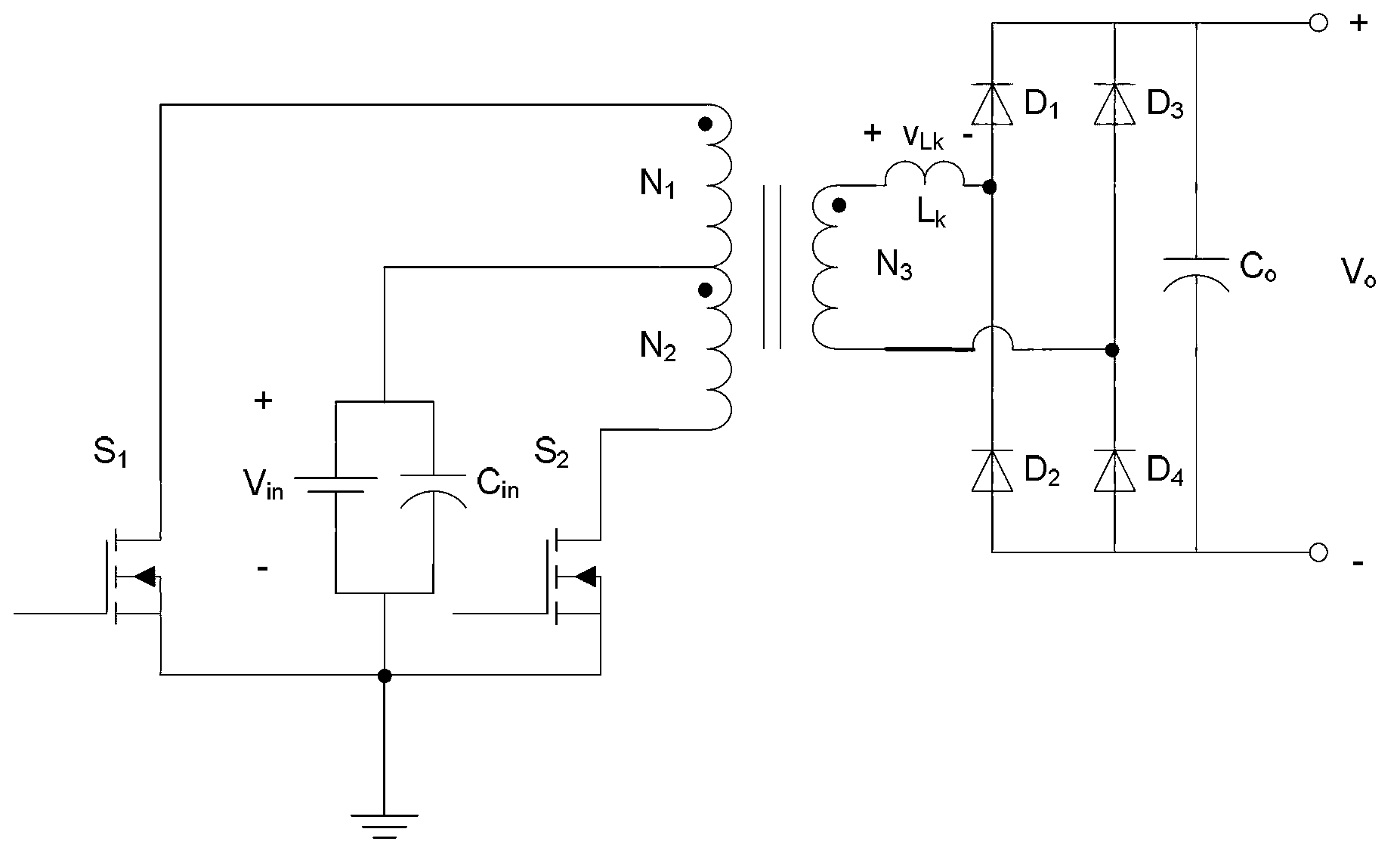
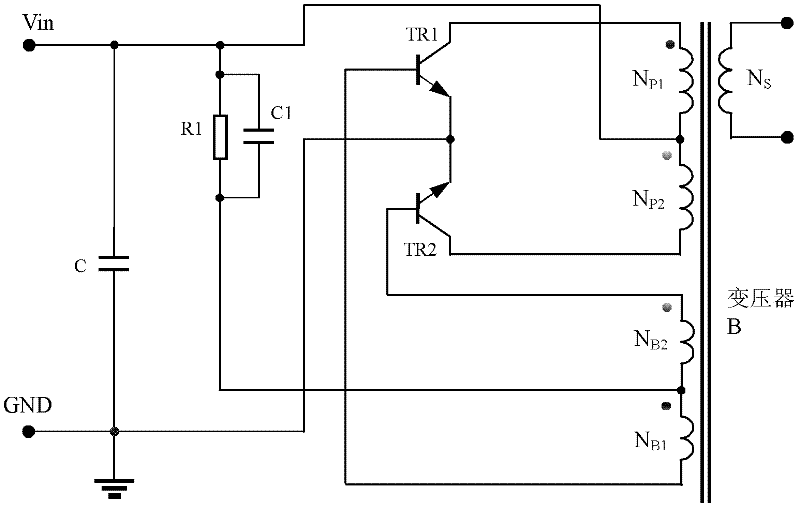
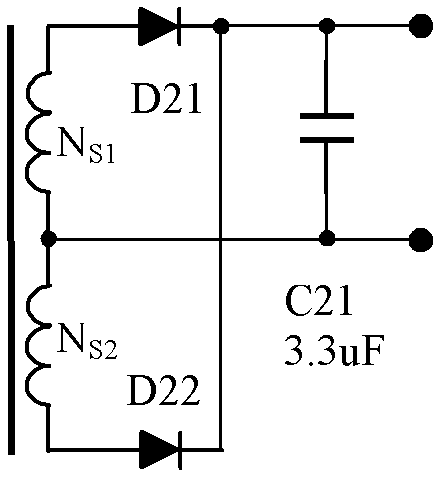
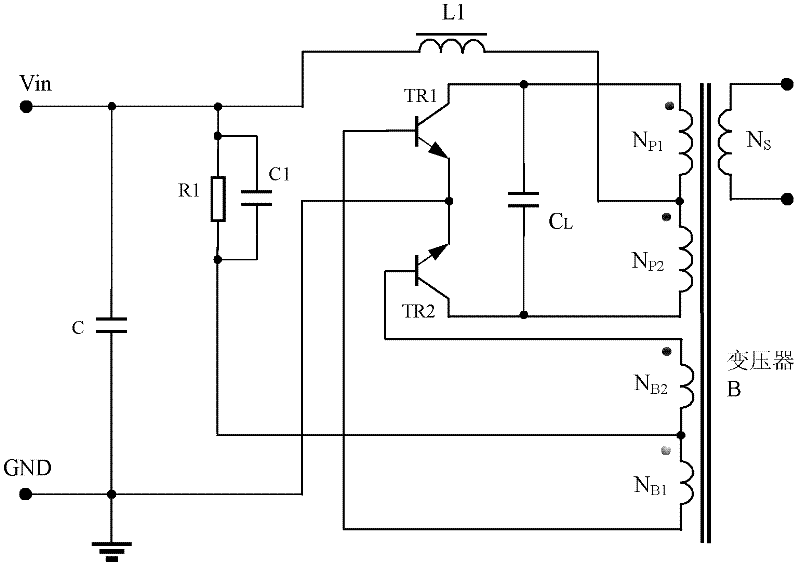
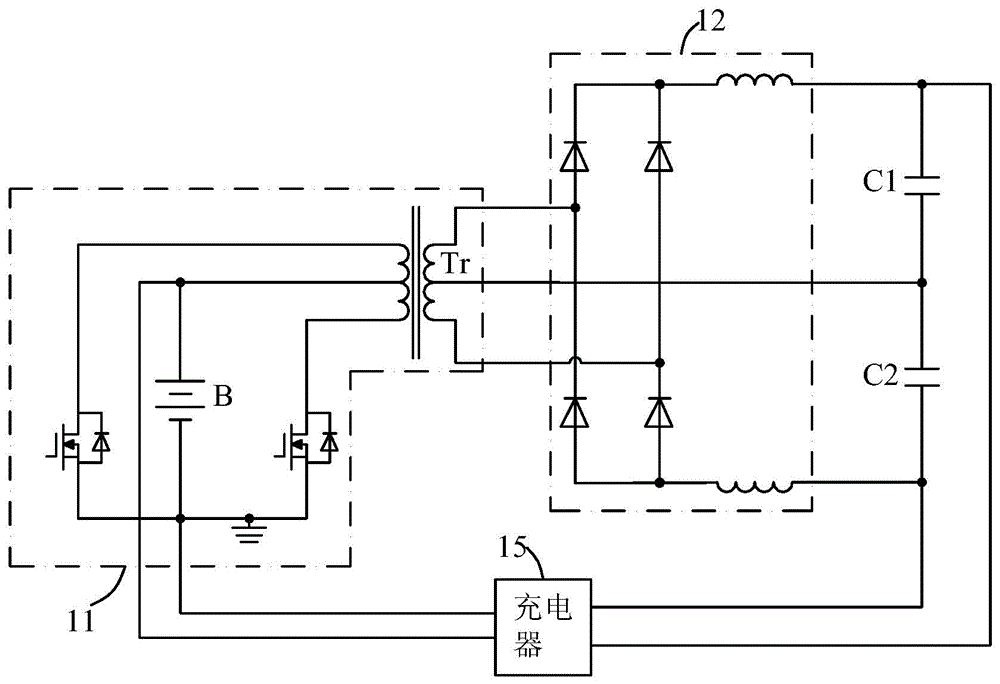
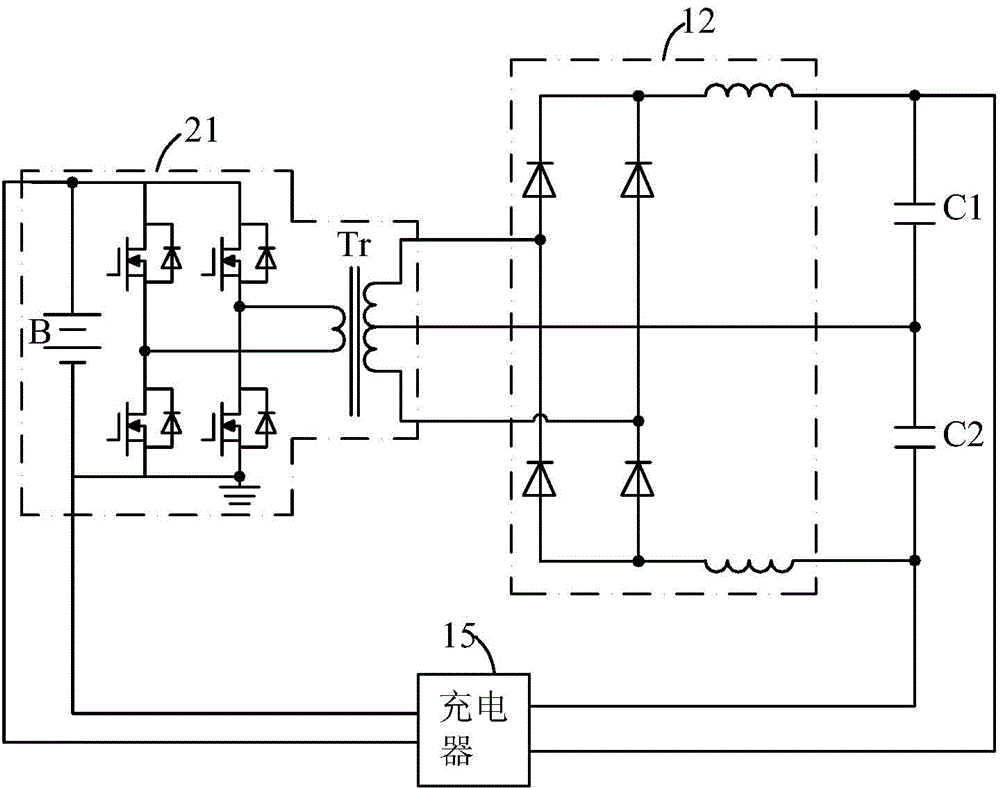
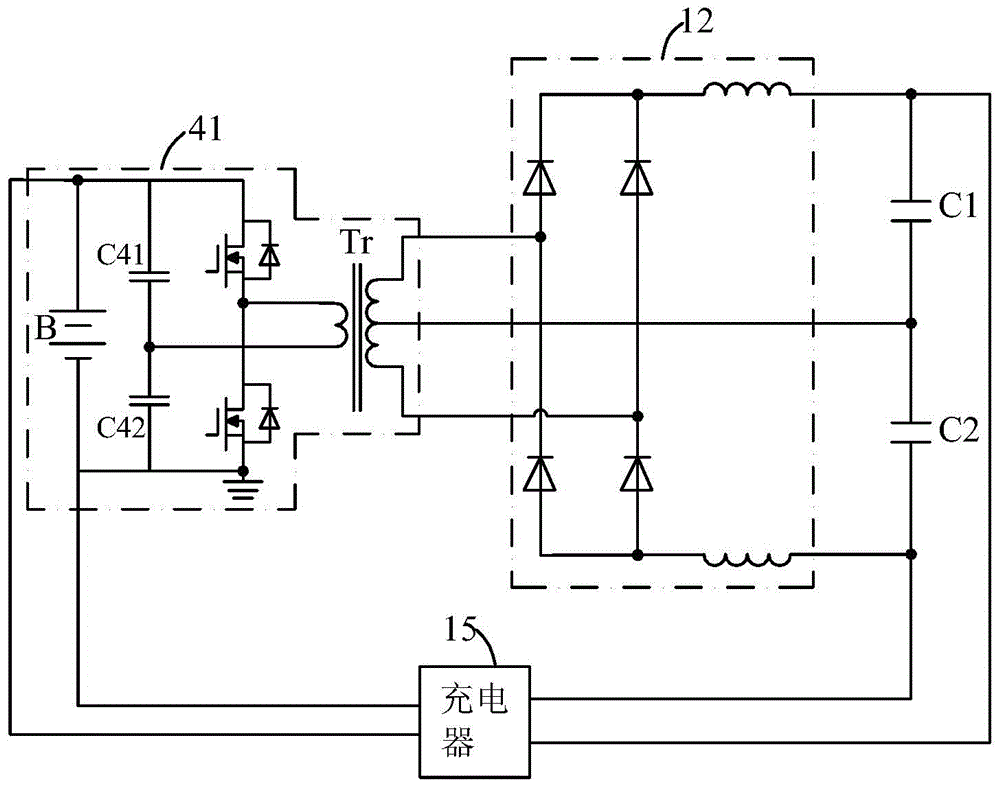
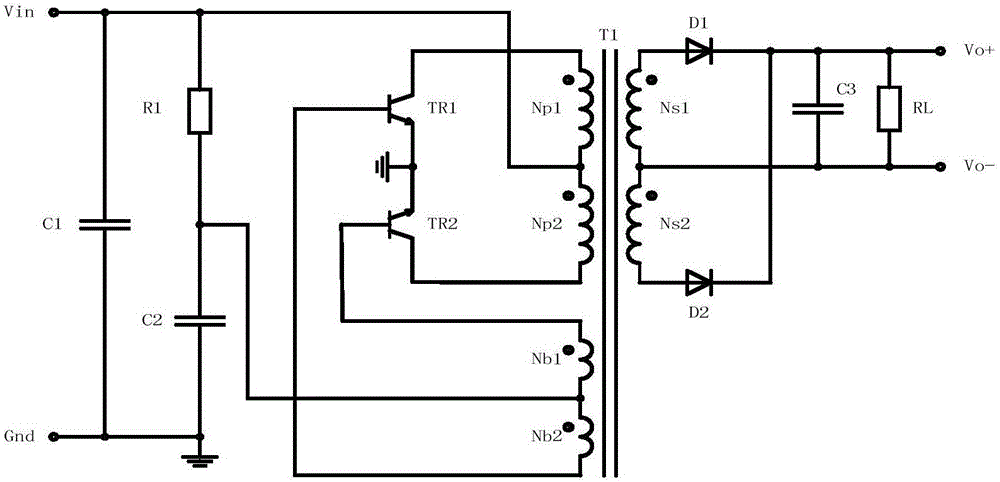
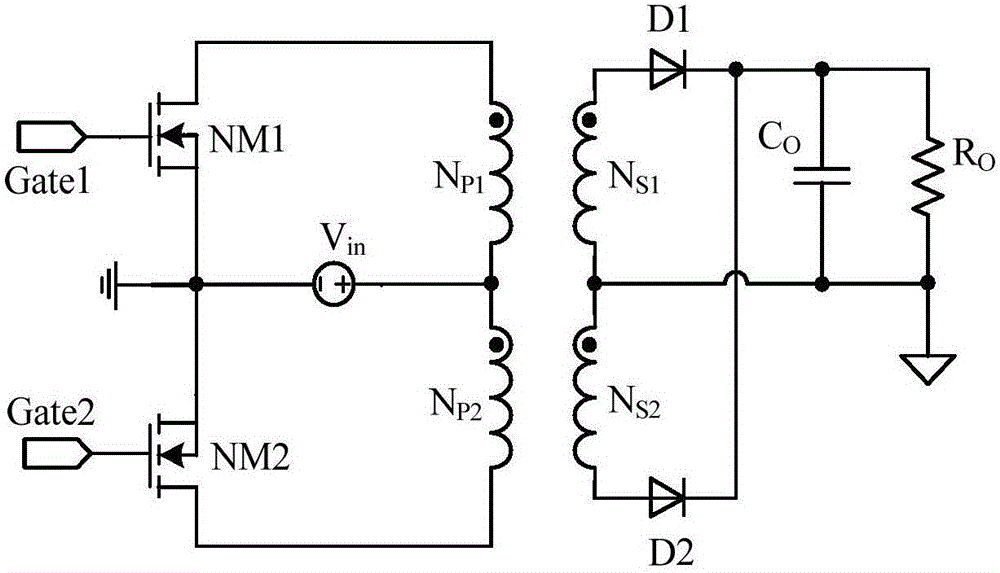
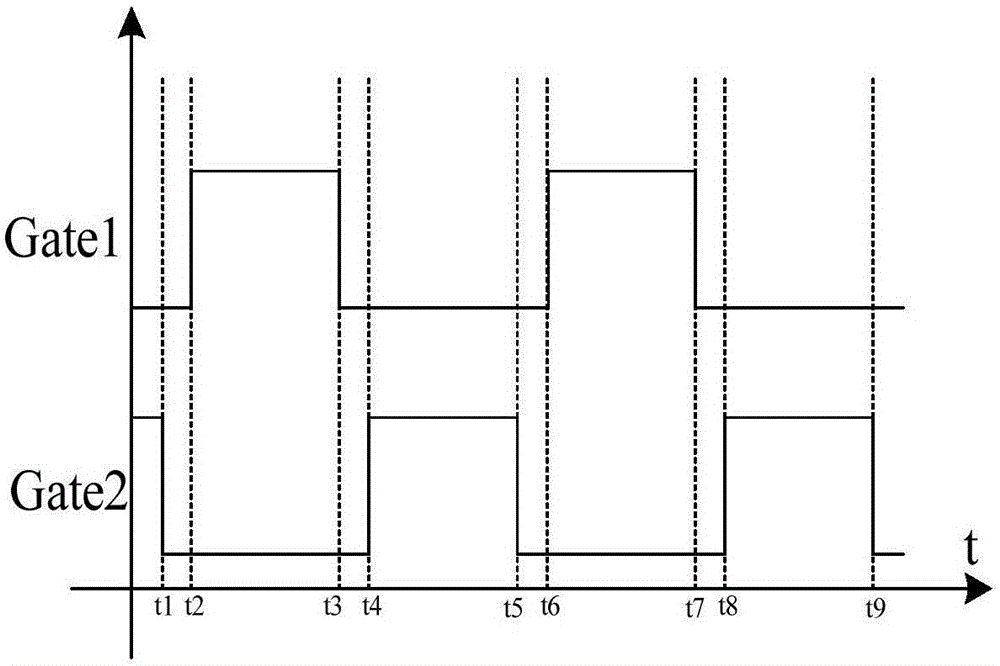
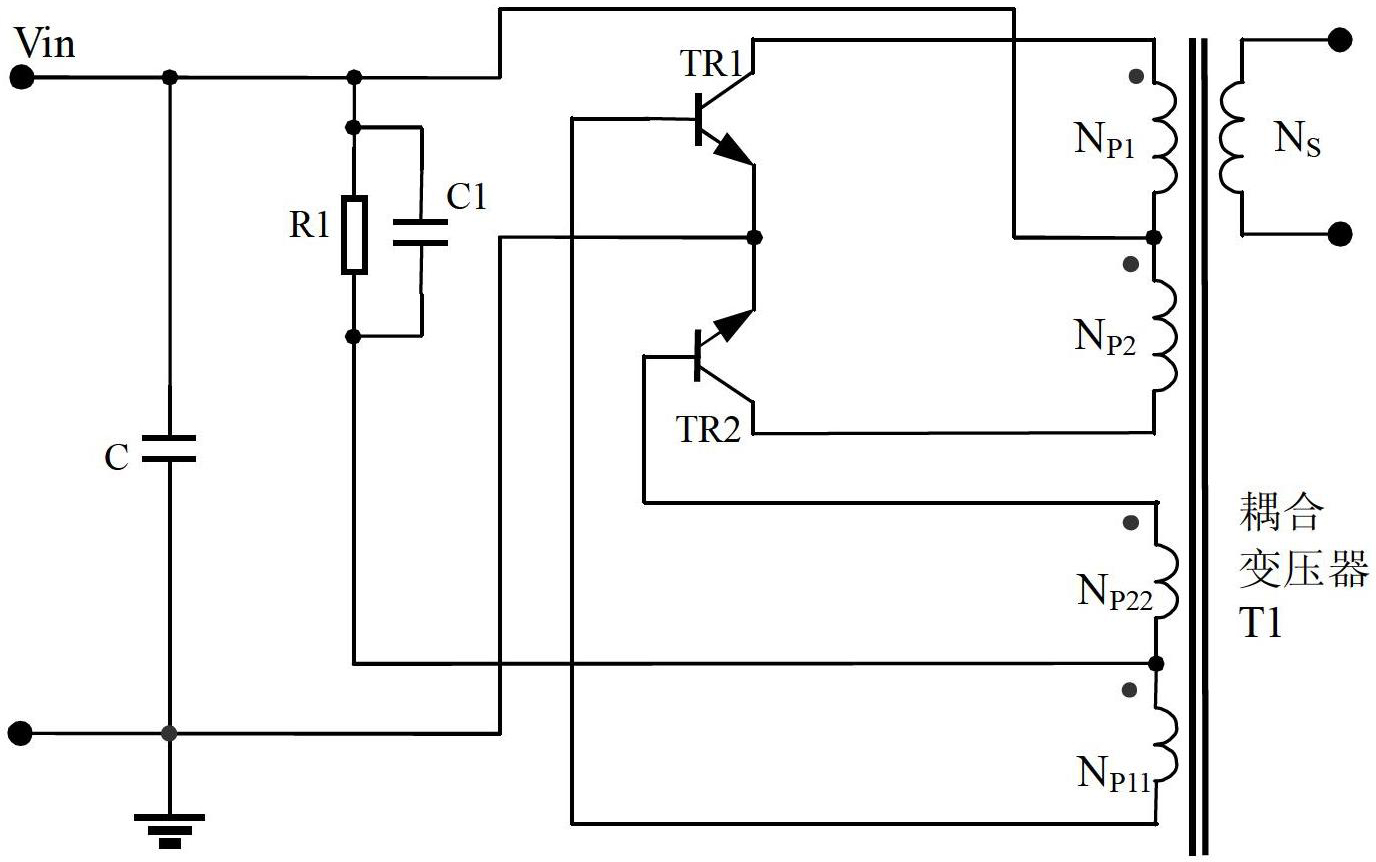
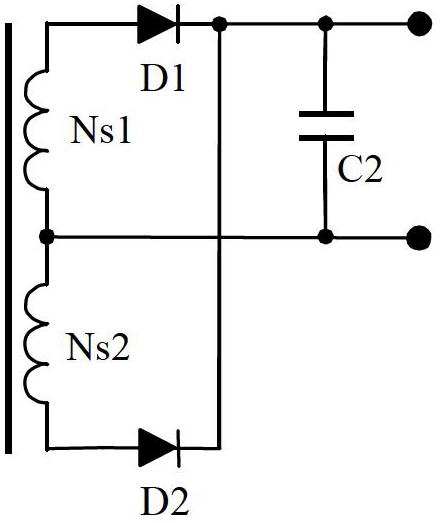
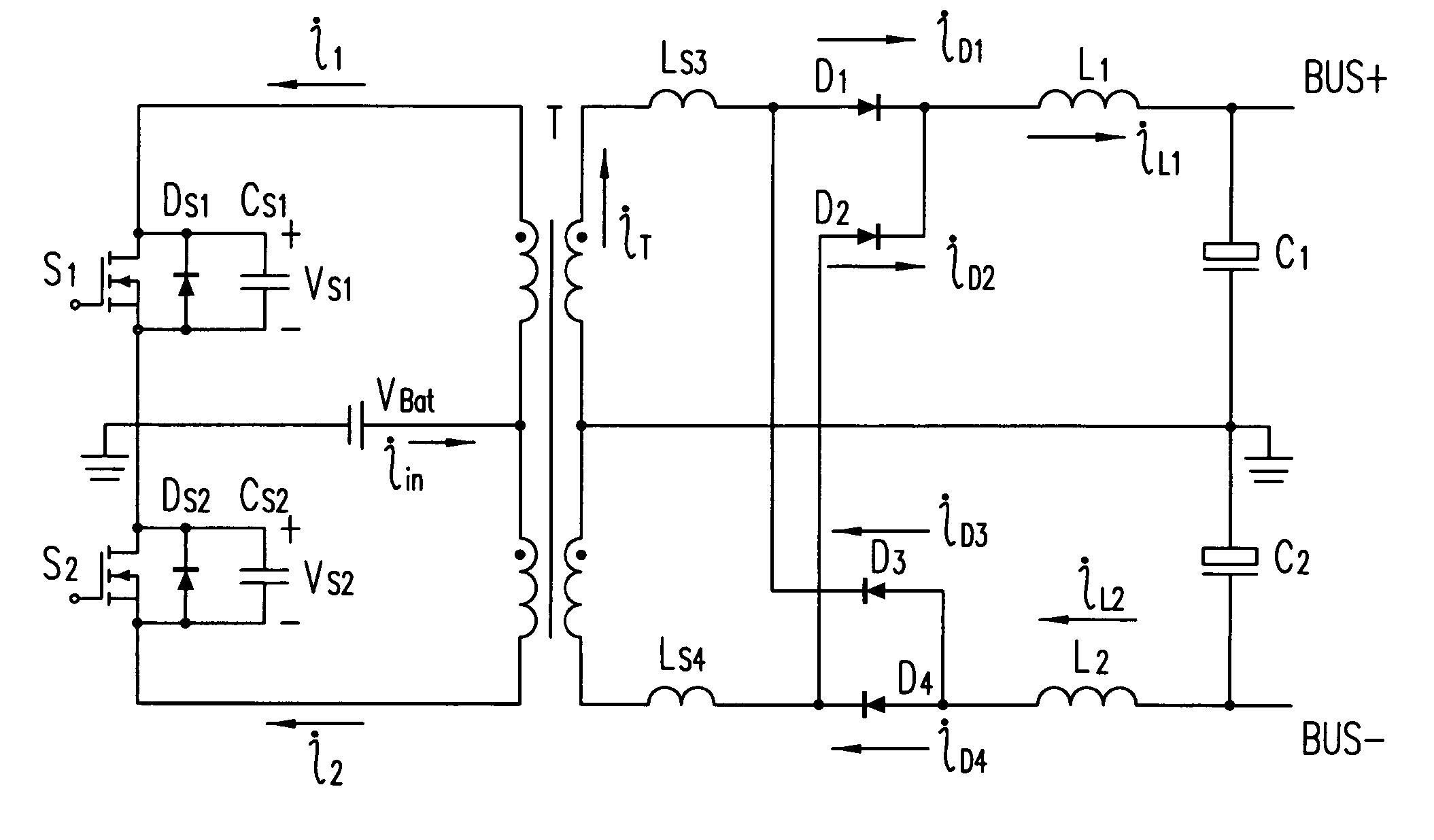
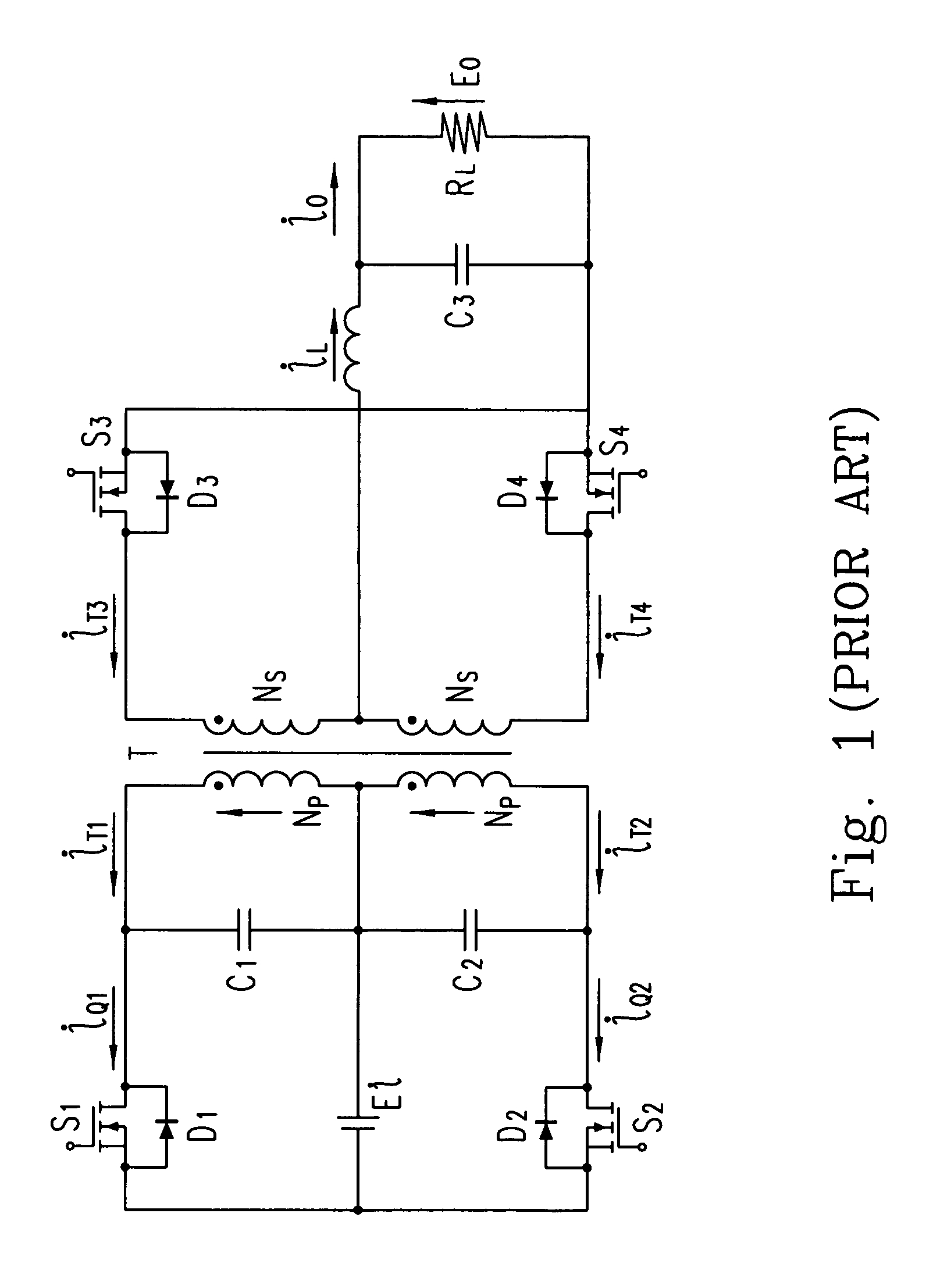
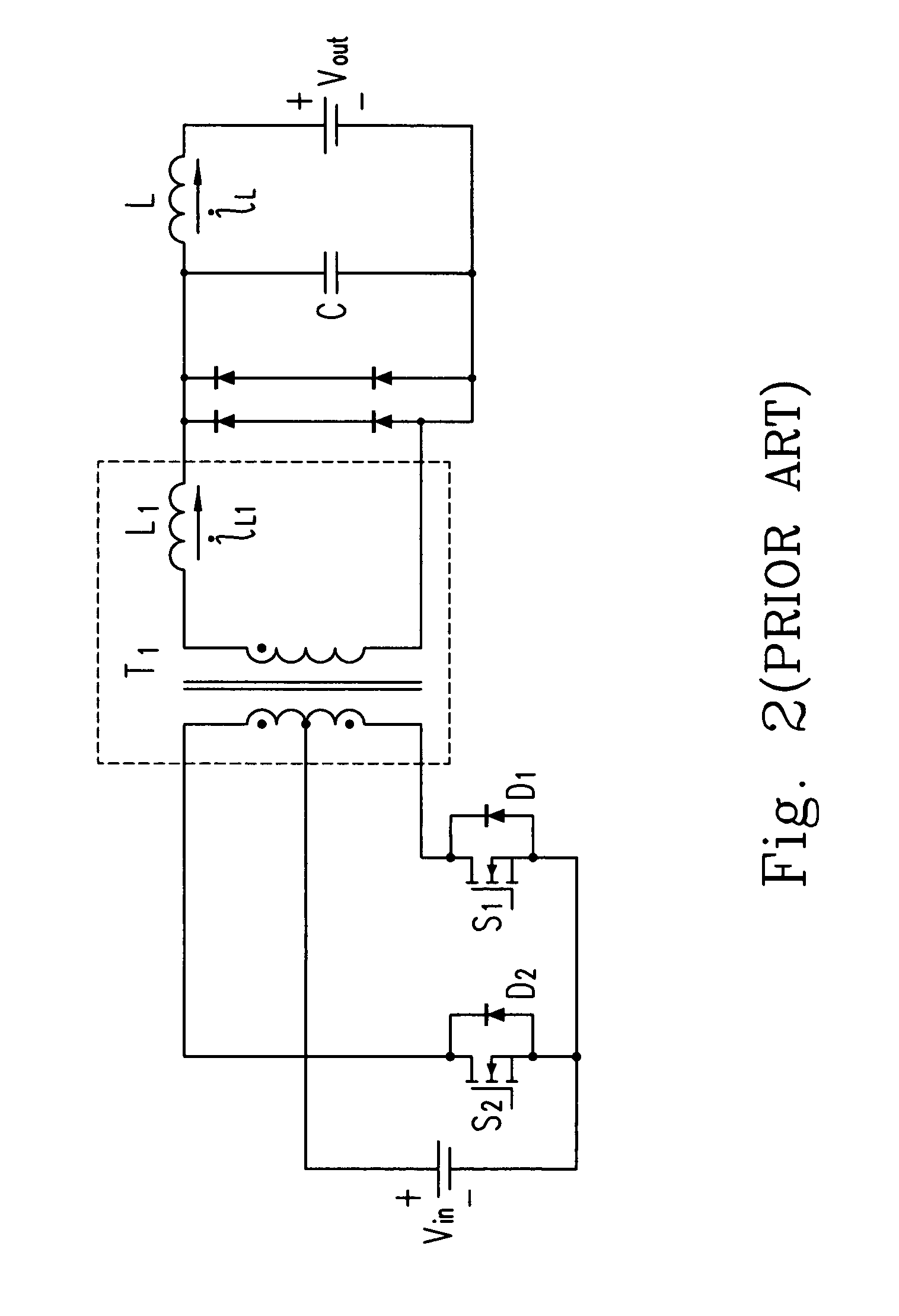
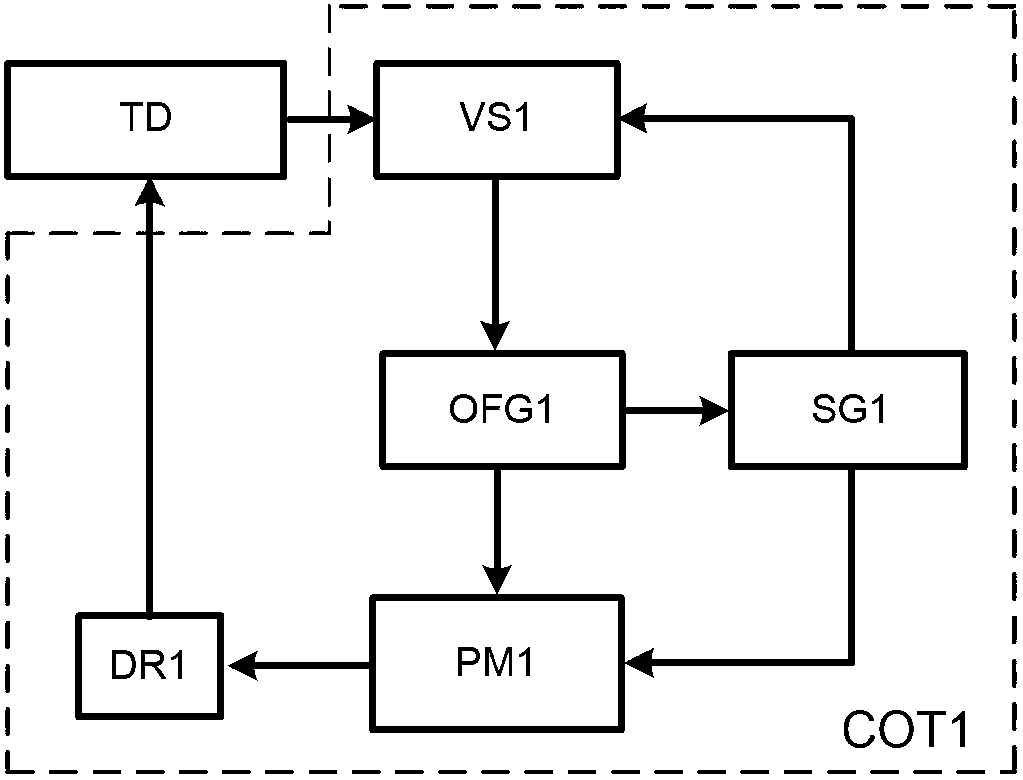
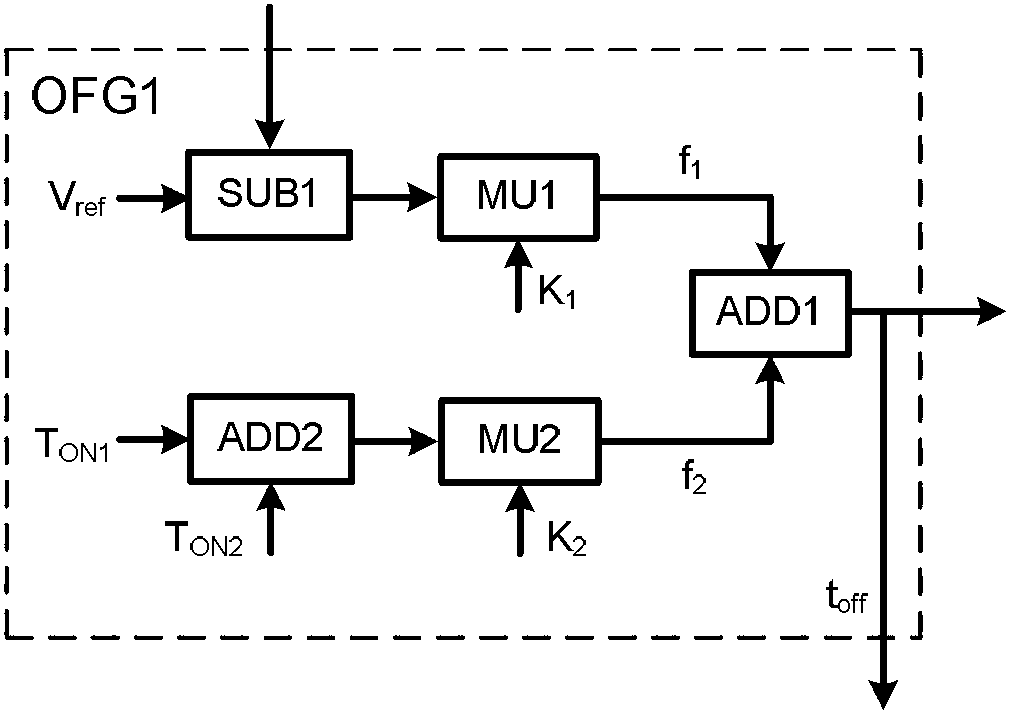
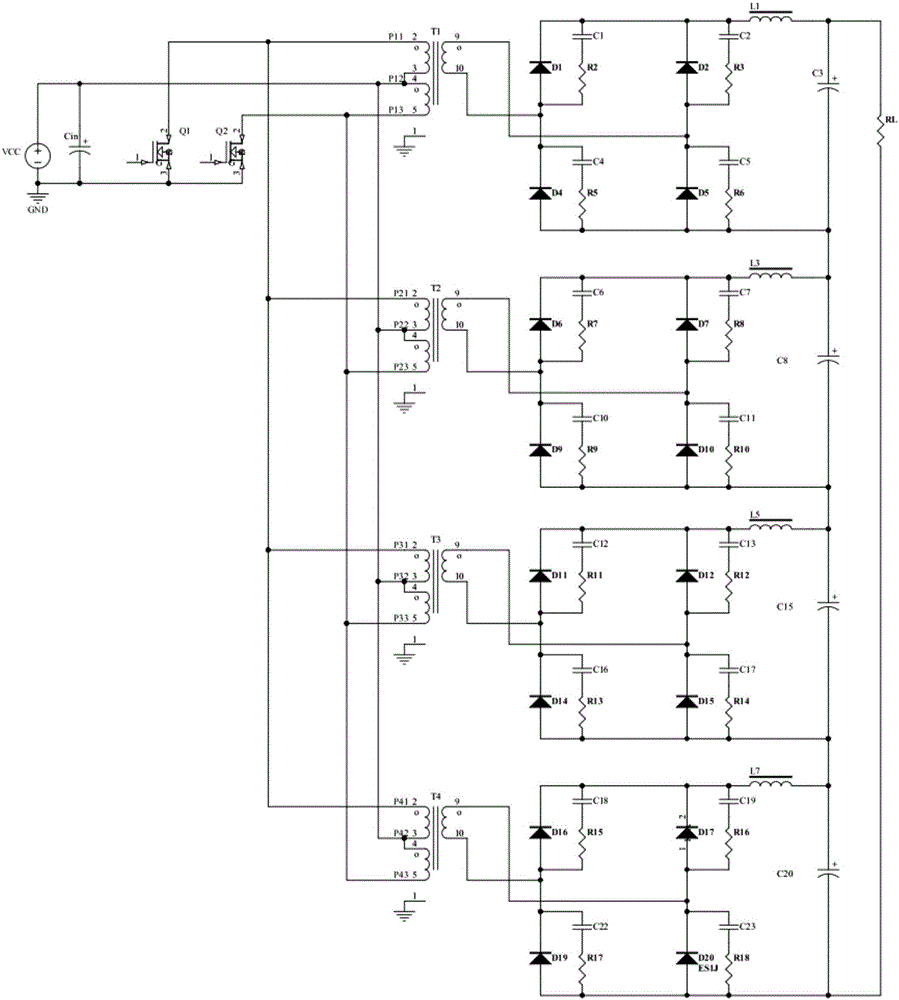
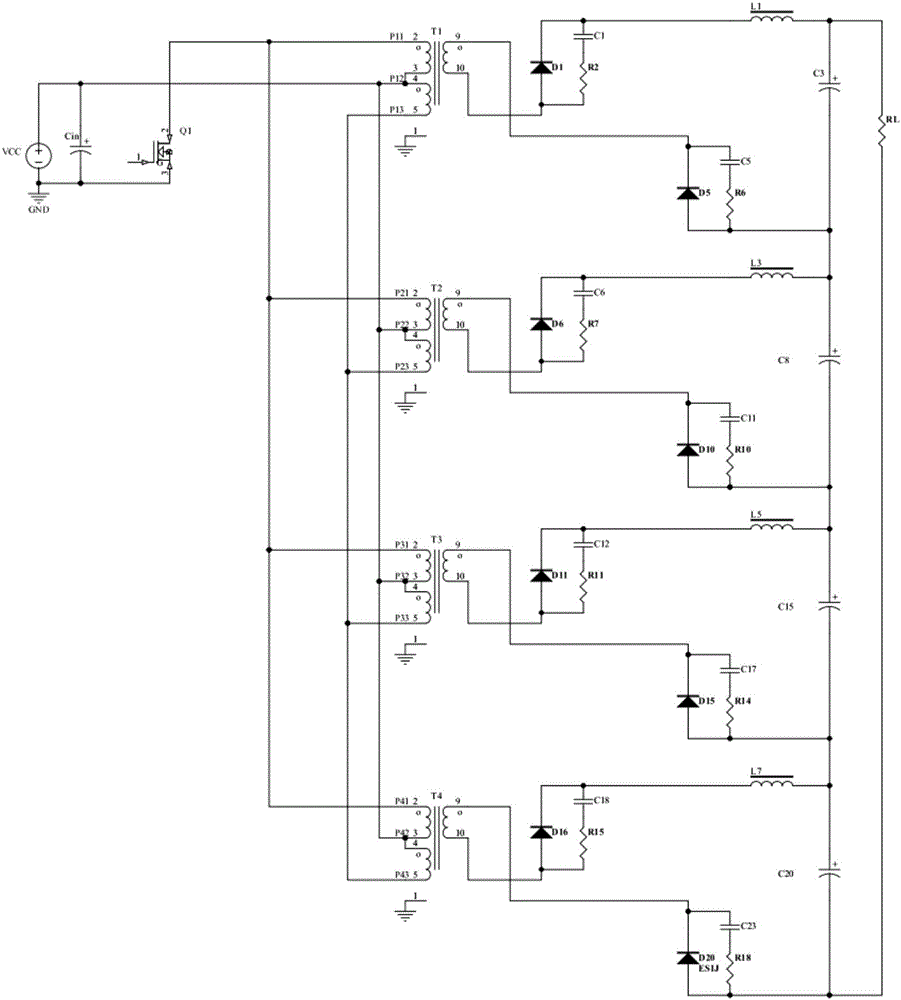
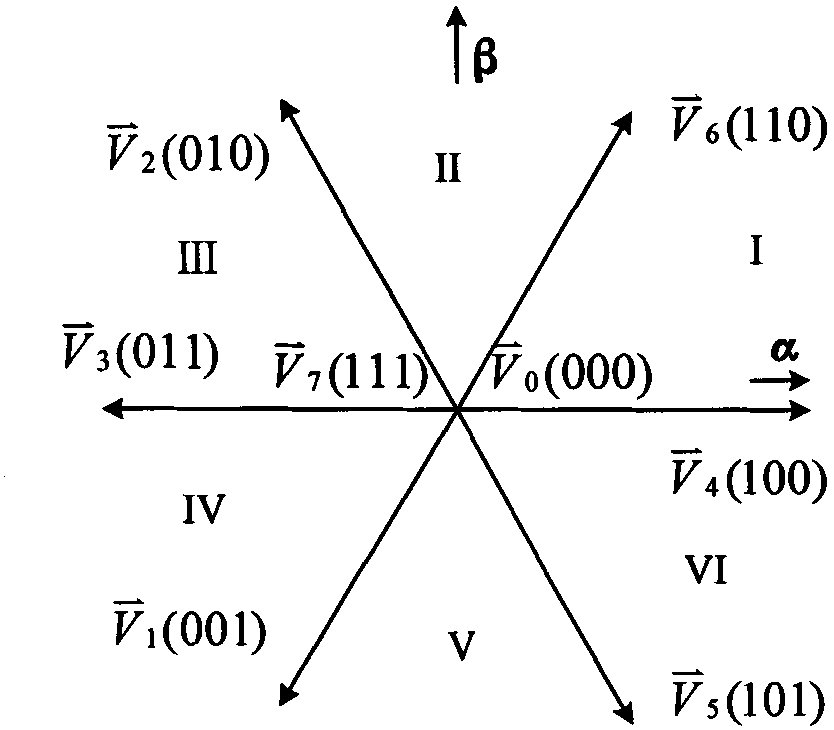Patents
Literature
107 results about "Push–pull converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
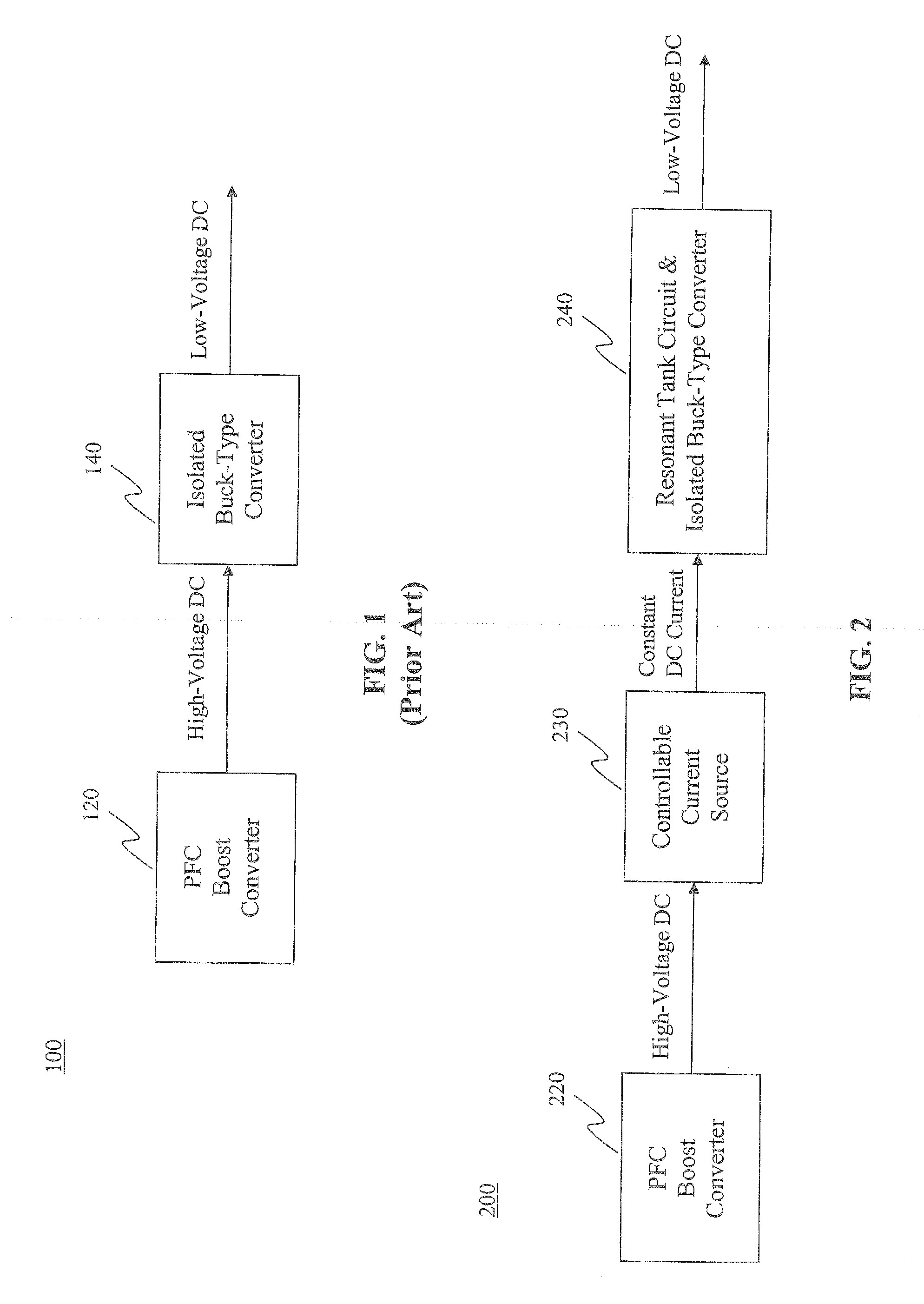
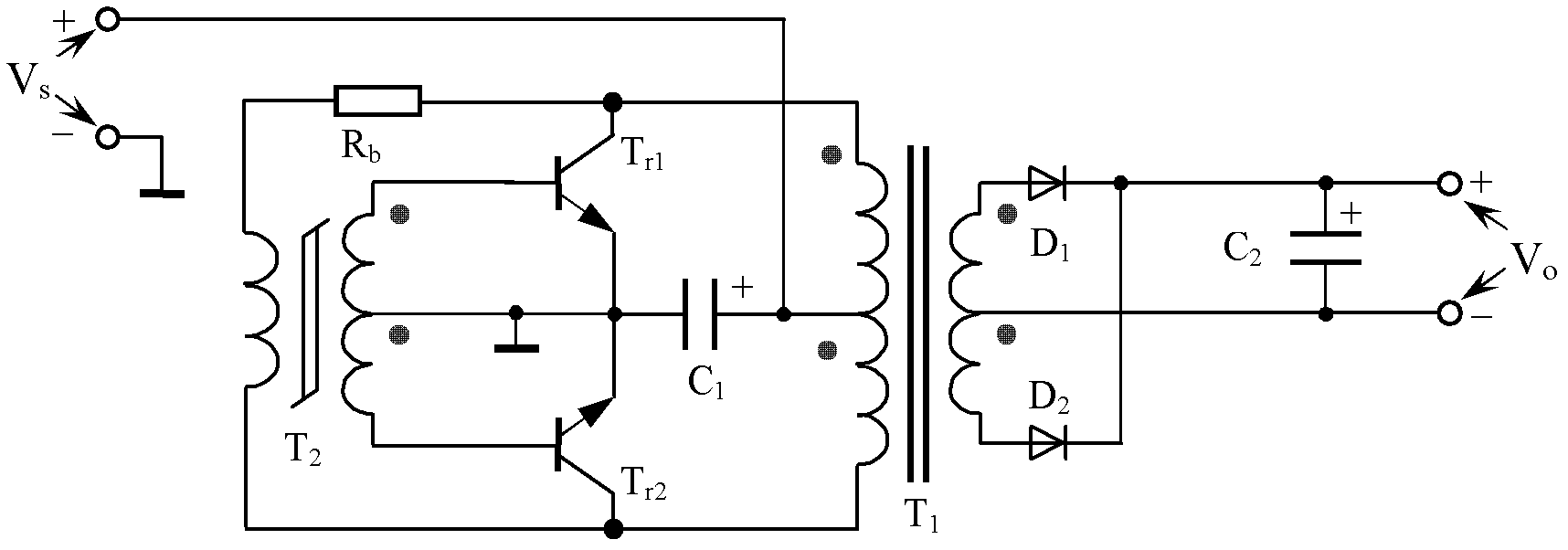
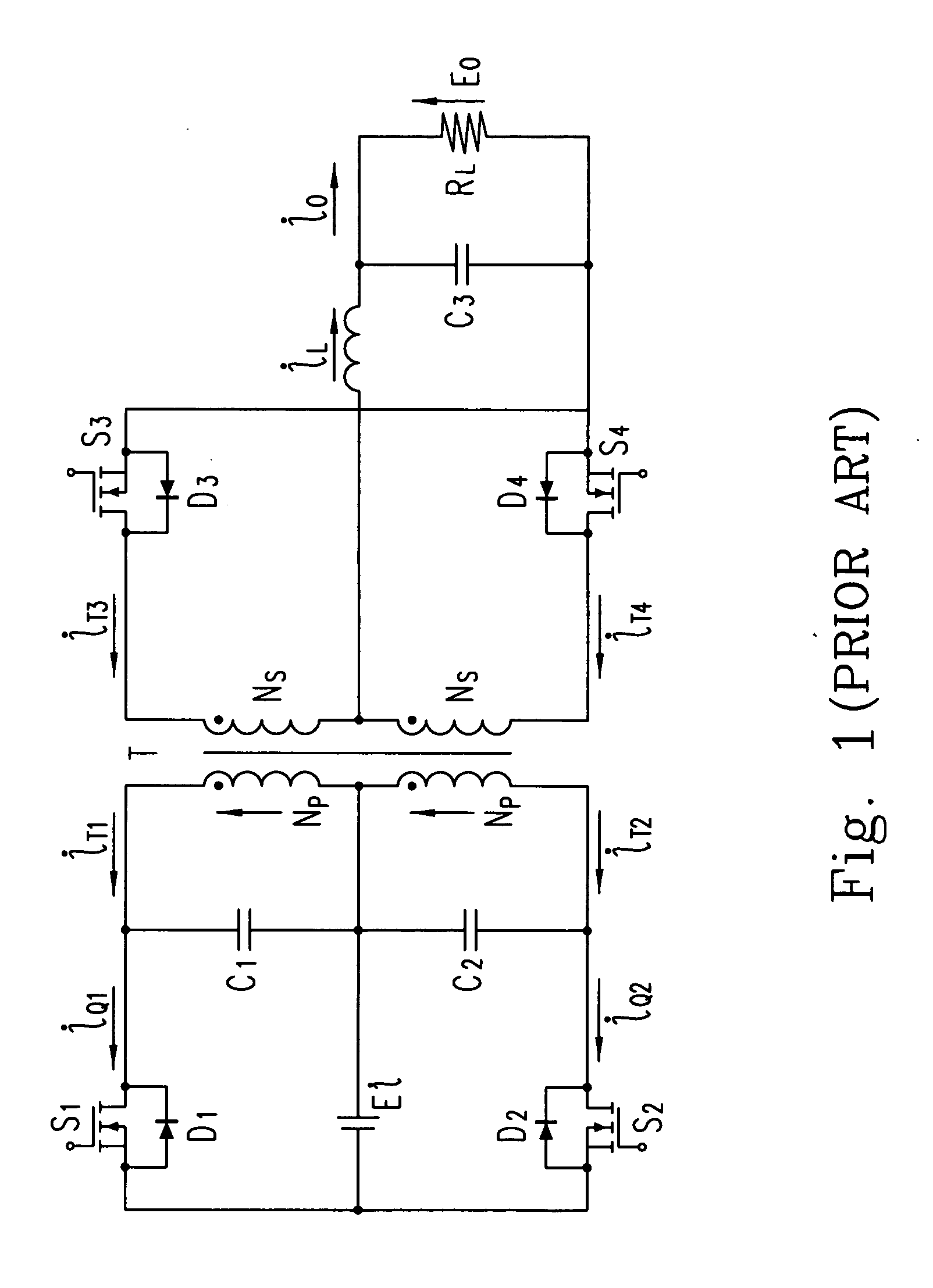
A push–pull converter is a type of DC-to-DC converter, a switching converter that uses a transformer to change the voltage of a DC power supply. The distinguishing feature of a push-pull converter is that the transformer primary is supplied with current from the input line by pairs of transistors in a symmetrical push-pull circuit. The transistors are alternately switched on and off, periodically reversing the current in the transformer. Therefore, current is drawn from the line during both halves of the switching cycle. This contrasts with buck-boost converters, in which the input current is supplied by a single transistor which is switched on and off, so current is only drawn from the line during half the switching cycle. During the other half the output power is supplied by energy stored in inductors or capacitors in the power supply. Push–pull converters have steadier input current, create less noise on the input line, and are more efficient in higher power applications.
Accelerated commutation for passive clamp isolated boost converters
InactiveUS6876556B2Efficient and cost-effectiveImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsVoltage spikeBuck converter
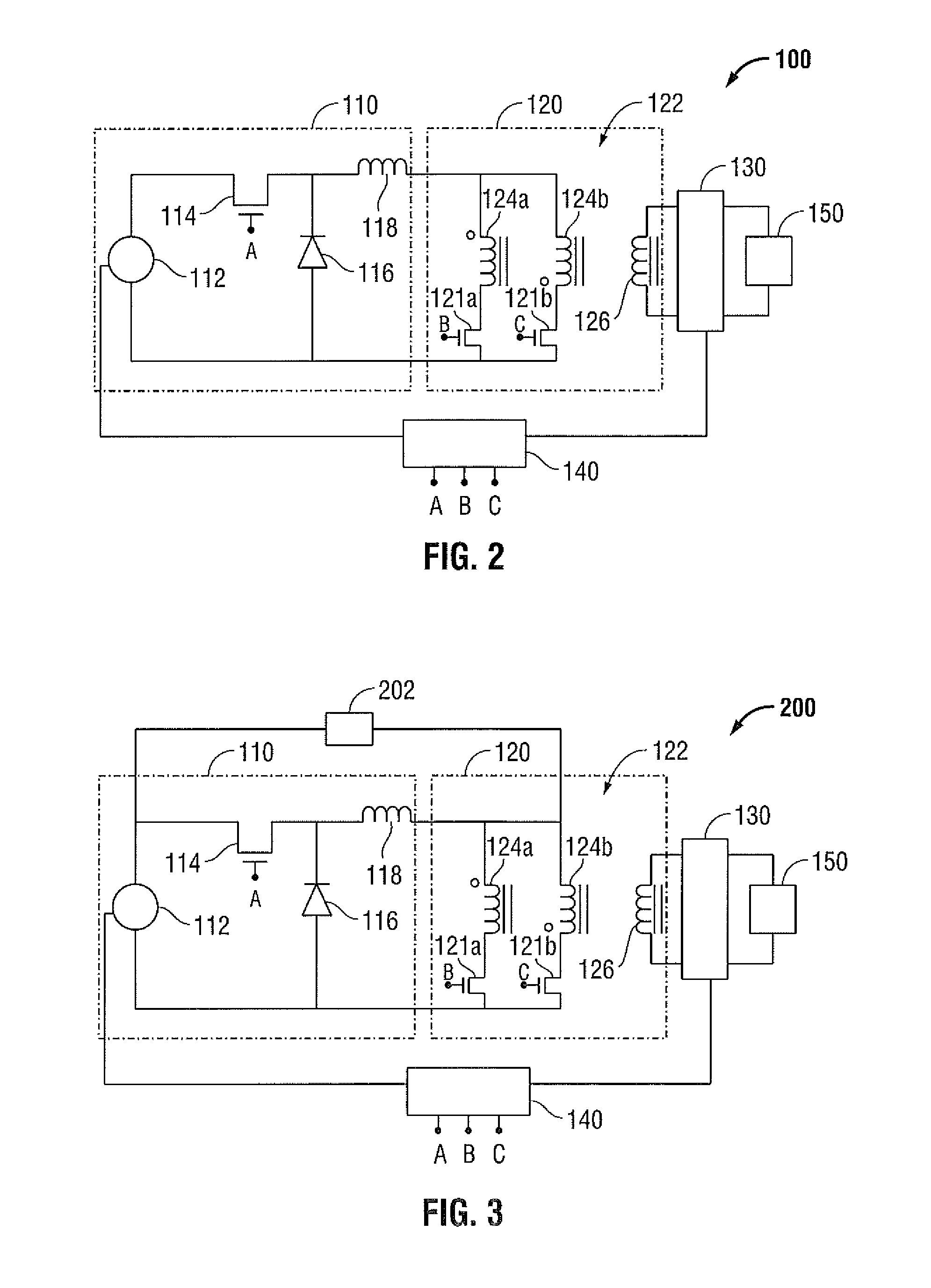
An efficient and cost effective bidirectional DC / DC converter reduces switch voltage stress via accelerated commutation allowing use of a low-cost passive clamp circuit in boost mode. The converter includes a primary circuit, transformer and secondary circuit. The primary circuit takes the form of a “full bridge converter,” a “push-pull converter,” or an “L-type converter.”. The primary circuit may include a dissipator such as a snubber circuit or small buck converter. A secondary side of the transformer is momentarily shorted by the secondary circuit by, for example, turning on at least two switches in the secondary circuit simultaneously for a minimal calibratable period when a pair of primary circuit controllers turn off to protect the primary circuit switches from voltage spikes during switching conditions.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
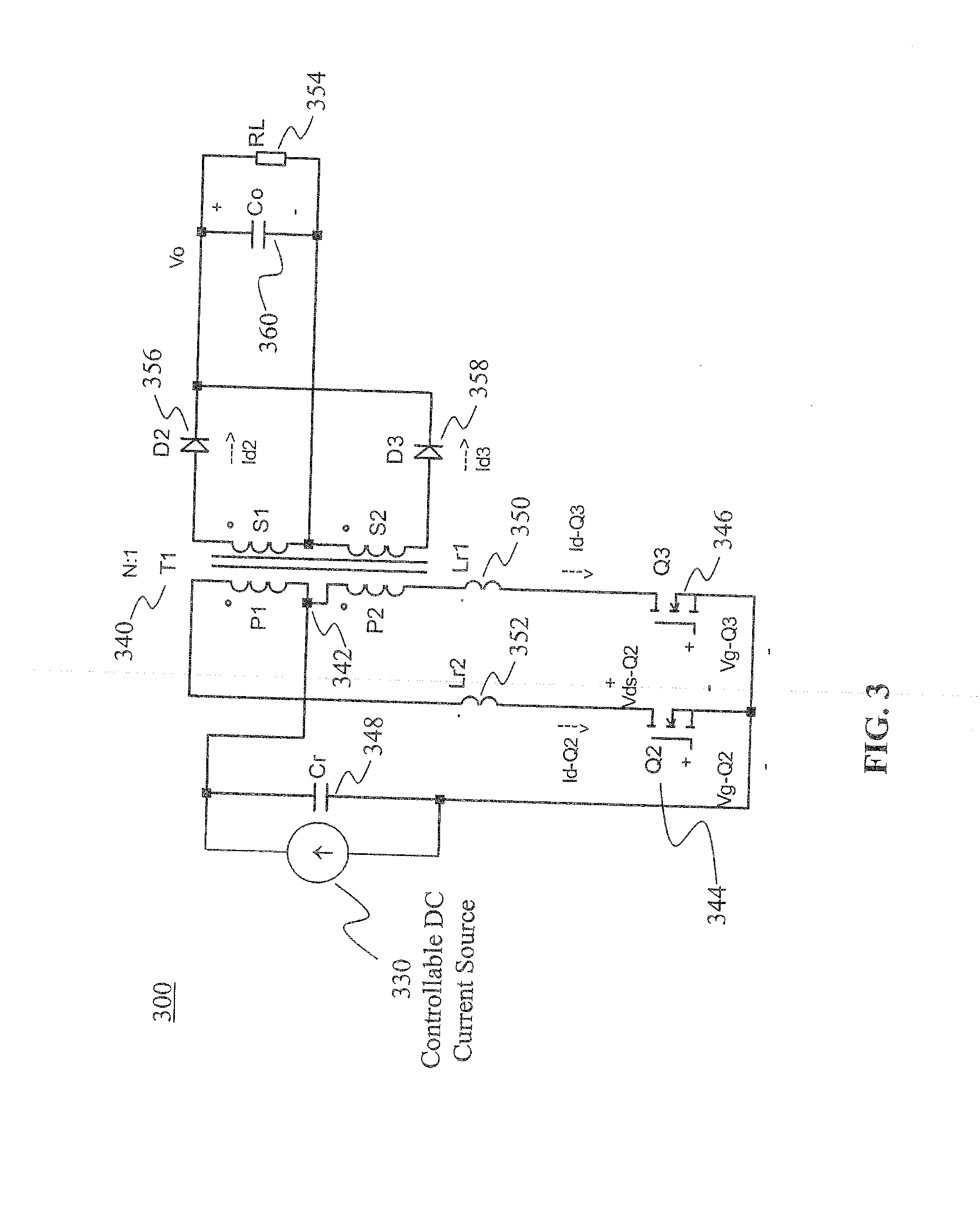
Two stage resonant converter
ActiveUS20110261590A1Efficient power electronics conversionEnergy industrySoft switchingResonant converter
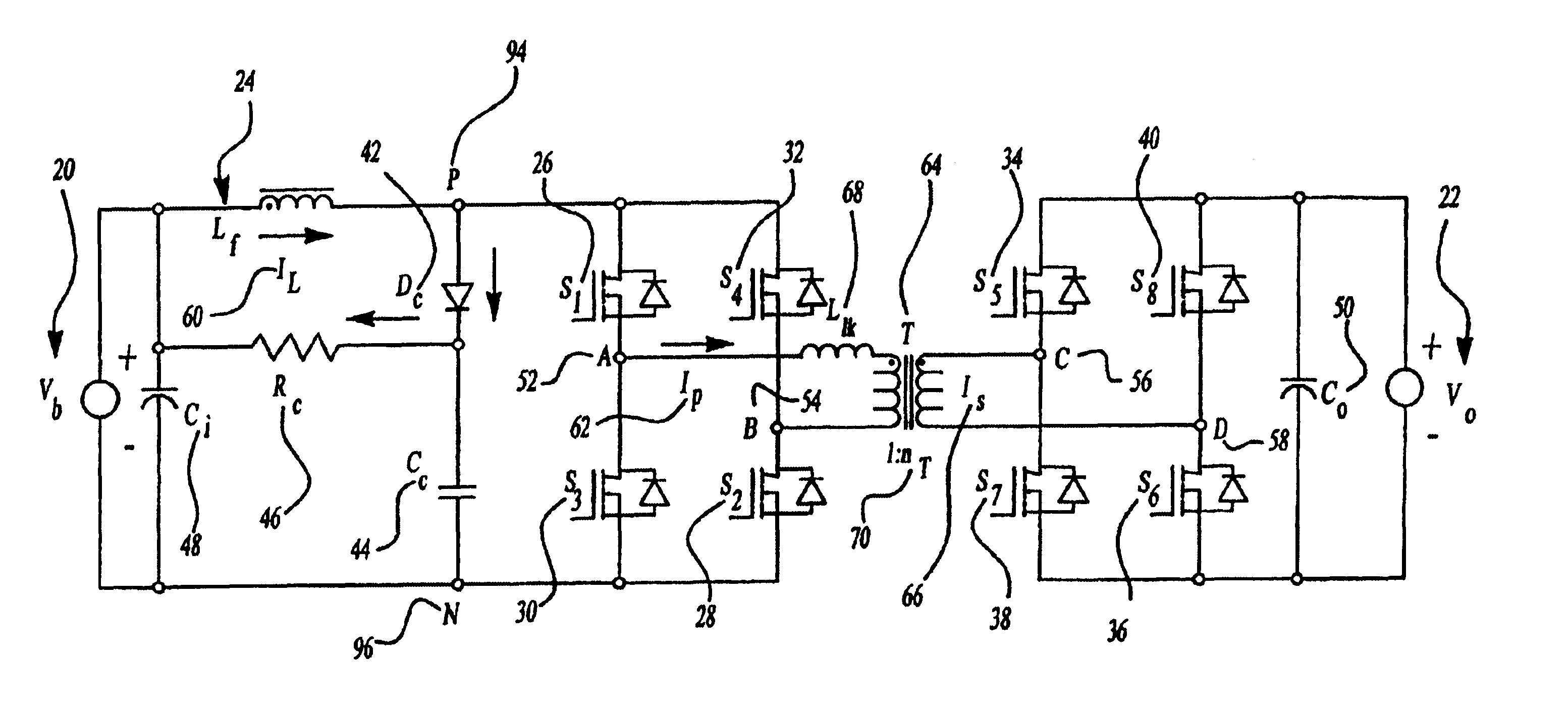
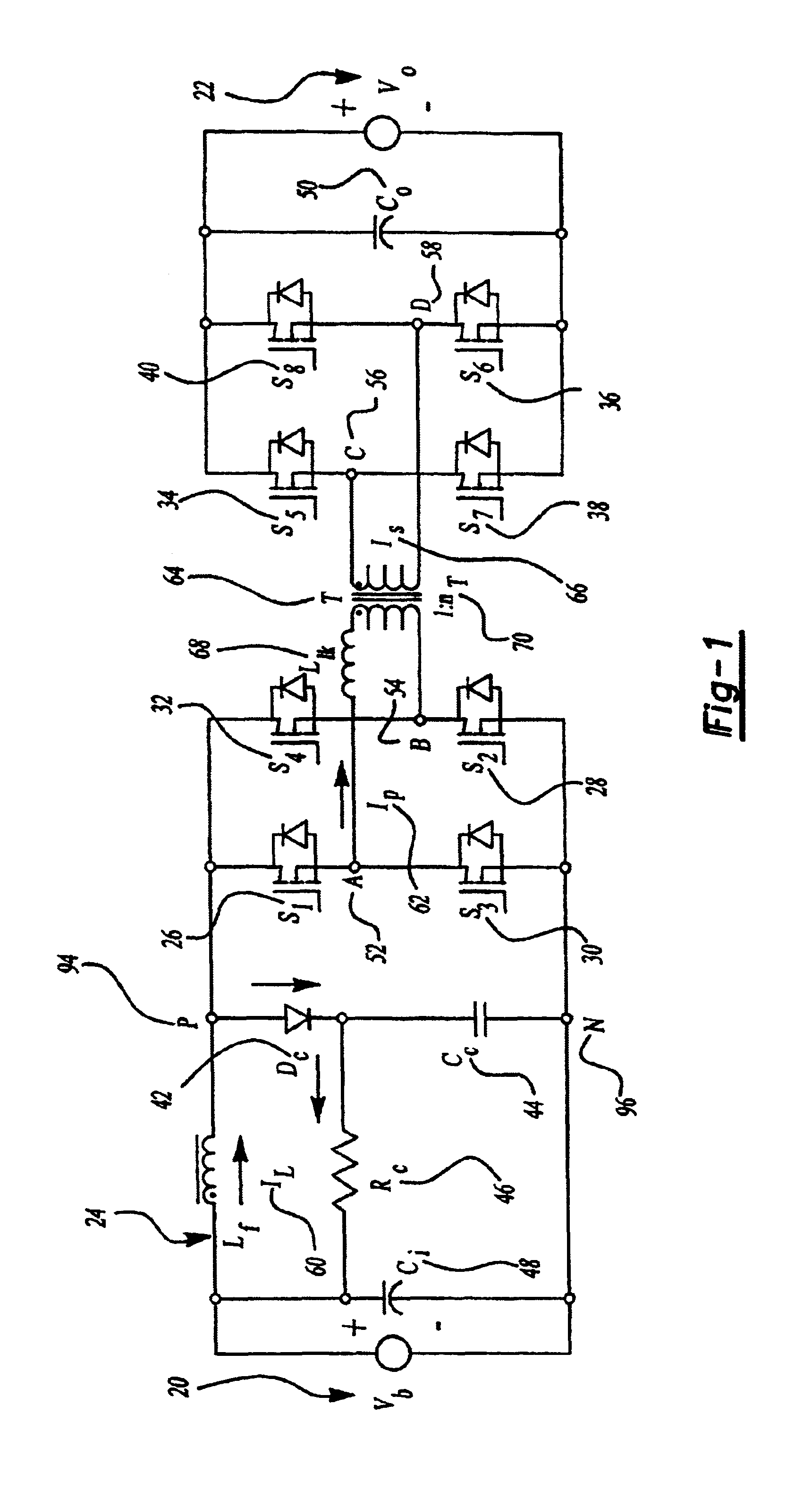
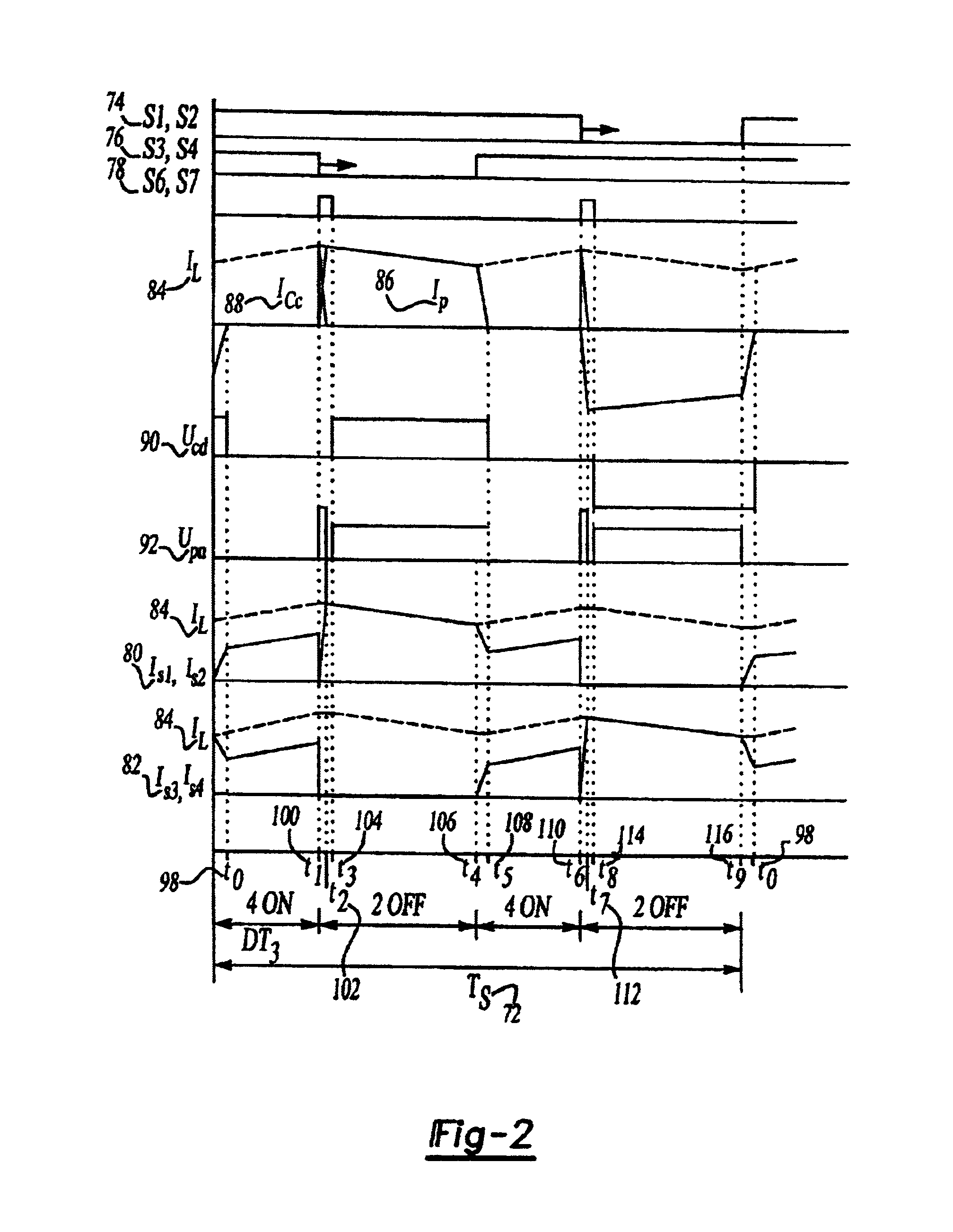
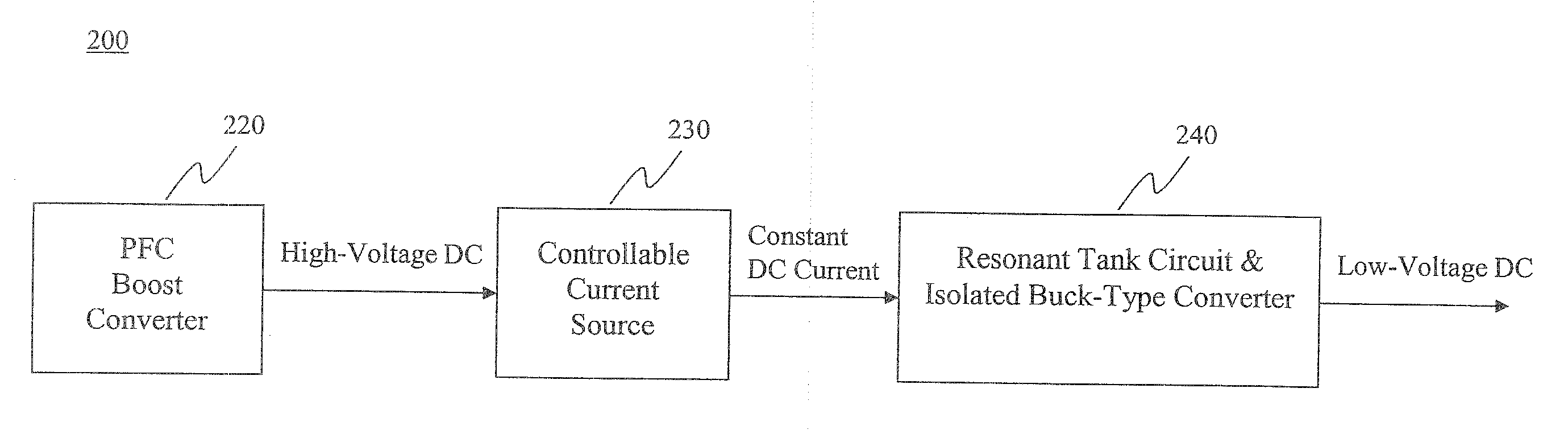
A resonant converter comprising: a controllable current source; a resonant tank circuit coupled to the current source; and an isolated buck-type converter coupled to the resonant tank circuit, the isolated buck-type converter having an output, wherein the resonant tank circuit enables switches in the isolated buck-type converter to switch under soft-switching conditions. In some embodiments, the controllable current source is a switch-mode-type current source. In some embodiments, the isolated buck-type converter comprises a half-bridge converter. In some embodiments, the isolated buck-type converter comprises a full-bridge converter. In some embodiments, the isolated buck-type converter comprises a push-pull converter.
Owner:FLEXTRONICS AP LLC
Electronic ballast for fluorescent lamps
InactiveUS6118228AElectric light circuit arrangementElectric discharge lampsResonant filterRadio frequency
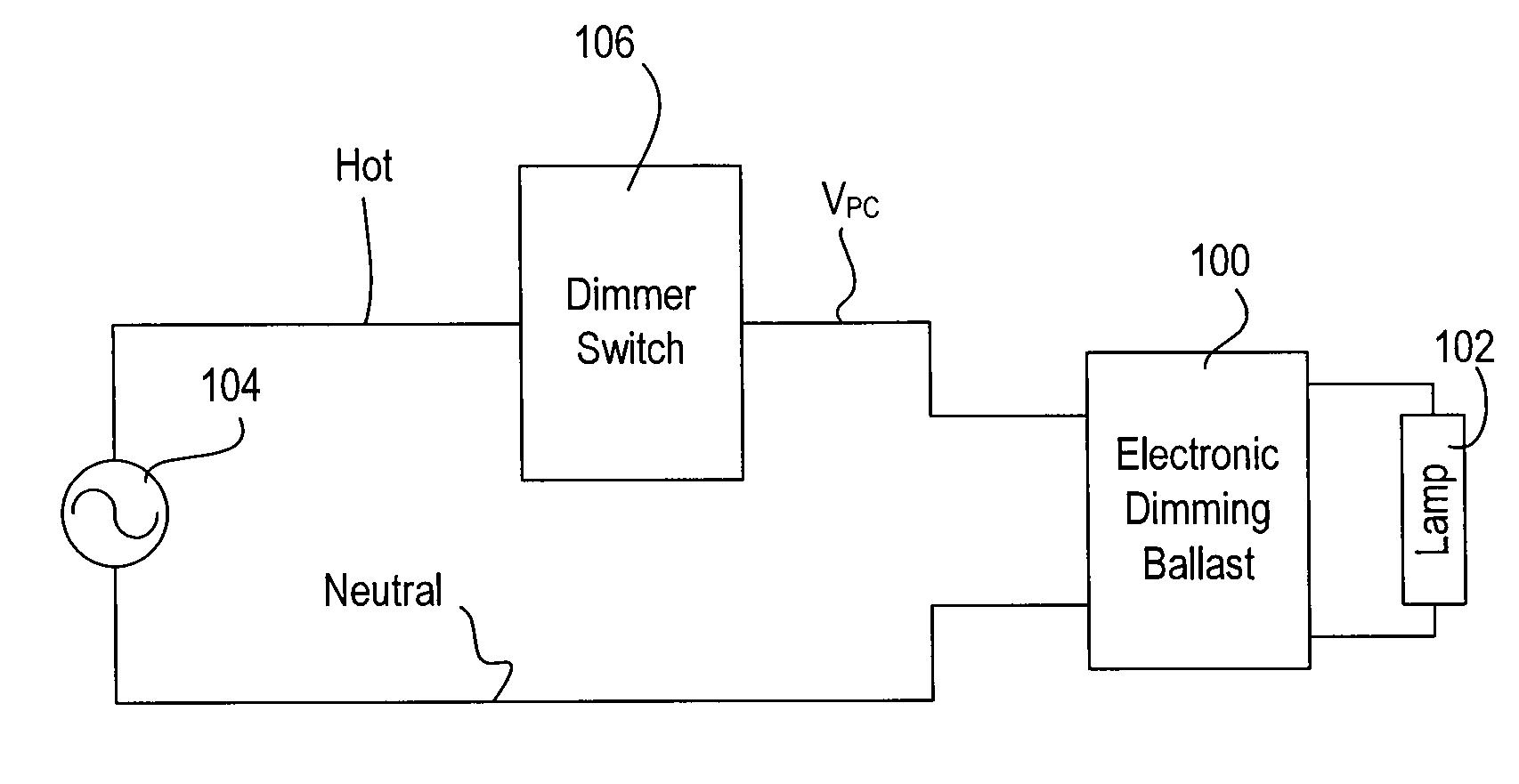
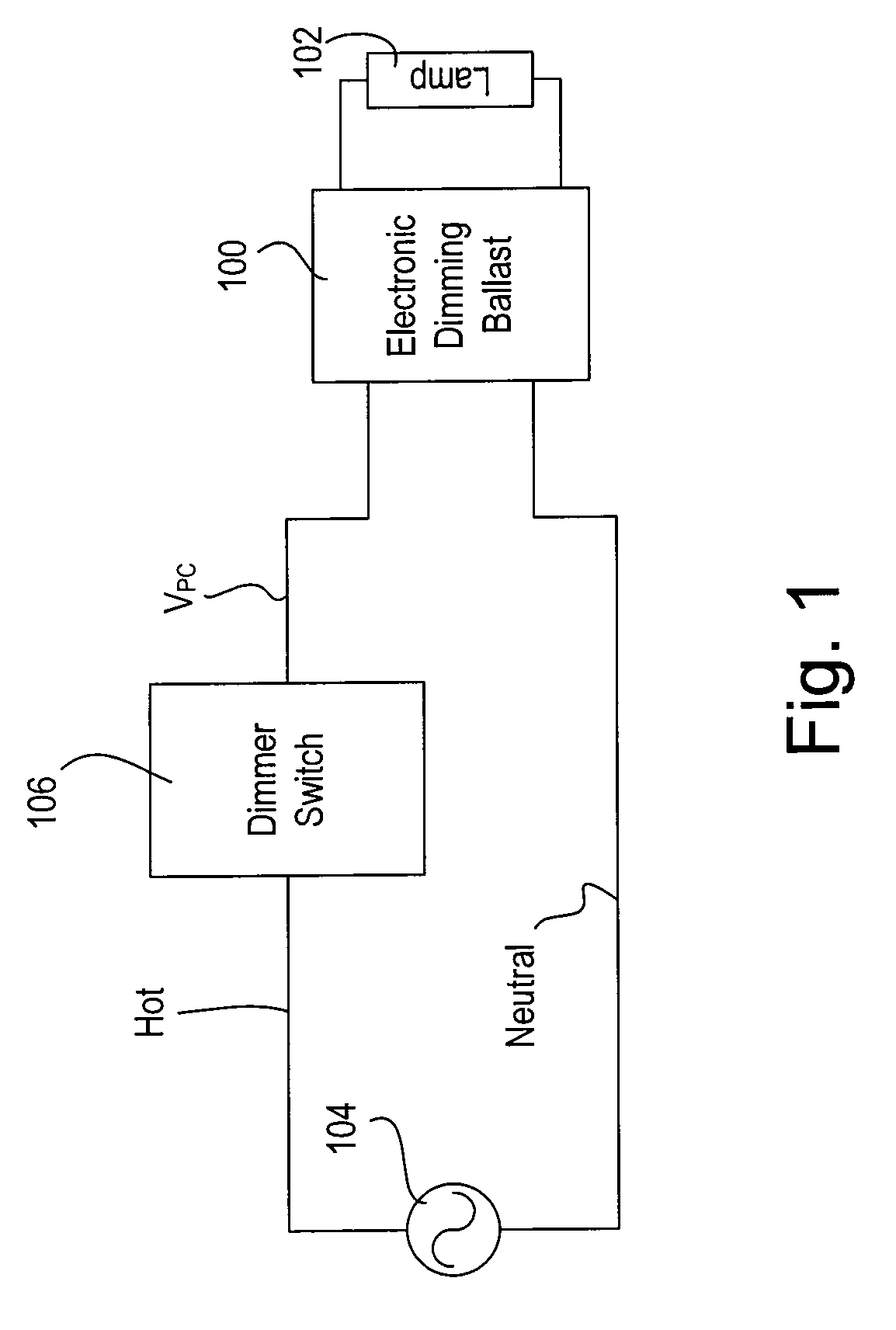
PCT No. PCT / HU95 / 00049 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 2, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 2, 1998 PCT Filed Oct. 3, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 13391 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 10, 1997A high-frequency filtered dimmable electronic ballast circuit for powering low-pressure fluorescent lamps includes an input protection device; a radio-frequency filter connected to an output of the input protection device; a rectifier connected to an output of the radio-frequency filter; a power factor correcting switching power supply device connected to an output of the rectifier; a current controlled push-pull converter connected to an output of the switching power supply device; a series-parallel resonant filter composed of a capacitor in series with two inductors having a common connection in parallel with an additional capacitor connected to an output of the push-pull converter to maintain voltage wave forms essentially sinusoidal and of constant amplitude regardless of loading; a fluorescent lamp connected to an output of the resonant filter; and an external on / off switching circuit connected directly or by an optical or magnetic insulation device to an input of the push-pull converter for renotely turning on and off the fluorescent lamp.
Owner:PAL SANDOR
Self-exited push-pull converter
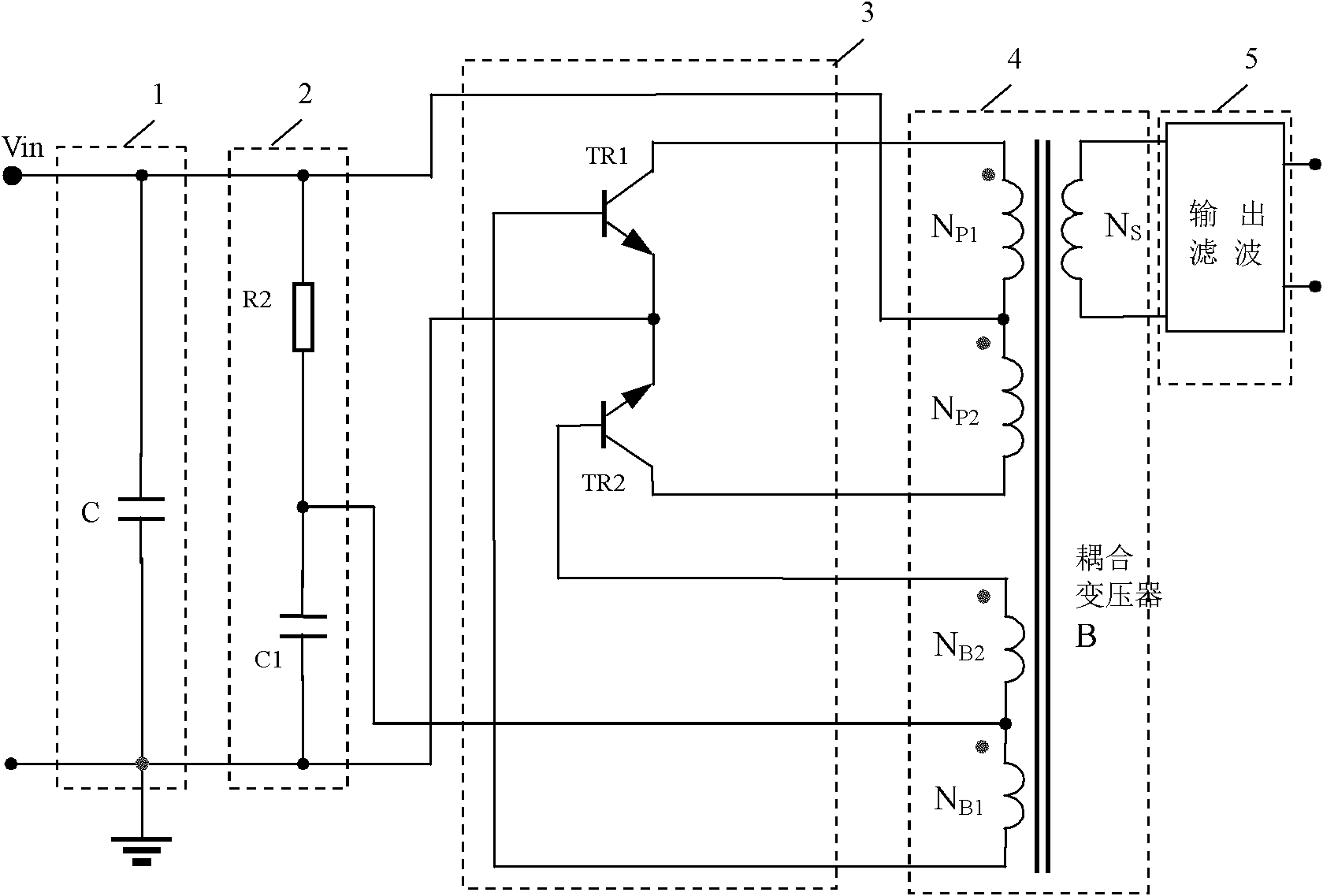
The invention discloses a self-exited push-pull converter, comprising an input soft starting circuit, a bipolar push-pull circuit, a coupling transformer and an output filter circuit, wherein the input soft starting circuit, the bipolar push-pull circuit, the coupling transformer and the output filter circuit are connected in order; the bipolar push-pull circuit comprises two triodes and a high frequency self-exited suppression circuit, wherein the two triodes are in push-pull connection; the emitters of the two triodes are grounded; the bases of the two triodes are respectively connected with two ends of a feedback winding of the coupling transformer; the collectors of the two triodes are connected with two ends of a primary winding of the coupling transformer; the high frequency self-exited suppression circuit is used for removing sine vibration generated due to high characteristic frequency when the triodes are electrified; and the high frequency self-exited suppression circuit is connected in the bipolar push-pull circuit. The self-exited push-pull converter can effectively control high frequency vibration.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
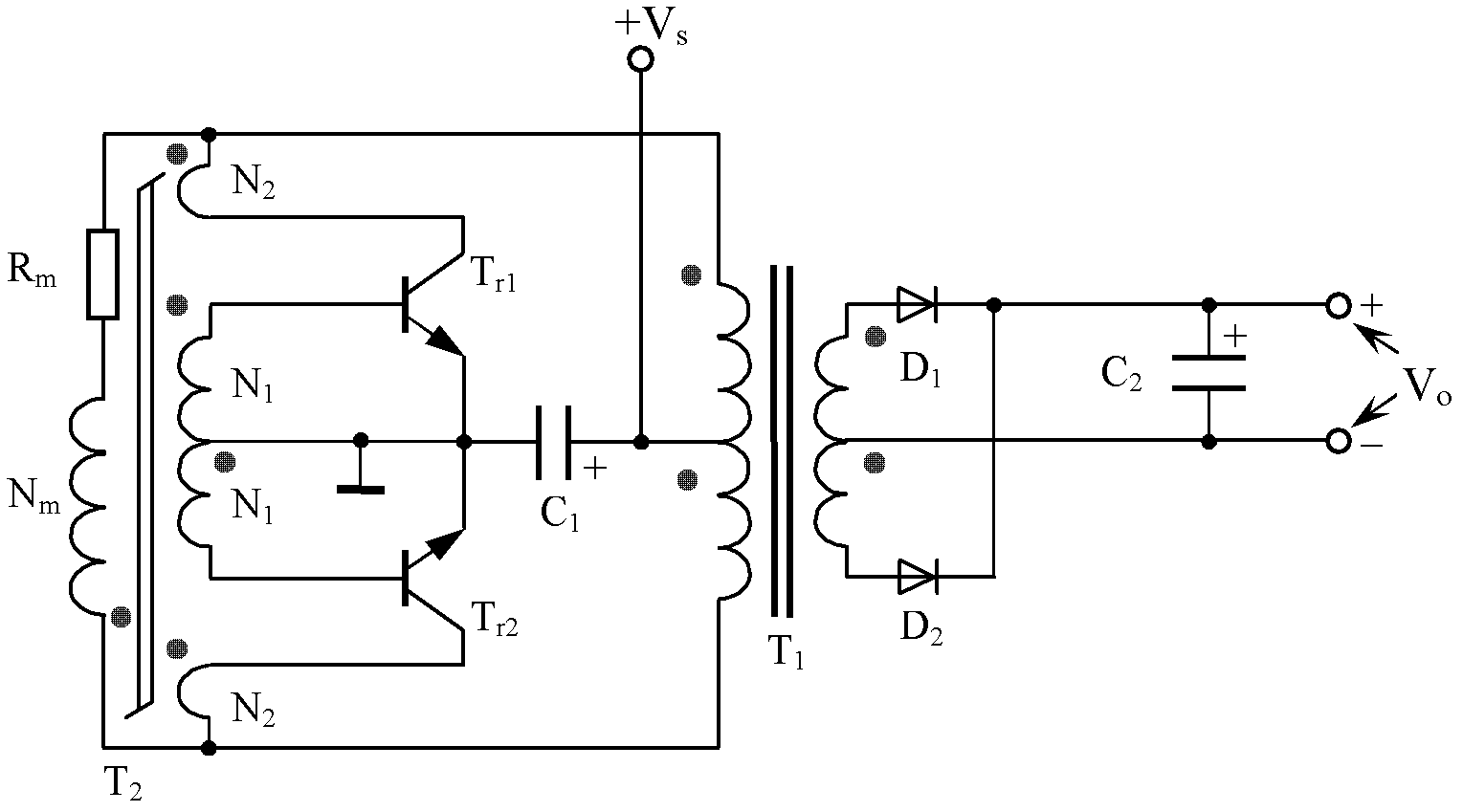
A self-excited push-pull converter
ActiveCN102291001AImprove self-protection performanceGood consistency of short circuit protection performanceApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationTransformerPush pull
The invention discloses a self-excitation push-pull type converter which comprises a Jensen circuit and is mainly characterized in that a two-terminal network with electric performance of accessing high frequency and stopping low frequency is formed between one end of magnetic saturation transformer primary winding in the Jensen circuit and one terminal of main transformer primary winding, namely the magnetic saturation transformer primary winding is connected in parallel with the main transformer primary winding through the two-terminal network. The self-excitation push-pull type converter disclosed by the invention has good self-protective capability, and can automatically recover normal work after disappearance of over-current and short circuit.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
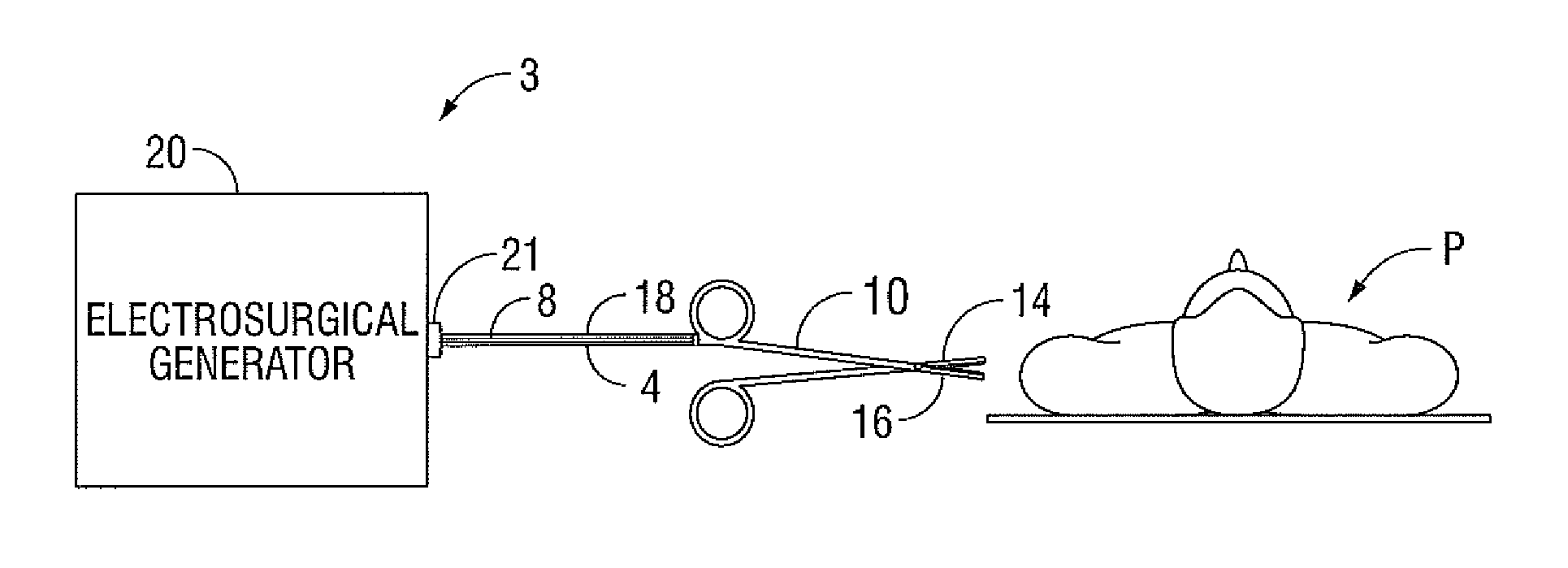
Current-Fed Push-Pull Converter with Passive Voltage Clamp
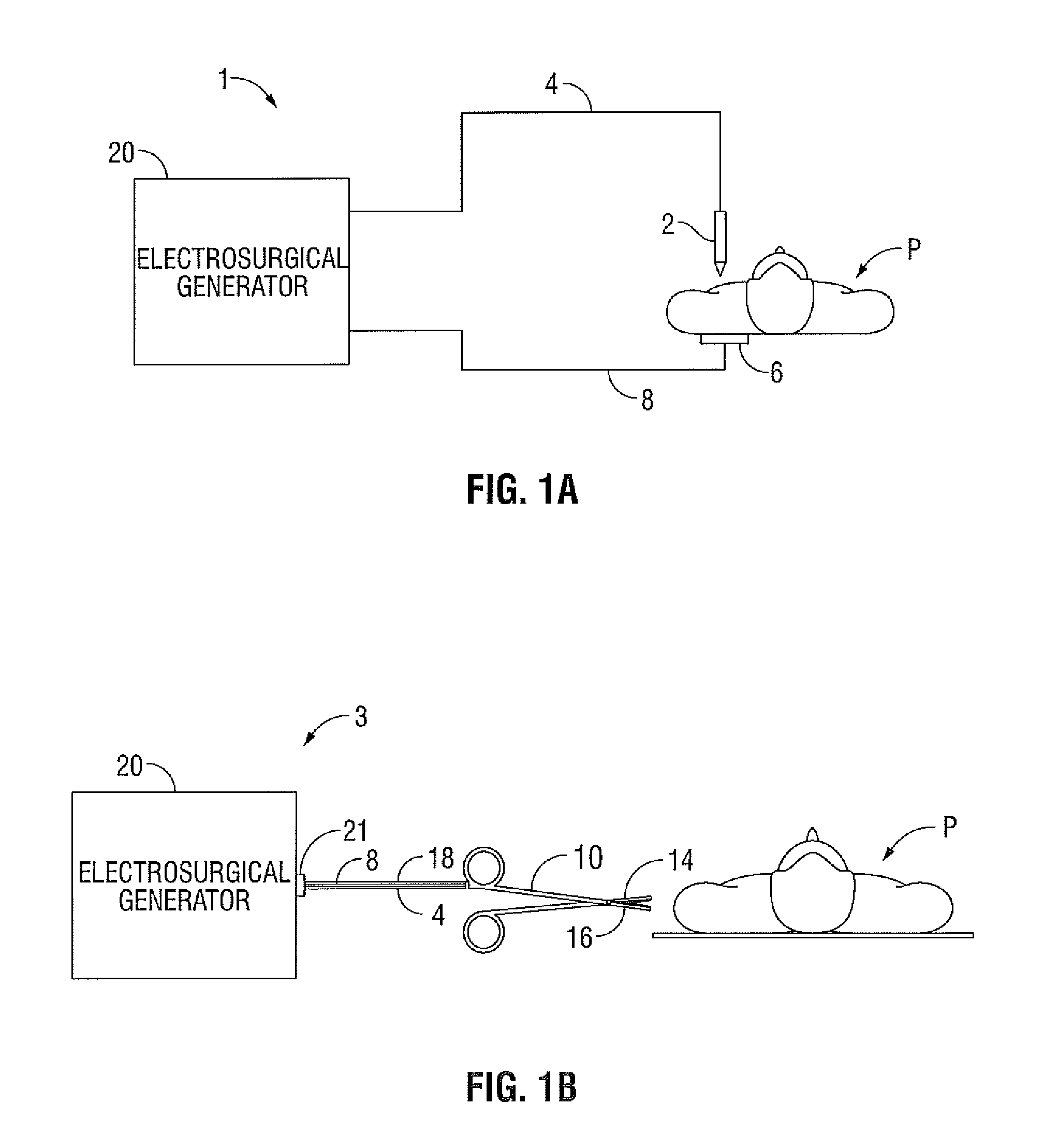
ActiveUS20110319881A1Controlling energy of instrumentSurgical instruments for heatingBuck converterInductor
An electrosurgical generator configured to output radio frequency (RF) energy having a current-source type behavior is provided. The generator has a buck converter having a voltage source, at least one switch and an inductor. The generator also has an RF stage configured to output the RF energy. A sensor circuit configured to measure at least one parameter of the RF energy and a controller configured to receive the measured parameter from the sensor circuit and control the output of the electrosurgical generator based on the measured parameter may also be provided in the electrosurgical generator.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Push-pull converter with voltage multiplying resonance capability
InactiveCN103078514AHigh gainReduce the turns ratioEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionCapacitancePush pull
The invention discloses a push-pull converter with voltage multiplying resonance capability. The push-pull converter comprises a primary side push-pull circuit, an isolation transformer, a secondary side voltage multiplying circuit and a secondary side resonance circuit. The push-pull converter has the advantages that on the basis of omitting the filter inductance, the secondary side utilizes the voltage multiplying structure, the gain of the converter is improved, the goal that the number of turns of the transformer is reduced to one half of the number of the original turns under the condition with the same voltage boosting ratio, and the size and the weight of the transformer are effectively reduced; in addition, a voltage multiplying capacitor also participates in the resonance of the secondary side equivalent leakage inductance of the transformer, the zero-current shutoff of a secondary side rectifier diode is realized, the reverse recovery problem of the rectifier diode is solved, the loss is reduced, and the integral efficiency of the converter is improved; and meanwhile, the primary side adopts the minimum element number, one capacitor and one group of transformer windings are reduced by the secondary side, miniaturization and light weight of the converter are realized, and in addition, the cost of the converter is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A self-excited push-pull converter
ActiveCN102299616AEasy to makeSimple production processAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionSelf excitedPush pull
The invention discloses a self-excited push-pull type converter which comprises a Royer circuit. An inductor connects a power supply terminal of the Royer circuit with a center tap of a transformer primary winding in the Royer circuit. An inductance value of the inductor is less than one-tenth of an inductance value of a primary winding in the transformer. The center tap of the primary winding isa connection point of two primary windings of the transformer. The self-excited push-pull type converter of the present invention has the characteristics of high consistency, easy debugging, low technology requirement, and good short circuit protection performance.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
Power switch device pulse transformer isolation driving circuit
InactiveCN103414354AImprove noise immunityImprove reliabilityConversion without intermediate conversion to dcBuck converterFull bridge converter
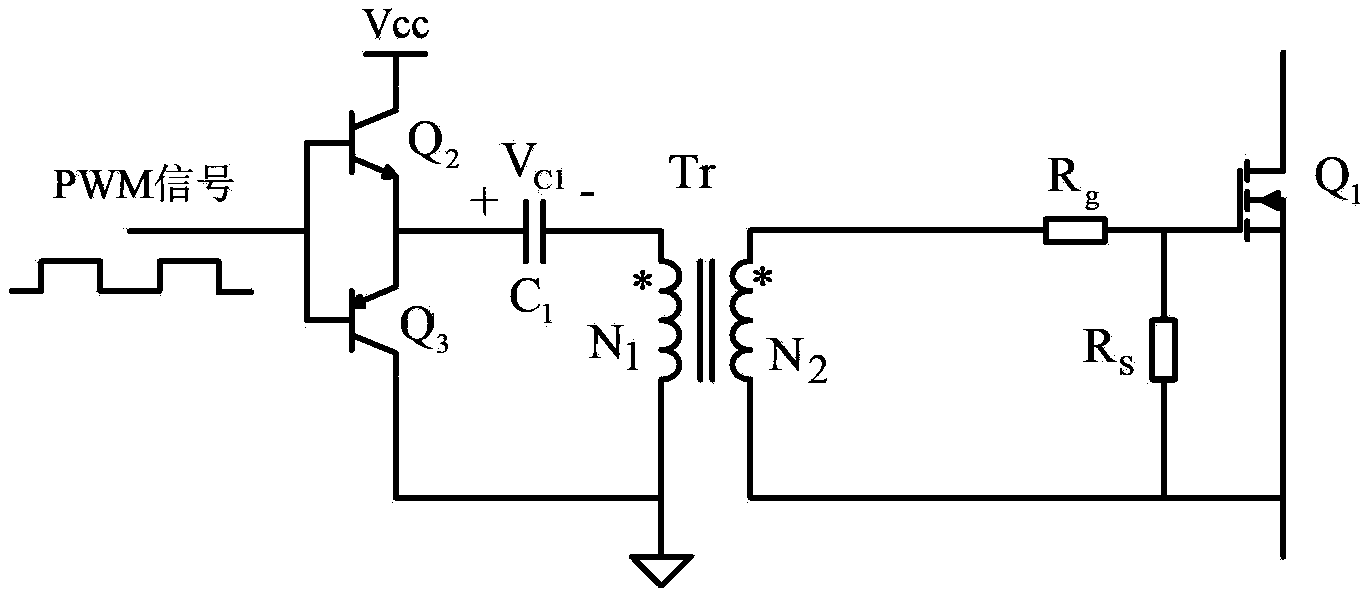
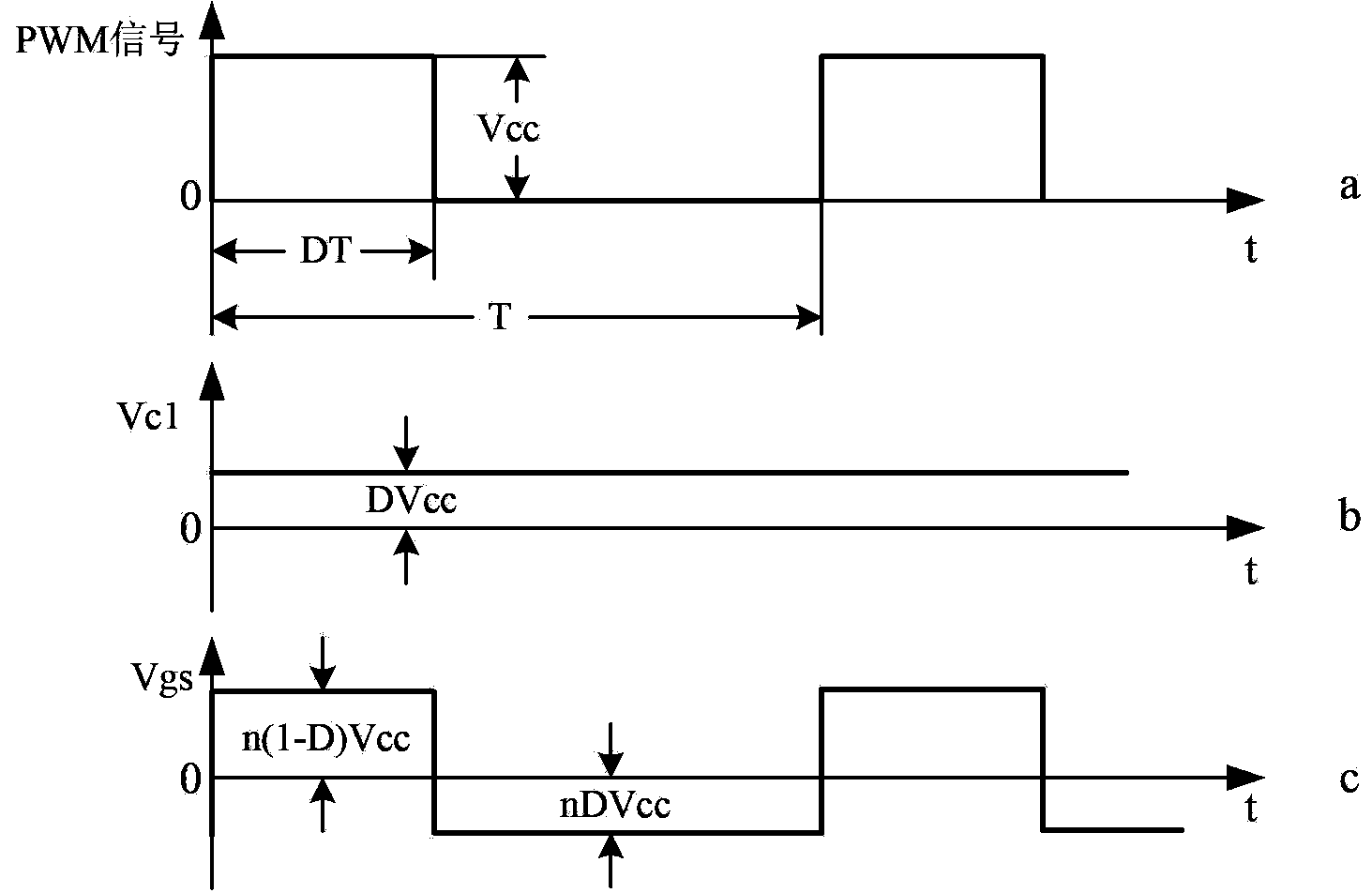
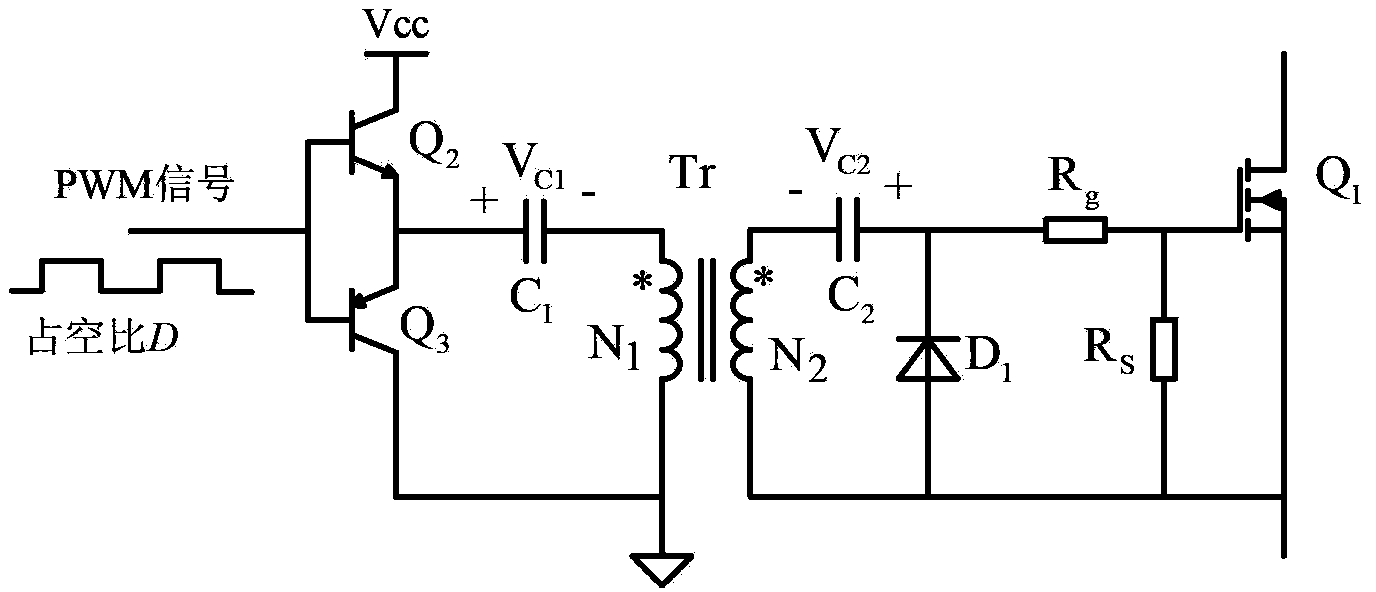
The invention discloses a power switch device pulse transformer isolation driving circuit. The power switch device pulse transformer isolation driving circuit comprises a primary-side circuit, a pulse transformer Tr and a secondary-side circuit, wherein the primary-side circuit comprises an NPN transistor Q2, a PNP transistor Q3 and a blocking capacitor C1, and the secondary-side circuit comprises a power switch device Q1, a driving resistor Rg, a gate discharge resistor Rs, a diode D1, a compensation capacitor C2, a voltage-regulator tube Z1 and a negative pressure holding capacitor C3. The power switch device pulse transformer isolation driving circuit of the invention can be applied to all switching converters such as a boost converter, a buck converter, a forward converter, a flyback converter, a half-bridge switching converter, a half-bridge converter, a full-bridge converter and a push-pull converter, and can effectively improve the reliability of the switching converters.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Push-pull converter and method for power supply device and uninterrupted power supply system
InactiveCN1592061AImprove efficiencyReduce switching lossesEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectricityEngineering
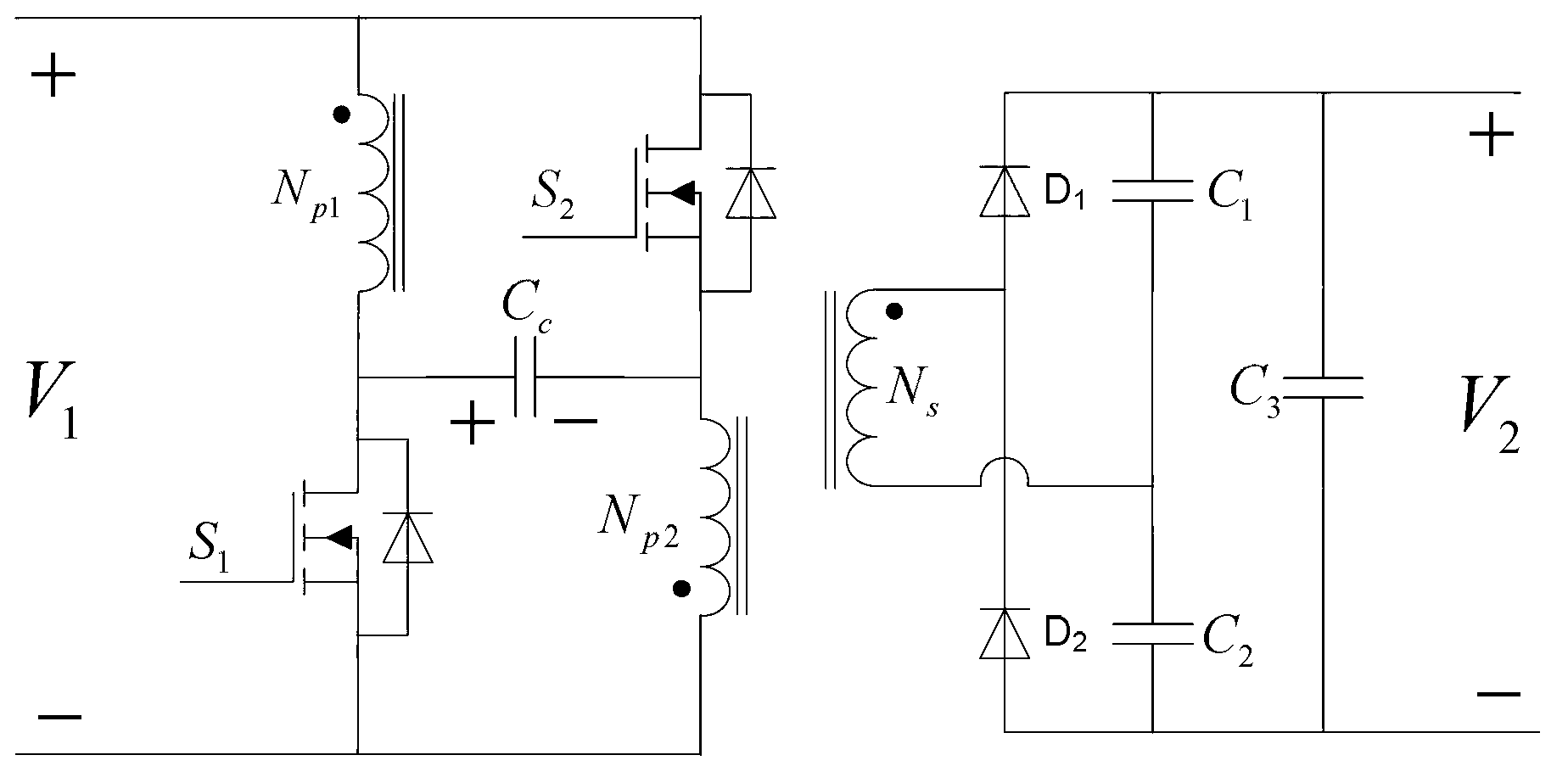
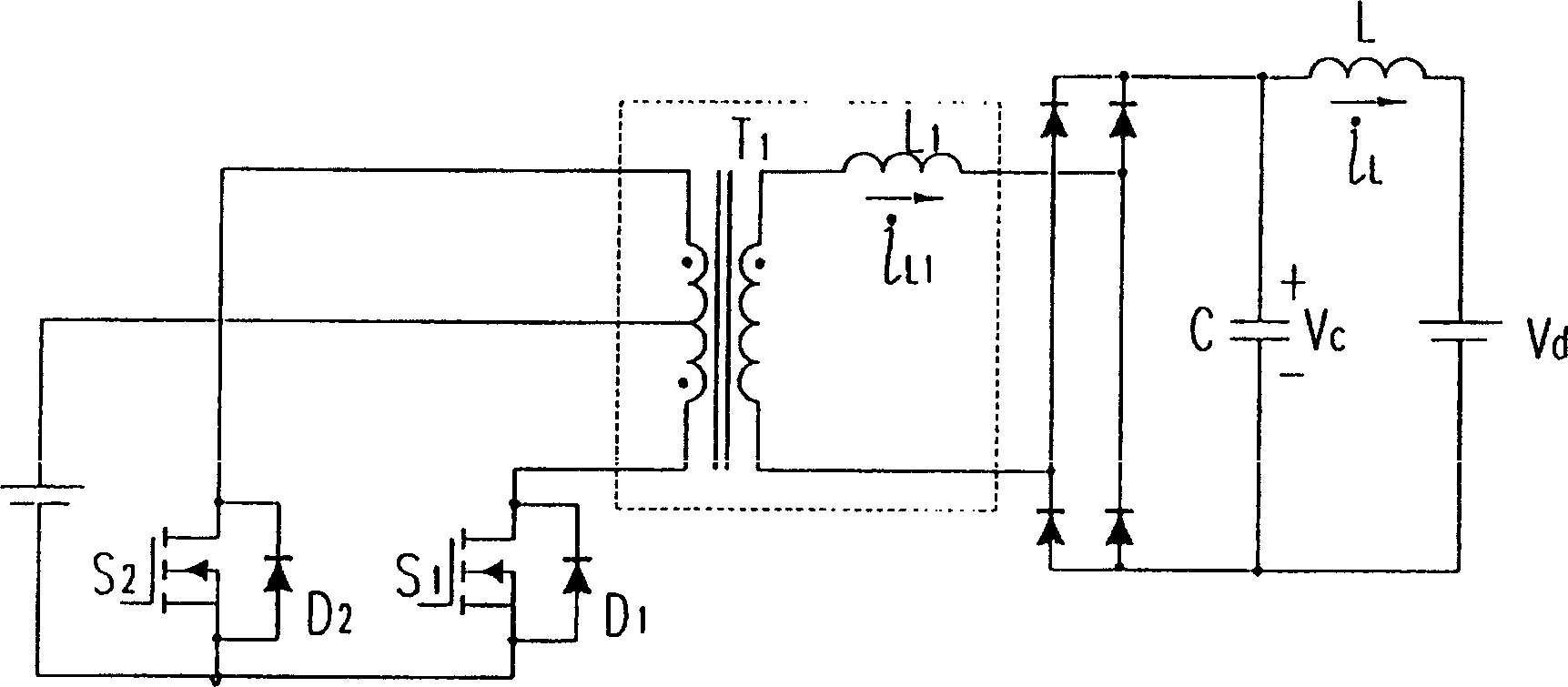
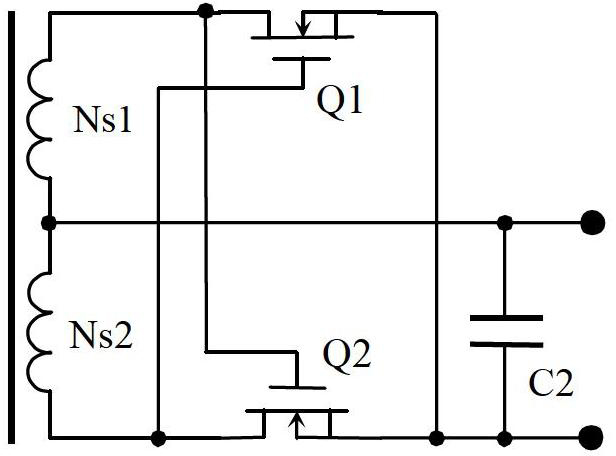
This invention provides a zero-voltage switch push-pull converter and a method for continuous supplying power system of a power source supplier, in which, the converter includes a transformer containing a primary winding with a central tap and a secondary winding, an electric energy storage supply device, one end of which is connected with the central tap of the primary winding, the other end to the earth, a first master switch element, the first end of which is linked to the first end of the primary winding, and the second to the earth, a second master switch element, its first end to the earth, the second to a second end of the primary winding and a commutating circuit connected to the second winding to convert AC to DC provided by it to let the primary circuit element switch at zero voltage.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Primary side ZVS push-pull converter having relatively less losses
ActiveUS20050024901A1Reduce switching lossesImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionConductor CoilCenter tap
The push-pull converter for zero-voltage switching of the switches on the primary side of the transformer to have a relatively lower loss is proposed. Which includes: a transformer having a primary winding with a center tap and a secondary winding, an electrical energy storage device having a first terminal coupled to the center tap of the primary winding and a second terminal coupled to a ground, a first switch having a first terminal coupled to a first terminal of the primary winding and a second terminal coupled to the ground, a second switch having a first terminal coupled to the ground and a second terminal coupled to a second terminal of the primary winding, and a rectifier circuit coupled to the secondary winding for transforming an AC output of the secondary winding to a DC output.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
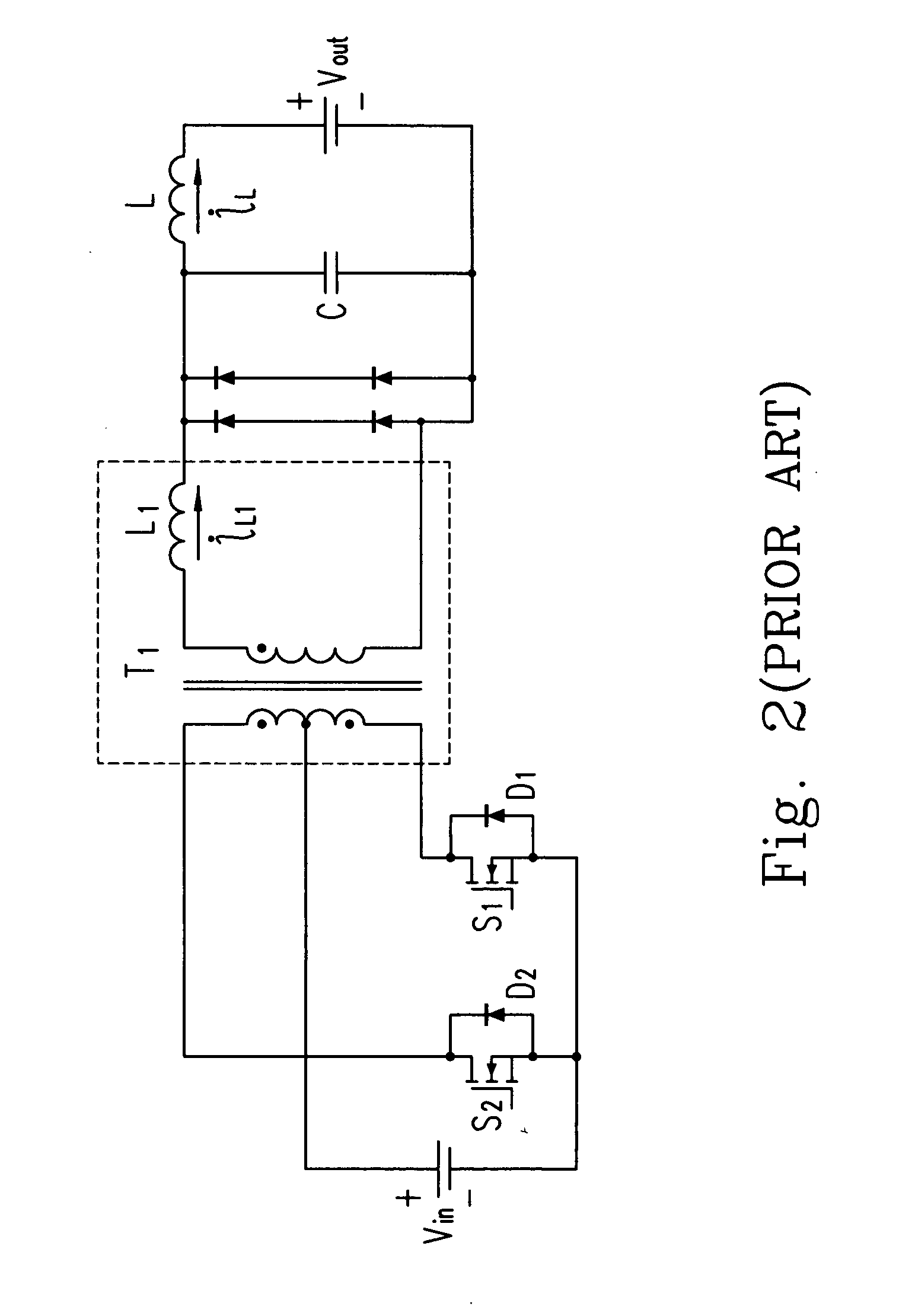
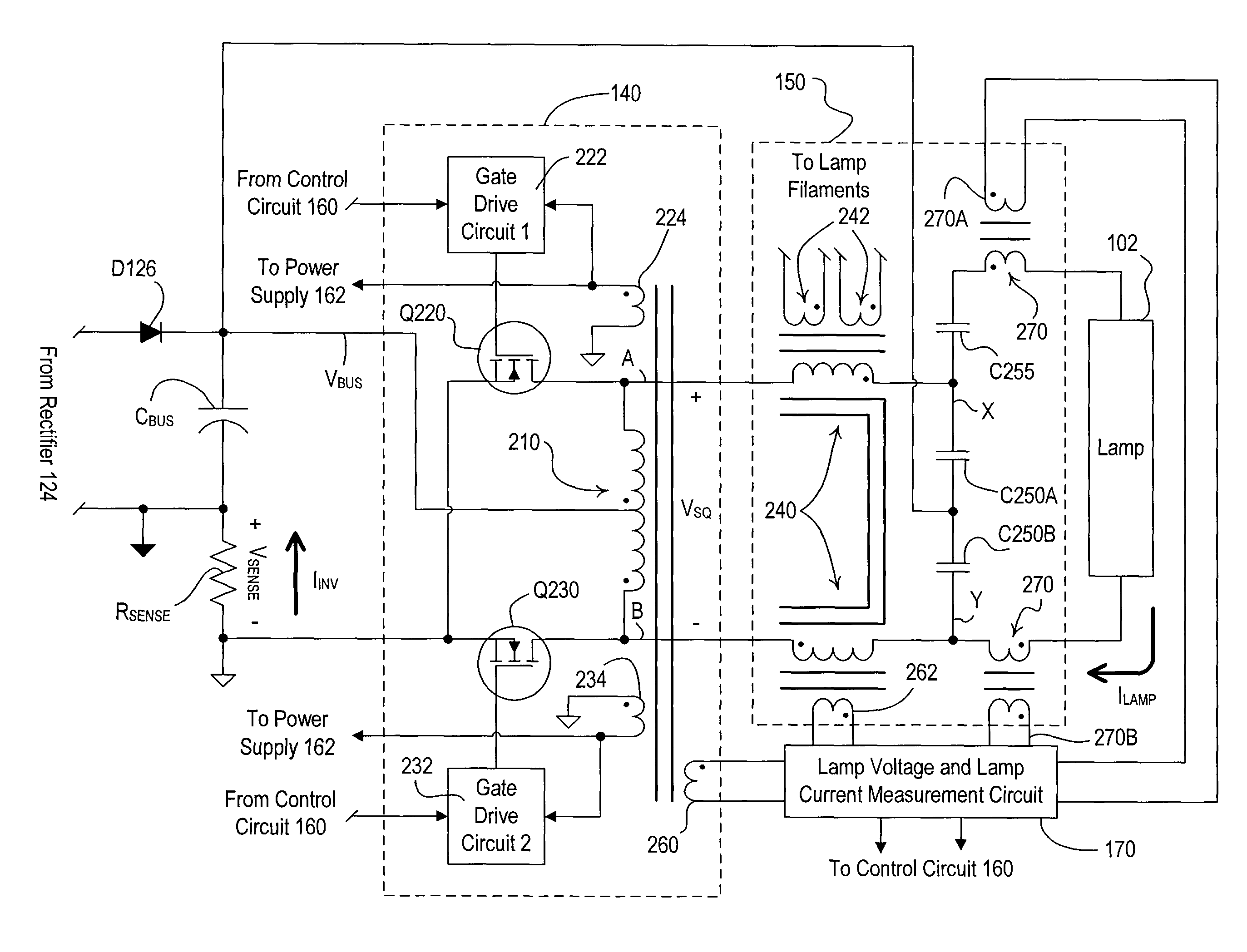
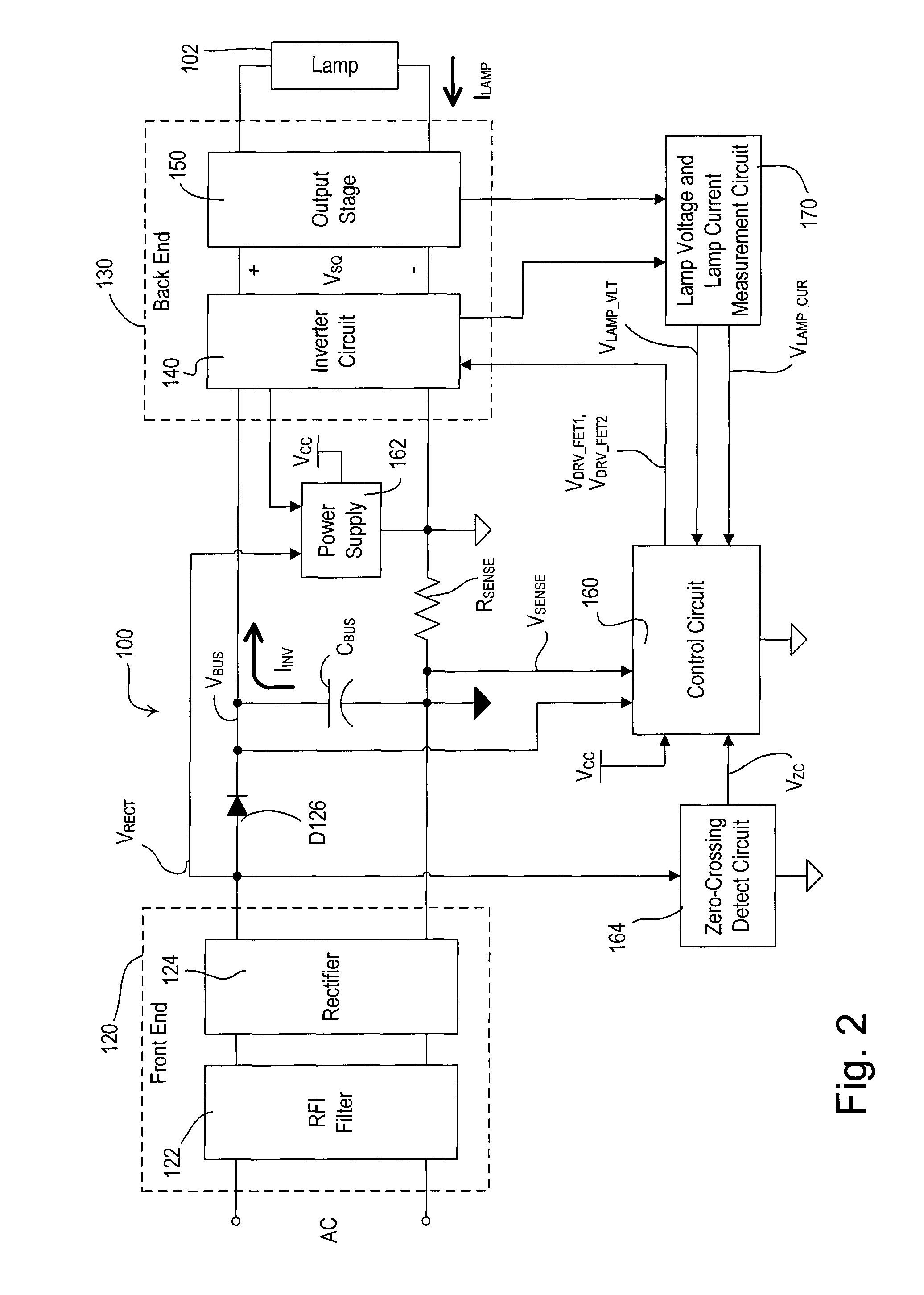
Electronic ballast having a partially self-oscillating inverter circuit
An electronic ballast for driving a gas discharge lamp comprises an inverter circuit that operates in a partially self-oscillating manner. The inverter circuit comprises a push-pull converter having a main transformer having a primary winding for producing a high-frequency AC voltage, semiconductor switches electrically coupled to the primary winding of the main transformer for conducting current through the primary winding on an alternate basis, and gate drive circuits for controlling the semiconductor switches on a cycle-by-cycle basis. The drive circuits control (e.g., turn on) the semiconductor switches in response to first control signals derived from the main transformer, and control (e.g., turn off) the semiconductor switches in response to second control signals received from a control circuit. The control circuit controls the semiconductor switches in response to a peak value of an integral of an inverter current flowing through the inverter circuit.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
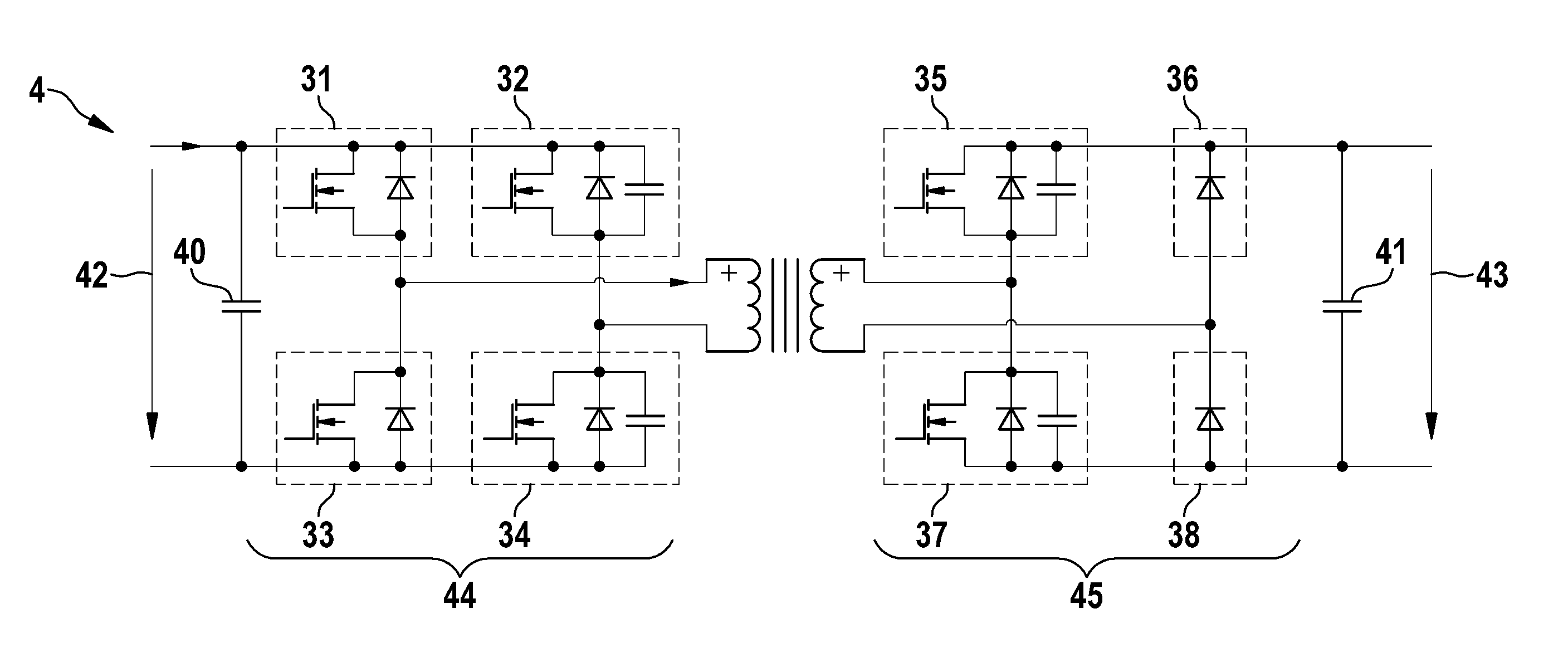
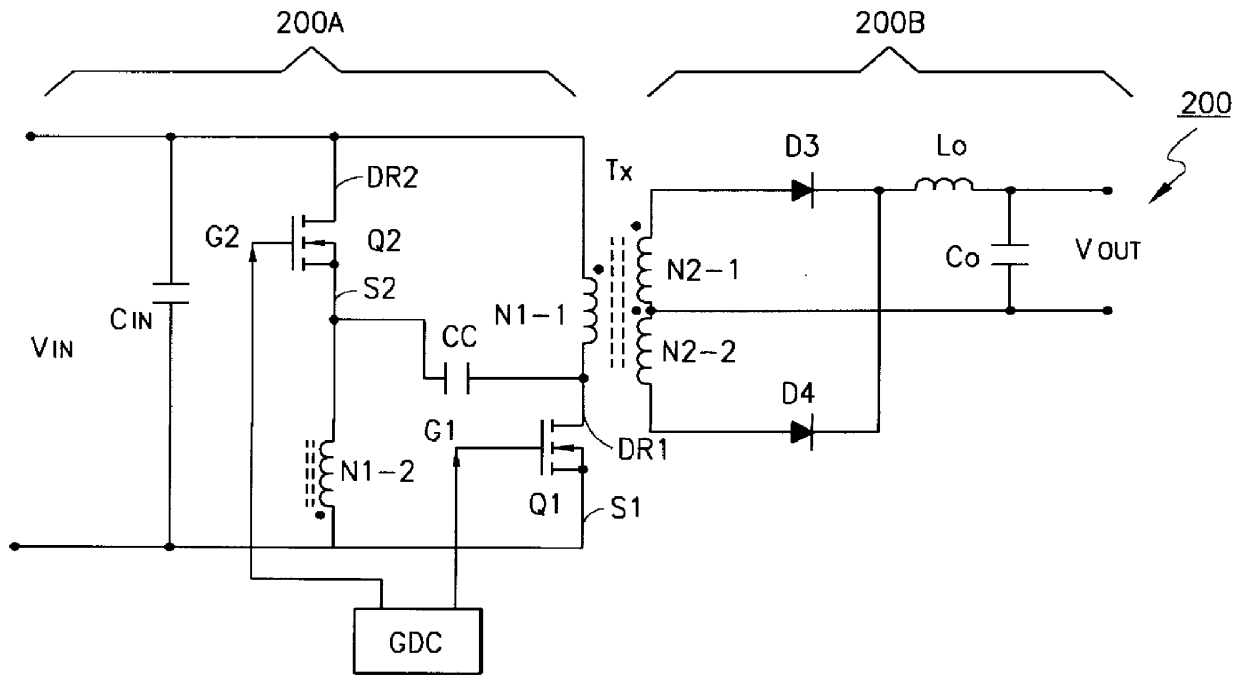
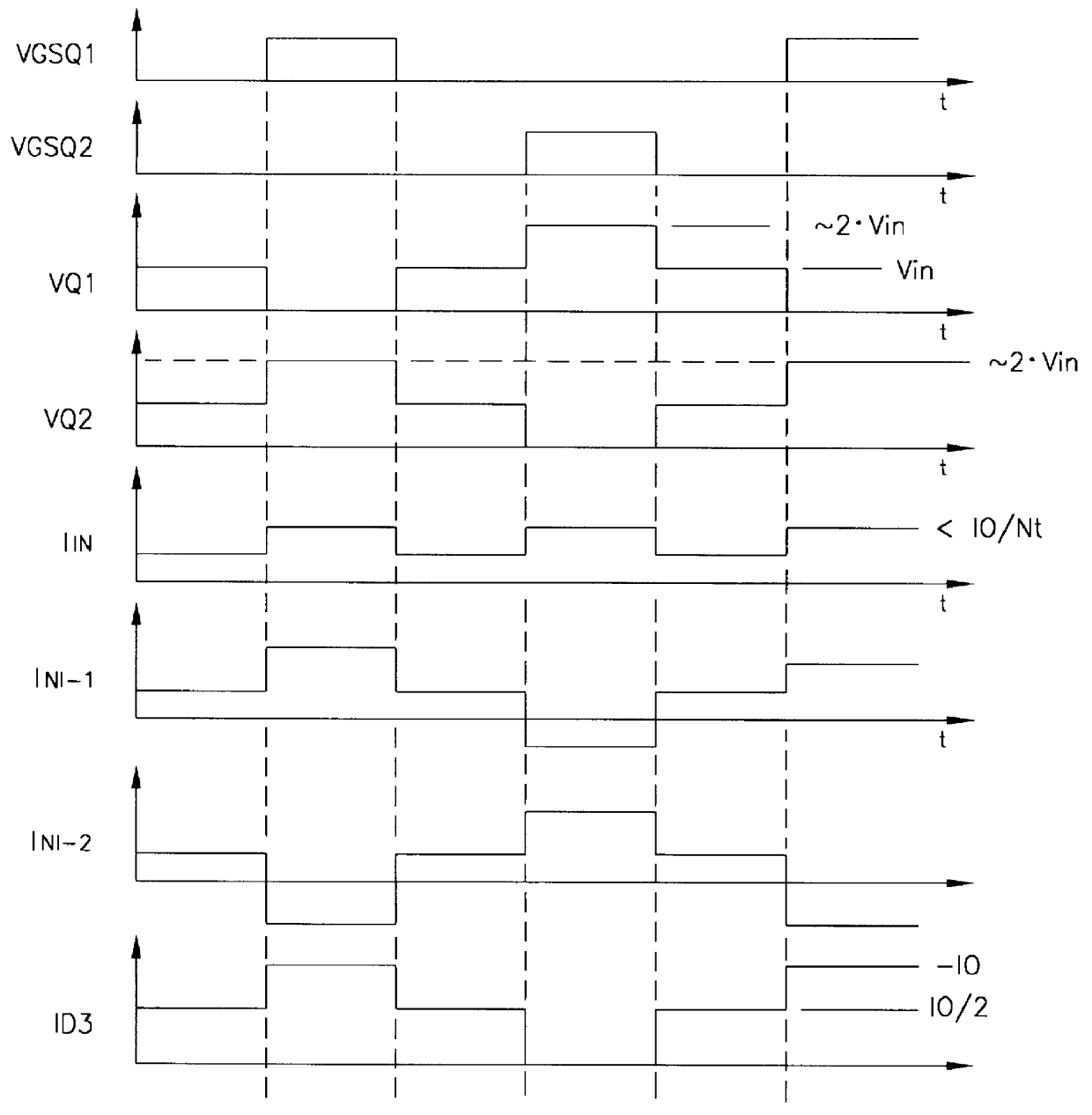
Push-pull converter and modulation method for controlling a push-pull converter
ActiveUS20130314950A1Reduce in quantityEasy to controlEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionFull bridgeSecondary side
The invention relates to a push-pull converter (4) comprising a primary-side input converter circuit (44) with a plurality of primary-side switching devices (31, 32, 33, 34) in a full-bridge circuit, said input converter circuit being designed to convert an input DC voltage (42) into a first AC voltage, and comprising a transformer (39) with a primary-side winding and a ON secondary-side winding, said transformer being designed to receive the first AC voltage on the primary-side winding and to generate a second AC voltage on the secondary-side winding. The push-pull converter also comprises a secondary-side output converter circuit (45) which is designed to convert the second AC voltage into an output DC voltage (43), comprising a first semi-bridge circuit, said semi-bridge circuit comprising a first secondary-side switching device (35), a second secondary-side switching device (37), and a first center to that is connected to a first connection of the secondary-side winding. The secondary-side output converter circuit also comprises a second semi-bridge circuit which comprises a first secondary-side diode (36), a second secondary-side diode (38), and a second center tap which is connected to a second connection of the secondary-side winding, said second semi-bridge circuit not comprising a switchable component.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
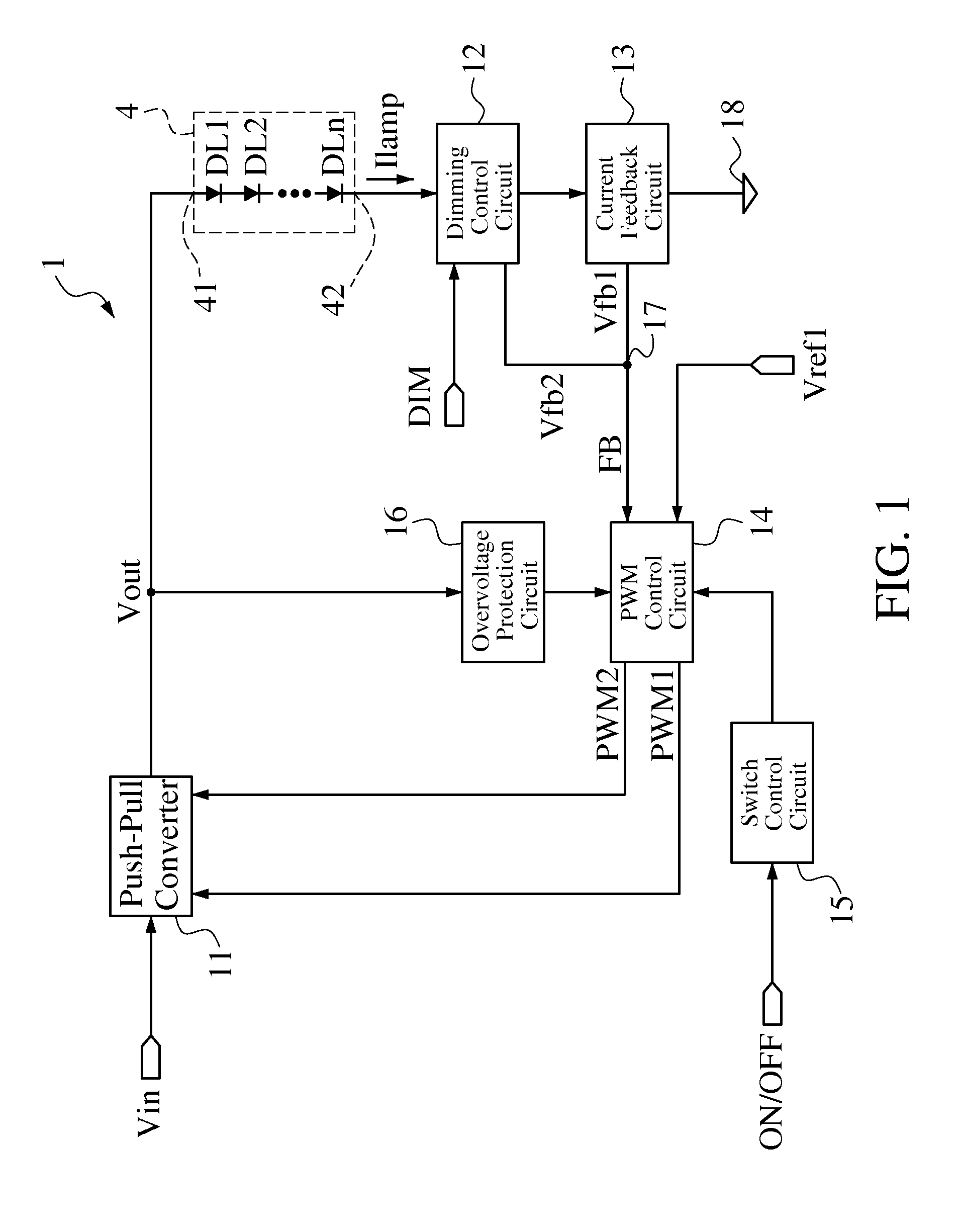
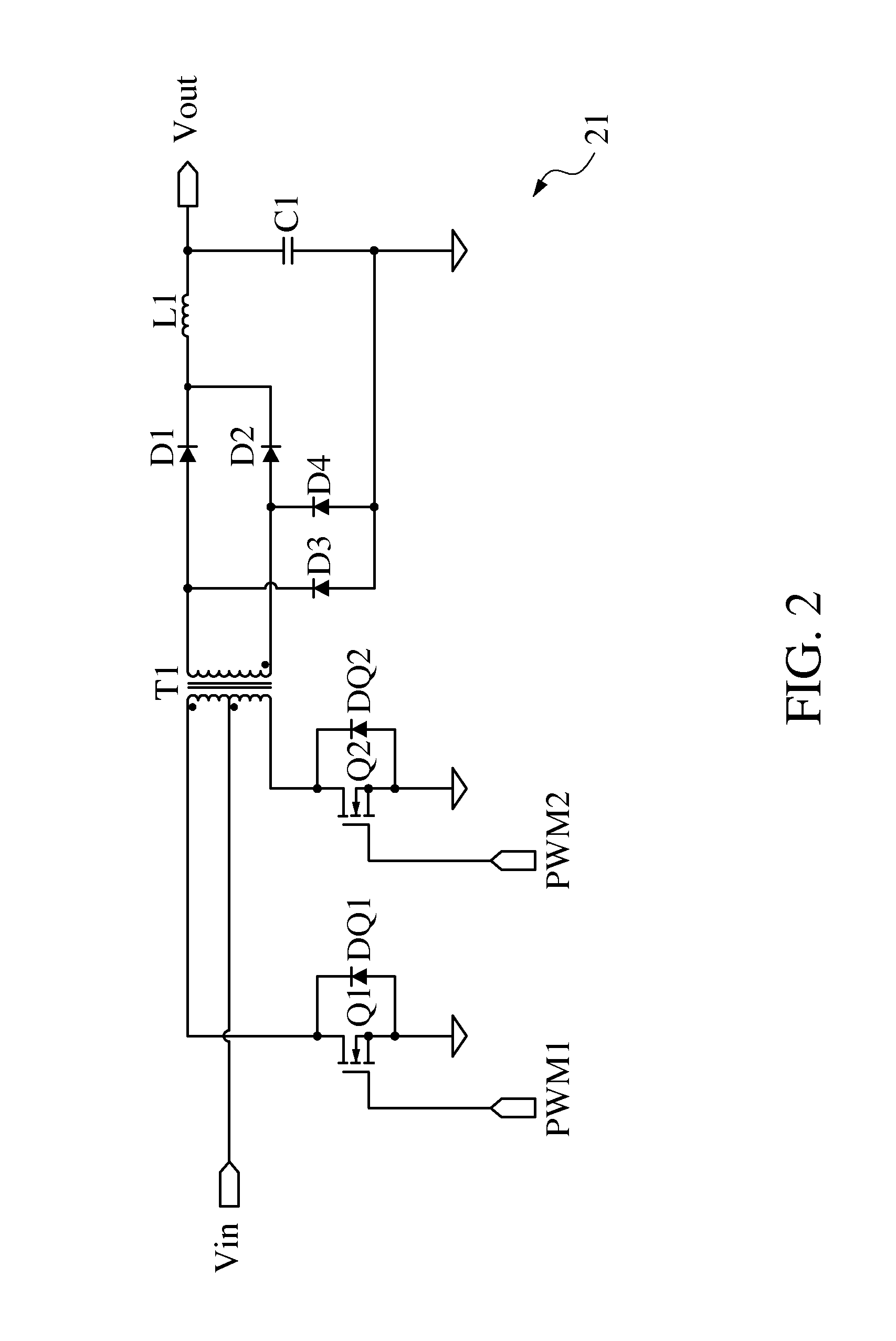
Driving circuit for single-string LED lamp
InactiveUS20120181950A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesGeneral purposeDriver circuit
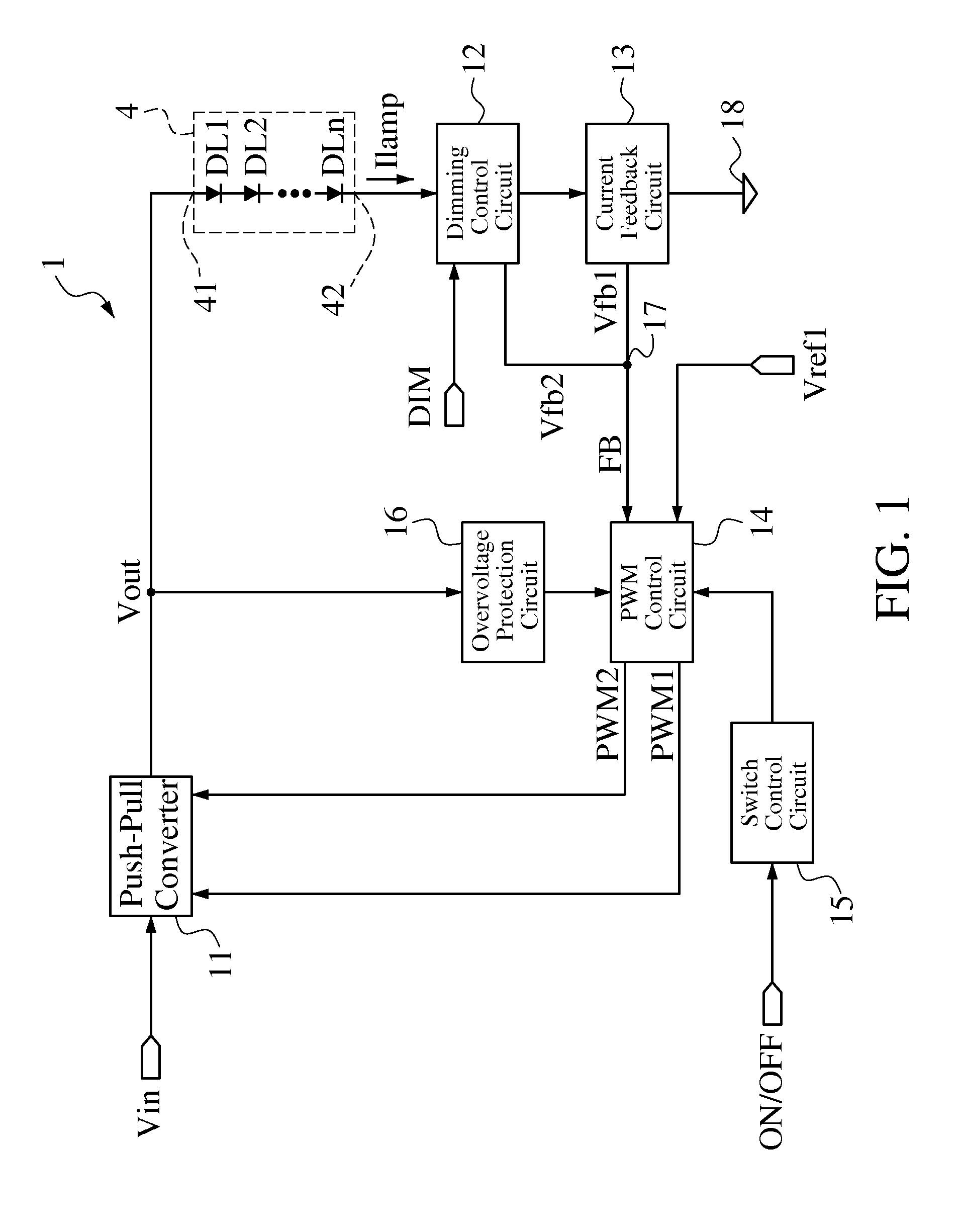
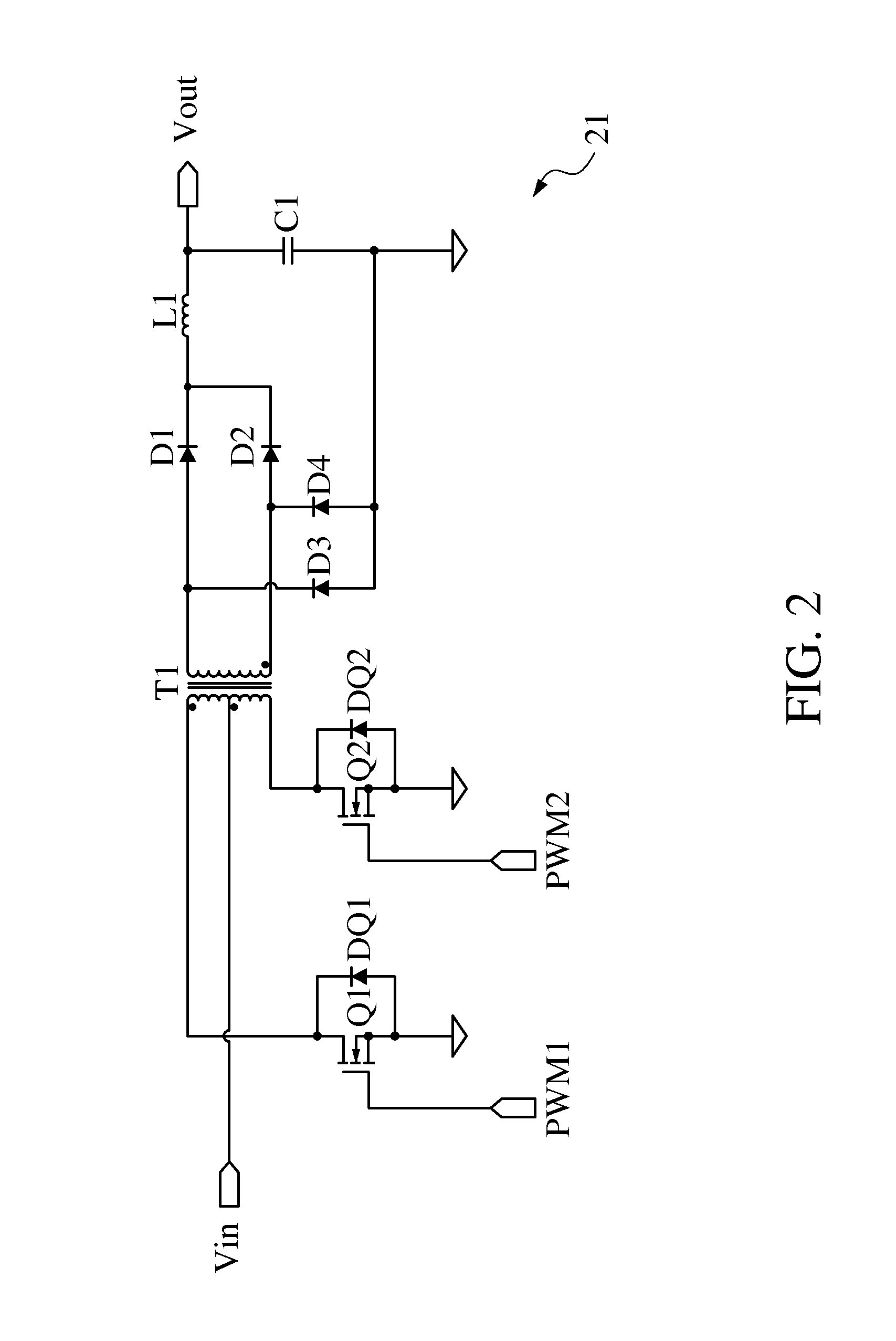
A driving circuit for a single-string light-emitting diode (LED) lamp includes a push-pull converter. The push-pull converter converts an input low DC voltage (such as 12-19V) to a high DC voltage (such as above 200V) to supply power to the single-string LED lamp. The driving circuit controls a lamp current flowing through the single-string LED lamp by means of constant current and adjusts brightness of the single-string LED lamp by means of pulse-width modulation (PWM) dimming. In addition, the single-string LED lamp provides the standardization design for connectors of the driving circuit used to connect to the single-string LED lamp so that the driving circuit has better common-use characteristic. Moreover, the driving circuit does not need a current balance circuit and only needs a cheaper and general-purpose integrated circuit to control the push-pull converter to reduce design cost of the driving circuit.
Owner:TPV ELECTRONICS (FUJIAN) CO LTD
Electronic ballast having a partially self-oscillating inverter circuit
ActiveUS20100060179A1Electrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementControl signalTransformer
An electronic ballast for driving a gas discharge lamp comprises an inverter circuit that operates in a partially self-oscillating manner. The inverter circuit comprises a push-pull converter having a main transformer having a primary winding for producing a high-frequency AC voltage, semiconductor switches electrically coupled to the primary winding of the main transformer for conducting current through the primary winding on an alternate basis, and gate drive circuits for controlling the semiconductor switches on a cycle-by-cycle basis. The drive circuits control (e.g., turn on) the semiconductor switches in response to first control signals derived from the main transformer, and control (e.g., turn off) the semiconductor switches in response to second control signals received from a control circuit. The control circuit controls the semiconductor switches in response to a peak value of an integral of an inverter current flowing through the inverter circuit.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Push-pull power converter circuit
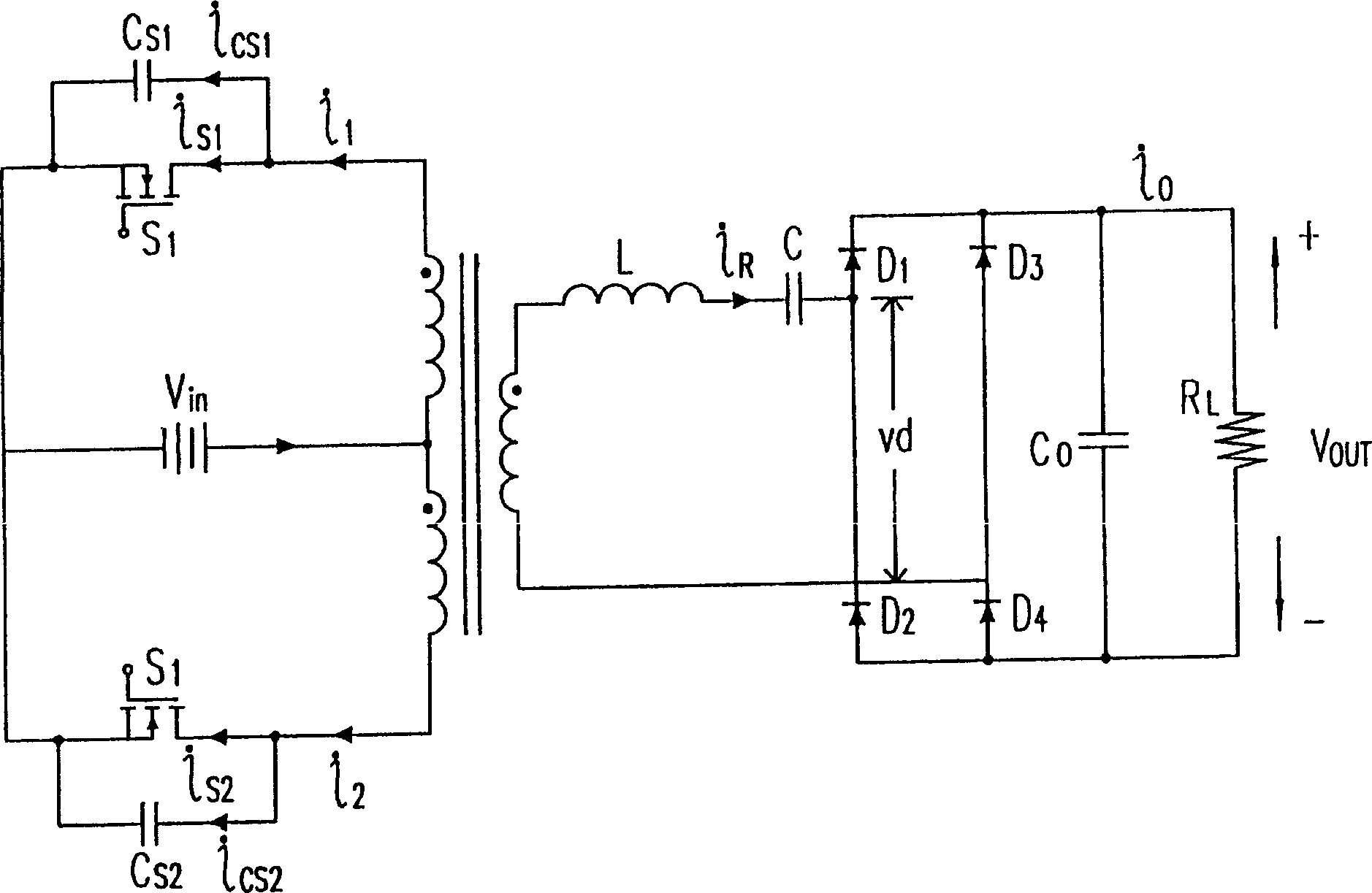
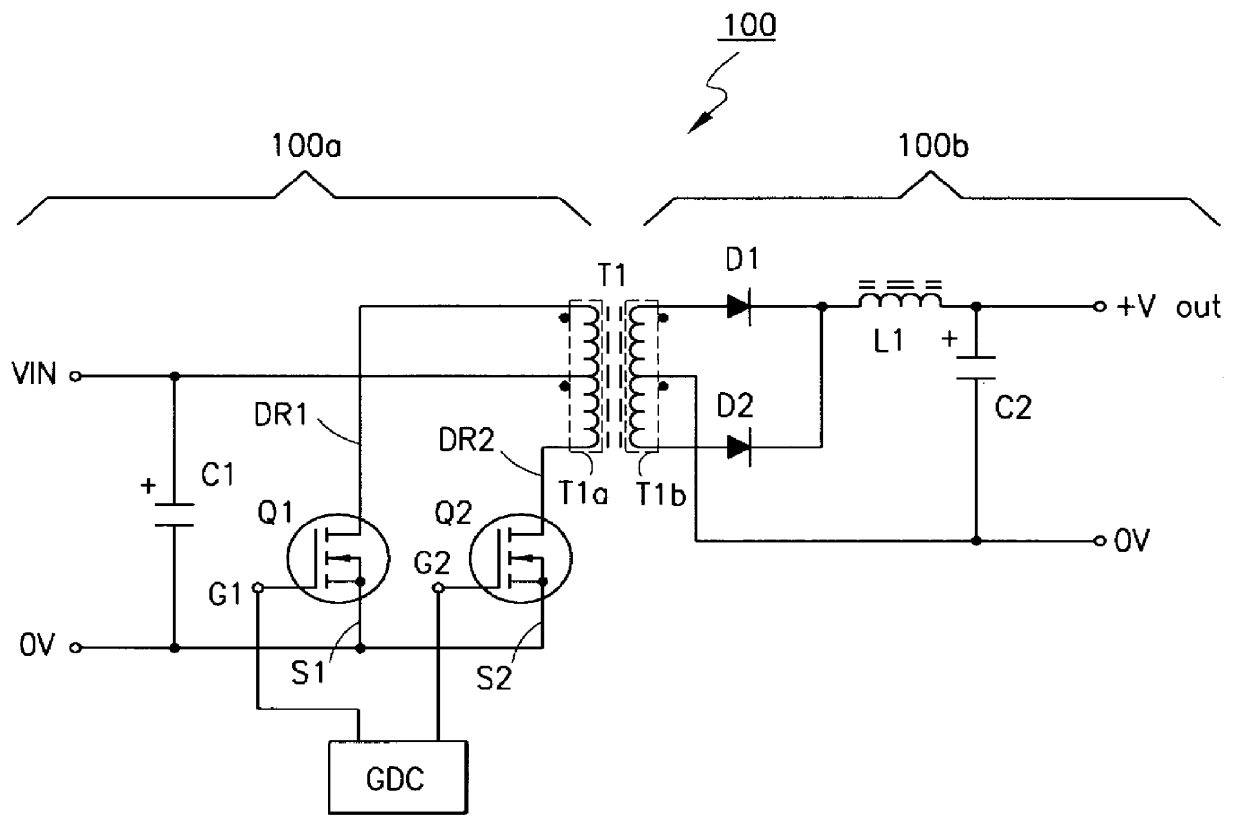
A push-pull converter for converting an input voltage to a selectable output voltage is disclosed. The push-pull converter includes a pair of primary switches and a pair of primary windings of a transformer. The voltage stress across the primary switches is regulated by means of a clamp capacitor. The clamp capacitor clamps the voltage of the primary switches during the reset of the primary windings of the transformer. An alternate embodiment is also disclosed in which the voltage stress across the primary switches is regulated by means of two clamp capacitors. The clamp capacitor clamps the voltage of the primary switches during the reset of the primary windings of the transformer. The clamp capacitors extend the transformer reset period to include the lagging dead time for the corresponding switches, as well as the complementary powering stage. Current in the output section during the dead times is permitted by means of an additional diode, therein.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Energy storage system and control method thereof
InactiveCN101944745AIncrease profitLow total harmonic contentAc network load balancingEngineeringGalvanic isolation
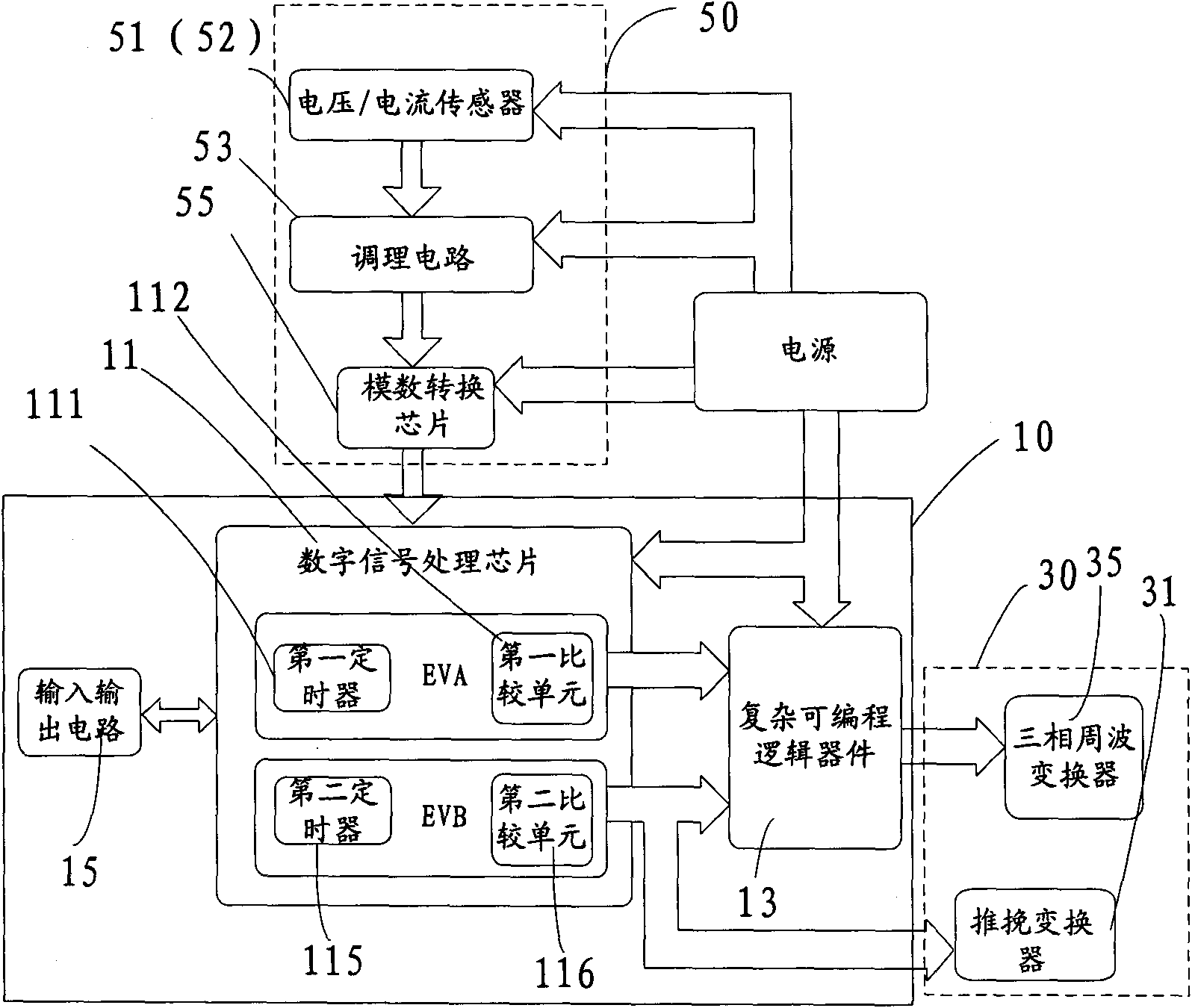
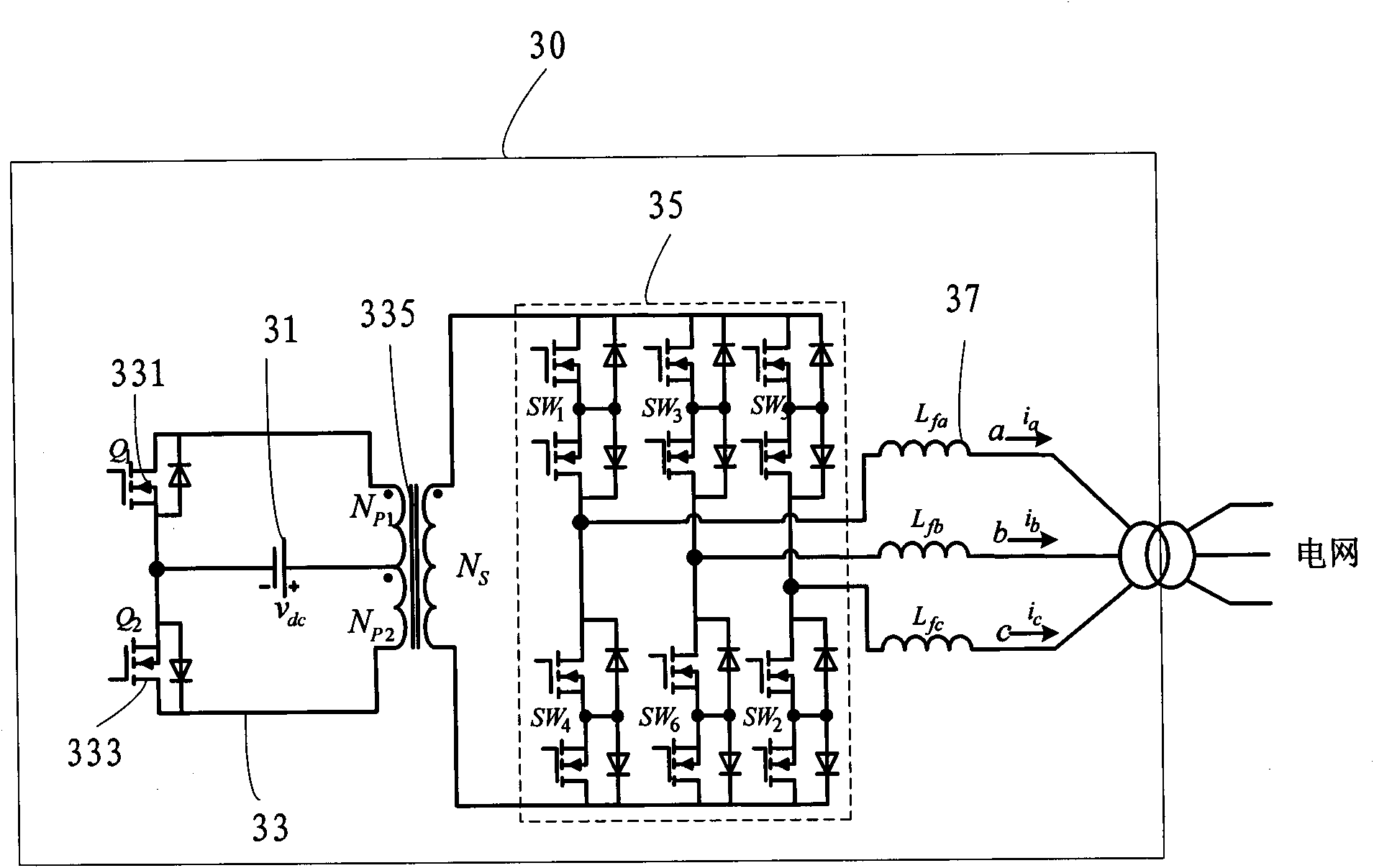
The invention provides an energy storage system which comprises a controller, a main circuit, a push-pull converter, a cycloconverter, a filter inductor and a sampling circuit. The controller is used for controlling the generation of an SVPWM (Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation) signal and a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal to obtain a discrete SVPWM signal, the main circuit comprises an energy storage device for storing and releasing electric energy, the push-pull converter comprises a high-frequency transformer and is boosted by adopting the high-frequency transformer to electrically isolate the input from the output of the energy storage system, the cycloconverter is used for converting a high-frequency alternating voltage into a power frequency alternating voltage, the filter inductor is used for filtering a grid current, and the sampling circuit is used for acquiring a voltage and a current of an external circuit. The energy storage system can generate discrete pulse-type SVPWM and has the advantages of higher utilization rate of the bus voltage, low total harmonic content and wide scope of application. The invention also provides a control method of the energy storage system.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Grid tied inverter, system and method
InactiveUS20120250359A1Dc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsGrid-tie inverterTransformer
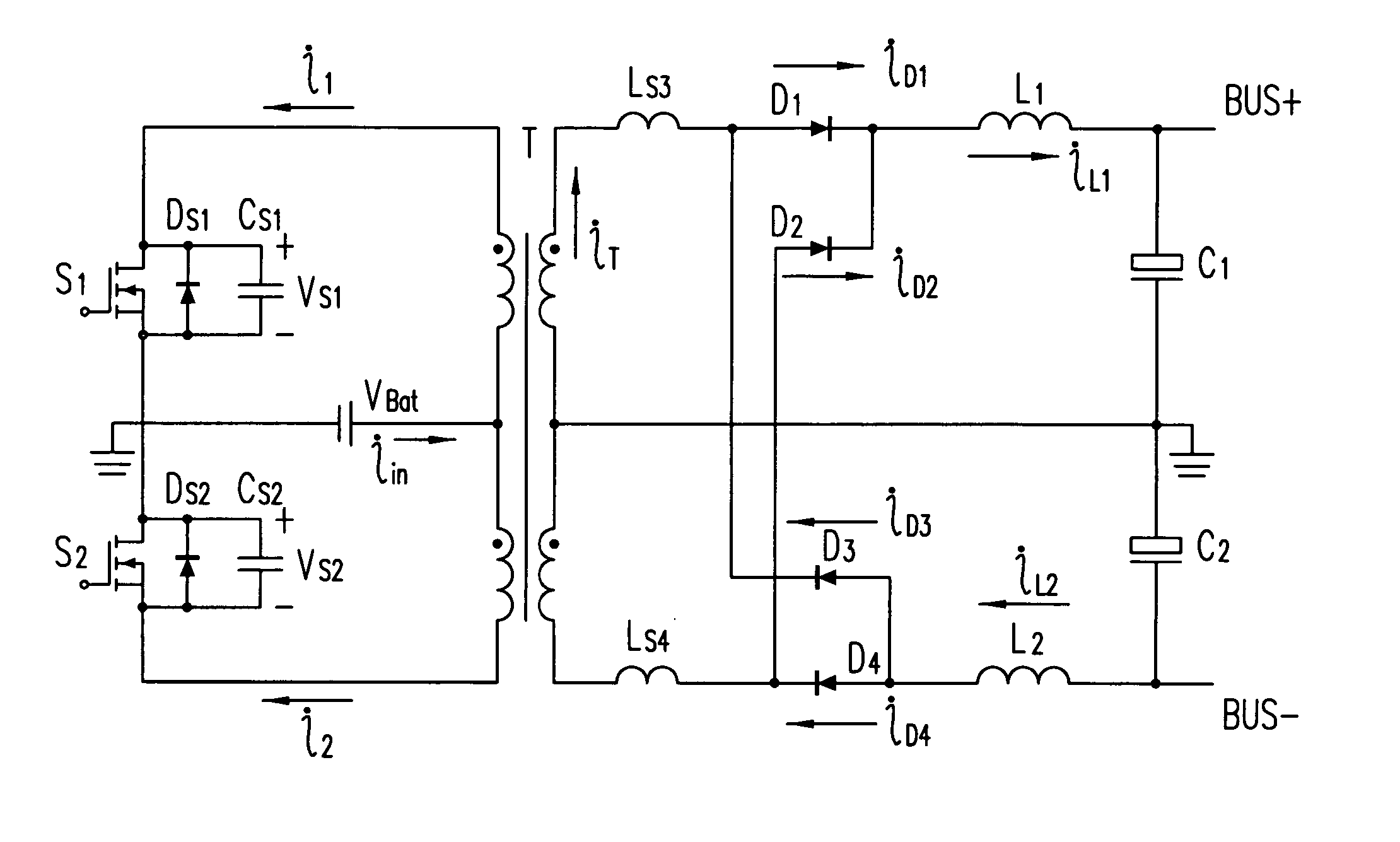
A grid tied inverter connectable to an electricity grid, the grid tied inverter comprising a DC to DC current fed push-pull converter operable to generate a current waveform from a DC voltage source, the current waveform being substantially synchronised to the electricity grid, the push-pull converter comprising a transformer having a first side connectable to a battery and a second side connectable to the grid, wherein each of the two primary sides is connected to ground via a switching transistor; andrespective voltage clamps are connected between the respective primary side of the transformer and the respective switching transistor, the voltage clamp commutating the current from the respective primary side of the transformer when the switching transistor is turned off.
Owner:SONY CORP
Control method of excited push-pull converter with zero-voltage switching and excited push-pull converter
ActiveCN103944402AReduce volumeLow costEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionParasitic capacitancePush–pull converter
The invention discloses a control method of an excited push-pull converter with zero-voltage switching and the excited push-pull converter. According to the magnitude of exciting current of a coupling transformer in the excited push-pull converter, the dead time of two main power MOS tube driving signals output by a controller is adjusted, in the dead time, the energy of the exciting current of the coupling transformer is used for completely releasing charges stored in a parasitic capacitor of one main power MOS tube, needing to be switched from the switch-off state to the switch-on state, in the excited push-pull converter, when diodes which are arranged in the main power MOS tube and are connected in an anti-parallel mode are switched on, the controller outputs a driving signal to control the main power MOS tube to be switched on, and zero-voltage switching is realized. The conditions for realizing zero-voltage switching of the primary MOS tube are irrelevant to the range of an input voltage and an output load, and it can be ensured that zero-voltage switching of a circuit is realized within the full-load range.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
Transforming device of push-pull circuit type
InactiveCN1479440AInhibition biasBias phenomenon preventionAc-dc conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionRectifier diodesPush pull
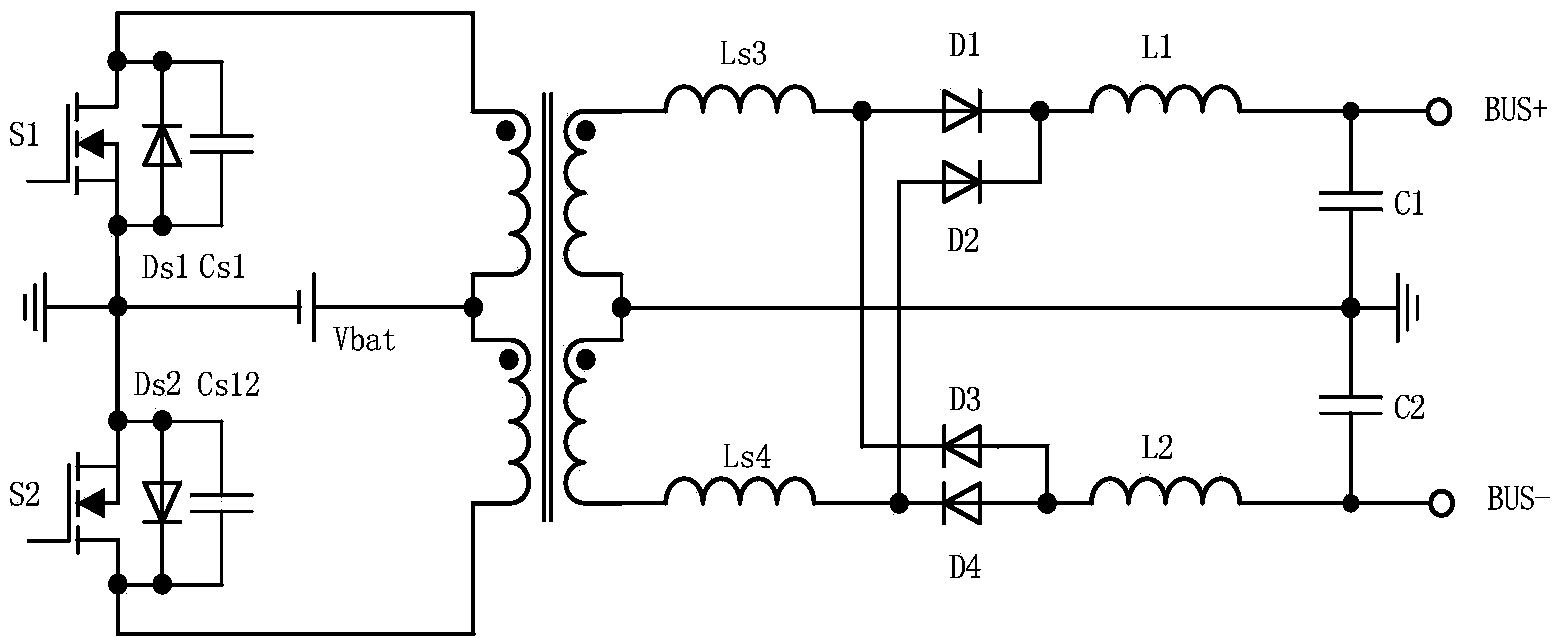
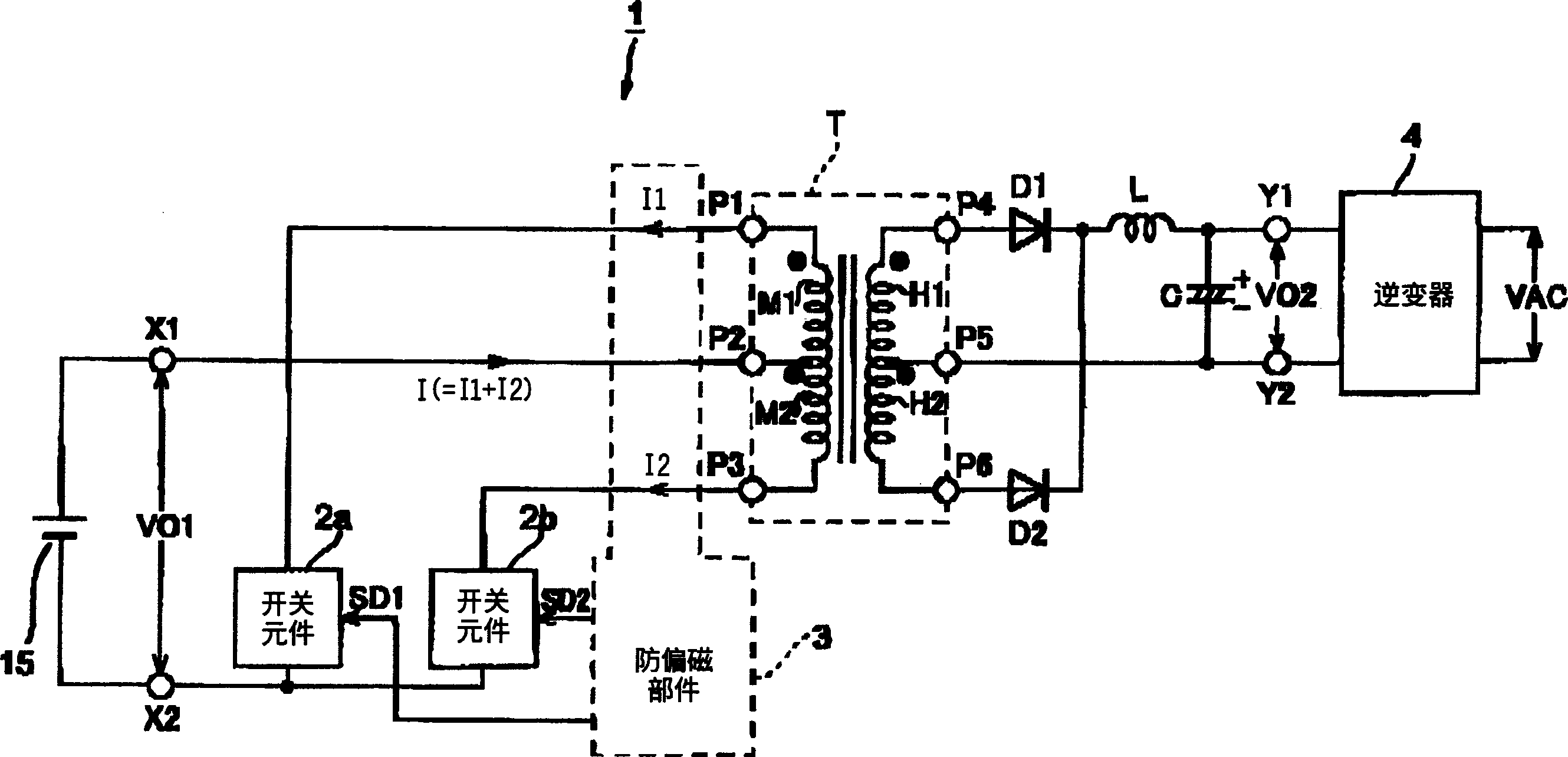
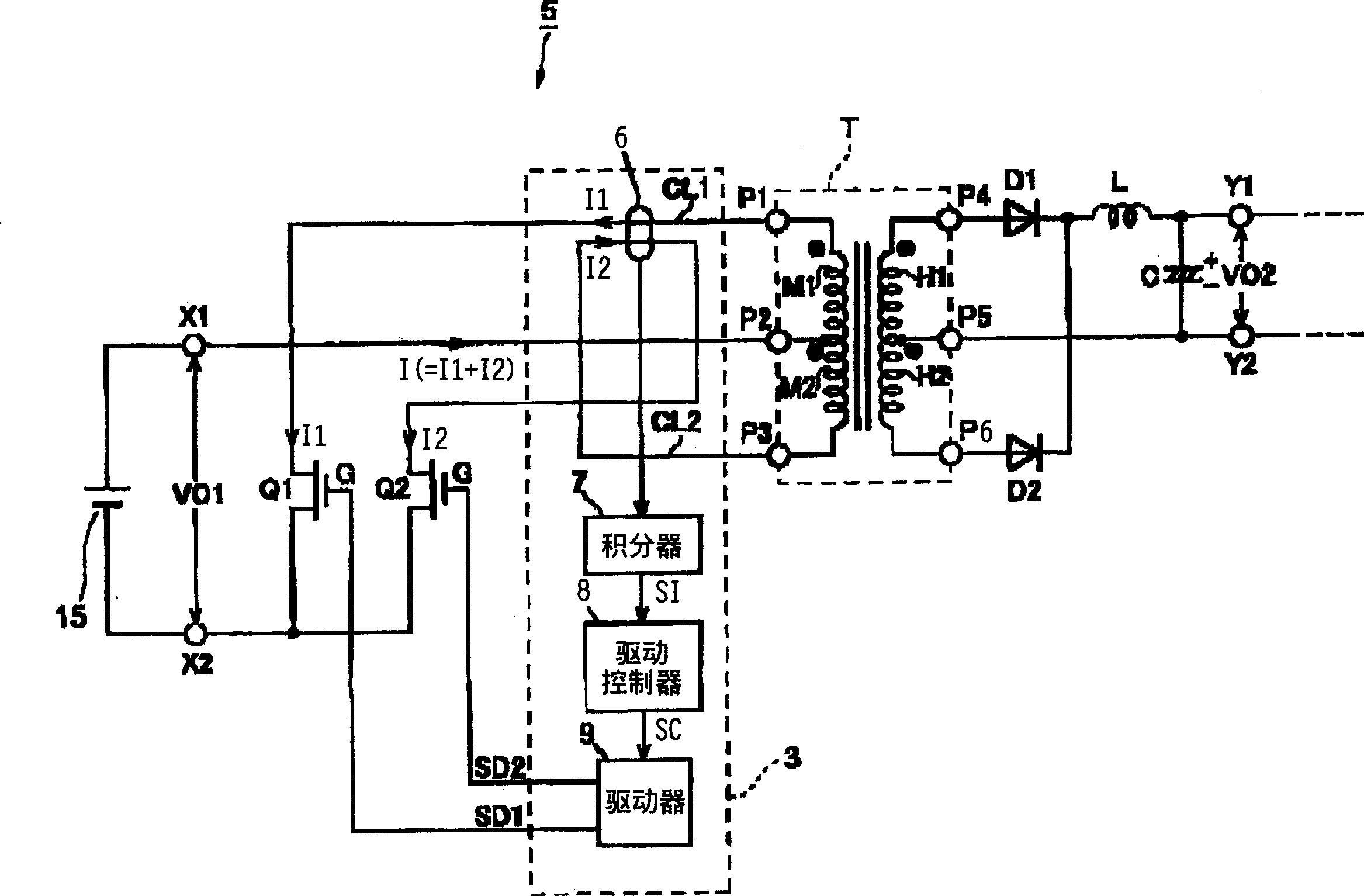
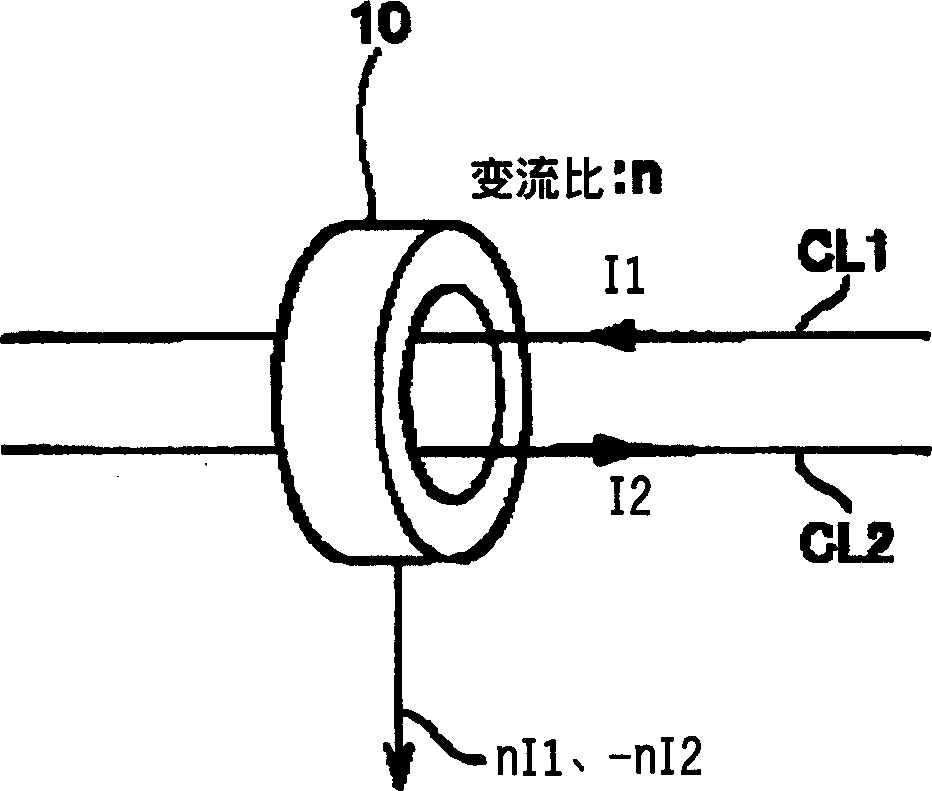
An electric power conversion device comprises switching elements 2a, 2b making up a push-pull converter, a pulse transformer T, a rectification diode D1, a rectification diode D2, a choke coil L, a smoothing capacitor C, a DC magnetic deviation prevention means 3, and an inverter 4. The DC magnetic deviation prevention means 3 detects the coil currents I1, I2 flowing in the primary windings M1, M2 of the pulse transformer T. By controlling (shortening) the on time of the switching element having a greater amount of current, the coil currents I1, I2 are balanced (I1=I2), thereby preventing the magnetic deviation phenomena of the pulse transformer.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Bidirectional DC-DC converter and control method thereof
ActiveCN106033931ALow costReduce in quantityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceDc dc converter
The invention provides a bidirectional DC-DC converter and a control method thereof. The bidirectional DC-DC converter comprises a full-bridge converter or a push-pull converter including a rechargeable battery and a transformer, a first winding, a second winding, a controllable one-way conductive device, a rectification filter circuit, a first capacitor, a second capacitor, a first switch tube, a second switch tube and a switch device, wherein the first capacitor and the second capacitor are connected; and the first switch tube and the second switch tube are connected. The switch device is used for making the rectification filter circuit, the first capacitor and the second capacitor form a discharging path in a discharging mode and making the first capacitor, the second capacitor, the first switch tube and the second switch tube form a half-bridge inverter capable of charging the rechargeable battery in a charging mode. Cost of the bidirectional DC-DC converter is low.
Owner:SANTAK ELECTRONICS SHENZHEN
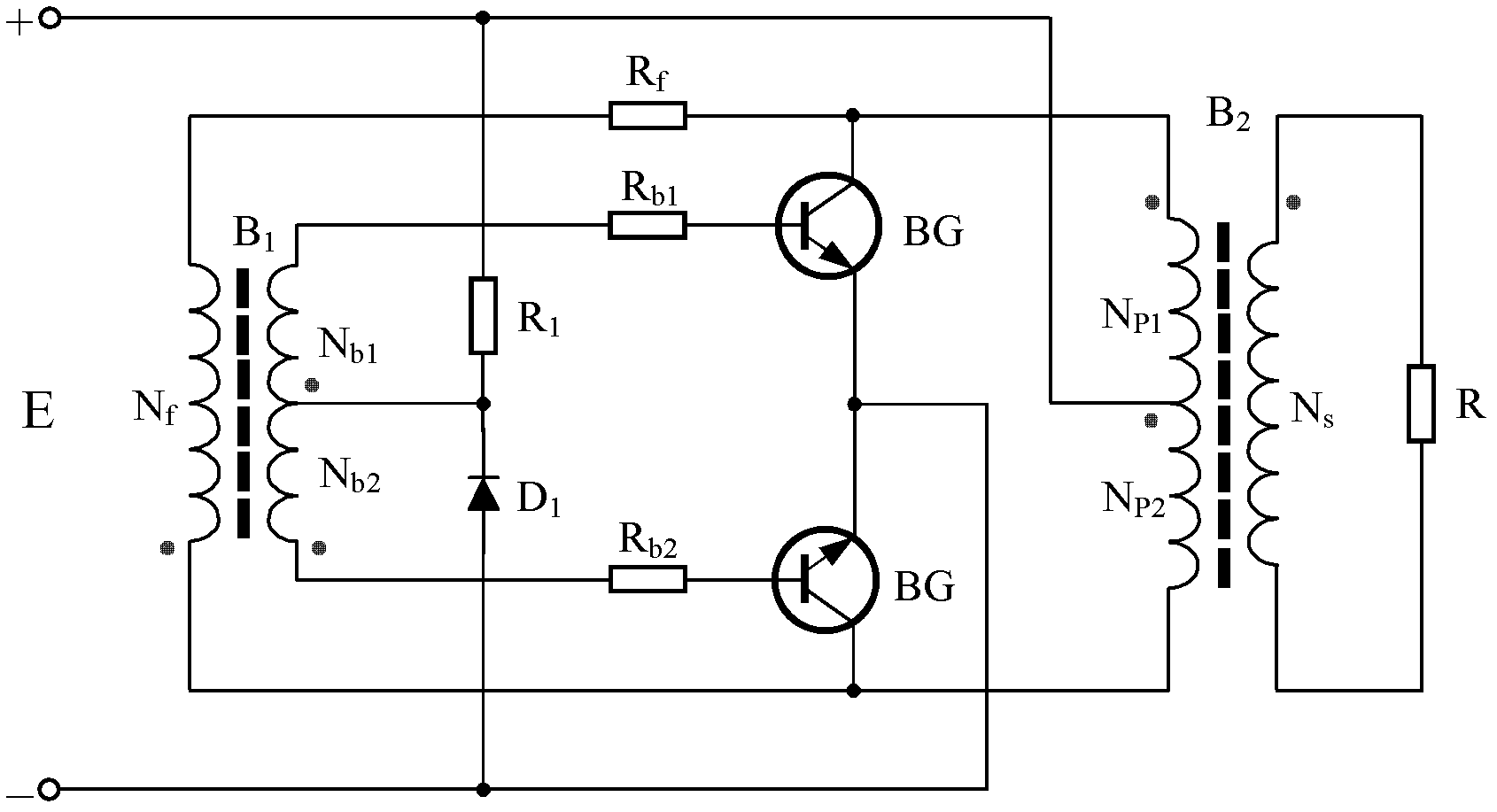
Transistor drive control method of push-pull converter and controller thereof
ActiveCN106130355AImprove reliabilityEffective self-protectionDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationTransformerPush pull
The invention relates to a push-pull converter, especially to a transistor drive control method of a push-pull converter and a controller thereof. The transistor drive controller that is suitable for driving control of two push-pull transistors comprises a quasi complementary pulse width generator that generates two paths of quasi complementary time sequence signals; one path of time sequence signal controls a first transistor and the other path of time sequence signal controls a second transistor, thereby carrying out external excited push-pull drive control of the two push-pull transistors. Compared with the prior art, the provided method and the controller have the following beneficial effects: transistors are in full conduction in a normal working sate and the working efficiency of the push-pull converter is not affected. When starting begins and the output of the converter is in a short-circuit mode, the inductor effect is out of action because the primary winding of the transformer is clamped and large voltages are applied on the two ends of the transistors; and when the state is detected continuously, entrance to a protection state is realized. Therefore, burning under heavy currents and high voltages can be avoided.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH +1
Method for improving working efficiency of self-excited push-pull converter and self-excited push-pull converter
ActiveCN102684506AImprove work efficiencyGood effectEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransformerLow voltage
The invention discloses a method for improving the working efficiency of a self-excited push-pull converter and the self-excited push-pull converter. The method comprises the steps of setting an output circuit of the converter as a synchronous rectification output circuit, and turning off a synchronizing signal of the synchronous rectification before overturning of a working state of the converter. The self-excited push-pull converter for realizing the method comprises a transformer and a synchronous rectification output circuit, wherein the synchronous rectification output circuit is connected to an output winding of the transformer, the synchronous rectification output circuit comprises two synchronous rectification metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) tubes, and the turnoff of the synchronizing signal of the synchronous rectification is ahead of the overturning of the working state of the converter. Due to the adoption of the method and the self-excited push-pull converter, the problem that the circuit cannot be overturned normally when the synchronous rectification circuit is applied to a Royer circuit can be solved; and the synchronous rectification circuit can be normally applied to the Royer circuit, the working efficiency of the Royer circuit is further improved, and especially the working efficiency of the Royer circuit in the low-voltage output application field can be improved.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH
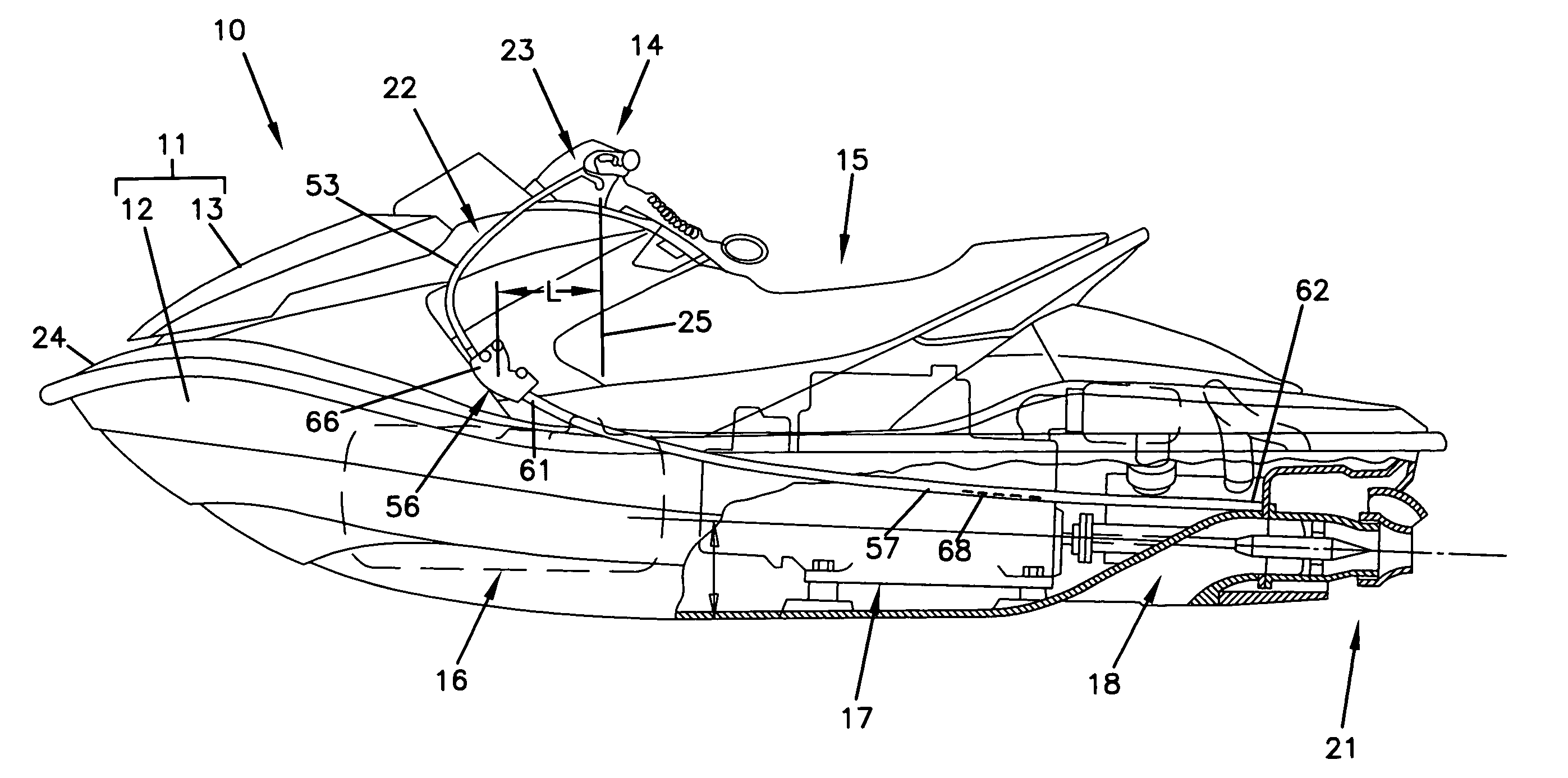
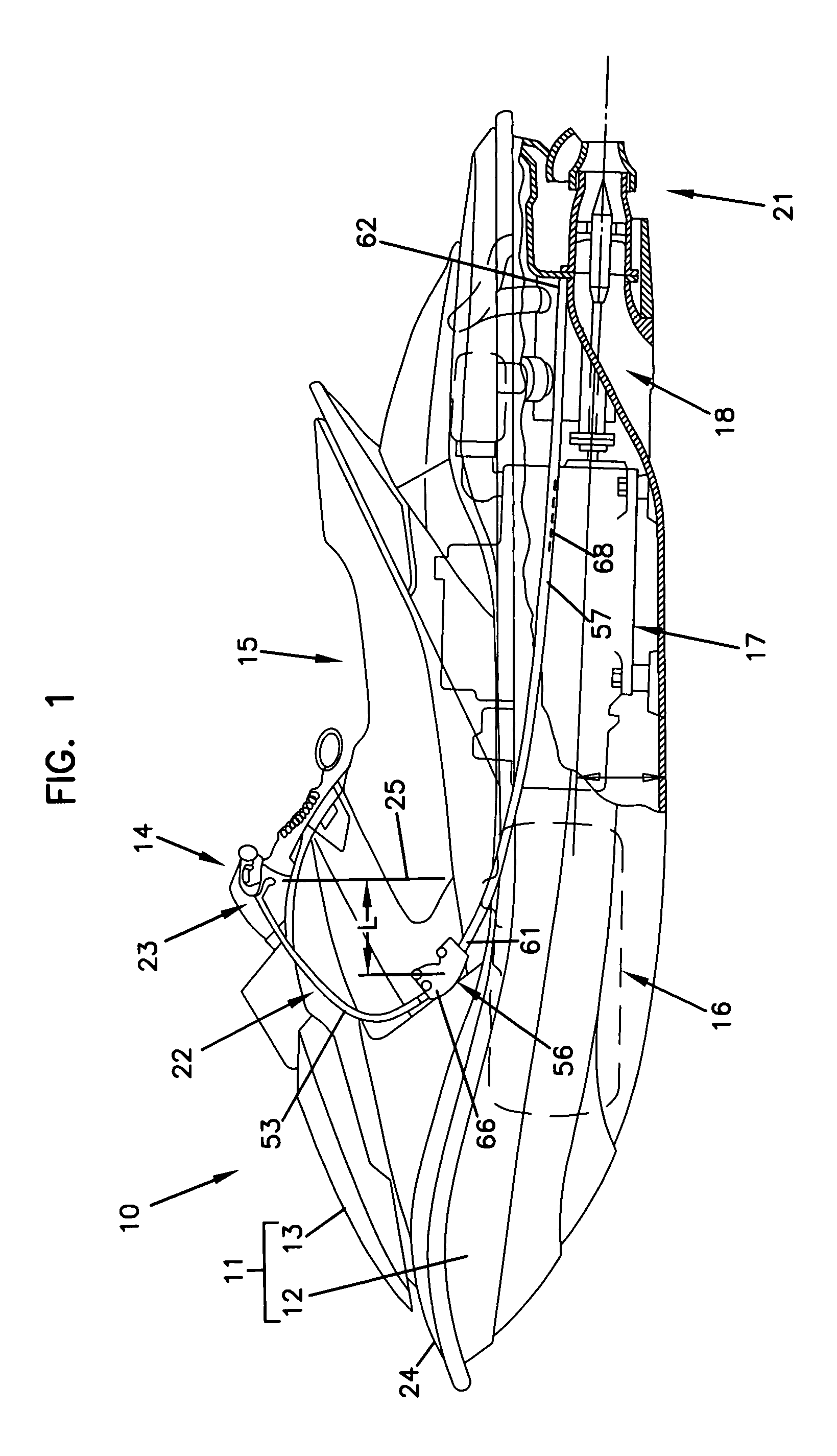
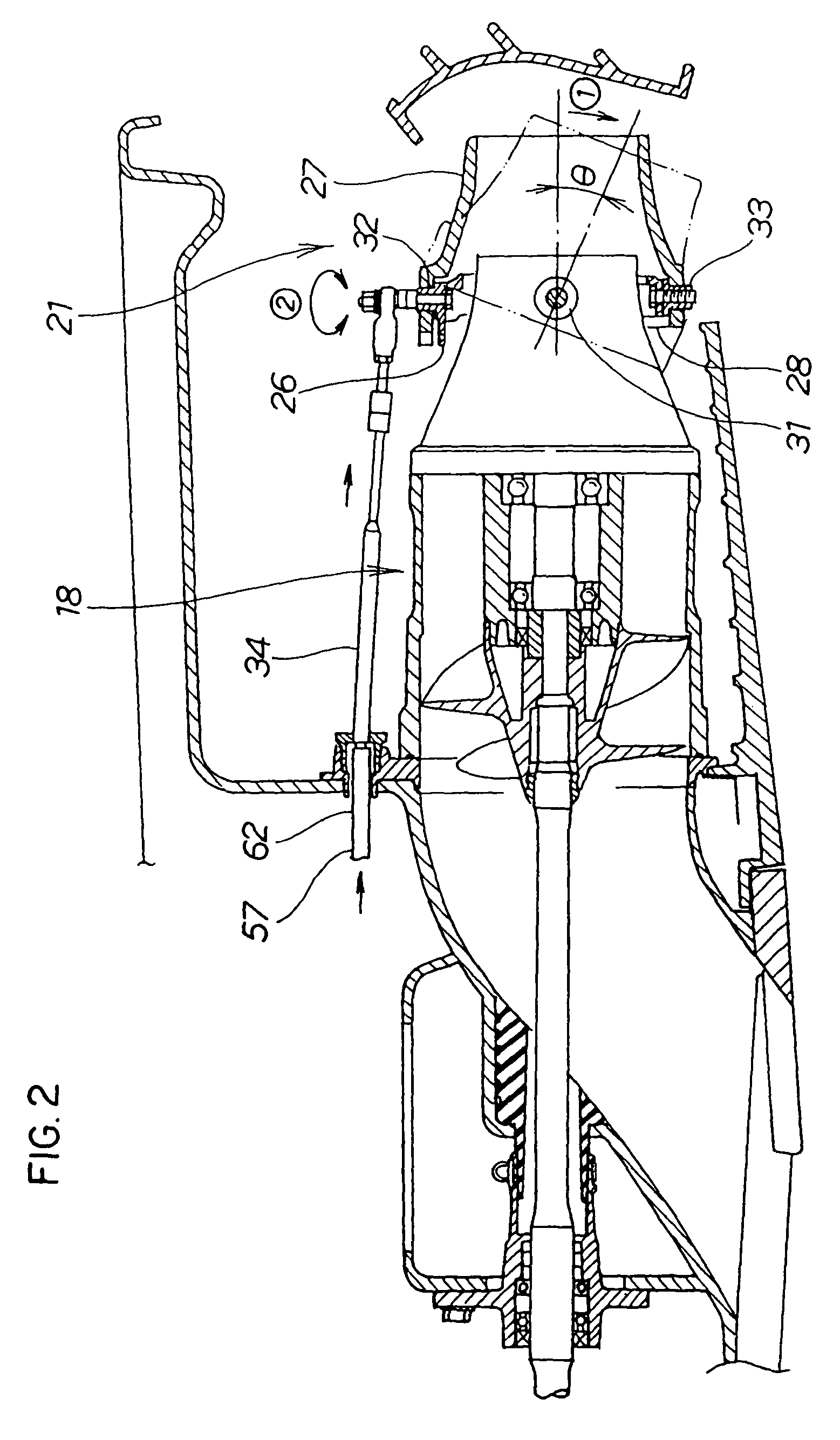
Trim operating wire structure for personal watercraft
A trim operating wire is disclosed wherein the length of the pull wire connecting between the push-pull converter and the trim operating lever can be made short, and the push wire can be made long. As a result, even where the pull wire, which is thin and highly flexible, is disposed in the state of being bent at several portions thereof, the sliding resistance of an inner wire of the pull wire is small, and operability is enhanced.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Primary side ZVS push-pull converter having relatively less losses
ActiveUS7049712B2Reduce switching lossesImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionEngineeringConductor Coil
The push-pull converter for zero-voltage switching of the switches on the primary side of the transformer to have a relatively lower loss is proposed. Which includes: a transformer having a primary winding with a center tap and a secondary winding, an electrical energy storage device having a first terminal coupled to the center tap of the primary winding and a second terminal coupled to a ground, a first switch having a first terminal coupled to a first terminal of the primary winding and a second terminal coupled to the ground, a second switch having a first terminal coupled to the ground and a second terminal coupled to a second terminal of the primary winding, and a rectifier circuit coupled to the secondary winding for transforming an AC output of the secondary winding to a DC output.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Switch converter double-edge constant breakover time modulation voltage type control method and device thereof
ActiveCN103066811AImprove transient performanceQuick adjustment of off timePower conversion systemsDouble tubeBuck converter
The invention discloses a switch converter double-edge constant breakover time modulation voltage type control method and a device thereof. According to relation between output voltages and voltage reference value, the switch converter double-edge constant breakover time modulation voltage type control method and the device thereof use a control time series formed by constant breakover, turn-off and constant breakover or a control time series formed by turn-off, constant breakover and turn-off for controlling breakover and turn-off of the switch converter switch tube. The switch converter double-edge constant breakover time modulation voltage type control method and the device thereof can be used for controlling a plurality of switch converters with a topological structure, such as a Buck converter, a Buck2 converter, a Cuk converter, a Zeta converter, a single tube normal shock converter, a double-tube normal shock converter, a push-pull converter, a push-pull normal shock converter, a half-bridge converter and a full-bridge converter. The switch converter double-edge constant breakover time modulation voltage type control method and the device thereof has the advantages of being simple in control, fast in transient response speed, high in voltage stabilization accuracy, and capable of not compensating network.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
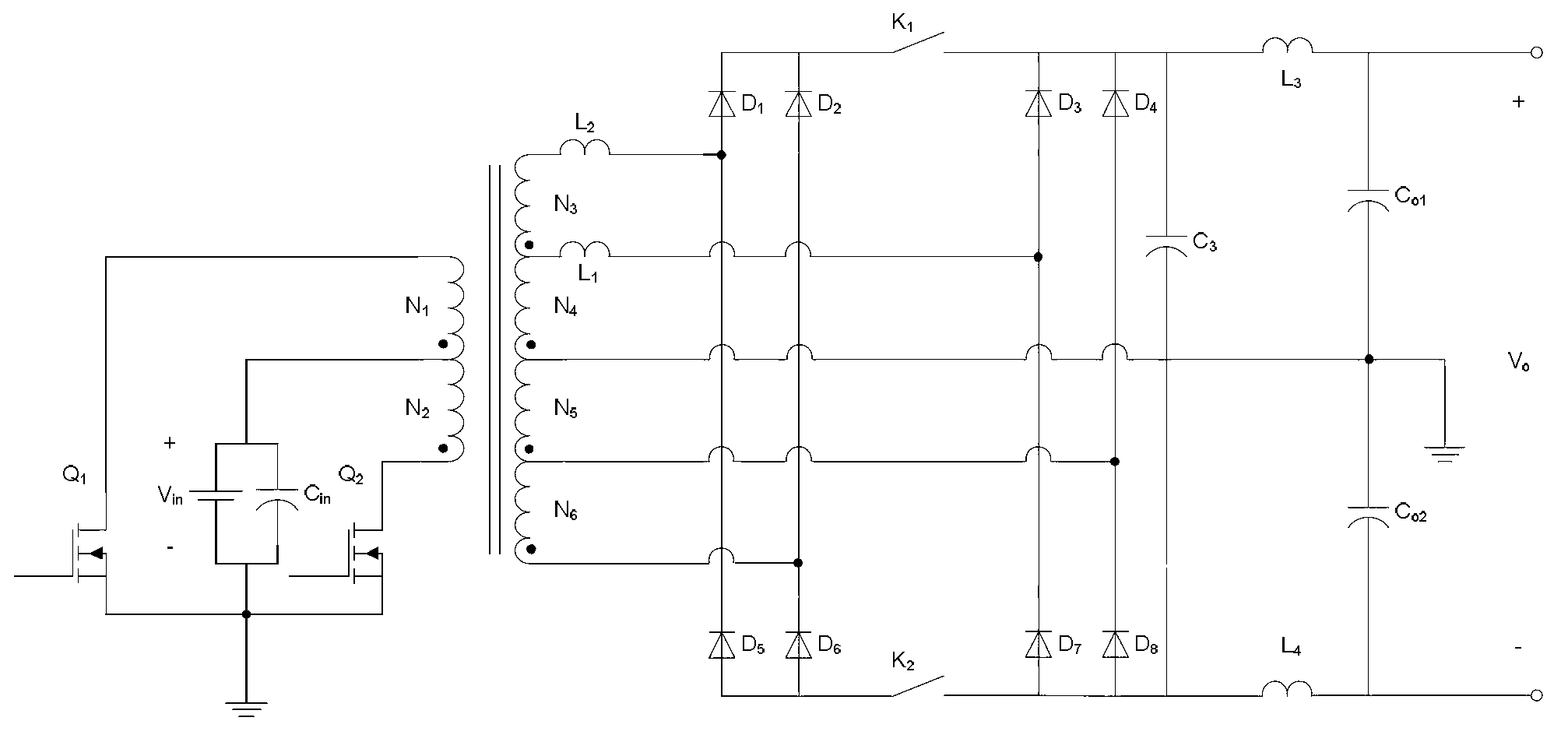
Input-parallel output-series converter based on push-pull topological structure
InactiveCN106849683AReduce AC lossReduce control difficultyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitancePush pull
The invention discloses an input-parallel output-series converter based on a push-pull topological structure. The converter comprises an external direct current voltage source, two power tubes, a push-pull topological structure booster circuit and a rectifier filter circuit. The external direct current voltage source is composed of a direct current power source and an input filter capacitor. A positive electrode of the direct current power source is connected with a positive electrode of the input filter capacitor, a negative electrode of the direct current power source is connected with a negative electrode of the input filter capacitor, and source electrodes of the first power tubes Q1 and Q2 are connected with the negative electrode of the direct current power source. The push-pull topological structure booster circuit comprises four paths of push-pull converters, dotted terminals of the primary sides of the four paths of push-pull converters are connected with a drain electrode of the power tube Q1, the heteronymous terminals of the primary sides of the four paths of push-pull converters are connected with a drain electrode of the power tube Q2, the auxiliary sides of the four paths of push-pull converters are connected with one path of rectifier filter circuit, and the output ends are connected in series. The two switching tubes are adopted for replacing multiple switching tubes, driving circuits of the switching tubes are reduced, the losses of the switching tubes are reduced, and the efficiency of the converter is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Direct-current draw-out power supply of IEGT power module
ActiveCN103683857ASafe and reliable workReduce the number of modulesApparatus with intermediate ac conversionFull waveHigh-voltage direct current
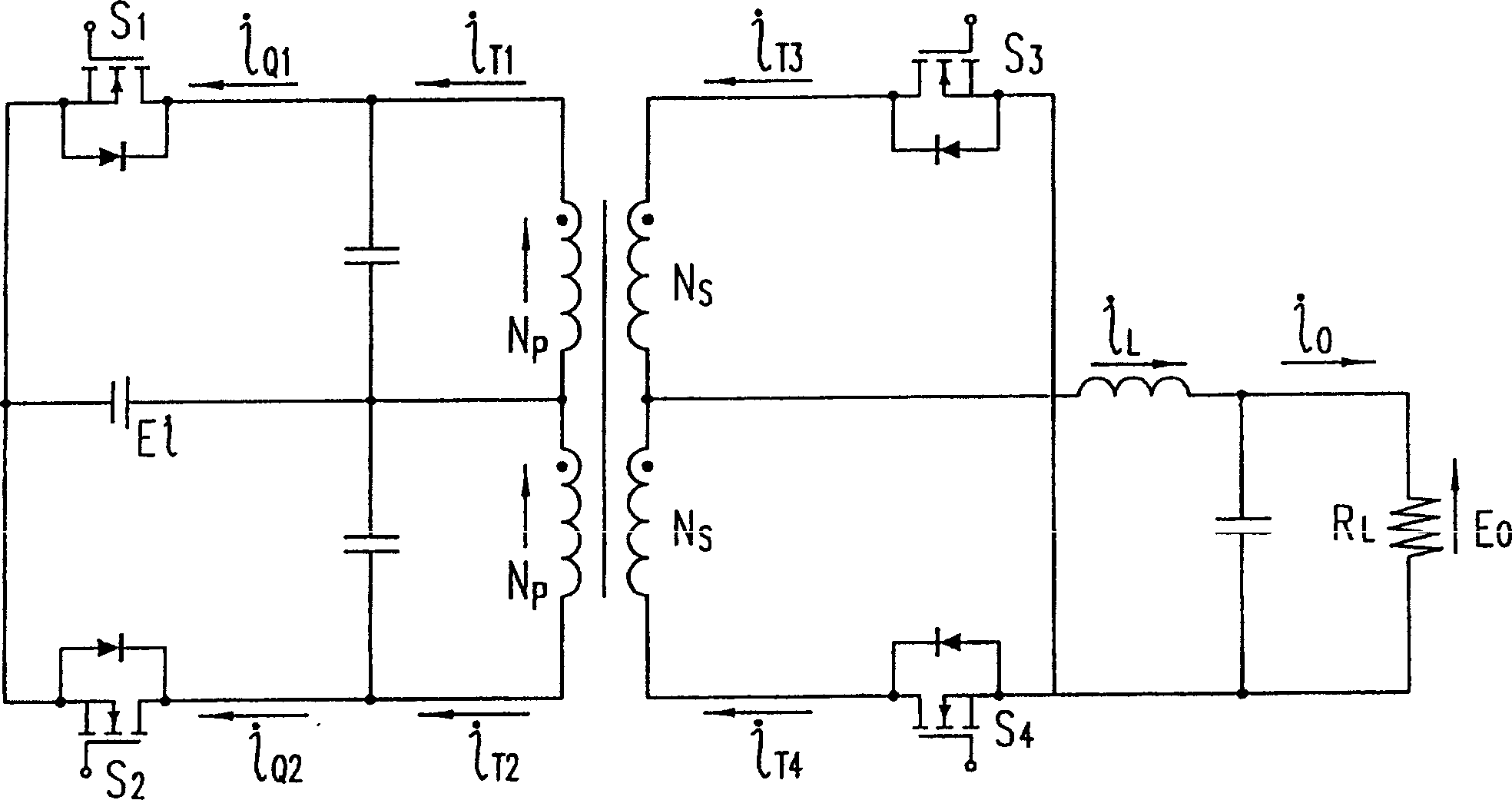
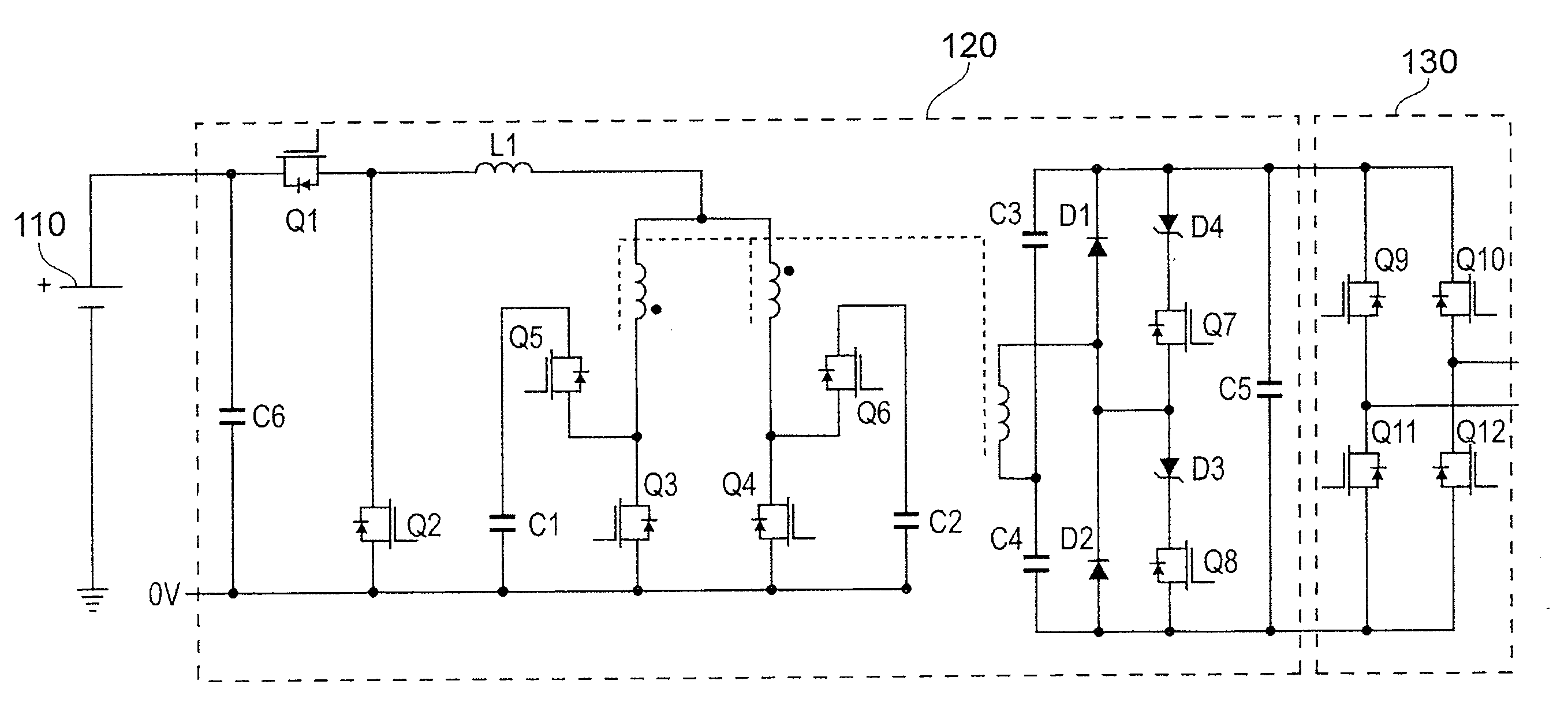
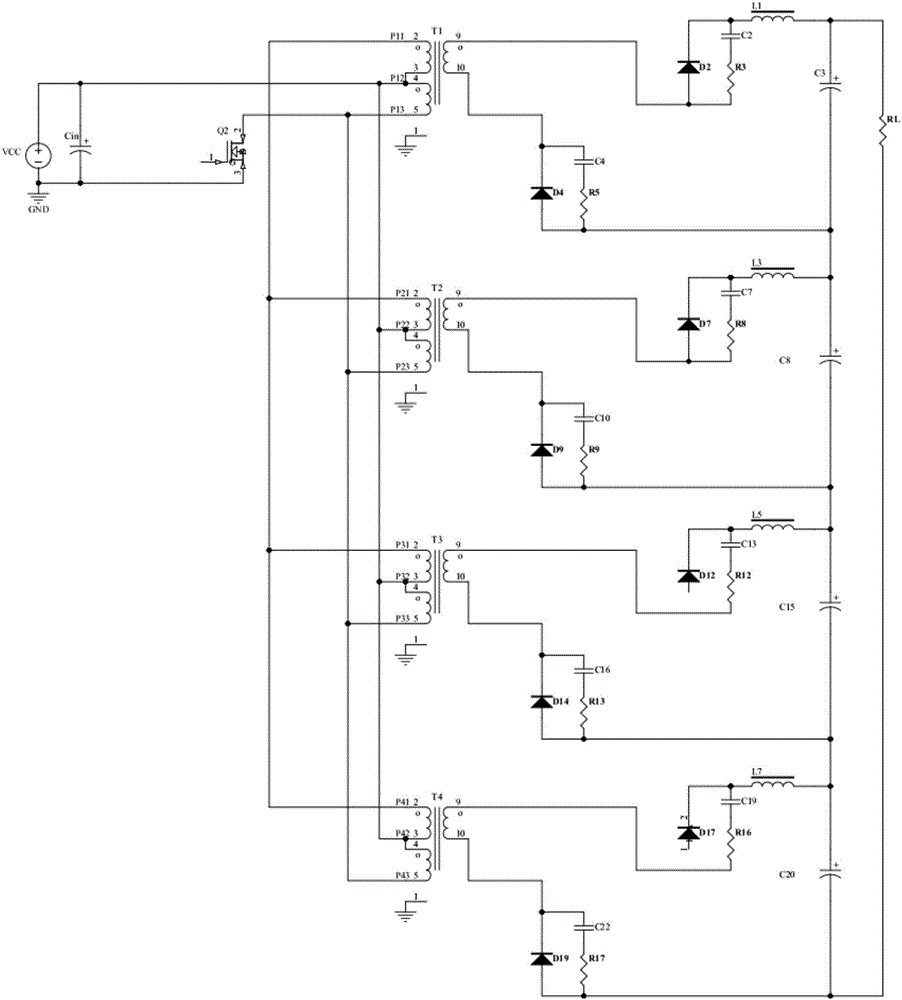
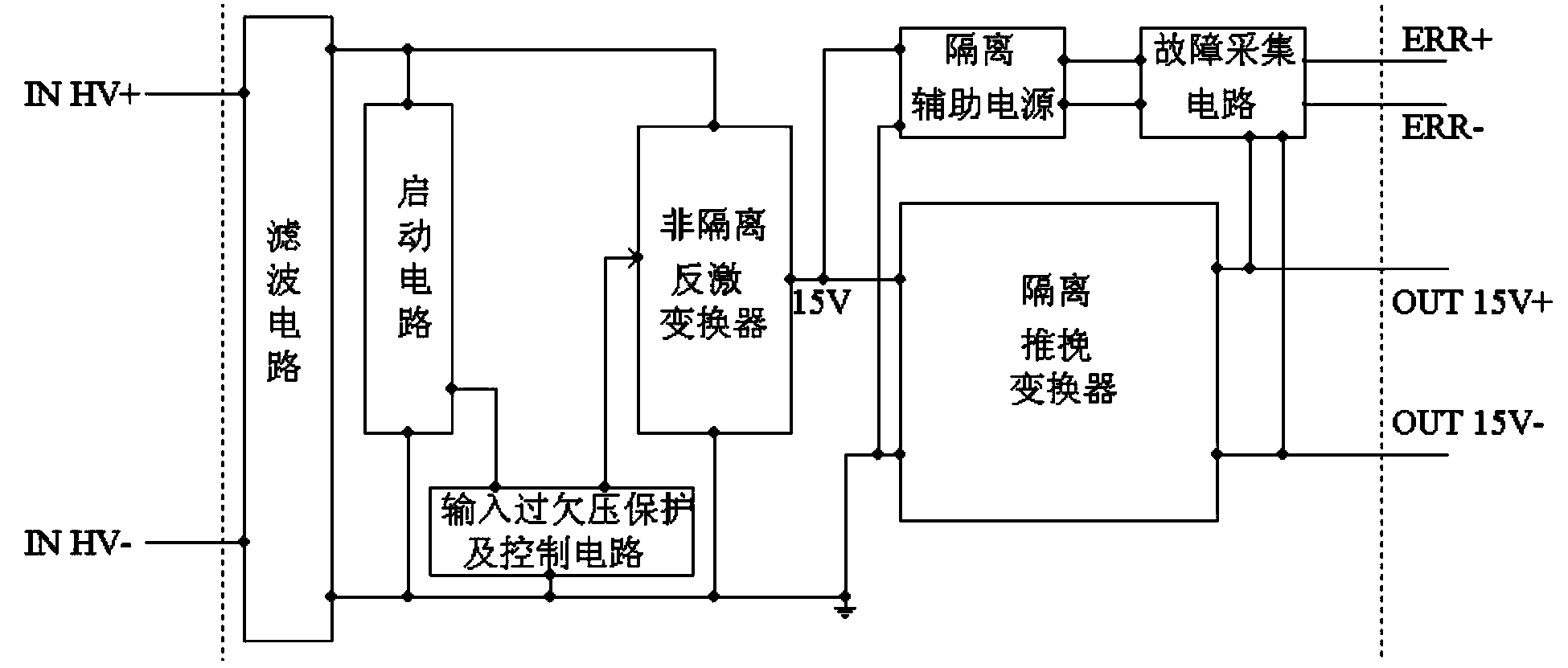
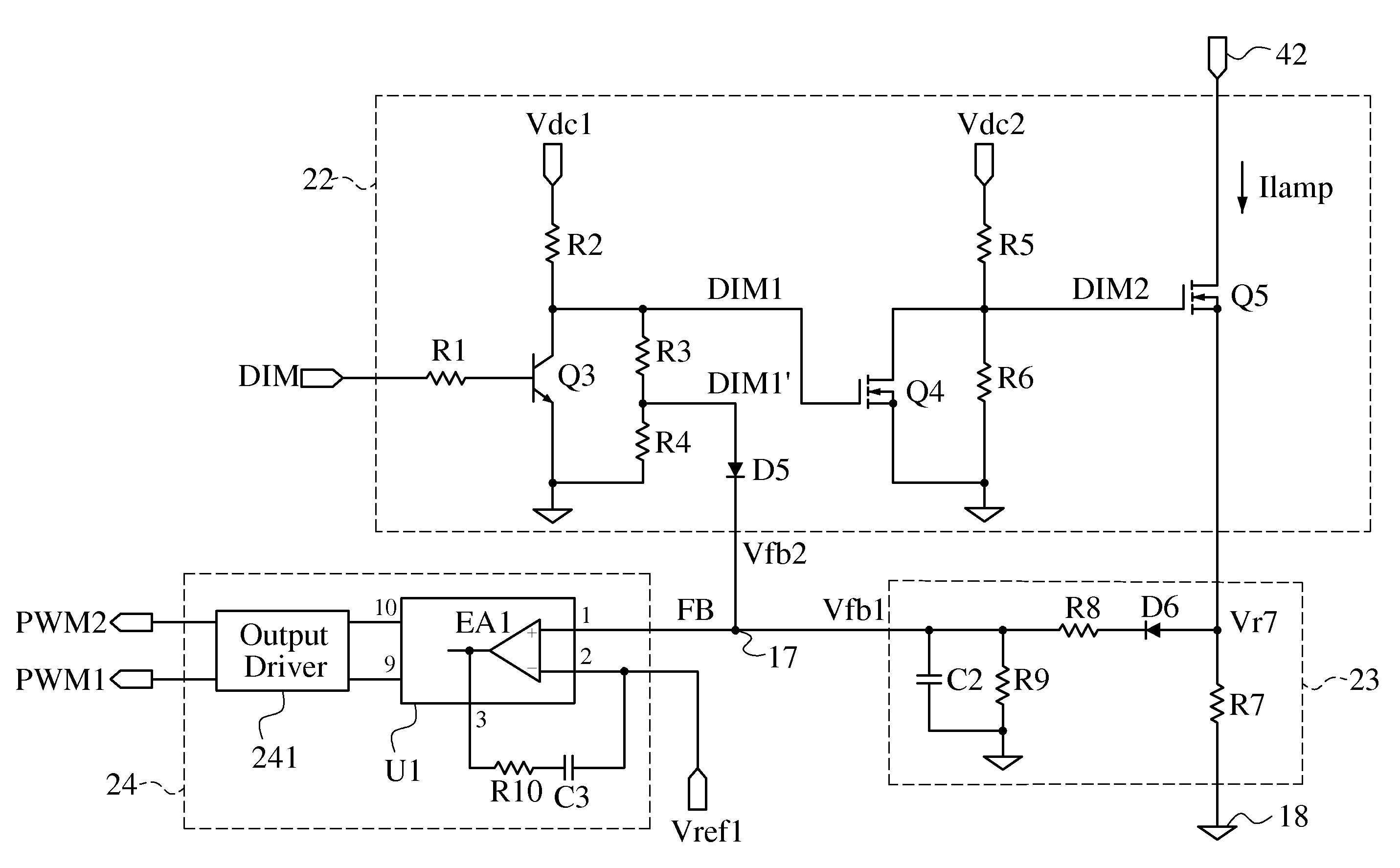
The invention relates to a direct-current draw-out power supply of an IEGT power module in the field of high-power electric and electronic converters. A main circuit comprises a filter circuit, a non-isolated flyback converter and an isolated push-pull converter. After input high-voltage direct-current electric energy is filtered through the filter circuit, first-stage conversion is performed on electric energy signals through the non-isolated flyback converter, bus high voltages are converted into DC400V electric signals, filtering processing is performed on the electric signals, then second-stage conversion processing is performed on the electric signals through the isolated push-pull converter, and finally a high-location draw-out power supply can output DC15V electric signals stably and safely after full-wave rectification is performed on the electric signals through a rectifying circuit (picture 4). The draw-out power supply can output direct-current input voltages within the range of 300Vdc-3700Vdc, and can be cooled naturally, provide electricity for operation of the IEGT power module and run safely and reliably in a complicated electromagnetic field environment.
Owner:RONGXIN HUIKO ELECTRIC TECH CO LTD +1
DC/DC conversion circuit and power supply device
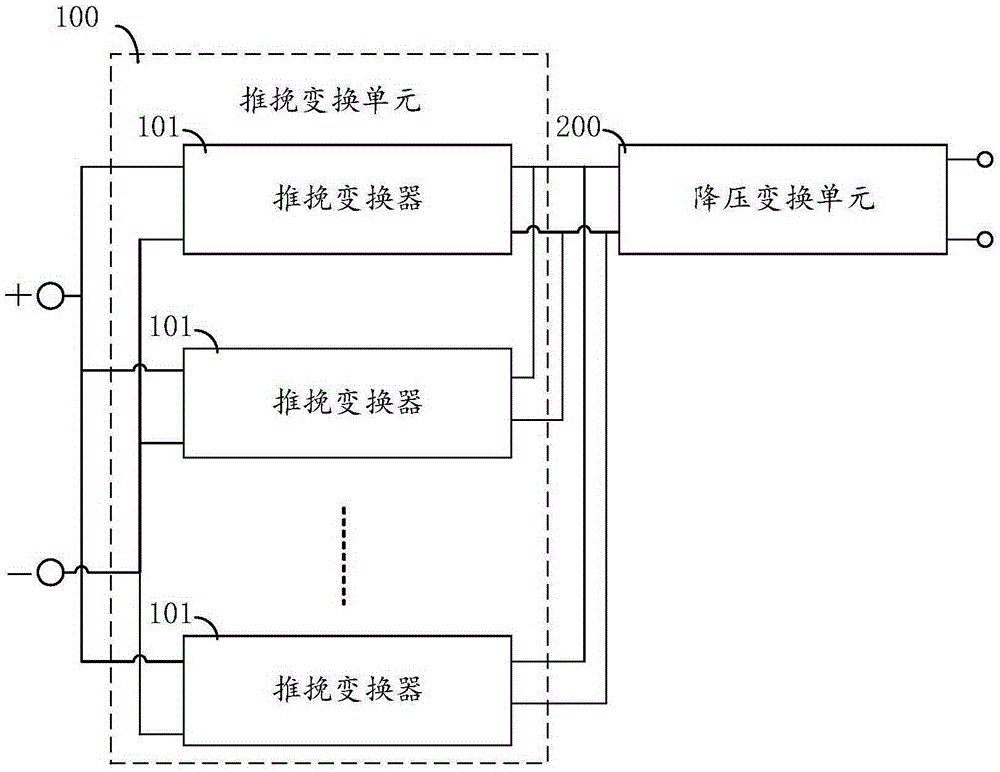
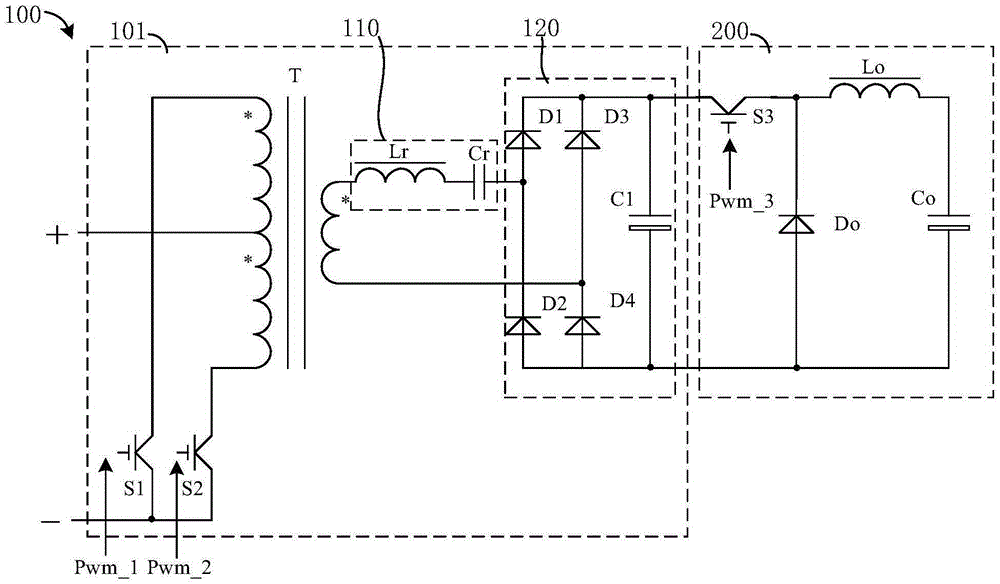
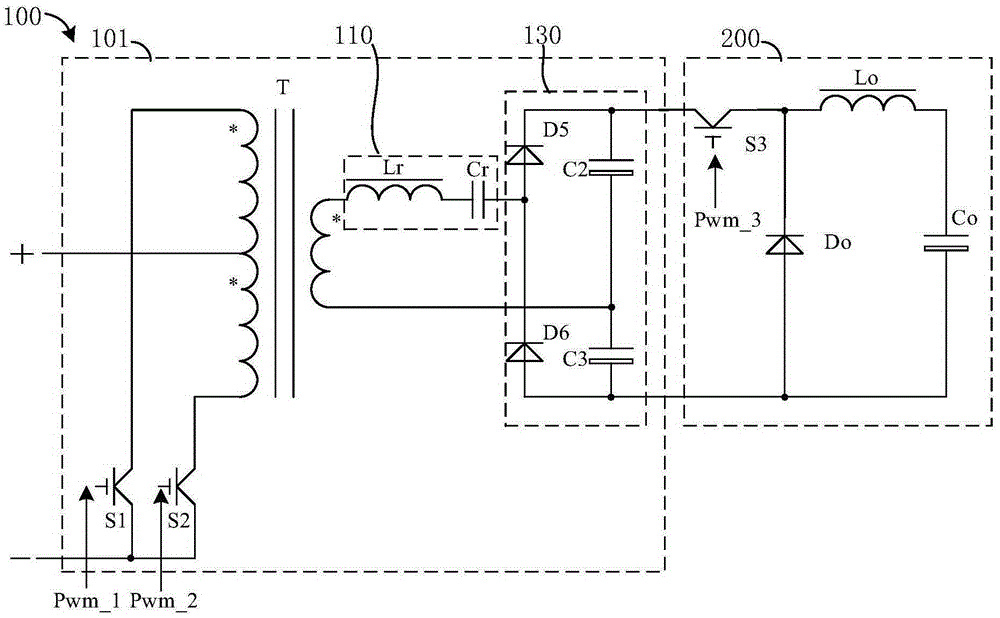
InactiveCN105337505AIncrease working frequencyImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationLoop controlSoft switching
The invention relates to a DC / DC conversion circuit and a power supply device. The DC / DC conversion circuit comprises a push-pull conversion unit and a buck conversion unit being a buck conversion circuit. The push-pull conversion unit includes one or more parallel push-pull converters connected to a direct-current power supply; with open-loop control of soft switching, the push-pull converters works near a frequency of a resonance point and carry out outputting to the buck conversion circuit. The output voltage and / or current of the DC / DC conversion circuit are / is controlled by adjusting a drive signal of the buck circuit. At the front push-pull stage, the open-loop working mode of resonant soft switch series connection is employed and the output voltage and current of the whole converter are controlled by adjusting the back-stage buck conversion circuit, thereby improving the working frequency and efficiency of the converter and reducing the size and cost of the converter. Switching tubes and rectifier tubes work in a soft switch state, so that the voltage stress of the power tube is reduced and reliability of the converter design is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN TIEON ENERGY TECH
Driving circuit for single-string LED lamp
A driving circuit for a single-string light-emitting diode (LED) lamp includes a push-pull converter. The push-pull converter converts an input low DC voltage (such as 12-19V) to a high DC voltage (such as above 200V) to supply power to the single-string LED lamp. The driving circuit controls a lamp current flowing through the single-string LED lamp by constant current and adjusts brightness of the single-string LED lamp by pulse-width modulation (PWM) dimming. In addition, the single-string LED lamp provides the standardization design for connectors of the driving circuit used to connect to the single-string LED lamp so that the driving circuit has a better common-use characteristic. Moreover, the driving circuit does not need a current balance circuit and only needs a cheaper and general-purpose integrated circuit to control the push-pull converter to reduce design cost of the driving circuit.
Owner:TPV ELECTRONICS (FUJIAN) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com