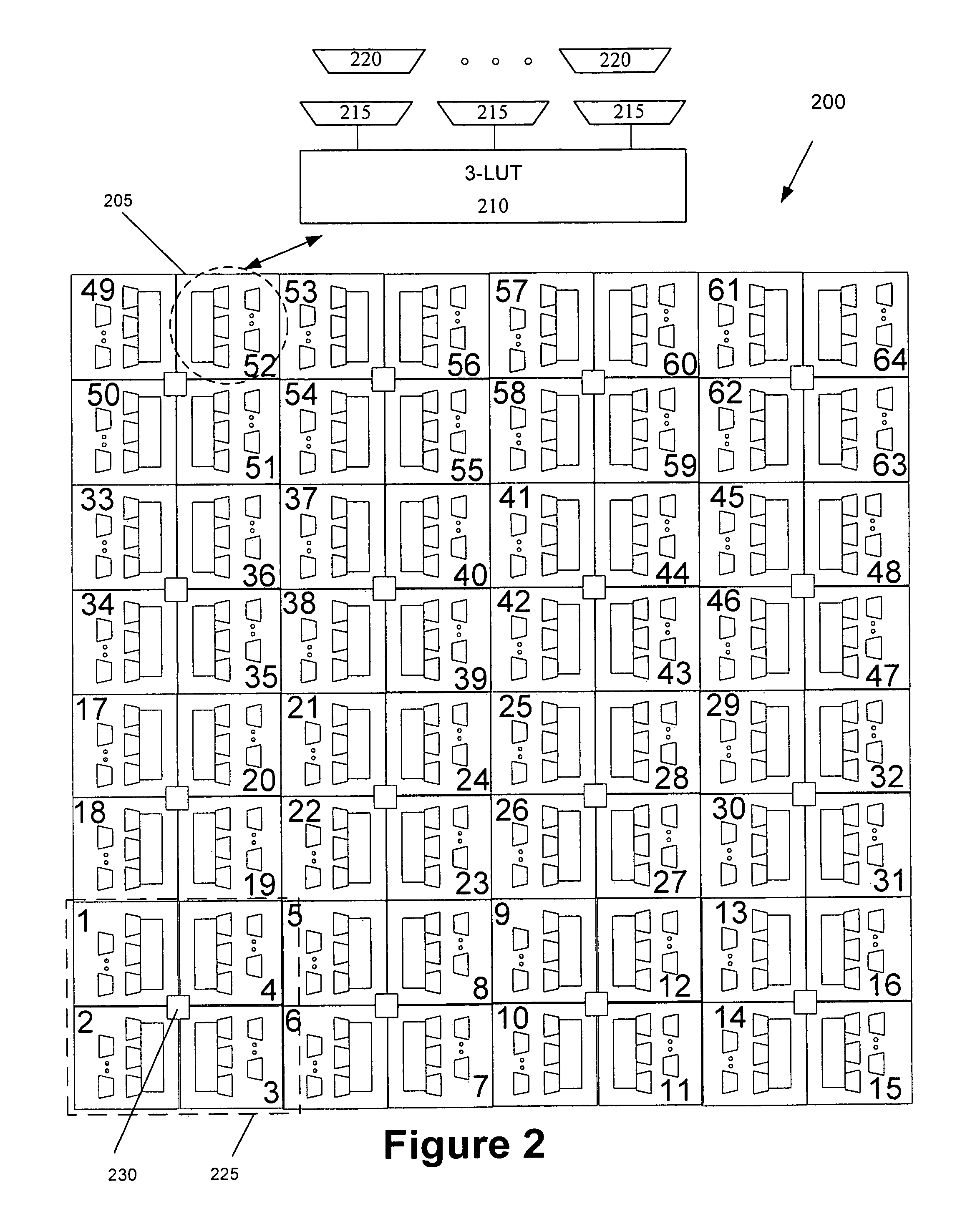
Patents
Literature
86 results about "Two's complement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Two's complement is a mathematical operation on binary numbers, and is an example of a radix complement. It is used in computing as a method of signed number representation. The two's complement of an N-bit number is defined as its complement with respect to 2. For instance, for the three-bit number 010, the two's complement is 110, because 010 + 110 = 1000. The two's complement is calculated by inverting the digits and adding one.
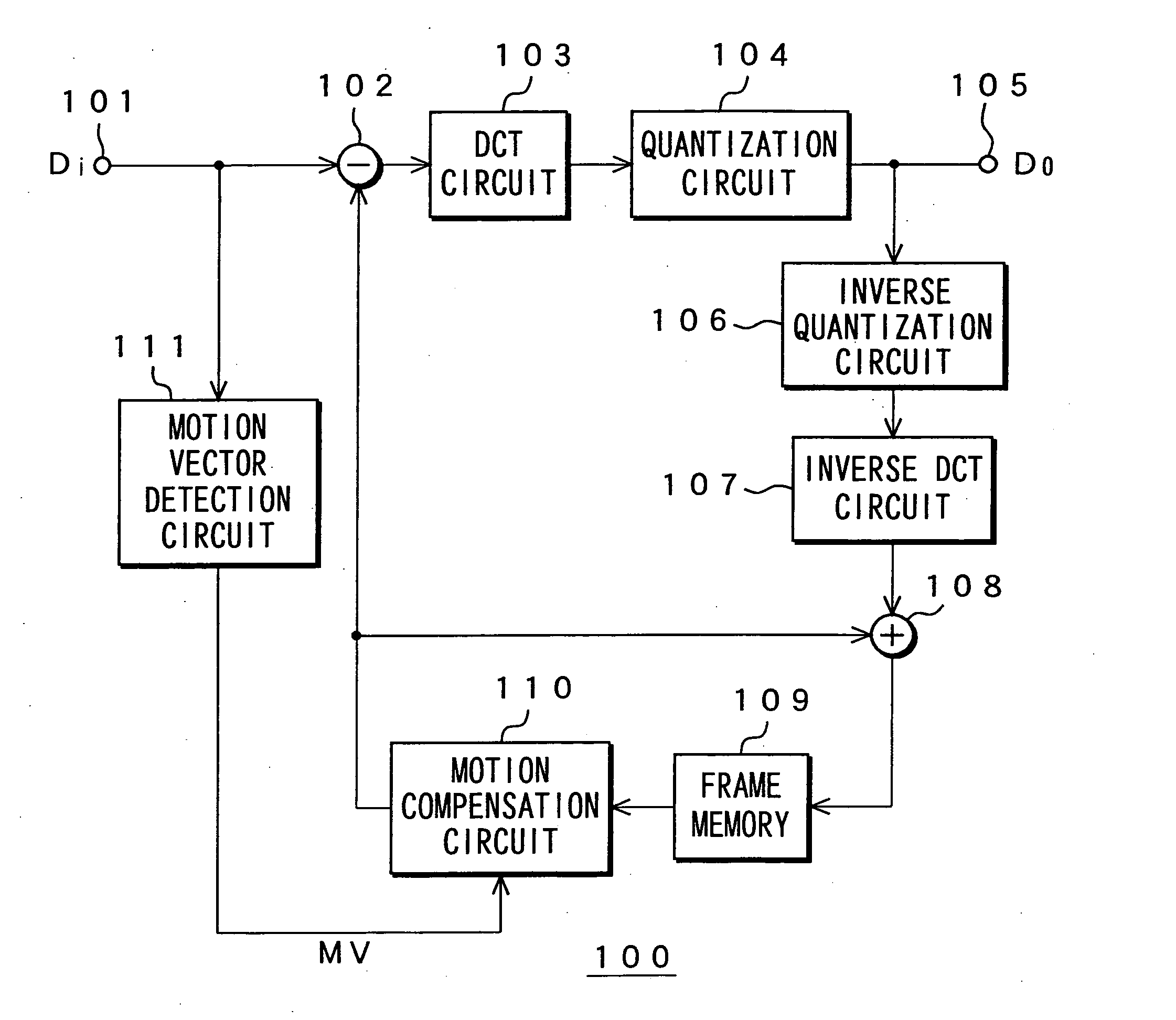
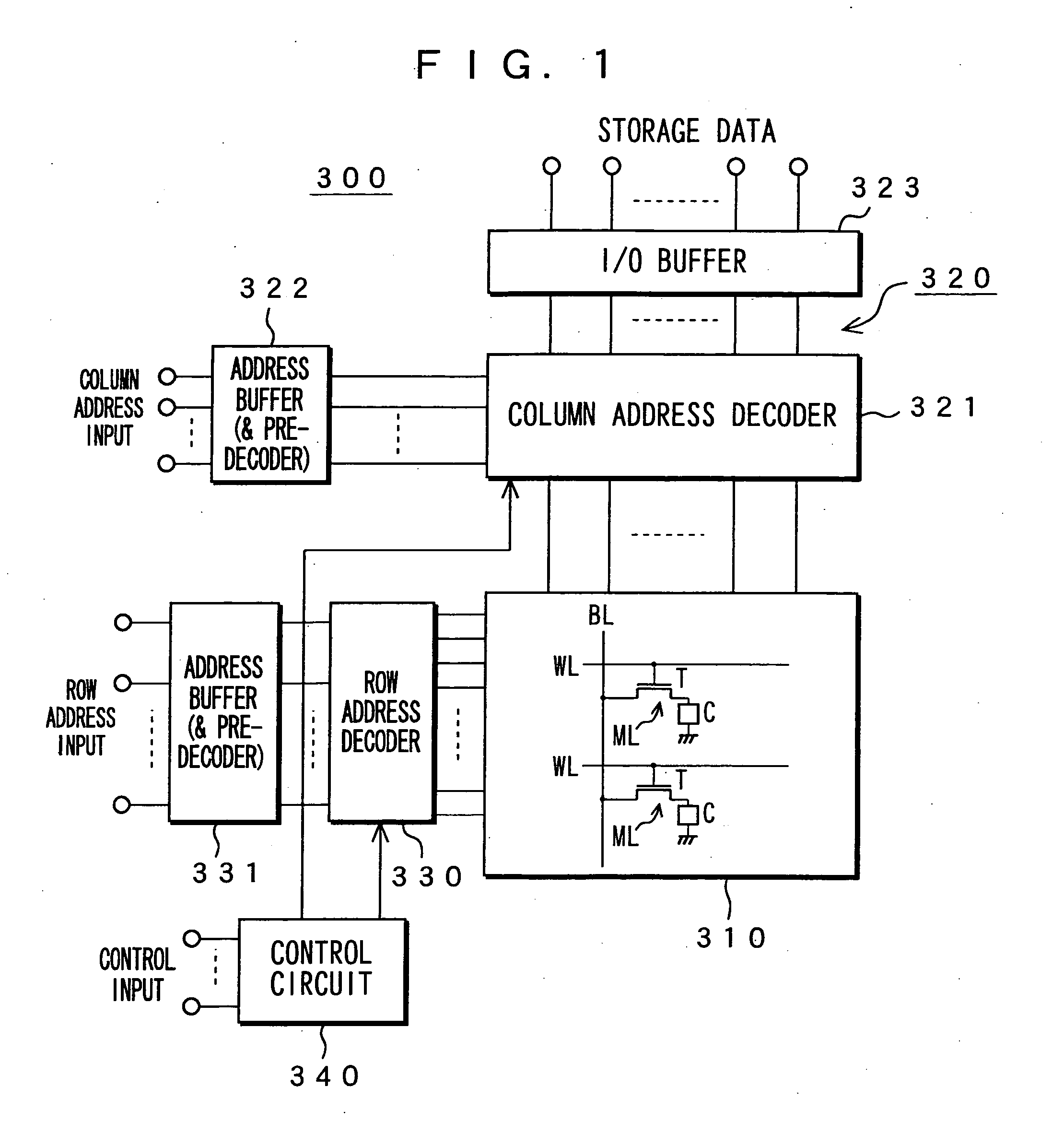
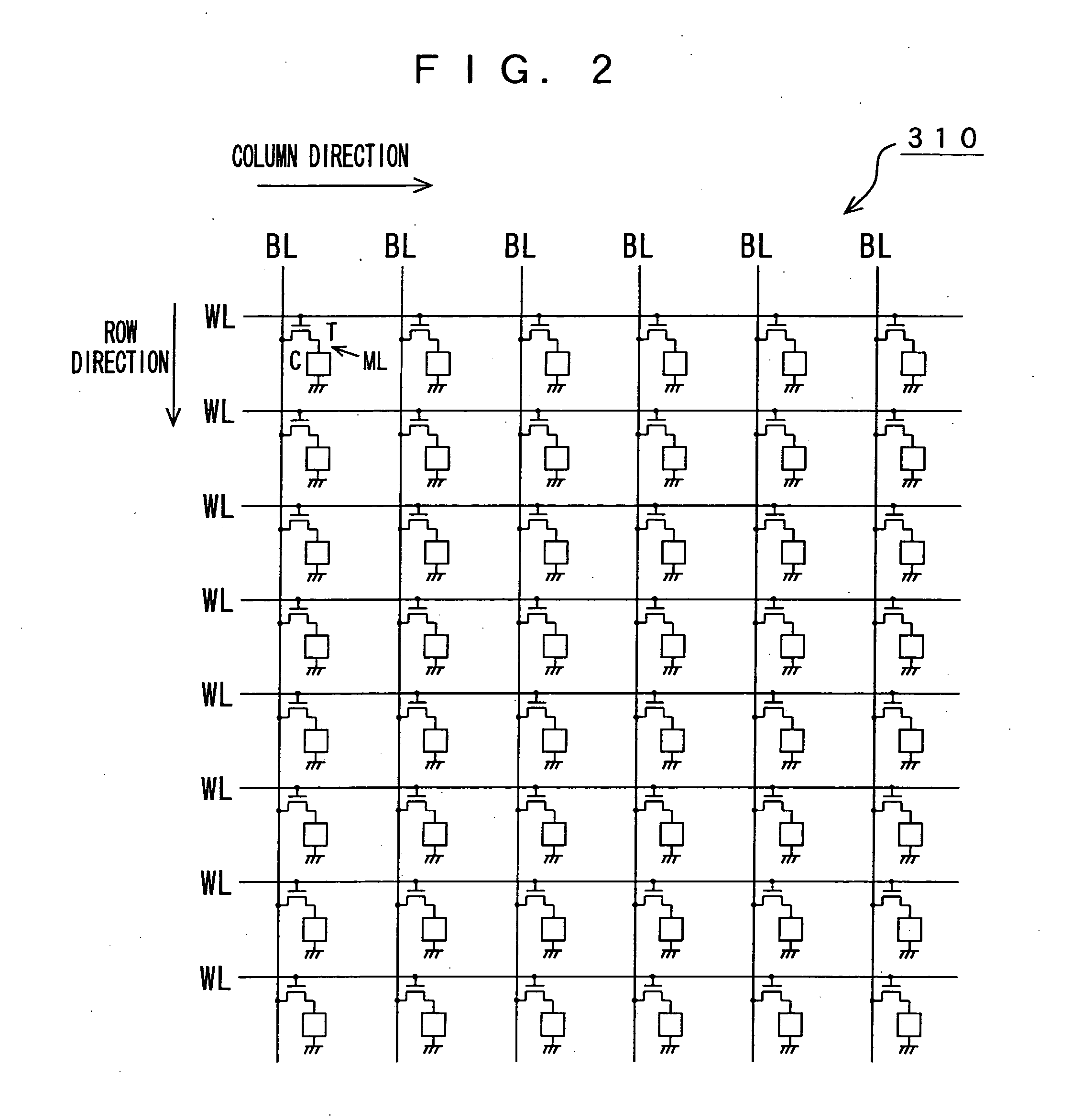
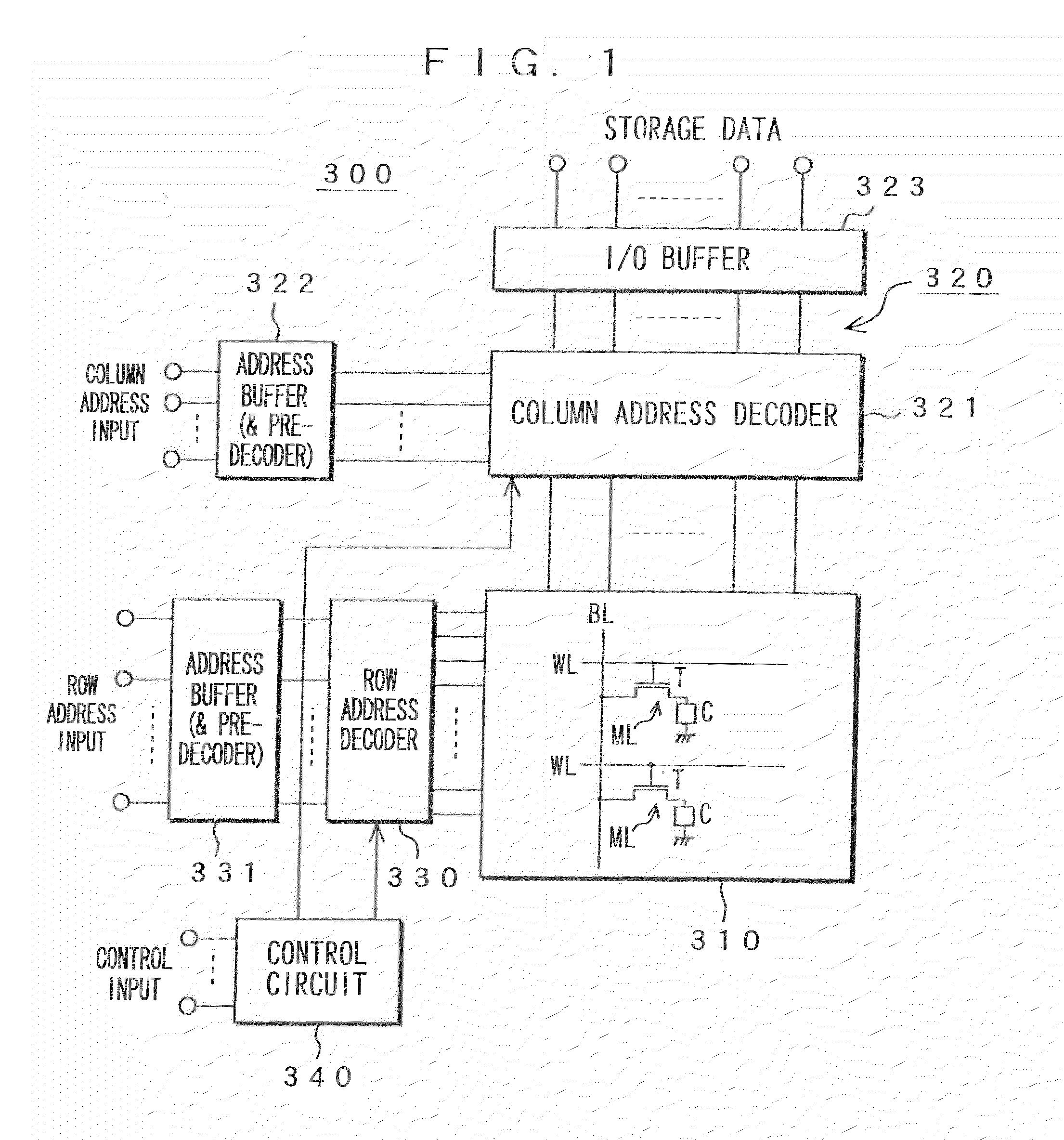
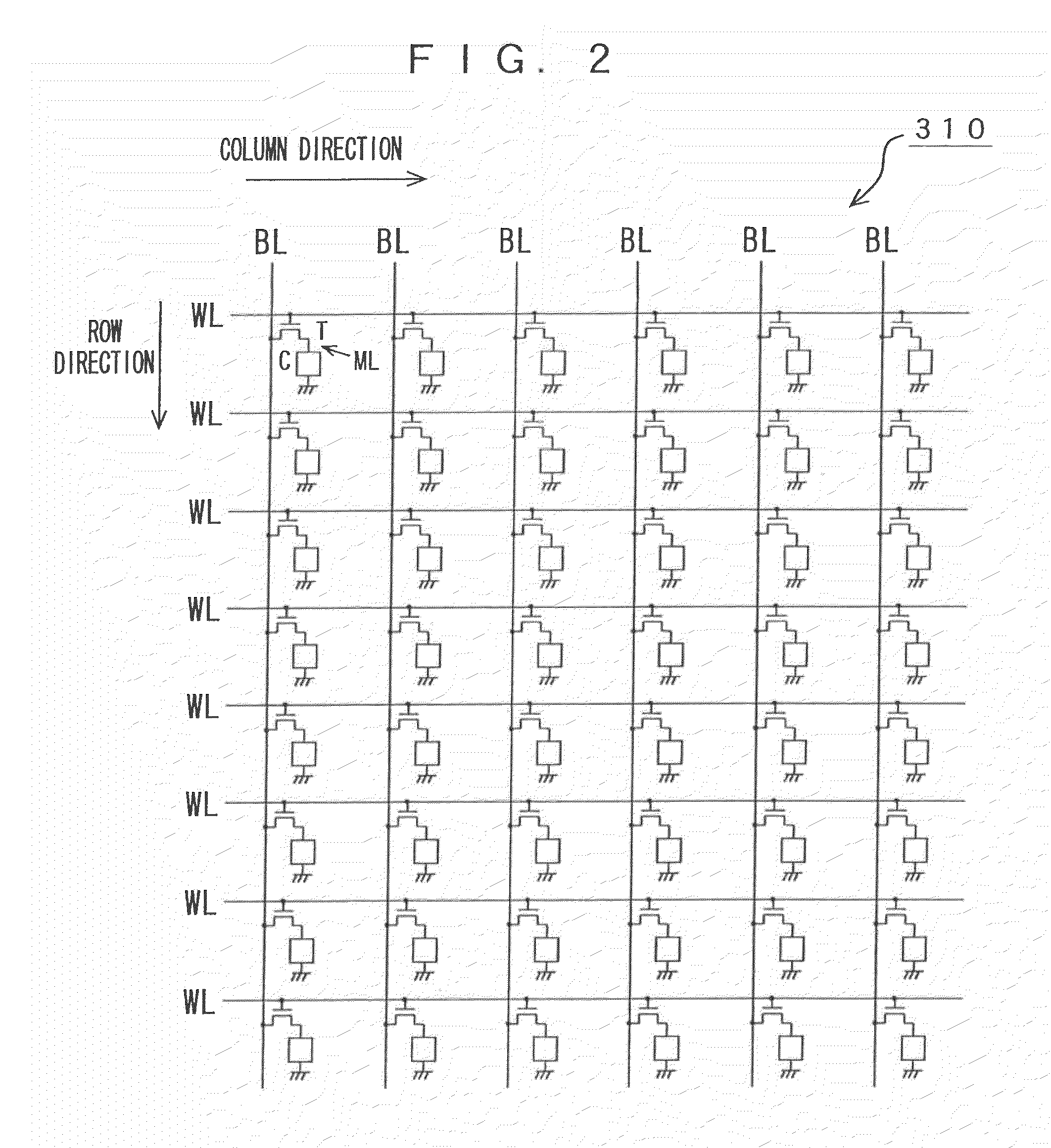
Memory device, motion vector detection device, and detection method
InactiveUS20060062483A1Increase computing speedLow costTelevision system detailsImage enhancementMotion vectorAbsolute difference
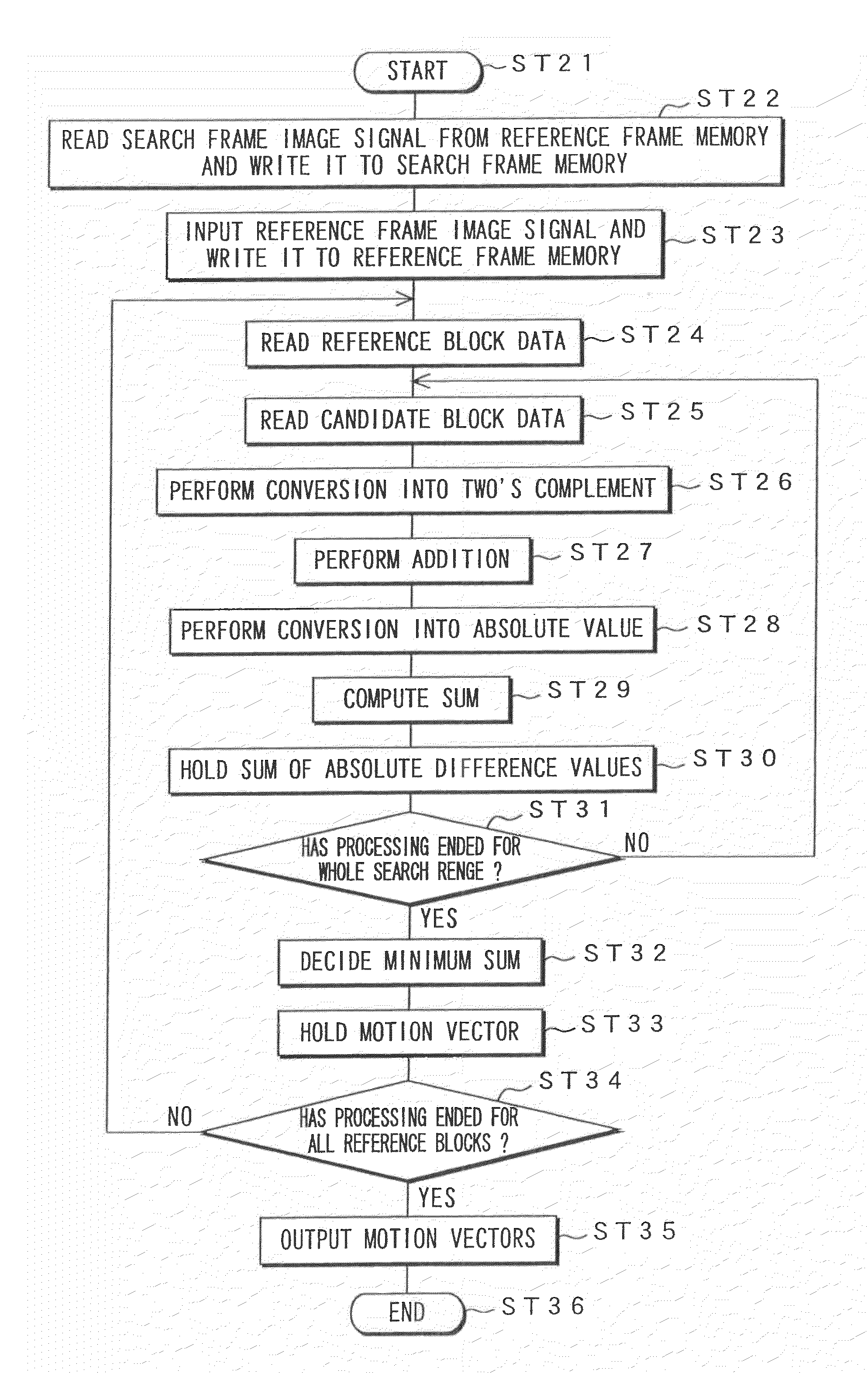
This invention relates to a memory device and the like that are preferably applied to a case where motion vector is detected using a block matching. Pixel data of a first frame (a reference frame) is stored in a unit A of memory cell array portion 20a in straight binary format. Pixel data of a second frame (a search frame) is stored in a unit B of memory cell array portion 20b in two's complement format. The units A and B have a plurality of memory cells, respectively. Word lines WL related to the pixel data of the first and second frames are simultaneously activated so that charges accumulated in capacitors of each of the memory cells can be combined along one bit line BL. A / D converter 53 outputs a digital signal (absolute difference value) having a value that corresponds to a total amount of charges. When reading the pixel data, a subtraction and a conversion into the absolute difference value are simultaneously performed.
Owner:SONY CORP
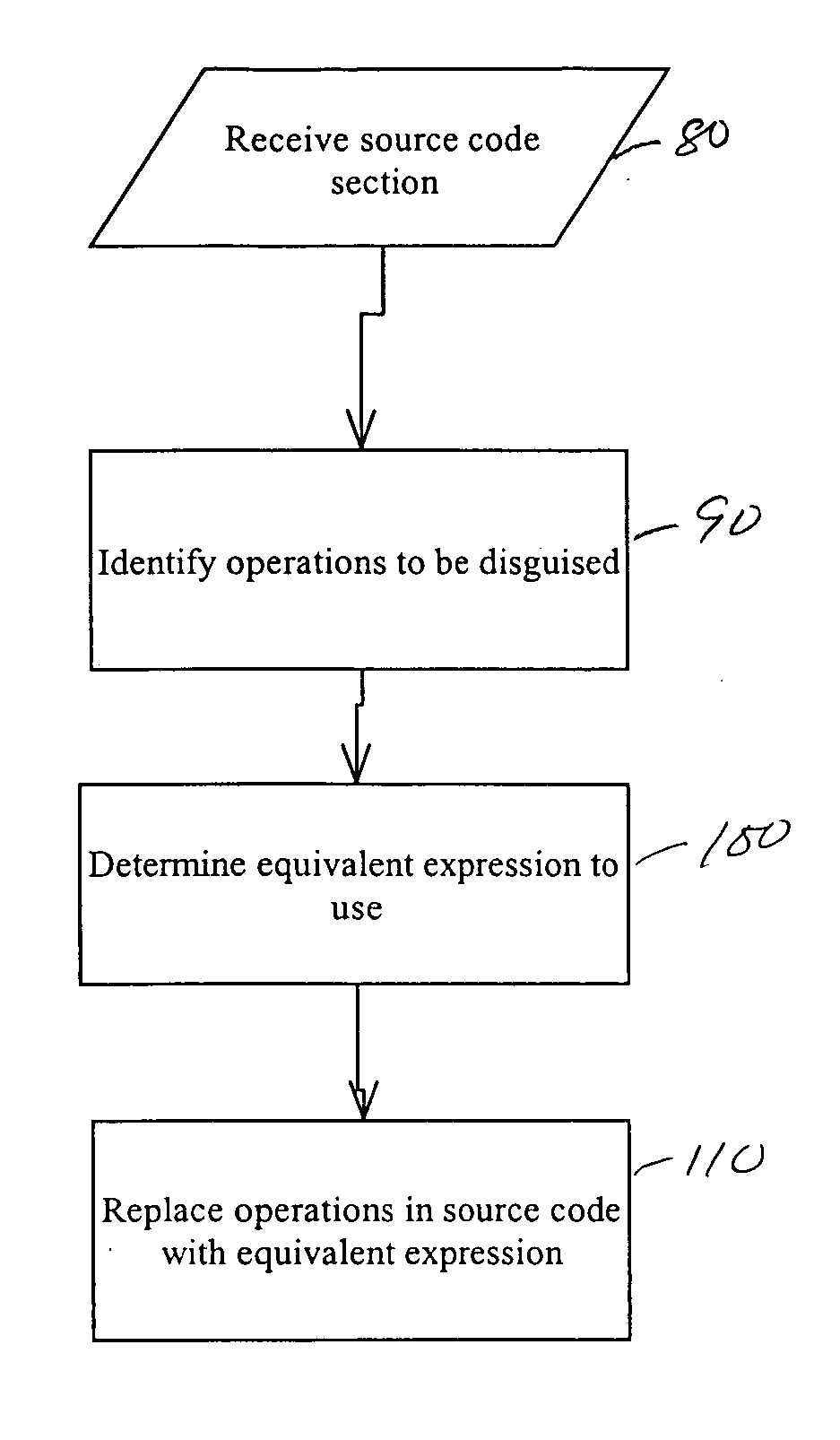
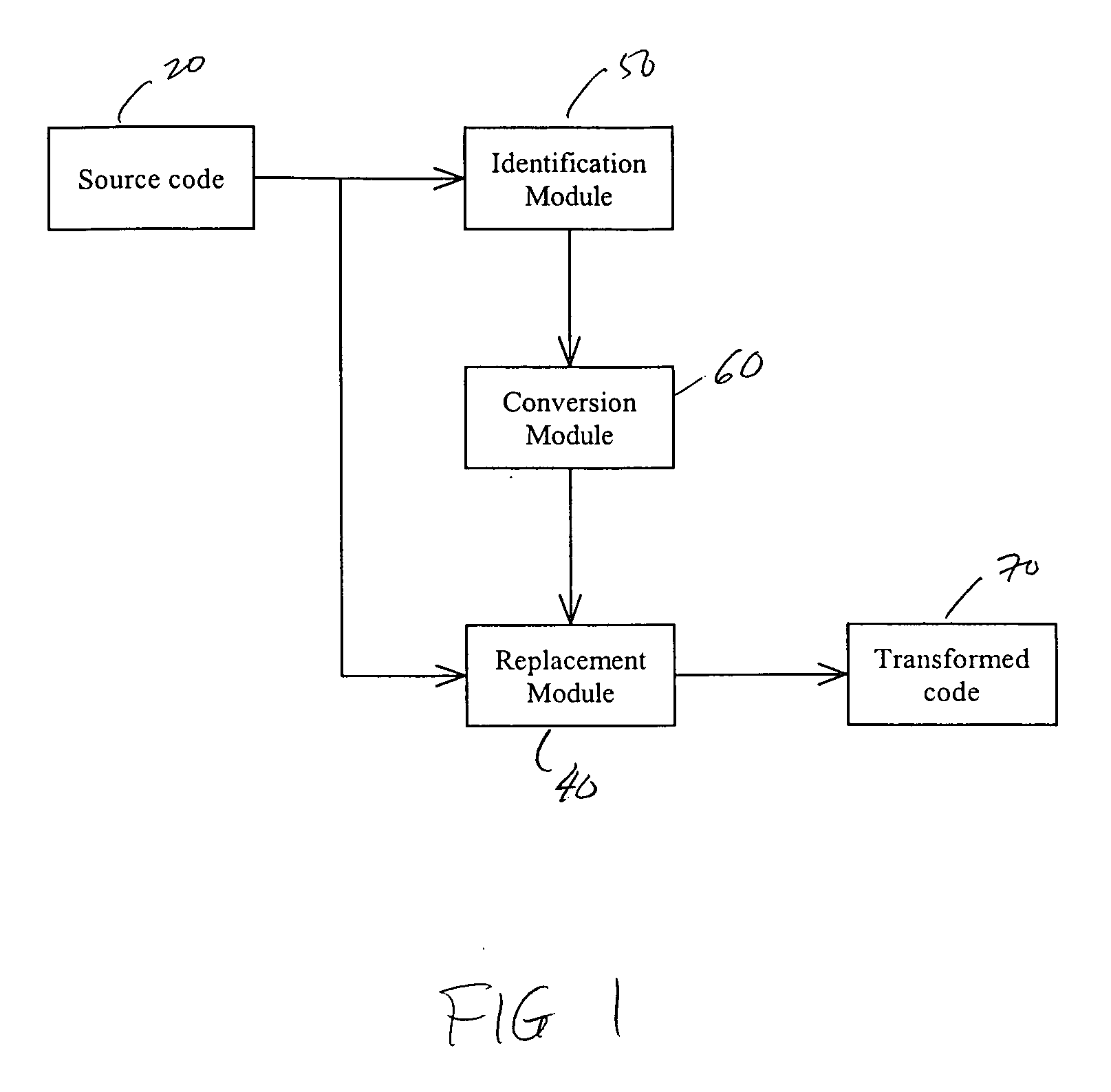
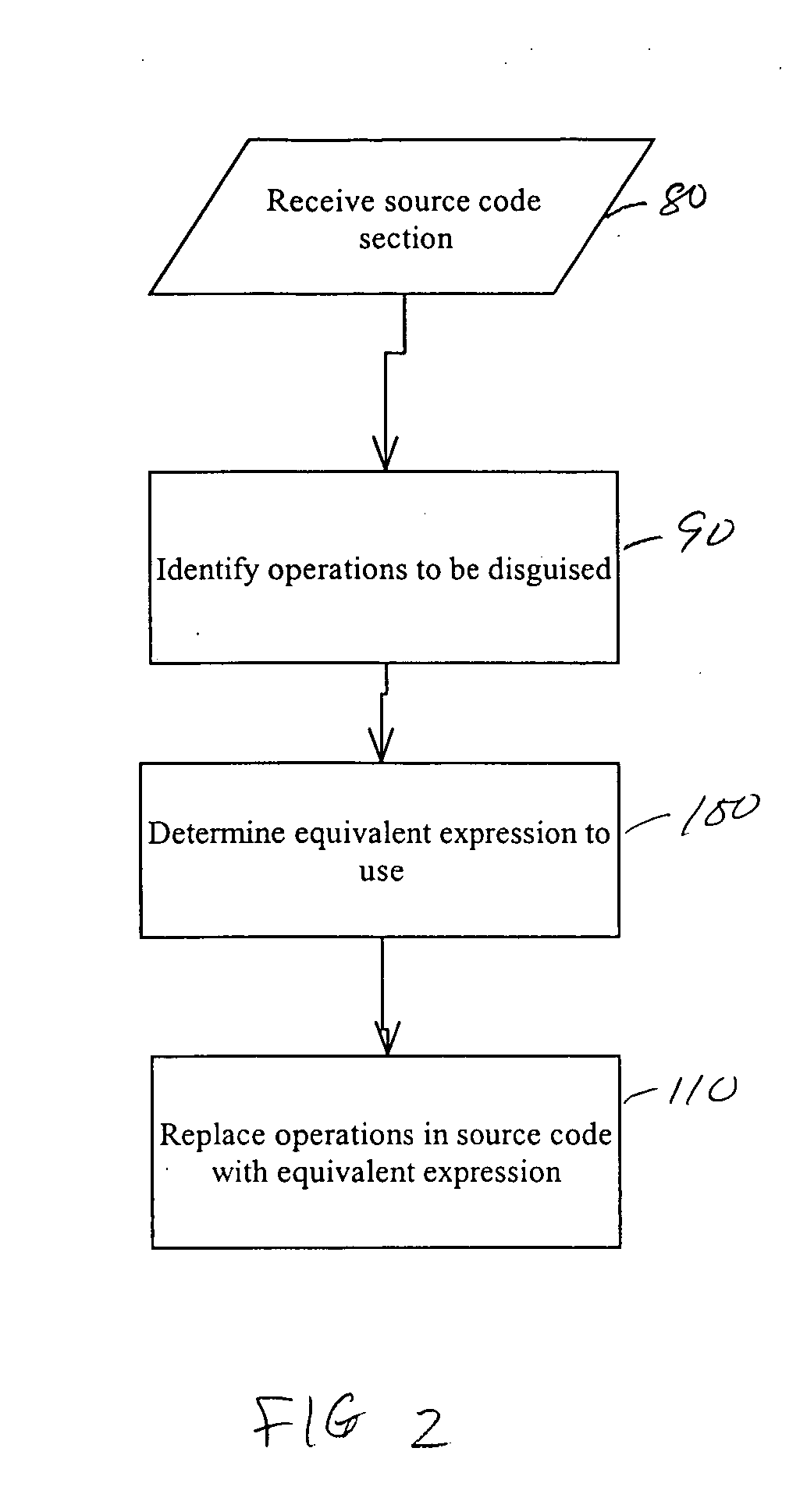
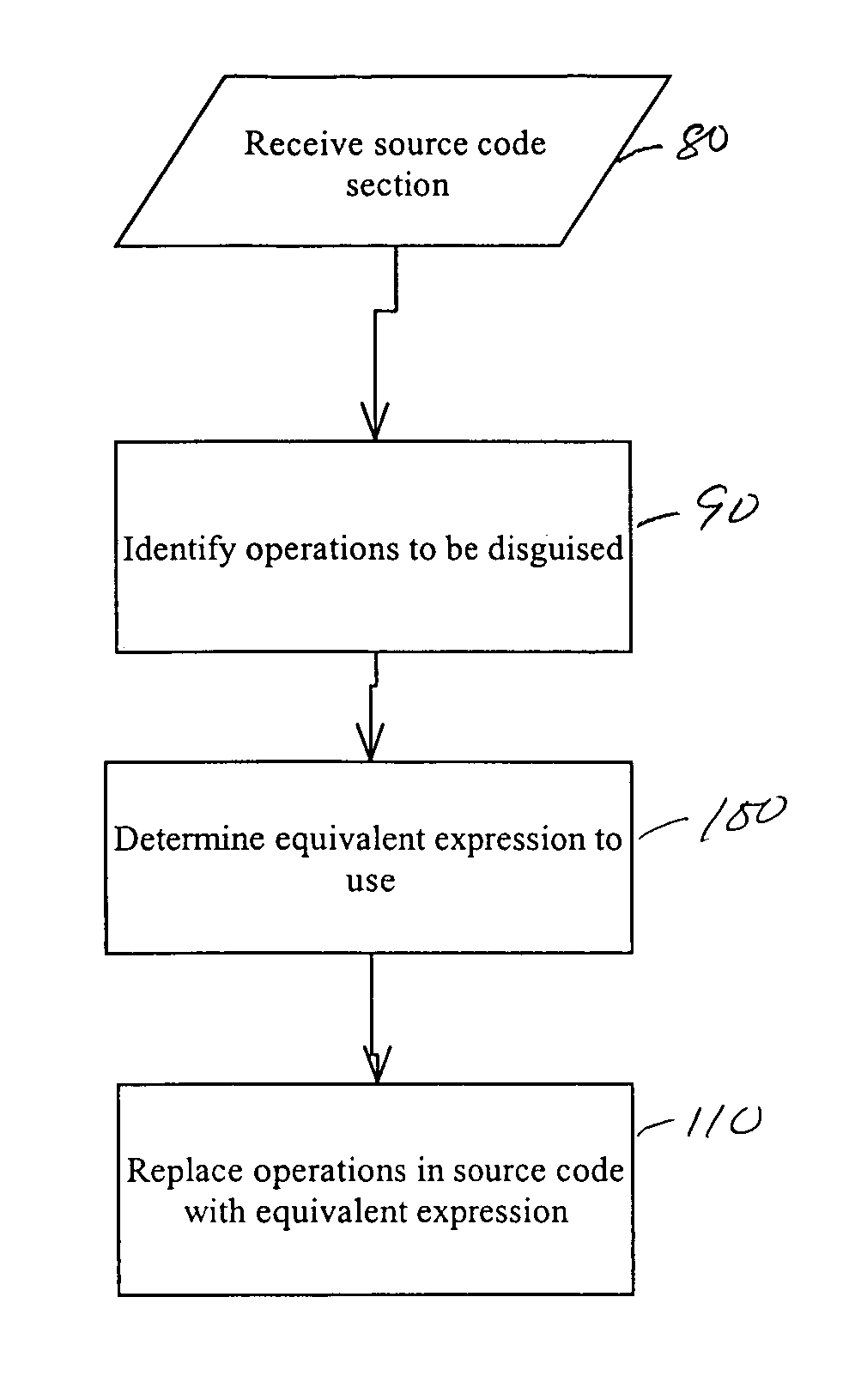
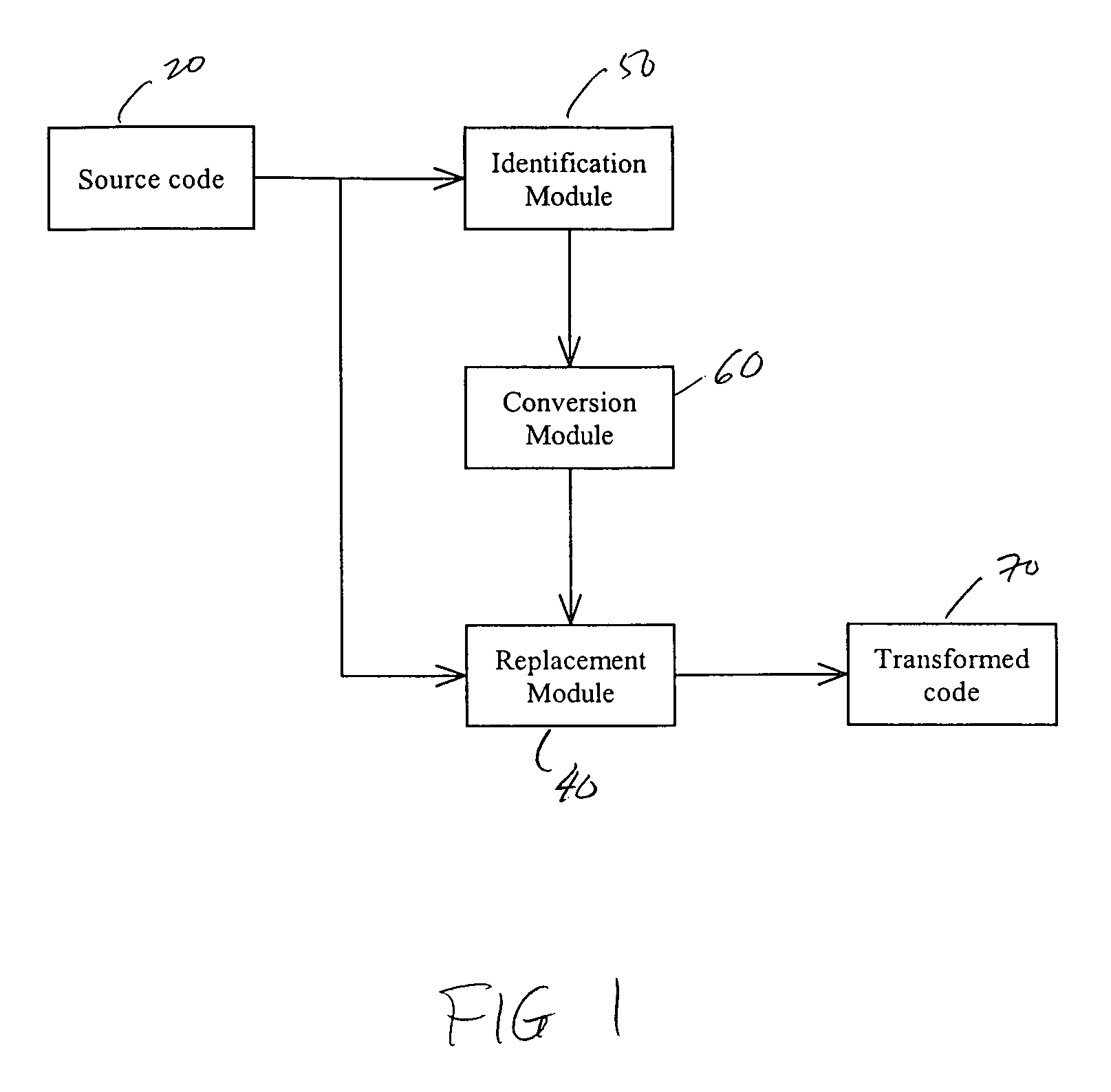
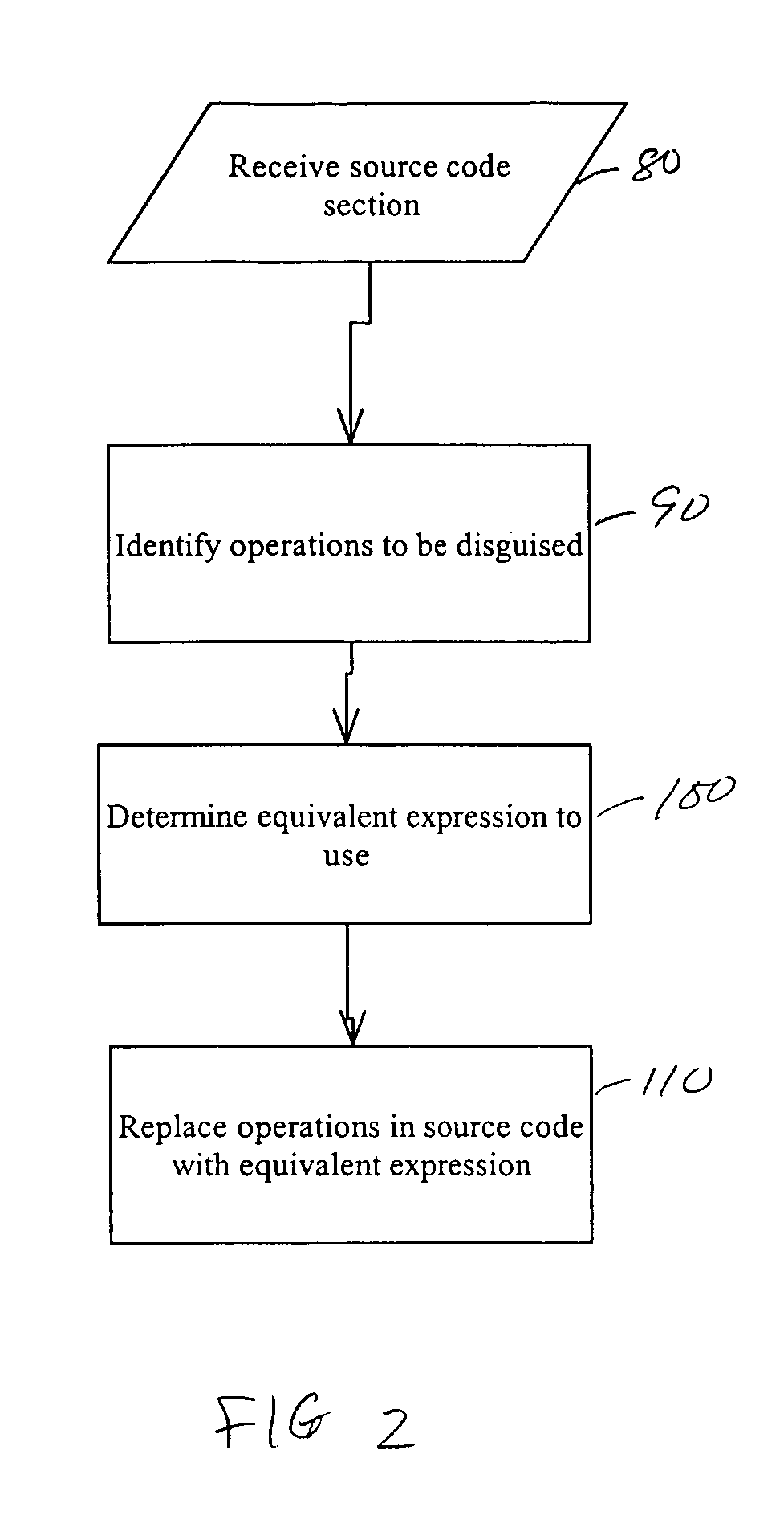
System and method for obscuring bit-wise and two's complement integer computations in software
ActiveUS20050166191A1True natureDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionSoftware systemTheoretical computer science
Systems and methods related to concealing mathematical and logical operations in software. Mathematical and logical operations are disguised by replacing them with logically equivalent expressions. Each equivalent expression has at least two expression constants whose values are based on scaling and bias constants assigned to variables in the original mathematical or logical operation. Each of the expression constants may also be based on additive or multiplicative inverses modulo n of the scaling and bias constants. By replacing the original operations with more complex but logically equivalent expressions containing variables that also involve more operations, the true nature of the original operations is disguised.
Owner:IRDETO ACCESS +1
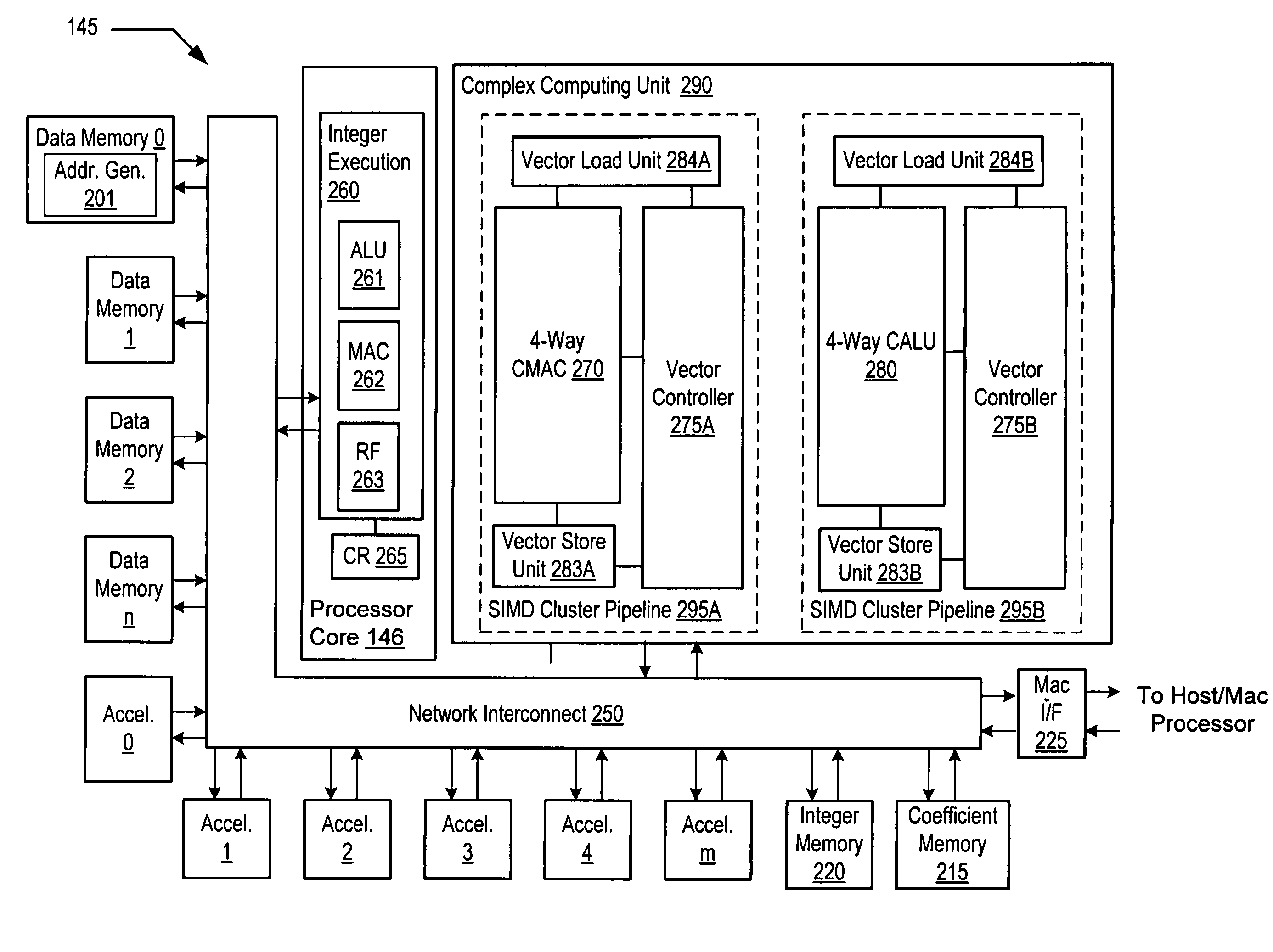
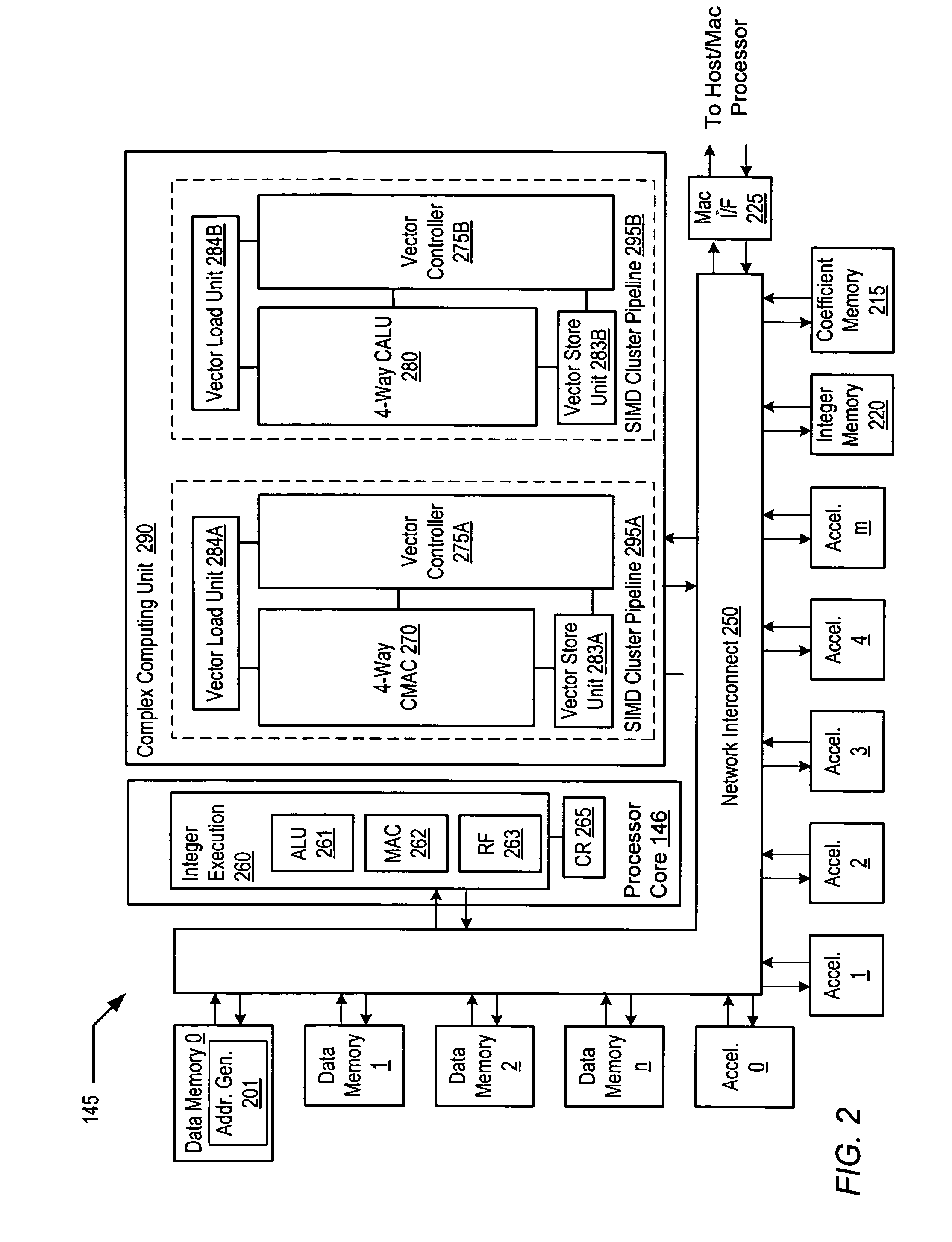
Complex vector executing clustered SIMD micro-architecture DSP with accelerator coupled complex ALU paths each further including short multiplier/accumulator using two's complement
ActiveUS7299342B2General purpose stored program computerSpecific program execution arrangementsArithmetic logic unitExecution unit
A programmable digital signal processor including a clustered SIMD microarchitecture includes a plurality of accelerator units, a processor core and a complex computing unit. Each of the accelerator units may be configured to perform one or more dedicated functions. The processor core includes an integer execution unit that may be configured to execute integer instructions. The complex computing unit may be configured to execute complex vector instructions. The complex computing unit may include a first and a second clustered execution pipeline. The first clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex arithmetic logic unit datapaths configured to execute first complex vector instructions. The second clustered execution pipeline may include one or more complex multiplier accumulator datapaths configured to execute second complex vector instructions.
Owner:CORESONIC AB
System and method for obscuring bit-wise and two's complement integer computations in software
ActiveUS7966499B2Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionSoftware systemLogical operations
Systems and methods related to concealing mathematical and logical operations in software. Mathematical and logical operations are disguised by replacing them with logically equivalent expressions. Each equivalent expression has at least two expression constants whose values are based on scaling and bias constants assigned to variables in the original mathematical or logical operation. Each of the expression constants may also be based on additive or multiplicative inverses modulo n of the scaling and bias constants. By replacing the original operations with more complex but logically equivalent expressions containing variables that also involve more operations, the true nature of the original operations is disguised.
Owner:IRDETO ACCESS +1
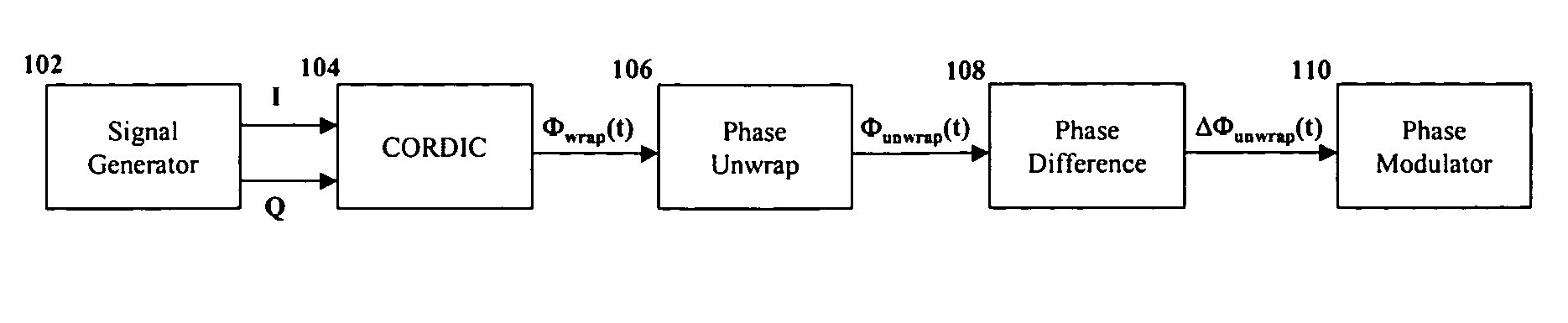
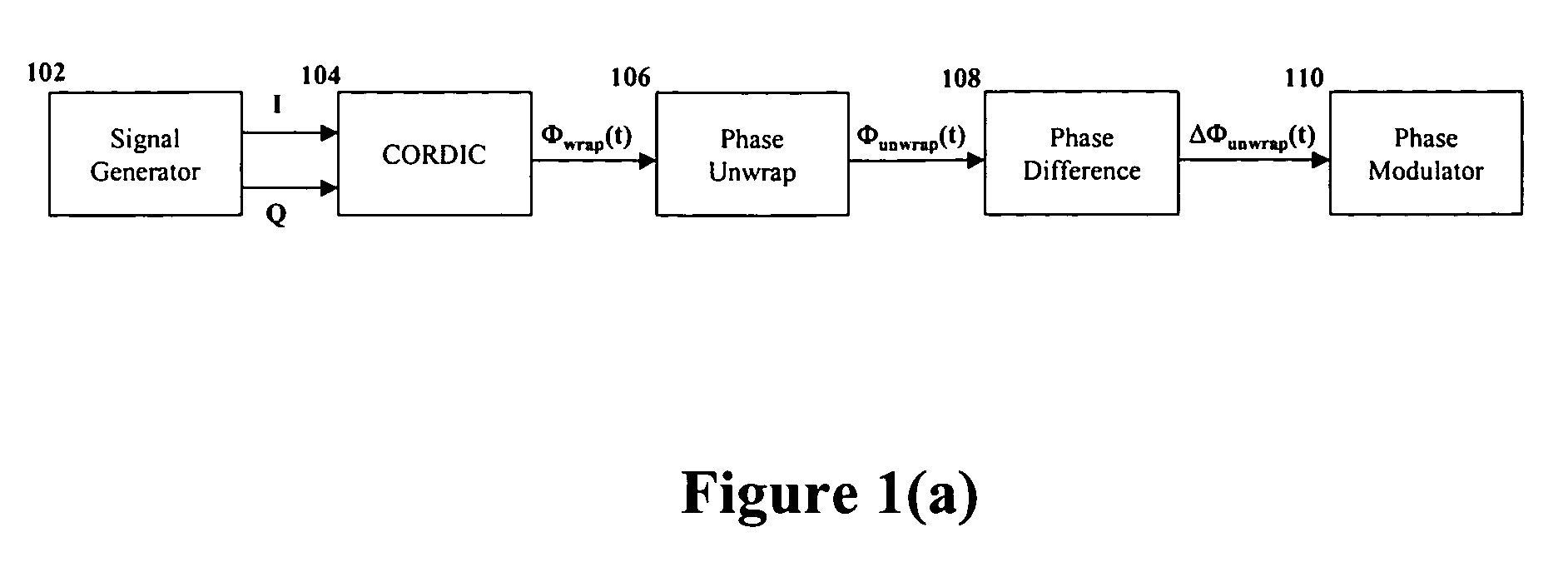
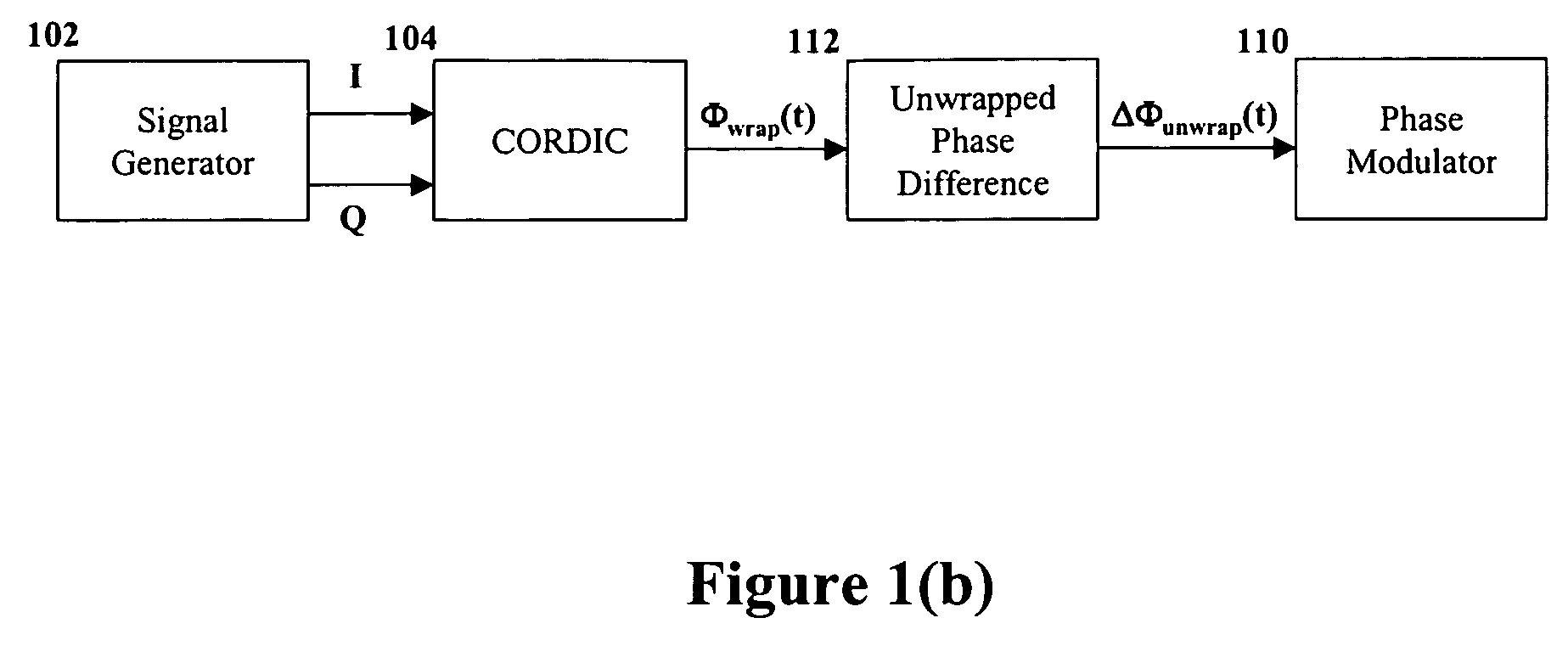
Apparatus, methods and articles of manufacture for signal propagation using unwrapped phase
InactiveUS7356091B2Angle modulation detailsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceTwo's complement
The invention relates to a system for processing an electromagnetic input signal in which processing circuitry may be used to produce a bounded phase signal, such as by calculating an n-bit 2's compliment number in the range of [−1, 1] from phase sample information for an input wave; and producing an unwrapped phase difference signal from the bound phase signal, such as by taking a 2's compliment subtraction using another wrapped phase signal from previous phase sample information. A corrected phase signal may also be used by taking a 2's complement addition using the bounded phase signal, wherein the unwrapped phase difference signal is produced using the corrected phase signal.
Owner:PINE VALLEY INVESTMENTS INC
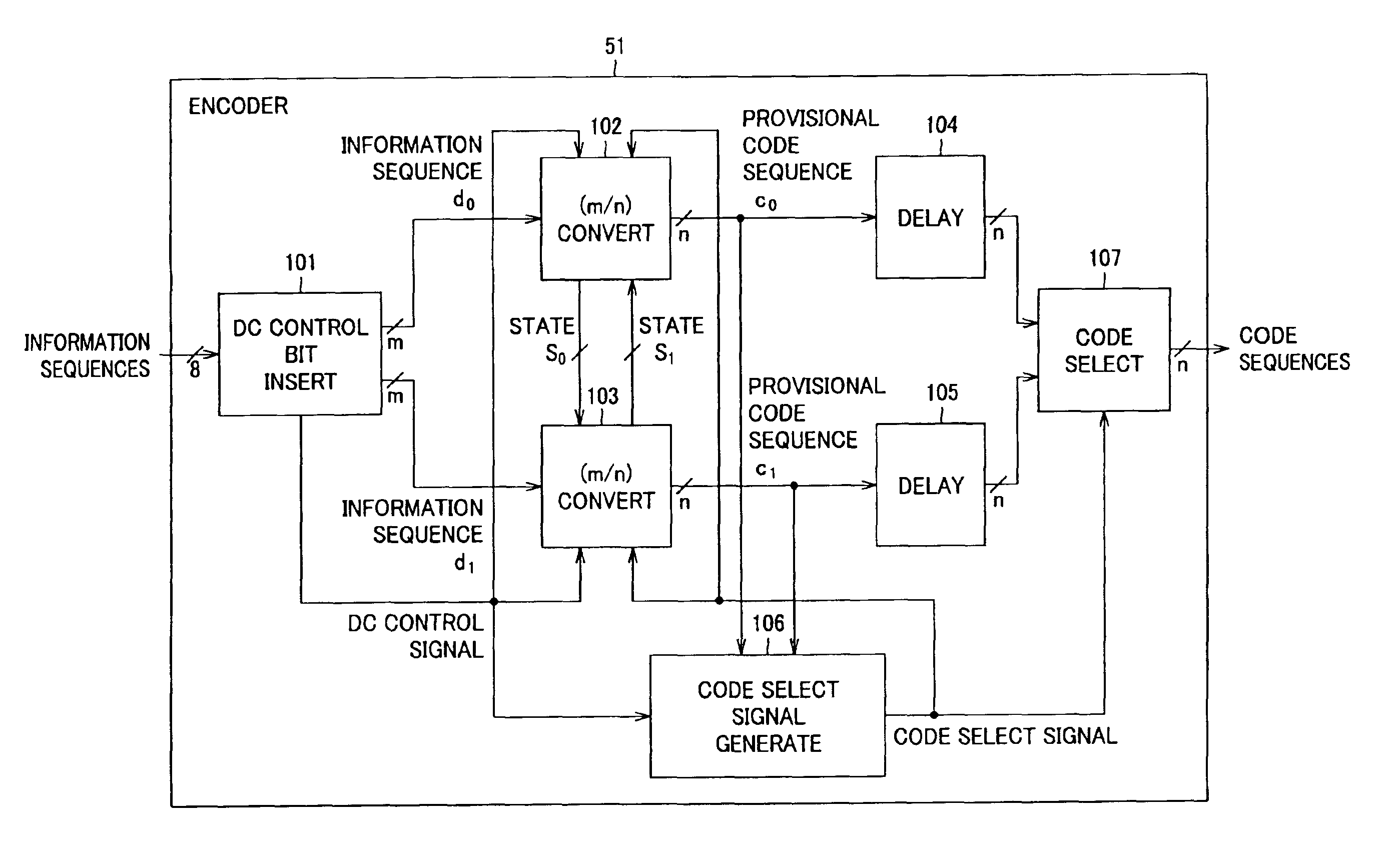
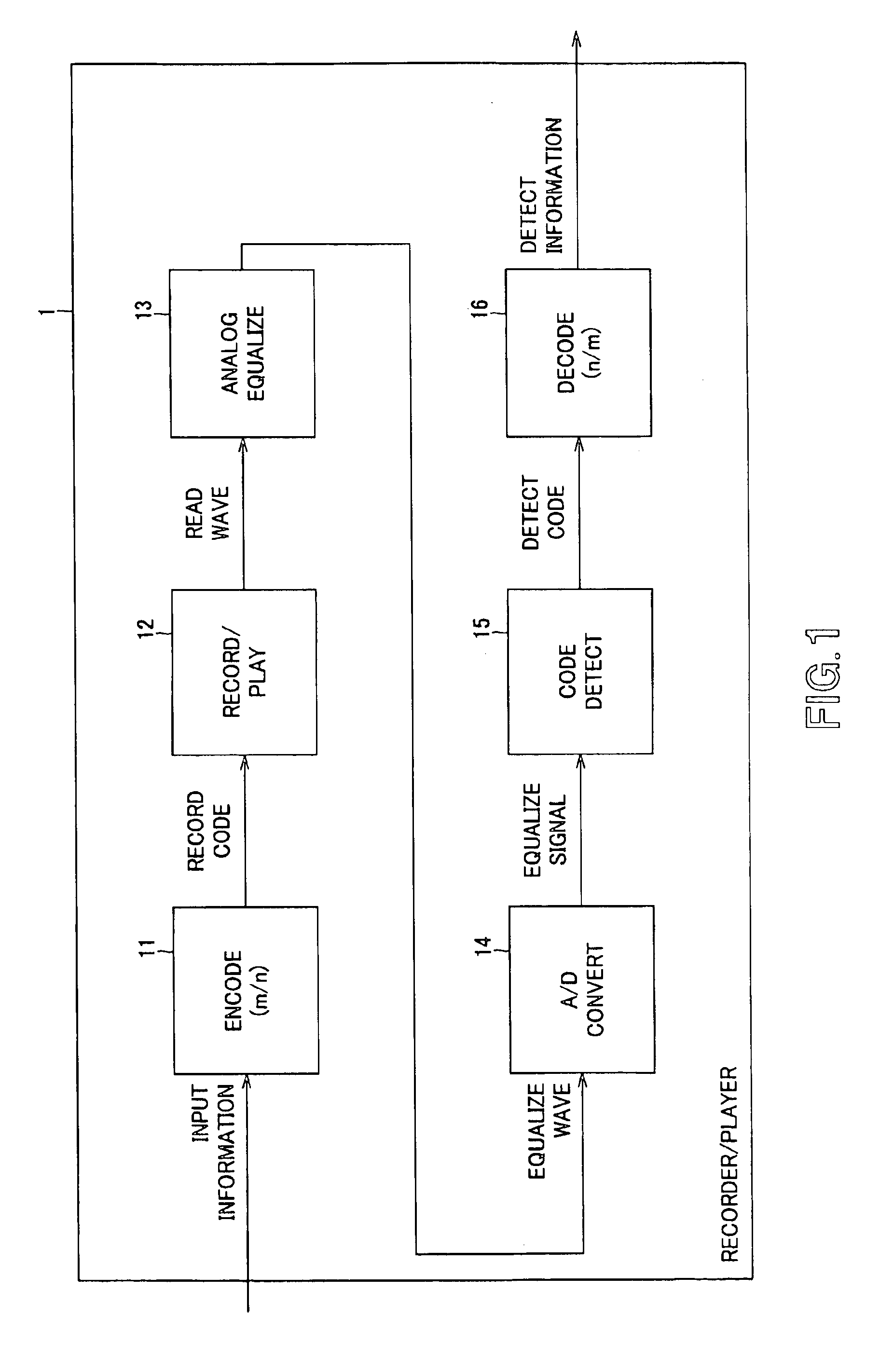
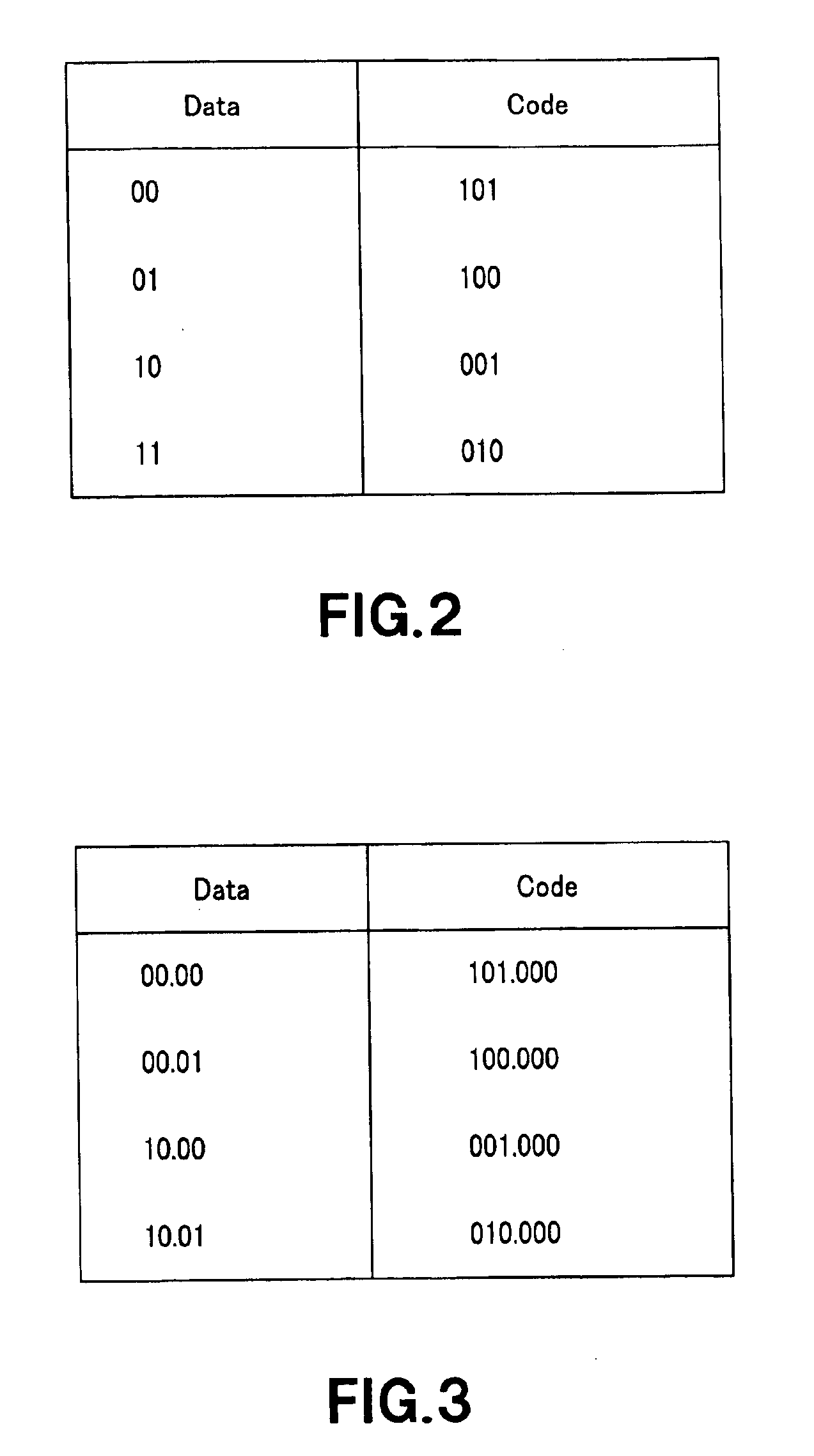
Encoding apparatus and method, recording medium and program
InactiveUS6891483B2Record information storageIndividual digits conversionComputer hardwareCode conversion
A code sequence is encoded using a code conversion table in which the parity of the code sequence varies until the code states become equal to each other. The code word assignment used in this code conversion table is such that the decoded code word constraint length is 3 blocks and q0≠q1 for an arbitrary information sequence is satisfied even if a DC control bit is inserted at any of the first and second bits of an information word. Code states s0 and s1 when information sequences d0 and d1 resulted from insertion of provisional DC control bits 1 and 0 inserted at the top of an information sequence “1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0” are encoded starting with a state 3 according to a predetermined code conversion table are equal to each other, namely, s0=s1=6, in a third block, and two's complement q0 of a sum of code sequences c0 up to a time when the code states are equal to each other is “0” while two's complement q1 of a sum of code sequences c1 up to that time is “1”. That is, the condition that q0≠q1 is met. The code sequence can be applied to a recorder / player or encoder.
Owner:SONY CORP
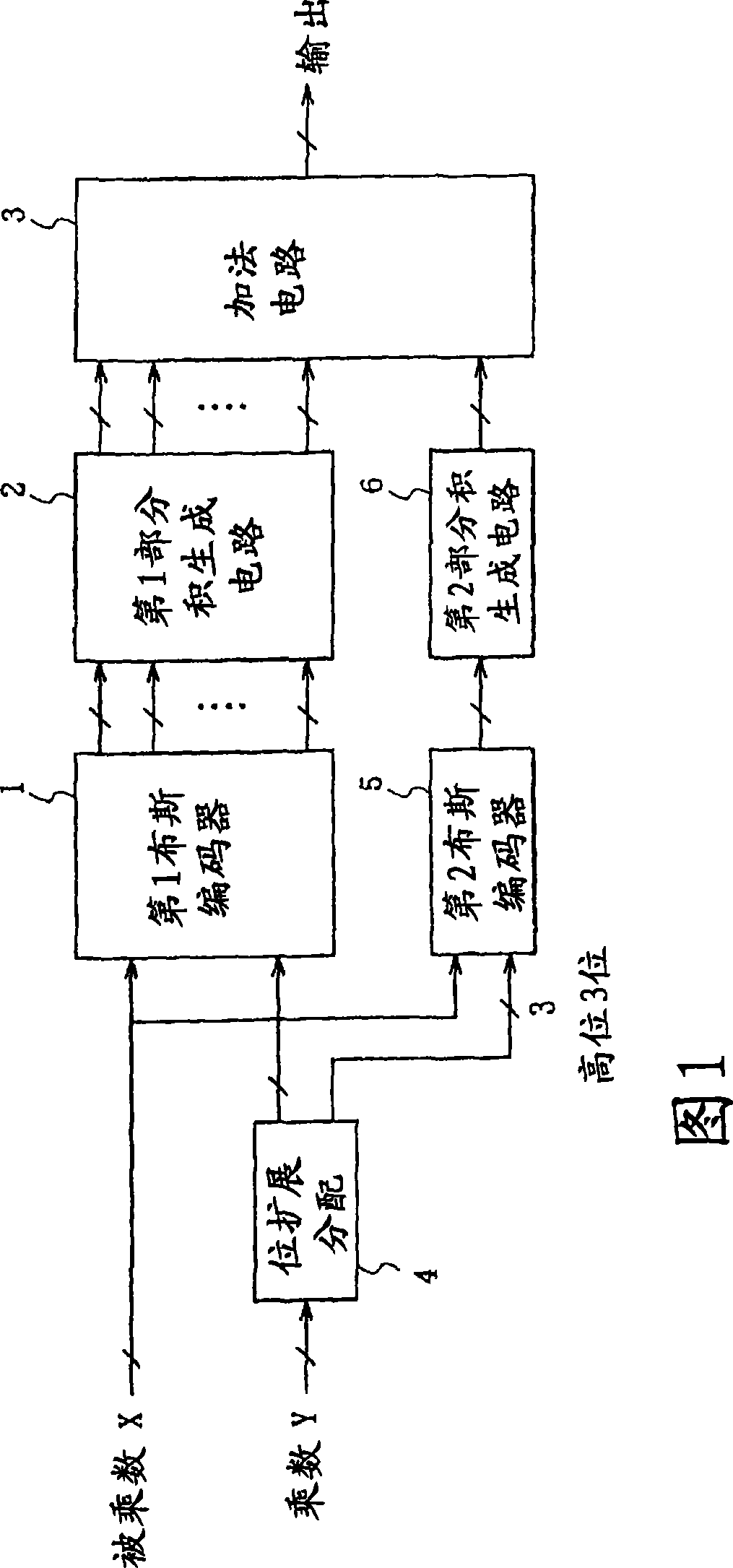
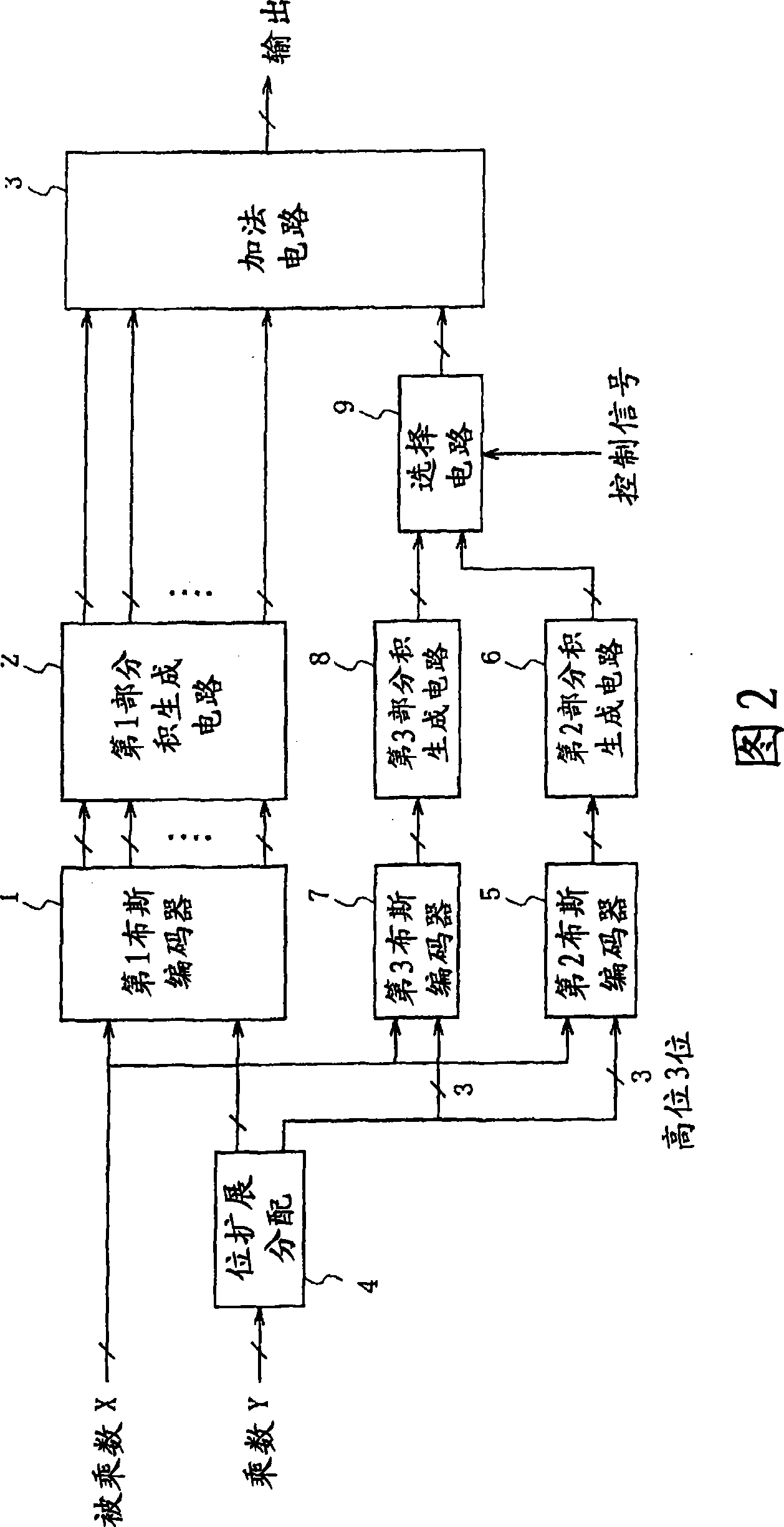
Multiplier, digital filter, signal processing device, synthesis device, synthesis program, and synthesis program recording medium
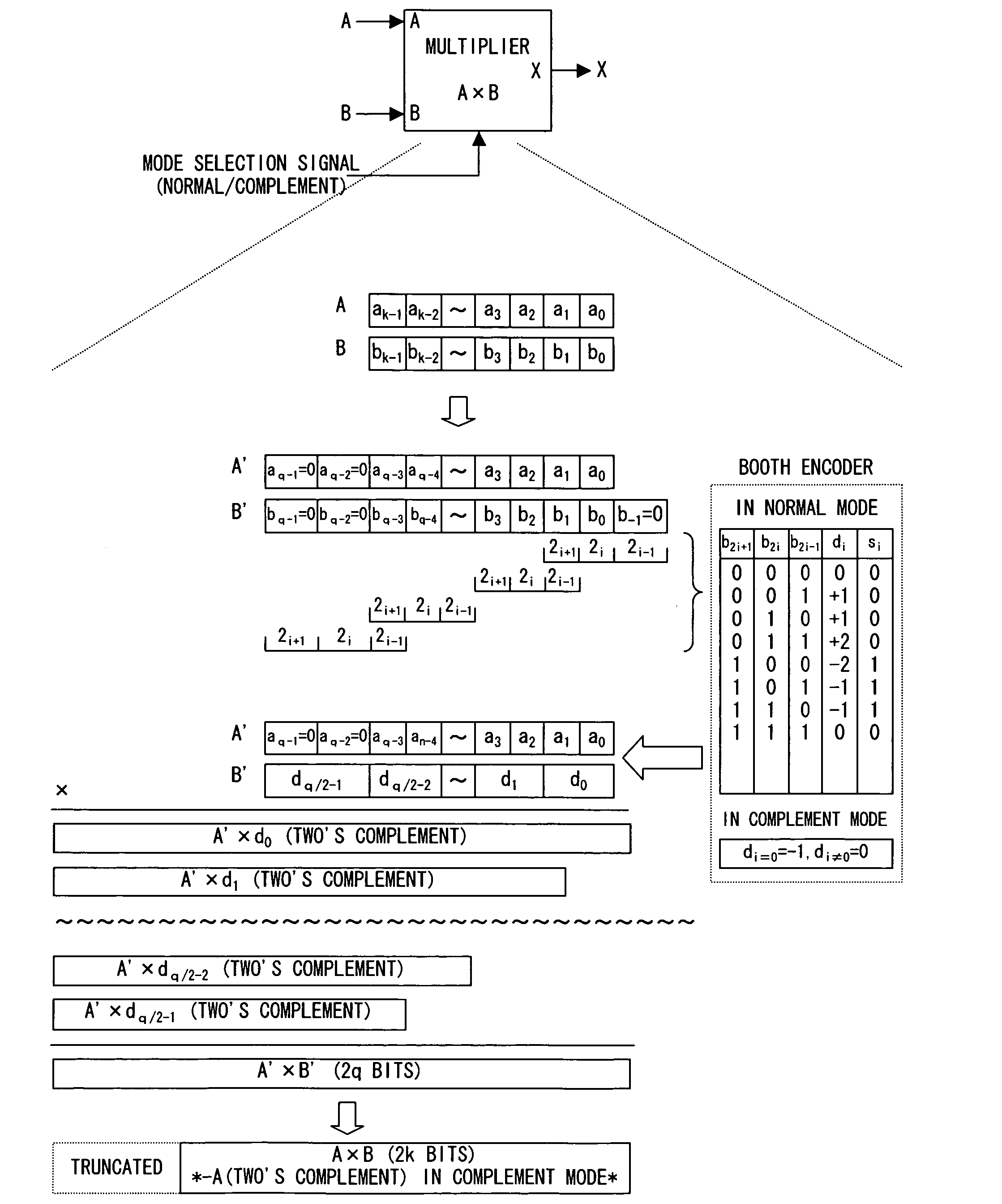
The invention provides a multiplier, digital filter, signal processing device, composition device, composition program and composition program recording medium.Conventional two's complement multiplier which is constituted by a Booth encoder, a partial production generation circuit, and an adder has a problem that the circuit scale would be increased because a bit extension is performed when the multiplier is adapted to an unsigned multiplication. A multiplication circuit of the present invention is provided with a first Booth encoder (1) for encoding lower-order several bits of a multiplier according to first rules of encoding using a Booth algorithm, and a second Booth encoder (5) for encoding most-significant several bits of the multiplier according to second rules of encoding using a Booth algorithm, which are different from the first rules of encoding, and thereby the most-significant several bits of the multiplier are encoded using the Booth algorithm which is different from that for the lower-order several bits.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Multiply and multiply and accumulate unit
InactiveUS20080243976A1Computation using non-contact making devicesFull adder cellLeast significant bit
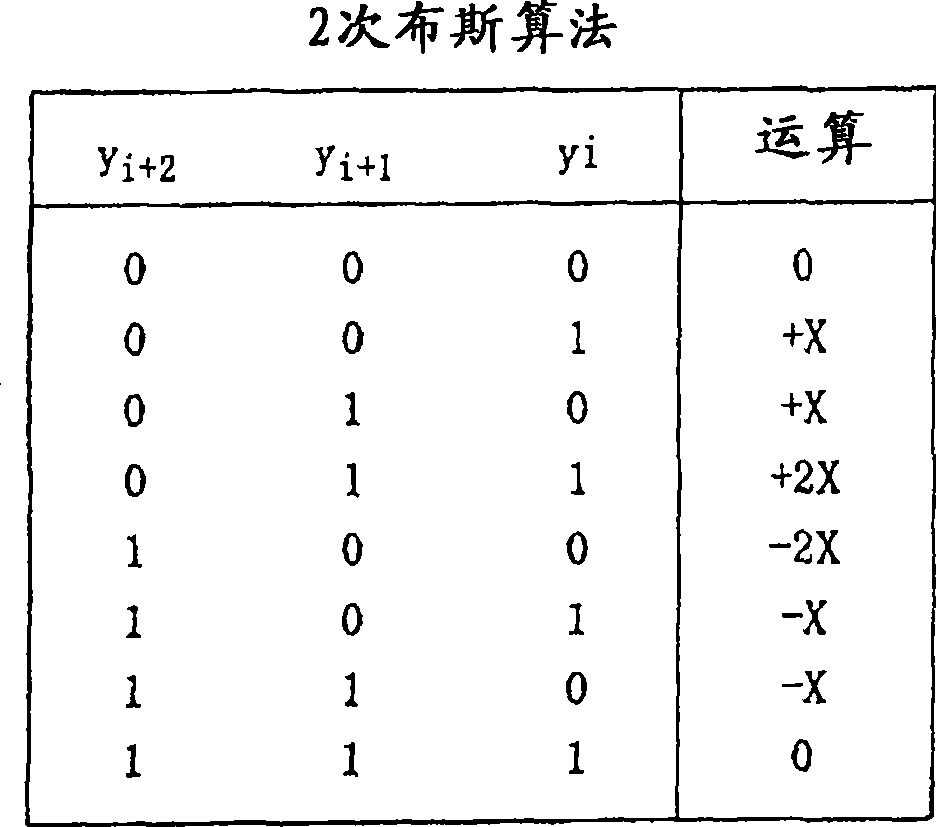
The present invention relates to a multiply apparatus and a method for multiplying a first operand consisting of na bits and a second operand consisting of nx bits. In one embodiment the multiply apparatus comprising a CSA (CSA) unit with nx rows each comprising na AND gates for calculating a single bit product of two single bit input values and adder cells for adding results of a preceding row to a following row and a last output row for outputting a carry vector and a sum vector, and logic circuitry for selectively inverting the single bit products at the most significant position of the nx−1 first rows and at the na−1 least significant positions of the output row in response to a first configuration signal before inputting the selectively inverted single bit products to respective adder cells for switching the CSA unit selectively between processing of signed two's complement operands and unsigned operands in response to the first configuration signal. In one embodiment the method comprising outputting a carry vector and a sum vector, and adding the carry vector and the sum vector provided by the output row of the CSA unit via a CPA unit consisting of a row of na full adder cells, wherein the carry input of the CPA unit is coupled to receive a first configuration signal to switch between processing of signed and unsigned two's complement operands.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
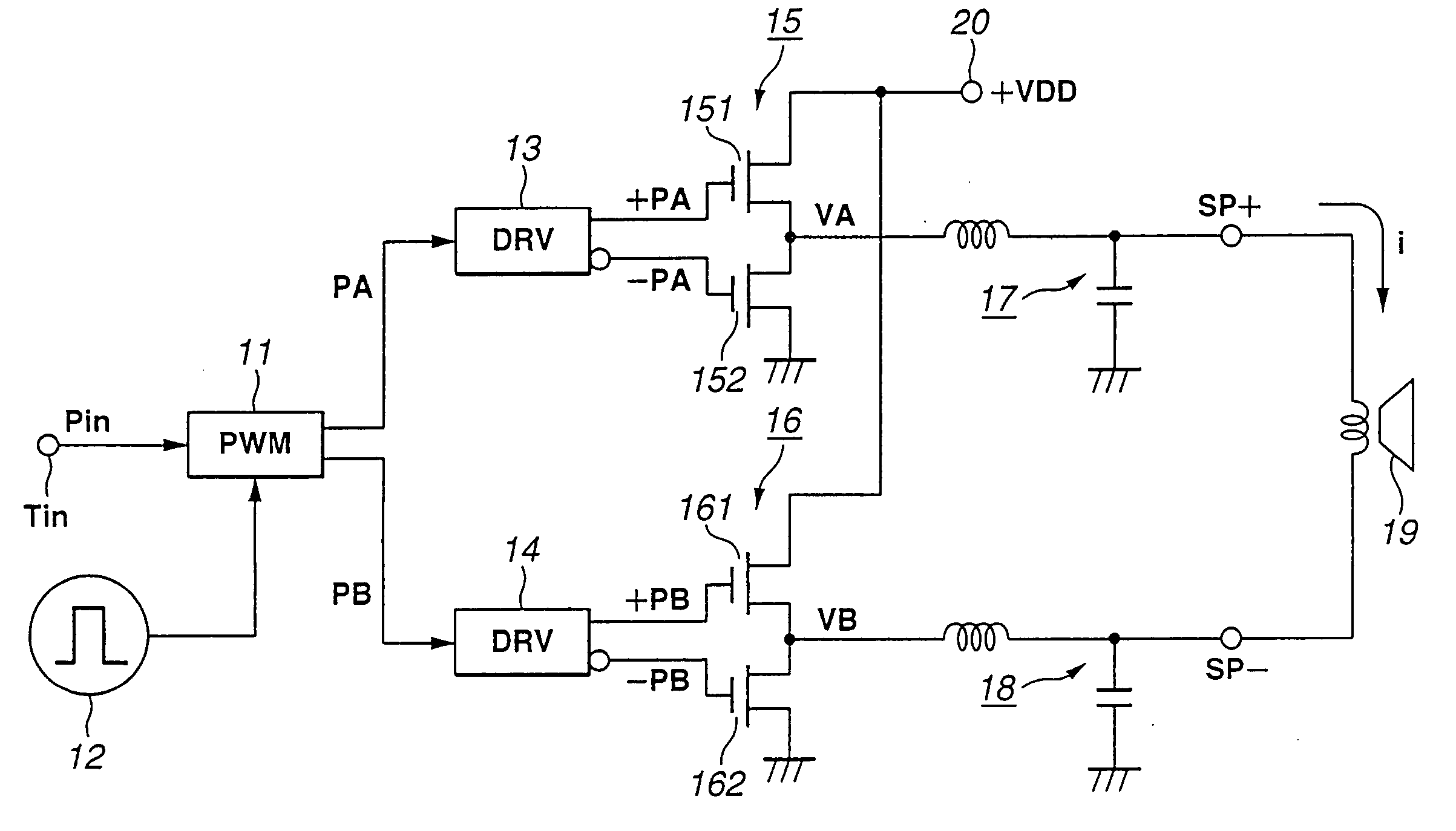
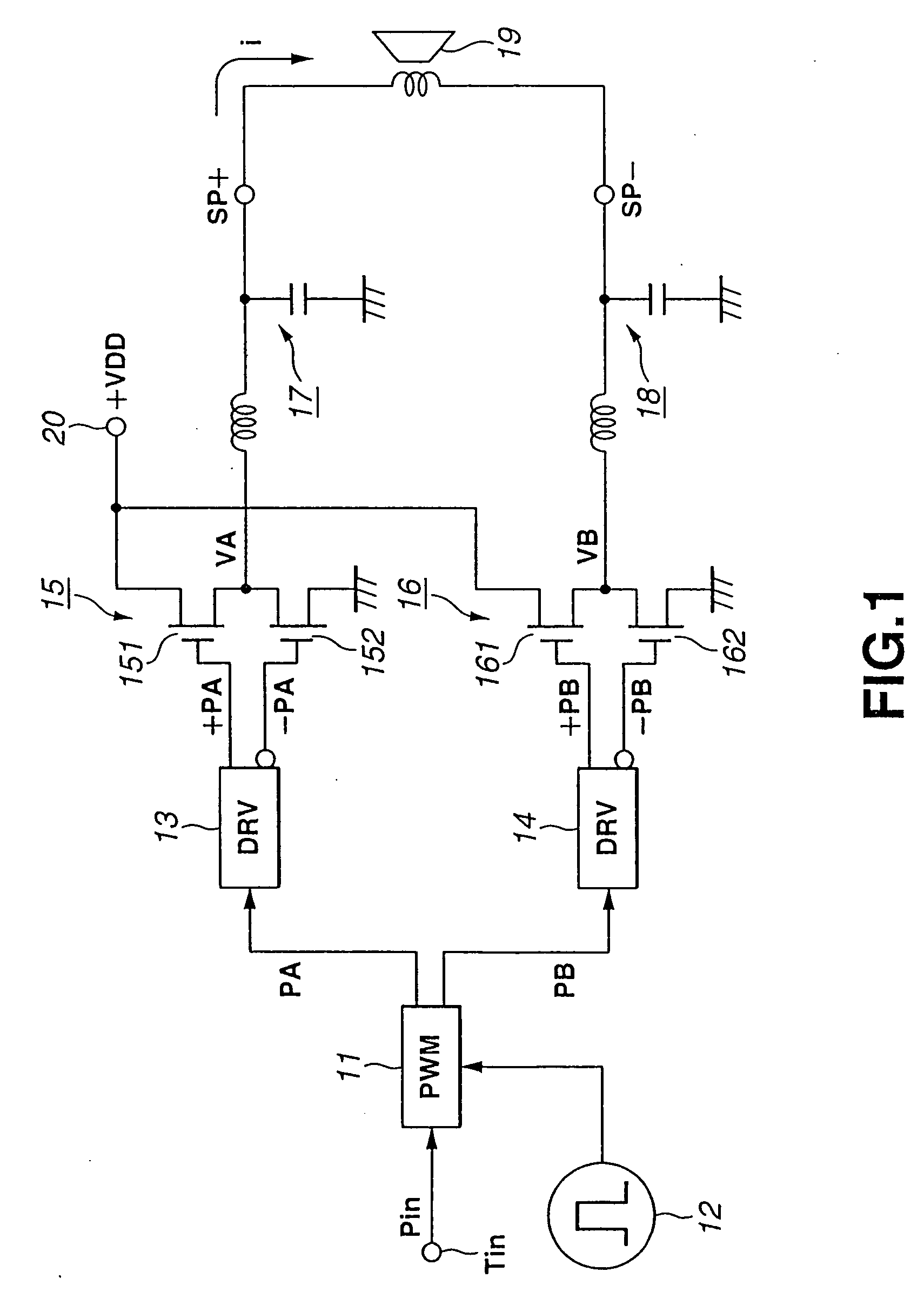
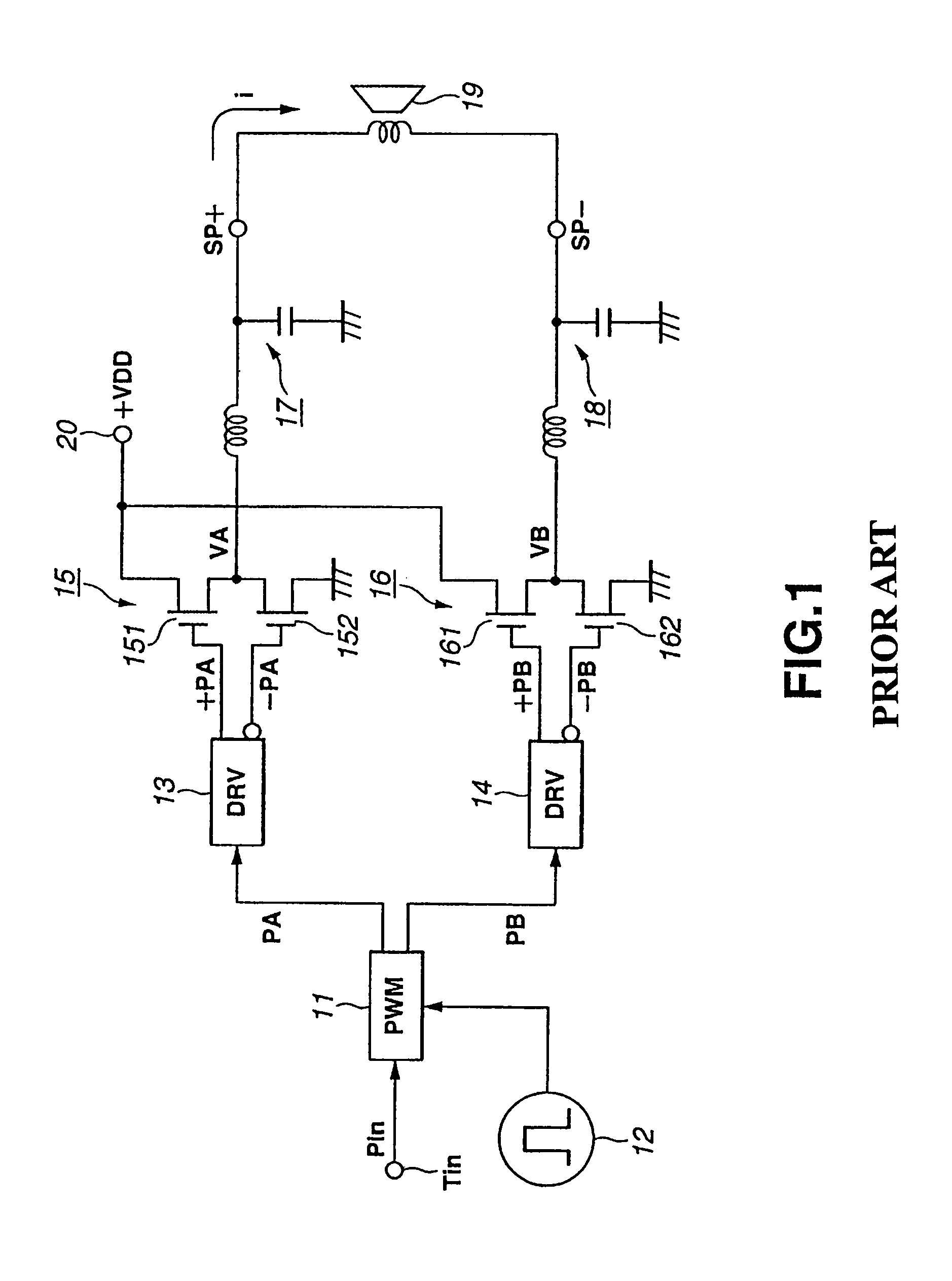
Power amplifier
InactiveUS20050231276A1Improved and novelPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersAudio power amplifierPush pull
In a power amplifier driven by a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal, a first pair of drive pulses opposite in level to each other is formed from a first pulse width modulation signal whose quantization level corresponds to its pulse width and supplied to a first push-pull circuit (15). A second pair of drive pulses opposite in level to each other is formed from a second pulse width modulation signal whose two's complement of quantization level corresponds to its pulse width, and supplied to a second push-pull circuit (16). A speaker (19) is connected between the first and second push-pull circuits (15 and 16). A deviation between potentials at the output terminals of the first and second push-pull circuits (15 and 16), respectively, is detected. When a deviation is detected, the push-pull circuits are substantially stopped from operating.
Owner:SONY CORP
Converting negative floating point numbers to integer notation without two's complement hardware
InactiveUS6965906B1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsMultiplexerParallel computing
For use in a processor having integer and floating point execution cores, logic circuitry for, and a method of, converting negative numbers from floating point notation to integer notation. In one embodiment, the logic circuitry includes: (1) a shifter that receives a number in floating point notation and shifts a fraction portion of the received number as a function of an exponent portion thereof to yield a shifted fraction portion and rounding data, (2) a one's complementer, coupled to the shifter, that inverts the shifted fraction portion to yield an unincremented inverted shifted fraction portion, (3) an incrementer, coupled to the one's complementer, that increments the unincremented inverted shifted fraction portion to yield an incremented inverted shifted fraction portion and (4) a multiplexer, coupled to the one's complementer and the incrementer, that selects one of the unincremented inverted shifted fraction portion and the incremented inverted shifted fraction portion based on the rounding data thereby to yield the received number in integer notation.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
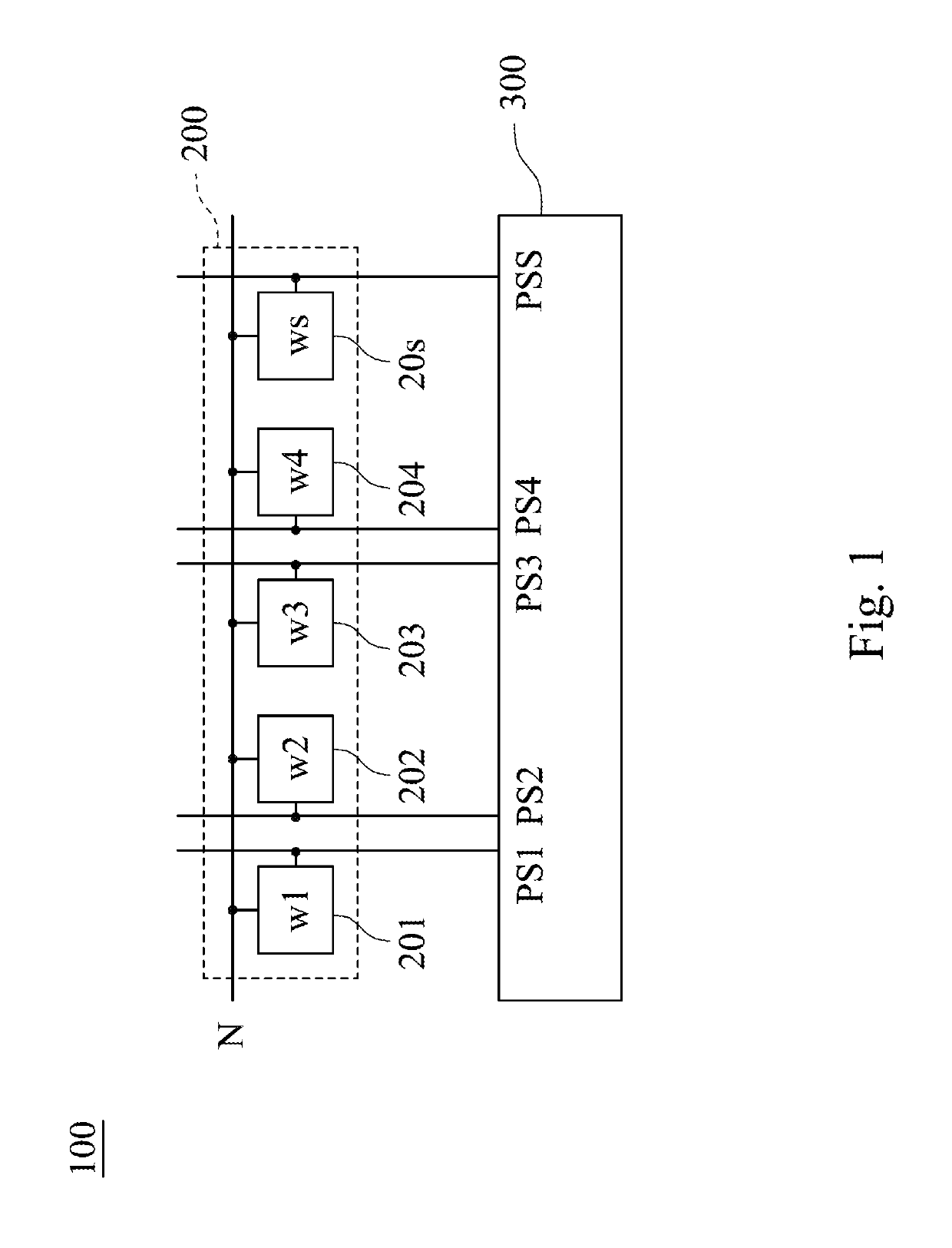
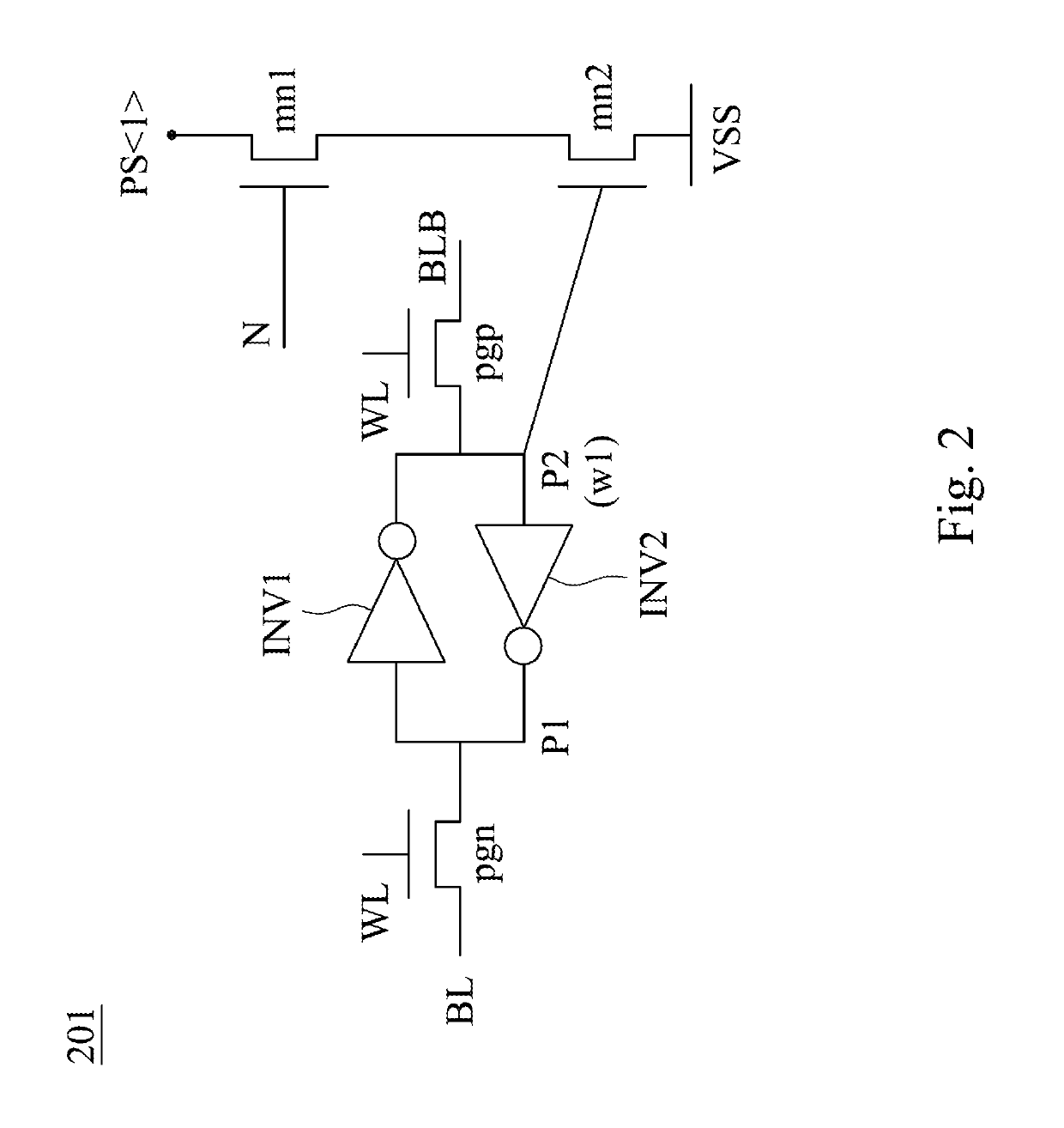
Multi-bit computing circuit for computing-in-memory applications and computing method thereof
A multi-bit computing circuit for computing-in-memory applications is controlled by an input port and includes a memory cell array and a capacitor sharing unit. The memory cell array includes a plurality of memory cells connected to the input port. The memory cells store a weight which is formed in two's complement. The capacitor sharing unit includes a plurality of switches, a plurality of capacitors and a sense amplifier. The switches are electrically connected to the memory cells, respectively. The capacitors are electrically connected to the switches, respectively. The sense amplifier is electrically connected to the capacitors and generates a total operational value. The capacitors are located among the switches and the sense amplifier, and the switches are switched to enable the total operational value to be equal to the input value multiplied by the weight. The present disclosure utilizes 8T SRAM cells without an extra DAC structure.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
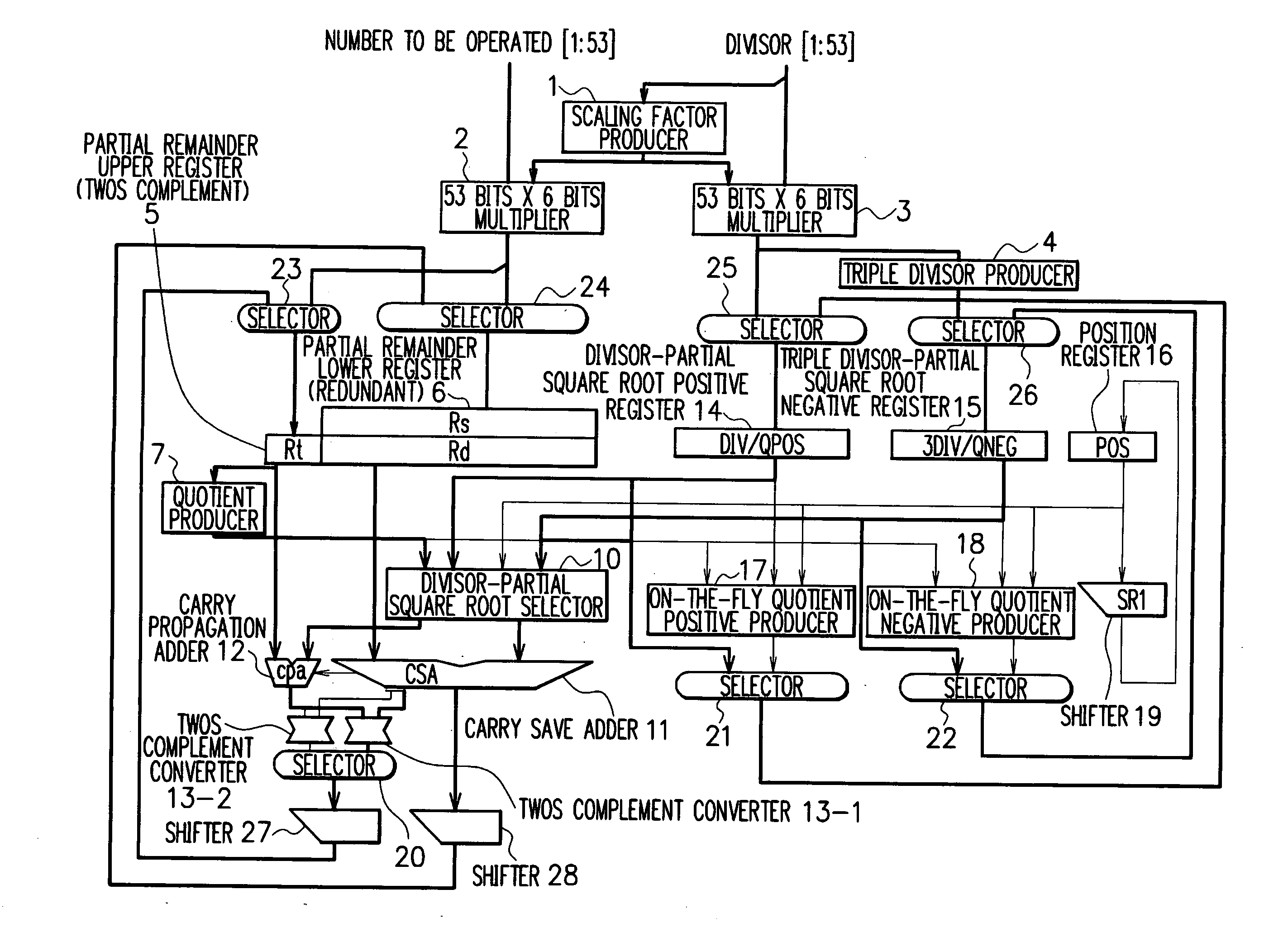
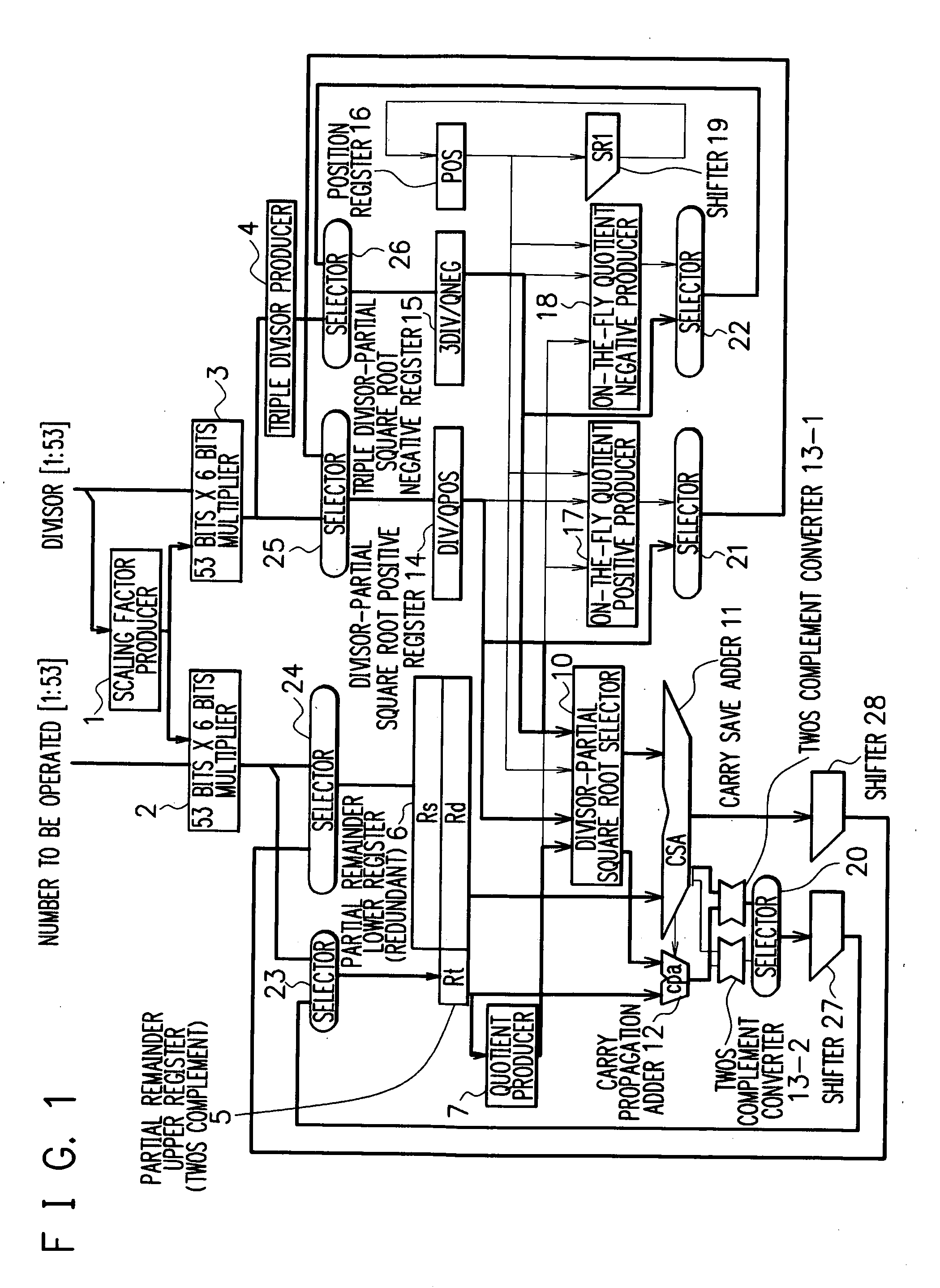
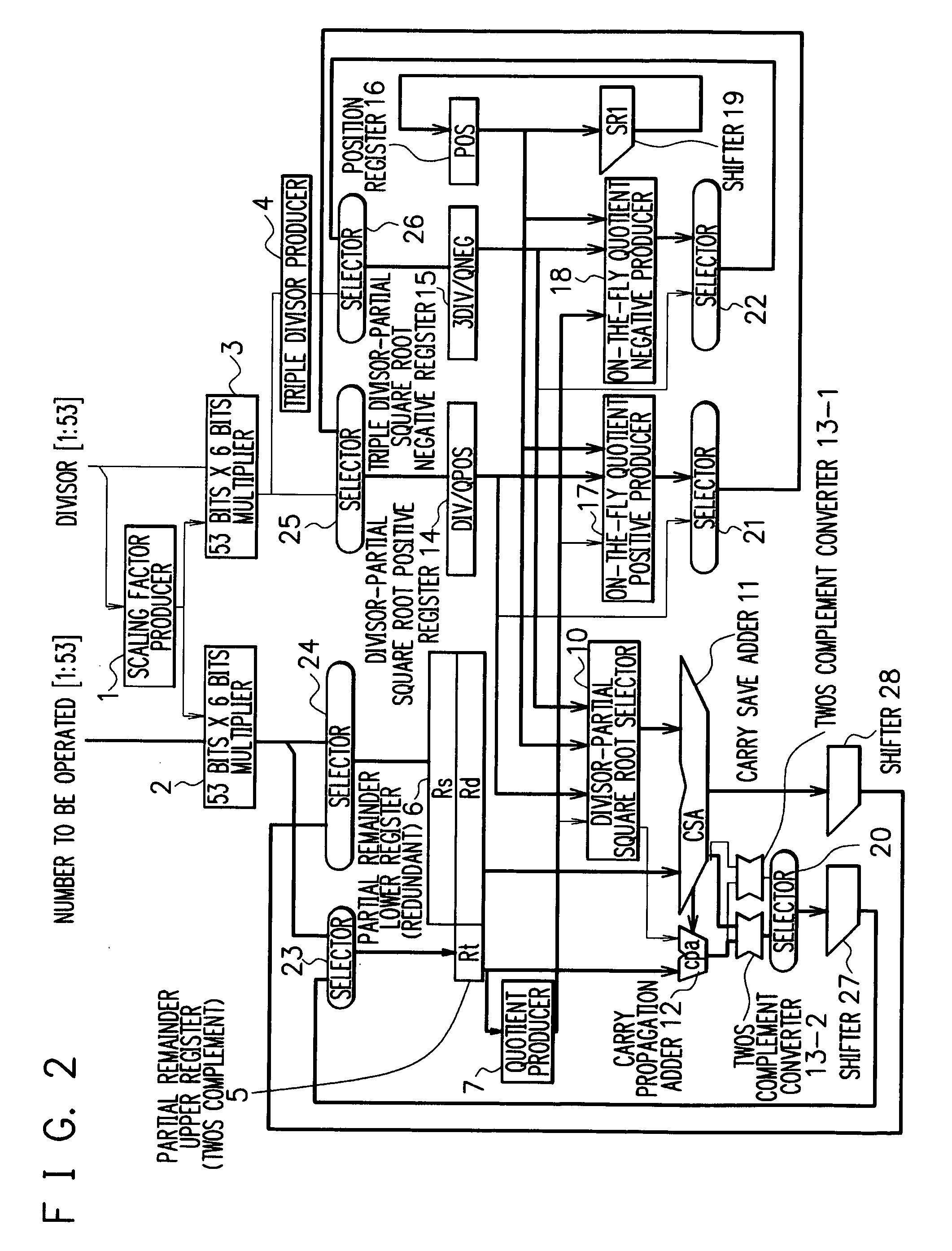
Division and square root arithmetic unit
ActiveUS20060129623A1Easy to processImprove processing speedComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesPartition of unityCarry-save adder
A division and square root arithmetic unit carries out a division operation of a higher radix and a square root extraction operation of a lower radix. A certain bit number (determined on the basis of a radix of an operation) of data selected from upper bits of the output of a carry save adder and the output of the adder are input to convert the data into twos complement representation data, and the twos complement representation data is shifted a certain bit number (determined on the basis of the radix of the operation) to use the shifted data for a partial remainder of the next digit. Hence, a large number of parts such as registers of a divisor and a partially extracted square root can be commonly used in a divider and a square root extractor to realize an effective and high performance arithmetic unit.
Owner:NEC CORP
Arithmetic device for multiple precision arithmetic for Montgomery multiplication residue arithmetic
InactiveUS7480691B2Reduce latencyComputation using non-contact making devicesCoding/ciphering apparatusComputer sciencePartial product
In an arithmetic device which performs a multiplication of a multiplicand A and a multiplier B expressed by bit patterns using a secondary Booth algorithm, an encoder selects a partial product indicating −A when the value of i specifying three consecutive bits of B is 0, and selects a partial product indicating 0 when the value of i is not 0. An addition circuit generates a two's complement of A from the partial product indicating −A, and outputs it as a multiplication result.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Memory device and device and method for detecting motion vector
InactiveUS20100002774A1Increase computing speedLow costImage enhancementTelevision system detailsBit lineMotion vector
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for generating the multiplicative inverse in a finite field GF(p)
ActiveUS7574469B2Eliminate the problemEasy to operateDigital computer detailsComputations using residue arithmeticTheoretical computer scienceExtended Euclidean algorithm
The essence of the invention is an effective method for generating the multiplicative inverse in a finite field GF(p) where p is prime, i.e. for generating the modular inverse. This method is derived from the Extended Euclidean Algorithm (EEA). The method is for binary execution of operations during the process of generating the modular inverse, with respect to the lowest number of addition, subtraction and shift operations possible. The proposed method avoids redundant operations for converting odd and negative values, which are performed in methods currently in use. To achieve that, negative numbers are represented in the two's complement code, values in the control part of the EEA are shifted to the left, and a new definition of the boundary and control conditions is utilized in the procedure. Minimizing the number of additions and subtractions is desirable for calculations with large numbers often encountered in cryptography.
Owner:CZECH TECH UNIV IN PRAGUE
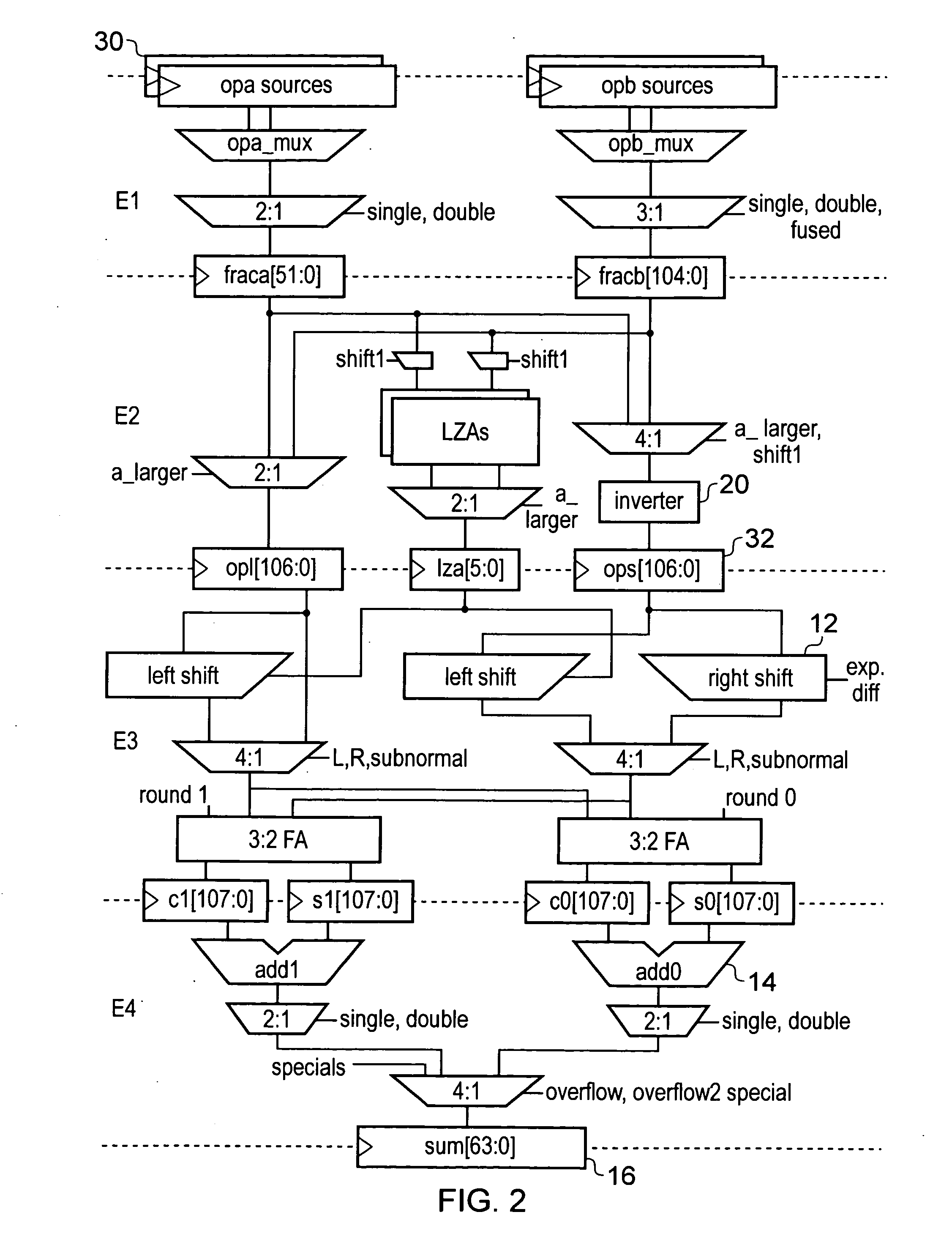
Floating-point arithmetic device
InactiveUS6571264B1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsLeading zeroComputer science
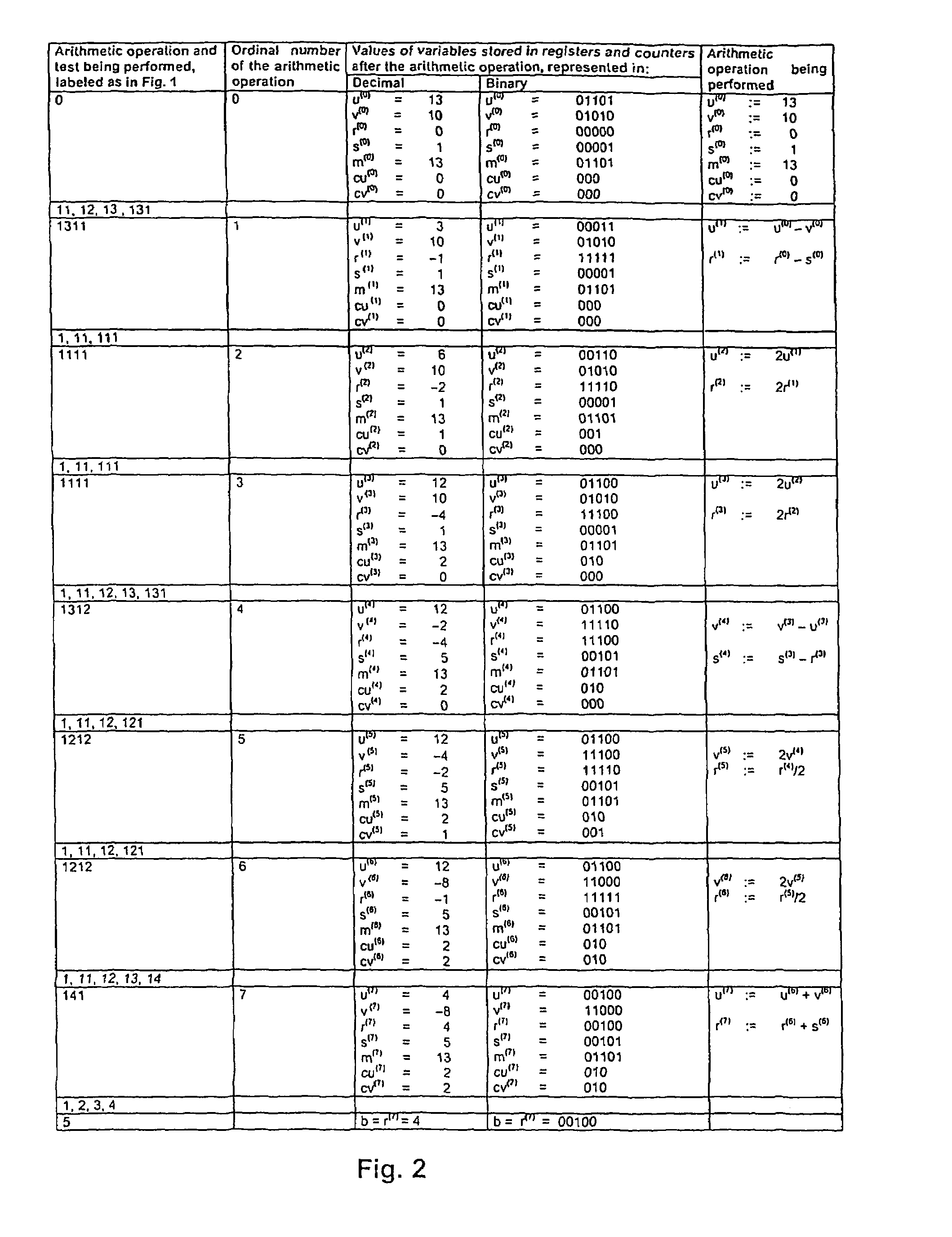
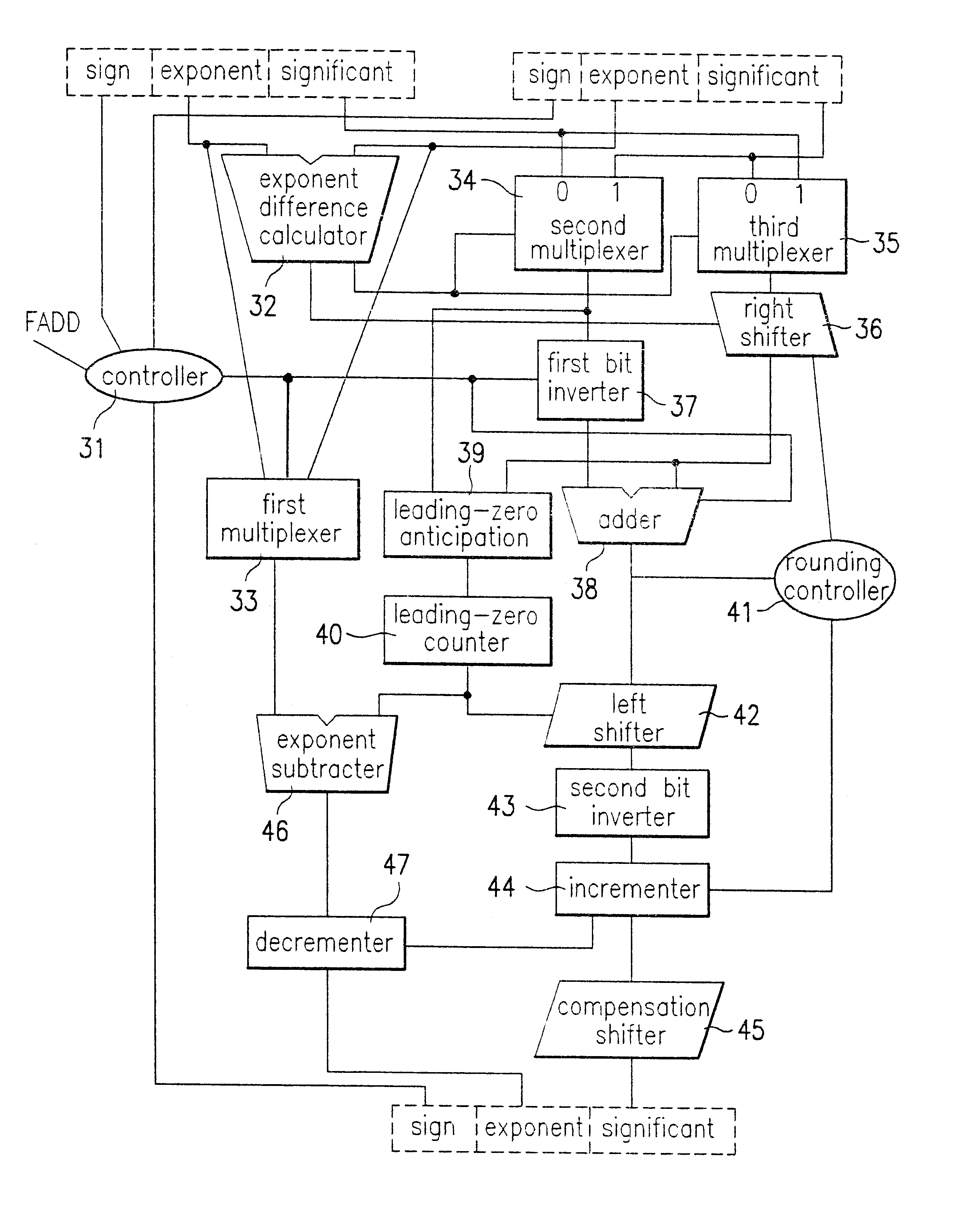
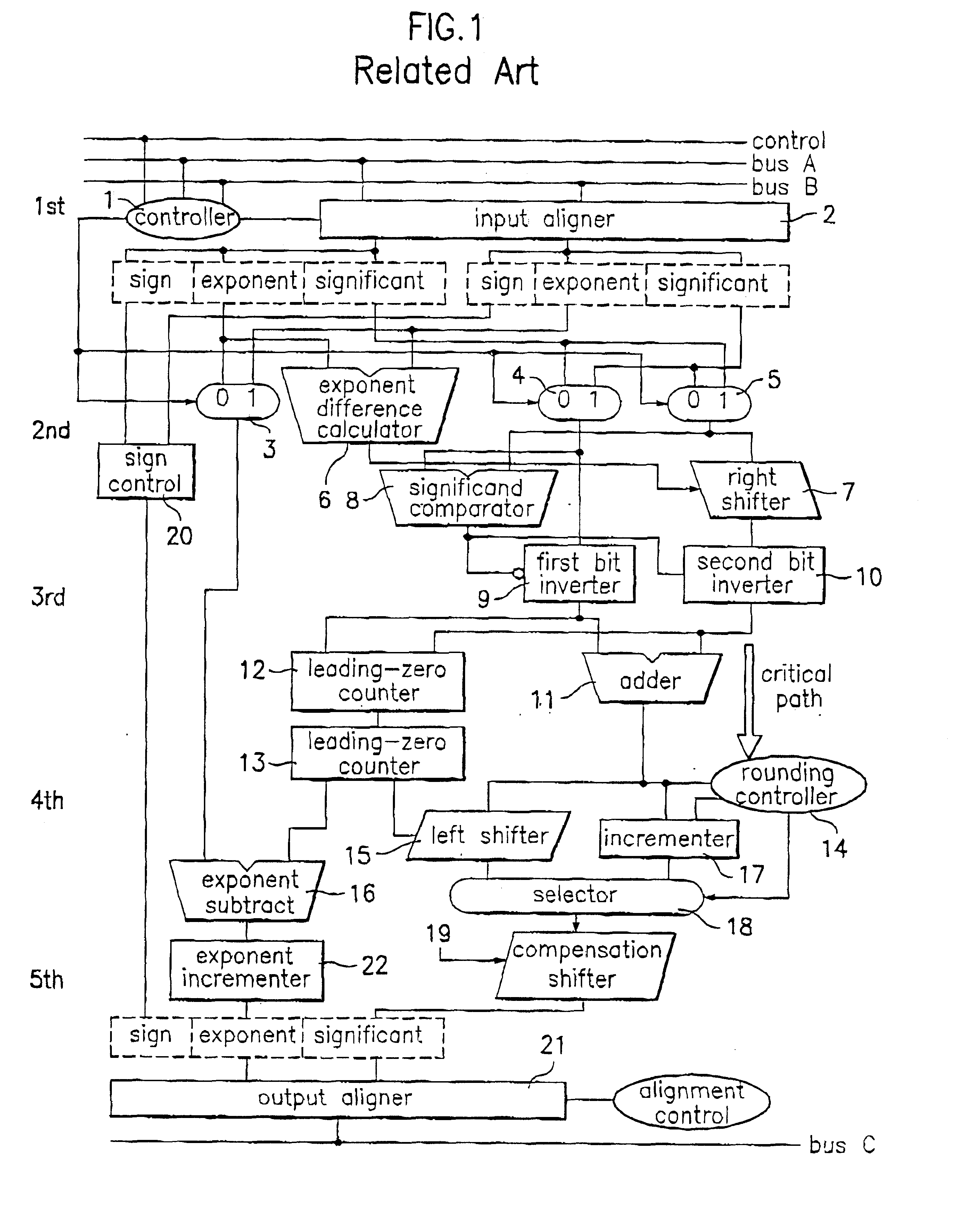
A floating-point arithmetic device, including a significand output circuit for calculating a difference between exponents, outputting a first significand with a larger exponent, and shifting the remaining significand by the calculated exponent difference, a first bit inverter, an adder, a leading-zero anticipation circuit for anticipating the consecutiveness of leading zeros from the significands, a leading-zero counter for counting the anticipated number of leading zeros, a left shifter for shifting an output value from the adder, a second bit inverter for taking two's complement of an output value from the left shifter, an incrementer for incrementing an output value from the second bit inverter by one, a compensation shifter for shifting an output value from the incrementer, an exponent subtracter for subtracting the number counted by the leading-zero counter from the larger exponent, and a decrementer for decrementing an output exponent from the exponent subtracter by one.
Owner:MAGNACHIP SEMICONDUCTOR LTD
Sign Operation Instructions and Circuitry
InactiveUS20090113174A1Improve efficiencyReduce in quantityProgram control using wired connectionsCode conversionOperating instructionSign bit
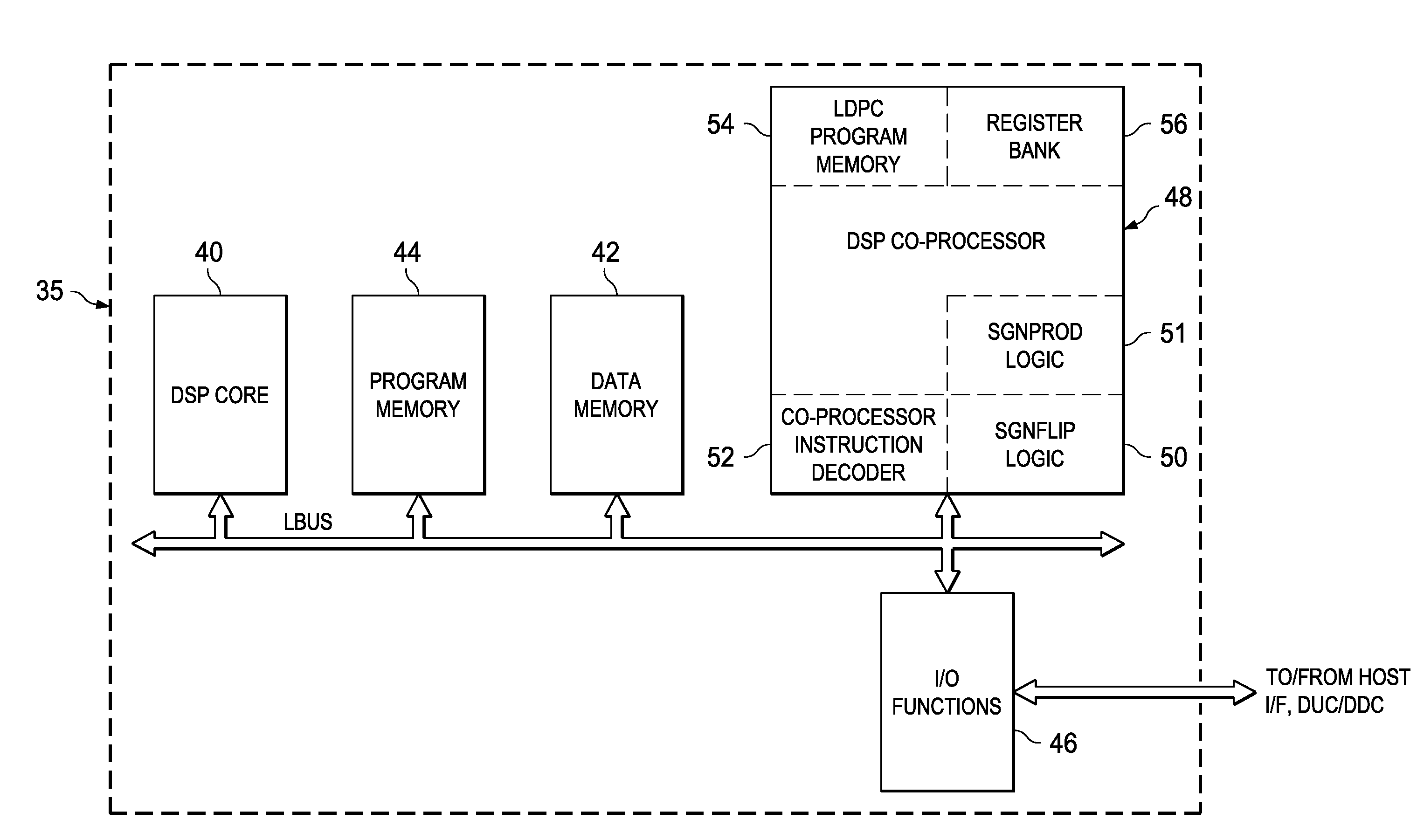
A co-processor for efficiently decoding codewords encoded according to a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code, and arranged to efficiently execute an instruction to multiply the value of one operand with the sign of another operand, is disclosed. Logic circuitry is included in the co-processor to select between the value of a second operand, and an arithmetic inverse of the second operand value, in response to the sign bit of the first operand. This logic circuitry is arranged to operate according to 2's-complement integer arithmetic, by also including invert-and-increment circuitry to produce a 2's-complement inverse of the second operand. A comparator determines whether the second operand is at a maximum 2's-complement negative value, in which case the arithmetic inverse is selected to be a hard-wired maximum 2's-complement positive value. Logic circuitry is also included in the co-processor to execute an instruction to multiple the signs of two operands; this logic circuitry is realized as an exclusive-OR function operating on the sign bits of the operands, and a multiplexer for selecting between digital words of the values +1 and −1 in response to the exclusive-OR function. The logic circuitry can be arranged in multiple blocks in parallel, to provide parallel execution of the instruction in wide datapath processors.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
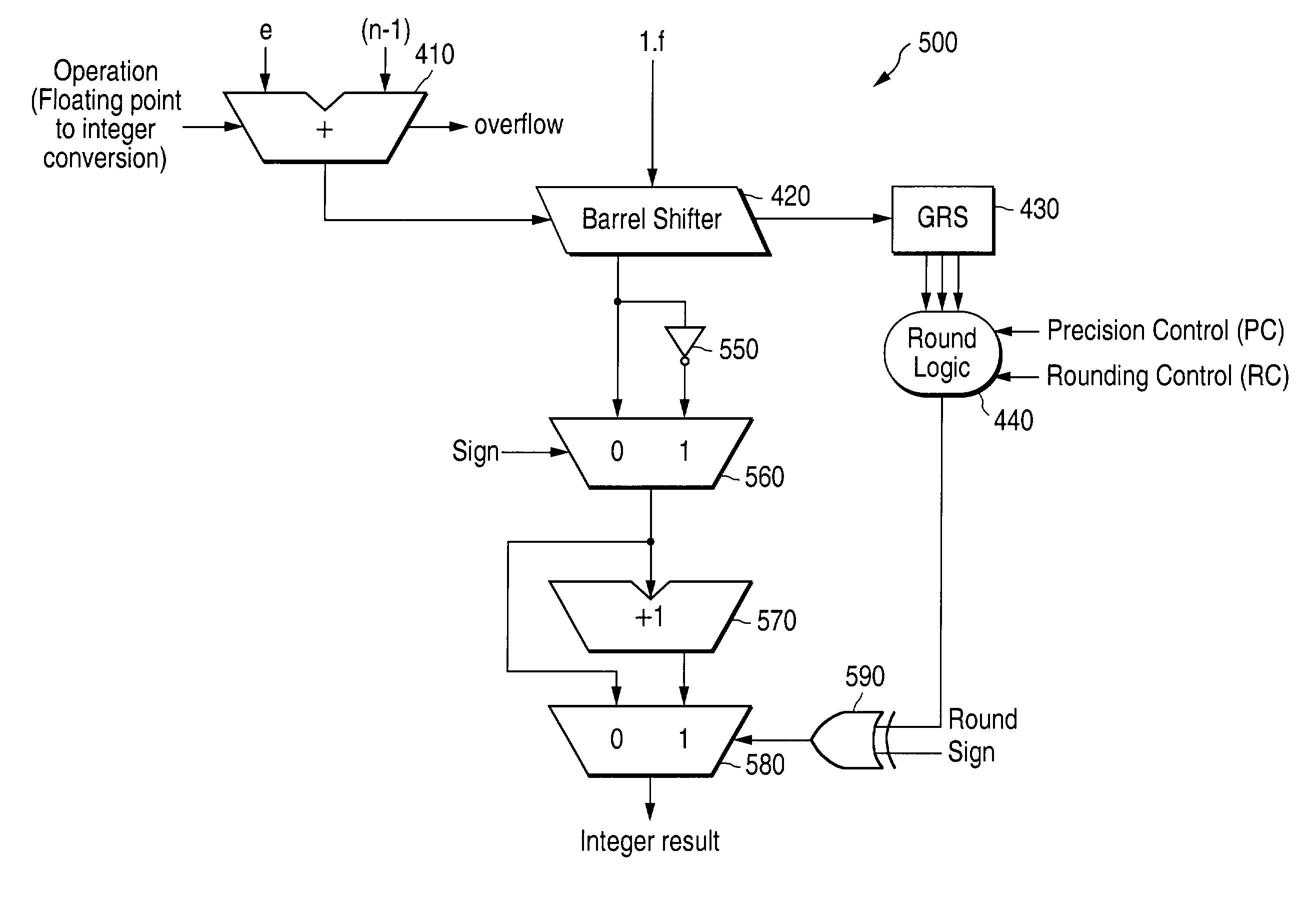
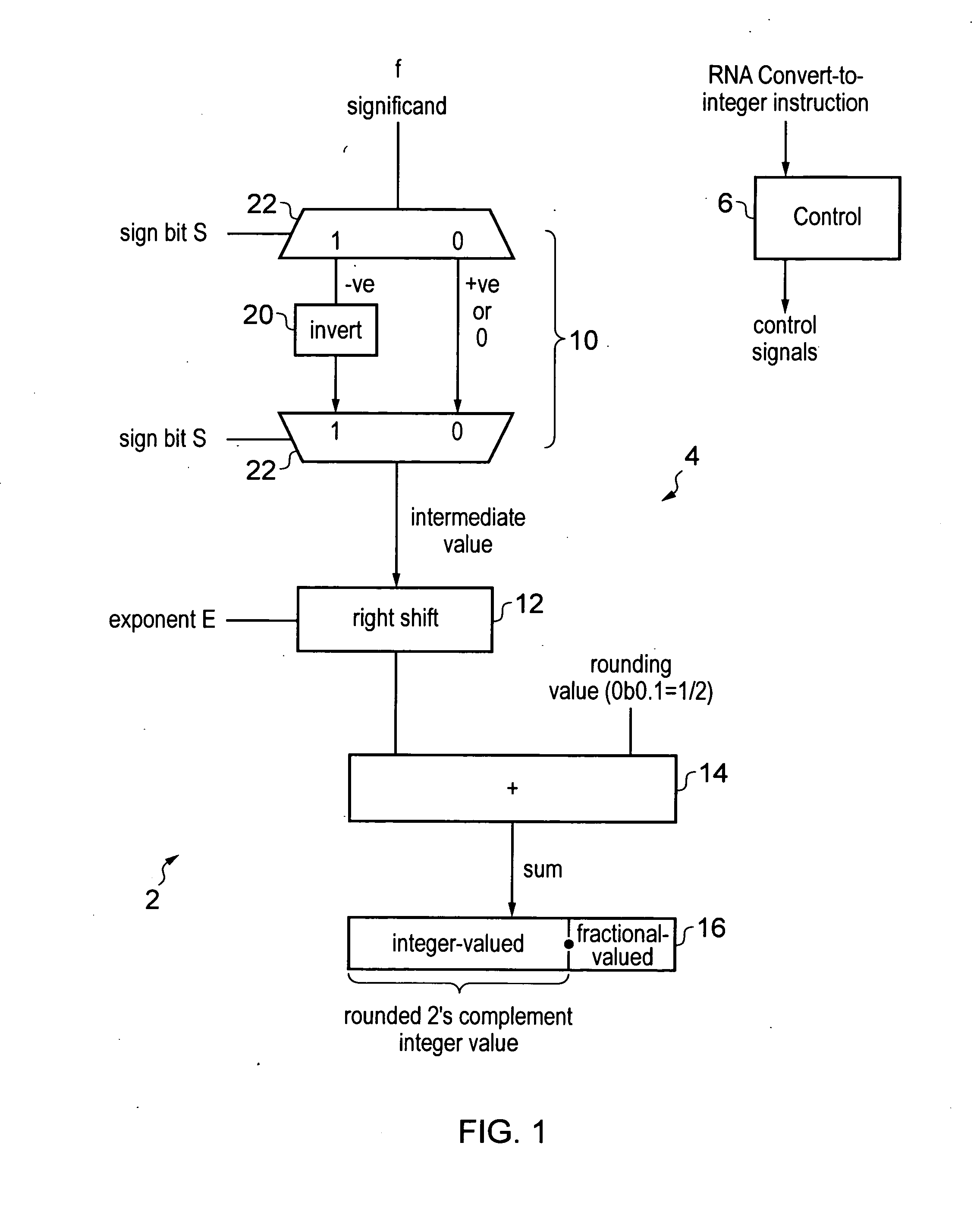
Apparatus and method for performing a convert-to-integer operation
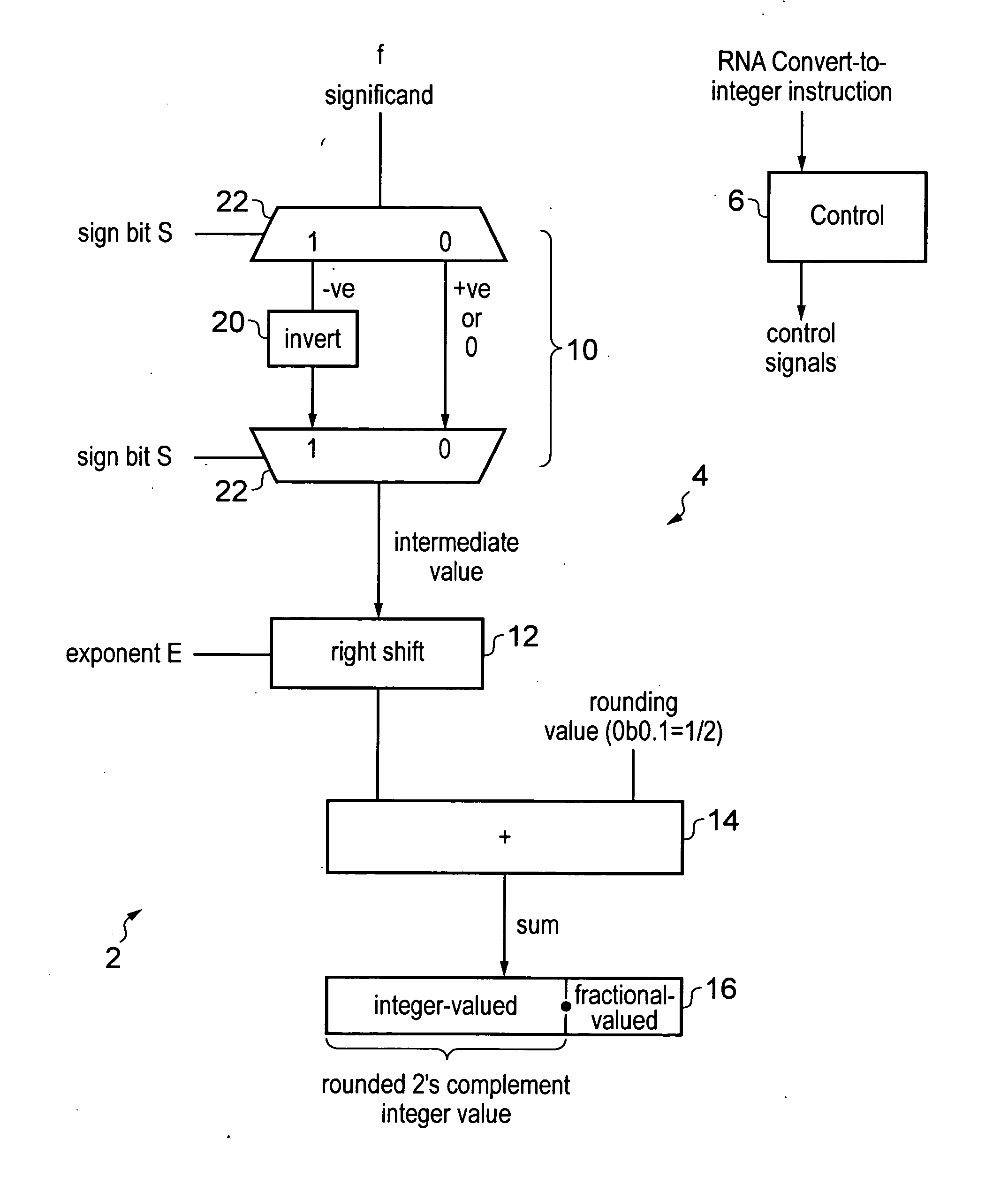
ActiveUS20130304785A1Performed quickly and efficientlyEasy to solveCode conversionProgram controlLeast significant bitFloating point
A data processing apparatus includes processing circuitry for performing a convert-to-integer operation for converting a floating-point value to a rounded two's complement integer value. The convert-to-integer operation uses round-to-nearest, ties away from zero, rounding (RNA rounding). The operation is performed by generating an intermediate value based on the floating-point value, adding a rounding value to the intermediate value to generate a sum value, and outputting the integer-valued bits of the sum value as the rounded two's complement integer value. If the floating-point value is negative, then the intermediate value is generated by inverting the bits without adding a bit value of 1 to a least significant bit of the inverted value.
Owner:ARM LTD
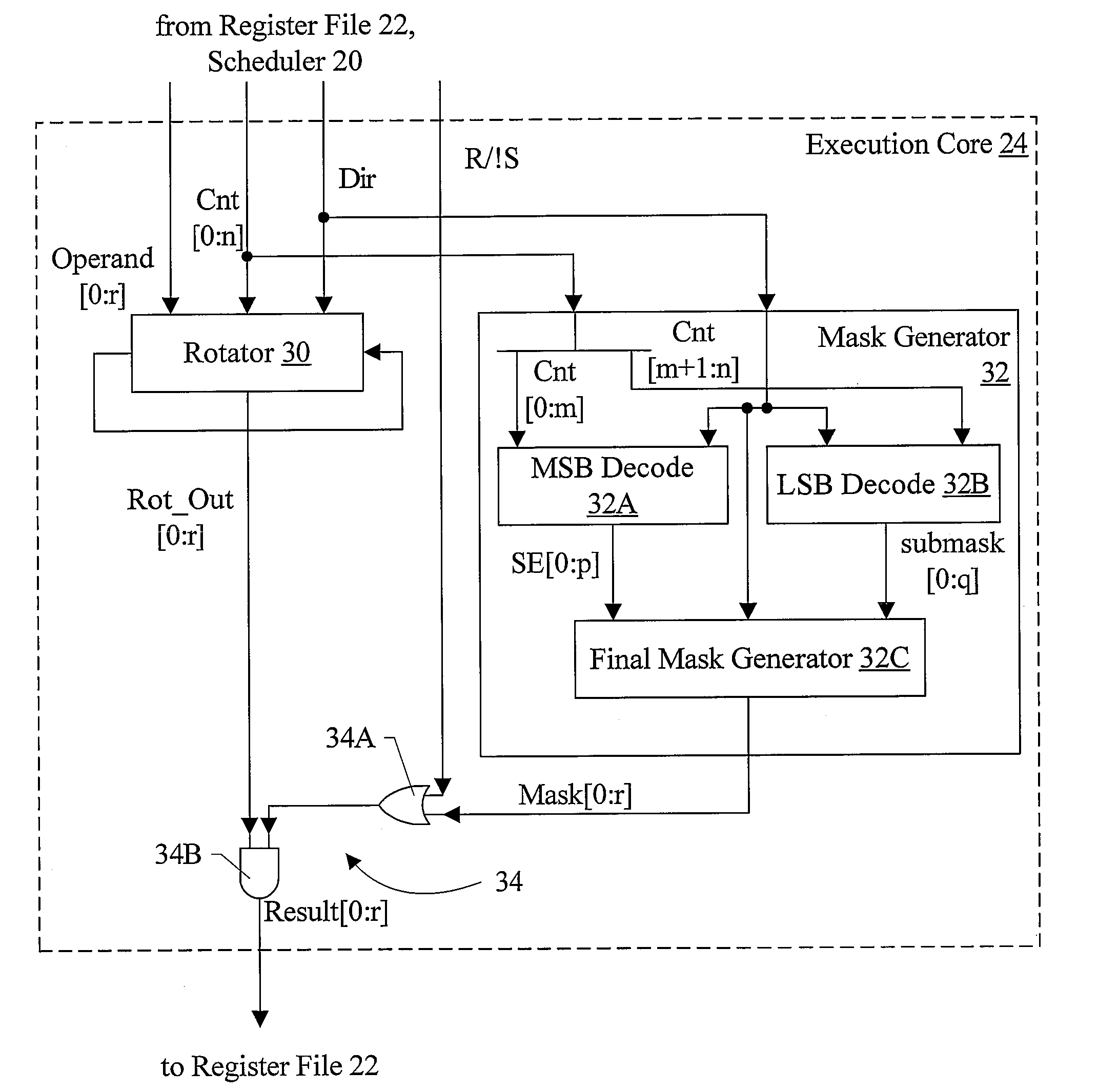
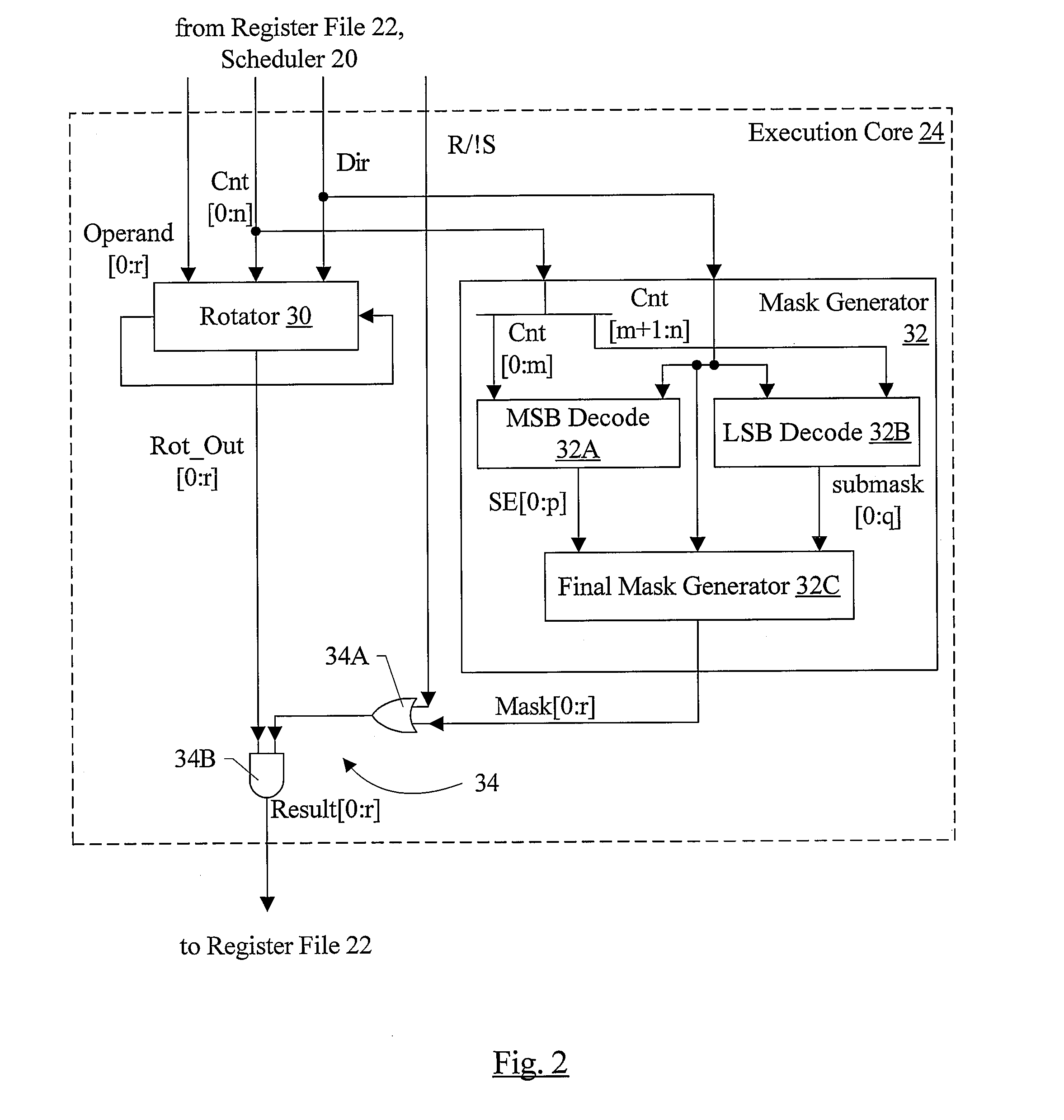
Fast Static Rotator/Shifter with Non Two's Complemented Decode and Fast Mask Generation
InactiveUS20080307204A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsLeast significant bitOperand
In one embodiment, a rotator, a mask generator, and circuitry configured to mask the rotated operand output by the rotator with the output mask generated by the mask generator perform a shift operation. Coupled to receive the input operand and the shift count, the rotator is configured to rotate the input operand by the shift count. Coupled to receive the shift count and the shift direction, the mask generator is configured to generate an output mask by decoding a most significant bit (MSB) field of the shift count to generate a first mask, decoding a least significant bit (LSB) field of the shift count to generate a second mask, logically ANDing the bits of the second mask with the corresponding bit of the first mask and logically ORing the result with an adjacent bit of the first mask that is selected responsive to the shift direction. Additionally, in one embodiment, the rotator may be configured to perform a right rotate / shift operation using a left rotate and without performing a two's complement operation on the rotate / shift count.
Owner:APPLE INC
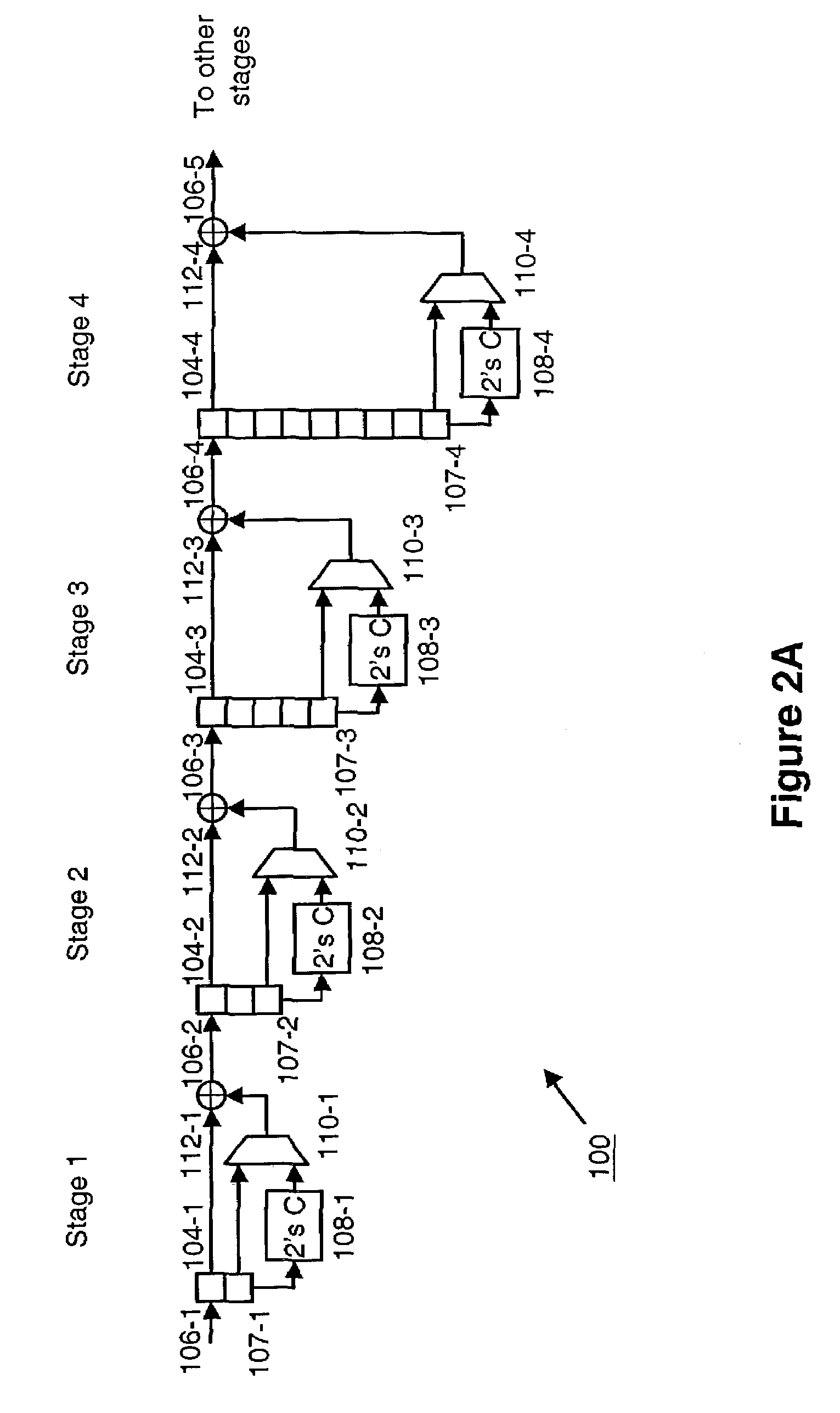
Apparatus and method for Fast Hadamard Transforms
InactiveUS7200629B2Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsHadamard transformShift register
A Fast Hadamard Transform generator serially performs a Fast Hadamard Transform of a sampled signal from a first channel. The Fast Hadamard Transform generator comprises a series of stages. Each stage includes a shift register for serially receiving samples of the signal. Each stage further includes a two's complement generator for producing a two's complement of a first sample of the signal and a first multiplexer for selecting between a first sample of the signal and the two's complement of the first sample. A first adder then generates a sum of a second sample of the signal and the first sample and a difference of the second sample and the first sample and supplies the sum and the difference to the shift register of the next stage. In one embodiment the shift registers are implemented in random access memory.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
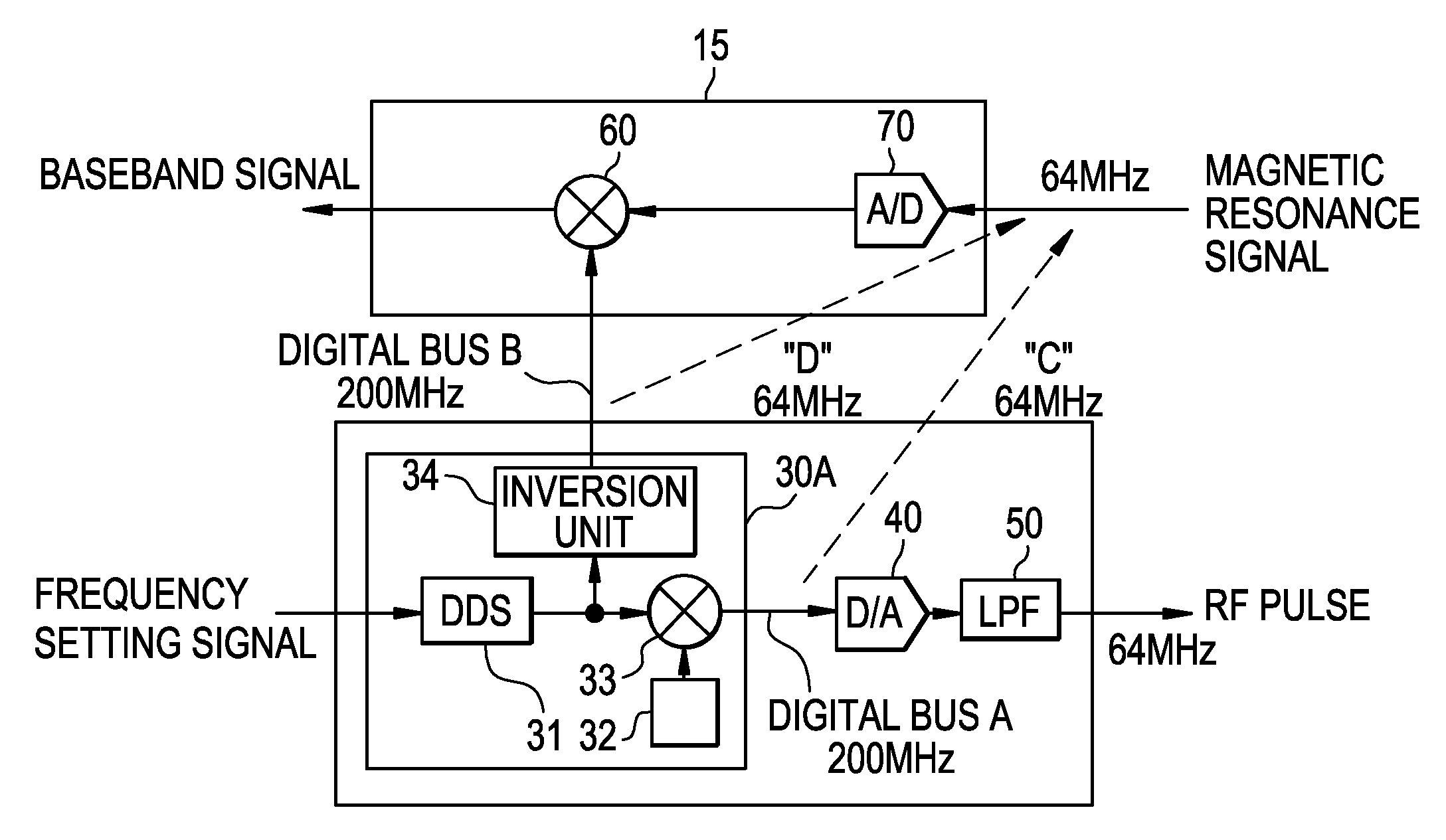
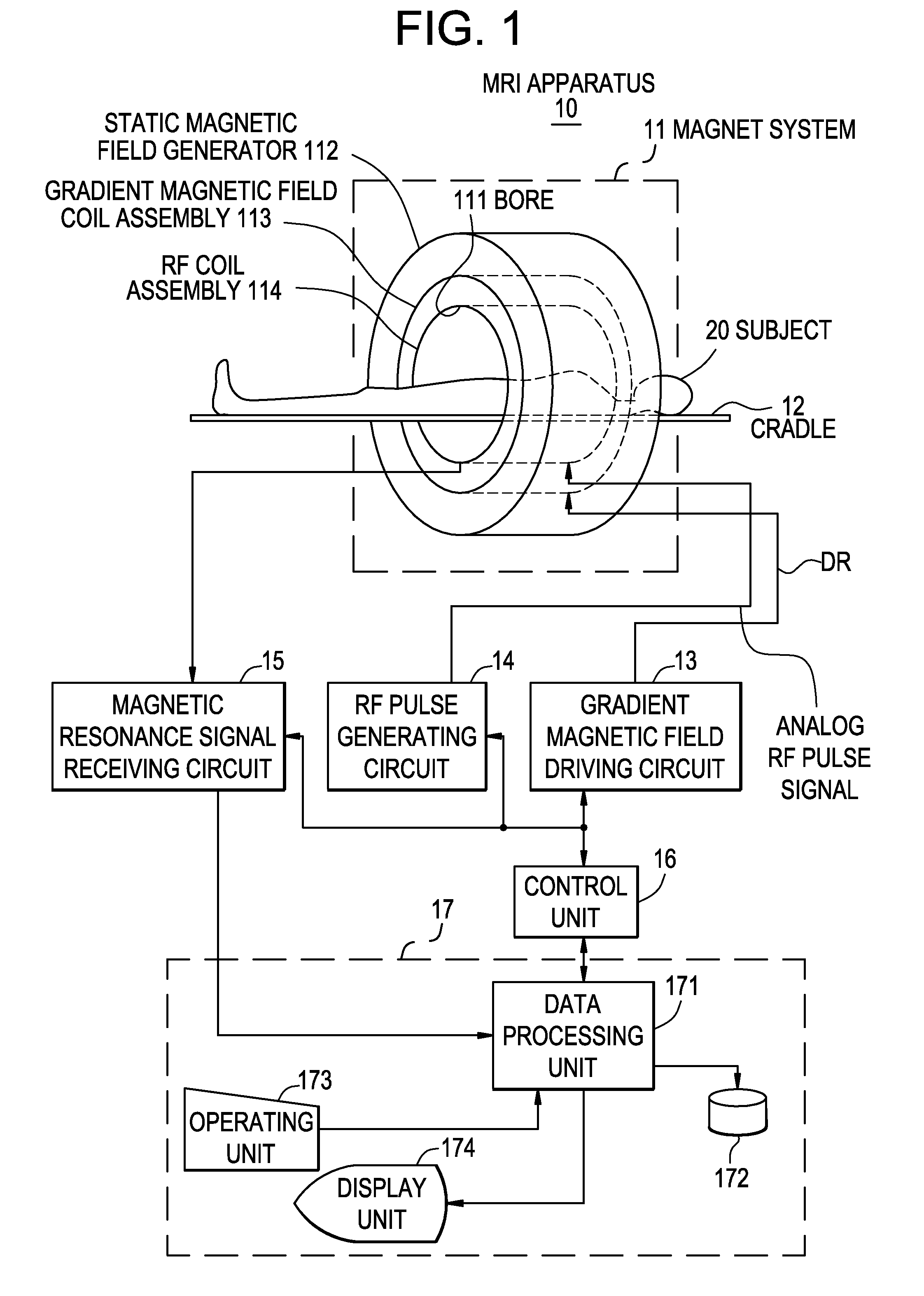
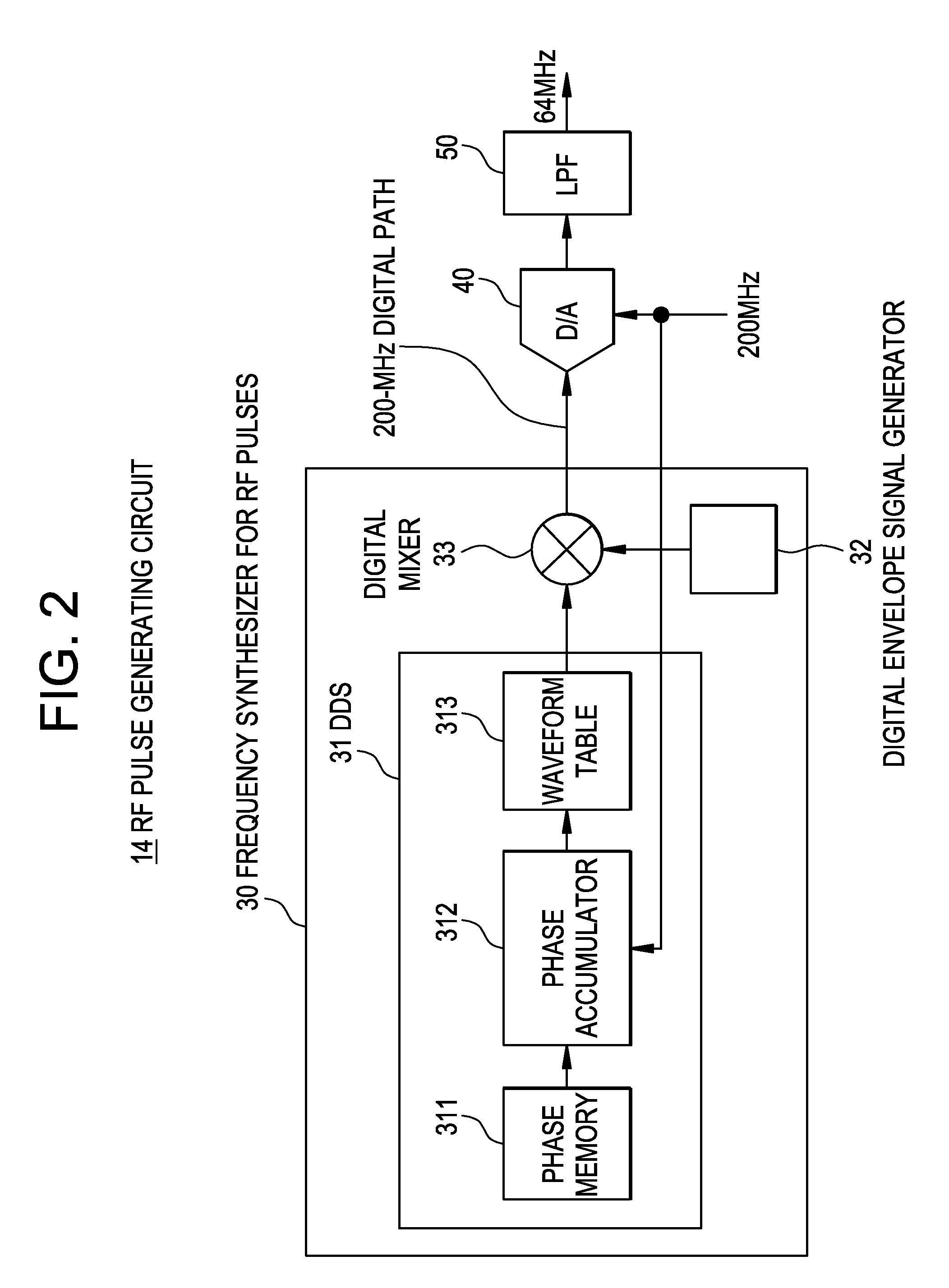
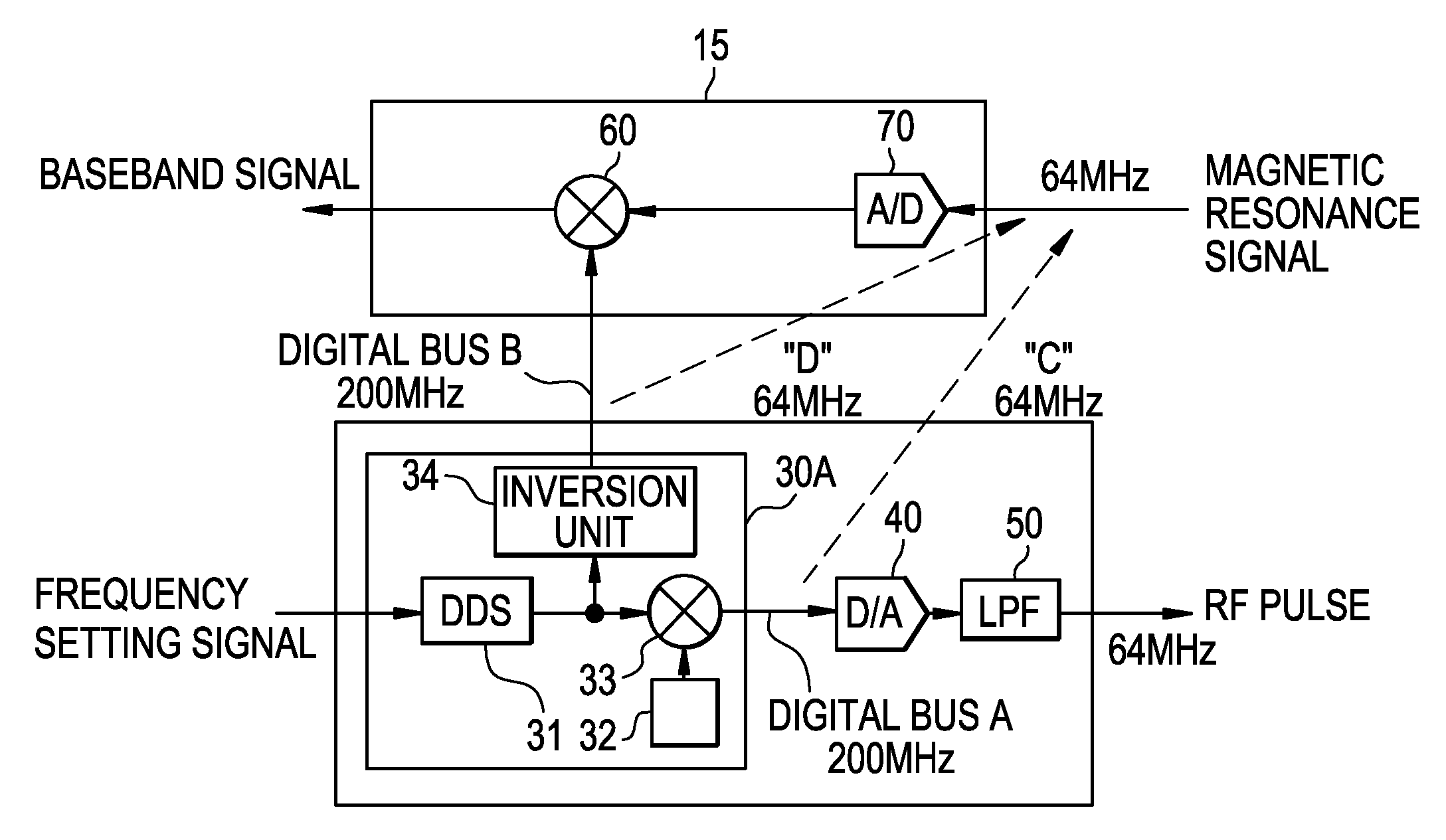
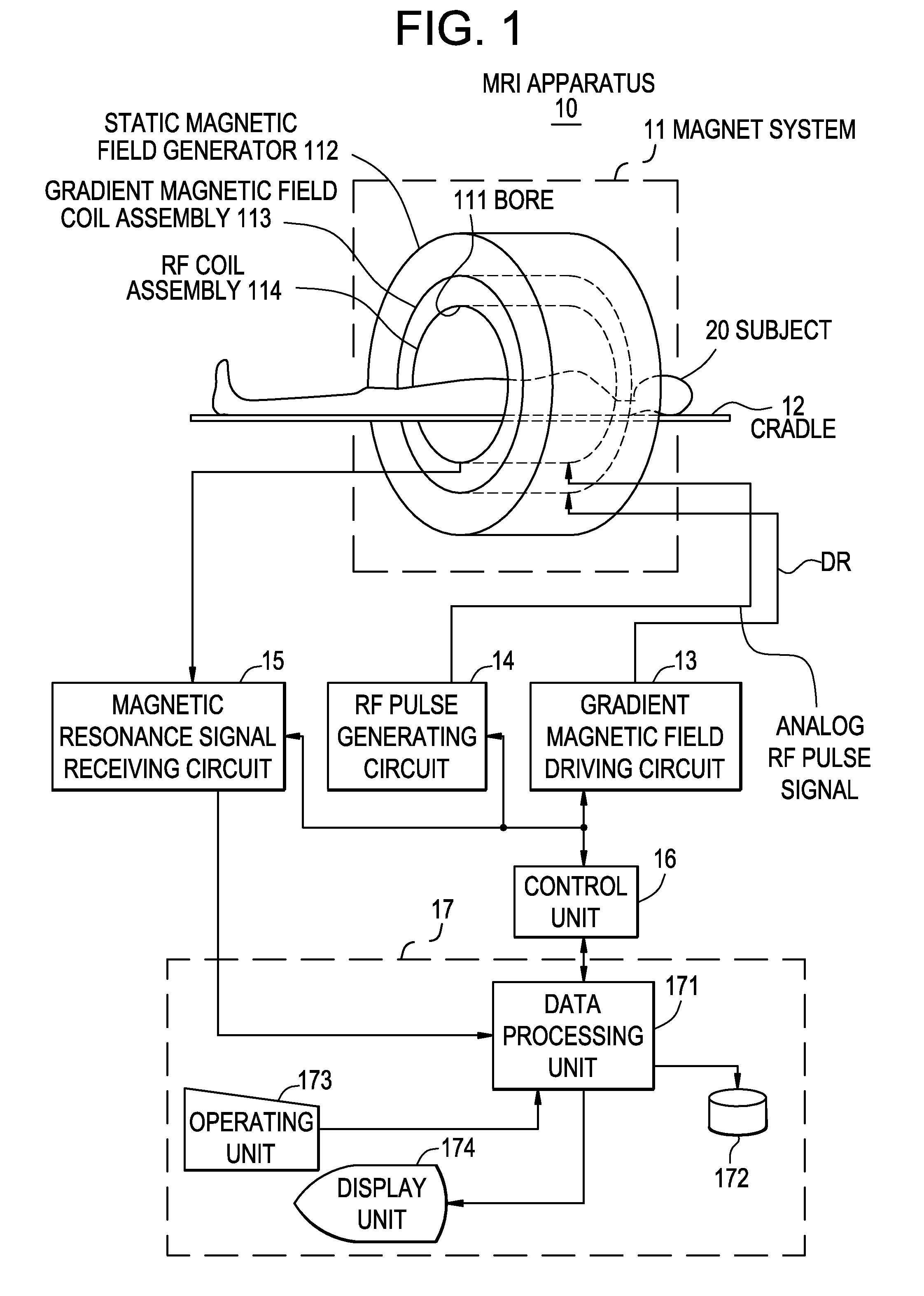
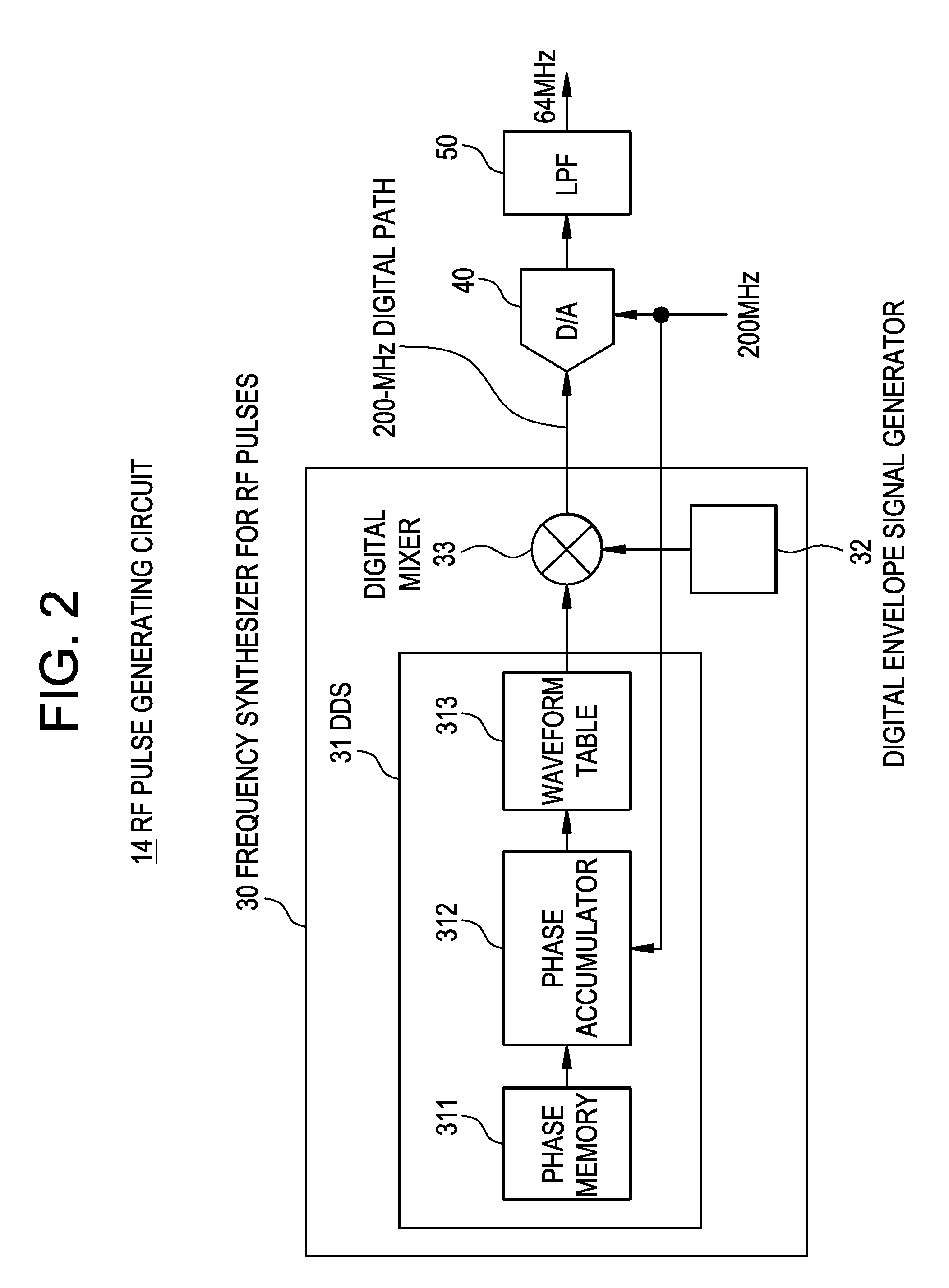
MRI apparatus and RF pulse generating circuit
InactiveUS20080258732A1Reduce decreaseReduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceDigital analog converterCarrier signal
An MRI apparatus includes: an RF coil to which analog RF pulse signals are applied; an RF pulse generating circuit which generates said analog RF pulse signals; and a magnetic resonance signal receiving circuit which receives analog magnetic resonance signals and converts these signals into baseband digital magnetic resonance signals, said RF pulse generating circuit comprising: a carrier signal generator which generates a digital carrier signal having a predetermined number of bits; a digital modulator which modulates said digital carrier signal with a digital envelope signal, thus generating digital RF pulse signals; a digital-analog converter which converts said digital RF pulse signals into the analog RF pulse signals; and an inversion unit which generates a digital inverted carrier signal having a two's complement relationship with said digital carrier signal and sends the digital inverted carrier signal to said magnetic resonance signal receiving circuit, said magnetic resonance signal receiving circuit comprising: an analog-digital converter which converts the analog magnetic resonance signals into digital magnetic resonance signals having a predetermined number of bits; and a digital demodulator which demodulates said digital magnetic resonance signals with said digital inverted carrier signal, thus converting these signals into the baseband digital magnetic resonance signals.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
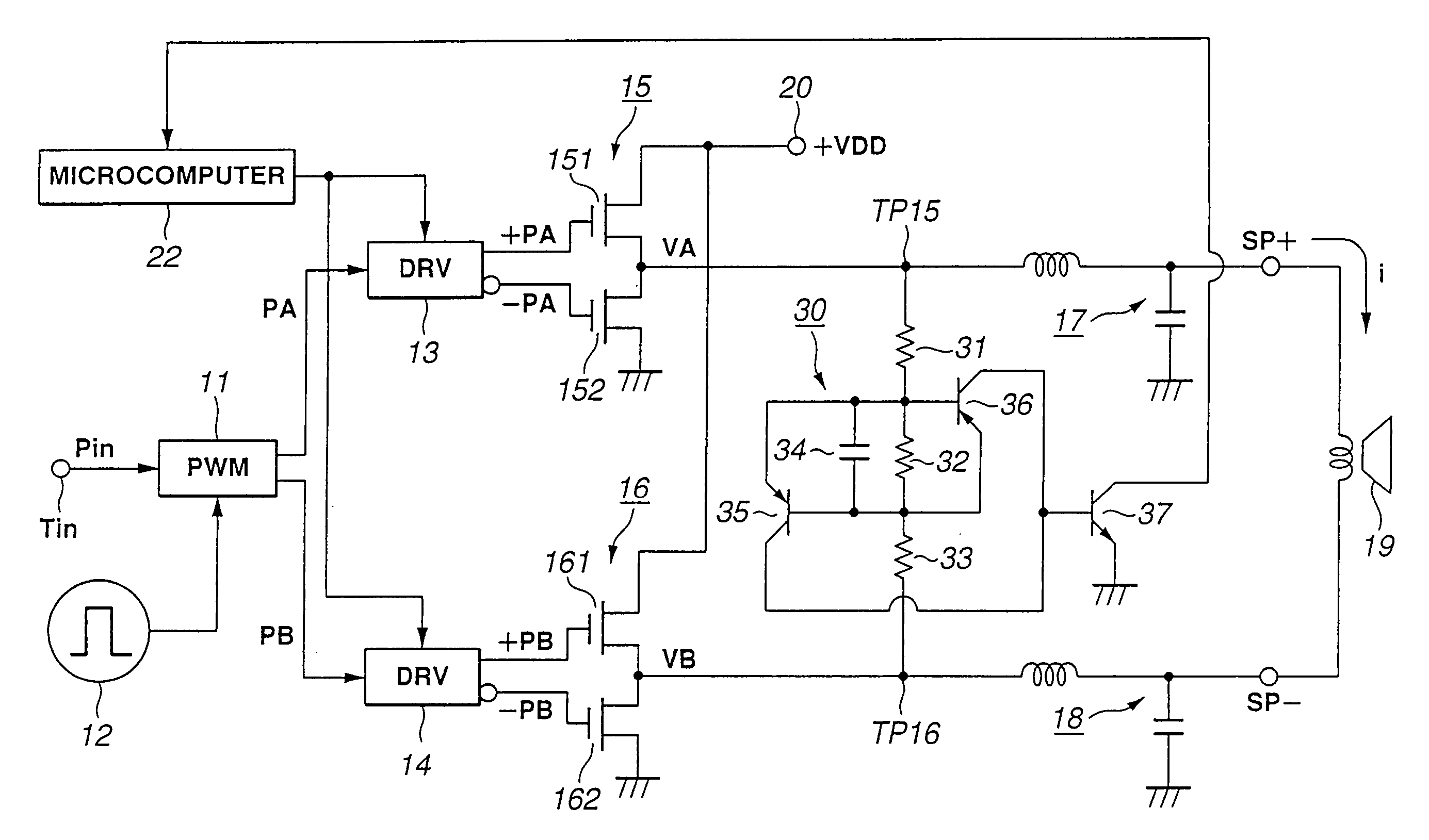
Power amplifier
In a power amplifier driven by a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal, a first pair of drive pulses opposite in level to each other is formed from a first pulse width modulation signal whose quantization level corresponds to its pulse width and supplied to a first push-pull circuit (15). A second pair of drive pulses opposite in level to each other is formed from a second pulse width modulation signal whose two's complement of quantization level corresponds to its pulse width, and supplied to a second push-pull circuit (16). A speaker (19) is connected between the first and second push-pull circuits (15 and 16). A deviation between potentials at the output terminals of the first and second push-pull circuits (15 and 16), respectively, is detected. When a deviation is detected, the push-pull circuits are substantially stopped from operating.
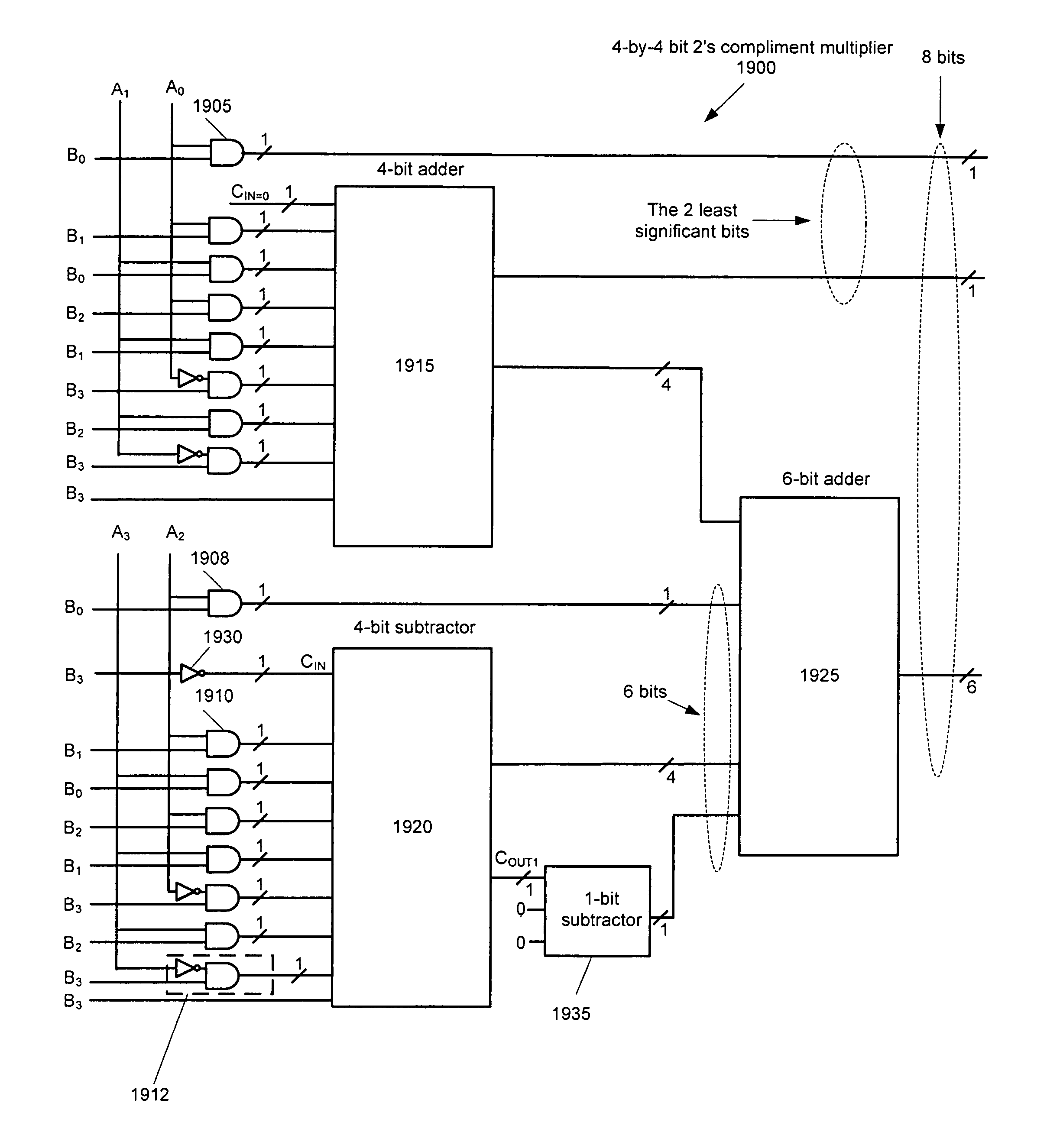
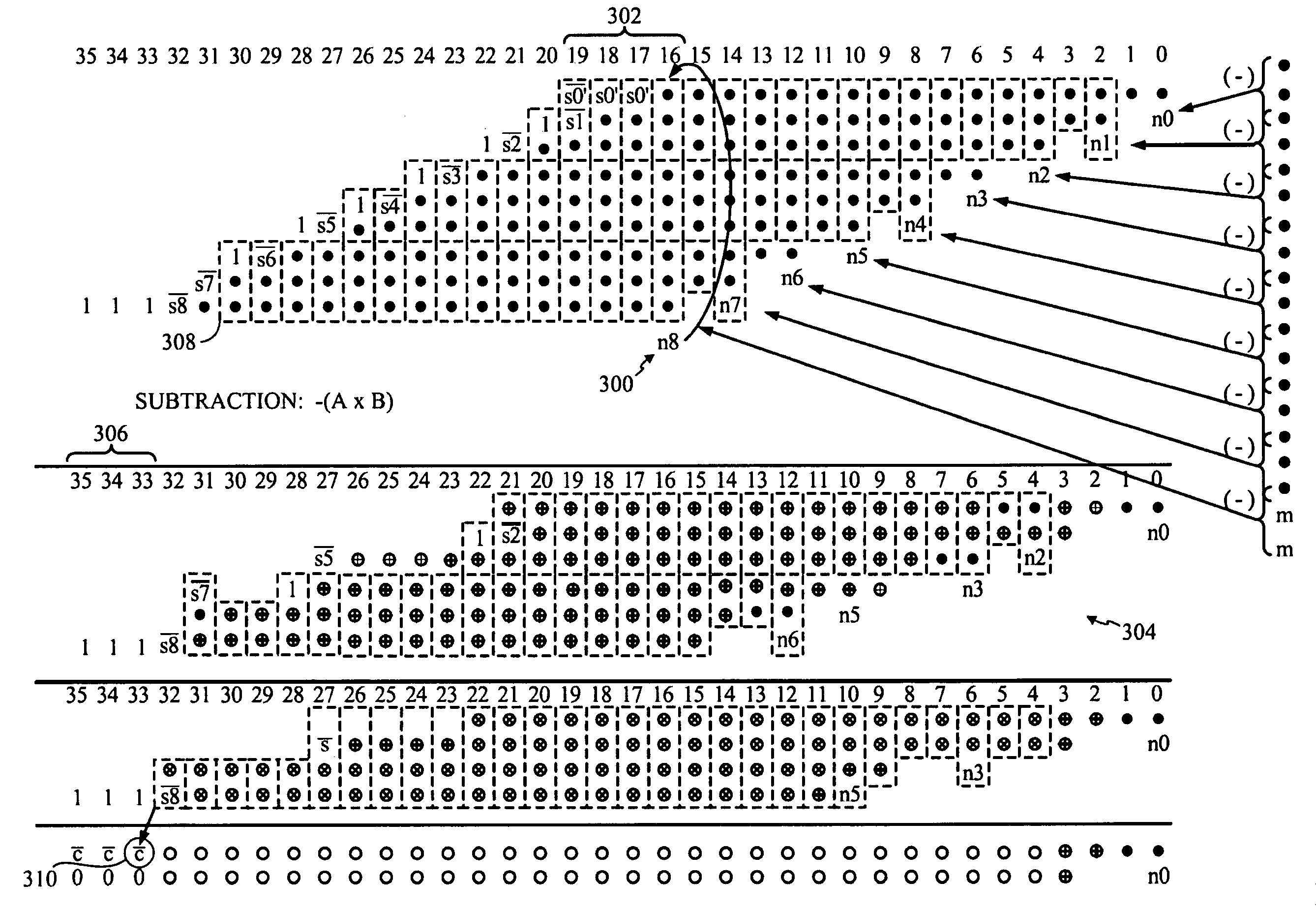
Method and apparatus for performing two's complement multiplication
InactiveUS7818361B1Reduce consumptionQuickly reconfiguredLogic circuits characterised by logic functionComputation using non-contact making devicesTheoretical computer scienceOperand
Some embodiments provide a novel way of performing a signed multiplication. Each individual bit of a first operand is multiplied by every bit of a second operand to generate partial multiplication results. Each partial result is shiftably added to other partial results except one partial result which is shiftably subtracted. For the partial result that is subtracted, the most significant bit of the second operand is negated and is utilized as carry in of the subtraction operation. The most significant bit of each operand is considered to have a negative sign when generating the partial multiplication results. Also, one of the partial results is appended with the most significant bit of the second operand. Some embodiments utilize a configurable IC that performs subtraction with the same circuitry and at the same cost as addition. The configurable IC also utilizes hybrid interconnect / logic circuits to perform part of the multiplication operation.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
MRI apparatus and RF pulse generating circuit
InactiveUS7560933B2Reduce noiseMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionDigital analog converterCarrier signal
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Multiplier restructuring algorithm and circuit thereof
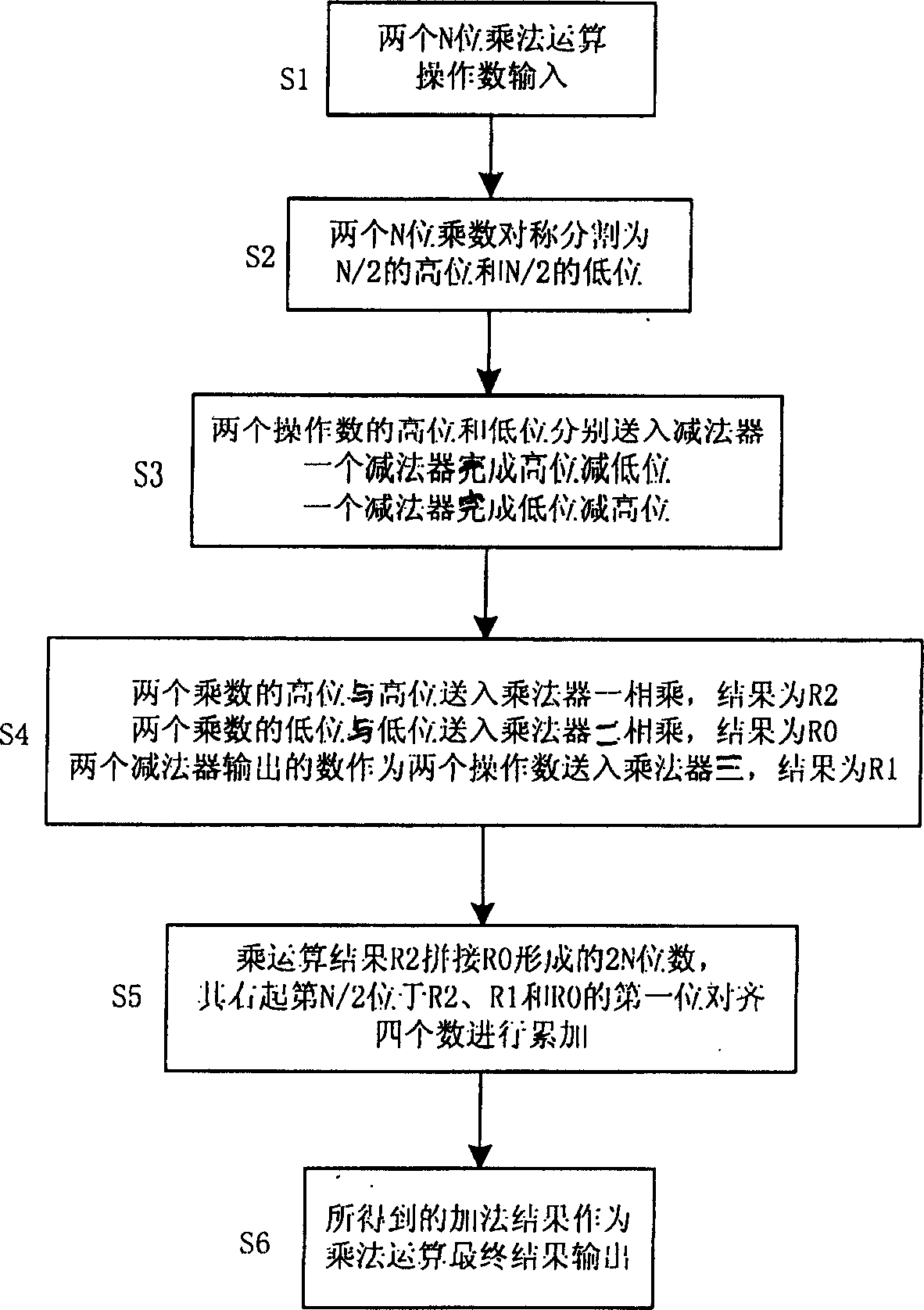
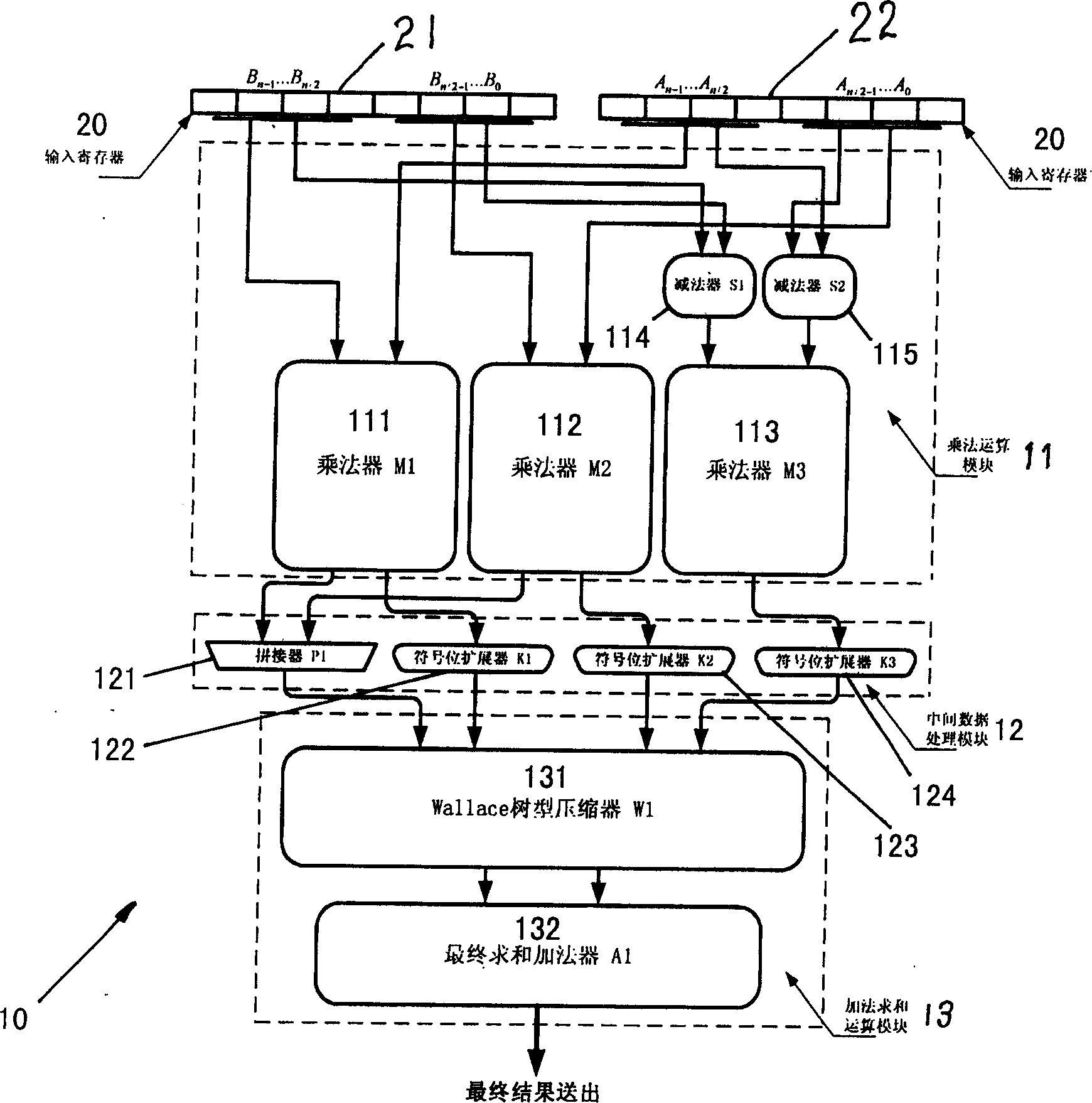
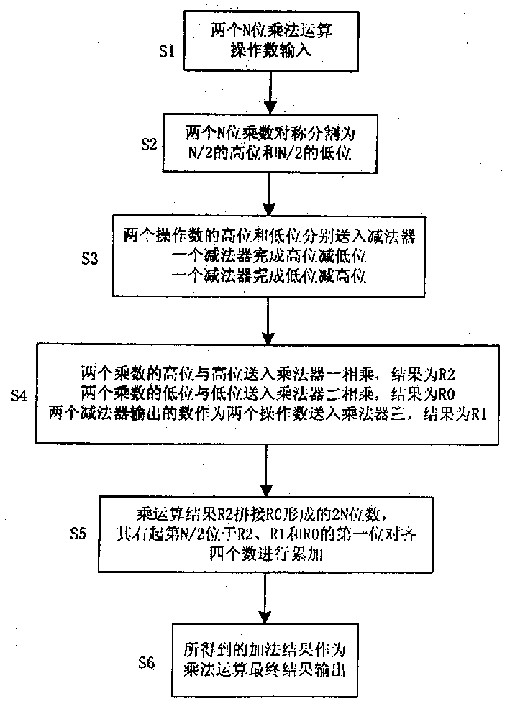
It is a new multiplier reconstructing algorithm which comprises the following: two N bit two's complement number with signs or number without signs which are used as multiply operation numbers into two input ends of the multiplier; to symmetrically divide the two N bit multiply operation numbers into half of the original bit width; to input the two N bit operation number N / 2 high order and N / 2 low order into two subtracters, wherein, one is to finish one operation number calculation and the other is to finish the other operation number low order minus high order calculation; to multiply two N bit numbers and get R2, and to multiply low order by low order input into multiplier and get R0 and the two output numbers from two subtracters is inputted into N / 2 bit multiplier 3 and get the result R1;The multiplier results R2 and R0 are joint into 2N bit number and the right No. N / 2 is in alignment with first bit of R2,R1 and R0 the additive result of which is used as multiply result to be outputted.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Booth multiplier with enhanced reduction tree circuitry
InactiveUS20070192398A1Minimize delayMinimize powerComputation using non-contact making devicesBooth encodingComputer science
Techniques for the design and use of a digital signal processor, including processing transmissions in a communications (e.g., CDMA) system. A modified Booth multiplication system and process determine a multiplicand, A, and a multiplier, B. Radix-m, (e.g., radix-4) Booth recoding on B generates “n” multiplication factors, where “n,” an integer, is approximating one half of the number of the multiplier bits. “n” partial products are generated using the “n” multiplication factors as multipliers of A. Then, a multiplication tree is formed using radix-m Booth encoding. The multiplication tree includes multiplier bits associated to generate a multiplication factors. In the event of a negative multiplication factor, a two's complement of A is formed by inverting the bits of A and associating a sticky “1” to complete the two's complementation. Furthermore, multiplication factors are reduced in multiple stages to a form sum and carry components of a pre-determined length. The additive inverse of A×B is formed by using novel techniques to calculate the product of A and −B.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Discrete cosine transform (DCT) implementation method and system based on randomized computation
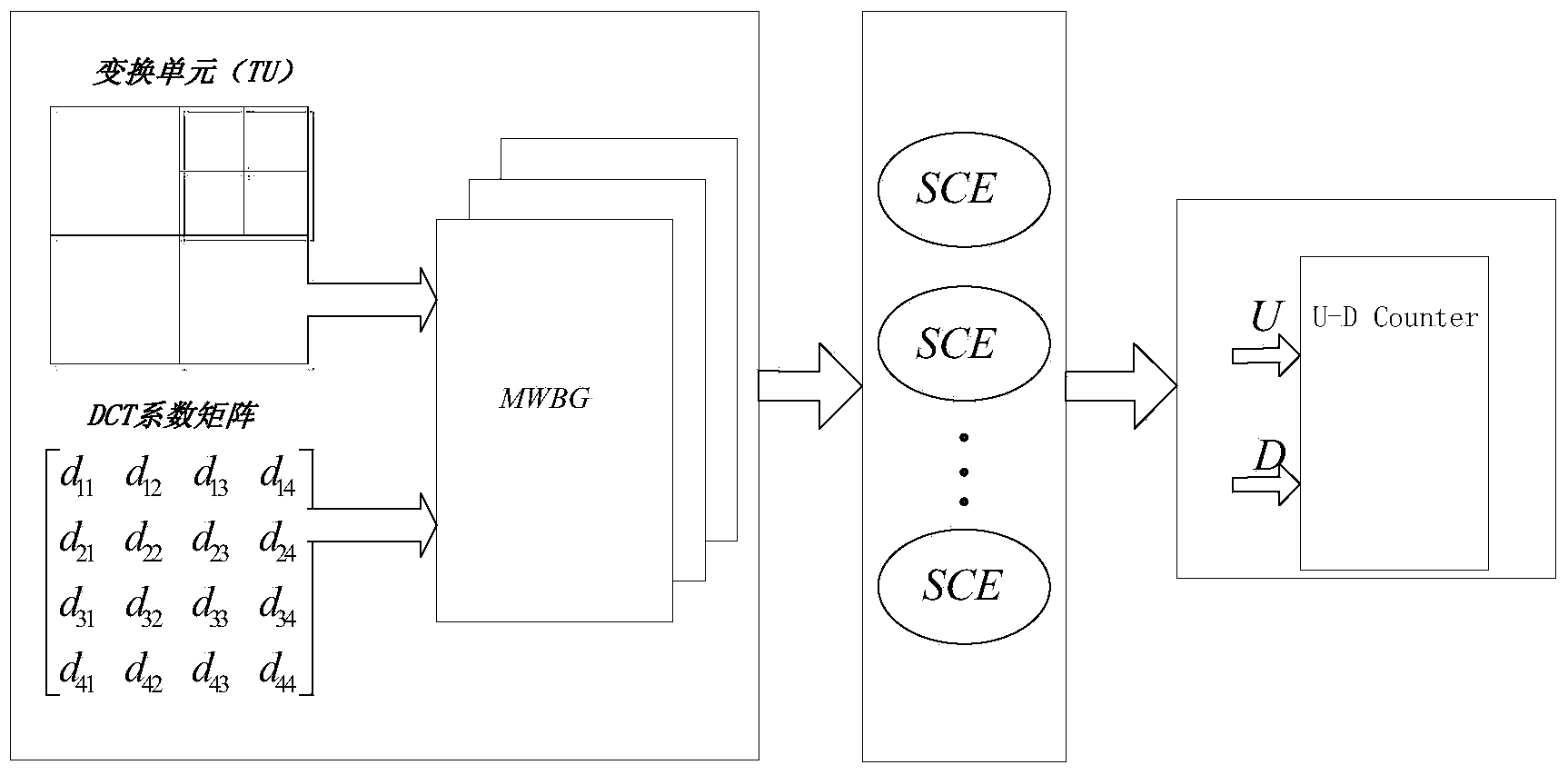
ActiveCN104038770AEasy to implementIncrease the operating clock frequencyDigital video signal modificationComplex mathematical operationsClock rateDiscrete cosine transform
The invention discloses a discrete cosine transform (DCT) implementation method and system based on randomized computation. The method comprises the following steps: mapping the ratio of an image transform unit (TU) to DCT into a decimal within a preset range, and transforming the decimal into a random sequence; transforming the random sequence into a randomized computation domain sequence, and computing by using a randomized computation multiplier and a randomized computation adder; transforming a computed result into a two's complement form in order to realize DCT. By adopting the method and the system, the hardware consumption can be lowered greatly, and the working clock frequency of the system is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
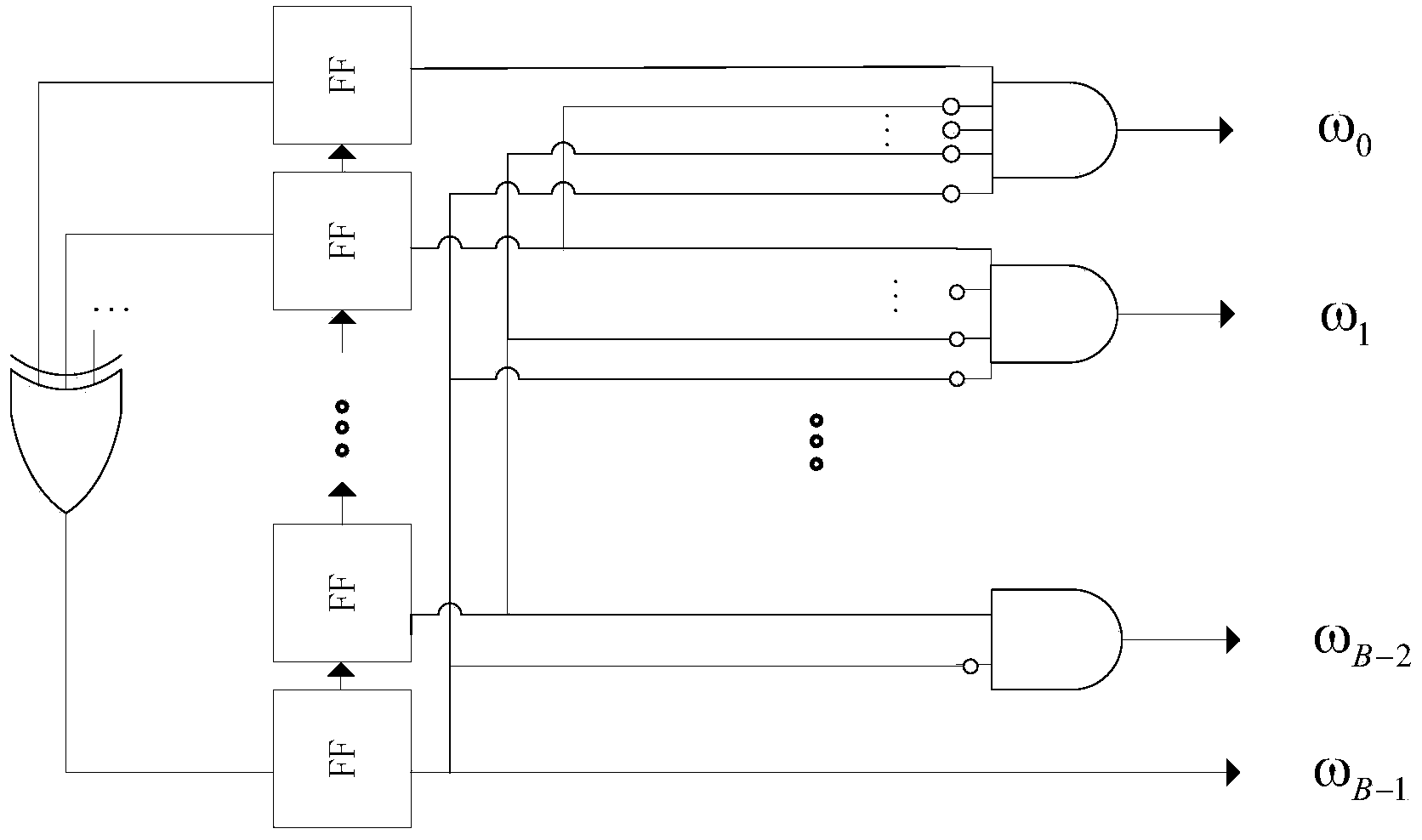
Reconfigurable two's-complement and sign-magnitude converter
InactiveUS20100042892A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelDigital computer detailsEngineeringSymbol of a differential operator
In one embodiment, a reconfigurable two's-complement-to-sign-magnitude (2TSM) converter has two five-bit non-reconfigurable 2TSM converters and is selectively configurable to operate in a five-bit mode or a ten-bit mode. In five-bit mode, the first and second non-reconfigurable 2TSM converters concurrently convert first and second five-bit messages, respectively, from two's-complement-to-sign-magnitude format. In the ten-bit mode, the first and second non-reconfigurable 2TSM converters concurrently convert first and second halves of a ten-bit message, respectively, from two's-complement-to-sign-magnitude format. The reconfigurable 2TSM converter then generates a ten-bit sign-magnitude message based on the conversions of the two non-reconfigurable 2TSM and a carry-over bit. In another embodiment, a reconfigurable sign-magnitude-to-two's-complement (SMT2) converter comprises the reconfigurable 2TSM described above. The reconfigurable SMT2 is selectively configurable to operate in (i) a five-bit mode to convert two five-bit messages concurrently and (ii) a ten-bit mode to convert one ten-bit message at a time.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
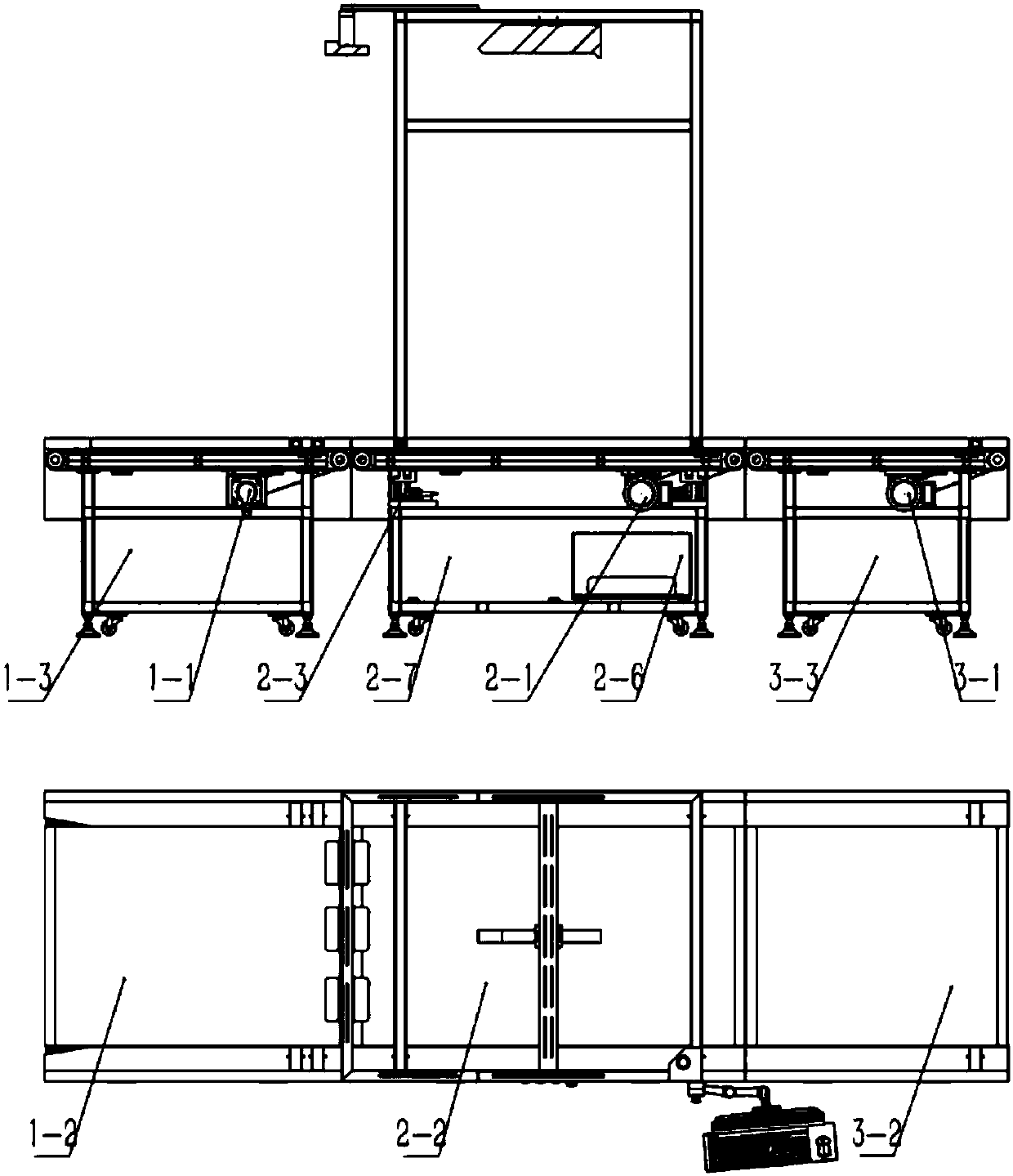
Dynamic package scale and method for dynamically weighing package
InactiveCN107944521ASave time and costSave operating costsLogisticsAutomatic testing and analysing marked record carriersStart stopData acquisition
A dynamic package scale includes a dynamic intelligent data acquisition device and a dynamic operating system integrating weighing, code scanning and volume detection. The dynamic intelligent data acquisition device adopts three-section type modular design, including a caching section, a weighing, code scanning and volume detection section and a code complementing section; and the dynamic operating system controls start-stop transmission and transmission distance of three sections of conveyer belts according to a detection result of the weighing, code scanning and volume detection section, sothat packages can be rapidly lined up and checked in an ordered manner, and a situation of missing detection is prompted in time through an alarm to perform code complementing. The dynamic package scale provided by the invention is easy to operate and is high in efficiency and precision, greatly improves work efficiency, and avoids unnecessary resource waste.
Owner:启东亦大通自动化设备有限公司
Booth multiplier with enhanced reduction tree circuitry
InactiveUS7809783B2Easy to operateReduce circuitComputation using non-contact making devicesBooth encodingComputer science
Techniques for the design and use of a digital signal processor, including processing transmissions in a communications (e.g., CDMA) system. A modified Booth multiplication system and process determine a multiplicand, A, and a multiplier, B. Radix-m, (e.g., radix-4) Booth recoding on B generates “n” multiplication factors, where “n,” an integer, is approximating one half of the number of the multiplier bits. “n” partial products are generated using the “n” multiplication factors as multipliers of A. Then, a multiplication tree is formed using radix-m Booth encoding. The multiplication tree includes multiplier bits associated to generate a multiplication factors. In the event of a negative multiplication factor, a two's complement of A is formed by inverting the bits of A and associating a sticky “1” to complete the two's complementation. Furthermore, multiplication factors are reduced in multiple stages to a form sum and carry components of a pre-determined length. The additive inverse of A×B is formed by using novel techniques to calculate the product of A and −B.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com