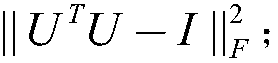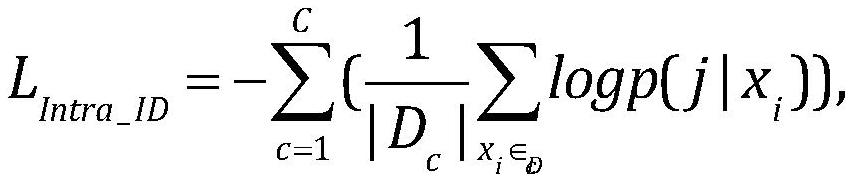Patents
Literature
71results about How to "Improve image recognition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
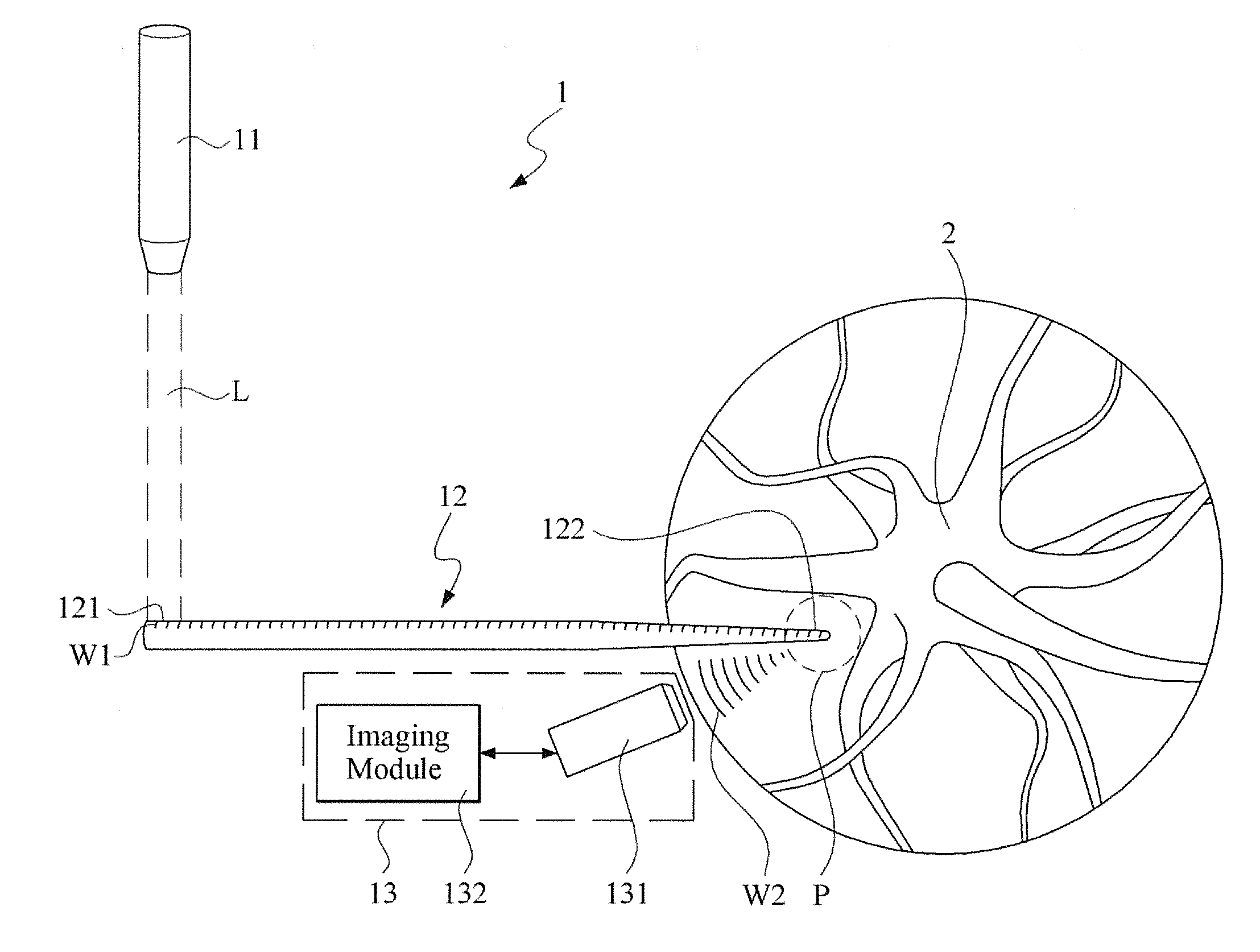
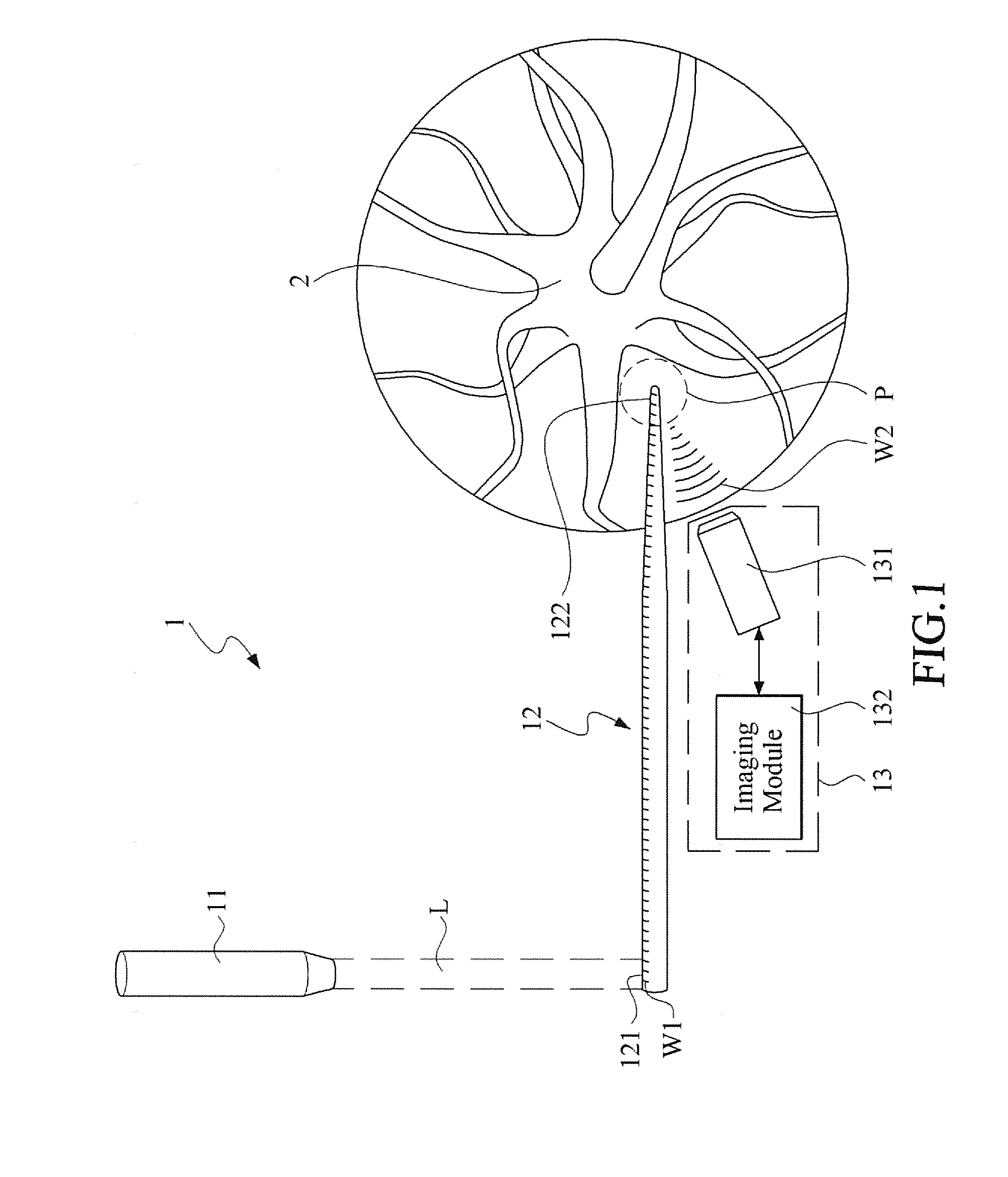
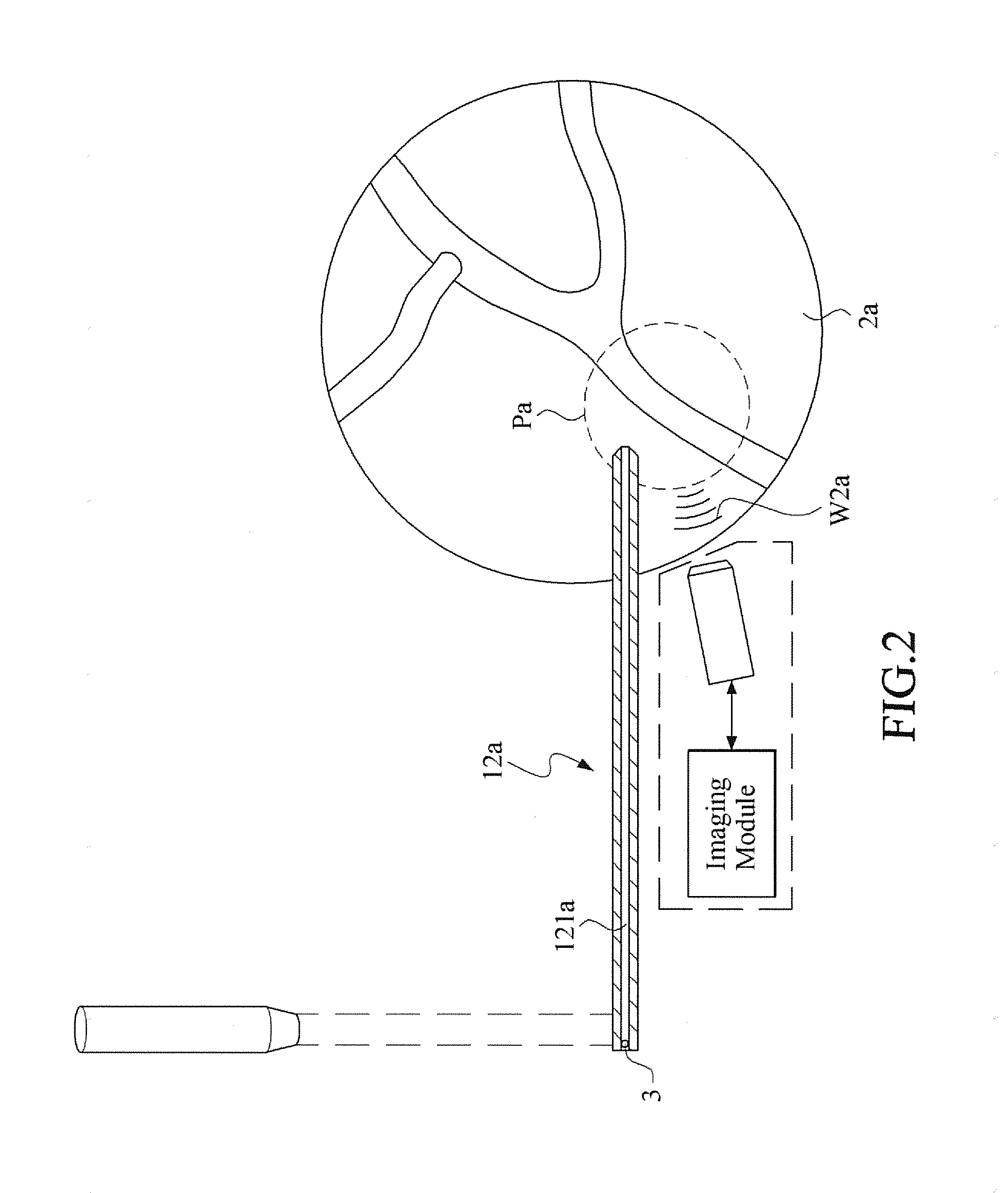
Intelligent luggage barrow of airport
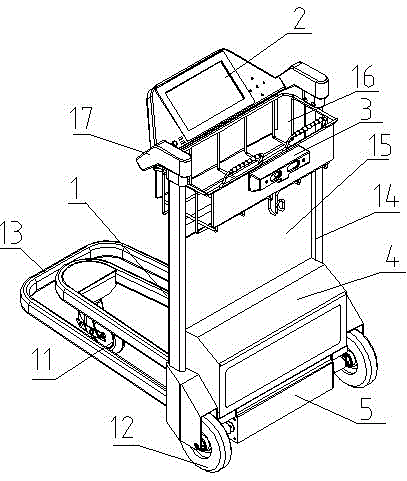
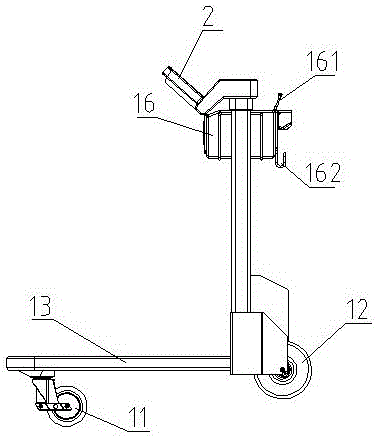
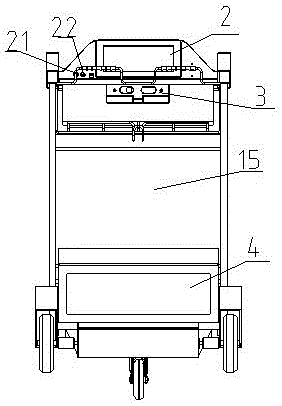
ActiveCN106741028AAchieve positioningSolve charging problemsGround installationsHand carts with multiple axesService experienceControl system
The invention discloses an intelligent luggage barrow of an airport. The intelligent luggage barrow is characterized in comprising a main body frame, a control panel, a deep visual identification device, a control box and a chassis driving device, wherein the main body frame comprises a luggage load bearing device and a functional frame; the functional frame comprises two supporting rods and an advertising space panel arranged between the two supporting rods; a small part luggage frame is arranged between the supporting rods on the top; two sides of the top end of each supporting rod are provided with panel supporting frames; the control panel is embedded into the panel supporting frames on two sides and is fixed by bolts; the deep visual identification device is fixed on a rear plate of the small part luggage frame; the chassis driving device is arranged on a wheel axle, and the supporting rods above the chassis driving device are riveted with the control box; a control system is integrated in the control box. According to the intelligent luggage barrow, functions including autonomous navigation, intelligent following, voice interaction, service consultation, on-line entertainment, convenient shopping, automatic weighting, forbidden article detection, automatic conversation, one-key recovery, kid missing prevention, automatic printing of boarding checks and the like are combined, and the intelligent luggage barrow of the airport can lead intelligent, fashionable, relaxed and convenient brand-new airport service experience.
Owner:四川西部动力机器人科技有限公司
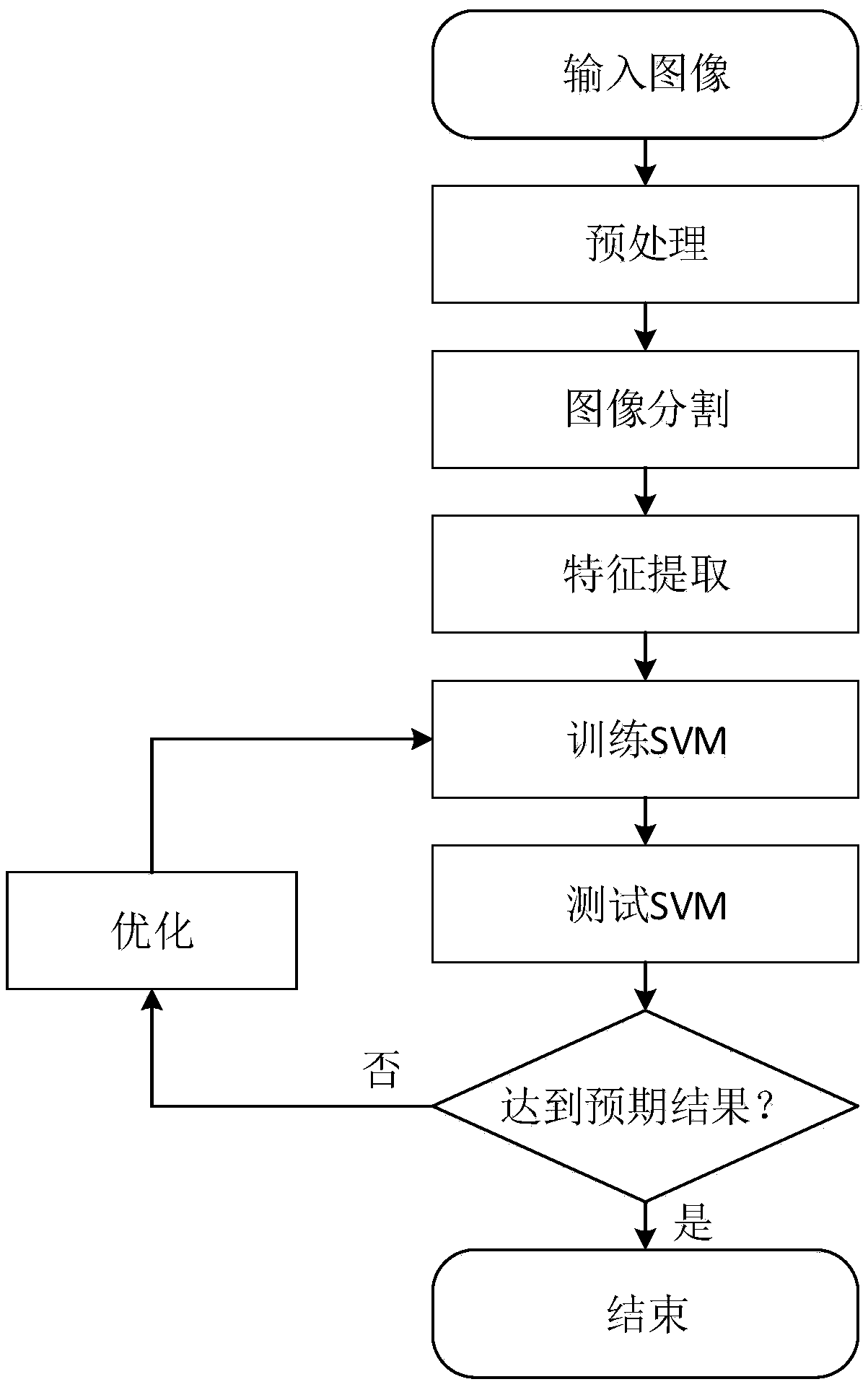
A method of leaf disease identification based on machine learning algorithm
PendingCN109308697AImprove image qualityRich image informationImage enhancementImage analysisSample imagePlant disease
The invention discloses a leaf disease identification method based on a machine learning algorithm, belonging to the technical field of image processing. The invention firstly performs preprocessing operations such as grayscale transformation, image enhancement and denoising on the collected leaf sample image; Then the preprocessed image is segmented by adaptive threshold algorithm to represent the texture information of the sample image effectively. The RGB color space is selected to extract the color features of the sample image, and the texture features of the segmented image are extractedaccording to the gray level co-occurrence matrix. Finally, support vector machine model is selected to classify and recognize the sample images by cross-validation algorithm. Firstly, the main parameters of SVM model are optimized by grid optimization method, and then the parameters with the best recognition accuracy are selected to establish SVM classification and recognition model. The inventioncan enable the computer to automatically identify the diseases and pests of the leaves through training, greatly reducing the space and time overhead, and improving the identification accuracy, and has the characteristics of fast, accurate and strong robustness.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Noncontact type book scanning equipment
InactiveCN105095894AImprove reading experienceImprove the problem of decreased recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionDimensional modeling
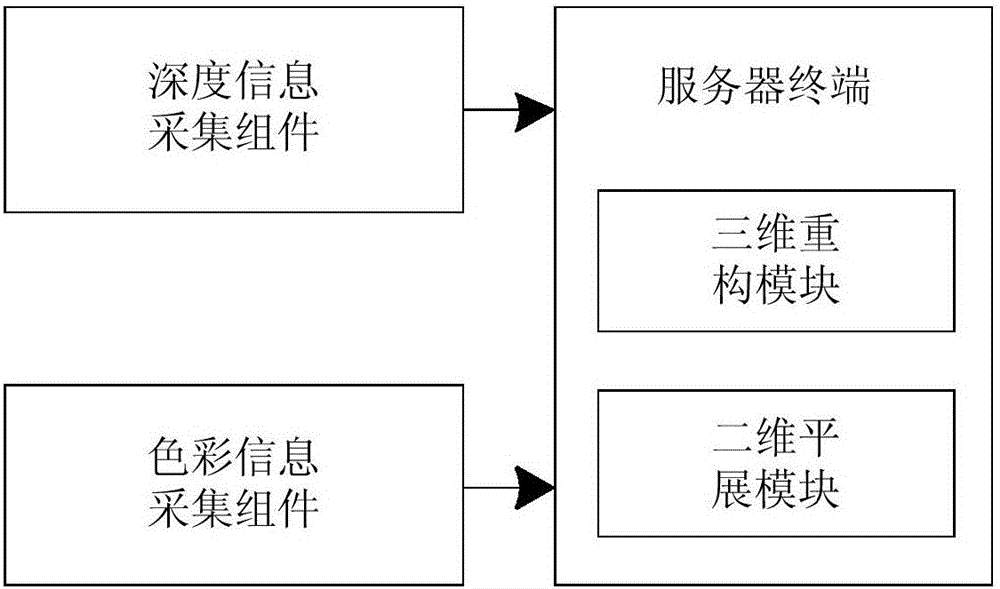
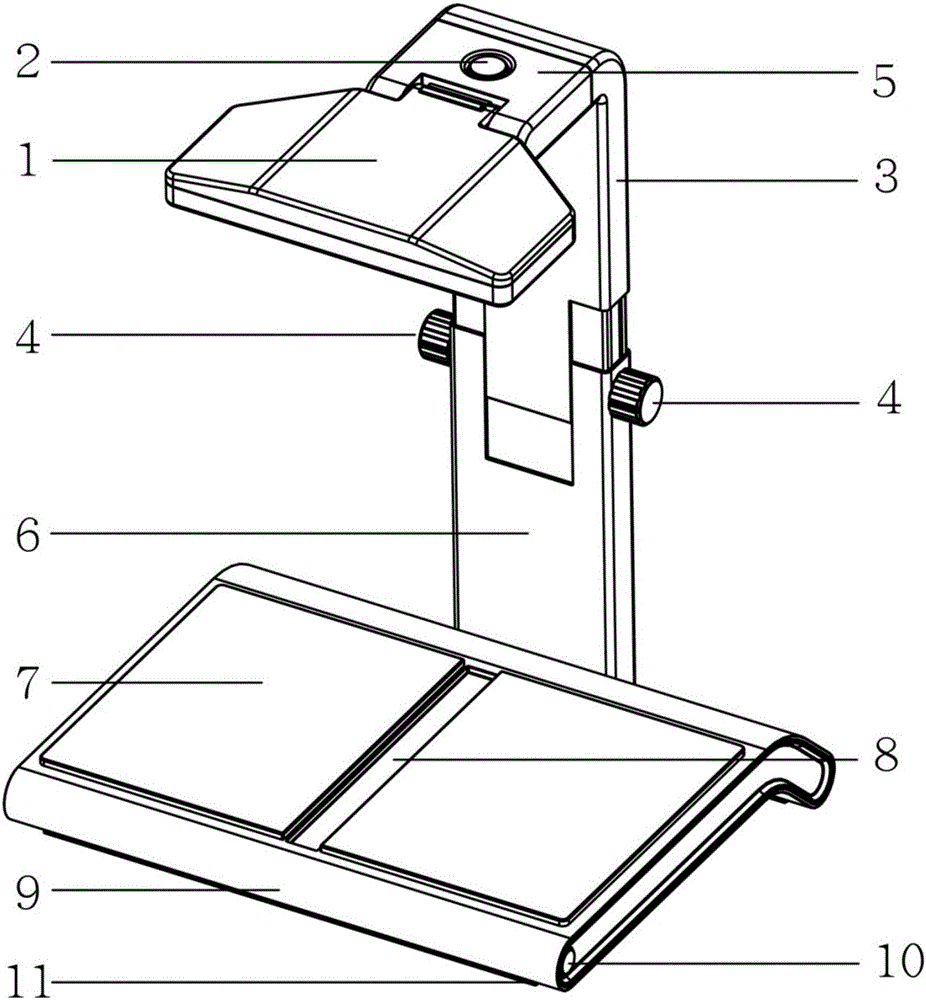
The disclosure provides noncontact type book scanning equipment. The noncontact type book scanning equipment comprises a depth information acquisition component which acquires depth information of a book to be scanned; a color information acquisition component which acquires color information of the book to be scanned; and a server terminal which receives the depth information acquired by the depth information acquisition component and the color information acquired by the color information acquisition component. The server terminal comprises a three-dimensional modeling module which is used for constructing a three-dimensional mesh model of the book to be scanned based on the received depth information; and a two-dimensional flattening module which is used for recovering a two-dimensional flat image of the book to be scanned based on the three-dimensional mesh model of the book to be scanned and the received color information. The scanning effect can be enhanced, reduction of image resolution can be improved and user reading experience can be improved by the noncontact type book scanning equipment.
Owner:PANOWIN TECH
Apparatus and method for image recognition
InactiveUS20150092057A1Efficient detectionEasy to reconfigureImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionLower limitTime efficient
Disclosed are image recognition apparatuses and methods which detect subject objects by configuring effective candidate regions for the subject objects in a target image. The apparatus includes an image inputting part receiving at least one image; an effective candidate region configuring part configured to receive a user input including information on reference positions of effective candidate regions and an upper limit and a lower limit of the effective candidate regions, and to configure the effective candidate regions based on the user input; and an effective region determining part configured to select an effective region meeting a preconfigured threshold among the effective candidate regions configured based on the user input. Therefore, since a complex conventional camera calibration procedure is not necessary, time and cost can be saved.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Nonnegative matrix factorization method based on discriminative orthogonal subspace constraint
ActiveCN108416374AImprove generalization abilityGood projection dimensionality reduction abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixAlgorithm
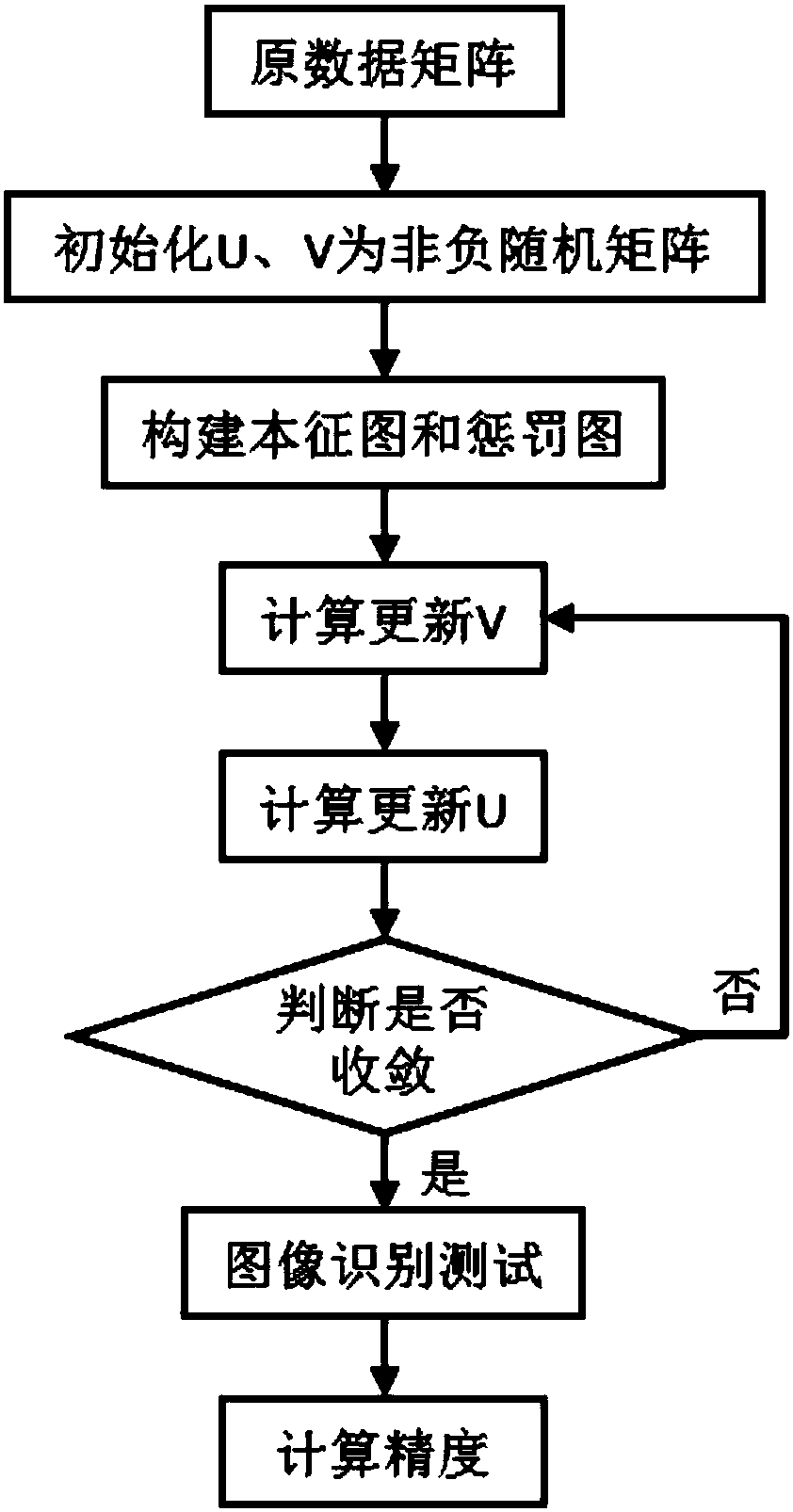
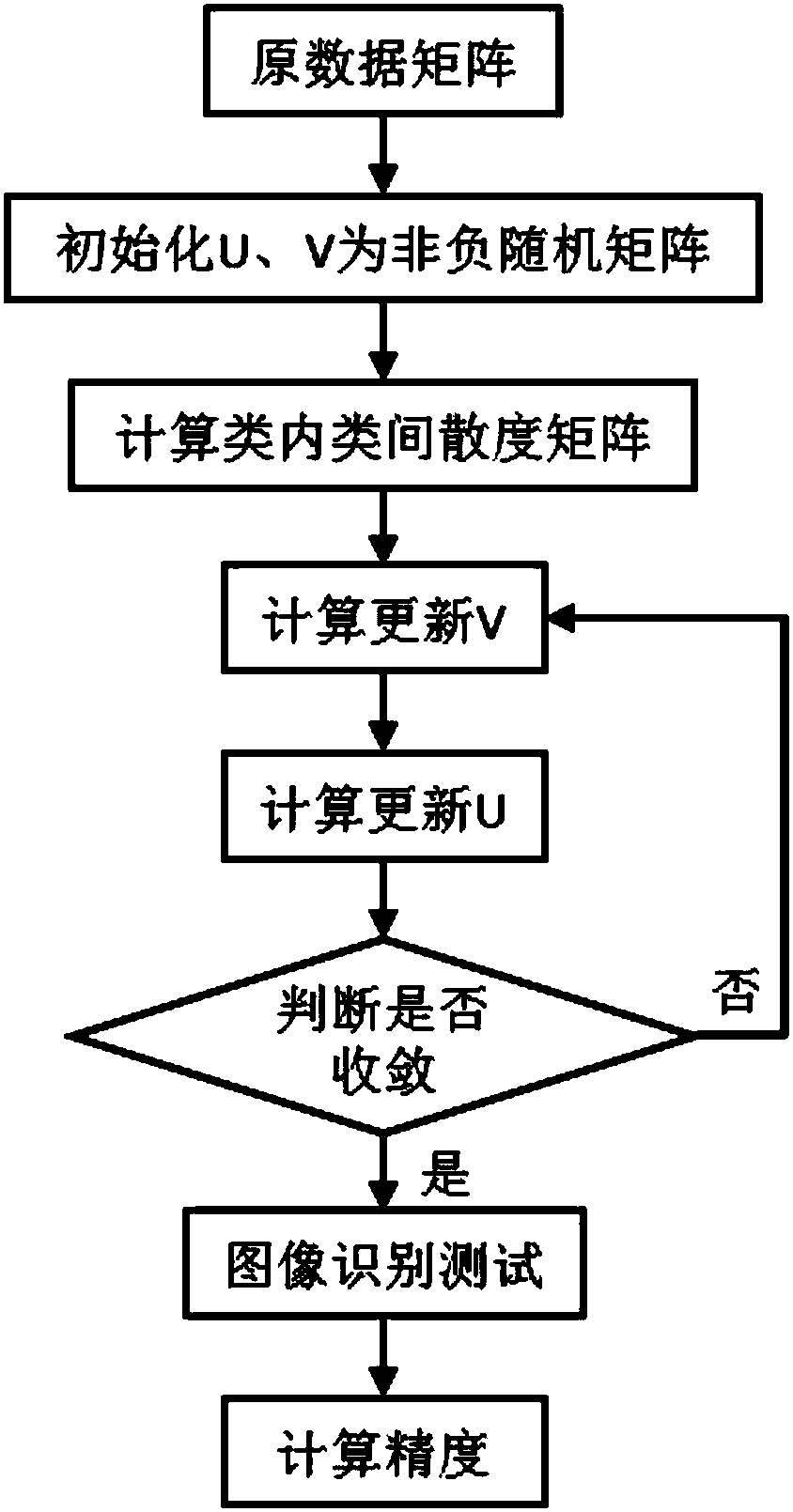
The invention discloses a nonnegative matrix factorization method based on a discriminative orthogonal subspace constraint. The method mainly comprises the following steps of (1) stretching an image in a training sample set into vectors to compose a training data matrix Xtrain, then factorizing the Xtrain in a nonnegative matrix factorization framework based on the discriminative orthogonal subspace constraint, and directly exerting a discriminative constraint item based on within-class and between-class associations to the basis matrix; (2) constructing a projection matrix W by use of the learned basis matrix U*, calculating projection expression of the training data Xtrain and test data Xtest in the projection matrix W, and performing an image recognition experiment with a nearest neighbor classifier; and (3) calculating the image identification precision. According to the nonnegative matrix factorization method based on the discriminative orthogonal subspace constraint, the discriminative structure information inside the data are explored and utilized, the discriminative constraint directly exerted to the basis matrix in the algorithm enhances the generalization performance of the algorithm and improves the image identification effect; and the method can be widely applied to the field of data mining and data analysis.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
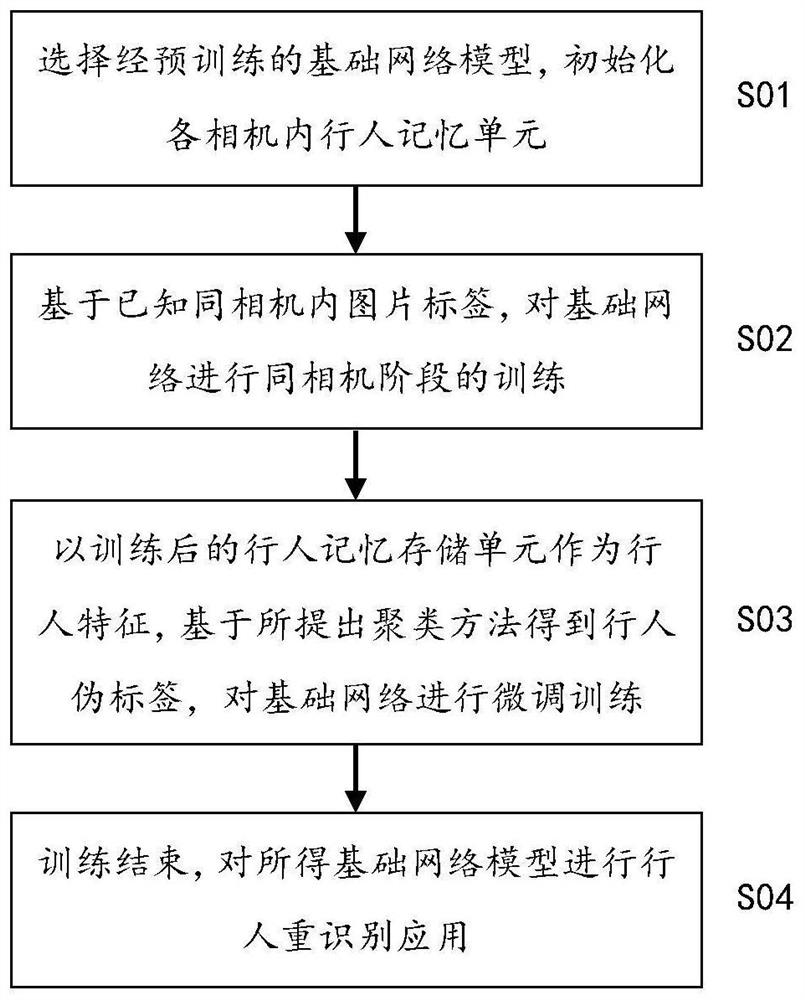
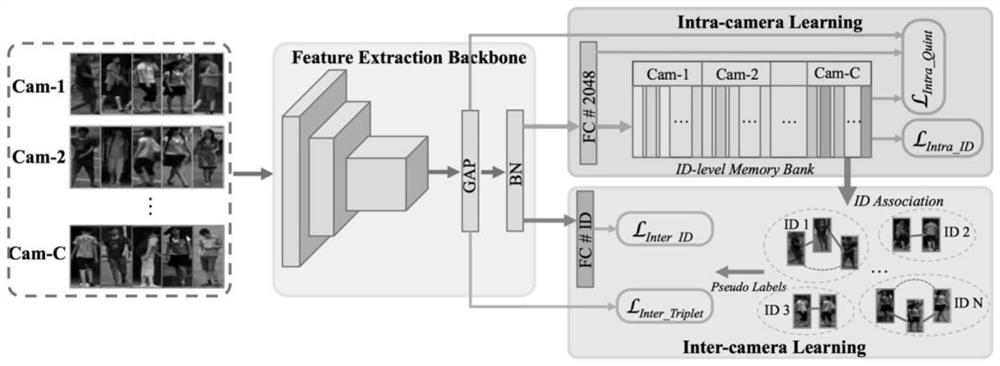
Multi-camera high-precision pedestrian re-identification method for supervised scenes in same camera
ActiveCN111723645AEffective use of globalImprove performanceInternal combustion piston enginesCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionRadiology
The invention discloses a multi-camera high-precision pedestrian re-identification method for supervised scenes in the same camera. The method comprises the steps of photograhing by adopting multiplecameras in the same pedestrian scene, selecting a basic network model, modifying after pre-training, acquiring a pedestrian picture set to be trained, establishing pedestrian memory features for eachcamera, and initializing the pedestrian memory features; based on an existing to-be-trained pedestrian picture set, performing training optimization and supervision in the same camera stage on the basic network model; obtaining a pedestrian pseudo-label by combining the trained pedestrian memory features with a clustering method, and performing fine tuning training on the basic network model by using the pedestrian pseudo-label; and performing cross-camera pedestrian re-identification application on the basic network model obtained by training. According to the method, the recognition performance can be effectively improved only by marking the pictures in the same camera in the scene, the re-recognition accuracy equivalent to that in a fully-supervised scene is achieved, and the pedestrianre-recognition accuracy equivalent to that in the fully-supervised scene is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
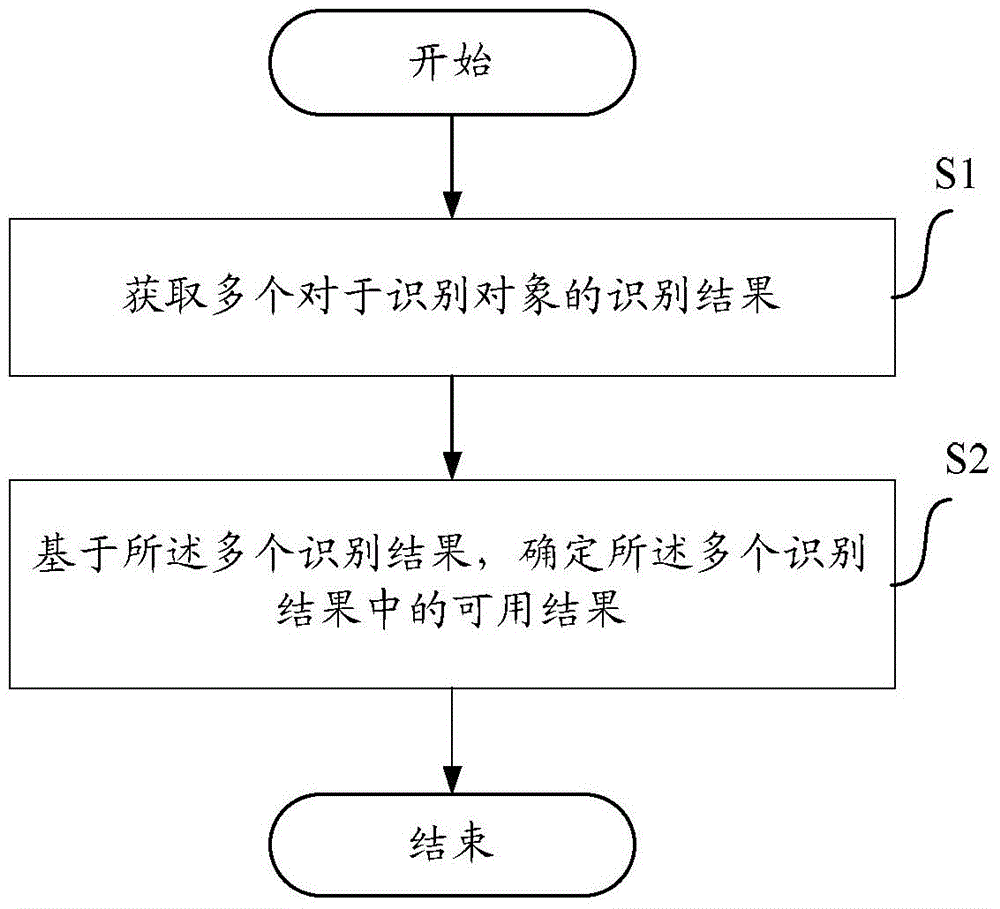
Method of face identification and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN104992146AEasy to identifyRecognition Effect SavingsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionData mining
The invention aims at providing a method of target identification and an apparatus thereof. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring a plurality of identification results for an identification target; based on the plurality of identification results, determining a usable result in the plurality of identification results. According to a scheme of the invention, through screening the plurality of identification results in image information, possible useless identification results are removed so that useless identification data storage is reduced, a processing capability of user equipment is increased, subsequent identification operations, such as face searching and the like, can be well performed and an identification effect to the image information is increased.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
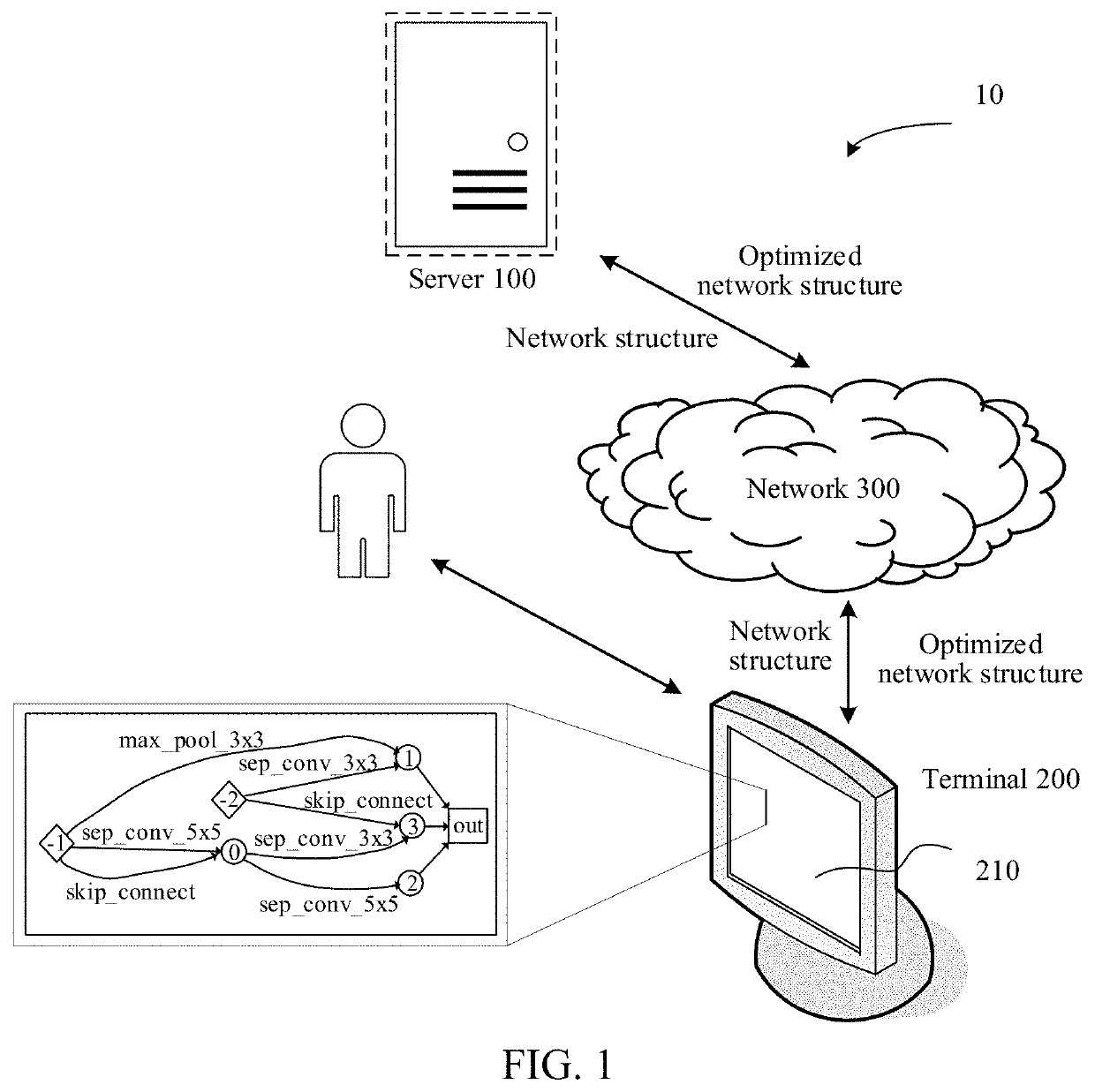
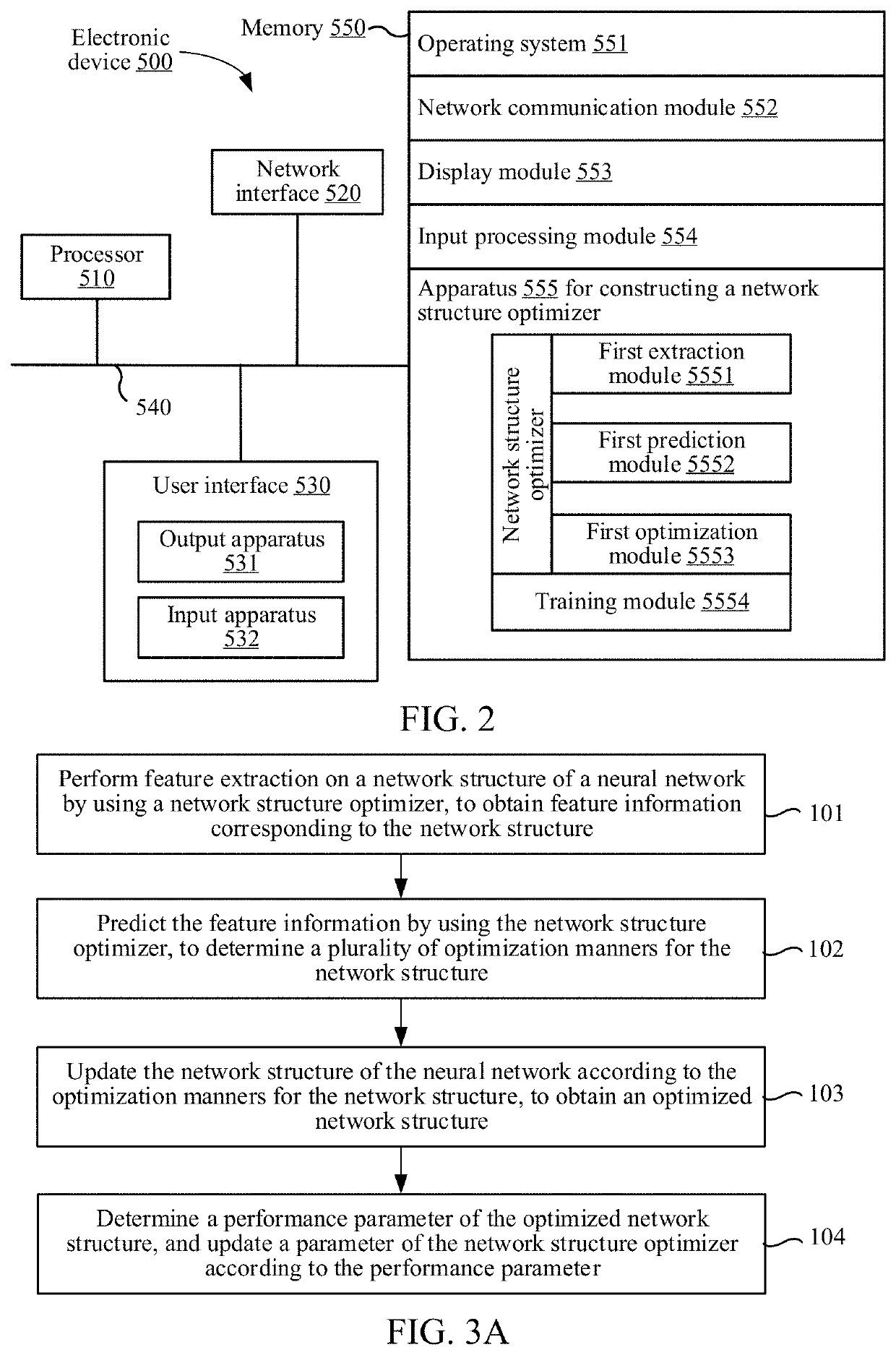
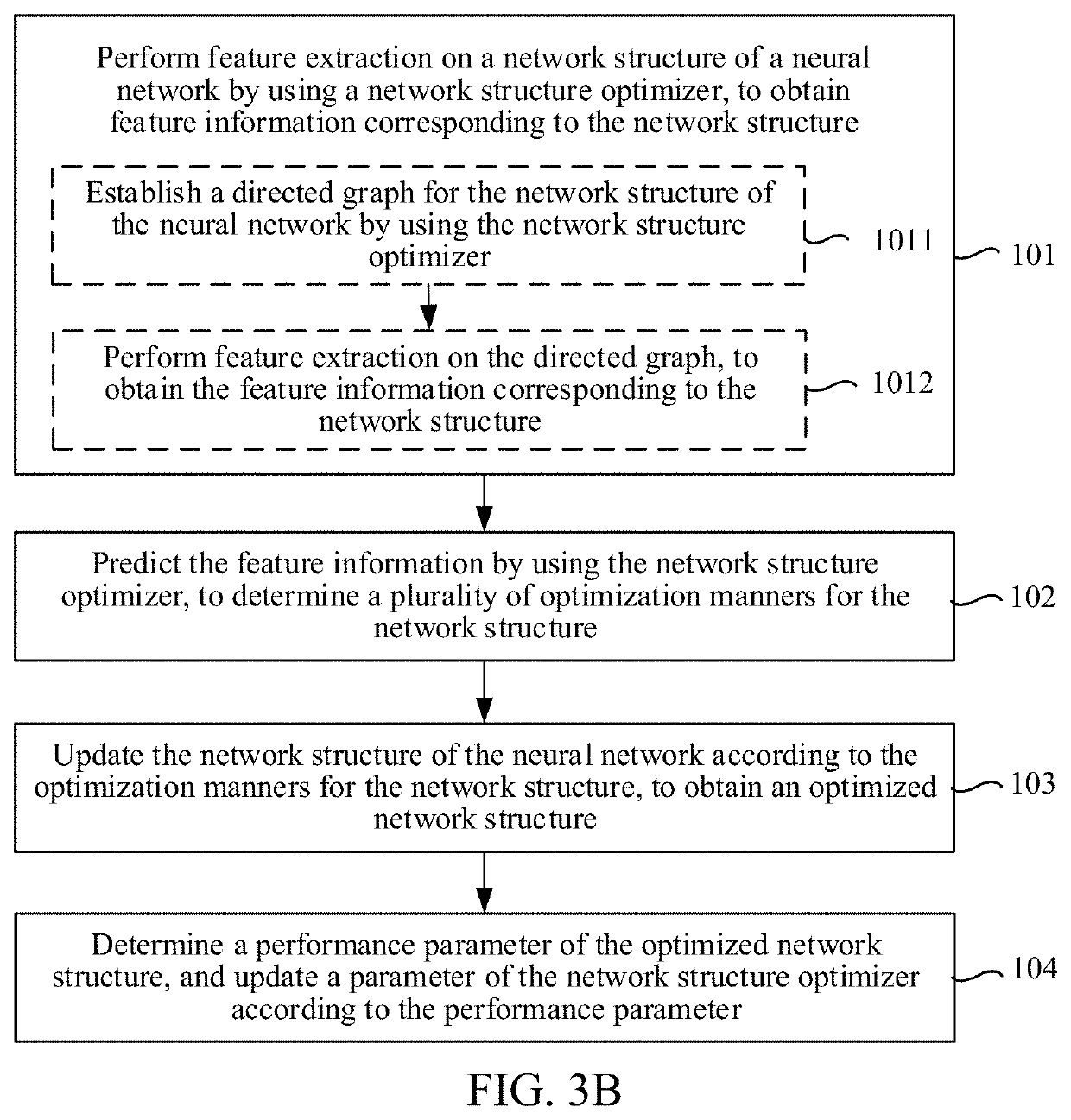
Method and apparatus for constructing network structure optimizer, and computer-readable storage medium
PendingUS20220044094A1Improve image recognitionImage recognition is accurateNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsFeature extractionNetwork structure
This application provides a method for constructing a network structure optimizer performed by an electronic device. The method includes: performing feature extraction on a network structure of an image recognition neural network by using a network structure optimizer, to obtain feature information corresponding to the network structure; predicting the feature information by using the network structure optimizer, to determine a plurality of optimization manners for the network structure; updating the network structure of the image recognition neural network according to the optimization manners for the network structure, to obtain an optimized network structure of the image recognition neural network; and determining an image recognition performance parameter of the optimized network structure of the image recognition neural network, and updating a parameter of the network structure optimizer according to the image recognition performance parameter, the network structure optimizer being configured to optimize the network structure of the image recognition neural network.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Method for detecting soil-wetted body in drip irrigation mode
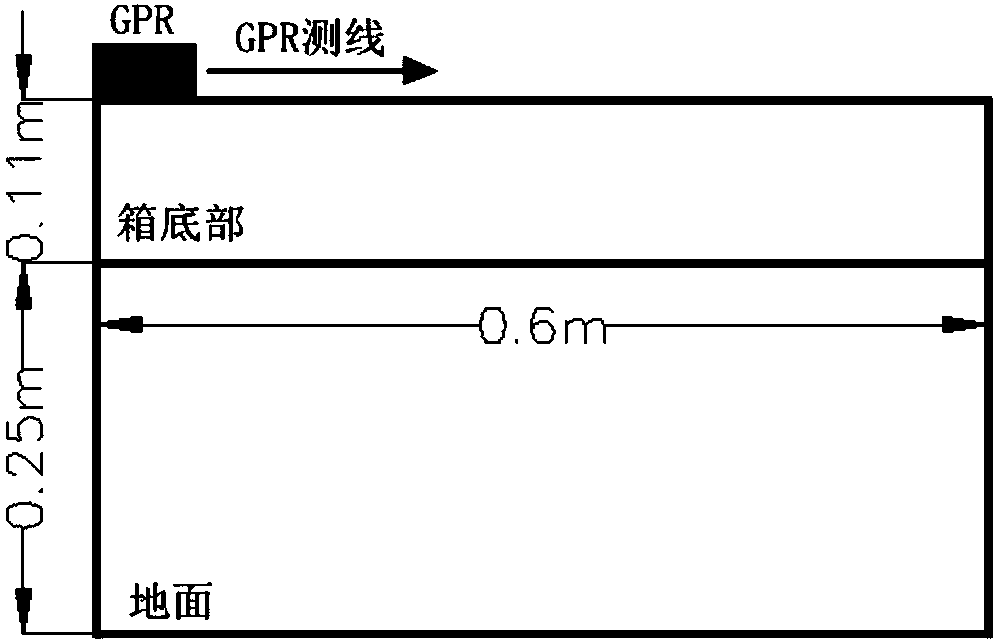
InactiveCN107727016AQuick detectionNon-destructive detectionUsing wave/particle radiation meansRadio wave reradiation/reflectionWater savingDielectric
The invention provides a method for detecting a soil-wetted body in a drip irrigation mode. The method comprises the following steps of collecting and processing GPR data, measuring the soil volume water content, establishing a relation model between the soil volume water content and the dielectric constant, and interpreting the processed GPR data. According to the invention, the established relation model between the soil volume water content and the dielectric constant is more accurate compared with a traditional Ttop model. The method provided by the invention is used for carrying out original detection on the premise that the soil-wetted body is not damaged at all. The change of the time scale and the spatial scale of the soil-wetted body is fully considered, so that the soil-wetted body can be rapidly and efficiently detected in the nondestructive and in-situ manner based on the ground penetrating radar technology. The application of the ground penetrating radar technology in thesoil-wetted body monitoring field is promoted. Meanwhile, the technical support is provided for the accurate agriculture and the water-saving agriculture.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Video processing method and device, computer readable storage medium and computer equipment
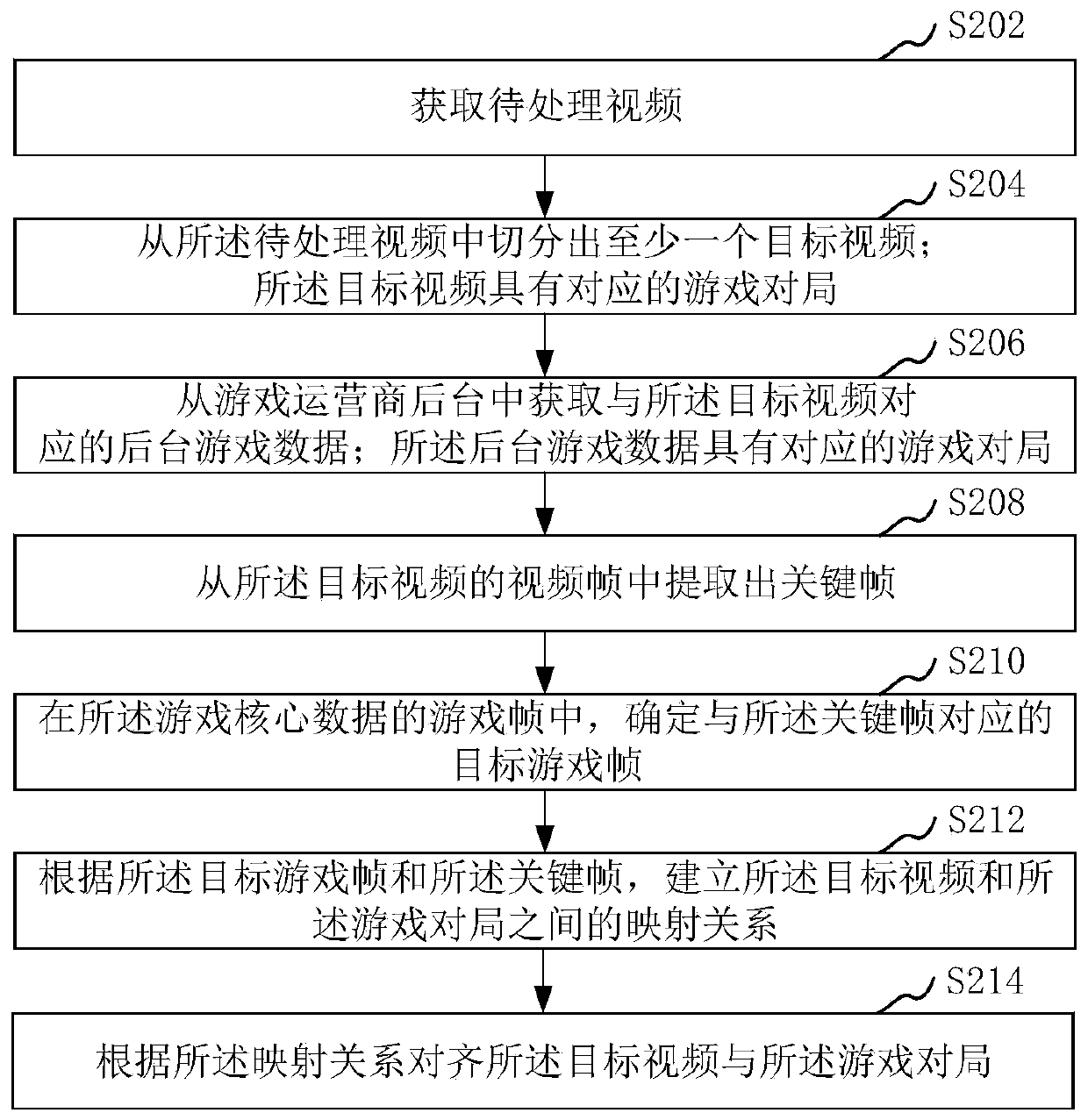
ActiveCN110841287AEmbedding precisionImprove image recognitionVideo gamesSelective content distributionVideo processingEngineering
The invention relates to a video processing method and device, a computer readable storage medium and computer equipment. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring a to-be-processed video;segmenting at least one target video from the to-be-processed video; acquiring background game data corresponding to the target video from a game operator background, wherein the background game datahave a corresponding game; extracting a key frame from video frames of the target video; in game frames of the game, determining a target game frame corresponding to the key frame; establishing a mapping relationship by adopting the target game frame and the key frame; and according to the mapping relationship, aligning the target video and the game. When a game commentary is required to be embedded in a certain position of the game, the embedded position in the video can be determined according to the mapping relationship, so that precise embedding of the game commentary is realized.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Image capture apparatus
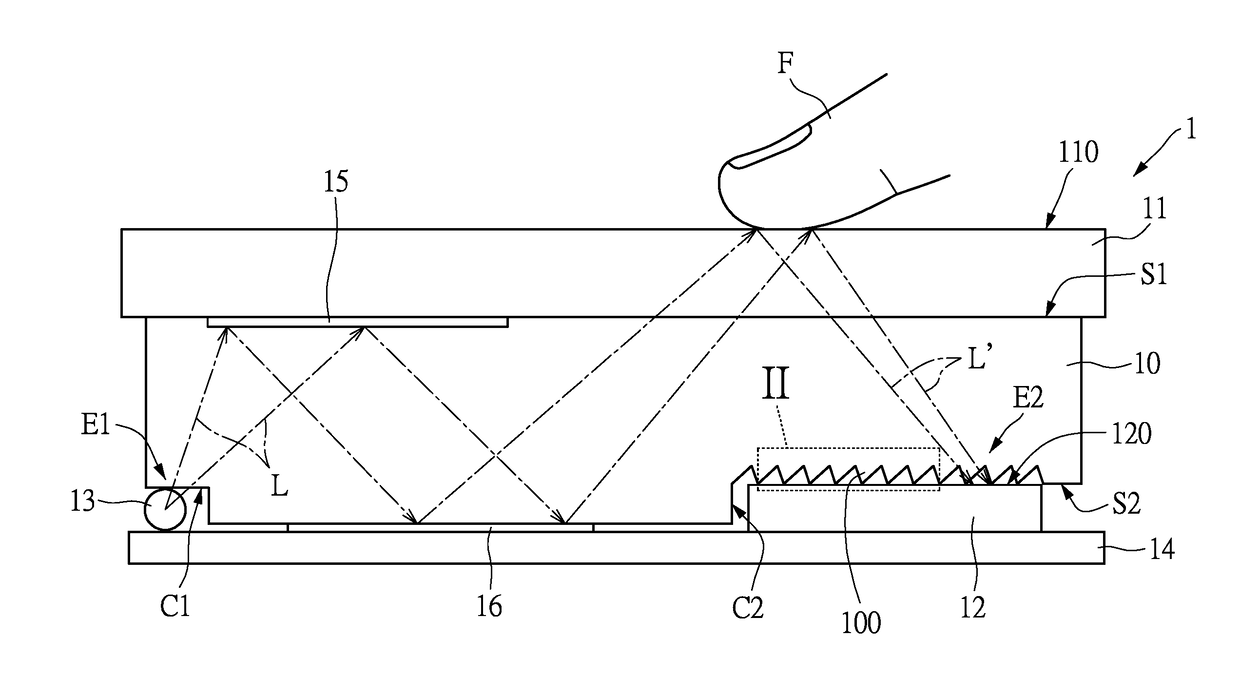
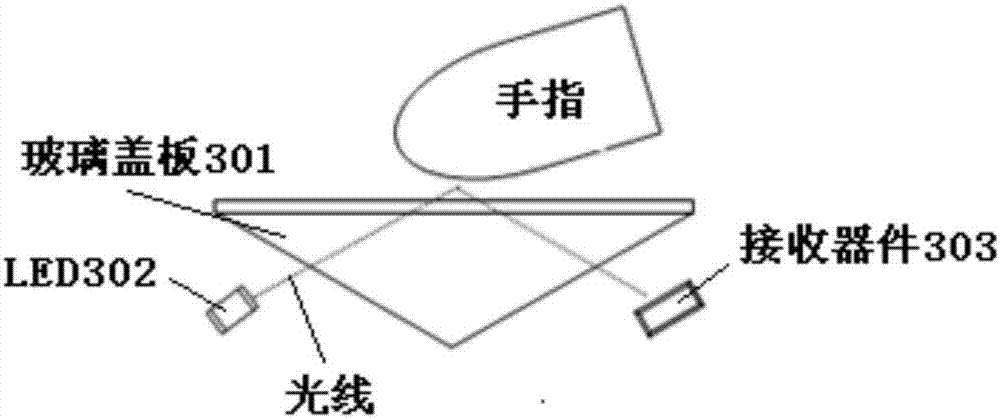
ActiveUS20180293423A1Improve visibilitySpread the wordMechanical apparatusSolid-state devicesLight guideLight beam
An image capture apparatus including a light guide element, an image capture device and a light emitting device. The light guide element has a first side, a second side and a light emitting portion located at the second side. The light emitting portion includes a plurality of enhanced transmission microstructures. The image capture device is disposed on the second side of the light guide element corresponding to the position of the enhanced transmission microstructures. A light beam, which is generated by the light emitting device and transmitted at least by the light guide element, is totally reflected to form a signal light beam. Thereafter, the signal light beam passes through the enhanced transmission microstructures and then is received by the image capture device.
Owner:GINGY TECH
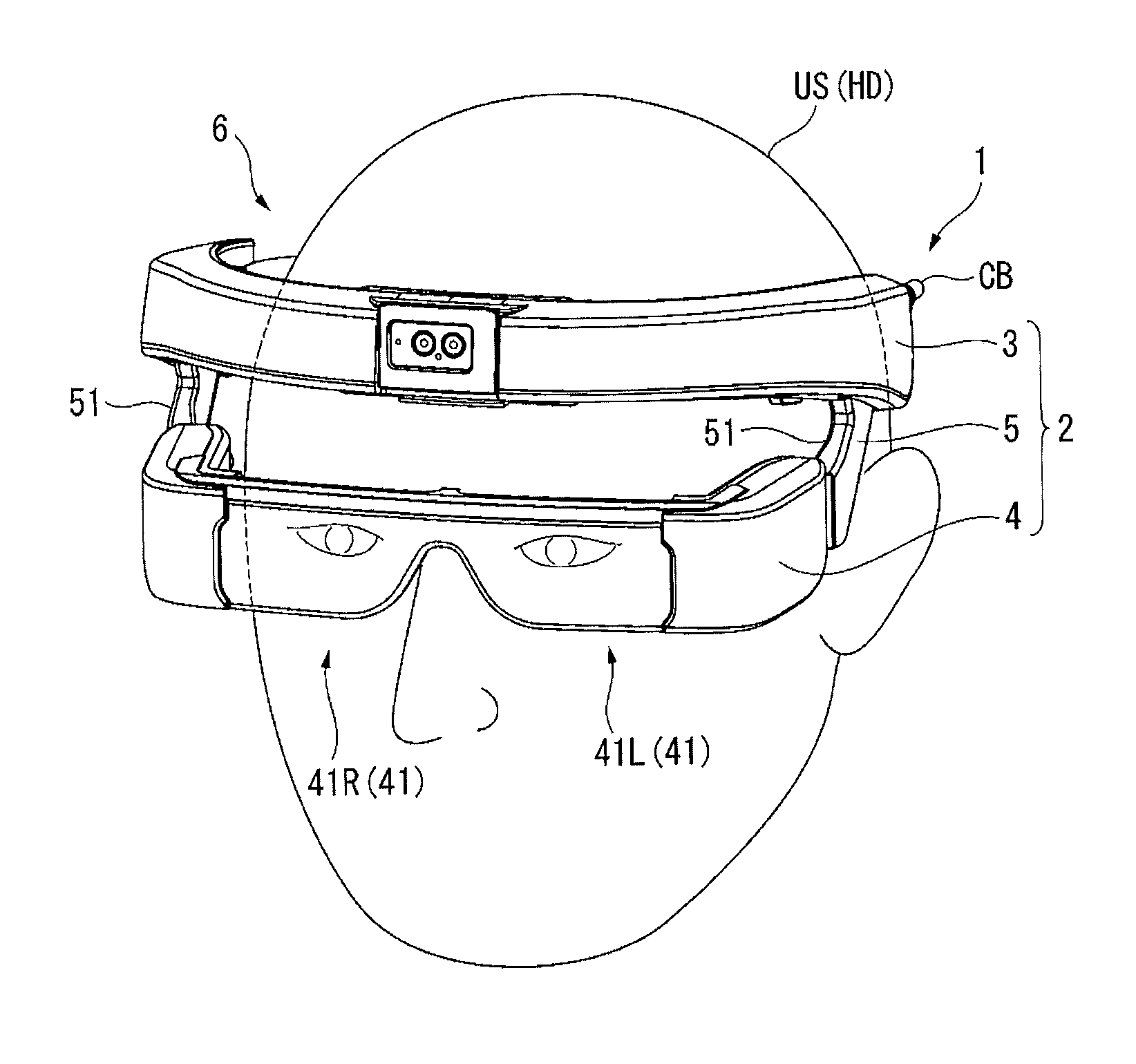
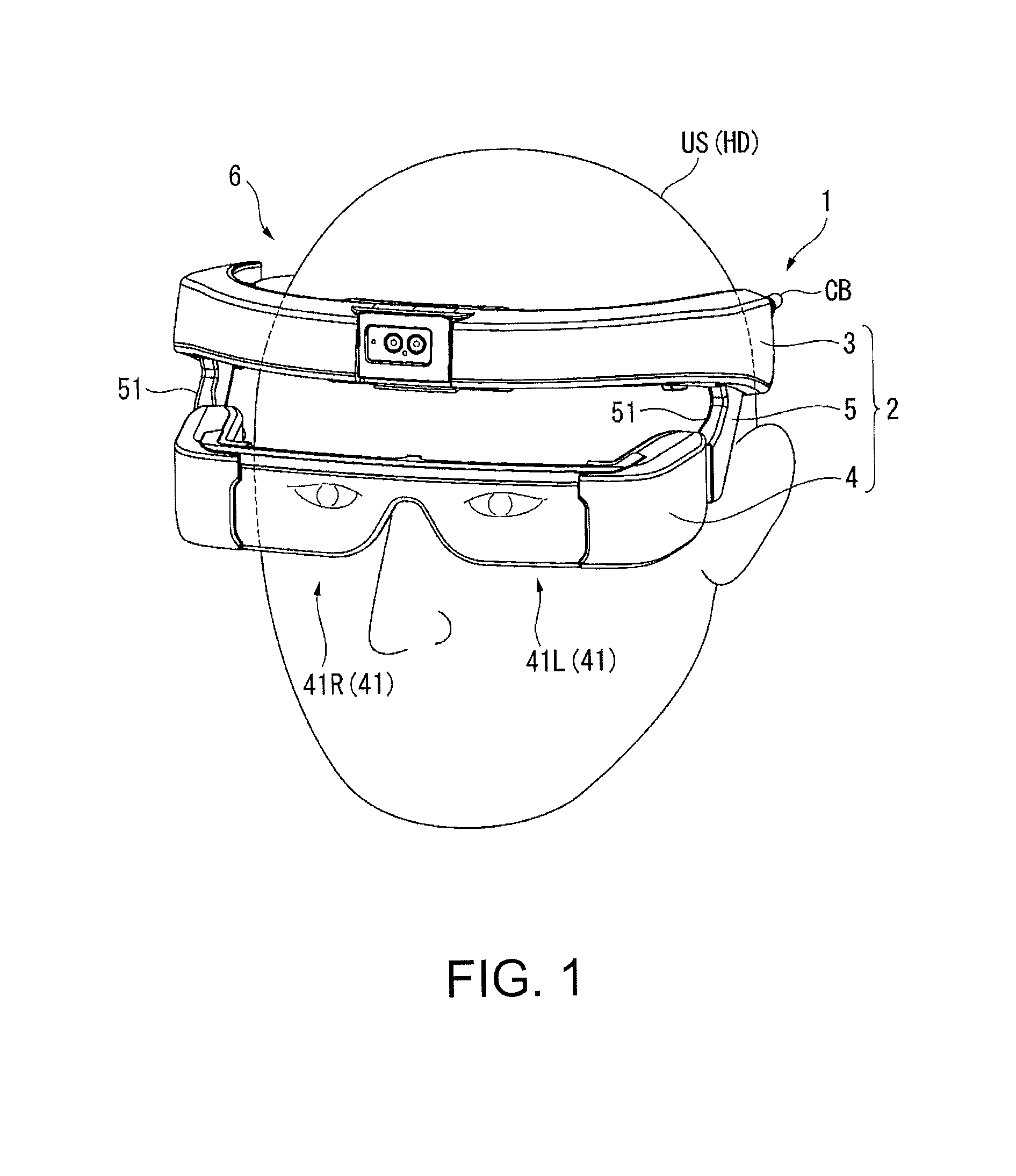
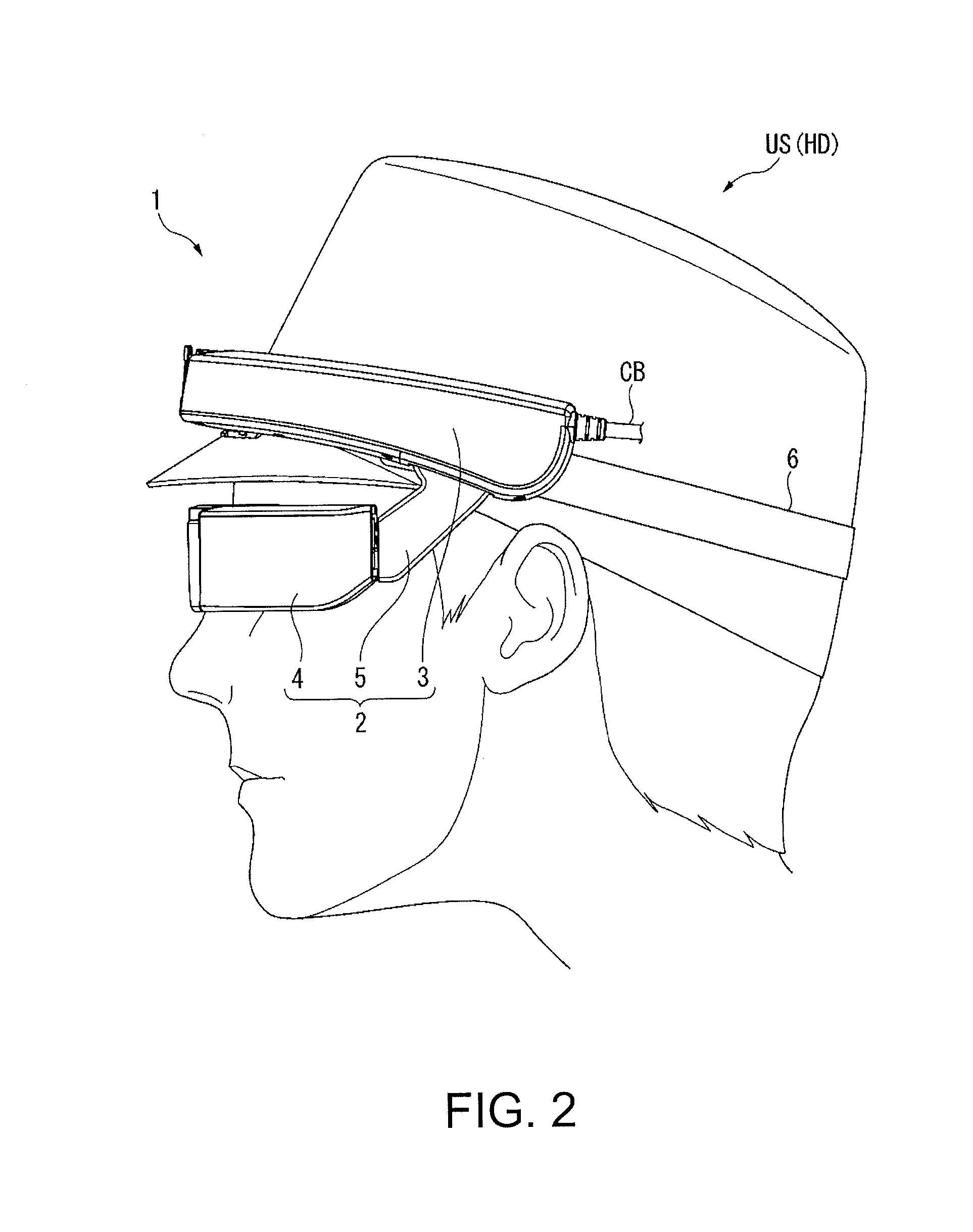
Image display apparatus
ActiveUS20160147071A1Reliably visually recognizeImprove image recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Computer science
An image display apparatus includes a frame along a head of an observer, a display unit that displays an image that can be visually recognized by the observer, and a supporting part attached to the frame and supporting the display unit, wherein the frame is fixed to a position in which the image displayed by the display unit connected to the frame via the supporting part is visually recognized by the observer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
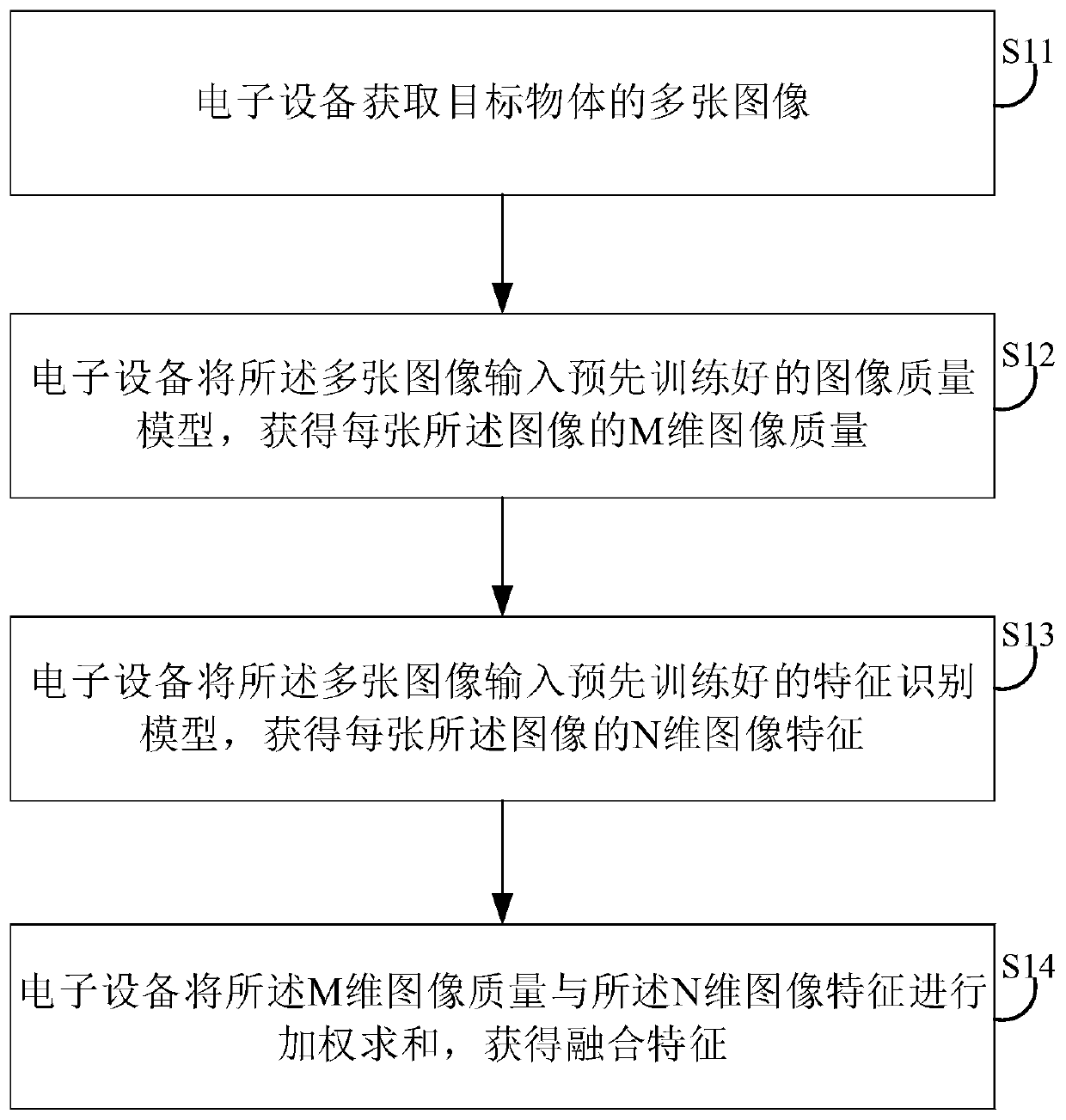
Feature fusion method and device, electronic device and storage medium
ActiveCN109766925AImprove image recognitionImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging qualityImaging Feature
The invention discloses a feature fusion method. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a plurality of images of a target object; inputting the plurality of images into a pre-trained image quality model to obtain the M-dimensional image quality of each image; inputting the plurality of images into a pre-trained feature recognition model to obtain N-dimensional image features of each image; performing weighted summation on the M-dimensional image quality and the N-dimensional image characteristics to obtain fusion characteristics, wherein M is a positive integer, N is a positive integer, when M is equal to 1, N is greater than or equal to 2, and when M is greater than or equal to 2, M is equal to N. The invention further provides a feature fusion device, an electronic device and a storage medium. According to the present invention, the image recognition effect can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INTELLIFUSION TECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
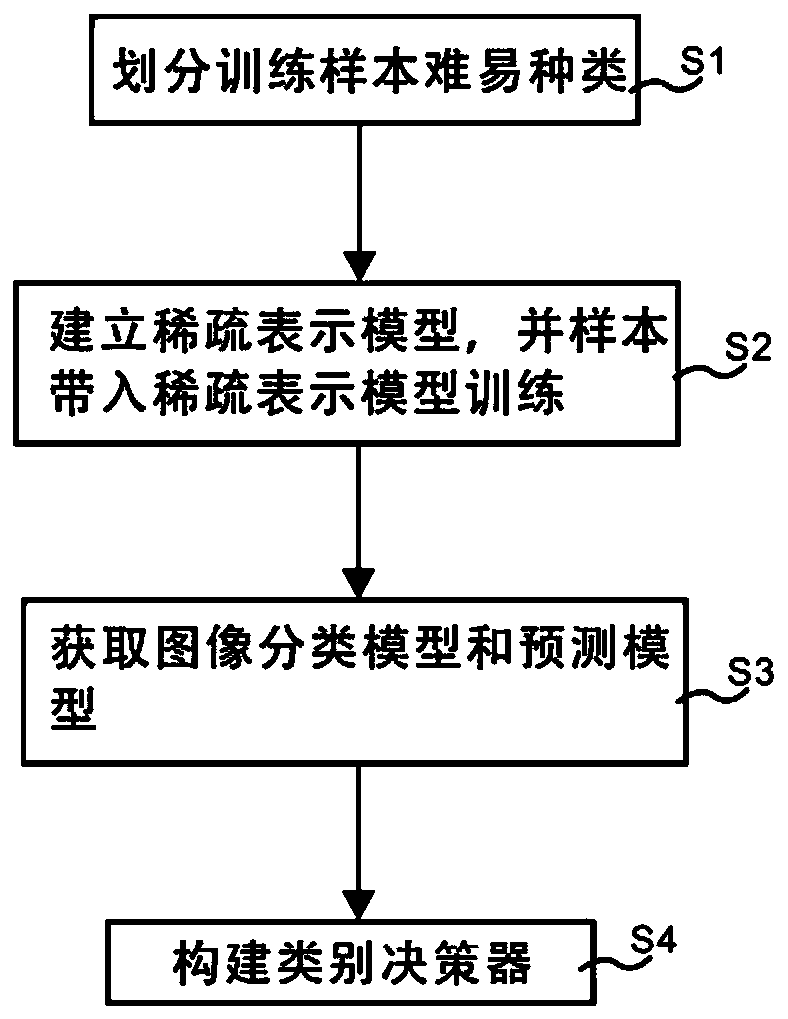
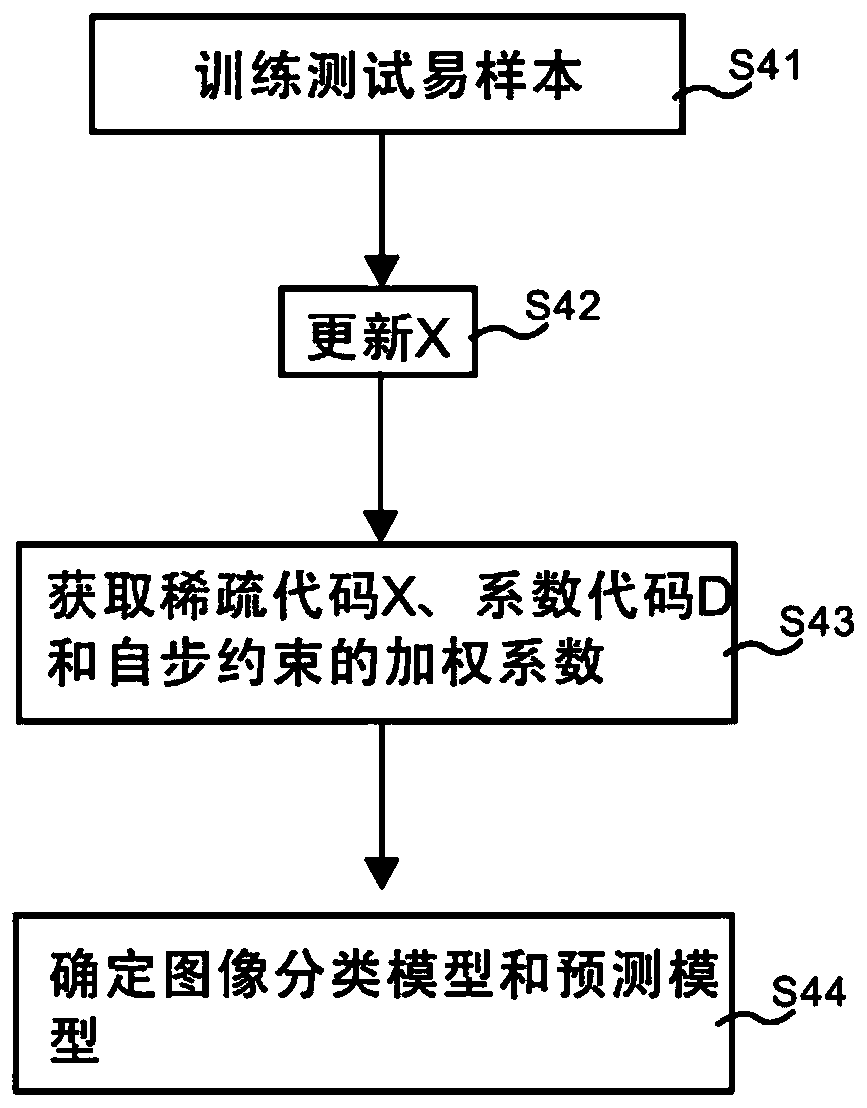
Supervised image classification method based on self-paced constraint mechanism
PendingCN110009049AEfficient use ofRobustCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningClassification methods
The invention discloses a supervised image classification method based on a self-paced constraint mechanism. The method comprises the following steps: dividing difficult types of training samples; establishing a sparse representation model, and substituting samples into the sparse representation model for training; obtaining an image classification model and a prediction model; constructing a category decision-making device, wherein the training sample difficult type comprises a training easy sample and a training difficult sample, and the division training sample difficultly-easy types are divided by adopting a self-step constraint matrix. According to the invention, the training samples are divided through the self-paced constraint matrix; the easy training sample and the difficult training sample are sequentially substituted into a defined sparse representation model for continuous training; a specific self-step constrained image classification scheme can be formed, more judgment information can be conveniently utilized, robustness is achieved on sample noise, and therefore the problem that a supervised dictionary learning mechanism is not suitable for complex samples containingnoise and huge intra-class changes can be solved, and the image recognition effect is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
System and imaging method for using photoacoustic effect
ActiveUS20160213256A1Improve image recognitionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterLight beamOrganic media
A system and an imaging method for using photoacoustic effect are provided in the present invention. The system includes a light source for generating a light beam, a wave-guide probe and an ultrasound receiving device. The wave-guide probe further has a reception portion and at least one transmission portion. The reception portion receives the light beam and then triggers a photoacoustic effect inside the reception portion so as thereby to generate at least one sound wave thereinside to be further transmitted to the at least one transmission portion. The transmission portion is merged into the organic medium. When the sound wave is transmitted to the transmission portion, an ultrasound area is generated inside the organic medium. The ultrasound receiving device is located adjacent to the organic medium, receives the ultrasound generated in the ultrasound area to form an ultrasound image of the organic medium, so as to achieve the imaging method.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
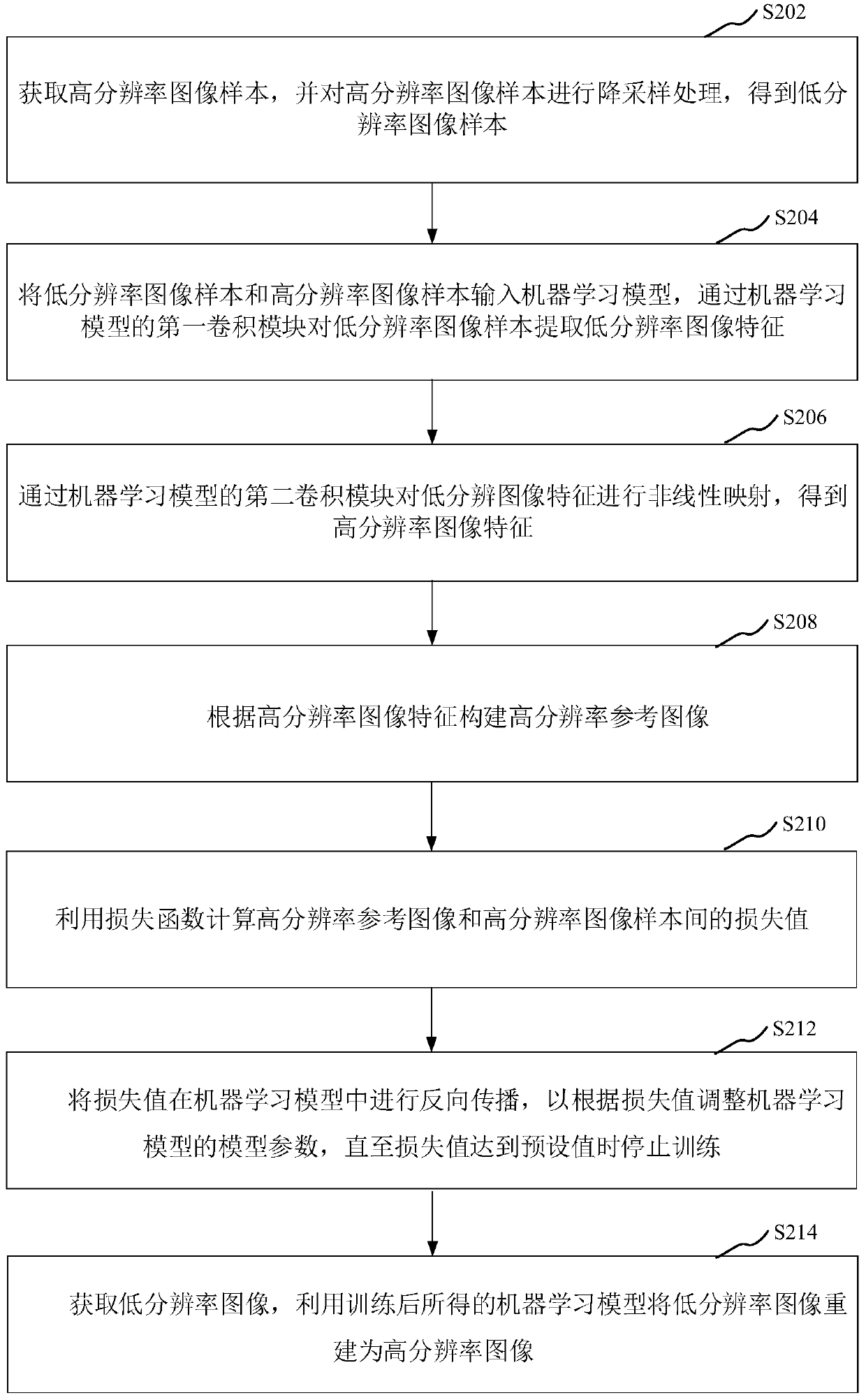
Image super-resolution reconstruction method and device, storage medium and computer equipment
ActiveCN111127317AEnhance the imageExcellent data indexGeometric image transformationReconstruction methodEngineering
The invention relates to an image super-resolution reconstruction method and device, a storage medium and computer equipment, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the downsampling of a high-resolution image sample, obtaining a low-resolution image sample, and extracting the low-resolution image features of the low-resolution image sample through a first convolution module of a machinelearning model; enabling the second convolution module to perform multiple times of nonlinear mapping on the low-resolution image features to obtain high-resolution image features; constructing a high-resolution reference image according to the high-resolution image features; calculating a loss value between the high-resolution reference image and the high-resolution image sample; performing backpropagation on the loss value in a machine learning model to adjust model parameters of the machine learning model according to the loss value; acquiring the low-resolution image; and reconstructing the low-resolution image into the high-resolution image by using the machine learning model obtained after training. The problem of poor recognition effect caused by low resolution of the face image can be avoided.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20150021781A1Improve image recognitionHigh precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesScattered lightContact hole
A semiconductor device has a plurality of first opening portions formed in an interlayer insulating film. The surface is covered with a metal film with a surface having concavities and convexities which scatter reflected light. Size of the first opening portion is of the same level as a contact hole of a component and cannot be recognized by an image recognition apparatus. The metal film can be recognized by the image recognition apparatus. By forming a TiN film serving as a reflection prevention film on an end of the metal film, portions that can easily scatter light and a portion that cannot easily reflect light are adjacent in an alignment marker. A passivation film is formed on the interlayer insulating film and the TiN film. Recessed portions disposed in the metal film are exposed to a second opening portion formed in the passivation film and the TiN film.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Camera viewer device
InactiveUS20070025724A1Good adhesionEasy detachmentTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringViewfinder
Owner:RICOH KK
Camera viewer device
InactiveUS7529479B2Improve image recognitionImprove visual effectsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringViewfinder
Owner:RICOH KK
Template creation method and image processor therefor
ActiveUS20090304286A1Reduce the differenceMatching rateMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Template based
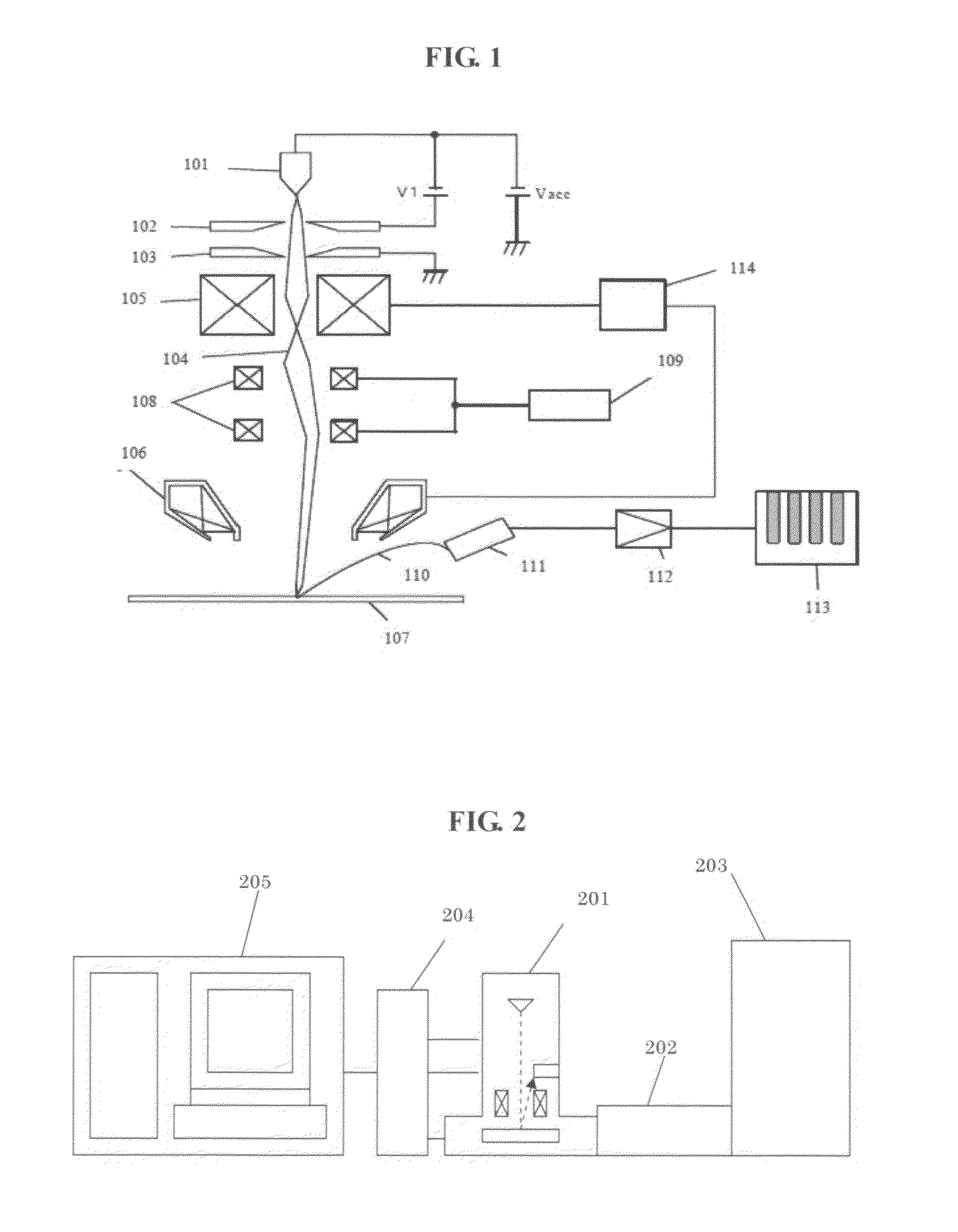
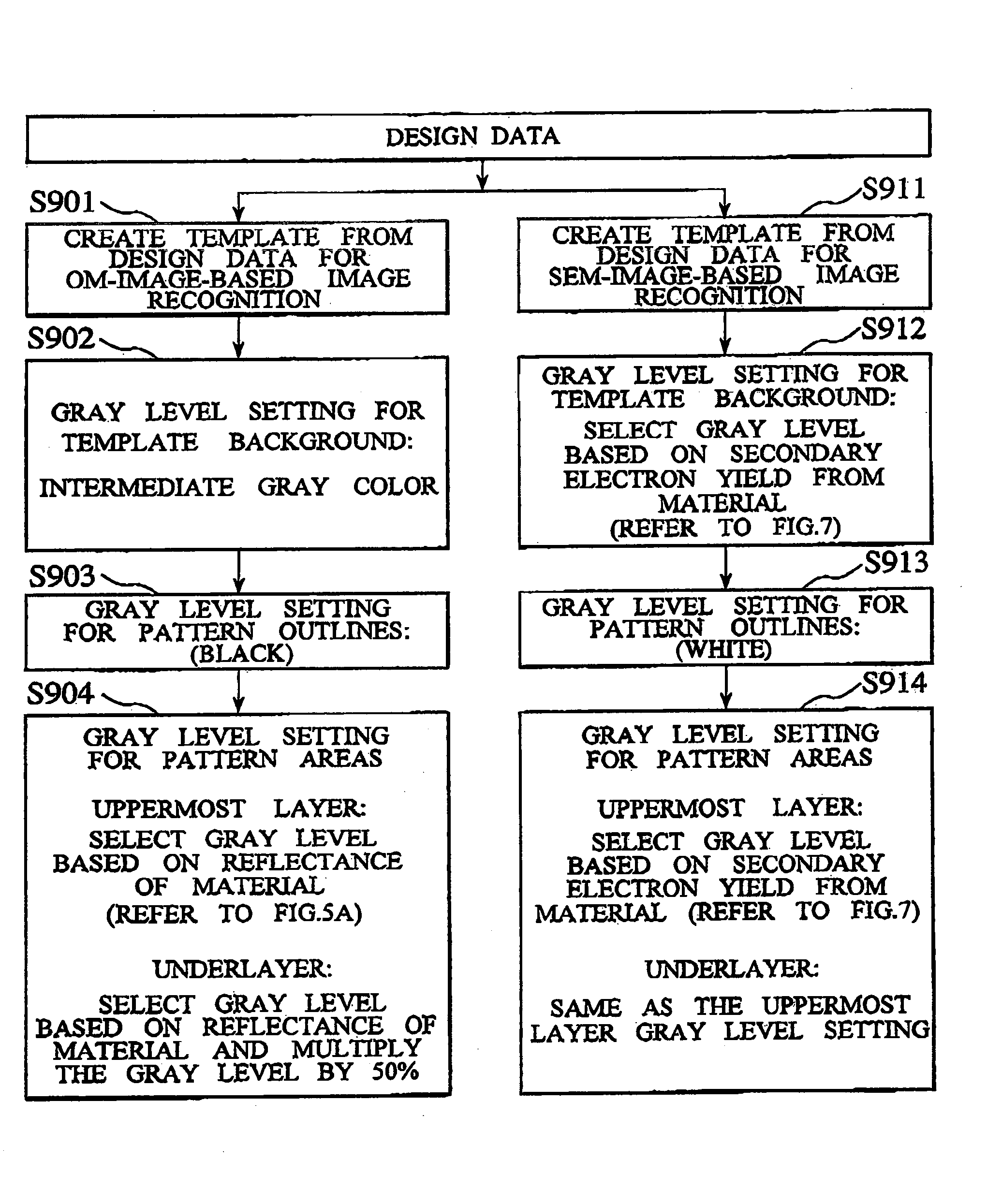
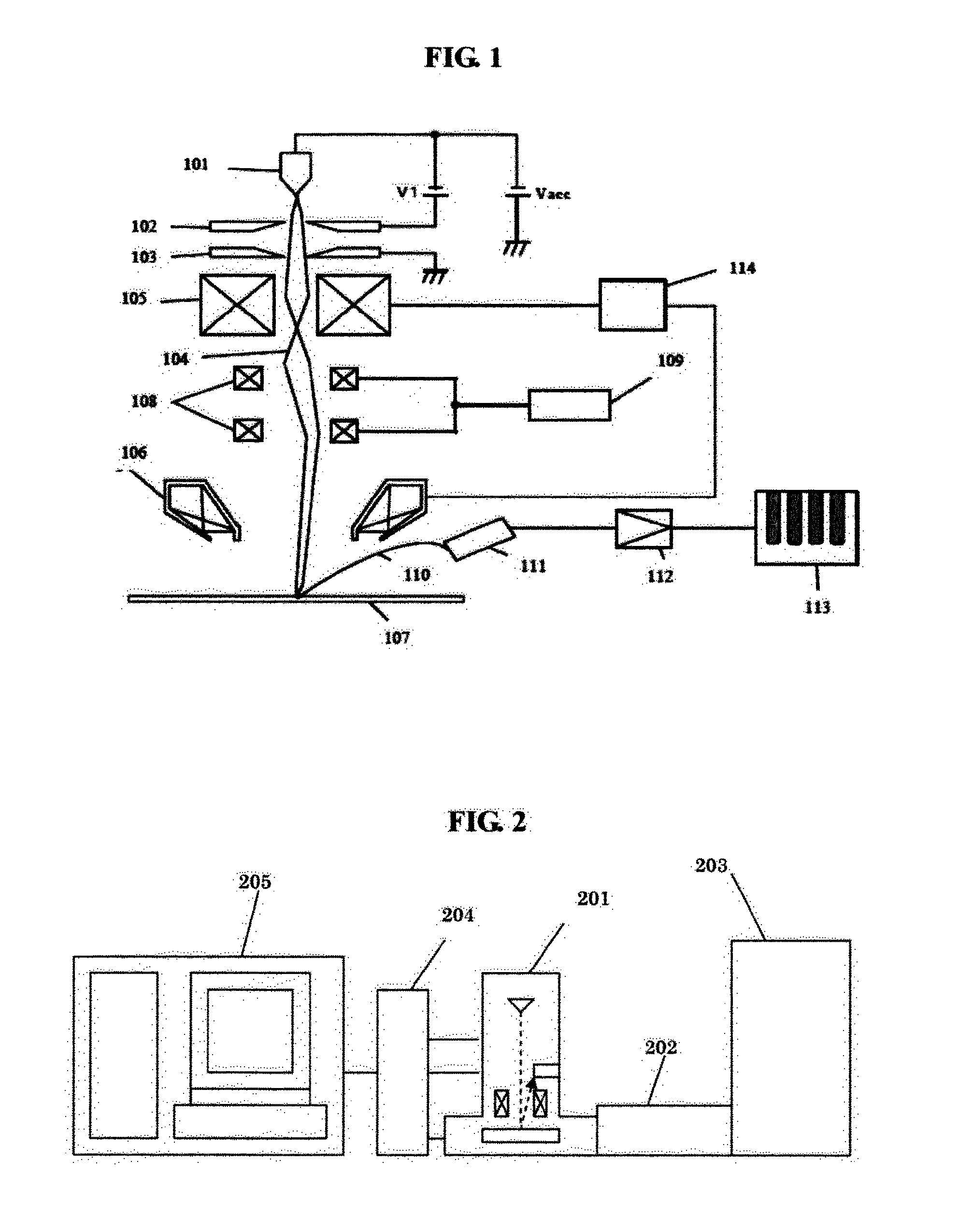
An object of the present invention is to maintain the ease with which a template is created based on design data without acquiring an actual image, which is achieved by providing the template with equivalent information contained by a template used for image recognition that involves same-type image comparison, and to improve image recognition performance by increasing the matching rate between a template and an actual image.To achieve the above object, the present invention provides a method, apparatus, and program for creating based on design data a template that is used for image recognition, wherein luminance information is set for each area in the template based on the material information of the region defined by the template. Specifically, the luminance information is set based on at least one of information from among the above material information, the pattern size information of a pattern arranged in the region defined by the template, the setup conditions of an imaging apparatus, the layer information of the region defined by the template, and the outline information of a pattern.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Template creation method and image processor therefor
ActiveUS8180140B2Reduce the differenceMatching rateMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Template based
To create a template for use in image recognition based on design data, luminance information is set for each area in the template based on the information regarding the region defined by the template. The luminance information may be set based on material information, pattern size information of a pattern arranged in the region defined by the template, and layer information of the region defined by the template. Alternatively, luminance information may be set based on material information, setup conditions of the scanning electron microscope, and pattern outline information of a pattern arranged in the region defined by the template.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Microelectromechanical probe, method of manufacturing the same and probe set
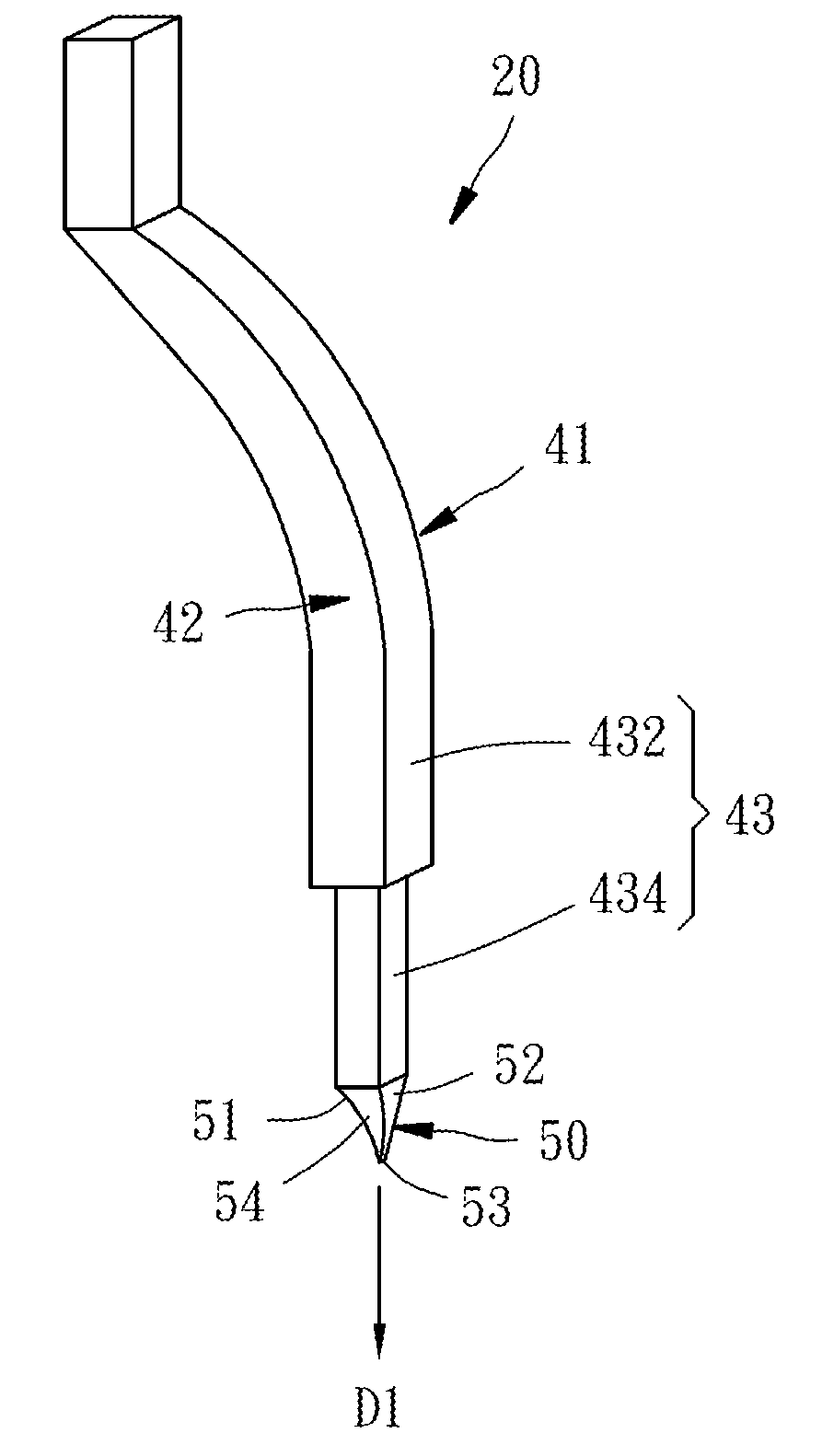
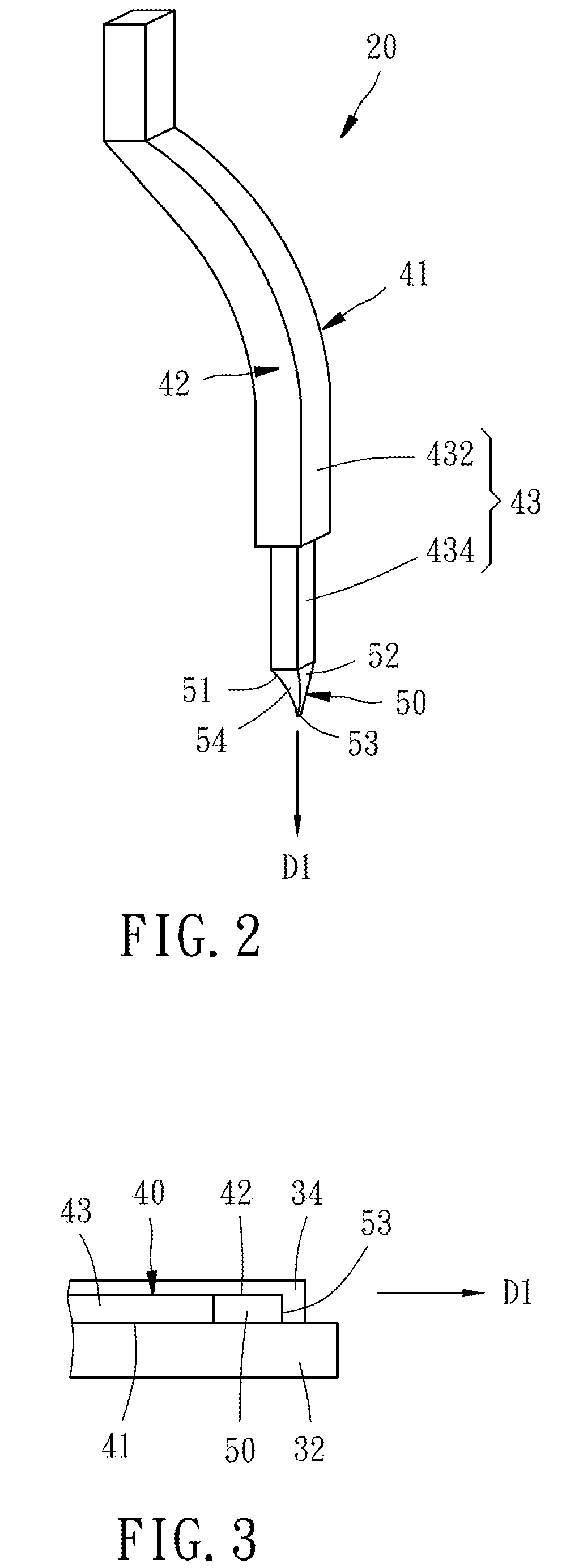
InactiveUS20170176497A1Small areaSmall probe markVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFixed microstructural devicesBiomedical engineeringMicroelectromechanical systems
A microelectromechanical probe is manufactured by a MEMS manufacturing process forming a probe body and a cutting process providing a pinpoint portion a cutting face. The probe has a top surface, a body portion, and a pinpoint portion extended in a probing direction from the body portion and provided with first and second sides and a probing end oriented in the probing direction. The cutting face is provided on the top surface, adjoins the first and second sides and the probing end, and has at least one cut mark formed by the cutting process, extended from the first side to the second side and non-parallel to the probing direction. The cutting face descends from an edge cut mark to the probing end.
Owner:MICROELECTRONICS TECH INC
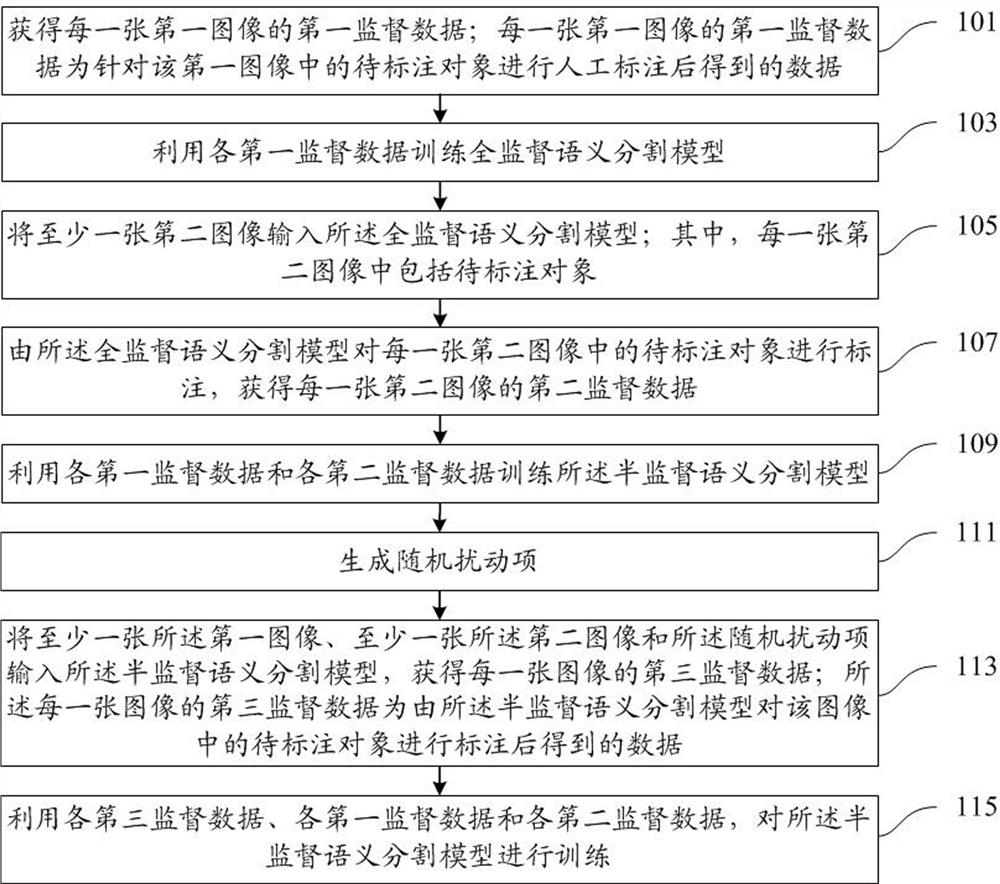
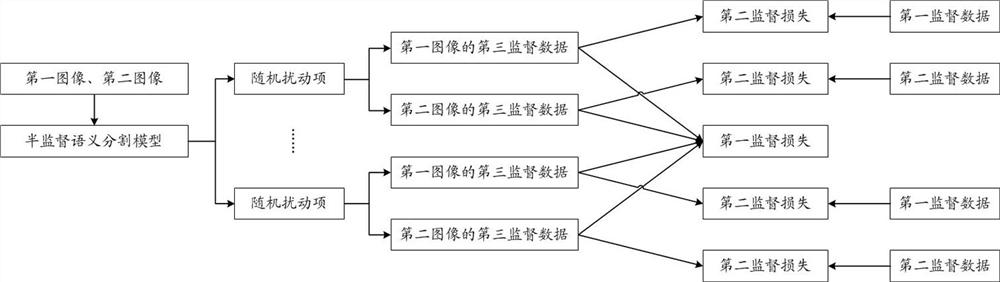
Semi-supervised semantic segmentation model training method, semi-supervised semantic segmentation model identification method and semi-supervised semantic segmentation model identification device
ActiveCN111898613AImprove accuracyImprove generalization abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionManual annotationMedicine
The embodiment of the invention provides a semi-supervised semantic segmentation model training method, a semi-supervised semantic segmentation model identification method and a semi-supervised semantic segmentation model identification device. The semi-supervised semantic segmentation model training method of the embodiment comprising obtaining first supervised data obtained by manually annotating a to-be-annotated object in a first image, and then obtaining a full-supervised semantic segmentation model with a relatively high recognition rate of the to-be-annotated object through training ofthe first supervised data; labeling the to-be-labeled object in the second image which is not manually labeled by utilizing the fully-supervised semantic segmentation model to obtain second superviseddata; training a semi-supervised semantic segmentation model by utilizing the first supervised data obtained through manual annotation and the second supervised data obtained through full-supervisedsemantic segmentation model annotation, and identifying the first image, the second image and the random disturbance item by utilizing the semi-supervised semantic segmentation model to obtain third supervised data; and finally, training the semi-supervised semantic segmentation model again through the first supervised data, the second supervised data and the third supervised data.
Owner:ALIPAY (HANGZHOU) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
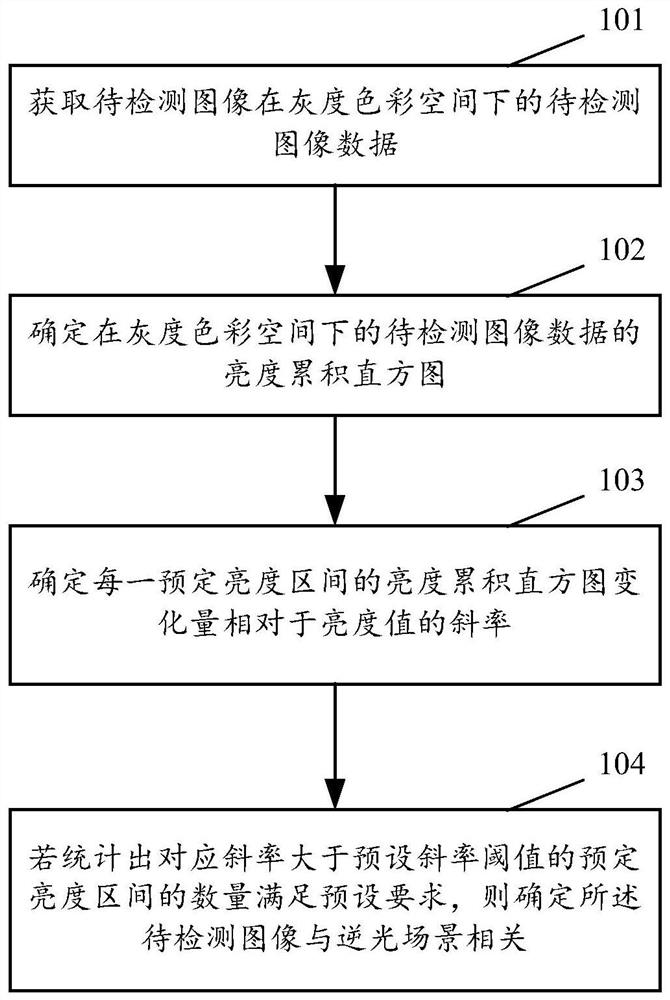
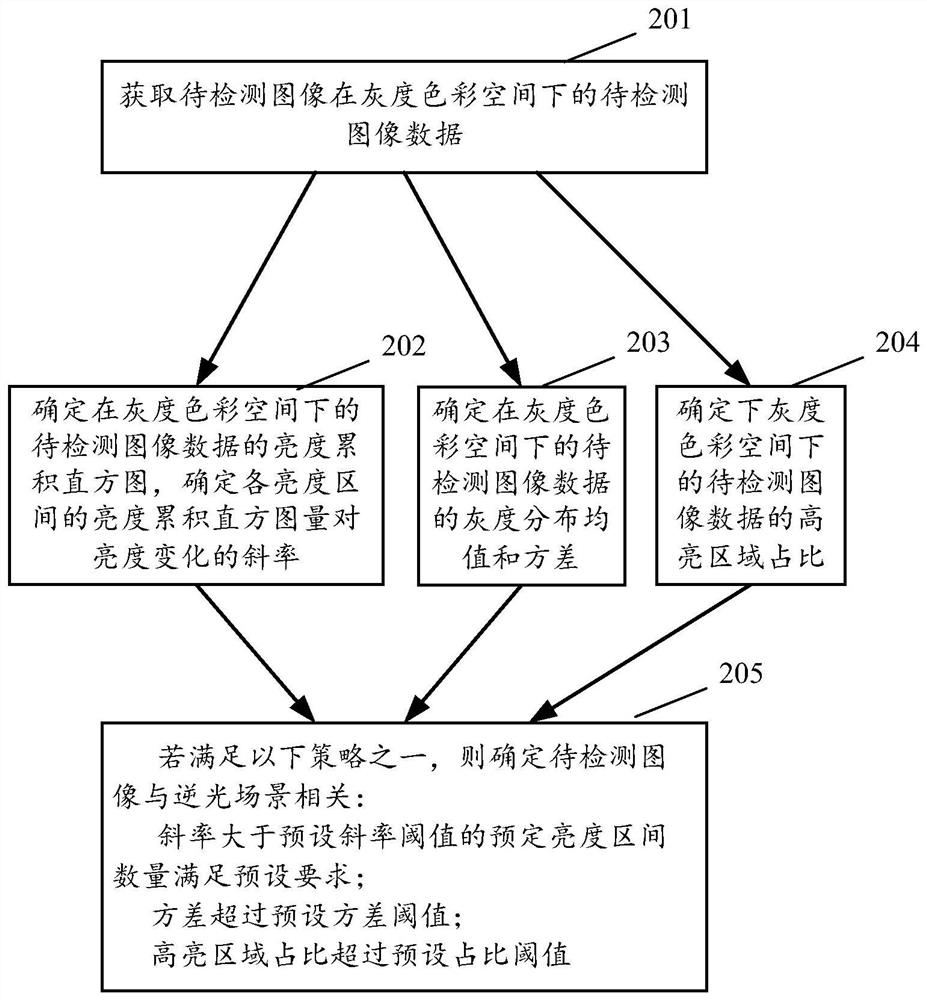
Image detection method, device and equipment and computer storage medium
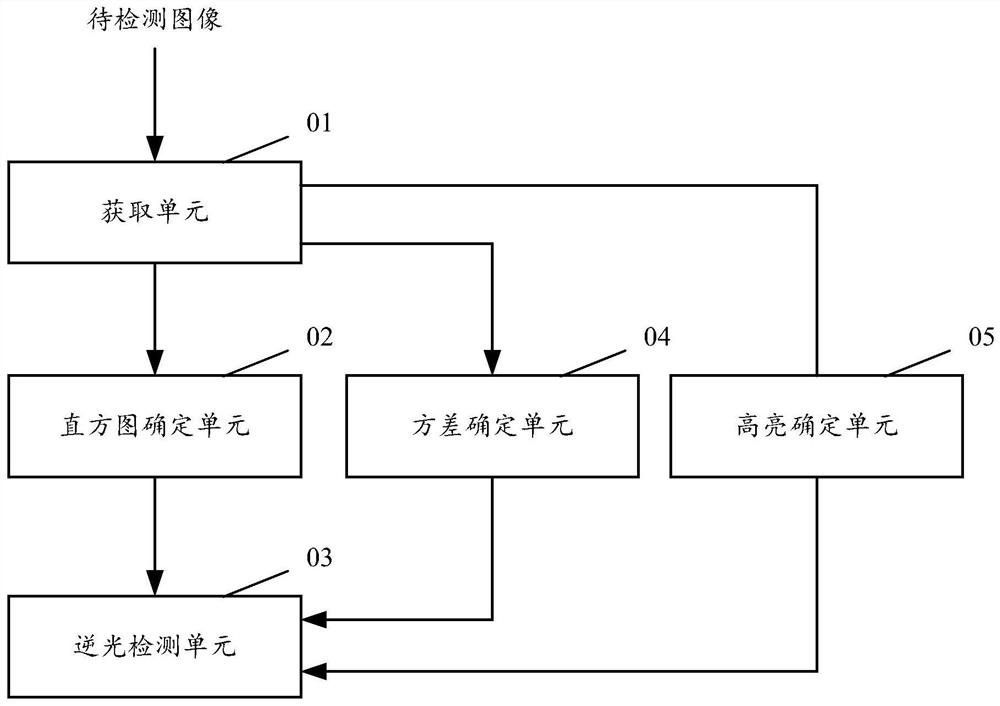
ActiveCN112312001AImprove Image Recognition PerformanceImprove image recognitionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHistogramColor space
The embodiment of the invention provides an image detection method, apparatus and device, and a computer storage medium. The method comprises the steps of obtaining to-be-detected image data of a to-be-detected image in a grayscale color space; determining a brightness accumulation histogram of the to-be-detected image data in the gray scale color space; determining the slope of the brightness accumulation histogram variation of each predetermined brightness interval relative to the brightness value; comparing the corresponding slope of each predetermined brightness interval with a preset slope threshold value; and determining that the to-be-detected image is related to a backlight scene if it is counted that the number of the predetermined brightness intervals of which the corresponding slopes are greater than a preset slope threshold meets a preset requirement. According to at least one embodiment of the invention, the image recognition performance under the condition of local backlight can be improved.
Owner:APOLLO INTELLIGENT DRIVING (BEIJING) TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Terminal and a fingerprint imaging method
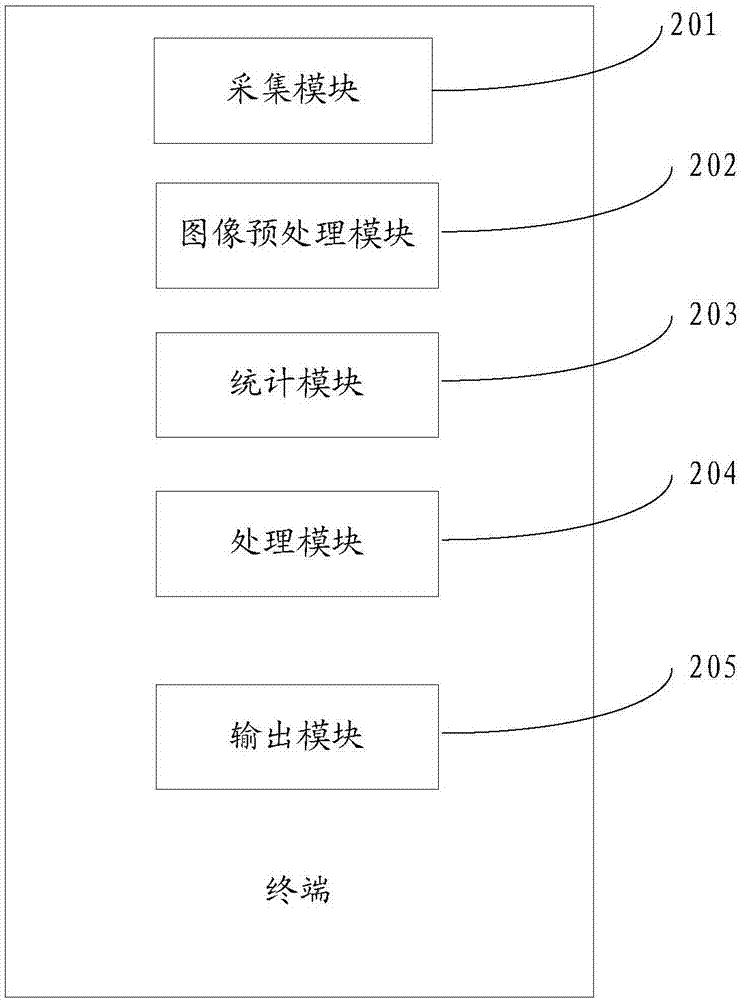
InactiveCN107247918AAccurately reflect the detailsImprove experienceCharacter and pattern recognitionFingerprintImage identification
The invention discloses a terminal and a fingerprint imaging method. The terminal comprises a collection module used for collecting a fingerprint, an image processing module used for preprocessing the image of the fingerprint to generate a grayscale map of the fingerprint, a statistical module used for doing statistics of the grayscale distribution in the grayscale map and generating a grayscale distribution map, a processing module used for cutting a section with the gray values smaller than a first threshold and / or a section with the gray values greater than a second threshold from the grayscale distribution map and stretching the grayscale of the grayscale distribution map after cutting according to preset rules, and an output module used for taking a fingerprint image corresponding to the grayscale distribution map after stretching as a target fingerprint image and outputting the target fingerprint image. Through the technical scheme, fingerprint imaging data of different skin colors can be processed differently, the details of user fingerprints can be reflected more accurately by enlarging difference, the ability of image identification is improved, and the user experience is improved.
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Device, system and method for drawing landmark map based on binocular vision
PendingCN113624244ALower requirementReduce complexityImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationImaging processingImage manipulation
The embodiment of the invention provides a device, system and method for drawing a landmark map based on binocular vision. The device comprises a first lens, a first prism, a second prism, an image sensor, an image processing module and a GNSS differential positioning module. The first lens and the first prism are symmetrically arranged along the central axis of the second prism, wherein the first lens and the first prism located on one side of the second prism sequentially form a left light path, and the first lens and the first prism located on the other side of the second prism sequentially form a right light path. The light along the left light path and the light along the right light path are reflected to the image sensor through the second prism. The image sensor is used for obtaining an image collected by a binocular lens and transmitting the image to the image processing module. The image processing module is used for analyzing and processing image data. The GNSS differential positioning module is used for obtaining the coordinate of the original point of the lens coordinate system in the world coordinate system through GNSS differential positioning. The requirement on a processor is reduced, the precision is high, and the cost is low.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE M2M +1
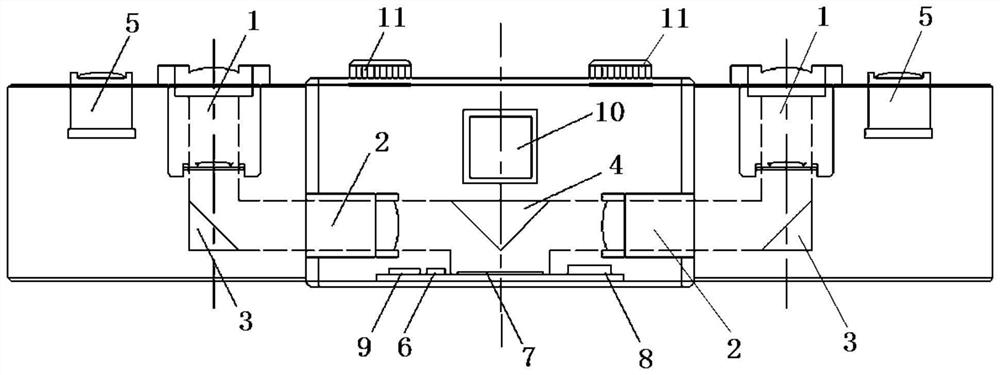
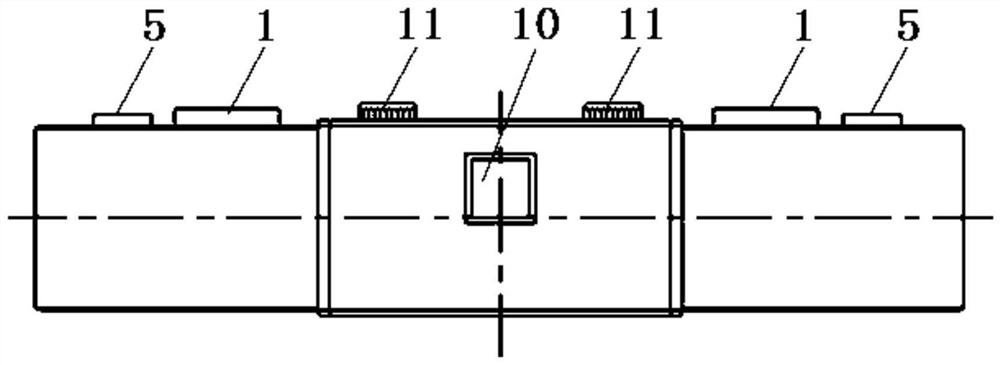
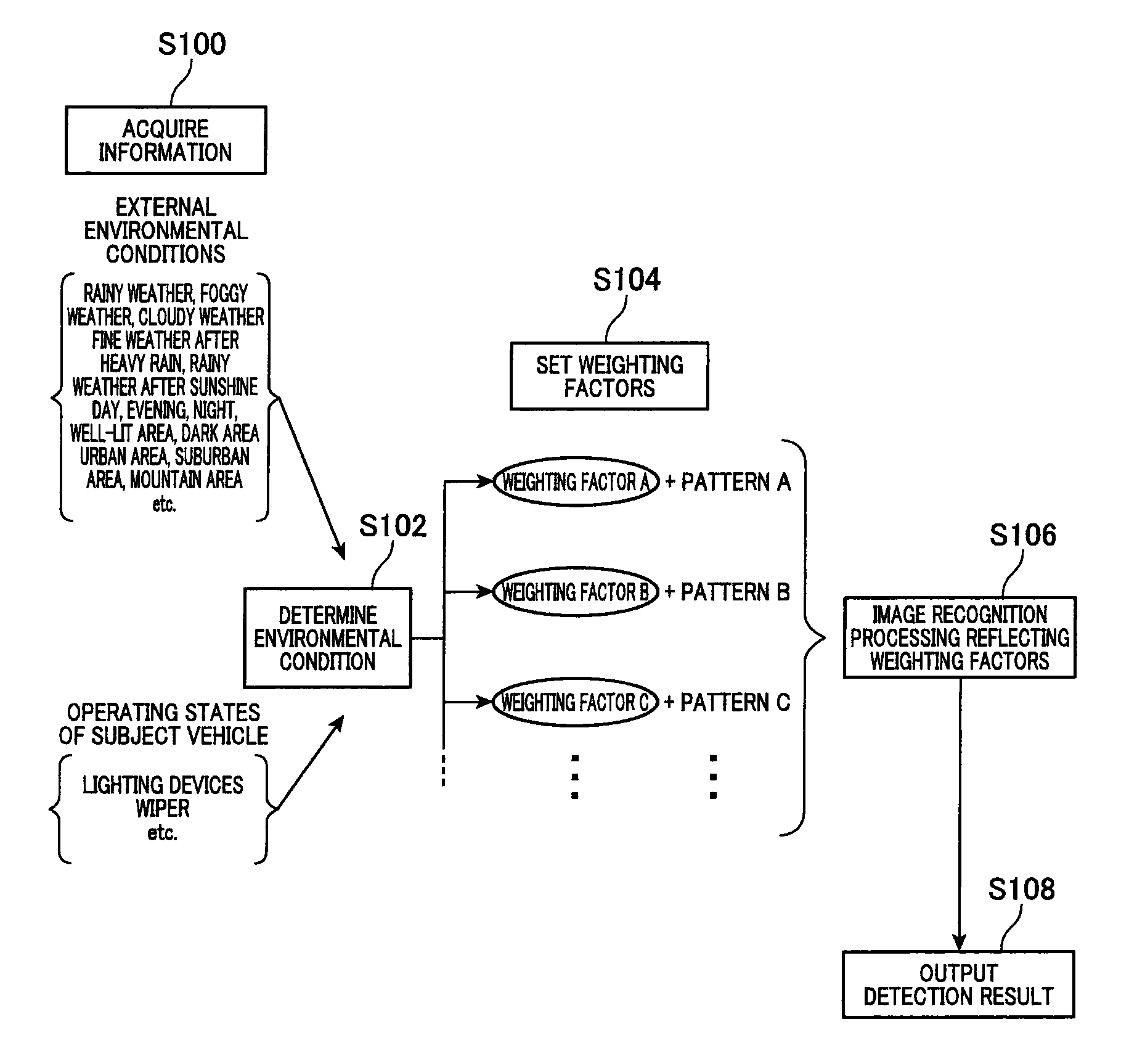
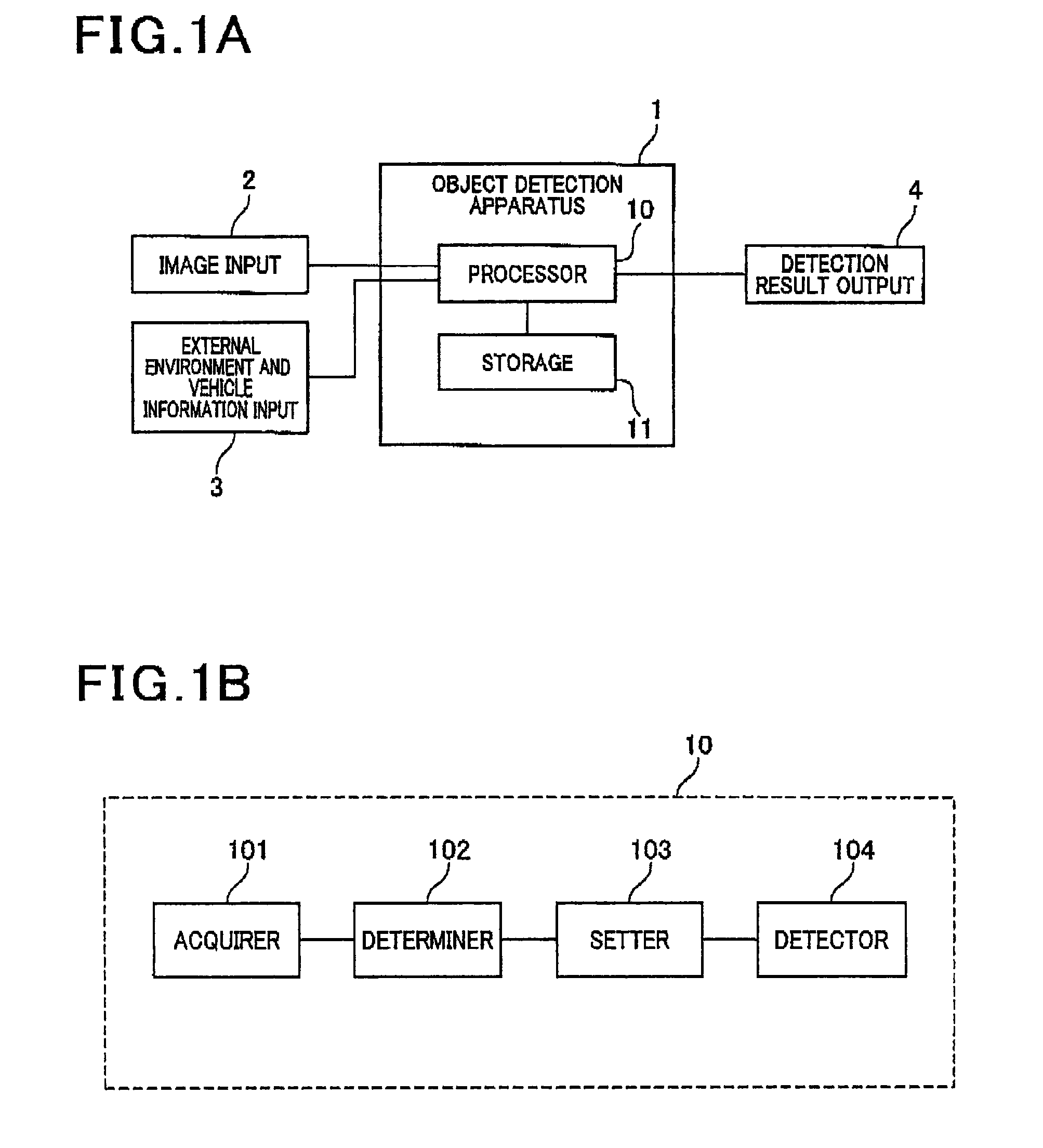
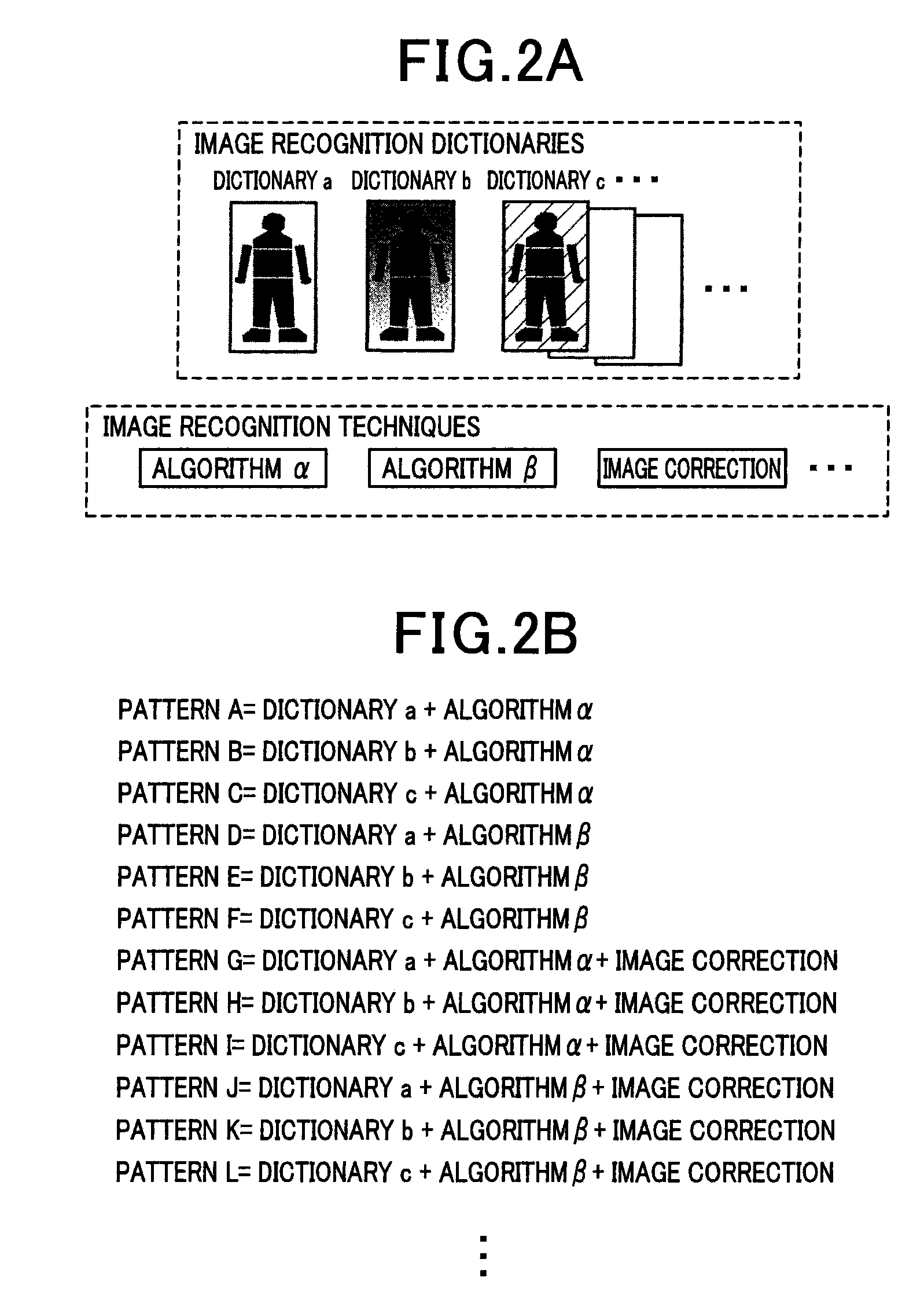
Object detection apparatus
ActiveUS9418287B2Higher weighting factorImprove image recognitionTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionObject detectionA-weighting
An object detection apparatus mounted in a system for detecting a target object in various changing environmental conditions. In the apparatus, an acquirer acquires either or both of information indicative of an external environment around the system and information indicative of an operating state of the system. A determiner determines an environmental condition with respect to an input image according to the acquired information. A setter sets, for each of plural image recognition methods each being a combination of one of the plural image recognition dictionaries and one of the plural image recognition techniques, a weighting factor according to the environmental condition determined by the determiner. A detector detects the object in the input image by applying each of the plural image recognition methods to the input image to obtain recognition results reflecting the weighting factors, and collectively evaluating the recognition results.
Owner:DENSO CORP
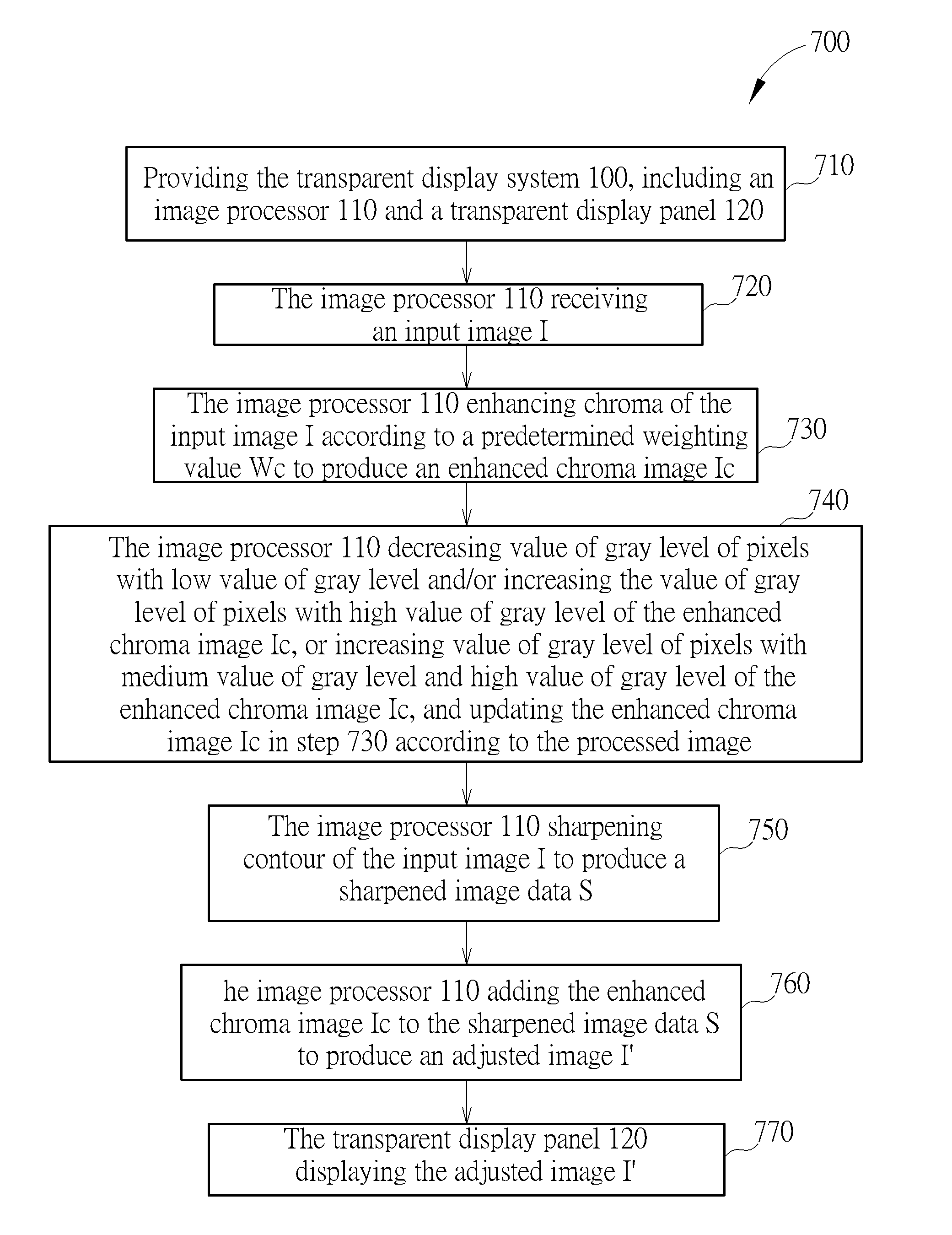
Image Processing Method for Transparent Display System
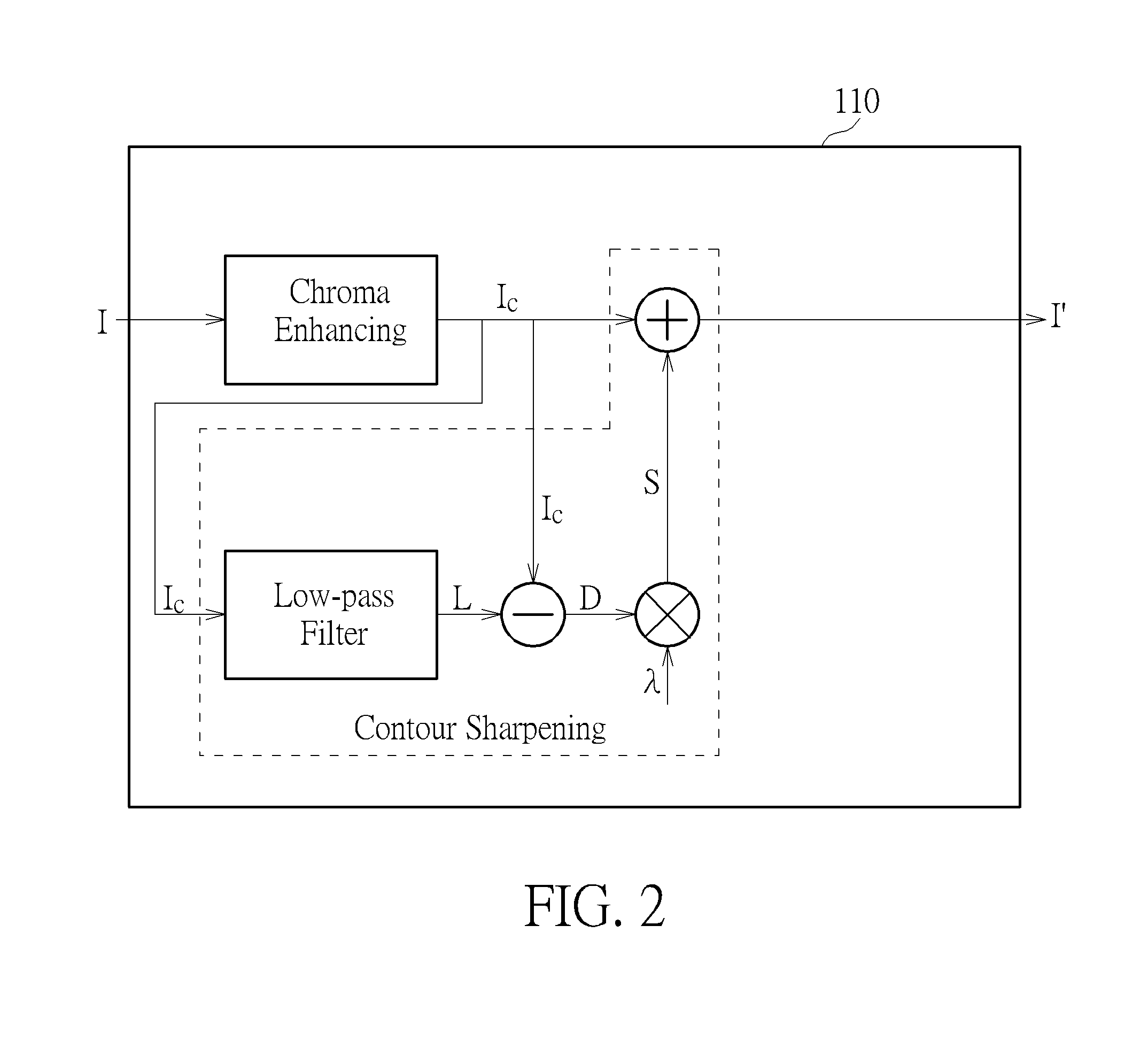
InactiveUS20160005190A1Improve image recognitionLight penetrabilityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging dataChrominance
An image processing method of a transparent display system includes providing the transparent display system, where the transparent display system includes an image processor and a transparent display panel. The image processor receives an input image. The image processor enhances the chroma of the image according to a predetermined weighting value to produce an enhanced chroma image. The image processor sharpens the contour of the image to produce a sharpened image data. The image processor adds the enhanced chroma image to the sharpened image data to produce an adjusted image. The transparent display panel displays the adjusted image.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Natural mode-based Logo generation method and intelligent Logo generator
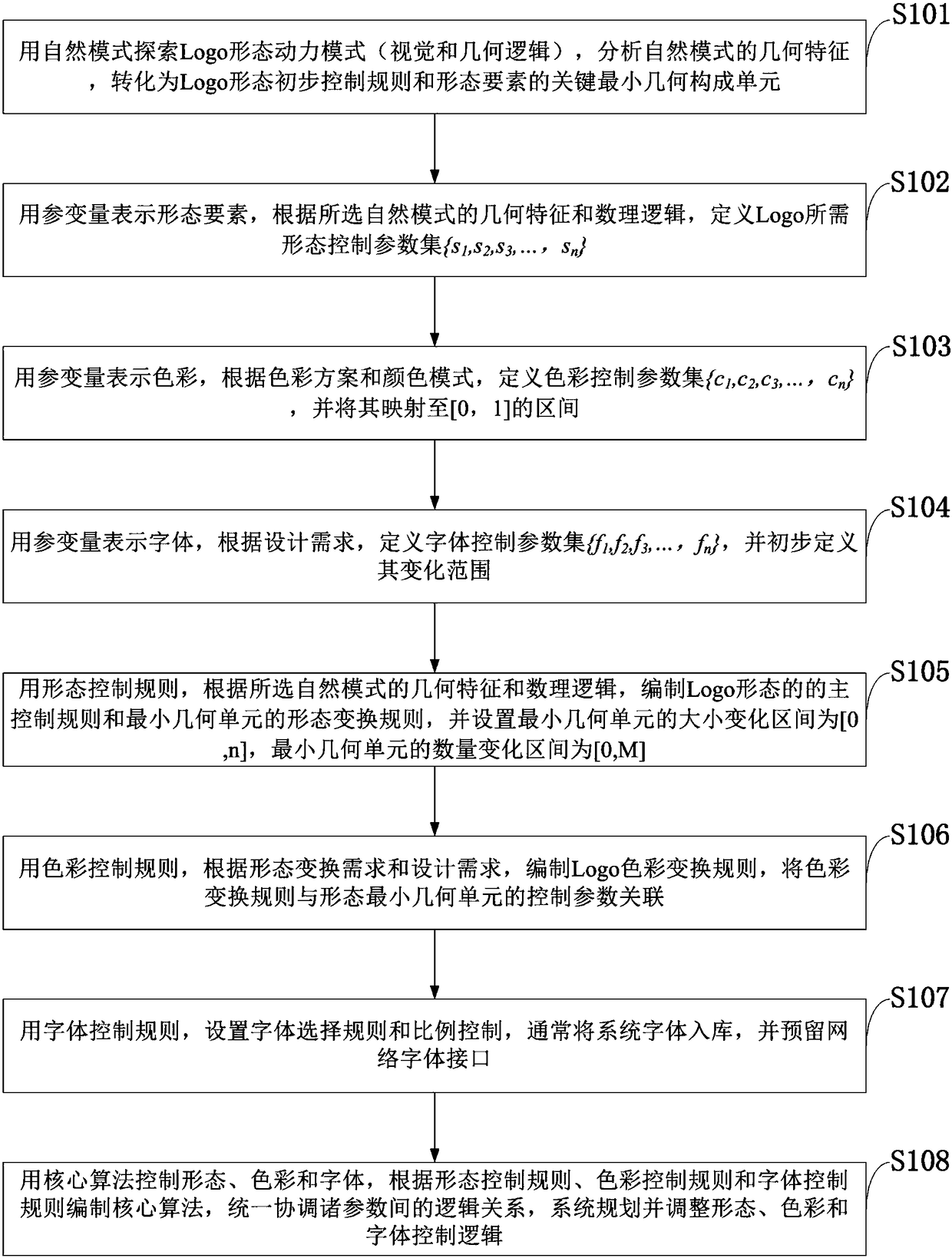
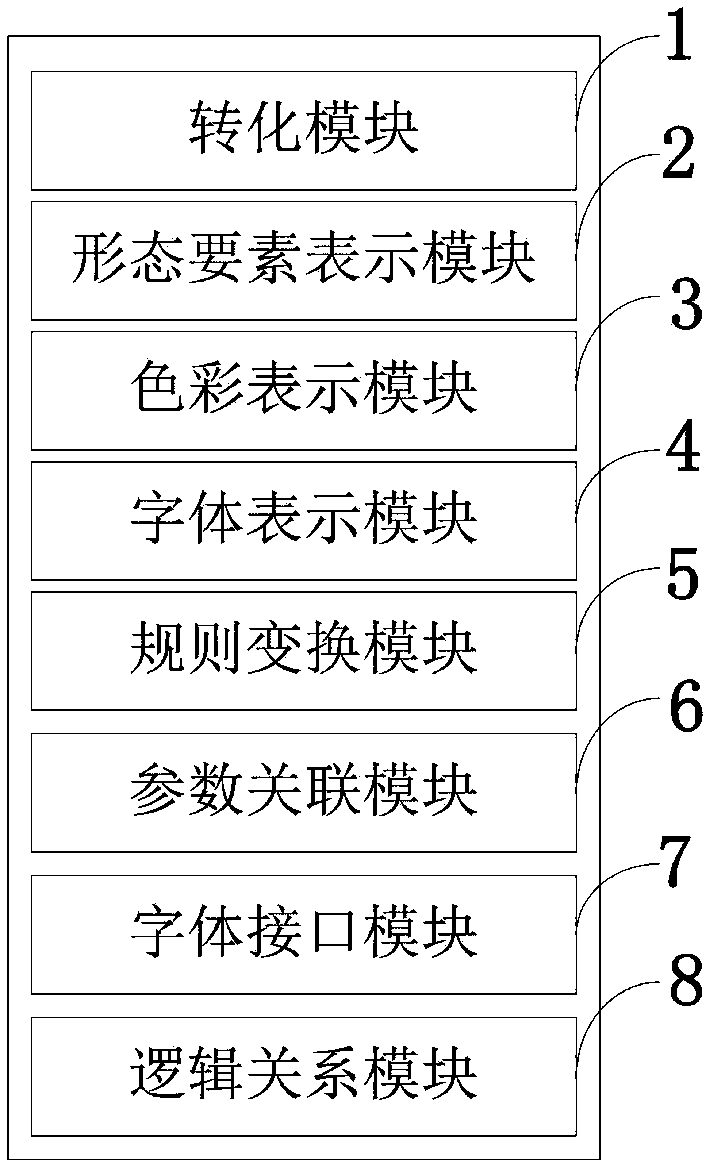
ActiveCN108549530AImprove corporate image recognitionBroaden the field of visionSoftware designFilling planer surface with attributesNature basedColor representation
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing and discloses a natural mode-based Logo generation method and an intelligent Logo generator. Source codes are written according to control rules and a core algorithm, and intelligent Logo design output is realized. The intelligent Logo generator comprises a conversion module, a form element representation module, a color representation module, a font representation module, a rule conversion module, a parameter association module, a font interface module and a logic relationship module. By use of design demands (generally from customers and competitive markets), a natural mode matched with the design demands is searched for; and the parametric intelligent Logo generator is realized by use of the core algorithm, the source codes are written according to the control rules and the core algorithm, the intelligent Logo design output is realized, Logo forms output by the generator are ever-changing, dynamic Logo design can be developed, and dynamic propagation can be realized for improving the enterprise image identification degree.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Image recognition method based on optimized deep neural network model
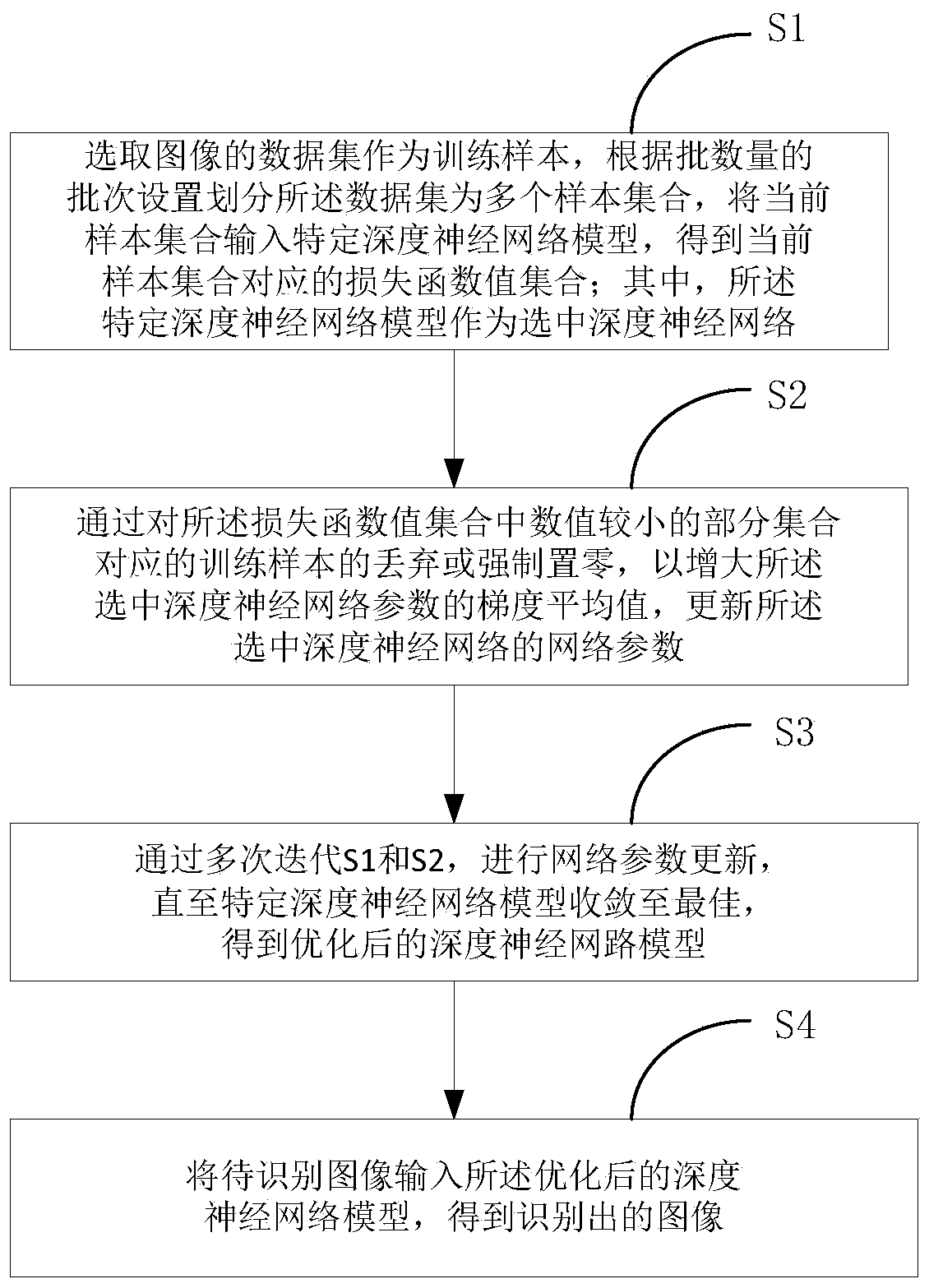
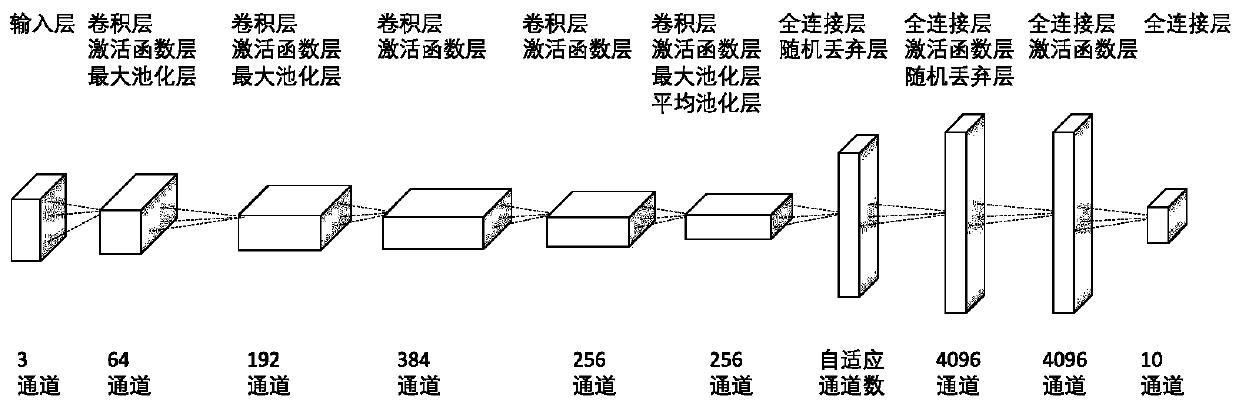
PendingCN111582442AIncrease training speedImprove image recognitionNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsPattern recognitionData set
The invention relates to an image recognition method based on an optimized deep neural network model, and belongs to the technical field of image recognition. The method comprises the following steps:S1, selecting a data set of an image as a training sample, dividing the data set into a plurality of sample sets according to batch setting of a batch number, and inputting a current sample set intoa specific deep neural network model to obtain a loss function value set corresponding to the current sample set, wherein the specific deep neural network model is used as a selected deep neural network; s2, updating network parameters of the selected deep neural network by discarding or forcibly zeroing training samples corresponding to a part of sets with smaller numerical values in the loss function value set; s3, iterating S1 and S2 for multiple times to obtain an optimized deep neural network model; and S4, inputting a to-be-identified image into the optimized deep neural network model toobtain an identified image. According to the method, the problem that the training performance of the deep neural network model under large-batch image data sets is greatly reduced is solved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com