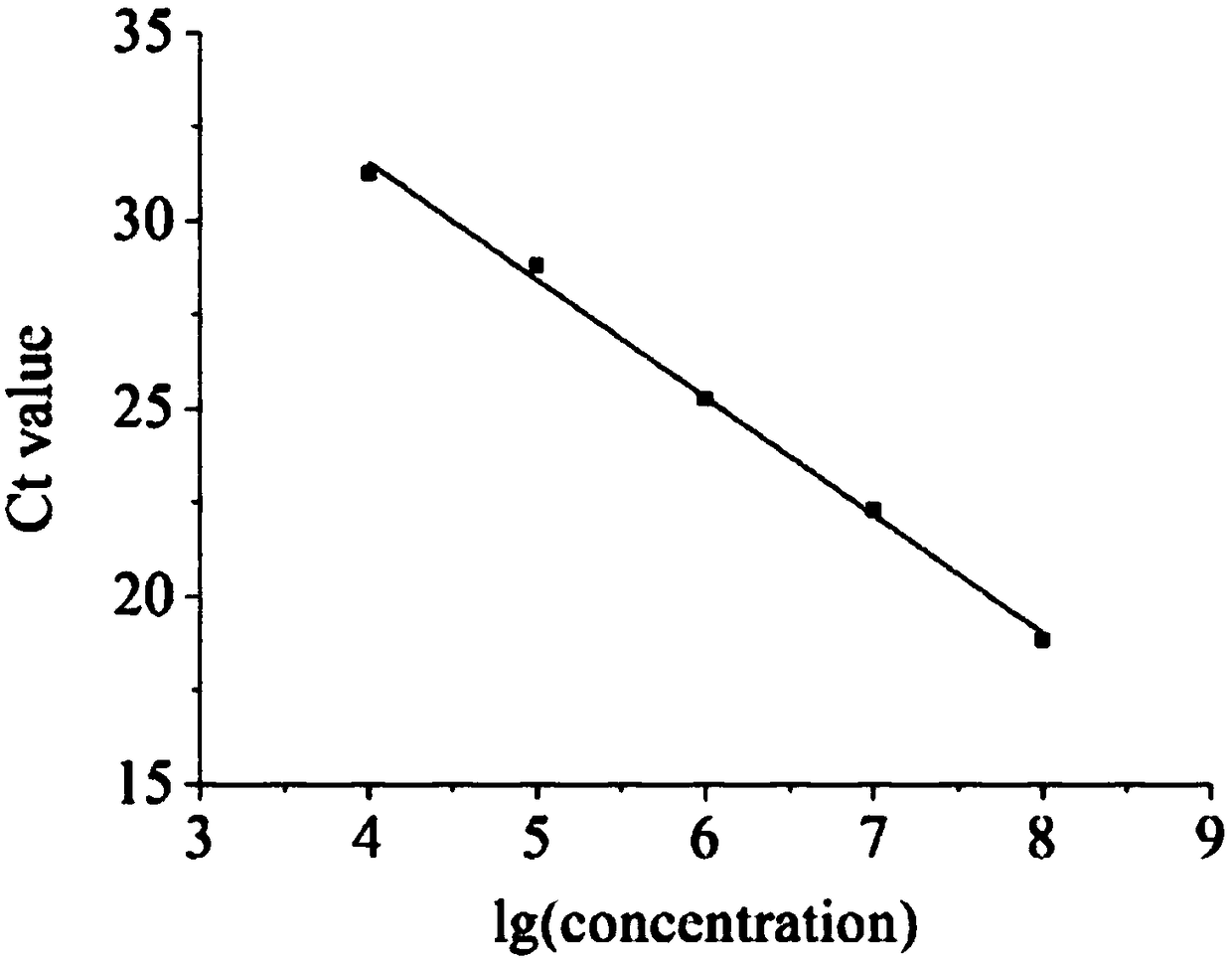
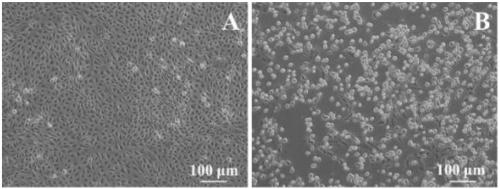
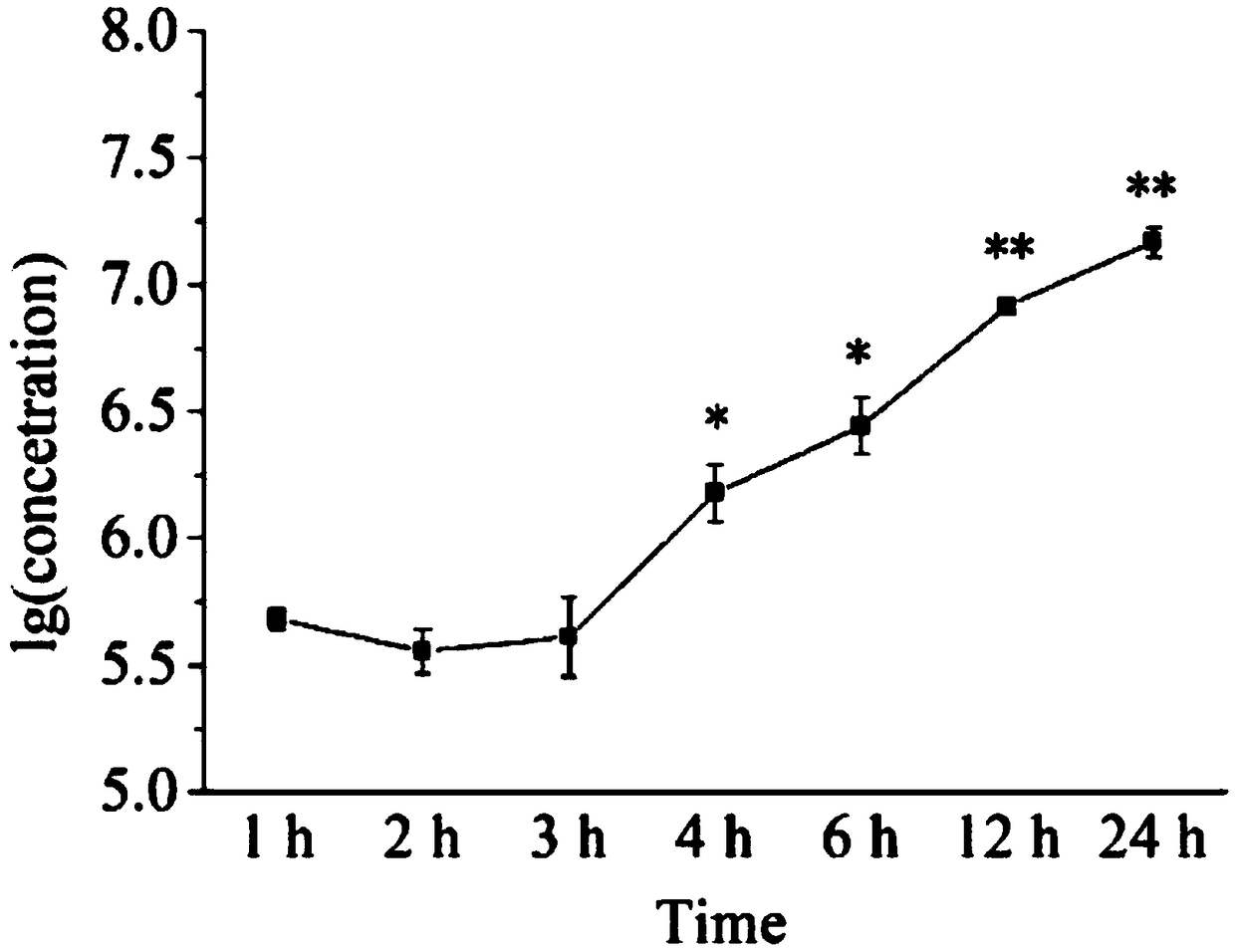
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Entry into host cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The invasion by an organism of a cell of its host organism. The host is defined as the larger of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction. [GOC:njm]
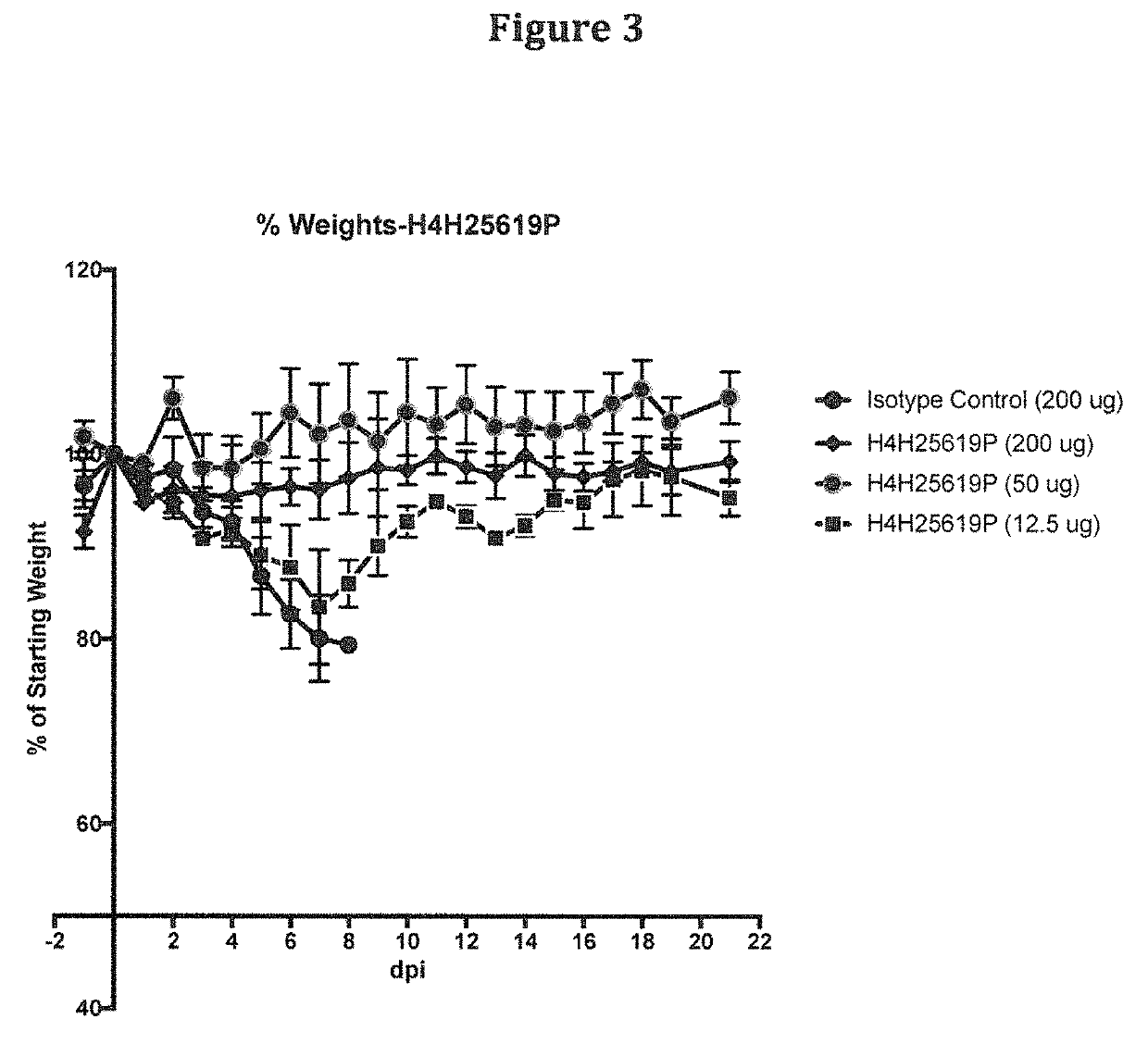
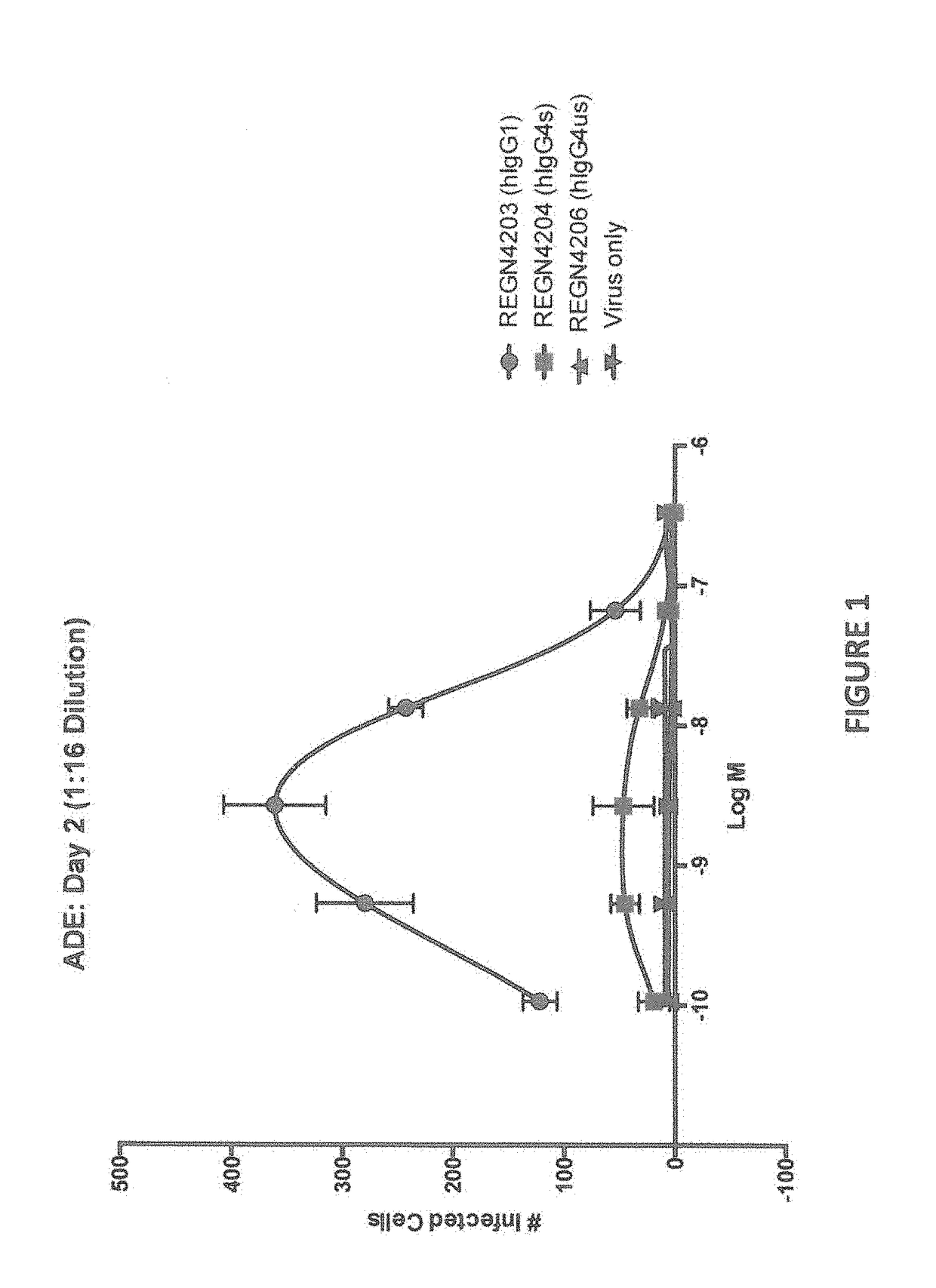
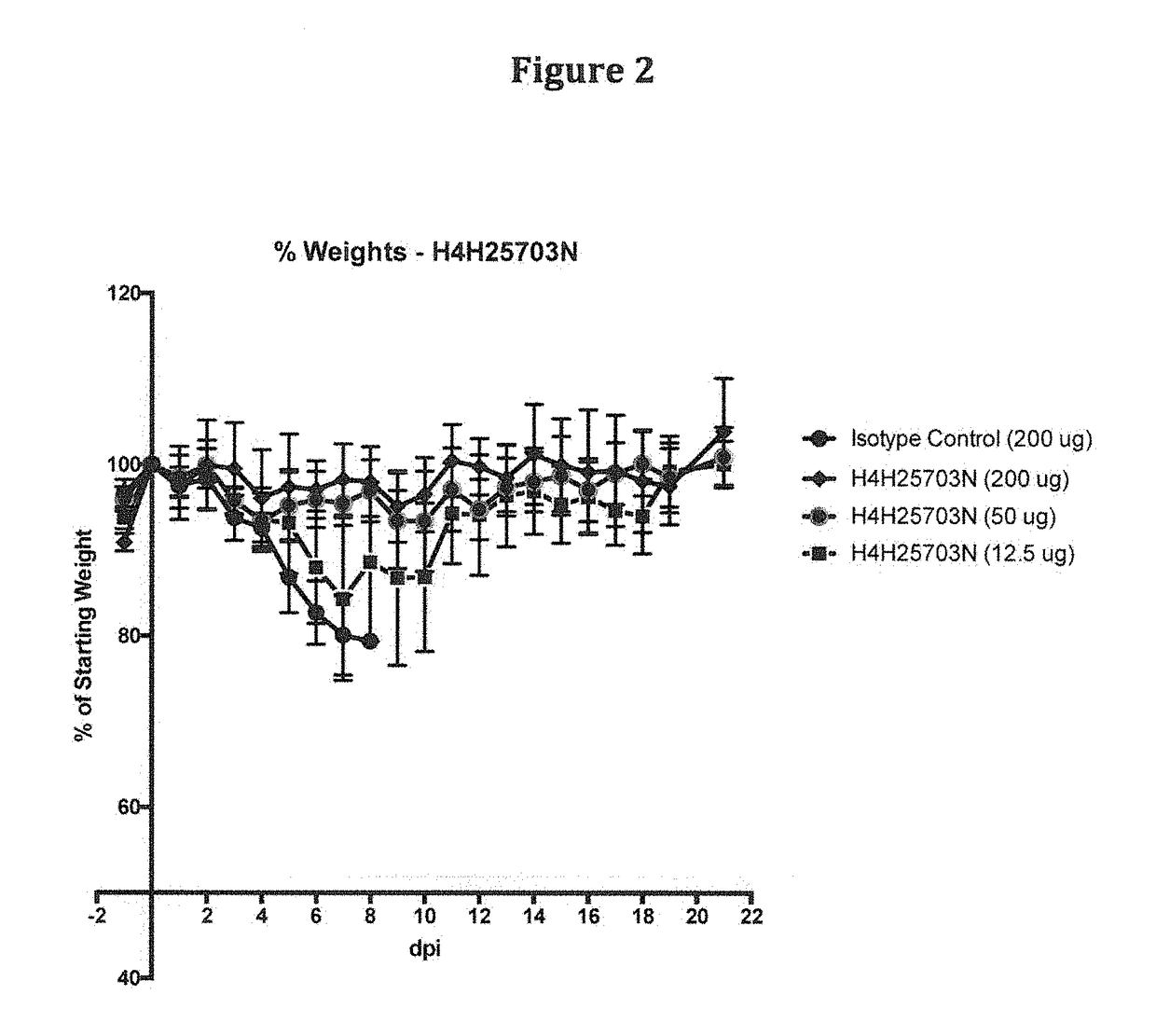
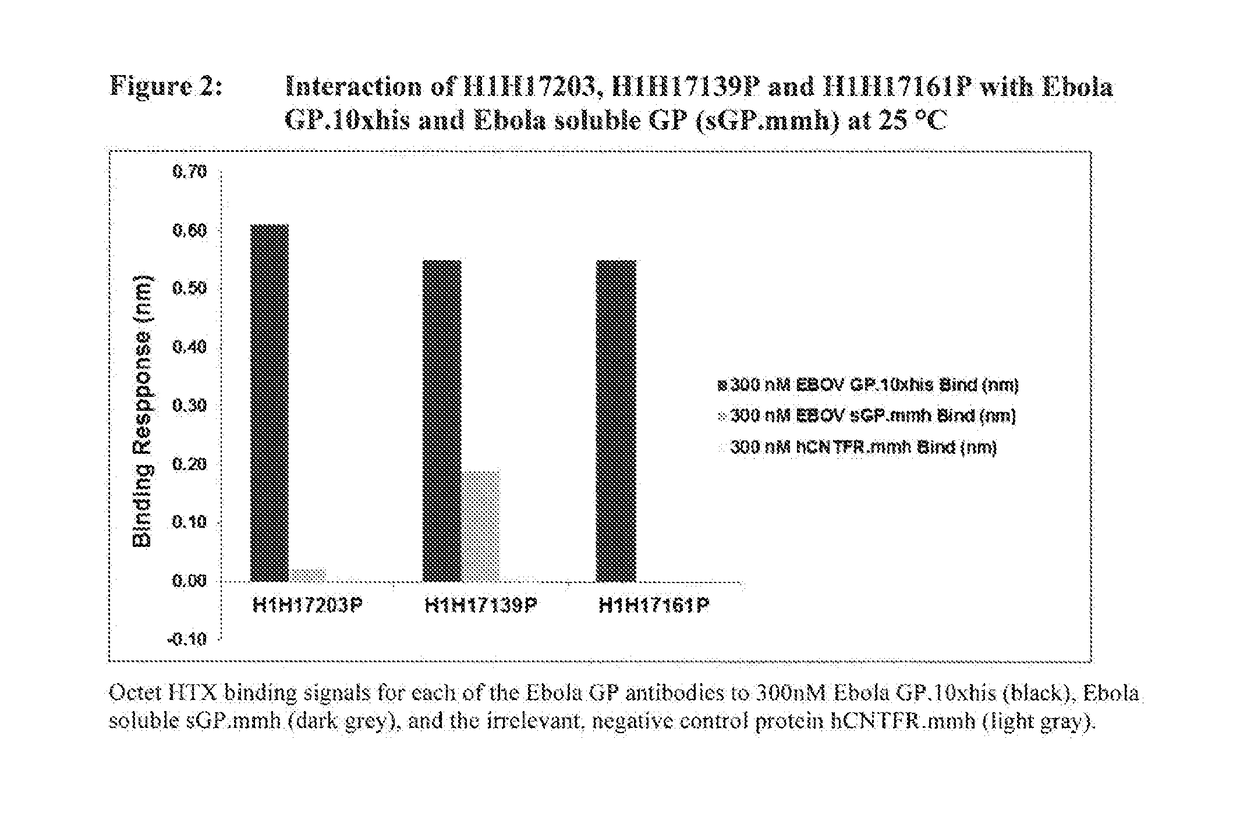
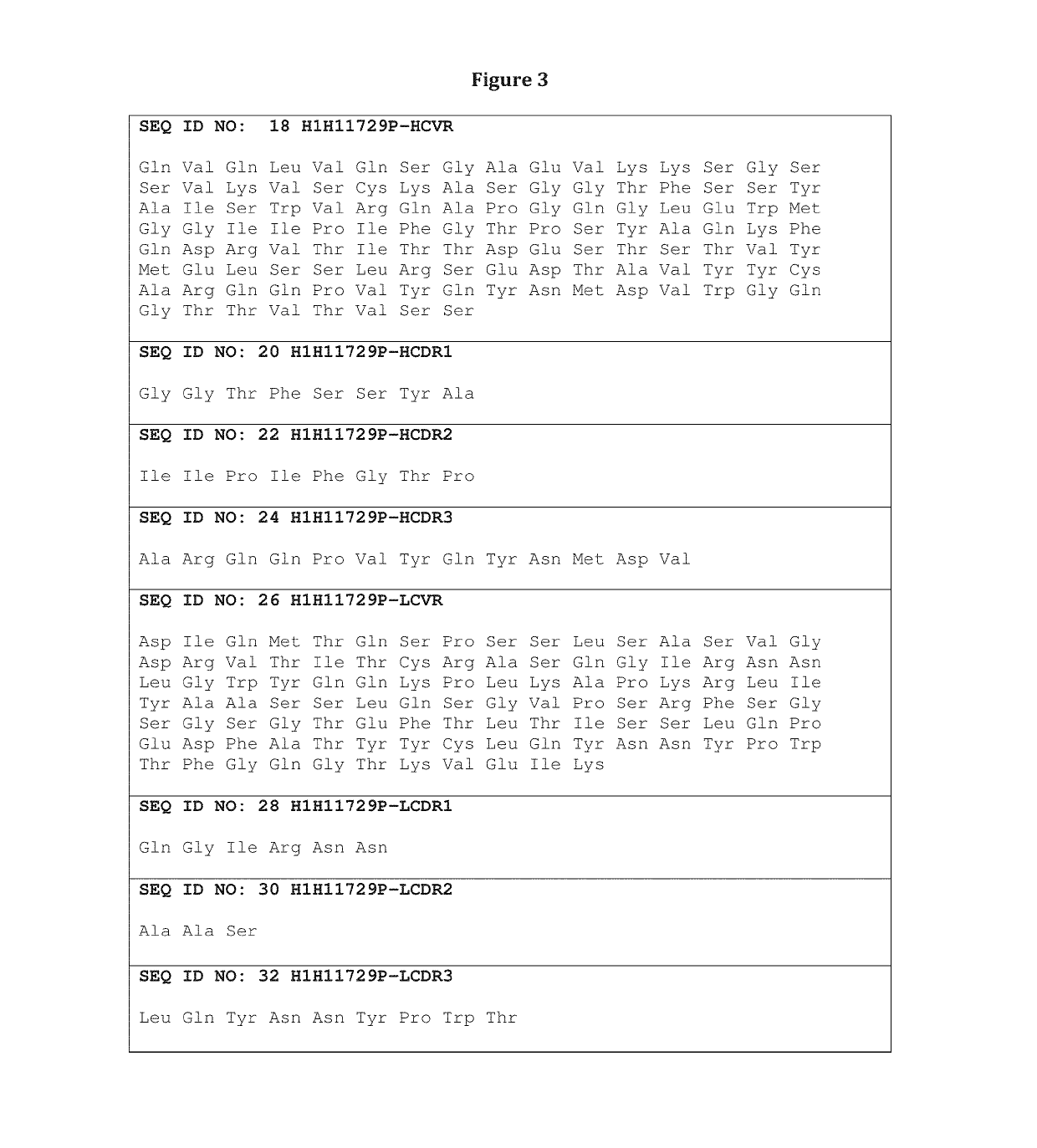
Human Antibodies to Ebola Virus Glycoprotein
ActiveUS20160215040A1Inhibiting and neutralizing activityAvoid enteringImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsViral glycoproteinAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides monoclonal antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, that bind to Ebola virus glycoproteins, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies and methods of use. The antibodies of the invention are useful for inhibiting or neutralizing Ebola virus activity, thus providing a means of treating or preventing Ebola virus infection in humans. In some embodiments, the invention provides for use of one or more antibodies that bind to the Ebola virus for preventing viral attachment and / or entry into host cells. The antibodies of the invention may be used prophylactically or therapeutically and may be used alone or in combination with one or more other anti-viral agents or vaccines.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Nucleic acid construct and expression vector for enhancing the production of recombinant protein, and method for the massive production of recombinant protein
InactiveUS20050287669A1High protein yieldResist protein toxicityFungiBacteriaGene productNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed herein are nucleic acid constructs and expression vectors for enhancing the production of recombinant polypeptides / proteins, and methods for the massive production of recombinant polypeptides / proteins, in which a first nucleic acid sequence encoding thioredoxin and a second nucleic acid sequence encoding hemoglobin are cloned into a host cell, thereby enhancing the capability of the thus formed recombinant host cell in producing a selected gene product, and thereby assisting said recombinant host cell in relieving intracellular stress due to the overproduction of said gene product.
Owner:FENG CHIA UNIVERSITY +1
Inhibitors of filovirus entry into host cells
Organic compounds showing the ability to inhibit viral glycoprotein (GP)-mediated entry of a filovirus into a host cell are disclosed. The disclosed filovirus entry inhibitor compounds are useful for treating, preventing, or reducing the spread of infections by filovirus including the type species Marburg virus (MARV) and Ebola virus (EBOV). Preferred inhibitors of the invention provide therapeutic agents for combating the Ivory Coast, Sudan, Zaire, Bundibugyo, and Reston Ebola virus strains.
Owner:MICROBIOTIX
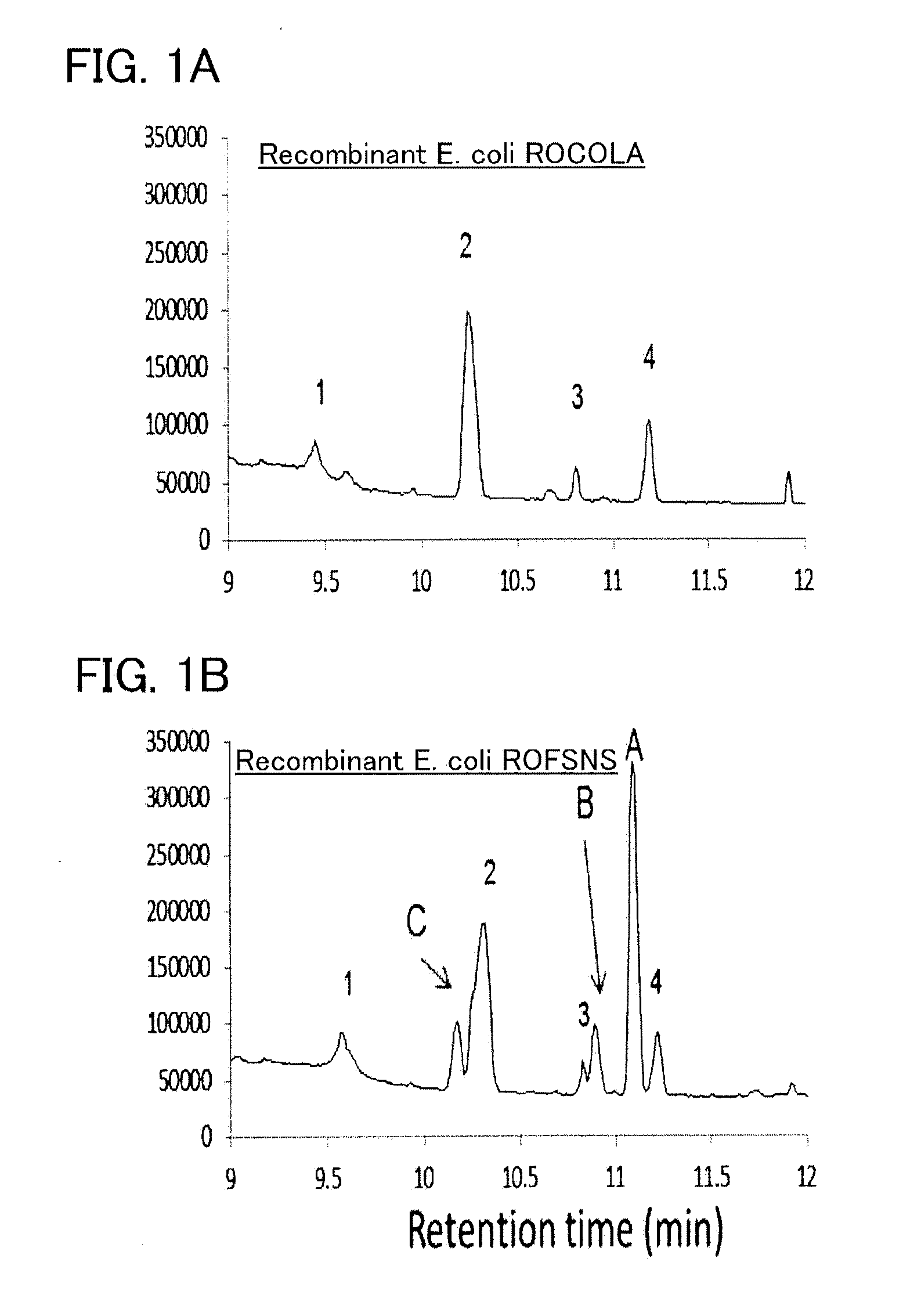
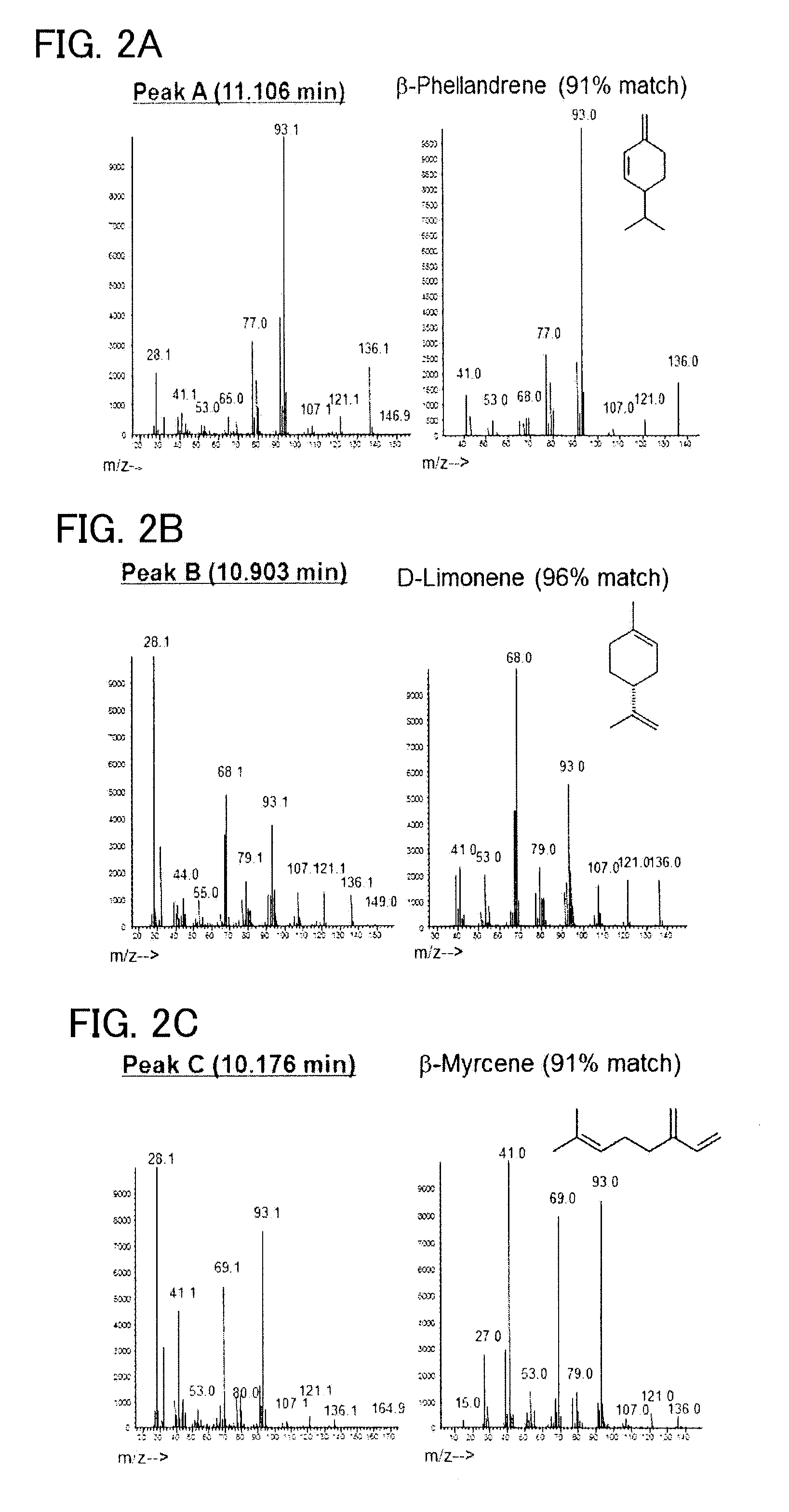
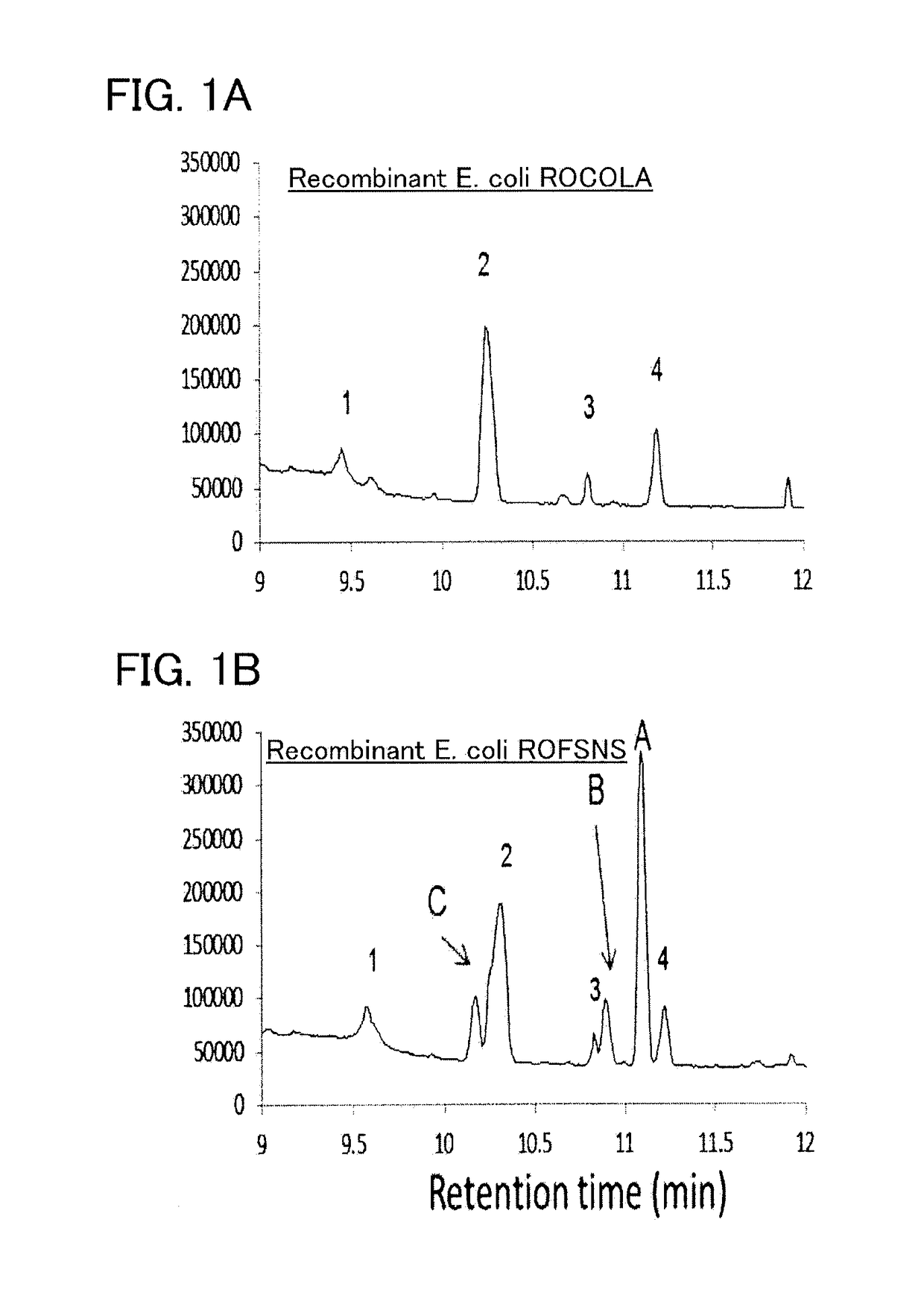
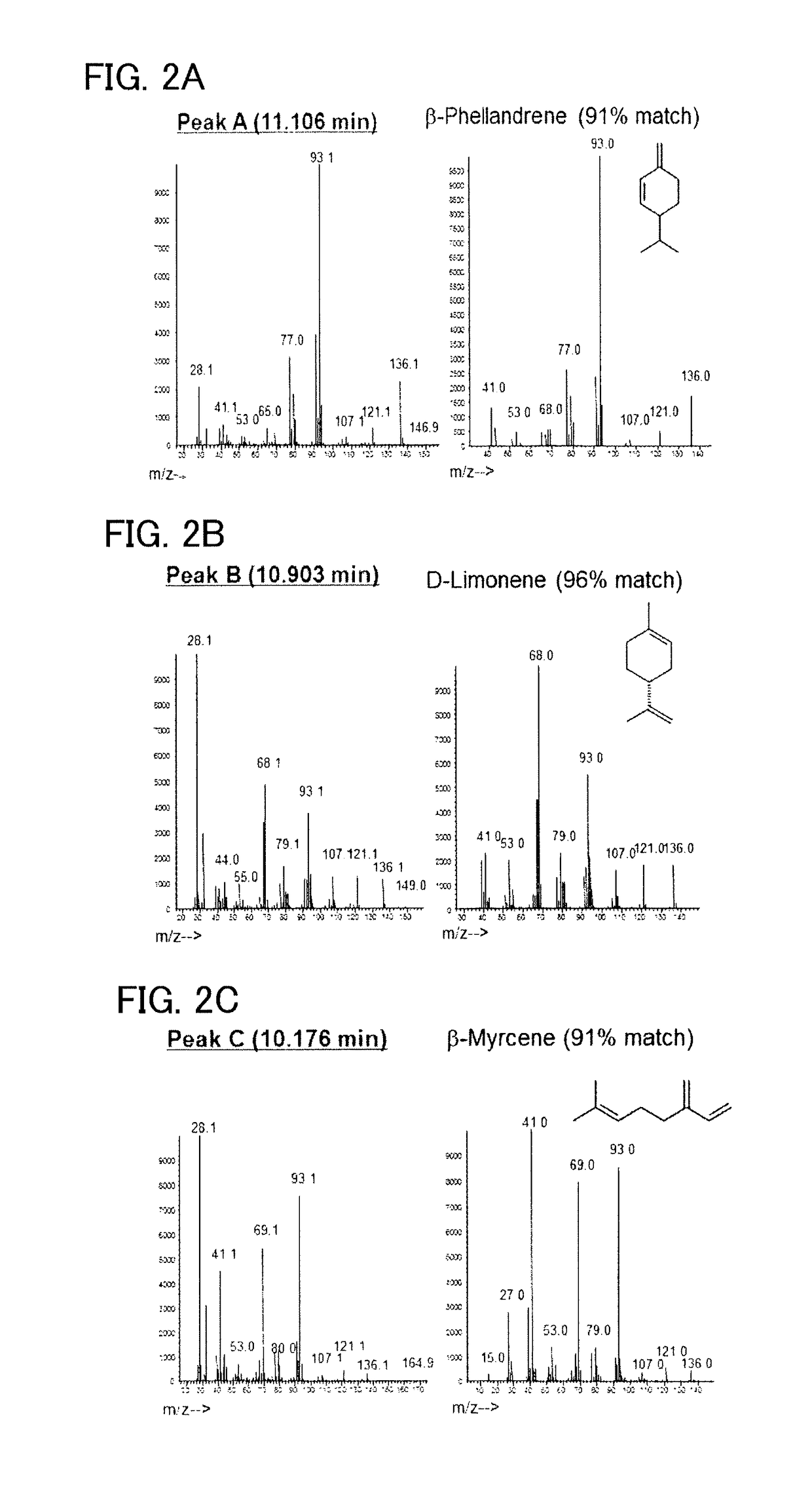
Recombinant cell, and method for producing beta-phellandrene
ActiveUS20150218589A1High purityAvoid small quantitiesBacteriaTransferasesPhellandreneNeryl pyrophosphate
To provide a series of techniques for obtaining β-phellandrene with high purity and in a large quantity.Provided is a recombinant cell capable of producing β-phellandrene, prepared by introducing at least one nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of a nucleic acid encoding geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) synthase and a nucleic acid encoding neryl pyrophosphate (NPP) synthase, and a nucleic acid encoding β-phellandrene synthase into a host cell in such a manner that these nucleic acids are expressed in the host cell. Also provided is a method for producing β-phellandrene by culturing the recombinant cell to produce β-phellandrene in the recombinant cell.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD +1
Carrier for gene transmission and preparation method thereof and application
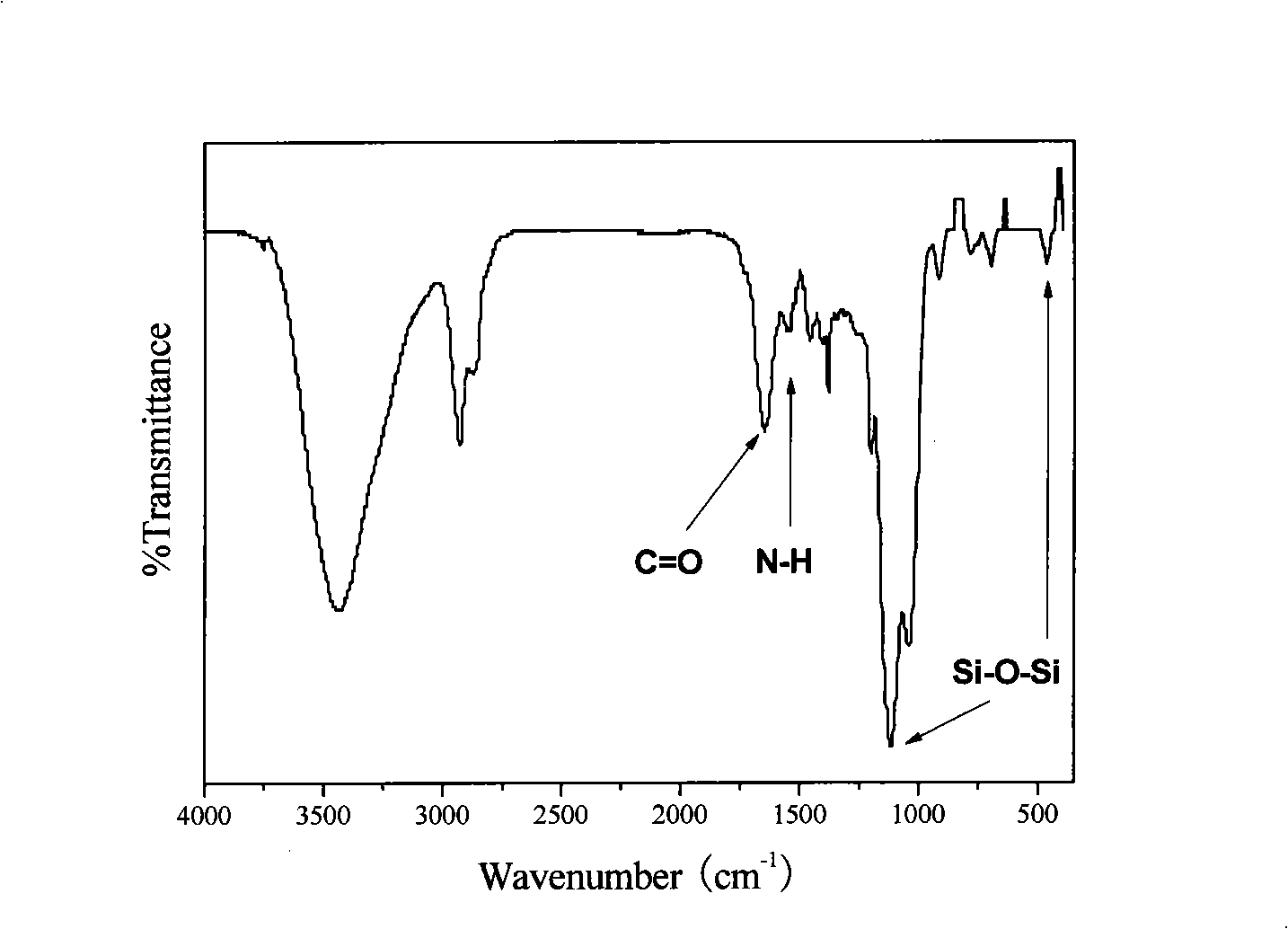
InactiveCN101284134AGood biocompatibilityNo side effectsGenetic material ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsGene deliverySide effect
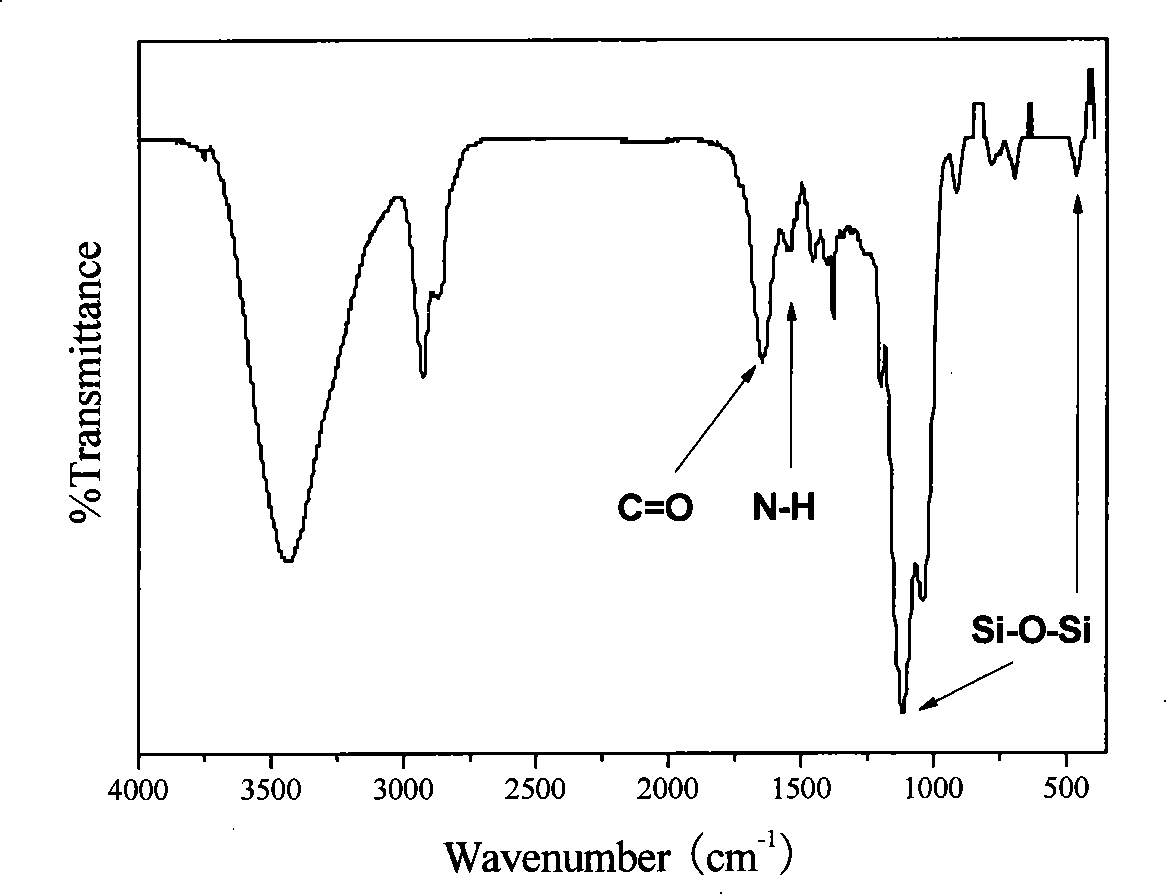
The invention relates to a carrier for gene delivery, gelatin-siloxane hybrid nano-material, a preparation method thereof by two-step sol-gel reaction and an application thereof. The gelatin-siloxane nano-particles are prepared from gelatin and 3-(2,3-epoxy propoxy )propyltrimethoxysilicane by performing chemical combination and hydrolytic reaction in acidic condition to obtain sol; and adjusting the pH value to slightly alkaline for performing polymerization reaction of silicane. The gelatin-siloxane hybrid nano-material has good biocompatibility, no toxic and side effect, and high stability; and is combined with exogenous gene to realize DNA transportation and expression, with high transduction efficiency, no immunogenicity, and no cytotoxicity. The size of the transferable exogenous gene is of several tens bp to several thousands kb, which overcomes size restriction to viral vector inserting into the exogenous gene. Thus the exogenous gene can be effectively carried into a host cell for performing effective transfection and expression.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Anti-Zika virus antibodies and methods of use
ActiveUS10421804B2Preventing entry of the virusInhibition of attachmentAntipyreticAnalgesicsAntigen Binding FragmentAntigen binding
The present invention provides monoclonal antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, that bind to ZIKV glycoproteins, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies and methods of use. The antibodies of the invention are useful for inhibiting or neutralizing ZIKV activity, thus providing a means of treating or preventing ZIKV infection in humans. In some embodiments, the invention provides for use of one or more antibodies that bind to the ZIKV for preventing viral attachment and / or entry into host cells. The antibodies of the invention may be used prophylactically or therapeutically and may be used alone or in combination with one or more other anti-viral agents or vaccines.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Application of teicoplanin to resisting Ebola virus
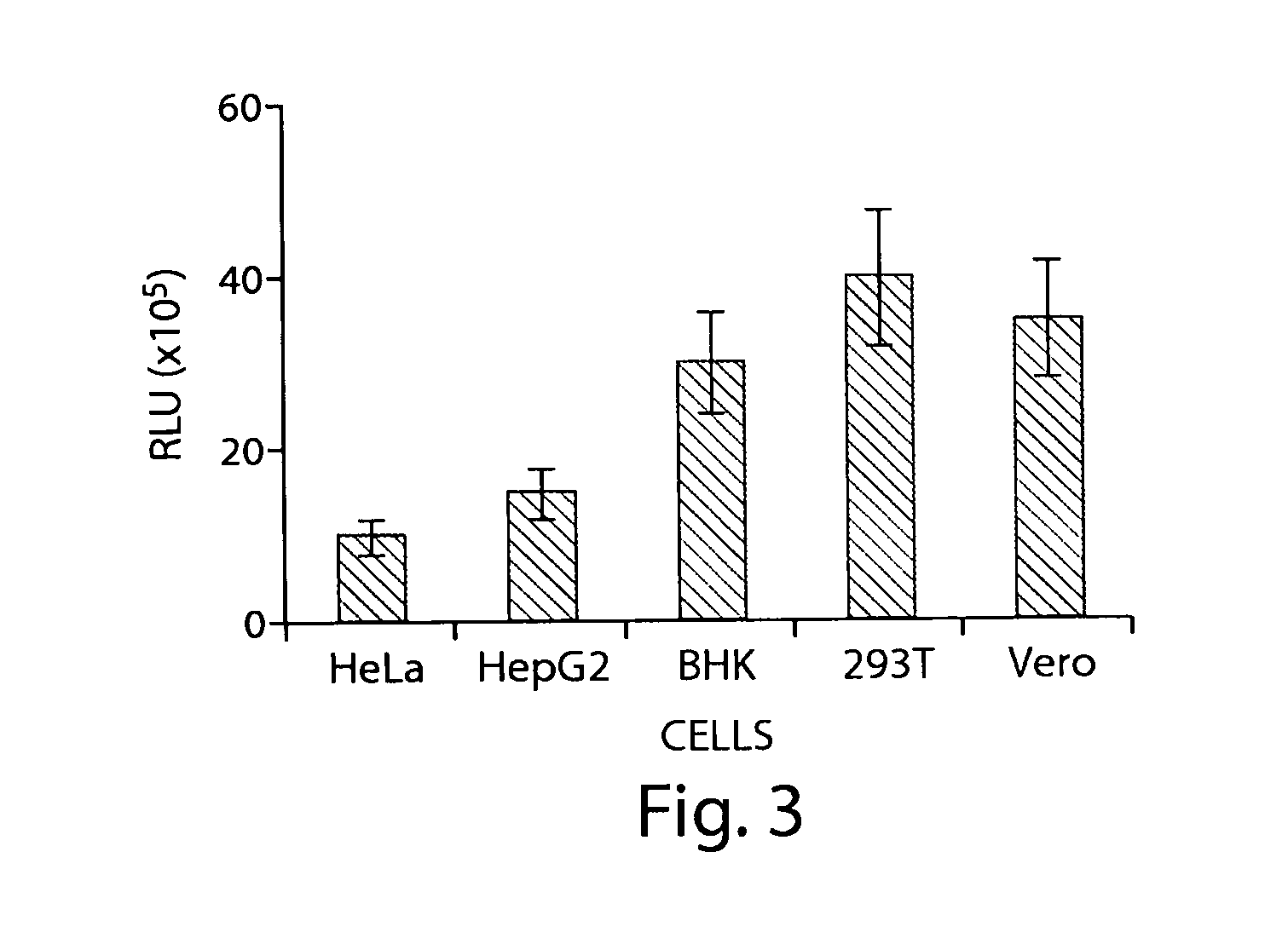
ActiveCN104873954AGood antiviral effectInhibition of the phenomenon of infection of 293T cellsAntiviralsSaccharide peptide ingredientsViral entry into host cellEbola virus
The invention provides application of teicoplanin to resisting Ebola virus. The teicoplanin can inhibit the envelope protein GP of Ebola virus. The envelope protein GP is the Zaire envelope protein of Ebola virus breaking out in 2014. The teicoplanin can inhibit Ebola virus from entering host cells and acting in host cells.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Anti-Zika Virus Antibodies and Methods of Use
ActiveUS20180016324A1Improve protectionImprove survivalAntipyreticAnalgesicsAntigen Binding FragmentAntigen binding
The present invention provides monoclonal antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, that bind to ZIKV glycoproteins, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies and methods of use. The antibodies of the invention are useful for inhibiting or neutralizing ZIKV activity, thus providing a means of treating or preventing ZIKV infection in humans. In some embodiments, the invention provides for use of one or more antibodies that bind to the ZIKV for preventing viral attachment and / or entry into host cells. The antibodies of the invention may be used prophylactically or therapeutically and may be used alone or in combination with one or more other anti-viral agents or vaccines.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Human antibodies to ebola virus glycoprotein
ActiveUS20170355751A1Inhibiting and neutralizing activityAvoid enteringImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsViral glycoproteinAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides monoclonal antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, that bind to Ebola virus glycoproteins, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies and methods of use. The antibodies of the invention are useful for inhibiting or neutralizing Ebola virus activity, thus providing a means of treating or preventing Ebola virus infection in humans. In some embodiments, the invention provides for use of one or more antibodies that bind to the Ebola virus for preventing viral attachment and / or entry into host cells. The antibodies of the invention may be used prophylactically or therapeutically and may be used alone or in combination with one or more other anti-viral agents or vaccines.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
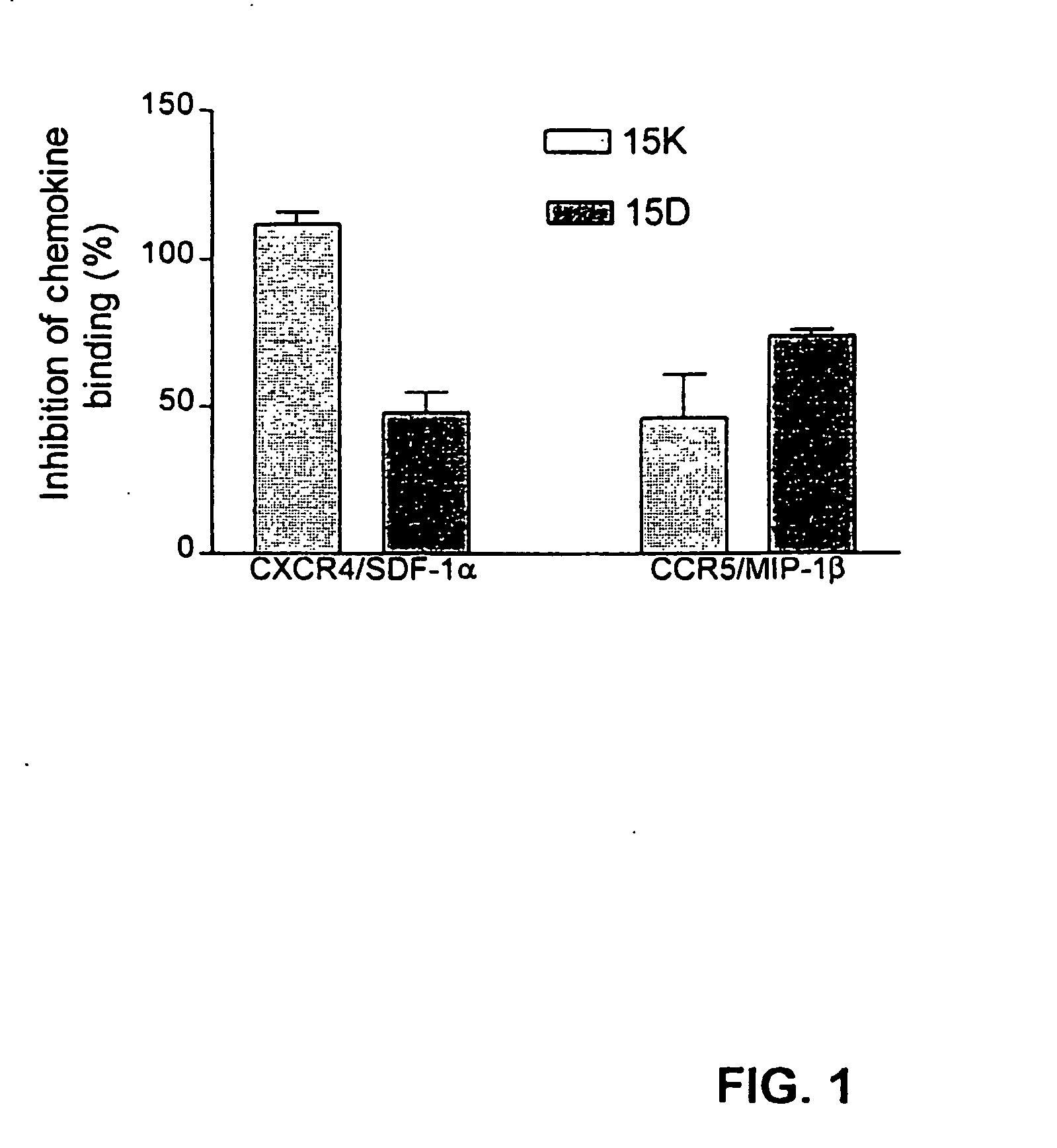
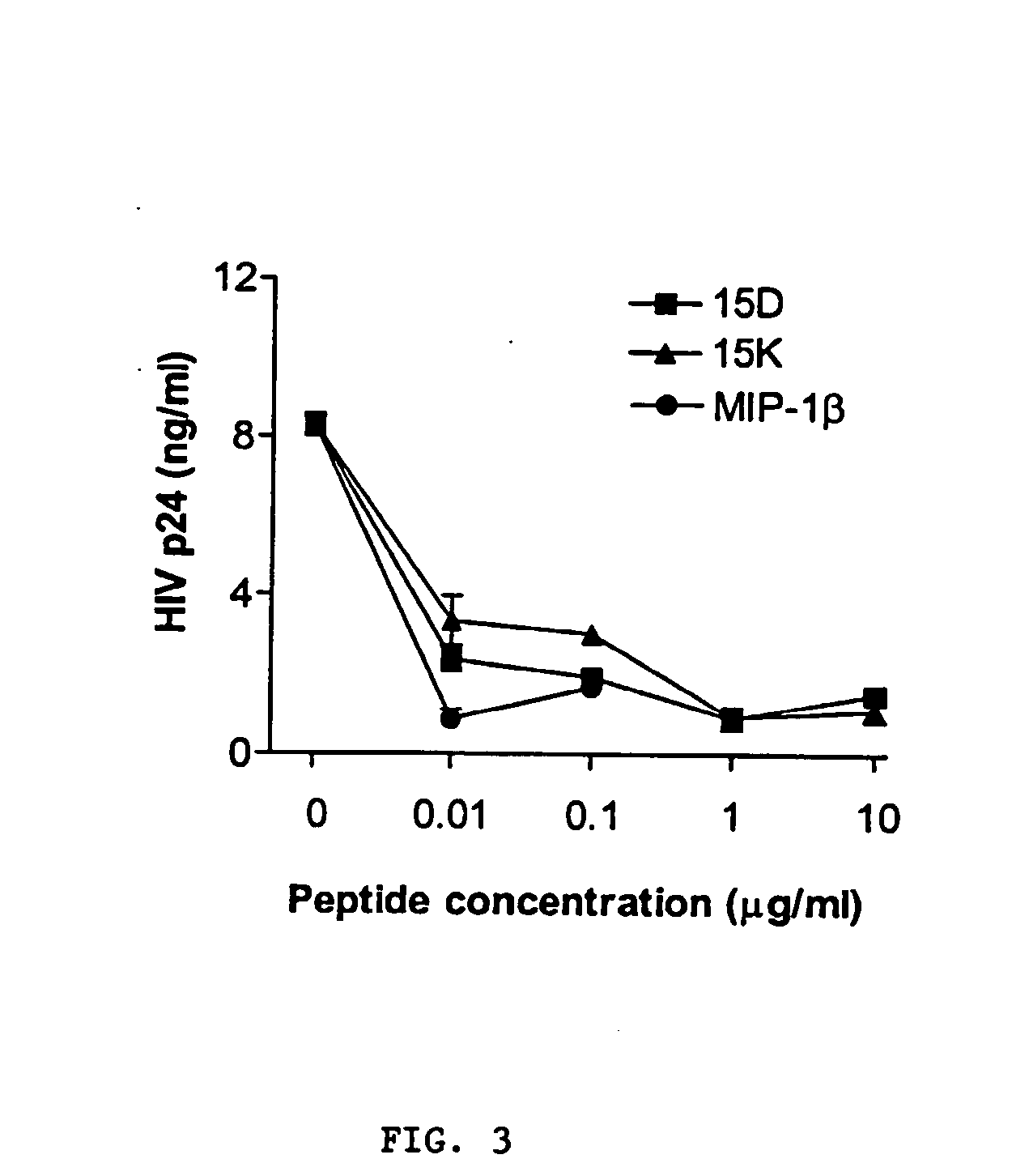
Methods and compositions for inhibiting hiv-coreceptor interactions
InactiveUS20060116325A1Elicit immune responseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseImmunodeficiency virus
Novel methods and compositions are provided for inhibiting interactions between human immunodeficiency viruses (HIVs) and viral coreceptors, including CXCR4 and / or CCR5 coreceptors. The anti-coreceptor binding agent includes a novel peptide portion of the gp120 envelope protein of HIV-1, as well as peptide analogs and mimetics of this peptide, that specifically binds to, or modulates activity of, the coreceptors(s). The anti-coreceptor binding agent is useful as a prophylactic or therapeutic treatment to prevent or inhibit HIV binding to a susceptible cell and thereby reduces infection and / or moderates or treats related diseases. In alternative embodiments, the peptides, analogs and mimetics are effective to inhibit direct co-receptor binding by HIV virus, coreceptor binding by HIV gp120 proteins or peptides, HIV fusion with target host cells, HIV virion entry into host cells, HIV replication, and HIV transmission between cells and hosts. In more detailed embodiments, the anti-coreceptor binding agents of the invention are multi-tropic by exhibiting activity against HIV interactions with multiple, CXCR4 and CCR5, coreceptors.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
Constructing method of oligo-amino acid plasmid
InactiveCN102242141AImprove connection efficiencySimple methodMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliDigestion
The invention discloses a constructing method of an oligo-amino acid plasmid, comprising the following steps of: A, designing and synthesizing two pairs of primers a, b and c, d; B, respectively performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on the two pairs of primers a, b and c, d with the same plasmid template; C, mixing the reaction liquids obtained in the step B, then performing denaturation and renaturation processes; D, after template digestion, directly converting into host cell escherichia coli BL21, i.e. digesting the PCR reaction product by DnpI enzyme in a reaction system of 17mL of PCR reaction product, 2mL of Tango buffer solution and 1mL of DnpI enzyme under the reaction condition of 37DEG C for 30 minutes, converting the competence of the escherichia coli BL21 by the reaction product, selecting monoclonal colonies, sequencing and identifying; and E, accurately sequencing. The method is simple, the materials and reagents are relatively cheap, and the connecting step of the blunt end ligase of a linear plasmid is omitted, thus obviously improving the connecting efficiency of plasmid oligo-amino acid mutation, and being favorable for industrial or medical scaled-up production. The success rate of sequencing is as high as 66% which is more than 5 times of that of the traditional method.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
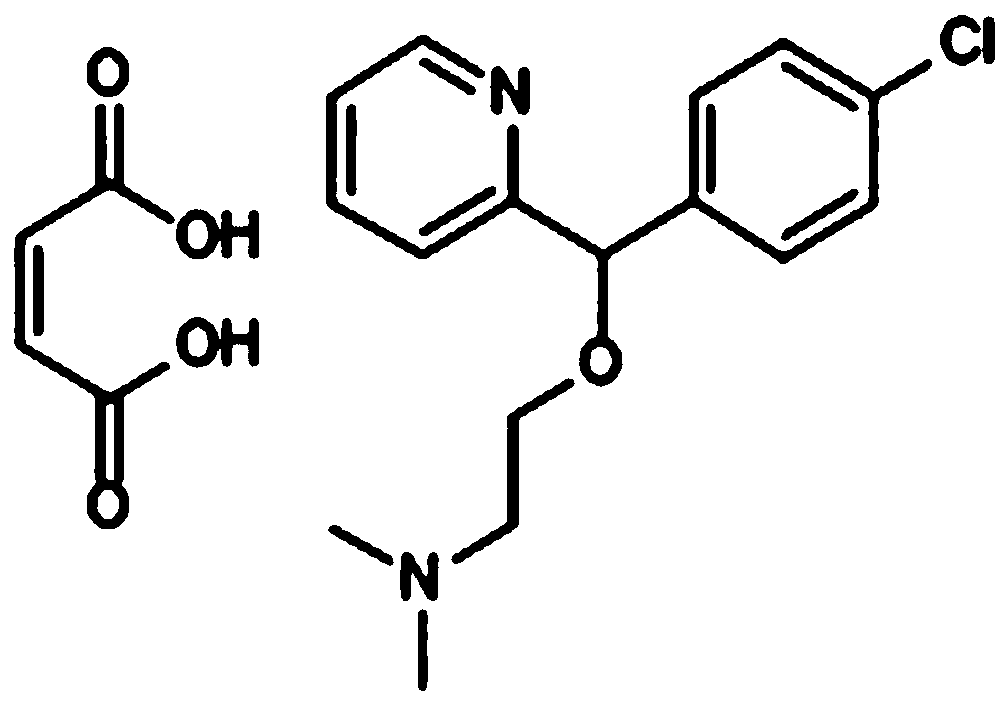
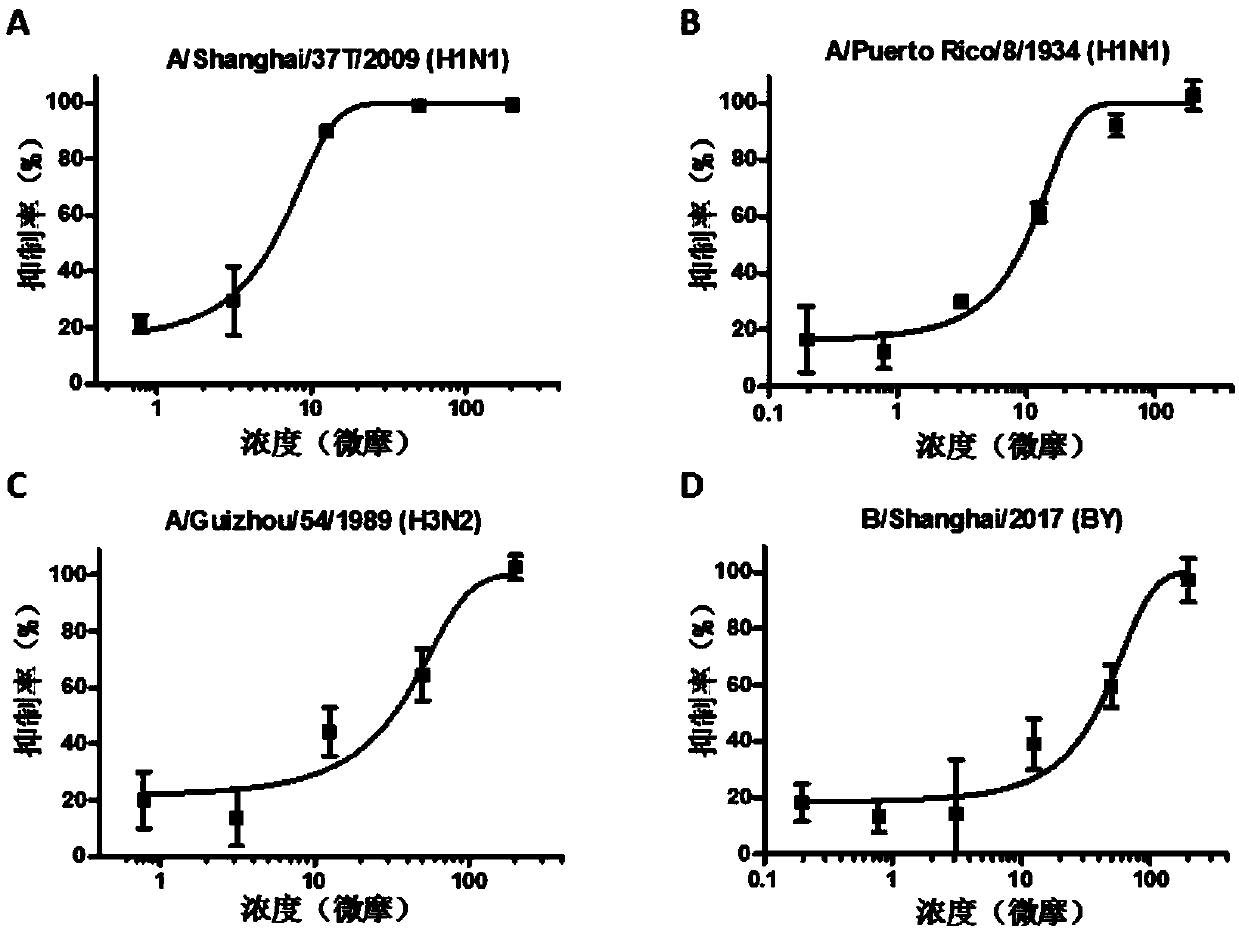
Application of carbinoxamine maleate in preparation of anti-influenza virus medicine
ActiveCN110870864AAvoid infectionBroad-spectrum antiviral activityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsEndocytosis InhibitionDose dependence
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and relates to an application of carbinoxamine maleate in preparation of an anti-influenza virus medicine. Experiments show that the carbinoxamine maleate has significant anti-influenza activity against different types and subtypes of influenza viruses in a completely non-toxic concentration environment, and inhibits the replication of alltested virus strains in a dose-dependent manner, so that the results indicate that the anti-influenza virus activity of the carbinoxamine maleate has a certain broad spectrum; influenza viruses described in the invention include influenza A and B viruses, including H1N1, H3N2, H7N9, H5N1, H7N1, H7N2, H7N3, H7N7, H9N2 or B type; the action mechanism study provided by the invention shows that the carbinoxamine maleate mainly inhibits the viruses from entering host cells by interfering with the endocytosis of the influenza viruses; and the carbinoxamine maleate can be used to prepare the medicinefor preventing and treating influenza, and provides a novel way and means for the prevention and treatment of the influenza.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
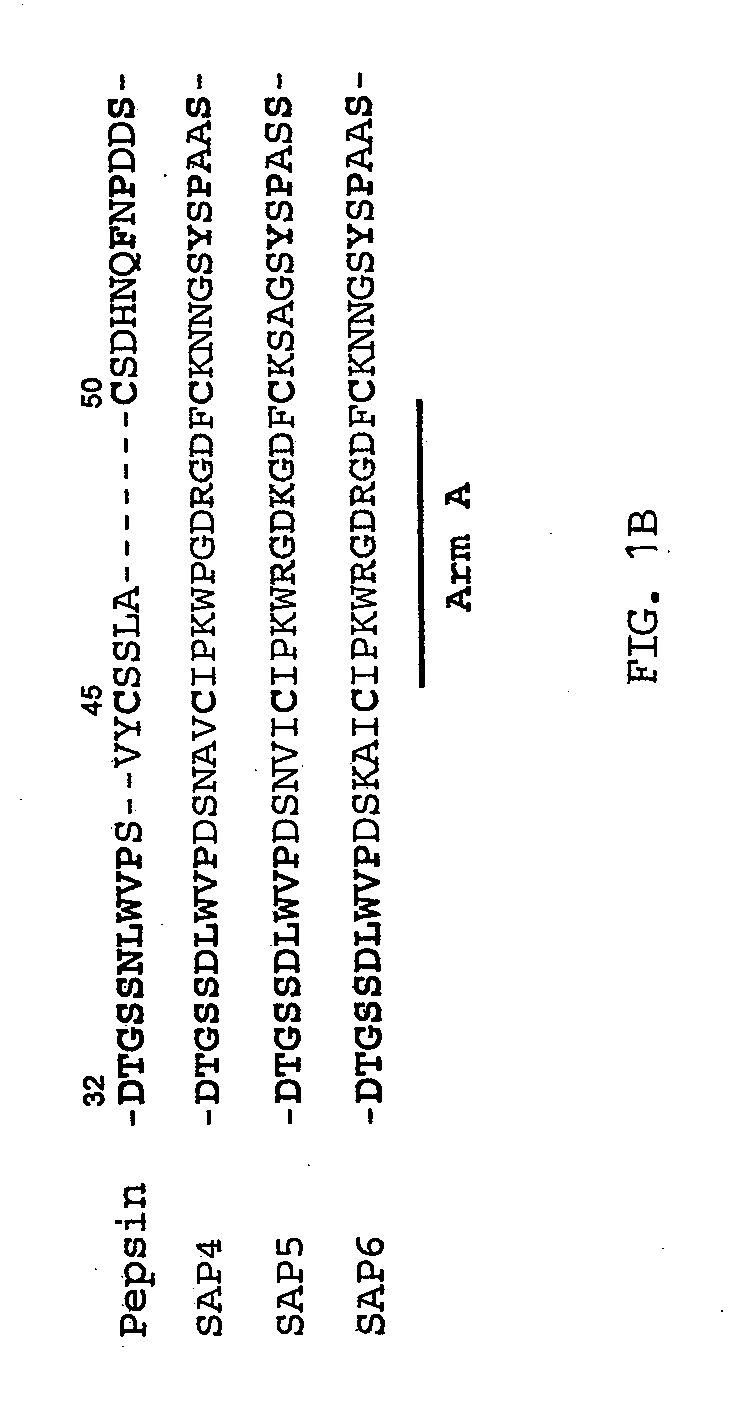
Methods and Compositions for Inhibiting Fungal Infection and Disease
The present invention describes a previously unknown interaction between secreted aspartic proteases (SAPs), including SAPs 4-6 of Candida albicans, and integrins on host cells. The SAPs secure entry into the host cell through RGD-like binding motifs and subsequently induce apoptosis, thereby clearing the way for systemic infection. The invention thus provide a new target for therapeutic intervention and describes peptides and antibodies that inhibit the action of SAPs in this context, including their interaction with integrins.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND
Human antibodies to influenza hemagglutinin
ActiveUS10392432B2Ameliorate and reduce and durationAmeliorate and reduce and and frequency of occurrenceOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against virusesHemagglutininAntigen Binding Fragment
The present invention provides monoclonal antibodies, or antigen-binding fragments thereof, that bind to the influenza hemagglutinin (HA) protein, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies and methods of use. The antibodies of the invention are useful for inhibiting or neutralizing influenza virus activity, thus providing a means of treating or preventing influenza infection in humans. In some embodiments, the invention provides for use of one or more antibodies that bind to the influenza HA for preventing viral attachment and / or entry into host cells. The antibodies of the invention may be used prophylactically or therapeutically and may be used alone or in combination with one or more other anti-viral agents or vaccines.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
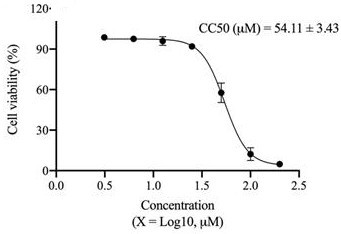
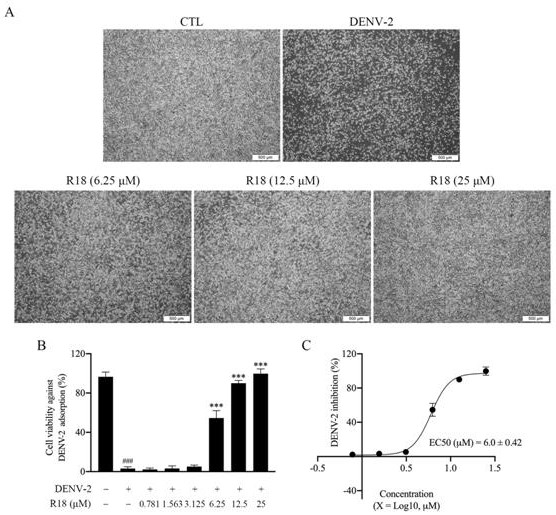
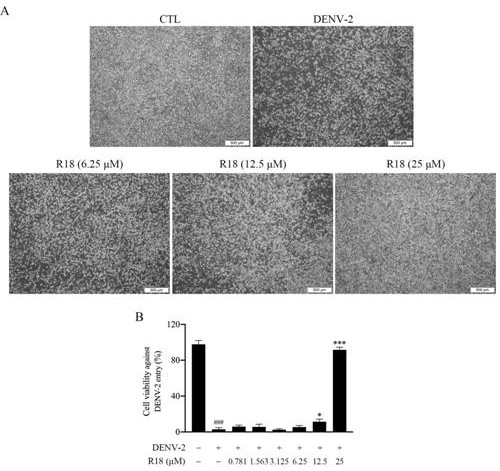
Application of Vina-ginsenoside R18 in preparation of anti-dengue virus pharmaceutical preparation
PendingCN113855688ABlocking adsorptionAvoid accessOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsIntracellularPharmaceutical formulation
The invention discloses application of a dammarane type tetracyclic triterpenoid monomeric compound vina-ginsenoside R18 in preparation of anti-dengue virus pharmaceutical preparation. In-vitro cell experiments of the compound show that the vina-ginsenoside R18 can play a role in resisting dengue virus through a plurality of links of blocking virus adsorption, entering host cells, inhibiting virus replication in the cells and the like, and has good antiviral activity. Therefore, the vina-ginsenoside R18 as an anti-dengue virus pharmaceutical preparation has a wide application prospect.
Owner:广东中诚生物科技有限公司
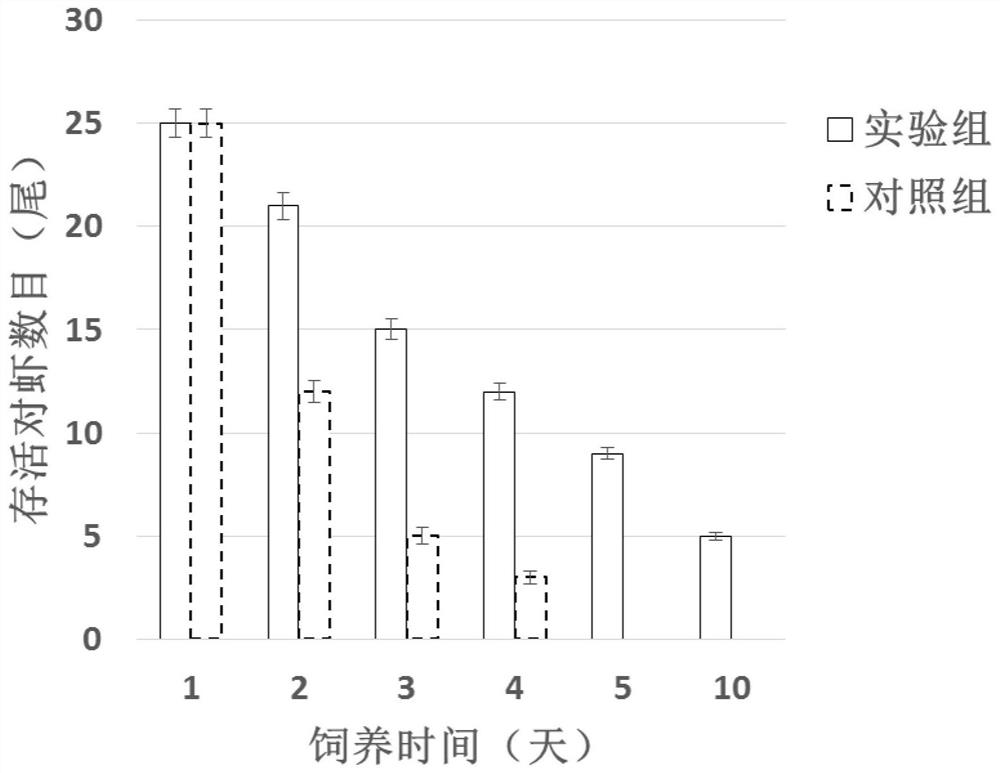
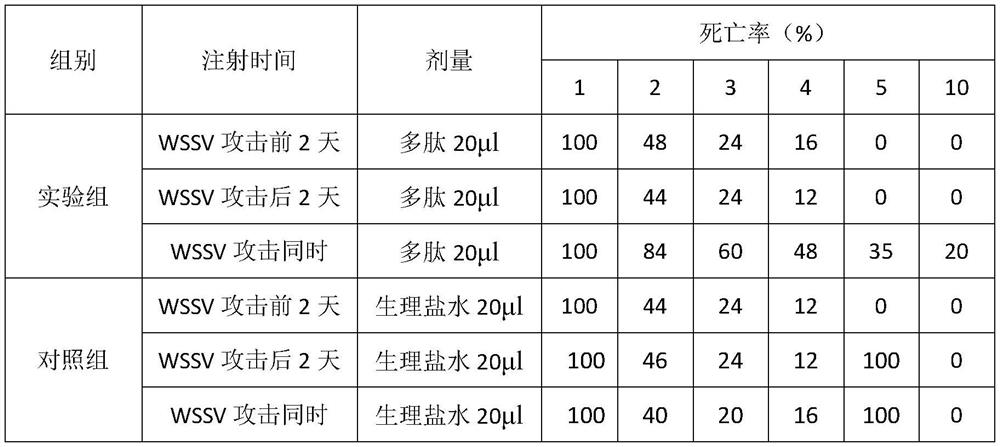
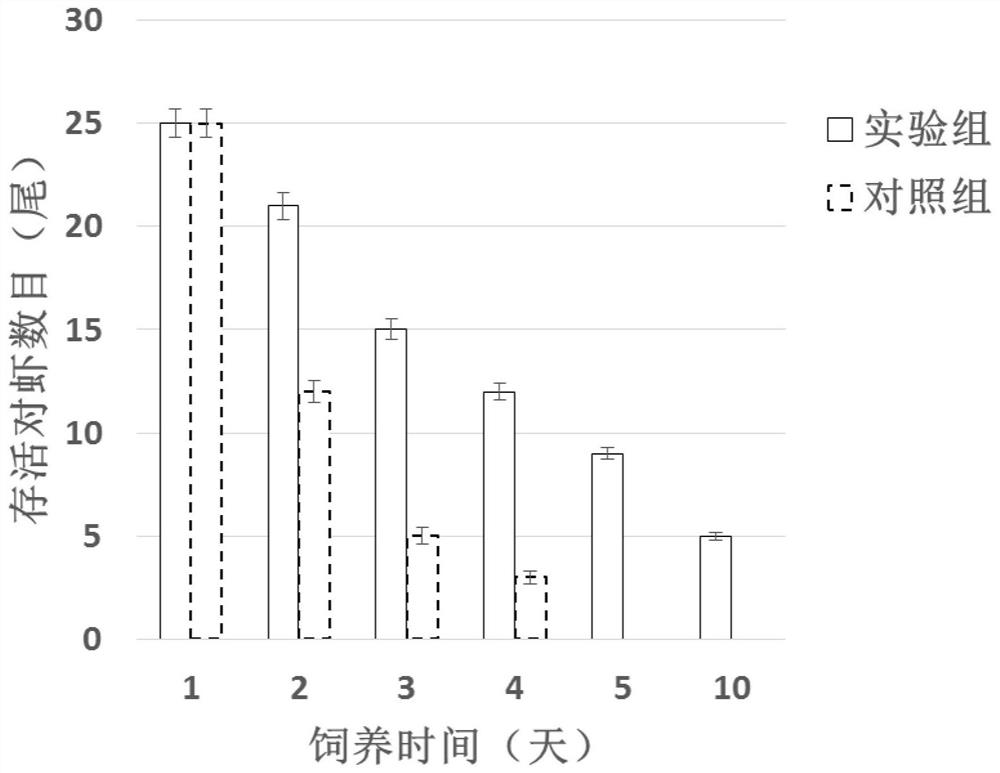
A prawn pcab7 protein and wssv envelope protein vp28 interaction blocker polypeptide
ActiveCN113121645BProlong survival timeRealize the role of anti-WSSVPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsCell membraneAmino acid
The invention provides a blocking polypeptide, which can block the interaction between Chinese prawn PcRab7 protein and WSSV envelope protein VP28, and has anti-WSSV effect. The amino acid sequence of the blocking polypeptide provided by the present invention is TAPLAITAIIAVFI. The polypeptide provided by the invention can block the binding of PcRab7 to VP28, thereby affecting the fusion of the virus envelope and the host cell membrane, so that the virus cannot enter the host cell and realize the anti-WSSV effect. The present invention uses shrimp infection experiments to verify that it can effectively prolong the survival time of shrimps infected with WSSV, can be used as an effective anti-WSSV candidate drug, and provides possible polypeptide drugs for the prevention and treatment of WSSV in the future.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Application of carbinoxamine maleate in preparation of anti-influenza virus medicine
ActiveCN110870864BAvoid infectionBroad-spectrum antiviral activityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsPharmaceutical SubstancesInfluenza Viruses Type A
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Inhibitors of filovirus entry into host cells
Owner:MICROBIOTIX
Recombinant cell, and method for producing β-phellandrene
ActiveUS9617563B2High purityAvoid small quantitiesFungiSugar derivativesNeryl pyrophosphatePhellandrene
To provide a series of techniques for obtaining β-phellandrene with high purity and in a large quantity.Provided is a recombinant cell capable of producing β-phellandrene, prepared by introducing at least one nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of a nucleic acid encoding geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) synthase and a nucleic acid encoding neryl pyrophosphate (NPP) synthase, and a nucleic acid encoding β-phellandrene synthase into a host cell in such a manner that these nucleic acids are expressed in the host cell. Also provided is a method for producing β-phellandrene by culturing the recombinant cell to produce β-phellandrene in the recombinant cell.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD +1
Novel expression regulating rna-molecules and uses thereof
The present application relates to a RNA molecule comprising a RNA-polymerase binding aptamer, wherein said RNA-polymerase binding aptamer has a length of 15 to 60 nt, wherein said RNA-Polymerase binding aptamer binds to a RNA-polymerase with a KD of 50 nM or lower. Furthermore, the application discloses a DNA molecule comprising a sequence encoding an RNA-polymerase binding aptamer of the invention, and a method of producing a protein or RNA of interest comprising providing a vector according to the invention, said vector comprising an expression, introducing said vector into a host cell, and culturing said host cell in culture medium under conditions inducing transcription from the promoter of the expression vector, and optionally recovering the protein of interest from the host cell or culture medium. Furthermore, the application pertains methods for in vitro transcription and expression employing the RNA-polymerase binding apatamers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VIENNA
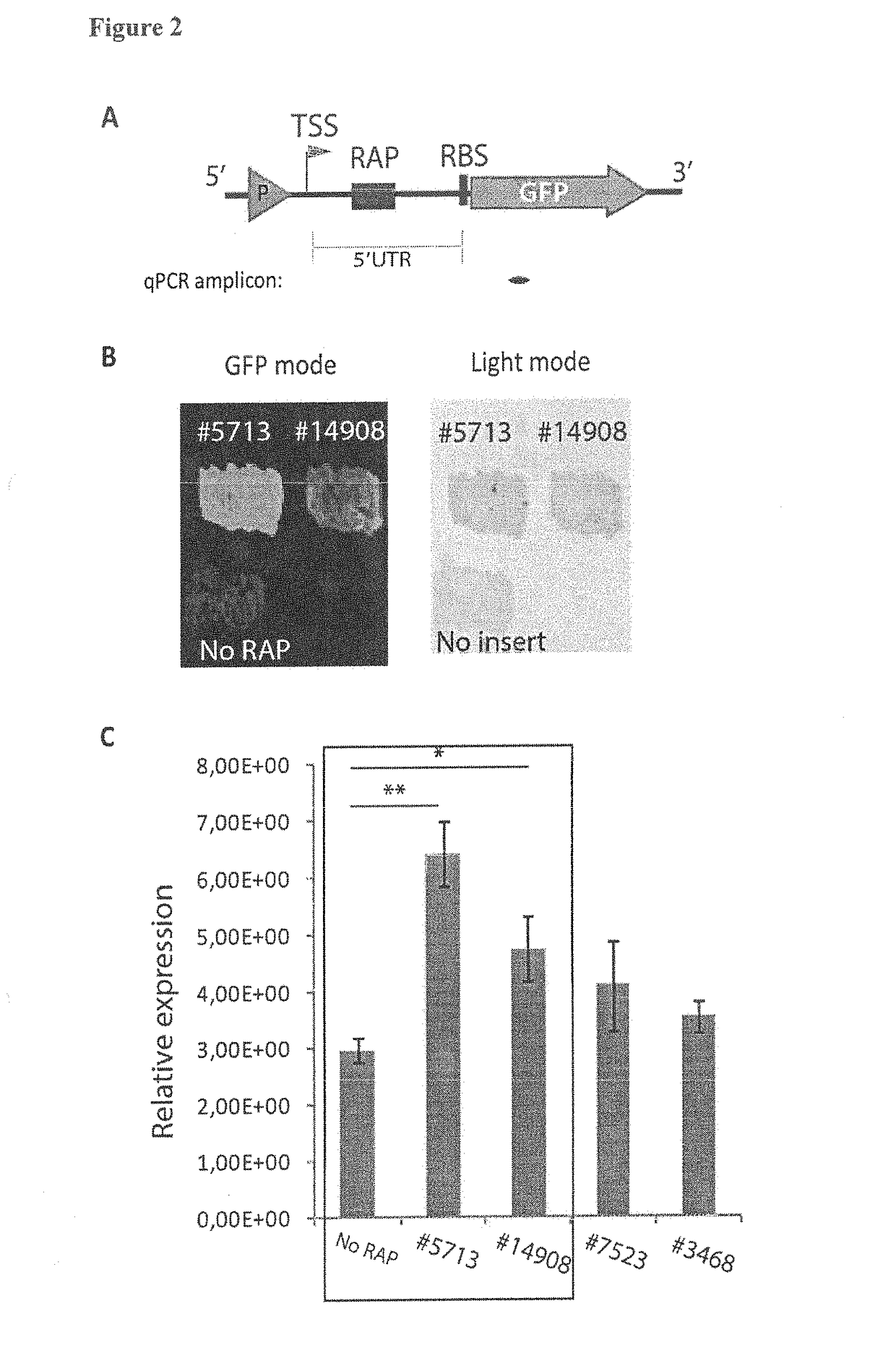
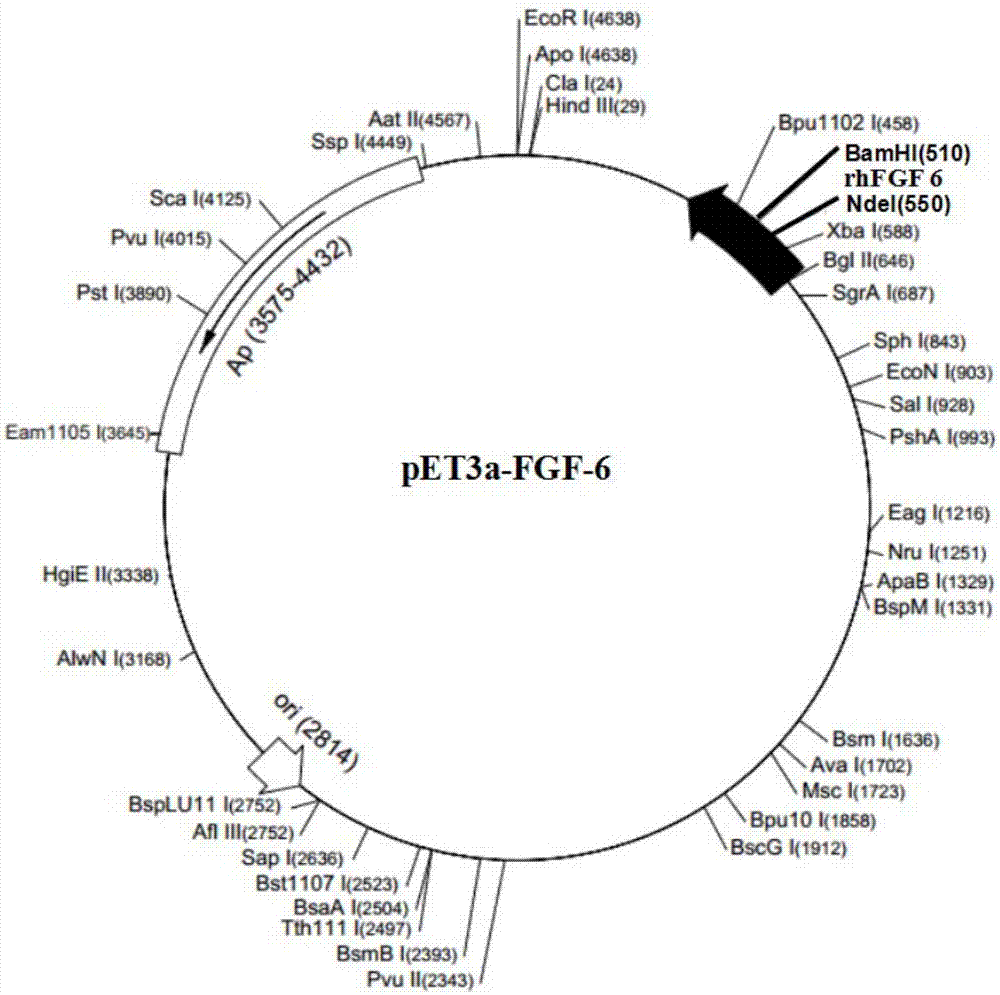
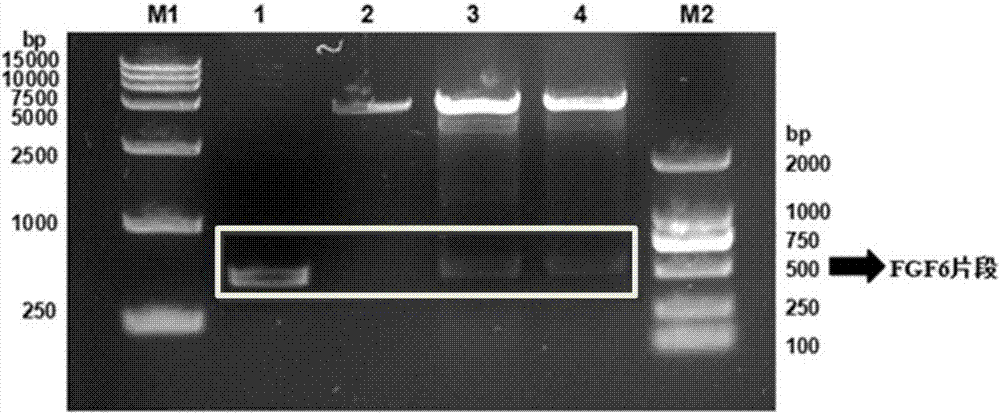
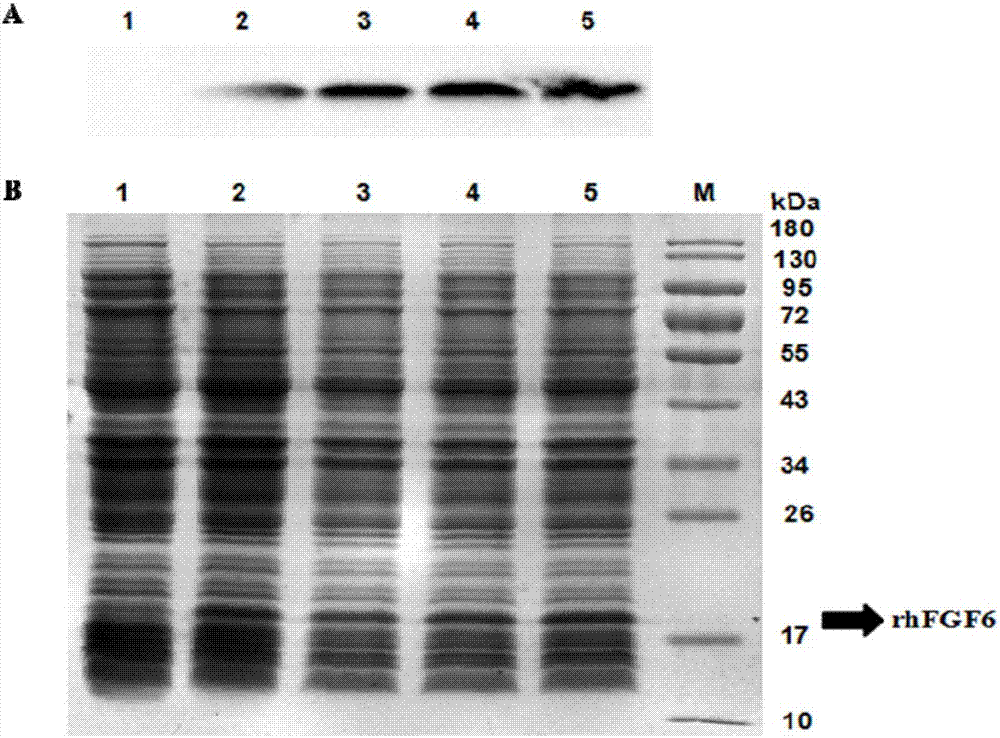
Nucleic acid fragment for encoding rhFGF-6, expression vector, host cell, production method and application
ActiveCN107058332APromote regenerationPromote generationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsSequence signalAmino acid
The invention discloses a nucleic acid fragment for encoding rhFGF-6, an expression vector, a host cell, a production method and an application and relates to the field of biological medicines. The nucleic acid fragment for encoding rhFGF-6, provided by the invention, is acquired by optimizing according to a natural sequence of rhFGF-6; 37 signal peptides are removed on the basis of the natural sequence and a secondary structure adverse to expression is eliminated, but an amino acid sequence of rhFGF-6 is not changed; the nucleic acid fragment is constructed onto a suitable carrier so as to form a recombinant expression vector; the recombinant expression vector is converted and then enters the host cell, so that the recombinant bacteria can be acquired; the recombinant bacteria are cultured and an inducer is adopted for inducing expression, so that rhFGF-6 can be highly expressed; the expressed rhFGF-6 has the activities of boosting tissue regeneration, boosting osteogenesis, repairing myocardial damage, boosting wound healing and promoting revascularization.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
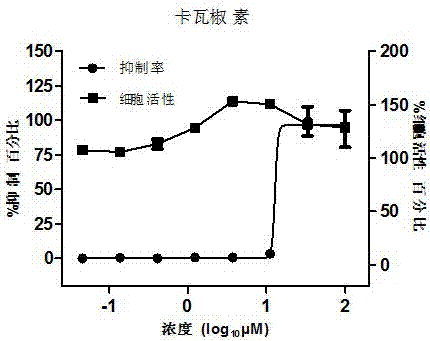
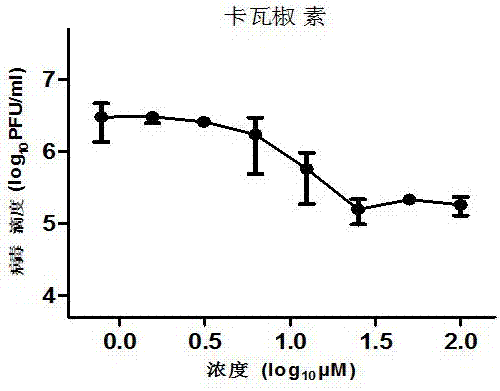
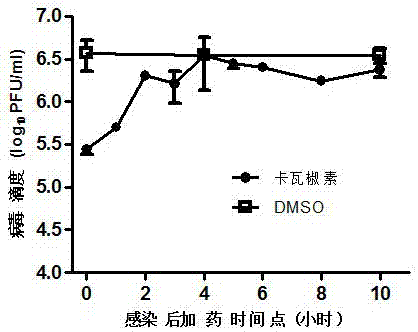
Application of kavalactone compound in preparing medicine for inhibiting infection of enterovirus 71
The invention relates to application of kavalactone in preparing medicine for inhibiting infection of enterovirus 71 (EV-A71). Through cytology and molecular biology experiments, it is shown that the compound can specifically act on the VP4 protein of the EV-A71virus and can specifically inhibit the EV-A71 virus to enter a host cell; and through cytotoxicity tests, it is shown that the compound almost has no cytotoxicity. Therefore the compound can safely be used for preparing medicines for treating and preventing related diseases caused by infection of the enterovirus EV-A71.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
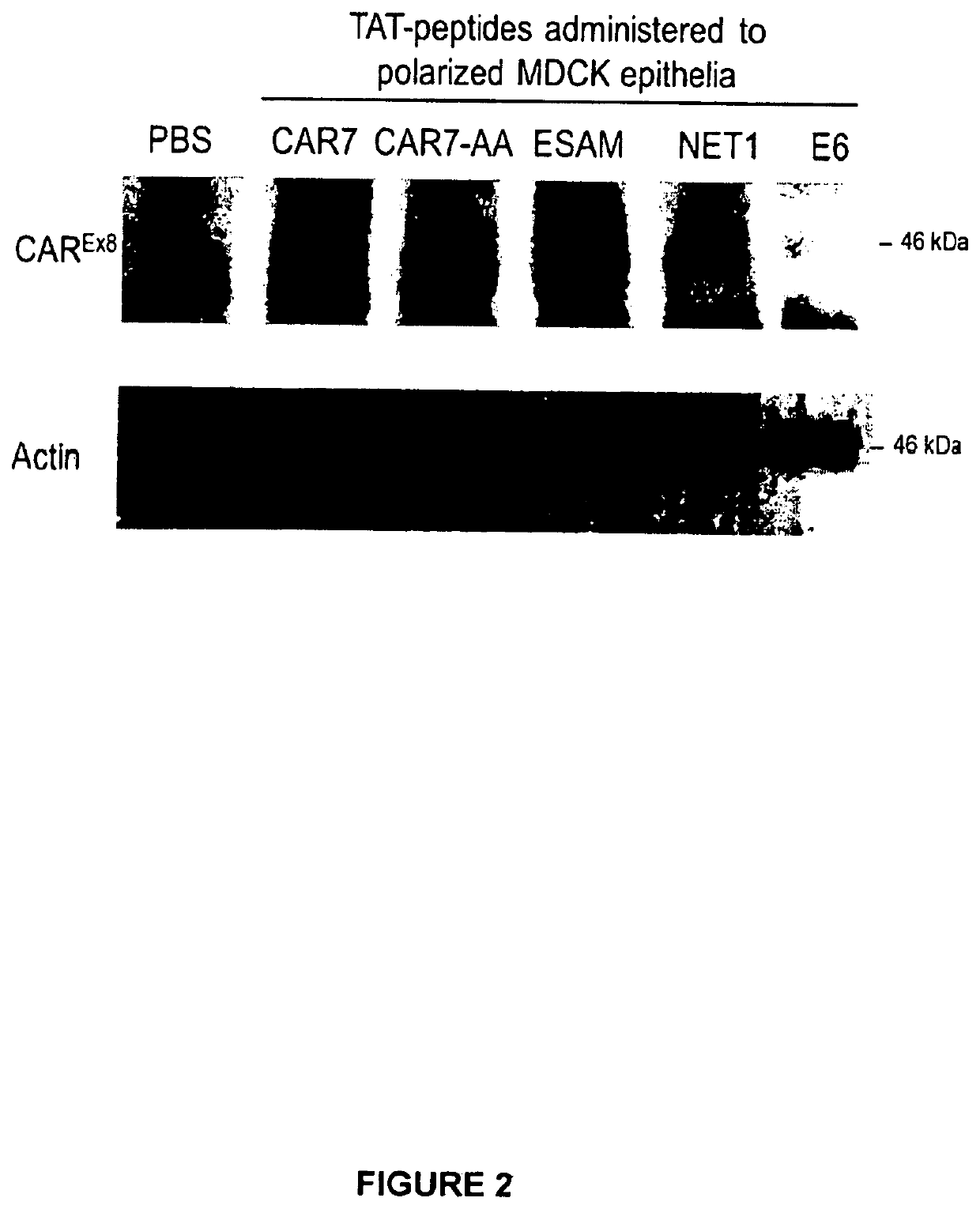
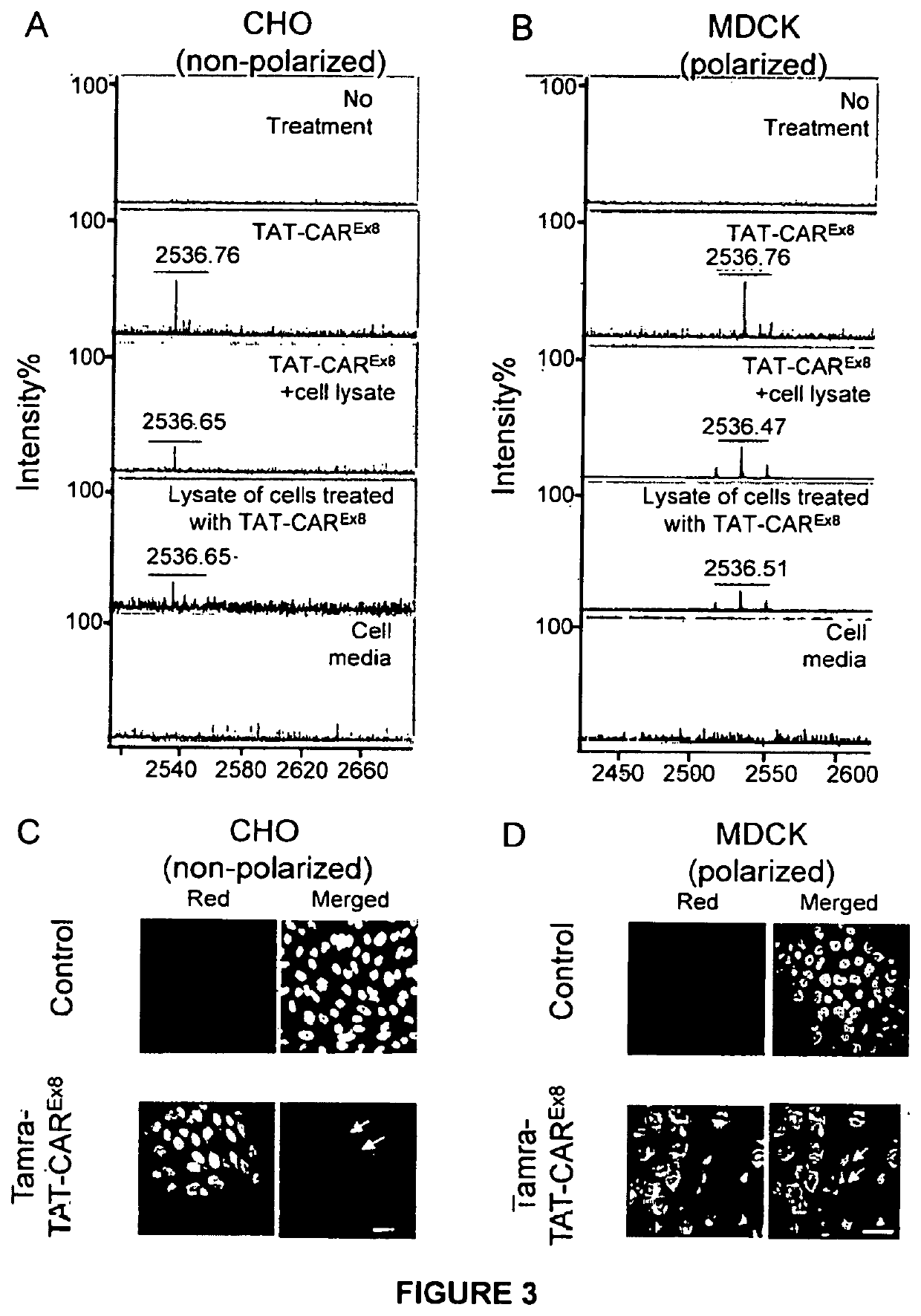
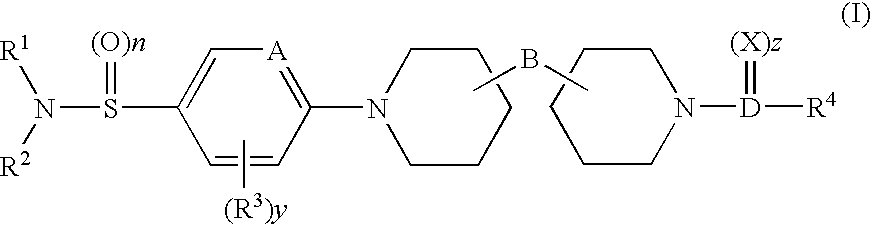
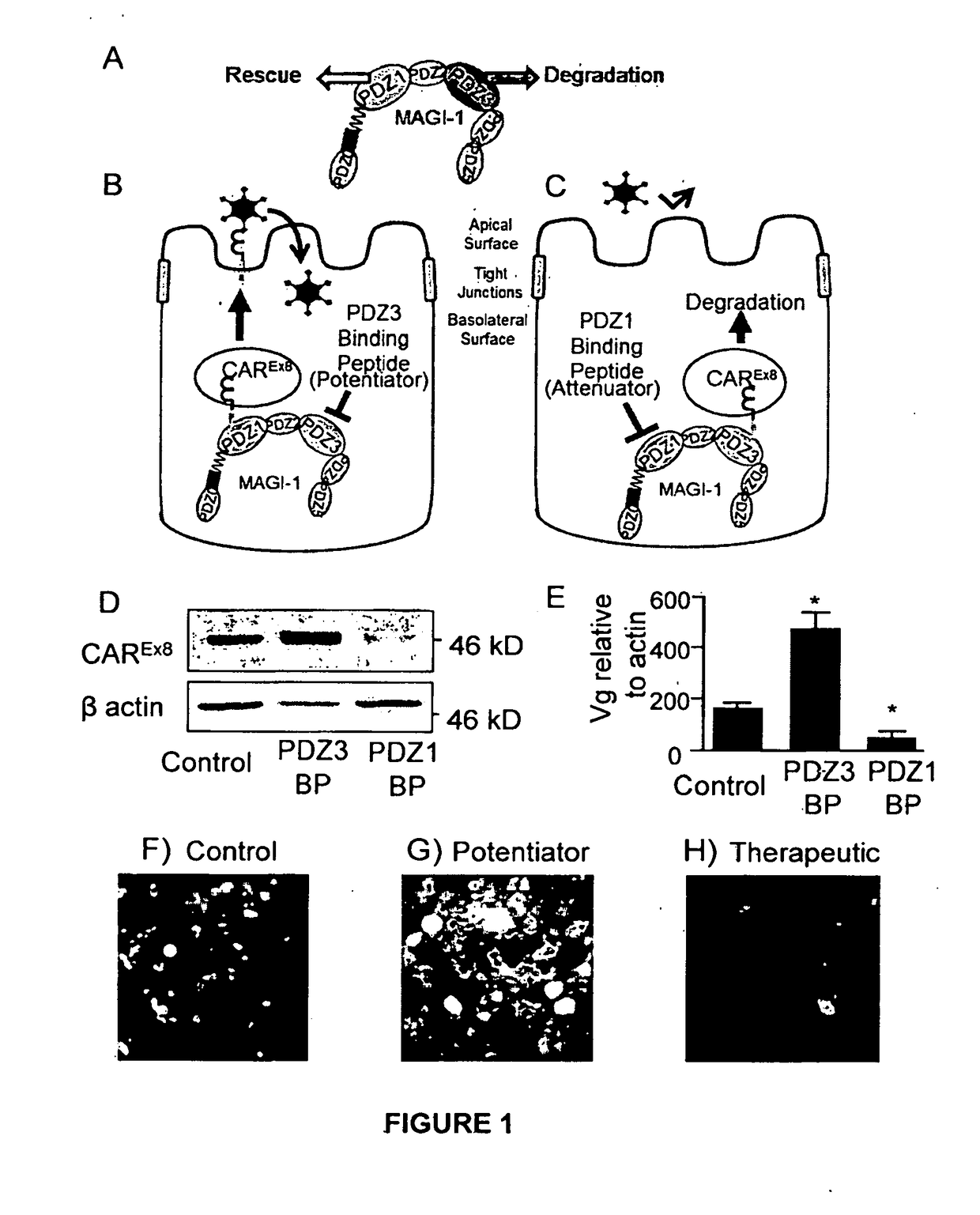
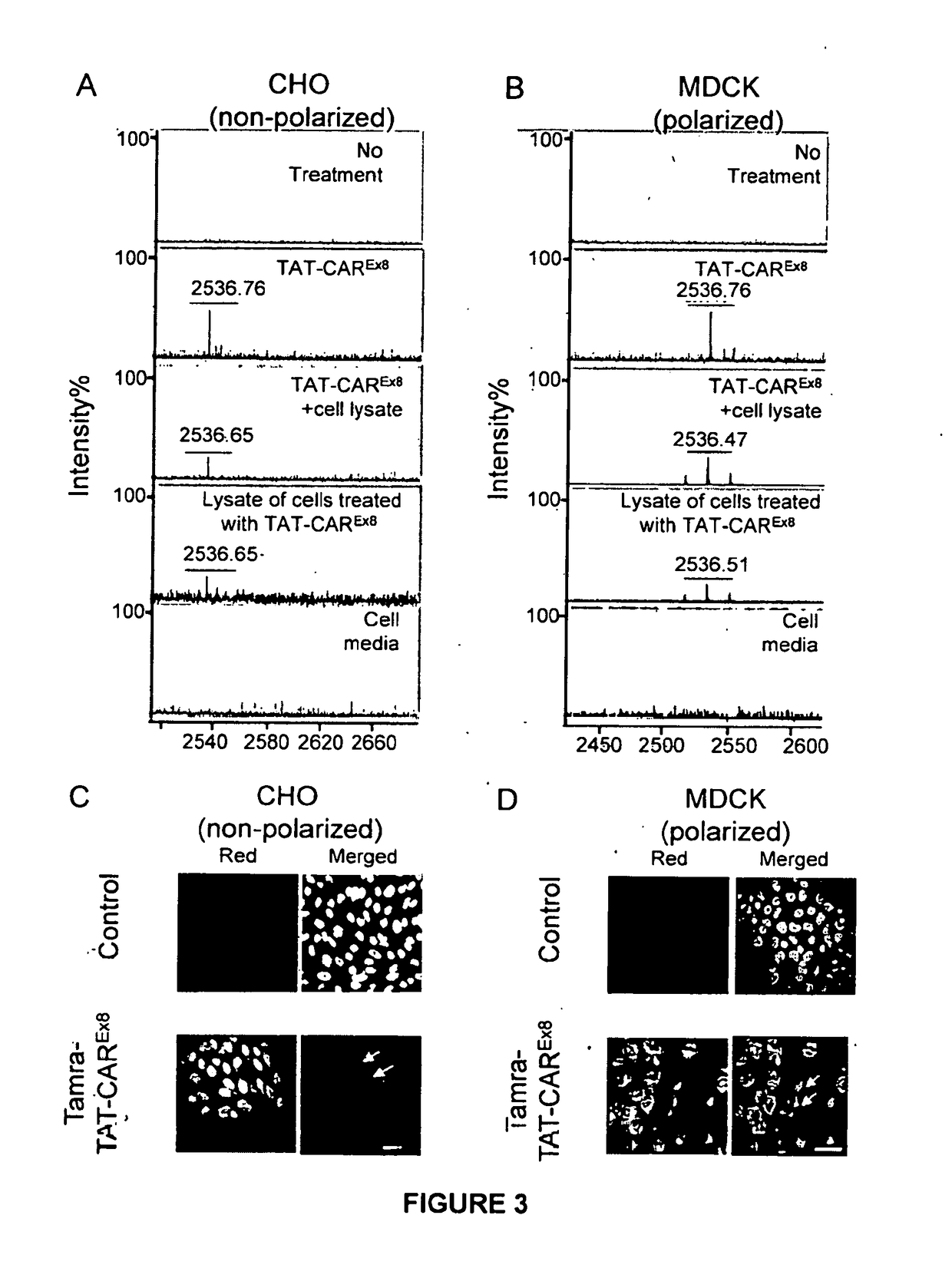
Peptide-based molecules for modulating car expression or accessibility and uses thereof
ActiveUS10736971B2Increasing or decreasing apical surface localization of CARGood curative effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsCoxsackievirusBinding domain
Peptide-based molecules for modulating expression or accessibility to the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR) are disclosed. Cell-permeable peptide-based molecules having a PDZ-decoy domain or PDZ-binding domain are used to modulate the expression or accessibility of CAR molecules, thereby affecting the ability of viral molecules, or molecules containing viral sequences or proteins able to bind CAR, to enter host cells.
Owner:WRIGHT STATE UNIVERSITY
Penaees chinensis PcRab7 protein and WSSV envelope protein VP28 interaction blocker polypeptide
ActiveCN113121645AProlong survival timeRealize the role of anti-WSSVPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsCell membranePost infection
The invention provides a blocking polypeptide. The blocking polypeptide can block the interaction between PcRab7 protein of Penaees chinensis and WSSV envelope protein VP28, and has an anti-WSSV effect. The amino acid sequence of the blocking polypeptide provided by the invention is TAPLAITAIIAVFI. The polypeptide provided by the invention can block the binding of PcRab7 to VP28, and can further influence the fusion of a virus envelope and a host cell membrane, so that the virus can not enter a host cell, and the anti-WSSV effect is realized. According to the invention, a Penaees chinensis infection experiment is adopted, and the experiment proves that the polypeptide can effectively prolong the survival time of Penaees chinensis infected with WSSV, and the polypeptide can be used as an effective anti-WSSV candidate drug, providing possible polypeptide drugs for prevention and treatment of WSSV in the future.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Rapid detection method of live virus and application of rapid detection method
InactiveCN109338013AGood for quantitative determinationQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesVirus inactivationTiter
The invention relates to a rapid detection method of live virus and application of the rapid detection method, and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. The rapid detection method comprises the following steps: transfection: inoculating viruses to be detected into single-layer host cells cultured in a cell culture plate in advance, transfecting and culturing; and detection: collecting samples at a sample collecting time when the inoculated viruses to be detected enter the host cells but are not amplified, cleaning for removing the viruses outside the host cells, then extracting viral DNA in the host cells for PCR detection to obtain the content of the live viruses in the viruses to be detected. The rapid detection method can effectively detect residual live viruses aftera virus inactivation process, has a quantification limit of 104 copies.muL-1 (approximately equivalent to 2 lgs) and a detection limit of 103 copies.muL-1 (approximately equivalent to -1 lg) and a minimum detection limit for detecting PRV infection titer of -1 lg, has the sensitivity higher than a traditional CPE method (-0.5 lg), can avoid the influence of subjective factors on judgment of results, and saves time and experiment costs.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
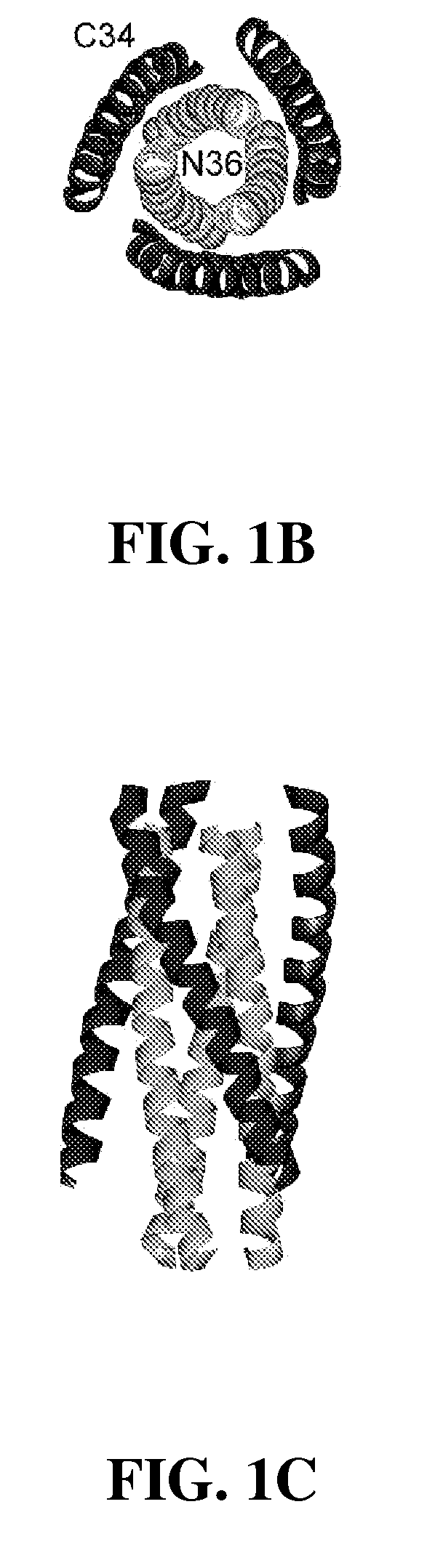
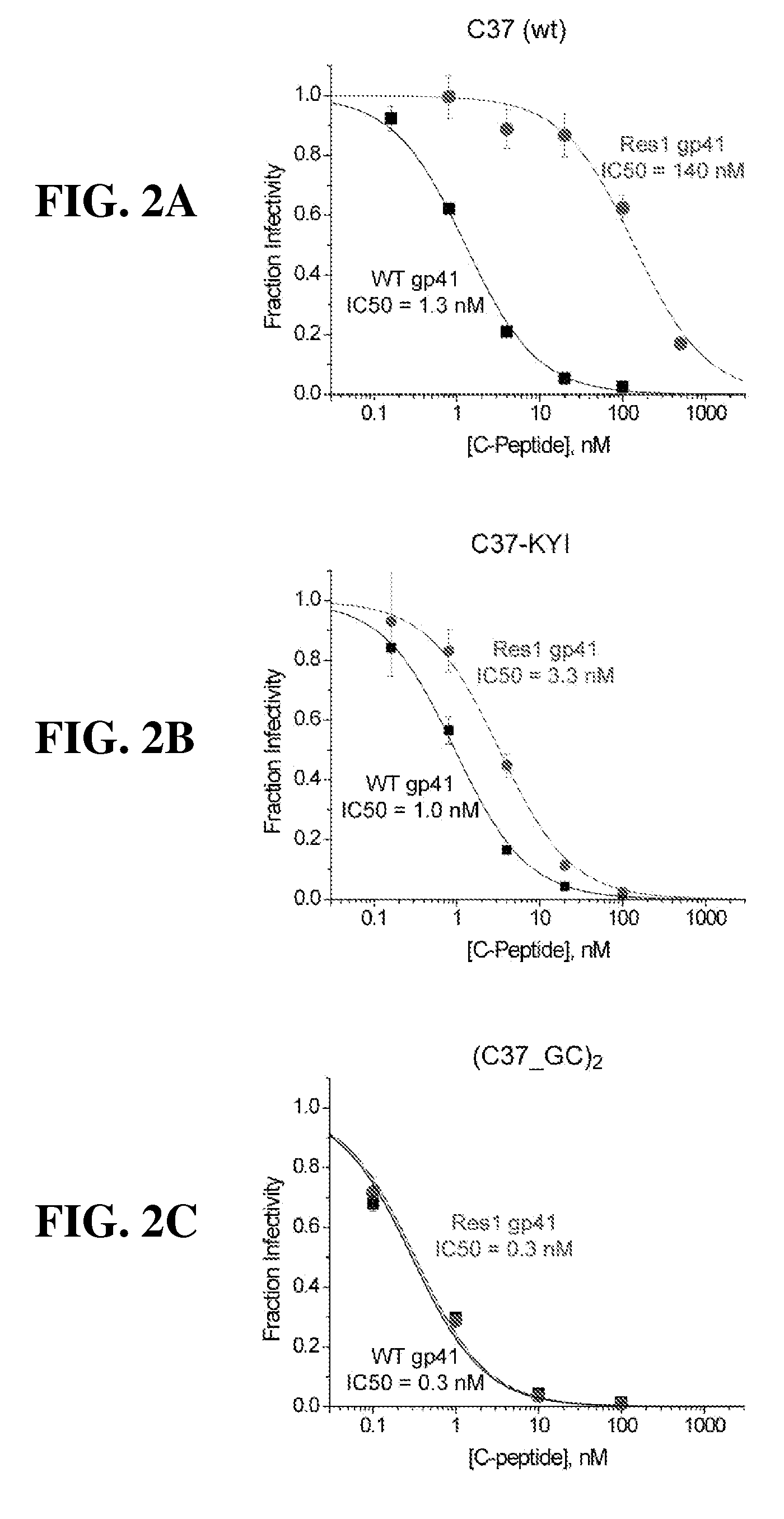
Tighter-binding c-peptide inhibitors of hiv-1 entry
InactiveUS20100029568A1Enhance of HIVSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsC-peptideEntry into host
The invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of HIV infection, inhibition against drug-resistant strains of HIV-1 and methods of enhancing the anti-HIV potency of peptide inhibitors against drug-resistant strains of HIV-1. In particular, oligomeric C-peptide inhibitors for inhibiting HIV entry into host cells are disclosed.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
N-aryl piperidine compounds
The present invention provides N-aryl piperidine compounds having antiinfective activity (i.e., antibacterial, antiviral), their compositions and methods of use. The compounds of the invention prevent the entry of HIV into host cells. More particularly, the compounds are effective at in inhibiting the binding interaction of HIV glycoprotein gp120 and the cell surface receptor CD4. The compounds can be used alone or in combination with other antivirals, antiinfectives, immunomodulators, or HIV entry inhibitors. More particularly, the invention relates to the prevention and treatment of HIV infectivity and AIDS.
Owner:PROPHARMACON
Peptide-based molecules for modulating car expression or accessibility and uses thereof
ActiveUS20180311369A1Reducing CAR-mediated viral infectionGood curative effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsDecoyCoxsackievirus
Peptide-based molecules for modulating expression or accessibility to the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR) are disclosed. Cell-permeable peptide-based molecules having a PDZ-decoy domain or PDZ-binding domain are used to modulate the expression or accessibility of CAR molecules, thereby affecting the ability of viral molecules, or molecules containing viral sequences or proteins able to bind CAR, to enter host cells.
Owner:WRIGHT STATE UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of carrier for gene transfer
InactiveCN101284134BGood biocompatibilityNo side effectsGenetic material ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsGene deliverySide effect
The invention relates to a carrier for gene delivery, gelatin-siloxane hybrid nano-material, a preparation method thereof by two-step sol-gel reaction and an application thereof. The gelatin-siloxane nano-particles are prepared from gelatin and 3-(2,3-epoxy propoxy )propyltrimethoxysilicane by performing chemical combination and hydrolytic reaction in acidic condition to obtain sol; and adjustingthe pH value to slightly alkaline for performing polymerization reaction of silicane. The gelatin-siloxane hybrid nano-material has good biocompatibility, no toxic and side effect, and high stability; and is combined with exogenous gene to realize DNA transportation and expression, with high transduction efficiency, no immunogenicity, and no cytotoxicity. The size of the transferable exogenous gene is of several tens bp to several thousands kb, which overcomes size restriction to viral vector inserting into the exogenous gene. Thus the exogenous gene can be effectively carried into a host cell for performing effective transfection and expression.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Novel mechanism for hiv-1 entry into host cells and peptides inhibiting this mechanism
InactiveUS20060234208A1Enhances virus entry into permissive cellsNovel mechanismBiocideCompound screeningHiv diseaseVirus strain
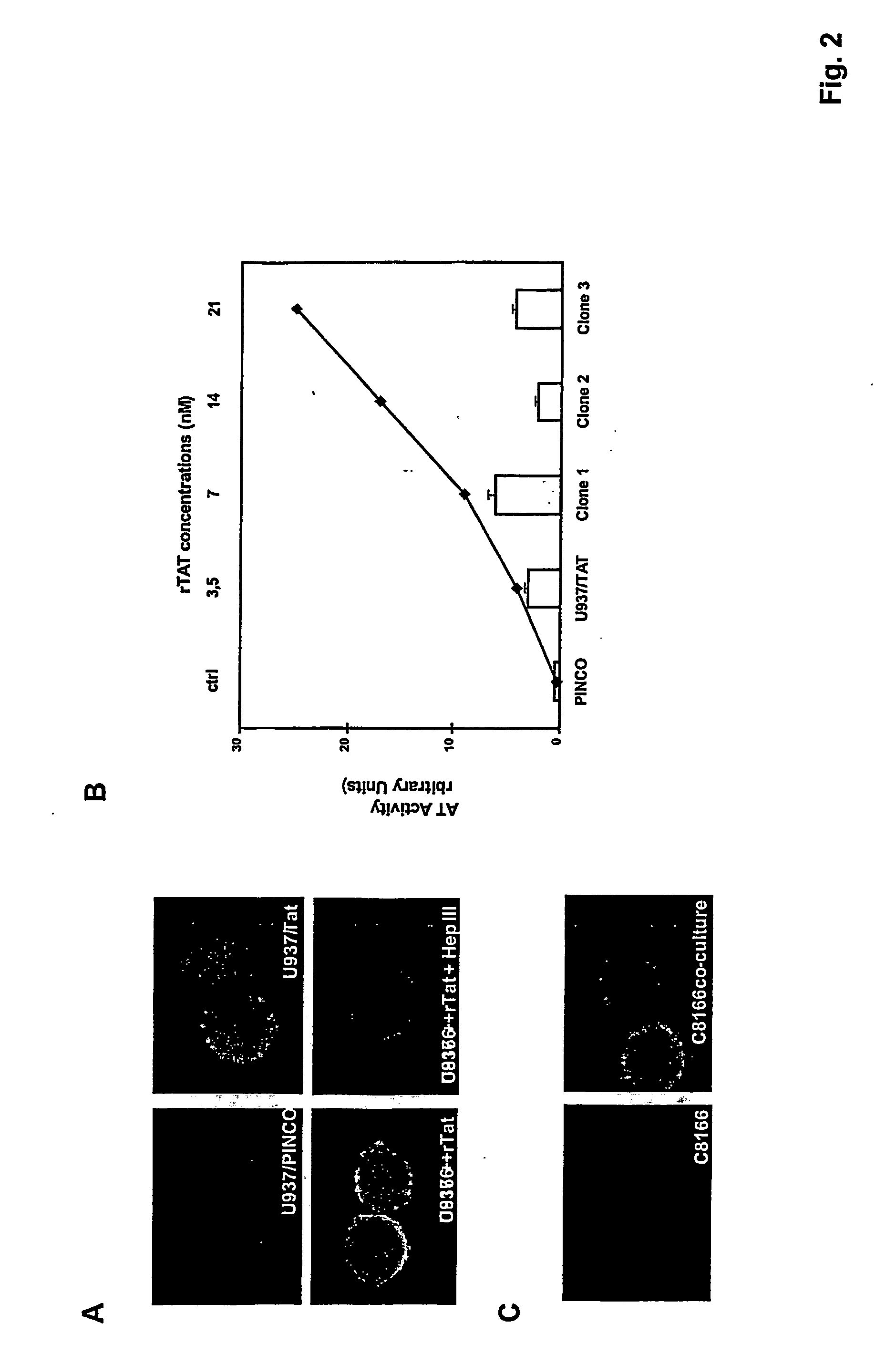
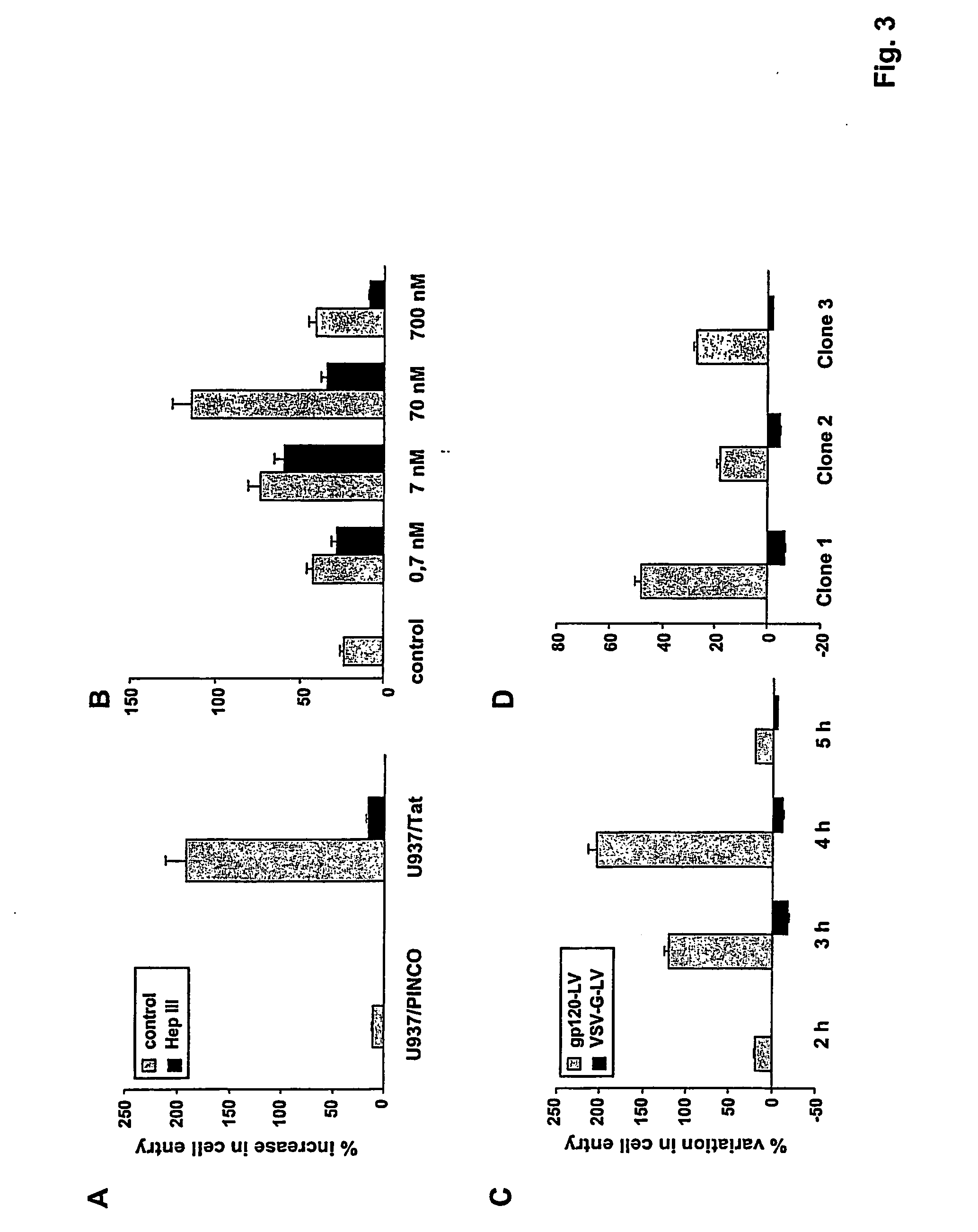
This invention relates to the finding that TAT interacts with gp120 at the cell surface and enhances HIV-1 entry into host cells. This invention also discloses modulators of this interaction, particularly peptides that mimic the region of gp120 involved in this interaction. These peptides interfere with TAT-mediated enhancement of infection regardless of virus strain, and are therefore suitable for the development in general of broad-range drugs against AIDS and other infectious diseases induced by HIV-1 related pathogens, and specifically for a class of chemicals active in the reduction or abrogation of virus and infectivity spreading.
Owner:CREABILIS THERAPEUTICS SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com