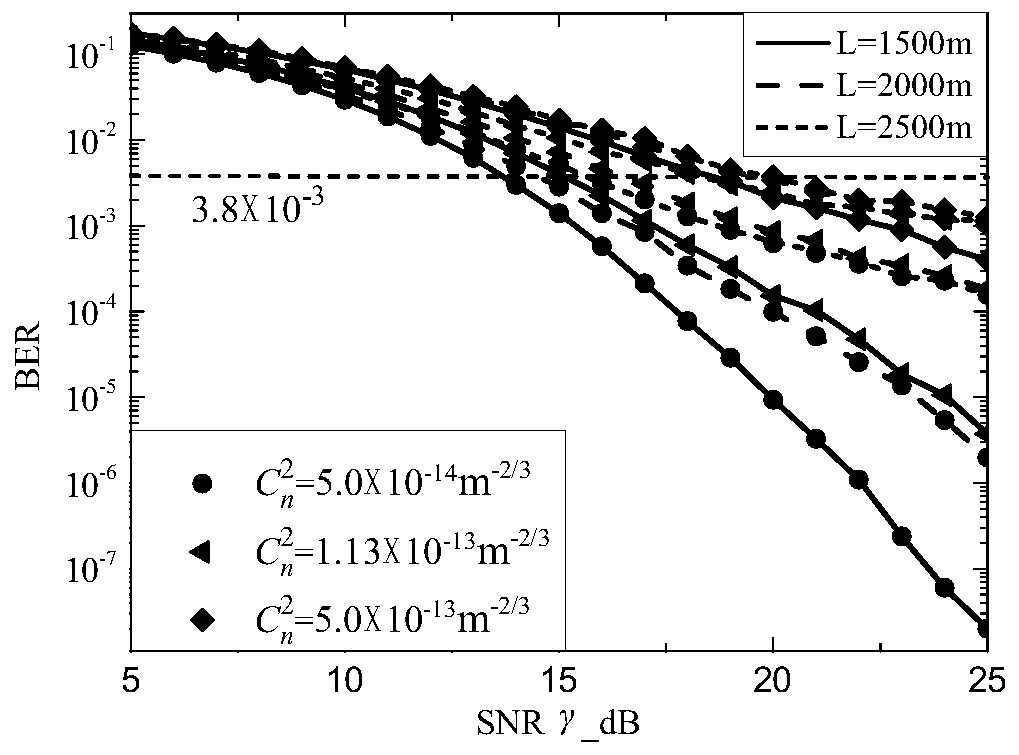
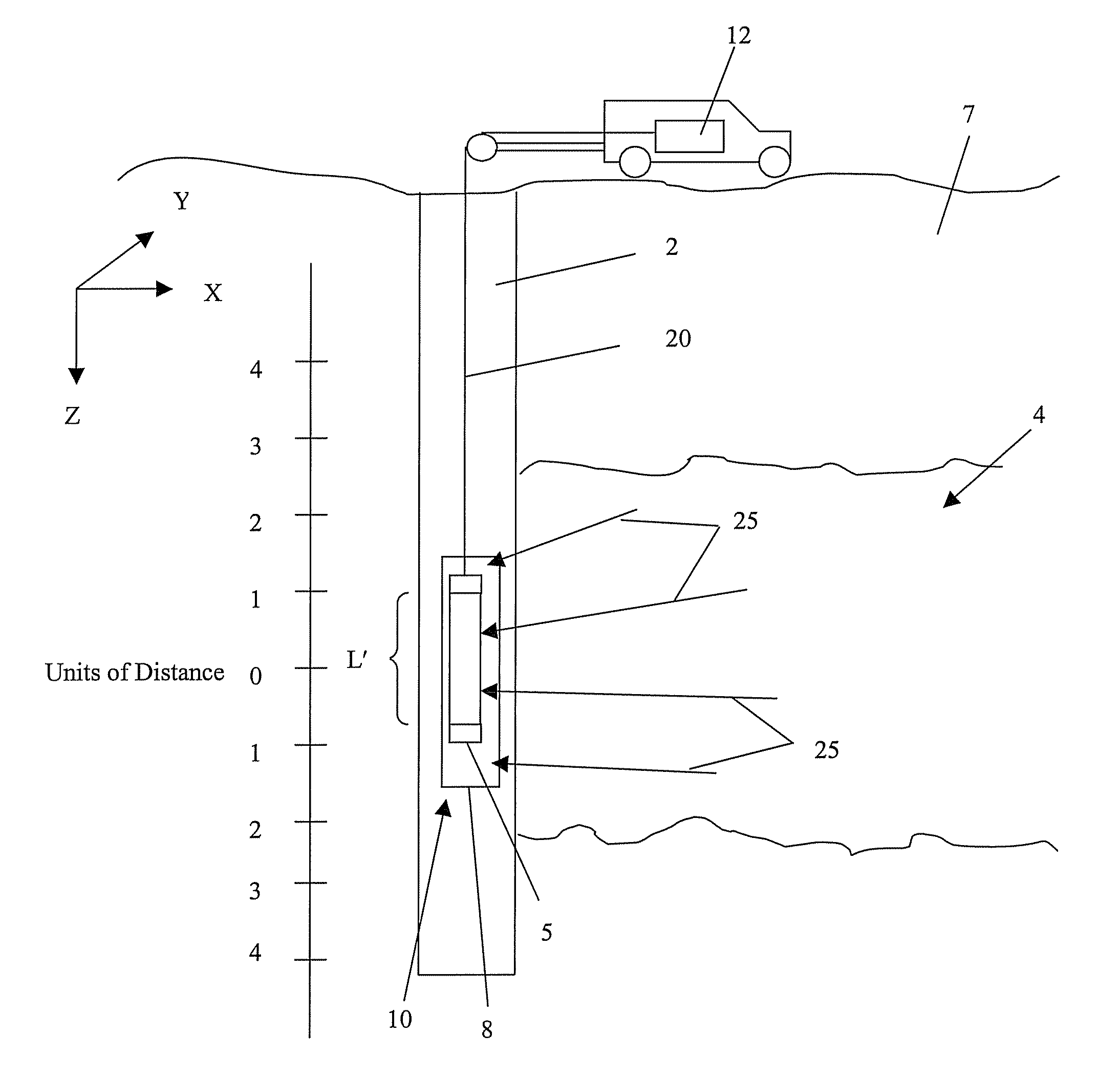
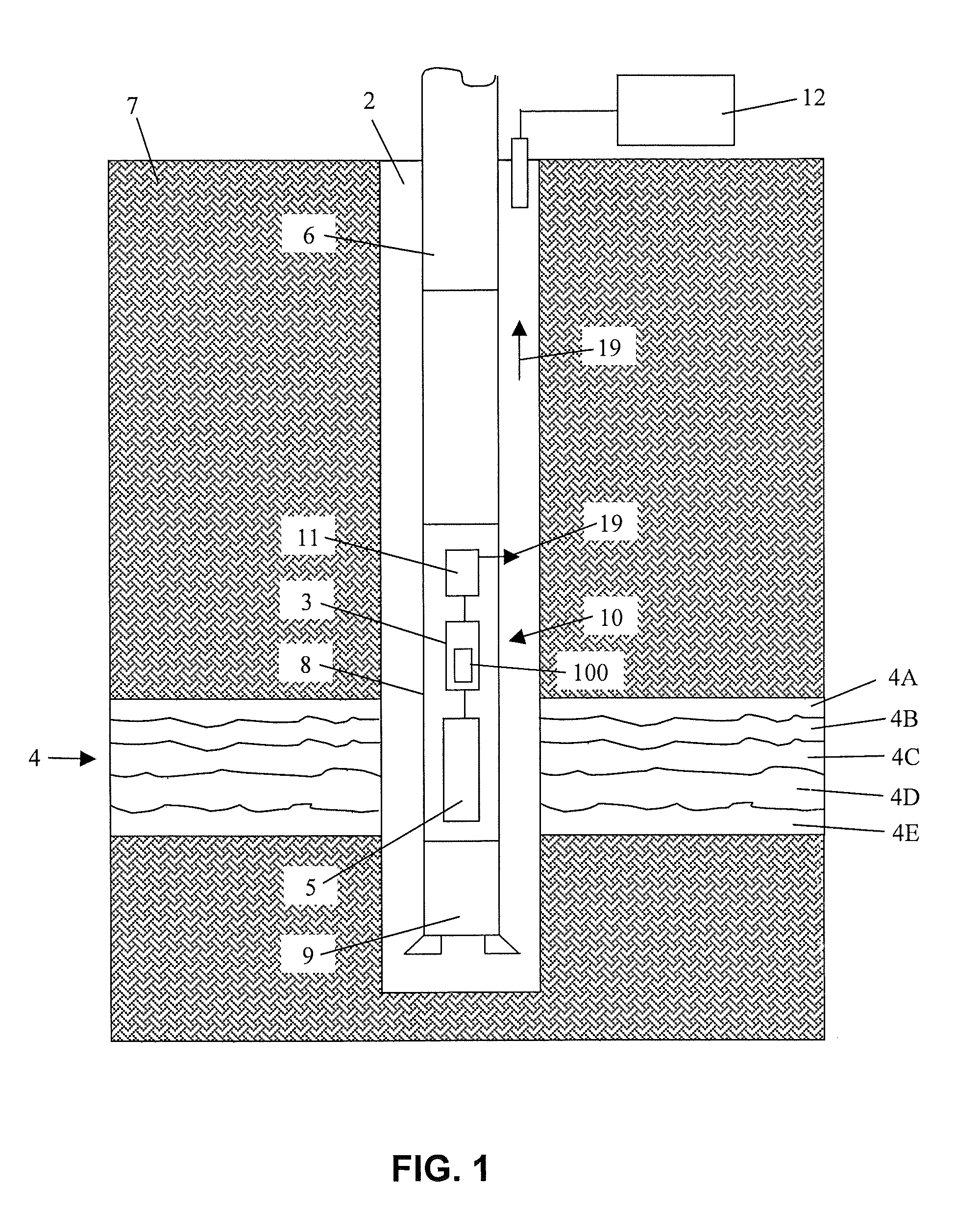
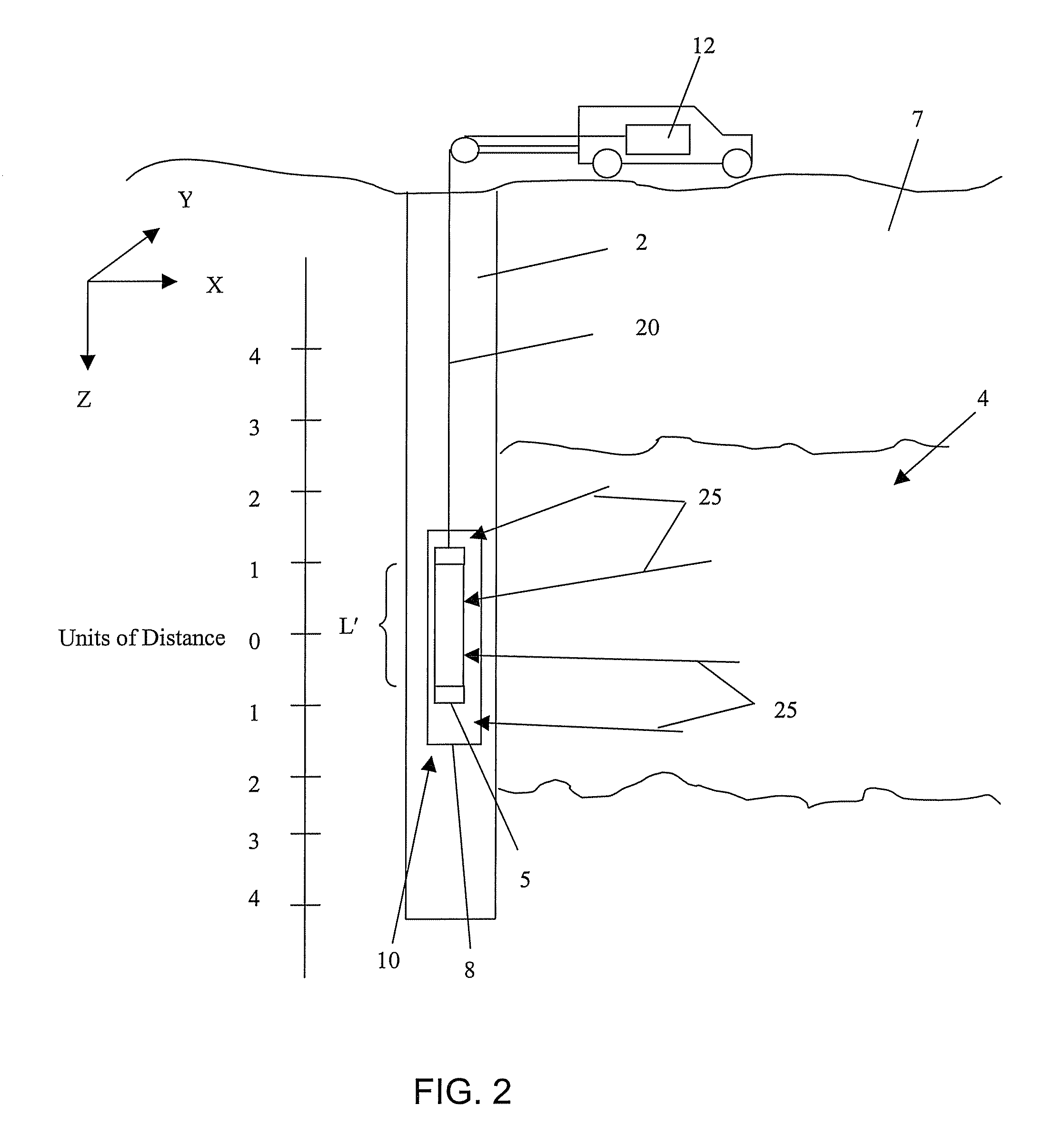
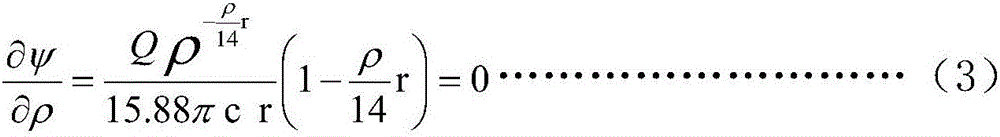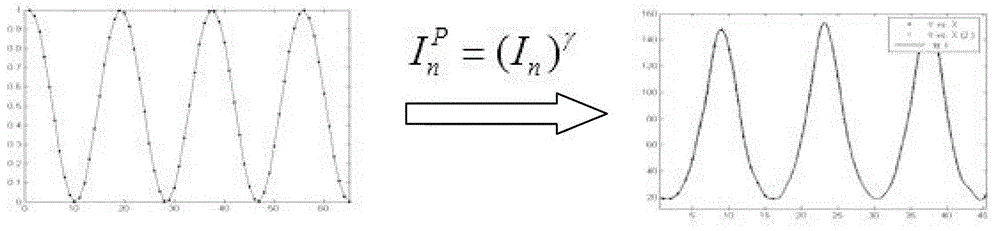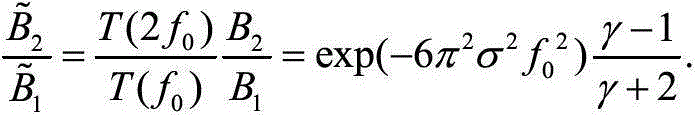Patents
Literature
34 results about "Gamma gamma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
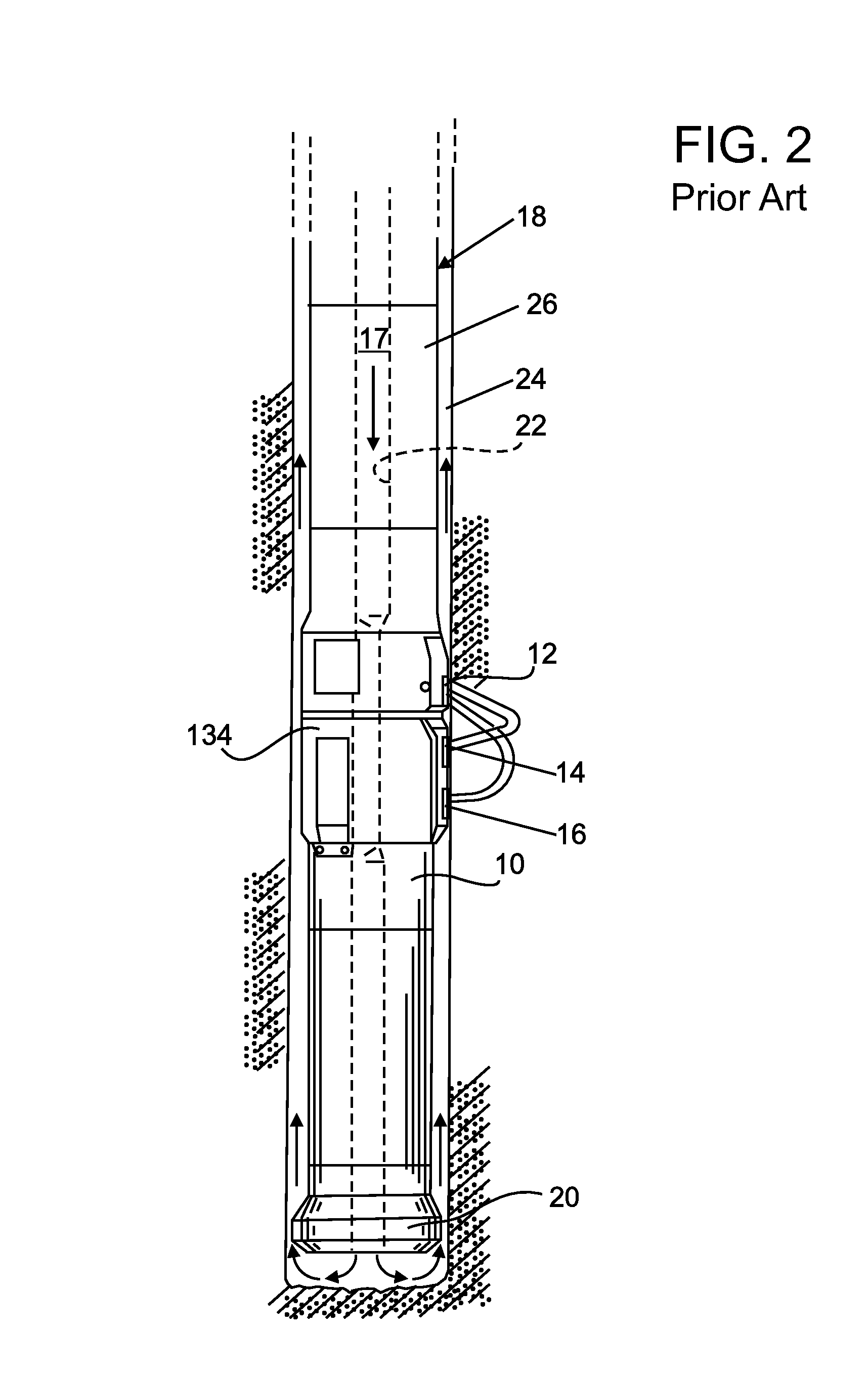
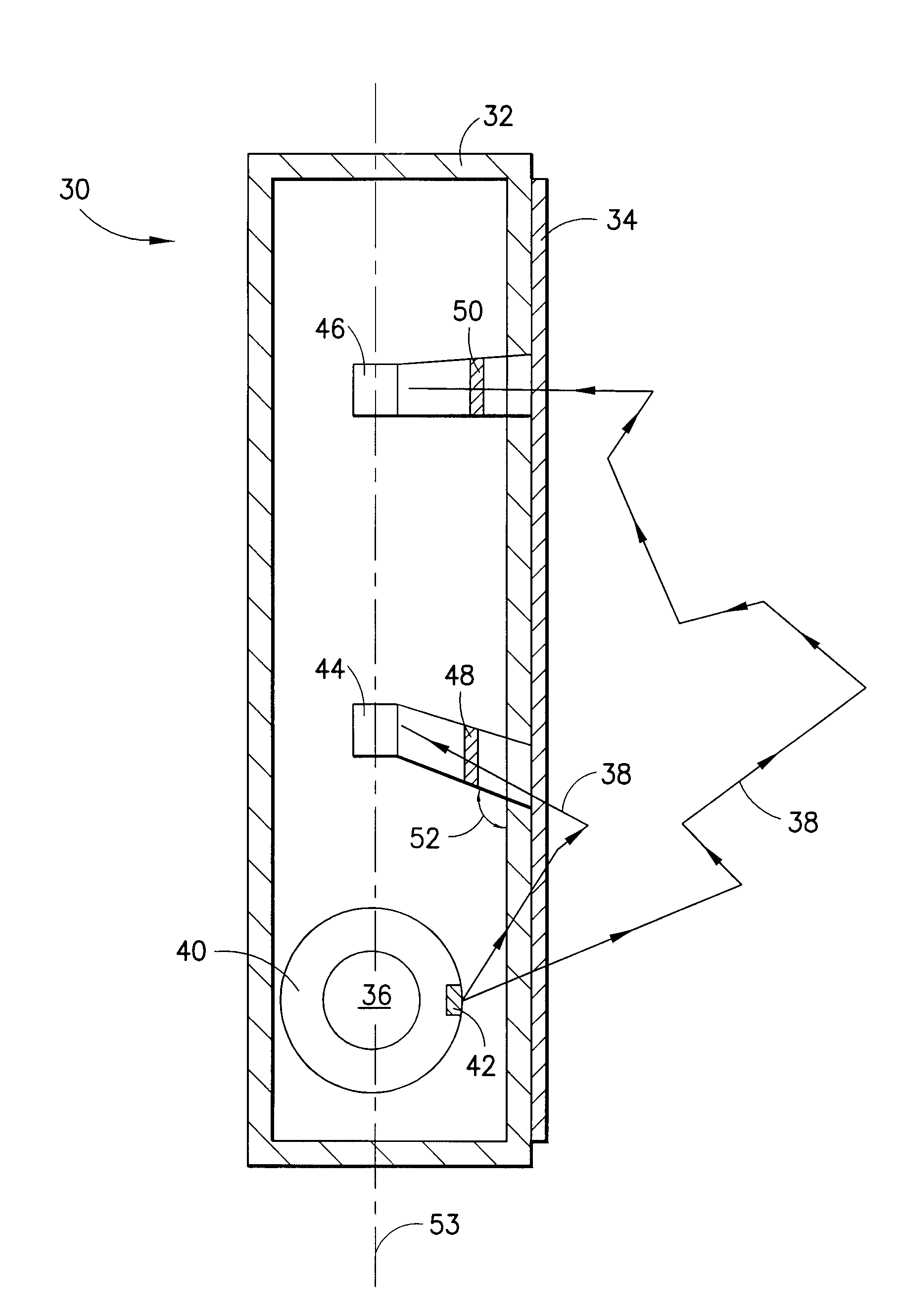
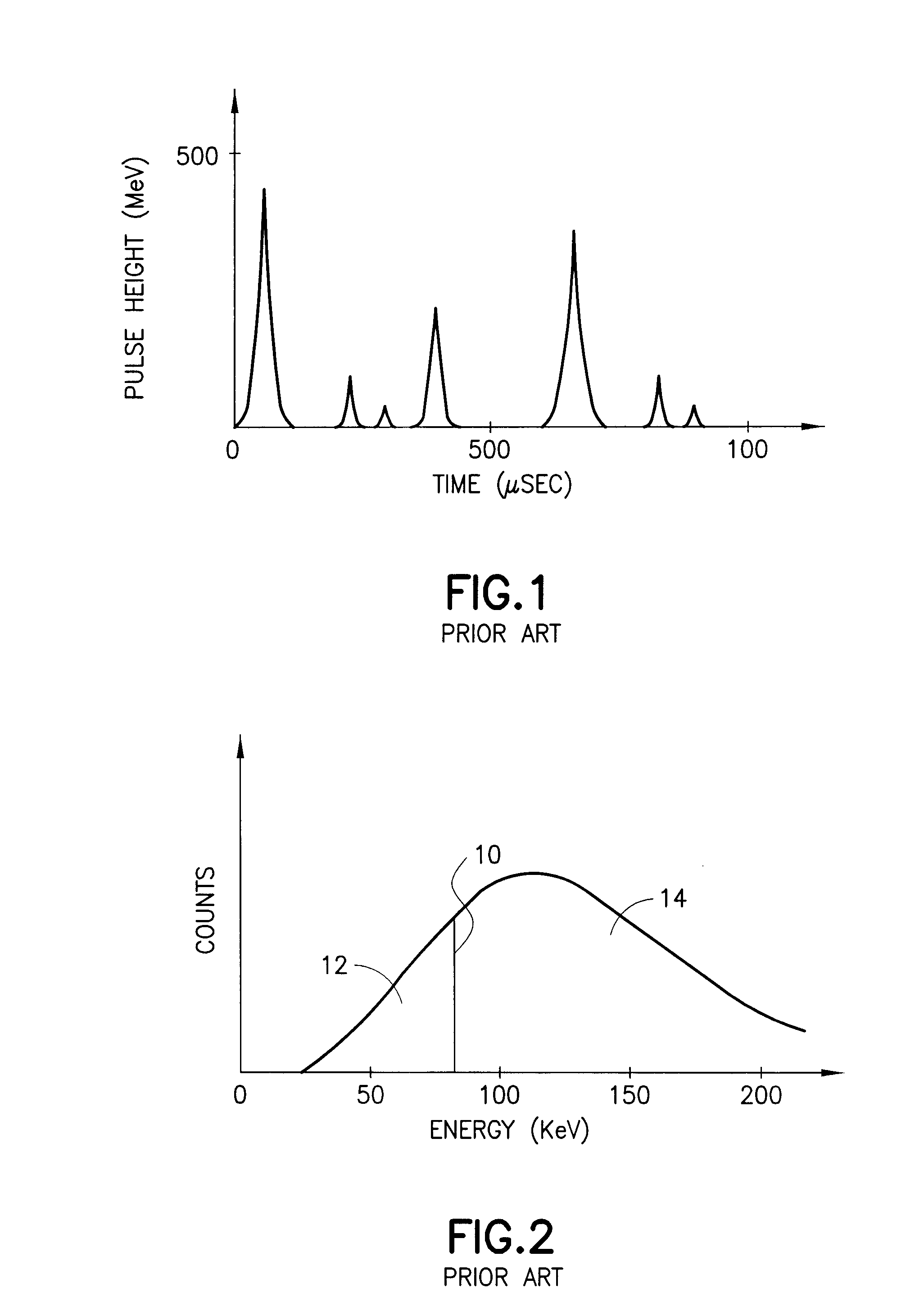
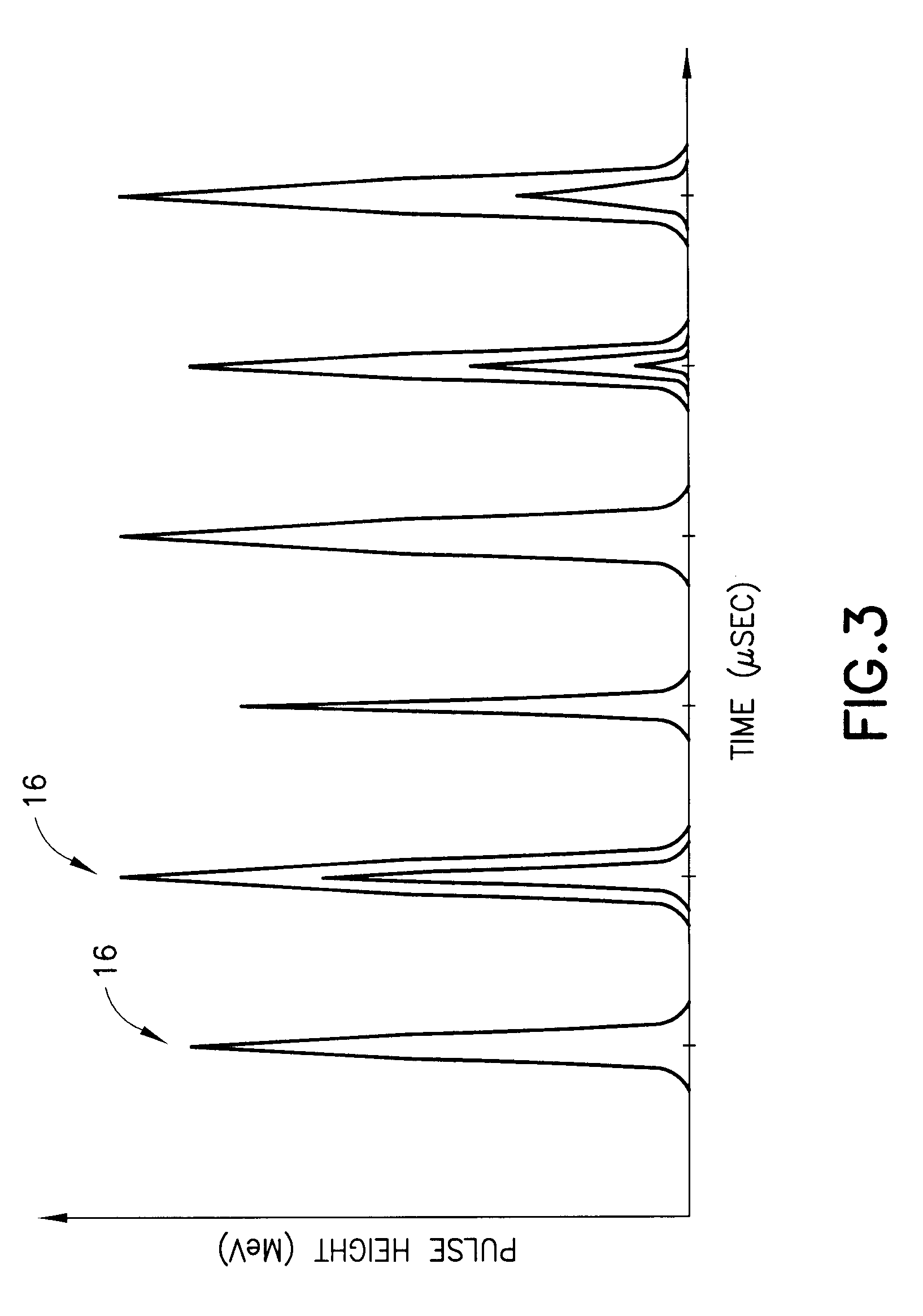
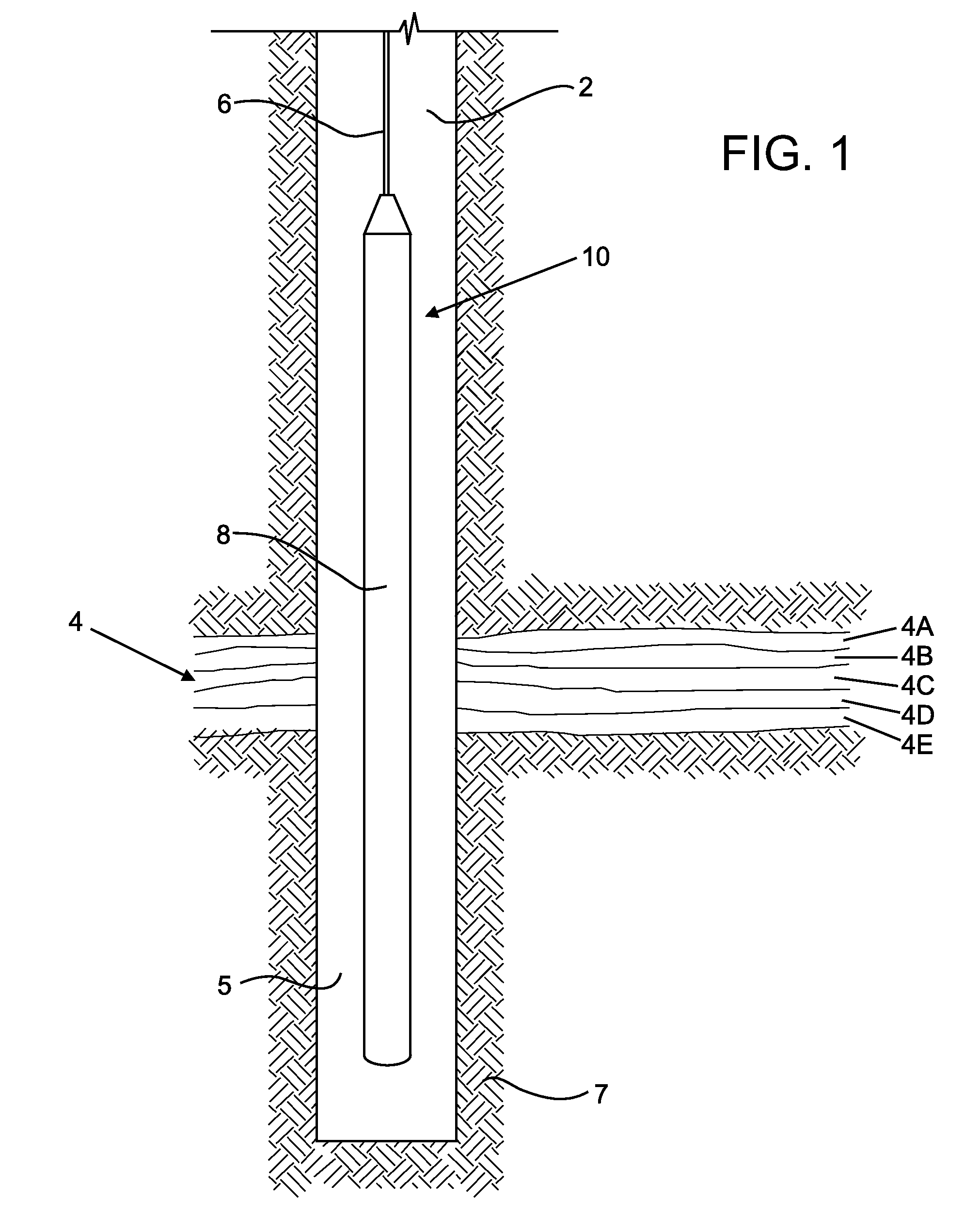
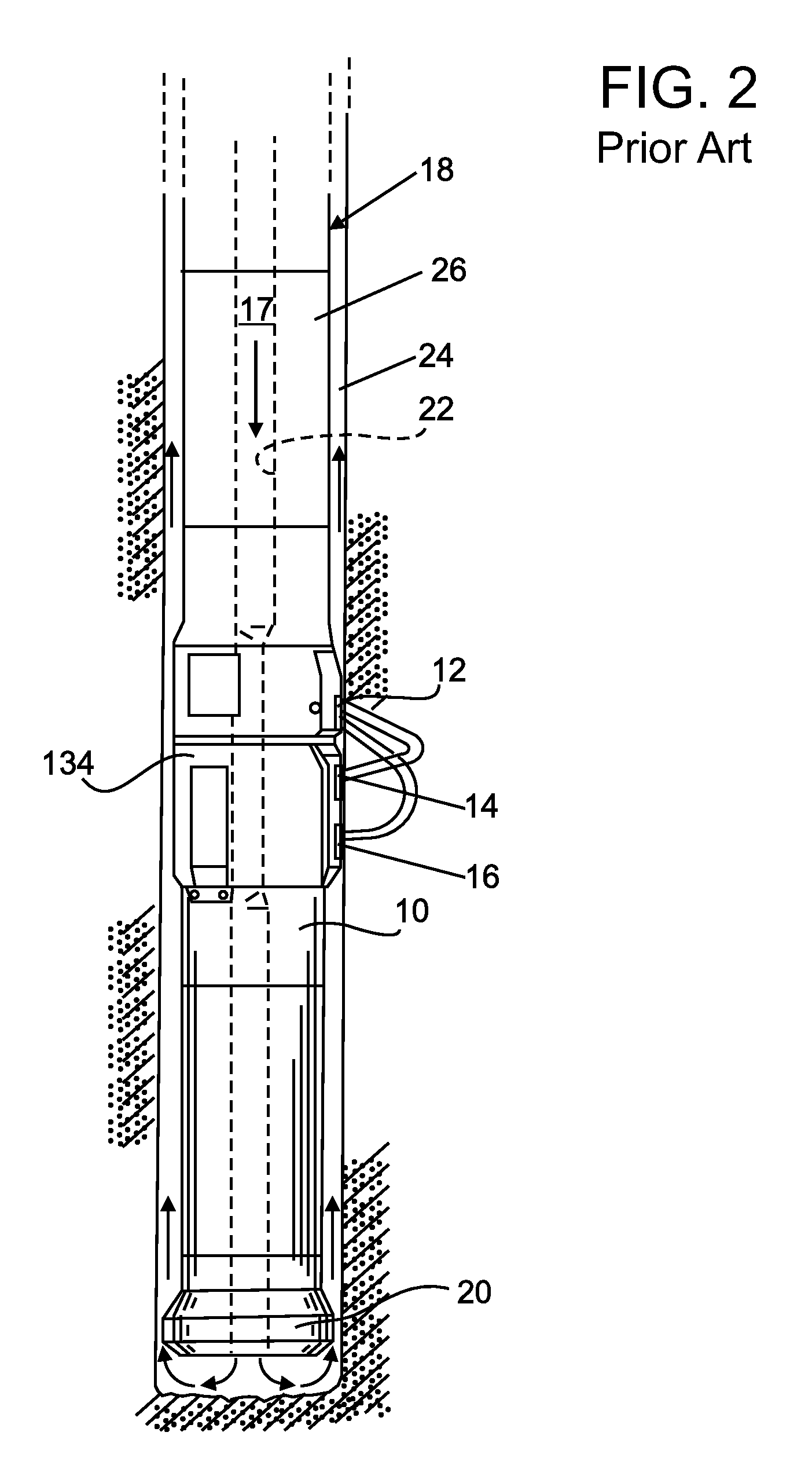
Gamma-ray camera system
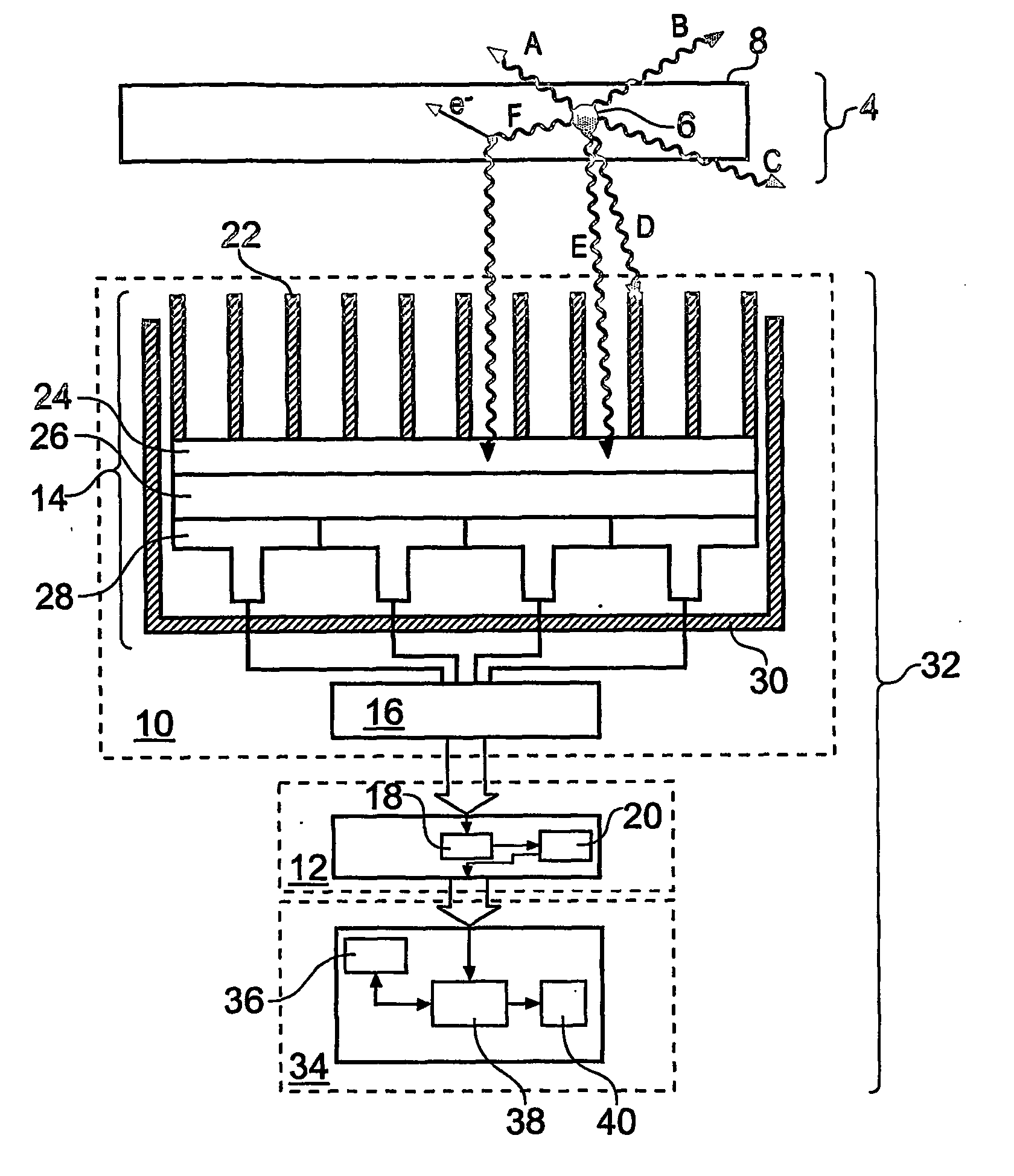
InactiveUS20060180767A1Improved energy resolutionEnhance the imageMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementEnergy windowGamma ray
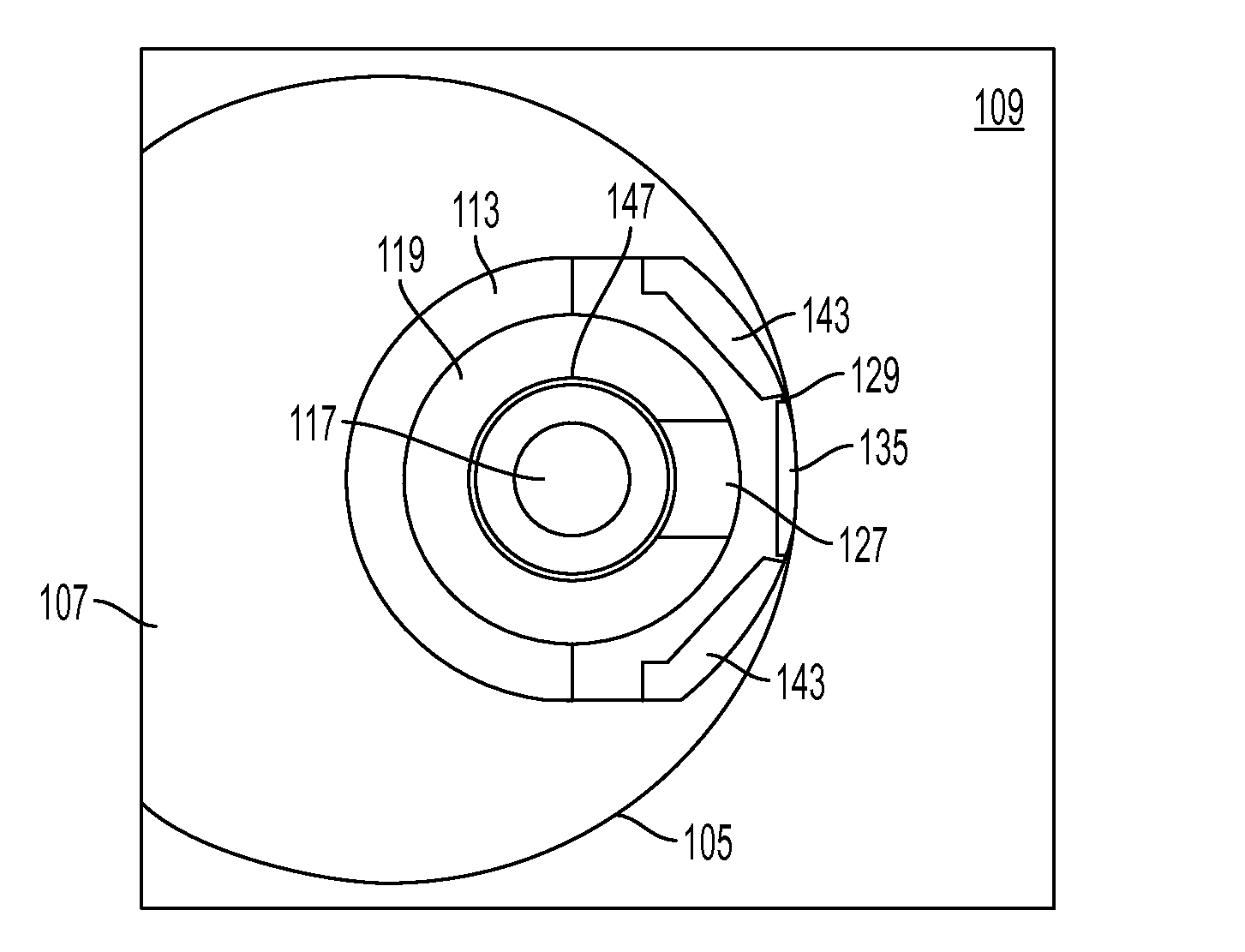
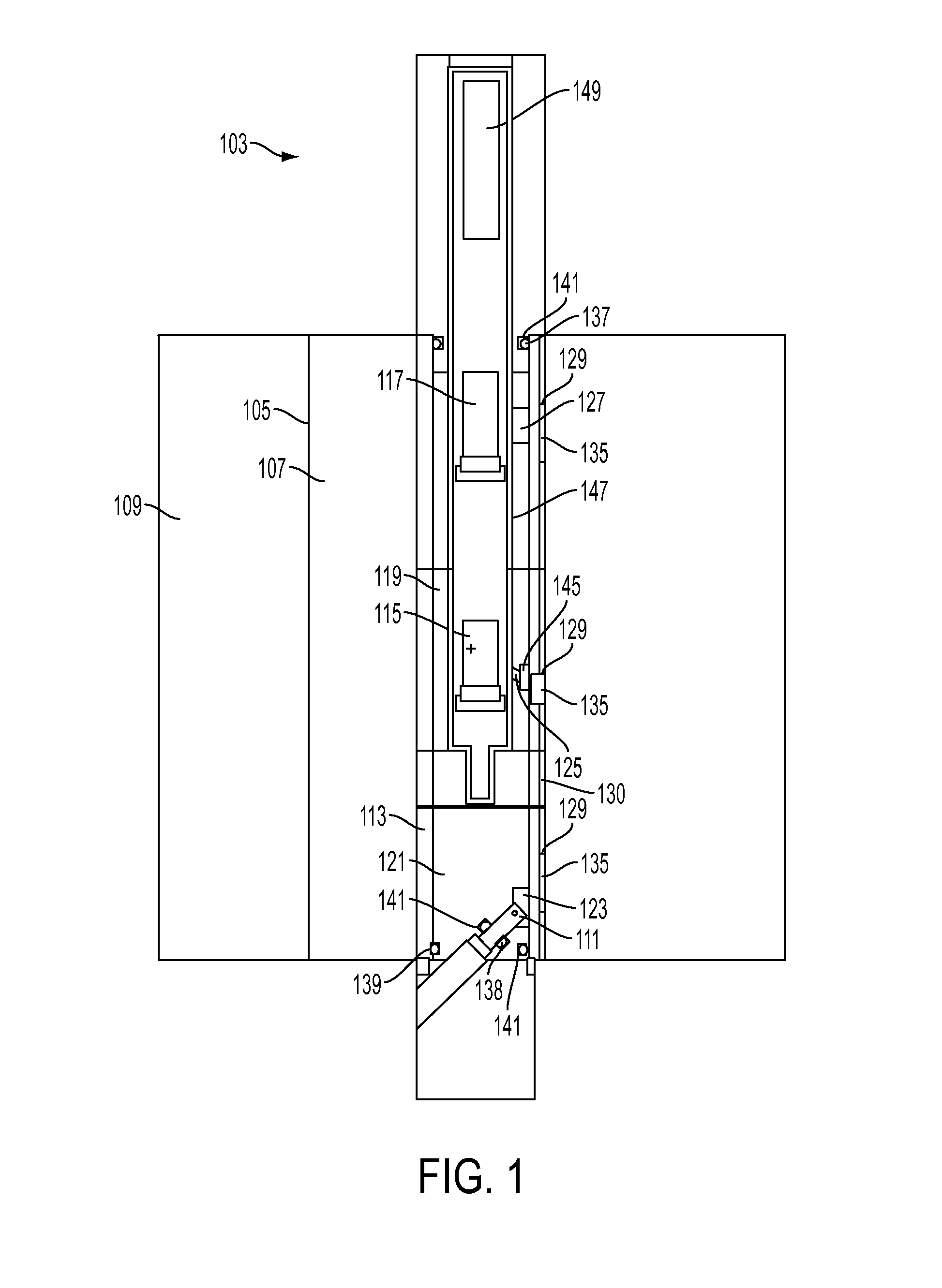
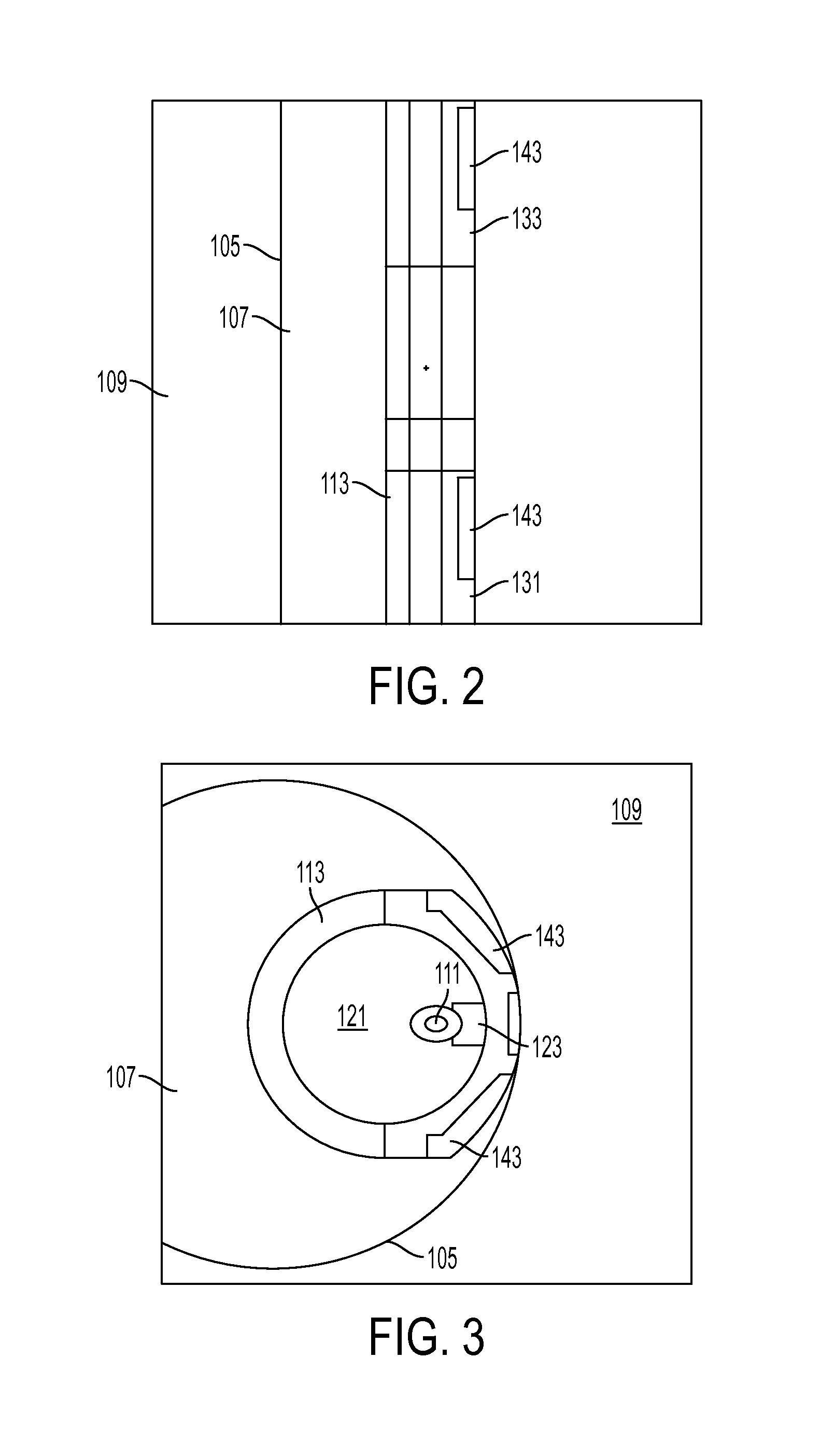
A scintillator crystal (26)=based gamma-ray camera system is described. The gamma-ray camera system includes a spectra processing component for (34) providing improved energy resolution over that seen in conventional gamma-ray camera systems. The spectra processing component operates to deconvolve detector response functions from observed energy spectra on a pixel by pixel basis. The pixel dependent to detector response functions are obtained by a combination of theoretical simulation, and empirical calibration. By deconvolving pixel specific detector response functions, variations in response of a gamma-ray camera system across its image plane can be accounted for. This offers significant improvements in energy resolution and many of the problems associated with conventional gamma-ray camera systems are reduced. For example, the improved energy resolution allows better rejection of photons associated with Compton scattering events occurring in a source being imaged. This is because a narrower energy window filter can be used without rejecting a significant fraction of non-Compton scattered photons. The spectra processing component can be easily implemented with different types of gamma-ray imagers, for example Anger-type cameras, and may also be retroactively fitted to existing gamma-ray camera systems.
Owner:SYMETRICA
Novel system and method of measuring concentration of radon in water
InactiveCN108802793AQuick measurementReduce measurement backgroundX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentCounting rateActivity concentration
The invention discloses a novel system and method of measuring concentration of radon in water. The novel system of measuring concentration of radon in water includes successively connected first Gamma detector, first linear amplifier, first single-channel pulse-height analyzer, first delay shaping circuit and first scaler, and successively connected second Gamma detector, second linear amplifier,second single-channel pulse-height analyzer, second delay shaping circuit and second scaler, wherein the output terminal of the first delay shaping circuit and the output terminal of the second delayshaping circuit are connected to the input terminal of a coincidence circuit; the coincidence output terminal of the coincidence circuit is connected with a third scaler; the novel system of measuring concentration of radon in water also includes a calculation module which is used for calculating the activity concentration C<222><Rn>: C<222><Rn>=n<Gamma Gamma 1> - n) / V<Elipson> <Gamma Gamma>of 222Rn in a sample to be measured, wherein n<Gamma Gamma 1> is the counting rate of the third scaler during the process of measuring the sample to be measured; n is the background counting rateof the third scaler; V is the volume of the sample to be measured; and Epsilon <Gamma Gamma> is the detection efficiency of a coincidence channel. The novel system and method of measuring concentration of radon in water can quickly reduce the measurement background and can achieve the effect of quickly and accurately measuring the concentration of radon in water.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
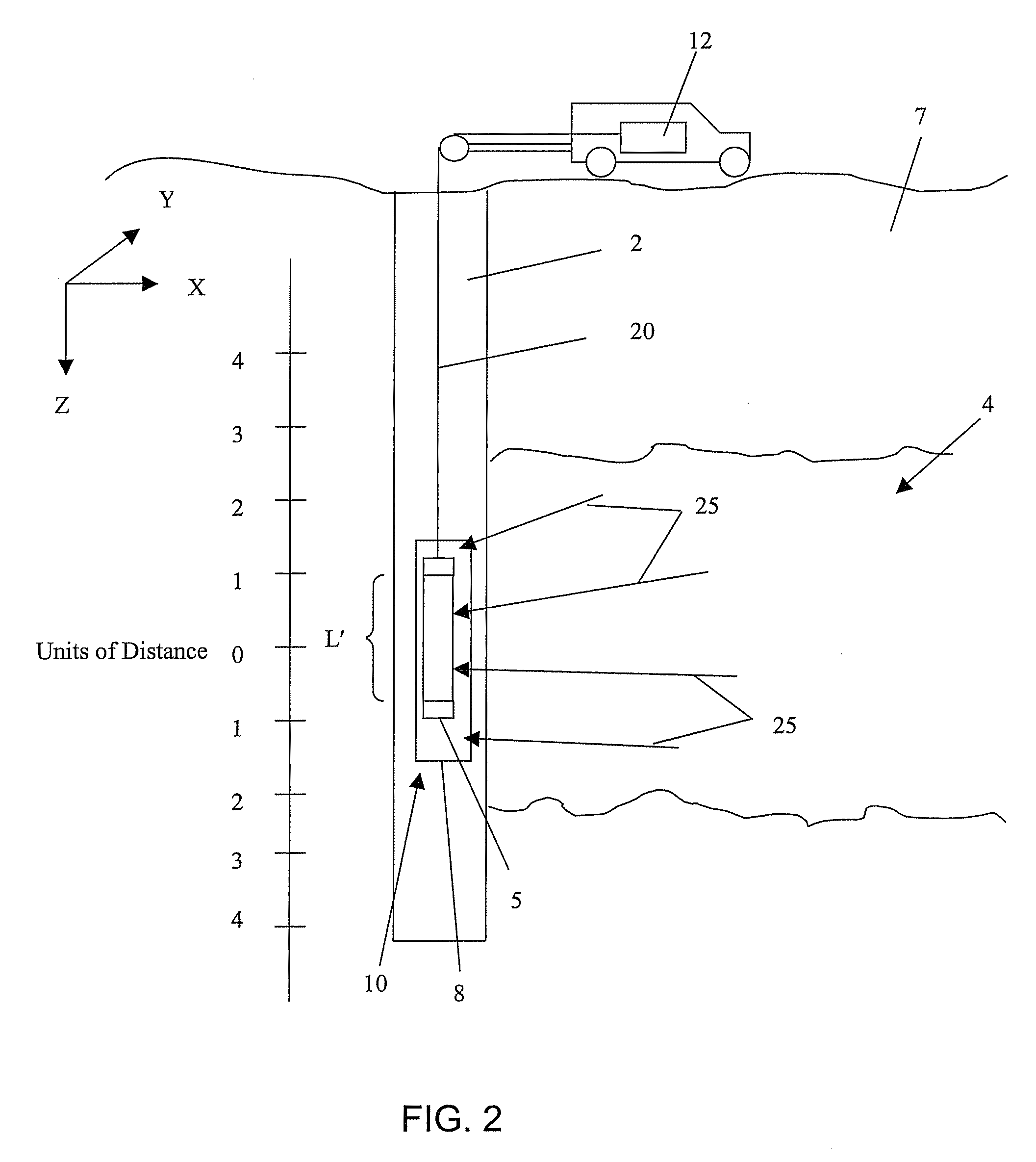
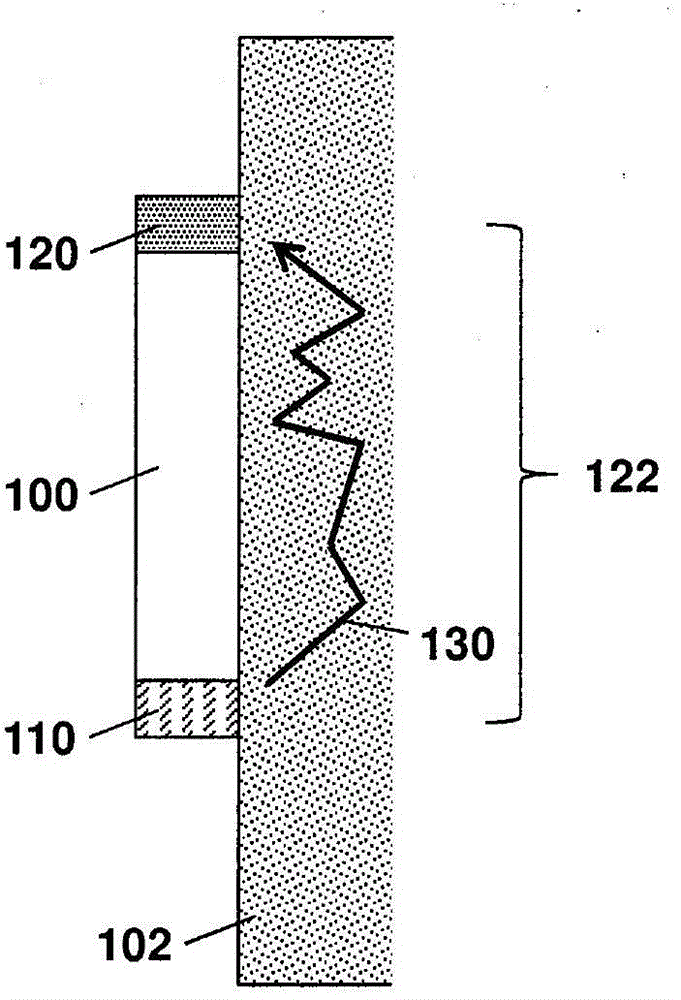
Gamma-gamma density measurement system for high-pressure, high-temperature measurements
InactiveUS20110204216A1Easy to replaceAccurate, precise density and photoelectric factor measurementsNuclear radiation detectionUltrasound attenuationGamma ray
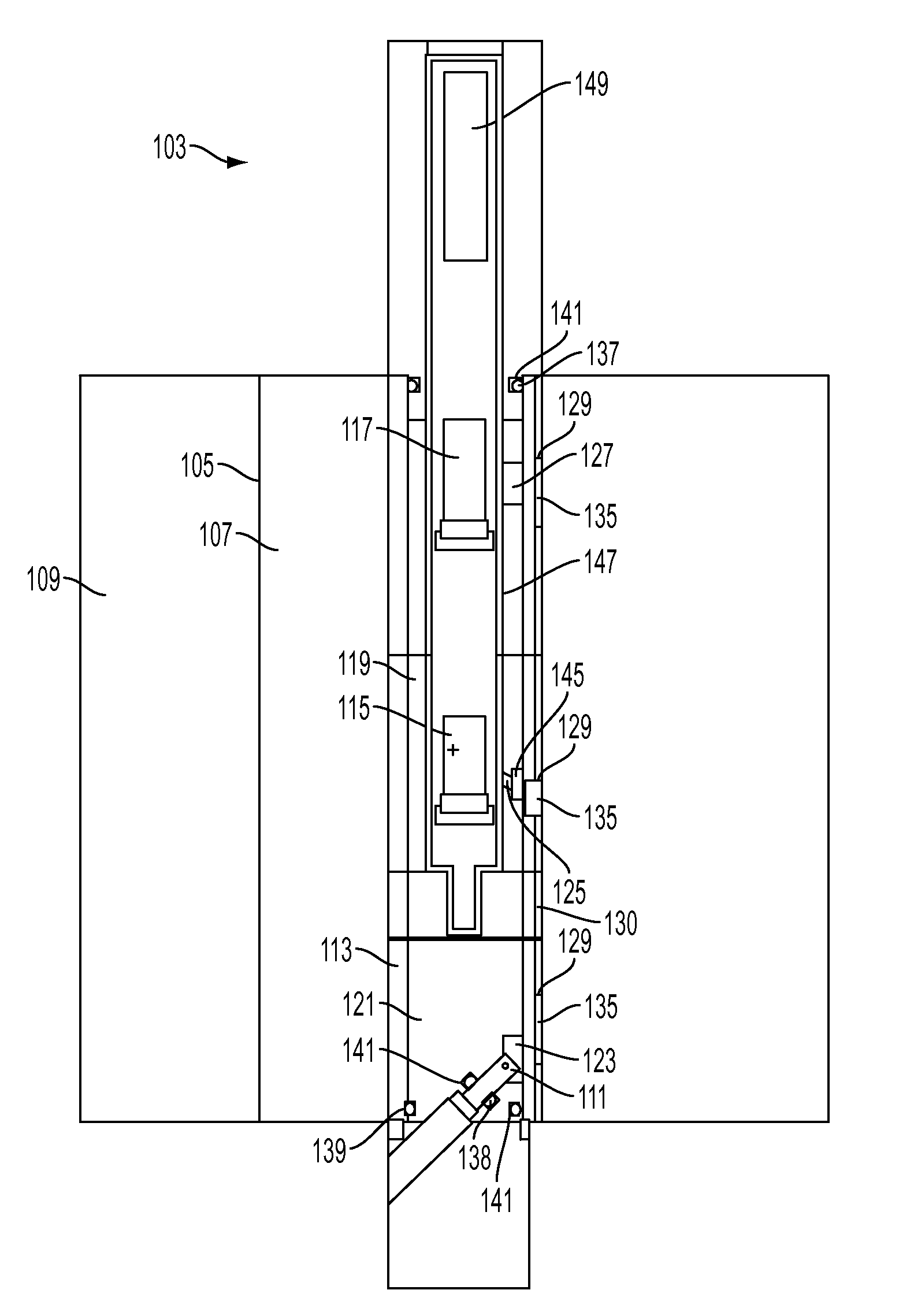
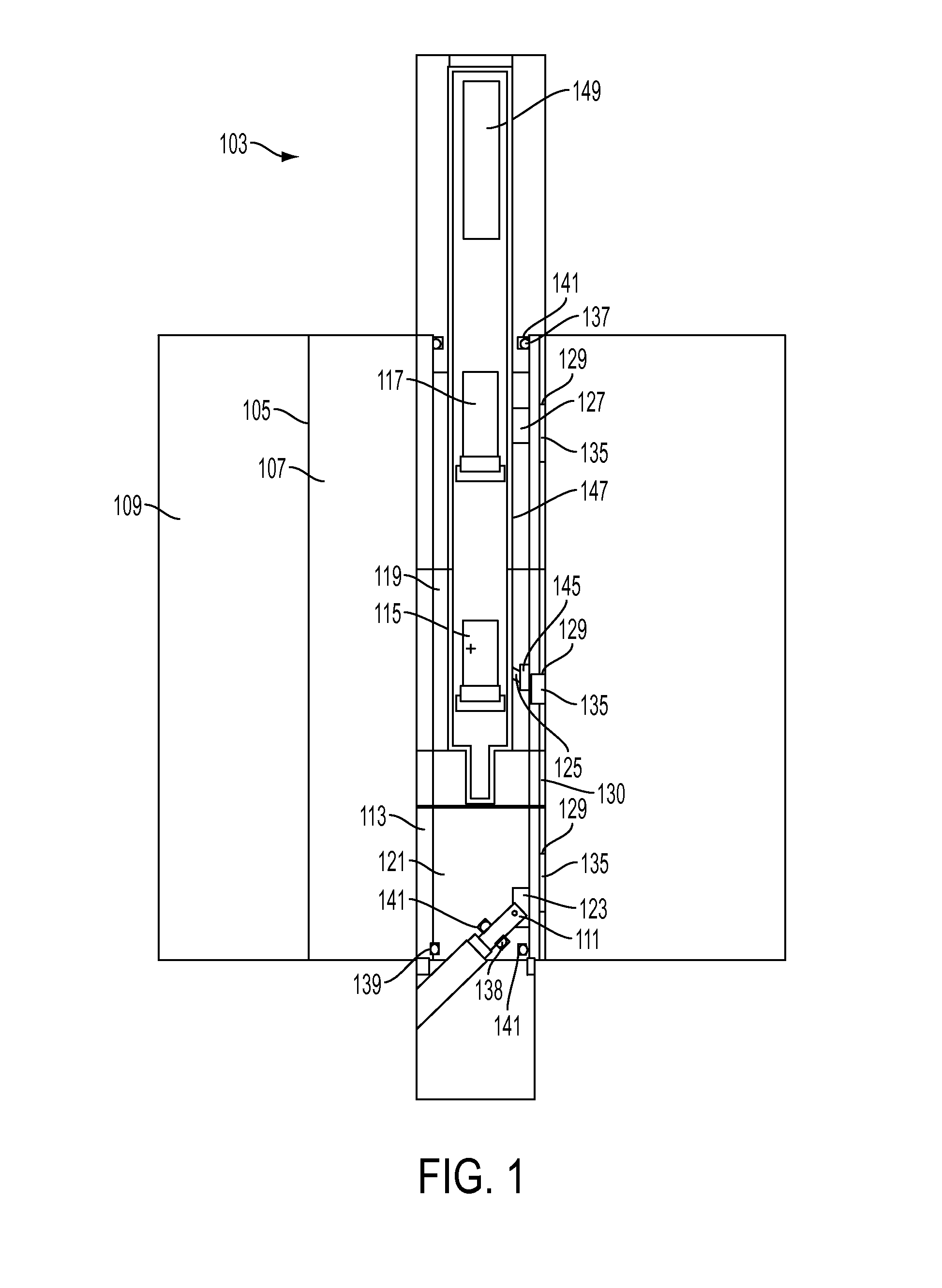
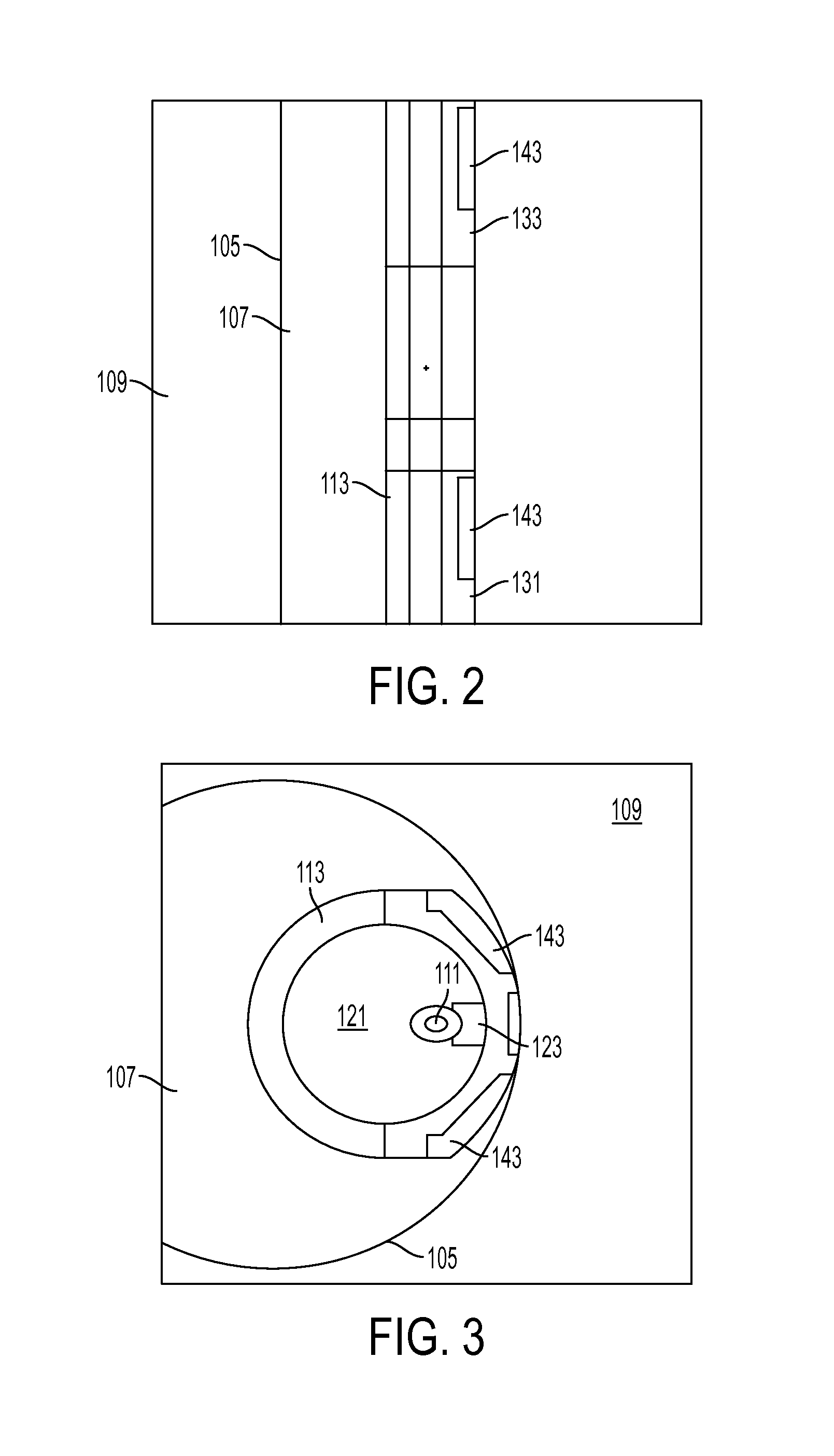
A downhole gamma ray density measurement system is described. The gamma ray density measurement system includes a pressure housing and a gamma ray source within the pressure housing. One or more detectors within the pressure housing detect gamma radiation. One or more low-attenuation inserts may be located in the pressure housing near the gamma ray source and / or one or more of the detectors. One or more high-attenuation inserts may be located in the pressure housing near the gamma ray source and / or one or more of the detectors.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
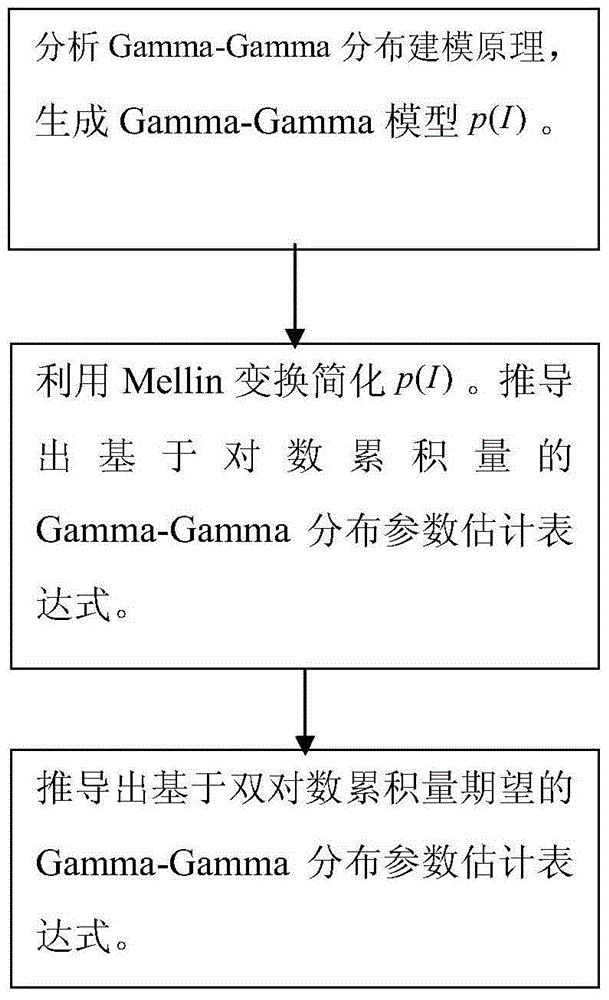
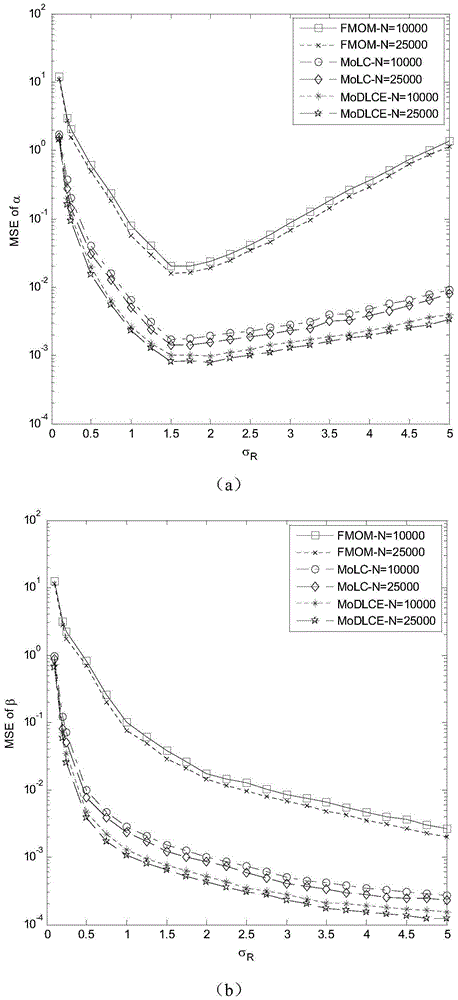
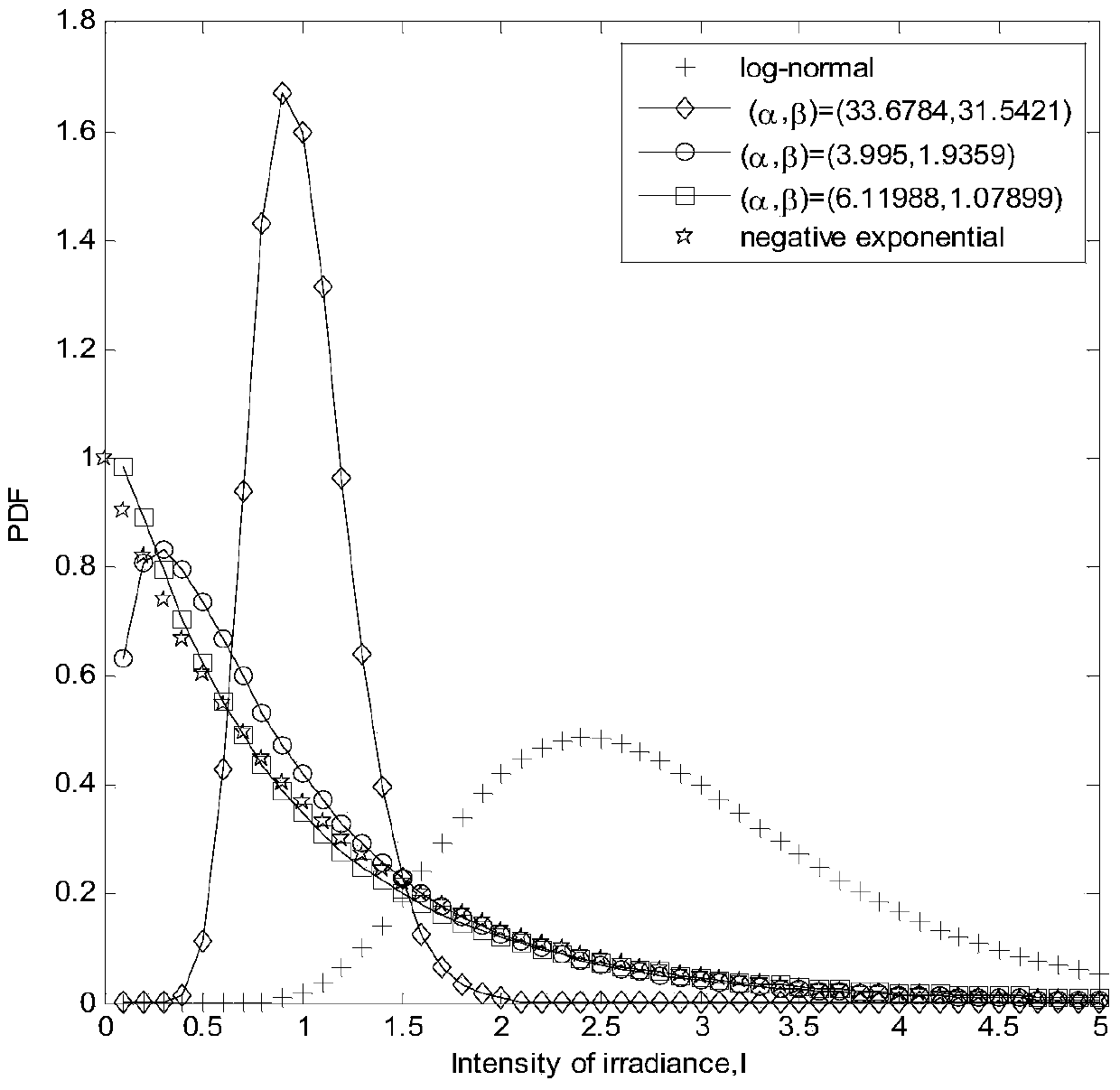
Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation method based on double logarithmic cumulant expectation
ActiveCN105743593AImprove estimation accuracyImprove computing efficiencyTransmission monitoringFree-space transmissionAlgorithmEstimation methods
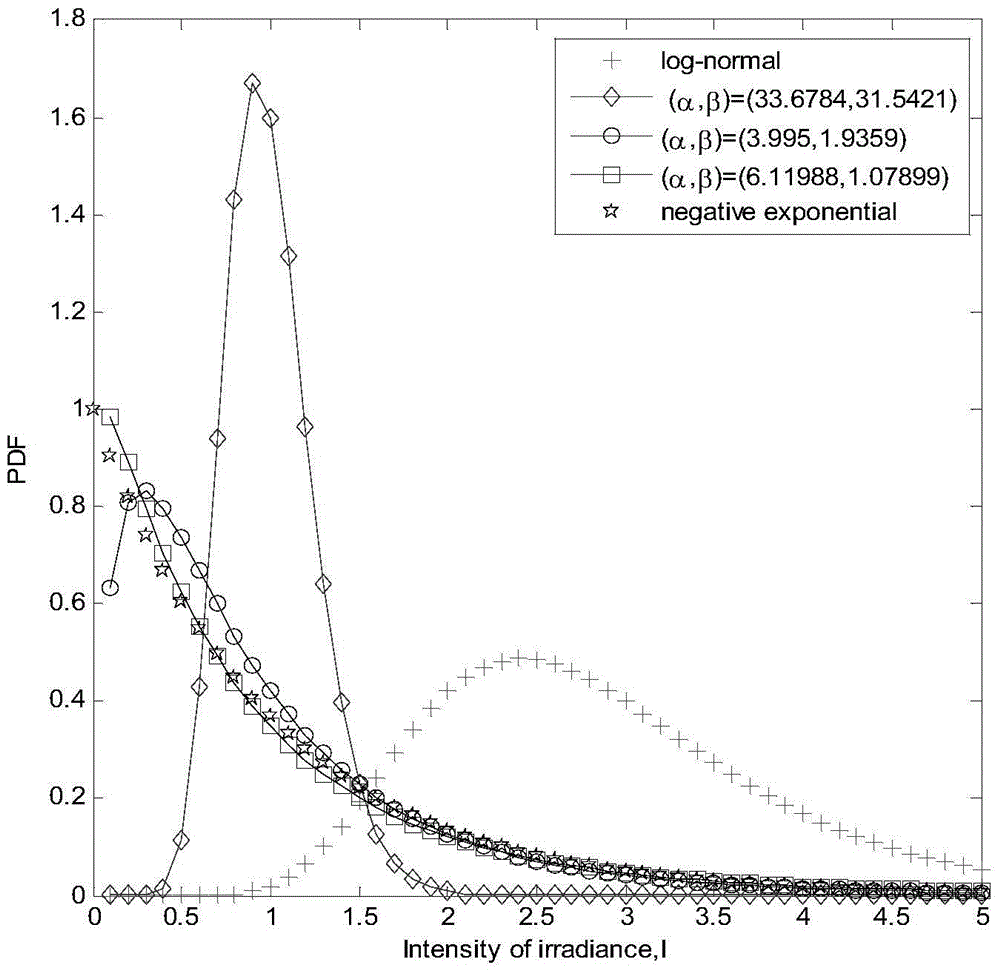
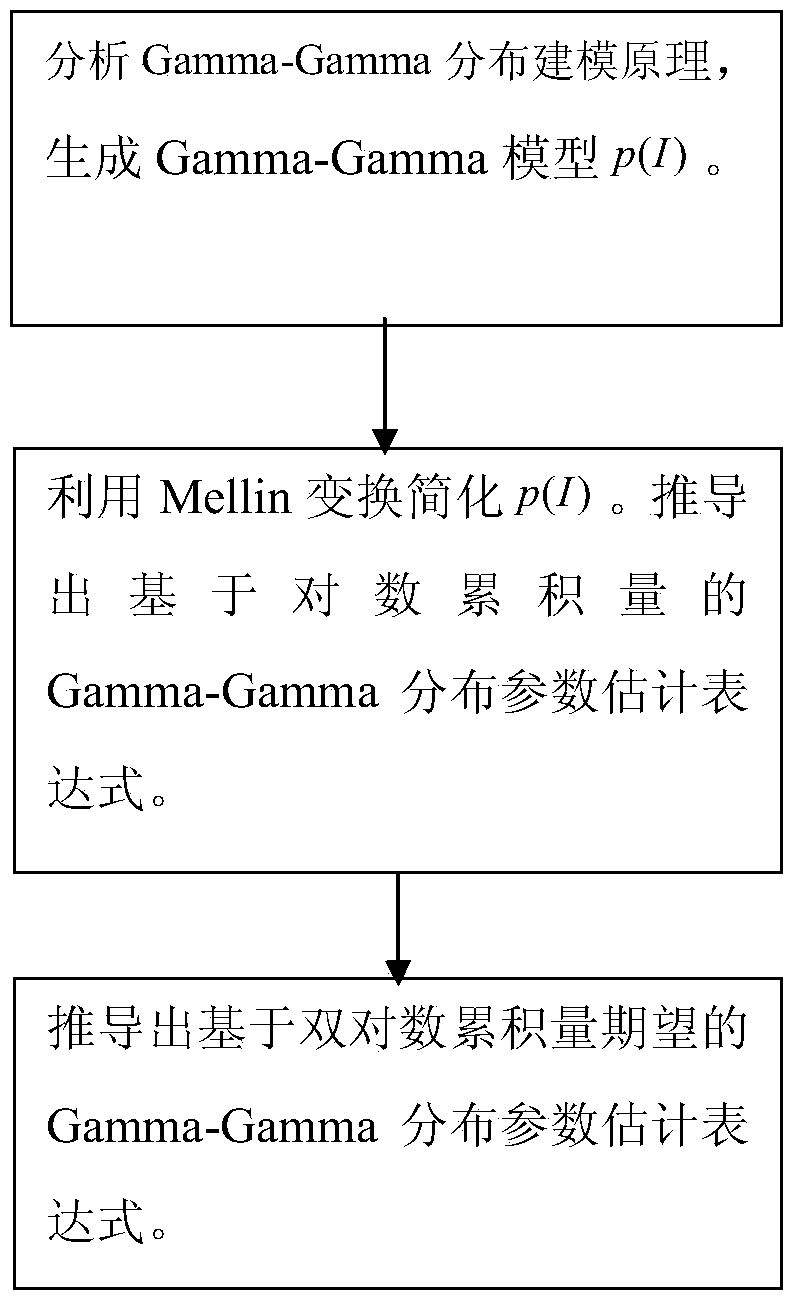
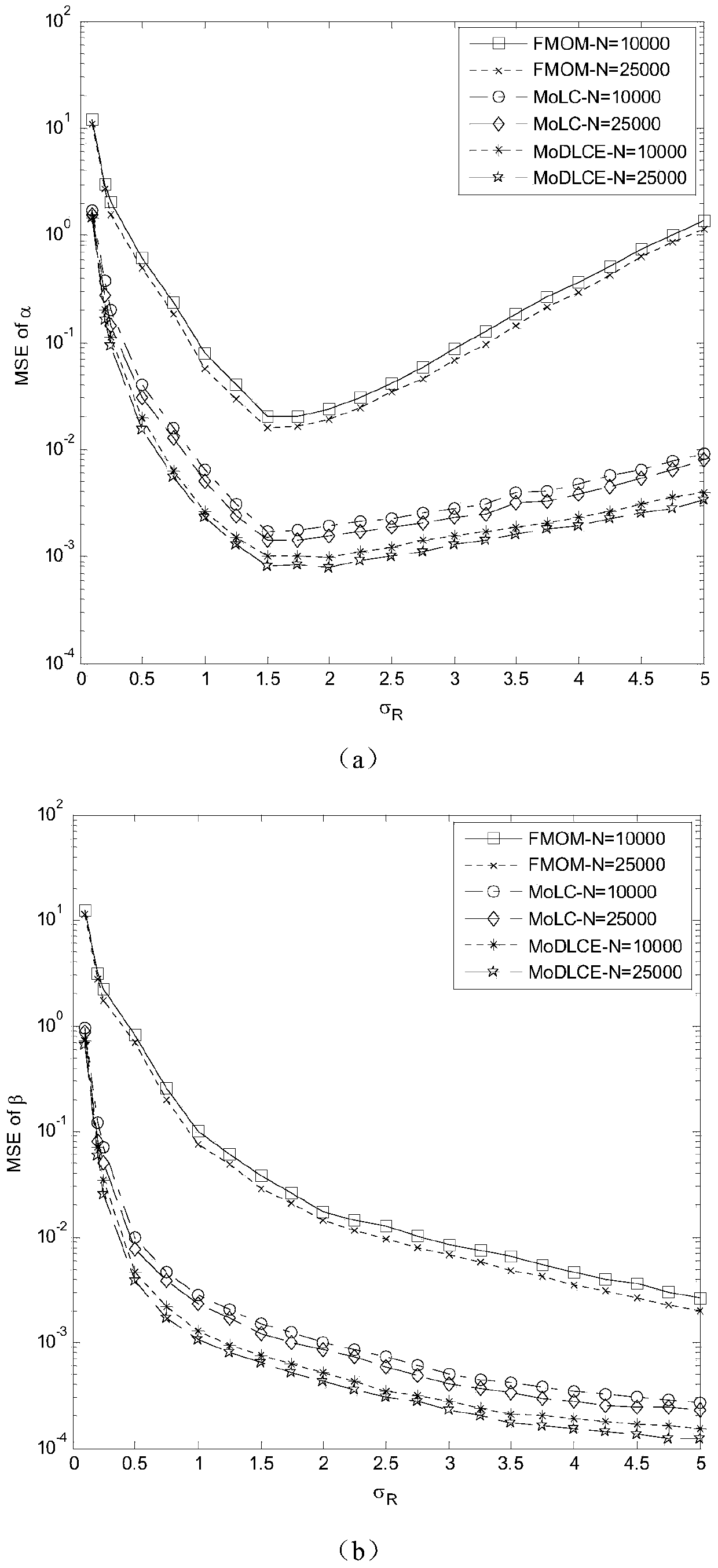
The invention relates to a Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation method based on a double logarithmic cumulant expectation, and belongs to the technical field of atmospheric turbulence channel parameter estimation of free space optical communication systems. According to the method, a Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation process is simplified greatly through Mellin transform, and a uniform parameter estimation method is built specific to the problems of low fractional moment (FMOM) parameter estimation accuracy and even error estimation in the prior art. Then, further improvements are made, and a concept of double logarithmic cumulant expectation is put forward, so that a finial parameter estimation expression is deduced. Compared with an FMOM, the Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation method has the advantages that relatively high computing efficiency is ensured, and the parameter estimation accuracy is increased.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
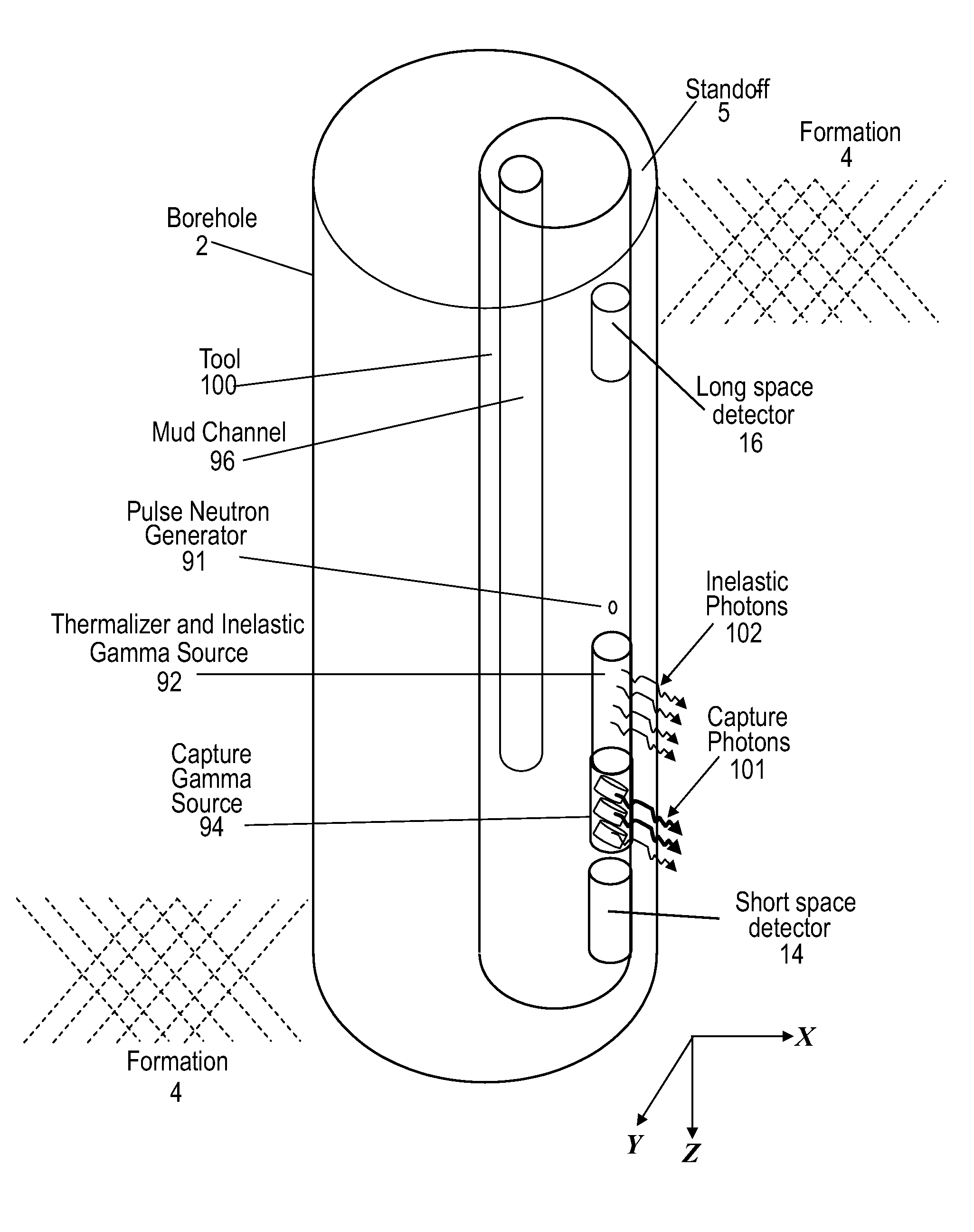
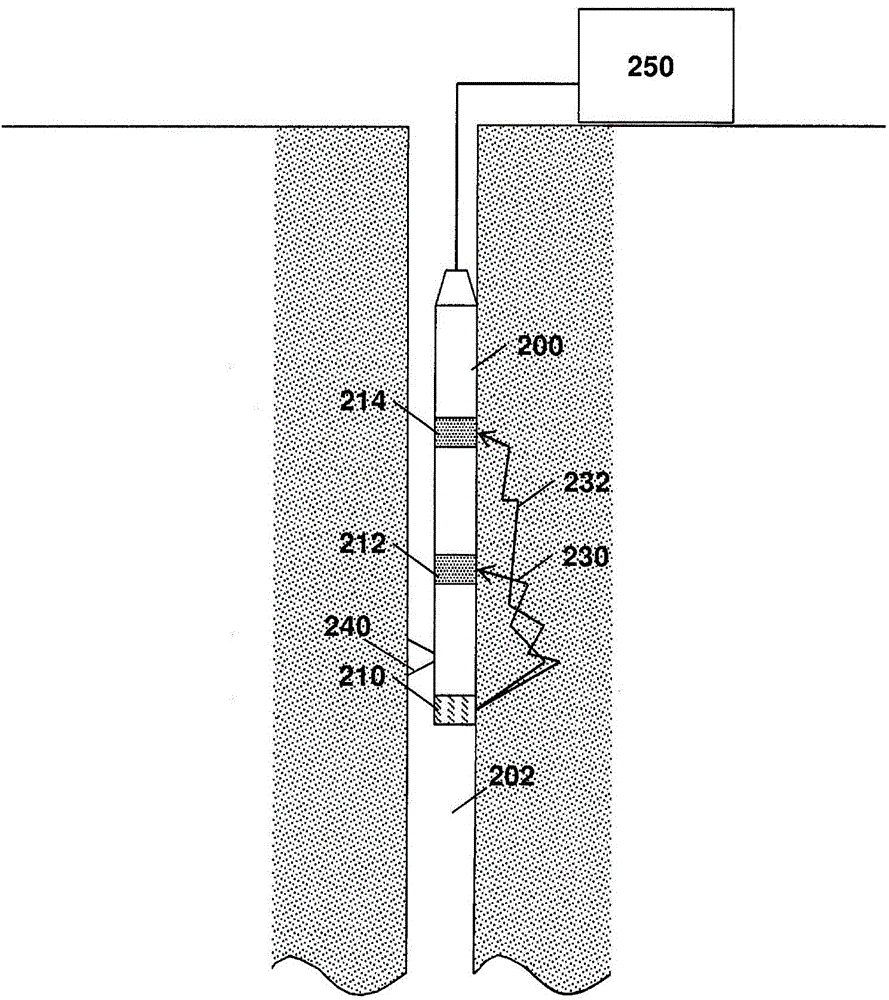
Method for taking gamma-gamma density measurements
InactiveUS20100252724A1Increase the sectionBorehole/well accessoriesNuclear radiation detectionGamma photonNeutron
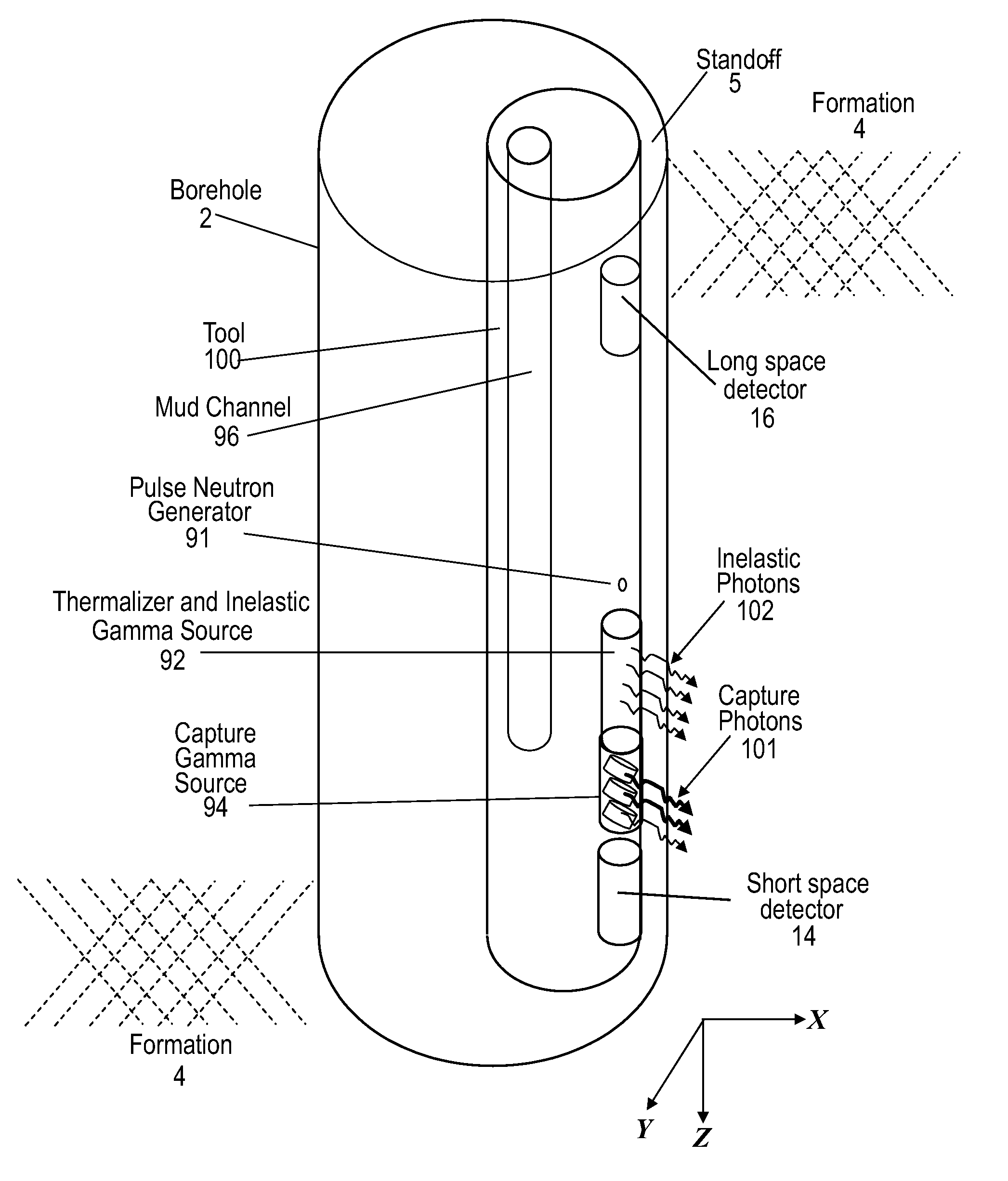
A method for performing a measurement of a property downhole includes: using an instrument including an irradiator including a pulsed neutron generator, a moderator and a material including a high cross section for capturing thermal neutrons downhole, generating inelastic gamma photons from neutron interactions in the moderator and generating capture gamma photons from neutron interactions in the material; irradiating sub-surface materials proximate to the instrument with the inelastic gamma photons and the capture gamma photons; detecting radiation scattered by the sub-surface materials; and estimating the property according to the detected radiation. A system is also disclosed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
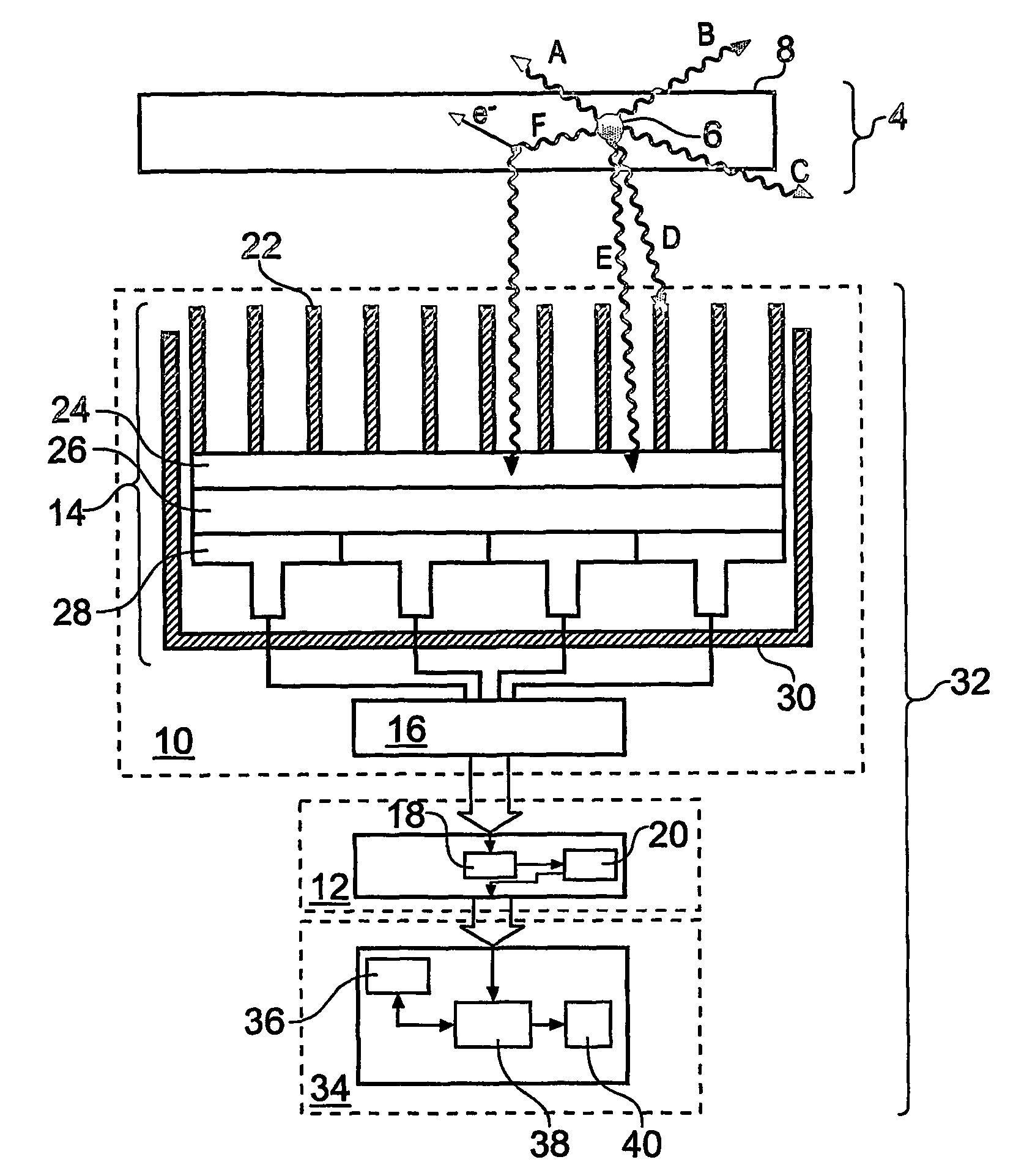
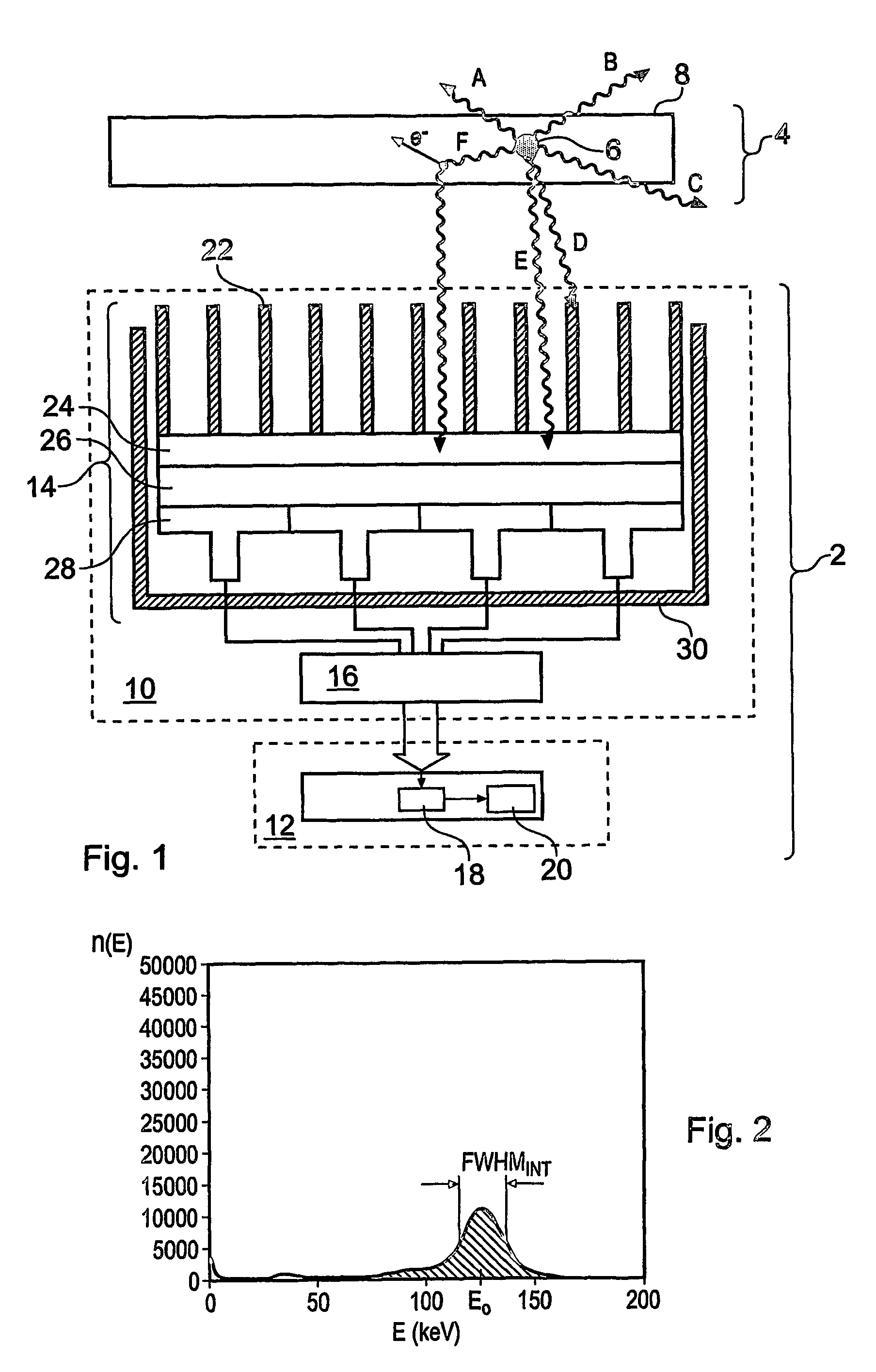
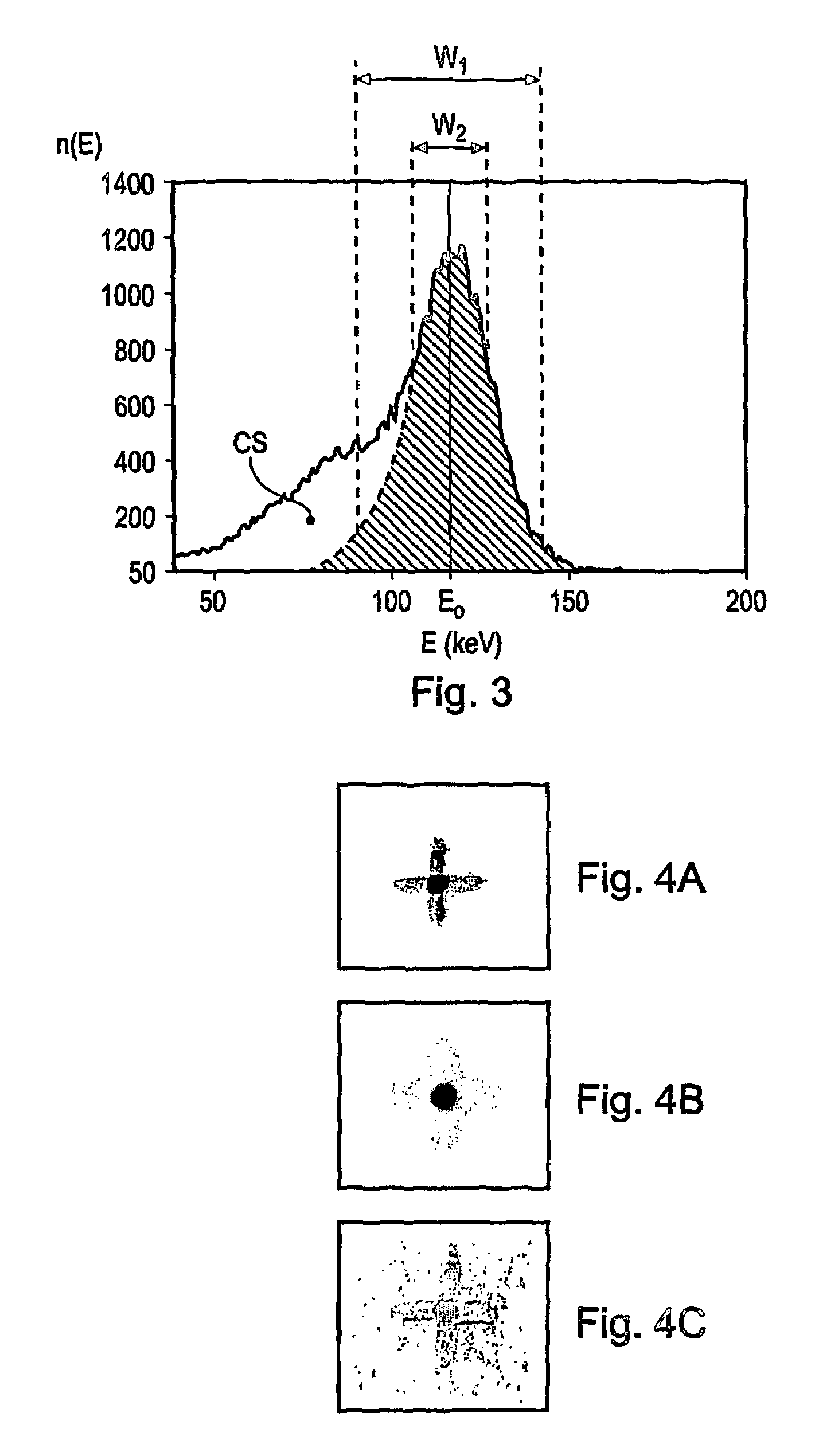
Gamma-ray camera system
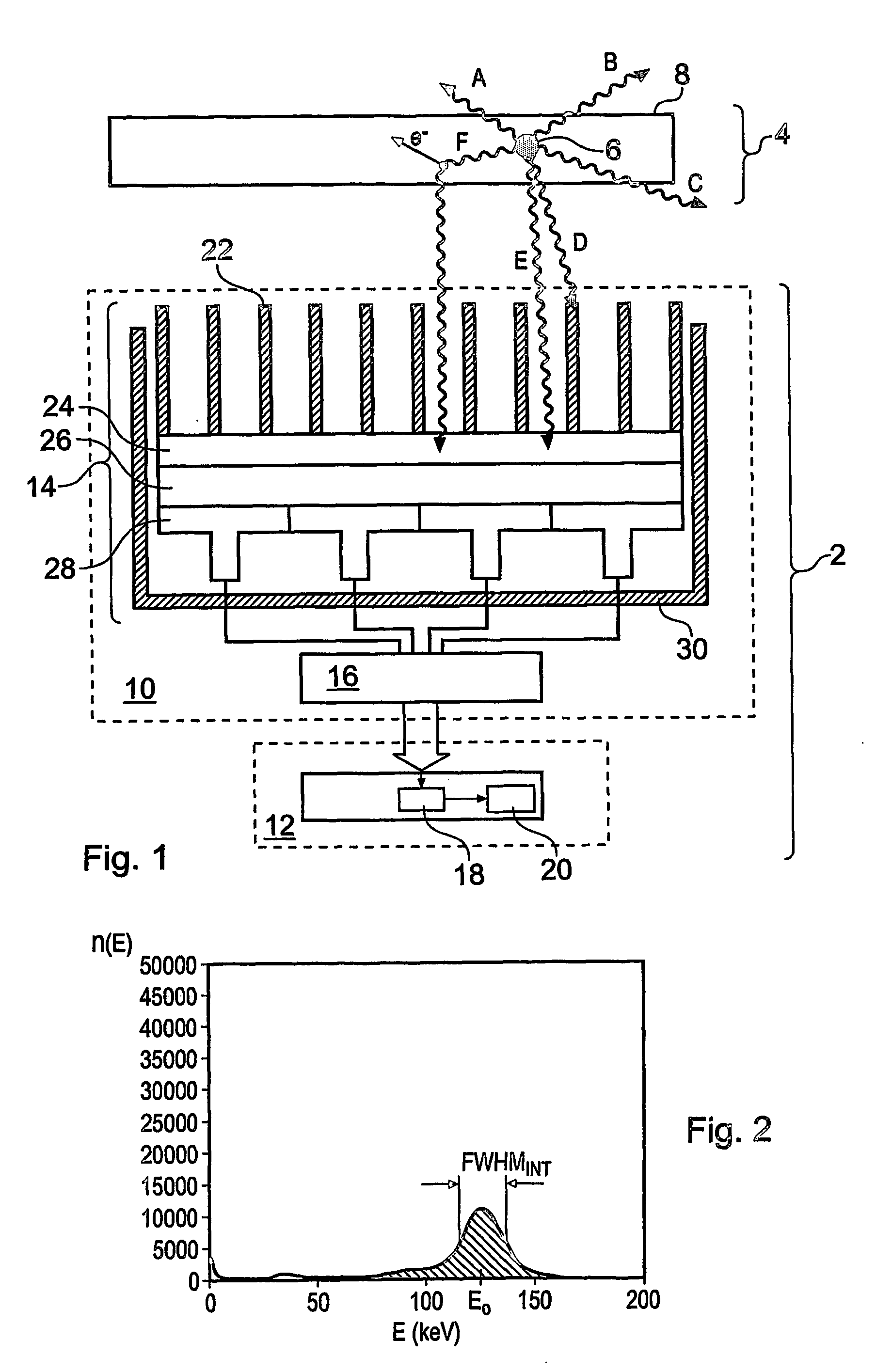
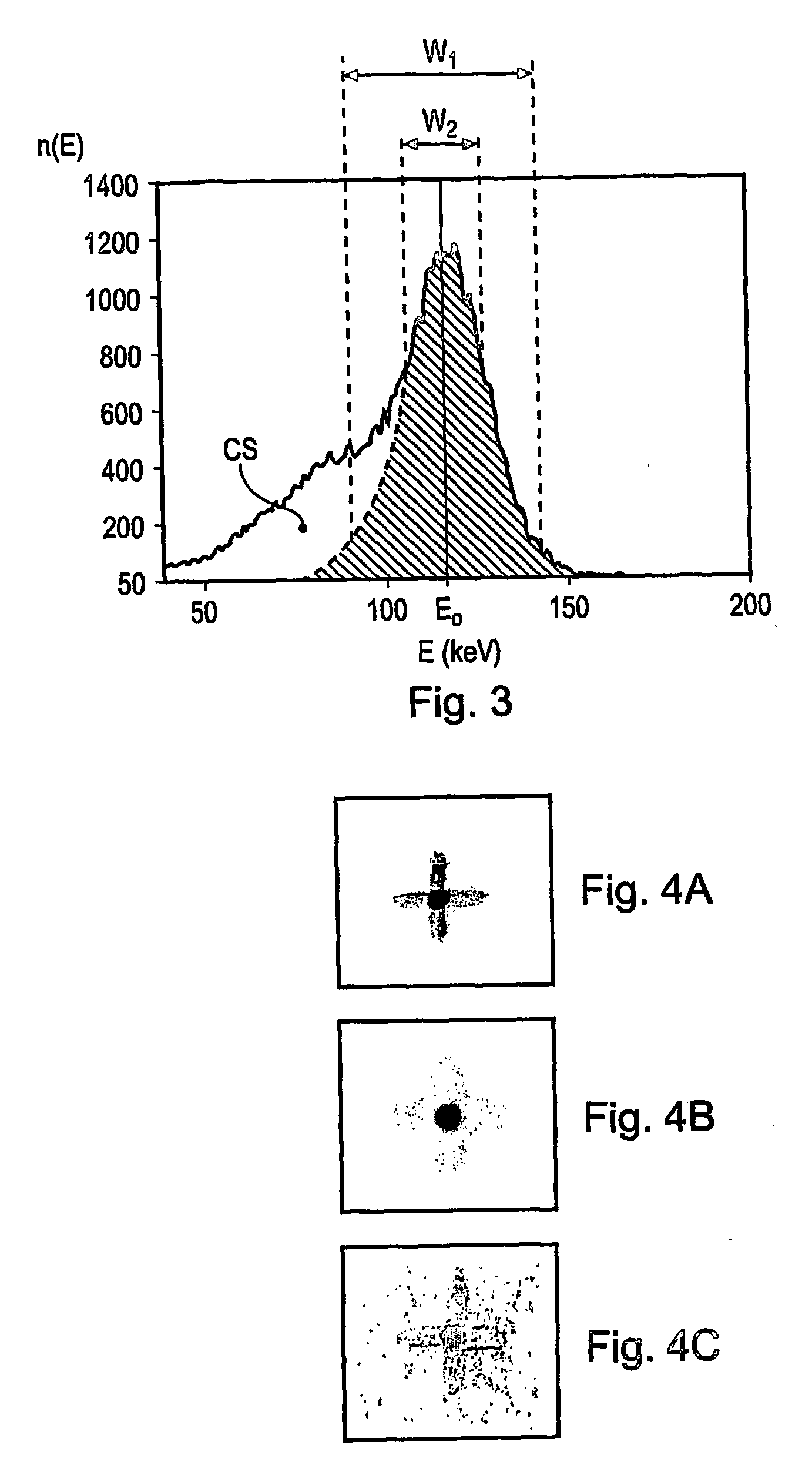
InactiveUS7504635B2Improved energy resolutionEnhance the imageMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation diagnosticsEnergy windowImage resolution
A scintillator crystal (26) based gamma-ray camera system is described. The gamma-ray camera system includes a spectra processing component for (34) providing improved energy resolution over that seen in conventional gamma-ray camera systems. The spectra processing component operates to deconvolve detector response functions from observed energy spectra on a pixel by pixel basis. The pixel dependent to detector response functions are obtained by a combination of theoretical simulation, and empirical calibration. By deconvolving pixel specific detector response functions, variations in response of a gamma-ray camera system across its image plane can be accounted for. This offers significant improvements in energy resolution and many of the problems associated with conventional gamma-ray camera systems are reduced. For example, the improved energy resolution allows better rejection of photons associated with Compton scattering events occurring in a source being imaged. This is because a narrower energy window filter can be used without rejecting a significant fraction of non-Compton scattered photons. The spectra processing component can be easily implemented with different types of gamma-ray imagers, for example Anger-type cameras, and may also be retroactively fitted to existing gamma-ray camera systems.
Owner:SYMETRICA
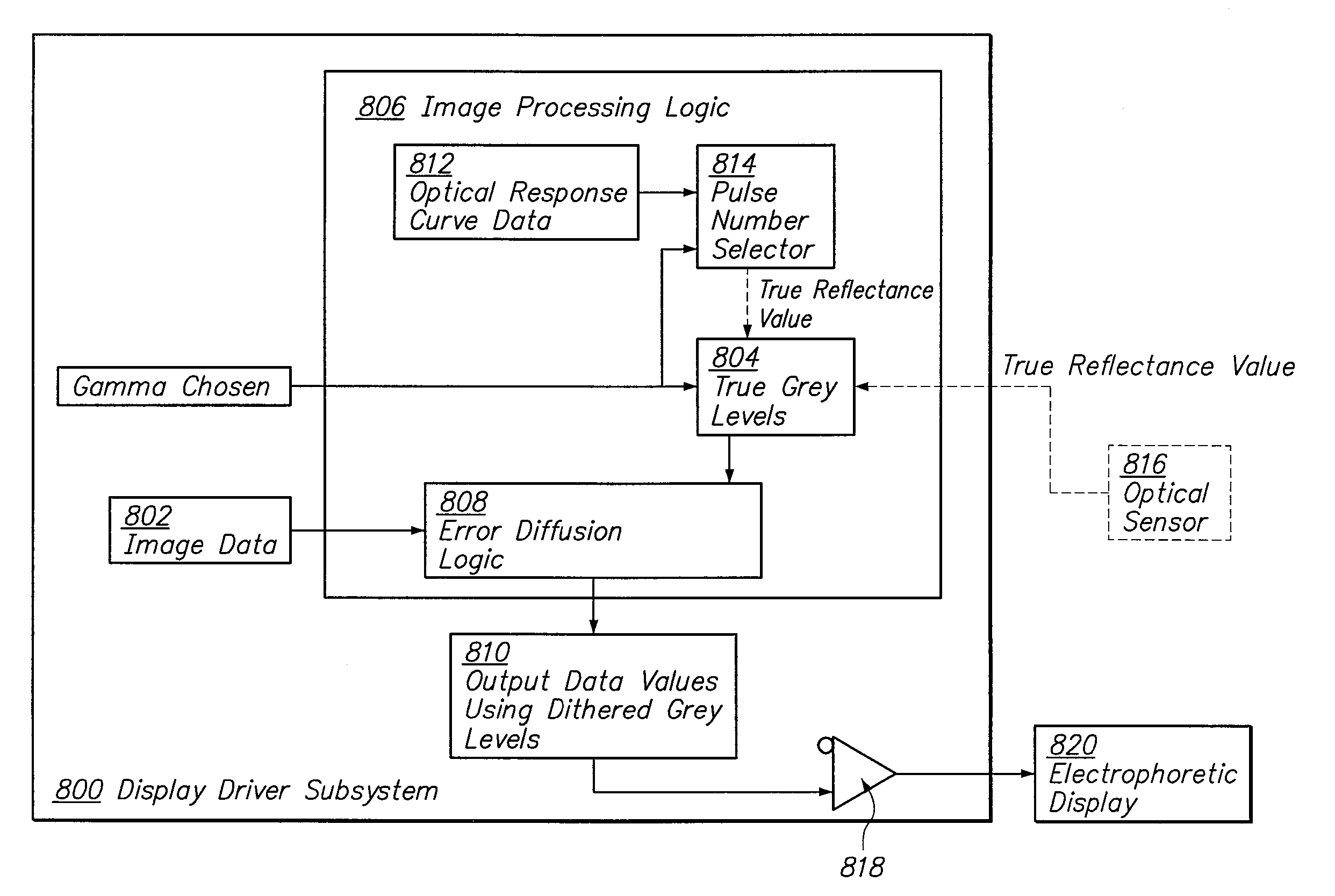
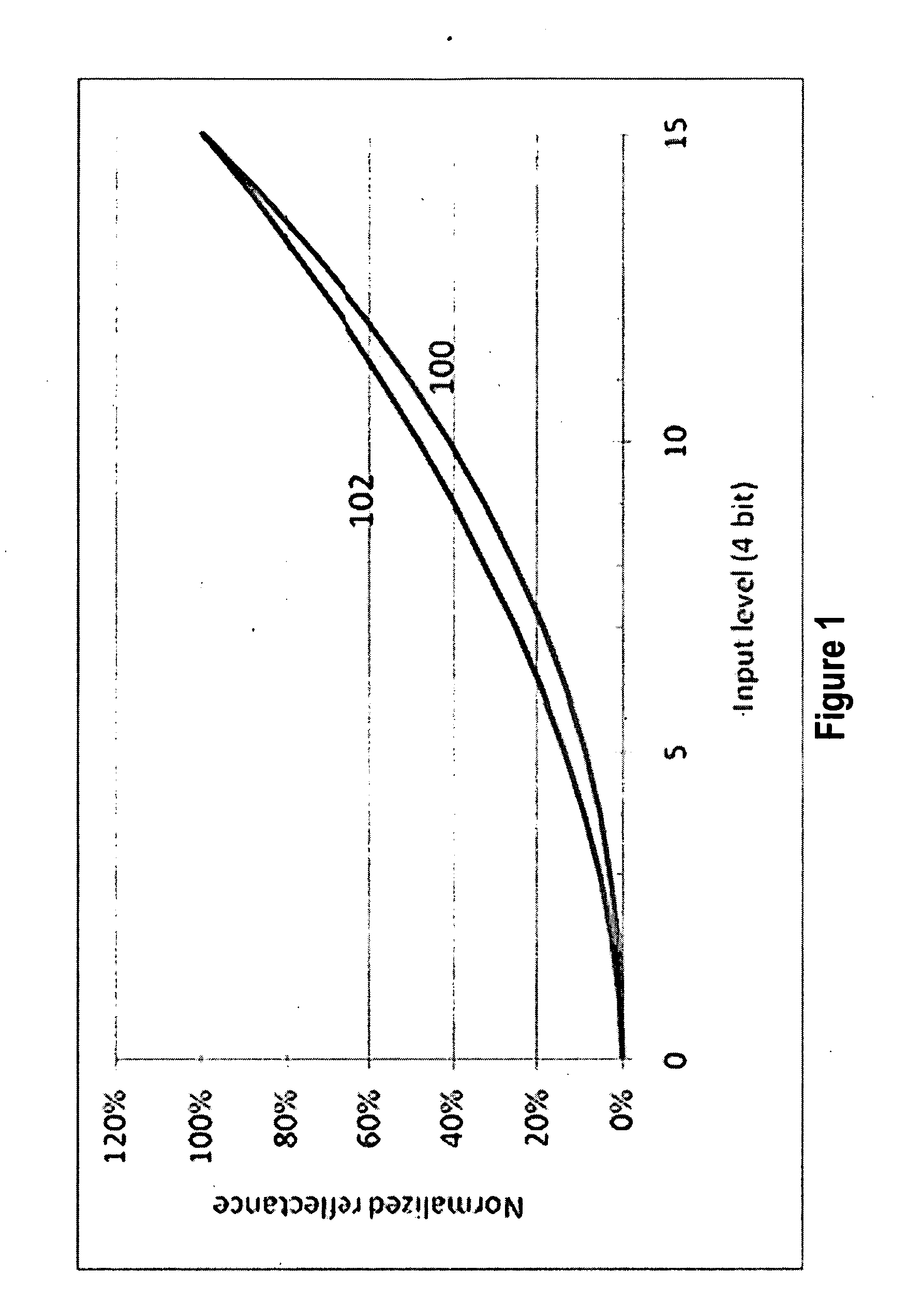
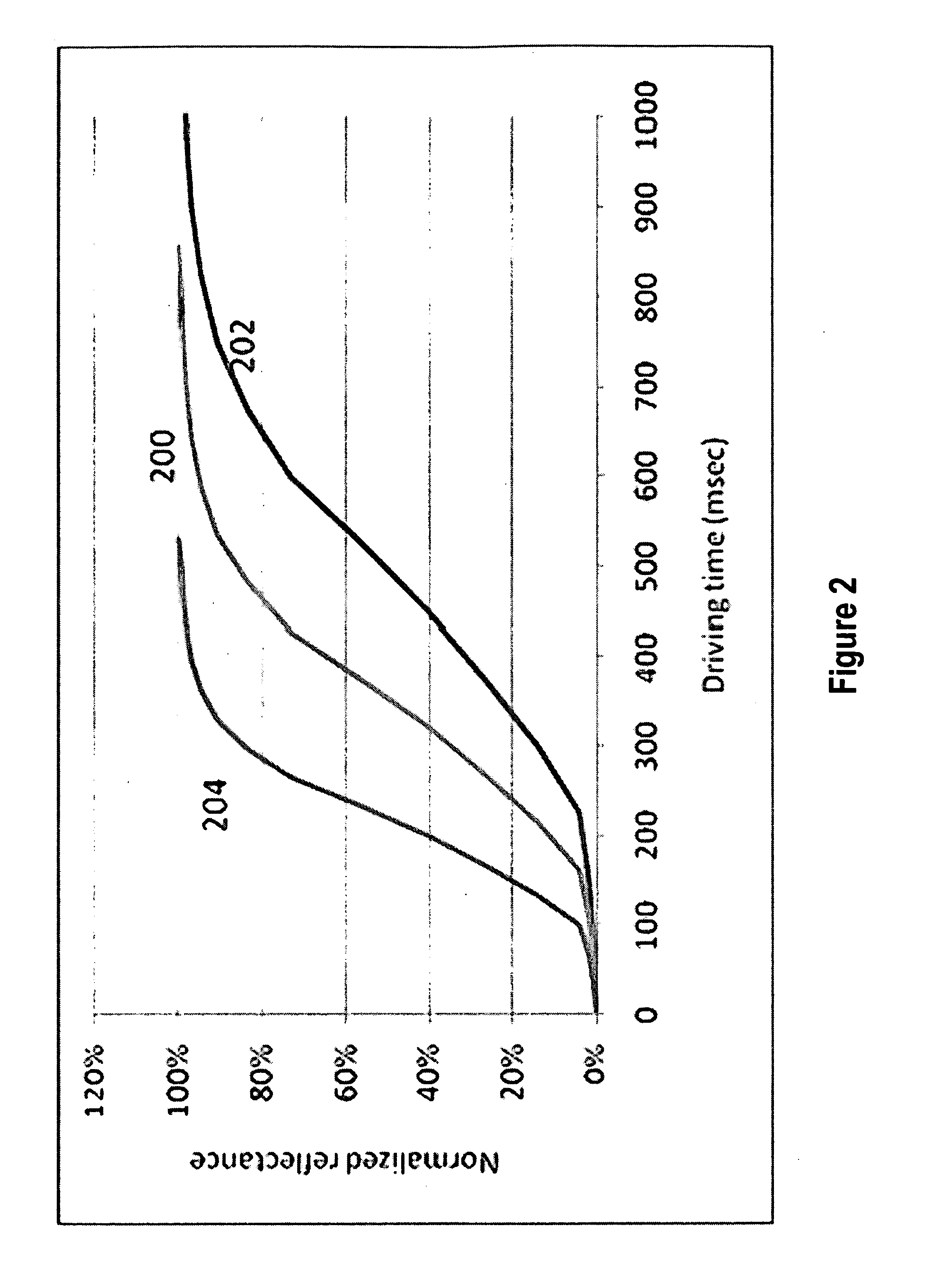
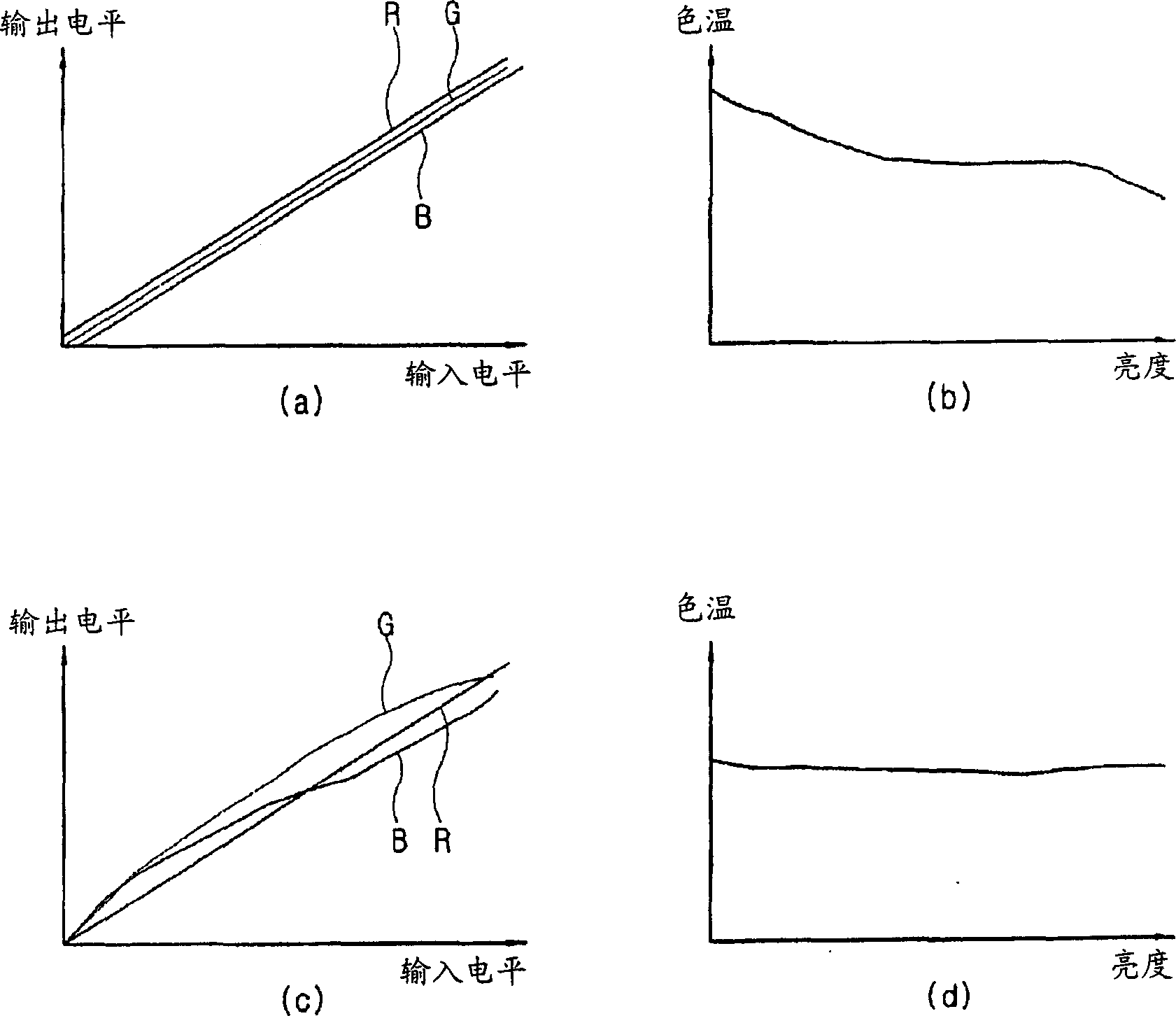
Gamma adjustment with error diffusion for electrophoretic displays
ActiveUS20100027073A1Improve display qualityComplex to useCathode-ray tube indicatorsVisual presentationImaging processingDisplay device
Embodiments are directed to image processing methods to improve display quality while using a limited number of pulses and to correct the error between the reflectance and the desired gamma. The complexity of the hardware used for driving a display device may then be reduced to minimum. In addition, in various embodiments the method can also be used to compensate for the change of an optical response curve due to batch variation, temperature change, photo-exposure or aging of the display device.
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
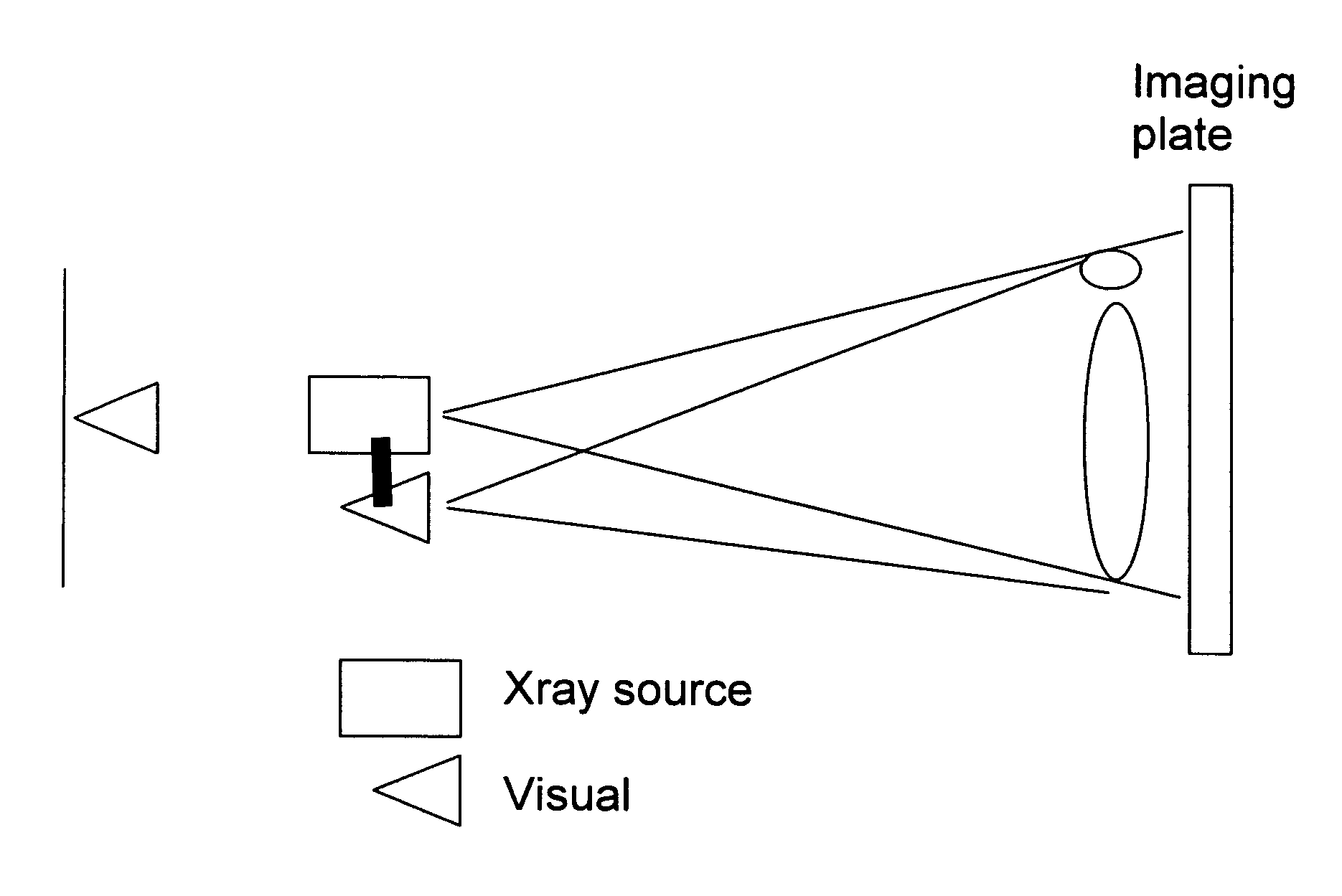
Fusion imaging using gamma or x-ray cameras and a photographic-camera
InactiveUS20070019787A1Facilitates combining the visualAccurately superimposeMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSoft x rayPhotographic camera
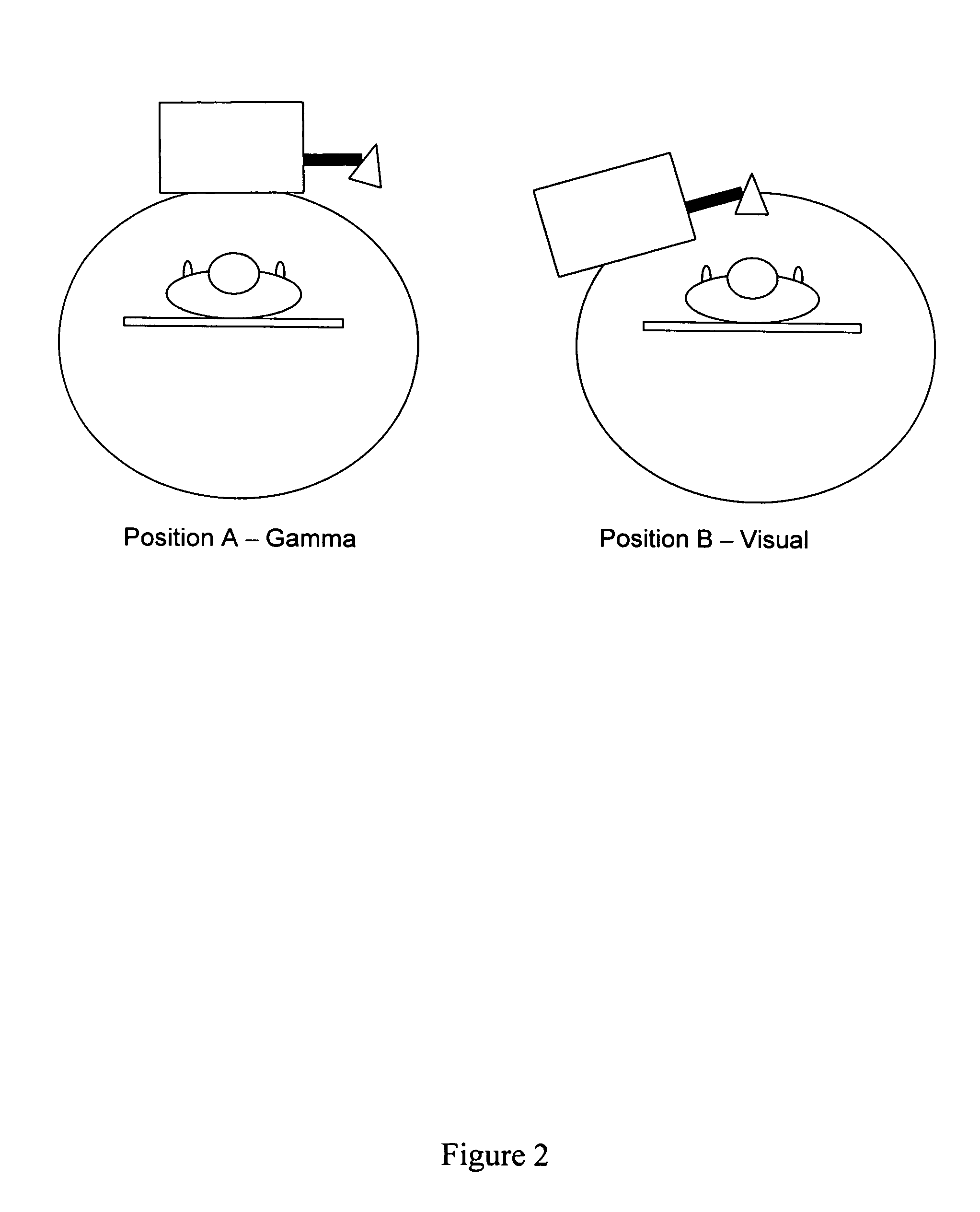
A visual photographic camera is utilized in a fixed geometric relationship together with another imaging or treatment source such as a standard gamma-camera or an x-ray source. The visual camera is either attached to the gamma camera gantry, the gamma camera head or mounted on a structure such as the ceiling in the imaging room. After the standard gamma camera image is obtained, the gamma-camera head can rotate either bringing the visual camera over the patient, or moving out of the way to expose the patient to the field of view of the gantry-mounted or ceiling mounted camera. On the fusion image, both the visual and scintigraphic parameters for each specific location on the patient's body may be coded in a display. The visual camera may be utilized together with x-ray imaging equipment. In that application, the visual camera could either be attached to the x-ray tube assembly, or be mounted on a structure in the imaging room. Based on a fixed relationship between the location of the x-ray machine and the photographic camera, the two images could be scaled and superimposed to generate a ‘fusion’ image.
Owner:ZUCKIER LIONEL S
Method for calculating average channel capacity of FTN transmission system on the condition of double Gamma turbulence channels
ActiveCN110572226AImprove spectral efficiencyLine-of-sight transmissionTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumTransport system
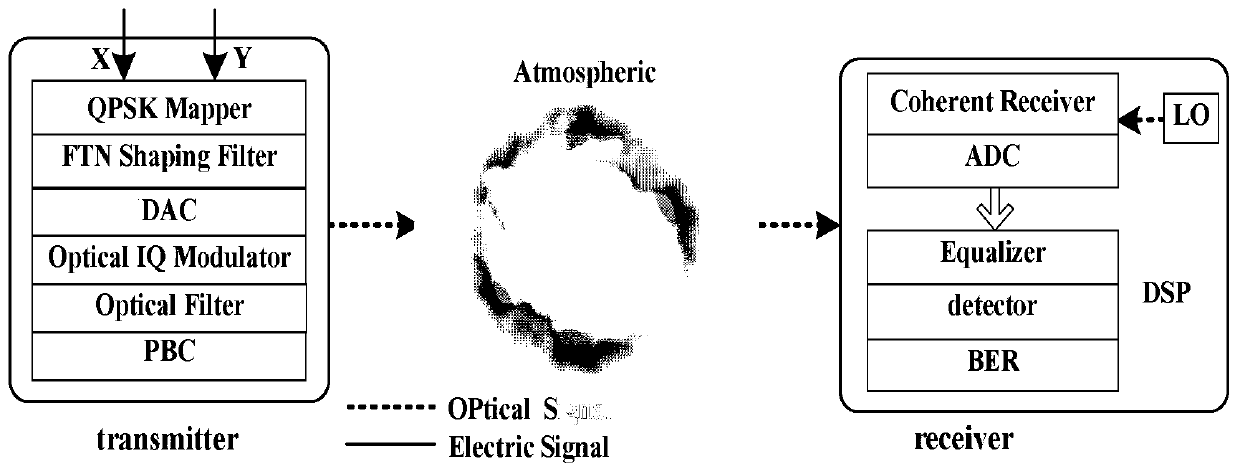
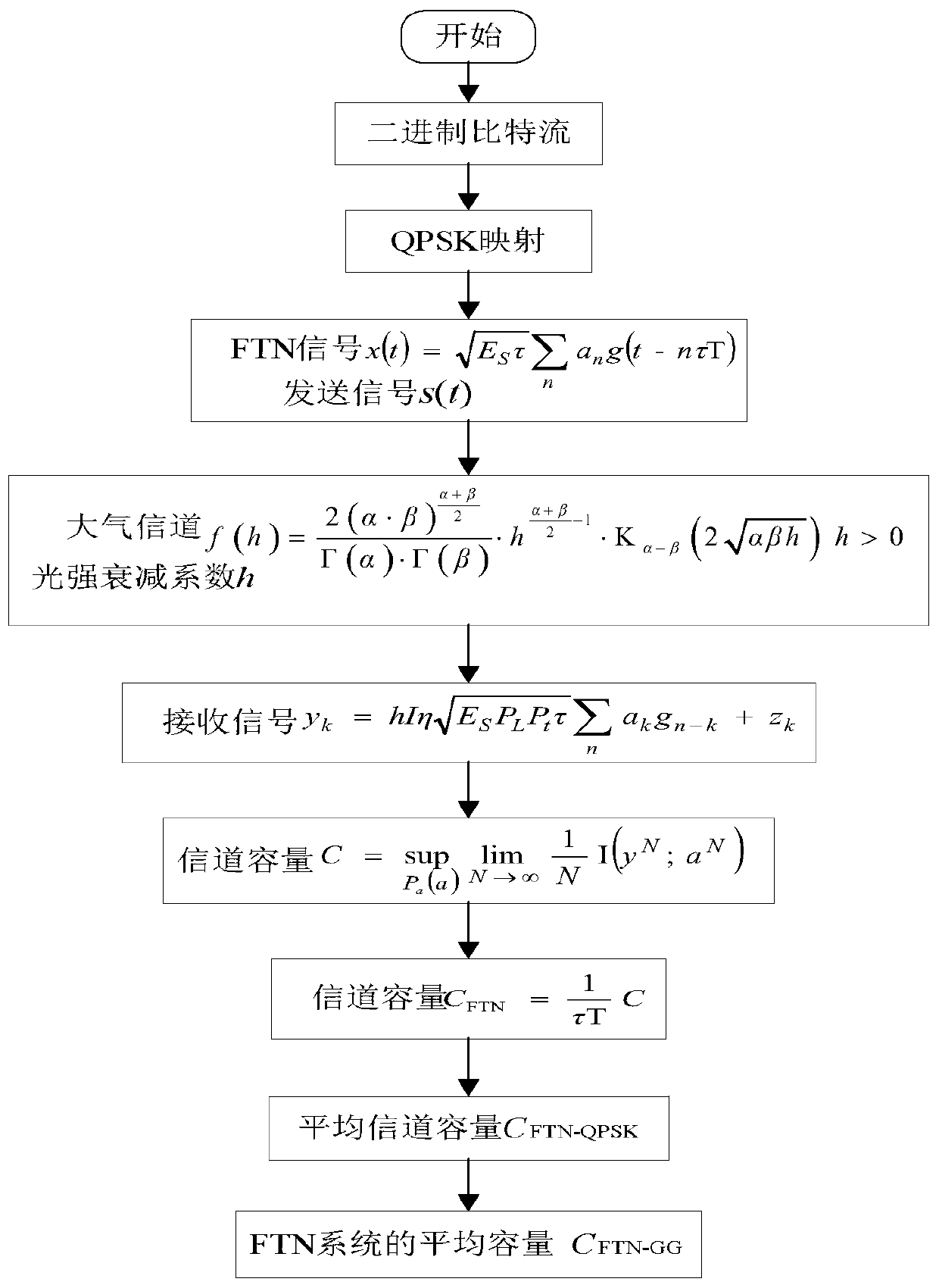
The invention discloses a method for calculating the average channel capacity of an FTN transmission system on the condition of double Gamma turbulence channels, and aims to introduce an FTN technology into a Gamma-Gamma turbulence channel, so that the symbol rate is greater than the Nyquist rate, the average capacity of the system is effectively improved, and the performance of an atmospheric transmission system is improved. The FTN signal is formed by performing QPSK mapping on input bit information an and then generating the FTN signal through an FTN shaping filter. The system channel capacity is obtained by using a received signal transmission model, and then normalizing the period of the channel capacity to obtain the average capacity of the FTN system. On the basis, an expression ofthe average capacity of the super-Nyquist optical transmission system under a Gamma-Gamma turbulence channel under a QPSK modulation format is derived according to QPSK modulation characteristics. Theconstruction of the super-Nyquist optical transmission system effectively improves the spectral efficiency of the system.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
High resolution gamma measurements and imaging
A method for measuring radiation in a borehole, the method including placing a detector comprising a scintillator and a plurality of photodetectors in the borehole; detecting a radiation interaction with a first photodetector; detecting the radiation interaction with at least a second photodetector; and determining a location of the interaction from the detecting; wherein the location provides information regarding formations surrounding the borehole.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method of extracting formation density and pe using a pulsed accelerator based litho-density tool
ActiveUS20110307179A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingElectron densityDensity change
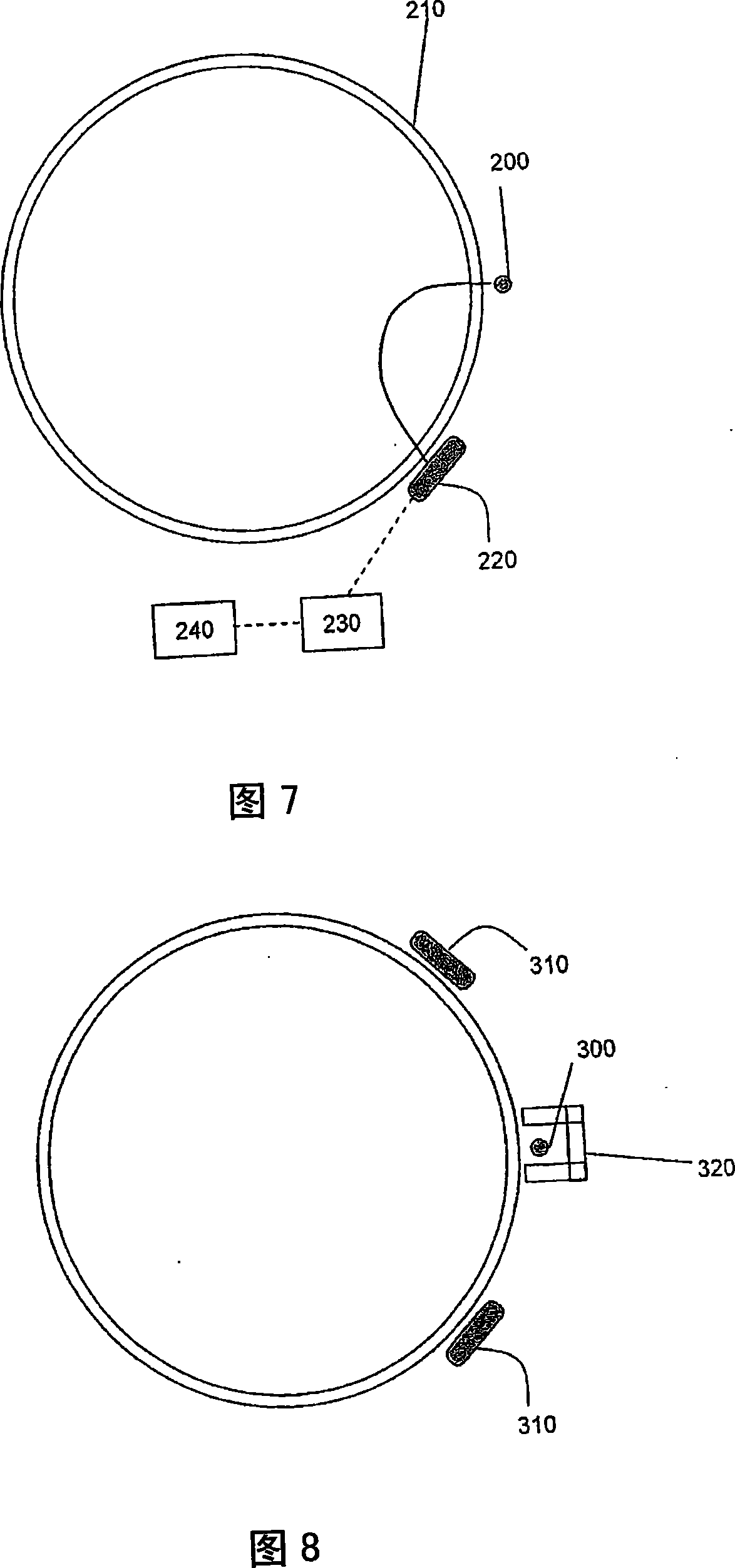
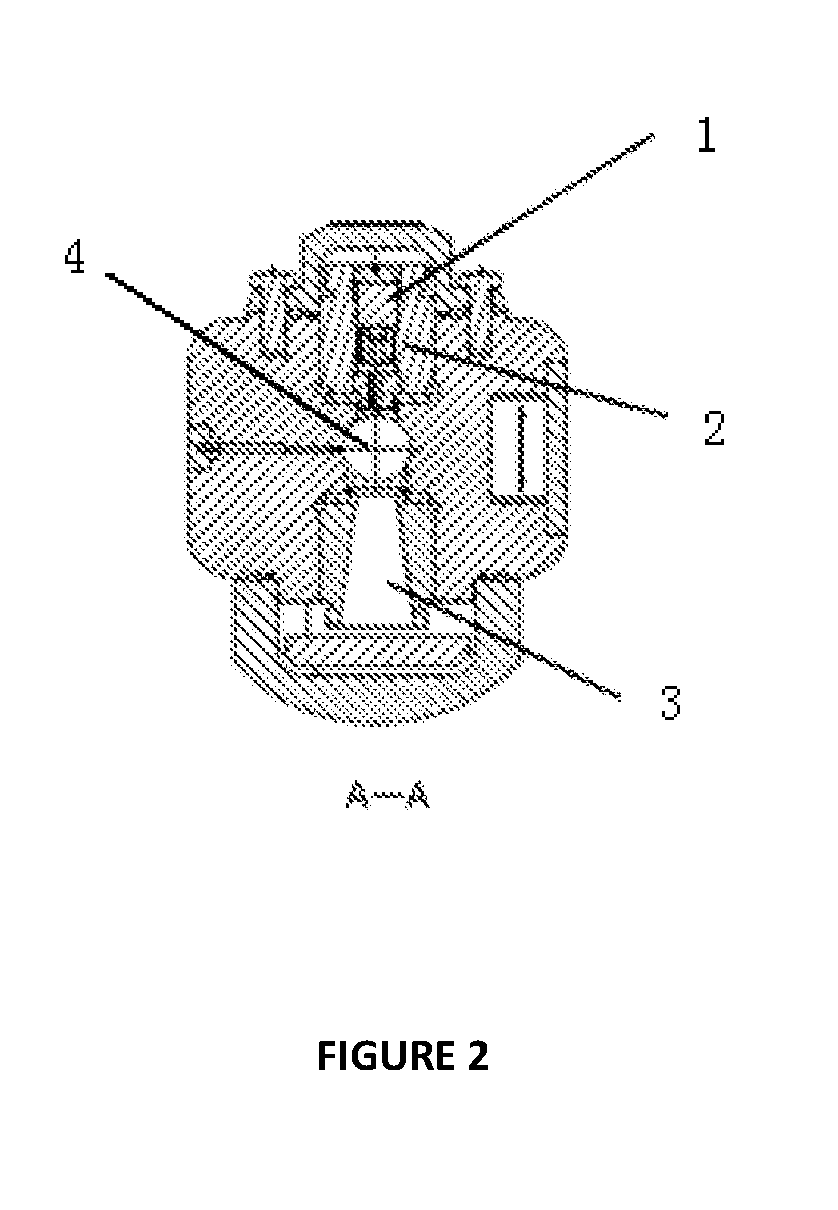
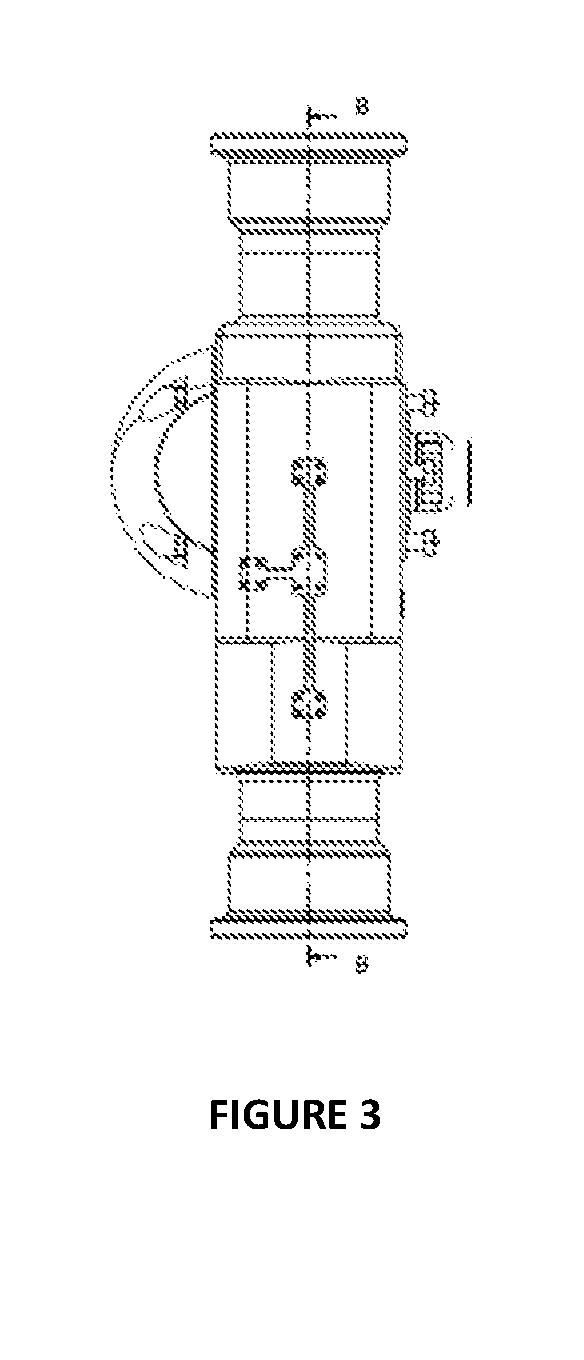
A method for a pulsed gamma-gamma density tool to simultaneously compensate for interactions due to the photoelectric effect and density variations caused by standoff enables a more precise determination of bulk formation density. This method includes the steps of providing a source of energetic particles and directing those energetic particles at a formation having a known photoelectric factor and electron density and capturing one or more photons either emitted or deflected from the formation either a first detector or a second detector. The first detector is spaced a first distance from the source, the second detector is spaced a second distance from the detector and a third distance separates the first detector from the second detector. Measuring a first total energy of the photons striking the first detector during a time interval and measuring a second total energy of the photons striking the second detector as a function of the time interval and disposing a first filter between the first detector and the formation effective to cause Pe response to match standoff influence thereby compensating for both effects simultaneously. In addition to the first filter, the required compensation may include a second filter between the second detector and the formation as well as adjustments to the respective first distance, second distance and third distance.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
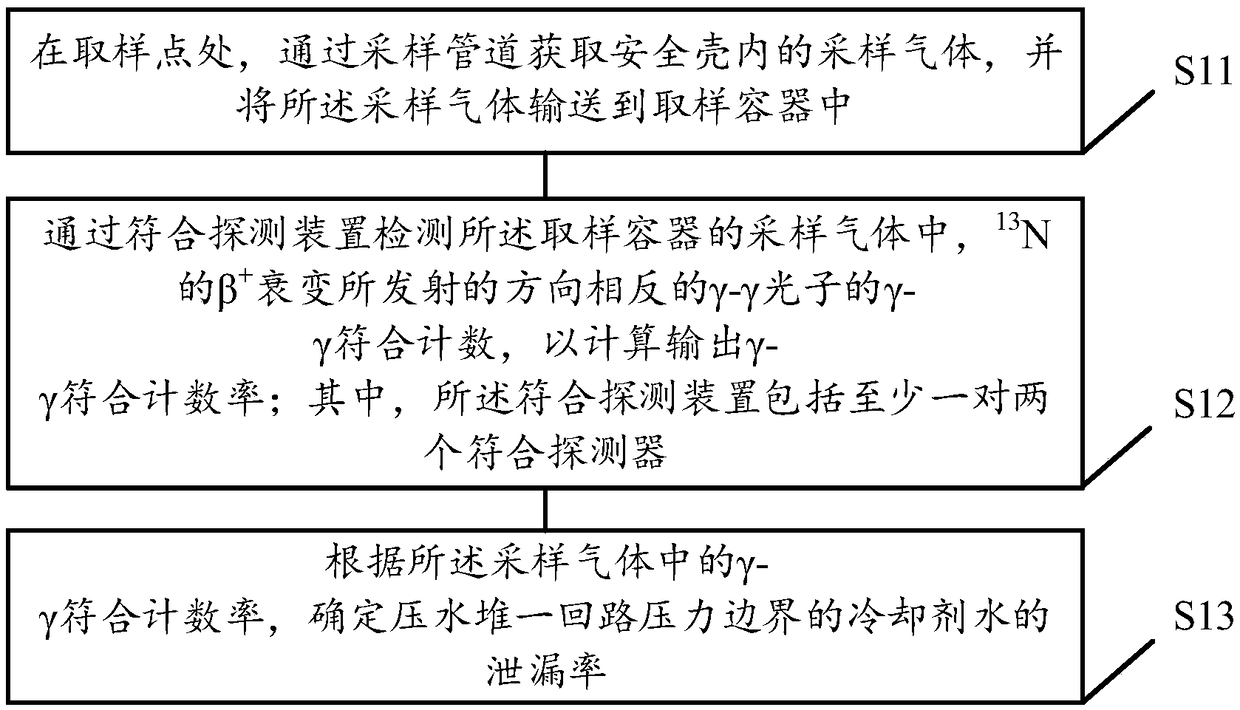
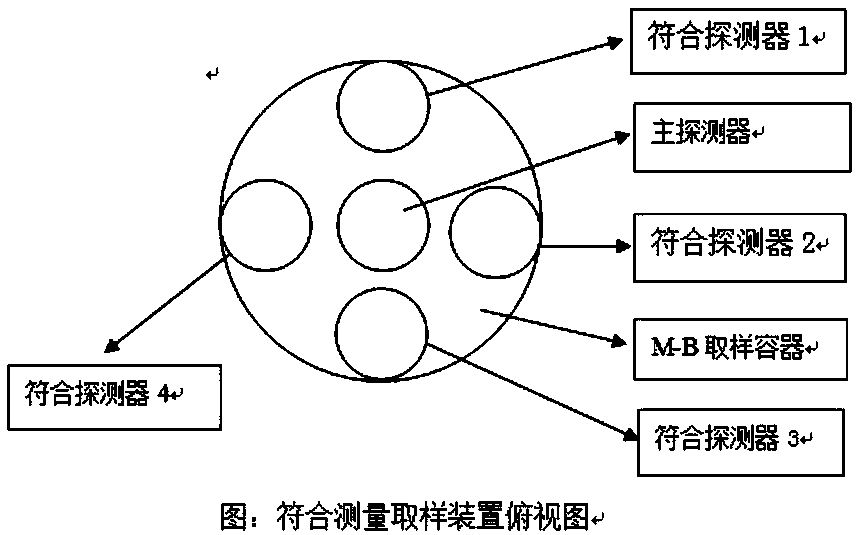
Pressurized water reactor primary coolant circuit boundary leakage monitoring method and system as well as monitoring instrument
InactiveCN108877970AImprove detection efficiencyLow stability requirementsNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear engineeringPressurized water reactor
The invention discloses a pressurized water reactor primary coolant circuit boundary leakage monitoring method and system as well as a monitoring instrument. The method comprises the following steps:on a sampling point, acquiring sampling gas in a safety shell by virtue of a sampling pipeline, and transporting the sampling gas into a sampling container; detecting gamma-gamma coincidence countingof gamma-gamma photons opposite to the emitted direction of beta+ decay of 13N in the sampling gas of the sampling container by virtue of a coincidence detection apparatus, and calculating and outputting a gamma-gamma coincidence counting rate, wherein the coincidence detection apparatus comprises at least two coincidence detectors; and according to the gamma-gamma coincidence counting rate in thesampling gas, determining a leakage rate of cooling agent water on the pressurized water reactor primary coolant circuit boundary, so that the pressurized water reactor primary coolant circuit leakage can be accurately and efficiently monitored.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
High resolution gamma measurements and imaging
ActiveUS20090101808A1Material analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A method for measuring radiation in a borehole, the method including placing a detector comprising a scintillator and a plurality of photodetectors in the borehole; detecting a radiation interaction with a first photodetector; detecting the radiation interaction with at least a second photodetector; and determining a location of the interaction from the detecting; wherein the location provides information regarding formations surrounding the borehole.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Natural gamma ray logging sub method and apparatus
A natural gamma tag marking materials for sub or permanent markers used in gamma logging operations, such natural gamma materials having a gamma count of between 200 and 1000 counts per second. The instant invention further discloses a typical Sub, for insertion in a drilling operation, utilizing natural gamma element compounds which are considered to be non-hazardous and effective as tag markers when used in wire-line logging operations.
Owner:TUMLIN DAVID M +1
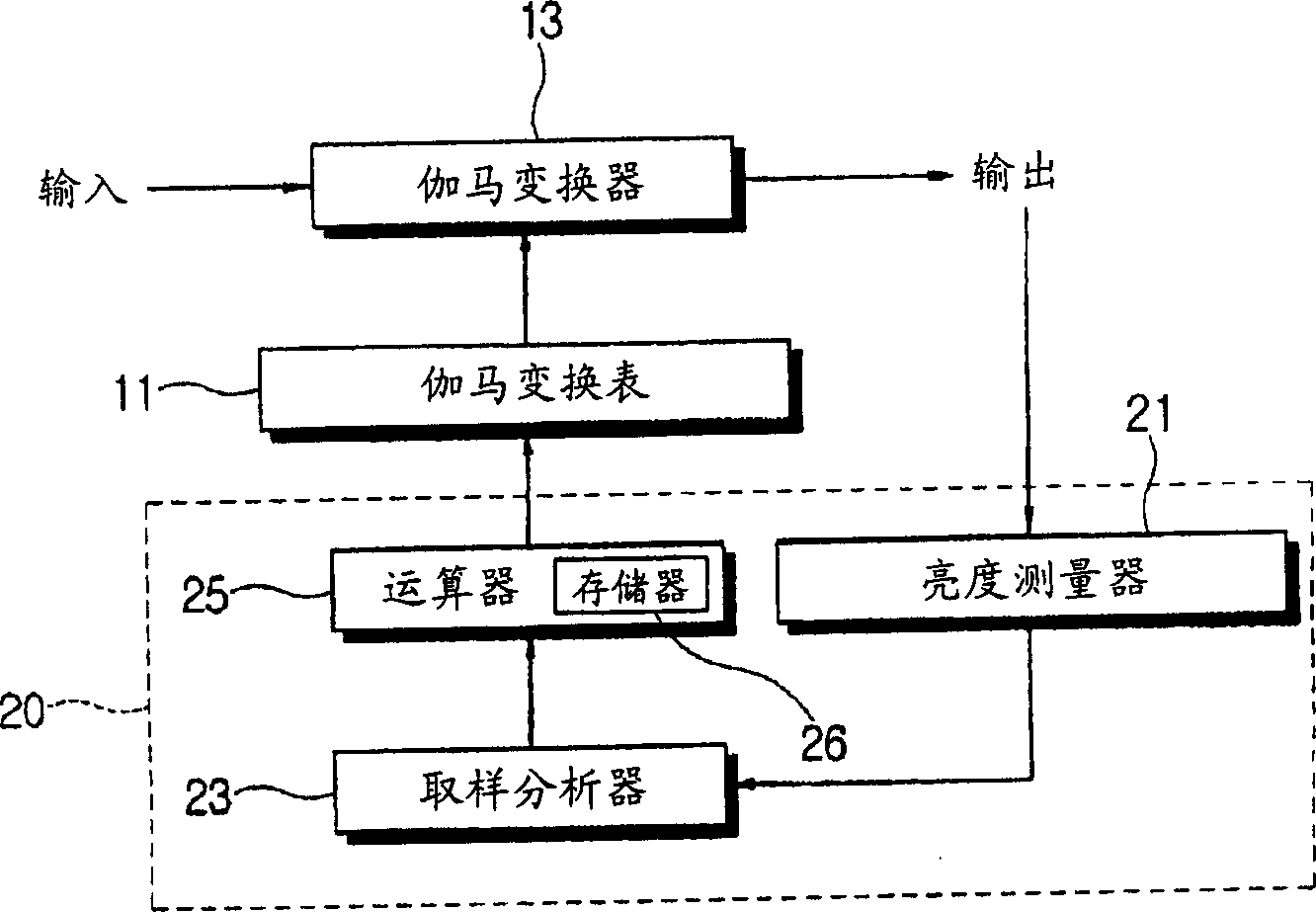
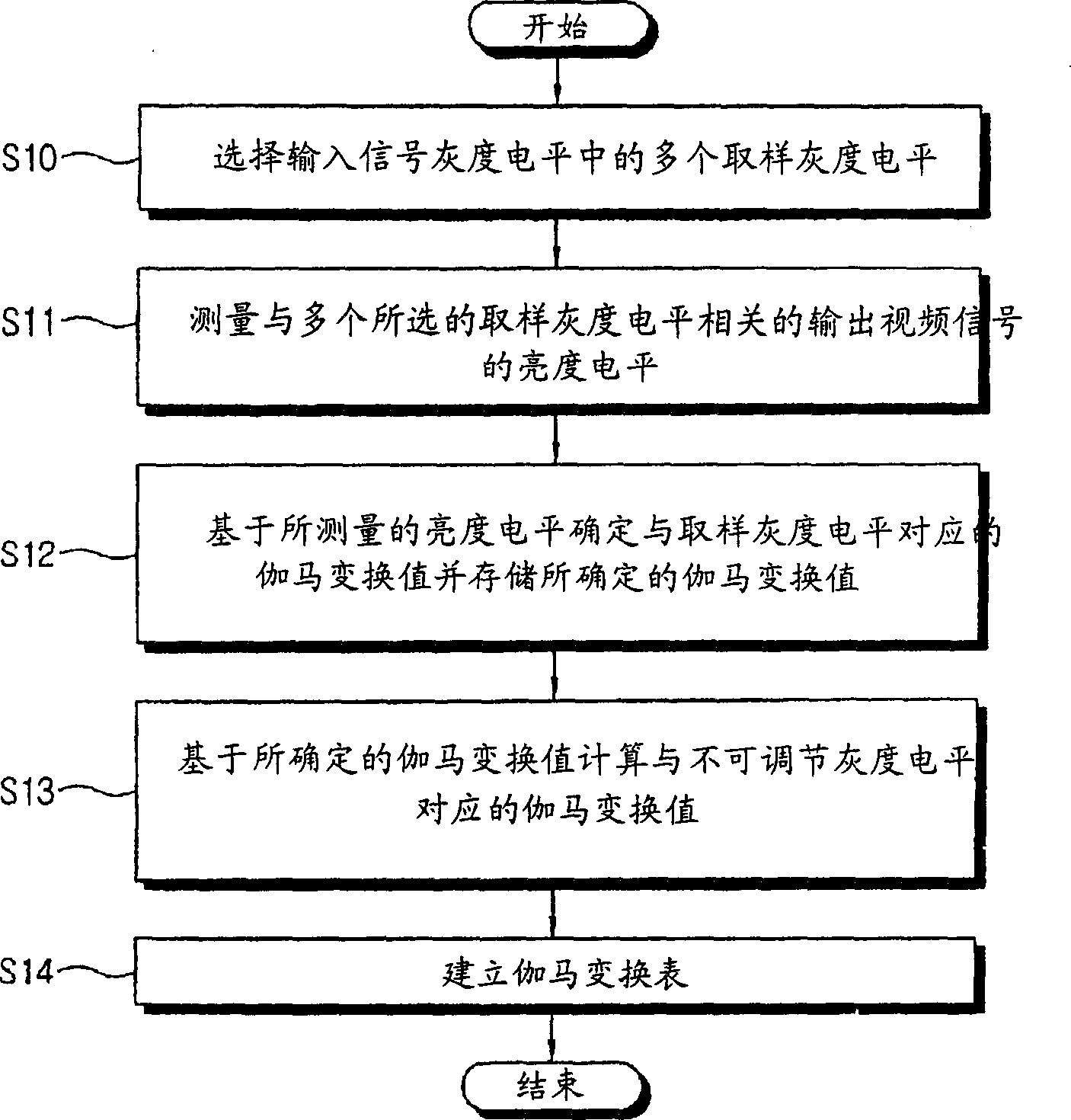
Method and system for gamma adjustment of display apparatus
InactiveCN1777294AColor signal processing circuitsStatic indicating devicesGray levelComputer science
A gamma adjustment method for a display device having a gamma conversion table of an input signal, the method comprising: selecting a plurality of sampled gray levels among the gray levels of the input signal; Sampling the brightness level of the output video signal related to the gray level; determining a first gamma conversion value corresponding to the sampling gray level based on the measured brightness level and storing the determined gamma conversion value; Calculating a second gamma conversion value corresponding to the gray level of the input signal excluding the sampled gray level based on the gamma conversion value corresponding to the gray level; and based on the stored first gamma conversion value and the calculated The second gamma transform value to set the gamma transform table.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
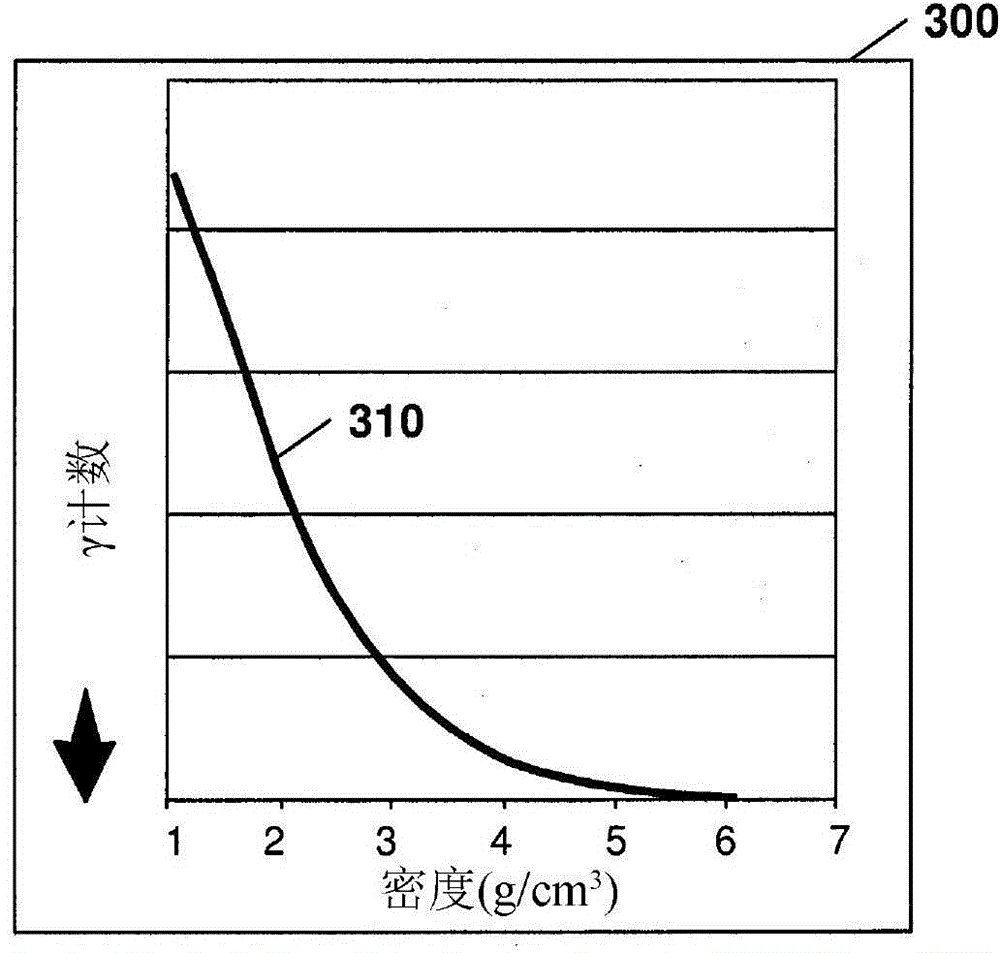
Density measurement with gamma backscattering
InactiveCN101183065AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSpecific gravity measurementUltimate tensile strengthCondensed matter physics
A system for measuring the density of a fluid in a vessel, the system including: at least one gamma-ray source positioned proximate to the vessel; at least one gamma-ray detector positioned proximate to the vessel, wherein the at least one gamma-ray detector is configured to detect gamma rays backscattered by the fluid from the at least one gamma-ray source; and a translator for converting the detected gamma-ray backscatter to a density value. A method to determine properties of a fluid in a vessel, the method including: positioning a gamma-ray source proximate to the vessel; positioning a gamma-ray detector proximate to the vessel; detecting gamma rays backscattered by the fluid from the gamma-ray source with the gamma-ray detector; determining a density of the fluid based upon an intensity of backscattered gamma rays received by the gamma-ray detector.
Owner:思姆菲舍尔科技公司
Gamma-gamma density logging distorted curve correction method
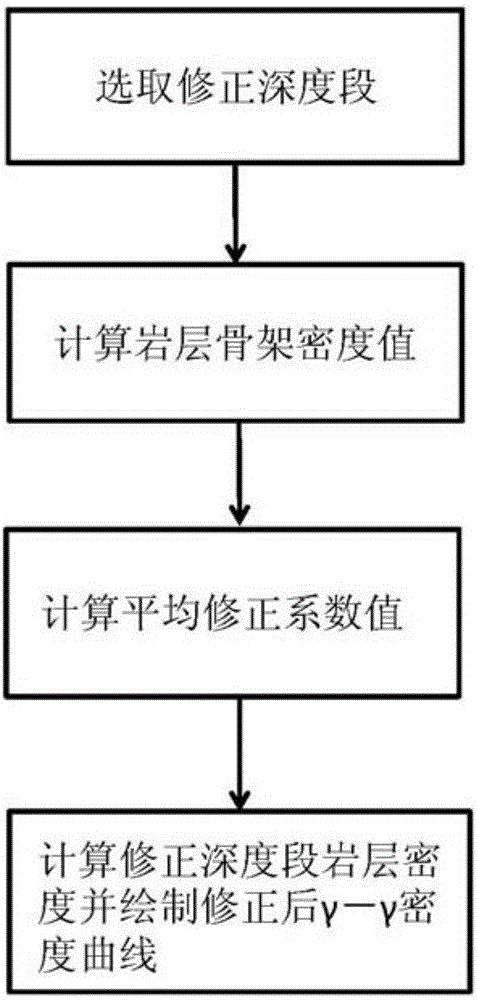
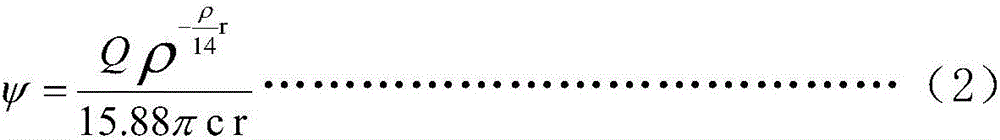
ActiveCN106094037AAvoid big swingsAccurate Acoustic Impedance DataSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingData sortingCorrection method
The invention belongs to the field of nuclear physics research and application, and specifically relates to a gamma-gamma density logging distorted curve correction method. The invention provides a correction method for eliminating gamma-gamma density logging curve distortion produced due to rock radiation in the stage of gamma-gamma density logging data sorting. The method comprises the following steps: S1, selecting a correction depth section; S2, calculating the density value of a rock skeleton; S3, calculating the average correction coefficient value; and S4, calculating the rock density of the correction depth section and drawing a corrected gamma-gamma density curve. The problem that a curve fluctuates drastically in a uranium enrichment section before correction is solved. Accurate acoustic impedance data can be provided for seismic exploration, and the quality of gamma-gamma density logging can be monitored effectively. The correction method is also applicable to a gamma-gamma density logging distorted curve affected by a hole enlarge section and a hole collapse section.
Owner:核工业二〇八大队
Display apparatus and method of driving the same
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
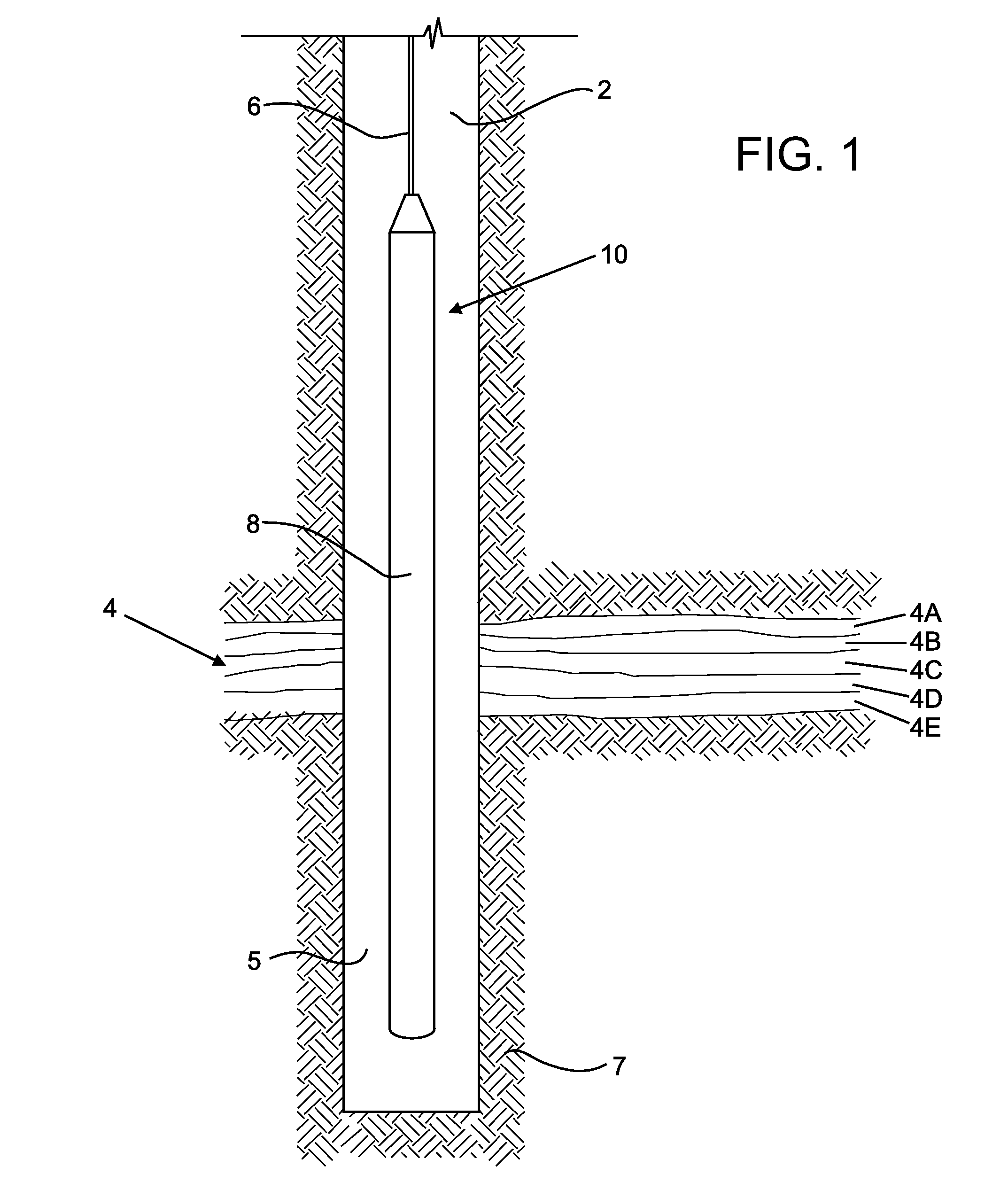
Method and system for evaluation of gamma-gamma well logging data in mineral exploration
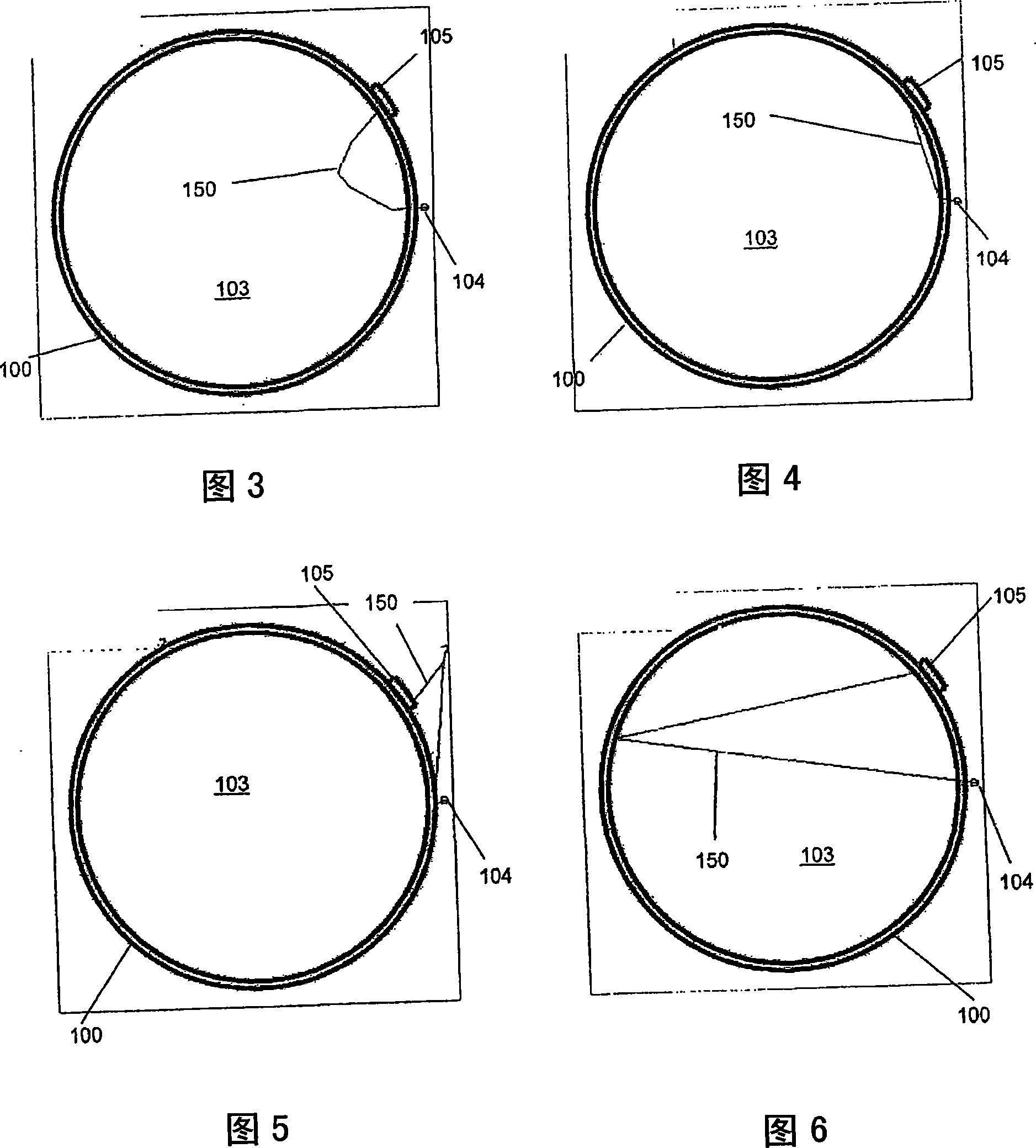
A calibration site for a gamma-gamma well logging tool for use in mineral exploration, the calibration site having a column consisting of a plurality of blocks of known densities; and a borehole through the column configured to accept the gamma-gamma well logging tool. Further, a method for calibrating a gamma-gamma well logging tool at the calibration site, the method including lowering the gamma-gamma well logging tool into a column consisting of a plurality of blocks of different known densities and having a borehole therein to receive the gamma-gamma well logging tool; raising the gamma-gamma well logging tool at a set rate; capturing a radiation count at a sensor of the gamma-gamma well logging tool; converting the radiation count to a recorded density for a particular depth at a computing device; and comparing the recorded density at each position of the column with the known densities.
Owner:VALE LIMITED
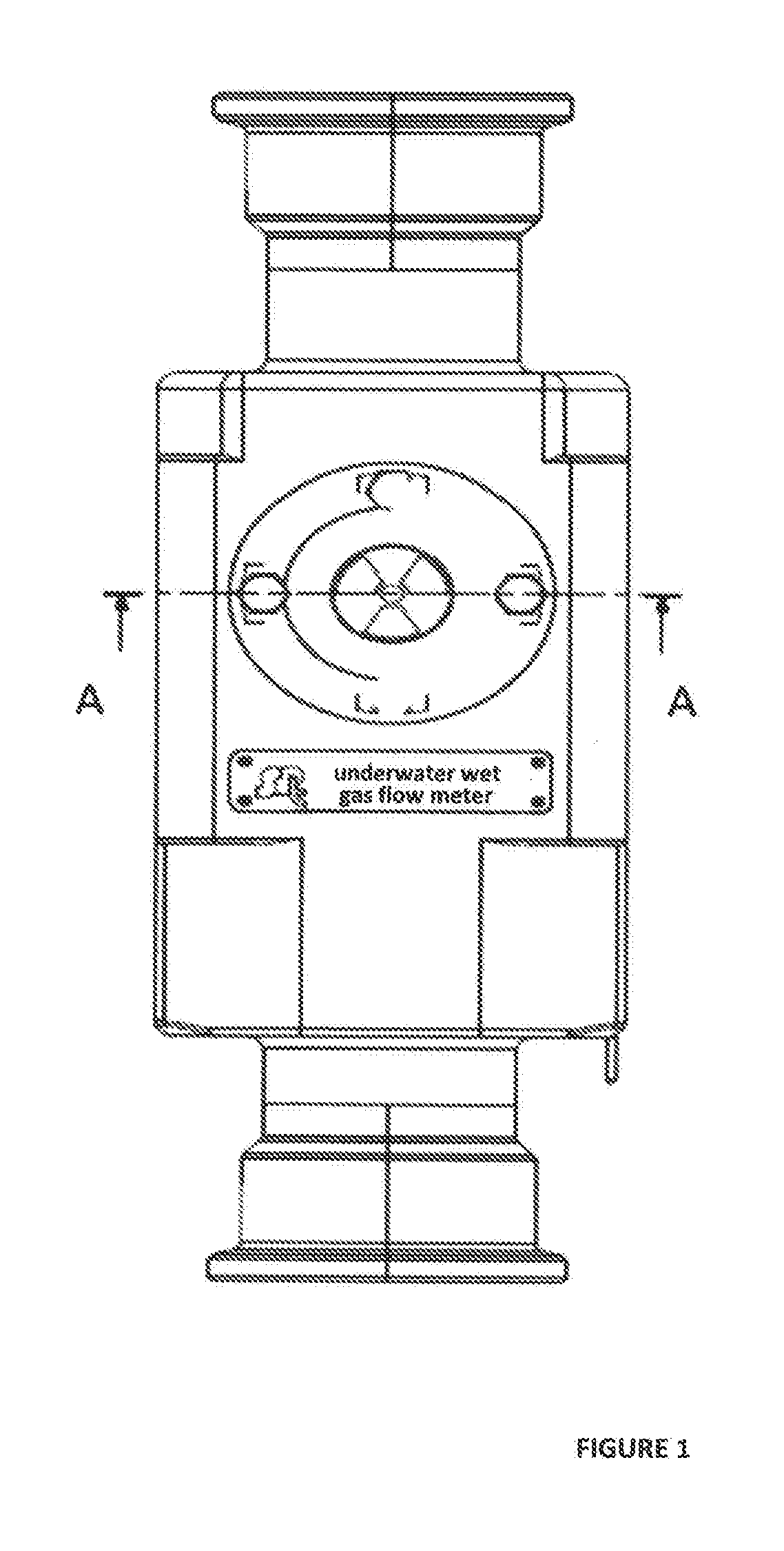
Apparatus and Method for Measuring Mass Flow-rates of Gas, Oil and Water Phases in Wet Gas
ActiveUS20190219432A1Improve convenienceConducive to simplificationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationIndirect mass flowmetersDifferential pressureRadioactive source
The invention is directed to apparatus for measuring mass flow-rates of the gas, oil and water phases in a wet gas, comprising the following parts: a differential pressure flow meter, having a throat section, and a gamma ray detector, comprising a gamma ray emitter and a gamma ray receiver that are arranged in such a manner that gamma rays emitted from the gamma ray emitter can pass through the throat section in diametrical direction to reach the gamma ray receiver; wherein a radioactive source in the gamma-ray emitter is a multi-energy radioactive source that can naturally emit at least three energy gamma rays, and a thermostatic device is not used in the gamma ray receiver. The invention further relates to a metering method for measuring mass flow-rates of the gas, oil and water phases in a wet gas, in which the above apparatus is used. As for the apparatus according to the invention, neither a thermostatic device nor the calibration for the empty tube value is in need, and thus it is very suitable for the uses under water or down-hole.
Owner:WUXI SEA PIONEERS TECH CO LTD
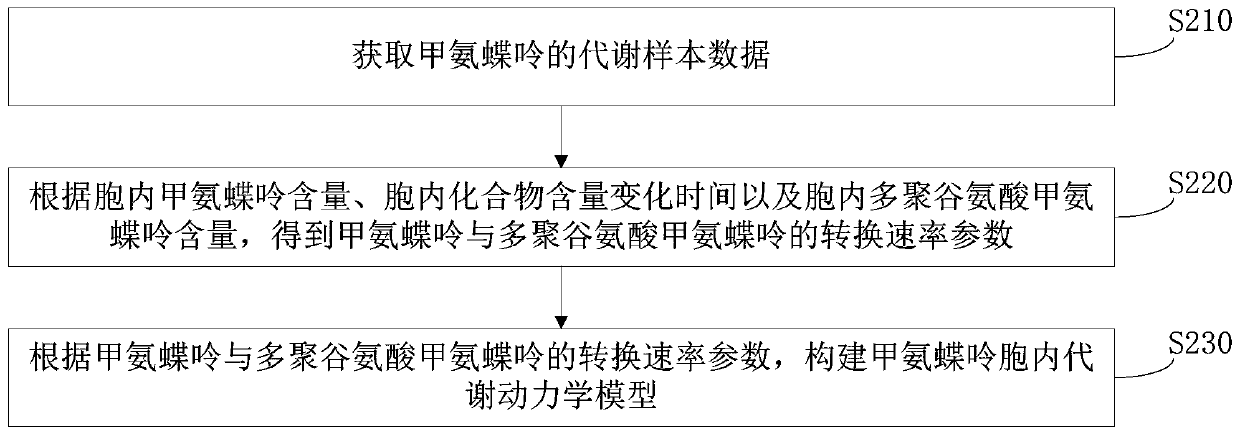
Methotrexate dosage regimen determining method, device, storage medium and equipment
The invention relates to a methotrexate dosage regimen determining method, a device, a storage medium and equipment. Through establishing a methotrexate inner metabolism dynamics model, in consideration of influence of different methotrexate metabolism related enzymes (folypolyglutamate synthetase and gamma-gamma-glutamyl hydrolase) contents to the methotrexate metabolism speed parameter, and thenthe metabolism condition of the methotrexate is simulated through the model, thereby determining the corresponding dosage regimen according to the methotrexate metabolism simulation condition, namelydetermining the dosage regimen according to the methotrexate metabolism related enzyme content differences between different patient individuals, thereby realizing more scientific and reasonable methotrexate dosage regimen, and realizing accurate medicament dispensing for aiming at different patient individuals.
Owner:余鹏
Method for taking gamma-gamma density measurements
A method for performing a measurement of a property downhole includes: using an instrument including an irradiator including a pulsed neutron generator, a moderator and a material including a high cross section for capturing thermal neutrons downhole, generating inelastic gamma photons from neutron interactions in the moderator and generating capture gamma photons from neutron interactions in the material; irradiating sub-surface materials proximate to the instrument with the inelastic gamma photons and the capture gamma photons; detecting radiation scattered by the sub-surface materials; and estimating the property according to the detected radiation. A system is also disclosed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
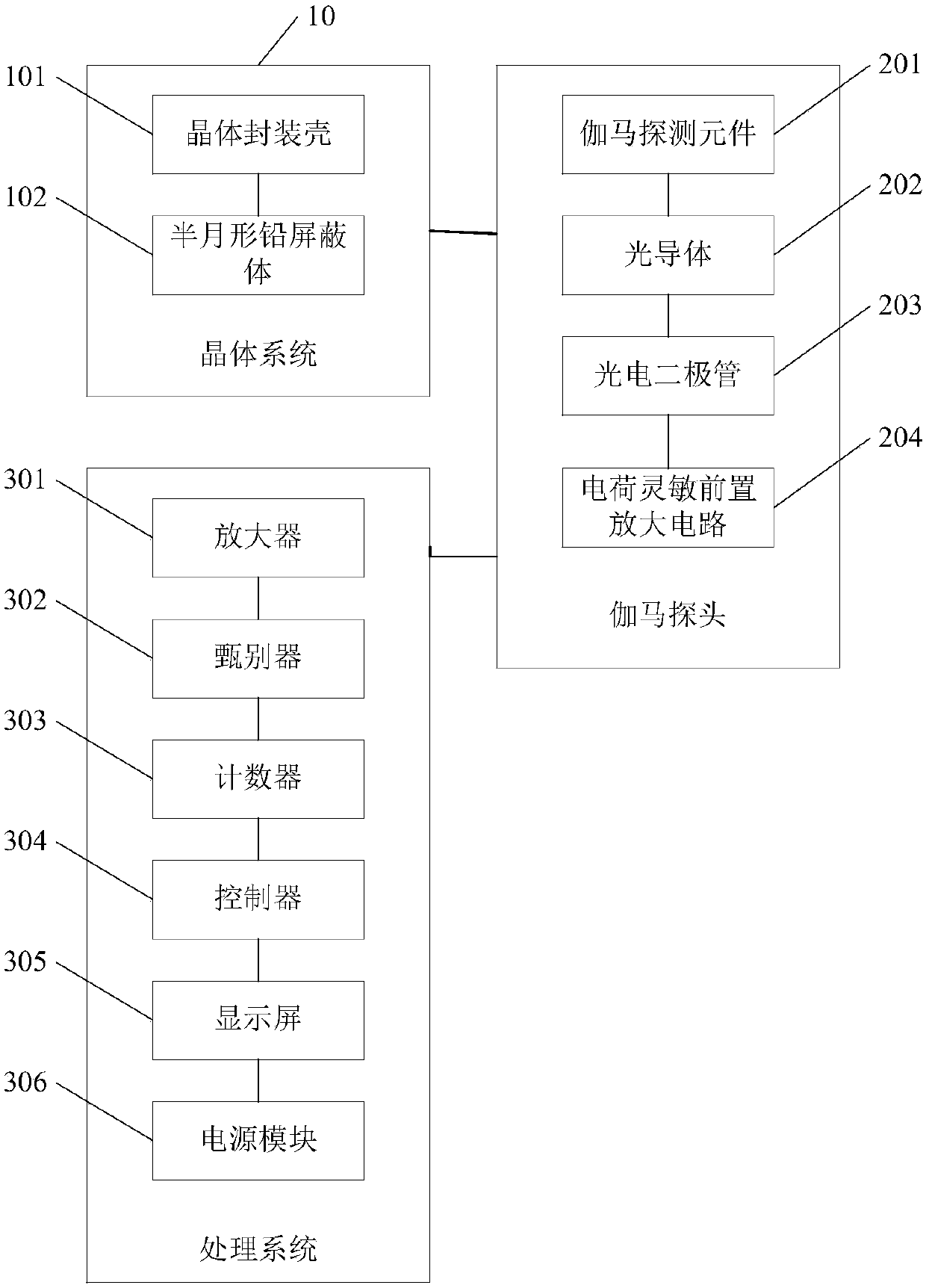
Gamma radiation detector
InactiveCN107748380AImprove detection resultsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentDiscriminatorCrystal system
The invention discloses a gamma radiation detector, which includes a crystal system, a gamma probe and a processing system, and the gamma probe includes a gamma detection element, a photoconductor, a photodiode and a charge-sensitive preamplifier circuit connected in sequence . The output end of the charge-sensitive preamplifier circuit is connected to the electronic signal input end, and the crystal system includes an externally sheathed crystal encapsulation shell, the crystal encapsulation shell is arranged in the shell of the detector, and wraps the gamma probe A half-moon-shaped lead shielding body is arranged in the gap between the crystal package shell and the outer shell of the detector, and the processing system includes an amplifier, a discriminator, a counter, a controller, a display screen and a power supply module, wherein the signal of the amplifier The input end is connected to the signal output end of the gamma probe, the display screen is connected to the controller, and the power supply module supplies power for the amplifier, discriminator, counter, controller, and display screen, thereby improving detection accuracy.
Owner:CHENGDU NEWRAY TECH CO LTD
A Parameter Estimation Method of Gamma-gamma Distribution Based on Double Log Cumulant Expectation
ActiveCN105743593BImprove estimation accuracyImprove computing efficiencyTransmission monitoringFree-space transmissionEstimation methodsAlgorithm
The invention relates to a Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation method based on a double logarithmic cumulant expectation, and belongs to the technical field of atmospheric turbulence channel parameter estimation of free space optical communication systems. According to the method, a Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation process is simplified greatly through Mellin transform, and a uniform parameter estimation method is built specific to the problems of low fractional moment (FMOM) parameter estimation accuracy and even error estimation in the prior art. Then, further improvements are made, and a concept of double logarithmic cumulant expectation is put forward, so that a finial parameter estimation expression is deduced. Compared with an FMOM, the Gamma-Gamma distribution parameter estimation method has the advantages that relatively high computing efficiency is ensured, and the parameter estimation accuracy is increased.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
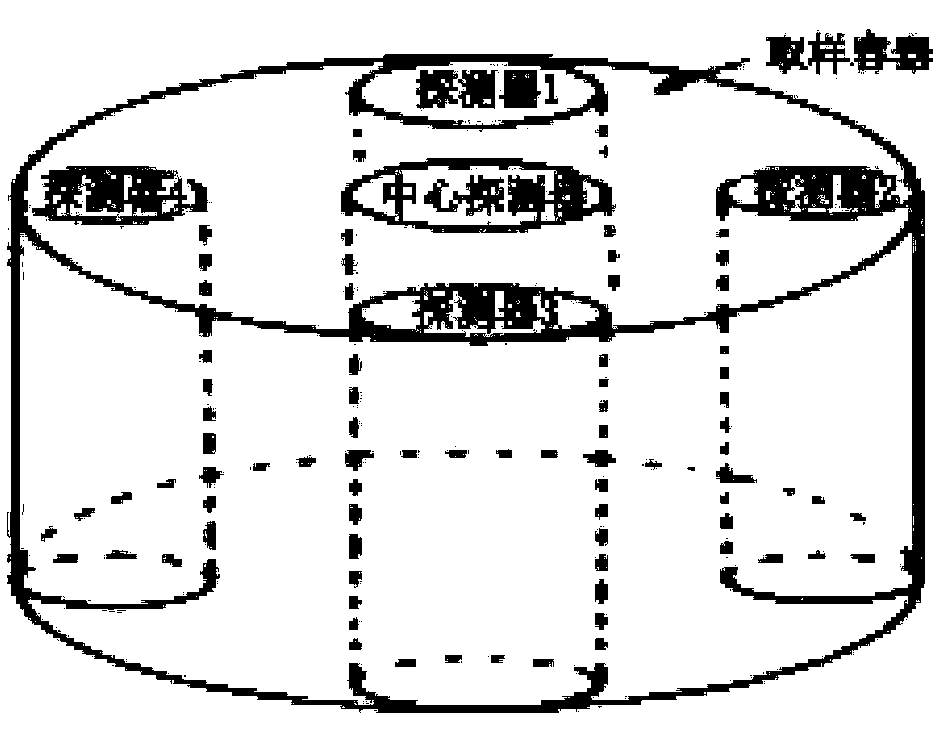
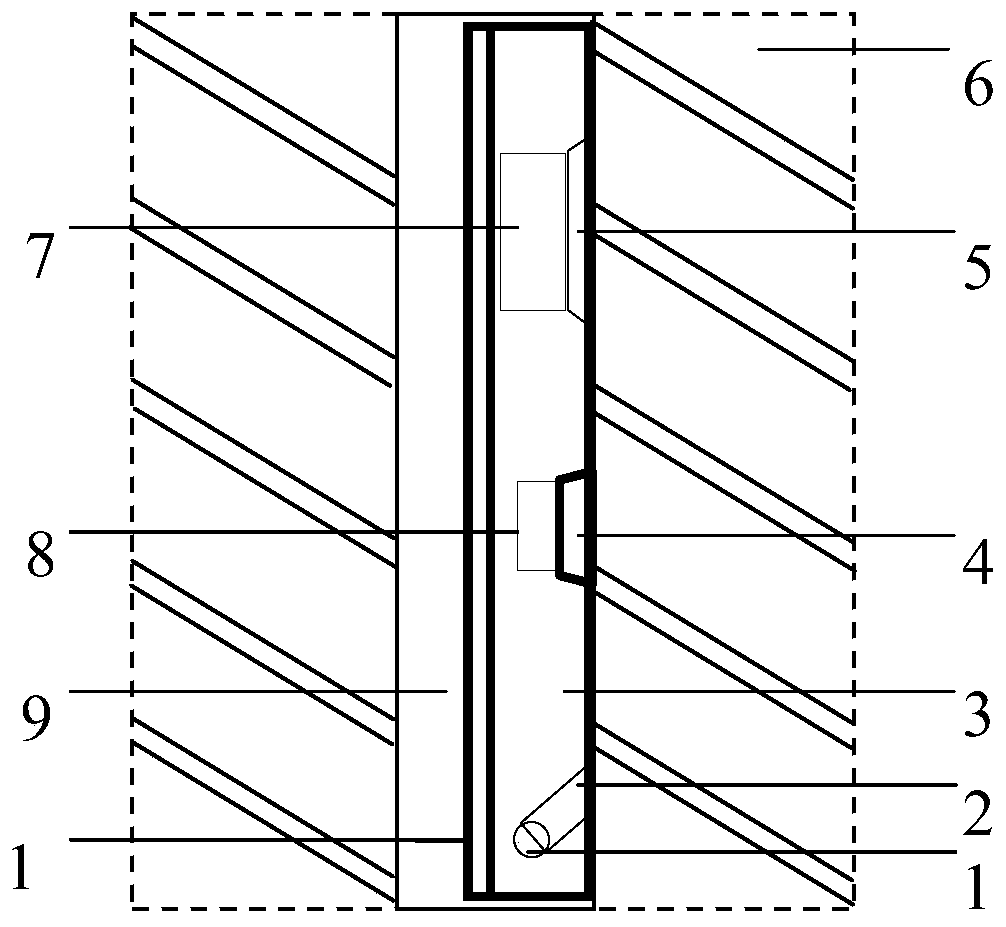
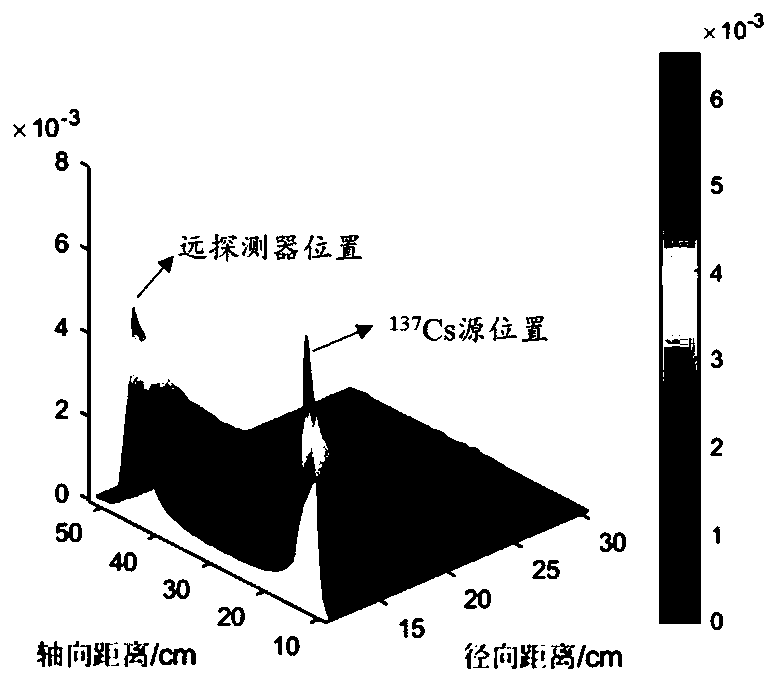
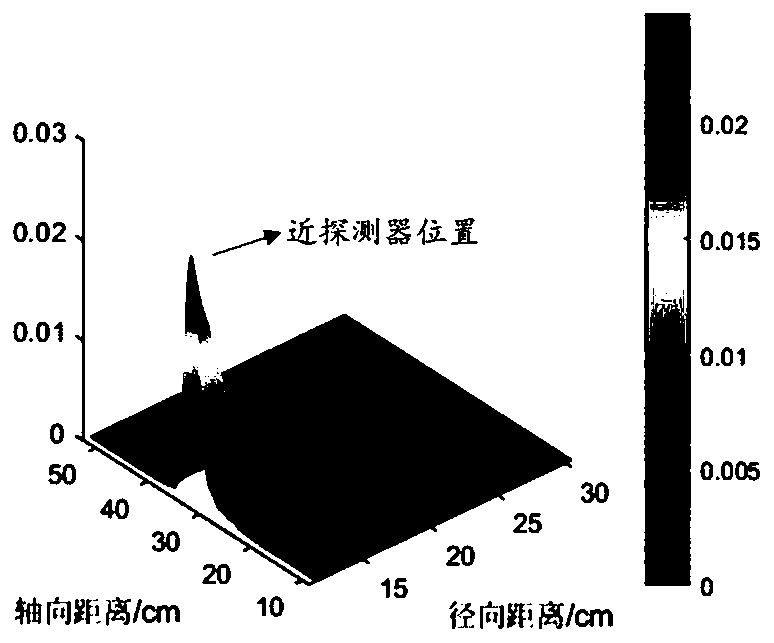
A kind of tomographic gamma scanning measurement method
ActiveCN103308534BGuaranteed uptimeReduced measurement timeMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
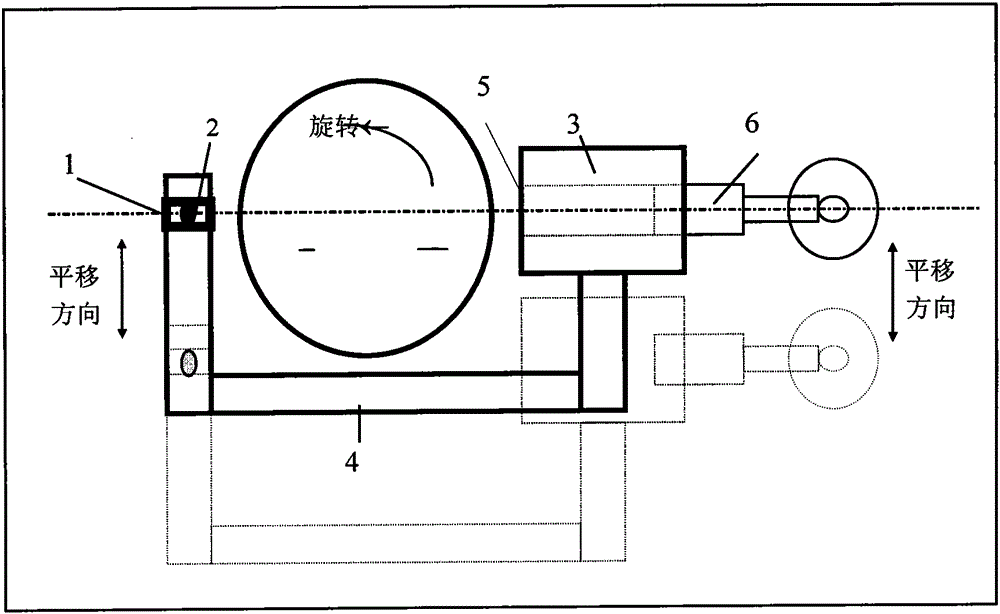
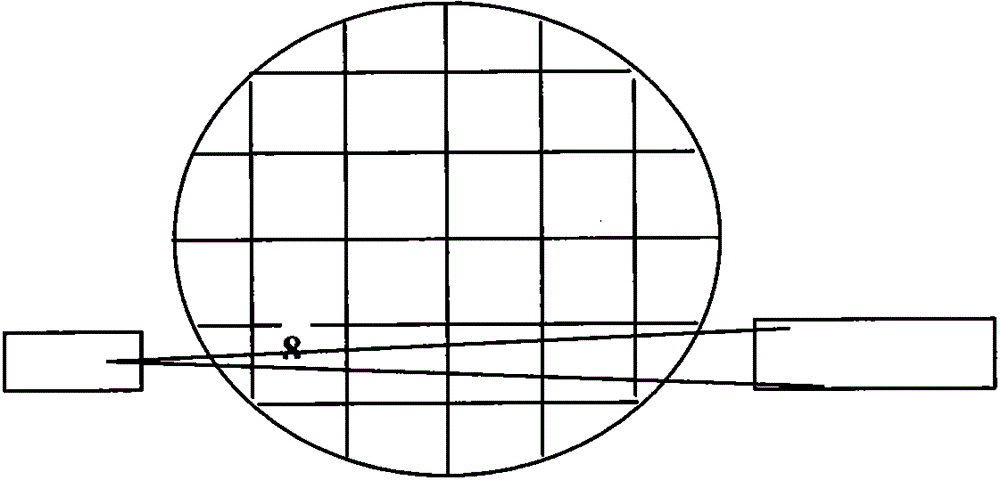
The invention discloses a tomographic gamma scanning and measuring method which comprises the following steps of: 1, performing transmitting measurement on a sample, namely (1) positioning and axially layering the sample; (2) selecting translation position points in equal interval on each layer; (3) rotating the sample around the central axis of a platform at each horizontal translation position point, and selecting eight rotating angles between 0 and 180 degrees in equal angle, wherein once measurement is performed while rotating once, and eight-time measurement is performed at each horizontal position point; 2, performing emission measurement on the sample; and 3, correcting the absorption attenuation of emitted gamma rays which penetrate through the measured sample by utilizing a dielectric wire attenuation coefficient obtained through transmitting gamma scanning measurement, and obtaining the radioactive content. The invention provides the tomographic gamma scanning and measuring method which is short in measurement time, high in analytical precision and high in measurement accuracy.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Gamma-gamma density measurement system for high-pressure, high-temperature measurements
InactiveUS8791407B2Easy to replaceAccurate, precise density and photoelectric factor measurementsNuclear radiation detectionUltrasound attenuationGamma ray
A downhole gamma ray density measurement system is described. The gamma ray density measurement system includes a pressure housing and a gamma ray source within the pressure housing. One or more detectors within the pressure housing detect gamma radiation. One or more low-attenuation inserts may be located in the pressure housing near the gamma ray source and / or one or more of the detectors. One or more high-attenuation inserts may be located in the pressure housing near the gamma ray source and / or one or more of the detectors.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Calibration Method of Gamma Value in Phase Measurement System
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Liquid crystal display device and display device
ActiveCN104123919BReduce mutual interferenceImprove qualityStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitLiquid-crystal display
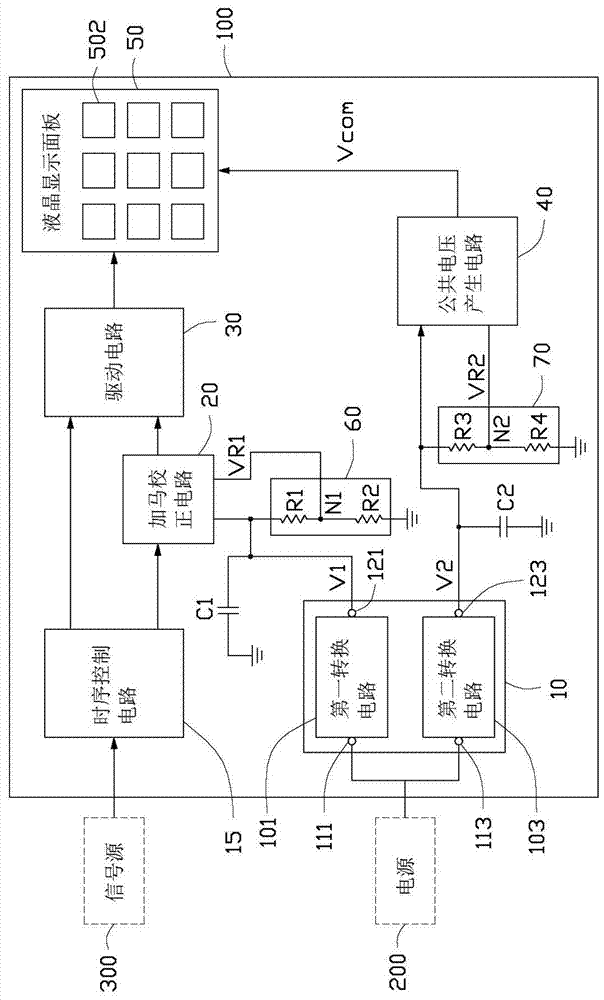
The invention provides a liquid crystal display device and a display device. The display device includes a display unit, a common voltage generation circuit, a gamma correction circuit, a drive circuit and a power conversion circuit. The common voltage generating circuit provides the common voltage to the display unit. The gamma correction circuit outputs a gamma voltage. The driving circuit provides grayscale voltages to the display unit according to the gamma voltage. The power conversion circuit includes a first conversion circuit and a second conversion circuit. The first and second conversion circuits are both input ends for connecting with a power supply, and the rest are two parallel branches separated from each other and not connected to each other. The first conversion circuit generates a first power supply voltage, the second conversion circuit generates a second power supply voltage, and the first and second power supply voltages are respectively output to the gamma correction circuit and the common voltage generation circuit. The gamma correction circuit uses the first power supply voltage as a reference voltage to generate a gamma voltage. The common voltage generation circuit generates a common voltage with the second power supply voltage as a reference voltage.
Owner:CENTURY DISPLAY (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Multi-purpose tender coconut essence
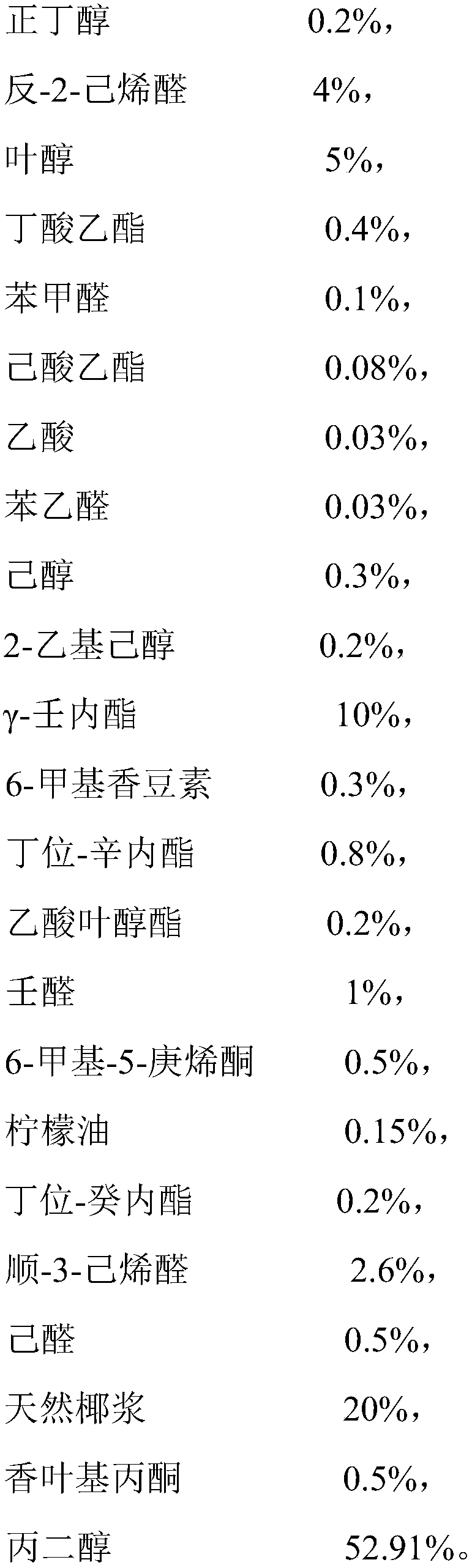
ActiveCN109090561ANatural aromaPerfect Green and Refreshing Coconut FlavorFood scienceCis-3-HexenalBenzaldehyde
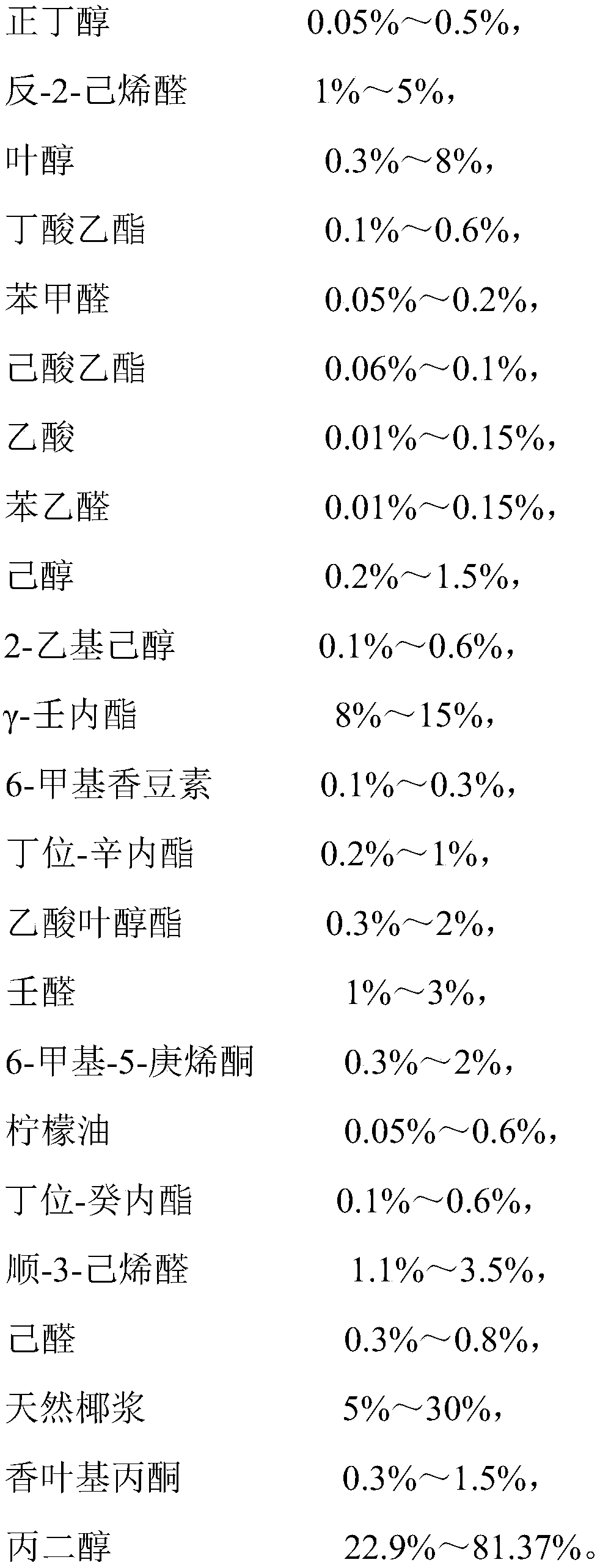
The invention discloses a multi-purpose tender coconut essence which is characterized by being composed of 0.05%-0.5% of n-butanol, 1%-5% of trans-2-hexenal, 0.3%-8% of leaf alcohol, 0.1%-0.6% of ethyl butyrate, 0.05%-0.2% of benzaldehyde, 0.06%-0.1% of ethyl caproate and 0.01%-0.15% of acetic acid and the like. According to the multi-purpose tender coconut essence, plenty of natural coconut milkis taken as a backing material, the leaf alcohol, cis-3-hexenyl acetate, cis-3-hexenal and trans-3-propyalacrolein coconut green peel fragrance raw material are added, gamma-gamma-nonanoic lactone andbutyl-octanolactone coconut meat and coconut juice fragrance raw materials are added, the coconut fragrance is made mellow and full well, the fragrance of the green coconut peel and fragrance of coconut juice and coconut meat are combined pleasantly, and thus the perfect, fragrant and tasty and refreshing coconut flavor is formed. In addition, the natural coconut milk in the essence is high in content, and natural oil lemon oil is added in the overall aroma for modification, so that the coconut fragrance is more natural, fuller and richer, which is in line with the trend that the essence tends to be natural and healthy.
Owner:广州市凯虹香精香料有限公司
Gamma density rapid-calculation method based on perturbation theory
ActiveCN110471120AHigh density calculation accuracyCalculation speedElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationComputational modelDensity response
The present invention discloses a gamma density rapid-calculation method based on a perturbation theory, and specifically relates to the field of petroleum and natural gas development. According to the method, from a gamma-gamma density response principle, the perturbation theory is introduced to a density response, different standard densities of strata are selected as a reference, and an instrument-stratum model is established in combination with MCNP for simulation to obtain first-order and second-order Compton and photolectric sensitivity function databases, thus forming a gamma-gamma density rapid-calculation method at last. The method specifically includes the following steps: step 1: introducing the perturbation theory into the density response, and performing expansion, deformationand simplification on a formula to obtain a spatial dynamic response function expression form; step 2: according to a parameter of a selected gamma-gamma density instrument, establishing a three-dimensional MCNP numerical calculation model, and simulating to obtain a spatial dynamic response function database; and step 3: performing multielement nonlinear regression on multiple hybrid density responses, and seeking for a coefficient of a rapid calculation formula to obtain the rapid calculation formula for density.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com