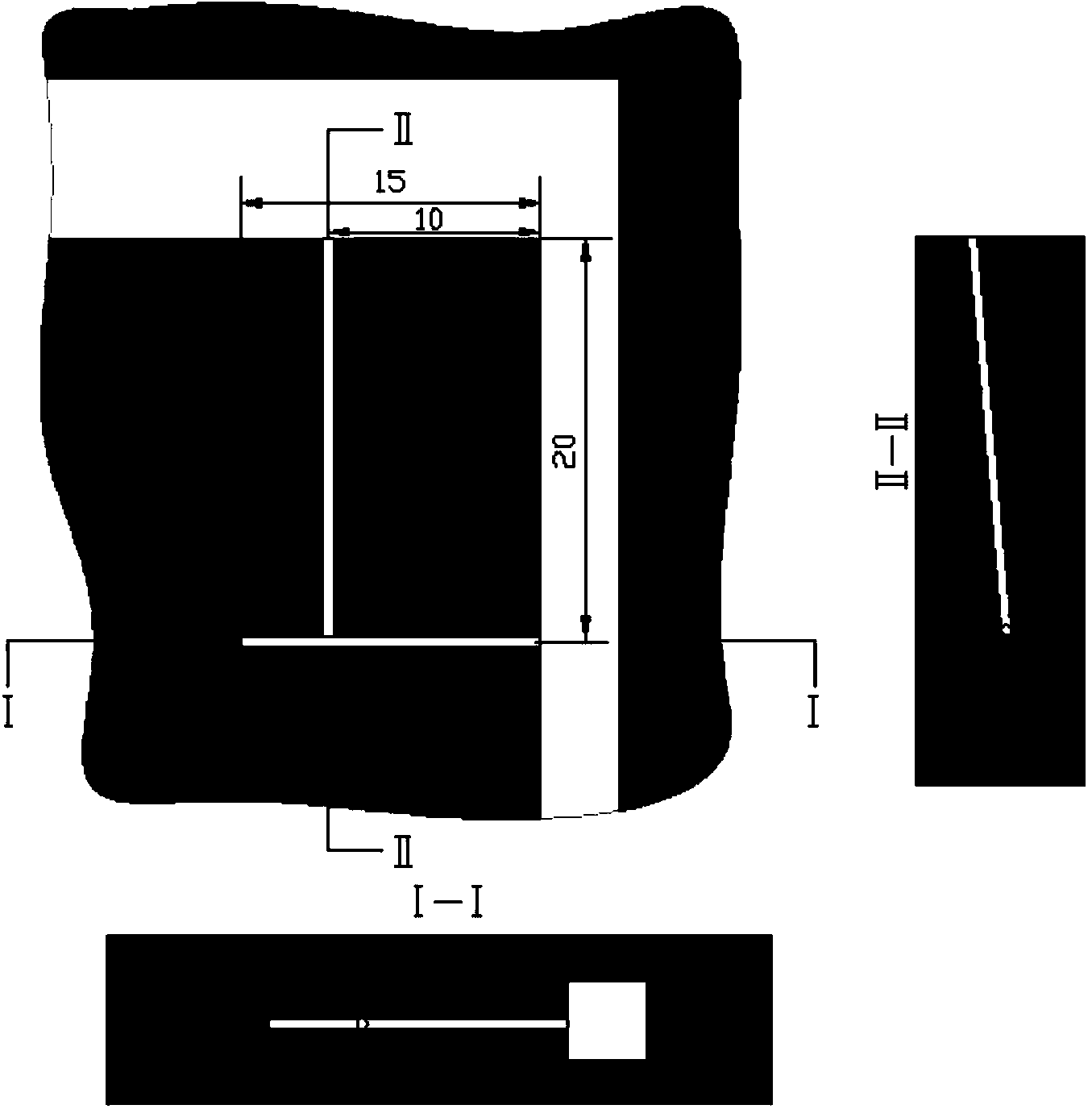
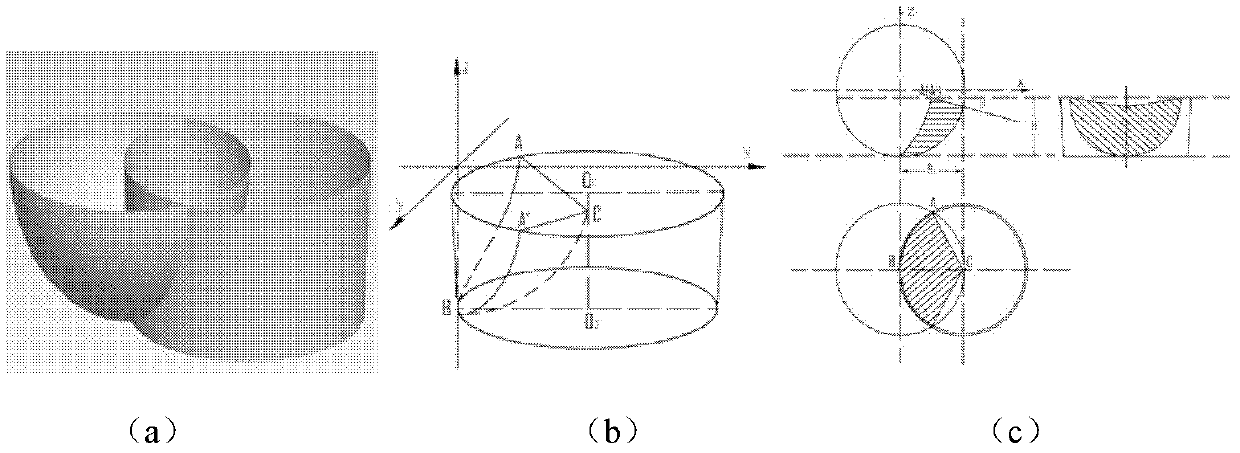
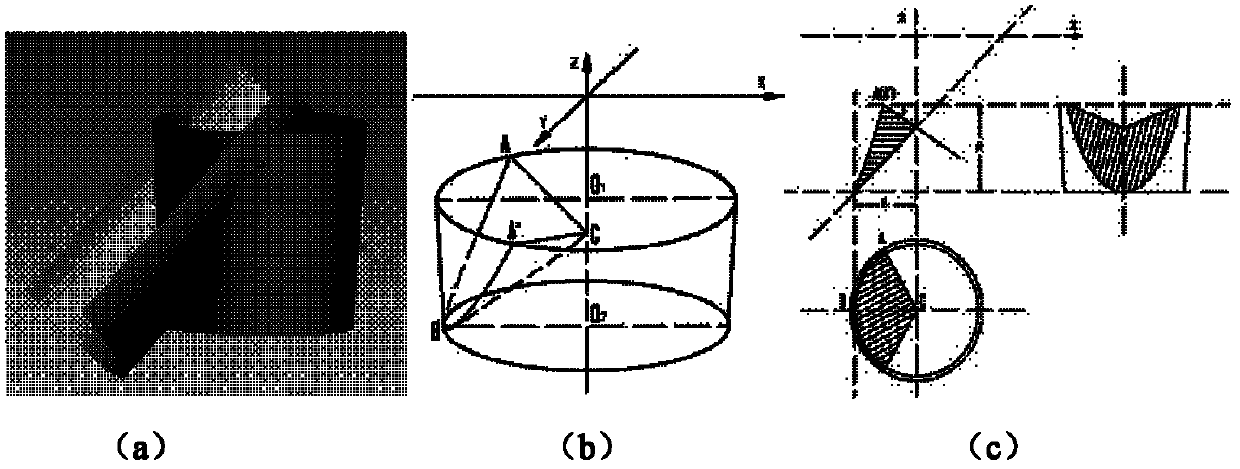
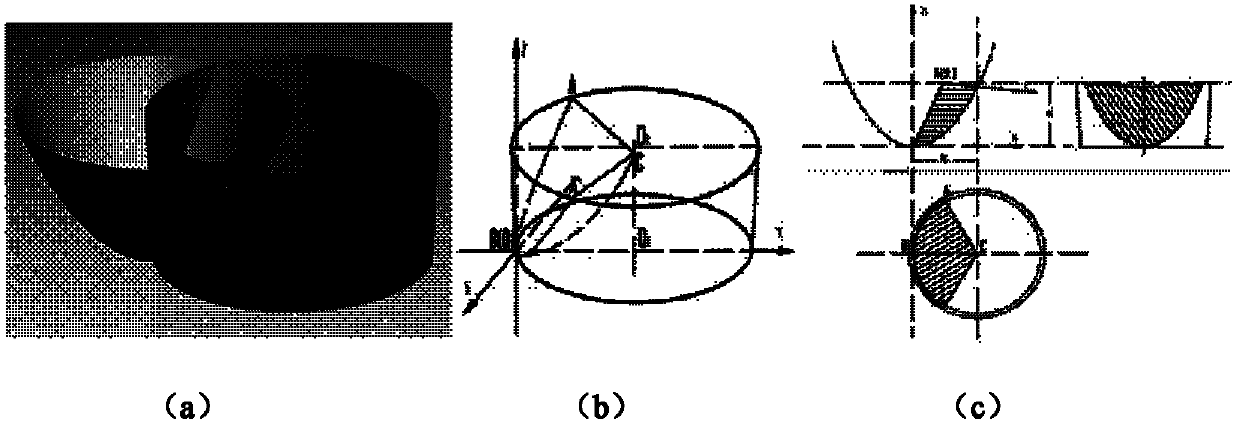
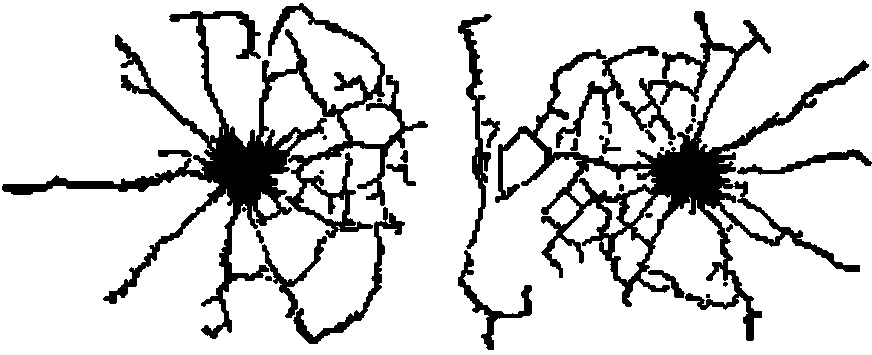Patents
Literature
37 results about "LS-DYNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
LS-DYNA is an advanced general-purpose multiphysics simulation software package developed by the Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC). While the package continues to contain more and more possibilities for the calculation of many complex, real world problems, its origins and core-competency lie in highly nonlinear transient dynamic finite element analysis (FEA) using explicit time integration. LS-DYNA is used by the automobile, aerospace, construction and civil engineering, military, manufacturing, and bioengineering industries.
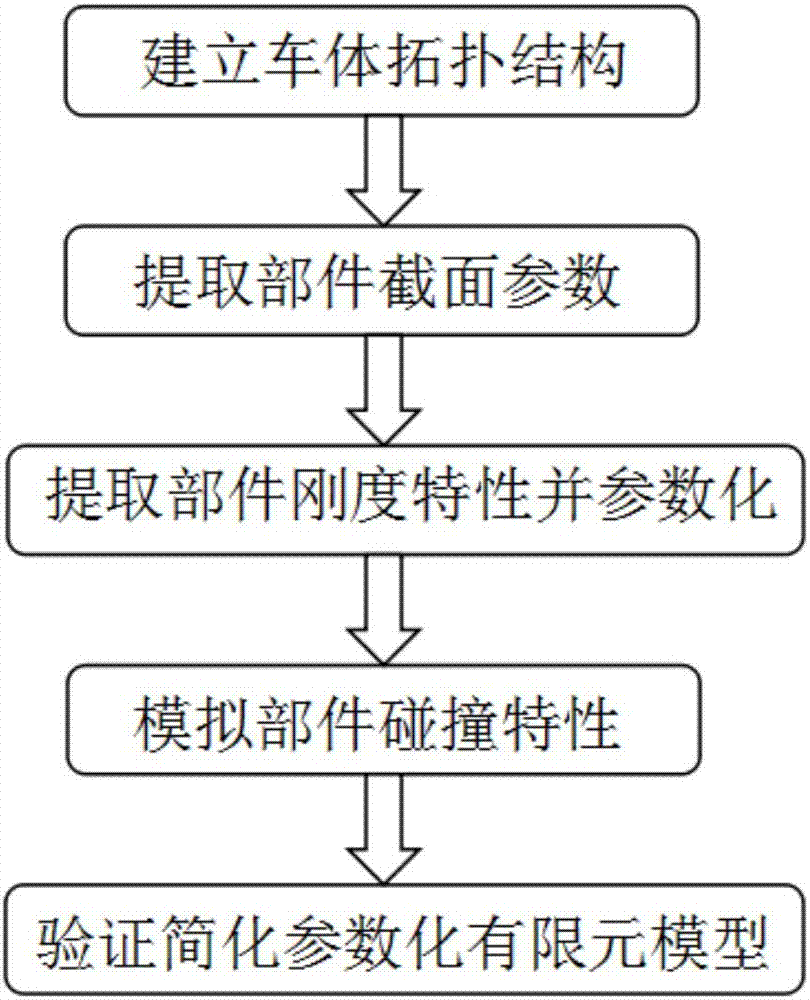
Method for building simplified parametric finite element model of car collision
InactiveCN107256289AQuick calculationEasy to modifyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelLS-DYNA
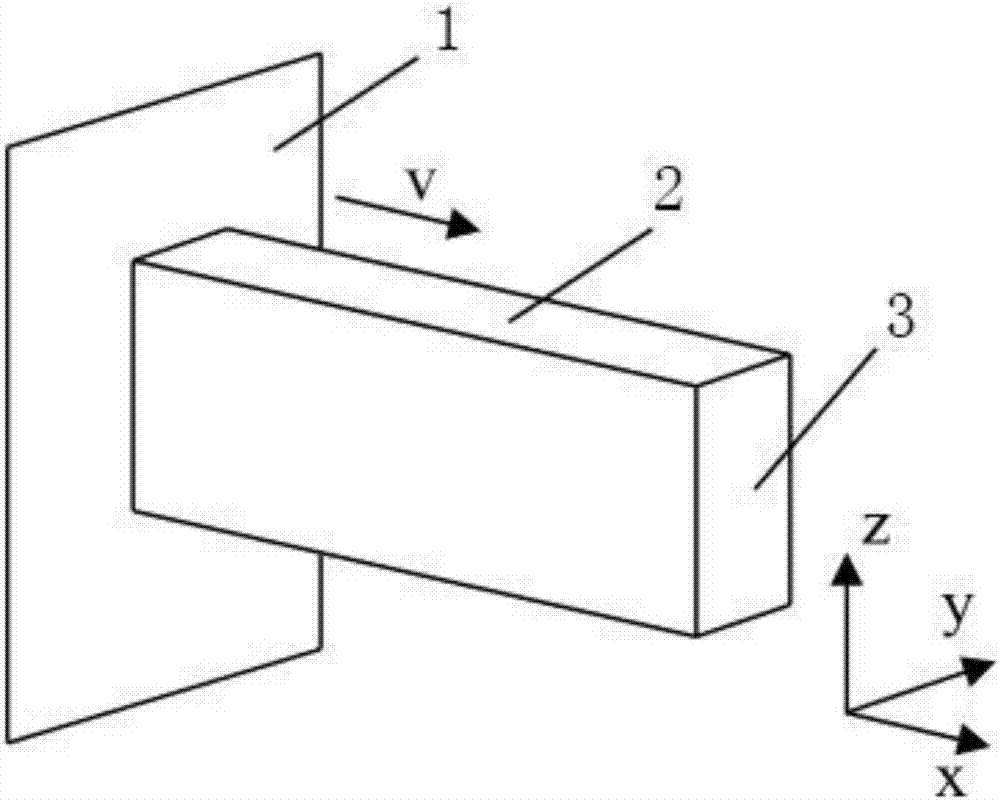
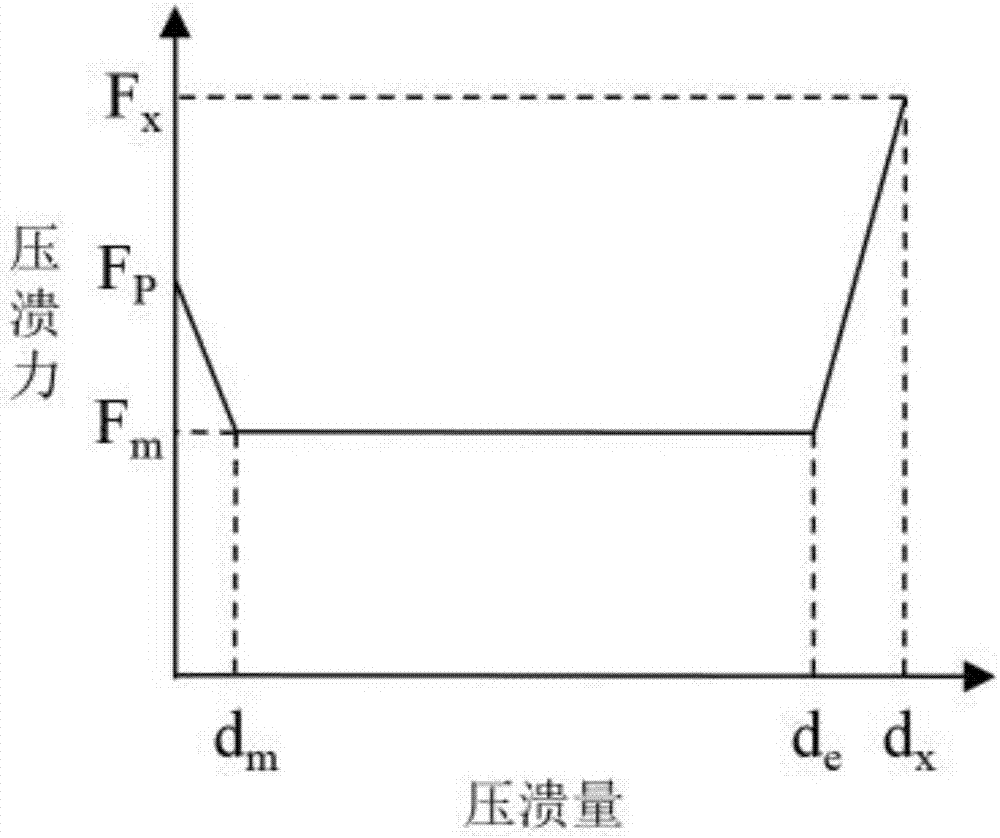
The invention discloses a method for building a simplified parametric finite element model of car collision, and aims to solve the problem of consumption of a large amount of modification and calculation time due to adoption of a conventional detailed finite element model in car body structure anti-collision design and improvement in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of 1) establishing a topological structure of a car body: (1) obtaining a detailed finite element model of a car; (2) building a one-dimensional unit topological model of the car body; and (3) building a topological structure model of the car body; 2) extracting cross section parameters of parts; 3) extracting stiffness characteristics of the parts and performing parameterization: (1) extracting crushing stiffness characteristics and performing parameterization; (2) building finite element simulation models of the crushing parts by utilizing Hypermesh software and performing calculation by utilizing LS-DYNA software to obtain a crushing force-crushing quantity curve; and (3) simplifying the crushing force-crushing quantity curve according to an absorbed energy equality principle and performing parameterization; 4) simulating collision characteristics of the parts; and 5) verifying the simplified parametric finite element model.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A method for determining loosening blasting danger-relieving range of coal beds with rock burst
The invention relates to a method for determining loosening blasting danger-relieving range of coal beds with rock burst, the method including: (1) theoretical calculation: calculating the specific drilling diameter and the fracture zone diameter on the condition of specific explosive parameters in accordance with site information and experience formulas, primarily determining the radius r of blasting pressure relief; (2) numerical simulation: simulating the drilling diameter and the fracture zone diameter on the condition of explosive parameters, which are identical to those in the theoretical calculation, by LS-DYNA dynamic simulation software and studying the influence of the blasting of the two drilling holes on the fracture zone and the distribution radius r; (3) on-site ultra-sonic test of the blasting fracture zone and verification.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Artificial cardiac valve and performance analysis method based on ANSYS/LS-DYNA thereof
The invention discloses an artificial cardiac valve. The thickness of the artificial cardiac valve ranges from 0.4mm to 0.6mm. A modeling equation of the curve face of the artificial cardiac valve is one the following four equations: 1 a round spherical face model parameter equation, 2 a cylindrical face model parameter equation, 3 a rotation paraboloid model parameter equation and 4 an ellipsoid model parameter equation, wherein x, y and z respectively represent a horizontal ordinate, a vertical ordinate and a longitudinal ordinate of a curve space ordinate, and alpha represents a conical inclined angle and is 3 degrees. The invention further discloses a performance analysis method based on ANSYS / LS-DYNA of the artificial cardiac valve and establishes a fluid-solid coupling model of the biological valve prosthesis so as to lay the foundation for fluid-solid coupling of the biological valve prosthesis. The artificial cardiac valve and the performance analysis method based on ANSYS / LS-DYNA of the artificial cardiac valve analyze and compare the four models according to bionics and the principle of the largest opening area and with the combination of bionic theory, the conclusion is obtained: a round spherical face cardiac valve has the best performance, so that powerful basis is provided for the research and optimization of the biological cardiac valves.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
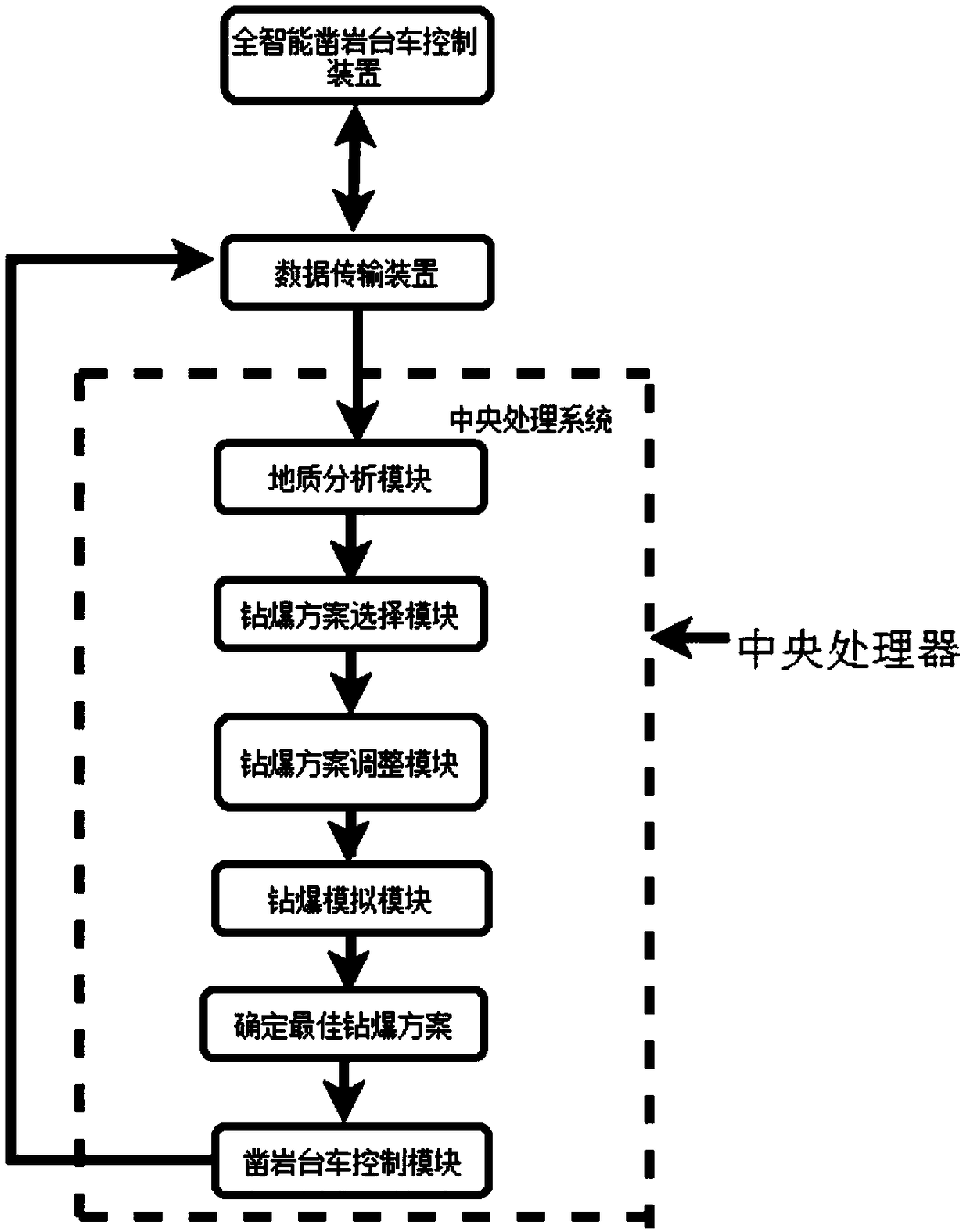
Method for overbreak-underbreak control of tunnel based on building information modeling (BIM)
ActiveCN108930539AEasy to controlRealize intelligent automation managementGeometric CADBlastingLS-DYNAComputer science
The invention discloses a method for overbreak-underbreak control of a tunnel based on building information modeling (BIM). According to the method, a full intelligent drill jumbo is connected with acentral processing unit of a user terminal, the precise positioning and multi-arm synchronous attitude adjustment of the drill jumbo are realized in the tunnel, multiple-drilling-arm automatic operation is achieved, and the peripheral contour of the tunnel and the positions of positioning boreholes are measured automatically. Geological analysis is carried out by combining advanced level drillinggeological exploration data with BIM technology analysis, according to drilling and blasting design matched with the implanted drilling and blasting design scheme, in cooperation with the constructionexperience of blasting personnel, the drilling and blasting design scheme is dynamically adjusted, and an LS-DYNA program is combined to perform drilling and blasting simulation, so that the best drilling and blasting program is formulated. The drill jumbo performs drilling according to the scheme, overbreak-underbreak is controlled strictly, and the intelligent and automatic management of personnel and machineries at a tunnel excavation construction site is realized, so that the control of overbreak and underbreak of the tunnel is achieved.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY 18TH BUREAU GRP CO LTD
Nonlinear topological optimization method for car body welding spot arrangement
ActiveCN106126849AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed reasonablenessGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationManufacturing cost reductionElement model
The invention discloses a nonlinear topological optimization method for car body welding spot arrangement. The method comprises the steps that a vehicle crash simulation finite element model is established, LS-DYNA calculation is submitted, and displacement values of crash performance key attention nodes are output; a white car body linear rigidity simulation finite element model is established, and GENESIS optimizing calculation is submitted; entity units are adopted for modeling of relevant welding spots in a crash model and a white car body model; an equivalent static load method is adopted for transforming crash nonlinear conditions into linear static conditions for topological optimization design; the welding spots are set to be topological variables, obtained welding spot density values are updated into the crash finite element model, and a new round of crash simulation analysis is conducted; lastly, a convergence result is postprocessed. According to the method, the entity welding spots are subjected to topological optimization, car body welding spot arrangement is realized on the premise that crash properties at all important moments are met, reasonability of car body welding spot arrangement is ensued, redundant welding spot arrangement is avoided, the number of the welding spots is reduced, manufacturing cost is lowered, and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:迅仿科技(上海)有限公司 +2
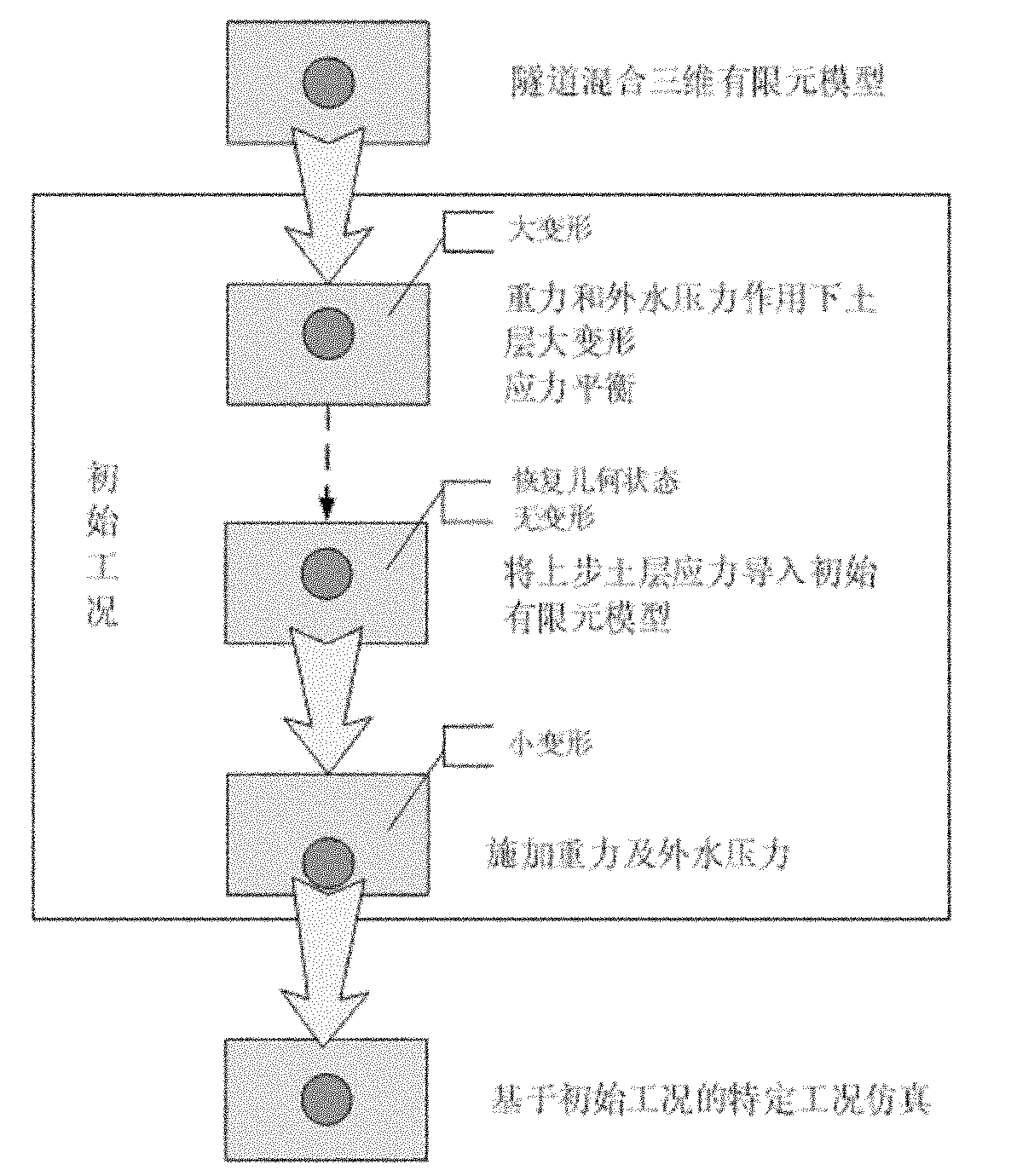
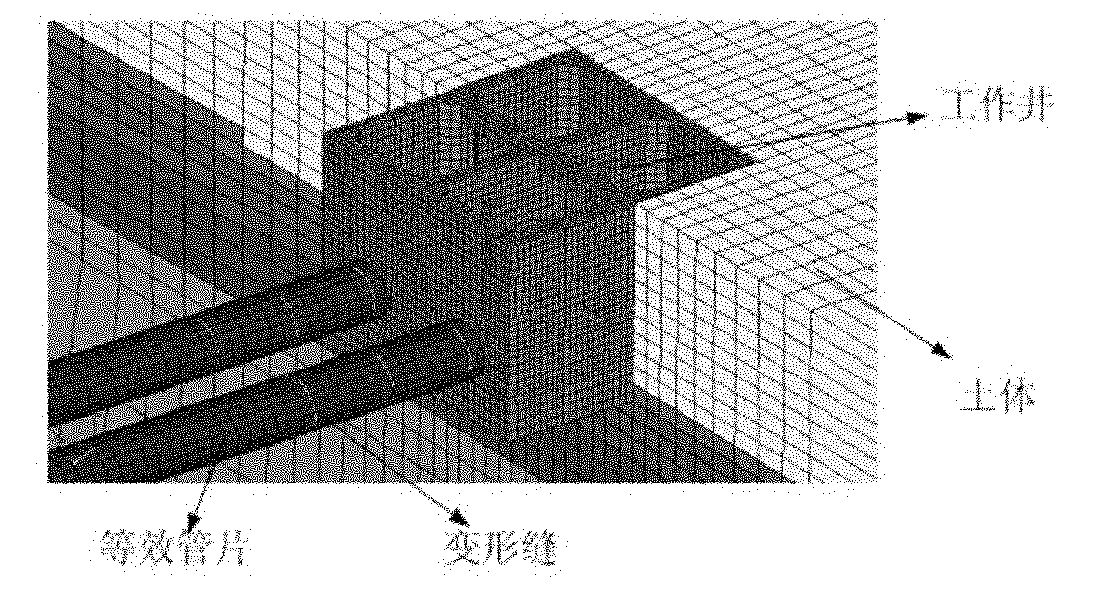
Water-conveyance tunnel simulating method based on mixed model
The invention relates to a water-conveyance tunnel simulating method based on a mixed model in the technical field of tunnel construction. The method comprises the following steps of: simulating the initial working condition after establishing a mixed three-dimensional finite element model of the tunnel and adding soil and the initial stress of a duct piece so as to obtain the initial state of anestablished tunnel; and then, adding an external simulation condition to the mixed three-dimensional finite element model of the tunnel in the initial state and then calculating through a nonlinear finite element displaying method LS-DYNA to obtain a model response to realize the simulation of the tunnel. The invention can obtain the response rule of the integral structure of the tunnel and analyze the key parts at the key position in detail; and meanwhile, integral equivalent calculation can be carried out firstly to obtain a local danger part or to specify the local danger part according tothe previous construction experience.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SUBEI RES INST
Cutting process simulation process for brittle materials
InactiveCN105512400AAvoid the difficult problem of online observationImprove surface qualitySpecial data processing applicationsMicro nanoSmoothed-particle hydrodynamics
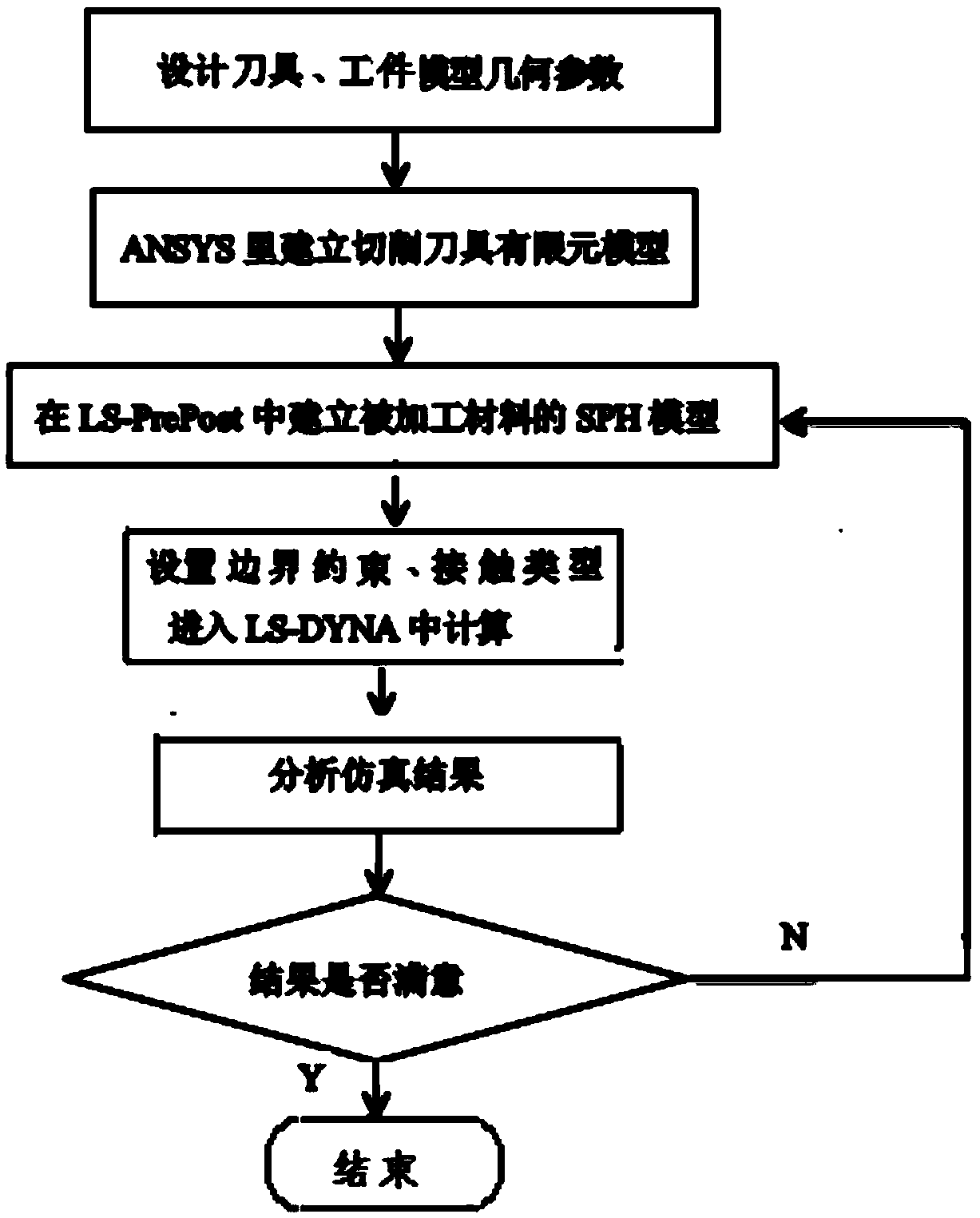
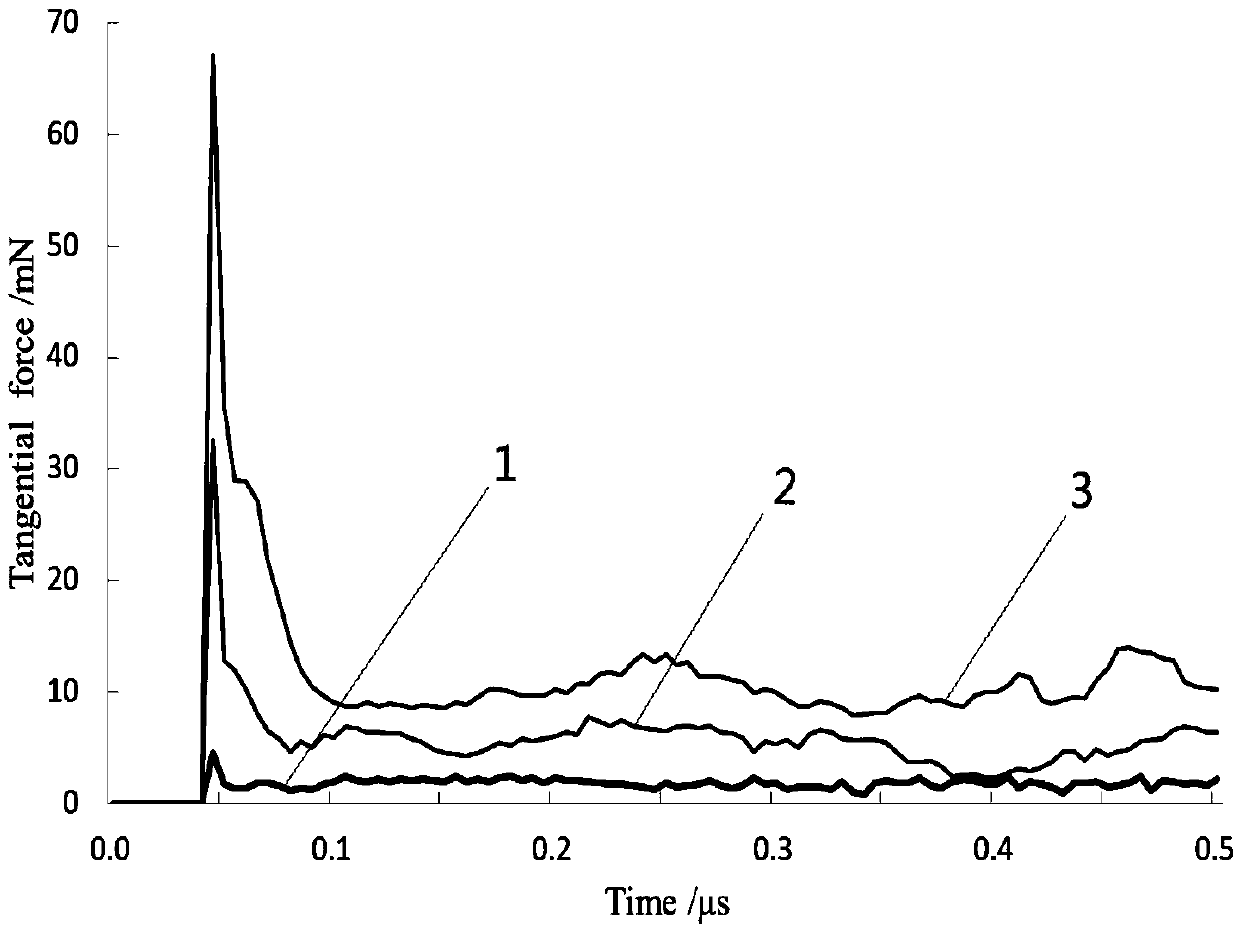
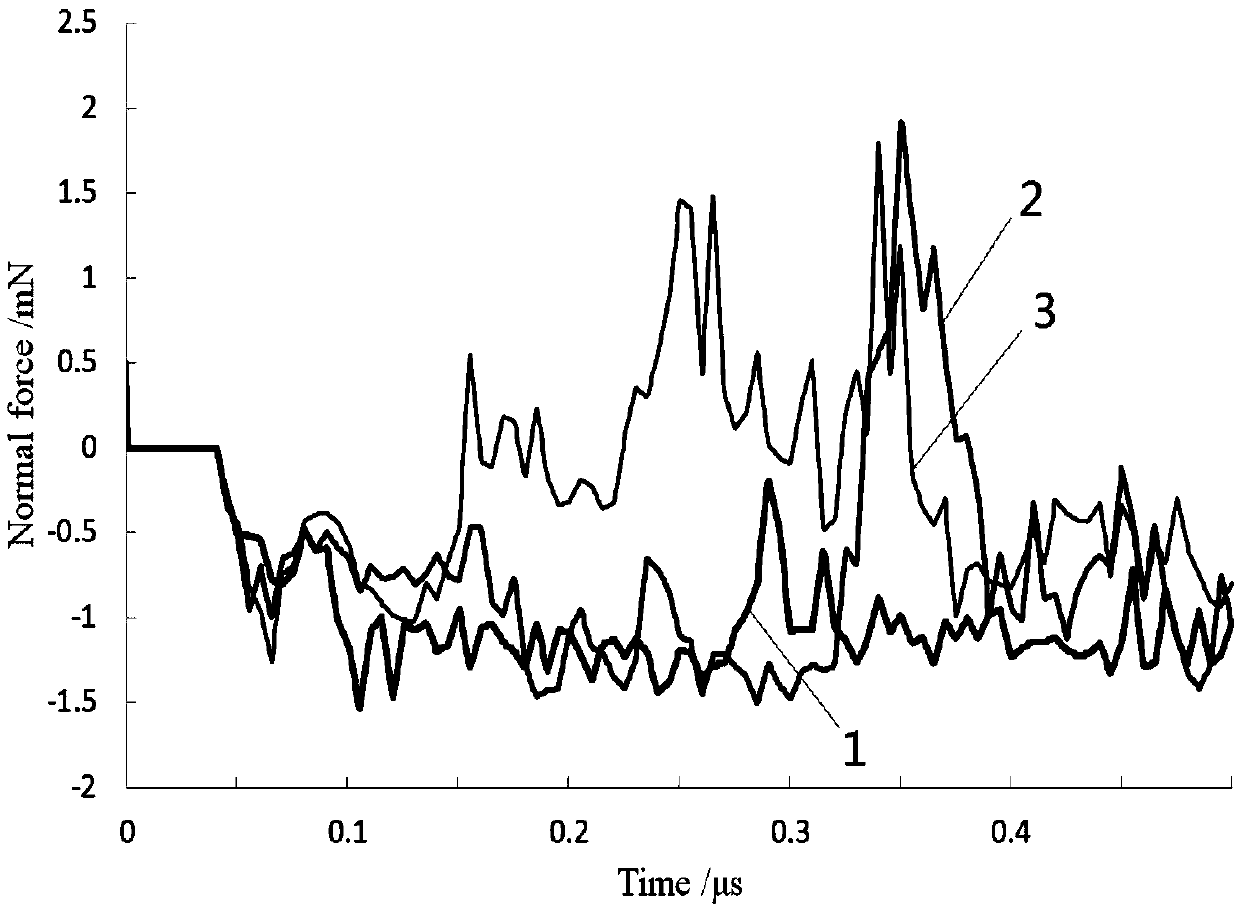
The invention provides a cutting process simulation process for brittle materials, belongs to the field of micro-nano ultraprecision machining numerical simulation and relates to a three-dimensional micro-nano cutting machining simulation method based on an SPH (smoothed particle hydrodynamics) method. According to the simulation method, dimensions of a cutter and a workpiece material are set firstly; then a three-dimensional cutter finite element model is established in ANSYS, an SPH model of the workpiece material is established in LS-PrePost, parameters of contact, boundary, the material and the like are set, and calculation is performed in LS-DYNA; finally, a simulation result is analyzed, and whether the result meets the actual machining condition is judged. The simulation method has the advantages that data including stress, strain, density and the like in a cutting machining process can be obtained more clearly and more accurately, the brittle materials are removed from a ductile region through control of cutting depth, and acquisition of more ideal surface quality is more facilitated. A large quantity of labor cost, experimental cost and economic cost is saved, and the problem of on-line observation difficulty of an experimental method is solved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
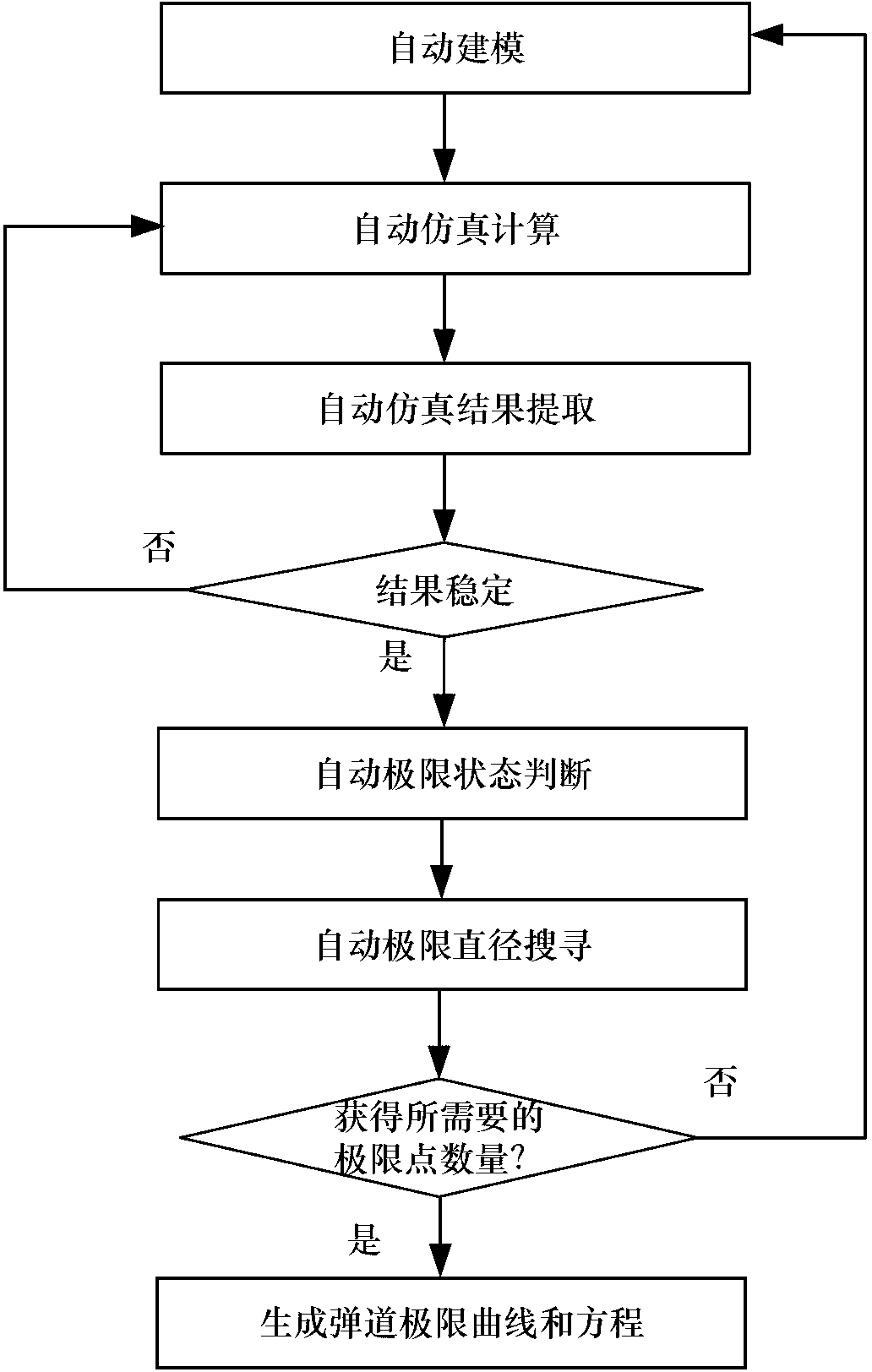
Numerical-value-simulation-based automatic ballistic limit acquisition method for satellite protective structure
ActiveCN103218490ALow costShorten acquisition cycleSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsLS-DYNA
The invention relates to a numerical-value-simulation-based automatic ballistic limit acquisition method for a satellite protective structure. The method comprises the following steps: a servo program creates modeling scripts according to key parameters and configurations of a simulation model to be created, calls pre-processing software to read the modeling scripts and execute modeling operations and outputs simulation model k files, an LS-dyna solver is started to calculate and output result files at fixed time intervals, simulation termination judgment is carried out by using the restart analysis function of the LS-dyna solver, simulation is ended until results are stable, data of the obtained result files are displayed graphically, limit points are directly obtained if critical penetration situations are obtained, the limit points are obtained through automatic limit diameter search if the critical penetration situations are not obtained, and a ballistic limit curve and a ballistic limit equation are finally created after the required limit points are obtained. The method has the advantages that the analysis cost is reduced, the cycle is shortened, and simulation results can be applied to engineering design through only being calibrated by a few assisted experiments.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
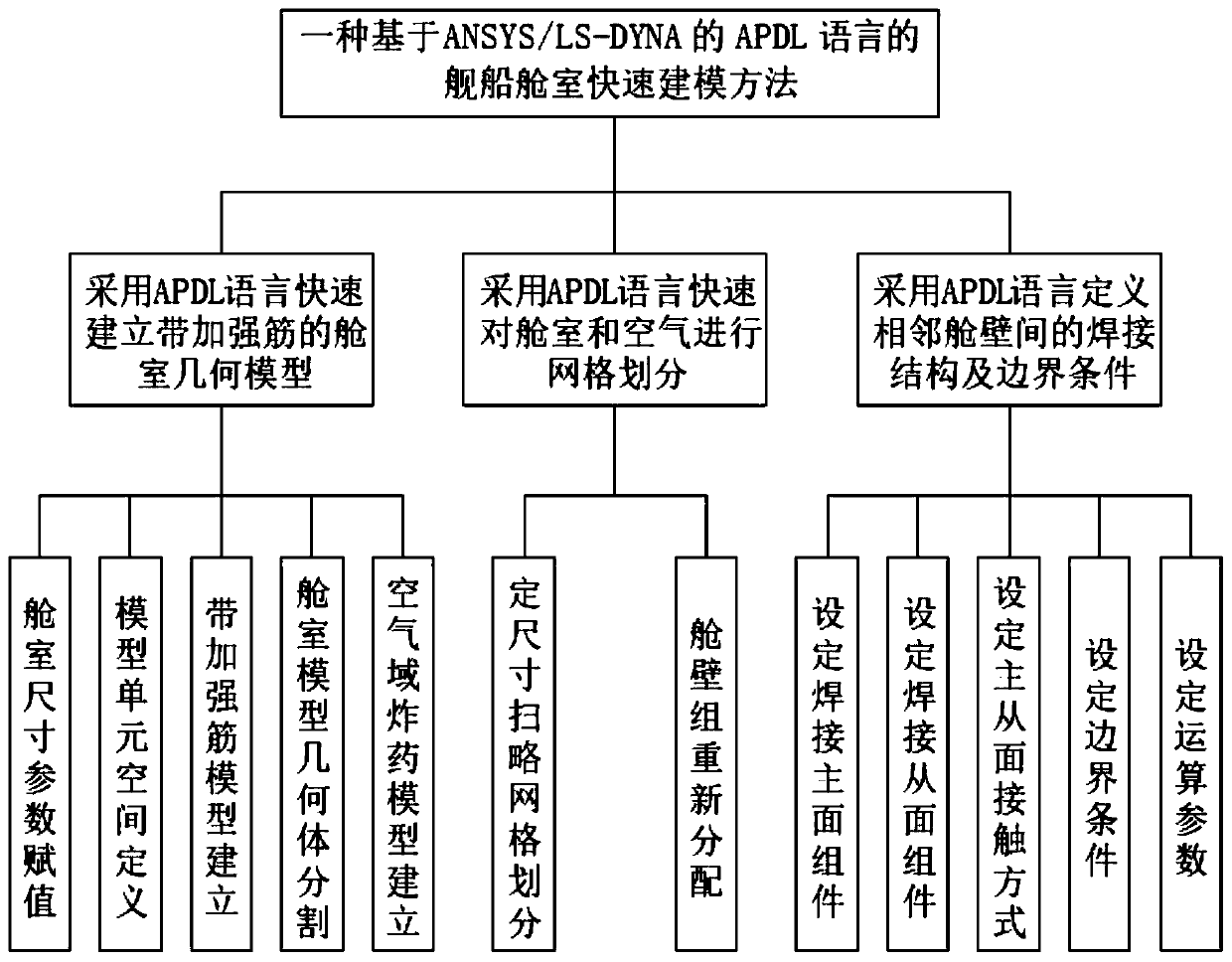
Ship cabin rapid modeling method based on APDL language of ANSYS/LS-DYNA
InactiveCN110427645AAccurate Response ResultsImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisLS-DYNA
The invention relates to a ship cabin rapid modeling method based on an APDL language of ANSYS / LS-DYNA. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, parameterizing each panel of a cabin and eachkey size of a reinforcing rib structure of the panel, then carrying out common node setting on an overlapping region of a cabin wall and a reinforcing rib by utilizing an APDL language, establishinga solid model of each panel and the reinforcing rib of the cabin, and quickly cutting the model by adopting a cyclic instruction, controlling a distance and changing the position and direction of a working surface; secondly, performing grid rapid division on the cabin model and the air domain by utilizing a hexahedron entity unit with a specific size, defining a welding structure between cabin walls by adopting a fixedly connected fracture contact model (TSTS), and establishing a ship cabin finite element analysis model. According to the method, a common node method and a fixed connection fracture failure method are adopted to define a single cabin wall inner welding structure, and the reliability of ship cabin indoor explosion test damage effect research is improved.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
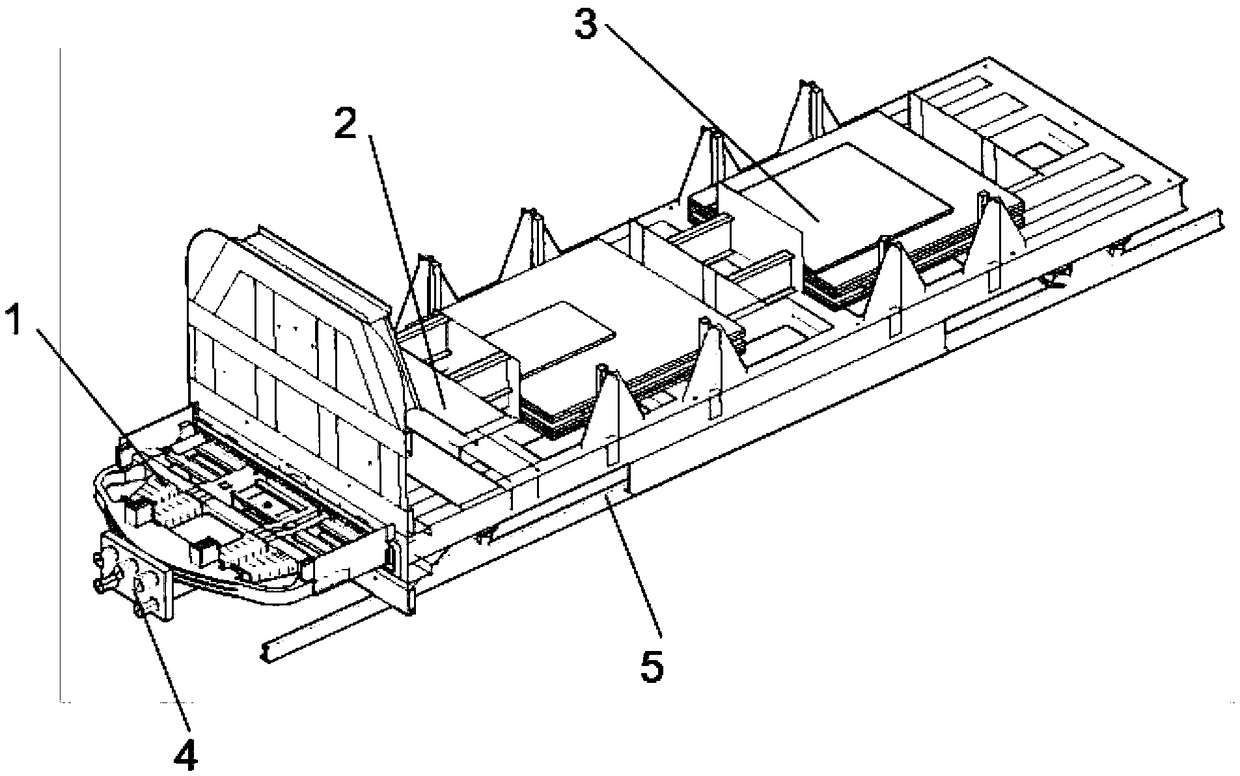
Rapid design and optimization method of energy absorbing structure at front end of rail vehicle chassis
PendingCN109002642AAchieve analytics optimizationAchieve deformationGeometric CADInternal combustion piston enginesElement modelLS-DYNA
Owner:CRRC CHANGCHUN RAILWAY VEHICLES CO LTD
Method for searching adjacent particles in analog simulation technology
InactiveCN102930087AAvoid dependenceImproved ability to simulate large-scale engineering problemsSpecial data processing applicationsLS-DYNAComputer science
The invention discloses a method for rapidly searching adjacent particles in an analog simulation technology. According to the method, the traditional point-in-box (PIB) searching method is greatly improved, the dependence of the PIB searching method on particle point distribution is avoided, and the method has higher calculation efficiency than the PIB searching method and a tree searching method. The method is applicable to various commercial computer simulation systems, such as ANSYS, LS-DYNA and ABAQUS and can be embedded into a computer simulation system, so that the calculation efficiency of searching adjacent particles is improved; and therefore, the capacity of software for simulating large-scale engineering problems is improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for selecting packing for roll bending of integral panel based on finite element analysis
InactiveCN103530448AShorten the design cycleReduce design costSpecial data processing applicationsSocial benefitsLS-DYNA
The invention discloses a method for selecting packing for roll bending of an integral panel based on finite element analysis. ANSYS / LS-DYNA calculation software is used in the method, and the method comprises the following steps of defining material models of rollers, panels and the packing, establishing and segmenting geometric models, dividing lattices on the geometric models, applying restrictions and speed load to an upper roller and a lower roller, carrying out solving, and analyzing and comparing the straightness, the residual stress and the unit strain obtained through post-processing results to obtain a preferred packing variety. According to the method, the optimized packing variety is obtained by selecting different varieties of packing to carry out comparison through the method of the finite element, the method can be directly used for guiding the selection of the packing in actual production, therefore, the design period is shortened greatly, design cost is reduced, and design efficiency is improved. Meanwhile, the method is an environment-friendly production mode, and large amount of economy, environment and social benefit can be generated for enterprises and the society.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
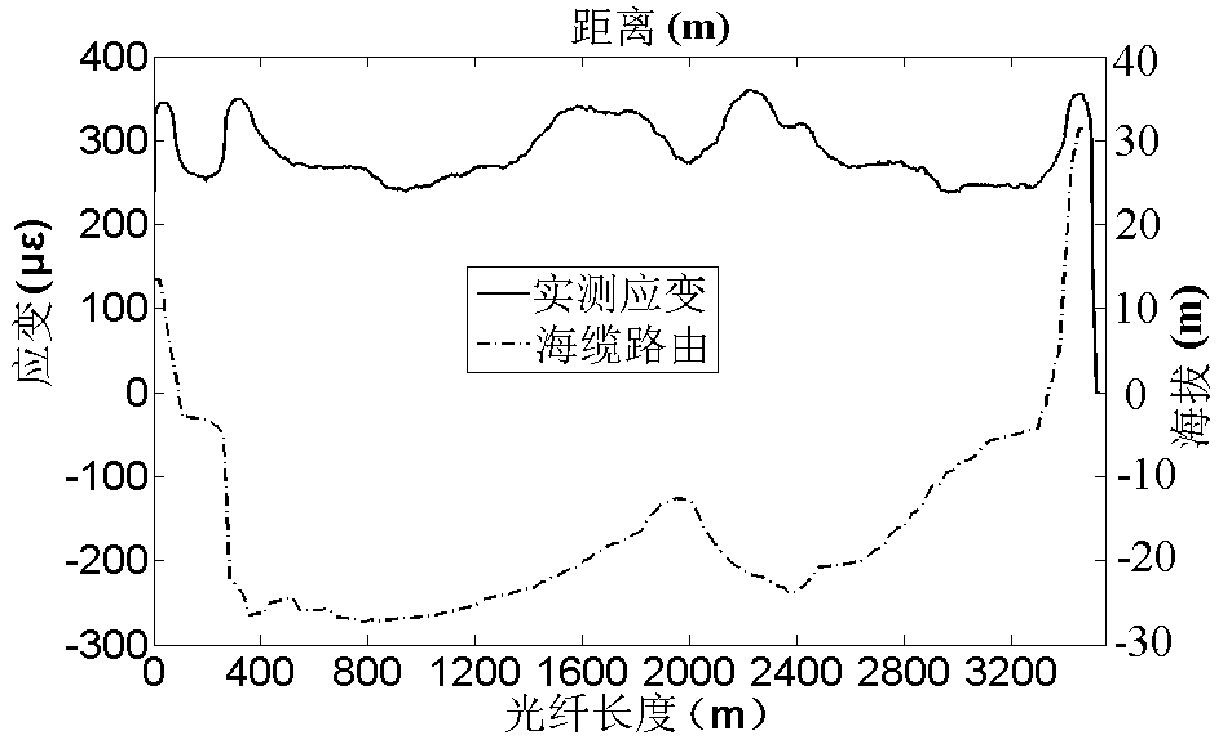
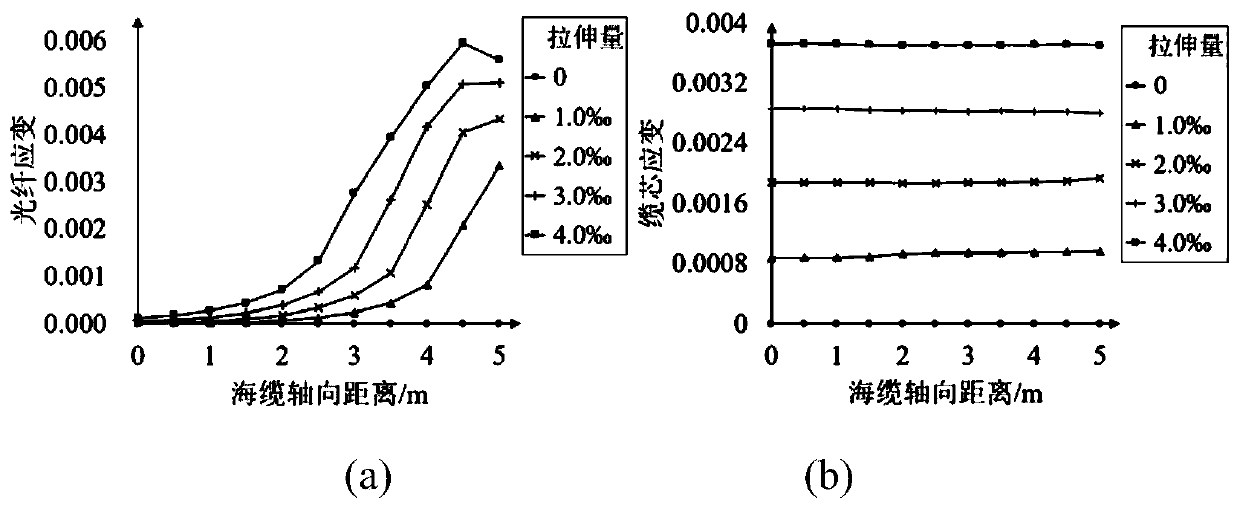
Mechanical fault monitoring method for photoelectric composite submarine cable
ActiveCN110296885AMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using single impulsive forceResearch ObjectElement model
The invention discloses a mechanical fault monitoring method for a photoelectric composite submarine cable, and belongs to the technical field of fault monitoring. According to the method, a 110kV YJQ41x300mm2 type submarine cable is used as a research object; based on ANSYS / LS-DYNA explicit dynamics analysis, a structural dynamics finite element model is established, modeling simulation is carried out on three typical fault conditions such as stretching, twisting and anchoring of the submarine cable, the strain distribution along a submarine cable composite fiber and a corresponding relationship between the strain and stress of a relevant structure in the submarine cable and the fiber strain in the fault development process are obtained, a functional relation between cable core and armorstrains and stress and optical fiber strains in the stretching and twisting states is established, and an evaluation index of the submarine cable damage state and the fiber strains under the anchoring condition is established. According to the mechanical fault monitoring method for the photoelectric composite submarine cable provided by the invention, the possible mechanical fault state types ofthe submarine cable can be identified, and preliminarily judgment is carried out on the development degree of corresponding faults by combining the established functional relation and a damage evaluation index.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
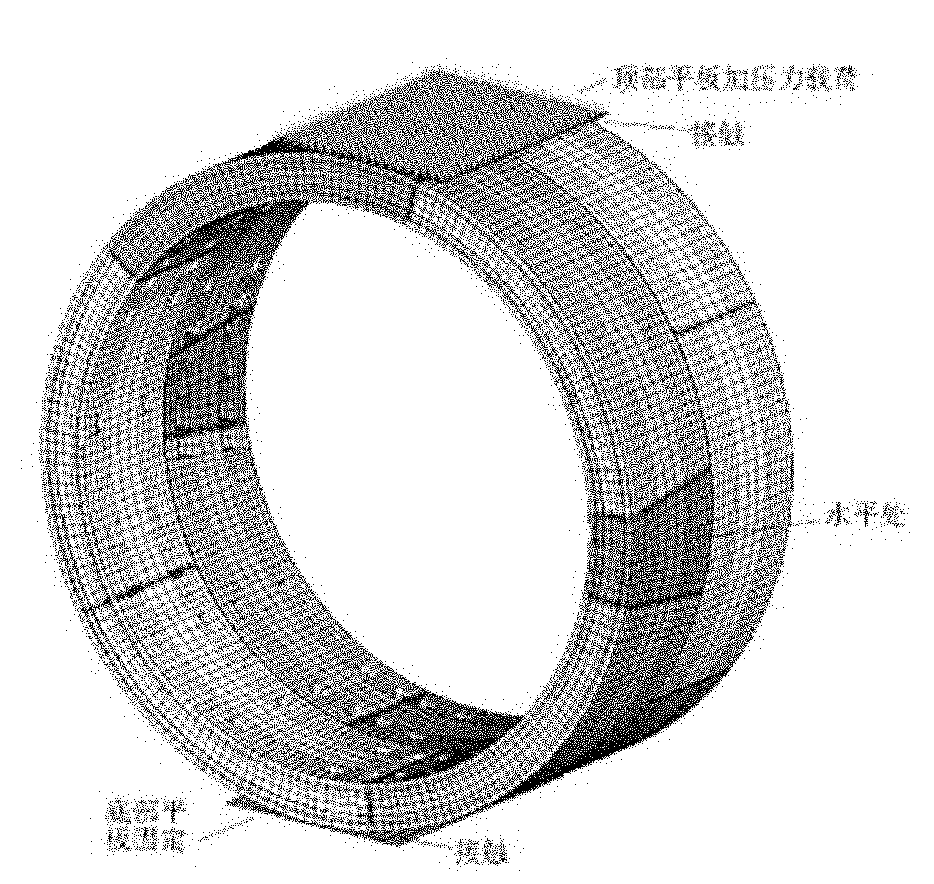
Computing method of mechanical dynamic compression property parameters of two-dimensional porous materials
InactiveCN102508934AAccurately determineReliable resultsSpecial data processing applicationsComputing MethodologiesLow speed
The invention discloses a computing method of mechanical dynamic compression property parameters of two-dimensional porous materials, which includes the following steps of establishing a finite element computing model by ANSYS / LS-DYNA software, placing the two-dimensional porous materials between an upper press plate and a fixed supporting plate horizontally, leading the upper press plate to move downwards so as to apply loads to the two-dimensional porous materials, dividing the finite element computing model of the two-dimensional porous materials into grids and starting computing; post-processing computed results by LSPREPOSTED software so as to obtain contact force and various curves between the two-dimensional porous materials and the upper press plate; and finally computing the mechanical dynamic compression property parameters of the two-dimensional porous materials according to formulas. The computing method can meet solution of the mechanical dynamic compression property parameters of the two-dimensional porous materials on the condition of high-speed and low-speed compression loading, is reliable in computing results and fast, simple and convenient in computing.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Car body beam frame collision modeling and analysis method considering characteristics of plastic hinge
ActiveCN106021701AImprove the efficiency of collision designShorten the design cycleGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationLS-DYNACollision analysis
The invention relates to a car body beam frame collision modeling and analysis method considering characteristics of a plastic hinge, and belongs to the field of car body design. The method comprises the steps of firstly solving a cross section area and a bending-twisting inertial moment characteristic of the cross section, with a complex shape, of a car body beam frame; secondly creating a car body beam frame model; thirdly generating a plastic hinge model characteristic of a thin-walled beam unit, and assigning a value to a material characteristic of a Belytschko-Schwer (BS) beam unit, wherein an MAT 29# material type of LS-DYNA software is selected for the material characteristic; and finally generating a keyword text file that can be solved by the LS-DYNA software, and calling the LS-DYNA software to perform collision solving. The car body frame model is established by adopting the beam unit; the plastic hinge model simulates bending, twisting and crushing deformation of a beam to perform collision analysis; a solving result is reliable, the user operation is convenient, and the modeling period is greatly shortened; and the method has an important guide effect for car body design.
Owner:左文杰 +1
Method for analyzing excessive opening of car doors
InactiveCN105989212AShort cycleImprove analysis efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsElement modelLS-DYNA
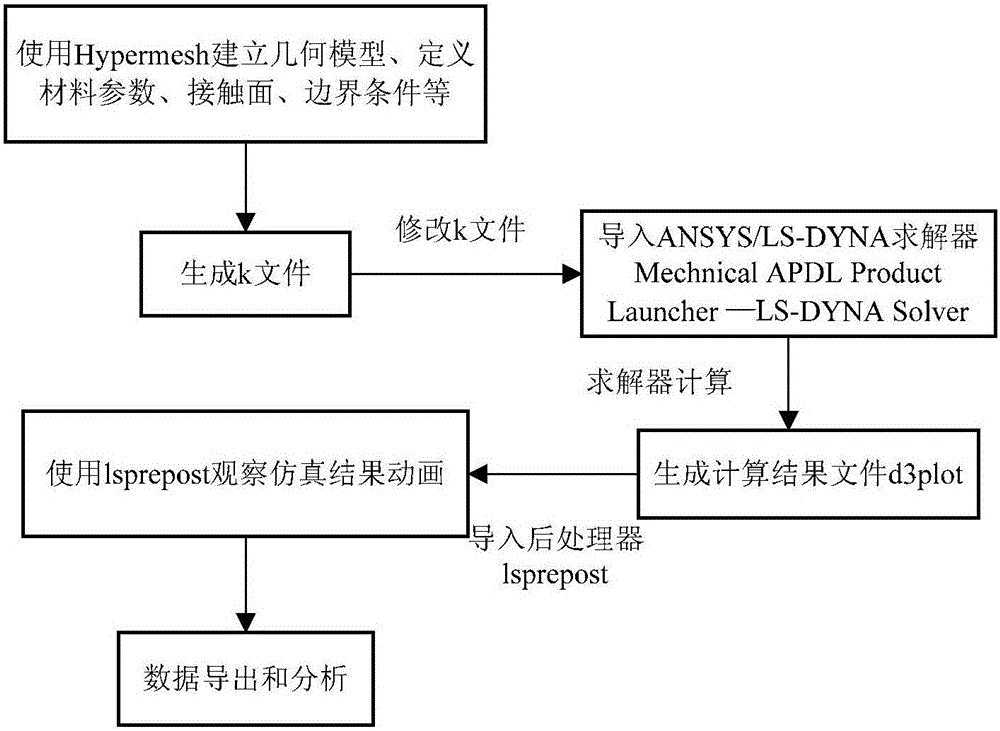
The invention provides a method for analyzing excessive opening of car doors. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an established car body CAD geometric model through Hypermesh, wherein the car body CAD geometric model comprises a car door and a car body, and the car door is in a maximum design opening angle state; establishing a finite element model of the car body CAD geometric model through the Hypermesh, and creating a K file, wherein the K file comprises contact relation information, material information, boundary condition information, load information and output result information, the boundary condition information comprises a full-constraint type of a section node of the car body, load application in the load information indicates applying gravity field load with 1 gravity acceleration on the finite element model and applying a rotation angle speed along the opening direction on the car door, and an output result in the output result information comprises a rotation angle of the car door and stress of a sheet metal part; and solving the K file through LS-DYNA so as to obtain a result file related to the output result.
Owner:JIANGLING MOTORS
Numerical simulation method for cutting process of bar cutter
ActiveCN104991991AImprove work efficiencyReduce power consumptionSpecial data processing applications3D modellingLS-DYNAEngineering
The invention relates to a numerical simulation method for a cutting process of a bar cutter. The method comprises following steps: establishing a simulation model, and simulating the cutting process of the bar cutter through the ANSYS / LS-DYNA software; analyzing an influence rule for the cutting process by angle factors, and determining cutting angle factor level values; changing the speed, diameter and cutting angle of a cutting steel wire, and performing dynamics simulation analysis on a moving process when the steel wire cuts clay strips; and designing a orthogonal test, analyzing important orders of the factors influencing the cutting power consumption and steel wire maximum equivalent stress, and finally obtaining an optimal combination of working parameters of the bar cutter. The method is advantageous in that the method can simulate actual working conditions of the bar cutter and can provide the basis for the selection of the working parameters of the bar cutter, and therefore the power consumption and production cost of the bar cutter can be reduced, the working efficiency of the bar cutter can be improved, and the qualified rate of adobe can be increased.
Owner:南通大学技术转移中心有限公司
High-rise building mechanical demolition method based on numerical simulation
PendingCN109933894ASafe Mechanical Demolition WorkControlled Mechanical Demolition OperationsSpecial data processing applicationsLS-DYNAEngineering
The invention discloses a high-rise building mechanical demolition method based on numerical simulation. The method comprises the following steps: finding out relevant data of the high-rise building required by modeling, establishing a model of the high-rise building, selecting the position of a simulation notch, selecting the notch length of the high-rise building during toppling, determining a demolition and collapse direction, carrying out notch field positioning, and carrying out notch mechanical processing until the high-rise building topples smoothly. On the basis of the principle, ANSYS / LS-DYNA numerical simulation software is adopted for carrying out toppling simulation on the high-rise building; the optimal notch length is determined through numerical simulation. The high-rise building mechanical demolition method has the advantages that the high-rise building mechanical demolition method is simple in operation, notch treatment is performed by machinery, safe and controllableconstruction requirements are met, toppling demolition of the high-rise building is achieved. The defects of blind construction of mechanical demolition and uncontrollable safety factors are effectively overcome, and the requirements of high-rise building mechanical demolition operation safety, controllability, low cost and high speed are met.
Owner:杭州建工集团有限责任公司
Dynamic fluid field hybrid analysis method of fabric fluid structure interaction model
InactiveCN102004821AAccurate flow field conditionsSolve the calculation problem of moving mesh flow fieldSpecial data processing applicationsLS-DYNAEngineering
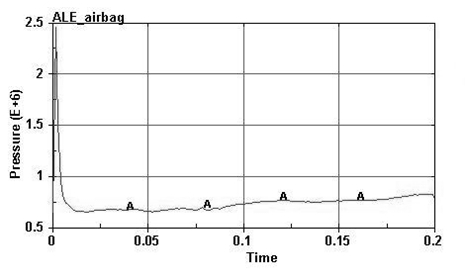
The invention discloses a dynamic fluid field hybrid analysis method of a fabric fluid structure interaction model, which adopts the calculation steps of: 1. building a fabric three-dimensional mesh model; 2. carrying out dynamic analysis on the fabrics by an ALE (Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian) method based on LS-DYNA to obtain the fabric dynamic change condition; 3. using an instant fabric appearance as the fluid boundary condition and dividing fit mesh; and 4. carrying out fluid field analysis on the basis of FLUENT. The invention uses the ALE method (Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian) based onthe LS-DYNA for the first time to obtain the dynamic fabric shape as the FLUENT boundary condition to analyze the fluid field condition, and the problems that the ALE method has inaccurate fluid field description and the dynamic mesh fluid field is difficult to calculate under the great deformation of flexible fabric are effectively solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
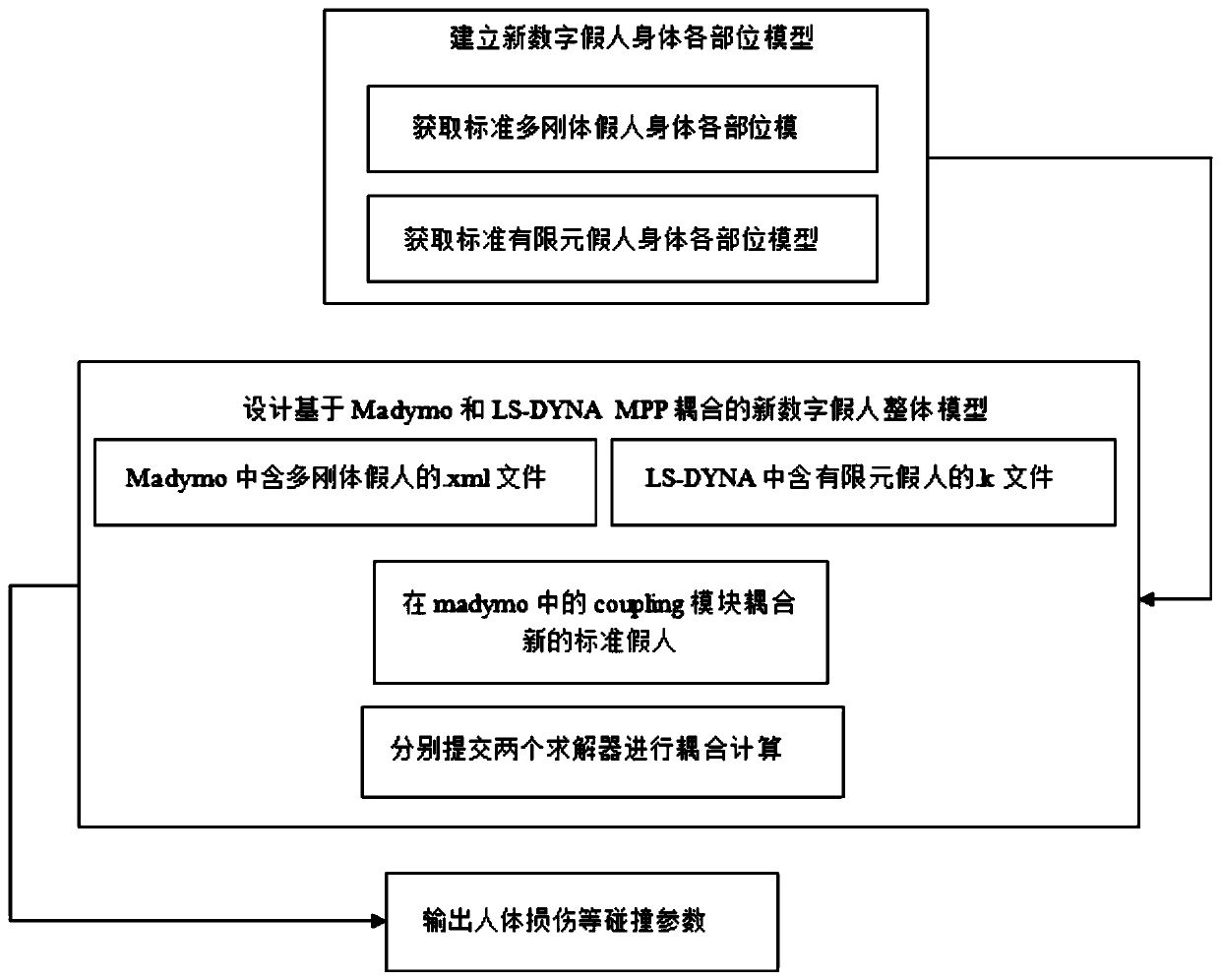
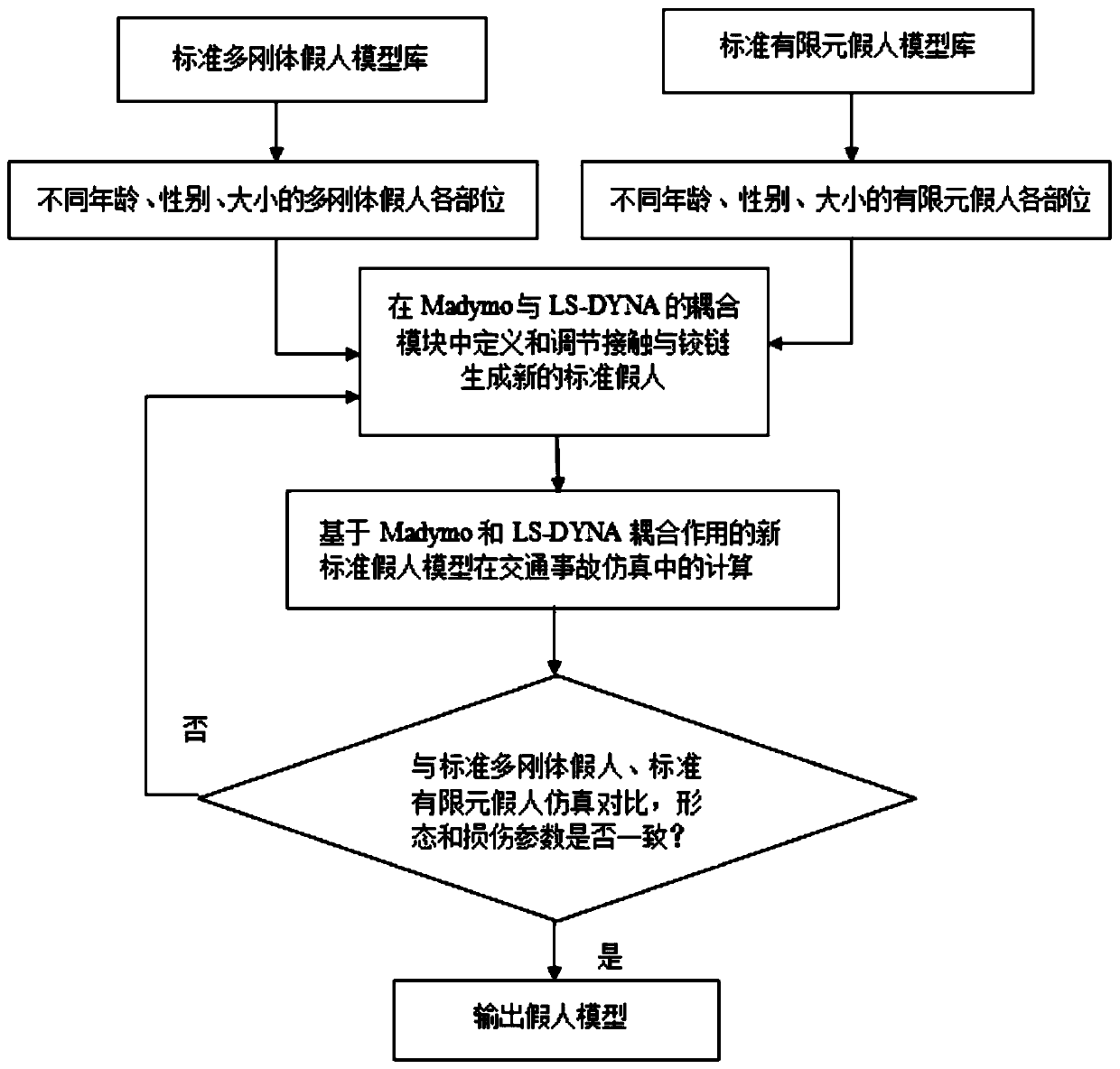
Digital dummy model modeling method based on multi-rigid-body and finite element coupling calculation
ActiveCN110362875ASet stableAvoid volumeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLS-DYNACoupling
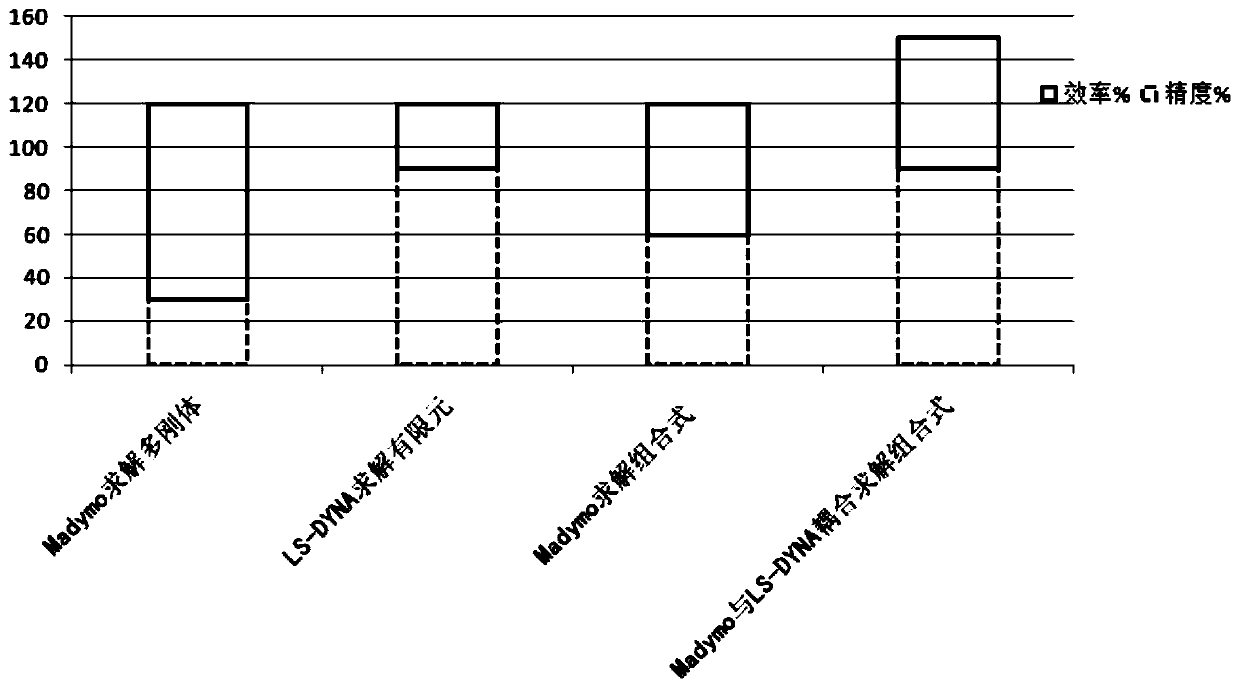
The invention relates to a digital dummy model modeling method based on a multi-rigid-body and finite element coupling calculation in the field of traffic accident safety, which comprises the following steps of: establishing a standard digital dummy model library which respectively comprises each body part model of a multi-rigid body digital dummy and each body part model of a standard finite element digital dummy; designing a new standard digital dummy model, and selecting LS-DYNA module is selected from coupling software of Madymo; ; defining a hinge and adjusting contact in the coupling module, generating a complete new standard digital dummy model by utilizing the standard multi-rigid body and the digital dummy model of each part of the standard finite element, and finally verifying the new model through coupling simulation calculation; and outputting and verifying the new standard digital dummy collision parameters. According to the method, the advantages of the two software can be brought into full play through a coupling solving calculation method, and the robustness of collision simulation calculation of the digital dummy model is greatly enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for drawing double-layer titanium alloy casing enthalpy curve
InactiveCN108647367AAccurate Simulation MethodImprove accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationLS-DYNATitanium alloy
The invention provides a method for drawing a double-layer titanium alloy casing enthalpy curve, and discloses a method for drawing a double-layer titanium alloy casing enthalpy curve. A smooth bore is used for the target test to simulate a high-speed blade impacting the casing, and the finite element simulation software LS-DYNA is used to perform numerical simulation on the target test, wherein the blade is made of the JOHNSON-COOK material model, and the target board adopts the SIMPLIFIED-JOHNSON-COOK material model. Compared with the accuracy of verifying the numerical simulation, appropriate simulation parameters are acquired. The simulation is used to simulate the tolerance critical speed of the double-layer titanium alloy casing under different condition, and the target test resultsare substituted for verification, thereby realizing the fitting of the tolerance curve formula of the casing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
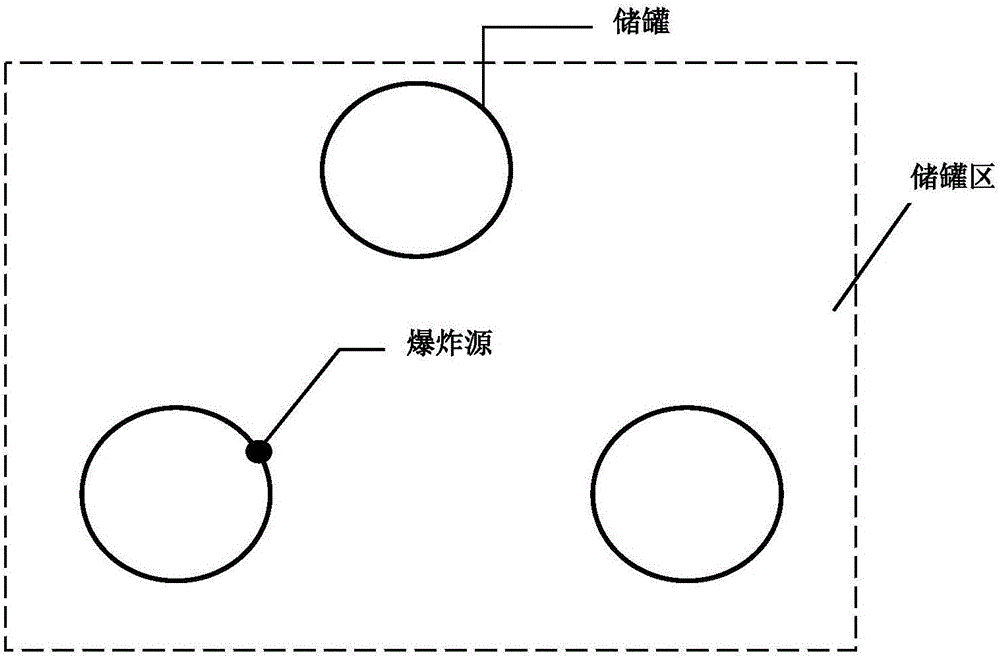
LS-DYNA based method for optimally designing layout of storage tank area of chemical industry park
InactiveCN105844002ALayout optimization design method is goodMulti-objective optimisationSpecial data processing applicationsChemical industryLS-DYNA
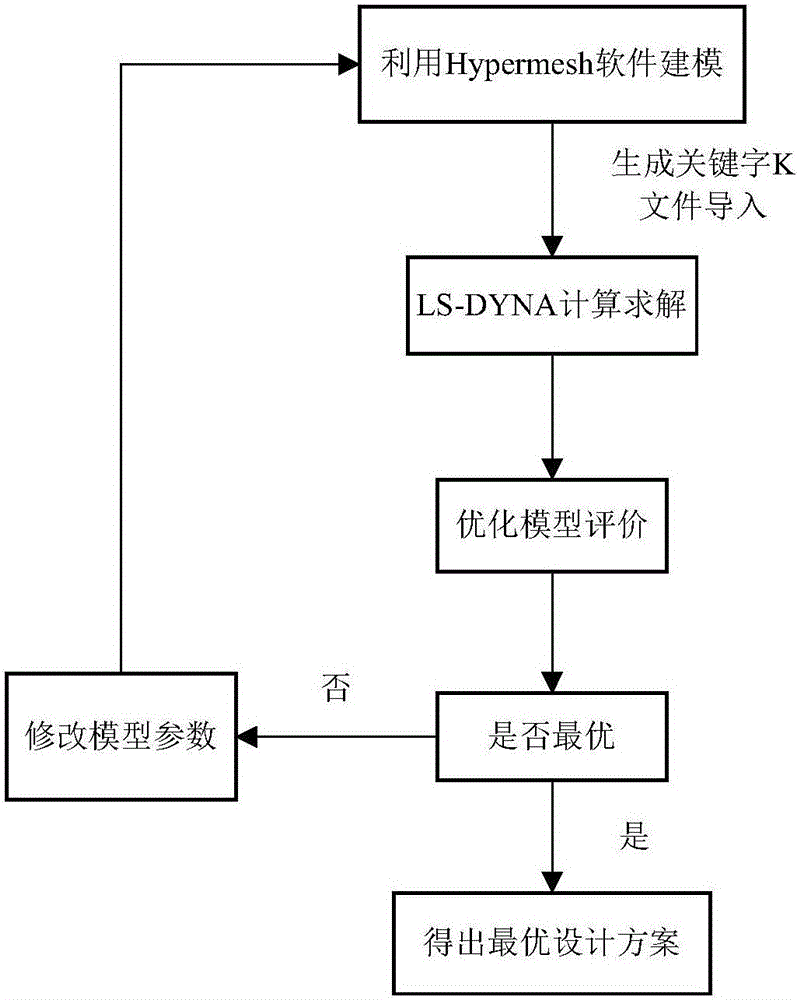
An LS-DYNA based method for optimally designing a layout of a storage tank area of a chemical industry park. The present invention relates to an LS-DYNA based method for optimally designing a layout of a storage tank area of a chemical industry park. An objective of the present invention is to solve the problems that the existing design method is poor and even unsuccessful in design, and basic materials may have expired, and actual on-site conditions have changes and the like. The method is specifically implemented according to the following steps: 1. defining a constraint condition of selecting a storage tank area of a chemical industry park as a model parameter of numerical simulation, and then generating a keyword k file; 2. inputting the keyword k file into LS-DYNA software to perform resolution so as to obtain a d3plot result file; 3. obtaining a breakage effect value of a whole explosion course; and 4. obtaining a layout manner with a smallest breakage effect value of the whole explosion course of the storage tank area, so as to obtain an optimized design scheme. The method provided by the present invention is applied to the field of layout optimization of the storage tank area of the chemical industry park.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
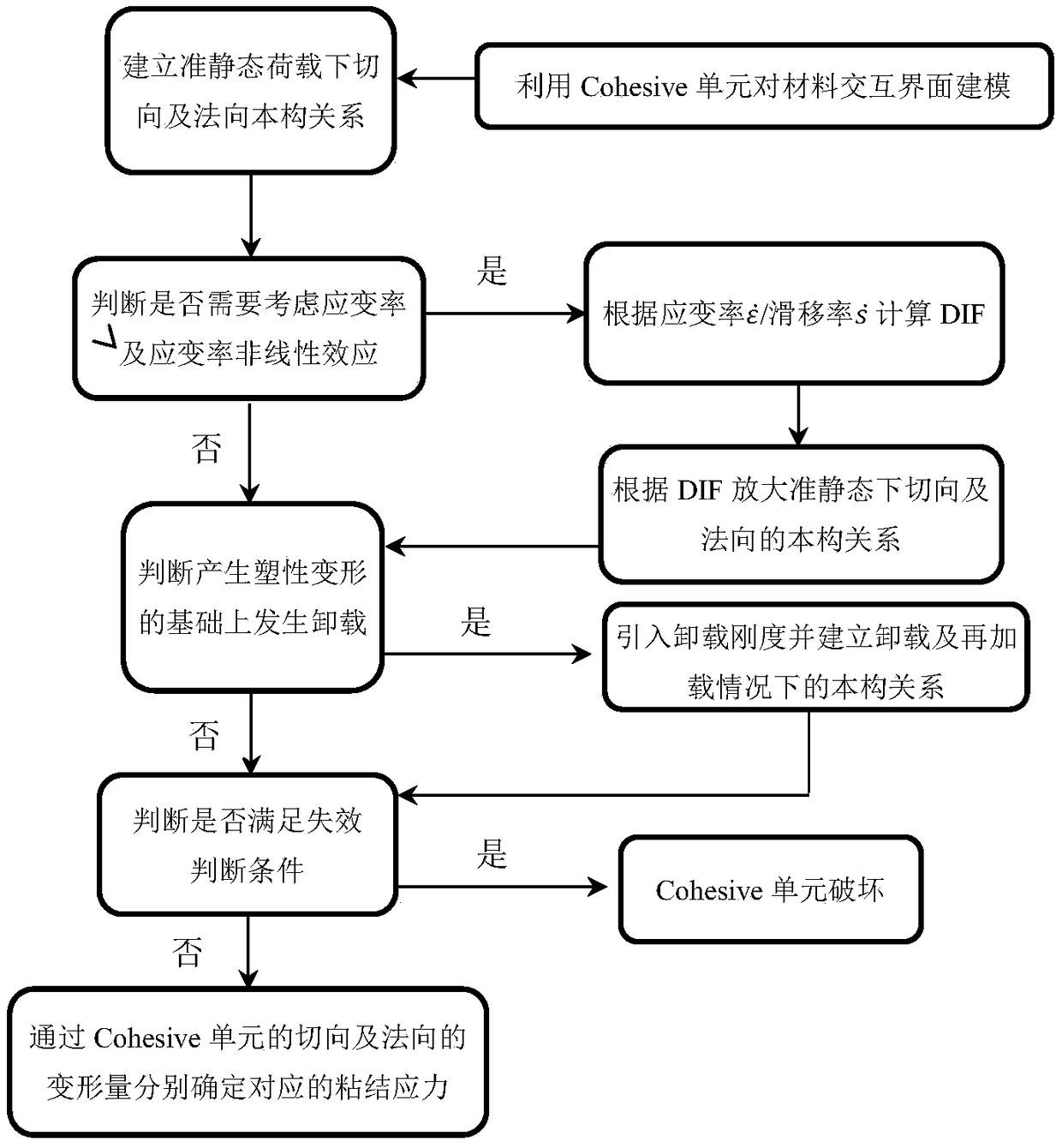
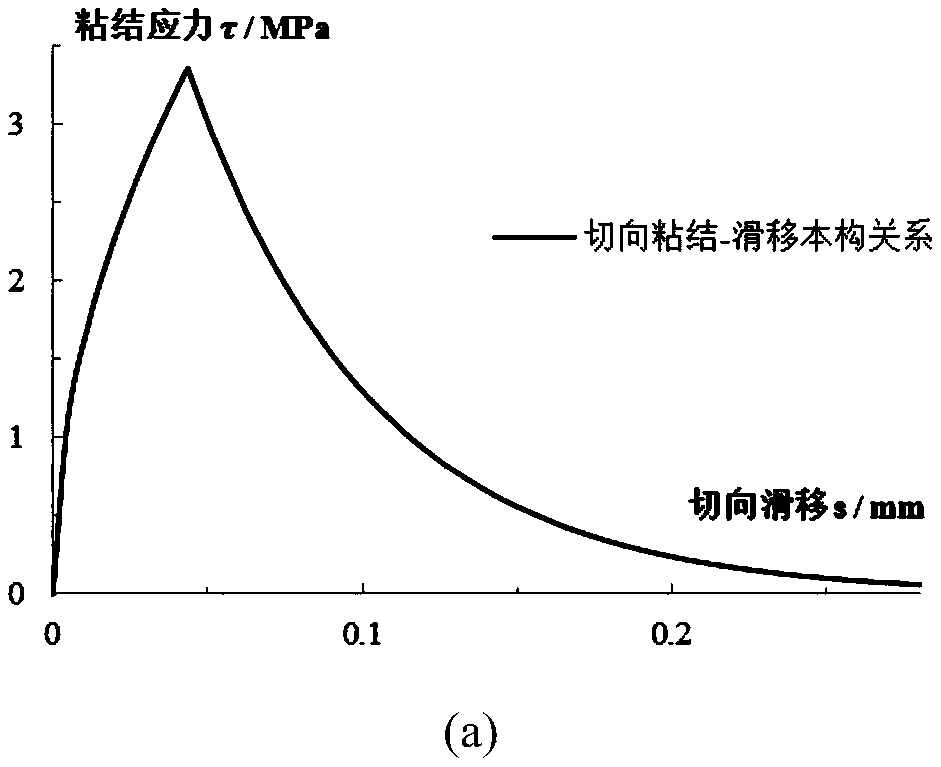
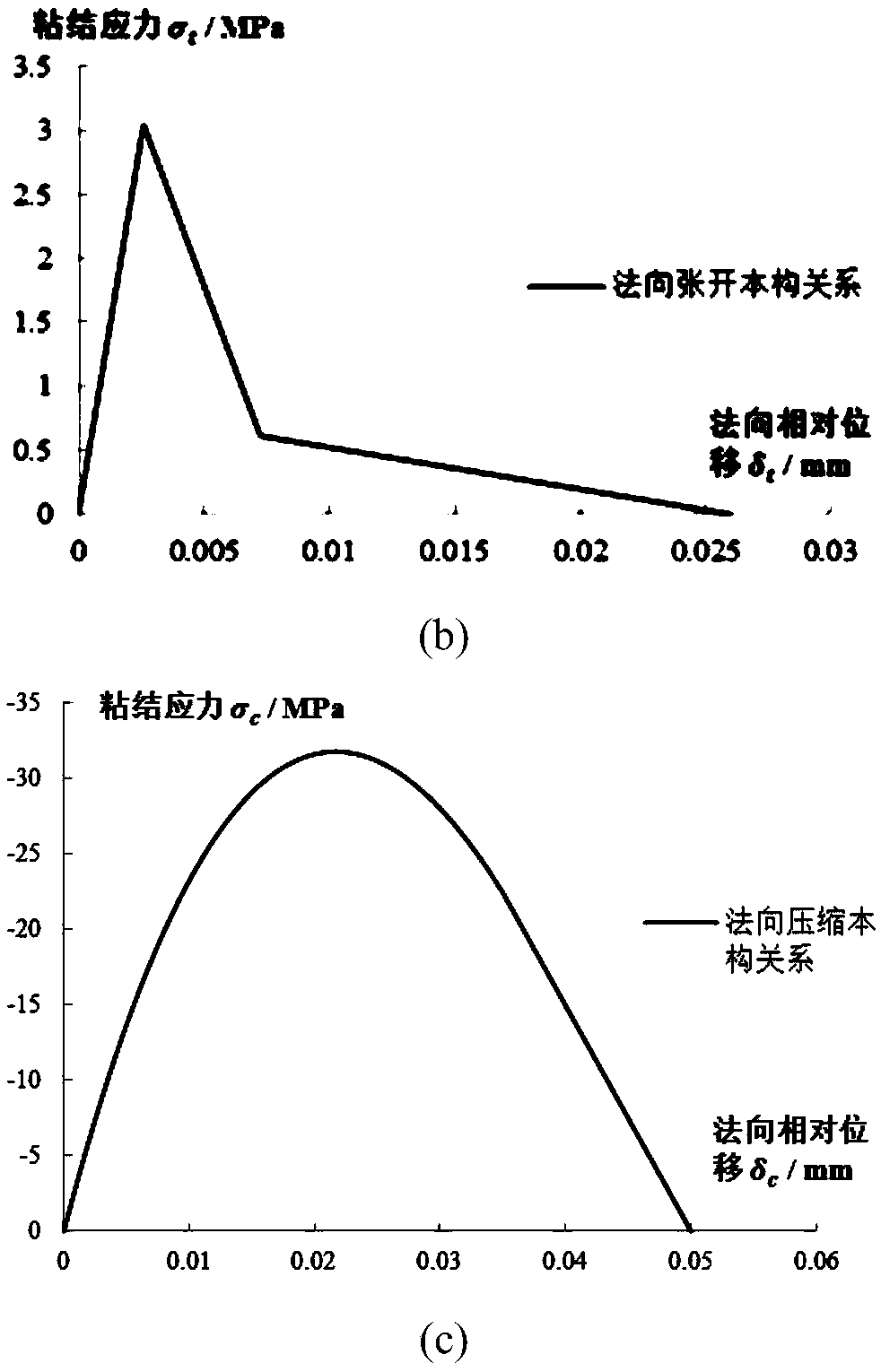
Material interactive interface numerical simulation method considering nonlinearity and strain rate effect
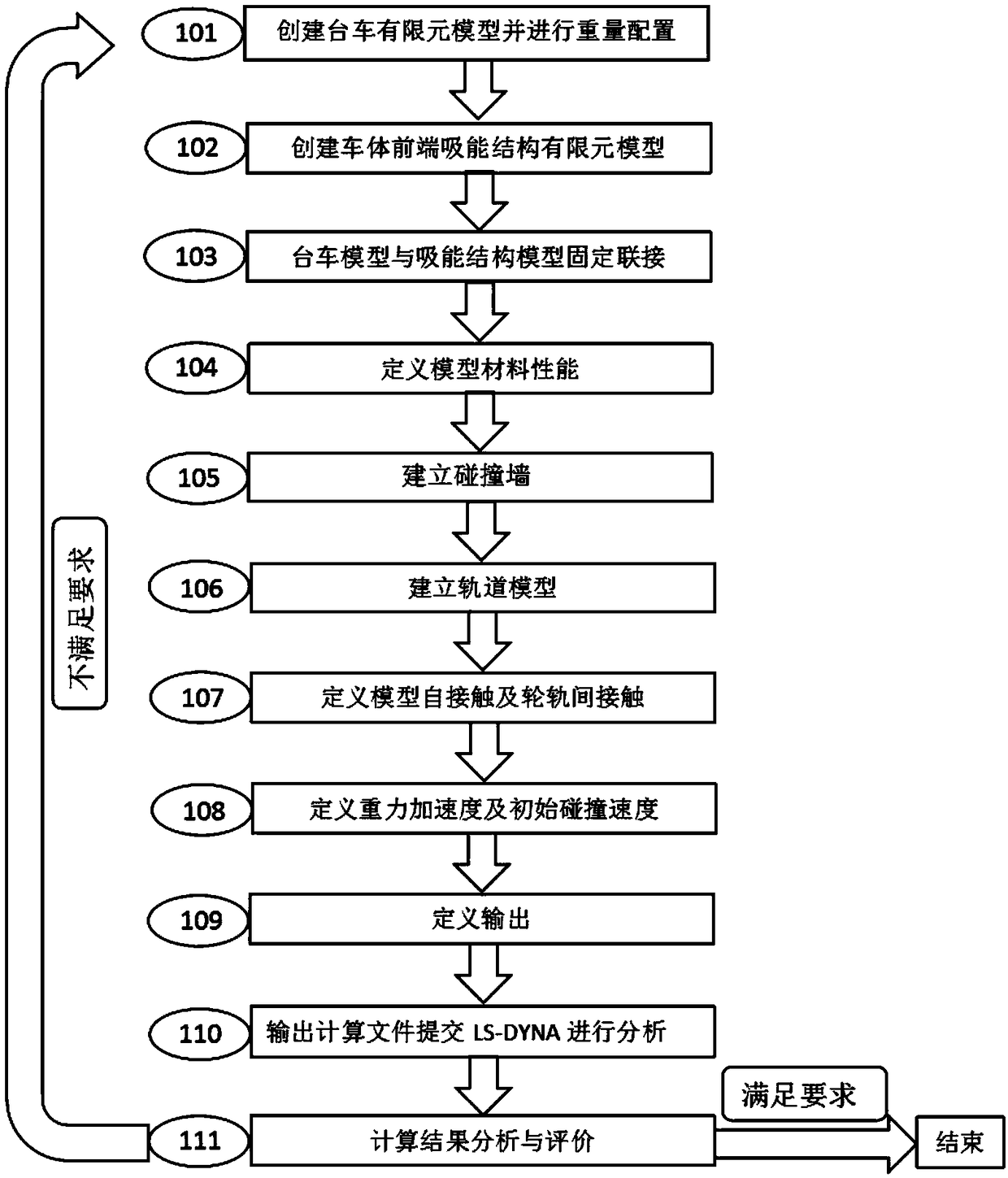
ActiveCN109187334AAccurate Mechanical PropertiesDescribe mechanical propertiesUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisRelational modelLS-DYNA
The present invention relates to a material interaction interface numerical simulation method considering nonlinearity and strain rate effect. The material interaction interface numerical simulation method considering nonlinearity and strain rate effect comprises the following steps of: establishing a constitutive relation model of tangential bonding-sliding and normal opening / compression nonlinearity of a material interaction interface under the action of a quasi-static load; quantifying the reinforcement effect of the strain rate effect and strain rate nonlinearity on the quasi-static constitutive relation model in the tangent direction and normal direction of the material interactive interface; defining the influence of the plastic damage effect on the tangential and normal constitutiverelation of the material interaction interface; establishing the failure judgment criterion of the material interaction interface in the hybrid mode; and defining a cohesive unit for the numerical simulation of the material interaction interface according to the material interaction interface constitutive relationship formed in the previous step based on LS-DYNA user-defined material module. Thematerial interaction interface numerical simulation method considering nonlinearity and strain rate effect can comprehensively and accurately describe the mechanical properties of the material interaction interface in the first and second modes, and reflects the dynamic performance of the material interaction interface under the strain rate effect and the nonlinearity and the influence of the plastic damage effect on the material interaction interface performance.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
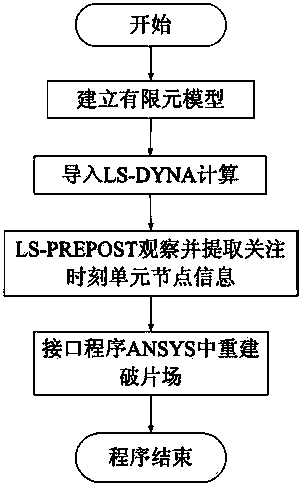
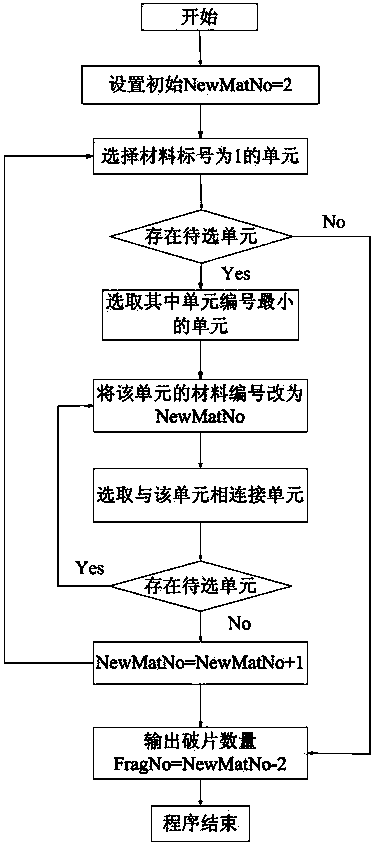
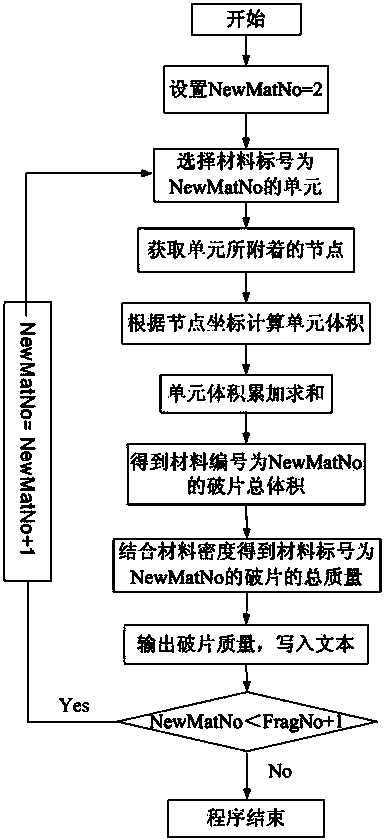
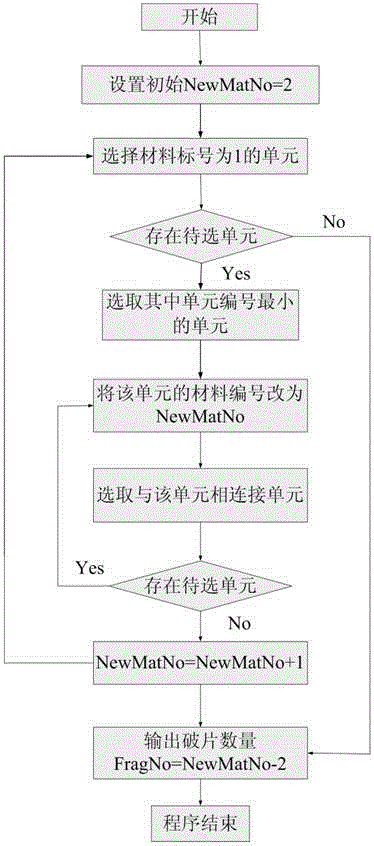
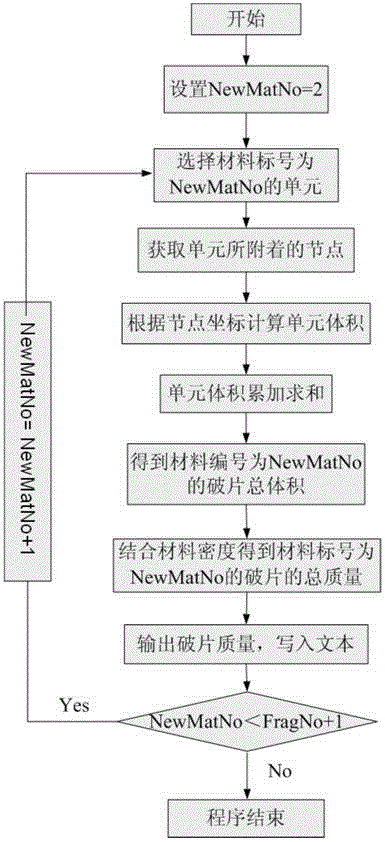
LS-DYNA calculation result-based automatic statistical method for quantitative information about fragments
The invention provides an LS-DYNA calculation result-based automatic statistical method for quantitative information about fragments. The number, the mass and the speed of each fragment in a calculation result can be obtained, and can be directly output as a text file for evaluating the efficiency of a warhead or providing references for the design of the warhead and a protective structure. The method comprises the following steps of first reconstructing a fragment data file on the basis of an LS-DYNA calculation result; then searching and identifying the fragments in groups, and endowing serial numbers to the fragments; next making statistics on the mass of each fragment, and outputting the mass data of each fragment to a result file; finally making statistics on the speed of each fragment, and outputting the speed data of each fragment to the result file.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
An automatic statistical method for fragment quantitative information based on ls-dyna calculation results
The invention provides an LS-DYNA calculation result-based automatic statistical method for quantitative information about fragments. The number, the mass and the speed of each fragment in a calculation result can be obtained, and can be directly output as a text file for evaluating the efficiency of a warhead or providing references for the design of the warhead and a protective structure. The method comprises the following steps of first reconstructing a fragment data file on the basis of an LS-DYNA calculation result; then searching and identifying the fragments in groups, and endowing serial numbers to the fragments; next making statistics on the mass of each fragment, and outputting the mass data of each fragment to a result file; finally making statistics on the speed of each fragment, and outputting the speed data of each fragment to the result file.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
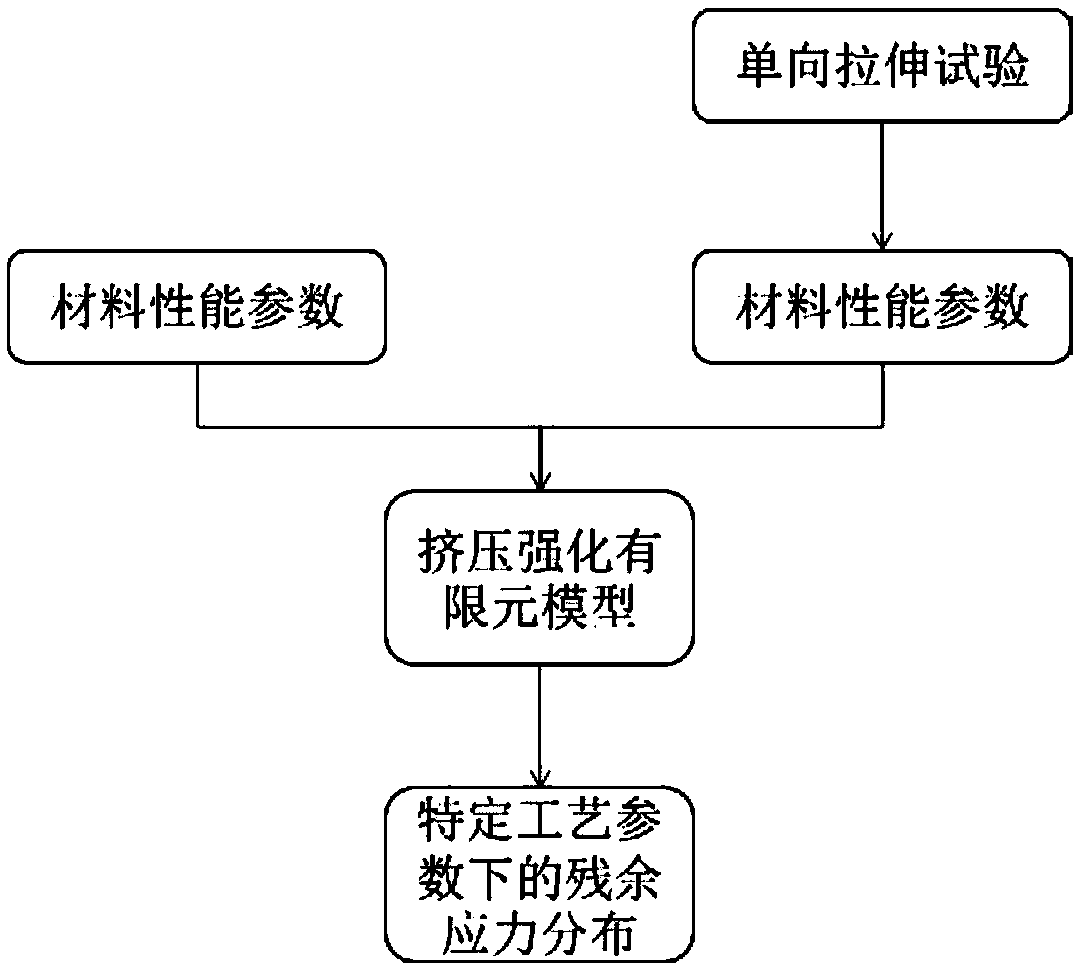
A three-dimensional numerical simulation method for extrusion strengthen process of turbine disk hole
The invention relates to a three-dimensional numerical simulation method for an extrusion strengthen process of a turbine disk hole, wherein, the three-dimensional modeling of the extrusion strengthening process establishes three-dimensional models of a central circular hole plate and a mandrel with a certain interference amount; the finite element model of extrusion strengthening process is established, and in the preprocessing module of the finite element analysis software ANSYS / LS-DYNA, according to the actual working conditions, the material properties and parameters are set, and the finite element mesh is divided. Load and boundary conditions are set to simulate the relative motion of the mandrel and the central circular hole plate; solution analysis and post-processing is performed to create an analysis job to solve the problem and obtain the residual stress field.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
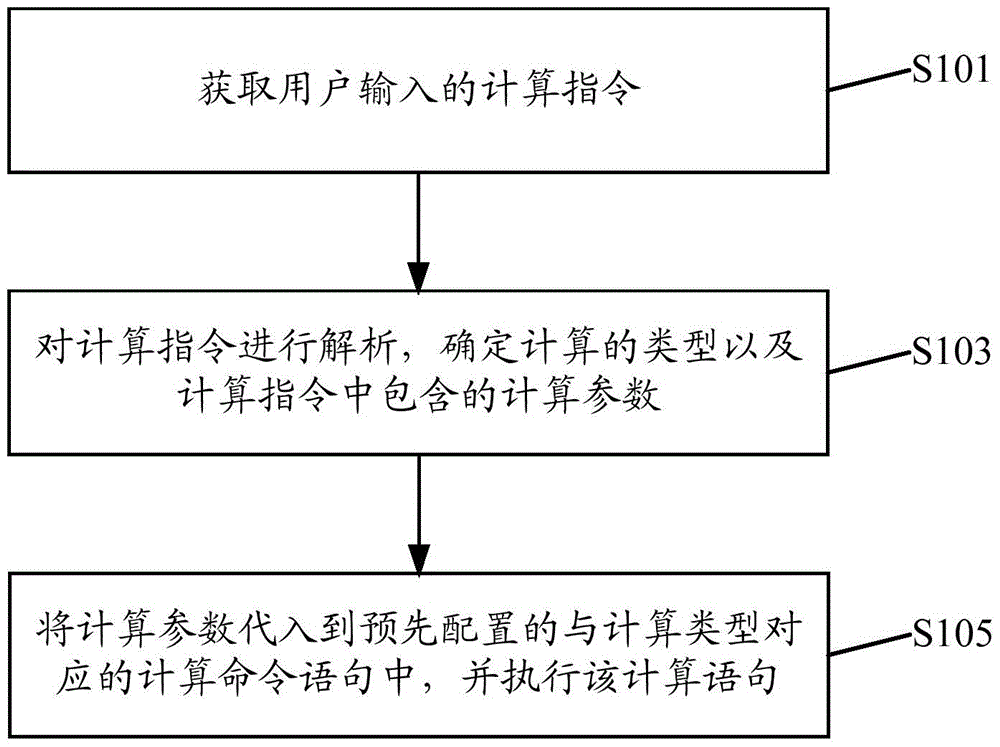
Method and device for realizing calculation tasks of ls-dyna
ActiveCN103559346BReduce difficultyReduce error rateSpecial data processing applicationsUser inputLS-DYNA
Owner:DAWNING INFORMATION IND BEIJING +1
An LS-Dyna based flying net-target collision dynamic analysis method
ActiveCN109446565AEasy to controlIncrease credibilityGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationCollision dynamicsCollision theory
The invention relates to an LS-Dyna based flying net-target collision dynamic analysis method, which uses the nonlinear finite element analysis software ANSYS / LS-Dyna for the typical flying net-targetrigid-flexible collision dynamics analysis, and comprises the steps of establishing a flying net-target collision dynamic model in the LS-Dyna; carrying out the data processing on the calculation result of the LS-Dyna in MATLAB; analyzing the characteristics during the flying net-target collision process. Compared with the prior art, the method is simpler than the traditional theoretical analysismethod, and the flying net carried by the multi-agent can better control the multi-agent to complete the corresponding task. By the flying net-target collision dynamic model established through the ANSYS / LS-Dyna, the traditional rigid-flexible collision theory also can be verified relatively.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
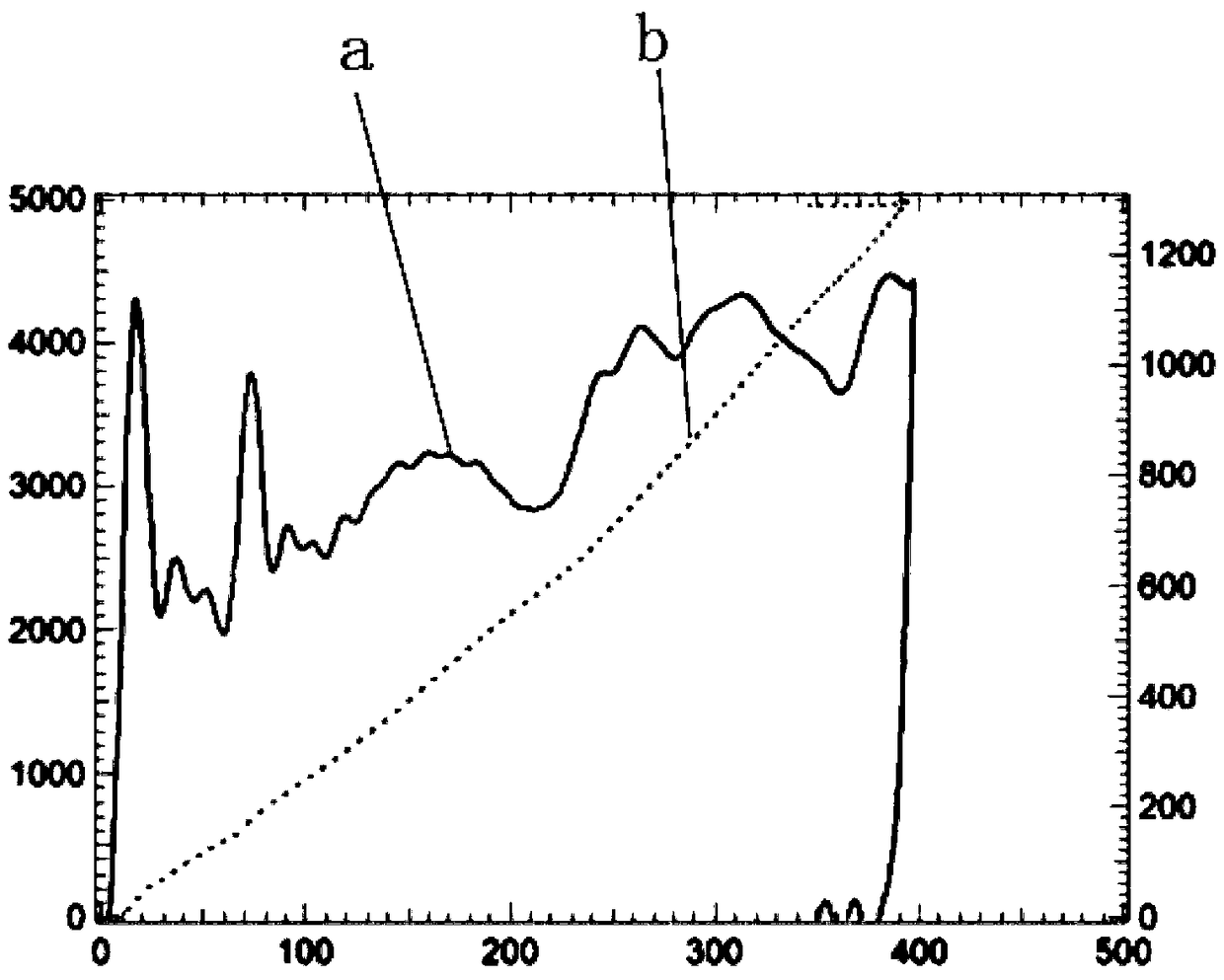
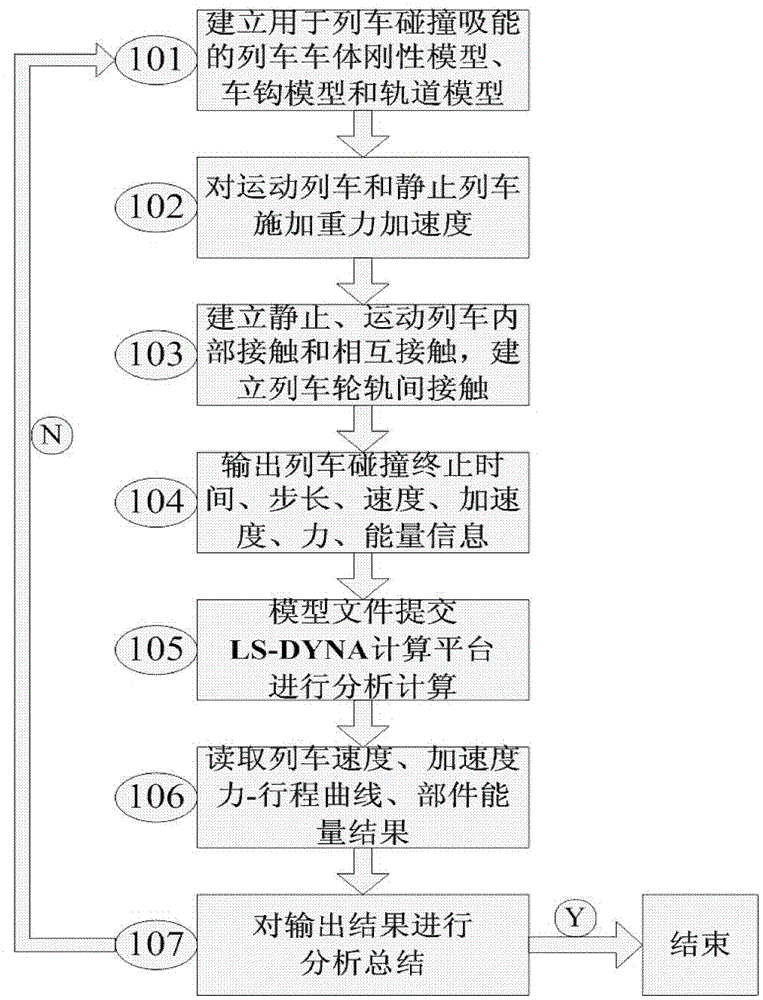
Rapid Analysis Method of Train Energy Distribution
InactiveCN102542102BFast implementation of allocation analysisMeet energy absorption requirementsElectric devicesOperating modesLS-DYNADegrees of freedom
Owner:CRRC CHANGCHUN RAILWAY VEHICLES CO LTD
Modeling and Analysis Method of Car Body Girder Skeleton Collision Considering Plastic Hinge Characteristics
ActiveCN106021701BImprove the efficiency of collision designShorten the design cycleGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMaterial typeCollision analysis
The invention relates to a car body beam frame collision modeling and analysis method considering characteristics of a plastic hinge, and belongs to the field of car body design. The method comprises the steps of firstly solving a cross section area and a bending-twisting inertial moment characteristic of the cross section, with a complex shape, of a car body beam frame; secondly creating a car body beam frame model; thirdly generating a plastic hinge model characteristic of a thin-walled beam unit, and assigning a value to a material characteristic of a Belytschko-Schwer (BS) beam unit, wherein an MAT 29# material type of LS-DYNA software is selected for the material characteristic; and finally generating a keyword text file that can be solved by the LS-DYNA software, and calling the LS-DYNA software to perform collision solving. The car body frame model is established by adopting the beam unit; the plastic hinge model simulates bending, twisting and crushing deformation of a beam to perform collision analysis; a solving result is reliable, the user operation is convenient, and the modeling period is greatly shortened; and the method has an important guide effect for car body design.
Owner:吉数研院(吉林省)信息技术咨询设计有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com