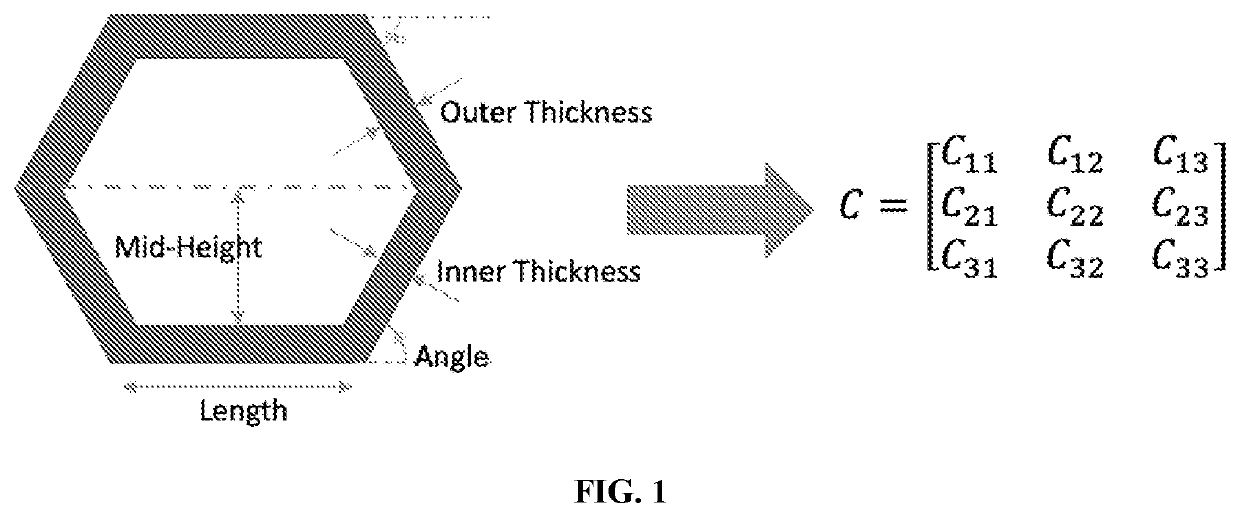
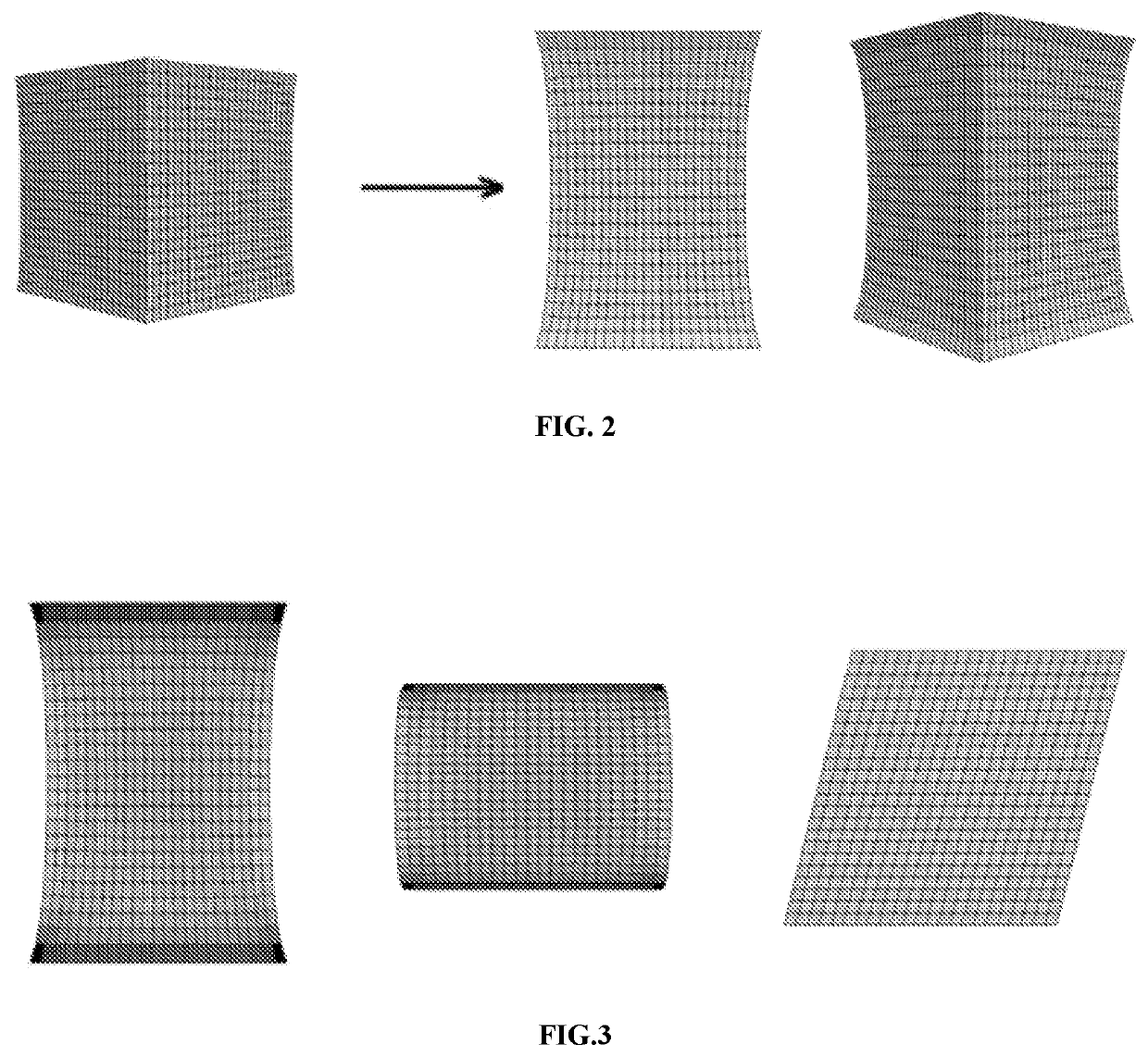
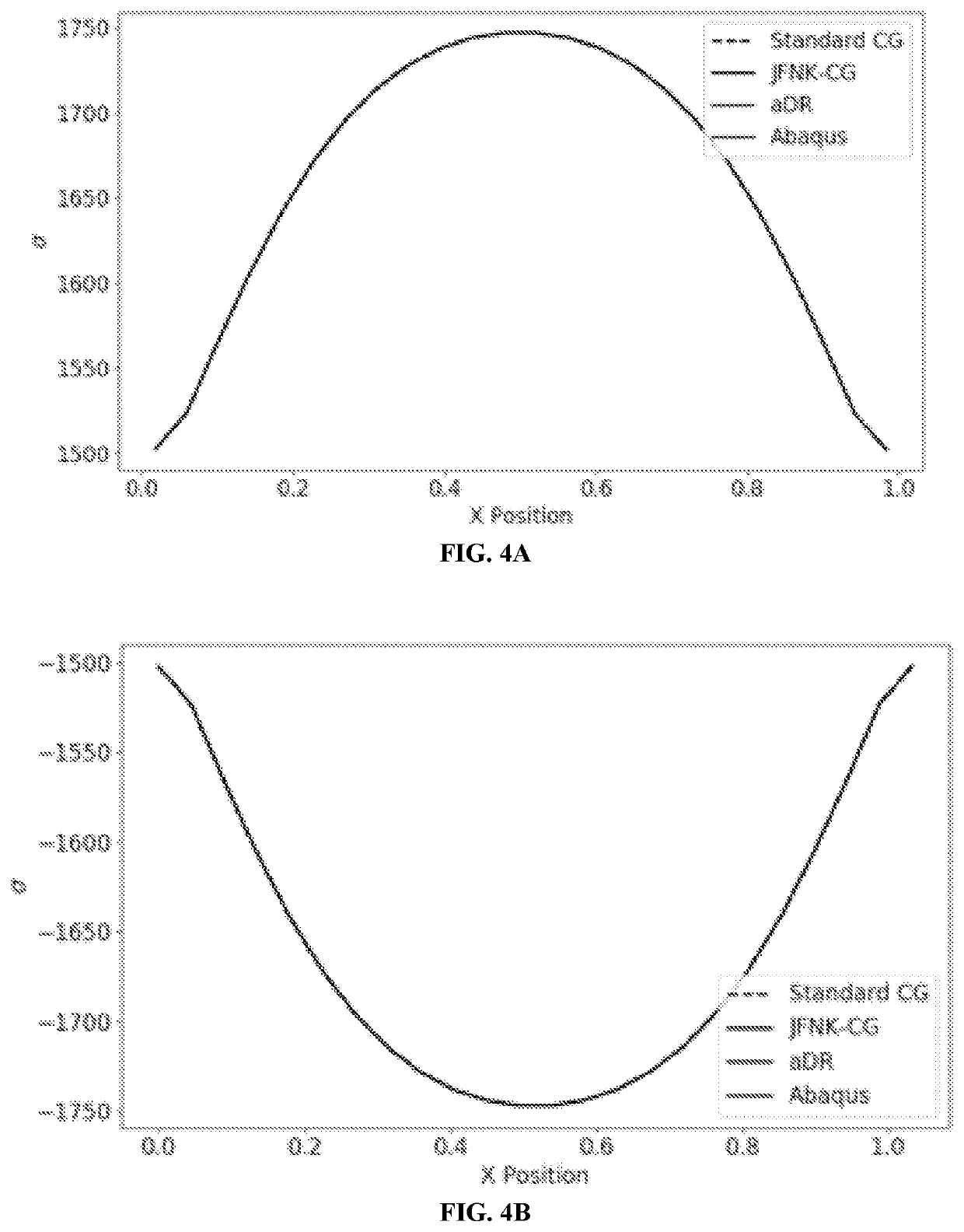
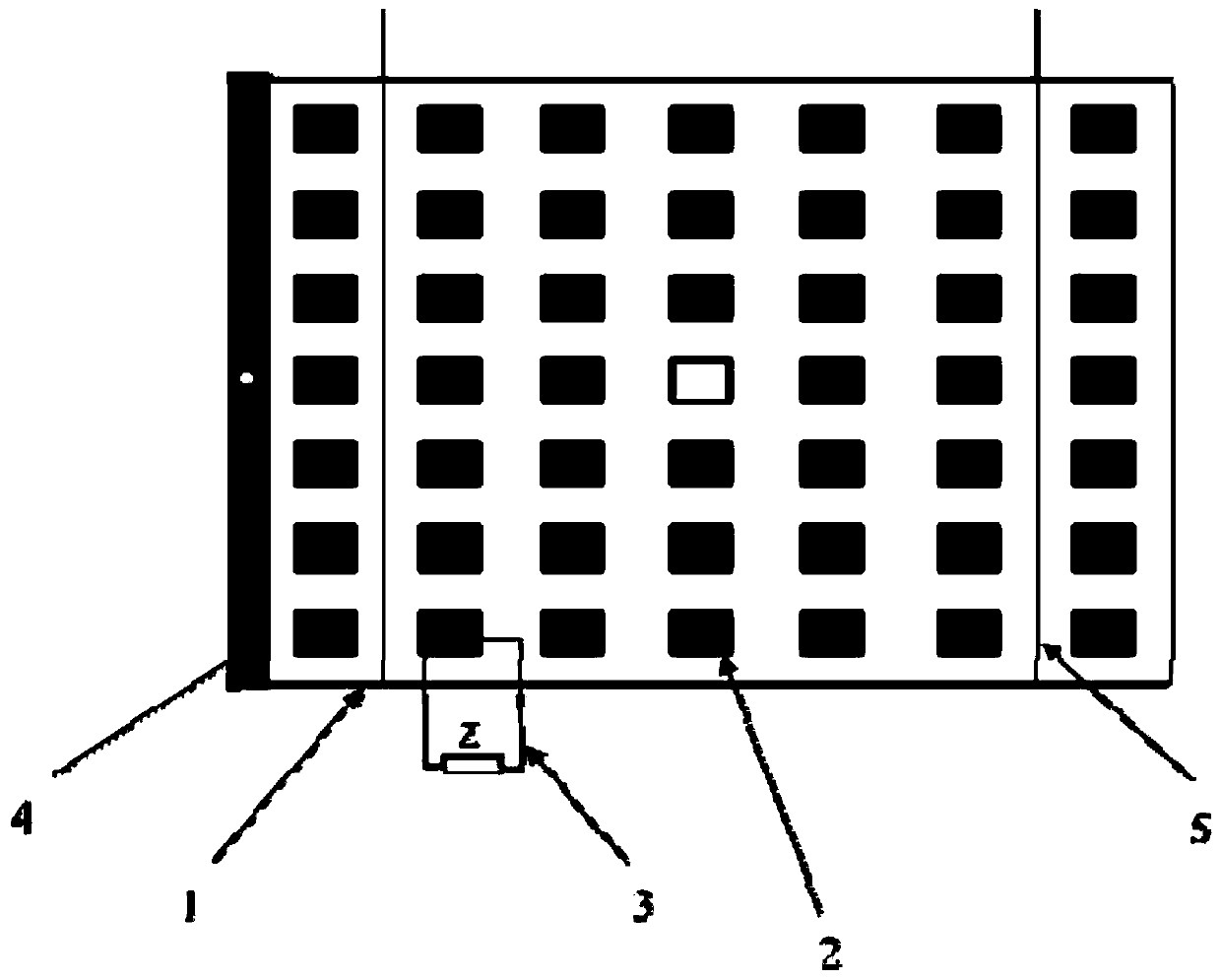
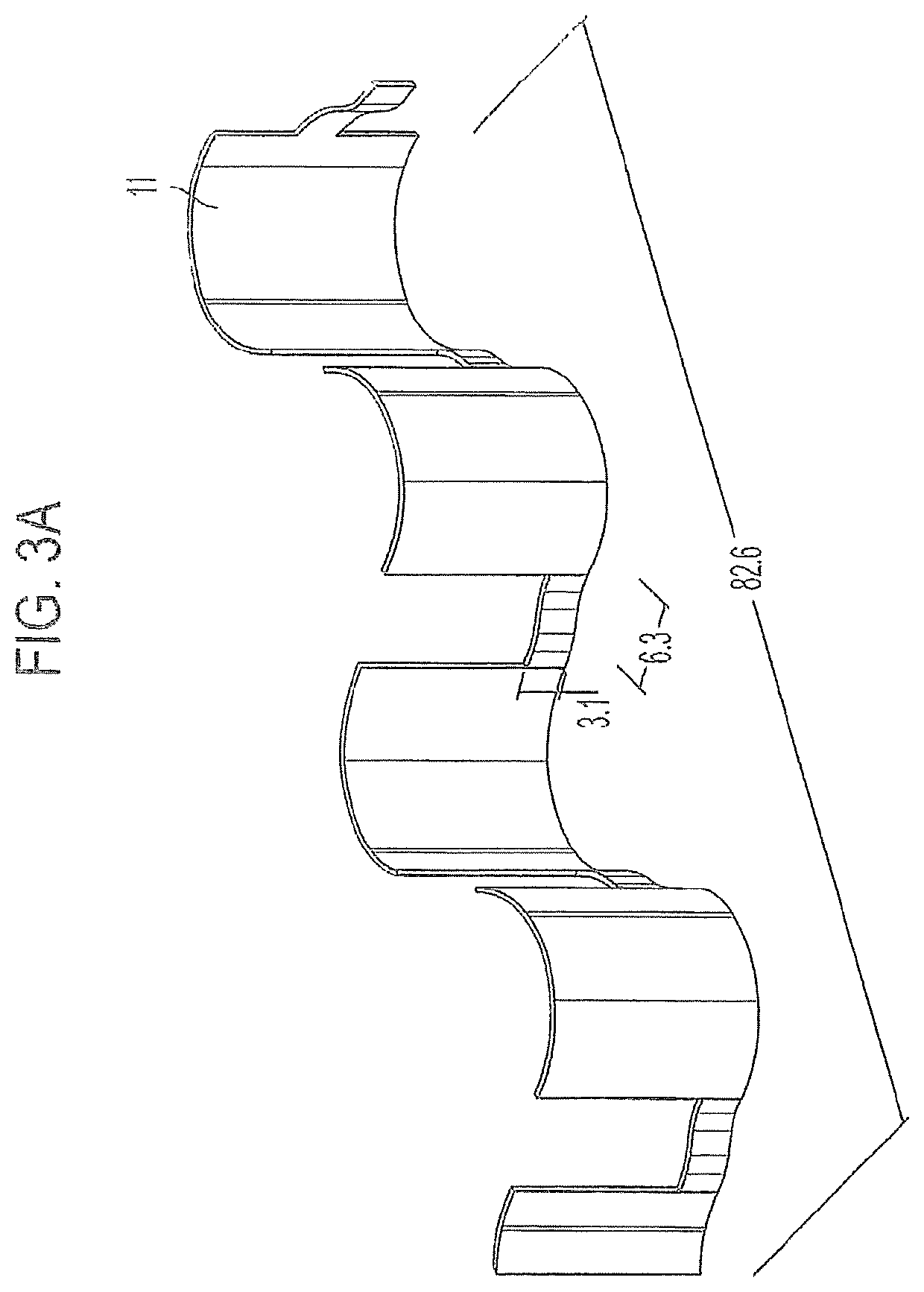
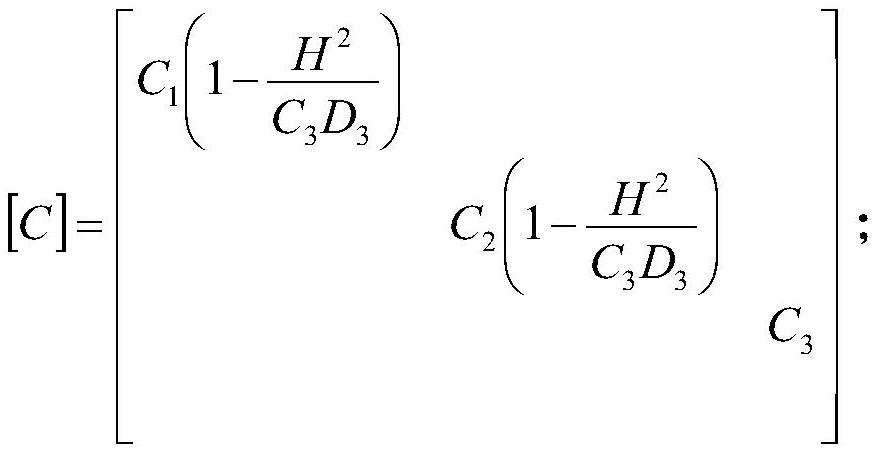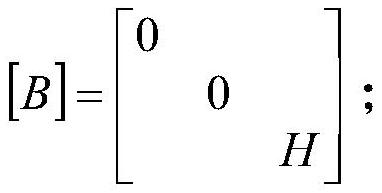Patents
Literature
38 results about "Mechanical metamaterial" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mechanical metamaterials are artificial structures with mechanical properties defined by their structure rather than their composition. They can be seen as a counterpart to the rather well-known family of optical metamaterials and include acoustic metamaterials as a special case of vanishing shear. Their mechanical properties can be designed to have values which cannot be found in nature.
Mechanical meta-materials
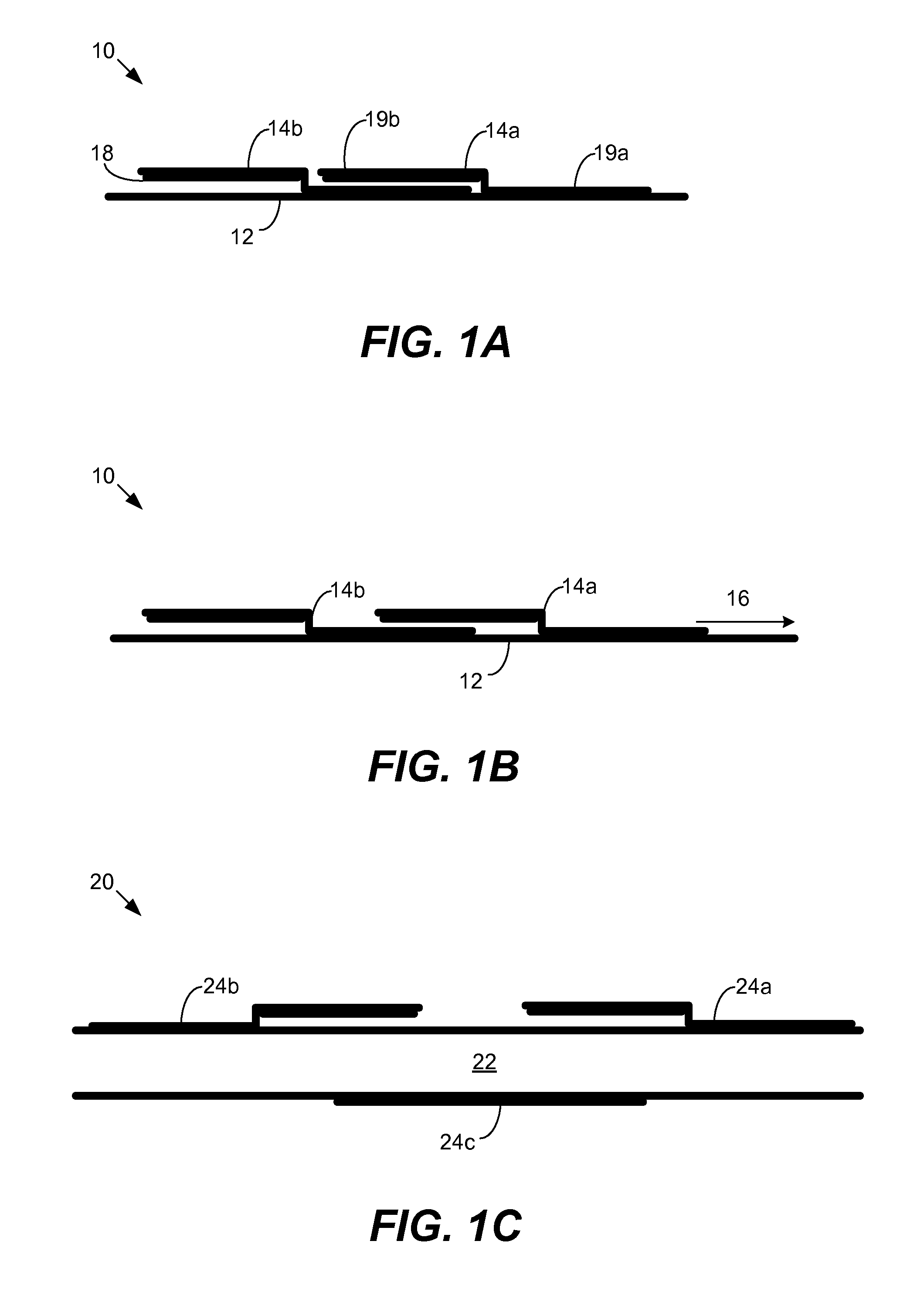
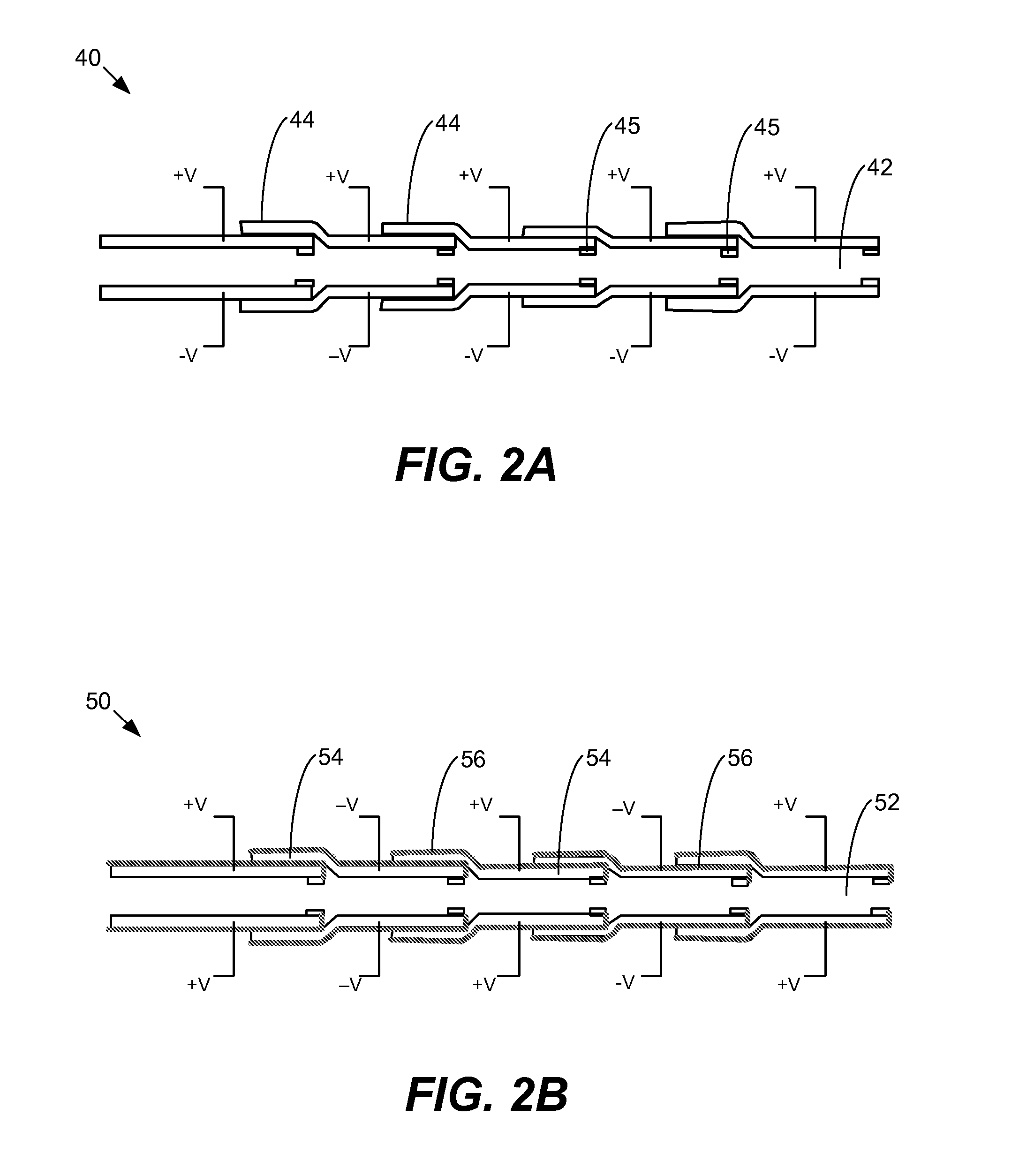
ActiveUS20060192465A1Minimize sizeMinimize massEfficient propulsion technologiesCatheterMechanical metamaterialEngineering
The present invention provides meta-materials with an actively controllable mechanical property. The meta-material includes a deformable structure and a set of activation elements. The activation elements are controllable between multiple states. The meta-material includes a first value for a mechanical property when one or more of the activation elements is in the first activation state and includes a second value for the mechanical property when the activation elements have been activated to the second activation state. In one aspect, the meta-material resembles a composite material where the connectivity between the component materials or shape and arrangement of the component materials is dynamically controllable so as to affect a mechanical property of the meta-material.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Mechanical meta-materials
ActiveUS20080075930A1Minimize sizeMinimize massLayered productsEfficient propulsion technologiesMechanical metamaterialEngineering
The present invention provides meta-materials with an actively controllable mechanical property. The meta-material includes a deformable structure and a set of activation elements. The activation elements are controllable between multiple states. The meta-material includes a first value for a mechanical property when one or more of the activation elements is in the first activation state and includes a second value for the mechanical property when the activation elements have been activated to the second activation state. In one aspect, the meta-material resembles a composite material where the connectivity between the component materials or shape and arrangement of the component materials is dynamically controllable so as to affect a mechanical property of the meta-material.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
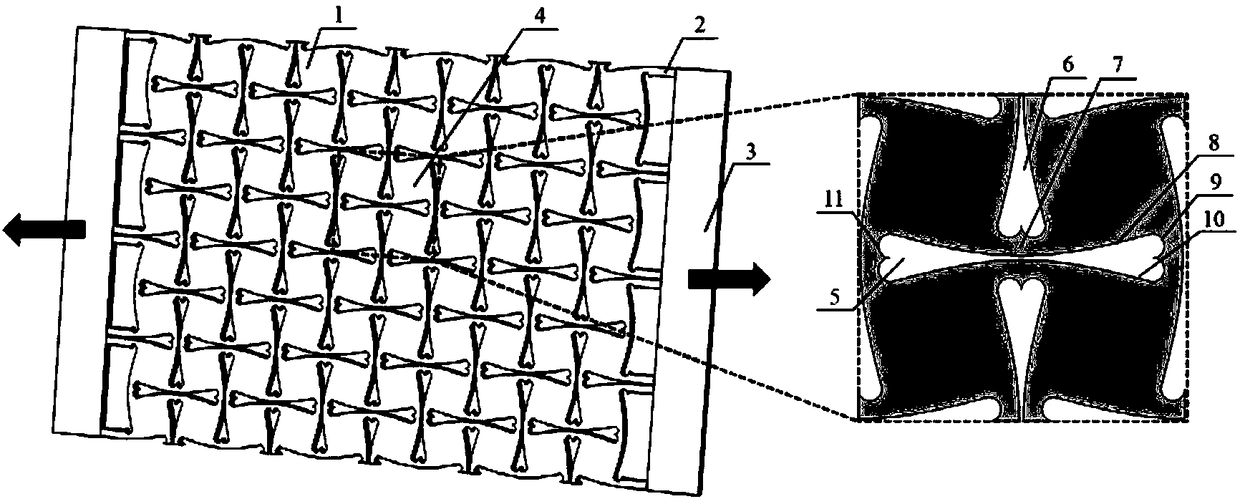
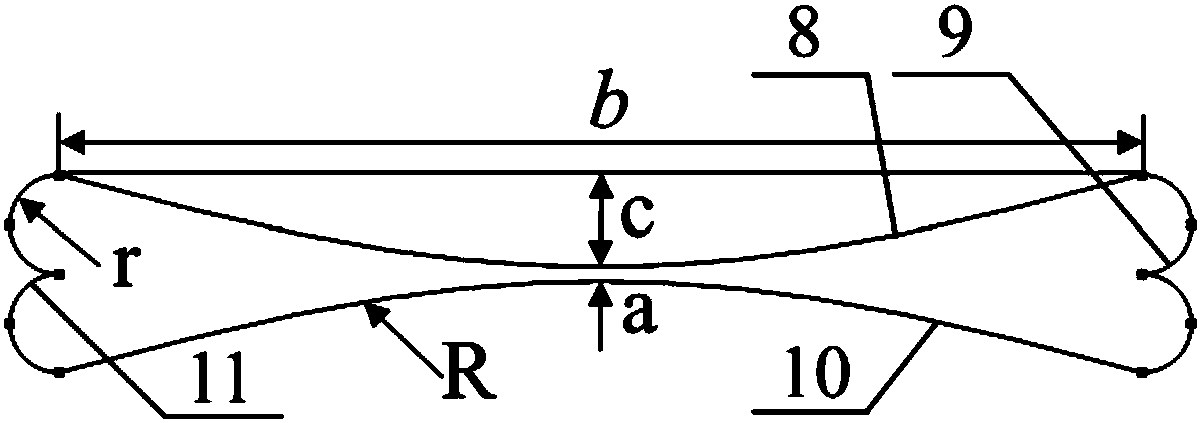
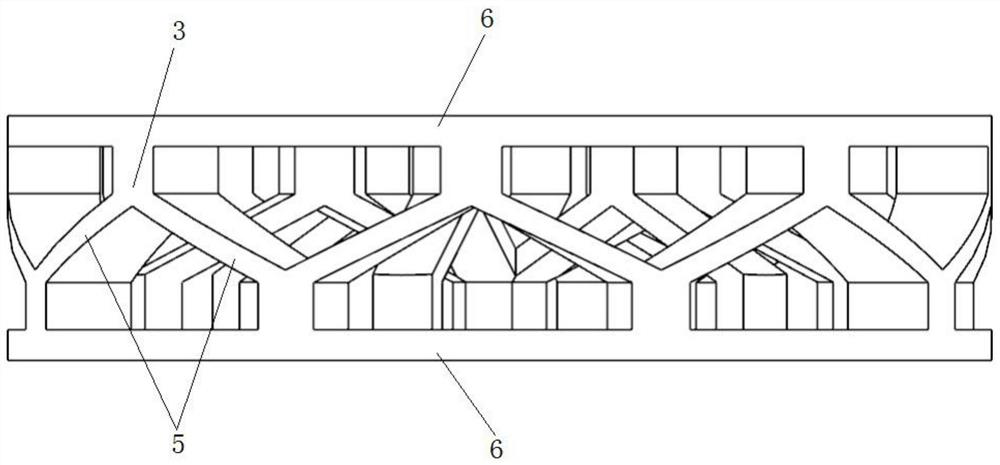
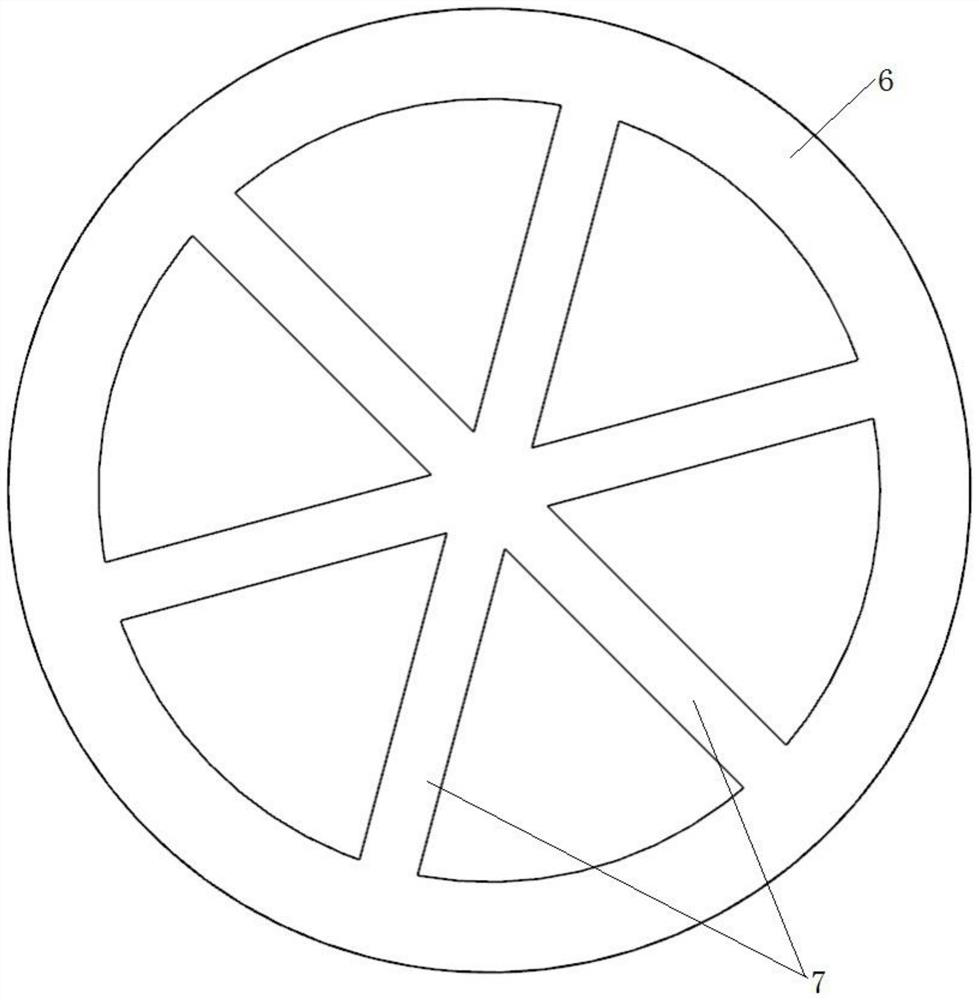
High-tensile-strength mechanical metamaterial adjustable in band gap
ActiveCN108591810AReal-time and continuous adjustmentGuaranteed reliabilitySheets/panelsMechanical metamaterialConfiguration design
The invention discloses a high-tensile-strength mechanical metamaterial adjustable in band gap. The high-tensile-strength mechanical metamaterial adjustable in band gap is characterized in that the metamaterial comprises an elastic perforated plate and a clamping plate; the elastic perforated plate is provided with a plurality of through holes arranged in a matrix form; each through hole is defined by an upper edge arc line, a right end arc line, a lower edge arc line and a left end arc line in sequence, the upper edge arc line and the lower edge arc line are in mirror symmetry, openings of the upper edge arc line and the lower edge arc line are away from each other, the left end arc line and the right end arc line in mirror symmetry, openings of the left end arc line and the right end arcline are away from each other; and the outer edge of the elastic perforated plate is connected with the inner edge of the clamping plate through a plurality of elastic connection bodies. According tothe high-tensile-strength mechanical metamaterial adjustable in band gap, the clamping plate is pulled by external mechanical force to drive the elastic perforated plate to move, so that a square celluar geometrical configuration is changed, real-time continuous adjusting of the band gap is achieved, operation is convenient and easy to achieve, in addition, the reliability of the metamaterial during drawing is ensured through the high-tensile-strength through hole configuration design, and the engineering practicality is high.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Novel three-dimensional structure with adjustable Poisson's ratio and thermal expansion coefficient and design method thereof
PendingCN112420134ALarge adjustment rangeRealize 3D Negative Poisson's RatioMolecular entity identificationMolecular designMechanical metamaterialThermal dilatation
The invention discloses a novel three-dimensional structure with adjustable Poisson's ratio and thermal expansion coefficient and a design method thereof, and the method comprises the following steps:firstly, selecting different triangular unit geometric parameters and material combinations, designing a triangular unit based on three materials, and then splicing two same triangular units into a parallelogram, constructing a three-dimensional cell element based on four same parallelograms; periodically arranging the three-dimensional cell elements in the direction where the horizontal straightrods are located and repeatedly performing mirroring in the other two directions, and finally obtaining the novel three-dimensional truss structure; and then performing mechanical analysis on a three-dimensional cell element of the three-dimensional truss structure, solving an equivalent formula of elastic parameters and a thermal expansion coefficient of the three-dimensional truss structure through a displacement method and a unit load method, and calculating a corresponding poisson ratio and a thermal expansion coefficient based on the equivalent formula. By selecting reasonable geometrical parameters and material combination, the Poisson's ratio and the thermal expansion coefficient of the three-dimensional mechanical metamaterial can be regulated and controlled in a large range.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Methods and systems for designing metamaterials
PendingUS20210034801A1Lighten the computational burdenDesign optimisation/simulationComputational materials scienceMechanical metamaterialEngineering
Systems and methods for computing linear and non-linear explicit, matrix-free, statics with applications to functionally graded mechanical metamaterials. In some aspects, these systems and methods use an algorithm based on a special finite element formulation called the Jacobian Free Newton Krylov (JFNK) method.
Owner:THORNTON TOMASETTI INC
Mechanical metamaterial fluctuation device with active regulation and control function
InactiveCN111541045AAchieve vibration protectionTo achieve the purpose of vibration isolationNon-rotating vibration suppressionAntennasMechanical metamaterialCapacitance
The invention discloses a mechanical metamaterial fluctuation device with an active regulation and control function. The mechanical metamaterial fluctuation device comprises a base plate, a piezoelectric plate and a negative capacitance circuit; and the base body plate is of a plate-shaped structure made of ABS materials and is hung on a support through a rope, a clamp is installed on one side ofthe base body plate, the piezoelectric patches of rectangular structures are periodically pasted on the front face and the back face of the base body plate respectively, and each piezoelectric patch is connected with a negative capacitance circuit to form a periodic structure capable of conducting active regulation and control.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Temperature sensor
ActiveCN112097936AHigh detection sensitivitySimple structureThermometers using material expansion/contactionMechanical metamaterialElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a temperature sensor, and the sensor comprises a substrate, two thermally-driven V-shaped beam structures, a frame-shaped mechanical metamaterial structure and a strain sensitive film. The two thermally-driven V-shaped beam structures are located on the two sides of the frame-shaped mechanical metamaterial structure respectively. The strain sensitive film is located in thecenter of the frame-shaped mechanical metamaterial structure. When the ambient temperature changes, the suspended thermally-driven V-shaped beam expands or contracts under the influence of the temperature, the rigid insulation connecting wire is driven to drive the frame-shaped mechanical metamaterial structure to expand or contract in multiple directions, and expansion or contraction of the mechanical metamaterial structure is transmitted to the strain sensitive film through the rigid insulation connecting wire; the strain sensitive film converts multi-directional strain into resistance valuechange, and the ambient temperature is measured by detecting the resistance change, so the detection sensitivity of the device is greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
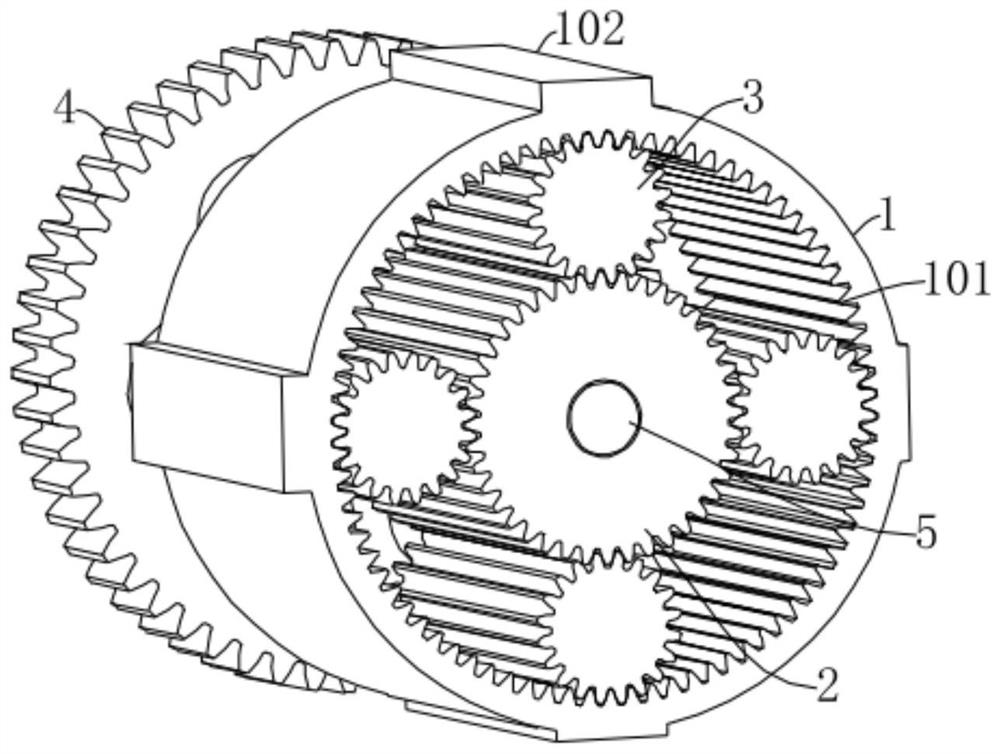
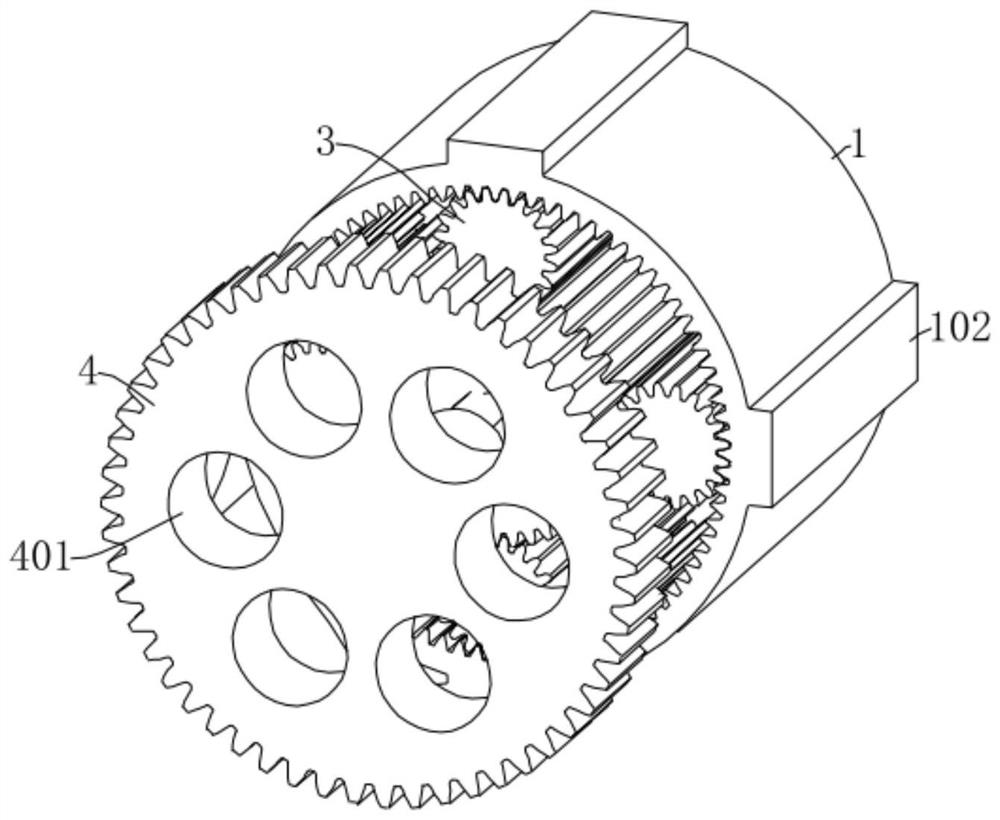
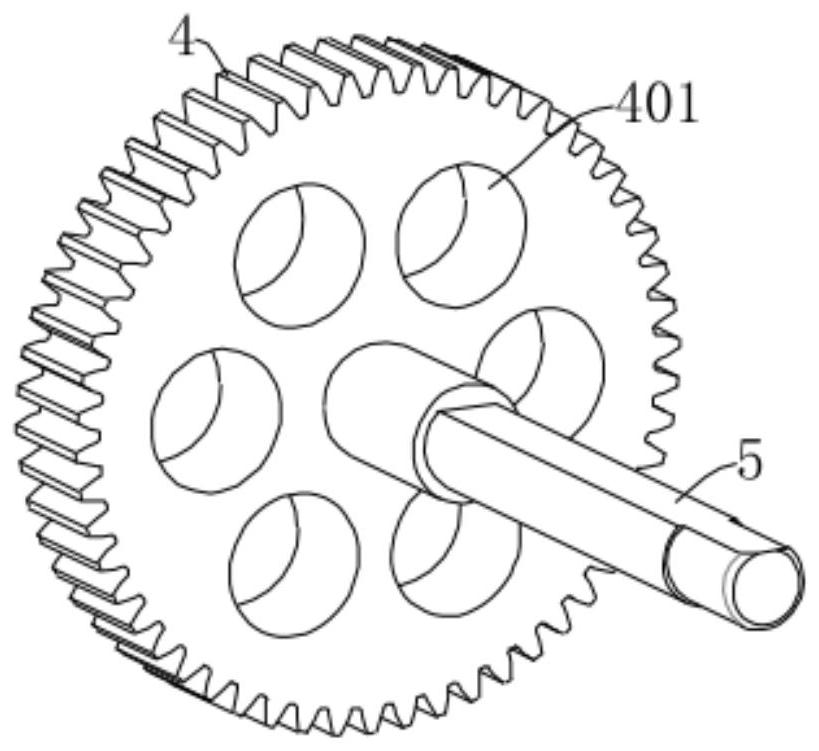
Super-cell and large-range variable stiffness mechanical metamaterial based on planetary gear system
ActiveCN113775702AAchieve regulationSame-sex natureToothed gearingsGearing detailsMechanical metamaterialGear wheel
The invention discloses a super-cell and large-range variable stiffness mechanical metamaterial based on a planetary gear system. The mechanical metamaterial is formed by periodically extending a plurality of super-cells in an x-axis direction and / or a y-axis direction, and each super-cell comprises a planetary gear mechanism and a transmission mechanism. Each planetary gear mechanism comprises an outer ring, a sun gear and a planetary gear assembly. Each transmission mechanism comprises a transmission gear and a center shaft, one end of each center shaft is fixedly connected with the center of the corresponding transmission gear, and the other end is fixedly connected with the center of the corresponding sun gear. According to the mechanical metamaterial, on one hand, the defects that in an existing reconfigurable mechanical metamaterial design technology, the adjustment range of elastic parameters is narrow, the number of stable states is small, and adjustment and control robustness is low are overcome; and on the other hand, the defects that a mechanical metamaterial based on a common plane gear is difficult to bear tensile load, the tensile modulus is difficult to adjust, and interference exists between a stress part and regulation and control deformation are overcome.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Acceleration sensor based on mechanical metamaterial structure
The invention provides an acceleration sensor based on a mechanical metamaterial structure. The acceleration sensor comprises a substrate, an acceleration sensing unit, at least one strain sensing unit, an anchor point group and a lead group, wherein the acceleration sensing unit, the at least one strain sensing unit, the anchor point group and the lead group are arranged on the substrate. Each strain sensing unit comprises a mechanical metamaterial structure and a resistance strain gauge. One end of each mechanical metamaterial structure is connected with the anchor point group through the lead group, and the other end of each mechanical metamaterial structure is connected with the acceleration sensing unit through the lead group so as to receive a single-direction strain generated by theacceleration sensing unit during acceleration motion and convert the single-direction strain into a multi-direction strain; and each resistance strain gauge is connected with the corresponding mechanical metamaterial structure so as to generate the change of the resistance value under the multi-direction strain and measure the acceleration according to the change of each resistance value. The acceleration sensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, a large measurement range, a small measurement error, a novel structure and the like.
Owner:NANJING GAOHUA TECH
Pressure sensor based on mechanical metamaterial structure
ActiveCN112284580AHigh sensitivityRealize measurementForce measurementMechanical metamaterialElectrical connection
The invention provides a pressure sensor based on a mechanical metamaterial structure. The sensor comprises a substrate, a pressure sensing unit, at least one thermal driving unit, a strain sensing unit, an anchor point group and a lead group, wherein the pressure sensing unit, the at least one thermal driving unit, the strain sensing unit, the anchor point group and the lead group are arranged onthe substrate. The strain sensing unit comprises the mechanical metamaterial structure and a strain sensitive film, wherein the pressure sensing unit is electrically connected with at least one thermal driving unit through the lead group and the anchor point group to form a current path. When a current in the current path changes, the thermal driving unit can generate a single-direction strain, and the mechanical metamaterial structure is connected with each thermal driving unit to convert the single-direction strain into multi-direction strain. The strain sensitive film is electrically connected with the mechanical metamaterial structure so that the pressure is measured by detecting the resistance value according to the multi-directional strain output resistance value, and the sensitivity of the pressure sensor to the pressure is further improved.
Owner:NANJING GAOHUA TECH
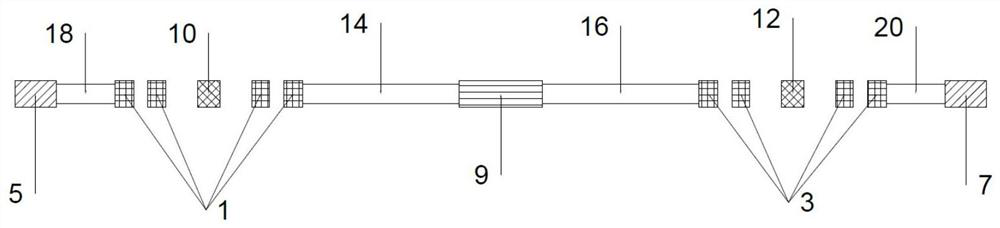
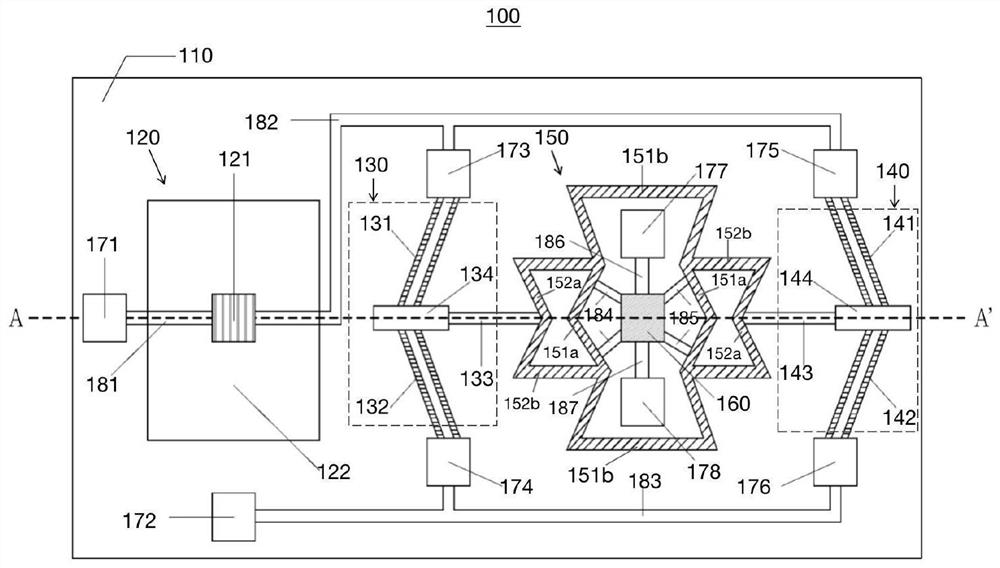
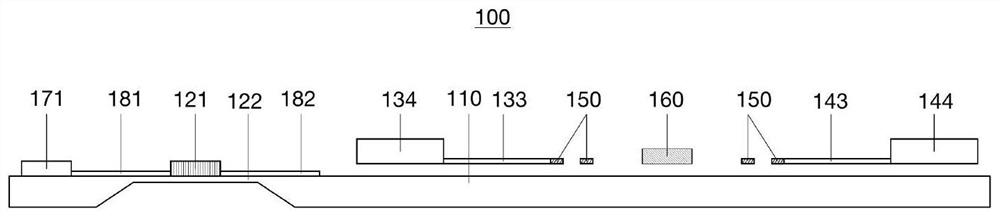
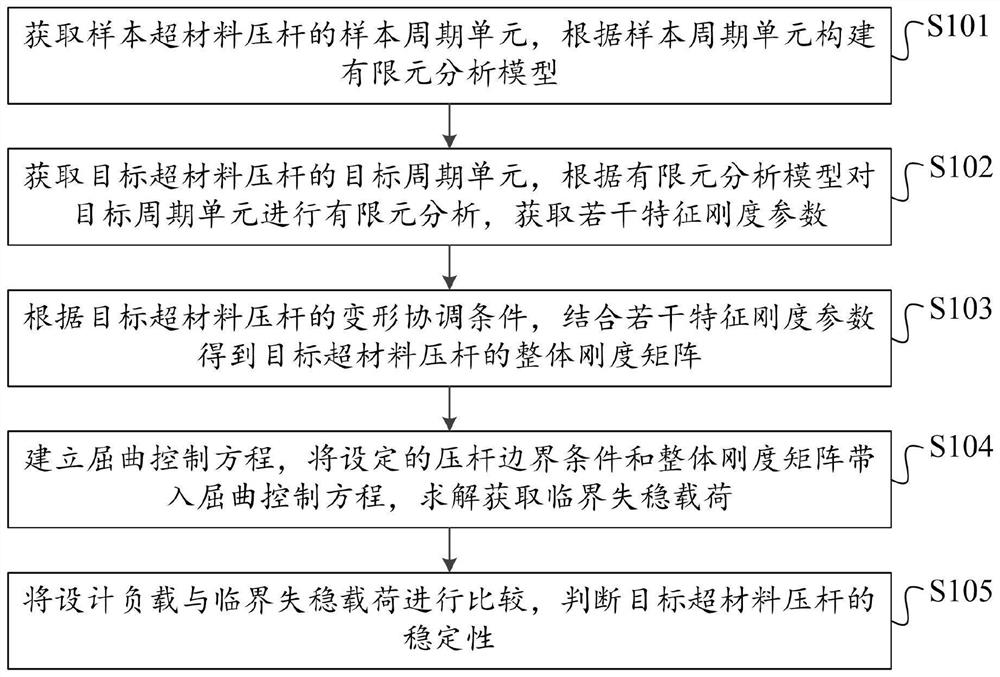
Mechanical metamaterial compression bar stability analysis method
ActiveCN112784460AShorten design timeImprove structural design efficiencyGeometric CADSustainable transportationMechanical metamaterialElement analysis
The invention provides a mechanical metamaterial compression bar stability analysis method which comprises the following steps of: obtaining a sample period unit of a sample metamaterial compression bar, and constructing a finite element analysis model according to the sample period unit; obtaining a target periodic unit of a target metamaterial compression bar, and performing finite element analysis on the target periodic unit according to the finite element analysis model to obtain a plurality of characteristic stiffness parameters; according to the deformation coordination condition of the target metamaterial compression bar, combining the plurality of characteristic stiffness parameters to obtain an overall stiffness matrix of the target metamaterial compression bar; establishing a buckling control equation, substituting a set pressure bar boundary condition and the overall stiffness matrix into the buckling control equation, and solving to obtain a critical instability load; and comparing a design load with the critical instability load, and judging the stability of the target metamaterial compression bar. According to the method, the time required for judging the structural stability of the metamaterial pressing rod is shortened, and the structural design efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:北京理工大学重庆创新中心 +1
Fluid-solid interaction mechanical metamaterial pipeline structure for vibration attenuation and noise elimination and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN113090847AIncrease stiffnessTaking into account the carrying capacityPipe elementsVibration attenuationMechanical metamaterial
The invention provides a fluid-solid interaction mechanical metamaterial pipeline structure for vibration attenuation and noise elimination and a manufacturing method thereof. The pipeline structure comprises a plurality of vibration attenuation and noise reduction pipeline primitive cells which are connected in series. Each vibration attenuation and noise reduction pipeline primitive cell comprises a first connecting pipe, a second connecting pipe and a third connecting pipe, and vibrator piece units, wherein the first connecting pipe, the second connecting pipe and the third connecting pipe are sequentially connected, the vibrator piece units are located on a part of the outer wall of the second connecting pipe and surround the second connecting pipe, the inner diameter of the first connecting pipe is gradually reduced in the direction from the first connecting pipe to the second connecting pipe, the second connecting pipe is in a straight pipe shape, and the inner diameter of the third connecting pipe is gradually reduced in the direction from the third connecting pipe to the second connecting pipe. The fluid-solid interaction mechanical metamaterial pipeline structure for vibration attenuation and noise elimination has good low-frequency broadband vibration attenuation and noise elimination functions.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
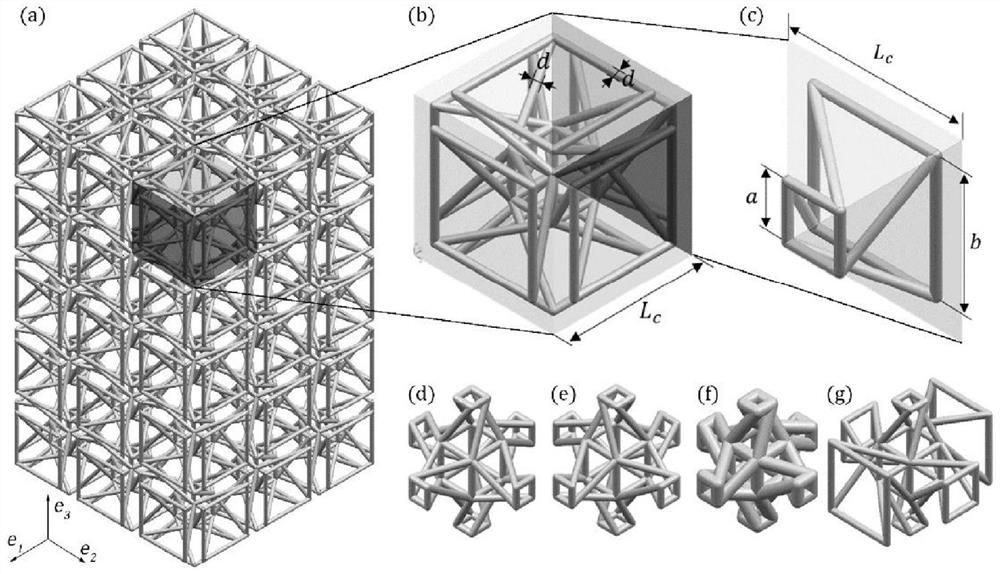
Ultralight high-rigidity mechanical metamaterial and optimization design method thereof
PendingCN114462275AHas ultra-light propertiesReduced ultralight propertiesGeometric CADBridge structural detailsMechanical metamaterialOctahedron
The invention discloses an ultralight high-rigidity mechanical metamaterial which comprises at least one structural unit capable of being spliced with each other, and each structural unit is of a cubic octahedral beam frame structure and is formed by splicing an internal structure and four external structures. The internal structure comprises a square plate, a cross beam and a straight beam connected with the center of the square plate and the center of the cross beam, the external structure is of a four-corner star-shaped flat plate structure, and one external structure is spliced between each corner of the square plate and each corresponding end of the cross beam. In other words, the upper outer end corner and the lower outer end corner of one external structure are spliced with one corner of the square plate and the corresponding end of the cross beam correspondingly, and the left outer end corner and the right outer end corner of every two adjacent external structures are spliced with each other; and the internal structure and the four external structures are spliced to form the cubic octahedral beam frame structure. The ultralight high-rigidity mechanical metamaterial disclosed by the invention has an ultralight characteristic and a relatively high axial elastic modulus.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
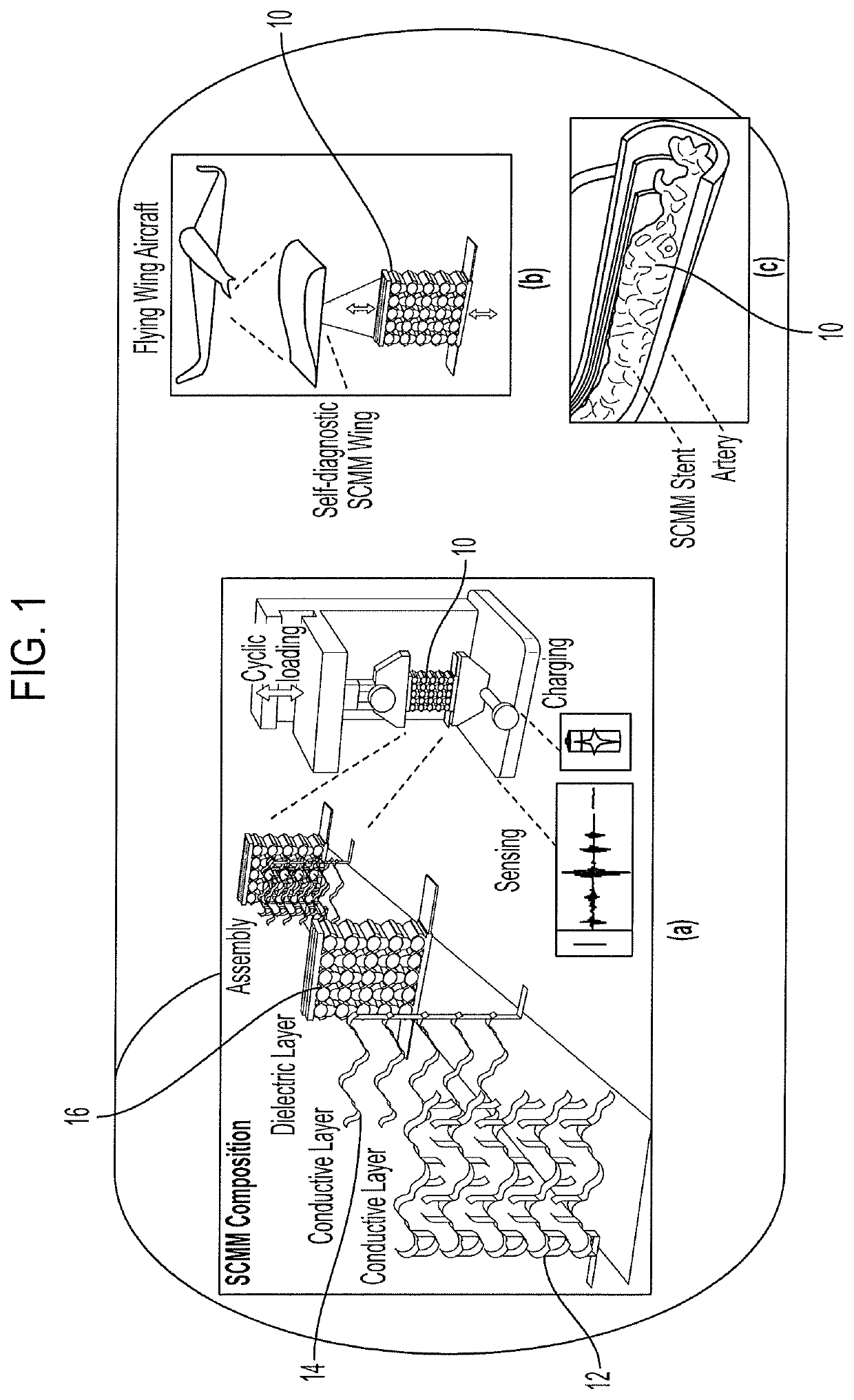
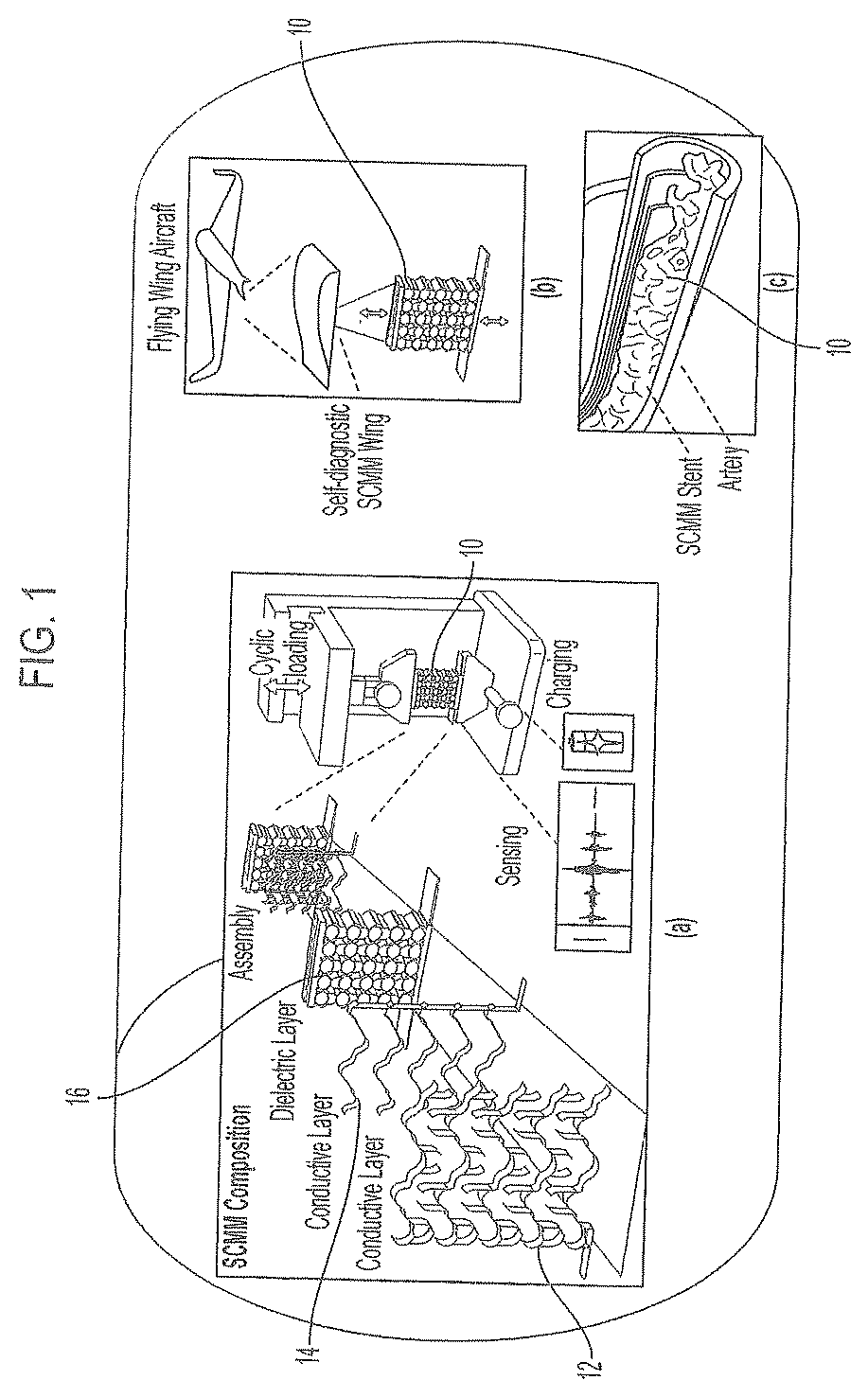
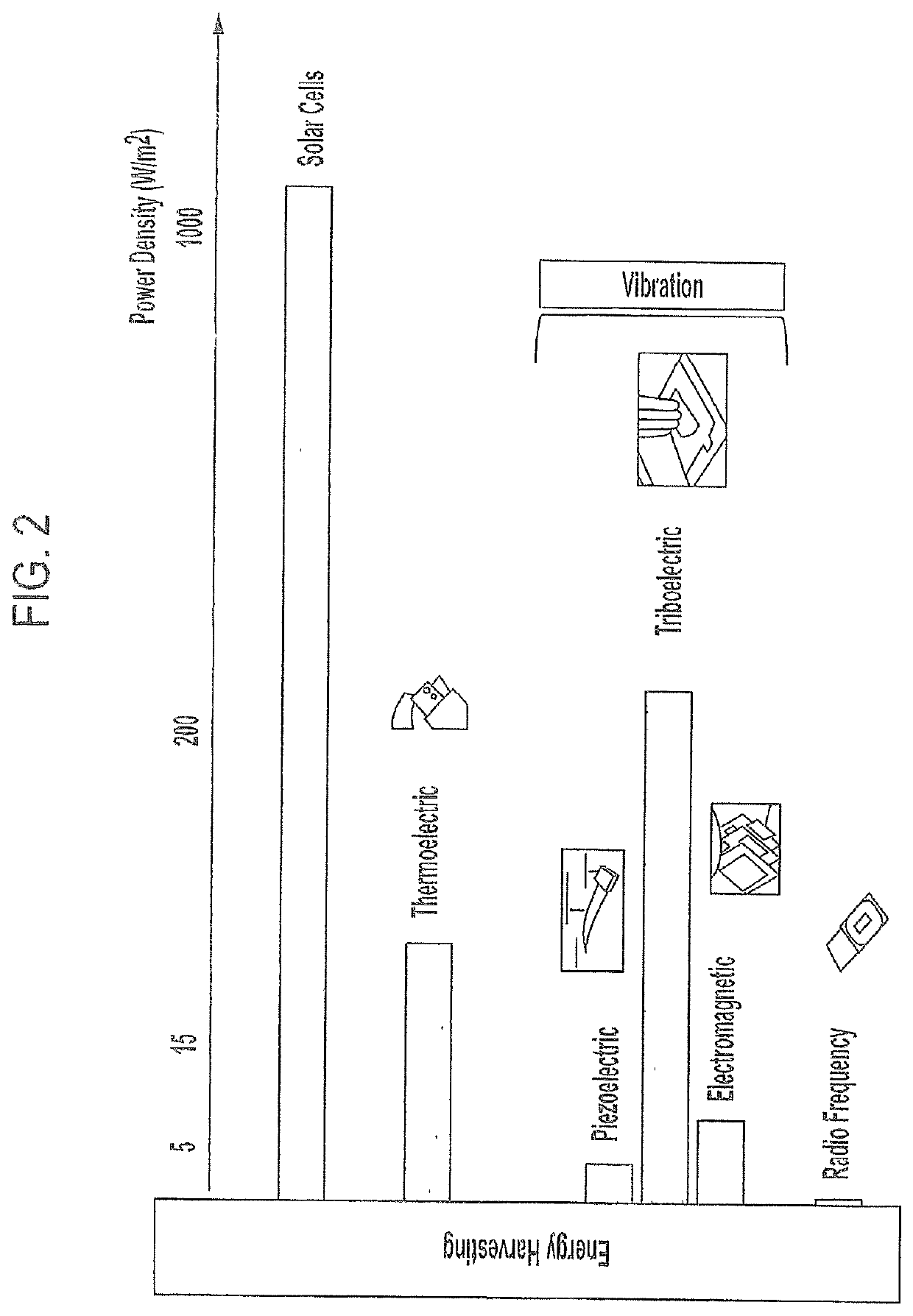
Self-aware composite mechanical metamaterials and method for making same
PendingUS20220011176A1StentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusMechanical metamaterialContact electrification
A self-aware composite mechanical metamaterial, comprising first and second electrically conductive components disposed relative to each other to act as opposite electrodes to induce contact electrification; wherein the first and second electrically conductive components, along with a dielectric component serving as a skeleton of the self-aware composite mechanical metamaterial, form a lattice of snapping curved semicircular-shaped segments, wherein each of the snapping curved semicircular-shaped segments has an elastic snap-through instability mechanism; and wherein the lattice comprises periodic repeatable parallel rows of the snapping curved semicircular-shaped segments.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Reinforced negative stiffness metamaterial structure
PendingCN114038518ATake advantage ofImprove impact resistanceComputational theoretical chemistryComputational materials scienceMechanical metamaterialShock resistance
The invention discloses a reinforced negative stiffness metamaterial structure, relates to the technical field of mechanical metamaterials, and solves the technical problems that the structure of a negative stiffness metamaterial is not simple enough and cannot be repeatedly used. According to the technical scheme, the metamaterial structure is characterized in that the space is fully utilized through an outer cylindrical surface and an internal periodic structure, and the impact resistance and the self strength of the metamaterial structure are improved. Meanwhile, the negative stiffness and the bistable performance of the metamaterial structure are rapidly calculated or verified through a buckling force displacement expression, the design time of the shock resistance of the reinforced metamaterial structure is shortened, and the structural design efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Self-aware composite mechanical metamaterials and method for making same
PendingUS20220209686A1Non-insulated conductorsFriction generatorsMechanical metamaterialContact electrification
A self-aware composite mechanical metamaterial, comprising first and second electrically conductive components disposed relative to each other to act as opposite electrodes to induce contact electrification; wherein the first and second electrically conductive components, along with a dielectric component serving as a skeleton of the self-aware composite mechanical metamaterial, form a lattice of snapping curved semicircular-shaped segments, wherein each of the snapping curved semicircular-shaped segments has an elastic snap-through instability mechanism; and wherein the lattice comprises periodic repeatable parallel rows of the snapping curved semicircular-shaped segments.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
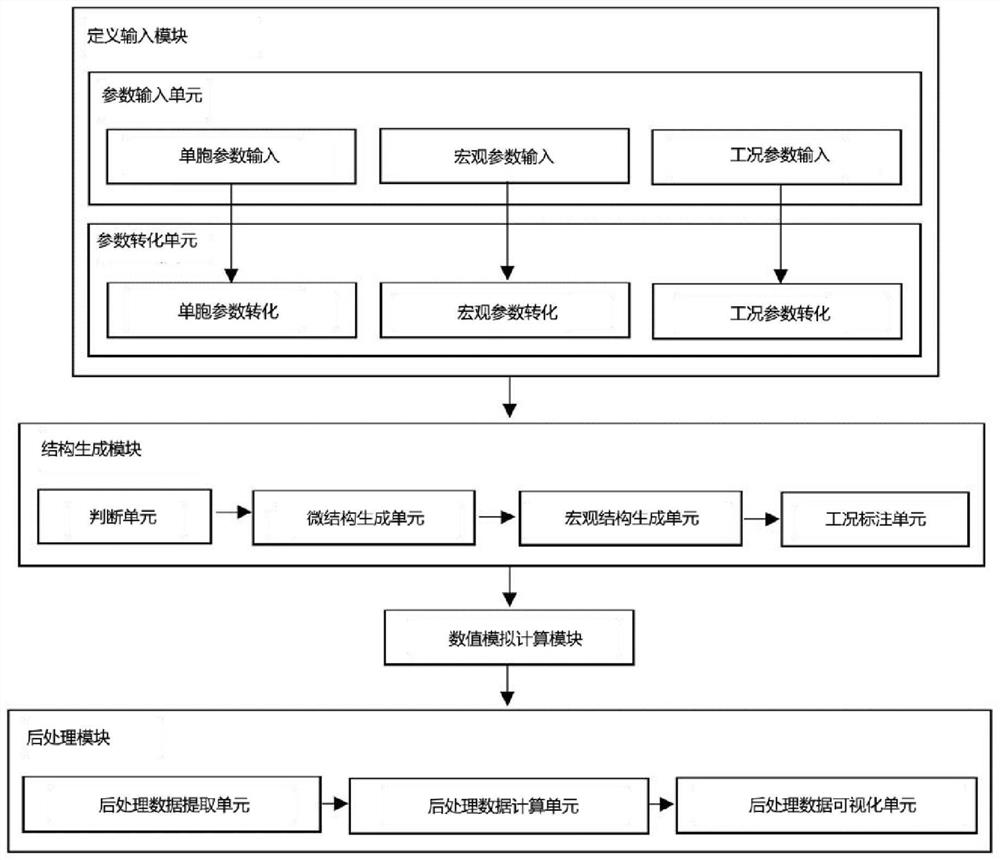
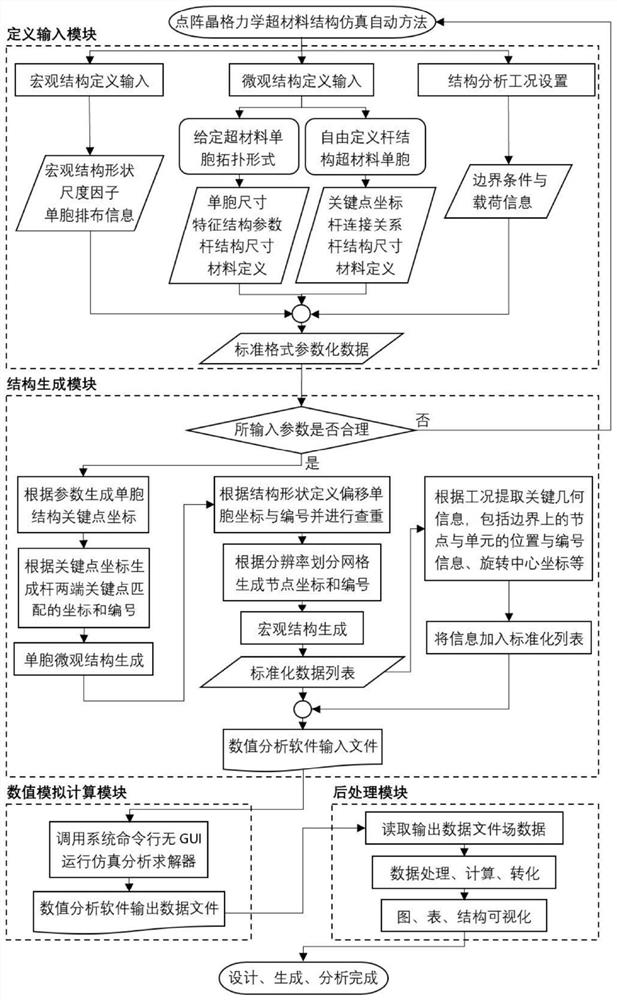
Multi-working-condition simulation automation system and method for rod structure and metamaterial structure
PendingCN114297877AActual engineering valueDesign optimisation/simulationComputational theoretical chemistryMechanical metamaterialAnalogue computation
The invention discloses a multi-working-condition simulation automation system and method for a rod structure and a metamaterial structure, and the system comprises a definition input module, a structure generation module, a numerical simulation calculation module and a post-processing module. A lattice mechanical metamaterial structure model is generated through a structure generation algorithm, simulation analysis of corresponding working conditions is automatically carried out, and post-processing is automatically carried out according to requirements to extract related data.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Two-dimensional mechanical metamaterial with designable deformation and non-contact control
ActiveCN111969327AStrong designabilityRealize deformation controlAntennasMechanical metamaterialEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of metamaterials and relates to a two-dimensional mechanical metamaterial with designable deformation and non-contact control. Each single cell element comprises a deformation unit and a motion unit; each deformation unit comprises an inwards-concave n-angle shape, n connecting rods and n control blocks; one end of each connecting rod is fixedly connected with the concave n-angle shape, the other end of each connecting rod is fixedly connected with the center of one control block; the two ends, far away from the center, of each control block are connected with one movement unit in a sliding mode. In the same single cell element, each movement unit is connected with two control blocks; in the deformation unit, n connecting rods are symmetricallyand fixedly connected to the periphery of the inwards-concave n-angle shape; the deformation unit is of a star-shaped structure with the size controlled by deformation parameters; the movement unit isof a plate-shaped structure with the fixed size; a control groove is formed in a plate-shaped structure and connected with the control blocks and the movement unit in a sliding mode. The material disclosed by the invention can realize negative Poisson's ratio effect, deformation designability and non-contact control.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Passive wireless temperature sensor based on mechanical metamaterial structure
ActiveCN112097938ASimple structureEasy to measureThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansMechanical metamaterialEngineering
The invention provides a passive wireless temperature sensor based on a mechanical metamaterial structure, the temperature sensor comprises a substrate, and at least one temperature sensing unit and astrain sensing unit which are arranged on the substrate, and the strain sensing unit comprises a mechanical metamaterial structure, an LC resonance circuit and a plurality of insulating support pieces, wherein the mechanical metamaterial structure is connected with at least one temperature sensing unit so as to receive single-direction strain generated by the temperature sensing unit due to temperature change and convert the single-direction strain into multi-direction strain, and the LC resonance circuit is connected with the mechanical metamaterial structure through a plurality of insulating supporting pieces, so that resonant frequency changes are generated under multi-direction strain, the resonant frequency is measured in a non-contact mode in a mutual inductance coupling mode, and temperature measurement is achieved. A passive wireless measurement mode is adopted, so the temperature sensor is low in power consumption and easy to measure and has the advantages of being simple instructure, small in measurement error, compatible in process and the like.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A mechanical energy absorbing metamaterial based on a buckle structure and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN107498934BAdjust mechanical propertiesMechanical properties can be adjustedProtective equipmentLaminationElastomerMechanical metamaterial
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A passive wireless robotic gripper based on a mechanical metamaterial structure
ActiveCN112025752BHigh precisionReduce volumeMicromanipulatorGripping headsCapacitanceMechanical metamaterial
The invention discloses a passive wireless machine grabbing hand based on a mechanical metamaterial structure, which includes a graphene oxide layer of a mechanical metamaterial structure, a graphene layer of a mechanical metamaterial structure, an upper plate of a capacitor, a dielectric layer, and a lower capacitor. Plates, planar inductors, vias, substrates, anchor regions, the graphene layer of the mechanical metamaterial structure is located below the graphene oxide layer of the mechanical metamaterial structure, the double-layer mechanical metamaterial structure is located on the front of the substrate, and the center of the mechanical metamaterial structure The place is a pressure-sensitive capacitor composed of the upper plate of the capacitor, the dielectric layer and the lower plate of the capacitor. The lower plate of the capacitor is connected to the anchor area, and the anchor area is connected to the planar inductance on the back of the substrate through the through hole. The present invention is based on the LC resonant circuit The change of resonant frequency can realize the detection of the object on the grasping hand, and apply infrared light excitation to the grasping hand to realize the purpose of grasping the object. It has the advantages of high sensitivity, small measurement error, small size, low power consumption, and novel structure. .
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
An acceleration-sensitive mechanism based on mechanical metamaterials and a composite-sensitivity micromachined accelerometer
ActiveCN109085382BMeet measurement needsCompact structureAcceleration measurementMechanical metamaterialAccelerometer
The invention discloses an acceleration sensitive mechanism based on mechanical metamaterial and a composite sensitivity micromechanical accelerometer. The accelerometer comprises an acceleration sensitive mechanism, a displacement sensing mechanism, and a sensitivity switching actuator; the acceleration sensitive mechanism comprises a mass, a folded beam and a mechanical metamaterial periodic structure; one end of the folded beam and one end of the mechanical metamaterial periodic structure are respectively connected to the two ends of the mass; the folded beam is used to provide the positivestiffness to the acceleration sensitive mechanism; the mechanical metamaterial periodic structure is used to provide positive and negative stiffness which are changed with the displacement; the sensitivity switching actuator is used to control the mass to move to different stiffness regions. The acceleration sensitive mechanism based on mechanical metamaterial and the composite sensitivity micromechanical accelerometer adopts a serial connection manner of the mechanical metamaterial periodic structure and the folded beam to form a flexible structure having a plurality of stress-strain linearregions with different slopes; the flexible structure of the acceleration sensitive mechanism can have different stiffness at different positions, thus has multiple sensitivities.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
a temperature sensor
ActiveCN112097936BHigh detection sensitivitySimple structureThermometers using material expansion/contactionMechanical metamaterialElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a temperature sensor, which comprises a substrate, two heat-driven V-shaped beam structures, a frame-shaped mechanical metamaterial structure, and a strain-sensitive thin film. Two thermally actuated V-shaped beam structures are located on either side of the frame-shaped mechanical metamaterial structure. A strain-sensitive membrane sits at the center of the frame-shaped mechanical metamaterial structure. When the ambient temperature changes, the suspended heat drives the V-shaped beam to expand or contract under the influence of temperature, drives the rigid insulated connecting wire to drive the frame-shaped mechanical metamaterial structure to expand or contract in multiple directions, and the expansion or contraction of the mechanical metamaterial structure The shrinkage is transmitted to the strain-sensitive film through the rigid insulated connection wire, and the strain-sensitive film converts multi-directional strain into a change in resistance value, and the ambient temperature is measured by detecting the change in resistance, so the detection sensitivity of the device is greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A chiral compression-twist superstructure material
ActiveCN112917894BStable torsional behaviorRealize the compression and torsion functionAdditive manufacturing apparatusConstructions elementsCrystallographyMechanical metamaterial
The invention belongs to the technical field of mechanical metamaterials, in particular to a high-strength chiral compression-torsion superstructure material. The chiral compression-twist superstructure material of the present invention is formed by repeatedly stacking several cells; each cell is a cube surrounded by six in-plane chiral structures with the same structure; the in-plane chiral structure consists of 8 beams and A ring is composed of coplanar; among the 8 beams, 4 long beams and 4 short beams are alternated, one end is tangent to the ring respectively, and is combined into a whole, and the other end is located at the four vertices of a square and the square of the square. At the midpoint of the four sides; in the cell, there are six in-plane chiral structures with the same structure, and the outer endpoints of the three adjacent beams of the two in-plane chiral structures are connected correspondingly to form a space cube. The superstructural material exhibits stable and significant torsional behavior under compression, and the maximum compression-torsional angle can be adjusted by the thickness of the beam, the number of cells and the number of layers.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
A pressure sensor based on mechanical metamaterial structure
ActiveCN112284580BHigh sensitivityRealize measurementForce measurementMechanical metamaterialElectrical connection
The present invention provides a pressure sensor based on a mechanical metamaterial structure, comprising: a substrate, a pressure sensing unit, at least one thermal driving unit, a strain sensing unit, an anchor point group and a lead group arranged on the substrate, wherein the strain sensing unit includes a mechanical A metamaterial structure and a strain sensitive film, wherein the pressure sensing unit is electrically connected with at least one thermal driving unit through a lead group and an anchor point group to form a current path, and when the current in the current path changes, the thermal driving unit can generate a single directional strain, the mechanical metamaterial structure is connected with each thermally driven unit to convert single-directional strain into multi-directional strain, and the strain-sensitive film is electrically connected with the mechanical metamaterial structure to output resistance values according to the multi-directional strain, through The resistance value is detected to realize the measurement of the pressure, thereby improving the sensitivity of the pressure sensor to the pressure.
Owner:NANJING GAOHUA TECH
Nonreciprocal bending mechanical metamaterials and their design methods
The present application discloses a non-reciprocal bending mechanical metamaterial and a design method thereof. The non-reciprocal bending mechanical metamaterial comprises a plurality of unit cell structures periodically arranged and interconnected in a three-dimensional space; , the unit cell structure includes the first division, the second division and the third division, along the second direction, the unit cell structure also includes the fourth division and the fifth division arranged oppositely; along the third direction, the unit cell structure The cellular structure also includes the sixth division and the seventh division which are arranged oppositely; a kind of non-reciprocal bending mechanical metamaterial provided by the present invention realizes the natural material by breaking the space inversion symmetry of the three-dimensional structure and introducing nonlinearity The asymmetric positive and negative bending stiffness properties that do not have provide a new paradigm for mechanical functional metamaterials.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
A passive wireless temperature sensor based on a mechanical metamaterial structure
ActiveCN112097938BSimple structureEasy to measureThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansMechanical metamaterialLc resonant circuit
The invention provides a passive wireless temperature sensor based on a mechanical metamaterial structure. The temperature sensor includes: a substrate, and at least one temperature sensing unit and a strain sensing unit provided on the substrate. The strain sensing unit includes a mechanical metamaterial structure, LC A resonant circuit and a plurality of insulating supports; wherein the mechanical metamaterial structure is connected to at least one temperature sensing unit to receive a single-directional strain generated by the temperature sensing unit due to temperature changes, and convert the single-directional strain into a multi-directional strain Strain, the LC resonant circuit is connected to the mechanical metamaterial structure through multiple insulating supports to produce changes in resonant frequency under multi-directional strain, and the resonant frequency can be measured non-contactly through mutual inductance coupling to achieve temperature measurement. The invention adopts a passive wireless measurement method, so that the temperature sensor has low power consumption and is easy to measure. At the same time, it also has the advantages of simple structure, small measurement error, and process compatibility.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Step-by-step elasticoplastic deformation mechanical metamaterial suitable for multiple working conditions
ActiveCN111341395APlay the role of impact bufferFully absorbedComputational materials scienceInstrumentsMechanical metamaterialEnergy absorption
The invention relates to a step-by-step elasticoplastic deformation mechanical metamaterial suitable for multiple working conditions. The metamaterial comprises a plurality of cells which are periodically arranged in the same plane, and each cell is composed of a vertical rod, two inclined rods and two supporting rods, wherein the two inclined rods are connected, the connecting point between the inclined rods is connected with one end of the vertical rod, the inclined rods and the supporting rod form a rhombus, the slenderness ratio of the inclined rods is not larger than 0.05, and the included angle between the inclined rods and the supporting rod is not larger than 40 degrees. The metamaterial provided by the invention can be used under various working conditions, and step-by-step elasticoplastic deformation is realized. Under a small impact load, the first stress platform can be used for absorbing energy, and elastic deformation correspondingly occurs, so that the material can be repeatedly utilized; under a large impact load, the second stress platform can participate in the energy absorption process, plastic deformation occurs in the stage, the energy absorption efficiency isimproved, and therefore a better buffering effect is achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Mechanical-metamaterial-based stretchable sustrate with negative poisson's ratio and manufacturing method thereof
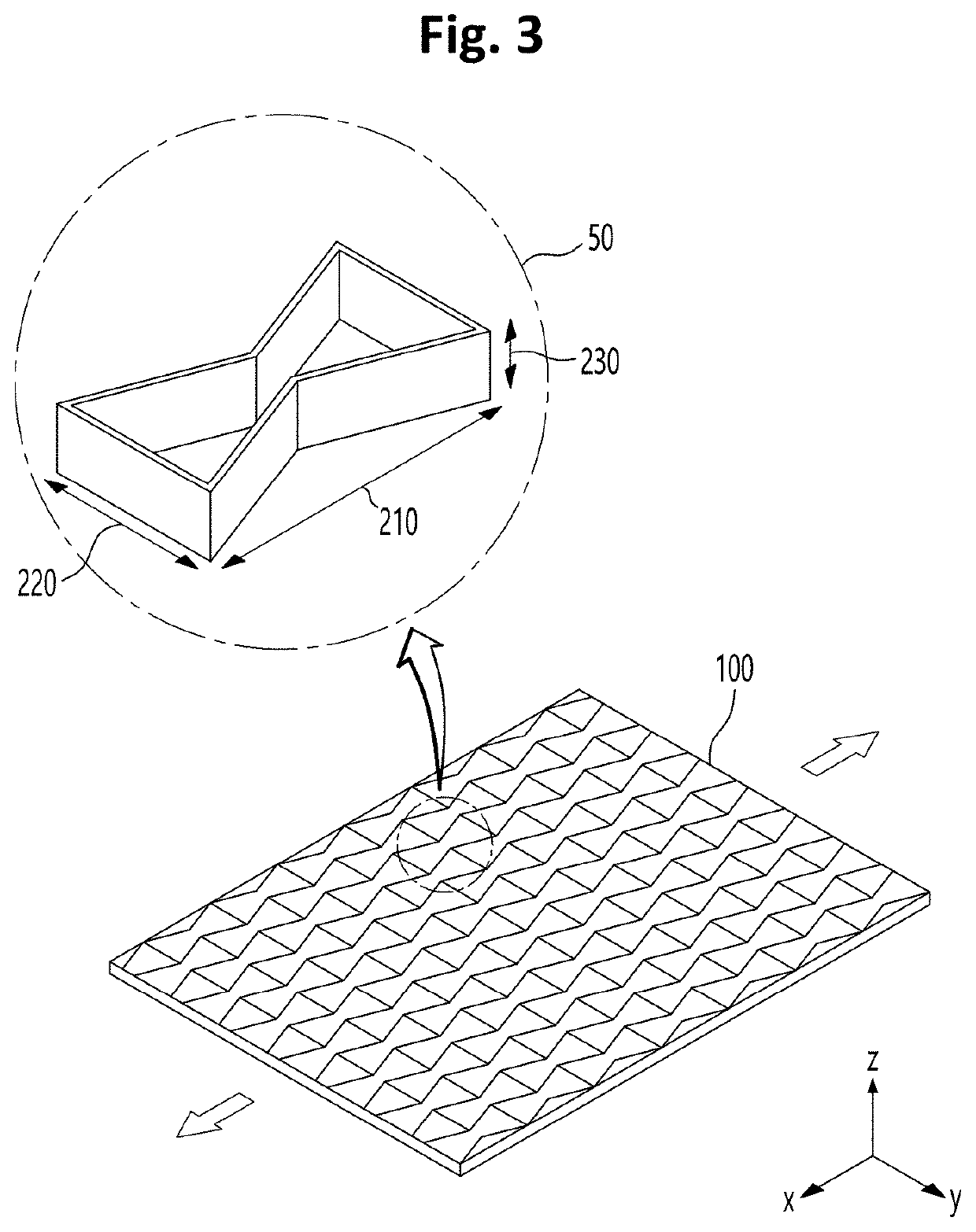
ActiveUS20220161517A1Porous dielectricsCircuit bendability/stretchabilityMechanical metamaterialMechanical engineering
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Discrete macroscopic metamaterial systems
PendingUS20220290570A1Reducing effective densityTurbinesAdditive manufacturing apparatusMechanical metamaterialComputer printing
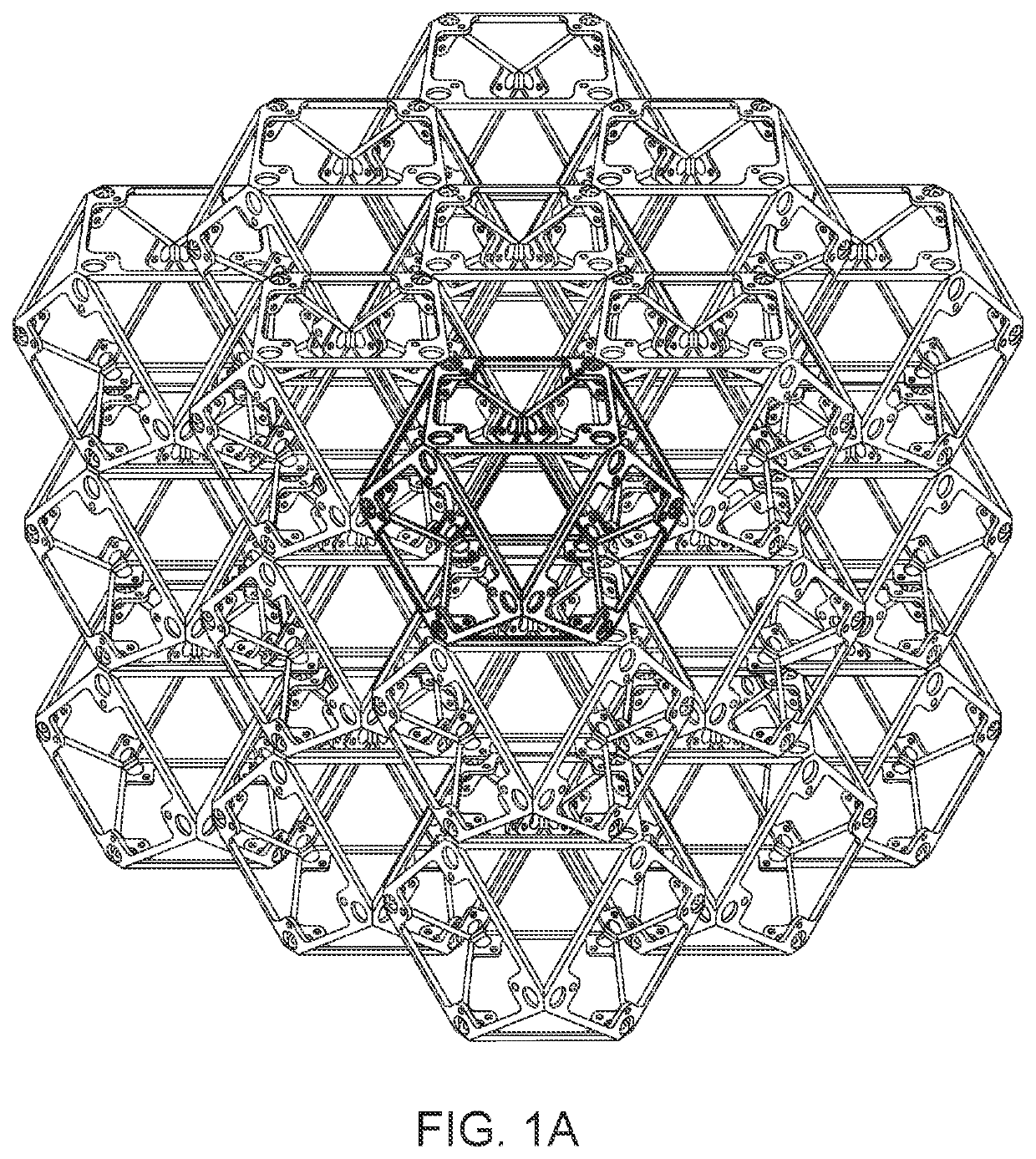
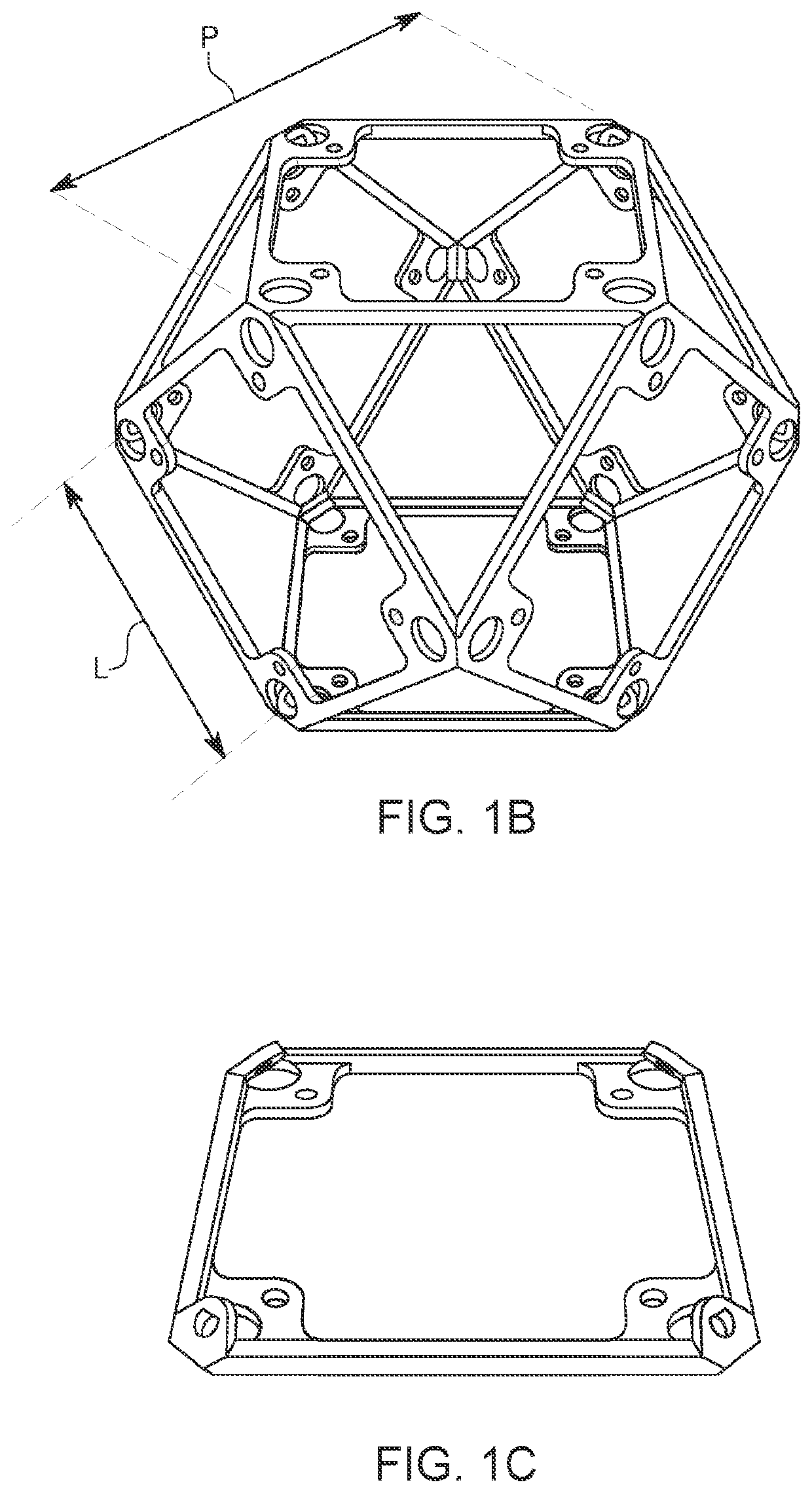
A construction system for mechanical metamaterials based on discrete assembly of a finite set of modular, mass-produced parts. A modular construction scheme enables a range of mechanical metamaterial properties to be achieved, including rigid, compliant, auxetic and chiral, all of which are assembled with a consistent process across part types, thereby expanding the functionality and accessibility of this approach. The incremental nature of discrete assembly enables mechanical metamaterials to be produced efficiently and at low cost, beyond the scale of the 3D printer. Additionally, a lattice structure constructed of two or more rigid, compliant, auxetic and chiral part types enable the creation of heterogenous macroscopic metamaterial structures.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com