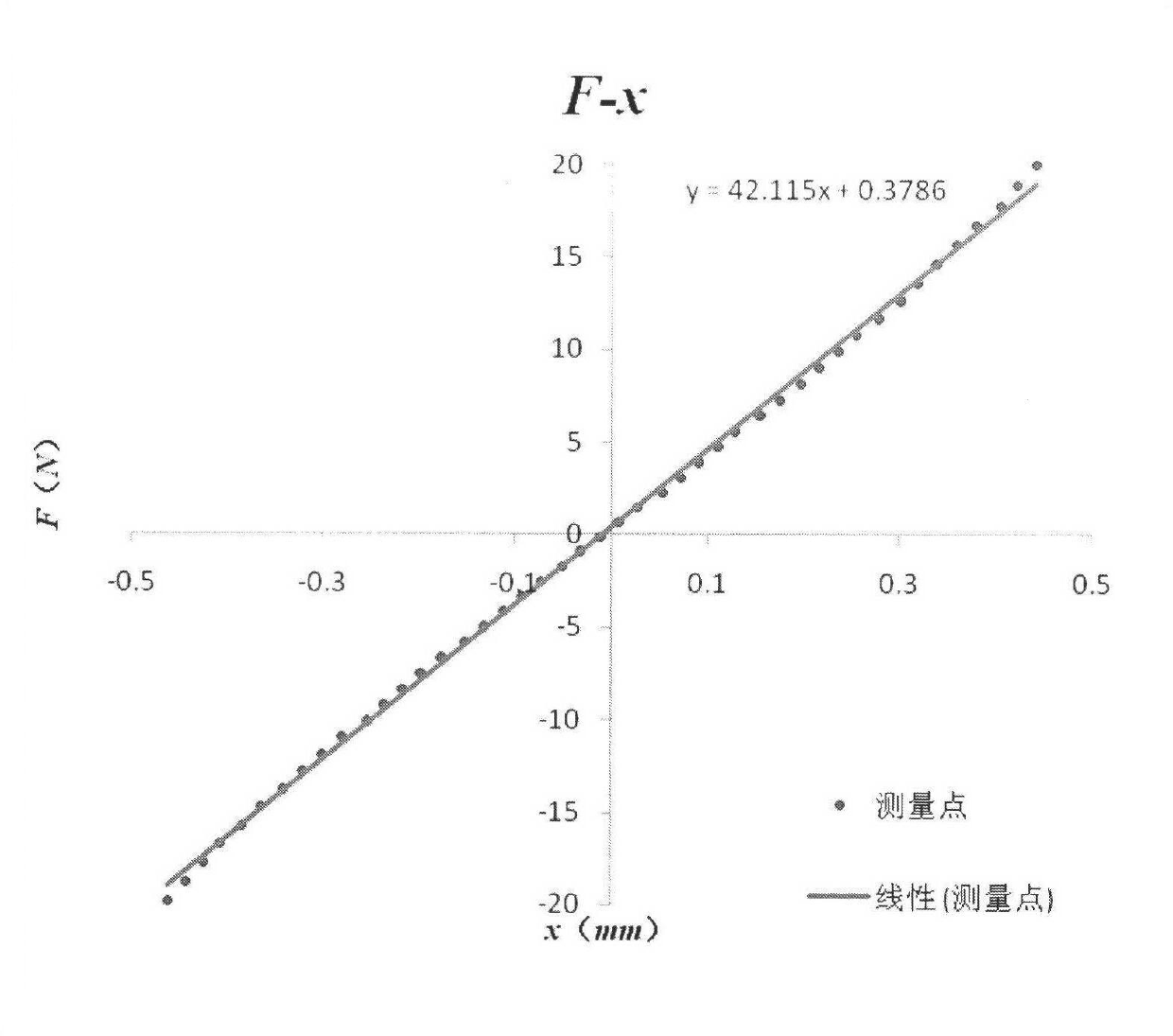
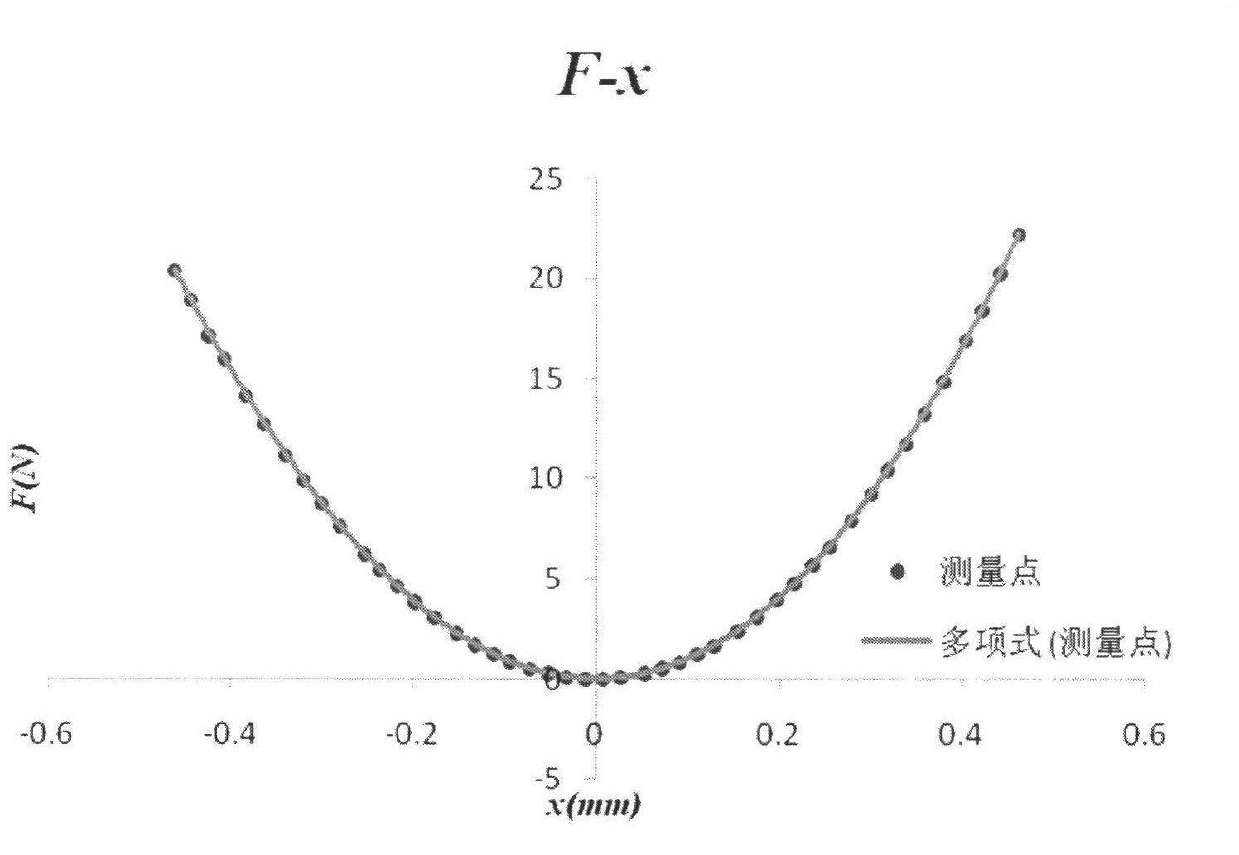
Patents
Literature
227 results about "Force displacement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Forced displacement or forced immigration is the coerced movement of a person or people away from their home or home region and it often connotes violent coercion.
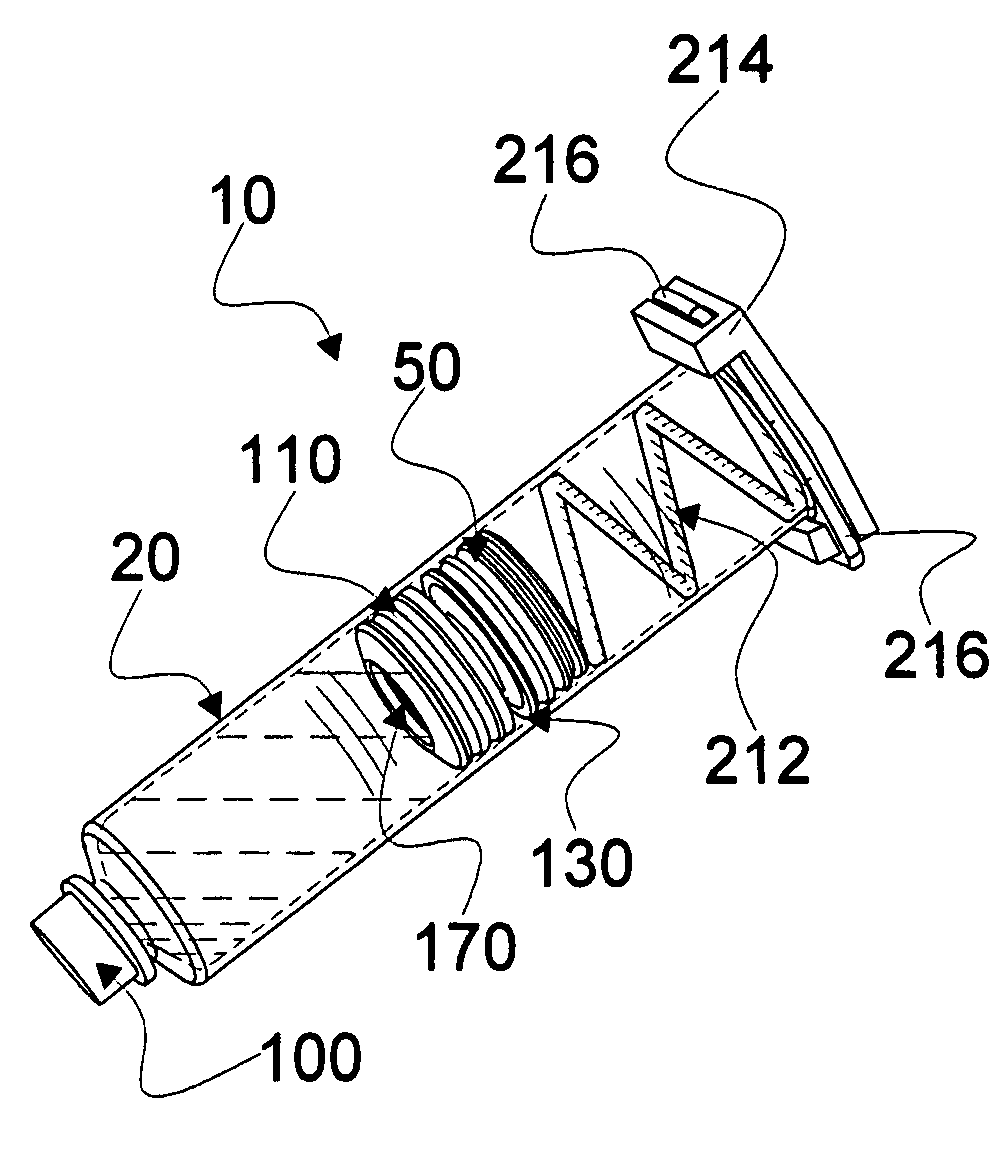
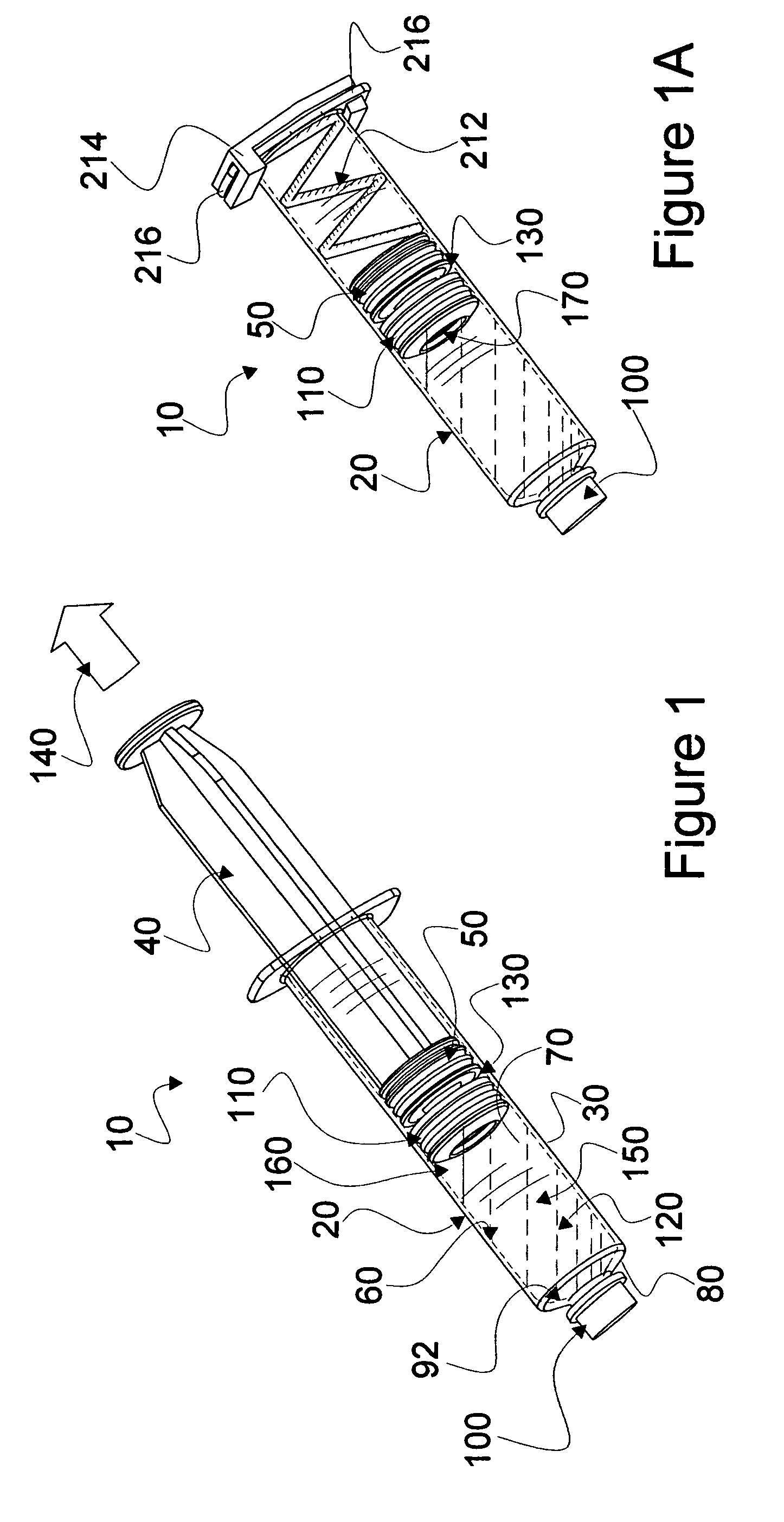
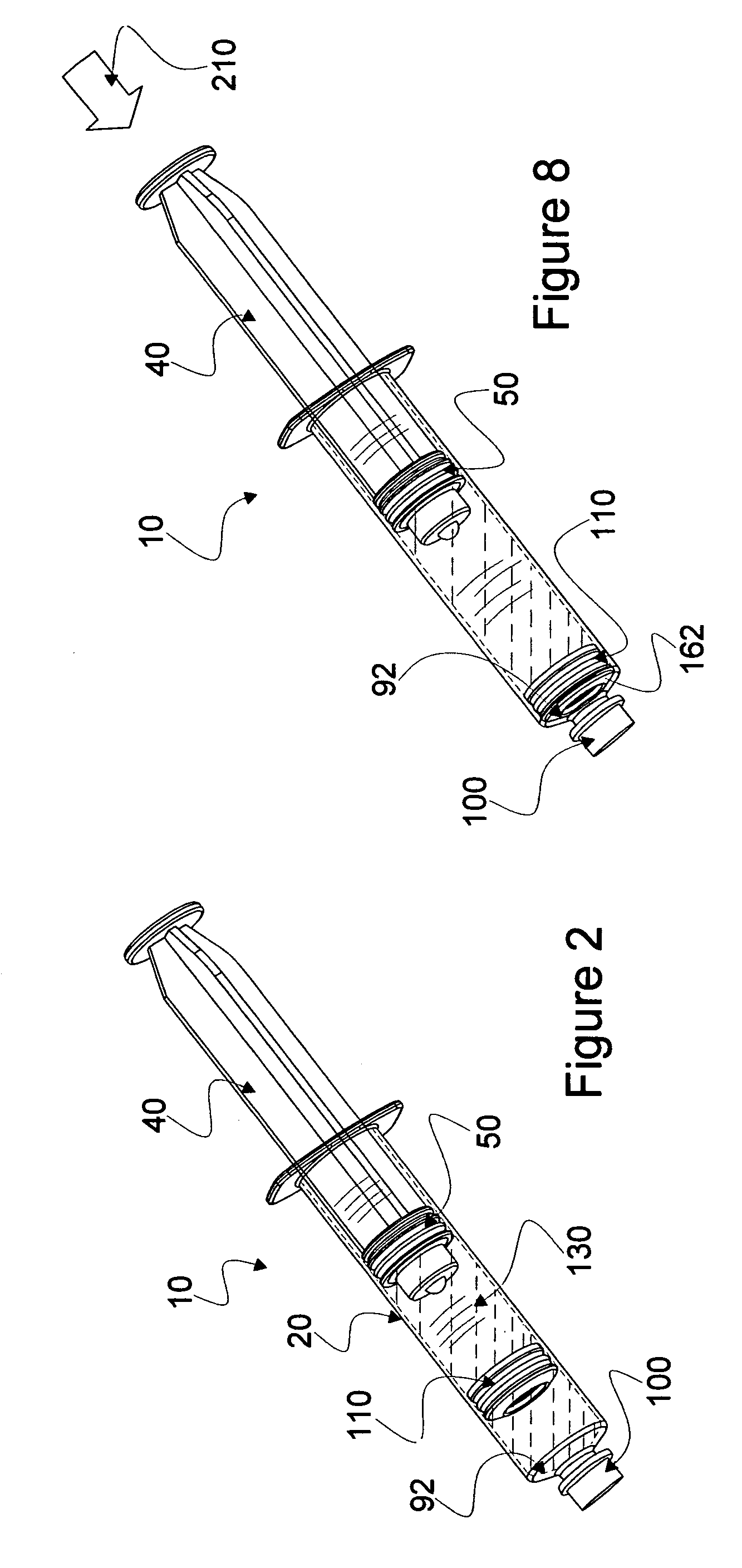
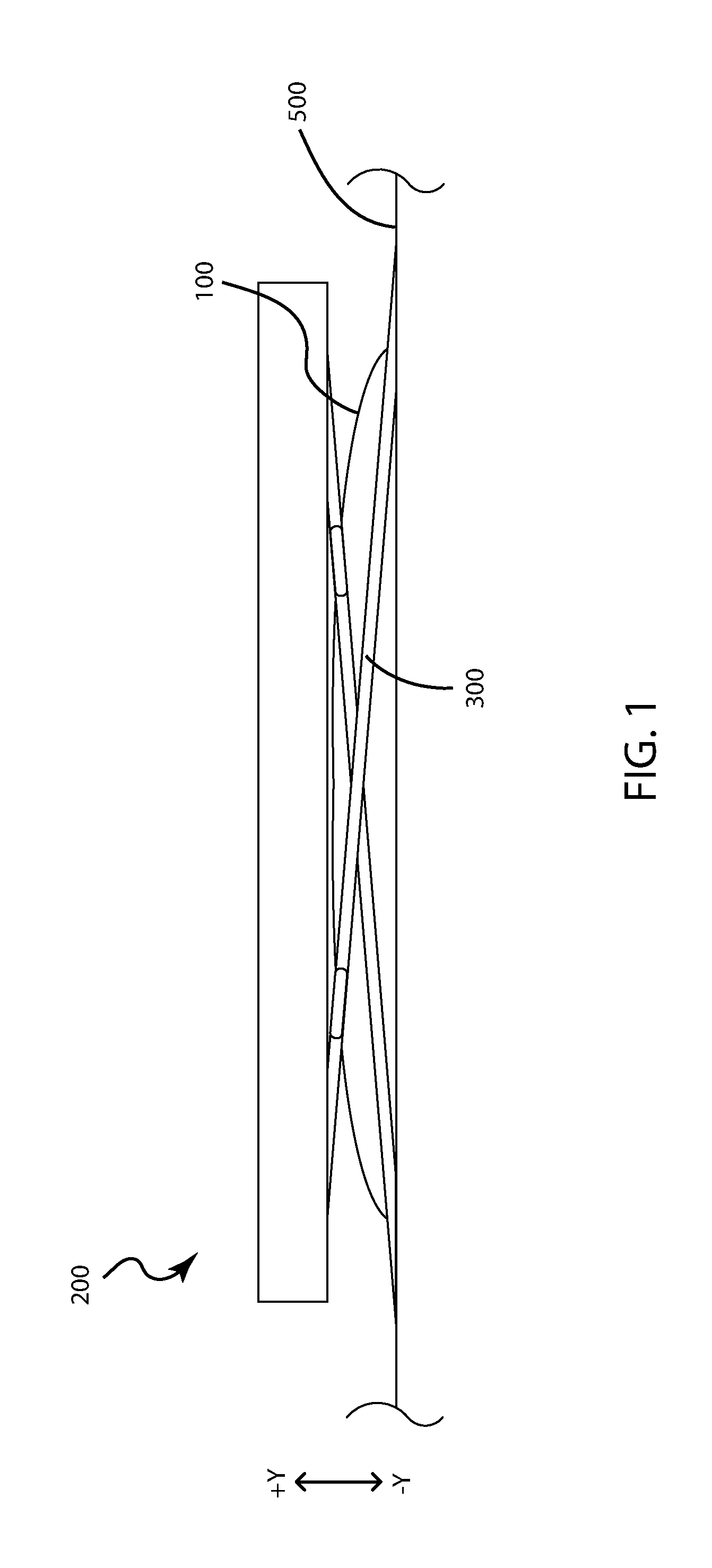
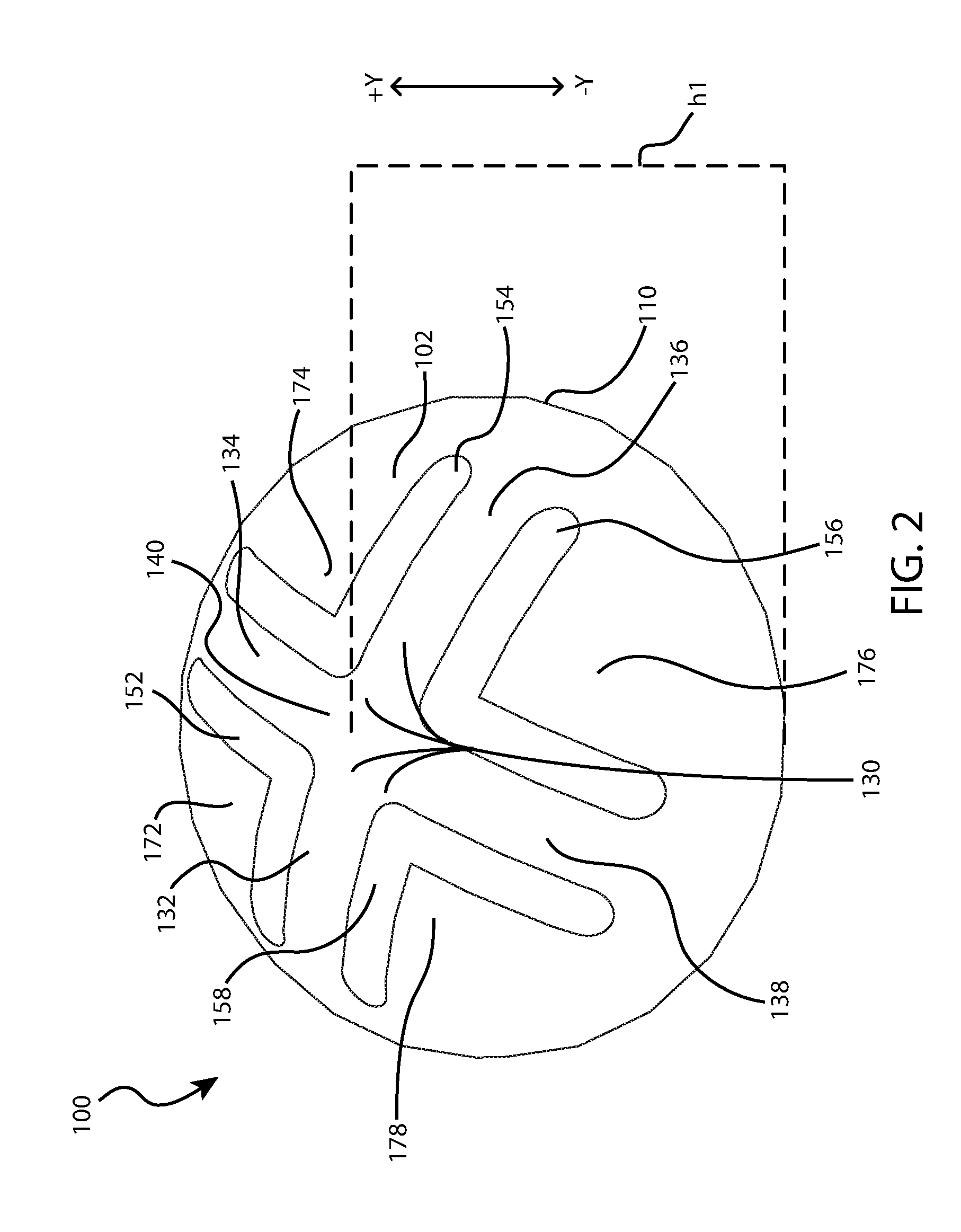
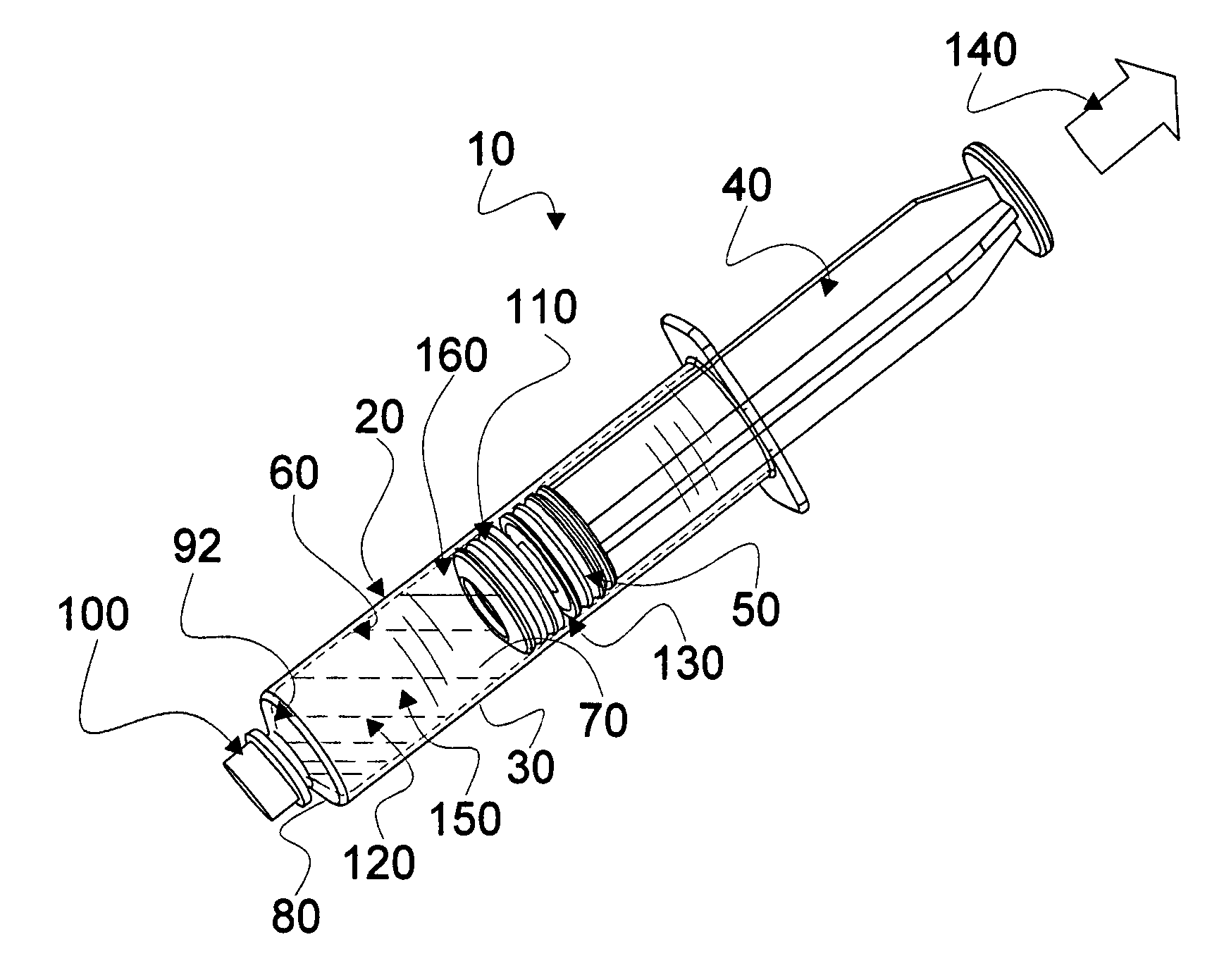
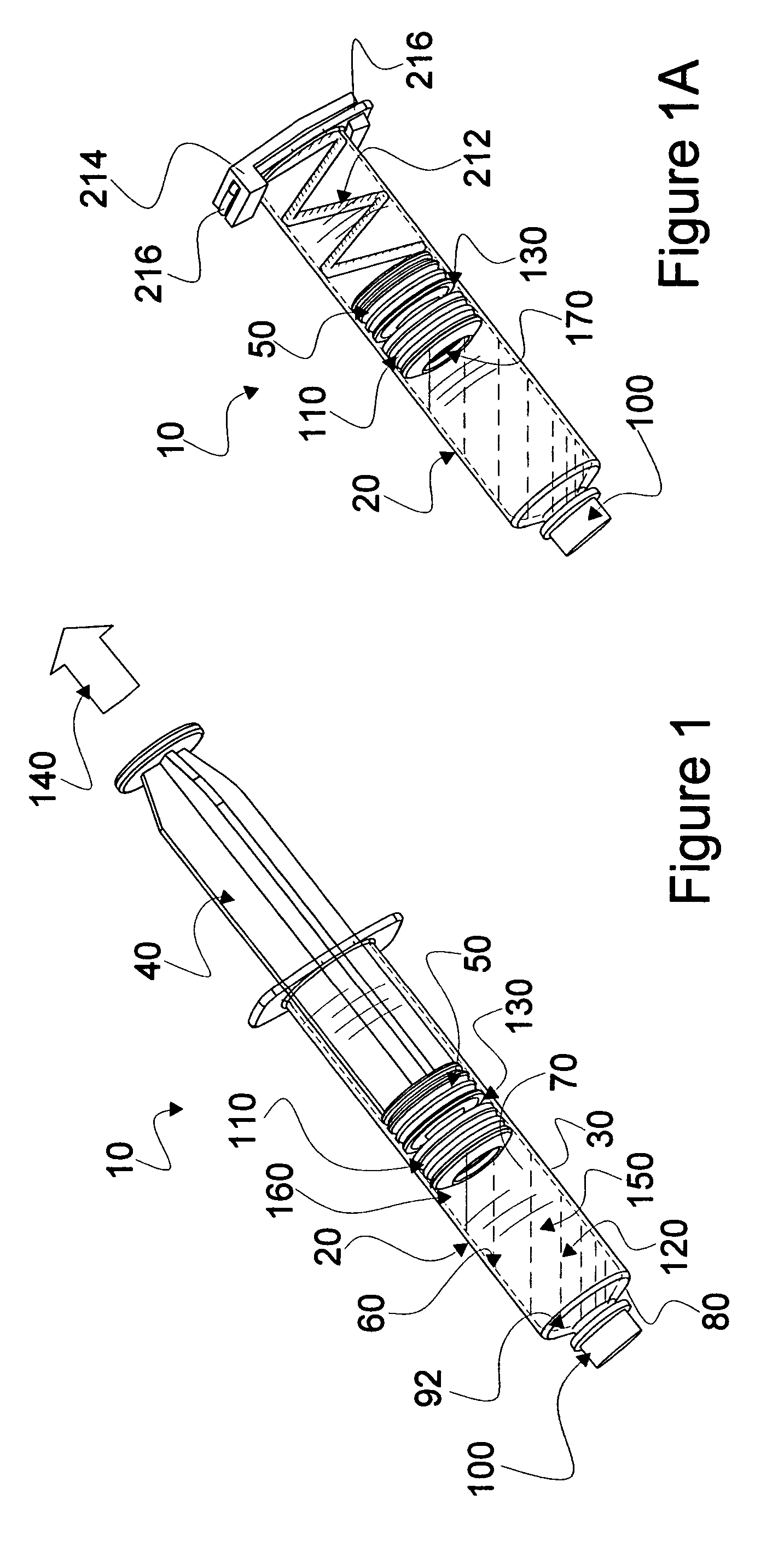
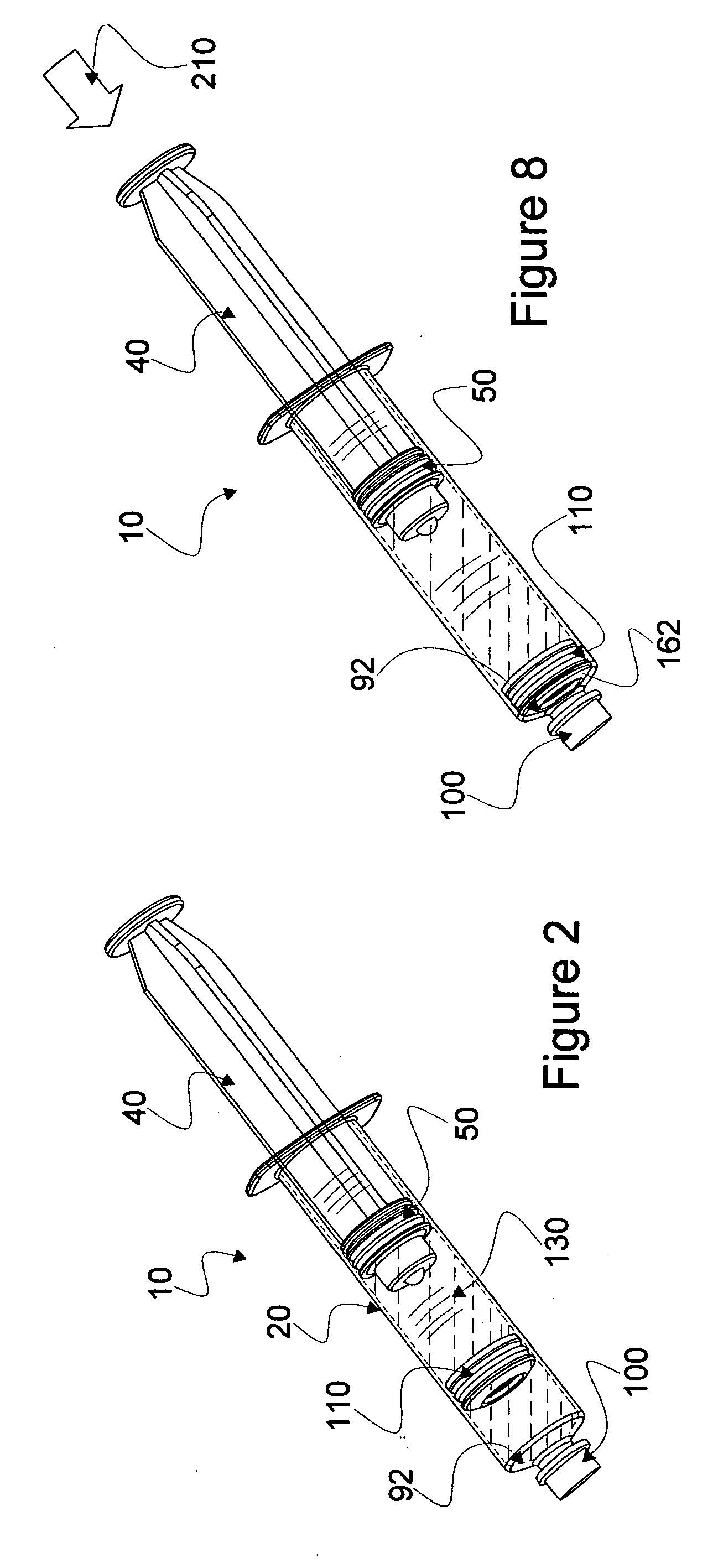
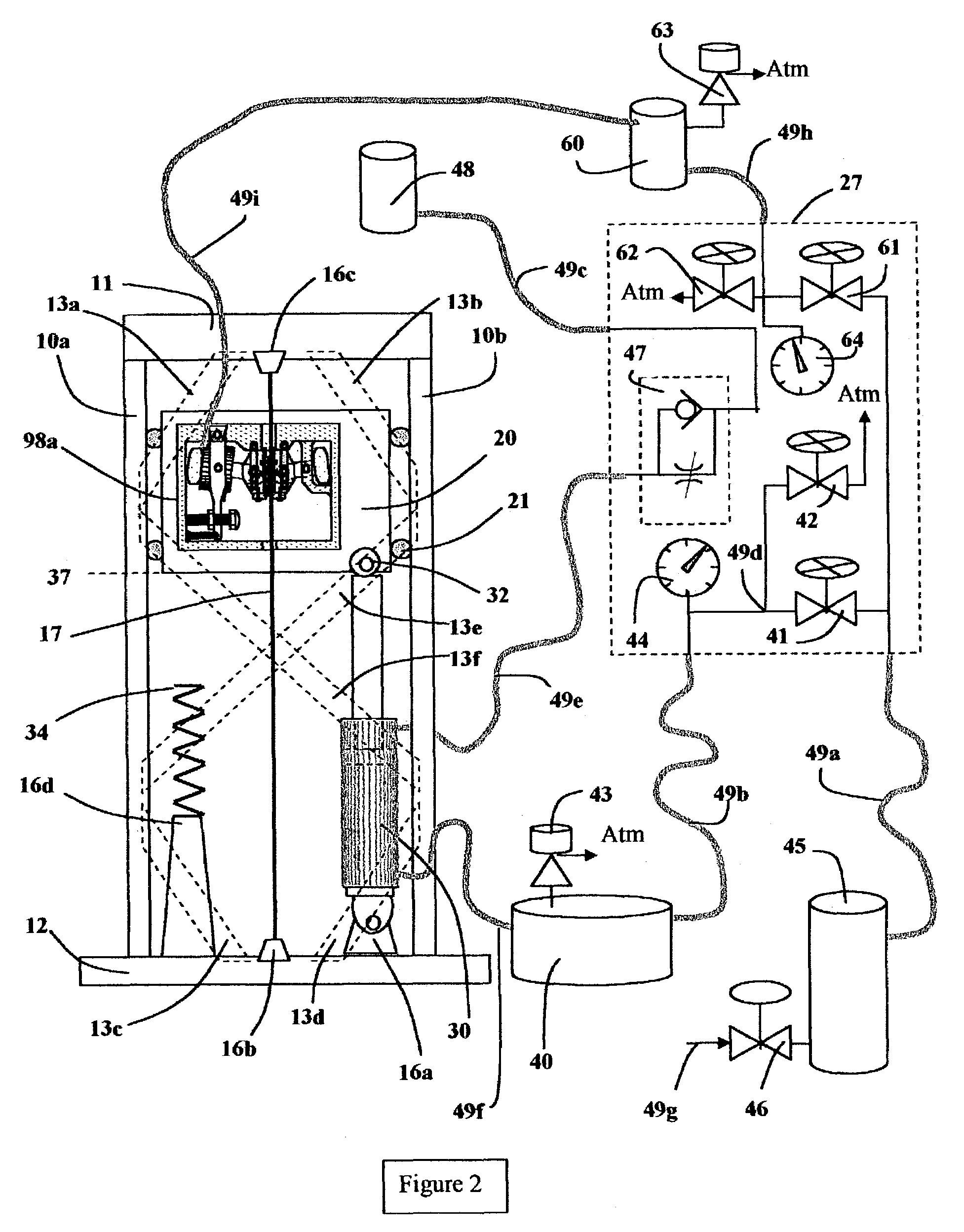
Mixing syringe with and without flush
Owner:INFUSIVE TECH LLC
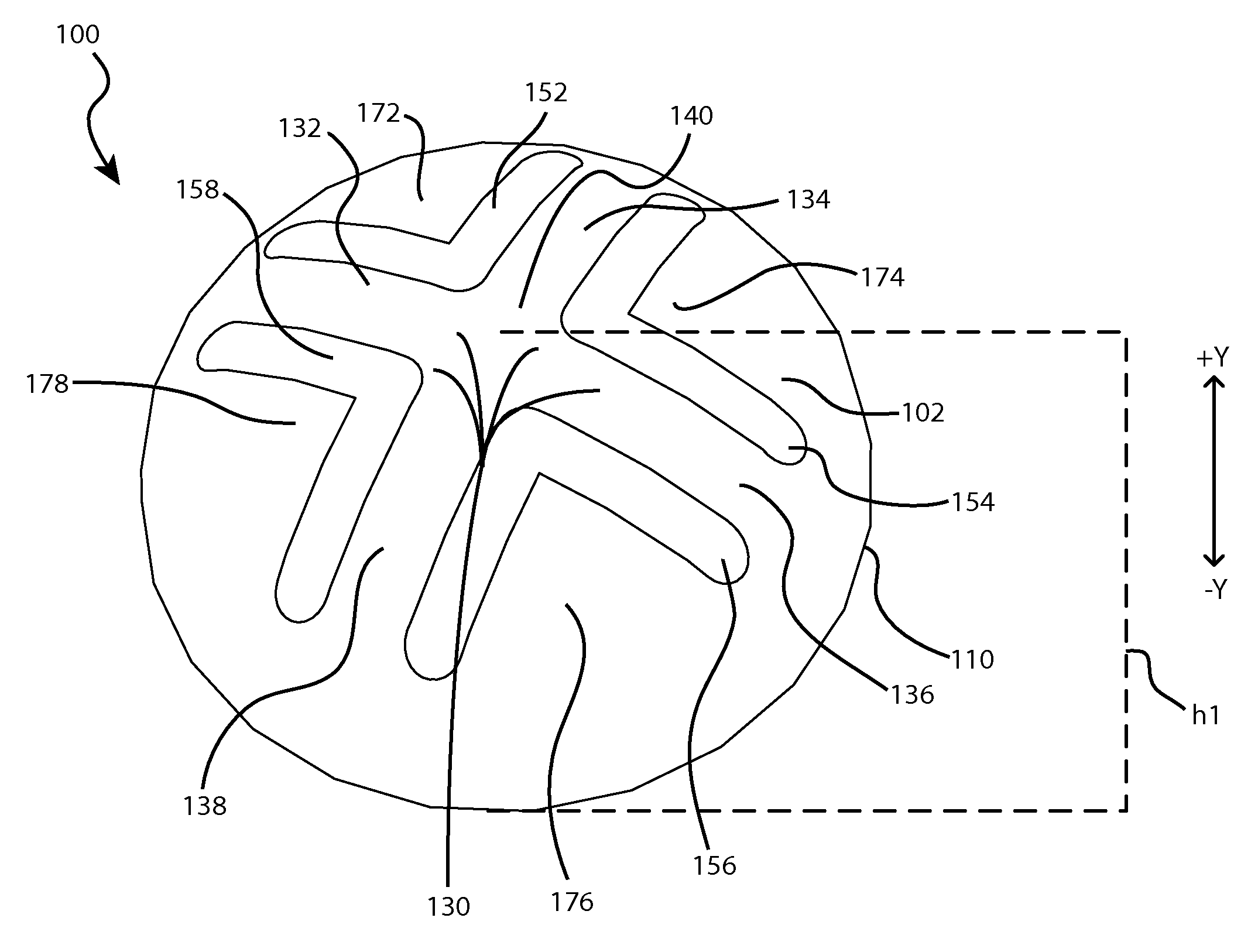
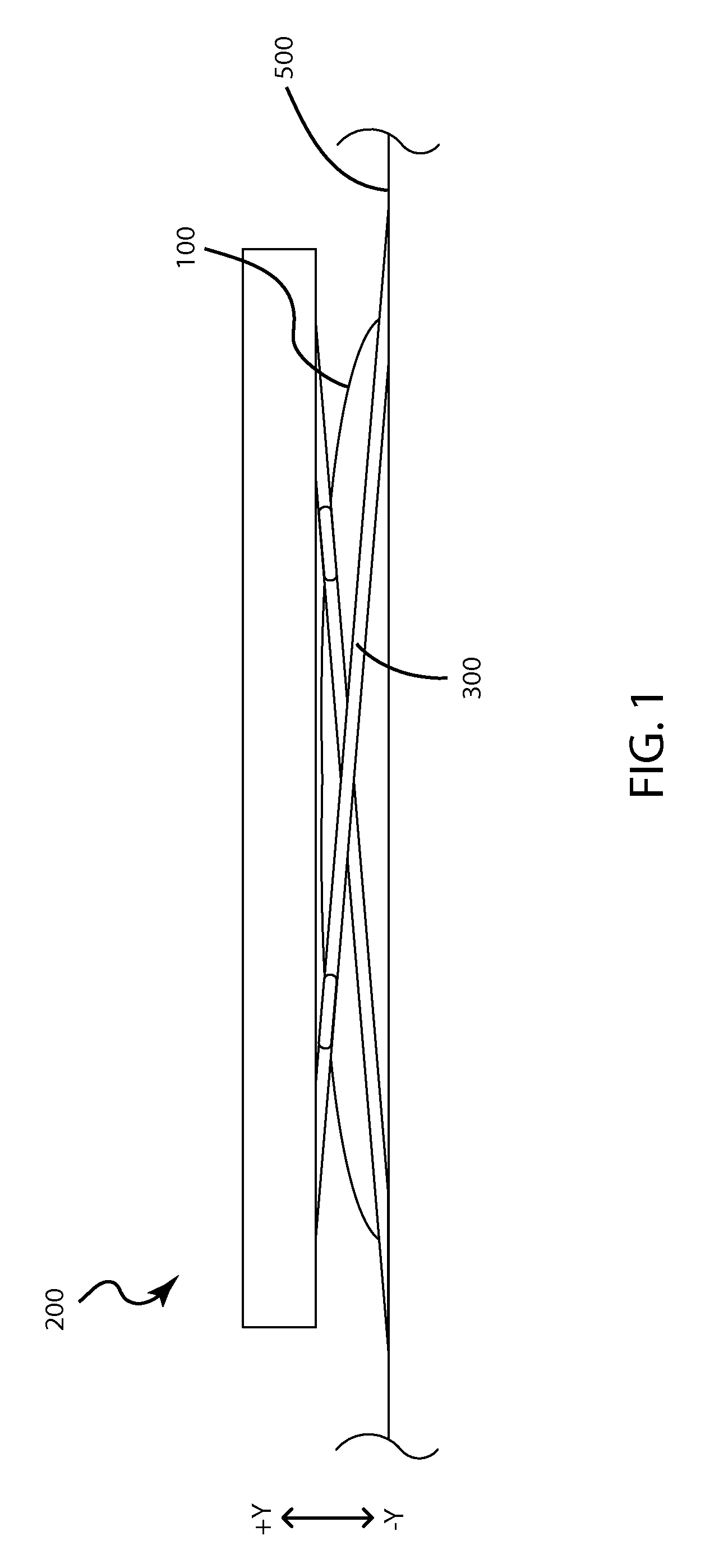
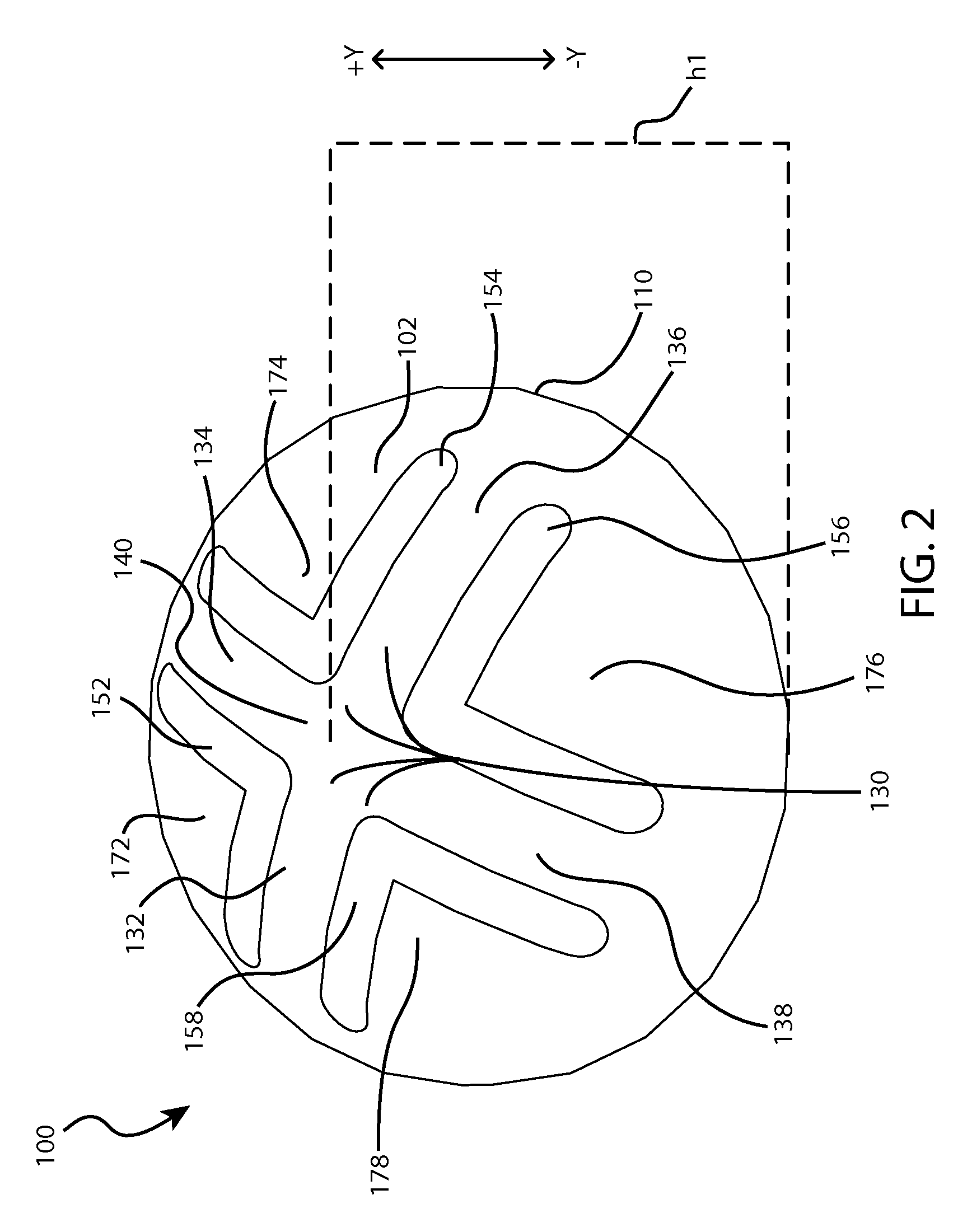
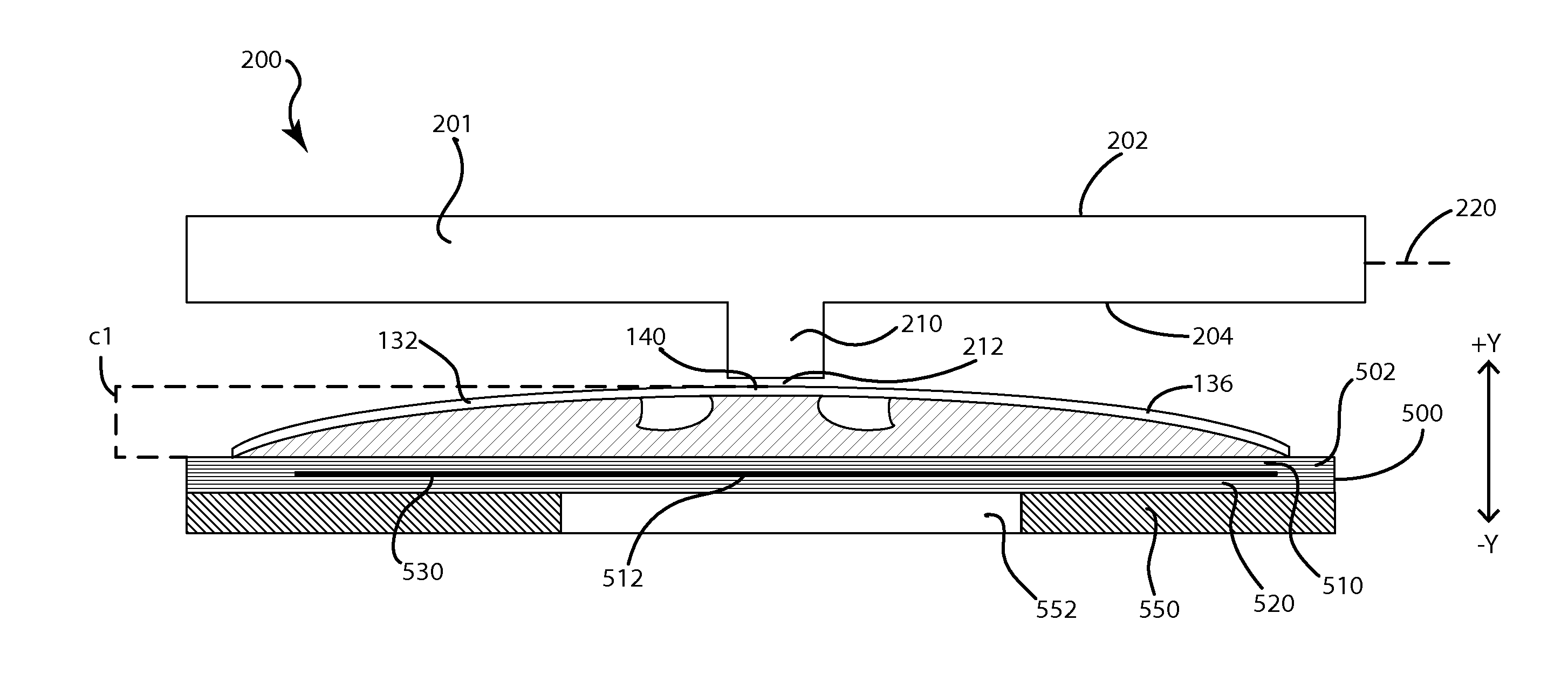
Low travel switch assembly
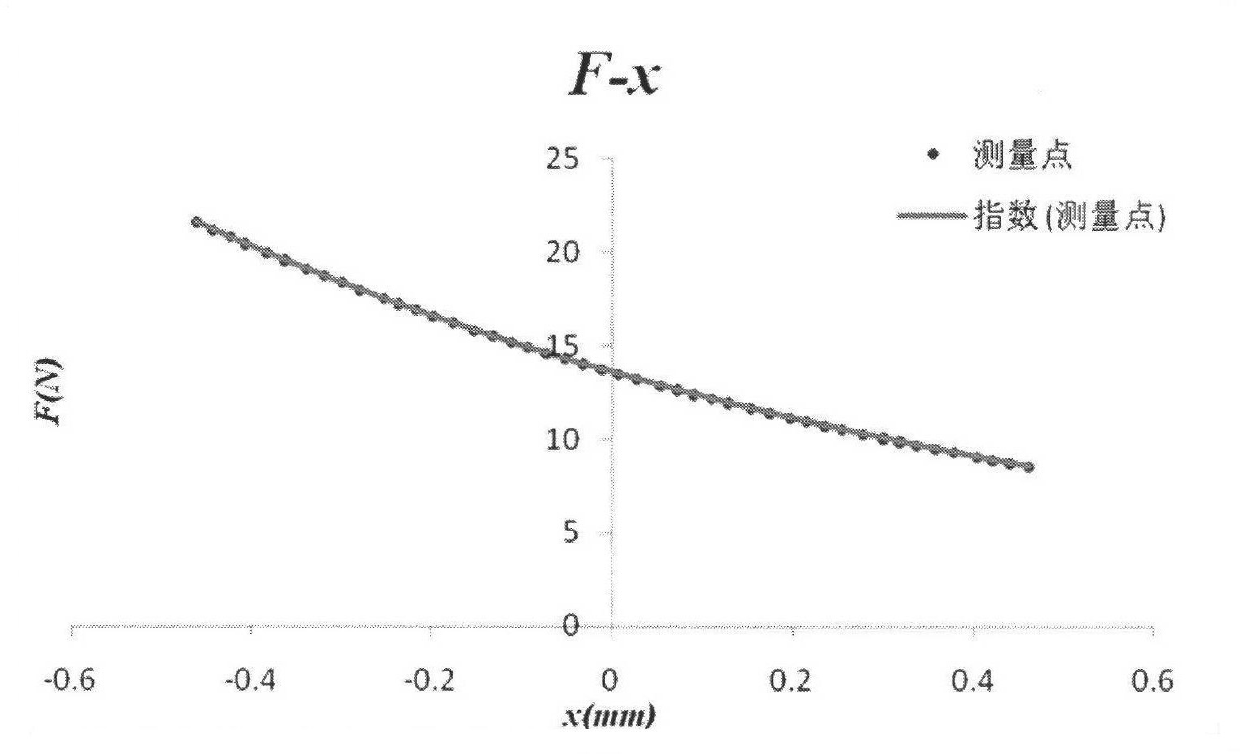
A low travel switch assembly and systems and methods for using the same are disclosed. The low travel dome may include a domed surface having upper and lower portions, and a set of tuning members integrated within the domed surface between the upper and lower portions. The tuning members may be operative to control a force-displacement curve characteristic of the low travel dome.
Owner:APPLE INC
Multi-chamber, sequentially dispensing syringe
A discharge assembly is disclosed which partitions a conventional syringe into proximal and distal chambers to provide a multi-chamber, sequentially dispensing syringe apparatus. Incorporated in the discharge assembly is a syringe stopper body and an associated valve stem which in combination form a valve. A syringe plunger communicates through fluid in the proximal chamber to force displacement of the discharge assembly. The valve is actuated by collision between a rigid member which is a part of the valve stem and the distal internal surface of the syringe. The discharge assembly may be made from two parts: (1) the stopper body (made from conventional syringe stopper material); (2) the valve (actuating) stem made from rigid material similar to material from which the syringe barrel is made. Key features of such a multi-chamber syringe apparatus are (1) fluids in the chambers are kept disparate; (2) the discharge assembly may be used in conventional syringes; (3) gas in a closed chamber, proximal to the discharge assembly, is retained in the proximal chamber while only liquid is dispensed therefrom.
Owner:THORNE CONSULTING & INTPROP
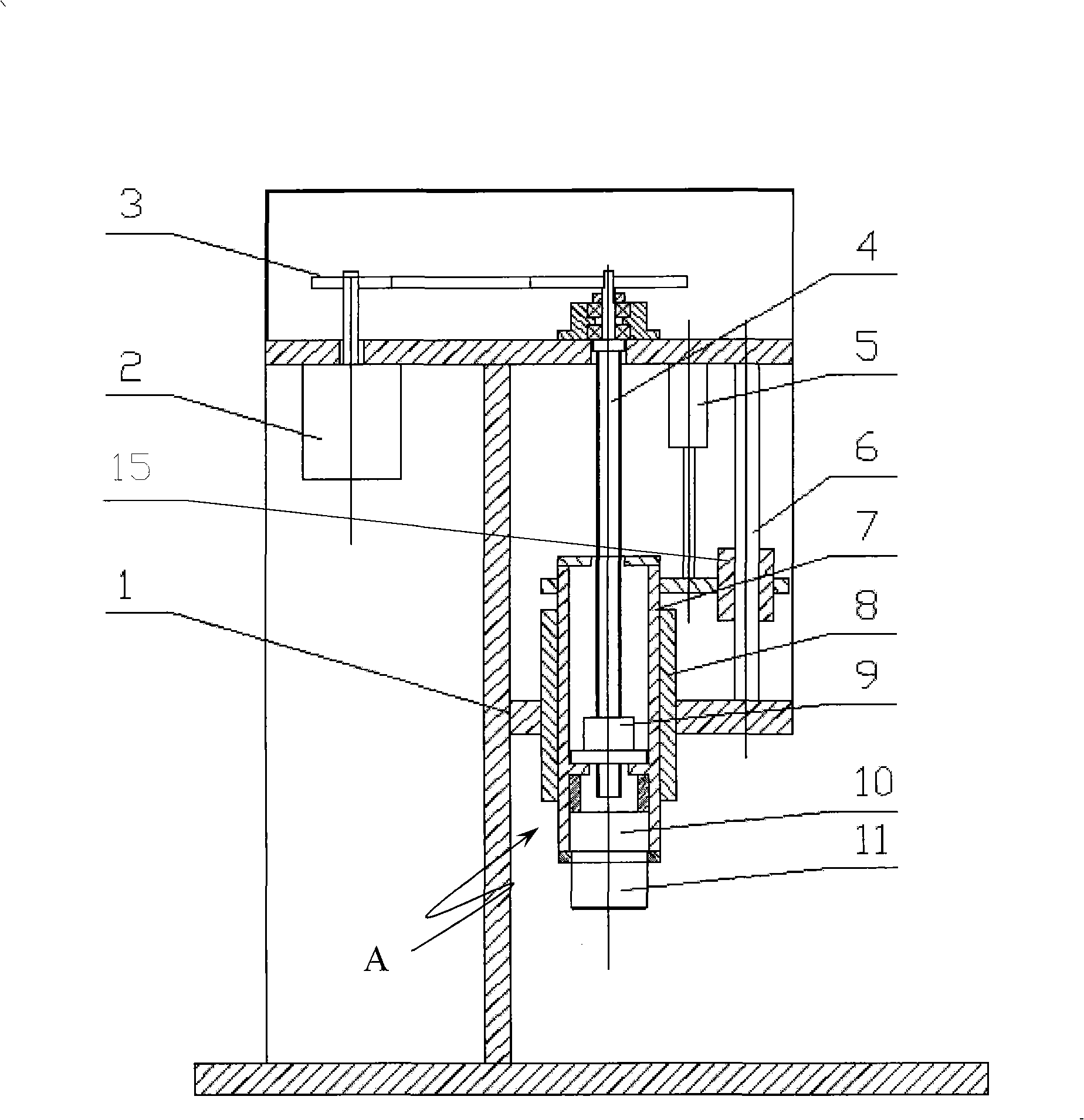
Servo press mounting device for monitoring press mounting force and displacement
ActiveCN101288934APress-in (return) speed is stable and adjustableReal-time display of pressing force-displacement curveMeasurement/indication equipmentsMetal working apparatusDisplay deviceDisplacement control
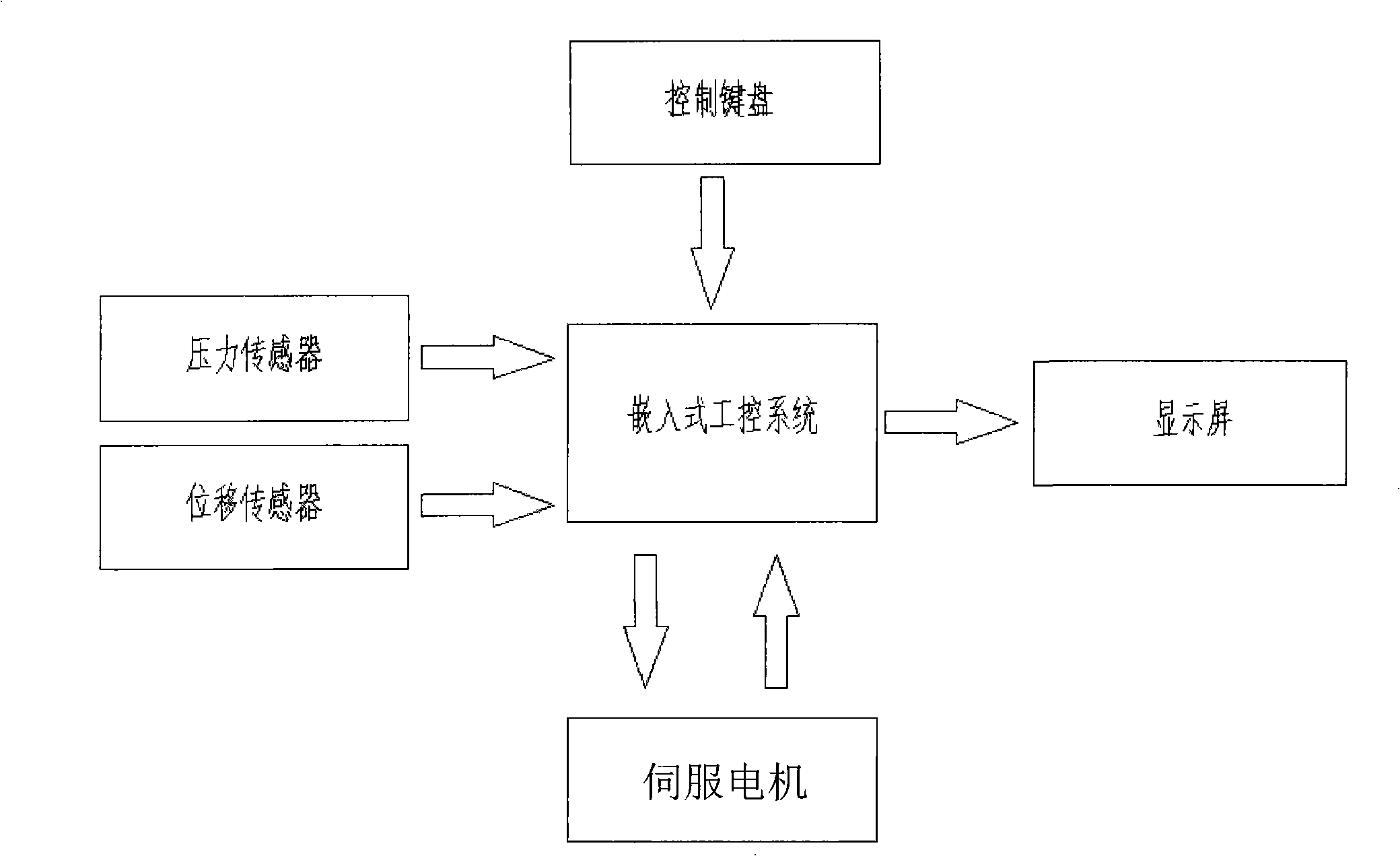
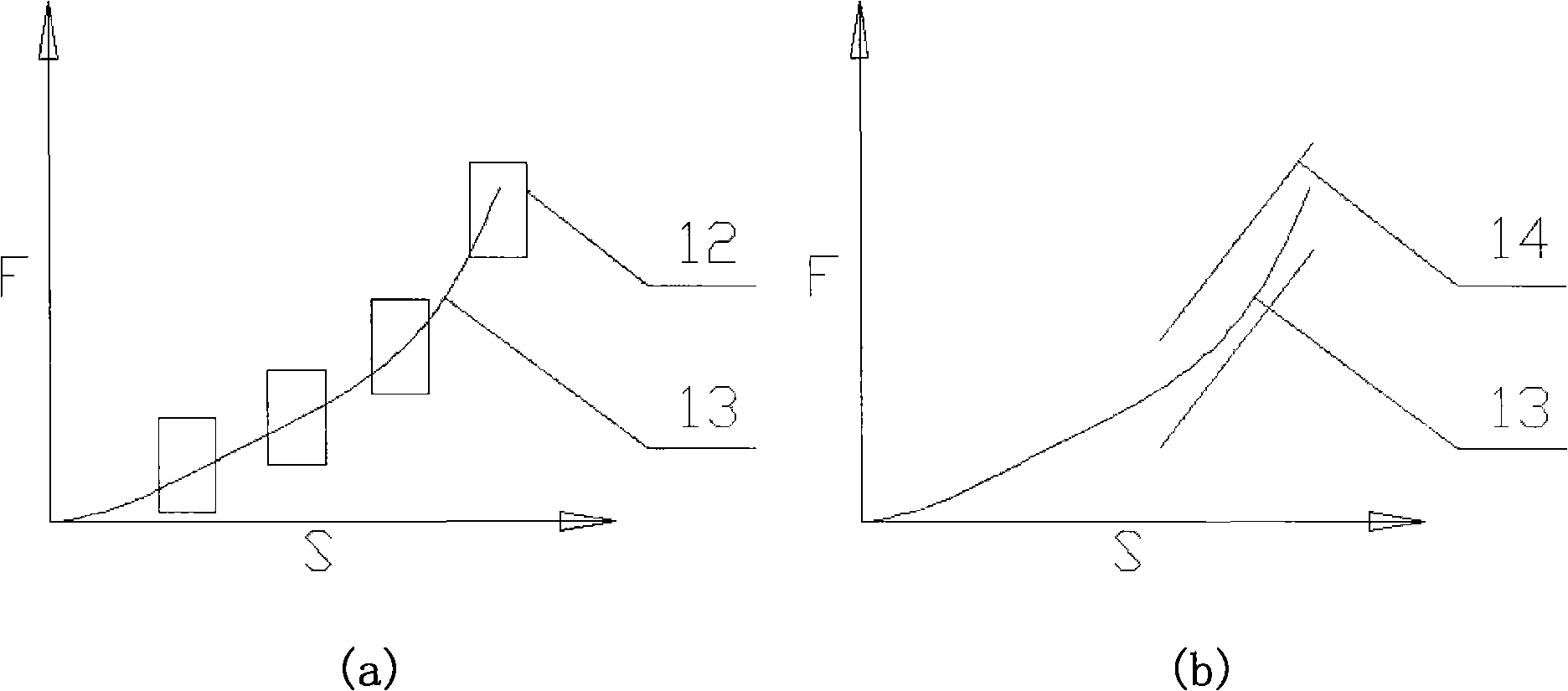
A servo press-mounting machine for monitoring press-mounting force and displacement pertains to a mechanical assembling device. The prior art has the defect that the press-mounting result needs additional detection equipment for detection. A power device provided by the present invention consists of a servo motor controlled by an embedded industrial control system and a drive piece matched with the servo motor in a transmission way; the drive piece is matched with a press-mounting head by screw thread; the press-mounting head is provided with a pressure sensor for sending signals to the embedded industrial control system and connected with a displacement sensor; the embedded industrial control system is connected with a display and a control keyboard. The present invention takes the servo motor as the source power, is equipped with the pressure sensor and the displacement sensor and takes the embedded industrial control system as the core of the control system. The machine provided by the present invention has the advantages of stable and adjustable pressining speed, accurate and convenient press-mounting force control and press displacement control, the real-time display of press-mounting force-displacement curve, qualification determination when in press mounting, scientific and diversified qualification determination ways, etc.
Owner:HANGZHOU SANHUA RES INST CO LTD
Low travel switch assembly
ActiveUS9412533B2Contact surface shape/structureEmergency casingsForce displacementElectrical and Electronics engineering
A low travel switch assembly and systems and methods for using the same are disclosed. The low travel dome may include a domed surface having upper and lower portions, and a set of tuning members integrated within the domed surface between the upper and lower portions. The tuning members may be operative to control a force-displacement curve characteristic of the low travel dome.
Owner:APPLE INC
Low travel switch assembly
ActiveUS20140346025A1Maintain positionContact member manufacturingContact surface shape/structureForce displacementElectrical and Electronics engineering
A low travel switch assembly and systems and methods for using the same are disclosed. The low travel dome may include a domed surface having upper and lower portions, and a set of tuning members integrated within the domed surface between the upper and lower portions. The tuning members may be operative to control a force-displacement curve characteristic of the low travel dome.
Owner:APPLE INC
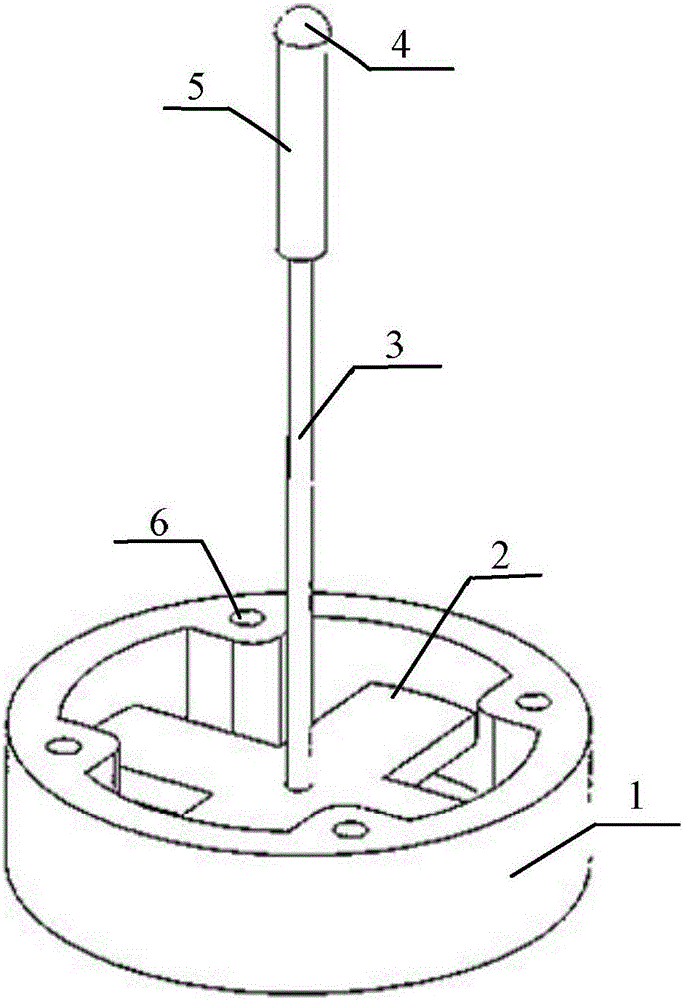
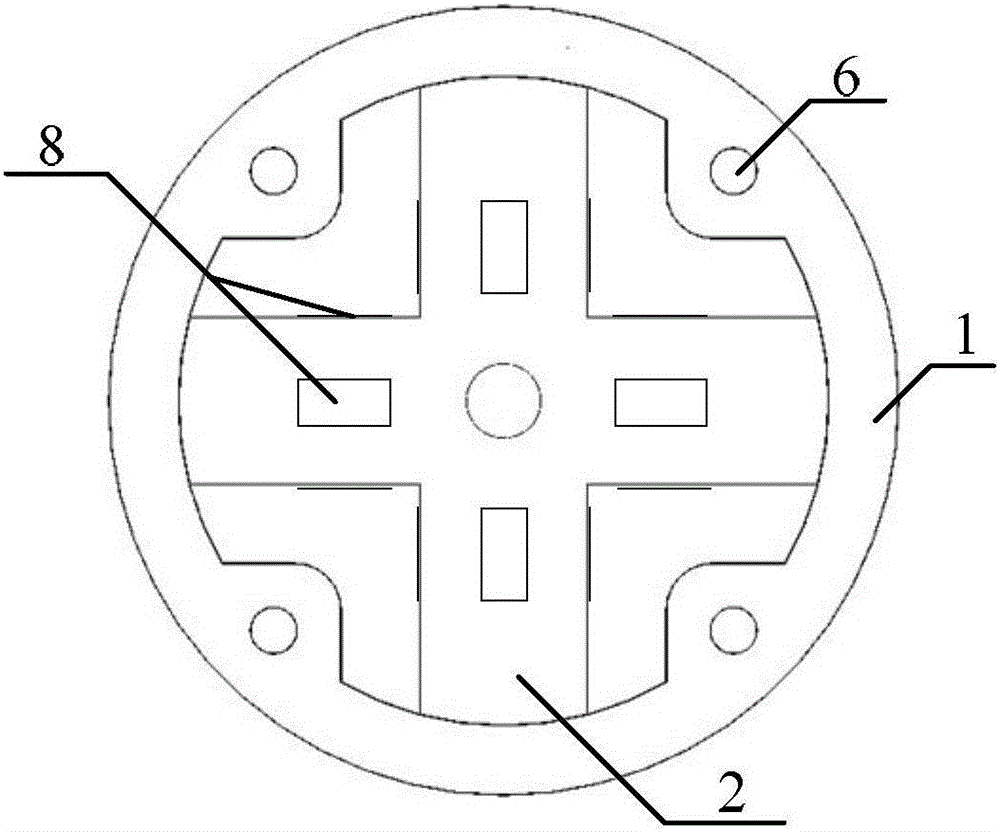
Whisker sensor for perceiving three-dimensional force displacement and three-dimensional force of contact point
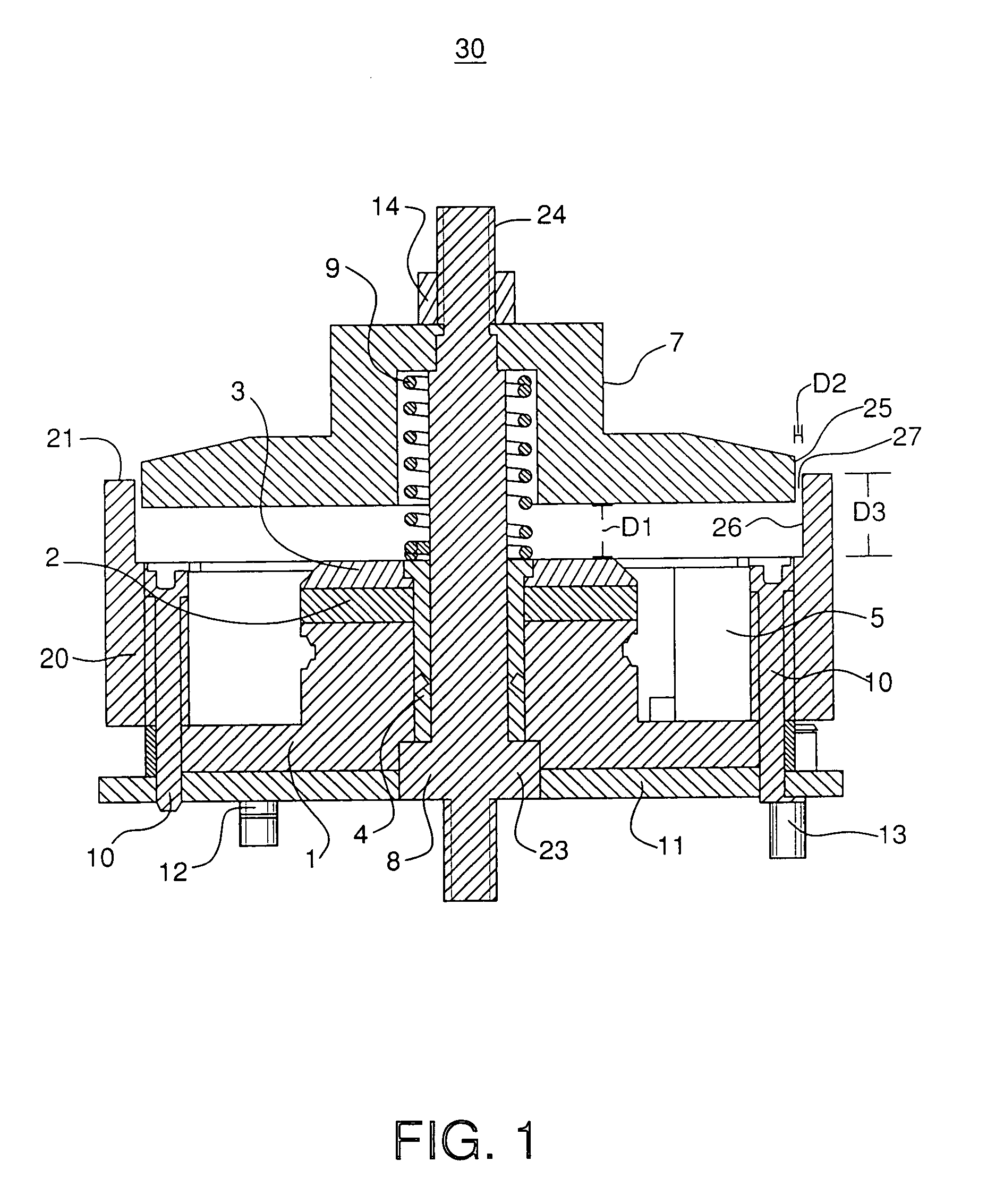
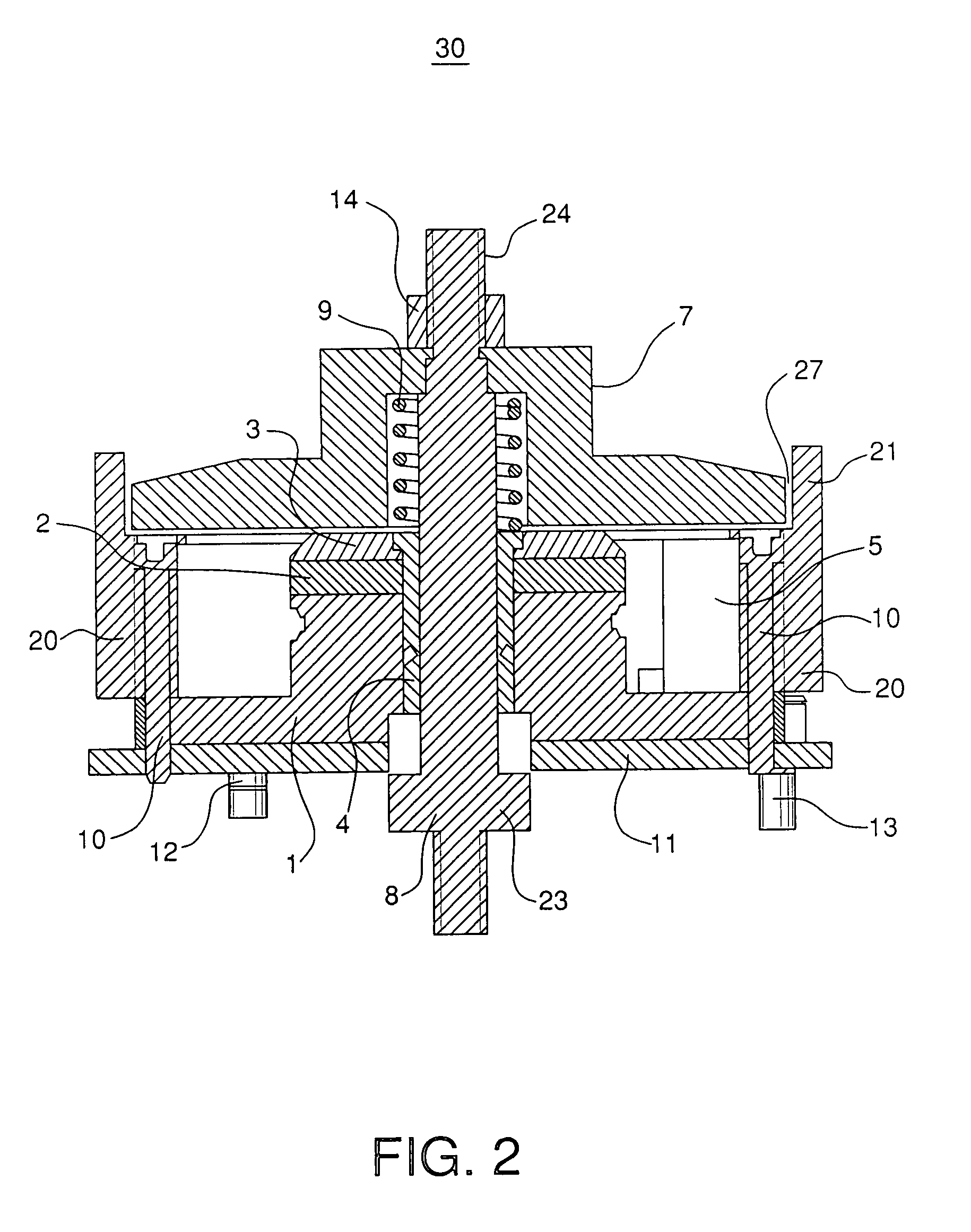
The invention discloses a whisker sensor for perceiving three-dimensional force displacement and a three-dimensional force of a contact point. The whisker sensor is installed on a robot body, the whisker sensor comprises a cross elastic beam (1), strain gauges (8), a flexible whisker (3), a contact ball (4), a spring (7) and a sleeve (5), wherein the cross elastic beam (1) is of a hollow structure and comprises four elastic beams (2) arranged inside, a wheel rim and four wheel rim screw holes (6), the four elastic beams (2) are intersected in pairs to form an angle of 90 degrees and thus form a cross shape, and the upper surface, the lower surface, the left side surface and the right side surface are each provided with a strain gauge (8) in an adhesive mode; the four wheel rim screw holes (6) are symmetrically distributed at the upper surface of the cross elastic beam (1) for fixing the position of the sensor; and the flexible whisker (3) is installed at the center of the cross elastic beam (1). According to the invention, accurate positioning of a target object can be realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Finite element analysis method for formula racing car frames
InactiveCN108170972ASolve problems that cannot be solved by manual calculation in experimentsImprove accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelVehicle frame
The invention provides a finite element analysis method for formula racing car frames, belongs to the technical field of computer aided engineering, and aims at solving the problem that existing racing car frame optimization and analysis are bad in correctness and long in design period. The finite element analysis method comprises the following steps of: A, constructing a three-dimensional model and carrying out meshing to convert the three-dimensional model into a finite element model; B, applying boundary conditions according to each working condition, carrying out finite element analysis and calculation on frame bending rigidity under each working condition, and comparing the analysis result with material bending strength to carry out structure optimization; C, respectively applying forced displacement in opposite directions on two sides of the car frame, carrying out finite element analysis and calculation to obtain torsional rigidity of the car frame, and carrying out structure optimization according to the analysis result; and D, analyzing and comparing whether a fixed frequency of each order modal of the car frame is different from an external main excitation frequency or not, and carrying out structure optimization according to the result. According to the method, the correctness of optimization and analysis is improved, the expenditure is decreased and the design period is shortened.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIRUN AUTOMOBILE +2
Device and method for ascertaining the force-displacement characteristic curve of one or more ligaments
ActiveUS8945026B2Improve sterilityIncrease flexibilitySurgeryPerson identificationLigament structureEngineering
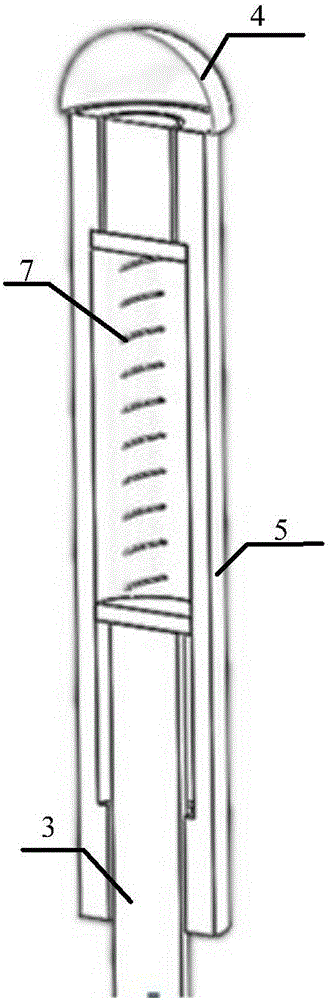
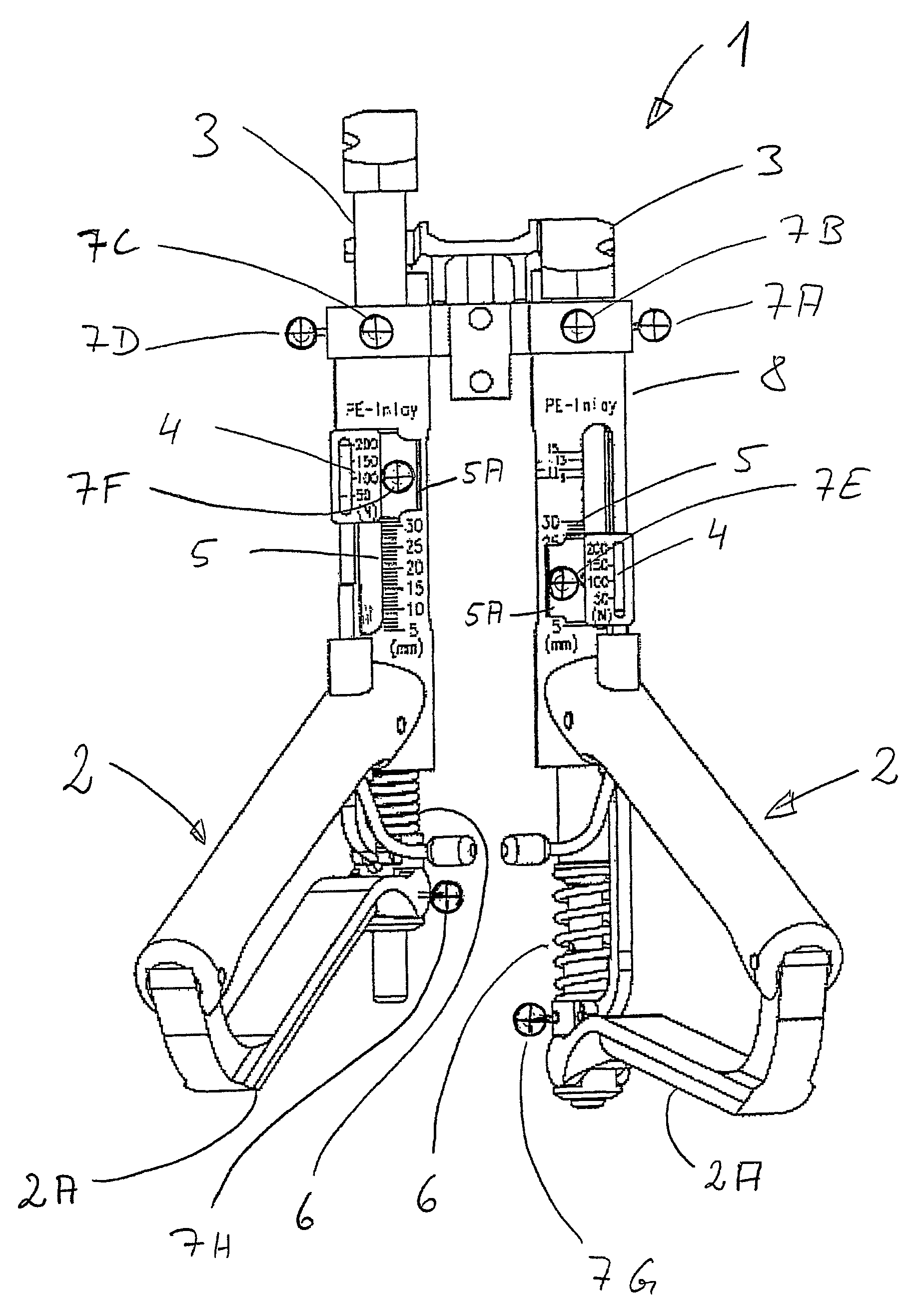
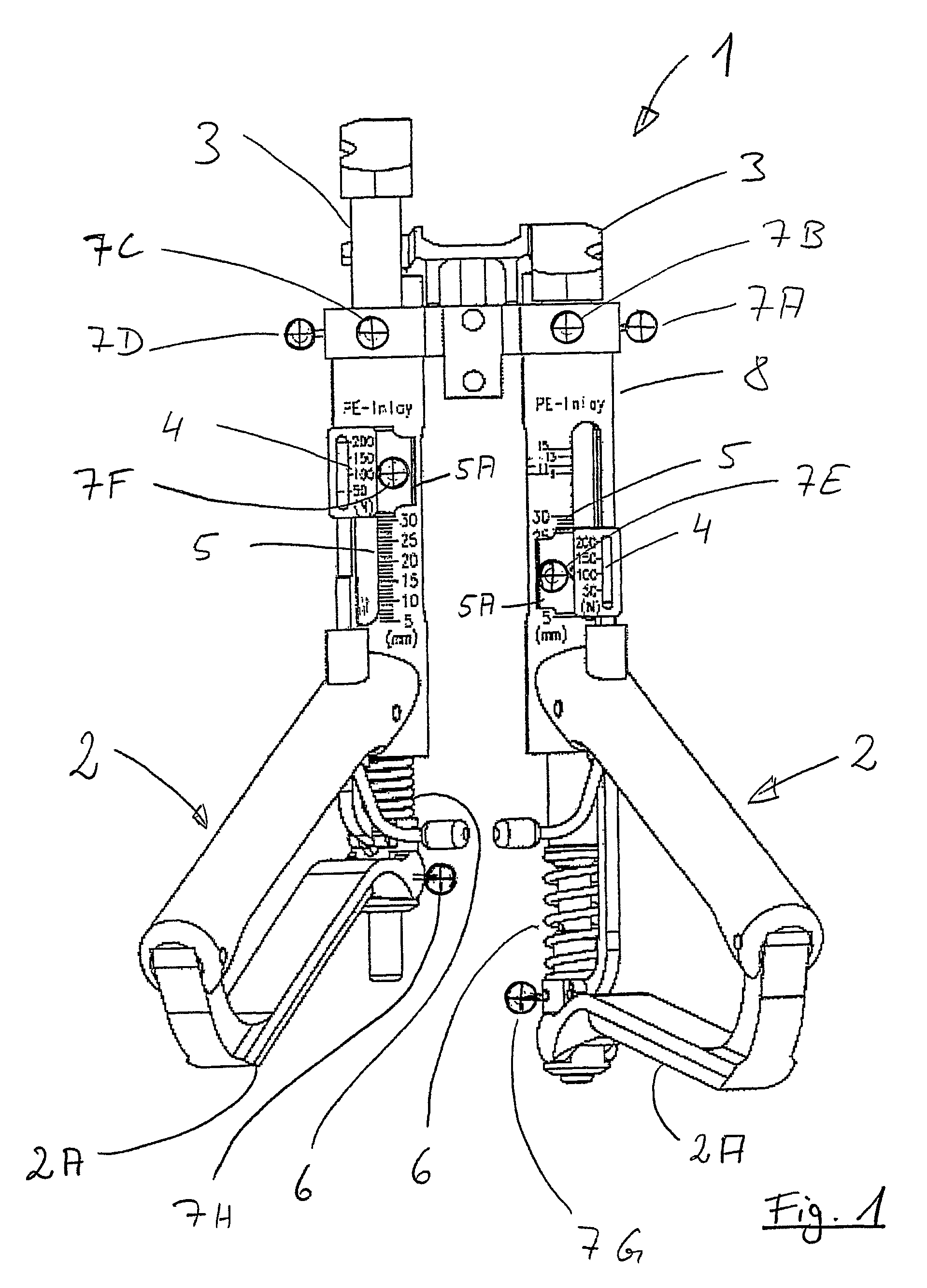
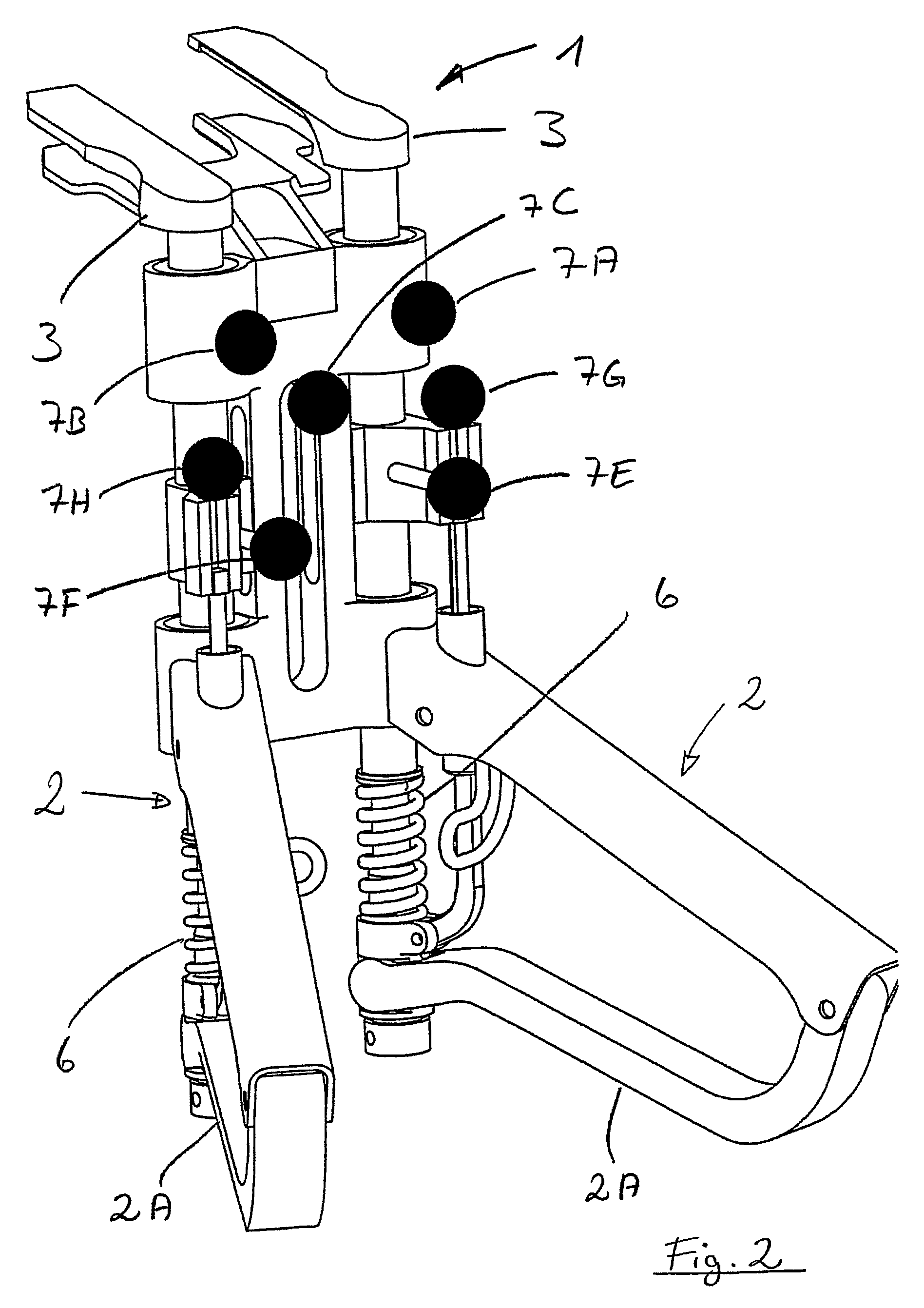
An appliance (1) for tensioning ligaments, especially articular ligaments, of a human or animal body, having at least one handle (2), the or each handle (2) being in operative engagement with, in each case, a tensioning element (3) associated therewith, and with the or each handle (2) in each case a force indicator (4), which indicates a force exerted on a or each tensioning element (3) associated with the or each handle (2) on tensioning of one or more ligaments, and a displacement indicator (5), which indicates the excursion of the tensioning element (3) in question from a reference position, and with the or each force indicator (4) and / or with the or each displacement indicator (5) there is / are associated at least one marker (7A-7H), which is arranged to be detected without contact by a measurement value ascertainment system (20) associated with the appliance (1), and also a device (20), comprising the appliance (1), for ascertaining force-displacement characteristic curves of ligaments, and also a method of ascertaining them.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW ORTHOPAEDICS
Force-displacement hybrid control motorcycle frame fatigue test method
InactiveCN103398859AIn line with the actual stress situationAchieving multi-axial loadingVehicle testingPilot systemVehicle frame
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH +1
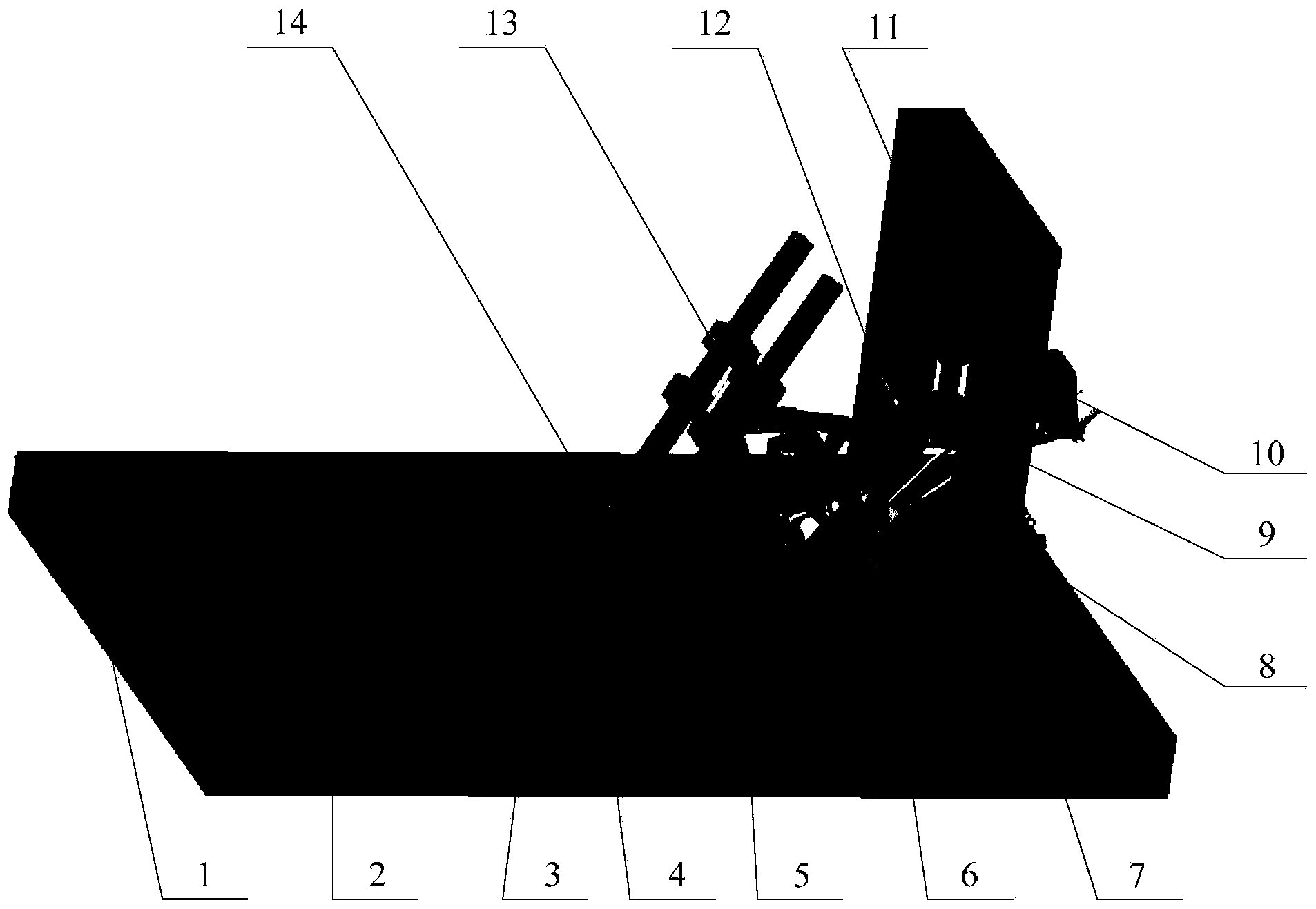
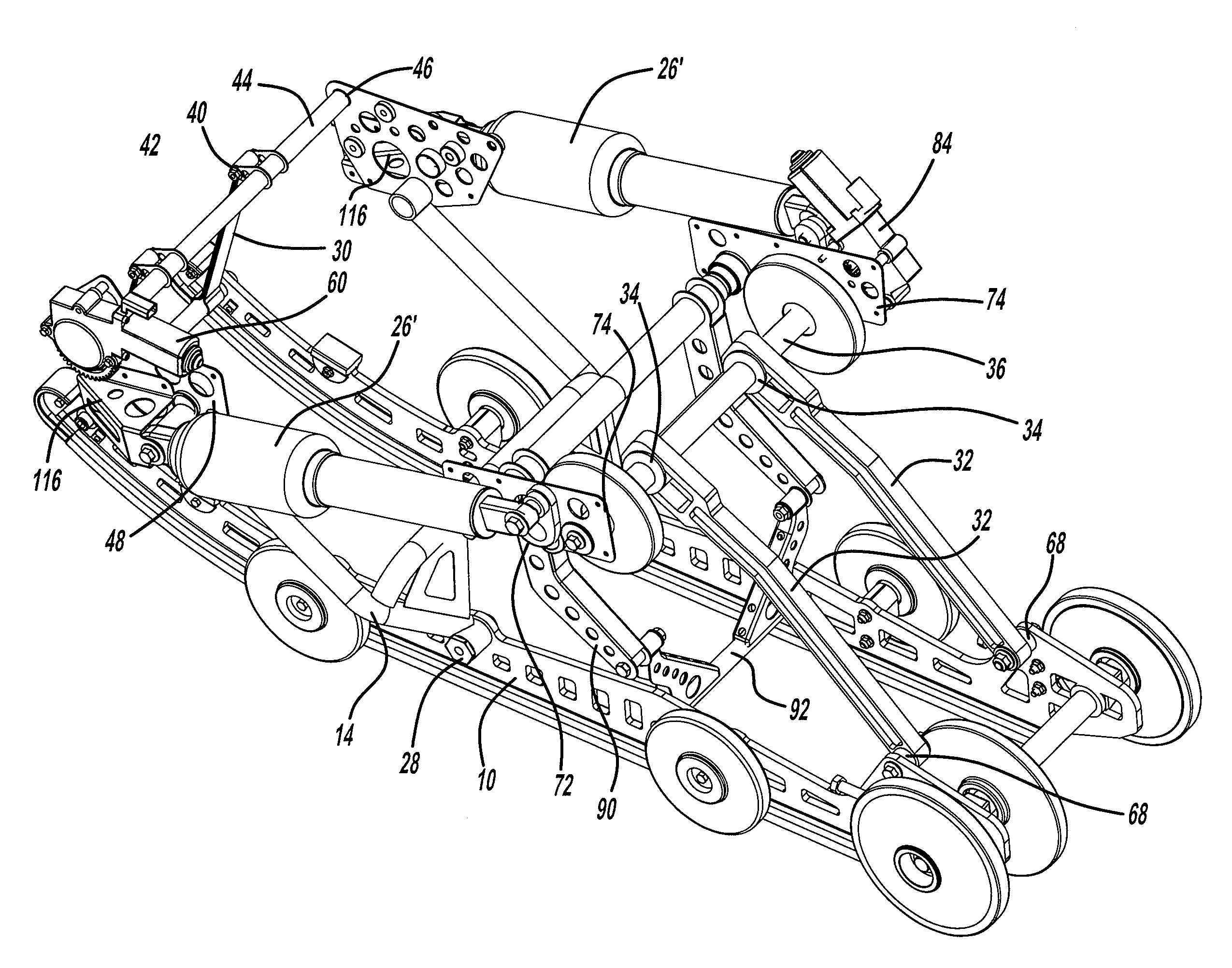
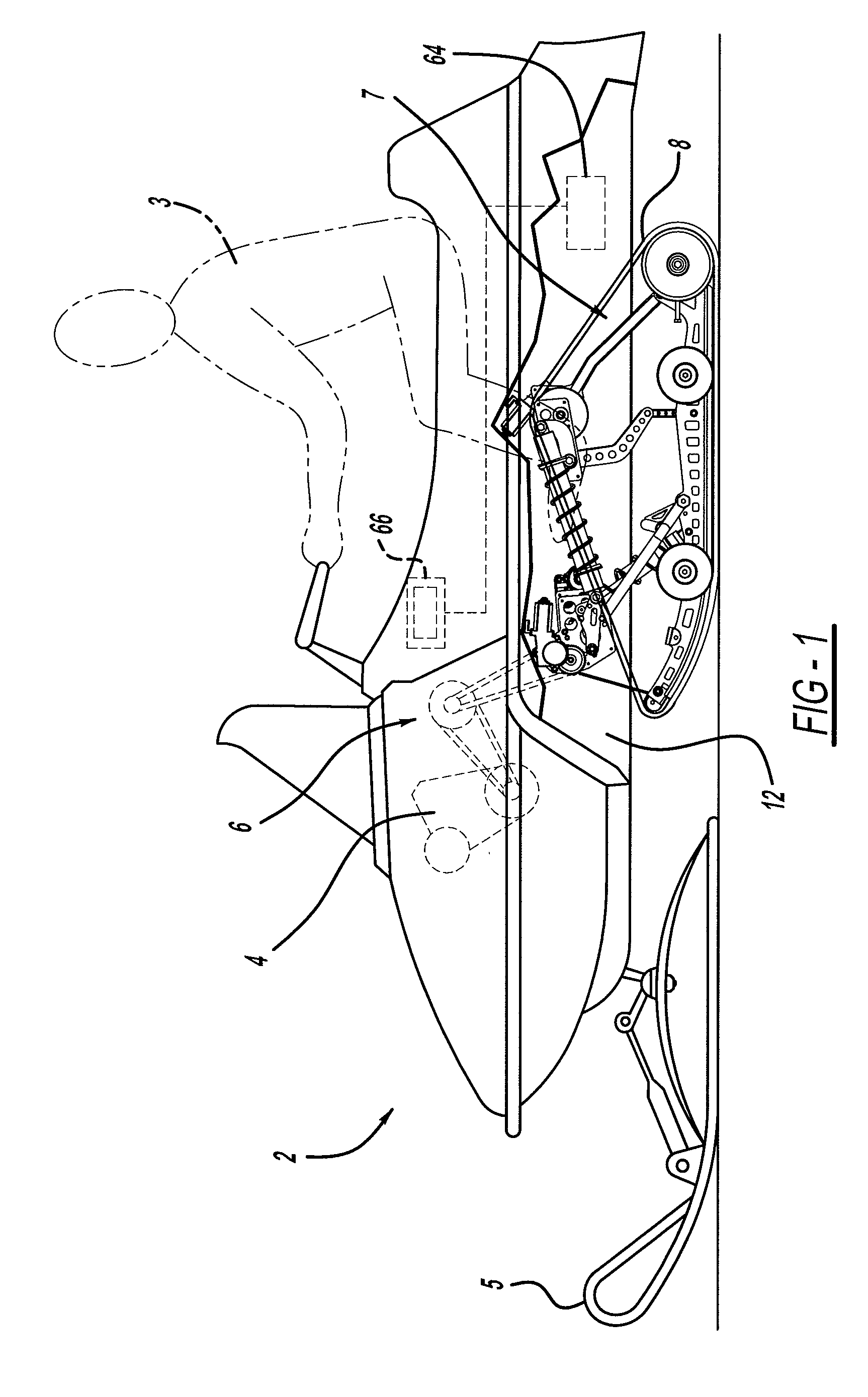
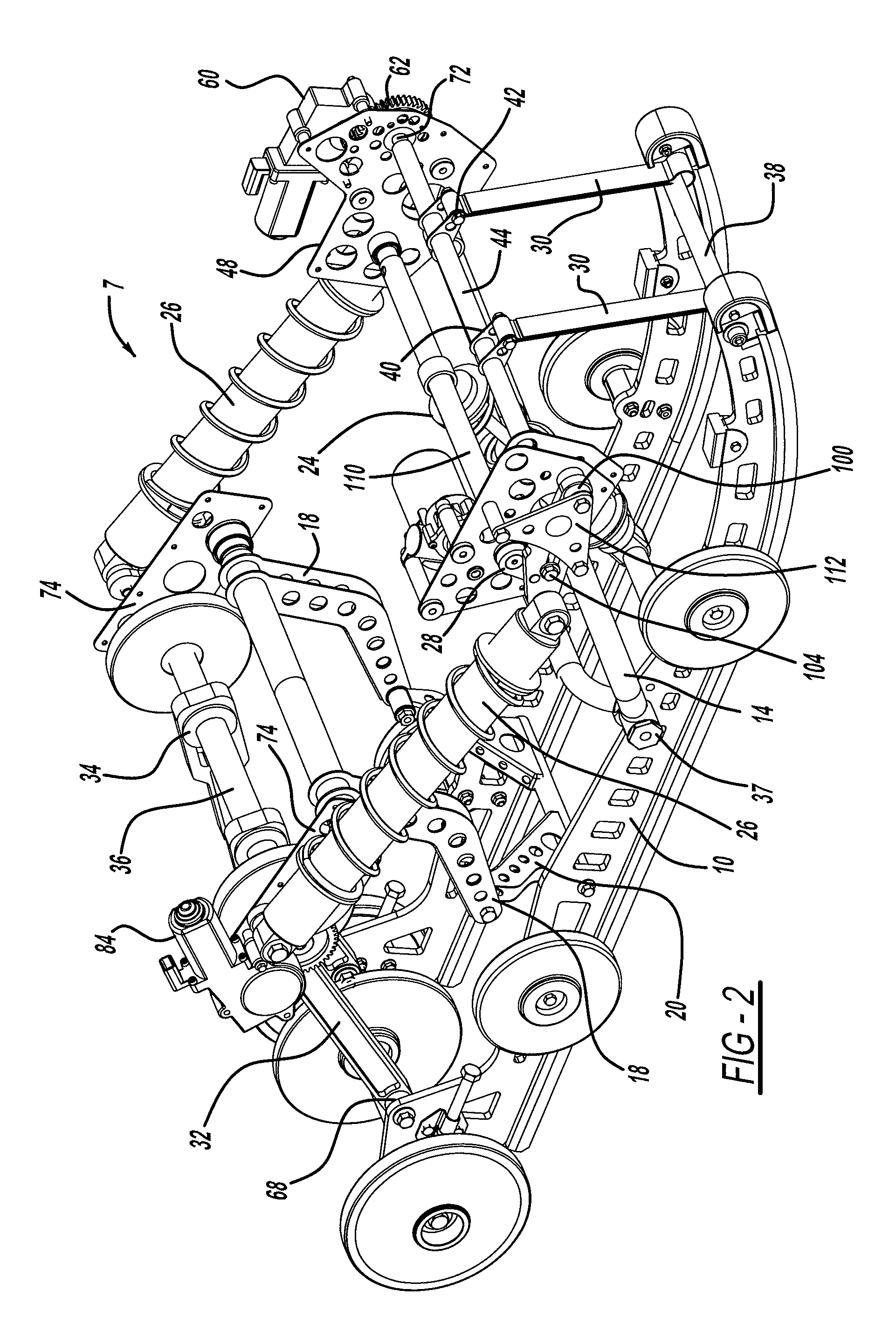
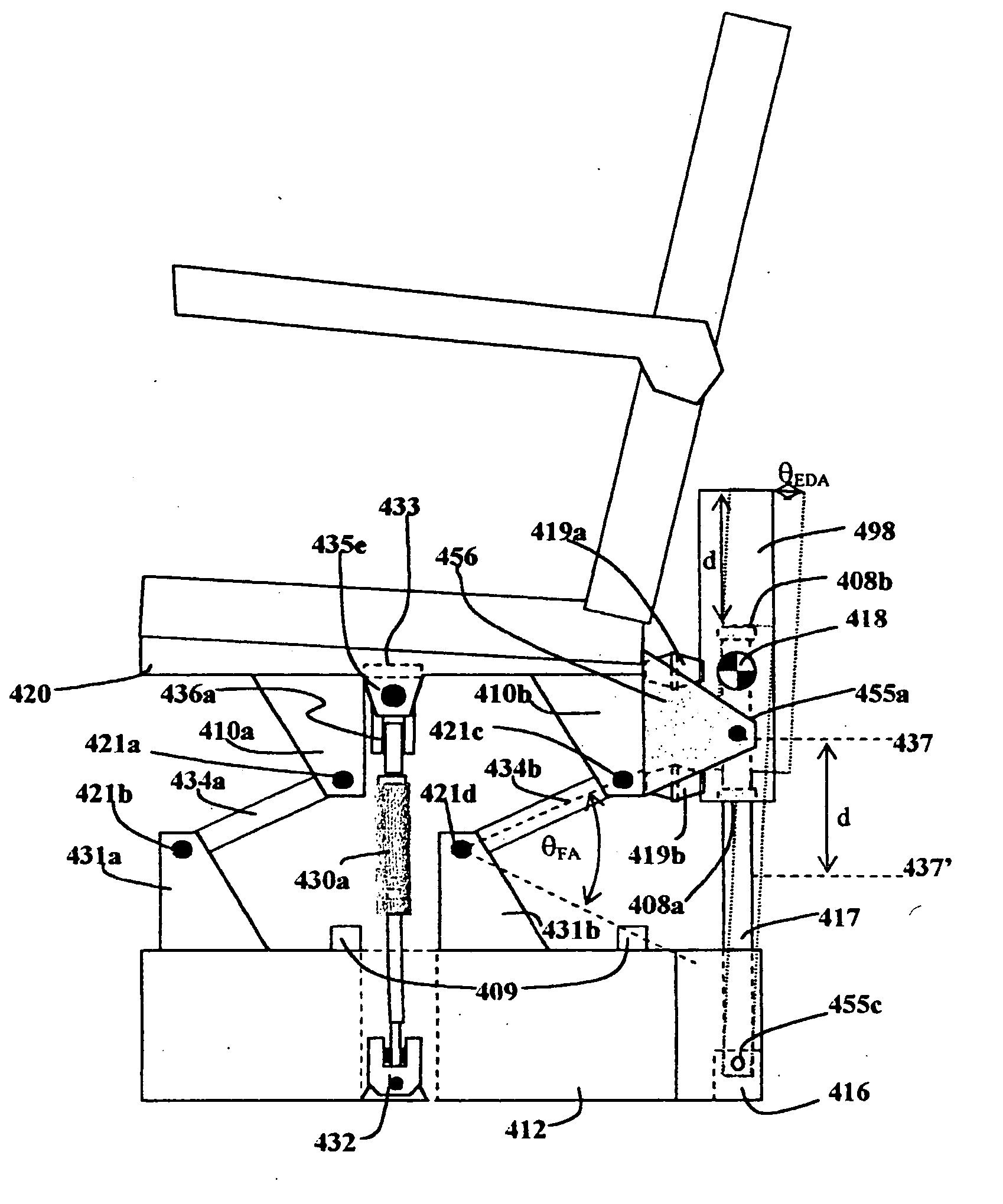
Semi-active snowmobile rear suspension
InactiveUS8676440B2Reduce unsprung massReduce feedbackSnowmobilesDigital data processing detailsSemi activeCoupling
A snowmobile suspension system connected between a skid frame positioned below a chassis of a snowmobile. A limiter strap adjustment mechanism is connected between the chassis and the at least one limiter strap and selectively adjusts the length of the at least one limiter strap. A coupling arm adjustment mechanism is connected between the chassis and at least one coupling arm and selectively adjusts the length of the at least one coupling arm. A linear force device adjustment mechanism is connected between the chassis and the linear force device for adjusting the length and angle of the linear force device relative to the at least one rear arm resulting in control of the force displacement characteristics of the at least one rear arm.
Owner:MAGNA INTERNATIONAL INC
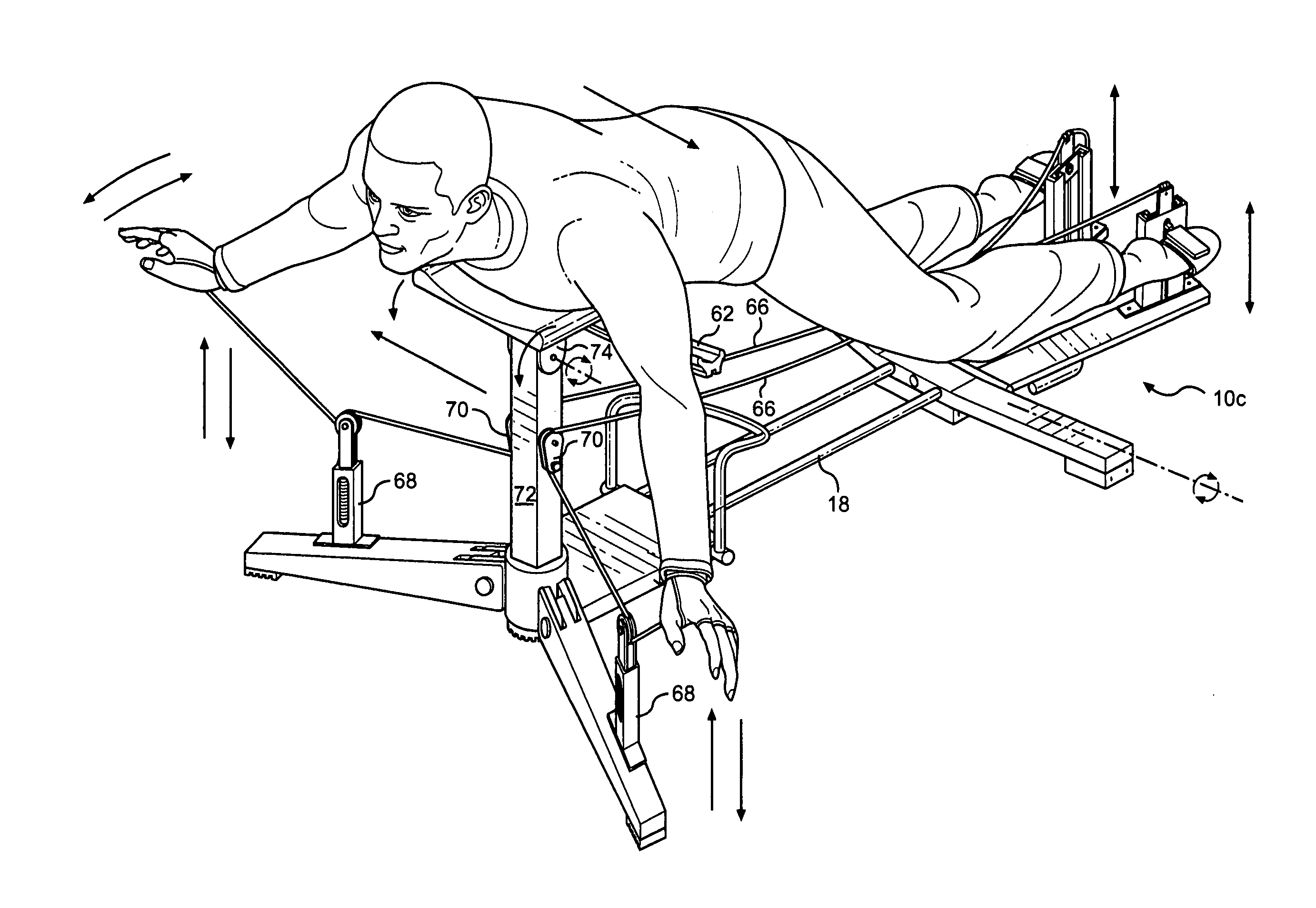
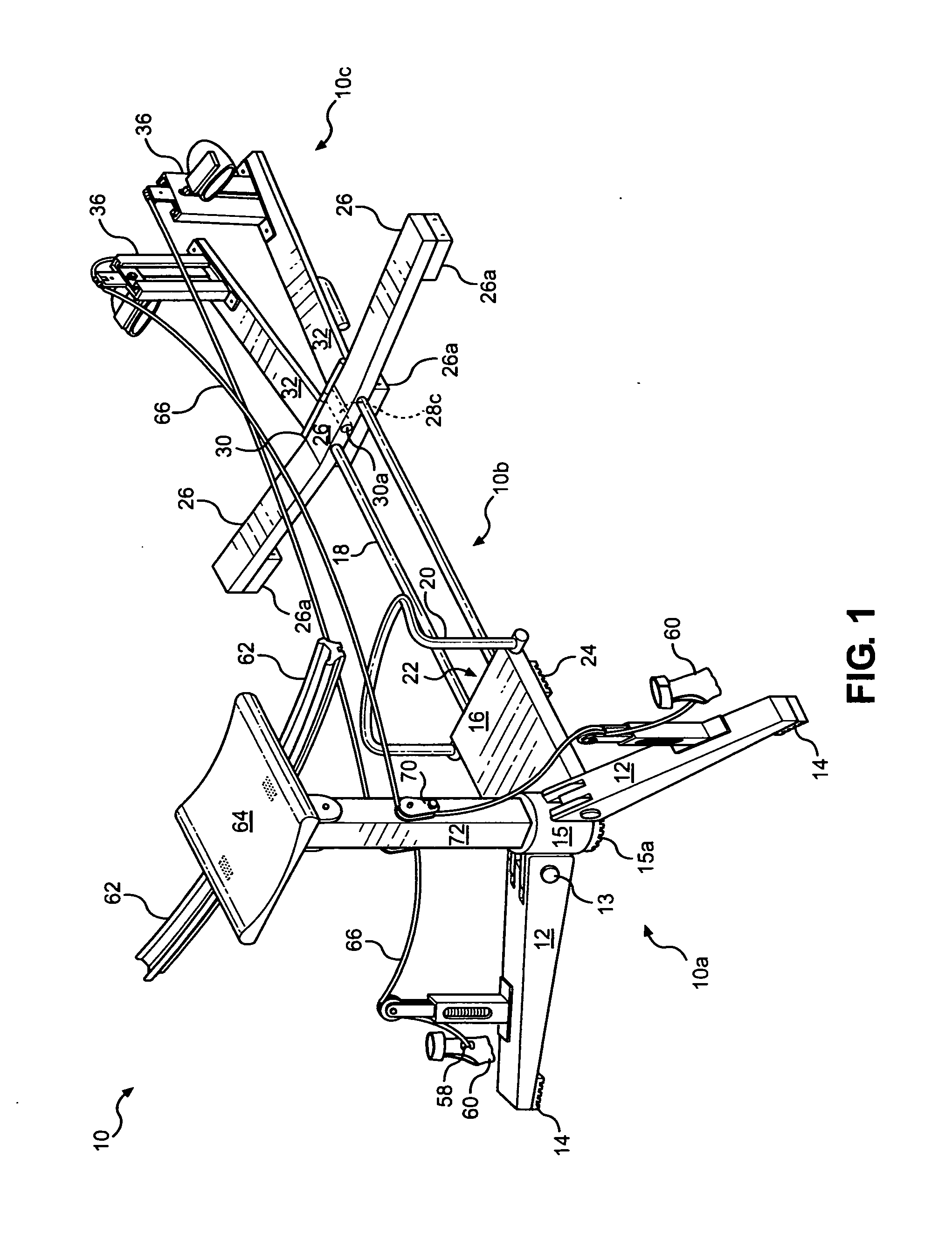
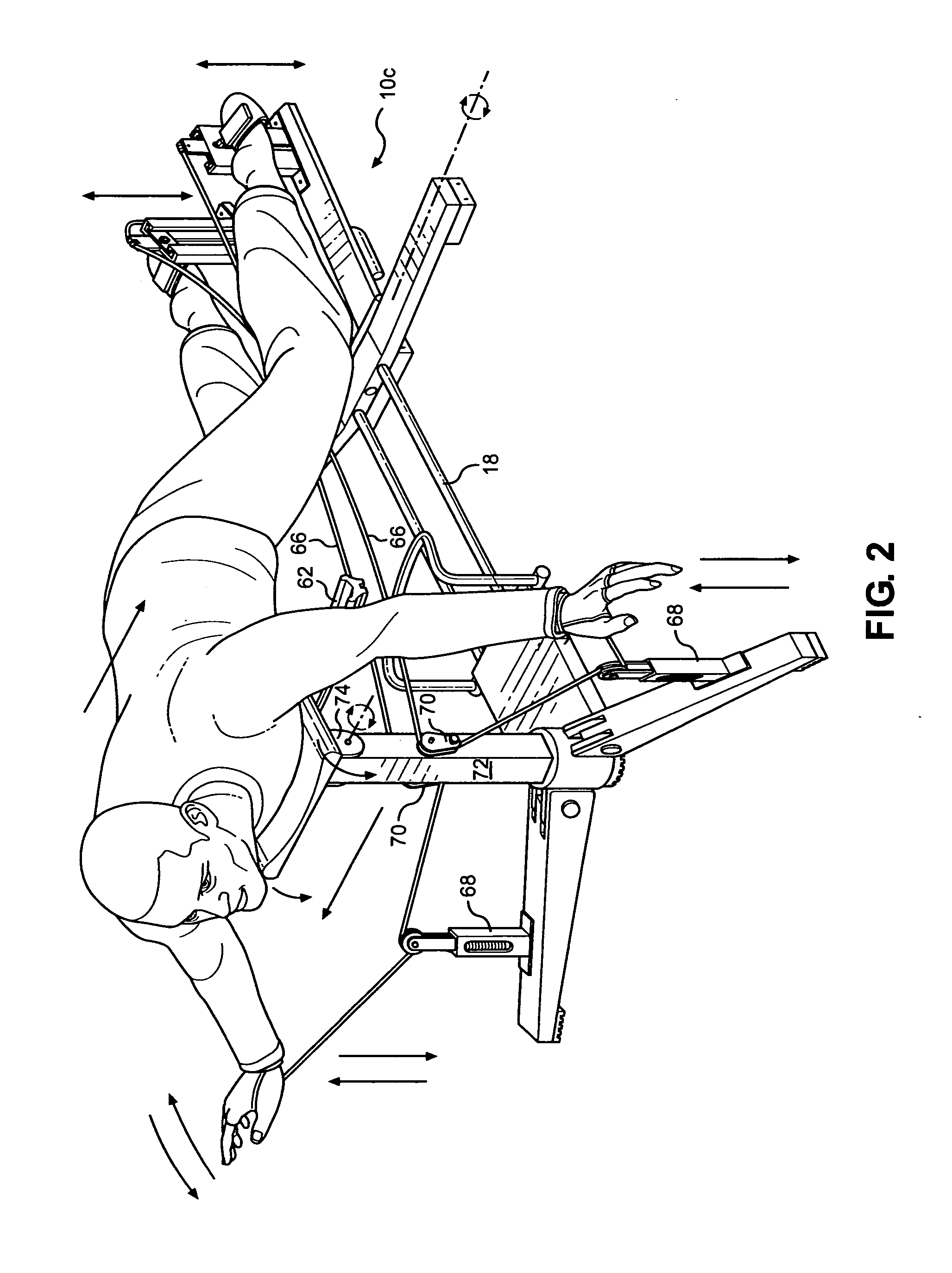
Hydro eliminator full body exercise swim machine
A new type of exercise machine for full body and cardiovascular fitness enthusiasts. It incorporates the properties of tension physics with applied tension force displacement wherein the users' torso is attached to a moving part that tilts and is centralized along a path of lease resistance (B) and the users' hands and feet are fixed at point A and point C of that path. Having the users' hands at point (A) attached to a cable that passes through the same central point (B) by why of a pulley and proceeding to the opposite foot; point (C). The user will then, in a simulated swim stroke assert force on both ends of the cable thus moving the entire body to the right or to the left. During this movement the user has at his / her discretion the amount of resistance applied between the hands and the feet.
Owner:BARNES PAUL AUGUSTINE
High initial force electromagnetic actuator
InactiveUS6950000B1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesCores/yokesMagnetic tension forceEngineering
An electromagnetic actuator is provided that comprises a housing, a solenoid coil, and an armature. The armature can move between a first position proximate a portion of the housing and a second position distal of the portion of the housing. The armature and the portion of the housing define a first gap and an extension member extends in an axial direction into the first gap, thereby defining a second gap. The width of the second gap is less than the width of the first gap. The length and shape of the extension member may be varied to produce increased initial magnetic force from the solenoid coil on the armature. The length and shape of the extension member may also be varied to produce a desired armature force-displacement curve over the stroke of the actuator.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
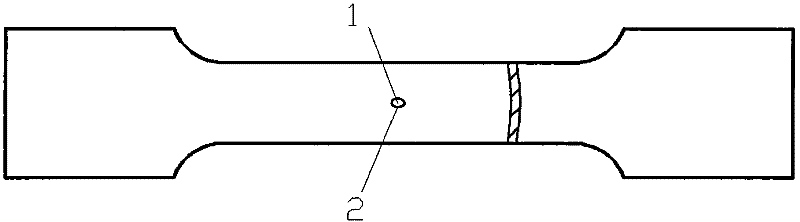
Test sample and method for testing performance parameters of pipe under complex stress state
ActiveCN102410957AFit plane stress-strain propertiesLarge strain rangeMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesTest performanceAxial compression
The invention relates to a test sample and method for testing performance parameters of a pipe under the complex stress state. A common uniaxial tension arc-shaped test sample is processed into an arc-shaped test sample with an elliptical hole. The center line of a long shaft of the elliptical hole is in superposition with a center line in the length direction of the uniaxial tension arc-shaped test sample; and the center of the circle of the elliptical hole is in superposition with the center of the shape of the arc-shaped tension test sample with the elliptical hole. Two sections of pipe compressed test samples are cut out along the axial direction of the pipe to be tested. The verticality of the cross section of each pipe compressed test sample to the axial line of the pipe is 0.08-0.1, and the degree of roughness of the cross section of each pipe compressed test sample is 0.8-0.2. The tension testing is performed on the arc-shaped tension test sample with the elliptical hole, the axial compression testing is performed on the pipe compressed test samples, the lateral compression testing is performed on the pipe compressed test samples and reverse engineering is further performed on obtained force-displacement data, thereby testing the performance parameters of the pipe under the complex stress state.By adopting the whole set of test sample for testing the performance parameters of the pipe under the complex stress state and the testing method, the testing precision and the efficiency of the performance parameters of the pipe are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU NEW HENGJI SPECIAL EQUIP
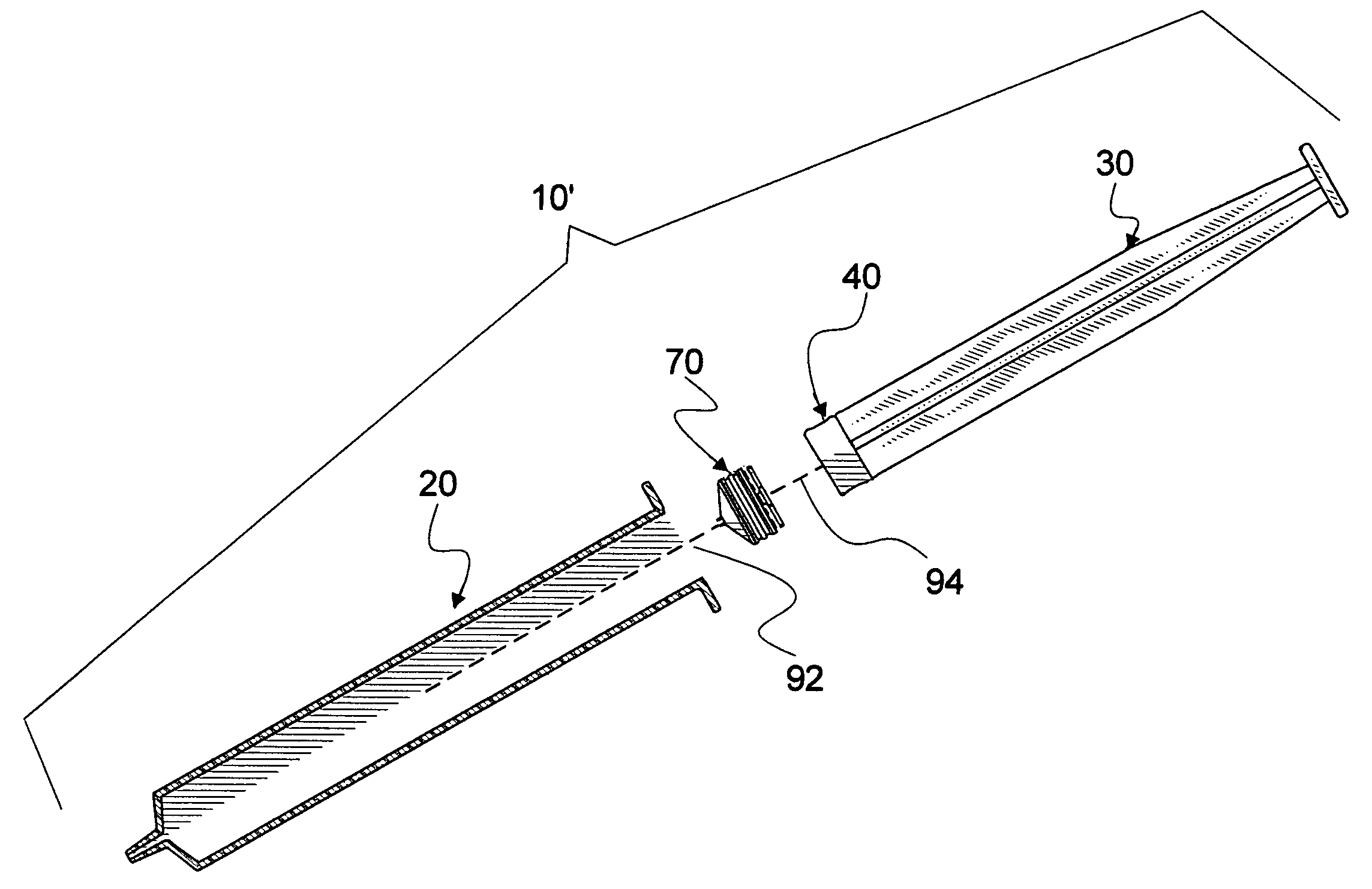
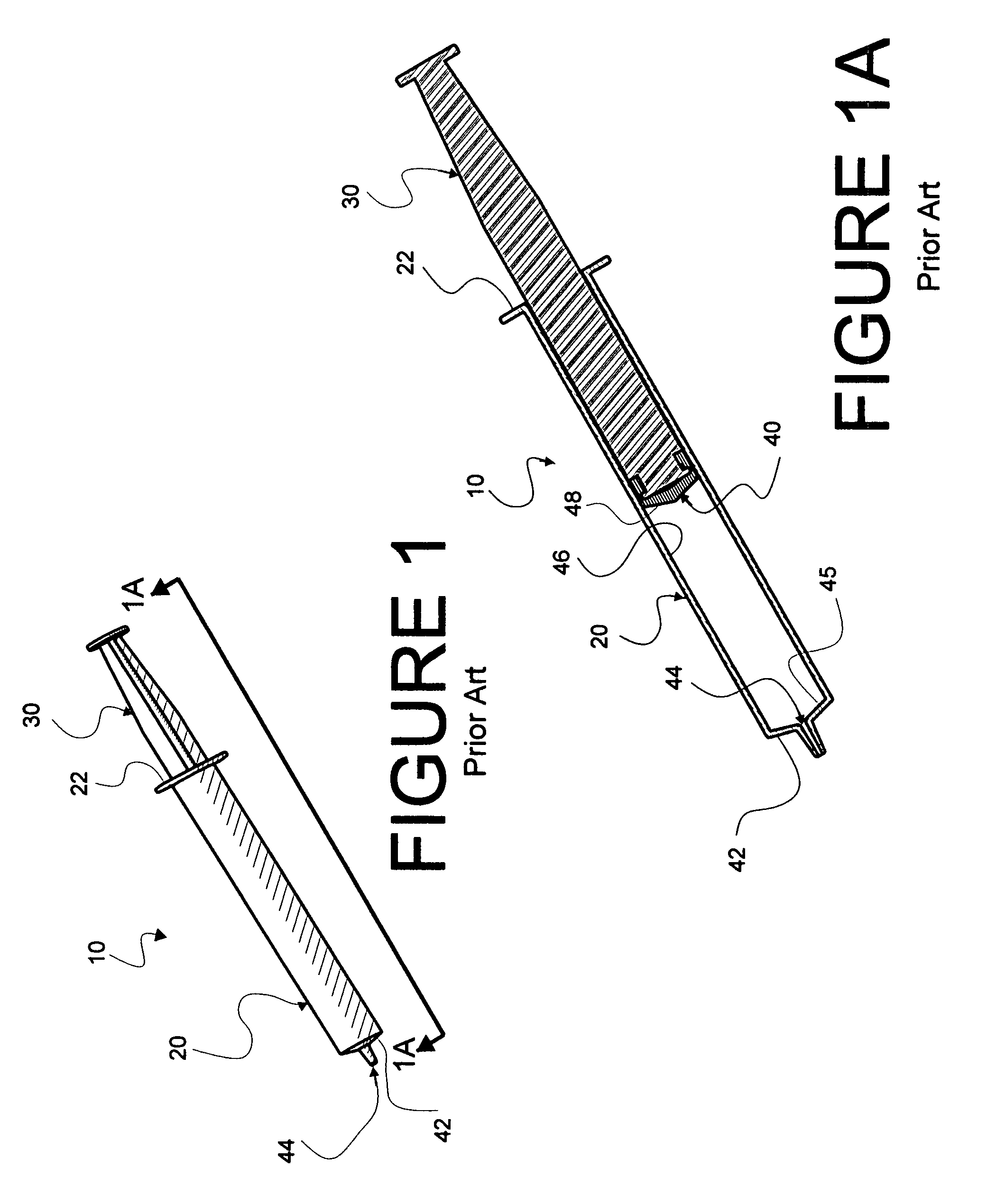
Mixing syringe with and without flush
InactiveUS20060142701A1Stable maintenanceInhibit refluxInfusion syringesIntravenous devicesDifferential pressureEngineering
A displaceable valved stopper is disclosed which partitions a conventional syringe into proximal and distal chambers to provide a multi-chamber, mixing syringe assembly. Also the valved stopper and a valve assembly are disclosed for use in a single conventional syringe to provide dual chamber mixing plus a disparate and sequentially dispensed flush. Incorporated in the valve assembly is another valved stopper and a separator which filters out gas from liquid being dispensed through the valve assembly. Each valved stopper is made as a single molded part which may be made from basic syringe plunger material. Also, each valved stopper may have a bi-state valve (e.g. a domed, slit valve). The separator is a single molded part which may be molded from basic syringe material. Each valve is actuated to a different state by differential pressure of a force greater than the associated valved stopper displacement force. A syringe plunger communicates through fluid in a more proximal chamber to force displacement of the valved stopper and valve assembly for both mixing and dispensing.
Owner:INFUSIVE TECH LLC
Pendulum bob type shearing-resistant impact testing machine and testing method thereof
ActiveCN104048885AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyMaterial strength using single impulsive forceMaterials testingCompressive strength
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
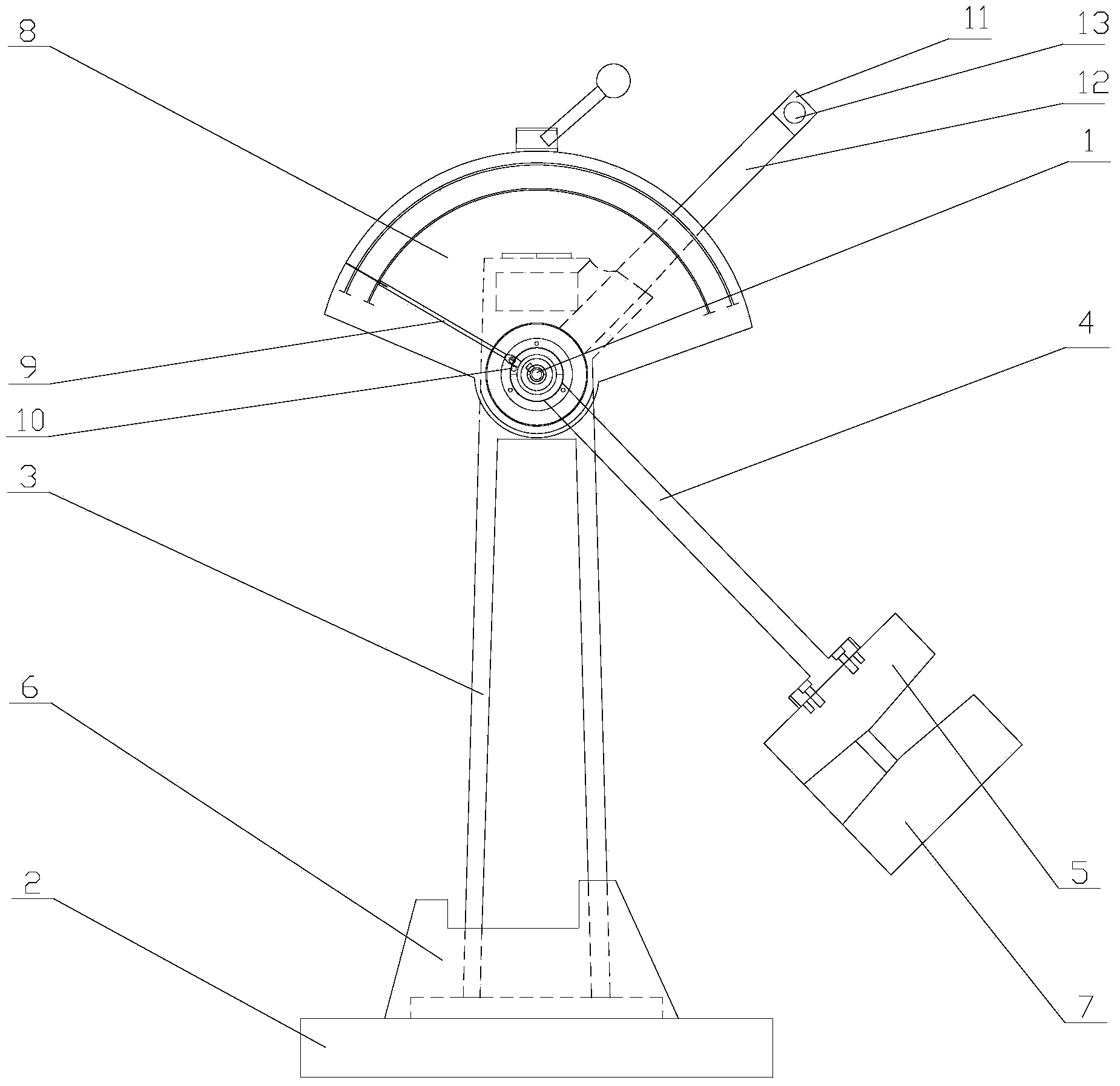
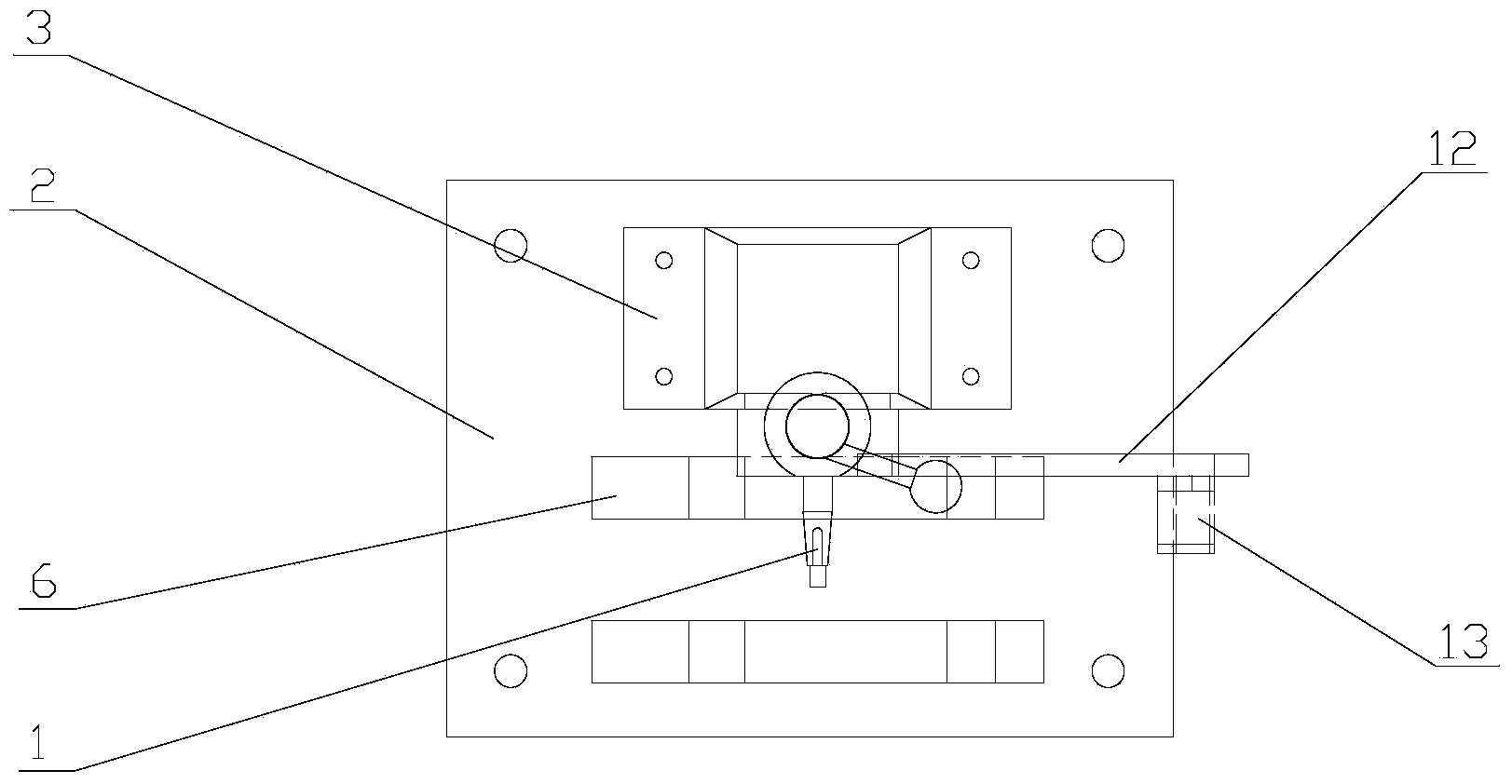
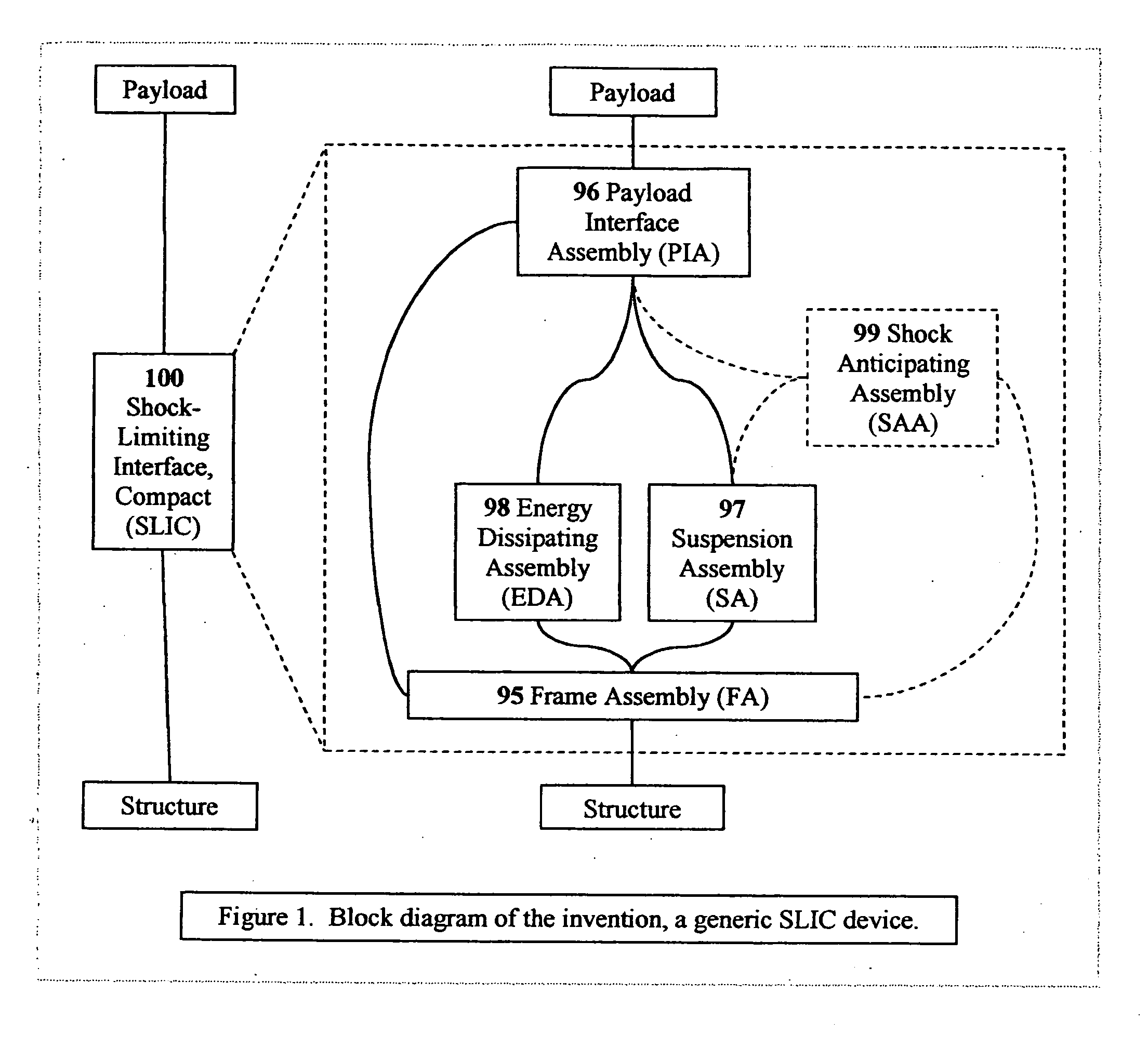
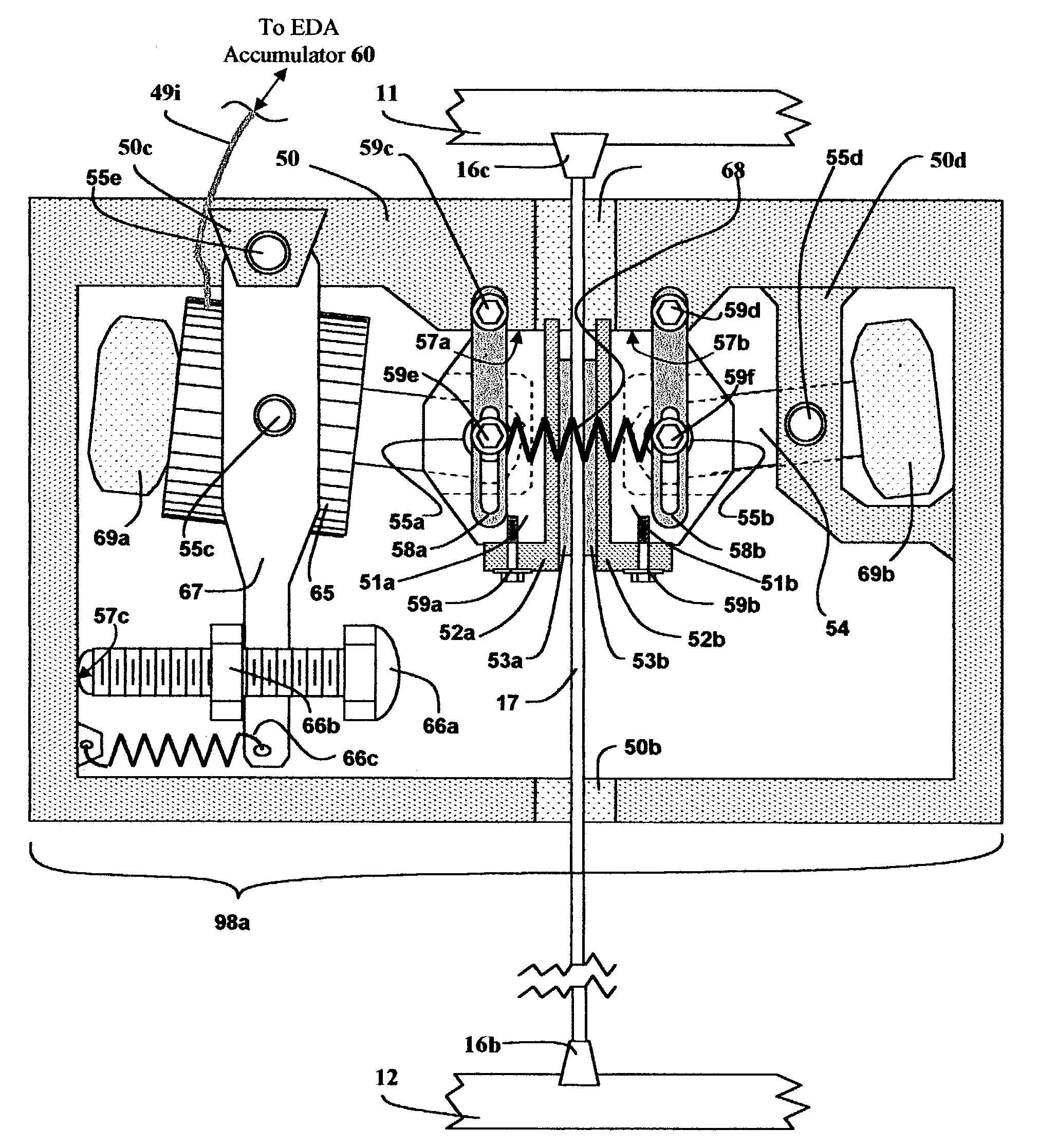
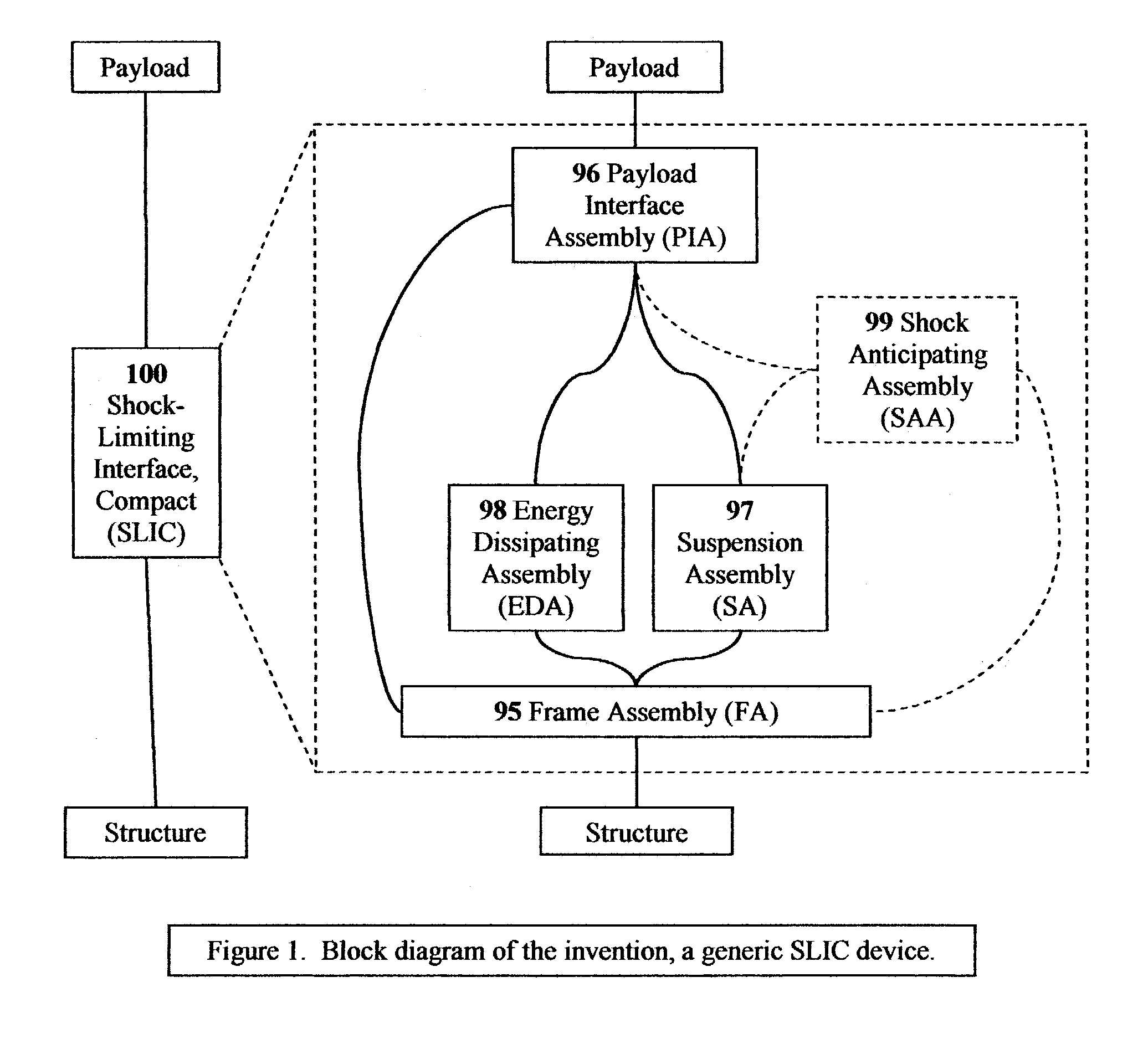
Shock-limiting interface, compact (SLIC)
InactiveUS20070034768A1Dissipate impact energyDisplacement minimizationVehicle seatsStands/trestlesEngineeringUsability
A passive / reactive device protests a Payload from injury or damage due to the shock caused by impact or explosion. When the vehicle or structure mounting the Payload receives a shock pulse, the invention limits the acceleration transmitted from the vehicle or structure to the Payload to an acceptably low, user-adjustable level which is substantially constant or is some other user-adjustable force-displacement function. The invention is capable of doing so even when the peak magnitude of the imposed shock is on the order of thousands of G's, with a rise time to peak on the order of microseconds. The invention can be embodied to operate passively, without any external source of power, sensor system, or CPU, although they can be added to improve certain usability features. The invention also absorbs or dissipates the shock energy in substantially the minimum distance possible without exceeding the user-defined acceleration limit on the Payload. The invention can also react when a shock-producing impact is imminent by repositioning the Payload away from the impact site. The Payload can be a person or persons, or shock-vulnerable equipment. The shock can be created in a number of ways, including an explosion, an impact or collision, the slamming on high-performance boats and some off-road vehicles, earthquake, or even intentional shocks on an amusement thrill ride. The ability of the invention to protect against shock is limited only by its ability to absorb or dissipate the energy of the shock pulse on the Payload. The device can be implemented to protect against shock from any arbitrary direction. The name Shock-Limiting Interface, Compact (SLIC) is coined for this invention.
Owner:STENARD JOHN
Three-slideway wing flap test method for simulating deformation of wings
ActiveCN103558019AReduce the size of the experimental designHigh precisionMachine part testingRelative displacementUltimate tensile strength
The invention belongs to the technical field of strength tests, and relates to a three-slideway wing flap test method of the strength test under the condition that the wings deform. By utilizing the relative displacement theory, the three-slideway wing flap test method largely reduces the design scale of the experiment, reduces test risks, largely improves the accuracy of the experiment design through the method that forced displacement and pneumatic loads are simultaneously loaded stage by stage, and fully tests the structures like wing flaps.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Magnetic drive peak force modulated atomic force microscope and multi-parameter synchronous measurement method thereof
ActiveCN107449939ALarge signal to noise ratioImprove signal-to-noise ratioScanning probe microscopyMicro nanoMechanical models
The invention provides a magnetic drive peak force modulated atomic force microscope and a multi-parameter synchronous measurement method thereof, relates to the technology of measurement of the material surface topography and mechanical properties under the micro-nano scale, and aims at solving the problems that the driving frequency range of the probe in the conventional method based on the force-displacement curve is limited and integrally driving the probe interferes the movement of the probe cantilever and influences the measurement accuracy under the liquid environment. A coil is arranged in a sample table. The probe tip is provided with magnetic particles which are magnetized along the length direction of the probe or have the magnetized component of the direction. Firstly the PSD voltage curve U<free> of vibration of the probe in the free state is acquired, then the PSD voltage curve U<inden> of the tip position when the probe intermittently contacts the sample is acquired, the voltage curve U<Force> of the probe under stress is acquired by U<free> and U<inden>, and the force-displacement curve is acquired according to all the curves so as to acquire the mechanical properties of the material through combination of the corresponding contact mechanical model. The driving frequency range of the probe is wide and the measurement accuracy is high so as to be suitable for the research of polymer composite material or biological cells.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Shock-limiting interface, compact (SLIC)
InactiveUS7070153B1Acceleration is limitedProvide supportVehicle seatsStands/trestlesEngineeringUsability
A passive / reactive device protects a Payload from injury or damage due to the shock caused by impact or explosion. When the vehicle or structure mounting the Payload receives a shock pulse, the invention limits the acceleration transmitted from the vehicle or structure to the Payload to an acceptably low, user-adjustable level which is substantially constant or is some other user-adjustable force-displacement function. The invention is capable of doing so even when the peak magnitude of the imposed shock is on the order of thousands of G's, with a rise time to peak on the order of microseconds. The invention can be embodied to operate passively, without any external source of power, sensor system, or CPU, although they can be added to improve certain usability features. The invention also absorbs or dissipates the shock energy in substantially the minimum distance possible without exceeding the user-defined acceleration limit on the Payload. The invention can also react when a shock-producing impact is imminent by repositioning the Payload away from the impact site. The Payload can be a person or persons, or shock-vulnerable equipment. The shock can be created in a number of ways, including an explosion, an impact or collision, the slamming on high-performance boats and some off-road vehicles, earthquake, or even intentional shocks on an amusement thrill ride. The ability of the invention to protect against shock is limited only by its ability to absorb or dissipate the energy of the shock pulse on the Payload. The device can be implemented to protect against shock from any arbitrary direction. The name Shock-Limiting Interface, Compact (SLIC) is coined for this invention.
Owner:STENARD JOHN KEVIN
Automobile door closing-force testing device
InactiveCN1710392ACorrectly evaluate the difficulty of closingSimple structureApparatus for force/torque/work measurementReal-time dataTransducer
A device for testing door close force of automobile is controlled by computer, it applies S-shape strain type of force test transducer and capacity type of displacement transducer to measure force and displacement as well as applies serial interface to input force displacement signal to portable computer for realizing real time data collection and communication . The device not only can realize test of door close force but also can realize test of door close displacement.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Semi-active snowmobile rear suspension
InactiveUS20120166043A1Motion ratio of to increaseRising rate force/displacement characterisitcSnowmobilesDigital data processing detailsSemi activeCoupling
A snowmobile suspension system connected between a skid frame positioned below a chassis of a snowmobile. A limiter strap adjustment mechanism is connected between the chassis and the at least one limiter strap and selectively adjusts the length of the at least one limiter strap. A coupling arm adjustment mechanism is connected between the chassis and at least one coupling arm and selectively adjusts the length of the at least one coupling arm. A linear force device adjustment mechanism is connected between the chassis and the linear force device for adjusting the length and angle of the linear force device relative to the at least one rear arm resulting in control of the force displacement characteristics of the at least one rear arm.
Owner:MAGNA INTERNATIONAL INC
Method for testing buffer performance of two-dimensional porous material under high-speed impact condition
InactiveCN104535407ASolve problems that cannot be used to study the cushioning properties of two-dimensional porous materials under high-speed impact loading conditionsSpecial data processing applicationsStrength propertiesEnergy absorptionStress–strain curve
The invention discloses a method for testing the buffer performance of a two-dimensional porous material under the high-speed impact condition. The method comprises the steps of carrying out buffer performance testing on the two-dimensional porous material to obtain a corresponding impact force displacement curve, standardizing the impact force displacement curve to obtain a corresponding standardized stress strain curve, and establishing and calculating buffer performance evaluation indexes such as optimal unit volume energy absorption, optimal specific energy absorption, impact force efficiency and a minimal dynamic buffer coefficient, so as to realize the testing of the dynamic buffer performance of the two-dimensional porous material under the high-speed impact load condition. According to the method, the problem that the buffer performance of the two-dimensional porous material under the high-speed impact load condition cannot be researched by virtue of an existing method is solved, samples of different thickness do not need to be tested, an evaluation method is simple, the load condition is similar to an actual impact load and does not influenced by the fluctuation of a curve amplitude value, and the method can be used for researching the influences of factors such as impact speed, structure parameters and unit forms to the buffer performance of the two-dimensional porous material.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
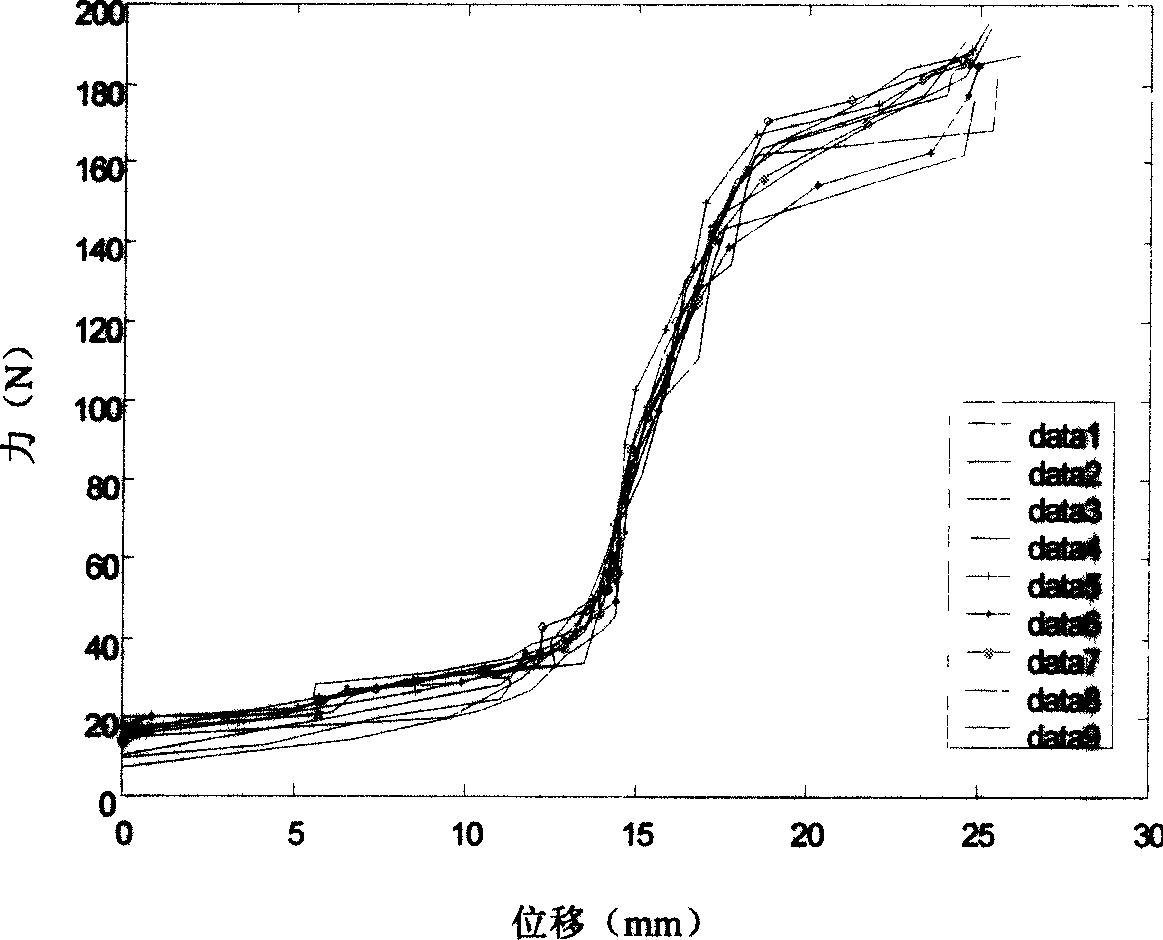
Device for automatically calibrating clamp rigidity and application method thereof
ActiveCN109100222AEfficient measurementThe stiffness test process is smooth and continuousMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesReduction driveElectric machinery
The invention discloses a device for automatically calibrating clamp rigidity and an application method thereof, and belongs to the field of machinery. The device for automatically calibrating clamp rigidity is used for fast and highly precise clamp rigidity calibration. In the process of calibrating the clamp rigidity, firstly an equilibrium position is adjusted, and a force sensor and a displacement sensor return to a home position; an industrial control computer sends out a command to control a stepping motor to drive a retarder to rotate, and to drive the entire screw nut slide table to move along a straight line through a screw nut pair; the displacement of the screw nut slide table is stably transmitted to a loading head through the action of a spring, and then the clamp is deformed;a collecting device synchronously collects signals from the force sensor and the displacement sensor and outputs the signals to the industrial control computer; the industrial control computer controls the stepping motor to stop rotating after the signal from the force sensor reaches a set value; and the stepping motor reverses again to a zero point when the stepping motor is reversed to a set reversed value. The device for automatically calibrating clamp rigidity and an application method thereof can obtain a force-displacement curve of the entire process through one-time clamping only, andobtain the rigidity of the clamp under a tension and compression state. The rigidity test process is smooth and continuous, and the rigidity measurement is accurate.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
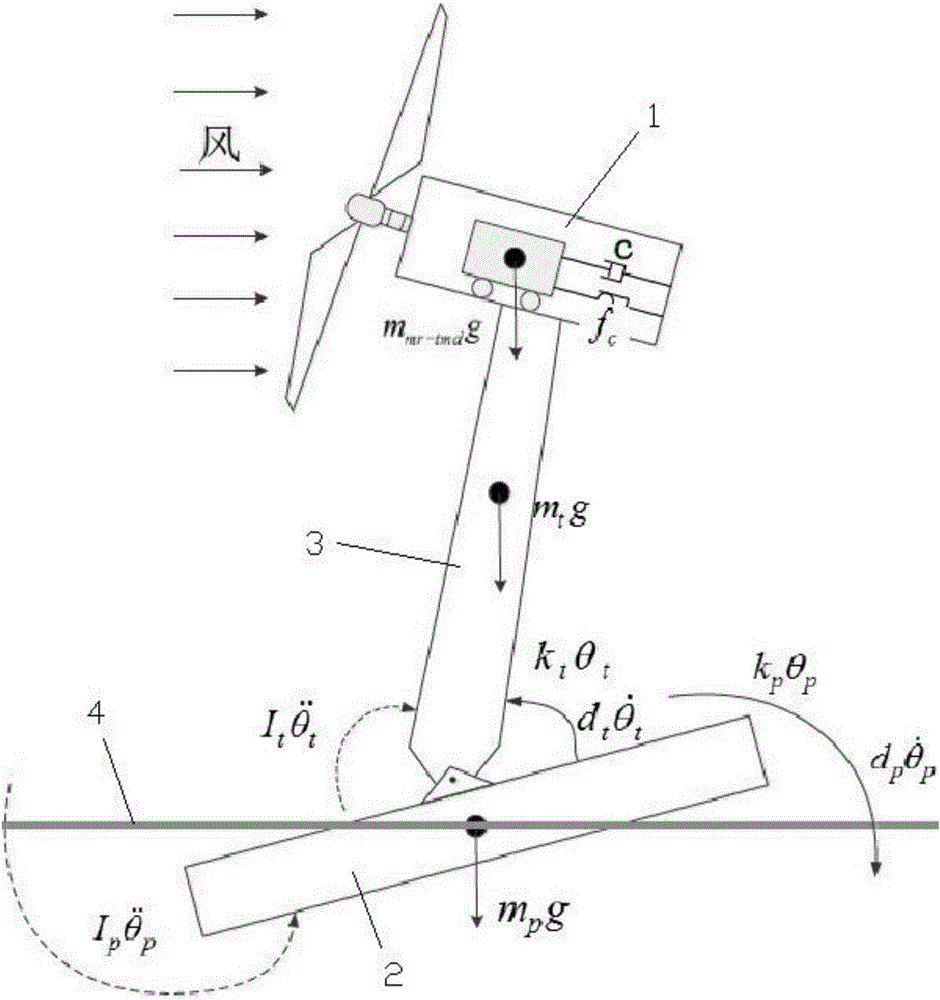
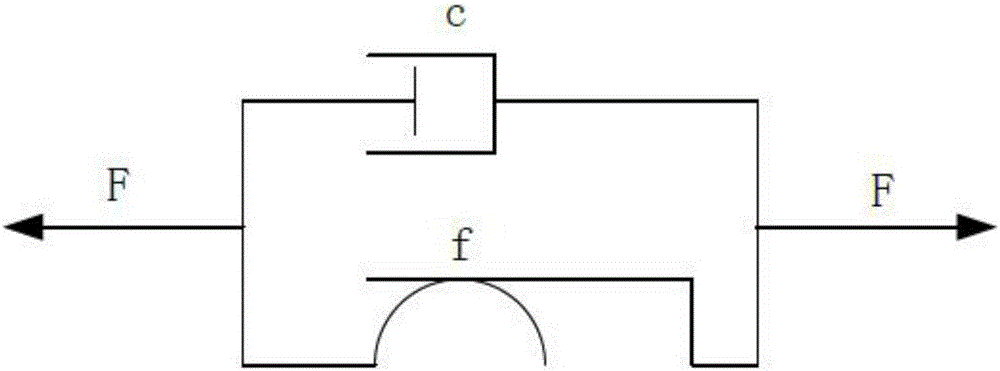
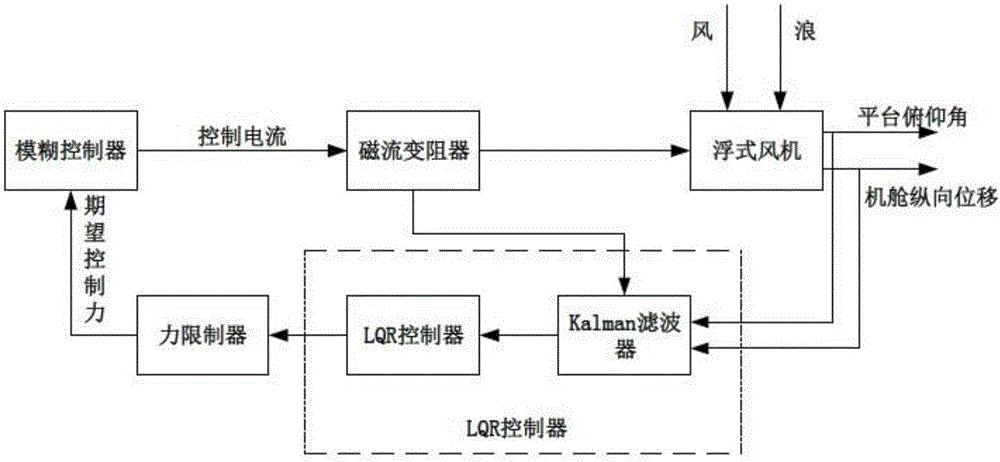
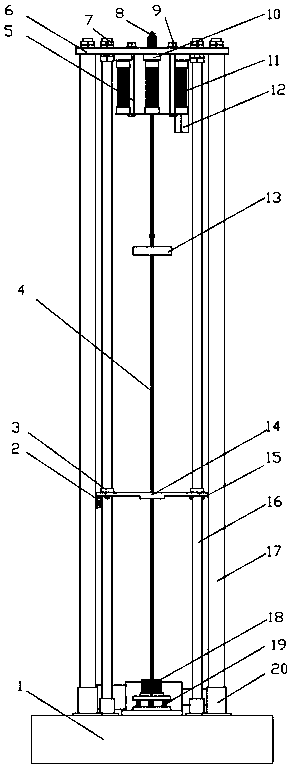
Method of load shedding of floating wind turbine generator system based on semi-active structure control of magneto rheological damper
The invention discloses a method of load shedding of a floating wind turbine generator system based on semi-active structure control of a magneto rheological damper. The method includes the following steps: (1) analyzing the structure of the magneto rheological damper, obtaining a force-displacement relationship of the magneto rheological damper; (2) establishing an equation of motion of a multi-degree of freedom system of an offshore floating wind turbine generator system which is configured with the magneto rheological damper, and establishing equations of motion of the wind turbine generator system and the magneto rheological damper; (3) controlling the magneto rheological damper through a LQR controller and a Fuzzy controller so as to reduce the pitch angle of the floating wind turbine generator system and the longitudinal displacement of a nacelle. According to the invention, the method overcomes the defects of passive control and active control in structural control of a damper, requires less extra energy, requires simple apparatus and is not less susceptible to stability loss, can effectively reduce total load of the floating wind turbine generator system, guarantees stability of a platform, and further increases service life and energy quality of output electricity of a wind turbine generator.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Drop hammer impact testbed capable of accurately measuring impact load and dynamic displacement and testing method of drop hammer impact testbed
PendingCN109115634ASimple structureLow processing and manufacturing costsMaterial strength using single impulsive forceData acquisitionEngineering
The invention relates to a drop hammer impact testbed capable of accurately measuring an impact load and dynamic displacement and a testing method of the drop hammer impact testbed. The drop hammer impact testbed capable of accurately measuring the impact load and dynamic displacement mainly comprises a main frame module, a lifting module, a forcing module, a hammer grabbing module, a hammer headmodule, a test piece fixing seat, a magnetic railing ruler, a dynamic force sensor, a data collection and processing module and the like. The magnetic railing ruler installed on the side surface of the hammer head can accurately measure displacement of the hammer head, while the dynamic force sensor which is installed below the test piece fixing seat can accurately measure the impact force appliedto an object to be measured. The drop hammer impact testbed is simple in structure and convenient to operate, can rapidly and reliably capture a force-displacement signal of the whole impact process,can accurately calculate the impact energy absorbed by the object to be measured and is beneficial to analyzing and studying the anti-impact performance of a material.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Device and method used for measuring axial and radial rigidity of magnetic suspension bearing
InactiveCN102435434AHigh degree of automationImprove handlingMachine bearings testingRotary stageFixed frame
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring the rigidity of a magnetic suspension bearing. The device mainly comprises three precise electronic control displacement tables, a turn table, three laser displacement sensors, a six-degree of freedom force / moment sensor, a tool converter, a mounting converter, a right angle fixing frame, a reference measuring plane and the magnetic suspension bearing, wherein the three precise electronic control displacement tables are controlled through a personal computer (PC); a stator of the magnetic suspension bearing is enabled to move in a certain direction in the horizontal plane, and a rotor of the magnetic suspension bearing is enabled to move in a vertical direction; force-displacement data is obtained through measuring the force borne by the rotor at a certain steeping point and the displacement of the stator / rotor relative to an equilibrium point for the time being; and the data is relatively processed through a selected fitting model, and then the rigidity in different positions in the direction is obtained. The device has the advantages of high precision, flexible measurement, high automation degree, good maneuverability and the like.
Owner:苏州同心医疗科技股份有限公司
Engagement arrangement
Retention of position and clamping of components is ideally performed with an engagement arrangement which is reconfigurabie. Magnetorheological (MR) fluids have been utilised for reconfigurabie engagement arrangements but typically require powerful electromagnets to activate the MR fluid. By providing enclosed chambers with a constriction in the form of a passage (30) between a reservoir portion (31) of the chamber and an engagement portion (32) of the chamber it is possible to utilise smaller permanent magnets (7) acting upon a smaller volume of MR fluid in the passage. In such circumstances initial positioning of engagement elements (9) is provided through forced displacement in the form of a plunger or pin (11) and then retention of the engagement element position achieved through positioning a magnetic field across and about a passage (30) to create an effective block retaining MR fluid volume and therefore presentation of the engagement element (9). In order to achieve such performance MR fluids which have an appropriate performance and durability are necessary. In such circumstances in accordance with other aspects of the present invention particular magnetorheological fluids are also described.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NOTTINGHAM
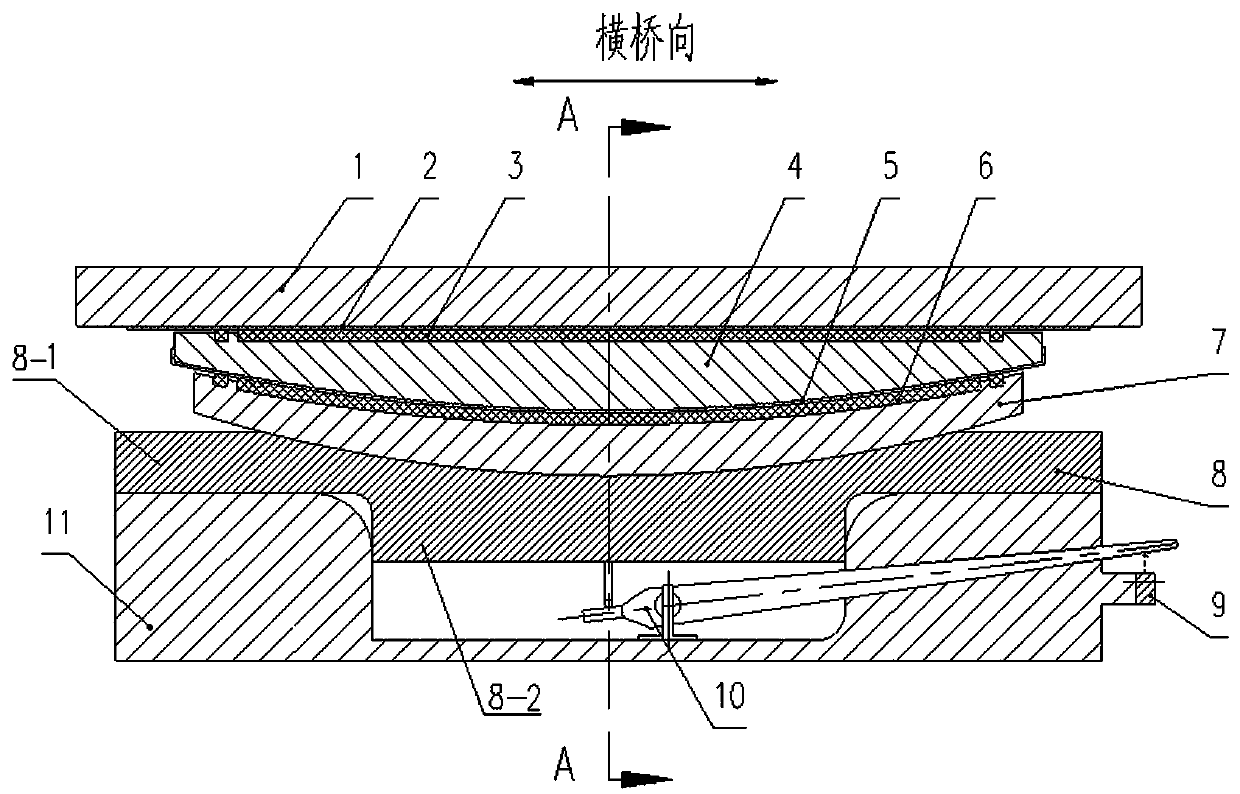
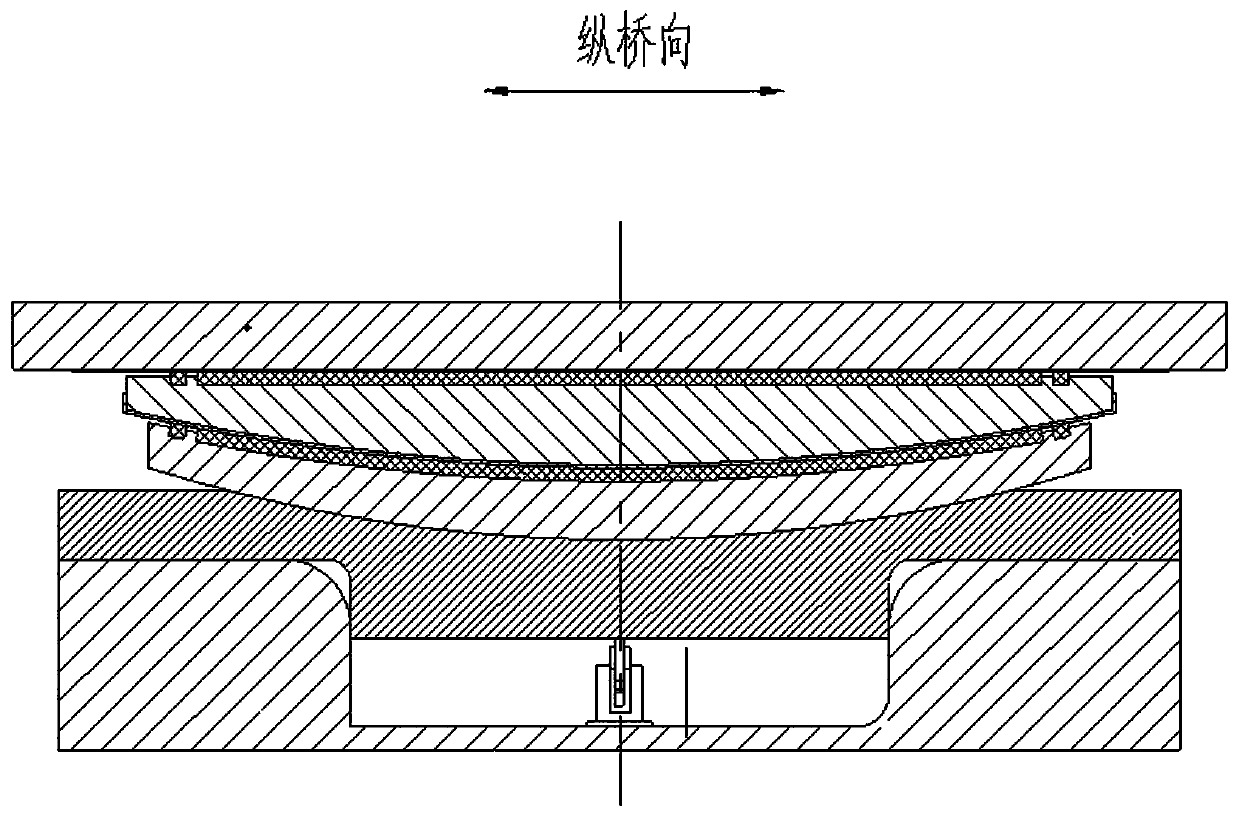
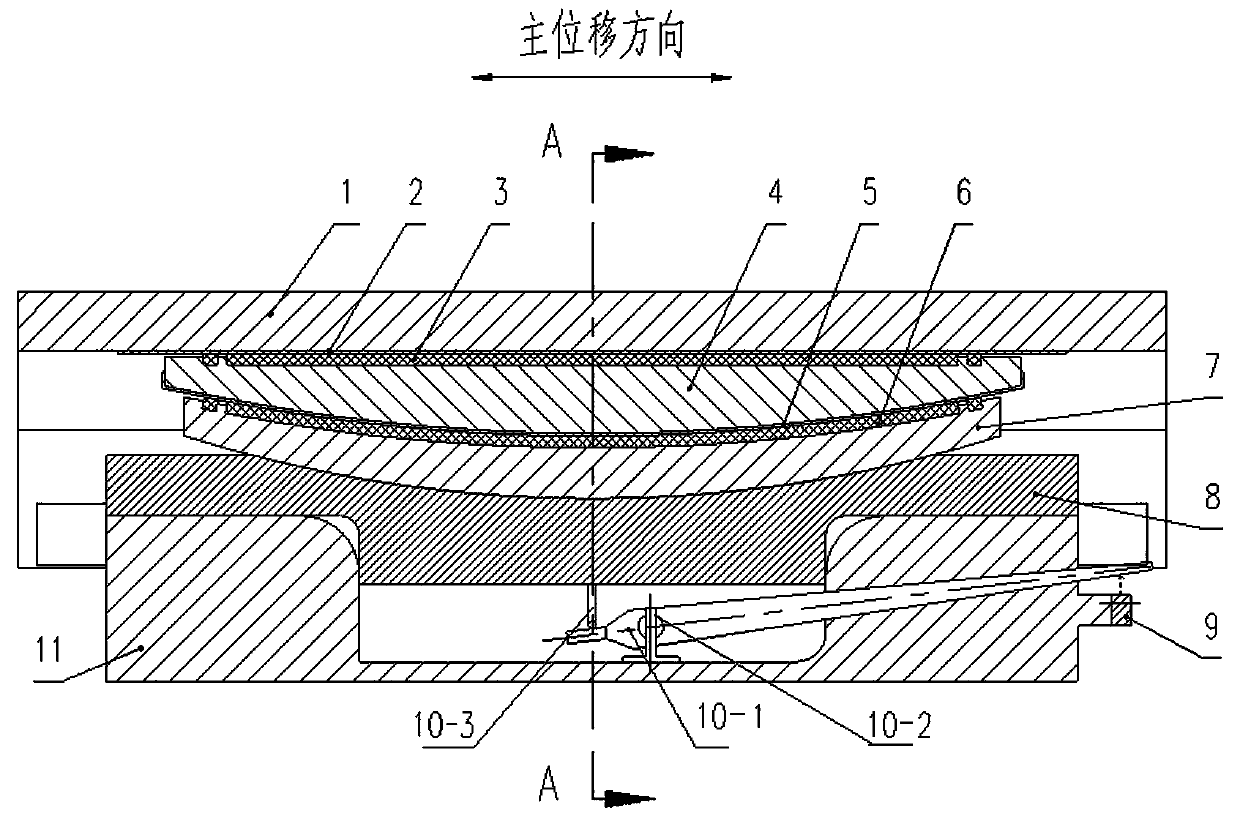
Vertical force measuring type bridge support and force measuring method
PendingCN110106782AThe measured data is sensitiveReal-time automatic collectionBridge structural detailsForce measurement by elastic gauge deformationEngineeringForce displacement
The invention provides a vertical force measuring type bridge support and a force measuring method. The vertical force measuring type bridge support comprises an upper support, a seat board, a bottombasin, a displacement amplification device and a displacement sensor; and the upper part of the support bears force-displacement conversion. After the support bears a vertical force, the center of a lower seat board generates a downward displacement; through the displacement amplification device, the displacement is amplified and led out of the support; through a load test, a relation between thevertical load force of the support and the reading of a displacement sensor is calibrated to realize purposes of force-displacement conversion and an easily detached and changed displacement measuringelement.
Owner:LUOYANG SUNRUI SPECIAL EQUIP
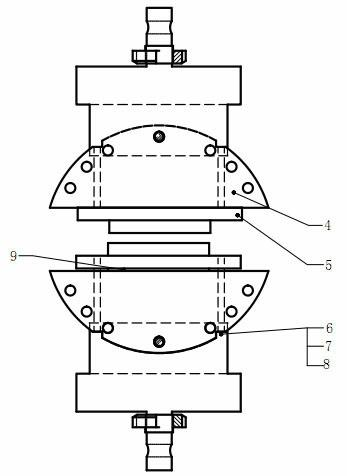
Clamp for mixed fracture test of dual-phase material interface
The invention belongs to the technical field of a material detection, and particularly relates to a clamp for mixed fracture test of a dual-phase material interface. The clamp is divided into an upper part and a lower part that are symmetric to each other; each of the upper part and the lower part consists of a pulling rod, a semiround plate and a sample table; the sample table is connected with the semiround plate by bolts; the semiround plate is connected with the pulling rod by a bolt; a plurality of round holes are symmetrically arranged at the edge of the semiround plate; and the upper pulling rod and the lower pulling rod are fixedly connected with an upper force-applying system and a lower force-applying system of a pulling machine respectively. The clamp can be used together with a universal mechanic tensile testing machine; a sample with a pre-crack is fixed on the clamp; subsequently the clamp can be rotated so as to apply the pull forces of different angles to the sample; the critical fracture strength of the interface crack can be calculated according to a force-displacement curve. The clamp can be used for conveniently determining the situations of the I-type mixed fracture mode and the II-type mixed fracture mode under different tensile loading angles, and is also applicable to determinine the I-type fracture situation of the dual-phase material interface.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com