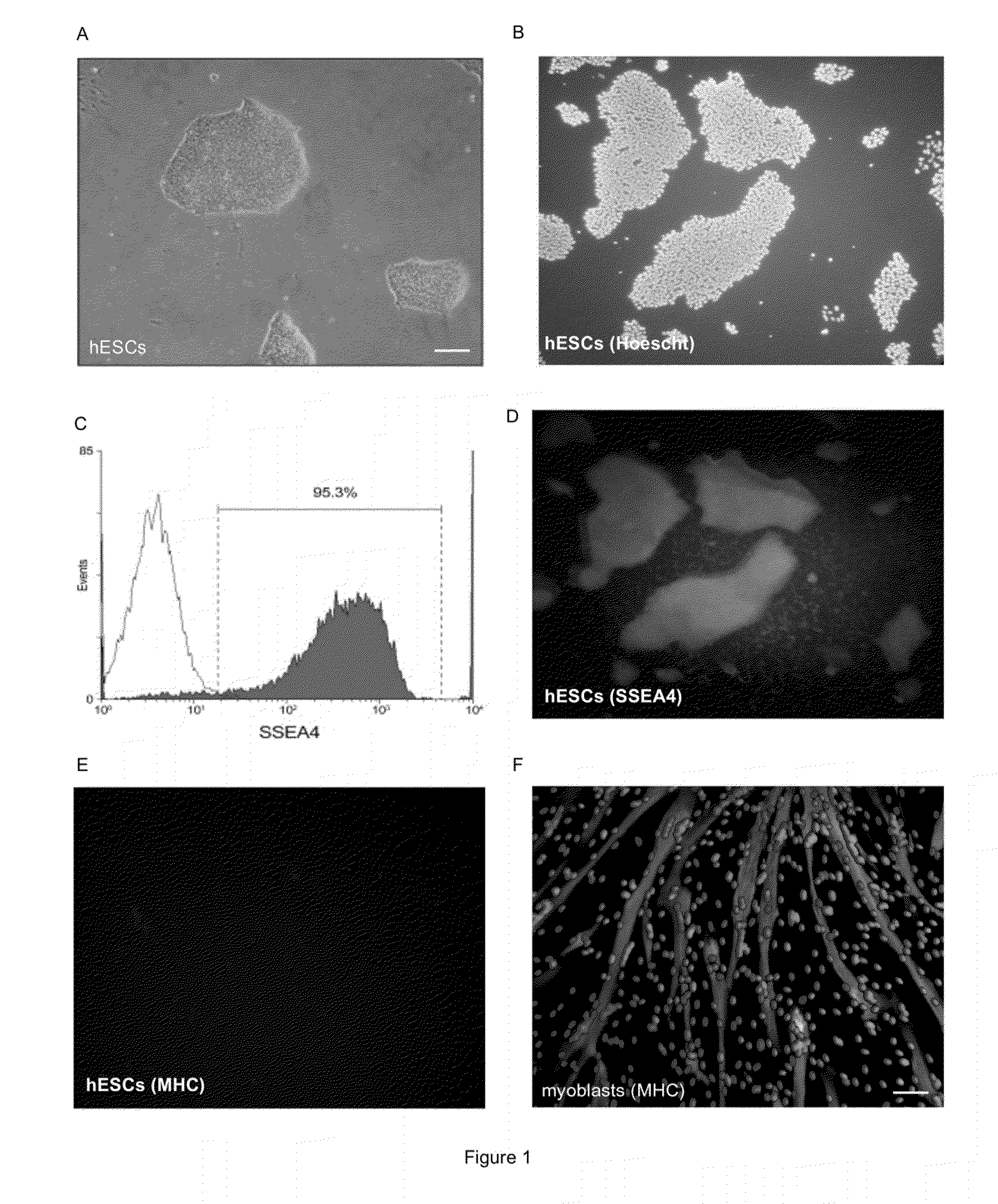
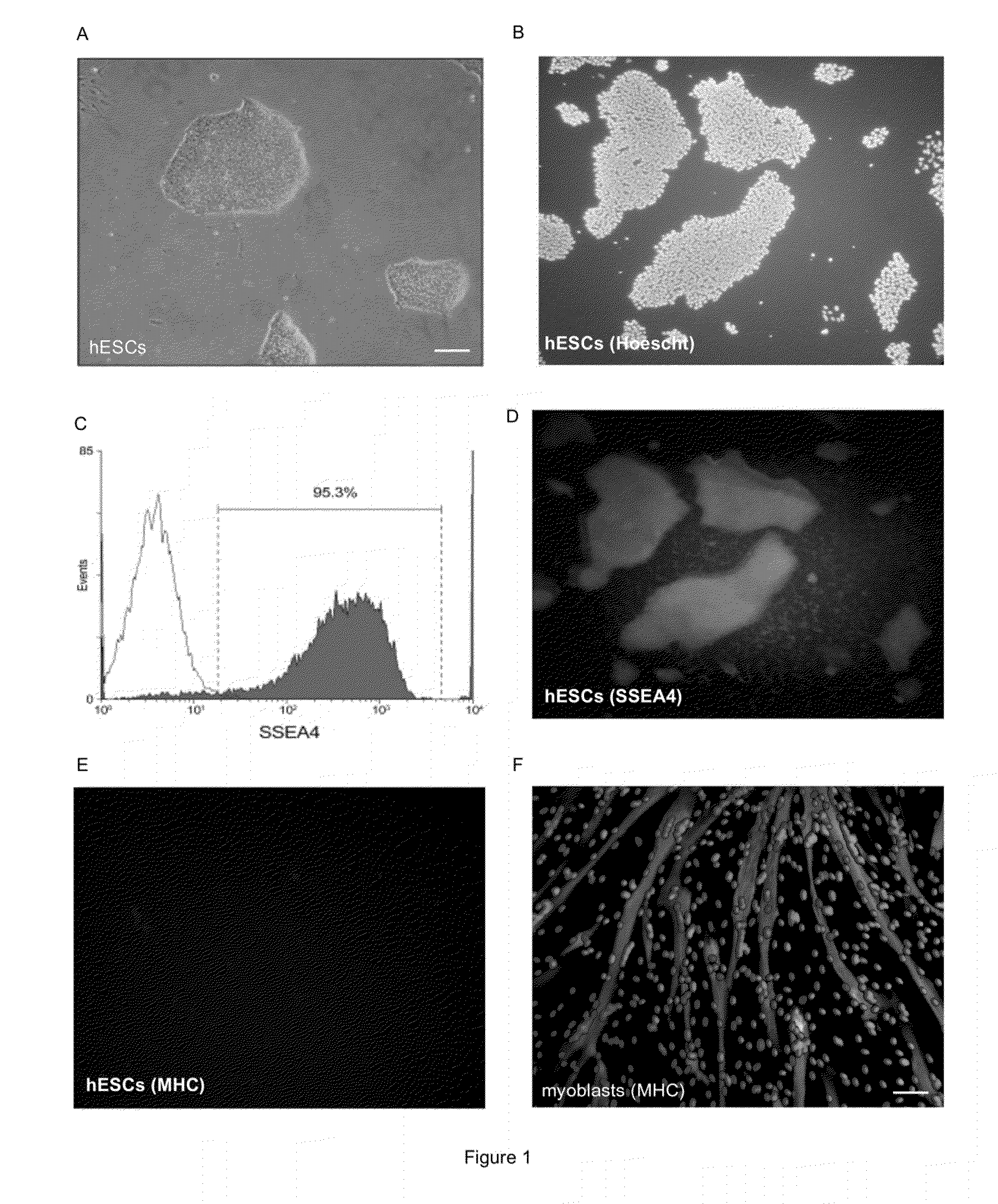
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Myogenic differentiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Directional knockout on sheep MSTN gene and detection method for influence thereof on myogenic differentiation
InactiveCN105821116ALow toxicityHigh targeted knockout efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSide effectGene targeting
The invention discloses directional knockout on sheep MSTN gene by applying the CRISPR / Cas9 technology, and a method for verifying the impact effect of directional knockout on skeletal muscle satellite cell differentiation. The concrete contents are as follows: firstly, target gene cloning; secondly, gRBA design and synthesis; thirdly, CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout vector construction; fourthly, CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout vector exogenous activity detection; fifthly, CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout vector endogenous activity detection; sixthly, CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout vector knockout effect detection. The method has the following advantages: firstly, the experimental period is shorter; secondly, the method is simple and practicable, has high repeatability, and can be performed in common laboratories; thirdly, active vector constructed through the method is small in toxic and side effects, and can be applied to the preparation and production of transgenic animals; fourthly, the method is small in non-specific shear, and obviously improves the gene targeting knockout efficiency; fifthly, the method is high in applicability.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Myogenic differentiation of stem cells and and uses thereof
Disclosed are methods of differentiating stem cells into muscle cells by growing the cells in a myogenic culture medium. The differentiated cells can be used as a source of cells for transplantation in a patient in need thereof.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Method for promoting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells
ActiveCN107287242ALittle influence on other biological characteristicsUseful for researchGenetically modified cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSkeletal Muscle Satellite CellsClinical research
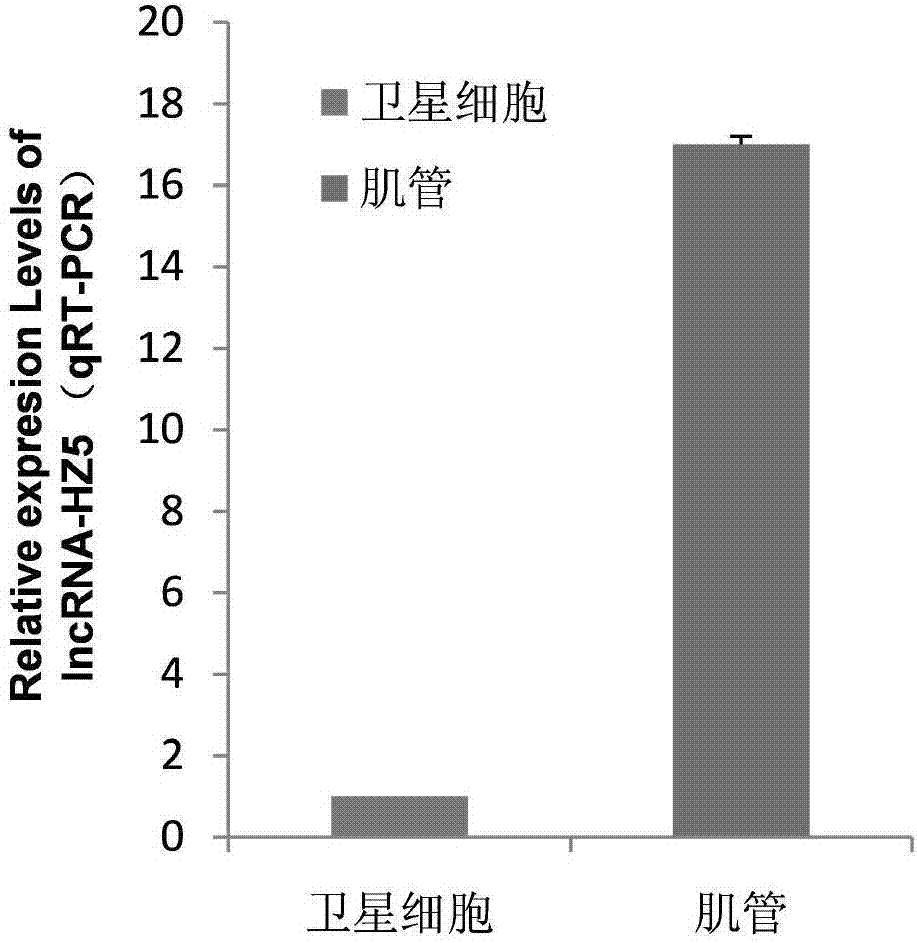
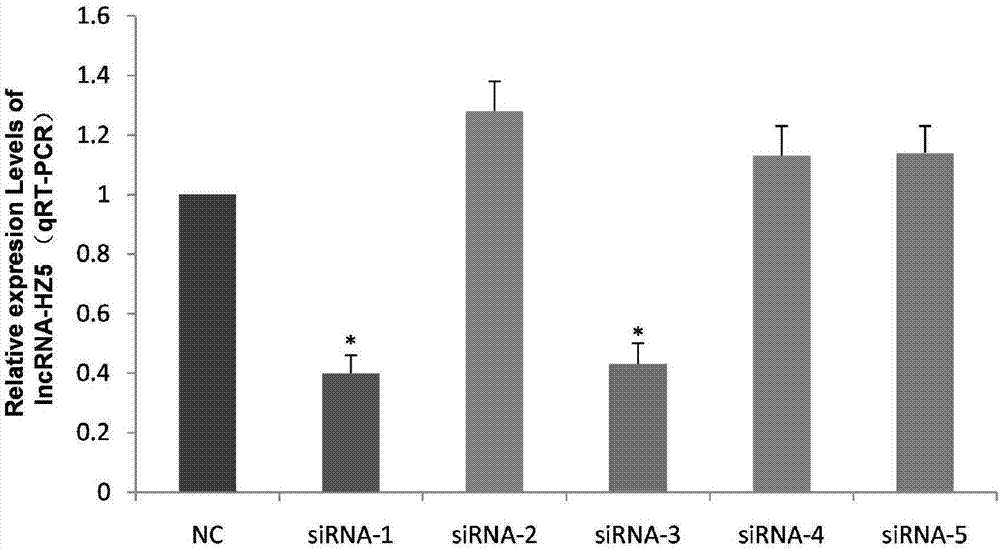
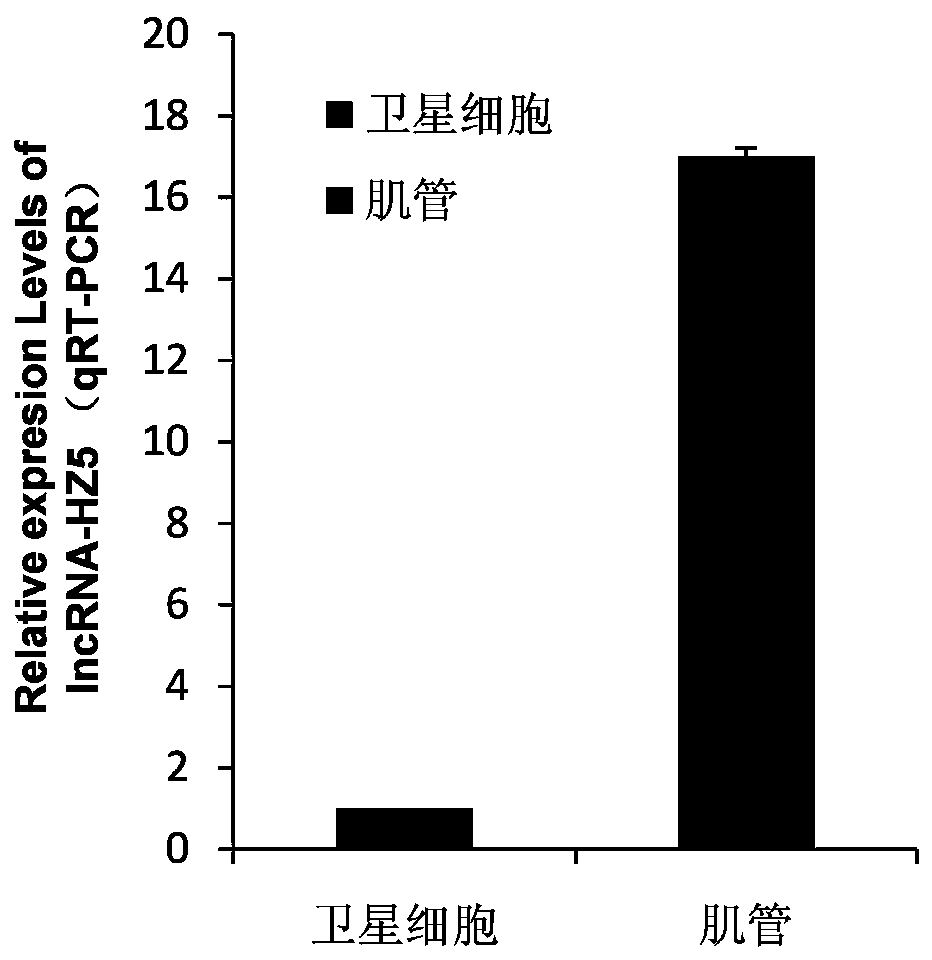
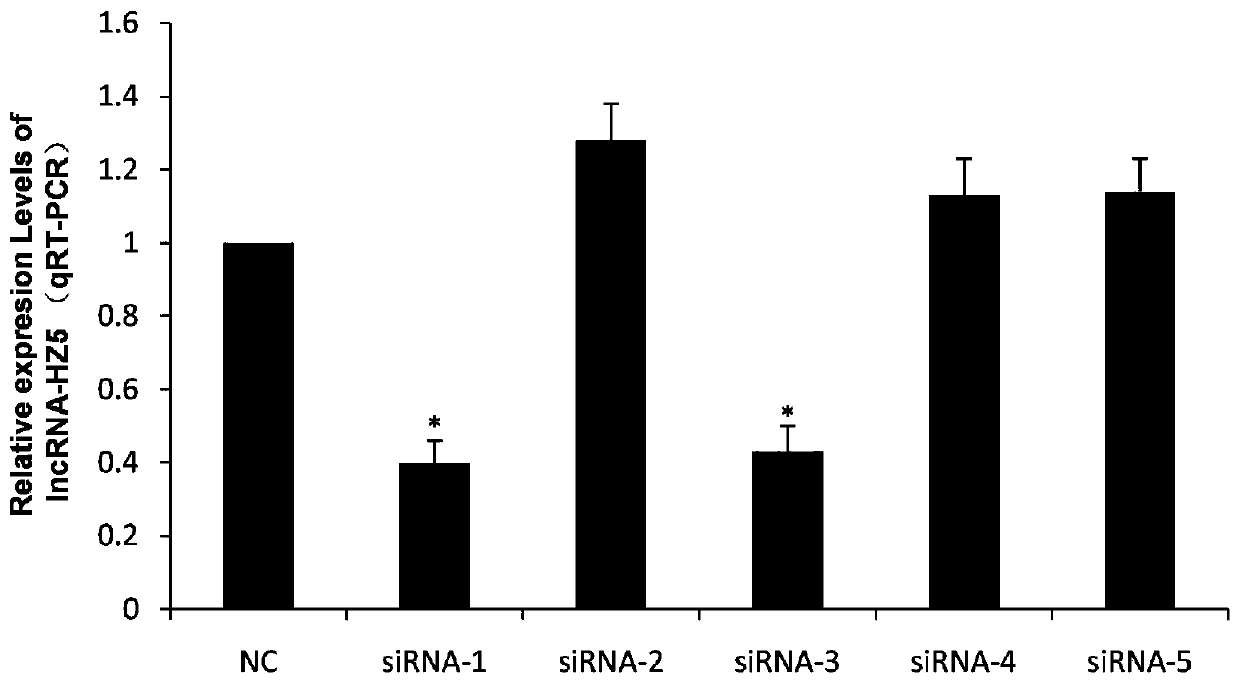
The invention relates to a method for promoting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells. According to the method, myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells is promoted by interfering lncRNA-HZ5 expression. The specific method comprises the steps as follows: siRNA of lncRNA-HZ5 is designed and synthesized according to an lncRNA-HZ5 base sequence, siRNA is used for transfection of the bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells, the expression level of lncRNA-HZ5 is lowered, and myogenic differentiation of the bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells is promoted, wherein the genome base sequence of lncRNA-HZ5 is shown in SQ1. The myogenic differentiation process of the bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells regulated by changing lncRNA-HZ5, enlightenment is provided for long non-coding RNA research of muscle development differentiation, and a new idea and reference are provided for clinical research, diagnosis and treatment of muscle development differentiation and damage repair.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
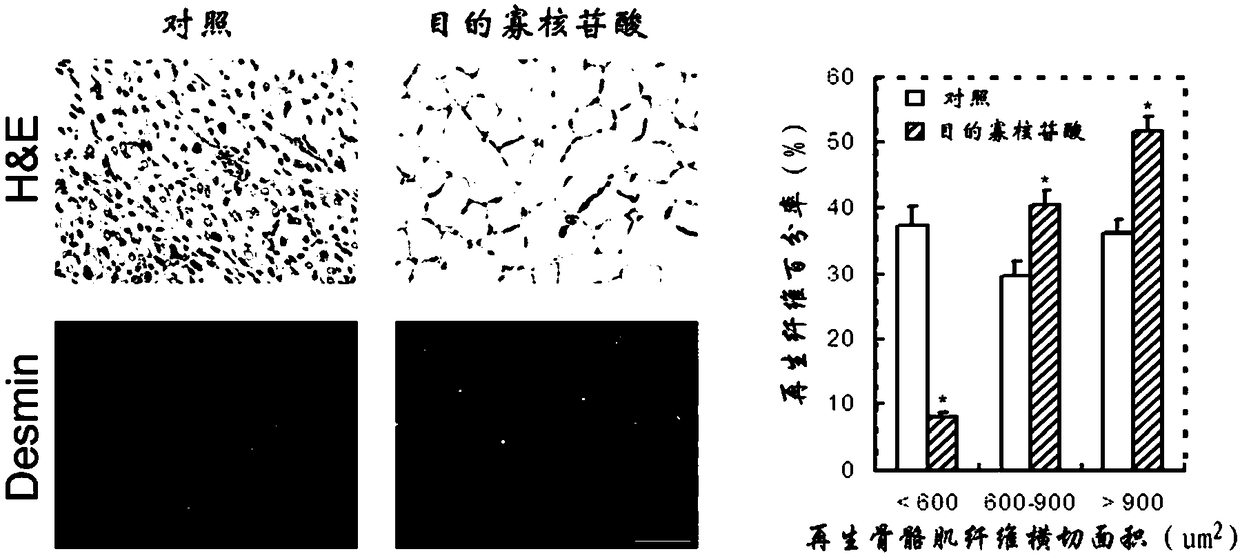
Oligonucleotide for promoting repair of skeletal muscle injury, medicine and application thereof
InactiveCN108728437APromote recoveryFast regenerationOrganic active ingredientsMuscular disorderFiberCvd risk
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine and particularly relates to oligonucleotide for promoting repair of skeletal muscle injury and an application method thereof. The invention firstly discloses oligonucleotide which is screened from transcripts of human-derived growth imprinted gene H19 and has a function of obviously promoting myogenic differentiation of skeletal-muscle myoblast. The oligonucleotide is characterized by being shown in sequences of SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2. The oligonucleotide and the application method have the advantages of simple operation, no risk, promotion for fast regeneration of new muscle fiber after skeletal muscle injury and good function restoration. Therefore, the oligonucleotide and the application method have good application prospect in genetherapy of skeletal muscle injury caused by acute contusion, crush injury, explosion injury or chemical substances.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
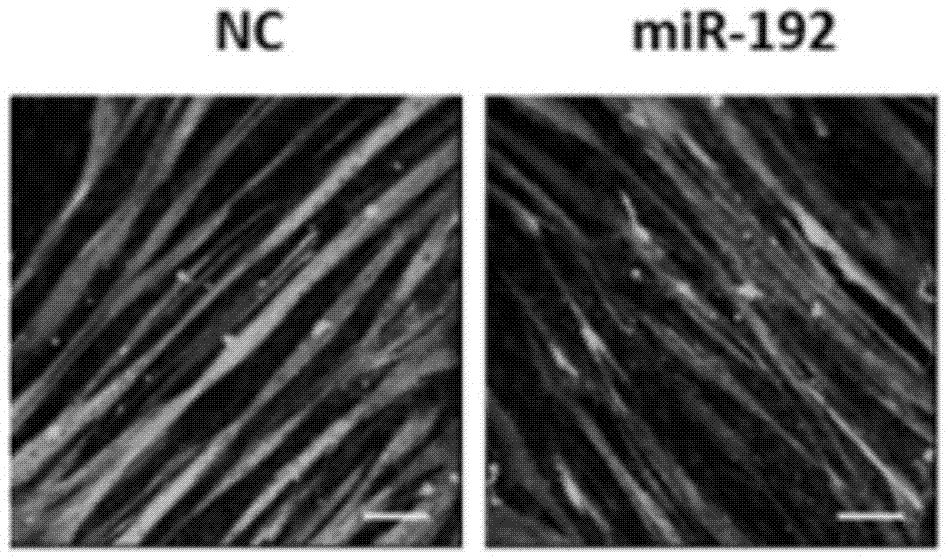
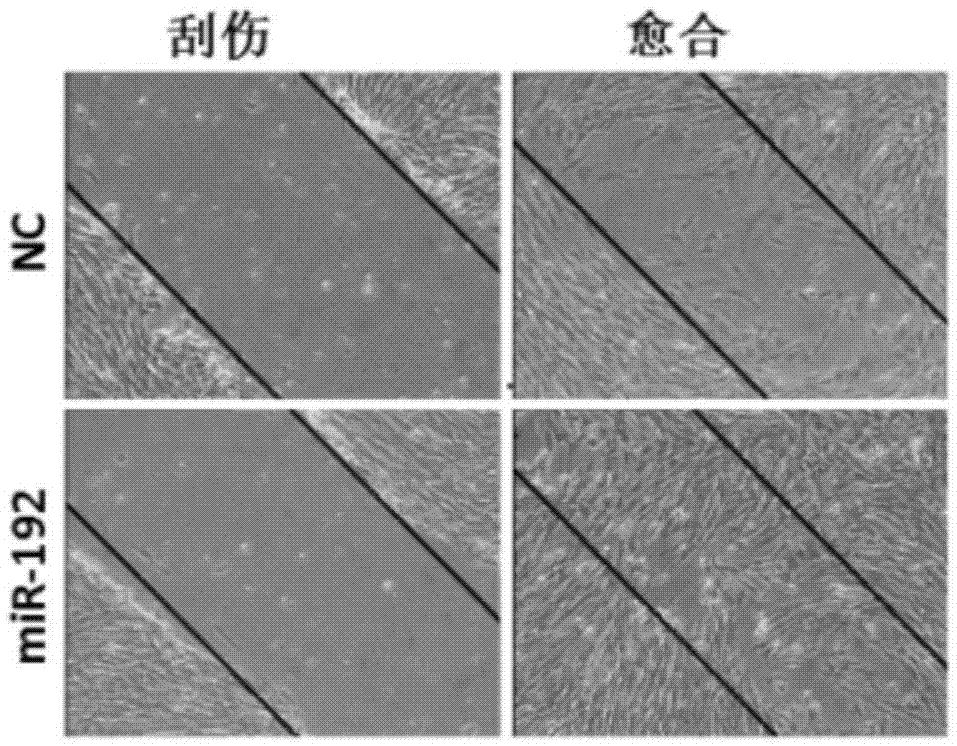
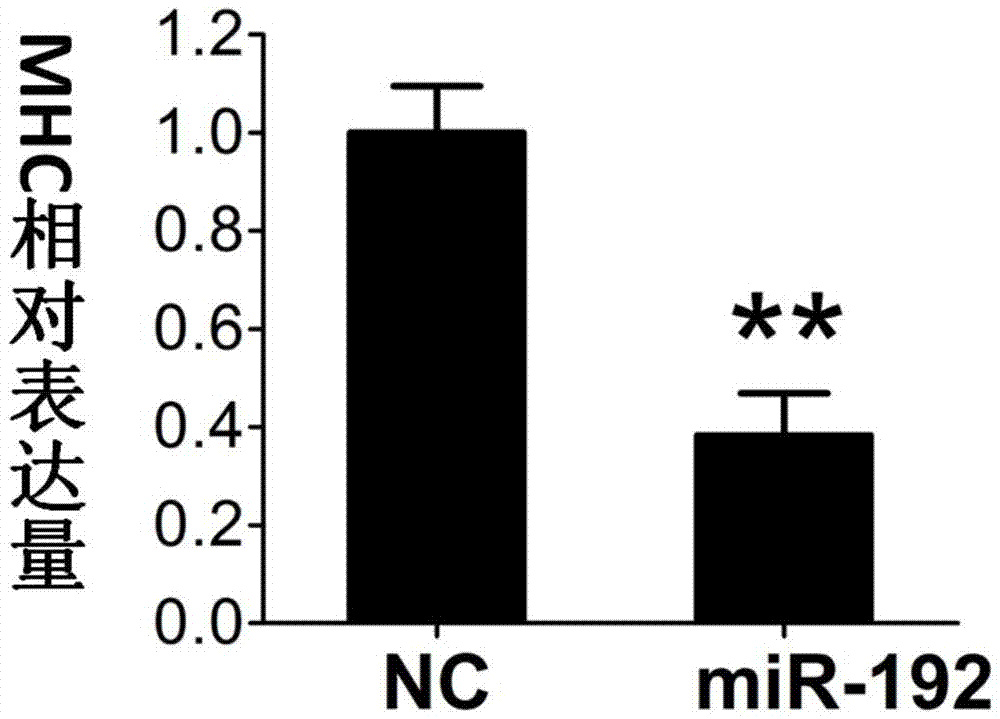
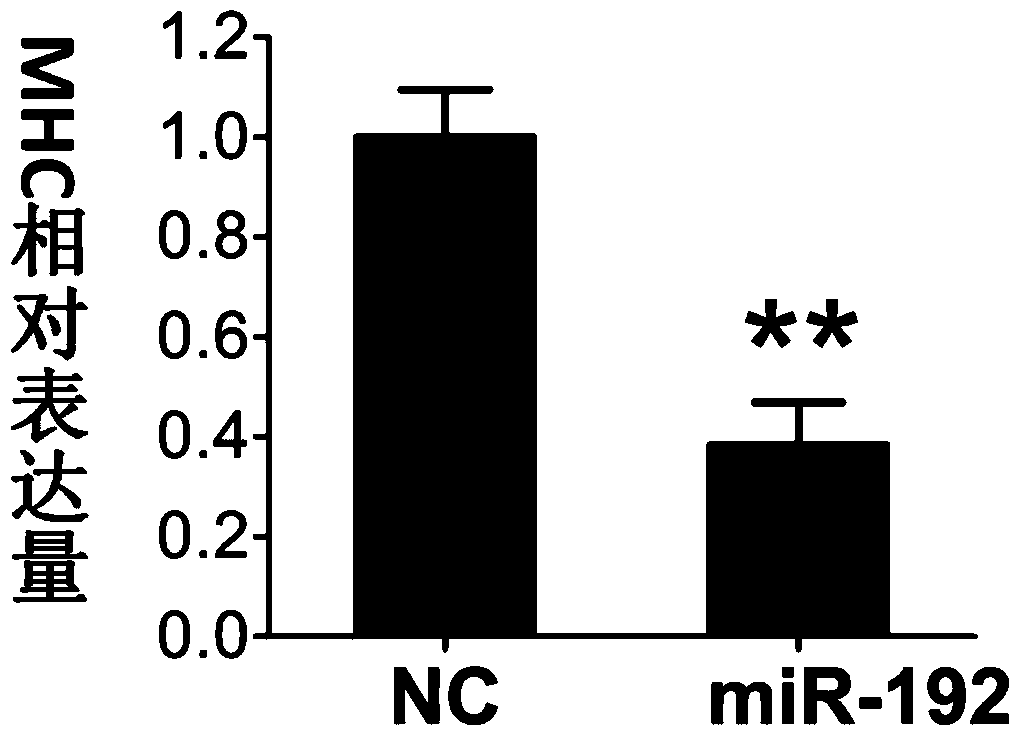
Application of miR-192 in regulation and control of proliferation and differentiation of sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells
ActiveCN105441448AIncrease meat productionImprove qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSkeletal Muscle Satellite CellsNucleotide sequencing
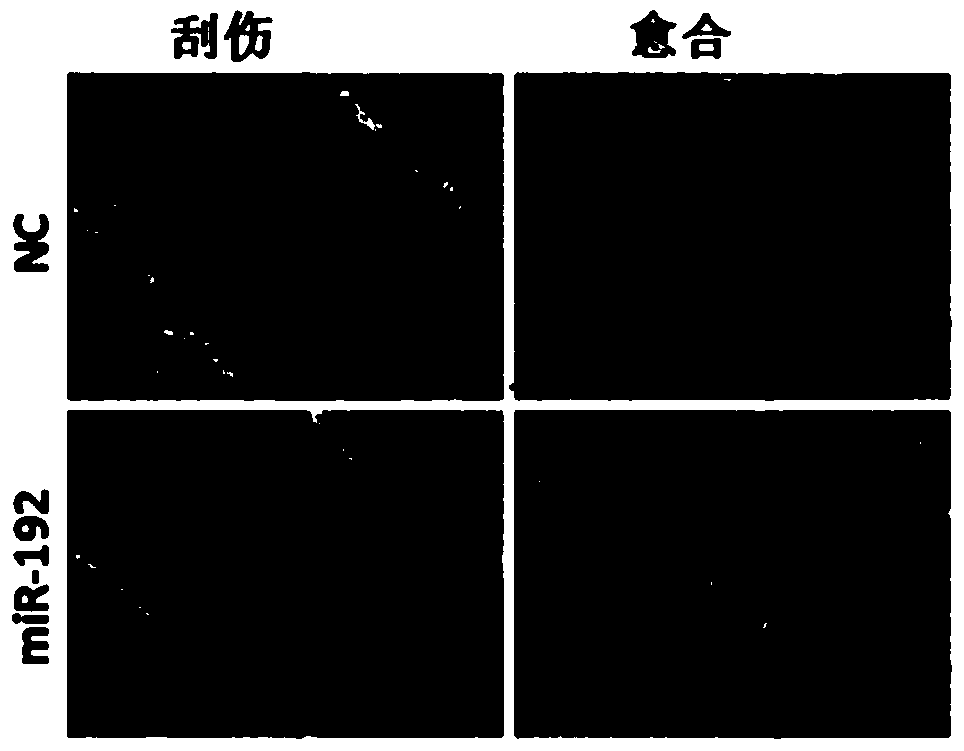
The invention discloses an application of non-coding small RNA (ribonucleic acid) miR-192 in inhibition of myogenic differentiation of sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells and promotion of proliferation of the sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells. Analogues of the non-coding small RNA miR-192 are transfected to the sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells to result in overexpression of miR-192 in the cells, the sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells with miR-192 overexpression are compared with cells with control nucleotide sequence overexpression, and the differentiation of the sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells is inhibited while the proliferation capacity is improved. The invention further provides an application of the miR-192 in inhibition of RB1 protein level expression in the sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells. According to the invention, functions of the miR-192 for negatively regulating and controlling the myogenic differentiation of the sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells and promoting the proliferation of the sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells are discovered for the first time.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Over-expression vector for muscle specific expression of pig IGF1 gene
InactiveCN102978202AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationAlpha-ActinWild type
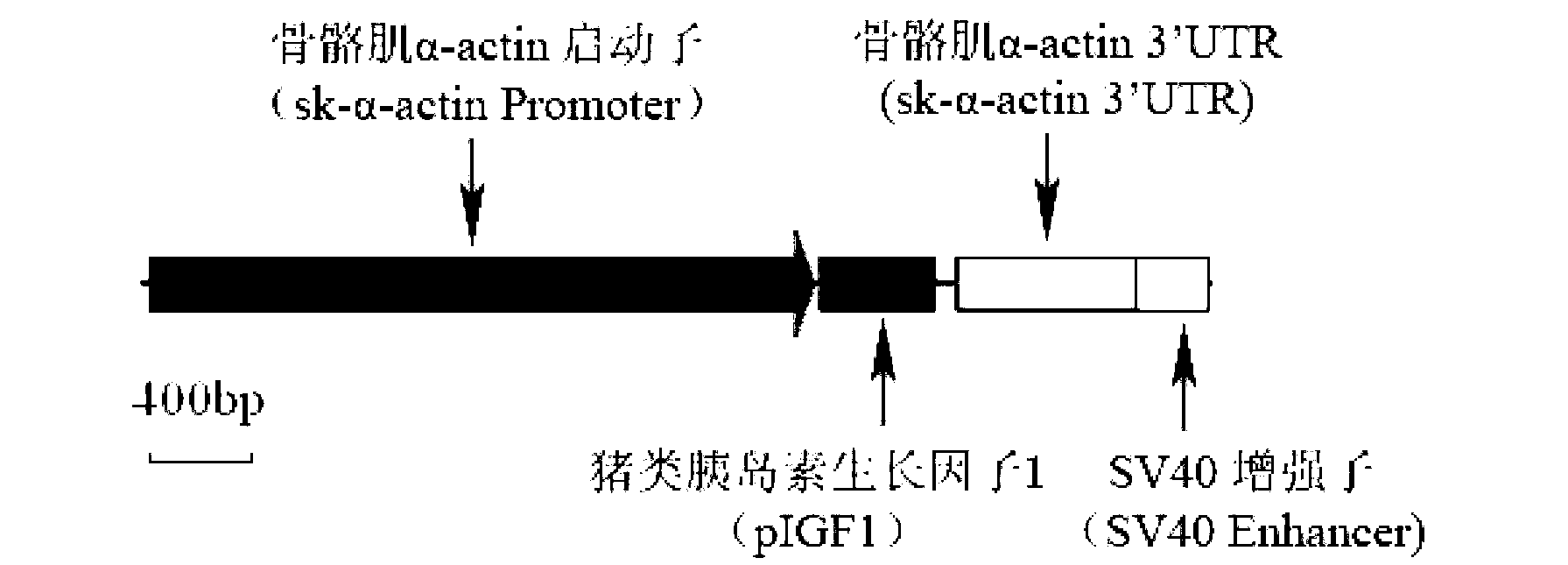
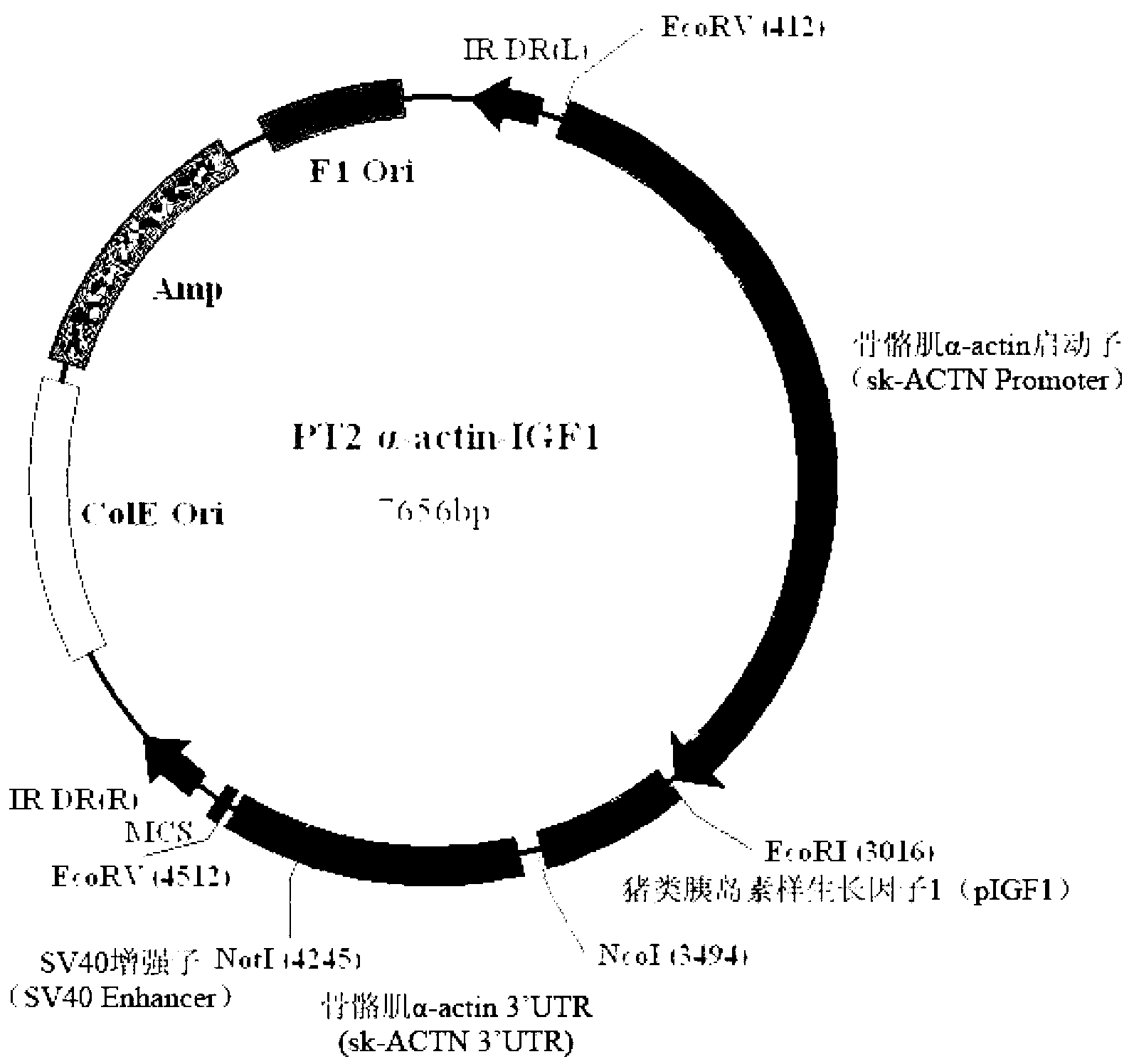
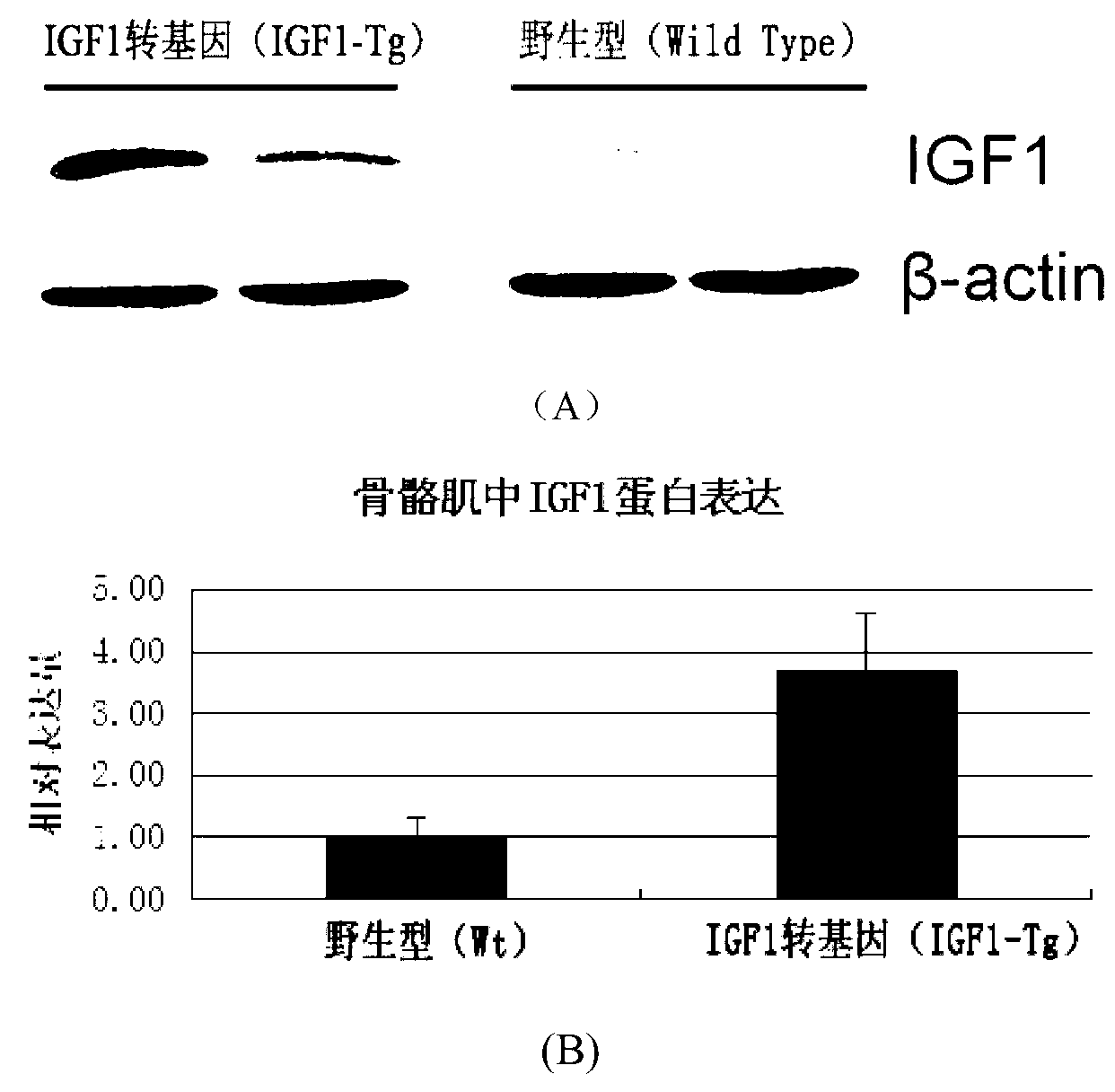
The invention provides a secure expression vector for specific over-expression of pig endogenous gene IGF1 (C1 : Ea) in pig skeletal muscle. The vector comprises an expression cassette composed of the pig endogenous sequence sk-alpha-actinPromoter / IGF1 (C1 : Ea) / sk-alpha-actin3'UTR / SV40 enhancer in series. The expression vector verifies on a cell scale that the skeletal muscle specific sk-alpha-actin promoter can be expressed efficiently in myoblasts, and expressed at lower level in PET cells having myogenic differentiation potential, but not expressed in other type cells. By using the constructed vector for preparing transgenic mice, the detected mRNA expression level and protein expression level of the IGF1 gene in the skeletal muscle of the transgenic mice via quantification PCR and WesterBlot are 15 times and 3.5 times that of the wild mice respectively; and the IGF1 gene can be only expressed in the skeletal muscle efficiently.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Pax-encoding vector and use thereof
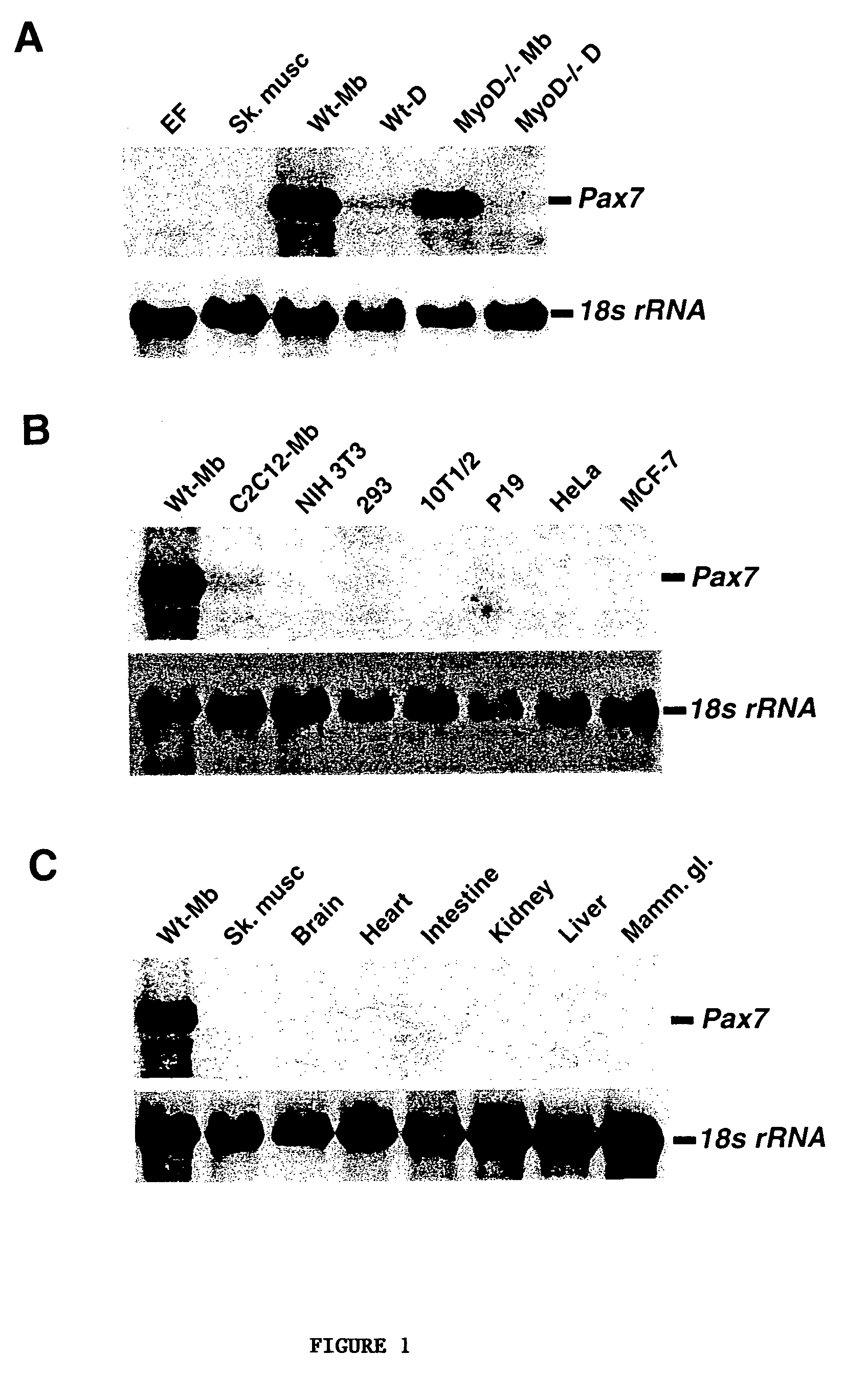
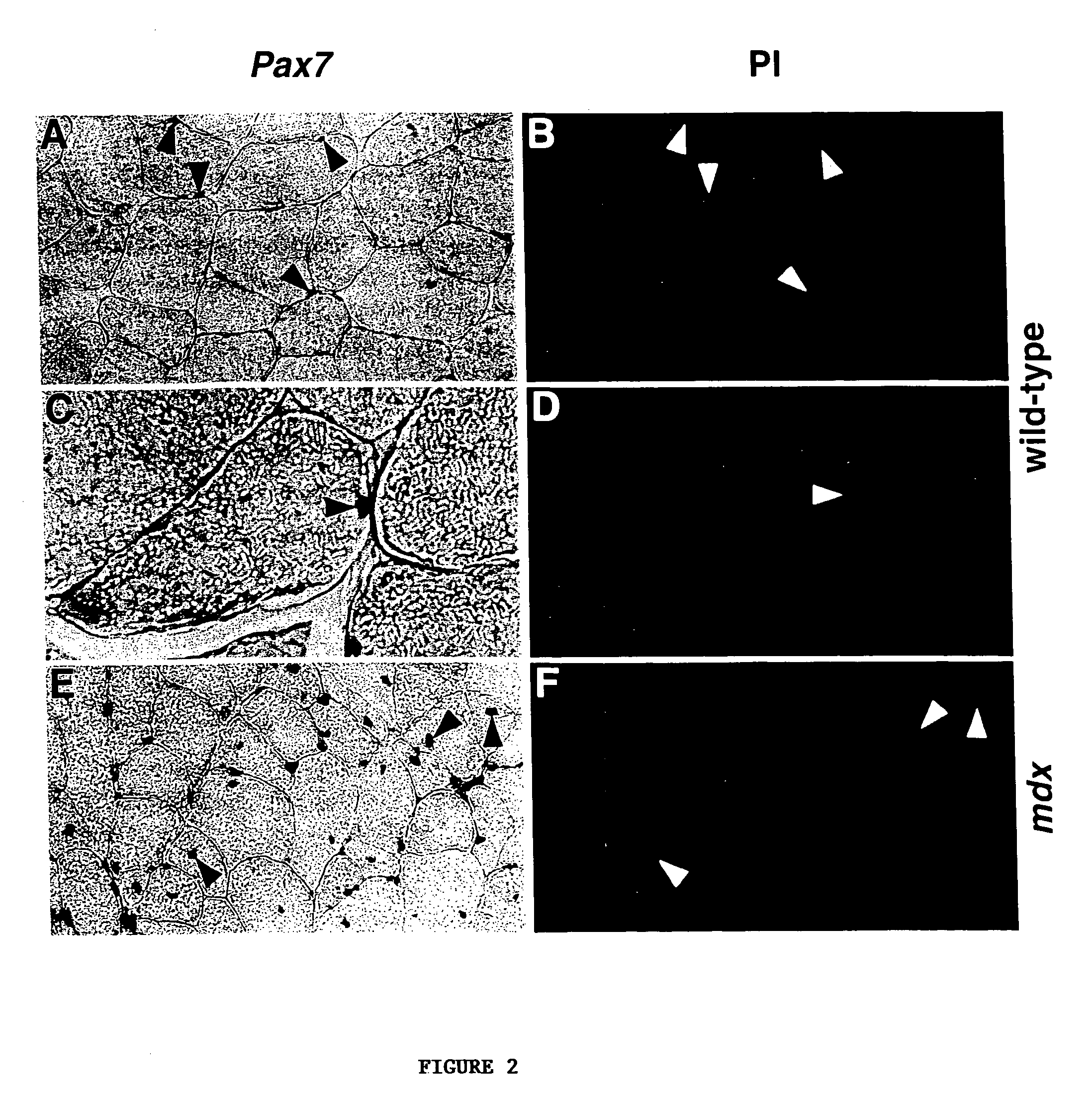
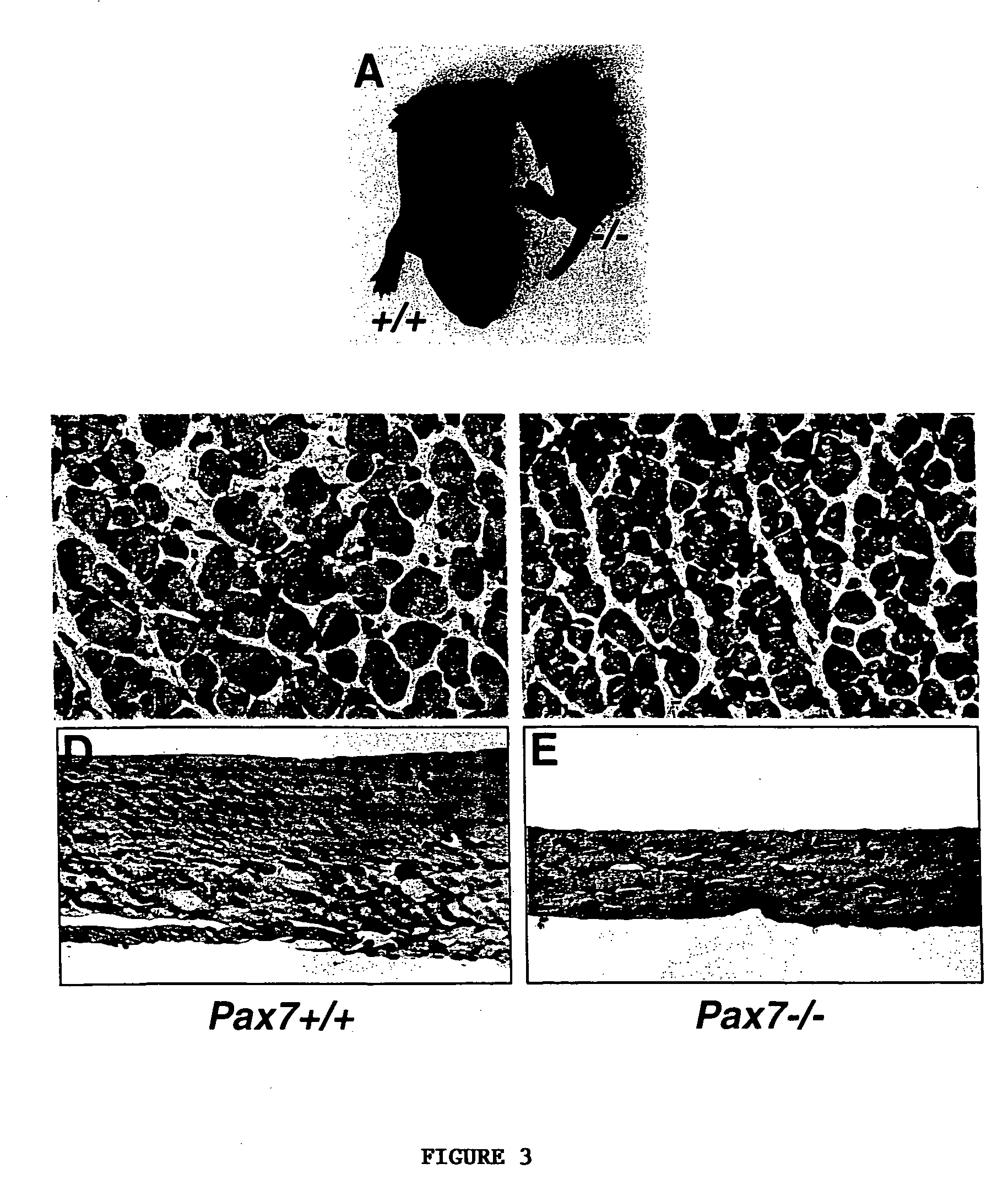
The present invention provides cells transformed with a nucleotide sequence encoding Pax7, Pax3 or both. The present invention also pertains to Pax-encoding vector that comprises a sequence encoding Pax7, Pax3 or an active variant or fragment thereof, which can be used to induce myogenic differentiation of stem cells. The present invention further pertains to methods of preparing the Pax-encoding vector. Also provided is a method of inducing myogenic differentiation in stem cells and treating a subject with the cells.
Owner:OTTAVA HEALTH RES INST (CA)
Culture method for improving oxidative metabolic capability of chicken skeletal muscle cells
The invention discloses a culture method for improving oxidative metabolic capability of chicken skeletal muscle cells, belonging to the technical field of biology. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: respectively inoculating separated and purified chicken skeletal muscle sarcoblasts and muscle-derived fibroblasts into an upper chamber and a lower chamber of a Transwell culture dish, wherein the chicken skeletal muscle sarcoblasts and the muscle-derived fibroblasts are separated by a PET membrane having a pore size of 1 mu m but share a myogenic differentiation culture medium with added H2O2; and performing myogenic differentiation induced culture for 7-10 days to obtain myotubes having an independent retraction capability, and performing low-temperature impact stimulation once every 8-12 hours in the culture period. According to the method provided by the invention, the mitochondrion content and transmembrane potential of the chicken skeletal muscle cells as well as the activity of aerobic metabolic enzymes can be obviously improved; and meanwhile, the activity of ATPase can be reduced. The method has the characteristics of short culture period and stable effect, and lays a foundation for researching a chicken skeletal muscle energy metabolism law, a fiber type formation mechanism and the like, thus having favorable research and application value.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Ex vivo expansion of myogenic stem cells by notch activation
InactiveUS20150166961A1Promoting muscle tissue regenerationEasy to transplantBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorHuman cell
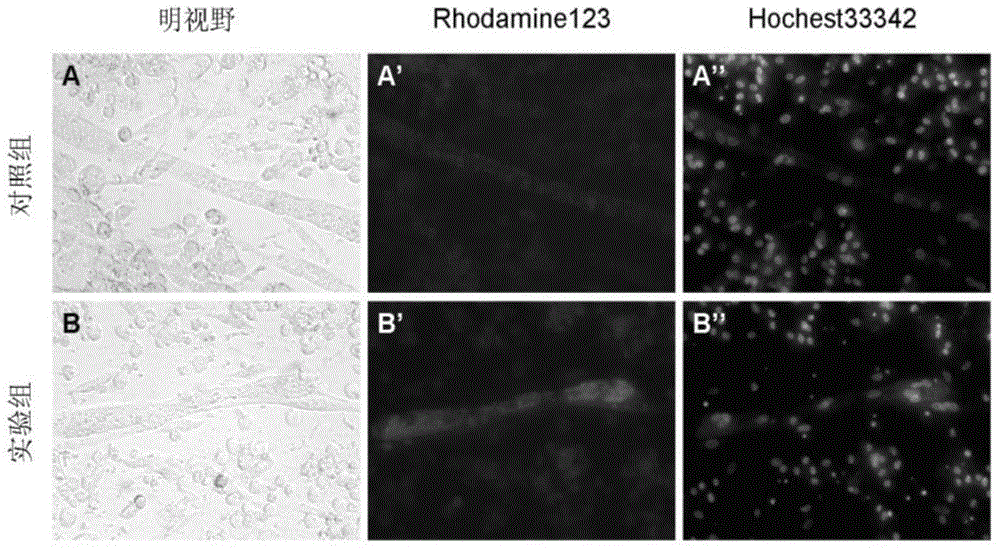
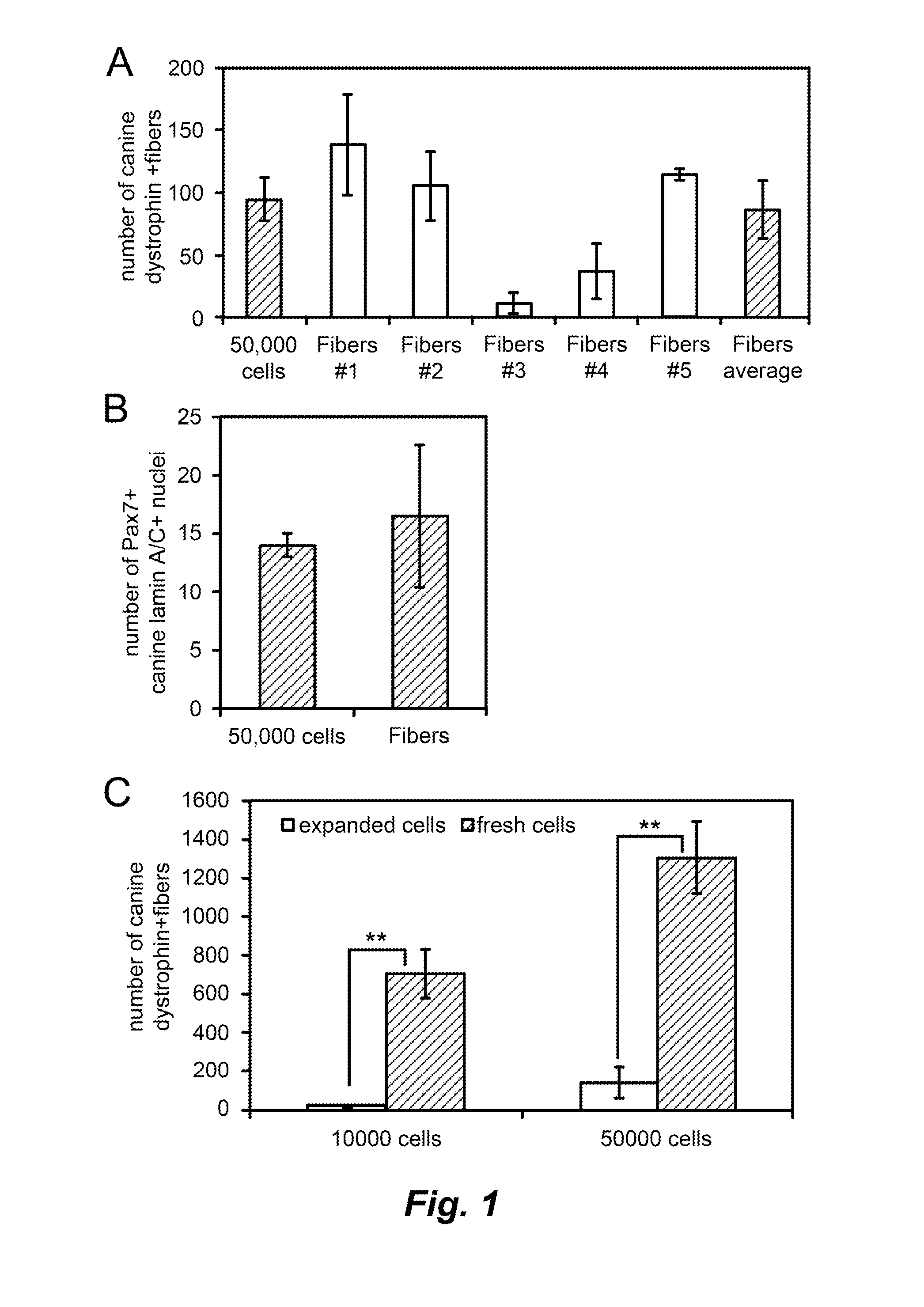
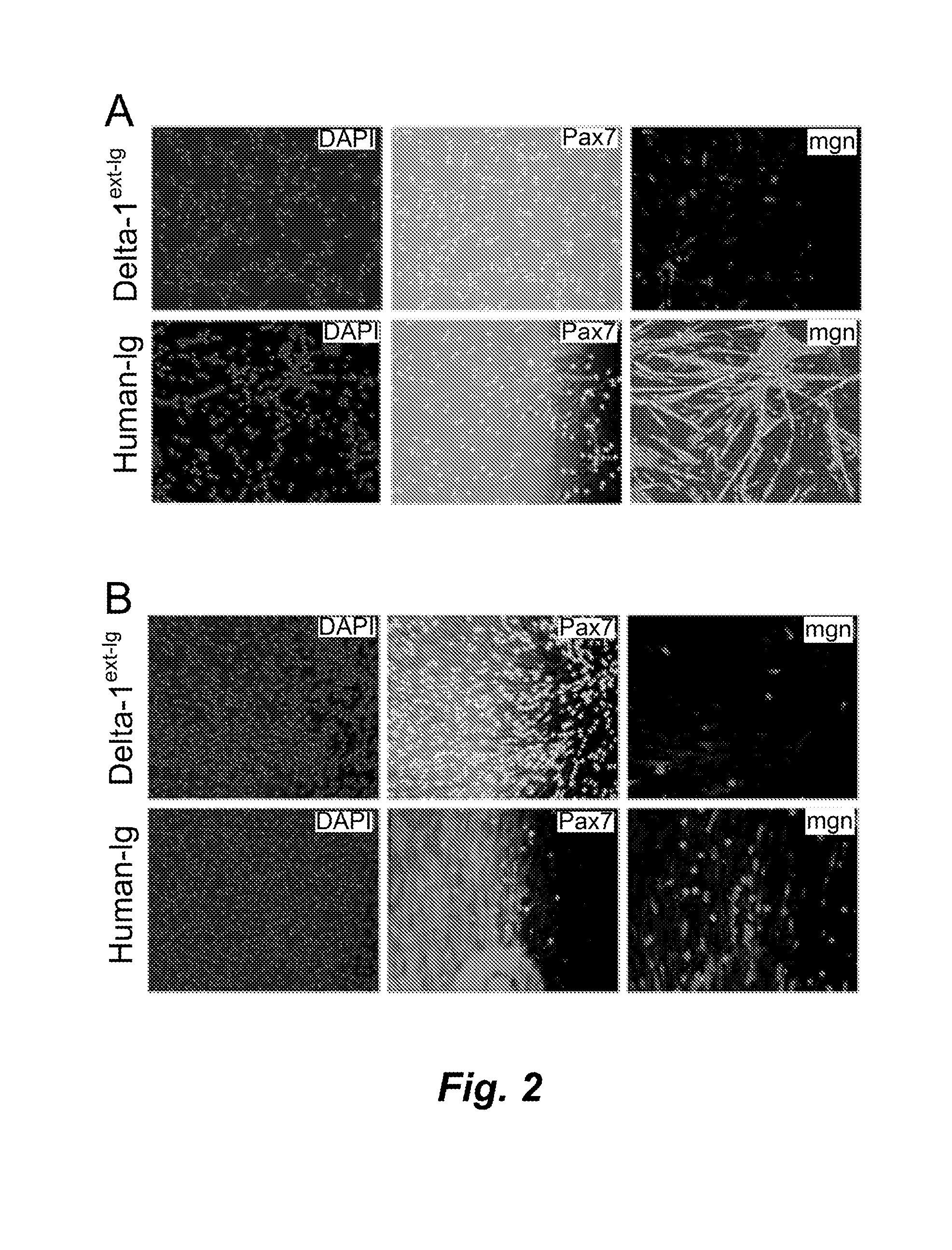
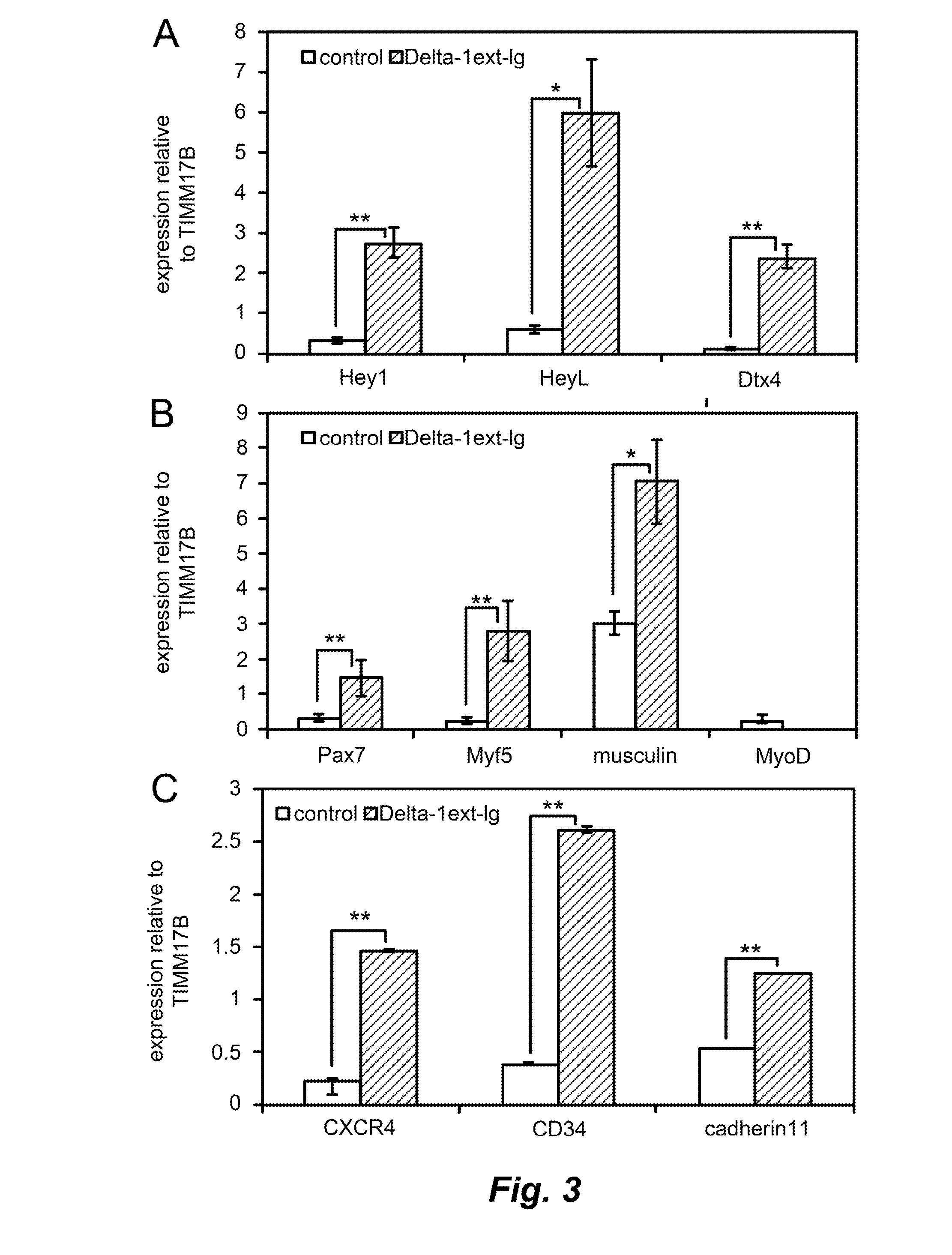
Activating Notch signaling in cultured canine muscle derived cells inhibited myogenic differentiation, and increased the number of myogenic progenitor cells that were similar to quiescent or newly activated satellite cells. Importantly, cells expanded in the presence of Notch activation maintained engraftment potential, indicating the potential for therapeutic benefit. Activation of Notch signaling to inhibit myogenic differentiation in cultured human muscle-derived cells is also contemplated, for maintaining engraftment potential using such human cells in transplantation.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Pax-encoding vector and use thereof
The present invention provides cells transformed with a nucleotide sequence encoding Pax7, Pax3 or both. The present invention also pertains to Pax-encoding vector that comprises a sequence encoding Pax7, Pax3 or an active variant or fragment thereof, which can be used to induce myogenic differentiation of stem cells. The present invention further pertains to methods of preparing the Pax-encoding vector. Also provided is a method of inducing myogenic differentiation in stem cells and treating a subject with the cells.
Owner:OTTAVA HEALTH RES INST (CA)
Primer for nile tilapia germ plasm purity identification and PCR identification method
InactiveCN105385759AStrong specificityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAntigenNile tilapia
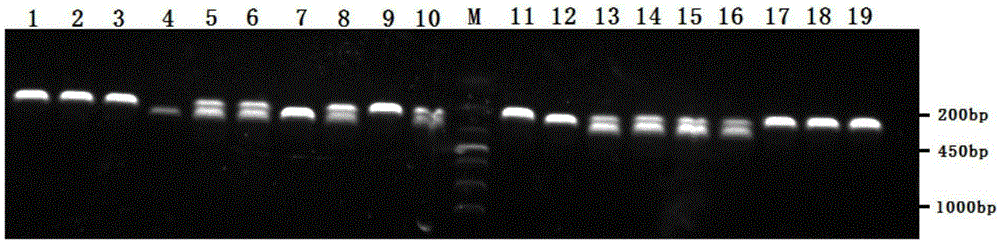
The invention discloses a primer for nile tilapia germ plasm purity identification and a PCR identification method. The primer is capable of amplifying an MyoD (Myogenic Differentiation Antigen) gene of nile tilapia, so as to generate a strip of 229bp specific amplification fragment. (1), the primer provided by the invention is used to amplify the genomic DNA of the nile tilapia, so as to generate the strip of 229bp specific amplification fragment, and a strip of 264bp band of blue tilapia, wherein two strips of hybrid tilapia are respectively 229bp and 264bp bands, which can be obviously distinguished, and thus the germ plasm purity identification of the nile tilapia can be simply and accurately carried out; (2), the specificity of the primer provided by the invention is high, and other fragments except the target fragment cannot be amplified; (3), the invention discloses the PCR identification method using the primer, and the method is fast and convenient in operation and accurate in result, so that the defect of unstable result brought about by adopting a conventional morphological method to identify the nile tilapia of different species is avoided.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for promoting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells
ActiveCN110747230AGood yieldImprove qualityGenetically modified cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSkeletal Muscle Satellite CellsBiochemistry
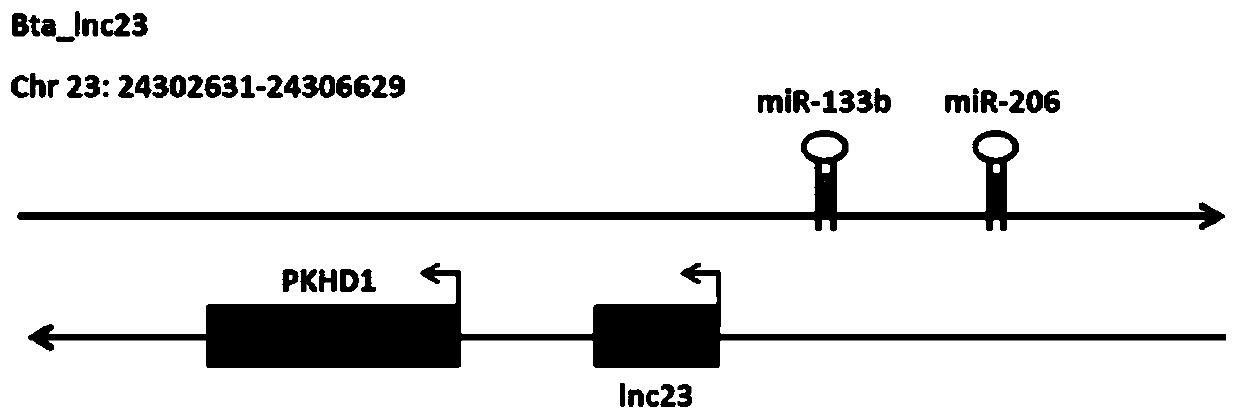
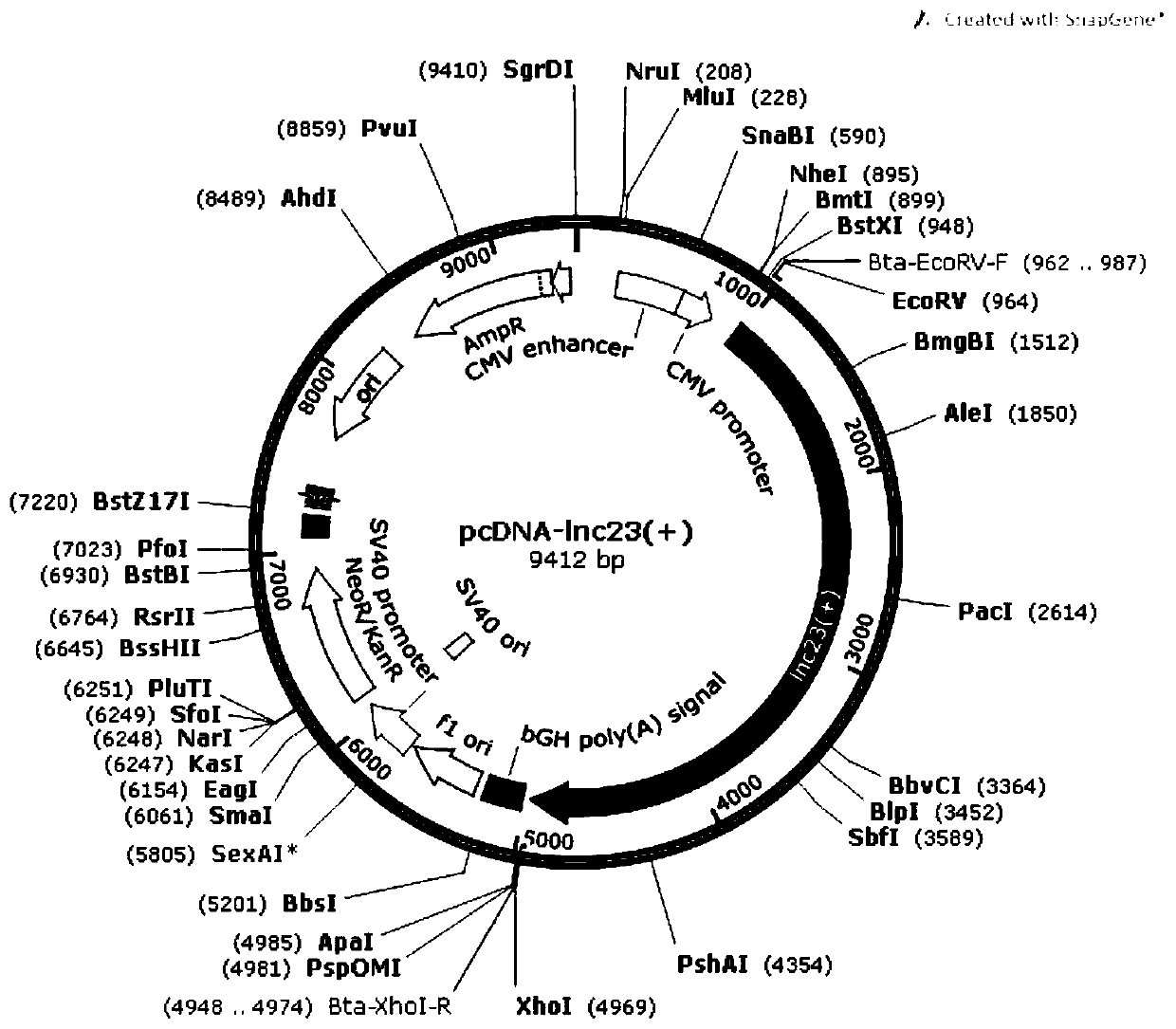
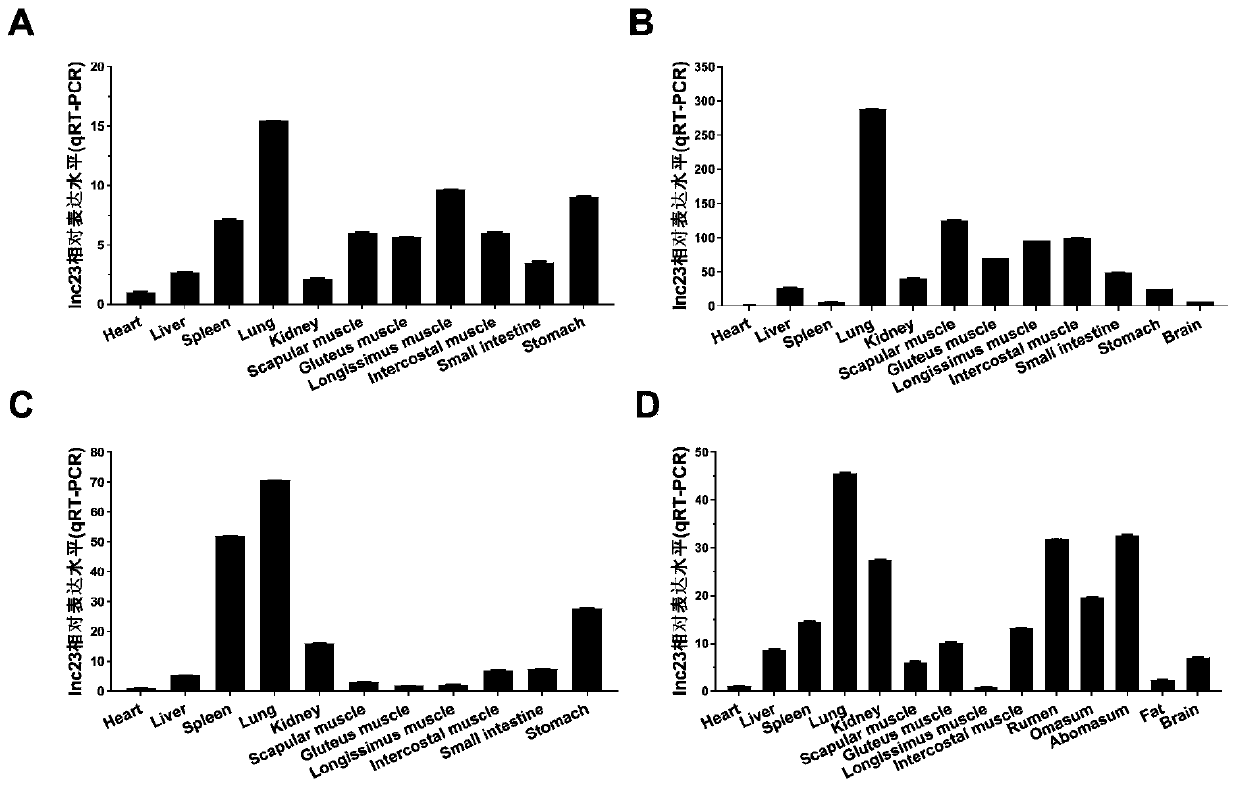
The invention relates to a method for promoting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells. The method is characterized in that according to the method, the myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells is promoted by increasing the expression of lncRNA-23, wherein the genome base sequence of the lncRNA-23 is SEQ NO.1. The method can provide inspirationfor researching long non-coding RNA of muscle development differentiation, can lay a good foundation for further researching the action mechanism of key lncRNA in the muscle development process, andprovides inspiration for exploring the muscle growth and development mechanism and improving the yield and quality of beef.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
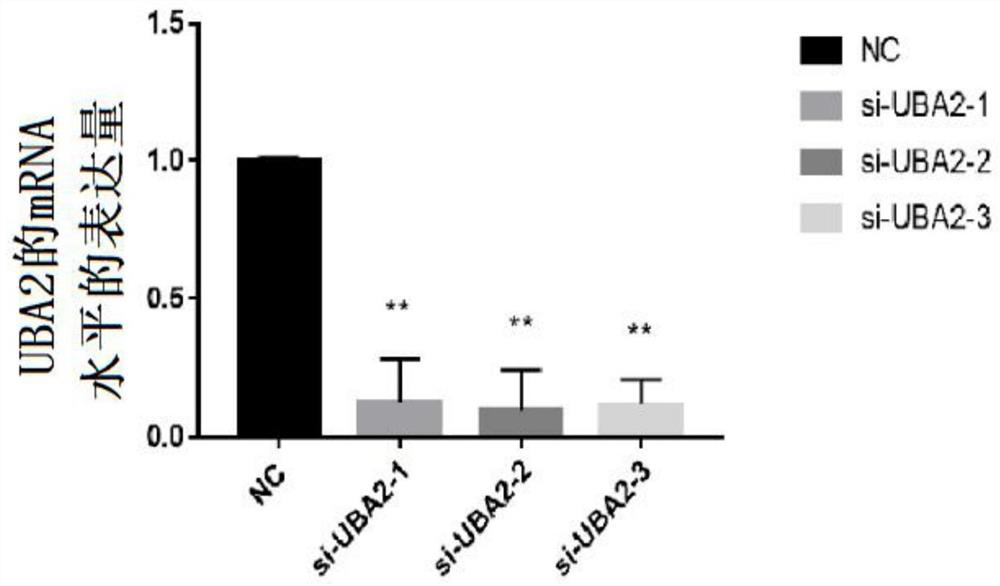
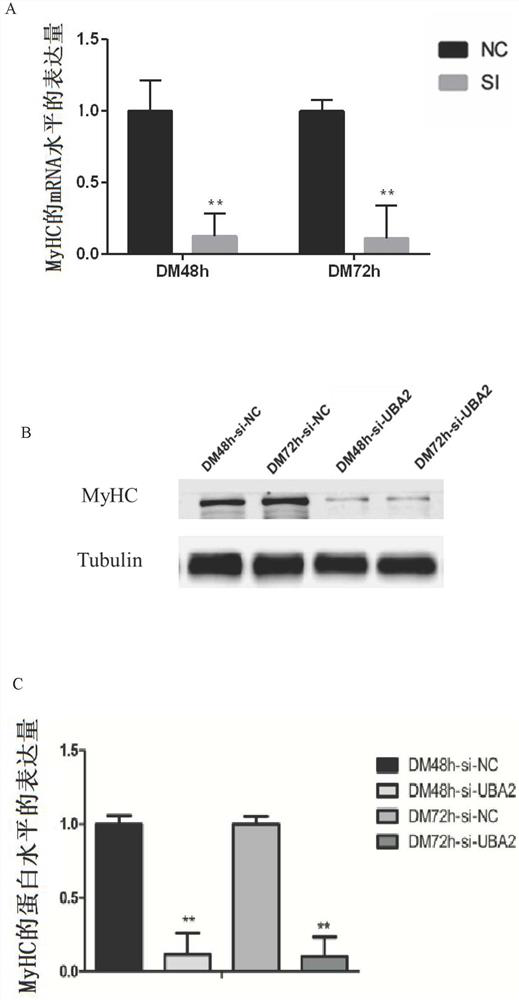
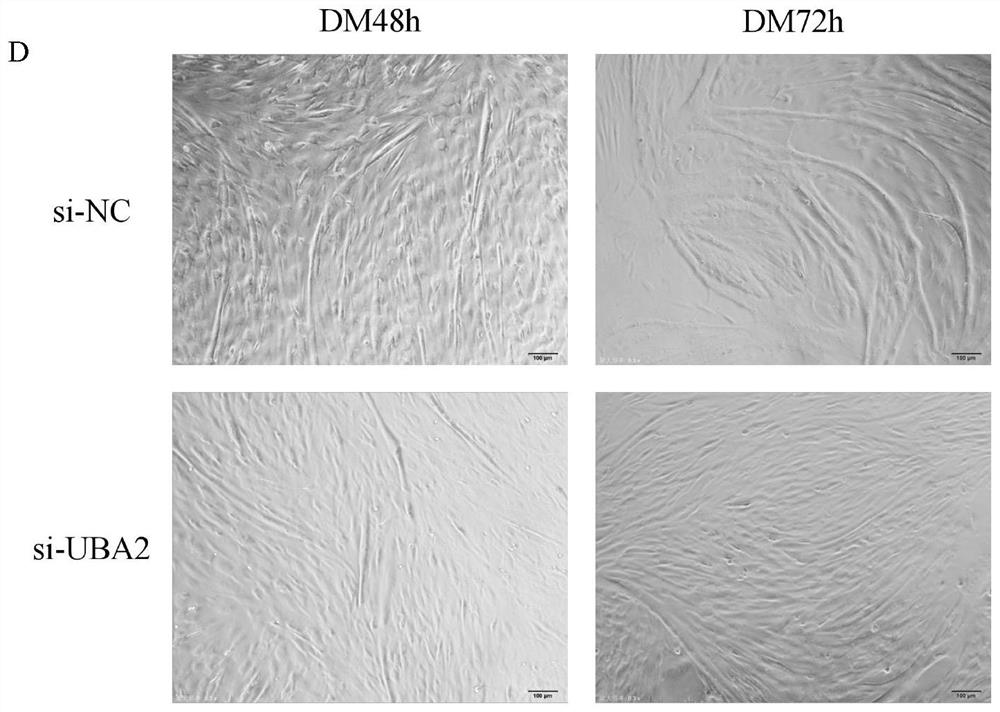
Method for inhibiting proliferation and myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by interfering UBA2 expression
ActiveCN113502269ARegulates the process of development and differentiationPrevent proliferationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsEnzymesSkeletal Muscle Satellite CellsMedicine
The invention discloses a method for inhibiting proliferation and myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by interfering UBA2 expression, the method realizes inhibition of proliferation and myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by interfering UBA2 expression, and the genome base sequence of UBA2 is SEQ NO.1. According to the method, the proliferation and myogenic differentiation process of the bovine muscle satellite cells is regulated and controlled by changing UBA2 expression, enlightenment can be provided for research of ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme for muscle development and differentiation, and a new thought and reference are provided for clinical research and diagnosis and treatment of muscle development and differentiation and damage repair.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Myogenic differentiation of stem cells and uses thereof
Disclosed are methods of differentiating stem cells into muscle cells by growing the cells in a myogenic culture medium. The differentiated cells can be used as a source of cells for transplantation in a patient in need thereof.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Method for low-cost in-vitro culture of porcine muscle stem cells
ActiveCN112458049ASupports in vitro growthEasy to grow on a large scaleCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsIn vitro growthMuscle stem cell
The invention discloses a method for low-cost in-vitro culture of porcine muscle stem cells, and belongs to the technical field of stem cell and animal cell culture. The invention discloses a culturemedium and the culture method for culturing the muscle stem cells at low cost, the muscle stem cells can keep in-vitro growth and myogenic differentiation capacity through the culture medium and the culture method, and the cost of the culture medium is greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
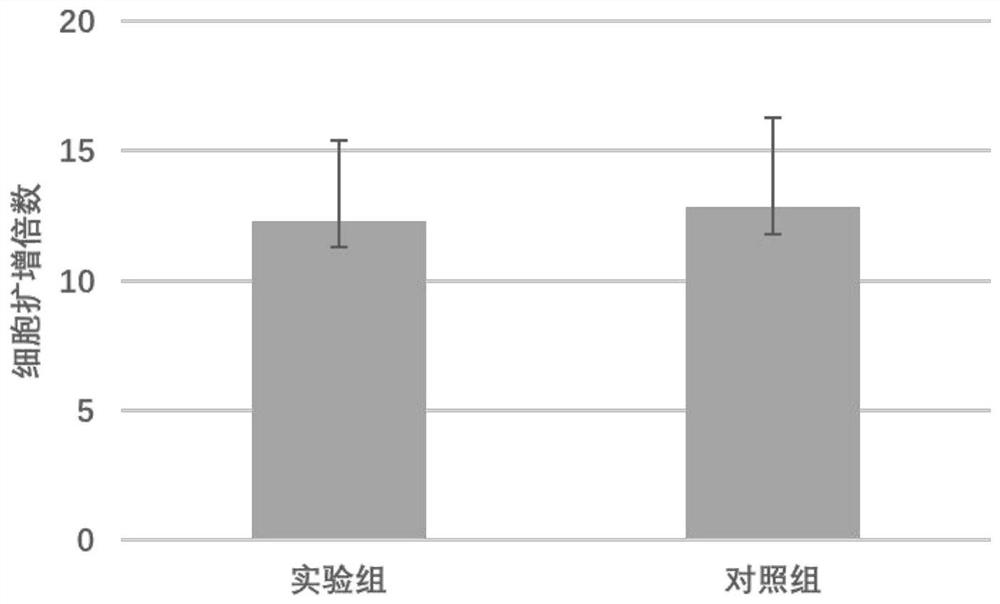
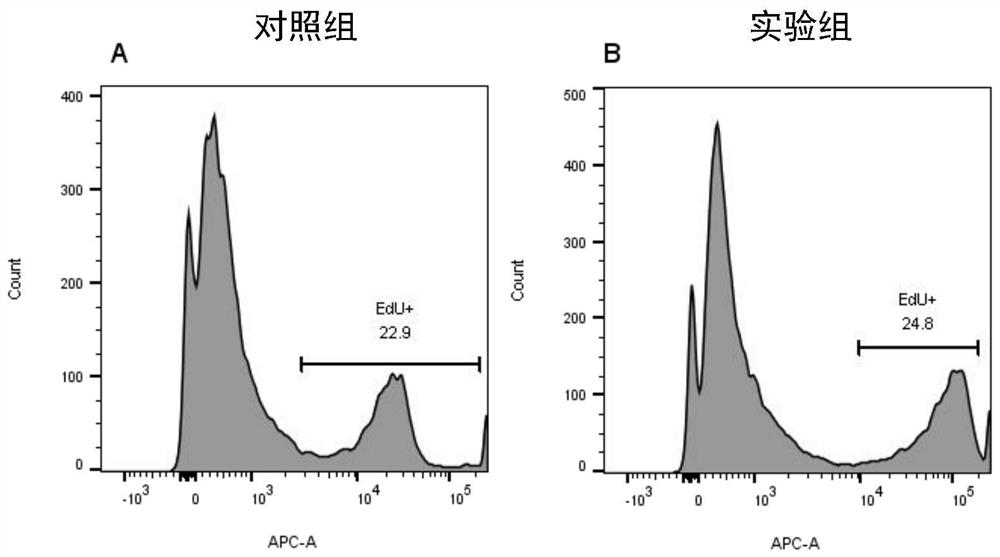
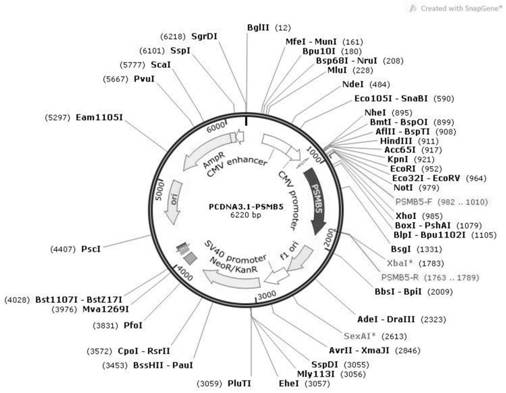
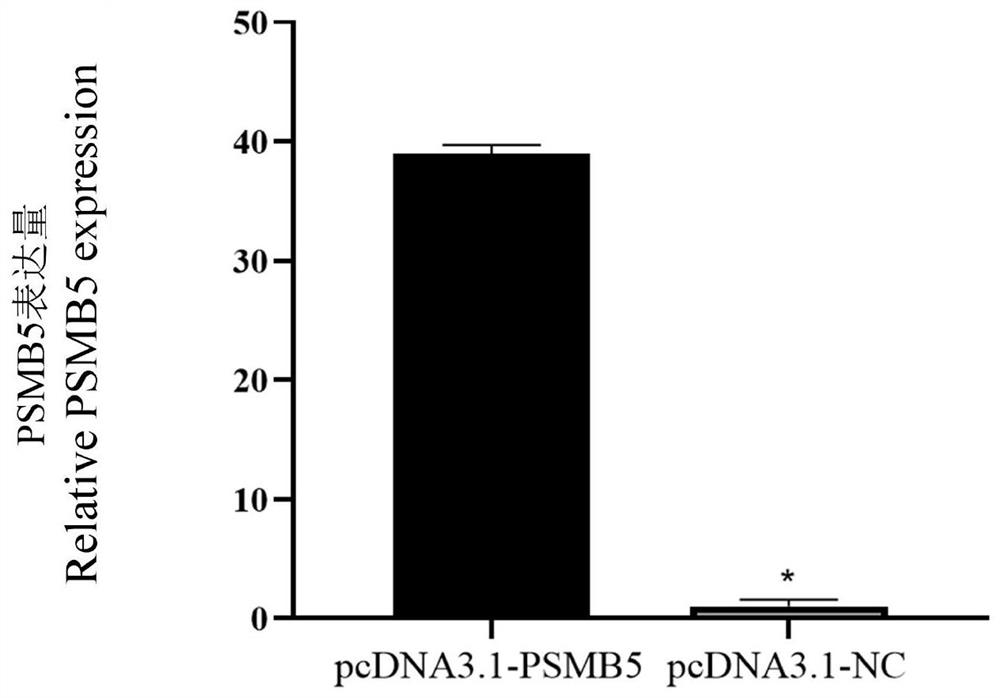
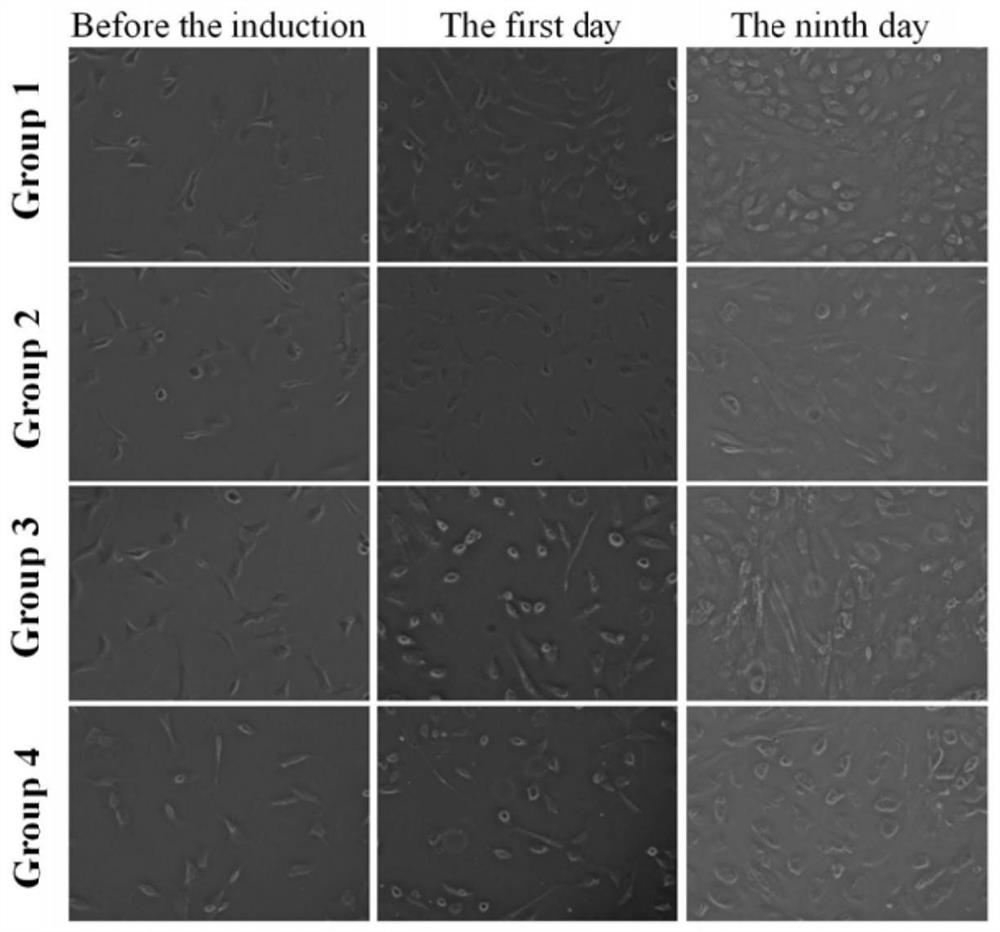
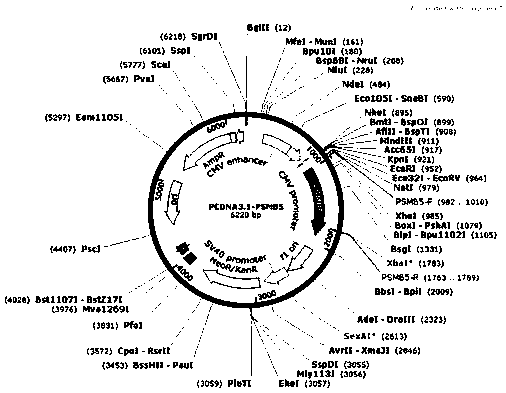
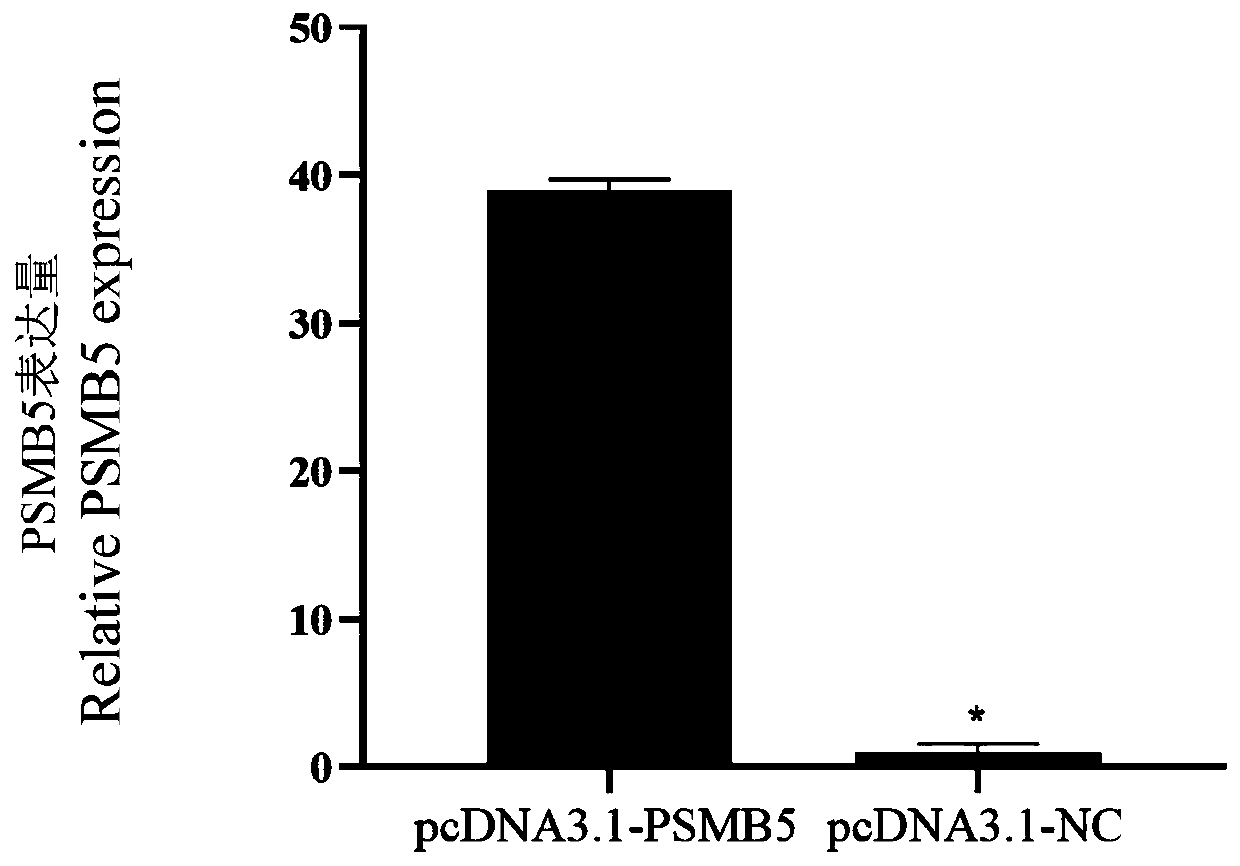
A method for promoting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by overexpressing psmb5
ActiveCN110964746BRegulates the process of development and differentiationPromote myogenic differentiationGenetically modified cellsNucleic acid vectorLipofectamineSkeletal Muscle Satellite Cells
The present invention relates to a method for promoting the myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by overexpressing PSMB5, the steps are as follows: (1) obtaining the target sequence comprising the bovine PSMB5 gene sequence; (2) constructing the expression vector pcDNA3.1-PSMB5; (3) pcDNA3.1 Transfect bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells with ‑PSMB5: use the obtained expression vector pcDNA3.1‑PSMB5, and use liposome transfection reagent to transfect bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells, so that bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells overexpress PSMB5, and utilize the effect of PSMB5 , to improve the in vitro differentiation capacity of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells. The method of the present invention uses PSMB5 to regulate the proliferation and myogenic differentiation of bovine muscle satellite cells, which can provide enlightenment for the study of the ubiquitination process of muscle development and differentiation, and provide new insights for clinical research and diagnosis and treatment of muscle development and differentiation and injury repair. ideas and references.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
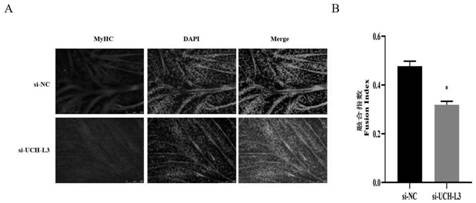
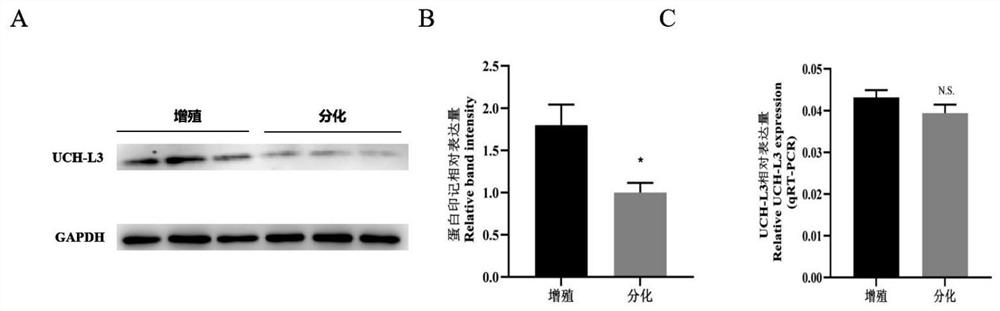
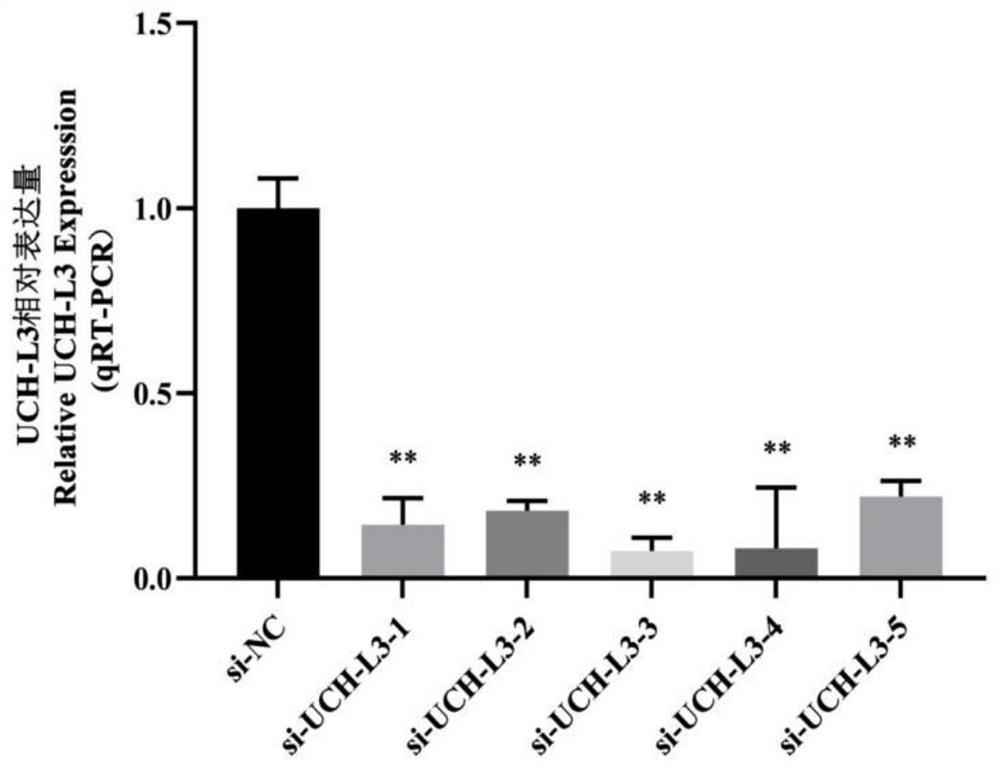
A method for inhibiting the myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by interfering with uch-l3 expression
ActiveCN110951783BRegulates the process of development and differentiationInhibition of myogenic differentiation processActivity regulationVector-based foreign material introductionSkeletal Muscle Satellite CellsDeubiquitinating enzyme
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting the myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by interfering with the expression of UCH-L3, wherein the method is to suppress the myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by interfering with the expression of UCH-L3, wherein the The genome base sequence of UCH‑L3 is: SEQ NO.1. The method of the present invention regulates the myogenic differentiation process of bovine muscle satellite cells by changing the expression of UCH-L3, which can provide enlightenment for the research on deubiquitinating enzymes of muscle development and differentiation, and provide clinical research, diagnosis and treatment for muscle development and differentiation and injury repair Provide new ideas and references.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Method for inhibiting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by interfering UCH-L3 expression
ActiveCN110951783ARegulates the process of development and differentiationInhibition of myogenic differentiation processActivity regulationVector-based foreign material introductionSkeletal Muscle Satellite CellsBovine muscle
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by interfering UCH-L3 expression, the myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells is inhibited by interfering UCH-L3 expression, and the genome base sequence of UCH-L3 is SEQ NO.1. The invention also relates to a kit for inhibiting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by interfering UCH-L3 expression. According to the method, the myogenic differentiation process of bovine muscle satellite cells is regulated and controlled by changing UCH-L3 expression, enlightenment can be provided for deubiquitination enzyme research of muscle development and differentiation, and new thought and reference are provided for clinical researchand diagnosis and treatment of muscle development and differentiation and injury repair.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Serum-free myogenic differentiation culture medium containing natural compound and application of serum-free myogenic differentiation culture medium
ActiveCN114752554AMitigate high cost issuesAvoid Pollution HazardsCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsBiotechnologyMyogenic cell
The invention discloses a serum-free myogenic differentiation culture medium containing a natural compound and application, and belongs to the technical field of animal cell culture and cell culture meat. According to the method, the influence of the improved serum-free culture medium on the differentiation state of the muscle-derived cells is represented through apparent observation of the cell differentiation state, muscle specific protein MyHC immunofluorescence staining and analysis of the differentiation rate and the fusion rate by virtue of Image J and other software. In addition, immunoblotting and fluorescent quantitative PCR prove that a serum-free myogenic differential medium added with growth factors, plant-derived natural products and other auxiliary factors can enable the protein synthesis capability of myogenic cells to be equivalent to that of myogenic cells under a 2% horse serum-containing differential medium. The cost of the cell culture meat technology in the differentiation process is greatly reduced, the biological safety of the product is further guaranteed, and technical support is provided for efficient and economical production of high-quality muscle protein in the cell culture meat industry.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
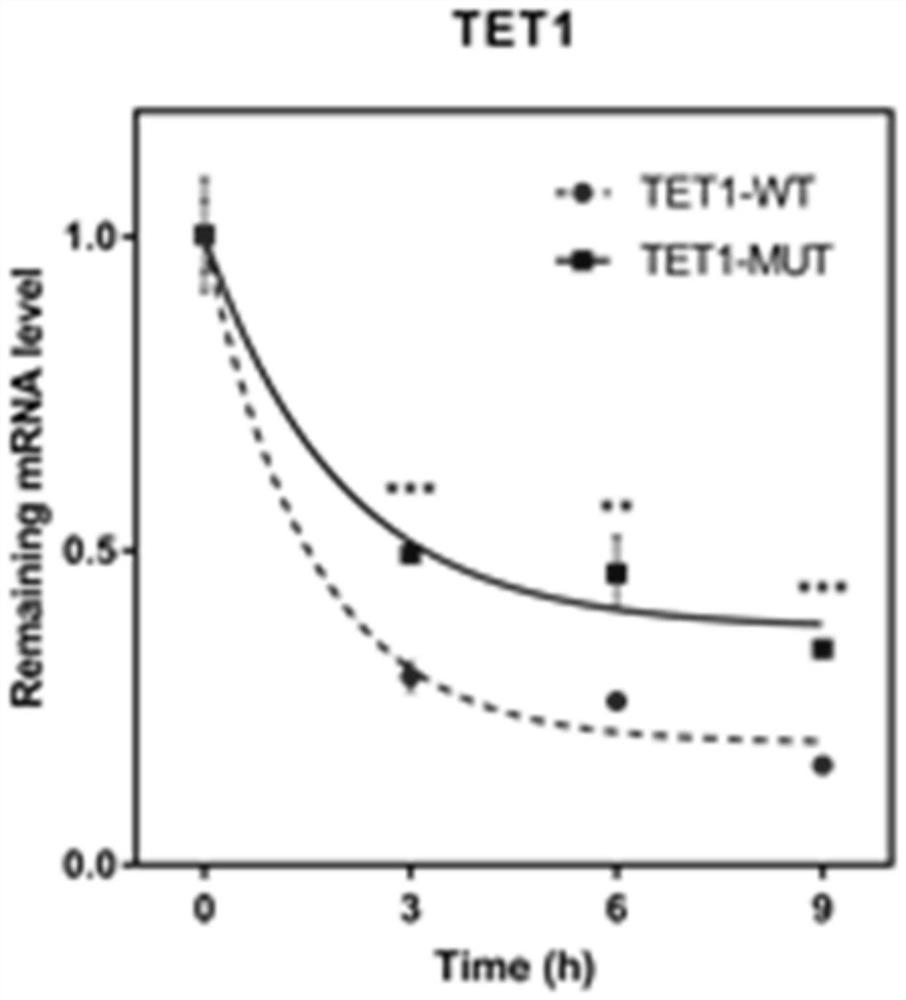
Interaction identification and application of bovine skeletal muscle differentiation related DNA methylase TET1 and m6A methylase METTL3
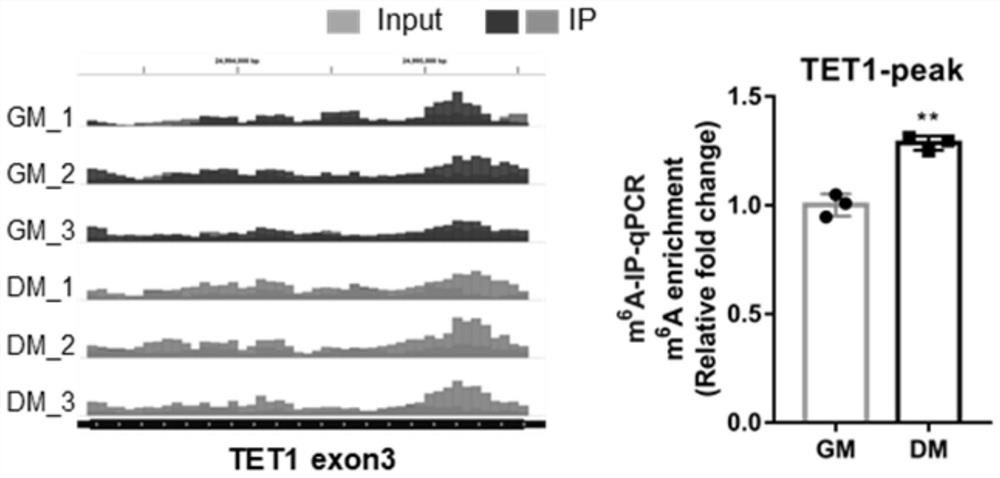
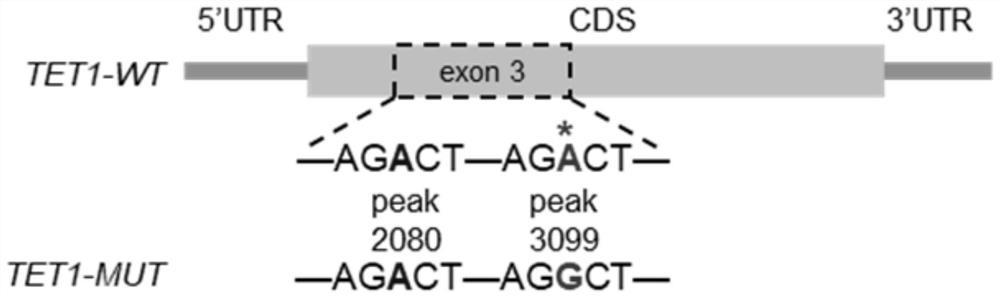
ActiveCN114480670AImpact generationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDNA methylationLuciferase
The invention provides a method for identifying an m6A methylation site on mRNA of DNA demethylase TET1 related to bovine skeletal muscle differentiation, provides a primer sequence and a method for identifying the m6A methylation level of TET1, and identifies the change of the m6A level of TET1 in myogenic differentiation according to m6A-seq sequencing and m6A-IP-qPCR; the m6A methylation level of TET1 is changed through synonymous mutation of the m6A site, and it is proved that m6A methylation of TET1 has the function of influencing skeletal muscle differentiation; the invention provides a method for detecting the regulation and control of TET1 by m6A methylation modification. A dual luciferase report system and an RIP experiment prove that the expression of TET1 is regulated and controlled by METTL3-m6A-YTHDF1; a method for detecting the influence of DNA methylation on m6A methylation modification is provided, and the interaction of DNA methylation and RNA methylation in bovine skeletal muscle differentiation is proved. Reference is provided for functional research of m6A methylation modification regulation and control of muscle growth and development, a new interaction mechanism in skeletal muscle development is identified, and a new molecular marker is provided for directional breeding of beef cattle.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
CD24 positive expression cell in urine as well as preparation method and application of CD24 positive expression cell
ActiveCN114504595AAchieve regenerative repairAchieving Autologous Cell TherapyCell dissociation methodsMuscular disorderSomatic cellBiology
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, in particular to a CD24 positive expression cell in urine and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the application, cells with CD24 positive expression in urine-derived cells are found and screened from urine of a muscle injury patient, and the cells with CD24 positive expression in the urine cells can be subjected to myogenic differentiation under an in-vitro induction condition and are fused with muscle cells to form fused muscular tubules; it is verified that after CD24 positive expression cells in urine cells are transplanted into animal bodies, inflammatory reaction symptoms can be relieved at muscle injury parts, muscle regeneration and repair can be achieved, the CD24 positive expression cells can be used for preparing related medicine for repairing muscle injury treatment, the cells for treatment are derived from patient bodies and have the characteristic of individualized precise treatment, and the CD24 positive expression cells can be used for preparing the related medicine for repairing muscle injury treatment. The autologous cell treatment of the patient can be quickly realized, and the immunological rejection of transplantation is avoided.
Owner:广东明珠生物技术有限公司
A method for promoting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells
ActiveCN107287242BLittle influence on other biological characteristicsRegulates the process of development and differentiationGenetically modified cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSkeletal Muscle Satellite CellsClinical research
The invention relates to a method for promoting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells. According to the method, myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells is promoted by interfering lncRNA-HZ5 expression. The specific method comprises the steps as follows: siRNA of lncRNA-HZ5 is designed and synthesized according to an lncRNA-HZ5 base sequence, siRNA is used for transfection of the bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells, the expression level of lncRNA-HZ5 is lowered, and myogenic differentiation of the bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells is promoted, wherein the genome base sequence of lncRNA-HZ5 is shown in SQ1. The myogenic differentiation process of the bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells regulated by changing lncRNA-HZ5, enlightenment is provided for long non-coding RNA research of muscle development differentiation, and a new idea and reference are provided for clinical research, diagnosis and treatment of muscle development differentiation and damage repair.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Application of mir-192 in regulation of proliferation and differentiation of sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells
ActiveCN105441448BIncrease meat productionImprove qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSkeletal Muscle Satellite CellsControl cell
The invention discloses the application of a non-coding small RNA miR-192 in inhibiting the myogenic differentiation of sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells and promoting the proliferation of sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells. The analog of the non-coding small RNA miR-192 is transfected into sheep The overexpression of intracellular miR‑192 in skeletal muscle satellite cells, compared with the cells overexpressing the control nucleotide sequence, the differentiation of sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells was inhibited, but the proliferation of sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells was inhibited. Capabilities are improved. The present invention also provides the application of miR-192 to inhibit the expression of RB1 protein level in sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells. The present invention discovers for the first time that miR-192 has the function of negatively regulating the myogenic differentiation of sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells and promoting the proliferation of sheep skeletal muscle satellite cells.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
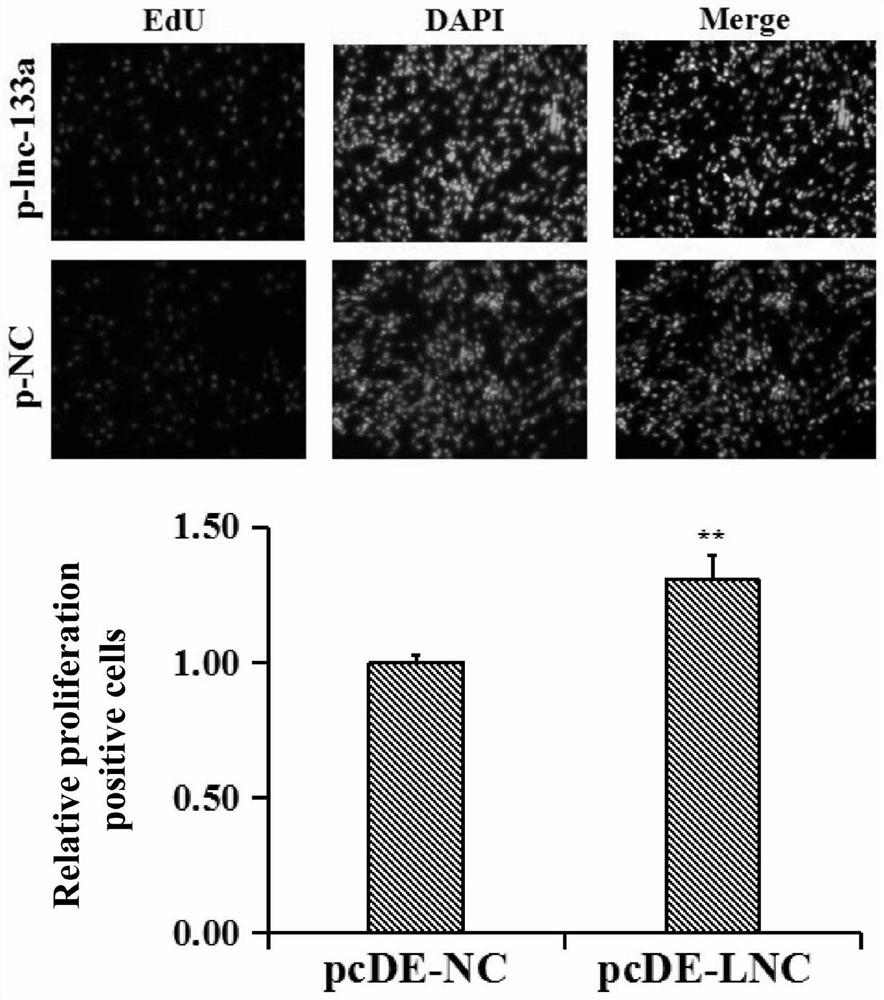
Bovine lncRNA-133a and its application and verification method in the regulation of proliferation and differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells
ActiveCN108753779BPromote proliferationPromote myogenic differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSkeletal Muscle Satellite CellsBovine muscle
The invention relates to a bovine lncRNA-133a sequence and its application and verification method in the regulation of proliferation and differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells. The present invention provides a sequence of long-chain non-coding RNA lncRNA-133a related to bovine muscle development. The present invention finds for the first time that lncRNA-133a has the function of promoting the proliferation and myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells, and can apply lncRNA-133a In regulation of proliferation and differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
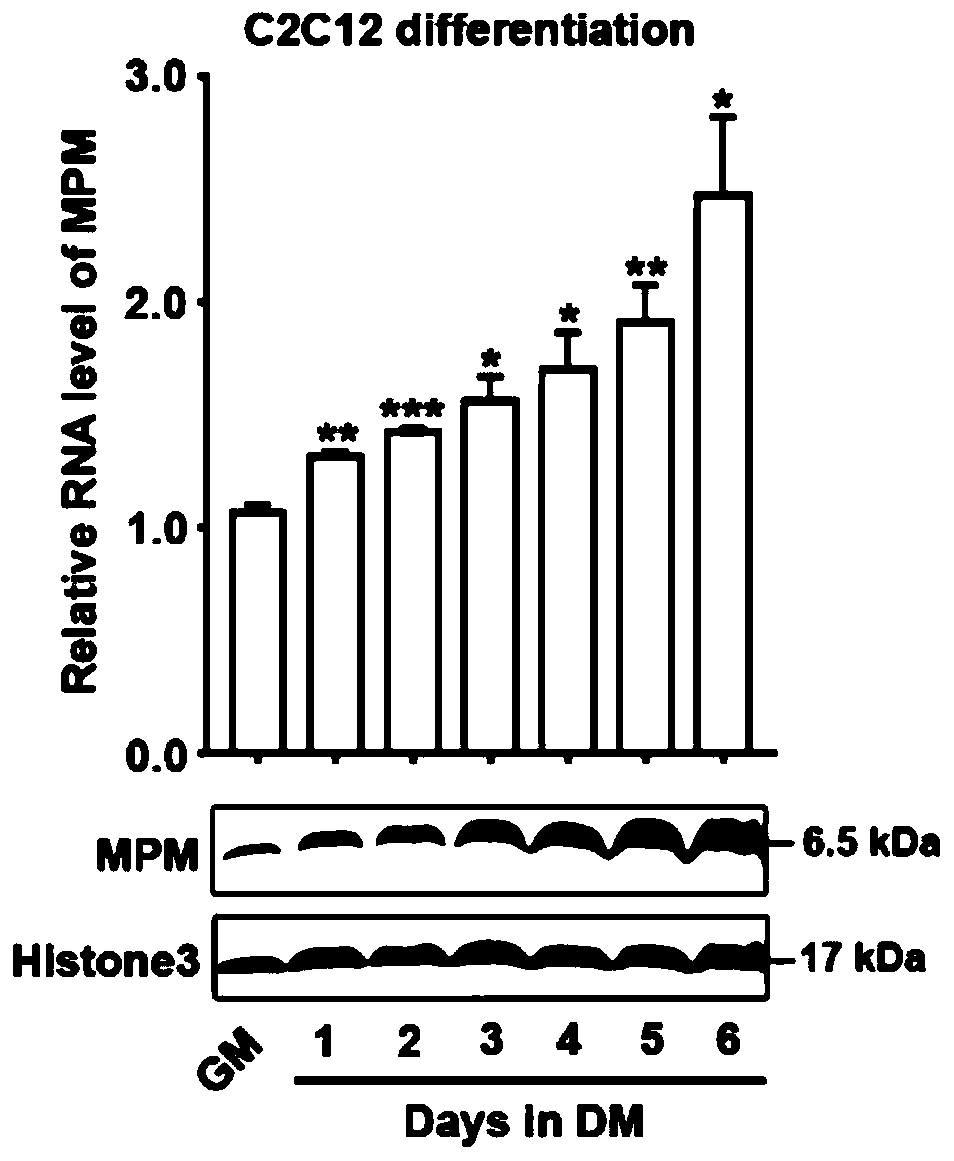
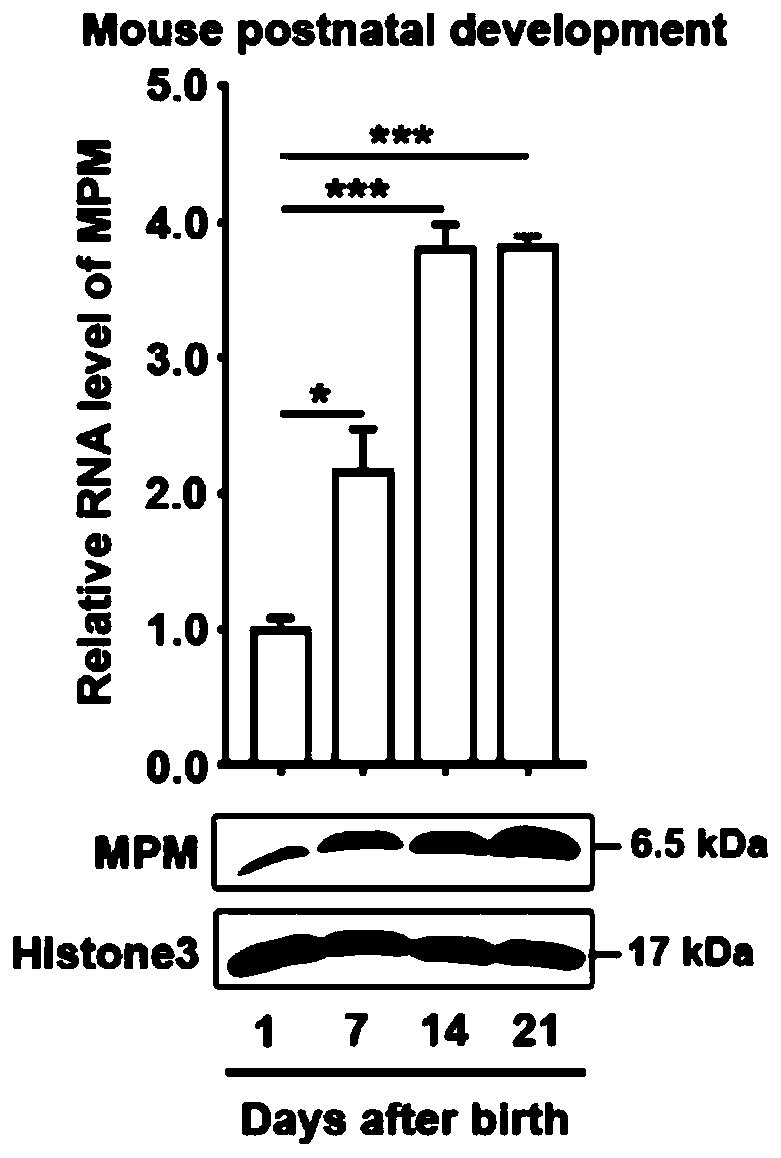
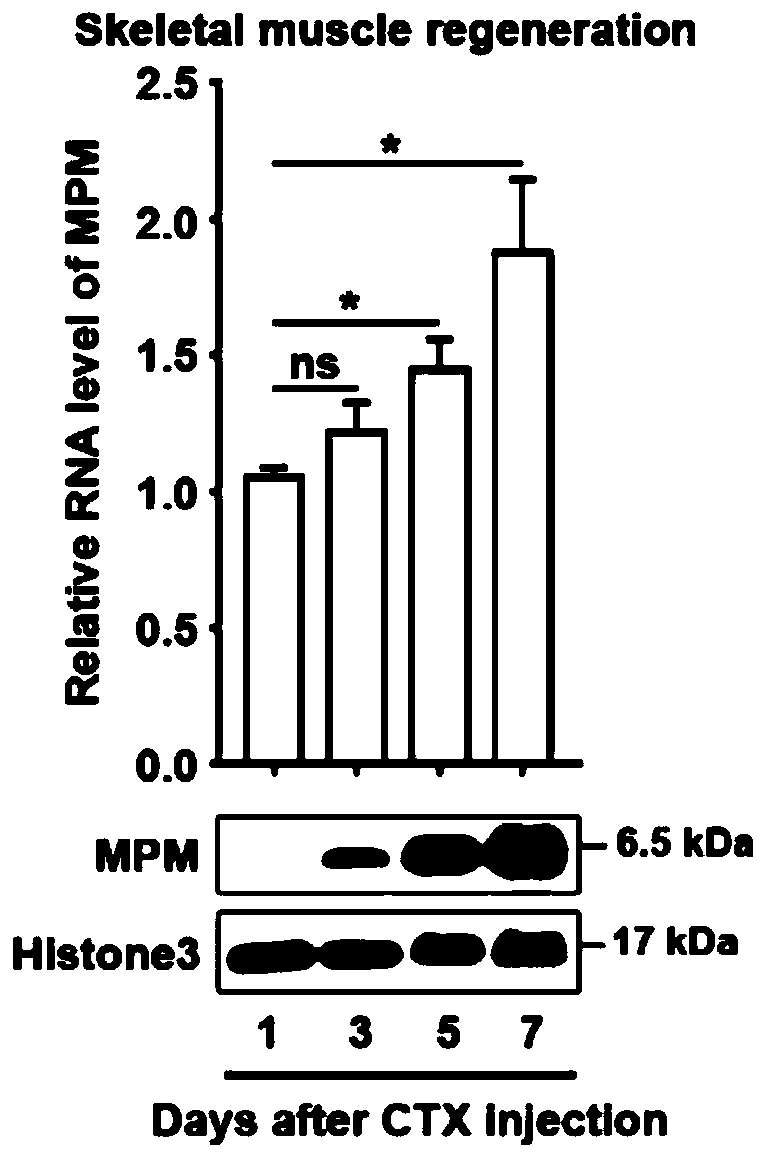
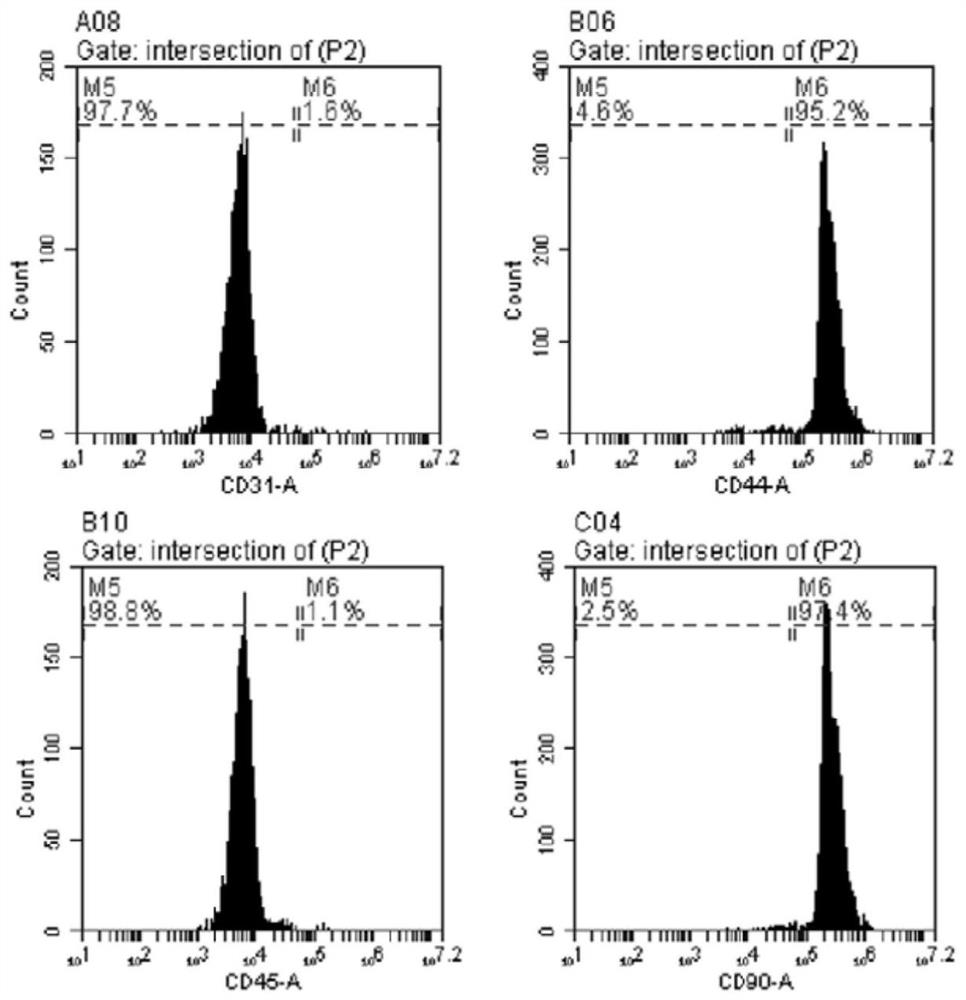
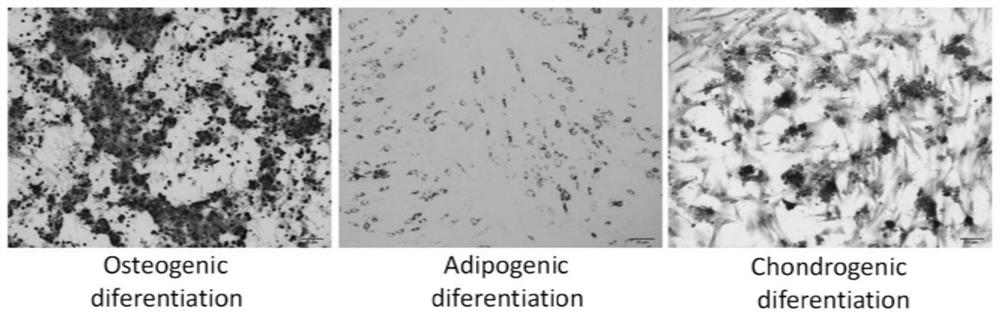
Application of short peptide MPM in the preparation of medicine for treating diseases related to muscle cell differentiation
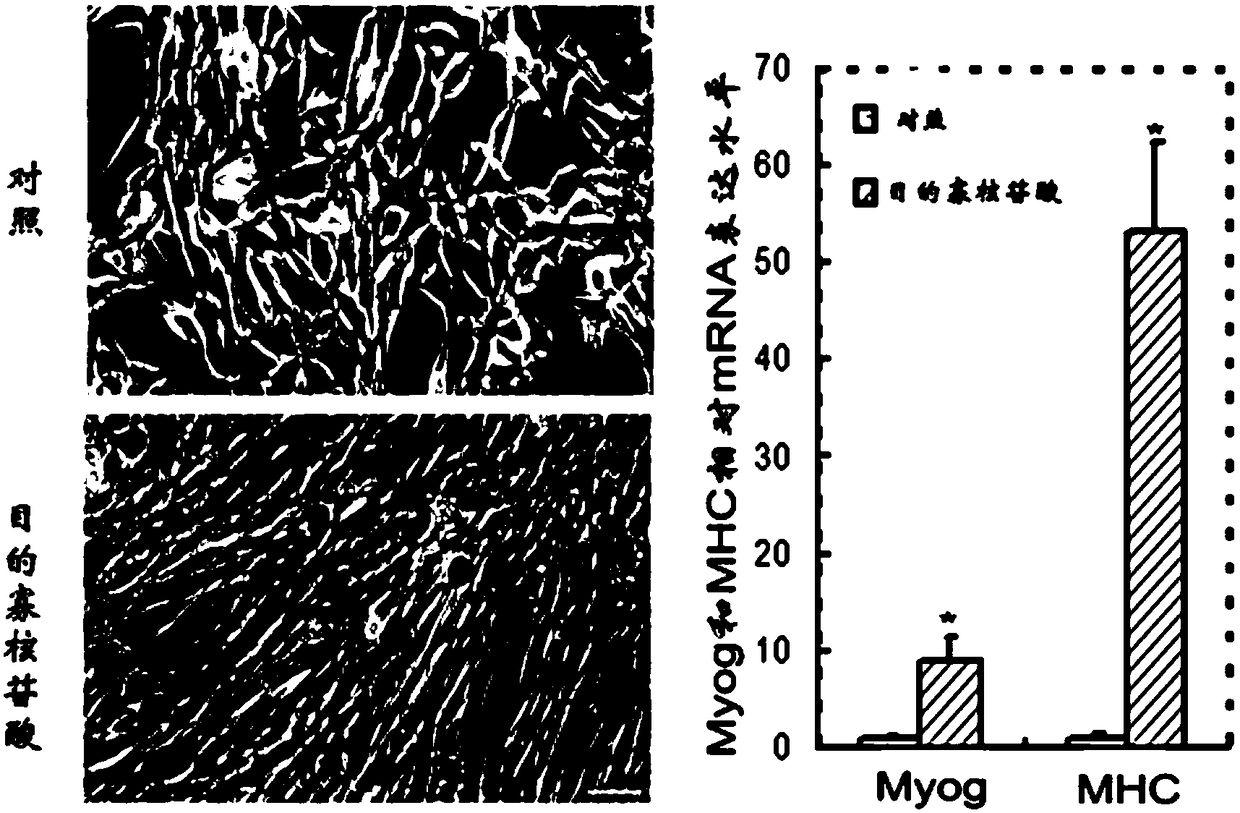
ActiveCN110404053AStrong differentiation abilityPromote myogenic differentiationPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderDiseaseFiber
The invention discloses application of a short peptide MPM in the preparation of a medicine for treating diseases related to muscle cell differentiation. An amino acid sequence of the short peptide MPM is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 or SEQ ID NO. 2, a nucleotide sequence of LINC00116 encoding the short peptide MPM is shown in SEQ ID NO. 3 or SEQ ID NO. 4. The application of the short peptide MPM in thepreparation of the medicine for treating the diseases related to the muscle cell differentiation finds that the short peptide MPM plays a key role in cell myogenic differentiation, skeletal muscle development and regeneration, muscle fiber development and regeneration; high MPM expression promotes cell myogenic differentiation, while low expression inhibits the myogenic differentiation of cells, and the expression level of MPM directly affects the maximum grip and mouse exercise tolerance. Compared with normal people, the expression level of the MPM is decreased in the diseased muscles of patients with tibial muscular dystrophy (DMD), Duchenne muscular dystrophy (TMD), rhabdomyosarcoma of different pathological types and the muscles of the elderly; and it indicates that the short peptide MPM is associated with muscle cell differentiation, the differentiation of the muscle cells can be promoted by promoting the expression of the MMP, and the medicine for treating diseases related to themuscle cell differentiation is prepared.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A method for inducing myogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN112342189BSimple differentiation methodNon-toxic and cheap differentiation methodCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMyosinMyogenic cell
Owner:NORTHERN JIANGSU PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Method for promoting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by overexpression of PSMB5
ActiveCN110964746ARegulates the process of development and differentiationPromote myogenic differentiationGenetically modified cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsLipofectamineSkeletal Muscle Satellite Cells
The invention relates to a method for promoting myogenic differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by overexpression of PSMB5. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining atarget sequence containing a bovine PSMB5 gene sequence; (2) constructing an expression vector pcDNA3.1-PSMB5; (3) transfecting bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by pcDNA 3.1-PSMB5, using the obtained expression vector pcDNA3.1-PSMB5 for transfecting bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by adopting a liposome transfection reagent so that the bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells overexpress the PSMB5, and improving the in-vitro differentiation capacity of the bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells by utilizing the effect of the PSMB5. According to the method, PSMB5 is used for regulating and controlling proliferation and myogenic differentiation of bovine muscle satellite cells, the enlightenment can be provided for research on the ubiquitination process of muscle development anddifferentiation, and a new thought and reference are provided for clinical research and diagnosis and treatment of muscle development and differentiation and injury repair.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
A culture method for improving oxidative metabolism of chicken skeletal muscle cells
InactiveCN104059876BInhibit apoptosisPromote maturityEmbryonic cellsBiotechnologySkeletal Muscle Fibers
The invention discloses a cultivation method for improving the oxidative metabolism ability of chicken skeletal muscle cells, which belongs to the field of biotechnology. The method provided by the present invention is to inoculate the separated and purified chicken skeletal muscle myoblasts and myogenic fibroblasts in the upper chamber and the lower chamber of the Transwell culture dish respectively, and the two are separated by a PET membrane with a pore size of 1 μm but shared. There is H 2 o 2 myogenic differentiation medium; Myotubes with voluntary contraction ability were obtained after myogenic differentiation induction culture for 7-10 days, during which low-temperature shock stimulation was performed every 8-12 hours. The method provided by the invention can significantly increase the mitochondrial content of chicken skeletal muscle cells, the transmembrane potential and the activity of aerobic metabolism enzymes, while reducing the activity of ATPase. This method has the characteristics of short cultivation period and stable effect, and it has laid a foundation for the study of chicken skeletal muscle energy metabolism, fiber type formation mechanism, etc., and has good research and application value.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
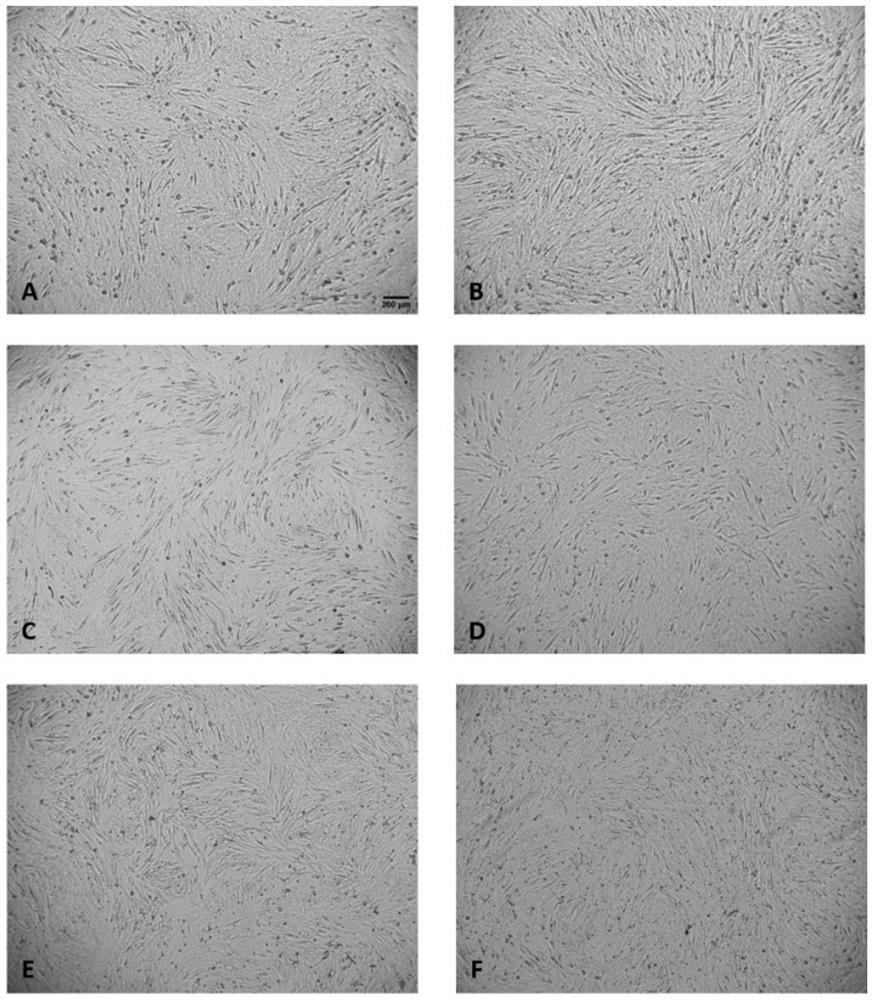
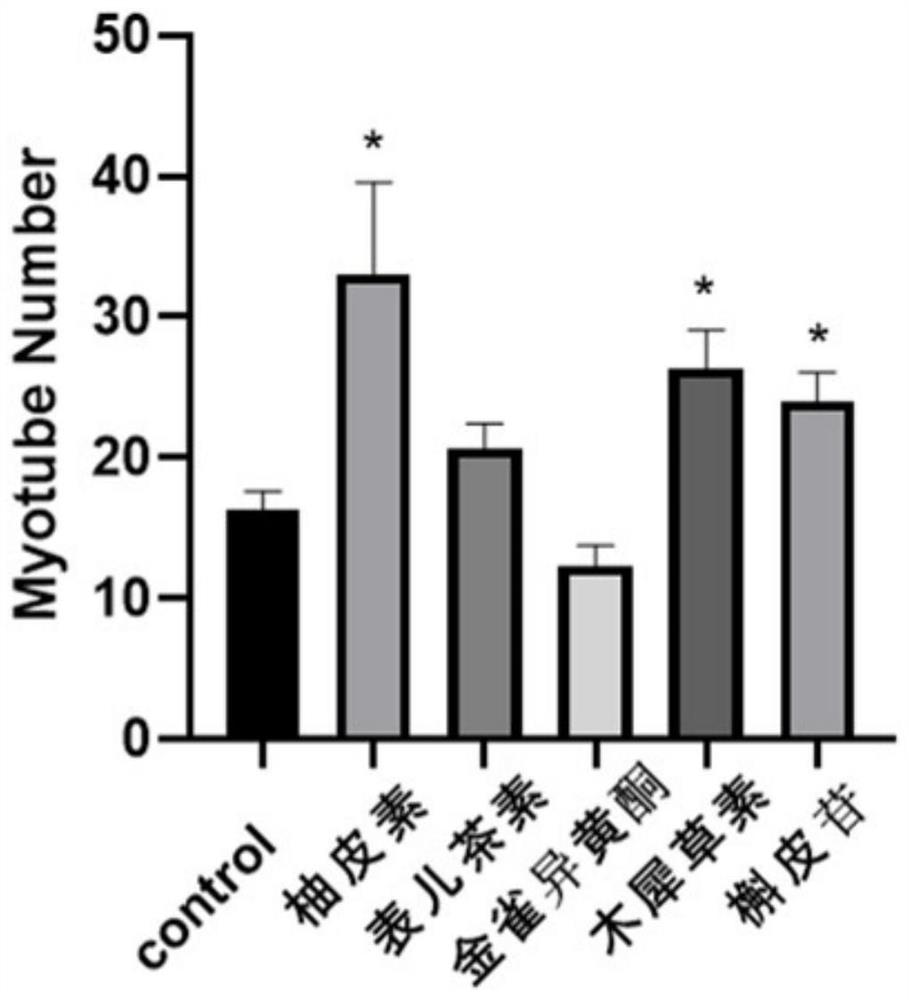
Application of flavonoid compound in induction of muscle-derived cell in-vitro efficient differentiation
PendingCN114752558AIncreased in vitro differentiation efficiencyIncrease MyHC expressionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsBiotechnologyXanthonoid
The invention discloses an application of a flavonoid compound in induction of muscle-derived cell in-vitro efficient differentiation, and belongs to the technical field of animal cell culture and cell culture meat. Influences of different flavonoid compounds on in-vitro myogenic differentiation of myogenic cells are investigated, one or more flavonoid compounds are found to be capable of effectively promoting in-vitro efficient differentiation of the myogenic cells to generate muscle fibers, meanwhile, the expression quantity of muscle fiber specific protein MyHC is remarkably increased, the synthesis time of high-quality muscle protein is shortened, and the development of muscle fibers is promoted. The efficient production of muscle stem cells is facilitated, and the rapid development of the cell culture meat industry is promoted.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
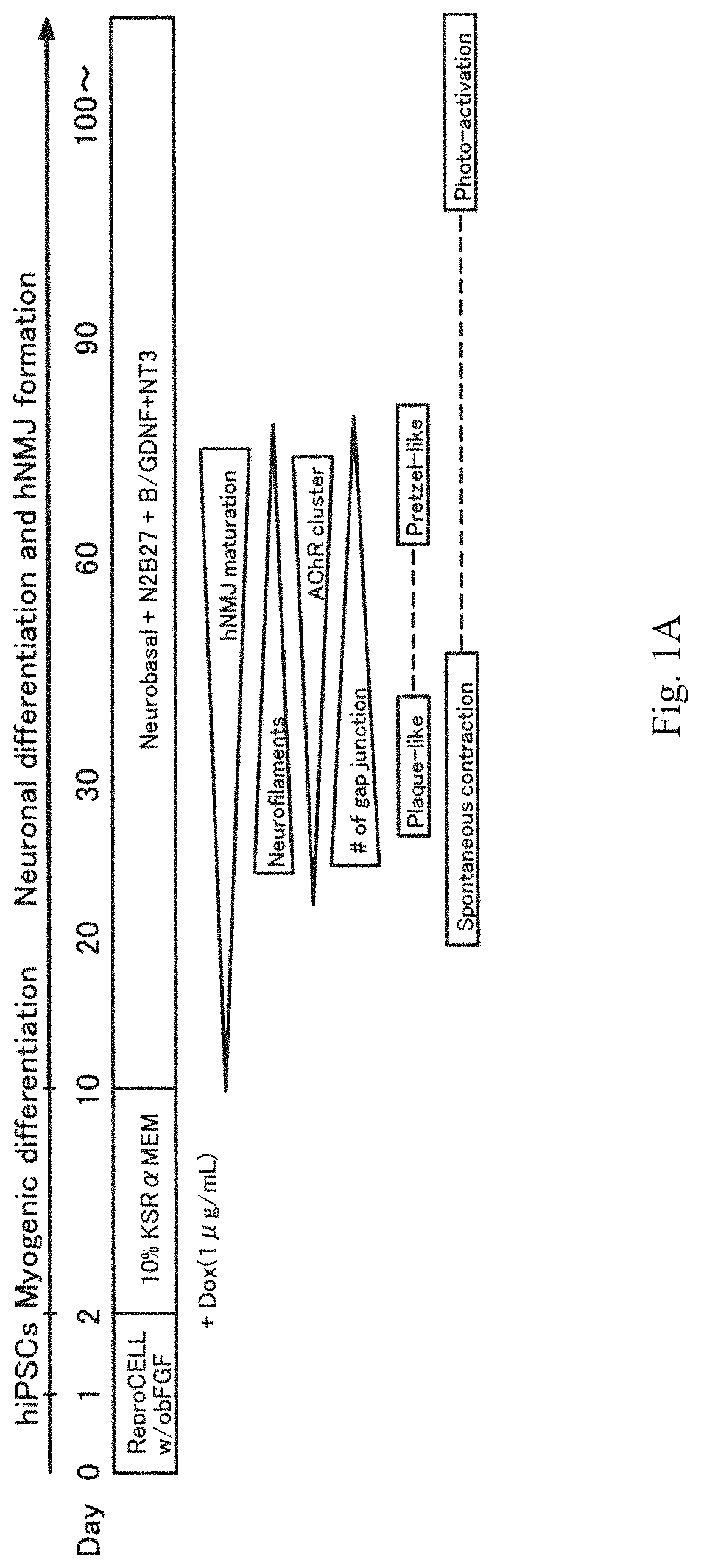
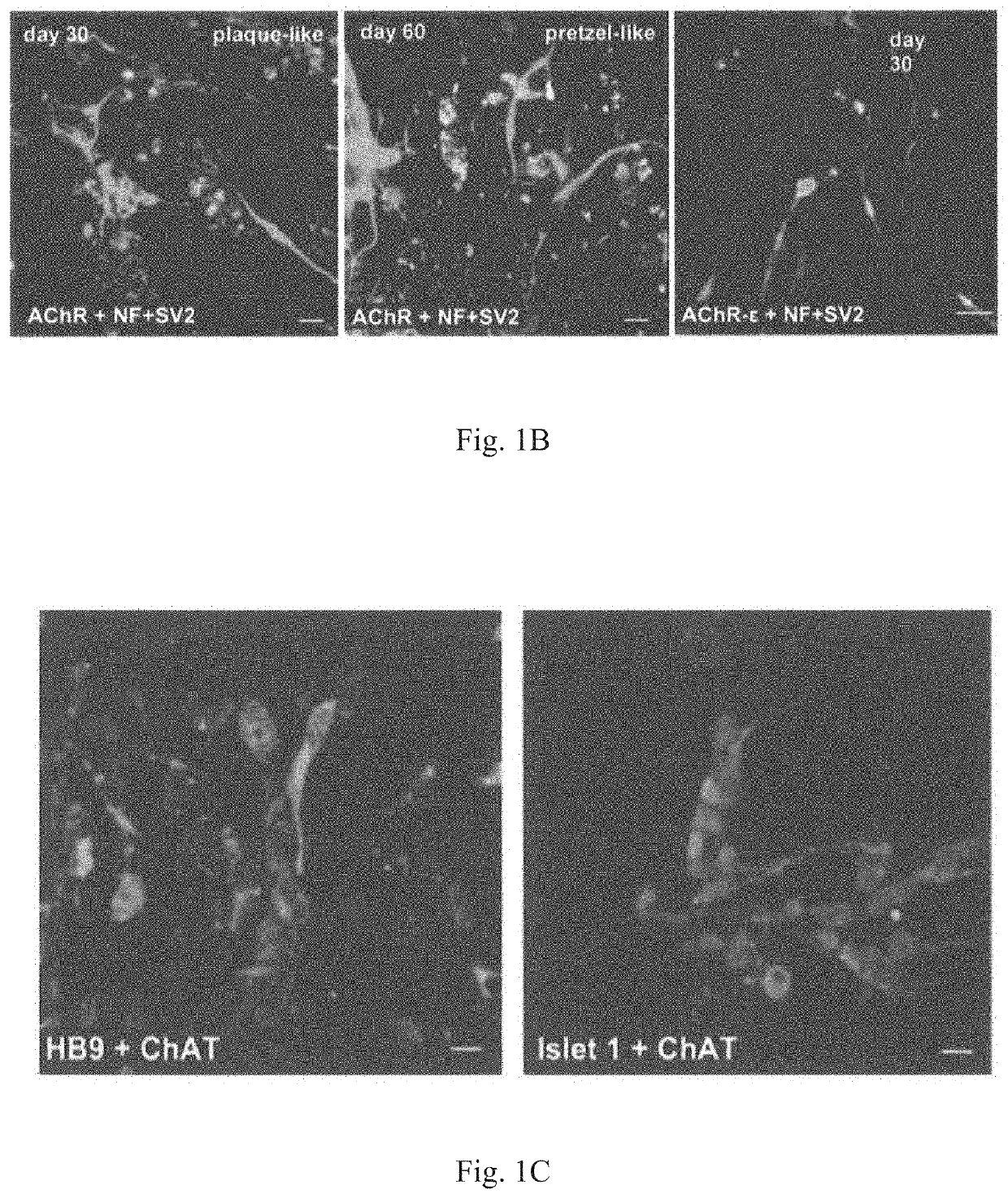
Method for obtaining artificial neuromuscular junction from pluripotent stem cells
PendingUS20210363496A1Efficiently obtainedPreparing a functional and mature NMJ in vitro easily and efficientlyMicrobiological testing/measurementMuscular disorderNeuronMultipotential stem cell
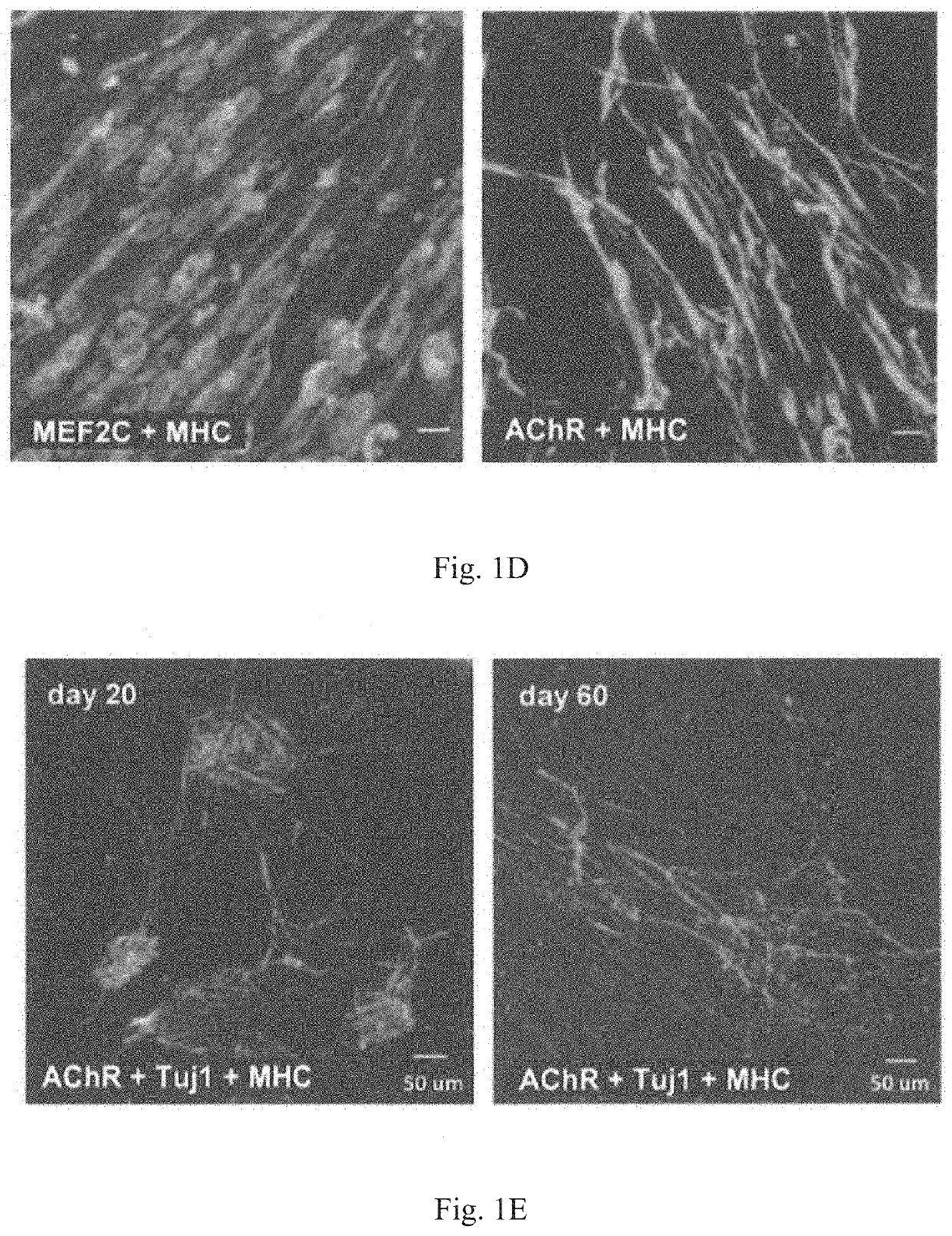
A method for easily and efficiently preparing a functional and matured neuromuscular junction (NMJ) in vitro includes producing an artificial neuromuscular junction by transiently expressing MyoD in pluripotent stem cells to induce myogenic differentiation, and culturing the cells obtained by transiently expressing MyoD in pluripotent stem cells to induce myogenic differentiation in a medium containing a neurotrophic factor to induce neuronal differentiation.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com