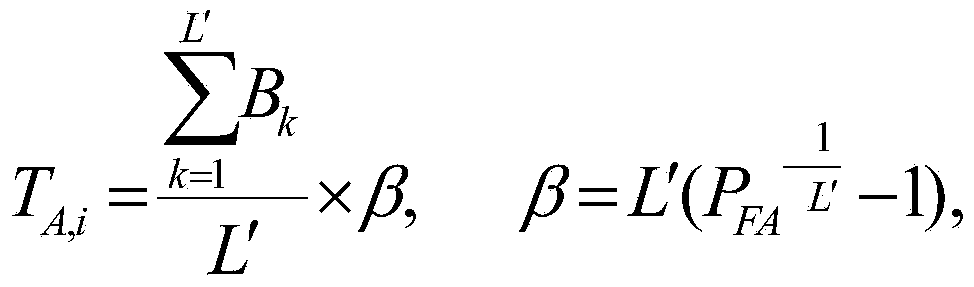Patents
Literature
193 results about "Ordered statistics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method, computer program, and system for automated real-time signal analysis for detection, quantification, and prediction of signal changes
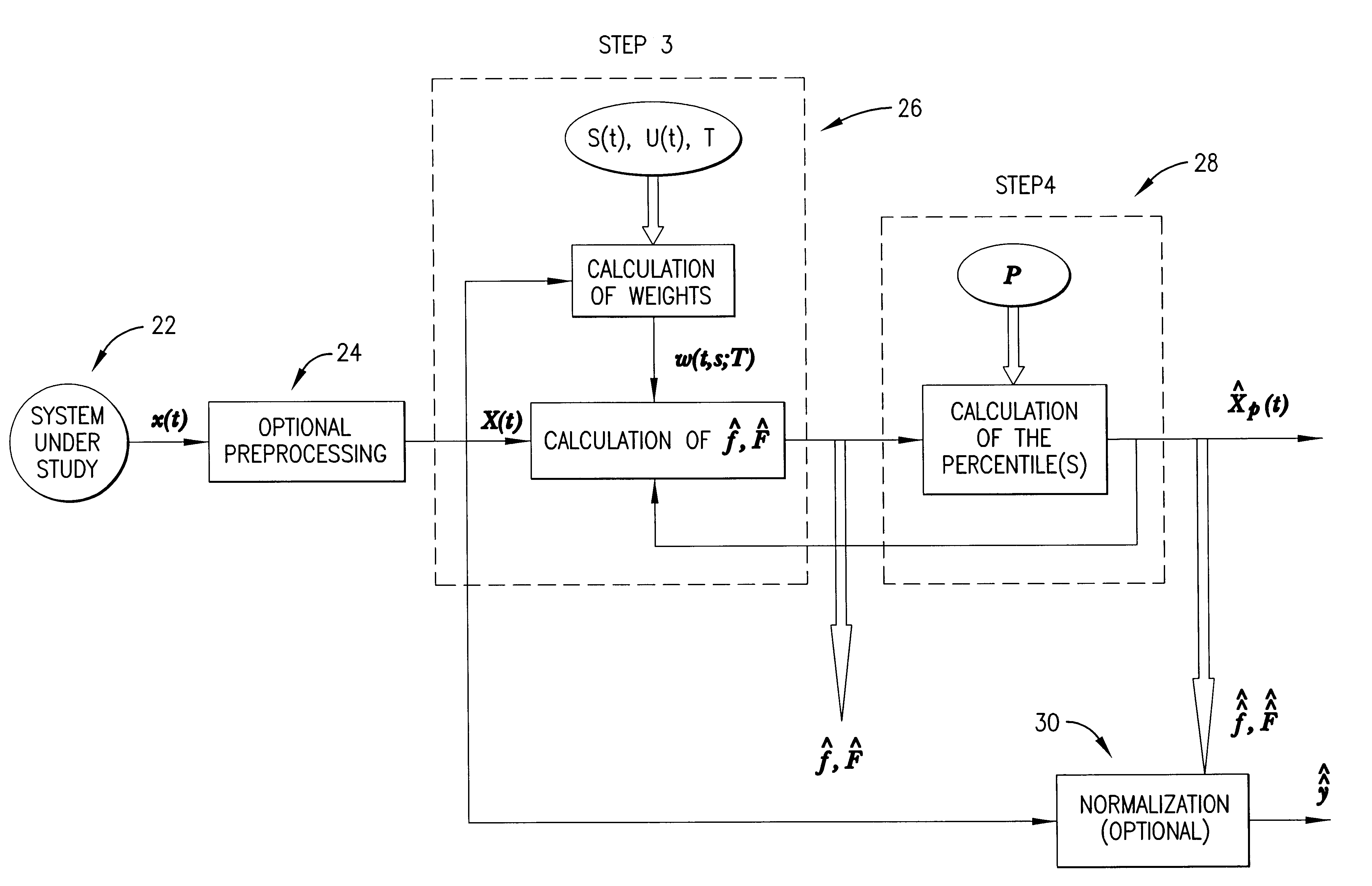
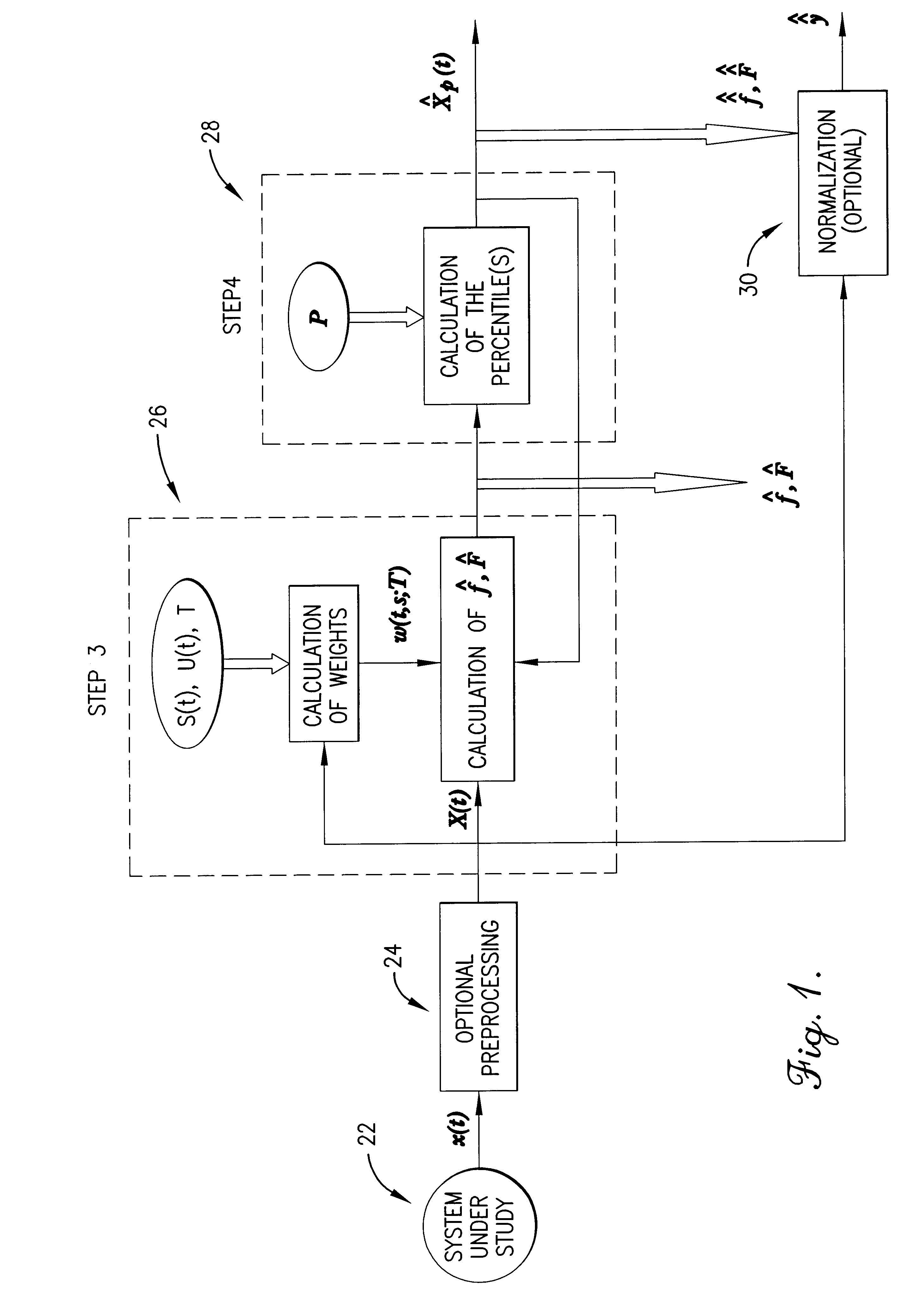
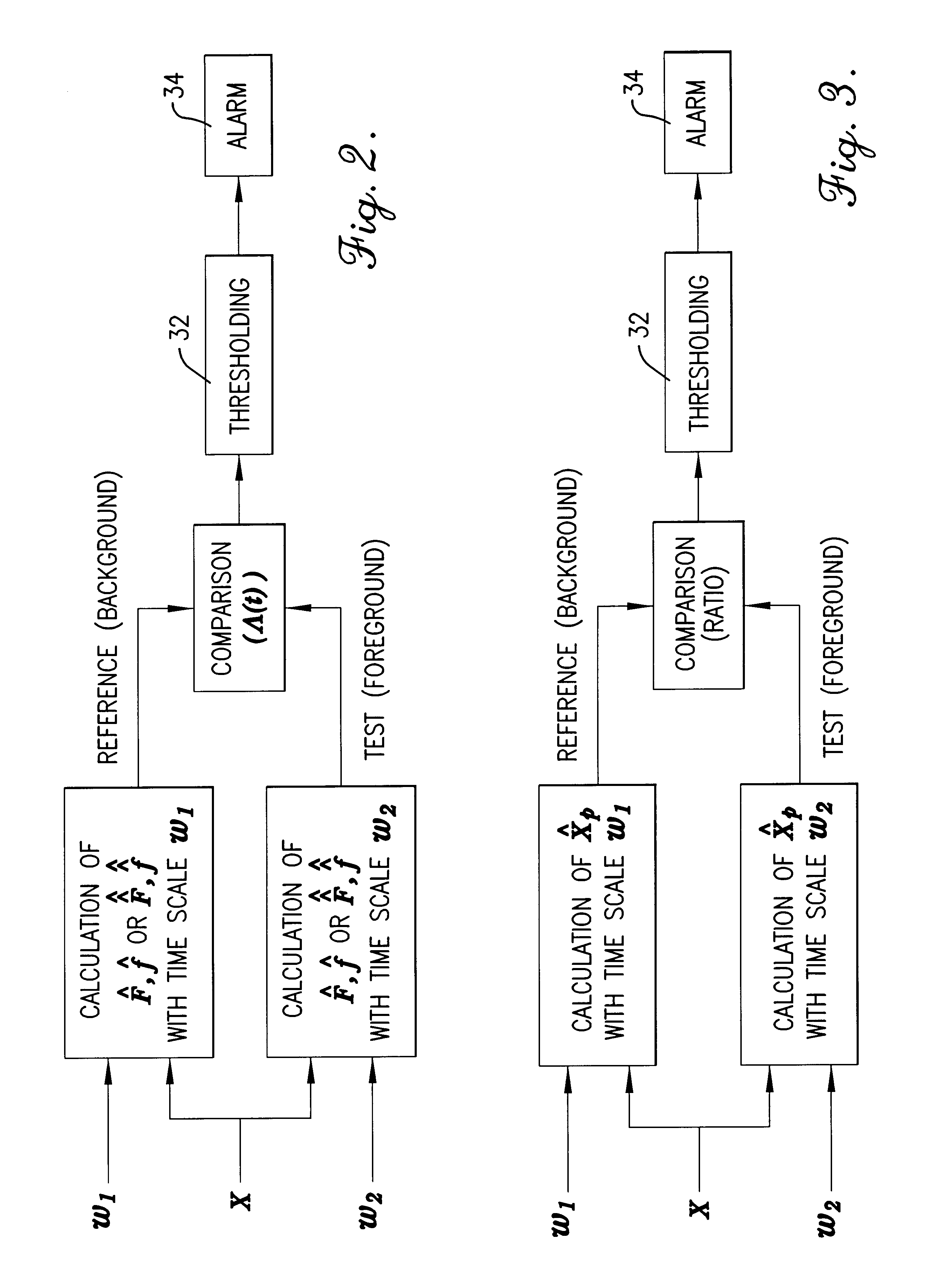
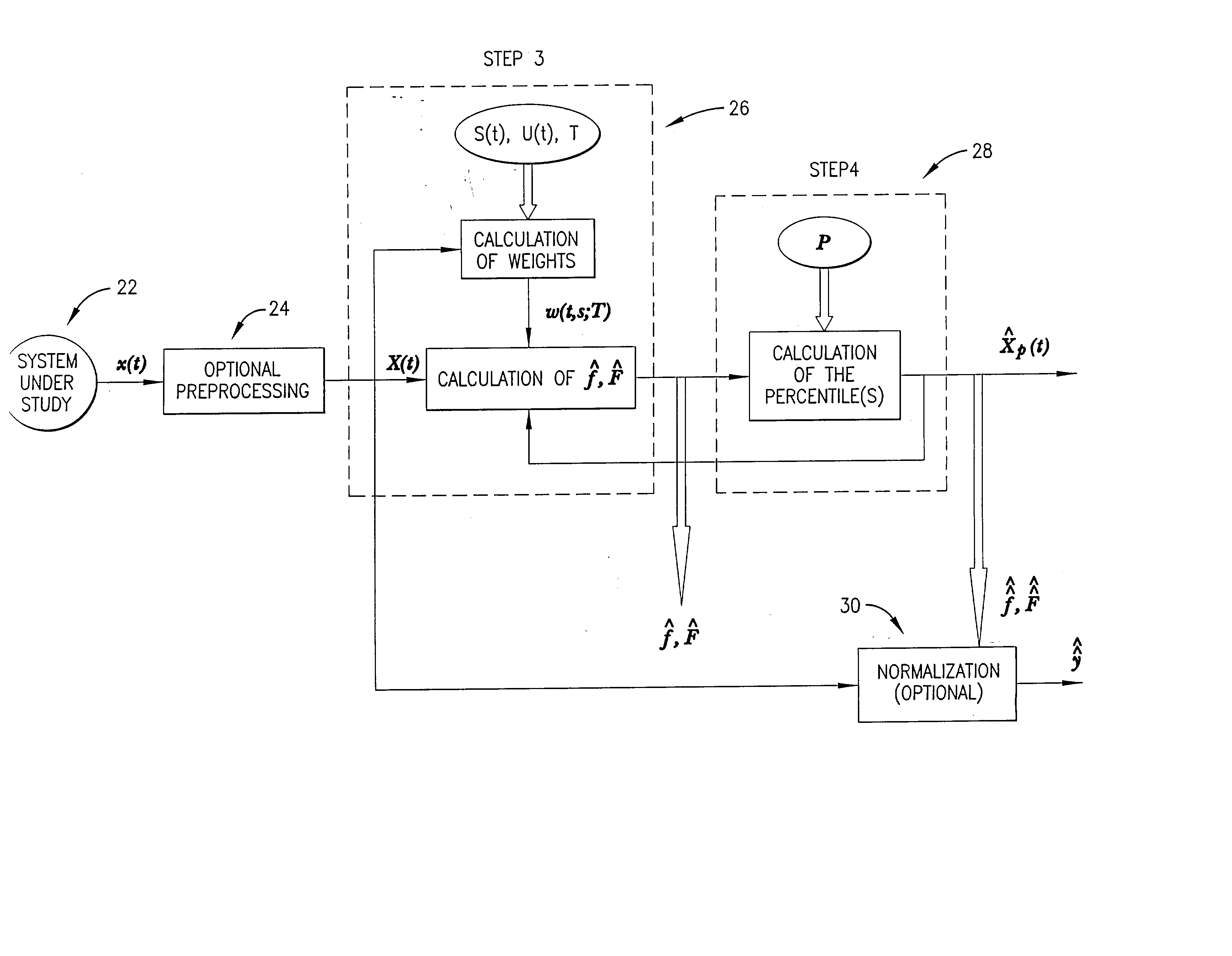
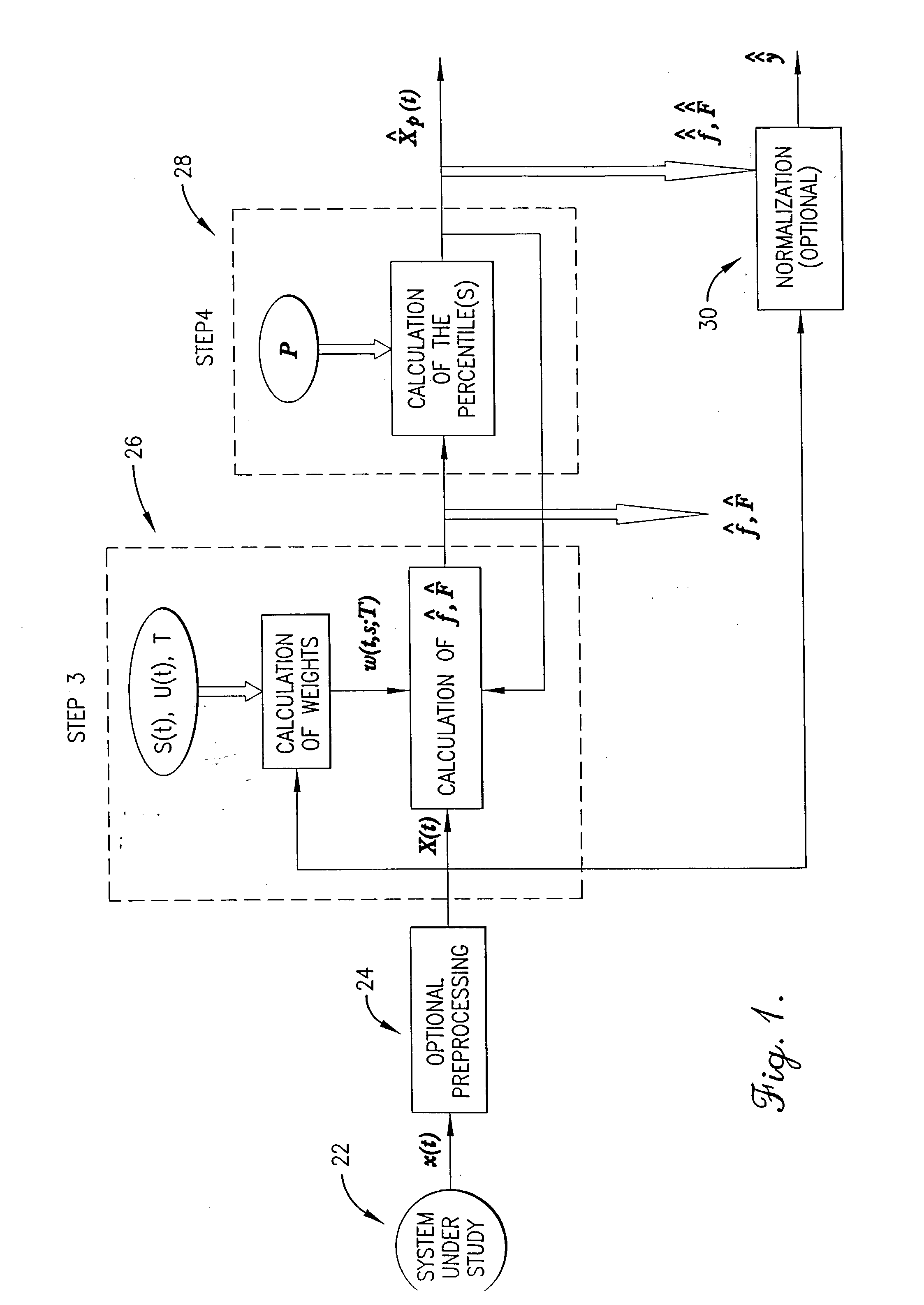
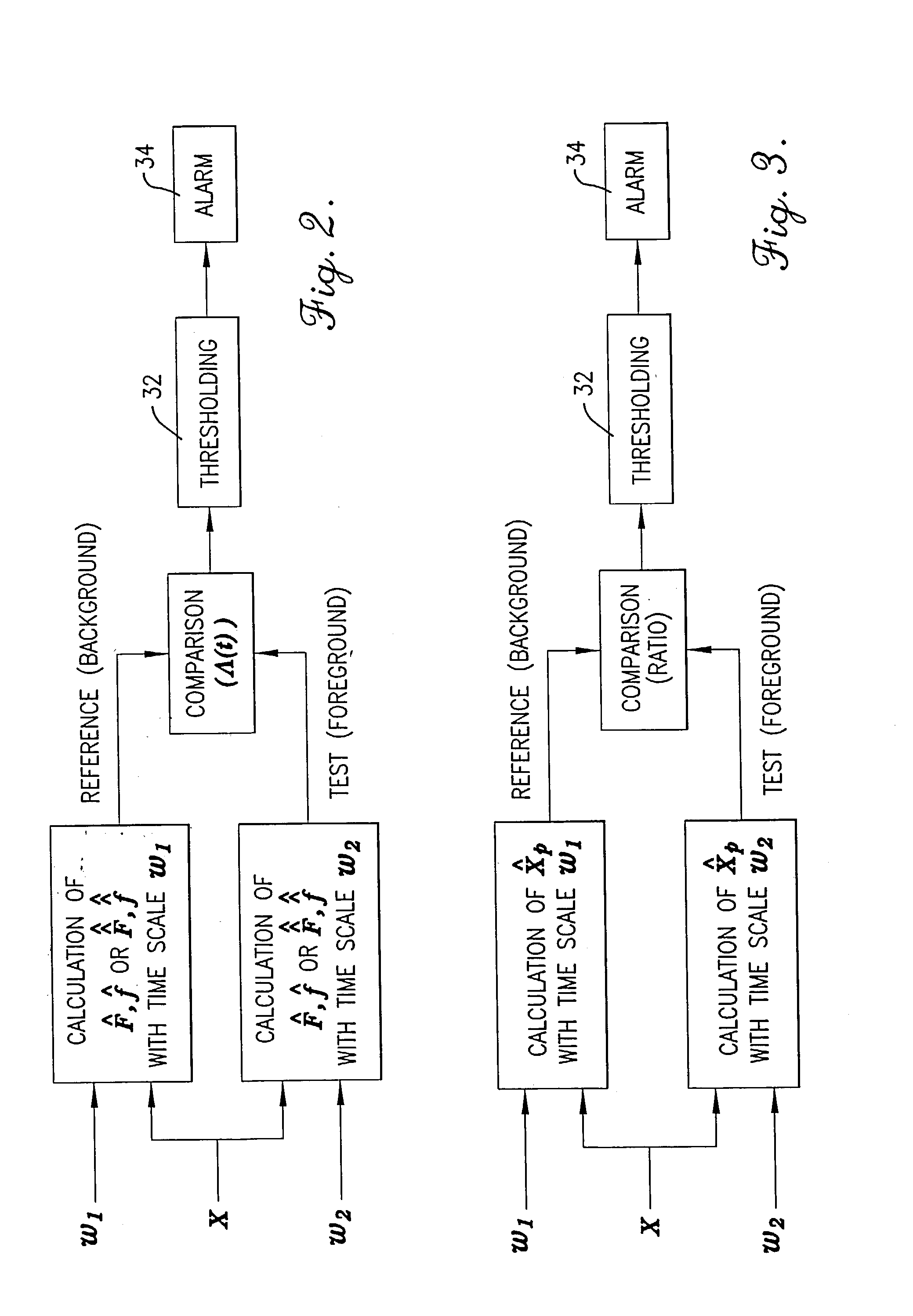
A method, computer program, and system for real-time signal analysis providing characterization of temporally-evolving densities and distributions of signal features of arbitrary-type signals in a moving time window by tracking output of order statistic filters (also known as percentile, quantile, or rank-order filters). Given a raw input signal of arbitrary type, origin, or scale, the present invention enables automated quantification and detection of changes in the distribution of any set of quantifiable features of that signal as they occur in time. Furthermore, the present invention's ability to rapidly and accurately detect changes in certain features of an input signal can also enable prediction in cases where the detected changes associated with an increased likelihood of future signal changes.
Owner:FLINT HILLS SCI L L C
Method, computer program, and system for automated real-time signal analysis for detection, quantification, and prediction of signal changes
InactiveUS20030187621A1Medical simulationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTime signalComputer science
A method, computer program, and system for real-time signal analysis providing characterization of temporally-evolving densities and distributions of signal features of arbitrary-type signals in a moving time window by tracking output of order statistic filters (also known as percentile, quantile, or rank-order filters). Given a raw input signal of arbitrary type, origin, or scale, the present invention enables automated quantification and detection of changes in the distribution of any set of quantifiable features of that signal as they occur in time. Furthermore, the present invention's ability to rapidly and accurately detect changes in certain features of an input signal can also enable prediction in cases where the detected changes associated with an increased likelihood of future signal changes.
Owner:FLINT HILLS SCI L L C
Method for forming a depth image from digital image data
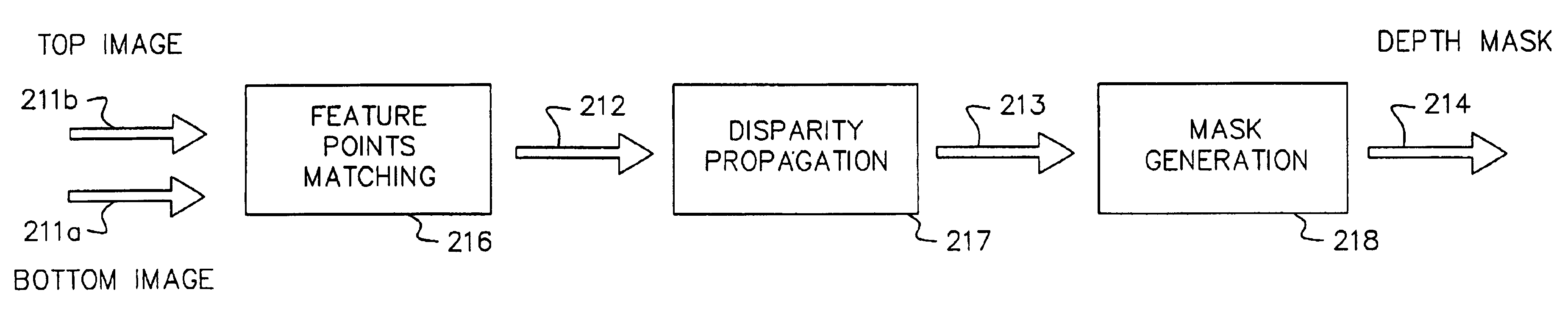
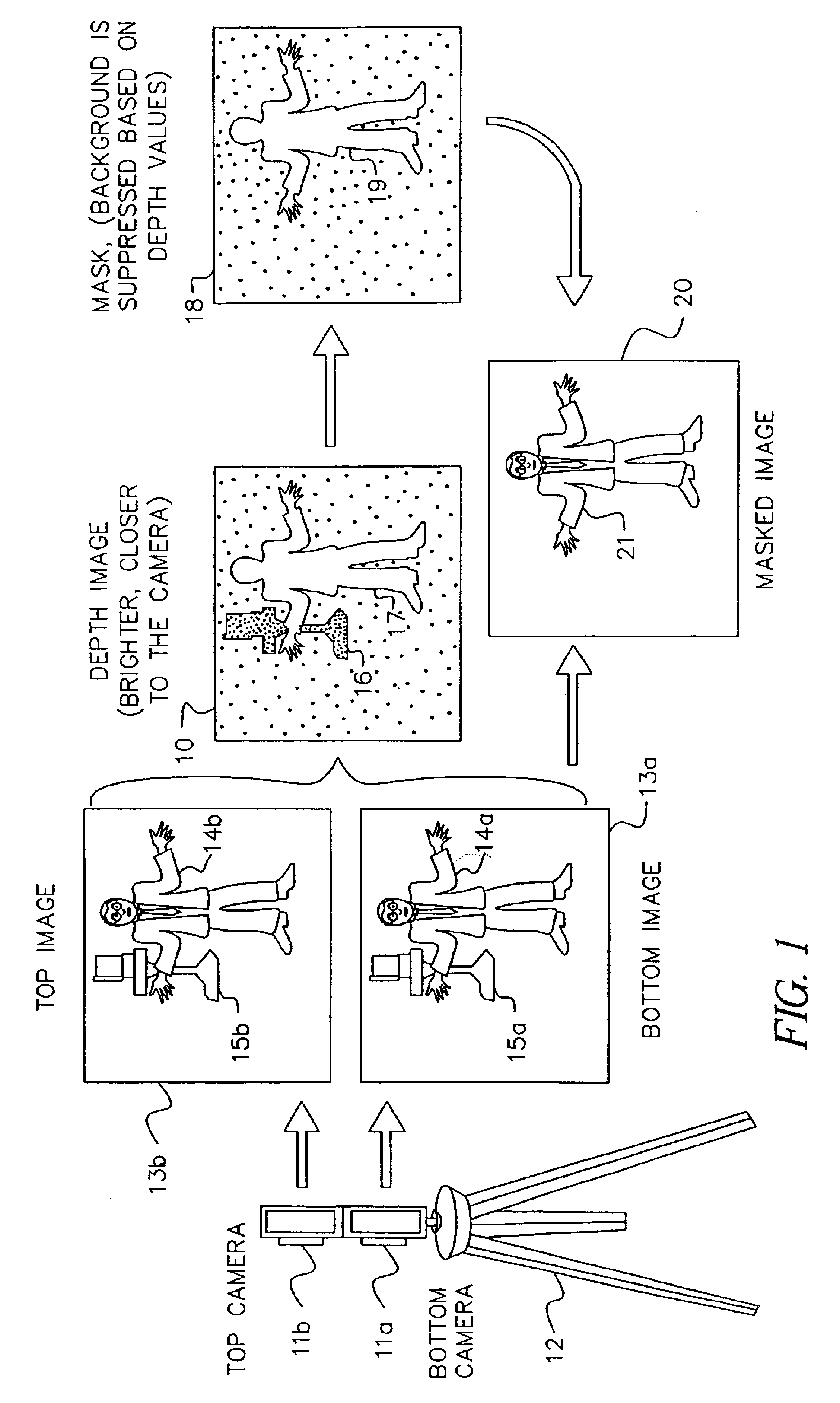
A computer vision / image processing method generates a depth map useful in producing a foreground depth mask for 2D / 3D image editing. The method uses image data from a plurality of scenes. Feature points on each of the vertical scan lines in each of the scene images are used to search for corresponding feature points on the corresponding vertical lines in other images. The corresponding feature-point search is performed by using a bipartite match network with a feature-point-ordering constraint and a disparity-limit constraint, and produces an individual feature-point depth map for each input image. A sparse feature-point depth map of the scene is obtained after applying a consistency test to all the individual depth maps. A complete feature-point depth map is produced by applying a color property assisted depth propagation process to the sparse feature-point depth map. Foreground and background separation is then conducted in the depth domain by using the order statistics of the depth data extracted the feature-point depth map. A foreground feature-point depth map is obtained from the separation operation. The final foreground depth mask is generated by applying a color aided eight-nearest-neighbor LMS interpolation process to the foreground feature-point depth map.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
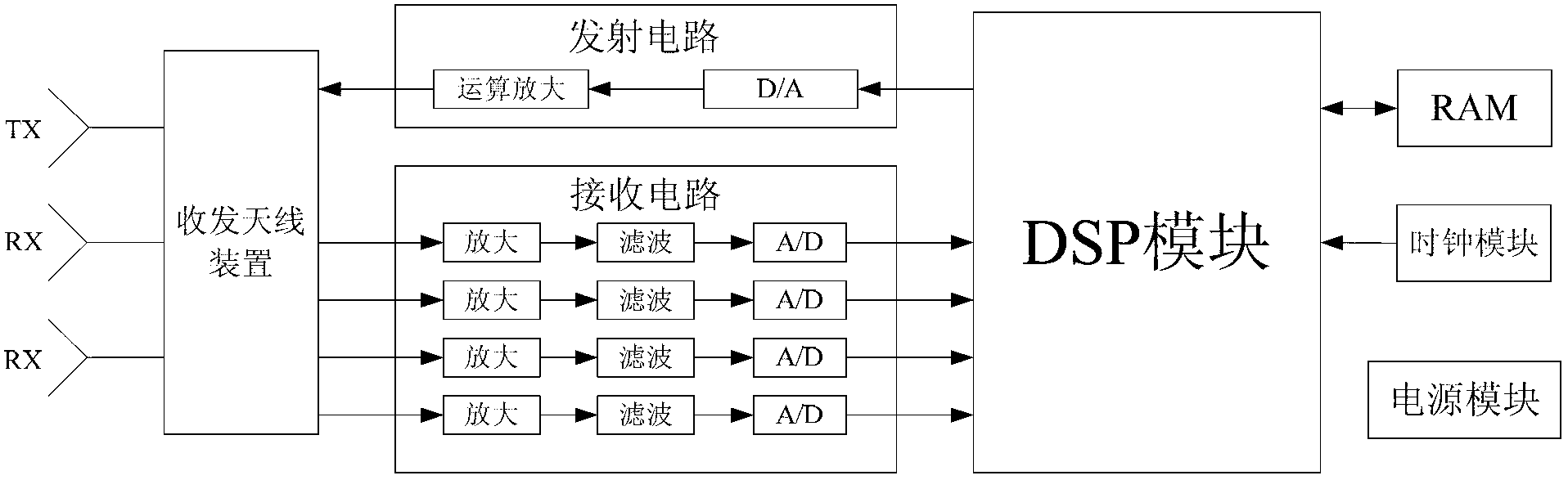
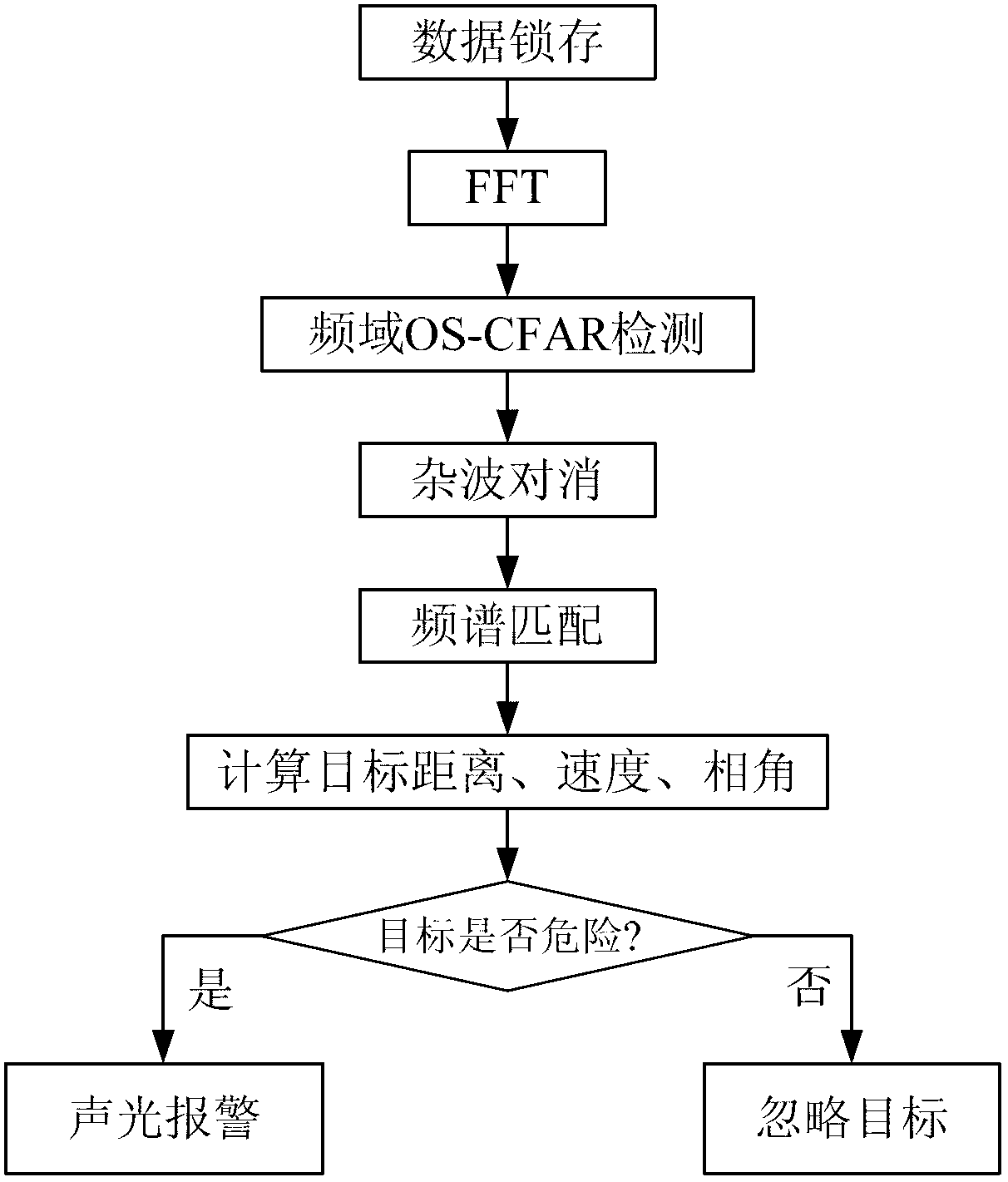
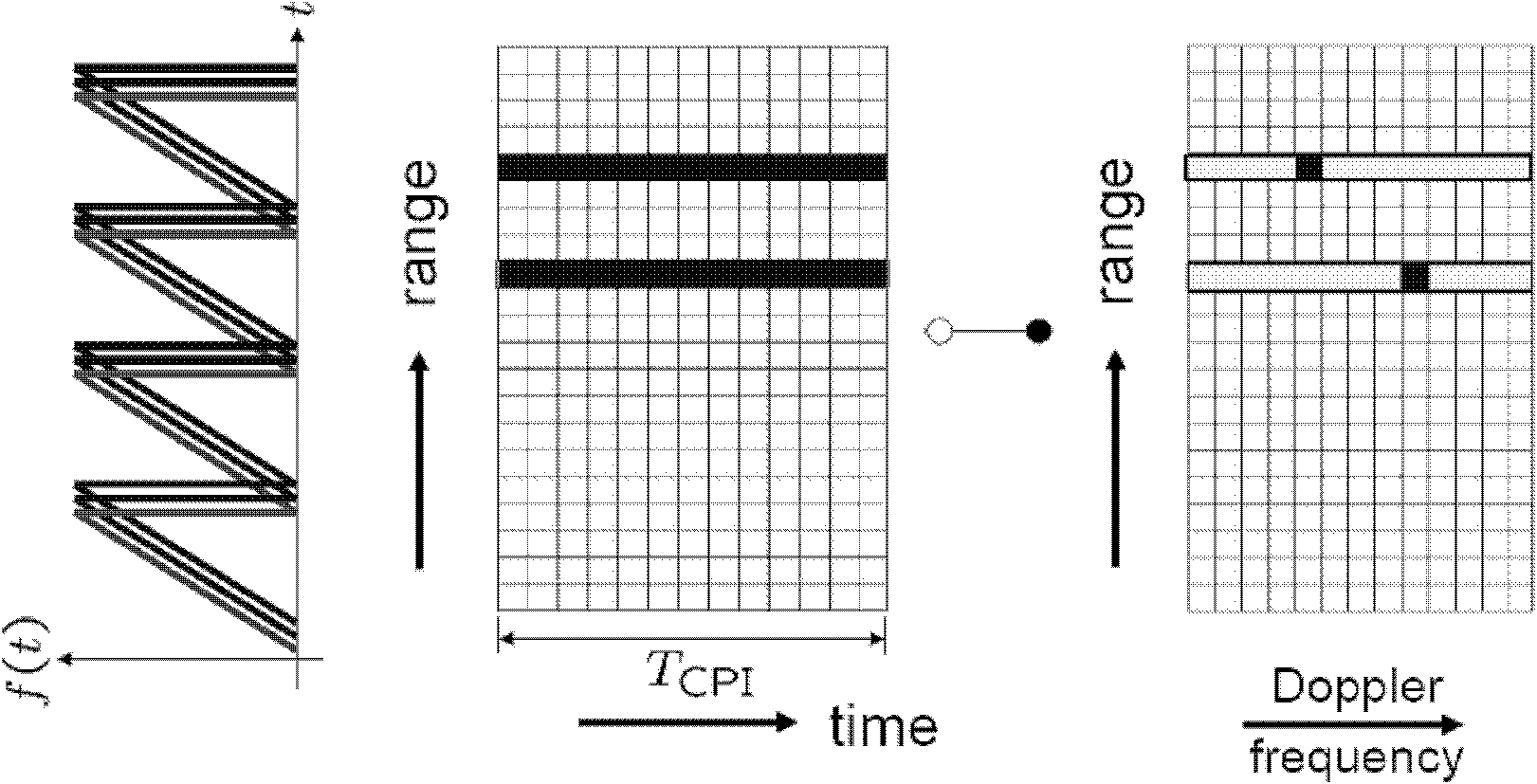
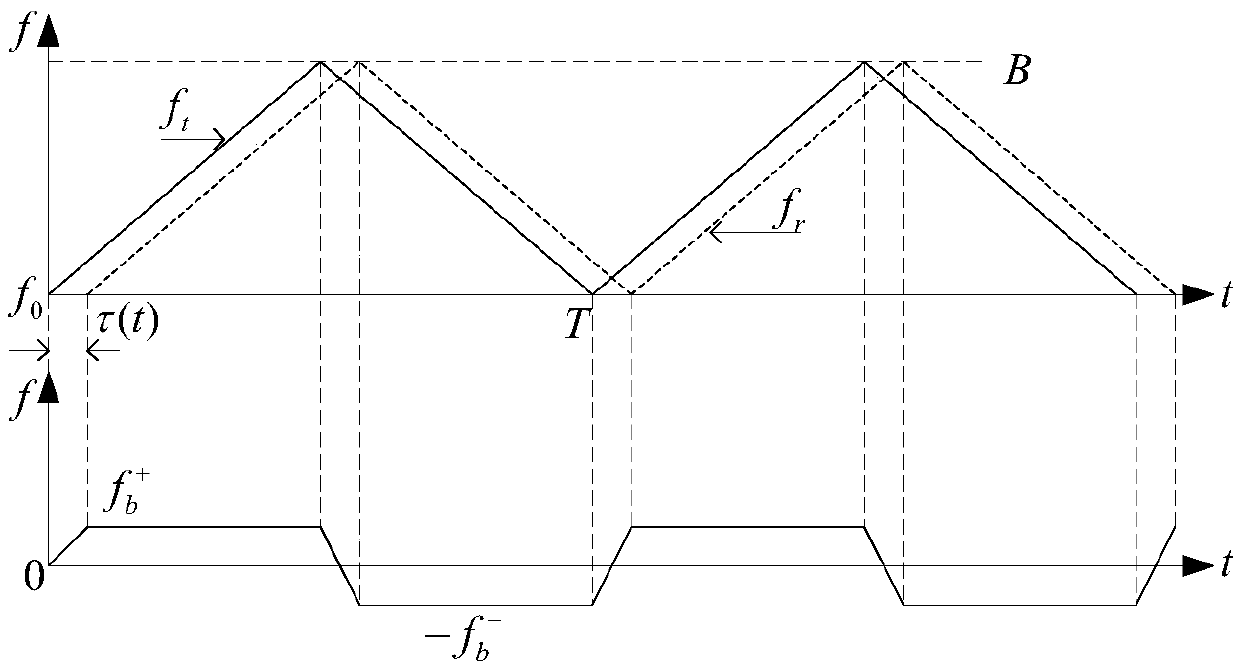
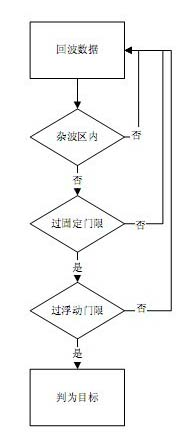
Method for detecting frequency domain constant false alarm of vehicle-mounted millimeter-wave anti-collision radar system
InactiveCN102707285AReduce false alarm rateLower requirementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a method for detecting frequency domain constant false alarm of a vehicle-mounted millimeter-wave anti-collision radar system, which belongs to the field of processing automotive anti-collision radar signals. The method comprises the following steps: when targets are located at the front of the anti-collision radar system, dividing the sampling data of the return signals which are pre-processed through a DSP (digital signal processor) module in the system into a frequency modulation ascending section and a frequency modulation descending section, and then storing the sampling data to an RAM (random access memory); conducting FFT (fast fourier transformation) template on the storage data, and then conducting the frequency domain constant false alarm detection on the obtained peak value points of a frequency spectrum based on order statistics, thus detecting the spectral lines of the effective targets from the signal frequency spectrum which contains noise waves; removing false targets by using the noise wave pairs; finally calculating the speed, the distance and the phase angle information of the targets according to the matched frequency spectrum information for analyzing and early warning of the system. According to the method in the invention, the false alarm rate of the detection of the anti-collision radar system is reduced effectively and the real time property and the effectiveness of the system are improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
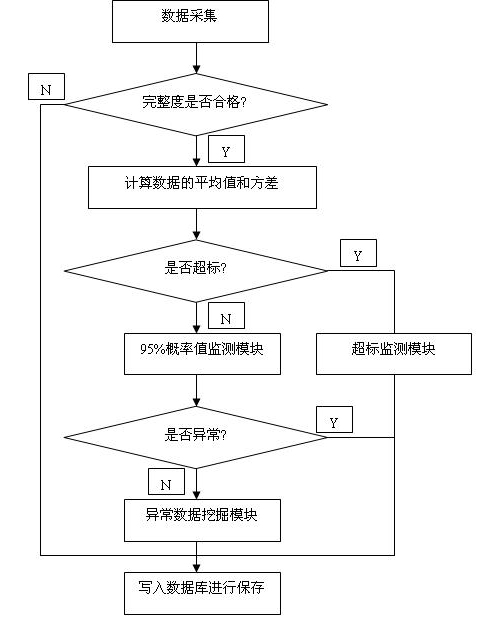
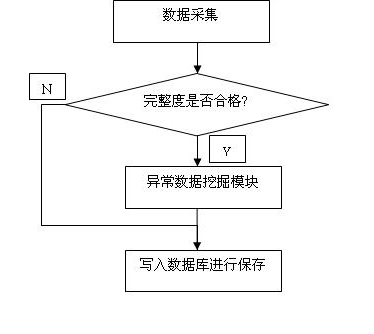
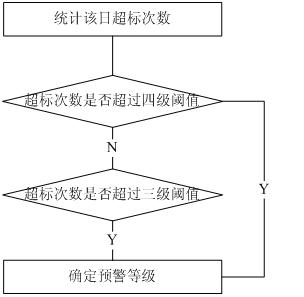
Early warning method of stable-state index of power quality
ActiveCN102170124AStructuredImprove accuracyAc network circuit arrangementsPower qualityQuality data
The invention discloses an early warning method of stable-state index of power quality. The method is realized by support from a power quality online monitoring device and a computer. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) selecting power quality indexes in advance, including voltage deviation, voltage total harmonic wave, short time flicking, etc, and setting earlywarning threshold values at four grades; (2) acquiring power quality data in real time, and analyzing each power quality index to carry out early warning grading; and (3) saving the values calculatedand a final early warning grade into a database. The early warning method of stable-state index of power quality establishes an early warning structure with two types, including index standard-exceeding type and index abnormal type, and four grades, and adopts time sequence mining algorithm based on high-order statistics in abnormal mining link to analyze potential abnormity of power quality datawith skewness and peakedness. Practice proves that the early warning method is clear in hierarchy, high in algorithm efficiency, strong in accuracy and good in operability. The early warning method is high-efficient and comprehensive.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST OF JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER +1
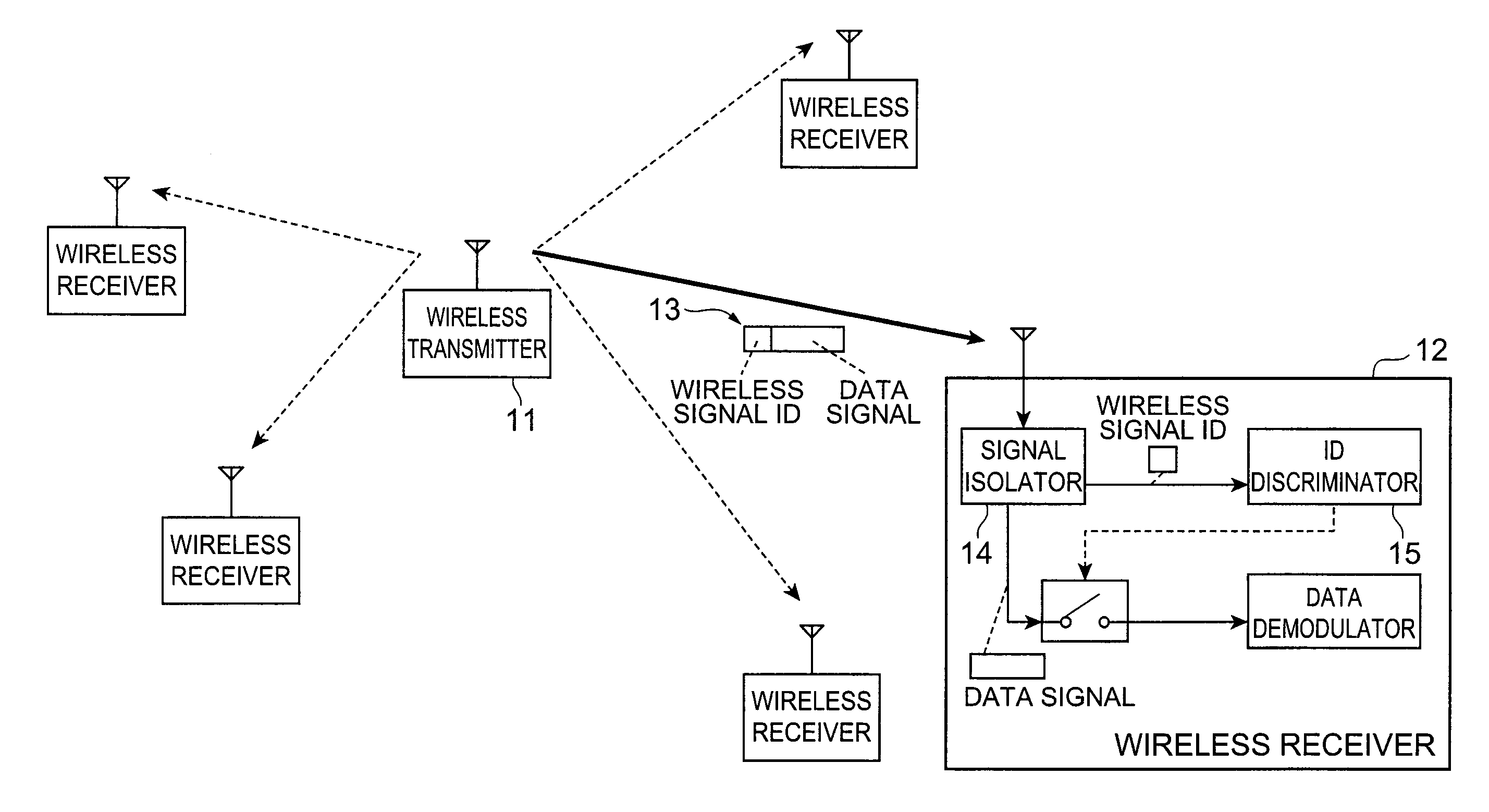
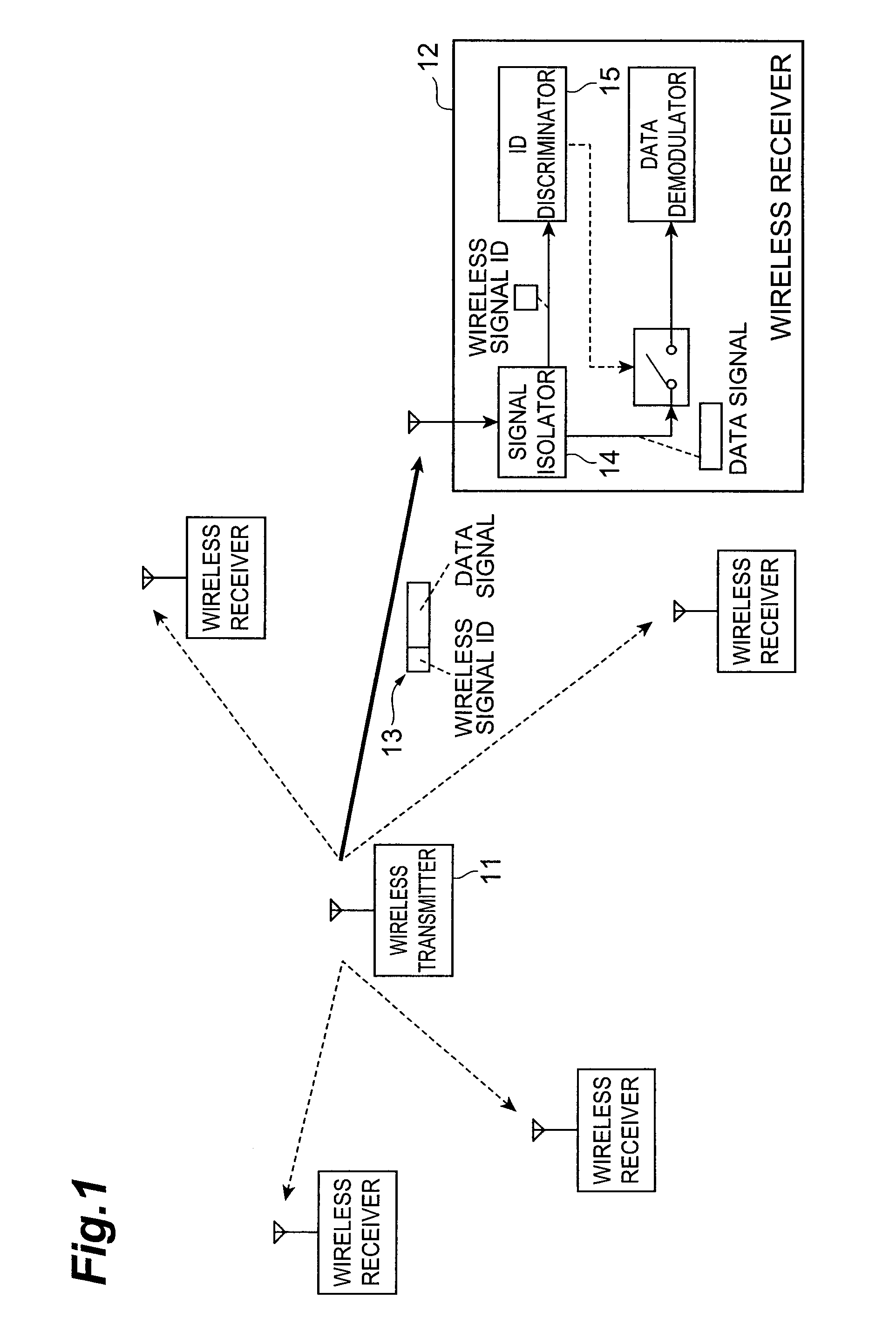
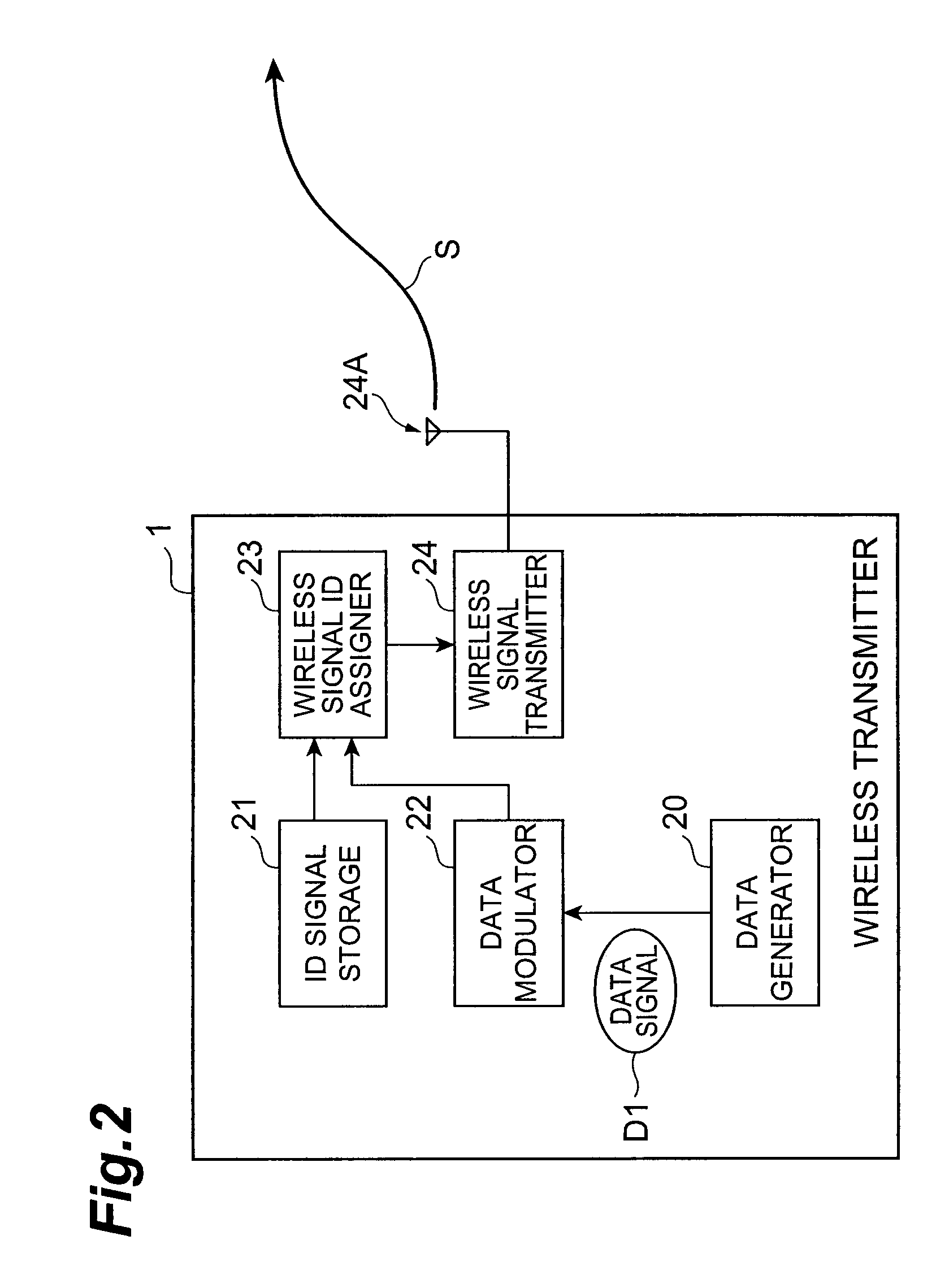
Wireless transmitter, wireless receiver, wireless communication system, and wireless signal control method
InactiveUS20080026704A1Accurate identificationAccurately determineBroadcast service distributionInter user/terminal allocationWireless transmissionCommunications system
A wireless transmitter comprises ID signal storage module for storing an ID signal that identifies a group to which a data signal to be transmitted belongs and provides, for each group, second or higher-order statistic properties unique to each group; modulator for modulating the data signal; wireless signal ID assignment module for associating the modulated signal thus modulated with the stored ID signal and for generating a signal to be transmitted, by assigning second or higher-order statistic properties that correspond with the ID signal to the modulated signal that is associated with the ID signal; and wireless signal transmission module for wirelessly transmitting the signal thus generated.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
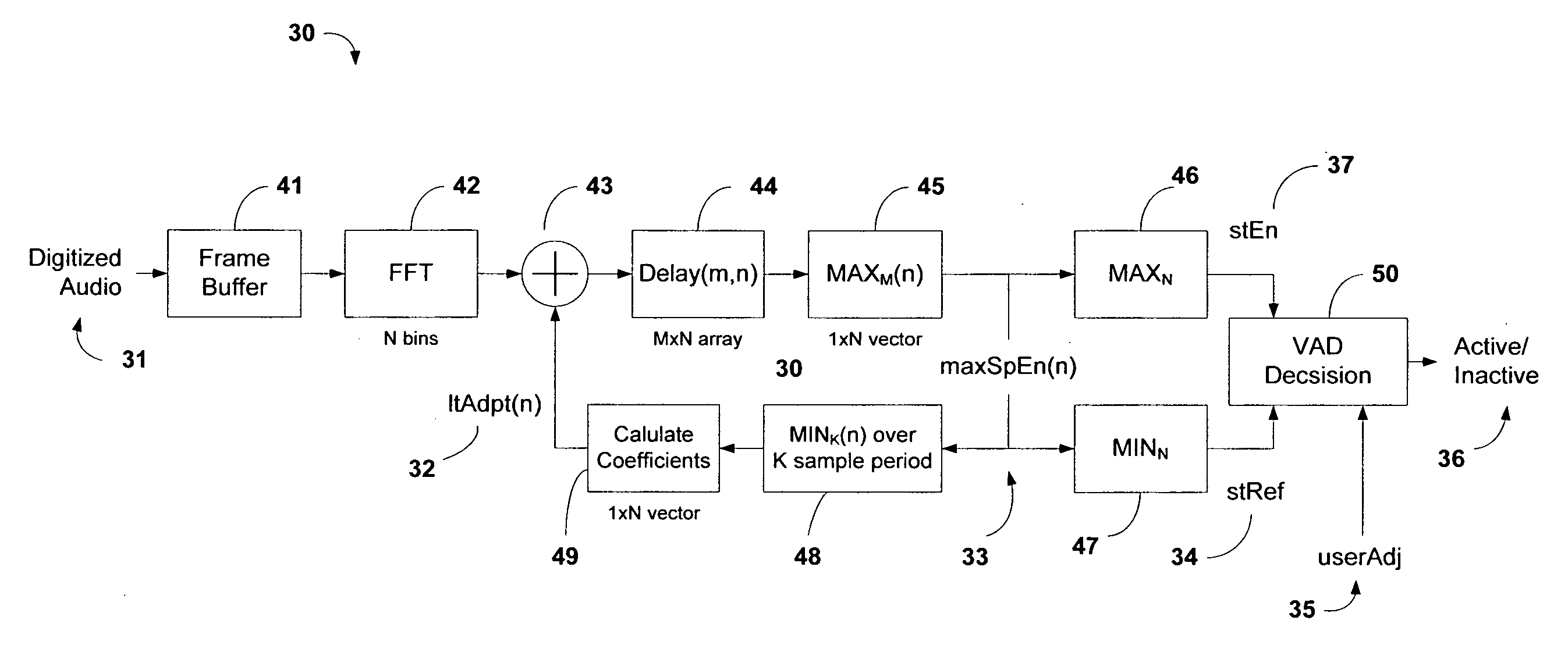
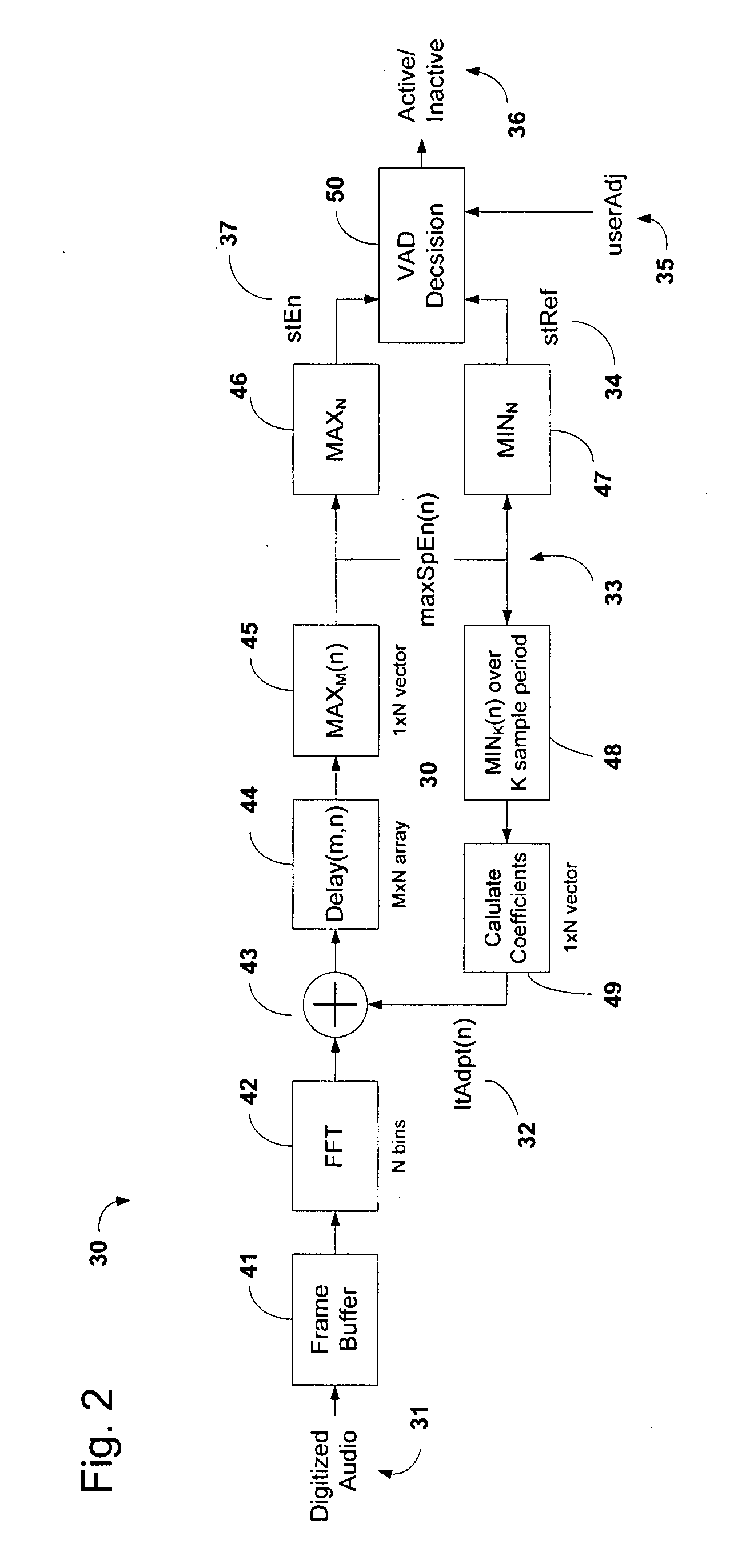
System and method of voice activity detection in noisy environments
InactiveUS20080249771A1Improve the detection rateImprove detection rateSpeech recognitionTraining periodHarmonic
An efficient voice activity detection method and system suitable for real-time operation in low SNR (signal-to-noise) environments corrupted by non-Gaussian non-stationary background noise. The method utilizes rank order statistics to generate a binary voice detection output based on deviations between a short-term energy magnitude signal and a short-term noise reference signal. The method does not require voice-free training periods to track the background noise nor is it susceptible to rapid changes in overall noise level making it very robust. In addition a long-term adaptation mechanism is applied to reject harmonic or tonal interference.
Owner:AVIDYNE CORPORATION
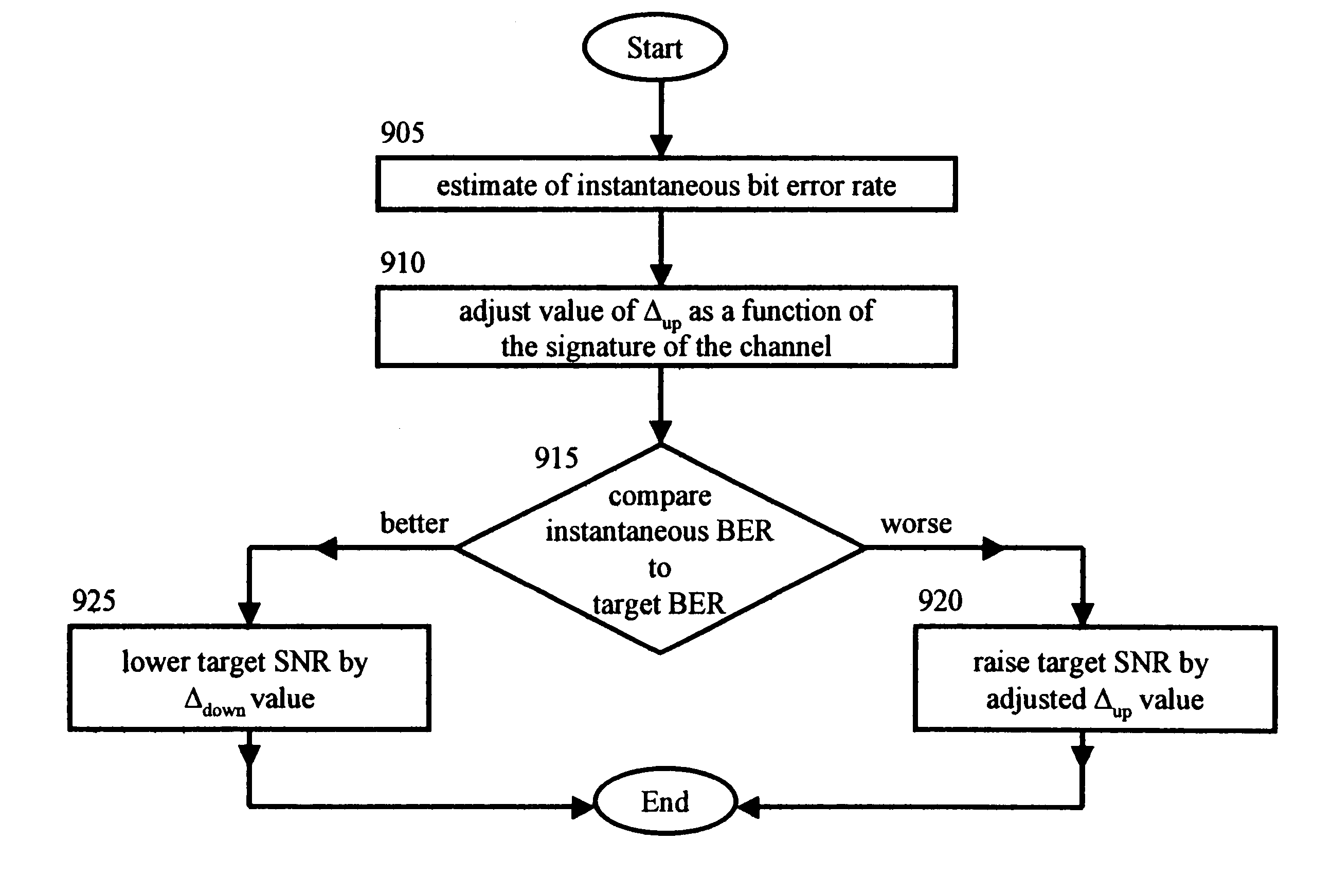
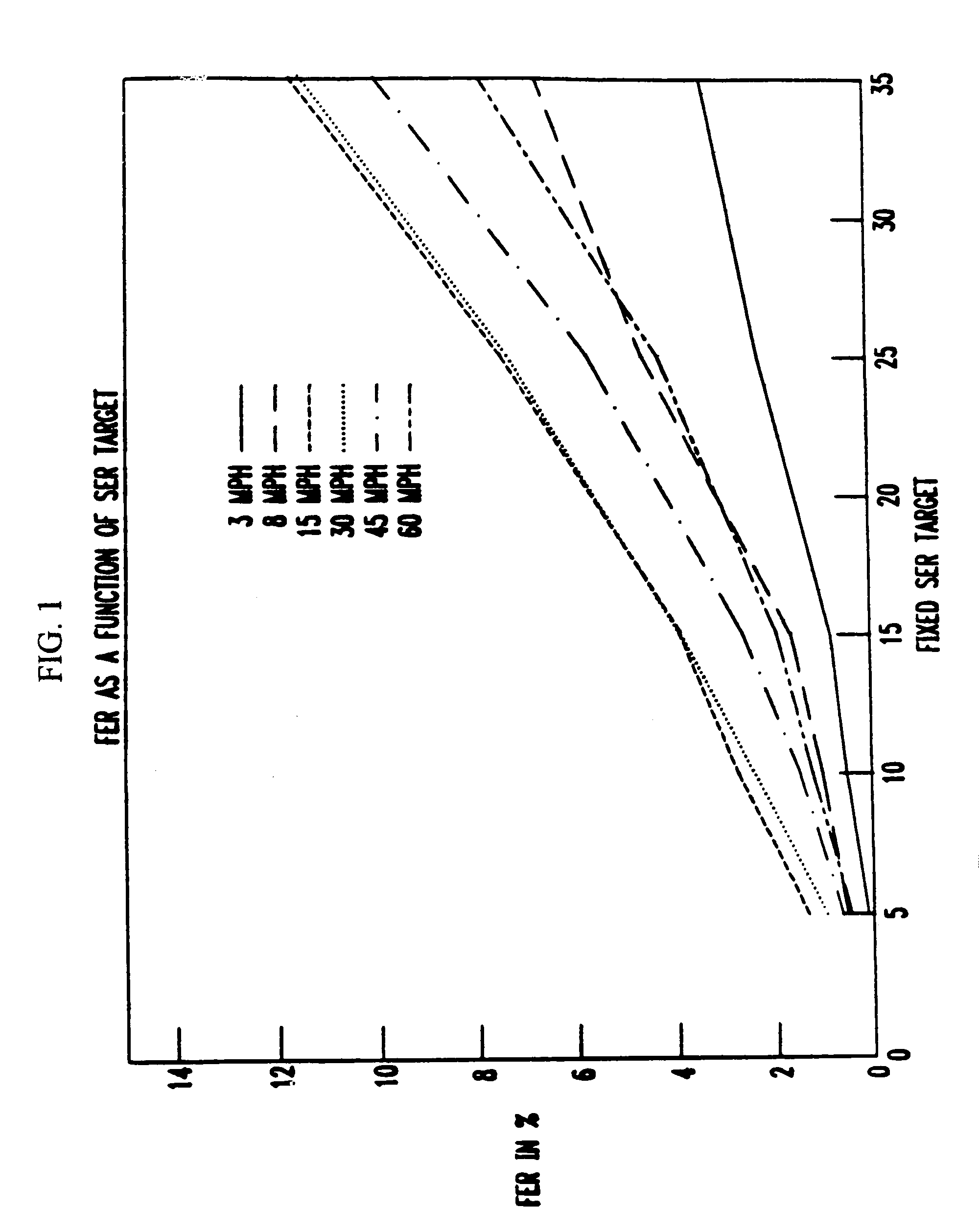
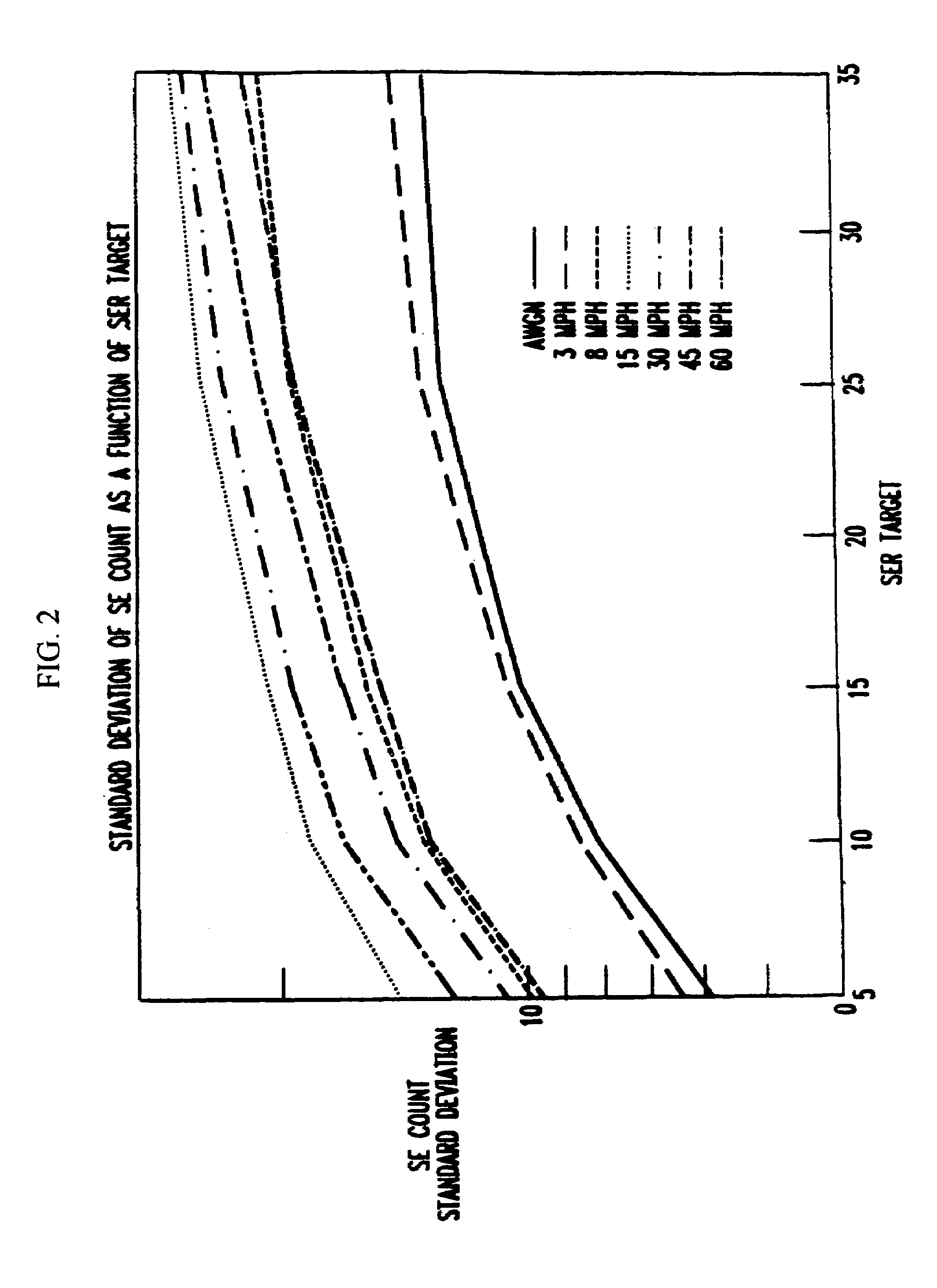
Reverse link outer loop power control with adaptive compensation
InactiveUS6965780B1Power managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
In a wireless communications system, a base station employs a bit error rate (BER) based Reverse Outer Loop Power Control (ROLPC) technique. The ROLPC technique uses either instantaneous or weakly filtered values of the BER for comparison with a BER target value for adjusting a target signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The BER target value is varied as a function of a second order statistic (e.g. variance, standard deviation) of the received SNR. In another embodiment, a symbol error count based ROLPC technique uses adaptive SER targets. In particular, a base station uses a 2nd order statistic, e.g., standard deviation (variance), to identify, or act as a signature of, a particular cellular (wireless) communications environment. The base station monitors the standard deviation of the symbol error count of a received signal (transmitted from a mobile station). The target signal-to-noise ratio ((Eb / N0)T) of this received signal is adjusted as a function of the value of the standard deviation and the adjusted (Eb / N0)T target is used to provide power control.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
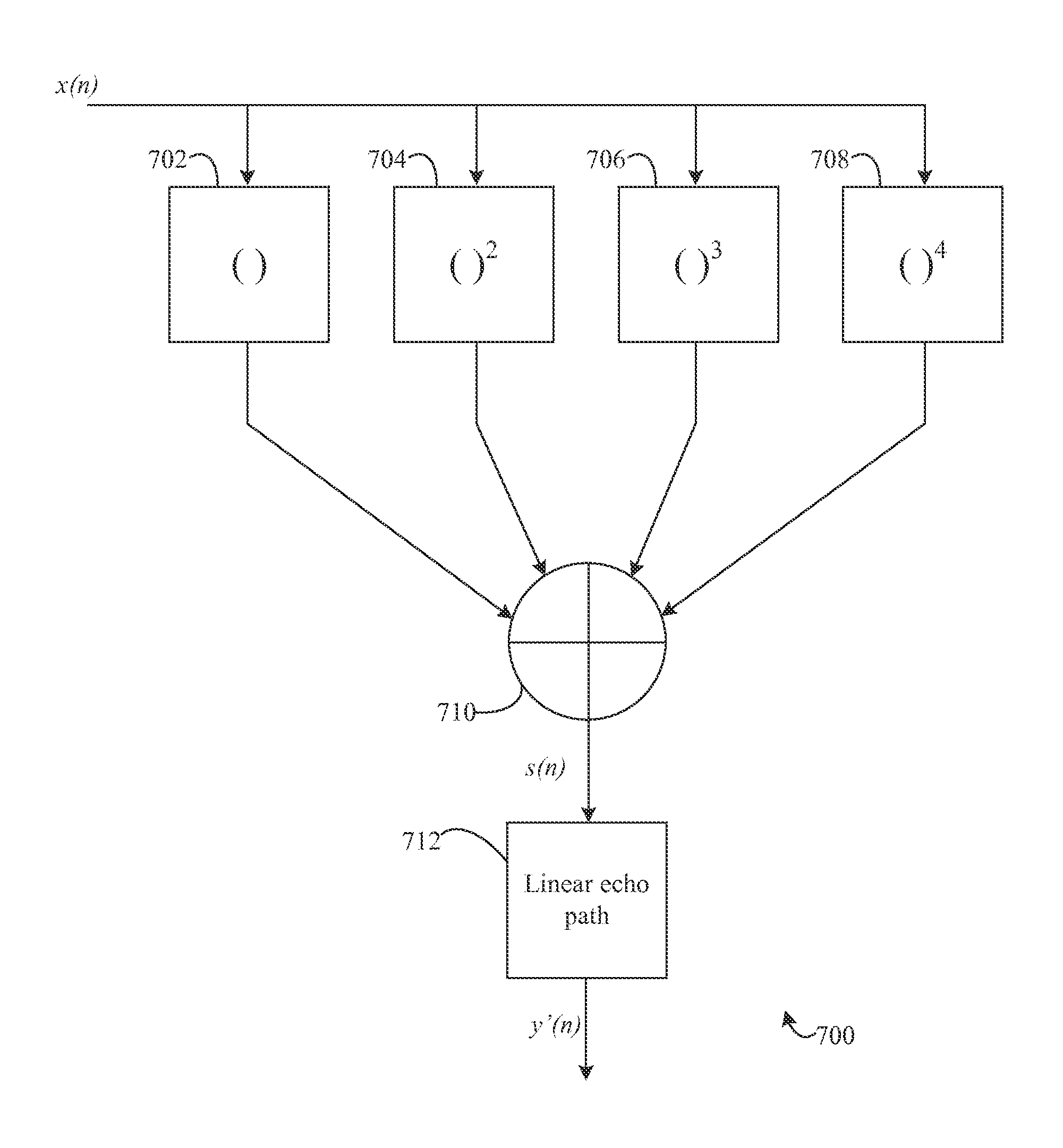
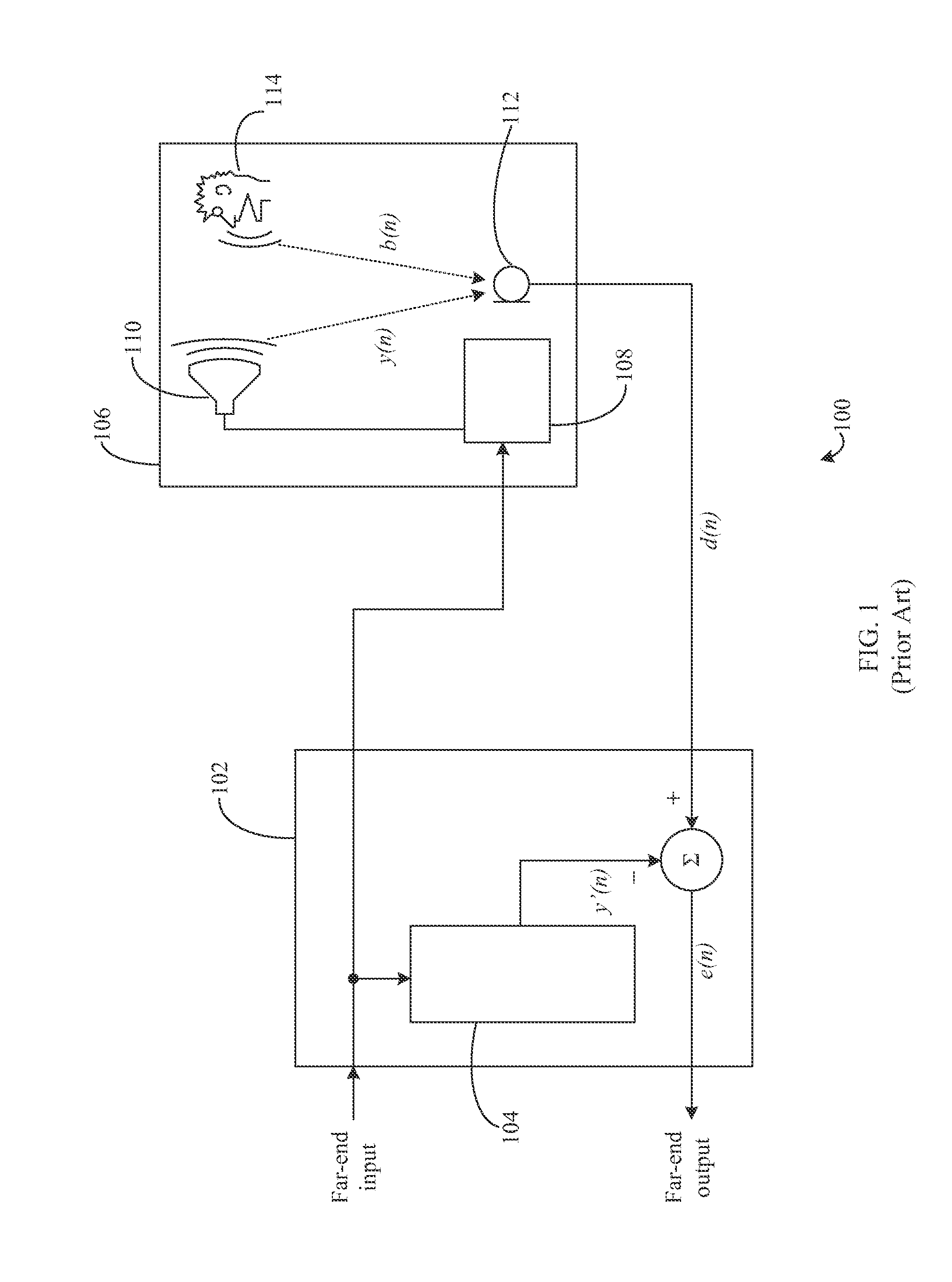
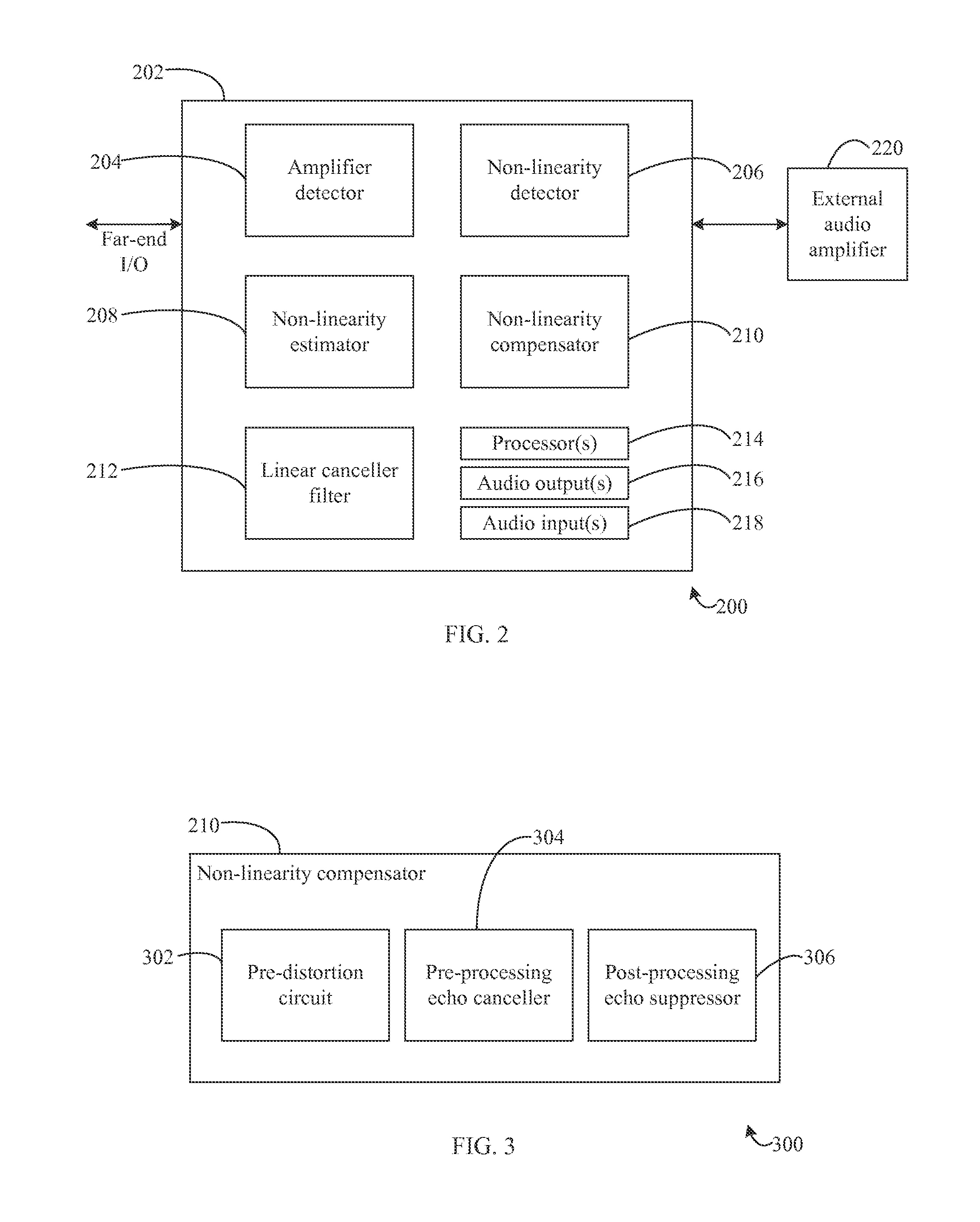
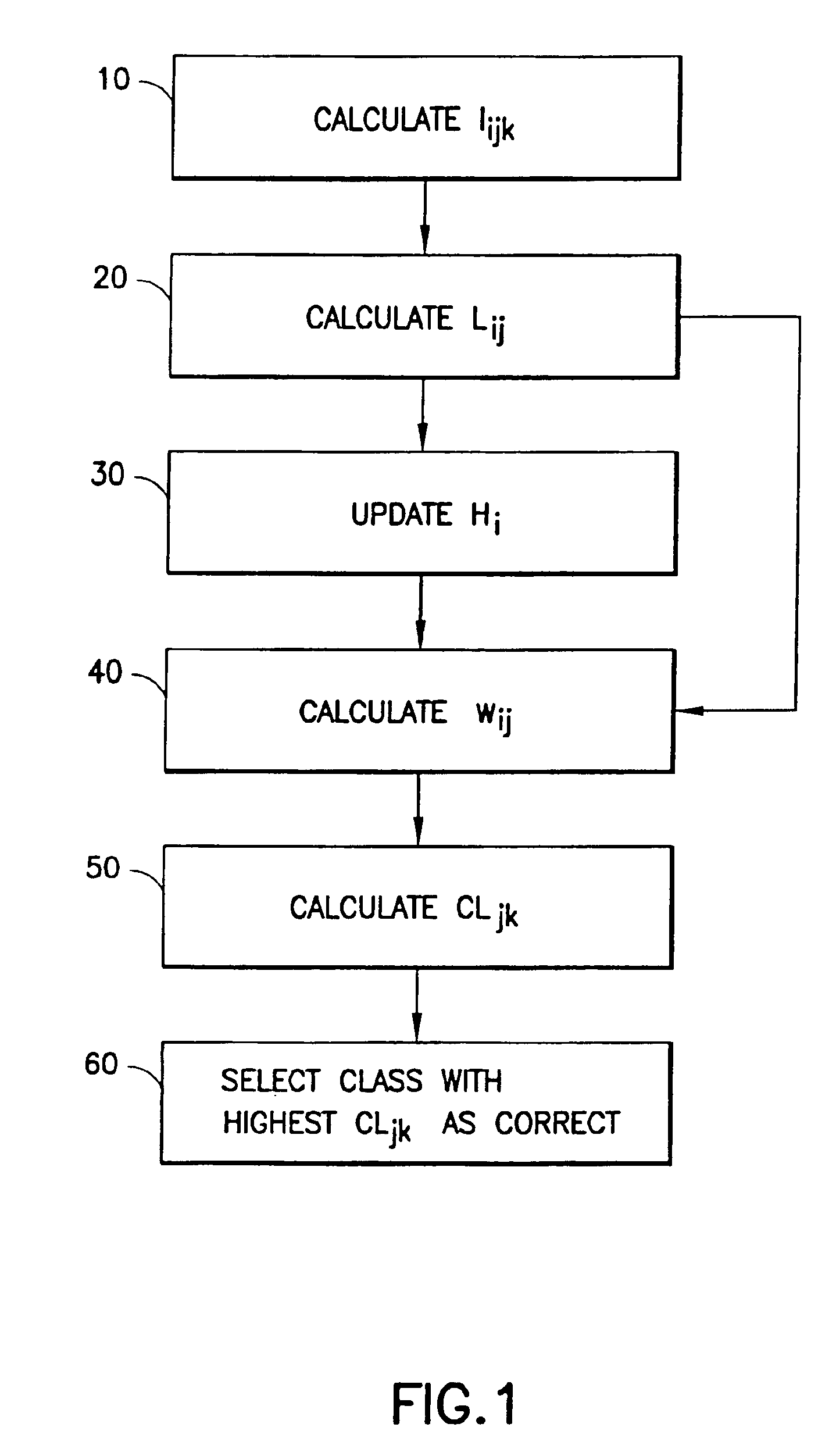
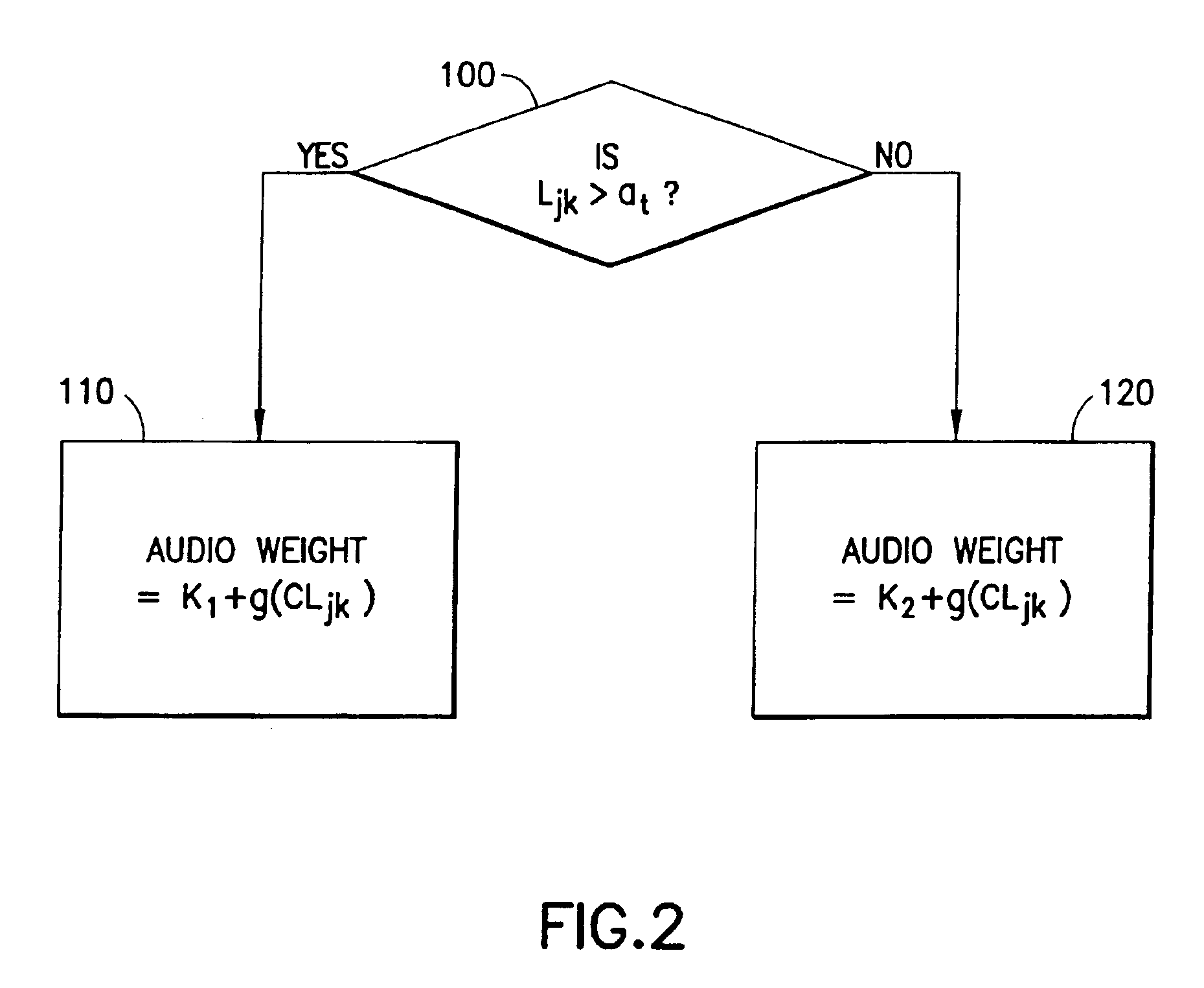
Detecting and quantifying non-linear characteristics of audio signals
InactiveUS20150003606A1Two-way loud-speaking telephone systemsEcho suppressors/cancellersDistortionVIT signals
Methods, systems, and apparatuses are provided for detecting, quantifying, and compensating for non-linear characteristics of audio signals. External audio devices are detected when coupled to electronic or communication devices. Tuning operations are initiated upon detection of external audio devices to estimate non-linear parameters imparted to audio signals by the external audio devices. The non-linear components of audio signals are compensated for based upon the estimations. Compensation is performed using pre-processing filters, distortion circuits, post-processing filters. Estimation and compensation for non-linearities is performed on the basis of models dynamically generated during estimation and the use of higher-order statistics.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Target signal detection method based on improved COSGO (Average Order Statistics Greatest of)-CFAR (Constant False Alarm Rate)
InactiveCN101872014AIncrease Target SNR GainReduce clutter missed detectionWave based measurement systemsTarget signalReference window
The invention discloses a COSGO (Average Order Statistics Greatest of)-CFAR (Constant False Alarm Rate) detection method in the work adopting a continuous wave system radar. In the COSGO-CFAR detection, firstly, n reference units in a left reference window and a right reference window of a target detection unit are sequenced from small to large according to powder; the left reference window and the right reference window respectively selects powers of former n-k units as clutter average power to respectively obtain two average clutter powders of the left reference window and the right reference window; the greater power of the two obtained average clutter powders is selected as the clutter power; and then the greater power is multiplied with a normalization threshold to obtain a real detection threshold, and the real detection threshold is compared with the power of the target detection unit to obtain a comparison result. The COSGO-CFAR detection method provided in the working adopting the continuous wave system radar realizes two-dimensional coherence accumulation through distance IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform) pulse pressure and orientation FFT (Fast Flourier Transform) pulse pressure, improves the target signal to noise ratio gain, and reduces the clutter detection omission under multi-object detection.
Owner:SHENZHEN KIGLESH TECH
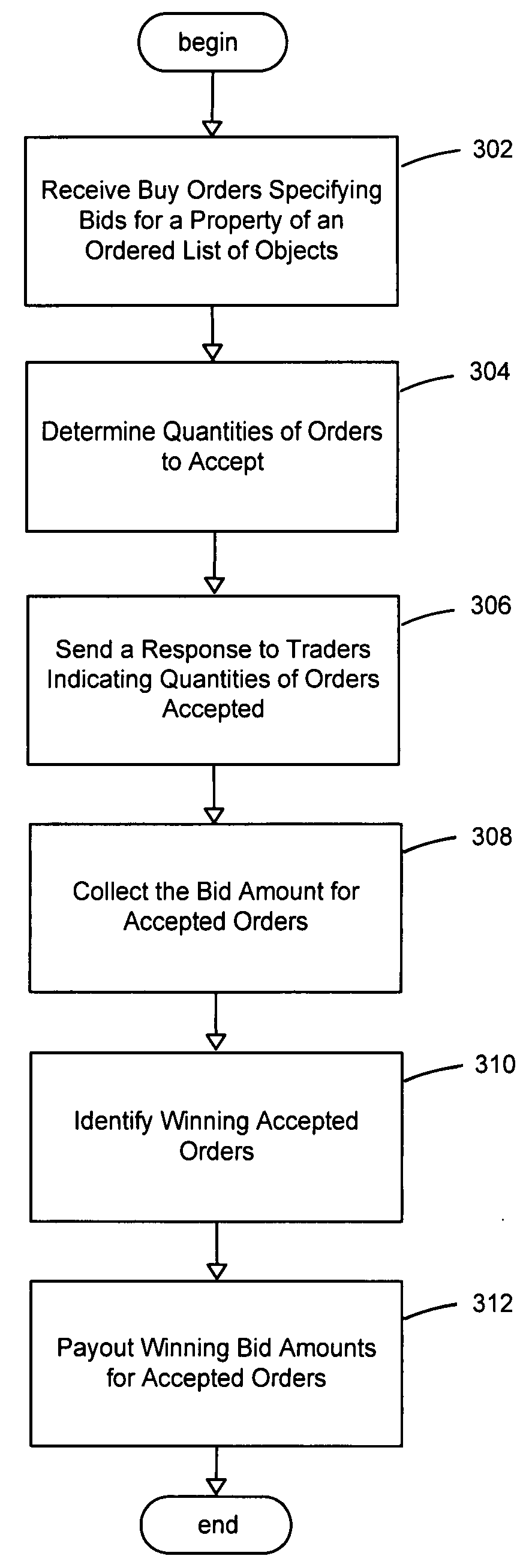
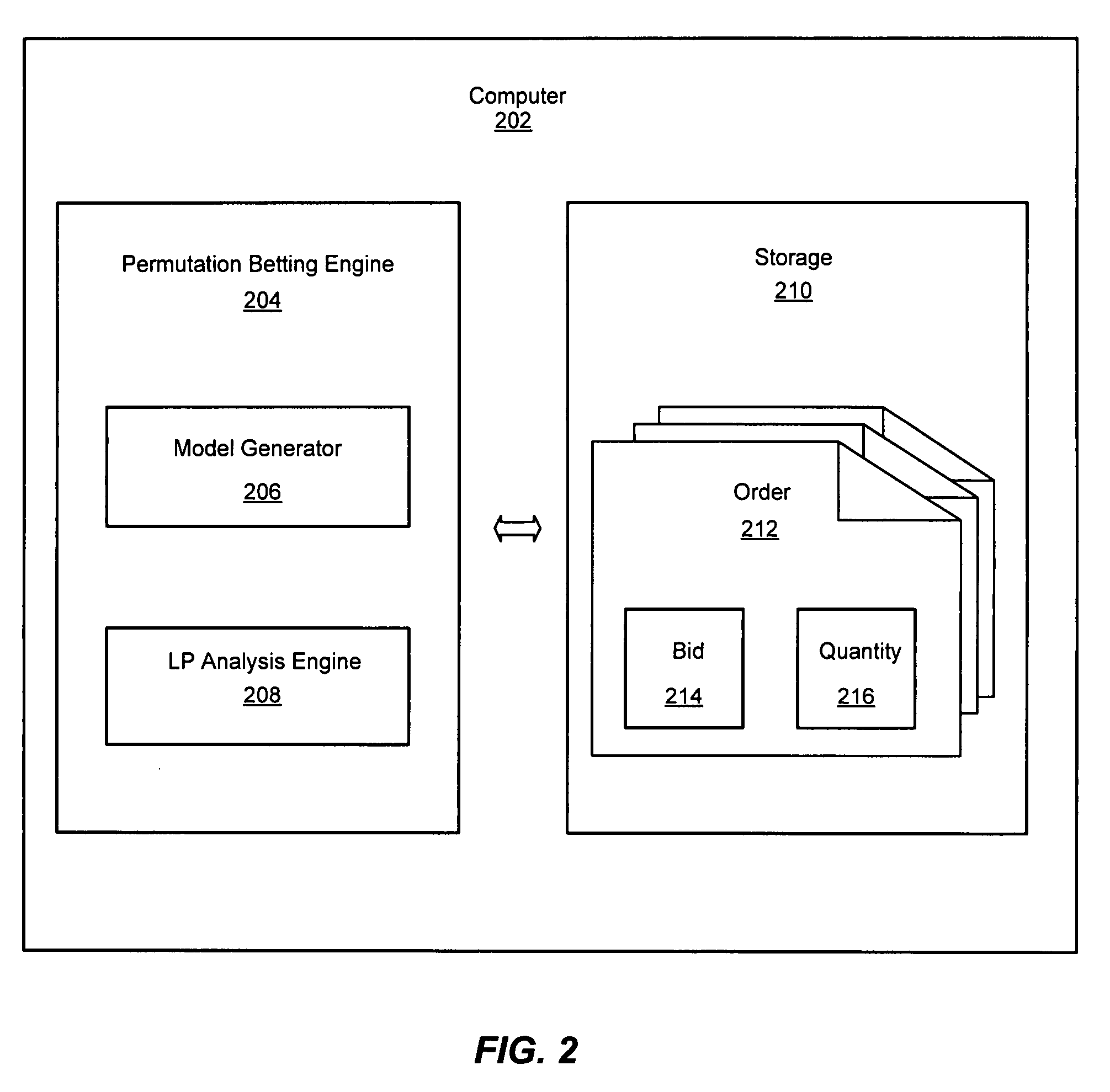
System and method for permutation betting
InactiveUS20080220855A1Maximizing a worst-case profit of an auctioneerImprove efficiencyApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesPaymentRanking
An improved system and method is provided for permutation betting. To do so, a permutation betting engine may be provided for providing services to support betting on an outcome resulting in an ordinal ranking of objects. Orders specifying a property of an ordering of one or more positions of an object in an ordinal ranking of objects may be received. The quantities for orders to accept may be determined, a response may be sent to traders indicating the quantities of orders for payment, and the amount owed for accepted orders may be collected. Winning accepted orders may be identified and payout may be made for winning accepted orders. Advantageously, the present invention may provide a framework for efficiently optimizing an auctioneer's objective using linear programming for a prediction market where the outcomes of interested events are ordered statistics.
Owner:OATH INC
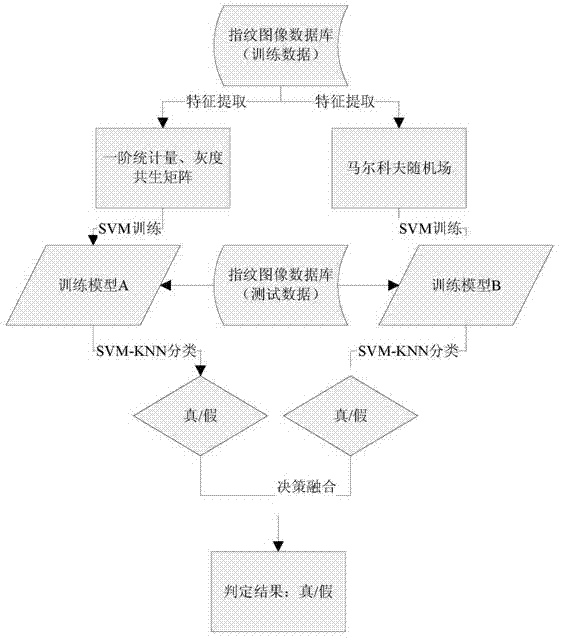
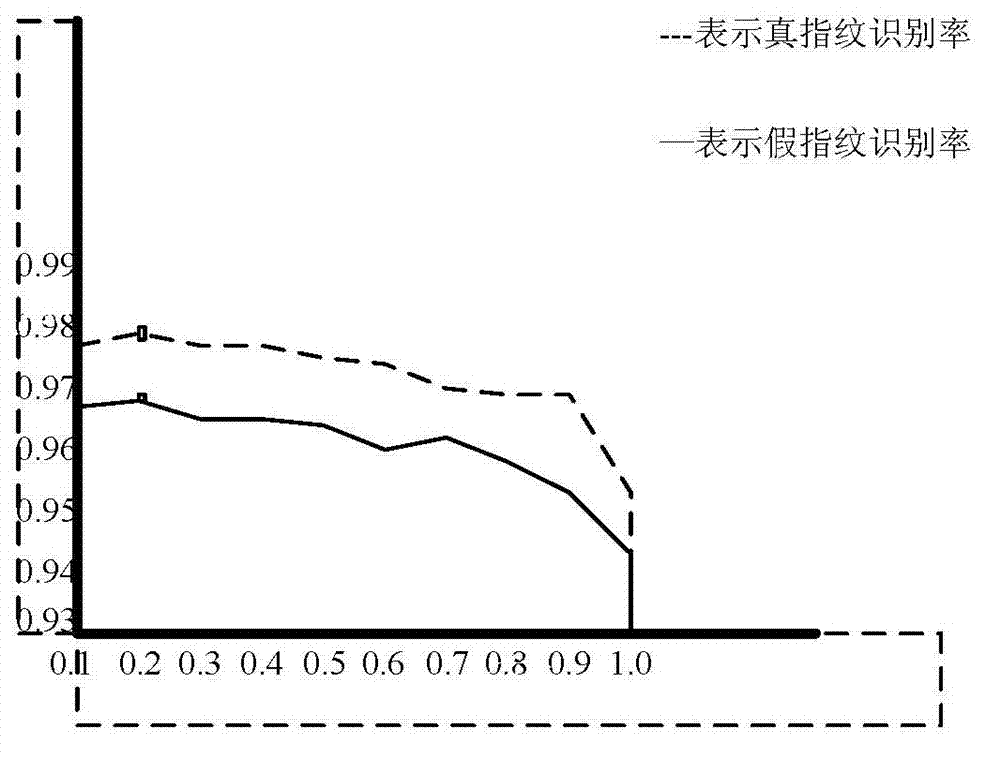
Fake fingerprint detection method based on markov random field (MRF) and support vector machine-k nearest neighbor (SVM-KNN) classification
ActiveCN103116744AImprove detection efficiencyImprove detection accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorSupport vector machine
A fake fingerprint detection method based on markov random field (MRF) and support vector machine-k nearest neighbor (SVM-KNN) classification includes steps: (1) fingerprint image feature extracting: (1.1) first-order statistics (FOS), (1.2) a gray level co occurrence matrix (GLCM) and (1.3) an MRF; (2) SVM training: training the FOS and the GLCM feature vector and the MRF feature vector to obtain a model A and a model B; (3) SVM-KNN classification: (3.1) the SVM classification mechanism and (3.2) SVM-KNN classifier forming; and (4) decision fusion for true and false fingerprint detection. Presently related articles for fake fingerprint detection by aid of the GLCM and the MRF are not found, and the fake fingerprint detection method achieves the purpose of identifying true and false fingerprints by aid of physical structures of the two feature quantized fingerprint images. Experiment results prove that the false accept rate and the false reject rate of the algorithm are respectively 1.84% and 1.79%, and therefore the fake fingerprint detection method is high in accuracy and good in practicality.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Approximate order statistics of real numbers in generic data
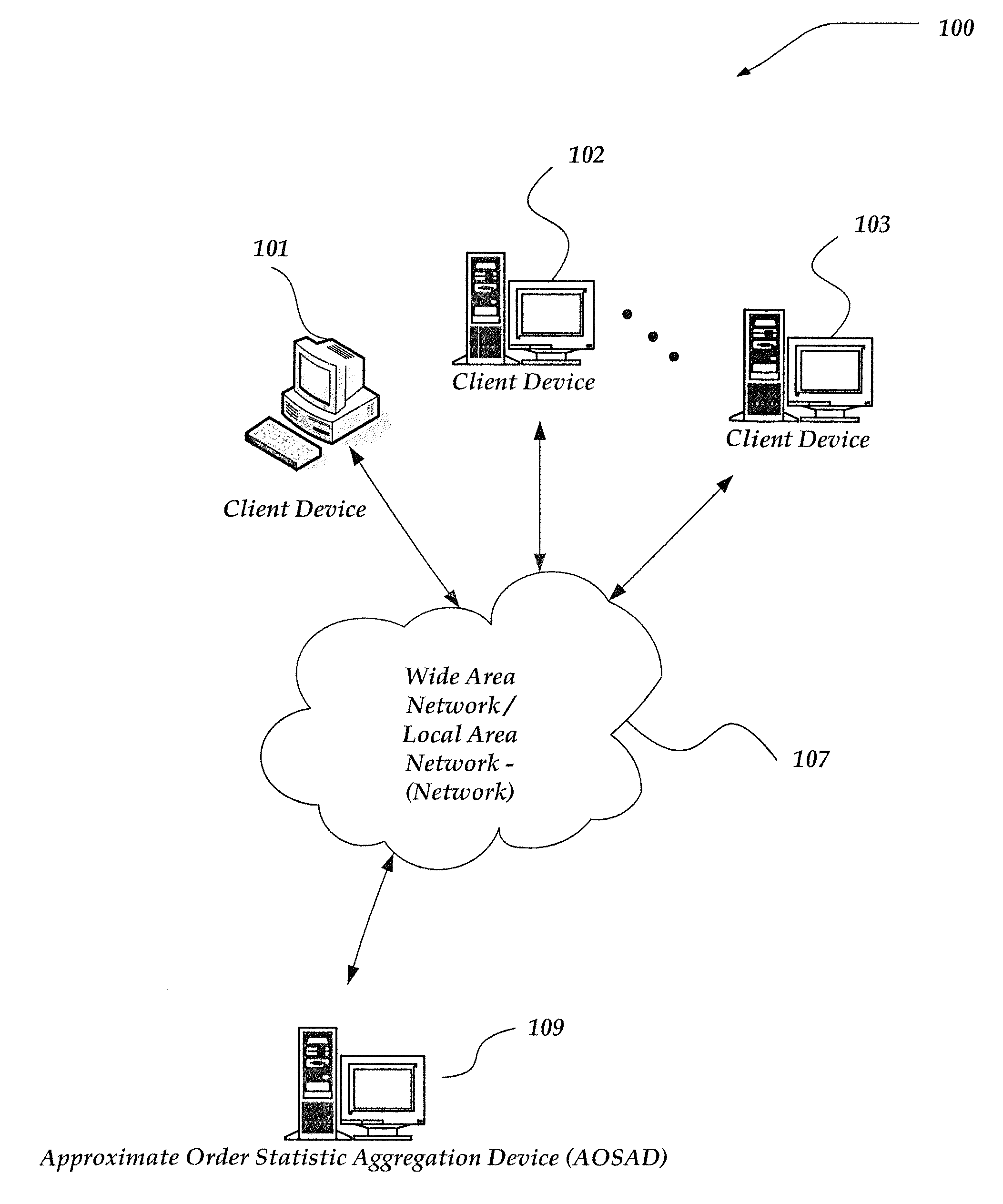
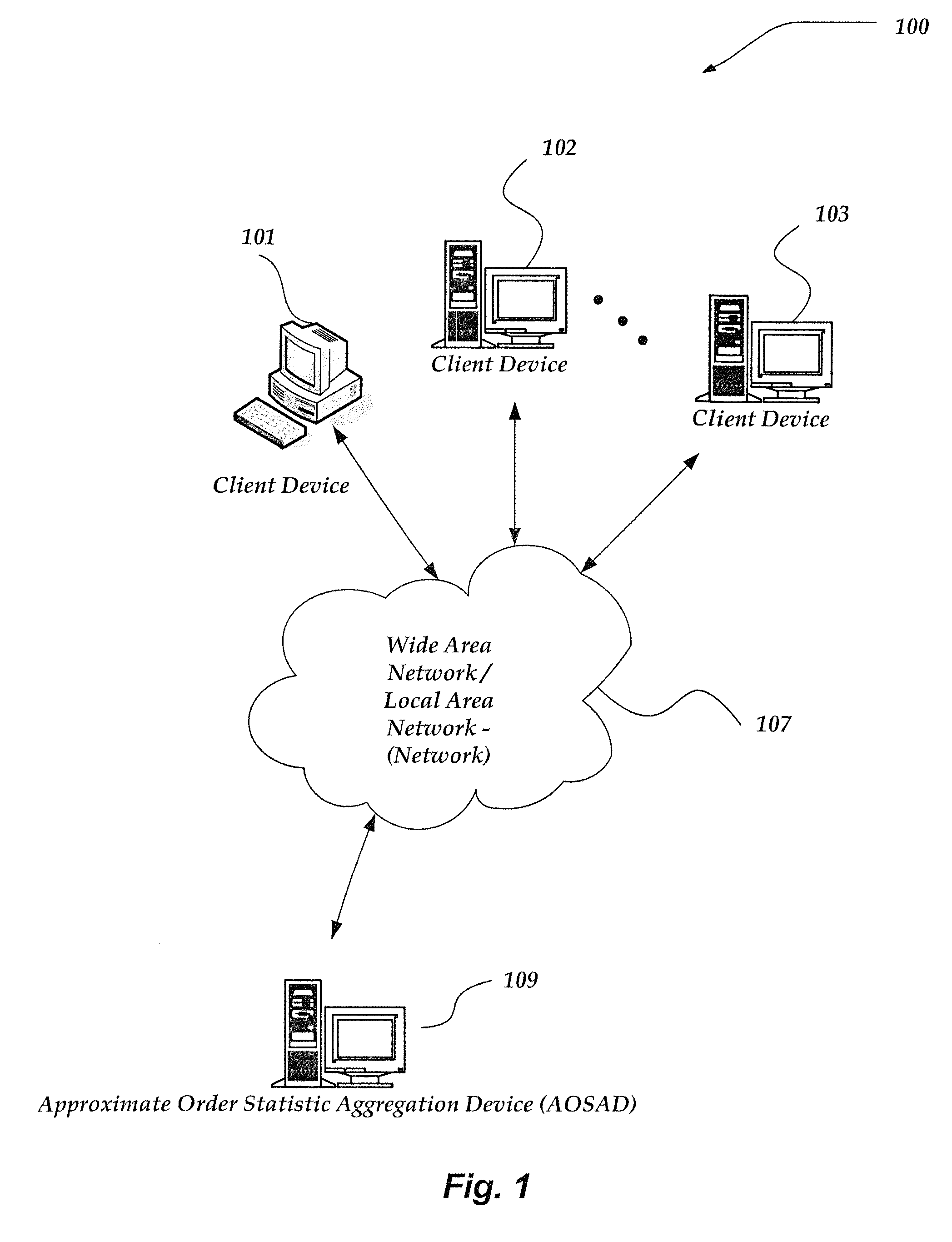
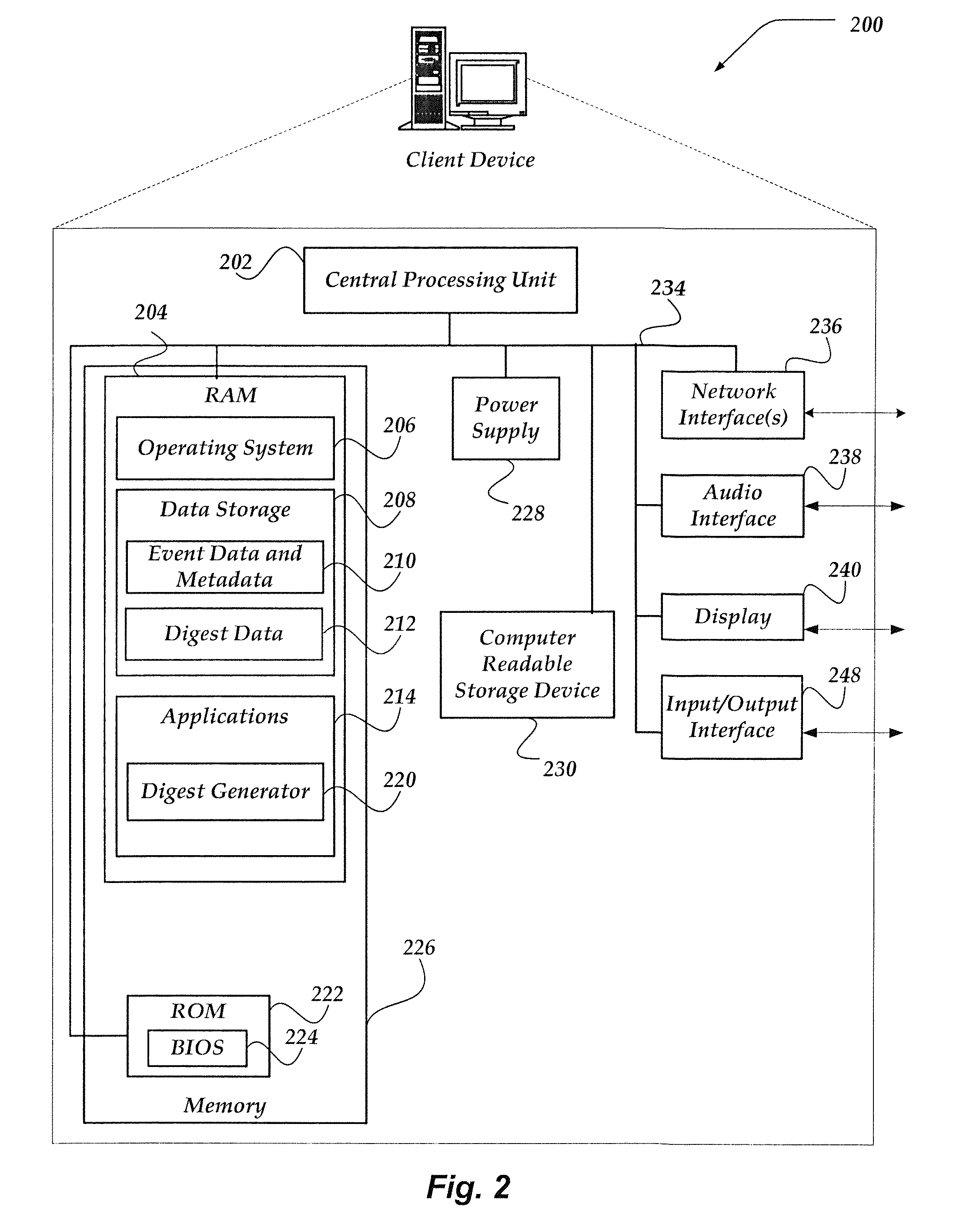
ActiveUS20130054660A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsReal arithmeticTheoretical computer science
A method, system, and processor-readable storage medium are directed towards calculating approximate order statistics on a collection of real numbers. In one embodiment, the collection of real numbers is processed to create a digest comprising hierarchy of buckets. Each bucket is assigned a real number N having P digits of precision and ordinality O. The hierarchy is defined by grouping buckets into levels, where each level contains all buckets of a given ordinality. Each individual bucket in the hierarchy defines a range of numbers—all numbers that, after being truncated to that bucket's P digits of precision, are equal to that bucket's N. Each bucket additionally maintains a count of how many numbers have fallen within that bucket's range. Approximate order statistics may then be calculated by traversing the hierarchy and performing an operation on some or all of the ranges and counts associated with each bucket.
Owner:SPLUNK INC
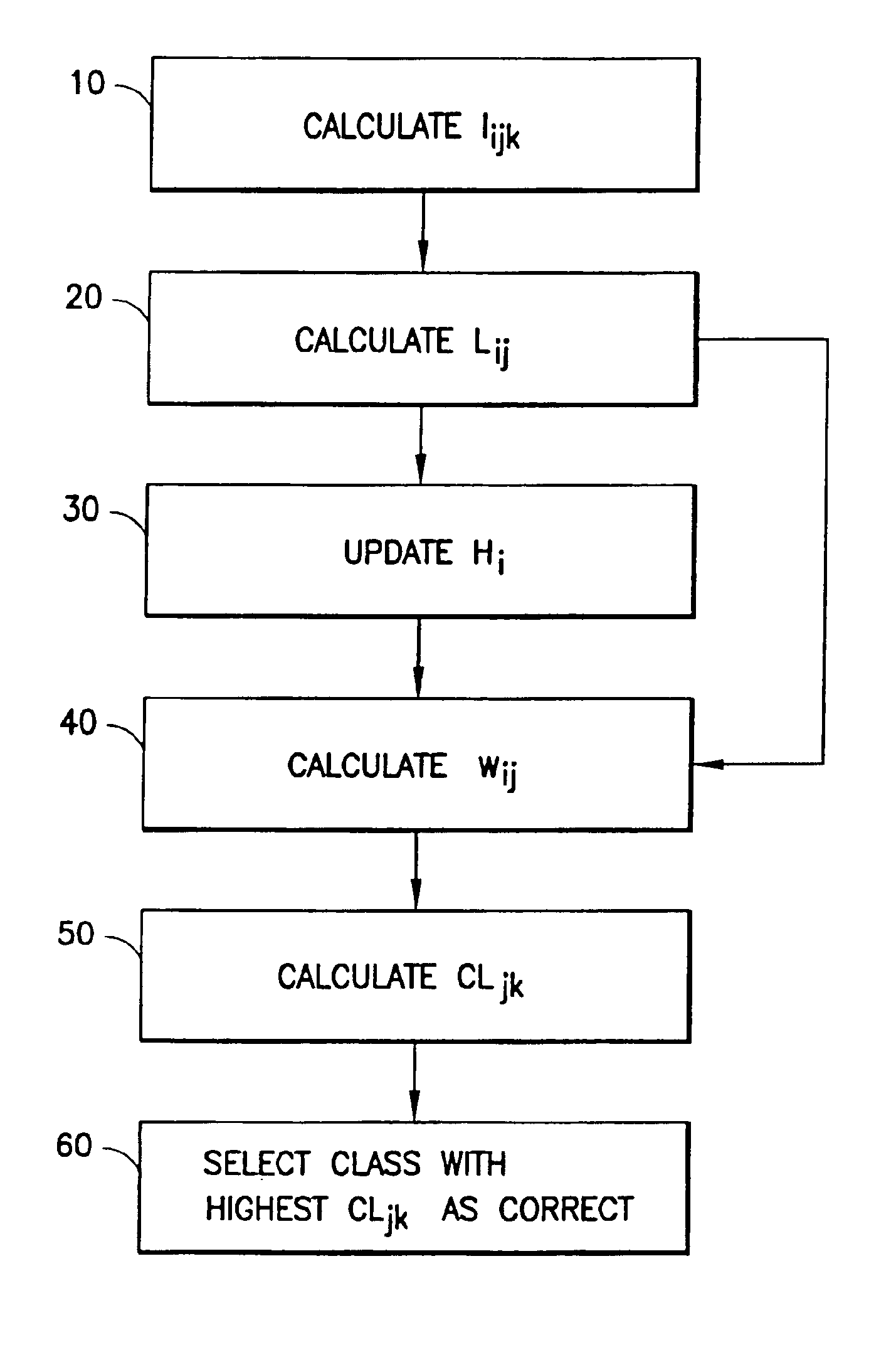
Decision making in classification problems
InactiveUS6931351B2Improve decision accuracyImprove classification accuracyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital data processing detailsAlgorithmClass model
Owner:IBM CORP
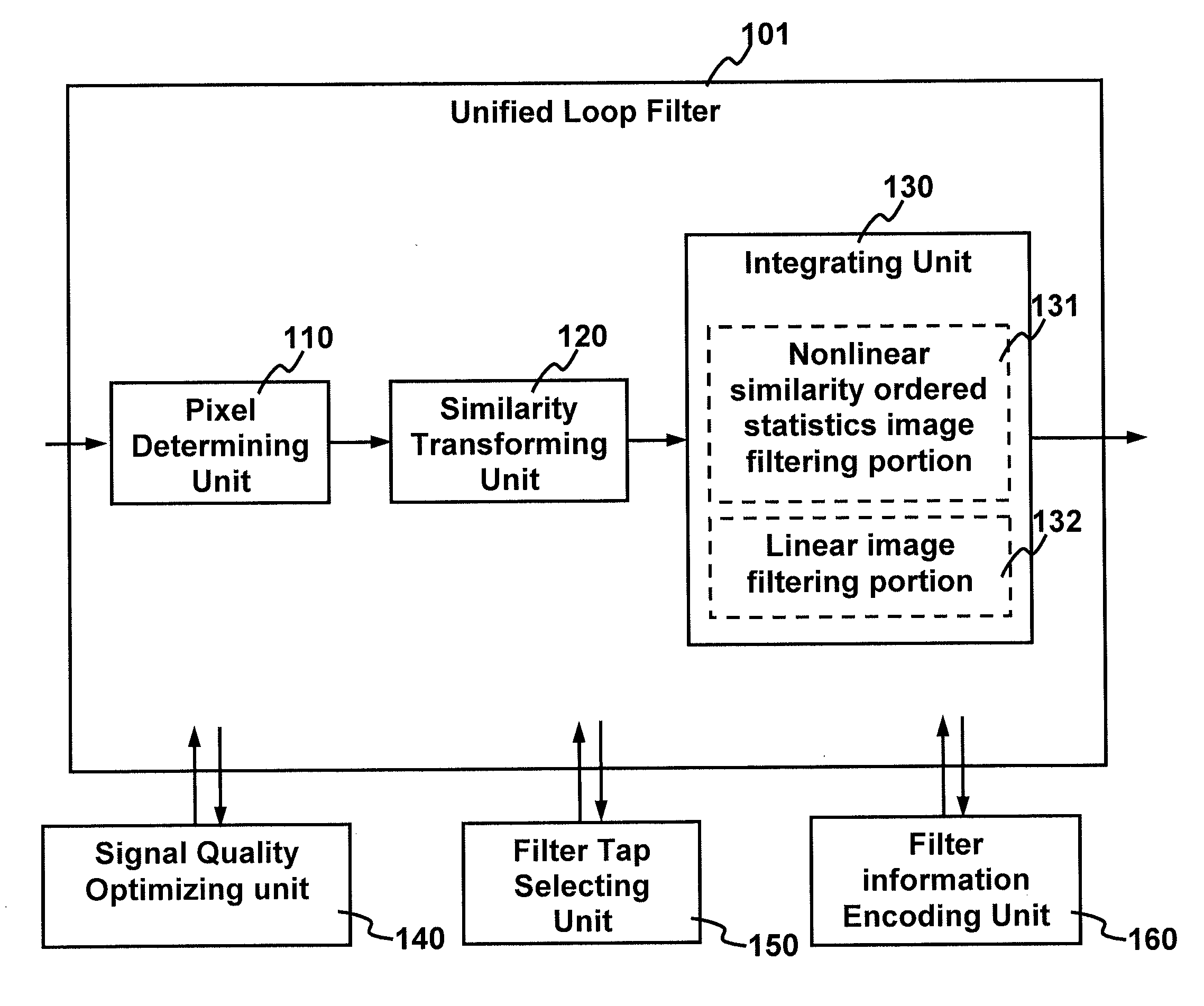
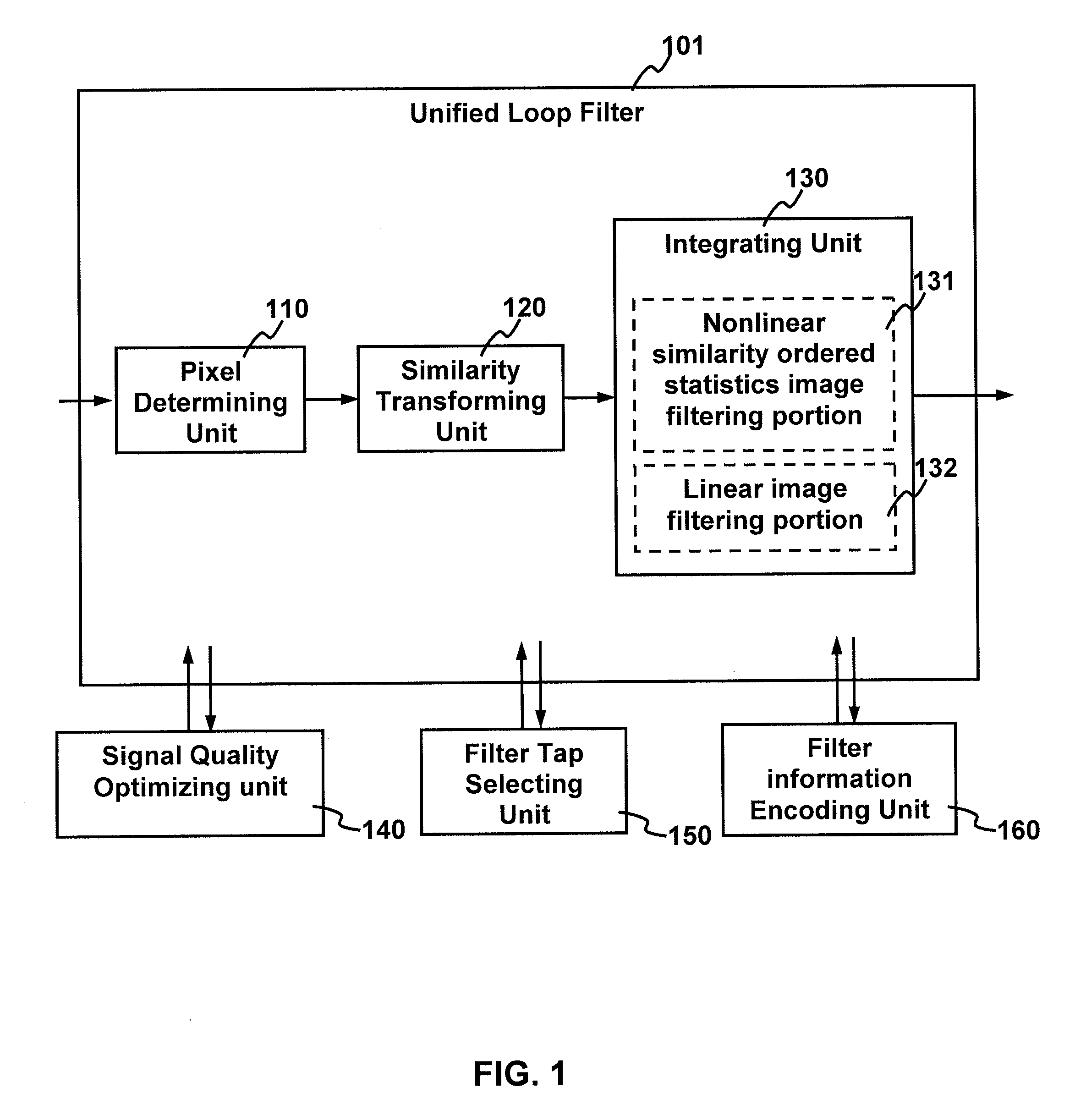
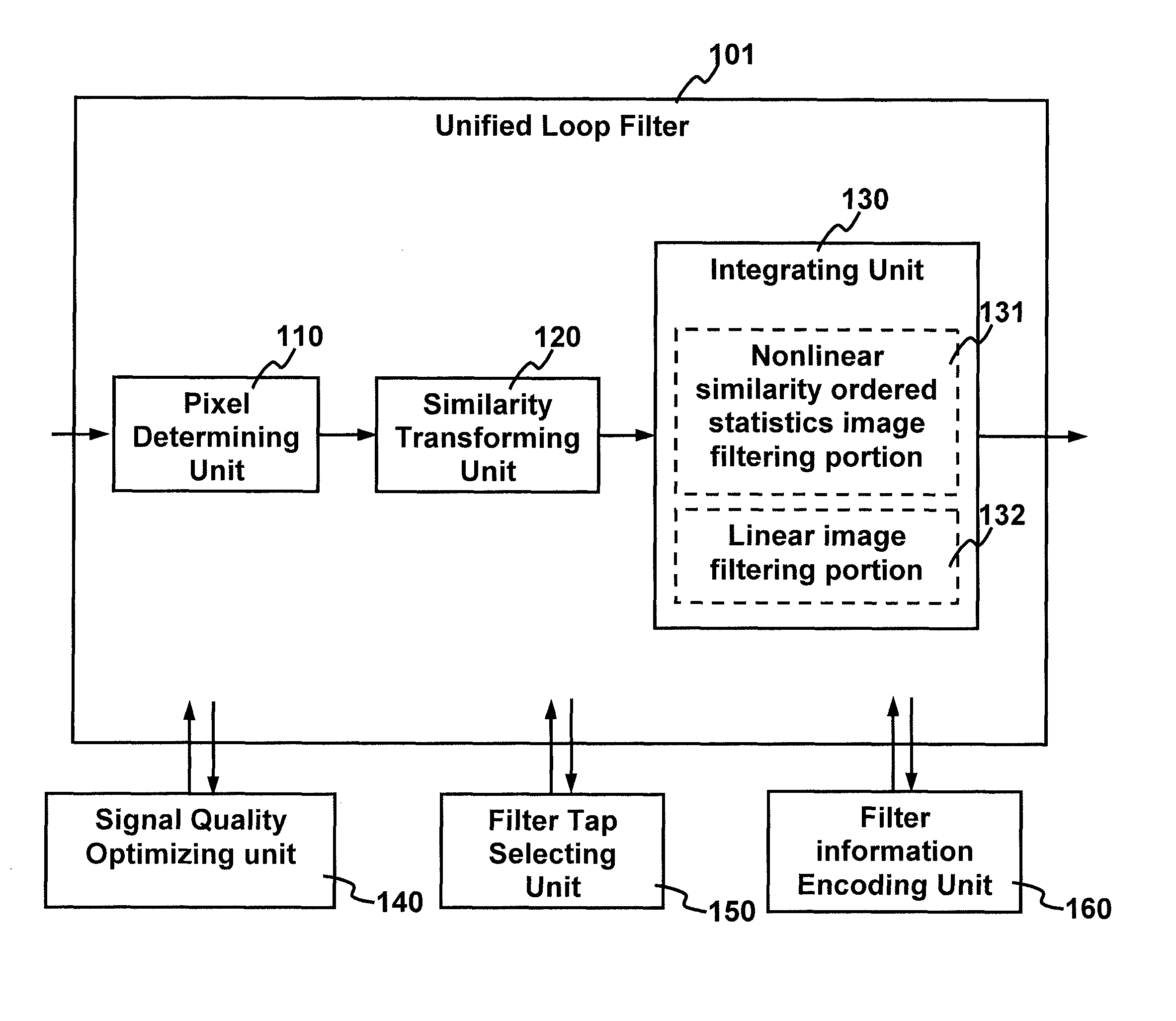
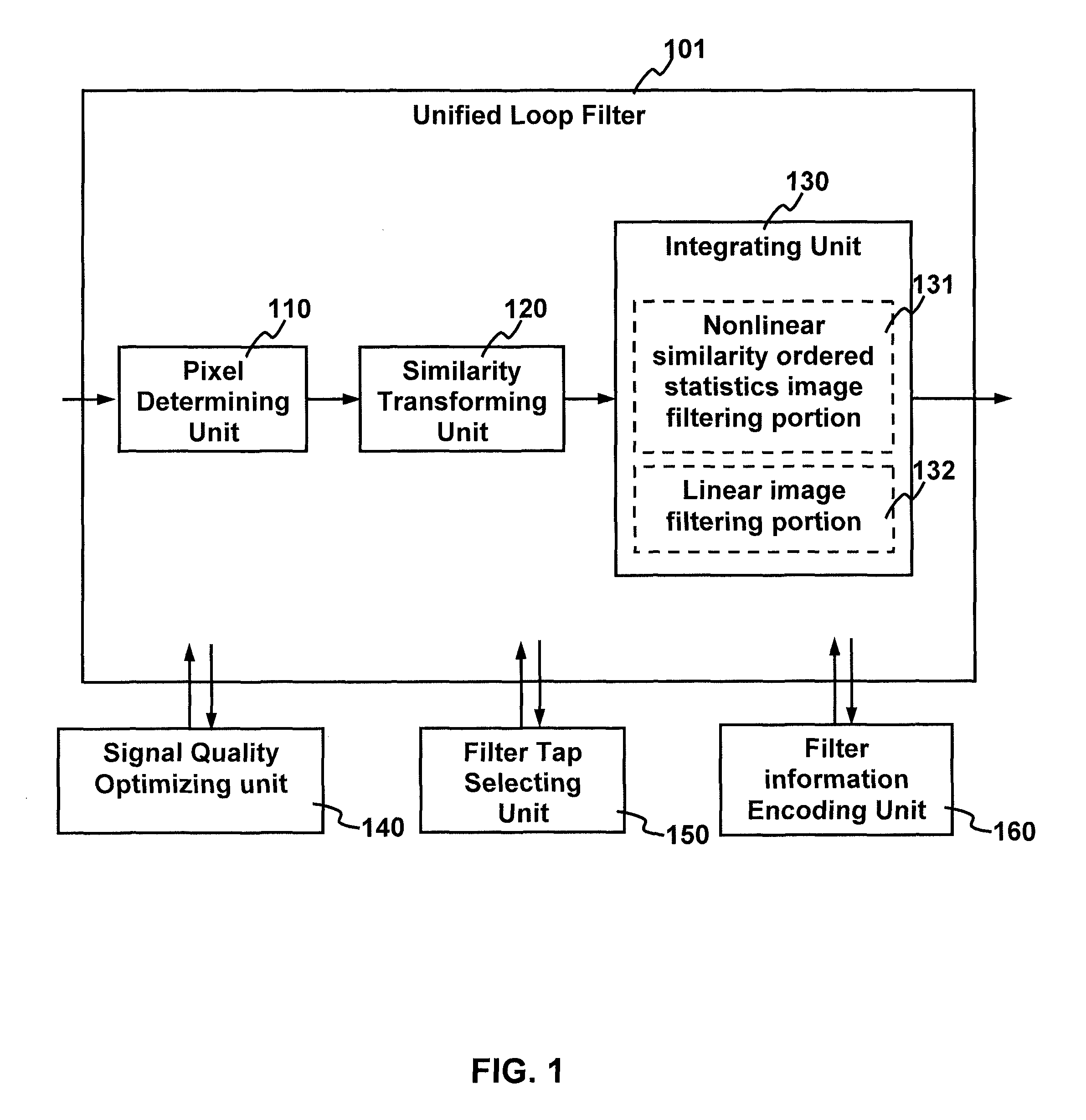
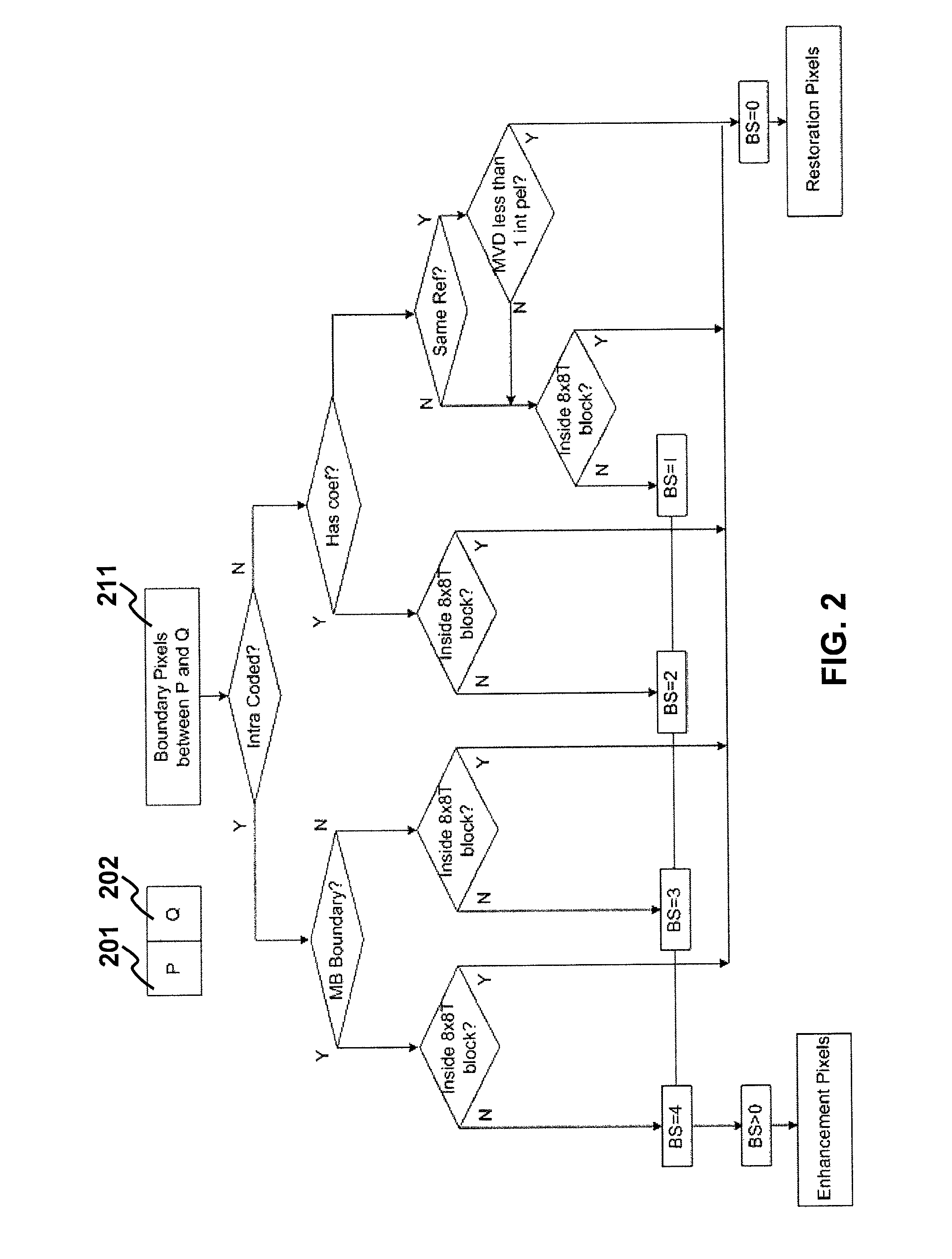
Method and apparatus for improving video quality
ActiveUS20110142136A1Improve objective qualityRaise the ratioImage enhancementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionLoop filter
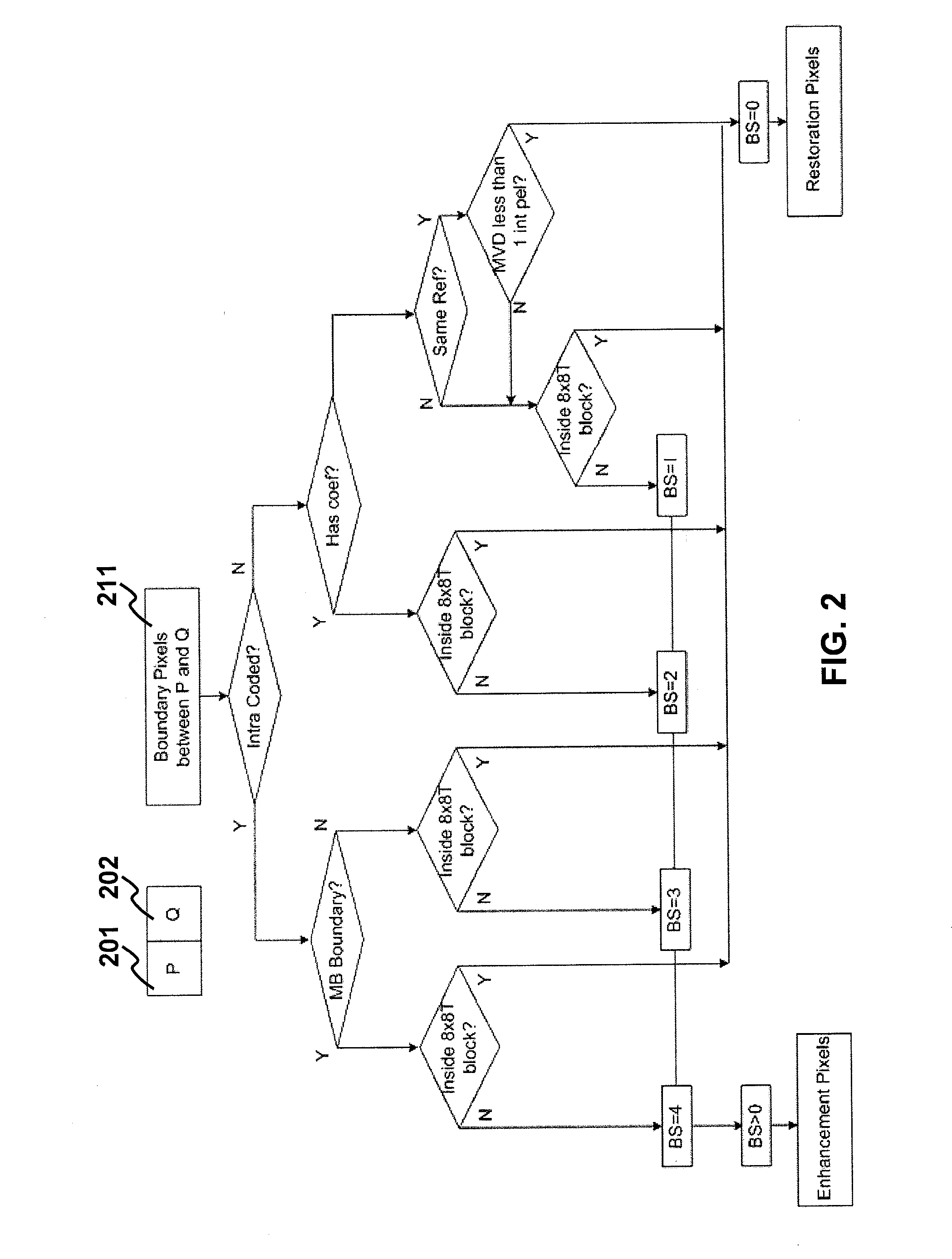
The present invention relates to method and apparatus for improving video quality. The present invention provides a unified loop filter including: a pixel determining unit which determines the type of a pixel based on boundary strength; a similarity transforming unit which transforms a nonlinear filter into a nonlinear similarity-ordered statistics filter; and an integrating unit which integrates the nonlinear similarity-ordered statistics filter with a linear image filtering portion. The unified loop filter is applicable to filter reconstructed frames when an encoder or a decoder is processing a video signal.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
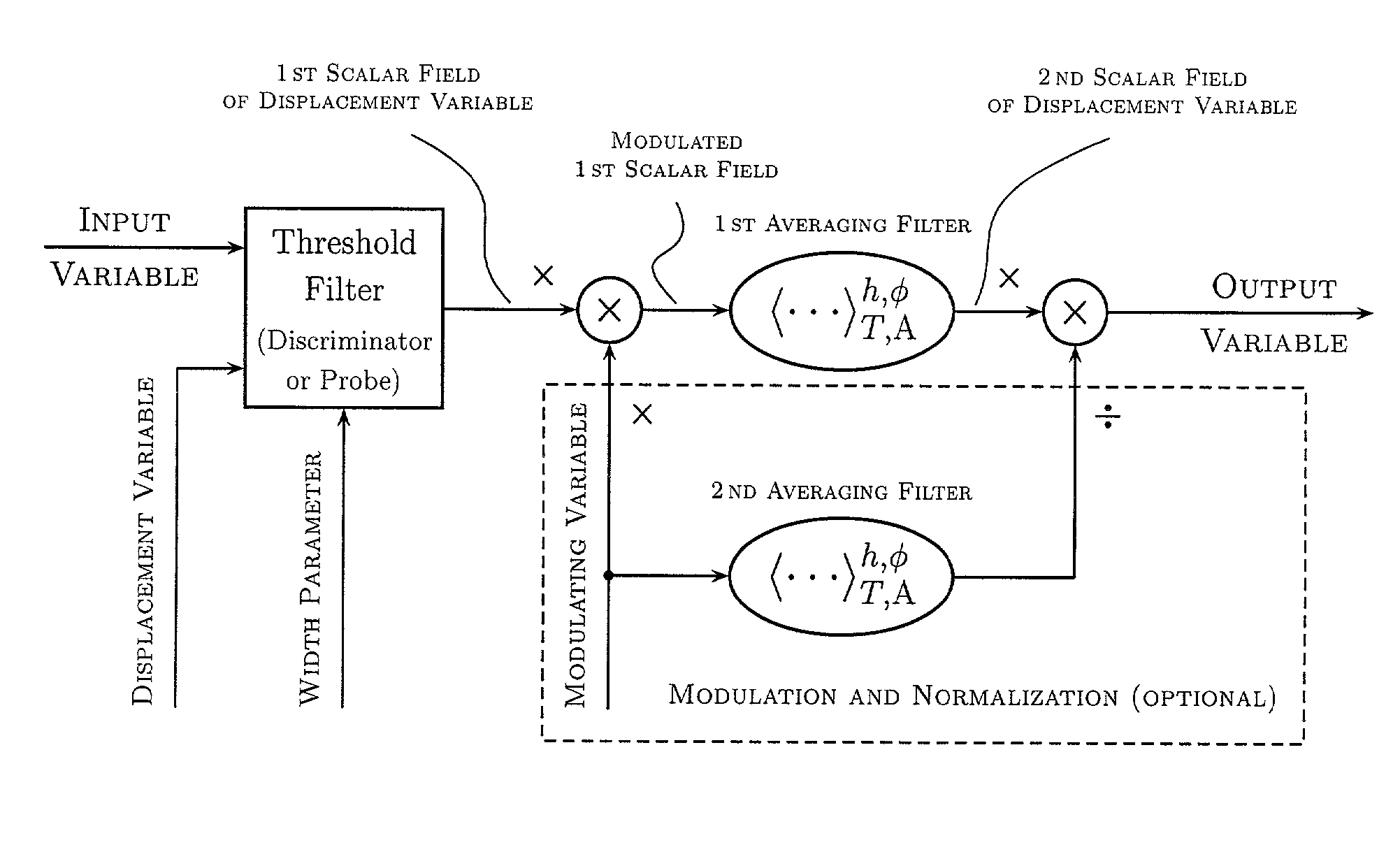
Method and apparatus for analysis of variables
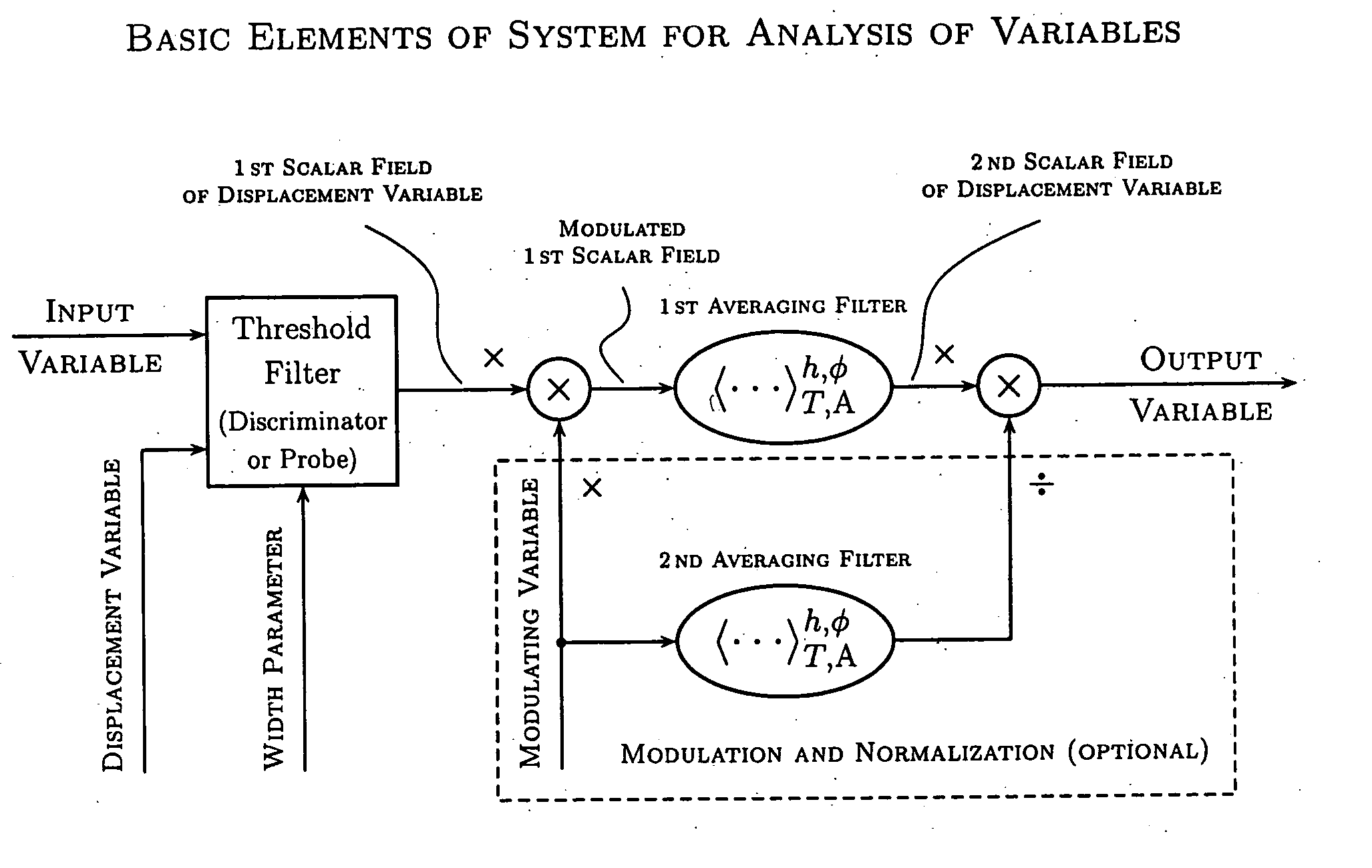
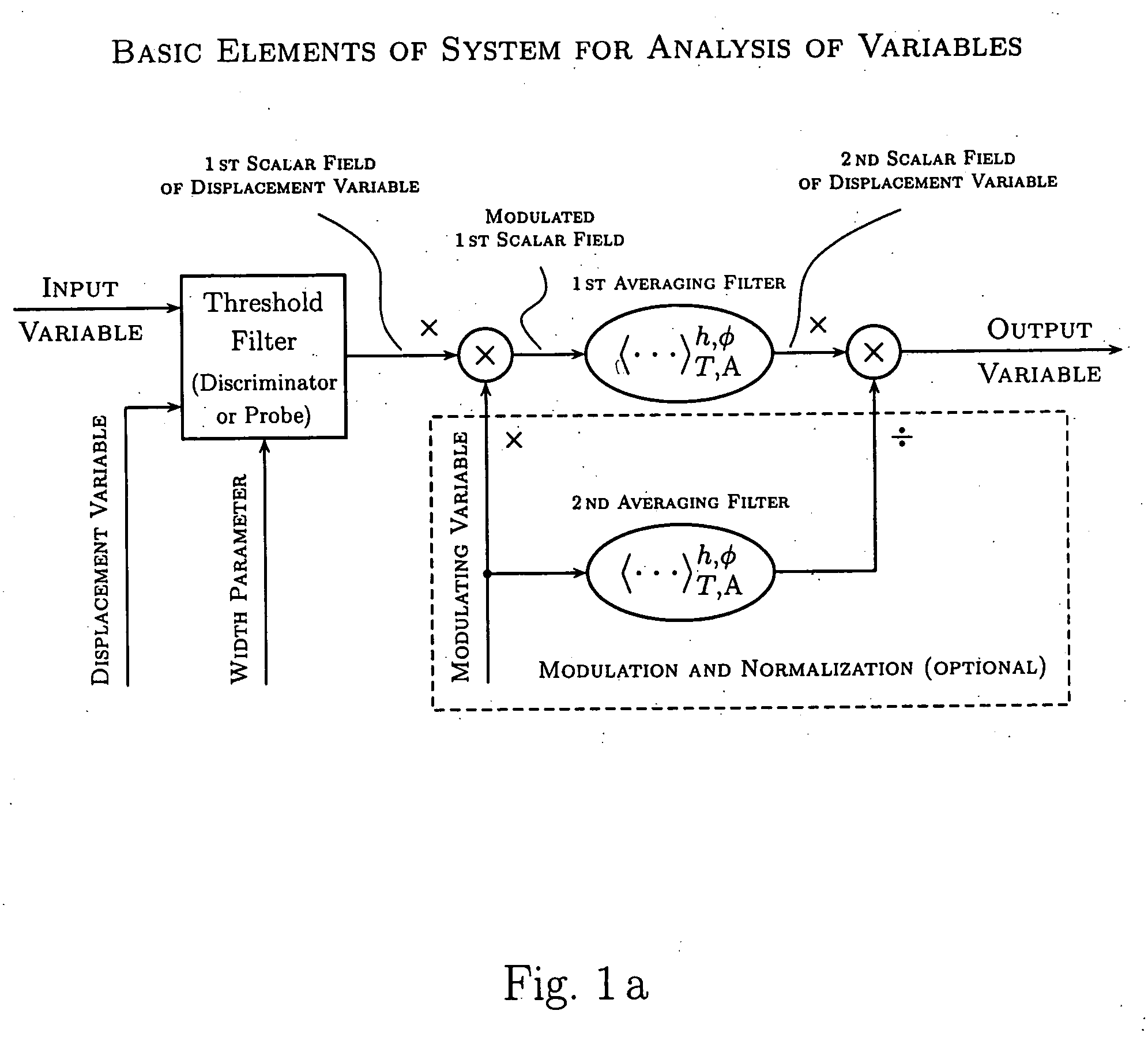
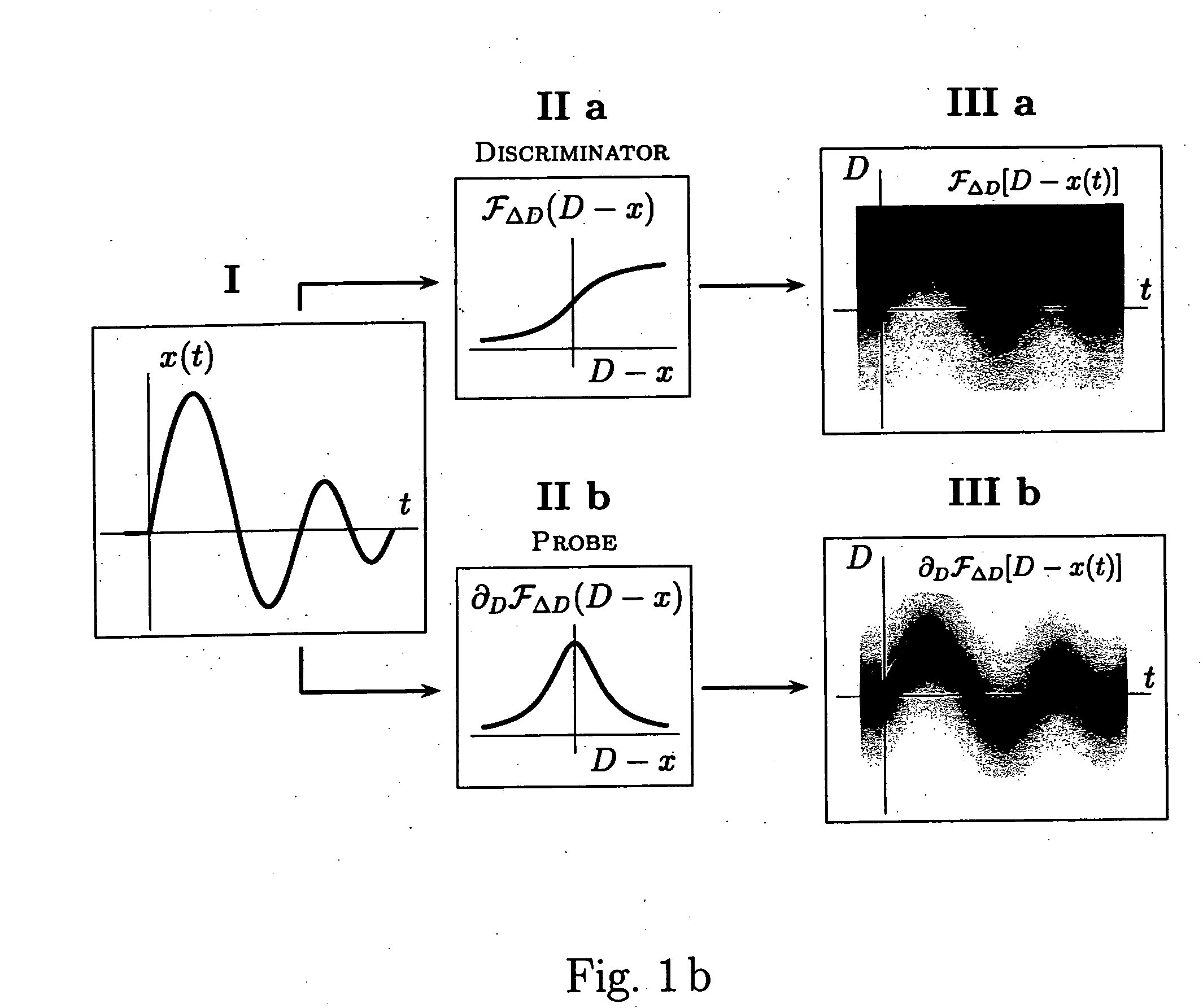
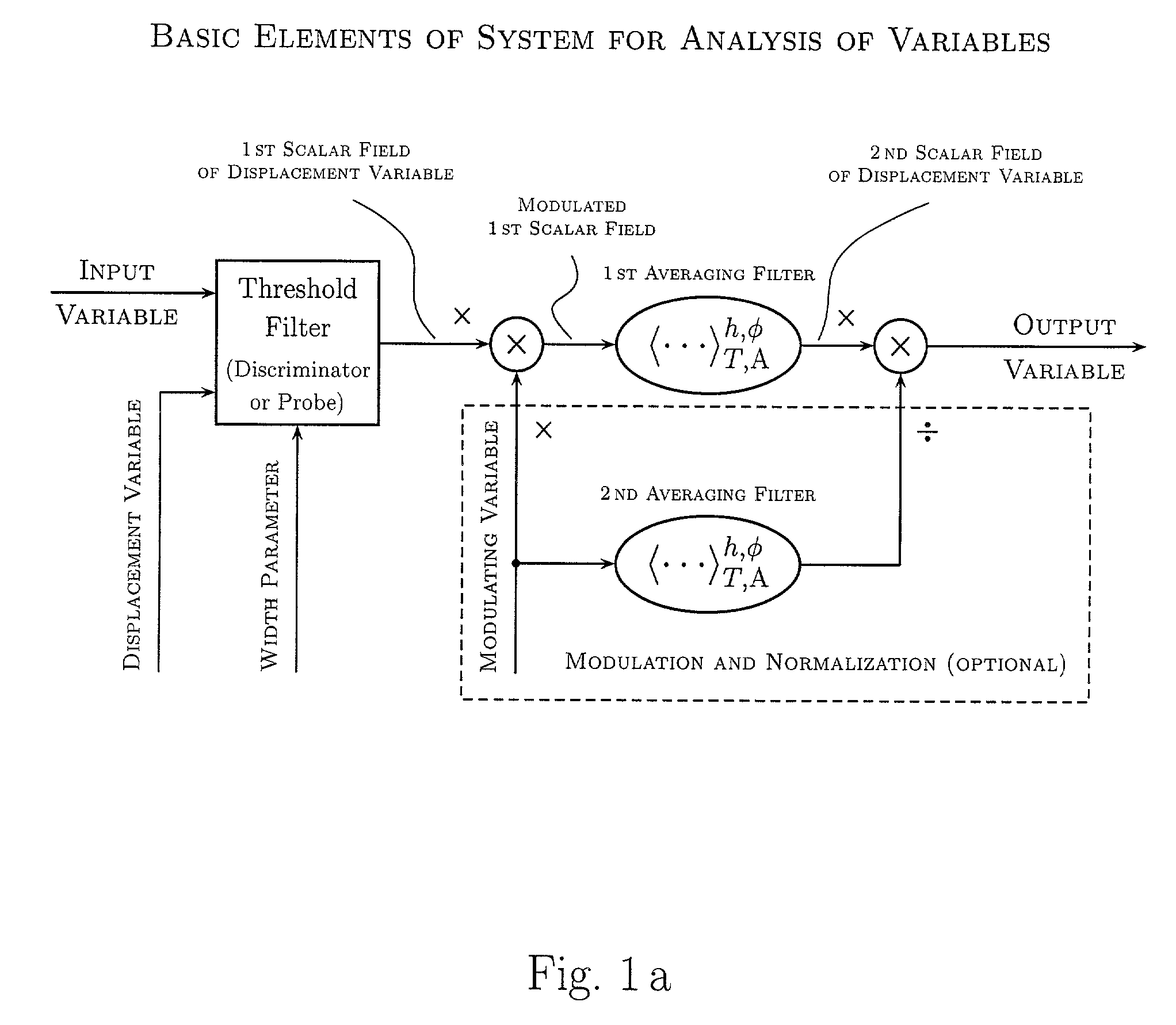
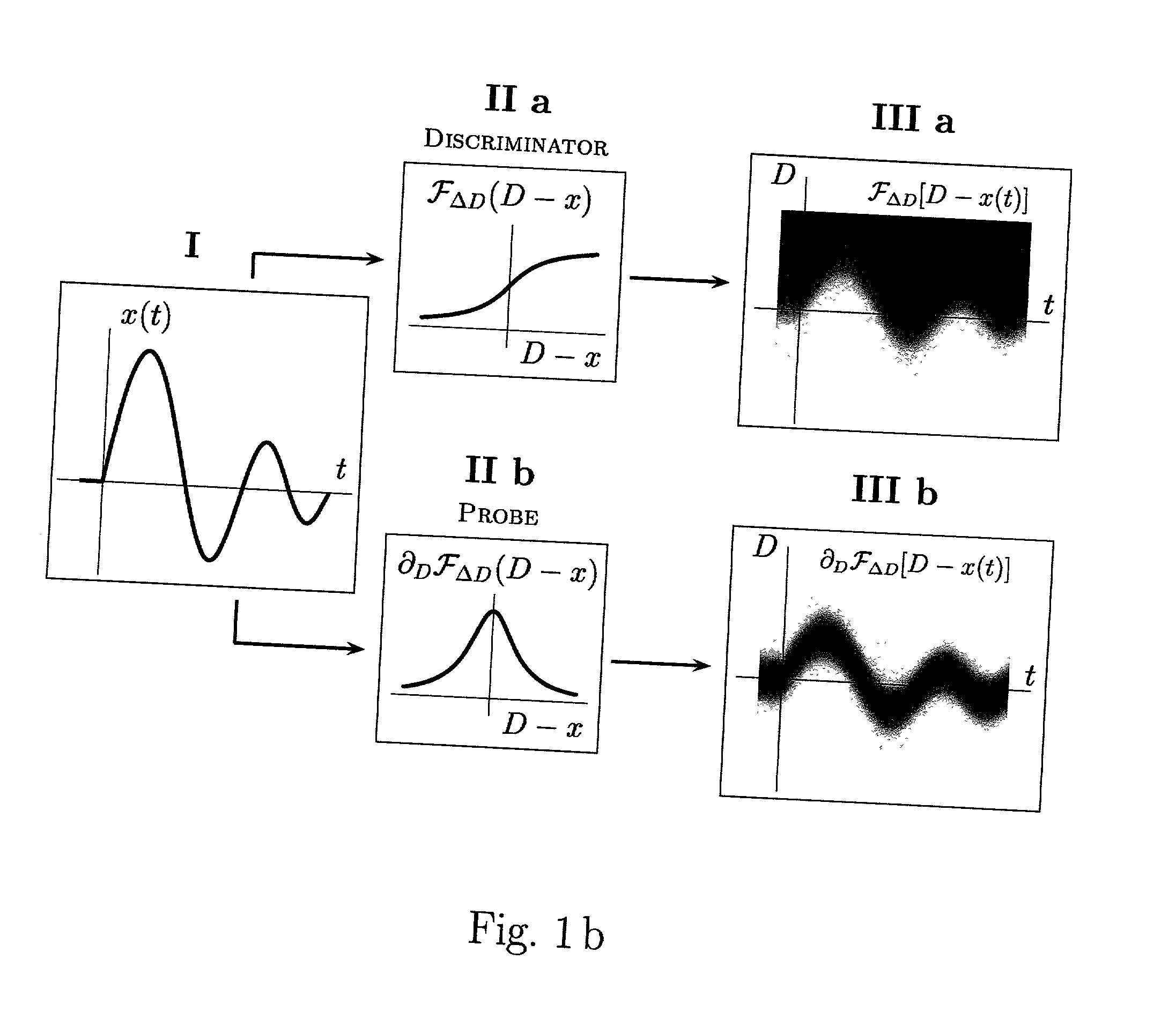
InactiveUS20040158592A1Simple and clear interpretationImprove applicabilityImage enhancementSpeech analysisVolumetric Mass DensityVector field
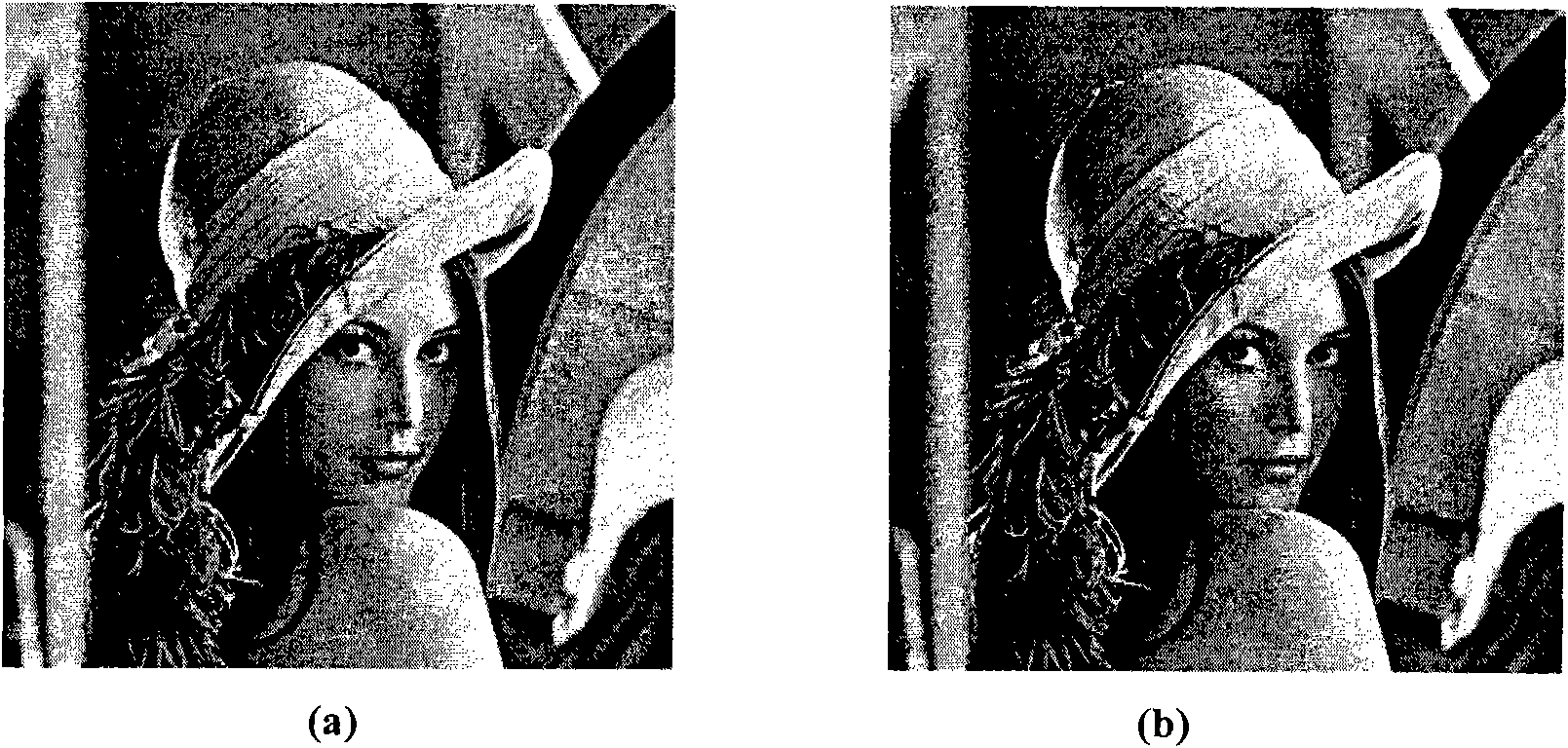
Various components of the present invention are collectively designated as Analysis of Variables Through Analog Representation (AVATAR). It is a method, processes, and apparatus for measurement and analysis of variables of different type and origin. AVATAR offers an analog solution to those problems of the analysis of variables which are normally handled by digital means. The invention allows (a) the improved perception of the measurements through geometrical analogies, (b) effective solutions of the existing computational problems of the order statistic methods, and (c) extended applicability of these methods to analysis of variables. The invention employs transformation of discrete or continuous variables into normalized continuous scalar fields, that is, into objects with mathematical properties of density and / or cumulative distribution functions. In addition to dependence on the displacement coordinates (thresholds), these objects can also depend on other parameters, including spatial coordinates (e.g., if the incoming variables are themselves scalar or vector fields), and / or time (if the variables depend on time). Moreover, this transformation of the measured variables may be implemented with respect to any reference variable. Thus, the values of the reference variable provide a common unit, or standard, for measuring and comparison of variables of different natures, for assessment of mutual dependence of these variables, and for evaluation of changes in the variables and their dependence with time. The invention enables, on a consistent general basis, a variety of new techniques for analysis of variables, which can be implemented through various physical means in continuous action machines as well as through digital means or computer calculations. Several of the elements of these new techniques do have digital counterparts, such as some rank order techniques in digital signal and image processing. However, this invention significantly extends the scope and applicability of these techniques and enables their analog implementation. The invention also introduces a wide range of signal analysis tools which do not exist, and cannot be defined, in the digital domain. In addition, by the present invention, all existing techniques for statistical processing of data, and for studying probability fluxes, are made applicable to analysis of any variable.
Owner:NIKITIN ALEXEI V +1
Double-threshold CFAR and trace point condensation method suitable for continuous wave radar
ActiveCN107861107AEnsure correct pairingReduce the number of statistical sortsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionGrazingDouble threshold
The invention discloses a double-threshold CRAR and trace point condensation method suitable for a continuous wave radar, belongs to a signal processing technology, and specifically relates to a continuous wave radar target constant false alarm detection and distance-speed two-dimensional trace point condensation method. Aiming at the characteristics of a relatively small wave beam grazing angle and relatively high resolution ratio of a continuous wave perimeter monitoring radar, a false alarm probability formula for ordered statistics of CRAR after Weibull clutter is subjected to linear detection and a corresponding clutter parameter estimation method are given; aiming at the problem that traditional OS-CRAR needs ranking operation and is relatively large in time consumption, a method fordouble-threshold CFAR is proposed, the number of times of statistical ranking is greatly reduced, and through addition of GO logic, running time is further reduced, and performance in clutter edges is improved; and joint realization of CRAR detection and trace point condensation is proposed, correct pairing of upper and lower frequency sweeping in subsequent processing of the continuous wave radar is guaranteed, and compared with traditional serial operation, computational complexity is greatly reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for analysis of variables
ActiveUS20050165879A1Improve applicabilityMore opportunityImage enhancementComputing operations for integration/differentiationPattern perceptionVector field
Various components of the present invention are collectively designated as Analysis of Variables Through Analog Representation (AVATAR). It is a method, processes, and apparatus for measurement and analysis of variables of different type and origin. AVATAR offers an analog solution to those problems of the analysis of variables which are normally handled by digital means. The invention allows (a) the improved perception of the measurements through geometrical analogies, (b) effective solutions of the existing computational problems of the order statistic methods, and (c) extended applicability of these methods to analysis of variables. The invention employs transformation of discrete or continuous variables into normalized continuous scalar fields, that is, into objects with mathematical properties of density and / or cumulative distribution functions. In addition to dependence on the displacement coordinates (thresholds), these objects can also depend on other parameters, including spatial coordinates (e.g., if the incoming variables are themselves scalar or vector fields), and / or time (if the variables depend on time). Moreover, this transformation of the measured variables may be implemented with respect to any reference variable. Thus, the values of the reference variable provide a common unit, or standard, for measuring and comparison of variables of different natures, for assessment of mutual dependence of these variables, and for evaluation of changes in the variables and their dependence with time. The invention enables, on a consistent general basis, a variety of new techniques for analysis of variables, which can be implemented through various physical means in continuous action machines as well as through digital means or computer calculations. Several of the elements of these new techniques do have digital counterparts, such as some rank order techniques in digital signal and image processing. However, this invention significantly extends the scope and applicability of these techniques and enables their analog implementation. The invention also introduces a wide range of signal analysis tools which do not exist, and cannot be defined, in the digital domain. In addition, by the present invention, all existing techniques for statistical processing of data, and for studying probability fluxes, are made applicable to analysis of any variable.
Owner:NIKITIN ALEXEI V +1
Blind hidden information detection method based on analysis of image gray run-length histogram
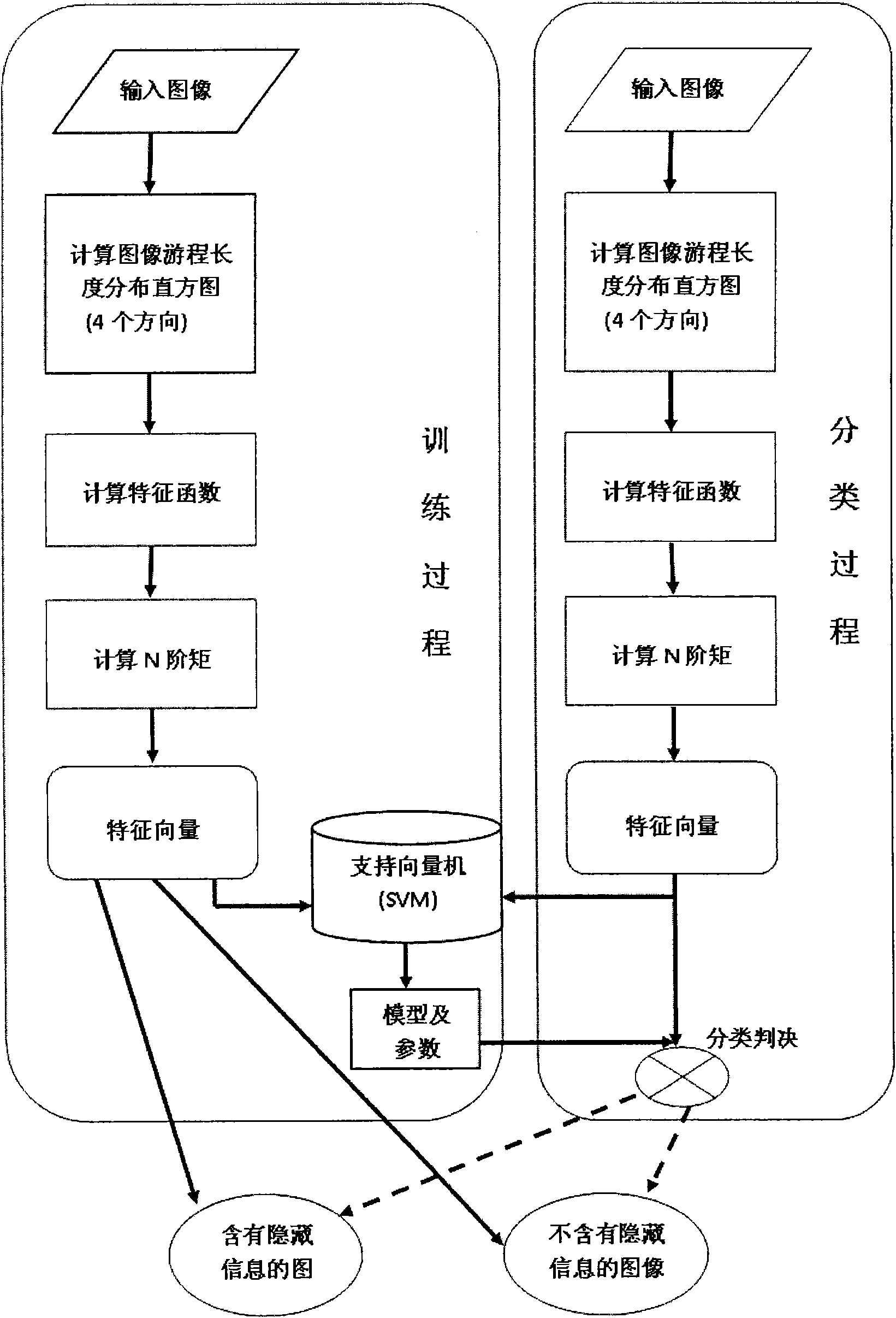
ActiveCN101615286AEasy extractionQuick extractionCharacter and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsFeature extractionModel parameters
The invention discloses a blind hidden information detection method based on analysis of an image gray run-length histogram, which judges whether an image possibly contains hidden information by analyzing the number distribution condition of long run lengths and short run lengths in the image gray run-length histogram. The method comprises the following steps: calculating a gray run-length matrix of gray images marked with class information in a training set to acquire a run-length histogram, extracting n-order statistic of a characteristic function of the run-length histogram as characteristics, and training and classifying the extracted characteristics to acquire classifier model parameters so to form a classifier model, wherein the marked class information contains or does not contain the hidden information; and calculating the gray run-length matrix of randomly inputted gray images to acquire an image run-length histogram, then carrying out characteristic extraction, and inputting the extracted characteristics into the classifier model to acquire the class information of the input images. The method realizes accurate and efficient blind hidden information detection of the images.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
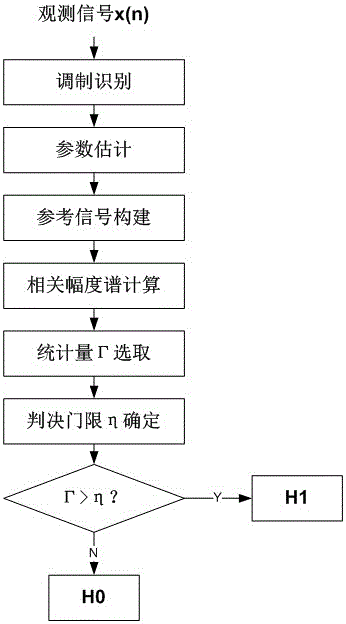
Hybrid modulation signal blind-processing result check method based on order statistic characteristics
ActiveCN106411803AIncrease credibilityImprove effectivenessMultiple carrier systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Peak value
The invention relates to a check problem for a linear frequency modulation / binary phase shift keying (LFM / BPSK) hybrid modulation signal blind-processing result, and provides a check method based on order statistic characteristics. A reference signal is constructed according to a signal model corresponding to a modulation identification result at first; then, a correlation spectrum of the reference signal and an observed signal is calculated; and thus, the LFM / BPSK signal blind-processing result is checked by detecting whether a peak value exists in the correlation spectrum or not. A computer simulation result shows that the method can perform effective check of the LFM / BPSK signal blind-processing result under a relatively low signal-to-noise ratio condition.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
Method for selecting algorithm in constant false alarm rate detection
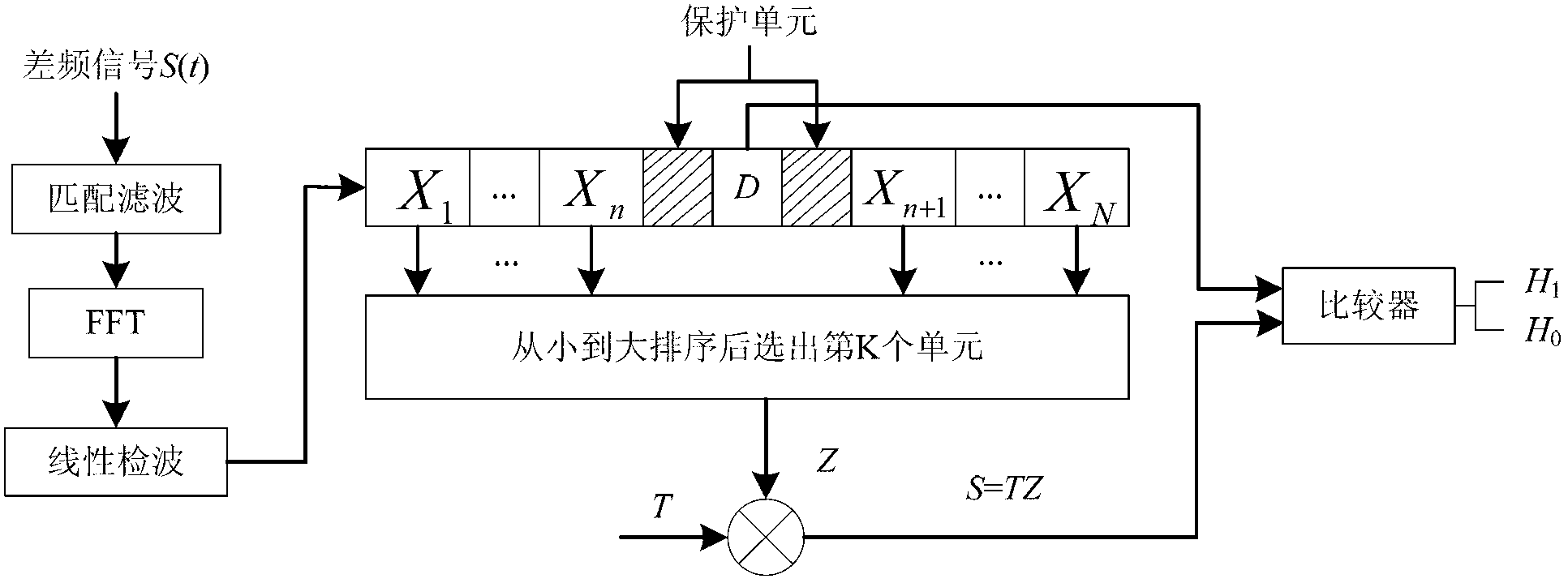
ActiveCN105373518AImprove performanceEasy to detectComplex mathematical operationsArray data structureReference window
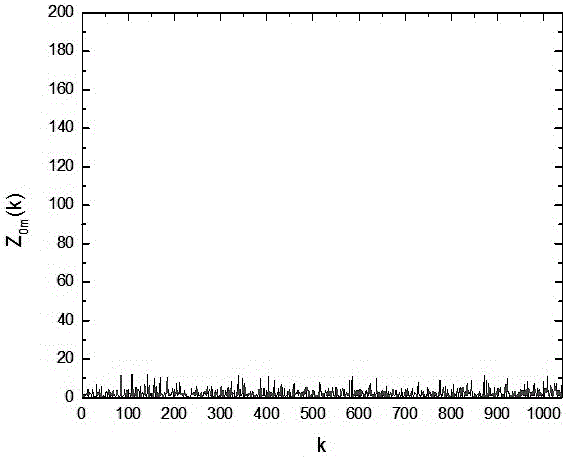
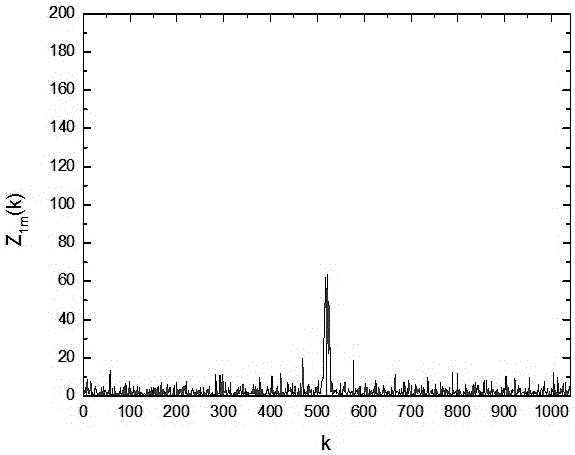
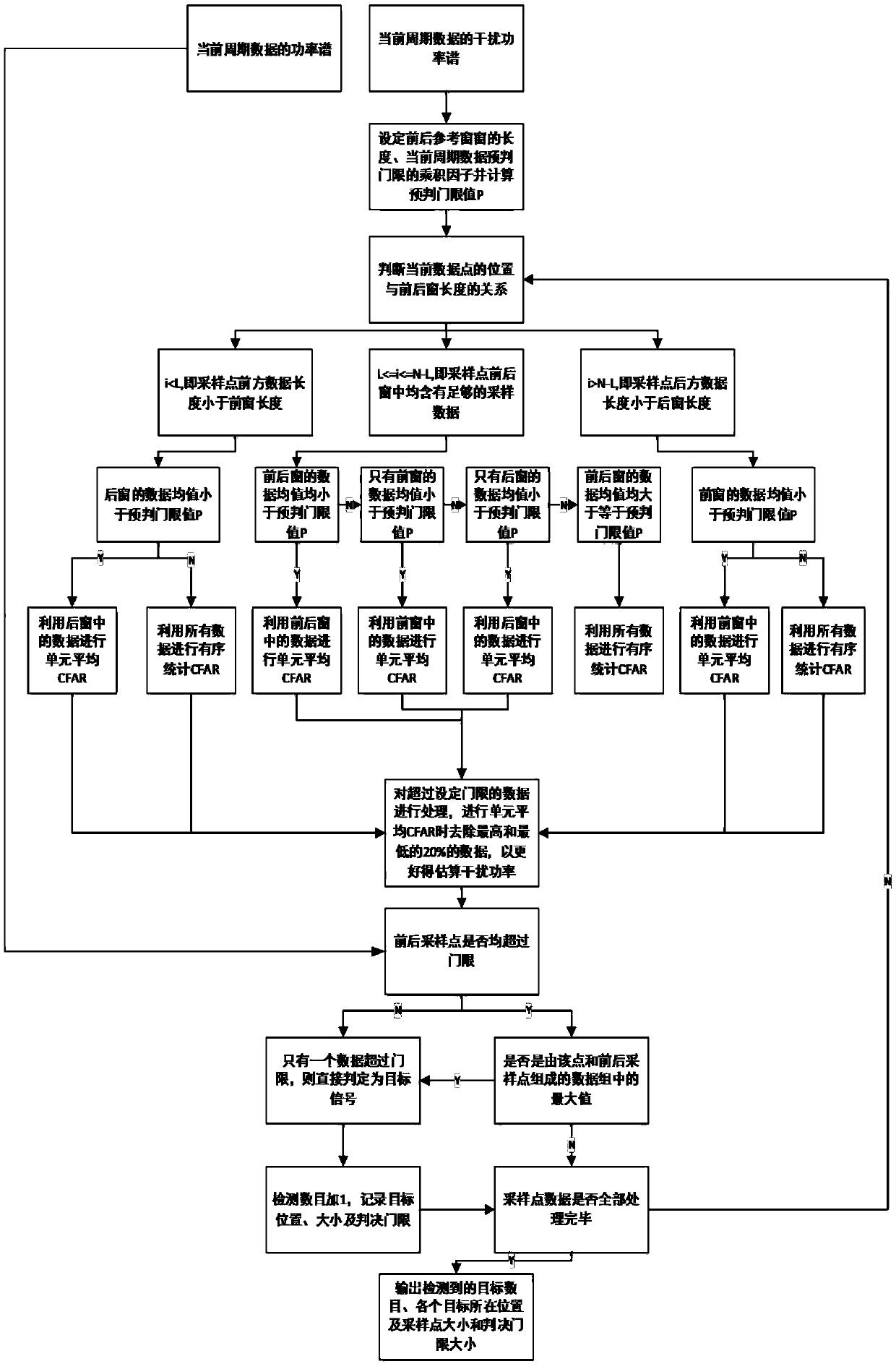
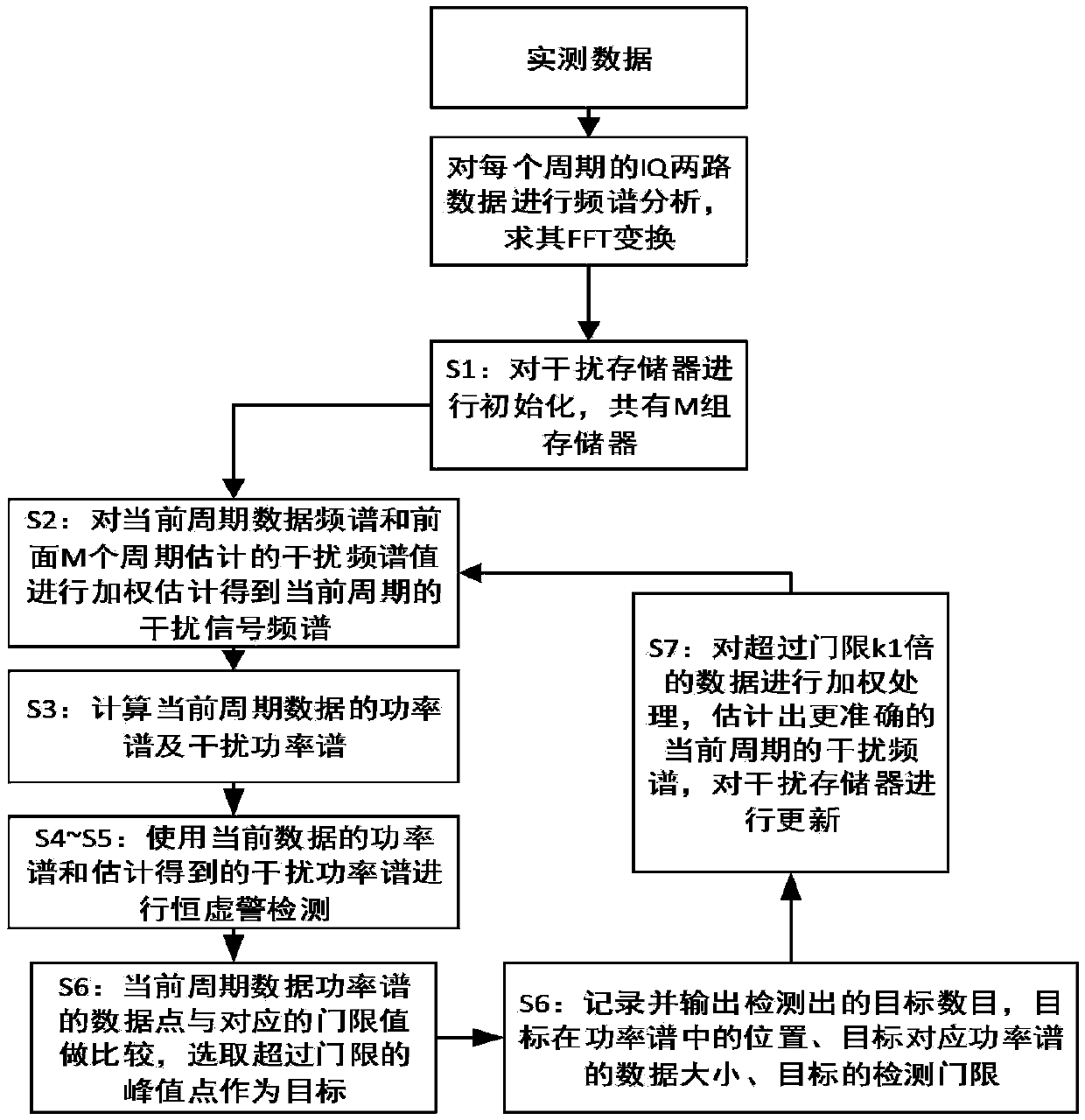
The invention discloses a method for selecting an algorithm in constant false alarm rate (CFAR) detection. The detection reference window length is L, the position of a current data point is i, and the data length is Q; if i<L, L data of a rear window in the position of an ith point in a corresponding interference power spectrum array are selected to calculate a judgment threshold, and if a data mean of the rear window is more than P, an order statistics CFAR method is adopted, otherwise, a cell averaging CFAR method is adopted; if L<=i<=Q-L, 2L data of front and rear windows in the position of the ith point in the corresponding interference power spectrum array are selected to calculate the judgment threshold; and if i>Q-L, L data of a front window in the position of the ith point in the corresponding interference power spectrum array are selected to calculate the judgment threshold. According to the method, the performance can be optimized with the cell averaging CFAR method in a uniform background, and the detection performance and the false alarm performance can be remarkably improved with the order statistics method in a non-uniform clutter background.
Owner:DALIAN ROILAND SCI & TECH CO LTD
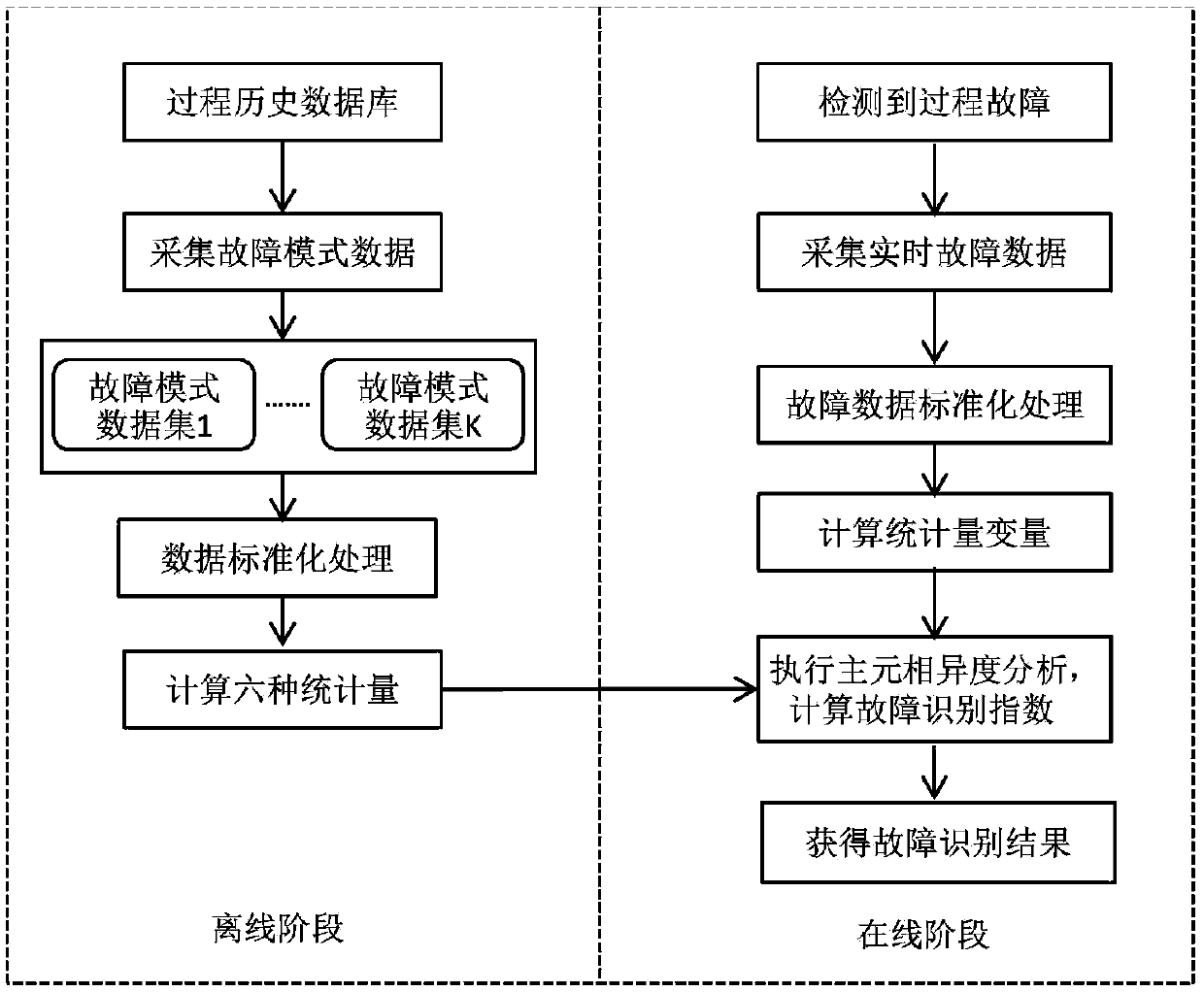
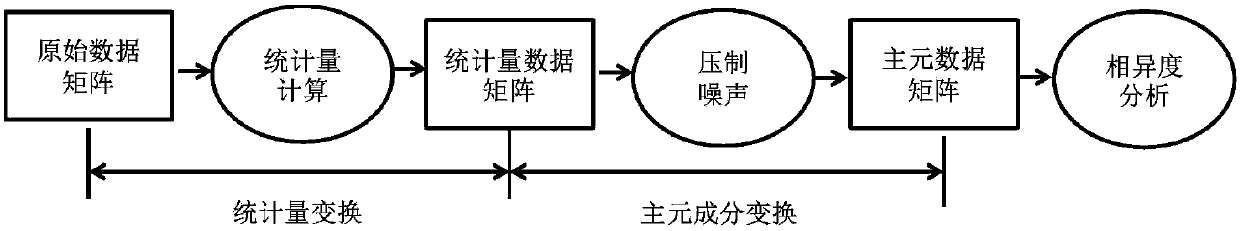
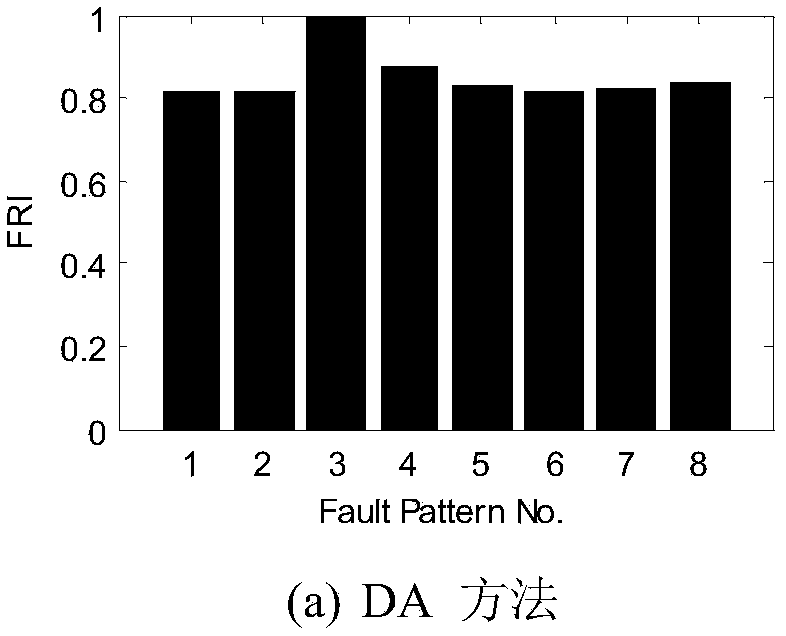
Multi-variable fault identification method of industrial process
InactiveCN105182955APrevent deterioration of recognition resultsFully excavatedElectric testing/monitoringData setData information
The invention relates to a multi-variable fault identification method of the industrial process. The method comprises the following steps that (1) a normal operation condition data set X and K types of known fault mode data sets of a historical database are collected, the mean value mean(X) and the standard deviation std(X) of the normal operation condition data set are calculated, and the known fault mode data sets are standardized to obtain a new fault mode data set; (2) data windows are constructed under the different fault mode data sets to calculate six types of statistical variables; (3) faults in the process are detected, and real-time fault data S is collected and standardized; (4) principal component dissimilarity analysis is implemented on the basis of the step (3), and the fault identification indexes FRI between a fault data set to be identified and the know fault mode data sets are calculated; and (5) the FRI are ordered to obtain a fault identification result. The method is based on the principal component dissimilarity analysis of the statistical quantity, in dissimilarity analysis, principal component information is extracted, minor data information is abandoned, influence of noise is inhibited, and high-order statistic information can be fully dug.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Speaker recognition in multimedia system
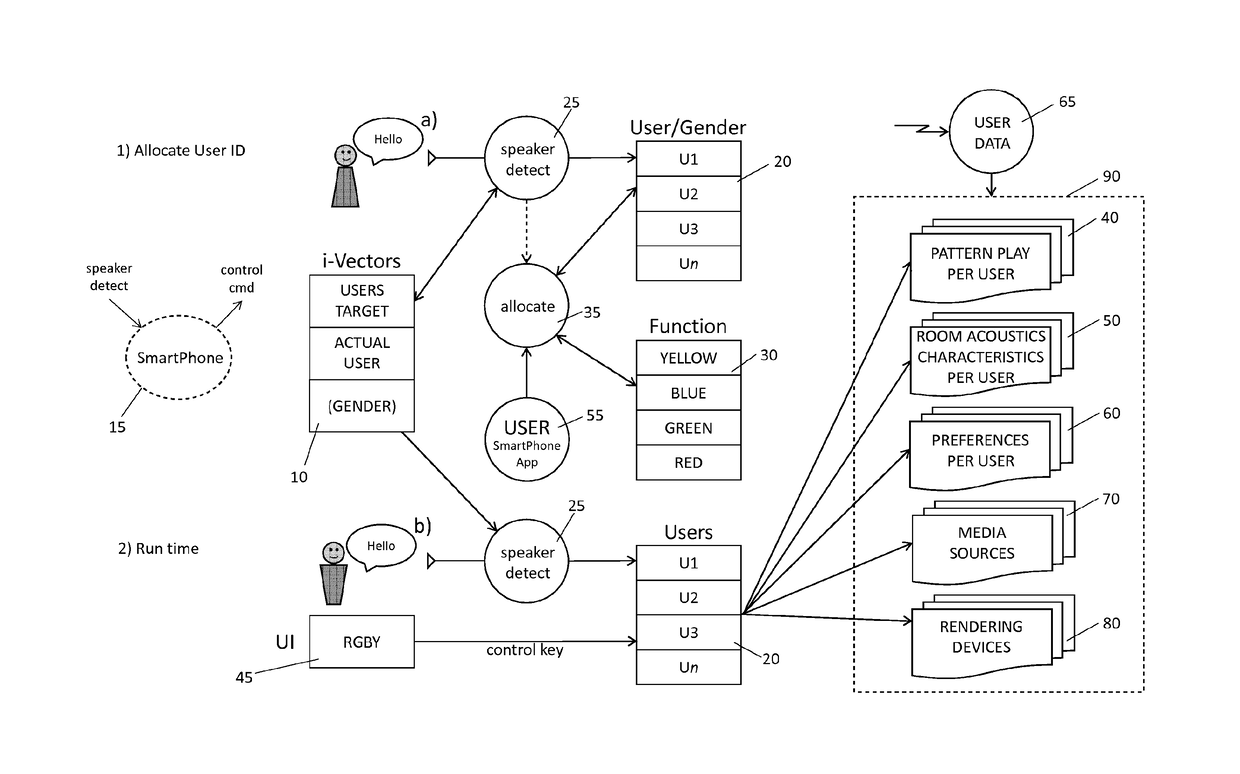
ActiveUS20170372706A1Improve performanceUnwanted variabilitySpeech analysisSpeech soundOrdered statistics
A method for identifying a user among a plurality of users of a multimedia system comprising extracting an i-vector for the speech utterance using total variability modeling, comparing the extracted i-vector with a collection of i-vector sets in order to identify a target set most similar to the extracted i-vector, and granting access to the multimedia system in accordance with an access profile associated with the identified target set. Further, source variation is minimized by, for each speech utterance acquired using a specific data source, re-centering first-order statistics of the speech utterance around the mean of an informative prior associated with the source, and using the co-variance of the informative prior associated with the source when extracting the i-vector for the speech utterance.
Owner:BANG & OLUFSEN
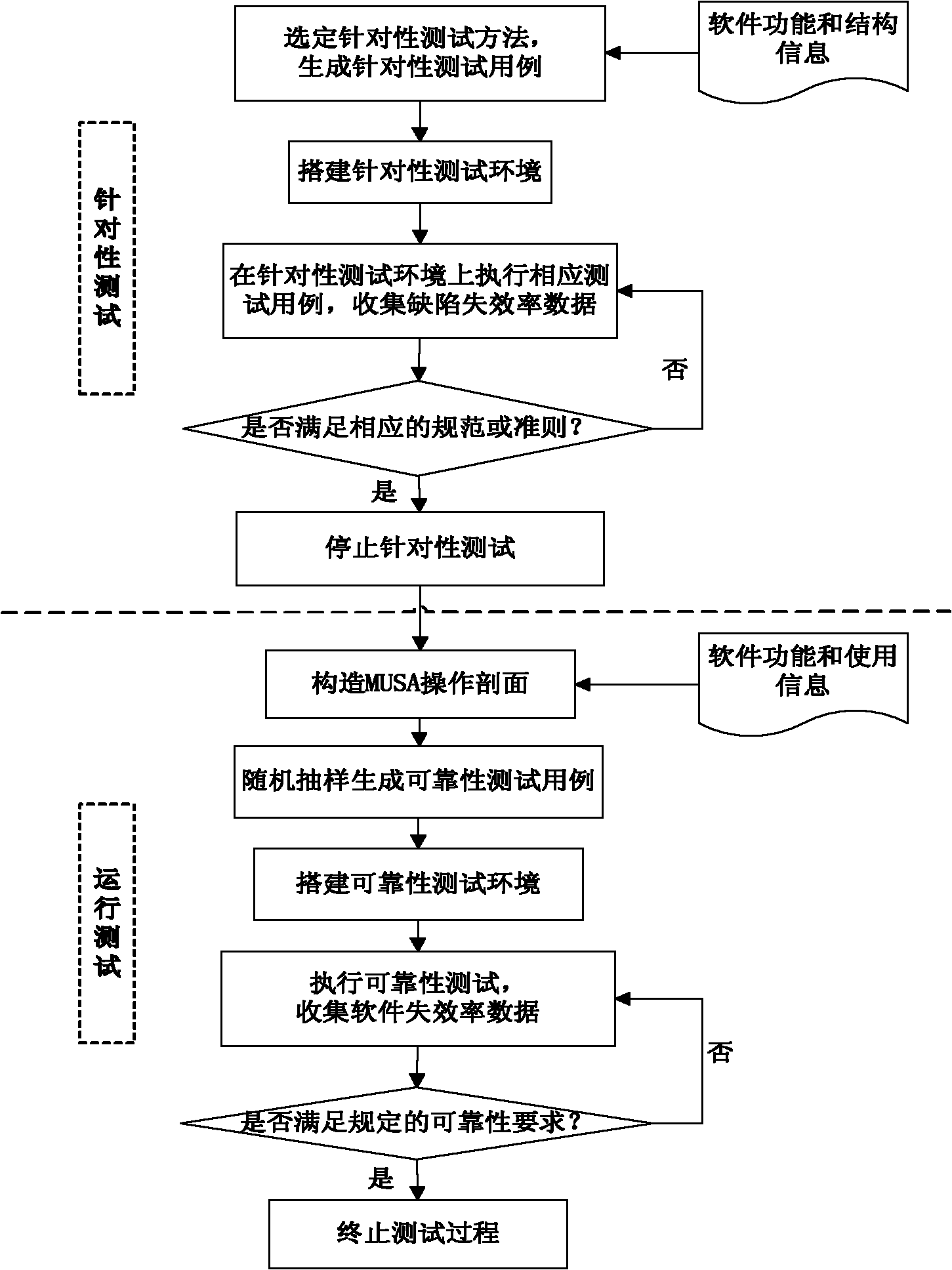
Software reliability assessment method and device based on hybrid testing
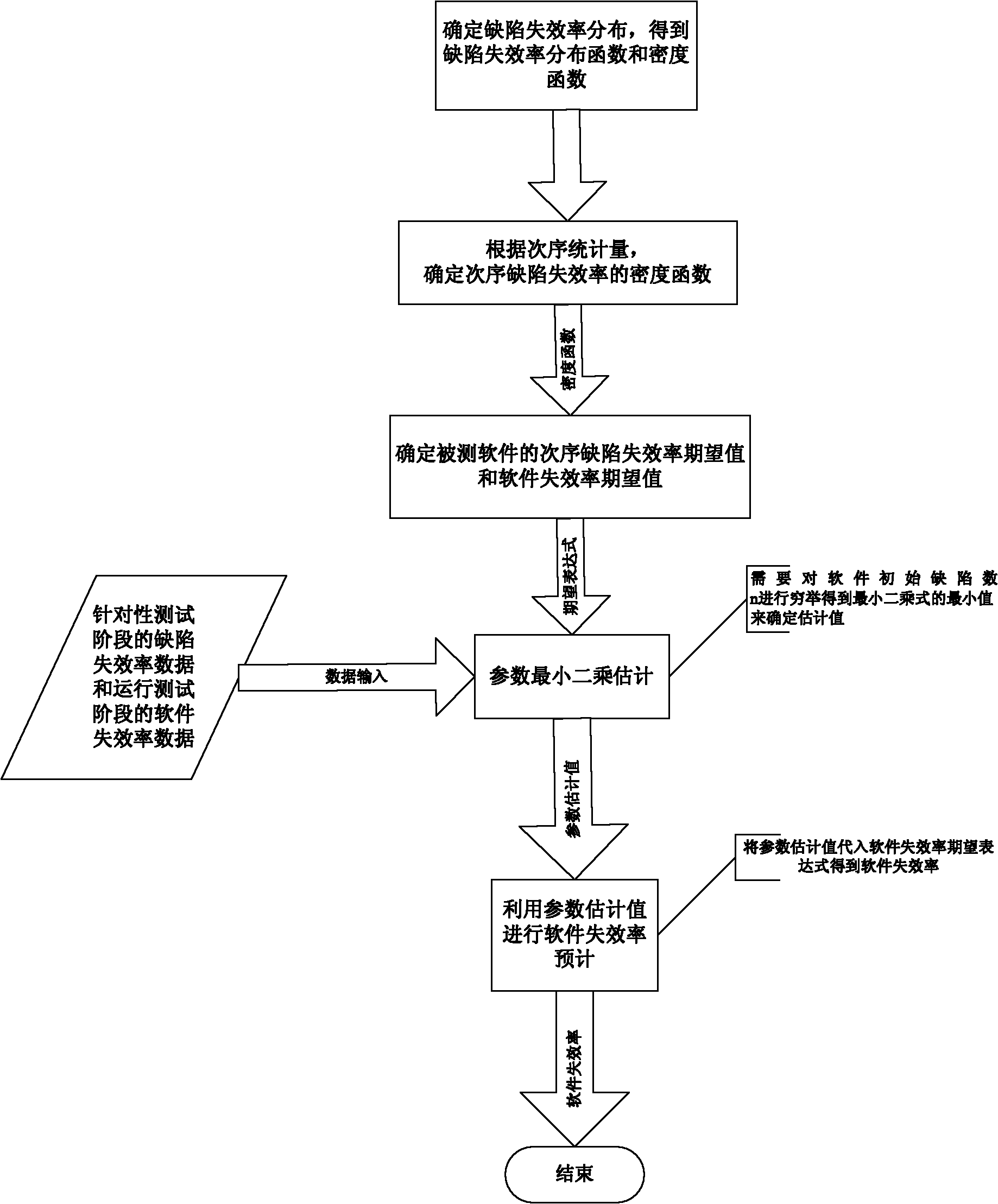
InactiveCN102063375AImprove reliabilityShorten the timeSoftware testing/debuggingFailure rateResource consumption
The invention discloses a reliability assessment method and device based on hybrid testing, belonging to the field of software reliability engineering. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining a defect failure rate distribution function and a density function through determining defect failure rate distribution of tested software; determining the density function of an order defect failure rate, an order defect failure rate expected value and a software failure rate expected value according to the order statistics; and hybrid-testing the tested software, and determining a distribution parameter according to a hybrid test result data. The invention overcomes the defects of more testing examples, neglecting of internal information, long testing time, large resource consumption and the like of the traditional reliability test by fully utilizing and combining the advantages of run tests and pertinence tests, thereby shortening the time of the software reliability tests, increasing thesoftware defect exposing speed and the progress of the software reliability tests, and greatly reducing the test cost and the resource consumption.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
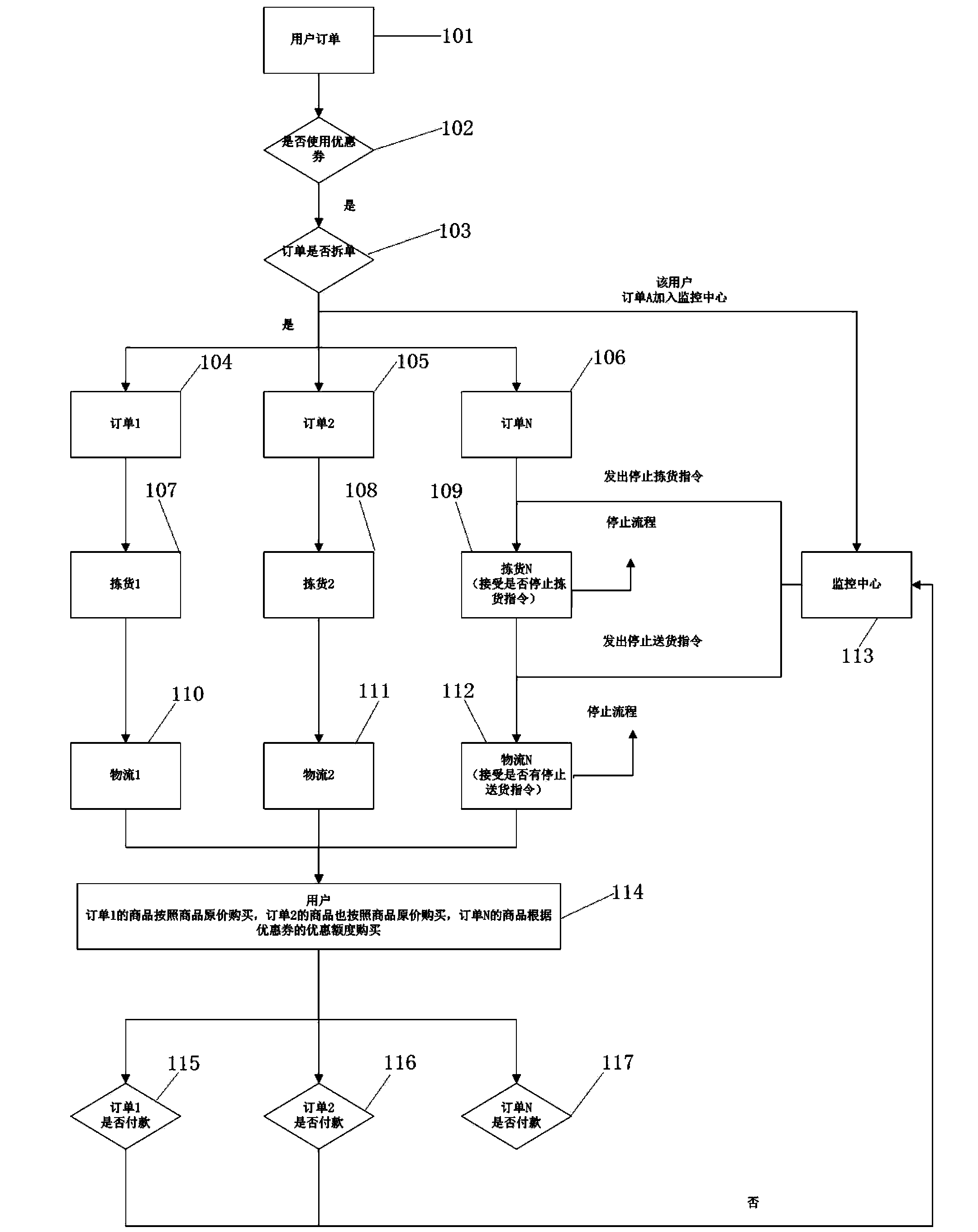
Discount monitoring system and method for multiple commodities
The invention discloses a discount monitoring system and method for multiple commodities. The system comprises an order separating module, an order statistics module, a payment statistics module and a discount rebating module. The order separating module separates commodities purchased by a client into multiple orders according to logistics, and sends order information to the order statistics module. The order statistics module counts up the logistics conditions of all the orders, selects the order with the logistics to be completed last according to the sequence of logistics, and sends the order and logistics information to the payment statistics module. The payment statistics module counts up the payment condition of all the orders, adds discount rebating information to the last order, and sends the discount rebating information to the discount rebating module. The discount rebating module takes the discount rebating information as the discount rebate of all the commodities before the order separating module conducts order separating. Due to the adoption of the technical scheme, the discount rebating operation is made to be conducted in the last step of the purchasing process, and merchants can be assisted in avoiding risks caused by sales logistics.
Owner:BEIJING JINGDONG SHANGKE INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Radar signal processing method
ActiveCN102495403AImprove detection rateMulti-objective feature optimizationWave based measurement systemsRadar signal processingPeak value
The invention relates to a radar signal processing method. The method comprises the following steps: a matched one-dimensional static clutter map applicable to the present angle can be extracted from an integral two-dimensional static clutter map, and range gates positioned within a clutter region are identified; target power data is traversed to identify a range gate outside the clutter region and with the power strength exceeding a deletion threshold; then one-dimensional OS-CFAR (Order Statistics Constant Alarm False Rate) filter processing is carried out; the target power data of each range gate is sequentially judged together with a fixed threshold and a floating threshold generated after one-dimensional OS-CFAR filtering to detect the target; all the detected target points are traversed to detect target peaks; and taking each target peak as the center, the positions of power data continually descending below a target separation threshold are searched to calculate the target length. By adopting the method, multi-target properties in the airport environment are optimized, and the probability of detecting smaller targets nearby larger targets is improved; and besides, the processor time is concentrated in regions interested by users, and only very few processor time is spent in the regions uninterested by the users.
Owner:无锡市雷华科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for improving video quality by utilizing a unified loop filter
ActiveUS8259819B2Improve subjective qualityRaise the ratioImage enhancementPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesLoop filterNonlinear filter
The present invention relates to method and apparatus for improving video quality. The present invention provides a unified loop filter including: a pixel determining unit which determines the type of a pixel based on boundary strength; a similarity transforming unit which transforms a nonlinear filter into a nonlinear similarity-ordered statistics filter; and an integrating unit which integrates the nonlinear similarity-ordered statistics filter with a linear image filtering portion. The unified loop filter is applicable to filter reconstructed frames when an encoder or a decoder is processing a video signal.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
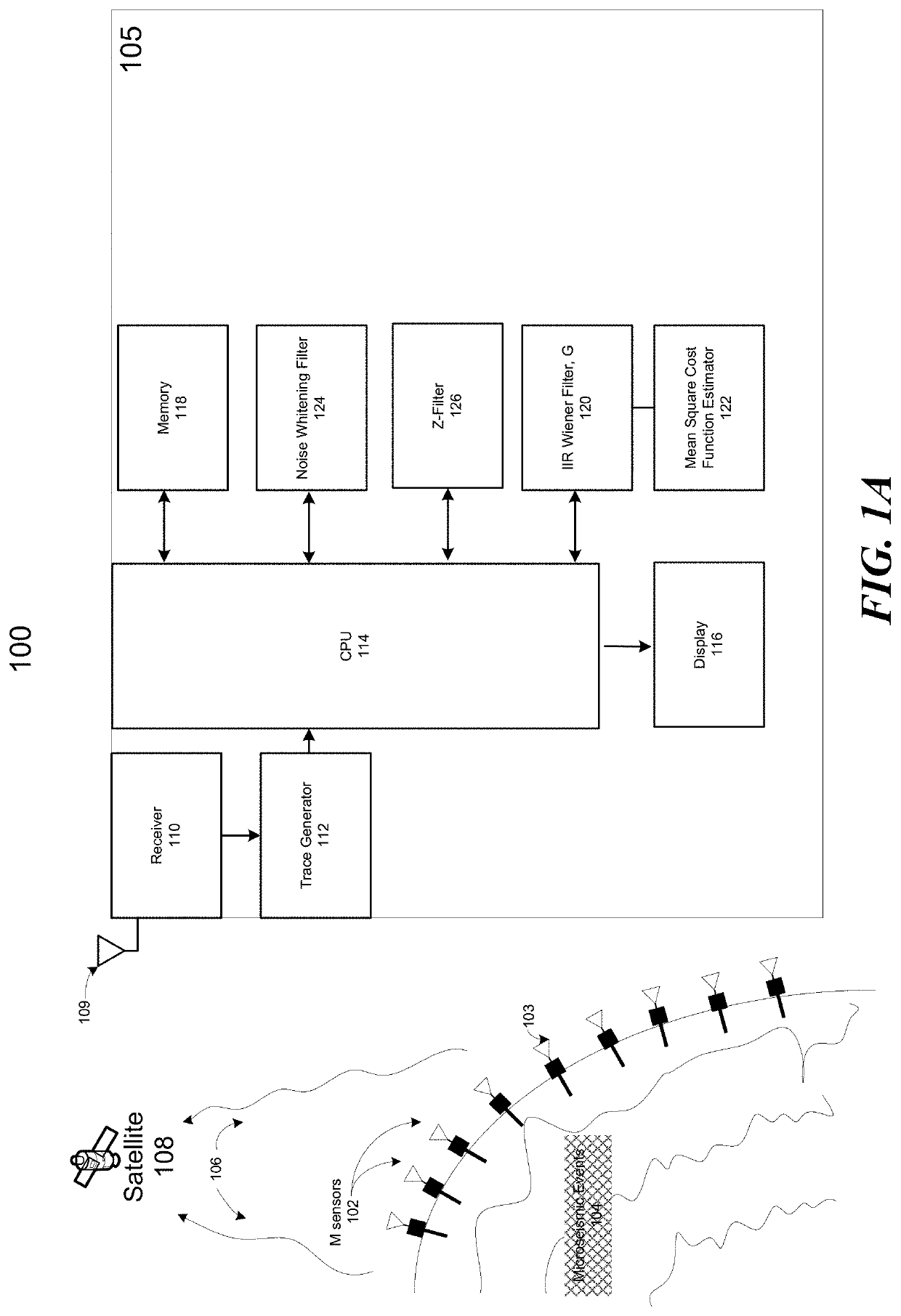
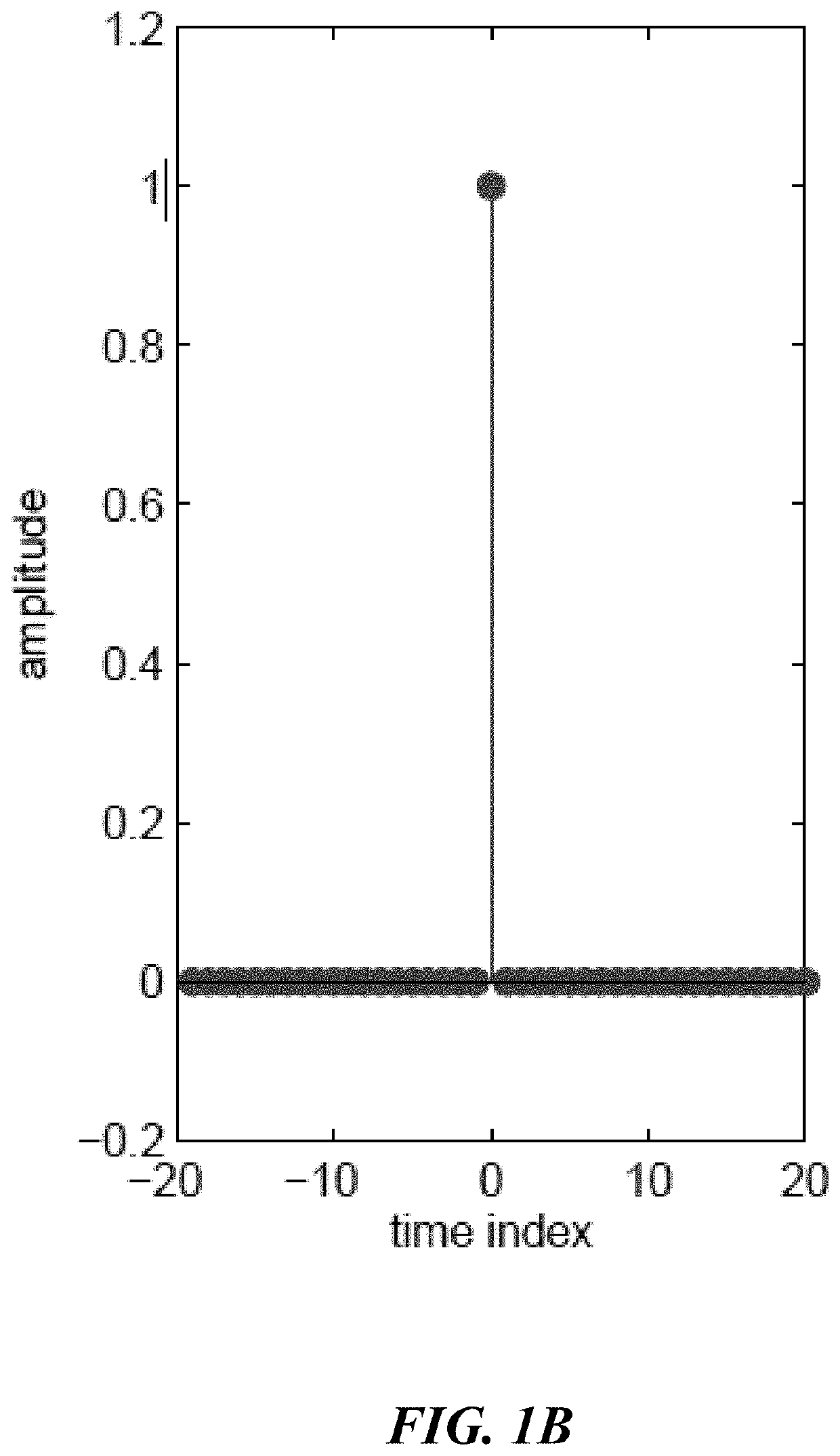
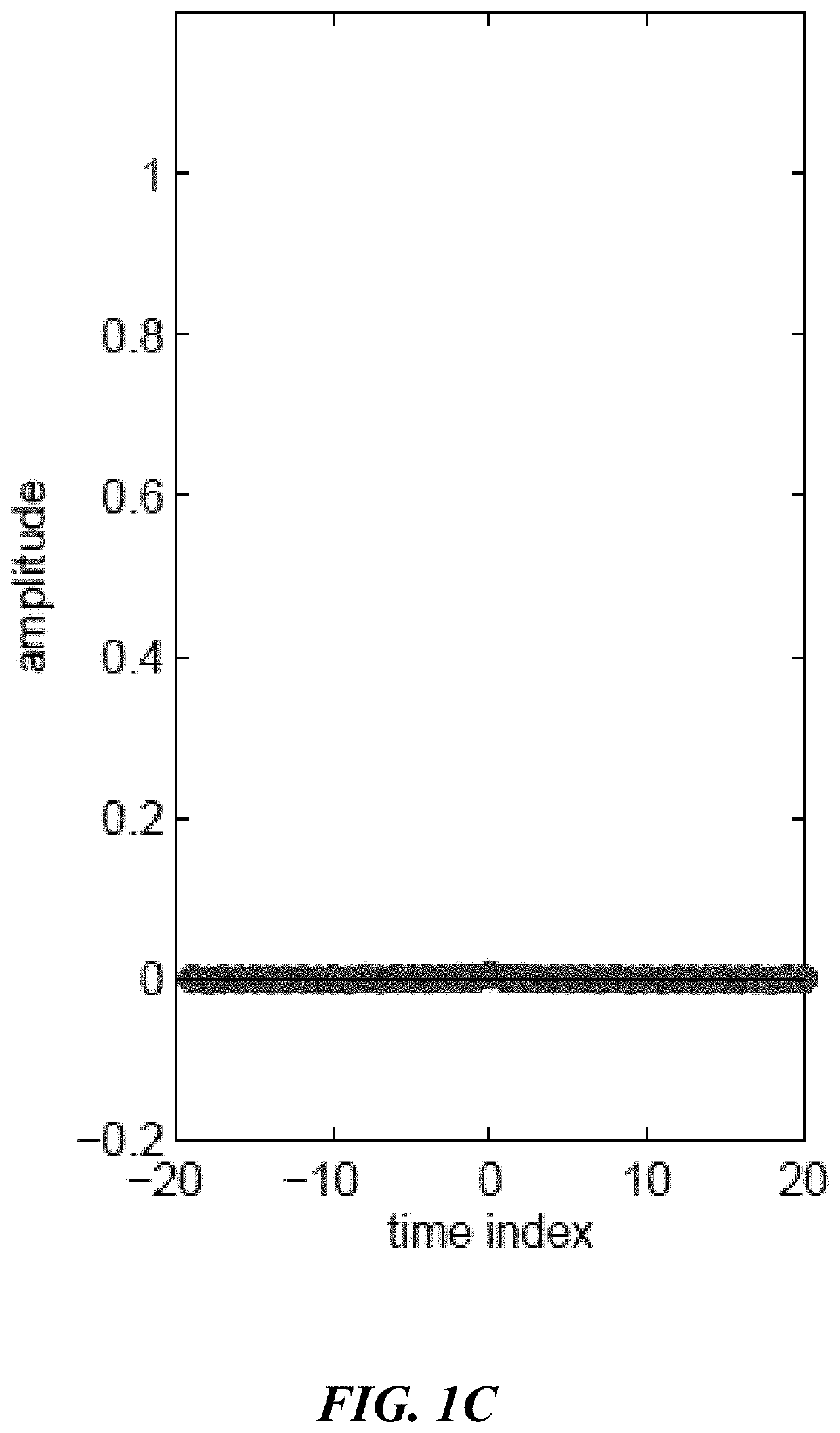
Observation-driven method based on iir wiener filter for microseismic data denoising
A system and method and non-transitory computer readable medium method for filtering signals representative of microseismic events with an infinite impulse response (IIR) Wiener filter which precludes the need for statistics or prior knowledge of the signal of interest. The second-order statistics of the noise and the noisy data are extracted from the recorded data only. The criteria used to optimize the filter impulse response is the minimization of the mean square error. The IIR Wiener filter was tested on synthetic and field data sets and found to be effective in denoising microseismic data with low SNR (−2 dB).
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
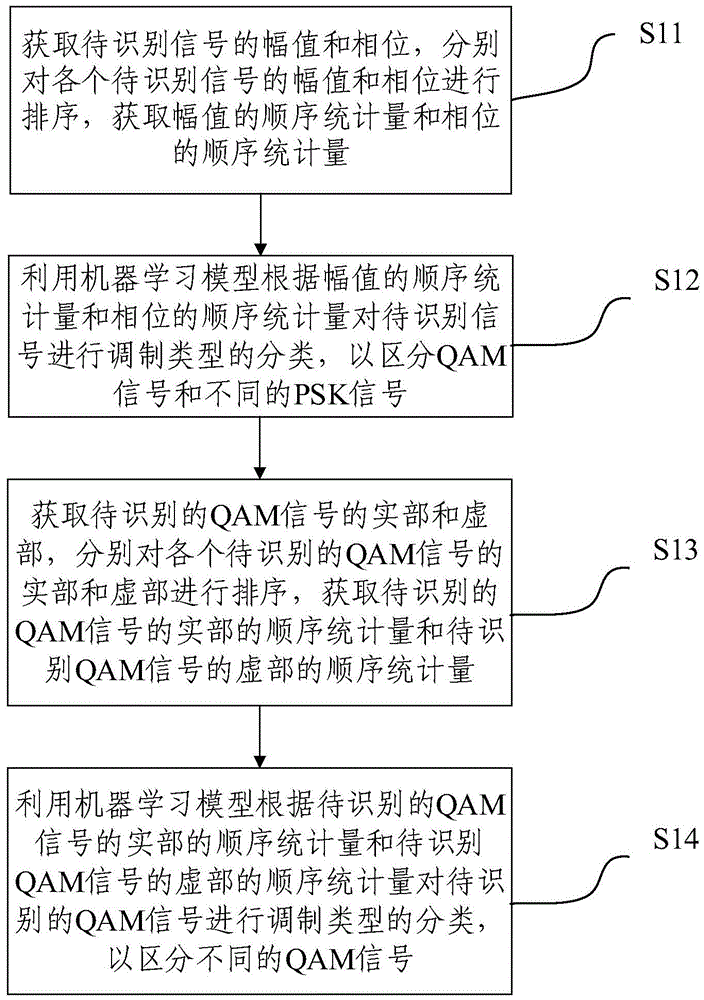
Modulation recognizing method and system based on order statistics and machine learning
ActiveCN105656826AEasy to classifyModulation type identificationPattern recognitionComputation complexity
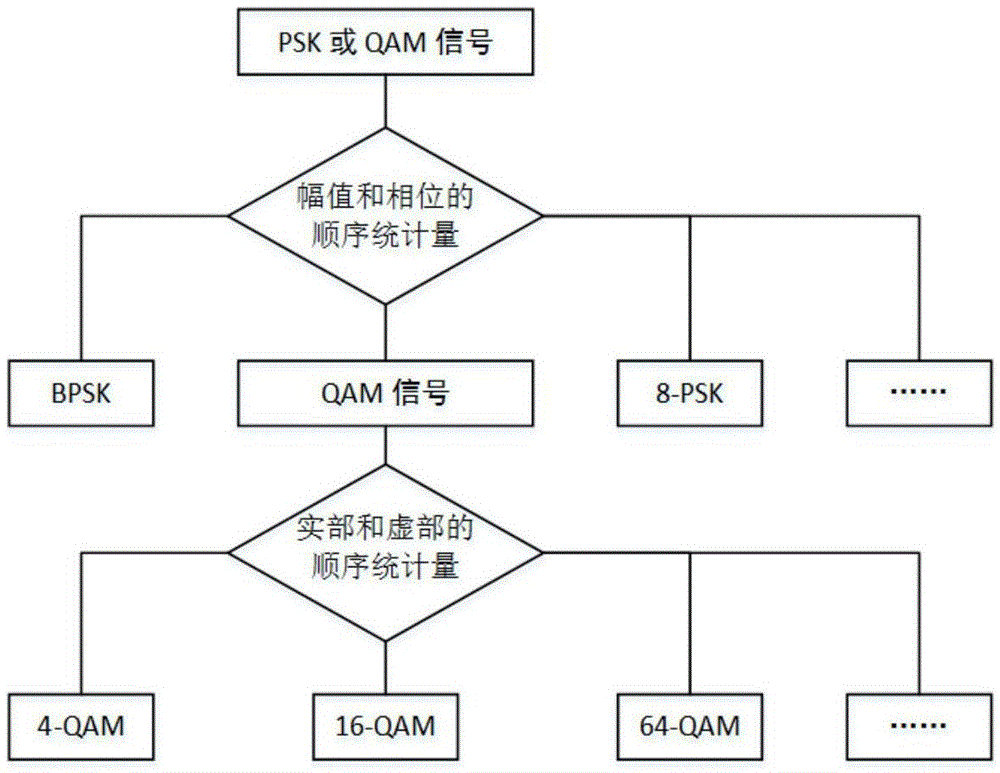
The invention relates to a modulation recognizing method and system based on order statistics and machine learning. The method includes the steps of obtaining the amplitude and phase of a to-be-recognized signal, obtaining the order statistics of the amplitude and the order statistics of the phase, classifying modulation types of the to-be-recognized signal through a robot learning model according to the order statistics of the amplitude and the order statistics of the phase to distinguish a QAM signal and different PSK signals, obtaining the real part and the visual part of the to-be-recognized QAM signal, obtaining the order statistics of the real part of the to-be-recognized QAM signal and the order statistics of the visual part of the to-be-recognized QAM signal, and classifying the modulation types of the to-be-recognized QAM signal through the robot learning model according to the order statistics of the real part of the to-be-recognized QAM signal and the order statistics of the visual part of the to-be-recognized QAM signal to distinguish different QAM signals. Good signal classifying performance is kept when the computation complexity is low.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Hybrid field signal source positioning method based on symmetrical nested array
InactiveCN108919178AReduce computational complexityOvercoming noisePosition fixationComputation complexityNested arrays
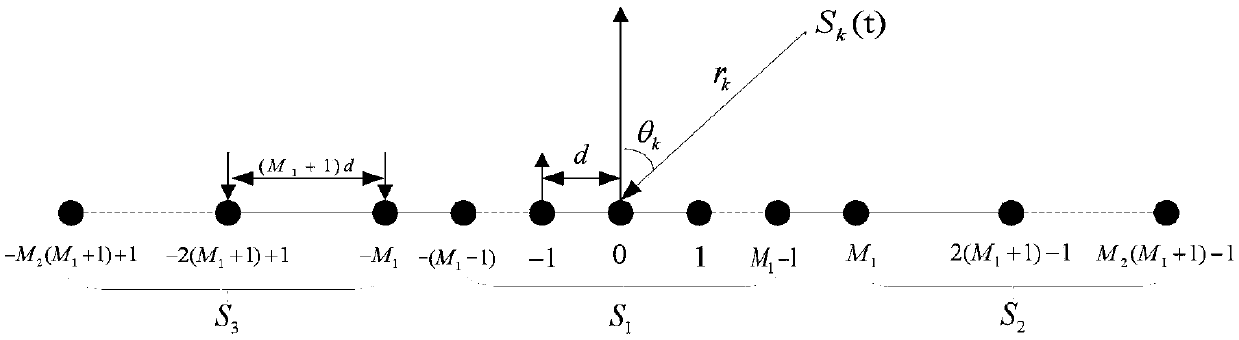
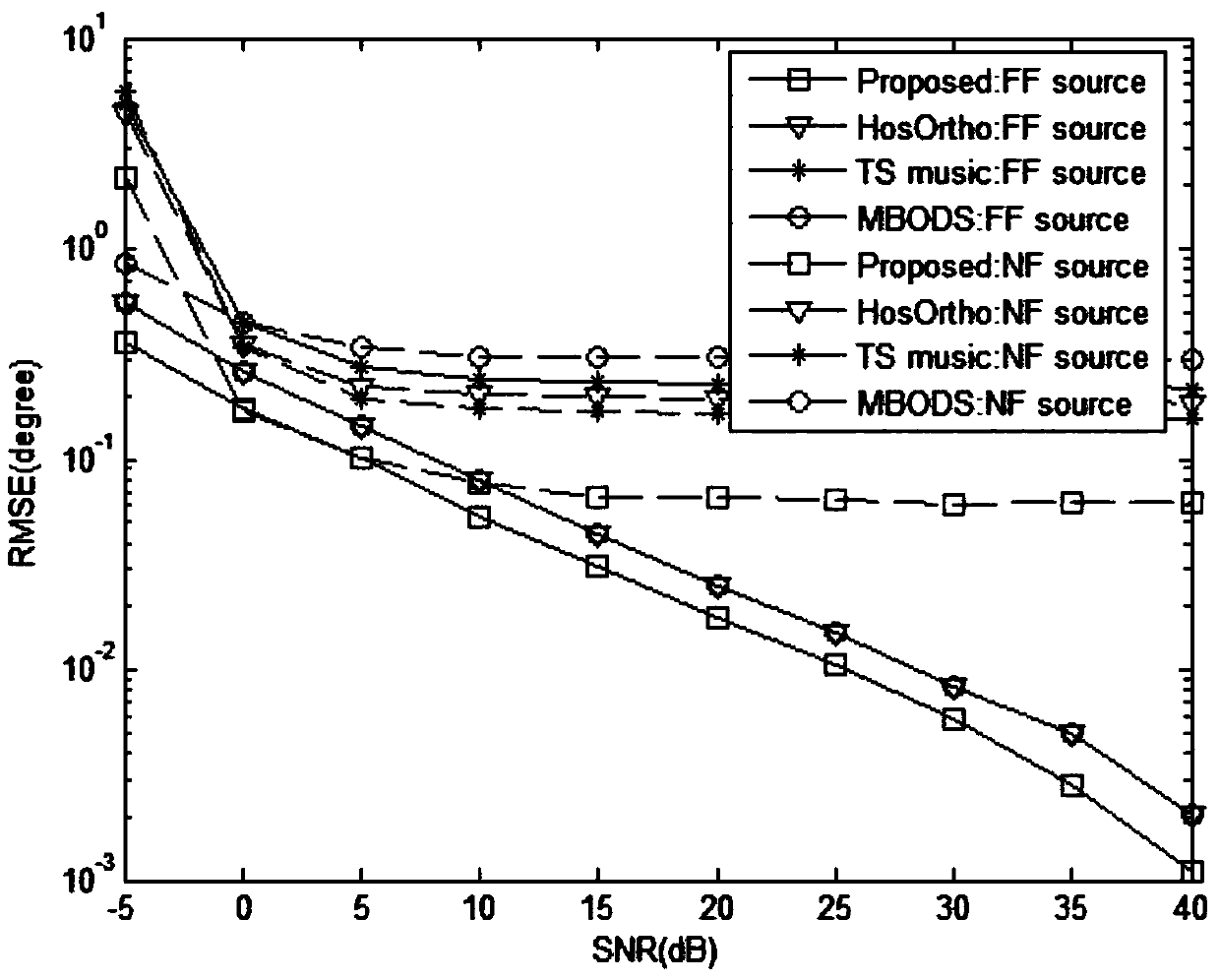
The invention provides a hybrid field signal source positioning method based on a symmetrical nested array. The hybrid field signal source positioning method comprises the following steps that an antenna array is set, wherein the antenna array is the symmetrical nested array; a far-field signal DOA is estimated to obtain an estimation value of the far-field signal DOA; the near field component isseparated from the far field component; a fourth-order cumulant virtual difference array of a near-field signal is calculated; an estimation value of the near-field signal DOA is obtained by using spectral peak search; and according to the near-field signal DOA estimation value, the near-field signal distance is estimated to obtain a near-field signal distance estimation value. The hybrid field signal source positioning method uses mixed-order statistics, and compared with a second-order statistic algorithm, the hybrid field signal source positioning method solves the problems of Gaussian noise interference and reduction of degree of freedom by half; the symmetric nested array and the fourth-order cumulant virtual differential array are used for improving the estimation accuracy of far-field DOA, near-field DOA and a near-field distance; oblique projection technology is utilized to separate the far-field and near-field components, and thus, it is not necessary to distinguish the far-field signal from the near-field signal according to distance parameters; and therefore, the number of search is reduced, and the computational complexity of the algorithm is further reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com