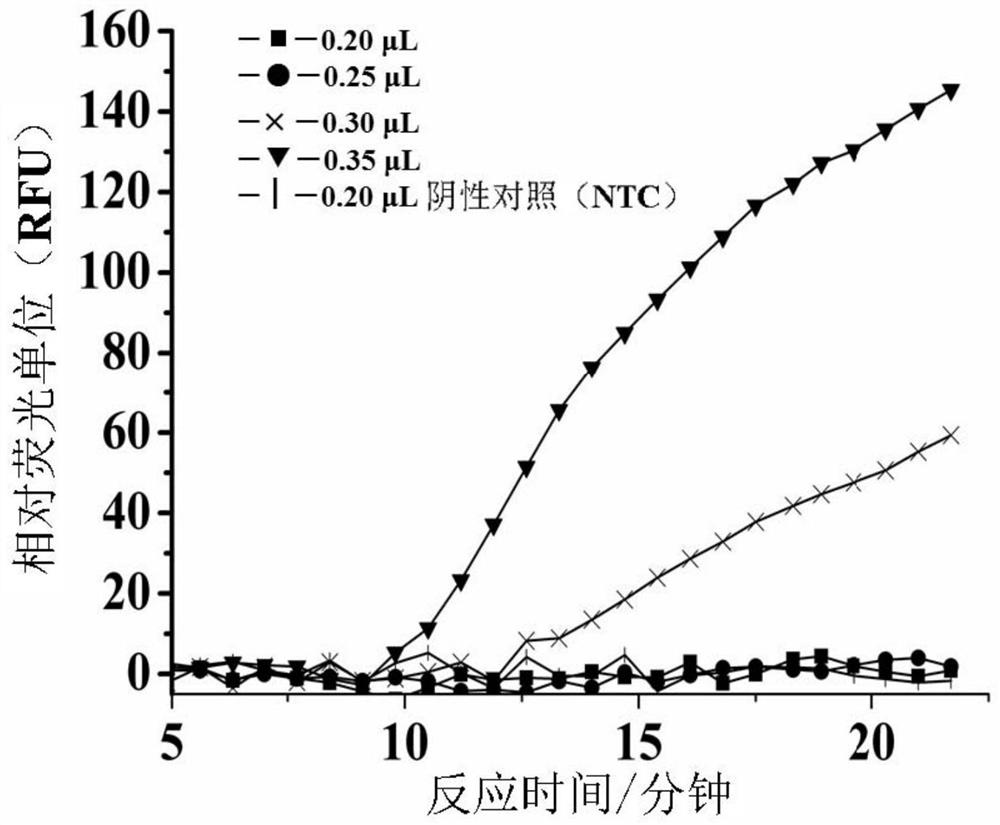
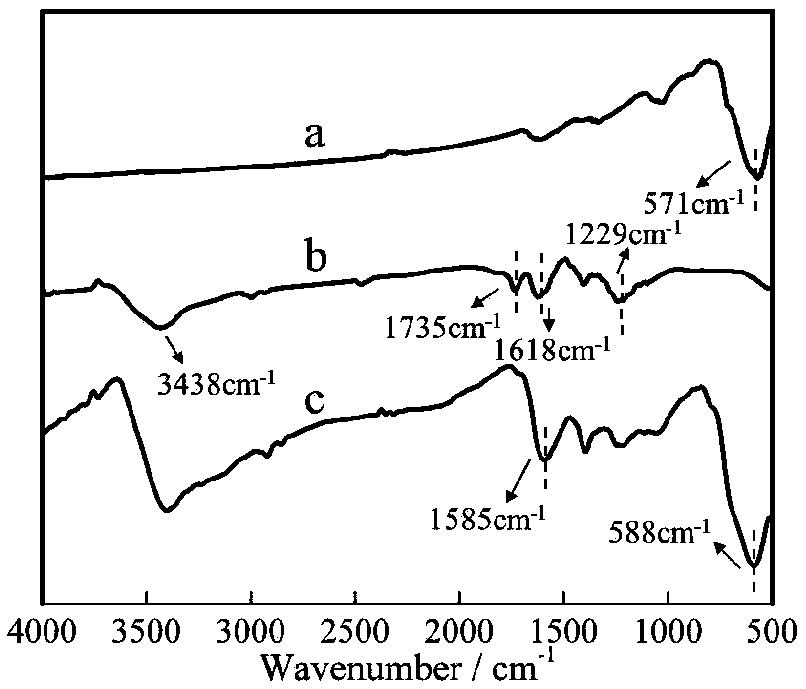
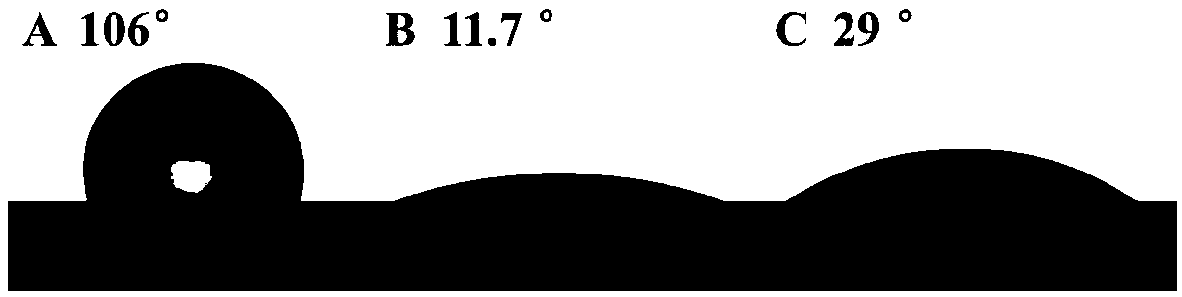
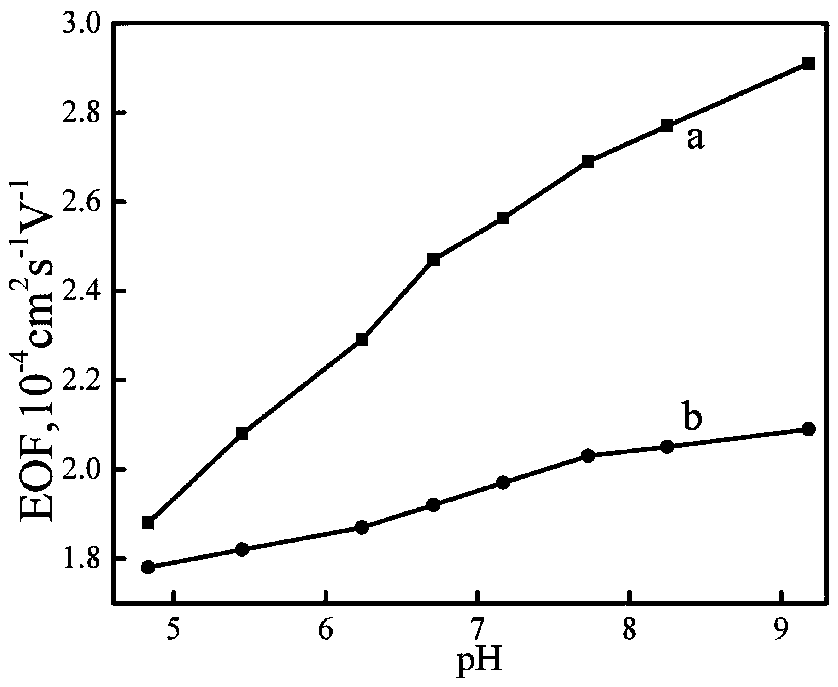
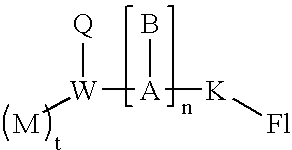Patents
Literature
36 results about "Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
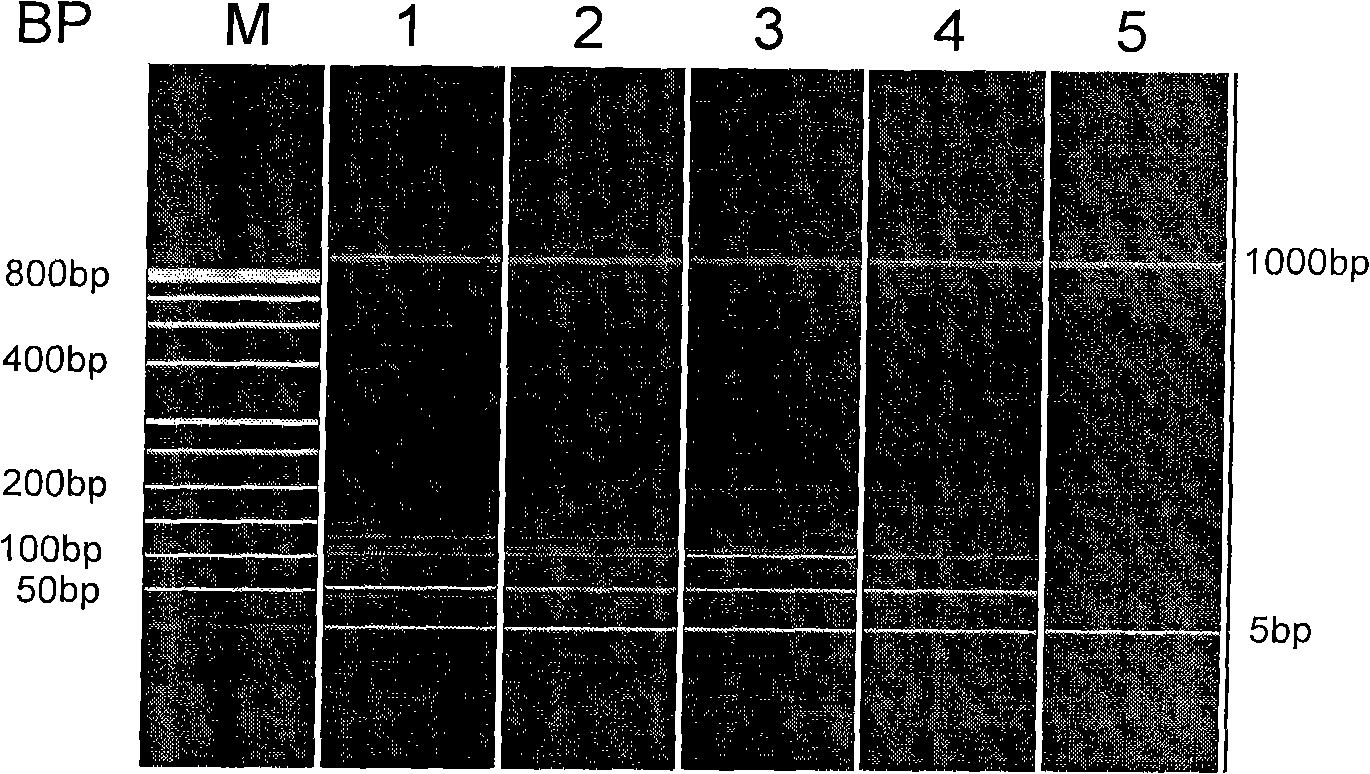
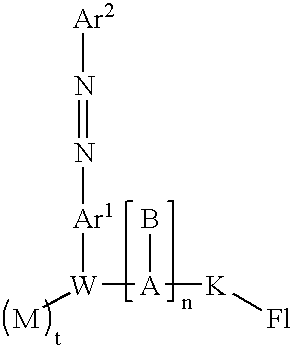
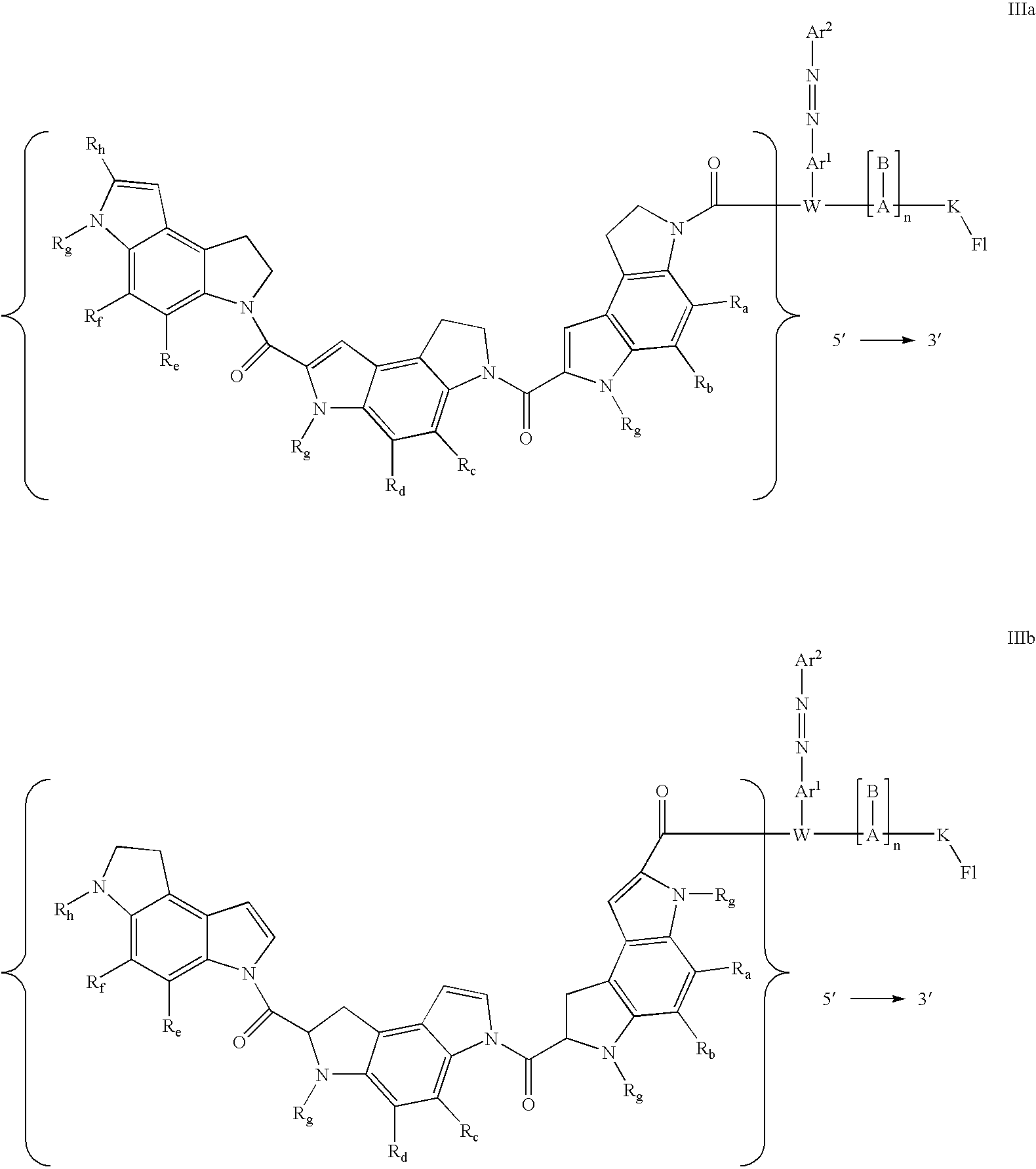
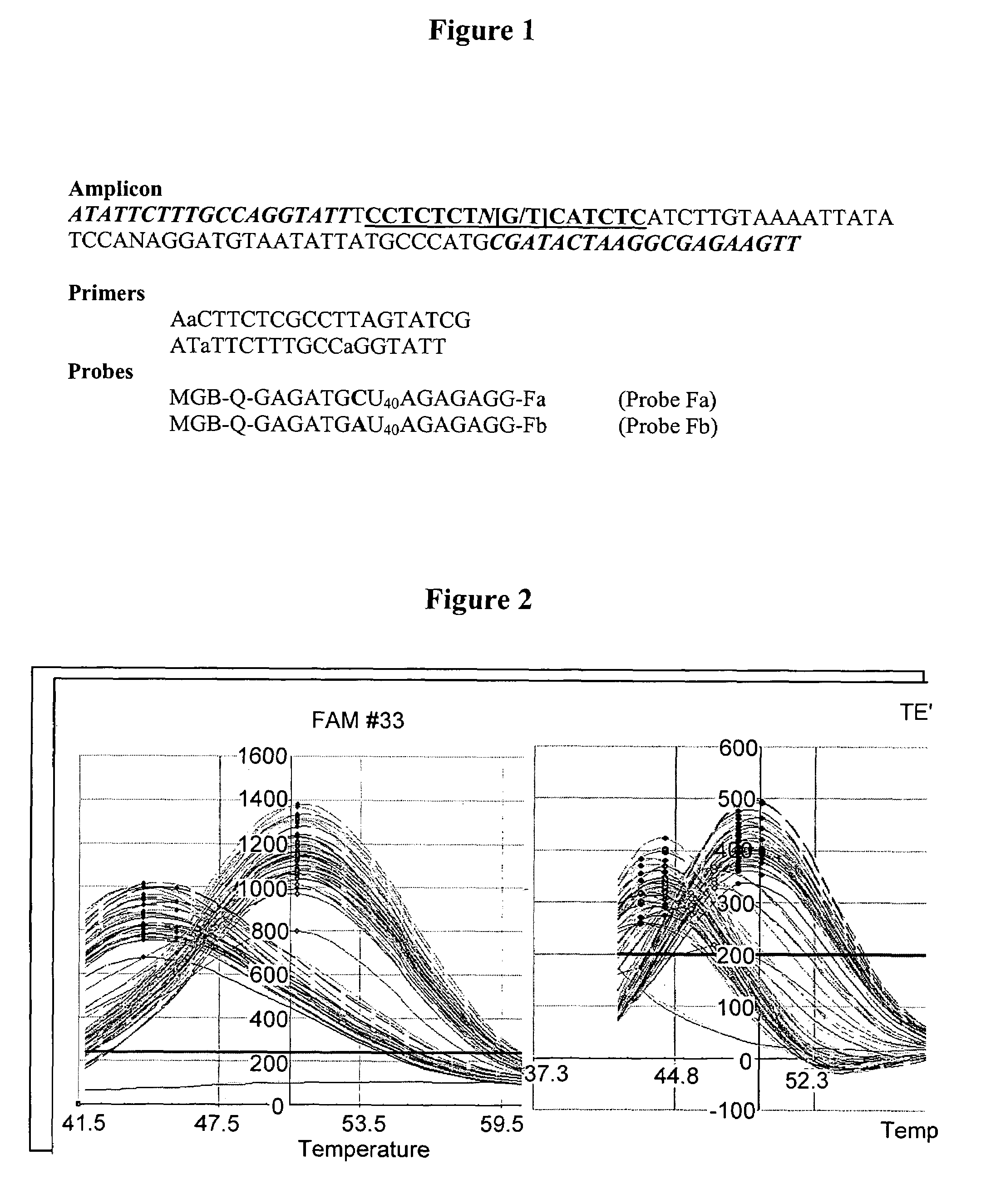
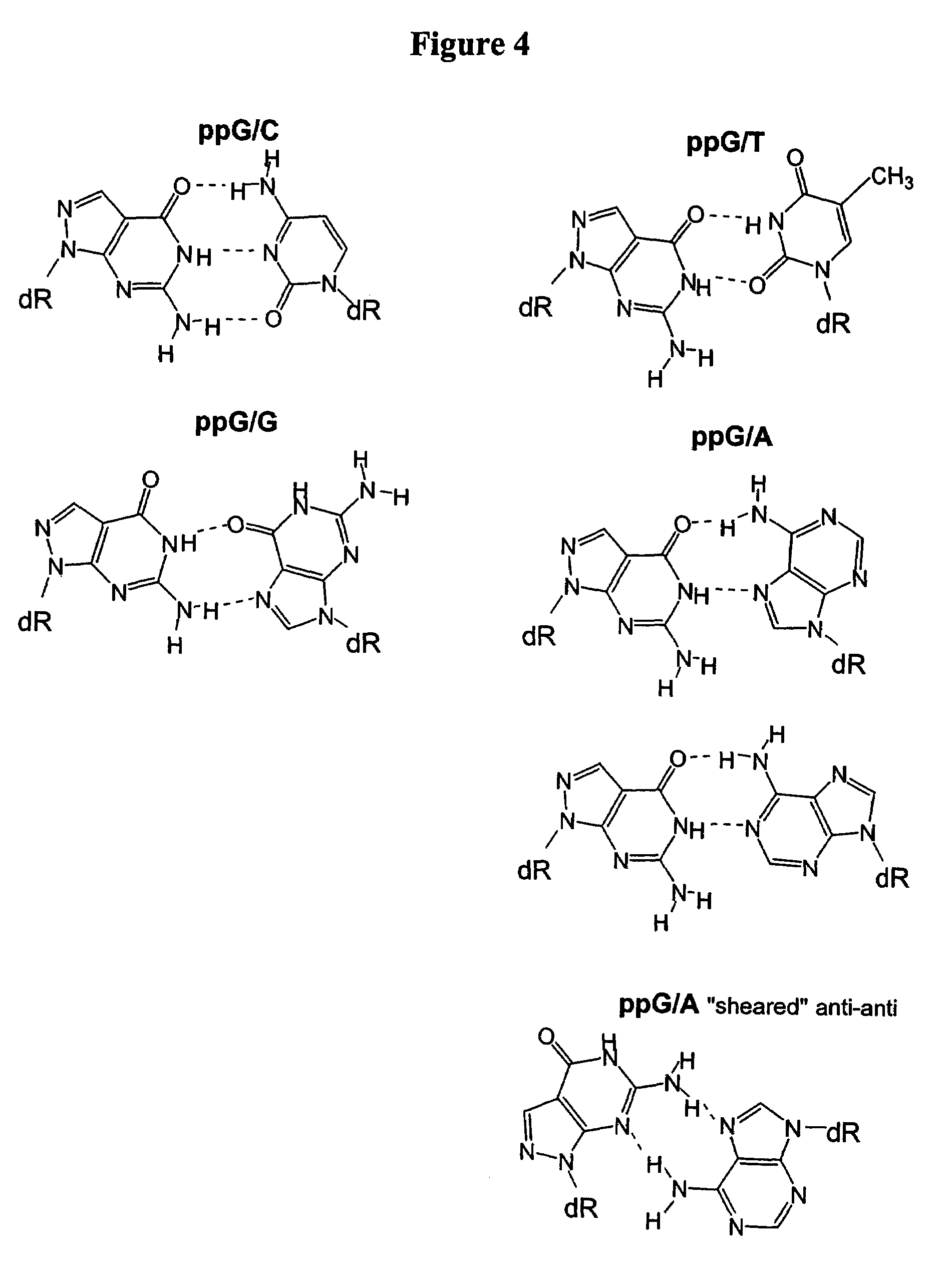
Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis of highly polymorphic target sequences
Owner:ELITECHGROUP MDX LLC
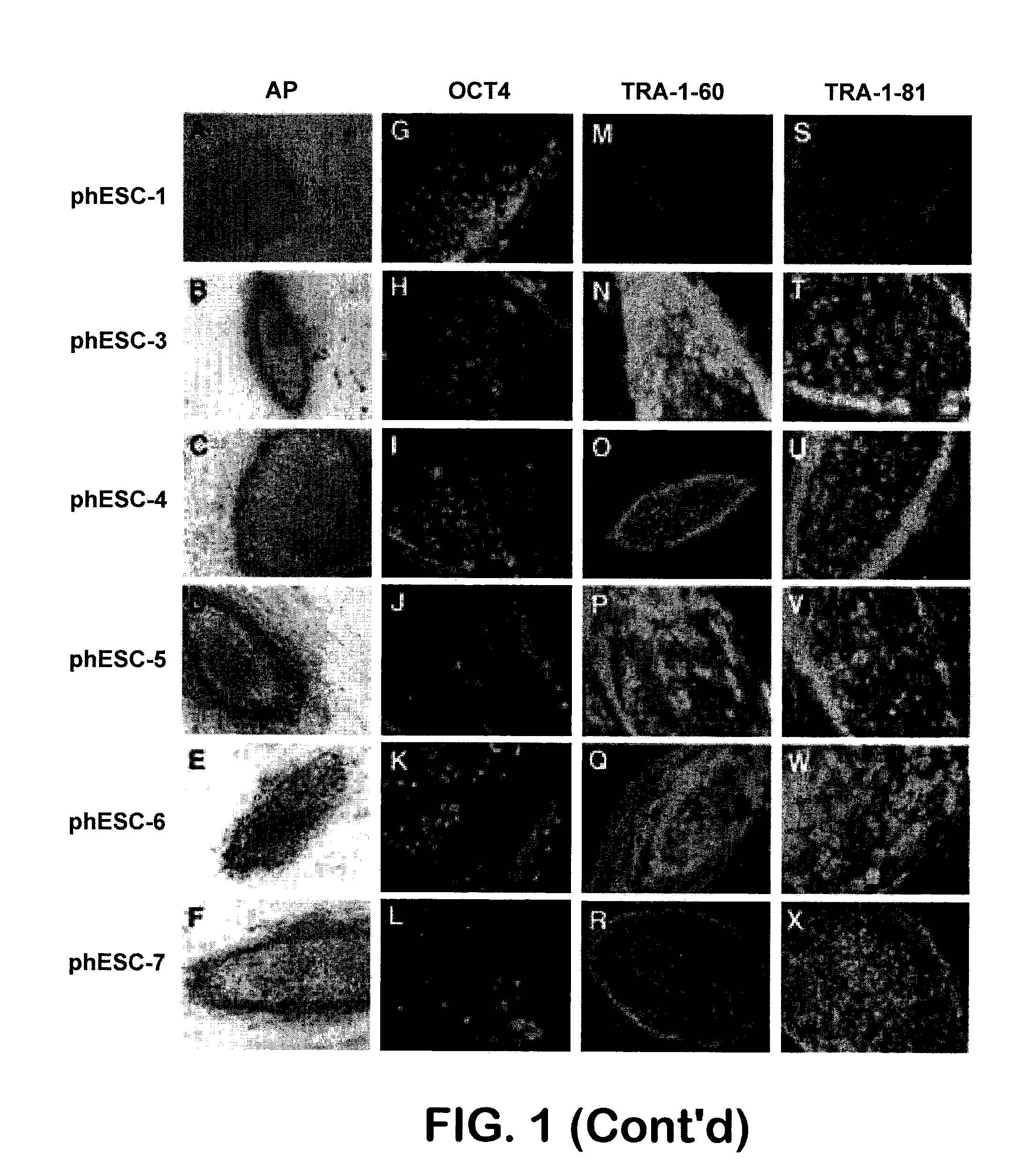
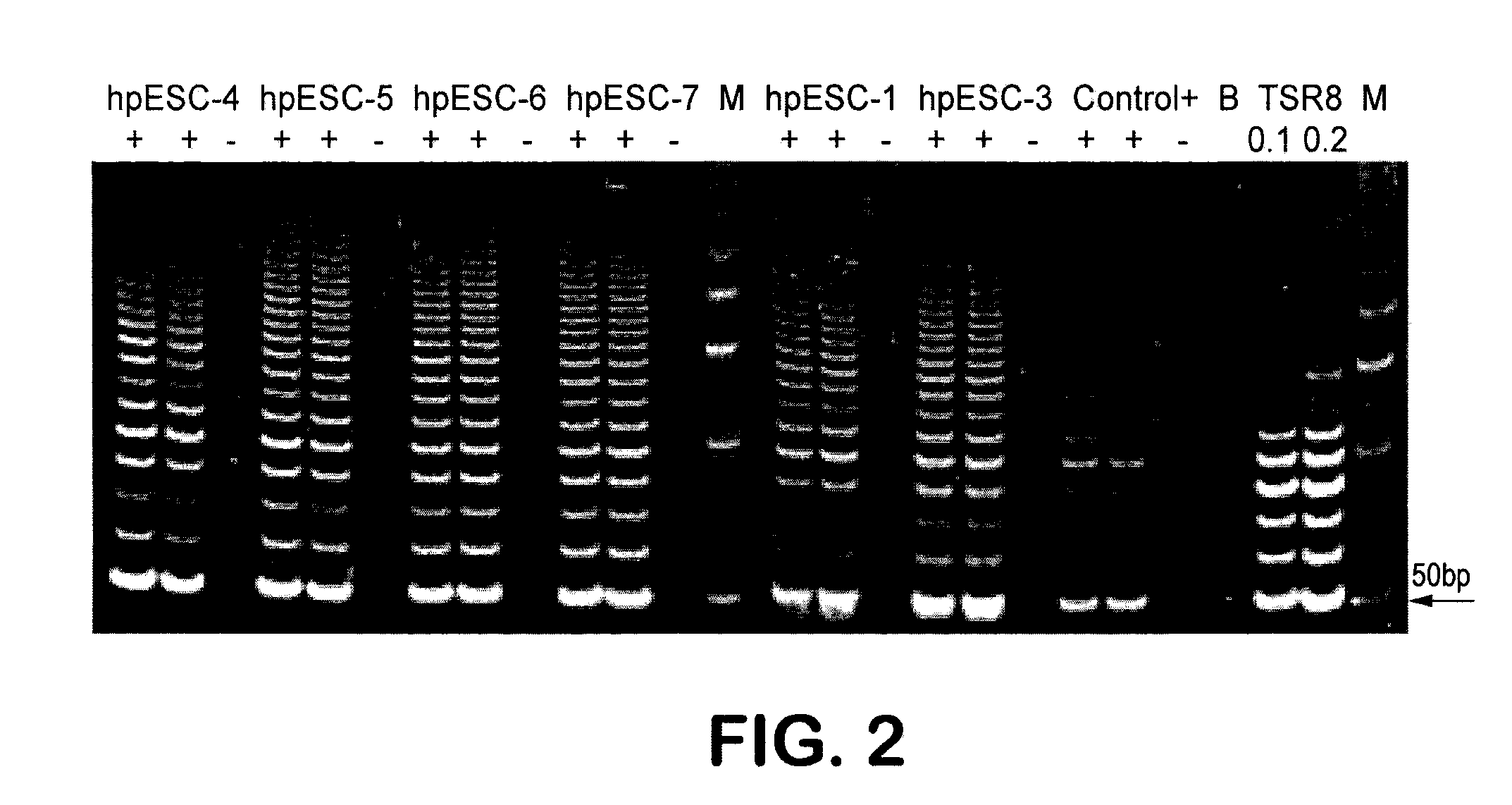
Patient-specific stem cell lines derived from human parthenogenetic blastocysts
InactiveUS20080299091A1Increase alkaline phosphatase activityHigh levelBiocideSenses disorderTelomeraseOocyte donor
Methods are disclosed for generating HLA homozygous parthenogenetic human stem cell (hpSC-Hhom) lines from both HLA homozygous and HLA heterozygous donors. These hpSC-Hhom lines demonstrate typical human embryonic stem cell morphology, expressing appropriate stem cell markers and possessing high levels of alkaline phosphatase and telomerase activity. Additionally, injection of these cell lines into immunodeficient animals leads to teratoma formation. Furthermore, in the case of HLA heterozygous donors, the hpSC-Hhom lines inherit the haplotype from only one of the donor's parents. SNP data analysis suggests that hpSC-Hhom lines derived from HLA heterozygous oocyte donors are homozygous throughout the genome as assessed by single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis. The protocol as disclosed minimizes the use of animal-derived components, which makes the stem cells more practical for clinical application.
Owner:INT STEM CELL CORP
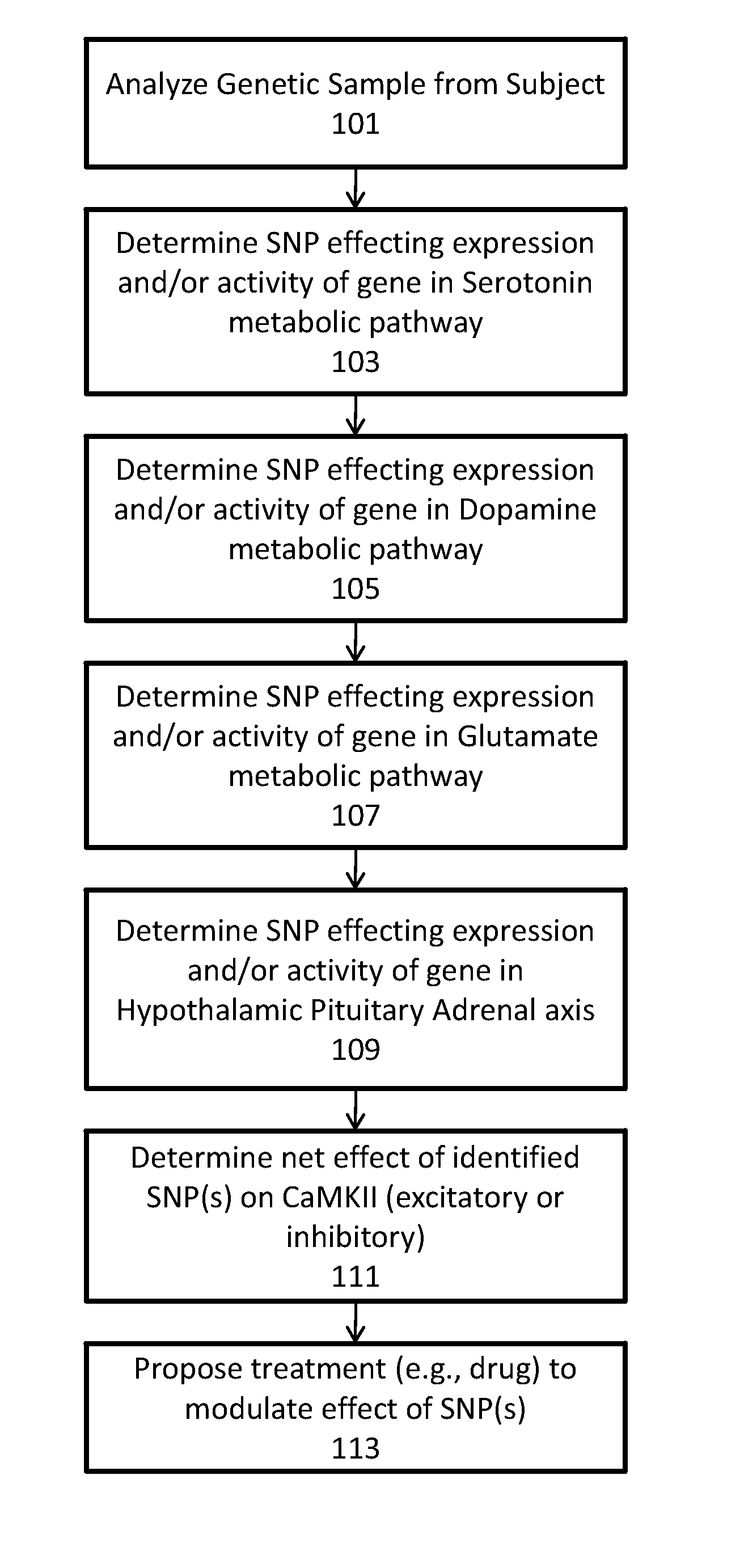
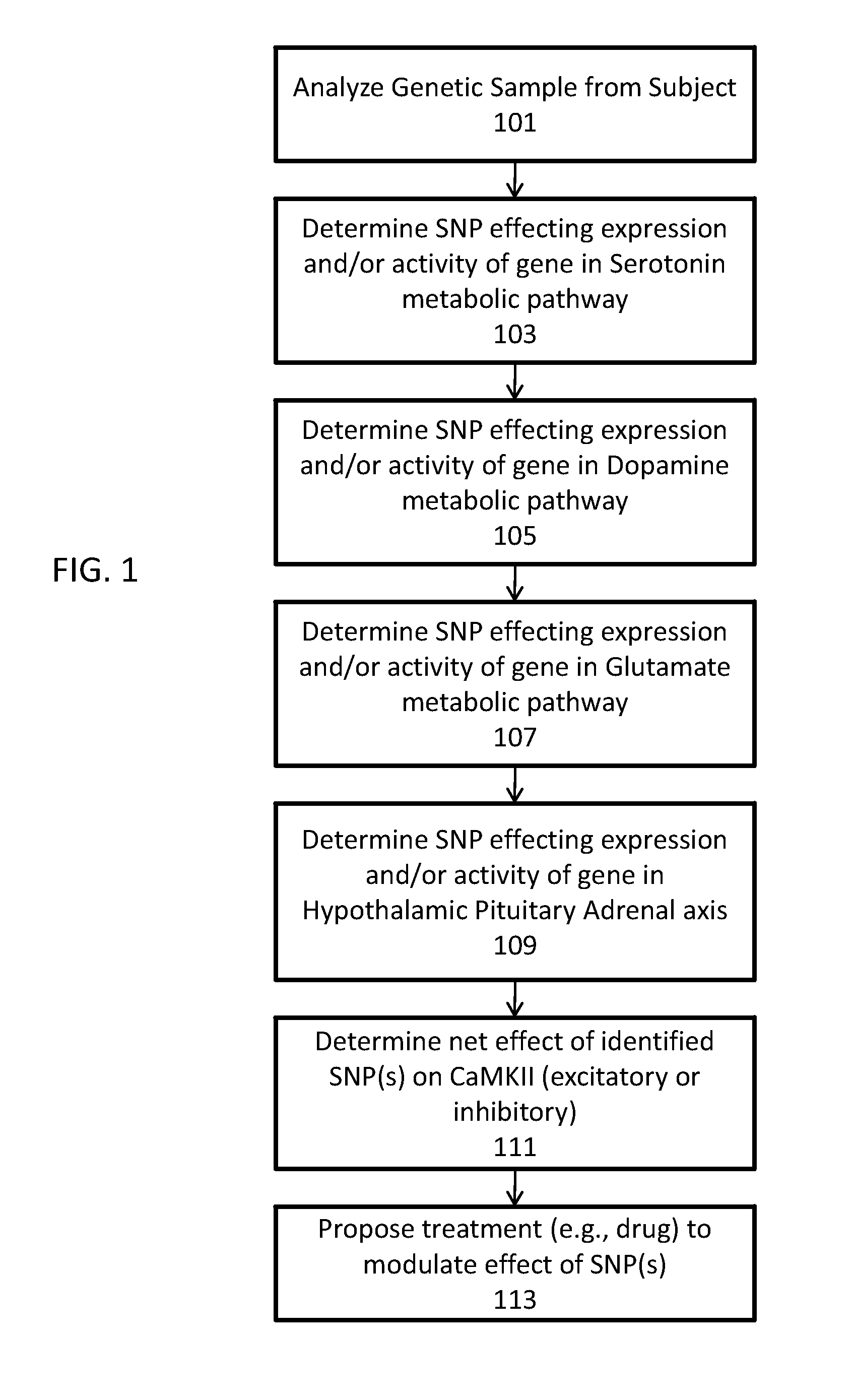
Methods for assessment and treatment of depression via utilization of single nucleotide polymorphisms analysis
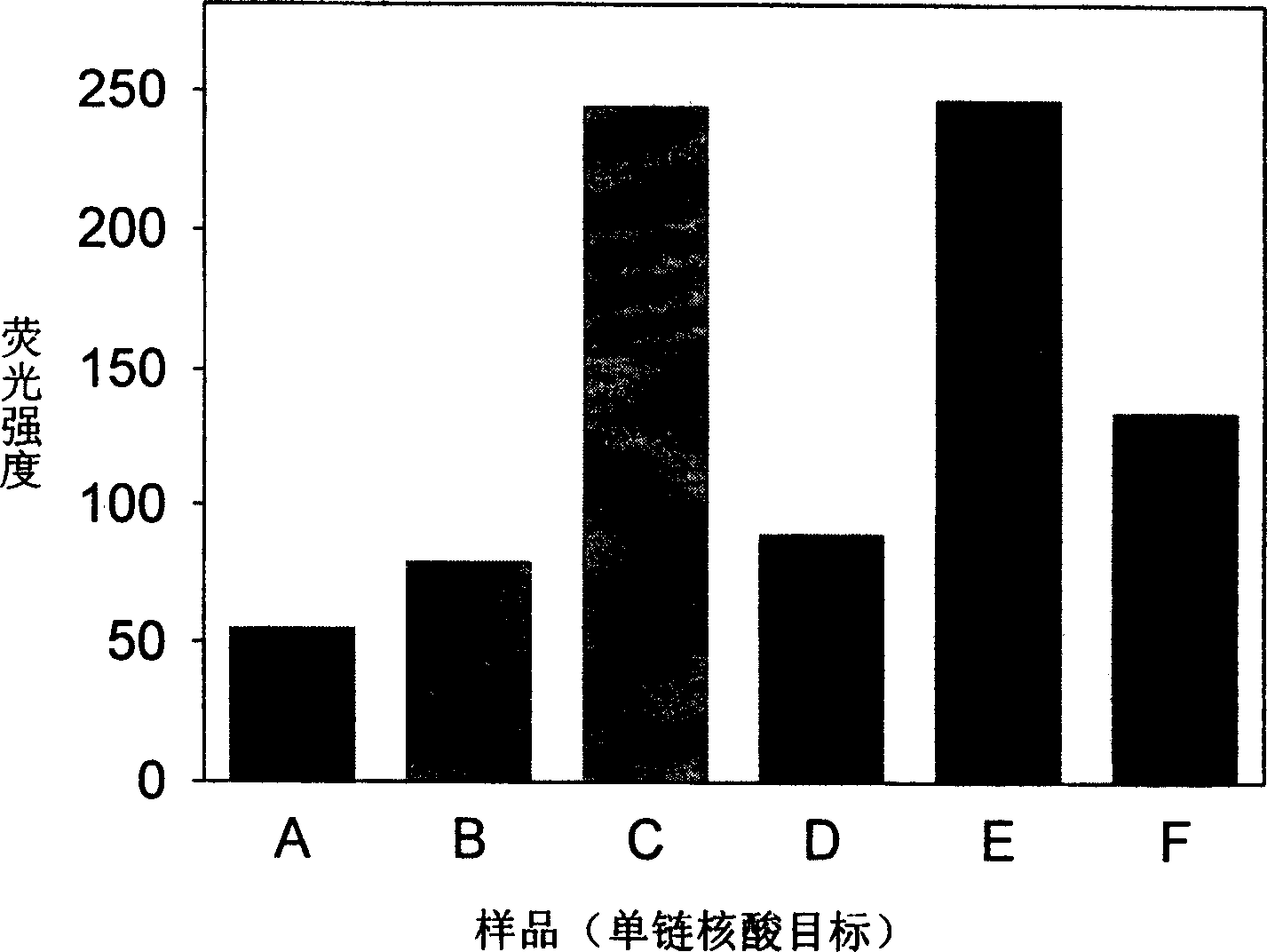
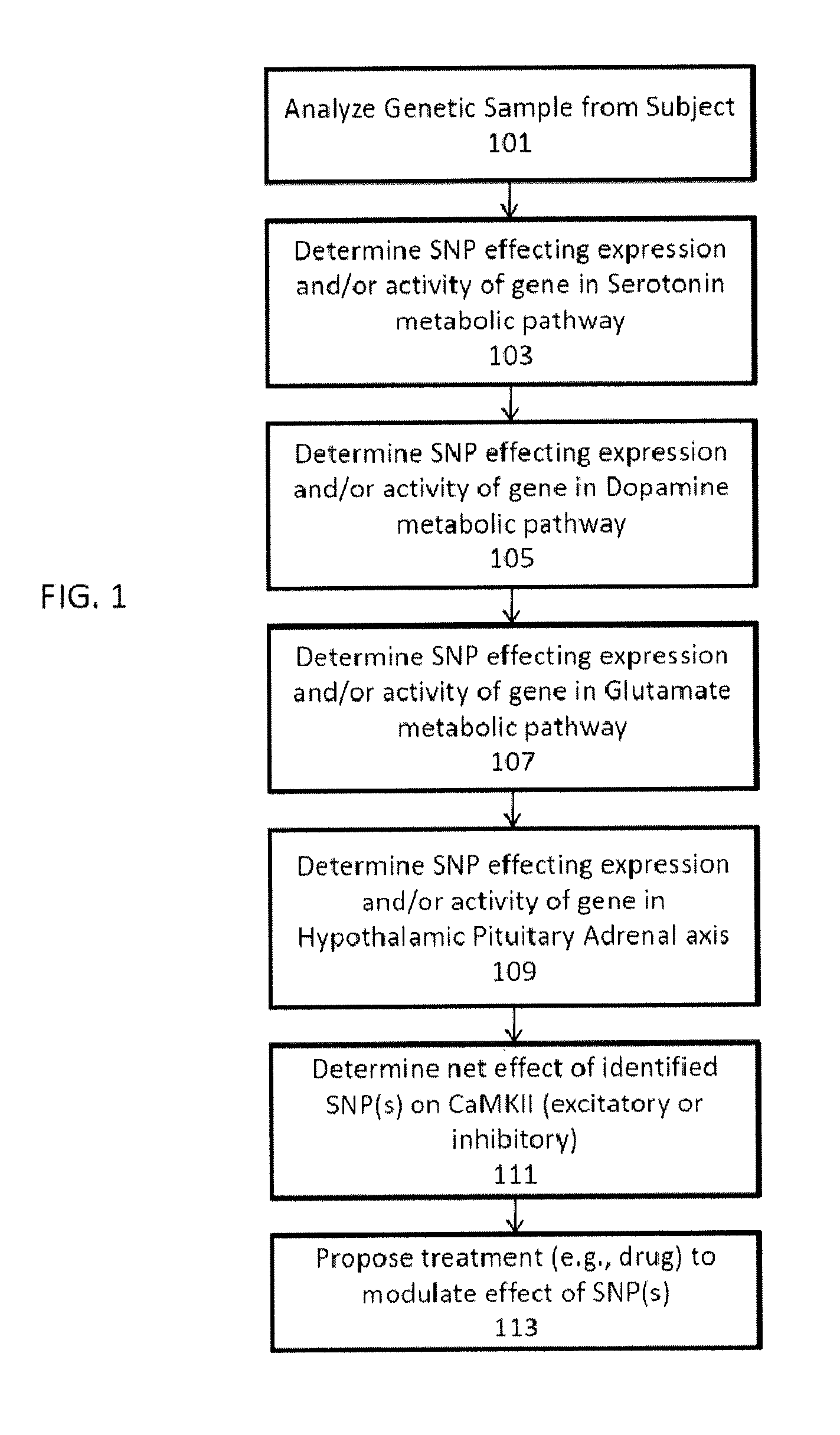
InactiveUS20100304391A1Avoid it happening againModulate long-term potentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetics predispositionCa2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase
Described herein are assays, kits and methods for treating depression, including the diagnosis and treatment of depression based on the determination of genetic predispositions towards inhibition or enhancement of Ca2+ / calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). For example, described herein are methods and kits (including assays) for determining if one or more gene in an excitatory or inhibitory pathway for modulating CaMKII activity or expression is likely to be inhibited or enhanced by an SNP. Also described are methods and kits (including assays) for prescribing treatment based on the identification of SNPs that may modulate CaMKII.
Owner:GENOMIND
Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis of highly polymorphic target sequences
Owner:ELITECHGROUP MDX LLC
MLCR probe, two-step reaction mode and suspension chip detection capture probe
InactiveCN101864482AOvercome the shortcomings of low detection sensitivityOvercome the disadvantage of difficult equalization signal amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideHigh flux
The invention relates to an MLCR probe, a two-step reaction mode and a suspension chip detection capture probe. The MLCR probe is one group of four single-chain DNA probes synthesized aiming at each point to be tested, the tail end of the MLCR probe is connected with a general sequence and used for converting LCR into MLCR; in the two-step reaction mode, the MLCR probe firstly carries out MLCR reaction to be converted into a connecting product, general sequences at the tail end of the connecting product are respectively matched with a general primer, and then PCR reaction for equally amplifying the connecting product is carried out; and the capture probe spans incision recognized by a heat-resisting lignase in the point to be tested, and can be hybridized with a product obtained by the second step PRC amplification at a chip inspection temperature. The invention overcomes the defects of low detection sensitivity of LCR and MLPA and difficult amplification of multiple PCRs by combining with the advantages of the LCR and the MLPA, has the characteristics of high flux, super sensitivity and high specificity, and is suitable for gene testing and Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis of various samples, especially traces and degraded DNA samples.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Selectivity of nucleic acid diagnostic and microarray technologies by control of interfacial nucleic acid film chemistry
InactiveUS20050181384A1High selectivityIncreased signal noiseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOligomerNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides methods for conducting hybridizations having increased selectivity of hybridization using substrates upon which probe nucleic acids are immobilized. The methods of this invention can be used to increase selectivity in nucleic acid diagnostic devices, such as biosensors and microarrays. The invention provides increased selectivity through control of the substrate surface chemistry and in particular, through control of the density of nucleic acids and other oligomers immobilized on a surface. The invention provides improved signal to noise in hybridization assays via enhanced differences in signal magnitude generated for fully matched target nucleic acid compared to partially matched target nucleic acid prior to signal processing. Specifically, invention provides methods for using substrates having medium-high to high immobilization densities to achieve higher hybridization The methods and substrates of this invention are particularly well-suited to assays for genetic targets in samples that contain genetic species that are very similar in nucleic acid sequence to the genetic target. The methods and substrates of this invention are also well-suite for single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis.
Owner:PIUNNO PAUL +3
Method for auxiliarily determining warfarin dosage for Chinese Han patients by utilizing single nucleotide polymorphism analysis and biological chip
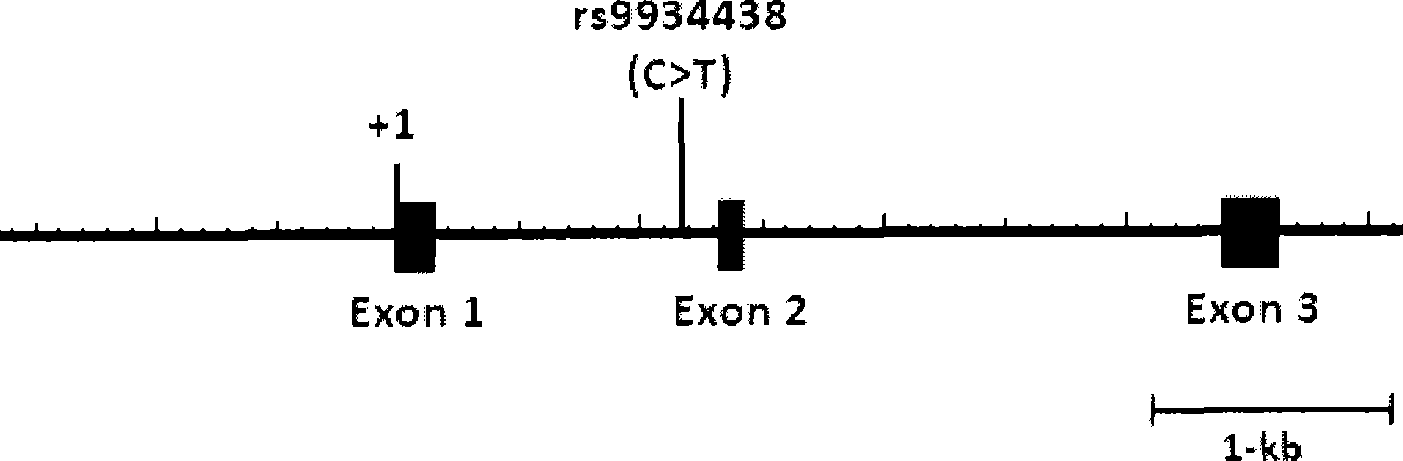
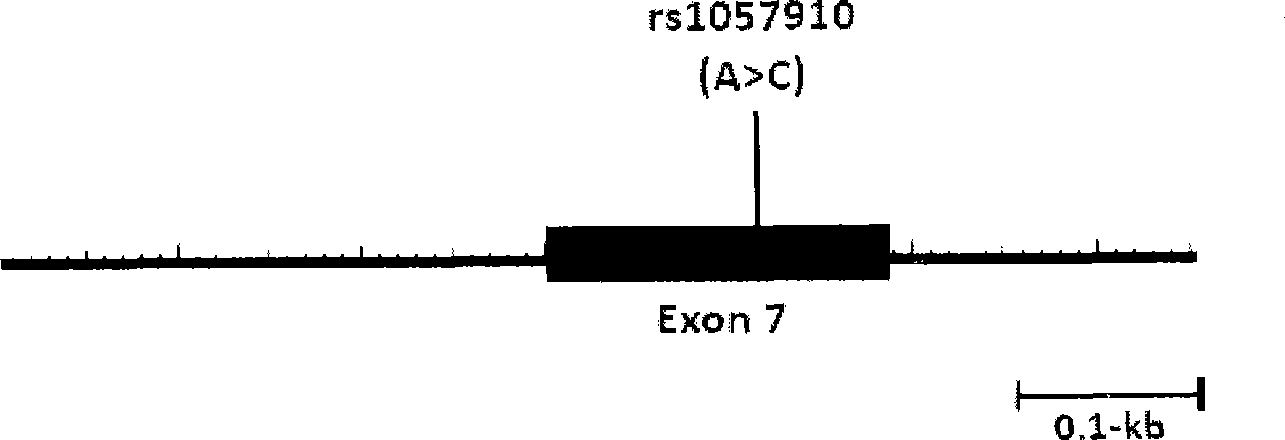
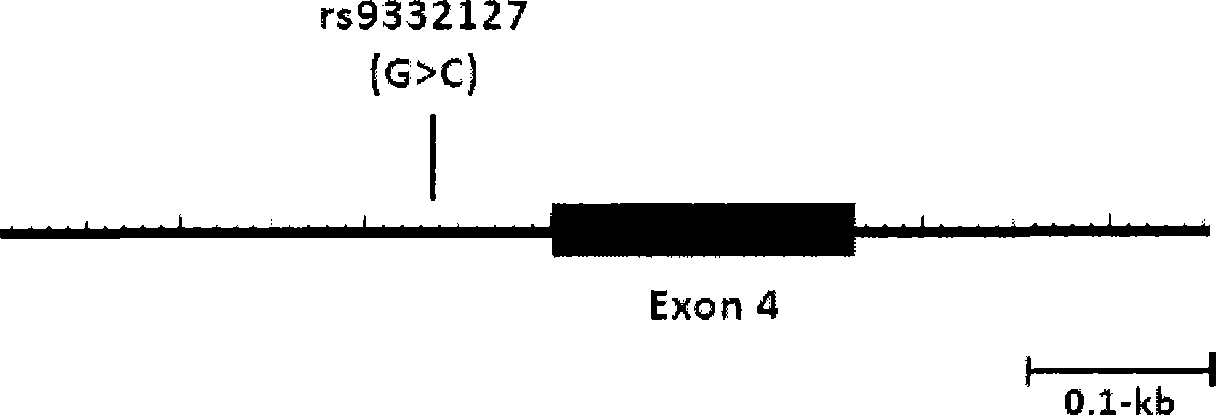
The invention relates to a method for auxiliarily determining warfarin dosage for Chinese Han patients by utilizing single nucleotide polymorphism analysis and a biological chip. In particular, the invention provides a method for acquiring grades useful in determining the warfarin dosage for the Chinese Han patients, which comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a nucleic acid sample from a patient; (2) detecting the nucleic acid sample aiming at one or more single nucleotide polymorphism sites selected from the following groups: rs9934438 site of VKORC1 gene, rs1057910 site and rs9332127 site of CYP2C9 gene, and rs4653436 site of EPHX1 gene; (3) determining genotypes of the single nucleotide polymorphism sites; and (4) grading the genotypes of the single nucleotide polymorphism sites, wherein the grades obtained in step (4) are helpful in determining the warfarin dosage for the patient. The invention also provides the biological chip used for the method.
Owner:李文正纳米研究院
Method of determining genetic predisposition for deficiency in health functions using SNP analysis
InactiveUS20070254306A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingDNA methylationInherited Predisposition
A method of determining genetic predisposition for deficiency in a specific health function of a person using single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis is provided. The method includes performing a SNP genotyping assay of three or more genes using a sample obtained from the person, obtaining a SNP panel which includes predetermined identifier SNPs, comparing the SNP panel with a predetermined criterion defining the genetic predisposition for deficiency in a specific health function; and reporting presence of genetic predisposition for deficiency in this health function if the SNP panel meets the predetermined criterion. The health function includes glycation, inflammation, DNA methylation, oxidation or DNA repair.
Owner:GIAMPAPA VINCENT C
Individualized gene information card for genome single nucleotide polymorphism analysis
InactiveCN102122326AServe as a health warningExpand your searchSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseInformation Card
The invention discloses an individualized gene information card for genome single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis, and relates to the technical field of molecular biology. The individualized gene information card is made by the following steps of: (1) making a sample acquisition packet; (2) detecting DNA; (3) analyzing data; (4) making individual gene card analysis software; and (5) making a gene health early warning network system. The individualized gene information card can predict the susceptibility of multiple diseases by monitoring the known SNP, assist a user in taking preventive measures in advance and prevent or delay the occurrence of the diseases. Therefore, the purpose of health early warning is fulfilled.
Owner:HEBEI JIANHAI BIO CHIP TECH
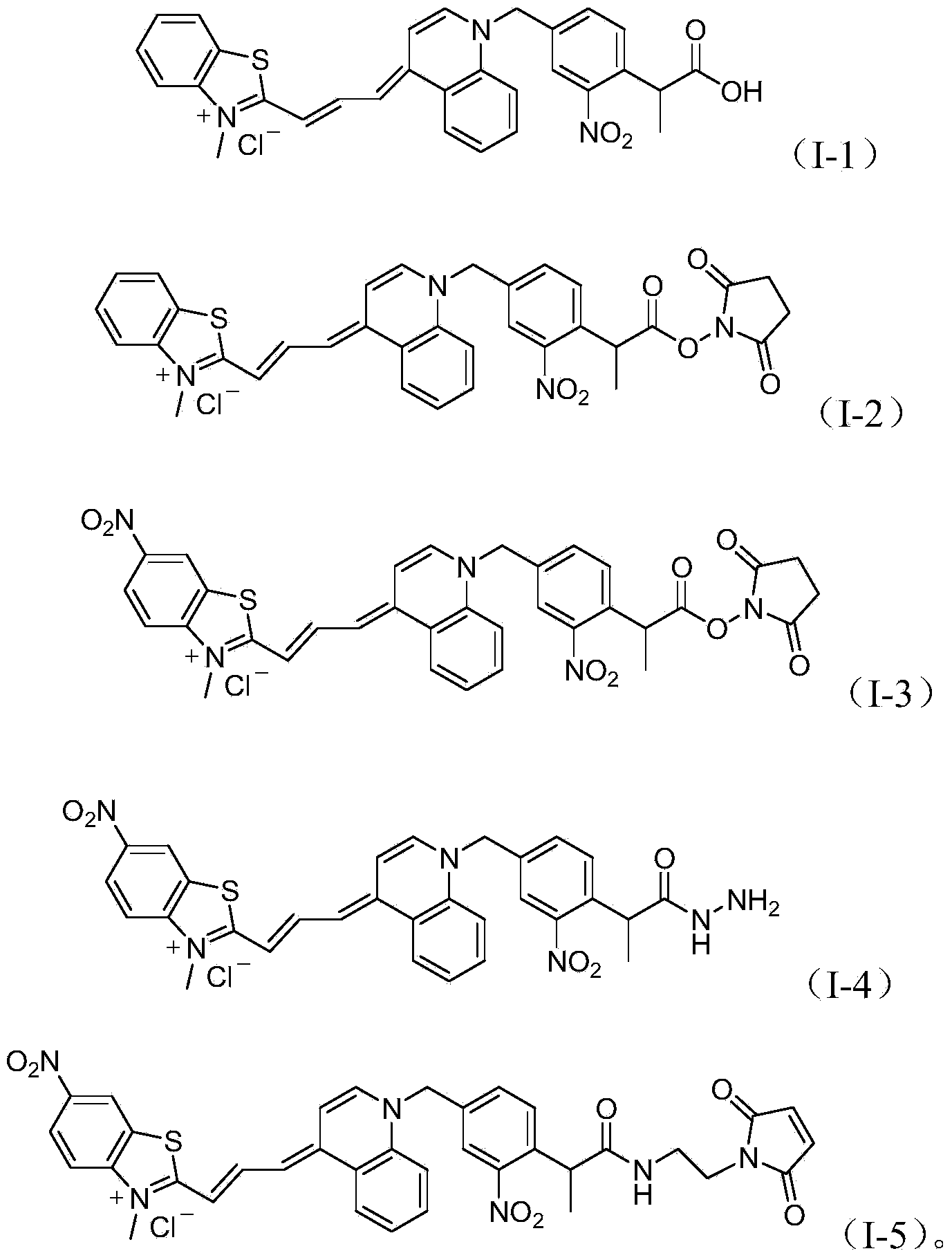
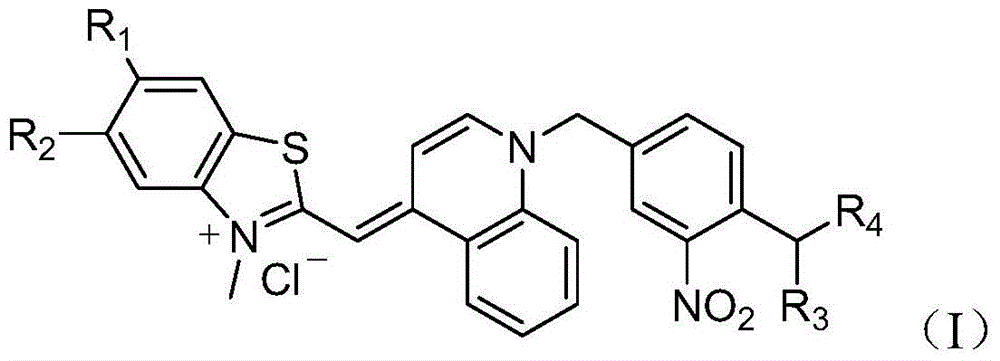
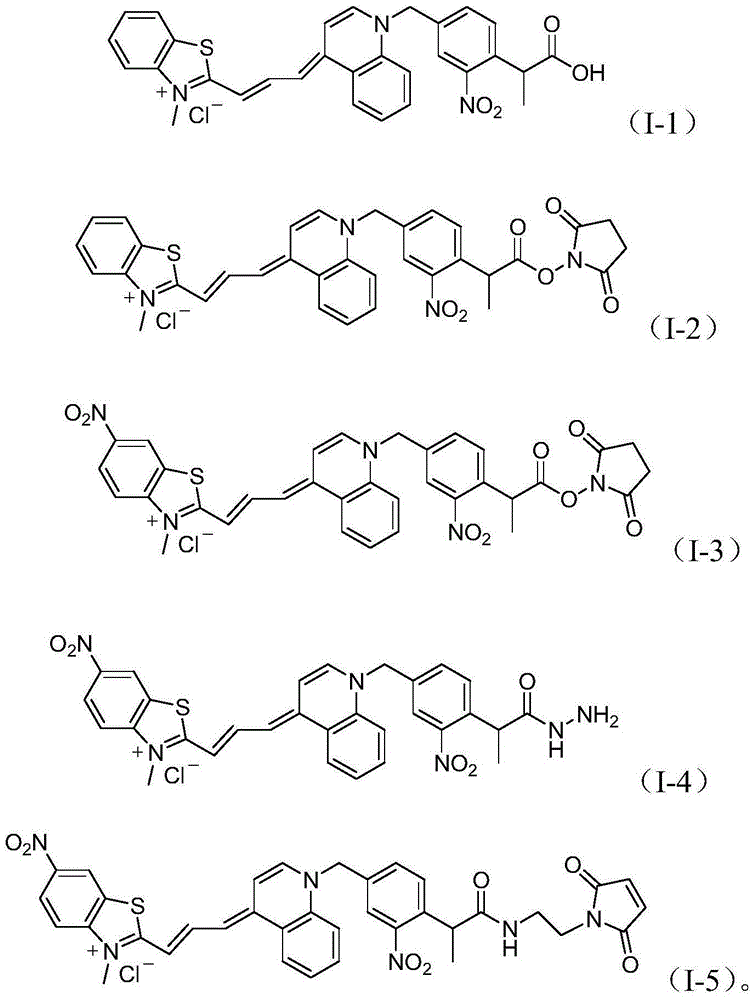
Asymmetric cyanine dye compound and application thereof
ActiveCN103554096AQuenching is effectiveHigh melting temperatureOrganic chemistryMethine/polymethine dyesCyanineDouble stranded
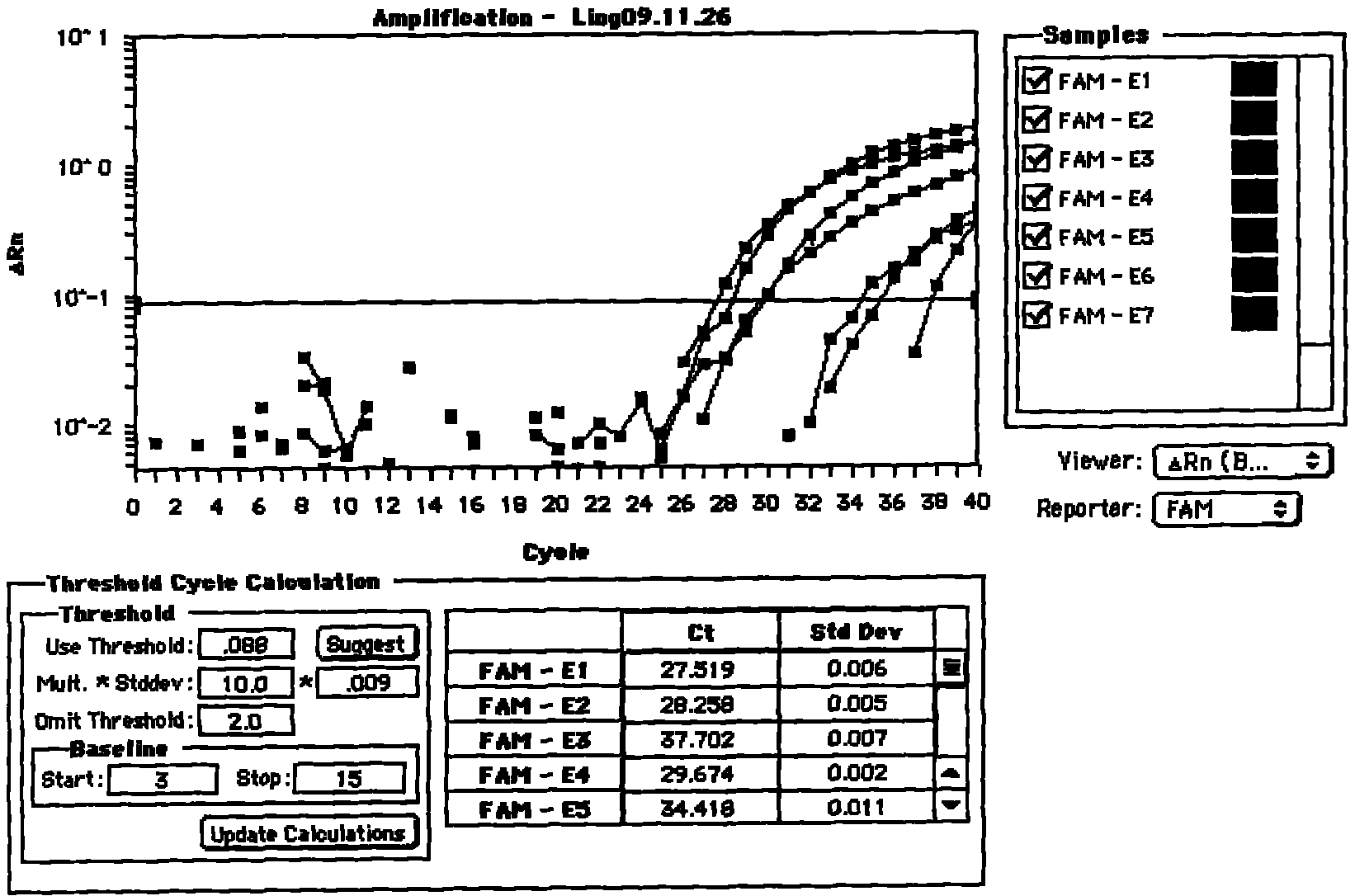
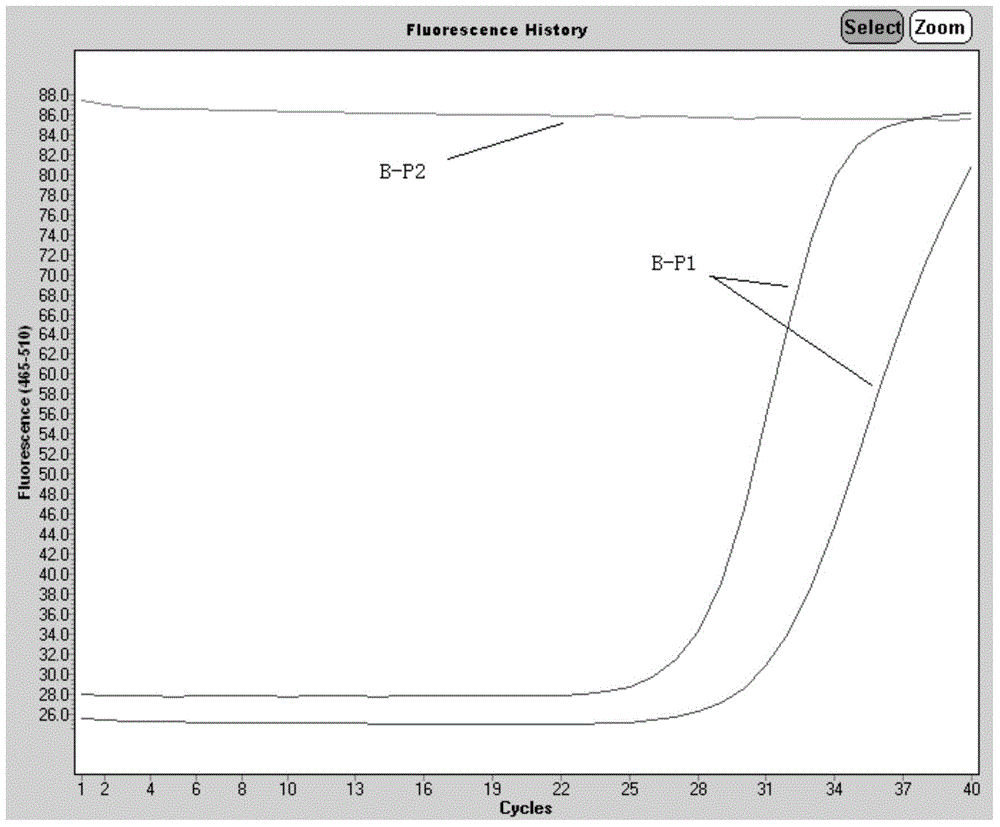
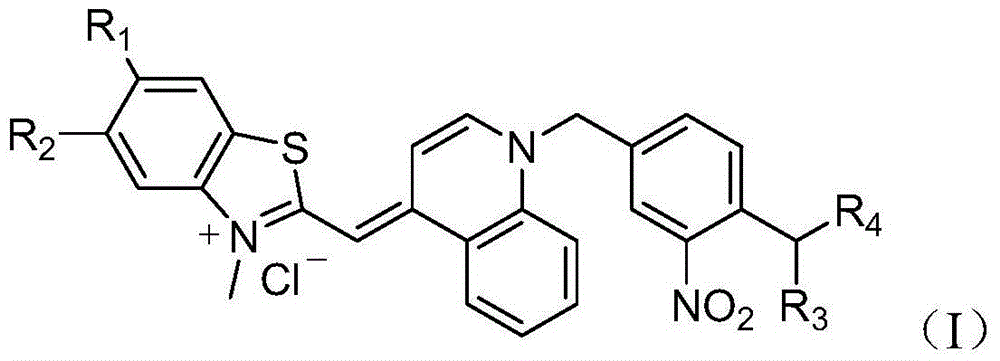
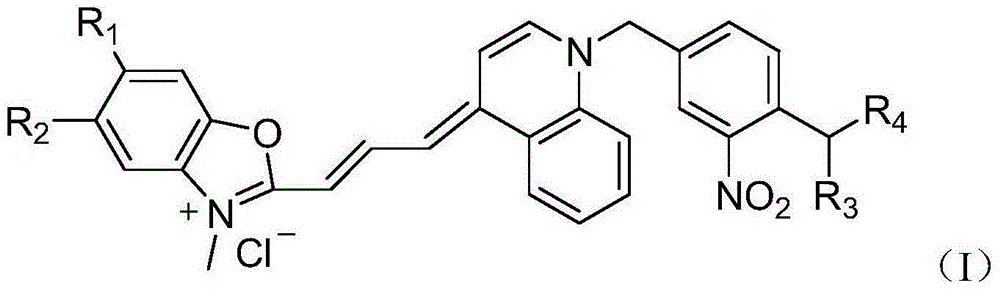
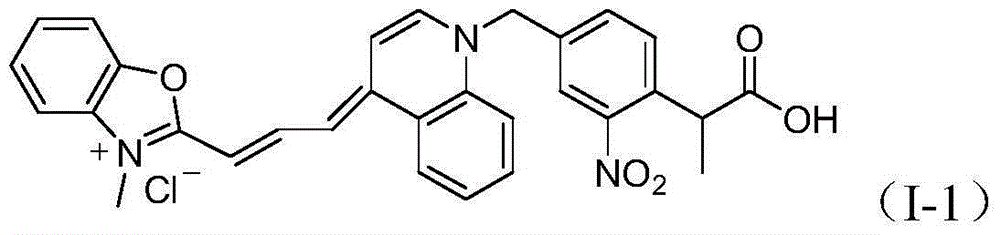
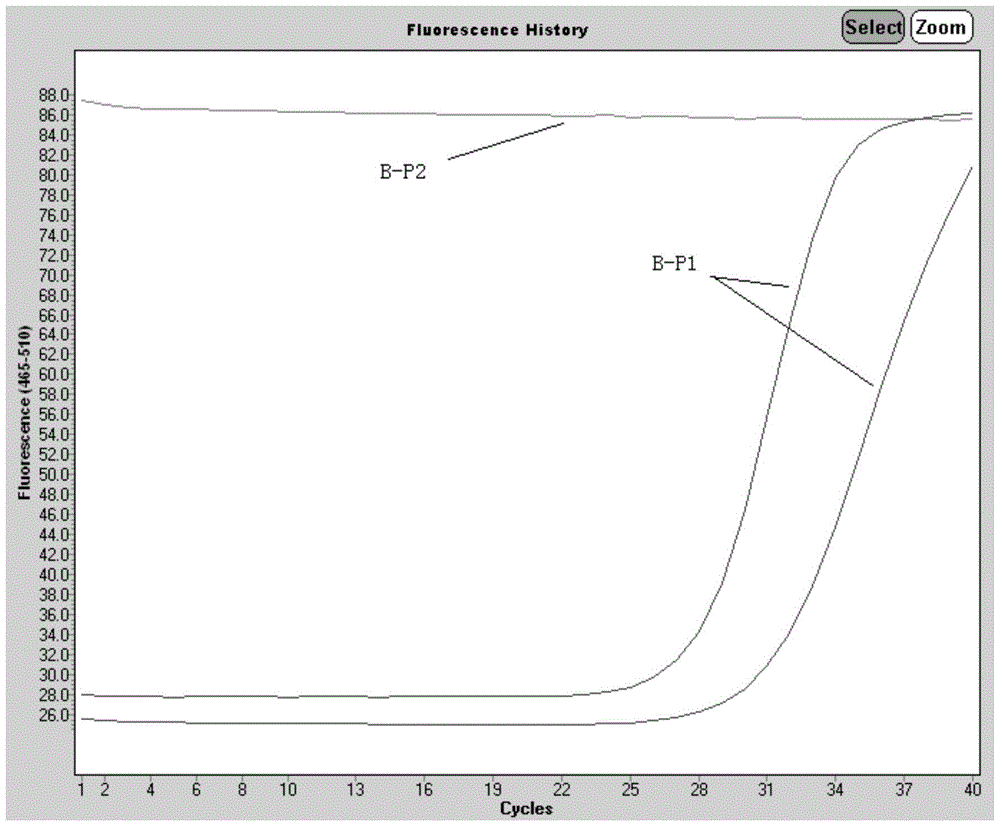
The invention provides an asymmetric cyanine dye compound (I) and application of the same as a quenching agent. The invention provides the asymmetric cyanine dye fluorescence quenching compound which can effectively quench fluorescence of FAM and stabilize DNA double strands, enables melting temperature in the PCR process to increase 2 to 3 DEG C, is applicable to a conventional real time fluorescence quantification PCR detection method and can be effectively applied to the field of analysis of single nucleotide polymorphism.
Owner:上海辉睿生物科技有限公司 +2
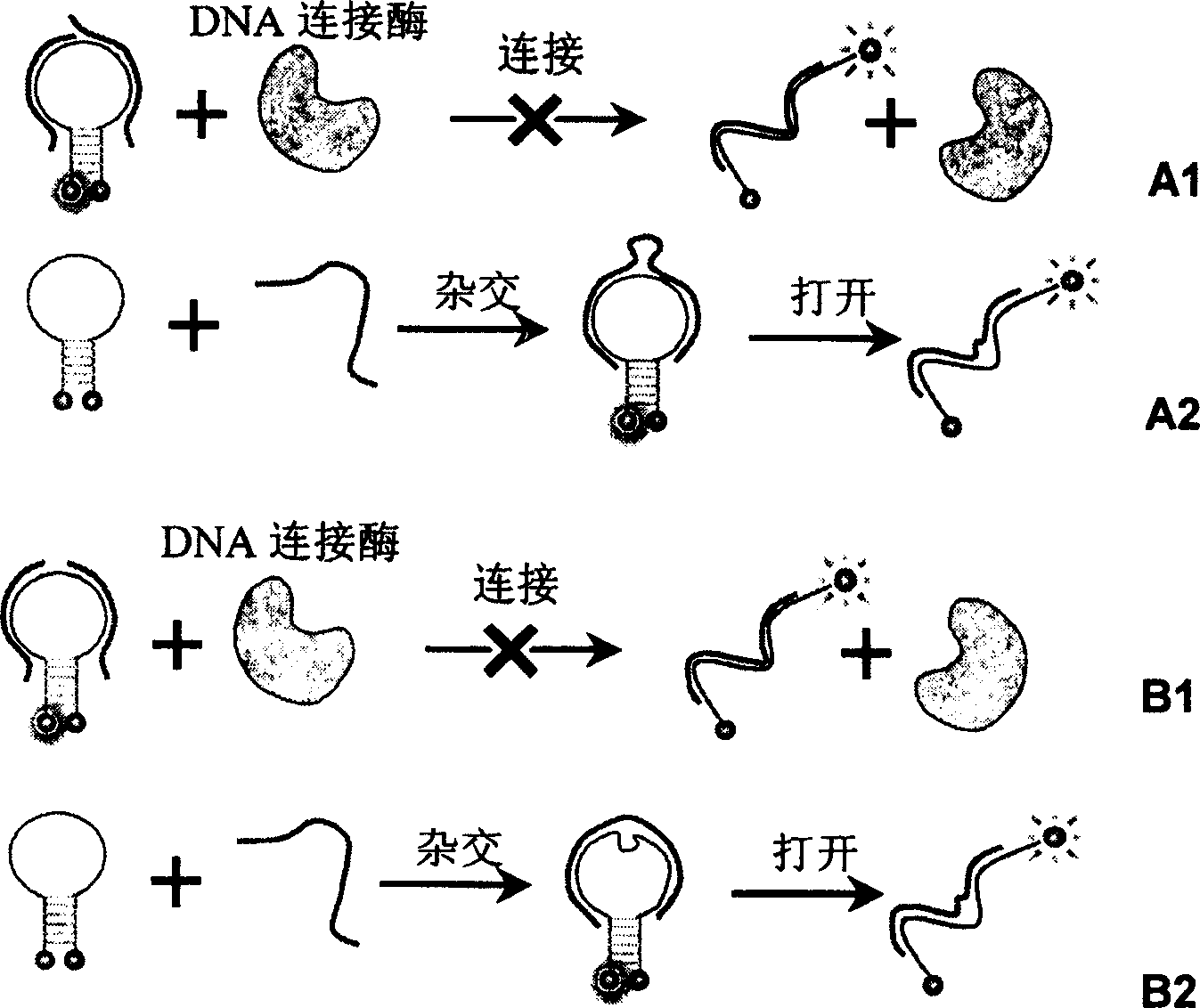
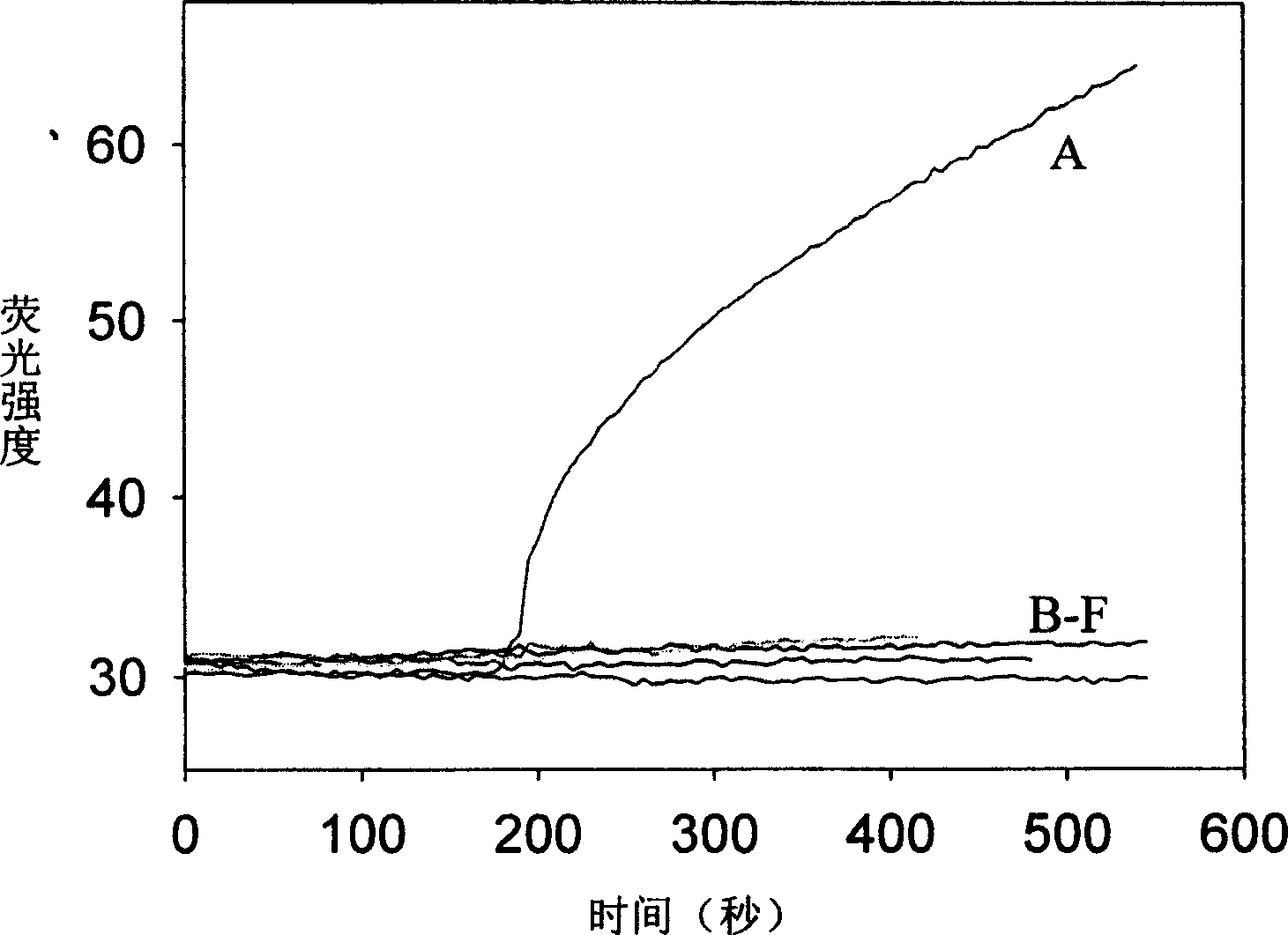
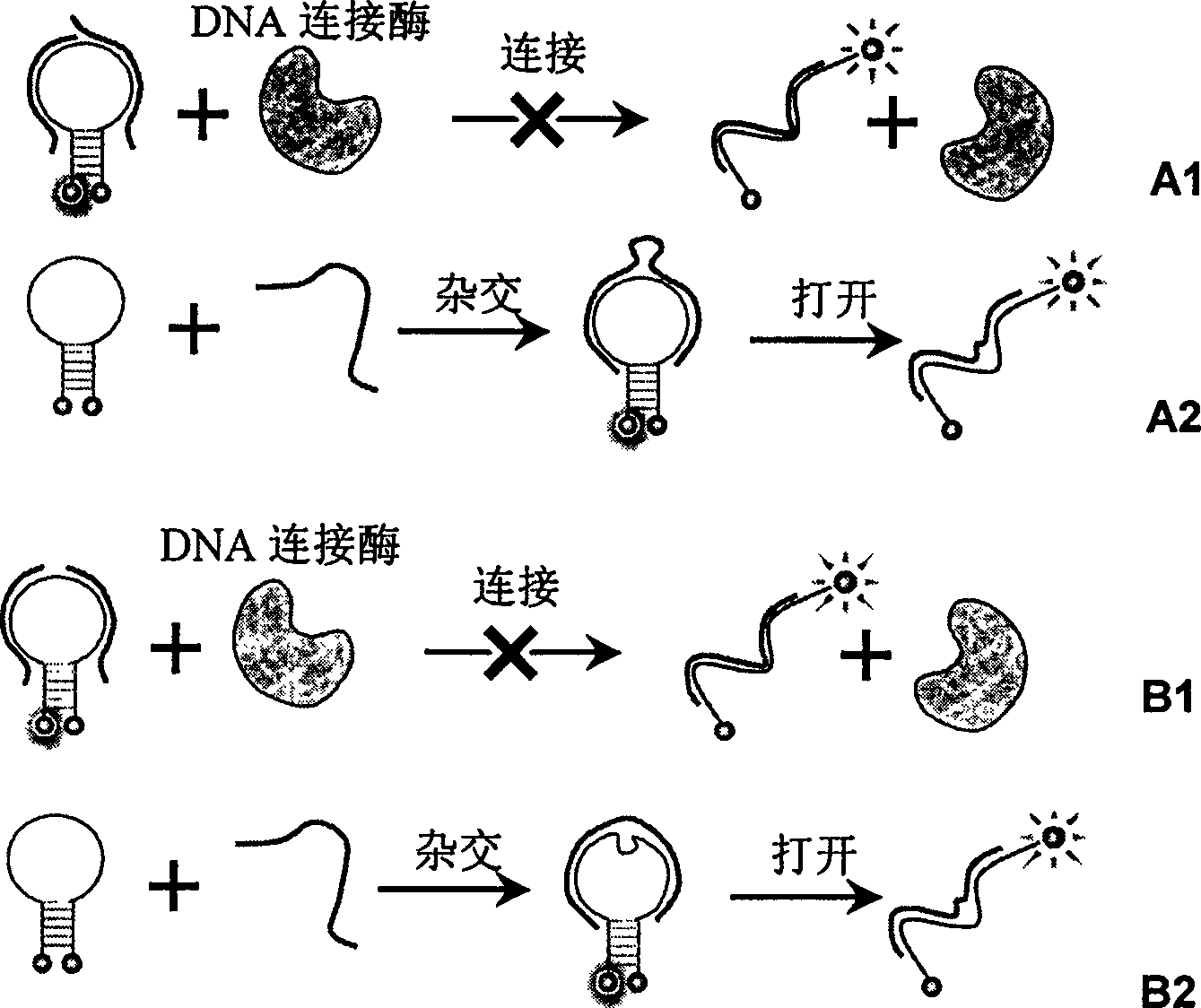
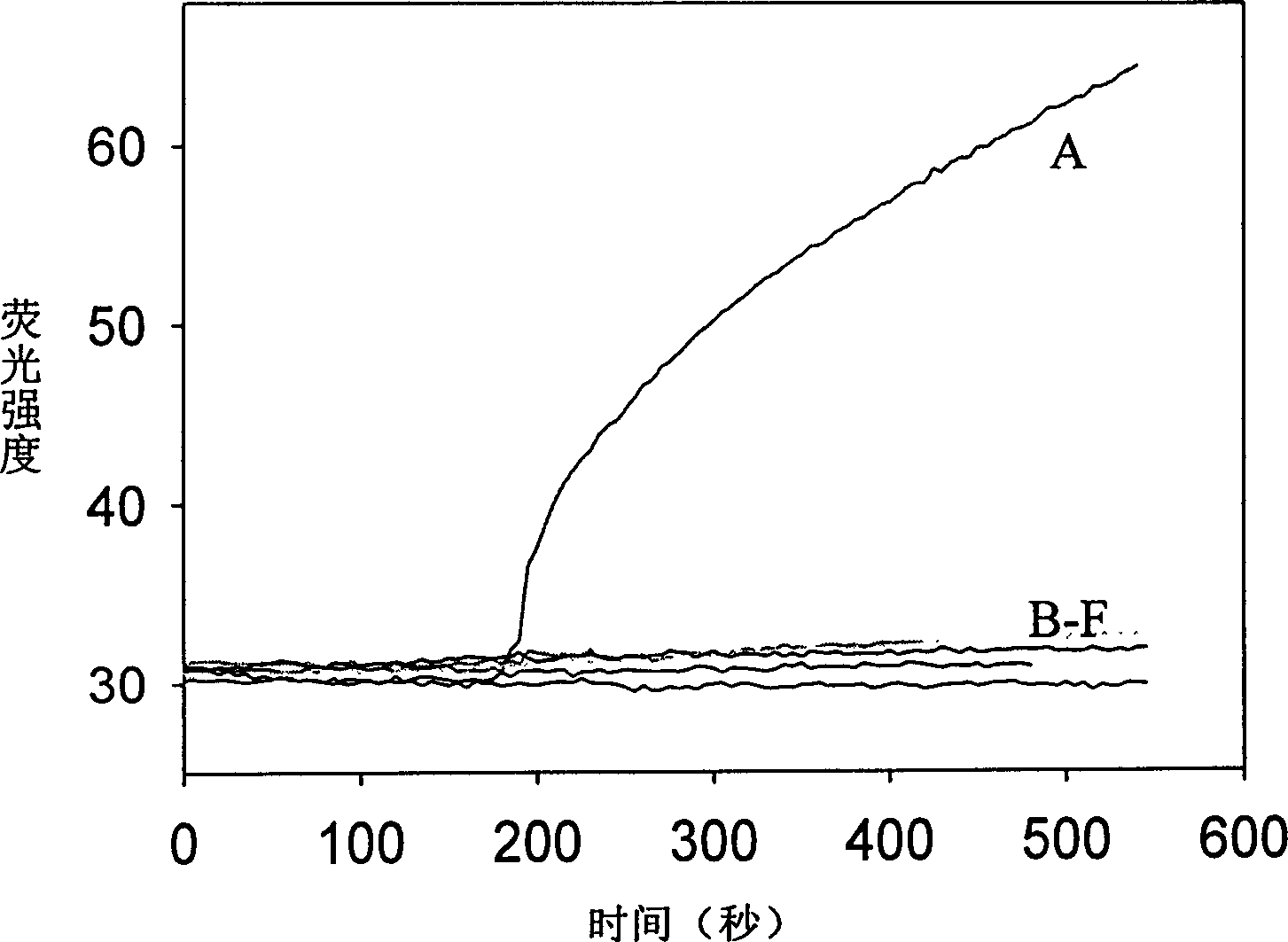
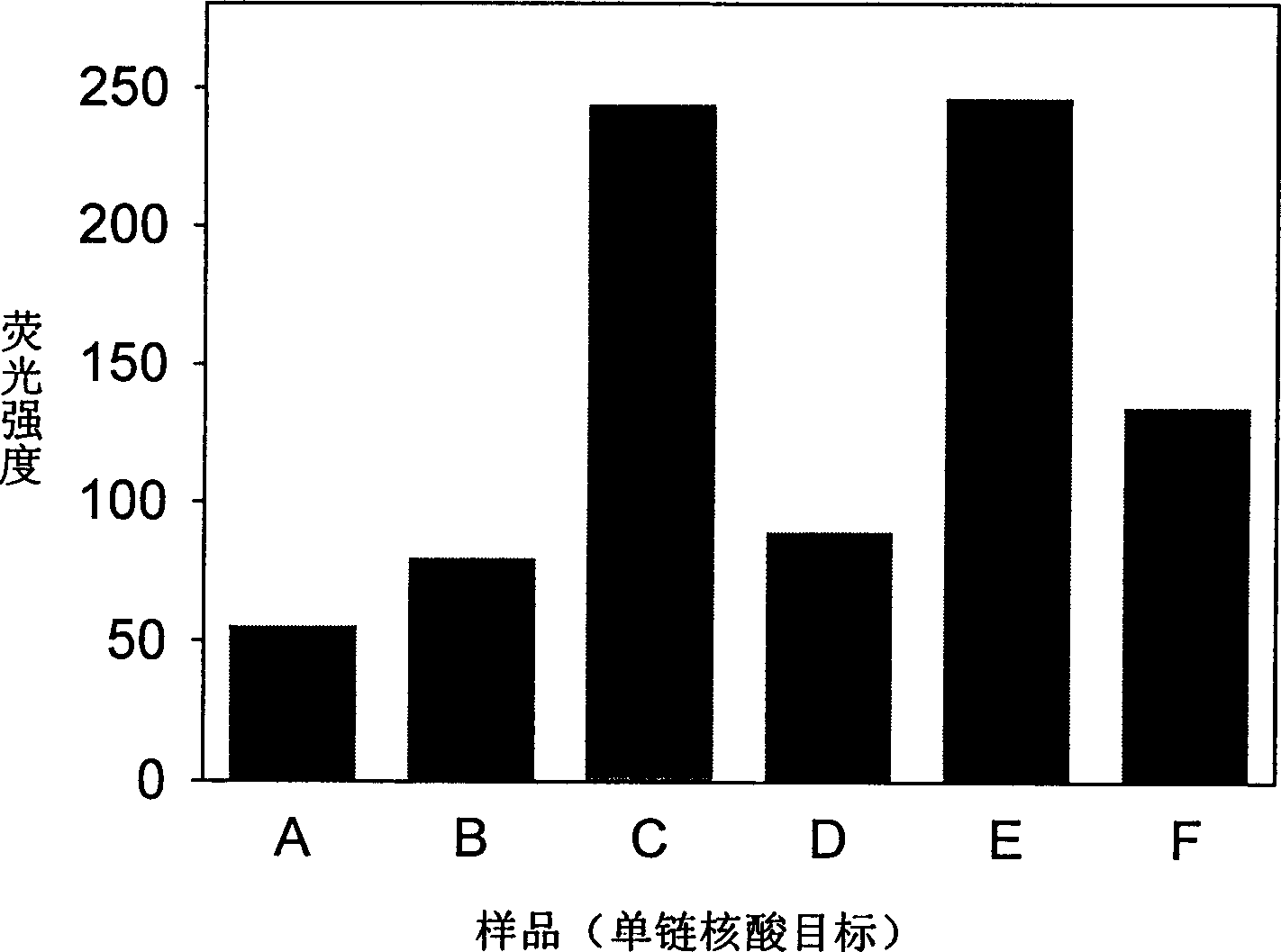
Real time method for detecting nucleic acid ligase reaction and nucleic acid ligase chain reaction
A system for detecting the ligase reaction of nucleic acid and the ligase chain reaction of nucleic acid is compose dof the nucleic acid probes of molecular label, amplified nucleic fragrance, Taq ligase and buffer solution. Its real-time analysis method includes such steps as adding molecular label, Taq ligase, amplifying primer, and single-chain or dual-chain target nucleic acid to the buffer solution, LDR or LCR temp cycle, and detecting the fluorescent intensity of specimen in low-temp cycle.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for detecting mutation of gene point through combination of amplification of equipmential specificity and Nano metal probe
InactiveCN1661094ASimple and fast operationOperational securityMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation detectionWild type
A method for deteting the mutation at gene site by combining allelic specific amplification with nano-gold probe inclues designing the allelic specific primer complementary with mutant gene but not with wild gene, allelic specific amplifying to obtain double-stranded DNA (product A) and residual single-stranded DNA-primer (product B), and sequentially adding said product and electrolyte solution to nano-gold sol. The color of solution is changed from red to blue for the product A or its not changed for the product B.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
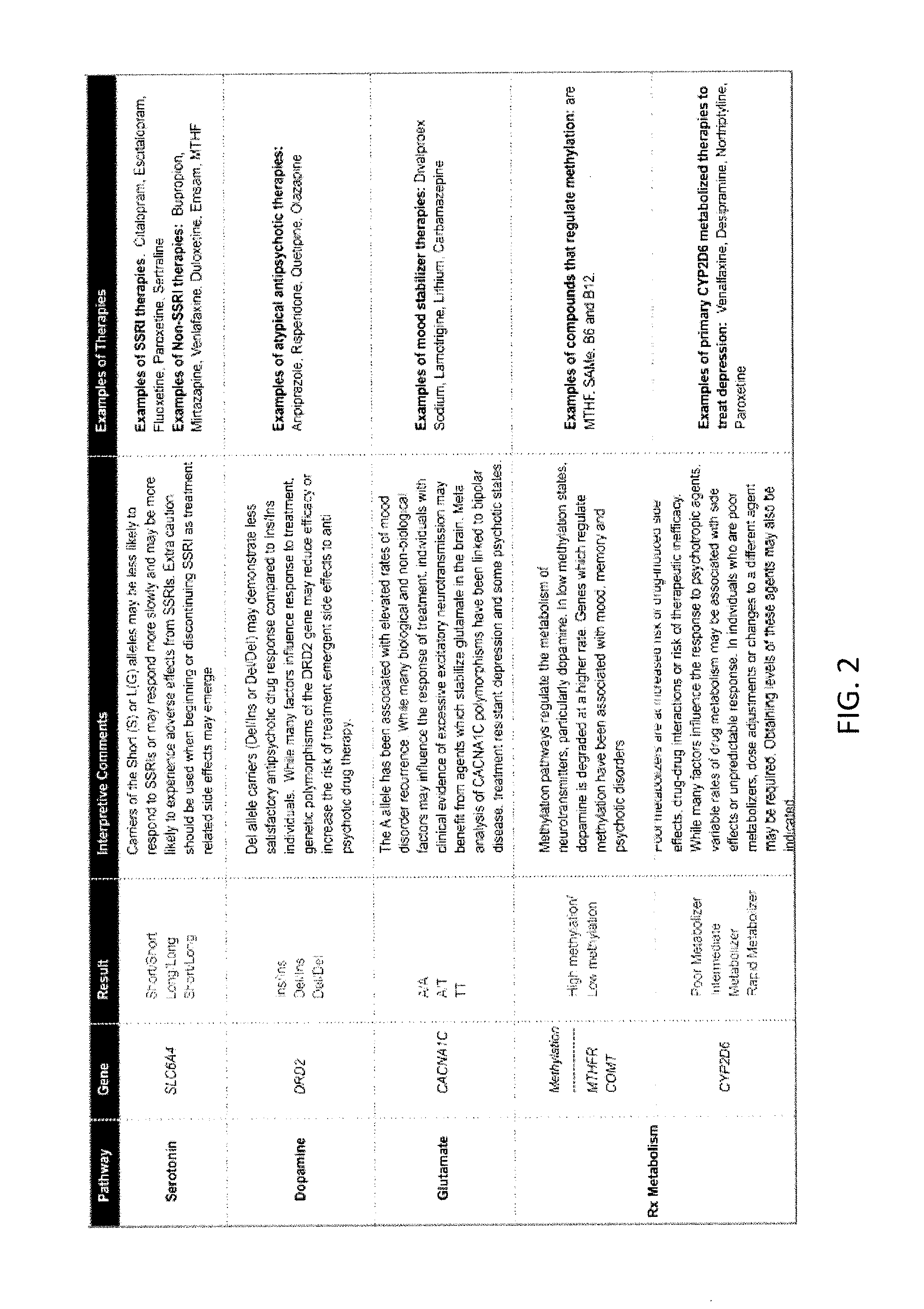
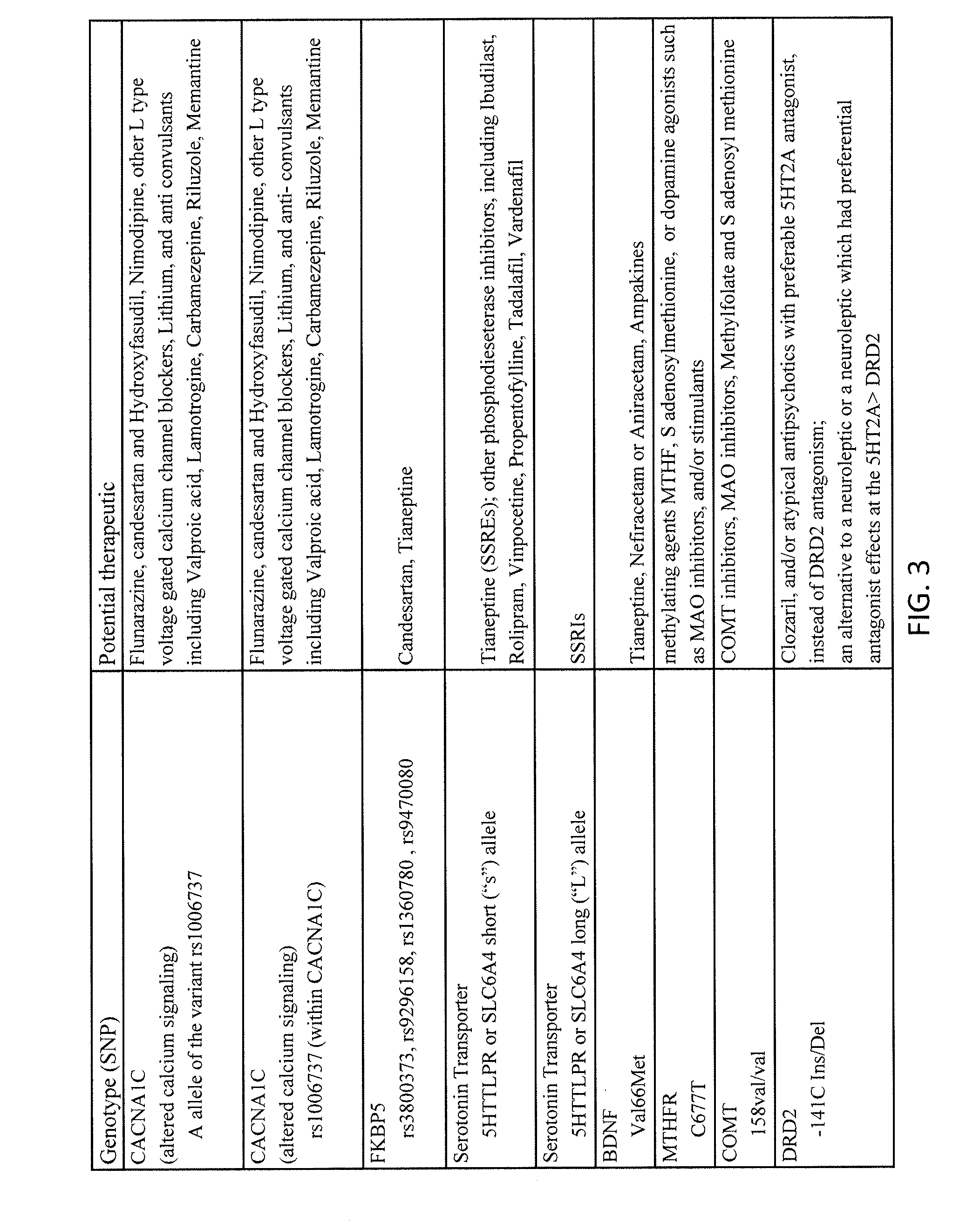
Methods for assessment and treatment of mood disorders via single nucleotide polymorphisms analysis
Described herein are assays, kits and methods for treating mood disorders by testing for one or more polymorphisms in a specific group of genes and for analyzing the results of polymorphism testing; the genes included may converge in one or more signaling pathways, and may be epigenetic. The genes are included based on the relationships of the proteins encoded by the genes in the context of particular signaling pathways and provide a diagnostically relevant nexus. Also described herein are methods of presenting the data collected by the screen, including methods of delivering interpretive comments and / or treatment guidance based on the results of the genetic screening either individually or based on the genetic composition of particular clusters of genes which may be related to each other. Importantly, drugs which modulate these genetic disturbances are described for targeted therapeutic use based upon companion diagnostic method.
Owner:GENOMIND
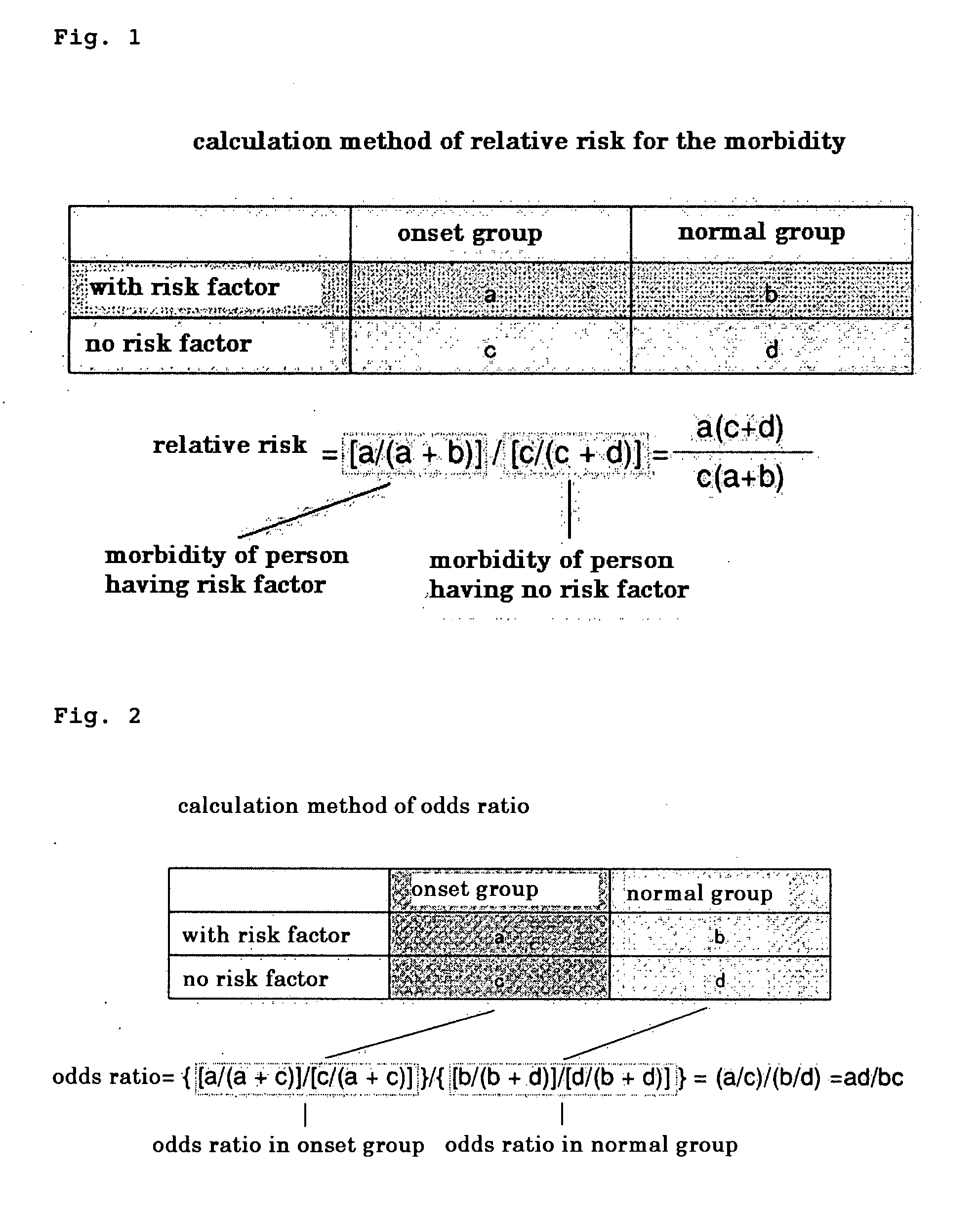
Method of Detecting Relative Risk for the Onset of Atopic Dermatitis by Gene Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Analysis
InactiveUS20090098107A1Increase probabilityPredict susceptibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsCvd riskOdds ratio
The present invention provides a method of discriminating a relative risk for the morbidity of atopic dermatitis of a test subject comprising: analyzing gene polymorphism of two or more of genes related to onset of atopic dermatitis using a sample isolated from a statistically significant number of normal persons and patients of atopic dermatitis to determine relative ratios (percentages (%)) related to the individual gene polymorphism of individual derived from the analysis; and calculating an odds ratio according to specified gene polymorphism from the relative ratio; and using, as a discrimination criterion, a combination of two or more of gene polymorphisms showing a synergetically higher odds ratio than odds ratios according to individual gene polymorphism. The method is useful for predicting susceptibility of an AD patient to chemicals based on genes and for selecting the diagnostic and / or therapeutic agent by eliminating harmful drug reactions from the analysis of principal factors related to onset and development of AD and interaction among these genes, and for determining a diagnostic method and therapeutic method using the detection method of morbidity risk.
Owner:ASUBIO PHARMA
Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis of highly polymorphic target sequences
ActiveUS20090087922A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBioinformaticsSingle nucleotide polymorphism analysis
Owner:ELITECHGROUP MDX LLC
A method and a kit for detecting nucleic acid sample pollution and application of the method
ActiveCN108823296AGuarantee the quality of inspectionEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymorphism analysisBiology
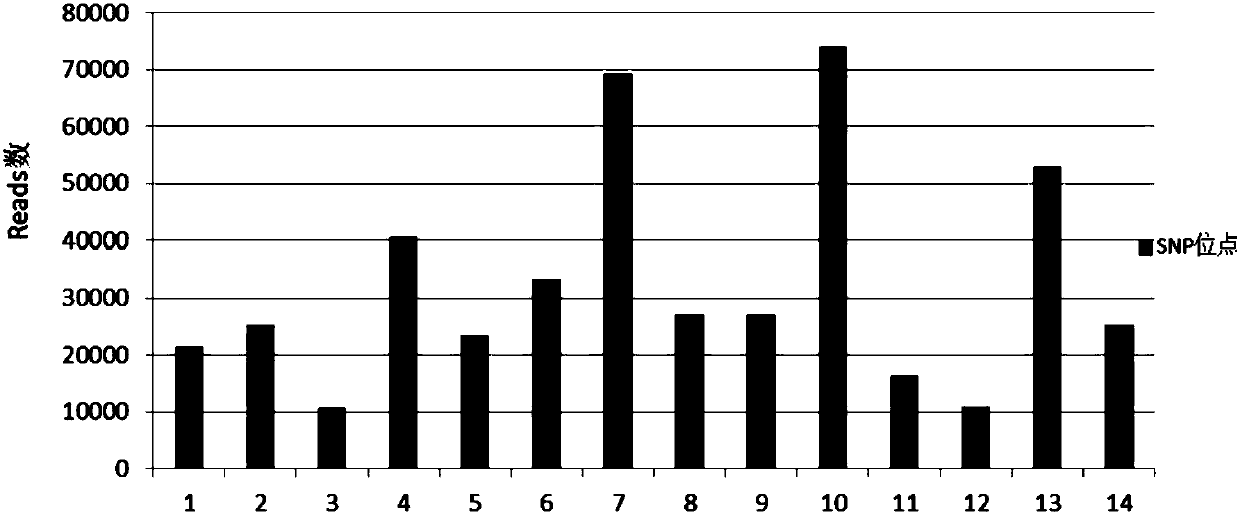
The application discloses a method and a kit for detecting nucleic acid sample pollution and application of the method. The method for detecting the nucleic acid sample pollution includes the following steps: PCR amplification is performed on a nucleic acid sample to be measured by adopting a SNP detection primer, mononucleotide polymorphism of the nucleic acid sample to be measured is analyzed, whether pollution of different individual sources is existed in the nucleic acid sample to be measured or not is judged according to a mononucleotide polymorphism analysis result; and the SNP detectionprimer is composed of at least an analysis primer pair of 14 SNP sites. The specificity of each individual SNP is creatively utilized and is used as specific identification information of the nucleicacid sample to be detected, if SNP information of the detected nucleic acid sample to be measured conforms to the self SNP information, the result that the nucleic acid sample to be detected is not polluted is judged, if not, and the result that the nucleic acid sample to be detected has pollution is judged. Whether the nucleic acid sample to be measured exists pollution or not can be accuratelyjudged by the detection method.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +2
Method and kit for amplifying and detecting nucleic acid
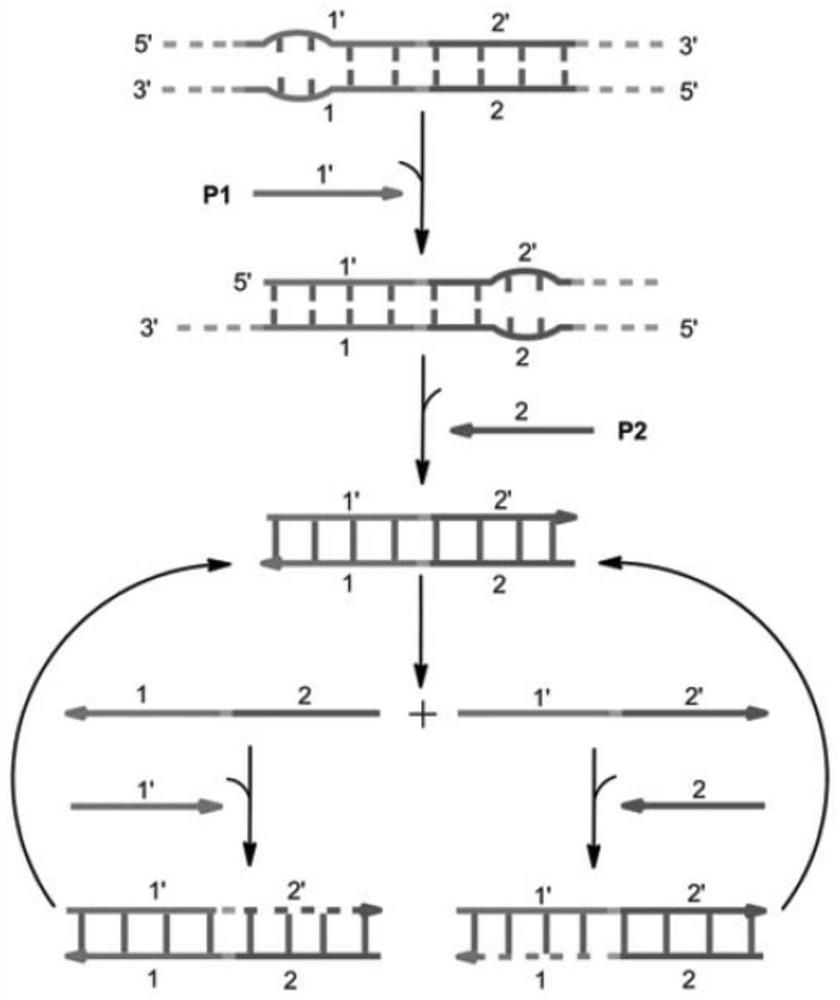
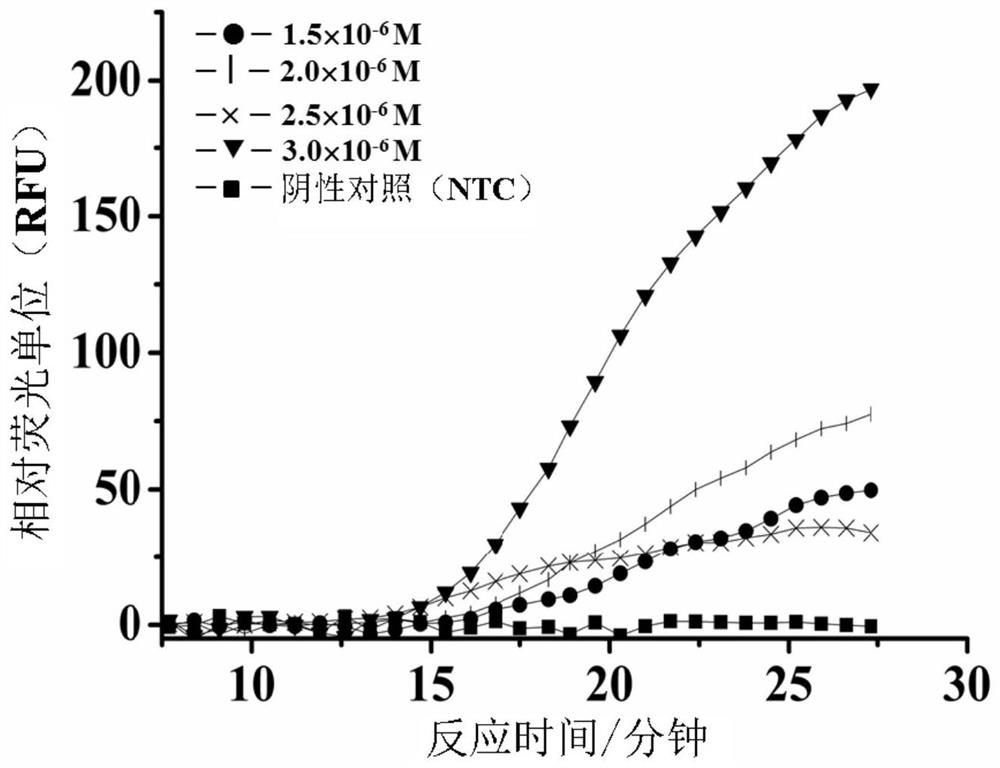
The invention relates to a method and a kit for amplifying and detecting nucleic acid. The invention provides a method for denaturation bubble mediated target nucleic acid amplification and a related kit and use thereof. According to the method, generation of denatured bubbles in double-stranded target nucleic acid molecules is promoted through rapid temperature-changing thermal circulation, so that the strand exchange amplification (SEA) reaction is accelerated. The kit comprises a specially designed primer and a polymerase for performing the method. The method and the kit disclosed herein can be used in various situations, such as diagnosis of infectious or genetic diseases, sample quality control, and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis.
Owner:青岛简码基因科技有限公司
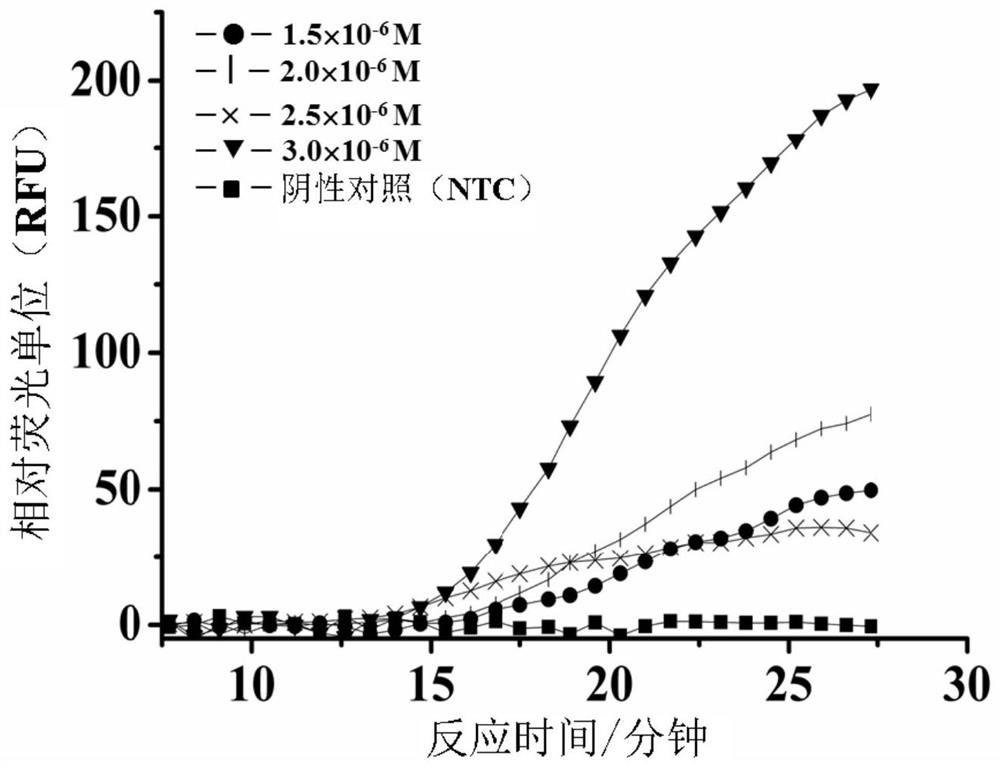
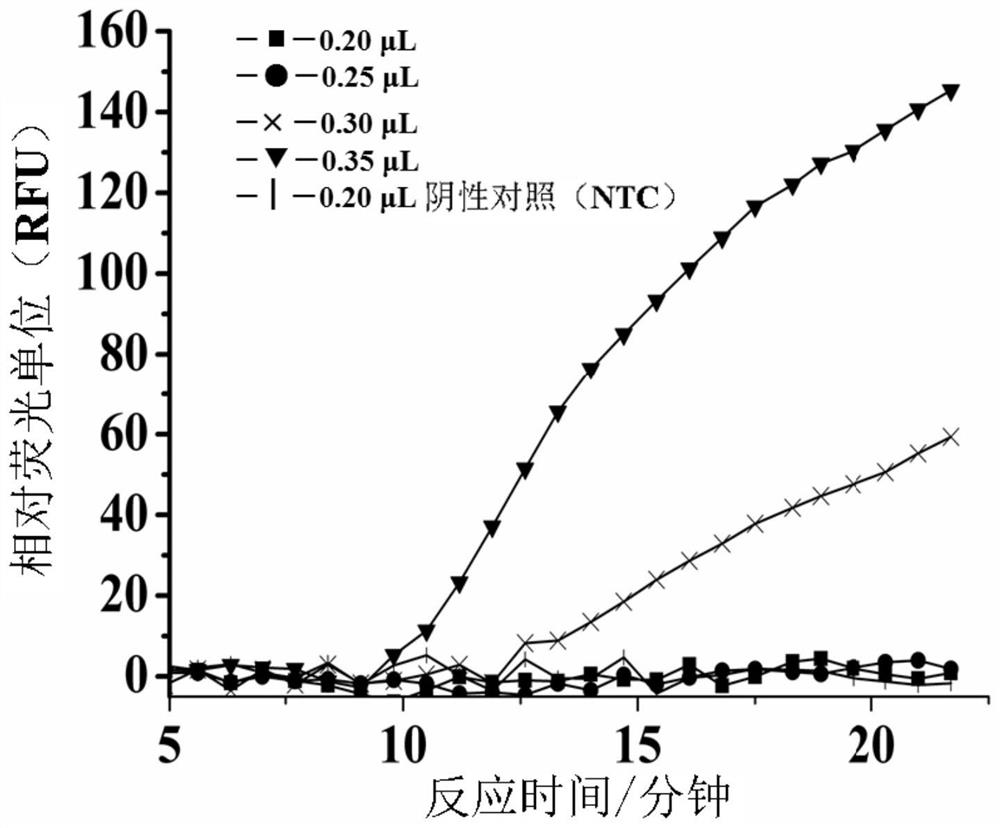
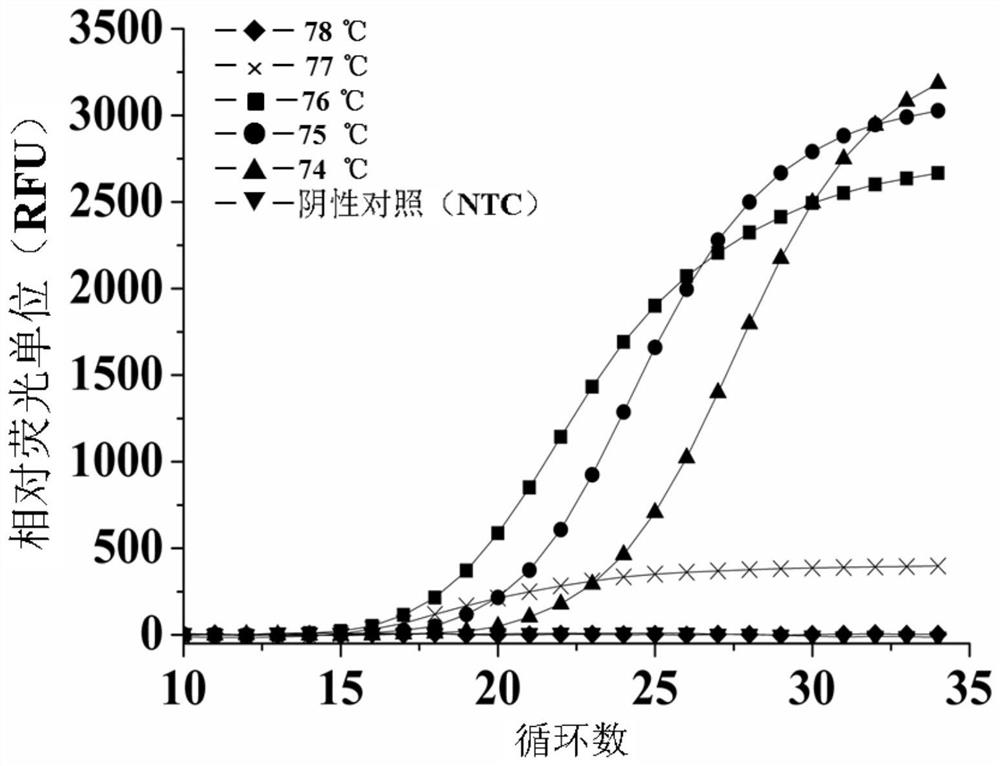
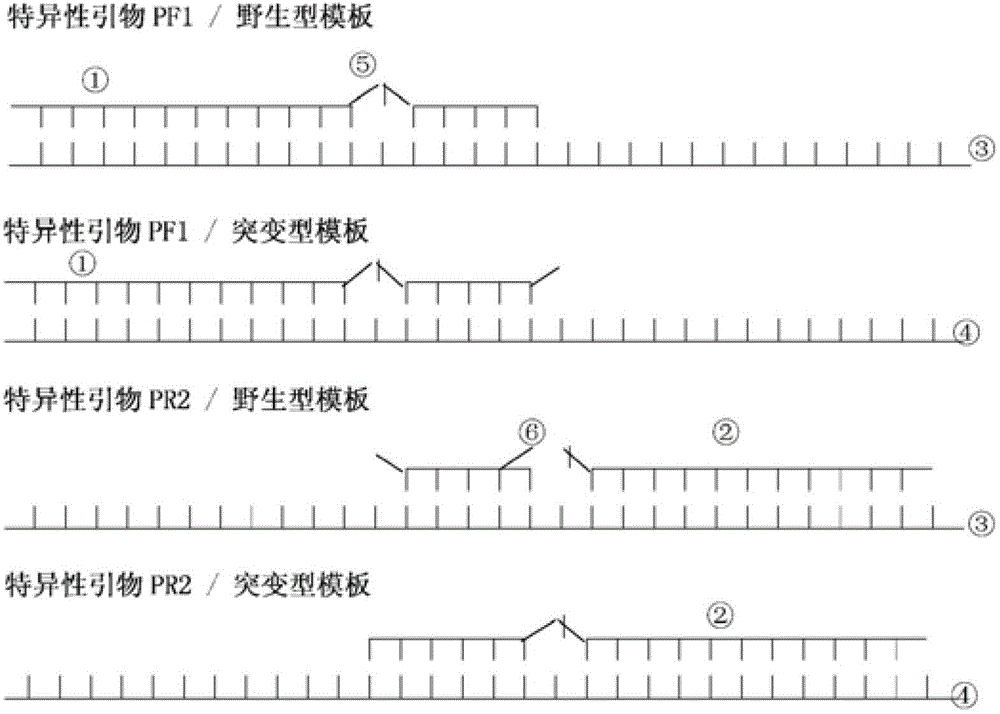
Analysis method for single nucleotide polymorphism
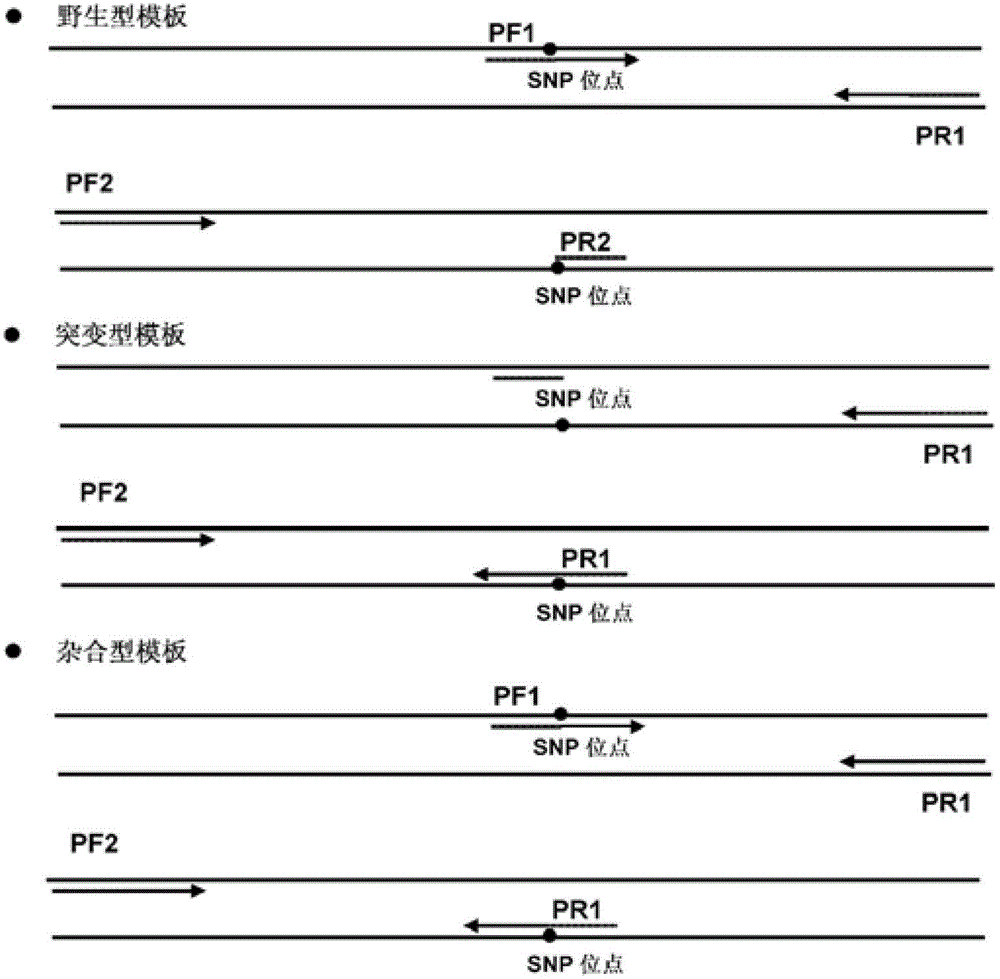
The invention relates to an analysis method for single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), and discloses a novel method for determining known SNP. According to the method, specific primers are designed to amplify toward two different directions for to-be-detected gene templates; amplification efficiency of other two peripheral primers matching the specific primers is controlled, so that the whole PCR reaction system has only one specific PCR product in detection of wide type or homozygous mutant type samples and has two PCR products in detection of heterozygous samples and wild type, hybrid type and mutant type can be distinguished clearly. An SNP analysis method with stable results, good repeatability and wide applicable types is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI TELLGEN LIFE SCI CO LTD
Method for amplifying and detecting nucleic acid and kit
The invention provides a method for denatured bubble mediated target nucleic acid amplification and a related kit and use thereof. According to the method, generation of denatured bubbles in double-stranded target nucleic acid molecules is promoted through rapid temperature-changing thermal circulation, so that the strand displacement amplification (SEA) reaction is accelerated. The kit comprises a specially designed primer and a polymerase for performing the method. The method and kit can be used in various situations, such as diagnosis of infectious or genetic diseases, sample quality control, and single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis.
Owner:青岛简码基因科技有限公司
Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis method based on magnetic functionalized microfluidic chip
ActiveCN109022552AEasy to separateEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis methodNanocomposite
The invention discloses a single nucleotide polymorphism analysis method based on a magnetic functionalized microfluidic chip, which belongs to the technical field of the microfluidic chip. The methodcomprises the following steps: Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles are loaded on the surface of graphene oxide to synthesize magnetic nanocomposites (GO@Fe3O4), under the action of an external magnetic field, GO@Fe3O4 is efficiently and controllably fixed in a separation channel of the microfluidic chip to obtain a GO@Fe3O4 functionalized microfluidic chip separation channel. In addition, the method successfully implements the analysis of single nucleotide polymorphism in the GO@Fe3O4 functionalized microfluidic chip separation channel, and the analysis method has the advantages of simplicity, convenience, high efficiency and short time.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
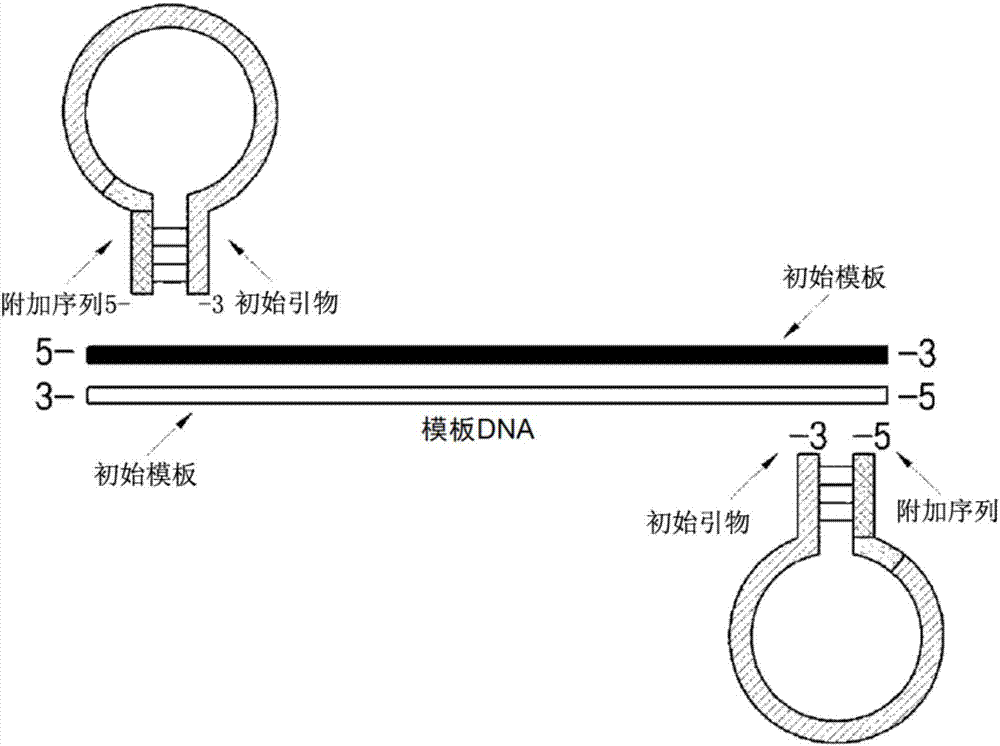
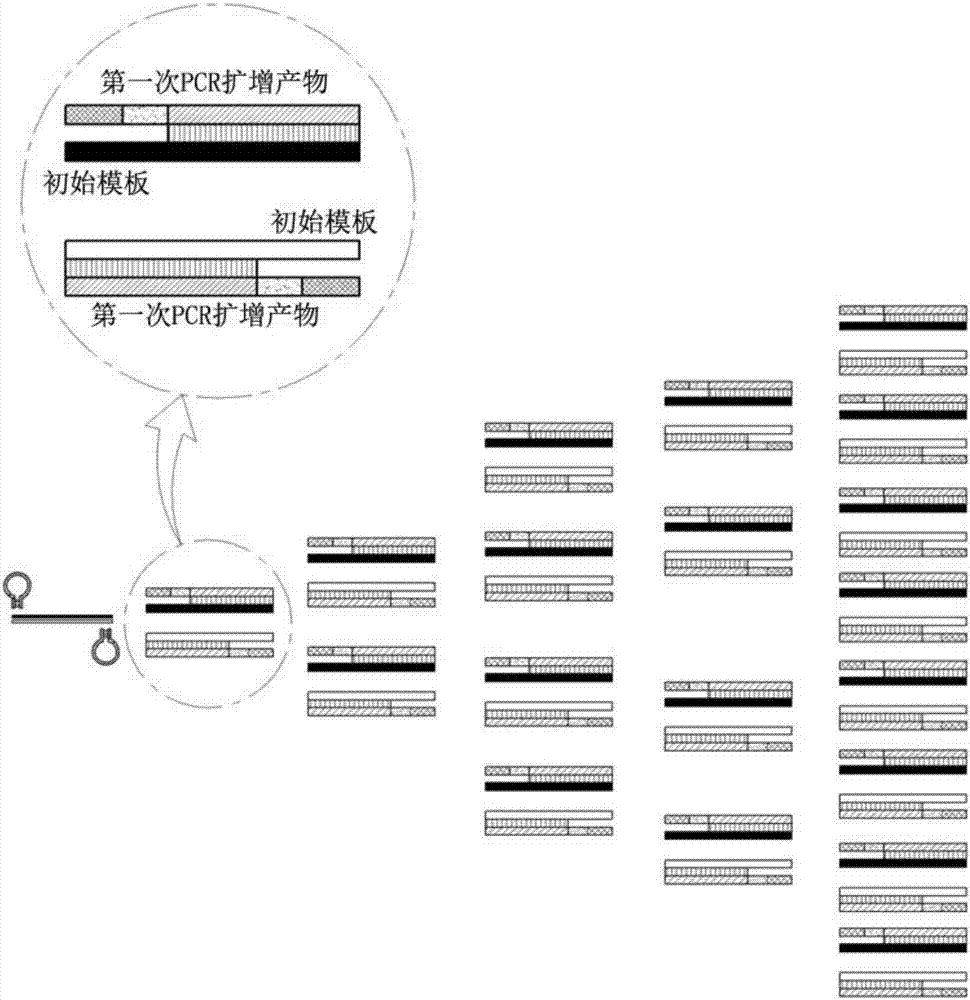
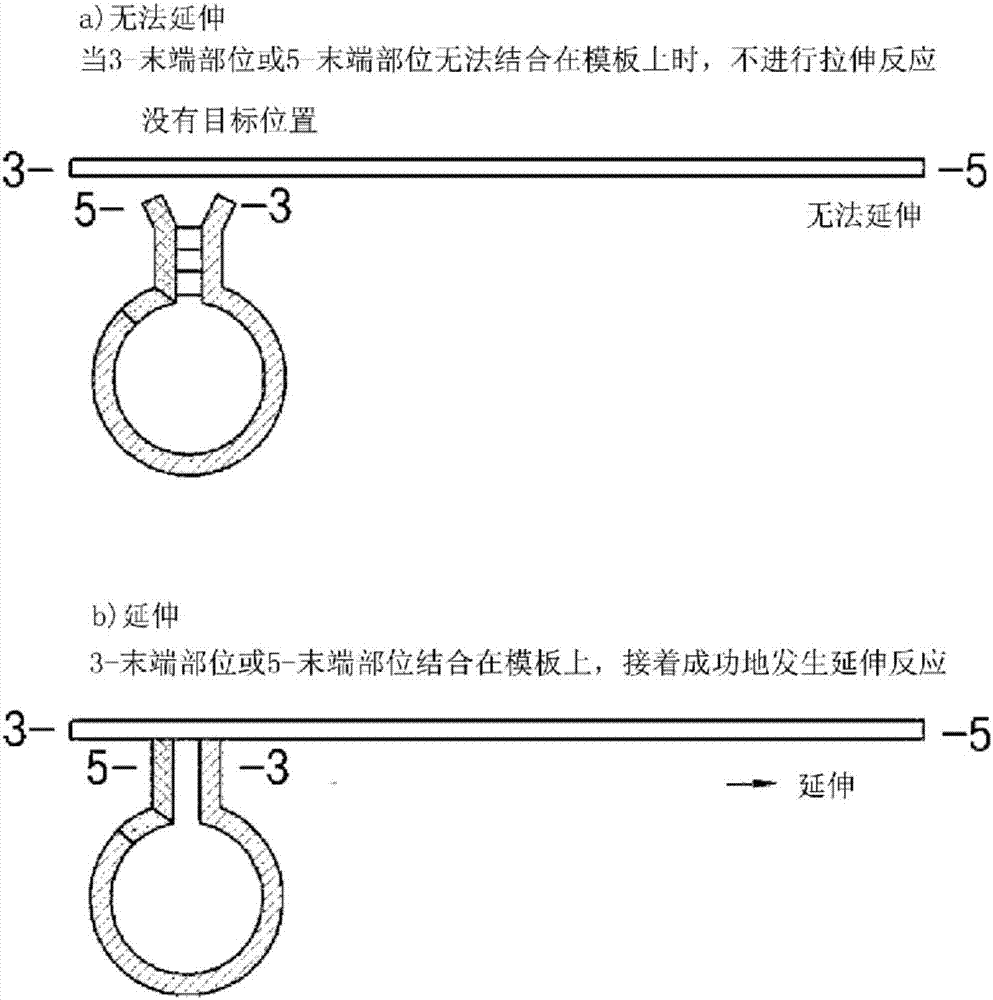
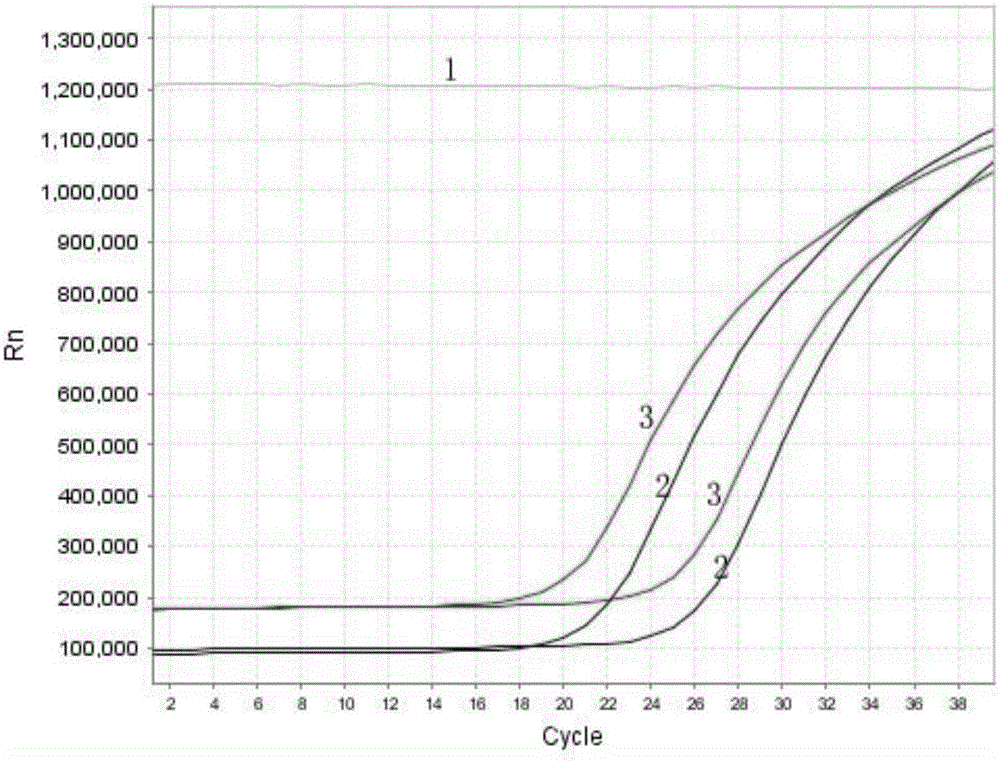
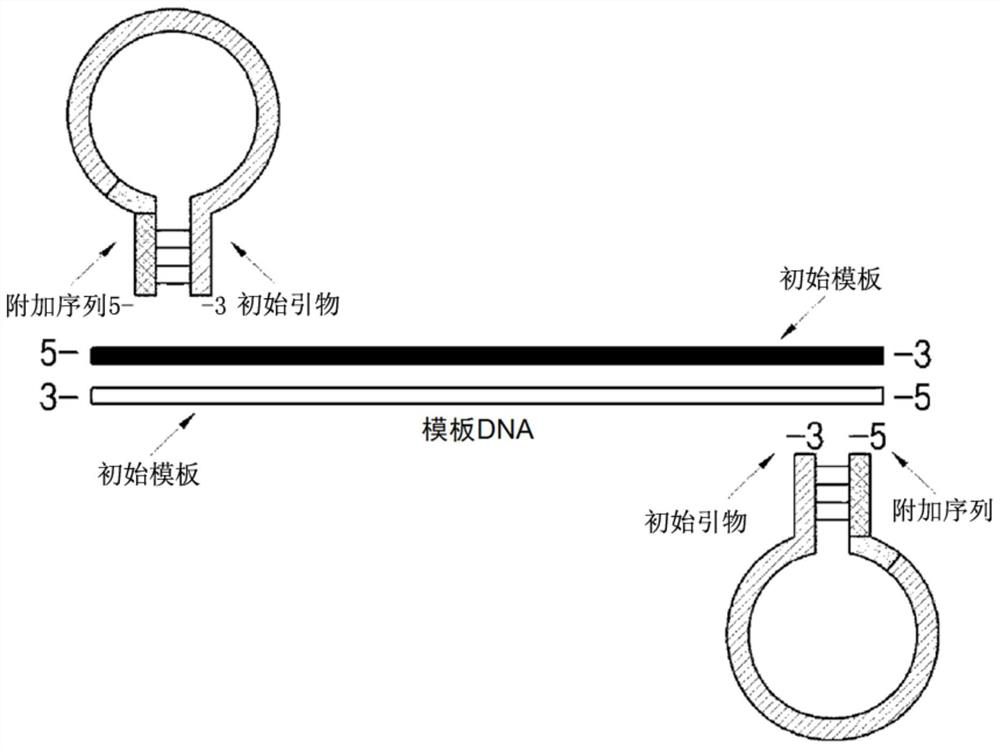
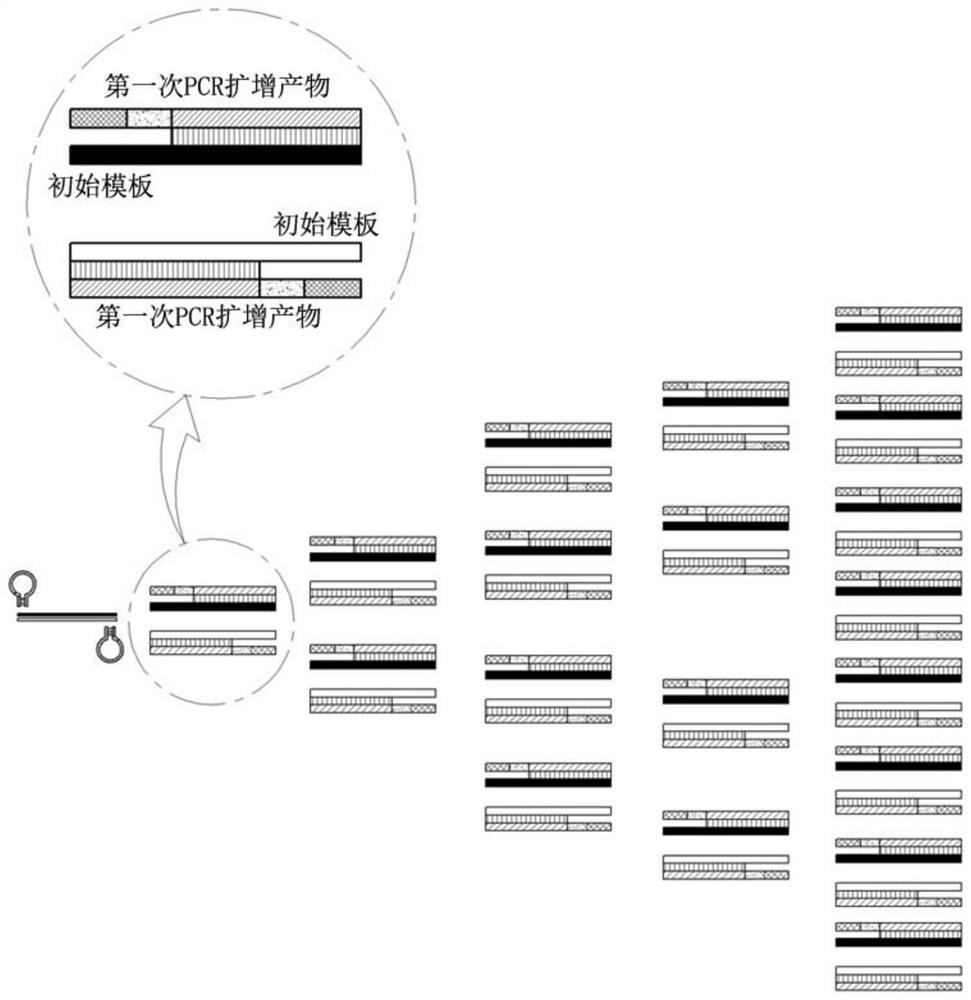
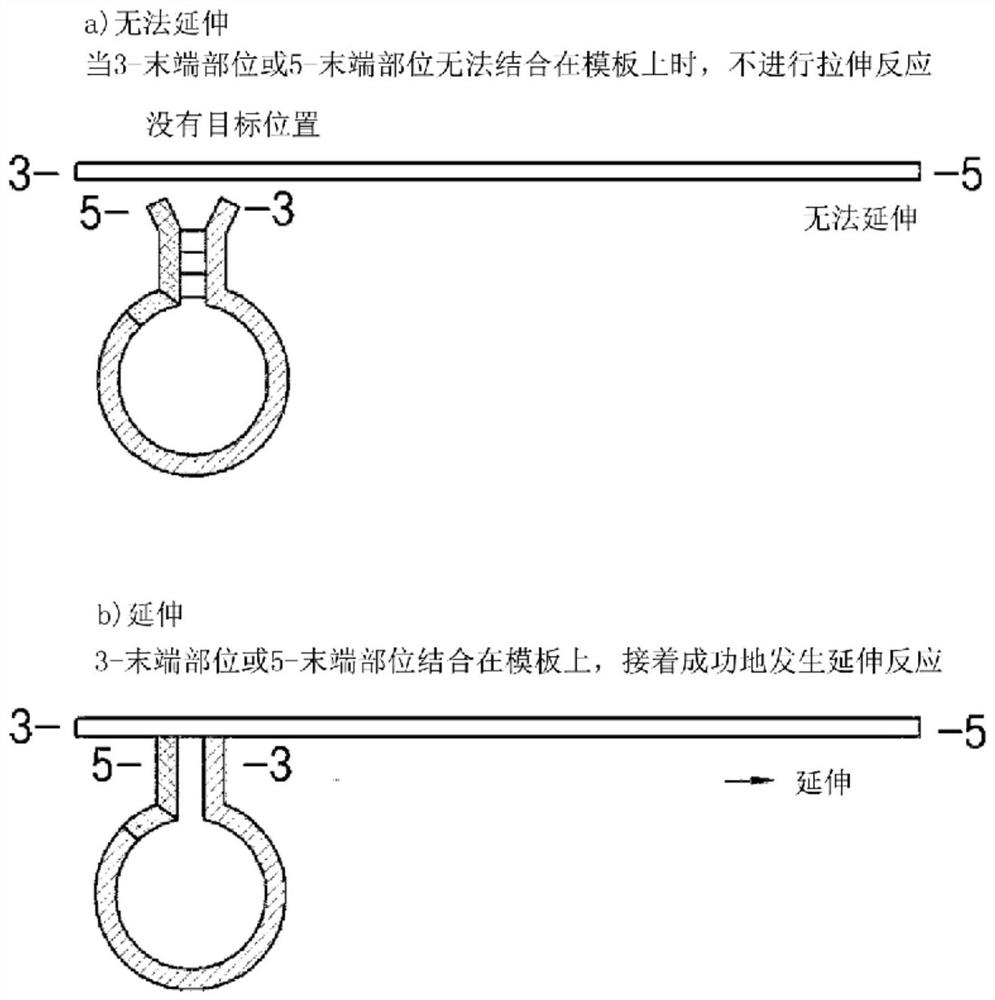
Dumbbell-structure oligonucleotide, nucleic acid amplification primer comprising same, and nucleic acid amplification method using same
ActiveCN107075576AImproved amplification methodEasy detection analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDumbbellNucleotide
The present invention relates to a dumbbell-structure oligonucleotide (DSO), a nucleic acid amplification primer comprising the same, and a nucleic acid amplification method using the same and, more specifically, to a method for multiple gene amplification and single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis using a dumbbell-structure oligonucleotide capable of excluding non-specific amplification products prior to binding to a template in a first cycle in performing a polymerase chain reaction. The present invention suppresses undesired amplification products at room temperature using a dumbbell structure oligonucleotide (DSO) generated by adding any nucleotide sequence designed to allow the 5'-terminal oligonucleotide and the 3'-terminal oligonucleotide to complimentarily bind to each other, a 3'-terminal template dependent specific nucleotide sequence, and a universal nucleotide pair for linking the two nucleotide sequences, prior to binding to a template in every first cycle at the time of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and as a result, efficiently increases sensitivity and specificity through the reduction in non-specific amplification products, thereby achieving the innovation of the gene amplification method.
Owner:精确诊断有限公司
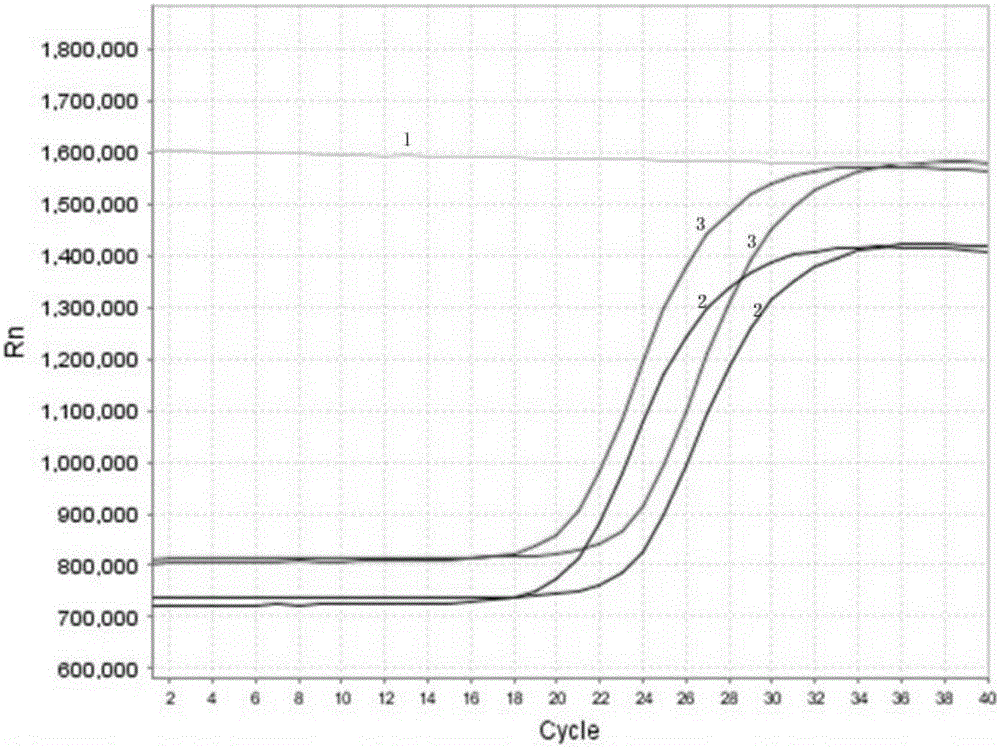
Asymmetric cyanine dye compound and its application
InactiveCN104059376BQuenching is effectiveEasy to useMethine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementCyanineQuenching
The invention provides an asymmetric cyanine dye compound (I) and application of the asymmetric cyanine dye compound serving as a quenching agent. The asymmetric cyanine dye fluorescence quenching agent compound can effectively quench fluorescence of an ROX channel, meanwhile, double DNA strands can be stabilized, the melting temperature in the PCR process is increased by 2 DEG C to 3 DEG C, the compound not only can be applied to a conventional real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method but also can be effectively used in the field of analysis for single nucleotide polymorphism. Please see the formula of the asymmetric cyanine dye compound in the specification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
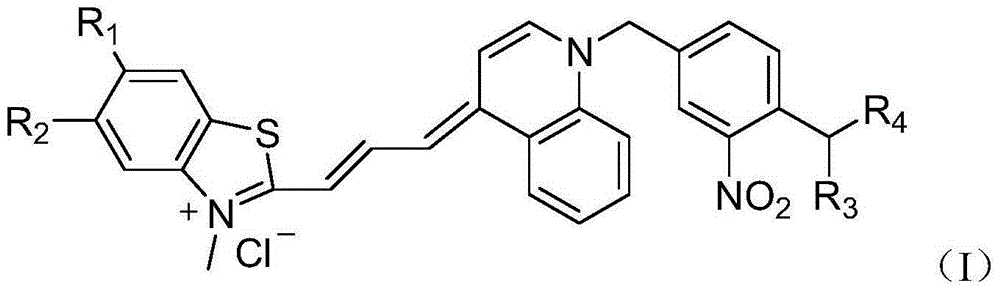
Asymmetric cyanine dye compound and application thereof
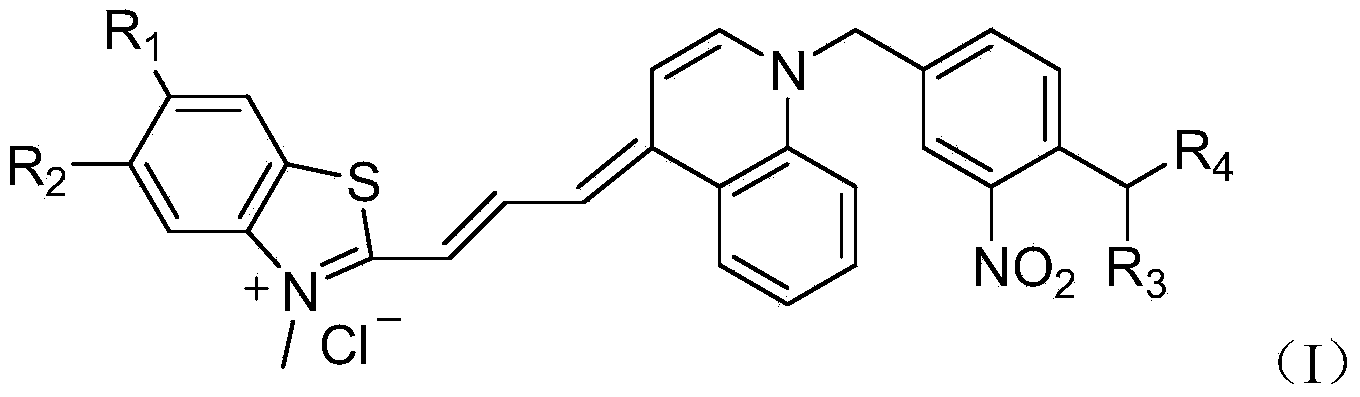
InactiveCN104073019AEffective quenchingHigh melting temperatureMethine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementCyaninePolymerase L
The invention provides an asymmetric cyanine dye compound (I) and an application of the cyanine dye compound as a quenching agent. By virtue of the asymmetric cyanine dye fluorescence quenching agent compound provided by the invention, 650nm-channel fluorescence can be effectively quenched and the melting temperature of stable double strands of DNA is increased by 2-3 DEG C in the PCR (Polymerase China Reaction) process. The asymmetric cyanine dye compound can be used for a conventional real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection method and can be also effectively used in the field of single nucleotide polymorphism analysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Real time method for detecting nucleic acid ligase reaction and nucleic acid ligase chain reaction
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Genotyping tool for improving the prognostic and clinical management of MS patients
InactiveUS8835111B2Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic linkage disequilibriumMedicine
Owner:BRAINCO BIOPHARMA
A kind of breeding method of soft-shelled soft-shelled turtle
ActiveCN112493204BImprove water qualityImprove the breeding effectWaste water treatment from animal husbandryBiological water/sewage treatmentBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a method for selecting and breeding soft-shelled soft-shelled turtles. SNP single nucleotide polymorphism analysis is used to determine Chinese soft-shelled soft-shelled turtle seedlings with excellent properties. Conduct non-specific viral pathogen detection on Chinese soft-shelled turtle seedlings, and screen out Chinese soft-shelled soft-shelled turtle seedlings without specific viruses; disinfect the breeding ponds to make them meet the breeding requirements; prepare multi-bacteria-sensitive bacteriophage microecological preparations; During the breeding process, the multi-bacteria-sensitive bacteriophage microecological preparations are regularly sprinkled; the water quality of the aquaculture water is regularly tested to determine the water quality, and the frequency of sprinkling the multi-bacteria-sensitive bacteriophage microecological preparations is adjusted as needed. The breeding method of the invention is highly operable, universal and economical.
Owner:温岭市万融特种生态养殖有限公司
Method for detecting mutation of gene point through combination of amplification of equipmential specificity and Nano metal probe
InactiveCN100395349CSimple and fast operationOperational securityMicrobiological testing/measurementMutation detectionWild type
A method for deteting the mutation at gene site by combining allelic specific amplification with nano-gold probe inclues designing the allelic specific primer complementary with mutant gene but not with wild gene, allelic specific amplifying to obtain double-stranded DNA (product A) and residual single-stranded DNA-primer (product B), and sequentially adding said product and electrolyte solution to nano-gold sol. The color of solution is changed from red to blue for the product A or its not changed for the product B.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of asymmetric cyanine dye compound and its application
ActiveCN103554096BQuenching is effectiveHigh melting temperatureOrganic chemistryMethine/polymethine dyesCyanineDouble stranded
The invention provides an asymmetric cyanine dye compound (I) and application of the same as a quenching agent. The invention provides the asymmetric cyanine dye fluorescence quenching compound which can effectively quench fluorescence of FAM and stabilize DNA double strands, enables melting temperature in the PCR process to increase 2 to 3 DEG C, is applicable to a conventional real time fluorescence quantification PCR detection method and can be effectively applied to the field of analysis of single nucleotide polymorphism.
Owner:上海辉睿生物科技有限公司 +2
A kind of asymmetric cyanine dye compound and application
InactiveCN104073019BEffective quenchingHigh melting temperatureMethine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementCyanineDouble stranded
The invention provides an asymmetric cyanine dye compound (I) and an application of the cyanine dye compound as a quenching agent. By virtue of the asymmetric cyanine dye fluorescence quenching agent compound provided by the invention, 650nm-channel fluorescence can be effectively quenched and the melting temperature of stable double strands of DNA is increased by 2-3 DEG C in the PCR (Polymerase China Reaction) process. The asymmetric cyanine dye compound can be used for a conventional real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection method and can be also effectively used in the field of single nucleotide polymorphism analysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Oligonucleotide with dumbbell structure, primer for nucleic acid amplification containing same, and nucleic acid amplification method using same
ActiveCN107075576BImproved amplification methodEasy detection analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMultiplexBase J
The present invention relates to a dumbbell structure oligonucleotide (dumbbell structure oligonucleotide, DSO), a nucleic acid amplification primer comprising the same and a nucleic acid amplification method using the primer, more specifically, to a method for performing polymerase chain reaction , a method for multiple gene amplification and single nucleotide polymorphism analysis using dumbbell structure oligonucleotides that can eliminate non-specific amplification products before combining with templates in each first cycle. In the polymerase chain reaction (polymerase chain reaction, PCR), the present invention utilizes dumbbell structure oligonucleotides (dumbbell structure oligonucleotide, DSO) to suppress unintended amplification products at room temperature, thereby reducing non-specific amplification products, Sensitivity and specificity can be improved efficiently, and the method of gene amplification can be improved. The dumbbell structure oligonucleotide can be obtained by attaching an arbitrary base sequence and a 3'-terminal template-dependent specific base sequence and connecting the two base sequences. , and the 5'-terminal oligonucleotide and the 3'-terminal oligonucleotide of the dumbbell structure oligonucleotide are designed to be in each first cycle before binding to the template Complementary binding.
Owner:精确诊断有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com