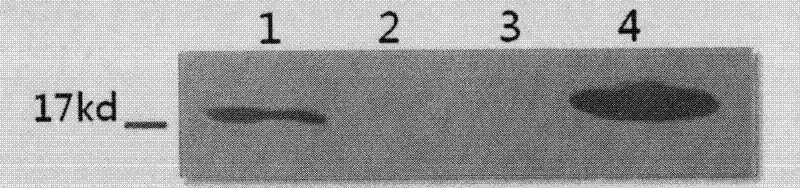
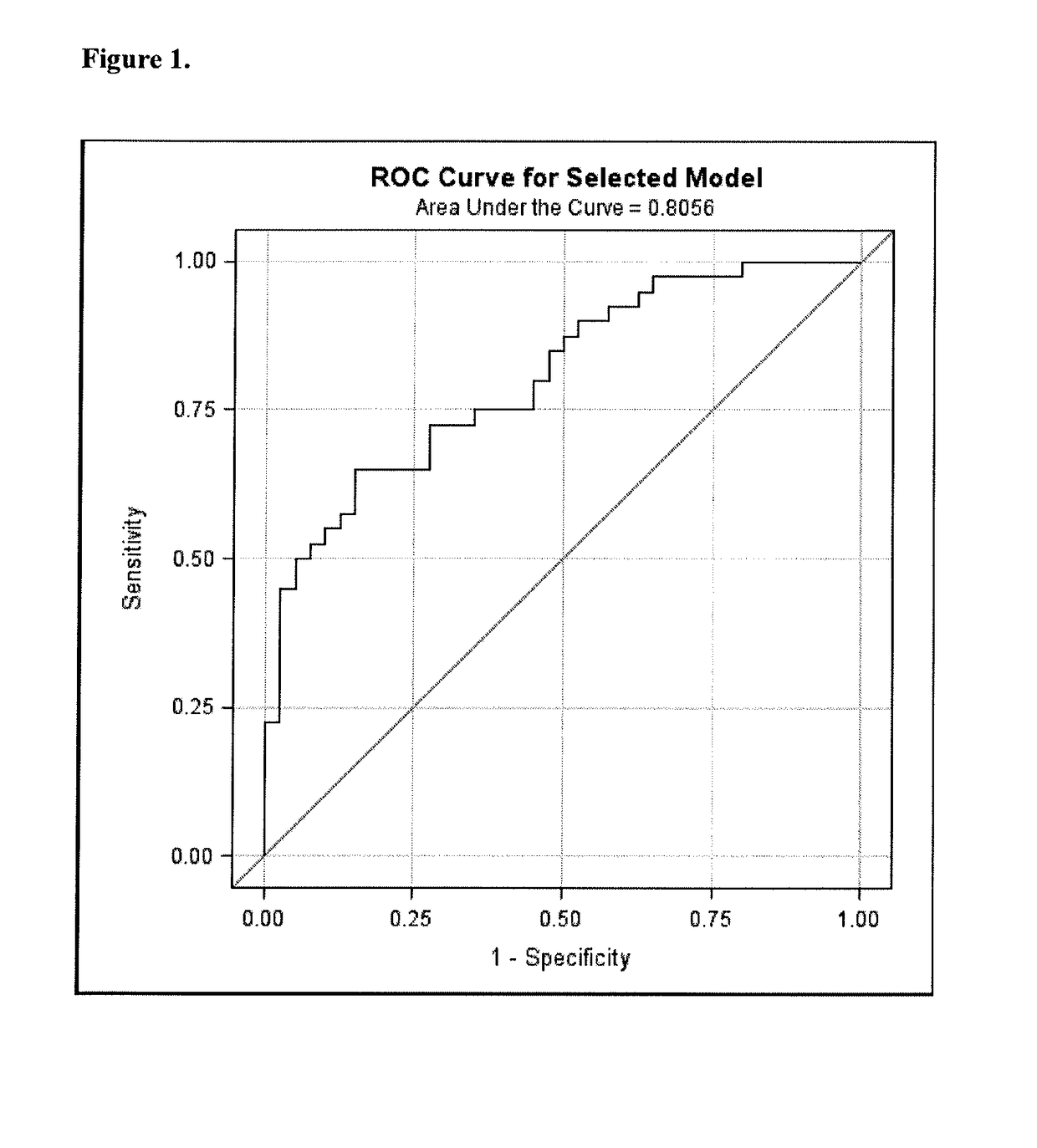
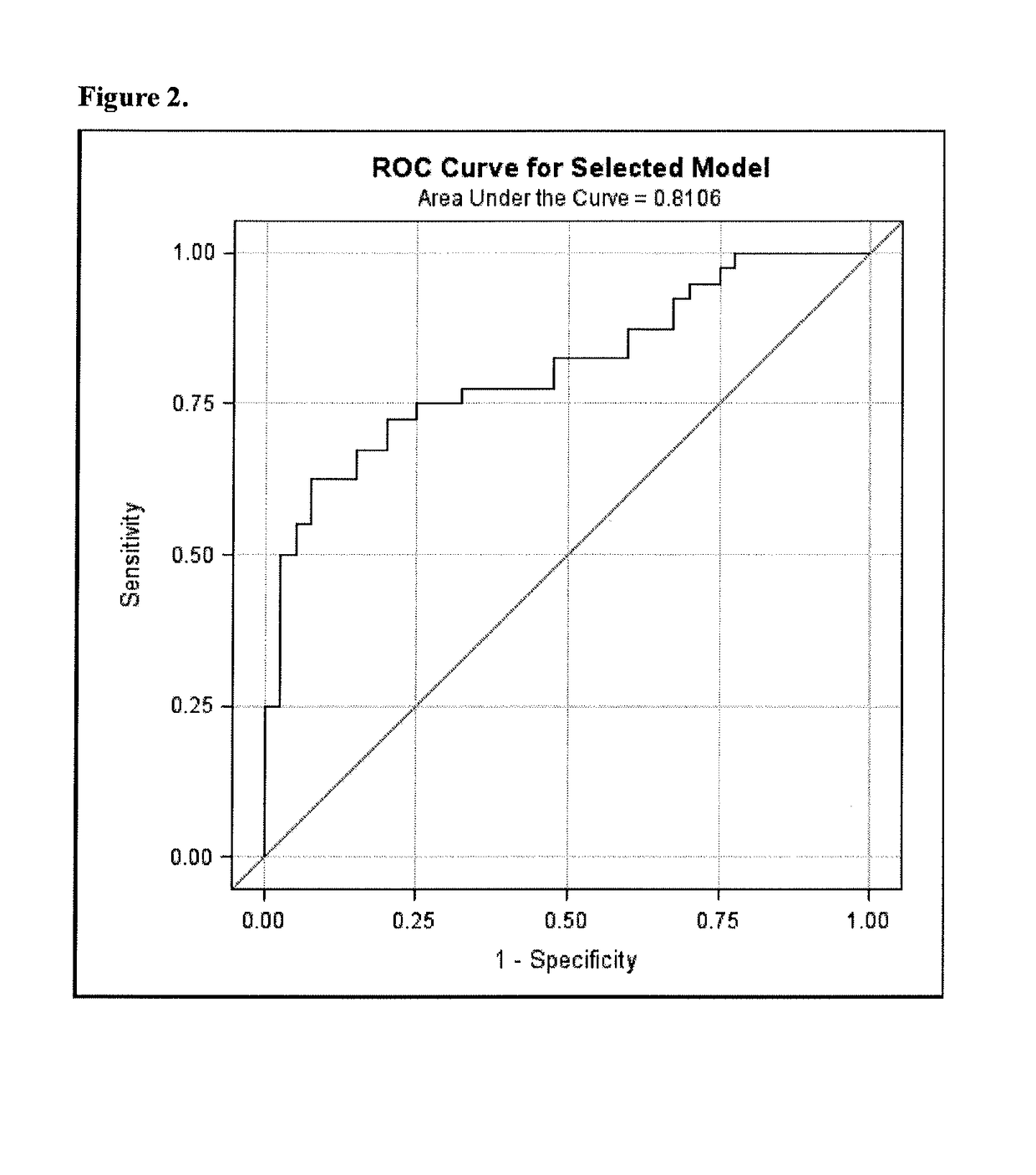
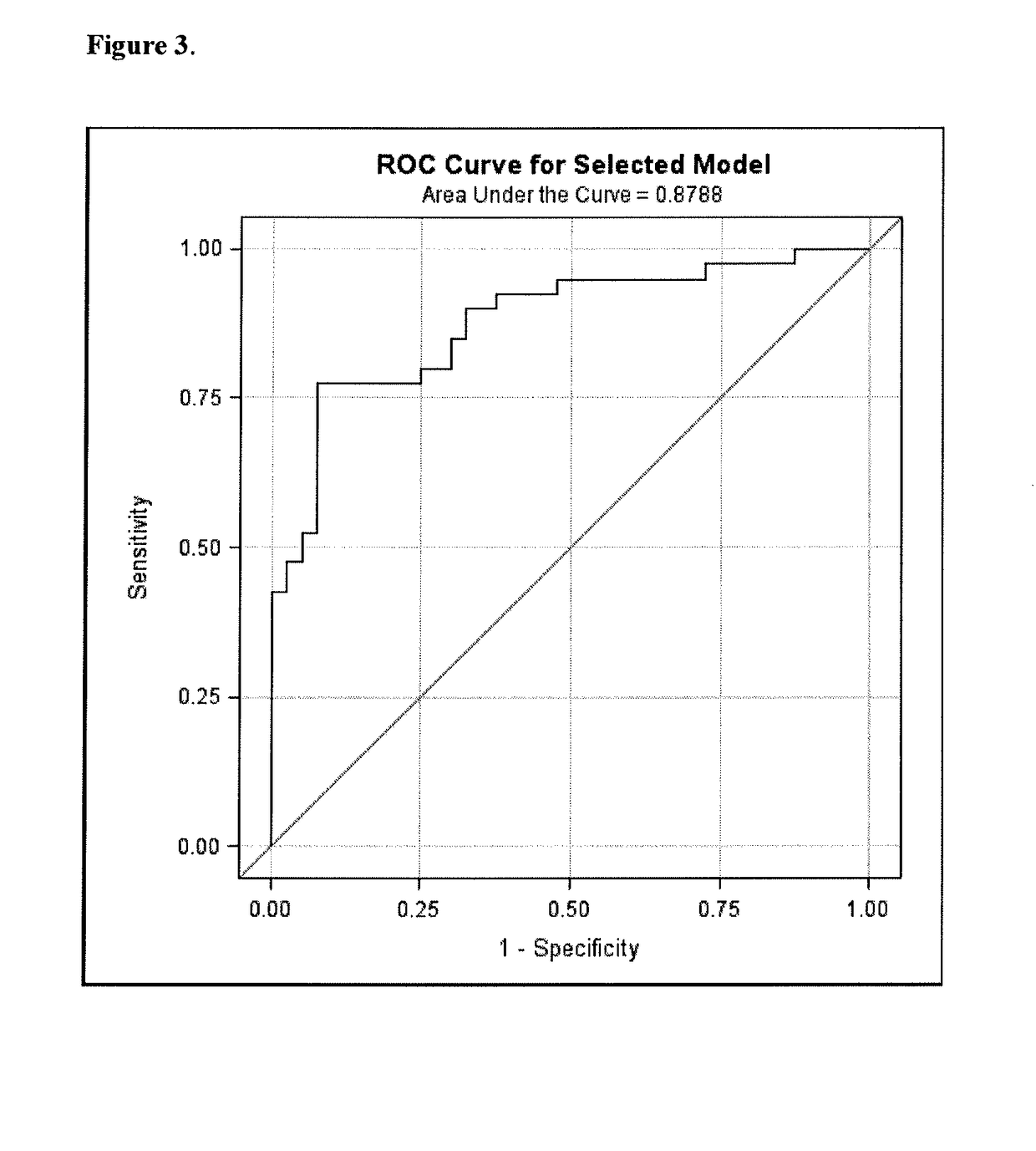
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Skeletal muscle damage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Damage to skeletal muscle may take various forms. Crush and other physical injuries cause damage to muscle cells directly or interfere with blood supply, while non-physical causes interfere with muscle cell metabolism. When damaged, muscle tissue rapidly fills with fluid from the bloodstream, including sodium ions.
Treatment Of Peripheral Vascular Disease Using Postpartum-Derived Cells
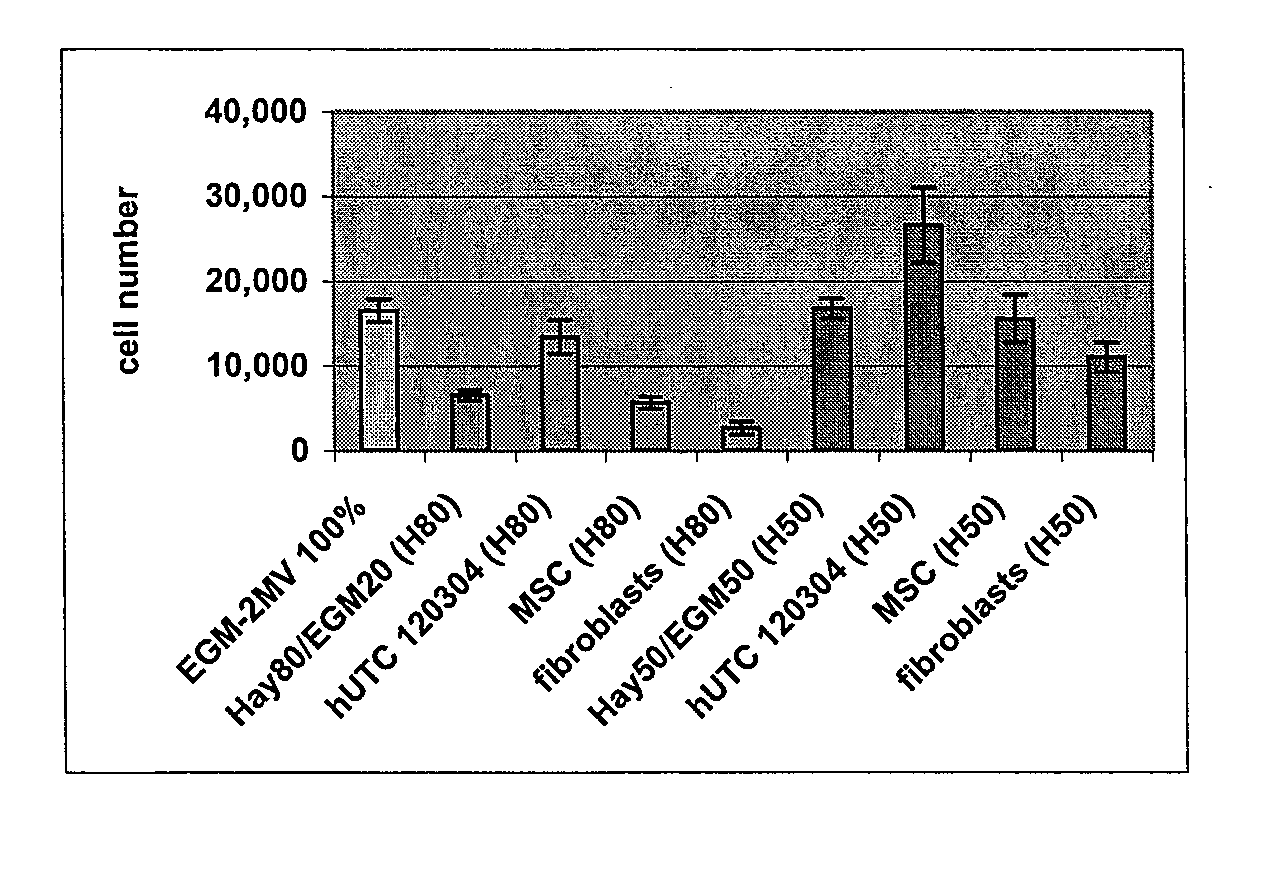
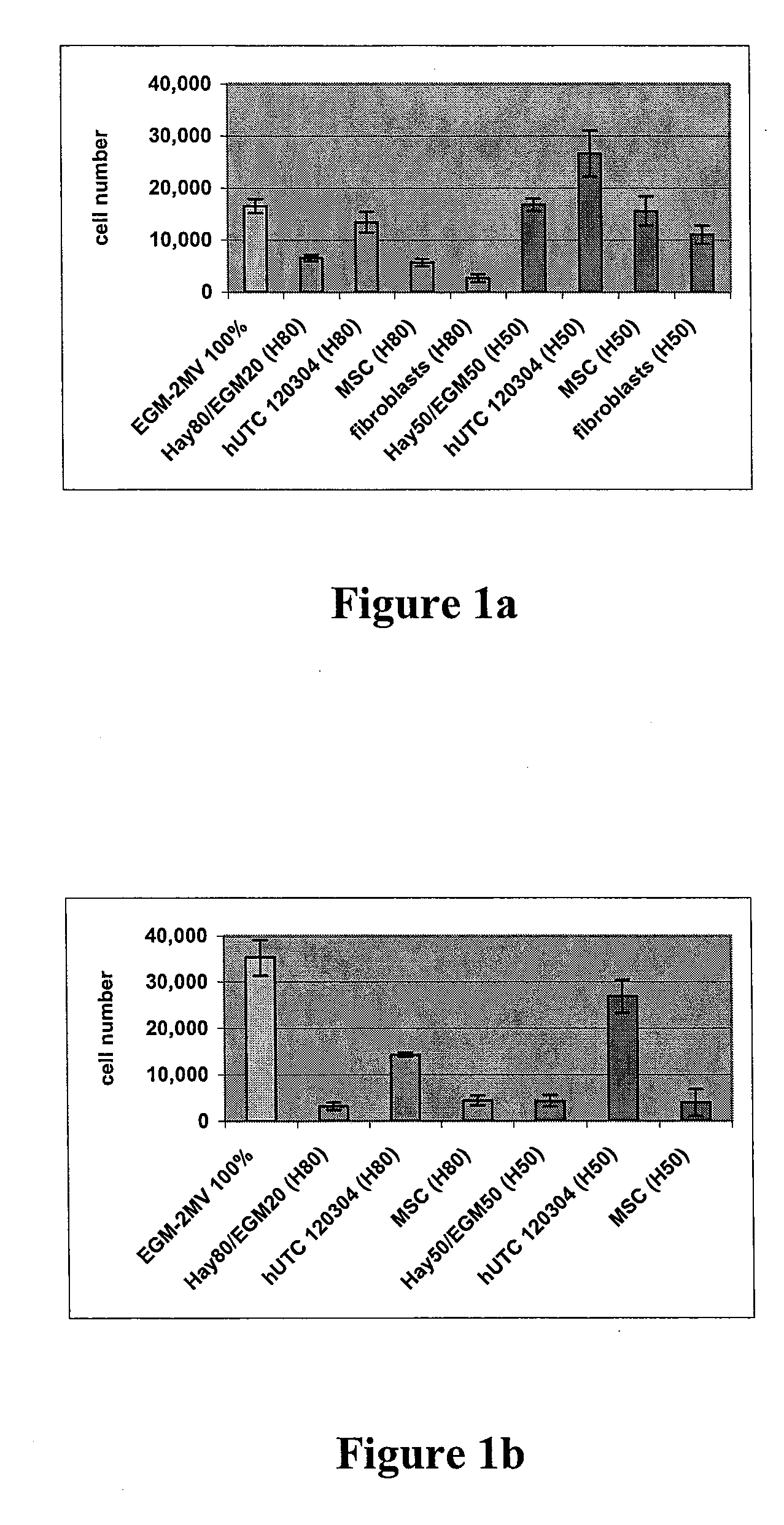
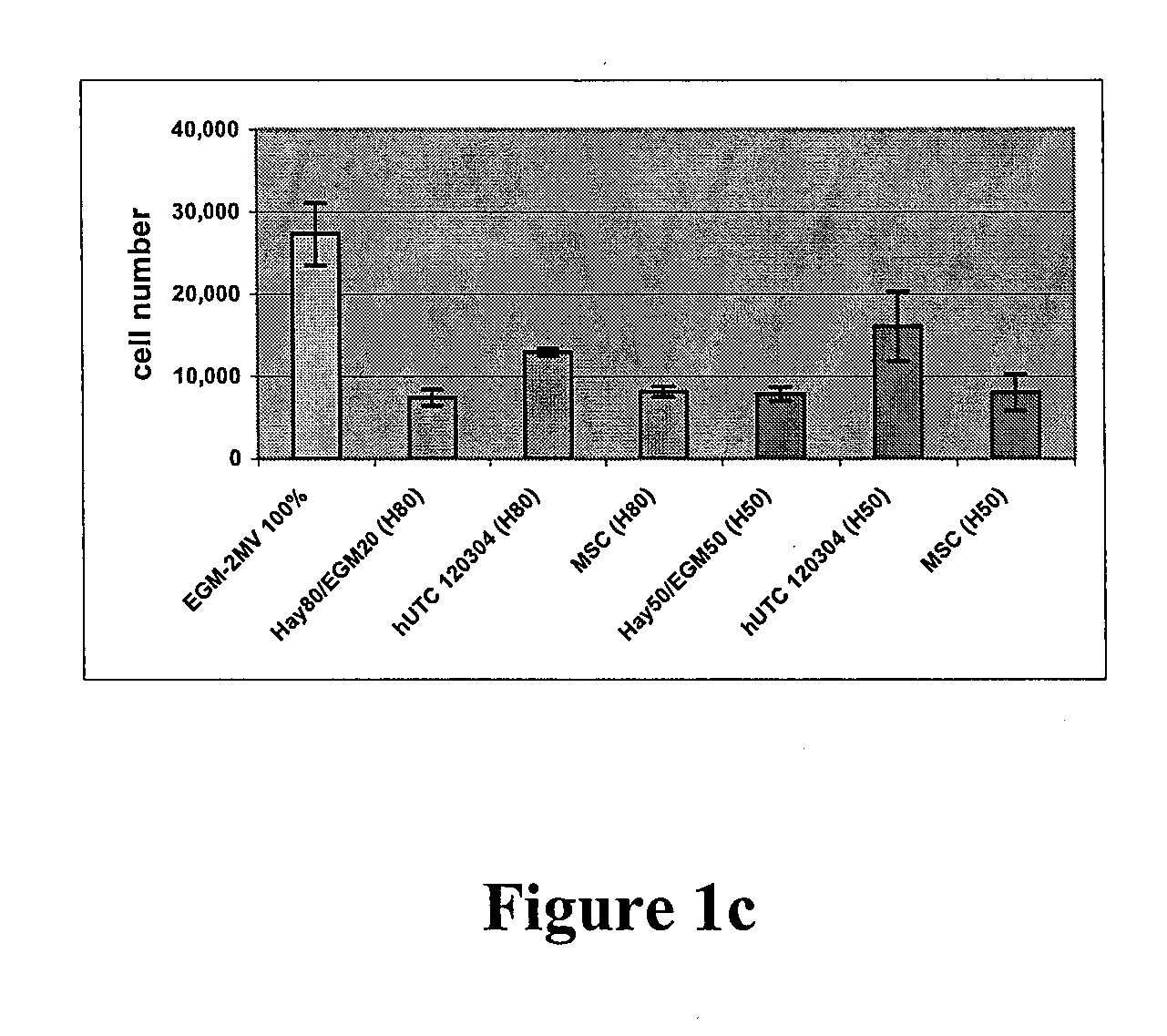
Compositions and methods of using cells derived from postpartum tissue such as the umbilical cord and placenta, to stimulate and support angiogenesis, to improve blood flow, to regenerate, repair, and improve skeletal muscle damaged by a peripheral ischemic event, and to protect skeletal muscle from ischemic damage in peripheral vascular disease patients are disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Treatment of muscle fatigue
PendingUS20060078596A1High metabolismUseful in treatmentBiocideMuscular disorderCardiac muscleBlood plasma
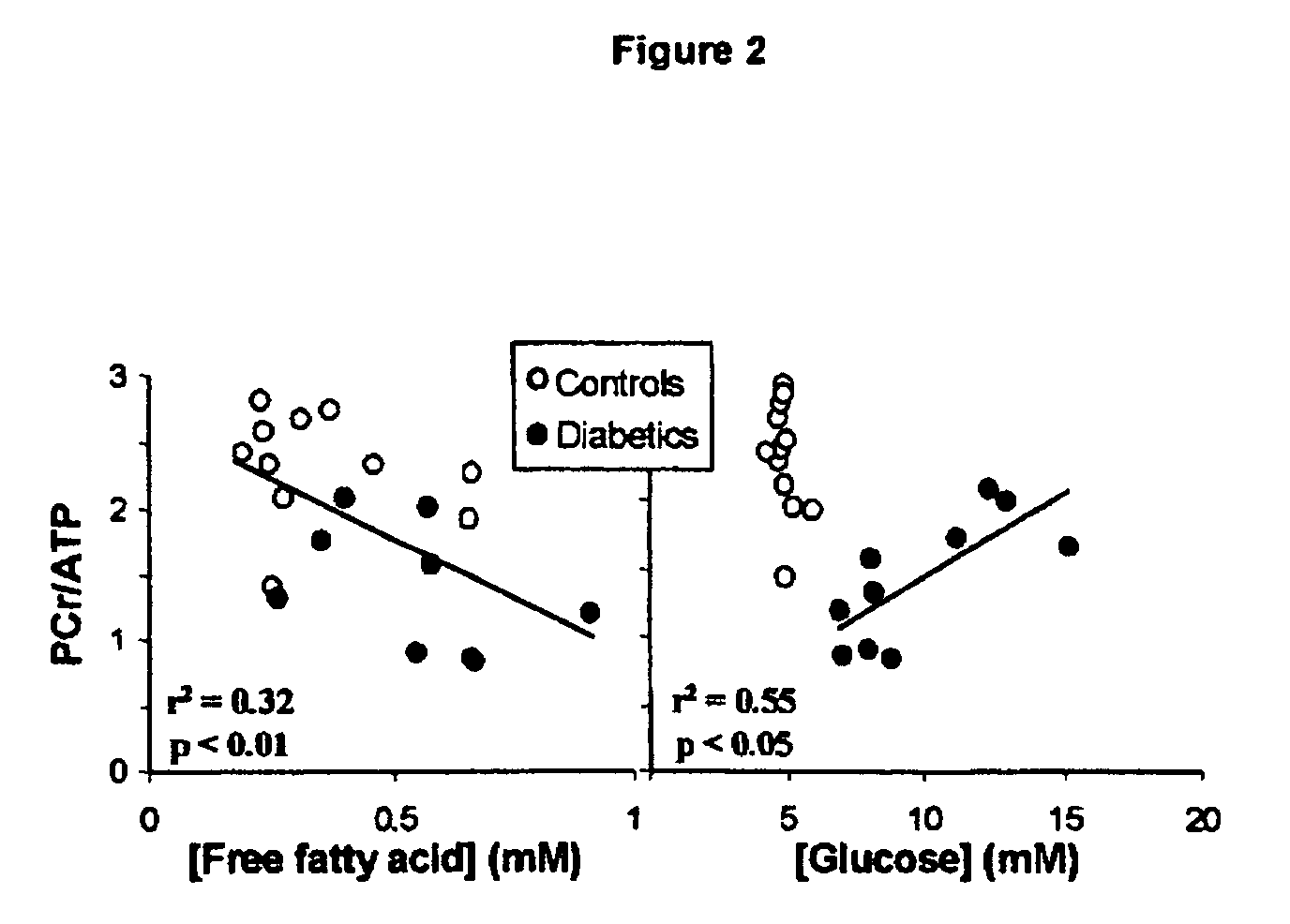
The present invention involves the use of a compound that reduces the level of free fatty acids circulating in the plasma of a subject in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of prevention of muscle (particularly cardiac or skeletal muscle) impairment or fatigue.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Combinations of HMG-COA reductase inhibitors and nicotinic acid and methods for treating hyperlipidemia once a day at night
InactiveUS20050255158A1Alter serum lipid levelReduce hyperlipidemiaSalicyclic acid active ingredientsMetabolism disorderLipid formationHMG-CoA reductase
The present invention relates to solid pharmaceutical combinations for oral administration comprising nicotinic acid or a nicotinic acid compound or mixtures thereof in an extended release form and an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, which are useful for altering lipid levels in subjects suffering from, for example, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis, without causing drug-induced hepatotoxicity, myopathy or rhabdomyolysis. The present invention also relates to methods of altering serum lipids in subjects to treat, for example, hyperlipidemia in hyperlipidemics, lipidemia in normolipidemics diagnosed with or predisposed to cardiovascular disease, and atherosclerosis, by administering such oral solid pharmaceutical combinations once per day as a single dose during the evening hours, without causing drug-induced hepatotoxicity, myopathy or rhabdomyolysis, or without causing in at least an appreciable number of individuals drug-induced hepatotoxicity, myopathy or rhabdomyolysis to such a level that discontinuation of such therapy would be required. More particularly, the present invention concerns oral solid pharmaceutical combinations comprised of, for example, (1) an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor for immediate or extended release, (2) nicotinic acid, a nicotinic acid compound or mixtures thereof, and (3) a swelling agent to form a sustained release composition for extended release of the nicotinic acid or nicotinic acid compound or mixtures thereof for nocturnal or evening dosing for reducing serum lipids and increasing HDL-cholesterol. In accordance with the present invention, and by way of example, a composition for oral administration during the evening hours to alter serum lipids comprised of nicotinic acid and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in the form of an extended or sustained release tablet or caplet coated with a coating comprising an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor in immediate release form is disclosed. Also in accordance with the present invention, the pharmaceutical combinations may include a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent for reducing the capacity of nicotinic acid or nicotinic acid compounds to provoke flushing reactions in individuals.
Owner:KOS LIFE SCI
Treatment of peripheral vascular disease using umbilical cord tissue-derived cells
Compositions and methods of using cells derived from umbilical cord tissue, to stimulate and support angiogenesis, to improve blood flow, to regenerate, repair, and improve skeletal muscle damaged by a peripheral ischemic event, and to protect skeletal muscle from ischemic damage in peripheral vascular disease patients are disclosed. In particular, methods of treating a patient having a peripheral vascular disease with umbilical derived cells and fibrin glue are disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Treatment of peripheral vascular disease using postpartum-derived cells
Compositions and methods of using cells derived from postpartum tissue such as the umbilical cord and placenta, to stimulate and support angiogenesis, to improve blood flow, to regenerate, repair, and improve skeletal muscle damaged by a peripheral ischemic event, and to protect skeletal muscle from ischemic damage in peripheral vascular disease patients are disclosed.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Methods of using zonisamide as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures
Methods of using zonisamide as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures are disclosed. In particular, the methods enhance the safety of patients taking pharmaceutical formulations of zonisamide by providing information that increases the awareness of rhabdomyolysis and / or elevated CPK as possible side effects; wherein the patients and / or prescribing physicians and other medical care providers are advised to monitor for such conditions and employ methods that will improve the therapeutic outcome in the few patients who experience rhabdomyolysis and / or elevated CPK associated with zonisamide therapy.
Owner:EISAI INC
Rosuvastatin calcium sustained-release preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101889975AOvercome the defect of "peak valley" fluctuation in blood drug concentrationImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderRosuvastatin CalciumBlood drug
The invention relates to a rosuvastatin calcium sustained-release preparation and a preparation method thereof. The rosuvastatin calcium sustained-release preparation basically contains 5 to 10mg of rosuvastatin calcium, and the balance of sustained-release framework material and other pharmaceutical excipients. The preparation method is simple; and all the materials are proportioned and the preparation is prepared by the preparation method for common tablets, granules or capsules. The rosuvastatin calcium sustained-release preparation prepared by the method avoids adverse reactions such as rhabdomyolysis, proteinuria, nephrosis, kidney failure, hepatotoxicity and the like caused by overdosage of medicaments; meanwhile, due blood concentration and time for treating diseases after the medicaments are taken can be maintained, and the peak valley phenomenon of the blood concentration is effectively avoided.
Owner:BEIJING HONGWAN PHARMA TECH
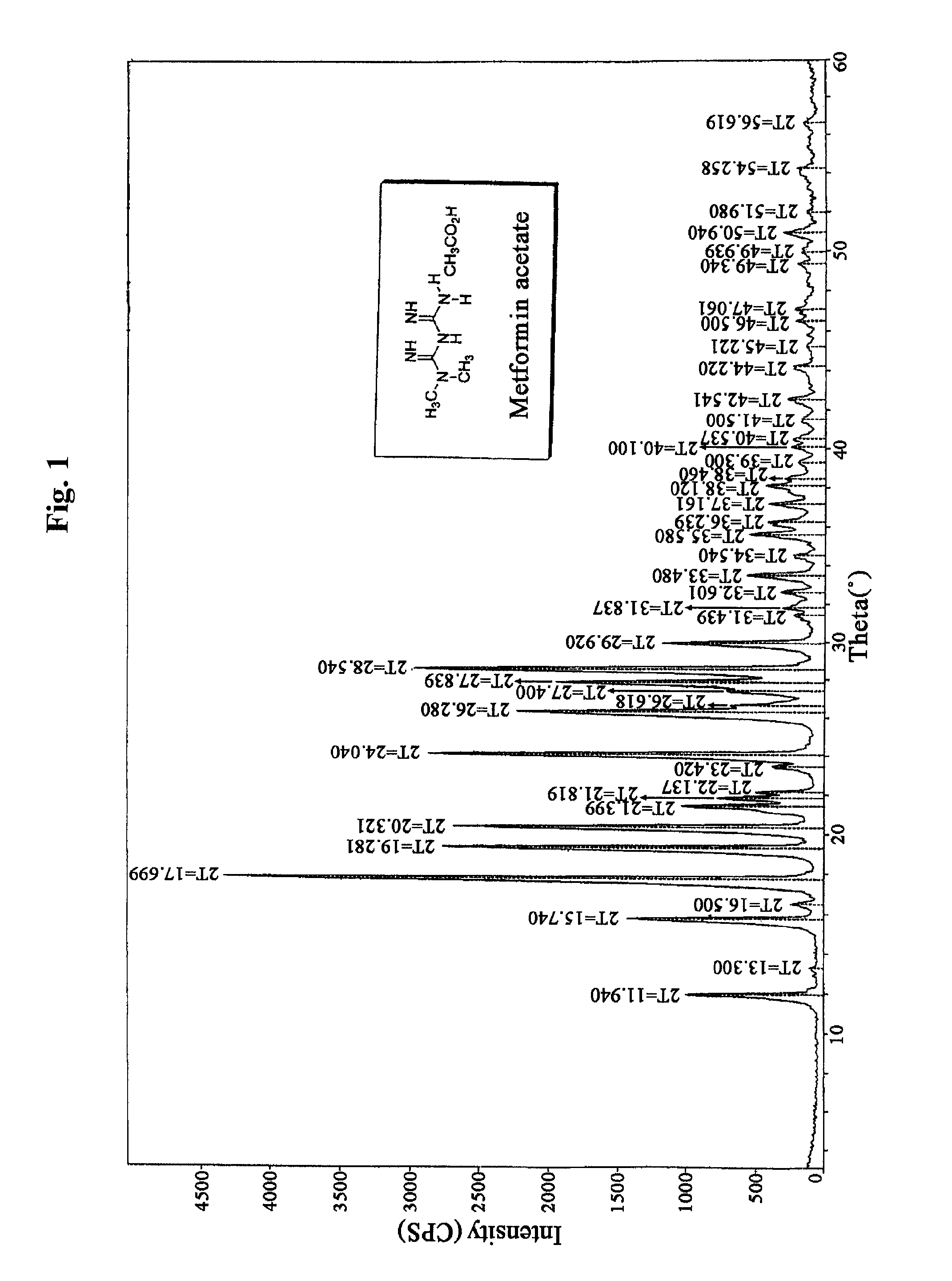
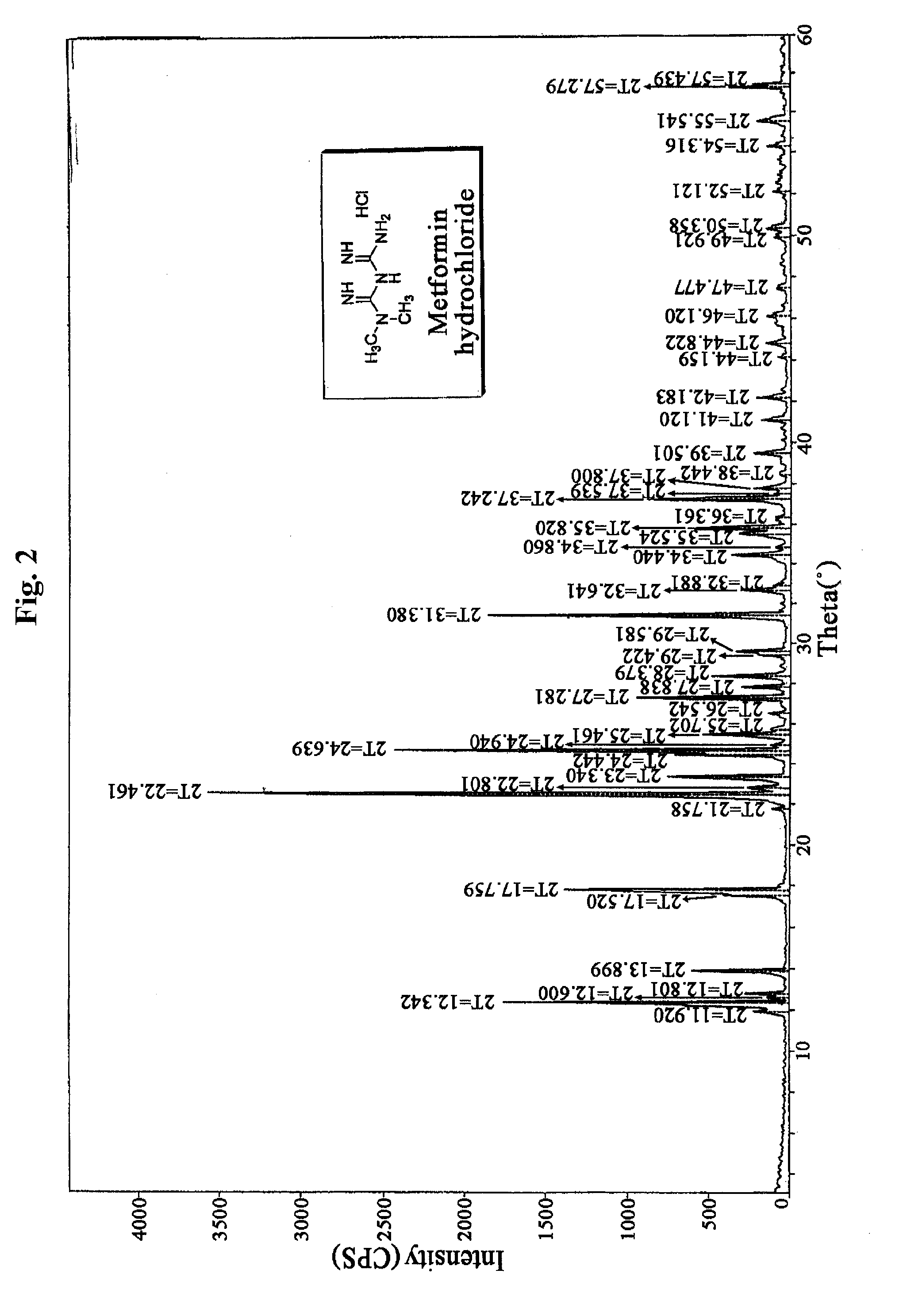
N, N-dimethyl imidodicarbonimidic diamide acetate, method for producing the same and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same
InactiveUS8058312B2Good effectSuperior in pharmaceuticalOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSolubilityCoronary heart disease
The present invention relates to N,N-dimethyl imidodicarbonimidic diamide acetate, a method of preparing the same and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, and more particularly, to N,N-dimethyl imidodicarbonimidic diamide acetate which is a crystalline acid addition salt prepared by reacting N,N-dimethyl imidodicarbonimidic diamide with acetic acid, and which is very effective as a therapeutic agent for treating metabolic syndromes that glycosuria and diabetes mellitus, obesity, hyperlipidemia, fatty liver, coronary heart disease, osteoporosis, polycystic ovarian syndrome, a cancer depleted of gene P53, etc. are complexly occurred; treating diabetes mellitus and preventing its complication; and treating a cancer and preventing myalgia, muscle cell cytotoxicity and rhabdomyolysis, etc. since the acid addition salt is excellent in physicochemical properties such as solubility, stability, non-hygroscopicity, anti-adhering property, etc., and low toxicity, a method of preparing the same and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same.
Owner:HANALL PHARMA CO LTD
N,N-dimethyl imidodicarbonimidic diamide dicarboxylate, method for producing the same and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same
ActiveUS8076377B2Good effectLowering blood glucoseOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSolubilityCoronary artery disease
Disclosed herein are a novel dicarboxylic acid salt of N,N-dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide, a preparation method thereof and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same. More specifically, disclosed herein are a novel dicarboxylic acid salt of N,N-dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide, a crystalline acid addition salt prepared by allowing N,N-dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide to react with a specific dicarboxylic acid, which has improved physical and chemical properties including solubility, stability, non-hygroscopicity and anti-adhesive properties, and low toxicity, and thus is very effective in the prevention and treatment of not only diabetes and its complications in patients with so-called metabolic syndromes, in which diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, fatty liver, coronary artery disease, osteoporosis, polycystic ovary syndromes, etc. appear in combination, but also p53 gene-deficient cancers, muscular pain, muscle cytotoxicity and rhabdomyolysis, as well as a preparation method thereof and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same.
Owner:HANALL PHARMA CO LTD
Biomarkers for sensitive detection of statin-induced muscle toxicity
InactiveUS20120258123A1Efficient mechanismSafety assessmentBiocideOrganic chemistryMyopathyConcentration ratio
The present invention inter alia provides a method, and uses thereof, of predicting statin-induced muscle toxicity or its complications, such as myalgia, myopathy and rhabdomyolysis, by detecting the lipid concentrations or lipid-lipid concentration ratios of a biological sample and comparing them to a control. This method has identified lipid markers that are more specific and sensitive in detecting these statin-induced muscle toxicity than the currently utilized clinical markers. Also provided is an antibody towards said lipids, and the use thereof for predicting, diagnosing, statin-induced muscle toxicity. The invention additionally relates to kits comprising lipids and / or an antibody thereto, for use in the prediction and / or diagnosis of statin-induced muscle toxicity.
Owner:ZORA BIOSCIENCES OY
Treatment of peripheral vascular disease using umbilical cord tissue-derived cells
Compositions and methods of using cells derived from umbilical cord tissue, to stimulate and support angiogenesis, to improve blood flow, to regenerate, repair, and improve skeletal muscle damaged by a peripheral ischemic event, and to protect skeletal muscle from ischemic damage in peripheral vascular disease patients are disclosed. In particular, methods of treating a patient having a peripheral vascular disease with umbilical derived cells and fibrin glue are disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Methods of using zonisamide as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures
Methods of using zonisamide as an adjunctive therapy for partial seizures are disclosed. In particular, the methods enhance the safety of patients taking pharmaceutical formulations of zonisamide by providing information that increases the awareness of rhabdomyolysis and / or elevated CPK as possible side effects; wherein the patients and / or prescribing physicians and other medical care providers are advised to monitor for such conditions and employ methods that will improve the therapeutic outcome in the few patients who experience rhabdomyolysis and / or elevated CPK associated with zonisamide therapy.
Owner:EISAI INC
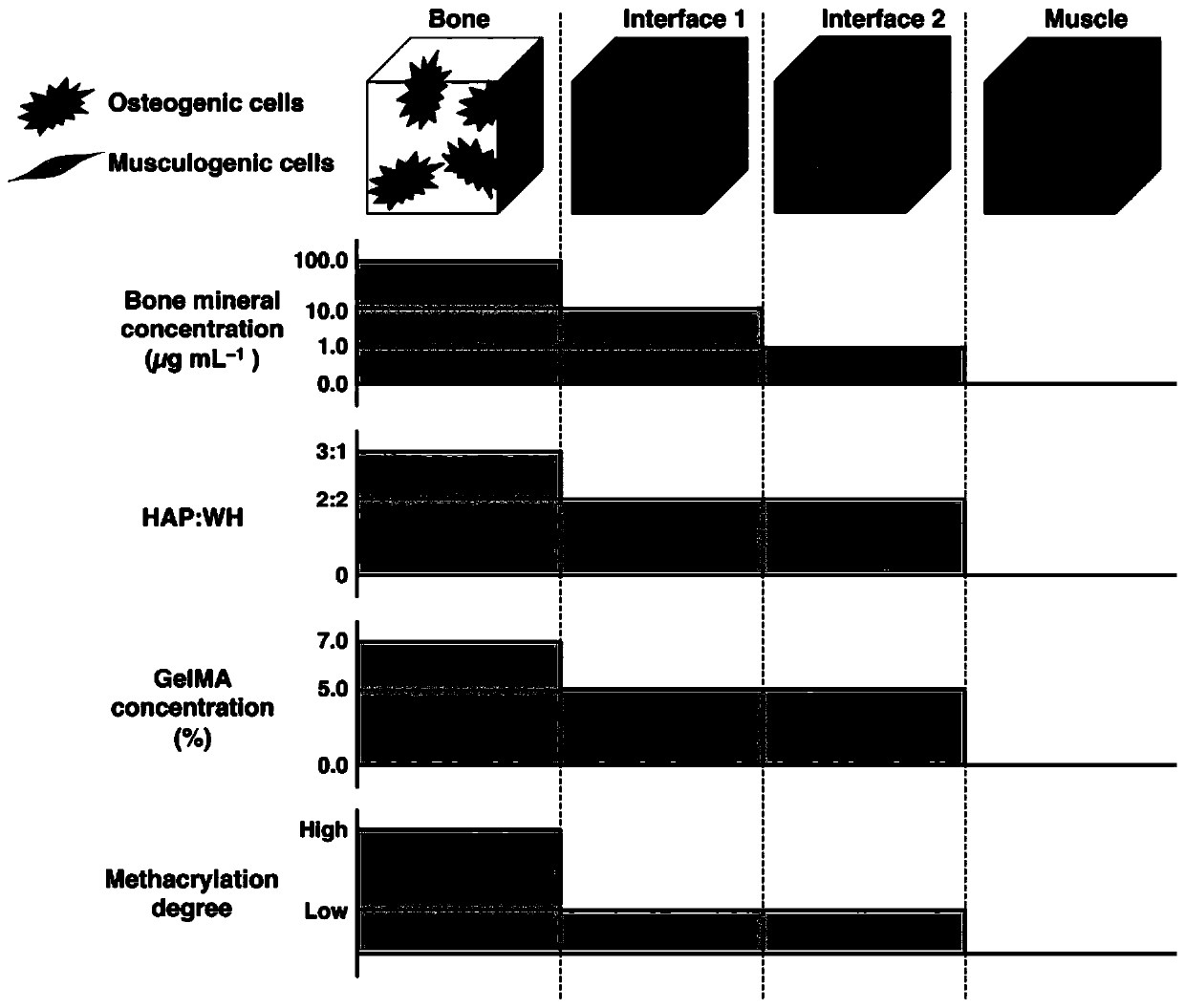
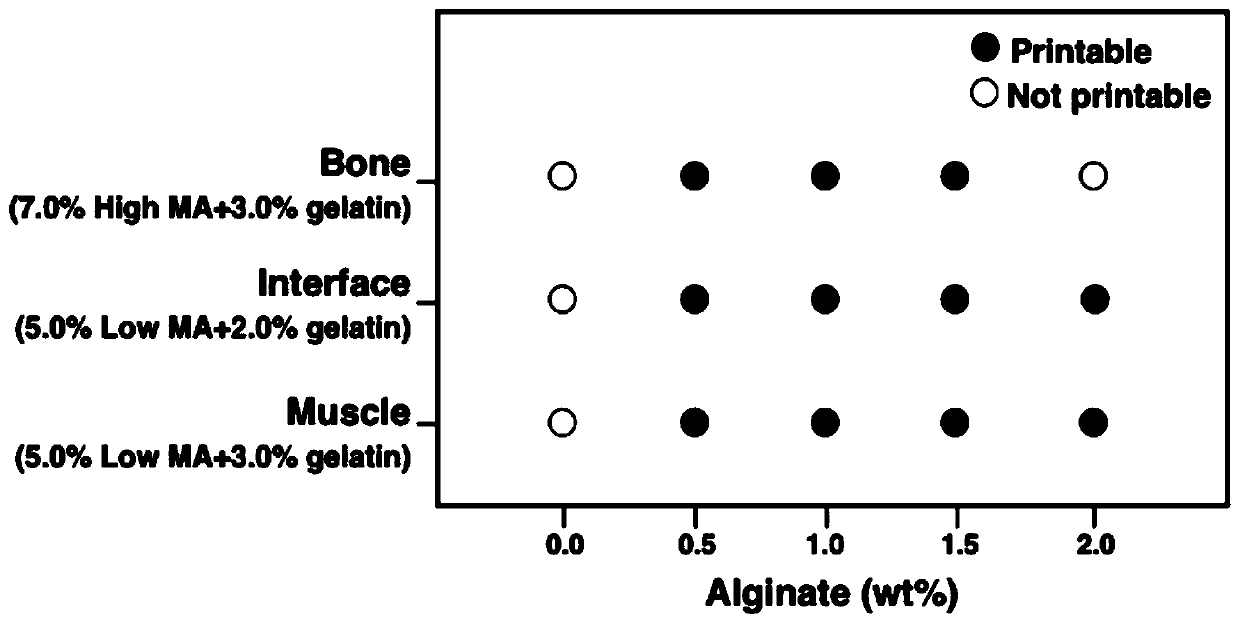
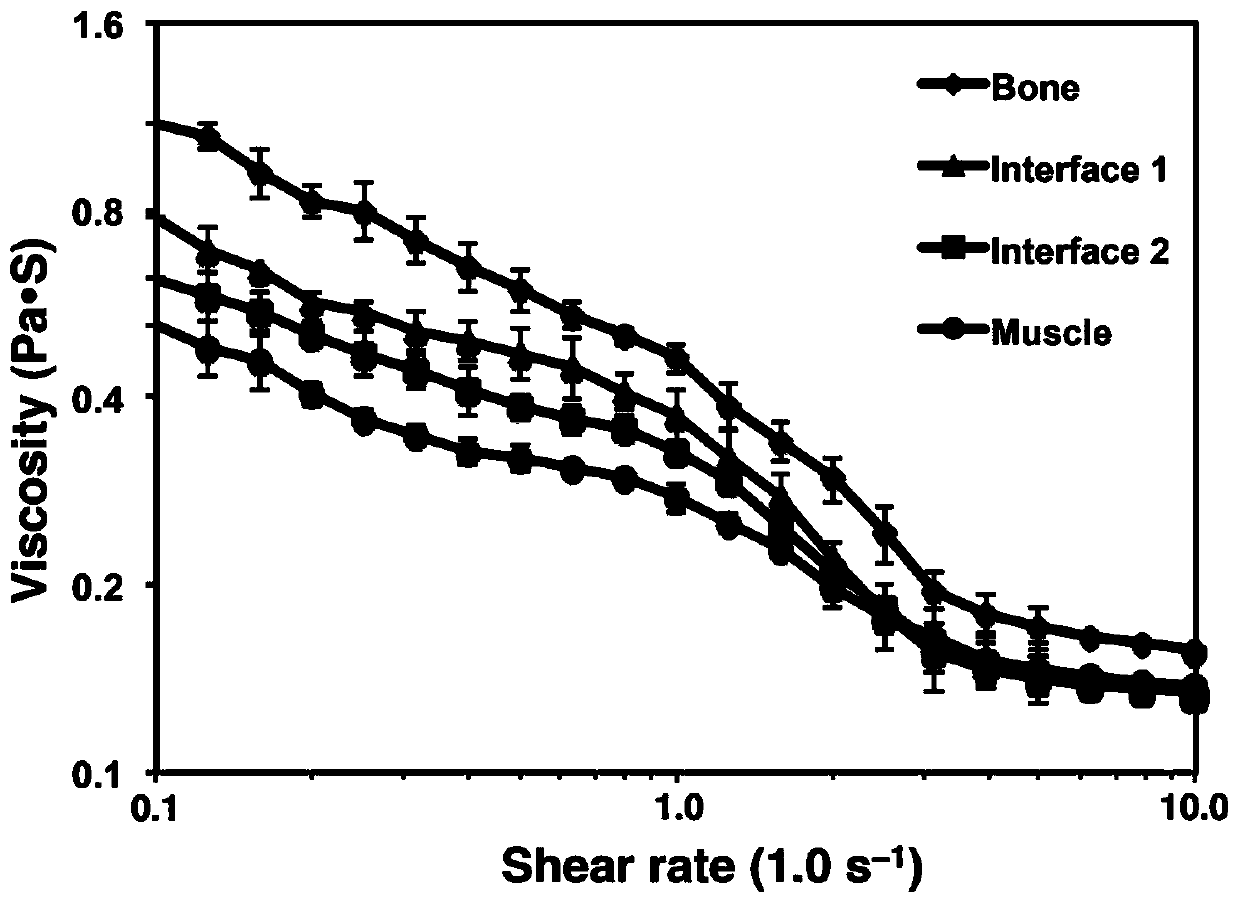
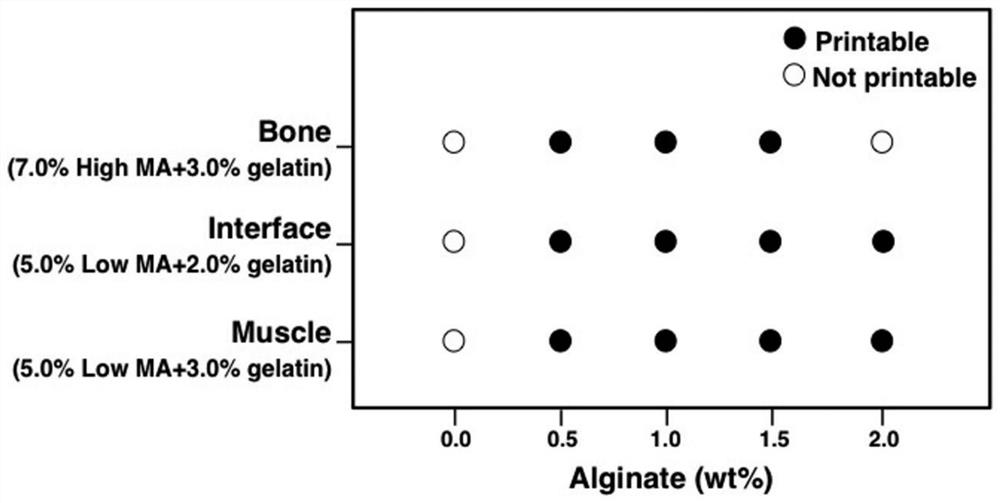
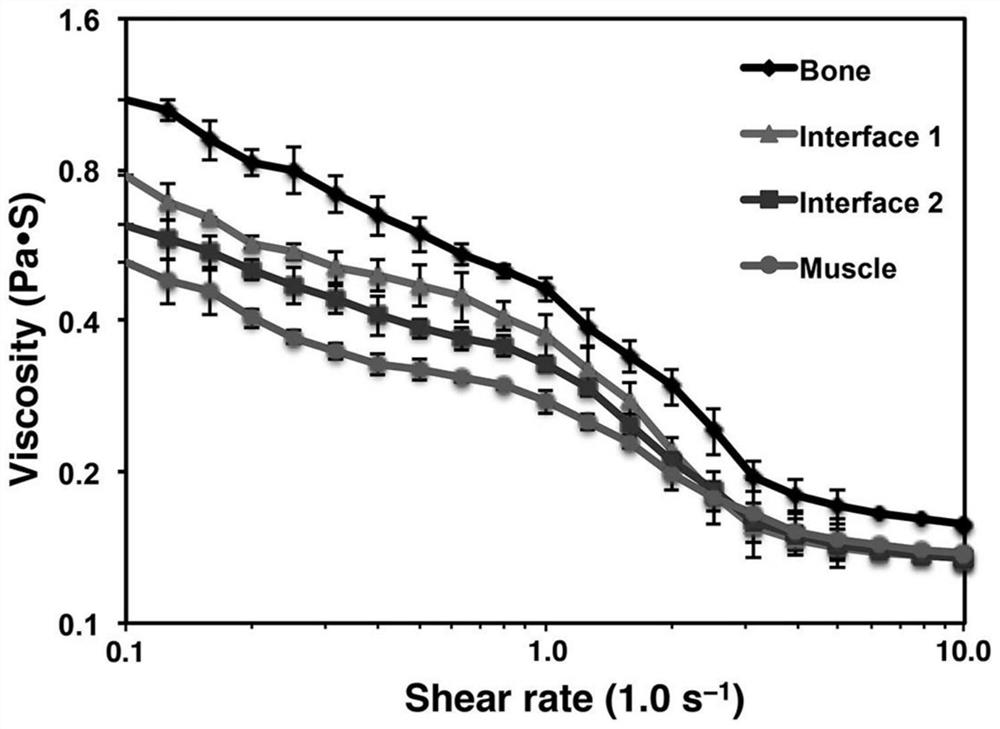
Method for preparing bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue through multi-channel extrusion 3D biological printing
ActiveCN110743040AReduce fibrosisEasy to customizeAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationMyogenic cellComputer printing
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue through multi-channel extrusion 3D biological printing. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing bone scaffold bionic bio-ink, periosteum bionic bio-ink, sarcolemma bionic bio-ink and muscle bionic bio-ink; respectively mixing MSCs and C2C12 with the corresponding bionic bio-inks; and printing and forming a bionic bone, bionic periosteum, bionic sarcolemma and bionic muscle four-layer composite tissue engineering scaffold by using a multi-channel extrusion 3D biological printer. Themethod for preparing the bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue through multi-channel extrusion 3D biological printing can minimize fibrosis during traumatic skeletal muscle injury recovery; the bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue prepared through multi-channel extrusion 3D biological printing can replace structures and functions of bones and skeletal muscles at the same time, and supports proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts and osteoblasts; and an implant is easy to customize by utilizing a 3D biological printing technology, so that the implant is suitable for any defect shape.
Owner:福建省安悦莱生物科技有限公司
Treatment of peripheral vascular disease using umbilical cord tissue-derived cells
Compositions and methods of using cells derived from umbilical cord tissue, to stimulate and support angiogenesis, to improve blood flow, to regenerate, repair, and improve skeletal muscle damaged by a peripheral ischemic event, and to protect skeletal muscle from ischemic damage in peripheral vascular disease patients are disclosed. In particular, methods of treating a patient having a peripheral vascular disease with umbilical derived cells and fibrin glue are disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
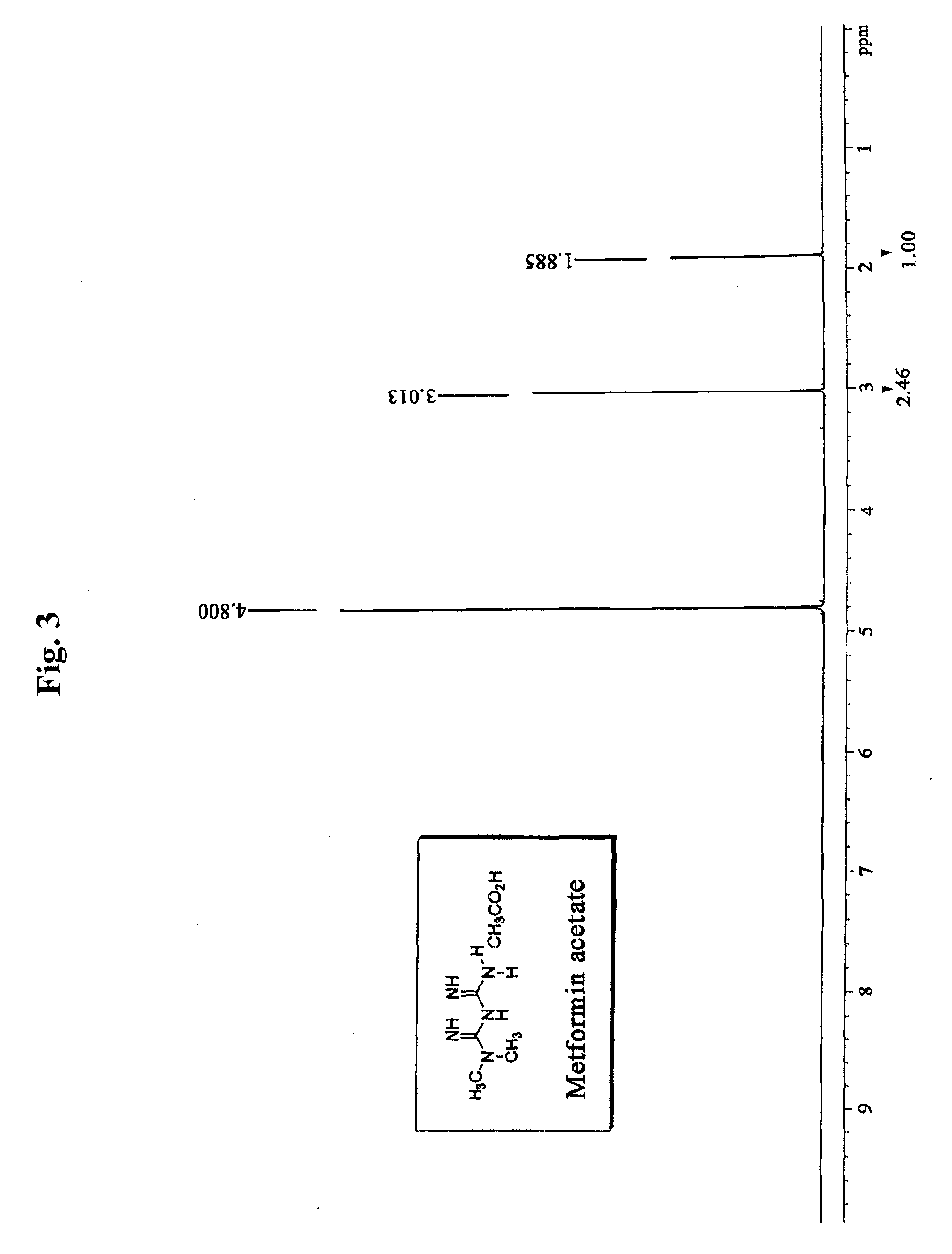
N, n -dimethyl imidodicarbonimidic diamide acetate, method for producing the same and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same
ActiveUS20100087544A1Increase insulin sensitivitySuperior in pharmaceuticalBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityCoronary heart disease
The present invention relates to N,N-dimethyl imidodicarbonimidic diamide acetate, a method of preparing the same and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same, and more particularly, to N,N-dimethyl imidodicarbonimidic diamide acetate which is a crystalline acid addition salt prepared by reacting N,N-dimethyl imidodicarbonimidic diamide with acetic acid, and which is very effective as a therapeutic agent for treating metabolic syndromes that glycosuria and diabetes mellitus, obesity, hyperlipidemia, fatty liver, coronary heart disease, osteoporosis, polycystic ovarian syndrome, a cancer depleted of gene P53, etc. are complexly occurred; treating diabetes mellitus and preventing its complication; and treating a cancer and preventing myalgia, muscle cell cytotoxicity and rhabdomyolysis, etc. since the acid addition salt is excellent in physicochemical properties such as solubility, stability, non-hygroscopicity, anti-adhering property, etc., and low toxicity, a method of preparing the same and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same.
Owner:HANALL PHARMA CO LTD
Peptide juice prepared by compounding mango juice with peptides having effects of resisting fatigue and increasing physical strength, and preparation method of peptide juice
The invention discloses a peptide juice compounded with anti-fatigue peptide and mango juice and a preparation method thereof, which belongs to the technical field of liquid processing and provides a new type of functional peptide juice food for the market. Kiwi peptide powder, seabuckthorn peptide powder, tiger palm peptide powder, Coprinus comatus peptide powder, golden mushroom peptide powder, bolete peptide powder, beet peptide powder, matsutake peptide powder, brown rice peptide powder, blueberry peptide powder, pea peptide powder , Chestnut mushroom peptide powder. These small molecular peptides can ensure the nutrition needed by athletes, have energy, strength and speed in competitions, reduce skeletal muscle damage, and help win championships. These are the main ingredients. Then take polysaccharides, vitamins, trace elements, essential oils, etc. as auxiliary materials. These main materials and auxiliary materials are weighed, mixed, granulated, dried and packaged to make mixed peptide powder. Take the pure mango juice and put it into the fresh-keeping can. According to the ratio of 1:50. Peptide Juice Made. It has the effect of supplementing nutrition.
Owner:TANGSHAN SHISAN TAIBAO BIOTECH CO LTD +2
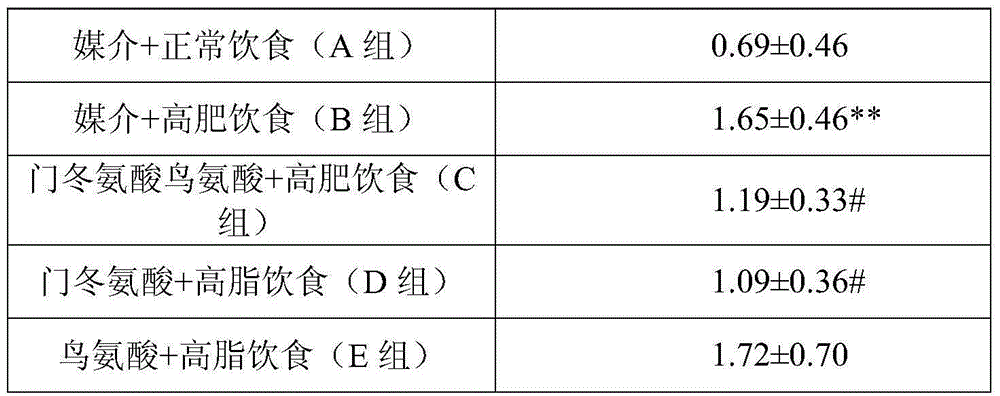
Ornithine- or aspartate-containing compositions and the uses thereof
Methods and compositions comprising ornithine and / or aspartate that are useful for lowering one or more hyperlipidemic risk factor levels are described. More specifically, compositions comprising ornithine and / or aspartate that are useful for lowering lipid and / or lipoprotein levels, such as triglyceride, cholesterol and LDL levels, in the bloodstream in a subject are described. Methods of using compositions comprising ornithine and / or aspartate for ameliorating the side-effect induced by a therapeutic agent (e.g., statin) or a condition that is associated with an elevation of CPK (e.g., rhabdomyolysis or myopathy) are also described.
Owner:WUHAN QR PHARMA CO LTD
Combinations of hmg-coa reductase inhibitors and nicotinic acid compounds and methods for treating hyperlipidemia once a day at night
InactiveUS20120164221A1Alter serum lipid levelReduce hyperlipidemiaBiocideAntipyreticHMG-CoA reductaseDrug induced hepatotoxicity
The present invention relates to solid pharmaceutical combinations for oral administration comprising nicotinic acid or a nicotinic acid compound or mixtures thereof in an extended release form and an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, which are useful for altering lipid levels in subjects suffering from, for example, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis, without causing drug-induced hepatotoxicity, myopathy, or rhabdomyolysis.
Owner:BOVA DAVID J +1
Use of ribose to alleviate rhabdomyolysis and the side effects of statin drugs
InactiveUS20060135440A1Relieve symptomsBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsSide effectSkeletal muscle damage
Owner:HOUSTON MARK C +1
Methods and pharmaceutical compostions for treating rhabdomyolysis
ActiveUS20180325890A1High affinityStrong specificityOrganic active ingredientsMuscular disorderSkeletal muscle damageRhabdomyolysis
Owner:UNIVERSITÉ PARIS CITÉ +4
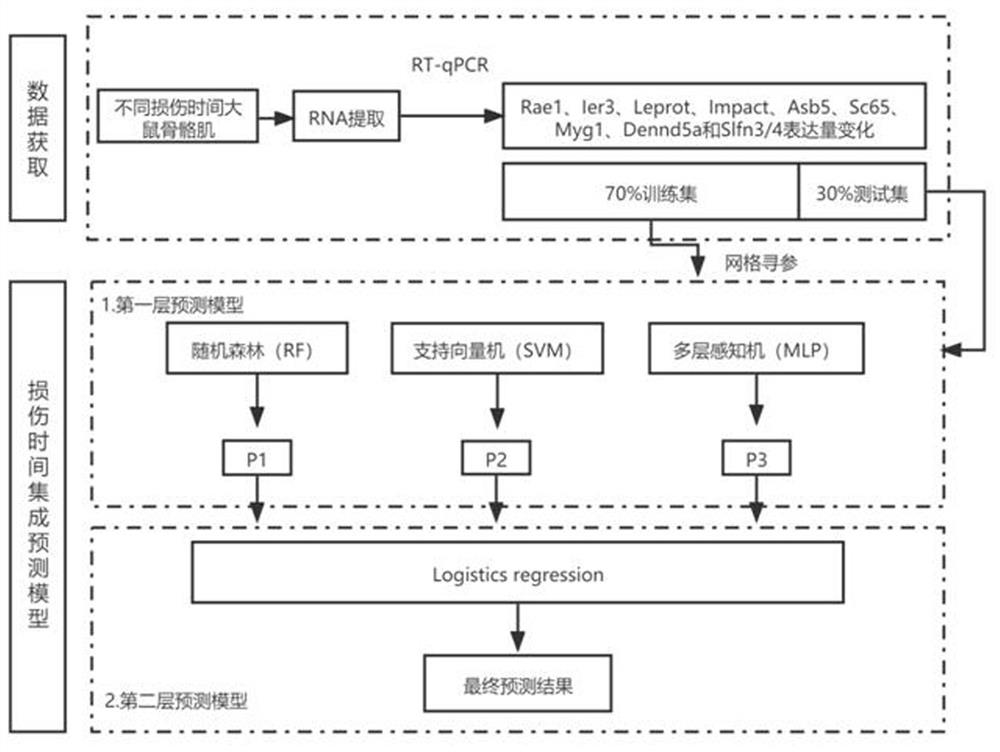
Skeletal muscle early injury time prediction method based on Stacking ensemble learning
ActiveCN114058691AImprove accuracyImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsAlgorithmPrediction probability
The invention relates to the field of forensic medicine, in particular to a skeletal muscle early injury time prediction method based on Stacking ensemble learning, which comprises the following steps: collecting skeletal muscle samples of rats at different injury time, and obtaining skeletal muscle injury repair related gene expression quantity; according to the prediction models of the three base classifiers, stacking the prediction probability values of the three base classifiers to form a new feature set, and conducting training to obtain a final Stacking ensemble learning model; and inputting the data of an unknown sample into the Stacking ensemble learning model so as to predict the damage time of the unknown sample. According to the prediction method, prediction results of the three base classifiers are integrated by adopting Stacking ensemble learning, and the three base classifiers are subjected to parameter optimization through grid search and cross validation, so that the accuracy and stability of skeletal muscle early injury time deduction are effectively improved.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
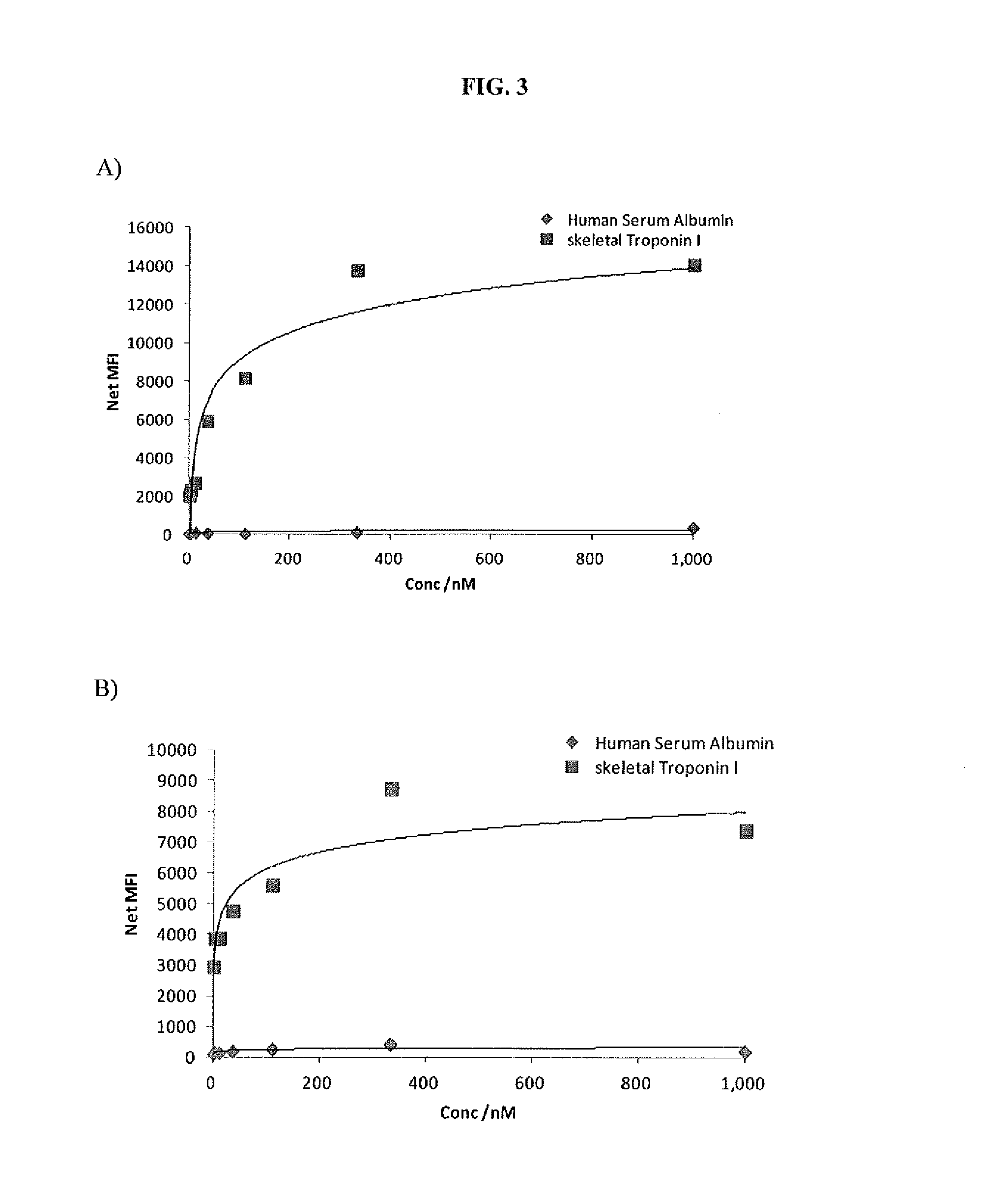
Troponin I protein binding compounds
ActiveUS8748104B1High sensitivityHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementAptamerSkeletal muscle damage
The invention provides aptamers capable of binding to the skeletal Troponin I protein useful as diagnostics of skeletal muscle damage in which the skeletal Troponin I protein has been implicated.
Owner:ENANO HEALTH
Myoglobin immunoadsorbent and immunoadsorption device
InactiveCN102526726AStrong specificityReduce dependencyOther blood circulation devicesMuscular disorderImmunosorbentsHaemodialysis machine
The invention discloses a myoglobin immunoadsorbent which comprises a solid phase carrier and a myoglobin polyclonal antibody coupled with the carrier; the myoglobin polyclonal antibody is a polyclonal antibody obtained by using a compound as an immunogen, wherein the compound is formed by crosslinking keyhole limpet hemocyanin with antigenic peptide; the amino acid sequence of the antigenic peptide is shown in sequence table SEQ ID:No.5. The invention also discloses a myoglobin immunoadsorption column which uses the myoglobin immunoadsorbent as a filler, a myoglobin immunoadsorption device containing the myoglobin immunoadsorption column, and a first aid tool kit. The immunoadsorbent and the device of the invention are established in a convenient blood perfusion treatment mode, can realize myoglobin adsorption with high specificity, and are especially suitable for on-site rescue of rhabdomyolysis. Compared with modes of hemodialysis or hemofiltration, the whole blood perfusion mode has less water and electricity consumption, is easier to realize, and more meets the requirements of disaster accident on-site rescue.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Biomarkers for sensitive detection of statin-induced muscle toxicity
InactiveUS9541565B2Safety assessmentFacilitate improving patient careBiocideOrganic chemistryMyopathyConcentration ratio
The present invention inter alia provides a method, and uses thereof, of predicting statin-induced muscle toxicity or its complications, such as myalgia, myopathy and rhabdomyolysis, by detecting the lipid concentrations or lipid-lipid concentration ratios of a biological sample and comparing them to a control. This method has identified lipid markers that are more specific and sensitive in detecting these statin-induced muscle toxicity than the currently utilized clinical markers. Also provided is an antibody towards said lipids, and the use thereof for predicting, diagnosing, statin-induced muscle toxicity. The invention additionally relates to kits comprising lipids and / or an antibody thereto, for use in the prediction and / or diagnosis of statin-induced muscle toxicity.
Owner:ZORA BIOSCIENCES OY
Biomarkers for sensitive detection of statin-induced muscle toxicity
InactiveUS9664698B2Safety assessmentFacilitate improving patient careComponent separationHealth-index calculationMyopathySkeletal muscle damage
Owner:ZORA BIOSCIENCES OY
Application of leucyl-tRNA synthetase 2
ActiveCN113769071APromote repairPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderSkeletal muscle damageBiochemistry
The invention provides application of leucyl-tRNA synthetase 2 to repair after skeletal muscle injury. The skeletal muscle repairing agent has the advantage of effectively promoting skeletal muscle repairing after injury.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation of biomimetic skeletal muscle composite tissue by multi-channel extrusion 3D bioprinting
ActiveCN110743040BReduce fibrosisEasy to customizeAnimal cellsAdditive manufacturing apparatusOsteoblastMyogenic cell
The invention discloses a bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue prepared by multi-channel extrusion 3D bioprinting. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing bone scaffold bionic bioink, periosteum bionic bioink, myofibrillar membrane bionic bioink, and muscle bionic bioink; Mix MSCs and C2C12 with the corresponding bionic bio-ink; use a multi-channel extrusion 3D bioprinter to print and form a four-layer composite tissue engineering scaffold of bionic bone, bionic periosteum, bionic sarcolemma, and bionic muscle. The bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue prepared by multi-channel extrusion 3D bioprinting of the present invention can minimize fibrosis during the recovery of traumatic skeletal muscle injury; the bionic skeletal muscle composite tissue prepared by multi-channel extrusion 3D bioprinting can simultaneously replace The structure and function of bone and skeletal muscle, supporting the proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts and osteoblasts; and using 3D bioprinting technology to make implants easy to customize to adapt to any defect shape.
Owner:福建省安悦莱生物科技有限公司
(monitoring only) combinations of hmg-coa reductase inhibitors and nicotinic acid compounds and methods for treating hypelipidemia once a day at night
InactiveUS20090226518A1Alter serum lipid levelReduce hyperlipidemiaBiocideAntipyreticLipid formationHMG-CoA reductase
The present invention relates to solid pharmaceutical combinations for oral administration comprising nicotinic acid or a nicotinic acid compound or mixtures thereof in an extended release form and an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, which are useful for altering lipid levels in subjects suffering from, for example, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis, without causing drug-induced hepatotoxicity, myopathy or rhabdomyolysis. The present invention also relates to methods of altering serum lipids in subjects to treat, for example, hyperlipidemia in hyperlipidemics, lipidemia in normolipidemics diagnosed with or predisposed to cardiovascular disease, and atherosclerosis, by administering such oral solid pharmaceutical combinations once per day as a single dose during the evening hours, without causing drug-induced hepatotoxicity, myopathy or rhabdomyolysis, or without causing in at least an appreciable number of individuals drug-induced hepatotoxicity, myopathy or rhabdomyolysis to such a level that discontinuation of such therapy would be required. More particularly, the present invention concerns oral solid pharmaceutical combinations comprised of, for example, (1) an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor for immediate or extended release, (2) nicotinic acid, a nicotinic acid compound or mixtures thereof, and (3) a swelling agent to form a sustained release composition for extended release of the nicotinic acid or nicotinic acid compound or mixtures thereof for nocturnal or evening dosing for reducing serum lipids and increasing HDL-cholesterol. In accordance with the present invention and by way of example, a composition for oral administration during the evening hours to alter serum lipids comprised of nicotinic acid and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in the form of an extended or sustained release tablet or caplet coated with a coating comprising an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor in immediate release form is disclosed. Also in accordance with the present invention. the pharmaceutical combinations may include a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent for reducing the capacity of nicotinic acid or nicotinic acid compounds to provoke flushing reactions in individuals.
Owner:BOVA DAVID J +1
Application of medicine in preparation of drugs for reducing muscle toxicity of statins
ActiveCN111773285AReduce muscle toxicityImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsMuscular disorderOxidative stressSkeletal muscle damage
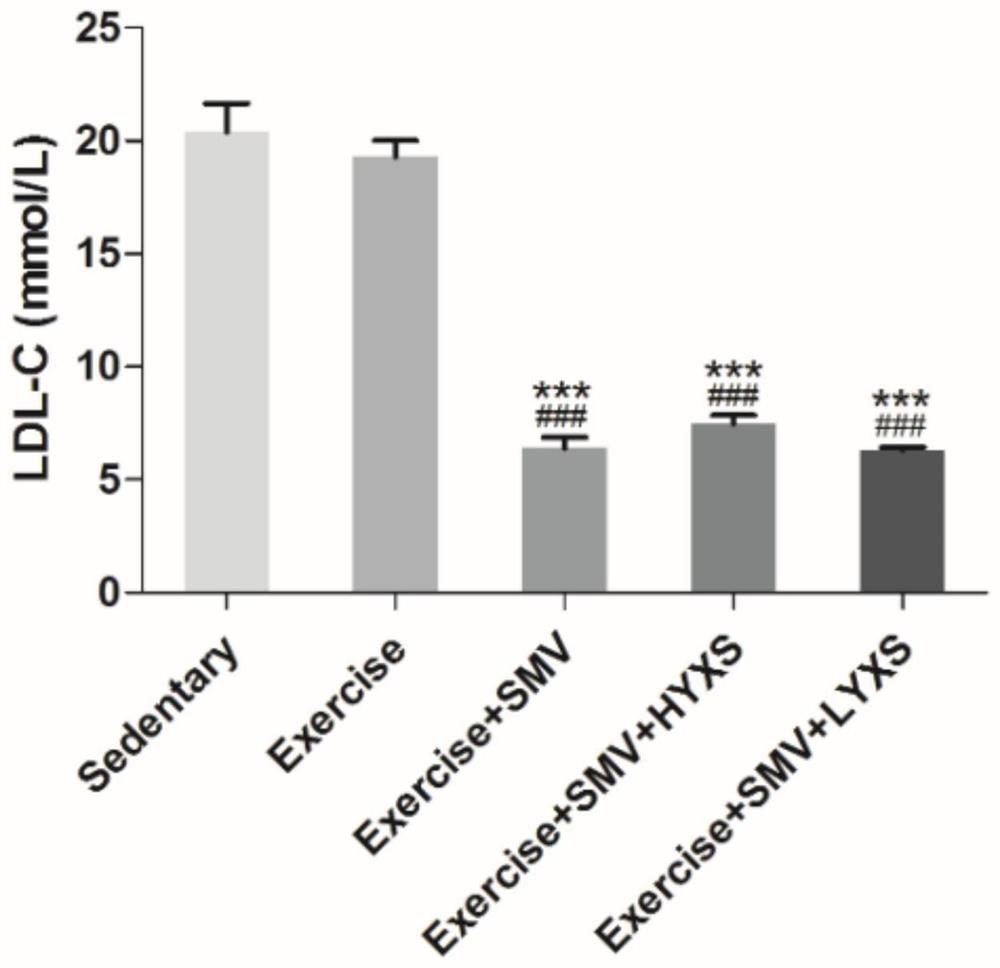
The invention discloses application of a medicine in preparation of drugs for reducing the muscle toxicity of statins. Experimental results show that a heart-nourishing tablet can reduce statins related skeletal muscle injury and improve exercise capacity by enhancing mitochondrial activity, improving oxidative stress and inhibiting myolysis of ApoE- / -mice fed with high fat in exercise training, and the effect is remarkable.
Owner:SHANGHAI PHARMA GRP QINGDAO GROWFUL PHARMA CO LTD
N,n-dimethyl imidodicarbonimidic diamide dicarboxylate, method for producing the same and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same
ActiveUS20100249241A1Good effectIncrease insulin sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSolubilityRhabdomyolysis
Disclosed herein are a novel dicarboxylic acid salt of N,N-dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide, a preparation method thereof and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same. More specifically, disclosed herein are a novel dicarboxylic acid salt of N,N-dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide, a crystalline acid addition salt prepared by allowing N,N-dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide to react with a specific dicarboxylic acid, which has improved physical and chemical properties including solubility, stability, non-hygroscopicity and anti-adhesive properties, and low toxicity, and thus is very effective in the prevention and treatment of not only diabetes and its complications in patients with so-called metabolic syndromes, in which diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, fatty liver, coronary artery disease, osteoporosis, polycystic ovary syndromes, etc. appear in combination, but also p53 gene-deficient cancers, muscular pain, muscle cytotoxicity and rhabdomyolysis, as well as a preparation method thereof and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same.
Owner:HANALL PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com