Patents
Literature
104 results about "Time-varying network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
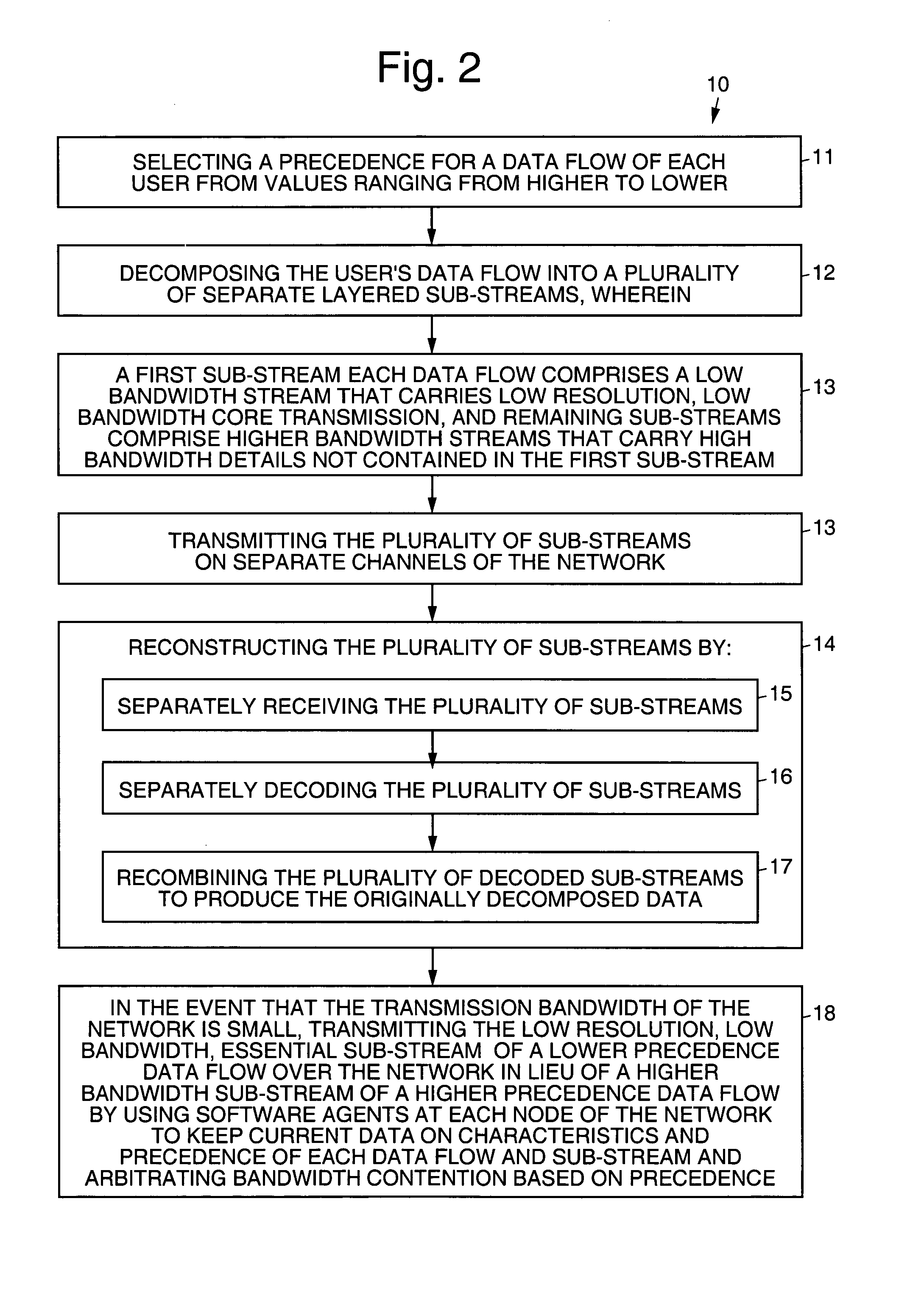
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A temporal network, also known as a time-varying network, is a network whose links are active only at certain points in time. Each link carries information on when it is active, along with other possible characteristics such as a weight. Time-varying networks are of particular relevance to spreading processes, like the spread of information and disease, since each link is a contact opportunity and the time ordering of contacts is included.
Adaptive quality-of-service reservation and pre-allocation for mobile systems
ActiveUS7289453B2Minimize impactDelay minimizationError preventionTransmission systemsAdaptive servicesQos management
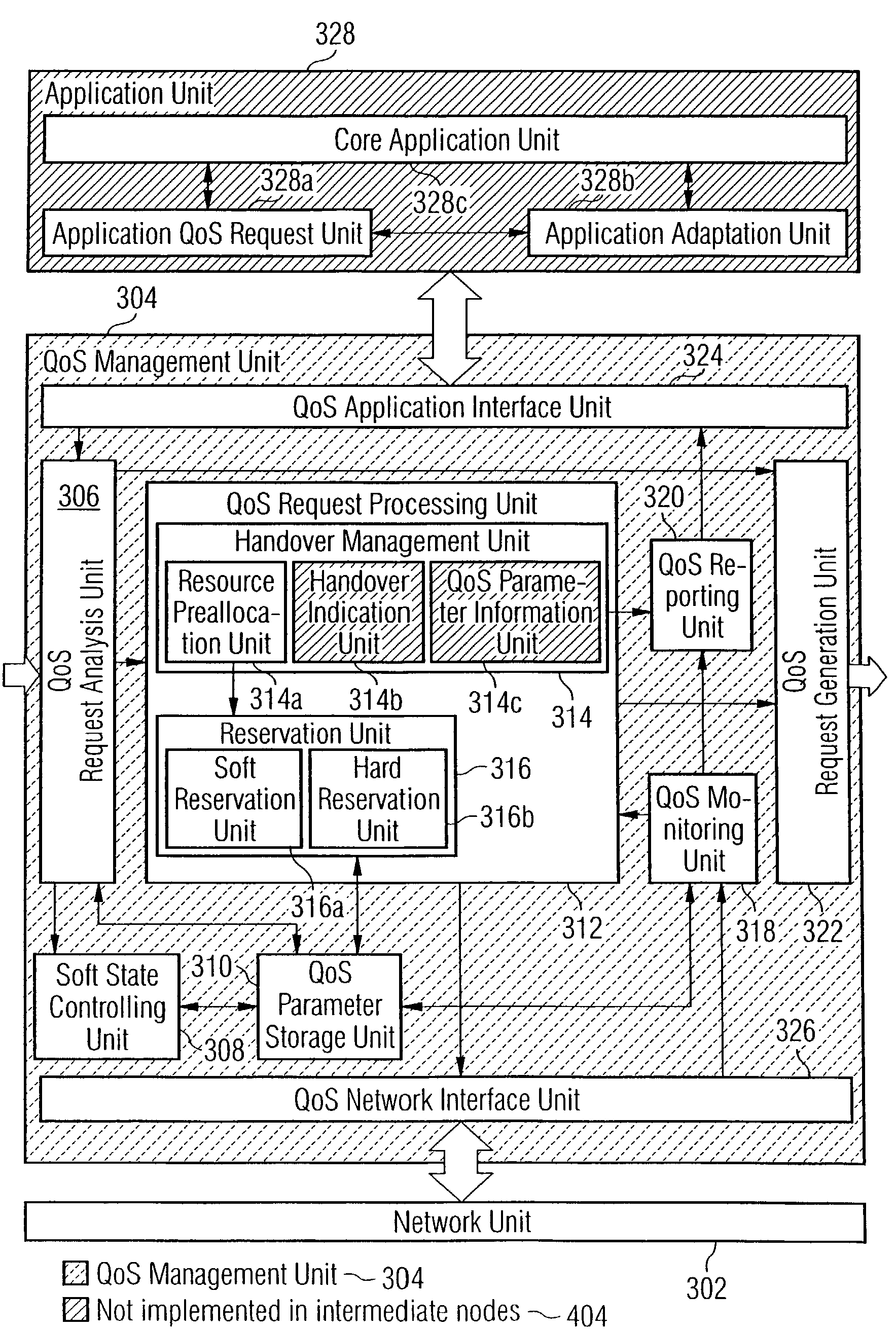
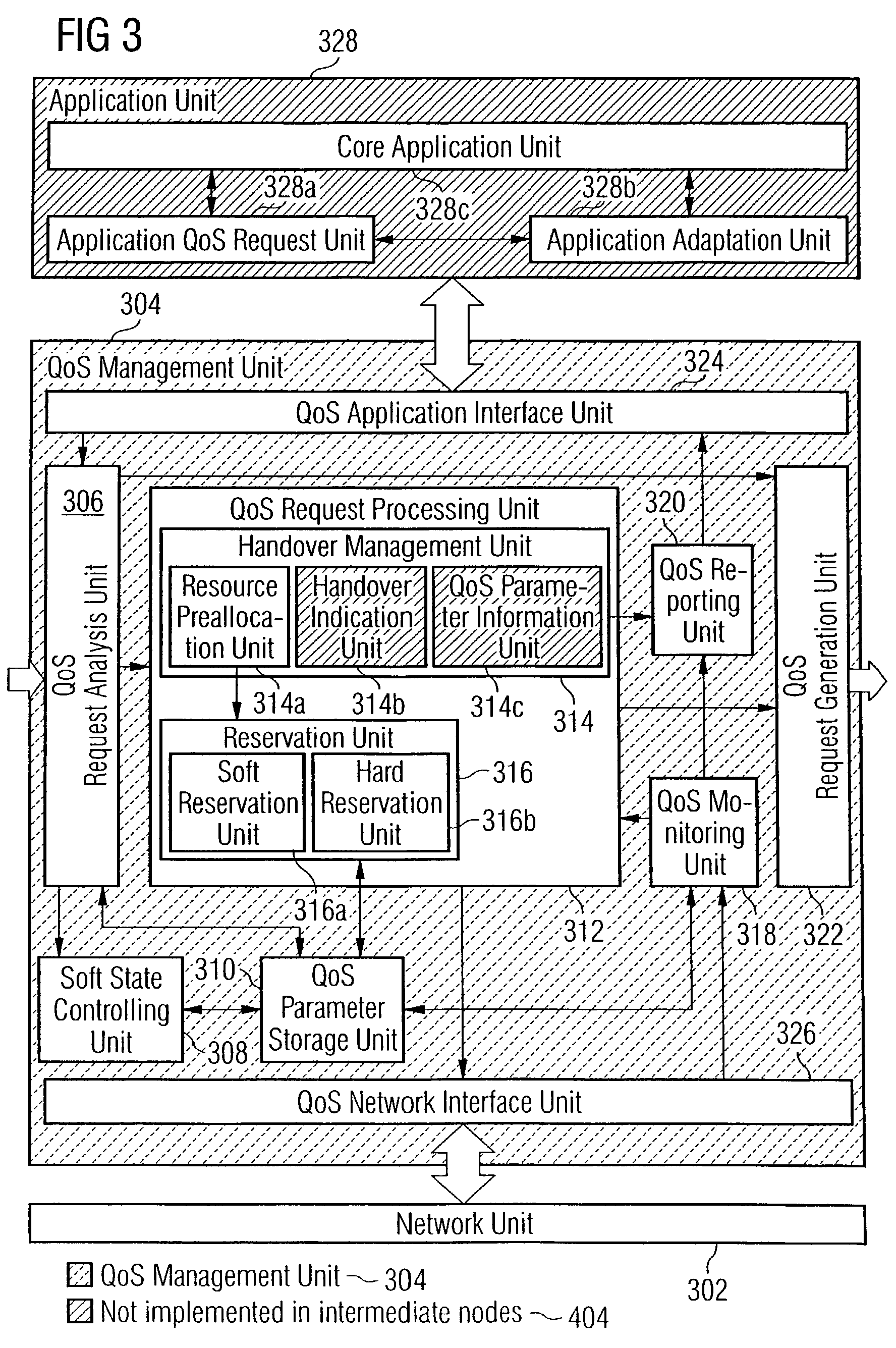
In the field of Quality-of-Service (QoS) management for adaptive real-time services running on mobile devices which support different access technologies in dynamic wireless Internet Protocol (IP) networks, the connectivity of the applied nodes is unpredictable time-varying. In this context, a QoS management unit (304) is proposed that allows adaptive applications with real-time requirements in typical mobile wireless scenarios—e.g. a radio link with a changing transmission quality and handover procedures (2900)—to adaptively and responsively react to a time-varying network topology and different radio link characteristics. Said QoS management unit (304) provides methods of pre-allocating, reserving, monitoring and adapting QoS-related parameters in a dynamic mobile environment.The QoS management unit (304) comprises at least one analysis unit (306) which evaluates QoS requests received from other nodes (402a / b, 404) to inform the application unit (328) of said mobile terminal (208) about the current QoS situation, at least one processing unit (312) that manages request messages (1200, 2000, 2400) for each type of QoS request, at least one monitoring unit (318) which monitors the current QoS situation within said mobile node (208) and initiates requests by activating the processing unit (312), and at least one generation unit (322) which is responsible for generating QoS requests or passing them on to the QoS management units (304) of other nodes (402a+b, 404).
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
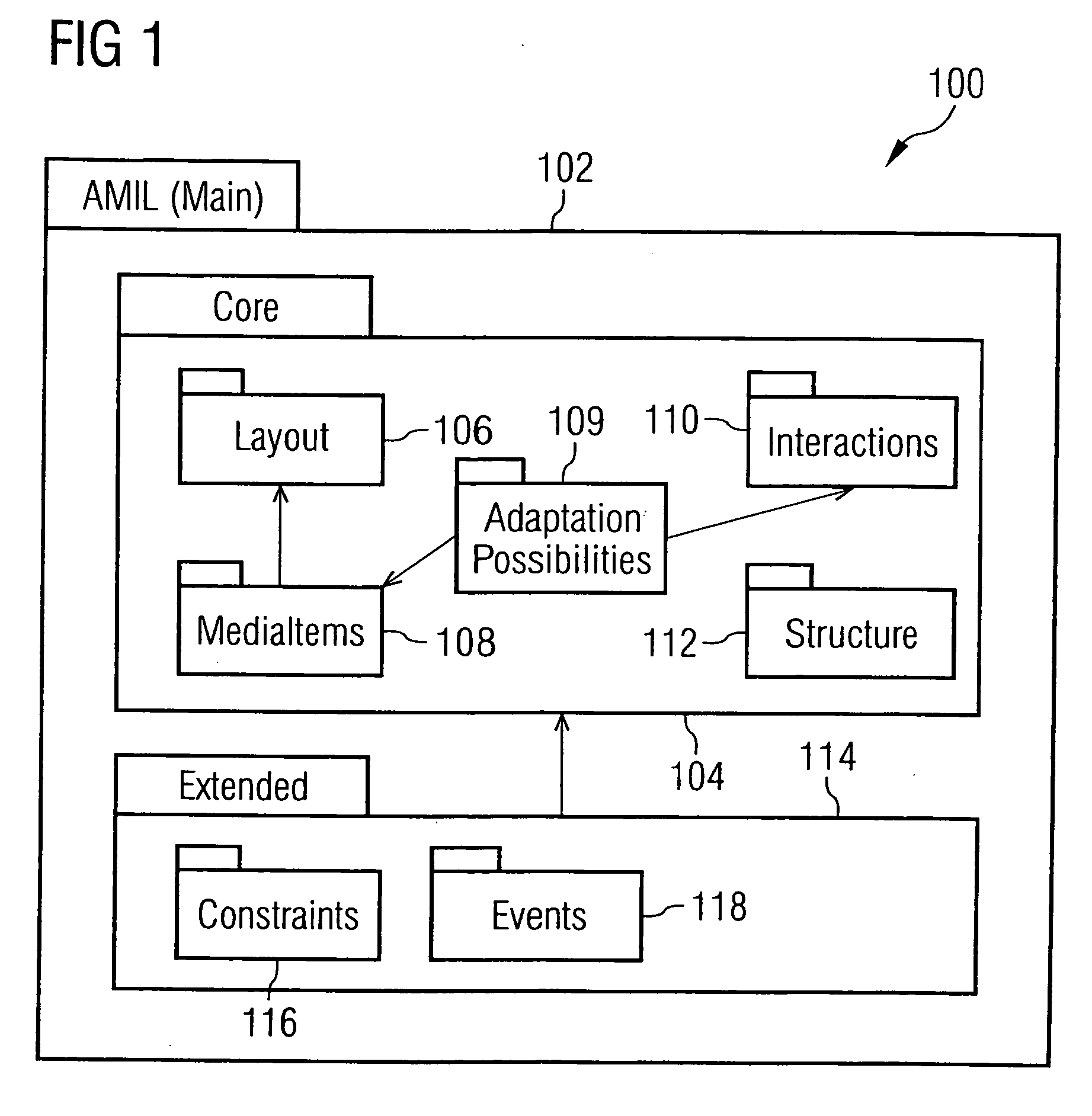
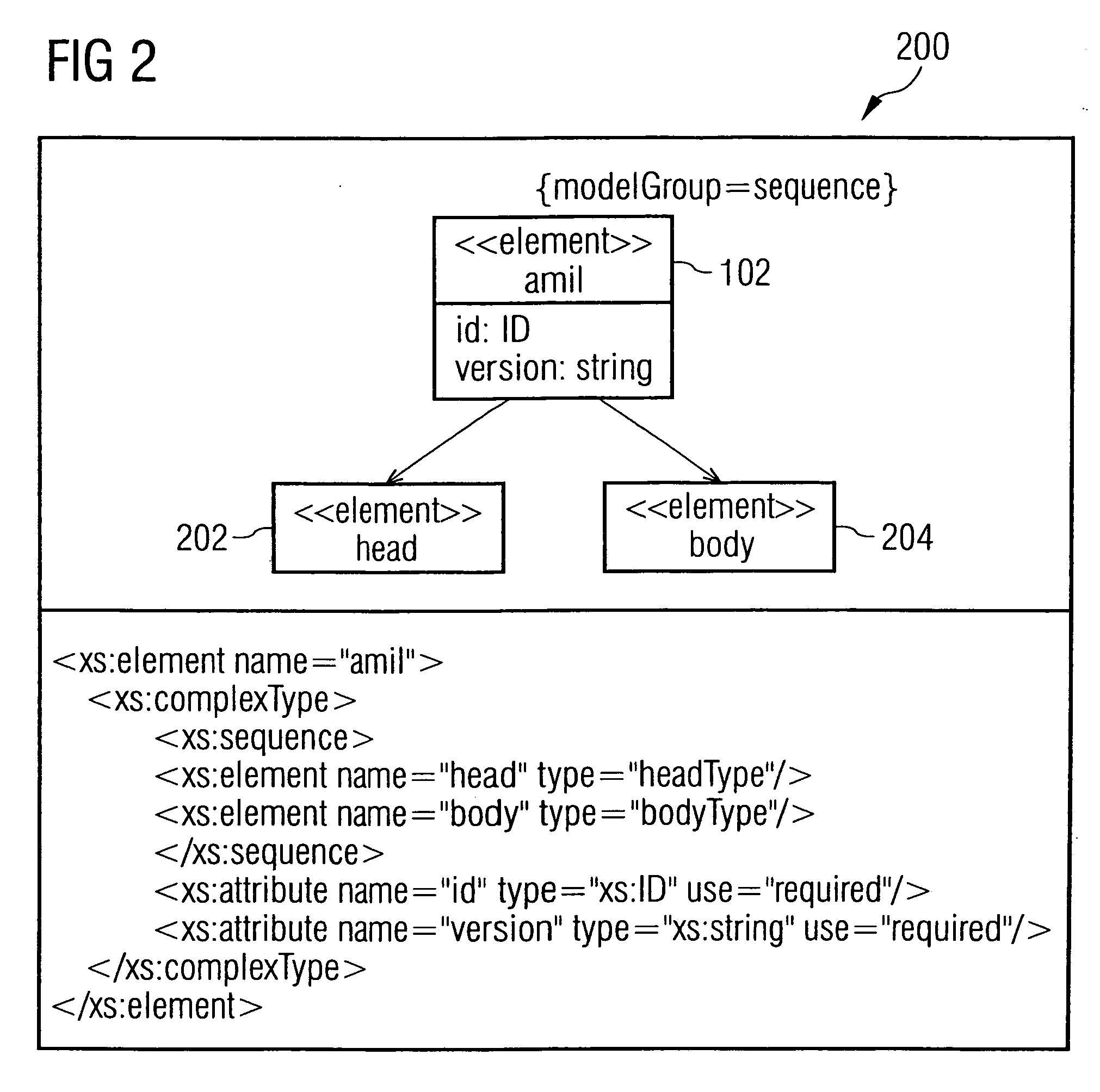
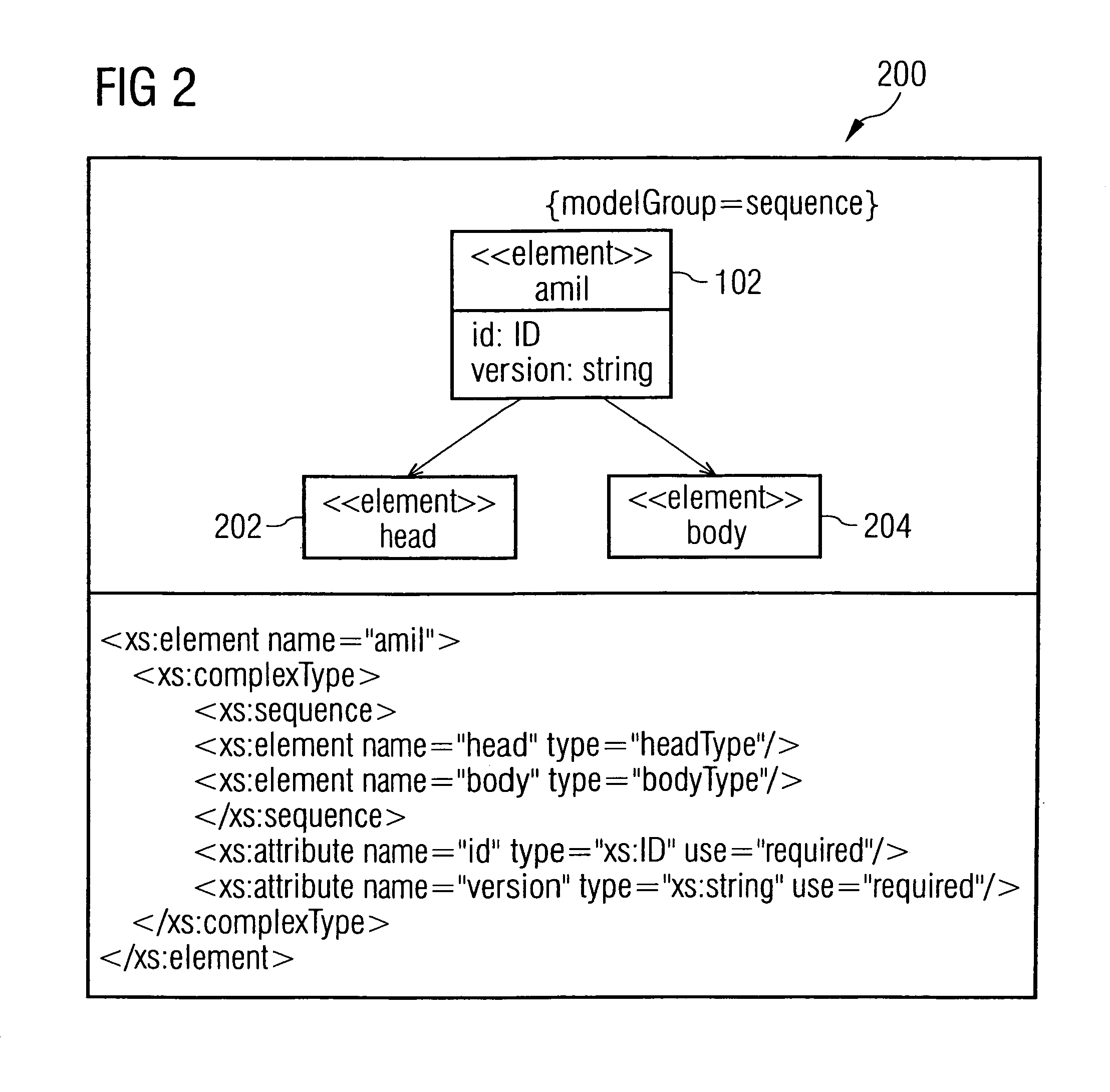
Adaptive multimedia integration language (amil) for adaptive multimedia applications and presentations
InactiveUS20060031749A1Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsPersonalizationDocument model
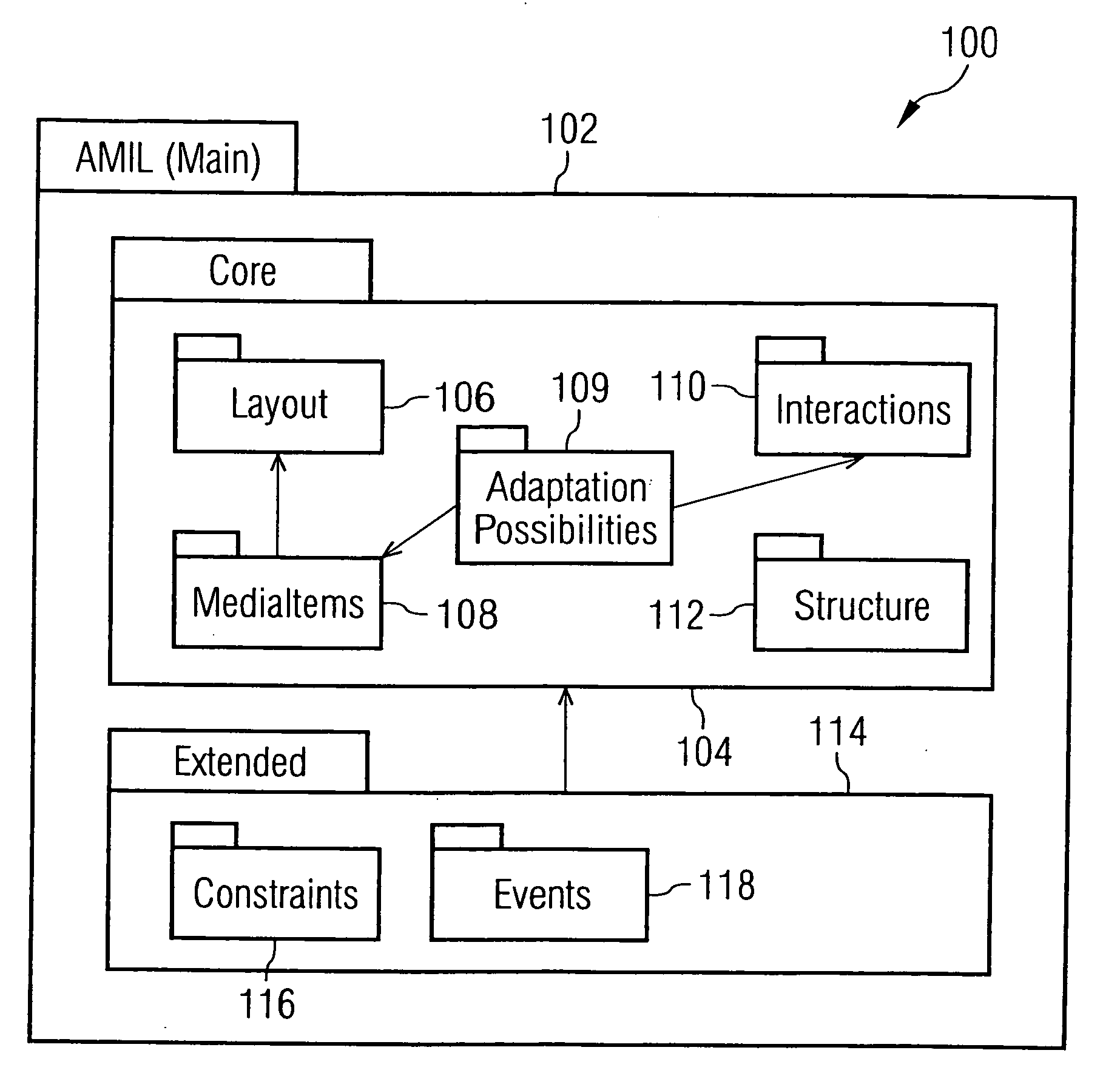
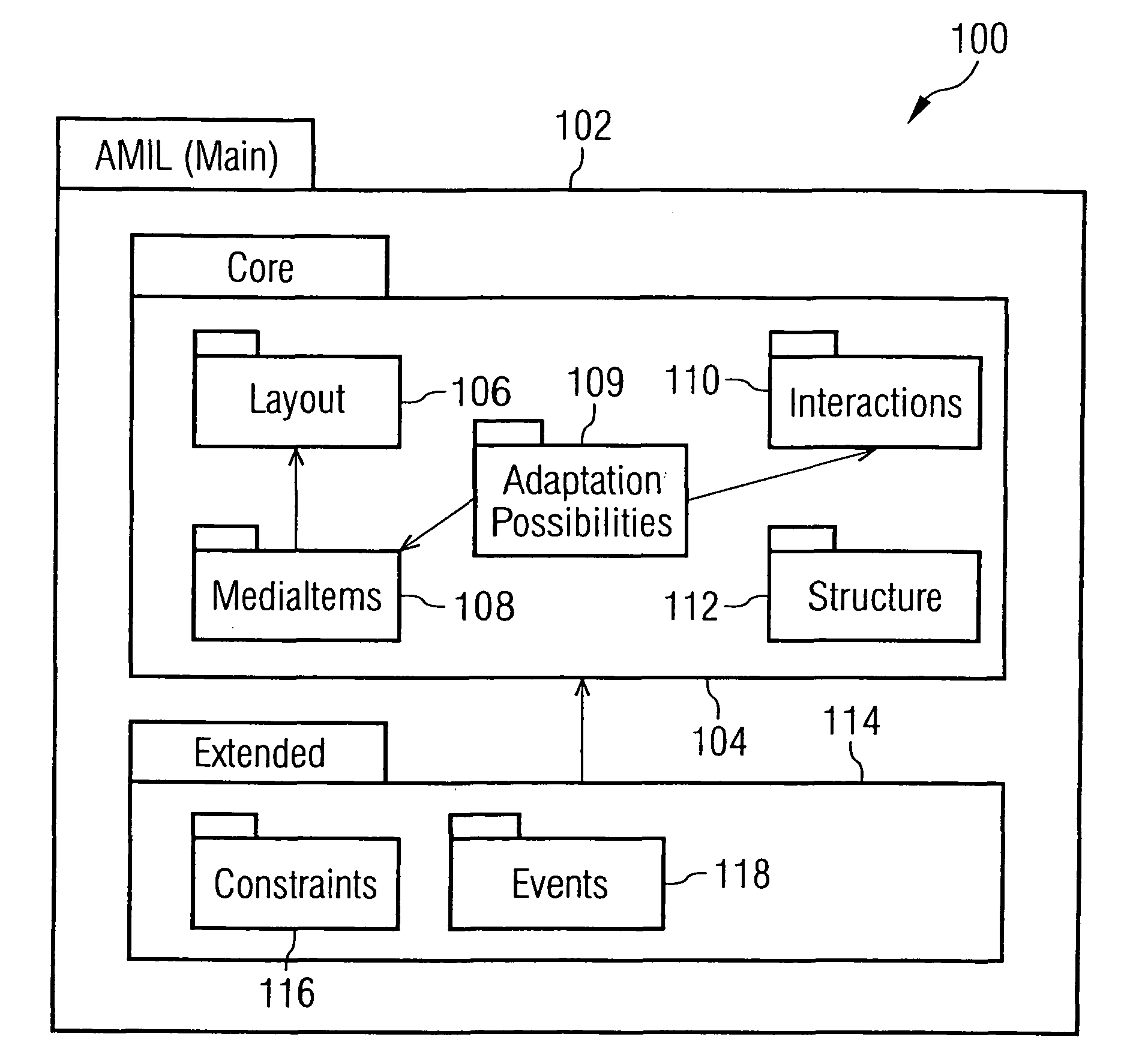
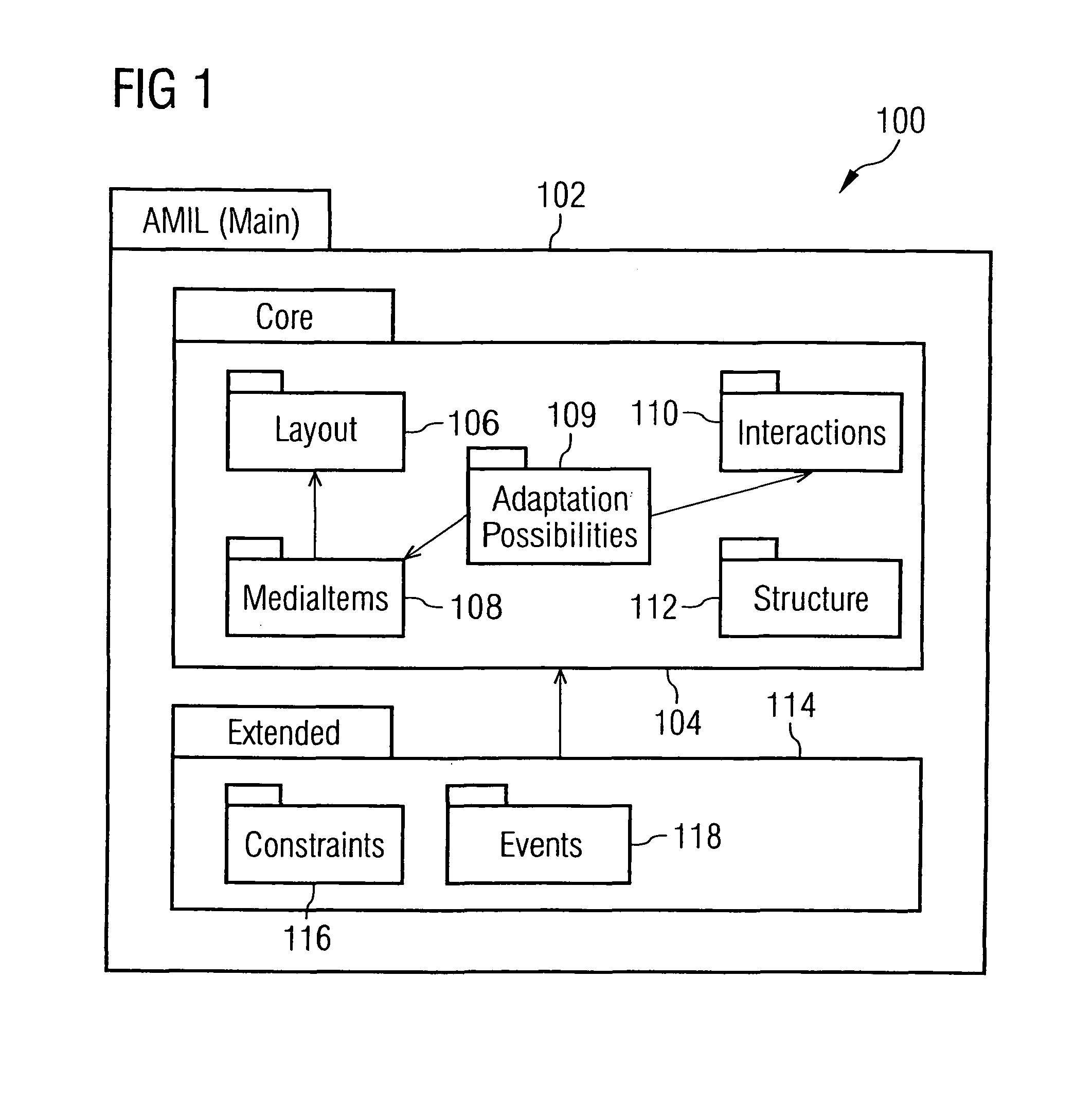
The invention generally relates to the field of markup languages used to describe adaptive mobile multimedia applications and / or presentations being inherently dependent on the dynamic mobile environment they are running in, which means that these mobile multimedia applications and / or presentations need to be adapted to the preferences of mobile users, the capabilities of their mobile computing devices, and their current situation. It allows adaptive mobile stream-based multimedia applications with real-time requirements in a typical wireless scenario (e.g. a radio link with a changing transmission quality and hand-over procedures) to adaptively and responsively react to a time-varying network topology and different radio link characteristics. Thereby, the underlying invention especially includes research and development issues in the field of describing adaptation possibilities (1500), adaptation constraints (802) and adaptation events (3802) directed to a personalization and context-aware adaptation of document-based multimedia applications by providing methods for pre-allocating, reserving, monitoring and adapting QoS-related parameters in a dynamic mobile environment using an XML-based multimedia presentation language. In this connection, a document model (100) consisting of vocabulary, document structure and linking means (1600) between the document model elements is presented which supports the description (700) of adaptive mobile multimedia applications and / or presentations. Besides, a document object model supporting a simplified transaction-oriented access is proposed.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
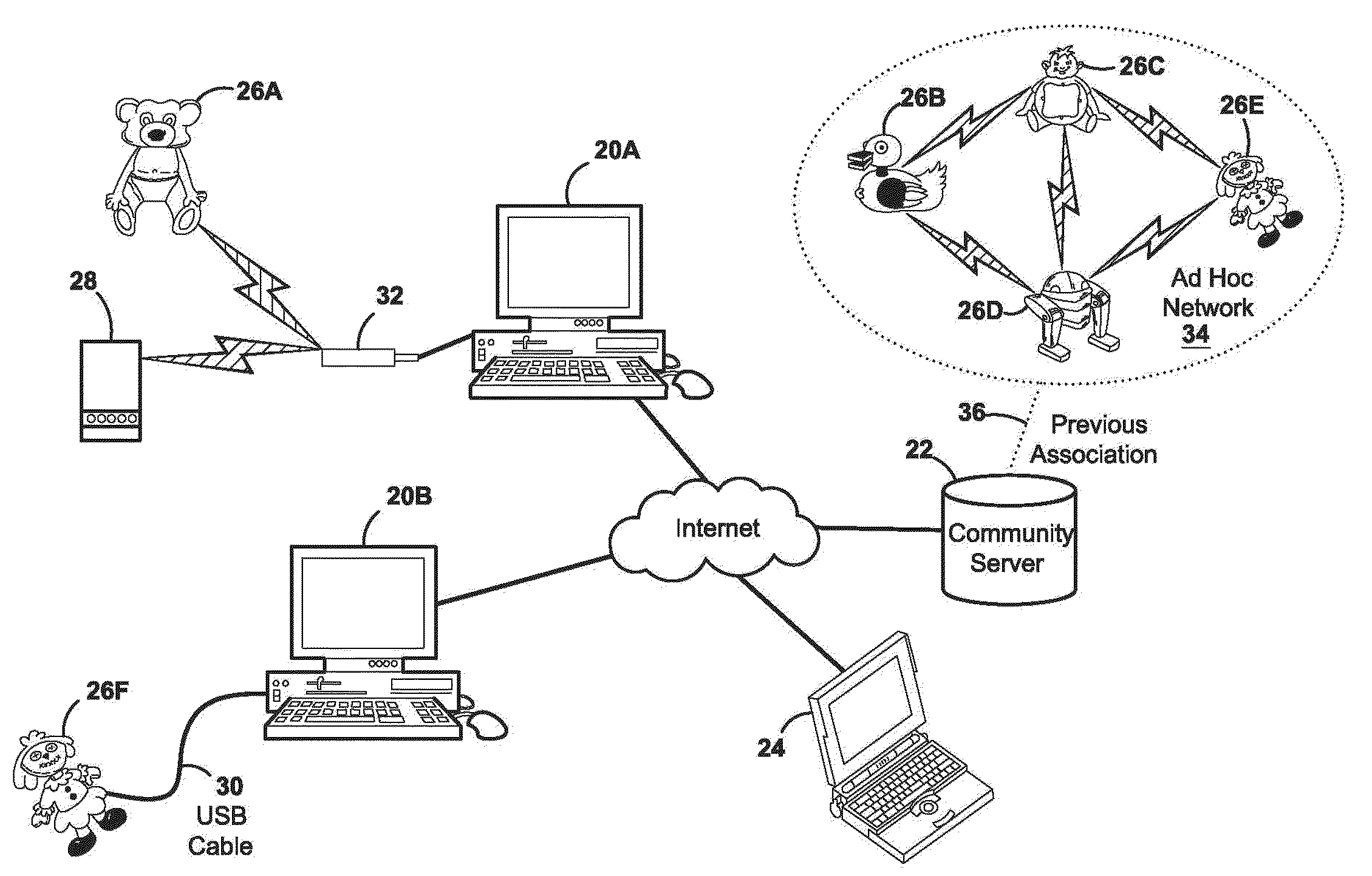
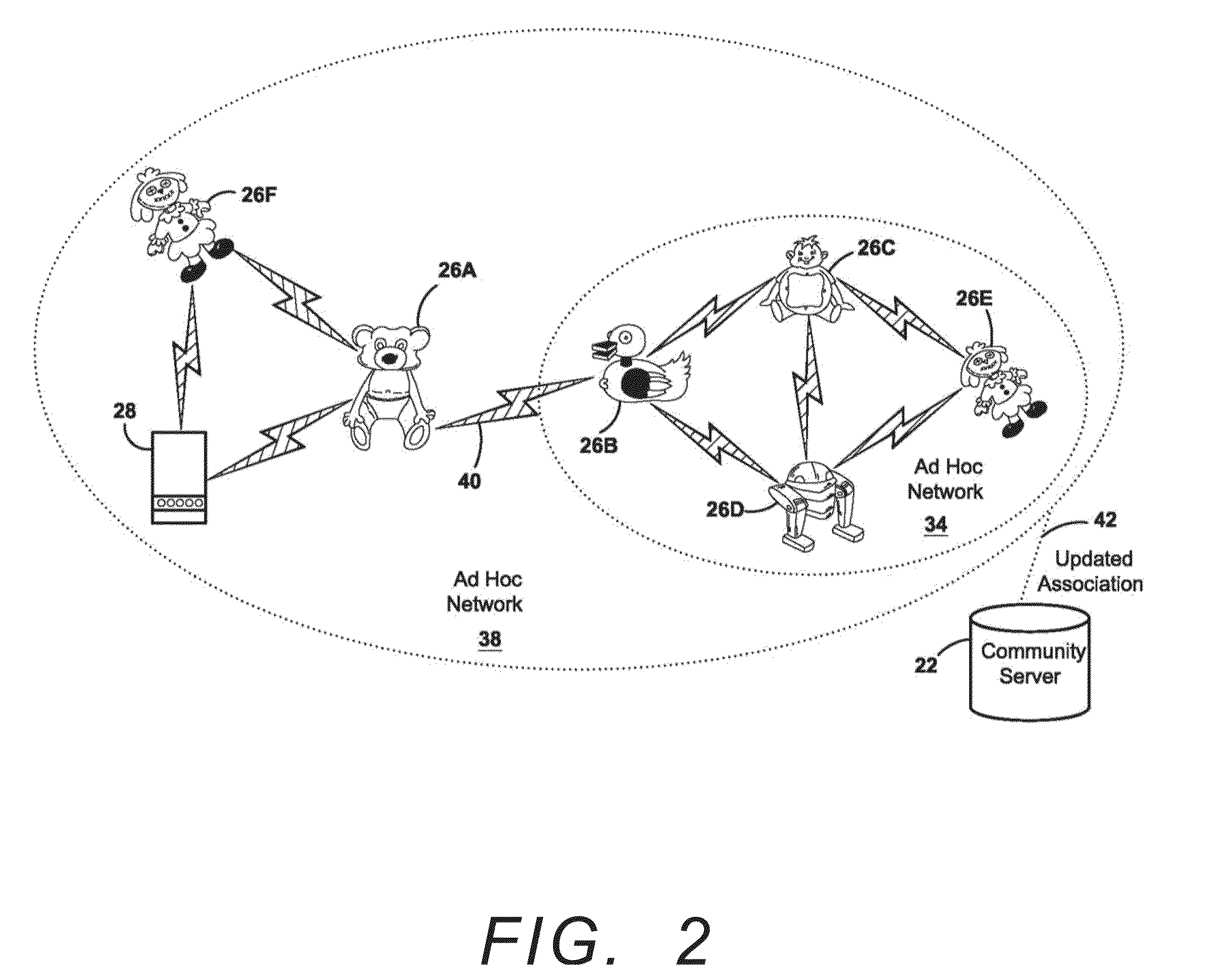
Temporal network server connected devices with off-line ad hoc update and interaction capability
InactiveUS20100172287A1Network topologiesWireless commuication servicesContext specificNetwork service
A system and method for using mobile network devices that are periodically connected to a network server are disclosed. The devices exchange data in an ad hoc manner when not connected to the server. In the preferred embodiment, independent mobile wireless network devices are connected to a network server through a client computing device acting as a gateway to the server. The presence of the mobile network device and the client computing device cause both devices to become users. The server pairs both the network device and the client computing device with a unique identity contained on the network device. Paired and independent identities that have presence on the server then interact with each other in such a manner that data on the connected mobile network devices is changed and stored in concordance with this community interaction. Unconnected mobile network devices search for other unconnected mobile network devices within range to form an ad hoc network. This allows the mobile network devices to exchange and store data related to their last community server interaction. This data is context specific in terms of the specific services used by the by the users that had presence on the community server. User interaction directly with mobile network devices can change this information locally even when not connected to a client computer. This information will also be exchanged and affect data stored on mobile devices that are part of an independent ad hoc network according to the context of the previous server data stored on the mobile devices.
Owner:KRIETER MARCUS
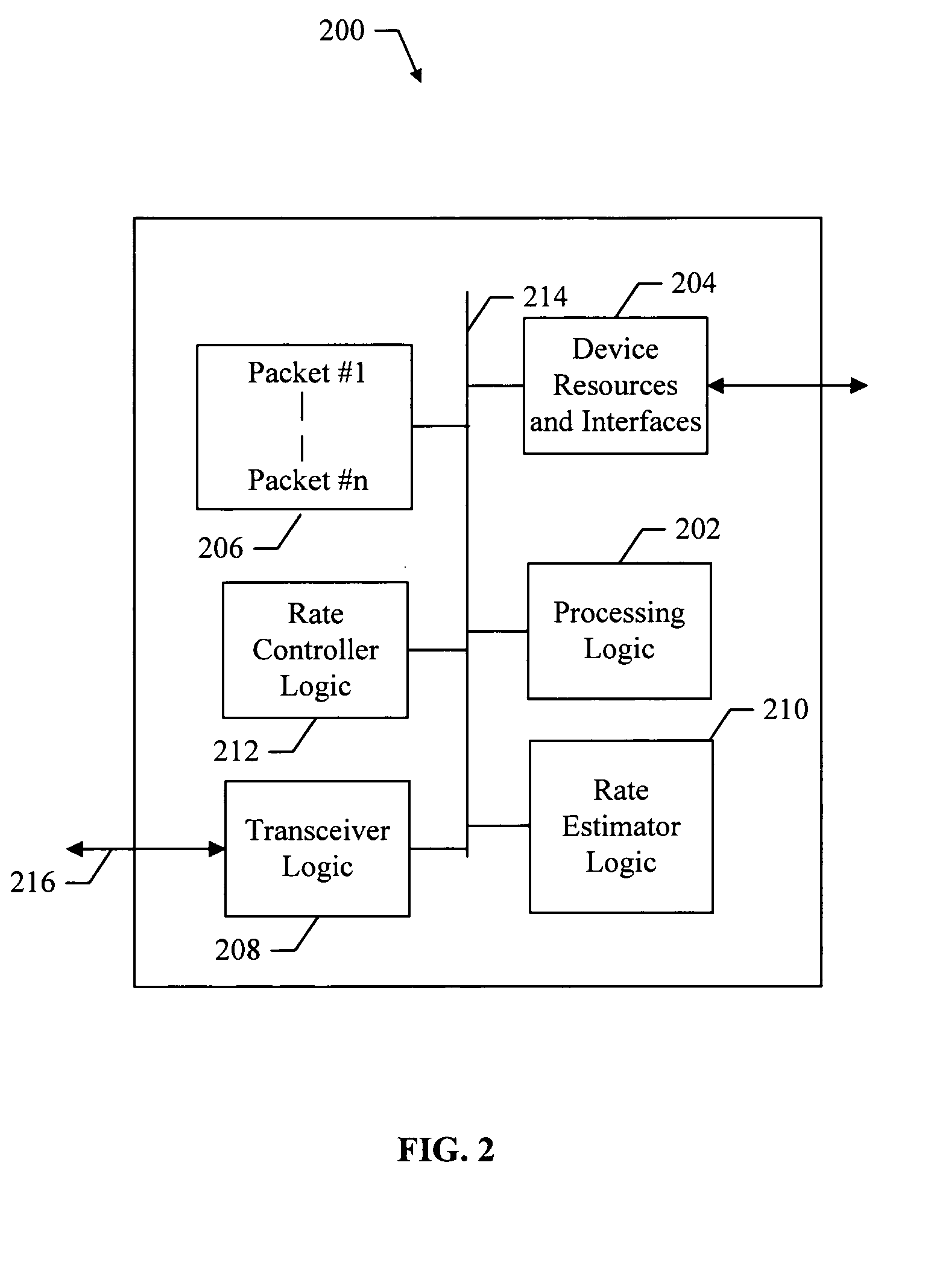
Method and apparatus for prioritized information delivery with network coding over time-varying network topologies
ActiveUS8861356B2Special service provision for substationError preventionTraffic capacityTopological graph
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
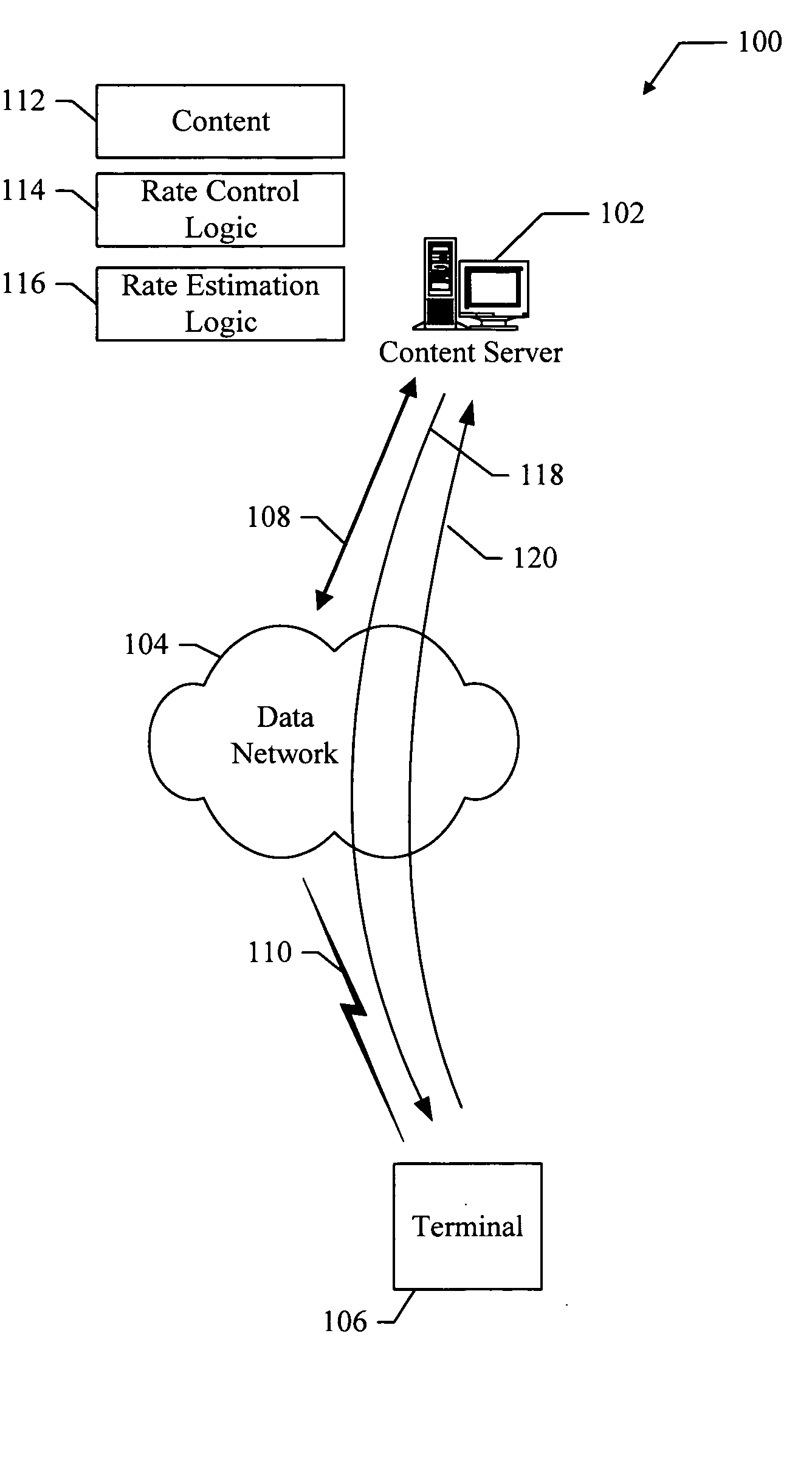
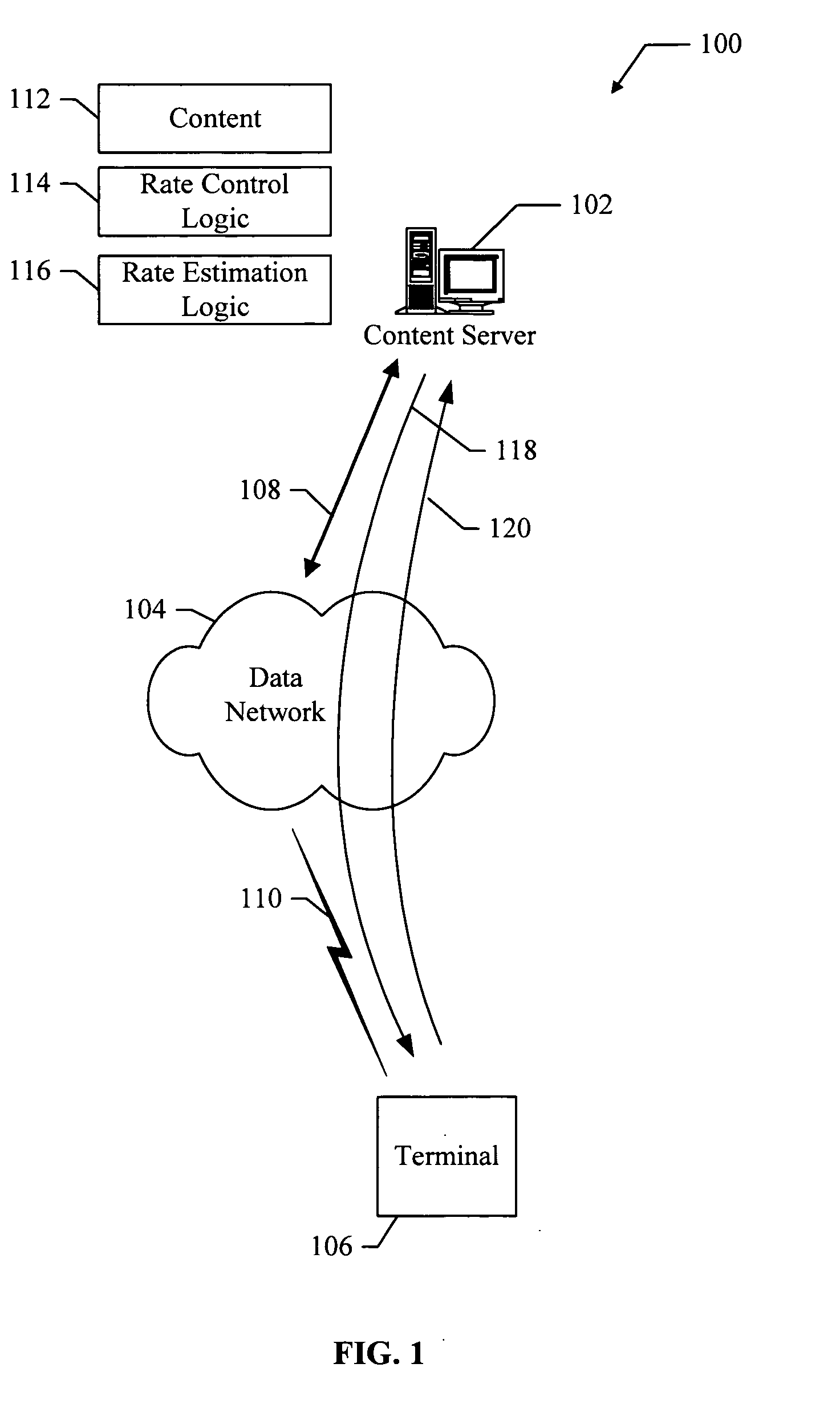
Methods and apparatus for optimum file transfers in a time-varying network environment
InactiveUS20060026296A1Efficient deliveryNetwork usageSpecial service provision for substationEnergy efficient ICTWeb environmentFile transfer
Methods and apparatus for optimum file transfers in a time-varying network environment. A method is provided for transmitting content in a data network. The method includes transmitting content at a selected transmission rate, and receiving one or more acknowledgement signals. The method also includes estimating a network delivery rate from the one or more acknowledgment signals, and adjusting the selected transmission rate of the content based on the network delivery rate.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adaptive network system with online learning and autonomous cross-layer optimization for delay-sensitive applications
InactiveUS20110019693A1Sub-optimal performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexReliable transmissionNetworked system
A network system providing highly reliable transmission quality for delay-sensitive applications with online learning and cross-layer optimization is disclosed. Each protocol layer is deployed to select its own optimization strategies, and cooperates with other layers to maximize the overall utility. This framework adheres to defined layered network architecture, allows layers to determine their own protocol parameters, and exchange only limited information with other layers. The network system considers heterogeneous and dynamically changing characteristics of delay-sensitive applications and the underlying time-varying network conditions, to perform cross-layer optimization. Data units (DUs), both independently decodable DUs and interdependent DUs, are considered. The optimization considers how the cross-layer strategies selected for one DU will impact its neighboring DUs and the DUs that depend on it. While attributes of future DU and network conditions may be unknown in real-time applications, the impact of current cross-layer actions on future DUs can be characterized by a state-value function in the Markov decision process (MDP) framework. Based on the dynamic programming solution to the MDP, the network system utilizes a low-complexity cross-layer optimization algorithm using online learning for each DU transmission.
Owner:SANYO NORTH AMERICA CORP +1
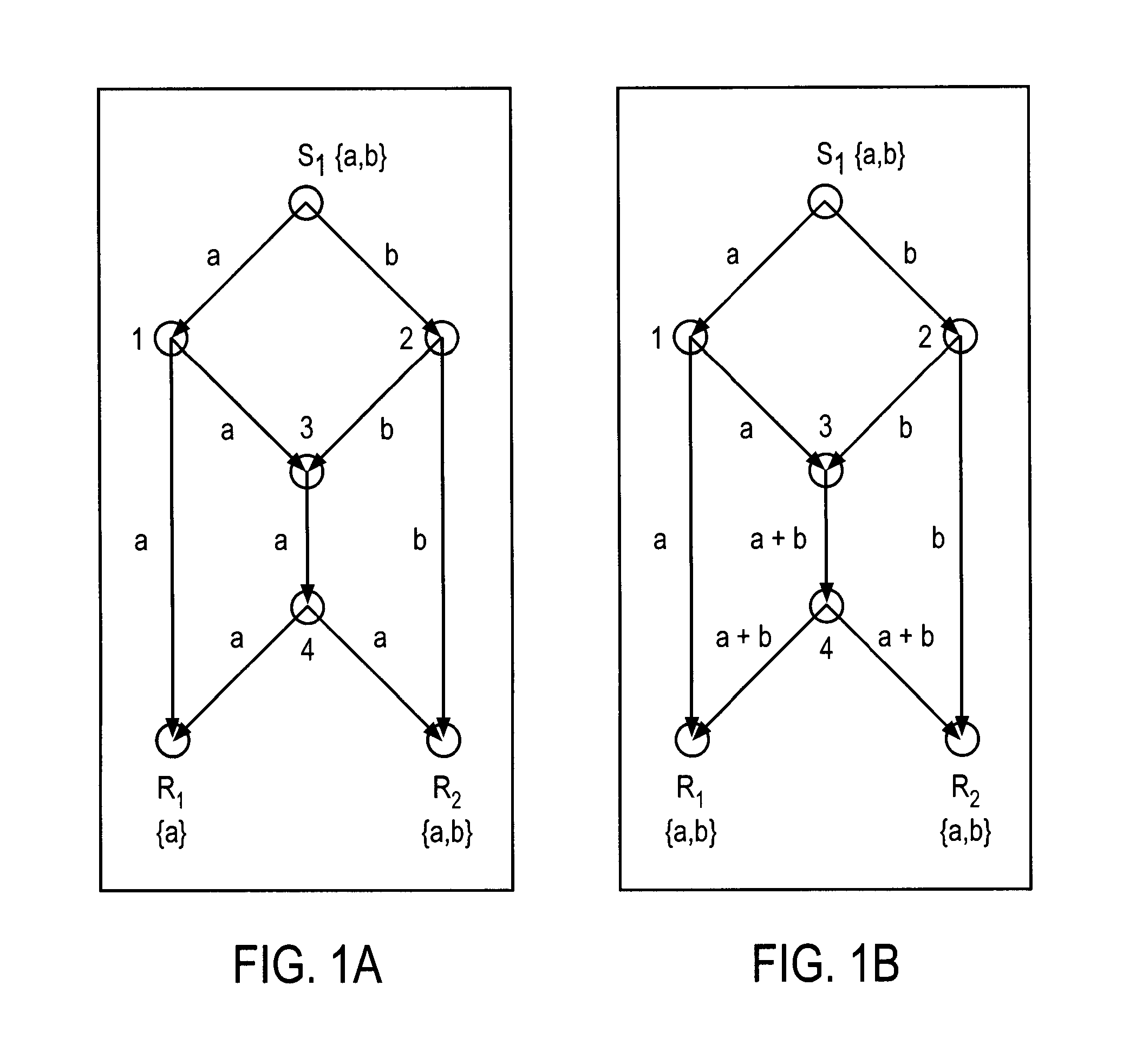
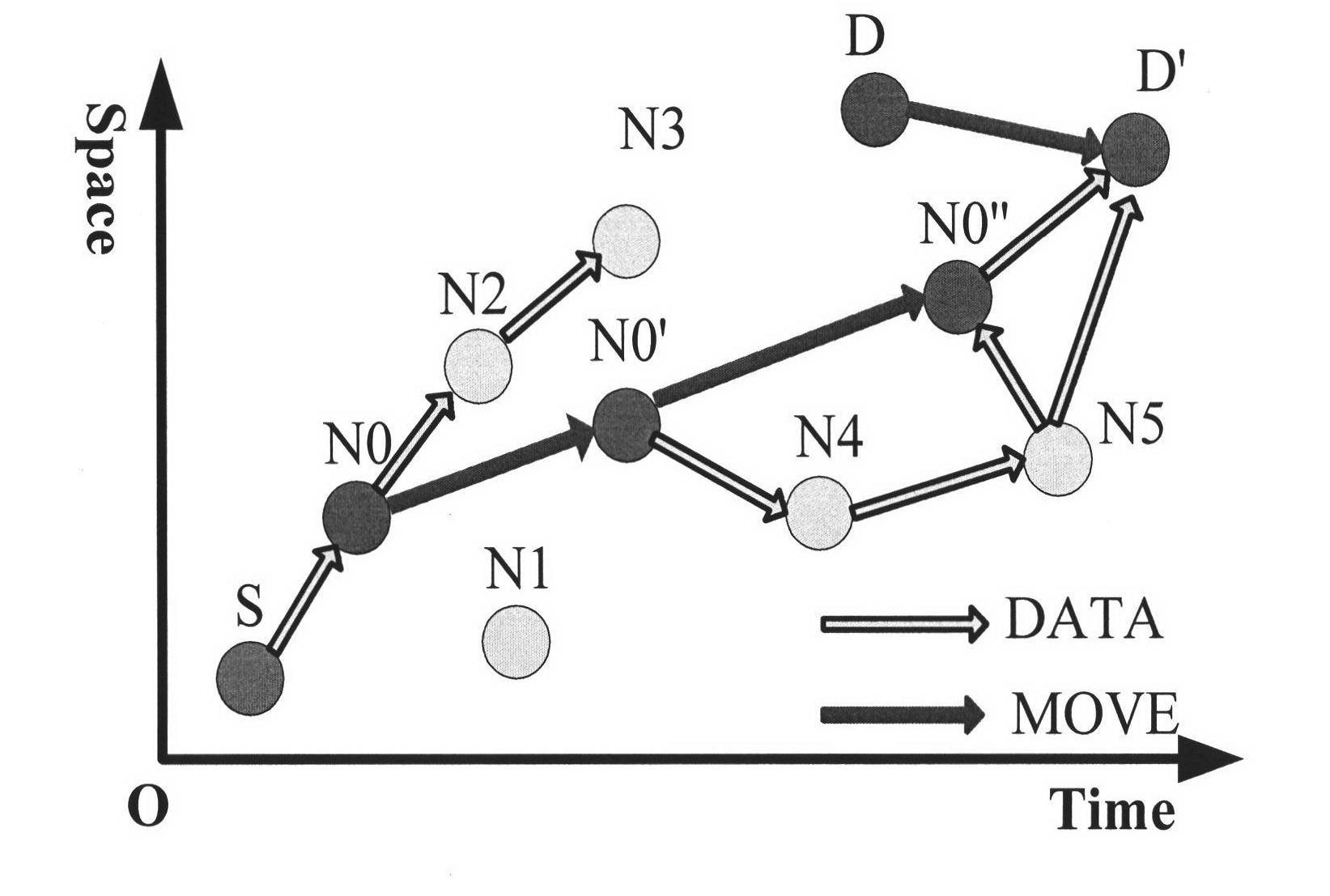
Information delivery over time-varying network topologies
InactiveUS20080089333A1Data switching by path configurationForward error control useVirtual network topologyNetwork code
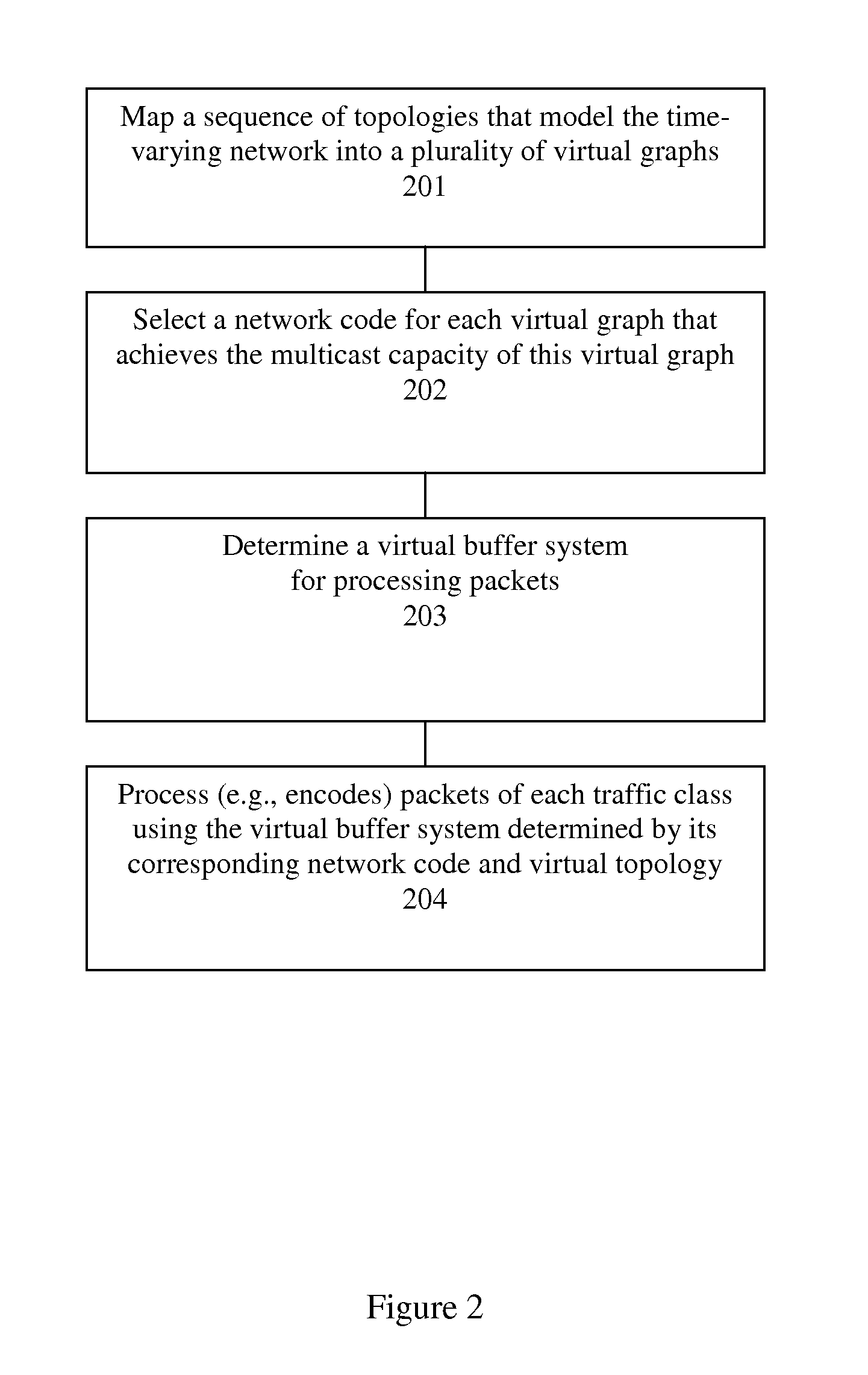
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for delivering information over time-varying networks. In one embodiment, the method comprises, for each of a plurality of time intervals, determining a virtual network topology for use over each time interval; selecting for the time interval based on the virtual network topology, a fixed network code for use during the time interval; and coding information to be transmitted over the time-varying network topology using the fixed network code with necessary virtual buffering at each node.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
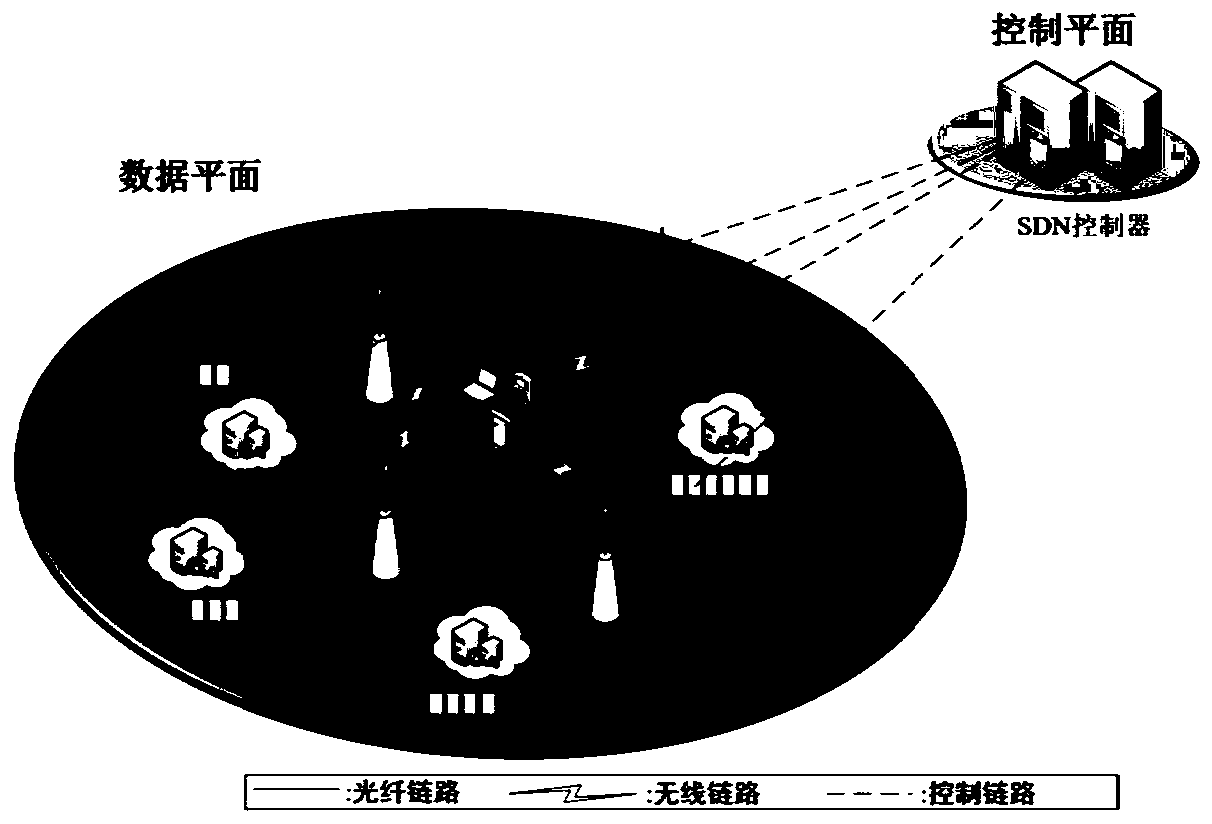
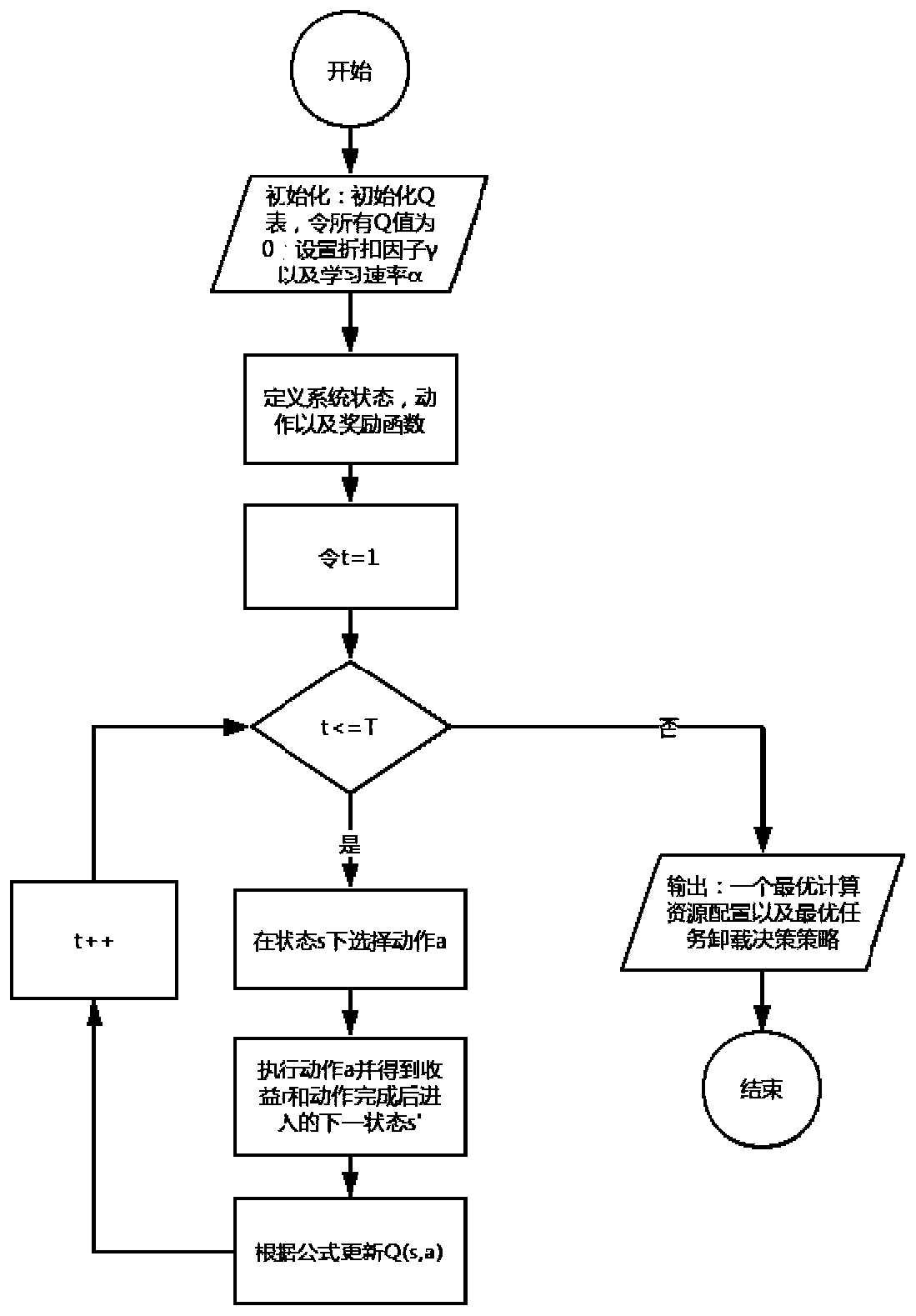
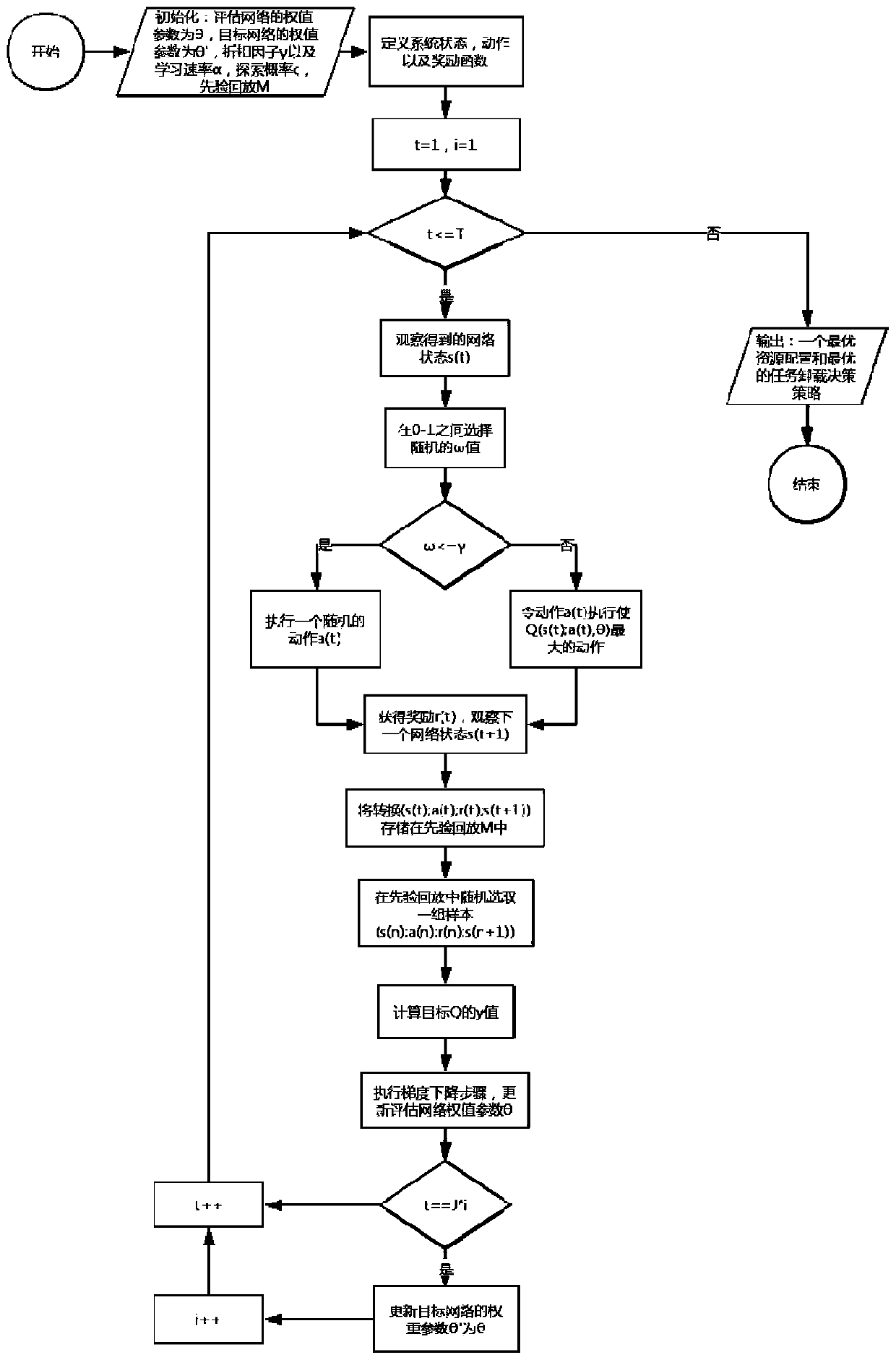
Computing resource allocation and task unloading method for edge computing of super-dense network
InactiveCN110798849AIncrease study timeFast convergenceWireless communicationMacro base stationsIndustrial engineering
A computing resource allocation and task unloading method for super-dense network edge computing comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a system model based on a super-dense network edgecomputing network of an SDN, and obtaining network parameters; step 2, obtaining parameters required by edge calculation: unloading the parameters to an edge server of a macro base station and an edgeserver connected with a small base station s through local calculation in sequence to obtain an uplink data rate of a transmission calculation task; step 3, adopting a Q-learning scheme to obtain anoptimal computing resource allocation and task unloading strategy; and step 4, adopting a DQN scheme to obtain an optimal computing resource allocation and task unloading strategy. The method is suitable for a dynamic system by stimulating an intelligent agent to find an optimal solution on the basis of learning variables. In a reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm, Q-Learning has good performancein some time-varying networks. A deep learning technology is combined with Q-learning, a learning scheme based on a deep Q network (DQN) is provided, the benefits of mobile equipment and an operatorare optimized at the same time in a time-varying environment, and compared with a method based on Q-learning, the method is shorter in learning time and faster in convergence. The method realizes simultaneous optimization of benefits of mobile devices (MDs) and operators in a time-varying environment based on the DQN.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
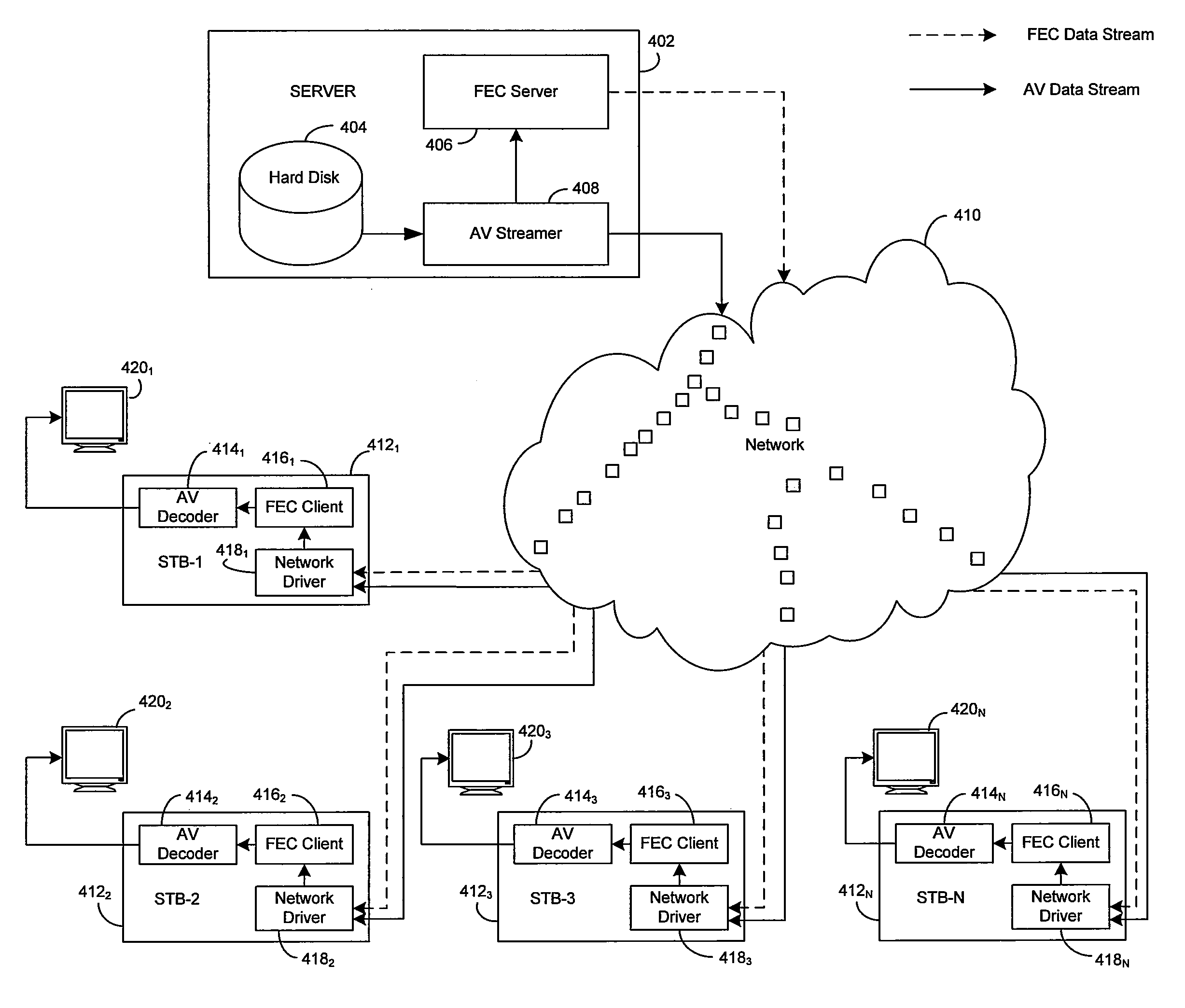
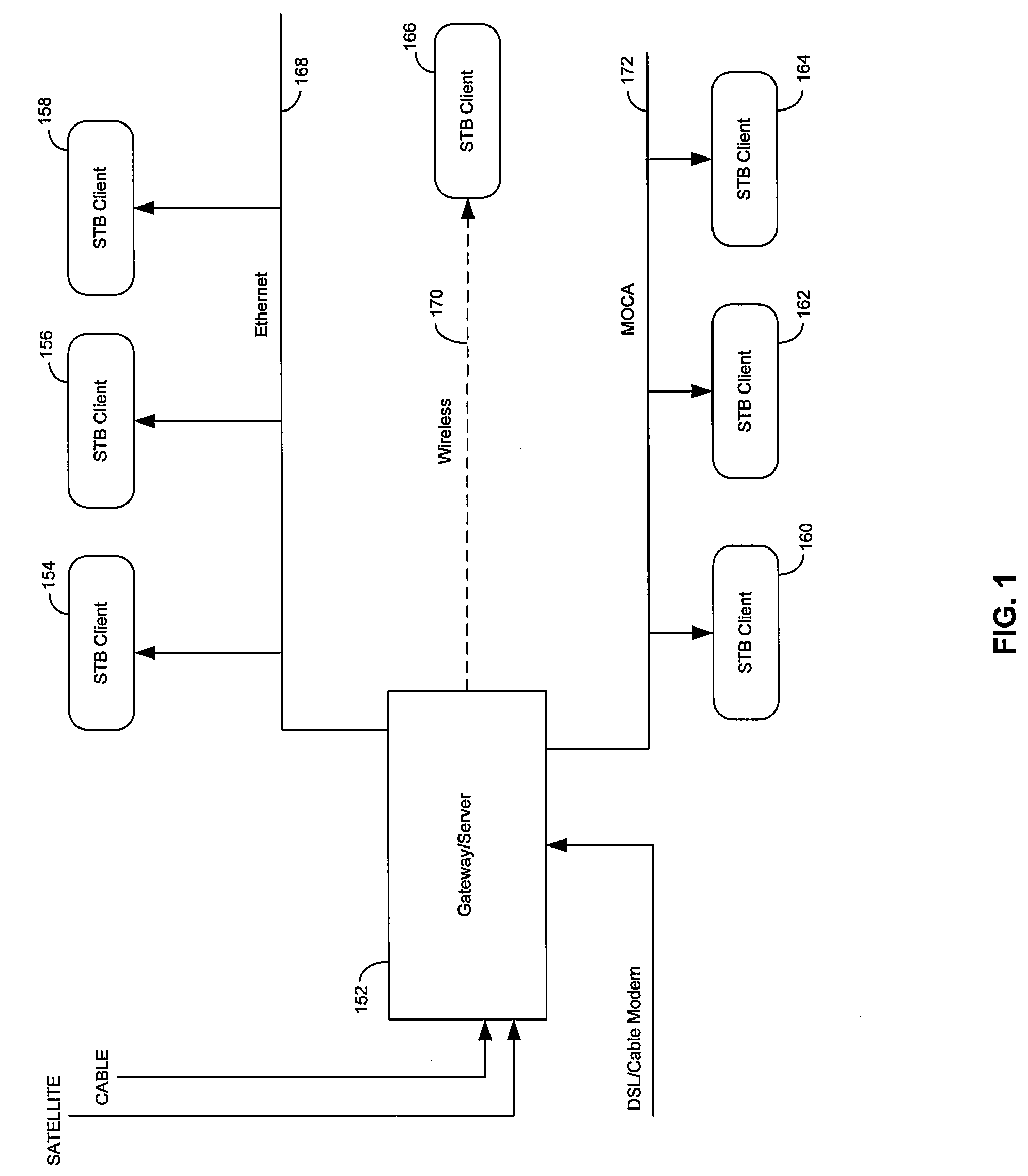
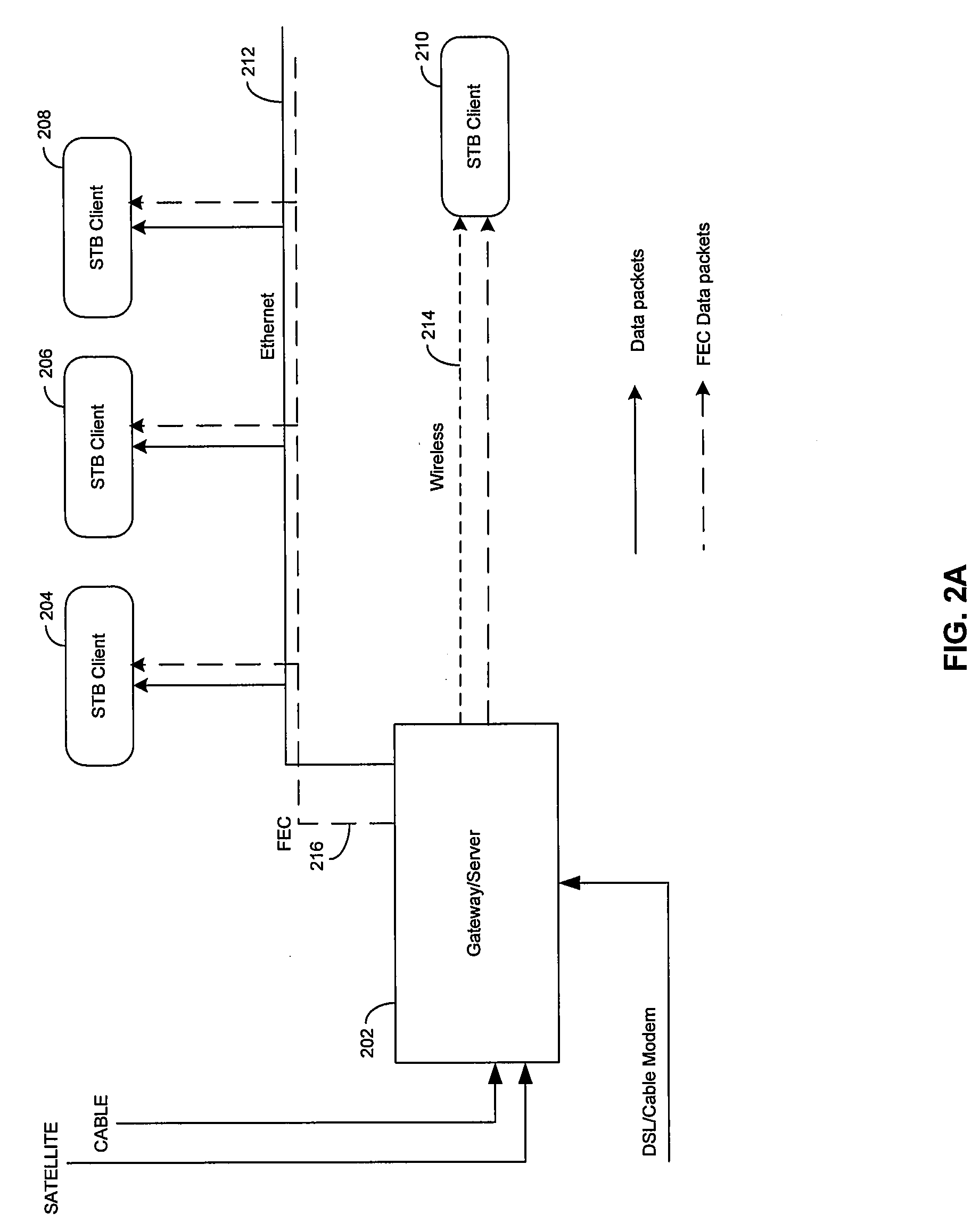
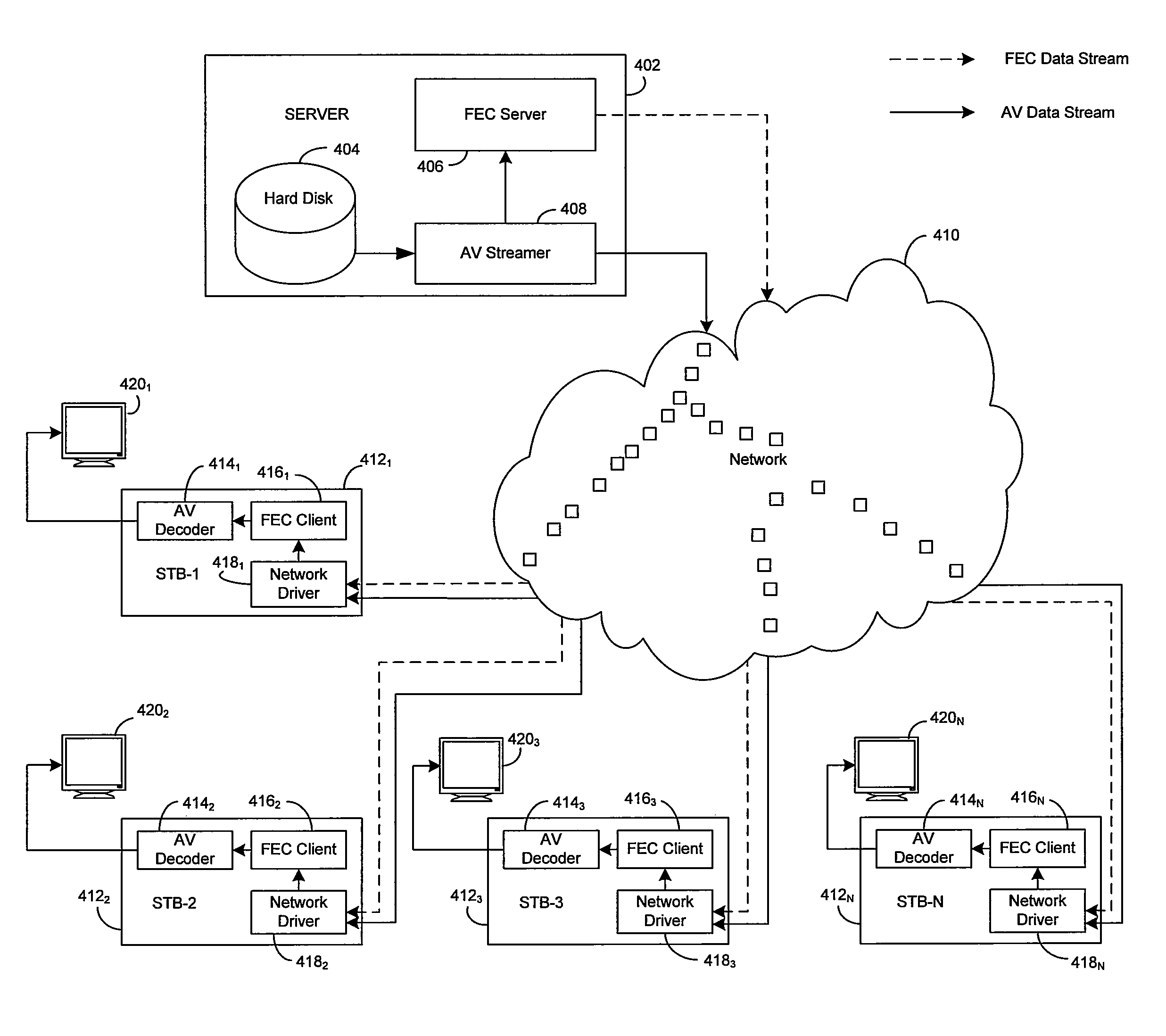
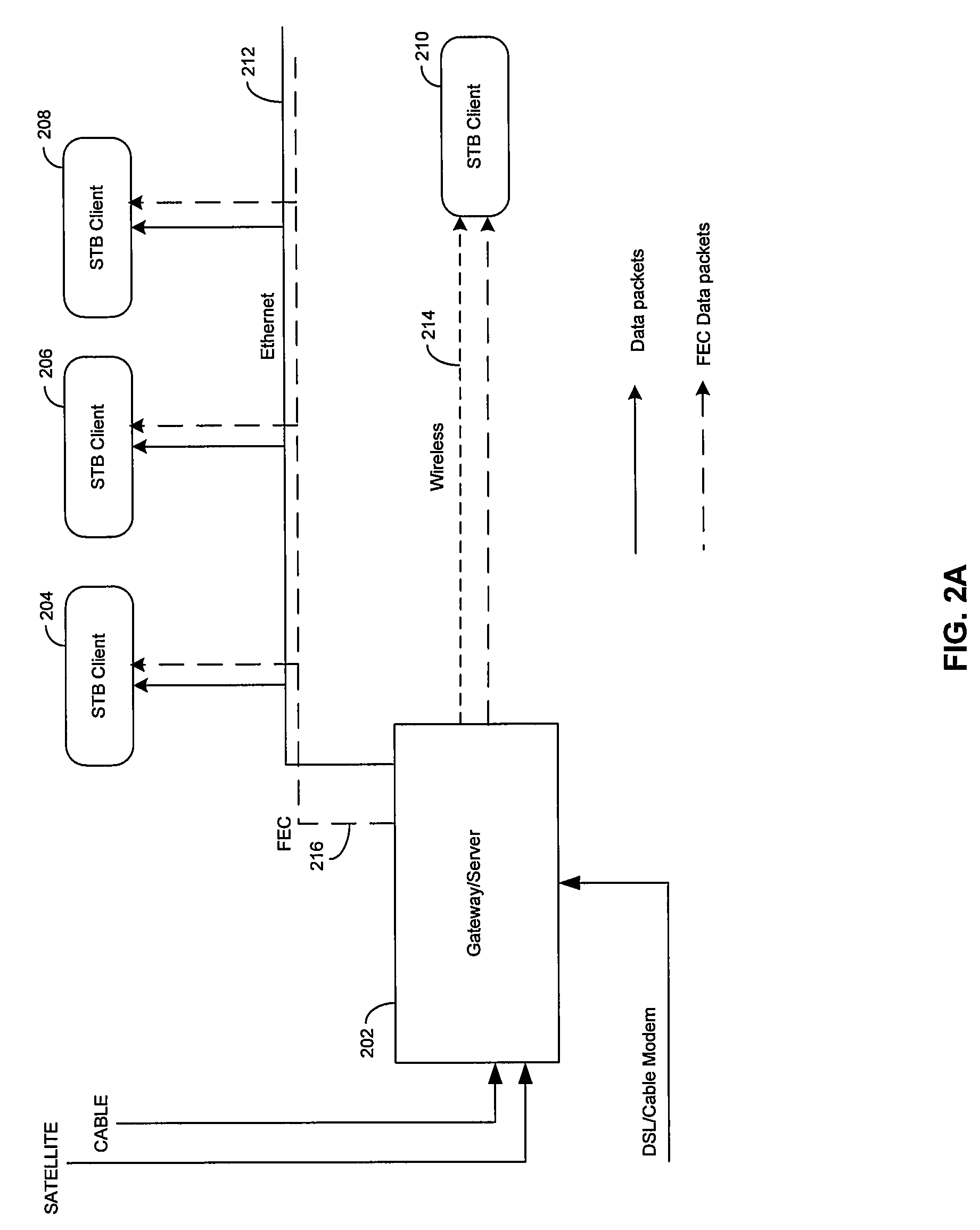
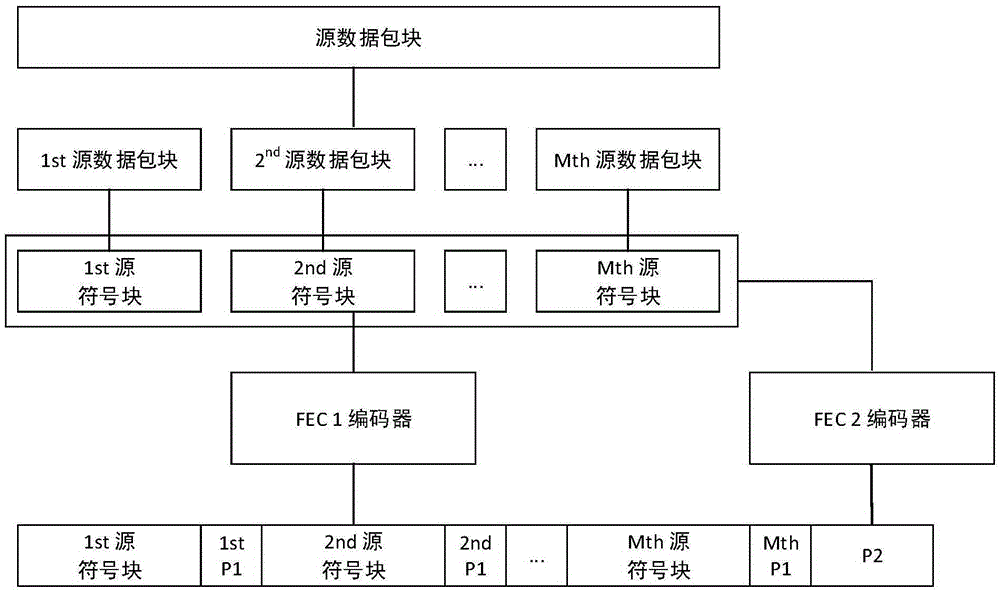
Method and System for Dynamically Adjusting Forward Error Correction (FEC) Rate to Adapt for Time Varying Network Impairments in Video Streaming Applications Over IP Networks
InactiveUS20090092152A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionCommunications systemForward error correction
Certain aspects of a method and system for dynamically adjusting forward error correction (FEC) rate to adapt for time varying network impairments in video streaming applications over IP networks may be disclosed. At a server side of a client-server communication system, a rate of transmission of forward error correction (FEC) packets to one or more clients may be dynamically adjusted based on receiving at least one upstream FEC packet from a plurality of clients. The rate of transmission of the FEC packets to the plurality of clients may be increased when a rate of occurrence of lost data packets is above a particular threshold value. The upstream FEC packets may comprise an urgent packet requesting transmission of a particular FEC packet in order to recover one or more particular lost data packets.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
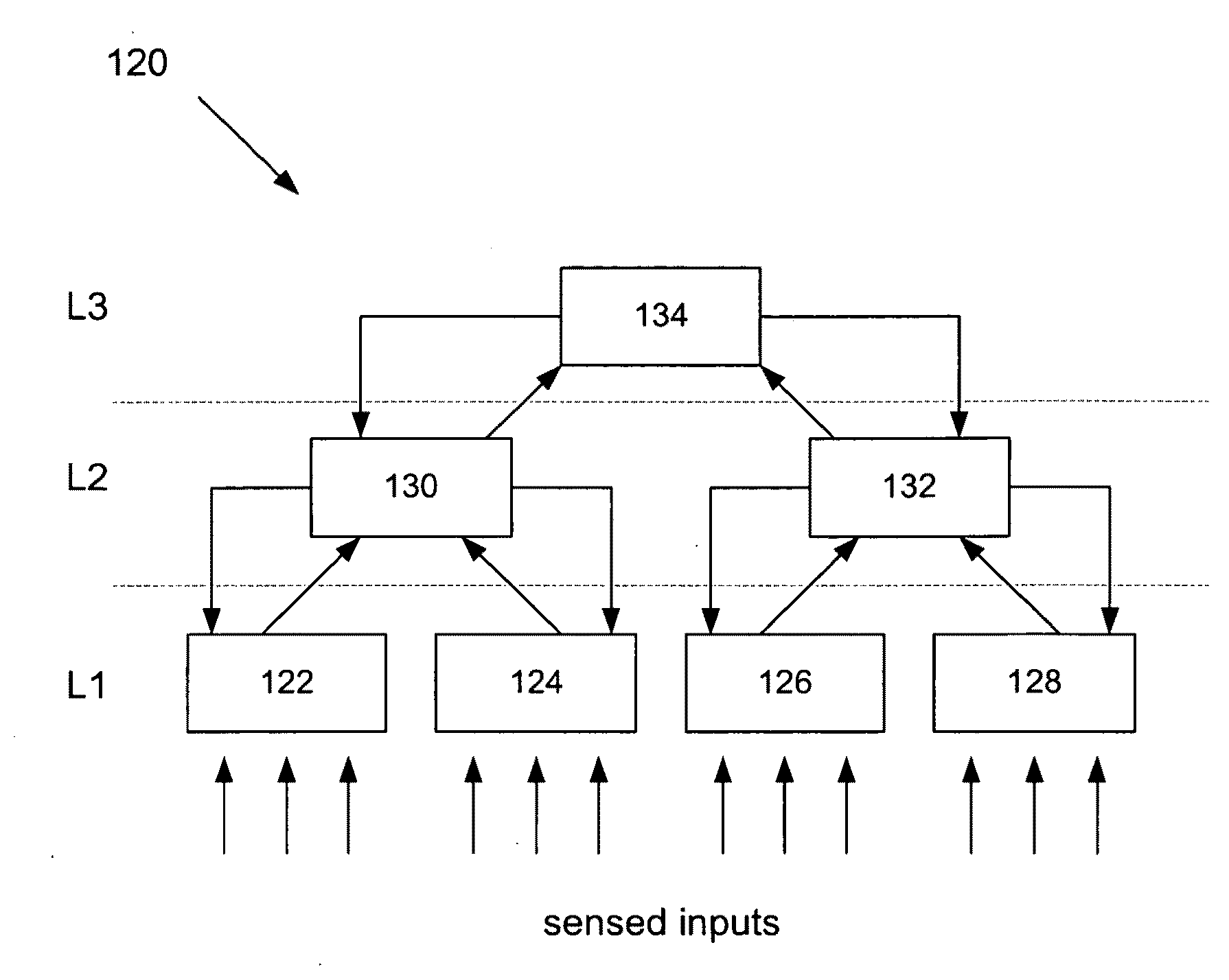
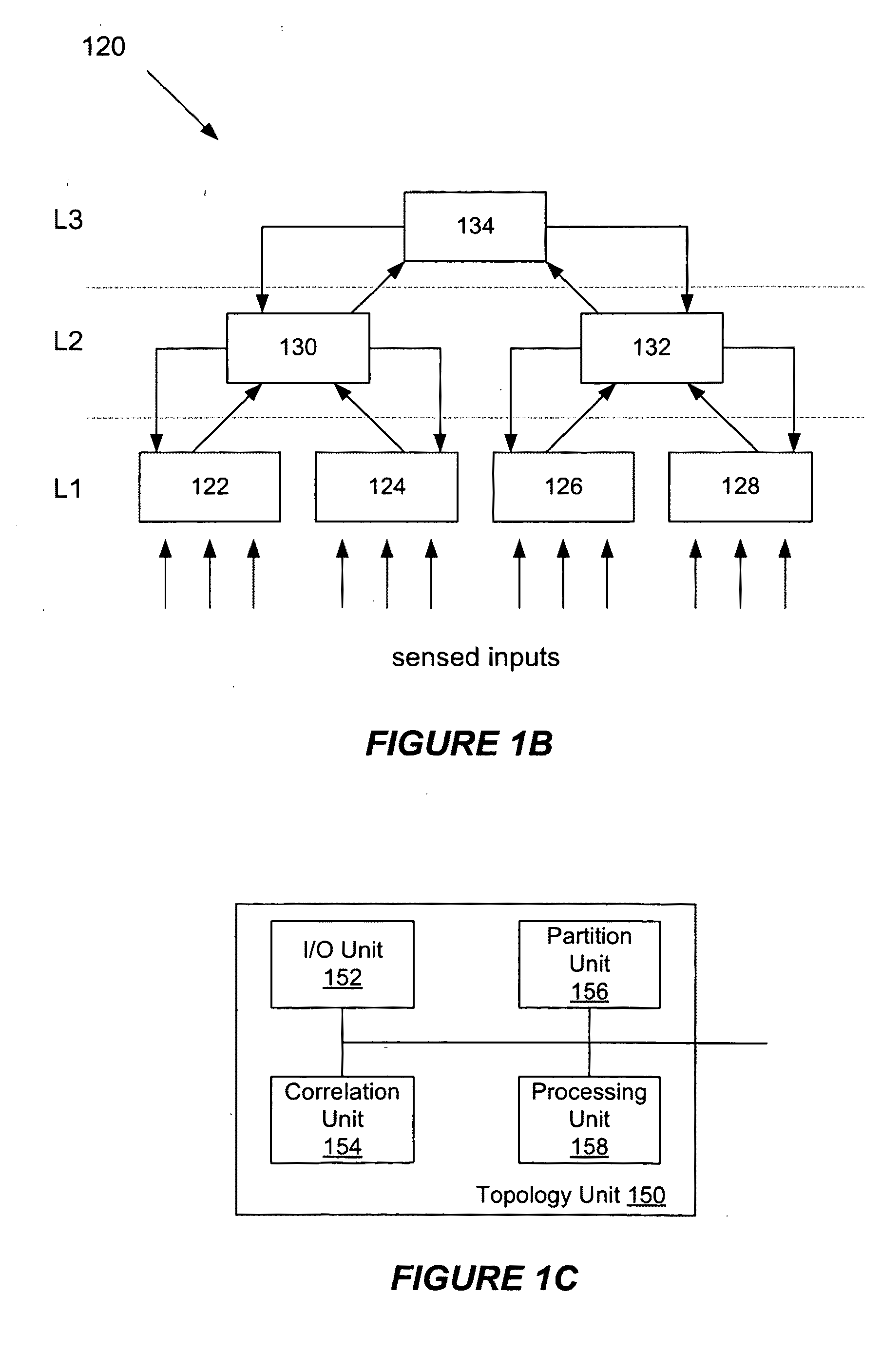
System and method for automatic topology determination in a hierarchical-temporal network
InactiveUS20090116413A1Data switching by path configurationNeural architecturesData streamNetwork topology
A system and method for automatically analyzing data streams in a hierarchical and temporal network to identify node positions and the network topology in order to generate a hierarchical model of the temporal or spatial data. The system and method receives data streams, identifies a correlation between the data streams, partitions / clusters the data streams based upon the identified correlation and forms a current level of a hierarchical temporal network by having each cluster of data streams be an input to a hierarchical temporal network node. After training the nodes, each of the nodes creates a new data stream and these data streams are correlated and partitioned / clustered and are input into a node at a next level. The process can repeat until a desired portion of the network topology is determined.
Owner:NUMENTA INC
Method and apparatus for prioritized information delivery with network coding over time-varying network topologies
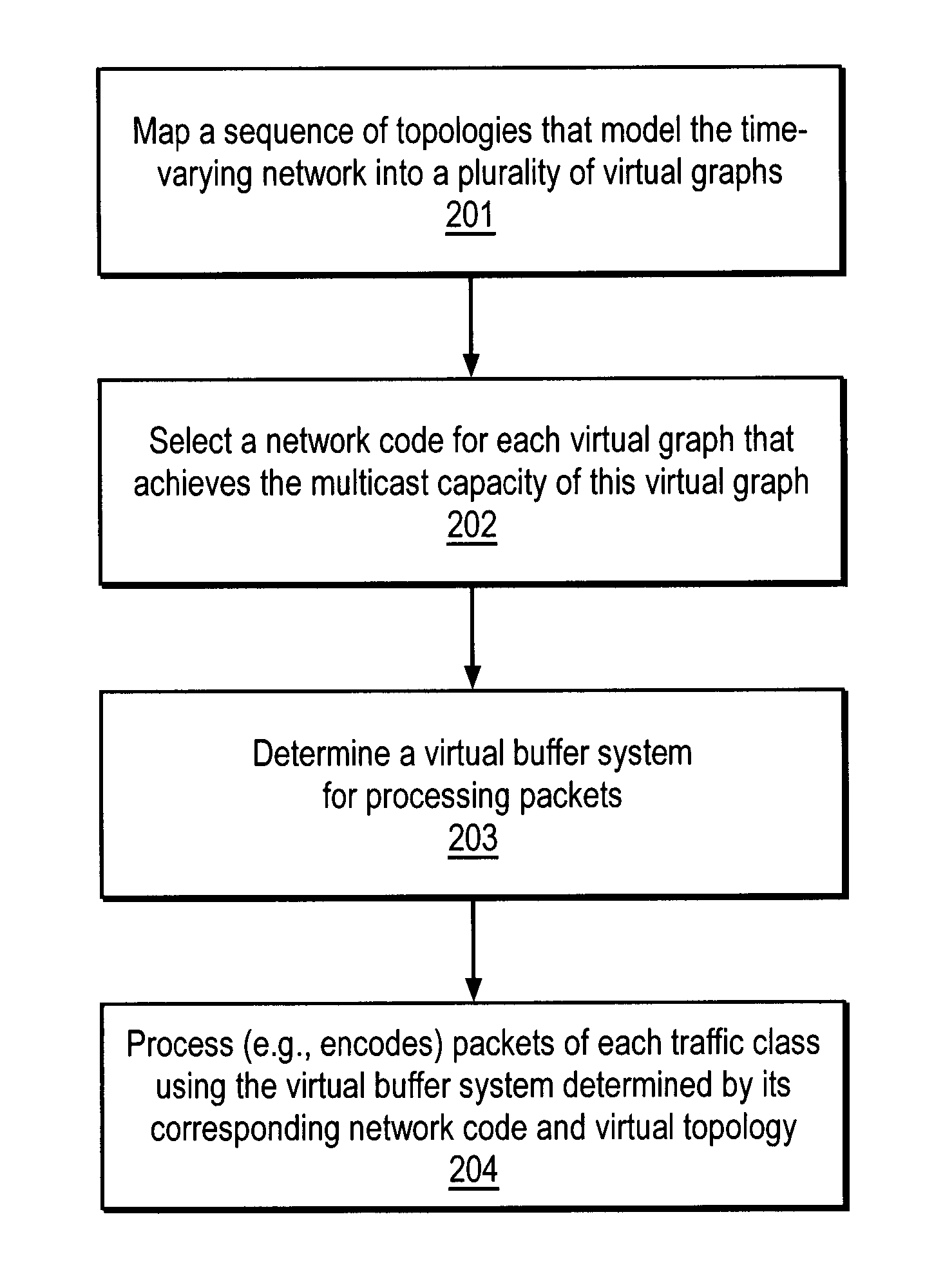
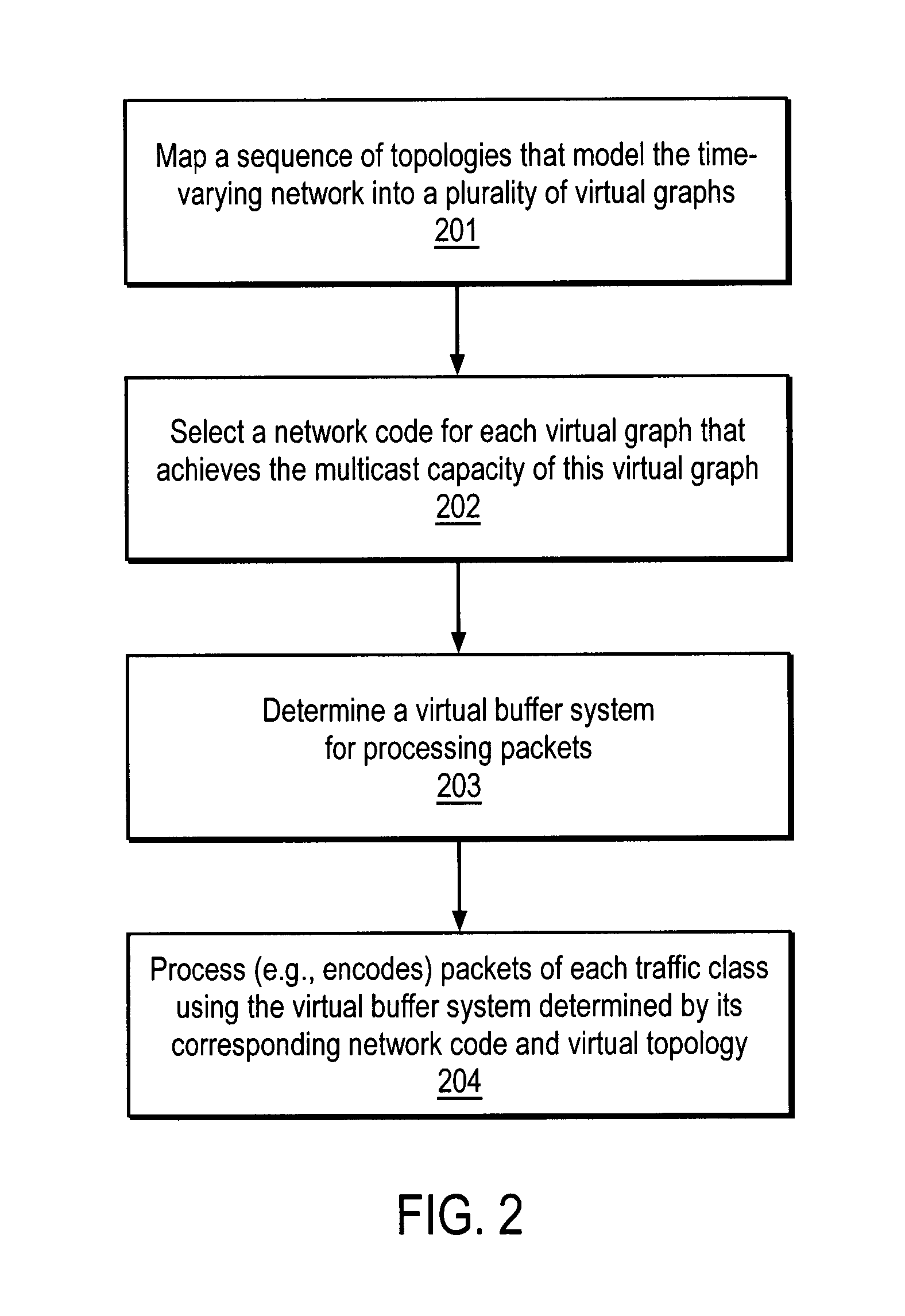
ActiveUS20080225751A1Data switching by path configurationWireless communicationTraffic capacityNetwork code
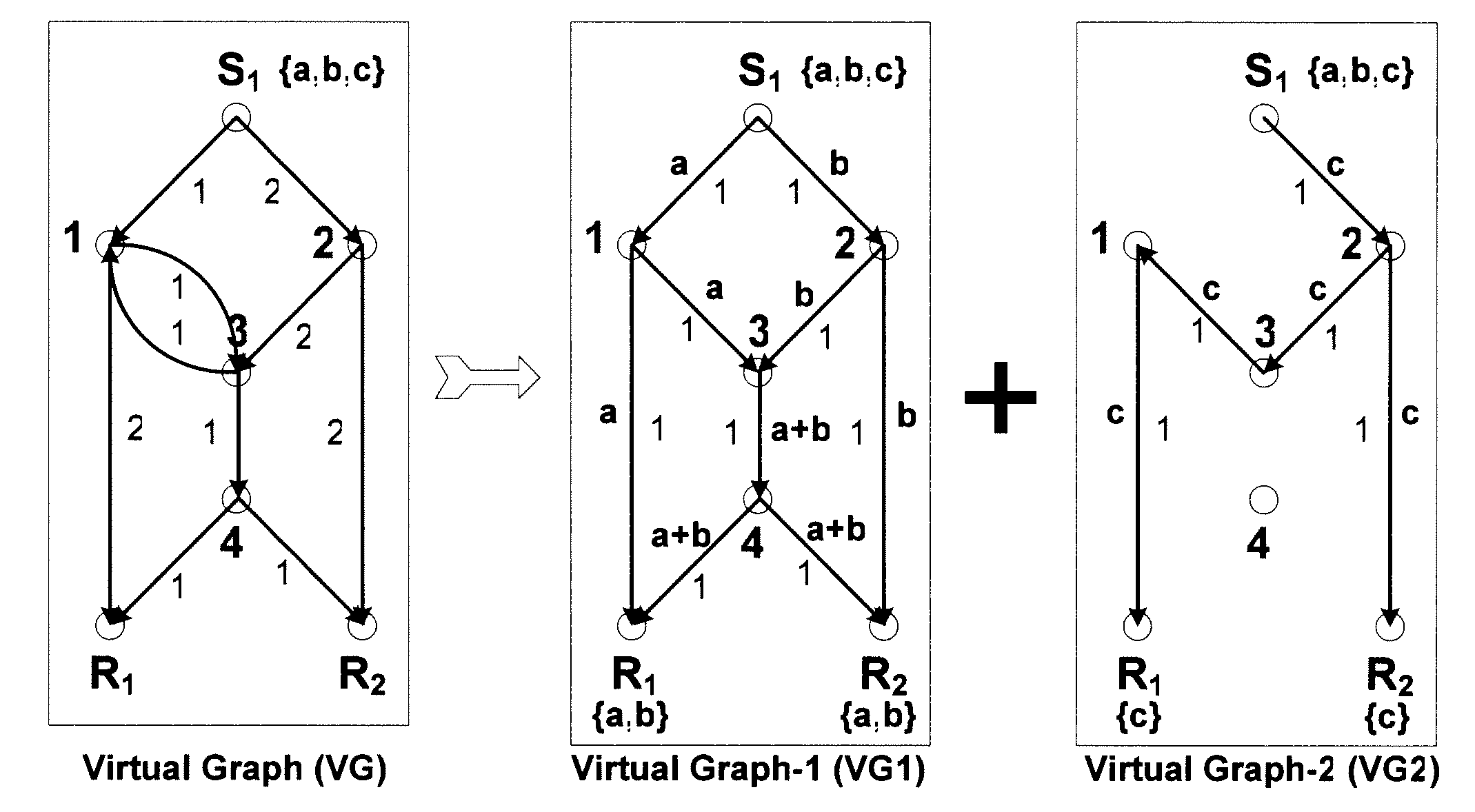
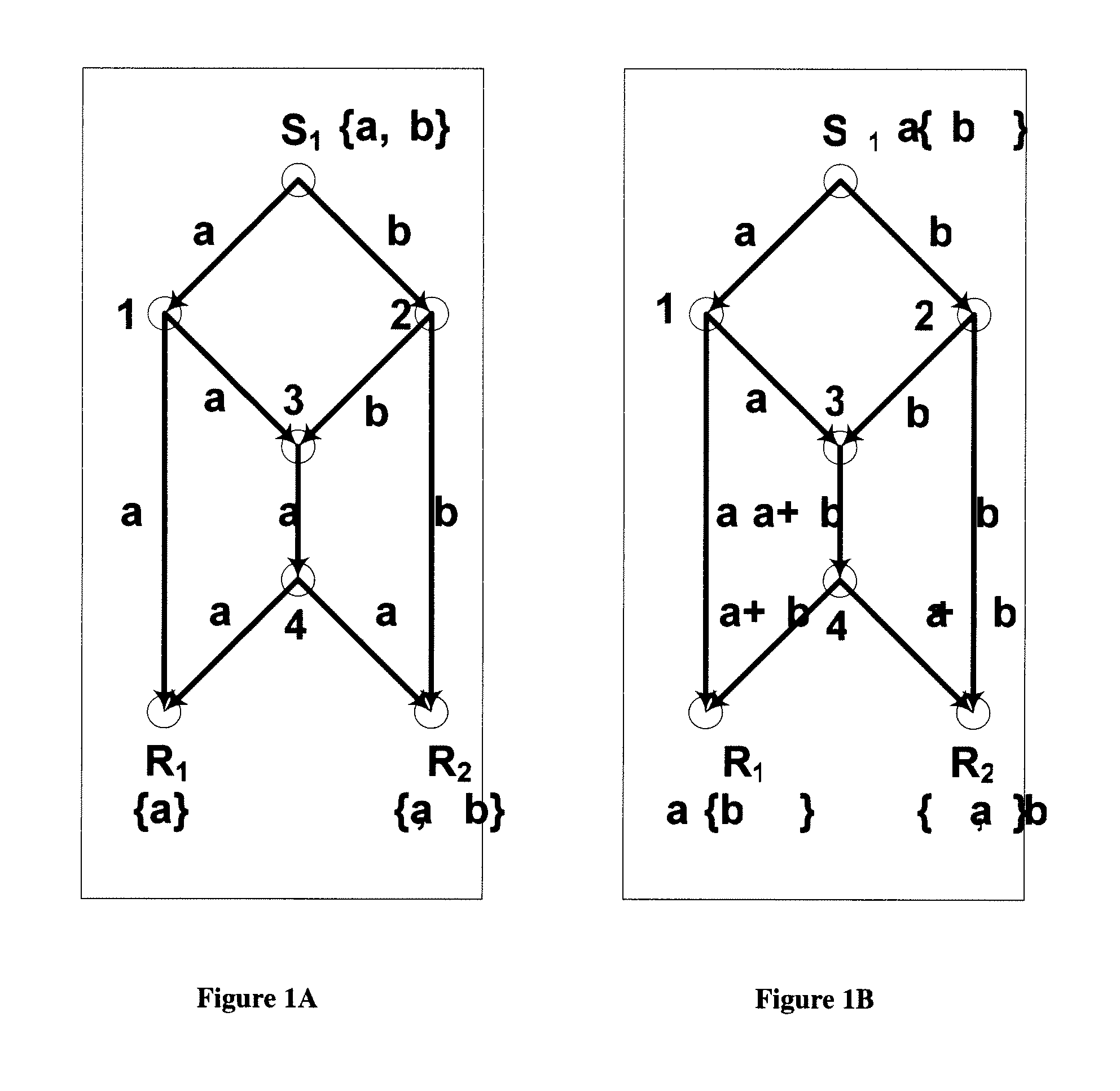
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for information delivery with network coding over time-varying network topologies. In one embodiment, the method comprises decomposing a sequence of topology graphs that model a time-varying network topology into a plurality of virtual graphs, where each virtual graph of the plurality of virtual graphs corresponds to a distinct traffic class, and the virtual topology graph representing a partial topology of a time-varying network. The method also includes selecting a network code for each virtual graph in the plurality of the virtual graphs to meet requirements of the distinct traffic class corresponding to said each topology graph, where the network code is used to encode packets of the associated traffic class, and processing packets of each traffic class using the network code determined by its corresponding virtual topology and the requirements of said each traffic class, including using a virtual buffer system to implement the network code corresponding to each traffic class over the physical network topology. The method also includes using a scheduler to determine the transmission schedules for each output packet from the virtual buffer system of each traffic class where the scheduling decisions are based, at least in part, on the QoS requirements of each class.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
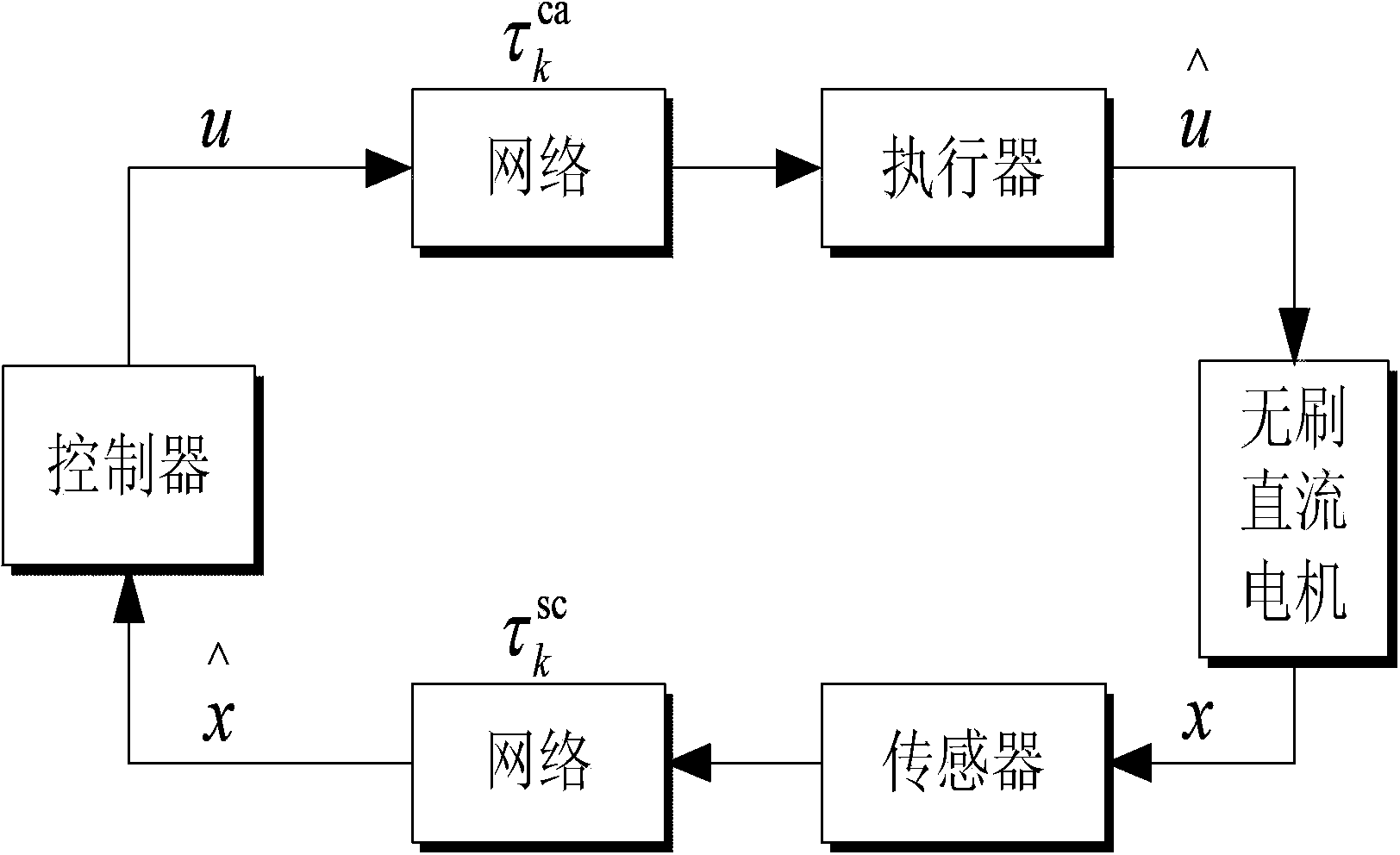
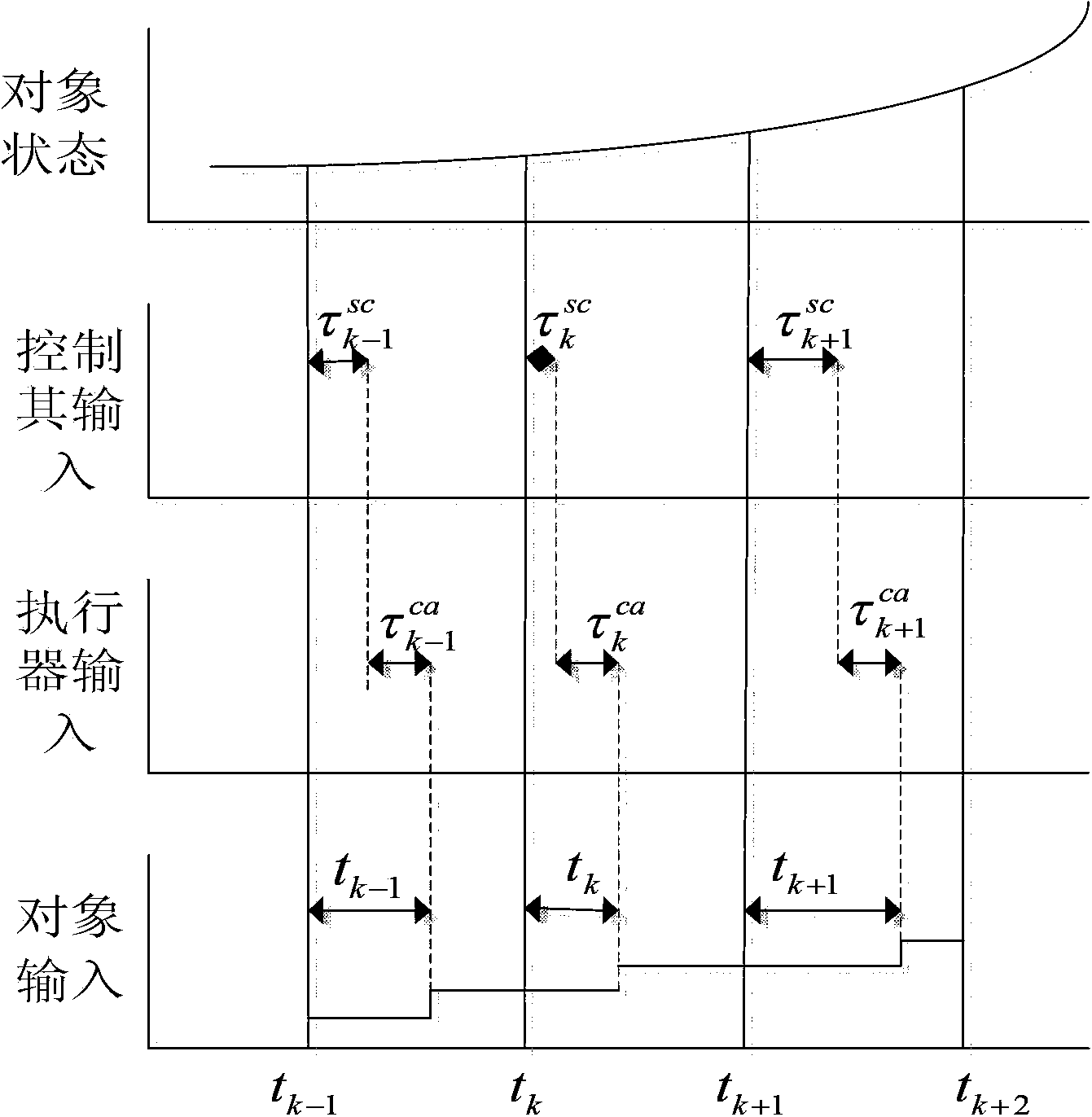
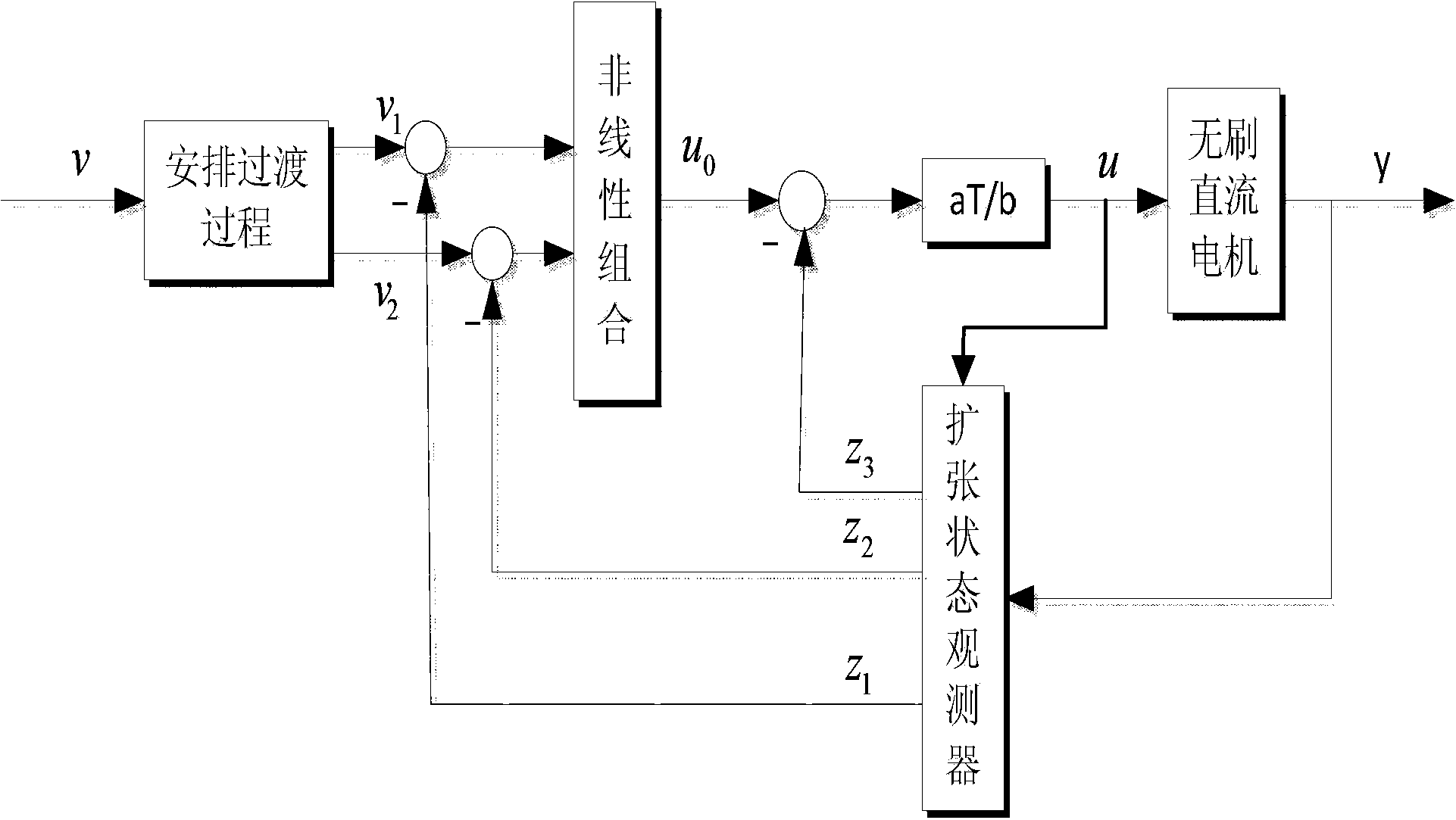
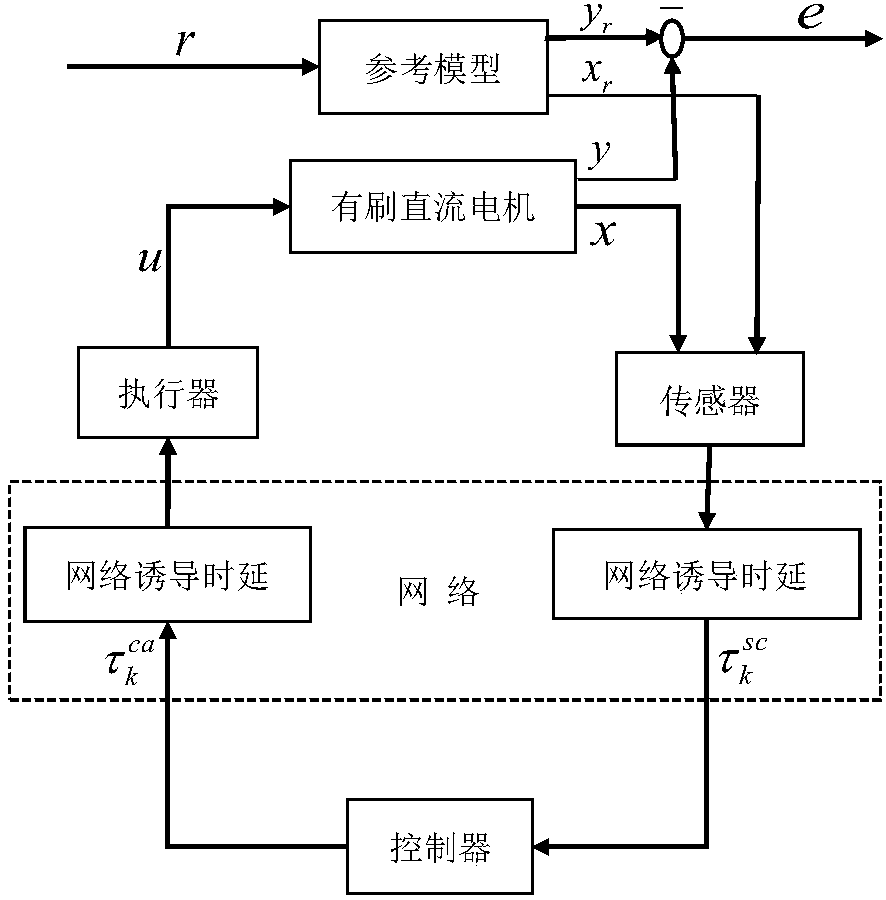
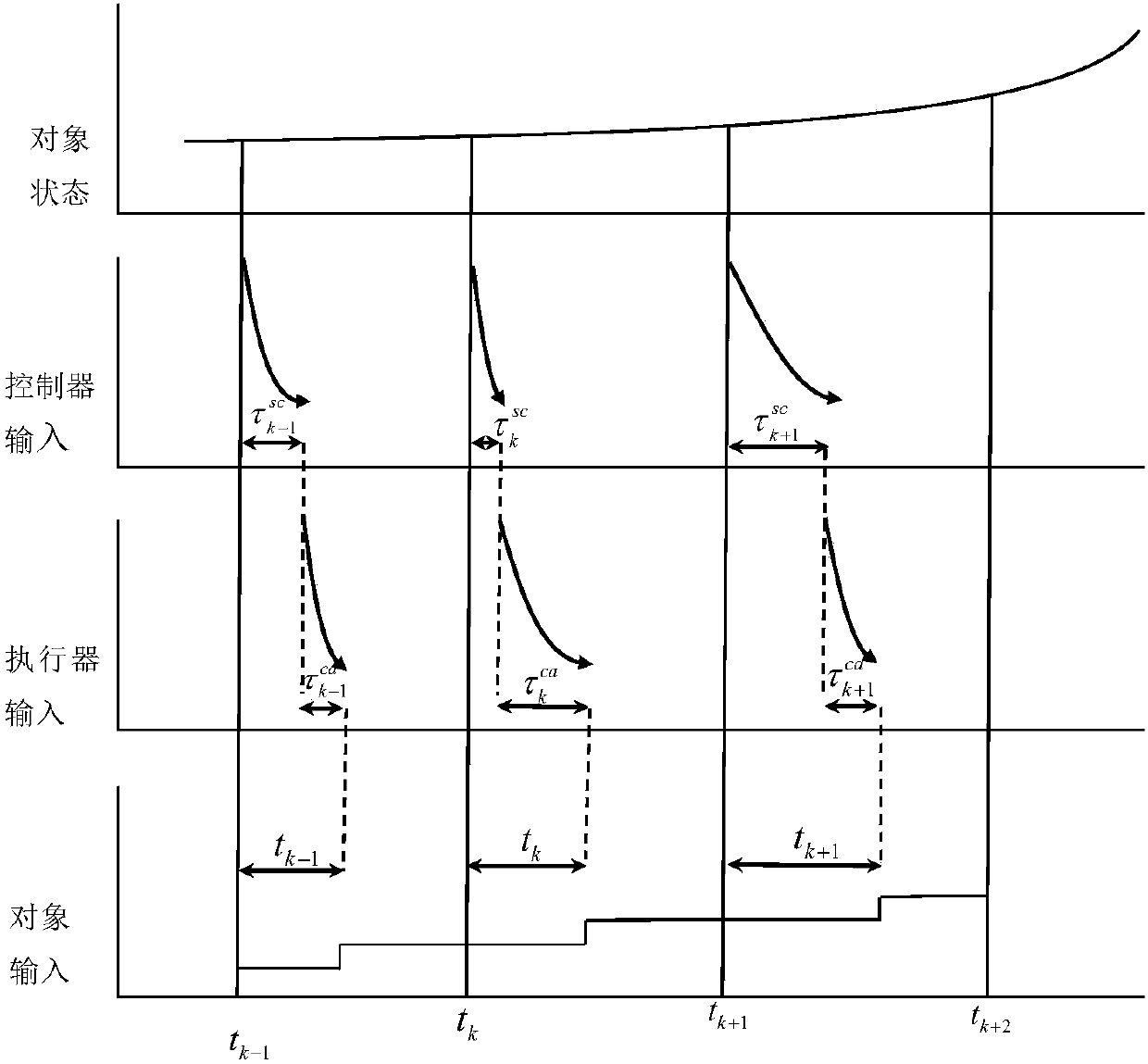
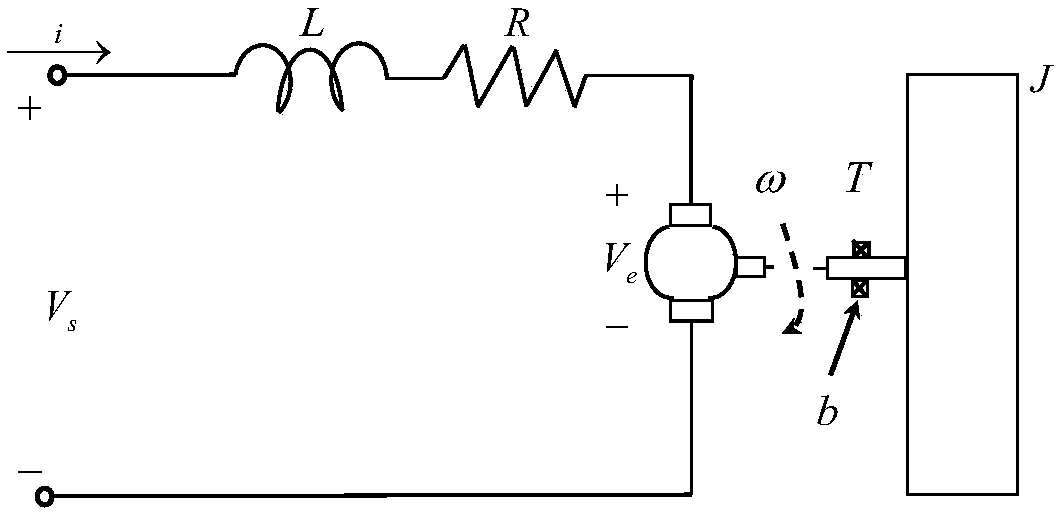
Networked brushless direct current motor time-delay compensation and control method using active-disturbance-rejection control technology
ActiveCN104142627AAccurate estimateSolving the difficult problem of accurate estimation of uncertain dynamicsAdaptive controlTime lagTime delays
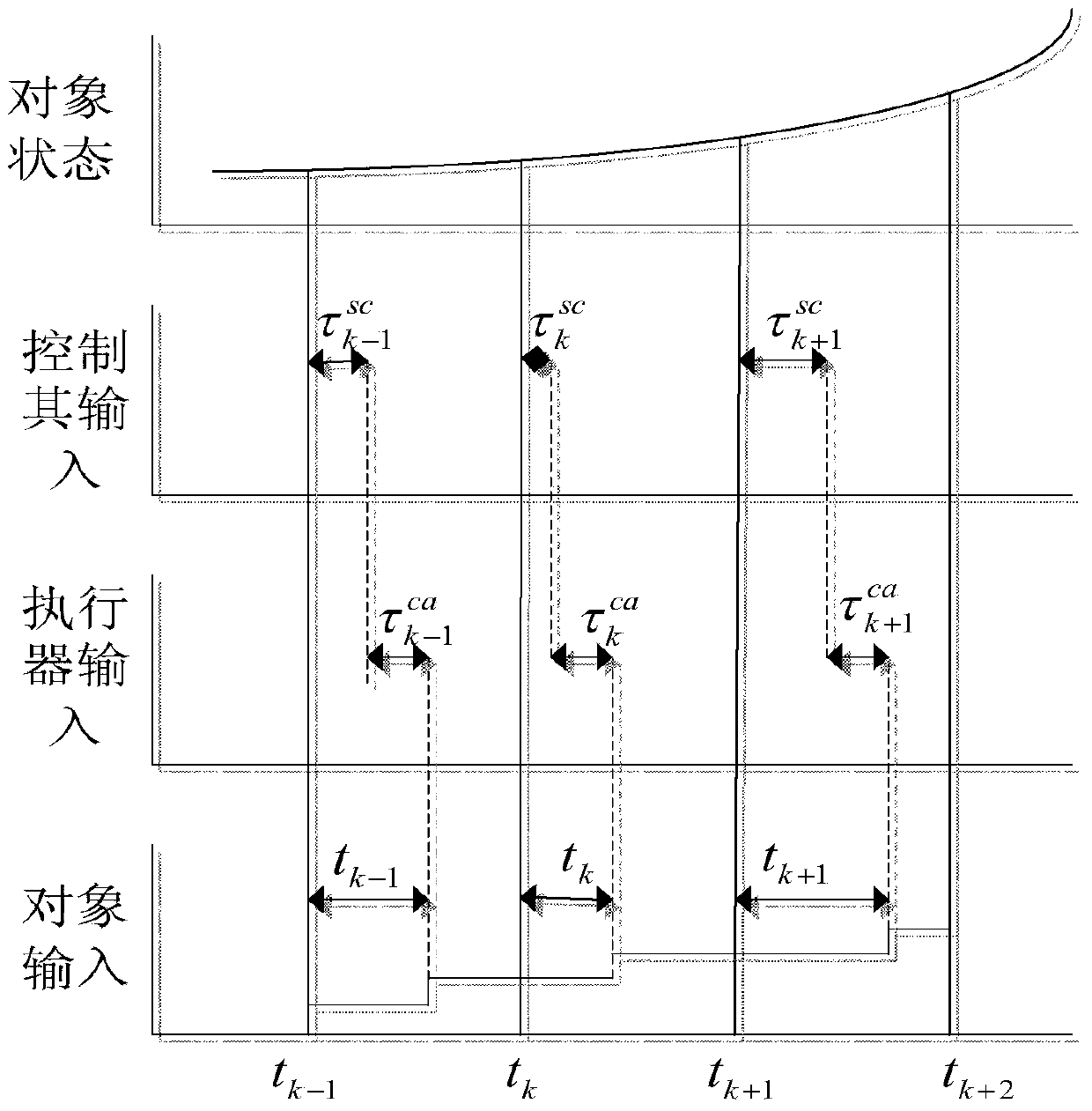
The invention discloses a networked brushless direct current motor time-delay compensation and control method using the active-disturbance-rejection control technology. The method comprises the steps of (1) establishing a brushless direct current motor control system model containing time-varying network-induced delay, wherein the brushless direct current motor control system is described as a discrete time linear time-varying system containing single-step input time lag, and then the uncertain dynamic state, caused by time-varying delay, of the system is partially described as the additive noise of the system; (2) designing an extended state observer which is used for estimating the uncertain dynamic state caused by time-varying delay as a part of total disturbance; (3) conducting compensation on the time-varying delay item in the brushless direct current motor control system. The method can be used for effectively conducting real-time estimation and compensation on the uncertain dynamic state caused by time-varying network-induced delay by means of the extended state observer, and can well restrain the uncertainty caused by time delay, internal and external disturbance of the system and model uncertainty.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Time diffusion route search method of satellite DTN (Delay/Disrupt-Tolerant Networking) network
ActiveCN105245451AGuaranteed successful delivery rateMinimum arrival timeRadio transmissionData switching networksTransmission qualityVisual perception
The invention provides a time diffusion route search method of a satellite DTN (Delay / Disrupt-Tolerant Networking) network, wherein the method is used for solving a route selection problem of an intermittent relay satellite network, and is obtained by CGR (Contact Graph Routing) principle improvement. An ERSA algorithm described in the invention calculates all information of a time-varying network, and the paths searched by the ERSA algorithm comprise a directly connected end-to-end path and a path for storage waiting for communication through a discontinuous link, and quantitative analysis is performed on the paths. Two new path measuring standards consider the transmission performance of the link, so as to guarantee the successful delivery rate and the shortest reach time of data. The increment of available paths improves the utilization rate of the algorithm for the system throughput performance. The time diffusion route search method of the satellite DTN network provided by the invention obtains a more efficient routing design and transmission quality by utilizing the overall inspection information of the network and the real-time network condition; therefore, compared with the traditional method, the method has certain advantages both in objective elevation index and subjective visual effect.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
DTN asynchronous routing algorithm based on node position projection
The invention relates to a DTN (Delay / Disruption Tolerant Networking) routing method. The DTN is a peculiar network model abstracted from challenged networks such as interstellar networks, satellite networks, AdHoc networks, sensor networks and the like, and is typically characterized in that a link between nodes has long time delay or intermittent distribution exists. Due to the distinct technical advantages in challenged network environments, the DTN becomes a research hotspot in the fields of battle field communication, deep-space communication, emergency communication and the like, and research results are practically applied in some fields. On the basis of studying the DTN asynchronous routing algorithm, analyzing and comparing typical algorithms, and finding the existing problems, a DTN time-varying model and a node position predictive model are built and a routing algorithm based on the node position projection is also proposed, and besides, the rationality and validity of the routing algorithm are verified through simulation.
Owner:NO 63 RES INST HEADQUARTERS OF THE GENERAL STAFF PLA
Method and system for dynamically adjusting forward error correction (FEC) rate to adapt for time varying network impairments in video streaming applications over IP networks
InactiveUS8091011B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionCommunications systemForward error correction
Certain aspects of a method and system for dynamically adjusting forward error correction (FEC) rate to adapt for time varying network impairments in video streaming applications over IP networks may be disclosed. At a server side of a client-server communication system, a rate of transmission of forward error correction (FEC) packets to one or more clients may be dynamically adjusted based on receiving at least one upstream FEC packet from a plurality of clients. The rate of transmission of the FEC packets to the plurality of clients may be increased when a rate of occurrence of lost data packets is above a particular threshold value. The upstream FEC packets may comprise an urgent packet requesting transmission of a particular FEC packet in order to recover one or more particular lost data packets.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Obstacle avoidance method and system of UAV formation under time-varying network topology
ActiveCN107491086AGuaranteed integrityAvoid defectsPosition/course control in three dimensionsObstacle avoidanceTime cost
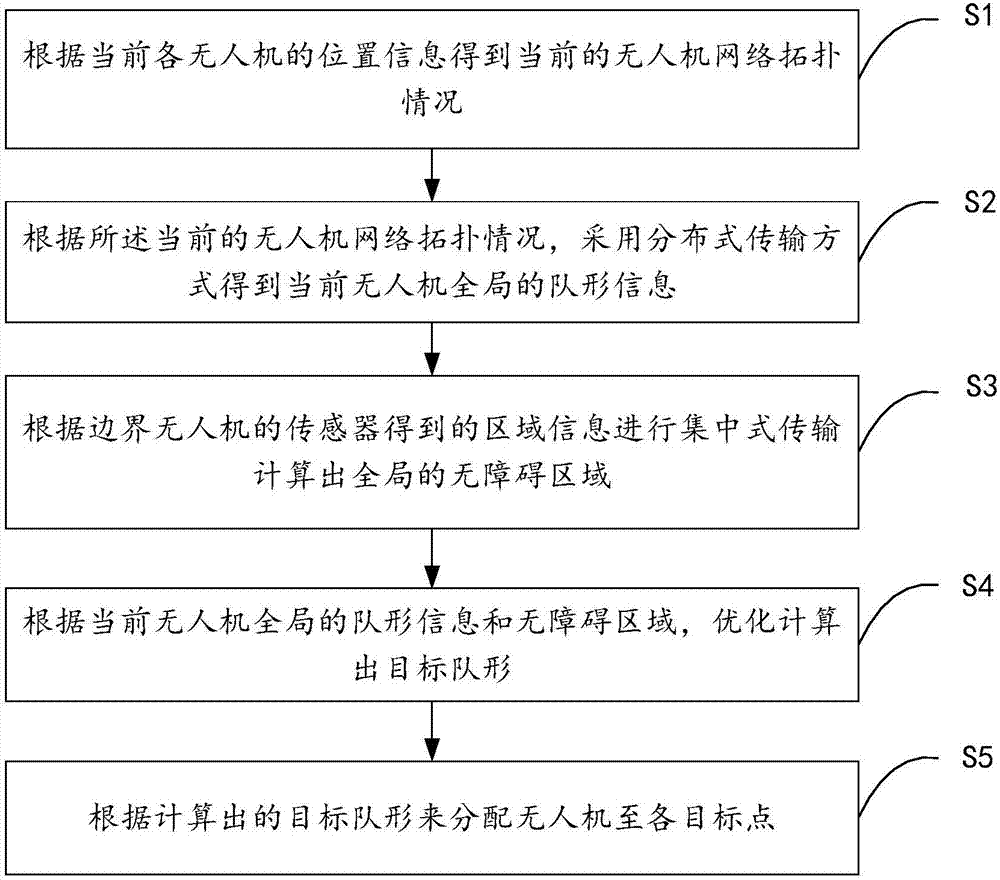
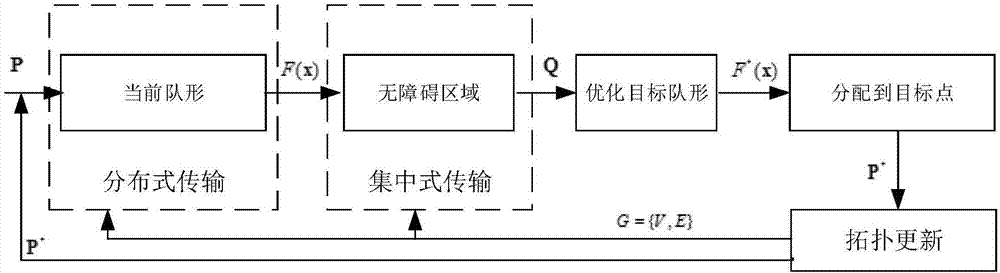
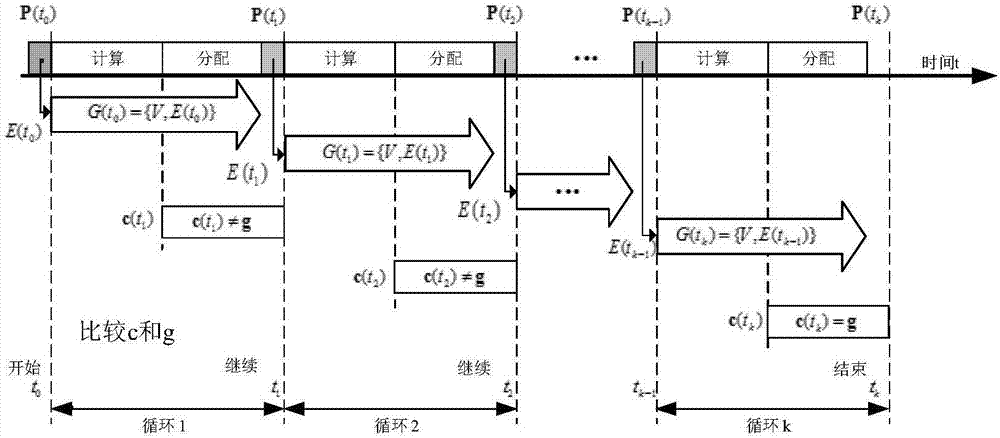
The invention discloses an obstacle avoidance method and system of a UAV (unmanned aerial vehicle) formation under time-varying network topology. The method comprises a step of obtaining a current UAV network topology condition according to position information of each UAV at present, a step of obtaining current UAV global formation information by using a distributed transmission mode according to the current UAV network topology condition, a step of carrying out centralized transmission according to regional information obtained by a sensor of a boundary UAV to calculate a global barrier-free area, a step of carrying out optimal calculation to obtain a target formation according to the current UAV global formation information and the barrier-free area, and a step of distributing a UAV to each target point according to the calculated target formation. According to the method and the system, the overall communication overhead and time cost are reduced, at the same time, a topology change caused by a formation change in the formation process is considered, a slice type topological model is established, different topologies are updated according to a current formation state in different time slots, and thus an algorithm is more close to the actual application. The integrity of the formation is ensured.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
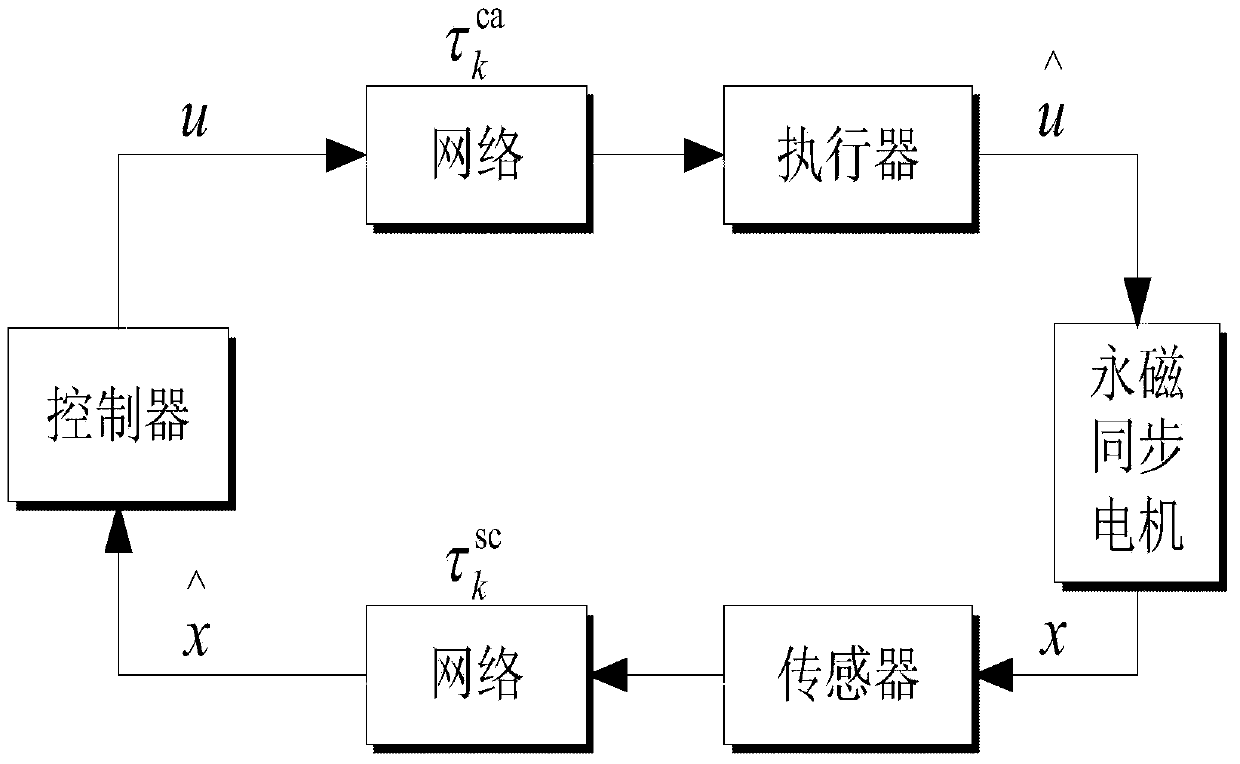
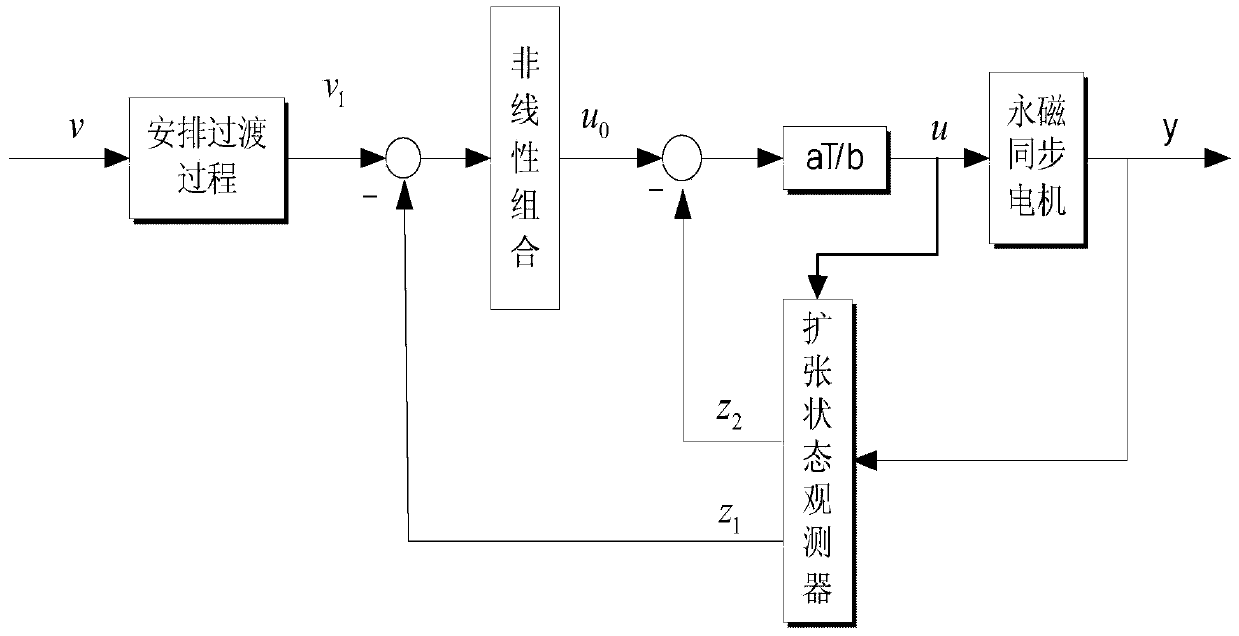
Networking time-delay compensation and control method using active-disturbance-rejection control technology for permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN104201967AAccurate estimateSolving the problem of accurately estimatingSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor parameters estimation/adaptationElectric machineTime delays
The invention provides a networking time-delay compensation and control method using the active-disturbance-rejection control technology for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: 1) building a permanent magnet synchronous motor control system model containing time-varying network-induced delay, and describing a permanent magnet synchronous motor control system as a discrete-time linear time-varying system with one-step input delay, so as to describe an undetermined dynamic part of the system caused by the time-varying delay as the additive noise of the system; 2) designing an expanding state observing device, and estimating the undetermined dynamic part caused by the time-varying delay as part of total disturbance through the expanding state observer; 3) compensating the undetermined dynamic state caused by the time-varying delay in the networking permanent magnet synchronous motor control system, wherein all undetermined dynamic parts caused by the time-varying delay and the internal and external disturbances in the system can be counteracted during compensating. The method shows high capability on inhibiting the nondeterminacy caused by time-varying delay, the internal and external disturbances of the system, and the nondeterminacy of a model.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A customized bus route optimization method for reliability shortest path
ActiveCN109447340ASatisfy high service punctuality requirementsIncrease share rateForecastingRush hourRoad networks
The utility model relates to a customized bus route optimization method for reliability shortest path, which comprises the following steps of establishing a road network, comprising establishing a spatio-temporal network and a reliability network; determining the passenger relaxation time window; determining the scope of service; calculating whether a passenger can be serviced by the opened vehicle k; finding the shortest path of reliability; opening the customized new bus routes. The invention discloses a custommized bus line optimization method for reliability shortest path, which can efficiently and quickly deliver passengers to a destination under the condition of satisfying passenger travel. Due to the delays caused by traffic congestion during the morning and evening rush hours of customized buses, the invention creatively proposes a method for searching the shortest path of reliability, which avoids the delay caused by driving, improves the stability and reliability of vehicle operation, meets the requirement of high punctuality of customized bus service by commuters during morning and evening rush hours, and finally improves the share rate of customized bus service.
Owner:TIANJIN MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN & RES INST
Adaptive FEC mechanism based on media content
ActiveCN106603192AFEC Mechanism RefinementGuaranteed content qualityChannel coding adaptationData streamCurrent channel
The present invention provides an adaptive FEC (Forward Error Correction) mechanism based on the media content. The mechanism classifies the media content and gives different significances, and the mechanism dynamically regulate the degrees of importance of frames included in the media data and the corresponding encoding schemes according to the current channel state in the condition without performing shunt of the current media data stream and transmits a data packet to a corresponding FEC encoder to perform protection with different degrees and finally encode one source data flow to an FEC code stream. The adaptive FEC mechanism based on the media content reduces the great data bulk caused by the FEC while ensuring the quality of the media content to the utmost extent; the adaptive FEC mechanism based on the media content does not need the shunt of the source data stream to reduce the complexity of the FEC encoding of a sending terminal and improve the efficiency of the FEC encoding; one source data stream only can encode and generate one FEC code stream so as to greatly reduce the increasing of the data bulk caused by the FEC encoding; and the adaptive FEC mechanism based on the media content can dynamically regulate the encoding scheme according to the changing of the current network state so as to has higher adaptability for the time varying network.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
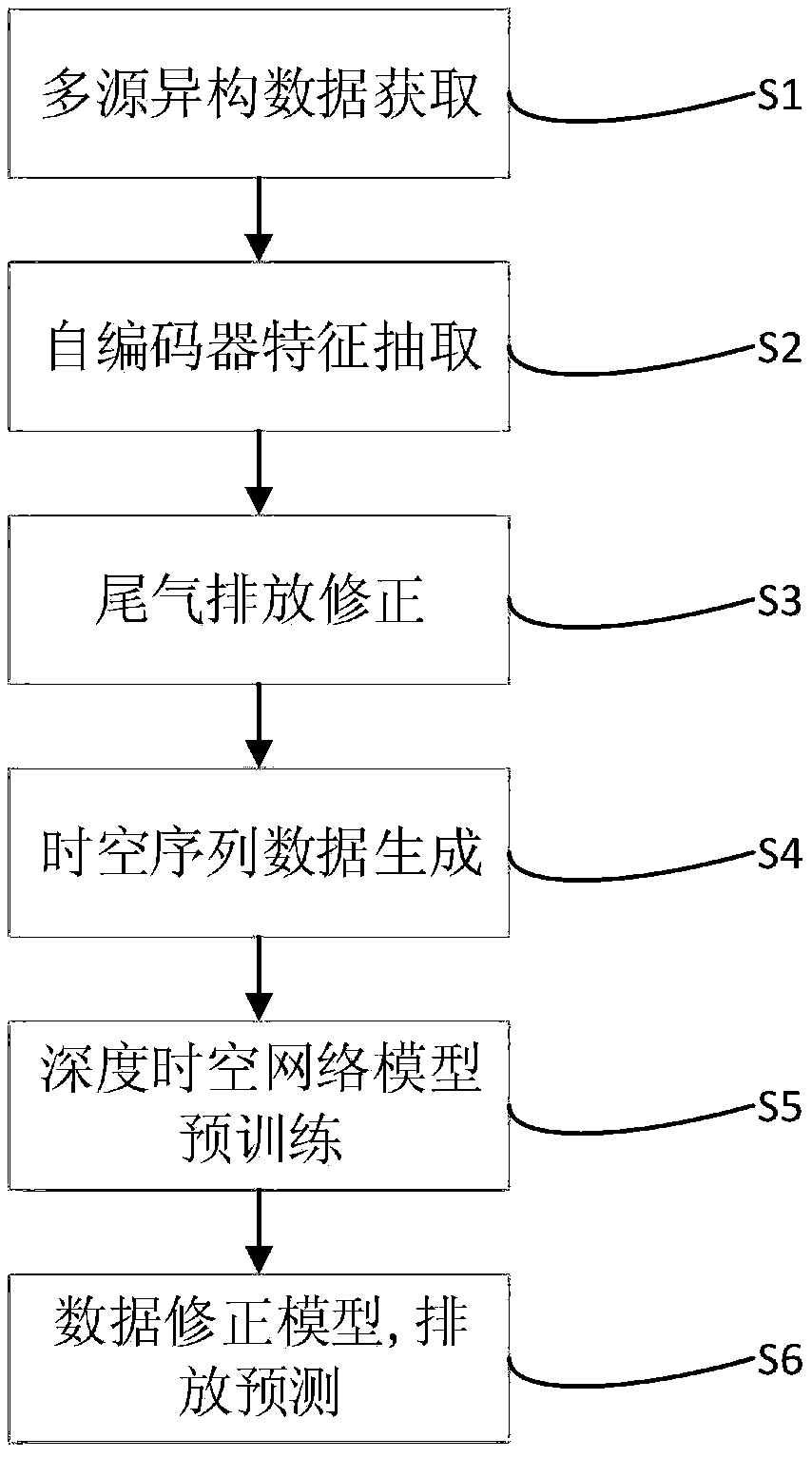
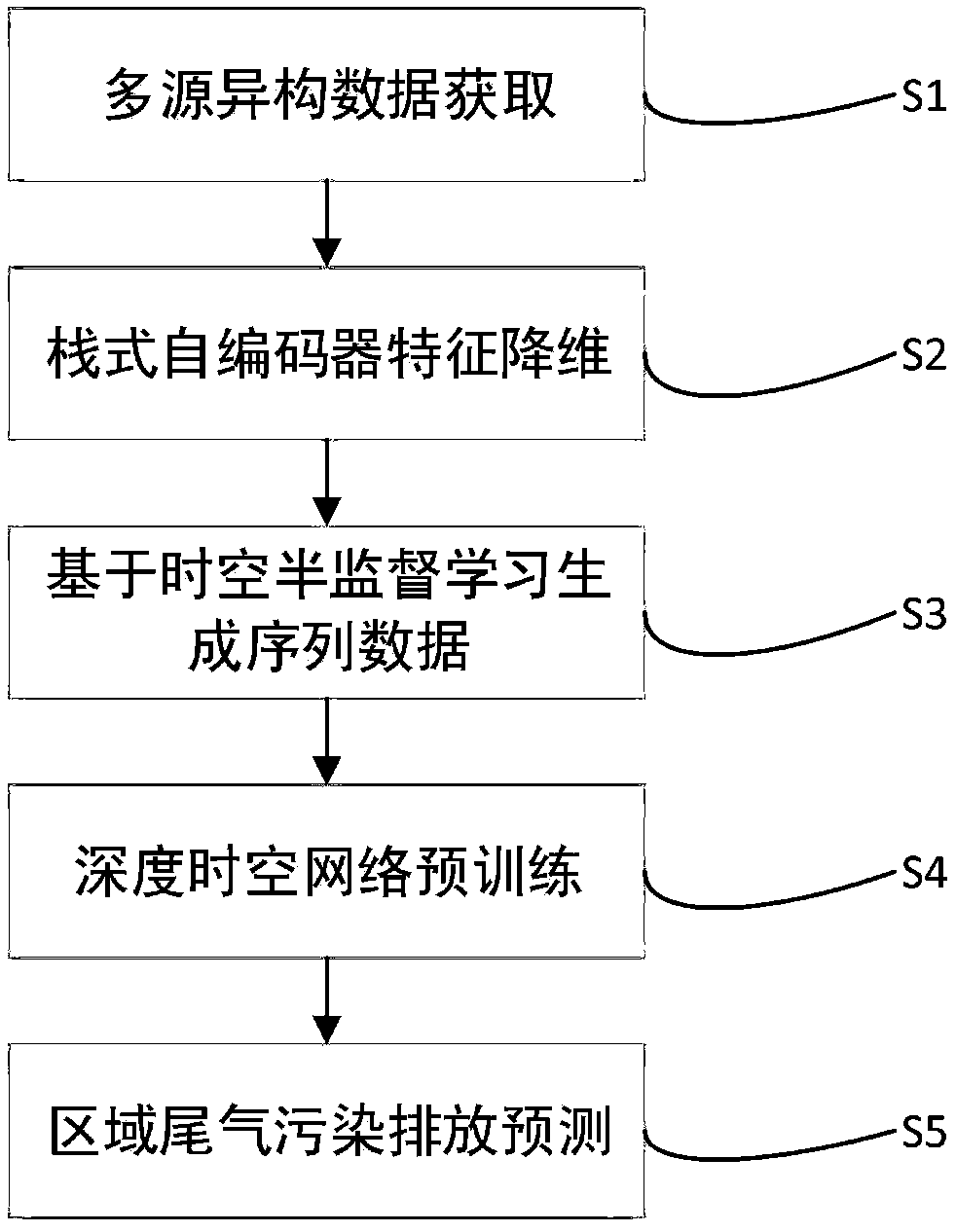
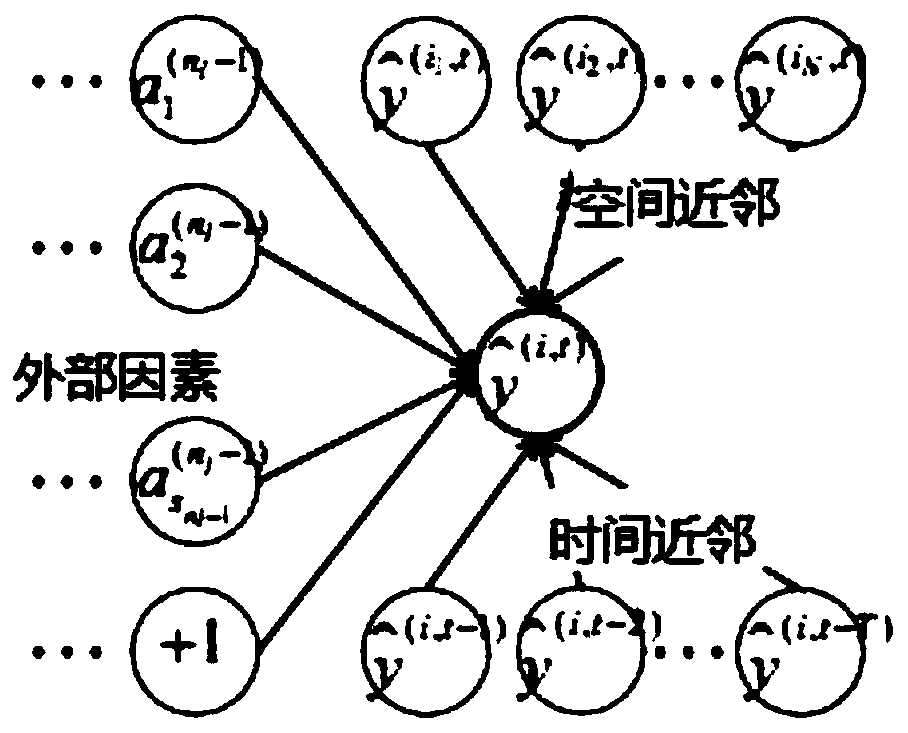
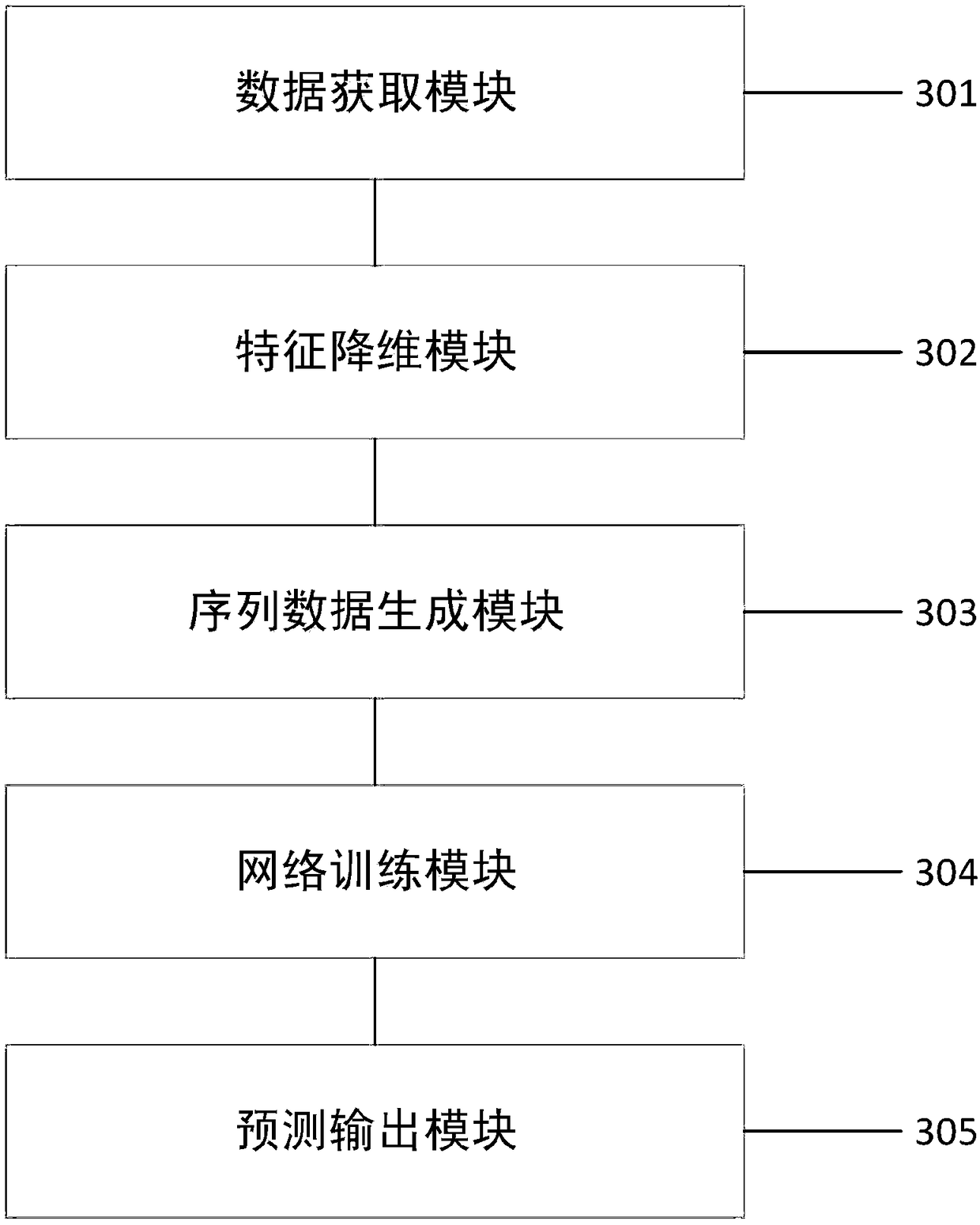
A prediction method of urban regional tail gas pollution based on depth spatio-temporal correction model
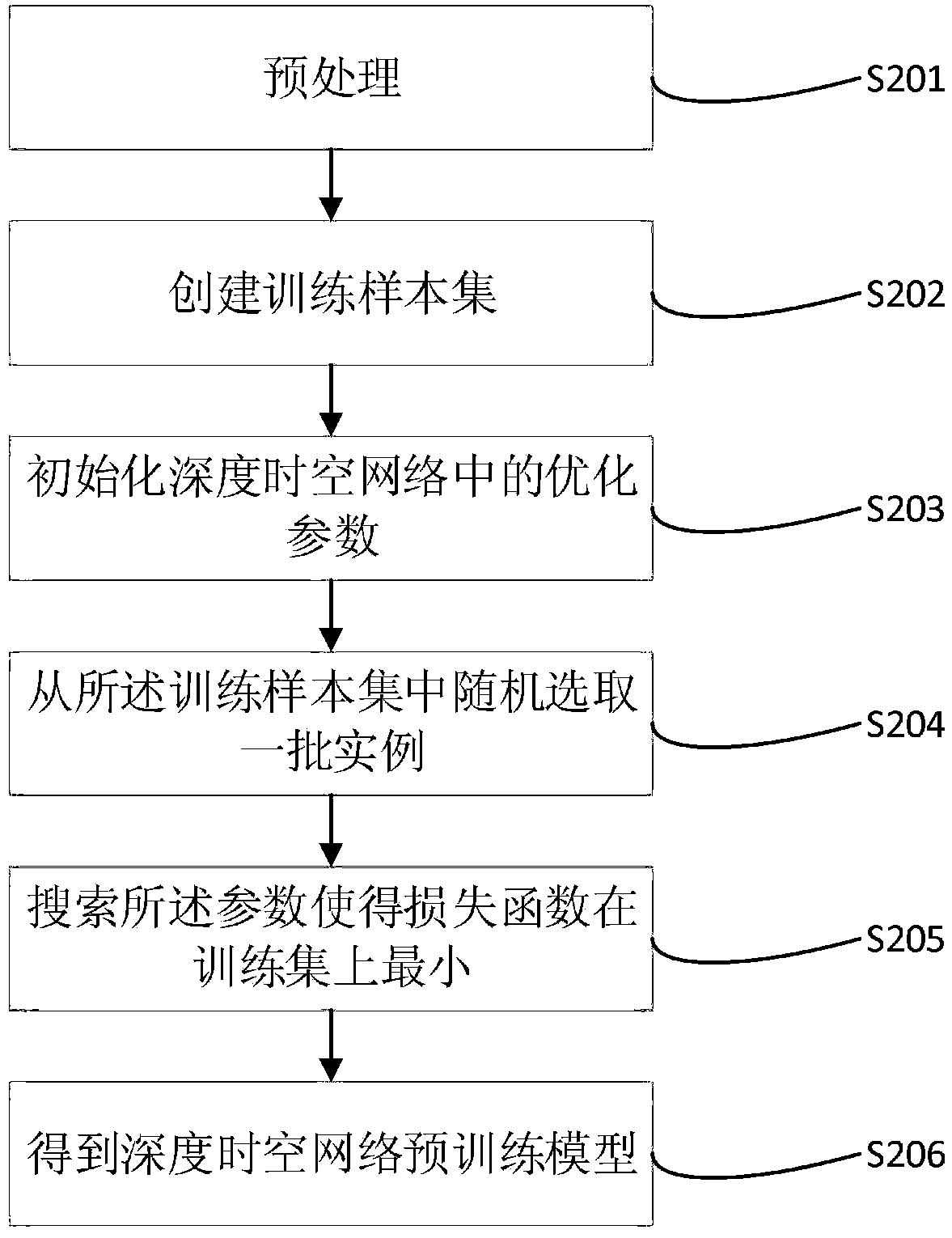
The invention provides an urban area tail gas pollution prediction method based on a depth space-time correction model, which comprises the following steps: acquiring multi-source heterogeneous data;a self-encoder feature extraction method realizes feature dimension reduction extraction of the multi-source heterogeneous data by constructing a three-layer self-encoder network structure; tail gas emission correction, substituting dimension reduction characteristic data of each data source extracted in the step 2 into the tail gas emission correction model; Spatio-temporal series data generation; deep spatio-temporal network model pre-training; replacing the corrected model data with the telemetry data of the real monitoring points, and re-training the corrected regional tail gas emission prediction model; the weighted parameters of the model are determined to obtain a depth spatio-temporal network model, and the multi-source heterogeneous data are input to obtain a predicted regional tail gas pollution emission result.
Owner:安徽优思天成智能科技有限公司
Adaptive multimedia integration language (AMIL) for adaptive multimedia applications and presentations
InactiveUS7966408B2Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsPersonalizationDocumentation procedure
The invention generally relates to the field of markup languages used to describe adaptive mobile multimedia applications and / or presentations being inherently dependent on the dynamic mobile environment they are running in, which means that these mobile multimedia applications and / or presentations need to be adapted to the preferences of mobile users, the capabilities of their mobile computing devices, and their current situation. It allows adaptive mobile stream-based multimedia applications with real-time requirements in a typical wireless scenario (e.g. a radio link with a changing transmission quality and hand-over procedures) to adaptively and responsively react to a time-varying network topology and different radio link characteristics. Thereby, the underlying invention especially includes research and development issues in the field of describing adaptation possibilities (1500), adaptation constraints (802) and adaptation events (3802) directed to a personalization and context-aware adaptation of document-based multimedia applications by providing methods for pre-allocating, reserving, monitoring and adapting QoS-related parameters in a dynamic mobile environment using an XML-based multimedia presentation language.In this connection, a document model (100) consisting of vocabulary, document structure and linking means (1600) between the document model elements is presented which supports the description (700) of adaptive mobile multimedia applications and / or presentations. Besides, a document object model supporting a simplified transaction-oriented access is proposed.
Owner:SONY DEUT GMBH
A method and a system for predicting the tail gas pollution distribution in a city road network
InactiveCN109165690AImprove forecastHigh precision predictionForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature DimensionENCODE
The invention provides a method for predicting the tail gas pollution distribution in a city road network. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring multi-source heterogeneous data; carryingout stack-type self-encode features dimension reduction, and constructing a multi-layer sparse self-encoder network structure to extract the features of the multi-source heterogeneous data; generating sequential data based on spatio-temporal semi-supervised learning; pre-training a deep spatio-temporal network model replacing the corrected model data with the telemetry data of the real monitoringpoints, and re-training the corrected regional tail gas emission prediction model; determining the weighted parameters of the model to obtain a deep spatio-temporal network model, and inputting the multi-source heterogeneous data t to obtain a predicted regional tail gas pollution emission result. The invention is based on a stack-type self-encoder dimension reduction feature extraction method, which can learn essential feature mapping between road network information, meteorological information, traffic flow information, POIs information and regional tail gas emission, and can realize higherprecision regional tail gas prediction on real telemetry data.
Owner:安徽优思天成智能科技有限公司
Method of DC motor networked tracking controller
The invention relates to a method of a DC motor networked tracking controller. The method comprises the steps of (1) establishing a DC motor discrete system state equation with the consideration of atime-varying network induced delay, describing the DC motor system as a discrete-time norm bounded uncertain system with a one-time input delay, and using an uncertain system method to process an exponential time-varying problem in a motor state equation, (2) establishing a closed-loop system model of a DC motor networked tracking control system containing uncertainties, wherein the closed-loop system is an uncertain augmented closed-loop system with the one-step input delay, and (3) designing the DC motor networked tracking controller including the steps of firstly carrying out H-infinity performance analysis on the closed-loop system to verify stability and then designing the networked tracking controller, wherein the time delay is divided into a mean part and an uncertainty part in modeling, a networked control system is described as a class of discrete-time norm bounded uncertain system, and a networked H-infinity tracking control strategy is used to design a state feedback controller.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
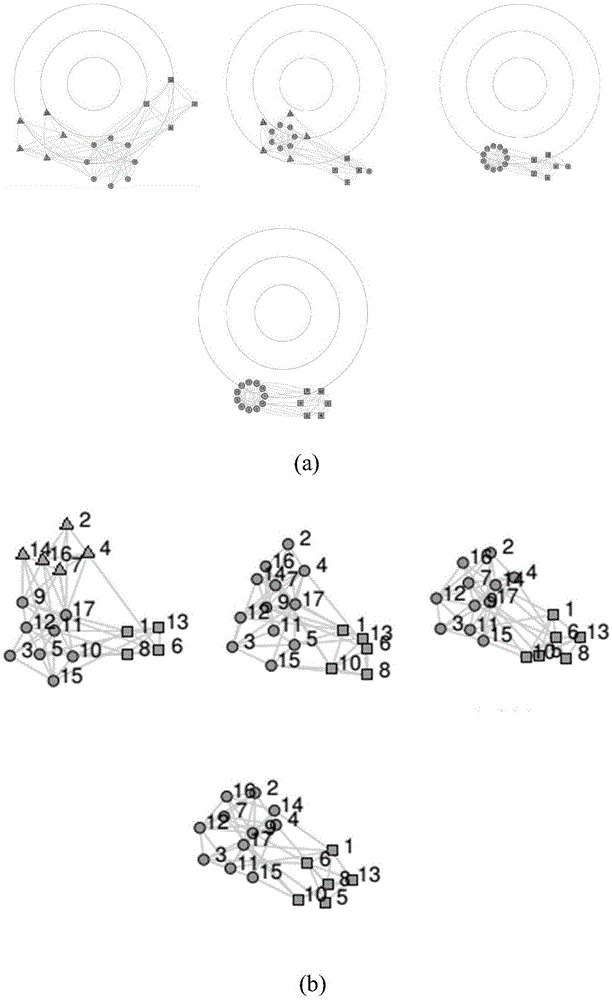
Time-varying network community evolution visualization method introducing quantitative index
ActiveCN105654387AEnsure layout stabilityImprove readabilityData processing applicationsNODALIndex mapping
The invention relates to the information visualization field and especially relates to a visualization method capable of reflecting community evolution in a time-varying network. Time-varying community division of the time-varying network is acquired. Global layout is performed on an abstract community network and a time-varying centripetal force is introduced so that an unstable community is close to a layout center and mapping of a community position and a time-varying characteristic is realized. A stability index is used to limit gravitation and a repulsive force in a gravitation model so as to guarantee layout stability and ensure a community layout position. Layout is performed on nodes in each community and node changes of a time-varying community in adjacent time slices are embodied. A concentric circular ring is used as a visual background and readability of the community position and stability quantification index mapping information is enhanced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
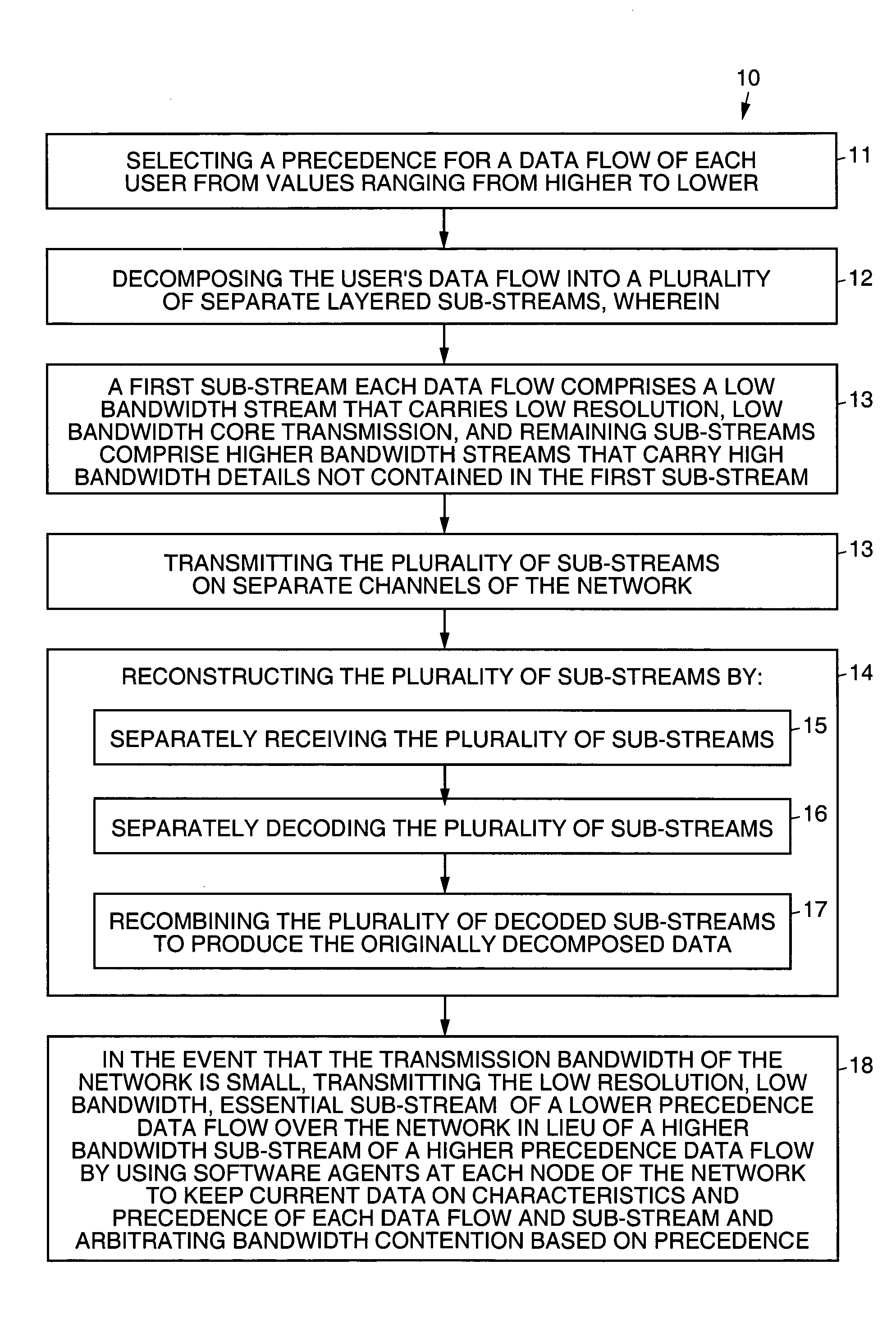
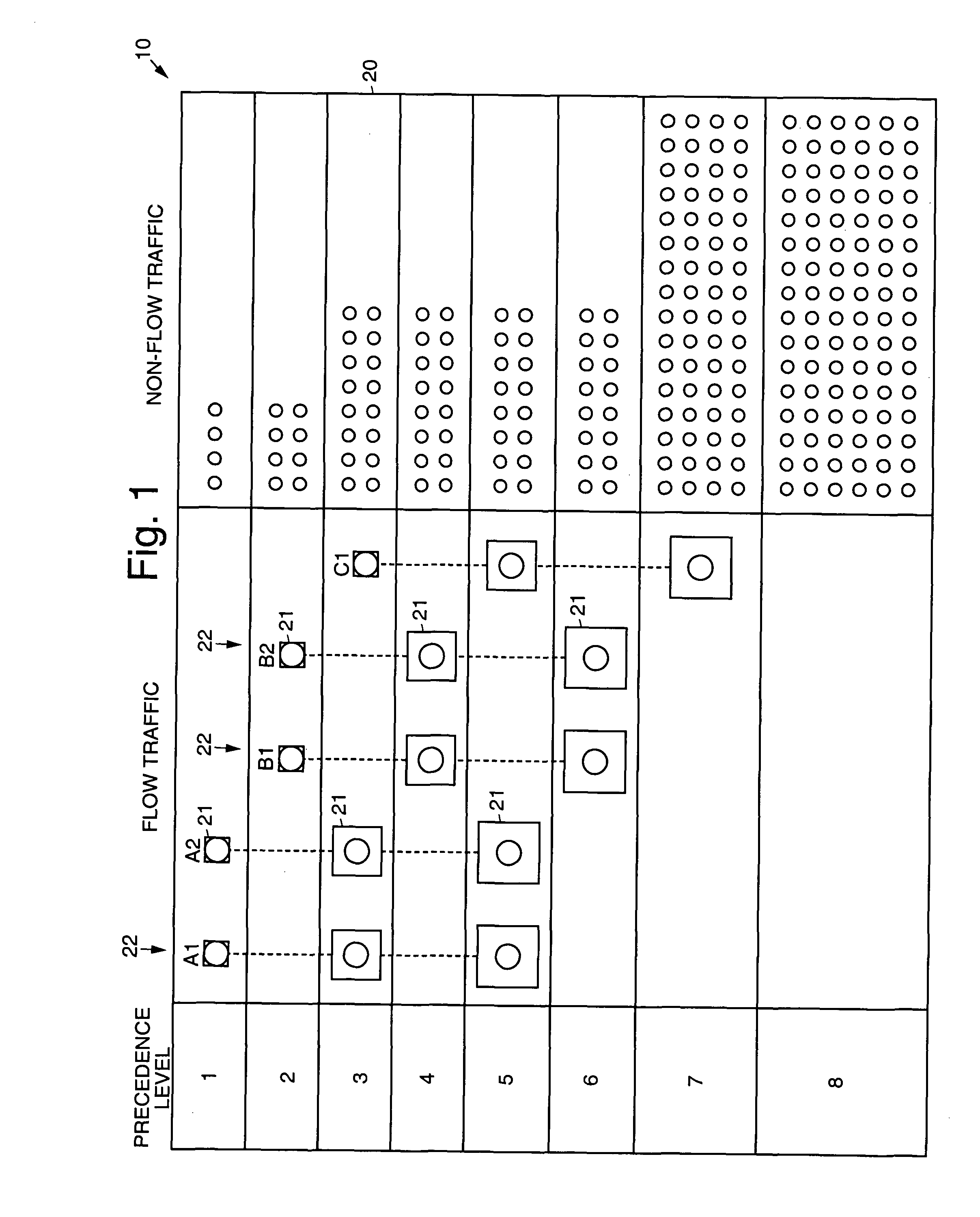
Precedence adjusted resource allocation
InactiveUS8239534B1Improve performanceReduce trafficError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPresent methodReal-time data
Methods that perform message and real-time data and computational flow routing across networks comprised elements with a dynamic time-varying network topology and loading. The unique algorithms and protocols for allocation of network resources embodied in the present methods provide optimal performance for high precedence traffic while providing as good as possible performance for lower precedence traffic.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
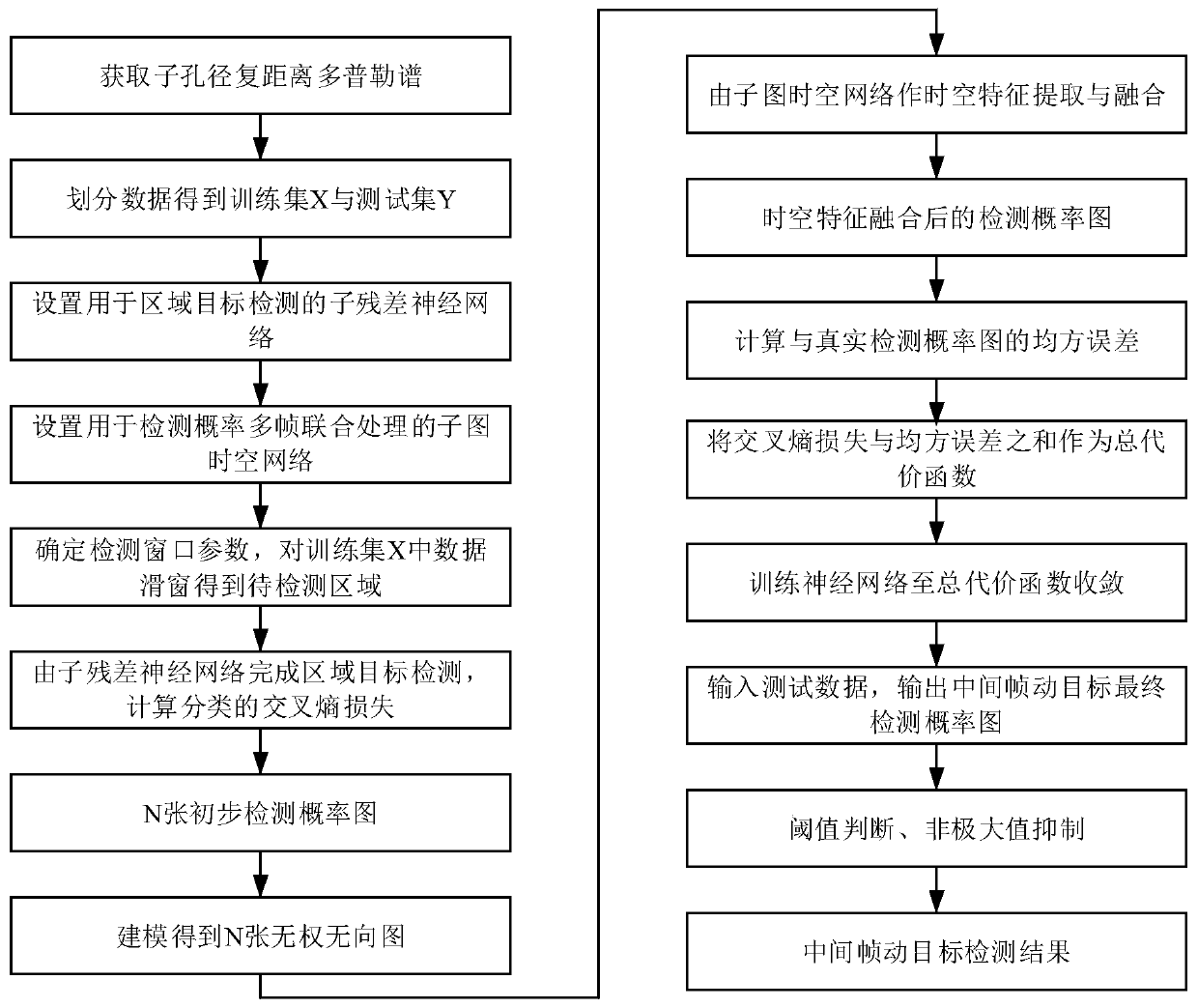
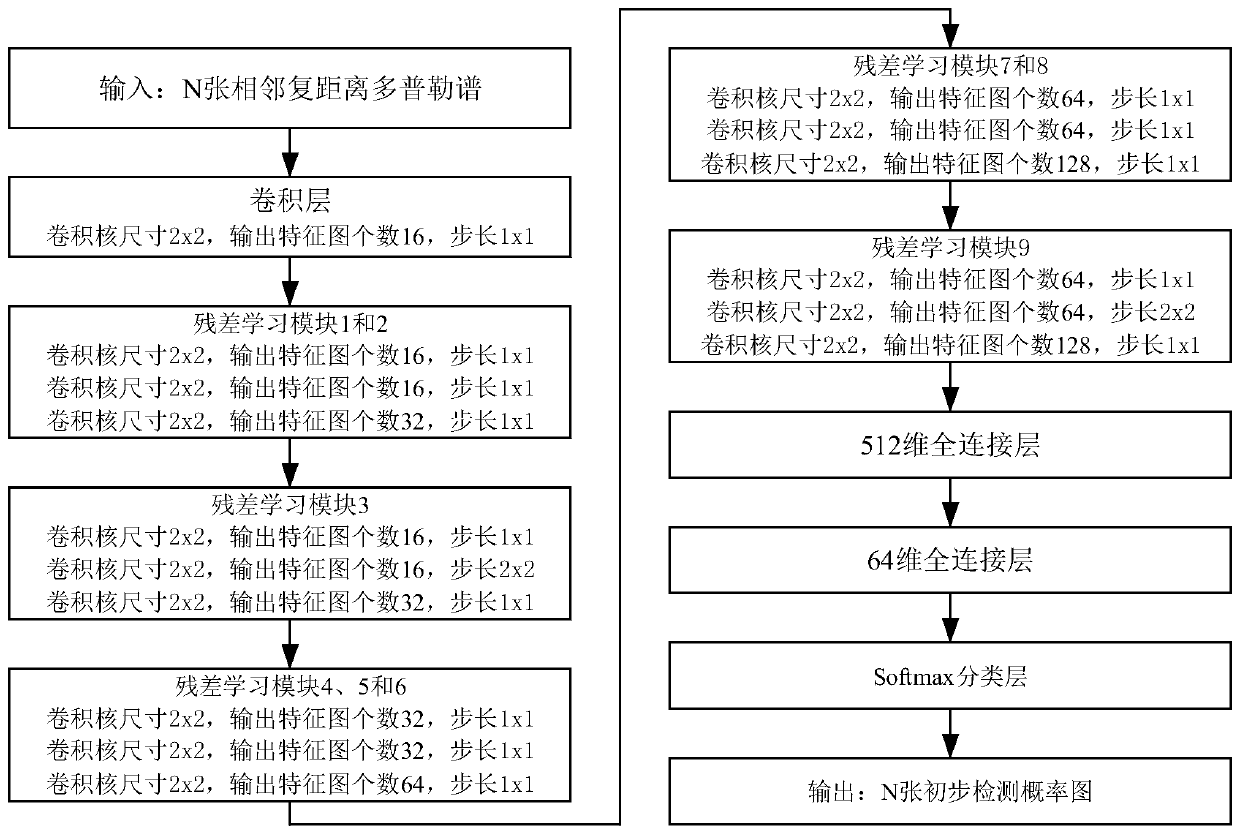
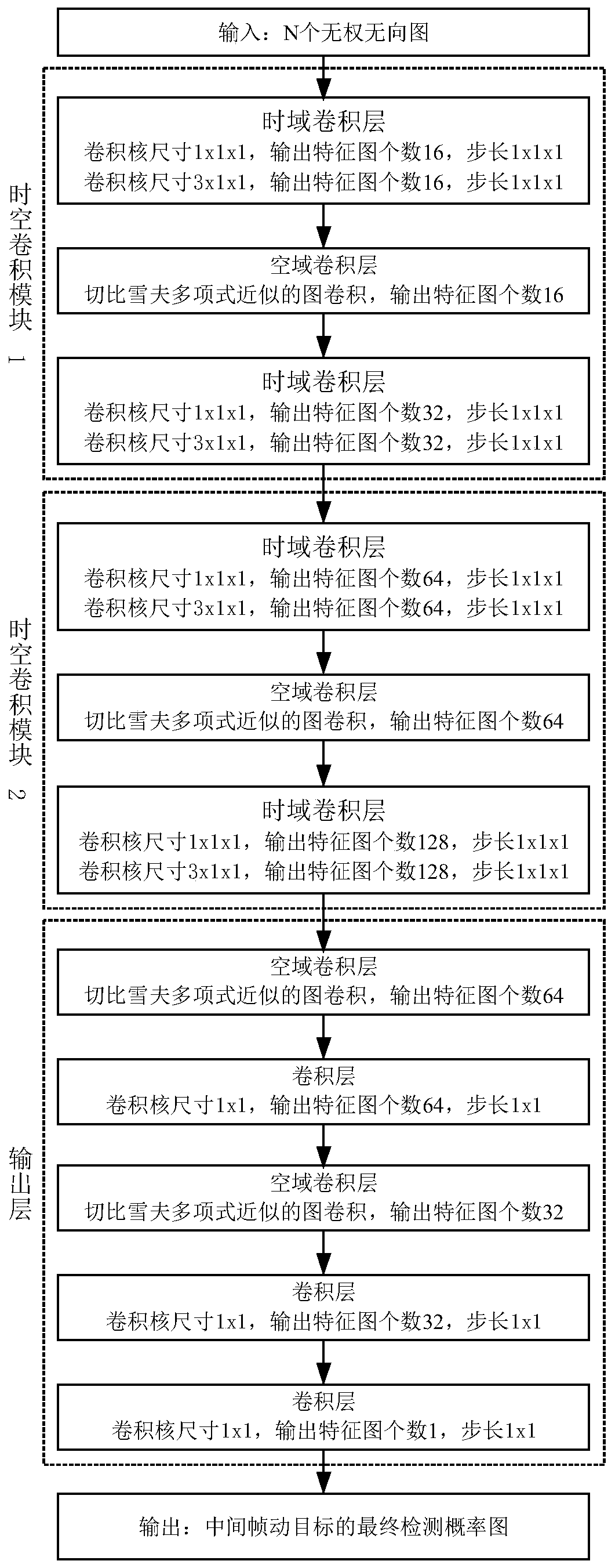
Radar moving target multi-frame joint detection method based on graph space-time network
ActiveCN111123257AReduce false alarm rateEasy to detectRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationFeature extractionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a radar moving target multi-frame joint detection method based on a graph space-time network. The method mainly solves the problem that in the prior art, the false alarm rate of moving target detection of a single-channel system is high. According to the scheme, the method comprises the steps of obtaining a sub-aperture distance Doppler spectrum; constructing a sub-residualnetwork and a sub-graph space-time network, and forming a neural network model for moving target detection by using the sub-residual network and the sub-graph space-time network; performing regionaltarget detection by using the sub residual network, outputting a preliminary detection probability graph, and calculating cross entropy loss; performing spatial-temporal feature extraction and fusionby using a sub-graph spatial-temporal network, outputting a final detection probability graph of an intermediate frame moving target, and calculating a mean square error; and taking the sum of the cross entropy loss and the mean square error as a total cost function, training the neural network until the total cost function is converged to obtain a trained neural network, inputting test data intothe trained neural network, judging an output threshold value of the trained neural network, and suppressing a non-maximum value to obtain a moving target detection result of an intermediate frame. According to the invention, the false alarm rate is reduced, and reliable moving target detection can be realized.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A method and a device for detecting time-varying stable communities in a time-varying network
ActiveCN109921921AImprove accuracyImprove reliabilityData switching networksComplex network analysisCommunity structure
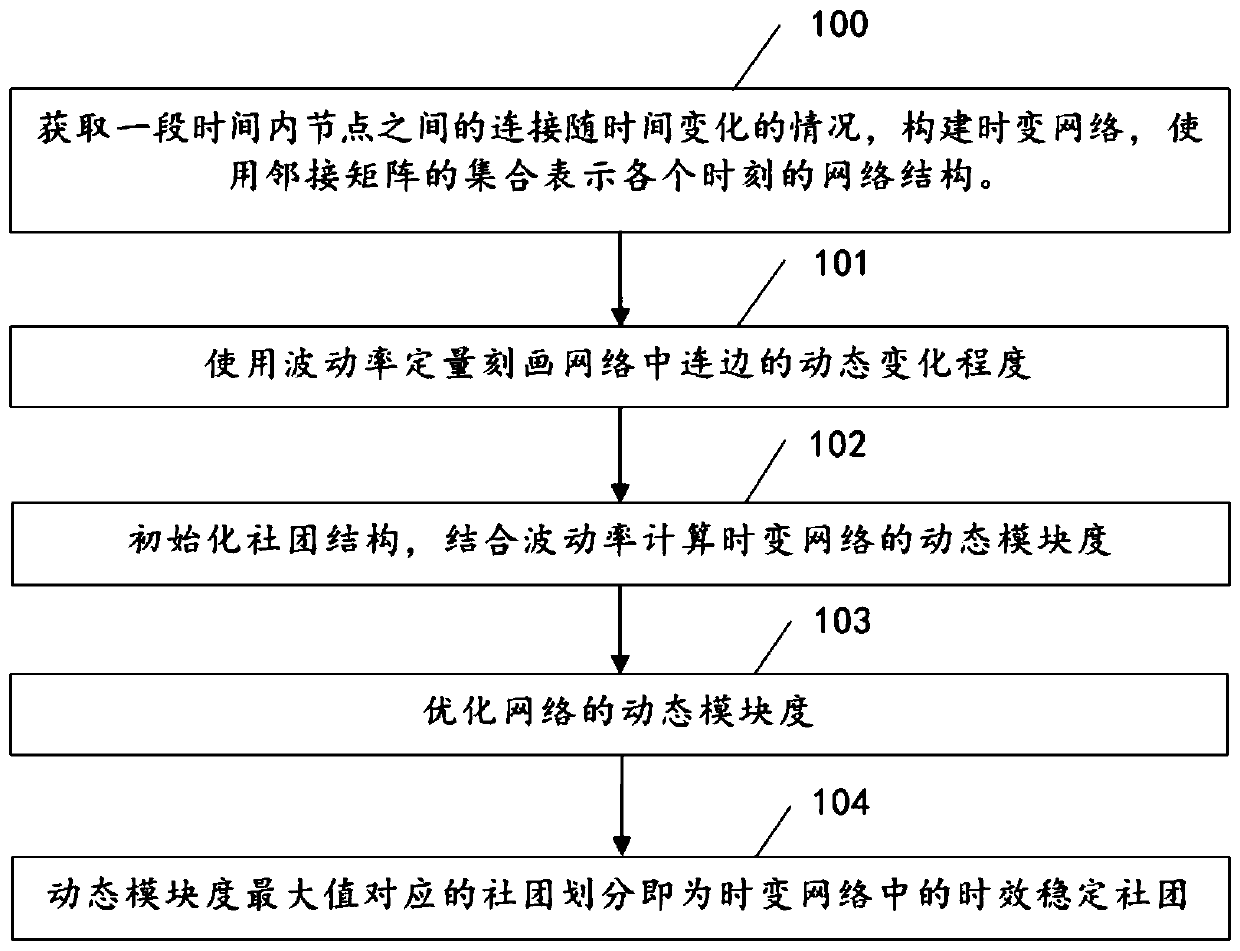
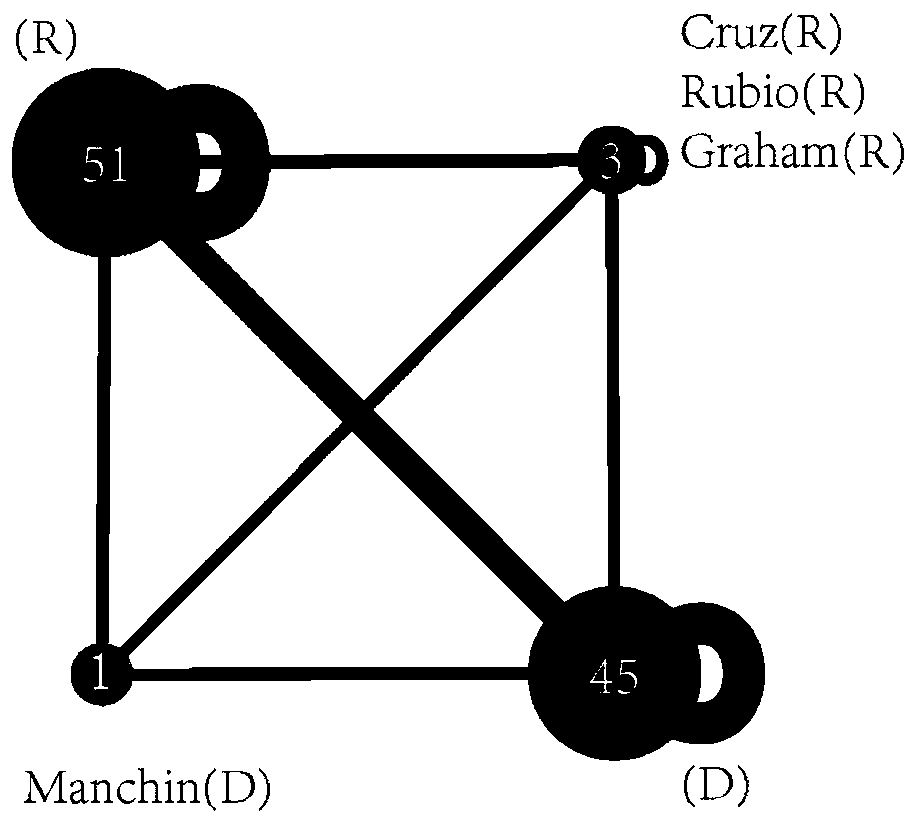
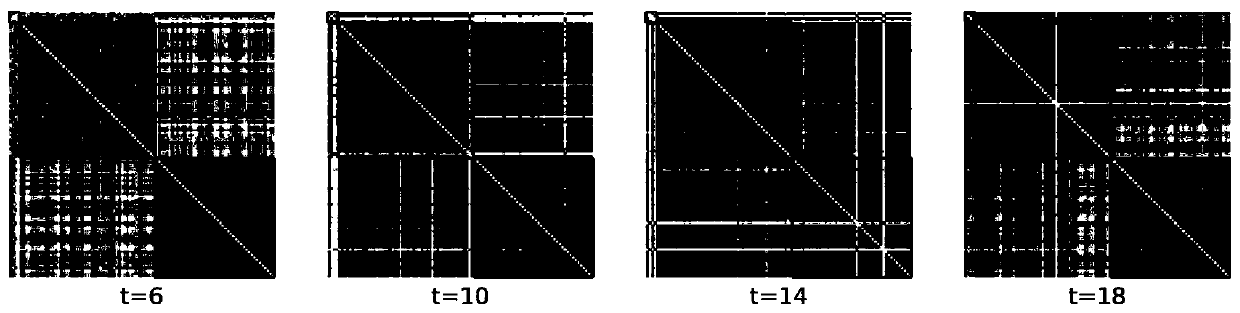
The invention belongs to the technical field of complex network analysis, and particularly relates to a method and a device for detecting aging stability communities in a time-varying network. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: acquiring the change condition of connection between nodes along with time, and constructing a time-varying network; Using the volatility to quantitatively describe the dynamic change degree of the connection edge in the network; Initializing a community structure, and calculating the dynamic modularity of the time-varying network in combination with the fluctuation rate; And optimizing the dynamic modularity, wherein the community structure corresponding to the maximum value is the time-varying stable community of the time-varying network. According to the invention, the network dynamic change is quantitatively described by using the volatility; the network dynamic change characteristics are combined with a community detection method; The method for identifying the stable community in the time-varying network is provided, the accuracy and reliability of community detection are improved, the method has wide application prospects in different fields of social networks, biological networks, traffic networks and the like, and meanwhile a new visual angle is provided for understanding the functions and the dynamic process ofthe community structure in a complex system in actual life.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Installation method and relative devices of business packet
InactiveCN102726025AInstallation supportDoes not cause coverageSpecial service provision for substationProgram loading/initiatingIp addressMedia access control
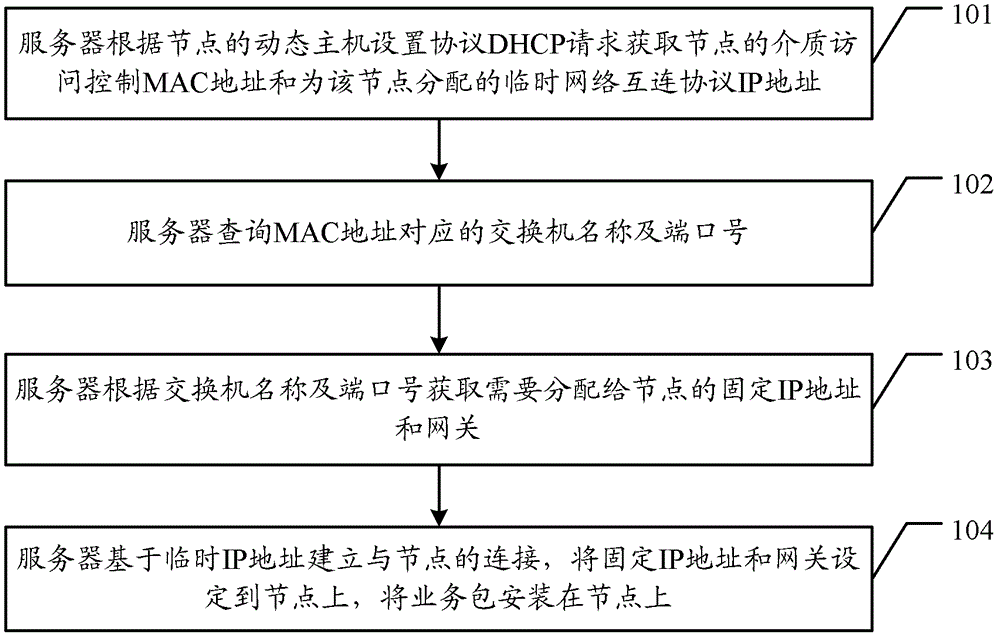
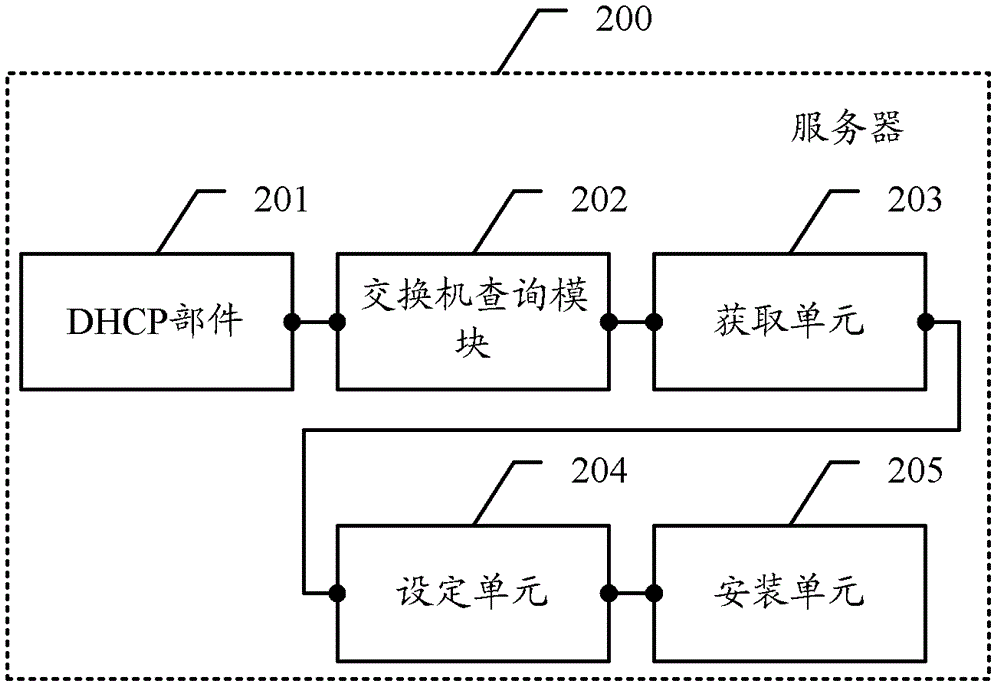
The present invention provides an installation method and relative devices of a business packet. The method comprises that: a server, according to a dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP) request of a node, acquires a media access control (MAC) address of the node and a temporal network Internet protocol (IP) assainged for the node; the server queries the switchboard name and a port number which are corresponding to the MAC address; the server, according to the switchboard name and the port number, acquires a fixed IP address and a gateway which are needed to be assigned to the node; the server, on the basis of the temporal IP address, builds a connection with the node, sets the fixed IP address and the gateway to the node, and installs the business packet on the node.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Incremental steady-state layout method for time-varying network data
InactiveCN109962811AImprove perceptionWeaken the visual effectData switching networksVisual presentationNetwork structure
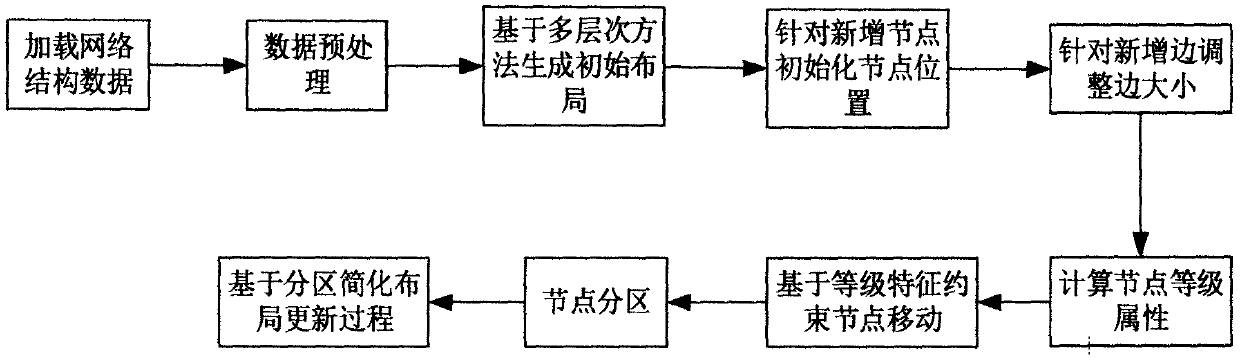
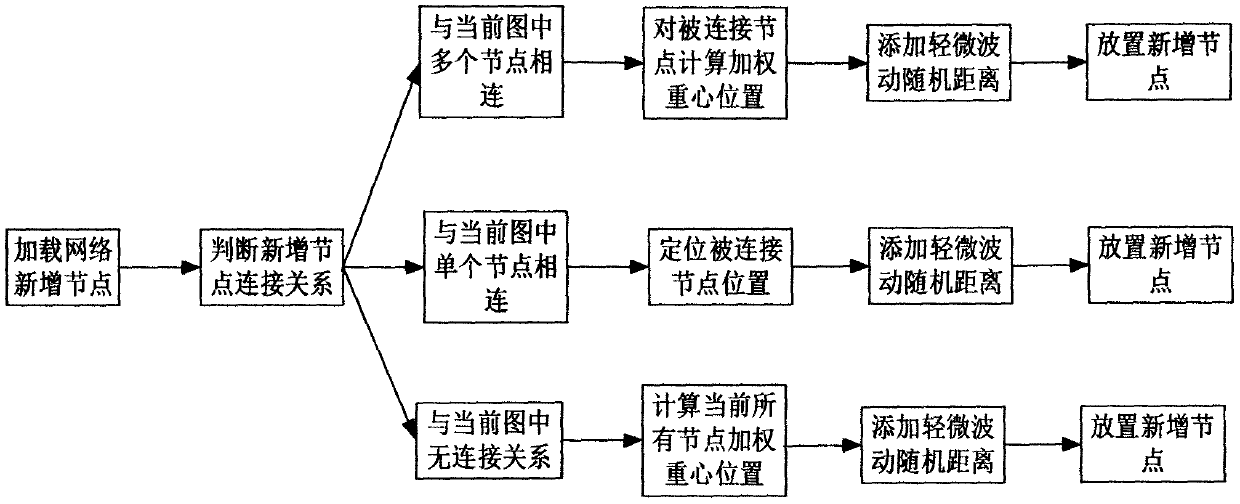
The invention discloses an incremental steady-state layout method for time-varying network data. The incremental steady-state layout method comprises the following steps: loading network structure data; preprocessing the data; generating an initial static graph by adopting a multi-level method; initializing node positions for newly added nodes; adjusting the length of the edge for the newly-addededge; calculating the level attribute of the node; partitioning the nodes, calculating the repulsive force in the form of pseudo nodes, and simplifying the layout updating process of the force guidingalgorithm. According to the invention, a stable layout method for time-varying network data is designed as a starting point; a force guide graph is used as a basic visual presentation mode; network structure characteristics such as'node level 'are introduced, it is guaranteed that focus of interest of a user does not change suddenly in the large-range change process of the network topology structure, the stability and continuity of the cognitive process of the user are kept, the user is helped to understand the topology structure of a complex network more effectively, and the understanding difficulty of the time-varying network topology structure is reduced.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
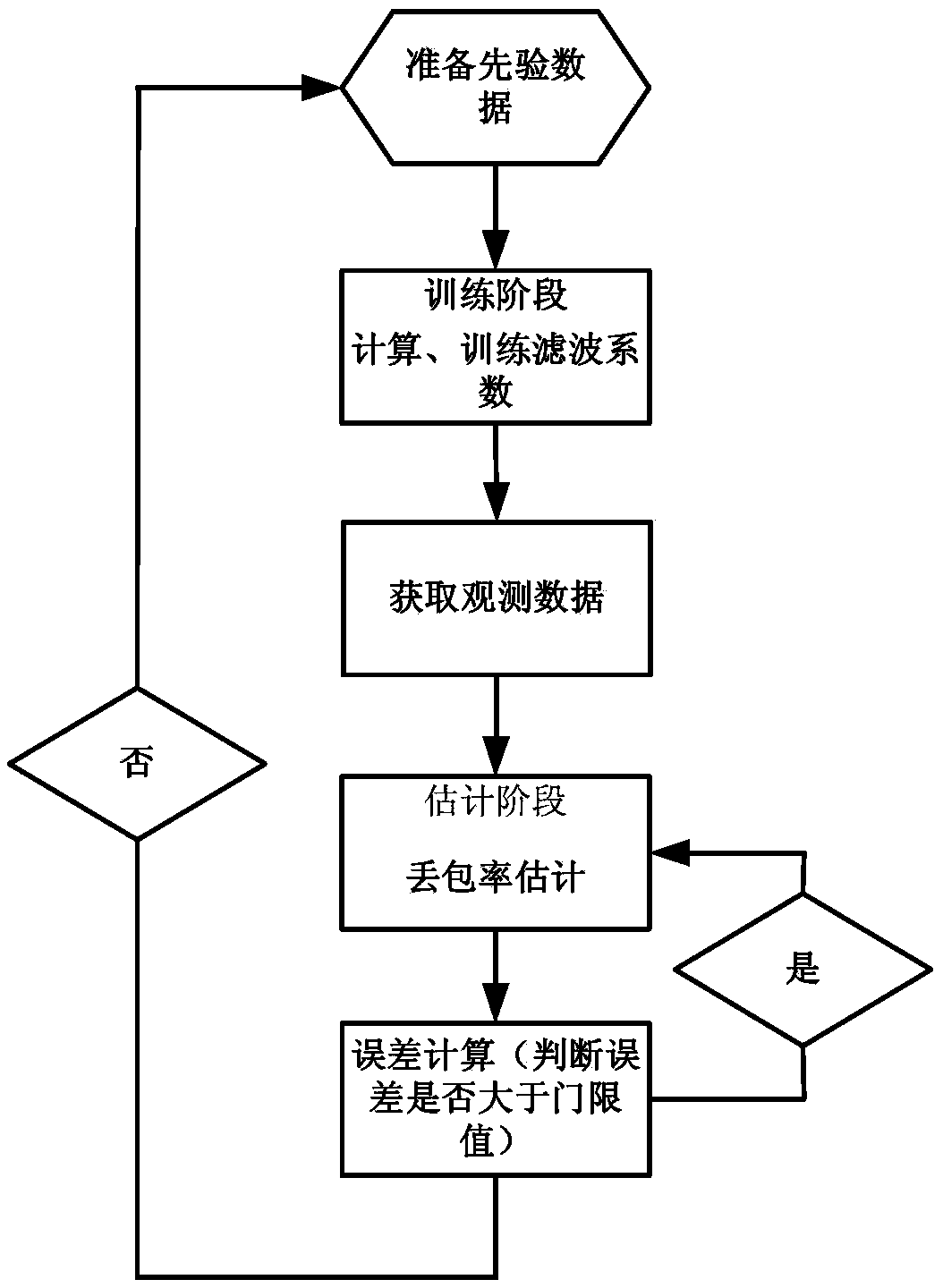
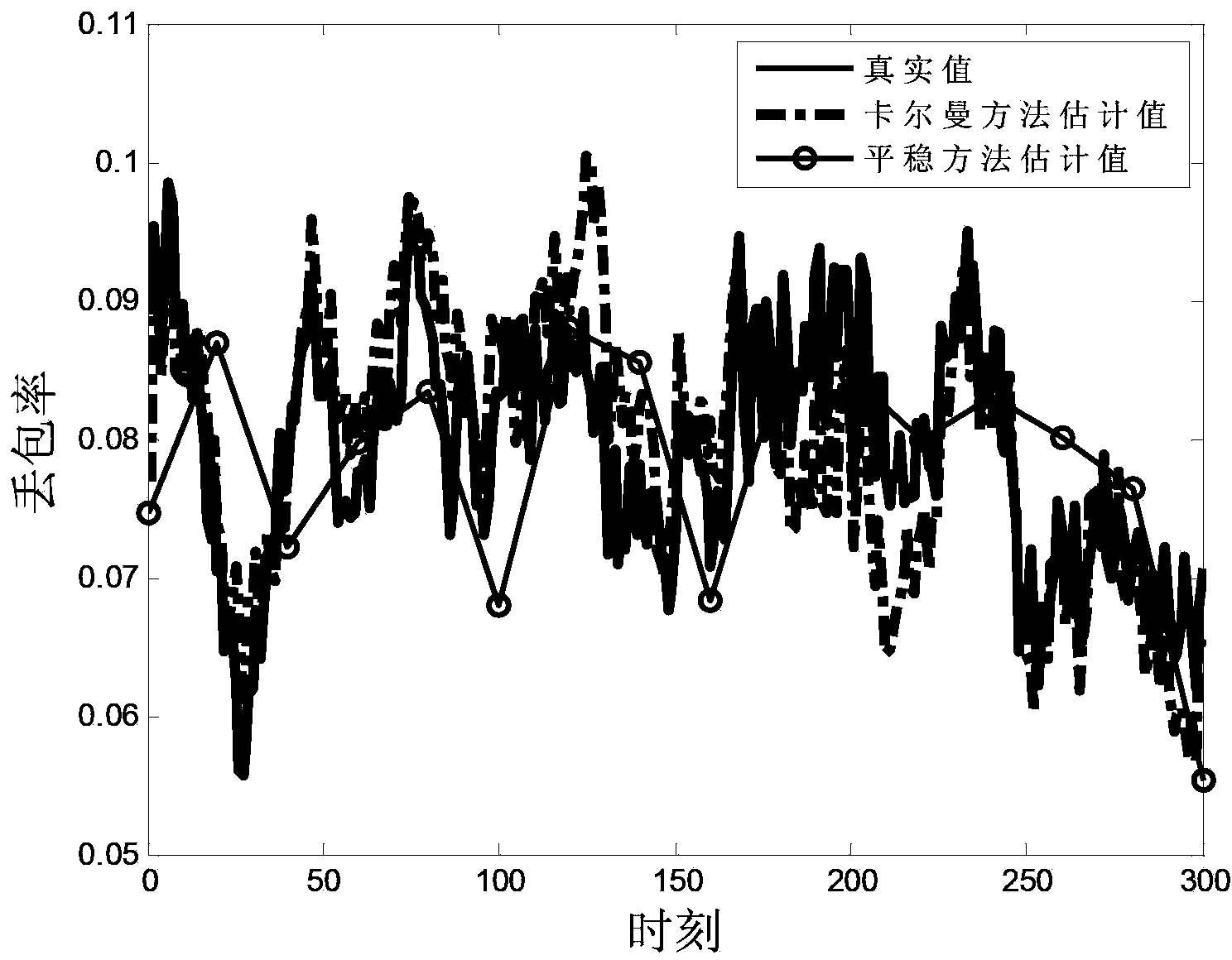
Time varying network link packet loss probability estimation method based on Kalman filter
InactiveCN103490955AReact to time-varying properties in real timeReduce mean square errorError preventionData switching networksPacket lossProbability estimation
The invention discloses a time varying network link packet loss probability estimation method based on a Kalman filter. The time varying network link packet loss probability estimation method based on the Kalman filter mainly comprises a training phase and an estimation phase. In the training phase, a source node sends back-to-back detection packets to multiple destination nodes so as to obtain path data, then, prior information of time varying link packet loss probability is estimated according to the path data, and a state transition equation of the Kalman filter is established. In the estimation phase, under the condition that the detection packets do not need to be sent, recursive computation and estimation of the time varying link packet loss probability are completed through a feedback control method according to the state transition equation and the path data obtained from network background flow. Due to the fact that a Kalman filter module is introduced to estimate the link packet loss probability of a time varying network, an obtained link packet loss probability estimated result has a minimum mean square error as well as high estimated accuracy, and the time-variation characteristic of the time varying network link packet loss probability can be reflected in real time.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com