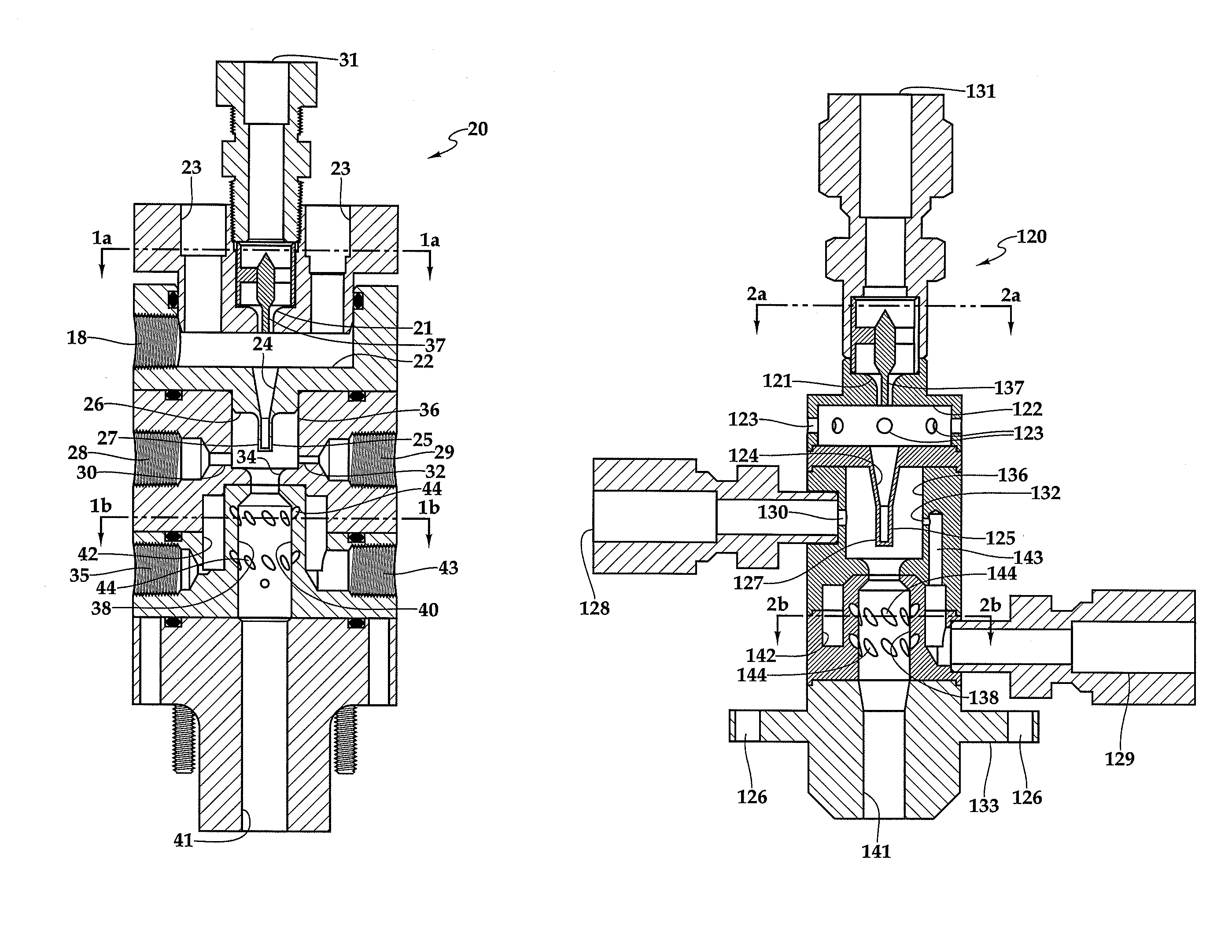
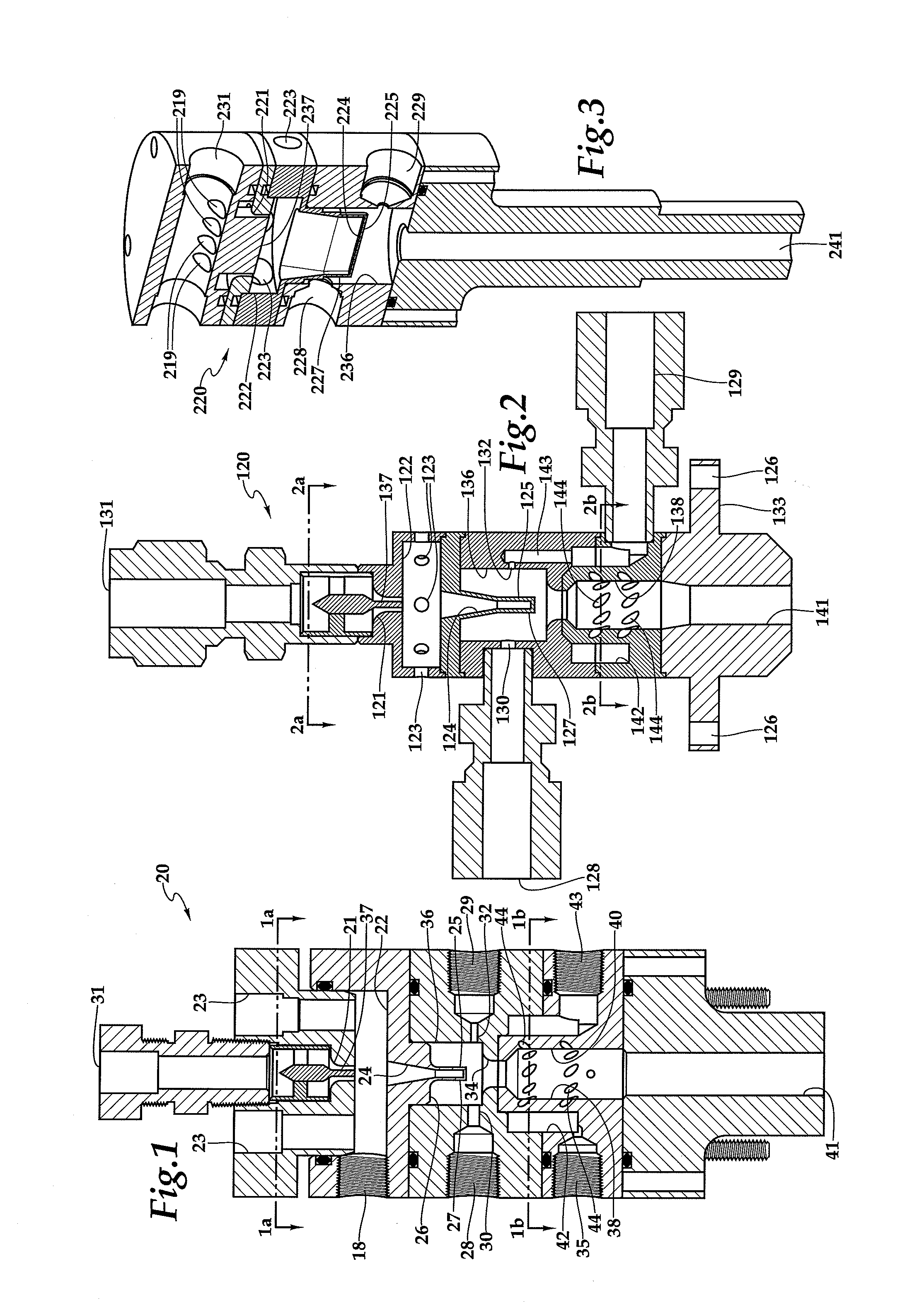
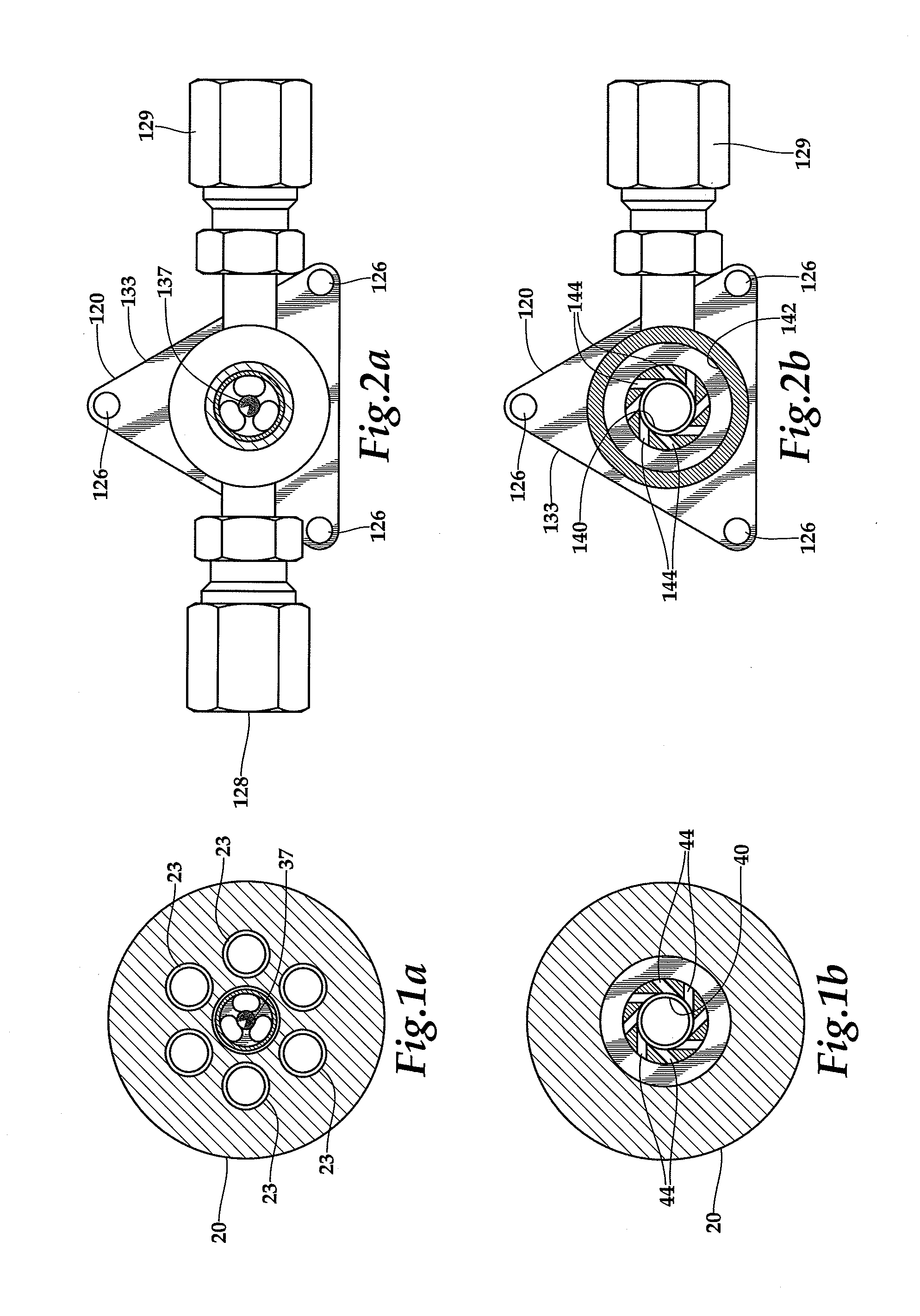
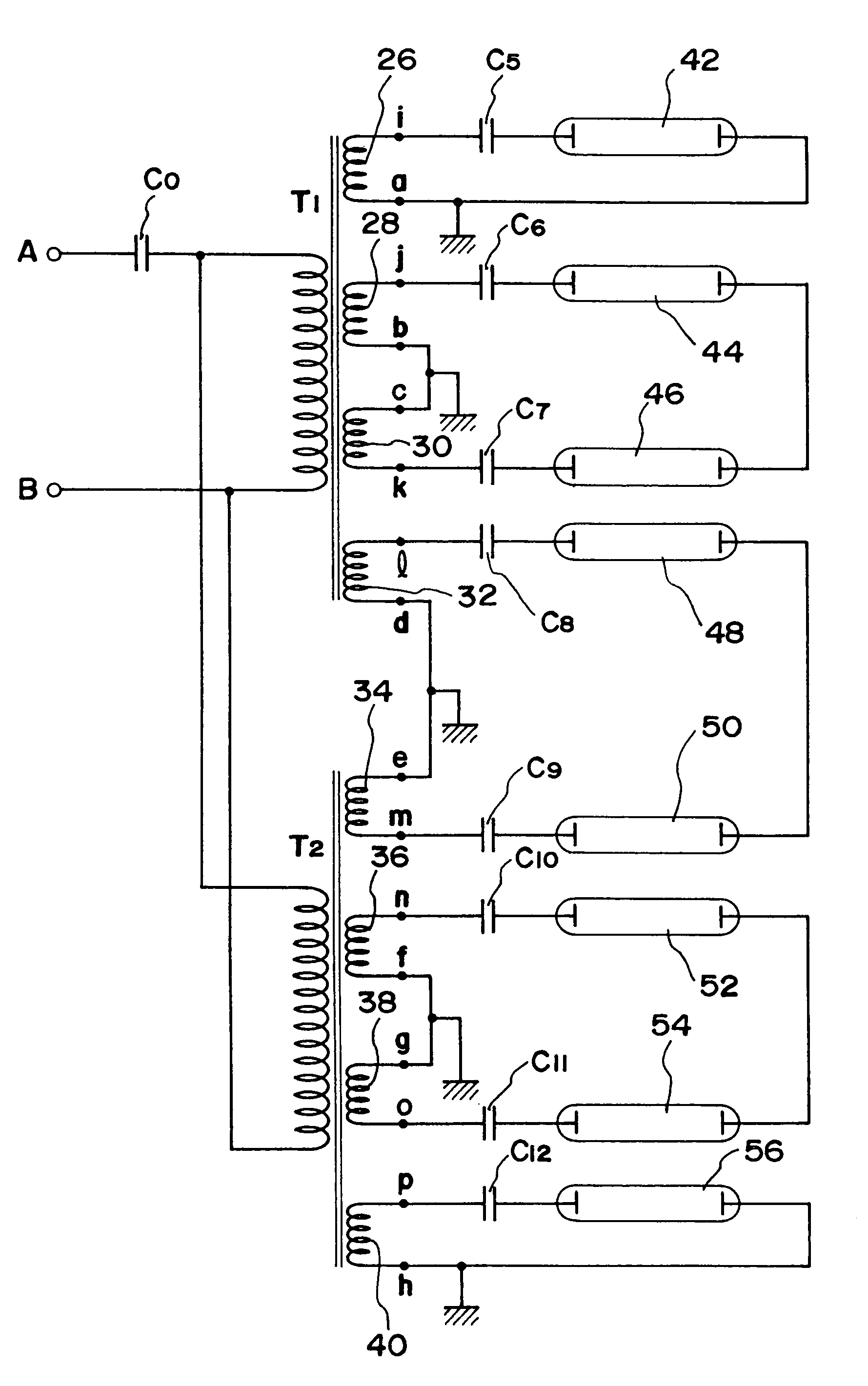
Patents
Literature
56results about "Electrostatic ignition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
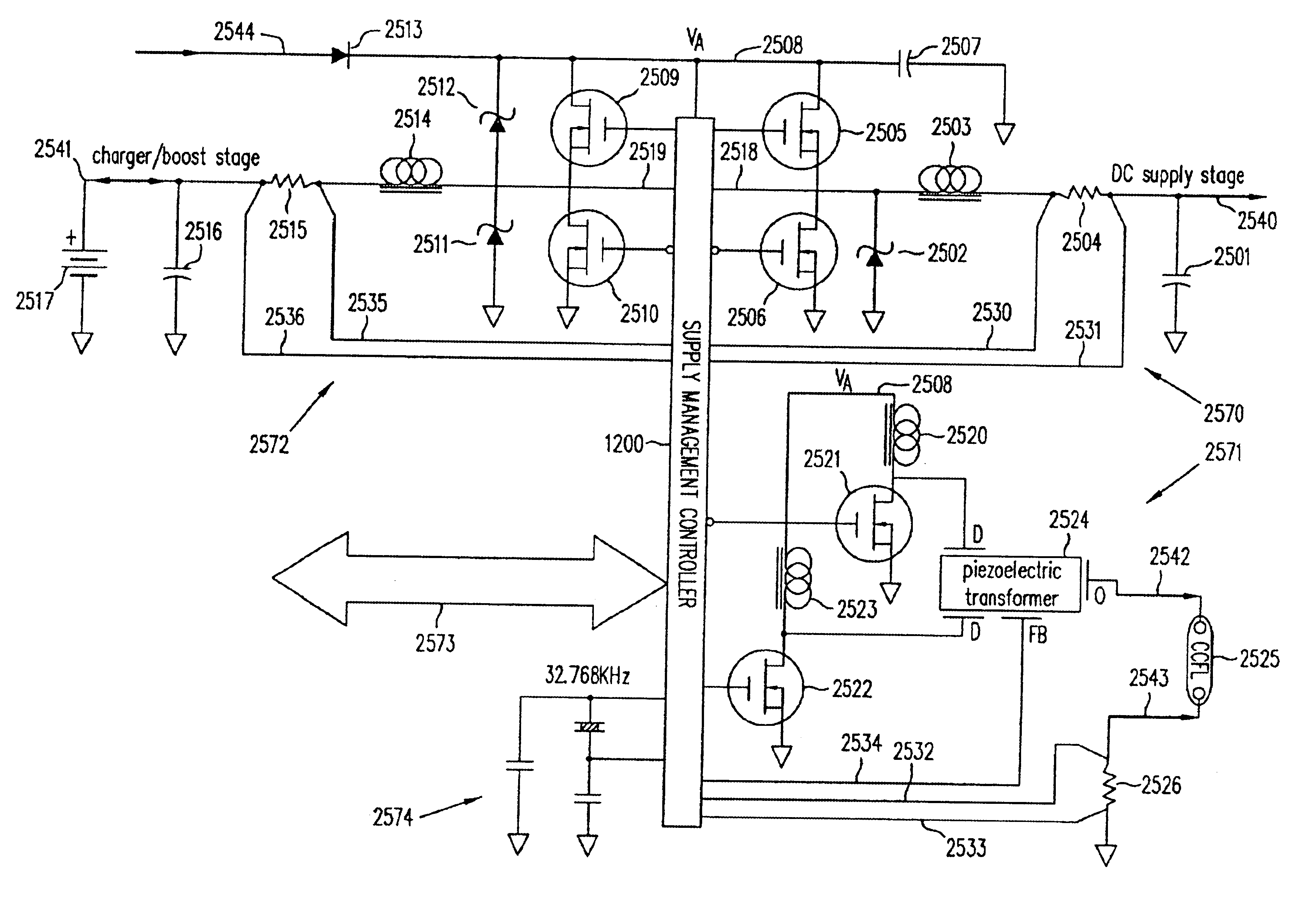
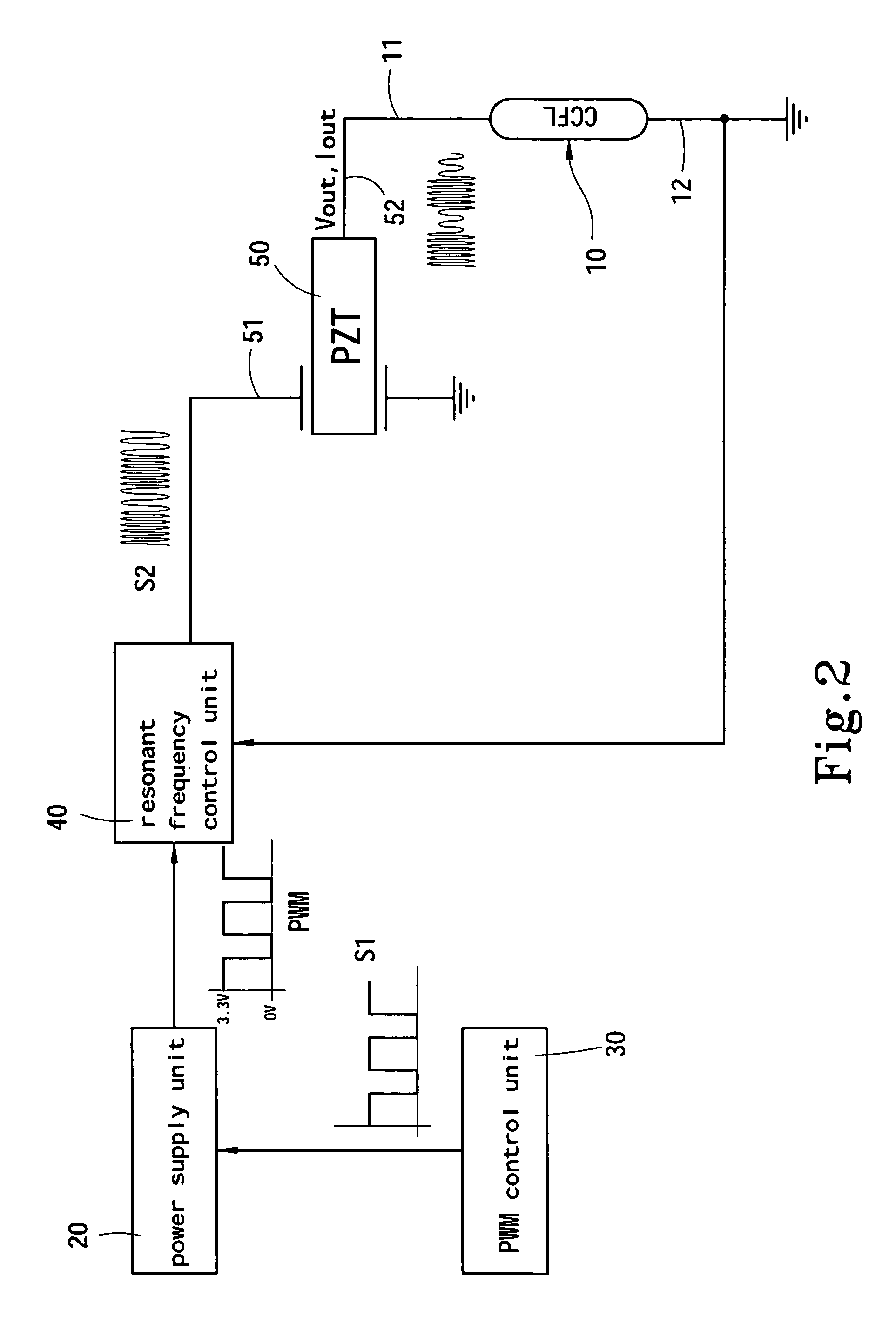
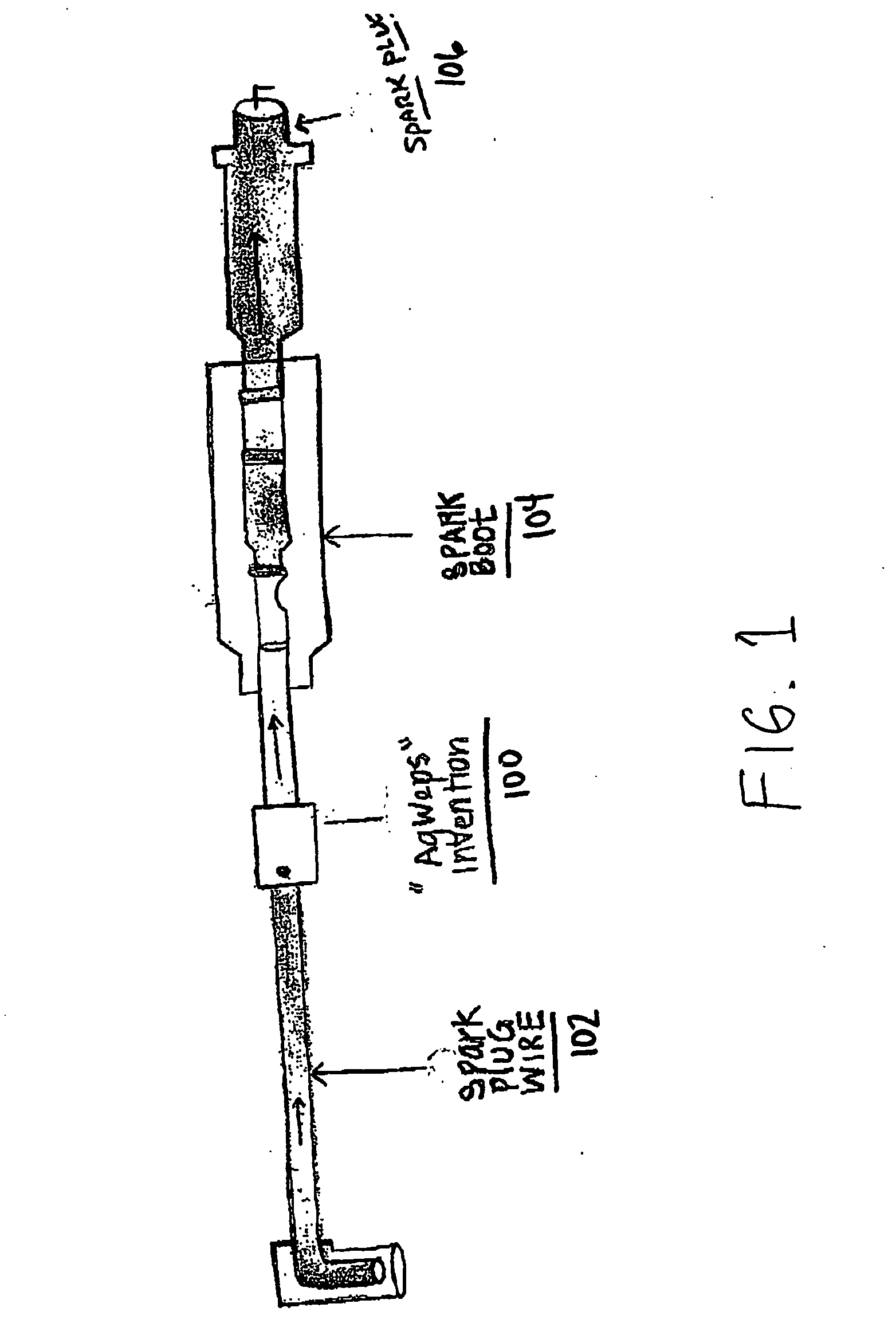
Method of tuning a circuit for energizing a cold cathode fluorescent lamp
Method of tuning a drive circuit for a cold cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL). The drive circuit includes a piezoelectric transformer coupled to an output of first and second transistors. The frequency of drive signals to the first and second transistors are varied until about a ninety degree phase relationship is achieved between the frequency of the drive signals and a frequency of voltage across a resistor connected to the CCFL is achieved. Alternatively, the frequency of the drive signals provided to the first and second transistor is adjusted as needed to achieve maximum output voltage.
Owner:EXAR CORP
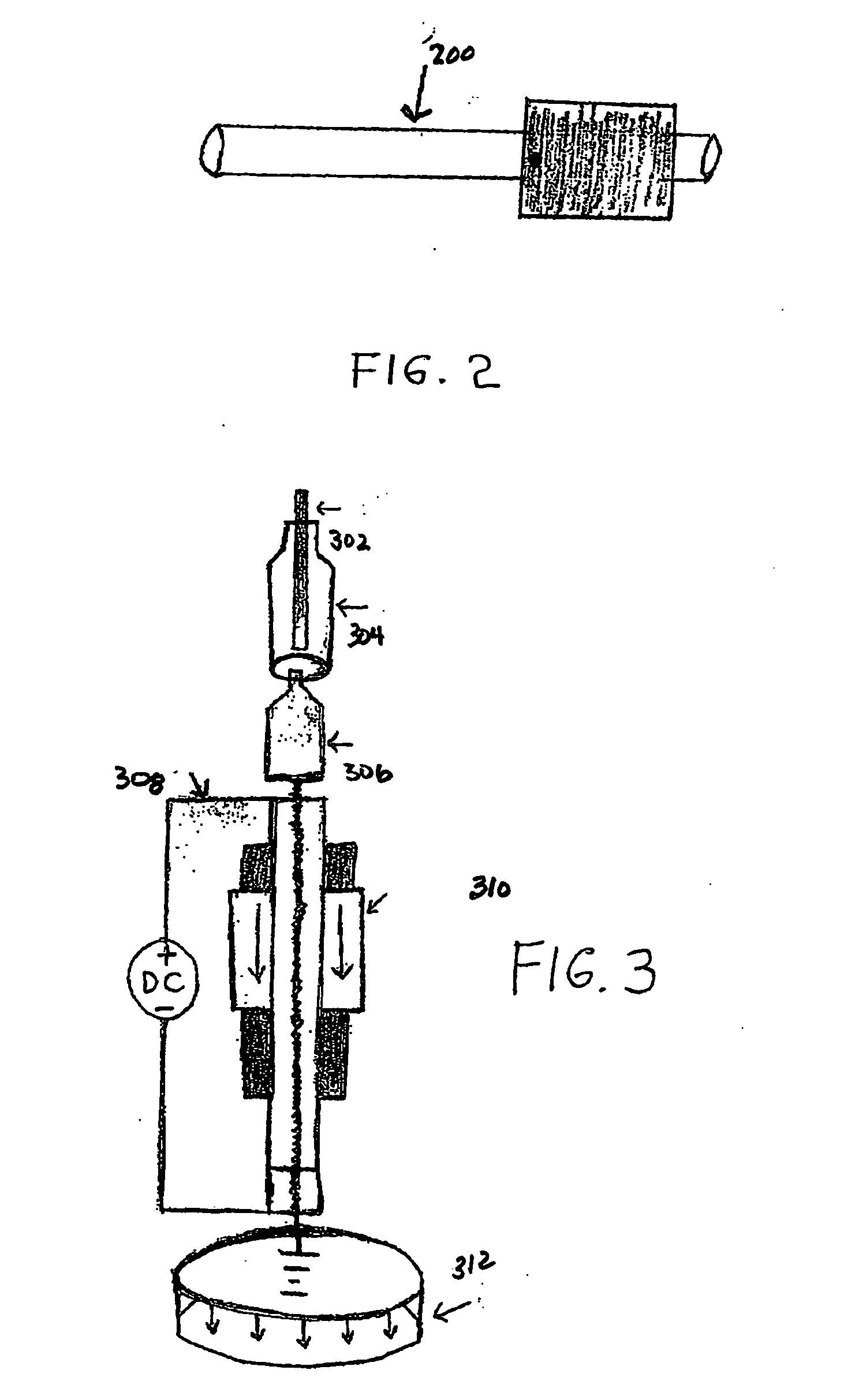
Plasma ignition for direct injected internal combustion engines
InactiveUS6883490B2Extend engine lifeGreater engine durabilitySparking plugsPower operated startersCombustion chamberPollutant emissions
Owner:JAYNE MICHAEL E
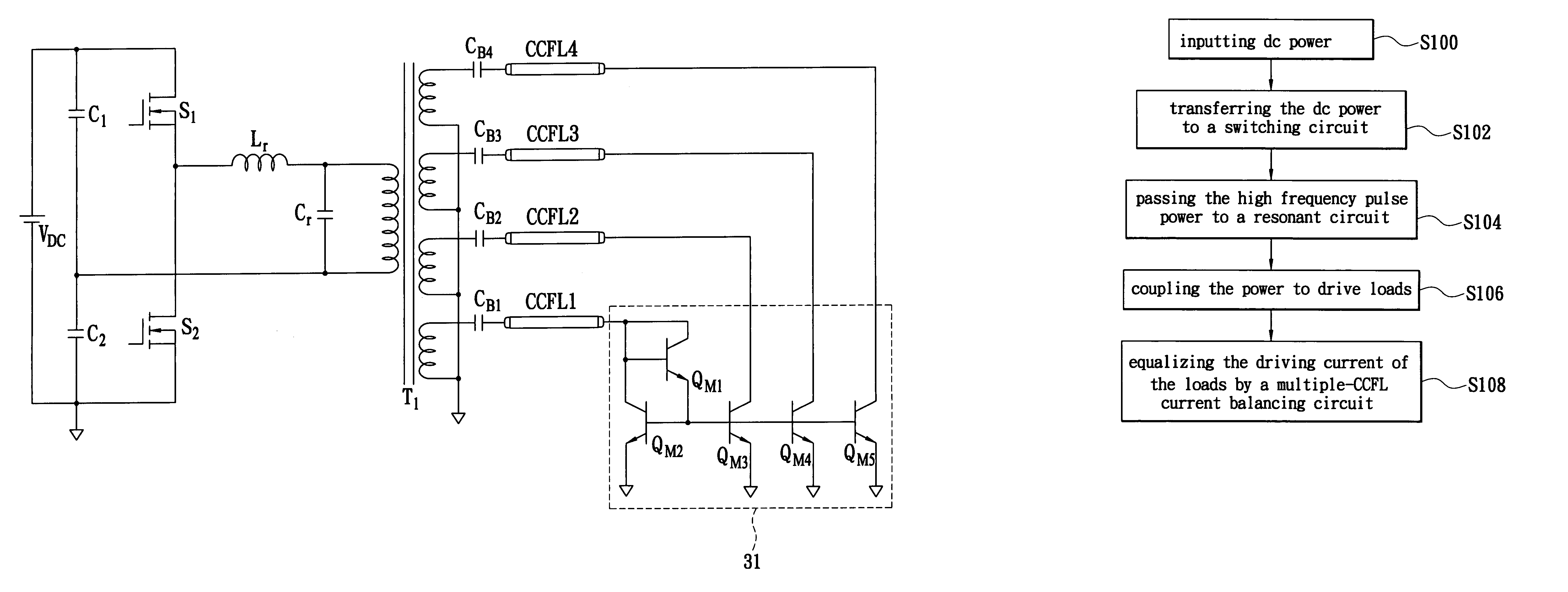
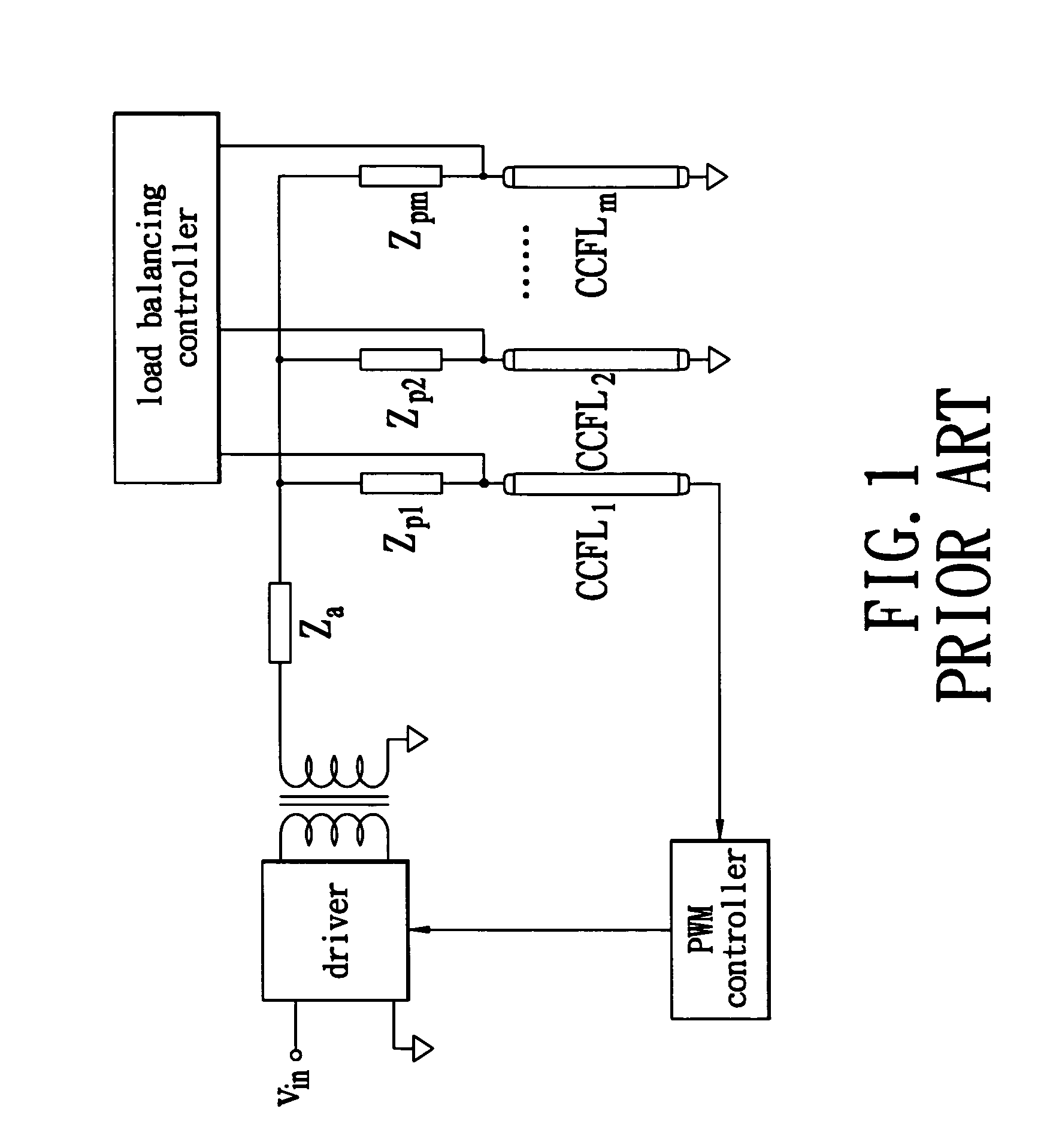
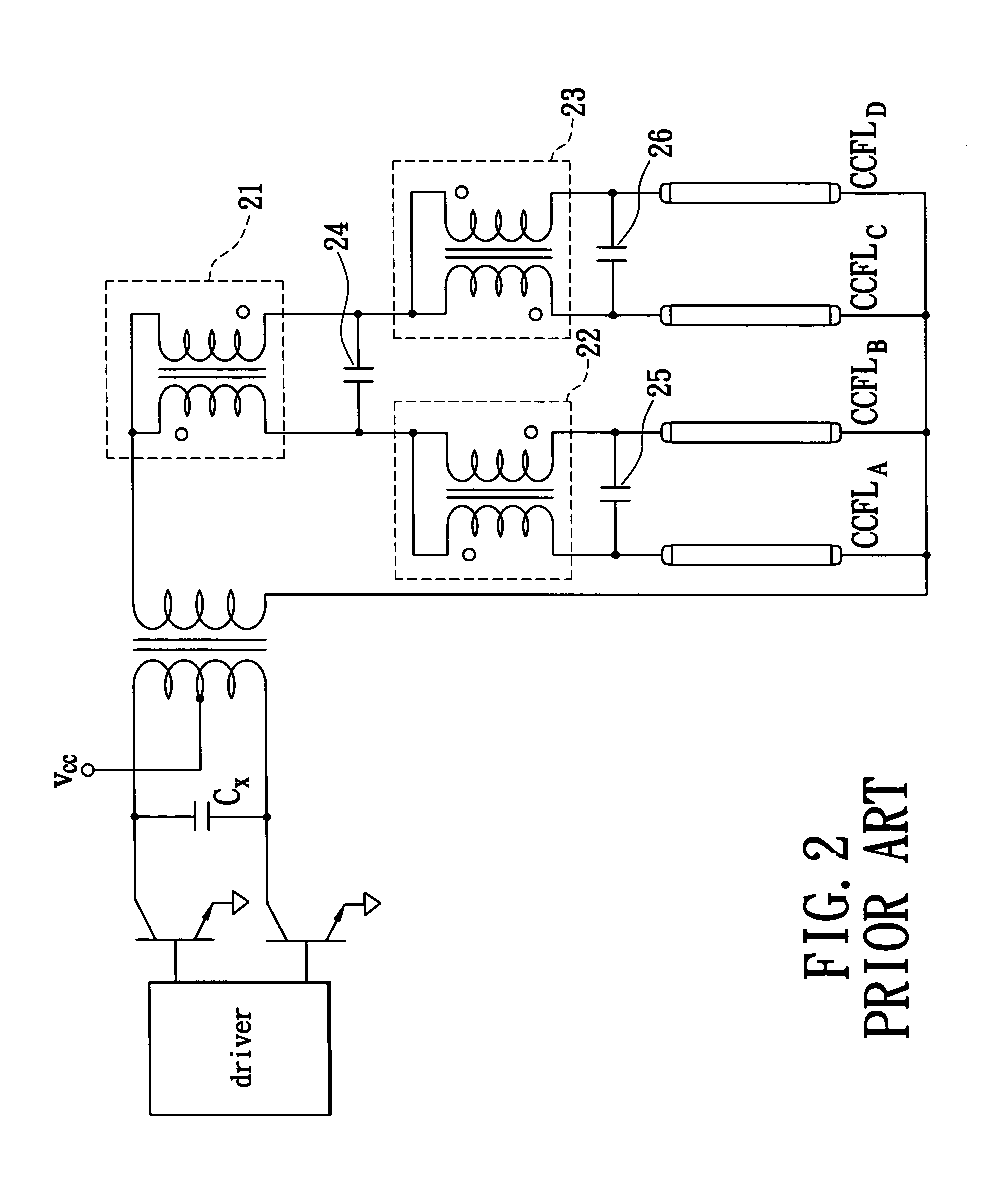
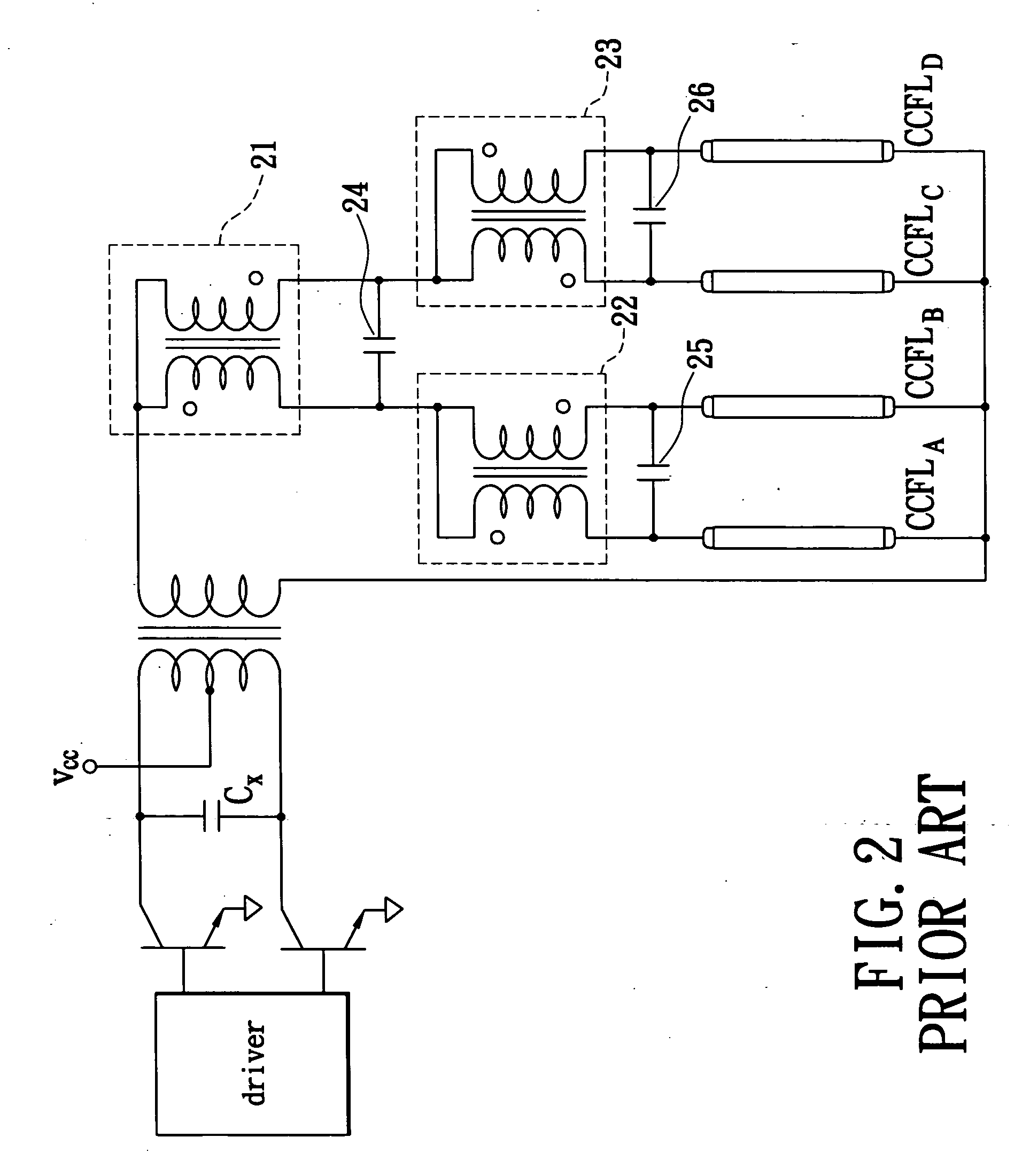
Multiple-CCFL parallel driving circuit and the associated current balancing control method for liquid crystal display
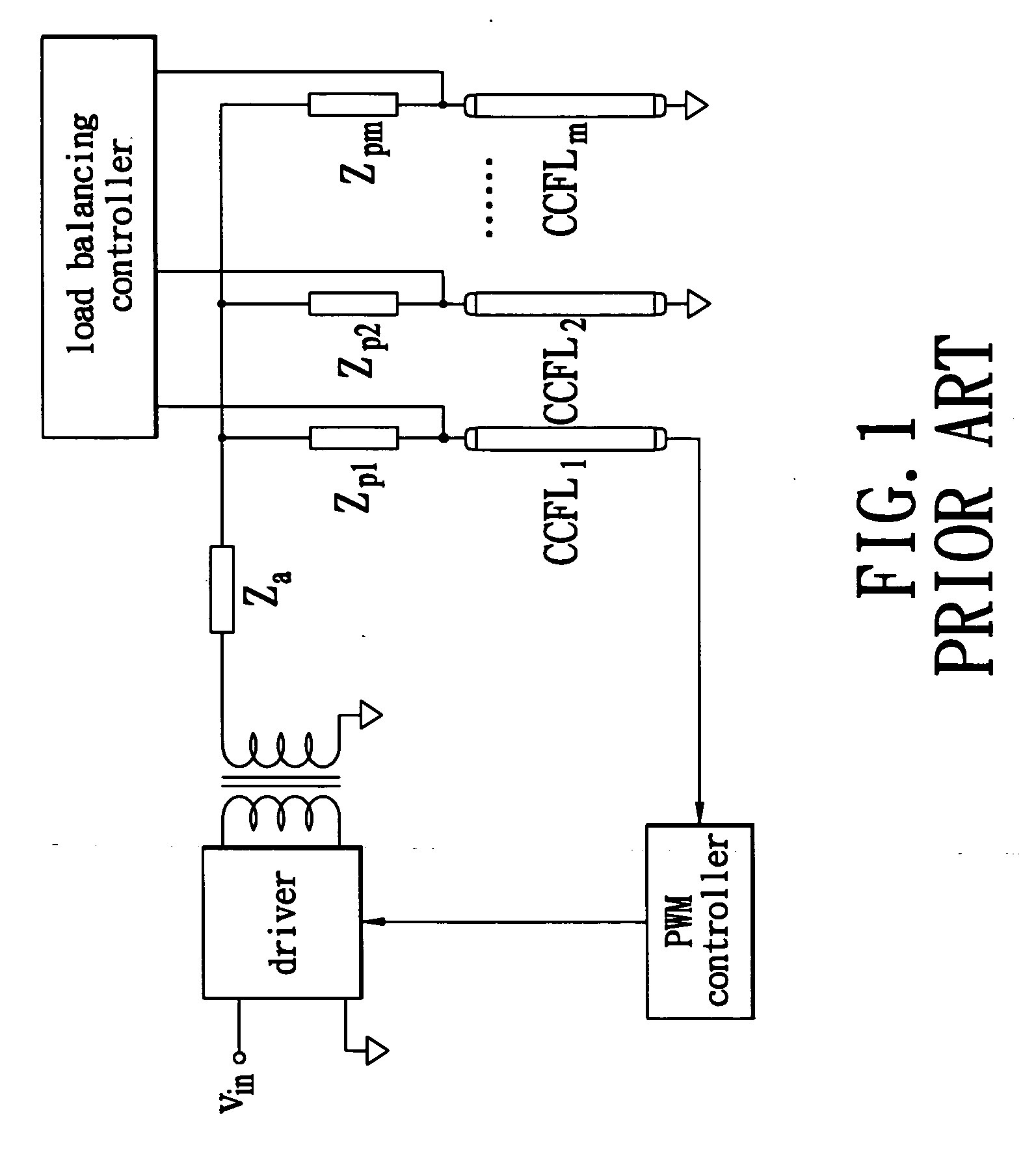
InactiveUS7042171B1Improve uniformityAchieve balanceElectric light circuit arrangementMachines/enginesDriving currentLiquid-crystal display
A multiple-CCFL parallel driving circuit and the associated current balancing control method for LCD are presented, wherein the circuit comprises a plurality of CCFLs for providing the backlight for a LCD; a boosting transformer with a plurality of outputs for providing the driving voltage and current for driving the plurality CCFLs; a plurality of ballast capacitors, the ballast capacitors connect between the boosting transformer and the CCFLs; and a multiple CCFL current balancing circuit. This invention uses a low cost current mirror circuit to equalize the driving current of a plurality of CCFLs and thus significantly improve the uniformity of the displayed image on a large-size LCD.
Owner:HSIU YING LI +3
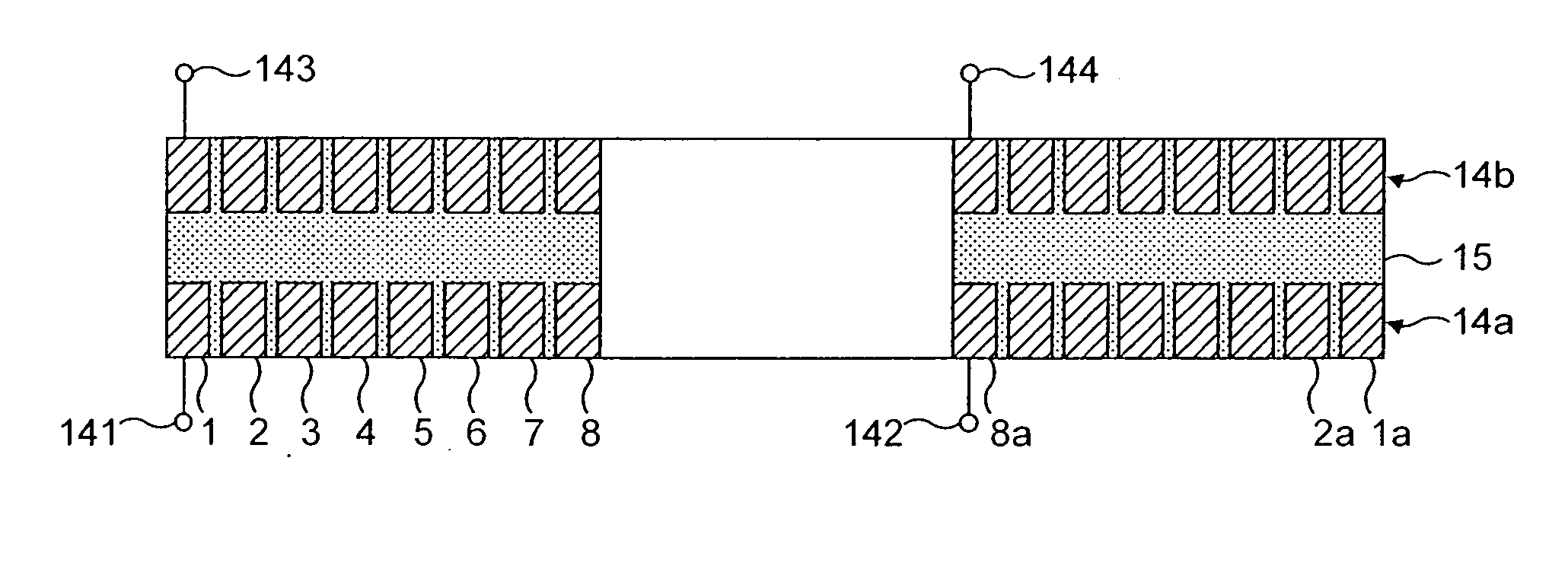
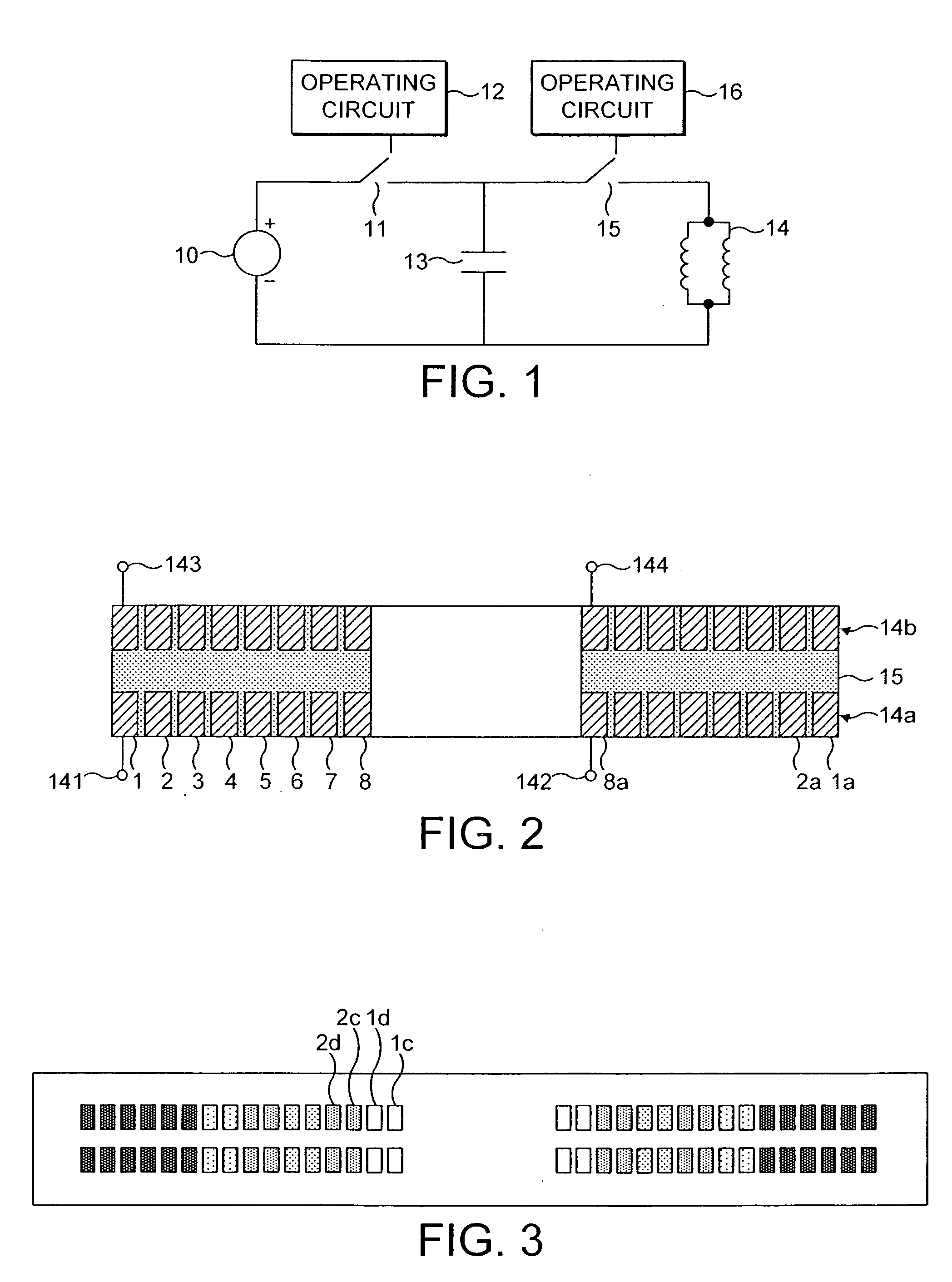
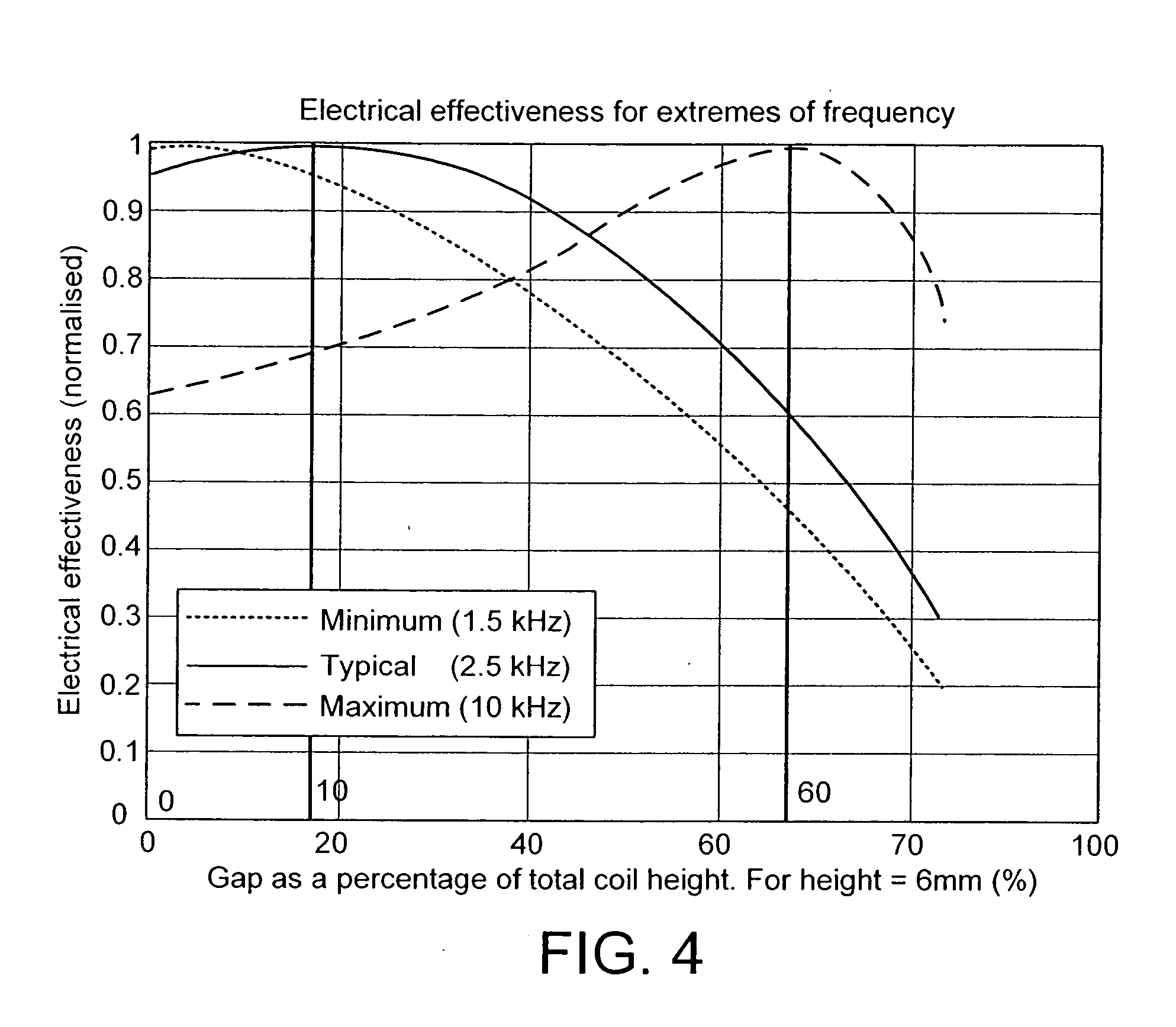
Magnetic stimulators and coils therefor
A magnetic coil inductor for use in magnetic stimulators comprises two face-to-face electrically connected windings each having a multiplicity of turns of a respective conductor. Corresponding turns are separated by a gap which typically is of the order of 18 to 20% of the total height of the coil. The magnetic stimulator includes a discharge capacitor and a switch arrangement operable to provide discharge pulses at a selected repetition rate through the inductor, the inductor and the capacitor constituting a resonant circuit of which the resonant frequency is substantially in excess of the repetition rate and is typically between 2 and 6 kHz.
Owner:THE MAGSTIM
Glow plug type acoustic resonance igniter
ActiveUS9476399B1High oxygen/fuelMinimal energyGas turbine plantsRocket engine plantsCombustion chamberHydrogen
An acoustic resonance igniter uses high-pressure helium to heat a resonance cavity so a hot surface of the resonance cavity forms a source of ignition to a combustion chamber. The resonance cavity may be round or may extend linearly to increase the size of the hot surface. The combustion chamber is cooled by arranging a feed of hydrogen and oxygen which is oxygen rich and which becomes more so when ignition occurs. A second combustion chamber receives the combustion chamber output and adds additional hydrogen through ports tangential to the wall of the second combustion chamber to enrich the fuel ratio and cool the second combustion chamber. The acoustic resonance igniter is used to ignite a large rocket engine or to form a rocket thruster.
Owner:SIERRA SPACE CORP
Drive circuit for illumination unit
InactiveUS7166969B2TransformersElectric light circuit arrangementOutput transformerOutput transformerless
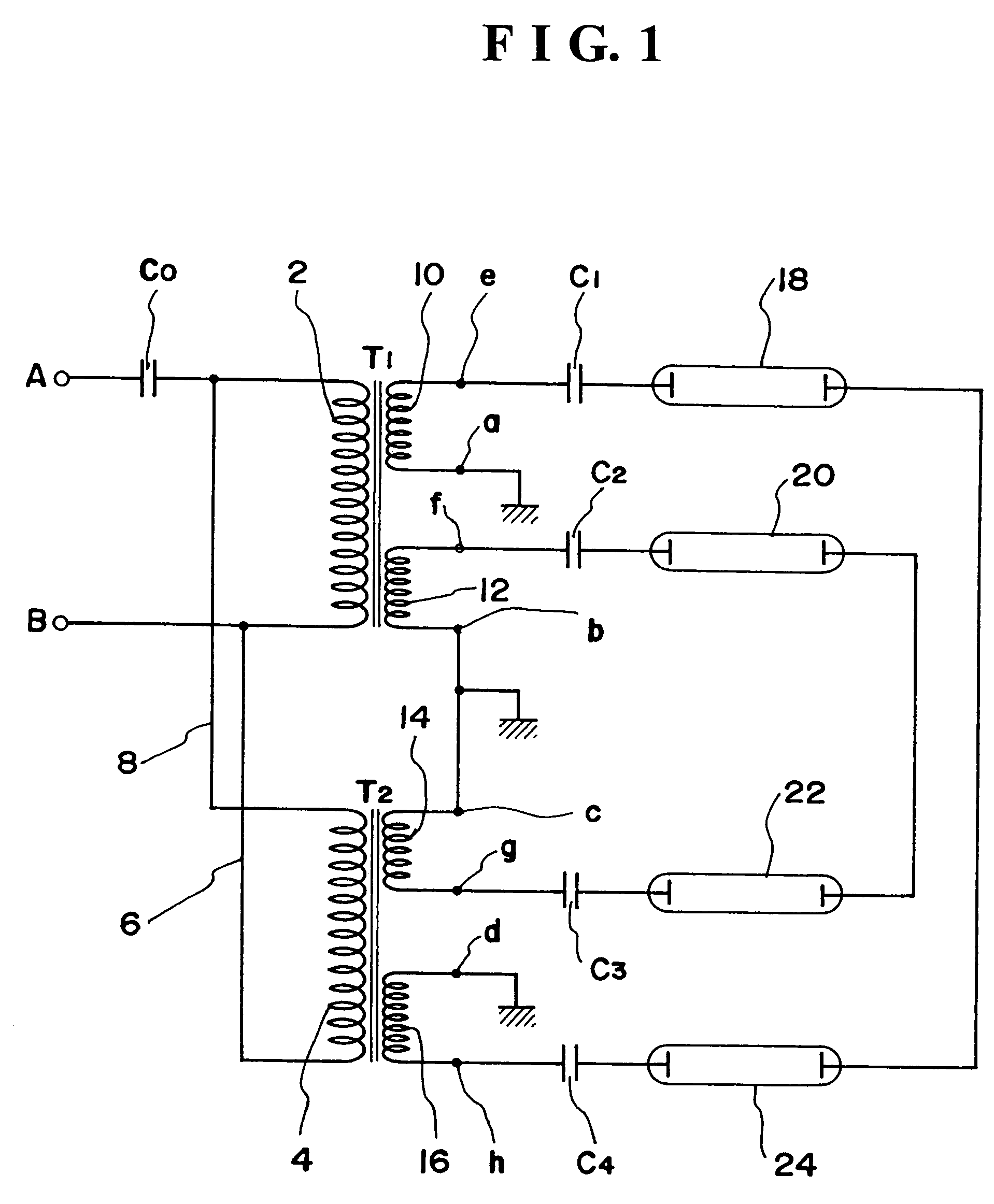
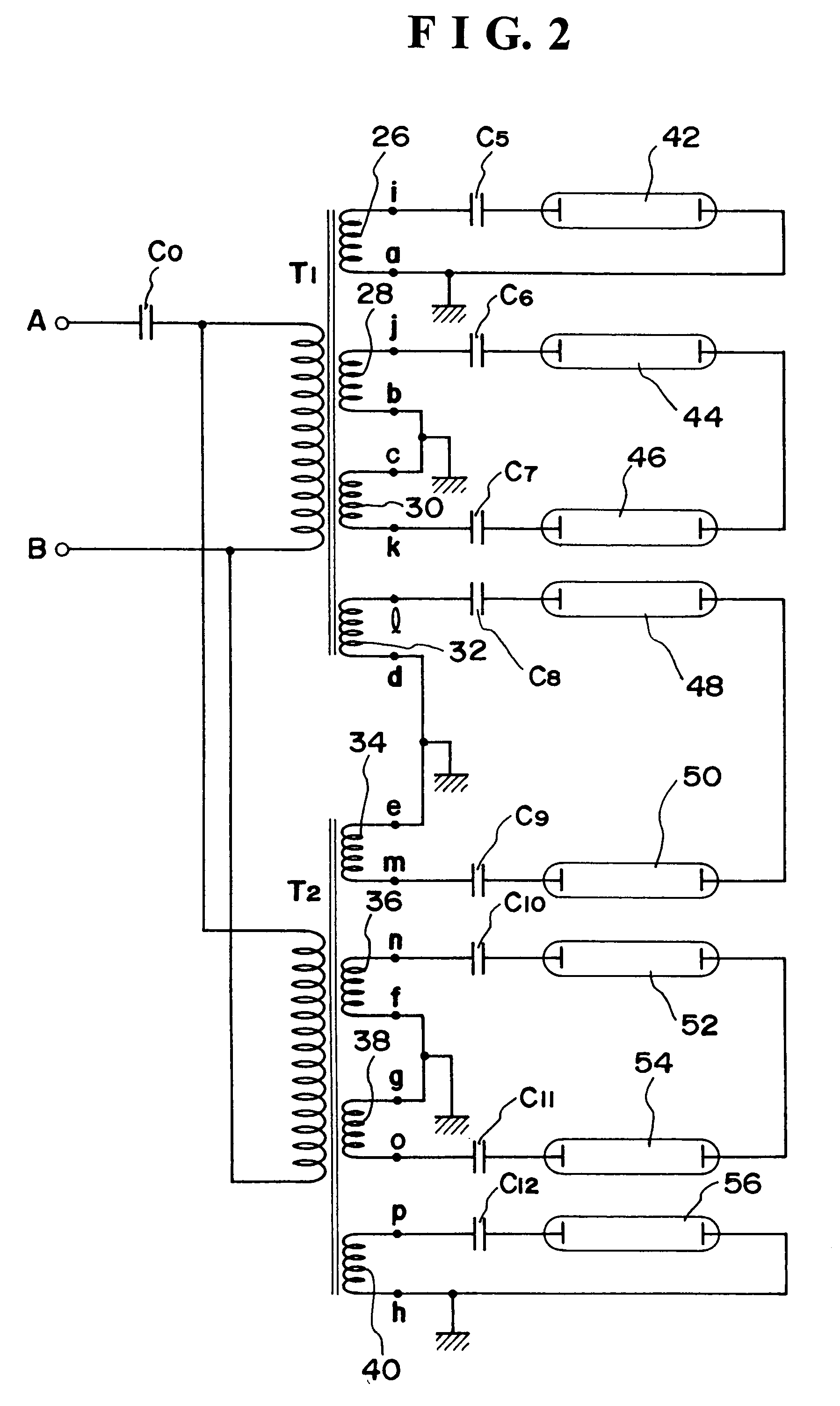
In case of driving a plurality of lamps with the use of a plurality of output transformers, a difference in the bright-ness of each lamp occurs by a dispersion of characteristics of the output transformers, and an object is to prevent such troubles. For this purpose, a primary side of a plurality of output transformers of a one input-plural output type are respectively connected, and illumination units are connected to the secondary side of each output transformer. All of the secondary output terminals of each output transformer are connected to the secondary output terminals of counter phase and are connected by forming a loop circuit with the connection of the output terminals in series in closed loom form. The illumination units are connected between the secondary output terminals of the output transformer and the output terminal of the other output transformer of counter phase with the output terminal.
Owner:KOHNO KAZUO
Multiple-ccfl parallel driving circuit and the associated current balancing control method for liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20060113926A1Improve uniformityAchieve balanceElectric light circuit arrangementMachines/enginesCapacitanceTransformer
A multiple-CCFL parallel driving circuit and the associated current balancing control method for LCD are presented, wherein the circuit comprises a plurality of CCFLs for providing the backlight for a LCD; a boosting transformer with a plurality of outputs for providing the driving voltage and current for driving the plurality CCFLs; a plurality of ballast capacitors, the ballast capacitors connect between the boosting transformer and the CCFLs; and a multiple CCFL current balancing circuit. This invention uses a low cost current mirror circuit to equalize the driving current of a plurality of CCFLs and thus significantly improve the uniformity of the displayed image on a large-size LCD.
Owner:HSIU YING LI +3
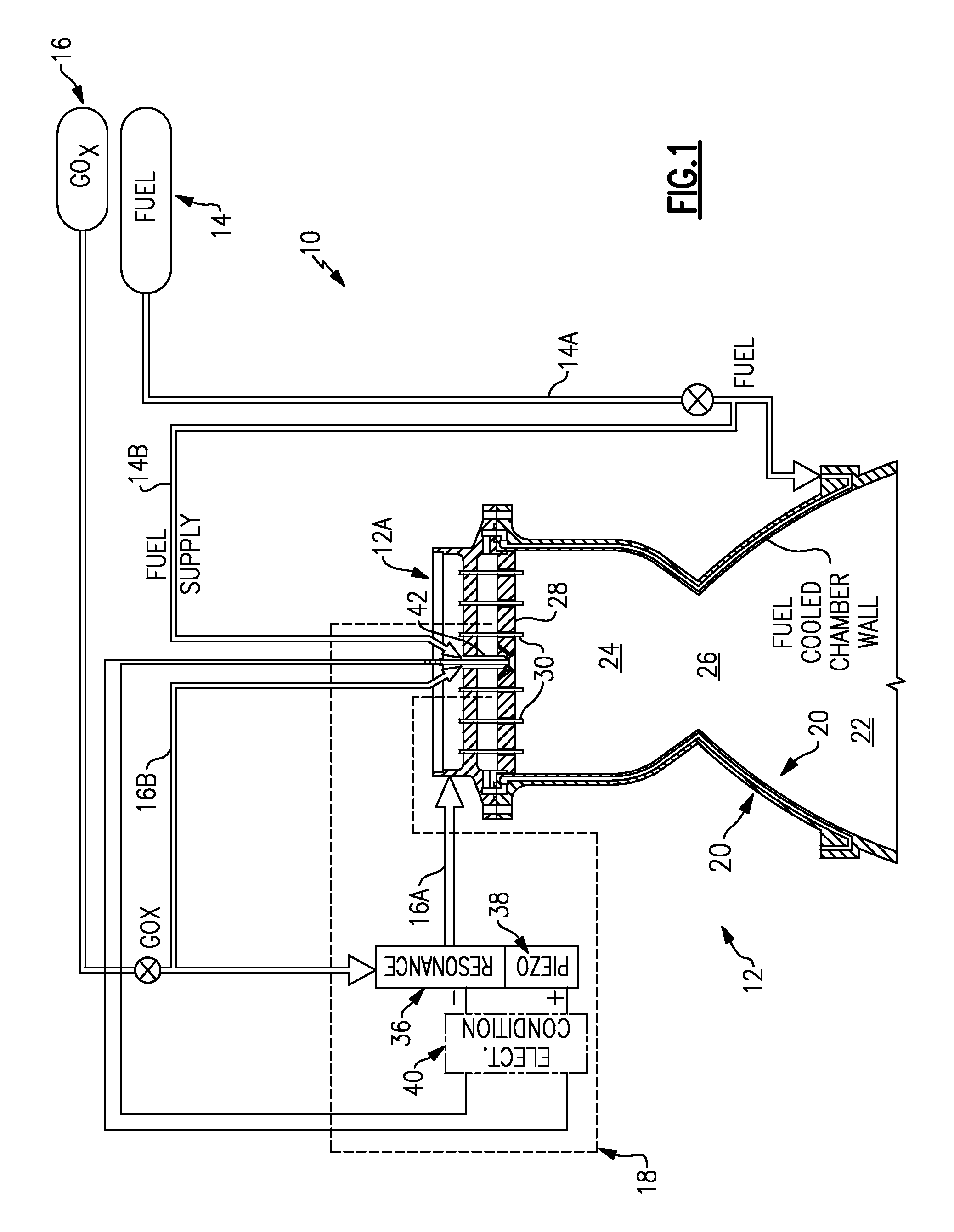
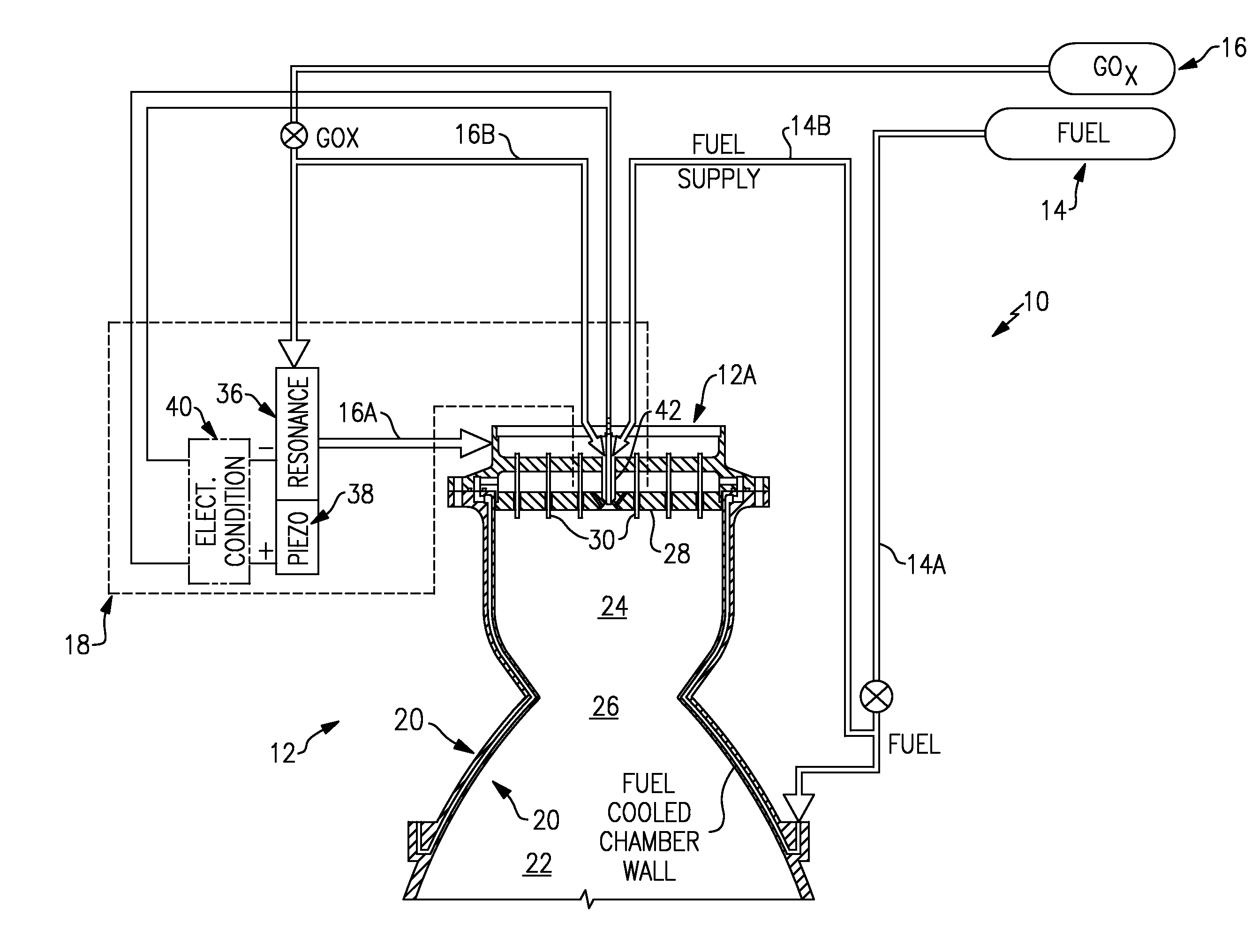
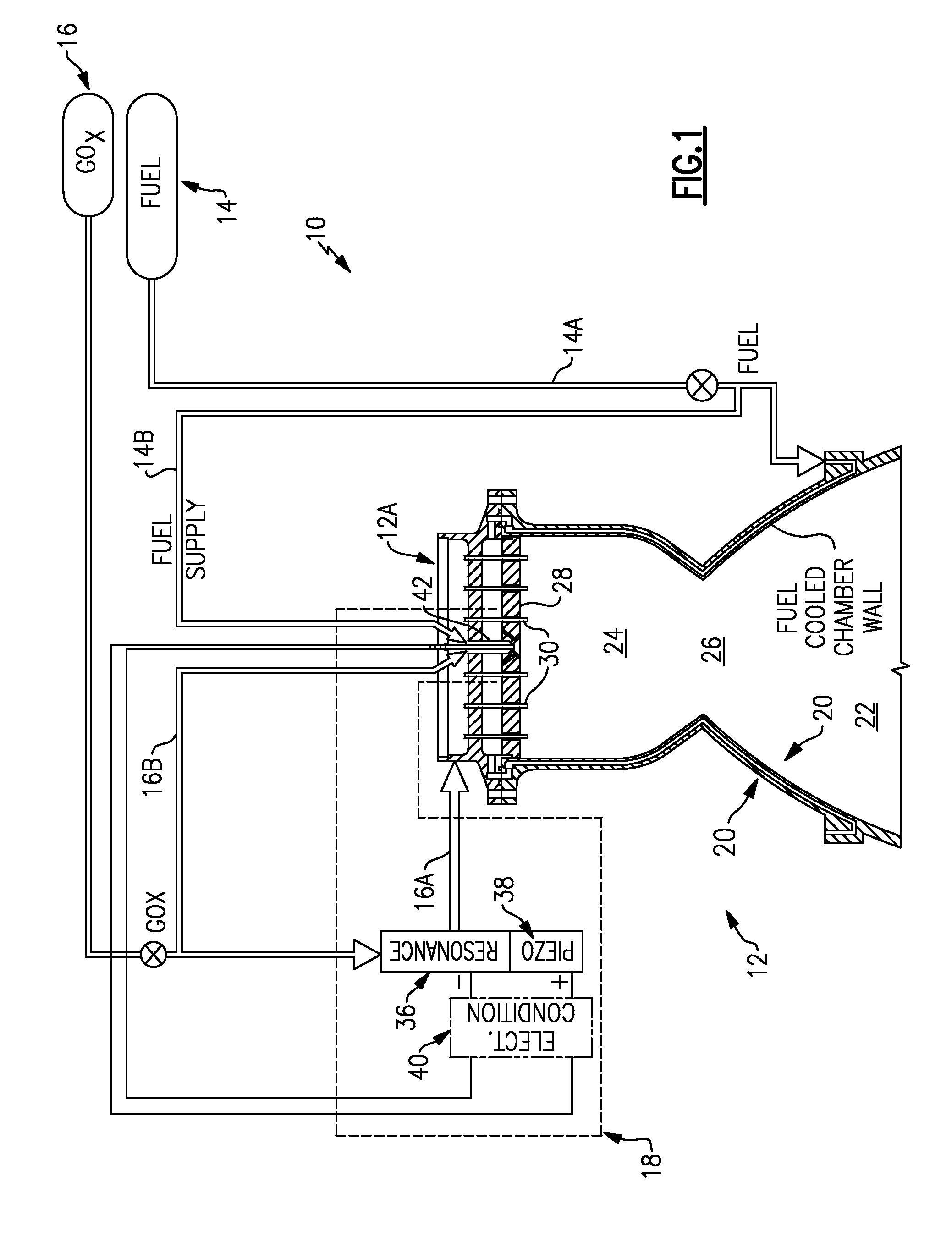
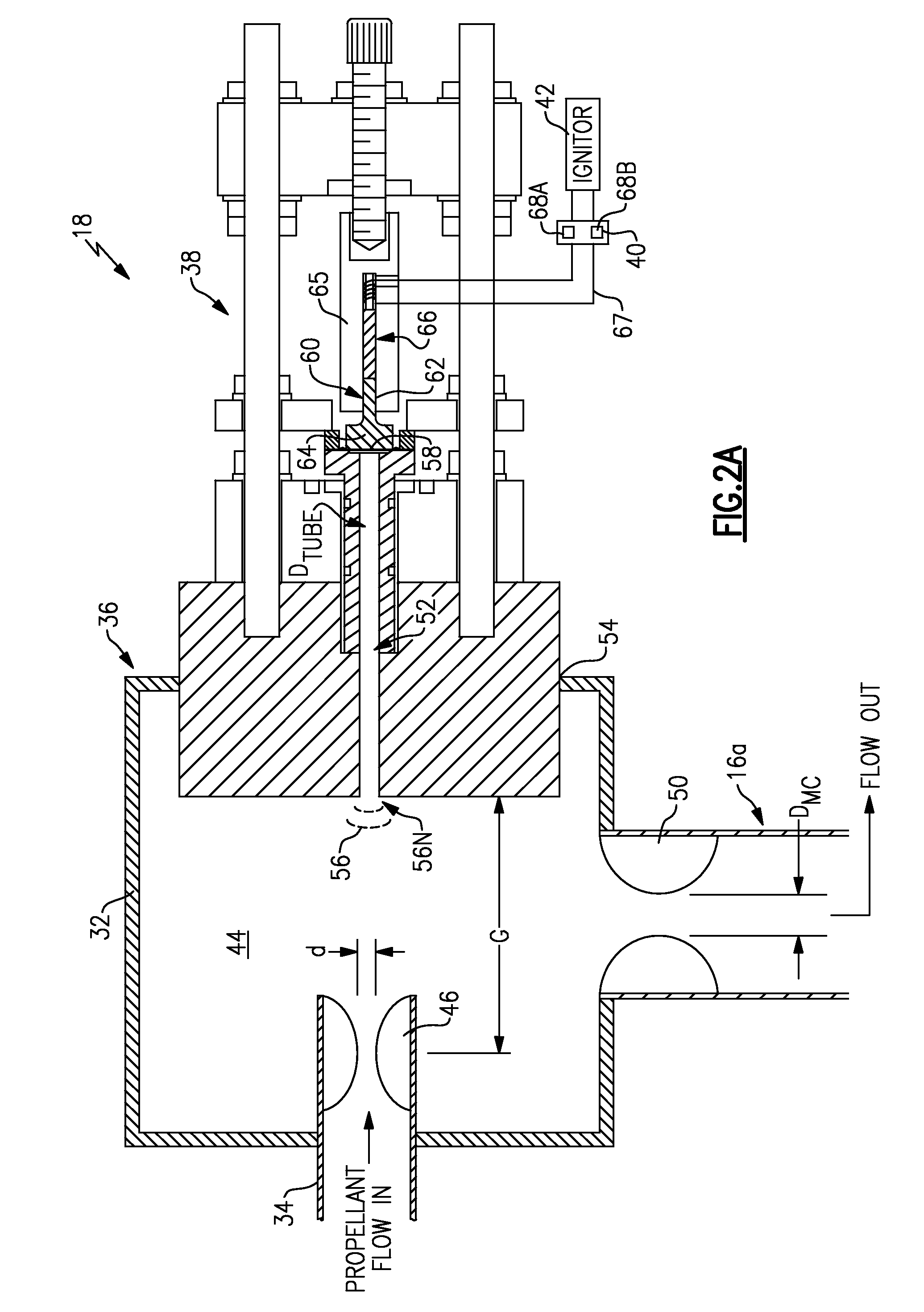
Piezo-resonance igniter and ignition method for propellant liquid rocket engine
ActiveUS7565795B1Increase net force outputAvoid smallCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCombustion chamberEngineering
Owner:AEROJET ROCKETDYNE OF DE
DA/AC convert for driving cold cathode fluorescent lamp
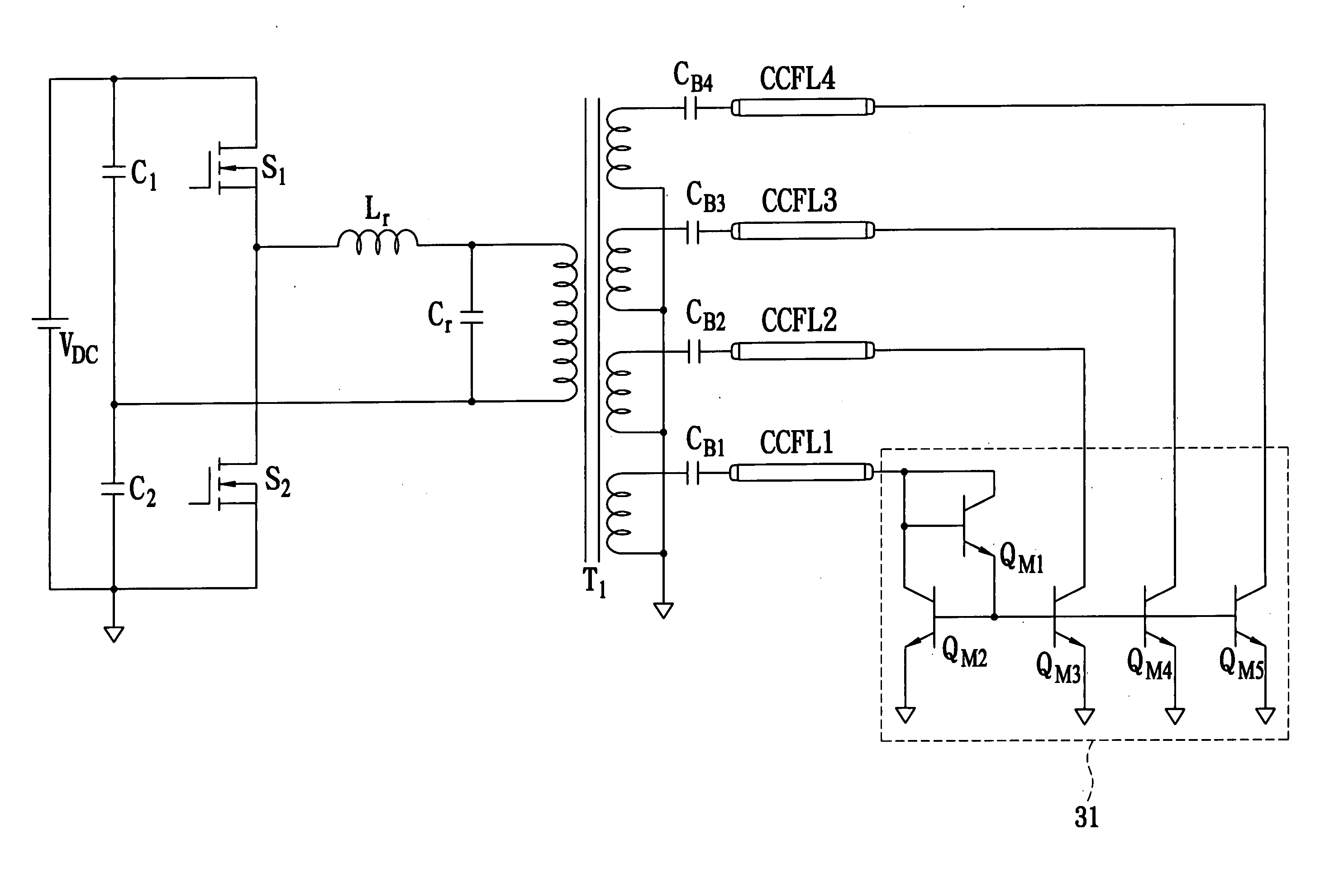
InactiveUS7825605B2Improve efficiencyAffects costPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDc-dc conversionFull bridgeCold cathode
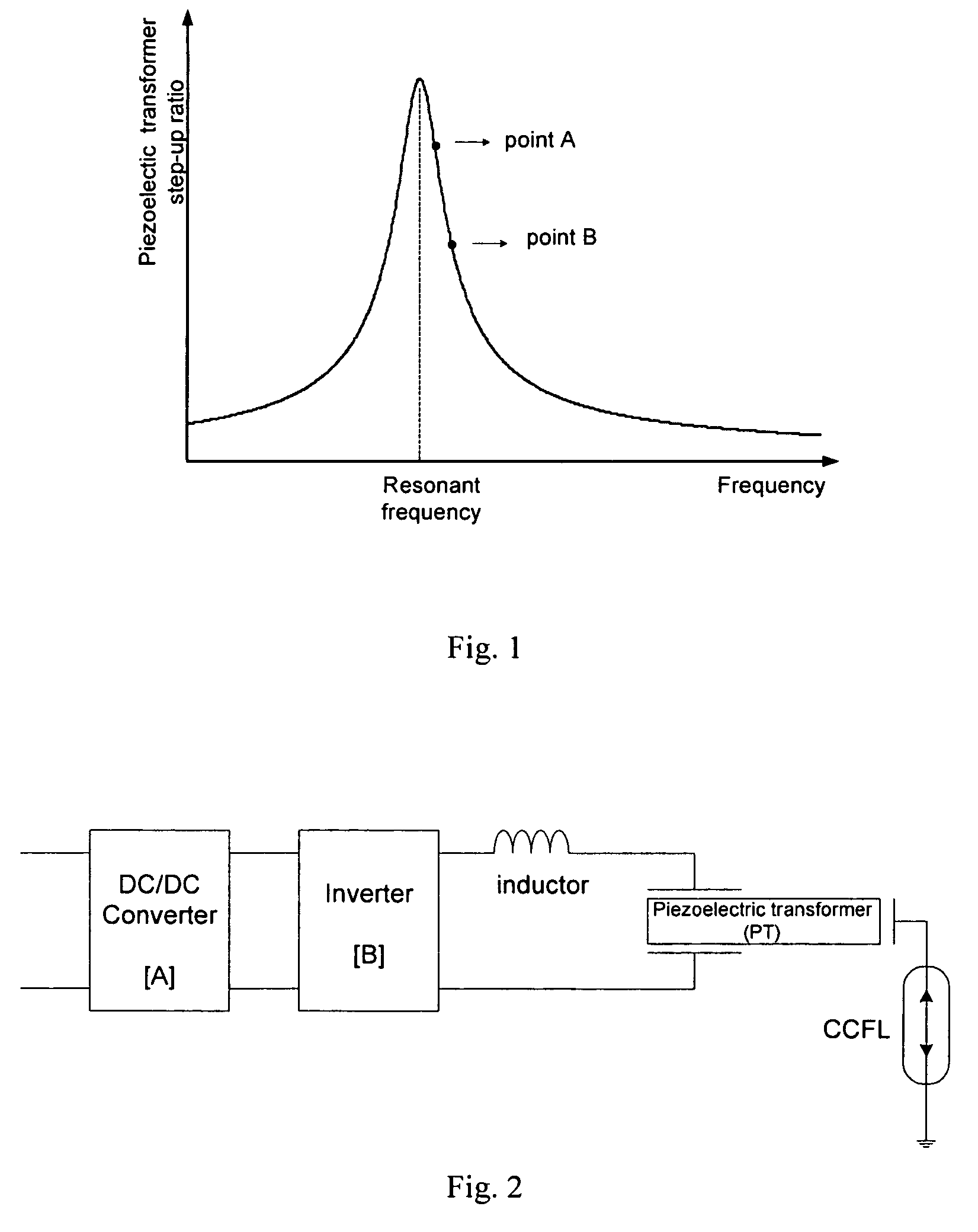
The present invention discloses a DC / AC converter in the backlight power supply system using cold cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL). The DC / AC converter comprises a front end DC / DC converter, a full-bridge or half bridge inverter, and a piezoelectric transformer. Even with a wide range of input voltages, the front end DC / DC converter produces a predetermined DC voltage or a DC voltage with a predetermined small range and the cascaded inverter operates with a switching frequency close to the resonant frequency of the piezoelectric transformer, which helps the backlight power supply system achieve high efficiency.
Owner:MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
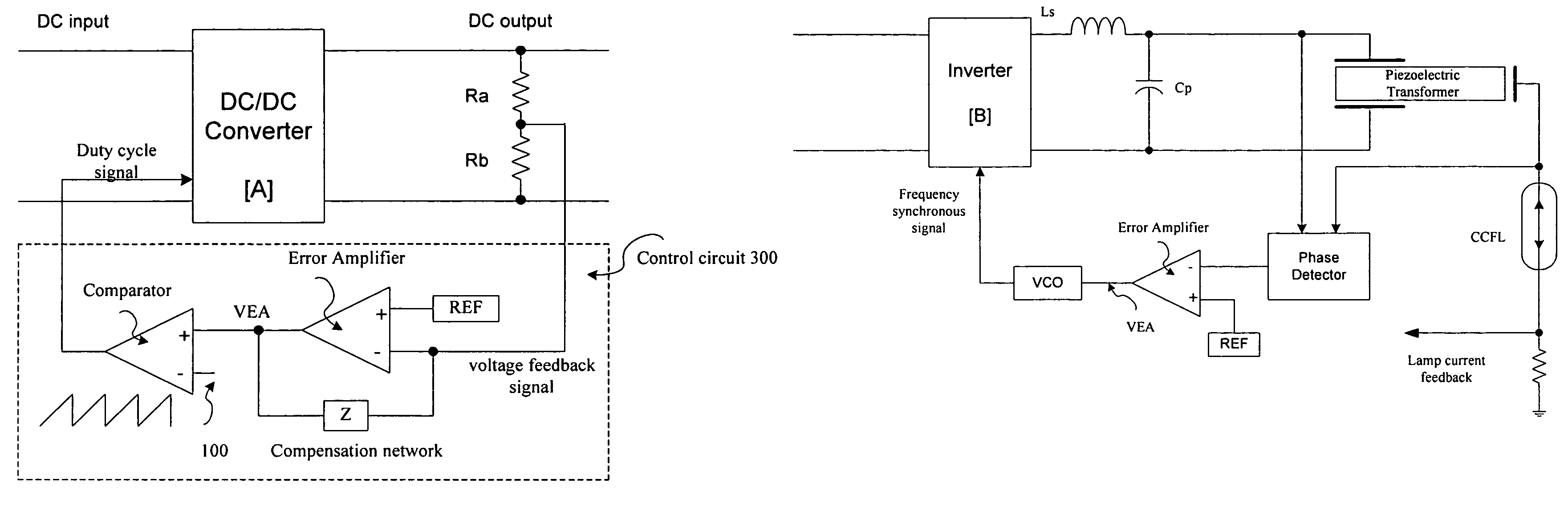
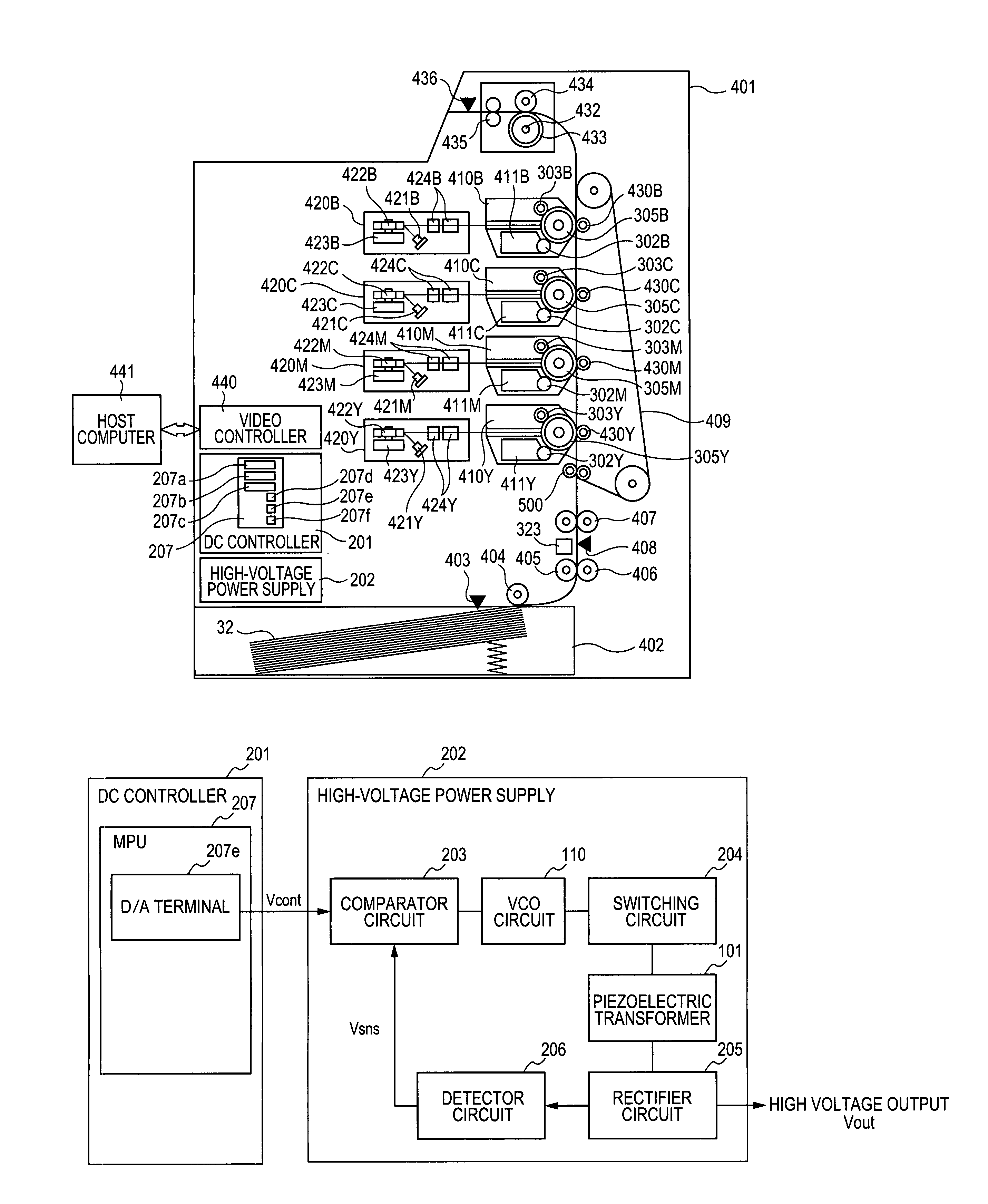
Image forming apparatus utilizing a piezoelectric-transformer high-voltage power supply and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS7196475B2Free from undesired latent response timesHigh voltagePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesDetector circuitsControl signal
Owner:CANON KK
Light modulation method and apparatus for cold cathode fluorescent lamps
InactiveUS7023142B2Negative effectExtend your lifeElectric light circuit arrangementMachines/enginesCold cathodeLuminosity
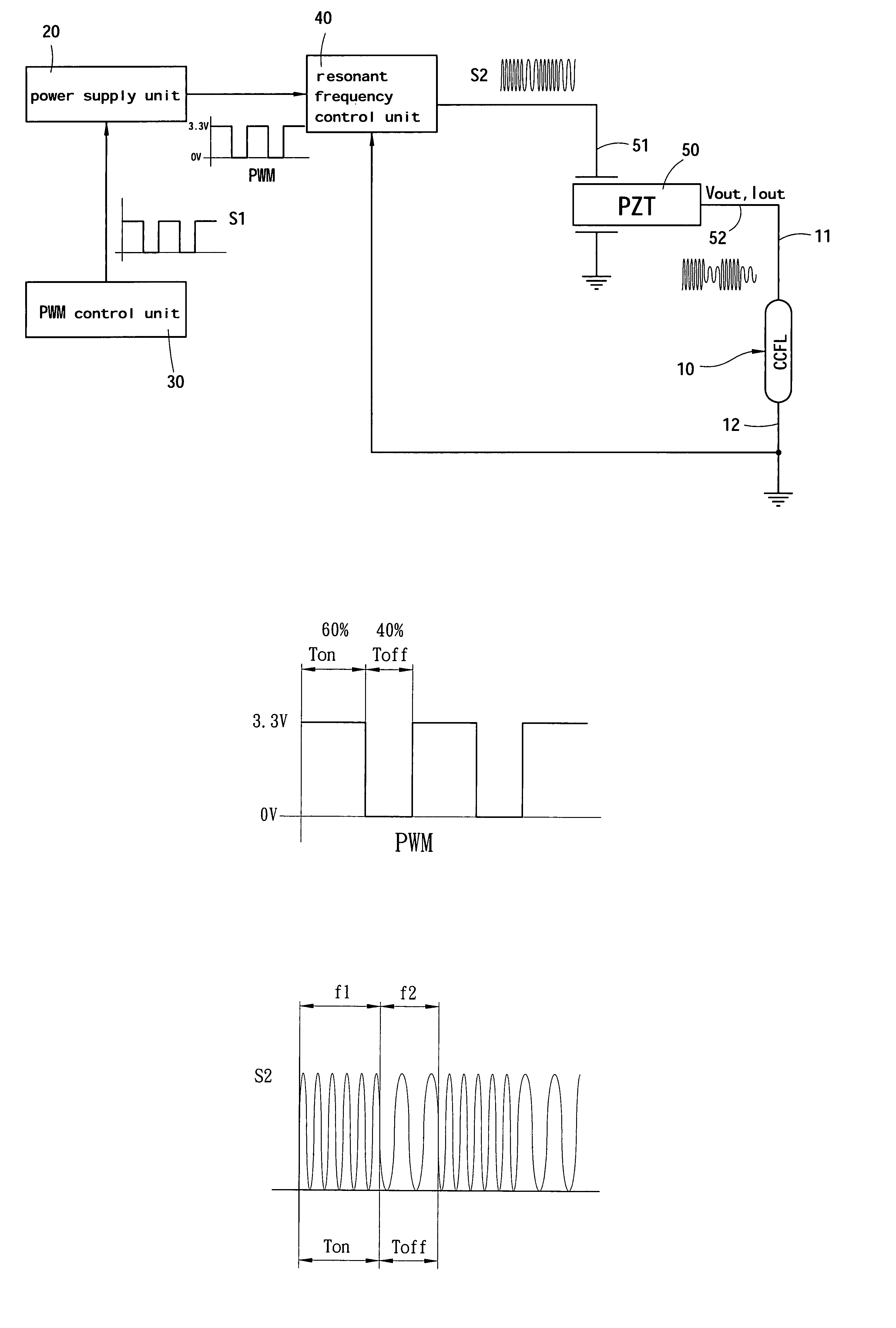
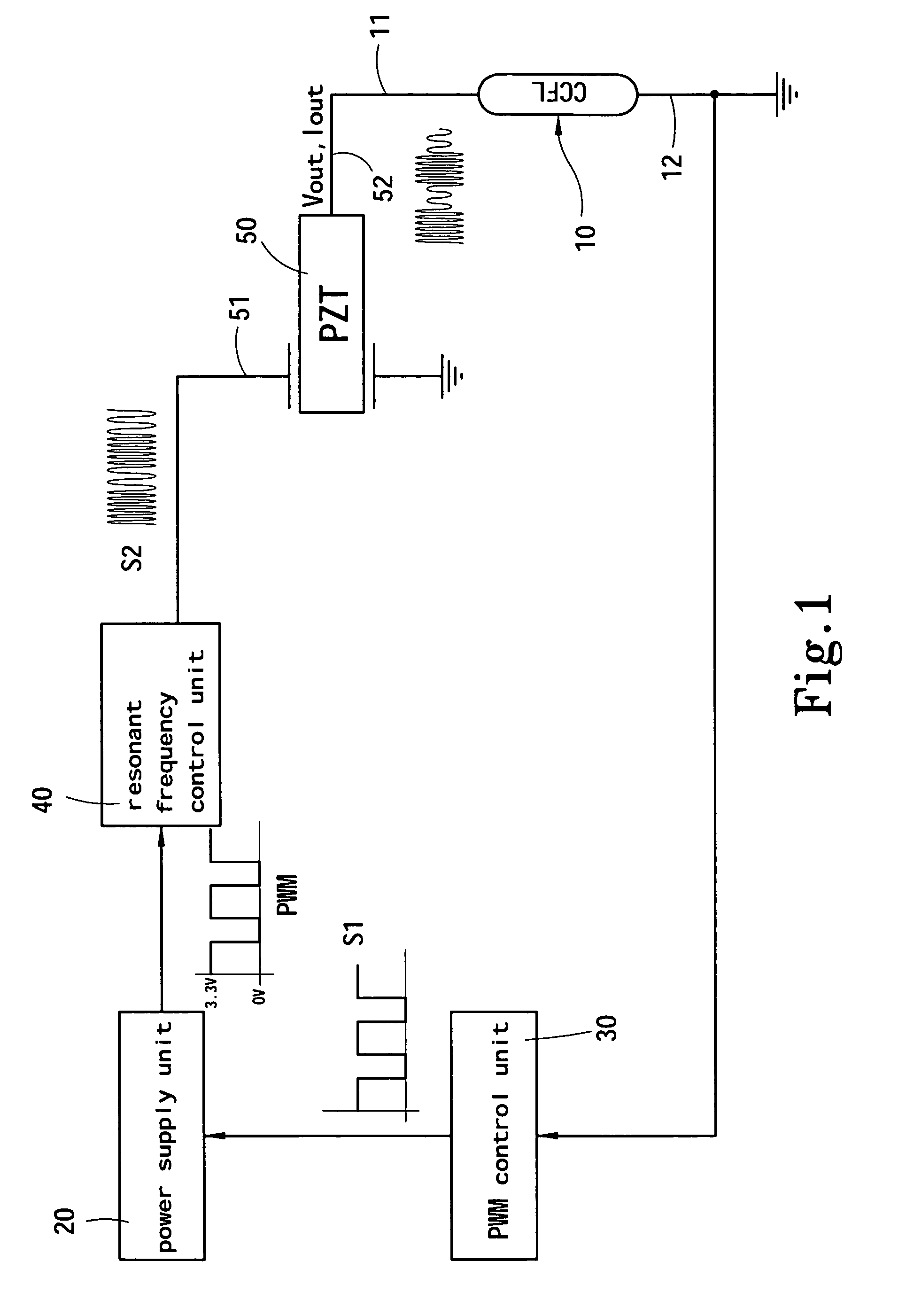
A method and apparatus for modulating light of CCFLs that couples frequency alteration and pulse width modulation (PWM) approaches to change output voltage and current of a piezoelectric transformer to modulate the luminosity of a CCFL. The invention includes a PWM controller to alter operation cycle and a frequency control IC to change resonant frequency that drives the piezoelectric transformer at different operation cycles thereby to modulate the luminosity of the CCFL and improve the life span of the piezoelectric transformer.
Owner:ZIPPY TECH
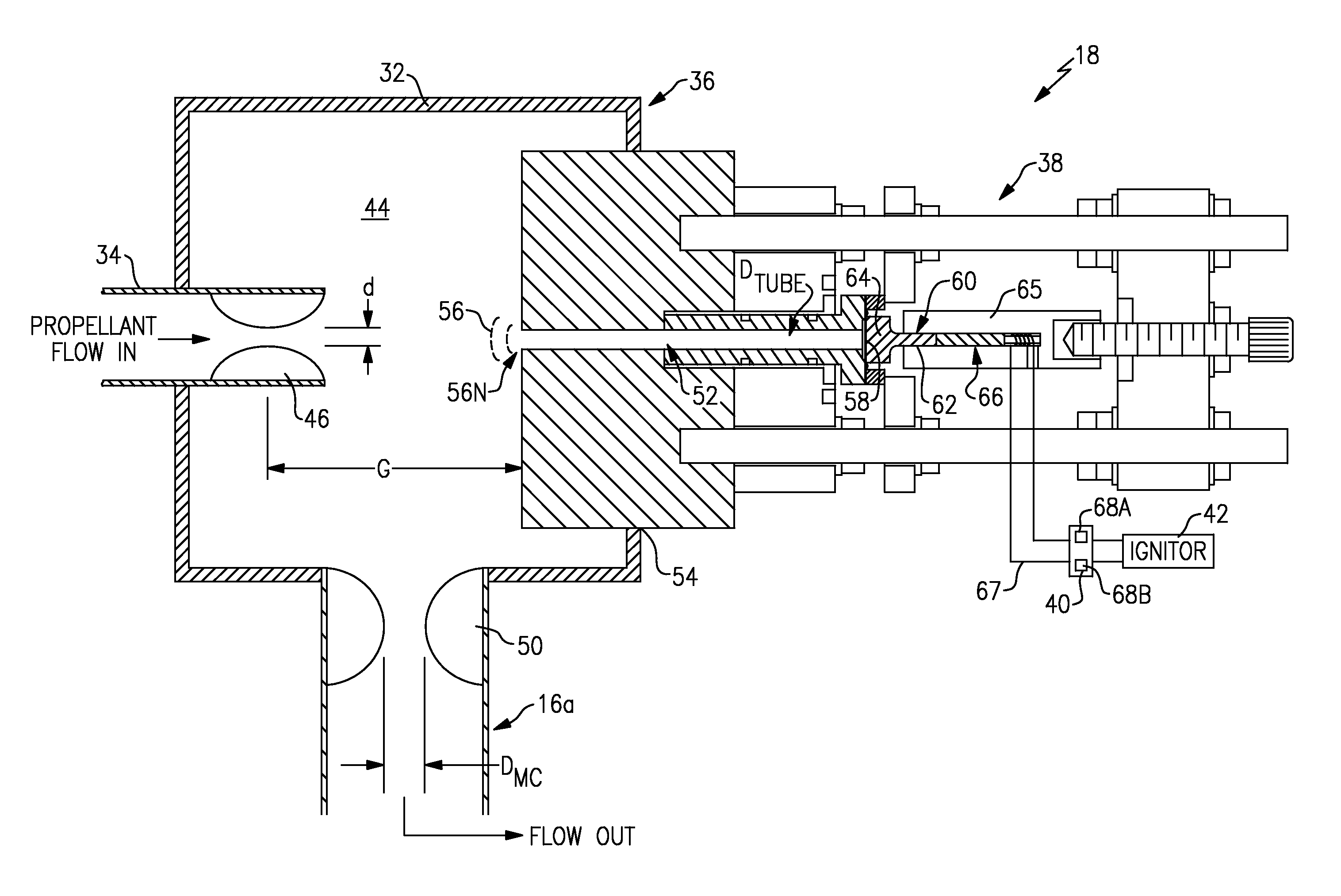
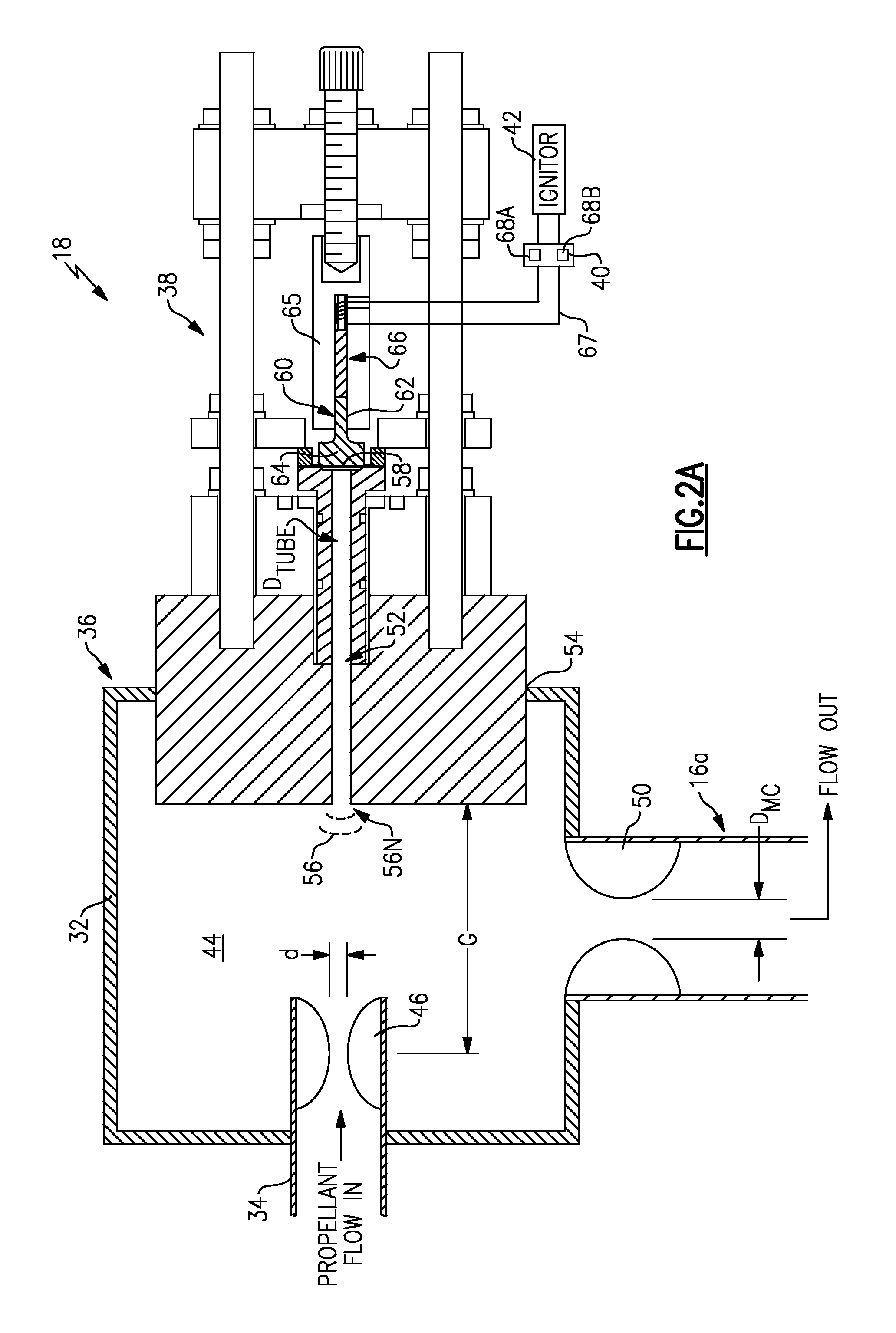
Piezo-resonance igniter and ignition method for propellant liquid rocket engine
ActiveUS20090173321A1Lower overall pressure dropEasy to controlCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusElectricityCombustion chamber
An ignition system for a rocket engine utilizes the pressure energy in a propellant flow. The propellant flow generates an oscillating pressure force in a resonance system which is then transmitted to a piezoelectric system. The electrical pulses are utilized to generate a spark in an igniter system spark gap, resulting in ignition. Since the spark energy production is driven by the resonance of the propellant flow, a fully passive auto-ignition system is provided. Once ignition occurs, the resultant backpressure in the combustion chamber “detunes” the resonance phenomena and spark production stops. Furthermore, should the engine flame out, spark production would automatically resume as the propellant valves remain open thereby providing relight capability.
Owner:AEROJET ROCKETDYNE OF DE
Propellant Flow Actuated Piezoelectric Igniter for Combustion Engines
InactiveUS20120094241A1Sufficiently and reliably strong spark responseSimple methodIncandescent ignitionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCombustionInternal combustion engine
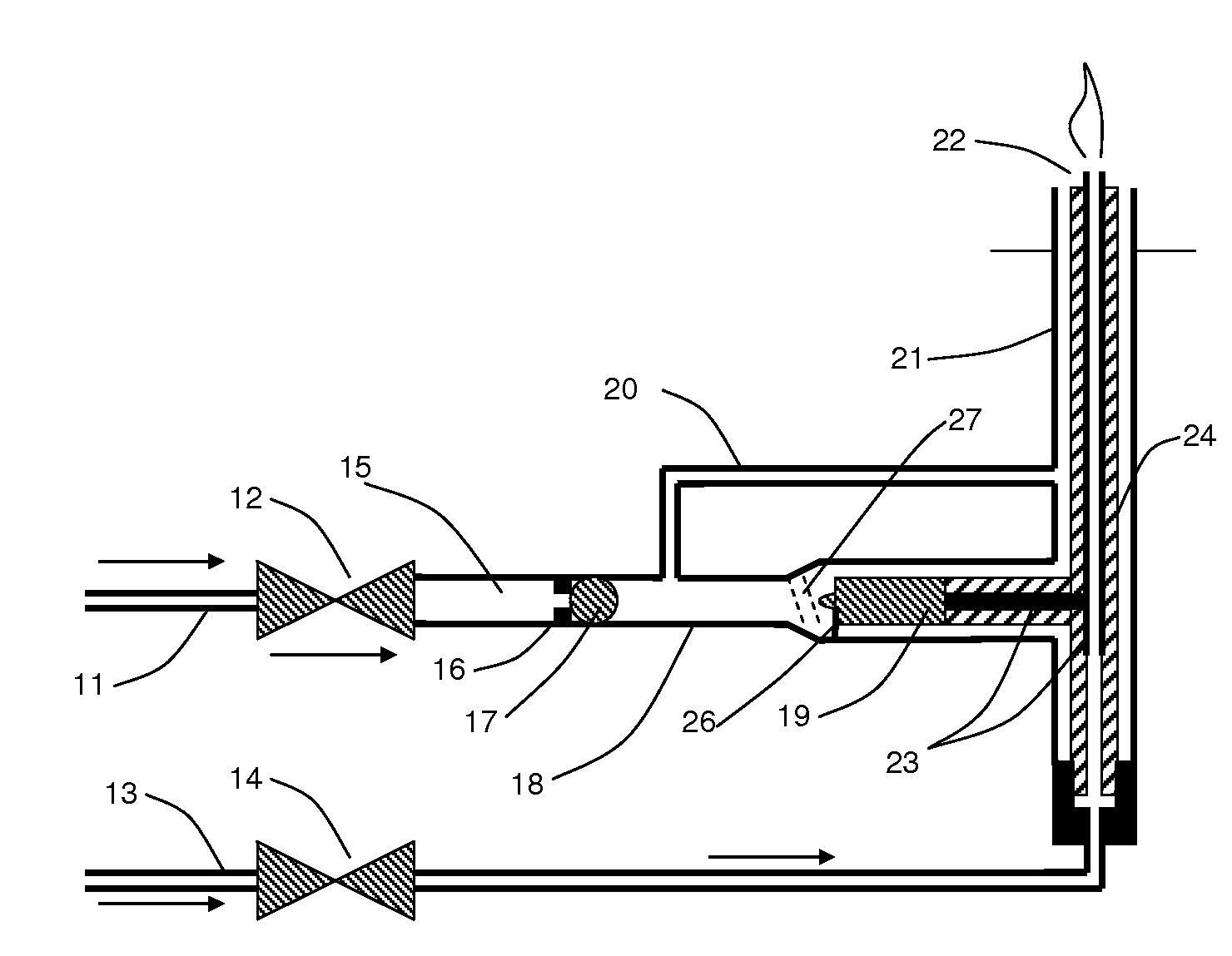
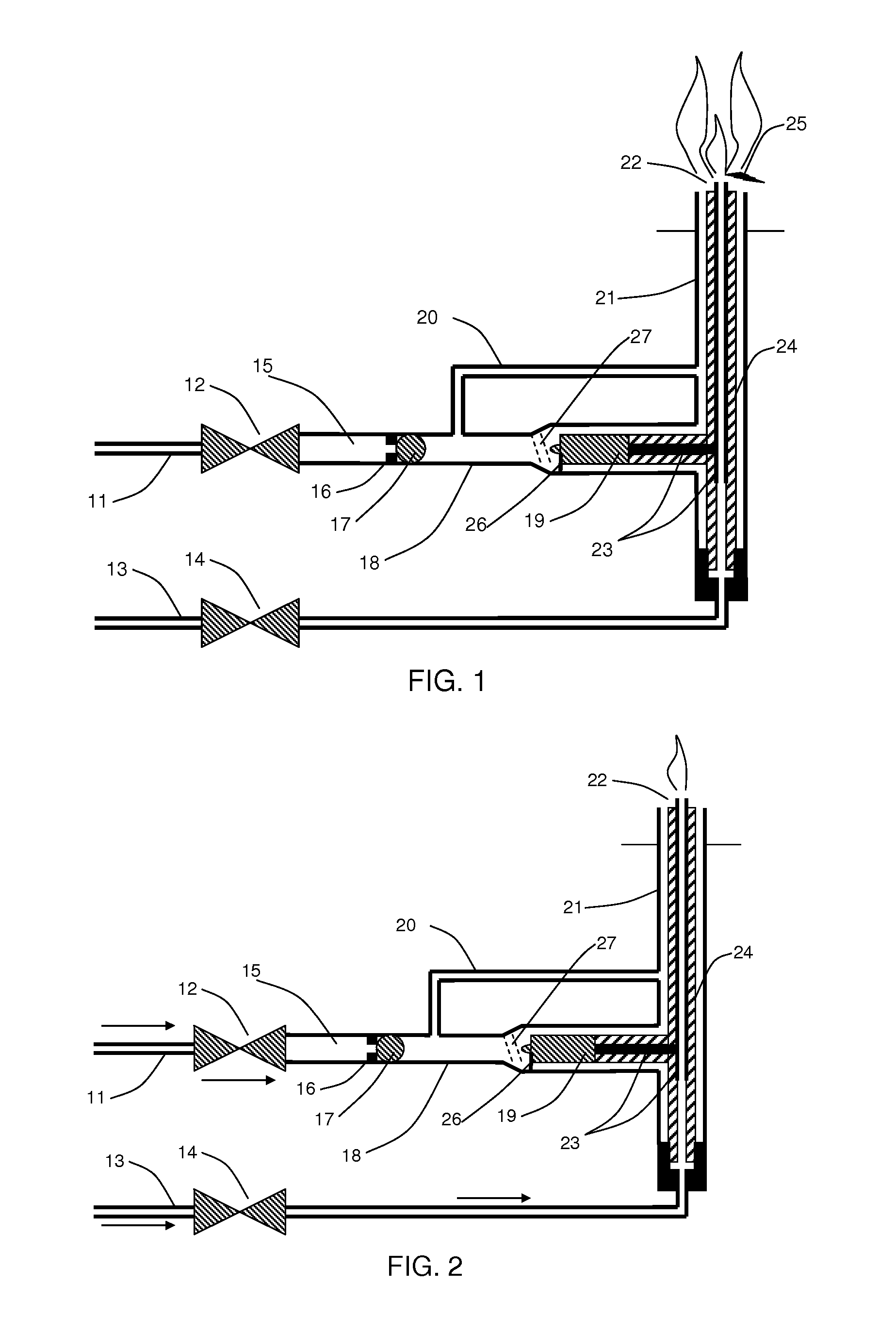
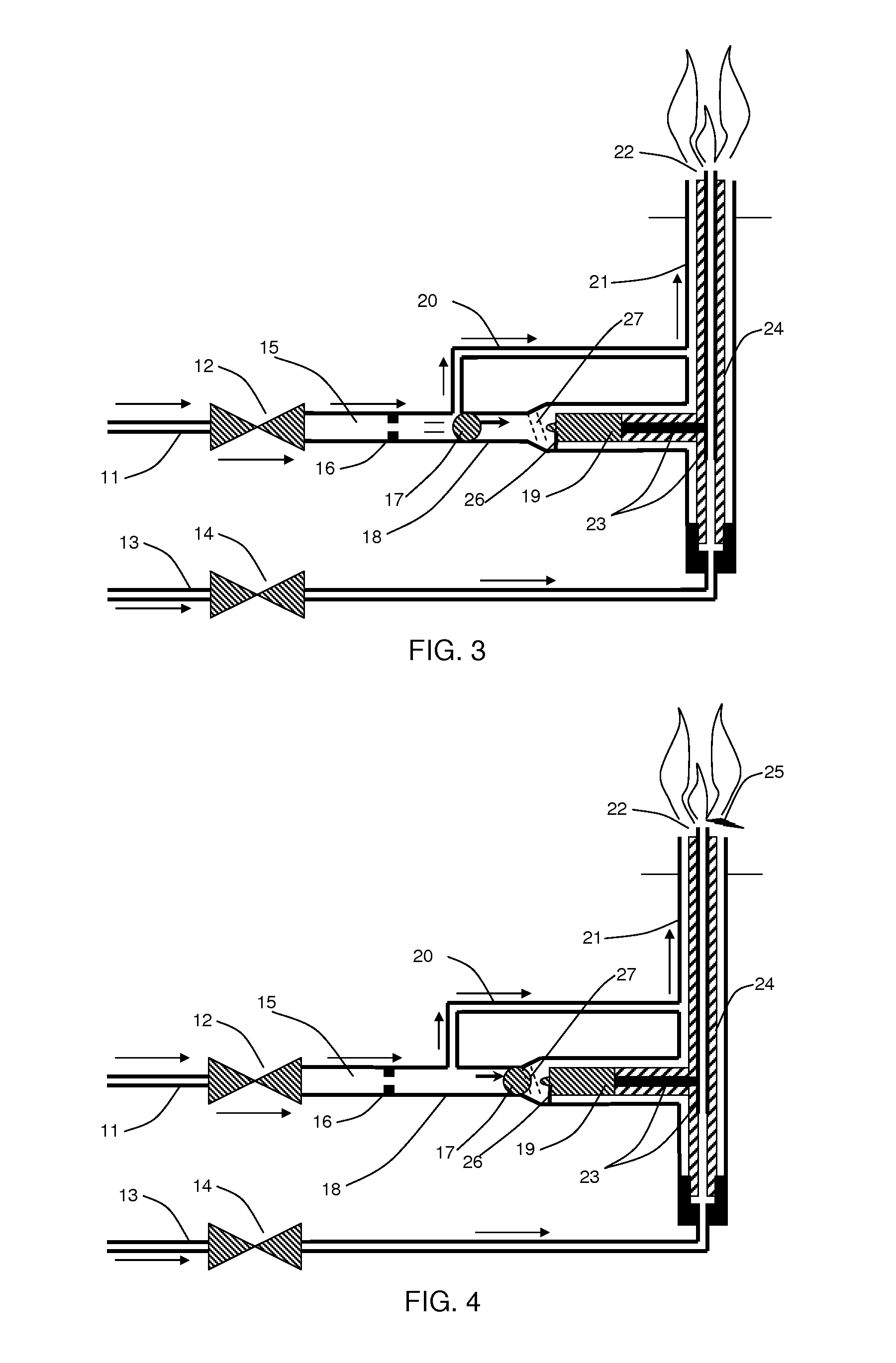
A propellant flow actuated piezoelectric igniter device using one or more hammer balls retained by one or more magnets, or other retaining method, until sufficient fluid pressure is achieved to release and accelerate the hammer ball, such that it impacts a piezoelectric crystal to produce an ignition spark. Certain preferred embodiments provide a means for repetitively capturing and releasing the hammer ball after it impacts one or more piezoelectric crystals, thereby oscillating and producing multiple, repetitive ignition sparks. Furthermore, an embodiment is presented for which oscillation of the hammer ball and repetitive impact to the piezoelectric crystal is maintained without the need for a magnet or other retaining mechanism to achieve this oscillating impact process.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENG SOLUTIONS
Image forming apparatus utilizing a piezoelectric-transformer high-voltage power supply and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20070018589A1Free from undesired latent response timesHigh voltageElectric light circuit arrangementMachines/enginesDriver circuitDetector circuits
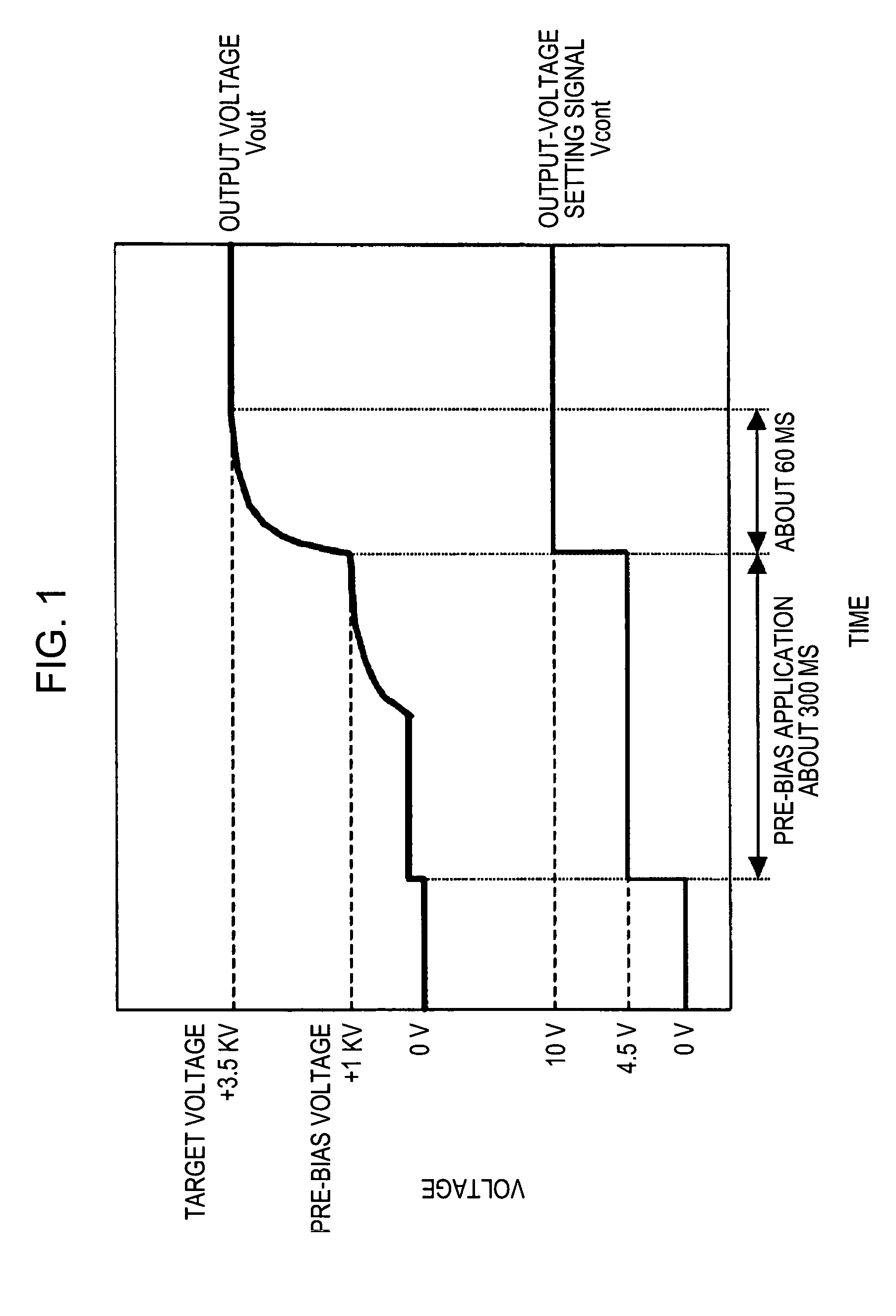
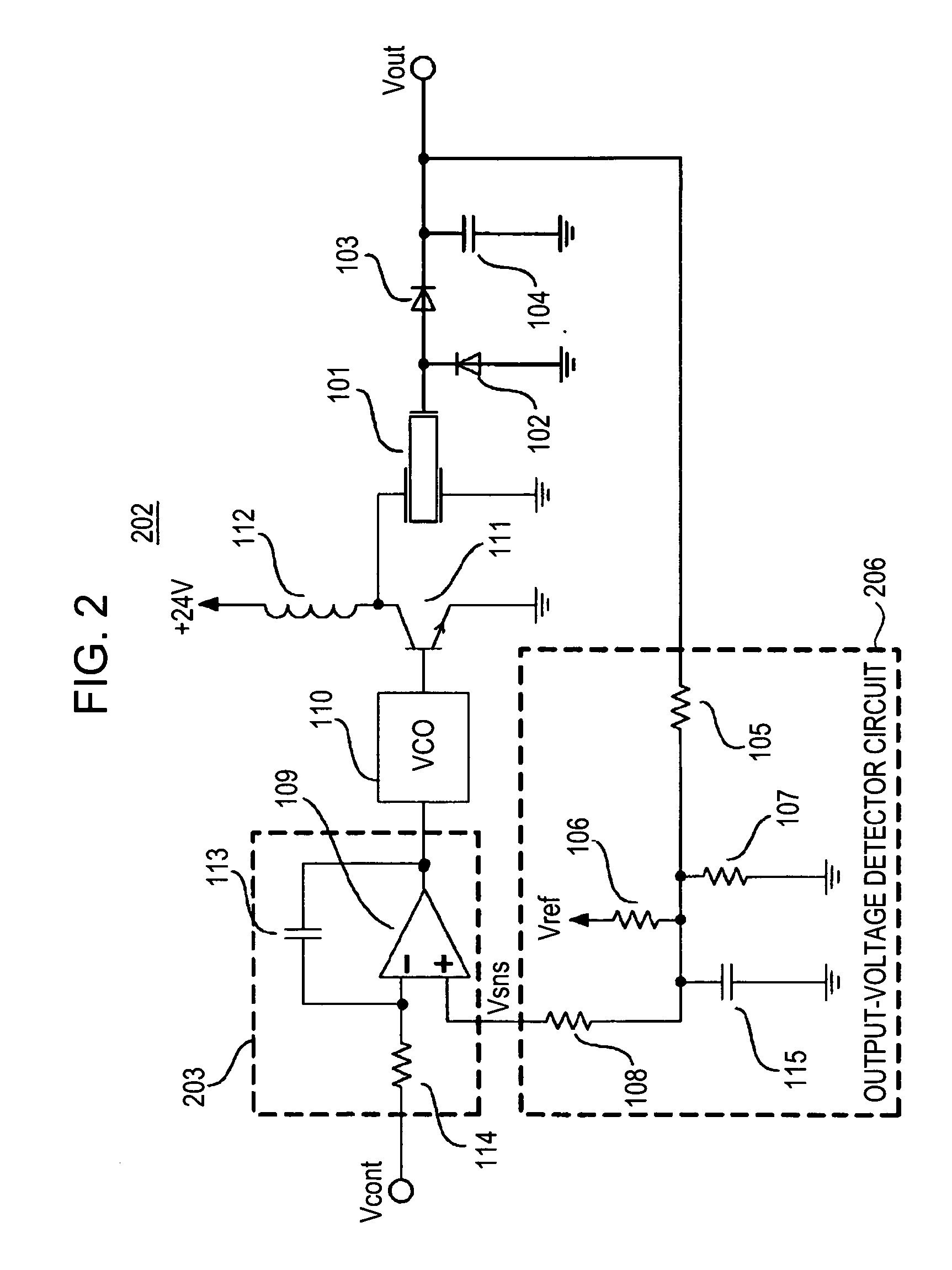
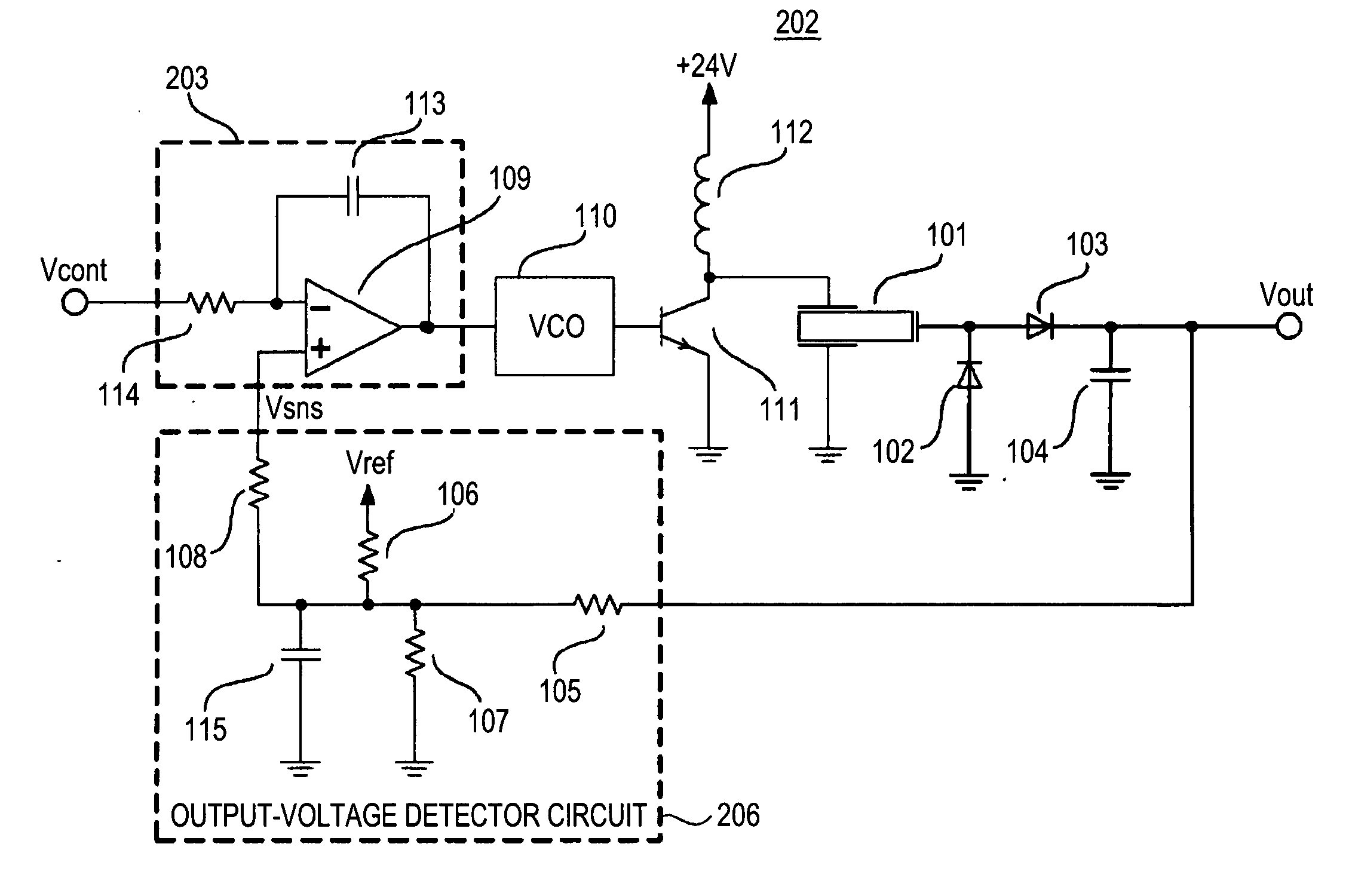
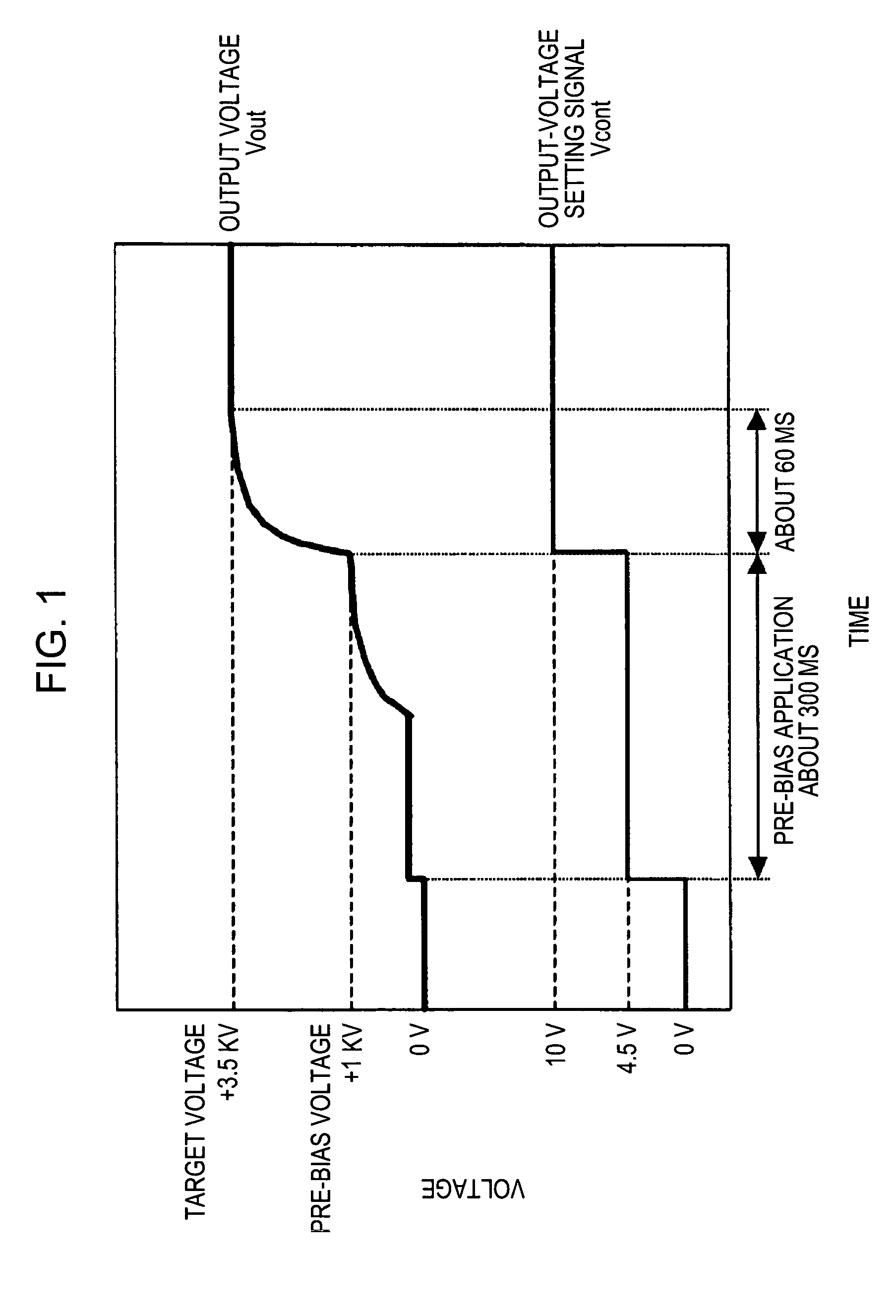
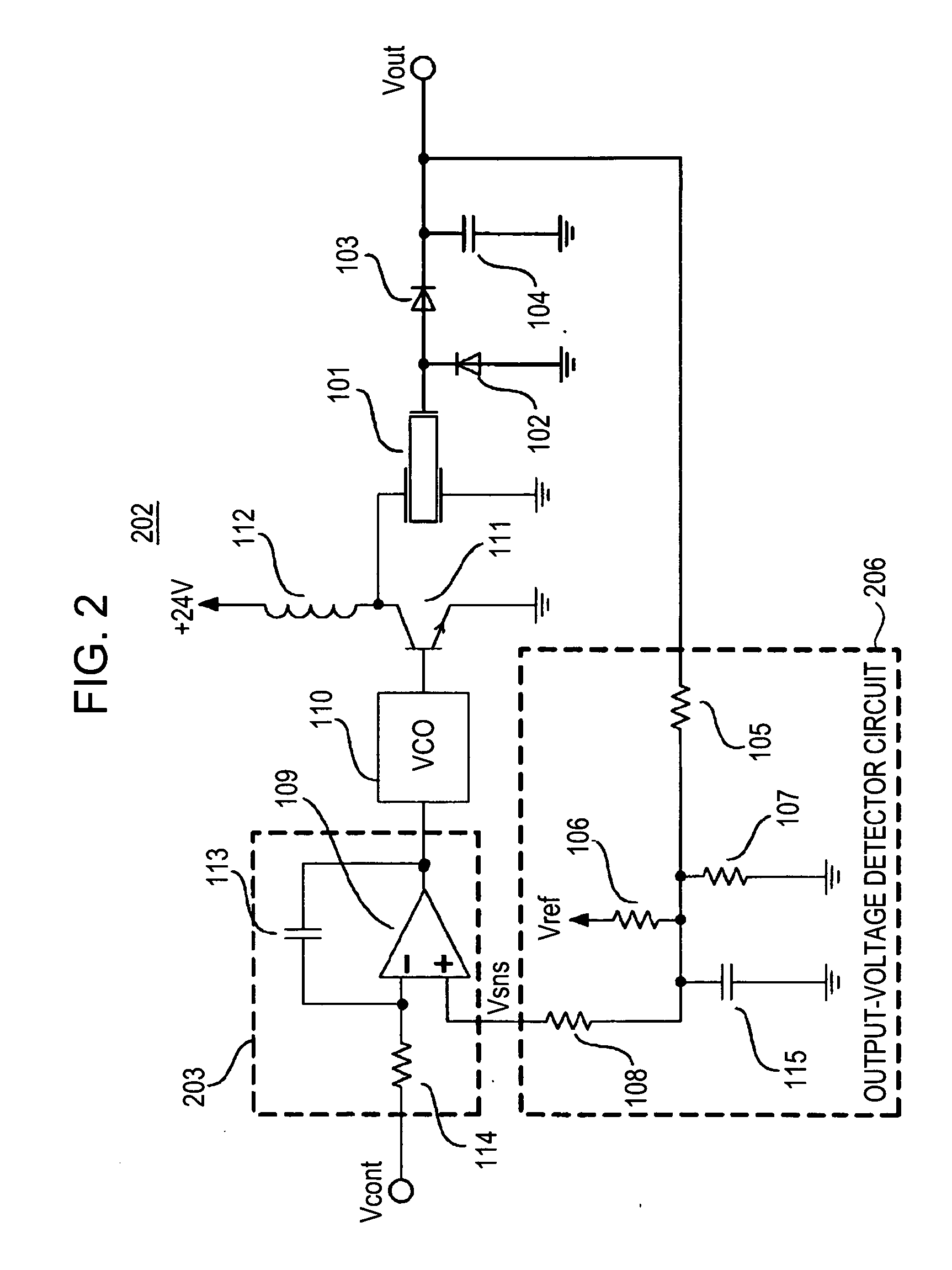
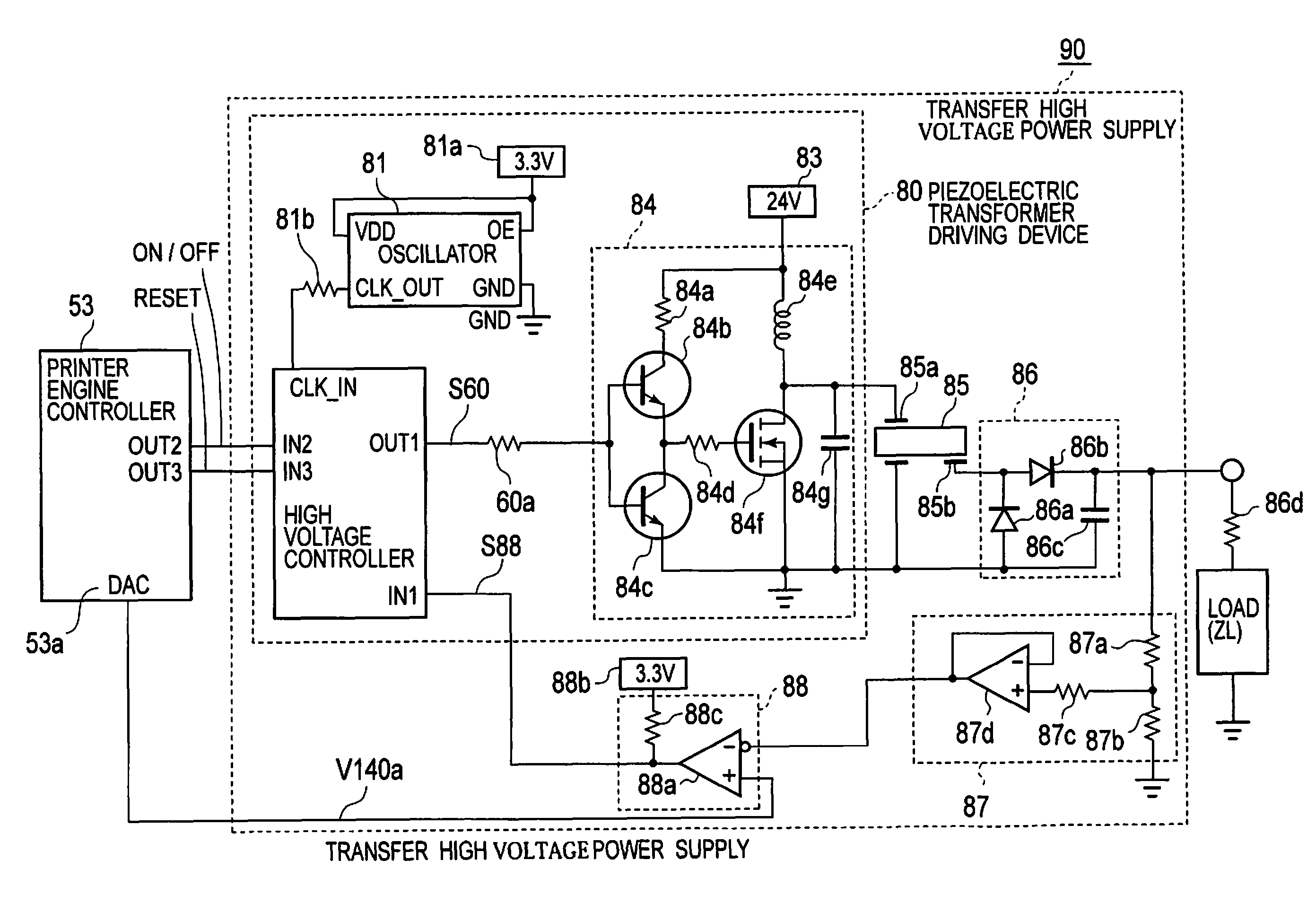
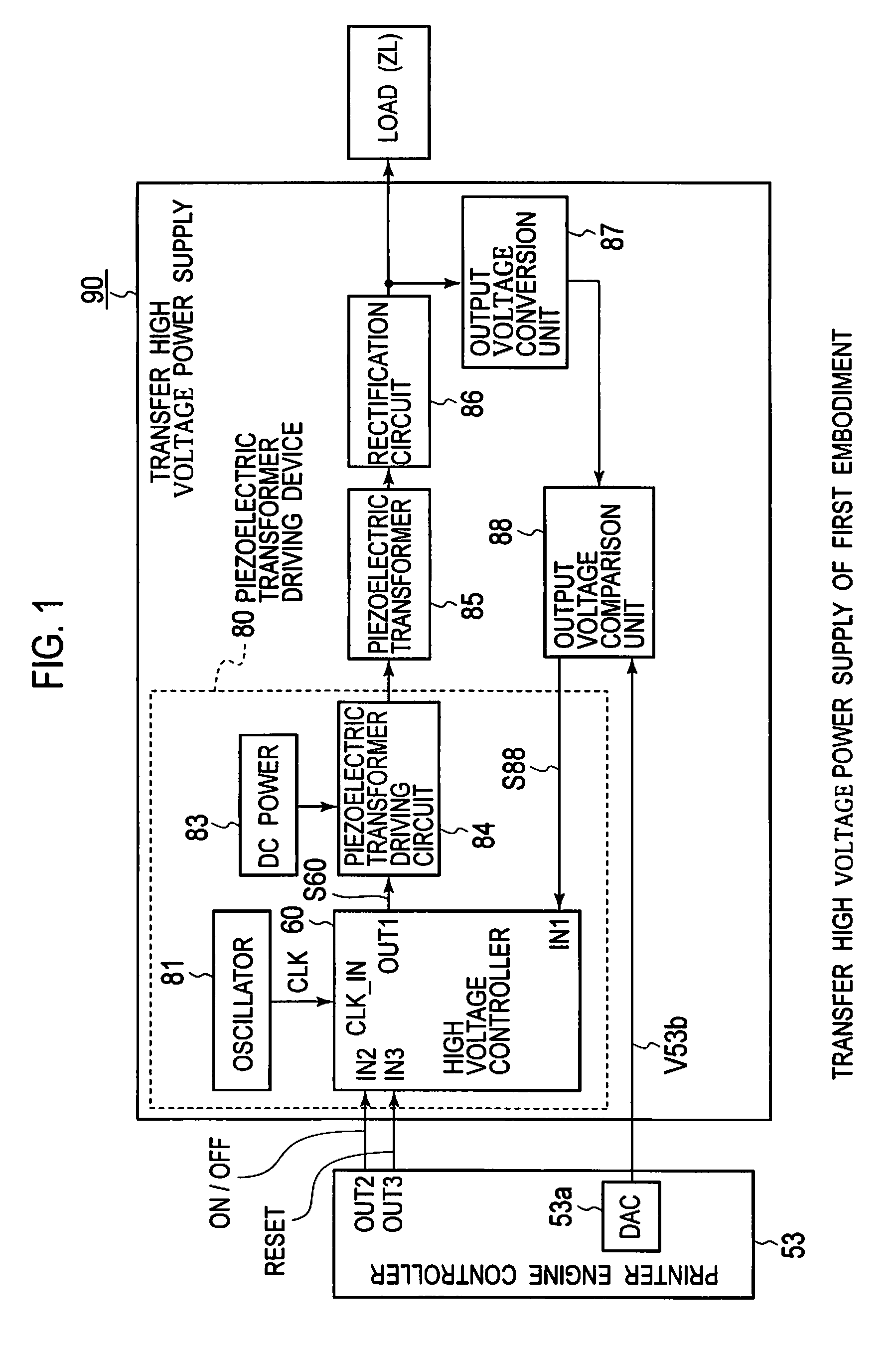
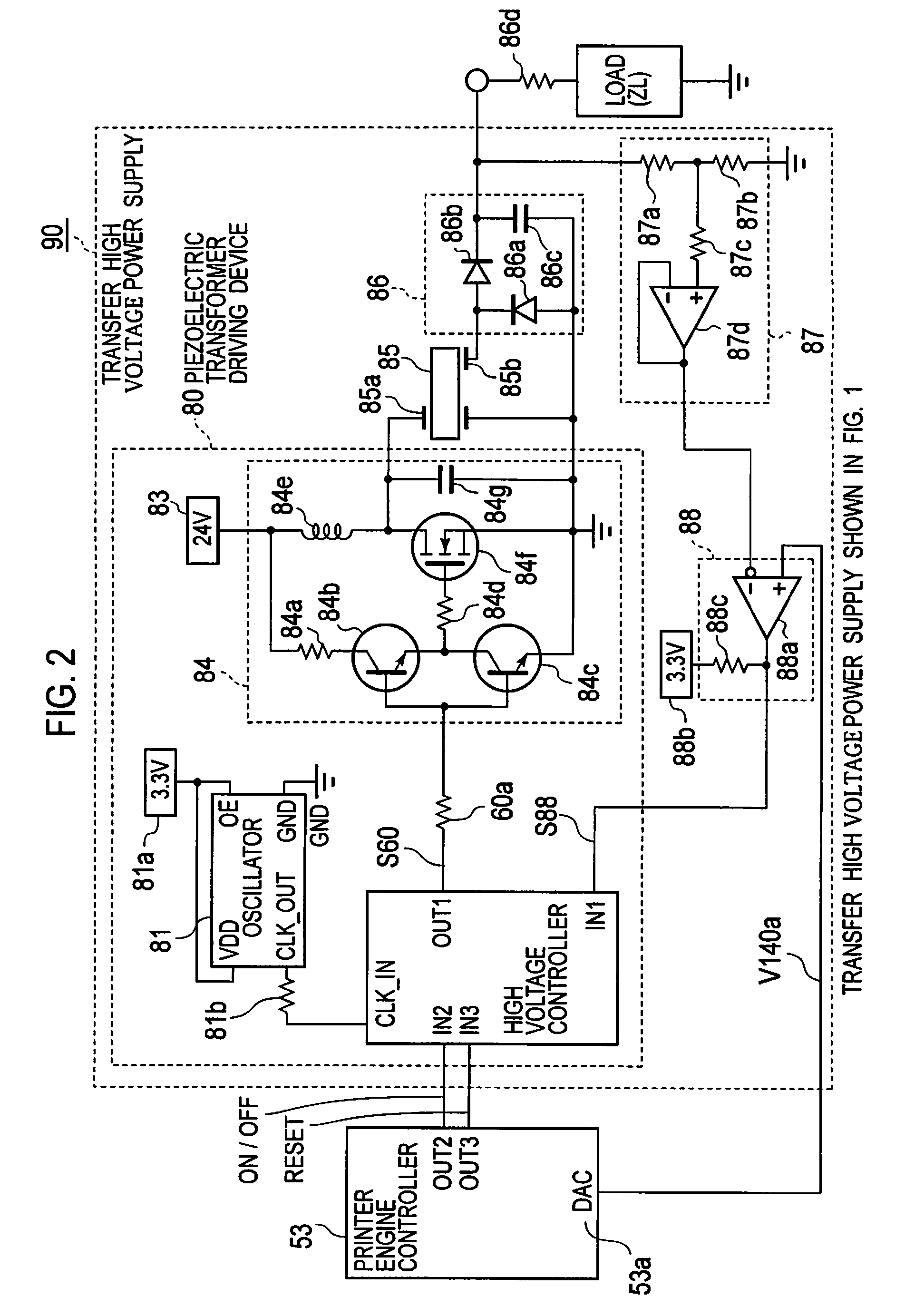
A piezoelectric-transformer high-voltage power supply in combination with an image-forming apparatus including a latent-image forming section configured to form an electrostatic latent image on an image carrier, a developing section configured to form a toner image on the electrostatic latent image, and a transfer section configured to transfer the toner image onto a transfer material includes a piezoelectric transformer; a piezoelectric-transformer drive circuit; an output-voltage setting-signal output circuit configured to output an output-voltage setting-signal; an output-voltage detector circuit, and a drive control circuit configured to output a control signal on the basis of a signal from the output-voltage detector circuit and the output-voltage setting-signal, for controlling the piezoelectric-transformer drive circuit. The output-voltage setting-signal output circuit outputs an output-voltage setting-signal corresponding to a voltage lower than a target voltage and, then, another output-voltage setting-signal corresponding to the target voltage.
Owner:CANON KK
Cold-cathode driver and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS6903517B2Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAc-dc conversionBurst dimmingPiezoelectric transformer
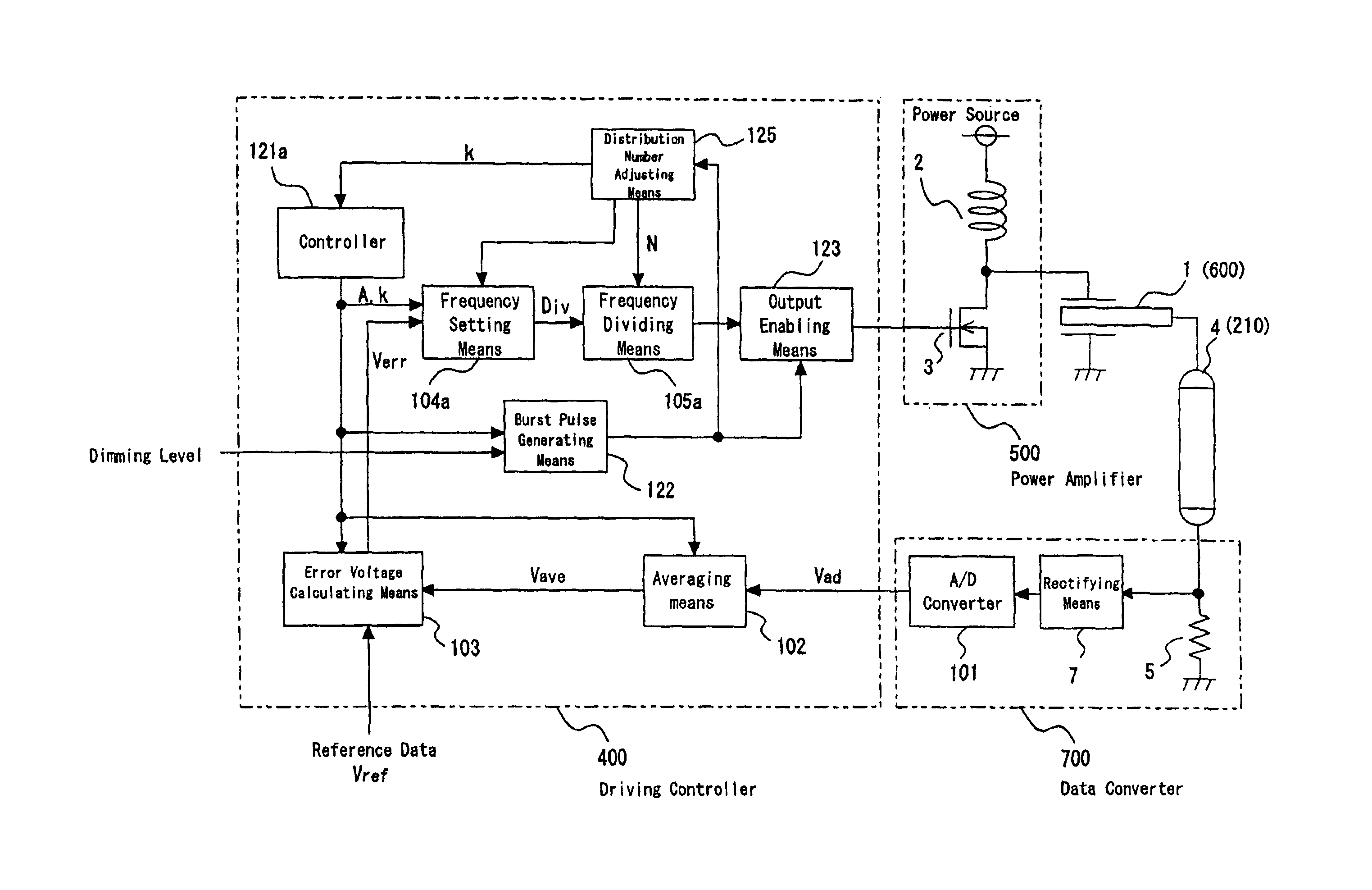
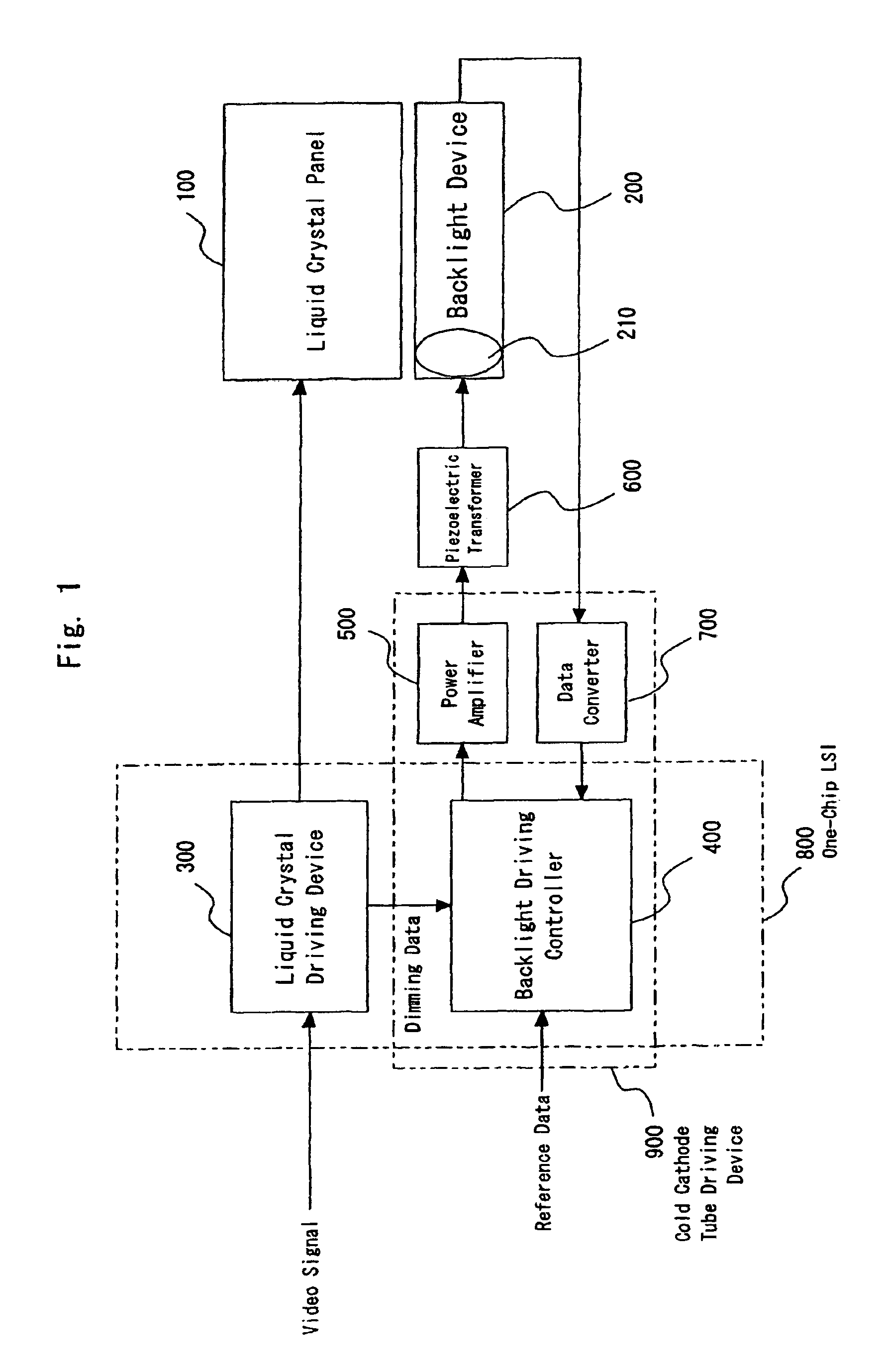
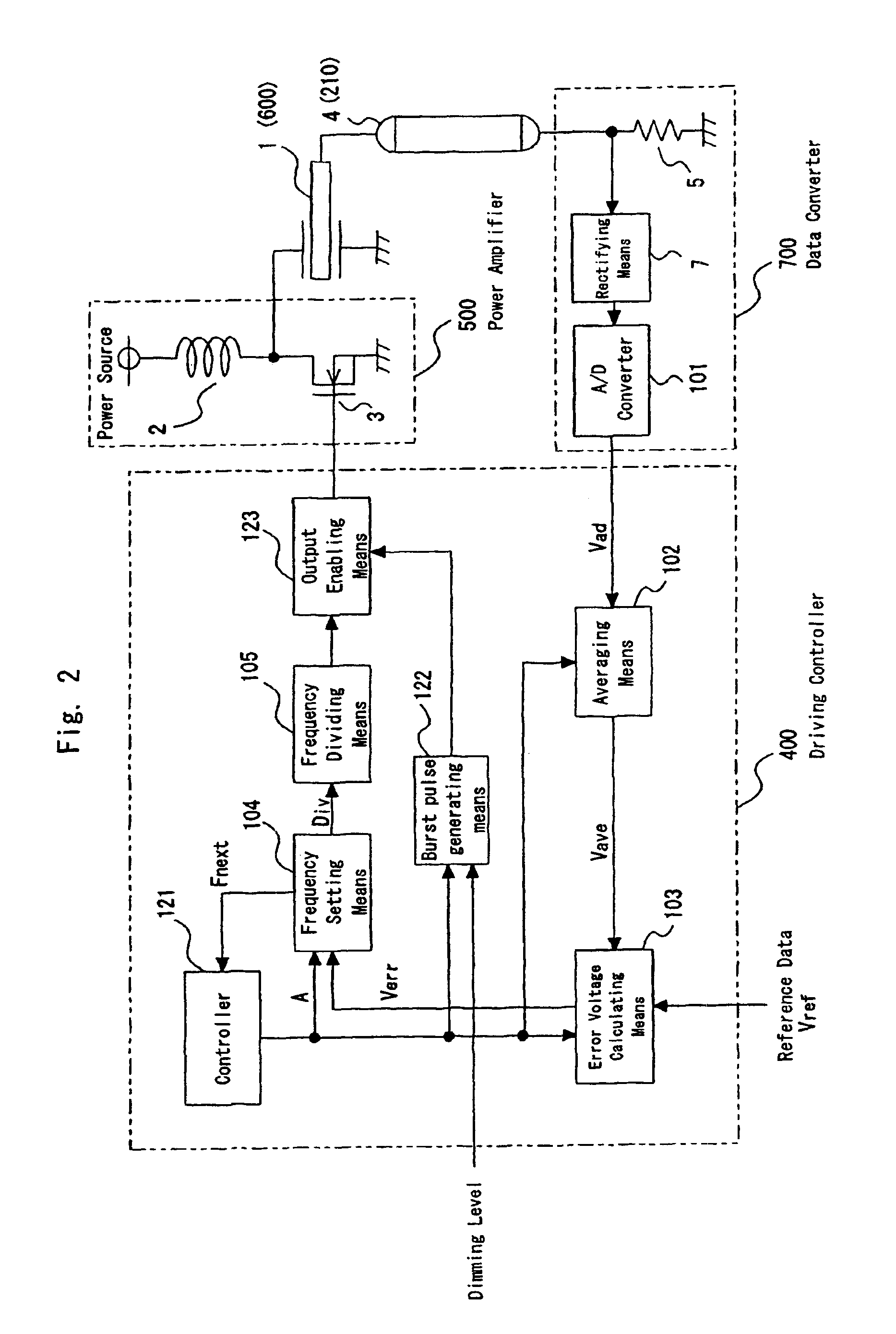
A cold cathode tube driving device using a piezoelectric transformer in which an output voltage varies depending on a frequency of an input voltage, as a booster transformer for driving a cold cathode tube, includes: a frequency dividing means which generates a driving pulse of an average frequency corresponding to frequency data outputted from a frequency setting means at a distribution cycle which is a driving pulse N cyclic period; a controller which controls a control cycle so as to perform the same driving for predetermined number of times A (A≧2) at the average frequency; and a burst pulse generating means which generates a pulse having a duty width in accordance with a dimming level externally applied thereto and having a frequency outputted from the controller.A control cycle is A times (natural number) the distribution cycle and the driving is performed A times at the same average frequency, whereby a digital driving system using the frequency distribution of the driving pulse is achieved. Consequently, a space for the driving circuit can be saved and cost can be reduced. Further, a frequency distribution system is adopted, thereby obtaining frequency resolution required for satisfactory dimming performance and lighting performance. Moreover, a burst dimming system is adopted, thereby suppressing brightness flicker seen in a tube current control system. Additionally, there is no electric power loss seen in a system in which a power source is turned on or off and further a shield circuit is unnecessary because of a system in which the driving pulse is turned on or off. In particular, the control cycle is A times the distribution cycle and the burst dimming is performed in which the driving is executed A times at the same average frequency, whereby the brightness flicker can be prevented by controlling the tube current to be constant with high dimming resolution assured.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Furnace using plasma ignition system for hydrocarbon combustion
InactiveUS20090104576A1Promote combustionImprove efficiencyBurnersPower operated startersCombustorFuel efficiency
An apparatus and method for the creation, placement and control of an area of electrical ionization within an internal combustion engine combustion chamber or a fuel burner for a furnace is disclosed. A furnace includes a fuel source, a fuel burner, a plasma nozzle and igniter assembly, and the associated housing and flue structures. The plasma nozzle and igniter assembly is arranged so that the fuel sprayed out from the nozzle into the combustion area passes through or in close proximity to the area of plasma ionization. A fuel burner equipped with this electrical ionization device has its fuel efficiency enhanced by the complete and immediate combustion of substantially all of the fuel that passes through the area of plasma ionization. Exhaust gas recirculation using this system is also disclosed.
Owner:JAYNE MICHAEL E
LED driver structure
InactiveUS7786676B2Less elementLow pricePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesStatic indicating devicesElectricityImpedance matching
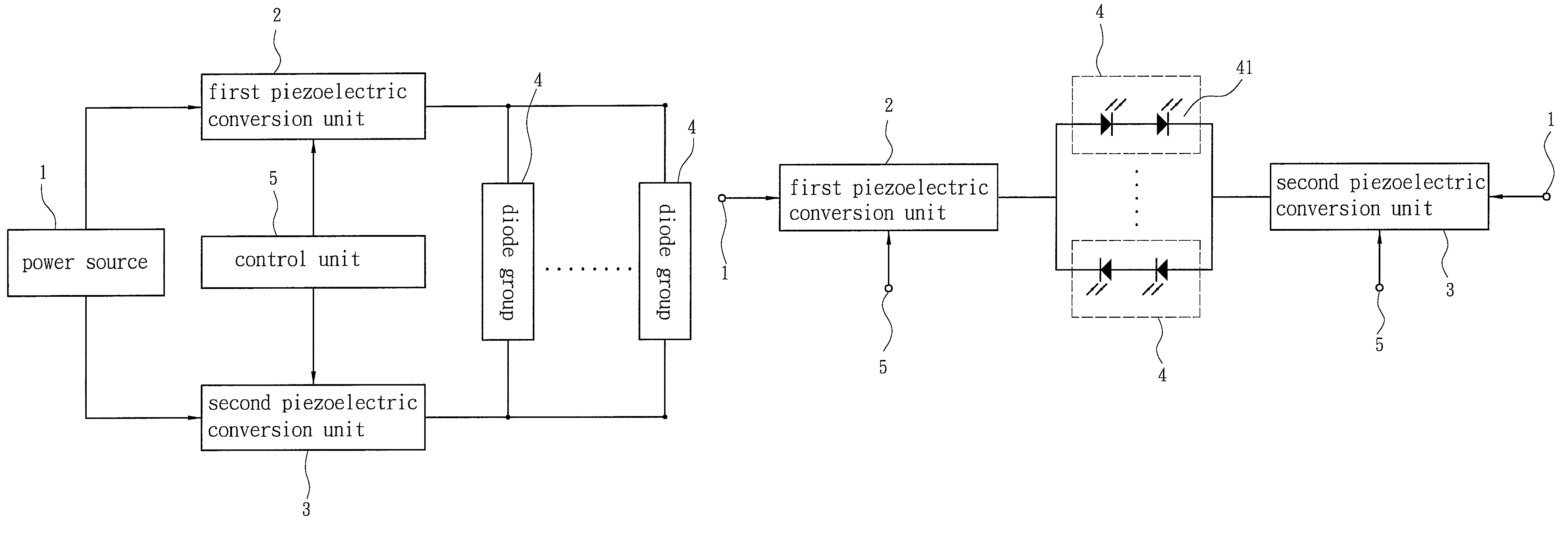
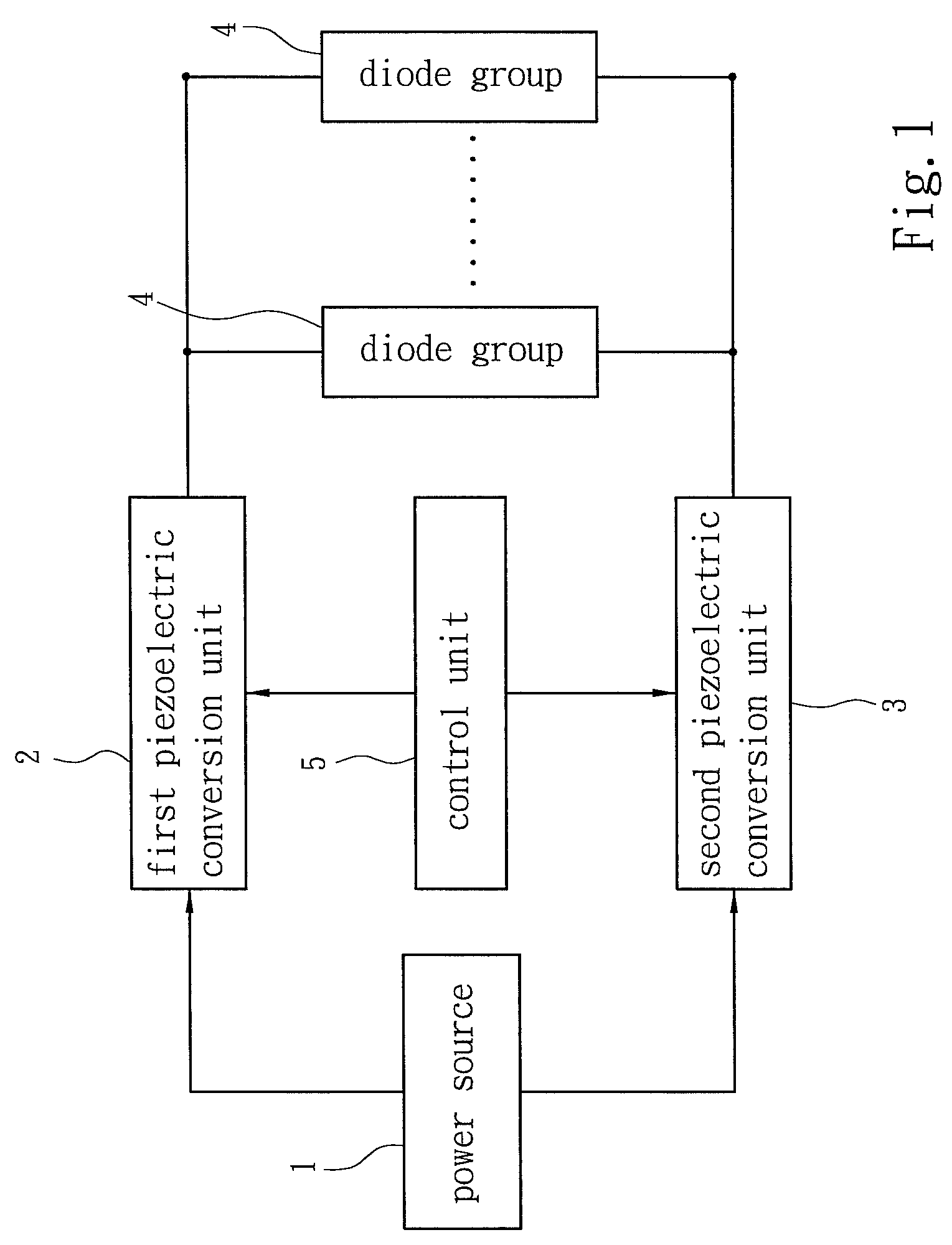
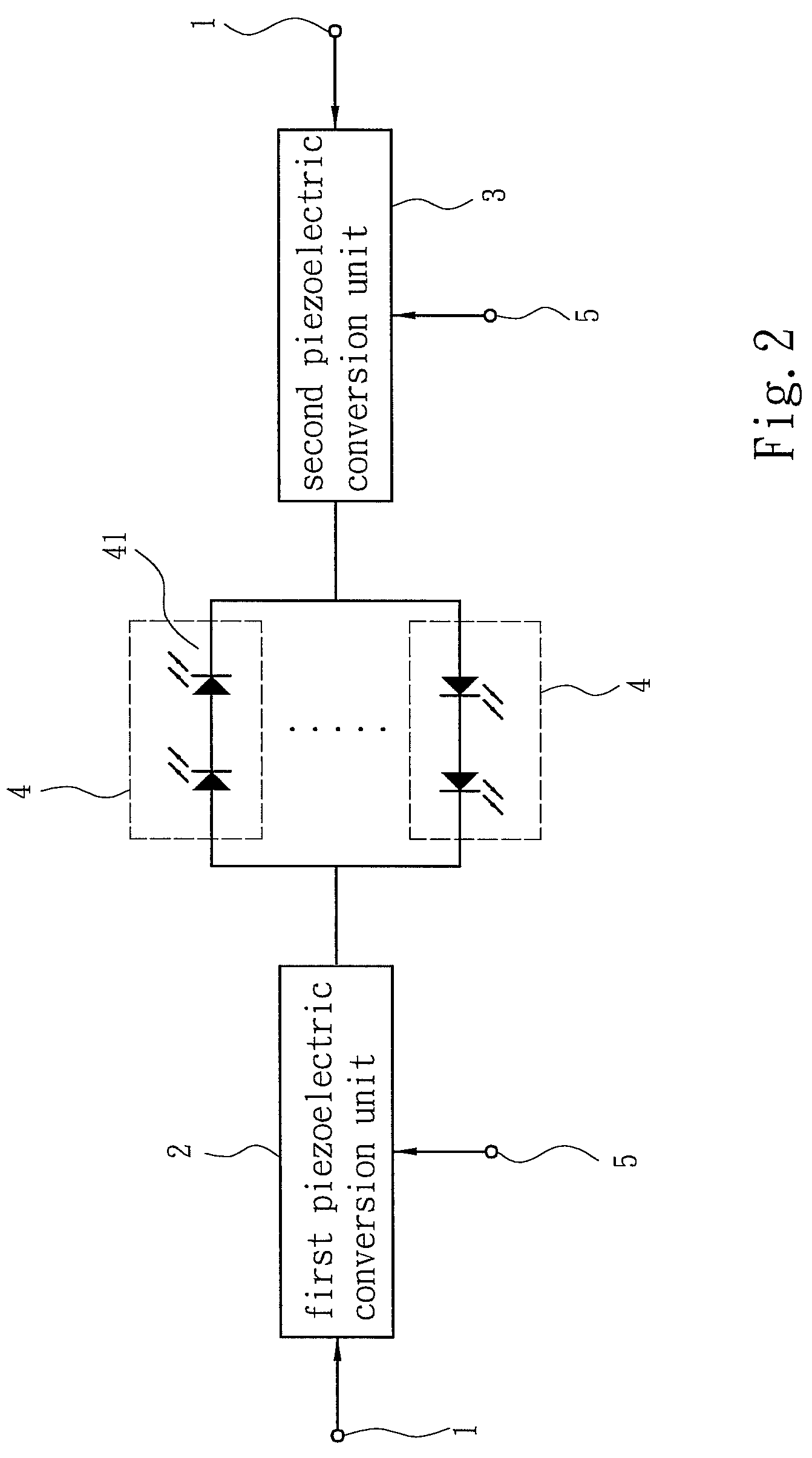
The present invention discloses an LED driver structure, which obtains input power coming from a power source to generate a constant-current power to drive a plurality of LEDs, and which comprises: a plurality of diode groups connected in parallel, a first piezoelectric conversion unit and a second piezoelectric conversion unit respectively arranged at both sides of the diode groups. The first and second piezoelectric conversion units receive the input power and opposite-phase convert the input power into driving powers to drive the diode groups. Among the plurality of diode groups, at least one diode group is formed of a plurality of LEDs. Each of the first and second piezoelectric conversion units has a piezoelectric inverter, which can easily achieve an impedance matching and a constant-current power to drive LEDs via a piezoelectric effect. Besides, the present invention also has the advantage of cost efficiency.
Owner:ZIPPY TECH
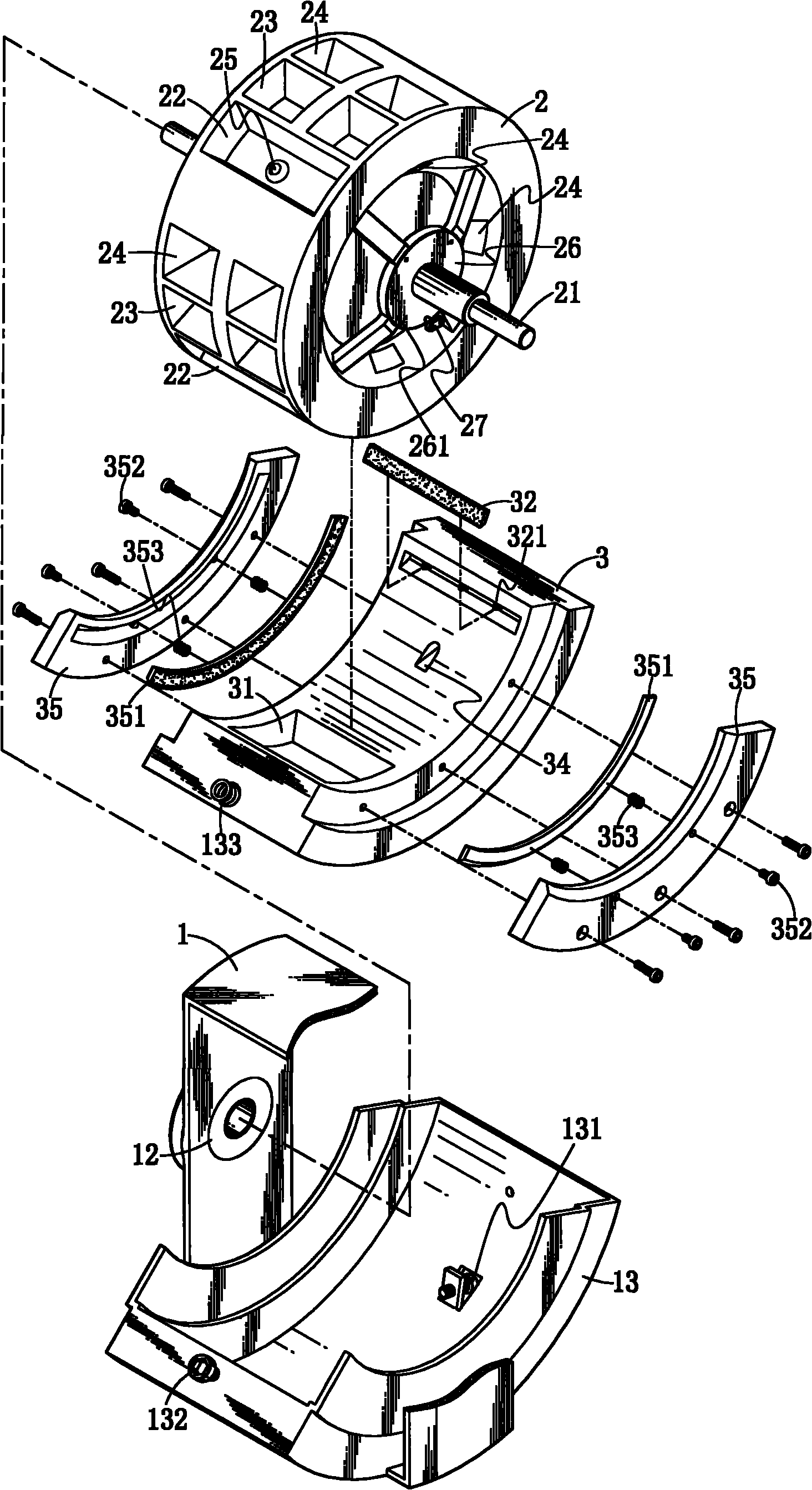
Improved structure of rotary engine
InactiveCN101845990AIncrease motivationSolve the disadvantages of loud explosion sound but no thrustInternal combustion piston enginesPiezo-electric ignitionCombustion chamberRotary engine
The invention relates to an improved structure of a rotary engine. A combustion chamber and an exhaust port are at least arranged in the periphery of a steamer, wherein the combustion chamber is additionally provided with a propulsion chamber in the front and a convex surface behind to propel and remove waste gas; the steamer can explode once per revolution or can explode several times per revolution. On a frame at the outside of the steamer, the indent inclined angle of a sliding block is supported by screws. An explosion space formed by the explosion chamber and the combustion chamber is arranged on the inner surface of the sliding block. Besides ignition time adjustable in advance after air enters the combustion chamber, during other strokes, due to the convex surface of the steamer, air-in can be prevented by sheltering the air inlet. Further, the invention can adjust the combustion time to generate greater explosive force and can remove the waste gas by post-explosion pressure.
Owner:周荣光
Camera flash circuit using a piezoelectric transformer to trigger firing of the camera flash tube
InactiveUS7049760B2Low costConvenient ArrangementElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementHigh voltage pulseEngineering
A camera flash circuit employing a piezoelectric transformer in the flash trigger circuit, the piezoelectric transformer having input terminals coupled to the main flash voltage storage capacitor and an output terminal coupled to the flash trigger terminal on the flash tube. When the camera flash trigger switch is closed, the input terminals of the piezoelectric transformer are driven directly from the charge voltage stored on the flash storage capacitor to generate the necessary high voltage pulse at the flash tube trigger terminal to initiate firing of the flash tube.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
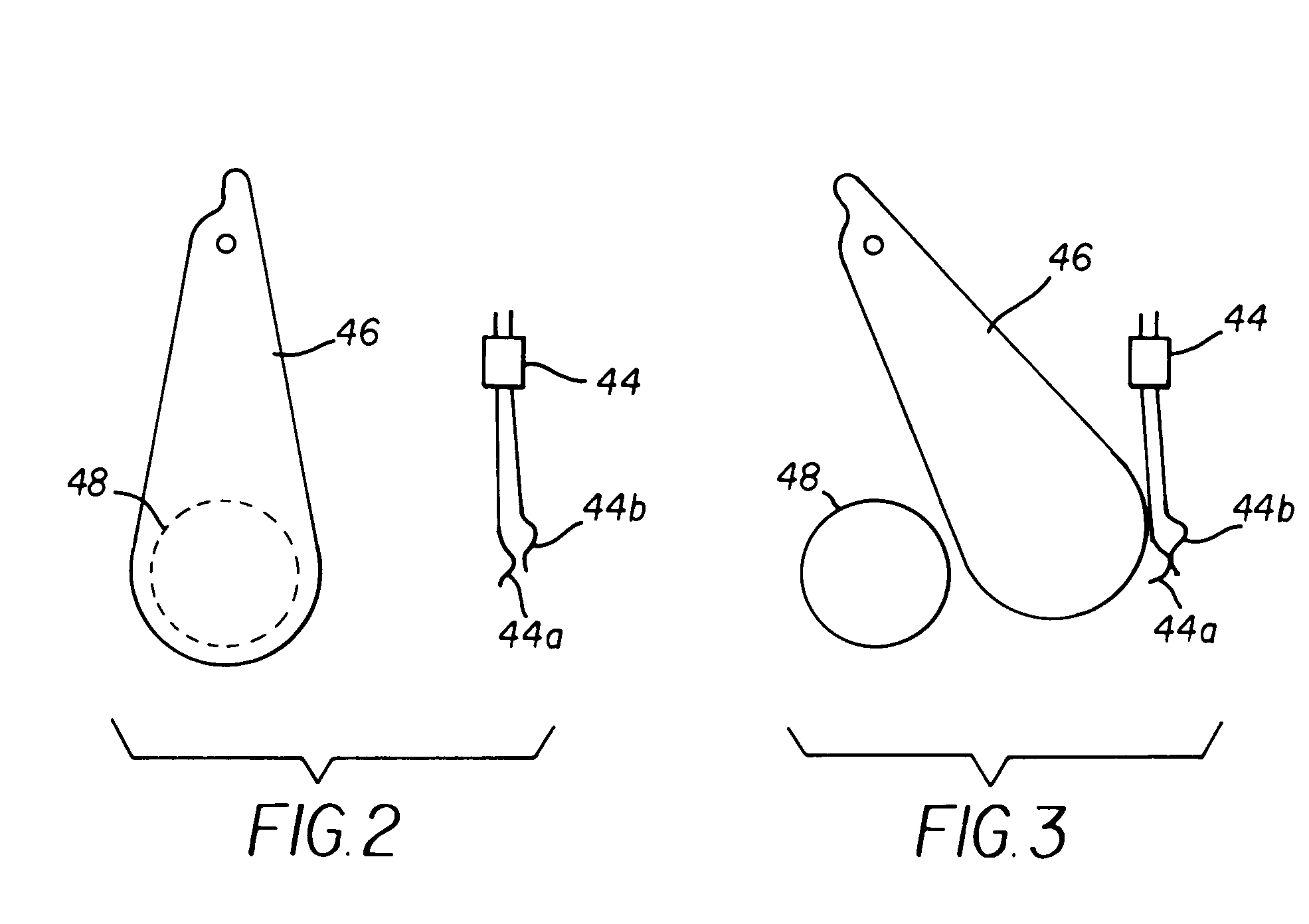
Piezoelectric transformer driving device, cold-cathode tube inverter, cold-cathode tube driving device, and image forming apparatus
A piezoelectric transformer driving device including: an oscillator; a frequency-divider outputting a pulse by dividing a clock signal from the oscillator by a frequency-divide ratio received thereto; a switching element driven by the pulse and intermittently applying a voltage to a primary side of a piezoelectric transformer; a frequency-divide ratio instructing unit holding a frequency-divide ratio instruction value of a real number having an integer part and an fractional part; a binarization unit binarizing the frequency-divide ratio instruction value into two different integer frequency-divide ratios and selectively outputting the frequency-divide ratios. The binarization unit adjusts an appearance ratio of the frequency-divide ratios such that an average of the frequency-divide ratios output from the binarization unit is equal to an average of the frequency-divide ratio instruction value.
Owner:OKI DATA CORP
Method for controlling the primary ignition current of an internal combustion engine with controlled ignition
ActiveUS6883508B2Improve approximationHigh precisionEngine testingMachines/enginesPower flowIgnition coil
Method for controlling a primary current in an ignition coil of an internal combustion engine with controlled ignition, the current is established in an inductive primary circuit over a given conduction time. The conduction time is calculated by:predetermining the predetermined conduction time,carrying out at least one measurement of the current in the primary circuit at an instant lying in the last tenth of the predetermined conduction time;estimating the current at the end of the predetermined conduction time, as a function of the measurement(s) carried out;optionally correcting the conduction time for the ignition cycle during which the last current measurement was carried out, as a function of the previous estimate and the current desired at the end of the conduction time.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE CORP
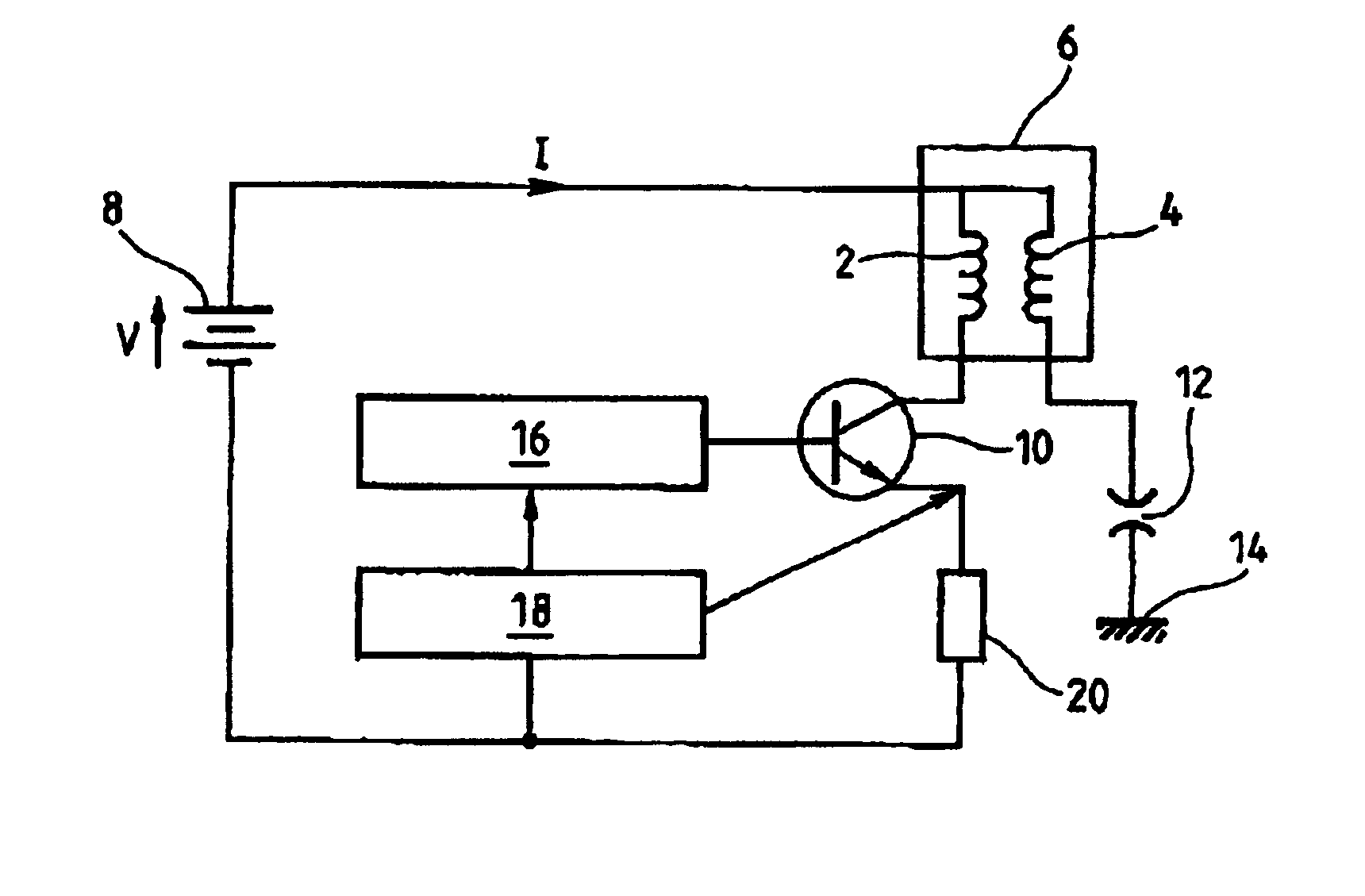
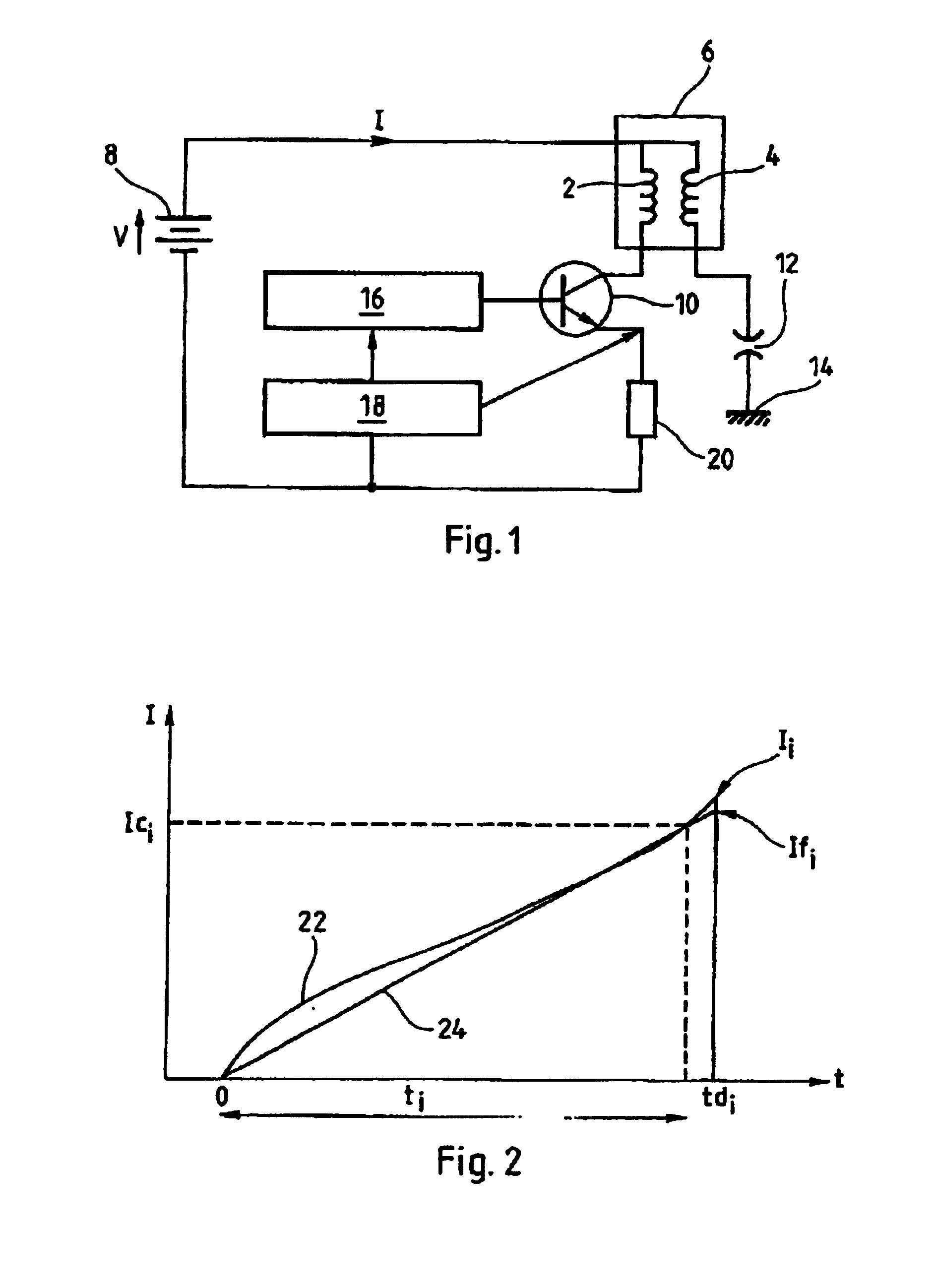
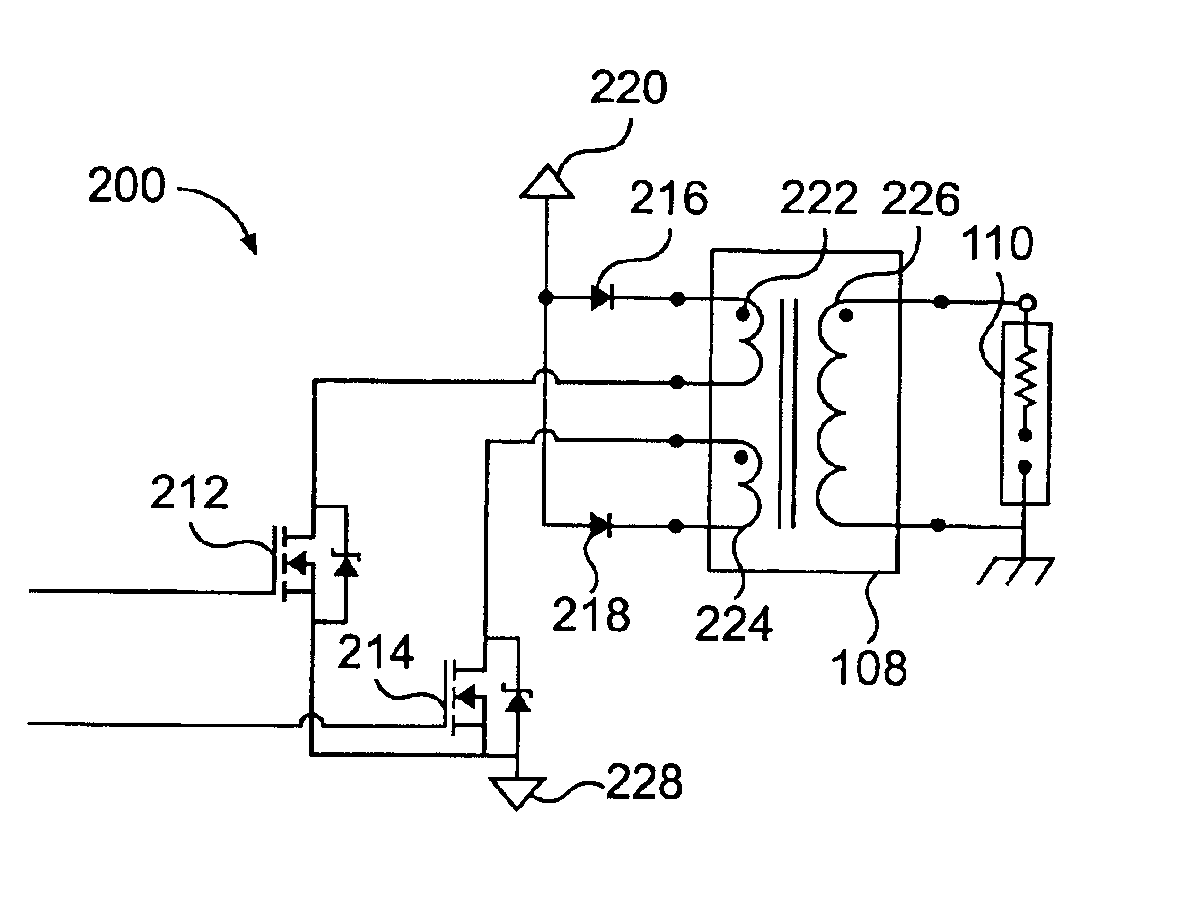
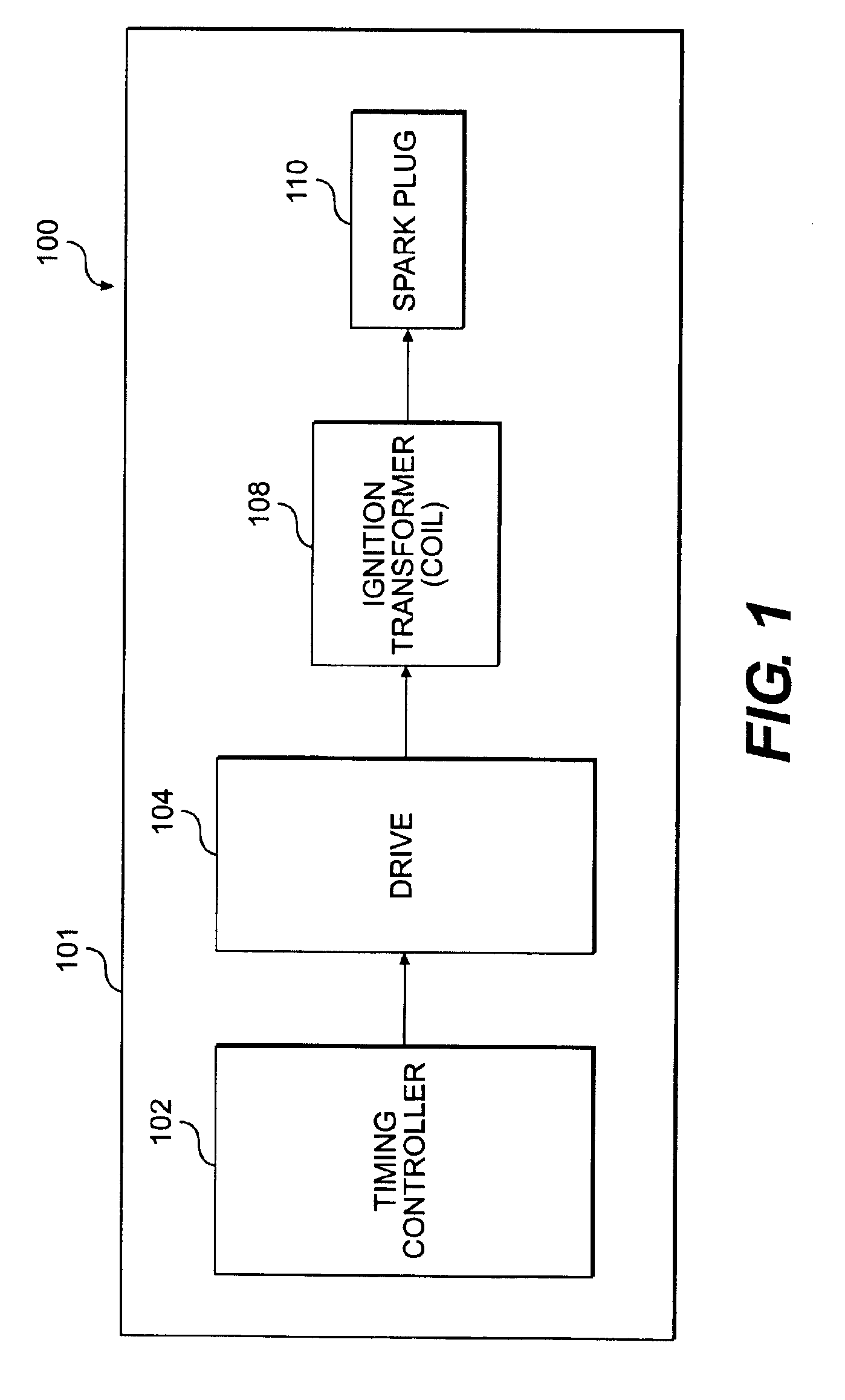
Low current extended duration spark ignition system
ActiveUS6935323B2Machines/enginesInstallations with induction energy storageTransformerConductor Coil
A system for firing a spark plug is disclosed. The system includes a timing controller configured to send a first timing signal and a second timing signal. The system also includes an ignition transformer having a primary winding and a secondary winding and a spark-plug that is operably associated with the secondary winding. A first switching element is disposed between the timing controller and the primary winding of the ignition transformer. The first switching element controls a supply of power to the primary winding based on the first timing signal. Also, a second switching element is disposed between the timing controller and the primary winding of the ignition transformer. The second switching element controls the supply of power to the primary winding based on the second timing signal. A method for firing a spark plug is also disclosed.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Driving method and driving circuit for piezoelectric transformer, cold-cathode tube light-emitting apparatus, liquid crystal panel and device with built-in liquid crystal panel
InactiveUS6911787B2Improve efficiencySuppress electromagnetic noiseStatic indicating devicesMachines/enginesTime ratioEngineering
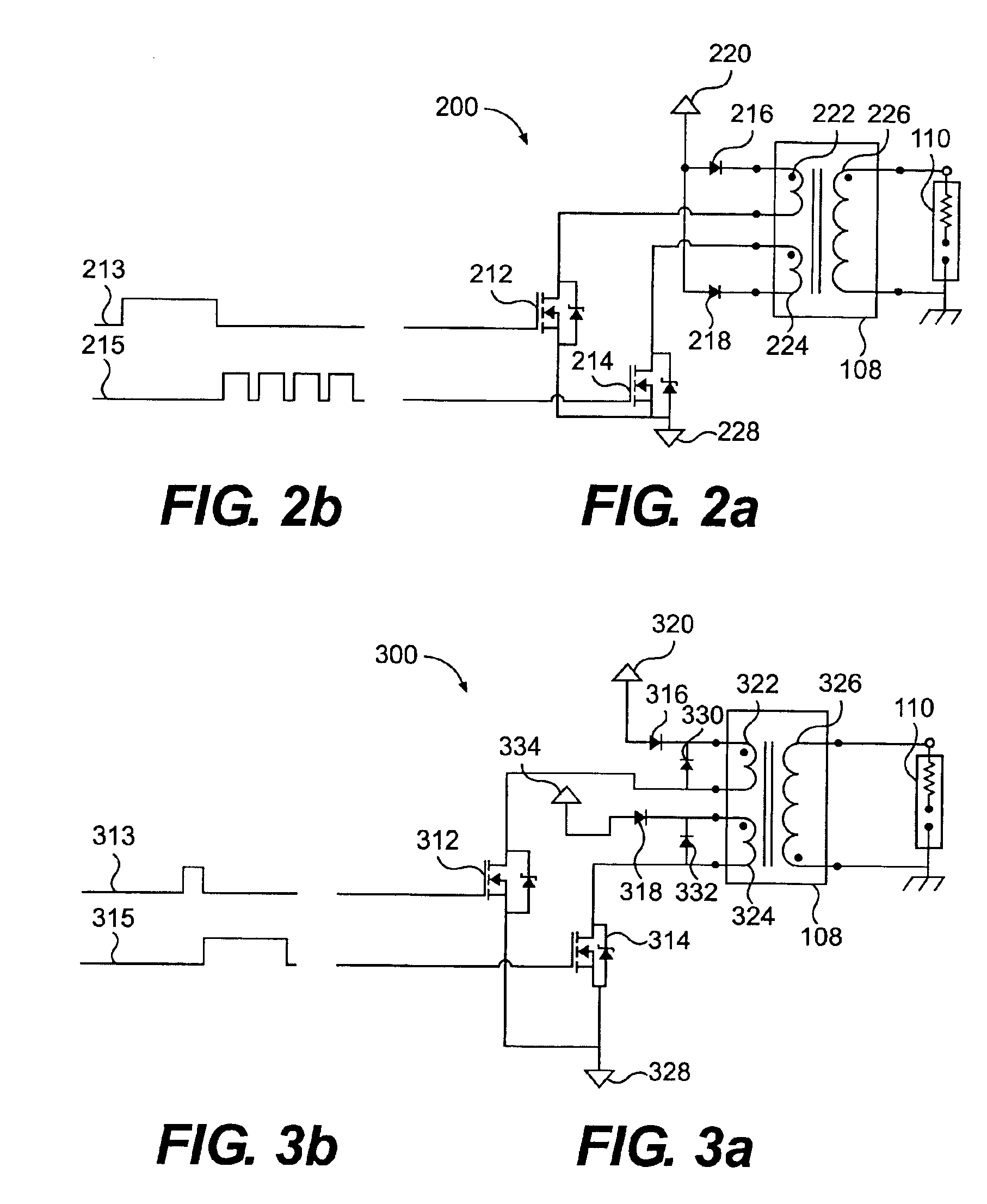
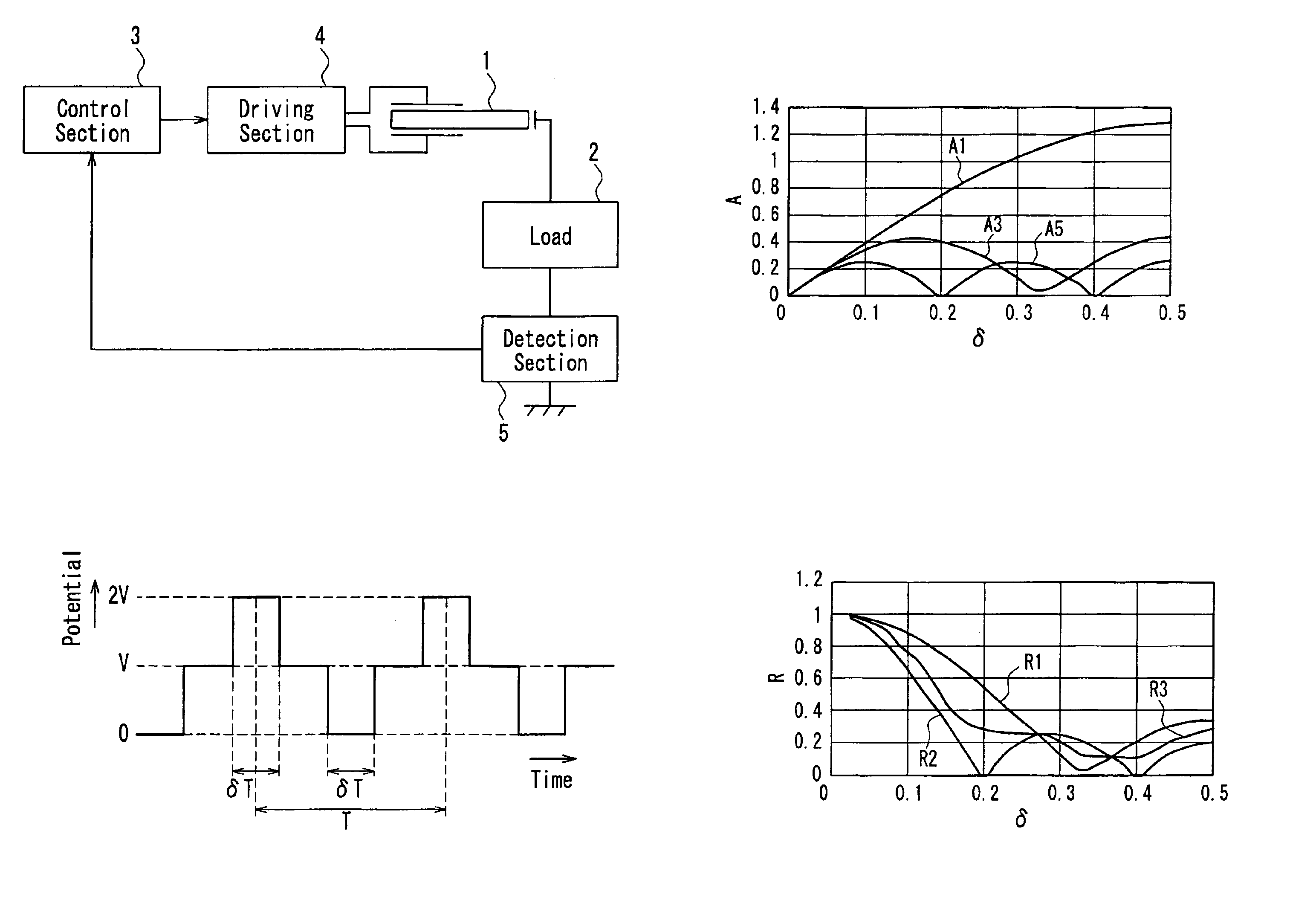
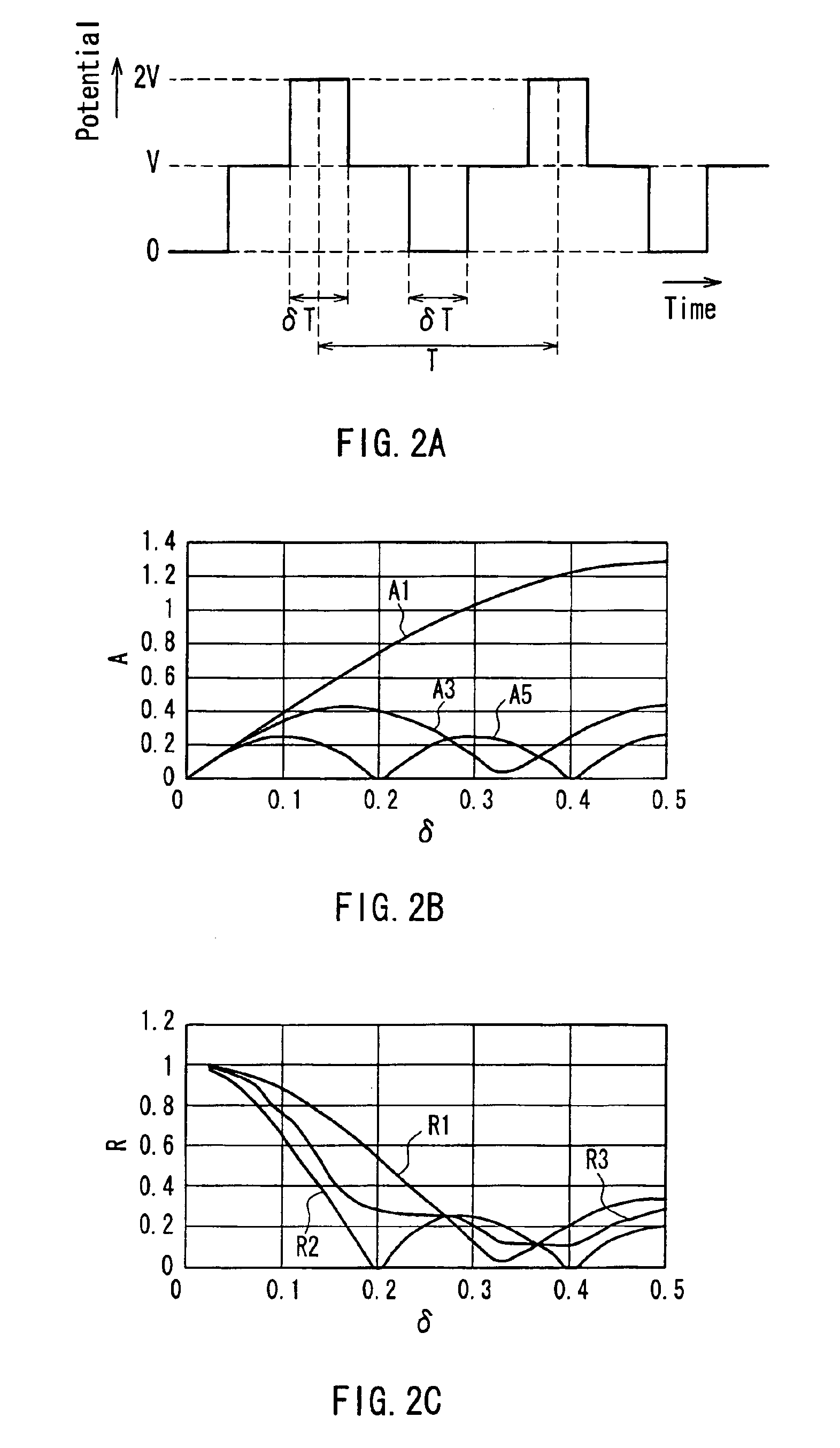
There is provided a method for driving a piezoelectric transformer in which a driving efficiency and the reliability in terms of withstand power and distortion can be enhanced by suppressing a higher order vibration mode exited by a harmonic component other than a driving frequency included in a driving signal of the piezoelectric transformer without using an inductive element. The driving signal applied to a primary side electrode of the piezoelectric transformer is a signal in a rectangular waveform having a time period δT in which a level is a maximum potential (2V) or a minimum potential (0), obtained by multiplying a period T of the driving signal by a predetermined time ratio δ. The time ratio δ is set to be smaller than 0.5 and so as to minimize a sum of ratios of amplitudes of respective higher order vibration modes with respect to an amplitude of a vibration mode exciting the piezoelectric transformer.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
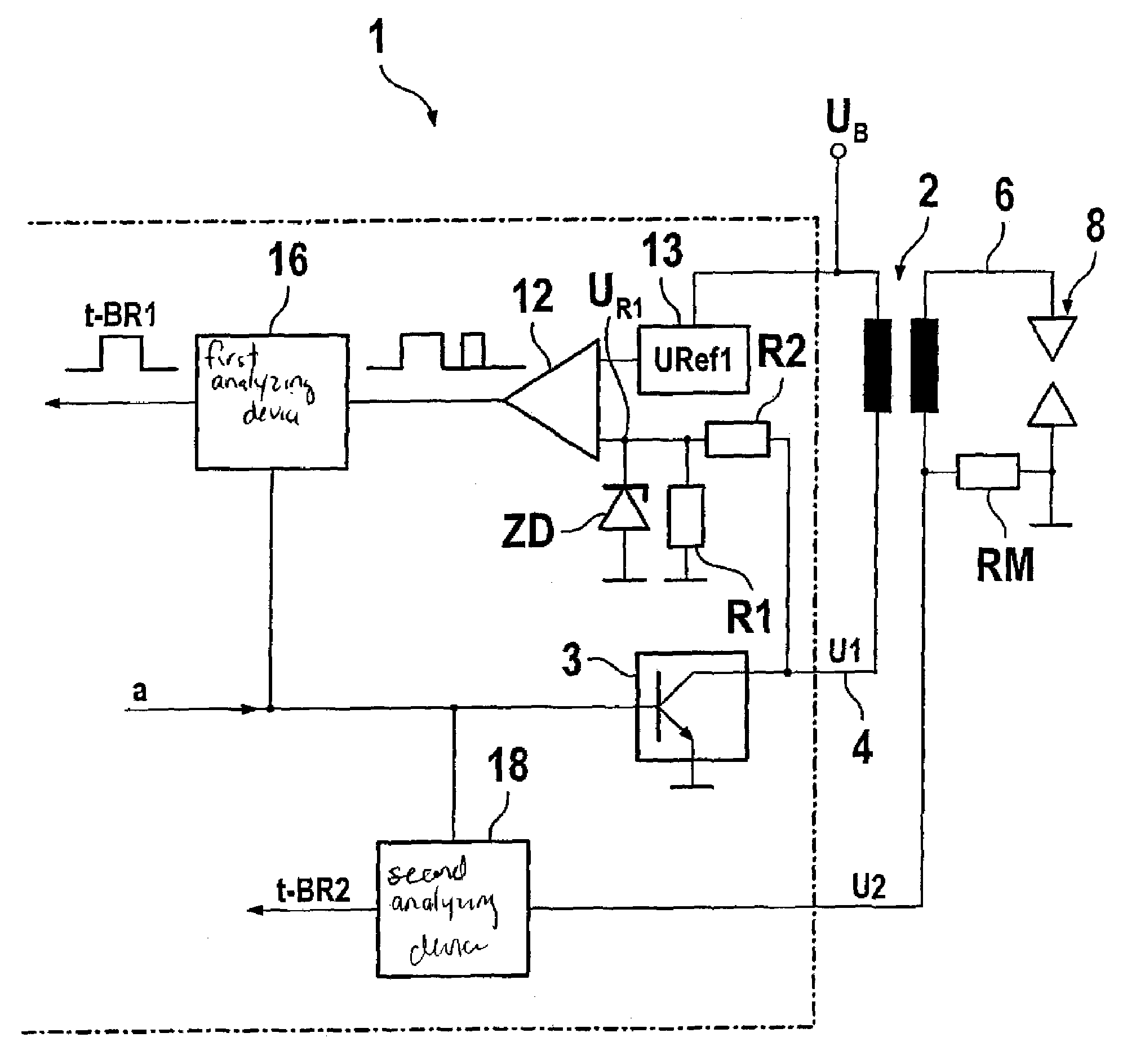
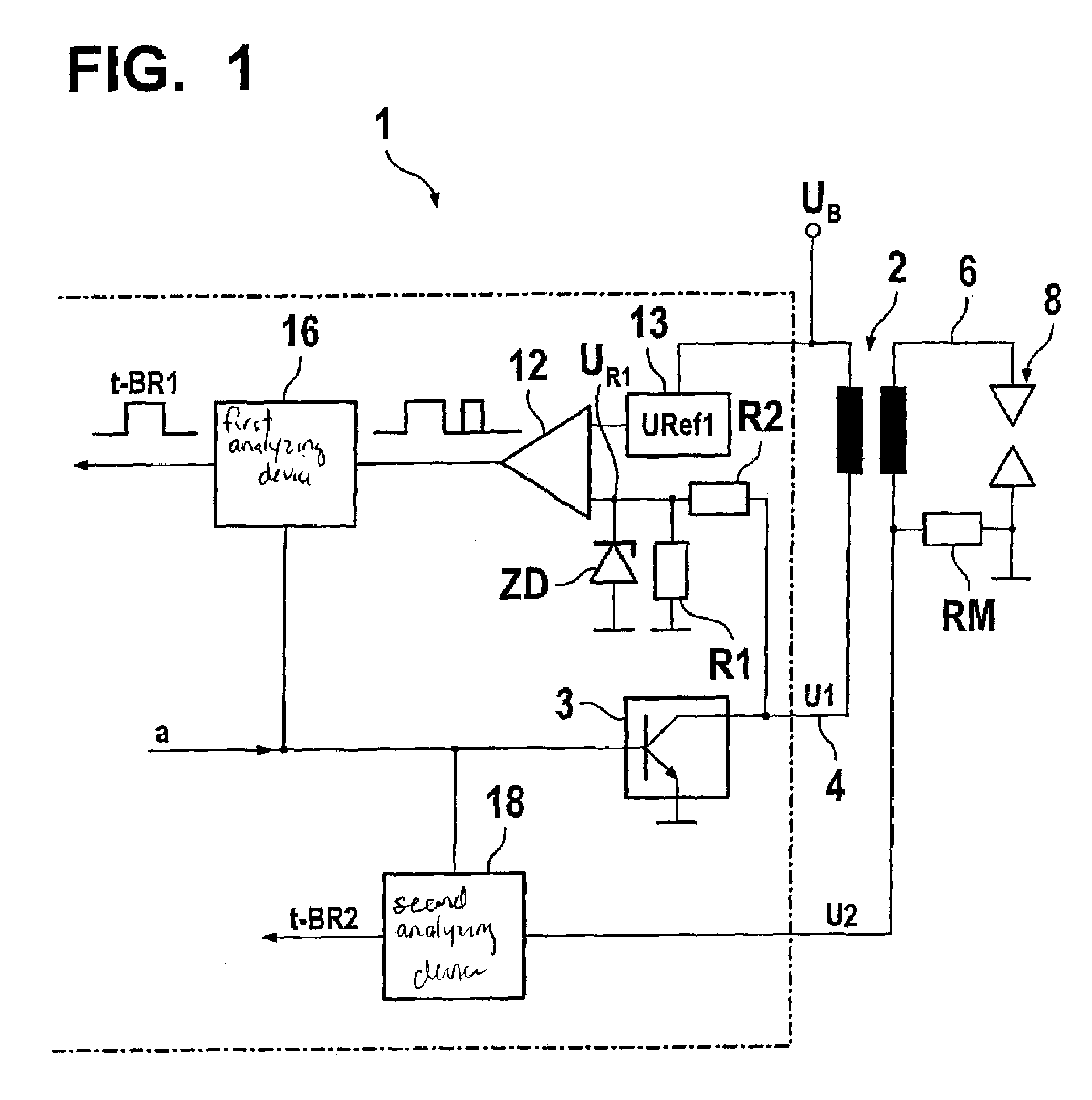
Driver circuit
InactiveUS6914434B2Easy to identifySuitable for integration in ICElectrical controlMachines/enginesDriver circuitMeasuring output
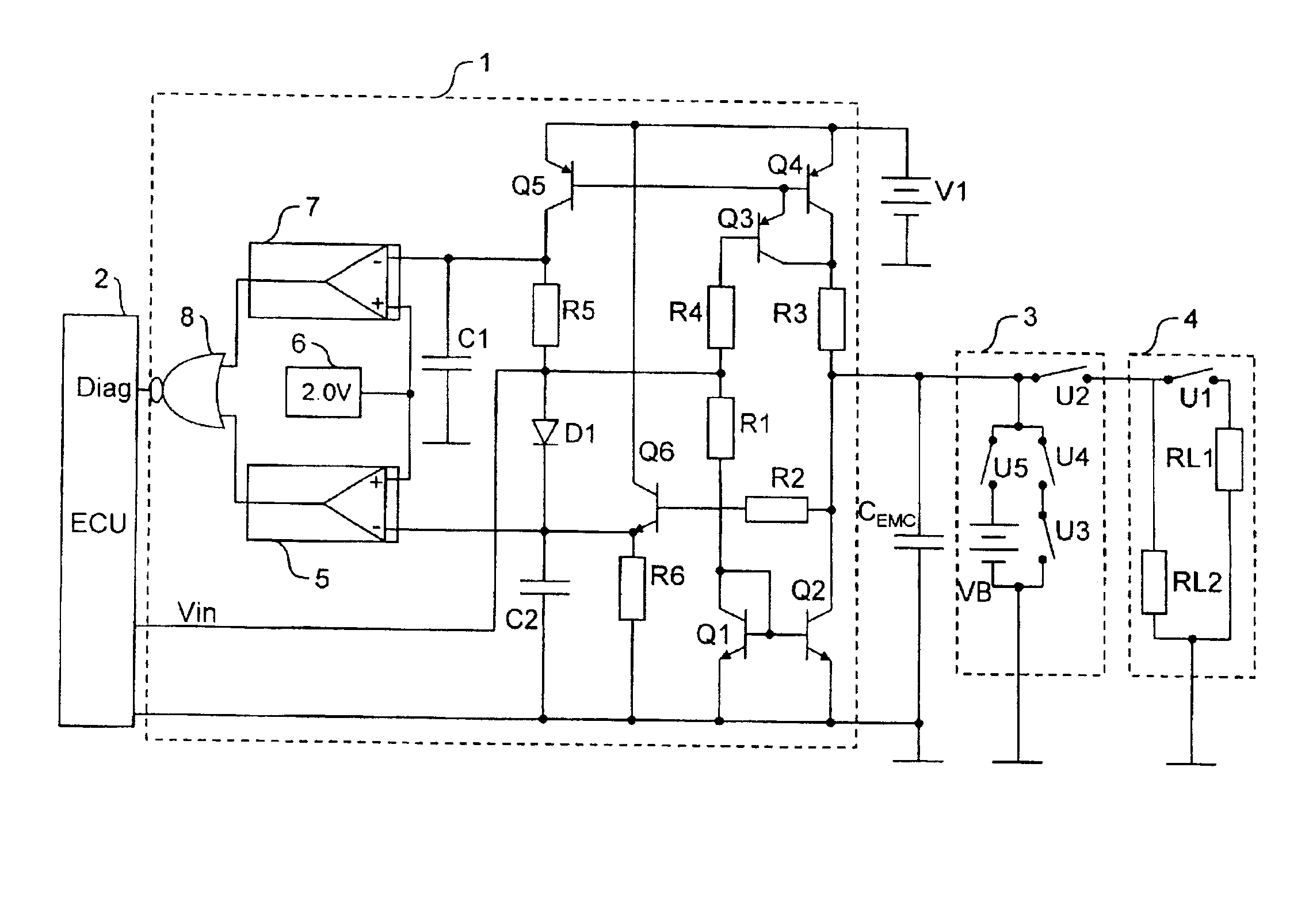
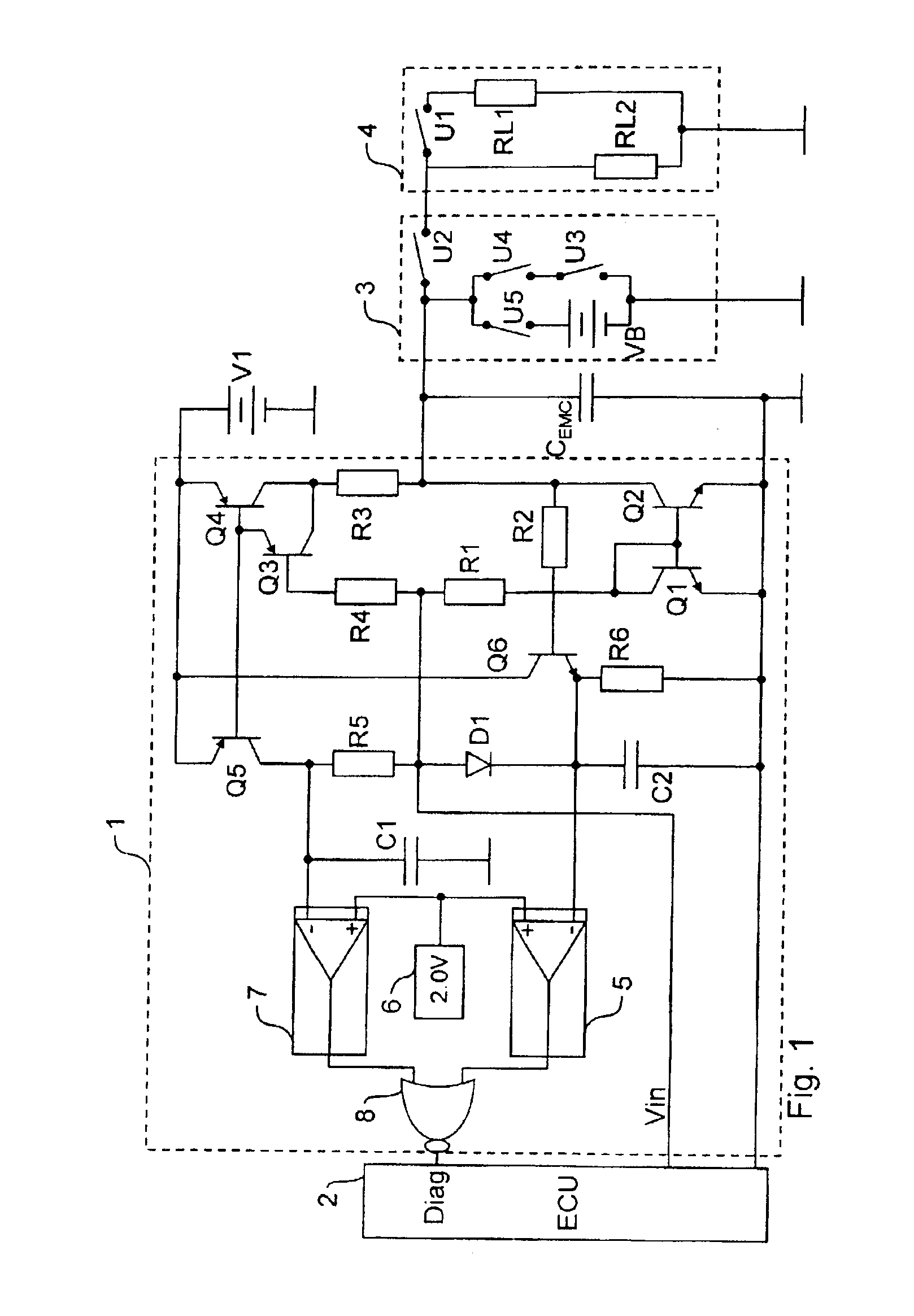
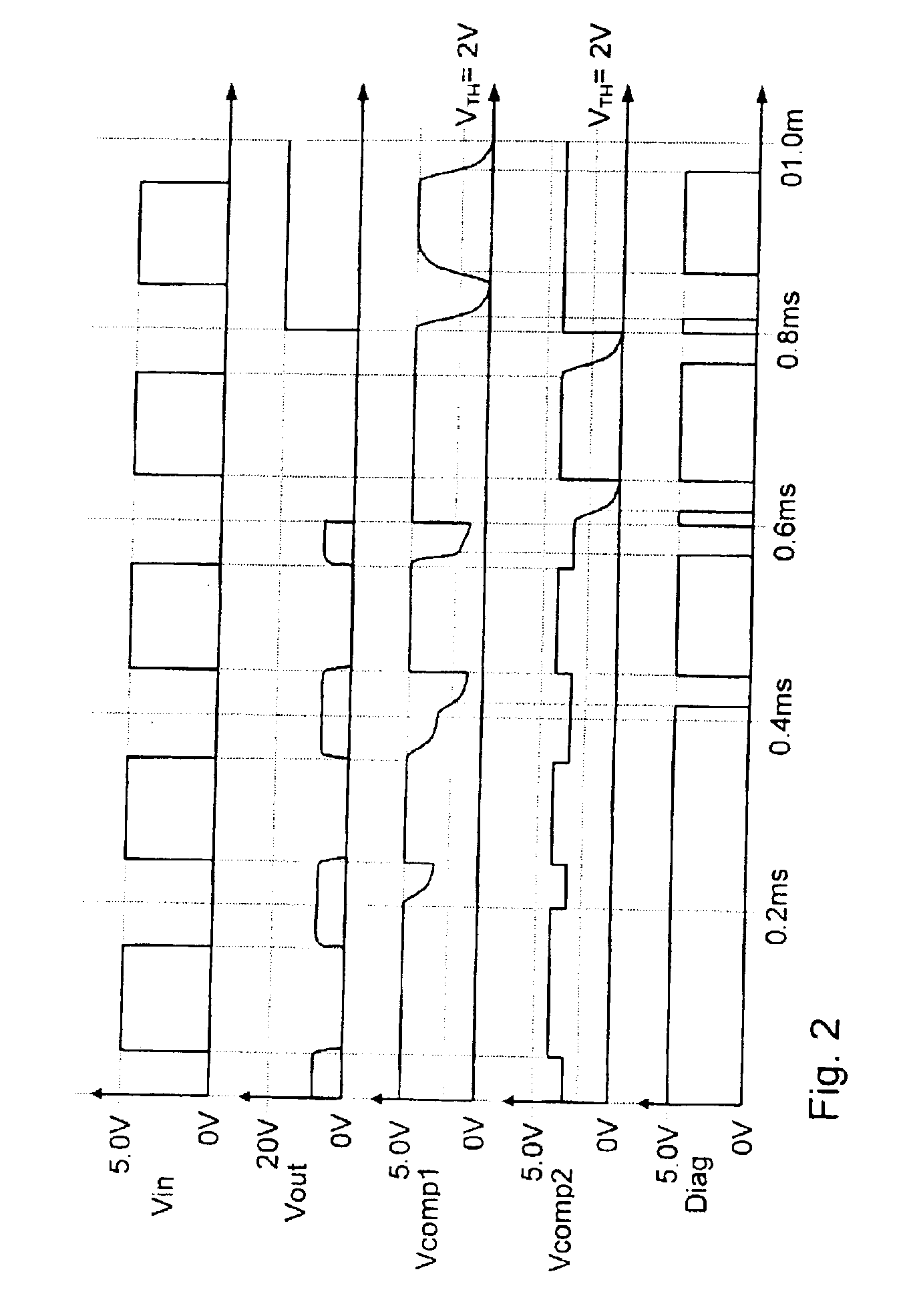
Driver circuit (1) for actuating an electrical device via a control line (3) and for diagnosing the state of the control line (3) and / or of the actuated device, having a test circuit (Q1-Q6, R1-R6), connected to the control line (3), for measuring the electrical output current flowing via the control line (3), and an evaluation unit (5-8), connected to the test circuit, for generating a diagnostic signal (DIAG) on the basis of the measured output current, the test circuit having at least one current mirror circuit (Q1, Q2; Q4-Q5).
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Anti global warming energy power system and method
InactiveUS20080271723A1Increase powerClean burningNon-insulated conductorsInsulated cablesElectricityCombustion chamber
A piezo-ceramic device is attached to the power wire of an engine to facilitate cleaner burning of fuel and improve to improve fuel consumption. In the presence of an electrical field around the power wire, the device directs acoustical energy of a subsonic frequency towards the combustion chamber which acts to ionize the fuel and impart a thrust on the piston.
Owner:COWDEN RALPH A
Method and device for detecting a phase of a four-stroke gasoline engine
InactiveUS6971372B2Accurate detectionCheap to achieveElectrical controlFuel injection apparatusTop dead centerGasoline direct injection
A method and a device for detecting the phase of a four-stroke gasoline engine, a gasoline direct injection engine in particular. For reliable phase detection involving relatively little expense during a starting phase, a crankshaft is turned together with at least one piston; ignition is triggered via an ignition coil in at least two successive top dead centers of the piston without a supply of fuel. A primary current or a secondary current, or a primary voltage or a secondary voltage are measured in a measuring period which extends at least over a spark duration after the ignition. From the comparison of the measuring signals of successive ignitions, a conclusion is drawn as to which of the successive top dead centers is an ignition top dead center and which is a charge cycle top dead center.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Piezoelectric cascade resonant lamp-ignition circuit
ActiveUS7902763B2Improve reliabilitySmall volumeElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectricityCapacitance
The present invention discloses a piezoelectric cascade resonant lamp-ignition circuit, which uses the intrinsic capacitors of a piezoelectric transformer as piezoelectric capacitors. One lamp is cascaded to one set of the piezoelectric capacitors. Several sets of the piezoelectric capacitors and a resonant inductor are cascaded to form a resonant lamp-ignition circuit. The lamp-ignition circuit of the present invention has advantages of low temperature, small leakage current, high breakdown voltage and high lamp ignition efficiency. When applied to drive several lamps, the present invention uses a fixed frequency to attain a fixed inner impedance of the equivalent circuit of the piezoelectric capacitor. Thereby, the currents of the lamps are balanced to have an identical value.
Owner:MIDAS WEI TRADING +1
Piezoelectric transformer
InactiveUS6989626B2Improve circuit efficiencyIncrease powerPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesStatic indicating devicesEngineeringPiezoelectric transformer
A compact and high-power piezoelectric transformer is realized by using higher order longitudinal extensional mode vibrations and increasing an effective electromechanical coupling factor by a primary electrode which consists of plural electrodes.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
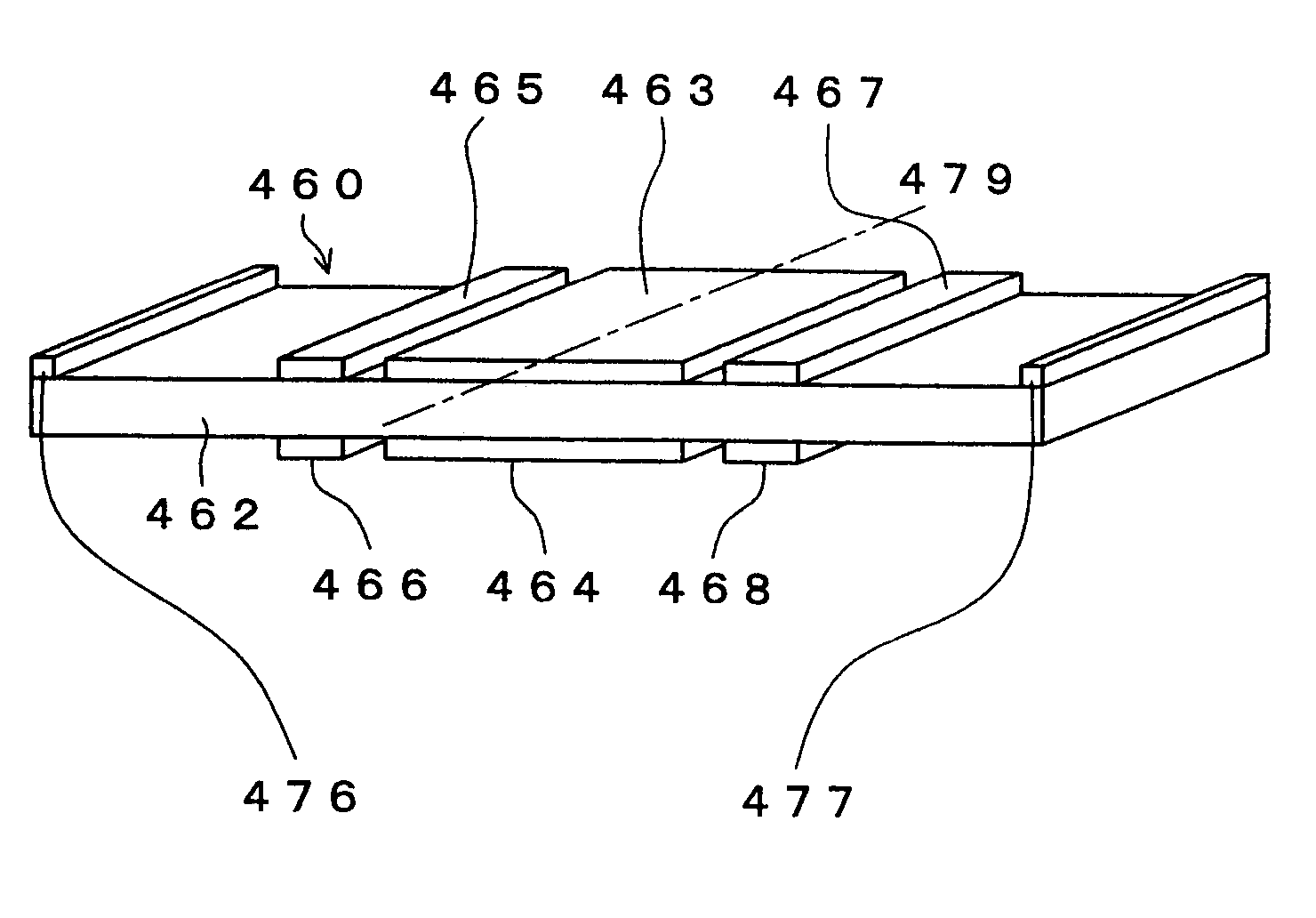
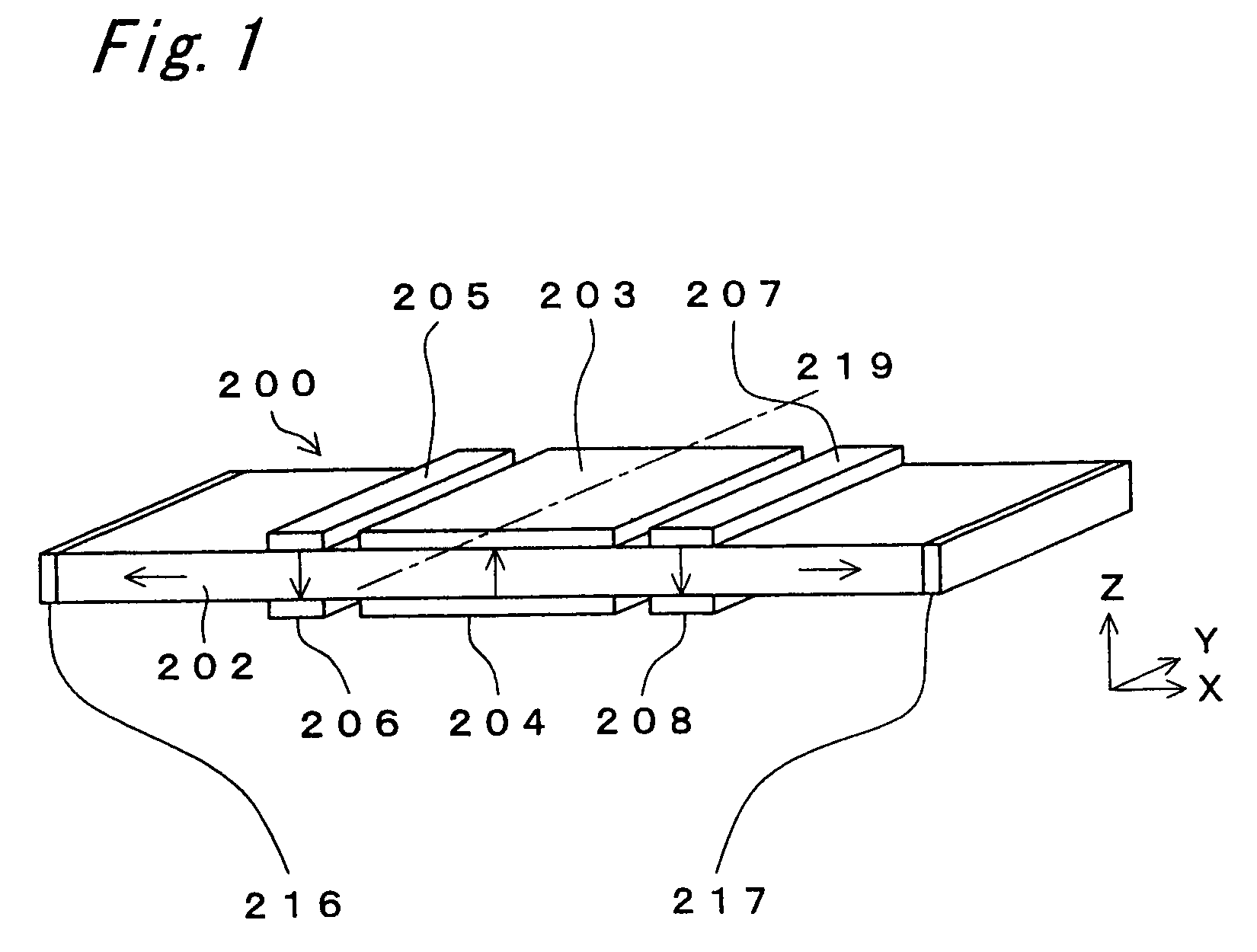
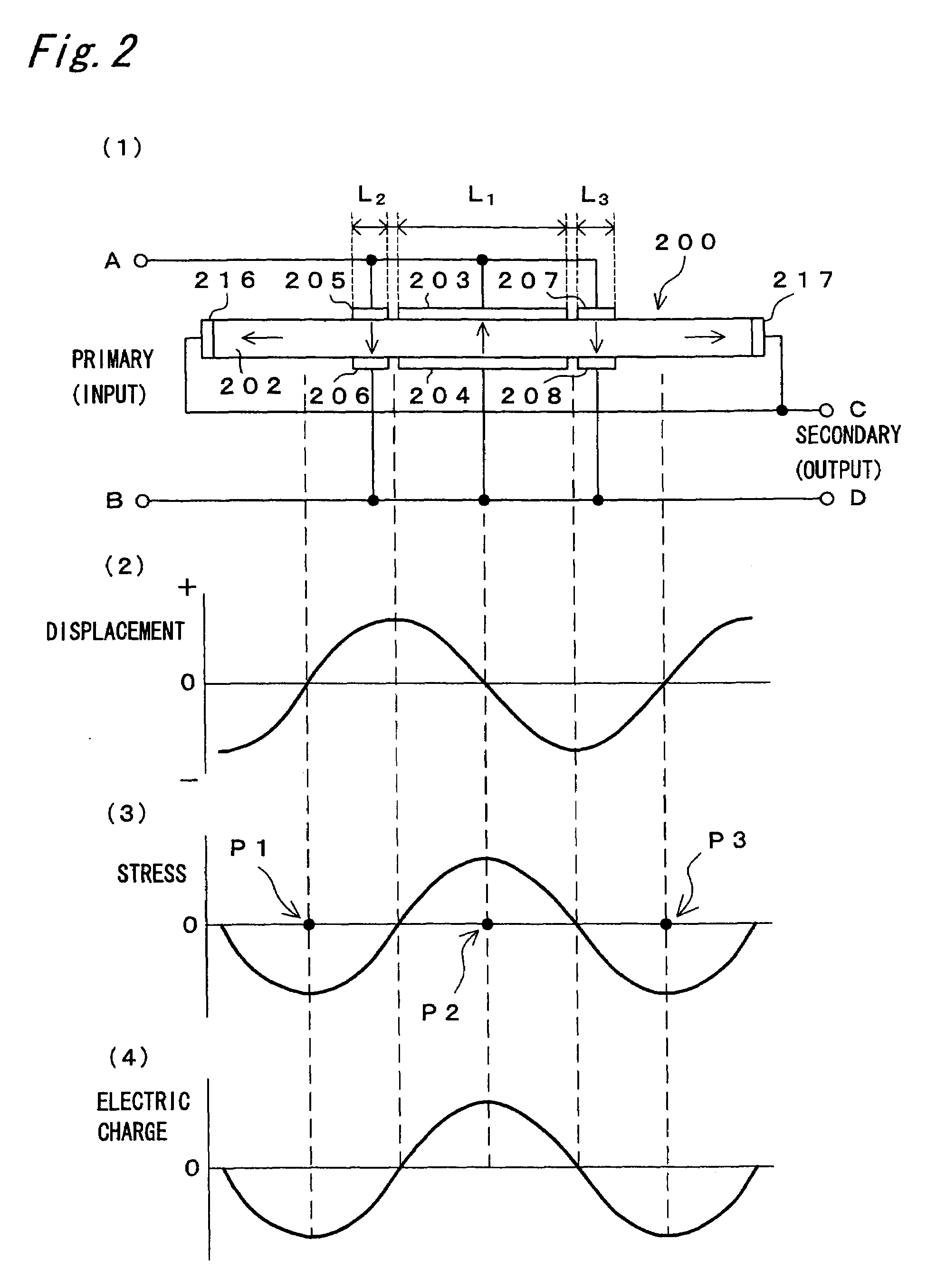
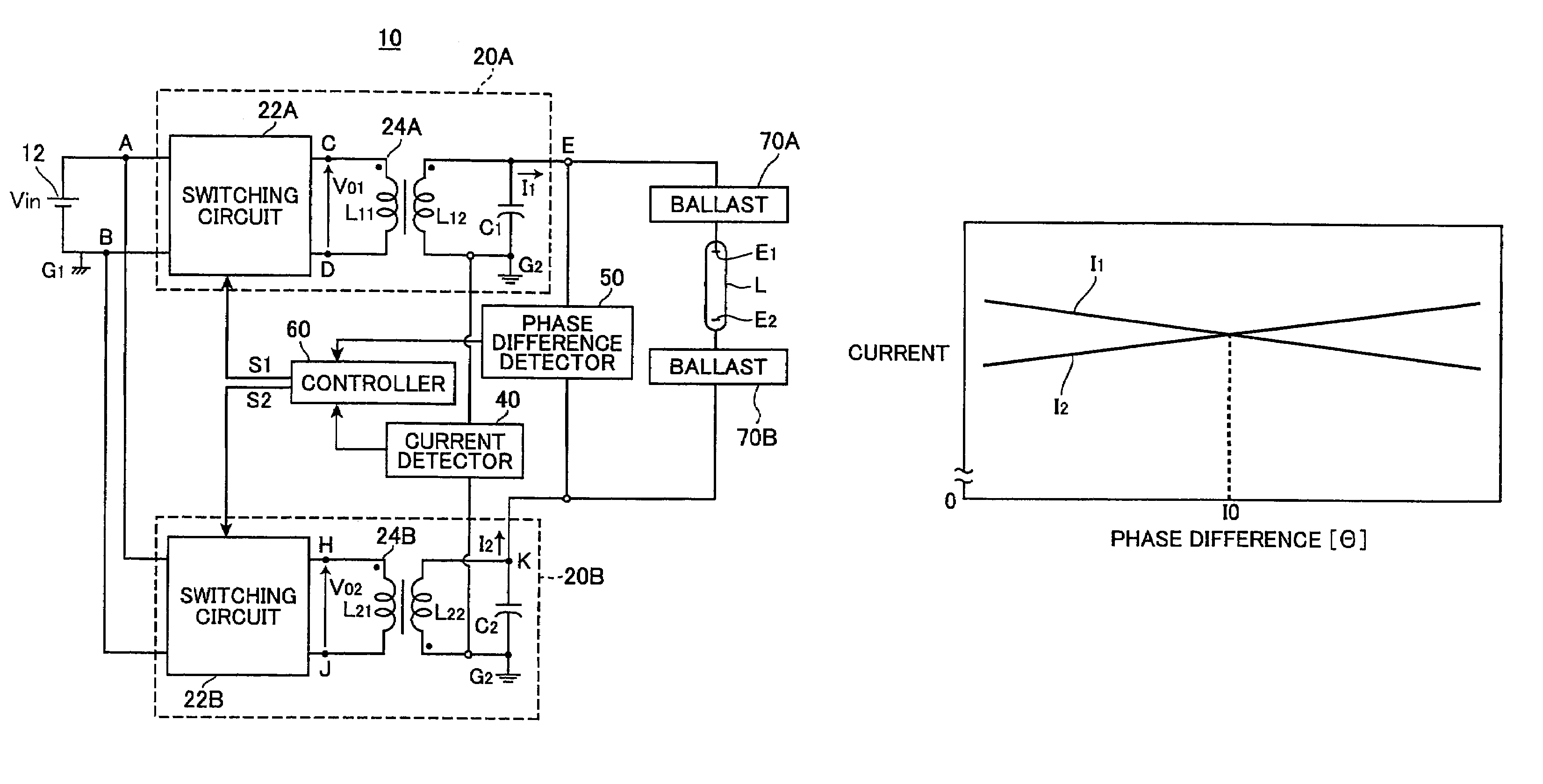
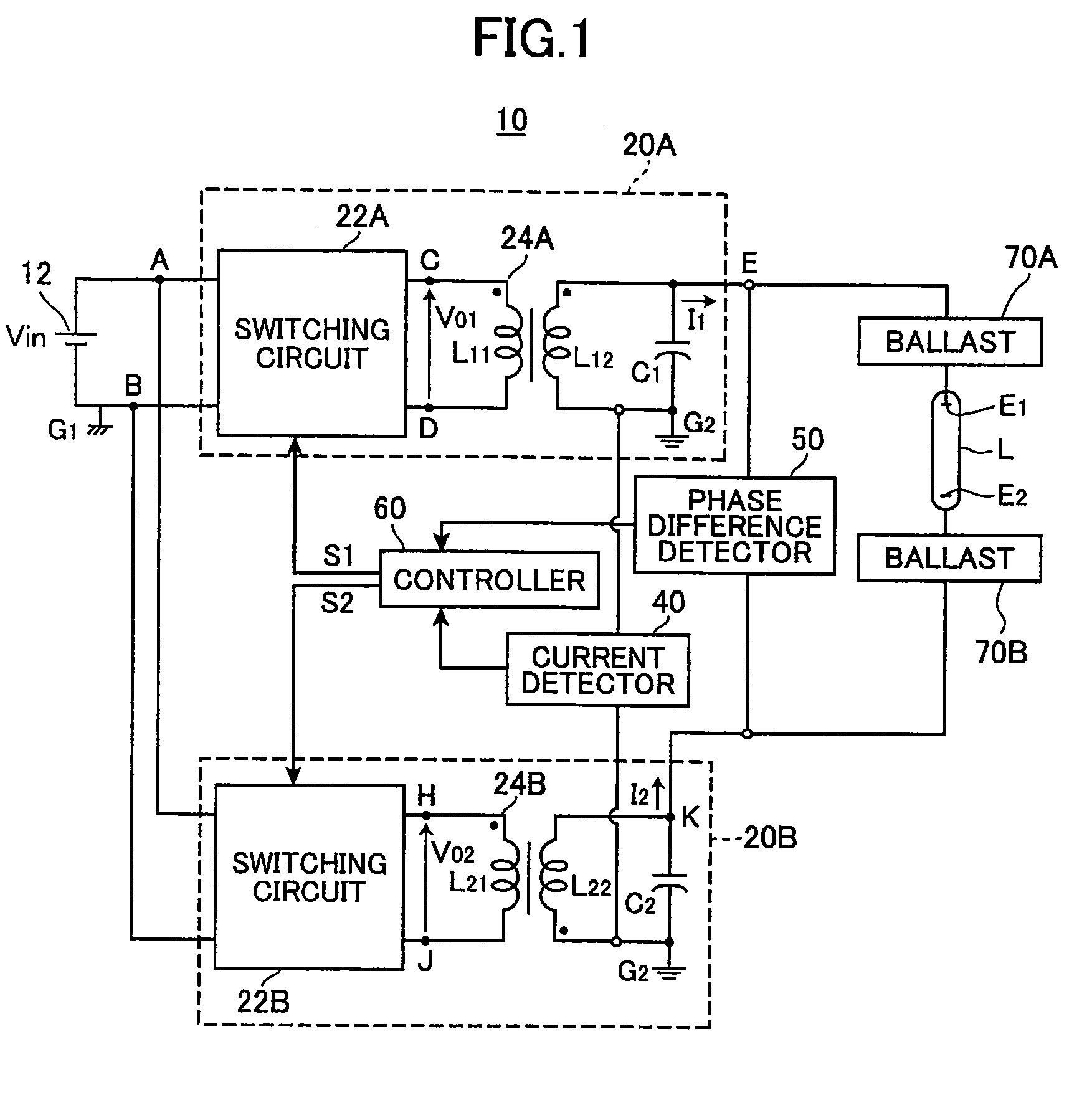
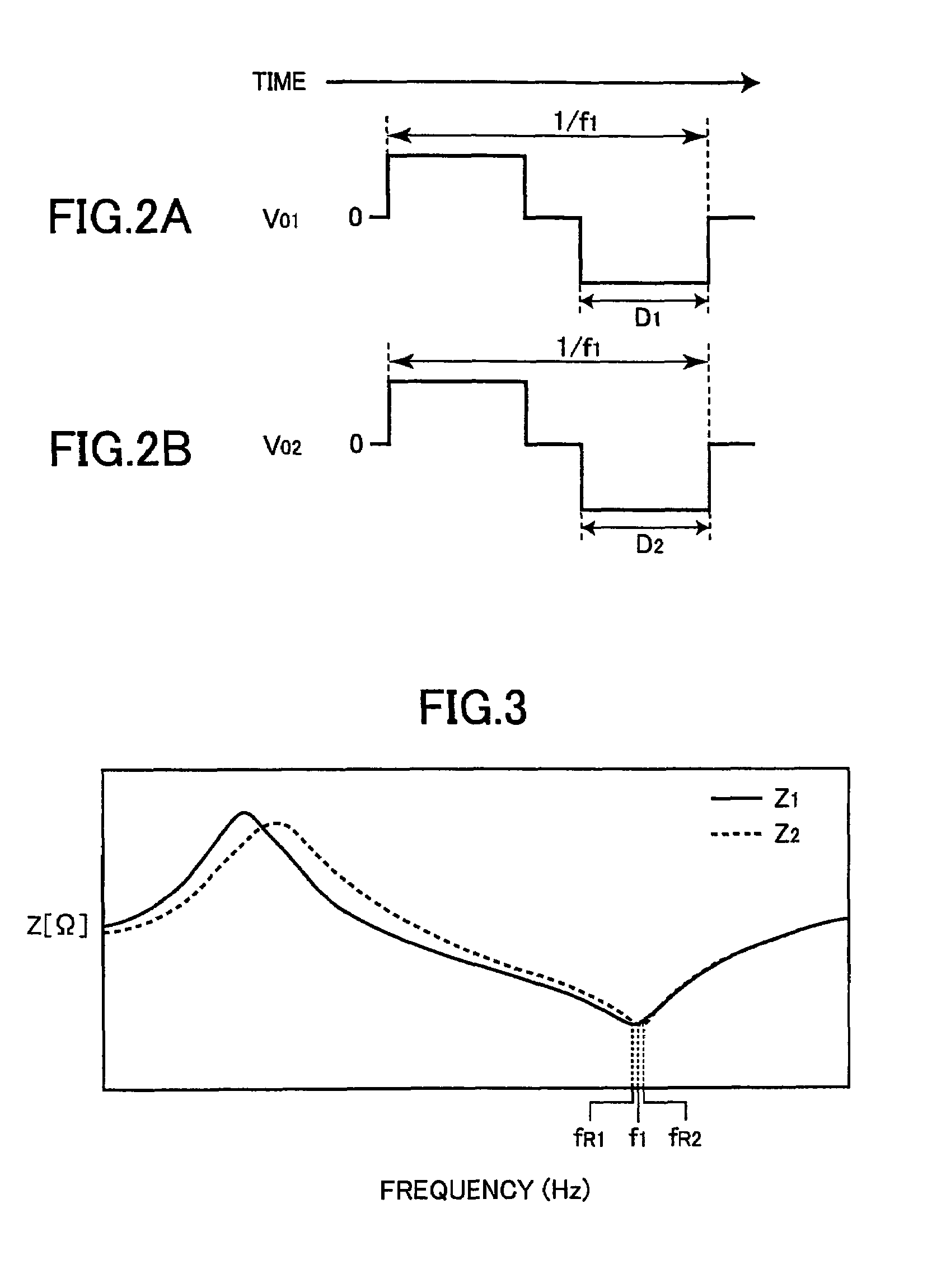
Discharge lamp lighting apparatus
InactiveUS7282866B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAc-dc conversionDriver circuitPhase difference
The present invention provides a discharge lamp lighting apparatus for lighting a discharge lamp having two electrodes, having: a first drive circuit, a second drive circuit, and a control circuit. The first drive circuit is connectable to one of the two electrodes to supply a first alternating current to the discharge lamp. The first alternating current has a frequency and a first effective value. The second drive circuit is connectable to the other of the two electrodes to supply a second alternating current to the discharge lamp. The second alternating current has the frequency and a second effective value. The second alternating current has an opposite phase to the first alternating current. The control circuit generates first and second drive pulses to drive the first and second drive circuits, respectively. The first and second drive pulses have a phase difference therebetween. The control circuit adjusts the phase difference to match the first and second effective values.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
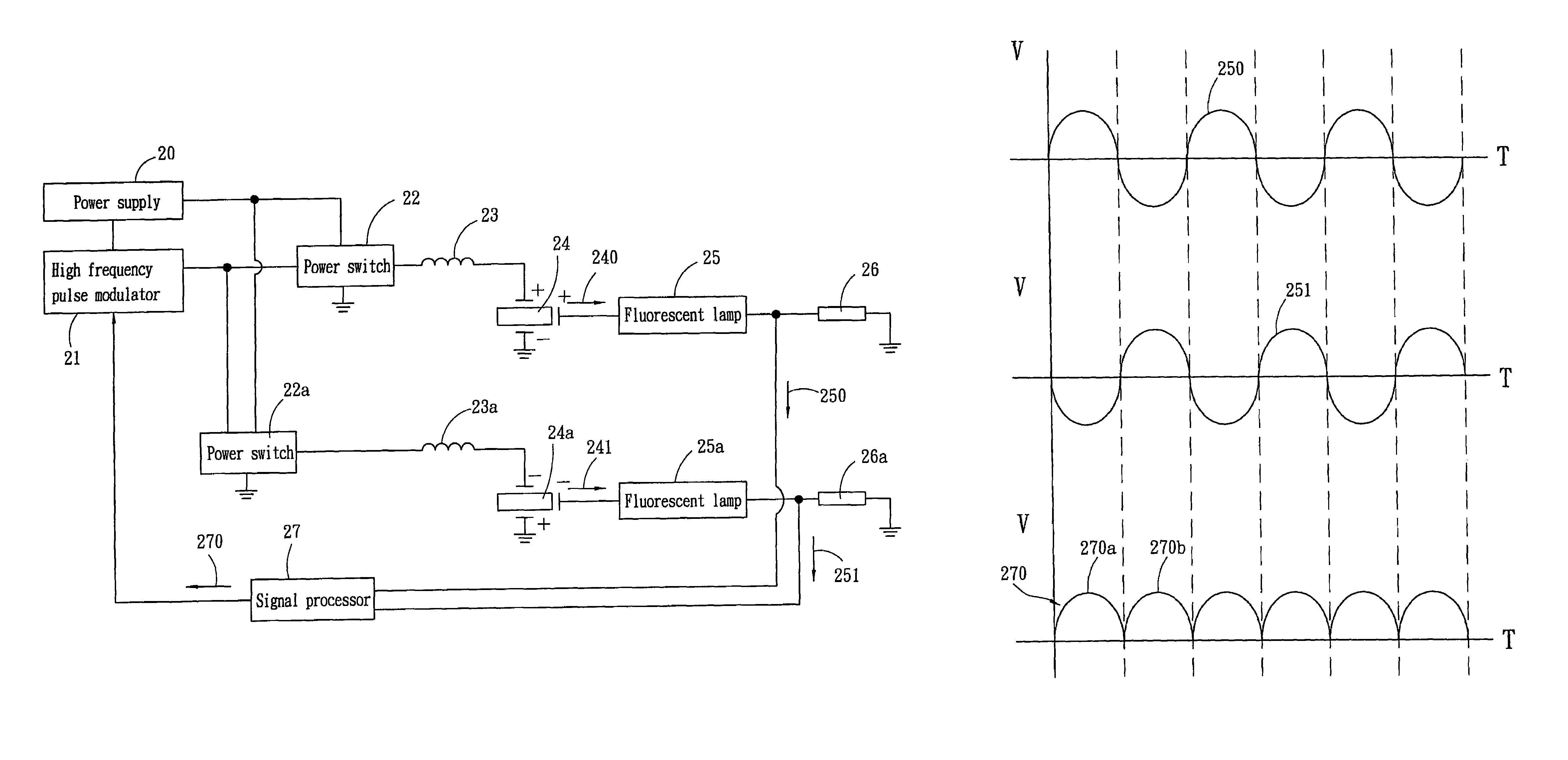
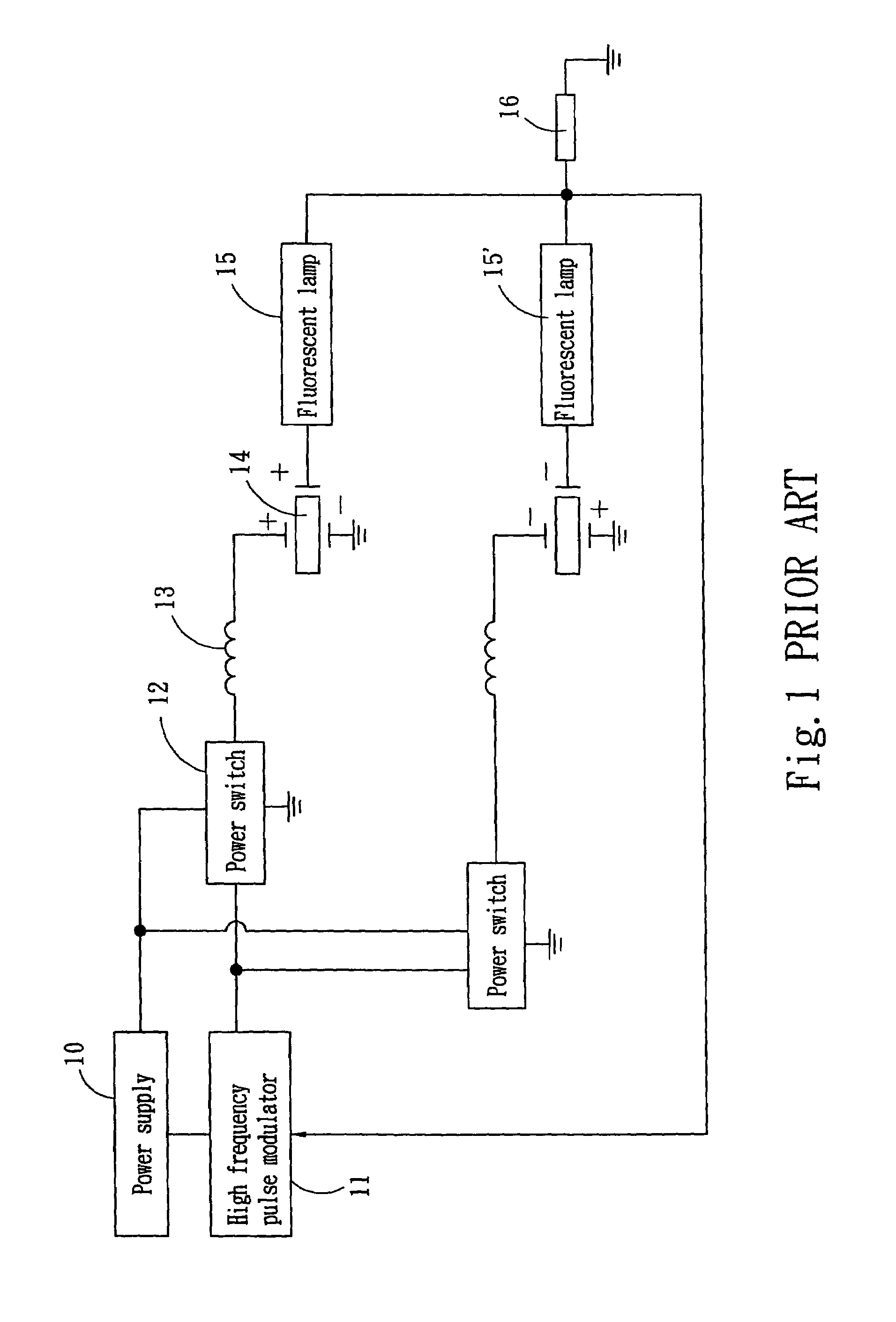
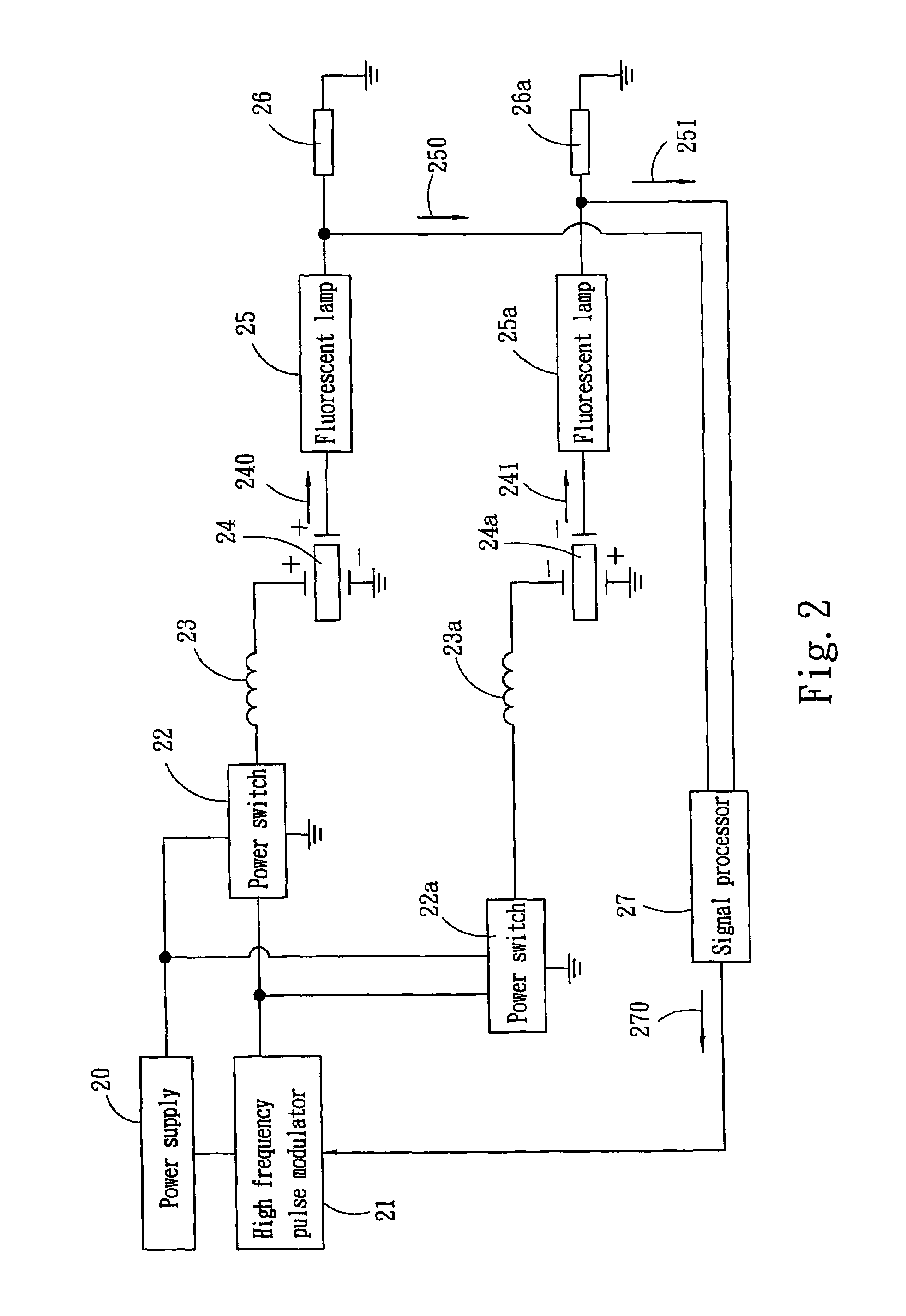
Current control apparatus for fluorescent lamps
A current control apparatus for fluorescent lamps adopted for use on high voltage actuated a fluorescent lamp includes a high frequency pulse modulator to provide voltage distribution signals, a power switch which is a MOSFET to output actuation signals, a conversion unit to receive the voltage distribution signals and perform voltage transformation, a piezoelectric transformer to receive the transformed voltage and perform voltage transformer, and the fluorescent lamp connecting to the piezoelectric transformer. The high frequency pulse modulator obtains a feedback current from the output ends of the fluorescent lamps through the signal processor to redistribute current and maintain evenness of the current in the fluorescent lamp.
Owner:ZIPPY TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com