Patents
Literature
32results about How to "Improving Q" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
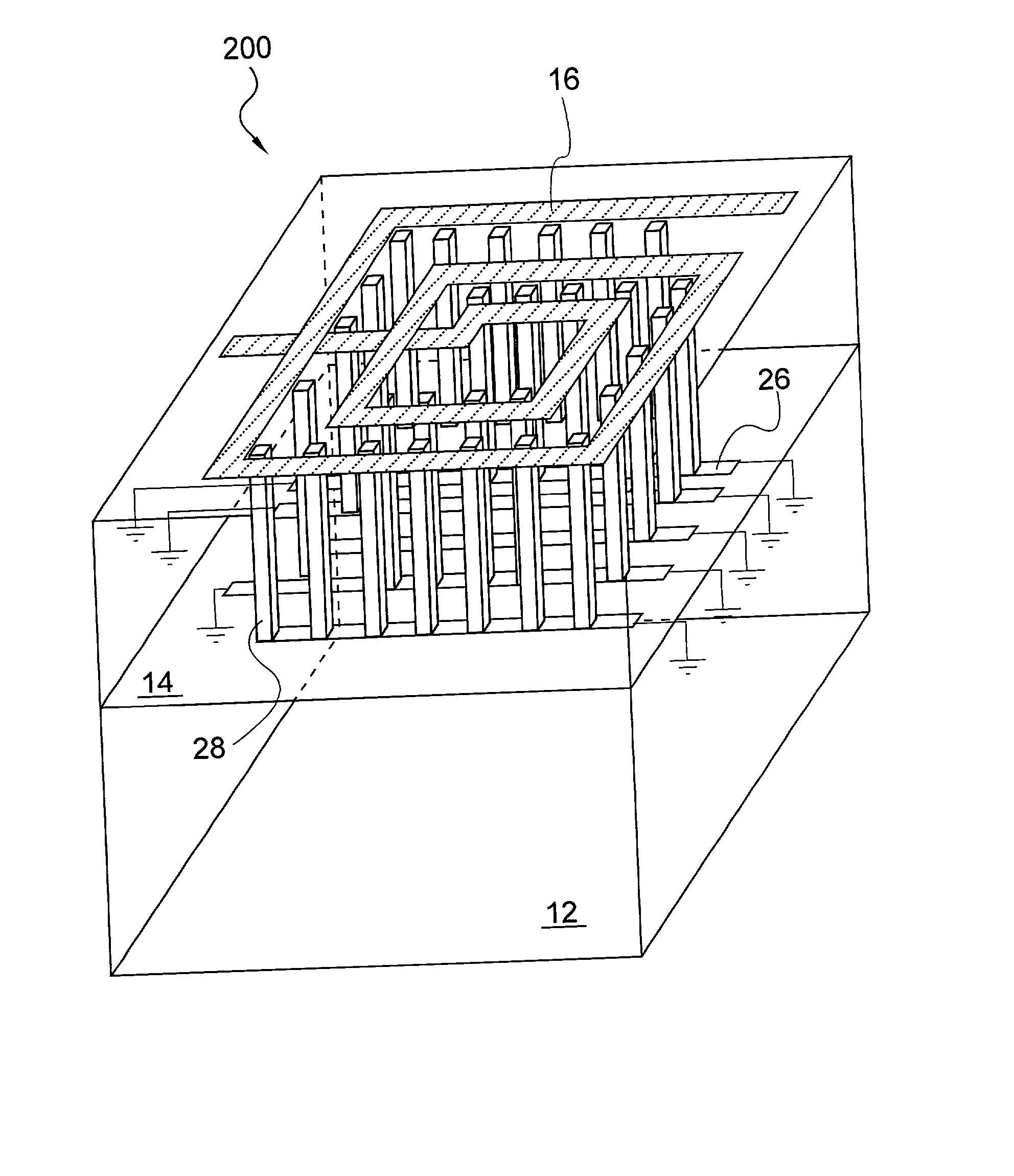
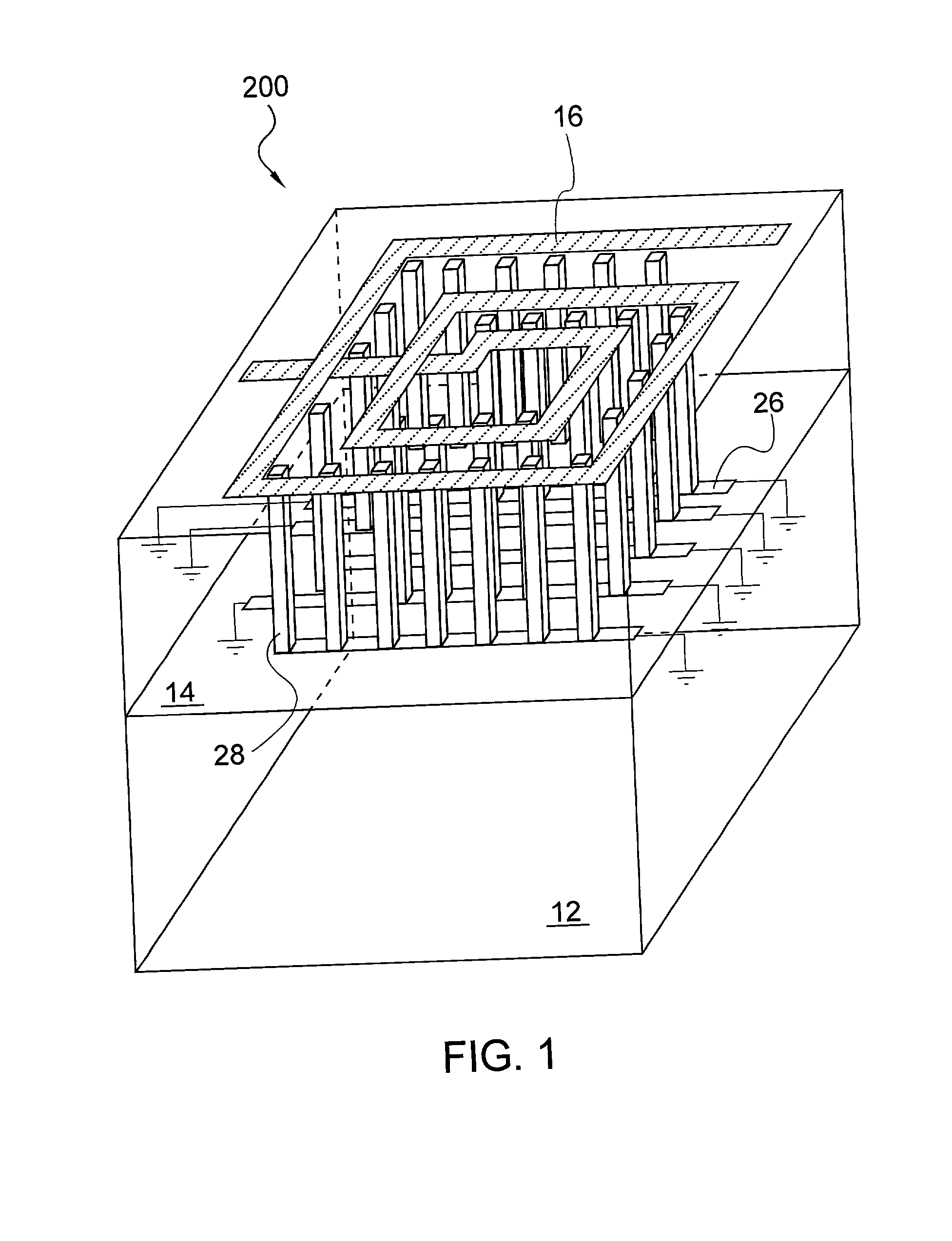
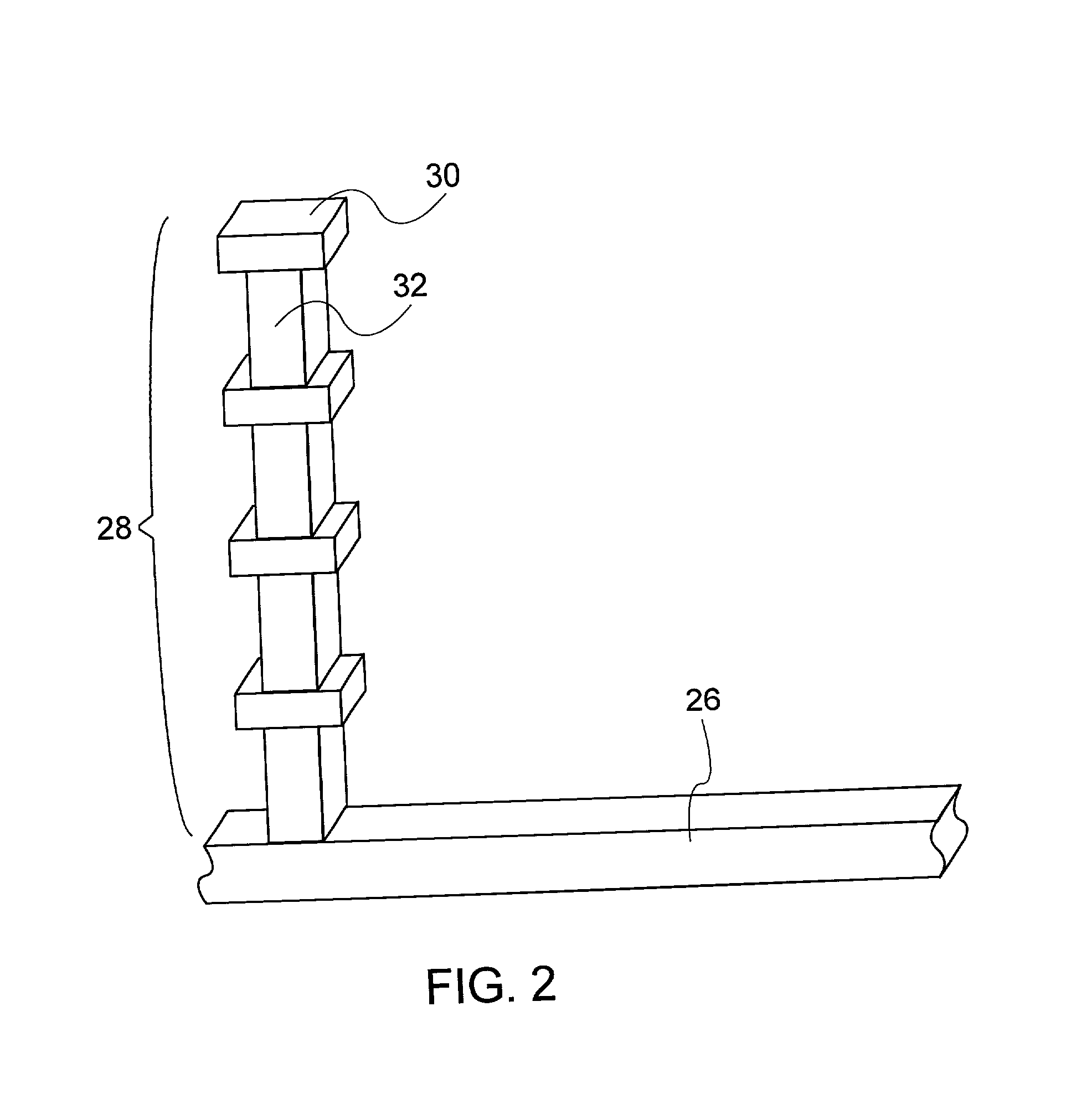
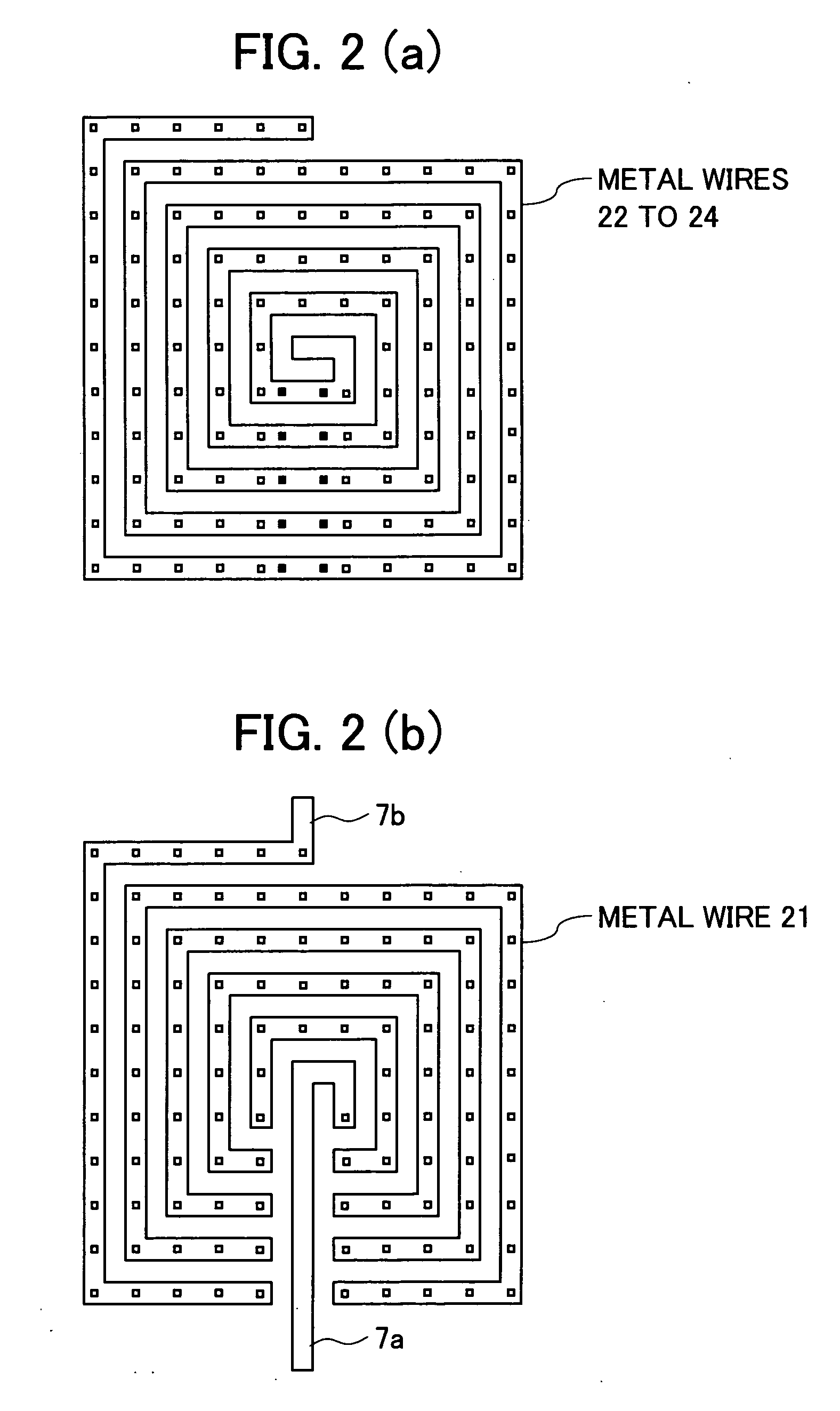
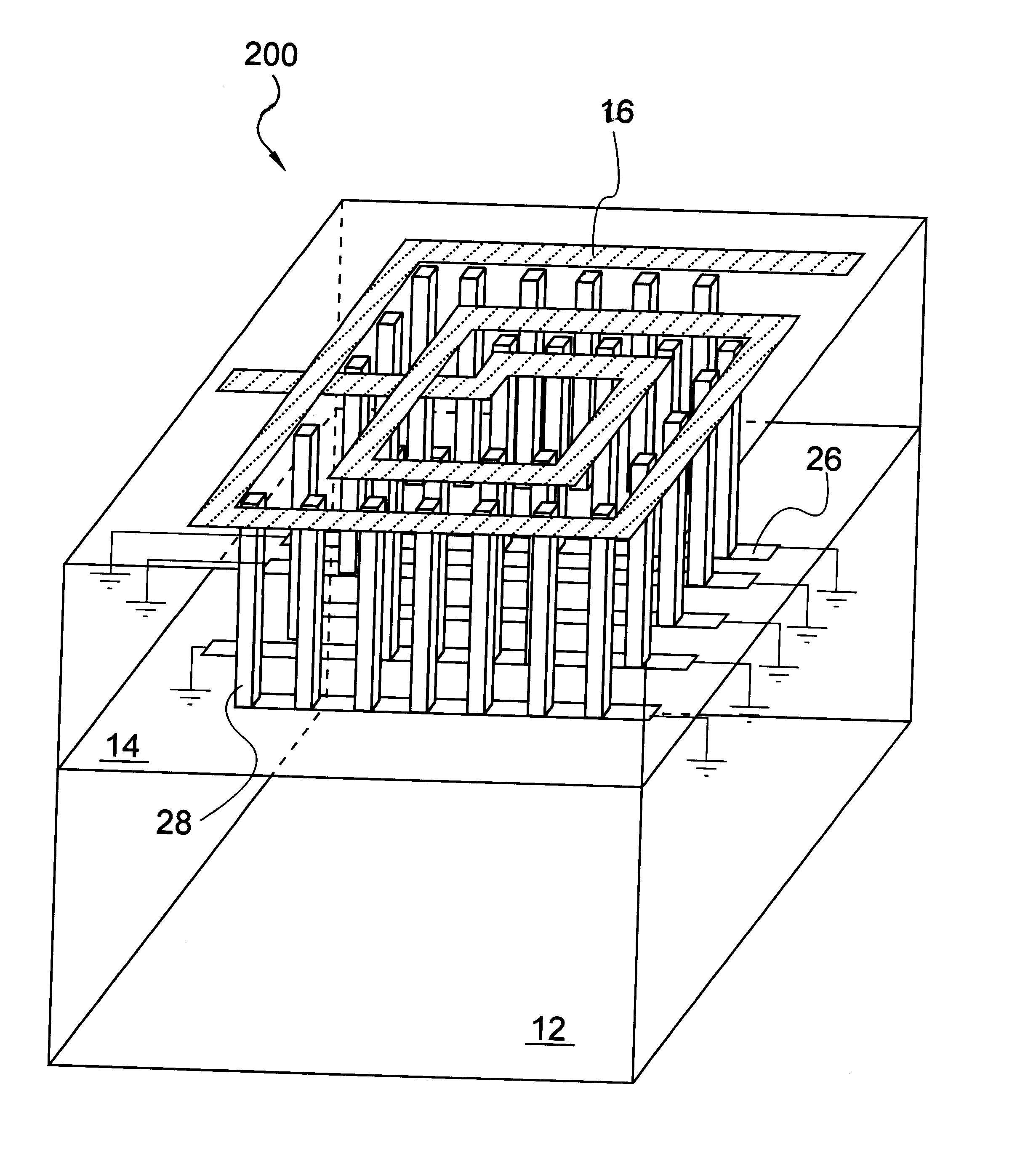
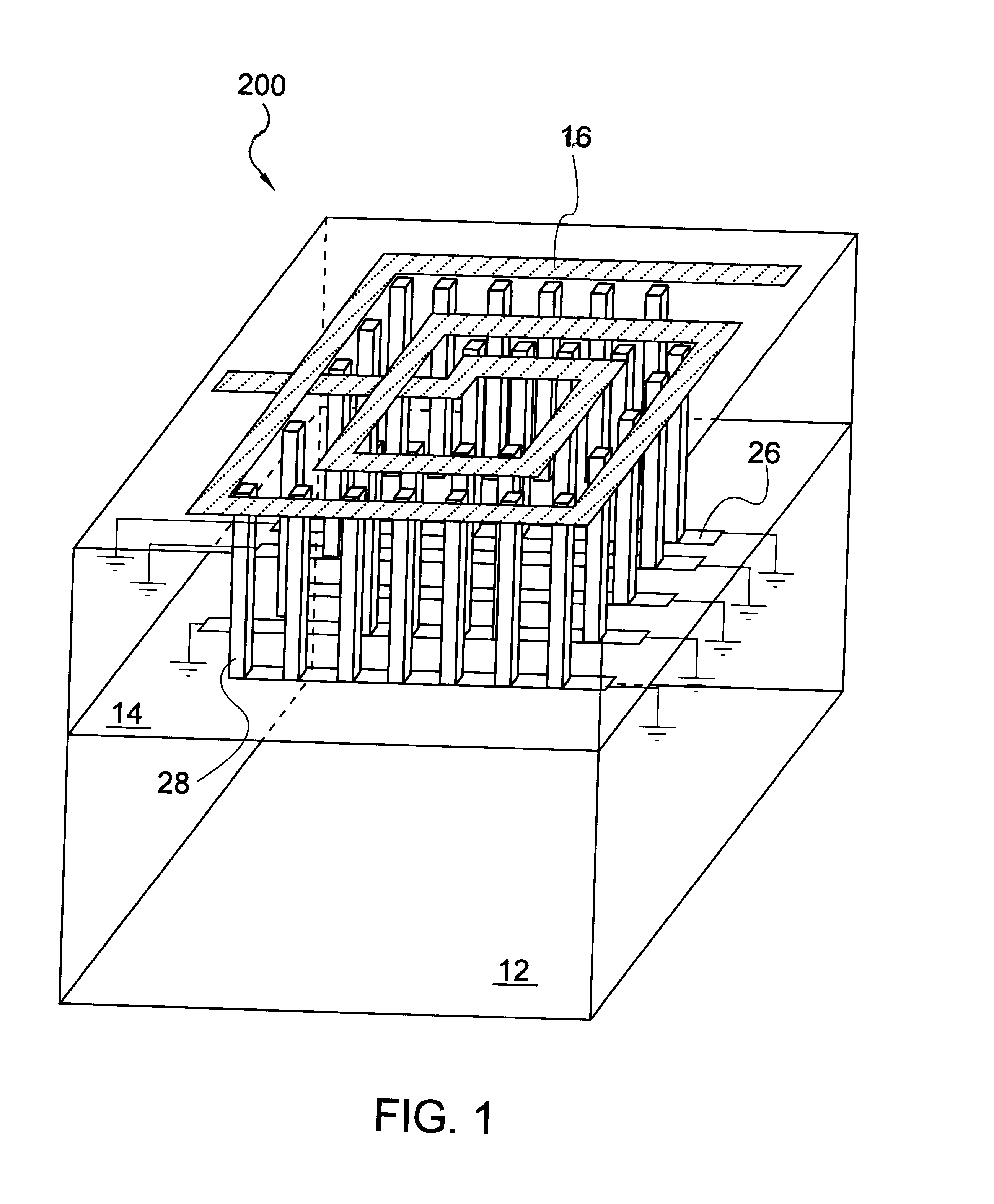
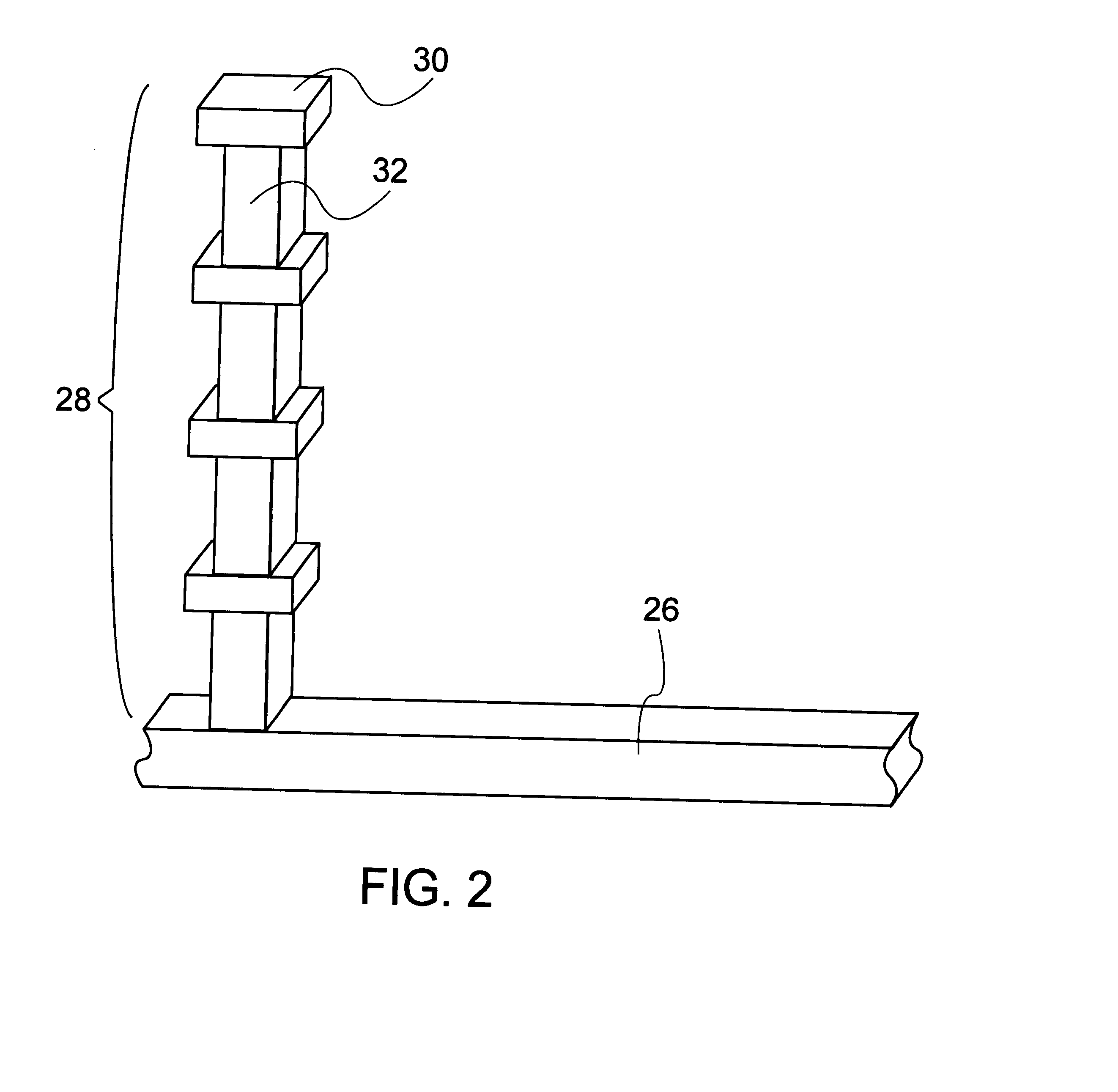
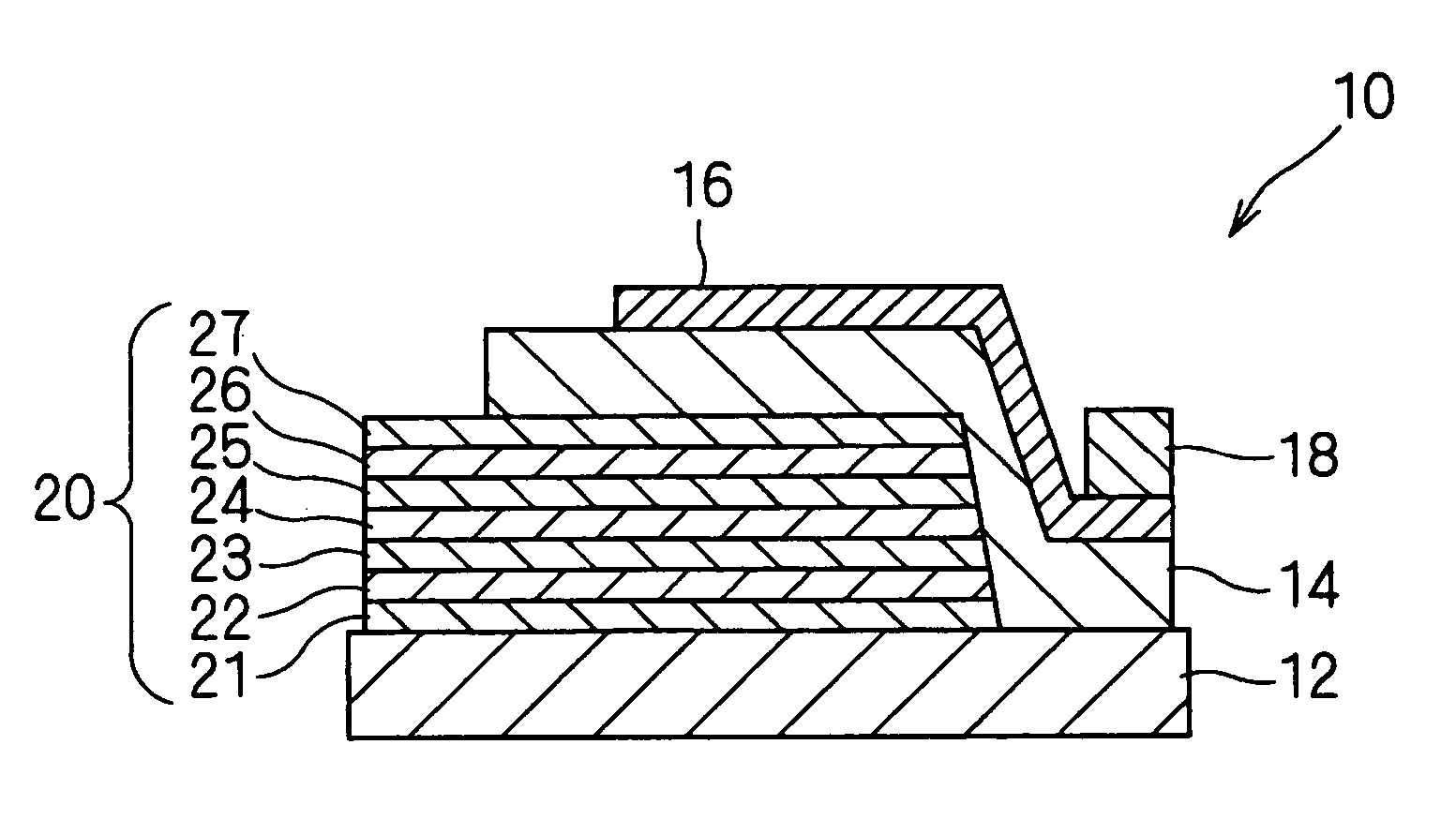
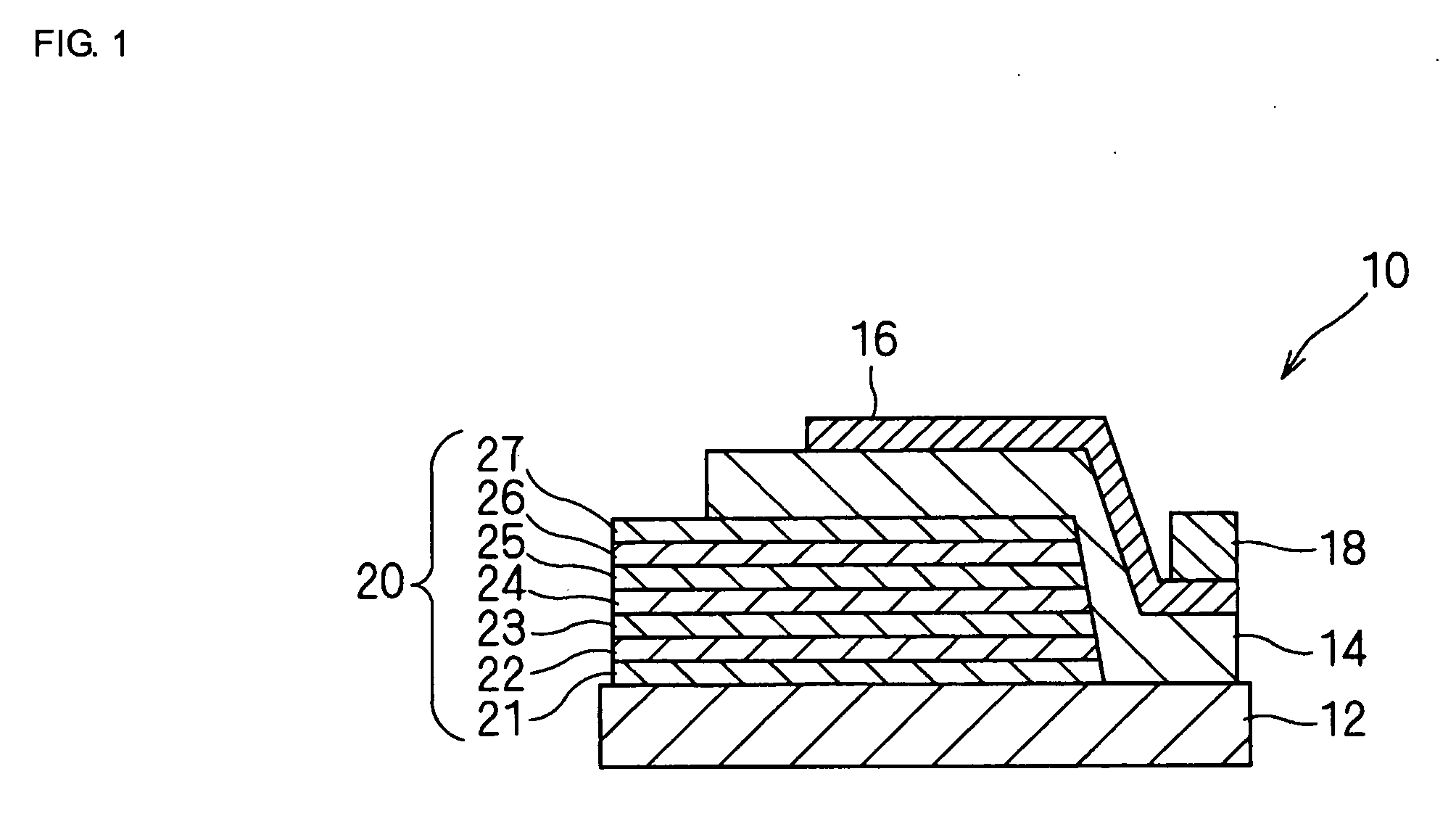
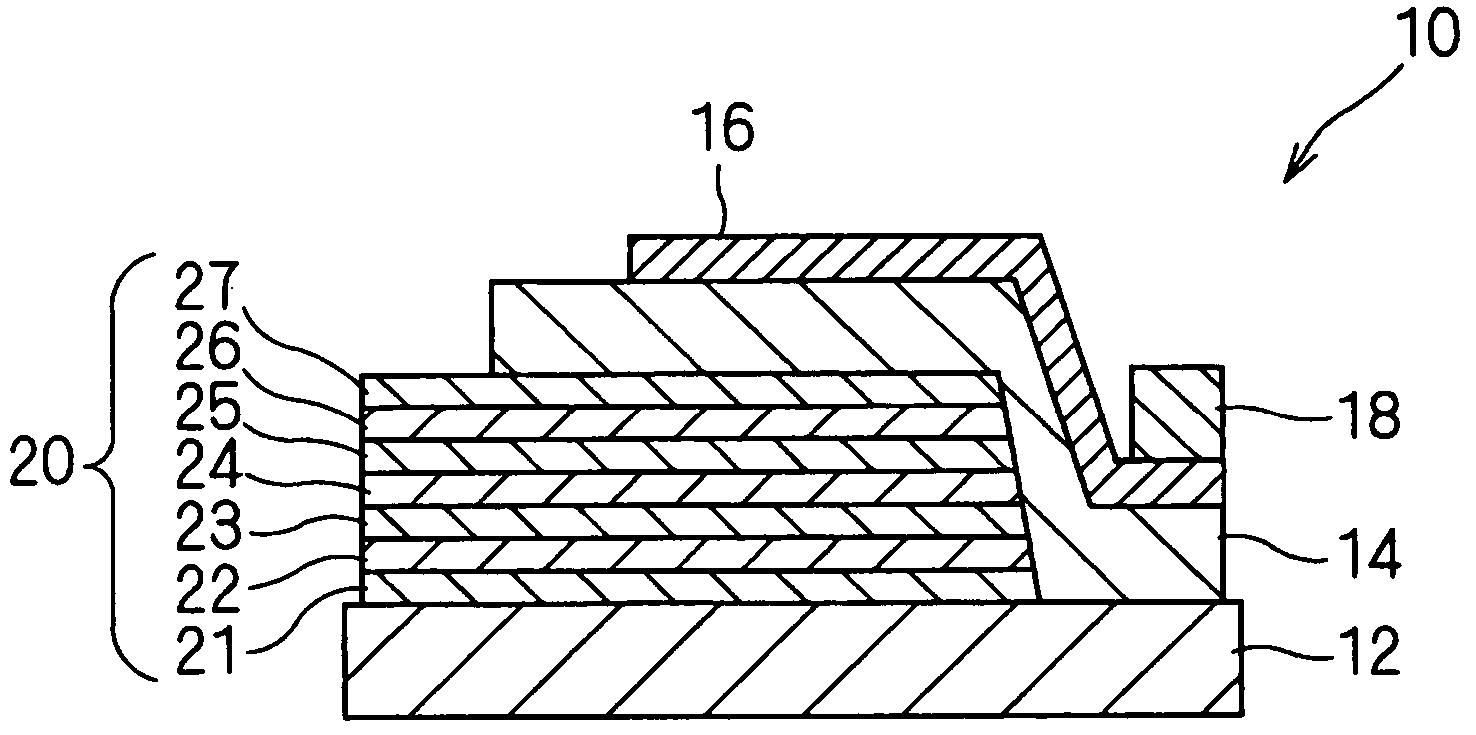
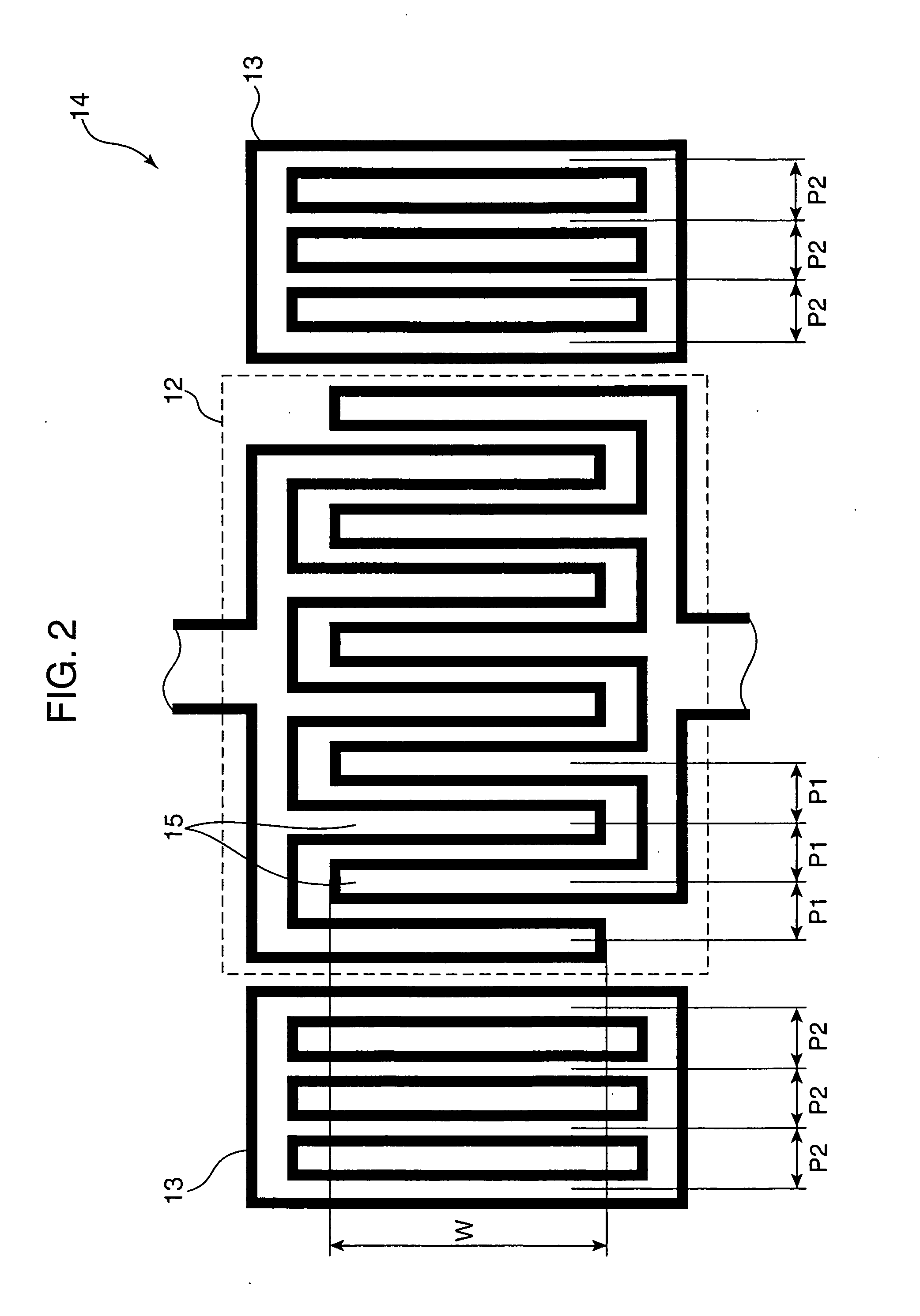
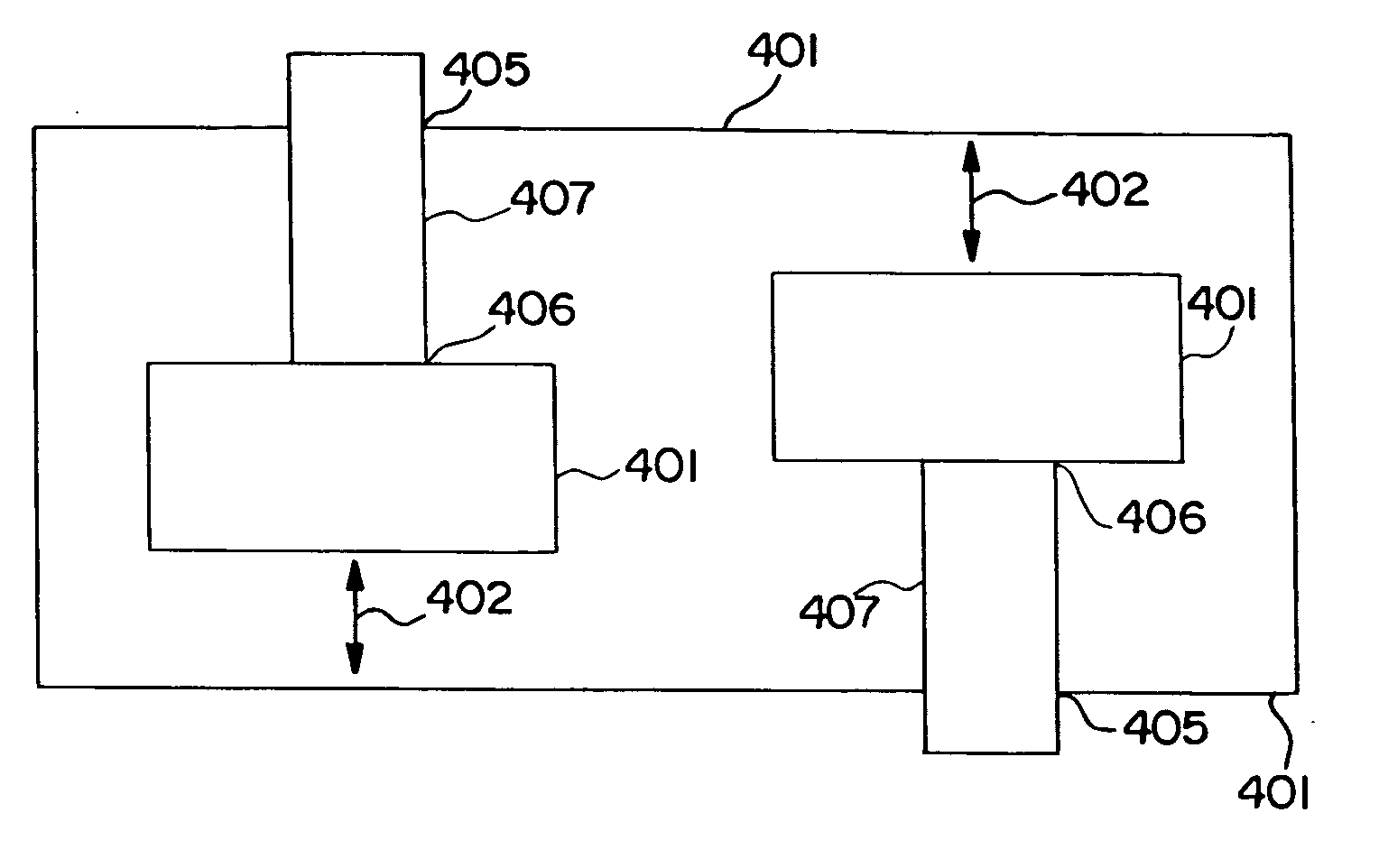
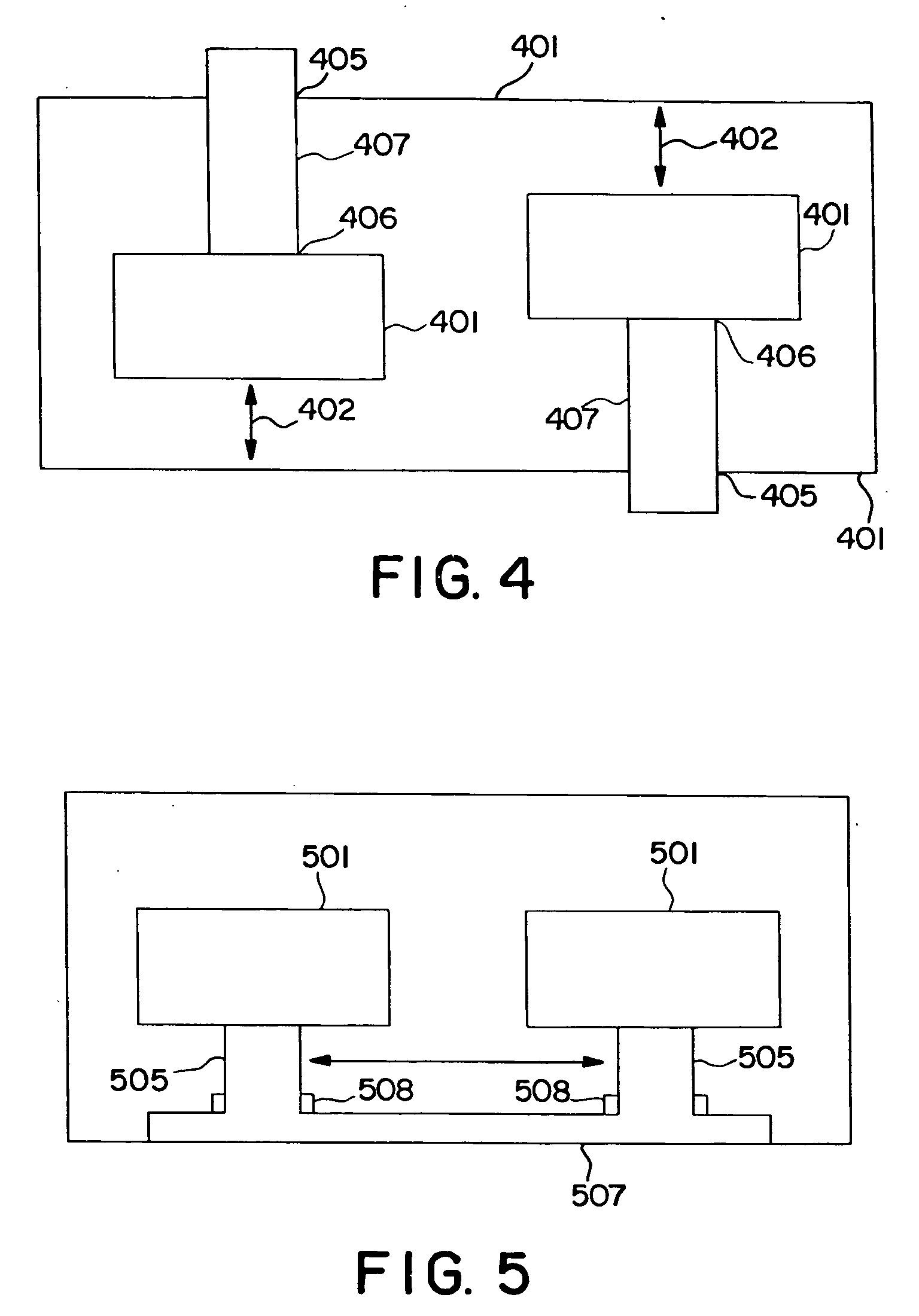
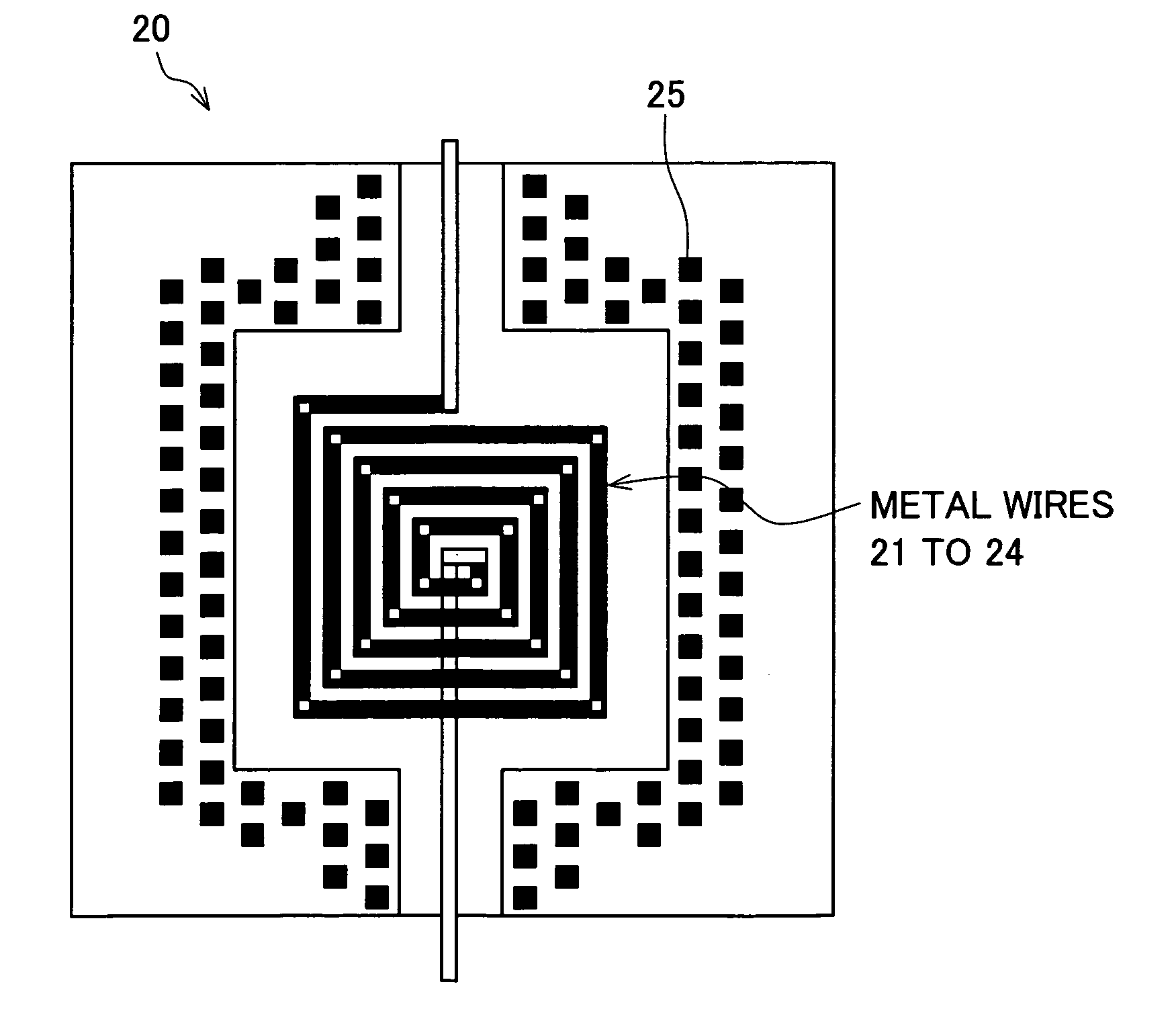
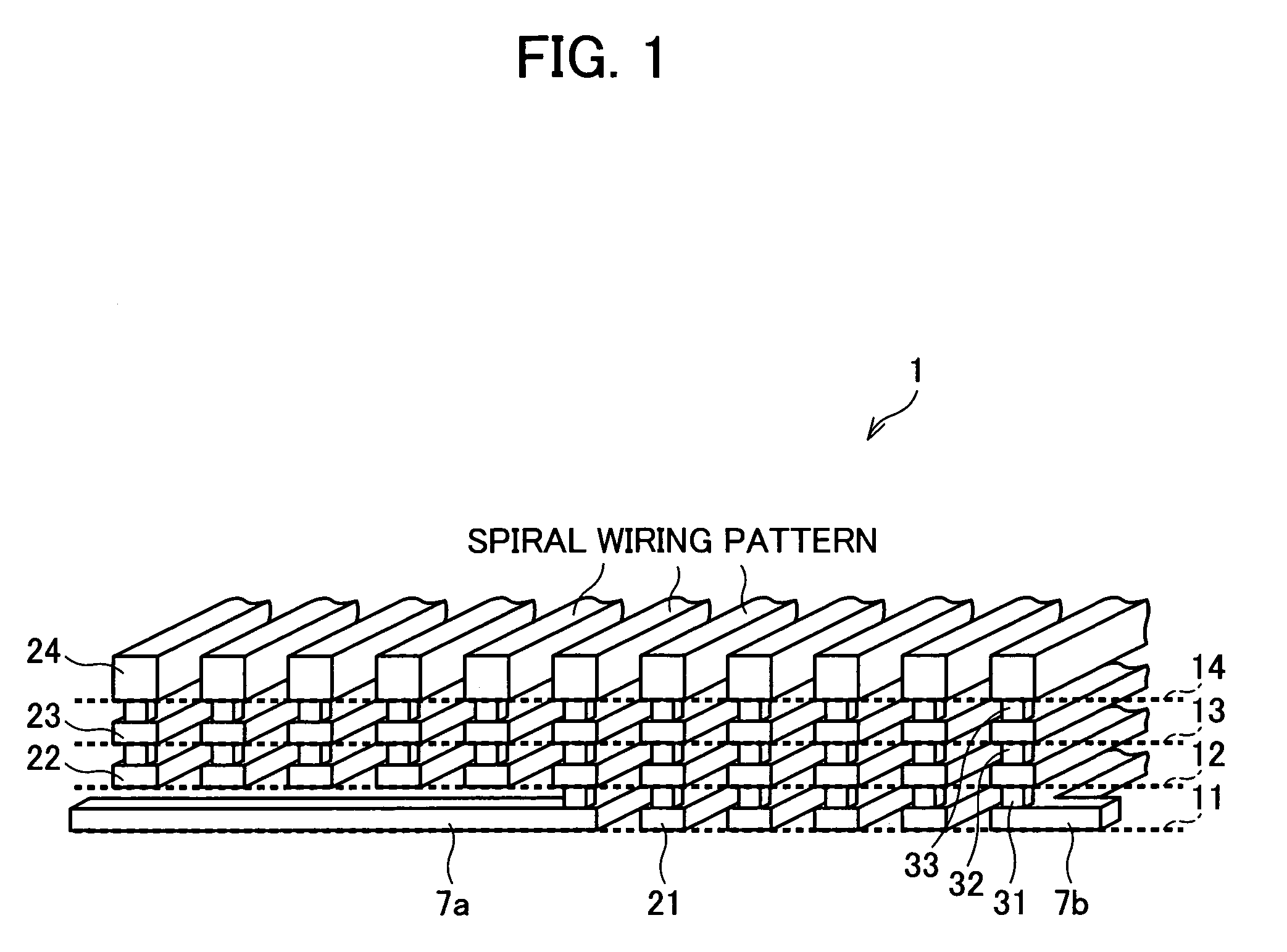
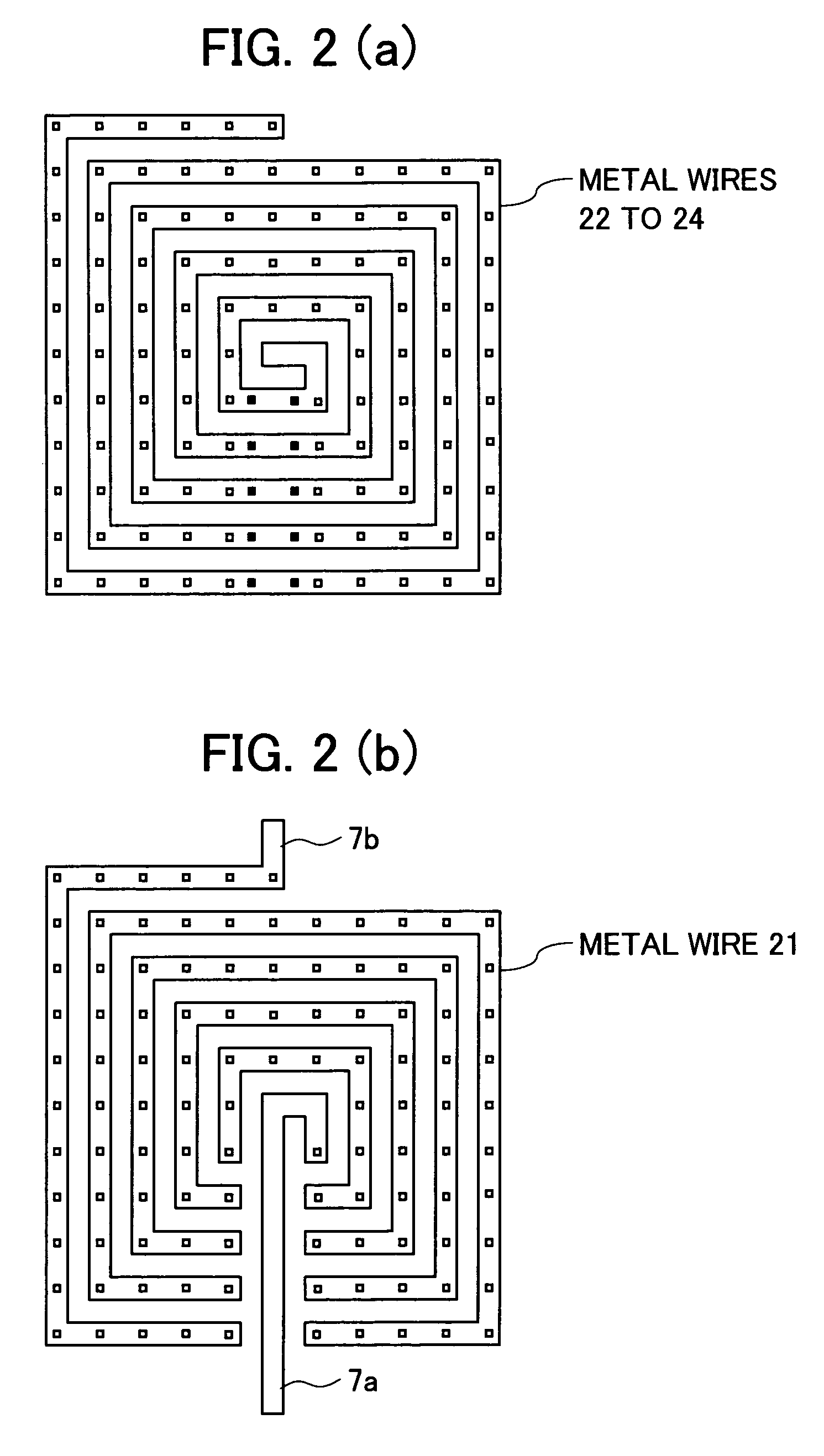
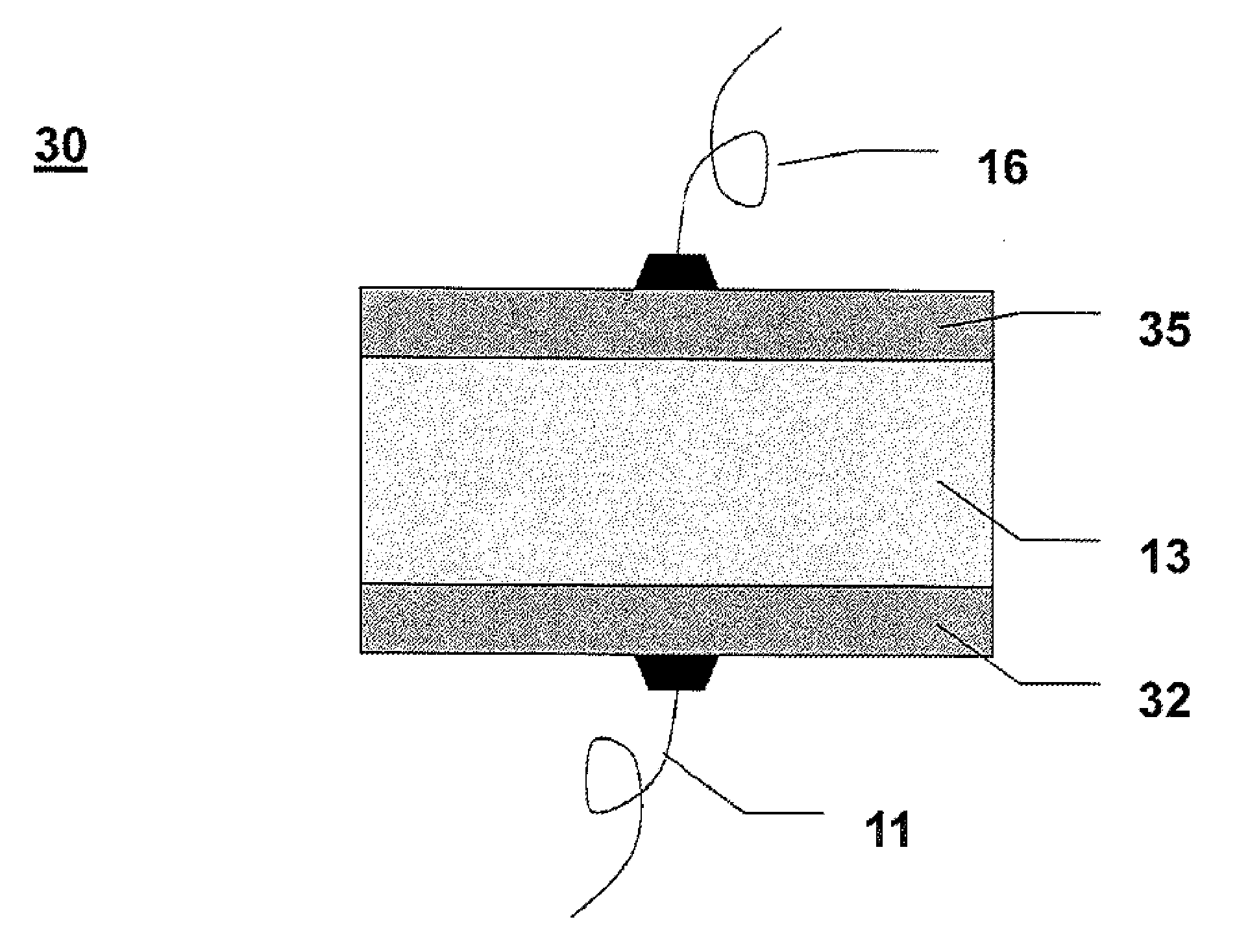
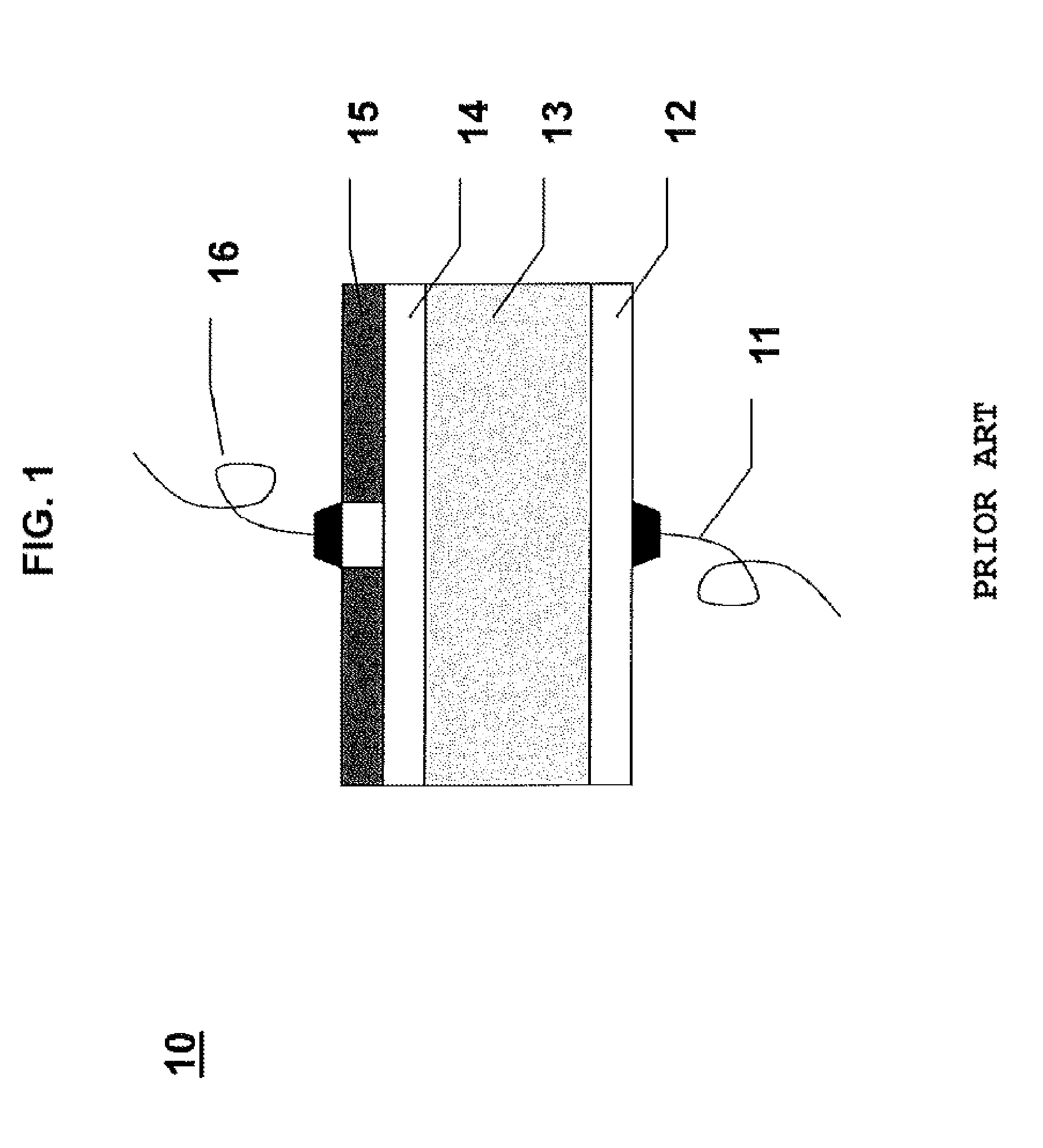
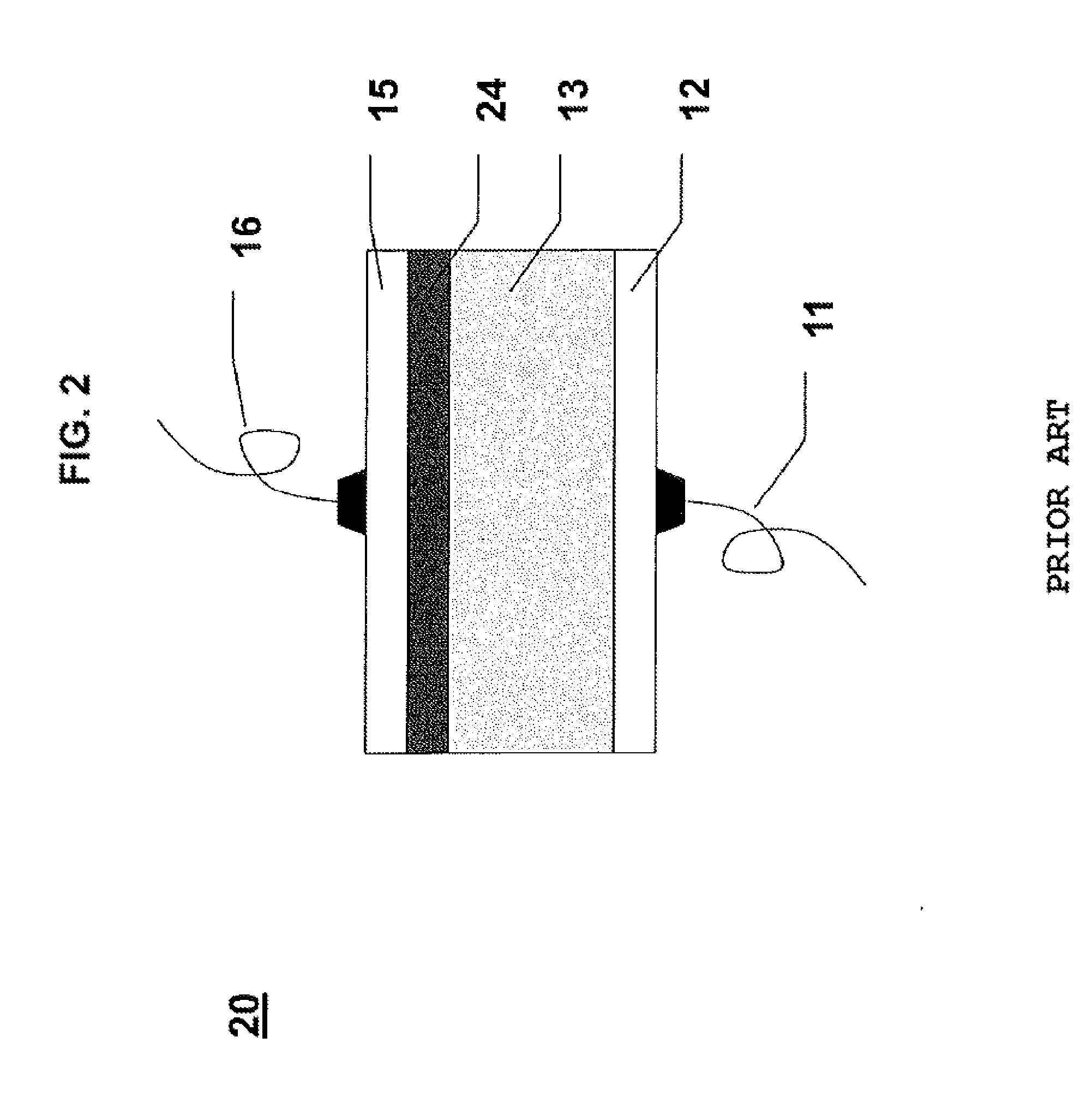
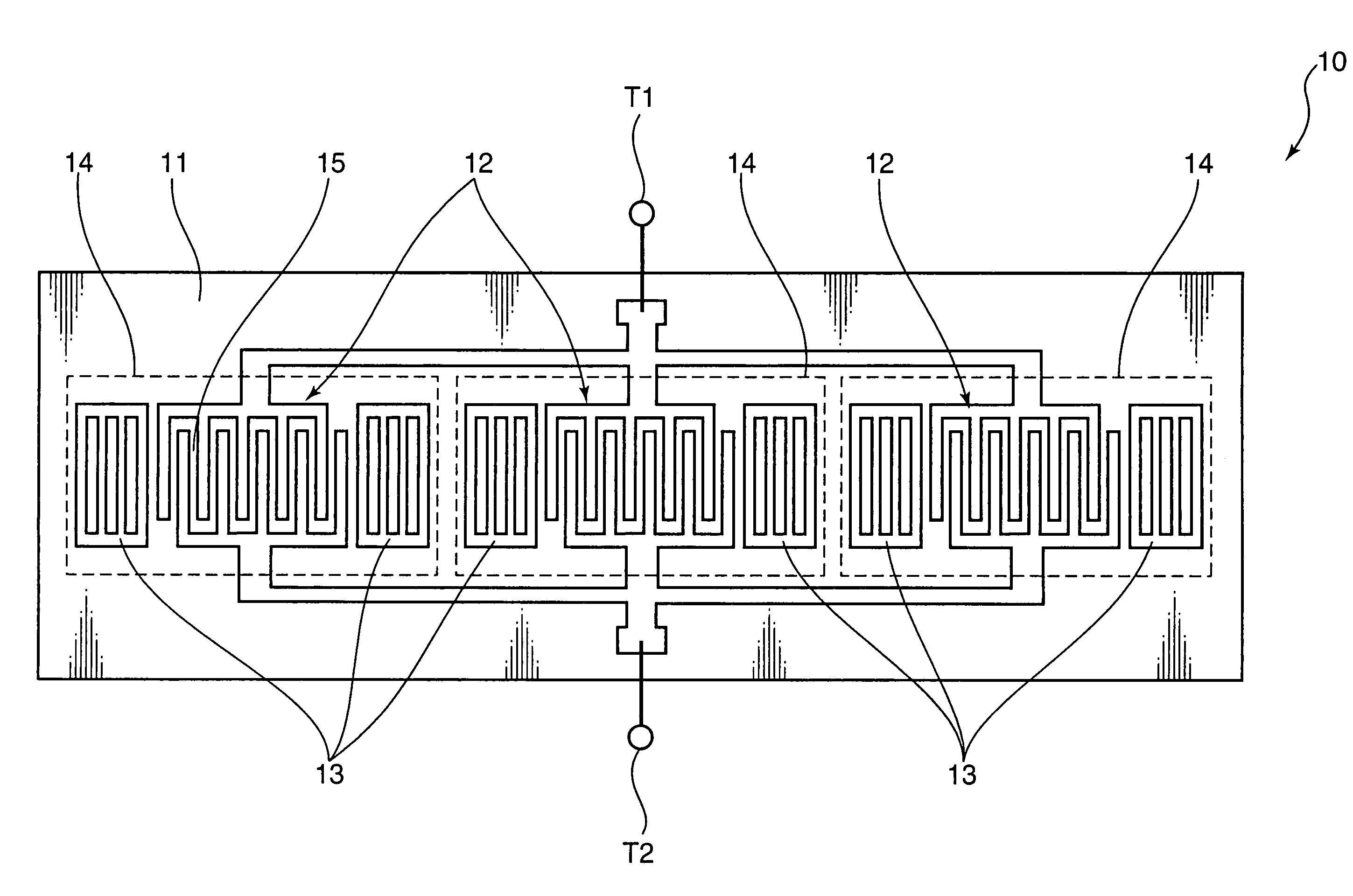
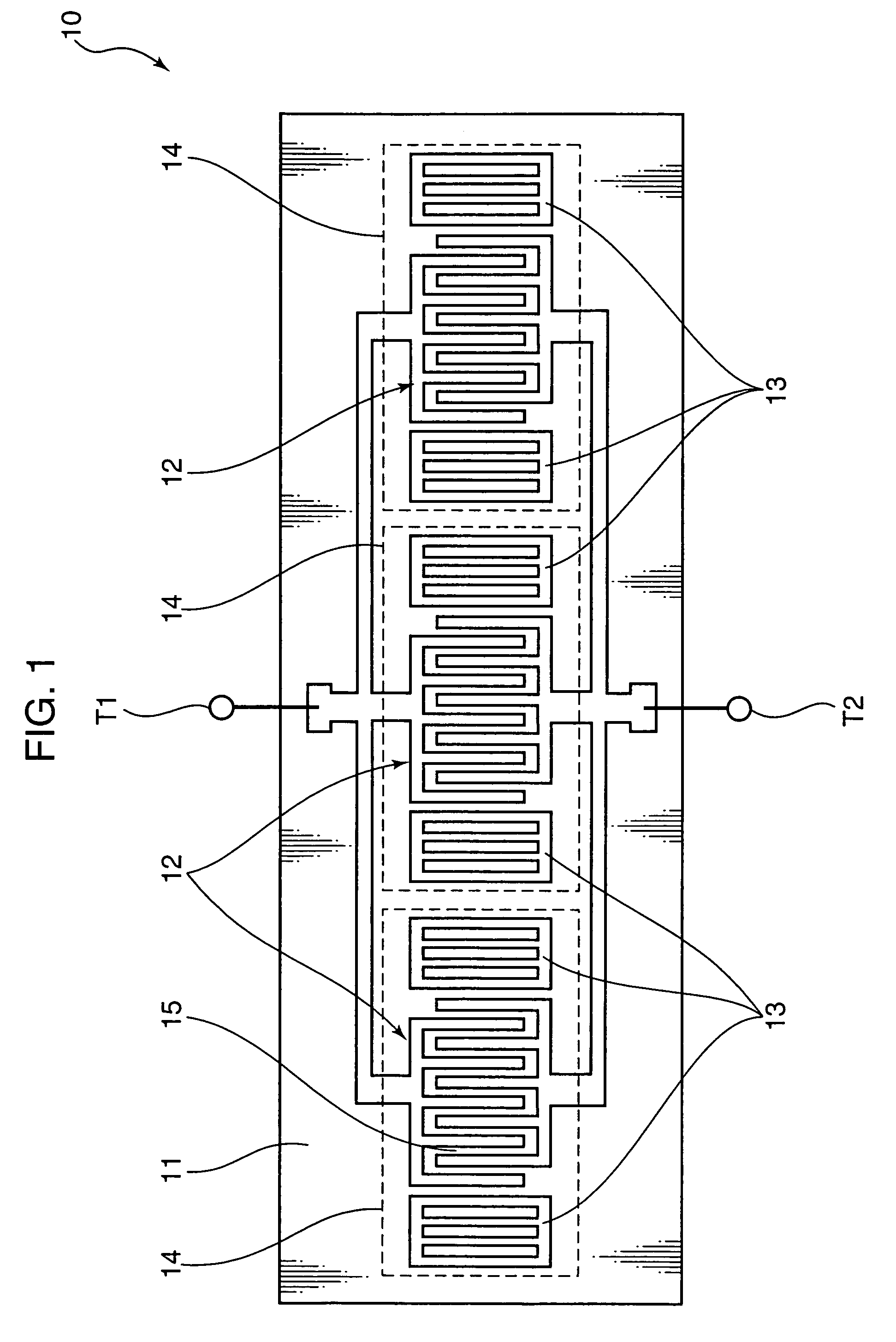
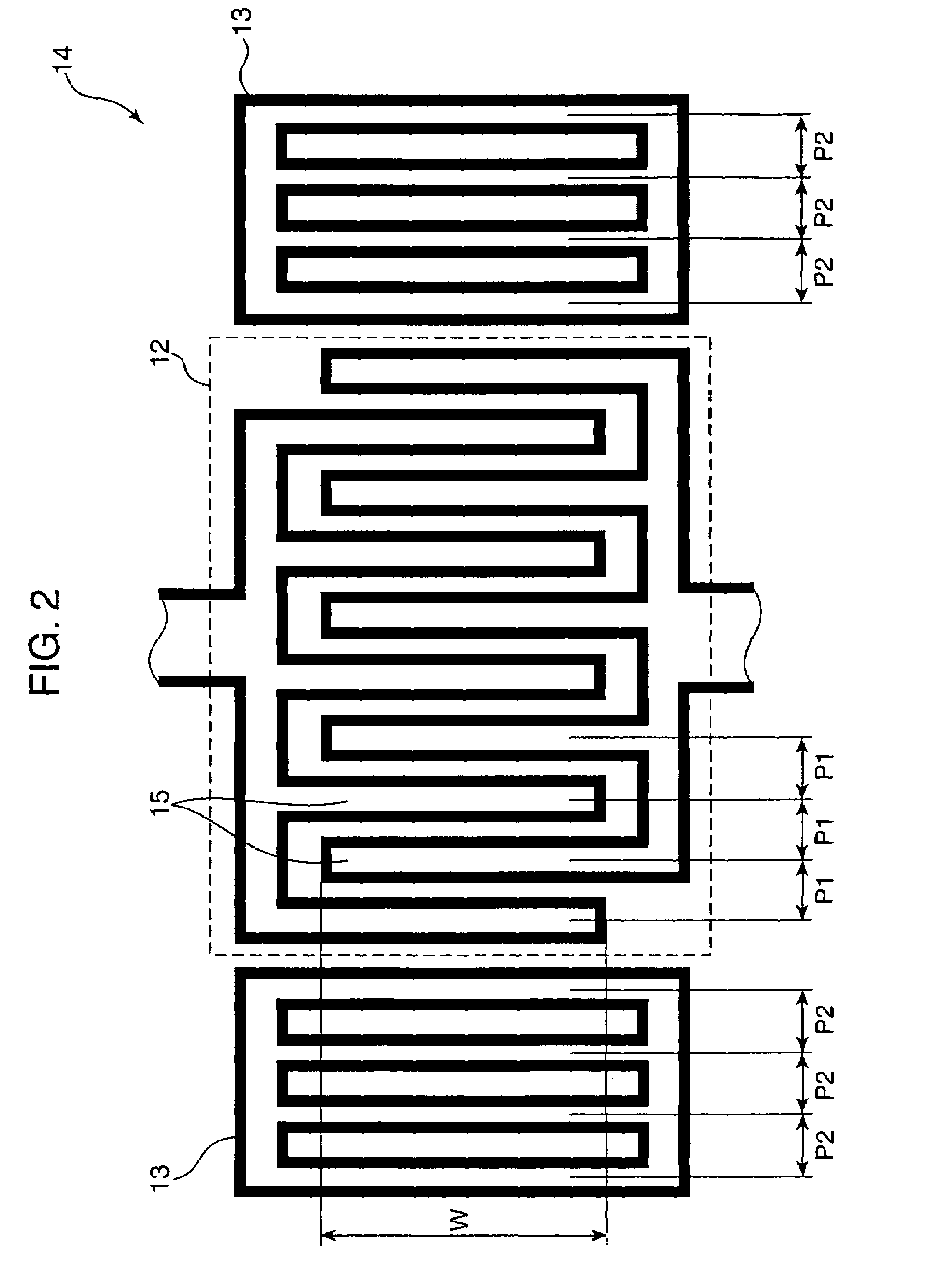
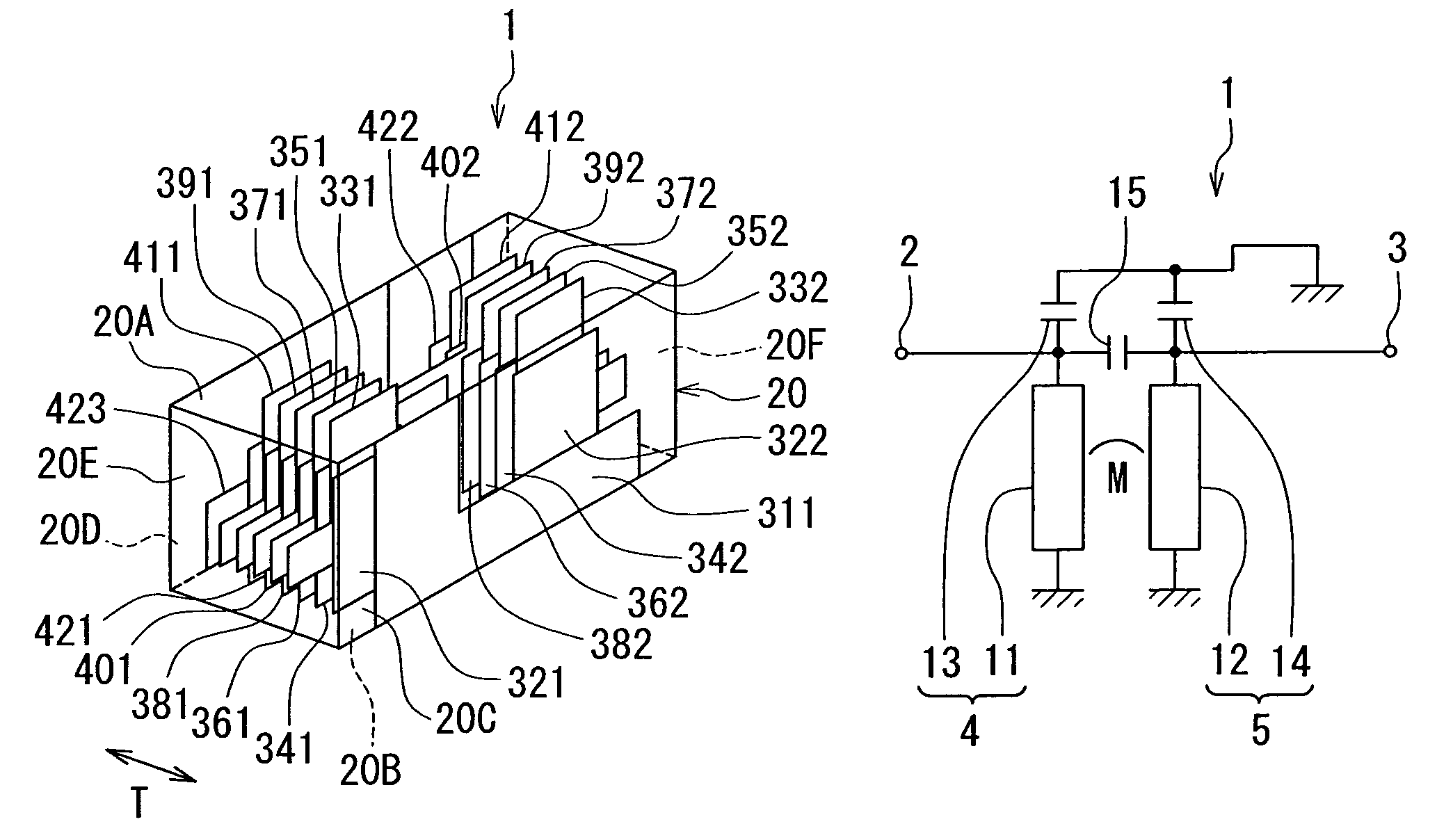
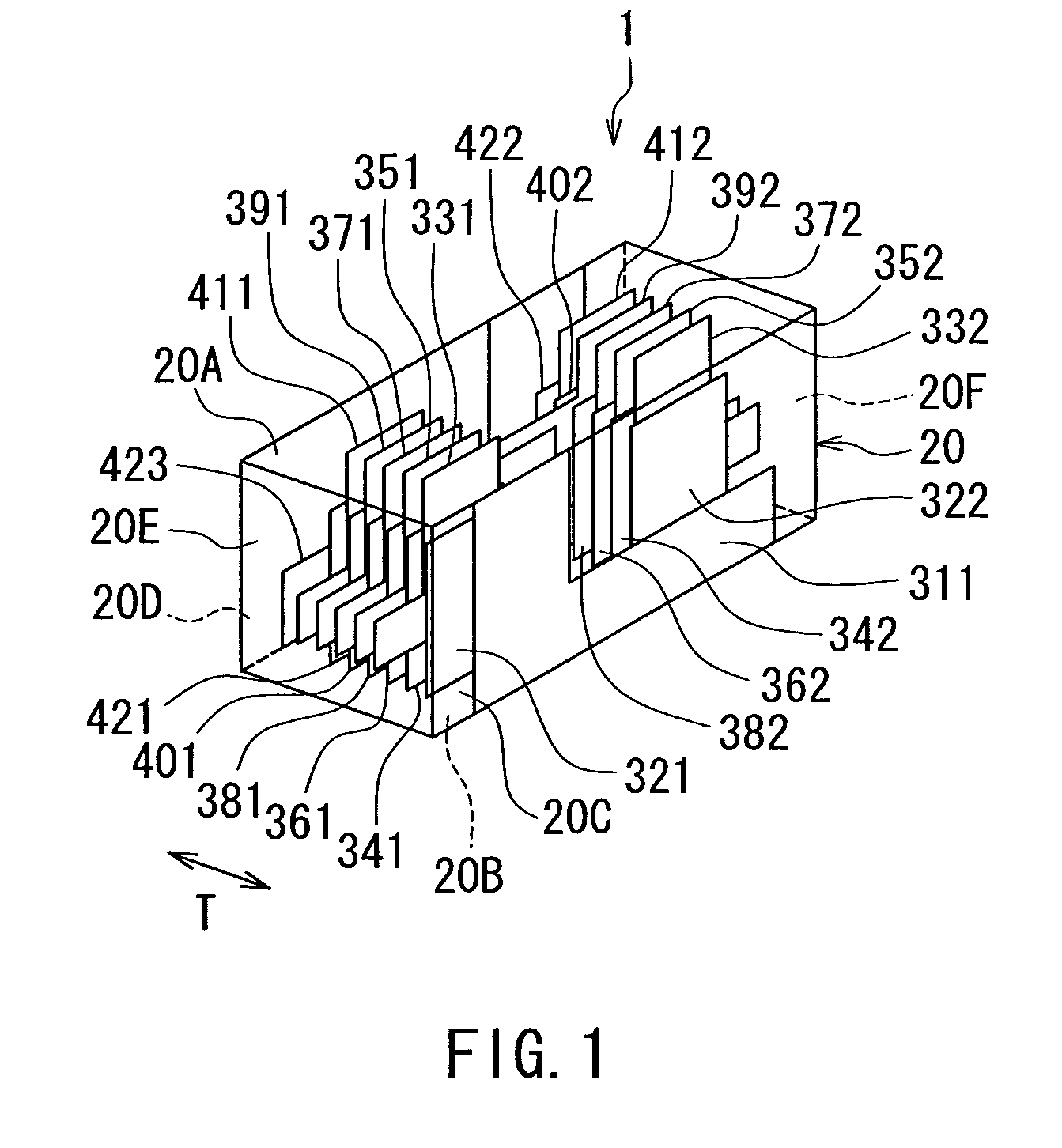
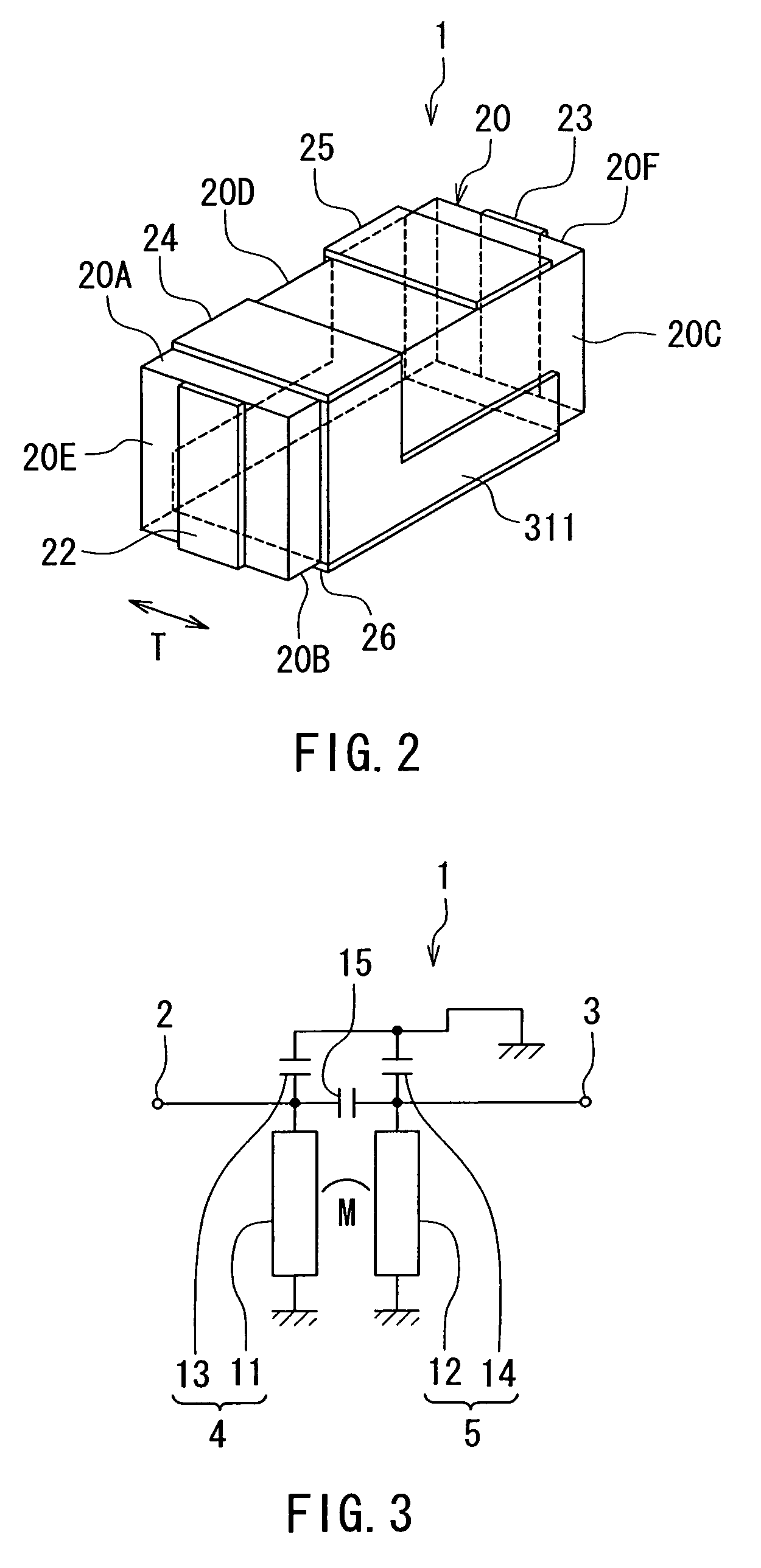
Spiral inductor semiconducting device with grounding strips and conducting vias
InactiveUS20020084509A1Useful operationGood effectTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceSpiral inductor
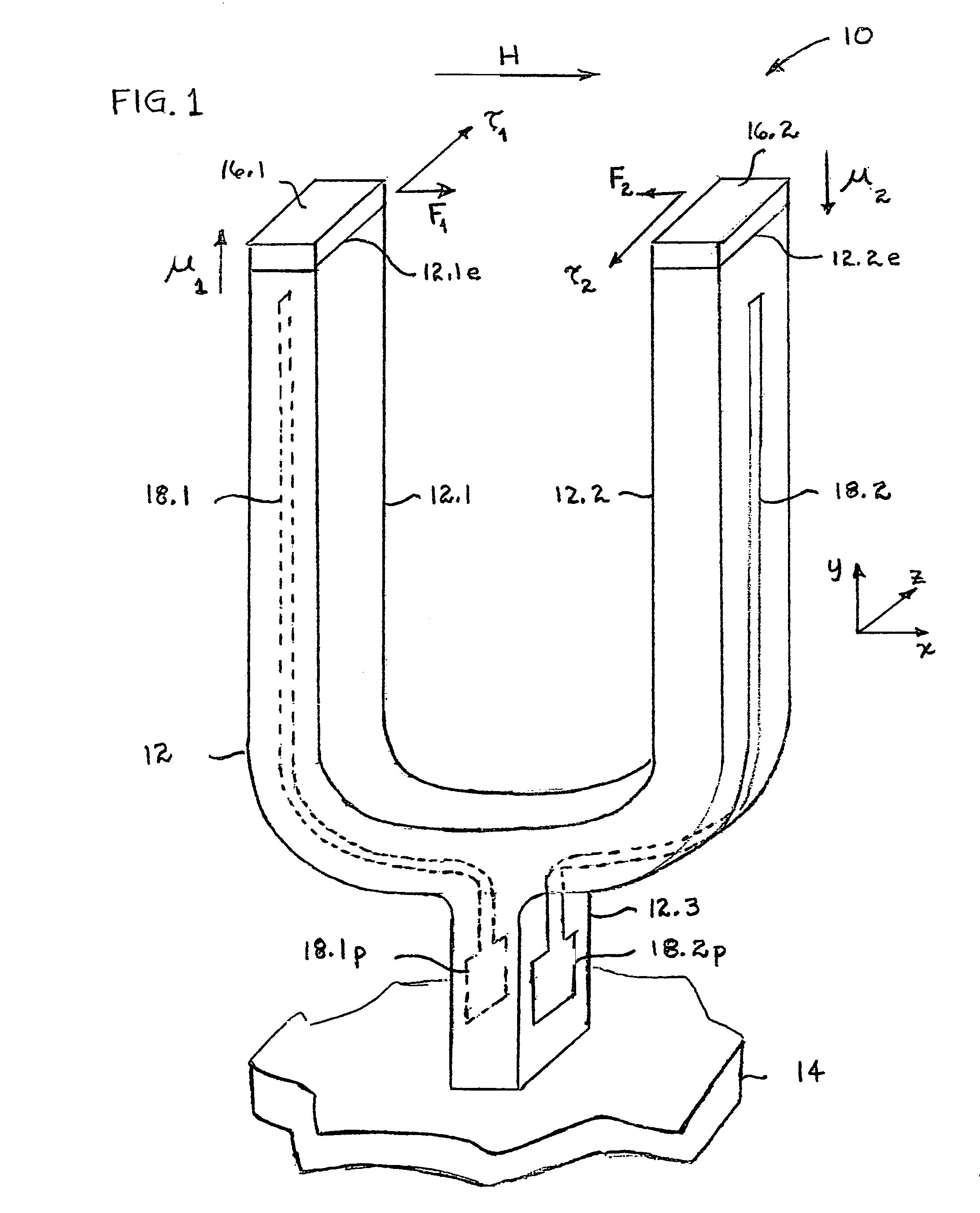
An integrated semiconducting device comprises a semiconducting substrate, a plurality of grounding strips disposed above the substrate in a lower metal level of the semiconducting device, an inductor positioned in an upper metal level of the semiconducting device, and a plurality of conducting vias connected to and extending away from the grounding strips towards the inductor. The inductor, conducting via, ground strips structure forms a Faraday cage that acts as a shield against electromagnetic radiation. The number and placement of the conductive vias are adjustable and can be optimized based on the relative importance of maximizing the quality factor Q of the inductor or minimizing the capacitance between the inductor and ground.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
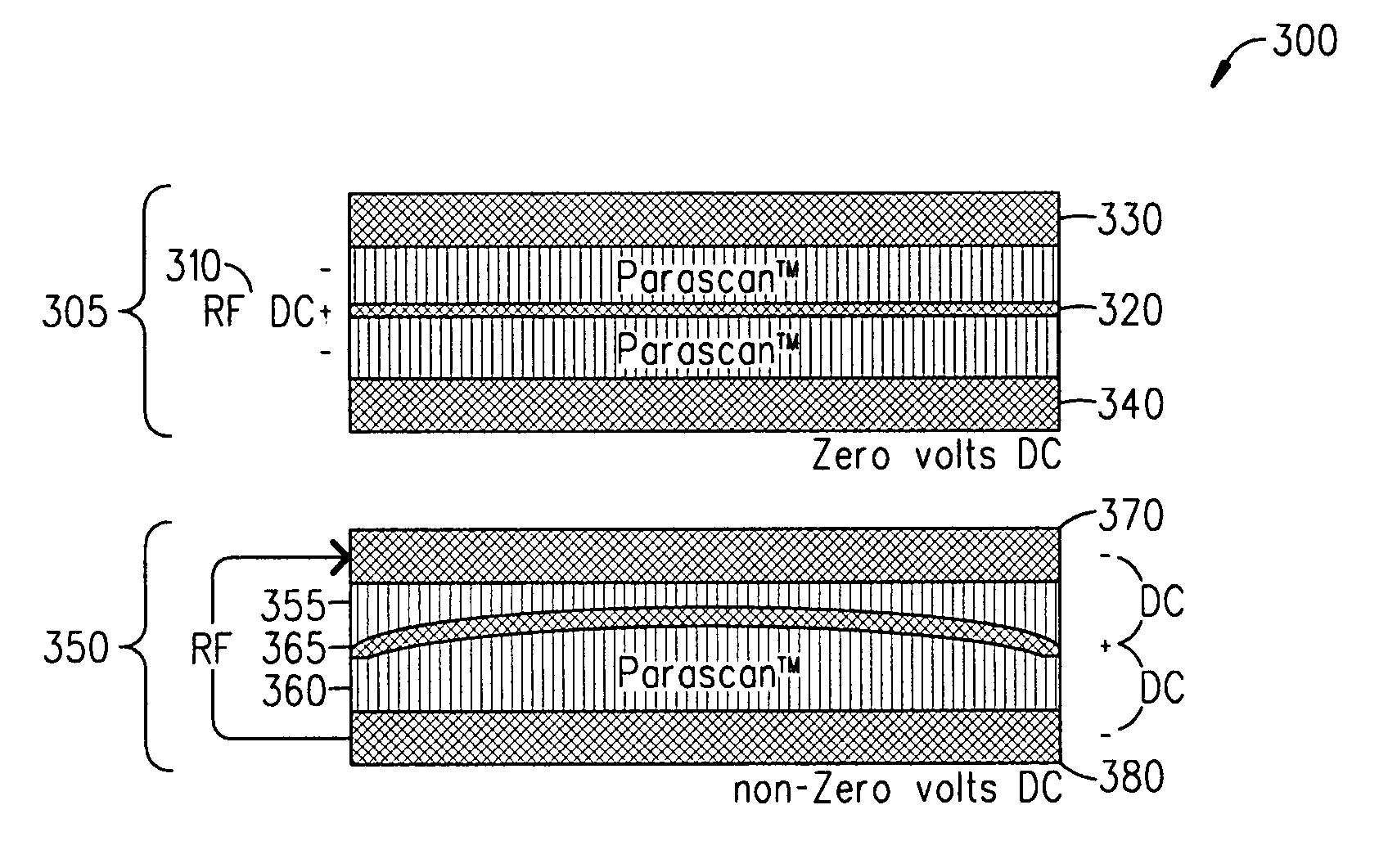
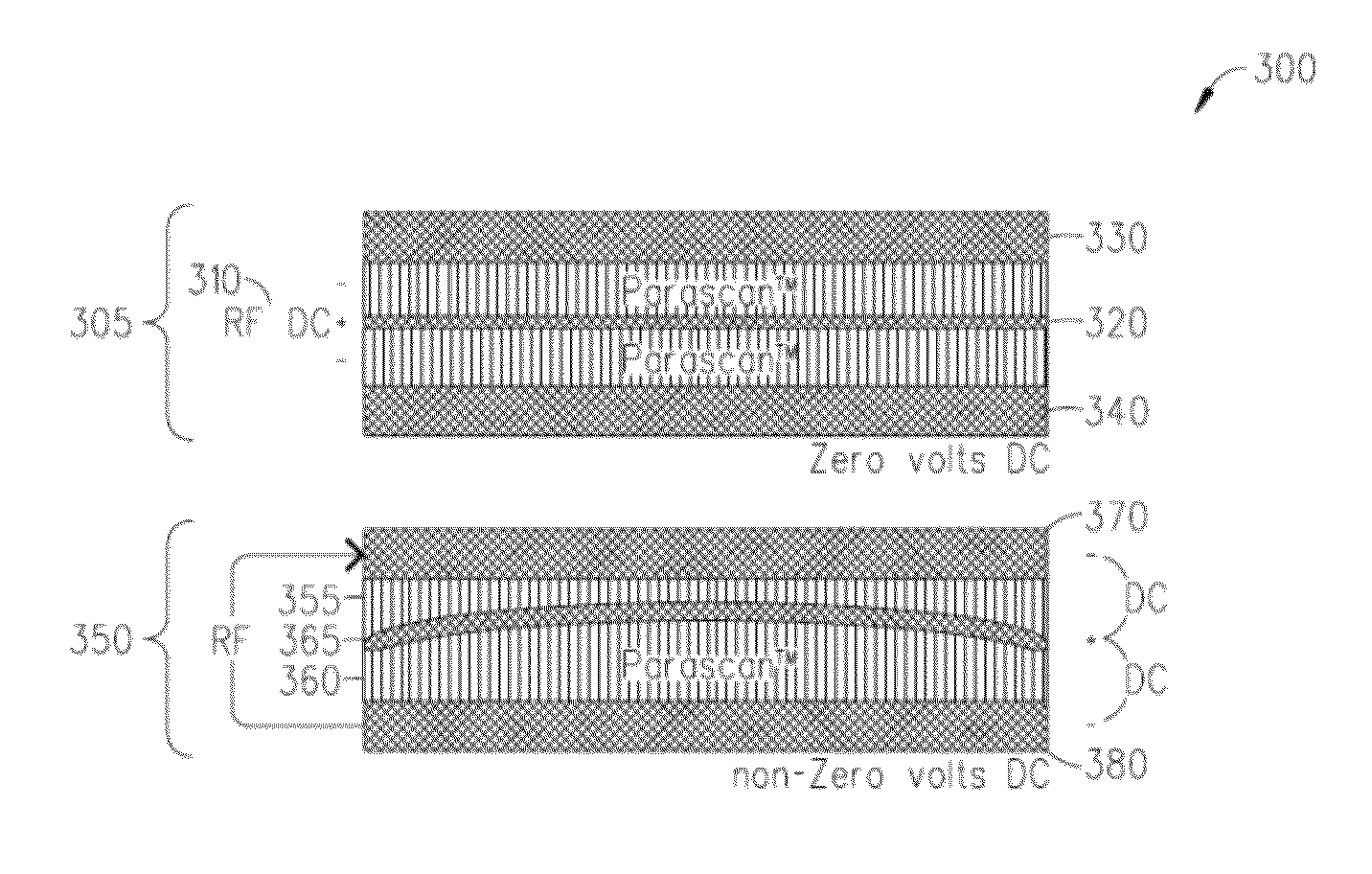
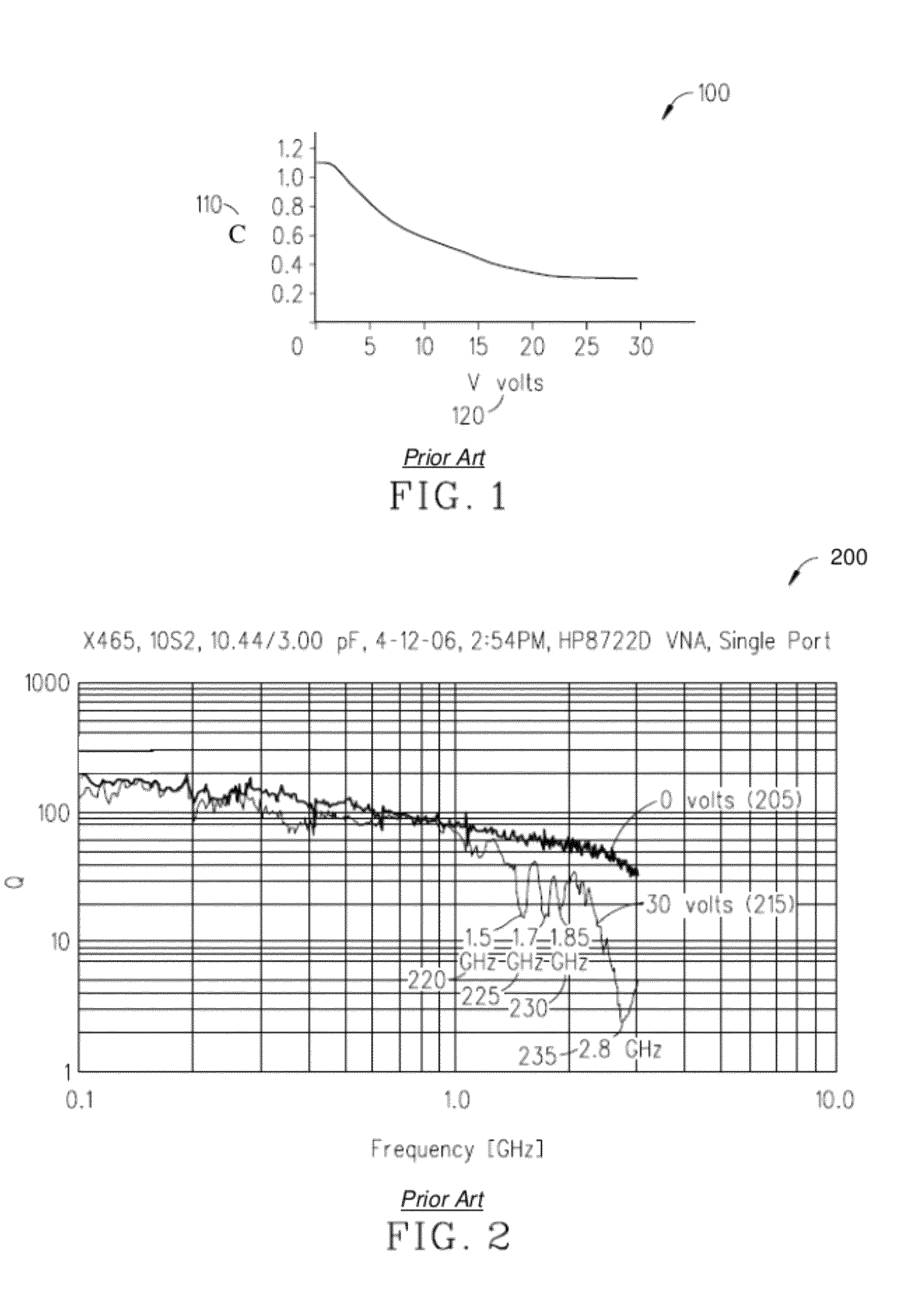
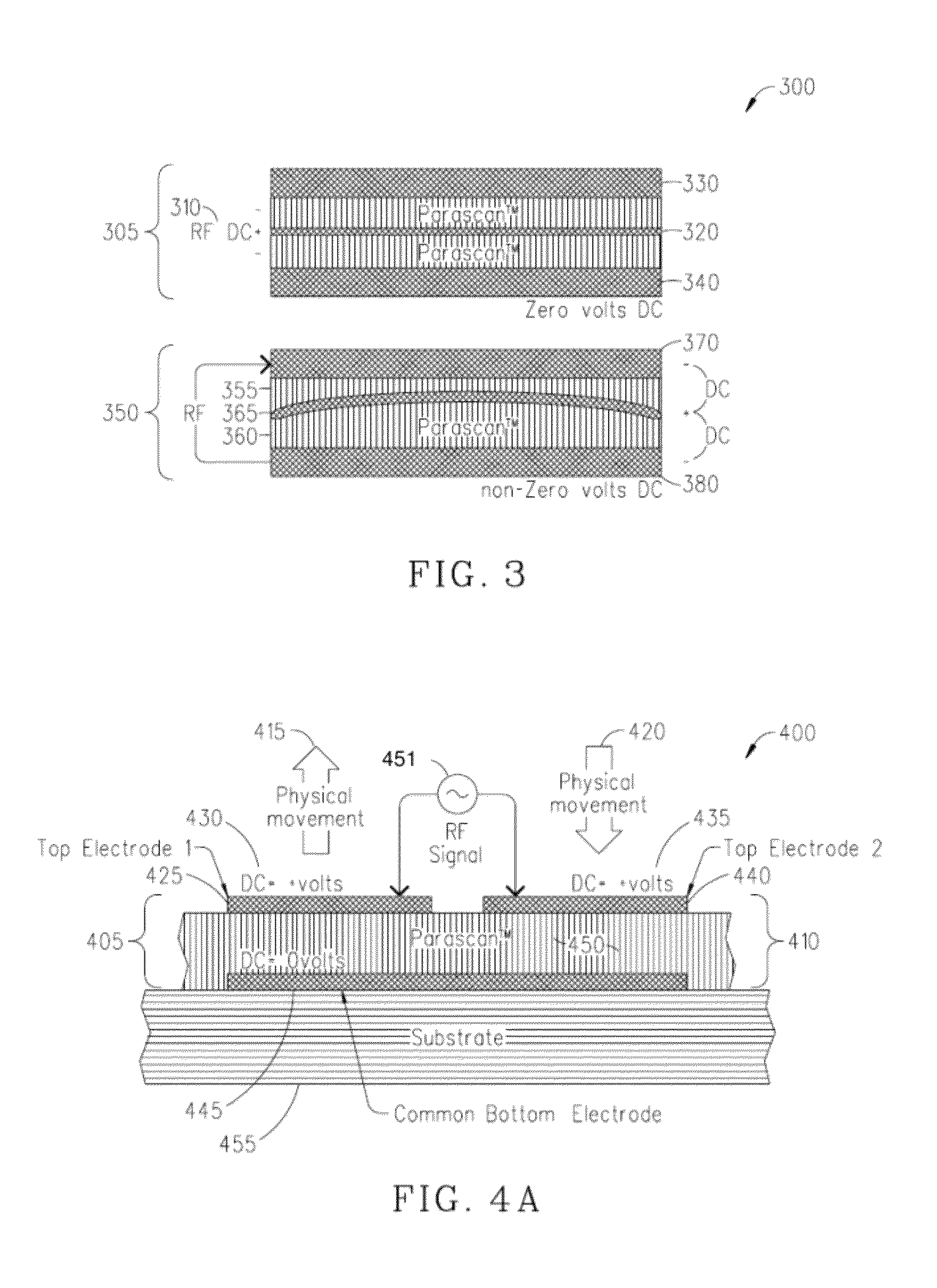
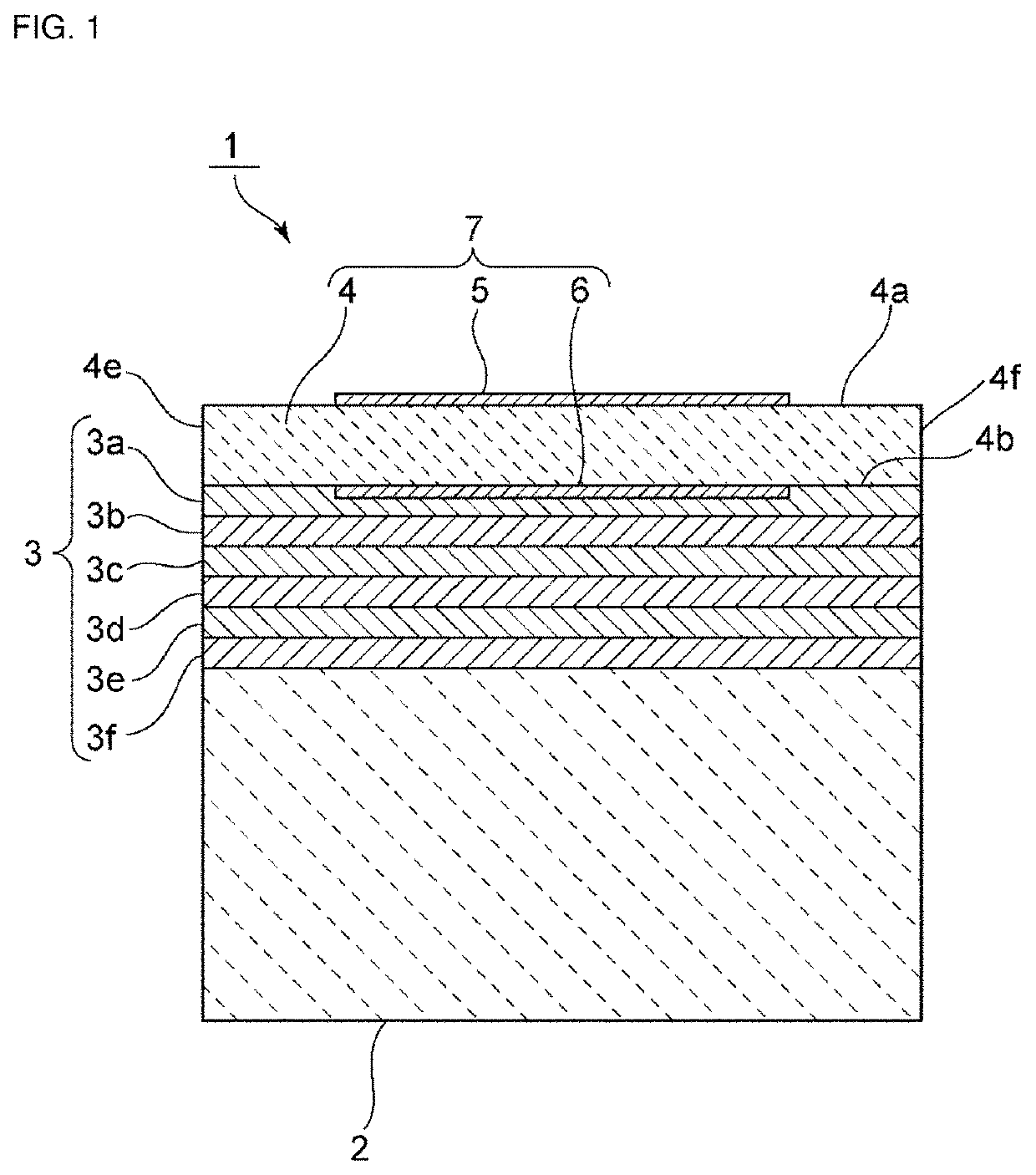
Capacitors adapted for acoustic resonance cancellation
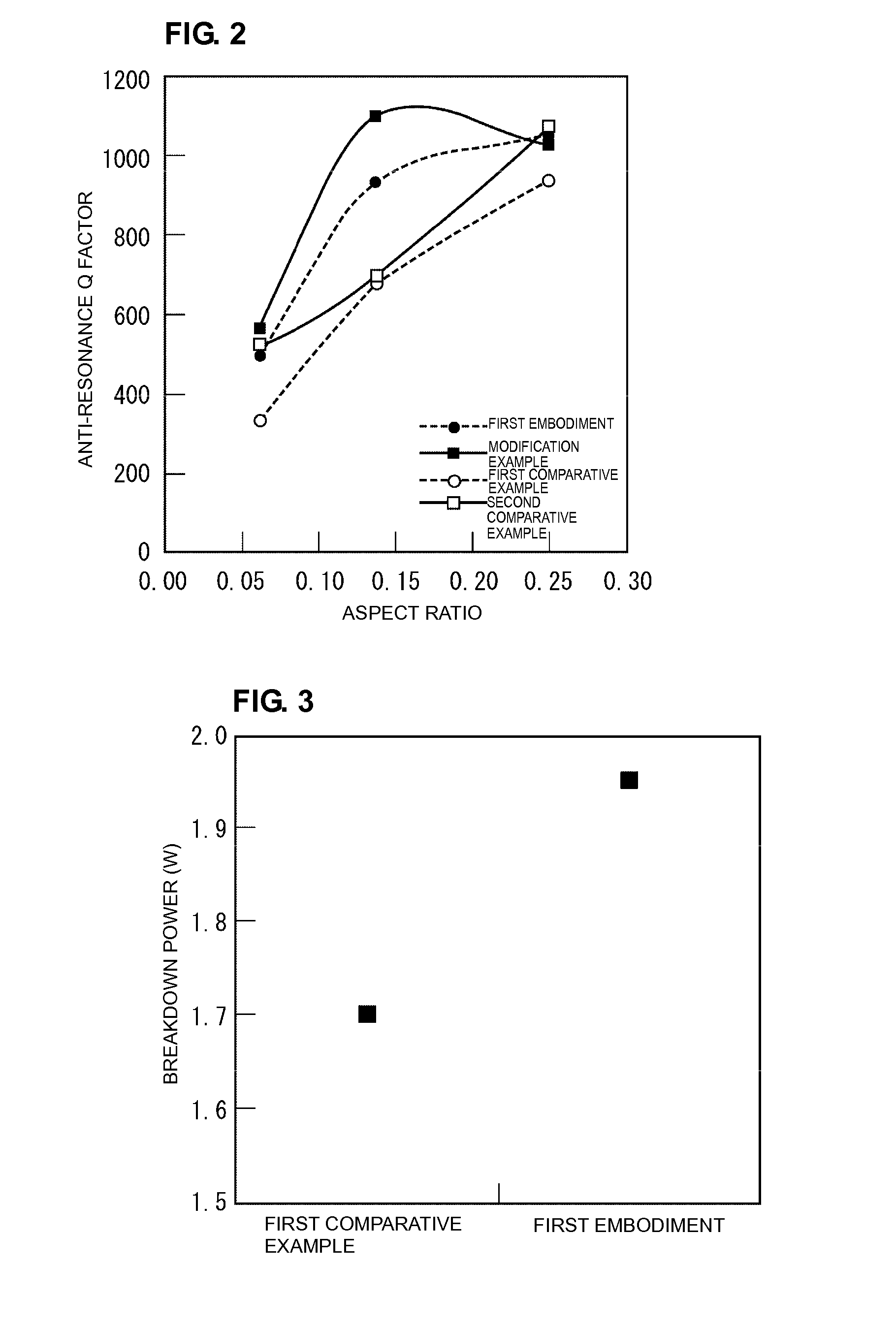
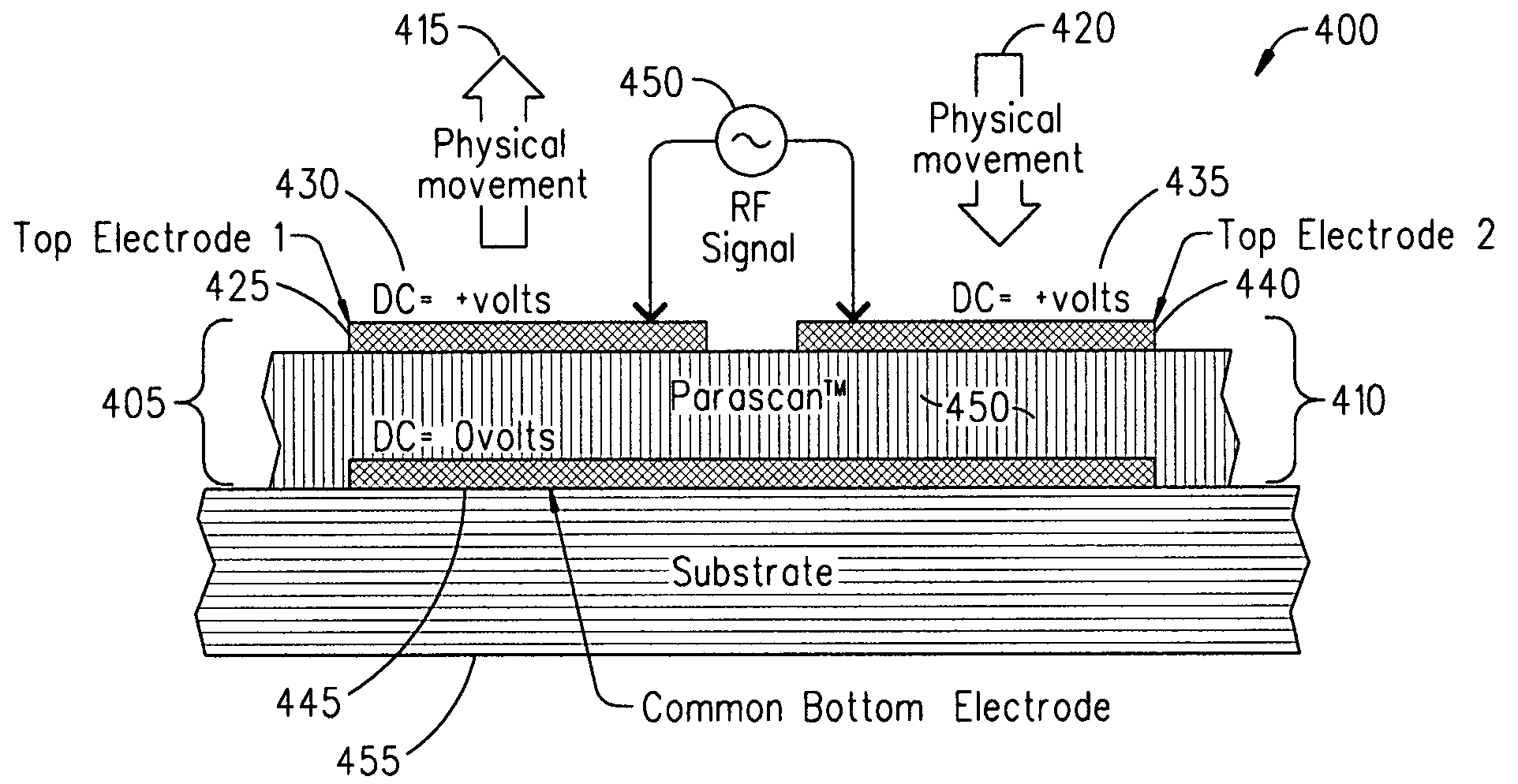
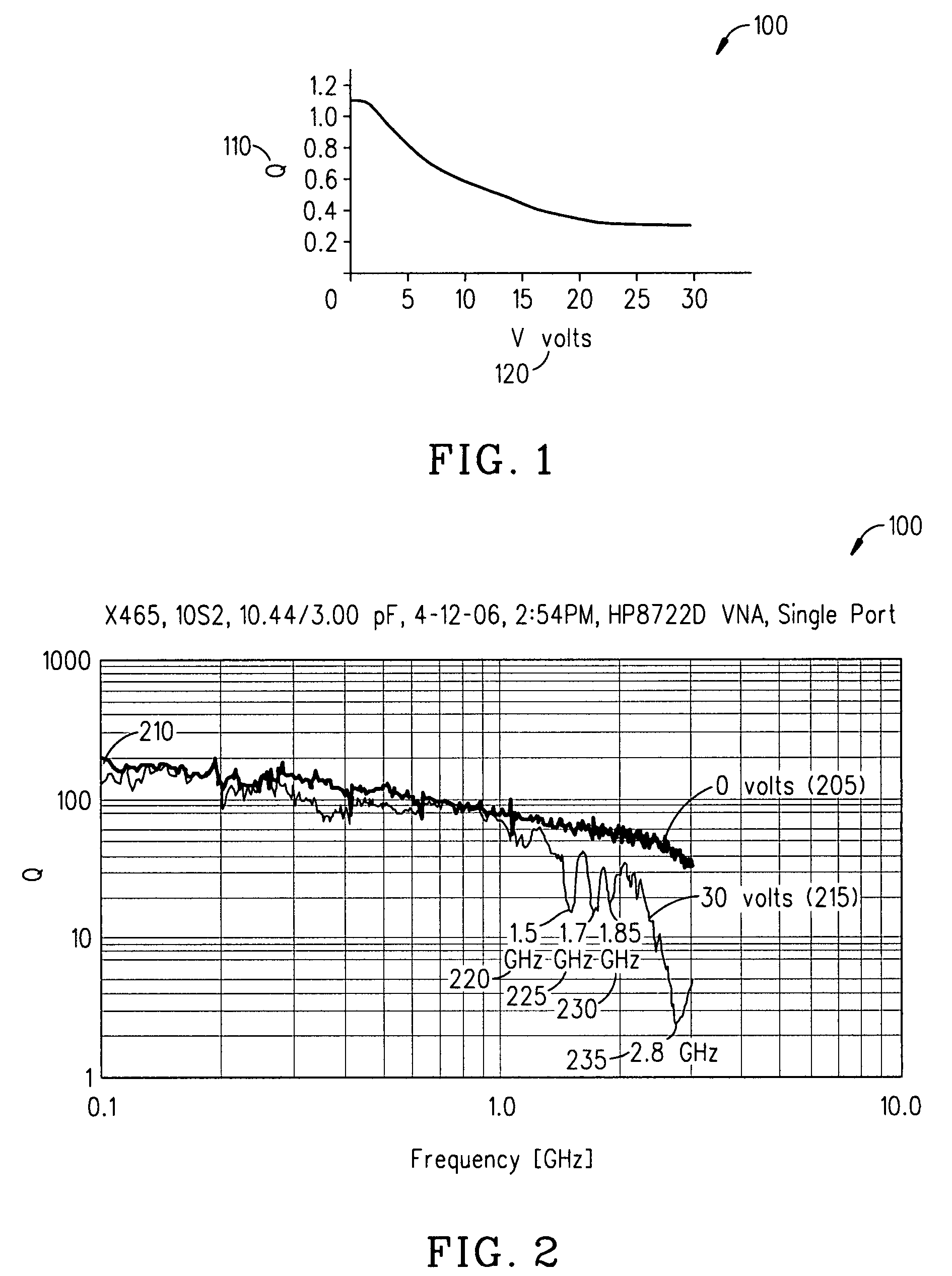
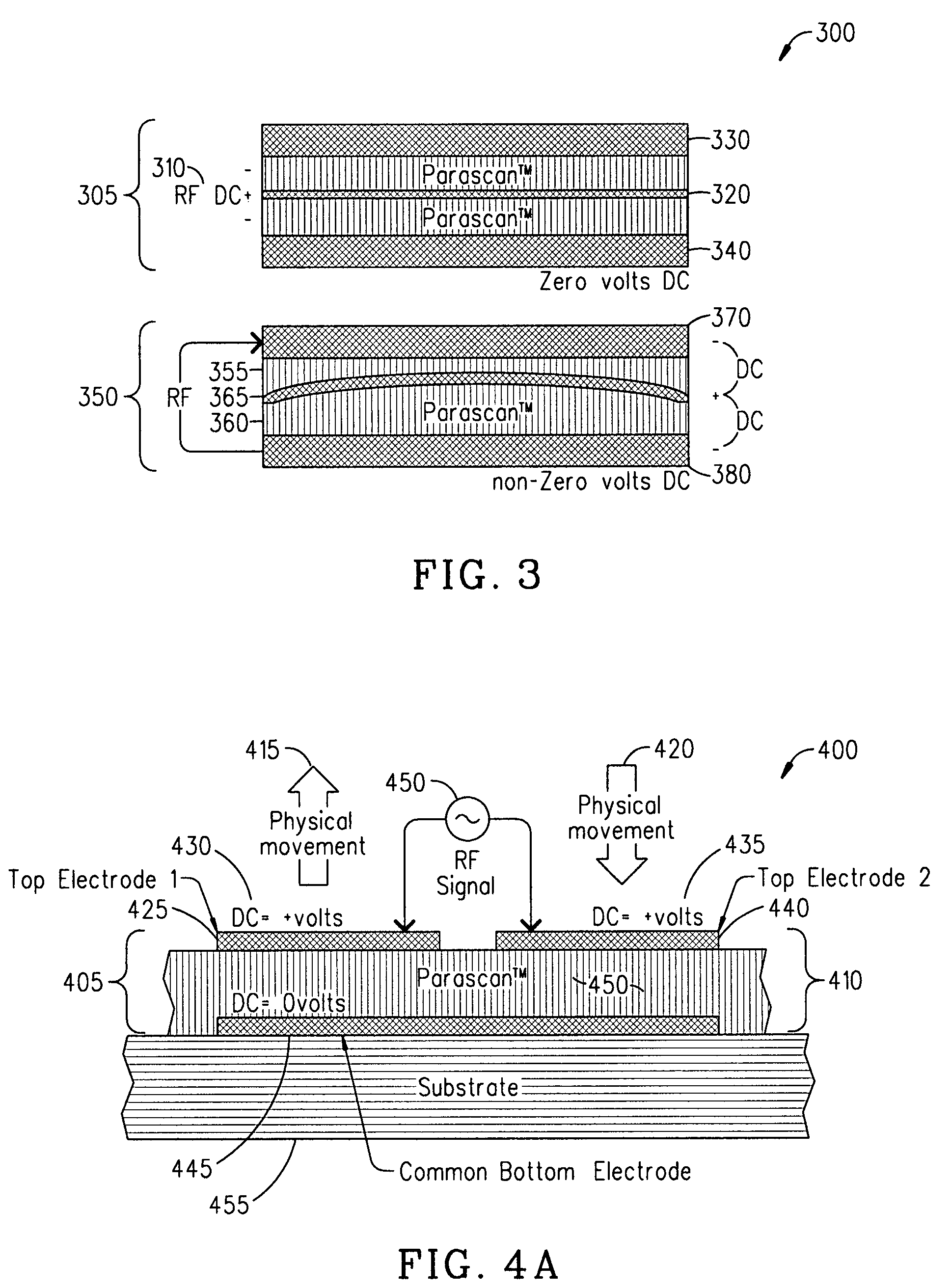
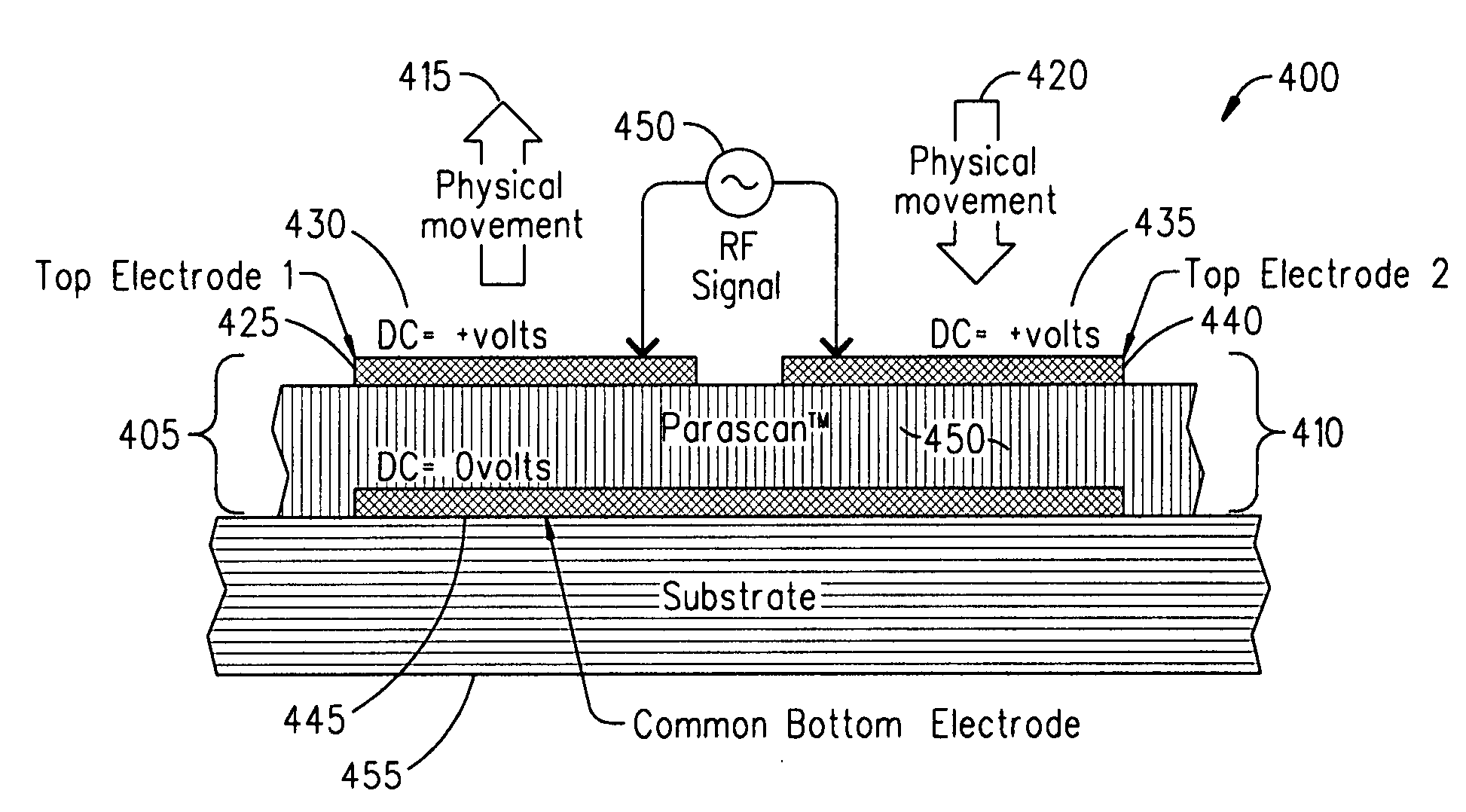
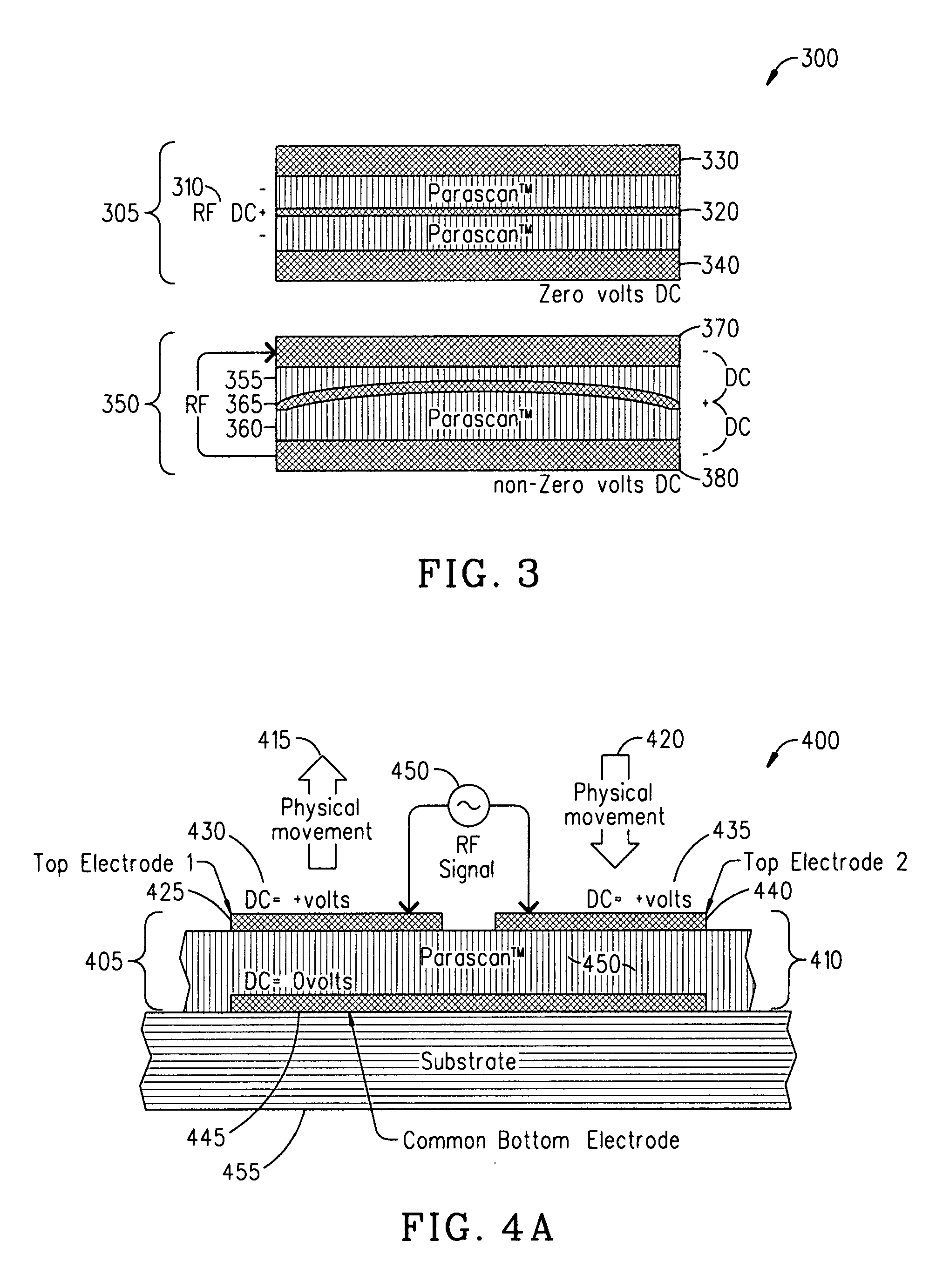
ActiveUS20080232023A1Reduce lossesImproving QMechanically variable capacitor detailsFixed capacitor electrodesAcousticsDielectric permittivity
An embodiment of the present invention provides a device, comprising a multilayered tunable dielectric capacitor, wherein said multilayers of tunable dielectric are adapted to be DC biased to reduce the dielectric constant; and wherein the DC bias is arranged so that the number of layers of tunable dielectric biased positively is equal to the number of layers of tunable dielectric biased negatively.
Owner:NXP USA INC
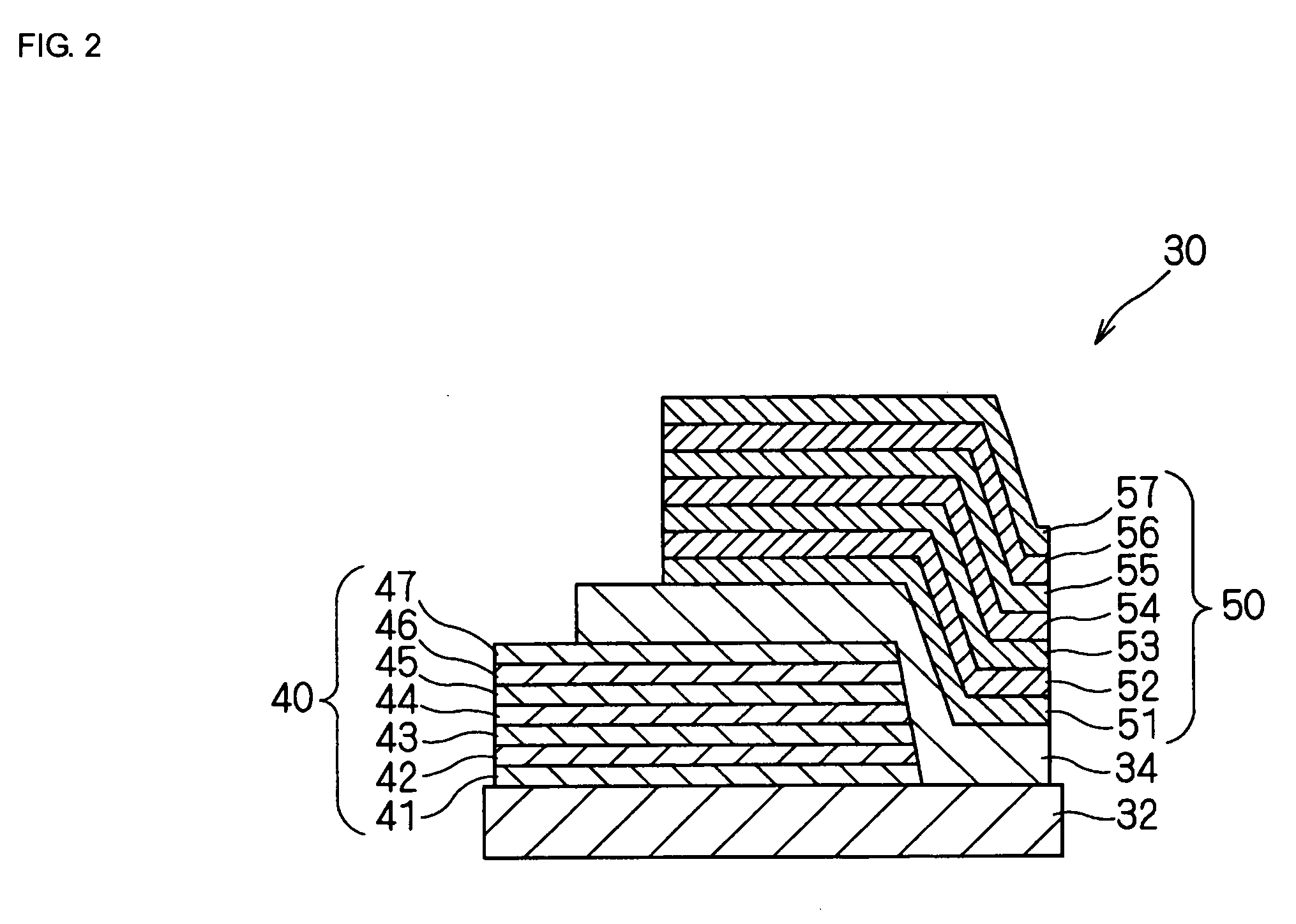
Inductor, resonant circuit, semiconductor integrated circuit, oscillator, and communication apparatus
InactiveUS20060125589A1Increase parasitic capacitanceHigh QTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsOscillations generatorsEngineeringInductor
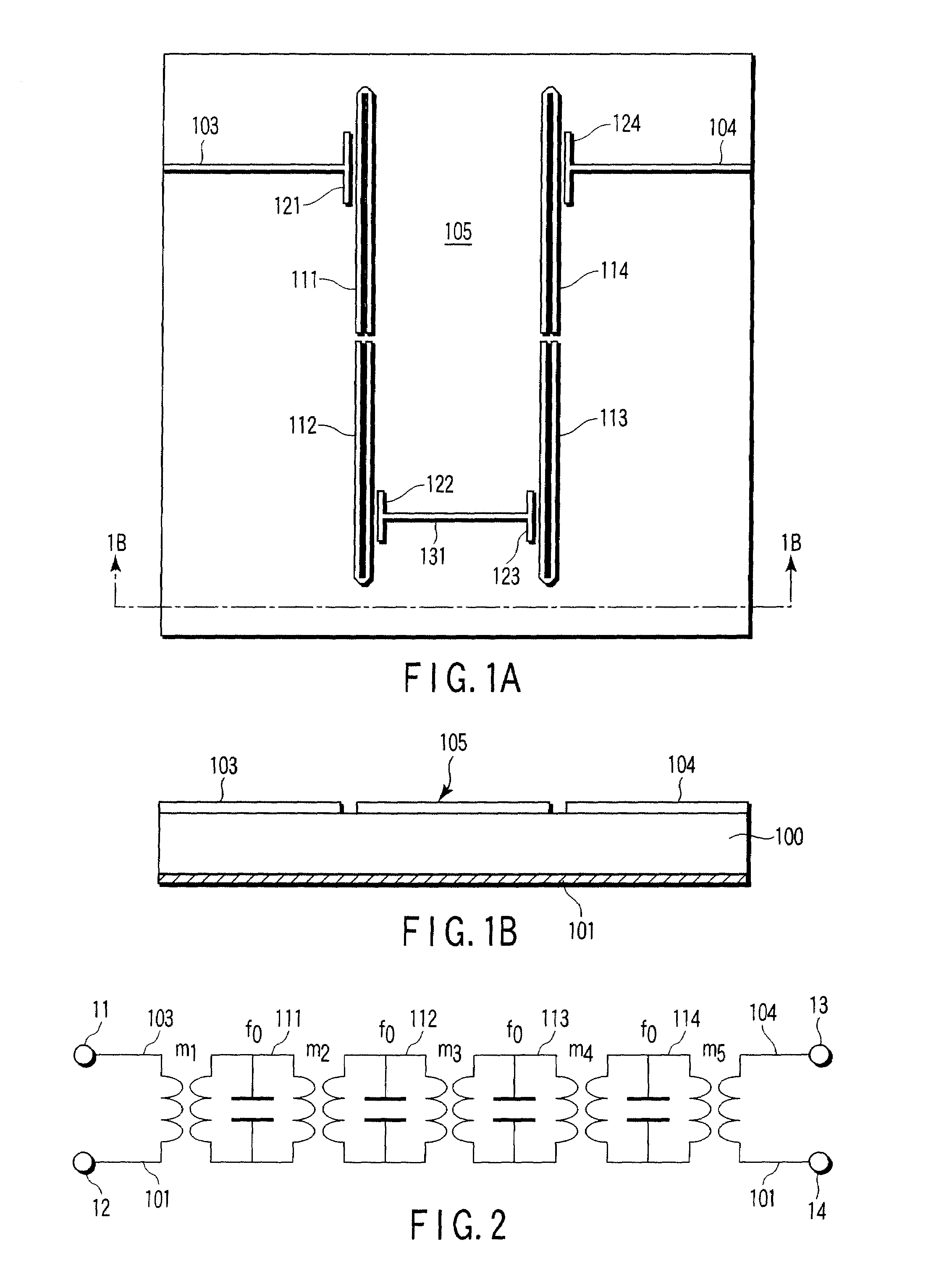
An inductor of the present invention includes a plurality of insulating layers being stacked and coil patterns respectively provided on predetermined layers of the insulating layers. The coil patterns are provided on at least two of the insulating layers, and electrically connected to each other. With this arrangement, it is possible to improve Q of the inductor without increasing the size of the inductor.
Owner:SHARP KK
Spiral inductor semiconducting device with grounding strips and conducting vias
InactiveUS6489663B2Good effectIncrease capacitanceTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCapacitanceSpiral inductor
An integrated semiconducting device comprises a semiconducting substrate, a plurality of grounding strips disposed above the substrate in a lower metal level of the semiconducting device, an inductor positioned in an upper metal level of the semiconducting device, and a plurality of conducting vias connected to and extending away from the grounding strips towards the inductor. The inductor, conducting via, ground strips structure forms a Faraday cage that acts as a shield against electromagnetic radiation. The number and placement of the conductive vias are adjustable and can be optimized based on the relative importance of maximizing the quality factor Q of the inductor or minimizing the capacitance between the inductor and ground.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
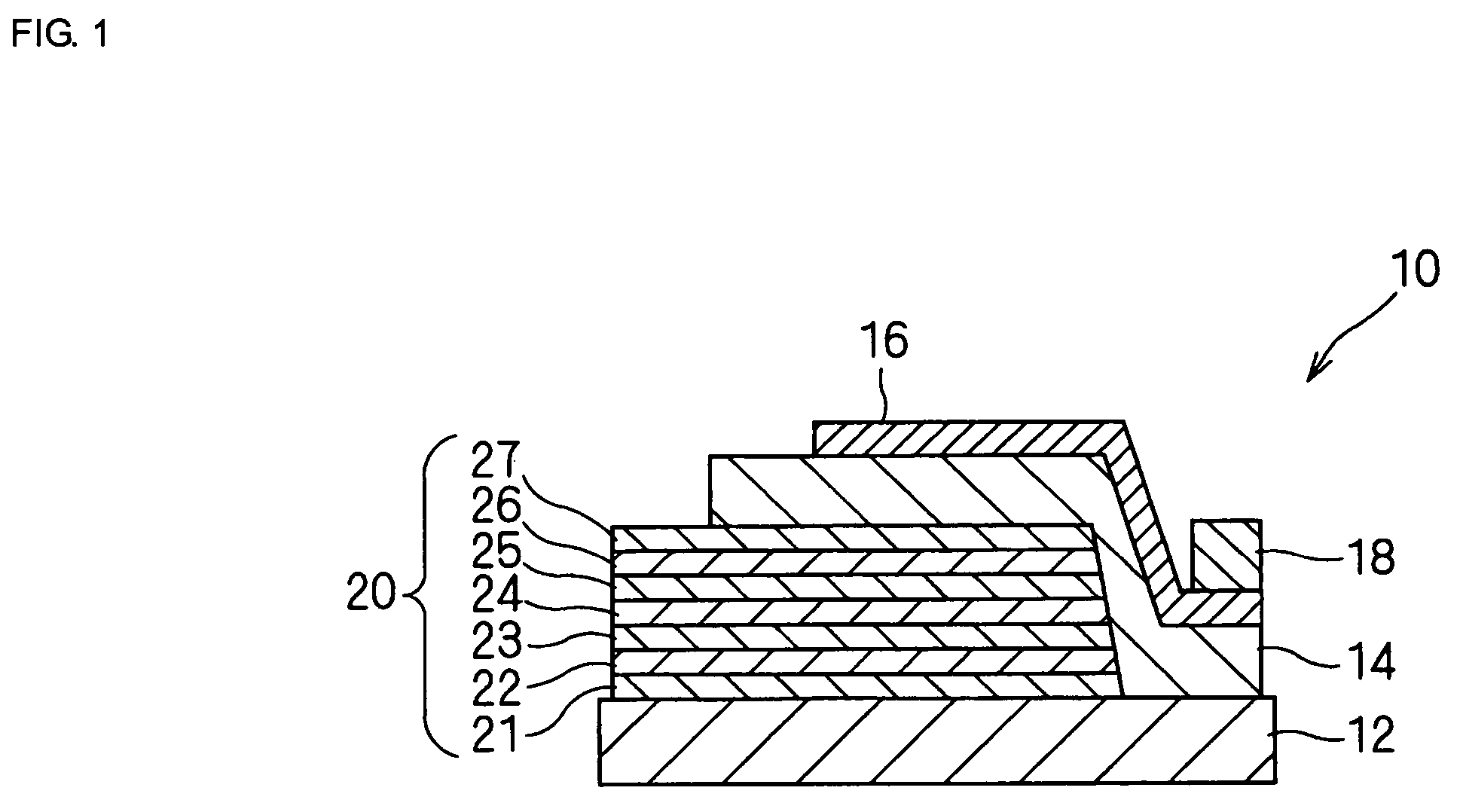
Piezoelectric thin-film resonator and process for producing same
InactiveUS20060119230A1Low costReduce energy lossPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSingle crystalConductive materials
A piezoelectric thin-film resonator includes a first excitation electrode and a second excitation electrode, the first excitation electrode being disposed opposite the second excitation electrode; a piezoelectric thin film disposed between the first excitation electrode and the second excitation electrode; and a substrate supporting the first excitation electrode, the substrate being composed of a LiTaO3 single crystal or a LiNbO3 single crystal, the first excitation electrode including an acoustic reflecting layer, the acoustic reflecting layer containing (a) at least one epitaxially grown first sublayer being composed of a conducting material and having a relatively high acoustic impedance; and (b) at least one epitaxially grown second sublayer being composed of another conducting material and having a relatively low acoustic impedance.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
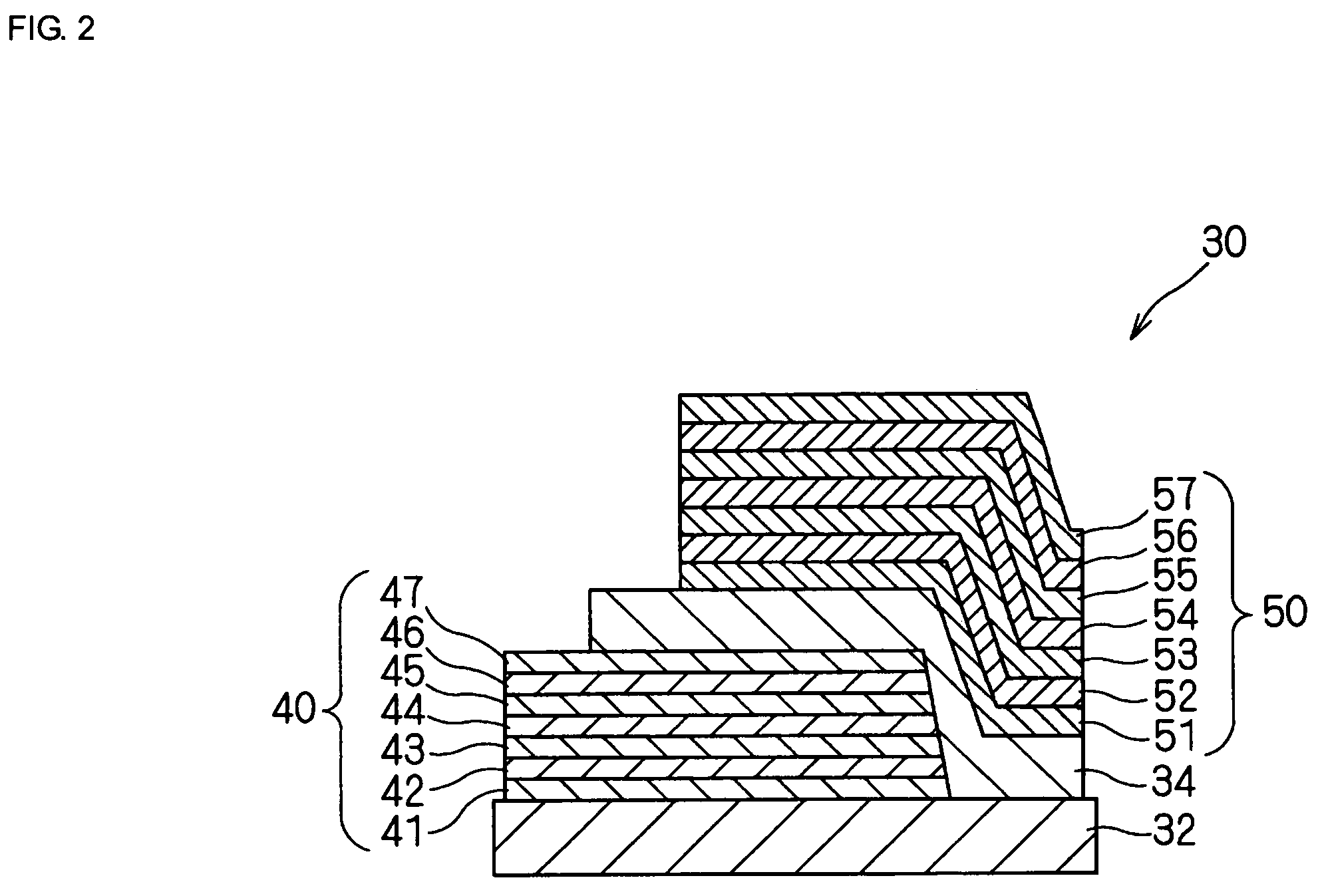
Piezoelectric thin-film resonator and process for producing same
InactiveUS7276836B2Reduce energy lossImproving QPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSingle crystalConductive materials
A piezoelectric thin-film resonator includes a first excitation electrode and a second excitation electrode, the first excitation electrode being disposed opposite the second excitation electrode; a piezoelectric thin film disposed between the first excitation electrode and the second excitation electrode; and a substrate supporting the first excitation electrode, the substrate being composed of a LiTaO3 single crystal or a LiNbO3 single crystal, the first excitation electrode including an acoustic reflecting layer, the acoustic reflecting layer containing (a) at least one epitaxially grown first sublayer being composed of a conducting material and having a relatively high acoustic impedance; and (b) at least one epitaxially grown second sublayer being composed of another conducting material and having a relatively low acoustic impedance.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
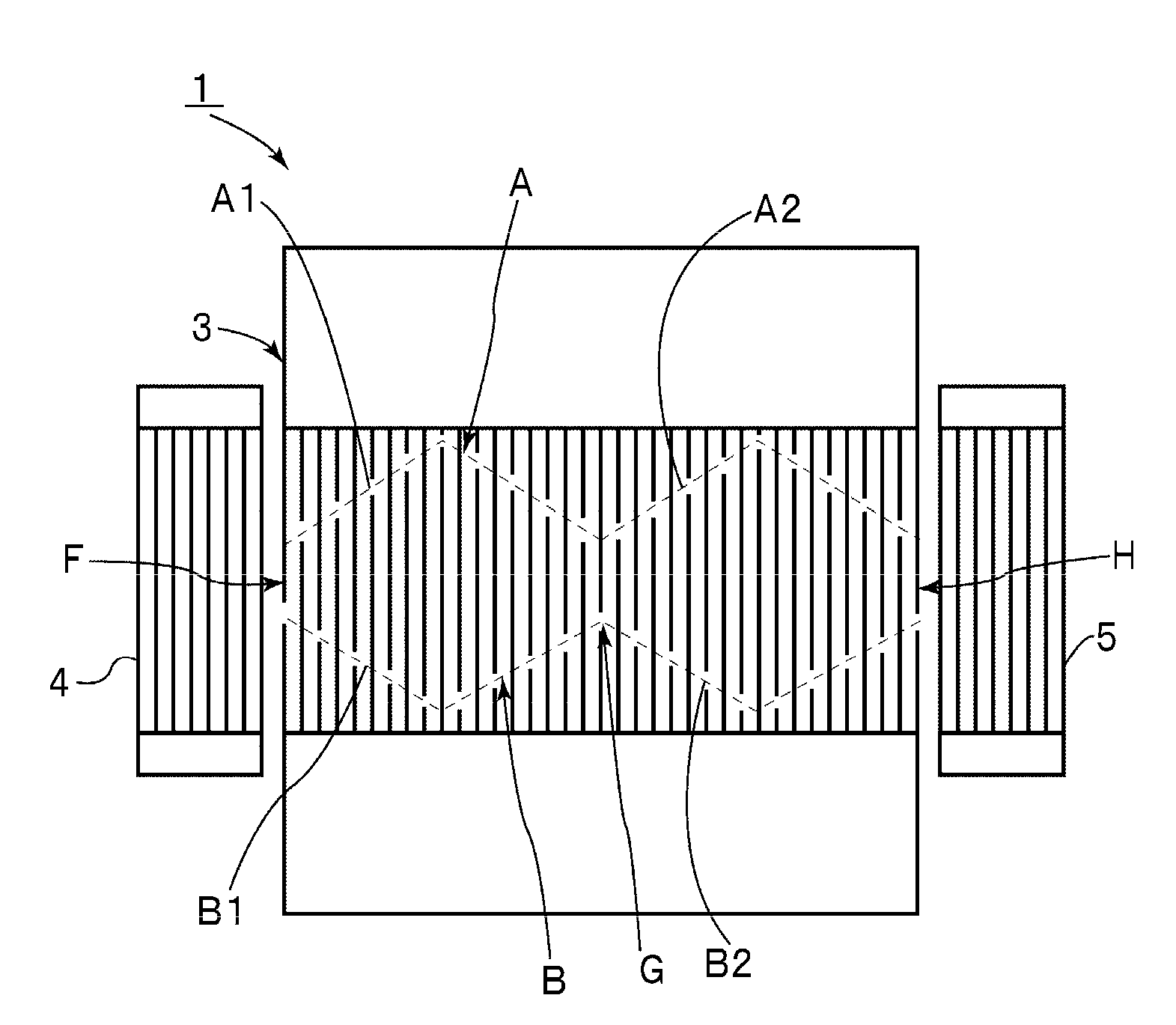
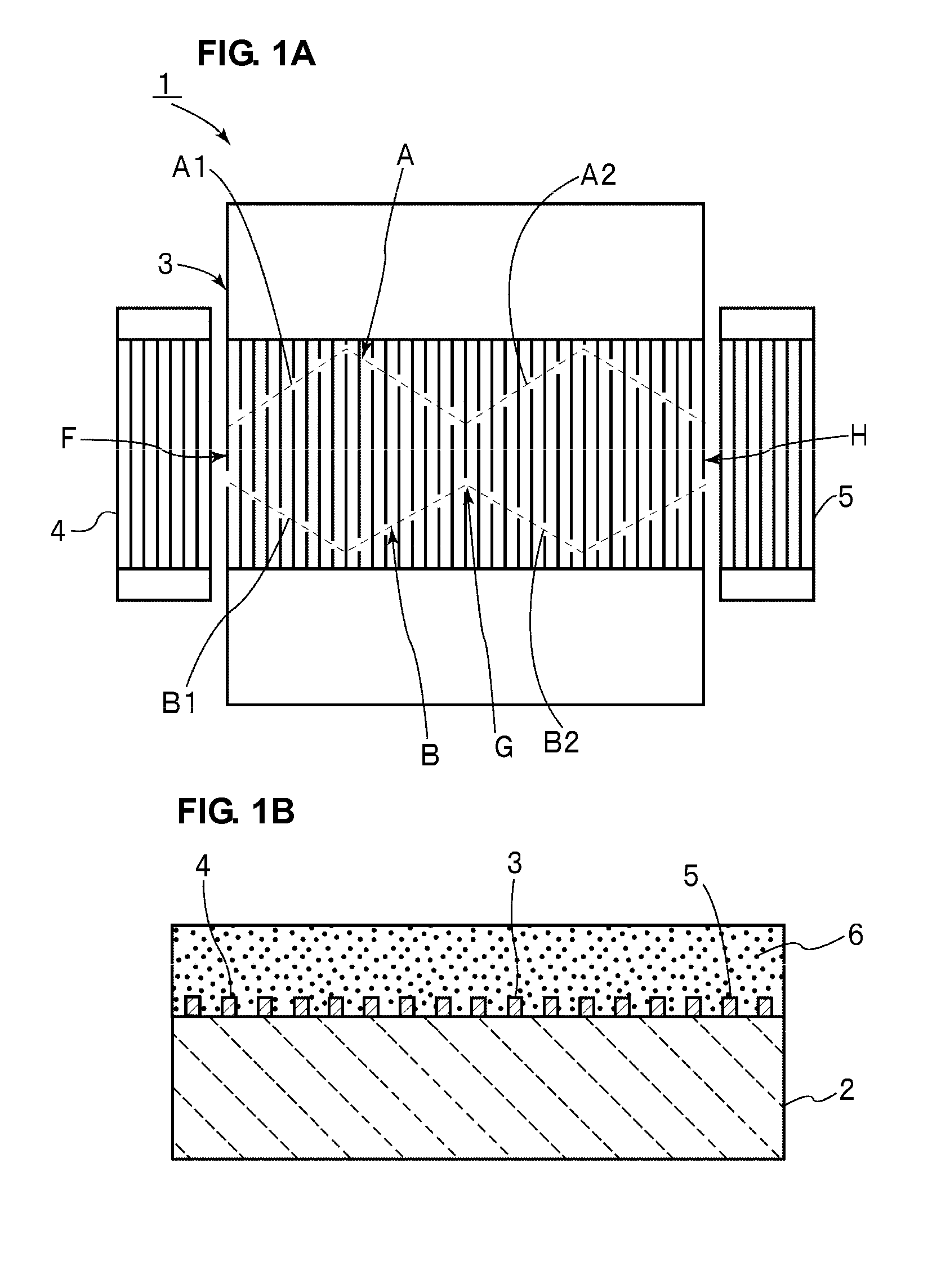
Acoustic wave resonator
ActiveUS20080309192A1Satisfactory resonance characteristicImproving QPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksApodizationResonator
In an acoustic wave resonator, an IDT electrode is provided on a piezoelectric substrate. The IDT electrode is apodization-weighted such that a plurality of maximum values of cross widths are provided in acoustic wave propagation directions. Alternatively, in apodization weighting, weighting is applied such that at least one of a pair of envelopes located at outer side portions of the IDT electrode in directions substantially perpendicular to acoustic wave propagation directions includes a plurality of angled envelope portions angled from a central portion of the IDT electrode toward an outer side portion of the IDT electrode in a direction substantially perpendicular to the acoustic wave propagation directions.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Capacitors adapted for acoustic resonance cancellation
ActiveUS7936553B2Improving QReduce lossesMechanically variable capacitor detailsFixed capacitor electrodesAcousticsDielectric permittivity
An embodiment of the present invention provides a device, comprising a multilayered tunable dielectric capacitor, wherein said multilayers of tunable dielectric are adapted to be DC biased to reduce the dielectric constant; and wherein the DC bias is arranged so that the number of layers of tunable dielectric biased positively is equal to the number of layers of tunable dielectric biased negatively.
Owner:NXP USA INC
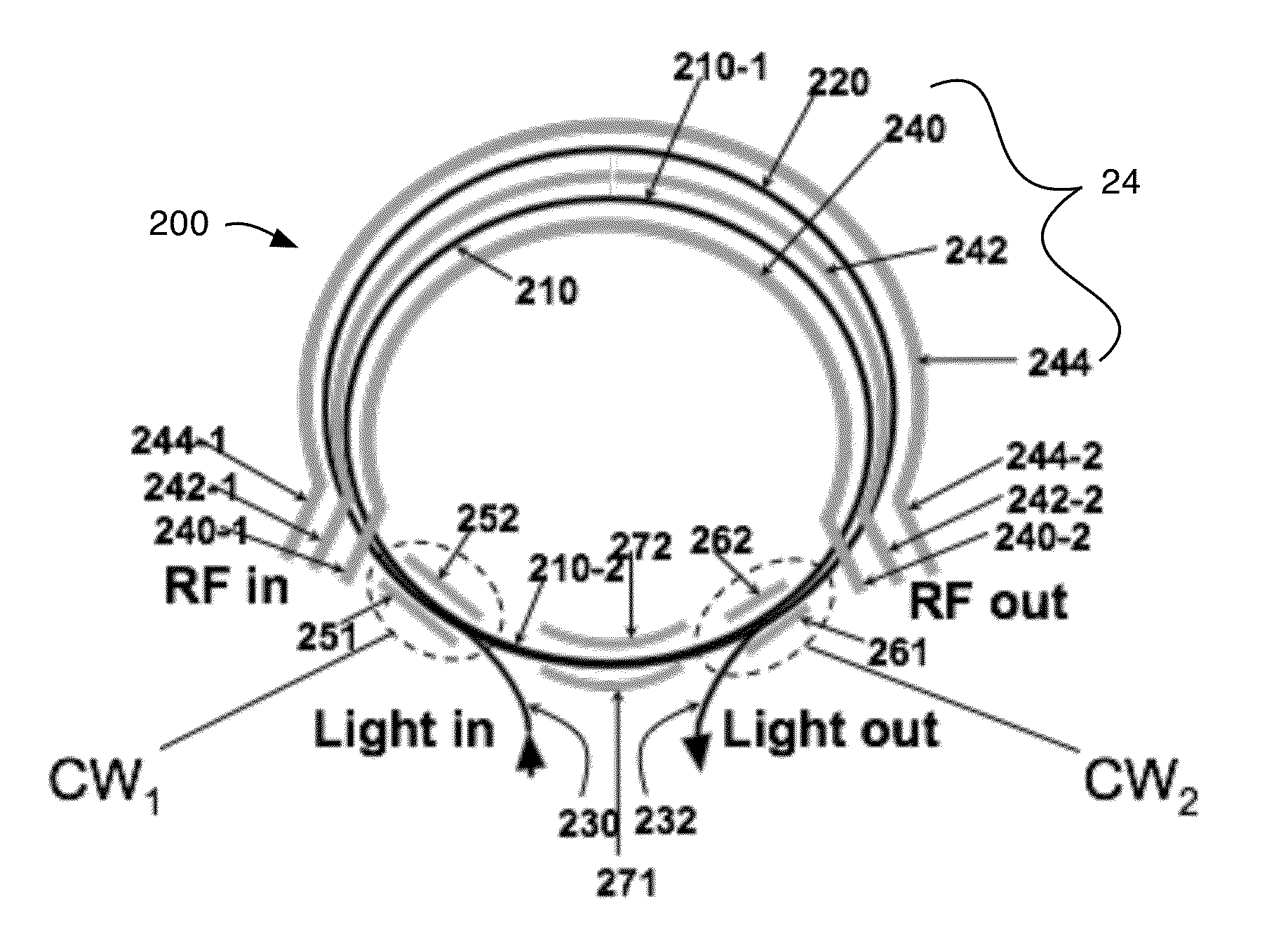
Re-circulation enhanced electro-optic modulator
ActiveUS9291837B1Wide modulation bandwidthImprove efficiencyNon-linear opticsMach–Zehnder interferometerEngineering
An optical modulator includes a waveguide Mach-Zehnder interferometer having a first and a second input and a first and a second output, a feedback waveguide segment connecting the second output with the second input, and a traveling-wave electrode; wherein the Mach-Zehnder interferometer, feedback waveguide segment and traveling-wave electrode are substantially arranged at or adjacent the perimeter of a smooth curve defining a closed geometric figure, the traveling-wave electrode extending along at least 50% of the length of the perimeter of the smooth curve.
Owner:HRL LAB
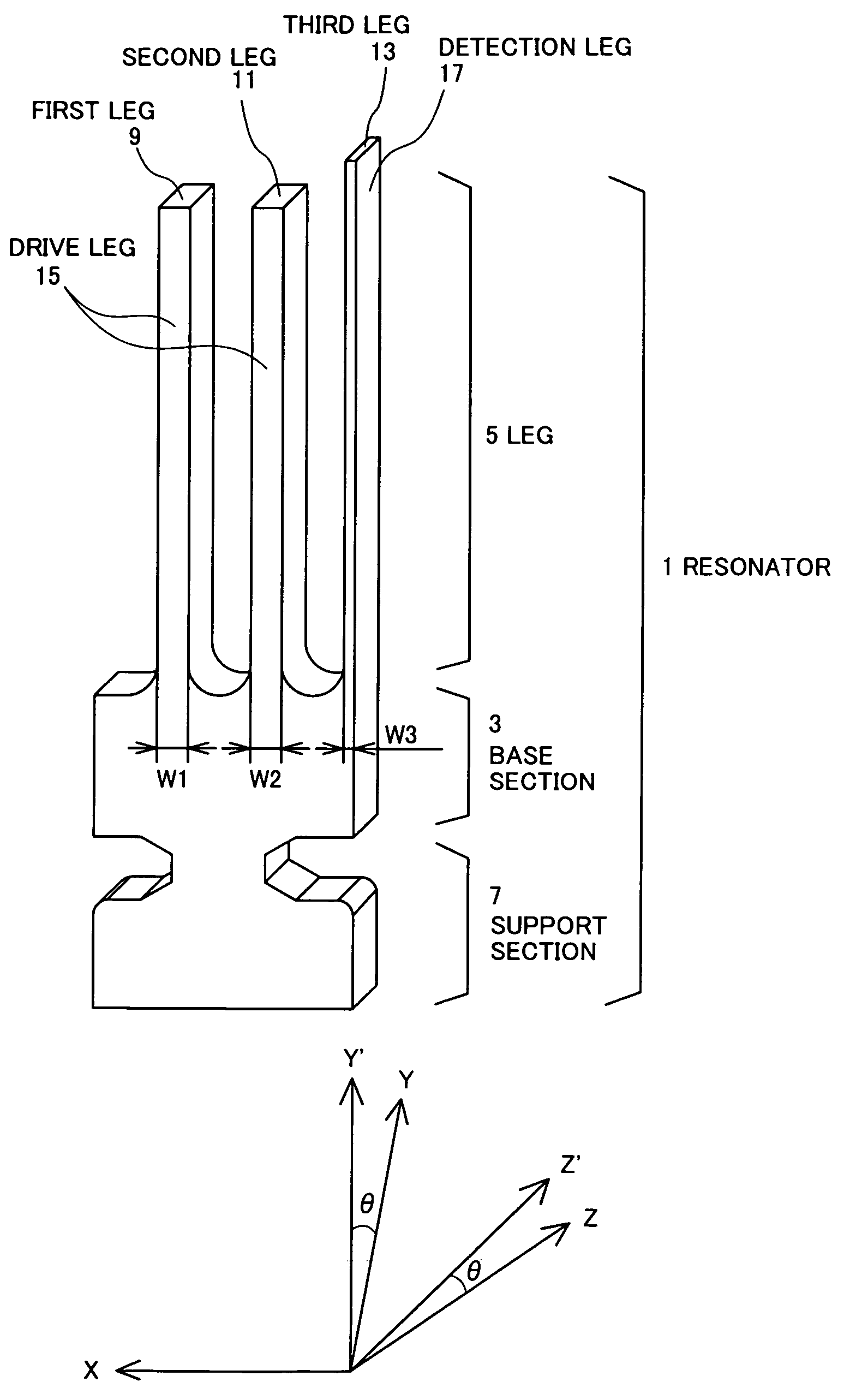
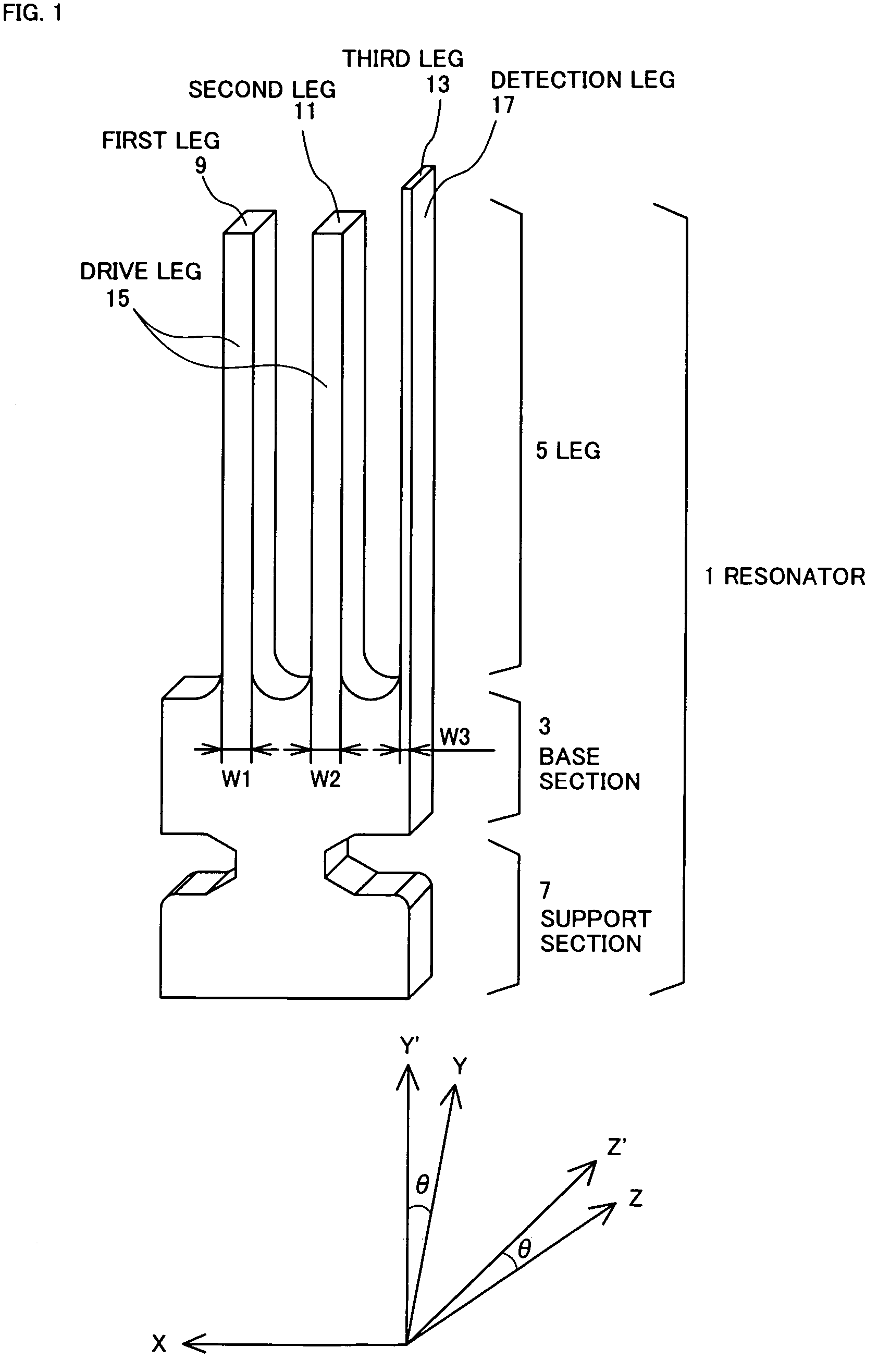
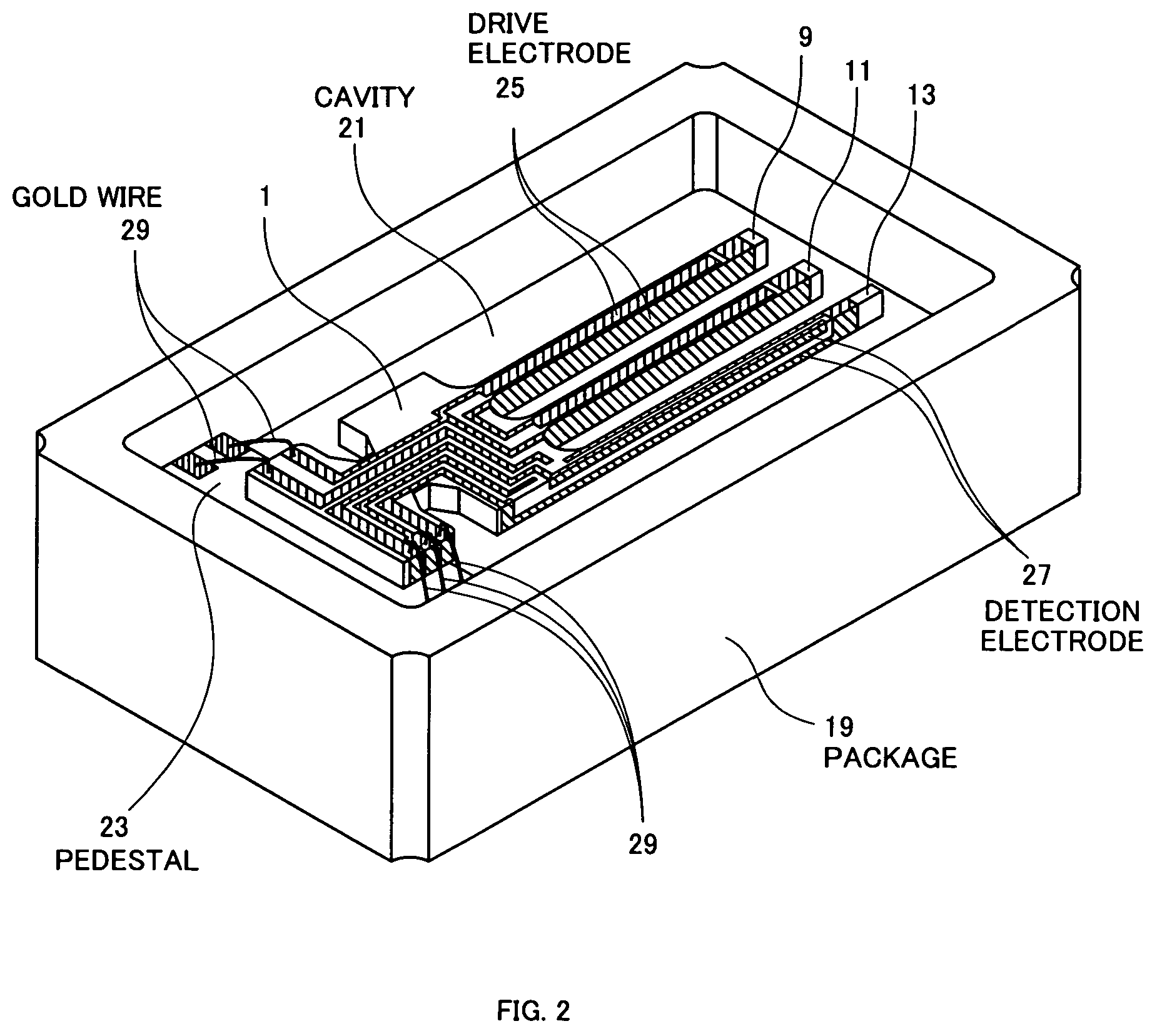
Vibration gyro
InactiveUS7673511B2Kinetic balanceVibrations can be prevented from leaking into the base sectionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesGyroscopeCoupling
A vibration gyro having a high accuracy, no vibration leak, and high S / N.The width of a detection leg of a resonator used in the vibration gyro is less than ⅗ of the width of drive legs. The length of the detection leg is larger than the length of the drive legs. As a result, the distance between the detection electrodes is decreased by comparison with the conventional vibration gyro and, therefore, the detection signal is increased and S / N is raised. Furthermore, increasing the leg length brings the natural vibration frequency of out-of-plane vibration of the drive legs close to the natural vibration frequency of the detection leg, providing good coupling and reducing vibration leak to the support section. As a result, Q is increased and S / N is accordingly further increased.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
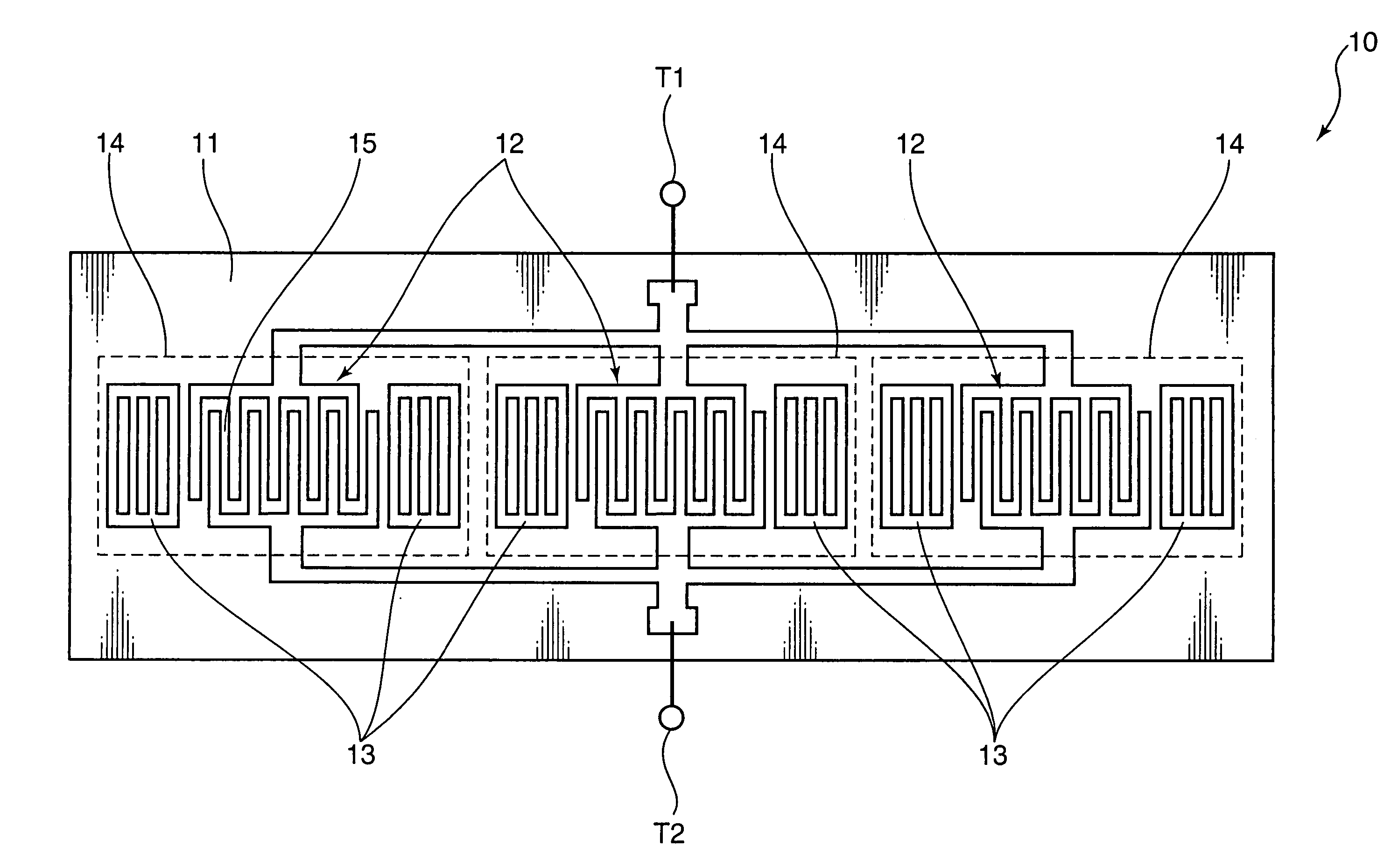
Surface Acoustic Wave Resonator and Surface Acoustic Wave Filter Using the Same
ActiveUS20080018417A1Reduced insertion lossIncrease steepnessImpedence networksResonanceSurface acoustic wave sensor
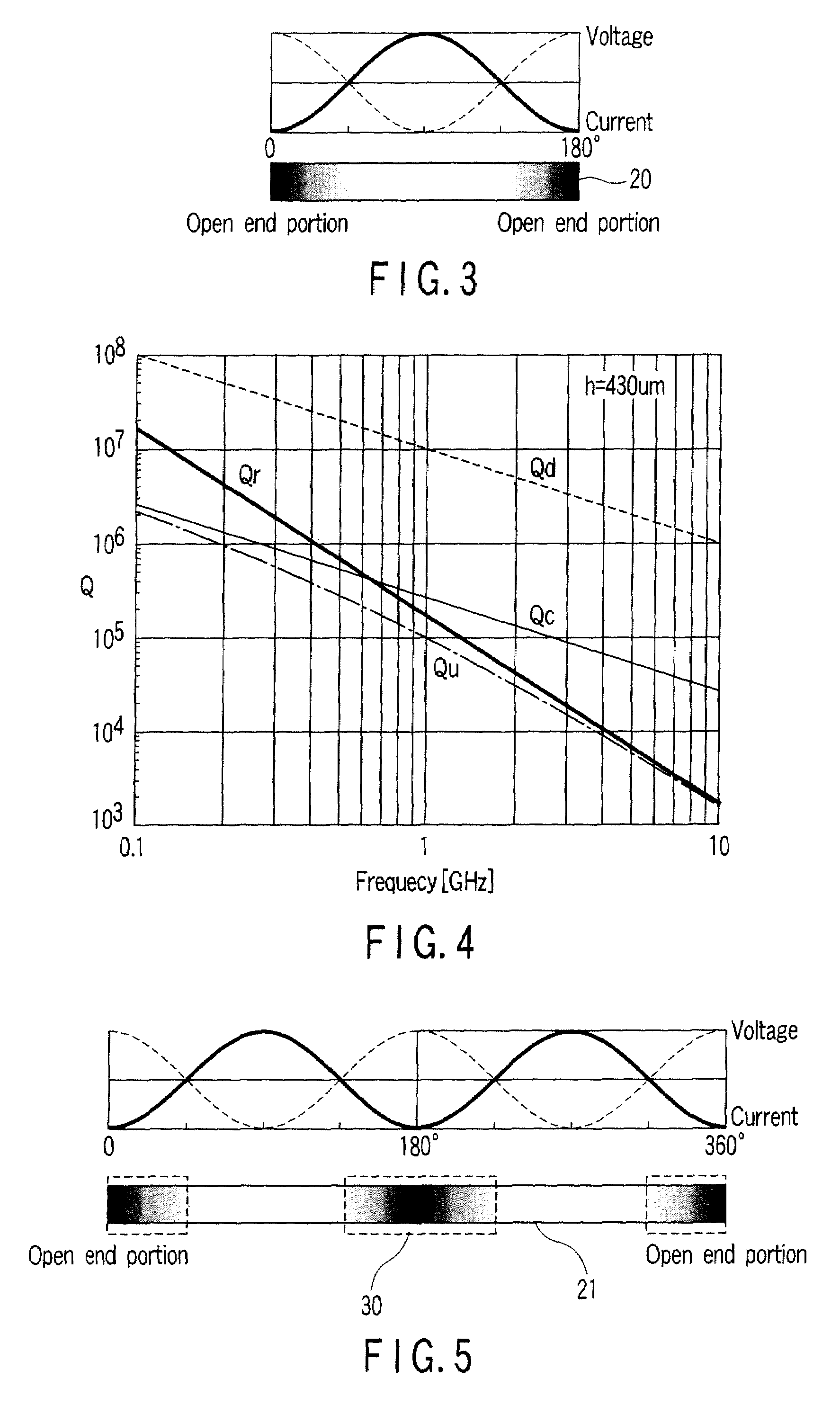
A Q-factor of a resonator at a high frequency is improved. An insertion loss of a filter using such a resonator and steepness of the filter are improved. A plurality of surface acoustic wave resonators including an interdigital transducer and reflecting electrodes provided on both sides thereof are connected in parallel on a piezoelectric substrate. Resonance frequencies of the surface acoustic wave resonators are rendered equal among all the resonators connected in parallel. In this way, Q-factor of resonance can be improved. A surface acoustic wave filter using such surface acoustic wave resonators is formed in order to improve the insertion loss and the steepness.
Owner:SKYWORKS PANASONIC FILTER SOLUTIONS JAPAN
Capacitors adapted for acoustic resonance cancellation
ActiveUS8467169B2Improving QReduce lossesMultiple-port networksFixed capacitor dielectricRadio frequency signalAcoustics
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and mechanism for tuning dielectric resonator circuits
InactiveUS20060197631A1Improving QReduced insertion lossResonatorsBridge strengtheningCouplingDielectric resonator
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
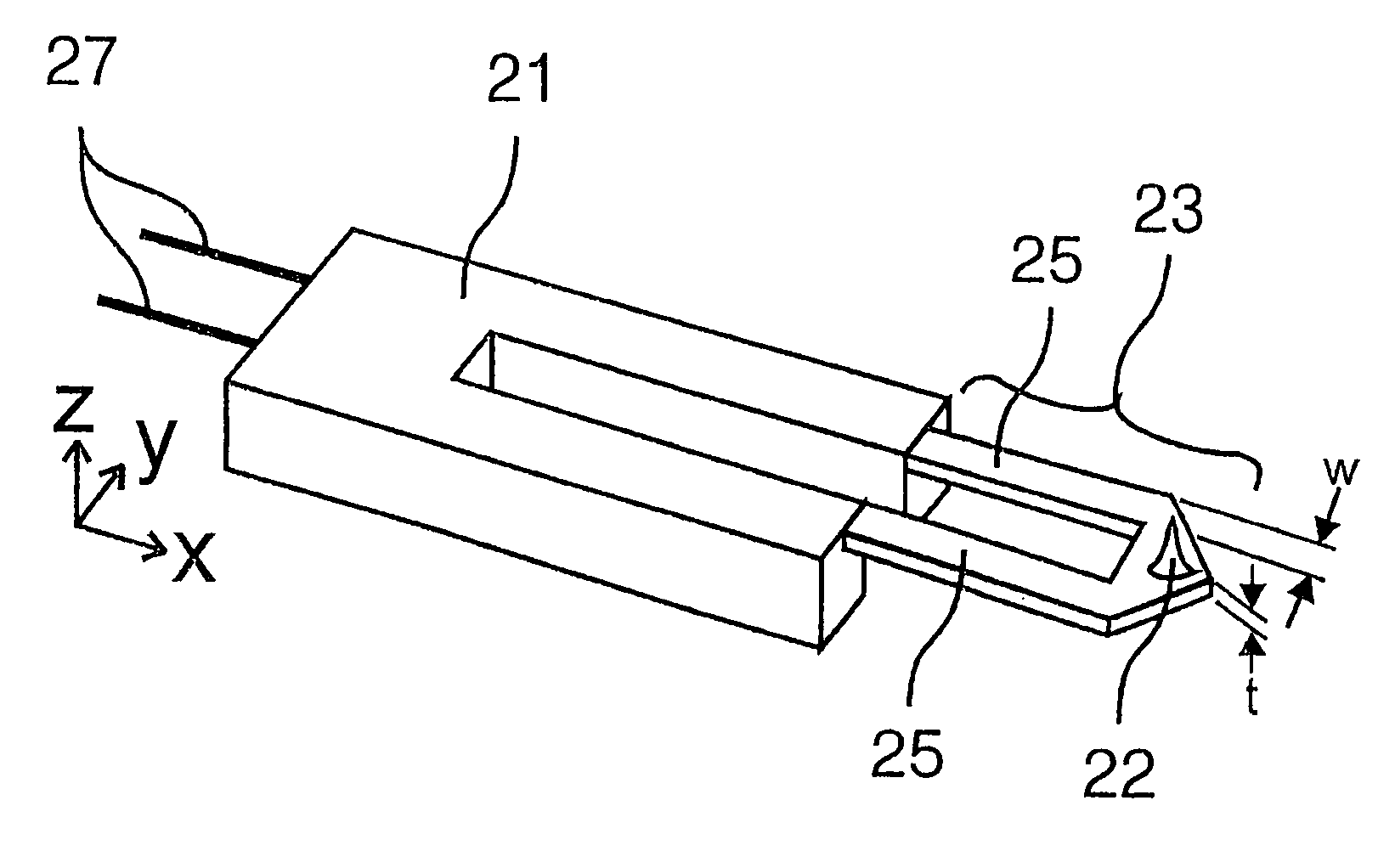
Inductor, resonant circuit, semiconductor integrated circuit, oscillator, and communication apparatus
InactiveUS7295096B2Reduced series resistanceIncrease in sizeTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsOscillations generatorsInductorInductance
Owner:SHARP KK
Actuating and sensing device for scanning probe microscopes
InactiveUS7051582B2Improving QMore forceMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTuning forkEngineering
An actuating and sensing device for scanning probe microscopes includes a tuning fork (21) containing two prongs, a connection device (23) such as a spring, and a probing tip (22). The tip (22) is connected to both prongs of the tuning fork (21) with the connection device (23). The tuning fork (21) is used as a mechanical resonator to vibrate. The movements of the prongs are transformed via the connection device (23) into movements of the tip (22), wherein the tip movements can be in different planes than the movement plane of the prongs.
Owner:UNIV DE NEUCHATEL INSTITUT DE MICROTECHN
Tuner for receiving television signal in VHF band and UHF band
InactiveUS6903783B2Stable characteristicsIncreased frequency rangeTelevision system detailsDiscontinuous tuning for band selectionEngineeringTransistor
In a television tuner, a predetermined bias voltage is applied to the anode of a first switching diode. A power supply voltage is applied to the collector of a switching transistor via a power supply resistor, and the emitter of the switching transistor is grounded. The collector of the switching transistor is connected to an input terminal of a first FET via a first resistor. The first switching diode and the switching transistor are both switched on or off correspondingly to whether a television signal in the UHF band is to be received or a television signal in the VHF band is to be received.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Temperature compensating electrodes
InactiveUS20140292152A1Reduce temperature driftPositive temperature coefficientPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksTitaniumTitanium alloy
Owner:CYMATICS LAB CORP
Filter and radio communication device using the same
A filter includes a resonant unit which has a plurality of resonators respectively formed of each microstrip line and connected in cascade with one another, and a coupling unit which has at least one inter-resonator coupling of the resonant unit in an area within a range of ±45° (⅛-wavelength) in an electrical length from a voltage maximum point at a intermediate of the microstrip line.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Nonreciprocal circuit device
ActiveUS20090206943A1Reduced insertion lossIncreases value of secondWaveguide type devicesDirect currentMagnet
A nonreciprocal circuit device includes a permanent magnet, a ferrite to which the permanent magnet applies a direct-current magnetic field, first and second central electrodes arranged on the ferrite, and a circuit board. The first central electrode includes electrode layers provided on main surfaces of the ferrite connected by an electrode provided on a top surface of the ferrite. A second central electrode includes electrode layers provided on the main surfaces of the ferrite connected by electrodes arranged on top and bottom surfaces of the ferrite. The second electrode is wound at least about three turns around the ferrite. A width dimension of the outermost electrode layers of the second central electrode is greater than a width dimension of the inner electrode layers of the second central electrode.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Capacitors adapted for acoustic resonance cancellation
ActiveUS20090040687A1Reduce lossesImproving QMultiple-port networksFixed capacitor dielectricAcousticsCapacitor
An embodiment of the present invention provides a method, comprising reducing the losses due to electro-mechanical coupling and improving Q in a multilayered capacitor by placing a first capacitor layer adjacent at least one additional capacitor layer and sharing a common electrode in between the two such that the acoustic vibration of the first layer is coupled to an anti-phase acoustic vibration of the at least one additional layer.
Owner:NXP USA INC
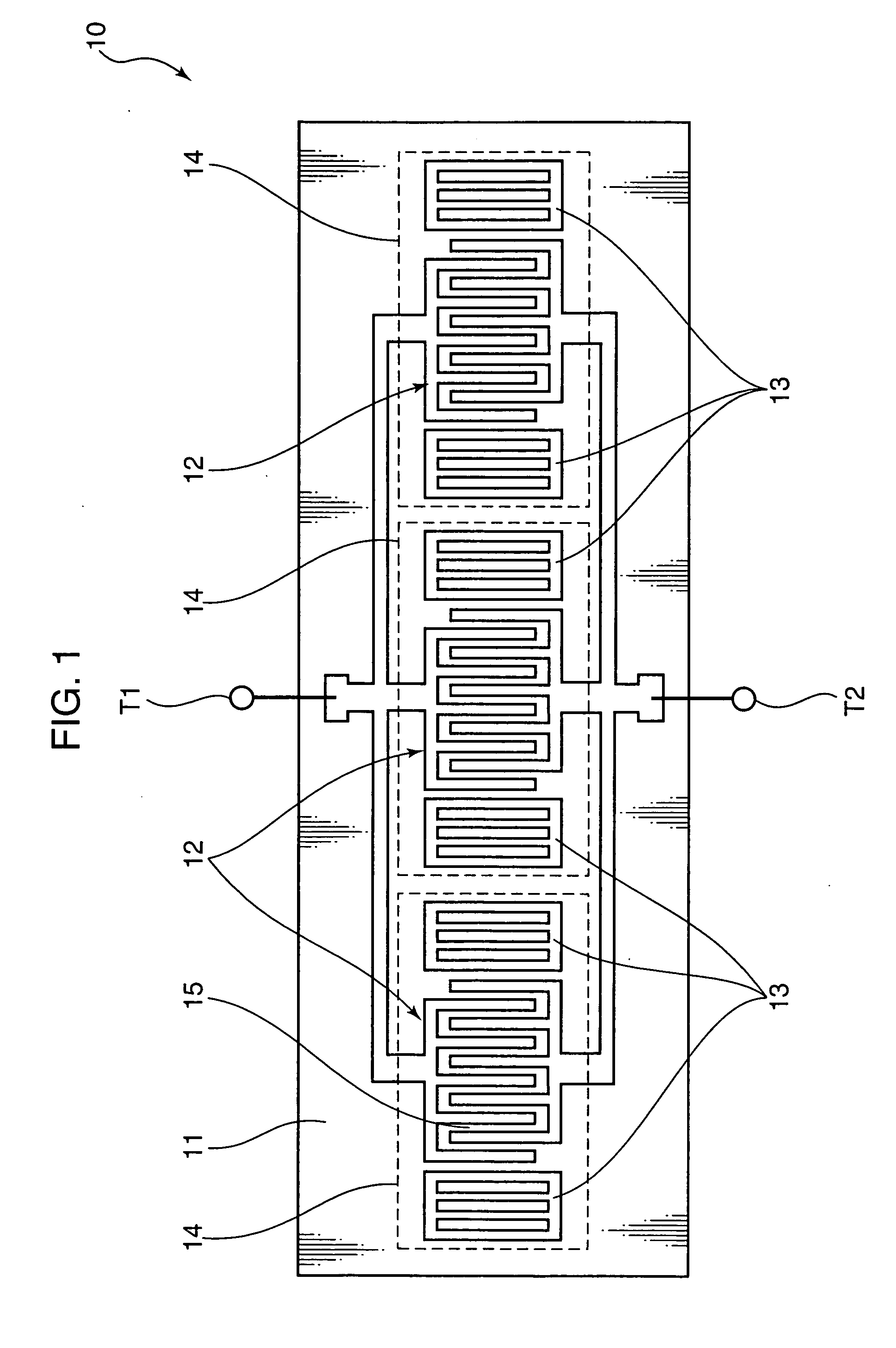
Surface acoustic wave resonator and surface acoustic wave filter using the same
ActiveUS7646266B2Improving QLow insertion lossPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksResonanceSurface acoustic wave sensor
A Q-factor of a resonator at a high frequency is improved. An insertion loss of a filter using such a resonator and steepness of the filter are improved. A plurality of surface acoustic wave resonators including an interdigital transducer and reflecting electrodes provided on both sides thereof are connected in parallel on a piezoelectric substrate. Resonance frequencies of the surface acoustic wave resonators are rendered equal among all the resonators connected in parallel. In this way, the Q-factor of the resonance can be improved. A surface acoustic wave filter using such surface acoustic wave resonators is formed in order to improve the insertion loss and the steepness.
Owner:SKYWORKS PANASONIC FILTER SOLUTIONS JAPAN
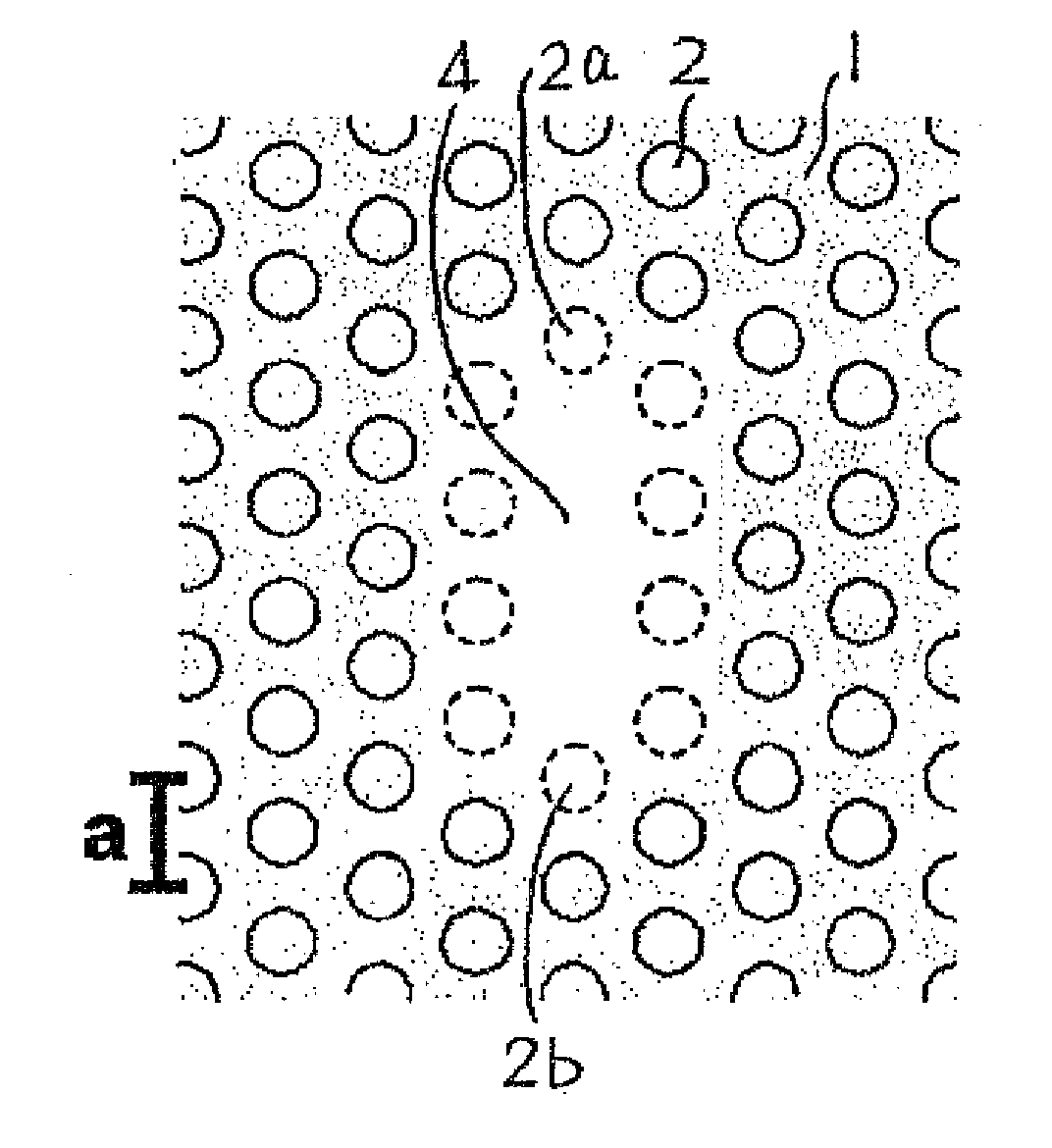
Two-Dimensional Photonic Crystal Cavity and Channel Add/Drop Filter
ActiveUS20070086716A1High resolutionSmall sizeCladded optical fibreNanoopticsPhotonic crystal cavityPhotonics
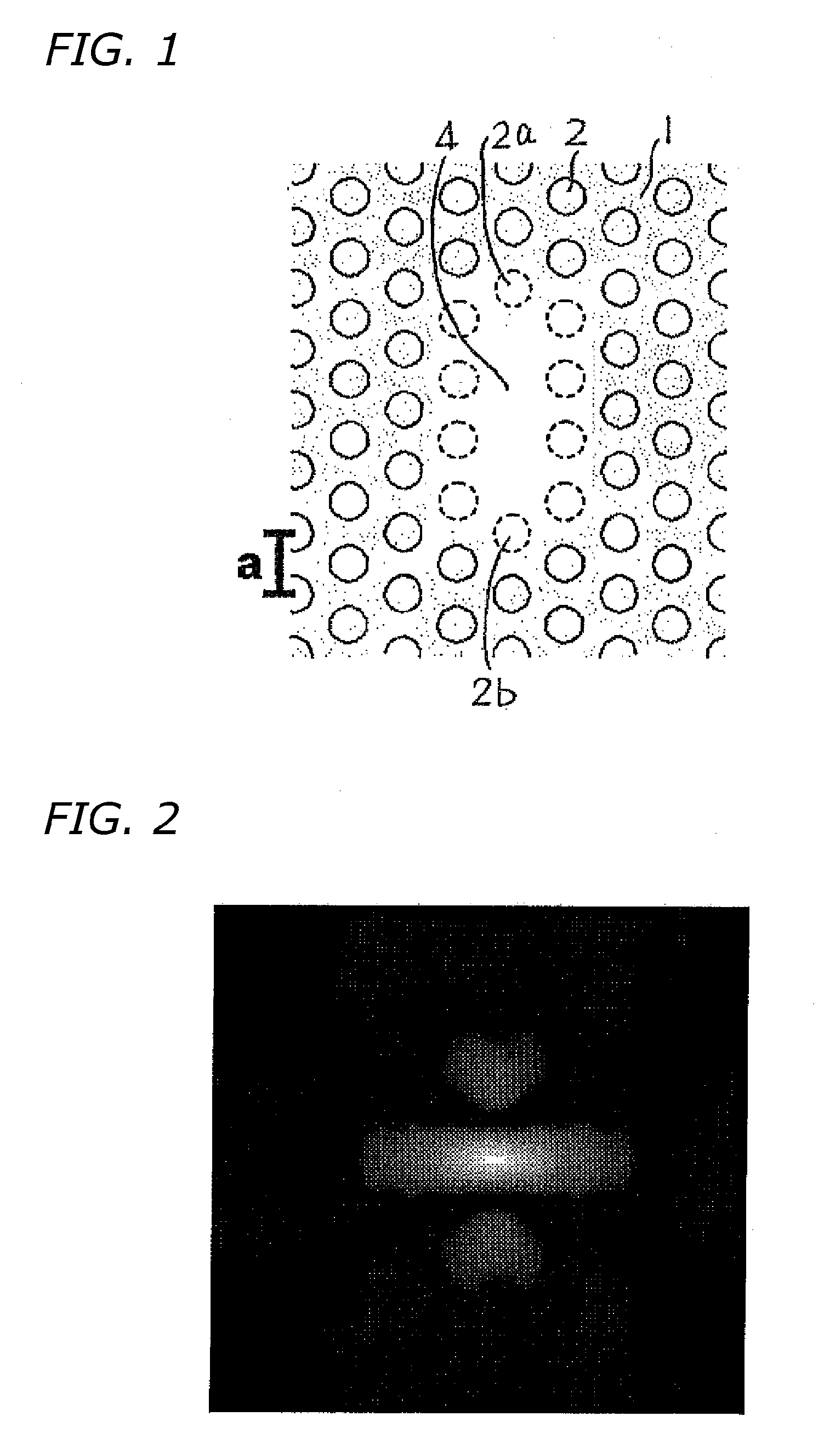
In 2D photonic crystals, cavities having a heightened Q factor are made available, wherein combining the high Q cavities with waveguides affords channel add / drop filters having high resolution. In a cavity constituted by a point defect within a 2D photonic crystal, the 2D photonic crystal is configured by an arrangement, in a two-dimensional lattice of points defined in a slab (1), of low-refractive-index substances (2) having a low refractive index relative to the slab (1) and being of identical dimension and shape. The point defect (4) contains a plurality of three or more lattice points that neighbor one another, and in these lattice points no low-refractive-index substances (2) are arranged; therein the dimension of the low-refractive-index substance (2) that should be arranged to correspond to at least one of the lattice points nearest the point defect (4) is dimensionally altered from a predetermined dimension.
Owner:PRESIDENT +1
Tuning fork magnetometer
Apparatus comprises a tuning fork having first and second tines, a first magnet disposed on the first tine, and a second magnet disposed on the second tine. In one embodiment the magnets comprise permanent magnets; in another they comprise electromagnets. In a preferred embodiment the magnets have magnetic moments oriented essentially parallel to the axis of the tines and anti-parallel to one another. In operation, the apparatus is made to oscillate at or near its resonant frequency, and in the presence of a magnetic field a parameter of the oscillation (e.g., its frequency, phase or amplitude) is altered in a fashion that allows the magnitude or direction of the magnetic field to be determined. In a preferred embodiment, the tuning fork is disposed within a vacuum enclosure, which increases the Q of the apparatus.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Power generating element
ActiveUS11329576B2Overall resonance can be greatly increasedIncrease power generationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesResonanceEngineering
A power generating element is provided that includes first and second plate-like structures, a pedestal that supports the first plate-like structure, and first and second piezoelectric elements that generate charges on the basis of the deflections of the two plate-like structures. A base end portion of the first plate-like structure is connected to the pedestal, and a direction from the base end portion toward the tip end portion of the first plate-like structure is a Y-axis positive direction. A base end portion of the second plate-like structure is connected to the tip end portion of the first plate-like structure via a connection body, and a direction from the base end portion toward the tip end portion of the second plate-like structure is a Y-axis negative direction. A frequency band of a half-value width of a resonance system formed on the basis of the flexibility of the second plate-like structure at least partially overlaps a frequency band of a half-value width of a resonance system formed on the basis of the flexibility of the first plate-like structure.
Owner:TRI FORCE MANAGEMENT CORP
Slotted dielectric resonators and circuits with slotted dielectric resonators
InactiveUS20050237135A1Improving QIncreasing center frequency of resonatorResonatorsDielectric resonatorEngineering
In accordance with the principles of the present invention, a resonator puck is provided with one or more vertical and / or horizontal, radial slits that improve the quality factor, Q, of circuits constructed from the resonators. Preferably, the slits are very narrow and, more preferably, about 100 to 1000 atoms wide. In some preferred embodiments of the invention, the surfaces of the resonators that define the slit are left relatively rough and may even contact each other such that the slit is not of uniform thickness, but essentially comprises a plurality of pockets between the two portions of the resonator.
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
Method and mechanism for tuning dielectric resonator circuits
InactiveUS20050200437A1Improving QReduced insertion lossResonatorsBridge strengtheningHemt circuitsEngineering
The invention comprises a technique and associated mechanisms by which dielectric resonator circuits, such as filters, can be tuned in both frequency, bandwidth or both without the need for irises, tuning screws and / or tuning plates. In accordance with the invention, the positions of the dielectric resonators are adjustable relative to each other within the cavity in multiple ways, including vertically and horizontally. The dielectric resonators also may tilt relative to each other. Furthermore, an off-center longitudinal hole can be machined in one or more of the dielectric resonators so as to make the electromagnetic field of the resonator non-uniform so that the dielectric resonator can be rotated about its longitudinal axis to alter the coupling between dielectric resonators. In accordance with another aspect of the invention, frequency tuning can be accomplished by using two separate dielectric resonators adjacent each other, one on top of the other, and adjusting the vertical spacing therebetween to achieve the desired center frequency within that dielectric resonator pair.
Owner:MA COM
Opto-electronic oscillator and method
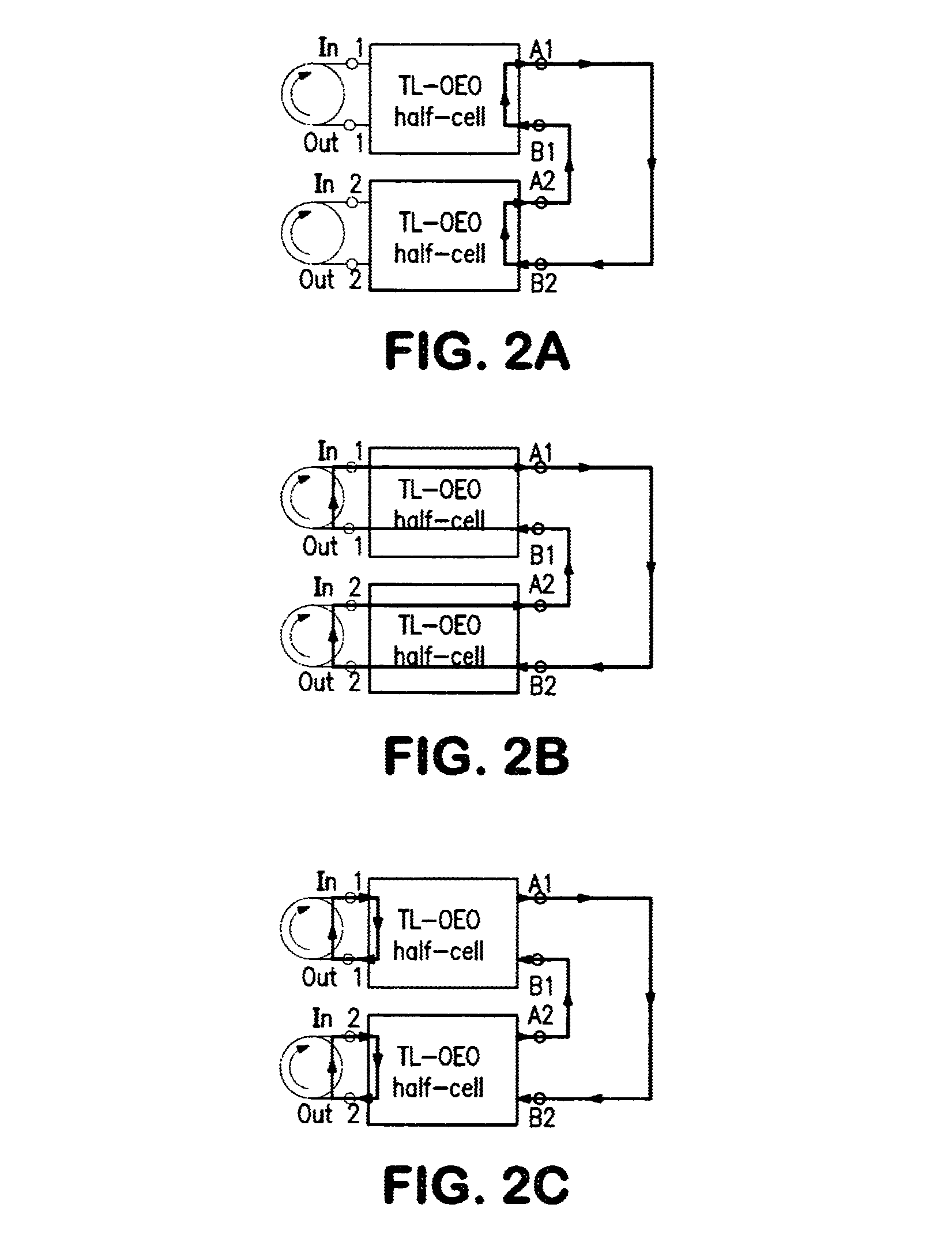
ActiveUS8842706B2Improve immunityEasily be cascadedLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionPhase shiftedPhotovoltaic detectors
An opto-electronic oscillator circuit, including: an opto-electronic circuit loop including an optical modulator that receives a first electrical signal and produces an optical output signal coupled with an optical resonator, a photodetector circuit optically coupled with the optical resonator, and a phase shifter coupled with the photodetector circuit for producing a phase shifted output signal that is fed back as the first electrical signal; an optical loop comprising the optical coupling of the optical resonator with the photodetector; and an electrical feedback circuit loop for coupling the first electrical signal with the photodetector circuit.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Nonreciprocal circuit device
ActiveUS7679470B2Reduced insertion lossIncrease valueWaveguide type devicesEngineeringDirect current
A nonreciprocal circuit device includes a permanent magnet, a ferrite to which the permanent magnet applies a direct-current magnetic field, first and second central electrodes arranged on the ferrite, and a circuit board. The first central electrode includes electrode layers provided on main surfaces of the ferrite connected by an electrode provided on a top surface of the ferrite. A second central electrode includes electrode layers provided on the main surfaces of the ferrite connected by electrodes arranged on top and bottom surfaces of the ferrite. The second electrode is wound at least about three turns around the ferrite. A width dimension of the outermost electrode layers of the second central electrode is greater than a width dimension of the inner electrode layers of the second central electrode.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Electronic component
ActiveUS8018305B2Improving QMultiple-port networksResonatorsElectrical conductorElectronic component
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Acoustic wave device
PendingUS20220014167A1Impedance ratio can be increasedImproving QImpedence networksEngineeringAcoustic wave
An acoustic wave device includes a support substrate, a piezoelectric body including LiTaO3, a first electrode on a first main surface of the piezoelectric body, a second electrode on a second main surface, an acoustic-layer laminated body between a support substrate and the piezoelectric body. The azimuth angle of the piezoelectric body is (about 85° to 95°, about 85° to 95°, about 5° to 65°) represented in Euler angles.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com