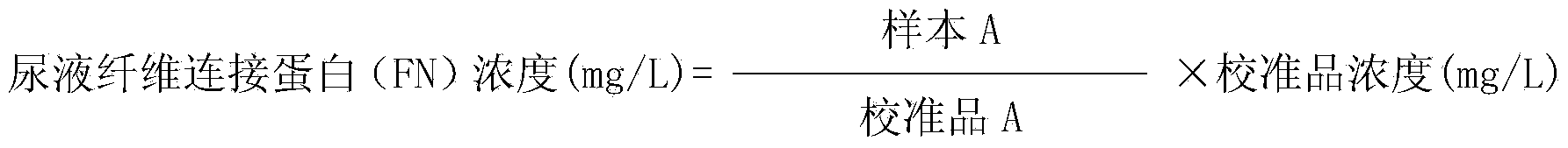Patents
Literature
55 results about "Automated analyser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An automated analyser is a medical laboratory instrument designed to measure different chemicals and other characteristics in a number of biological samples quickly, with minimal human assistance. These measured properties of blood and other fluids may be useful in the diagnosis of disease.
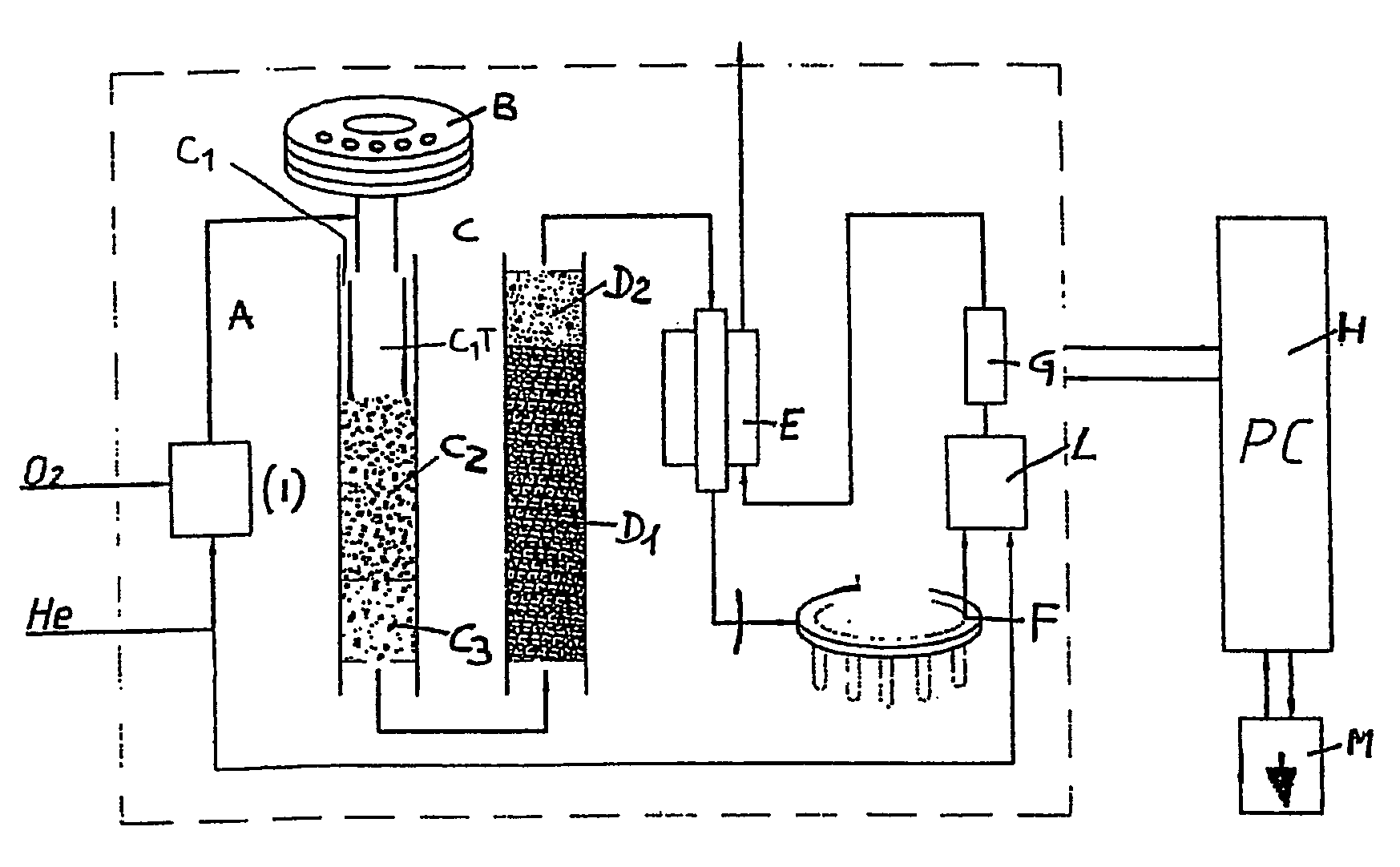
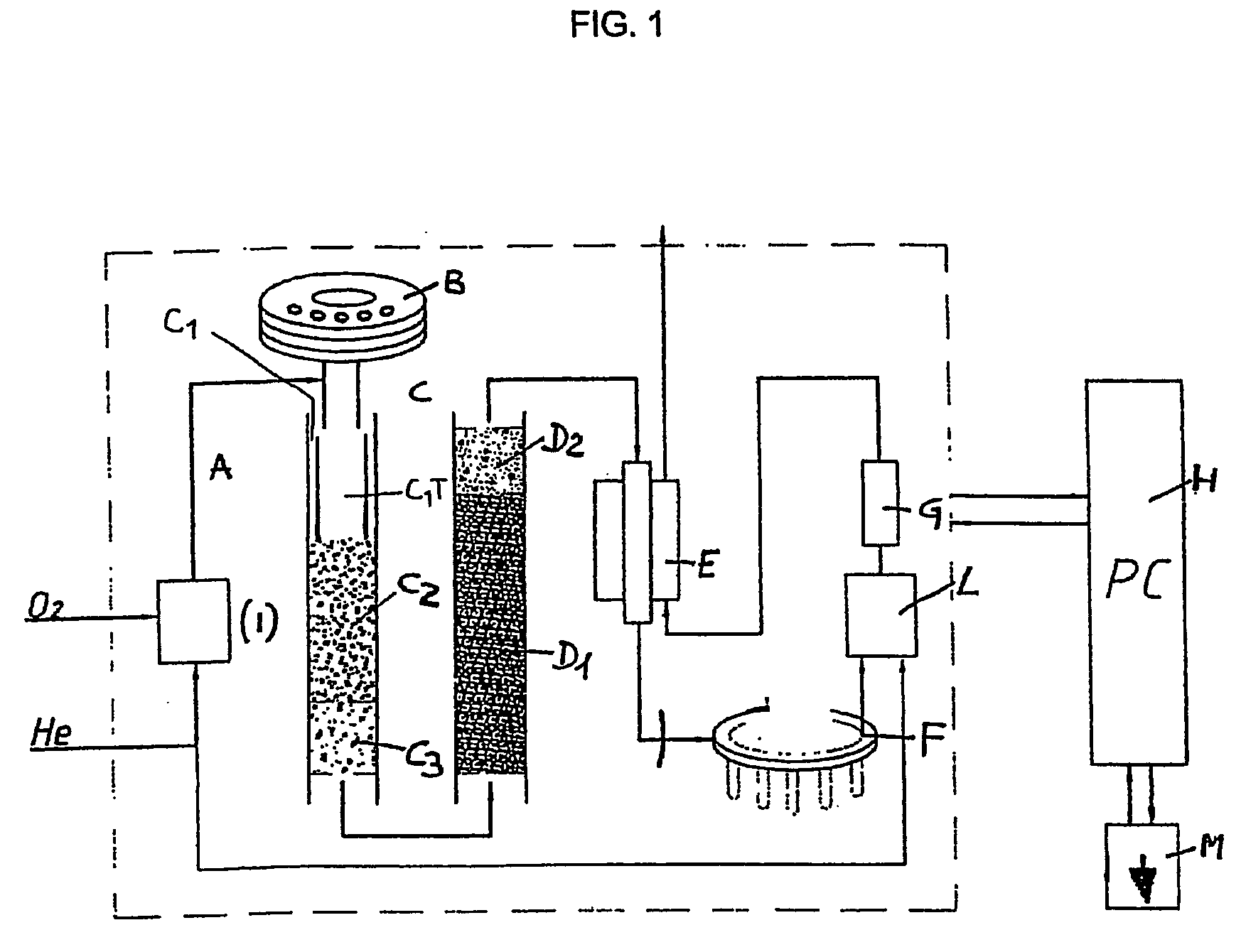
Automated process for isolating and amplifying a target nucleic acid sequence
InactiveUS20050130198A1Efficient and high through-put operationEfficient comprehensive utilizationRotating receptacle mixersBioreactor/fermenter combinationsIsolation proceduresTemperature control
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
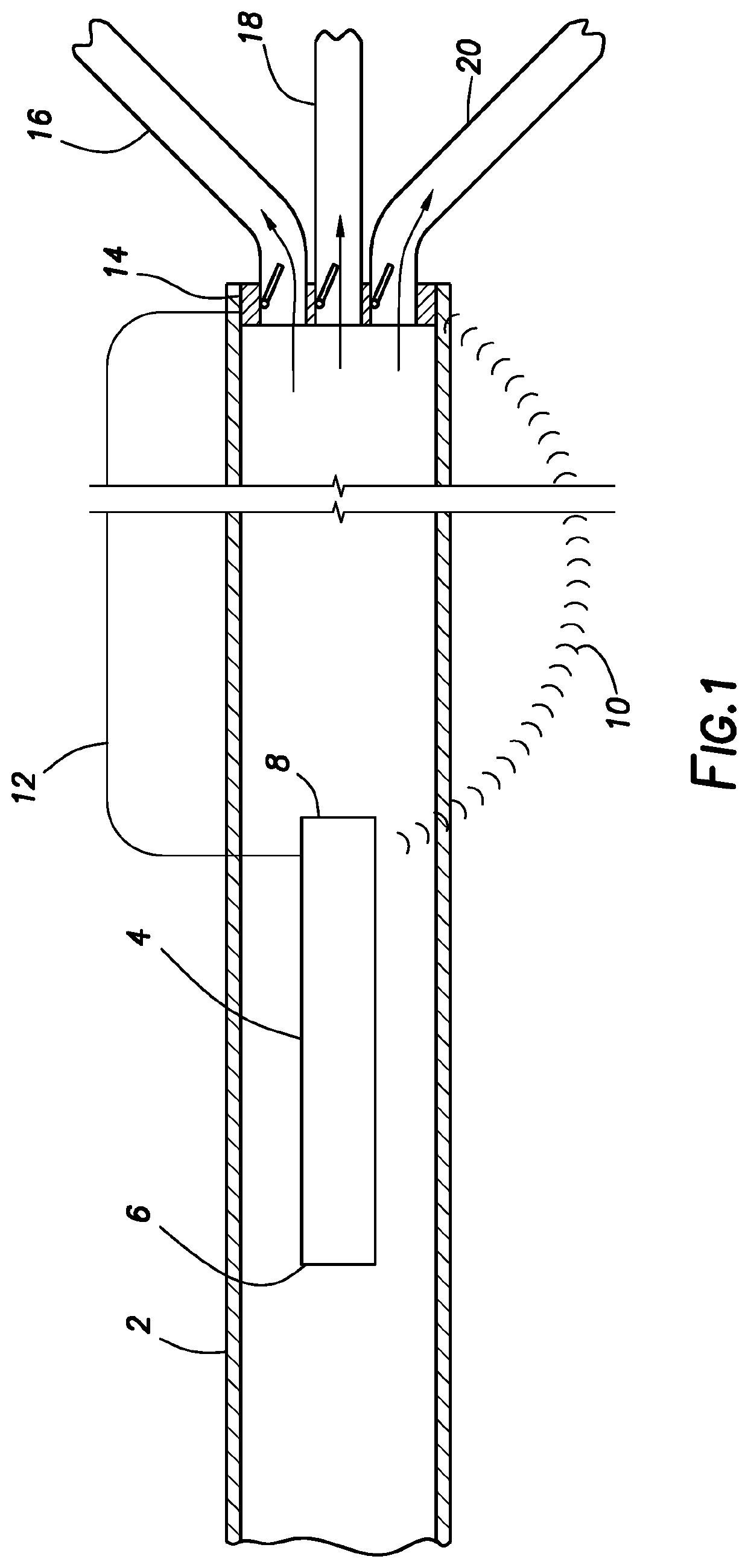
Containers for reducing or eliminating foaming
InactiveUS20060286004A1Reducing and eliminating aspirationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionEngineeringAutomated analyzer
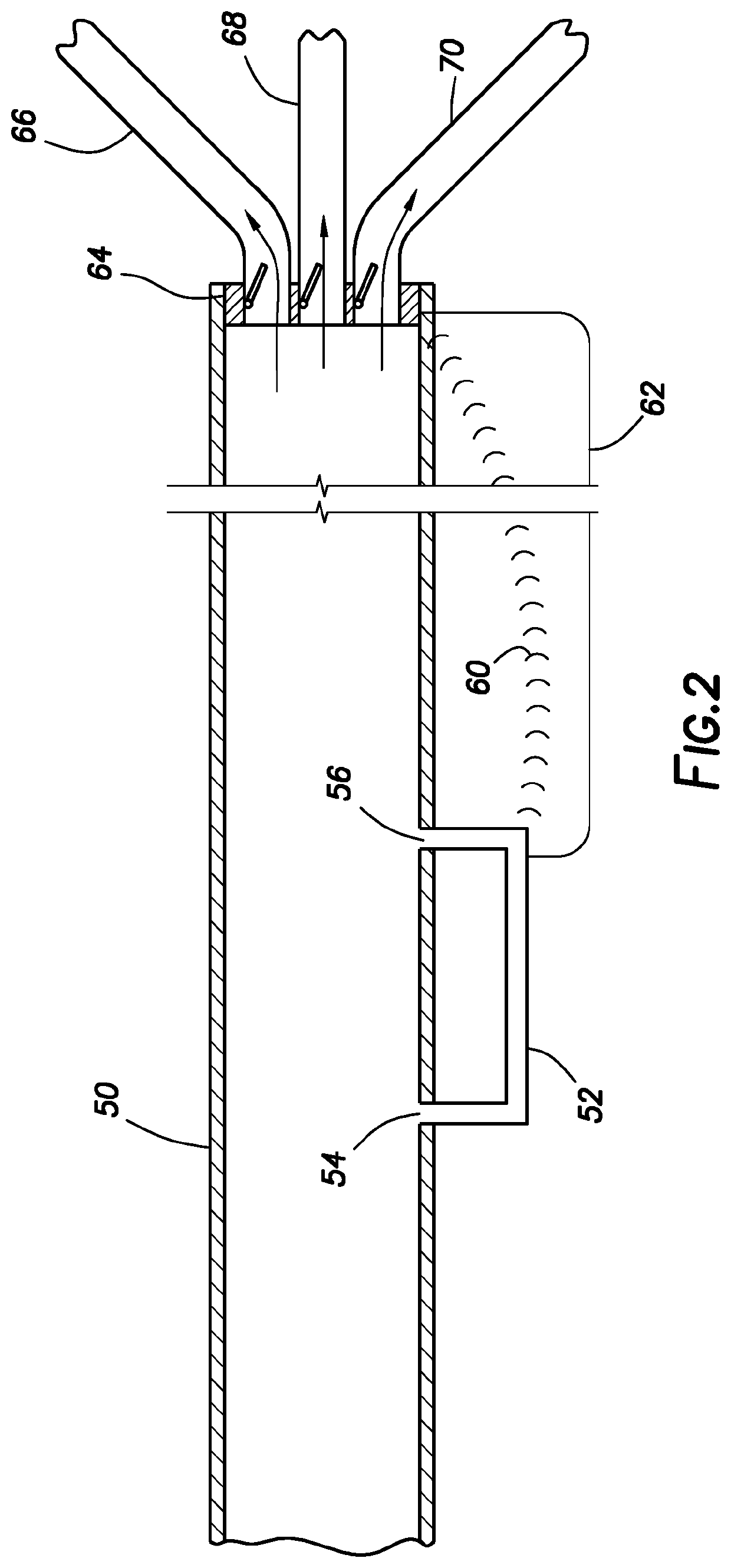
A foam reducing or eliminating container for containing a liquid includes: a container body having a top portion, a bottom portion and an opening for adding a liquid to or removing a liquid from the container body; and a hollow baffle located within the container with first and second openings therein. The first and second openings are covered with a pierceable seal, wherein the first opening of the baffle is at least partially aligned with the opening of the container. In a preferred embodiment, the container is a reagent supply container for an automated analyzer, which includes: a container as described above; and a closure which is movable away from the opening of the container to be in an open position and movable into contact with the opening to be in a closed position. In another preferred embodiment a reagent supply for an automated analyzer includes: the reagent supply container as described above; and a liquid reagent therein. The second opening of the baffle is submerged in liquid. A method for reducing or eliminating the aspiration of foam into a metering probe includes: providing a reagent supply as described above; providing a metering probe movable in a direction toward and away from the reagent supply; moving the closure away from the opening of the container; piercing both seals covering the first and second openings of the baffle allowing liquid to enter the baffle from the end of the baffle submerged in the liquid, wherein the seals may or may not be pierced with the metering probe; moving the metering probe into the first opening of the baffle and into contact with the liquid in the baffle; aspirating a selected amount of liquid in the baffle; and moving the metering probe out of the baffle.
Owner:ORTHO-CLINICAL DIAGNOSTICS
System and Method for Incubating the Contents of A Reaction Receptacle
InactiveUS20080089818A1Efficient and high through-put operationEfficient comprehensive utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusIsolation proceduresTemperature control
An automated analyzer for performing multiple diagnostic assays simultaneously includes multiple stations, or modules, in which discrete aspects of the assay are performed on fluid samples contained in reaction receptacles. The analyzer includes stations for automatically preparing a specimen sample, incubating the sample at prescribed temperatures for prescribed periods, performing an analyte isolation procedure, and ascertaining the presence of a target analyte. An automated receptacle transporting system moves the reaction receptacles from one station to the next. The analyzer further includes devices for carrying a plurality of specimen tubes and disposable pipette tips in a machine-accessible manner, a device for agitating containers of target capture reagents comprising suspensions of solid support material and for presenting the containers for machine access thereto, and a device for holding containers of reagents in a temperature controlled environment and presenting the containers for machine access thereto. A method for performing an automated diagnostic assay includes an automated process for isolating and amplifying a target analyte. The process is performed by automatically moving each of a plurality of reaction receptacles containing a solid support material and a fluid sample between stations for incubating the contents of the reaction receptacle and for separating the target analyte bound to the solid support from the fluid sample. An amplification reagent is added to the separated analyte after the analyte separation step and before a final incubation step.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
On-line macrocontaminant analyser and method
InactiveUS20130120556A1Water treatment parameter controlInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsImaging analysisOptical measurements
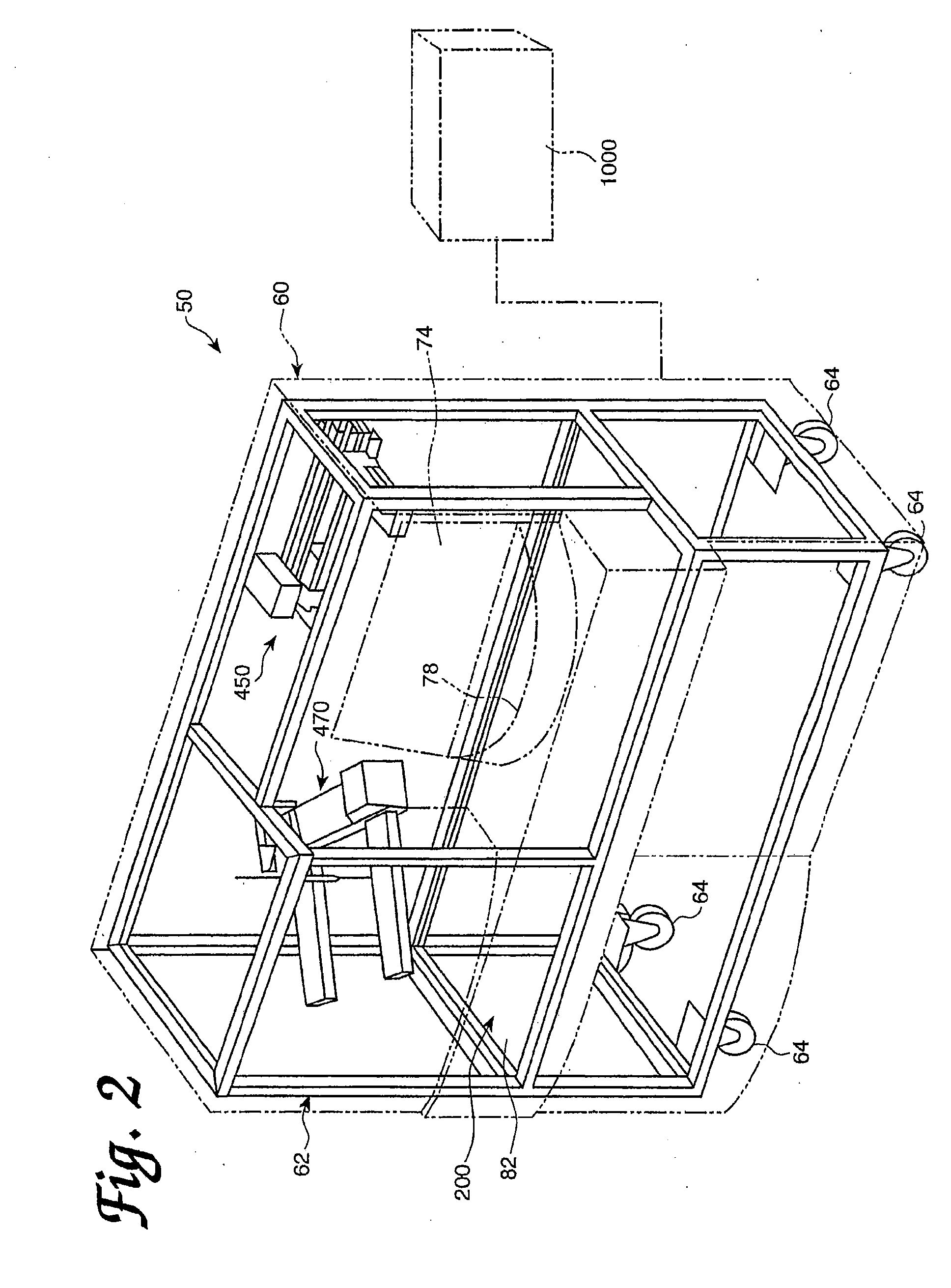
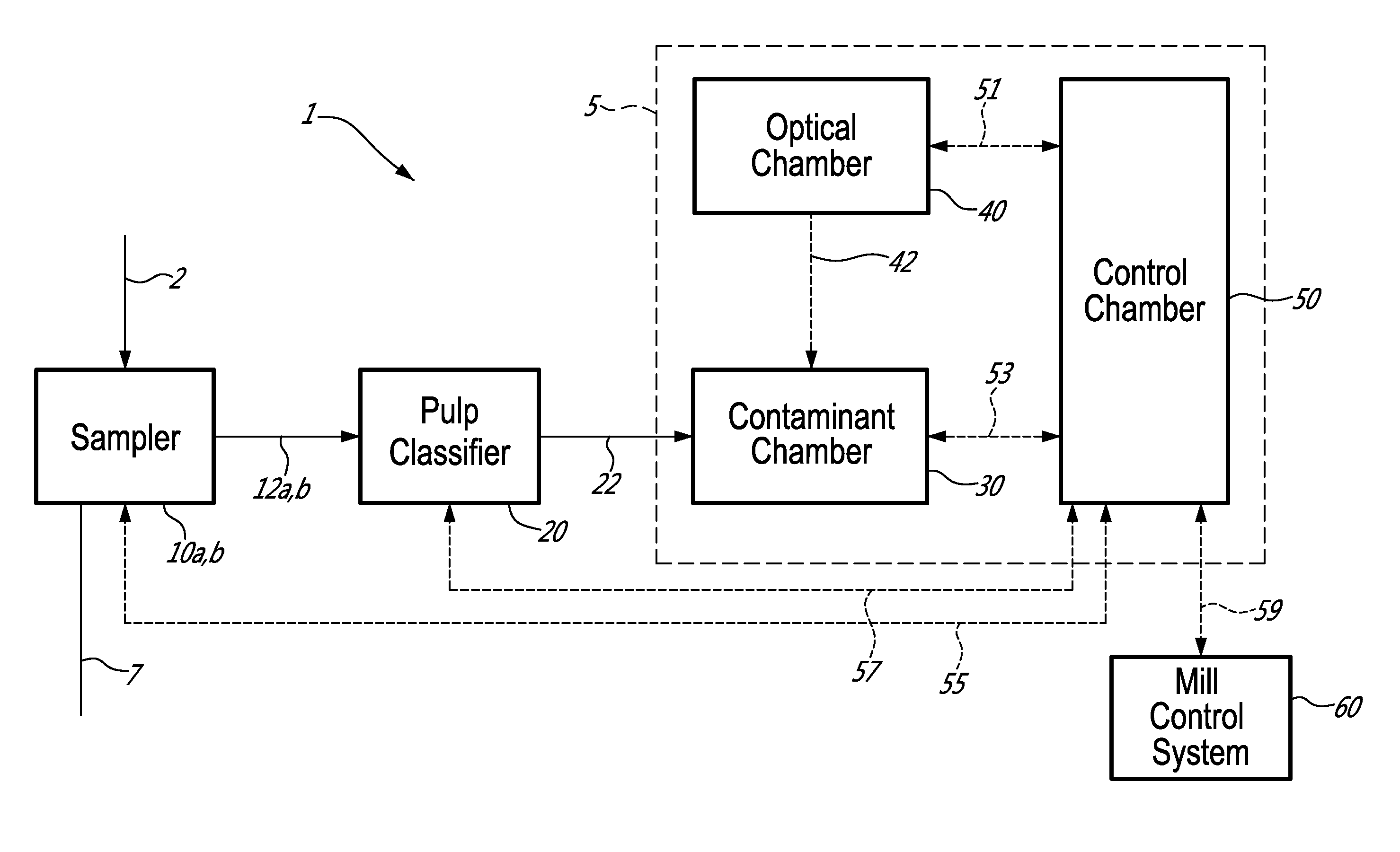
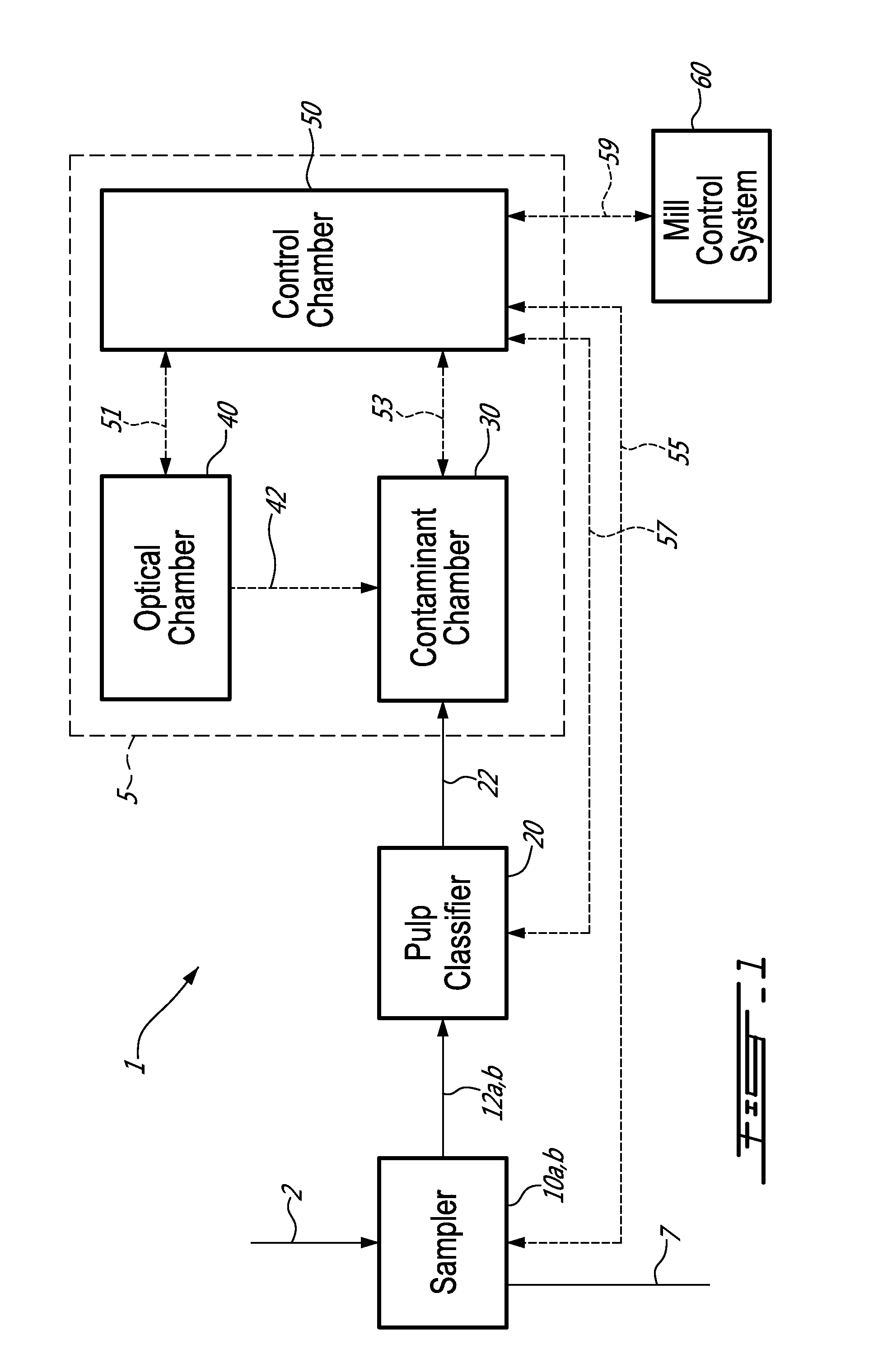
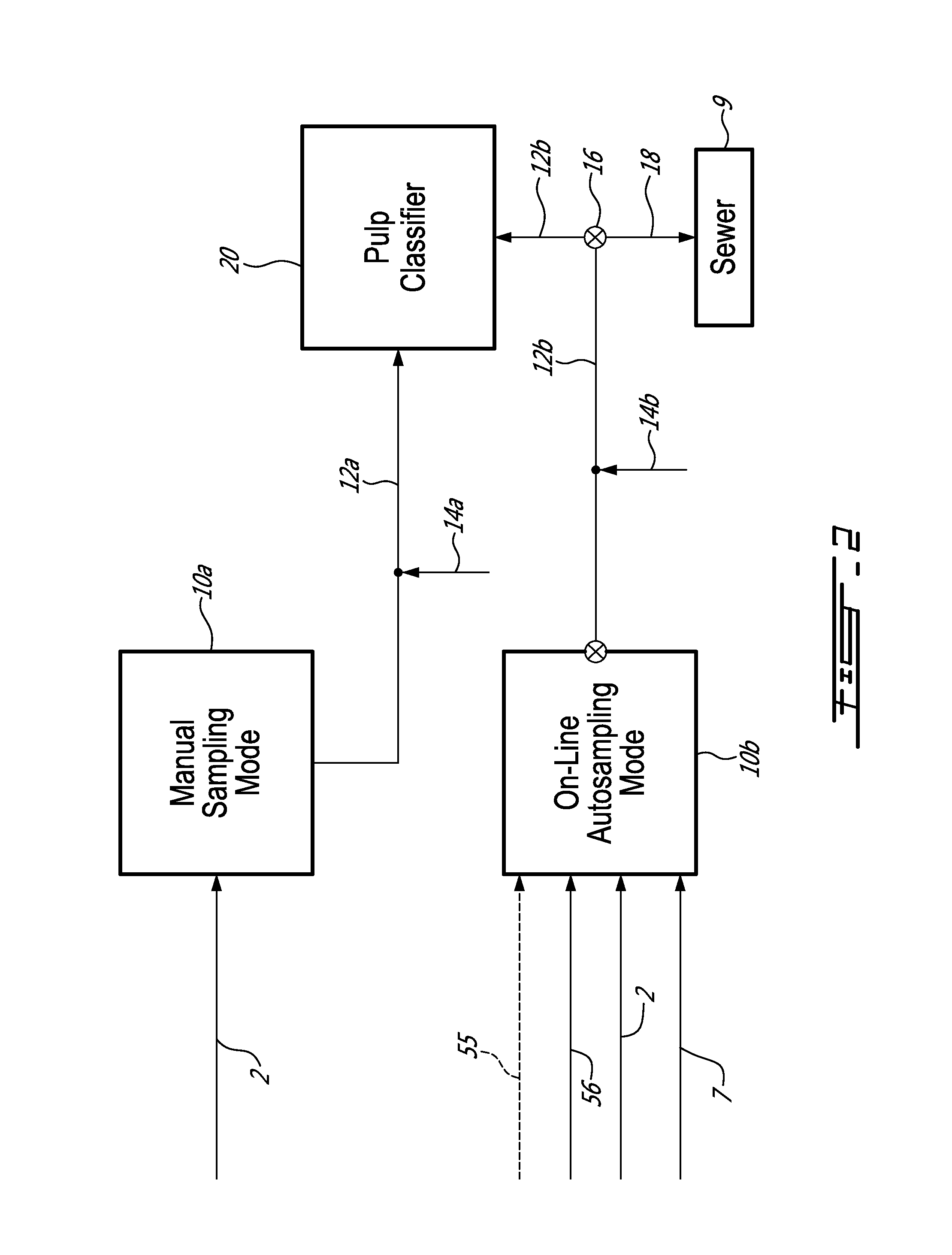
An on-line automated analyser of macrocontaminants is described. The analyser is for a pulp and / or a white water stream, the analyser comprises: a pulp classifier separating a sample from the stream into a fraction of macrocontaminants; a contaminant chamber enclosing a contaminant cell receiving the fraction; an optical chamber comprising an optical detector connected to the cell capturing at least one detected image; and a control chamber taking the at least one detected image and conducting an image analysis to determine type and quantity of at least one macrocontaminant in the fraction. The method of analysis of macrocontaminants is also described herein, the method comprises: separating a sample from the stream into a fraction of macrocontaminants; producing at least one detected image by optical measurement of the fraction; and analysing the at least one detected image and determining the quantity and type of at least one macrocontaminant in the fraction.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
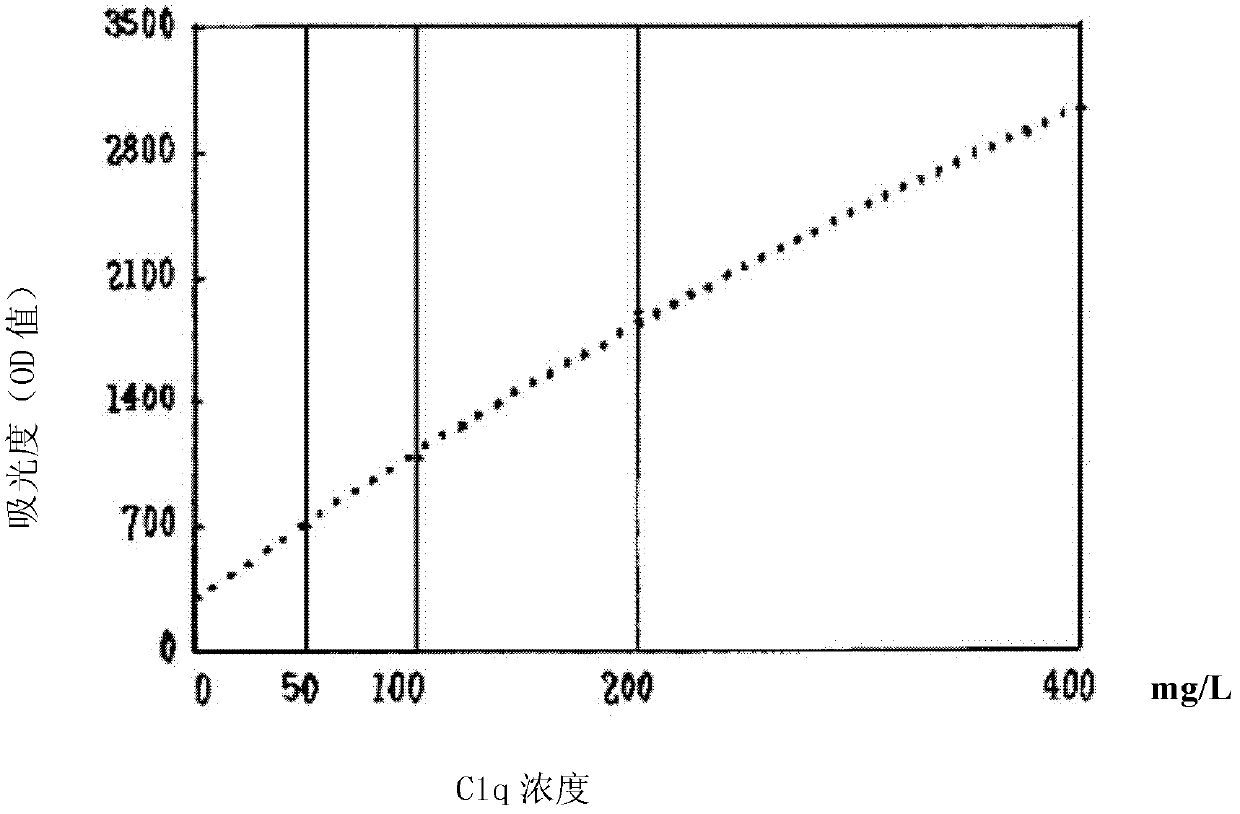
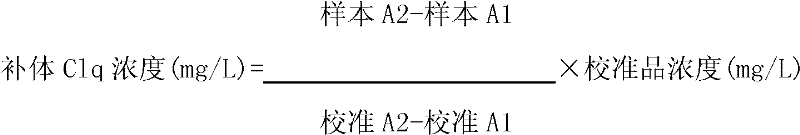
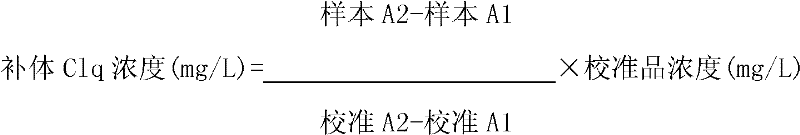
Kit and method for detecting concentration of complement Clq in human serum
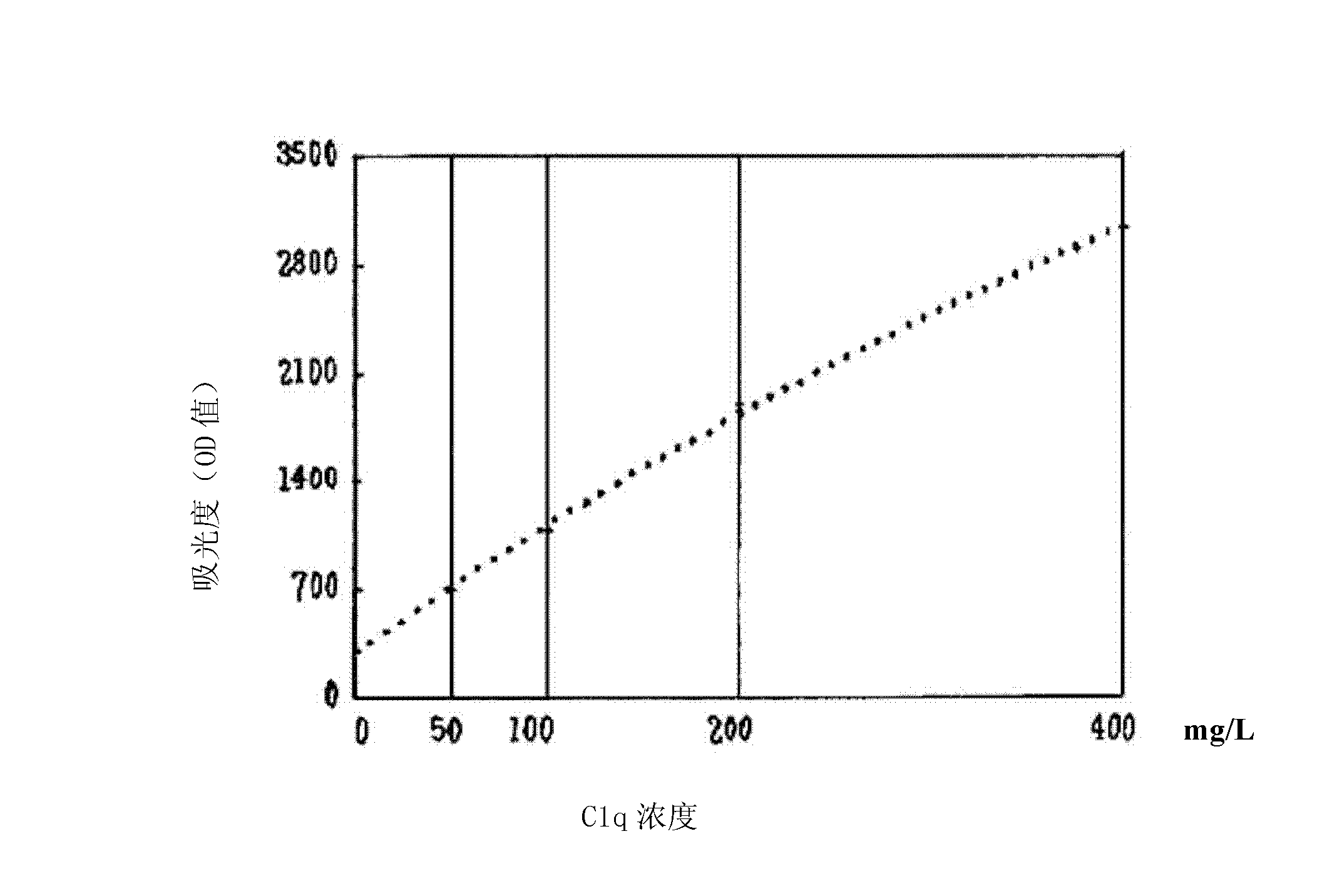
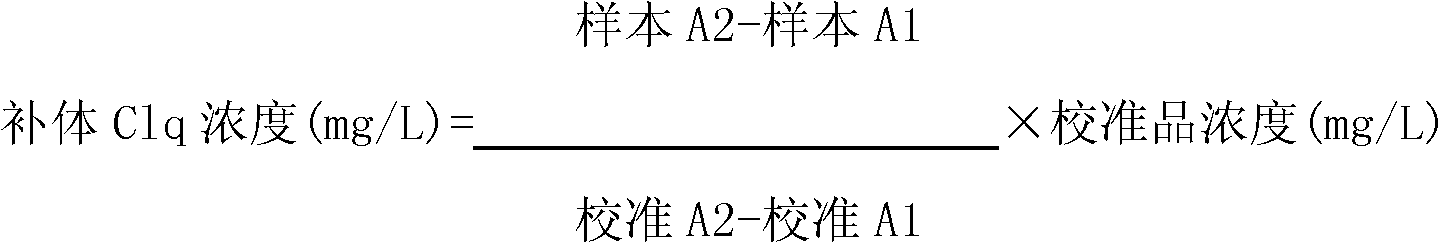
ActiveCN102323427ASignificant technological progressEasy to measureMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingSorbentTurbidimetry
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering, and provides a kit for detecting the concentration of a complement Clq in human serum by an immune transmission turbidimetry and an immune scattering turbidimetry. The kit solves the technical problems that an immune diffusion method and an enzyme-linked immune sorbent assay (ELISA) double antibody sandwich technology for measuring theconcentration of the complement Clq have complicated steps and are low in accuracy and repeatability in the prior art. The kit comprises two reagents, wherein a first reagent consists of disodium hydrogen phosphate, monopotassium phosphate, polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG6000), ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA)-NA2 and TX-100; and a second reagent consists of the disodium hydrogen phosphate,the monopotassium phosphate, the PEG 6000, the EDTA-NA2, the TX-100 and rabbit antihuman complement Clq antiserum. The invention also provides a method for detecting the concentration of the complement Clq in the human serum by using the kit. The kit and the method for measuring the concentration of the complement Clq have simple and convenient steps, are high in accuracy and repeatability and are used for automated analysis meters.
Owner:上海北加生化试剂有限公司
Mixer and circulating type photometric testing automatic analyzer
ActiveCN103785314AHigh degree of automationWithout human interventionFlow mixersColor/spectral properties measurementsInstrumentationAutomated analyser
A mixer and a circulating type photometric testing automatic analyzer are used for testing specific components of solutions or studying on chemical reaction dynamics. The mixer comprises a liquid inlet tube, a mixer body, an upper liquid outlet pipe communicated with the inner cavity of the mixer body and a lower liquid outlet pipe communicated with the inner cavity of the mixer body. One end of the liquid inlet pipe is vertically inserted into the inner cavity from bottom to top and is communicated with the inner cavity, the upper liquid outlet pipe is connected with the top portion of the mixer body, and the lower liquid outlet pipe is connected with the bottom of the mixer body. The automatic analyzer further comprises a mixer, an automatic injection valve, a reagent selector value, a three-way valve, a reagent pump, a water sample pump, a multi-channel switching valve, a reagent quantitative loop, a spectrophotometric detector and a control circuit. By the adoption of the automatic analyzer, the photometric testing is not interfered by air bubbles in a flow path, automation degree is high, the automatic sample feeding and the on-line mixing are added, no reagents need to be added repeatability, the utilization rate of reagents is improved efficiently, operation is flexible, the degree of reaction can be controlled by adjusting the mixing time, and the sensitivity can be adjusted to meet the measurement requirements of target objects with different concentrations.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
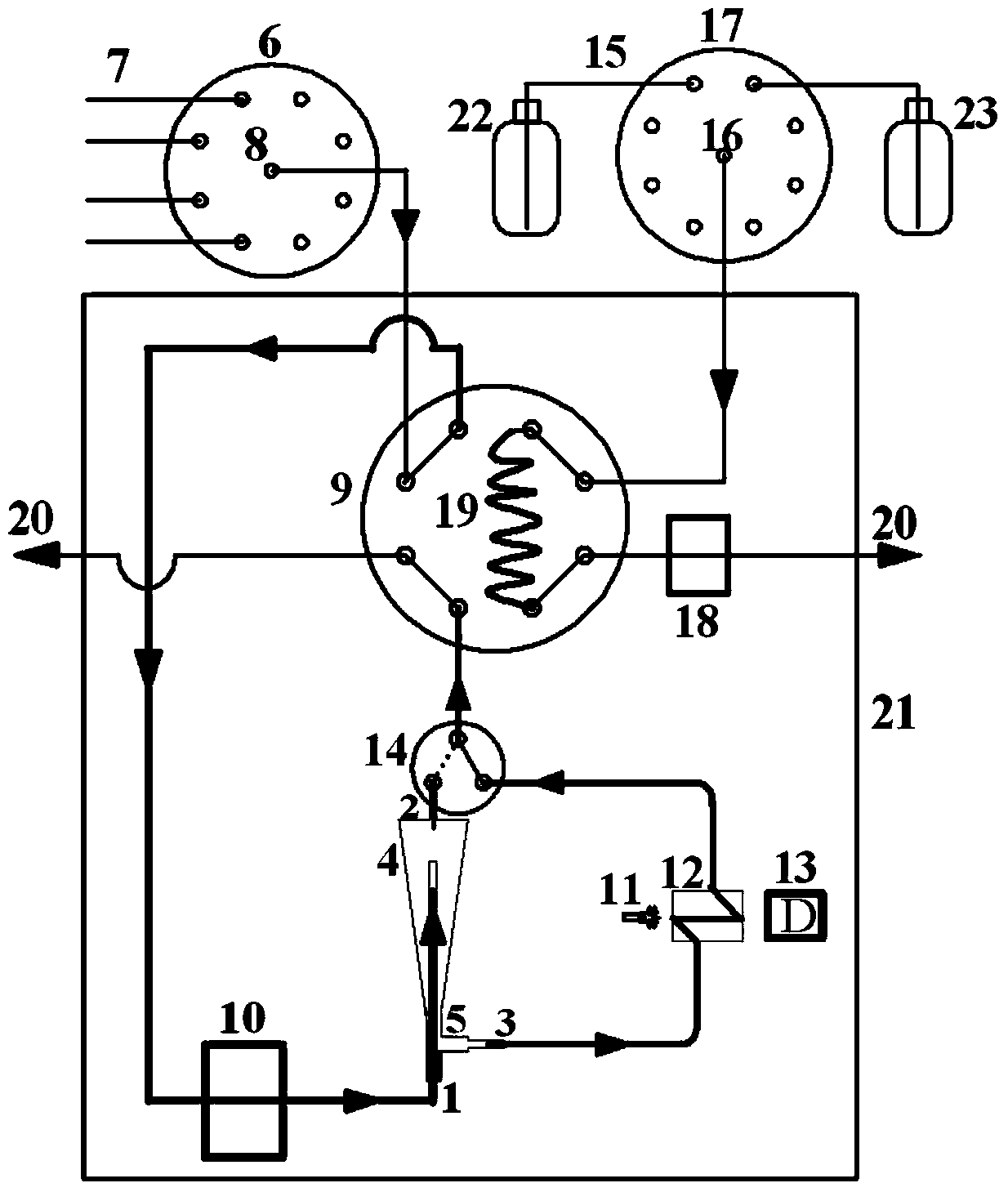
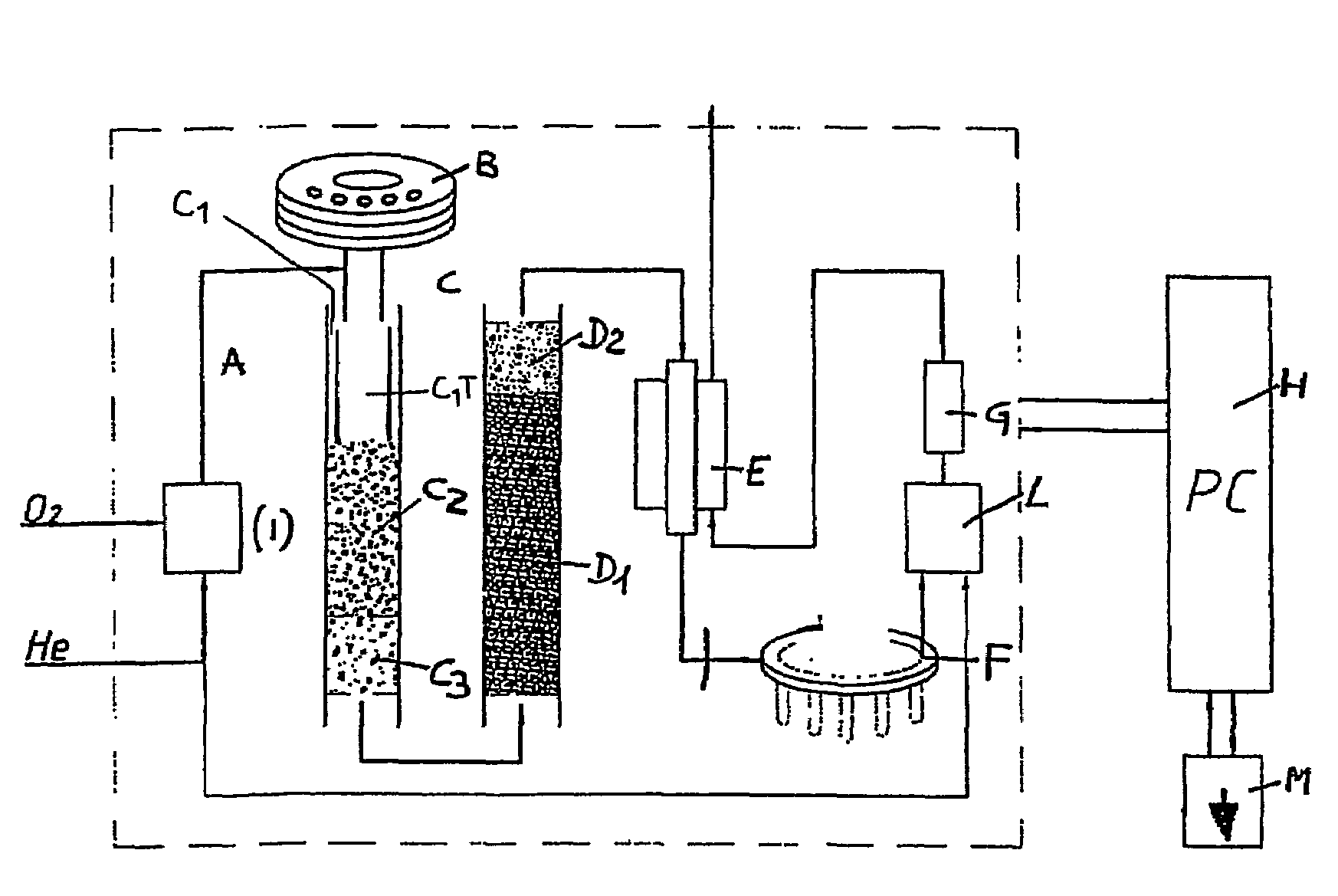
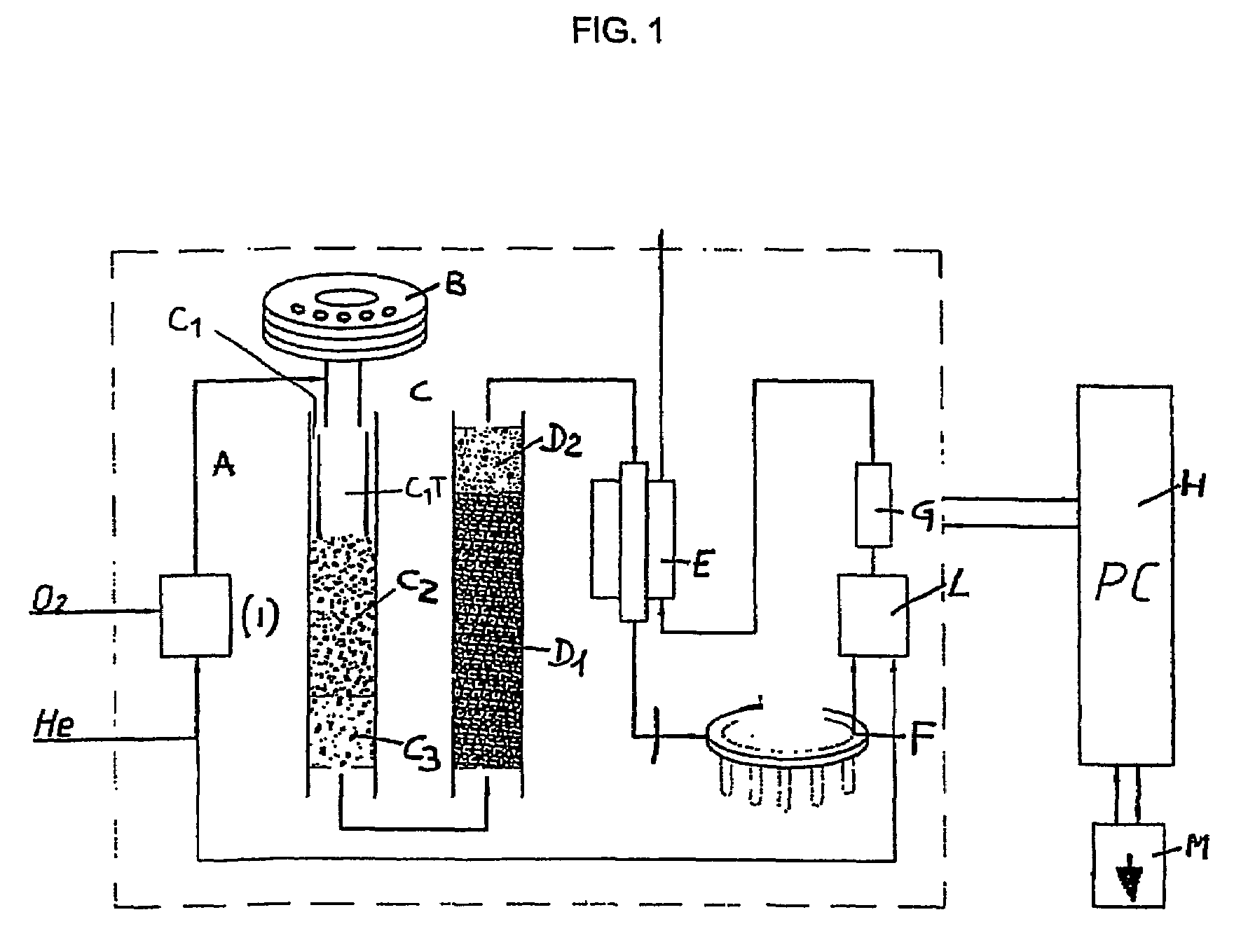
Automated analyser for determining nitrogen derived from organic compounds
ActiveUS20050266580A1Reduce usageEasy to disassembleChemical analysis using catalysisChemical analysis using combustionCo2 absorptionSorbent
An automated analyser is described for determining, by way of combustion, nitrogen contained in organic compounds, in particular proteins present in foods, animal feeds, polymers, fuels etc., characterised in that the carbon dioxide absorption device upstream of the nitrogen detector is self-regenerating and comprises: a distributor valve able to switch different gas circuits without contaminations and losses from one gas sample to another, a carousel consisting of a plurality of absorber elements inside which is placed an adsorbent material, a furnace suitable for said adsorbers, in such a manner that each of said adsorbers presents itself in turn for each analysis and that on completion of said analysis the same adsorber is conveyed to the furnace for degassing of the absorbent material and thus for its relative regeneration.
Owner:FOSS ANALYTICAL AS
Biochip and chip control method
PendingCN109174220AEasy dischargeImpact on test resultsLaboratory glasswaresBiochemical engineeringBiochip
The invention discloses a biochip and a chip control method. The biochip includes a chip substrate, and a quantitative sampling device, a plurality of reagent chambers and a reactor which are on arranged on the chip substrate; every reagent chamber is provided with a pipeline communicated with the reactor, and every pipeline is provided with a normally closed micro-valve; and the quantitative sampling device is provided with a sample outlet, and the sample outlet is communicated with the reactor. The biochip combines all the advantages of a large automatic analyzer and a biochip, strictly realizes the analysis precision of the traditional automatic analyzer, and even is better than the traditional automatic analyzer in some functions.
Owner:HUNAN LEGEND AI CHIP BIOTECH CO LTD
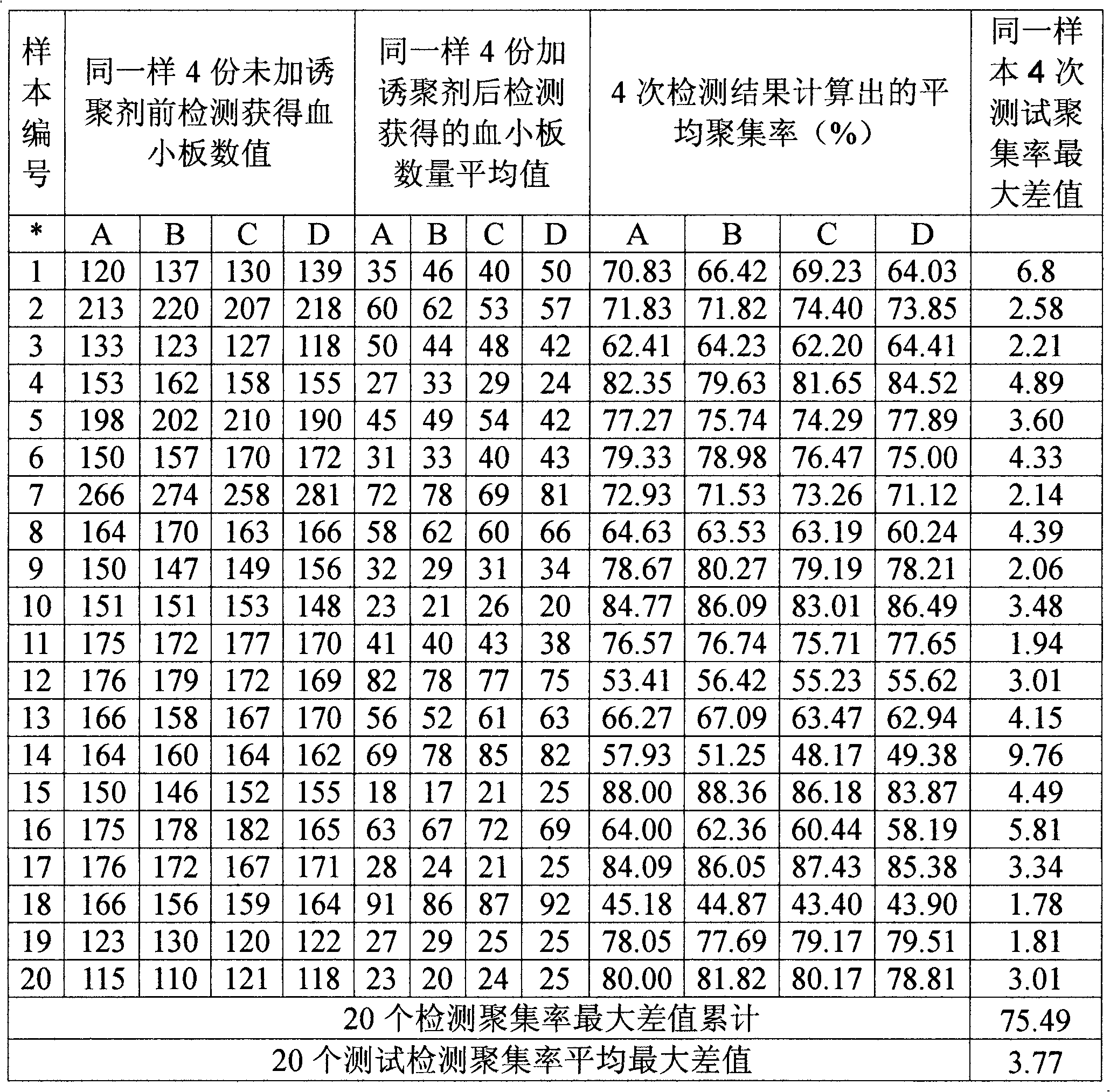
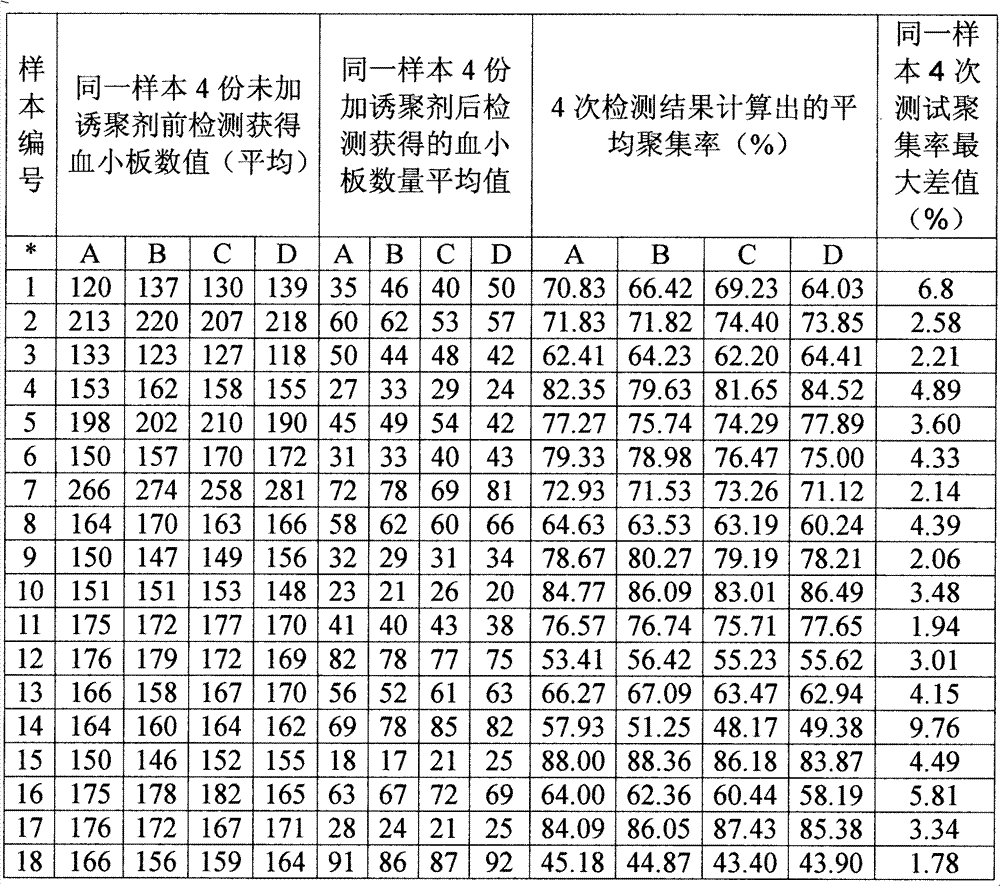
Optimized automation-adaptable platelet aggregation function inspection and analysis method
The invention provides an optimized automation-adaptable platelet aggregation function inspection and analysis method, and belongs to the field of clinical laboratory medicine. The method is an improvement and optimization of a platelet aggregation function inspection and analysis method using an automation counting method. The method is suitable for platelet aggregation function automatic analysis instruments using the counting method. According to the method, the number of platelets is inspected and recorded and an aggregation rate is calculated. A laboratory test result shows that the method is better in repeatability of the obtained result of platelet aggregation rate compared with a previous largest aggregation rate method.
Owner:SINNOWA MEDICAL SCI & TECH
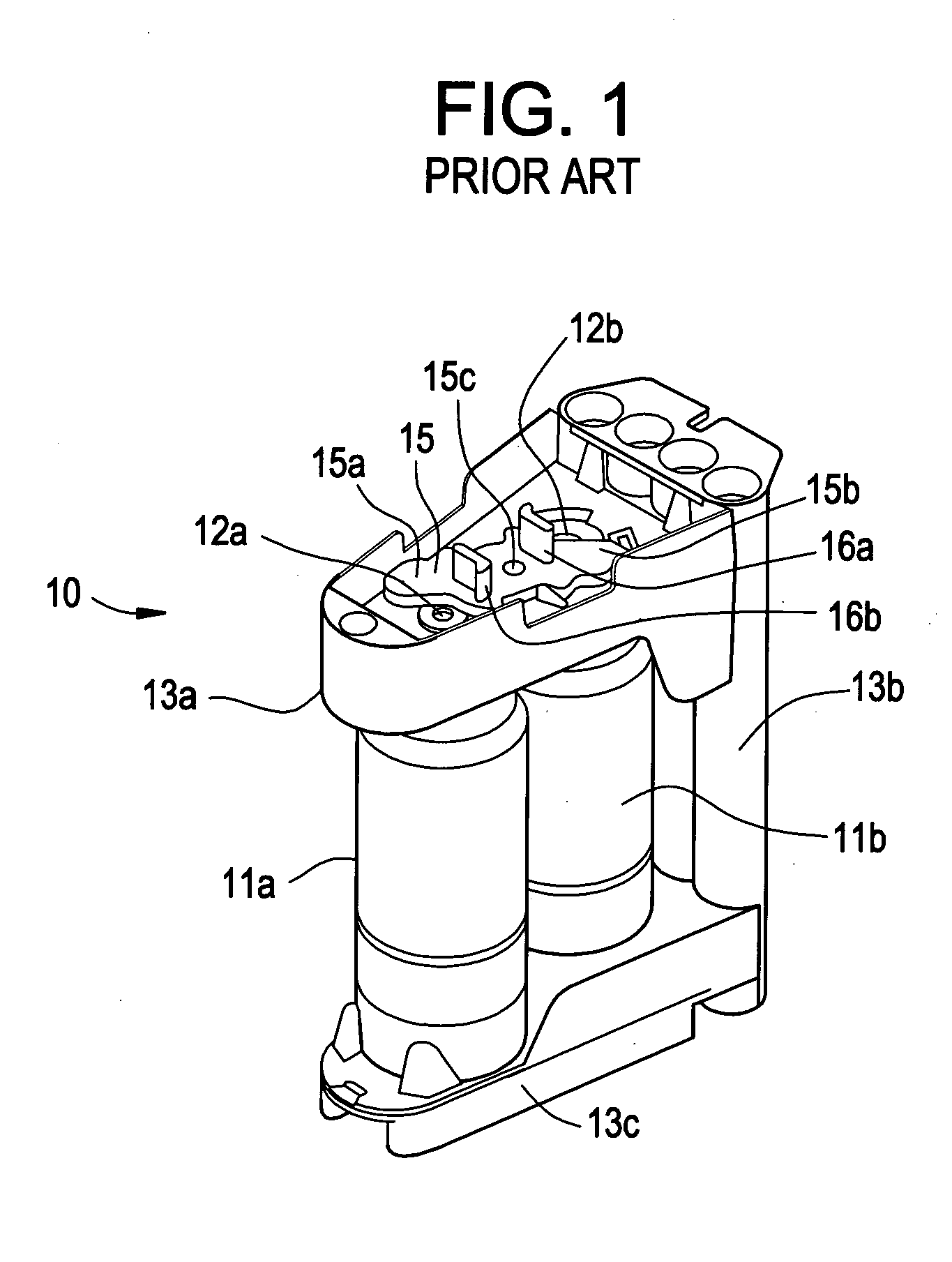
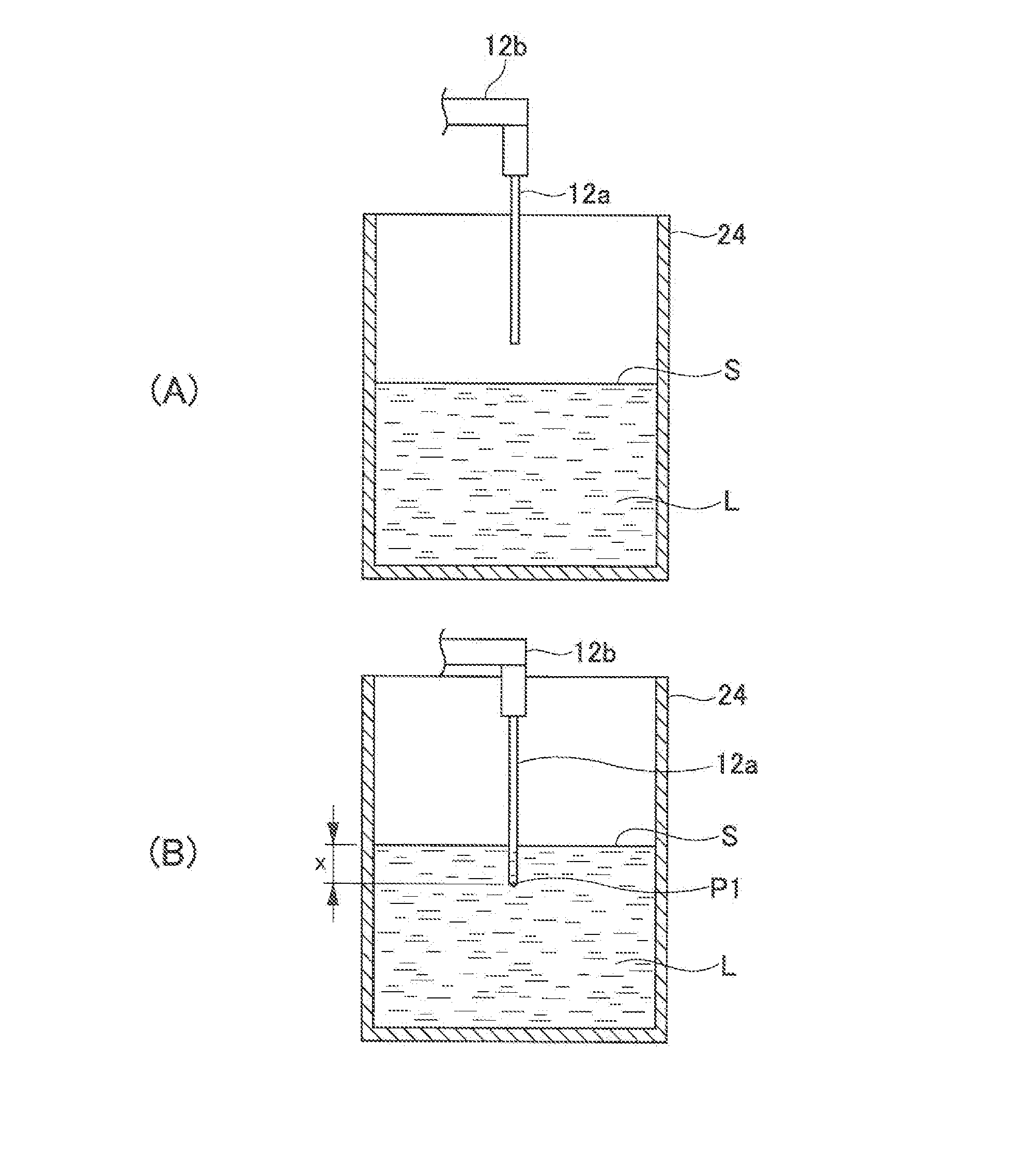
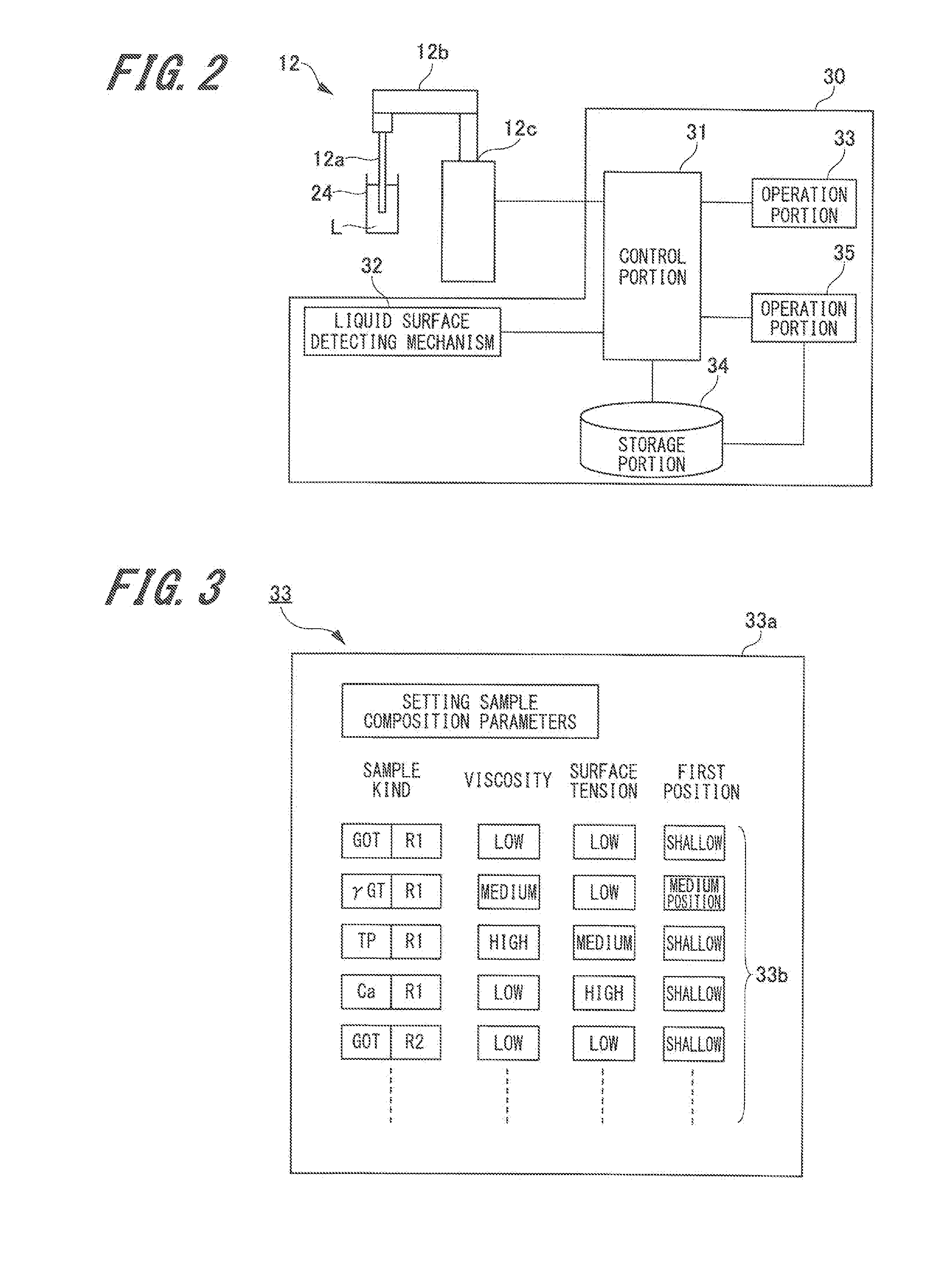
Automated Analyzer and Method for Lifting and Lowering Rod-Like Member in Automated Analyzer
ActiveUS20160187365A1Reduce adhesionImprove analytical accuracyTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersEngineeringAutomated analyzer
An automated analyzer includes a rod-like member 12a, a driving portion 12c, and a control mechanism 30. The driving portion 12c lifts and lowers the rod-like member 12a a direction of being inserted into and removed from the container 24. The control mechanism 30 controls the driving portion 12c so that the rod-like member 12a is lifted after being lowered so that a tip portion of the rod-like member 12a reaches a first position in the liquid L, and at a time when the rod-like member 12a reaches a second position where the tip portion is not separated from the liquid, an upward motion of the rod-like member 12a is stopped for a given period of time to reduce liquid film adhering to the rod-like member.
Owner:JEOL LTD
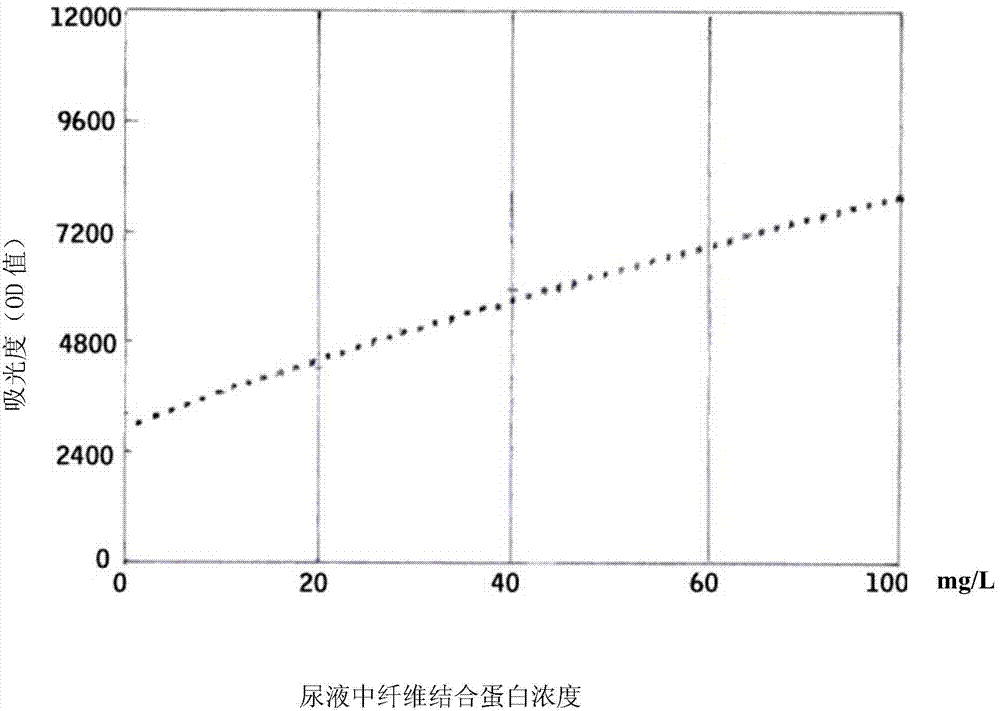
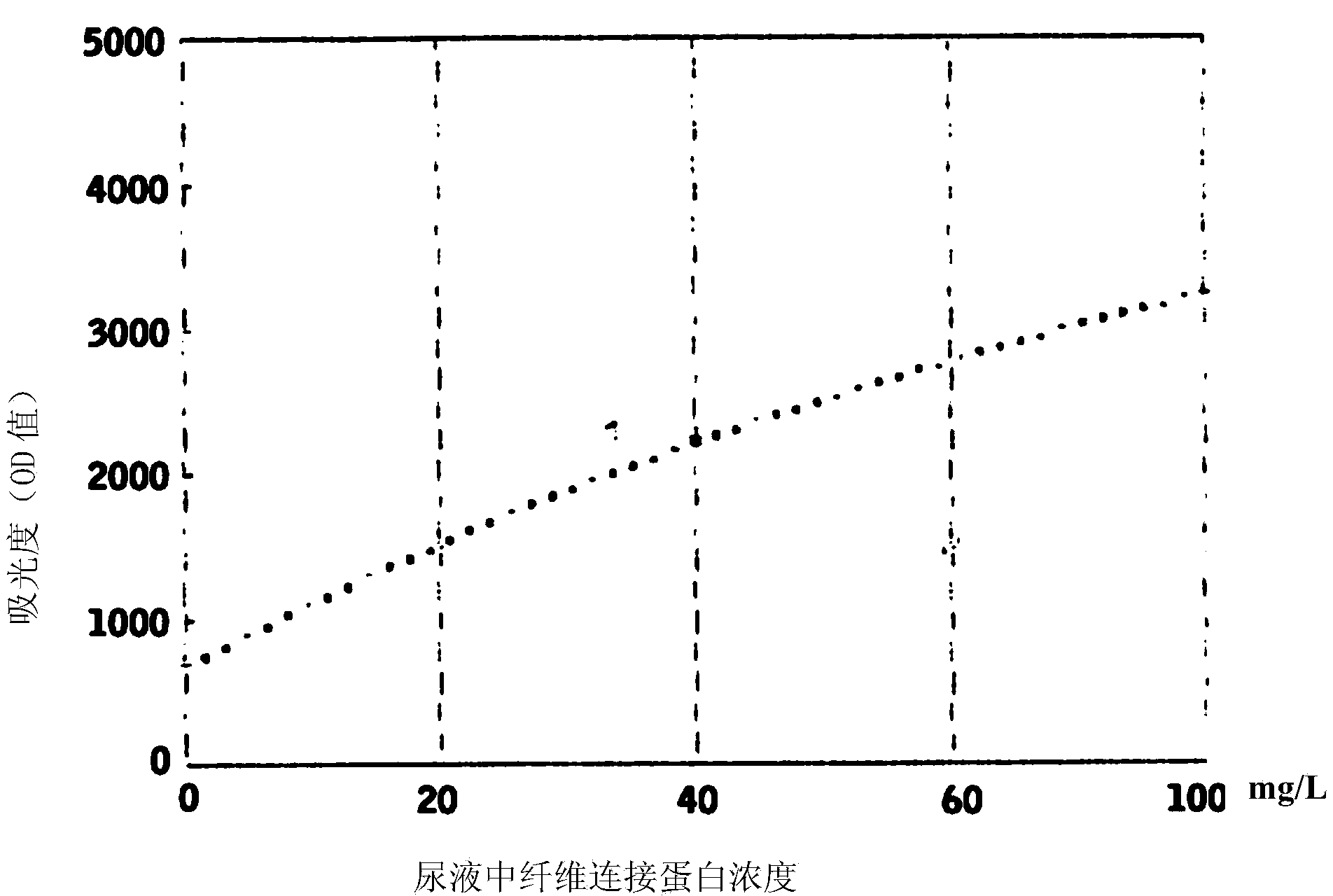
Kit and method for detecting concentration of fibronectin in urine
InactiveCN103675299ASignificant technological progressEasy to measureColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingCross-linkPhosphate
The invention provides a kit for detecting the concentration of fibronectin in urine, which comprises two reagents. A reagent I comprises phosphate buffer; a reagent II is suspension formed by cross-linking a rabbit anti-human fibronectin antiserum, a goat anti-human fibronectin antiserum, a rat anti-human fibronectin antiserum or a rat anti-human fibronectin monoclonal antibody on latex particles. The invention solves the problems of complex steps, low accuracy and poor repeatability when a radial immunodiffusion method and an ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) double-antibody sandwich technology are adopted to measure the concentration of the fibronectin in the prior art. The invention also provides a method for detecting the concentration of the fibronectin in human urine by adopting the kit. The kit and the method which are provided by the invention are used for measuring the concentration of the fibronectin in the urine, adopt simple steps, have high accuracy and good repeatability and are used for an automatic analysis meter.
Owner:上海北加生化试剂有限公司
Kit for determining concentration of human serum complement Clq and method thereof
InactiveCN102636654ASignificant technological progressEasy to measureBiological testingPhosphatePotassium
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering, provides a kit for determining the concentration of serum complement Clq, and solves the technical problem of complicated procedures, low accuracy and poor repeatability of immunodiffusion method and ELISA double-antibody sandwich technology adopted in the prior art to determine the concentration of complement Clq. The method involves the following two reagents: reagent I is composed of disodium hydrogen phosphate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, PEG6000, EDTA-Na2 and TX-100, and reagent II is composed of disodium hydrogen phosphate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, PEG6000, EDTA-Na2, TX-100, complement C1q antiserum or complement C1q monoclonal antibody. The invention also provides a method for determining the concentration of human serum complement Clq using the above kit. The kit and the method for determination of the concentration of complement C1q, provided by the invention, have the advantages of simple and convenient procedures, high accuracy and good repeatability, and are used for automated analyzers.
Owner:上海北加生化试剂有限公司
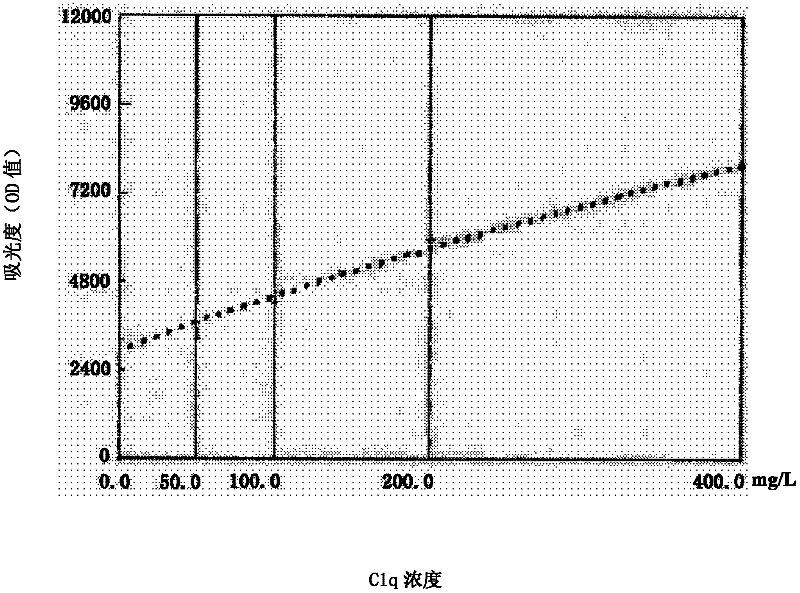
Kit and method for detecting C1q concentration of complement with nanosized-latex enhancing immune turbidimetry
ActiveCN102650641AHigh and low turbidityReduce light transmittanceBiological testingSorbentLatex particle
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering, and provides a kit for detecting C1q concentration of a complement in blood serum with a nanosized-latex enhancing immune turbidimetry, solving the problems of complex steps, low accuracy and poor repeatability in the prior art adopting an immunodiffusion method and an ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) double-antibody sandwich technology to detect the C1q concentration of the complement. The kit comprises two reagents, wherein a reagent I is prepared from disodium hydrogen phosphate, monopotassium phosphate, PEG6000, EDTA-NA2 and TX-100; and a reagent II is prepared from suspensions of rabbit anti-human complement C1q antiserum or goat anti-human complement C1q antiserum or rat anti-human complement C1q antiserum or rat anti-human complement C1q monoclonal antibodies crosslinking on latex particles. The invention also provides a method using the kit to detect the C1q concentration of the complement in human blood serum. The kit and the method have simpleness and convenience in steps for detecting the C1q concentration of the complement, high degree of accuracy and good repeatability and are used for automatic analyzers.
Owner:上海北加生化试剂有限公司
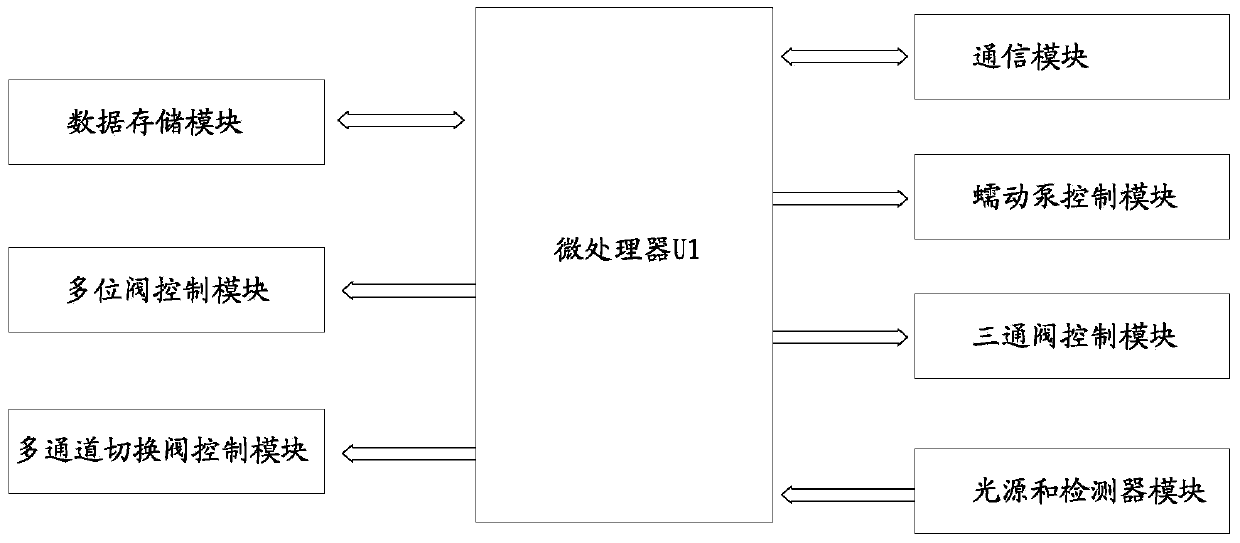
Automatic analysis instrument and system for microfluidic immunodetection chip
The invention discloses an automatic analysis instrument and system for a microfluidic immunodetection chip. The automatic analysis instrument comprises an instrument framework and a mechanical motion module, a liquid moving and sucking module and a detection module which are fixed on the instrument framework, wherein the mechanical motion module comprises a three-dimensional mechanical arm and a metal working pipe fixed on the three-dimensional mechanical arm; the motion of the three-dimensional mechanical arm drives the metal working pipe to move to assemble and disassemble a sucking head; the liquid moving and sucking module is communicated with the metal working pipe and is used for sucking and injecting liquid; the detection module is used for reading and transmitting a chemiluminescence signal on the microfluidic immunodetection chip. The analysis instrument is connected with a computer to form a system and comprehensively realizes organic integration of sample pretreatment, target protein separation purification, sample and reagent injection and suction, chip cleaning and signal acquisition and analysis processing, so that a microfluidic technology is automatic, miniaturized, and more accurate and simple.
Owner:BEIJING NANO ACE TECH CO LTD
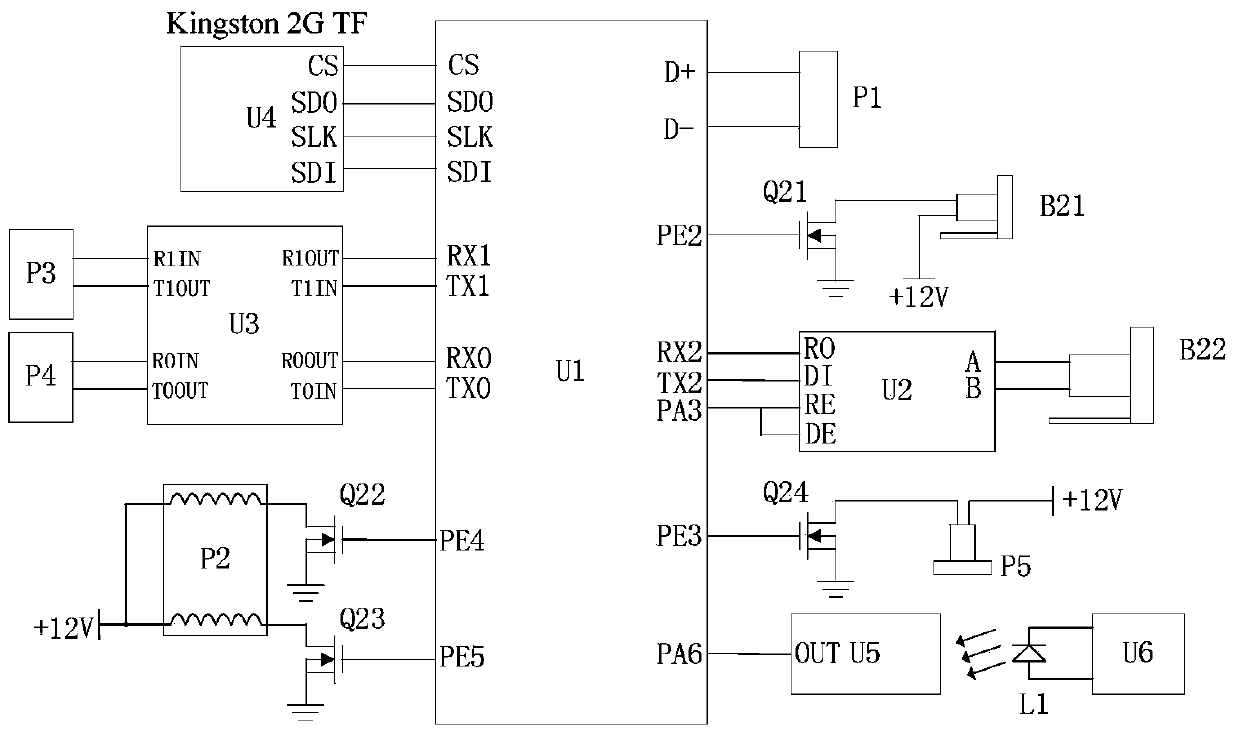
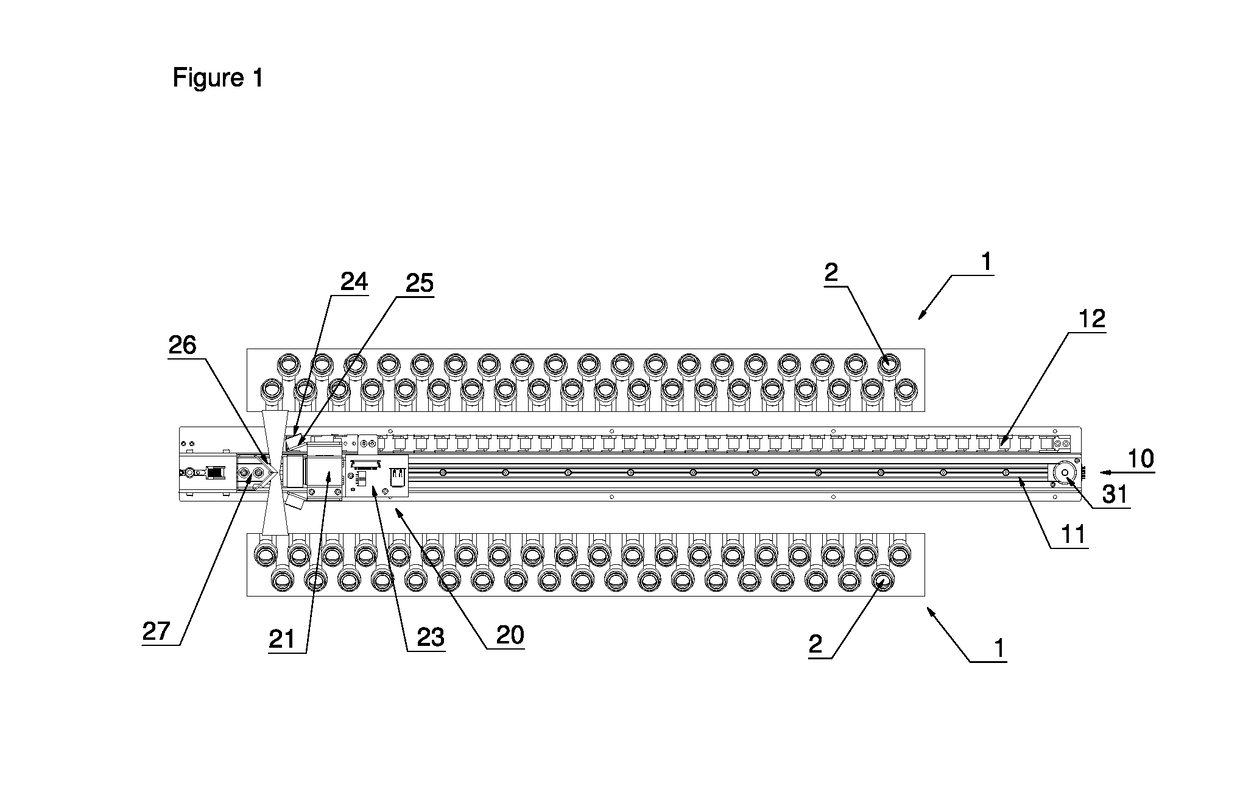
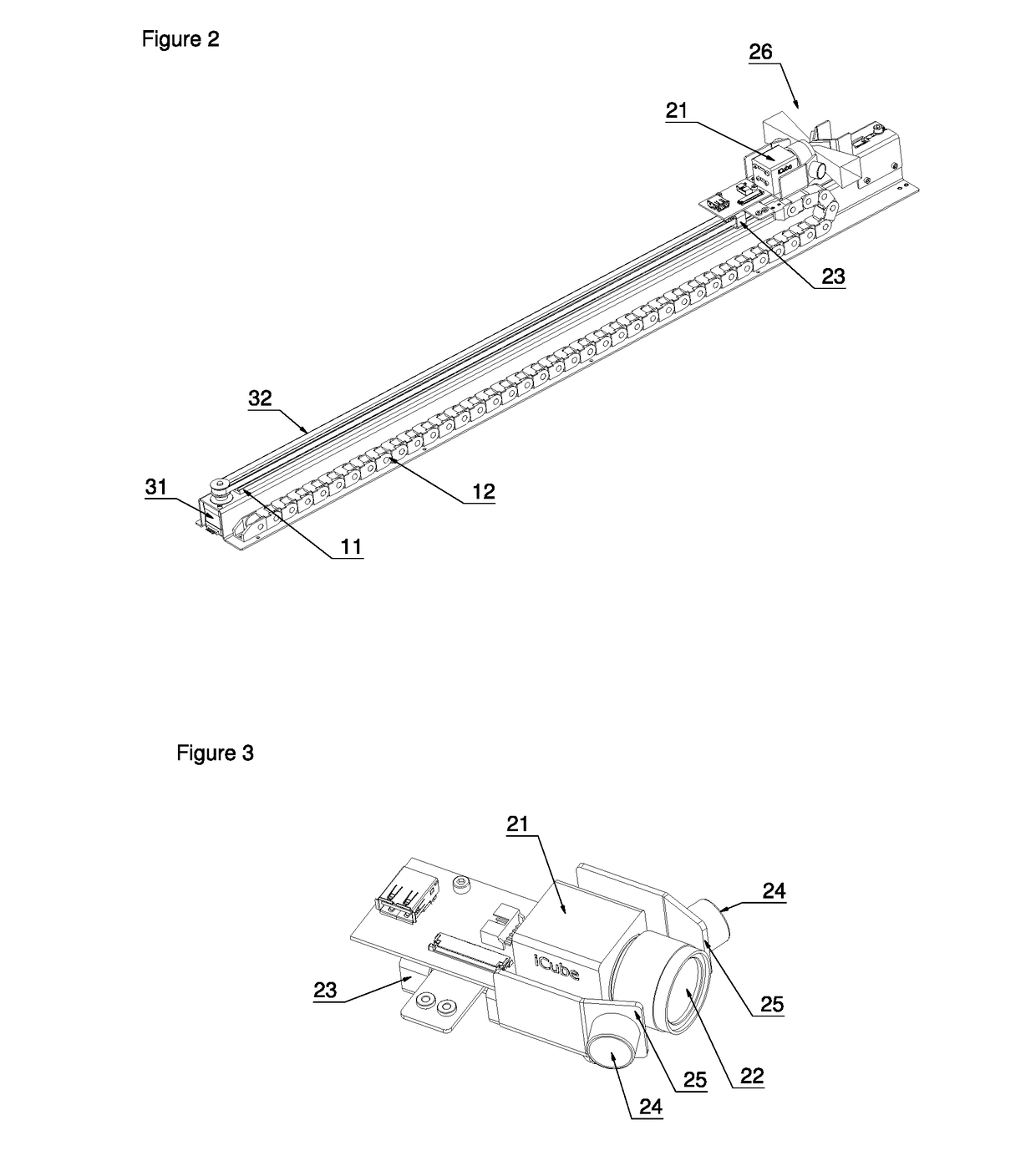
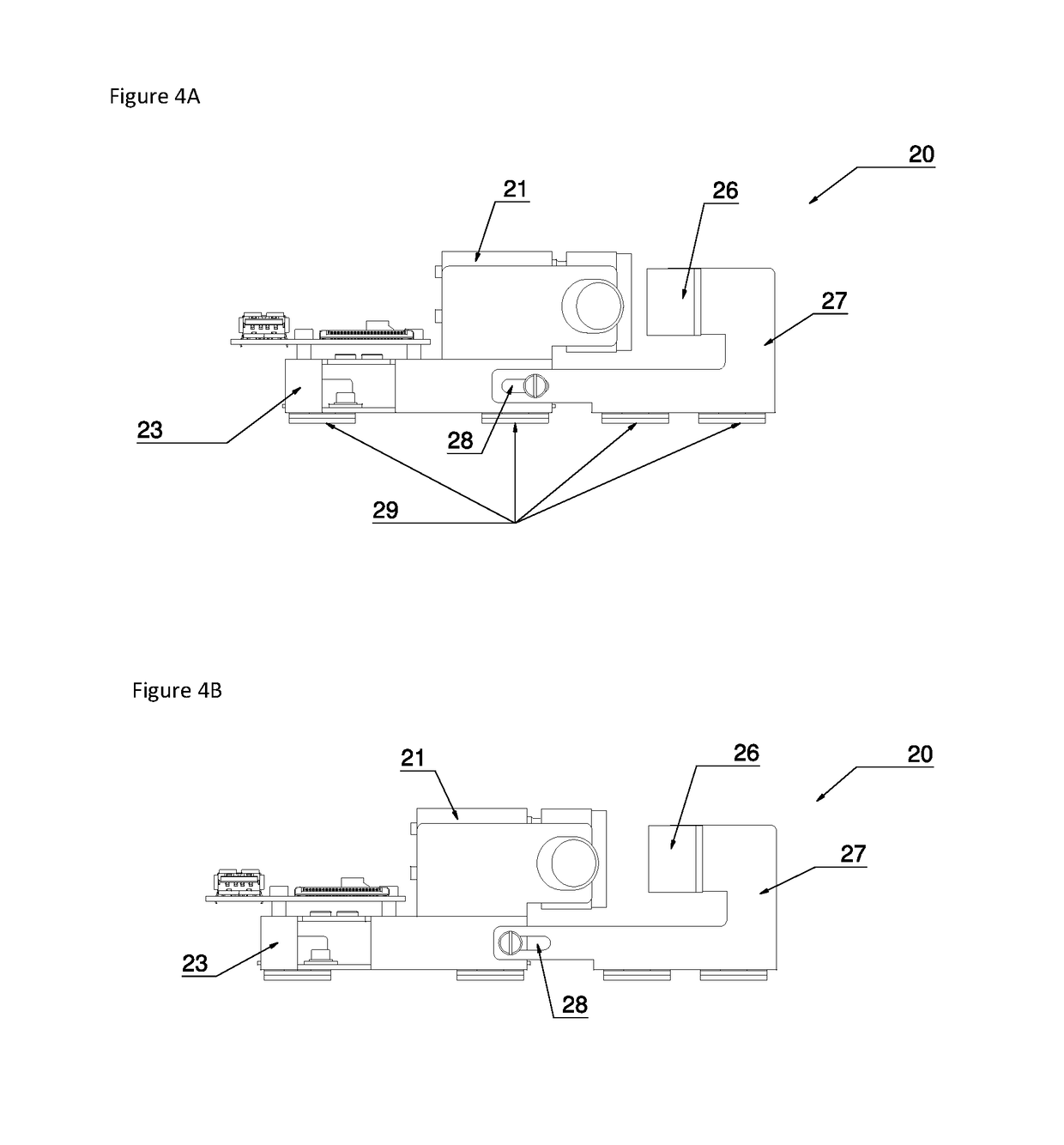
Scanning Device and Method for Use in an Automated Analyser
ActiveUS20190087616A1Simple mechanicsWide rangeMountingsSensing by electromagnetic radiationComputer scienceAutomated analyser
A scanning method with simple mechanics for use in an automated analyser to scan objects or codes on objects. The invention enables one to move a scanning unit comprising a camera and two deflection mirrors and to set two different focus levels with one and the same drive unit.
Owner:STRATEC BIOMEDICAL AG
Pipeline interchange/transmix
ActiveUS20210254793A1Programme controlFlow control using electric meansProcess engineeringAutomated analyzer
In one embodiment, a pipeline interchange is described where a first product flows through a first pipeline and a second product flows through a second pipeline. In this embodiment, a first product automated analyzer is situated near the first pipeline to physical and / or chemically analyze the first product and generate first product data. Additionally, in this embodiment, a second product automated analyzer is situated near the second pipeline to physical and / or chemically analyze the second product and generate second product data. A pipeline interchange is connected downstream to both the first pipeline and the second pipeline, wherein the pipeline interchange blends the first product flowing through the first pipeline with the second product flowing through the second pipeline. A third pipeline is connected downstream to the pipeline interchange, wherein the third pipeline flows a blended product created from the blending of the first product and the second product in the pipeline interchange. A data analyzer is also positioned to interpret the first product data and the second product data and communicate adjustments to the flow of both the first product and the second product to achieve desired physical and / or chemical characteristics in the blended product.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
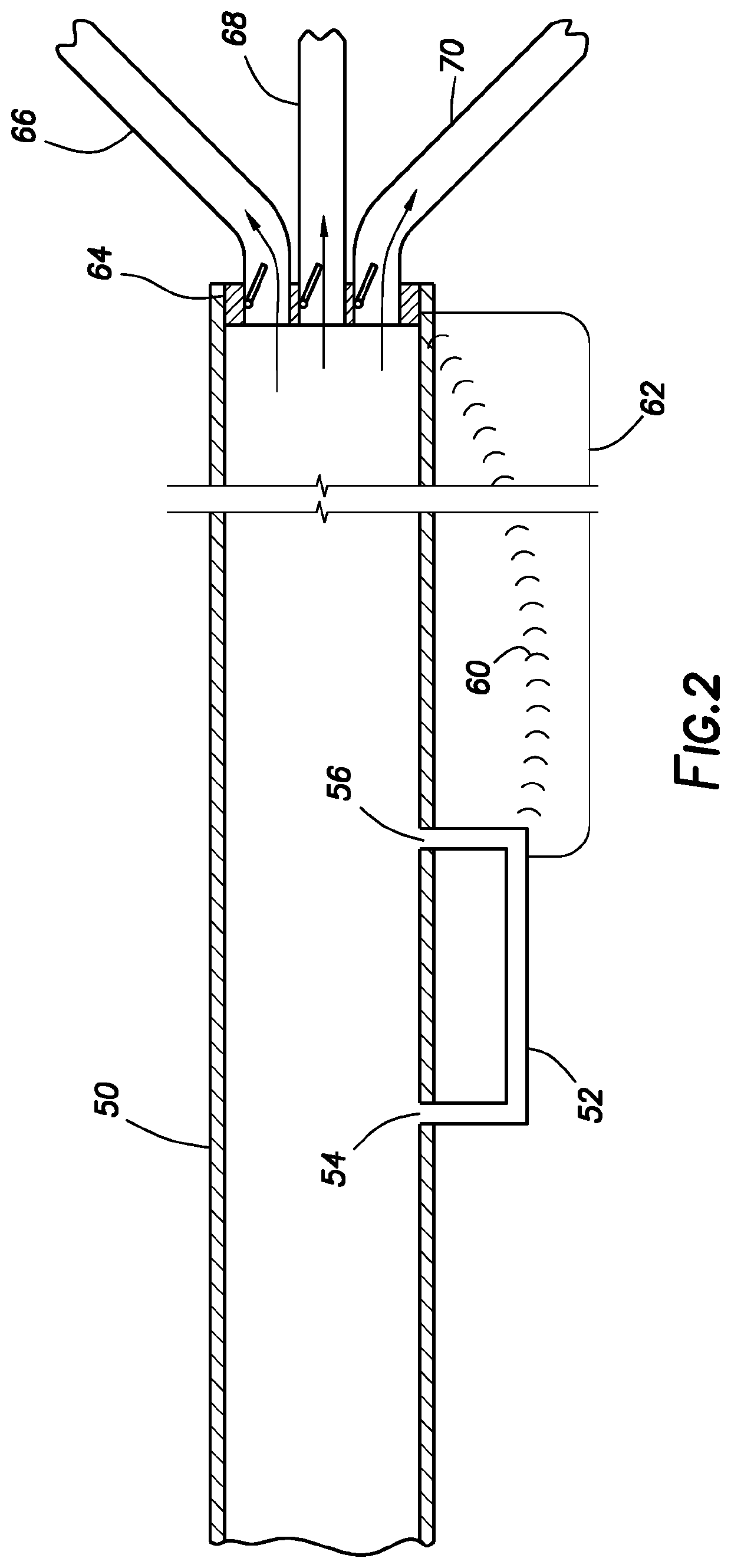
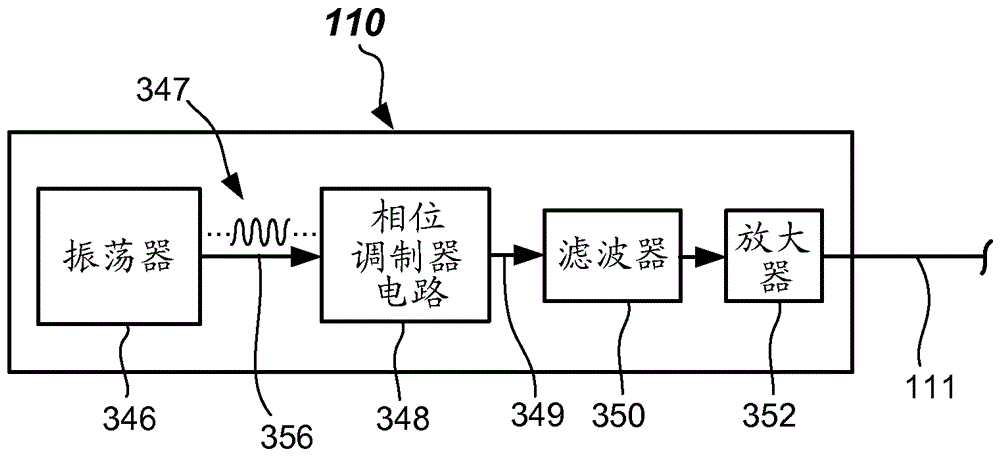
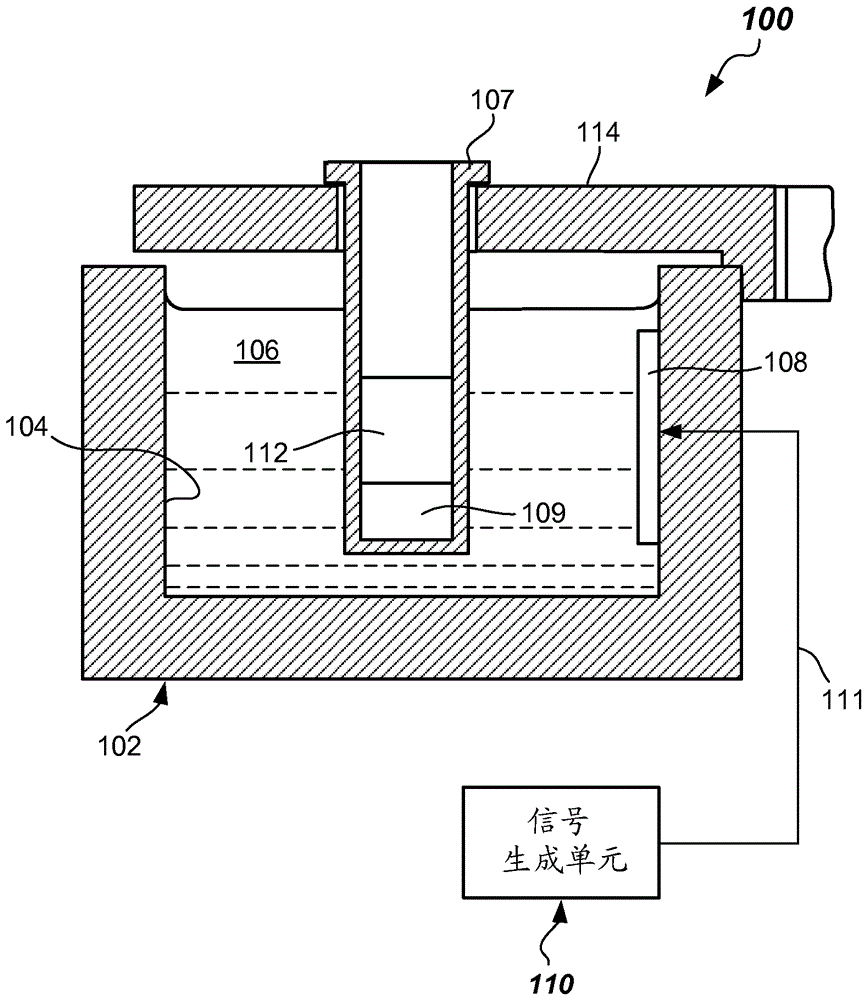
Phase-modulated standing wave mixing apparatus and methods
ActiveCN106687797AShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersTransportation and packagingTransducerEngineering
Disclosed are mixing apparatus adapted to provide mixing of components in an automated analyzer. The mixing apparatus includes a reservoir configured to contain a coupling liquid, a transducer configured to be driven at a frequency and communicate with the coupling liquid, and a signal generation unit configured to provide a phase modulatable drive signal to the transducer. In some embodiments, improved patient sample and reagent mixing may be provided. Systems and methods are provided, as are other aspects.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Automated analyser for determining nitrogen derived from organic compounds
ActiveUS7687029B2Reduce usageEasy to disassembleChemical analysis using catalysisChemical analysis using combustionAbsorbent materialNitrogen gas
An automated analyzer is described for determining, by way of combustion, nitrogen contained in organic compounds, in particular proteins present in foods, animal feeds, polymers, fuels etc., characterized in that the carbon dioxide absorption device upstream of the nitrogen detector is self-regenerating and comprises:a distributor valve able to switch different gas circuits without contaminations and losses from one gas sample to another,a carousel consisting of a plurality of absorber elements inside which is placed an adsorbent material,a furnace suitable for said adsorbers,in such a manner that each of said adsorbers presents itself in turn for each analysis and that on completion of said analysis the same adsorber is conveyed to the furnace for degassing of the absorbent material and thus for its relative regeneration.
Owner:FOSS ANALYTICAL AS
Kit and method for detecting fibronectin concentration in human urine
InactiveCN103645331ASignificant technological progressImprove accuracyBiological testingAntiserumProtein C
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering and provides a kit for detecting fibronectin concentration in human urine. The problems that the method for measuring the fibronectin concentration is complex in steps, low in accuracy and low in repeatability by adopting an immunodiffusion method and an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) double-antibody sandwich technology are solved. The kit comprises two reagents, namely a reagent I consisting of a phosphate buffer solution, and a reagent II consisting of a phosphate buffer solution and goat (rabbit) anti-human fibronectin antiserum or fibronectin monoclonal antibody. The invention also provides a method for detecting the fibronectin concentration in the human urine by adopting the kit. The kit and the method are used for measuring the fibronectin concentration in urine, are simple and convenient in step, high in accuracy and high in repeatability and are used for automatic analyzers.
Owner:上海北加生化试剂有限公司
Pipeline interchange/transmix
ActiveUS20210255162A1Optimize dataProgramme controlControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsProcess engineeringAutomated analyzer
In one embodiment, a process is taught where the process begins by flowing a first product through a first pipeline and flowing a second product through a second pipeline. In this embodiment, the first product in the first pipeline is analyzed with a first product automated analyzer that is capable of physical and / or chemically analyzing the first product in the first pipeline and generating a first product data. Additionally, in this embodiment, the second product in the second pipeline is analyzed with a second product automated analyzer that is capable of physical and / or chemically analyzing the second product in the second pipeline and generating a second product data. The process then produces a blended product by mixing both the first product and the second product within a pipeline interchange which is connected downstream to both the first pipeline and the second pipeline. The blended product then flows from the pipeline interchange to a third pipeline that is connected downstream of pipeline interchange. The first product data and the second product data is then interpreted in a data analyzer by comparing the physical and / or chemical characteristics of the physical and / or chemical characteristics of the first data to an optimal first data and the physical and / or chemical characteristics of the second data to an optimal second data. The data analyzer then determines the adjustments in the flow of the first product and the flow of the second product to achieve optimal blended data from the blended product. The adjustments are then communicated to adjust the flow of the first product in the first pipeline and the flow of the second product in the second pipeline.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
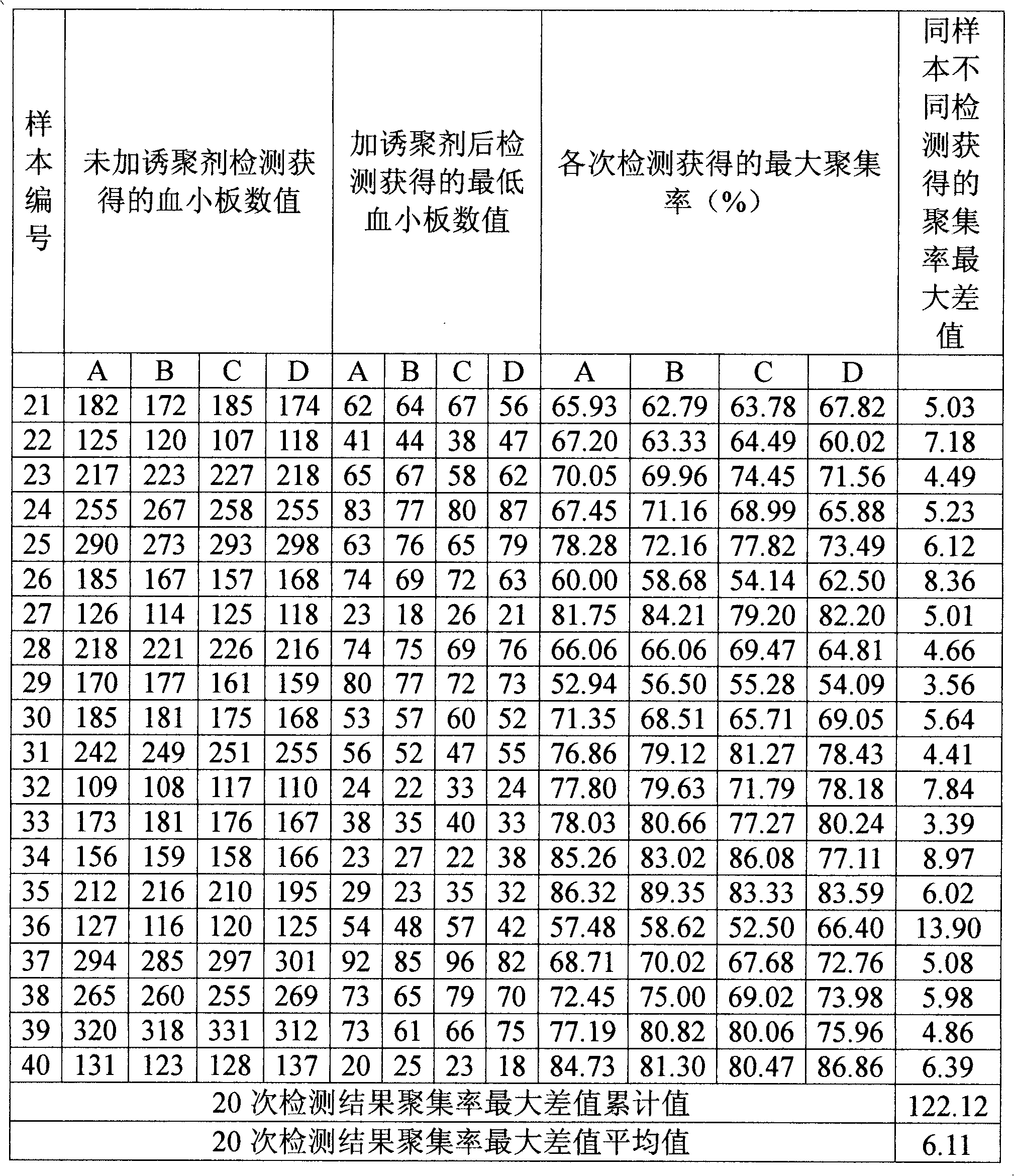
Optimized platelet aggregation function detection analysis method suitable for automated instrument
An optimized platelet aggregation function detection analysis method suitable for automated instrument belongs to the field of clinical laboratory medicine. The method is an improvement and optimization of an automatic counting detection method for detection analysis of platelet aggregation function. The process is applicable to platelet aggregation function automated analytical instrument employing a counting method. The method detects and records the amount of platelet and calculates aggregation rate. Test results by the laboratory show that the repeatability of the platelet aggregation rate result obtained by the method is superior to that of a prior maximum aggregation rate method.
Owner:SINNOWA MEDICAL SCI & TECH
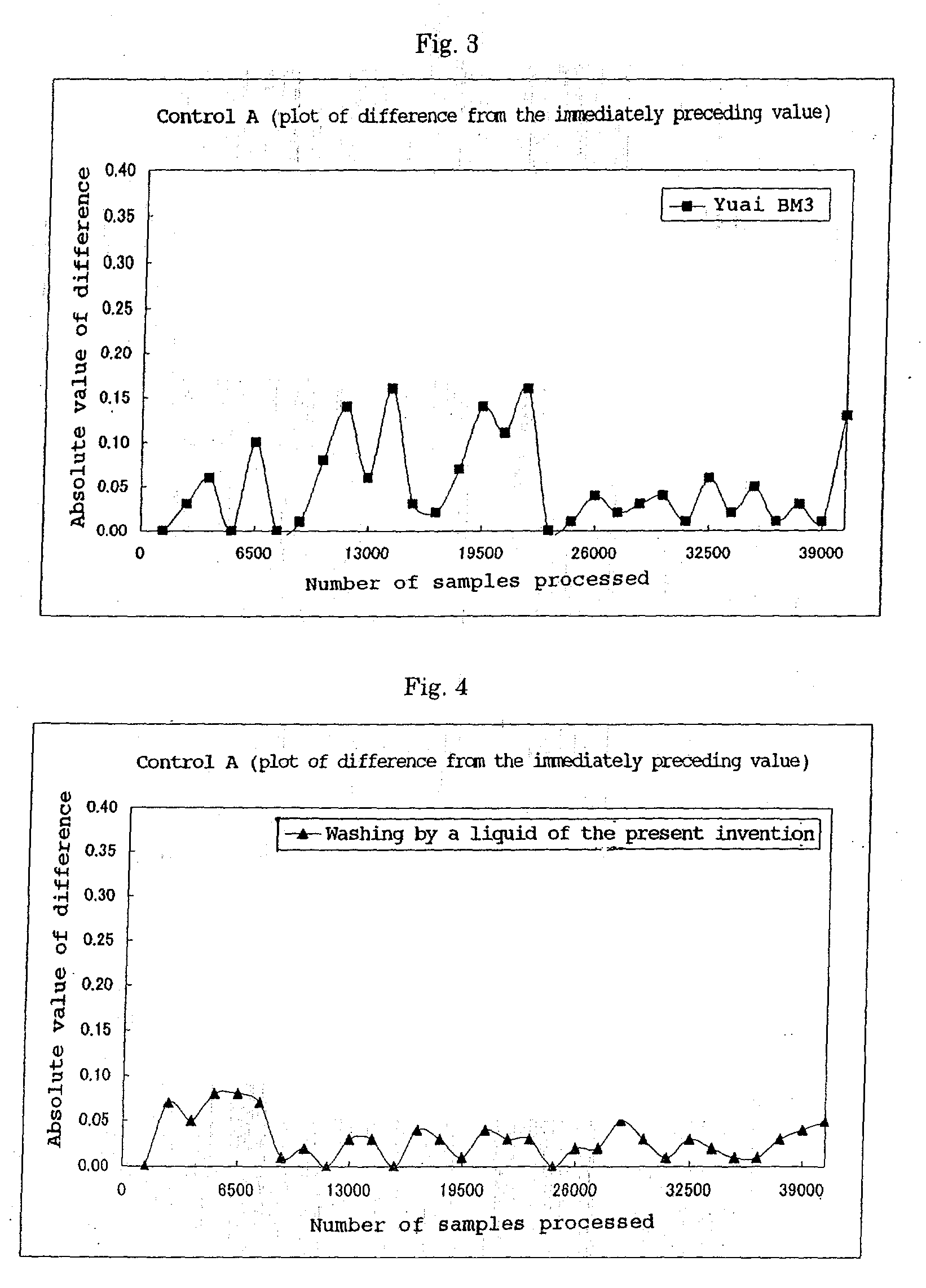
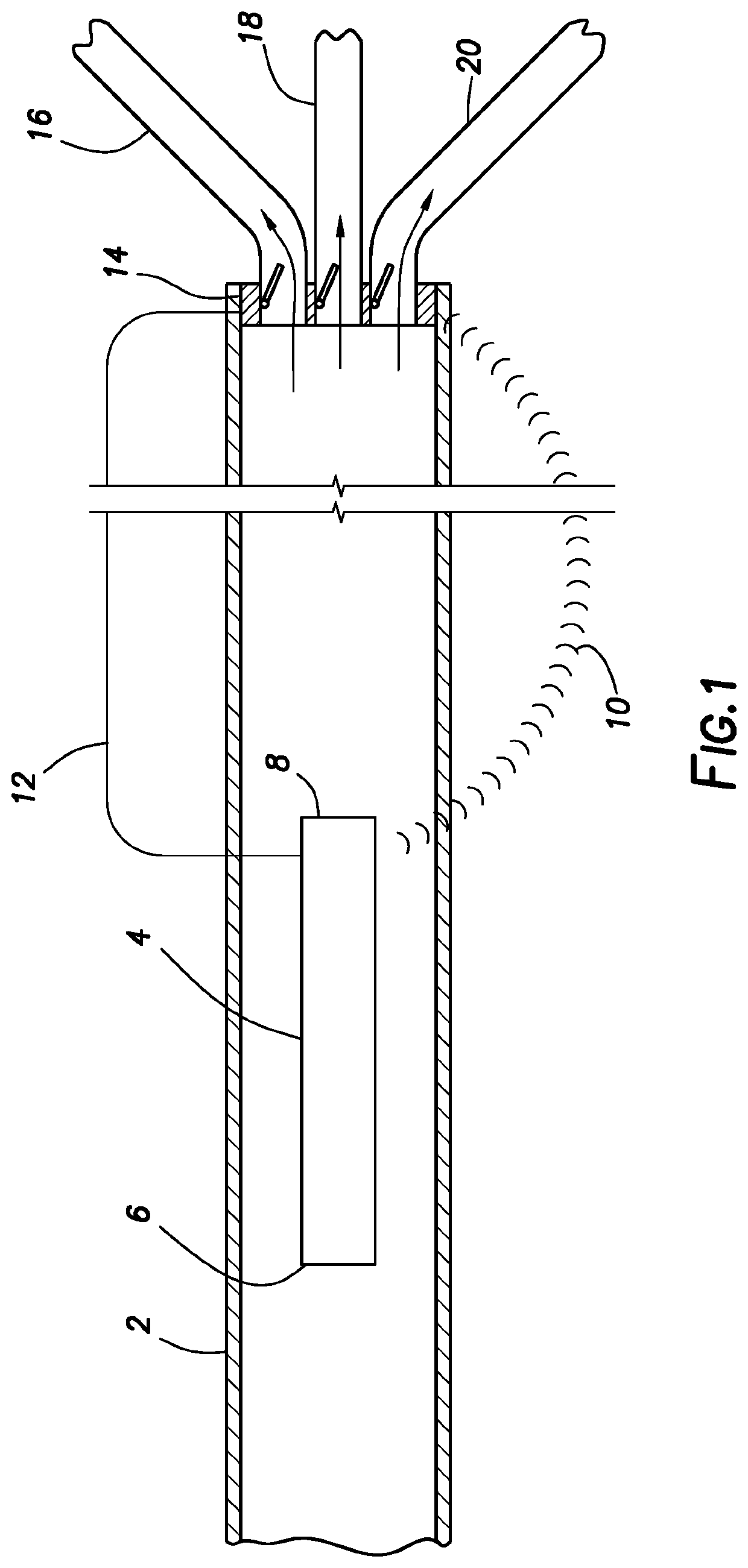
Alkaline washing liquid for automated clinical analyzer
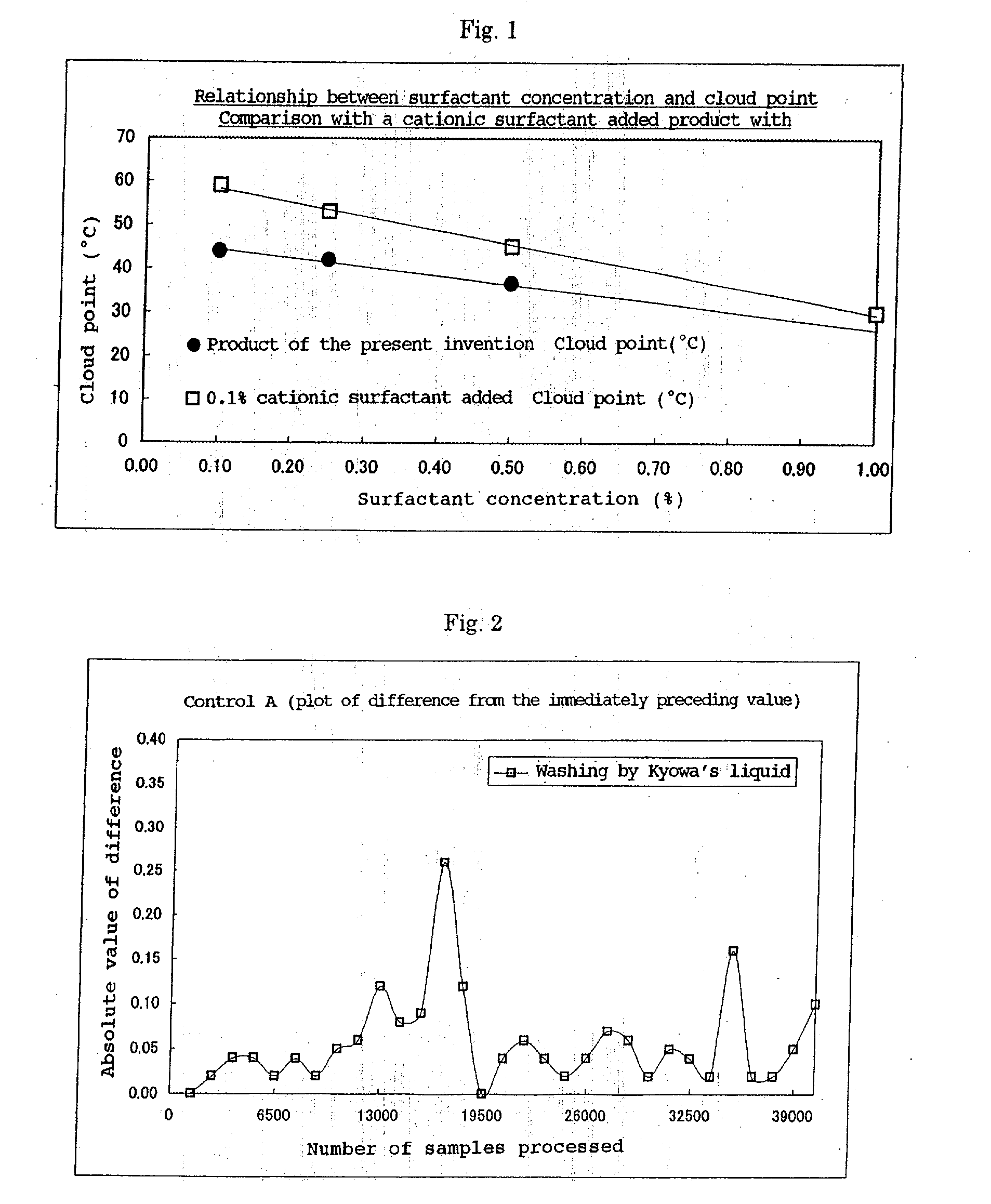
InactiveUS20020165116A1Improve washing effectImprove accuracyInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCationic surface-active compoundsCLOUD experimentCloud point
An alkaline washing liquid for an automated clinical analyzer is provided that allows measurement to be carried out with higher accuracy when simultaneously analyzing multiple items by preventing abnormal measurement due to reagent migration from other items, etc. A production process for the washing liquid and a washing method using it are also provided. The washing liquid has a cloud point of 36° C. to 50° C. and is formed from at least two kinds of polyoxyethylene alkyl ether type nonionic surfactants having different cloud points.
Owner:KANTO CHEM CO INC +1
Pipeline interchange/transmix
ActiveUS20210270796A1Programme controlAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyPetroleum productProcess engineering
In one embodiment, a pipeline interchange flows a product through an upstream pipeline. An automated analyzer is connected to the upstream pipeline to analyze different physical and / or chemically properties in the product and generate data from the product without extracting a sample from the upstream pipeline. An automatic splitter is placed downstream of the automated analyzer, capable of receiving and interpreting the data from the automated analyzer and directing the refined petroleum product into at least three different downstream pipelines, wherein at least one of the downstream pipelines is a transmix pipeline.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Pipeline interchange/transmix
ActiveUS20210270795A1Absorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyPipeline systemsProcess engineeringAutomated analyzer
In one embodiment, a pipeline interchange flows a product through an upstream pipeline. An automated analyzer is connected to the upstream pipeline, wherein the automated analyzer analyzes a sample of the product, and wherein the analyzer is capable of analyzing different physical and / or chemical characteristics of the product and generating a data sample. An automatic splitter is then placed downstream of the automated slipstream analyzer. In this embodiment, the automatic splitter is capable of receiving and interpreting the data sample from the automated analyzer and directing the product into at least three different downstream pipelines, wherein at least one of the downstream pipelines is a transmix pipeline and wherein at least one of the downstream pipelines returns the product upstream of the automated analyzer.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Supply module for an automated analyzer
ActiveUS9733264B2Optimize workflowReduce interventionImmunoassaysProcess engineeringAutomated analyzer
A method is described for supplying consumables to an automated analyzer by providing at least one reagent and at least one solid consumable from a supply module which is docked to the analyzer, followed by undocking the supply module from the analyzer and removing it therefrom. Also described is a respective system and a supply module for supplying consumables to an automated analyzer.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH +1
Pipeline interchange/transmix
ActiveUS11320095B2Radiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyProcess engineeringAutomated analyzer
In one embodiment, a pipeline interchange flows a product through an upstream pipeline. An automated analyzer is connected to the upstream pipeline, wherein the automated analyzer analyzes a sample of the product, and wherein the analyzer is capable of analyzing different physical and / or chemical characteristics of the product and generating a data sample. An automatic splitter is then placed downstream of the automated slipstream analyzer. In this embodiment, the automatic splitter is capable of receiving and interpreting the data sample from the automated analyzer and directing the product into at least three different downstream pipelines, wherein at least one of the downstream pipelines is a transmix pipeline and wherein at least one of the downstream pipelines returns the product upstream of the automated analyzer.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Transfer tool for use in automated analyser systems
InactiveUS20180156833A1Laboratory glasswaresSupporting apparatusBiomedical engineeringAutomated analyser
A device for storing and transferring liquids like samples and regents. The present disclosure provides a device for storing and transferring liquids in an automated analyser system, comprising at least one cavity for taking up a liquid and further at least one transfer tool for taking up a liquid, wherein the transfer toll is connected by at least one predetermined breaking member with the device.
Owner:STRATEC BIOMEDICAL AG
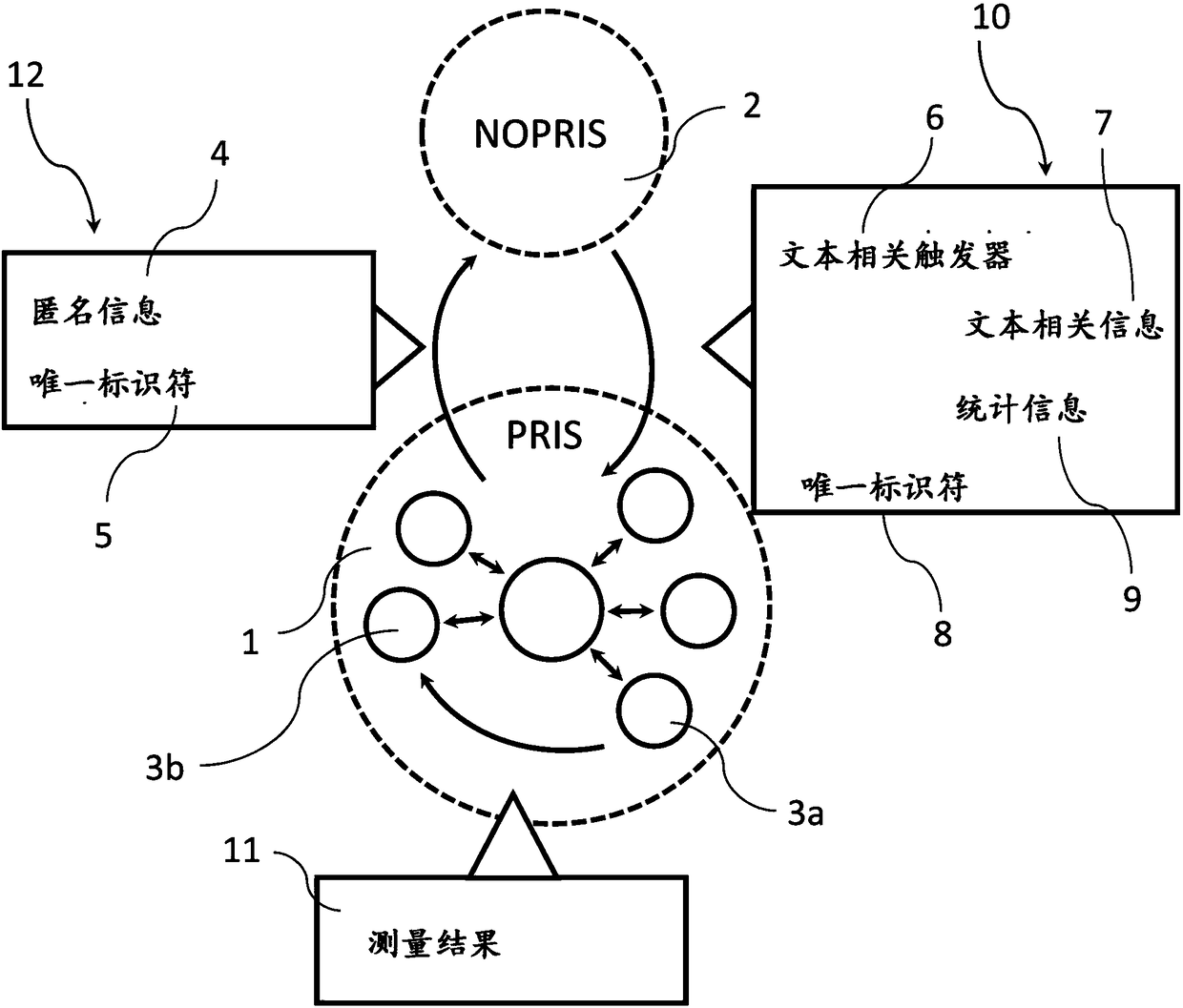
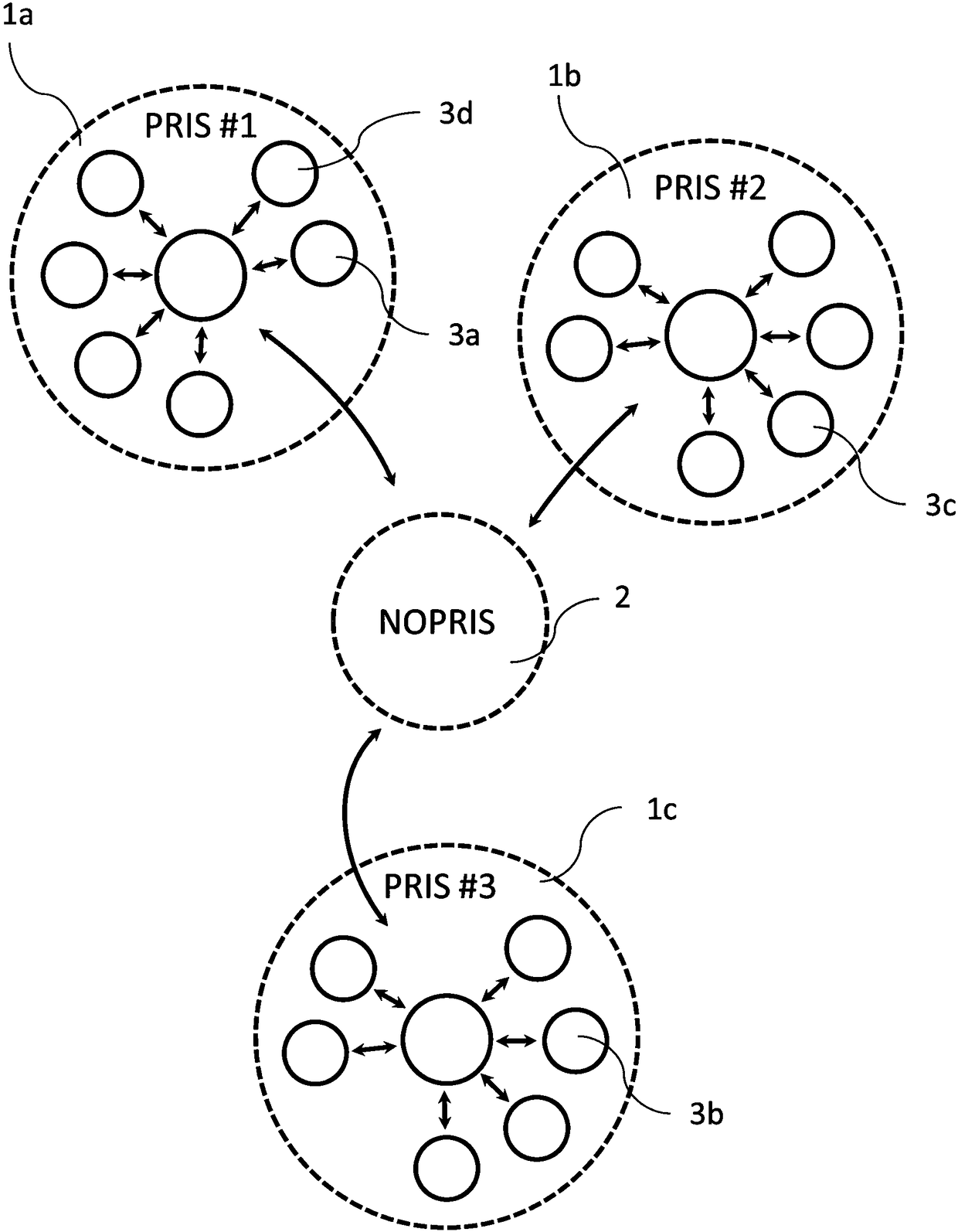
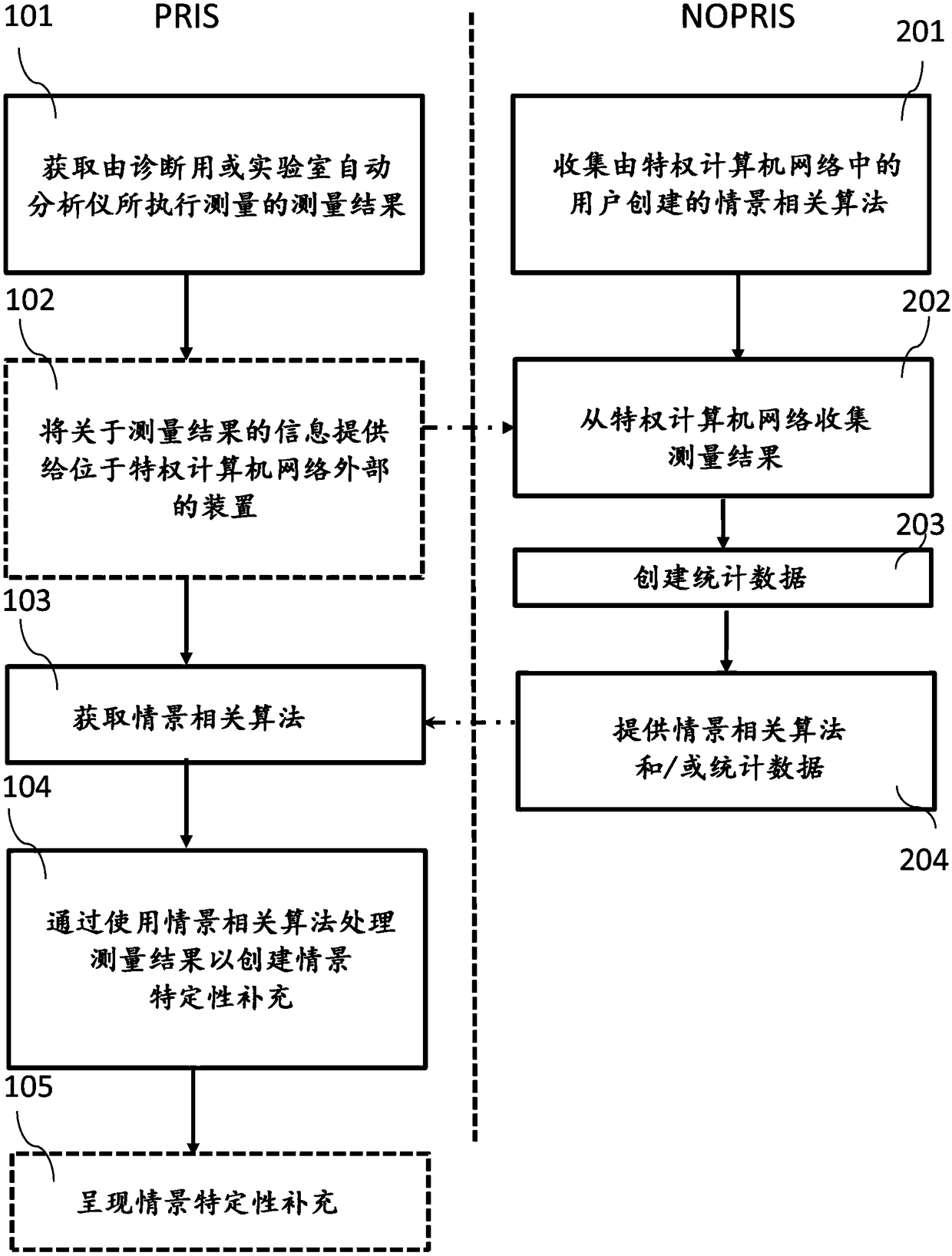
Supplementing measurement results of automated analyzers
PendingCN108091390AInformativeImprove the quality of treatmentComputer security arrangementsMedical equipmentSimulationSoftware engineering
In one aspect, a computer-implemented method for supplementing measurement results of automated analyzers is presented. The method includes obtaining, at a computer device, a result of a measurement performed by an automated analyzer, the computer device and the automated analyzer being located within a privileged computer network; obtaining a context related algorithm associated with the result of the measurement defining one or more triggering conditions and context related information from a computer device residing outside of the privileged computer network at the computer device and processing the result of the measurement by using the context related algorithm to generate a context specific supplement to the result of the measurement at the computer device.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Pipeline interchange/transmix
In one embodiment, a pipeline interchange is described where a first product flows through a first pipeline and a second product flows through a second pipeline. In this embodiment, a first product automated analyzer is situated near the first pipeline to physical and / or chemically analyze the first product and generate first product data. Additionally, in this embodiment, a second product automated analyzer is situated near the second pipeline to physical and / or chemically analyze the second product and generate second product data. A pipeline interchange is connected downstream to both the first pipeline and the second pipeline, wherein the pipeline interchange blends the first product flowing through the first pipeline with the second product flowing through the second pipeline. A third pipeline is connected downstream to the pipeline interchange, wherein the third pipeline flows a blended product created from the blending of the first product and the second product in the pipeline interchange. A data analyzer is also positioned to interpret the first product data and the second product data and communicate adjustments to the flow of both the first product and the second product to achieve desired physical and / or chemical characteristics in the blended product.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
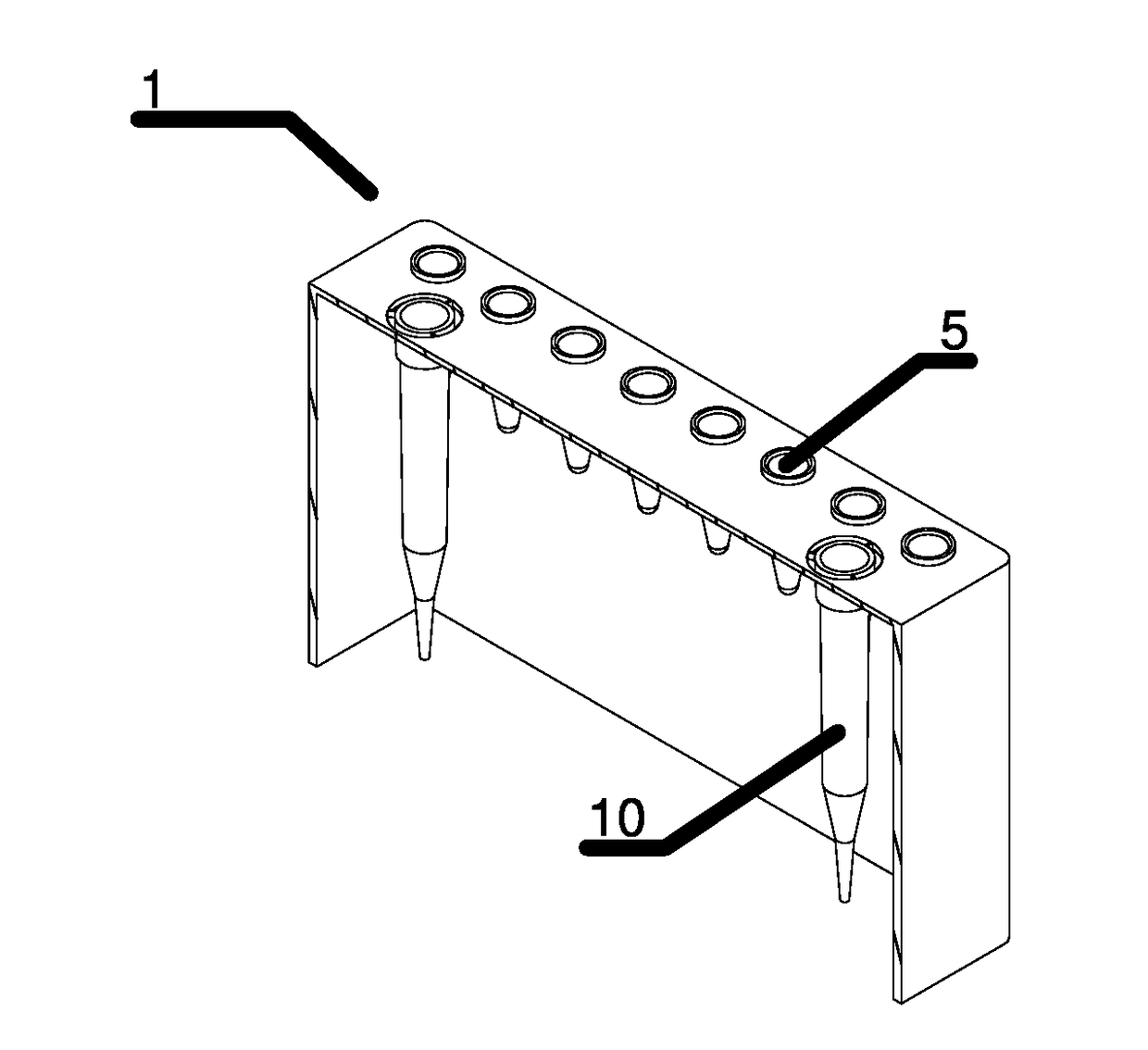
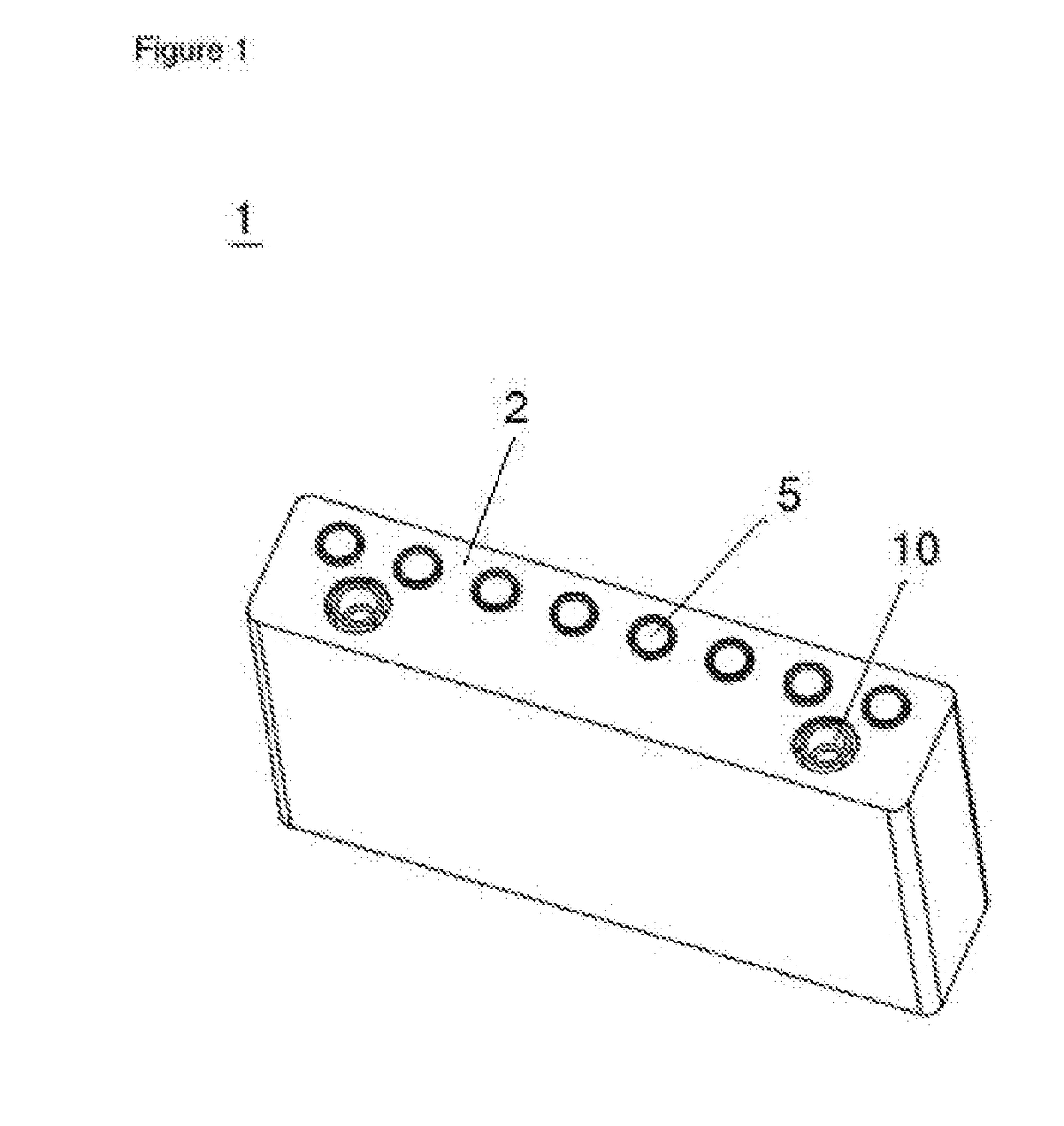
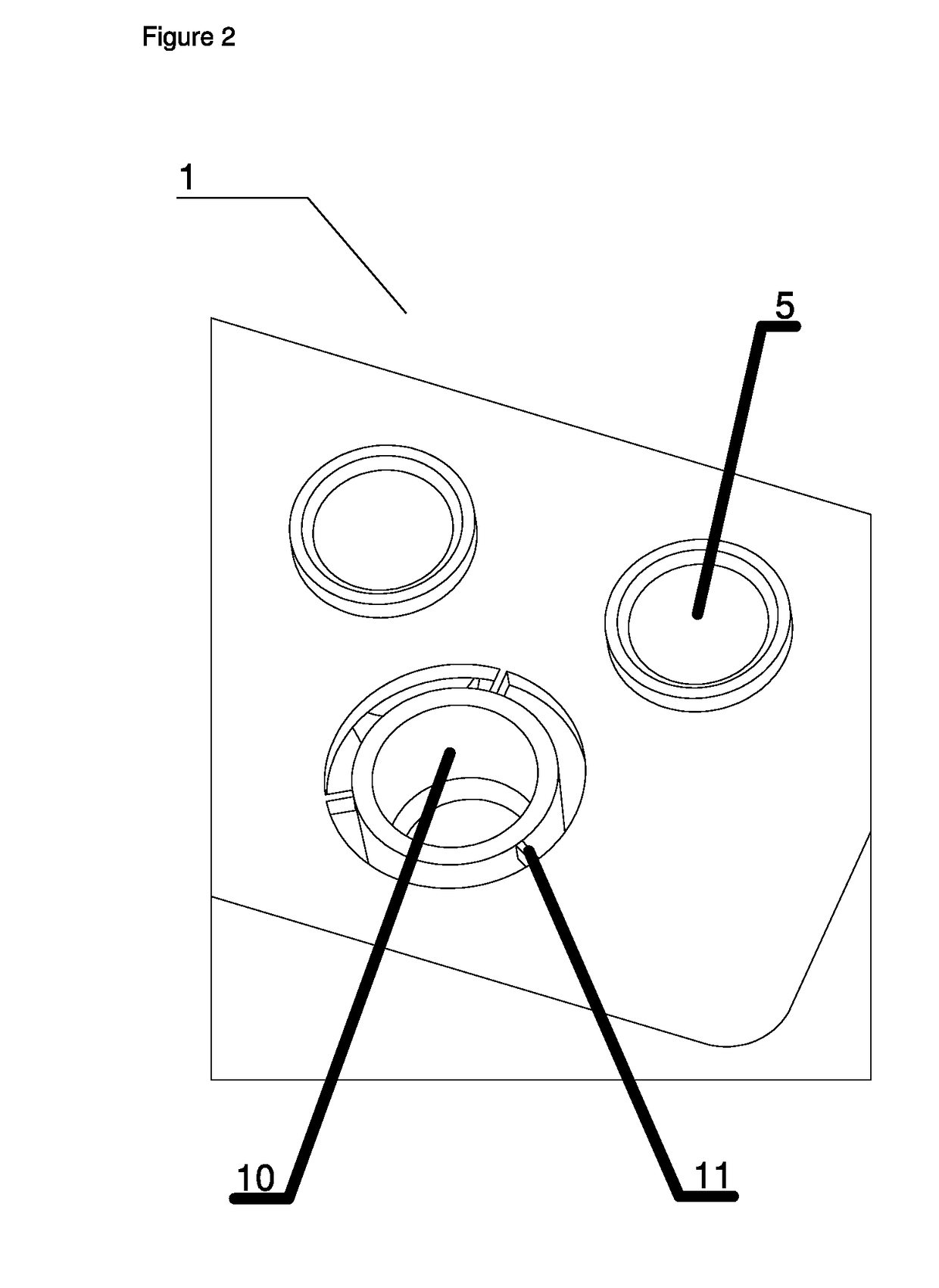
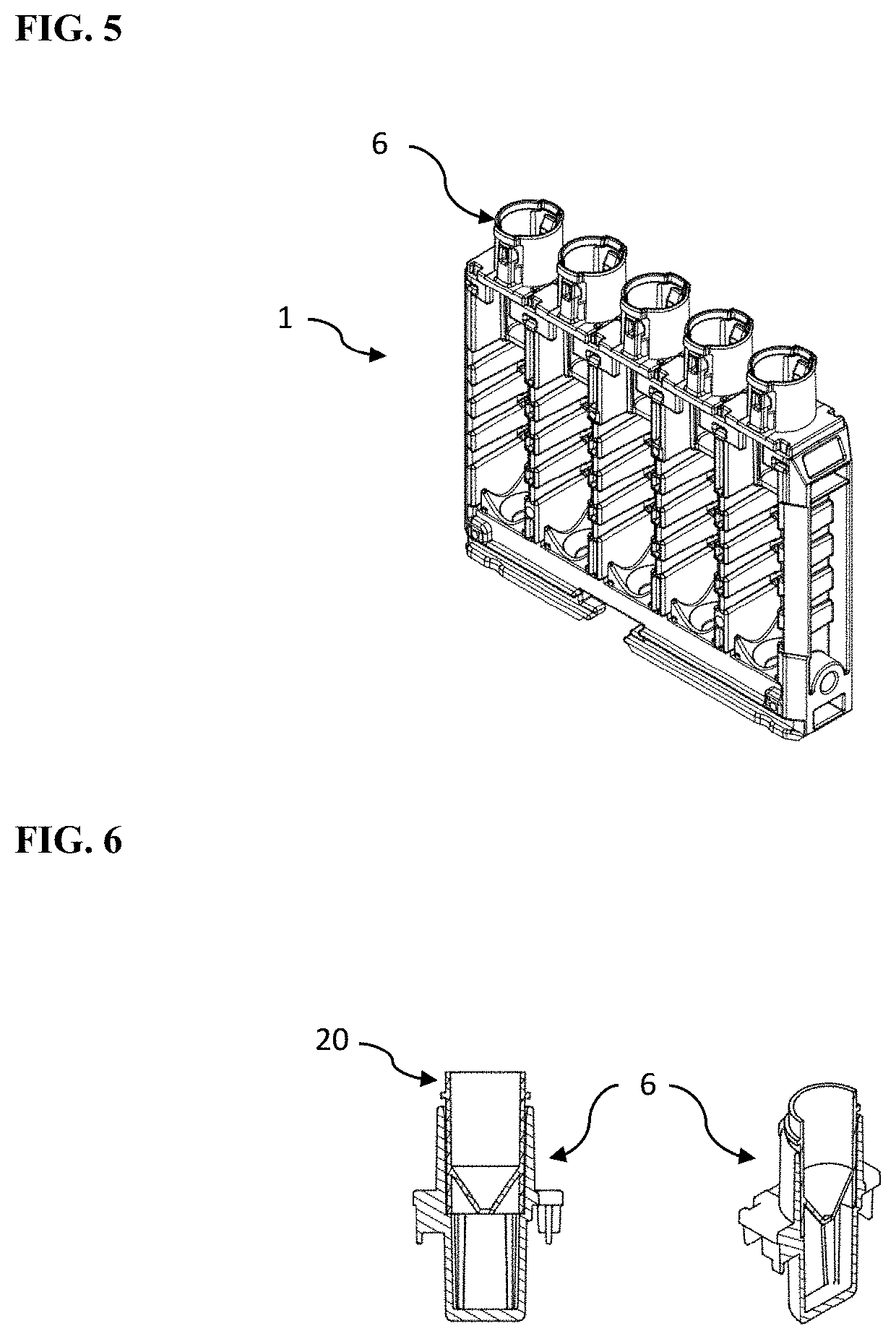
Rack for automated anaylzer
PendingUS20210156877A1Reducing available heightBurette/pipette supportsMaterial analysisMechanical engineeringAutomated analyser
A rack for automated analyser systems and provides a rack for automated analyser systems, the rack comprising a main body having an extended front side and a corresponding extended reverse side as well as at least two side walls defining at least one opening that is accessible from the main body's upper side for taking up a container for a sample that is to be processed; an upper insert that is arranged onto an upper end of the main body, wherein the upper insert has openings with a predefined diameter defining the upper surface of the rack.
Owner:STRATEC BIOMEDICAL AG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com