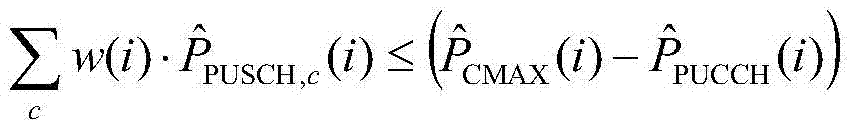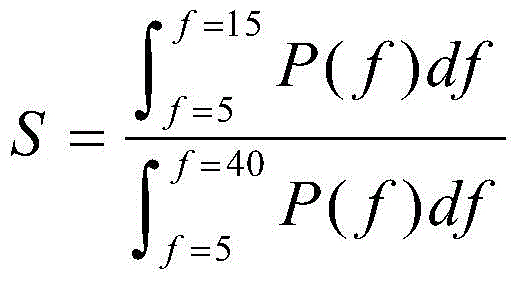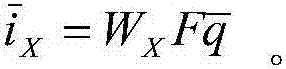Patents
Literature
93 results about "Noise spectral density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In communications, noise spectral density, noise power density, noise power spectral density, or simply noise density (N₀) is the power spectral density of noise or the noise power per unit of bandwidth. It has dimension of power over frequency, whose SI unit is watts per hertz (equivalent to watt-seconds). It is commonly used in link budgets as the denominator of the important figure-of-merit ratios, such as carrier-to-noise-density ratio as well as Eb/N₀ and Eₛ/N₀.
SINR measurement method for OFDM communications systems
ActiveUS7260054B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplexEngineeringMulti carrier
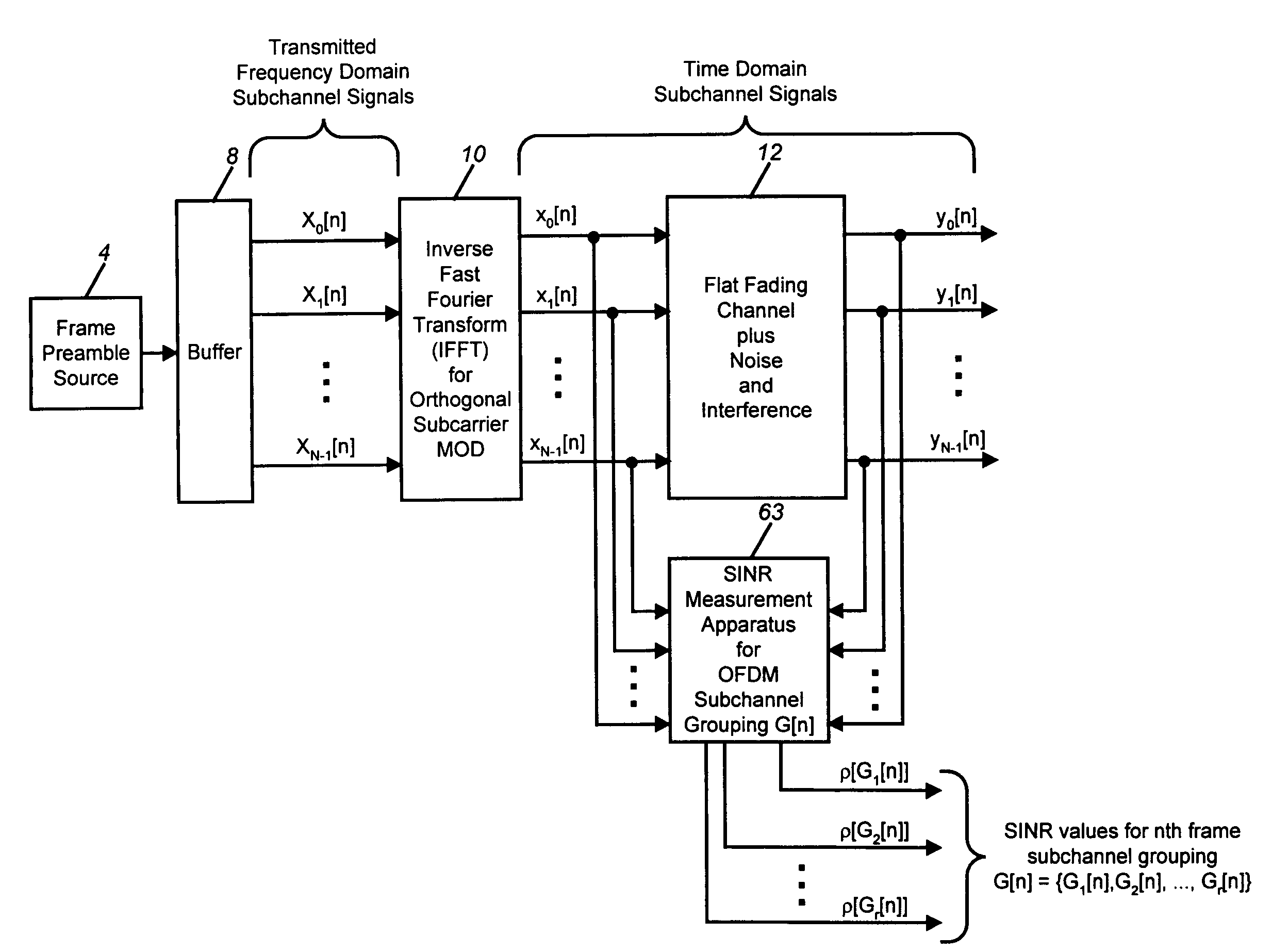
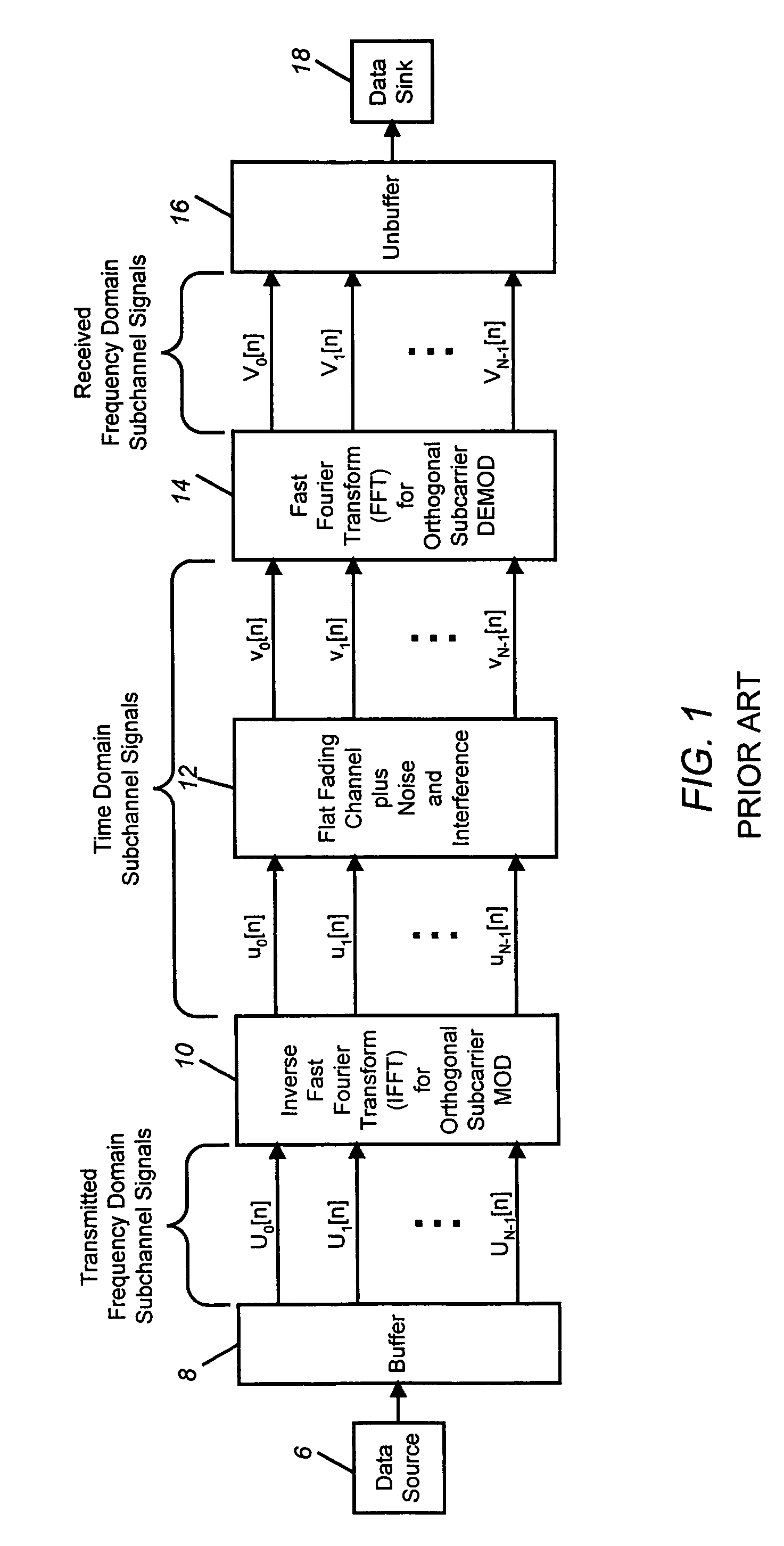
A signal to interference-plus-noise power ratio (SINR) measurement method for wireless communications systems which employ orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) for multicarrier data transmission is disclosed. Fast-Fourier transform (FFT)-based SINR measurements can be computed on frame-by-frame or greater interval for individual or groupings of subchannel signals. Given a known transmitted time-domain OFDM frame preamble, and the corresponding channel and interference-plus-noise (IPN) corrupted received time-domain frame preamble, the disclosed method first computes the power spectral densities of the received signal of interest and of a received unwanted interference-plus-noise signal. The FFT-computed power spectral densities are then used to compute average received signal and received IPN power measurements for specified individual or groupings of OFDM subchannel signals. The power measurements are then frame-averaged using a recursive exponential smoothing method. The frame-averaged signal and IPN power measurements are then used to form quantized measurements of SINR for the specified OFDM subchannel signals of the received frame.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and system for performing outer loop power control in discontinuous transmission mode
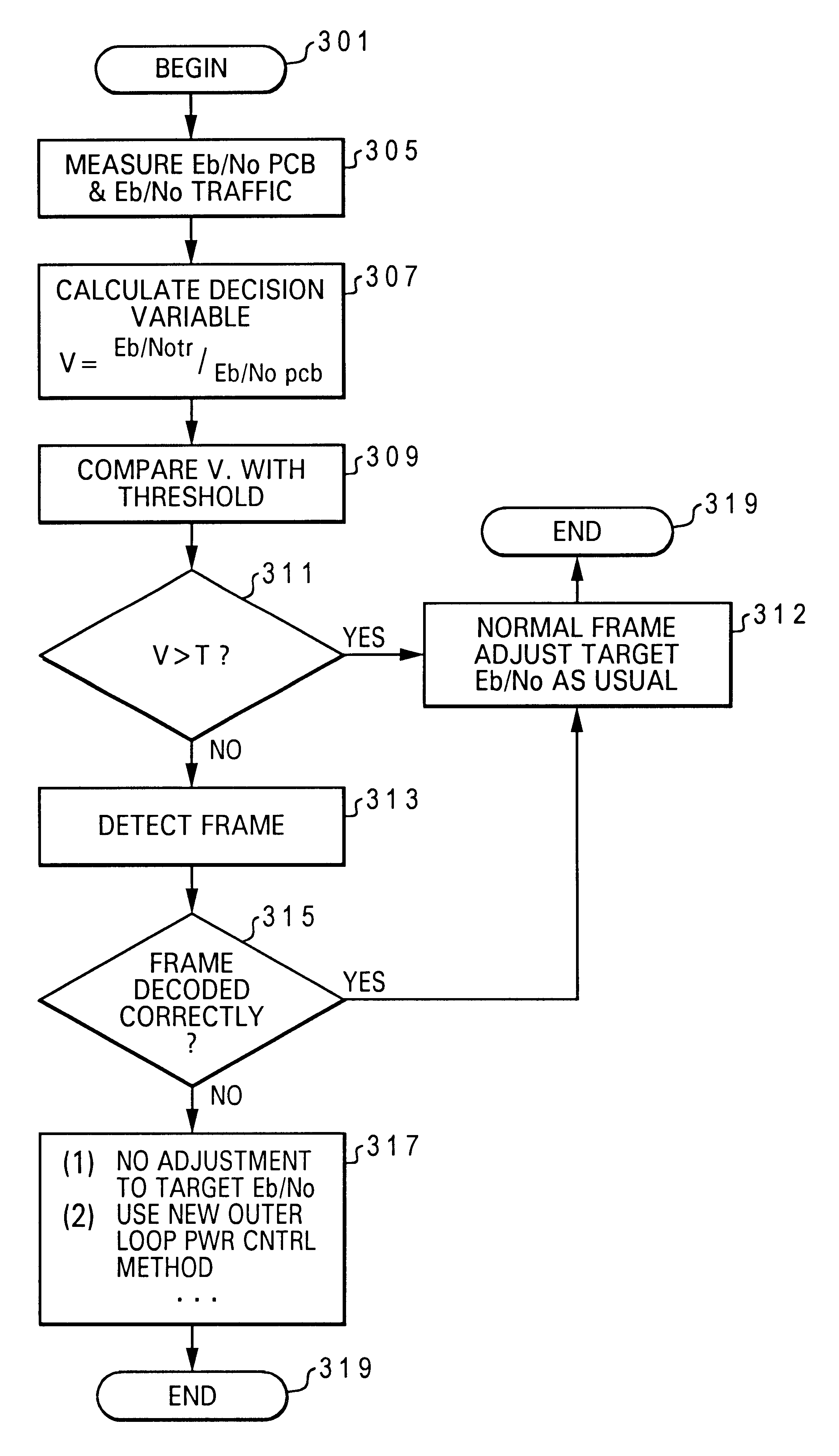
A method for controlling unnecessary power increases and call drop during discontinuous transmission (DTX) mode of a frame-based transmission system. The method comprises the steps of (1) detecting, at a receiver end of the transmission system a status of a transmitted frame indicating one of two possible transmission modes including (a) when a gating-off of the traffic channel occurs, and (b) when no gating-off of traffic occurs and normal traffic is being transmitted, and (2) controlling a change in the receiver target bit energy to noise spectrum density ratio Eb / No in response to the detection step so that a receiver target Eb / No is increased only when the detecting step does not indicate a gating-off of traffic has occurred.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for implementing outer loop power control in discontinuous transmission mode using explicit signalling
A signalling method for controlling unnecessary power increases and call drop during discontinuous transmission (DTX) mode of a frame-based transmission system. The signalling method comprises the steps of (1) detecting, at a receiver end of the transmission system a status of a transmitted frame indicating one of two possible transmission modes including (a) when a gating-off of the traffic channel occurs, and (b) when no gating-off of traffic occurs and normal traffic is being transmitted, and (2) controlling a change in the receiver target bit energy to noise spectrum density ratio Eb / No in response to the detection step so that a receiver target Eb / No is increased only when the detecting step does not indicate a gating-off of traffic has occurred.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method of characterizing the performance of a payload of a satellite in orbit and associated IoT system
ActiveUS20170134103A1Simple methodWiden characterization angular rangeTransmitters monitoringCosmonautic vehiclesFrequency spectrumEngineering
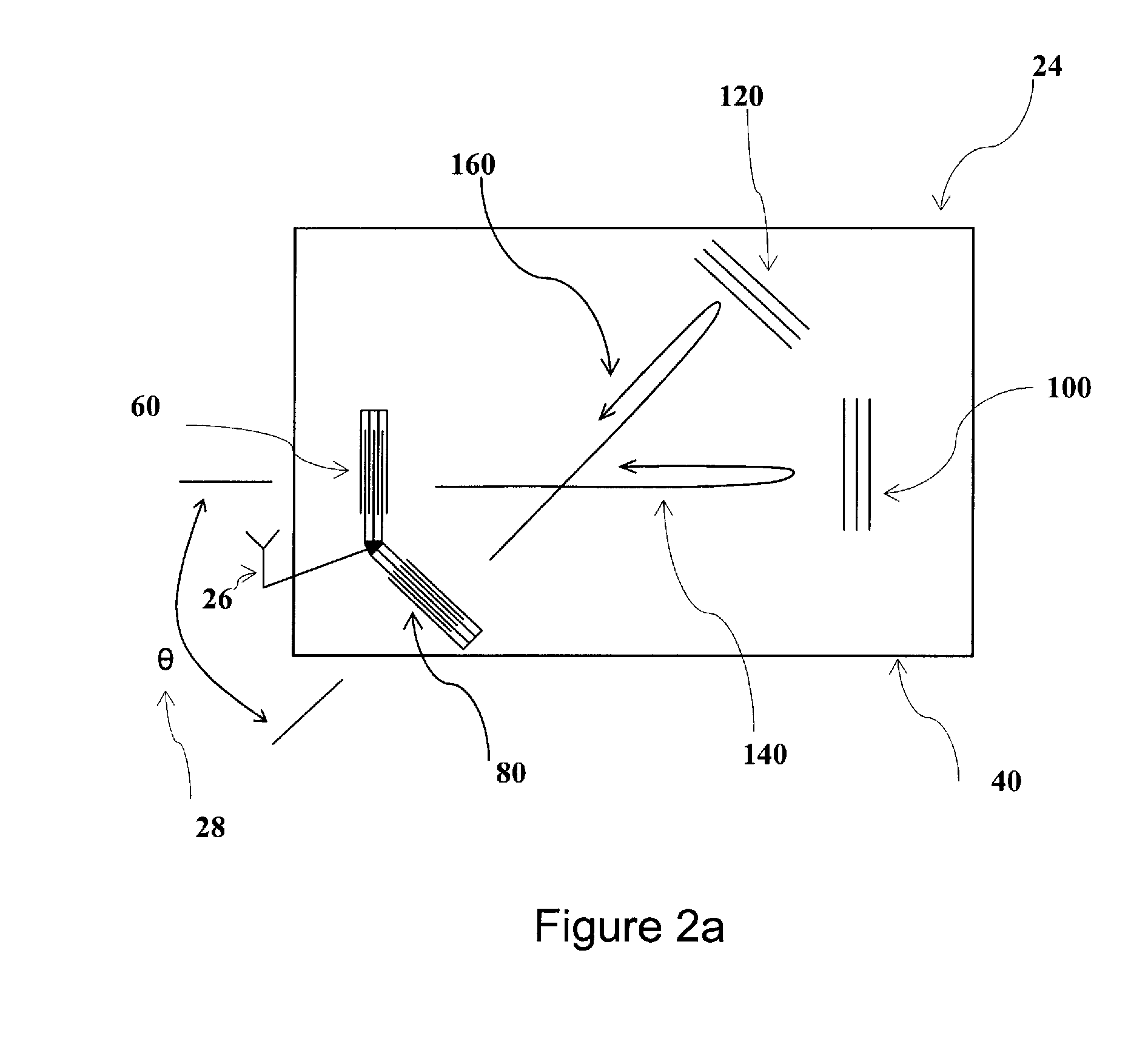
A method of characterizing the performance of the payload of a satellite in orbit is executed with the aid of a test ground station including first radio-frequency amplification means and a radio-frequency transmit ground antenna. The method includes a step of providing first amplification means that can be configured to generate at the input of the transmit ground antenna a wide-band test thermal noise the power spectral density of which can be adjusted to a test thermal noise reference power spectral density Dref so that the ratio of the test thermal noise spectral density received at the input of the transponder and that corresponds to it to the thermal noise floor spectral density generated by the satellite alone internally and the natural thermal noise of the Earth is greater than or equal to a first threshold Ds1 equal to 10 dB. An IOT system is configured to execute the method.
Owner:THALES SA
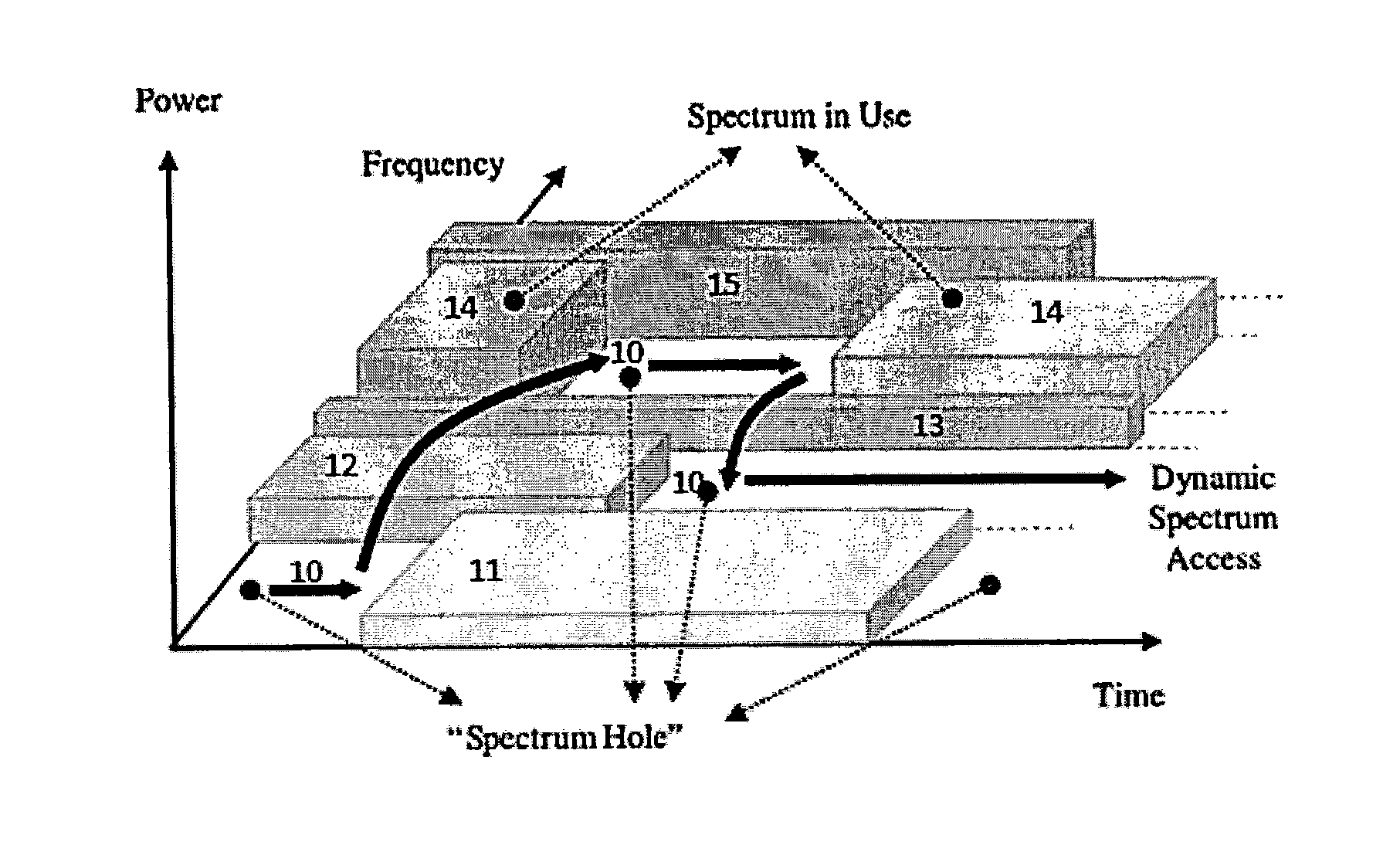
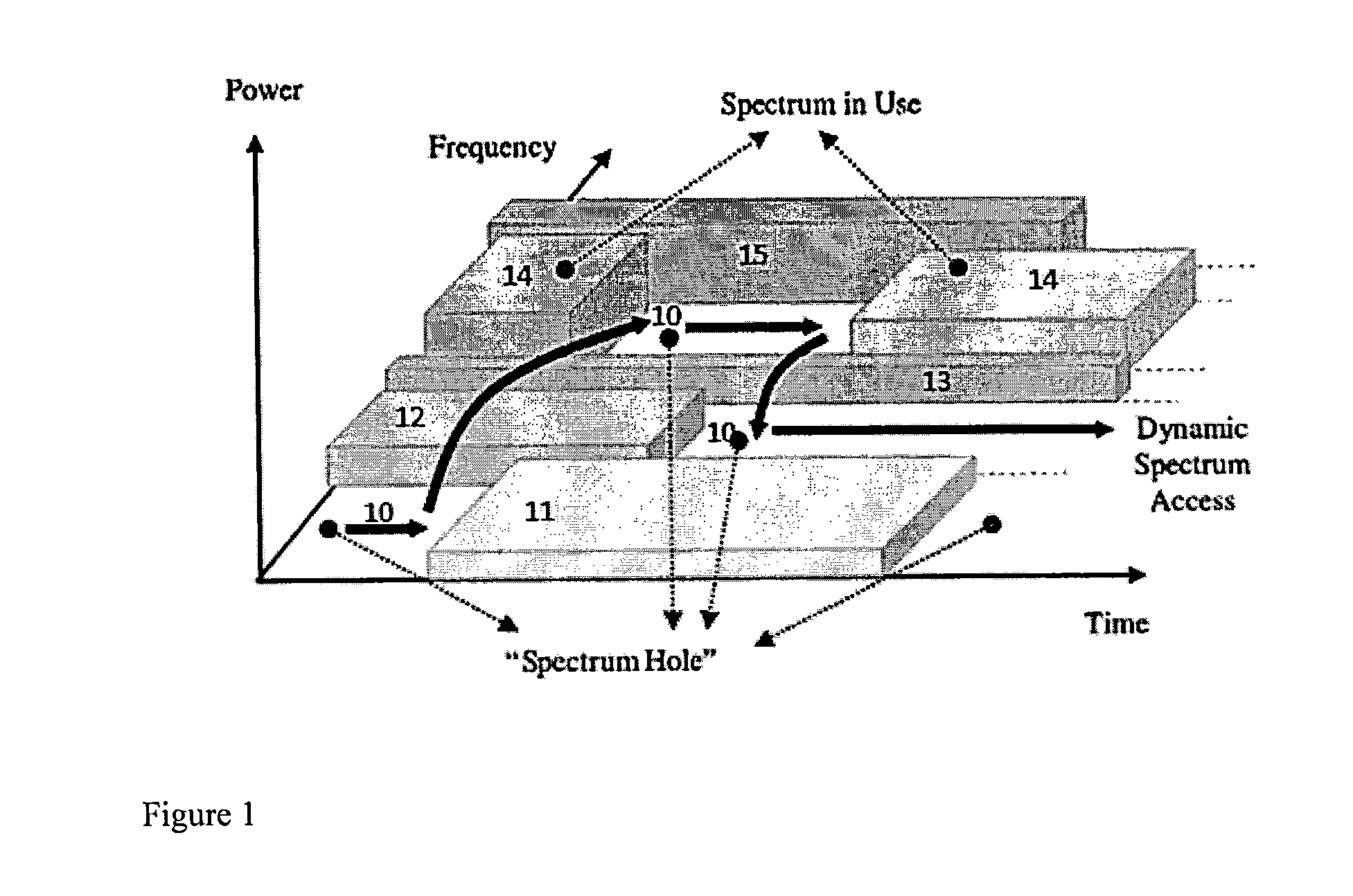
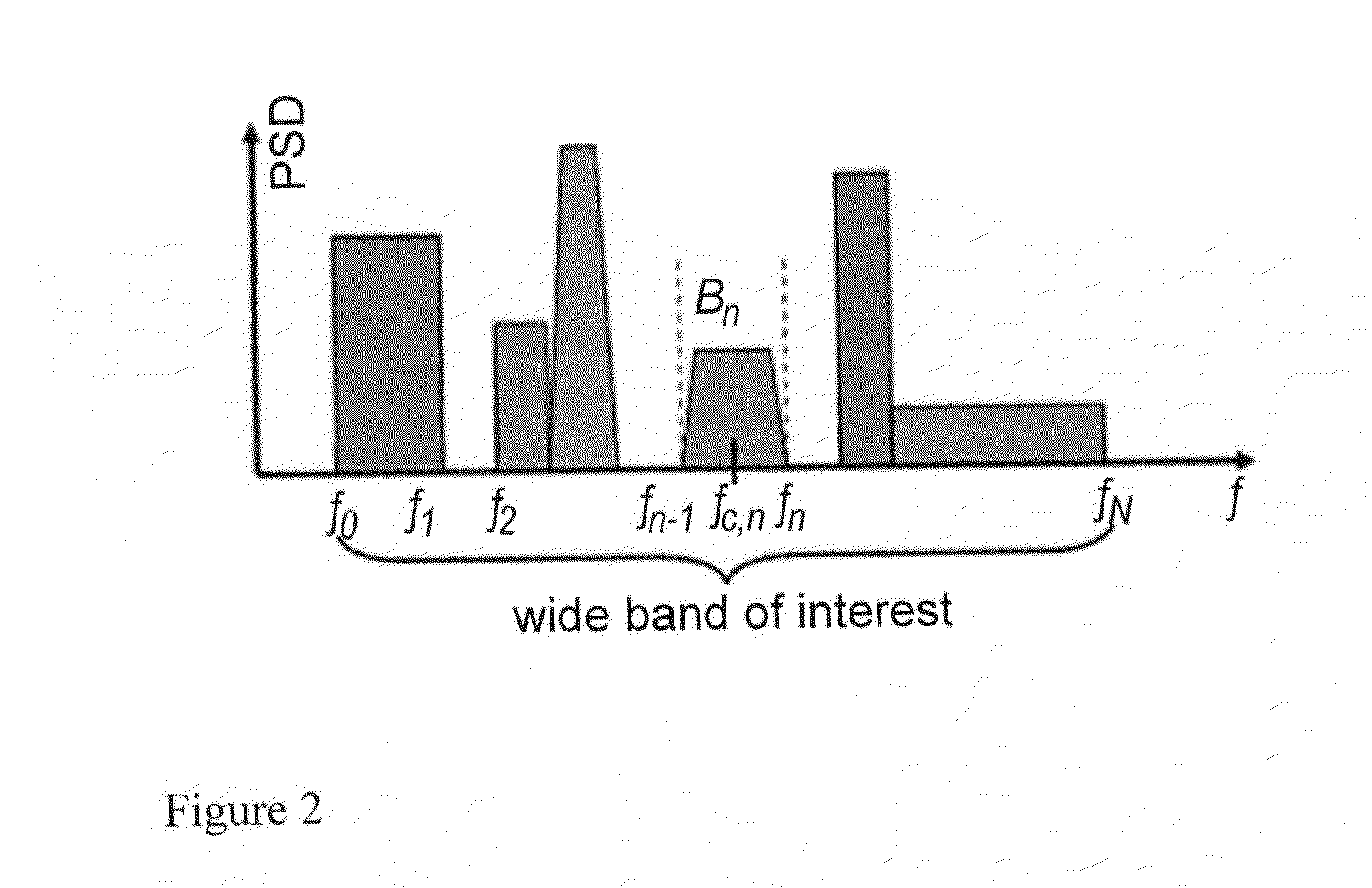
Cognitive radio spectrum sensing with improved edge detection of frequency bands
ActiveUS20150180689A1Efficient and robustSimple methodSpectral gaps assessmentTransmission path divisionFrequency spectrumSpectral density
A spectrum sensing method for cognitive radio wherein spectrum holes are detected in a wireless environment having spectrum scarcity. First, a cognitive radio user (CR) determines the power spectral density (PSD) of a wideband signal and detects subbands within the wideband using wavelet transforms (WT). WT coefficients are calculated by convolving the PSD with first derivatives of wavelet smoothing functions. The extrema of the WT coefficients demark frequency subband edges. Detecting subband edges becomes more robust against noise by median filtering the PSD before calculating WT coefficients, summing over WT coefficients with different scale factors, and suppressing WT coefficients below a noise threshold. After identifying subbands, the CR determines subband availability by measuring the subband power and signaling the power to a fusion center receiving power measurements from multiple cooperating CRs, and final decisions are based on data and decision fusion.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
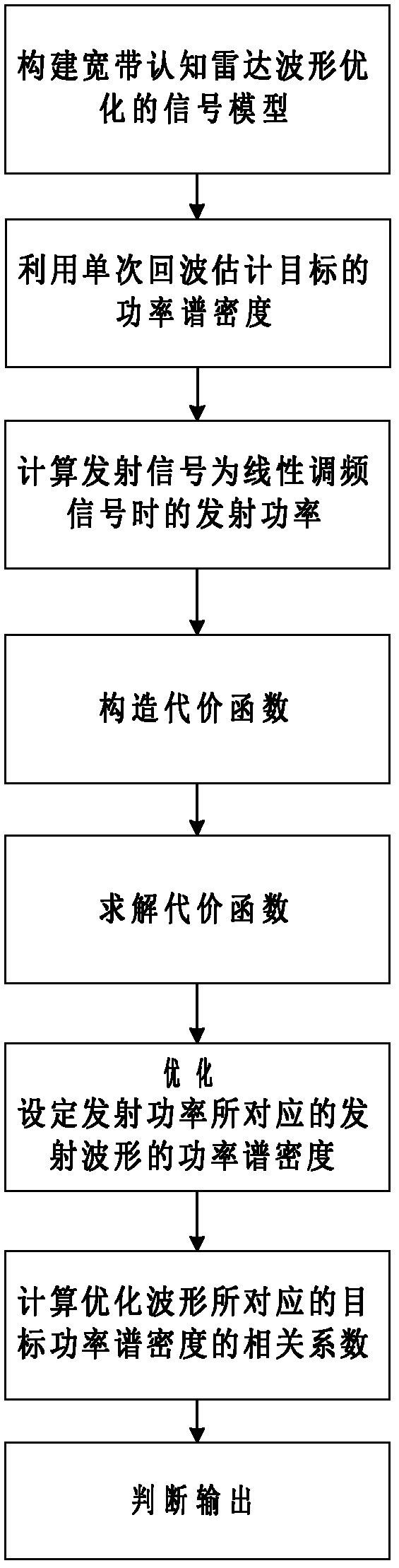
Waveform optimization method based on target cognition and transmitted power distribution
ActiveCN102565762ACognitive accuracyImprove estimation performanceWave based measurement systemsRadar waveformsTransmitted power
The invention discloses a waveform optimization method based on target cognition and transmitted power distribution, which mainly solves the problem that the current waveform optimization algorithm is not suitable for a broadband radar. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) building a waveform-optimized signal model of a cognitive radar of a broadband; (2) utilizing a single echo to estimate the power spectral density of a target; (3) calculating the transmitted power of a transmit signal being a linear frequency modulation signal to be used as a constrained initial value of the transmitted power; (4) constructing a cost function; (5) solving the cost function; (6) optimally setting the power spectral density of transmitted waveform corresponding to the transmitted power; (7) calculating the related coefficient of the estimated value and the true value of the power spectral density of the target corresponding to the optimized waveform; (8) and judging and outputting the power spectral density of the transmitted power and the transmitted waveform according to whether the related coefficient meets the requirements. According to the method, the transmitted waveform optimization and power distribution of a cognitive radar system of the broadband can be realized, and the efficiency and overall performance of the system are increased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Broadband high power light source
ActiveUS20120099340A1High optical peak powerSimplify Optical DesignMechanical apparatusLaser using scattering effectsStimulate raman scatteringLight beam
The present invention relates to a super continuum light source comprising a pump source arranged to emit light having a center wavelength λcenter arranged to provide pump pulse to a generator fibre, where the refractive index profile of the core is arranged to allow modal cleaning of the light is it propagates, such as via stimulated Raman scattering. An example of invention is the application of a relatively high power pump laser utilized to provide an optical super continuum with relatively high spectral density and / or good beam quality even though the pump laser may provide a beam with a high M2.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Detection of signals contianing sine-wave components through measurment of the power spectral density (PSD) and cyclic spectrum
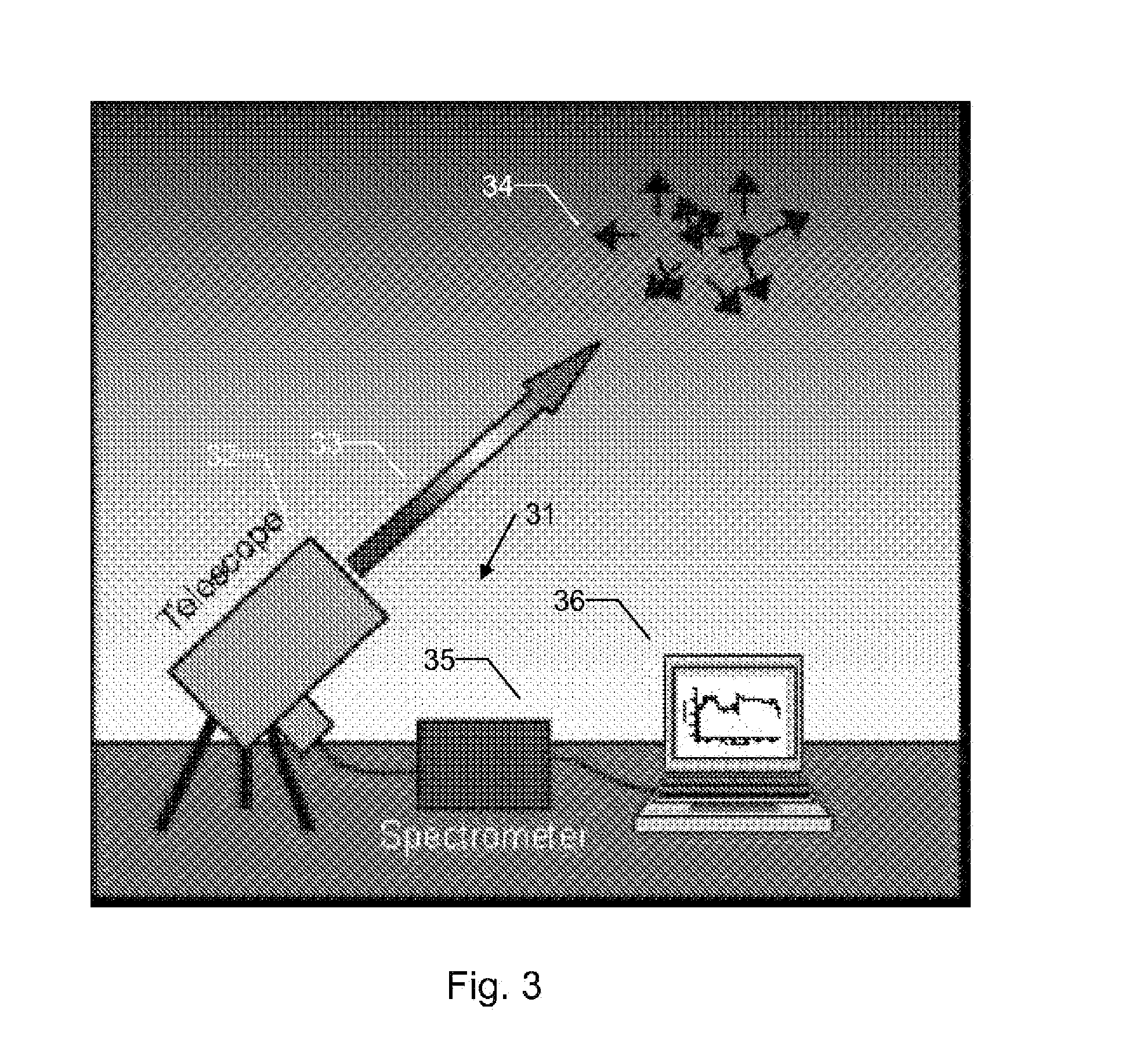
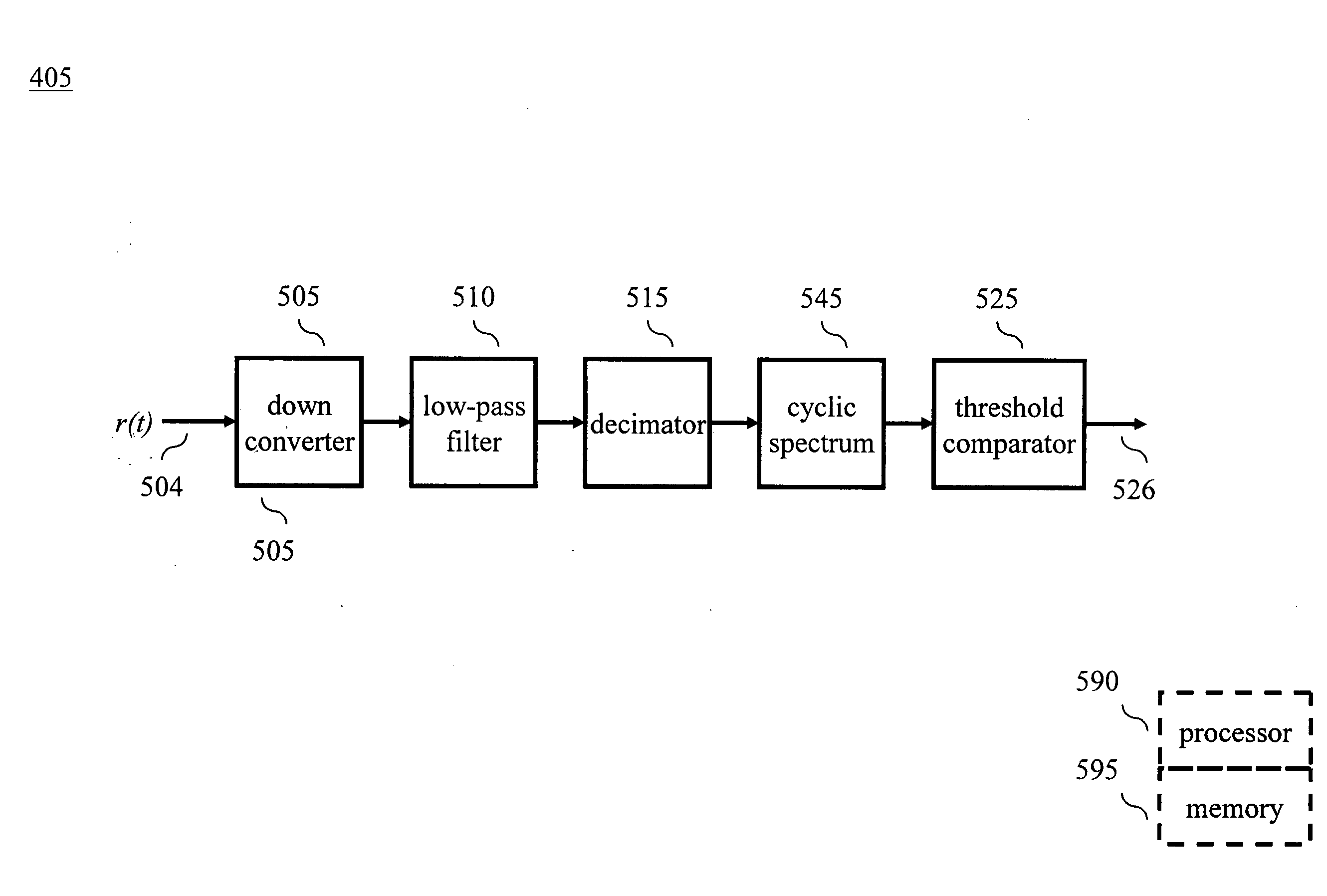
A Wireless Regional Area Network (WRAN) receiver comprises a transceiver for communicating with a wireless network over one of a number of channels, and a signal detector for use in forming a supported channel list comprising those ones of the number of channels upon which an Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) DTV (digital television) broadcast signal was not detected. The signal detector performs spectrum sensing as a function of power spectral density (PSD) and cyclic spectrum.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
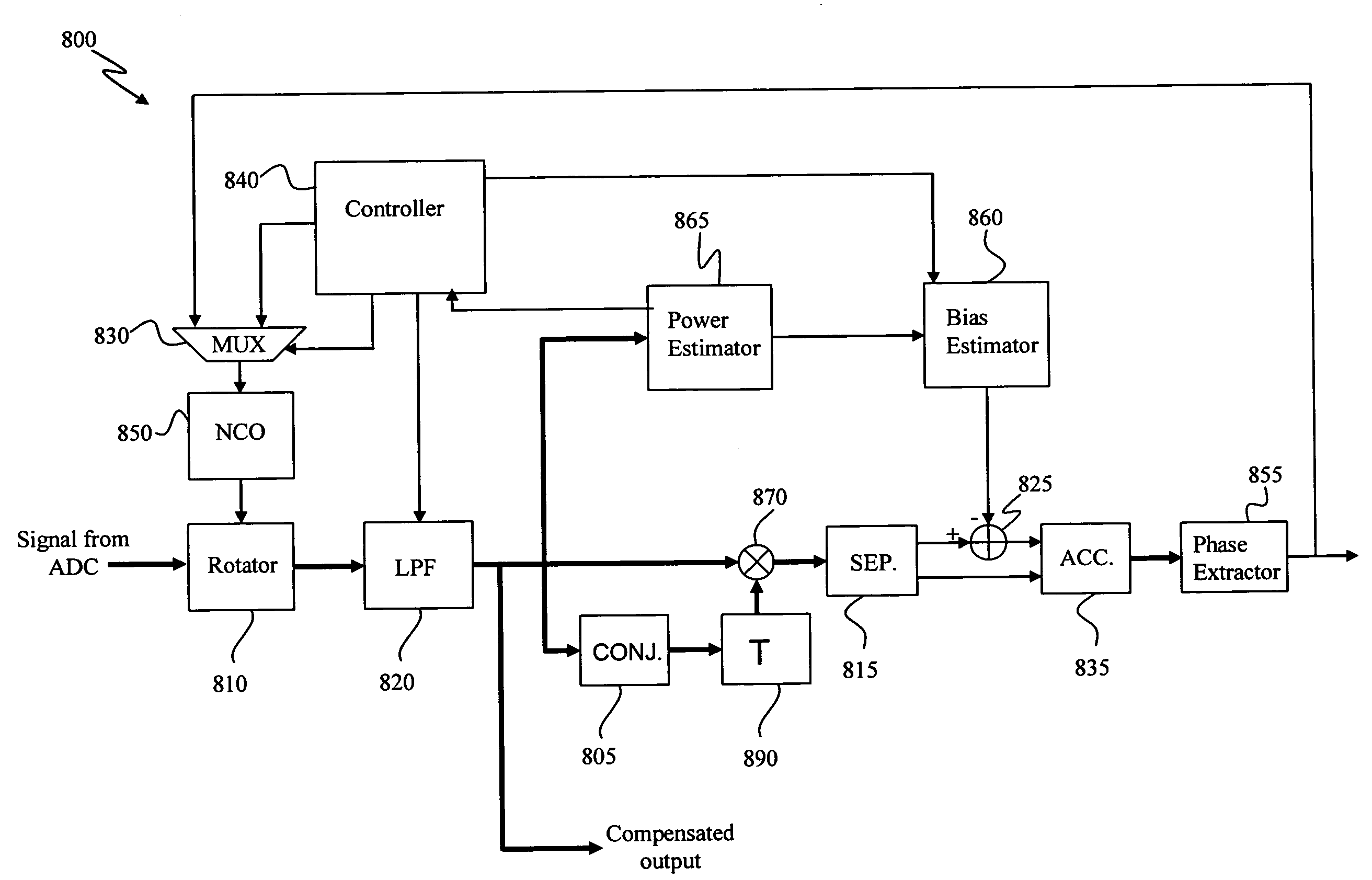
Apparatus and method for frequency estimation in the presence of narrowband gaussian noise
InactiveUS20090122928A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsFrequency spectrumReceiver function
A method of compensating for a frequency estimation bias due to sampled filtered noise of a channel filter, comprises: estimating autocorrelation functions for the impulse response of the channel filter over a range of frequencies; selecting one of the frequencies for use; estimating a noise spectral density of the sampled filtered noise; reading the autocorrelation function corresponding to the selected frequency; estimating the frequency bias as a function of the noise spectral density and the autocorrelation function for the selected frequency; and using the estimate to compensate for the frequency offset. The compensated signal is useful in such standard receiver functions as, automatic gain control (AGC), timing recovery, matched filtering / equalization and phase estimation and compensation.
Owner:DIGITALPTICS CORP INT
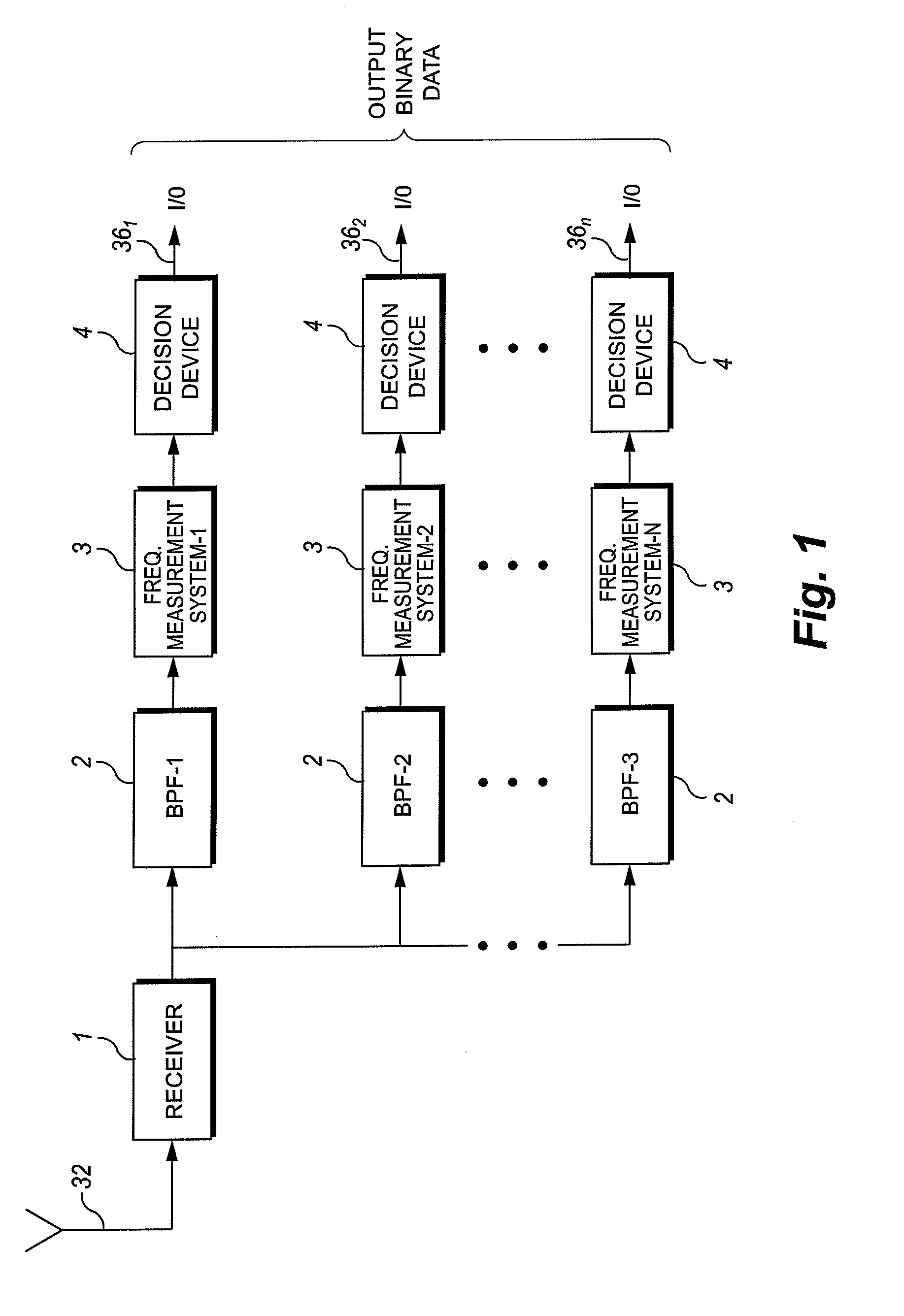
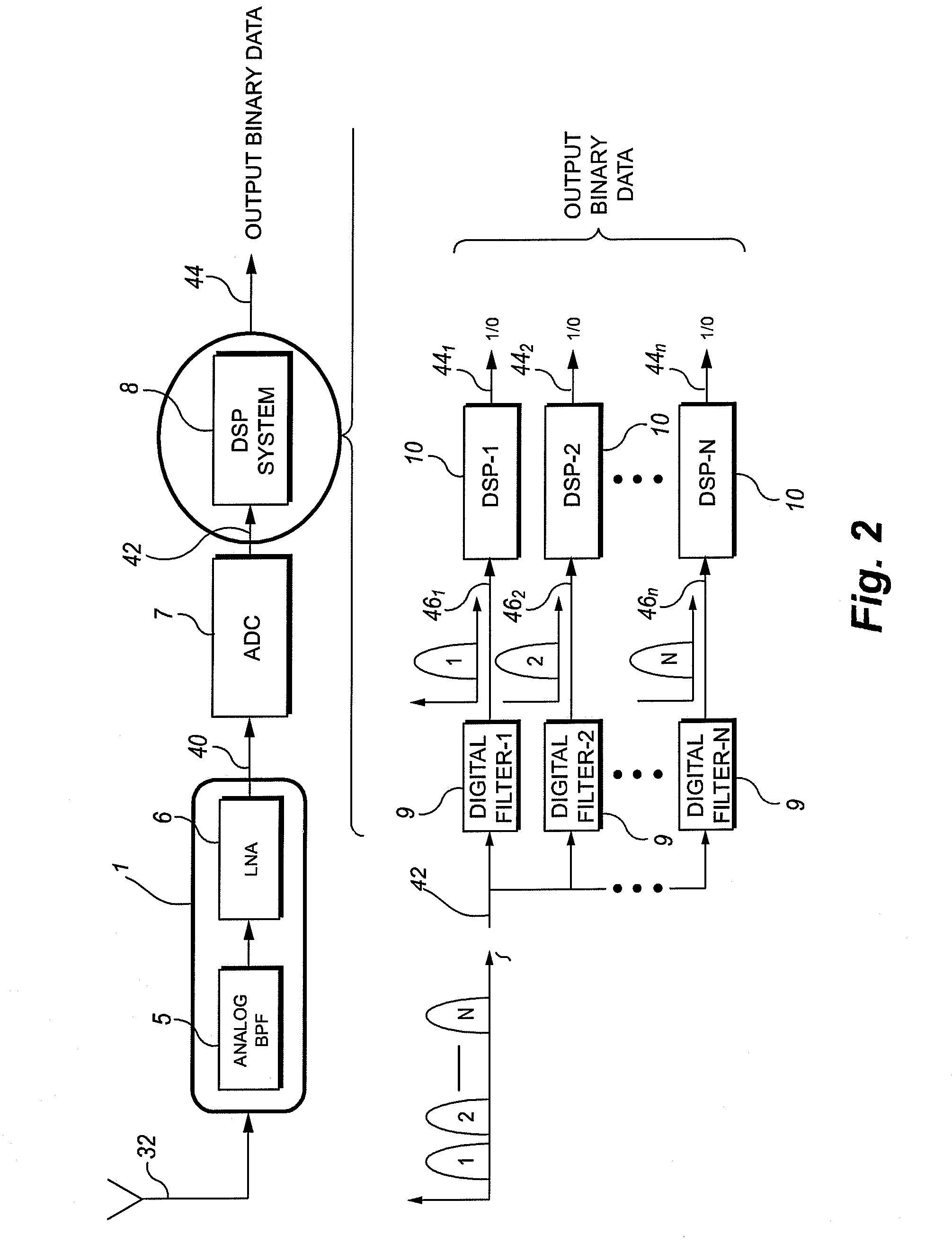
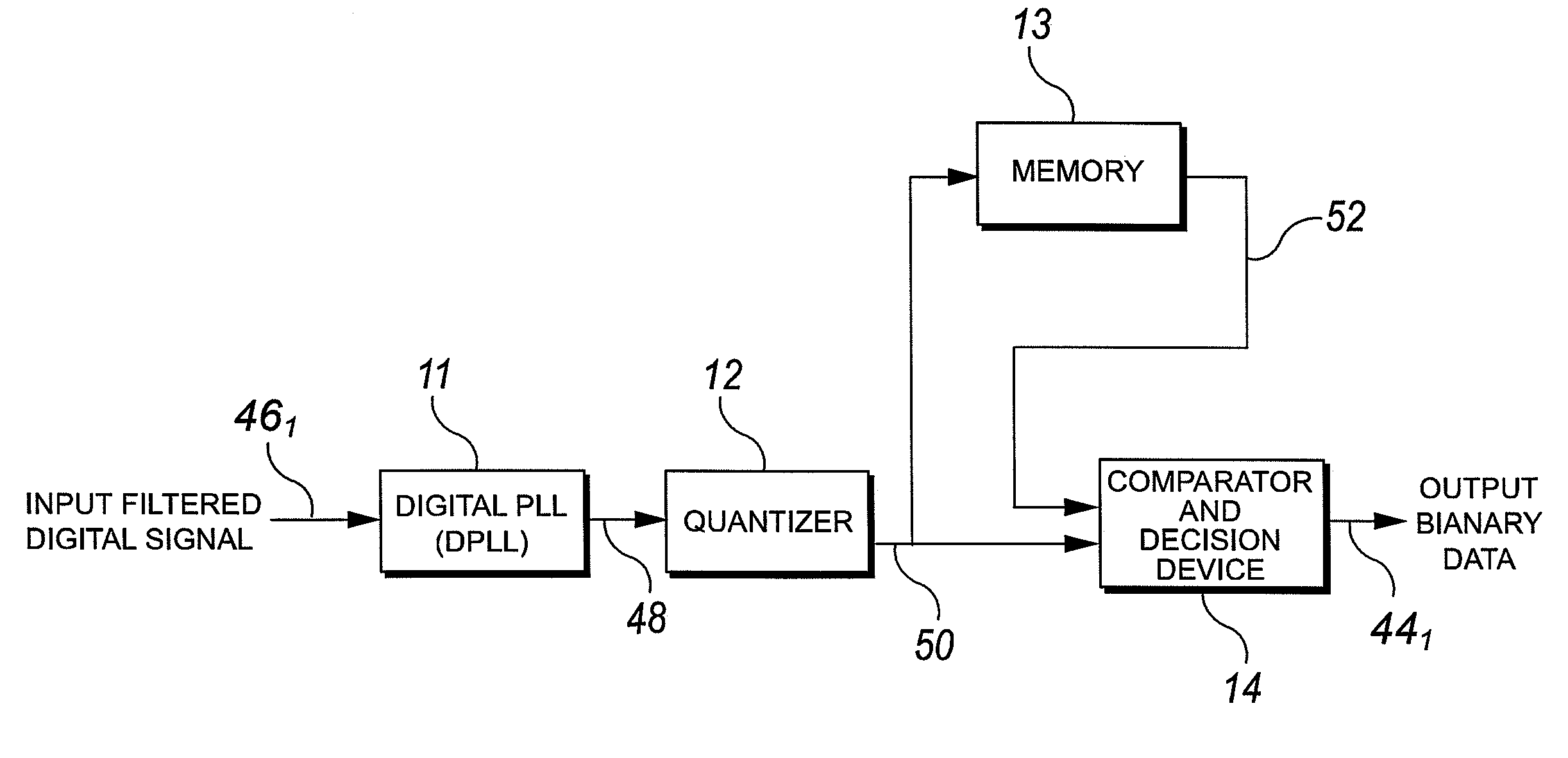
Frequency measurement system for low modulation index digital fm/pm communication
ActiveUS20080025439A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsDigital signal processingFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and methods for data demodulation in FM-FSK communication systems may include comparing the power spectral density (PSD) of the received frequency spectrum with that of the previously received samples using digital signal processing on a multi-sample message. A narrow band FM-FSK receiver may include a filter configured to pass FM signal components of a predetermined signal band, a memory configured to store the filtered signal component, and a DSP operably connected to the filter and the memory. The DSP may be configured to output a digital signal based upon a comparison of successive DSP calculated frequencies associated with a peak power of a power spectrum density (PSD) of successive samples of the filtered multi-sample message.
Owner:AL EIDAN ABDULLAH A
Coded acoustic wave sensors and system using time diversity
ActiveUS20090121847A1Increase the number ofIncrease diversityFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsThermometers using physical/chemical changesTime delaysMultiple sensor
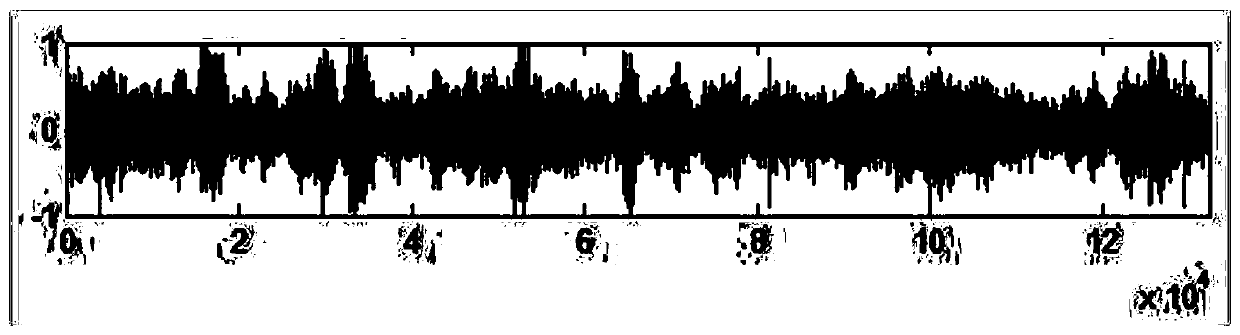
An apparatus and method for distinguishing between sensors that are to be wirelessly detected is provided. An interrogator device uses different, distinct time delays in the sensing signals when interrogating the sensors. The sensors are provided with different distinct pedestal delays. Sensors that have the same pedestal delay as the delay selected by the interrogator are detected by the interrogator whereas other sensors with different pedestal delays are not sensed. Multiple sensors with a given pedestal delay are provided with different codes so as to be distinguished from one another by the interrogator. The interrogator uses a signal that is transmitted to the sensor and returned by the sensor for combination and integration with the reference signal that has been processed by a function. The sensor may be a surface acoustic wave device having a differential impulse response with a power spectral density consisting of lobes. The power spectral density of the differential response is used to determine the value of the sensed parameter or parameters.
Owner:SENSANNA
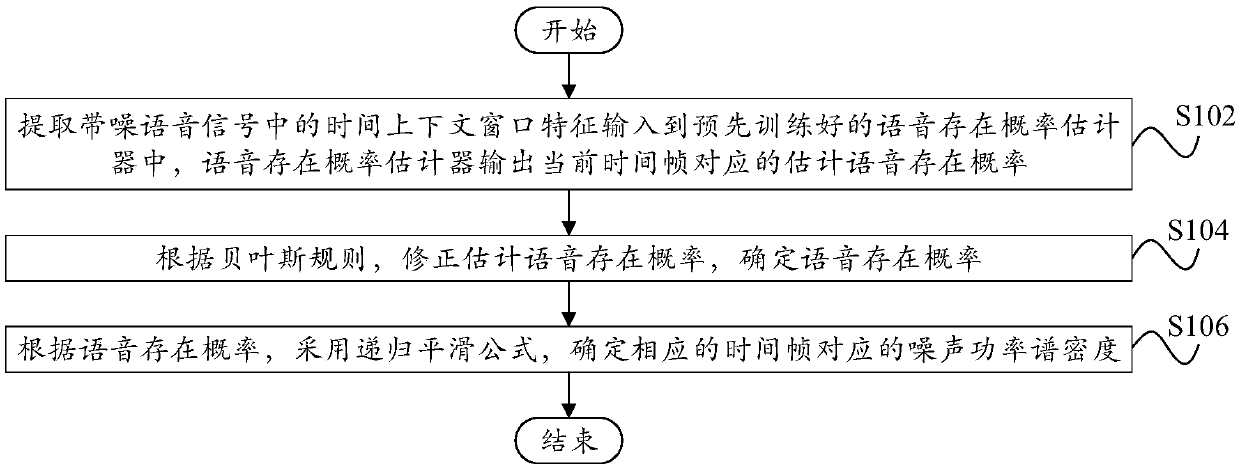
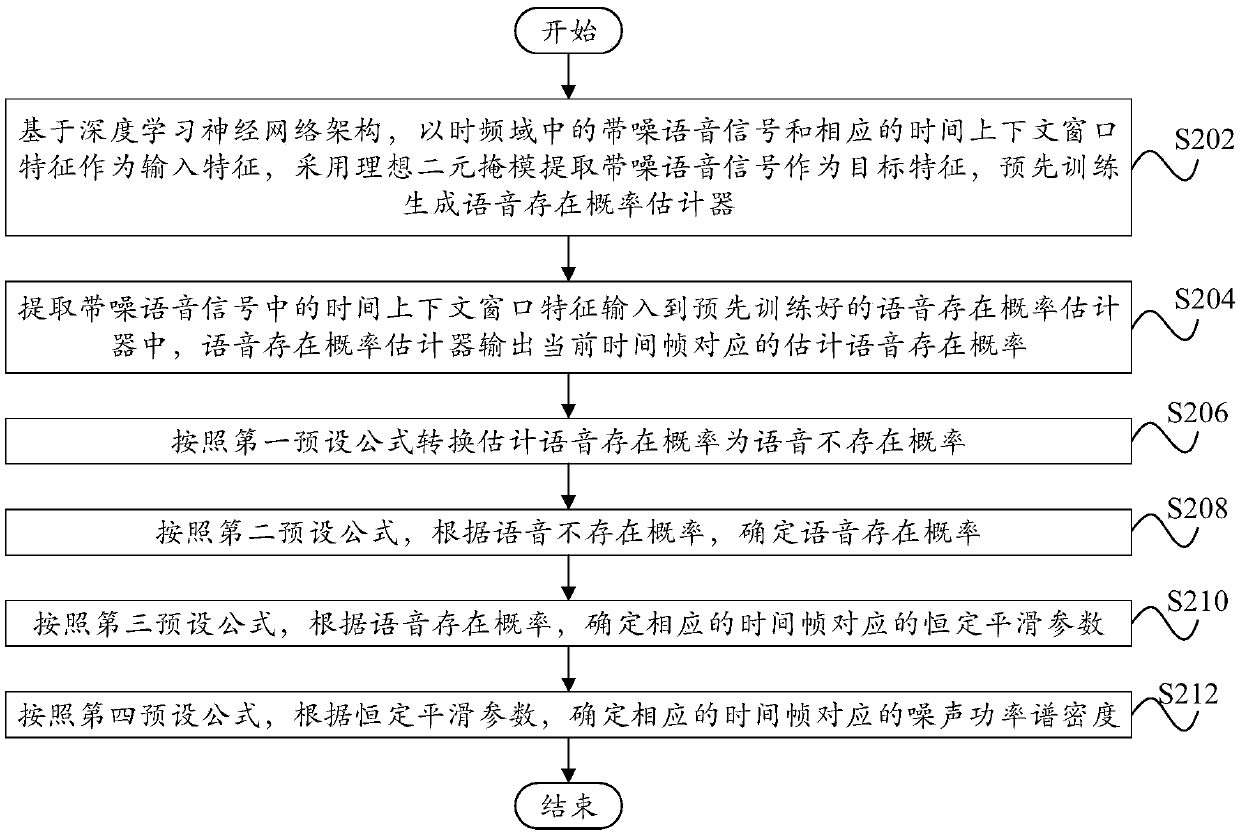
Method and device for estimating noise power spectral density of speech signal
PendingCN109616139AImprove estimation accuracyImprove speech enhancement performanceSpeech analysisBayes' ruleNoise power spectrum
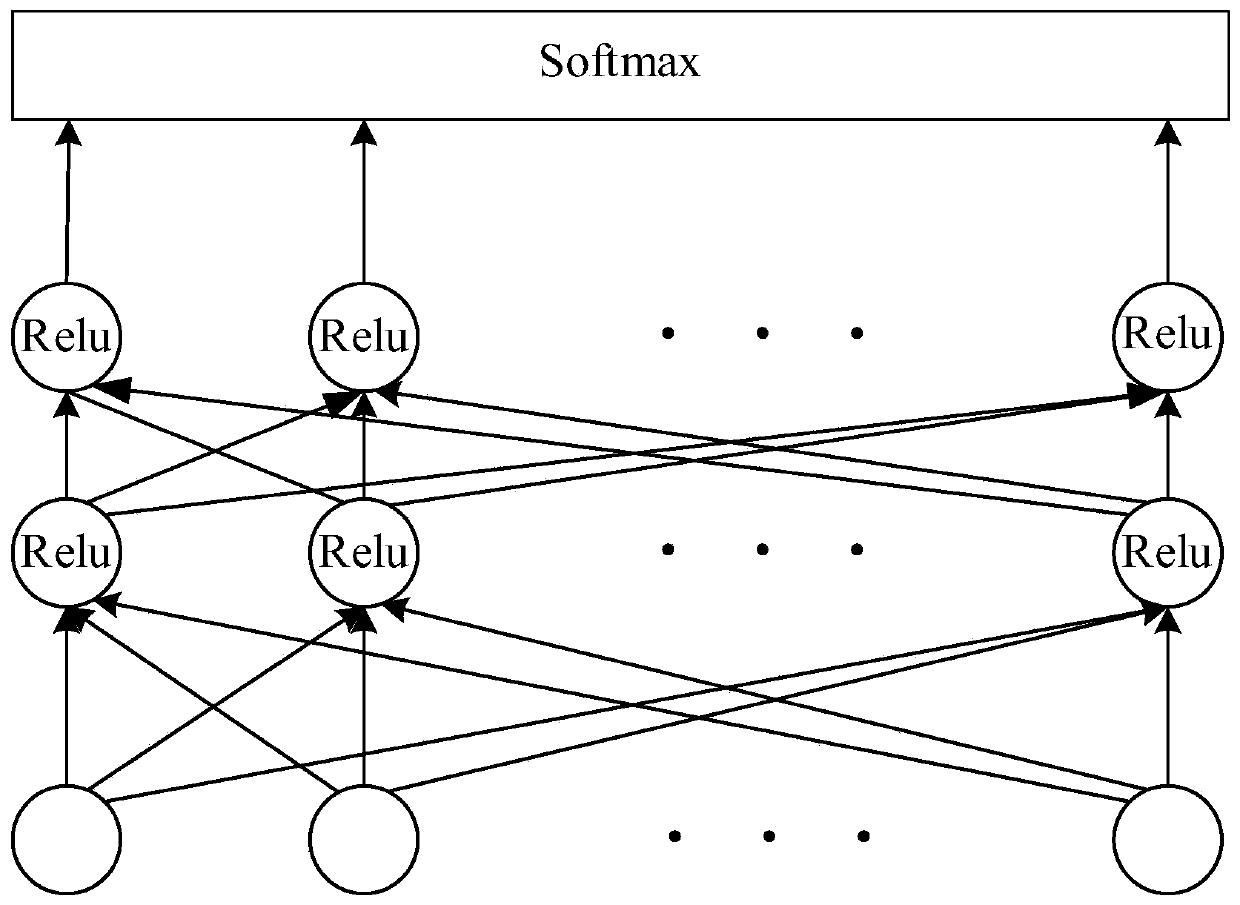
The invention relates to the technical field of speech processing and specifically provides a method and a device for estimating a noise power spectral density of a speech signal. The method comprisesthe following steps: extracting a time context window feature from a noise speech signal, inputting the time context window feature to a pre-trained speech existence probability estimator which outputs an estimated speech existence probability corresponding to a current time frame; correcting the estimated speech existence probability according to a Bayes rule to determine a speech existence probability; determining the noise power spectral density corresponding to the corresponding time frame based on the speech existence probability according to a recursive smoothing formula. Through the technical scheme of the invention, the estimation accuracy of the noise power spectral density is improved in the case of small computing resources, thereby being beneficial to effectively eliminating noise signals, minimizing distortion in the speech processing process and improving speech enhancement performance.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Frequency measurement system for low modulation index digital FM/PM communication
ActiveUS7653152B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsFrequency-modulated carrier systemsDigital signal processingFrequency spectrum
Owner:AL EIDAN ABDULLAH A
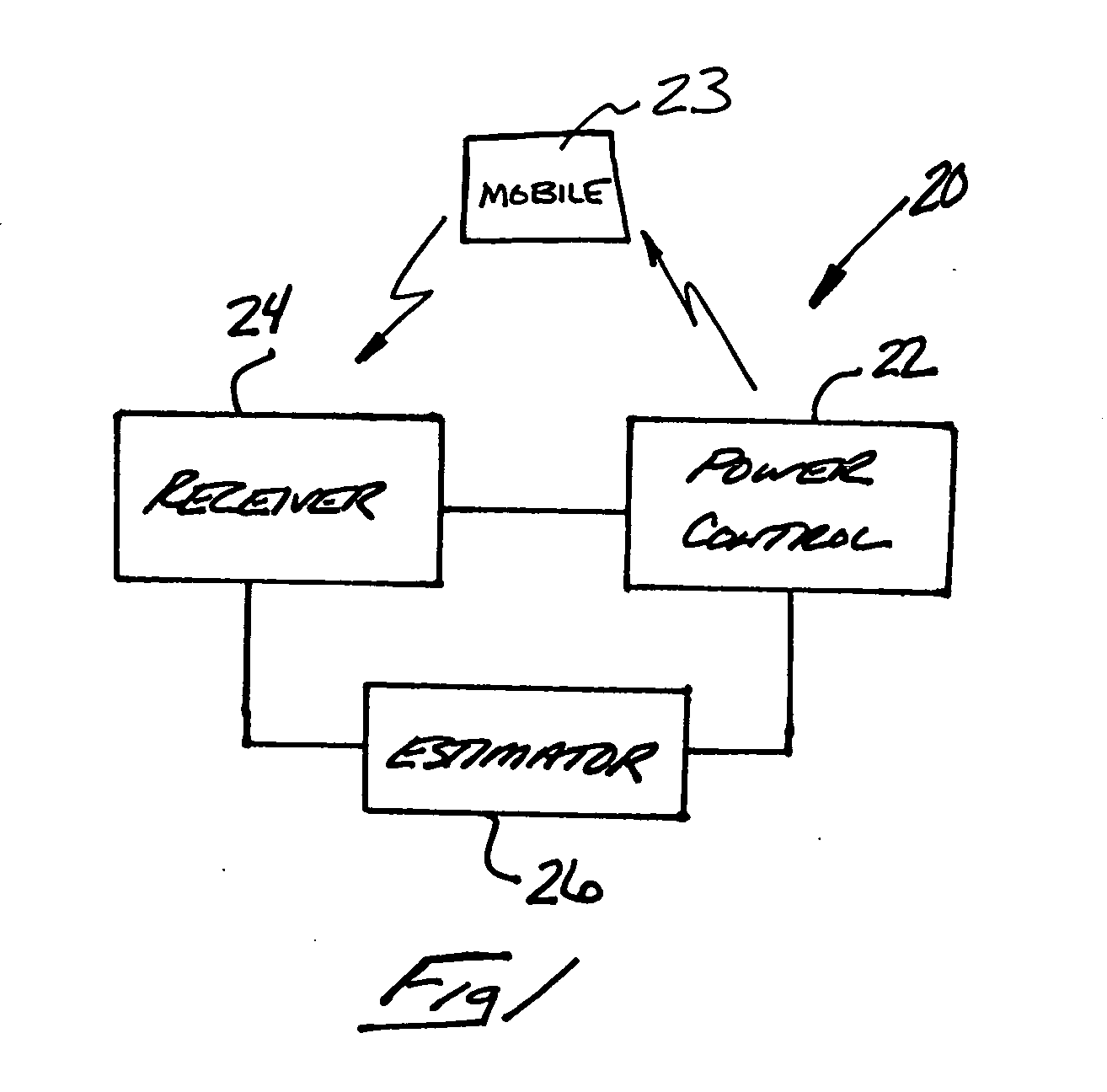
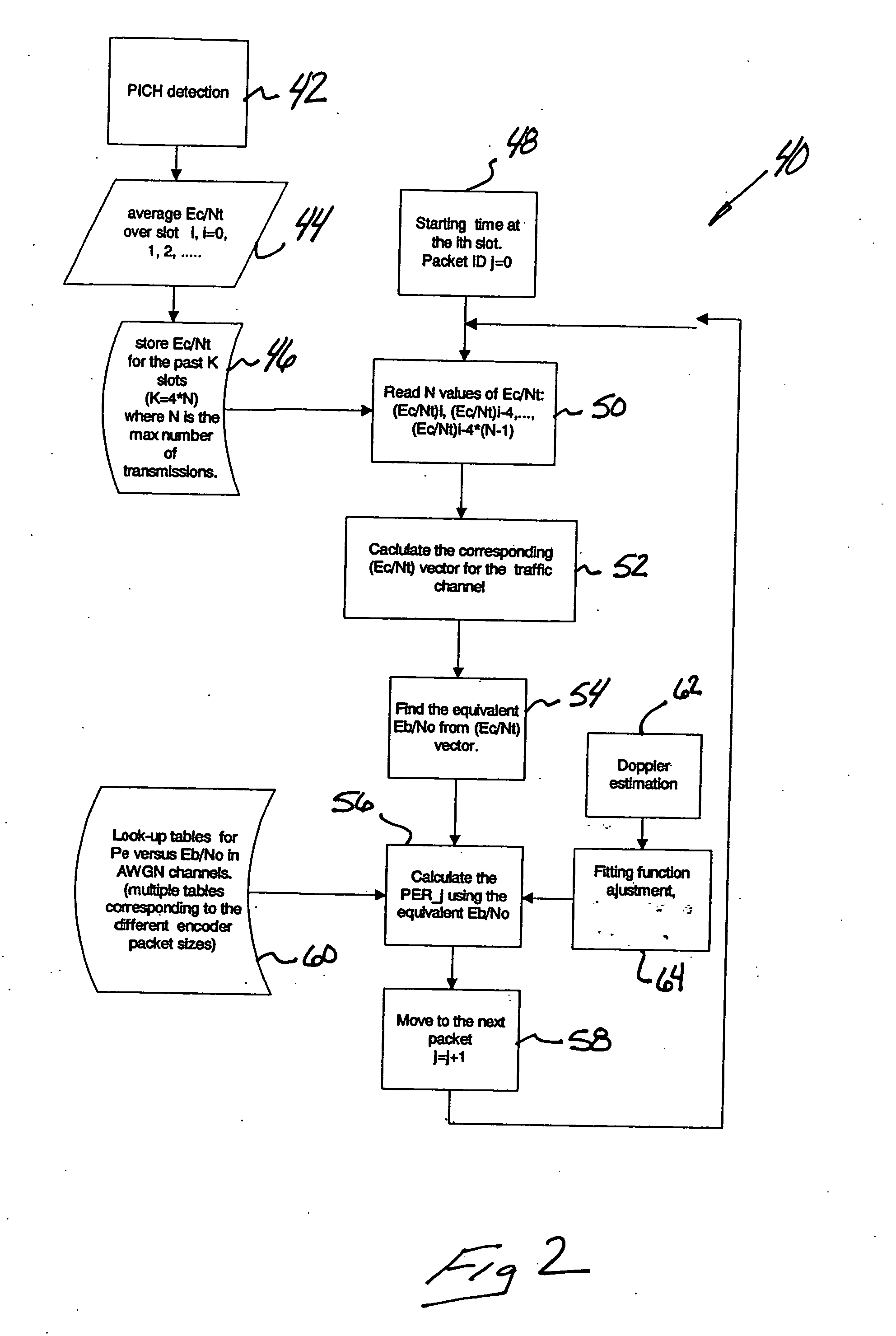
Packet error rate estimation in a communication system
InactiveUS20060067242A1Power managementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency spectrumCommunications system
Data communication includes an estimate of packet error rate that is useful, for example, when there is insufficient data transmission to provide a direct measurement of packet error rate. At least one pilot channel output provides a basis to determine an estimated packet error rate. One example includes using a pilot channel ratio of an energy-per-chip to a noise spectrum density. Another example includes using a pilot symbol error rate from the pilot channel as the basis for determining the traffic channel packet error rate.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Dual-channel voice enhancement method based on noise power spectral density
InactiveCN107680609AAvoid distortionImprove portabilitySpeech analysisNoise power spectrumAccurate estimation
The invention discloses a dual-channel voice enhancement method based on noise power spectral density, and the method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: 1), carrying out the short-time Fourier transform of voice signals received by two channels; 2), constructing a cross-power spectrum reduction filter; 3), constructing a spectrum correction filter, and carrying outthe preliminary estimation of the power spectral density of ta noise signal; 4), carrying out the accurate estimation of noise in the noise-containing voice signals. The method can reduce the coherentnoise residual, can improve the inhibition of non-coherent noise, is high in transportability, and is very good in application prospect for small-size intelligent mobile equipment.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Coded acoustic wave sensors and system using time diversity
ActiveUS8094008B2Increase the number ofIncrease diversityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsTime delaysMultiple sensor
An apparatus and method for distinguishing between sensors that are to be wirelessly detected is provided. An interrogator device uses different, distinct time delays in the sensing signals when interrogating the sensors. The sensors are provided with different distinct pedestal delays. Sensors that have the same pedestal delay as the delay selected by the interrogator are detected by the interrogator whereas other sensors with different pedestal delays are not sensed. Multiple sensors with a given pedestal delay are provided with different codes so as to be distinguished from one another by the interrogator. The interrogator uses a signal that is transmitted to the sensor and returned by the sensor for combination and integration with the reference signal that has been processed by a function. The sensor may be a surface acoustic wave device having a differential impulse response with a power spectral density consisting of lobes. The power spectral density of the differential response is used to determine the value of the sensed parameter or parameters.
Owner:SENSANNA
Power control method and power control device
InactiveCN106998583AReduce energy consumptionAvoid wasting powerPower managementHigh level techniquesResource elementResource block
The invention provides a power control method and a power control device. The method comprises steps: information is determined to be transmitted on an unlicensed carrier; power control is carried out on the unlicensed carrier in at least one of the following manners: power control is carried out according to a power spectral density (PSD) based on a resource element (RE); the PSD based on the RB is adjusted, and power control is carried out according to the adjusted PSD; power control is carried out according to the PSD of actual data and the PSD of an occupying signal, wherein the actual data are data actually transmitted by a transmitting terminal and the occupying signal is a signal used for occupying a channel; power control is carried out according to a power offset; power control is carried out by means of adaptive adjustment or semi-static adjustment CCA detection of a threshold; and power control is carried out by means of controlling the range of values of at least one parameter related to power control. Thus, the problem that the power of the unlicensed carrier can not be controlled effectively in a related technology can be solved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
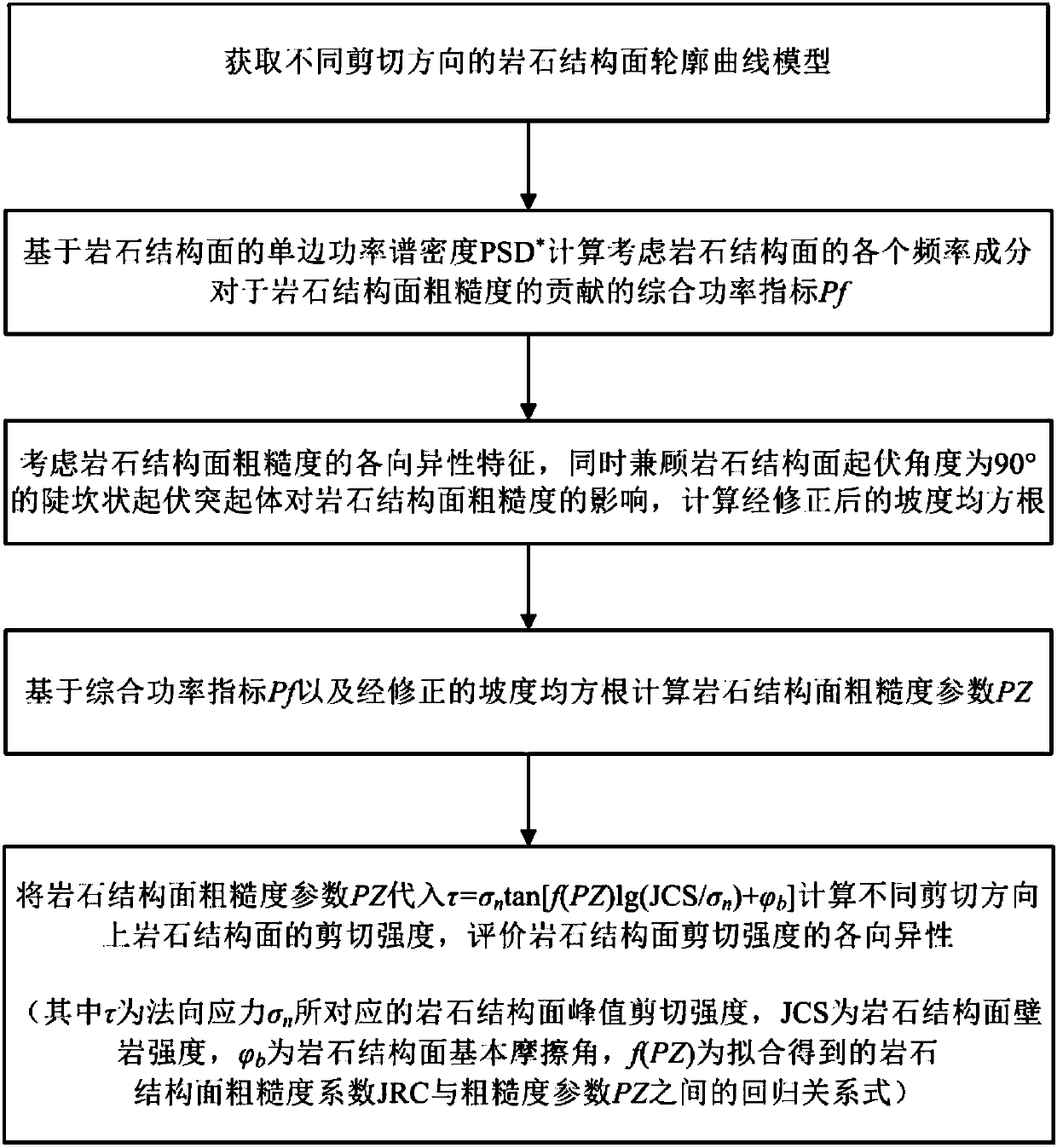
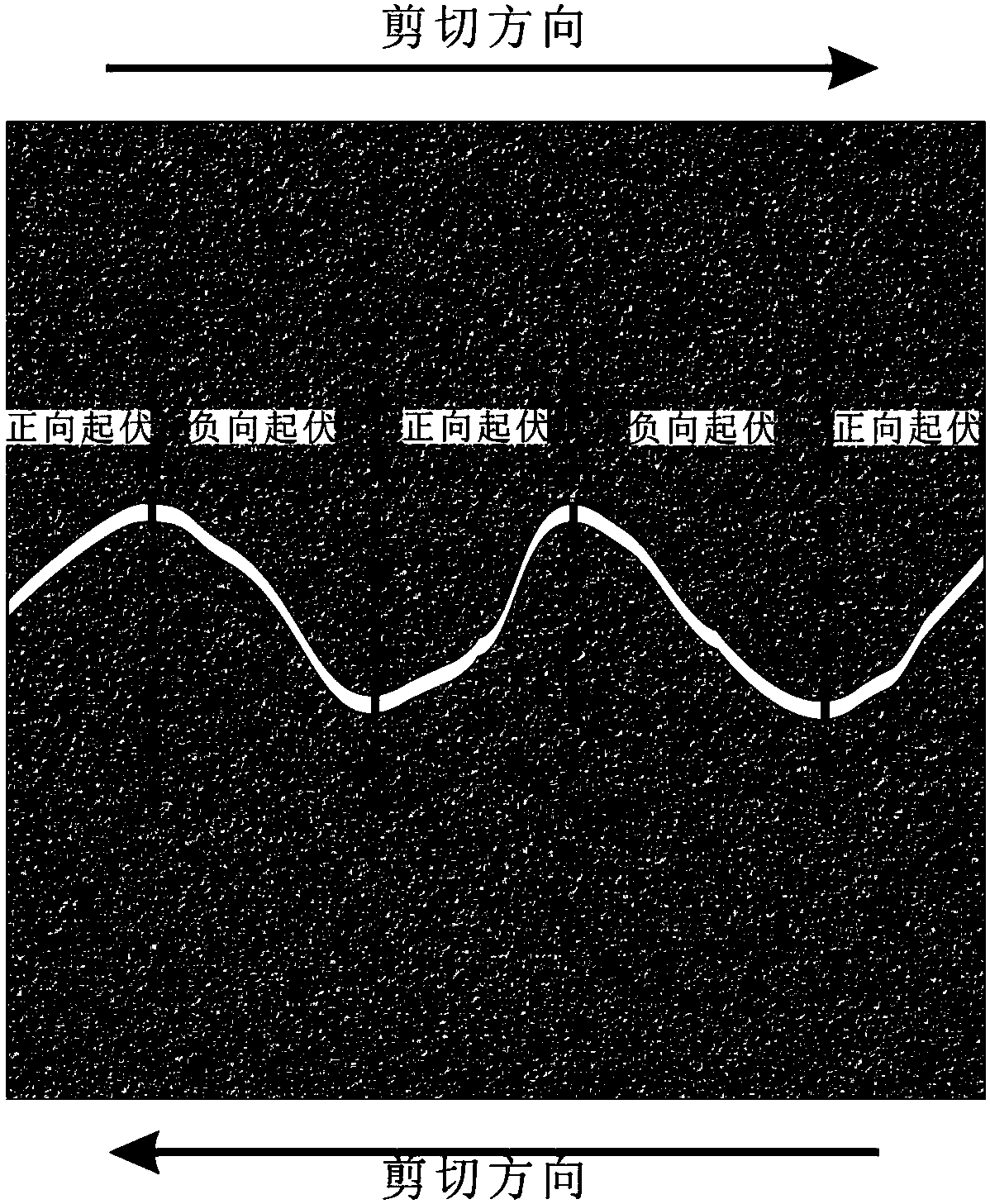
Anisotropy evaluation method for rock structural surface shear strength
InactiveCN108446431AComprehensive quantitative evaluationGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsAdditive ingredientSpectral density
The invention discloses an anisotropy evaluation method for rock structural surface shear strength. The method comprises the following steps that: S1: obtaining the rock structural surface outline curve models of different shearing directions; S2: on the basis of the one-side PSD (Power Spectral Density)* of the rock structural surface, calculating the comprehensive power index Pf of each frequency ingredient which forms the rock structural surface for the roughness contribution of the rock structural surface; S3: calculating a corrected gradient mean square root Z2<*>; S4: on the basis of thecomprehensive power index Pf and the gradient mean square root Z2<*>, calculating the roughness parameter PZ of the rock structural surface; and S5: calculating the shear strength in different sheardirections of the rock structural surface. By use of the method, on the basis of the power spectral density, the contribution of each frequency ingredient which forms the rock structural surface for the roughness of the rock structural surface and the anisotropy characteristic of the roughness of the rock structural surface are analyzed, and therefore, the anisotropy of the shear strength of the rock structural surface can be more comprehensively subjected to quantitative evaluation.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
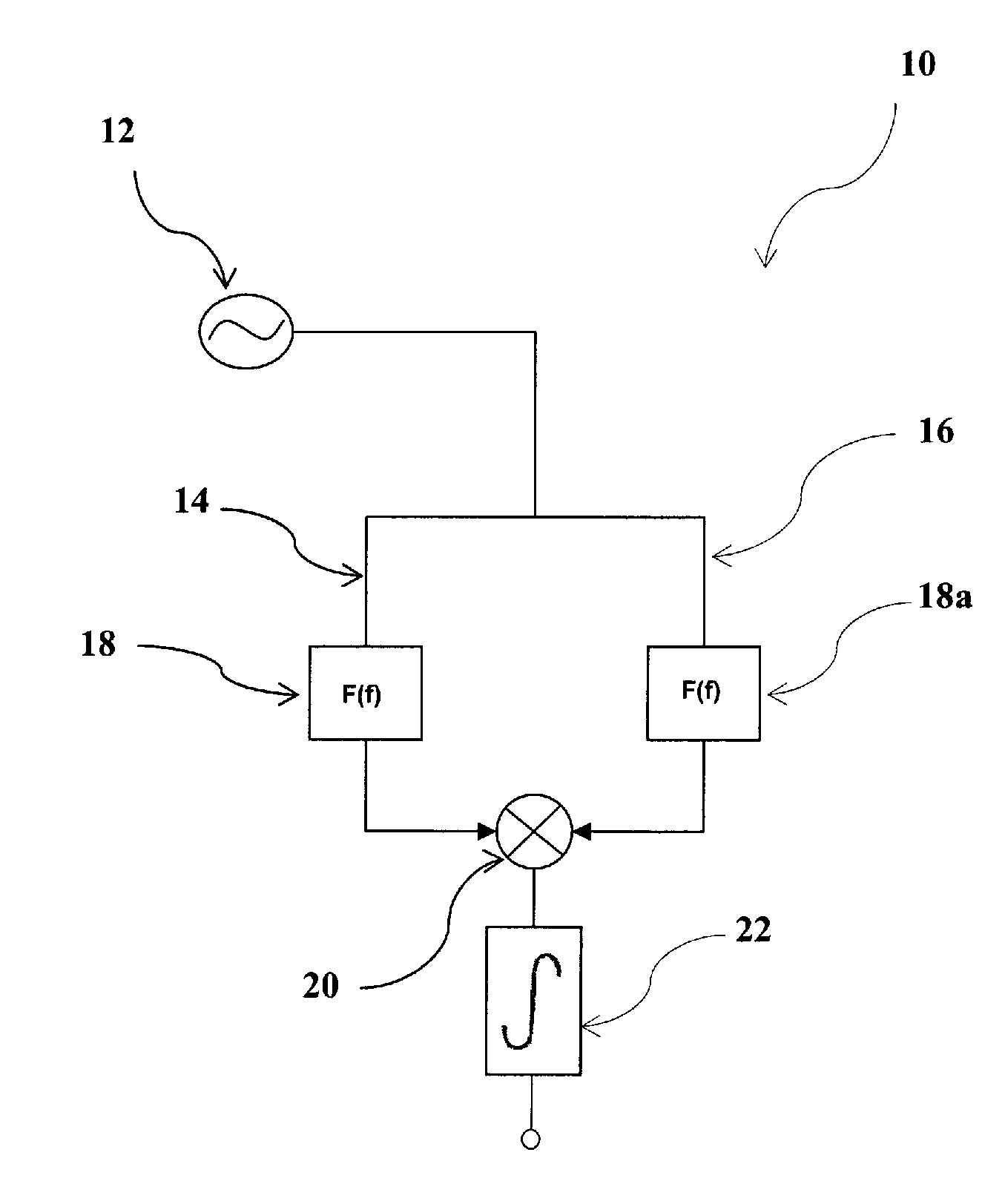
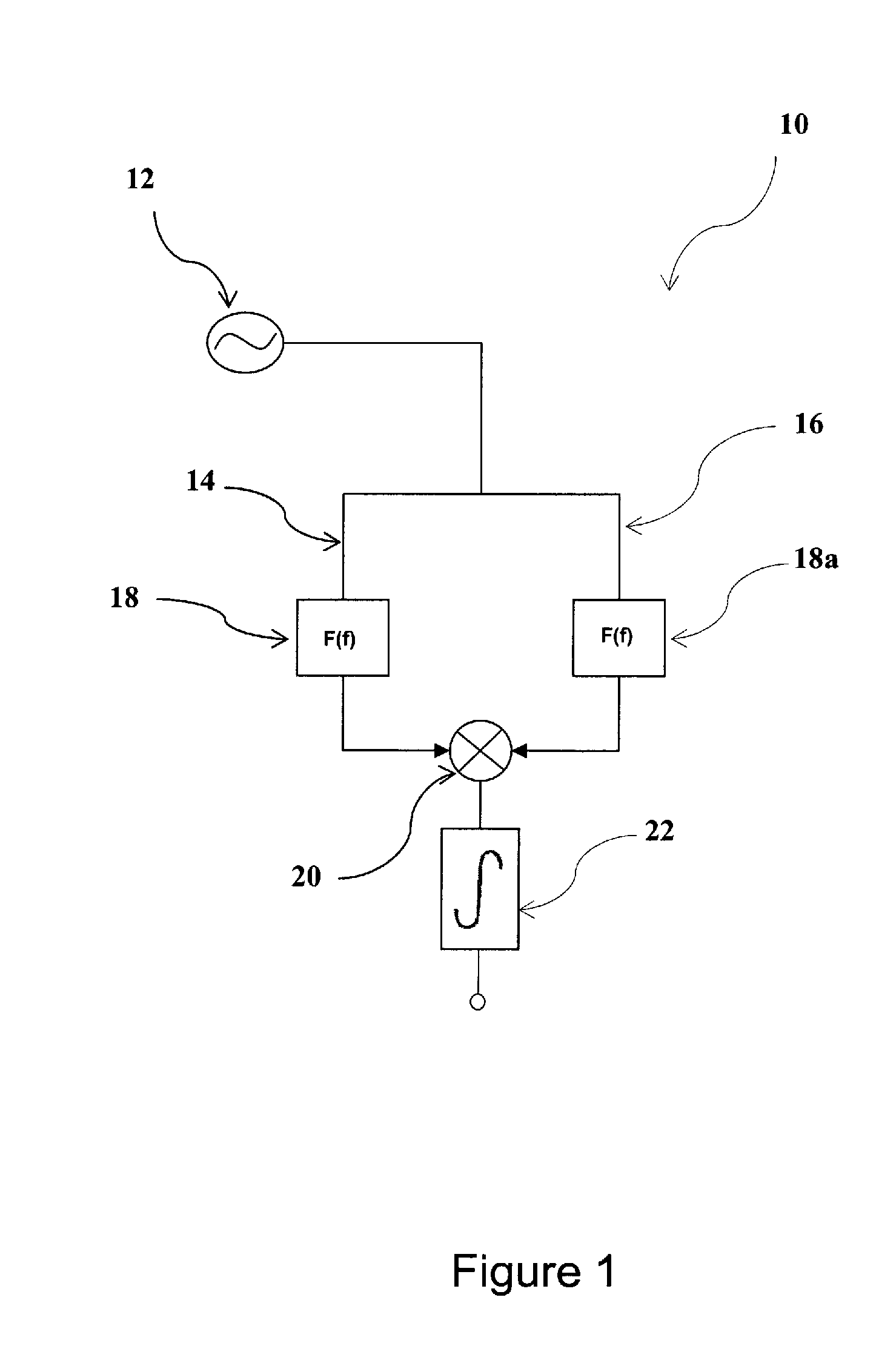
Determination of Statistical Error Bounds and Uncertainty Measures for Estimates of Noise Power Spectral Density
ActiveUS20130093770A1Drawing from basic elementsNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementFrequency spectrumNoise power spectrum
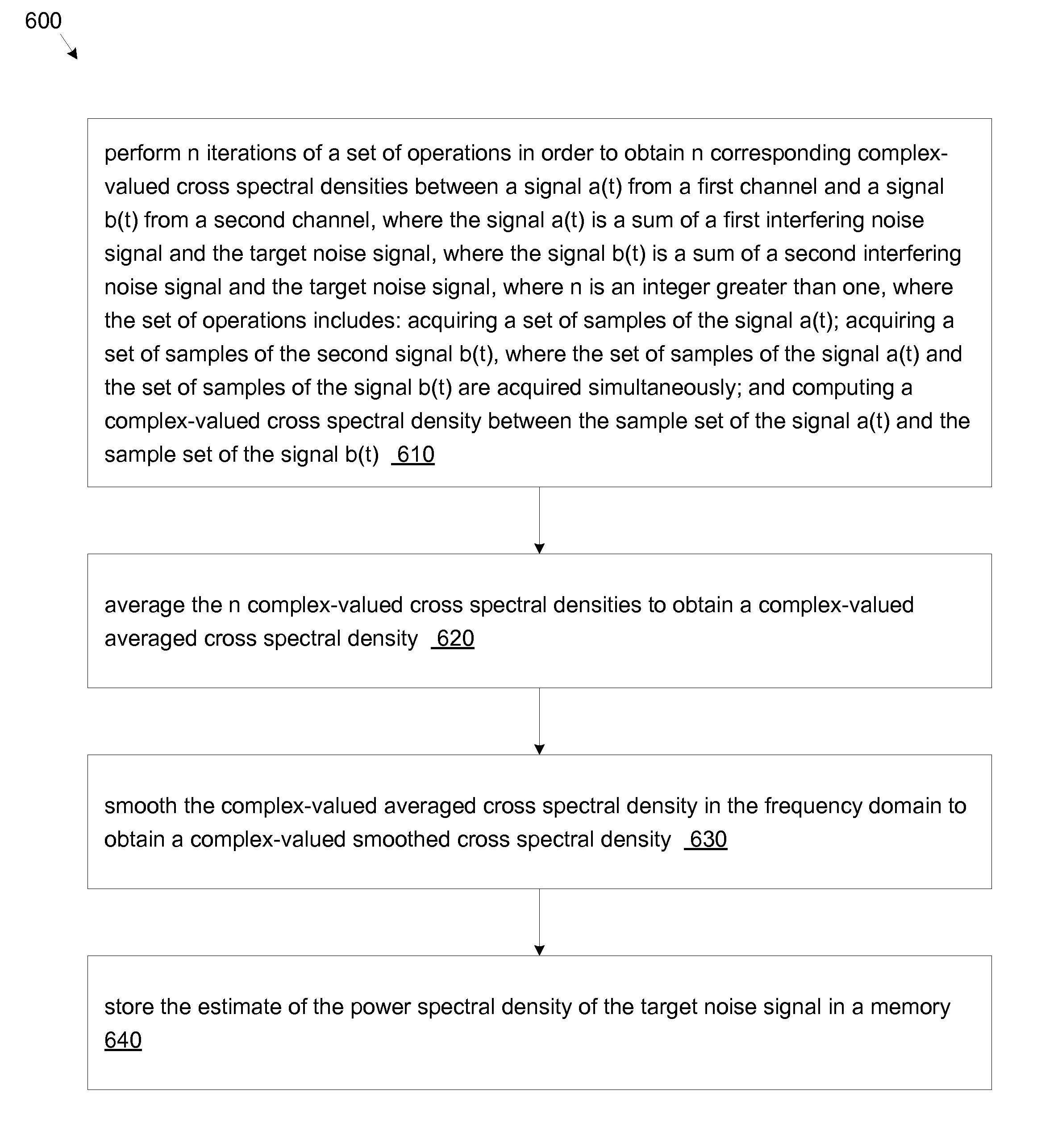
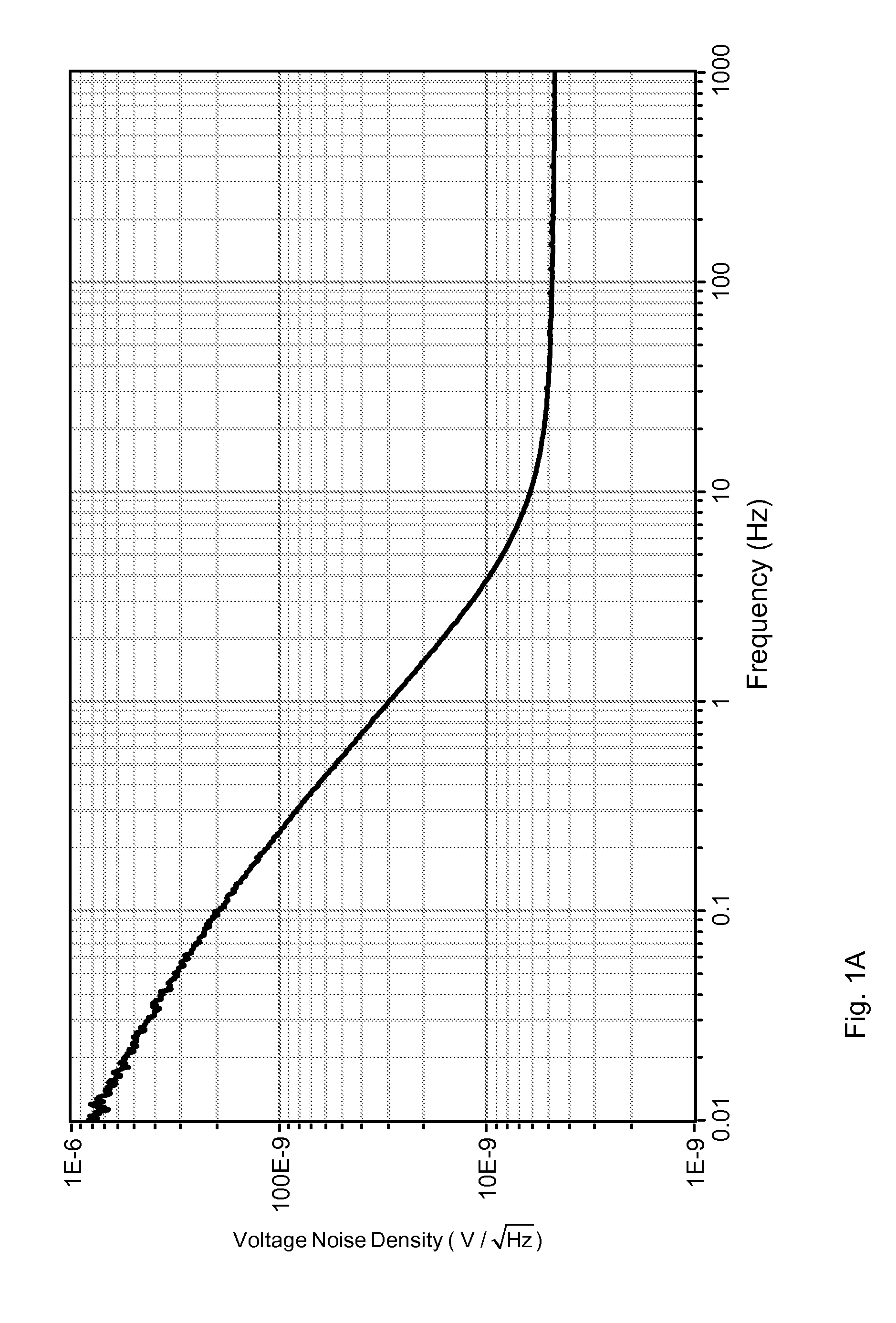
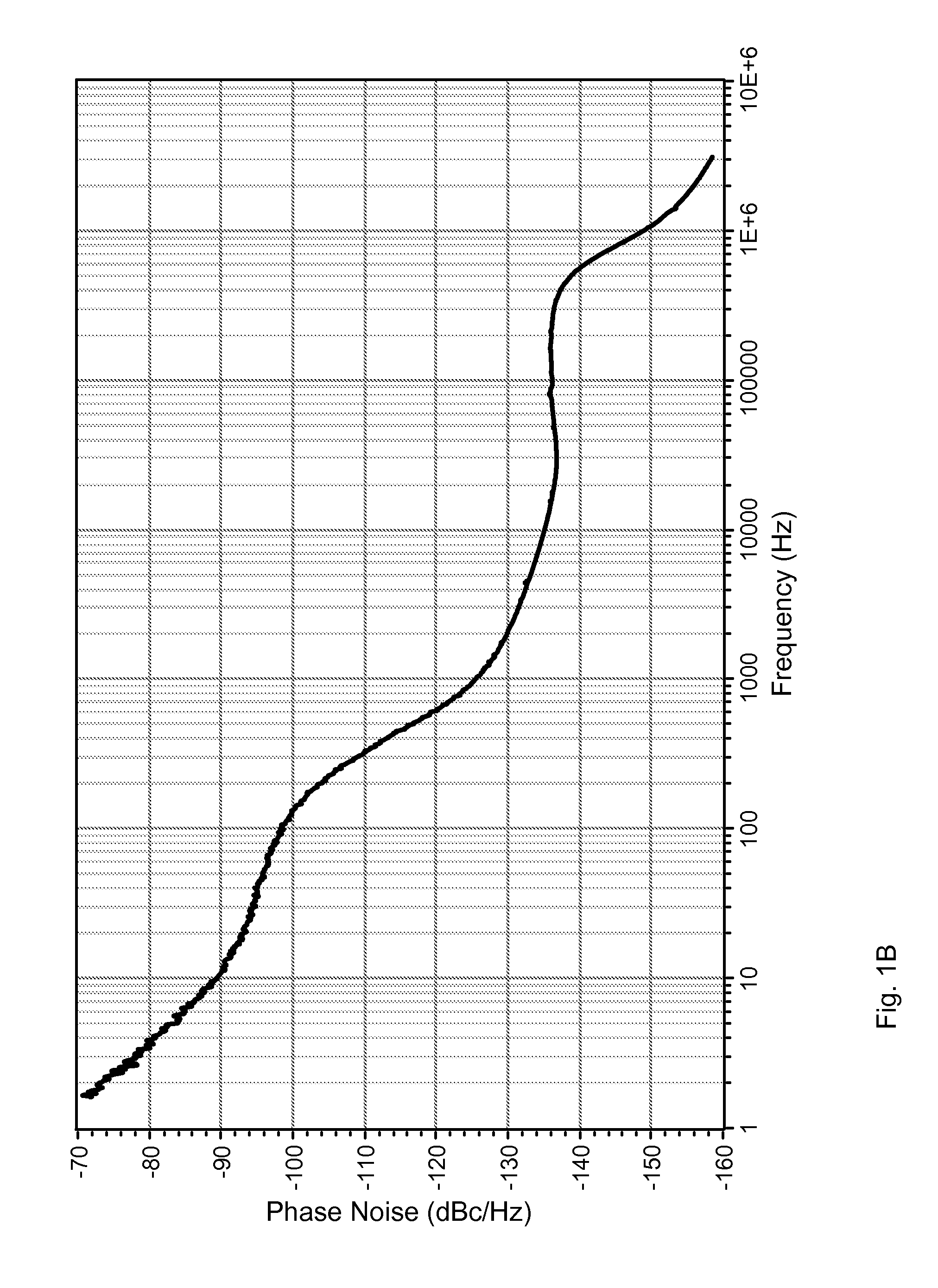
Systems / methods for computing a power spectral density estimate for a noise signal. Where the noise signal appears in two channels (a single channel), n successive data acquisitions from the two channels (the single channel) are used to compute n respective cross (power) spectral densities, which are then averaged. The averaged cross (power) spectral density may then be smoothed in the spectral domain. The magnitude of the smoothed cross (power) spectral density comprises an estimate for the noise power spectral density. An effective number of independent averages may be computed based on the number n, the time-domain window applied to the acquired sample sets, the amount of overlap between successive sample sets, and the shape of the frequency-domain smoothing function. A statistical error bound (or uncertainty measure) may be determined for the power spectral density estimate based on the effective number of averages and the averaged single-channel and cross-channel spectral estimates.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
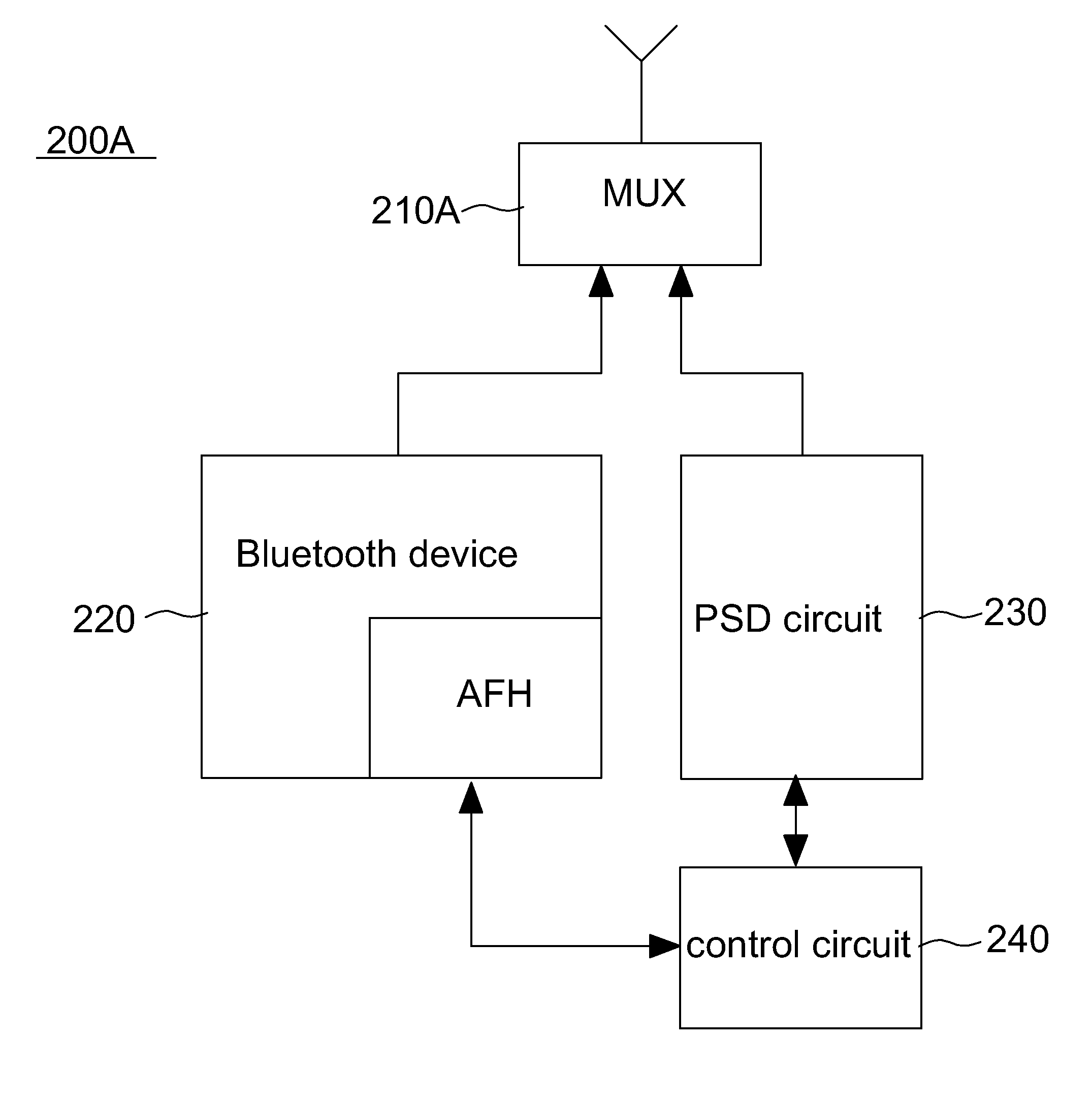
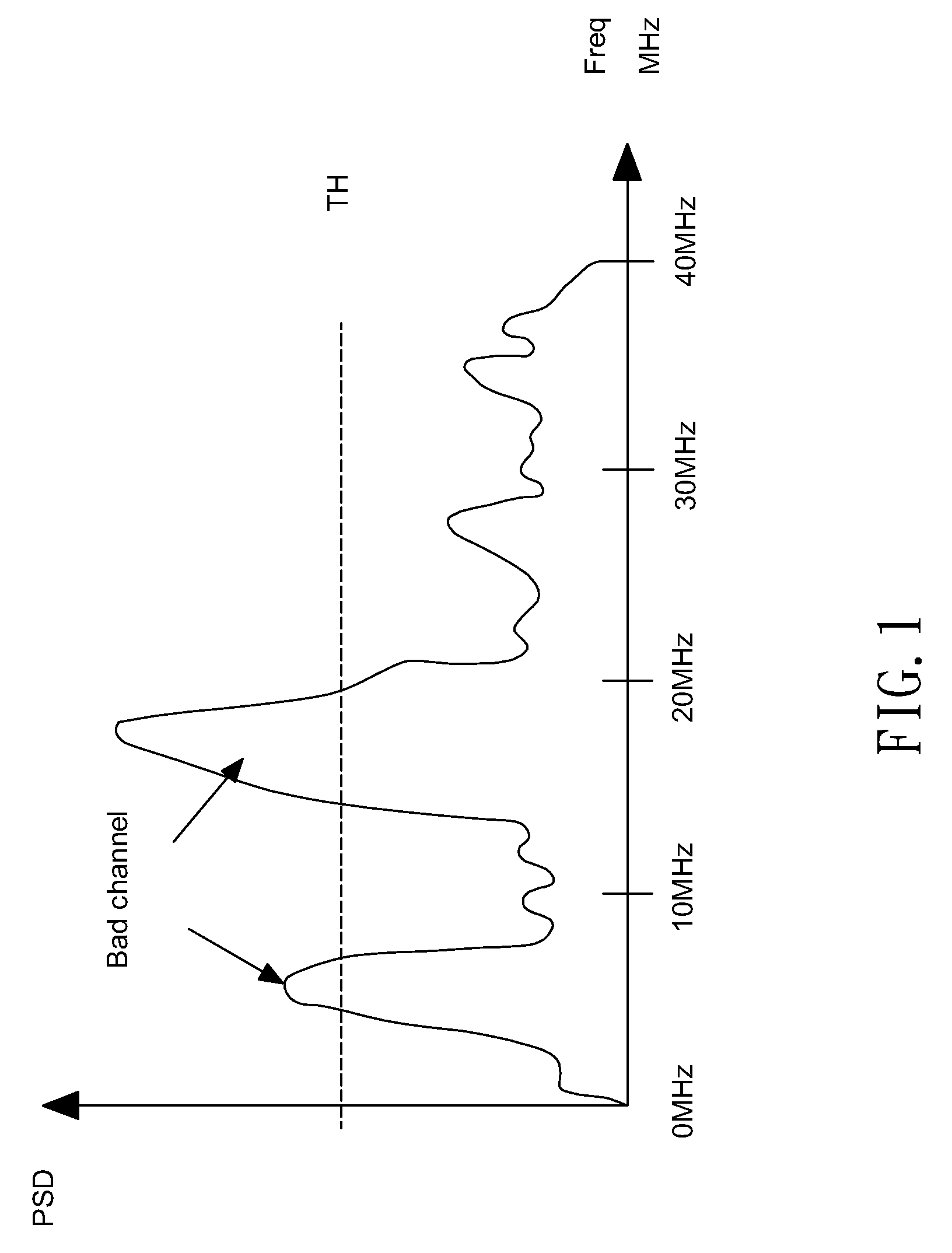
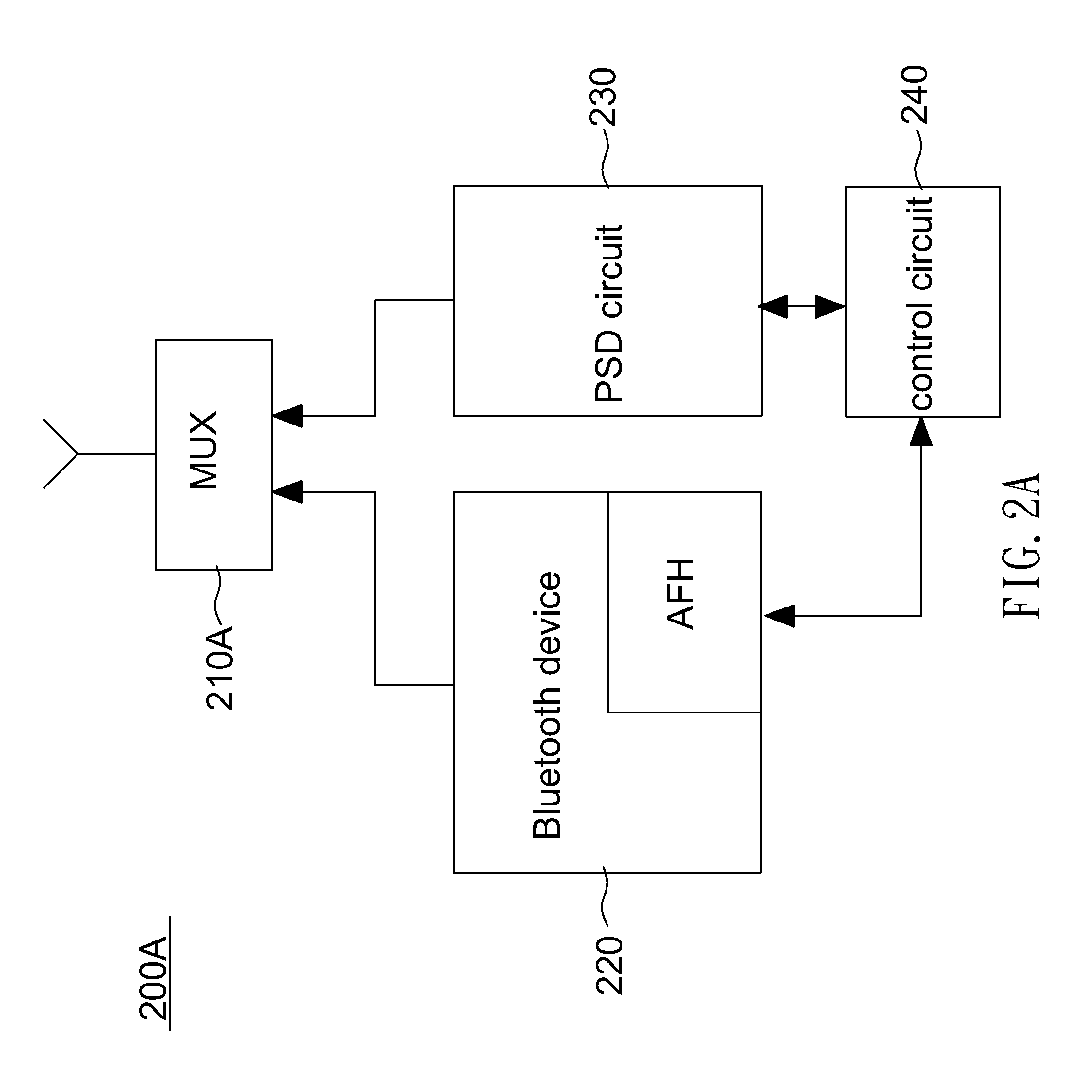
Method and device for implementation of adaptive frequency hopping by power spectral density
ActiveUS9136902B2Rapidly and correctly performance of channelFarther transmission distanceTransmissionFrequency spectrumSelf adaptive
A wireless communication device is disclosed. The wireless communication device includes a frequency hopping communication circuit, a power spectral density circuit and a control circuit. The frequency hopping communication circuit includes a channel map. The frequency hopping communication circuit selects one of channel in a channel map to connect to another frequency hopping communication circuit according to the channel map. The power spectral density circuit for generating a power spectral density signal by measuring spectrums on all channels connected to the frequency hopping communication circuit. The control circuit receives the power spectral density and output statistical distribution data to the frequency hopping communication circuit. The frequency hopping communication circuit updates the channel map according to the statistical distribution data.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
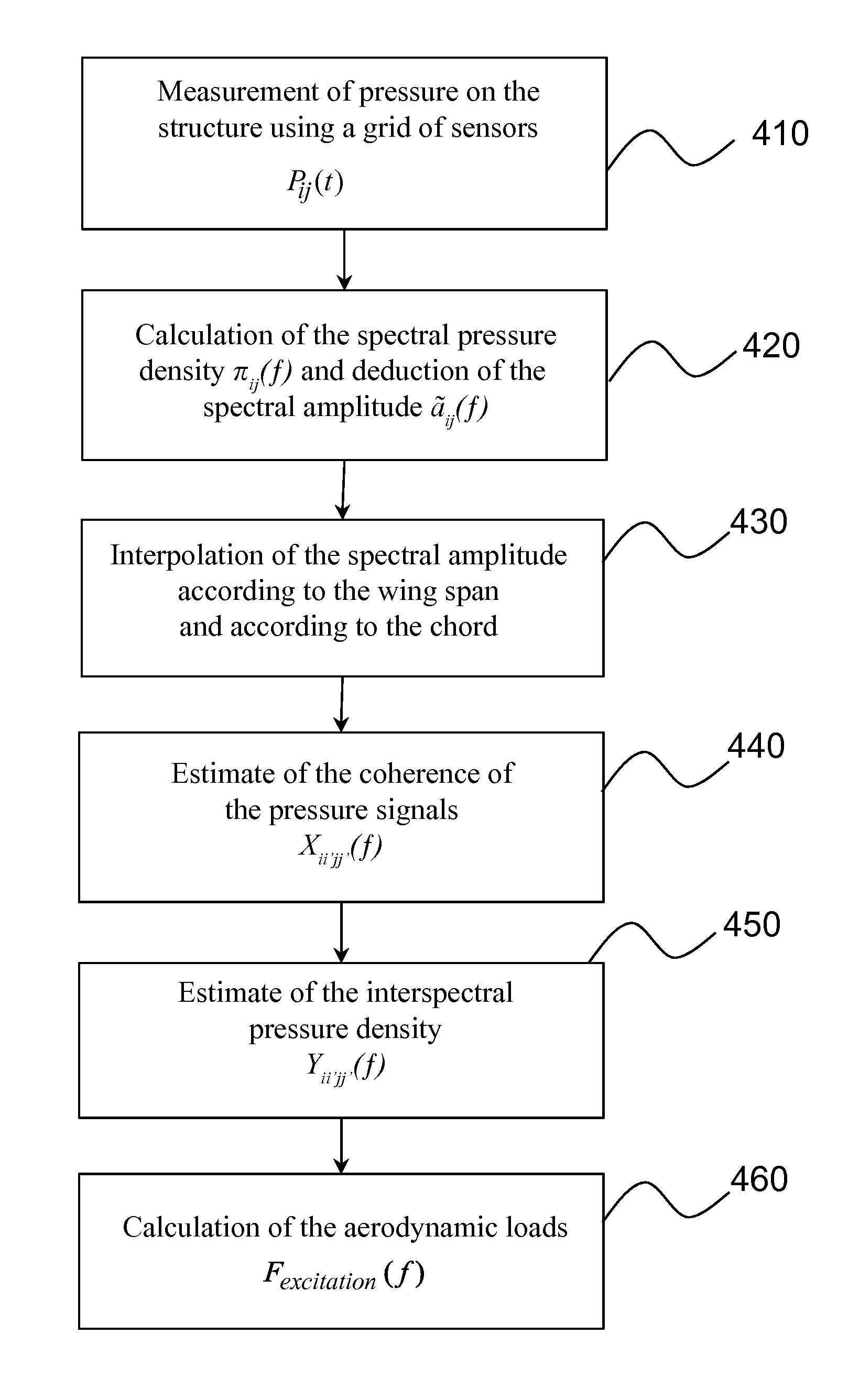
Method of simulation of unsteady aerodynamic loads on an external aircraft structure
InactiveUS20140081609A1Aerodynamic testingComputation using non-denominational number representationFrequency spectrumAerodynamic load
The invention relates to a method for simulating the unsteady aerodynamic loads being exerted on the external structure of an aircraft, notably in the context of a simulation of the buffeting of a wing surface in an airflow. The method includes a step of measurement of pressure (410) at different points of a grid, a step of calculation of the spectral density at these points (420) followed by extrapolation / interpolation operations to calculate the missing measurements (430), a step of estimation of the pressure coherence (440) for each pair of points of the grid, a step of estimation of the interspectral pressure density (450) for these same pairs of points, from the coherence thus estimated, and a step of calculation of the aerodynamic loads (460) by summing the real part of the interspectral density for the area of the wing surface having a separation of the boundary layer.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Electrocardiosignal quality discrimination method based on neural network model
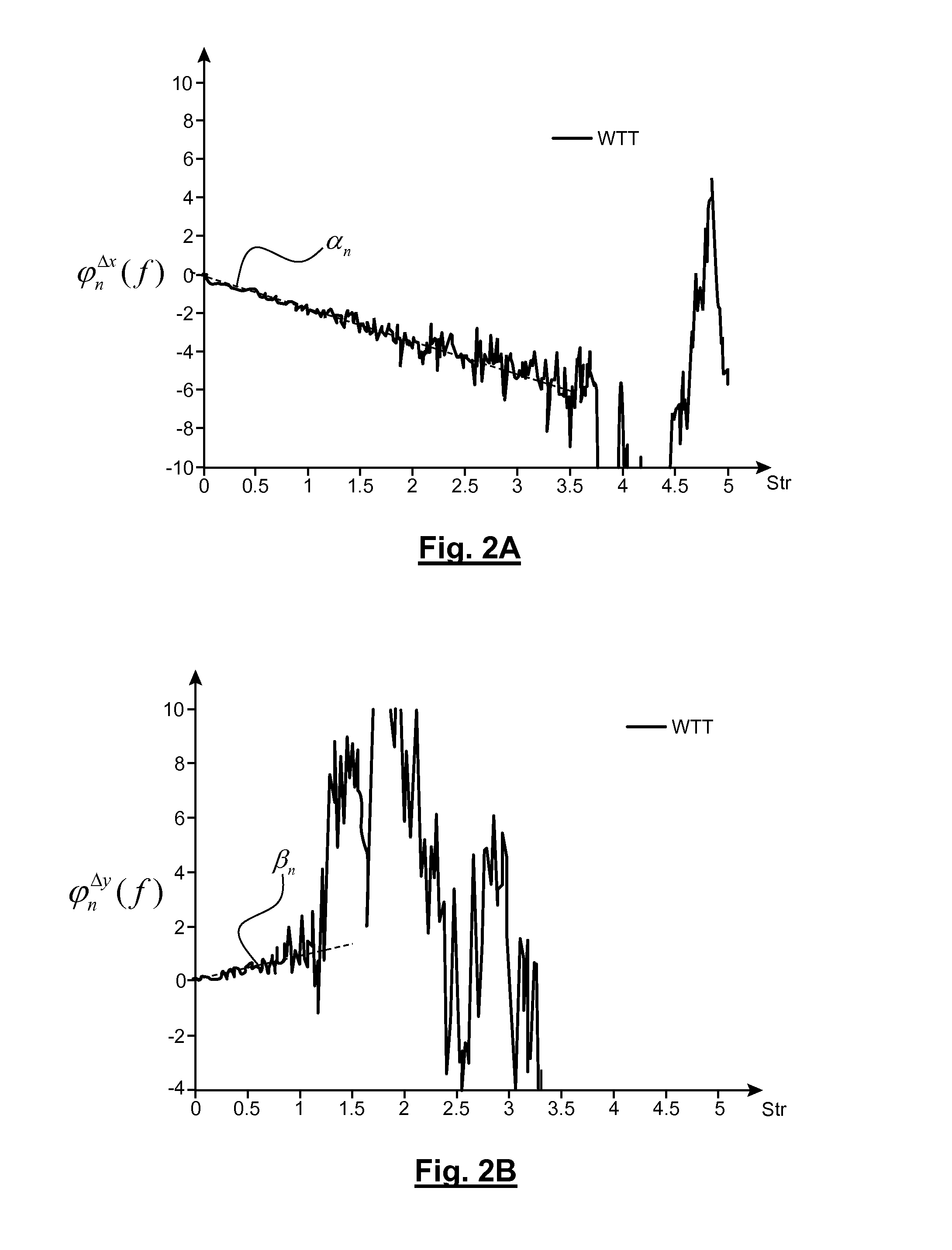
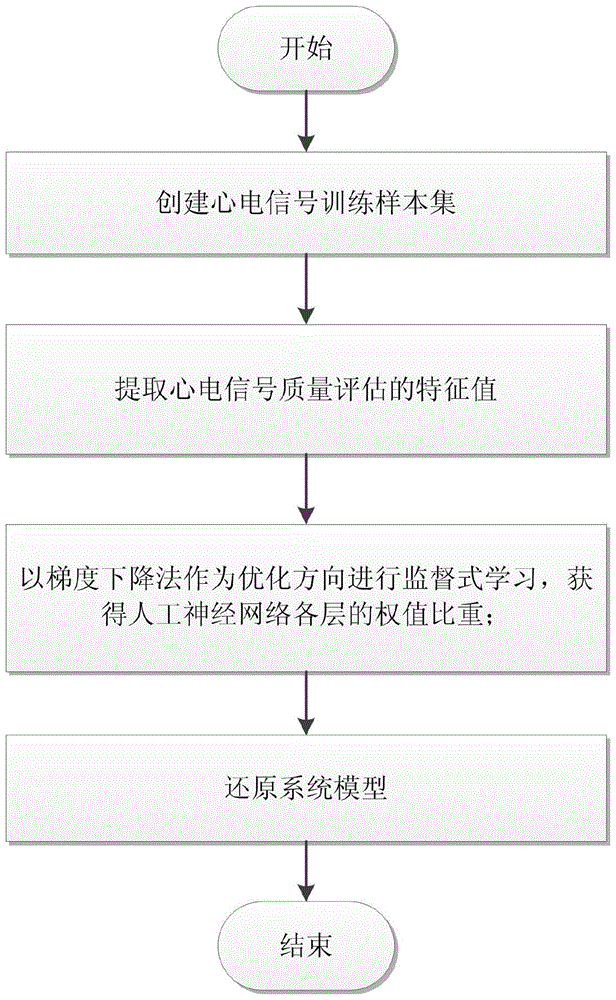
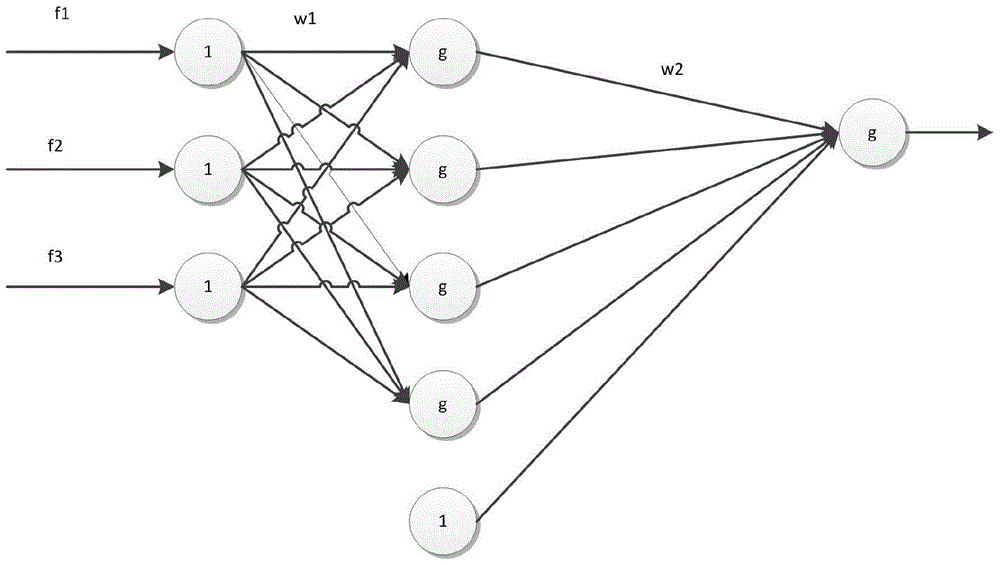
InactiveCN105725966ADiscriminant method implementationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalAlgorithm
The invention discloses an electrocardiosignal quality discrimination method based on a neural network model. The method comprises the steps that an independent and single-channel electrocardiosignal is converted into three feature values, namely, a QRS energy specific value, signal kurtosis and a base line energy specific value before learning through a technological means of solving an integral and a kurtosis coefficient through power spectral density, and then a discrimination model is accurately set up in an optimizing mode of gradient descent through an artificial neural network learning algorithm according to the feature values. The electrocardiosignal quality discrimination method is achieved by restoring a system model, and then whether the electrocardiosignal can be used for diagnosis or not is effectively discriminated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEDZONE BIOMEDICINE VENTURE INVESTMENT +2
Speech separation method and system based on Ultra Gaussian prior speech model and deep learning and storage medium
InactiveCN109767781ASuppression of non-stationary noise signalsSpeech analysisNoise power spectrumSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a speech separation method and system based on Ultra Gaussian prior speech model and deep learning and a storage medium. The speech separation method comprises the steps of: utilizing a pure speech power spectrum density estimated value and a noise power spectrum density estimated value so as to obtain a prior signal-to-noise ratio in a gain function; bringing the prior signal-to-noise ratio into the gain function to obtain a value of the gain function; multiplying the value of the gain function by noisy speech spectrum to obtain an estimated value of a pure speech amplitude spectrum; and by utilizing an overlapping-adding technology, obtaining a recovered speech signal. The speech separation method and system and the storage medium have the beneficial effects that by combining a conventional statistic model with a deep learning technology, not only can a non-stationary noise signal be effectively inhibited, but also a problem of weak generalization ability caused by high dependence of the deep learning technology on training data is solved. Combination of the conventional statistic model and the deep learning technology enables enhancement performance of themethod to show very robust in various noise environments and signal-to-noise ratio cases.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
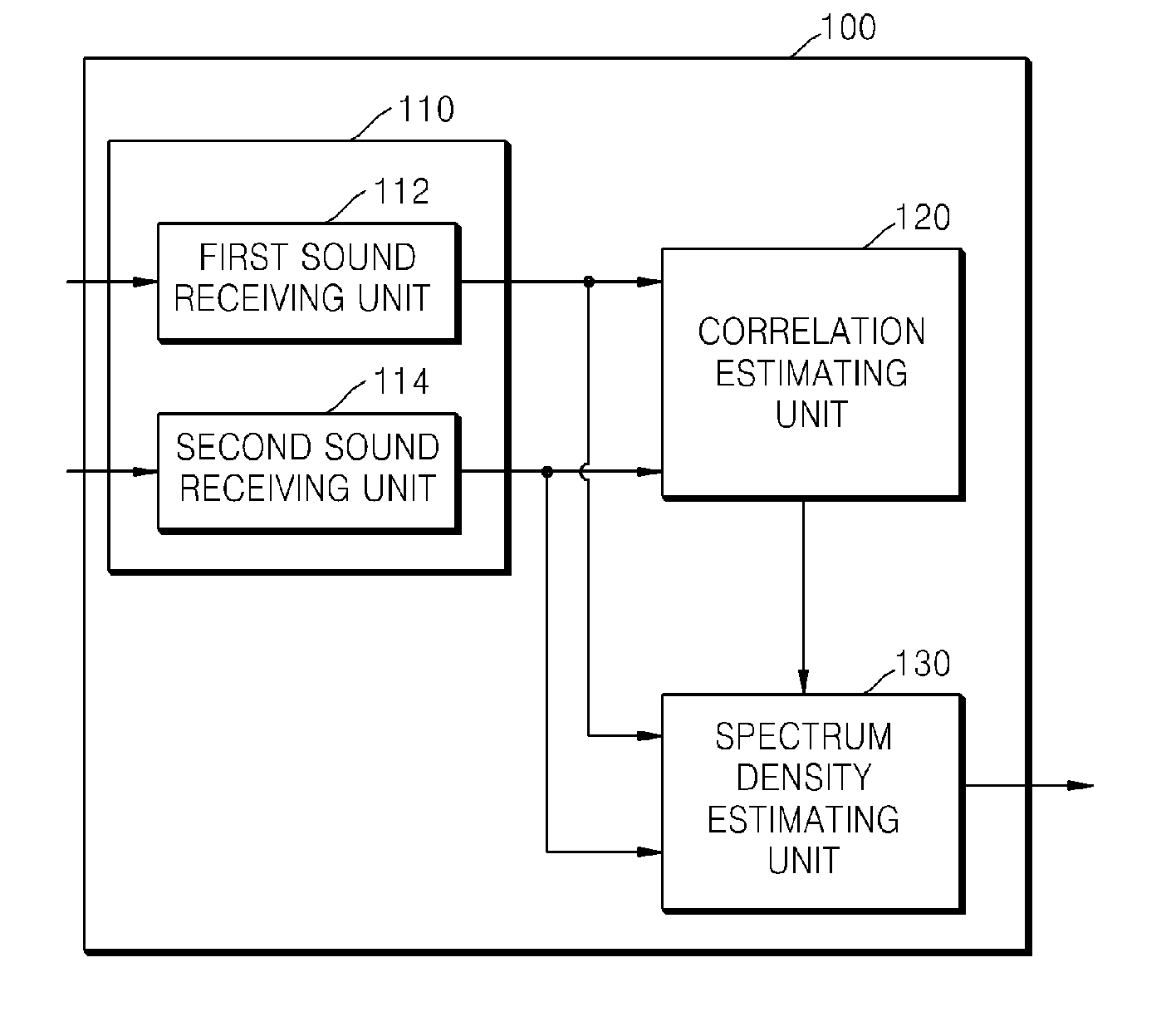
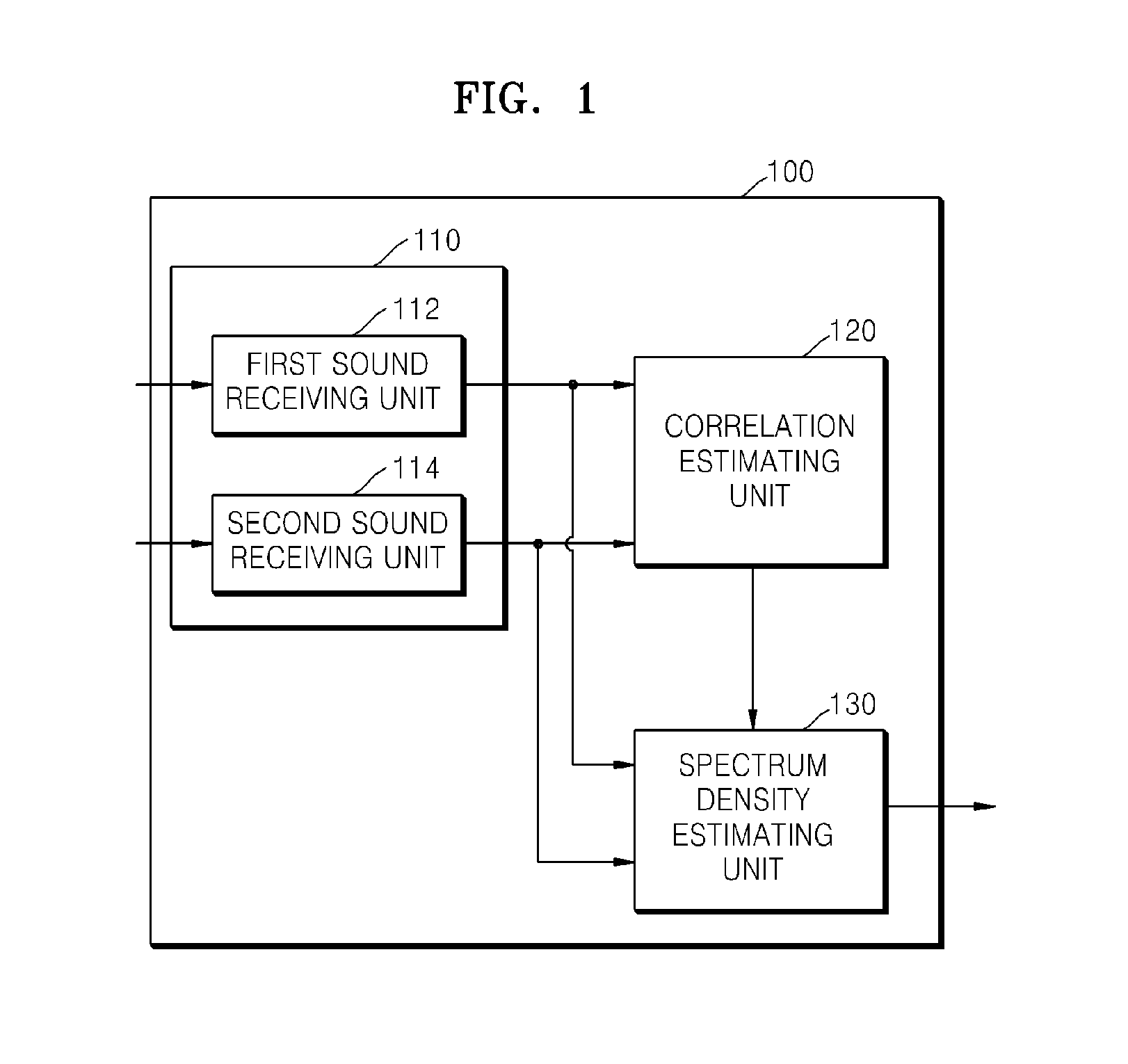
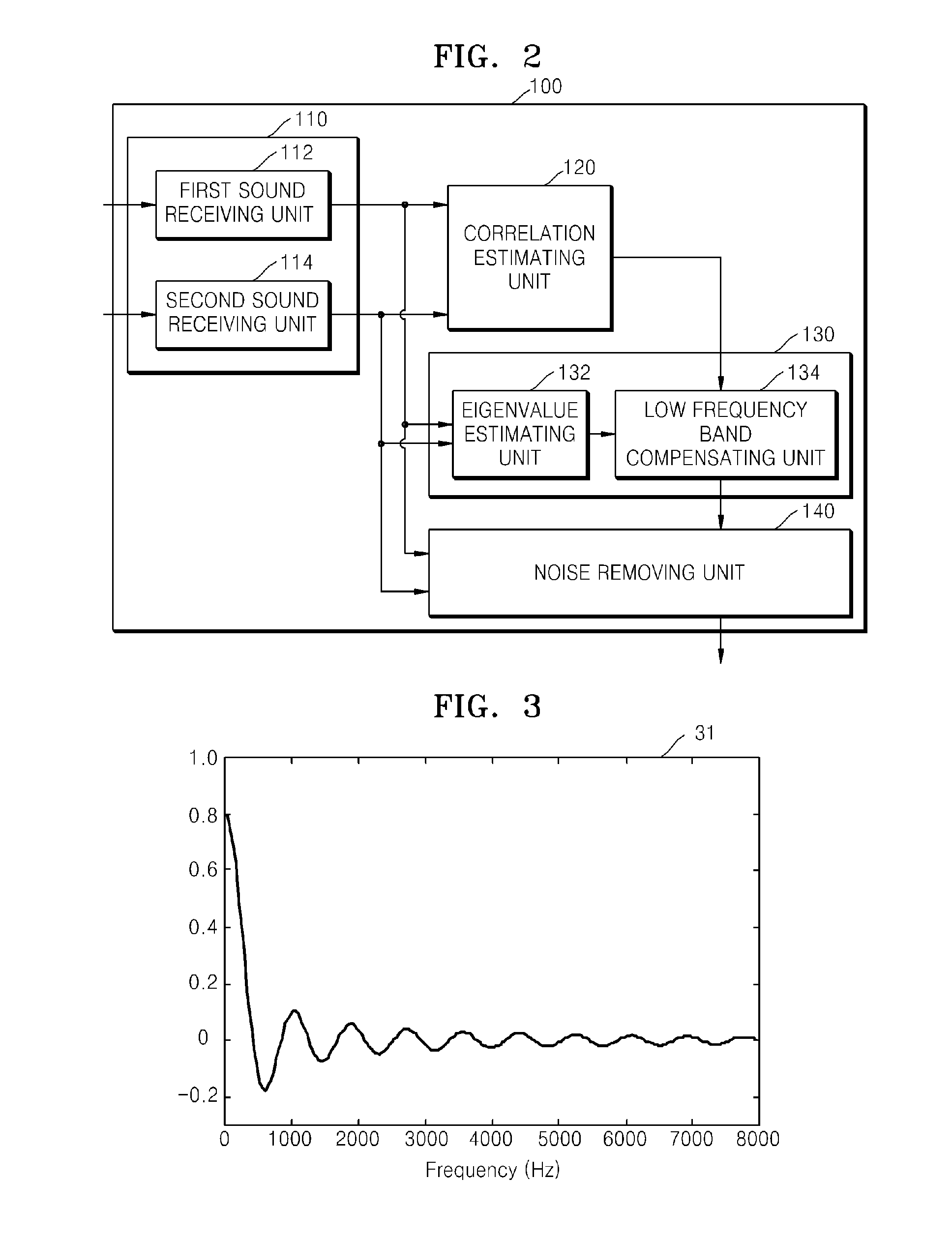
Method and apparatus for estimating spectrum density of diffused noise
InactiveUS20120243695A1Increase weightHearing device energy consumption reductionMicrophones signal combinationFrequency spectrumSpectral density estimation
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
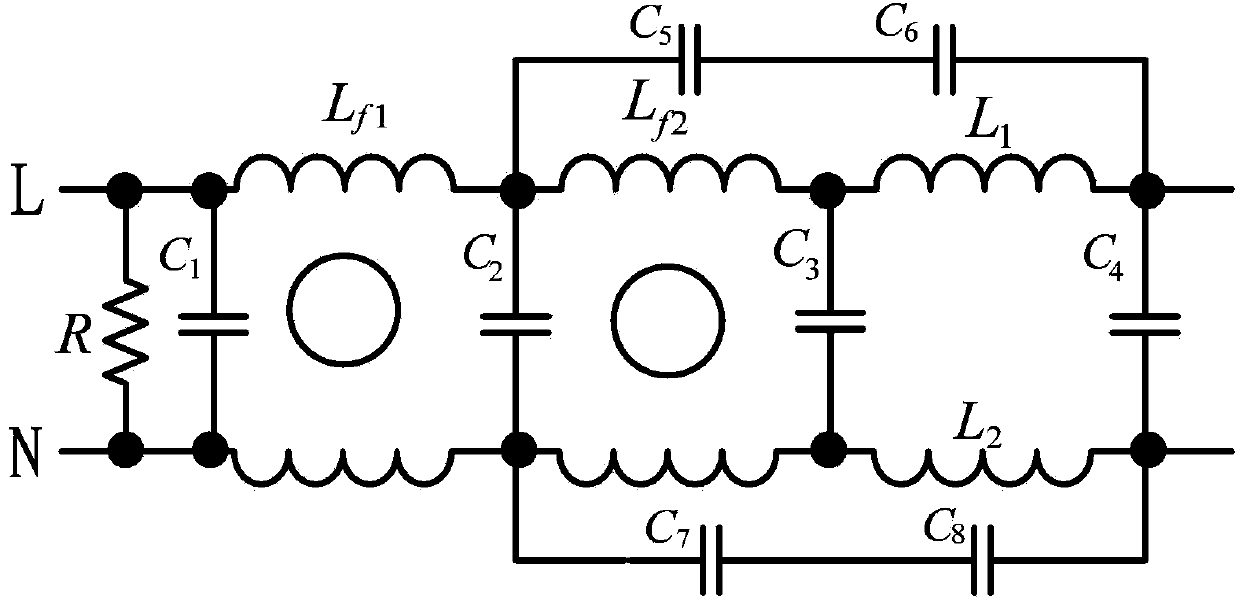
Filter at front end of outer part of household appliance for improving power spectral density of power line communication
ActiveCN103701427ASimple structureReasonable designMultiple-port networksPower distribution line transmissionCapacitanceCarrier signal
The invention discloses a filter at the front end of the outer part of a household appliance for improving the power spectral density of power line communication. The filter comprises a bleeder resistor R, common mode chokes Lf1 and Lf2, X capacitors C1, C2, C3 and C4, difference mode inductors L1 and L2, and high-voltage pulse absorbing capacitors C5, C6, C7 and C8, wherein the bleeder resistor R and the X capacitors C1, C2, C3 and C4 are connected between a null line and a live wire in parallel in sequence, two coils of the common mode chokes Lf1 are connected to a null line and a live wire between the capacitor C1 and the capacitor C2 in series respectively, two coils of the common mode chokes Lf2 are connected to a null line and a live wire between the capacitor C2 and the capacitor C3 in series respectively, the difference mode inductors L1 and L2 are connected to a null line and a live wire between the X capacitor C3 and the X capacitor C4 in series respectively, the high-voltage pulse absorbing capacitors C5 and C6 are connected in series, and the high-voltage pulse absorbing capacitors C7 and C8 are connected in series. The filter can be used for inhibiting an EMI (electro magnetic interference) signal conducted by the household appliance into a power grid, and blocking a power line carrier signal from being lost in the household appliance, so that the power spectral density of the power line communication is improved.
Owner:陕西翌鑫科技发展有限公司
System and method for spread spectrum ADC noise reduction
ActiveUS9455733B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersProcessor registerAnalog signal
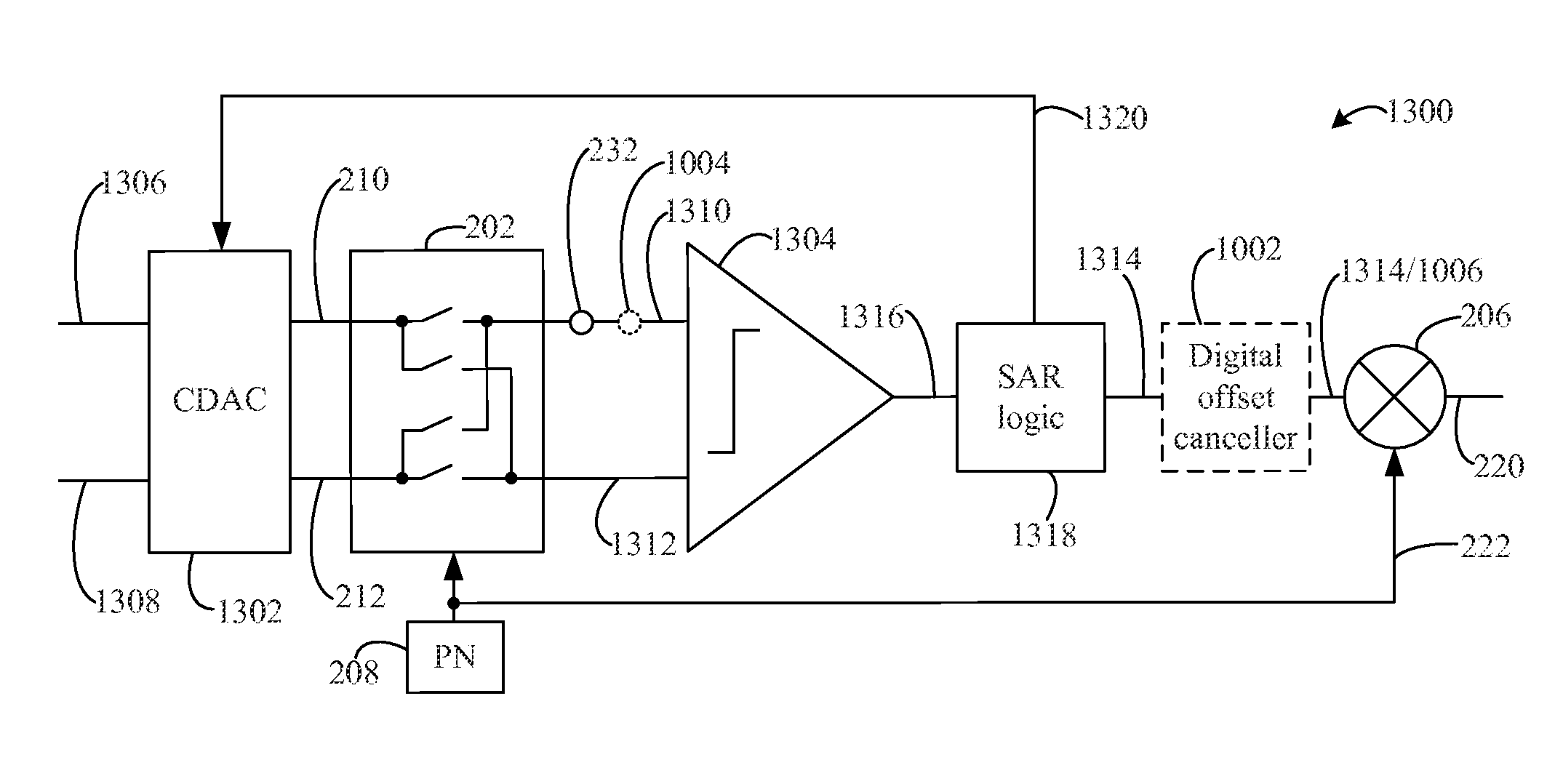
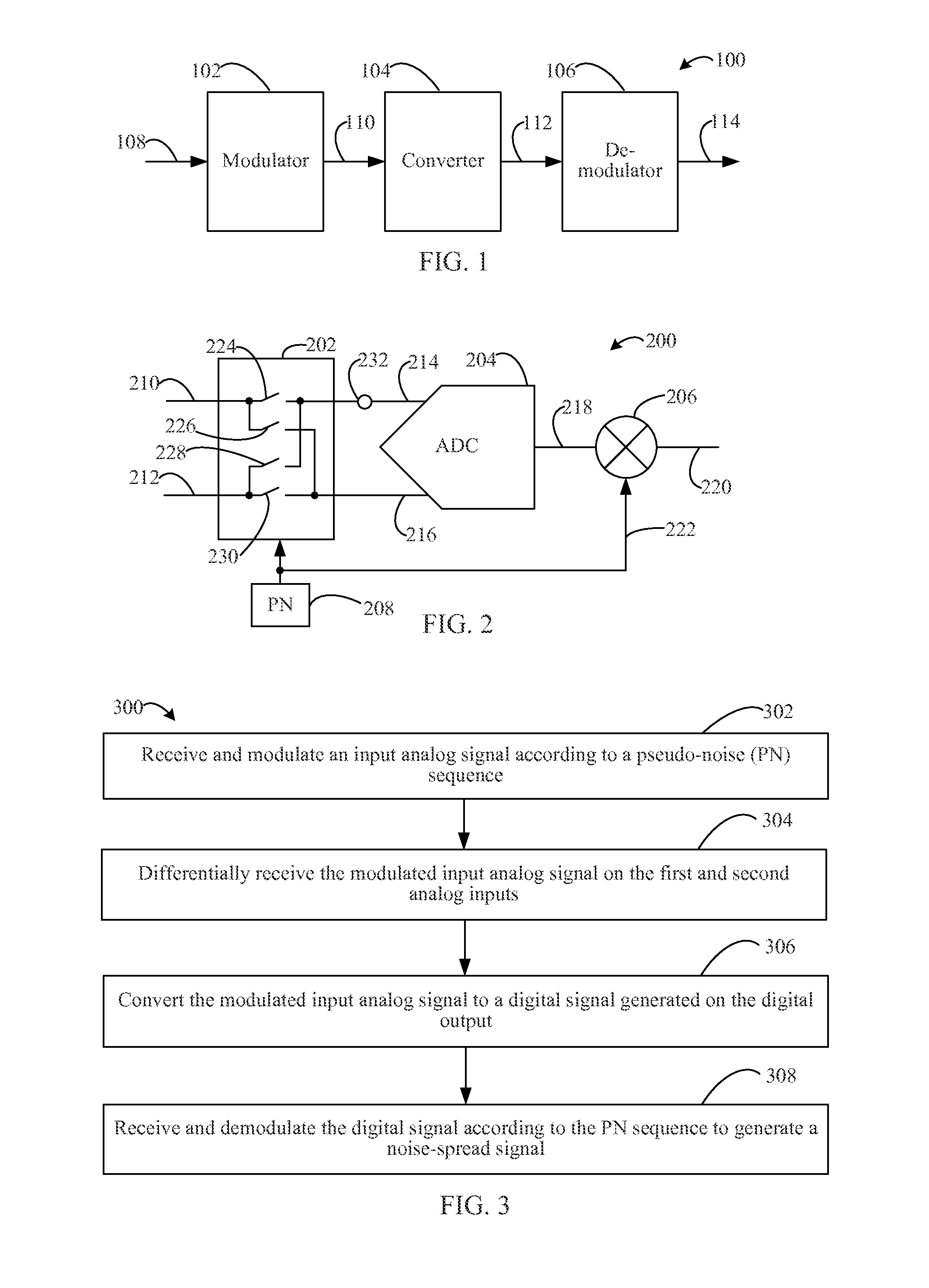
Methods, systems, and apparatuses, including electrical circuits, are described for spread spectrum ADC noise reduction. An analog-to-digital converter may include an analog modulator to modulate an input analog signal according to a pseudo-noise sequence. An ADC core may convert the modulated analog input signal to a digital signal representation thereof. The digital signal may be demodulated using the pseudo-noise sequence to generate a noise-spread signal with reduced noise spectral density. The analog modulator and digital demodulator may also be configured in an analog-to-digital converter that includes a comparator and successive approximation register (SAR) logic, rather than an ADC core, in a SAR implementation. Multi-lane, interleaved analog-to-digital conversion circuits are also described using the inventive techniques. Analog-to-digital converters including DC offset components and methods performed according to the inventive techniques are also described.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
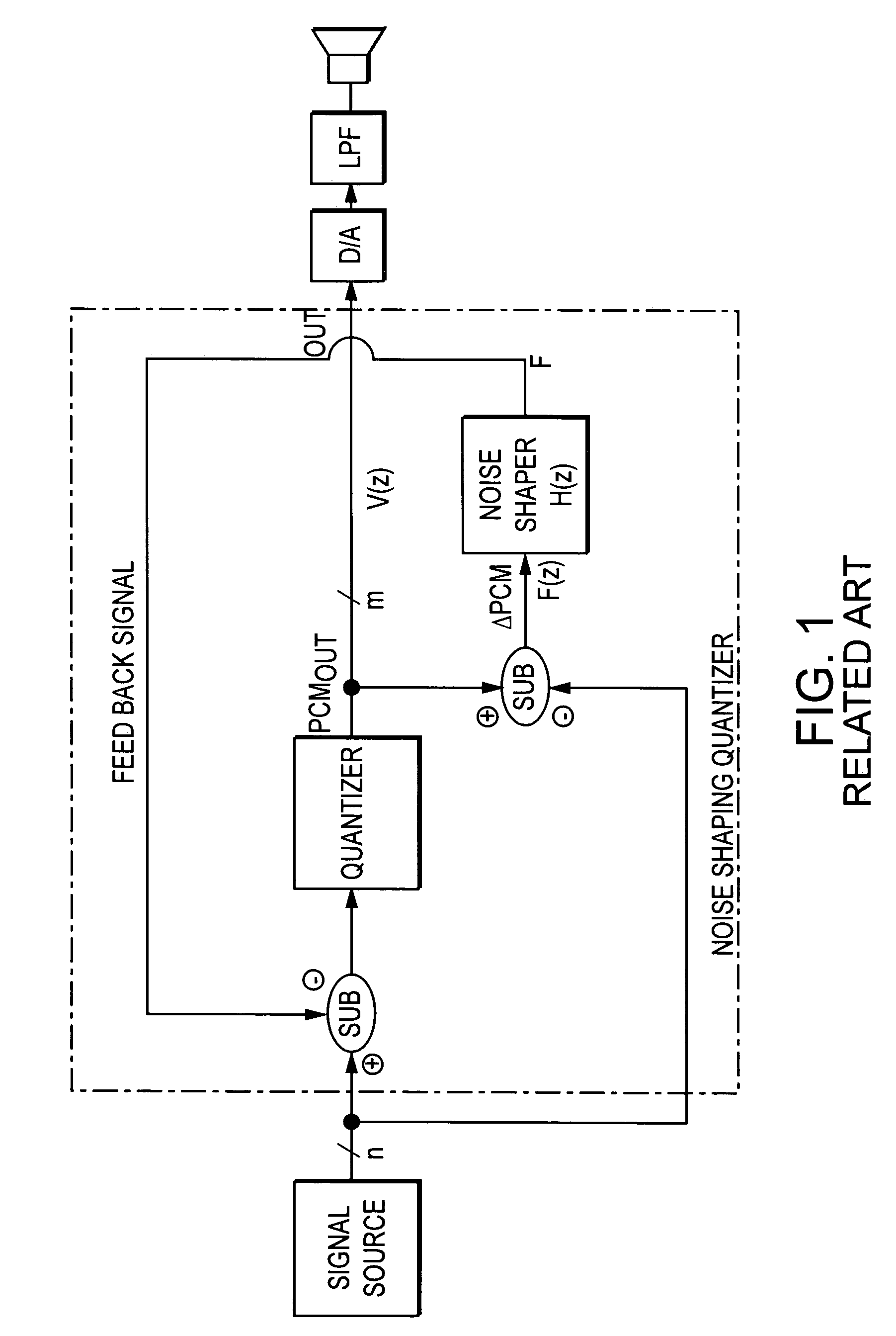
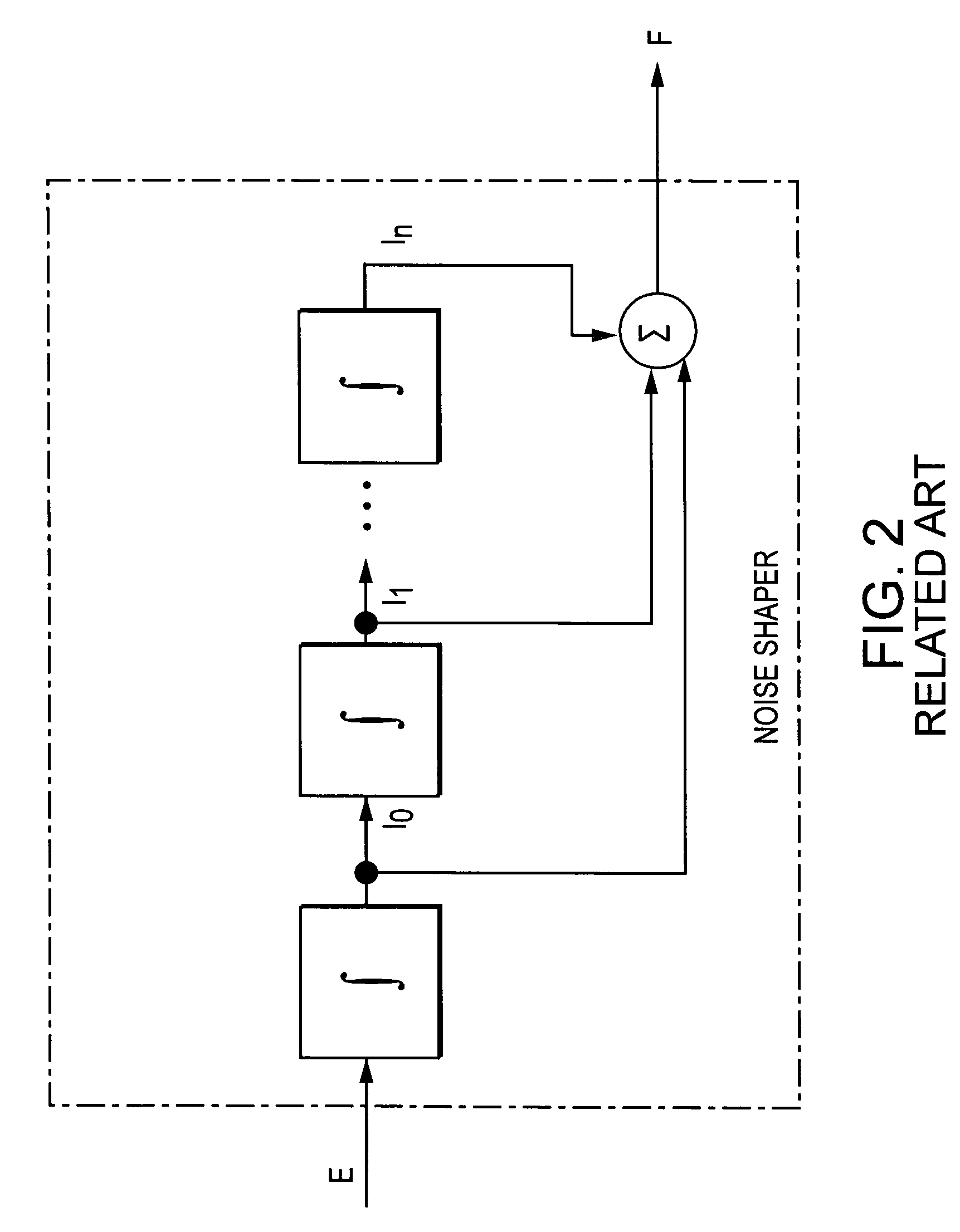
Noise shaper for shaping a power spectral density of an error signal and method therefore
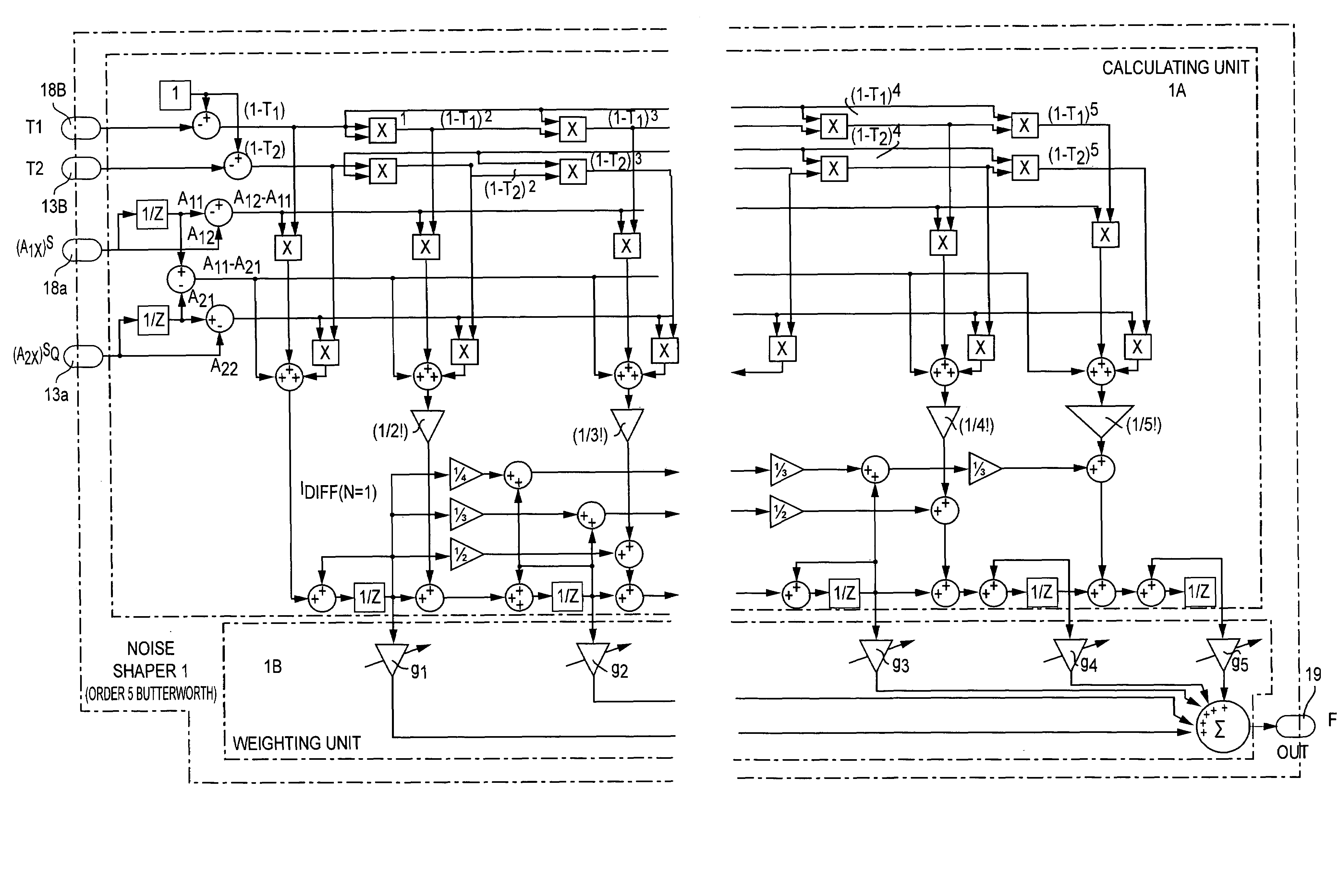
ActiveUS7307557B2Code conversionAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesIntegratorNoise shaping
A noise shaper for shaping a power spectral density of an input signal which consists of signal intervals, wherein each signal interval has a corresponding signal amplitude being constant for a variable interval duration time of the signal interval, said noise shaper comprising a calculation unit having at least one serial connected integrator wherein each integrator calculates an integrated signal of different order from said input signal, and a weighting unit for weighting each integrated signal with a corresponding adjustable weighting coefficient according to a noise transfer function.
Owner:CAMCO PRODN & VERTRIEBS
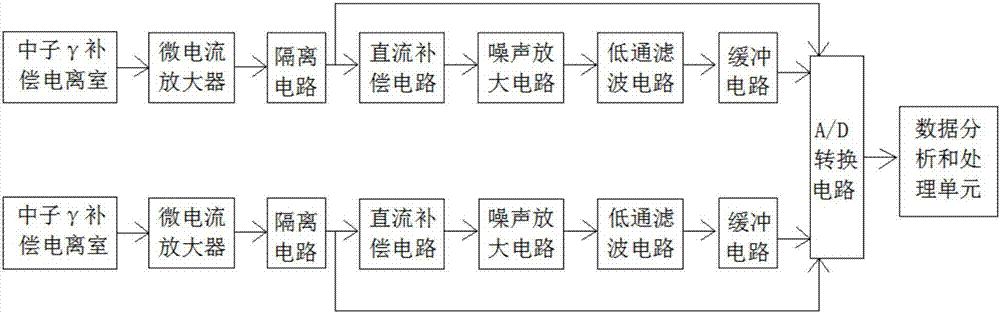
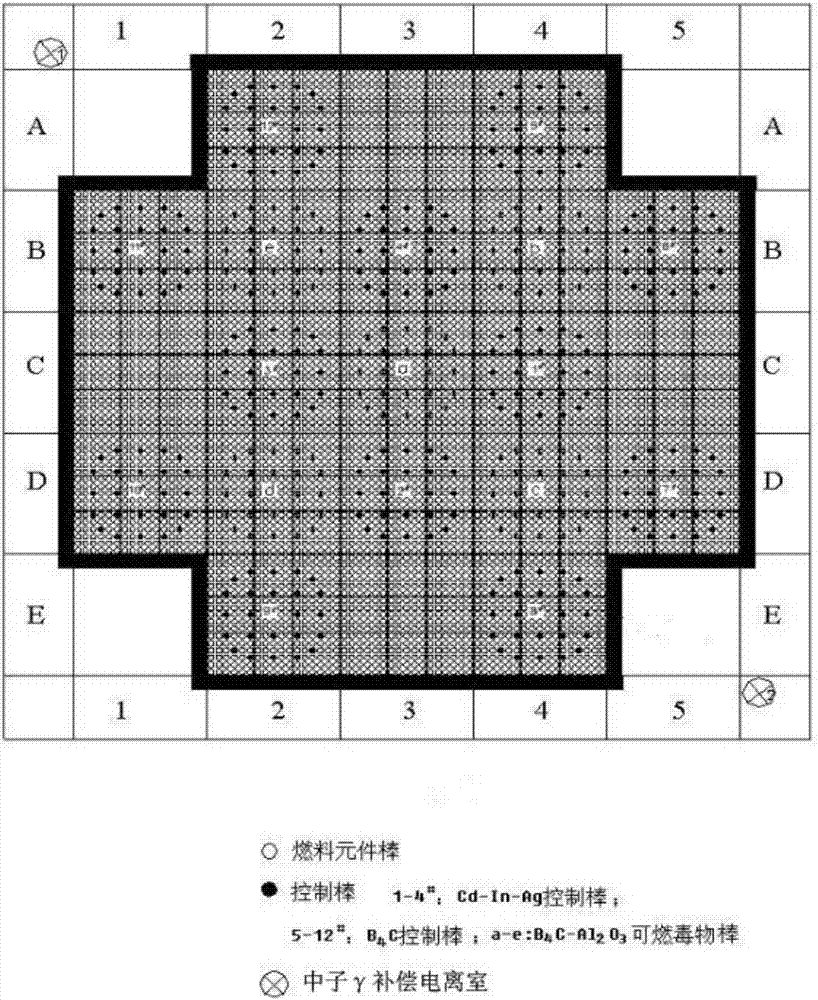
Reactor nuclear power monitoring method and system
InactiveCN107230505ASolve the errorAvoid complicatedNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringNuclear powerNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a reactor nuclear power monitoring method and system. The method comprises A, after the reactor power level is stable, measuring neutron noise signals through two symmetrically arranged neutron gamma compensation ionization chambers, B, calculating time signal FFT through the two neutron noise signals, calculating cross-spectral density phi XY and carrying out normalization, C, fitting the cross-spectral density and calculating cross-spectral density phi XY (omega 1) at frequency omega 1, and D, according to the fitted parameters, acquiring a reactor fission rate F and reactor absolute power P. The method and system can realize parameter measurement without interference on normal operation of the reactor, is suitable for all reactors and realizes fast and convenient measurement.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
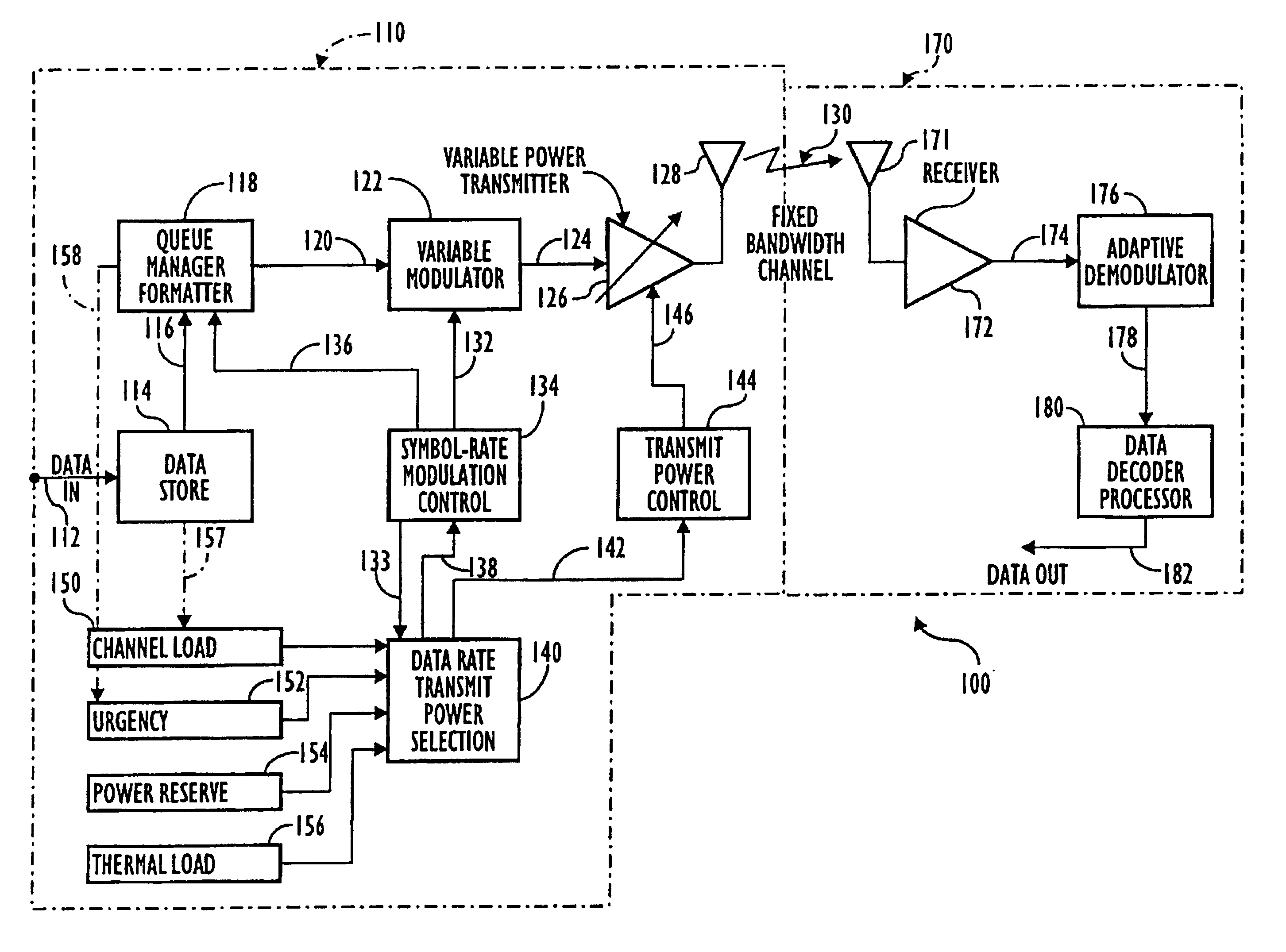
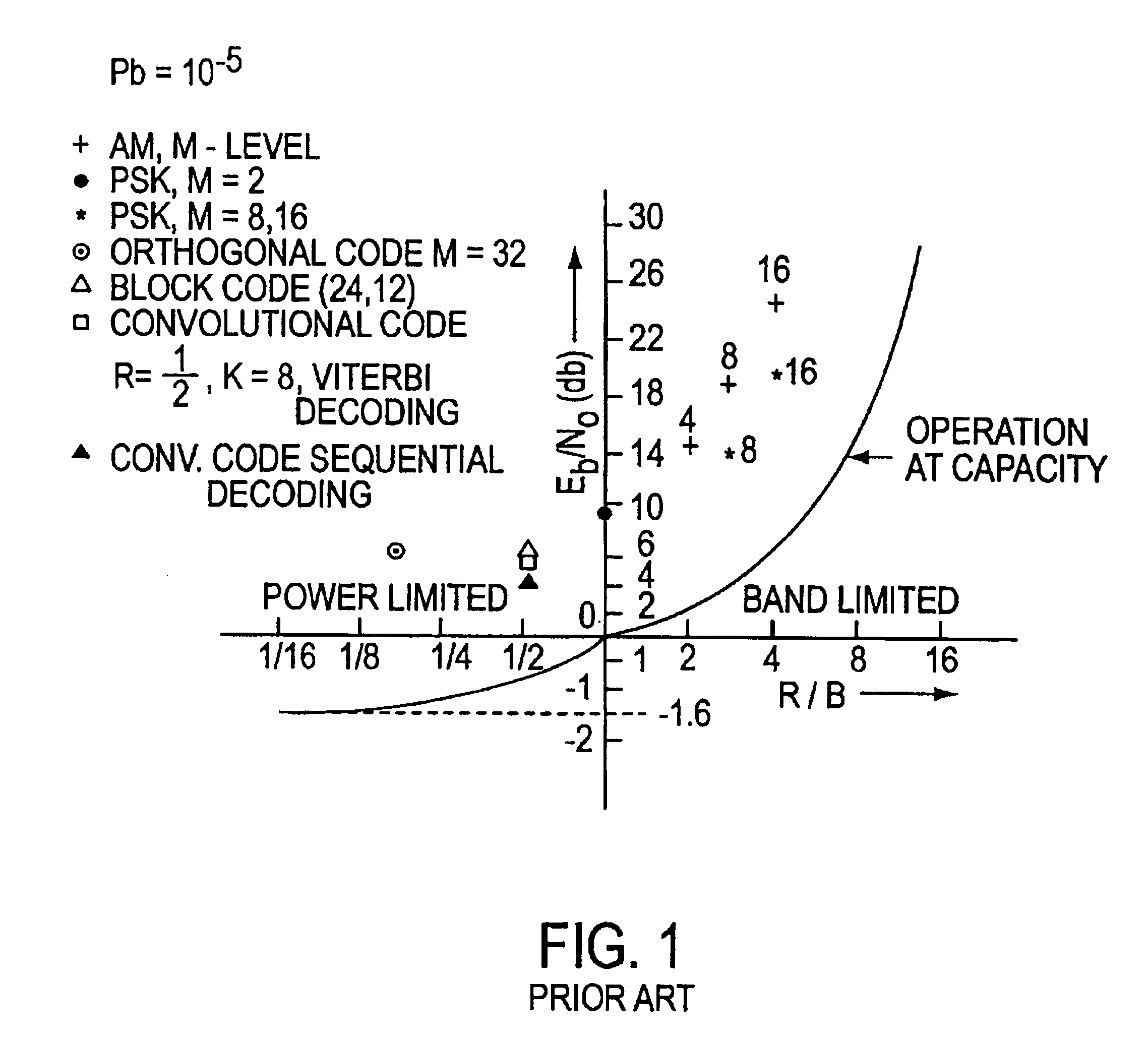
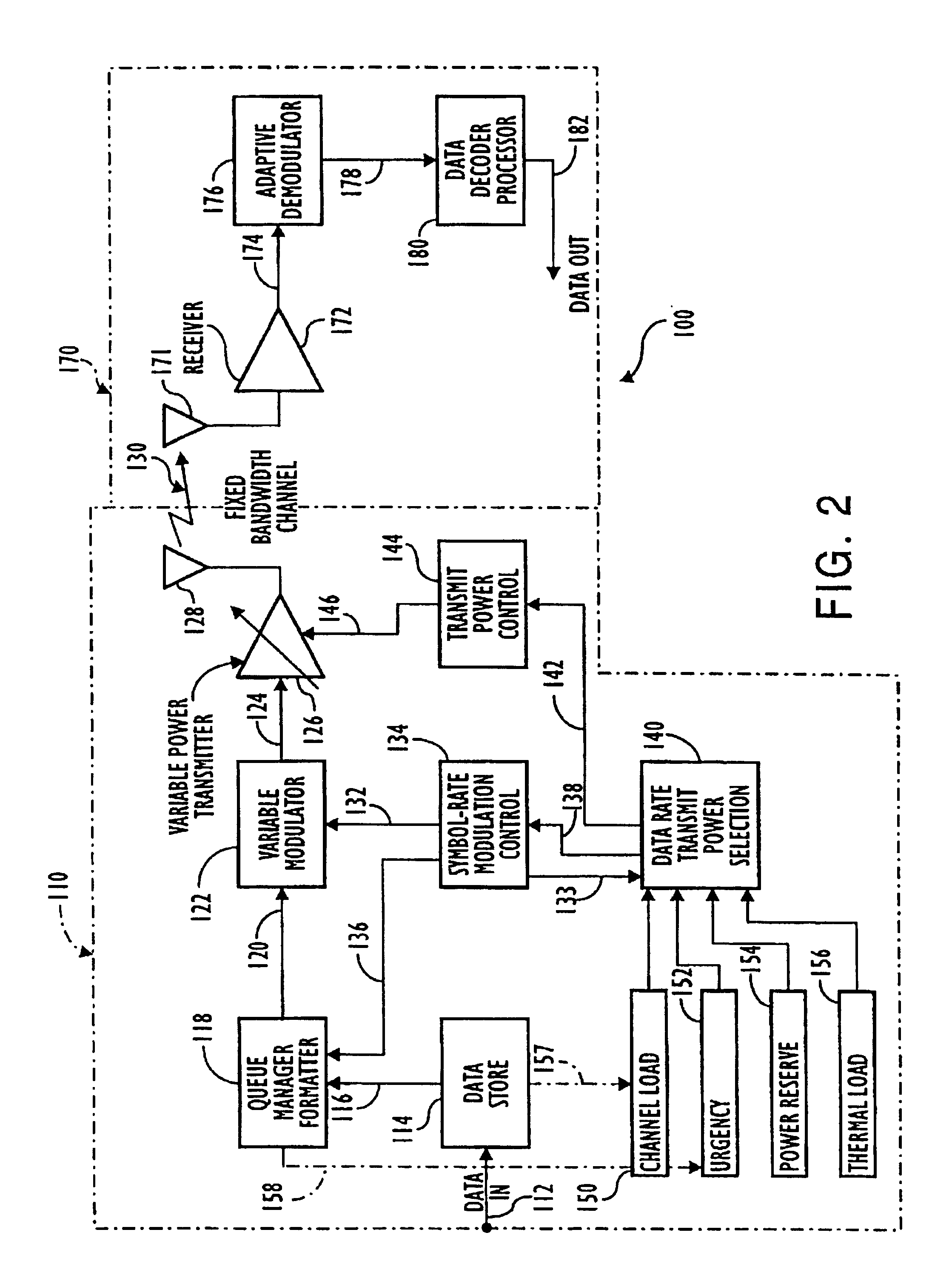
Demand-based power and data rate adjustments to a transmitter to optimize channel capacity and power usage with respect to data transmission traffic over a fixed-bandwidth channel
InactiveUSRE40078E1Easy to useLow costFrequency-division multiplex detailsData switching switchboardsTransmitted powerPower usage
In a communication system in which a transmitter transmits data over a communication channel of a fixed bandwidth to a receiver, the method according to which the transmit data rate is continuously adjusted to a rate which is substantially equal to a short-term average data rate. The channel capacity and / or other characteristics of the system, is continuously adjusted, through changes in transmit power, symbol rate and modulation format, to a level at which the ratio of received signal energy per bit to noise spectral density (Eb / N0) at the receiver is close to but above its minimum acceptable level, thereby matching the channel capacity and / or other characteristics of the system to the traffic. The system has further attributes which adjust the transmit data rate responsive to conditions involving at least one of data traffic levels, power reserve emergency, thermal load and message priority.
Owner:MOBILE SATELLITE VENTURES LP
Determination of Statistical Upper Bound for Estimate of Noise Power Spectral Density
ActiveUS20130097112A1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumNoise power spectrum
Systems / methods for computing a power spectral density estimate for a noise signal. Where the noise signal appears in two channels (a single channel), n successive data acquisitions from the two channels (the single channel) are used to compute n respective cross (power) spectral densities, which are then averaged. The averaged cross (power) spectral density may then be smoothed in the spectral domain. The magnitude of the smoothed cross (power) spectral density comprises an estimate for the noise power spectral density. An effective number of independent averages may be computed based on the number n, the time-domain window applied to the acquired sample sets, the amount of overlap between successive sample sets, and the shape of the frequency-domain smoothing function. A statistical error bound (or uncertainty measure) may be determined for the power spectral density estimate based on the effective number of averages and the averaged single-channel and cross-channel spectral estimates.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com