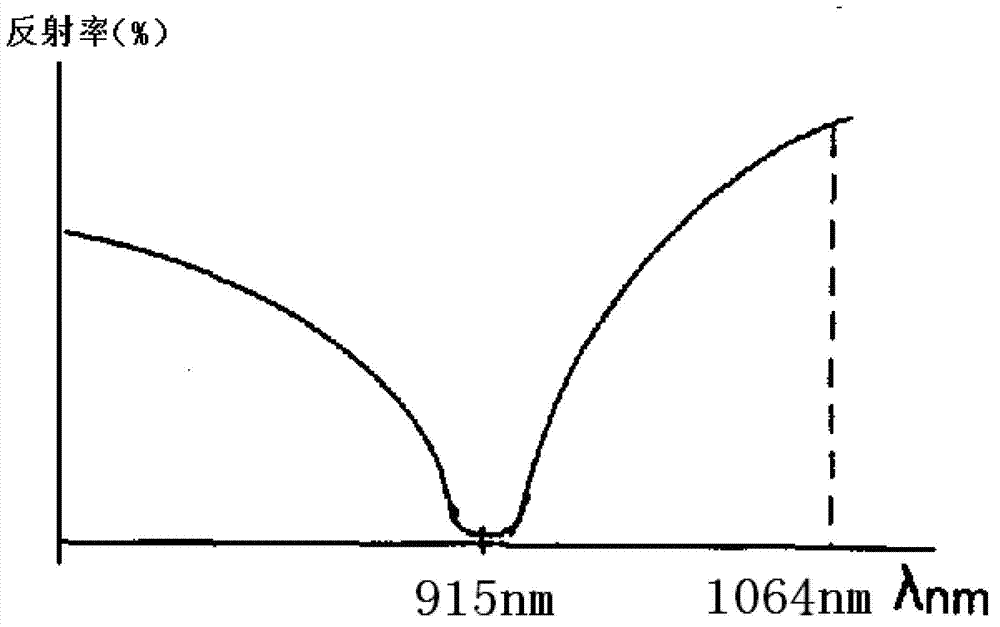
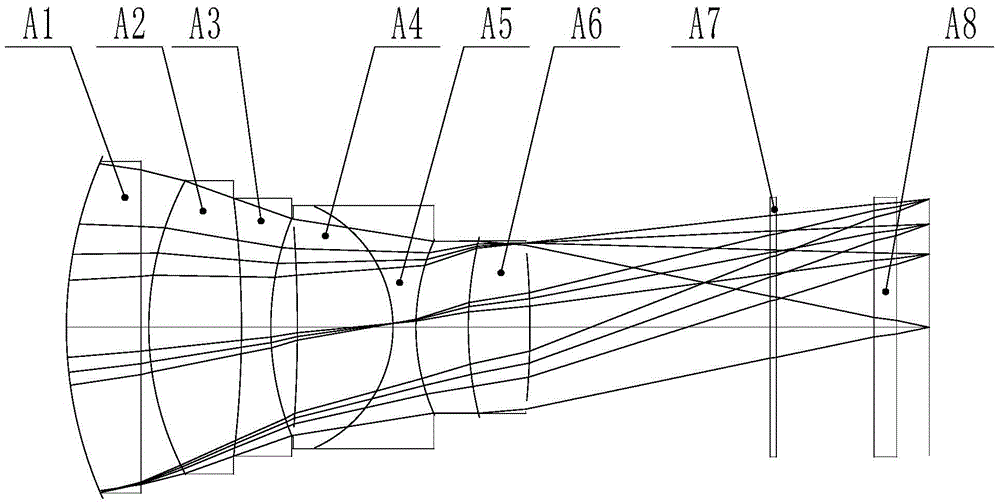
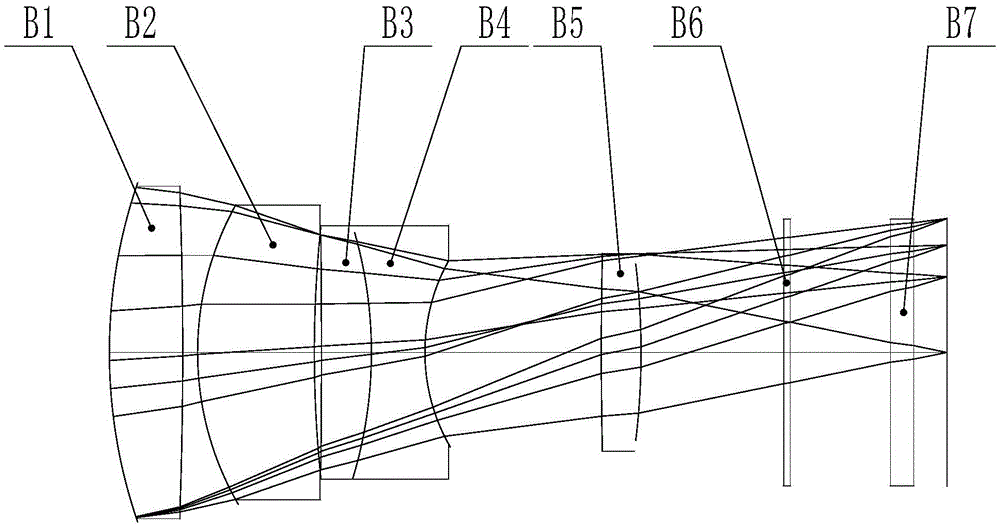
Patents
Literature
83results about How to "Simplify Optical Design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
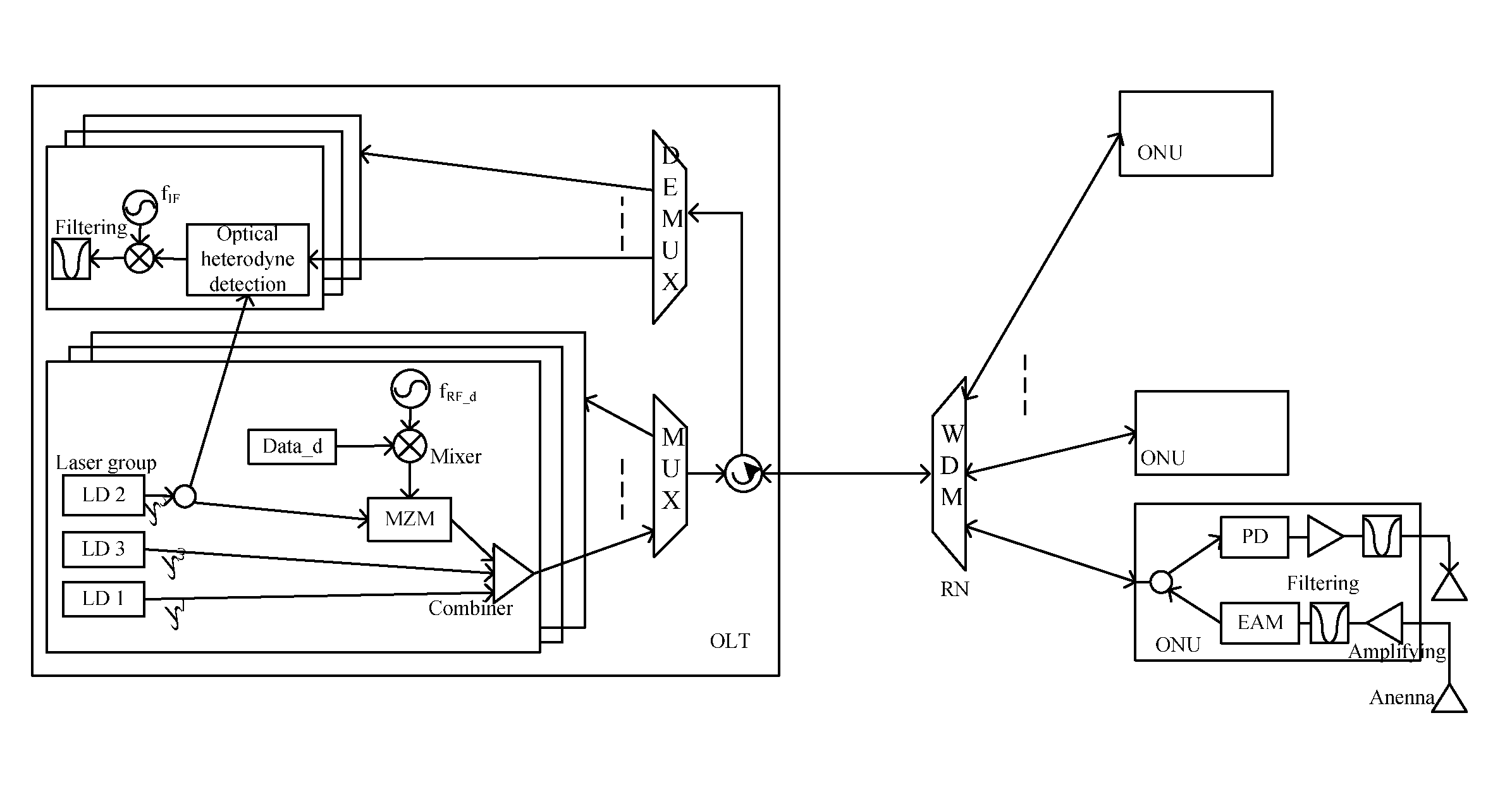
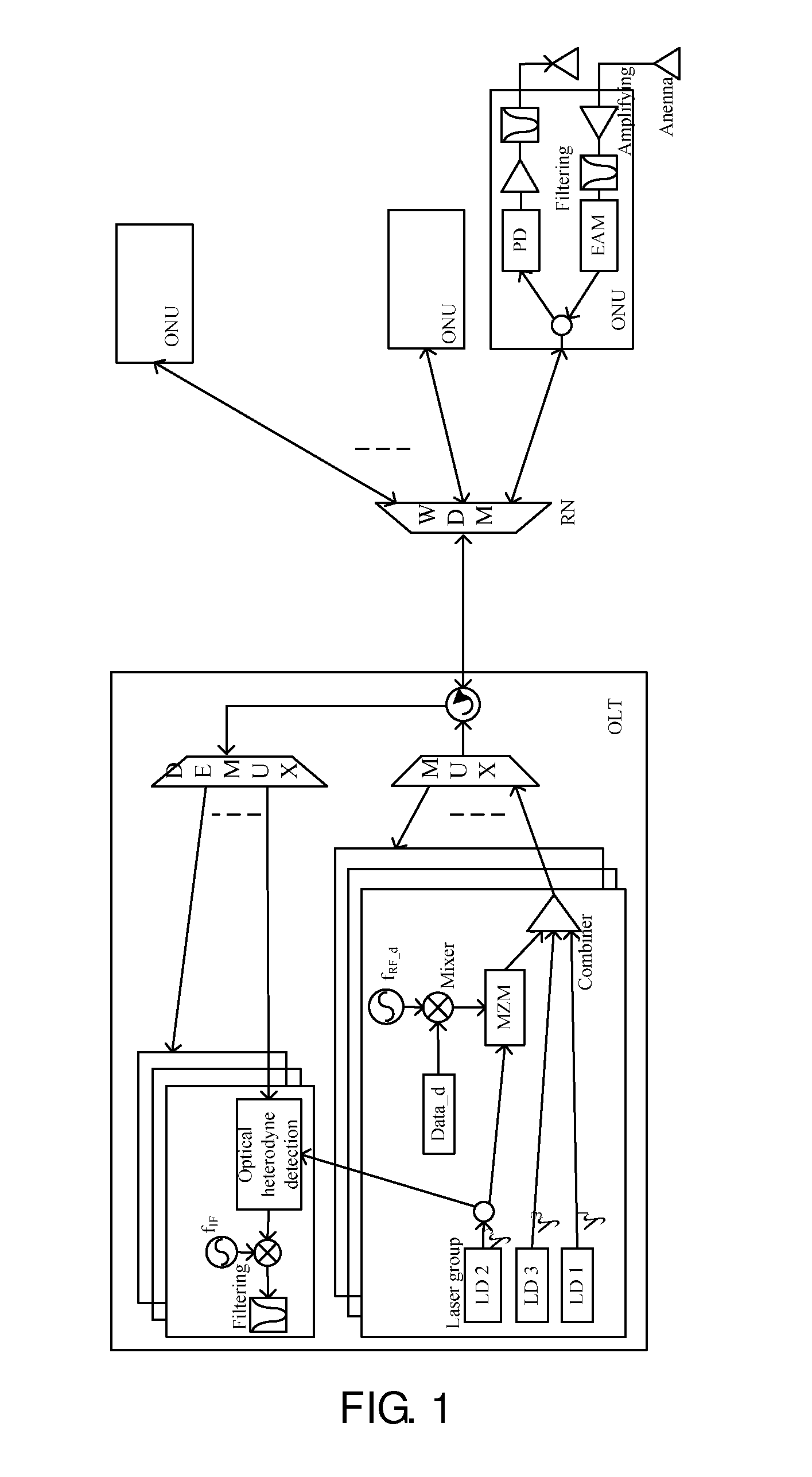
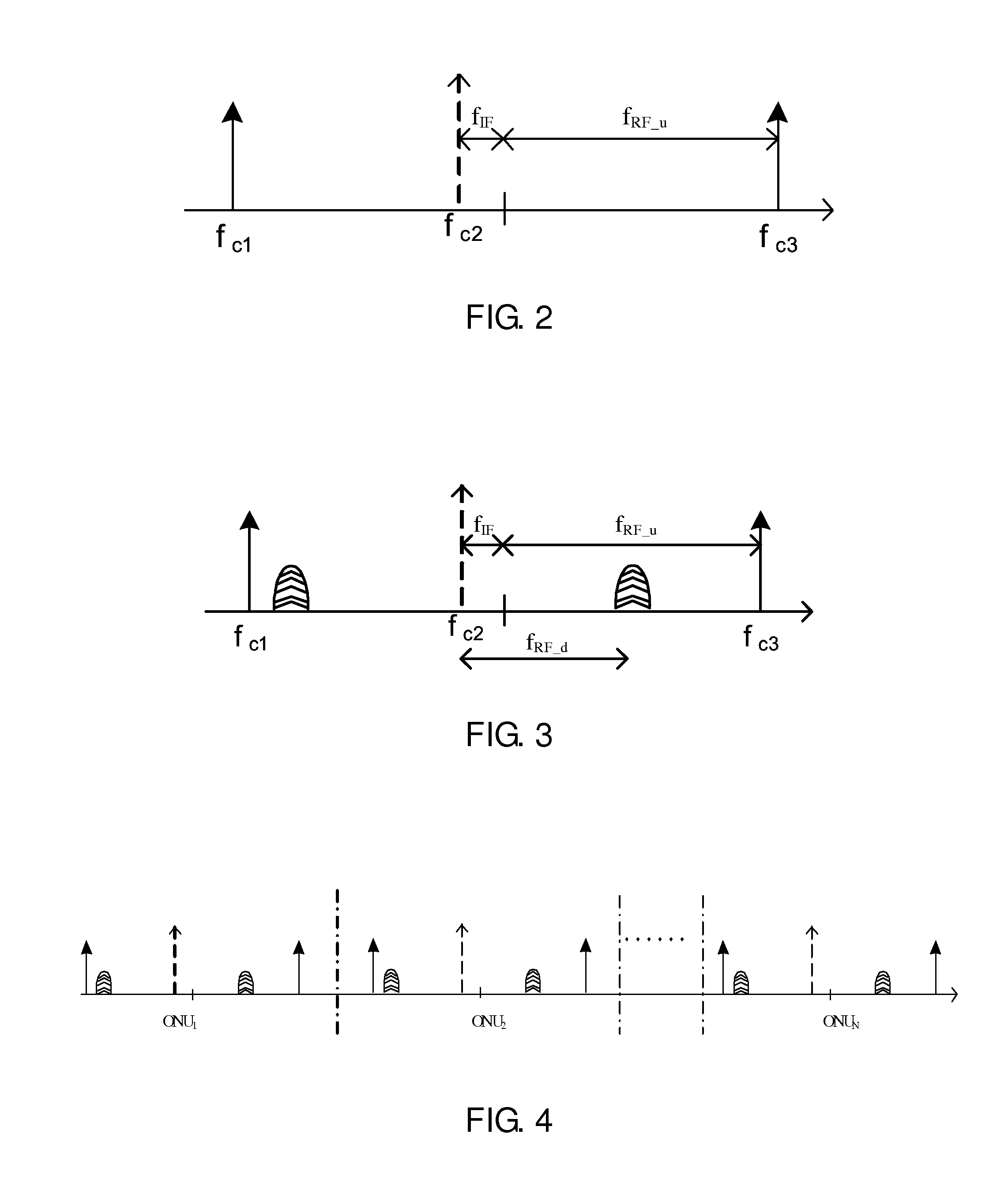
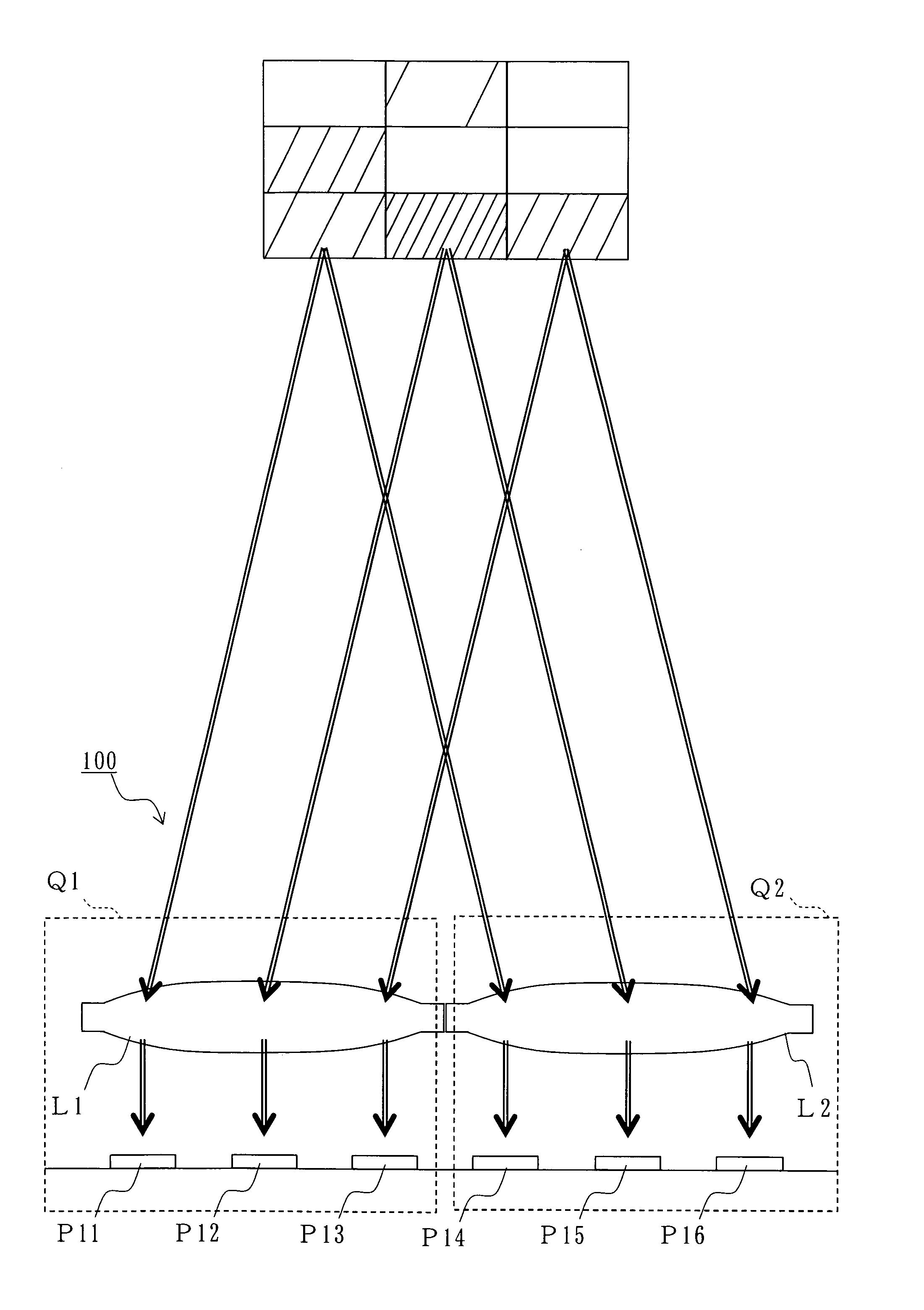
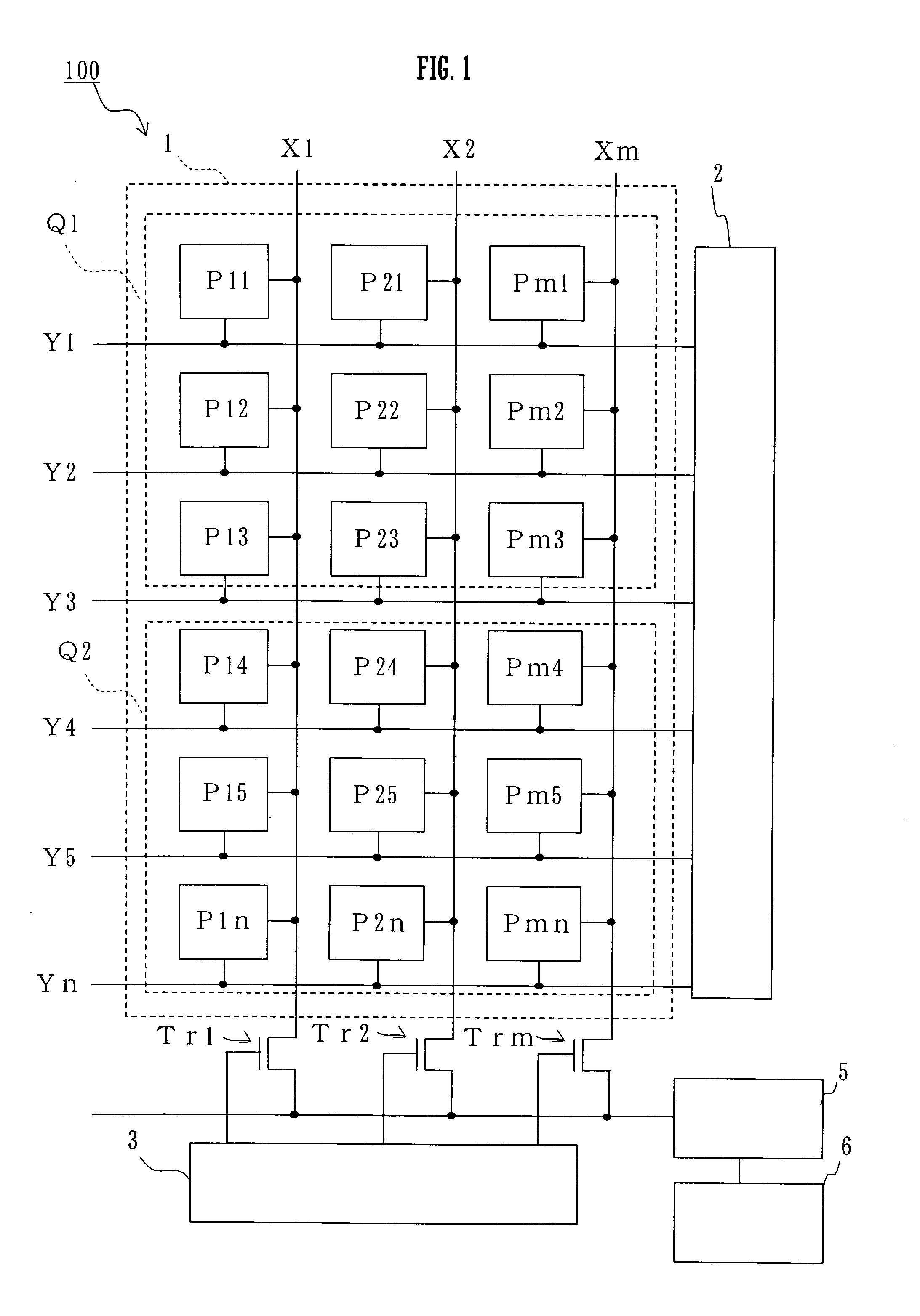
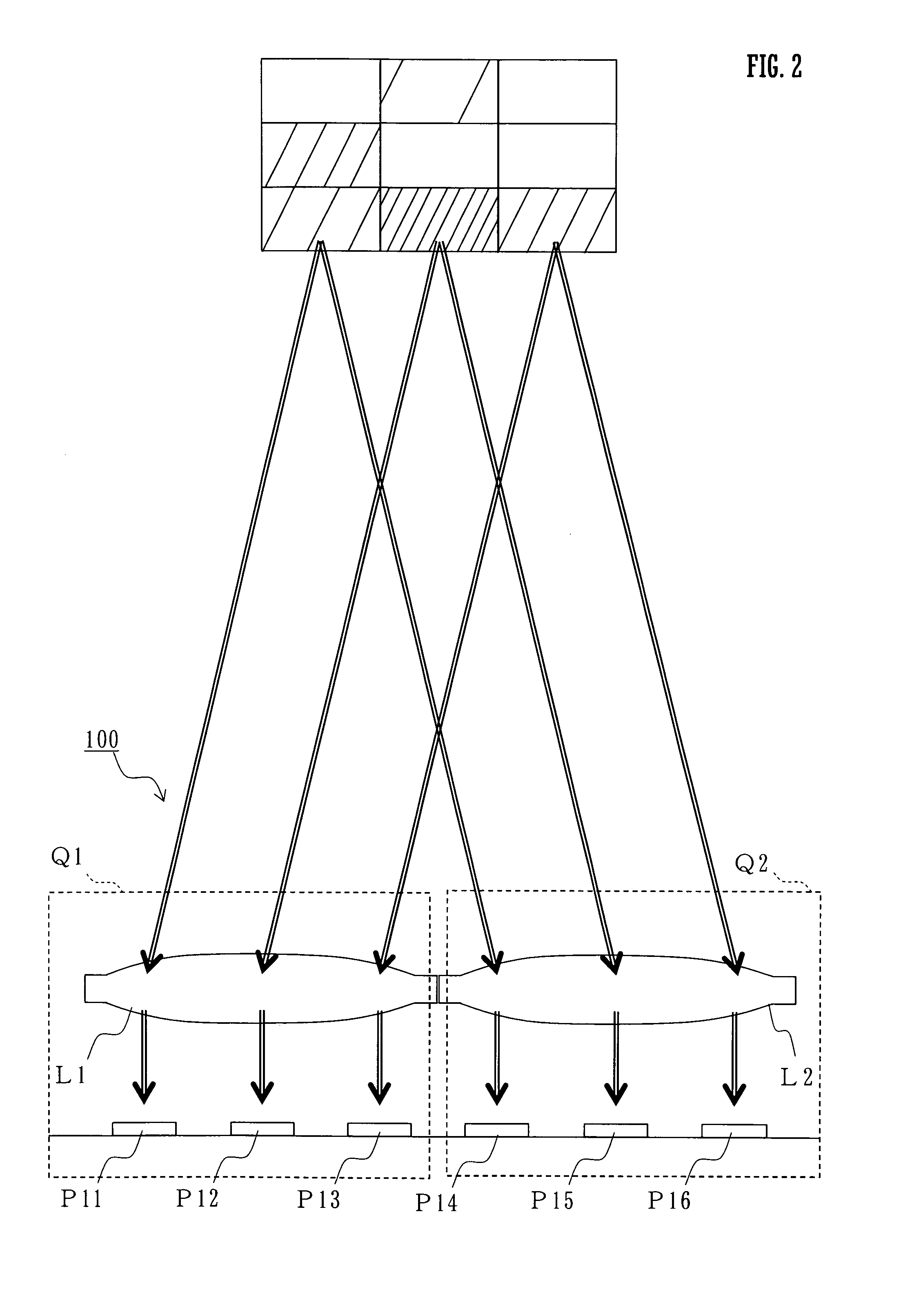
Optical line terminal, passive optical network and radio frequency signal transmission method
InactiveUS20100142955A1Additional wireless bandwidthPower spectrum is enhancedWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiple station single light sourceMultiplexingAccess network
An optical line terminal, a passive optical network and a radio frequency signal transmission method in the communication technical field are provided. The passive optical network comprises: an OLT, an ODN and at least one ONU. The OLT comprises: at least one transmitting unit, which provides one dedicated downstream optical carrier and two dedicated upstream optical carriers for ONU; the two dedicated optical carriers for ONU are configured to carry ONU upstream radio frequency signals; a multiplexing / demultiplexing unit; and at least one receiving unit which obtains the upstream signal from the demultiplexed upstream optical signal. The bandwidth of wireless access network is enhanced, and the design of ONU is simple.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
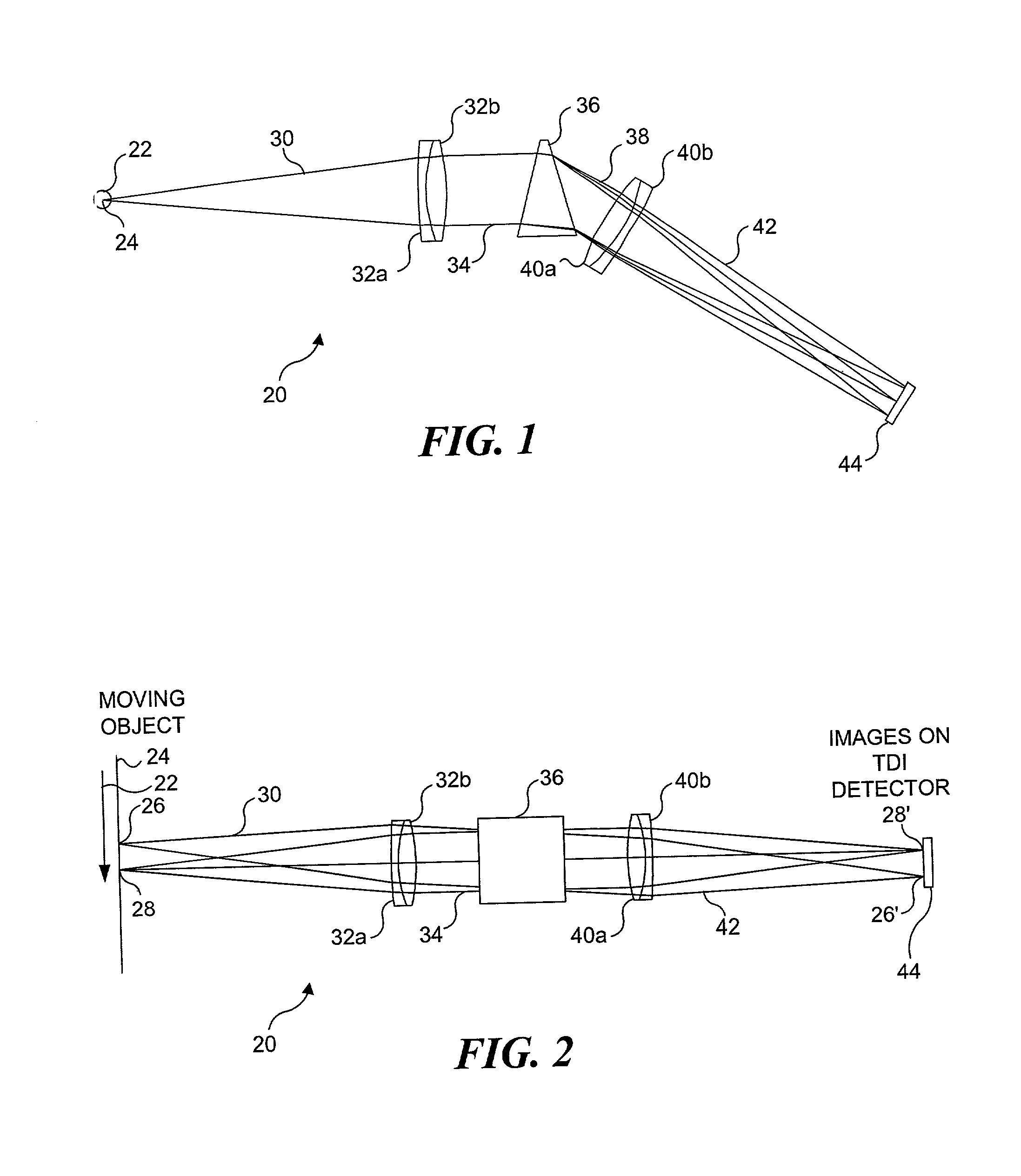
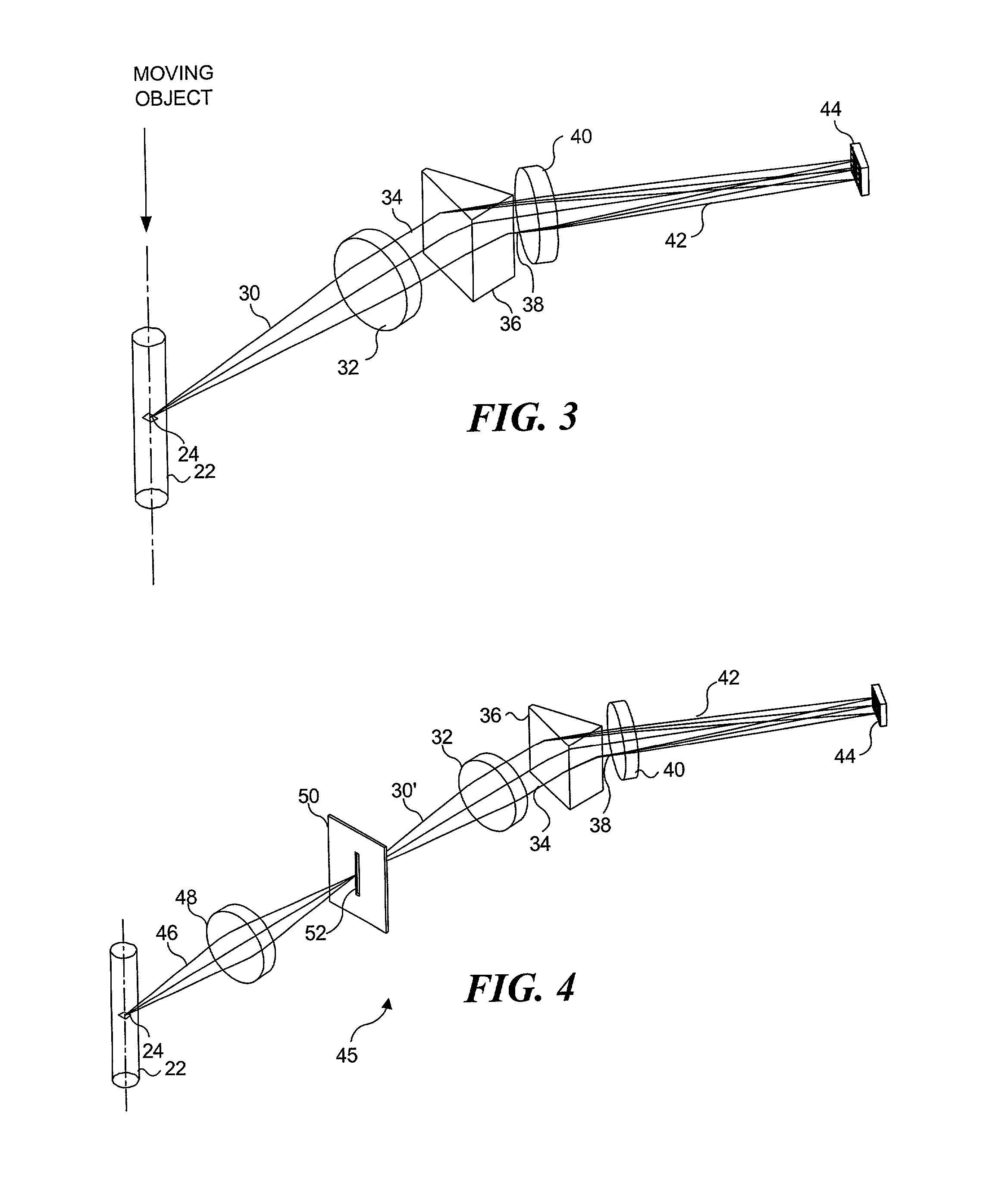
Imaging and analyzing parameters of small moving objects such as cells
InactiveUS20020071121A1High sensitivitySimplify Optical DesignOptical radiation measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementImaging lensLight filter
Light from an object such as a cell moving through an imaging system is collected and dispersed so that it is imaged onto a plurality of separate detectors. The light is spectrally dispersed by a plurality of spaced-apart dichroic reflectors, each detector receiving light from a different one of the dichroic reflectors. Each dichroic filter reflects light of a different predefined color, passing light of other colors. The output signal from each detector is indicative of a different characteristic of the object. In one configuration, each detector is provided with a separate imaging lens. In another configuration, the detectors are spaced at varying distances from the corresponding dichroic reflectors, so that separate imaging lenses are not required.
Owner:CYTEK BIOSCI
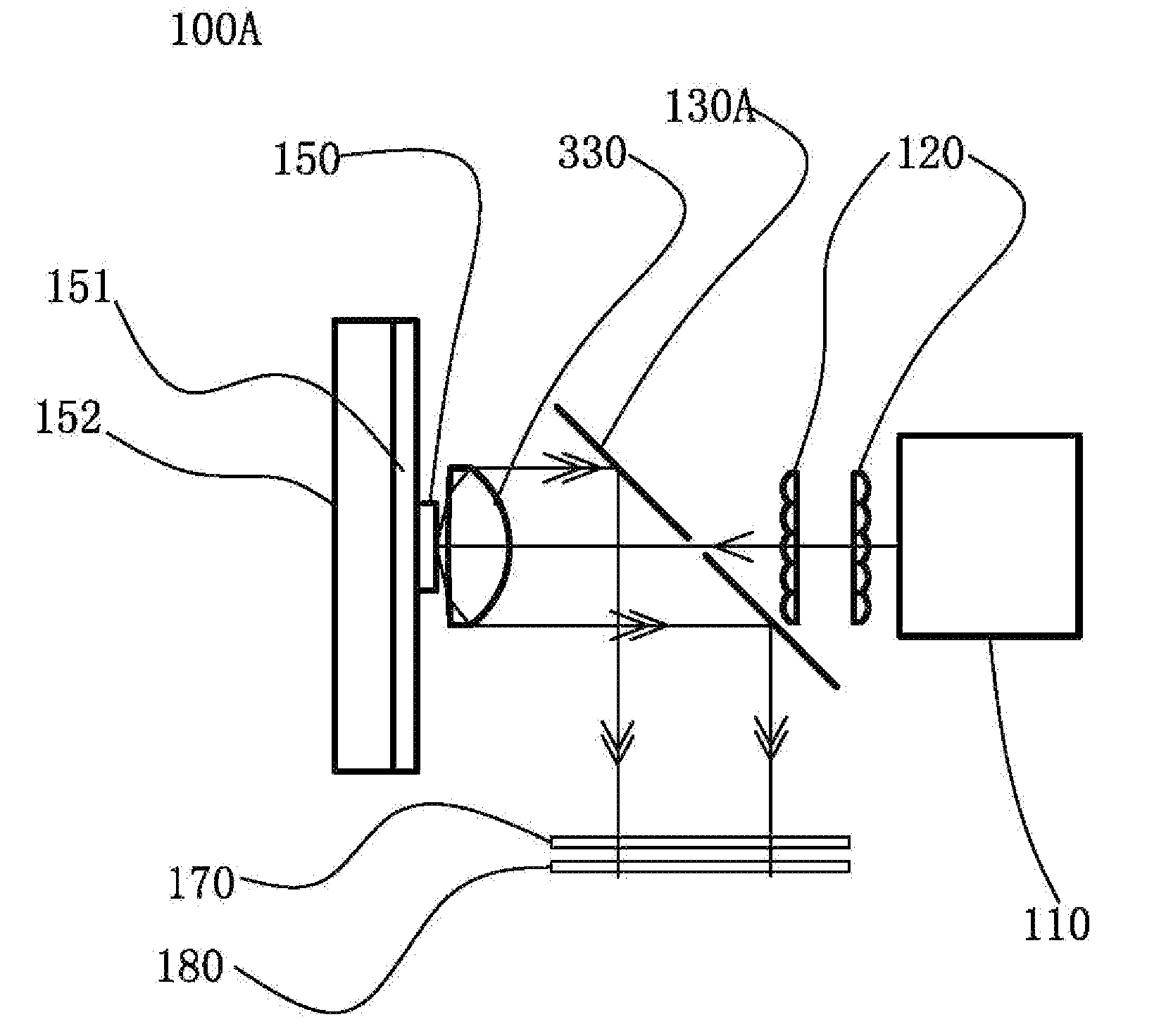
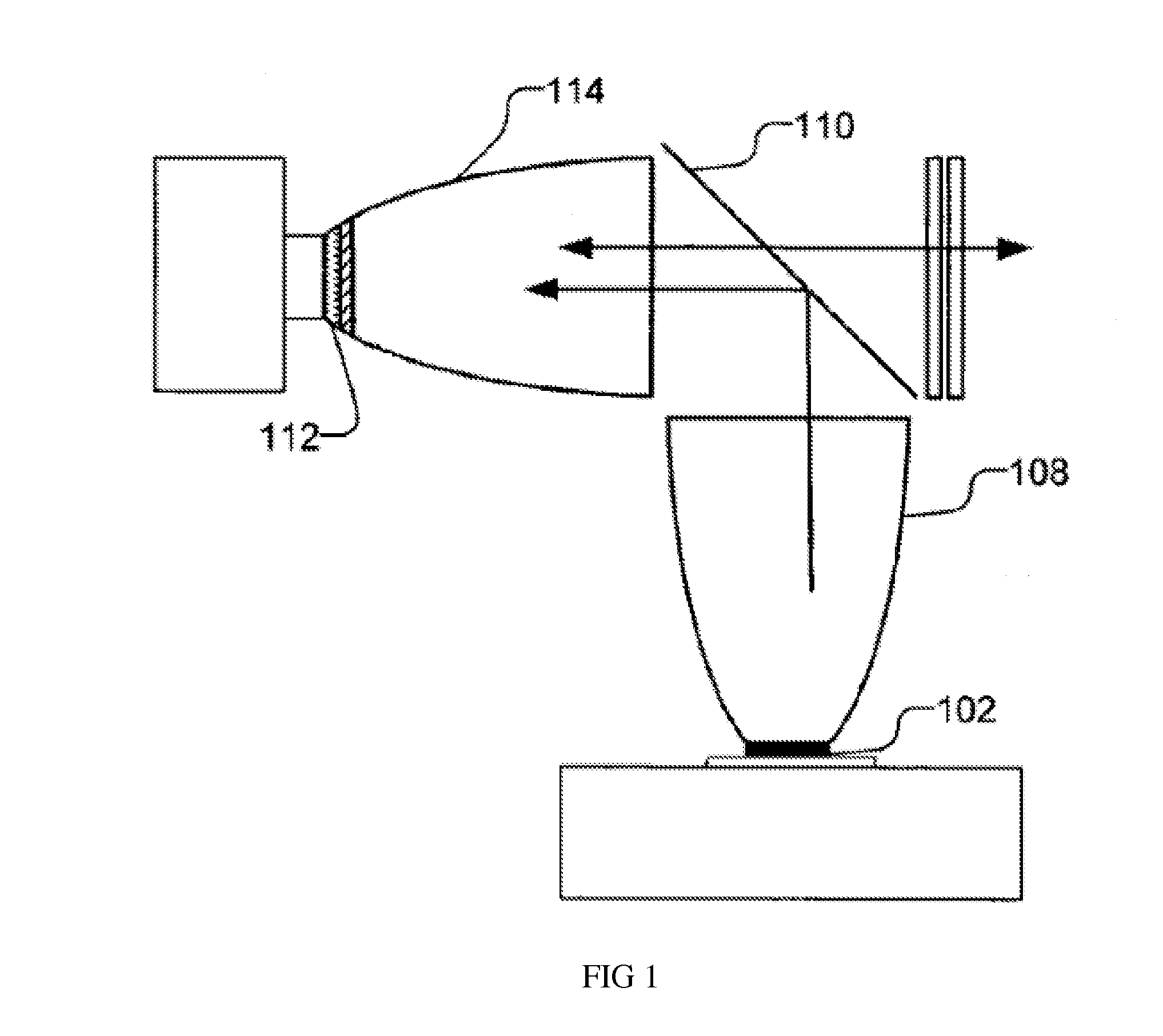
Light source
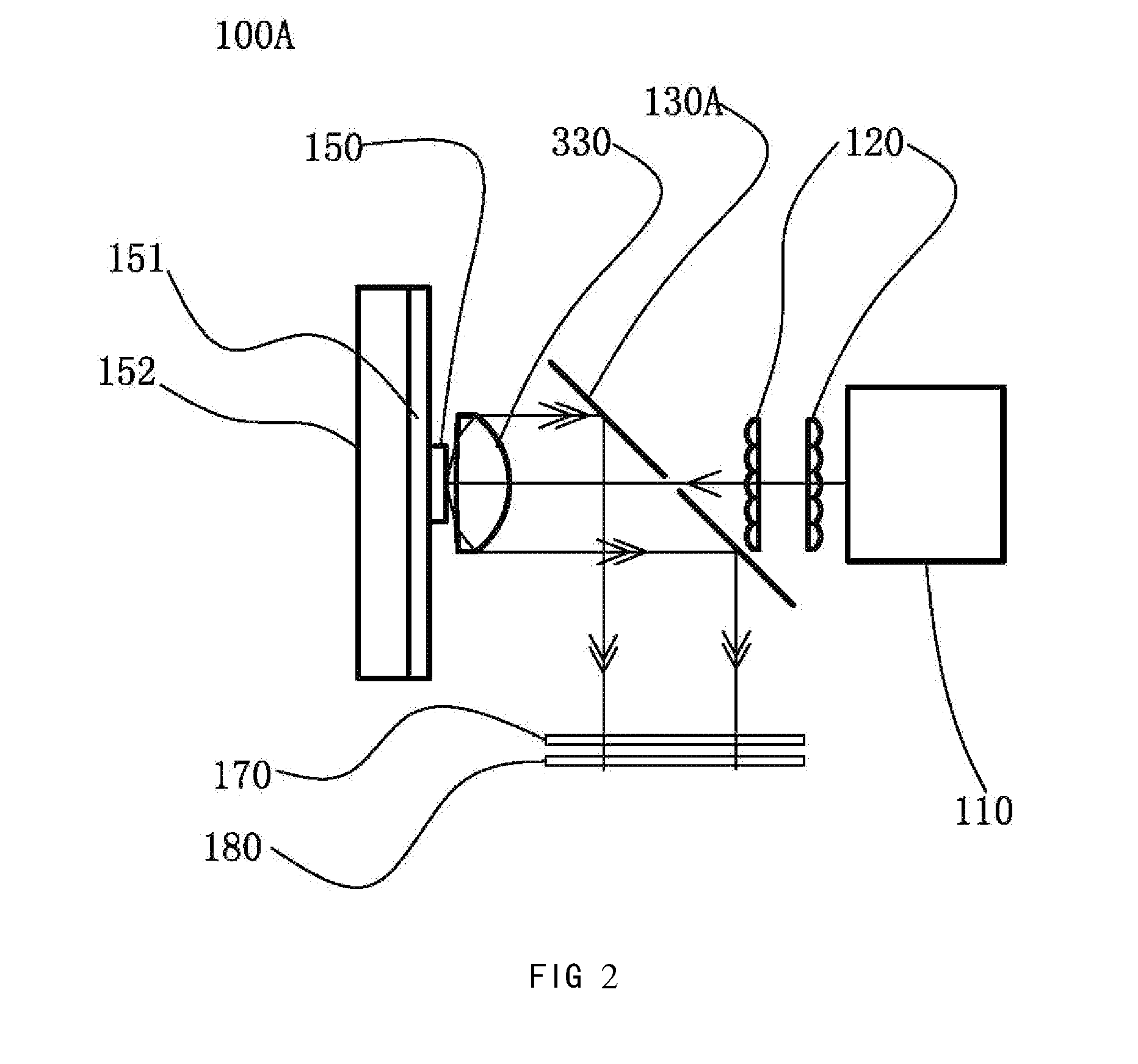
ActiveUS20130250546A1Simplify Optical DesignEasy to manufacturePoint-like light sourceProjectorsLight sourceLaser
A light source comprising an excitation light source (110) for providing excitation light, and an optical wavelength conversion member disposed at a distance from the excitation light source. The optical wavelength conversion member comprises an optical wavelength conversion material (150) for converting the excitation light into stimulated light. The light source also comprises an optical-guiding member that allows the excitation light to be incident on the optical wavelength conversion material, and an optical-collecting member (130A) for collecting stimulated light originating from the optical wavelength conversion material. To separate the paths of the stimulated light and the excitation light, the etendue of the optical-guiding member is less than or equal to ¼ of the etendue of the optical-collecting member. This allows the optical-guiding member to draw in the excitation light while preventing the excessive escape of the stimulated light through the optical-guiding member. The advantages of the light source are that it can separate the paths of the excitation light and the stimulated light, the light path is simple, and the optical members are easy to manufacture.
Owner:APPOTRONICS CORP LTD
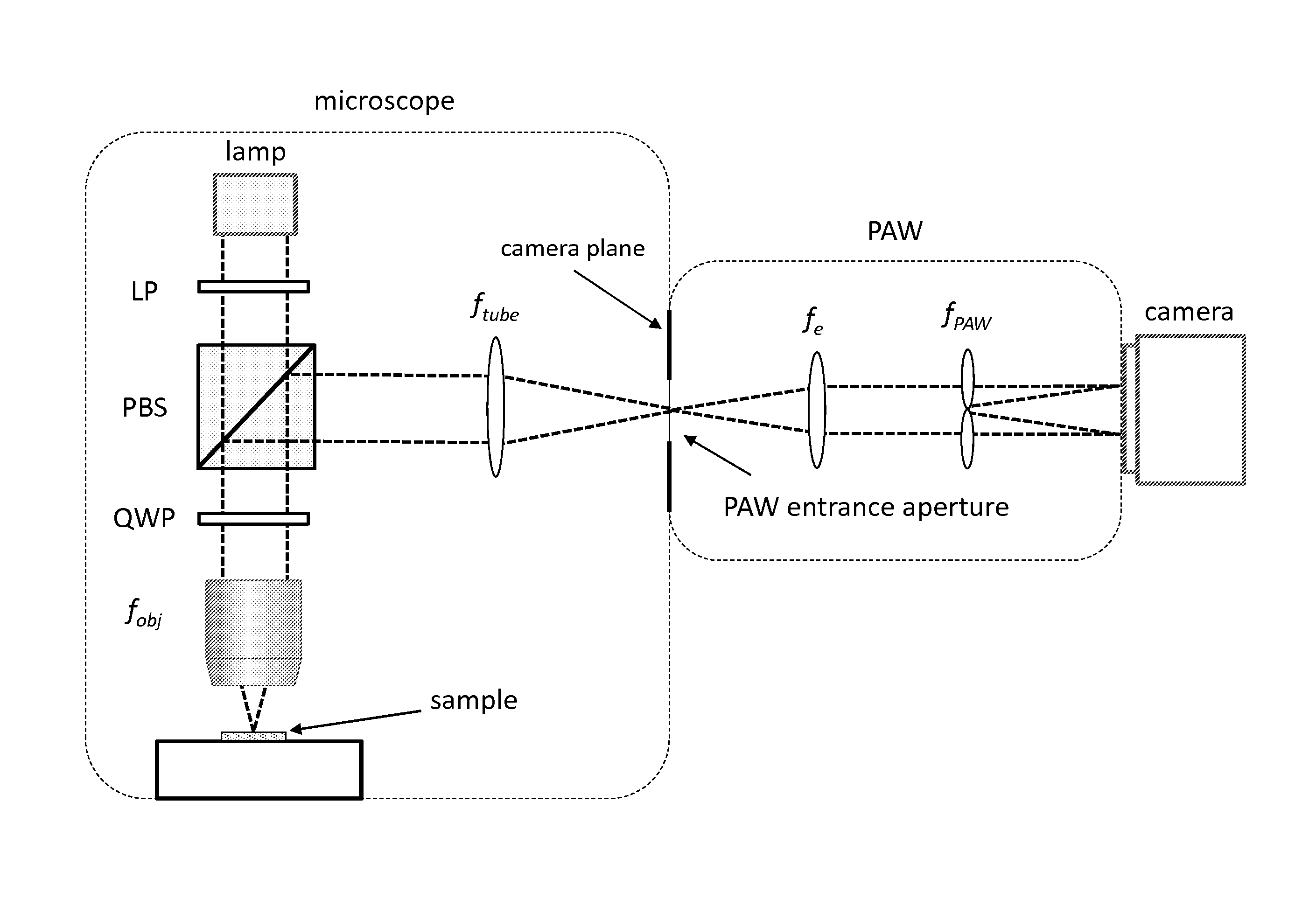
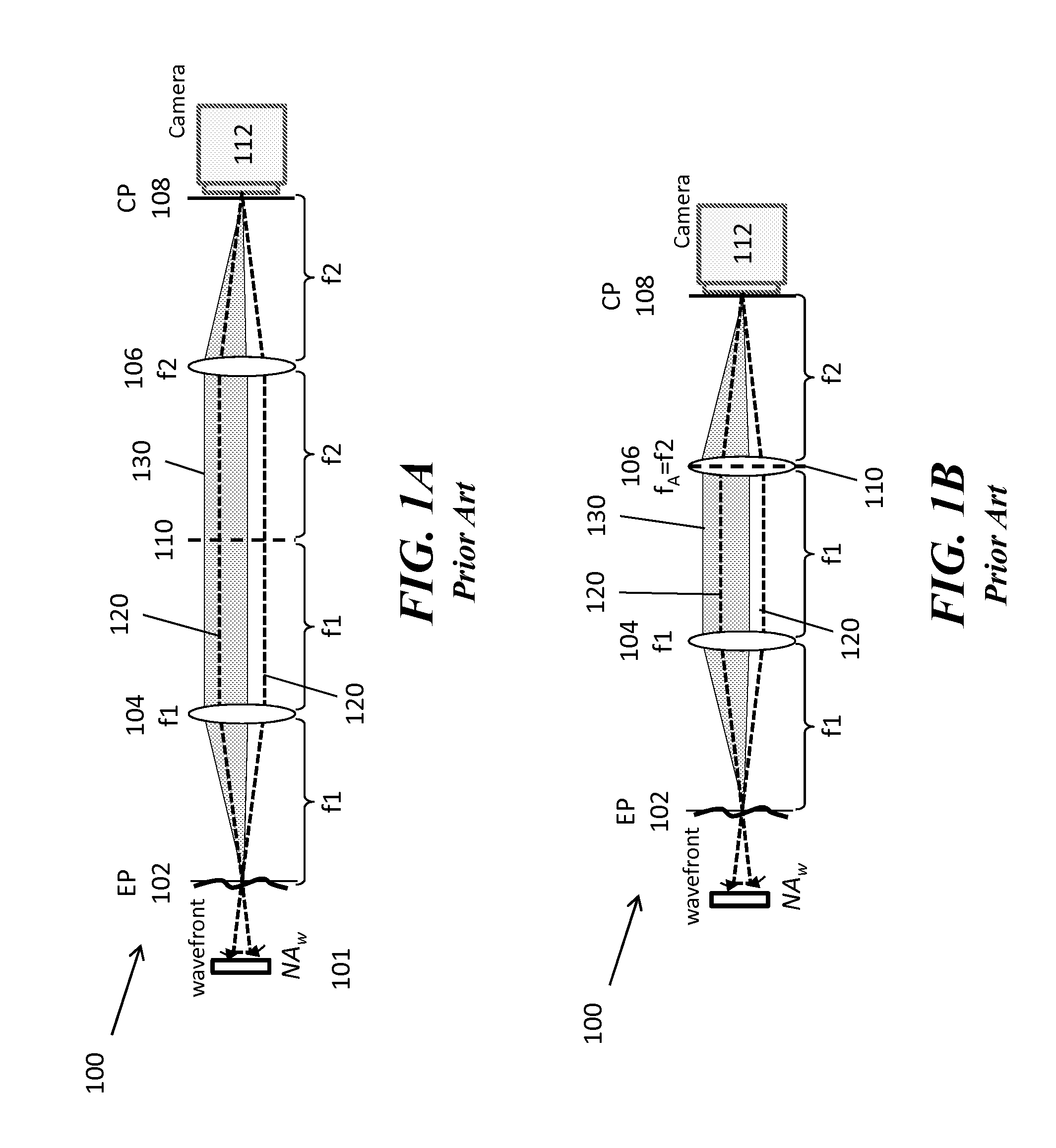
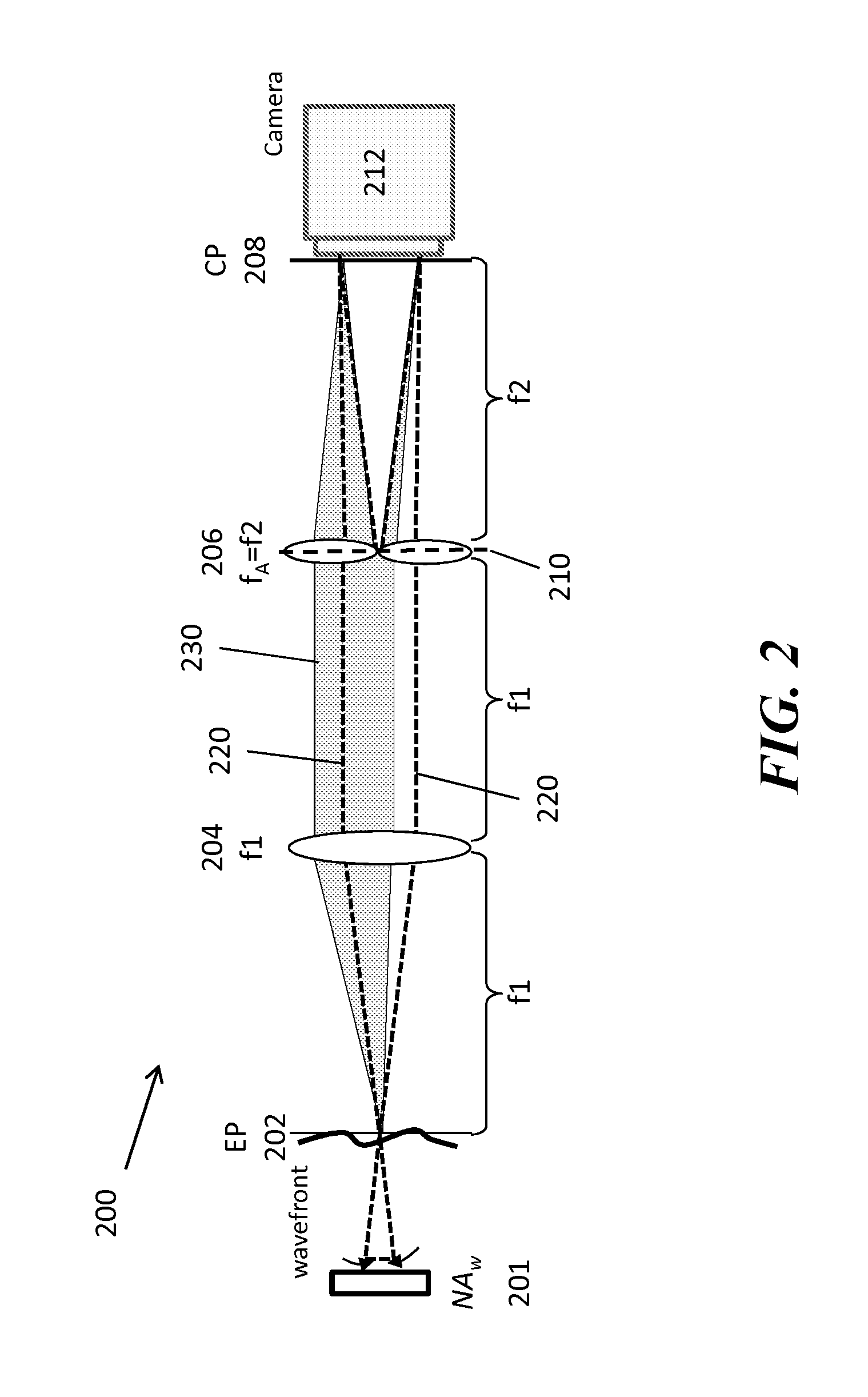
Partitioned aperture wavefront imaging method and system
InactiveUS20140267674A1Improve spatial resolutionHigh quality optical lensOptical measurementsColor television detailsIntermediate imageWavefront
A partitioned aperture wavefront imaging system includes an imaging system comprising a partitioned aperture lens array positioned at the aperture plane or Fourier plane between the entrance plane and camera plane of an imaging system. The partitioned aperture lens array can include 2 or more off-axis lenses symmetrically distributed about an optical axis, and adapted to produce simultaneously at the camera plane at least two images of an object, or intermediate image of an object, presented at the entrance plane. Preferably, the partitioned aperture lens array includes from 3 to 5 off-axis lenses and produces 3 to 5 images at the camera plane from which phase and amplitude information about the light field can be determined. The partitioned aperture wavefront imaging system provides enough information about the light field presented at the entrance plane to enable reconstruction of the light field at other planes relative to the entrance plane.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Single-path color video projection systems employing reflective liquid crystal display devices
InactiveUS6839095B2Light collection efficiency be improveMinimize étendueMirrorsStatic indicating devicesIntegratorProjection system
A multimedia projector (100) includes a single-path frame-sequential color optical system in which light rays emitted by a light source (14) propagate through a color wheel (102) and an optical integrator (16, 120, 122), and are directed toward a transflective polarizing beam splitter (40) that separates them into P-polarized components (76) and S-polarized components (78). The P-polarized components are transmitted toward a reflective LCD (26) in which pixels in a dark state reflect the light rays without a polarization change and return them through the transflective polarizing beam splitter, whereas pixels in a bright state reflect the light rays with a 90° polarization change as S-polarized light rays (112), which are reflected by the transflective polarizing beam splitter toward a projection lens (27).
Owner:STRAIGHT SIGNALS
Localized surface plasmon resonance sensing system, appartatus, method thereof
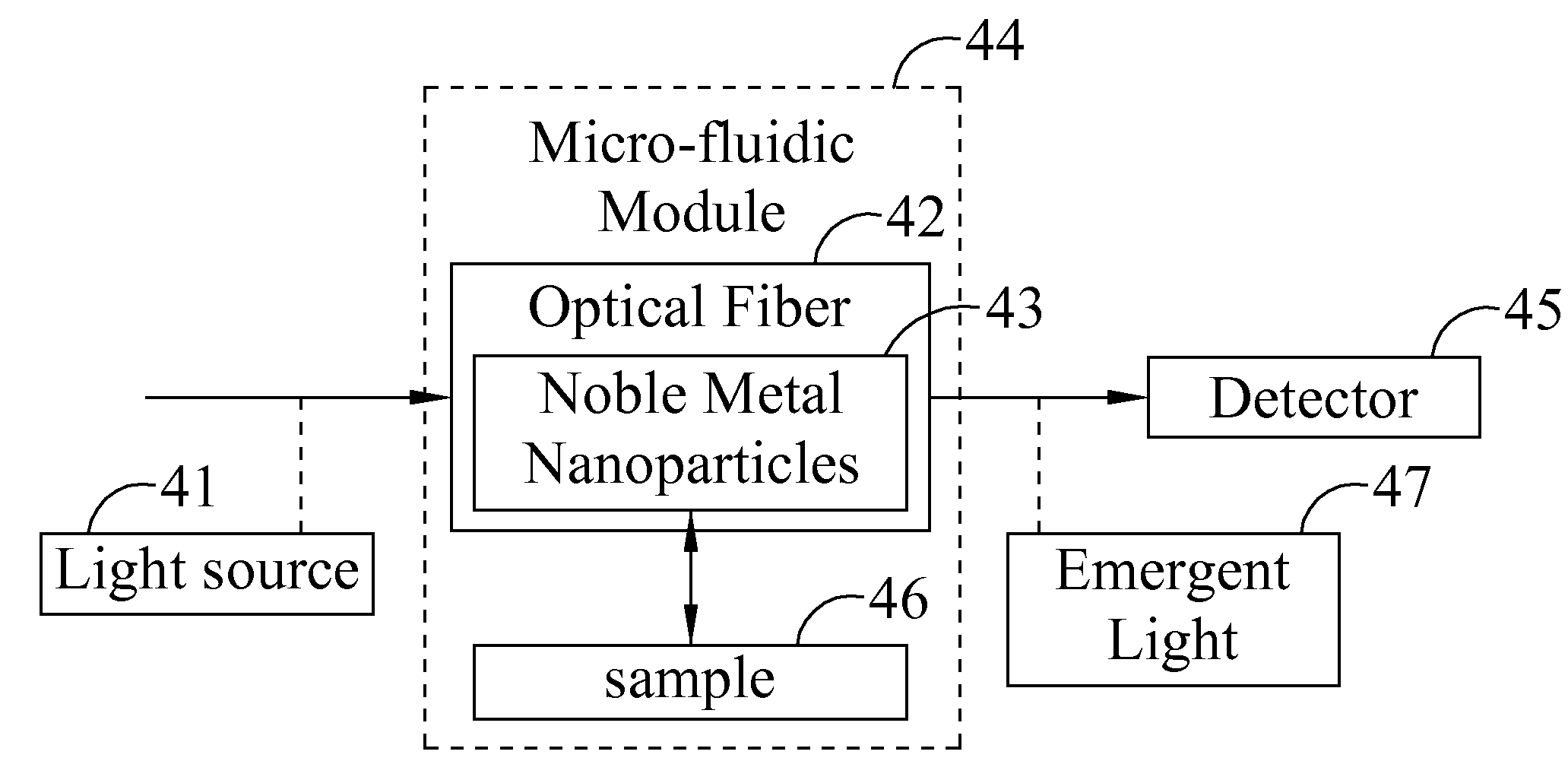
ActiveUS20100128275A1Sensor smallEasy to set upScattering properties measurementsLaboratory glasswaresOpto electronicLocalized surface plasmon
A sensing system comprises a light source, an optical fiber, a plurality of noble metal nano-particles, a micro-fluidic module and a photo detector. The optical fiber couples an incident light. The plurality of noble metal nano-particles are disposed on a surface of the optical fiber to form a noble metal nano-particle submonolayer, the noble metal nano-particles are substantially separated from each adjacent noble metal nano-particles such that the conductivity of the noble metal nano-particle submonolayer is smaller than that of a metal film. The micro-fluidic module accommodates the optical fiber and a sample, and the sample is driven to contact with the noble metal nano-particles. The photo detector detects an emergent light from the optical fiber. When the incident light interacts with the noble metal nano-particles, a signal derived from localized surface plasmon resonance in form of attenuated light or elastic scattered light is outputted through the photo detector.
Owner:INSTANT NANOBIOSENSORS CO LTD
Broadband high power light source
ActiveUS20120099340A1High optical peak powerSimplify Optical DesignMechanical apparatusLaser using scattering effectsStimulate raman scatteringLight beam
The present invention relates to a super continuum light source comprising a pump source arranged to emit light having a center wavelength λcenter arranged to provide pump pulse to a generator fibre, where the refractive index profile of the core is arranged to allow modal cleaning of the light is it propagates, such as via stimulated Raman scattering. An example of invention is the application of a relatively high power pump laser utilized to provide an optical super continuum with relatively high spectral density and / or good beam quality even though the pump laser may provide a beam with a high M2.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Broadband high power light source
ActiveUS8731009B2Increase powerLong lastingLaser using scattering effectsLighting support devicesFiberStimulate raman scattering
The present invention relates to a super continuum light source comprising a pump source arranged to emit light having a center wavelength λcenter arranged to provide pump pulse to a generator fiber, where the refractive index profile of the core is arranged to allow modal cleaning of the light is it propagates, such as via stimulated Raman scattering. An example of invention is the application of a relatively high power pump laser utilized to provide an optical super continuum with relatively high spectral density and / or good beam quality even though the pump laser may provide a beam with a high M2.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
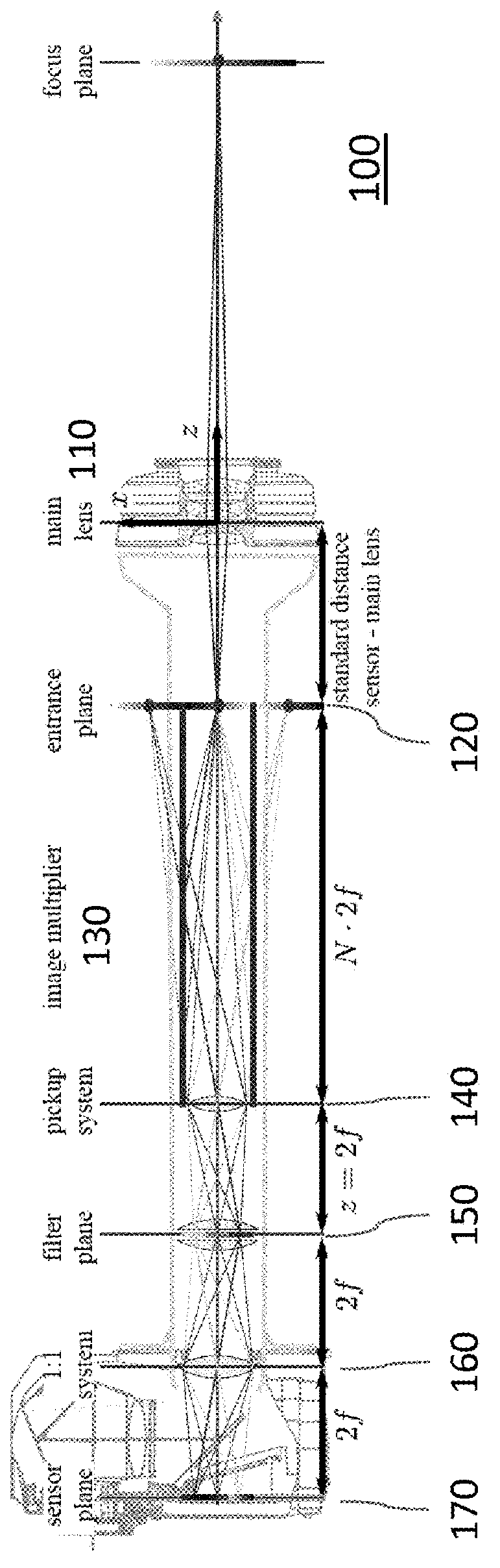
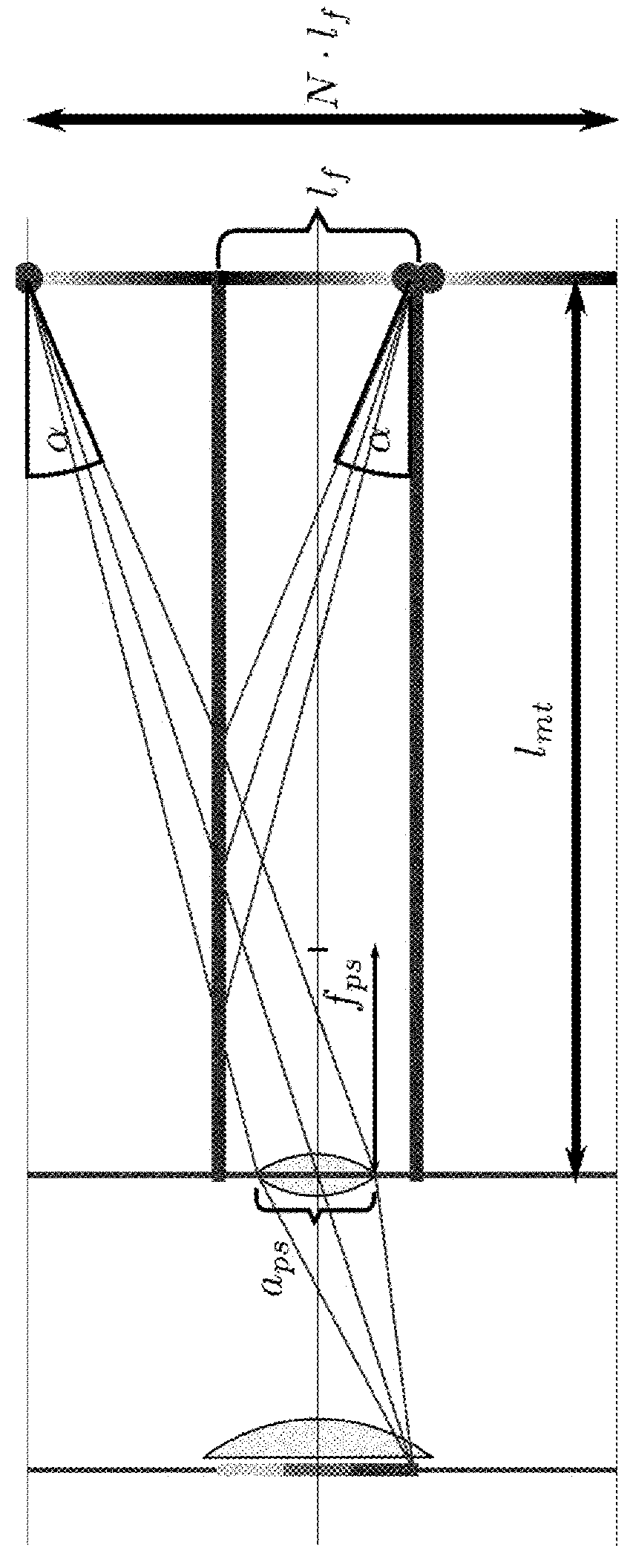
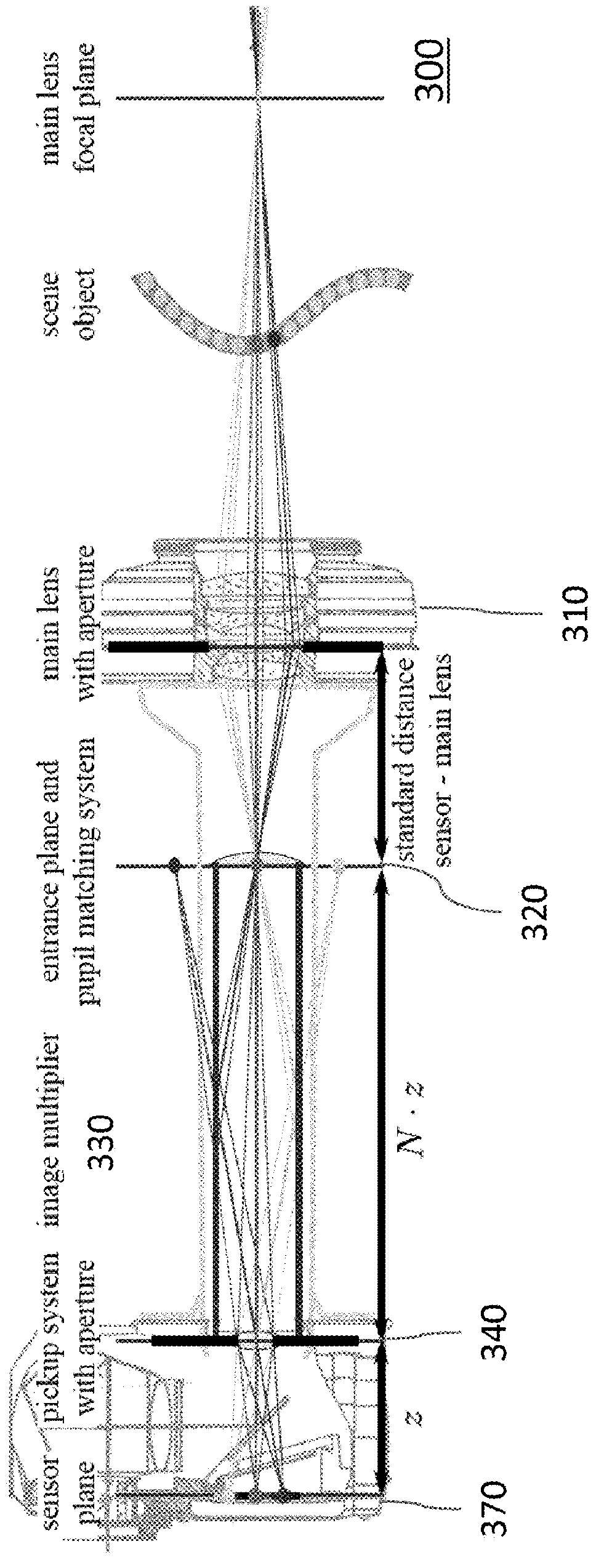
Plenoptic imaging device
ActiveUS20160057407A1Wide-spread adoption of plenoptic imaging by usersAvoid necessityTelevision system detailsPrismsImaging equipmentOptical image
A plenoptic imaging device according to the invention comprises an image multiplier (130) for obtaining a multitude of optical images of an object or scene and a pick-up system (140) for imaging at least some of the multitude of images to a common image sensor (170) during the same exposure of the sensor.
Owner:KLENS GMBH
Optical-fiber type laser wavemeter
ActiveCN102155997AReduce mirrorReduced Alignment DifficultyOptical measurementsGratingMeasurement device
The invention provides an optical-fiber type laser wavemeter that consists of a lens, fusing quartz optical fiber, an optical fiber coupler, a wavelength calibrating device, a grating monochromator, a wavelength precise measurement device, a linear CCD (Charge Coupled Device), a signal processor and a data wire. In the invention, the fusing quartz optical fiber is used for guiding light and the optical fiber coupler is used for splitting beam so that the spatial dimension and complexity of the wavemeter can be effectively reduced; and the calibration, coarse measurement and precise measurement of the wavelength are effectively combined so as to realize high-precision real-time measurement on the central wavelength and spectrum bandwidth of the laser. In the invention, the linear width and the central wavelength of the continuous laser and the pulse laser can be measured precisely and conveniently at high speed, and the optical-fiber type laser wavemeter is particularly used for measuring the laser wavelength of an excimer laser.
Owner:南京海莱特激光科技有限公司
Two Pi solid angle high resolution optical system
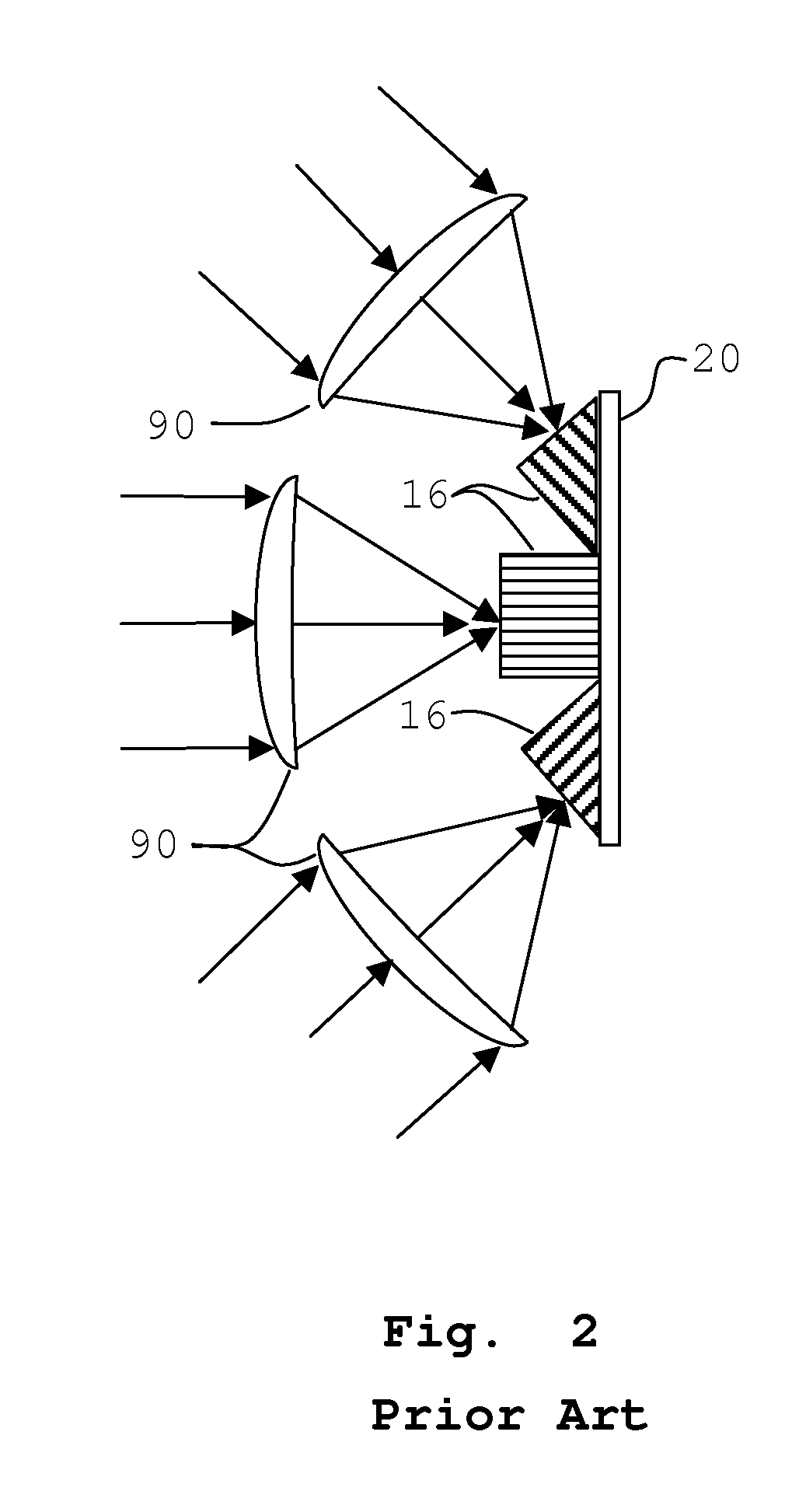
InactiveUS8488257B2Simplify Optical DesignSmall sizeClosed circuit television systemsPanoramic photographyFiberCMOS
This invention is a wide field surveillance, monocentric, refractive optical system with inherent features being, non-mechanical, compact, high resolution, a field of view up to two Pi steradians solid angle. The optics design uses a single optical system and multiple flat image collection devices. Multiple fiber plates translate and map the image off of the curved image surface to the flat image collection devices. The fiber plates also act to translate the image into a larger volume as compared to the curved image surface, allowing required volume for the multiple image collection devices. This invention uses a single refractive optical system with multiple CCD or CMOS detectors. Advantages over prior art are simple optical system, rugged optics, high resolution and single optics which is easily manufactured.
Owner:STARK DANIEL LEE
Polarization converter and projection system using same
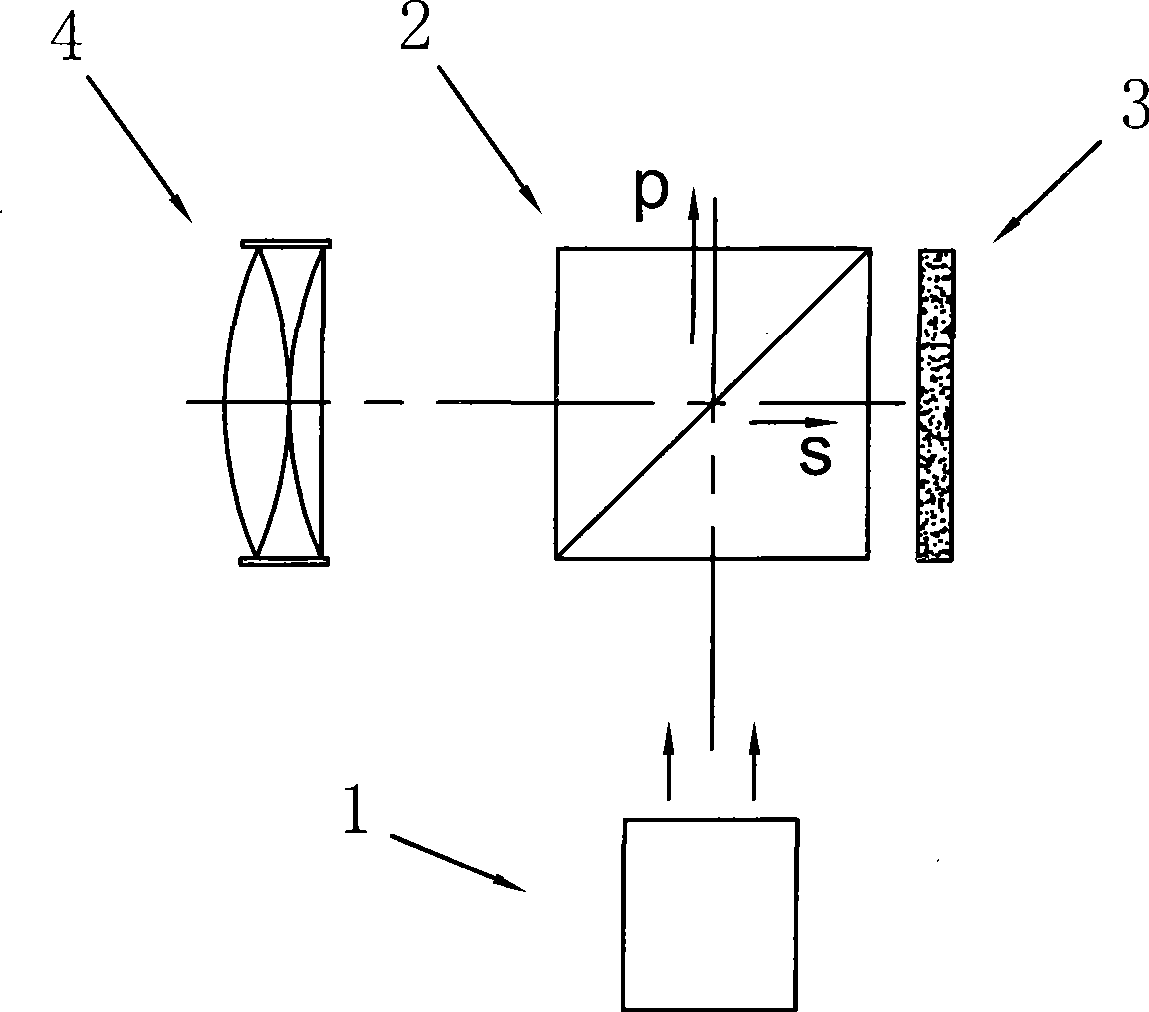
ActiveCN101546045ASimple structureLarge light output areaProjectorsOptical elementsBeam splittingLight beam
The invention provides a polarization converter with a novel structure and a projection system using the same. The polarization converter consists of seven small prisms which are arranged in an array and glued together; partial combining surfaces of the prisms are plated with polarization beam-splitting film layers or full reflective film layers; and light emergent surfaces of partial prisms are provided with half wave plates; therefore, the polarization converter can be used for converting all incident non-polarized light into S polarized light or P polarized light for emergence, and has good uniformity of emergent polarized light due to a PCS array. Beams emitted by a light source of the projection system can be directly incident into the polarization converter, and are converted into the S polarized light or P polarized light completely, and a micro lens system is not needed to adjust the beams emitted by the light source, so the optical design is simplified and the cost is saved; and the projection system has high light utilization rate and improves the image display quality.
Owner:BUTTERFLY TECH SHENZHEN
Color video projection system employing reflective liquid crystal display devices
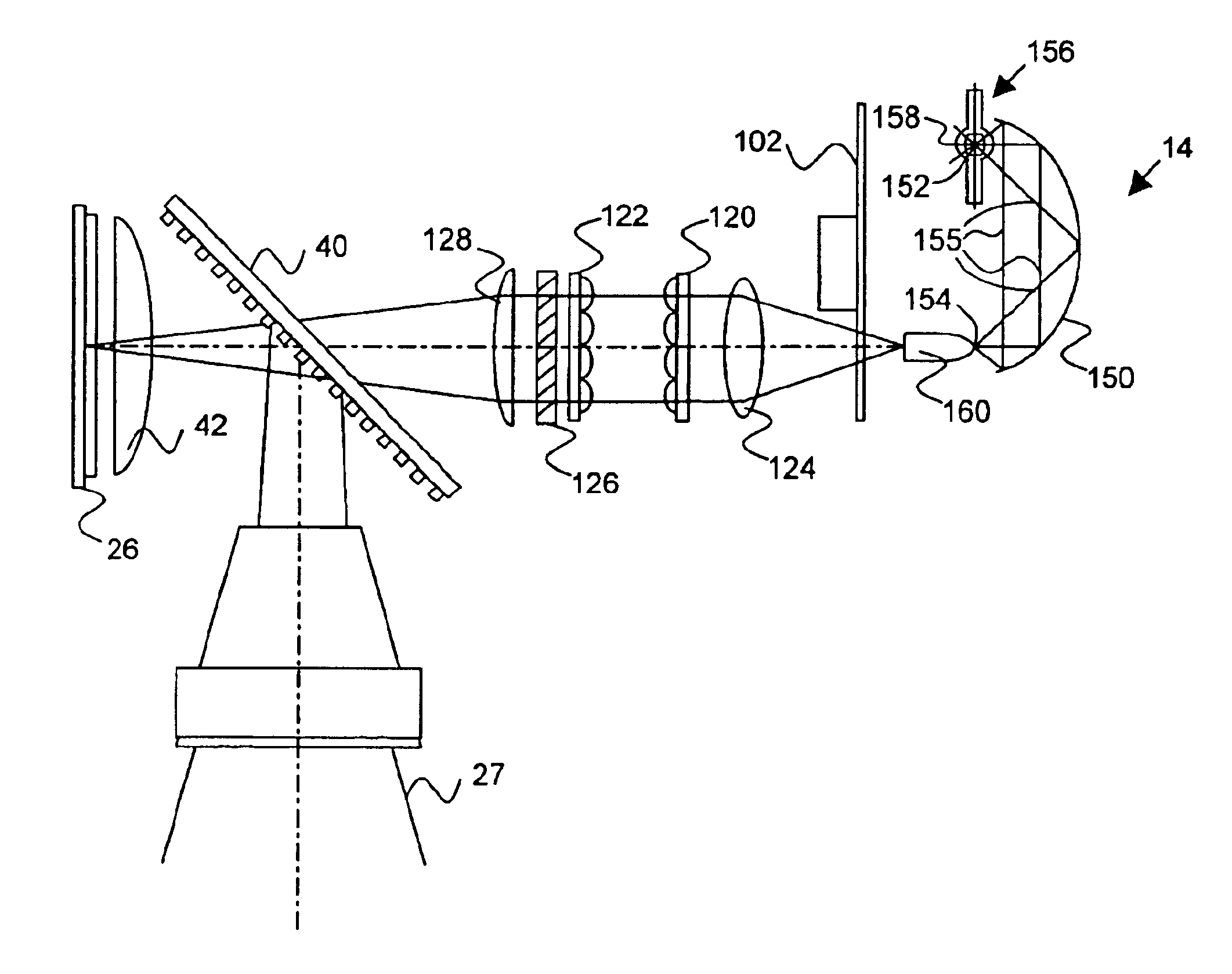
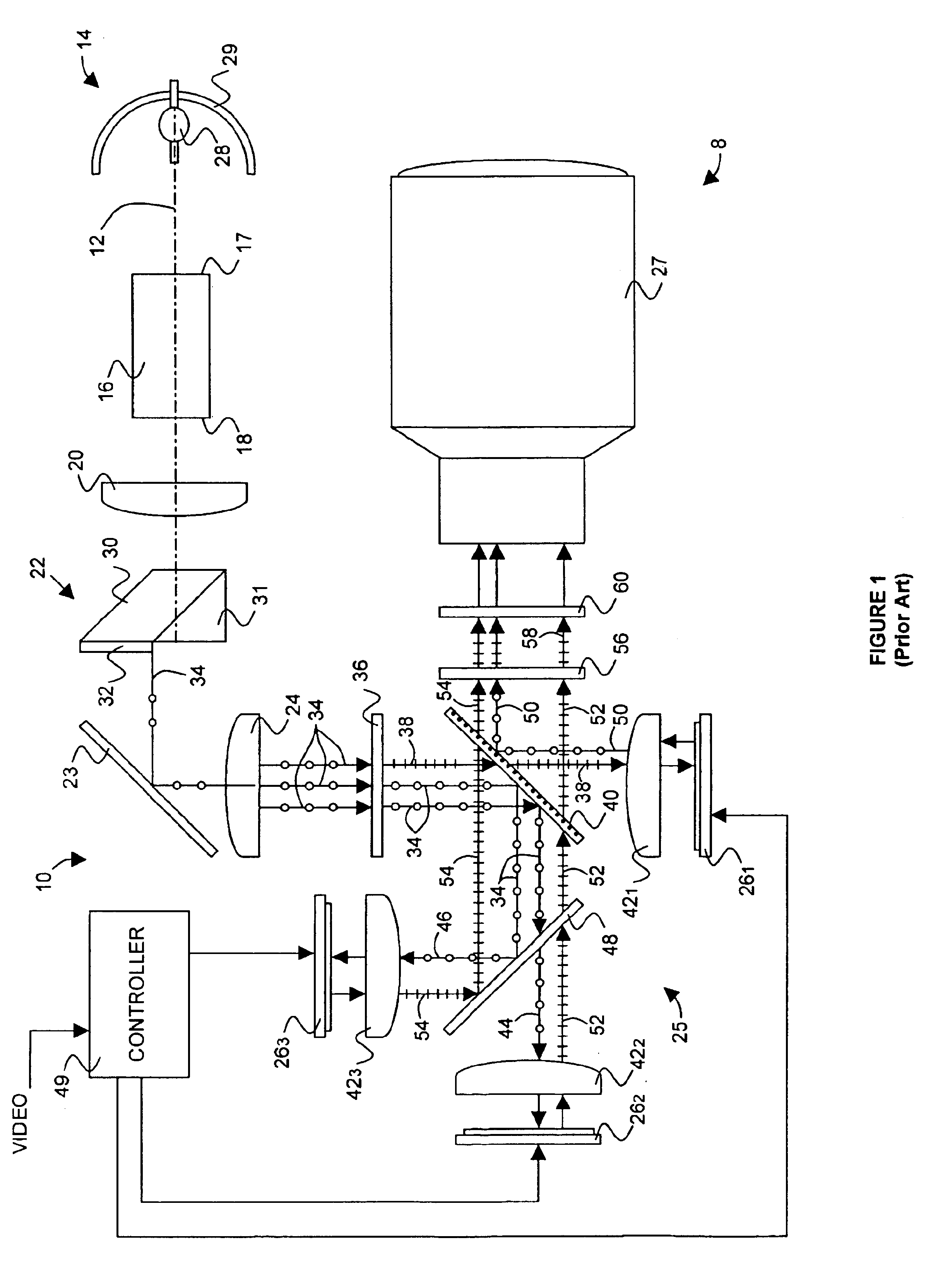
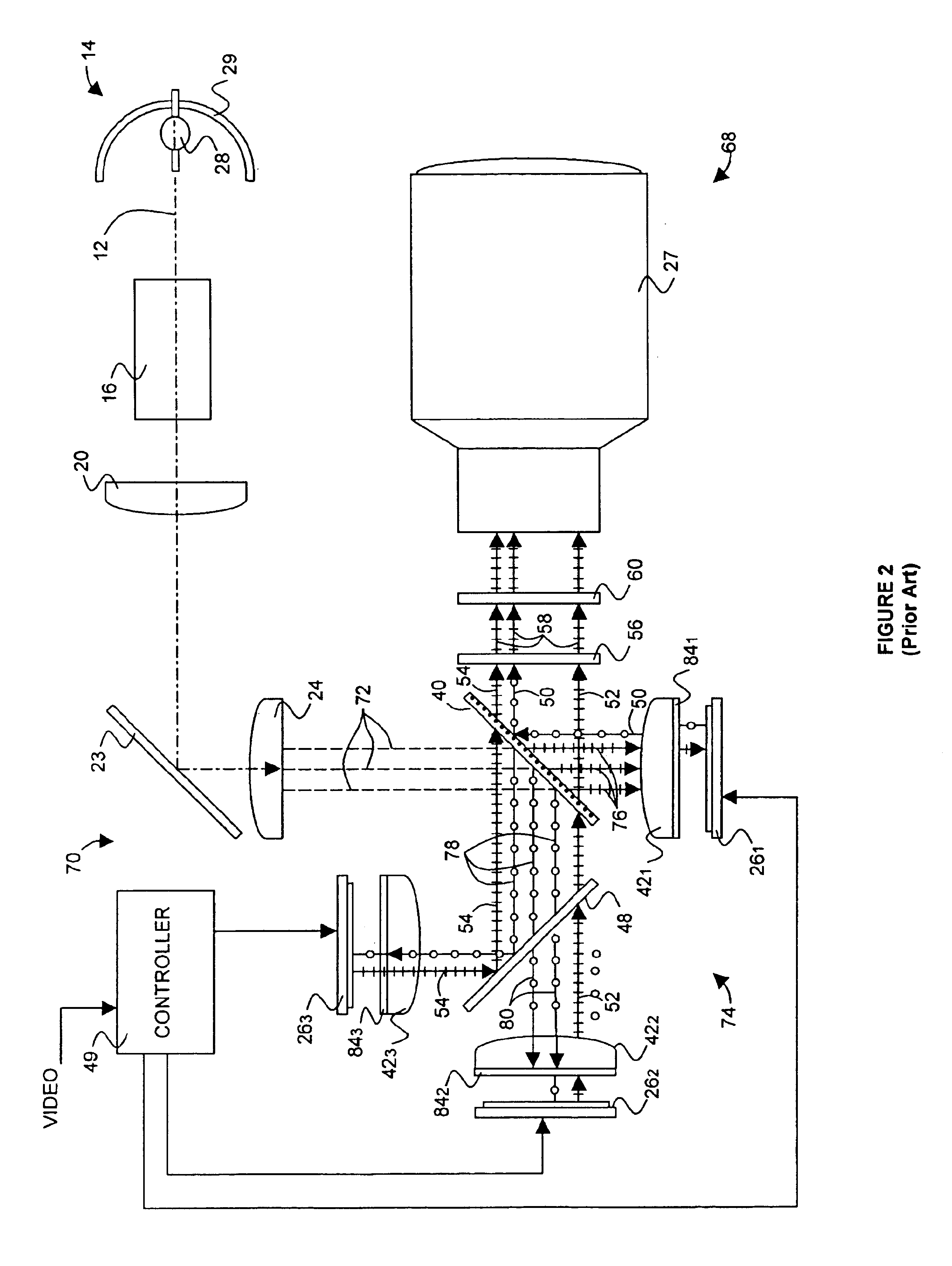
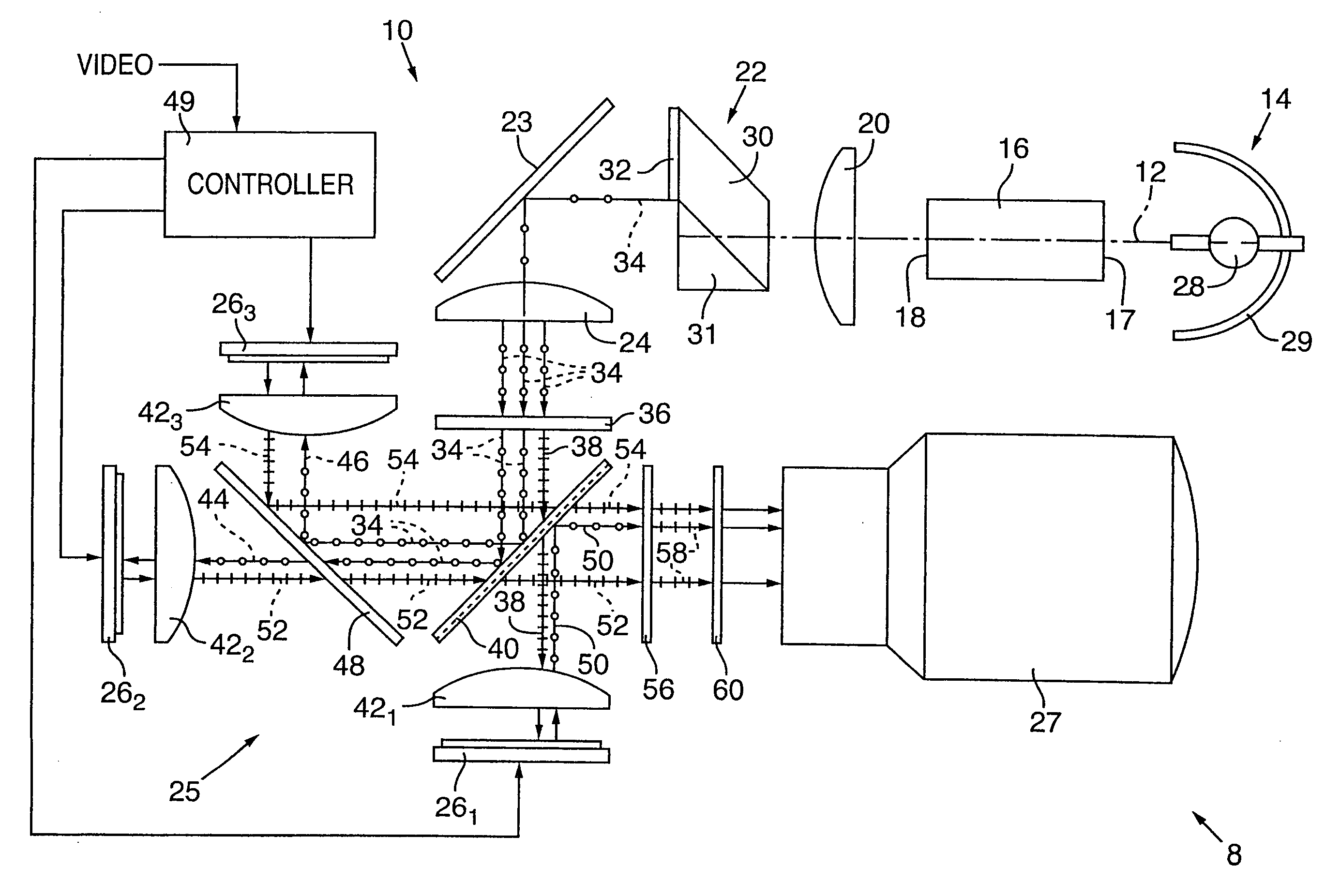
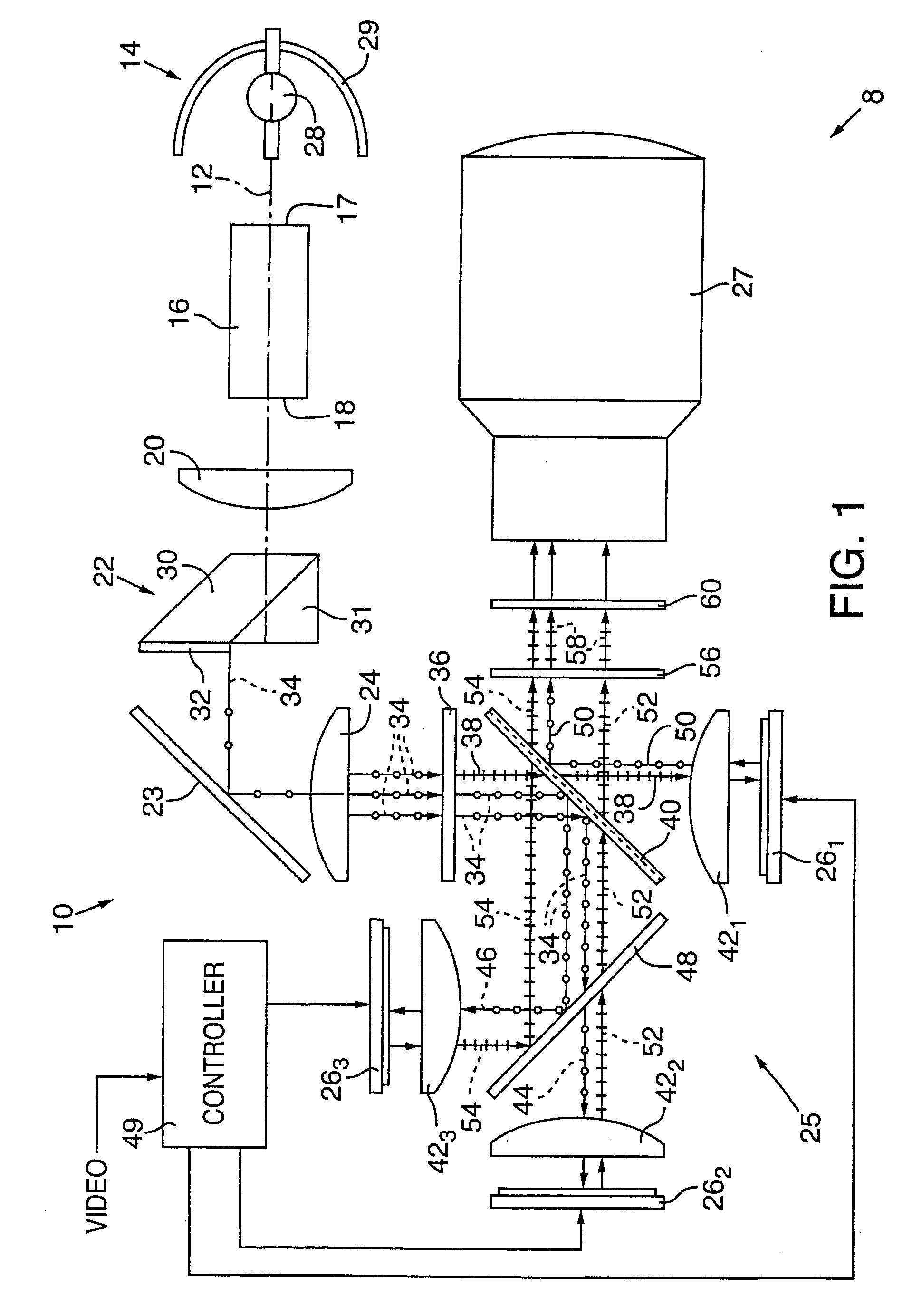
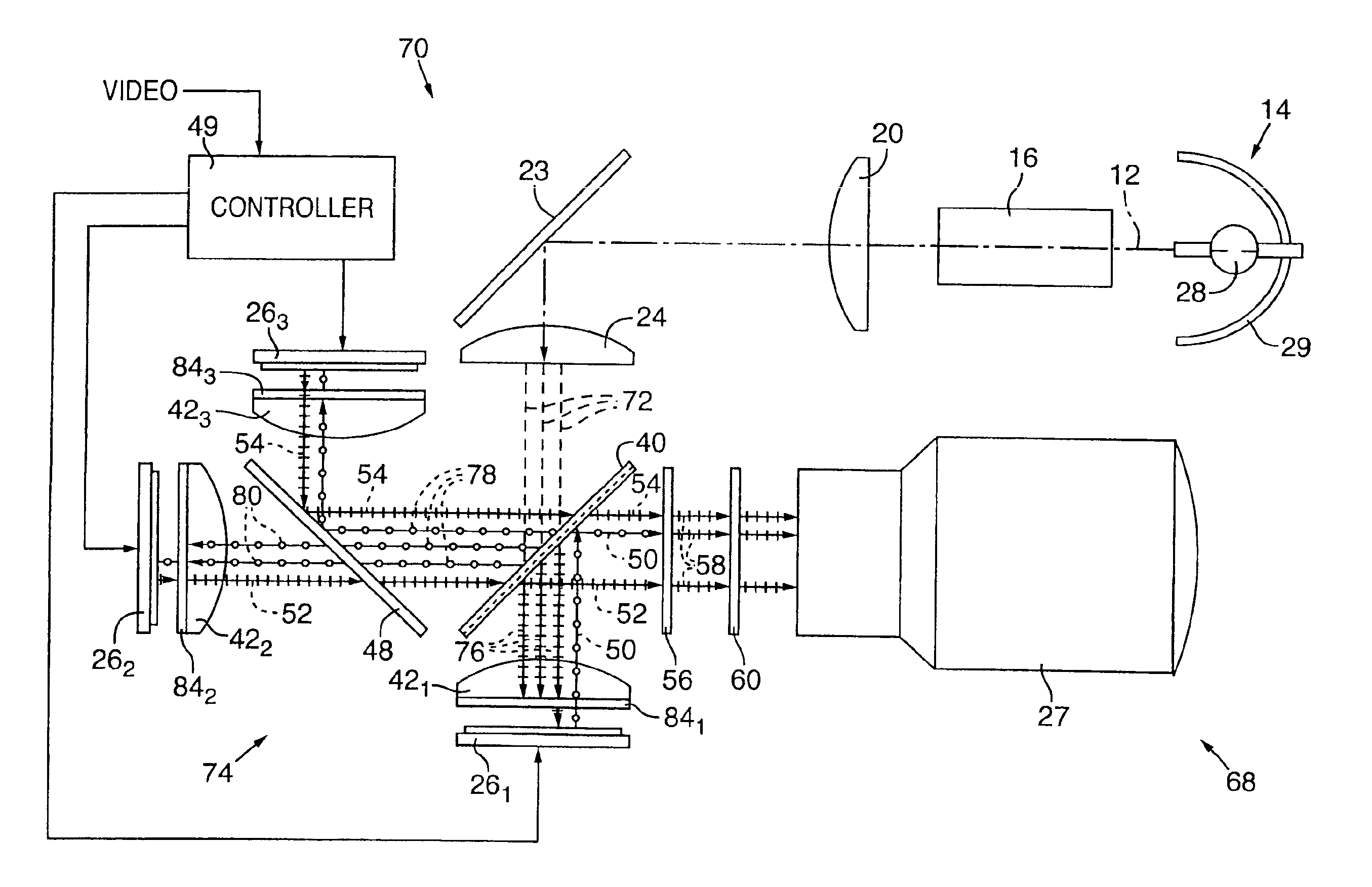
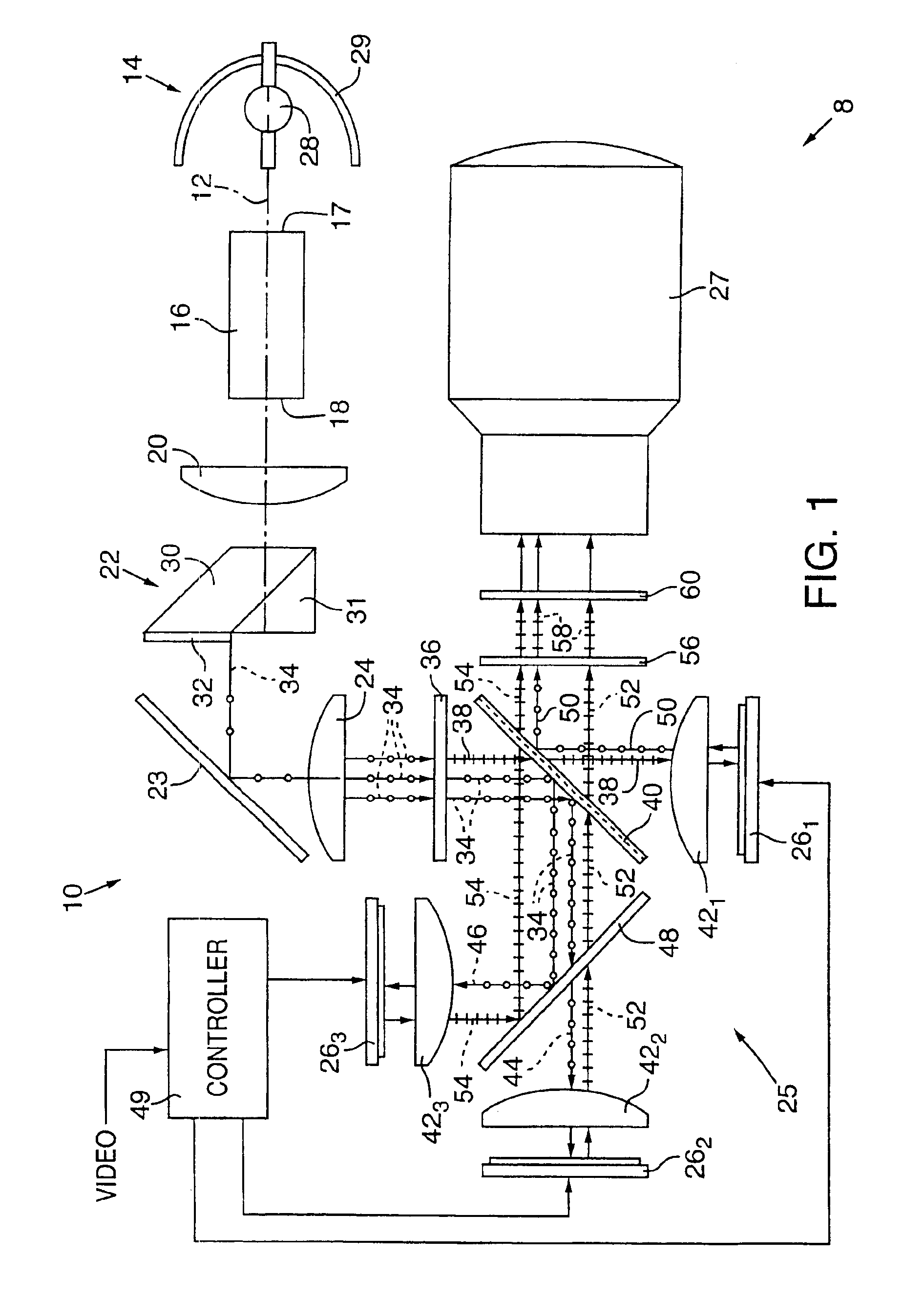
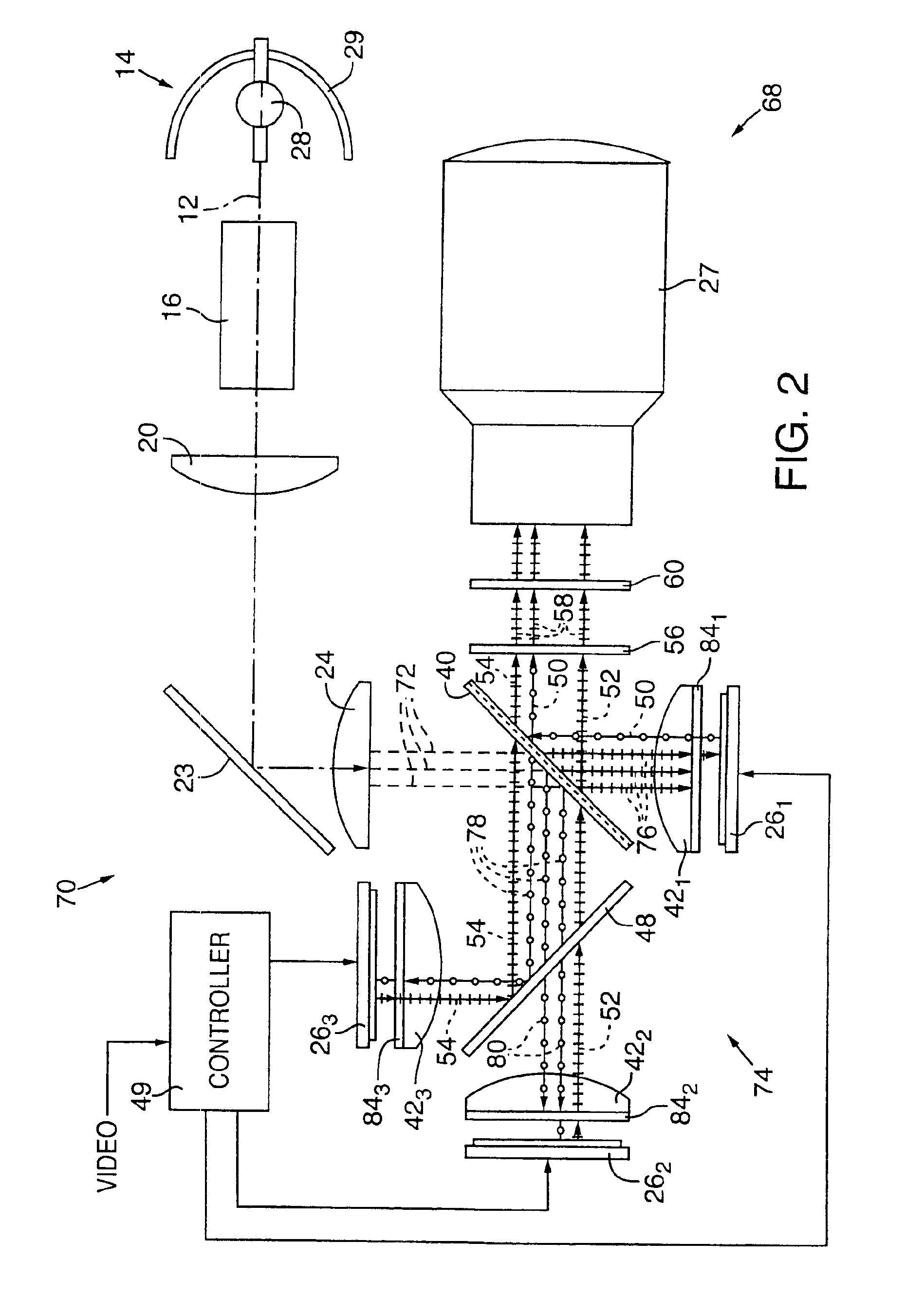
InactiveUS20040085634A1Light weightSimplify Optical DesignProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesCamera lensBeam splitter
An image projector (8, 68) includes a light source (14) that illuminates a three-path reflective LCD assembly (25, 74) that produces images for projection by a projection lens (27). The light source produces S-polarized light rays that are received by a spectrally selective wave plate (36) that changes a first wavelength range of light to P-polarized light rays (34) and transmits without polarization change second and third wavelength ranges of light. A plate-type transflective polarizing beam splitter (40) transmits the P-polarized first wavelength range light rays and reflects S-polarized second and third wavelength range light rays (34). The P-polarized first wavelength range light rays transmit through a field lens (421) and impinge on a first reflective LCD light valve (261). The S-polarized second and third wavelength range light rays strike a pleochroic filter (48), which divides them into second and third wavelength range light rays (44, 46) that propagate through field lenses (422, 423) and impinge on respective second and third LCD light valves (262, 263). The light rays impinging on dark state pixels on the first LCD light valve are reflected without polarization direction change and return toward the light source along their original paths. However, the light rays impinging on illuminated state pixels on the first LCD light valve are reflected with a 90° change in polarization direction and are reflected toward the projection lens by the transflective polarizing beam splitter. The light rays impinging on illuminated state pixels on the second and third LCD light valves are reflected with a 90° change in polarization direction, are recombined by the pleochroic filter, and transmit through the transflective polarizing beam splitter toward the projection lens.
Owner:DISPLAY VECTORS LLC
High power LED road lamp
InactiveCN1945104ASolve the cooling problemGood light distributionMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceEffect lightEngineering
The present invention relates to the application of high power LED in semiconductor lighting, and is especially high power LED street lamp. The high power LED street lamp of the present invention includes lamp body at least one LED light source and its heat sink, and metal PCB board for the circuit connection of LED light source. The metal PCB board fixed on the lamp body has at least one hole for the heat sink to be installed in, the heat sink has one metal column as the main body, disc bottom fixed on the inside surface of the lamp body and top for connecting the LED light source. The high power LED street lamp of the present invention has good heat dissipating effect, reliable operation, simple light path design and easy assembling.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Compressive plenoptic microscopy
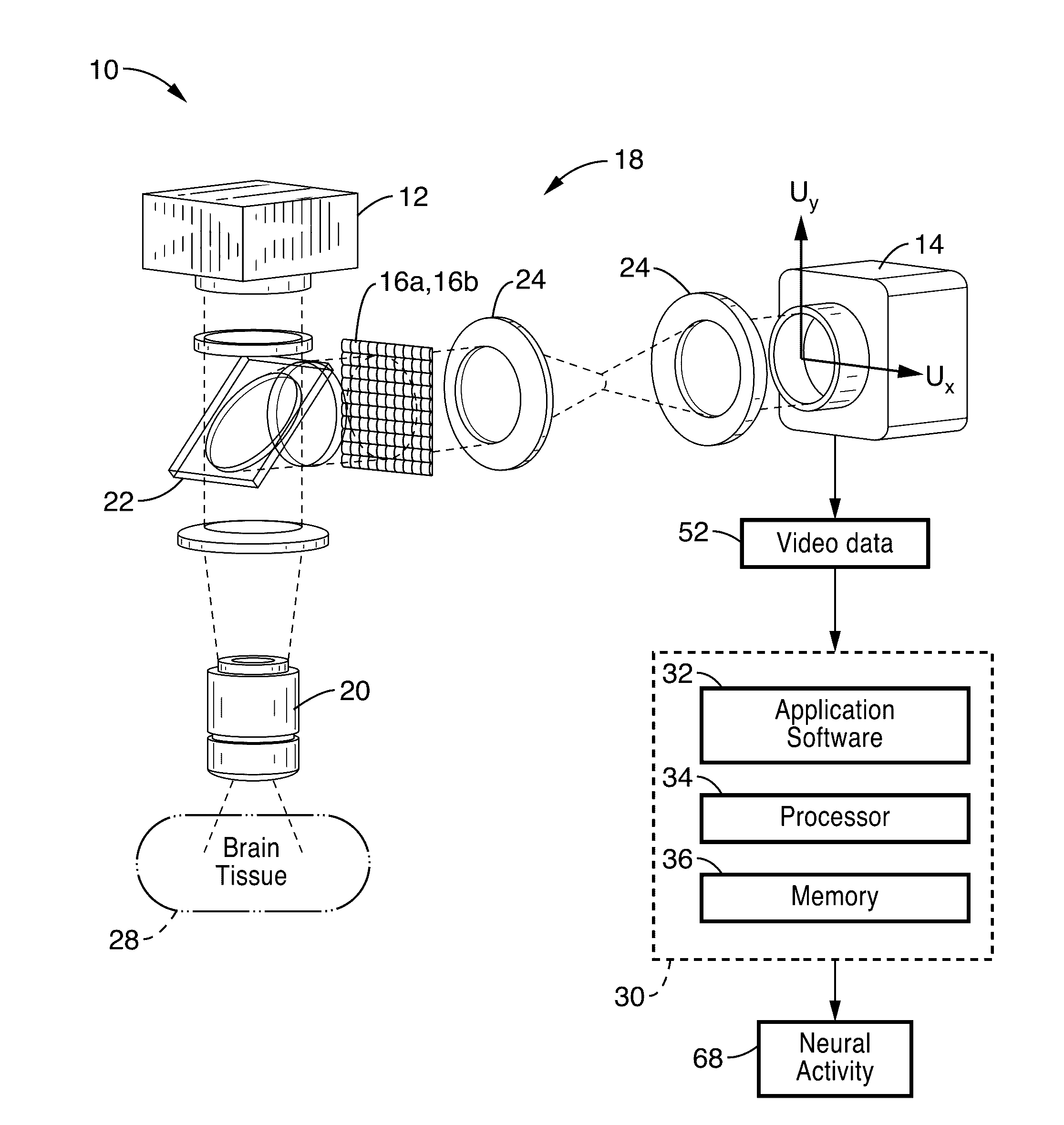
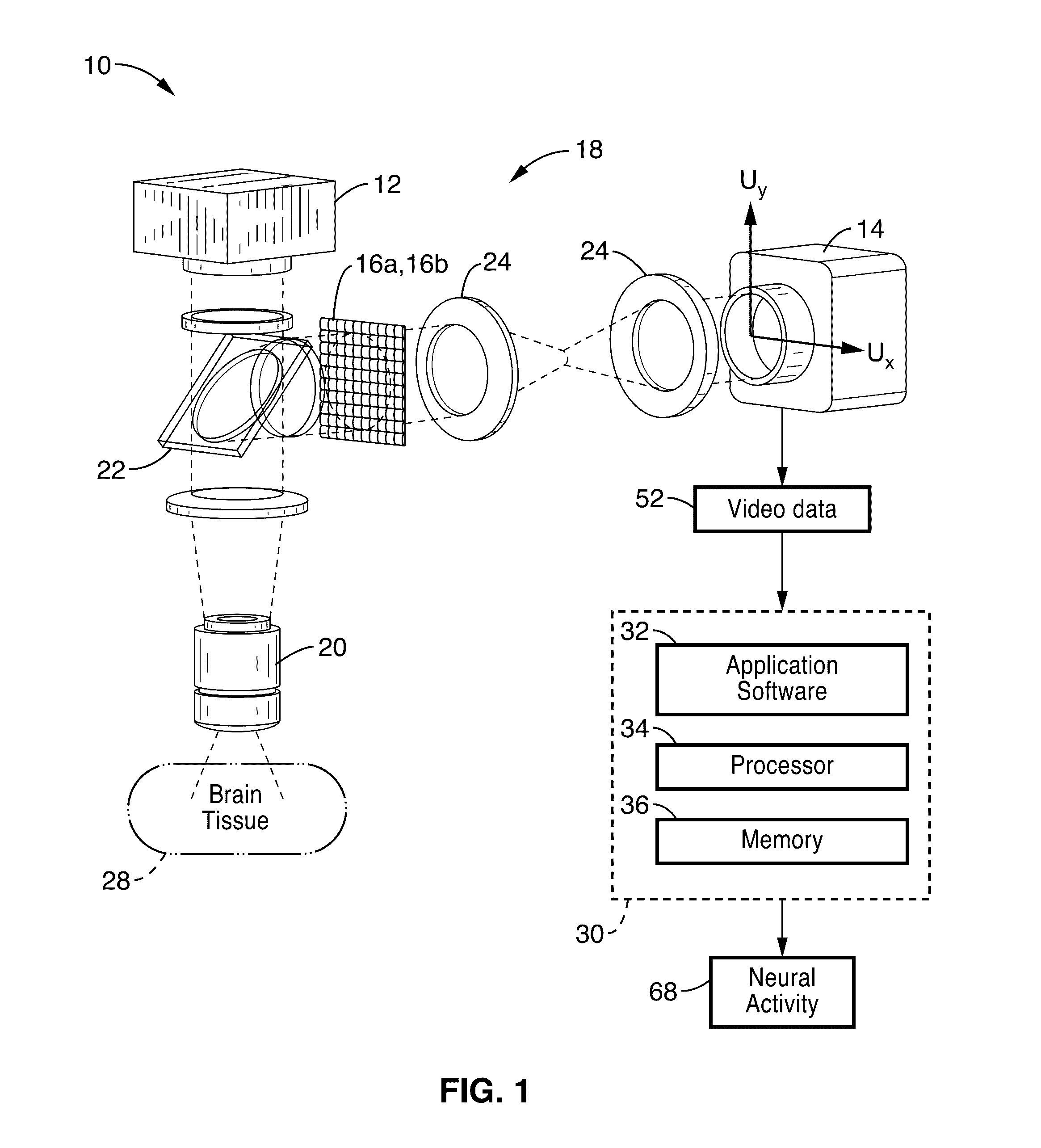
ActiveUS20170003491A1Rapid quantitationMaximises informationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingNeuron
A system and method for quantitative functional neuroimaging through thick brain tissue in live animals. A computational imaging method is disclosed that uses plenoptic image acquisition including a first initialization step that identifies individual neurons by their optical signature and provides a reliable estimate of their position in space and a second stimulation-based image processing step that used acquired calibration data to quickly quantify activity in each identified neuron at video frame-rate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Polarization conversion apparatus and projection system using same
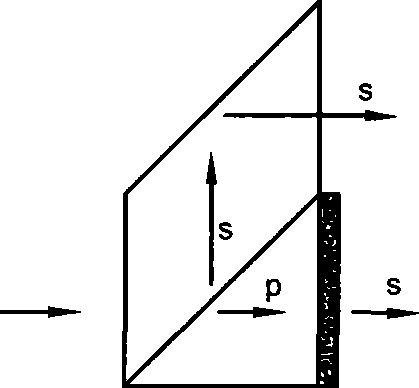
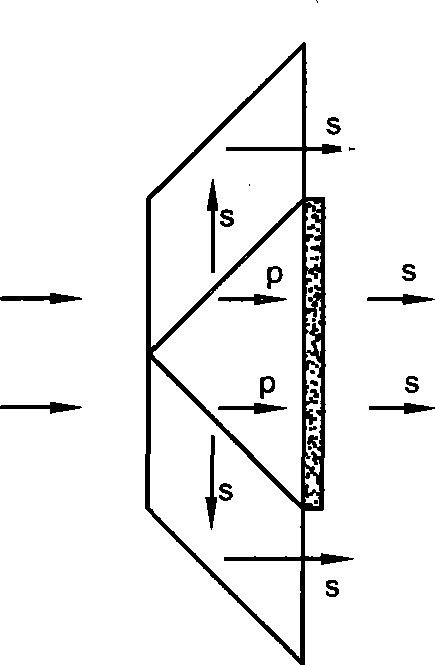
InactiveUS20110051093A1Good optical performanceReduce design difficultyProjectorsOptical elementsBeam splittingOptoelectronics
A polarization conversion apparatus capable of converting natural incident light into linear light with single polarization for emission includes a plurality of prisms arrayed as a whole component, a plurality of half-wave plates arranged at emission surfaces of some of the prisms, and a plurality of faying surfaces defined inside and a plurality of side surfaces defined outside. Some of the faying surfaces include polarization beam splitting films formed thereon to form polarization beam splitting surfaces, and one faying surface and the side surfaces include total reflection films formed thereon to form total reflection surfaces.
Owner:BUTTERFLY TECH SHENZHEN
Color video projection system employing reflective liquid crystal display devices
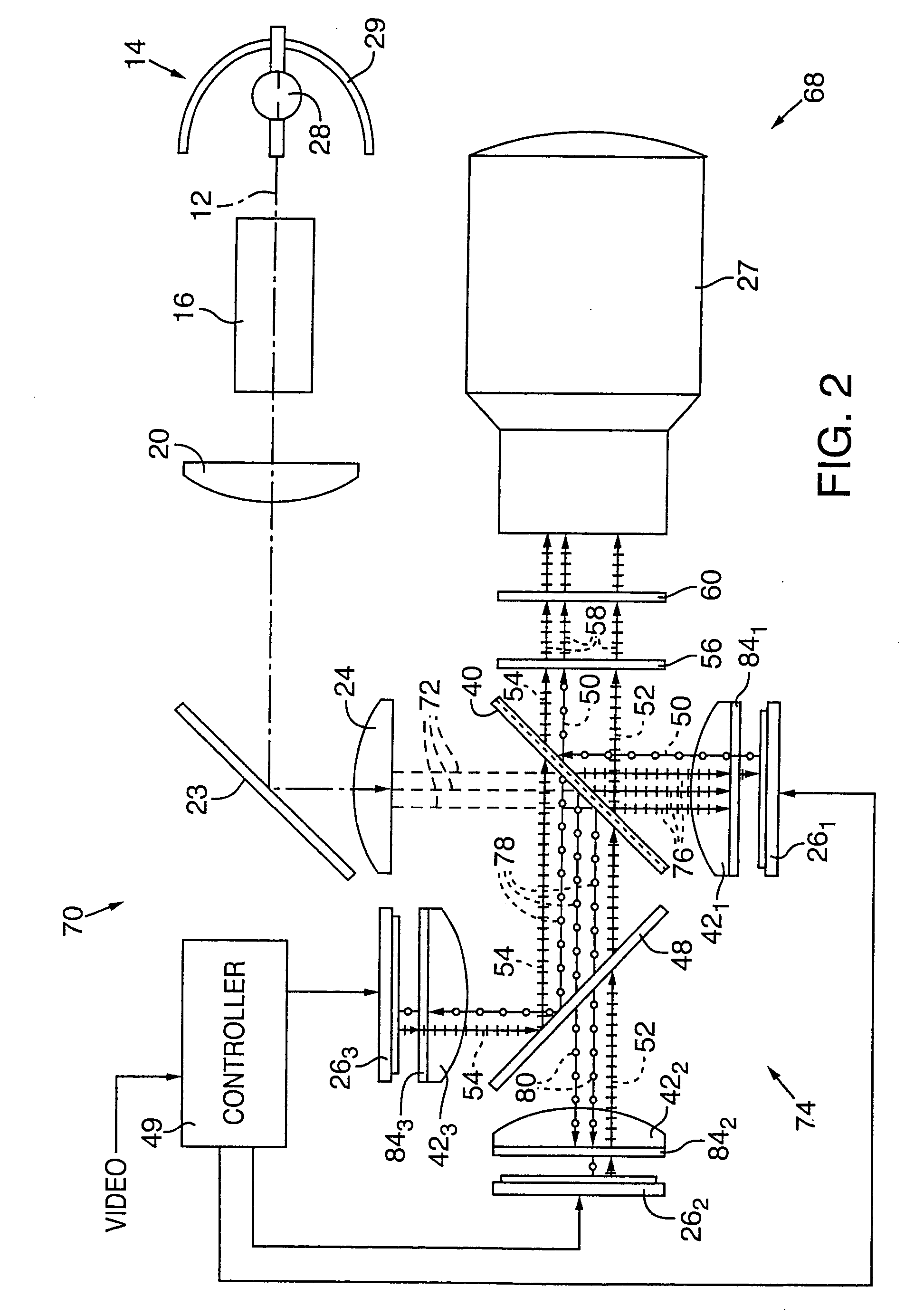
InactiveUS7072003B2Light weightSimplify Optical DesignProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesBeam splitterProjection system
An image projector (8, 68) includes a light source (14) that illuminates a three-path reflective LCD assembly (25, 74) that produces images for projection by a projection lens (27). The light source produces S-polarized light rays that are received by a spectrally selective wave plate (36) that changes a first wavelength range of light to P-polarized light rays (34) and transmits without polarization change second and third wavelength ranges of light. A plate-type transflective polarizing beam splitter (40) transmits the P-polarized first wavelength range light rays and reflects S-polarized second and third wavelength range light rays (34). The P-polarized first wavelength range light rays transmit through a field lens (421) and impinge on a first reflective LCD light valve (261). The S-polarized second and third wavelength range light rays strike a pleochroic filter (48), which divides them into second and third wavelength range light rays (44, 46) that propagate through field lenses (422, 423) and impinge on respective second and third LCD light valves (262, 263). The light rays impinging on dark state pixels on the first LCD light valve are reflected without polarization direction change and return toward the light source along their original paths. However, the light rays impinging on illuminated state pixels on the first LCD light valve are reflected with a 90° change in polarization direction and are reflected toward the projection lens by the transflective polarizing beam splitter. The light rays impinging on illuminated state pixels on the second and third LCD light valves are reflected with a 90° change in polarization direction, are recombined by the pleochroic filter, and transmit through the transflective polarizing beam splitter toward the projection lens.
Owner:DISPLAY VECTORS LLC
Microstructure multifunction optical film diaphragm
InactiveCN101359066AAdjust the glow rateBest light angle rangeOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsConvex structureLong axis
The invention discloses a micro-structure multi-functional optical film, comprising a light entry surface and a light exit surface which face each other; the light exit surface is provided with a plurality of micro-convex structures, wherein, the micro-convex structure is a semi-ellipsoid-similar structure which comprises a long shaft, a short shaft, a height, as well as four arc surfaces connecting the long shafts, the short shafts and the height; the four arc surfaces mutually intersect at four arc lines; the four arc lines intersect at the highest point of the micro-convex structure; the four arc surfaces intersect the light exit surface to form a closed semi-ellipsoid; and the long shafts of the micro-convex structures are arranged in a mutually parallel way. The micro-structure multi-functional optical film effectively integrates the effects of optical films of different types and helps to simplify the structure and optical design of backlight module groups so as to facilitate the manufacturing and reduce costs.
Owner:上海广电光电子有限公司
Two Pi Solid Angle High Resolution Optical System
InactiveUS20130114147A1High resolutionDesign issueClosed circuit television systemsPanoramic photographyFiberCMOS
This invention is a wide field surveillance optical system with inherent features being, non mechanical, compact, high resolution, a field of view up to two pi steradians solid angle. The optics design uses a single optical system and multiple flat image collection devices.Multiple fiber plates translate the image off of the curved image surface to a plane for flat image collection devices. The fiber plates also act to translate the image into a larger volume as compared to the curved image surface, allowing required volume for the multiple image collection devices.This invention uses a single optical system with multiple CCD or CMOS detectors. Advantages over prior art are simple optical designs, rugged optics because it can be manufactured as a single piece, and wider field of view without the sacrifice of resolution.
Owner:STARK DANIEL LEE
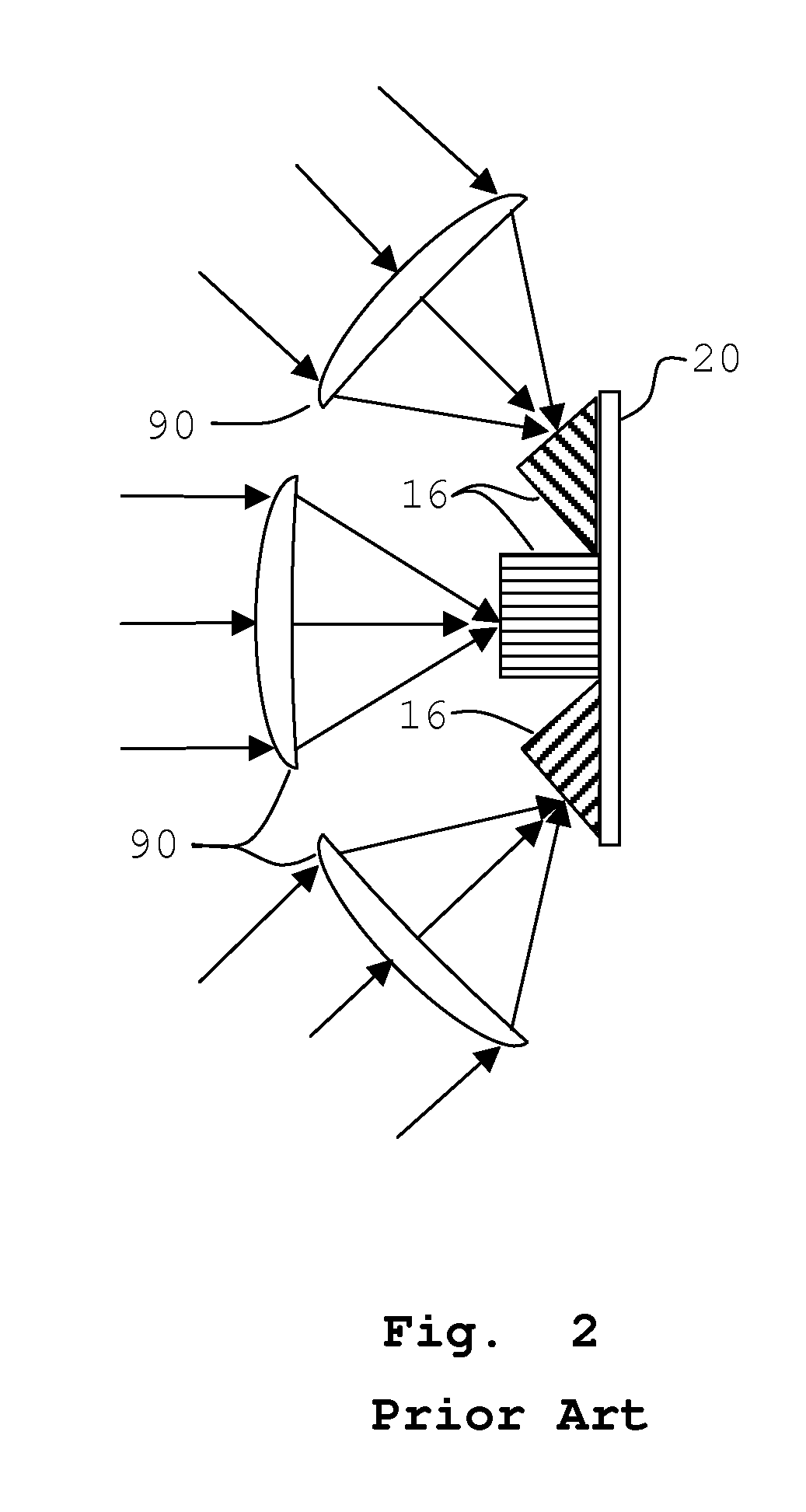
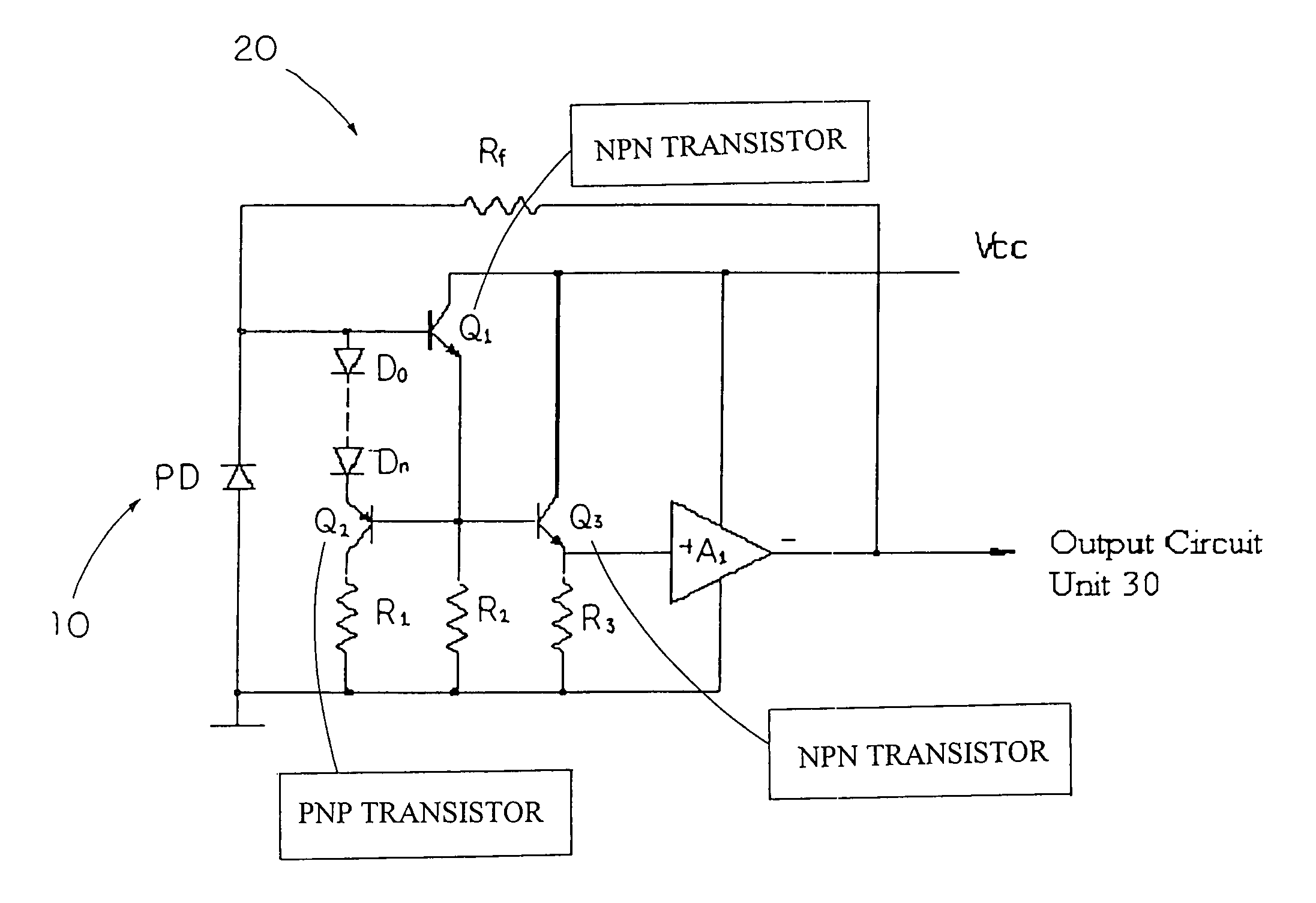
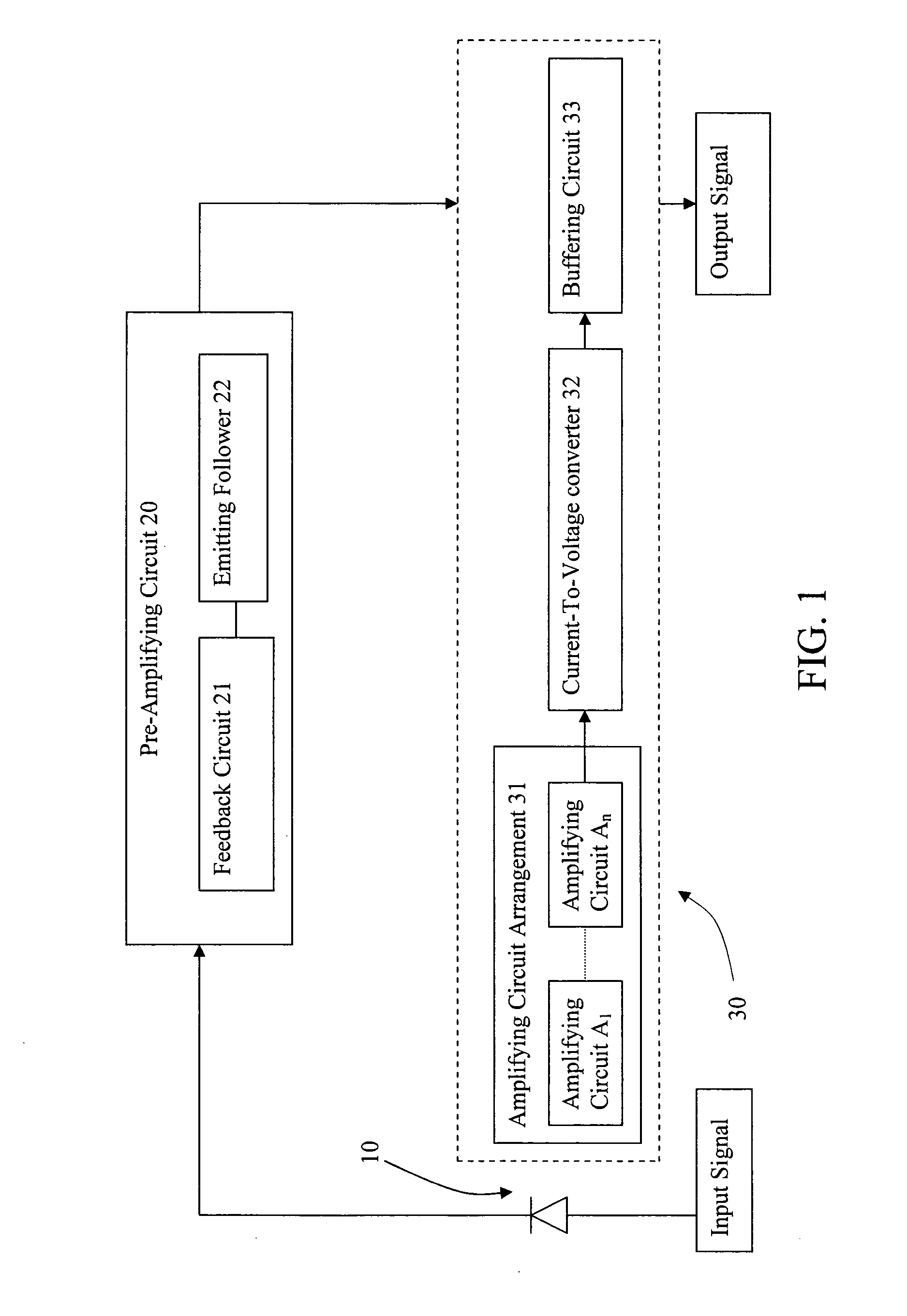
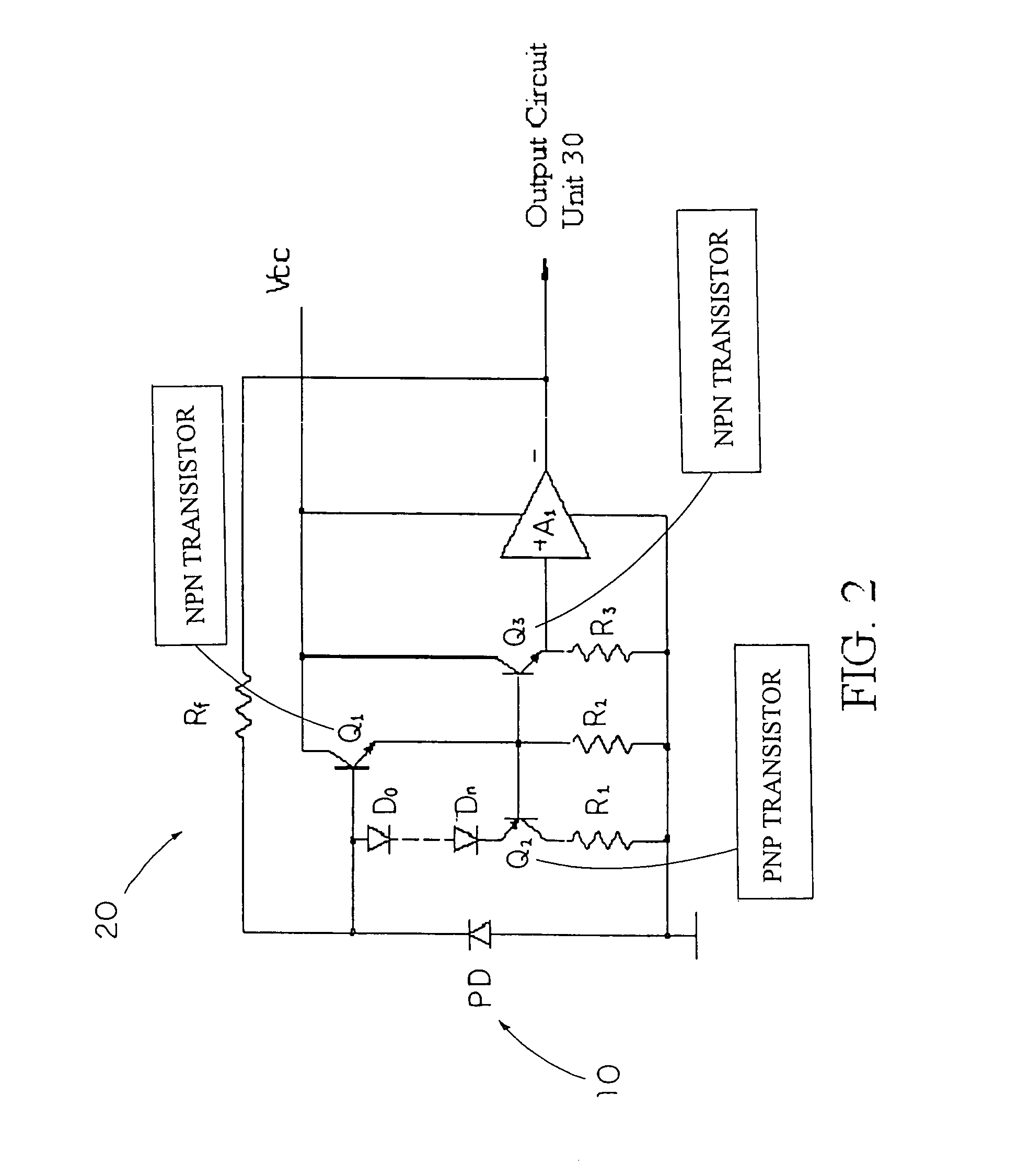
Optical input preamplifier
InactiveUS7026877B2Reduce inputHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansAmplifiers controlled by lightAudio power amplifierLight signal
An optical input preamplifier includes a photodiode for converting an input optical signal into a photocurrent as an output current, pre-amplifying circuit for pre-amplifying the output current from the photodiode wherein the output current is pre-amplified to form a pre-amplifying current, and an output circuit device converting the pre-amplifying current into an output signal. Therefore, the output current from the photodiode passes through the pre-amplifying circuit and the output circuit unit to substantially enhance the sensitivity of the optical input preamplifier.
Owner:YI HEQING
Laser Diode Array Based Photopolymer Exposure System
InactiveUS20170050377A1Simplify Optical DesignLow costAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor laser arrangementsSingle mode laserPhotopolymer
The invention uses a scanned two dimensional array of single mode laser diodes to generate a large number of beams scanning a large area of liquid photopolymer. The optical design is further simplified by using interleaved scanning generated by tilring a glass plate. Using a wavelength of 405-410nm allows the use of low cost laser diodes and a simplified optical design.
Owner:GELBART DANIEL
Optical detection apparatus and method thereof
InactiveUS20070051903A1Reduce dark currentSimplify Optical DesignPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansImage signalImaging Signal
An optical detection apparatus and method thereof is provided, which is applicable for detecting the image signals of a labeled sample. First, a laser module provides excitation light, and the excitation light is continuously reflected by a scan module for providing linear scanning light by changing a reflection angle. The carrier moves the light module in a direction nonparallel to the linear direction so as to provide a two-dimensional testing zone. The labeled sample placed in the testing zone is excited by the linear scanning light and generates emission light to be received by the light receiver. Therefore, the light receiver forms the image signals of the labeled sample corresponding to the emission light.
Owner:DR CHIP BIOTECH
Breast duct endoscope imaging probe
ActiveCN108670177AThe overall structure is simpleSimplify Optical DesignSurgeryEndoscopesHigh bandwidthEndoscope
The invention provides a breast duct endoscope imaging probe. Pulse laser is coupled to enter one end of an excitation optical fiber and focused at the other end through a collimating convergence element, irradiates onto a reflecting element and then is reflected, then the pulse laser is focused under the inner surface of a living body through a capsule, and an ultrasonic signal is generated because of acousto-optical effects; the ultrasonic signal which is reflected back penetrates through the capsule and irradiates onto the reflecting element and then is reflected and focused onto an opticalresonance element, and the resonant frequency of the optical resonance element is changed; probe laser is coupled to enter one end of a receiving optical fiber, and coupled at the other end of the receiving optical fiber to enter the optical resonance element, and the probe laser for changing the resonant frequency is reflected back from the receiving optical fiber, and subjected to three-dimensional imaging through an optical detector and an imaging unit. According to the breast duct endoscope imaging probe, the device is higher in integrating degree and smaller, low-cost, small, optically transparent and high-bandwidth all-optical acoustic-optical signal collection is achieved, and an existing clinical breast duct endoscope technology is greatly improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Host, optical lens module and digital diagnostic system including the same
ActiveUS9901242B2Simplify Optical DesignGreat mechanismTelevision system detailsBronchoscopesCamera lensOptical Module
A digital diagnostic system with interchangeable lenses includes a host and at least one optical lens module, wherein the host without any optical lens having curved surface includes a focus adjustment module which drives an image capture module to linearly move. Therefore, the optical system of the optical lens module can be designed independently, and no need to include focus adjustment mechanism, so that the optical design of the optical lens module can be greatly simplified, and the system allows a greater mechanism tolerance, thereby reducing manufacturing difficulty and manufacturing cost.
Owner:MEDIMAGING INTEGRATED SOLUTION INC
Light scanning unit, image forming apparatus employing the same and light scanning methods
InactiveCN101551521ASimplify Optical DesignReduce product sizeElectrographic process apparatusPictoral communicationOptical beam deflectionLight beam
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Stimulated polariton scattering optical amplifier
InactiveUS6924925B2Improve technical flexibilitySimple optical designLaser using scattering effectsPhysicsActive medium
The stimulated polariton scattering optical amplifier includes a first control optics assembly, a driver element, a second control optics assembly, a polariton active medium and egressing optics. The first control optics assembly receives an incoming laser beam and adjusts that incoming laser beam in accordance with first desired wavelength, polarization and beam propagation parameters. A driver element produces a driver laser beam. A second control optics assembly receives the driver laser beam and adjusts that driver laser beam in accordance with second desired wavelength, polarization and beam propagation parameters. A polariton active medium receives an output from the first control optics assembly and an output from the second control optics assembly. The polariton active medium provides a non-linear optical interaction between the outputs such that the incoming laser beam is amplified, producing an amplified polariton active medium output laser beam and a depleted driver laser beam. Egressing optics receives the amplified polariton active medium output laser beam and the depleted driver laser beam. The egressing optics controllably transmits the amplified polariton active medium output laser beam in accordance with third desired wavelength, polarization, and beam propagation parameters and prevents transmission of the depleted driver laser beam. The output of the egressing optics includes an amplified egressing optics output laser beam.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Signal and pumping laser hybrid integrated device
ActiveCN102820607ASimplify Optical DesignCompact structureActive medium shape and constructionOptical pathAll optical
The invention relates to a signal and pumping laser hybrid integrated device which is structurally characterized in that a plurality of multimode pump laser dies, at least one single-mode signal laser die and all optical path shaping lenses and 90-degree reflectors are mounted in a same laser shell and are coupled in a same output optical fiber. An output port of each single-mode signal laser die corresponds to the optical path shaping lens and the 90-degree reflector which are in a set, an output port of each pump laser die corresponds to the optical path shaping lens and the 90-degree reflector in another set, all the 90-degree reflectors are not overlapped with one another in space, and corresponding reflected light of all the 90-degree reflectors aligns with a same condenser lens and is coupled to the same output optical fiber to be outputted after passing through the condenser lens, wherein signal light is coupled to a fiber core of the output optical fiber, and pump light is coupled to the section of the output optical fiber. The signal and pumping laser hybrid integrated device structurally substitutes for a traditional complicated optical path system and is simpler in optical design, compact, reliable and stable in structure and excellent in performance.
Owner:WUHAN RAYCUS FIBER LASER TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Day-and-night dual-purpose lens system free of day-and-night confocal design and implementation method thereof
InactiveCN105527781AIncrease the number ofReduce manufacturing costCamera body detailsCamera lensOptical axis
The invention relates to a day-and-night dual-purpose lens system free of day-and-night confocal design and an implementation method thereof. The day-and-night dual-purpose lens system comprises a lens, a chip and a light filter switcher, wherein the light filter switcher is arranged inside the lens or is arranged at the front end of the lens or is arranged between the lens and the chip; a light filter I and a light filter II used for days and nights respectively are arranged on the light filter switcher; the light filter I and the light filter II are vertical to an optical axis and can be switched to the position of the optical axis for filtering light with different wave bands respectively; the light filter I is an infrared light cut-off filter capable of filtering infrared light; and the light filter II is a visible light cut-off filter capable of filtering visible light. The system and the method do not need to take a complicated day-and-night confocal design of the lens into account, a day-and-night confocal effect can be realized through a simple structure or method, and the system is low in manufacturing cost and excellent in performance.
Owner:FOCTEK PHOTONICS LNC
Photographic device
InactiveUS20070153116A1Reduce processing timeSimplify Optical DesignTelevision system detailsImage analysisImaging processingComputer science
A photographic device includes an image sensor in which a plurality of pixels are arrayed. A horizontal scan circuit selects in order vertical drive lines to which the pixels are connected. And a vertical scan circuit reads voltages, due to accumulated electric charges, from the pixels in the horizontal row which is selected. A plurality of lenses are provided to the image sensor, arranged along the direction parallel to the vertical drive lines. Each of these lenses images an image of the same photographic region upon a pixel region which it confronts. The accumulated electric charges are read out from each pixel, arrayed in order. An image processing unit acquires a plurality of images of the photographic region spaced apart in time. And a moving body detection unit performs moving body detection from the differences between this plurality of images of the photographic region.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
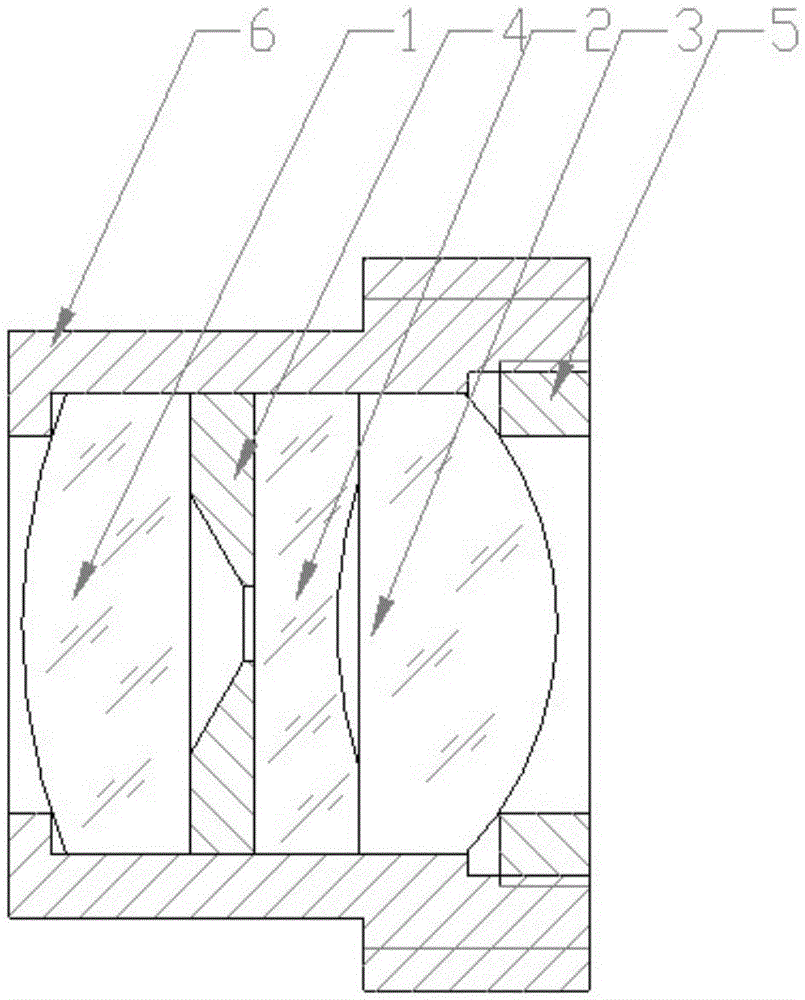
Imaging objective lens suitable for RGB-D camera
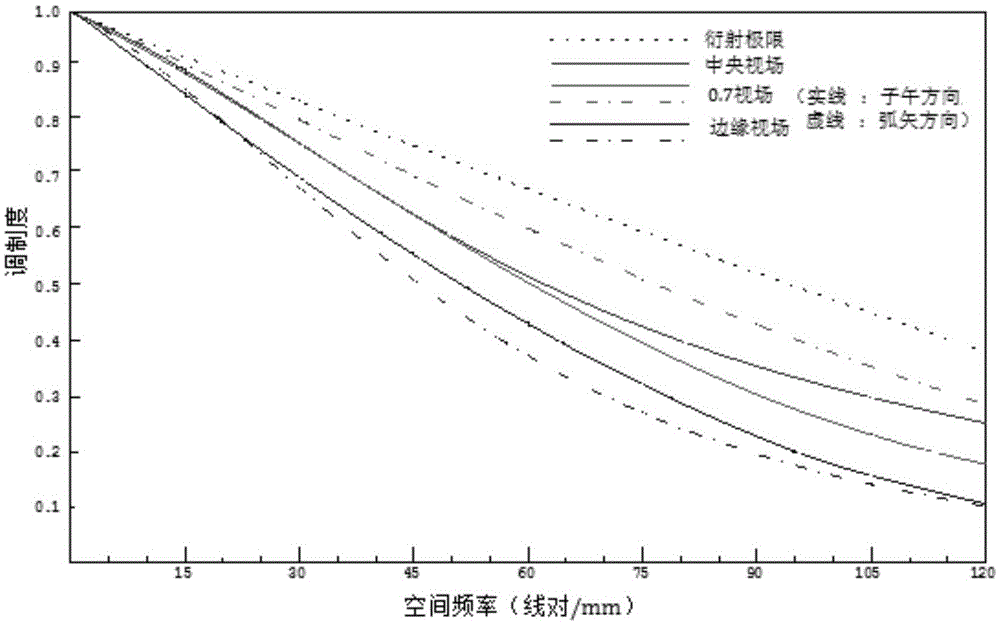
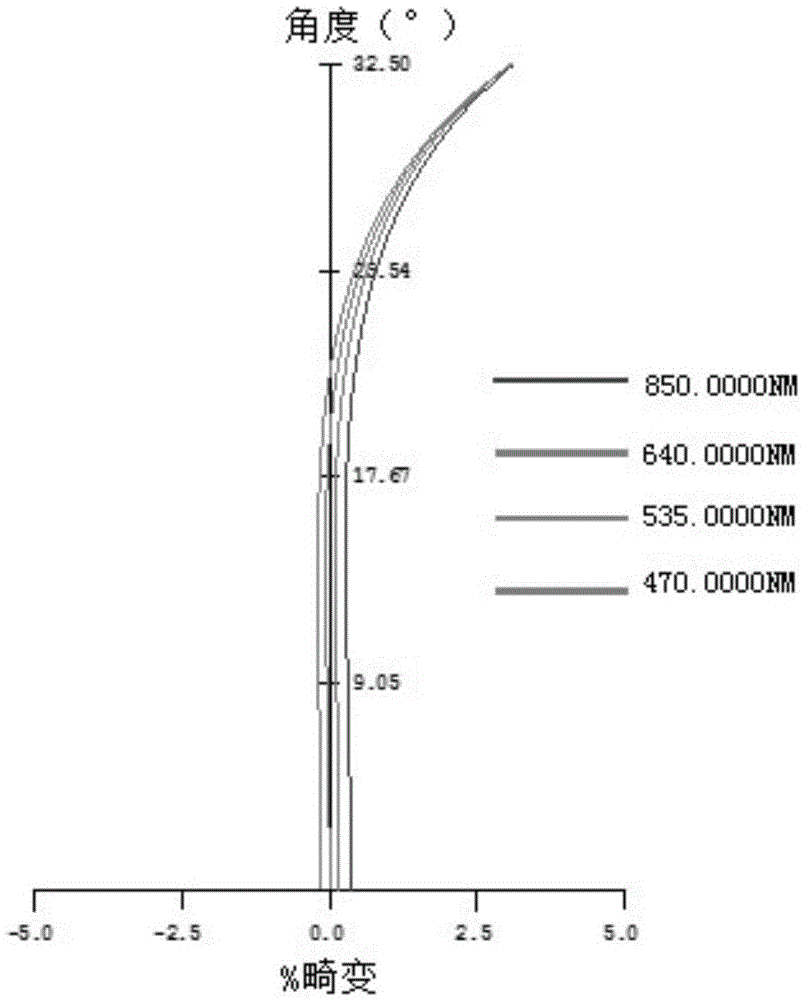
The invention discloses an imaging objective lens suitable for an RGB-D camera. A first lens, a first spacer ring, a second lens and a third lens which are attached in a lens cone in sequence from the objective space to the image space form the imaging lens. The imaging objective lens is of a three-piece spherical mirror structure, one mirror surface of each lens is a plane, the other mirror surface of each lens is a spherical surface, and thus machining cost is low; meanwhile, the second lens and the third lens are tightly attached, no spacer ring is needed, and thus the imaging objective lens is compact in structure and small in size; besides, the three lenses are the same in radius, and thus the assembling process is simple. In a broad spectrum region from visible light to near infrared rays, imaging definition is high, optical performance is excellent, and a large view field of 65 degrees and distortion smaller than 3.2% can be achieved. The imaging objective lens is suitable for a deep imaging system with infrared-assisted lighting and achieves user-friendly and easy-to-use natural man-machine interaction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com