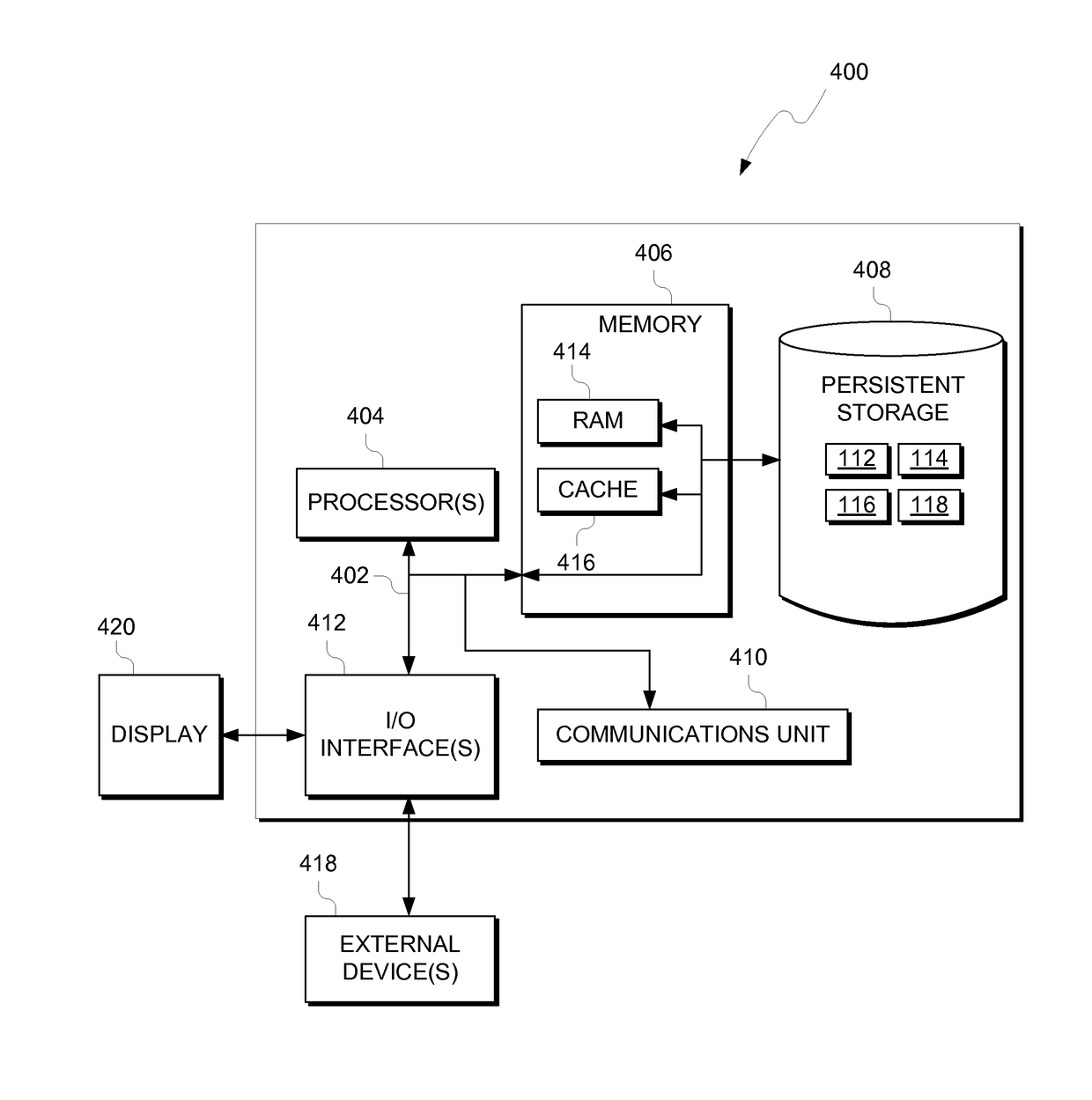
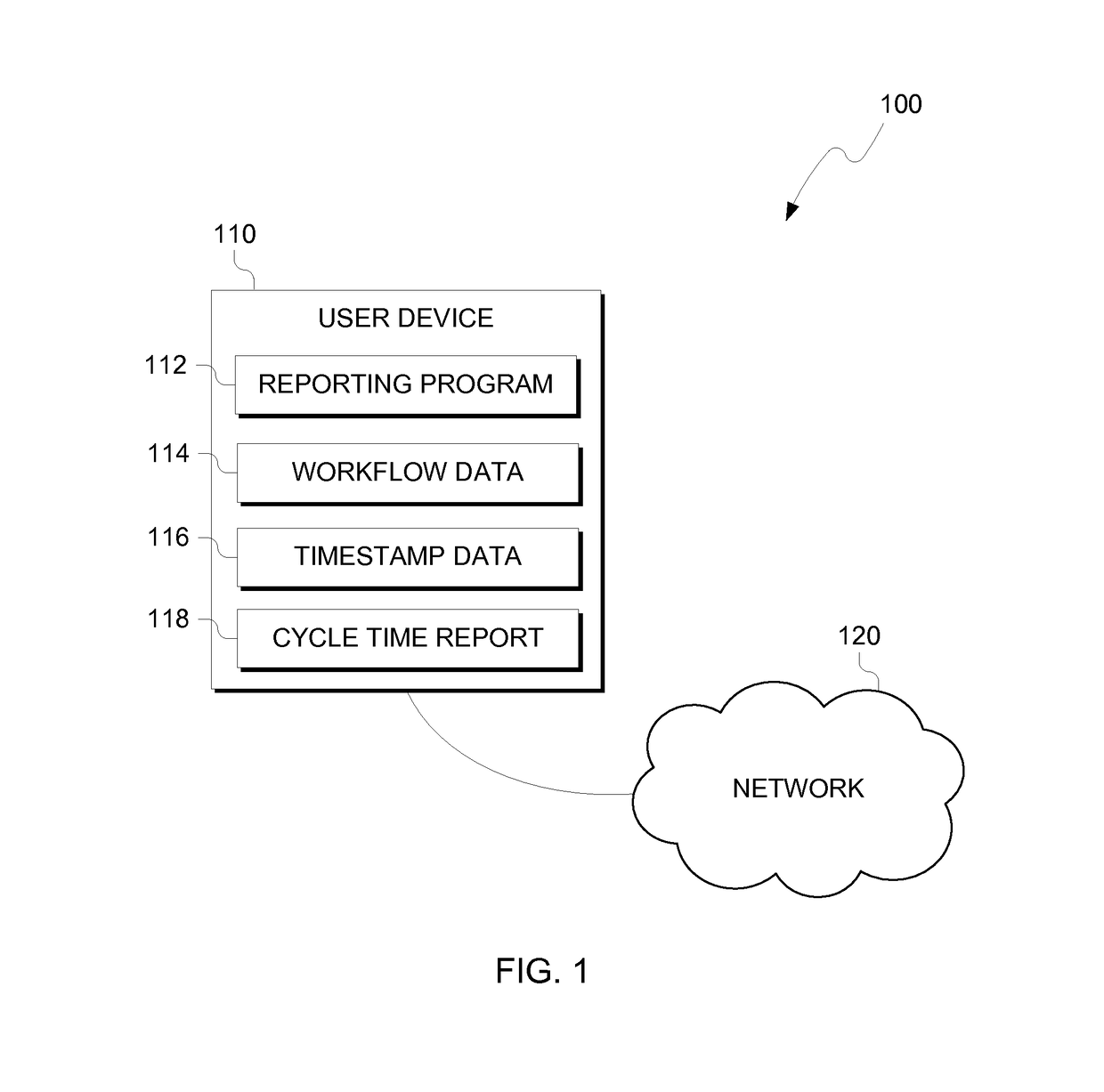
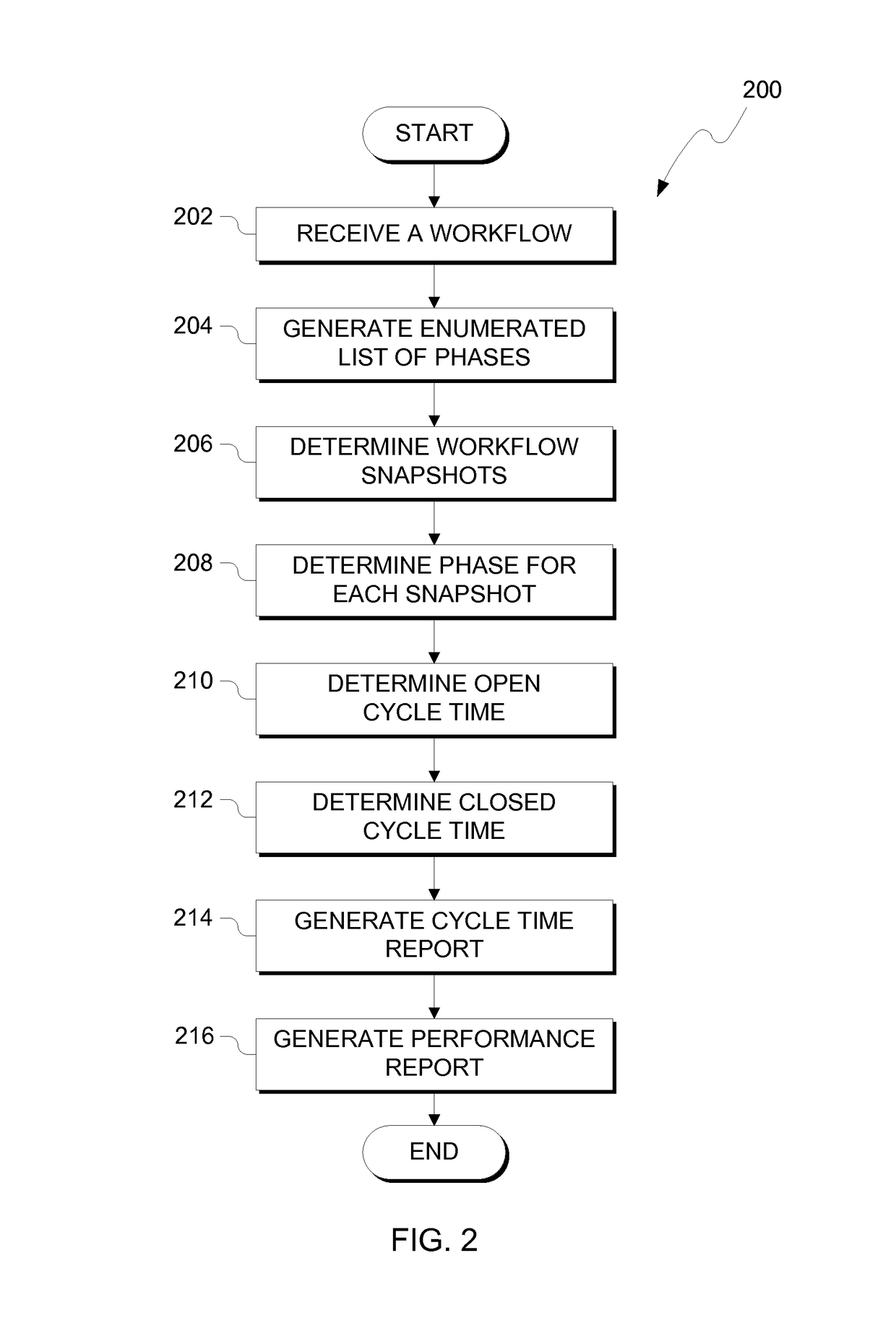
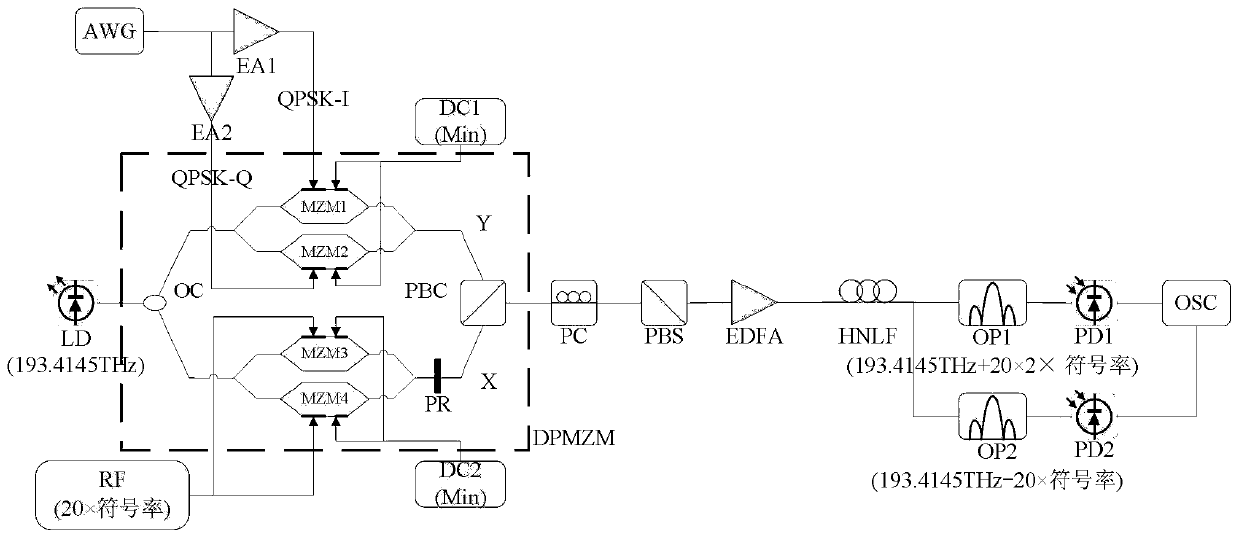
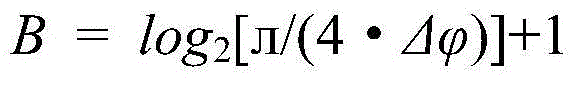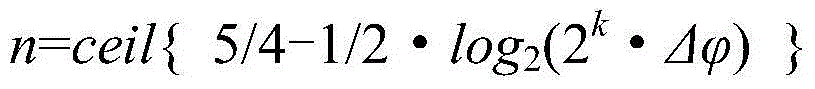Patents
Literature
44 results about "Phase mapping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
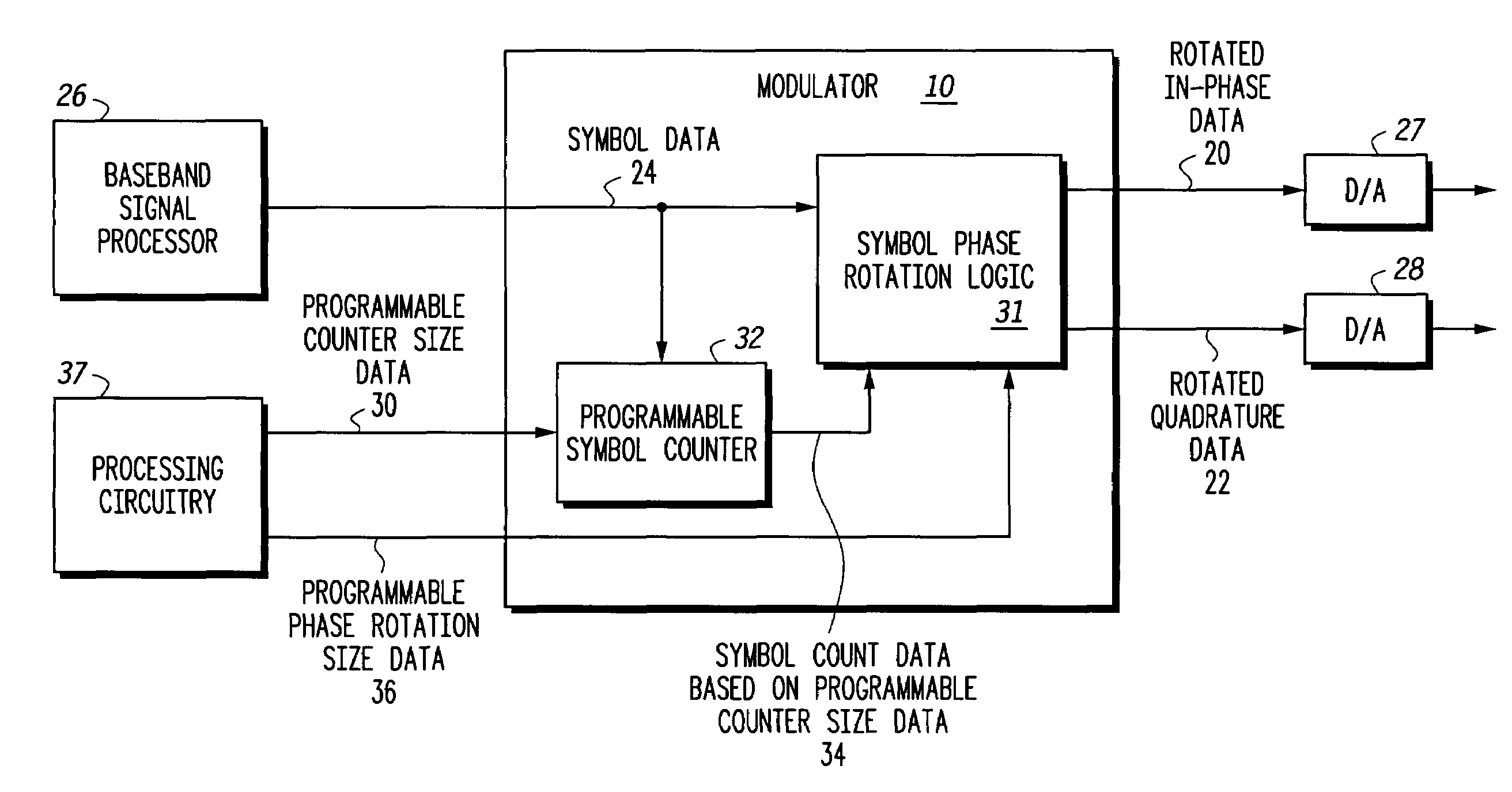
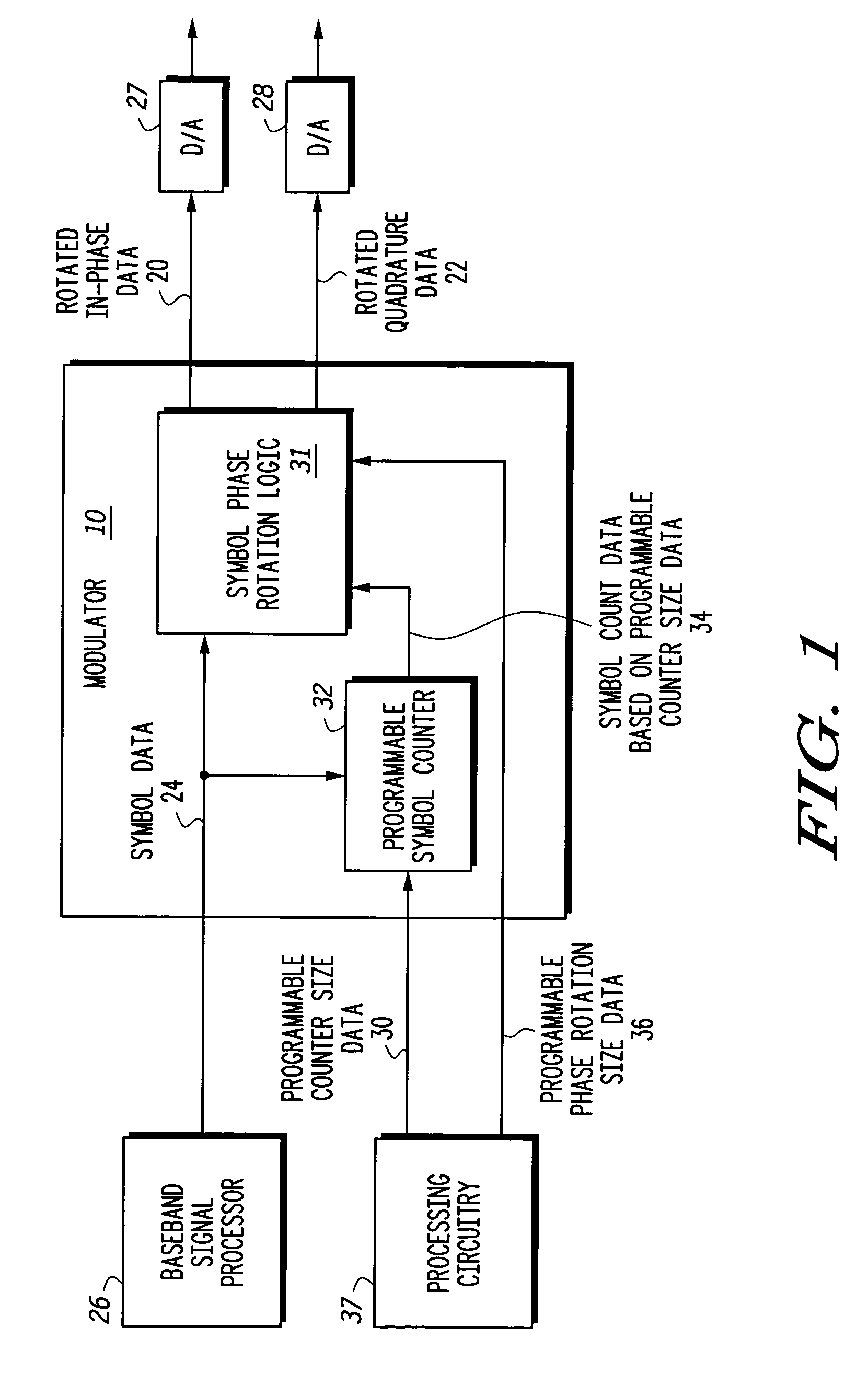
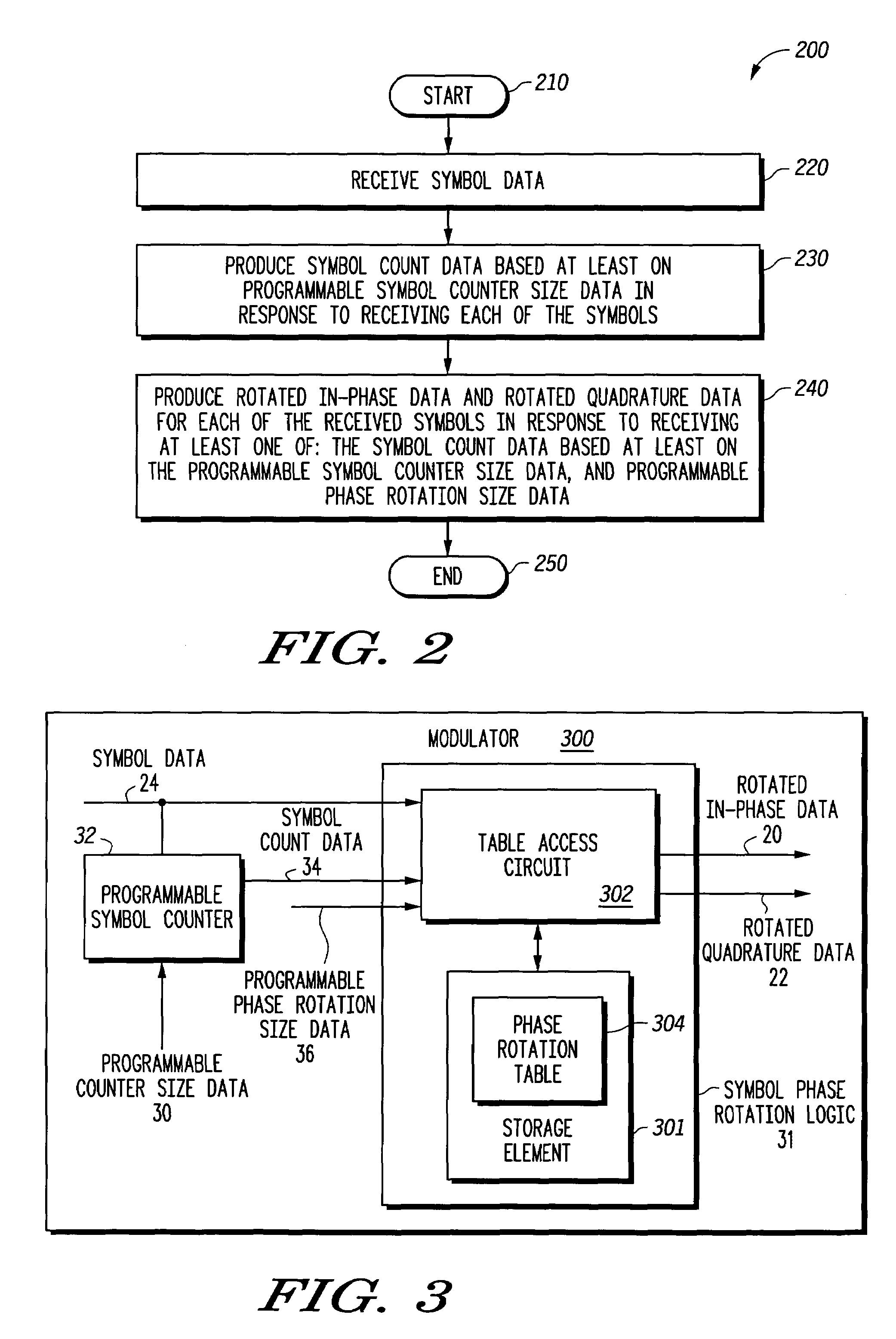
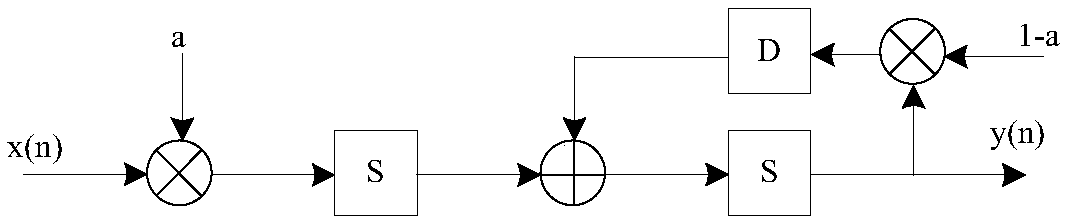
Programmable phase mapping and phase rotation modulator and method
ActiveUS7412008B2Angle modulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemPhase mapping
A modulator (10) and method provides a programmable phase rotation for supporting different modulation formats and different phase rotations. The modulator (10) includes a programmable symbol counter (32) and symbol phase rotation logic (31) operatively responsive to programmable phase rotation size data (36) and programmable counter size data (30). The modulator (10) can be used to communicate with different modulation formats employing different phase rotation conventions as used in different communication systems. The symbol phase rotation logic (31) produces rotated in-phase data (20) and rotated quadrature data (22) in response to receiving at least received symbol data (24), programmable phase rotation size data (36), and symbol count data (32) based on programmable counter size data (30). According to another embodiment, the phase rotations of the modulator (10) may be dynamically selectable such that the phase rotations may be selected to accommodate changes in channel characteristics in real time.
Owner:APPLE INC
Digital broadcast receiving apparatus and receiving method
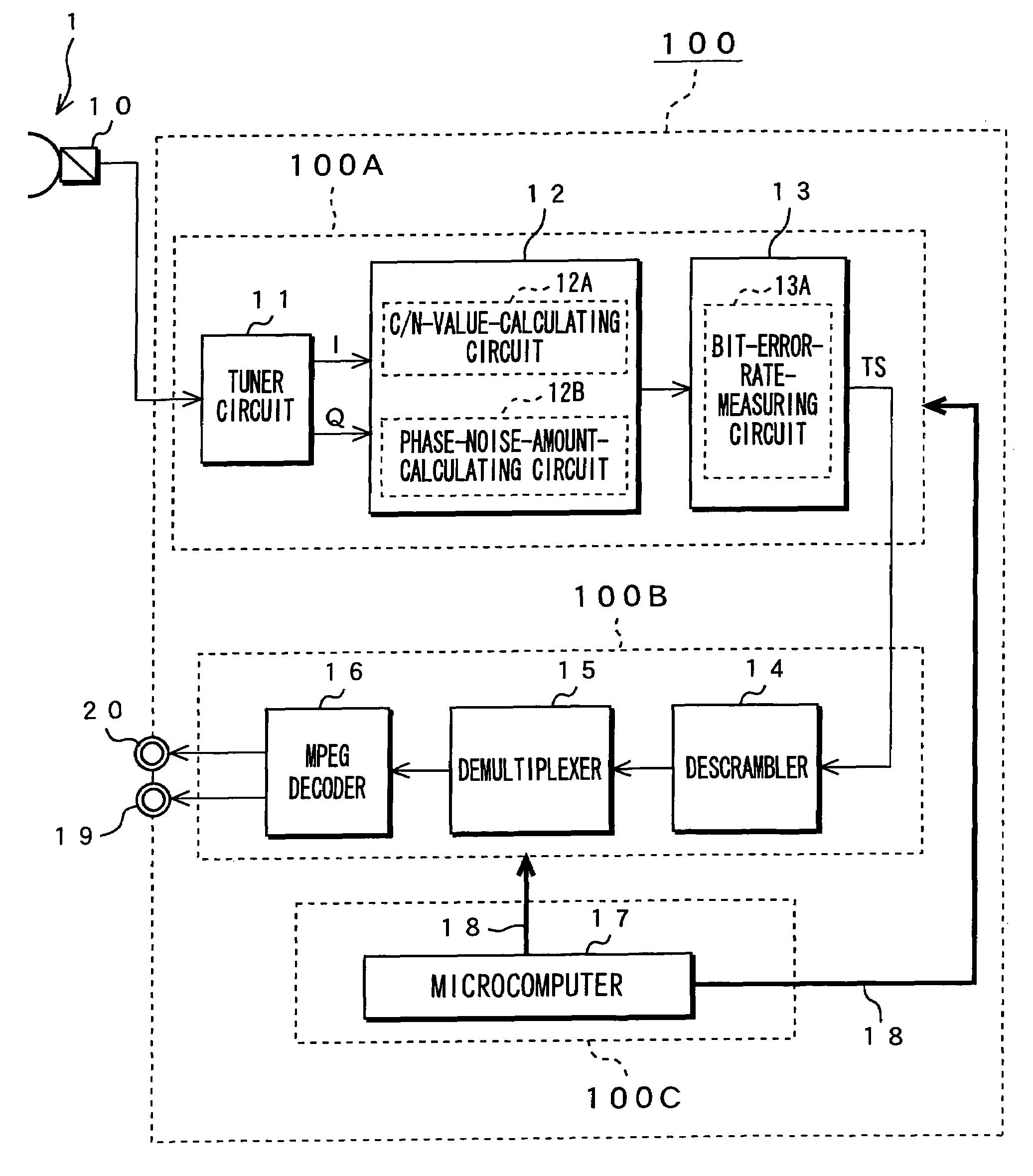
InactiveUS7561212B2Improve deteriorationDeterioration of characteristicTelevision system detailsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPhase noisePhase mapping
Owner:SONY CORP
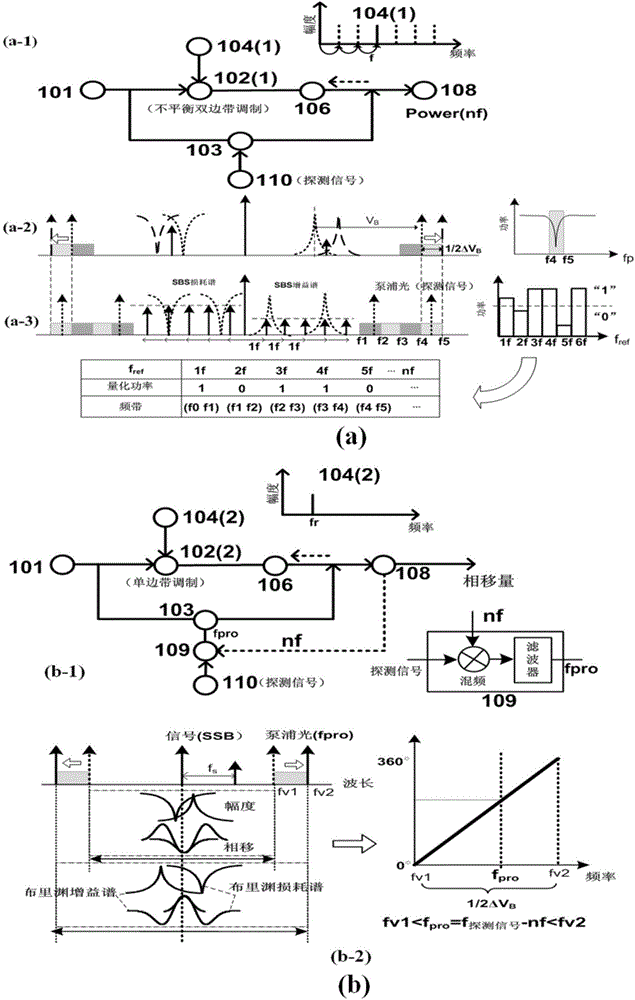
Multi-frequency high-precision microwave photon frequency measuring scheme based on stimulated brillouin effect
ActiveCN104614585ARealize frequency instantaneous detectionLow costFrequency measurement arrangementElectricityMicrowave
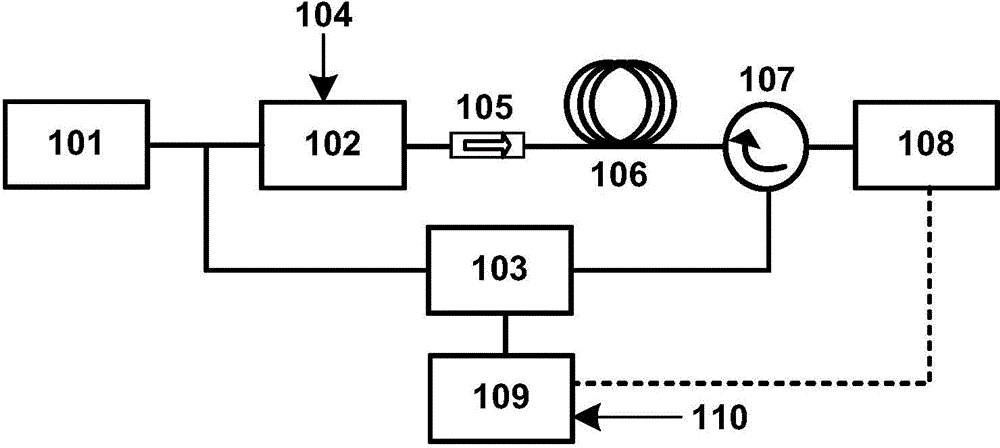
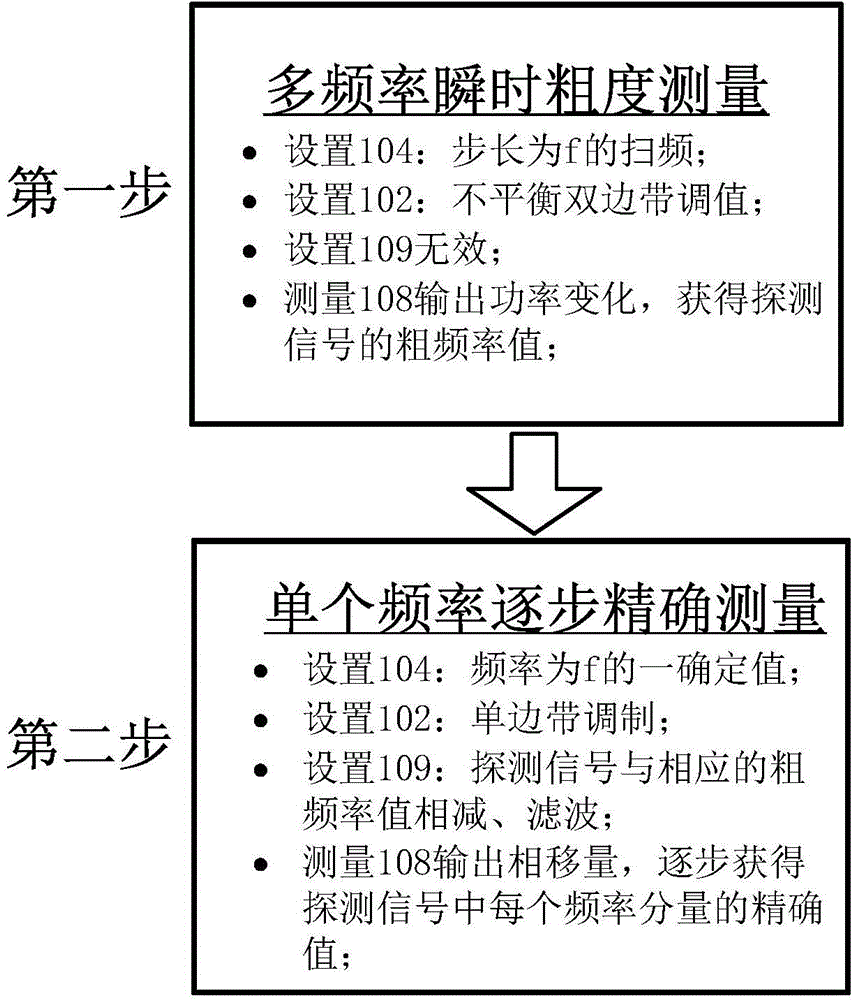
The invention discloses a multi-frequency high-precision microwave photon frequency measuring scheme based on stimulated brillouin effect. The multi-frequency high-precision microwave photon frequency measuring scheme comprises a single-wavelength laser device (101), a dual-drive mach-zehnder modulator (102), a mach-zehnder modulator (103), a optical isolator (105), a dispersion-shift optical fiber (106), an optical circulator (107), a photoelectric detector (108), an electric processing unit (109), a reference microwave source (104). Compared with other microwave photo frequency measuring schemes, double mapping relationship which are dynamic frequency-power mapping and frequency-phase mapping in the brillouin effect are respectively utilized, the multi-frequency instant measuring and the single-frequency error measuring are combined, so that the multi-frequency high-precision microwave photo frequency measuring is realized. The multi-frequency high-precision microwave photon frequency measuring scheme can be applied to the electronic countermeasure and the microwave detecting field.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
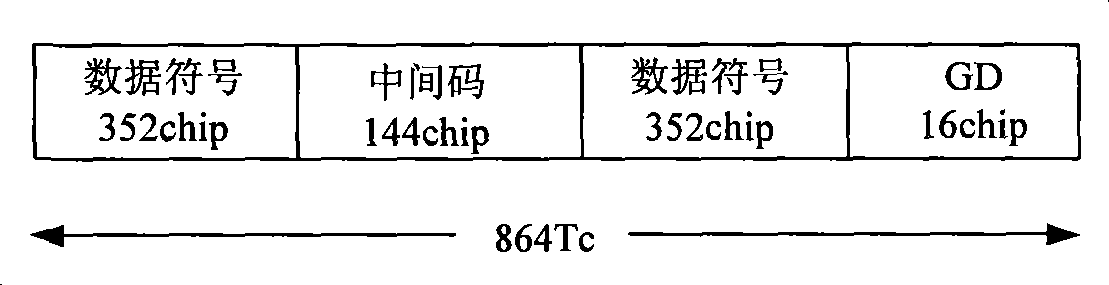
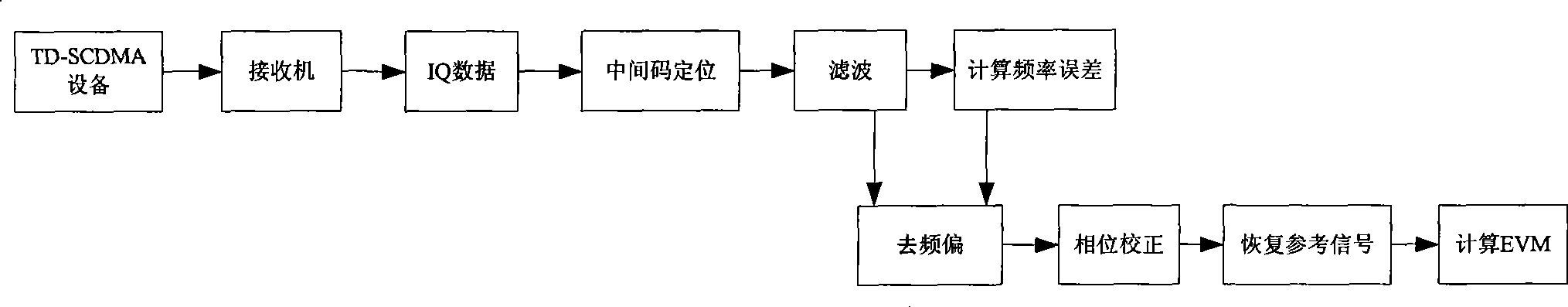
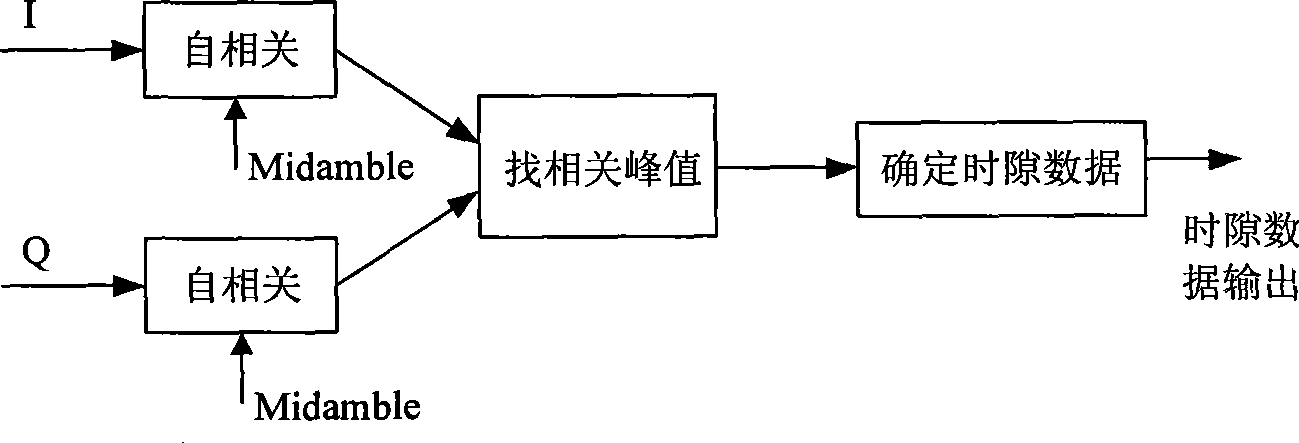
Method and device for measuring vector amplitude error for TD-SCDMA equipment testing
InactiveCN101534159AImprove test efficiencyReceivers monitoringPhase-modulated carrier systemsPhase correctionTD-SCDMA
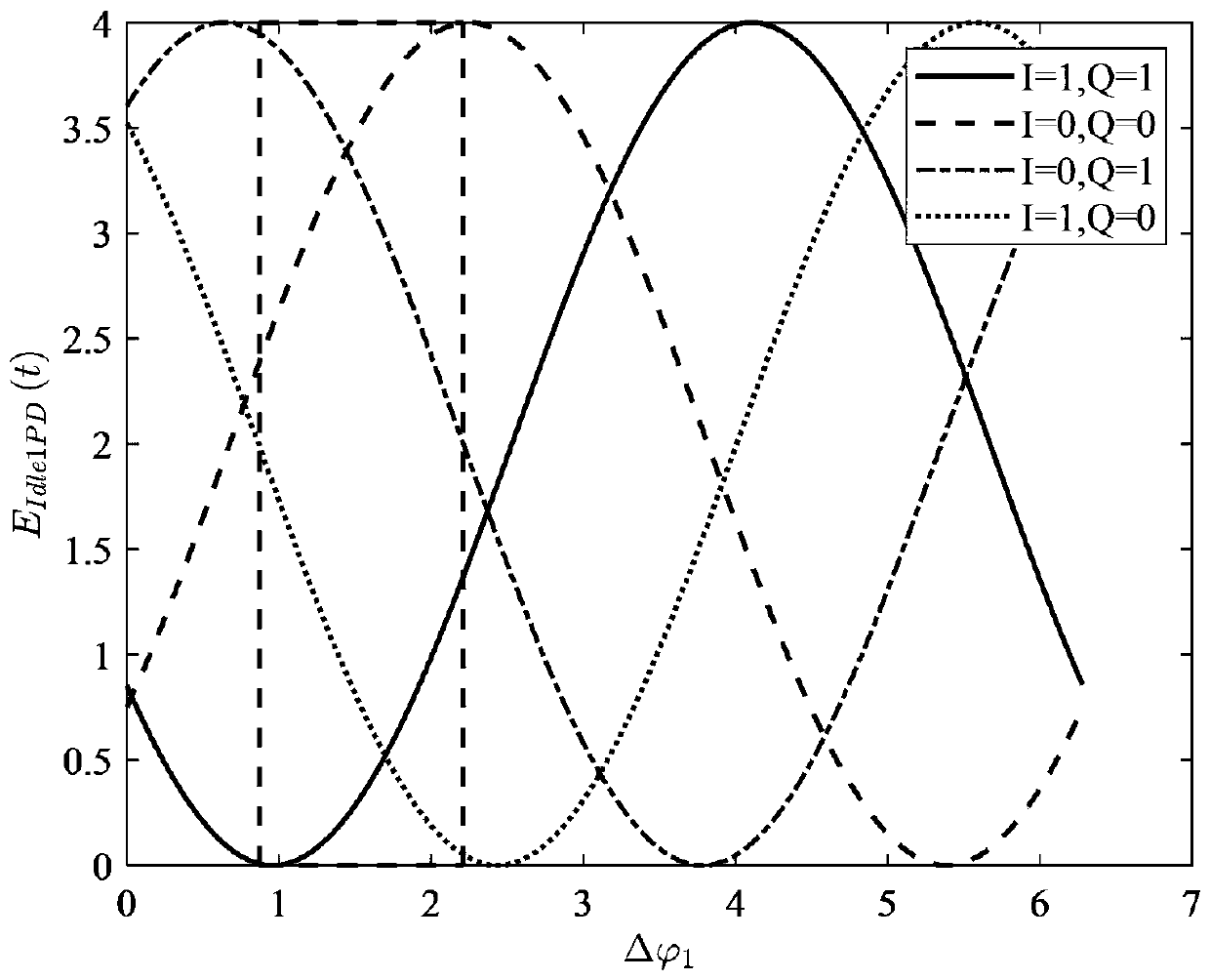
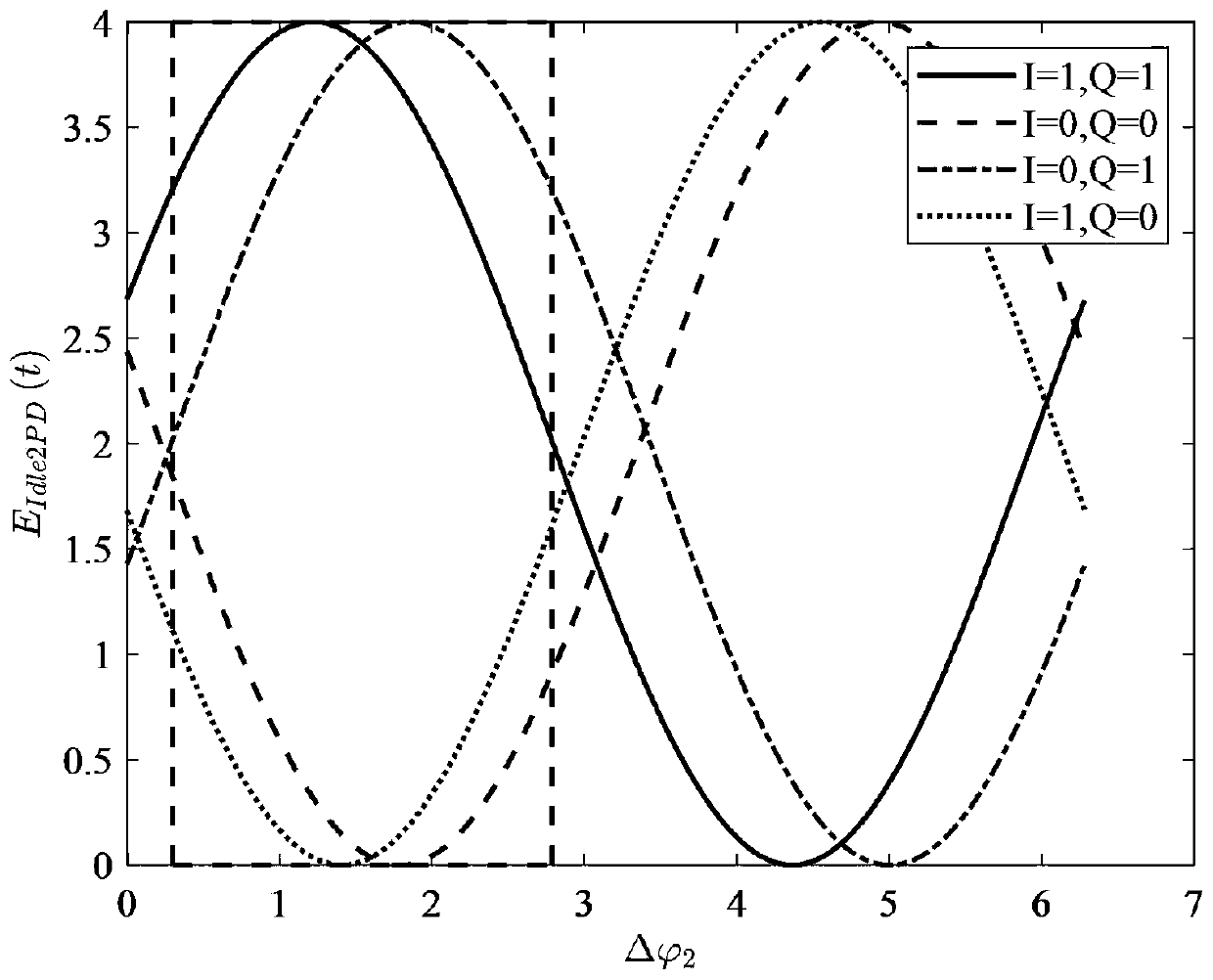
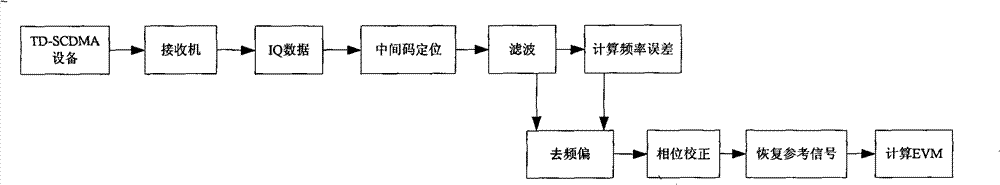
The invention relates to a method and a device for measuring a vector magnitude error for TD-SCDMA equipment testing, wherein a receiving device filters a received signal, divides data into 24 groups, and selects two groups of data in the middle to calculate. The calculation comprises that: a frequency deviation removing device is used to remove a phase error generated by frequency deviation in a signal; a phase correction device corrects the phase of the signal to correct an error of an initial phase; then, a module value of the signal is subjected to normalization processing to acquire a normalized measurement signal Z; the signal is divided into three types according to the magnitude of the module value of the signal and calculated, the equalizing value of the three types projected on coordinate axes are respectively calculated; the equalizing value is used as a module value of an ideal signal to acquire a reference signal R through phase mapping; a value of EVM is calculated according to a formula; and the result with the smaller numerical value in two calculating results is taken as the EVM value of the signal.
Owner:湖北众友科技实业股份有限公司
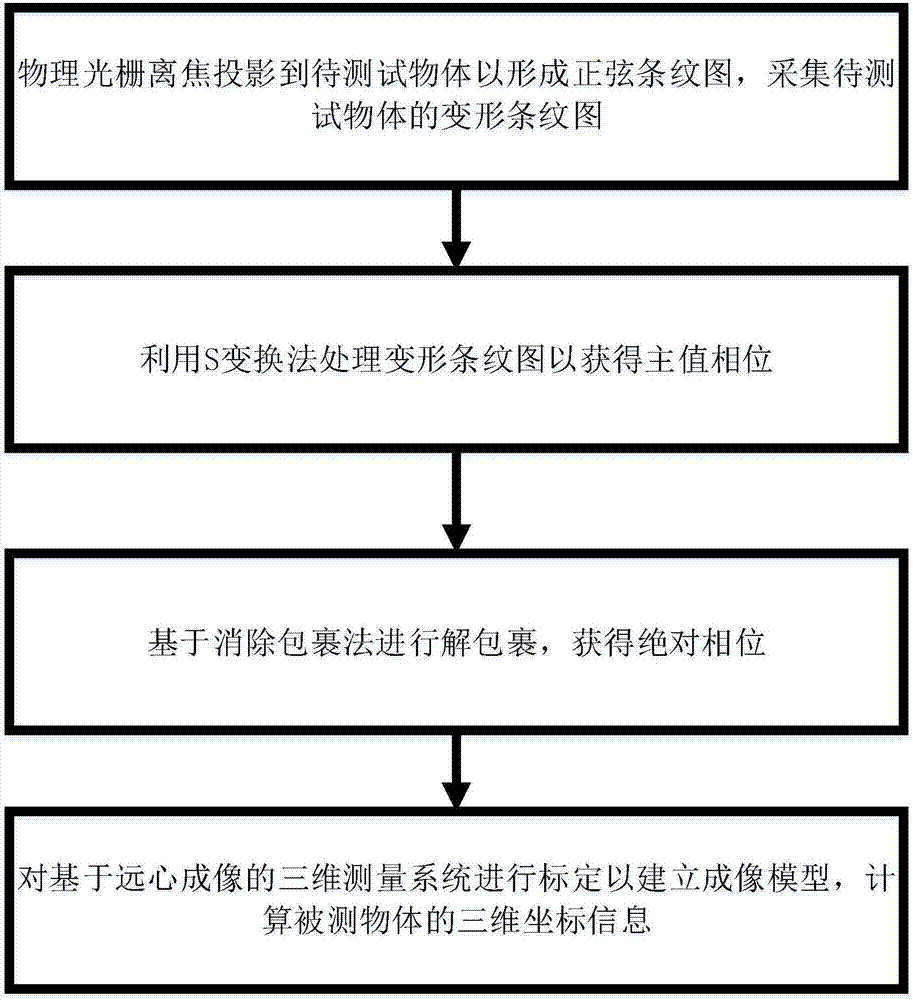
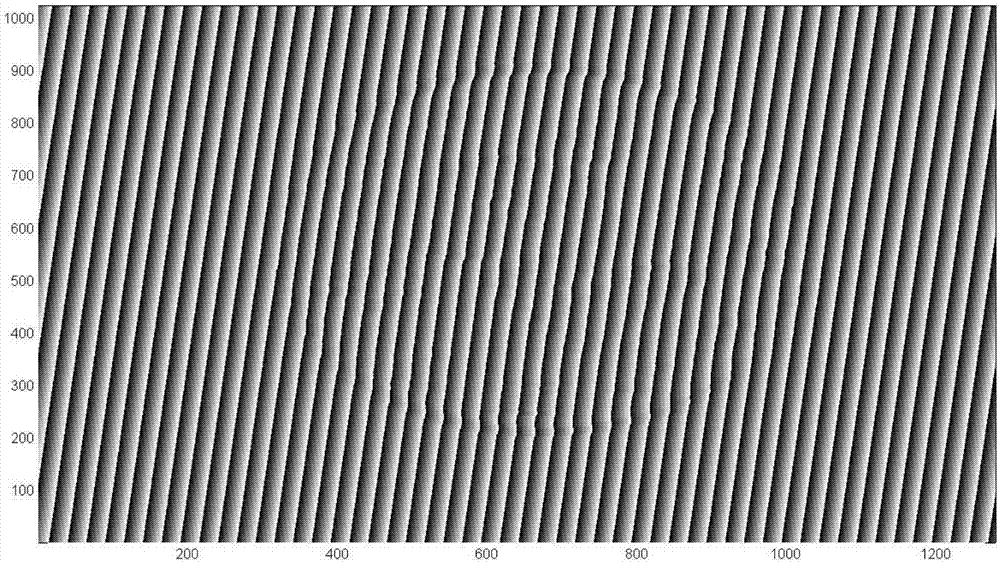
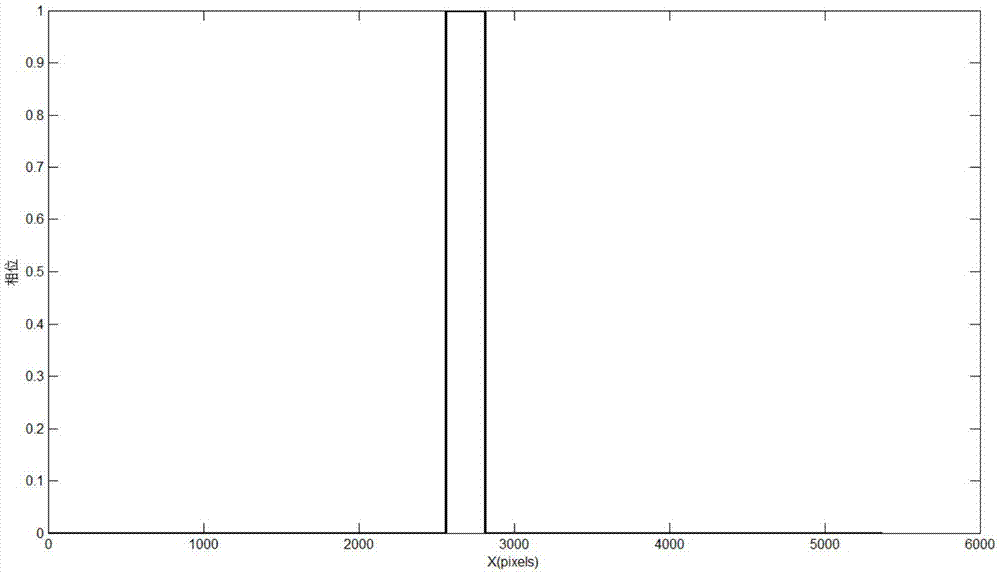
Three-dimensional measurement method and system based on single grating projection
ActiveCN107356212AEliminate phase componentsSimple stepsUsing optical meansGratingFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a three-dimensional measurement method and system based on single grating projection. The three-dimensional measurement method comprises the steps that a physical grating is projected to an object to be tested in an out-of-focus manner so as to form a sinusoidal fringe pattern, and a deformed fringe pattern of the object to be tested is collected; the deformed fringe pattern is processed by using an S-transform method to obtain the principal value phase Phi(x, y); unwrapping is performed based on a wrapping elimination method to obtain the absolute phase phi(x, y), and a three-dimensional measurement system for telecentric imaging is calibrated so as to build an imaging model, and three-dimensional coordinate information of the tested object is calculated. The three-dimensional measurement system is used for executing the method. The three-dimensional measurement method is based on the single fringe pattern, zero padding is performed on both ends of the principal value phase after the principal value phase is obtained according to the S-transform method so as to acquire up-sampling in the frequency domain, the frequency spectrum of the phase is shifted to the original position according to frequency shift characteristics of Fourier transform, a phase component of carriers is eliminated, the height-phase mapping relationship is fitted by adopting the telecentric imaging model, the three-dimensional measurement system is calibrated, the three-dimensional coordinate information of the tested object is obtained, the steps are simple, and the measurement speed is higher.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
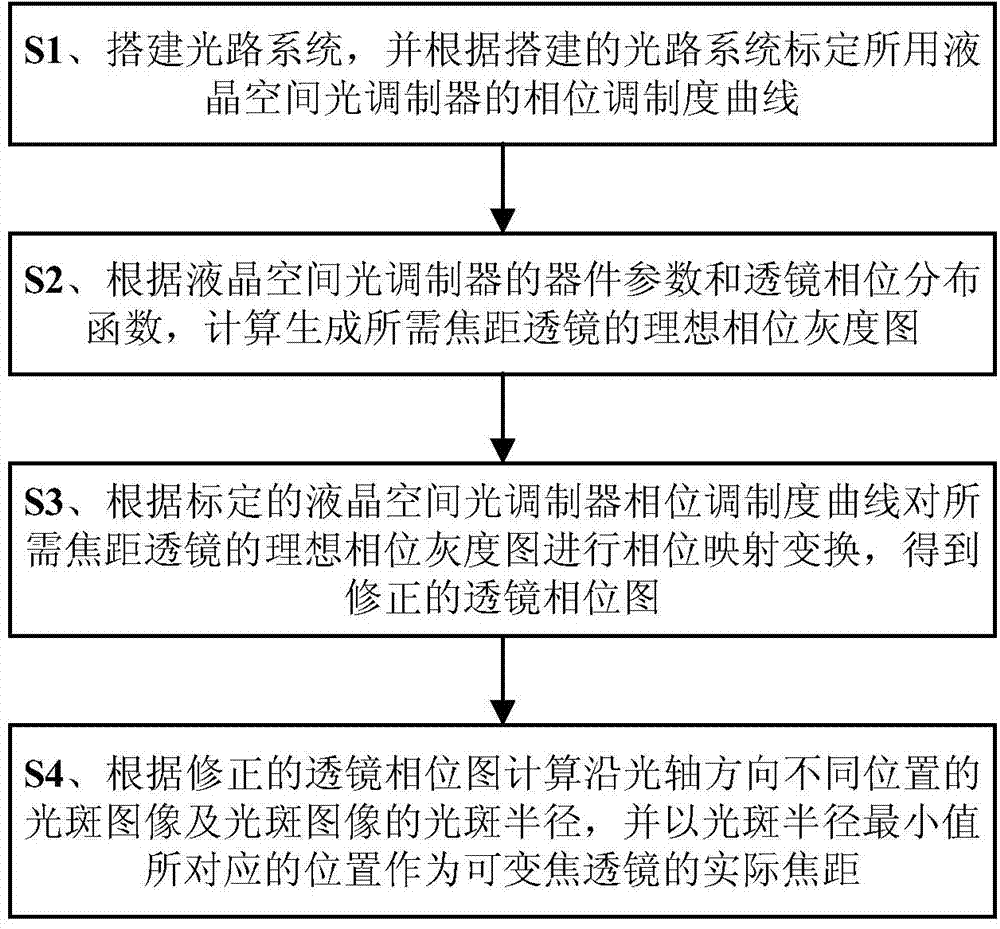
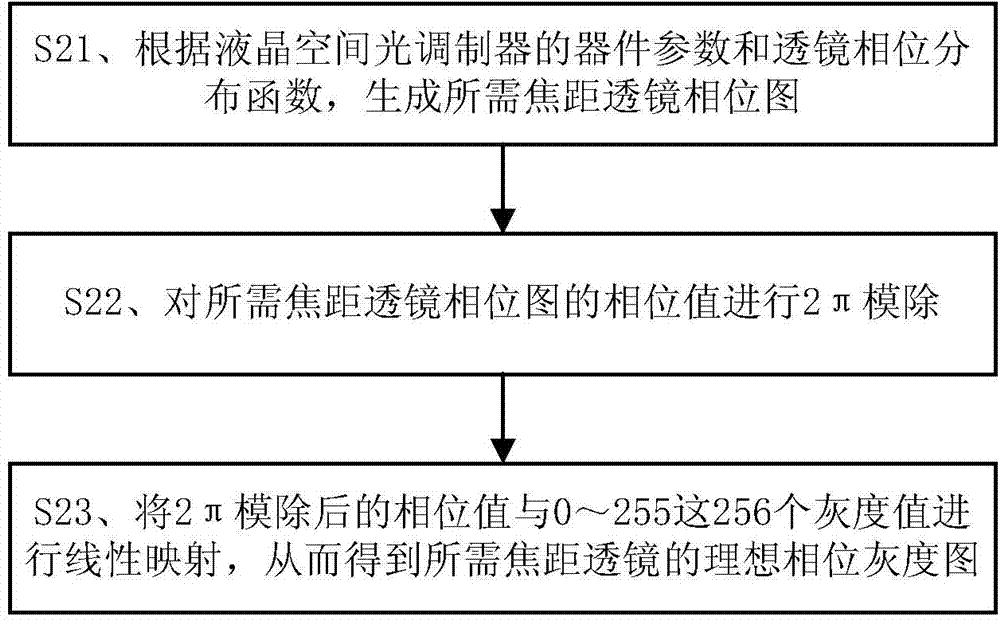
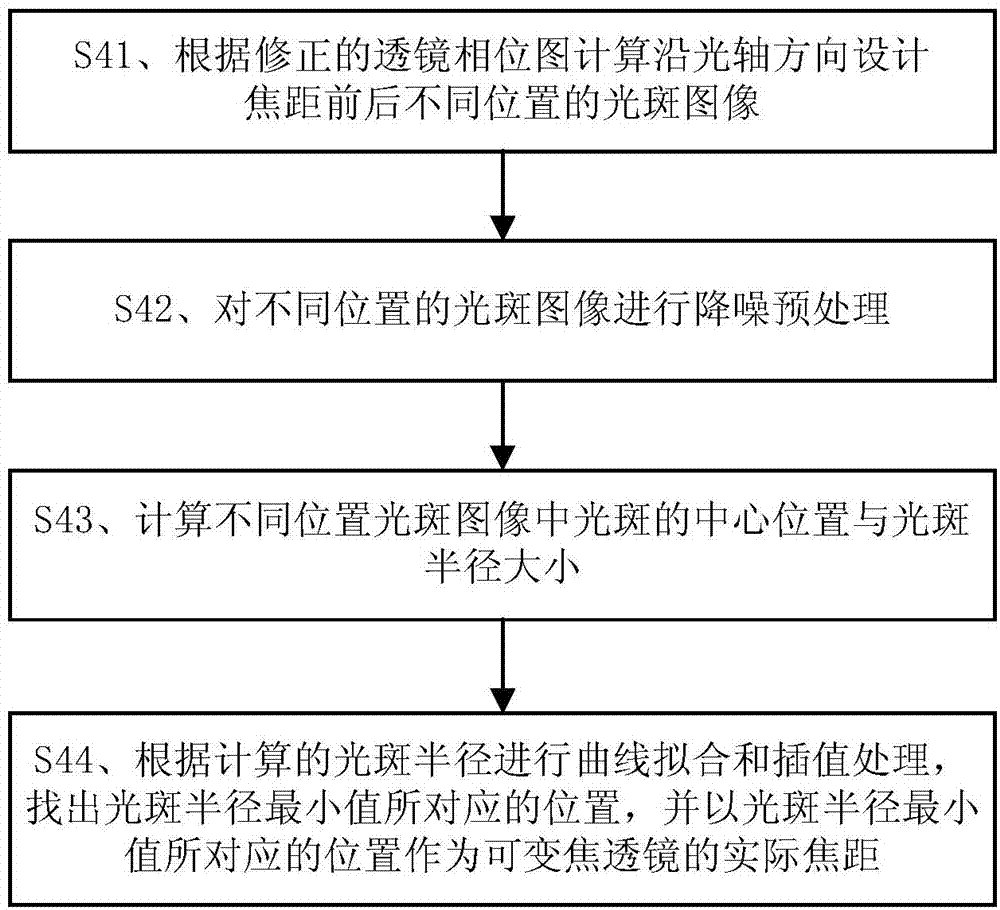
Method for computing actual focal length of variable-focal-length lens based on liquid crystal spatial light modulator
ActiveCN104122609AImprove image qualityWide adaptabilityNon-linear opticsLensPhase mappingLight spot
The invention discloses a method for computing an actual focal length of a variable-focal-length lens based on a liquid crystal spatial light modulator. The method includes: constructing a light path system and calibrating a phase modulation degree curve of the liquid crystal spatial light modulator according to the constructed light path system; computing an ideal phase grey-scale image for generating the lens with a required focal length according to device parameters of the liquid crystal spatial light modulator and a lens phase distribution function; subjecting the ideal phase grey-scale image of the lens with the required focal length to phase mapping transformation according to the calibrated phase modulation degree curve of the liquid crystal spatial light modulator so as to obtain a modified lens phase image; computing light spot images at different positions along the light axis direction and spot radiuses of the light spot images according to the modified lens phase image, and taking the position corresponding to a minimum spot radius value as the actual focal length of the variable-focal-length lens. The method has the advantages that the actual focal length of the variable-focal-length lens can be obtained quickly by computation based on the liquid crystal spatial light modulator, and the method is accurate in computing and wide in applicability and can be widely applied to the technical field of photology.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
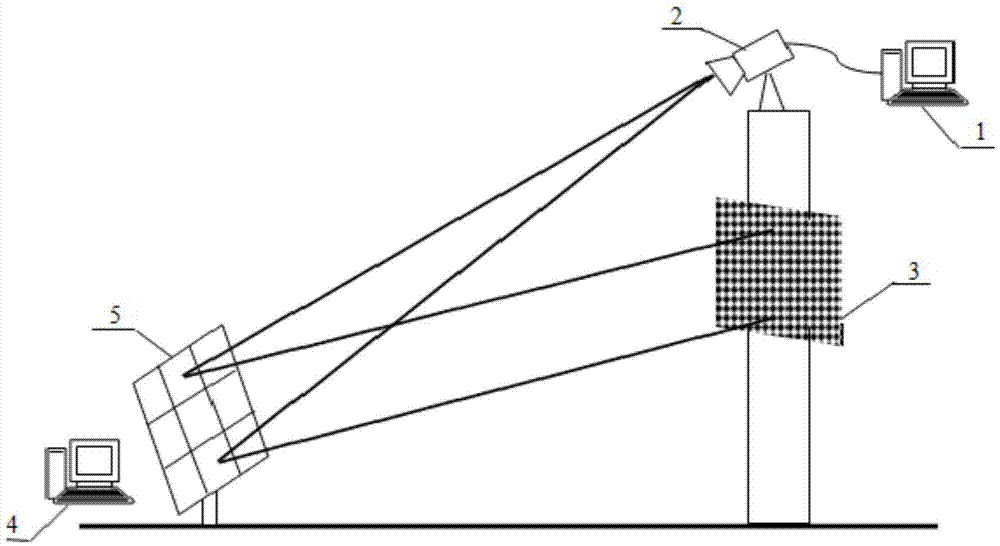
Plane shape detection method of heliostat for tower type solar power generation
ActiveCN104729430AReduce the impactImprove real-time performanceSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersHeliostatPhase mapping
A plane shape detection method of a heliostat for tower type solar power generation includes the steps that an industrial personal computer (4) controls the heliostat (5) to be detected, a CCD camera (2) can collect a deformed image, reflected by the heliostat (5), of a complex stripe image screen (3), a computer (1) controls the CCD camera (2) to collect a deformed complex stripe image reflected by the heliostat (5), and the slope distribution situation of the heliostat plane is obtained in combination with constructed virtual reference plane phase distribution and a heliostat plane slope and phase mapping model. The plane shape of the heliostat plane of the heliostat (5) to be detected can be obtained on the basis of the generalized Hermite interpolation method.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
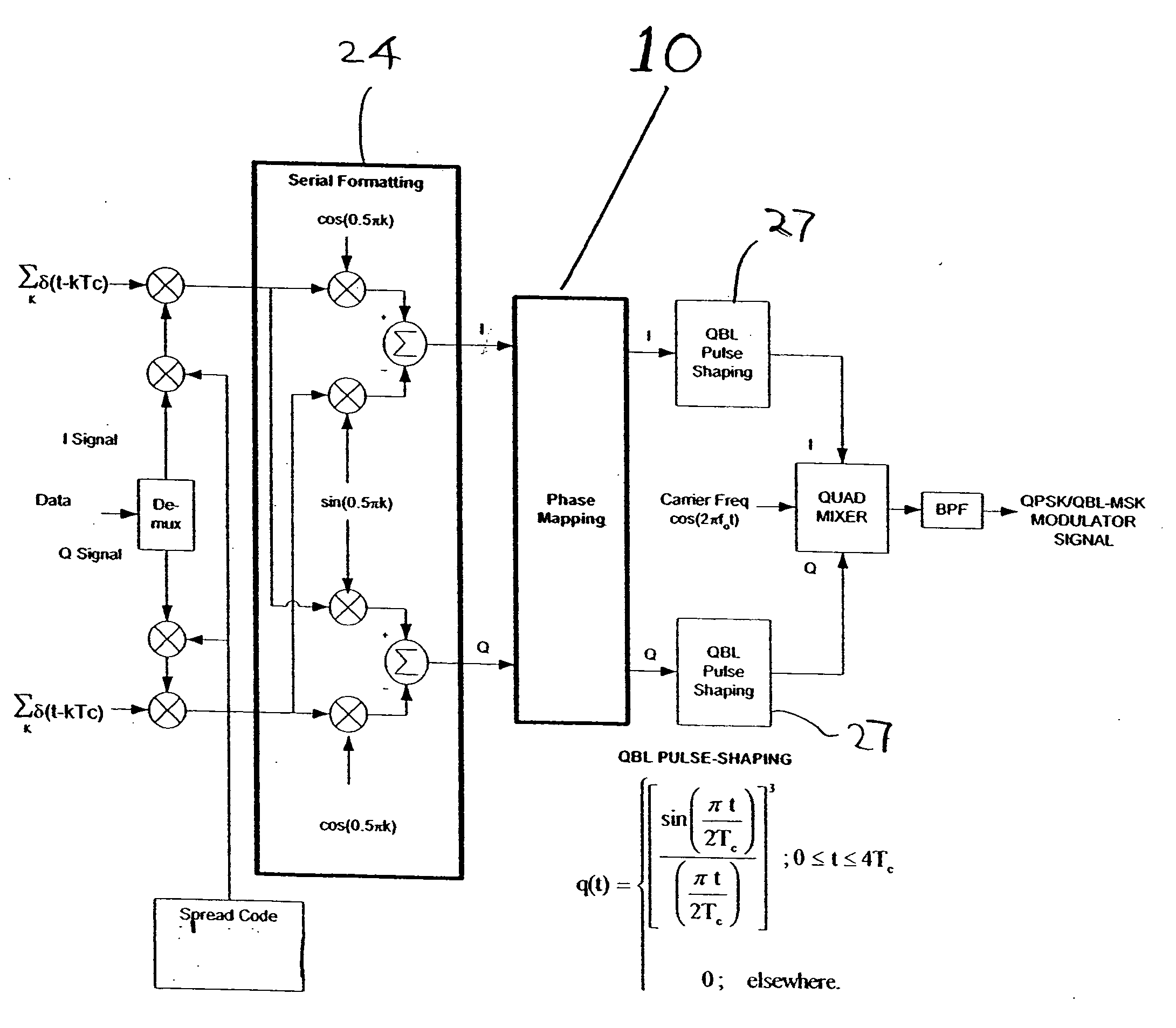
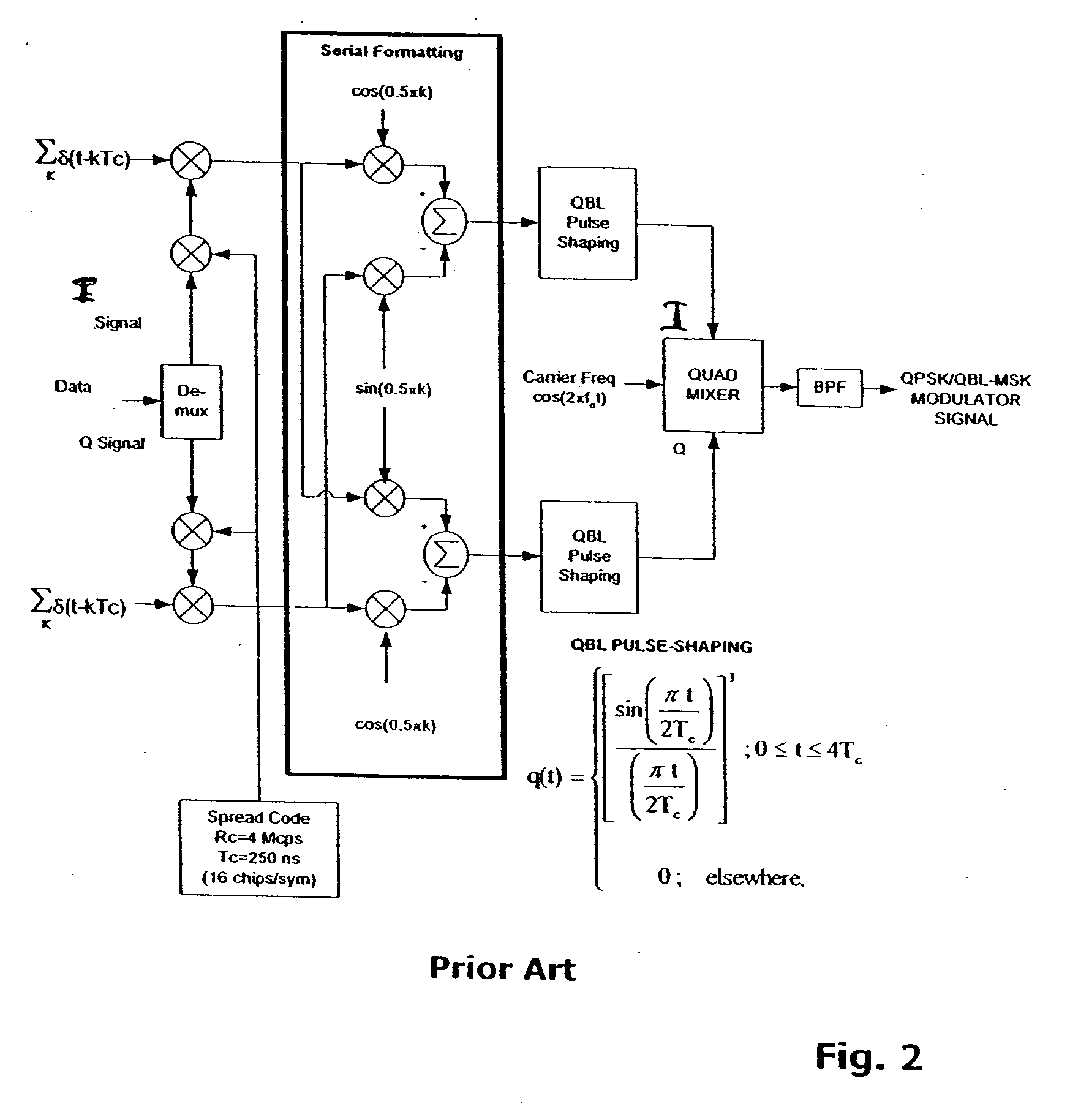
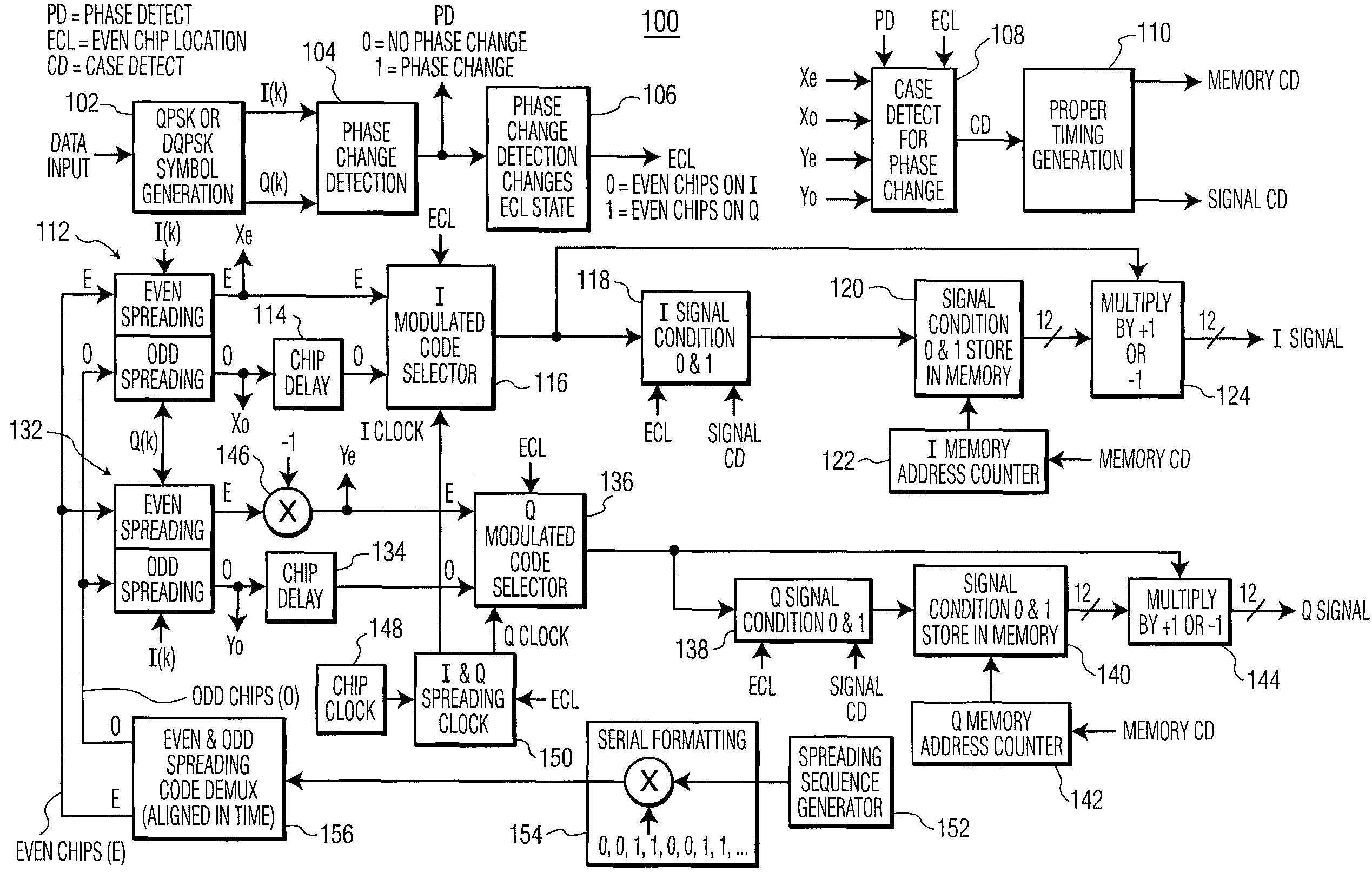
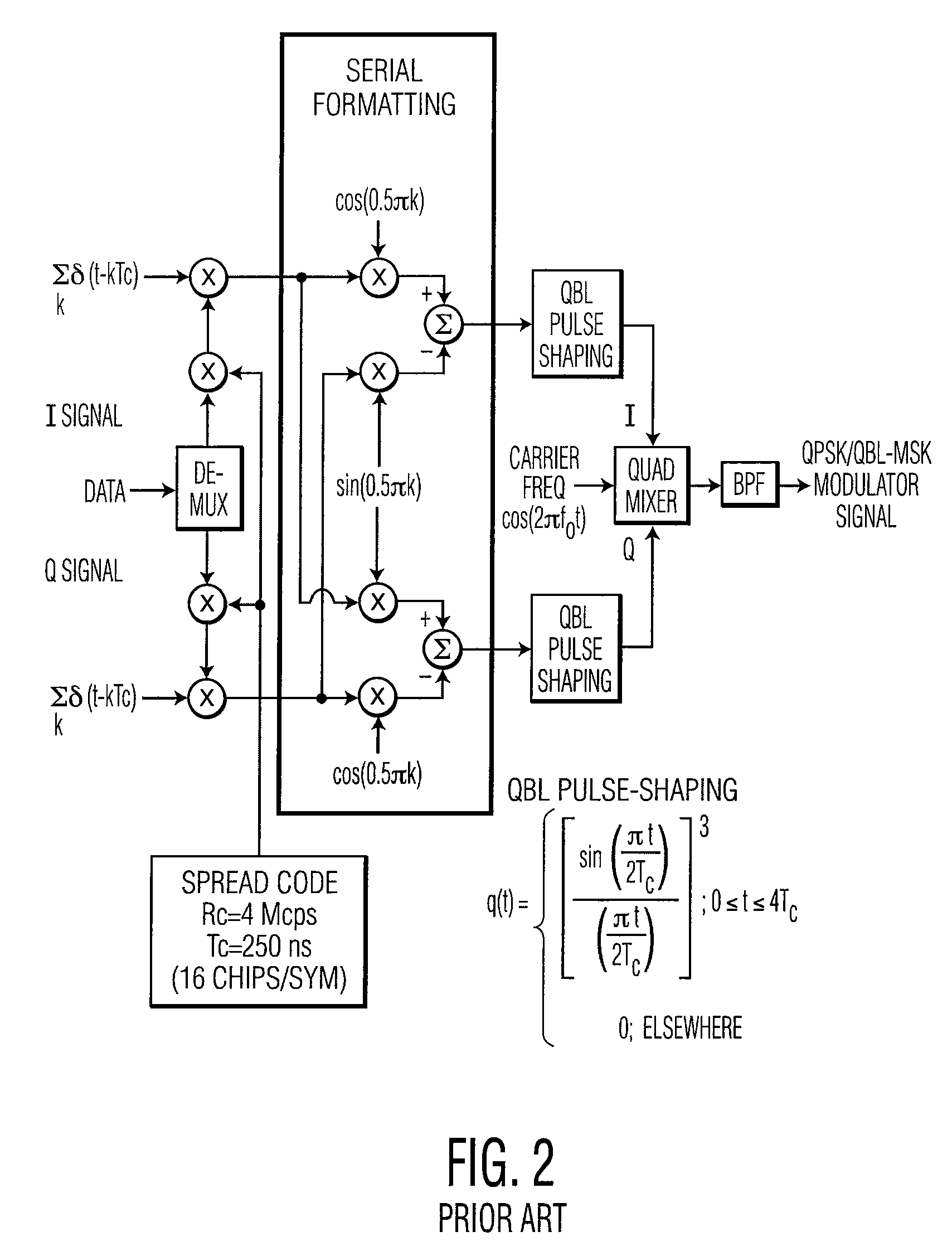
Phase mapping for QPSK/QBL-MSK waveform
ActiveUS20070025235A1Reduces processing gain degradationReduces look-up table complexityModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionPhase mappingWave shape
A method is described of pulse shaping a modulated sequence spread signal having serially formatted in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) waveforms, each waveform includes a predetermined number of chips per symbol. The method includes (a) examining adjacent chips of the I and Q waveforms at a symbol boundary; (b) determining that one of the I or Q waveforms, at the symbol boundary, includes two adjacent first and second chips separated by a single chip period, where the first chip belongs to a previous symbol and the second chip belongs to a present symbol; (c) determining whether the first and second chips are of the same value; (d) if step (c) determines that the chips are of the same value, then extending a peak value between the first and second chips, and zeroing the other waveform of the I or Q waveform during the extended duration of the peak value; and (e) if step (c) determines that the chips are of opposite values, then zeroing one of the first chip or second chip, and inserting a chip into the other waveform of the I or Q waveform during the duration of the zeroed one pulse. Step (e) includes inserting the chip into the other waveform, wherein the inserted chip has a value that is the same as an immediately previous chip value; and extending a peak value between the immediately previous chip and the inserted chip to provide a flat-top there-between.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMMUNICATIONS INC
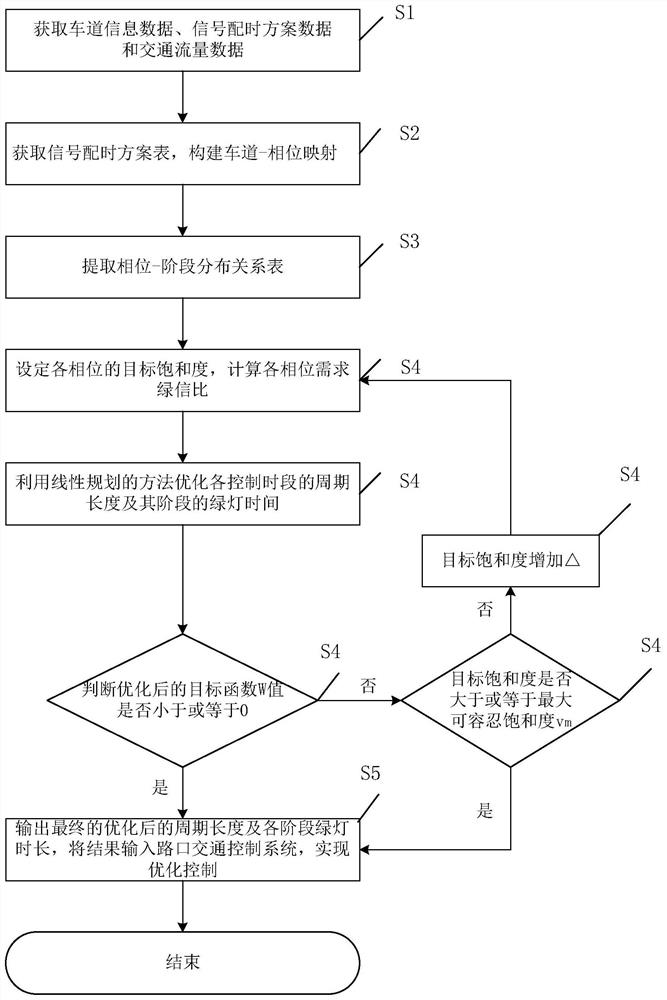
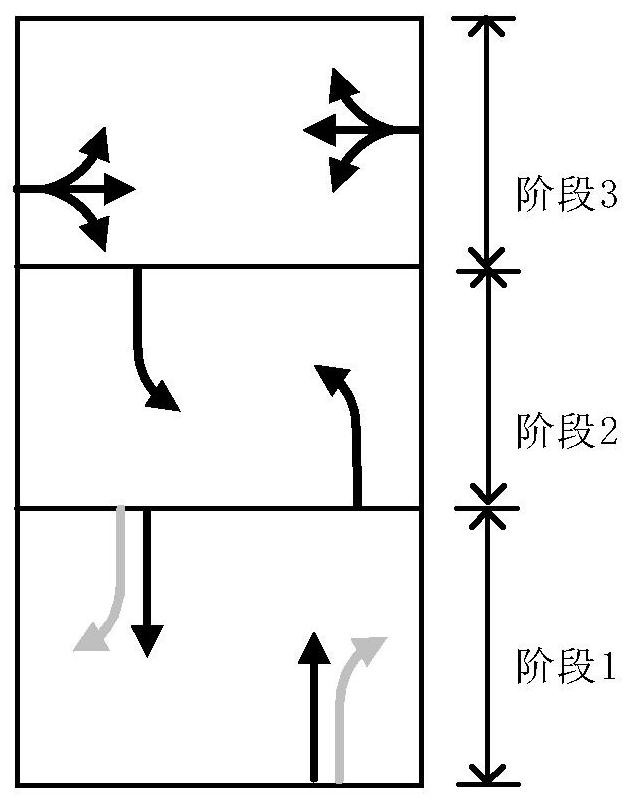
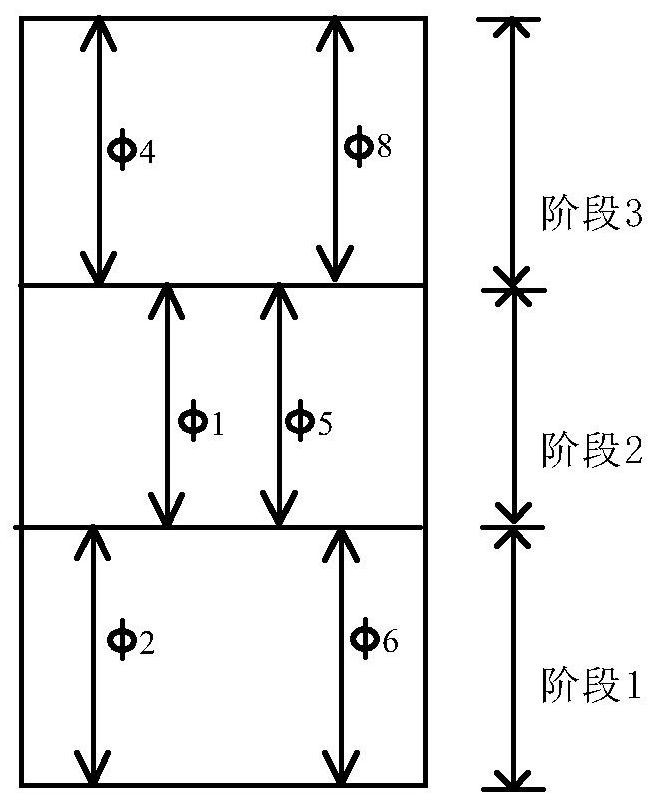
Stage-phase signal control scheme-oriented timing parameter optimization method
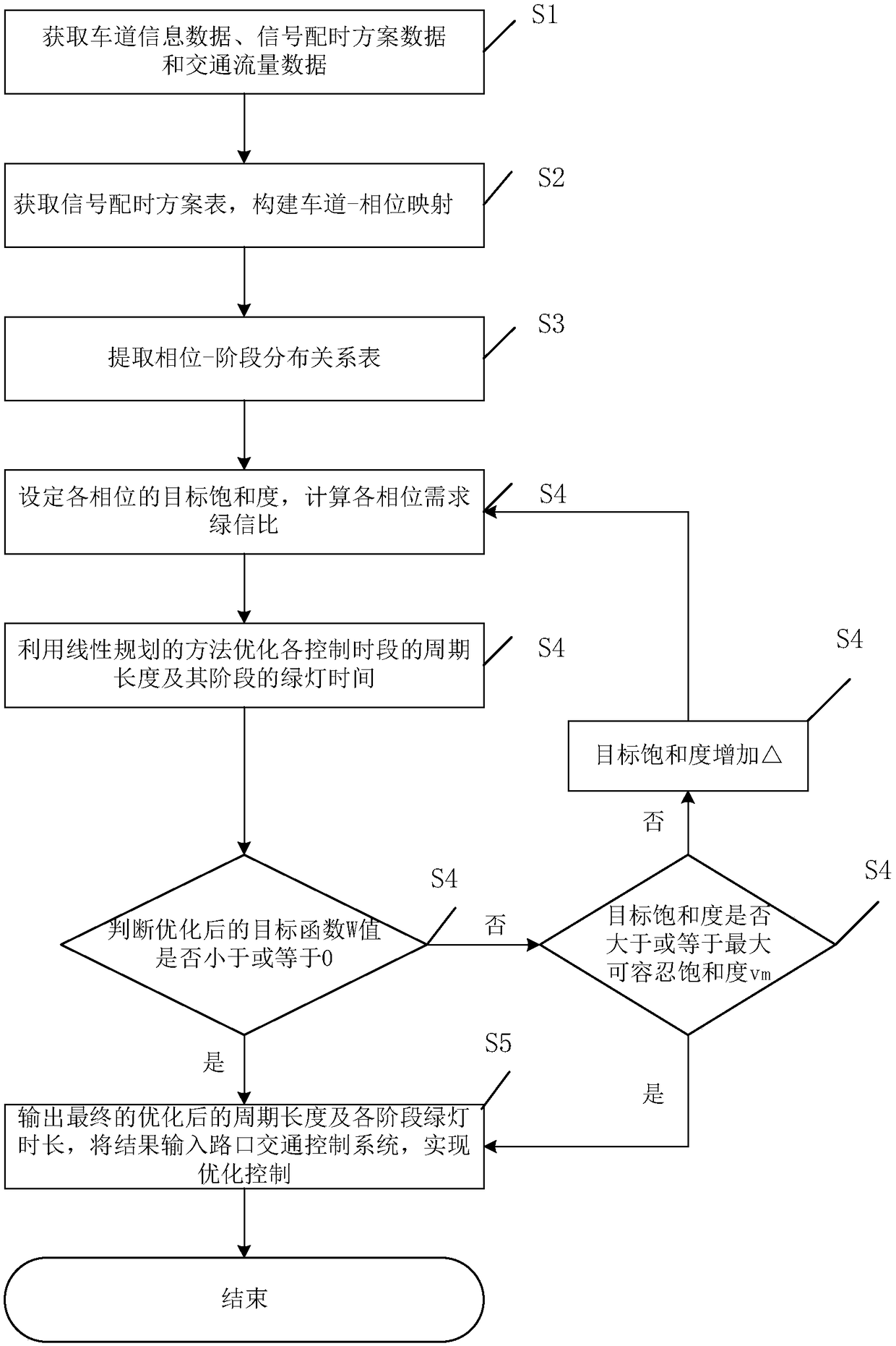
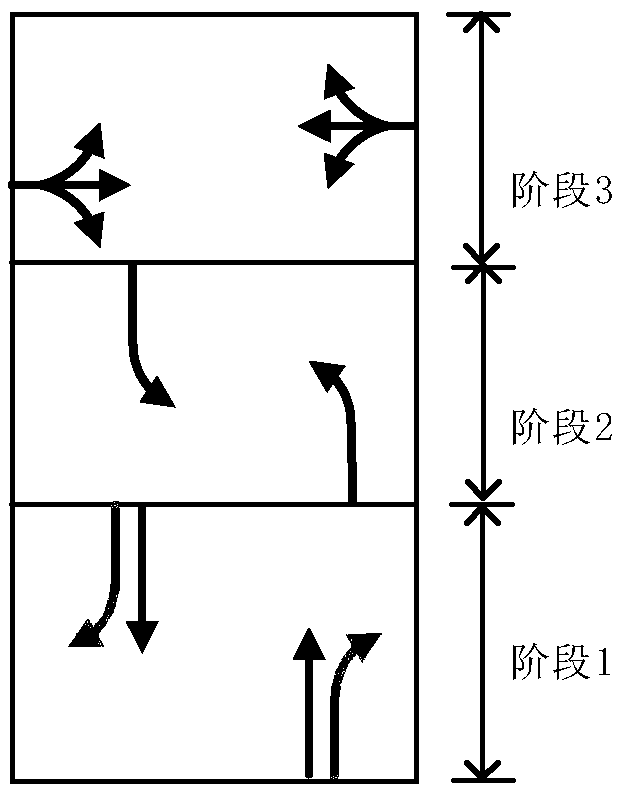
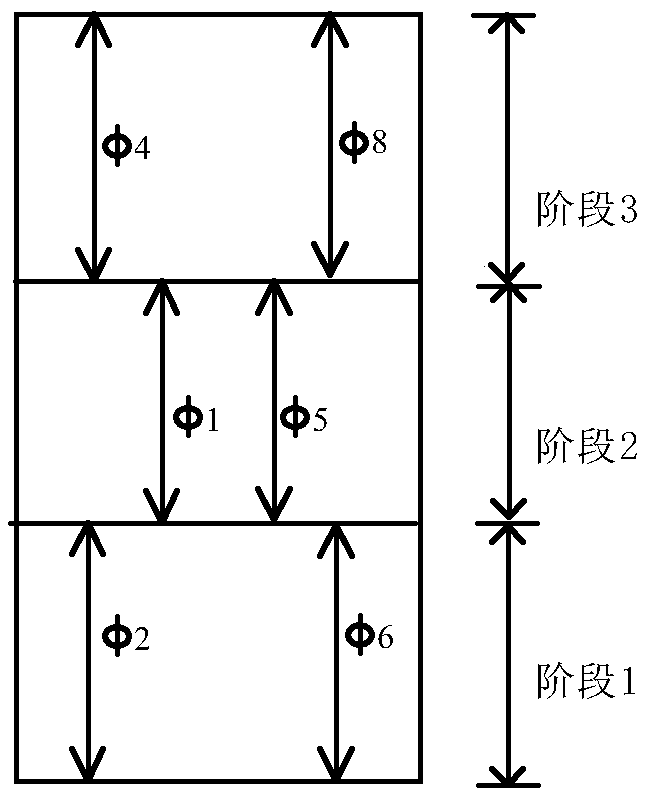
ActiveCN109410574AImprove scienceAvoid the Mistakes of EmpiricismControlling traffic signalsDetection of traffic movementPhase mappingGreen-light
The invention discloses a stage-phase signal control scheme-oriented timing parameter optimization method. The method includes the following steps that: 1, the lane information of a signalized intersection, the signal control scheme of the signalized intersection and the traffic volume of each lane are acquired, a lane information table and a signal timing plan table are generated; 2, the two tables form lane-phase mappings; 3, a phase-stage distribution relationship table is extracted; 4, the demand green signal ratio of each phase is obtained according to the target saturability of each phase, a linear programming equation model is constructed with the saturability of the intersection adopted as an optimization target, and an optimal cycle duration and the green light duration of each stage are obtained and are adopted as signal timing scheme optimization results; and 5, the signal timing scheme optimization results are inputted into an intersection traffic signal controller. The stage-phase signal control scheme-oriented timing parameter optimization method of the invention satisfies a domestic single-loop signal timing scheme structure, and can realize self-optimization and high accuracy of signal timing.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Apparatus for high rotation rate low I/O count phase interpolator
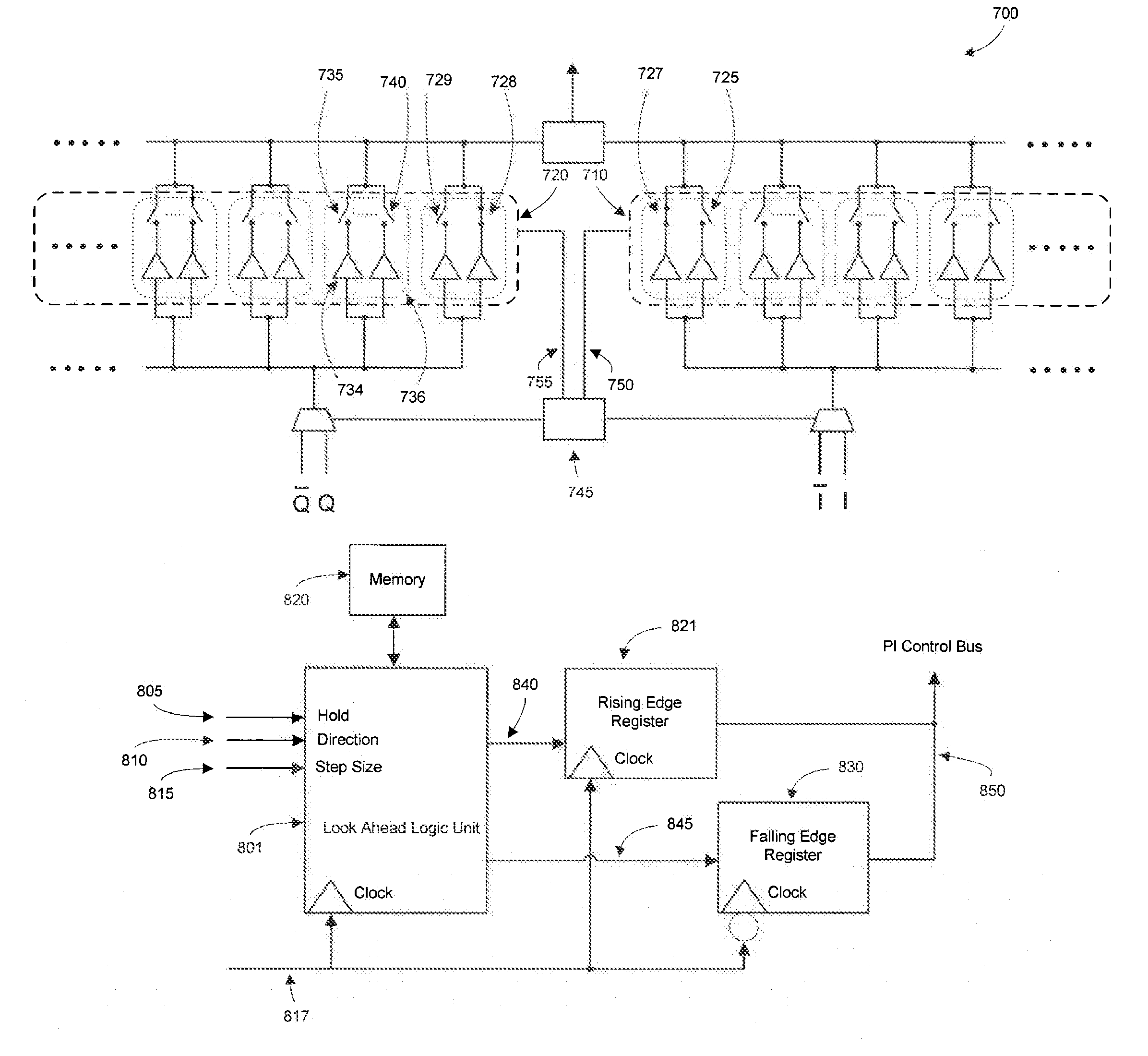
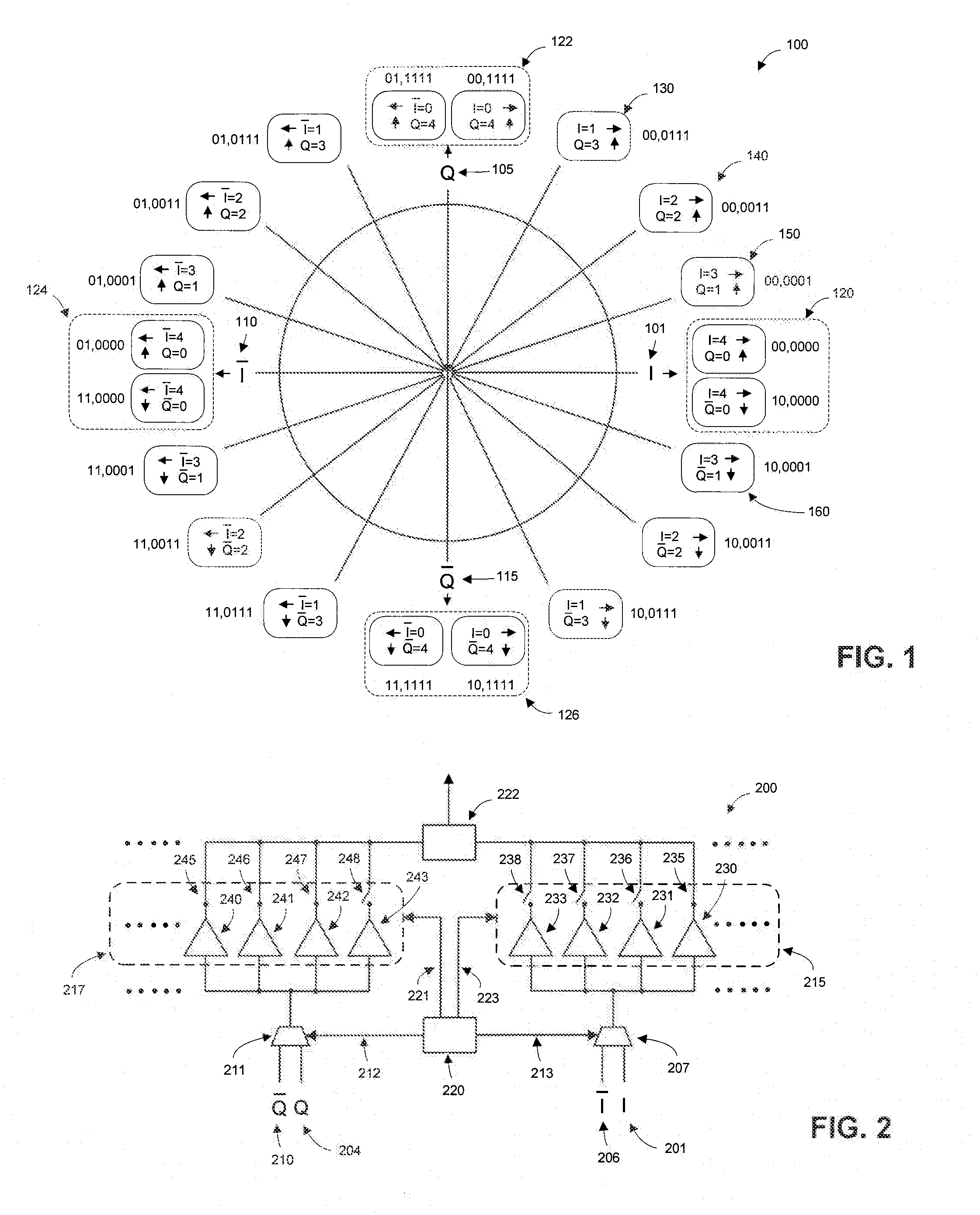
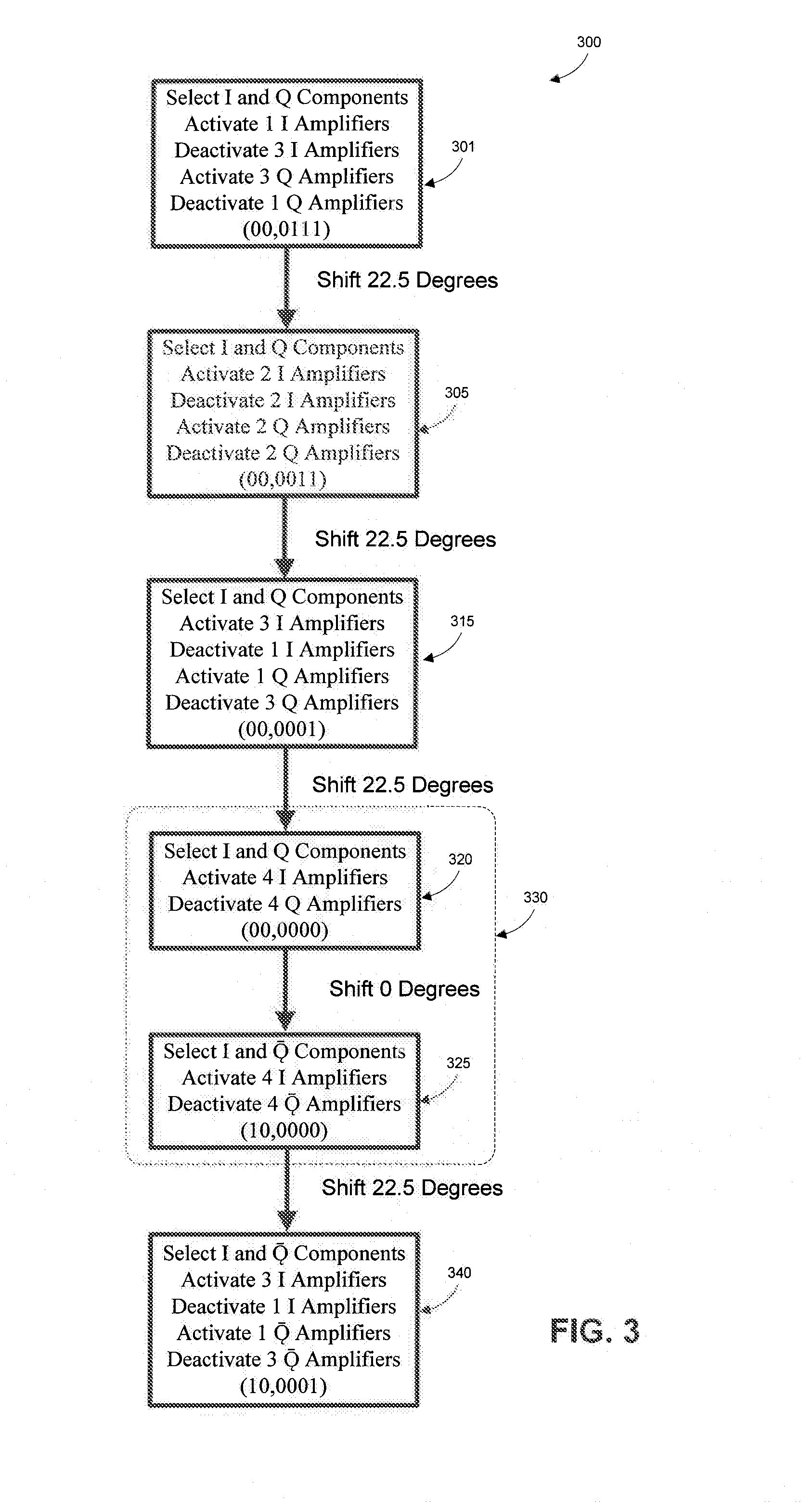
InactiveUS8947147B1Single output arrangementsElectric pulse generatorAudio power amplifierPhase mapping
Methods and apparatuses for high rotation rate low I / O count phase interpolation are disclosed, including techniques to reduce redundant phase interpolation coding and method steps by modifying phase mapping and generation with pluralities of amplifiers. I / O reduction count is achieved while maintaining resolution and allowing scalability in phase interpolation. Control circuits include techniques to interpolate phases at a high rotation rate while reducing discontinuities and risk for logic hazards.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
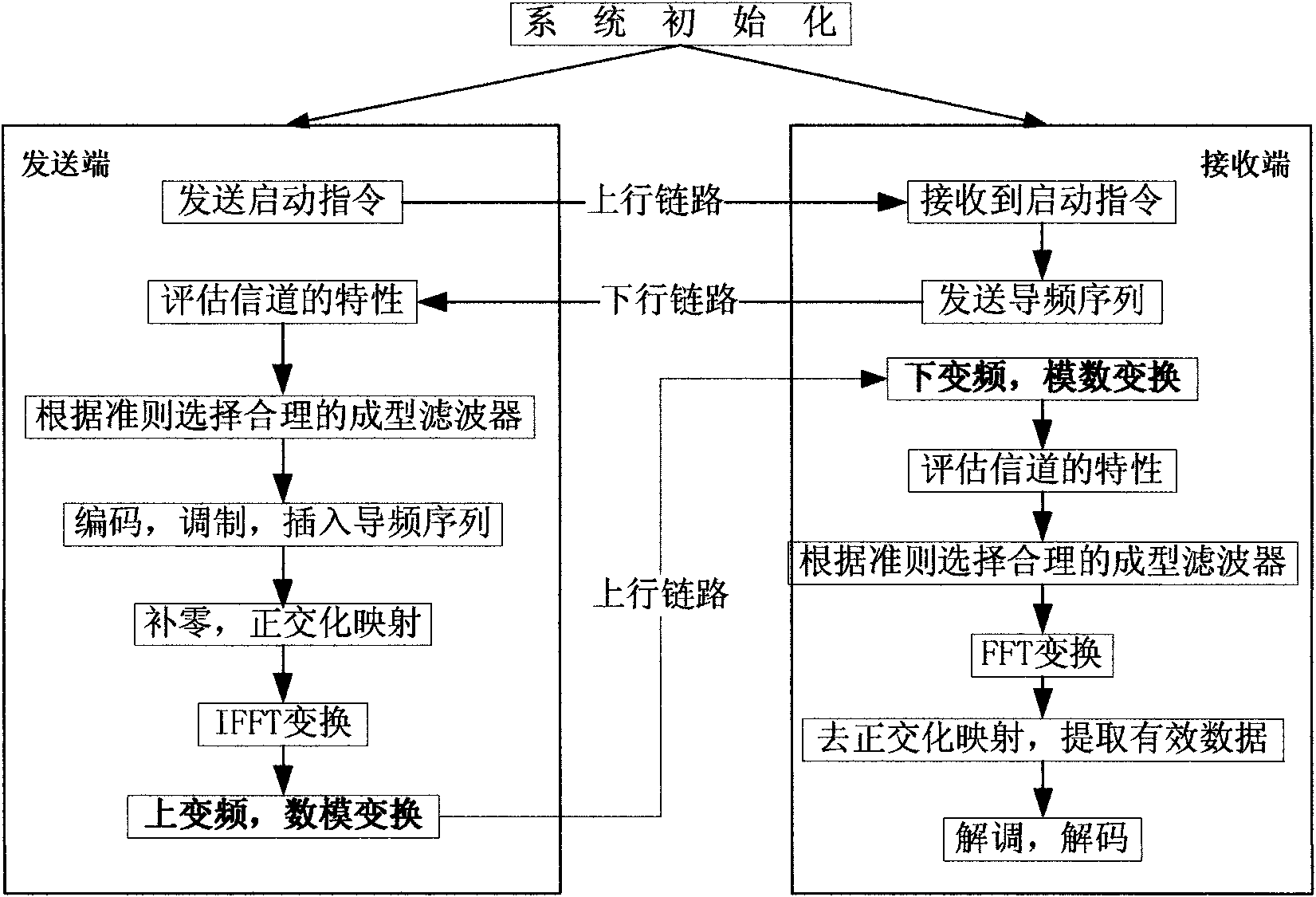
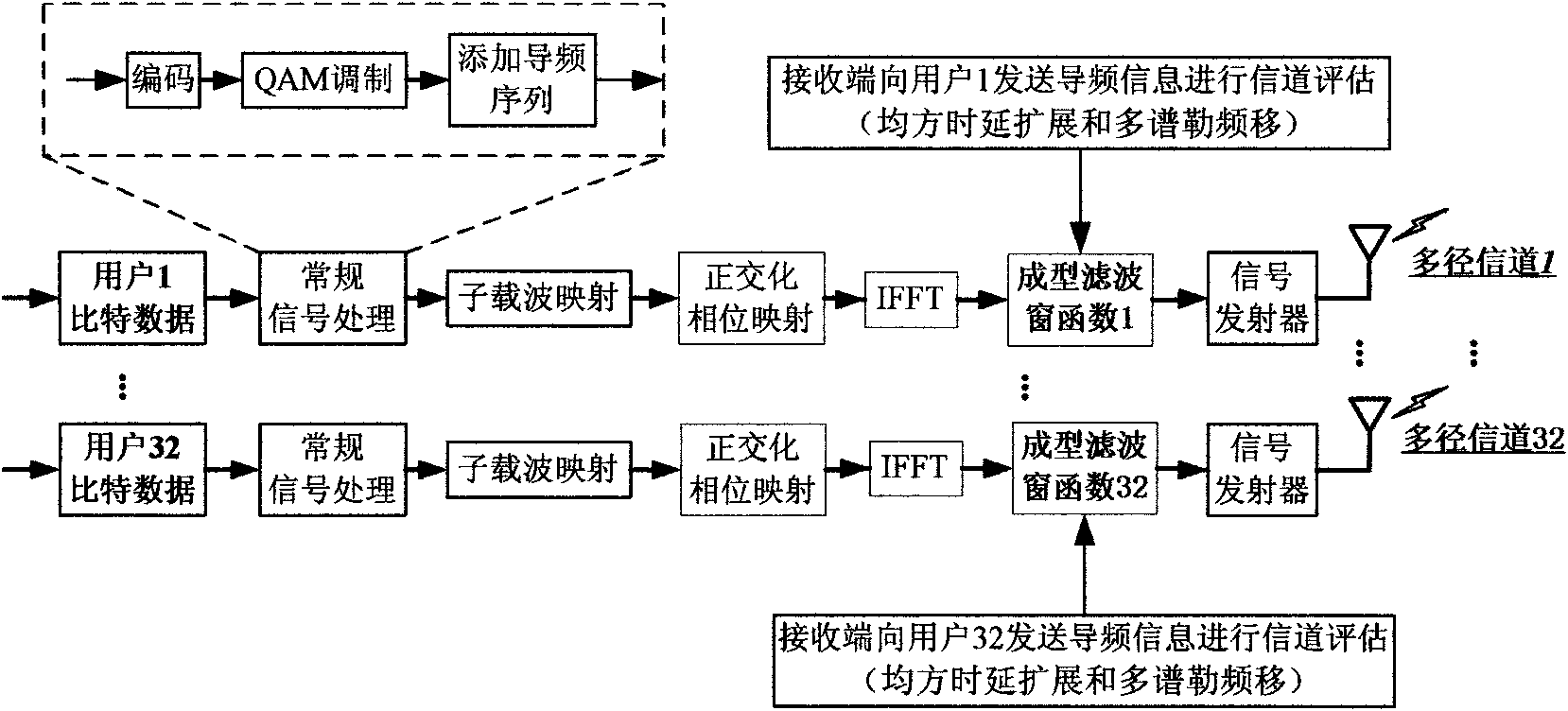
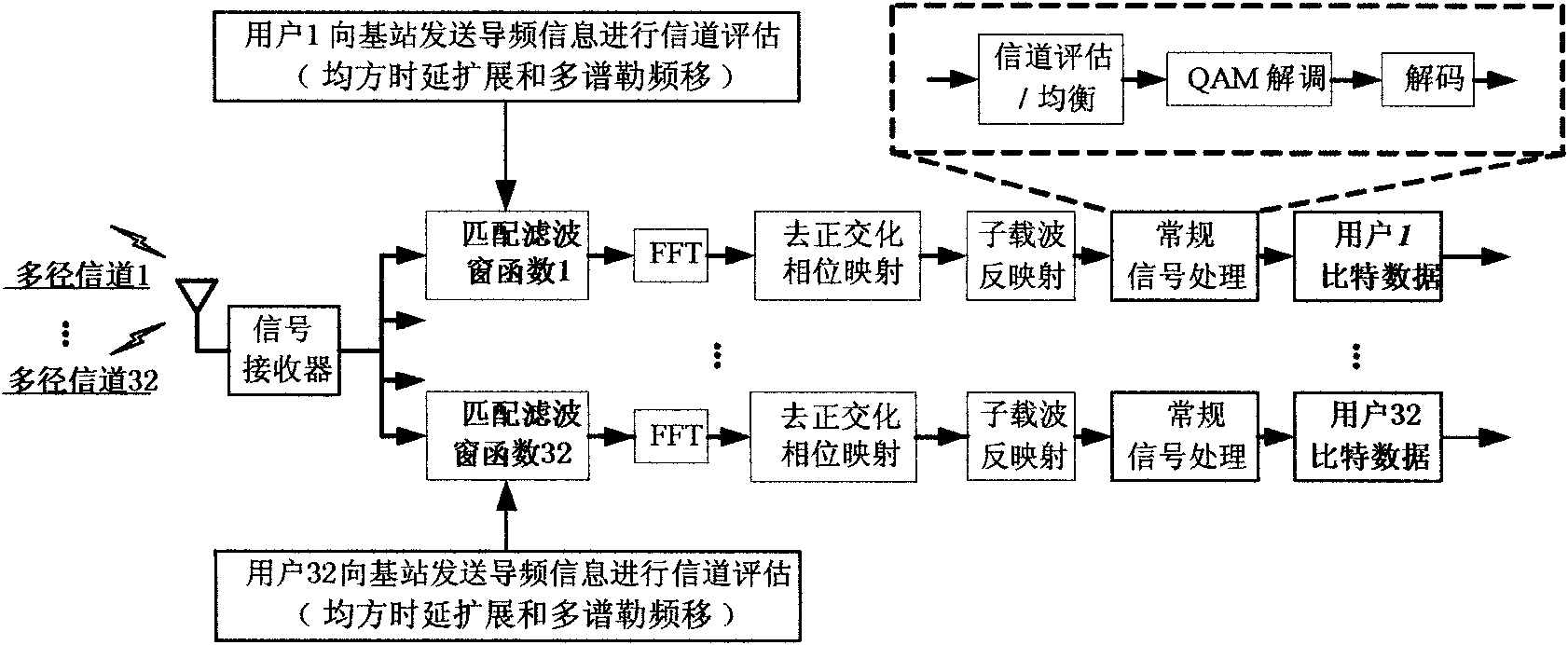
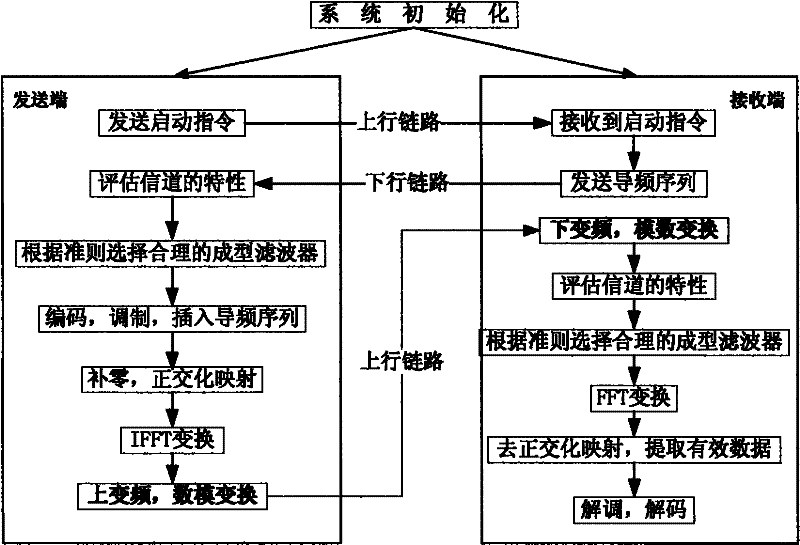
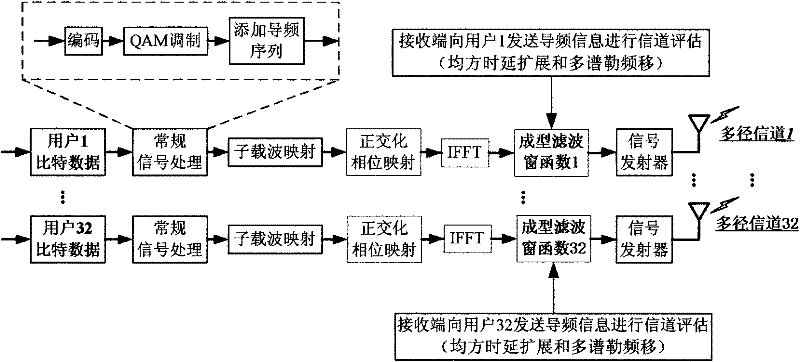
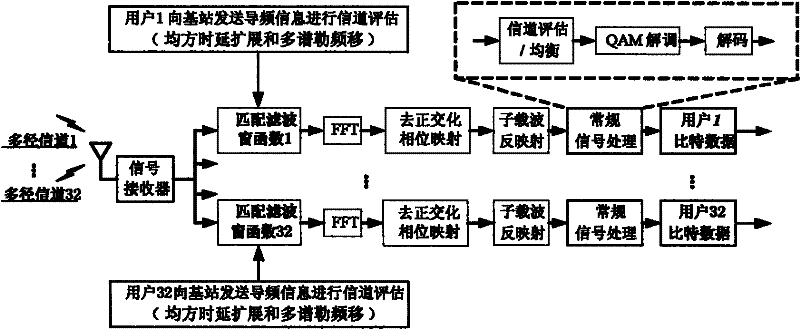
Uplink multiple access technology capable of automatically adapting to channel characteristic variation
InactiveCN101783782AReduce distractionsSmall distortionMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexFrequency spectrumSystem capacity
The invention belongs to an uplink multiple access technology capable of automatically adapting to channel characteristic variation in network access technologies. The invention comprises system initialization processing, which includes the following processes: a transmitting end: selecting a shaping filter matched with the characteristics of the current channel, quadrature amplitude modulating the send information, zero insertion processing, orthogonalization phase mapping, multi-carrier modulating, signal shaping and sending the signal; and a receiving end: processing the receiving signal, selecting the shaping filter matched with the characteristics of the channel, multi-carrier modulating, de-orthogonalization phase mapping, extracting valid data, isostatic compensating and storing the data. Because OQAM (technology) is introduced into OFDMA (technology) and the shaping filter with good time-frequency focusing characteristic is adopted to substitute for cyclic prefix, the invention has the characteristics of effectively improving the spectrum efficiency, system capacity and data transmission performance and resisting Doppler expansion, reducing the disturbance between users and distortion of the signal in the channel, better satisfying the requirement of high-speed mobile communications and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
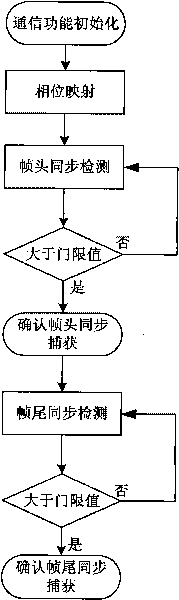
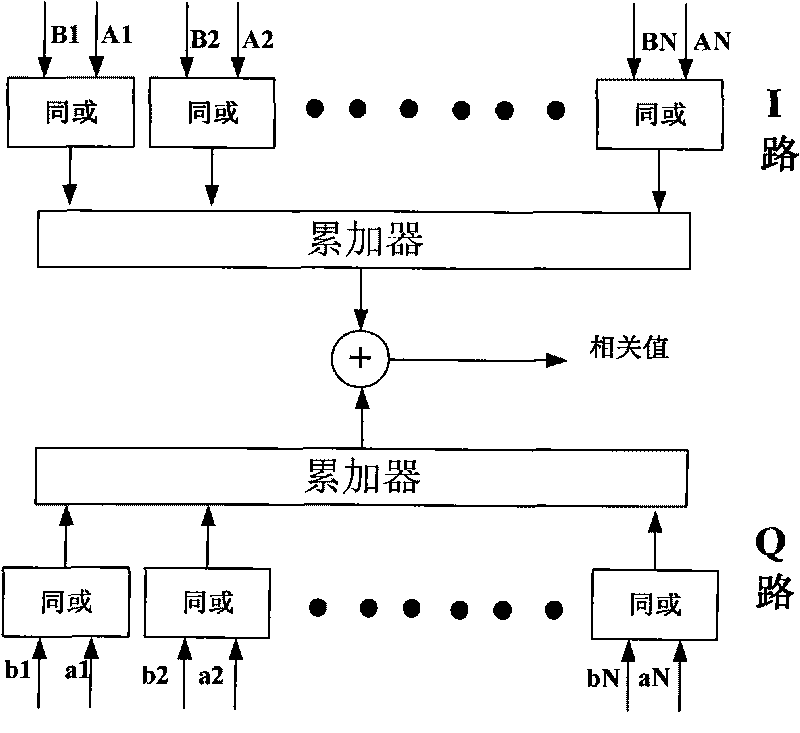
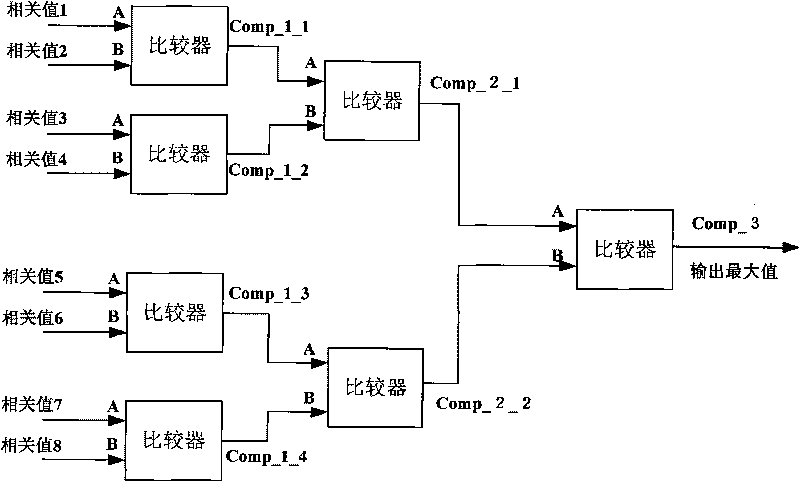
Frame synchronized method for unmanned air vehicle downstream data chain
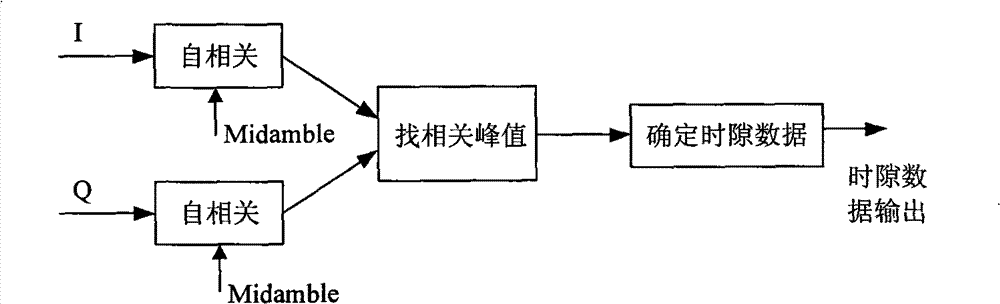
InactiveCN101702706AGood autocorrelationLeaky SynchronizationMulti-frequency code systemsResource consumptionPhase mapping
The invention discloses a frame synchronized method for an unmanned air vehicle downstream data chain, aiming at a data chain which takes QPSK as a modulating mode; the method comprises the following steps: step I, communication function initialization; step II, phase mapping; step III, frame header synchronized detection; step IV, frame header synchronized capture acknowledgement; step V, frame trail synchronized detection; step VI, frame trail synchronized capture acknowledgement. On the basis of carrying out phase mapping and eliminating phase ambiguity, the synchronized detection of the frame header and the frame trail is carried out, so as to carry out frame synchronized capture; in the method, the frame header and the frame trail adopt PN codes which have good autocorrelation and meet the low probability requirements of missed synchronization and false synchronization in frame synchronization; the method is simple and is easy to realize, the same module can realize two functions, the hardware realization is simple and convenient and the resource consumption is low.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
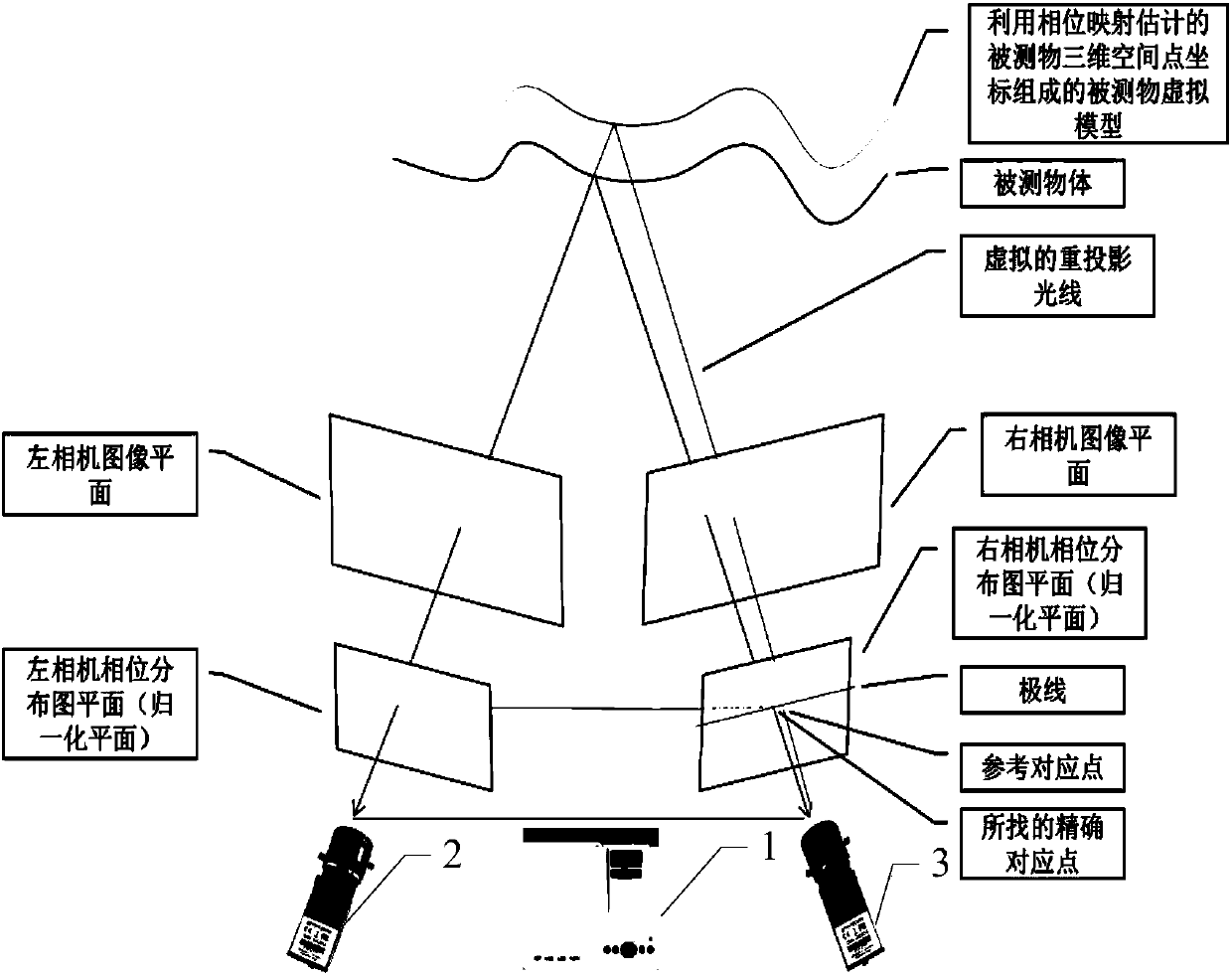
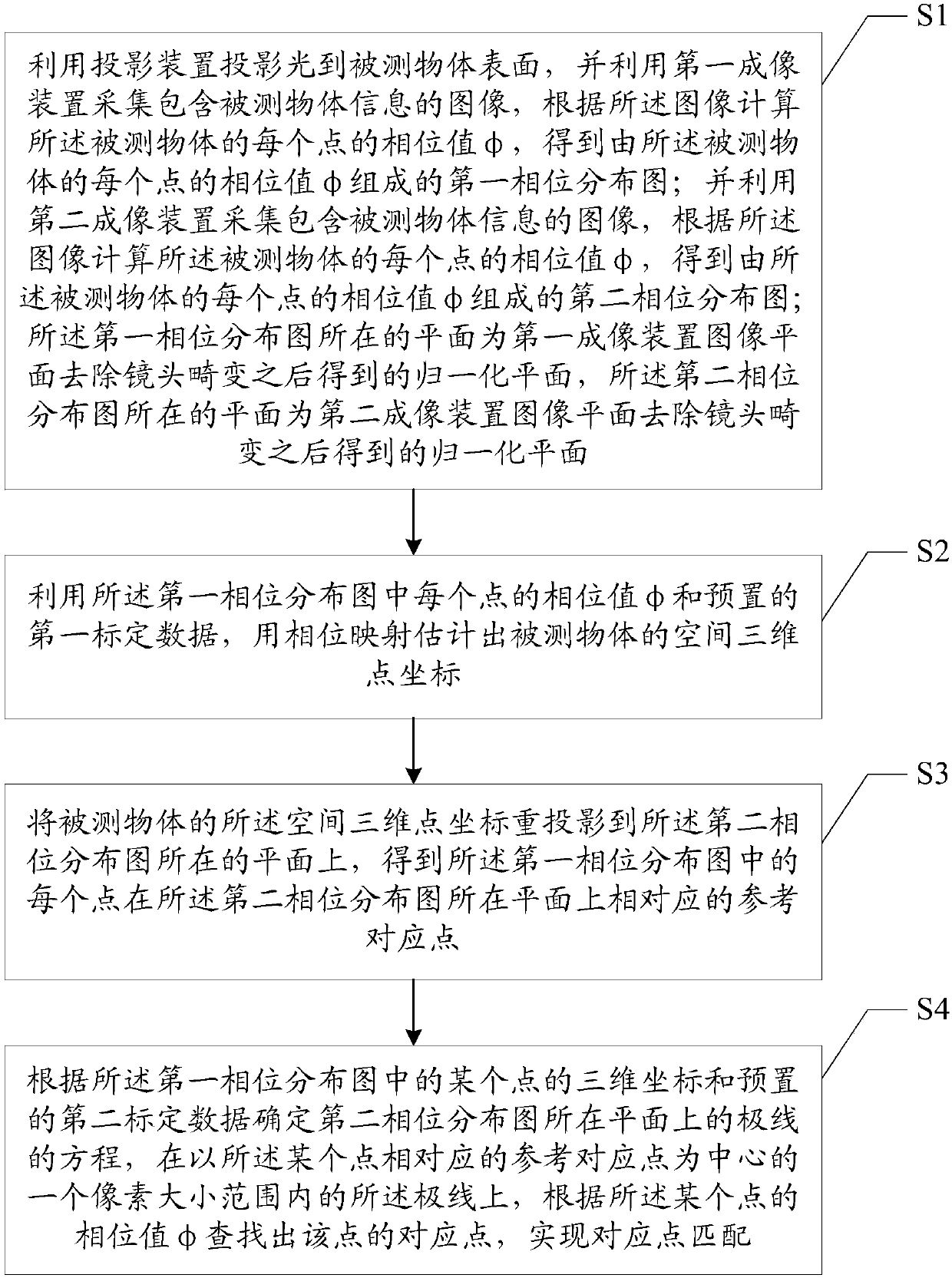
Rapid matching method and device of corresponding points for phase mapping assisted three-dimensional imaging system
ActiveCN106767405AReduce search rangeShorten the timeUsing optical meansDigital imagingPhase mapping
The invention is applicable to the technical field of optical three-dimensional digital imaging and provides a rapid matching method of corresponding points for a phase mapping assisted three-dimensional imaging system; the method comprises the steps of S1, acquiring an image including information of an object under measurement, and calculating to obtain first and second phase distribution diagrams composed of phase values Phi of points acquired; S2, using the phase values Phi of the points in the first phase distribution diagram and preset first calibration data to estimate spatial three-dimensional point coordinates of the object under measurement by means of phase mapping; S3, re-projecting the spatial three-dimensional point coordinates to a plane of the second phase distribution diagram to obtain reference corresponding points; S4, on polar lines of one-pixel range using one reference corresponding point, corresponding to a certain point in the first phase distribution diagram, as a center, finding a corresponding point to the certain point according to the phase value Phi of the certain point so that the corresponding point is matched. The method provided herein has narrowed finding range and shortened finding time.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
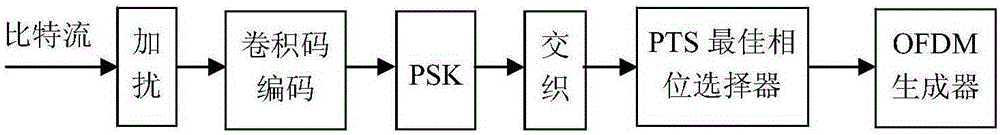
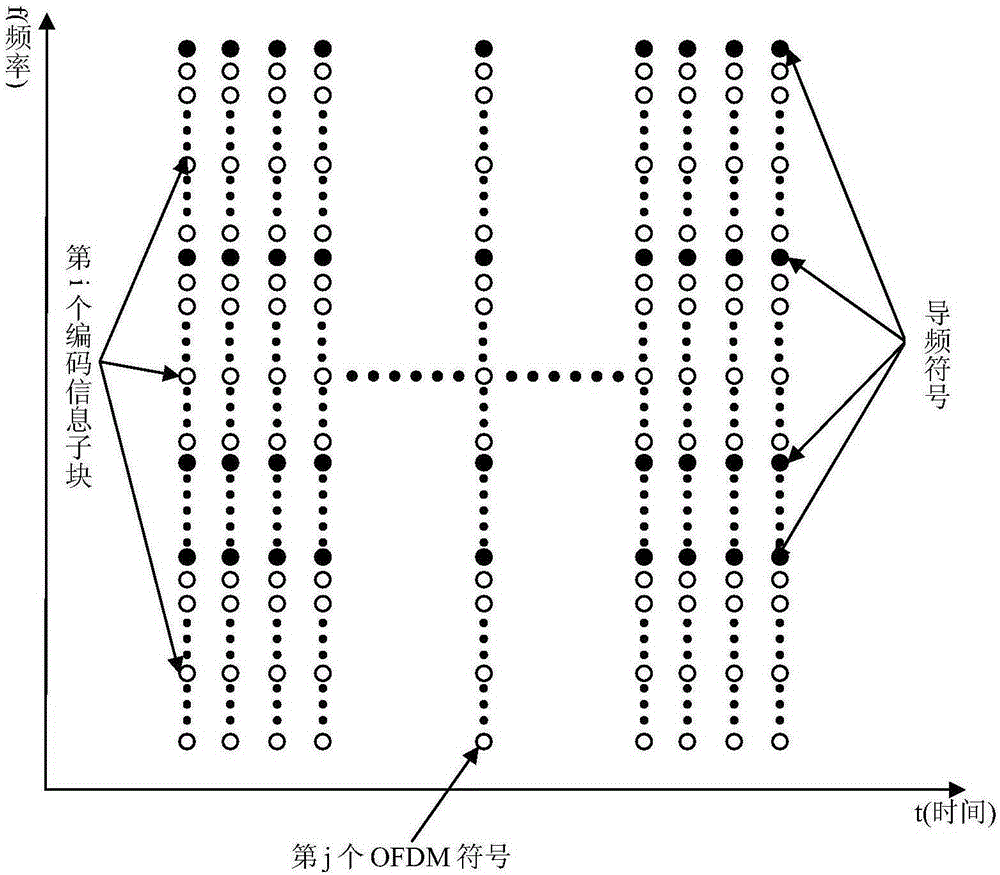
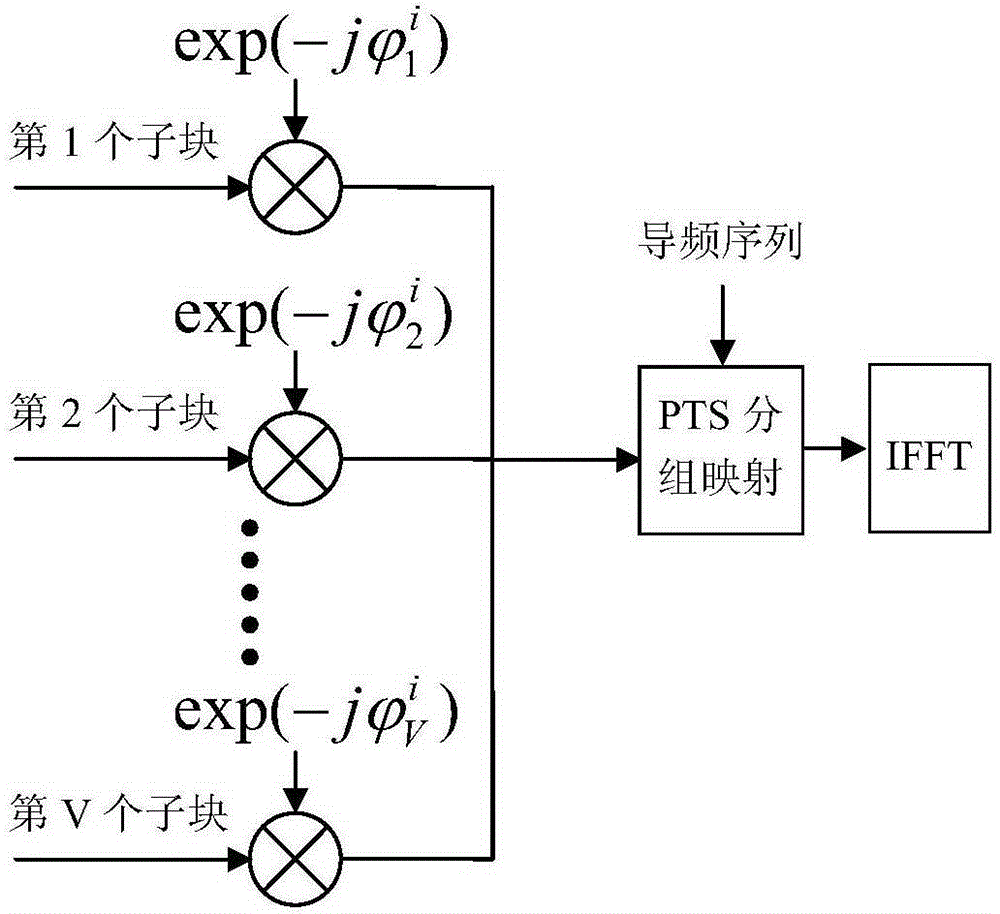
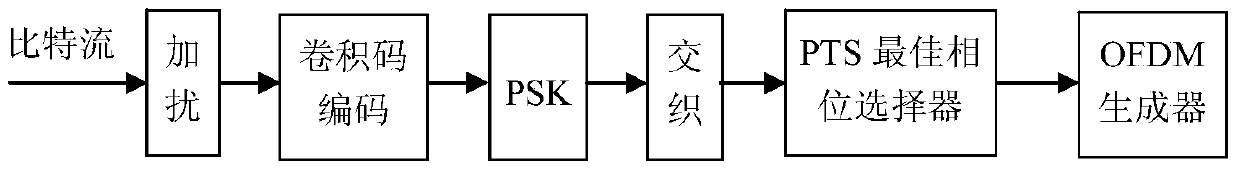
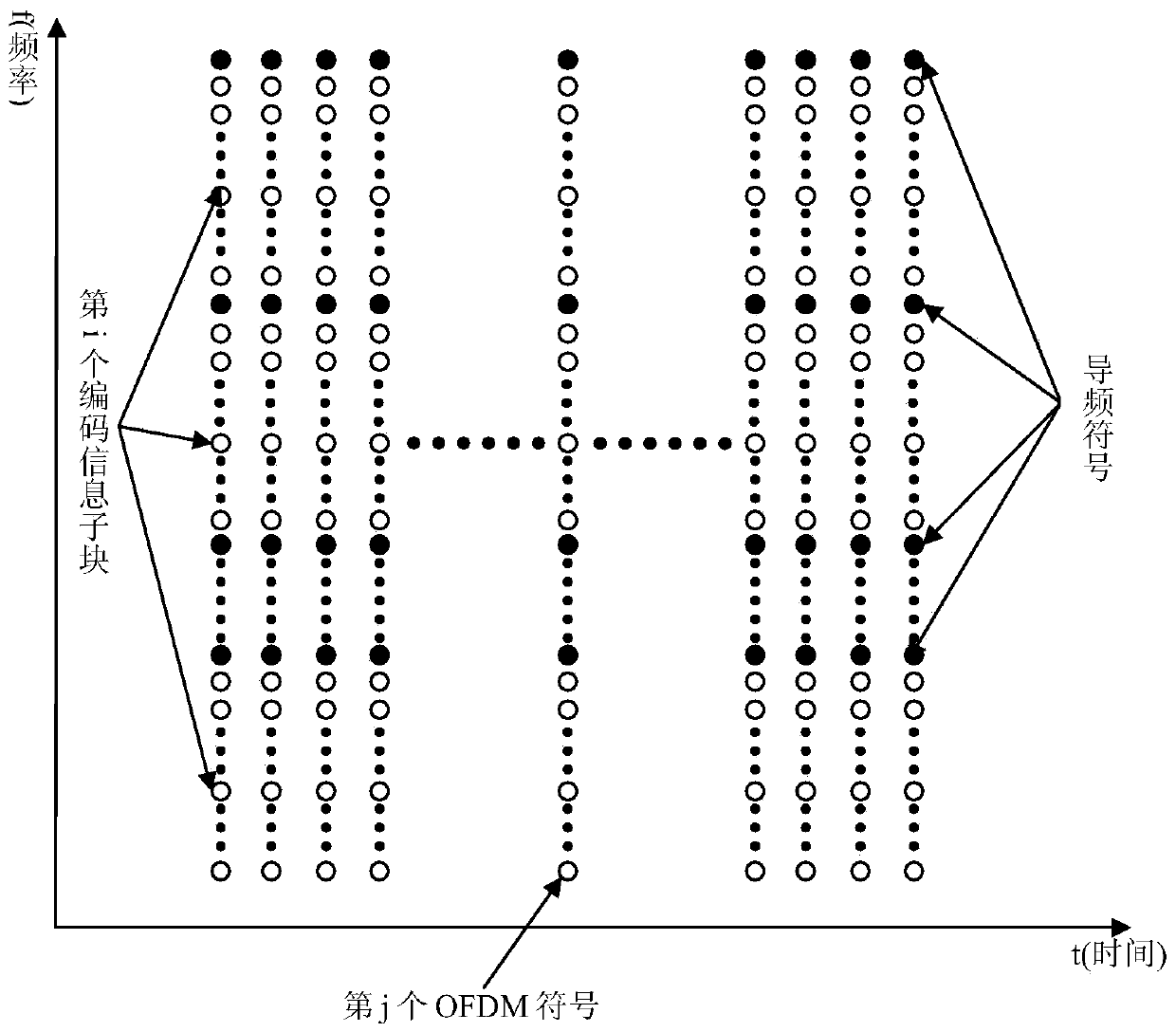
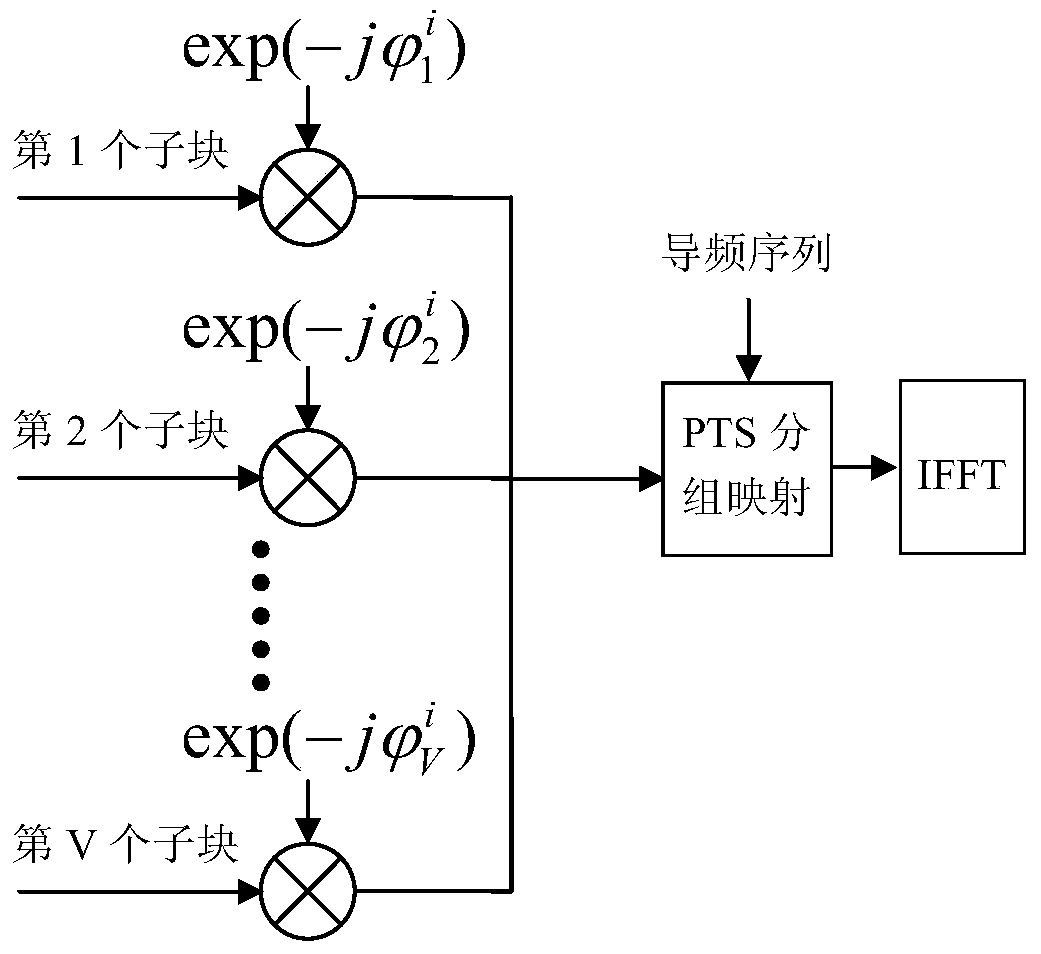
Method for suppressing OFDM communication signal peak-to-average power ratio based on PTS technology
ActiveCN105187354AAvoid efficiencyReduce riskMulti-frequency code systemsPhase correctionPhase mapping
The invention discloses a method for suppressing an OFDM communication signal Peak-to-Average Power Ratio (PAR) based on a PTS technology. A transmitting end generates an OFDM signal with a low PAR, and encoding and modulating steps include: (1) after performing scrambling processing on an information bit stream to be transmitted, feeding into a convolutional code encoder, and completing PSK phase mapping of a bit output by the encoder; (2) feeding a code element phase sequence into K*V-dimensional row-column interleaver to complete interleaving, and building a K*V-dimensional matrix, wherein K=N / (V+1), and N is the number of subcarriers of OFDM symbols; and (3) taking out code element phases of the K*V-dimensional matrix to form V subblocks of a size K, multiplying by exp(j(phi<h>)) to perform phase correction, performing OFDM modulation, and using optimal phase grouping to generate an OFDM signal with a minimum PAR again as a transmitting signal, thereby realizing PAR suppression. The method for suppressing the OFDM communication signal PAR based on the PTS technology has the beneficial effect that original information can be restored without using side information.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Phase mapping for QPSK/QBL-MSK waveform
ActiveUS7822100B2Reduce complexityReduce degradationModulated-carrier systemsRadio transmissionPhase mappingWave shape
A method of pulse shaping a spread signal of serially formatted in-phase (I) and quadrature (Q) waveforms, where each waveform includes a predetermined number of chips per symbol, includes (a) examining adjacent chips of the I and Q waveforms at a symbol boundary; and (b) determining that one of the I or Q waveforms, includes two adjacent first and second chips separated by a single chip period, where the first chip belongs to a previous symbol and the second chip belongs to a present symbol. If the chips are of the same value, the method extends a peak value between the first and second chips, and zeros the other waveform of the I or Q waveform during the extended duration. If the chips are of opposite values, then the method zeroes one of the chips and inserts a chip into the other waveform.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
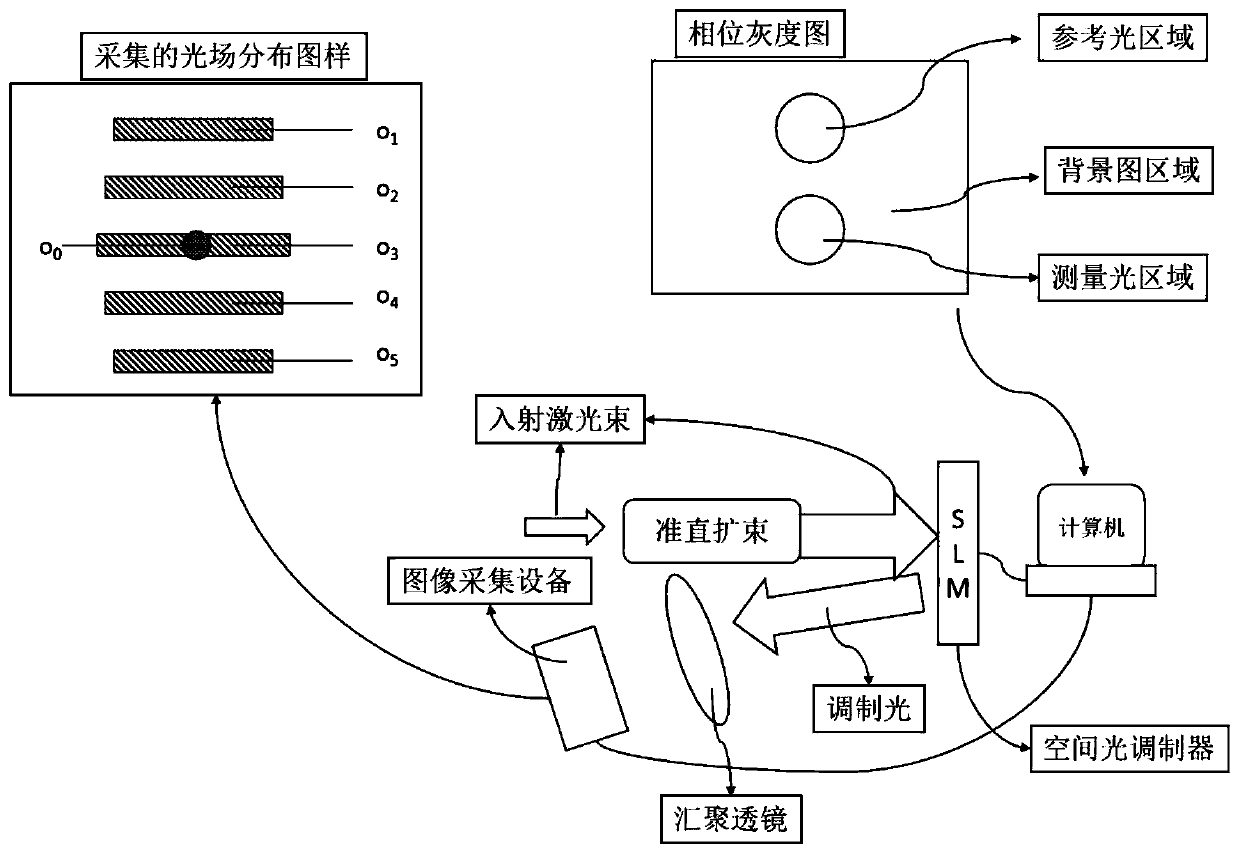
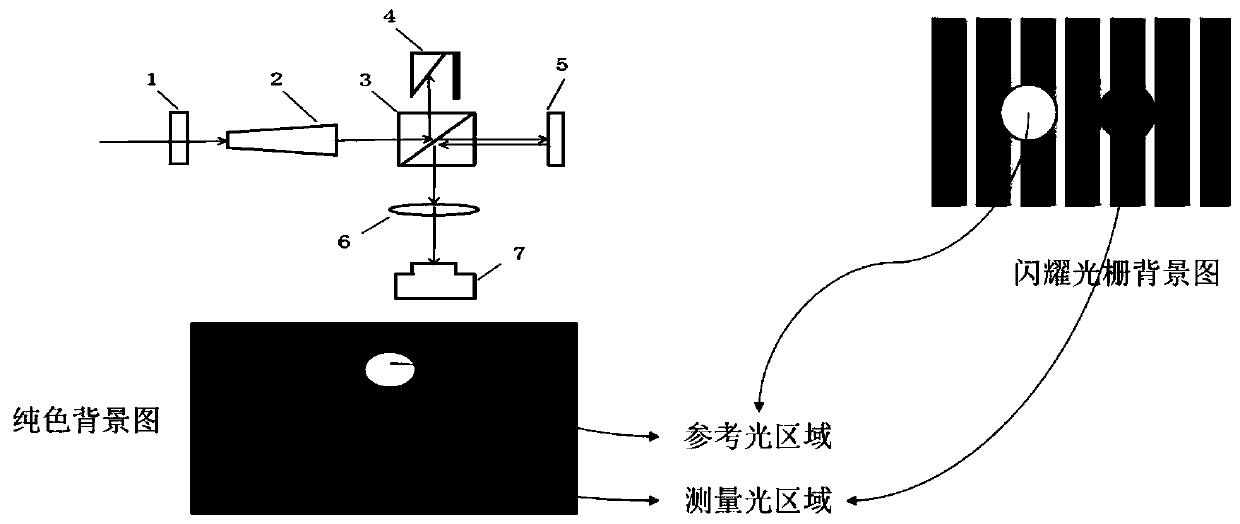
General calibration method for phase measurement of spatial light modulator
The invention discloses a general calibration method for phase measurement of a spatial light modulator. The method comprises the following steps: (a) generating a phase grey-scale map, and collectinga light field distribution map; (b) when the image quality is judged to be good manually, generating a 0-255 phase grey-scale map; (c) periodically, circularly and sequentially loading, automaticallycollecting a light field distribution diagram, calculating fringe and zero-order centroid offset, and further calculating a gray-scale phase mapping table; (d) carrying out data fitting on the gray-scale phase mapping table, carrying out comparative analysis on the data fitting and expected gray-scale phase mapping, if the data fitting and the expected gray-scale phase mapping meet the expectation, finishing calibration, and if not, performing Gamma correction on the acquired and calculated data and the expected data to form a new Gamma mapping table, and returning to the step (c) when writing the new Gamma mapping table into the Gamma mapping table until the calibration is completed.
Owner:SHANGHAI REALIC INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
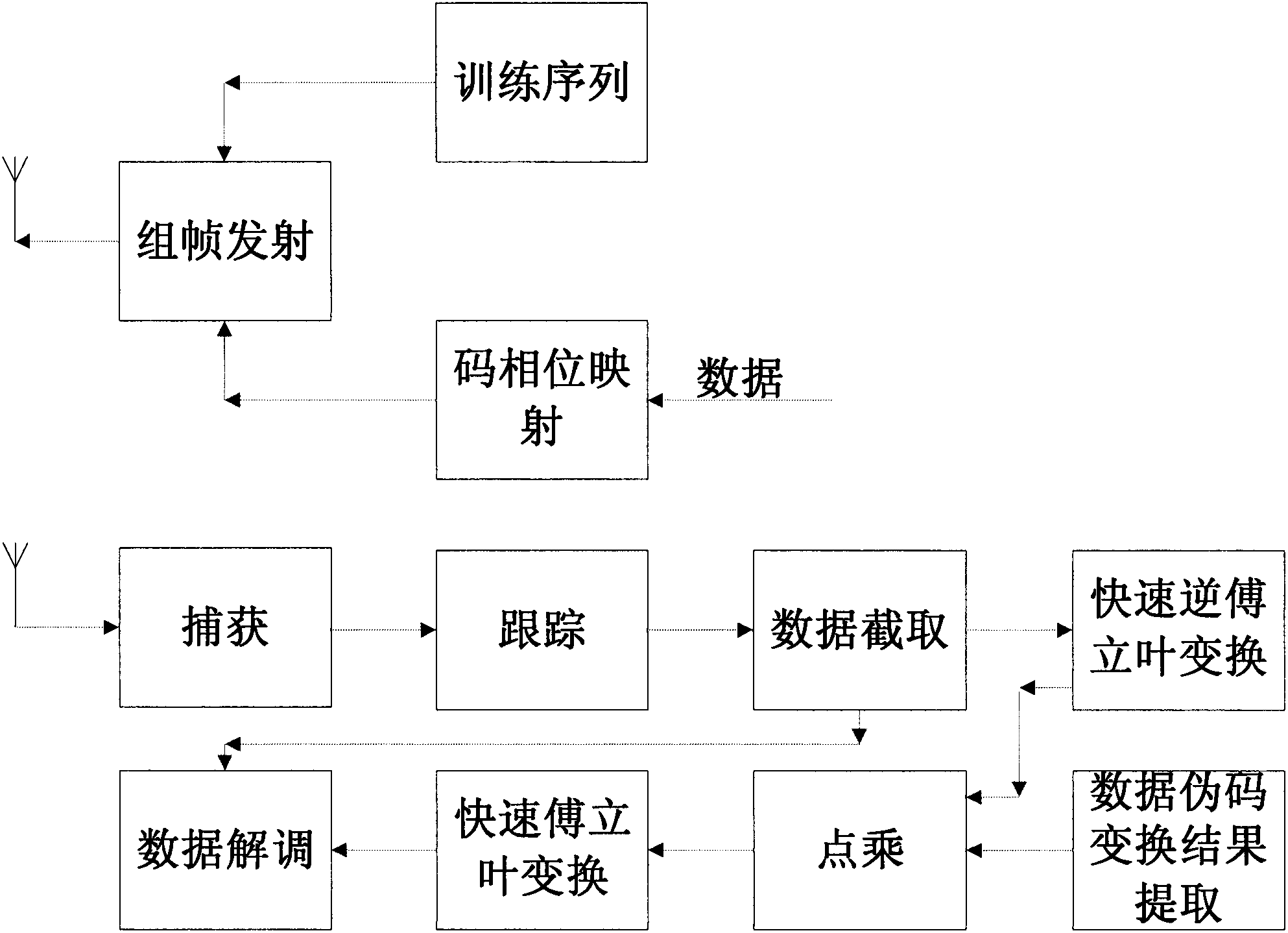
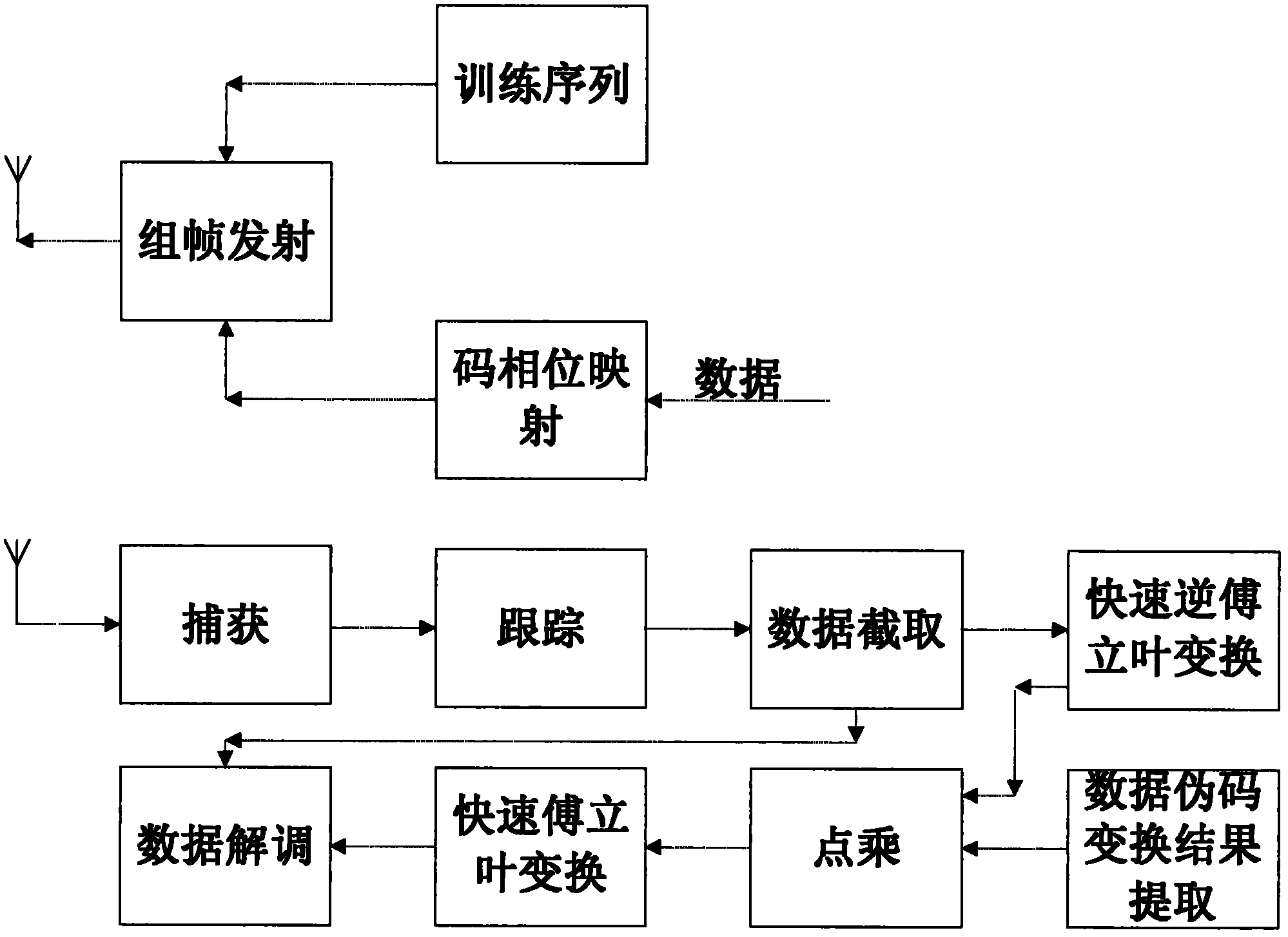
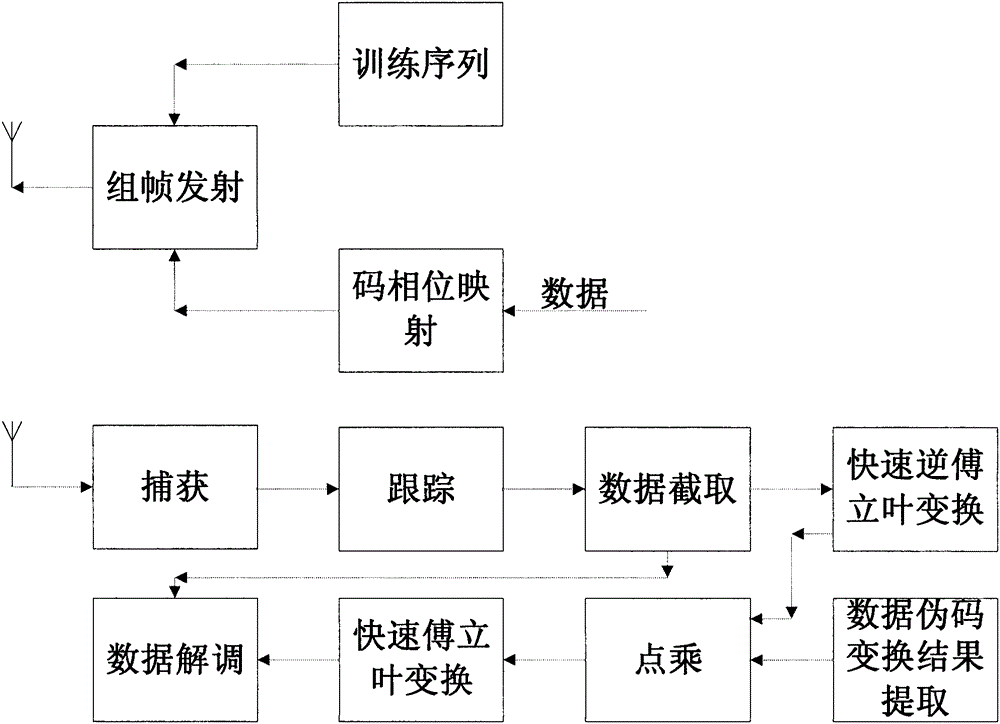
Tamed spread spectrum communication system based on fast Fourier transformation
ActiveCN102510298AIncrease resourcesIncrease the number ofBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsTelecommunicationsPhase mapping
The invention discloses a tamed spread spectrum communication system based on fast Fourier transformation. The tamed spread spectrum communication system comprises a training sequence module, a code phase mapping module, a framing transmitting module, a capturing module, a tracking module, a data interception module, a fast inverse Fourier transformation module, a point multiplication module, a fast Fourier transformation module, a data pseudo code transformation result extraction module and a data demodulation module. By adoption of the tamed spread spectrum communication system, the code length of a spread spectrum code is not limited by the number of correlators, and anti-interference capacity and confidentiality are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
OFDM-based anonymous communication waveform generation method
InactiveCN106101047AAchieve the effect of concealmentMulti-frequency code systemsPhase mappingGuard interval
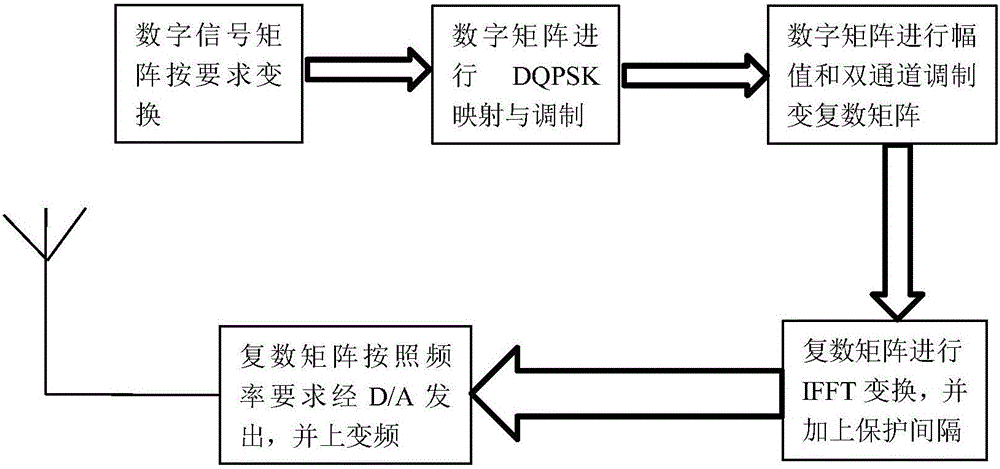
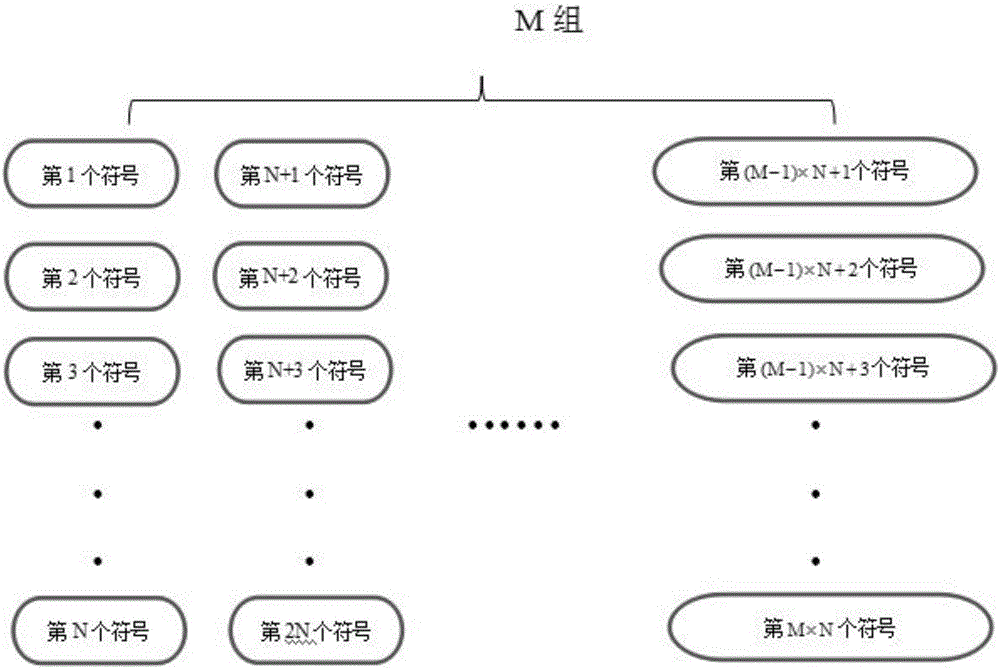
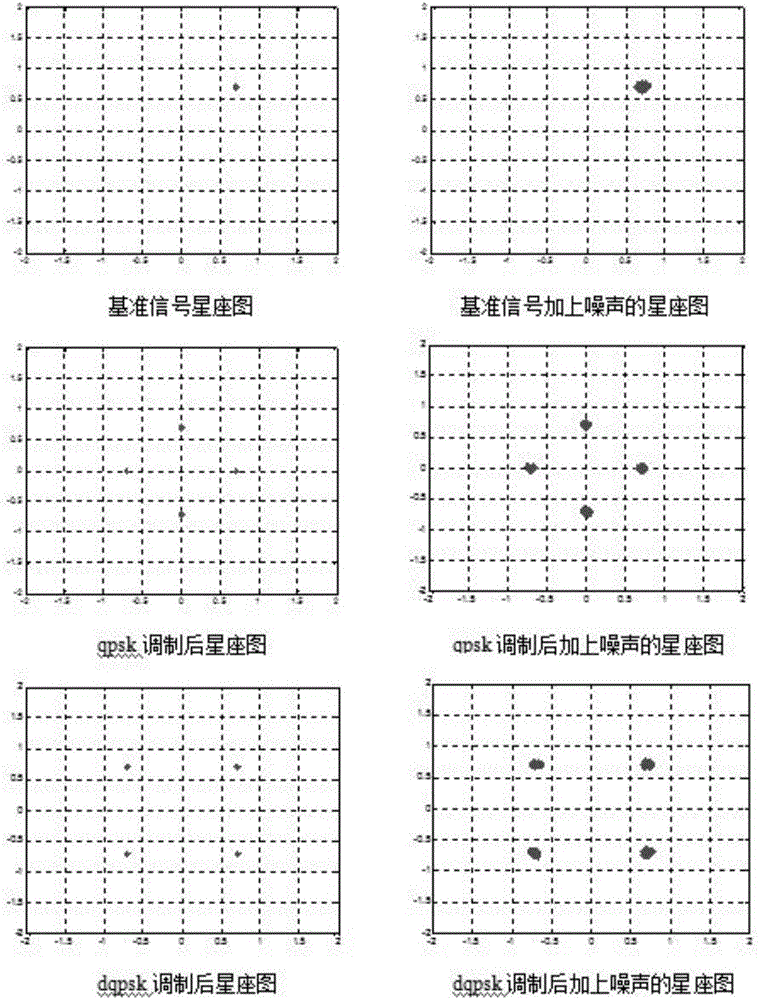
The invention provides an OFDM-based anonymous communication waveform generation method. The method comprises the following steps: S1, defining the total number of OFDM channels N and the number of OFDM channels for actual signal transmission n for digital signals, and carrying out serial-to-parallel conversion grouping according to the number of OFDM carriers and the QPSK signal mode; S2, carrying out phase mapping on the basis of digital symbols in the QPSK signal format; S3, carrying out IFFT conversion for a plurality of generated symbol matrixes in the DQPSK format, modulating the digital signals to the corresponding carriers so as to form digital multi-carrier symbol matrixes, and carrying out additional guard interval processing and additional noise processing of each frame of the matrixes; and S4, forming emitting digital symbol row matrixes, and finally carrying out digital-to-analogue conversion to form communication signals based on the DQPSK and the OFDM digital modulation modes. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that a flexible selection of the channels can achieve the anonymous effect, so that communication decryption is difficult; and the internal signal modulation mode of communication adopts the DQPSK modulation mode.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
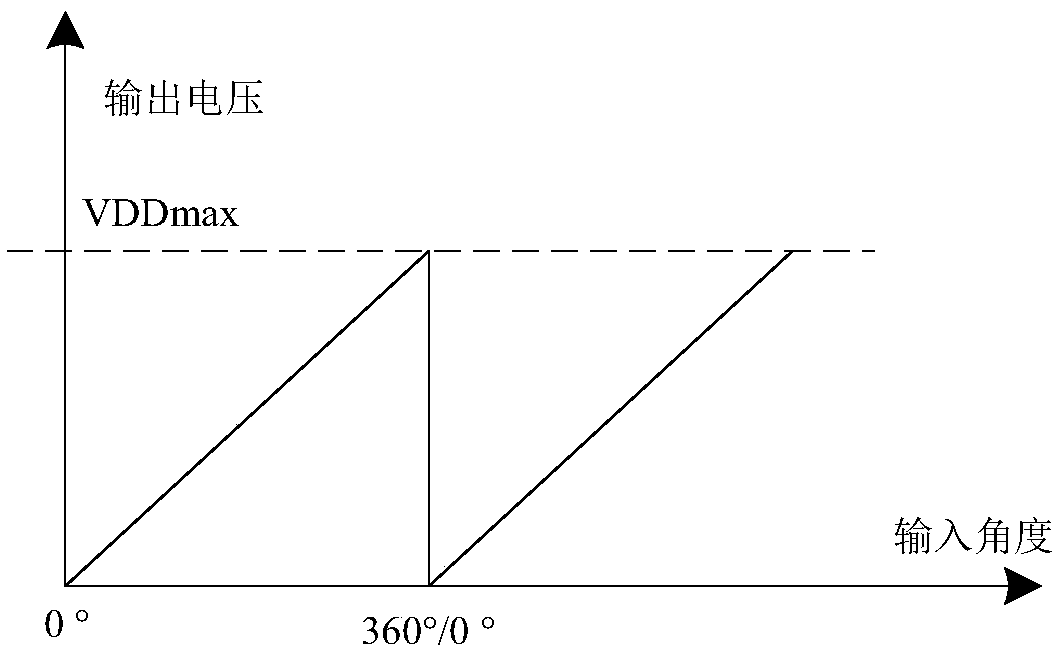
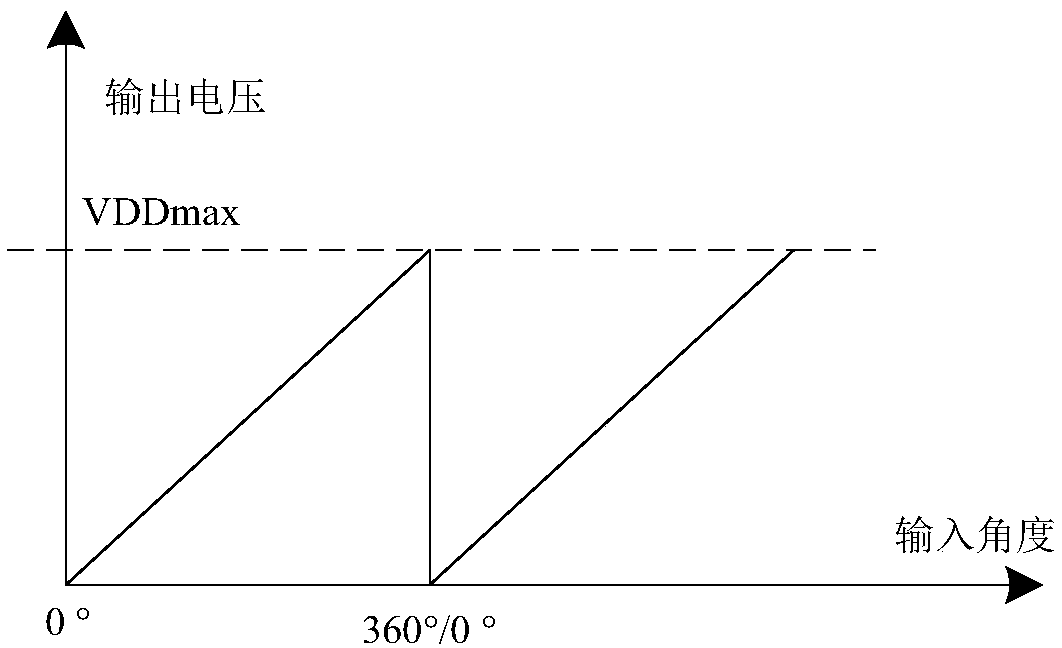
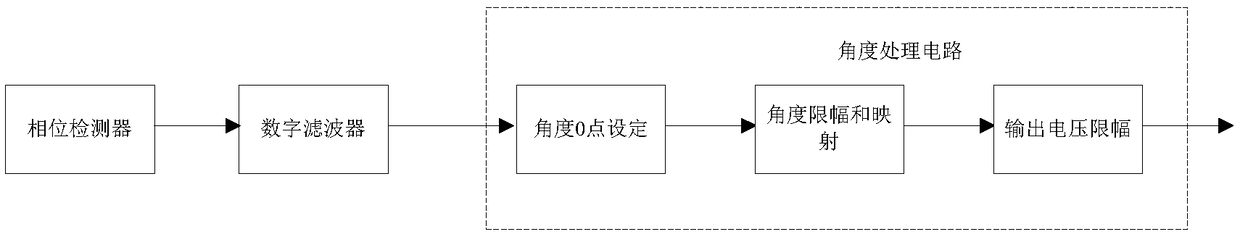
Digital implementation architecture of absolute magnetic angle encoder
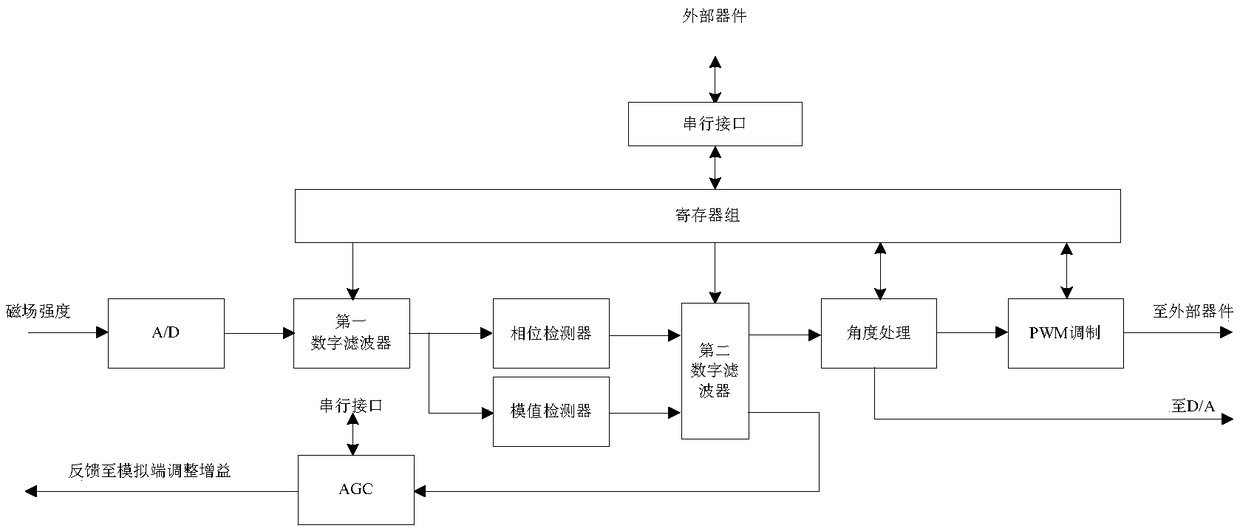
InactiveCN109506680AClear and simple digital architectureImprove Angle Detection AccuracyConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyPhase detectorComputer architecture
The invention discloses a digital implementation architecture of an absolute magnetic angle encoder. The digital implementation architecture involves the digital terminal processing steps: convertinganalog terminal data into digital signals via A / D (analog / digital) conversion, correcting with a first digital filter, processing with a phase detector, processing with a module detector, smoothing and filtering with a second digital filter, processing with an angle processing module, and allowing PWM (pulse width modulation) modulated output or D / A output. The digital implementation architecturehas inherent advantages of an absolute encoder; the angle output range can be optionally adjusted; phase mapping and zooming of the optional angle range from 0 degrees to 360 degrees are achieved. Thedigital implementation architecture is clear and simple, has high angle detection precision, stable power and high anti-interference capacity, and allows the angle limit range and output voltage limit range to be optionally adjusted according to configurations so as to meet the different actual application needs.
Owner:CROSSCHIP MICROSYST
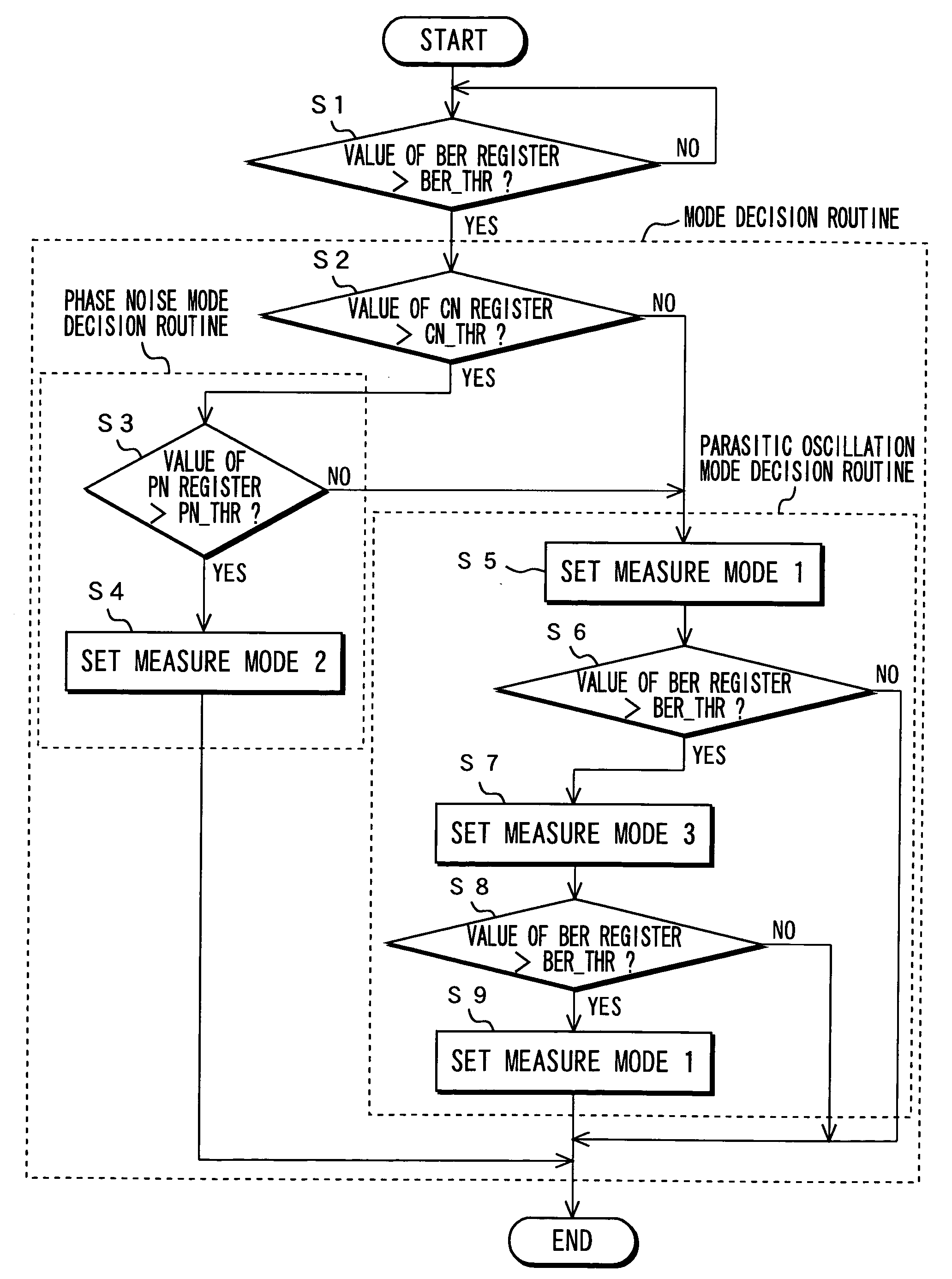
Digital broadcast receiving apparatus and receiving method
InactiveUS20070060184A1Deterioration of characteristicImprove deteriorationTelevision system detailsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorPhase noisePhase mapping
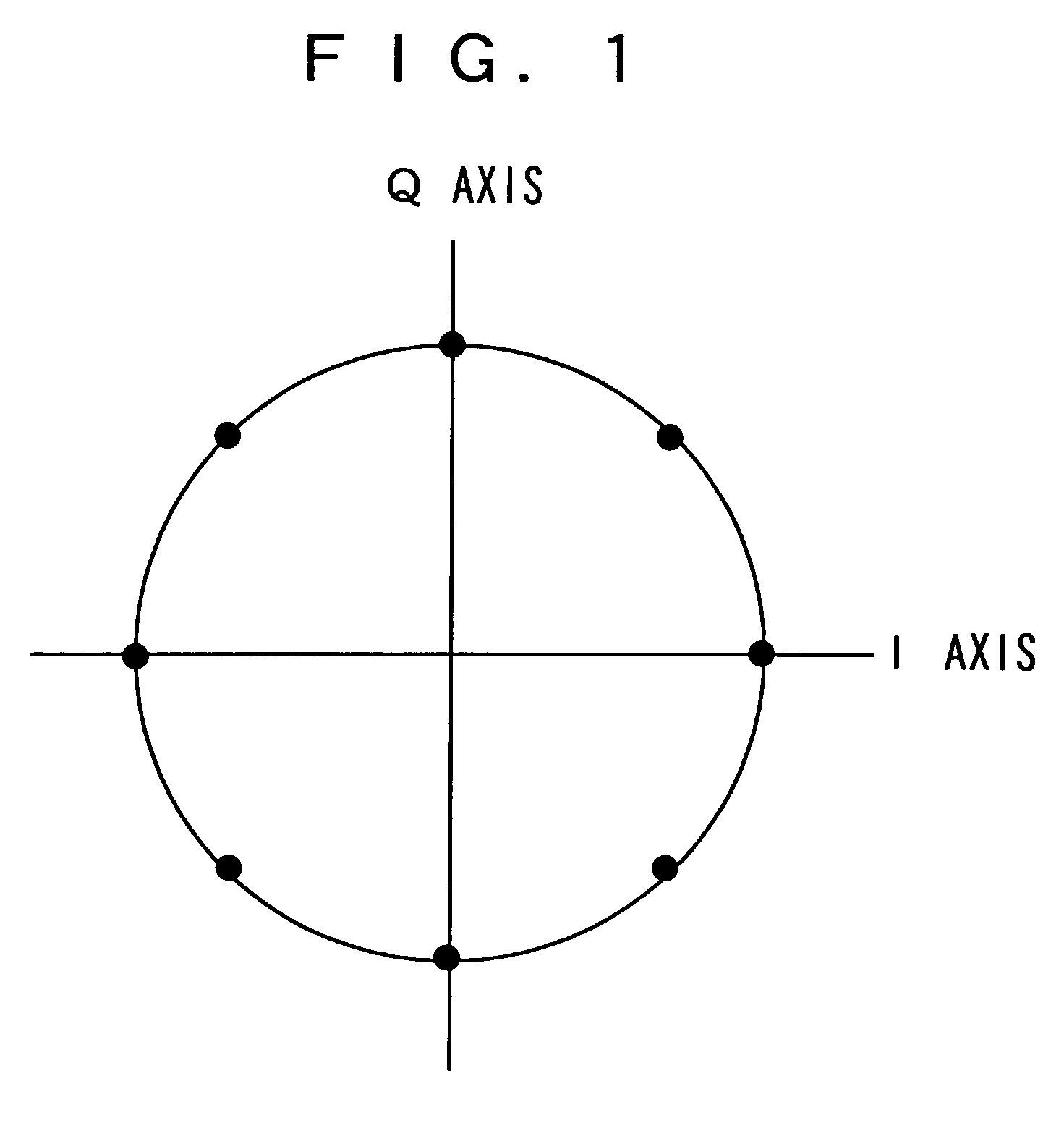
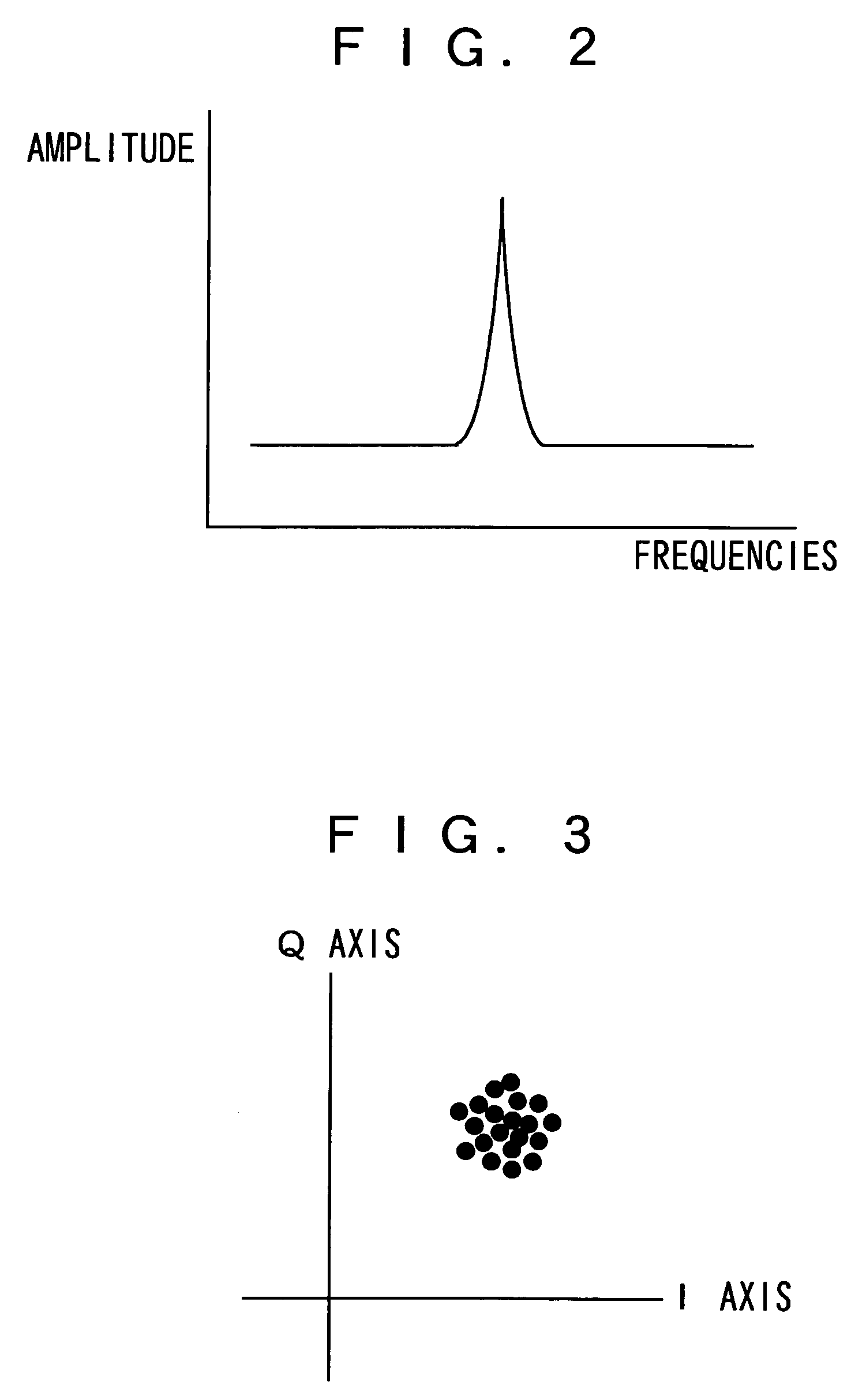
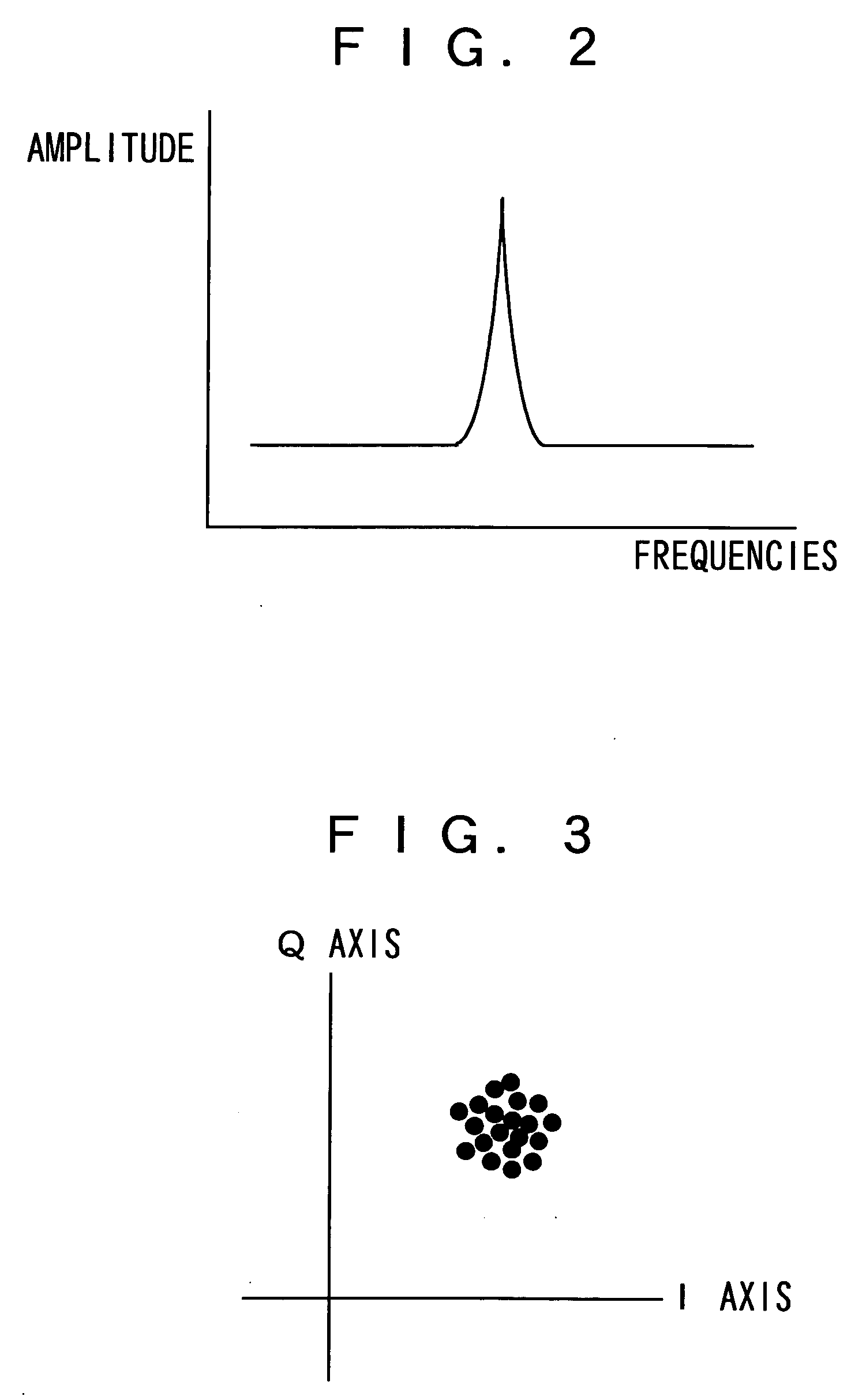
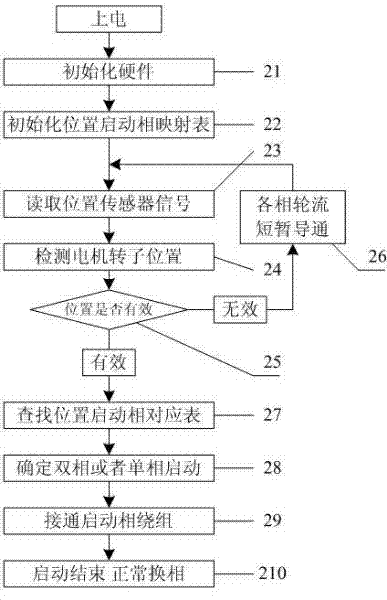
This invention allows a factor in deterioration for receiving characteristics of the antenna to be automatically determined and the deterioration for receiving characteristics to be automatically improved. In an apparatus 100 for receiving digital broadcast signal, when receiving the signal, a received signal sent from the antenna 1 is orthogonally detected to a baseband signal; an average value of amplitude in radial direction of signal points of phase mapping of the baseband signal is then measured to calculate a C / N value for the received signal; an average value of amplitude in circumferential direction of signal points of the phase mapping of the baseband signal is measured to calculate an amount of phase noise of the received signal; a bit-error rate of transport stream that is given by demodulating the baseband signal is then measured; a factor in deterioration for receiving characteristics of the antenna is determined based on these results; and a desired measure mode is set based on the determination result thereof.
Owner:SONY CORP
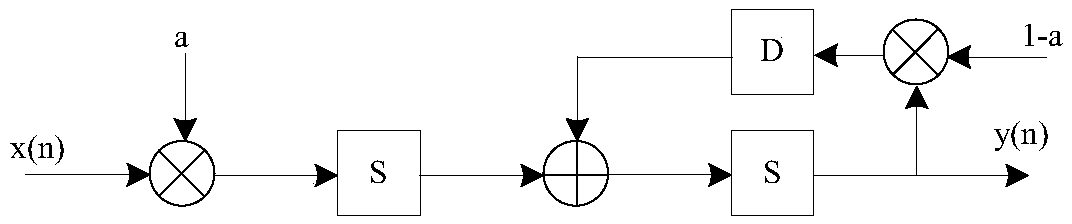
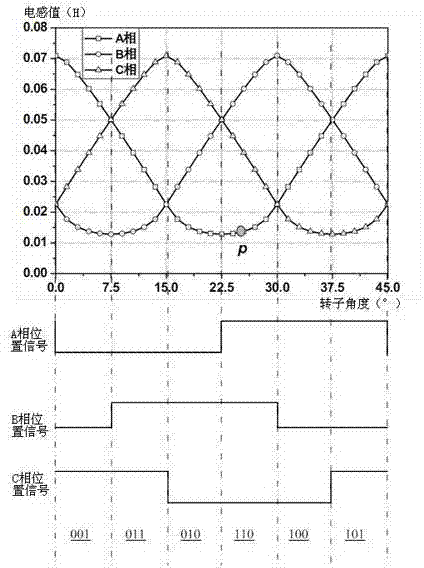
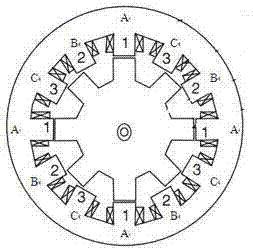
Method for launching three-phase switched reluctance motor (SRM)
InactiveCN102082536BIncrease starting torqueClear structureStarter arrangementsPhase mappingElectric machine
The invention discloses a method for launching a three-phase switched reluctance motor (SRM), which is characterized in that when a system is initialized, a position signal and a starting phase mapping table are built and initialized; when a motor is started, the position signal and the starting phase mapping table are searched in accordance with a rotor position; if the rotor of the motor is arranged at a position in which inductance variation is smaller, a two-phase starting mode is adopted; and if the rotor of the motor is arranged at a position in which inductance variation is larger, a one-phase starting mode is adopted. In the method, aiming at different rotor positions at the time of startup, the position signal and the starting phase mapping table are built; and by searching and determining an existing starting phase in the mapping table, the starting torque of the SRM is improved. Meanwhile, the method provided by the invention is clear in structure, strong in anti-interference and easy to realize.
Owner:南通通微电机科技有限公司 +1
Tabular phase mapping for cycle time reporting
A method, computer program product, and a computer system is provided. A processor receives a workflow, where the workflow includes a plurality of processes. A processor generates an enumerated list corresponding to the plurality of processes of the workflow. A processor maps a plurality of workflow snapshots to a value in the enumerated list. A processor generates a table, where the table comprises rows of a plurality of work requests and columns of the mapped plurality of workflow snapshots. A processor determines one or more open cycle times for open processes of the plurality of work requests. A processor determines one or more closed cycle times for closed processes of the plurality of work requests. A processor displays a report including the table, the one or more open cycle times, and the one or more closed cycle times.
Owner:IBM CORP
QPSK -to-BPSK all-optical modulation format conversion system based on DPMZM
ActiveCN111541490AIncrease symbol rateSimple structureElectromagnetic transmissionHigh level techniquesTelecommunicationsPhase mapping
The invention relates to a QPSK-to-BPSK all-optical modulation format conversion system based on DPMZM, and belongs to the technical field of communication. The system includes: a phase mapping mode of performing QPSK-to-BPSK format conversion based on FWM, a DPMZM bias point setting and electric signal input mode for QPSK-to-BPSK format conversion based on FWM; a signal processing mode for QPSK-to-BPSK format conversion based on FWM, and a signal extraction mode after QPSK-to-BPSK format conversion based on FWM. According to the system, as long as limit parameters of used devices allow, the symbol rate of input signals can be directly improved without changing the structure of the system; i-path and Q-path signals can be simultaneously converted and directly demodulated, a coherent receiver and a phase-locked loop are prevented from being used, and the system is simple in structure.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and device for measuring vector amplitude error for TD-SCDMA equipment testing
The invention relates to a method and a device for measuring a vector magnitude error for TD-SCDMA equipment testing, wherein a receiving device filters a received signal, divides data into 24 groups, and selects two groups of data in the middle to calculate. The calculation comprises that: a frequency deviation removing device is used to remove a phase error generated by frequency deviation in a signal; a phase correction device corrects the phase of the signal to correct an error of an initial phase; then, a module value of the signal is subjected to normalization processing to acquire a normalized measurement signal Z; the signal is divided into three types according to the magnitude of the module value of the signal and calculated, the equalizing value of the three types projected on coordinate axes are respectively calculated; the equalizing value is used as a module value of an ideal signal to acquire a reference signal R through phase mapping; a value of EVM is calculated according to a formula as a diagram; and the result with the smaller numerical value in two calculating results is taken as the EVM value of the signal.
Owner:湖北众友科技实业股份有限公司
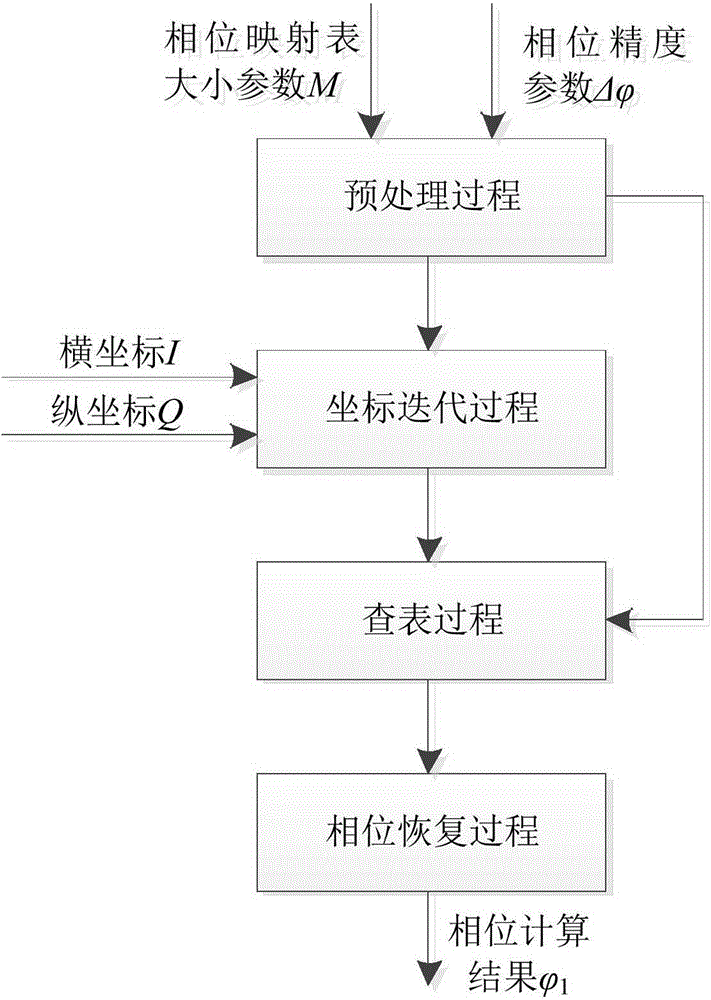
Calculation method with high-accuracy phase and small-memory capacitance lookup
ActiveCN104636632AReduce capacityLow phase resolutionSpecial data processing applicationsCapacitancePhase mapping
The invention provides a calculation method with a high-accuracy phase and the small-memory capacitance lookup. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the calculation method comprises the following steps: firstly, pretreatment process, namely, calculating the quantization position width and an iteration number value of a target point coordinate value, and constructing a phase mapping table; secondly, coordinate iterative process, namely, calculating a lookup coordinate of a target point; thirdly, lookup process, namely, looking up a phase value corresponding to the coordinate by utilizing a phase mapping table; and fourthly, phase retrieval process, namely, calculating a final phase result. The calculation method is capable of greatly improving the phase calculation accuracy under the condition of same memory capacitance with a phase mapping table in a traditional lookup table method, or greatly reducing the scale of the phase mapping table under the condition of keeping the same phase calculation accuracy, or simultaneously greatly improving the phase calculation accuracy and greatly reducing the scale of the phase mapping table.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Uplink multiple access method capable of automatically adapting to channel characteristic variation
InactiveCN101783782BReduce distractionsSmall distortionMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexSystem capacityFrequency spectrum
The invention belongs to an uplink multiple access technology capable of automatically adapting to channel characteristic variation in network access technologies. The invention comprises system initialization processing, which includes the following processes: a transmitting end: selecting a shaping filter matched with the characteristics of the current channel, quadrature amplitude modulating the send information, zero insertion processing, orthogonalization phase mapping, multi-carrier modulating, signal shaping and sending the signal; and a receiving end: processing the receiving signal, selecting the shaping filter matched with the characteristics of the channel, multi-carrier modulating, de-orthogonalization phase mapping, extracting valid data, isostatic compensating and storing the data. Because OQAM (technology) is introduced into OFDMA (technology) and the shaping filter with good time-frequency focusing characteristic is adopted to substitute for cyclic prefix, the invention has the characteristics of effectively improving the spectrum efficiency, system capacity and data transmission performance and resisting Doppler expansion, reducing the disturbance between users and distortion of the signal in the channel, better satisfying the requirement of high-speed mobile communications and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A method of suppressing the peak-to-average ratio of ofdm communication signals based on pts technology
ActiveCN105187354BAvoid efficiencyReduce riskMulti-frequency code systemsPhase correctionSide information
The invention discloses a method for suppressing an OFDM communication signal Peak-to-Average Power Ratio (PAR) based on a PTS technology. A transmitting end generates an OFDM signal with a low PAR, and encoding and modulating steps include: (1) after performing scrambling processing on an information bit stream to be transmitted, feeding into a convolutional code encoder, and completing PSK phase mapping of a bit output by the encoder; (2) feeding a code element phase sequence into K*V-dimensional row-column interleaver to complete interleaving, and building a K*V-dimensional matrix, wherein K=N / (V+1), and N is the number of subcarriers of OFDM symbols; and (3) taking out code element phases of the K*V-dimensional matrix to form V subblocks of a size K, multiplying by exp(j(phi<h>)) to perform phase correction, performing OFDM modulation, and using optimal phase grouping to generate an OFDM signal with a minimum PAR again as a transmitting signal, thereby realizing PAR suppression. The method for suppressing the OFDM communication signal PAR based on the PTS technology has the beneficial effect that original information can be restored without using side information.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
An absolute magnetic angle encoder output voltage control system and method
ActiveCN109217743AFlexible configurationIncrease the angleElectric motor controlVector control systemsRegister allocationPhase detector
The invention discloses an absolute magnetic angle encoder output voltage control system and method, On the basis of conventional angle detection and phase mapping, the invention adds the functions ofangle limiting and electric compression and amplification, which can map to the voltage output of full volt according to the angle range configured by the register, at the same time, the voltage of full volt can be limited, and finally the required output result can be obtained. The invention has the characteristics of small scale, low power consumption, simple control, flexible configuration ofangle limiting range and voltage limiting range, etc. At the same time, the phase detector of the invention can realize the operation processing of arbitrary input precision, the operation result is high in precision, simple in realization and small in area power consumption. Flexible angular and voltage limiting configurations allow multiple ranges of output voltages to be constructed.
Owner:CROSSCHIP MICROSYST
A Timing Parameter Optimization Method for Phase-Phase Signal Control Scheme
ActiveCN109410574BImprove scienceAvoid the Mistakes of EmpiricismControlling traffic signalsDetection of traffic movementPhase mappingControl engineering
The invention discloses a timing parameter optimization method oriented to a phase-phase signal control scheme, comprising the following steps: 1. Obtain lane information, signal control scheme and traffic volume of each lane at a signalized intersection, and generate lane information table and signal allocation 2. Construct the two tables into a lane-phase mapping; 3. Extract the phase-phase distribution table; 4. According to the target saturation of the phase, obtain the demand green signal ratio of each phase; use the saturation of the intersection Taking the degree as the optimization goal, a linear programming equation model is constructed to obtain the optimal cycle duration and green light duration of each stage as the optimization result of the signal timing scheme; 5. Input the optimization result of the signal timing scheme into the intersection traffic signal controller. The invention satisfies the structure of domestic single-ring signal timing scheme, and can realize self-optimization and accuracy of signal timing.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Tamed spread spectrum communication system based on fast Fourier transformation
ActiveCN102510298BIncrease resourcesIncrease the number ofBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsTelecommunicationsPhase mapping
The invention discloses a tamed spread spectrum communication system based on fast Fourier transformation. The tamed spread spectrum communication system comprises a training sequence module, a code phase mapping module, a framing transmitting module, a capturing module, a tracking module, a data interception module, a fast inverse Fourier transformation module, a point multiplication module, a fast Fourier transformation module, a data pseudo code transformation result extraction module and a data demodulation module. By adoption of the tamed spread spectrum communication system, the code length of a spread spectrum code is not limited by the number of correlators, and anti-interference capacity and confidentiality are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com