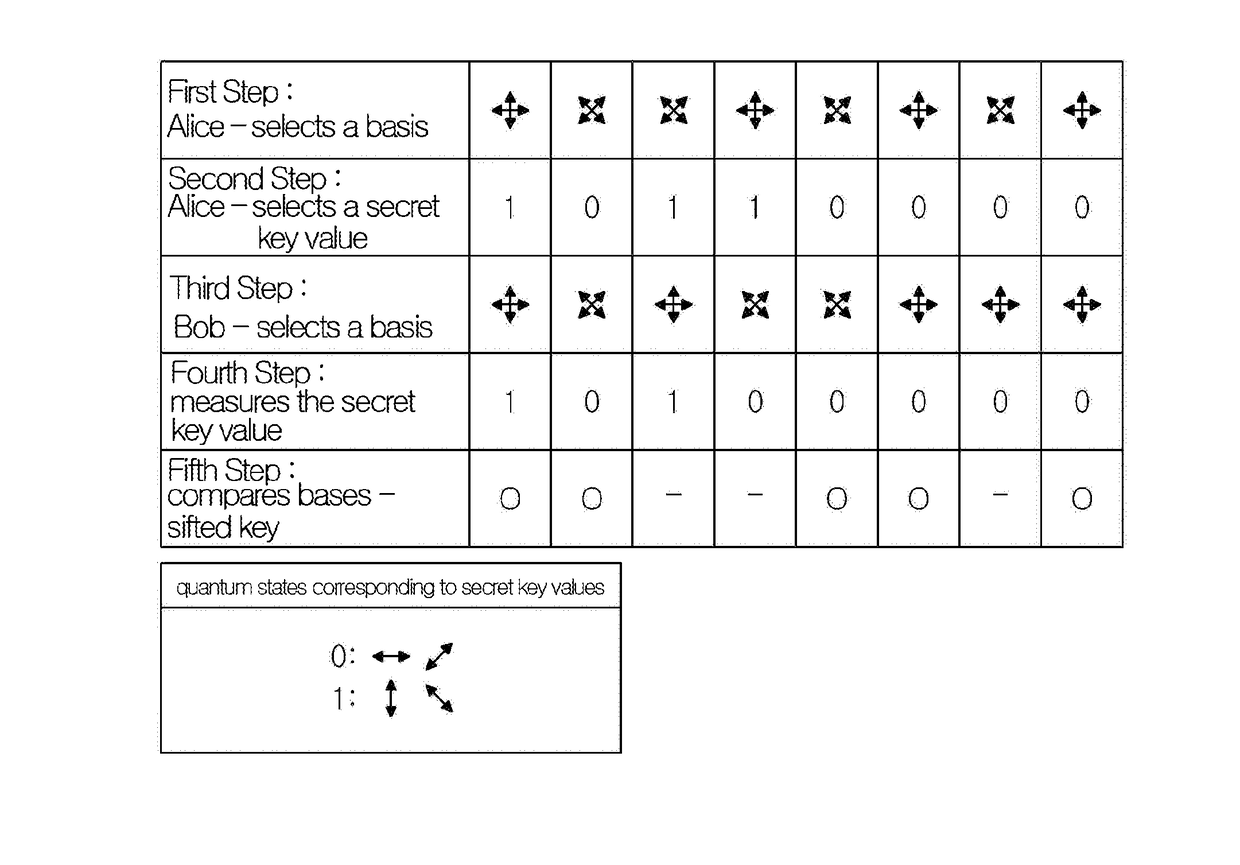
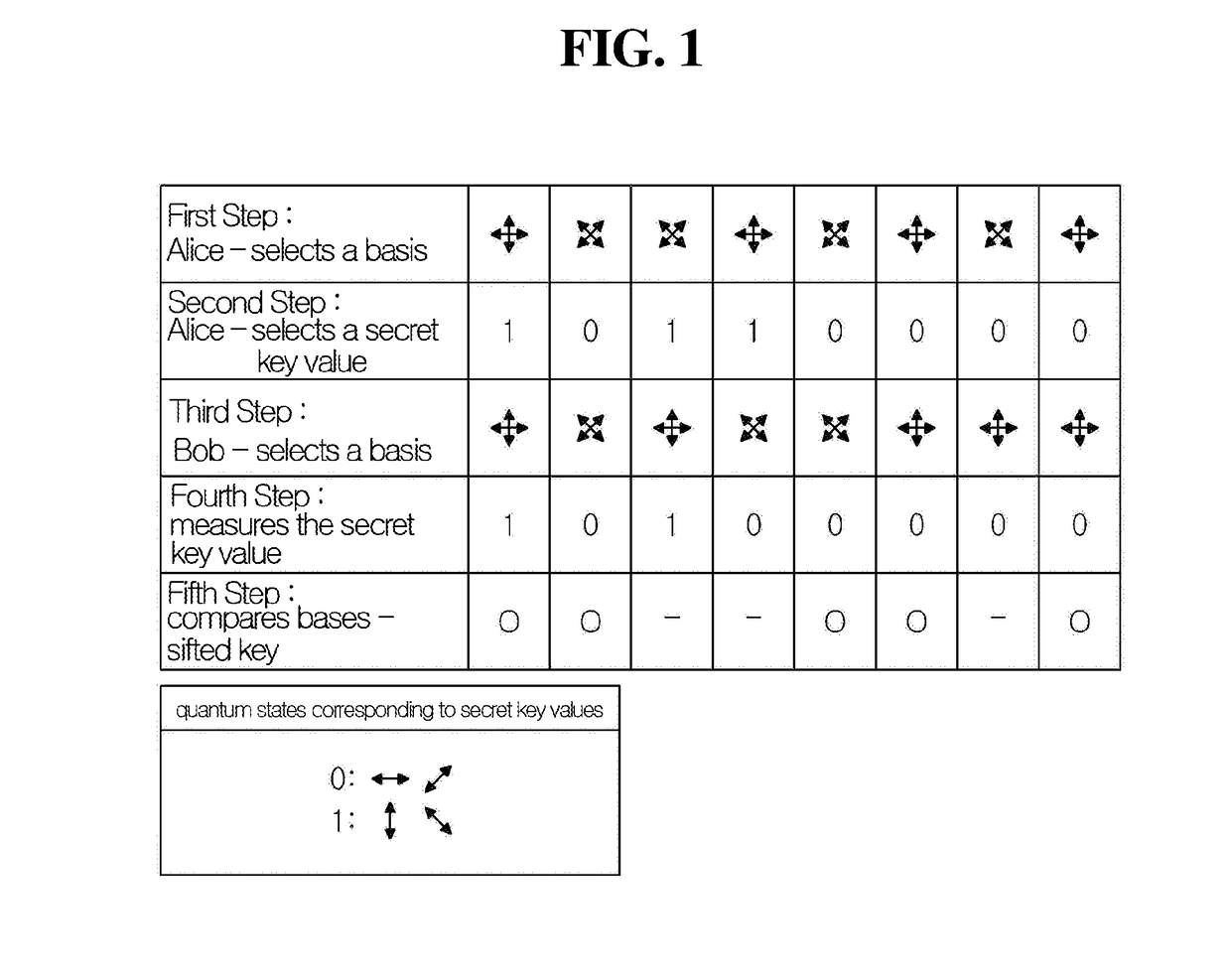
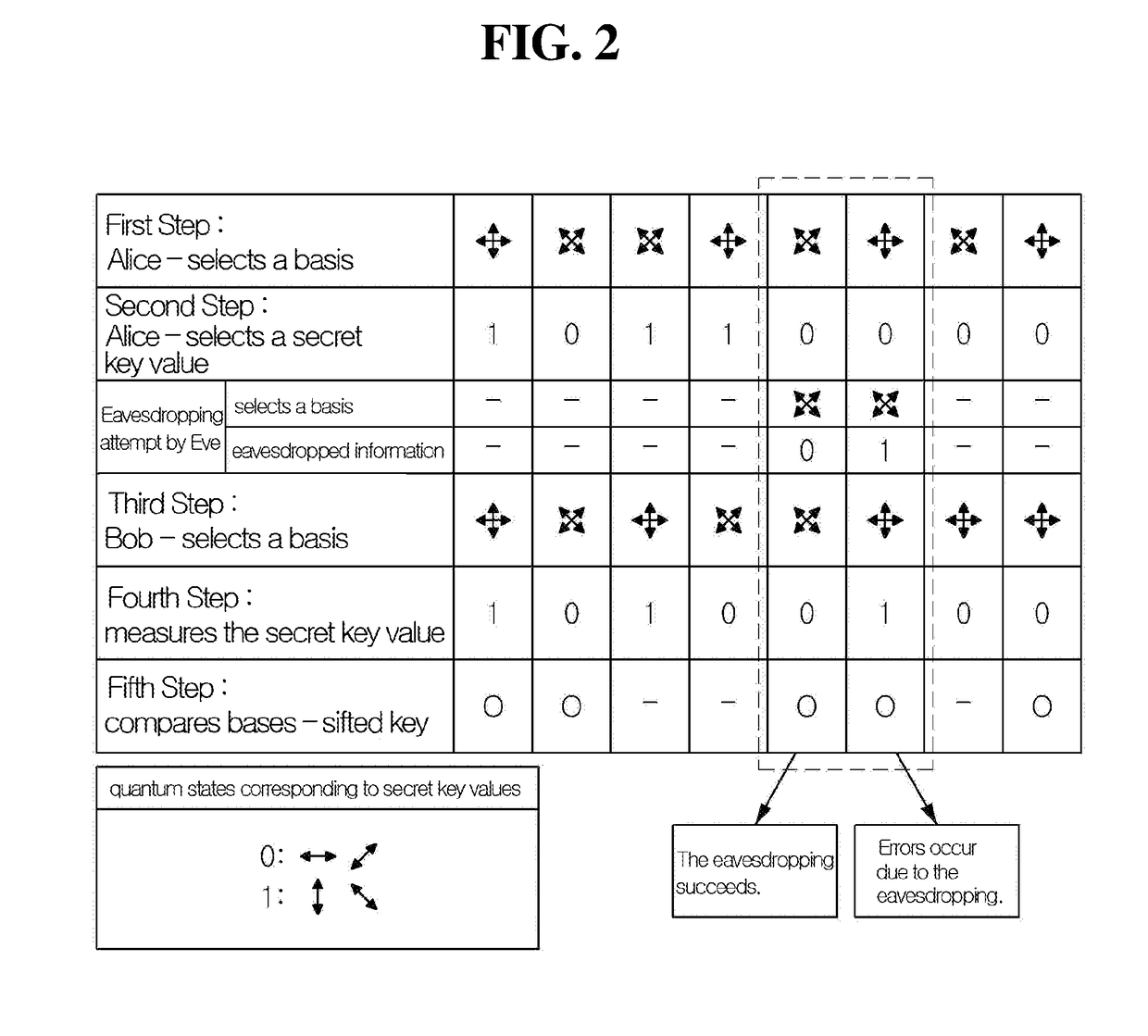
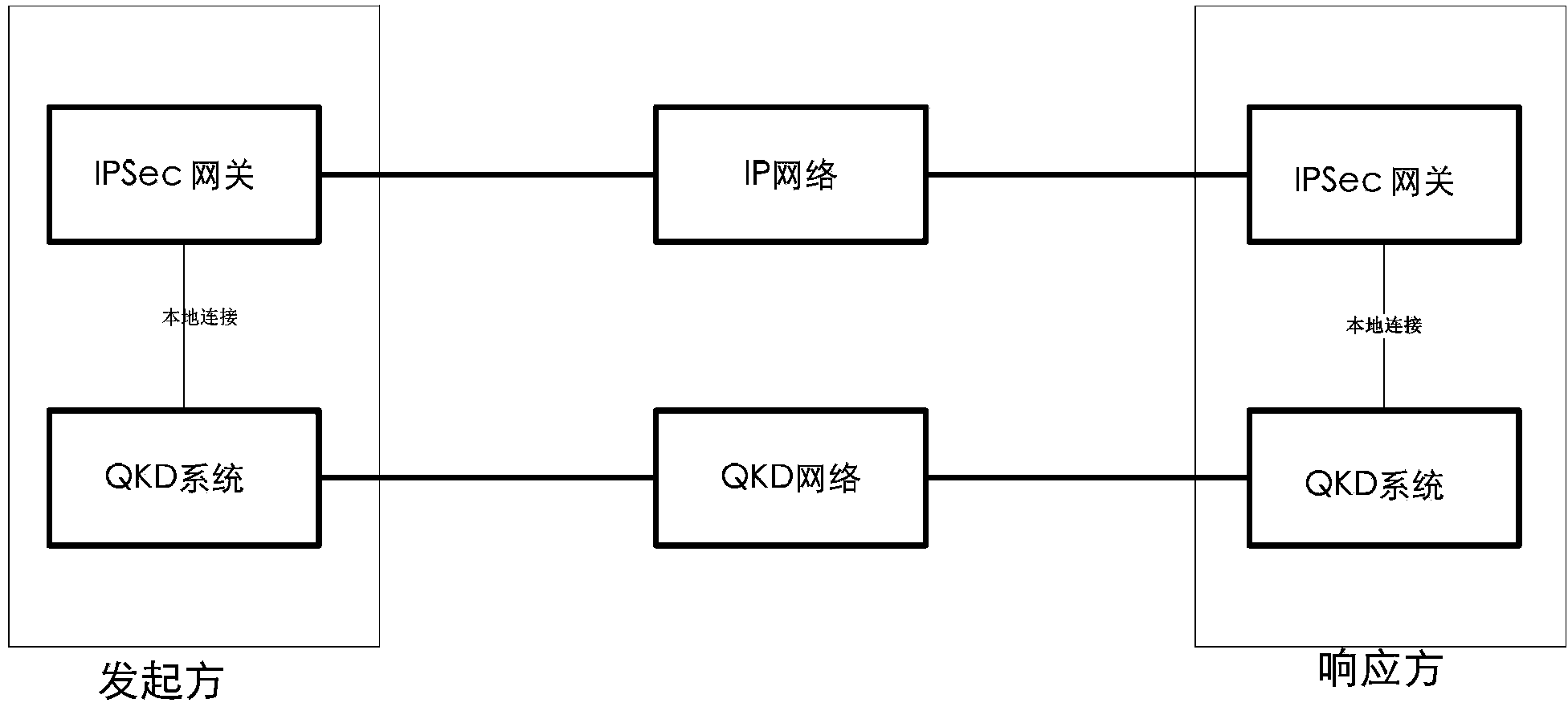
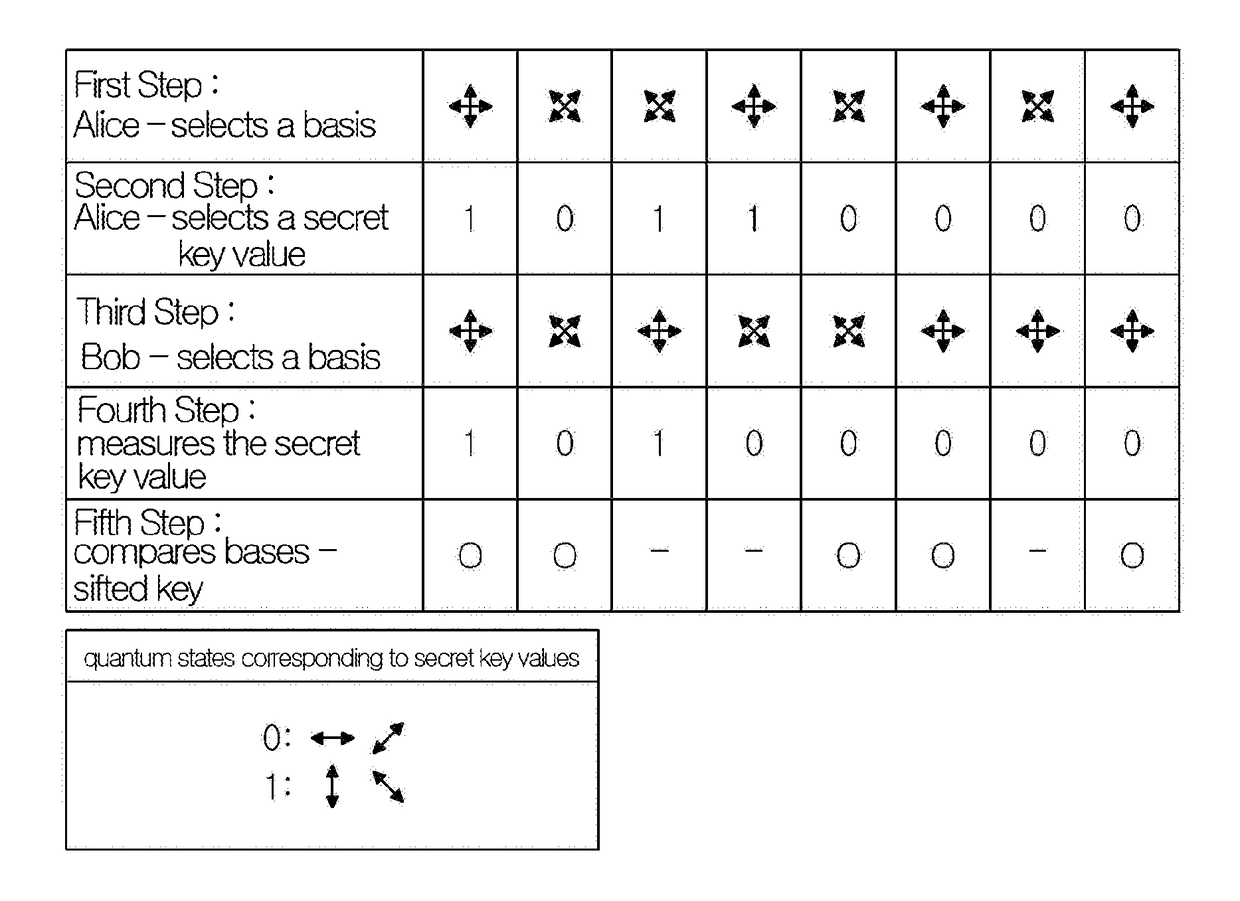
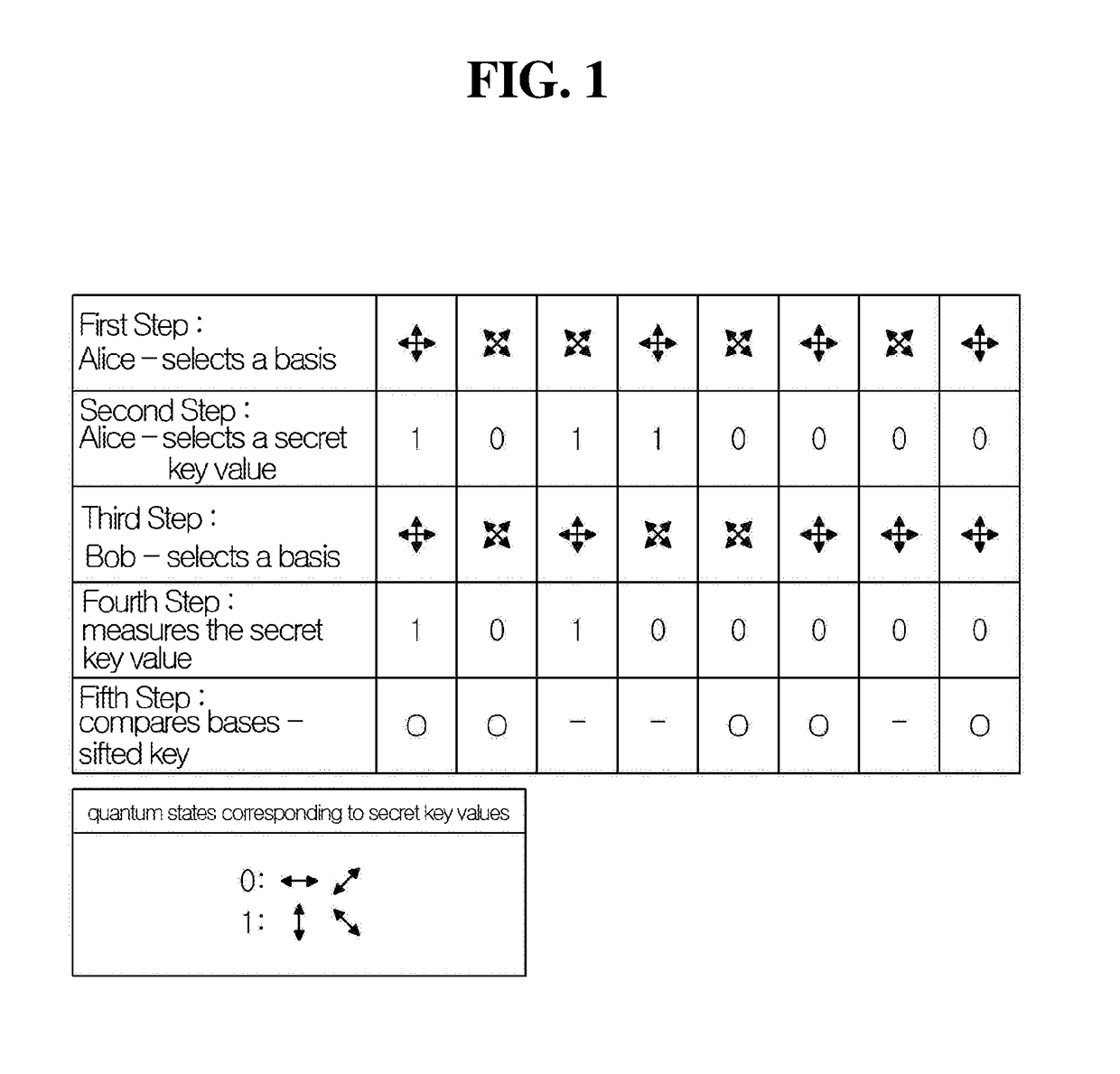
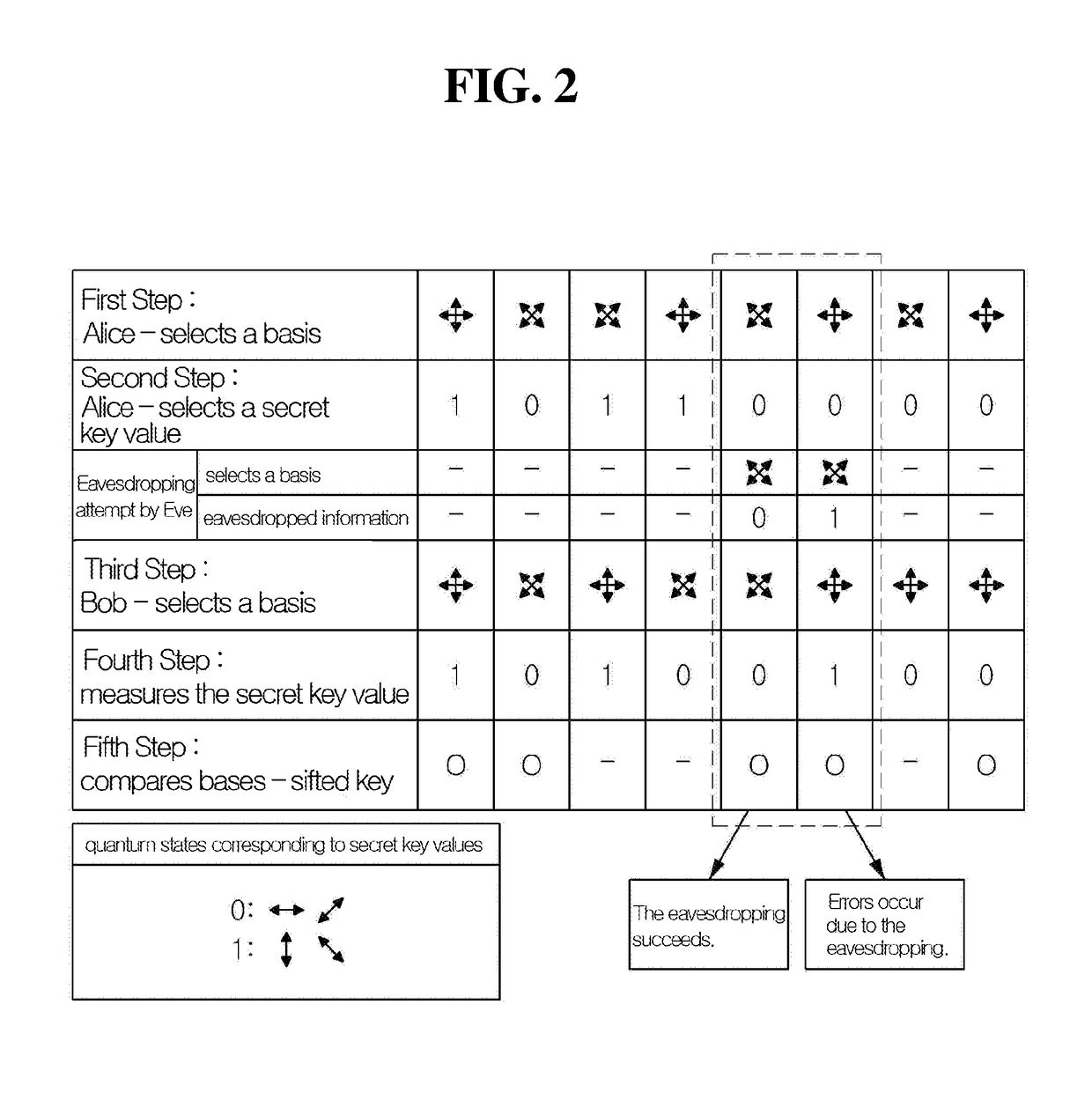
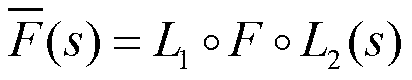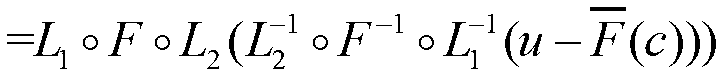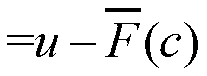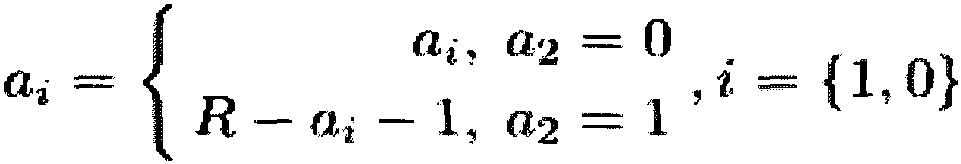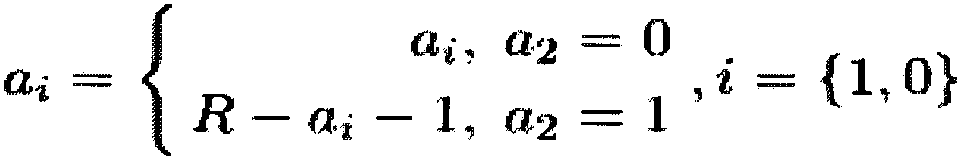Patents
Literature
31 results about "Post-quantum cryptography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
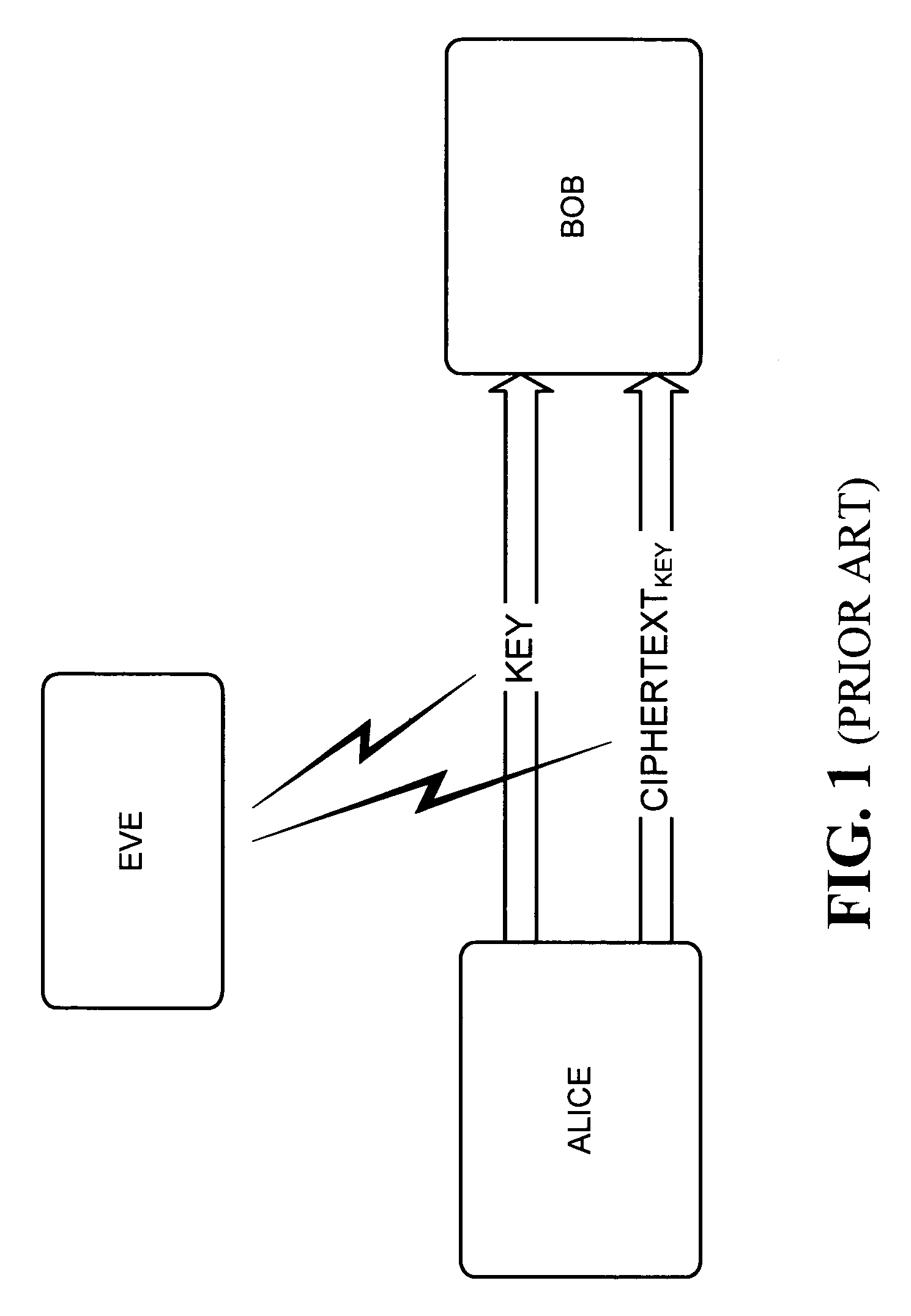
Post-quantum cryptography (sometimes referred to as quantum-proof, quantum-safe or quantum-resistant) refers to cryptographic algorithms (usually public-key algorithms) that are thought to be secure against an attack by a quantum computer. As of 2019, this is not true for the most popular public-key algorithms, which can be efficiently broken by a sufficiently strong quantum computer. The problem with currently popular algorithms is that their security relies on one of three hard mathematical problems: the integer factorization problem, the discrete logarithm problem or the elliptic-curve discrete logarithm problem. All of these problems can be easily solved on a sufficiently powerful quantum computer running Shor's algorithm. Even though current, publicly known, experimental quantum computers lack processing power to break any real cryptographic algorithm, many cryptographers are designing new algorithms to prepare for a time when quantum computing becomes a threat. This work has gained greater attention from academics and industry through the PQCrypto conference series since 2006 and more recently by several workshops on Quantum Safe Cryptography hosted by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) and the Institute for Quantum Computing.
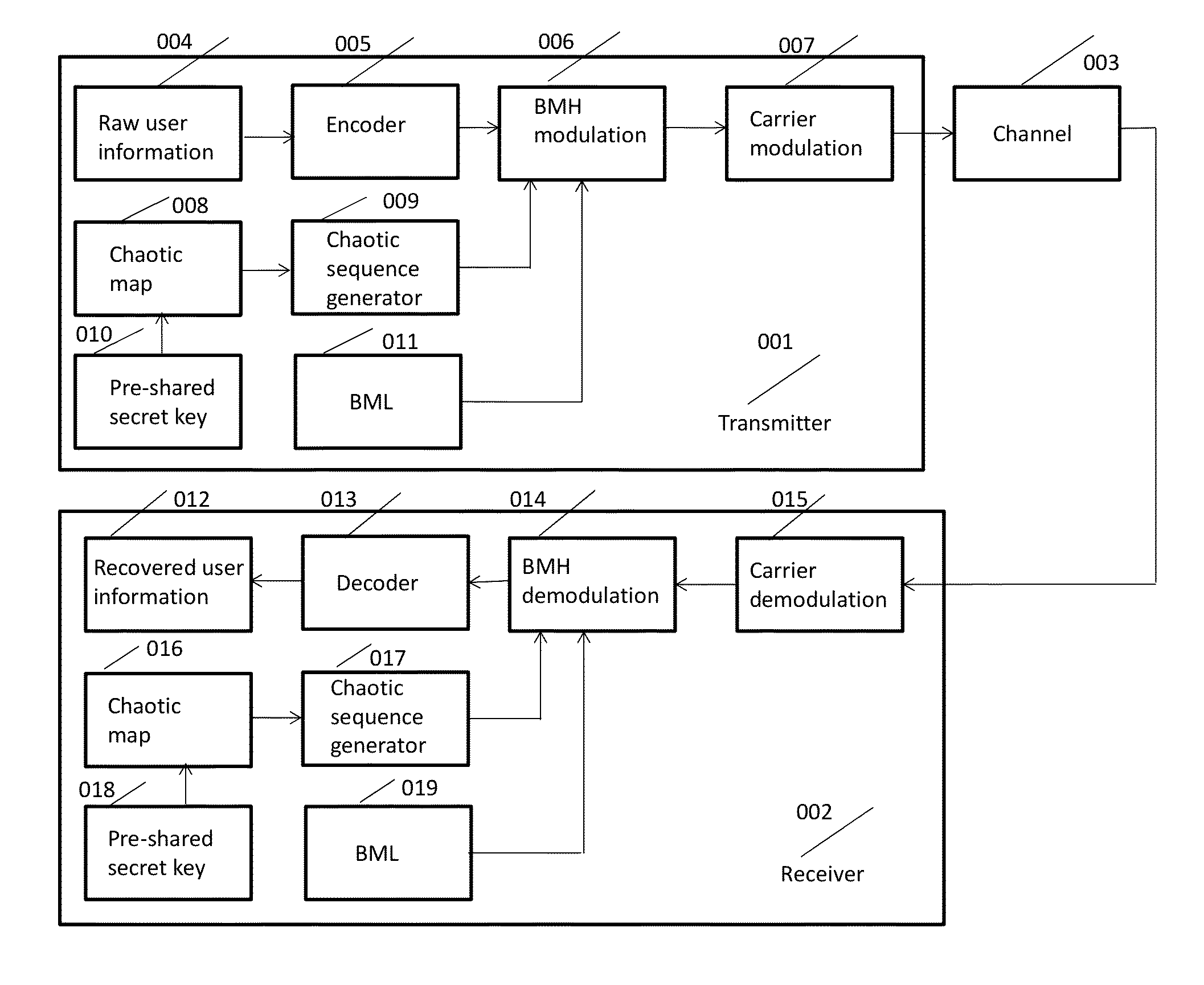
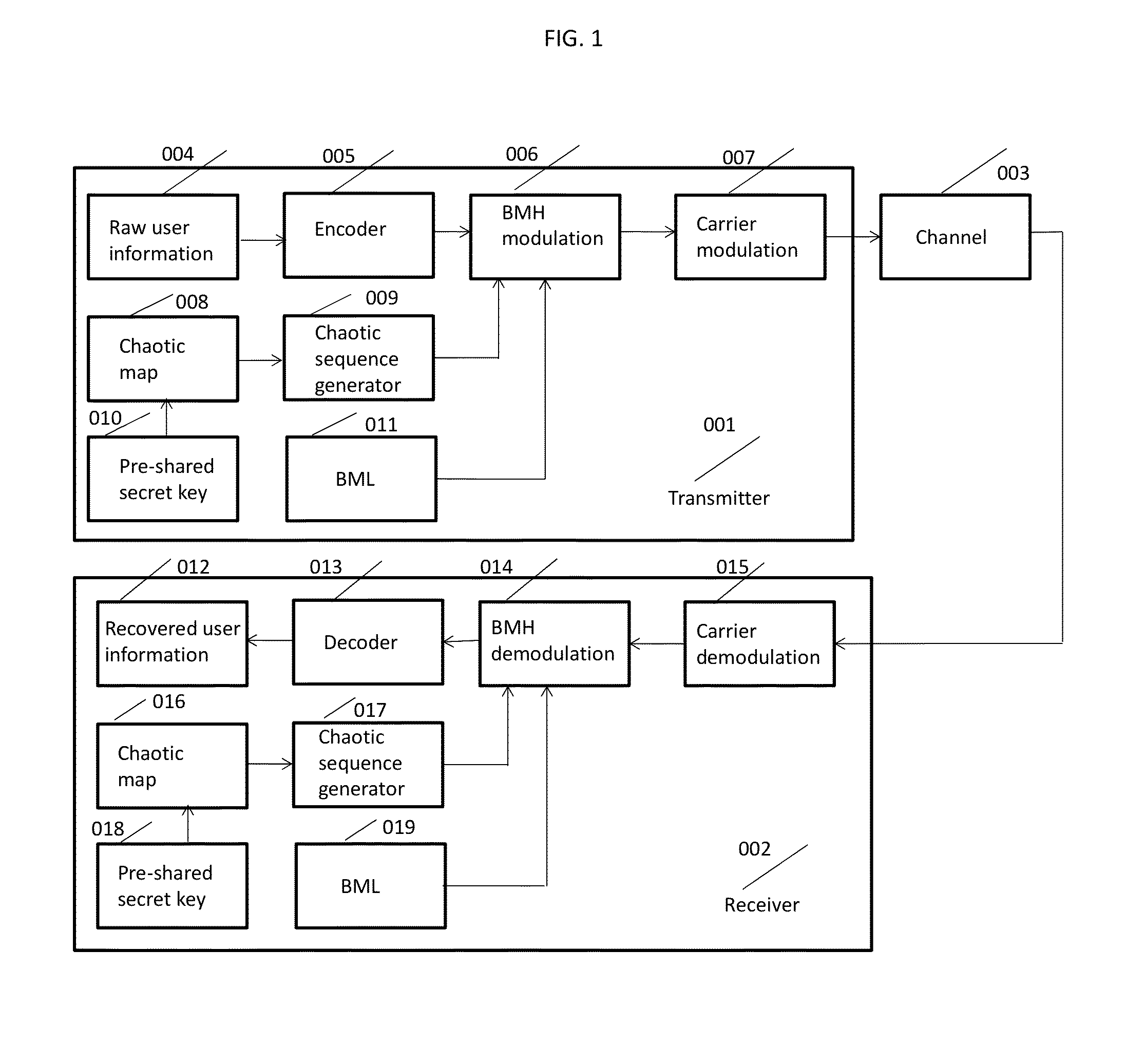
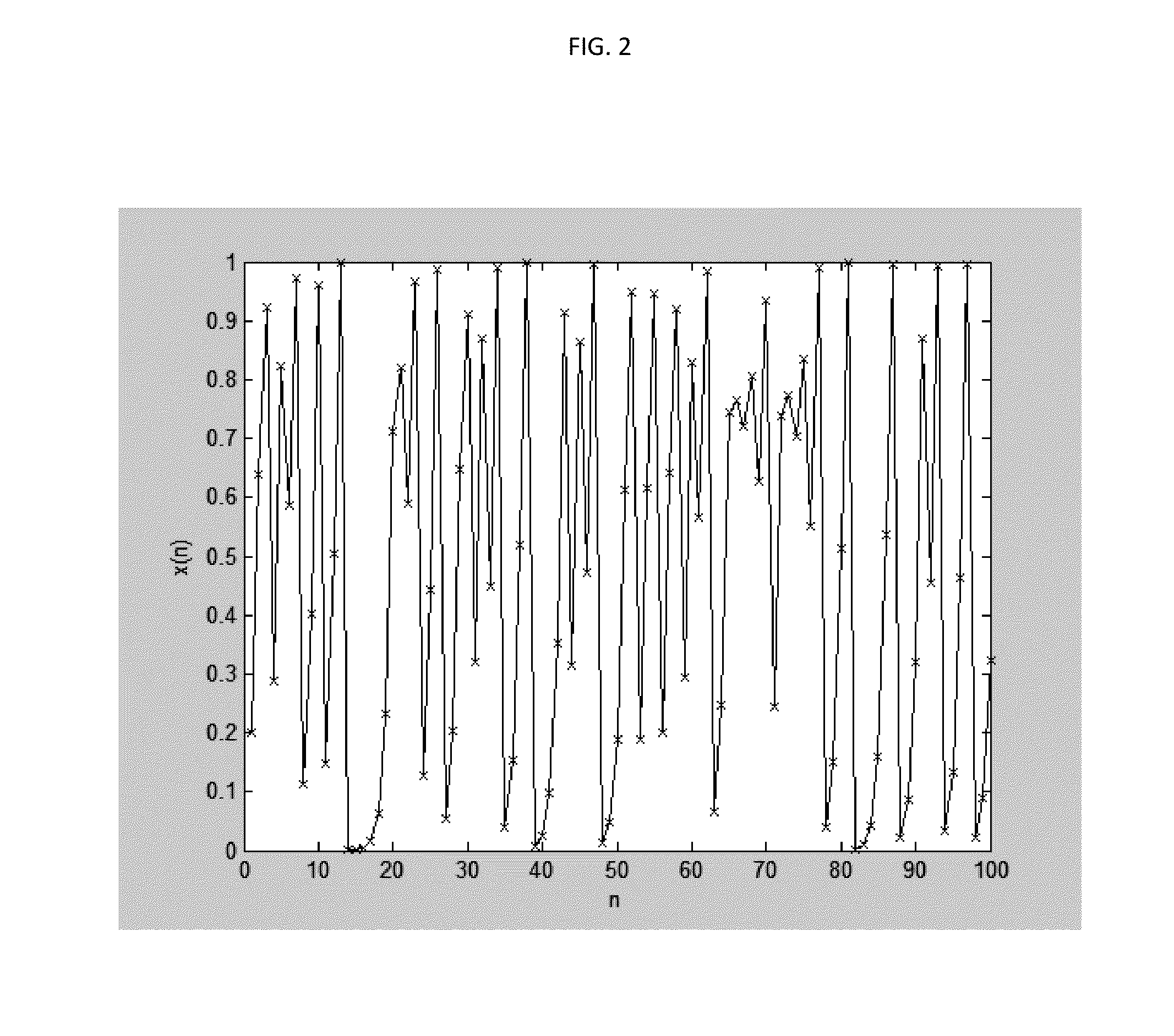
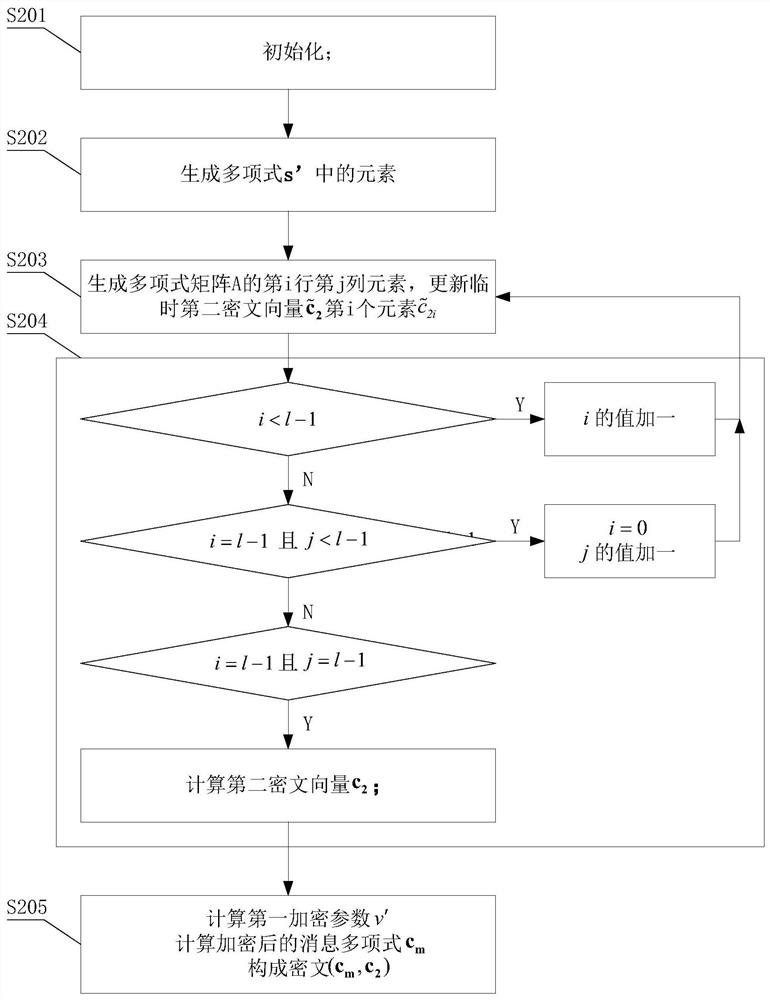
Chaotic Baseband Modulation Hopping Based Post-Quantum Physical-Layer Encryption
A post-quantum physical-layer encryption / decryption system based on chaotic Baseband Modulation Hopping (BMH). The baseband constellation, mapping, power level, and phase will vary symbol-by-symbol according to assigned random sequences. Pre-shared secret keys are used as the chaotic system parameters, initialization, and quantization parameters to generate the BMH codes. The BMH physical-layer encryption / decryption system can be combined with digital-domain based encryption algorithms such as AES, code-based post-quantum cryptography, and other physical-layer secure communication techniques such as Frequency Hopping (FH) and Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS). It can also be combined with Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) to provide mutual authenticated key distribution. This invention can be applied to all kinds of communication systems including wireless (radio frequency, optical, quantum channel, sonar) and wire (optical fiber, power-line, telephone line, wire quantum channel, etc.), single carrier and multi-carrier, OFDM, MIMO channels.
Owner:LI WENHUA +1
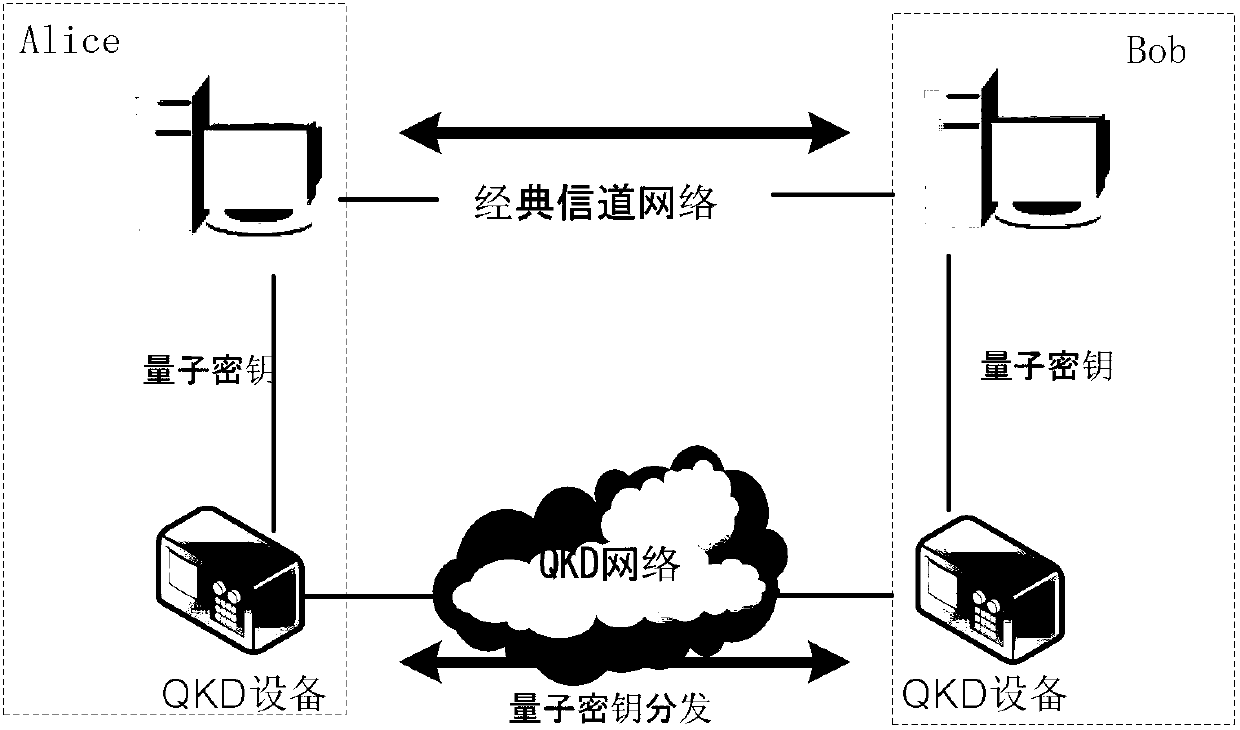
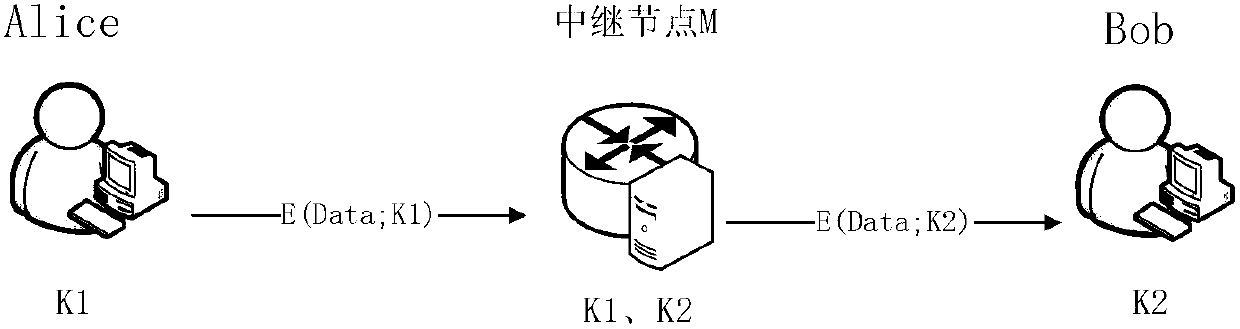
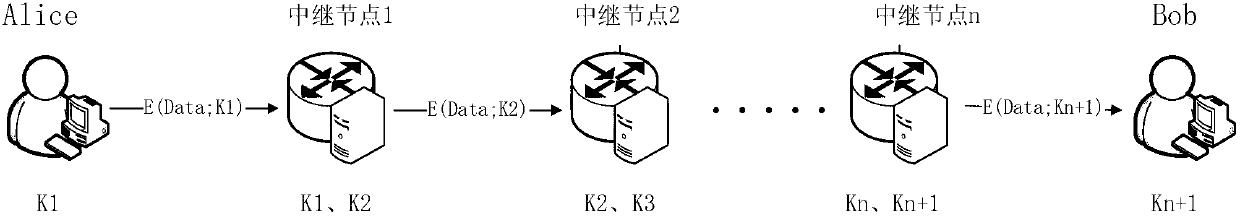
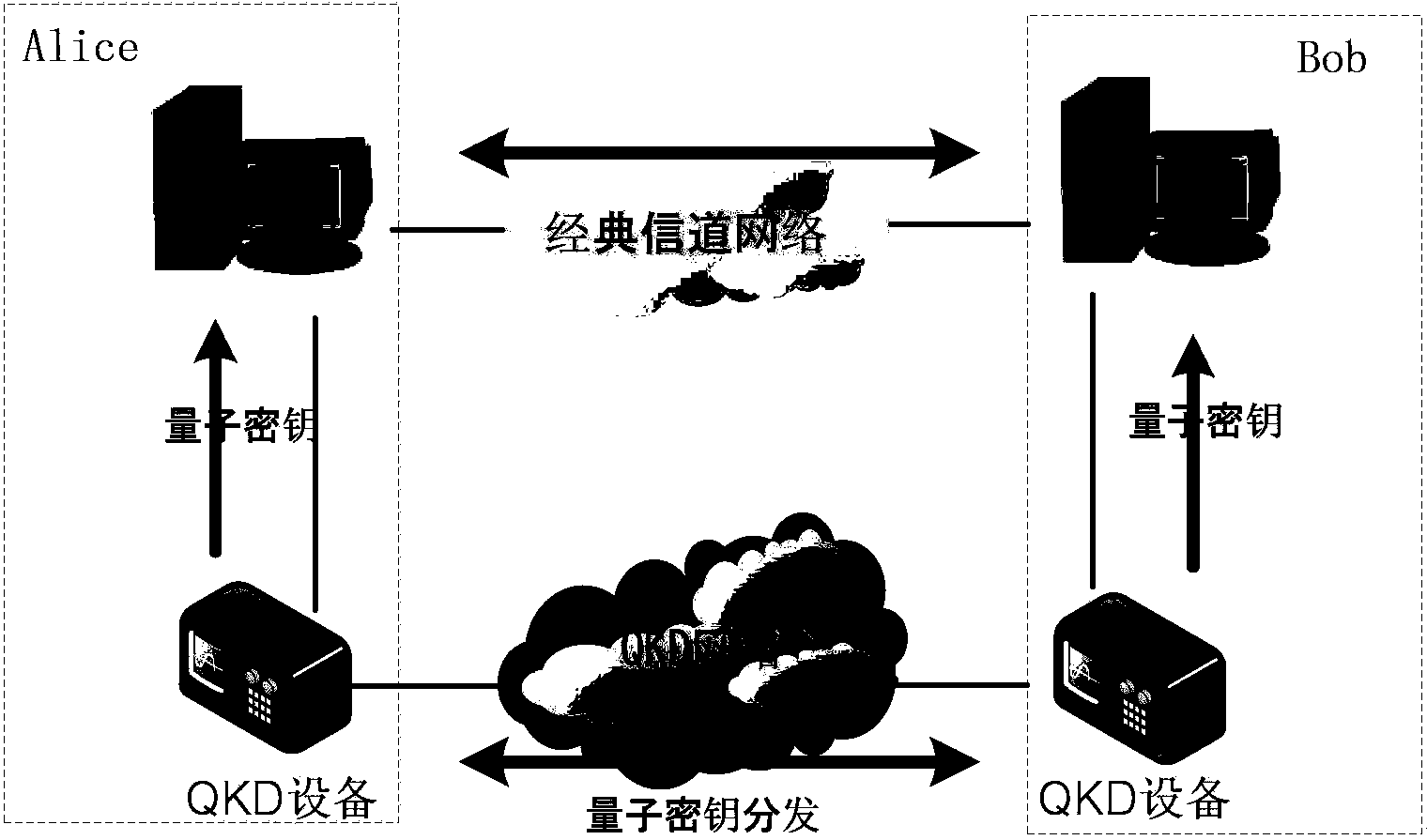
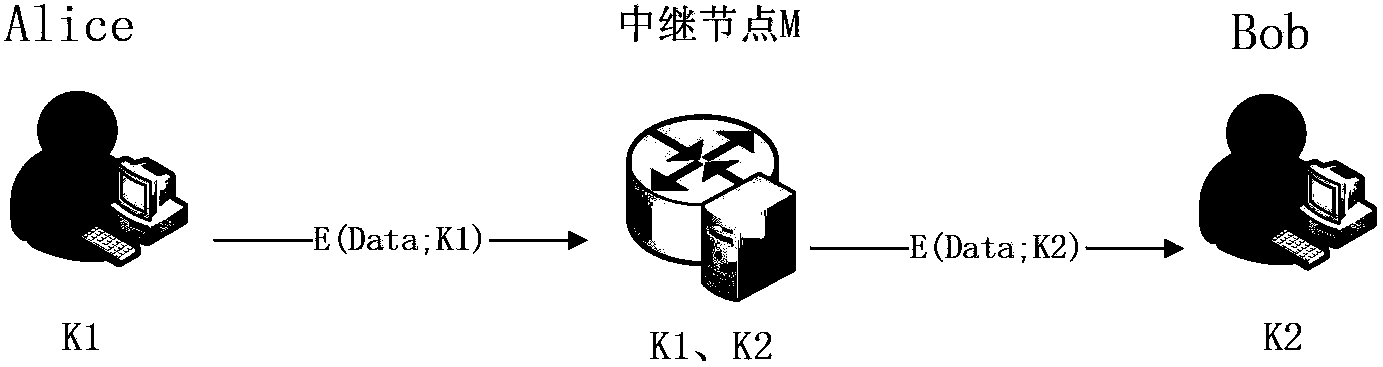
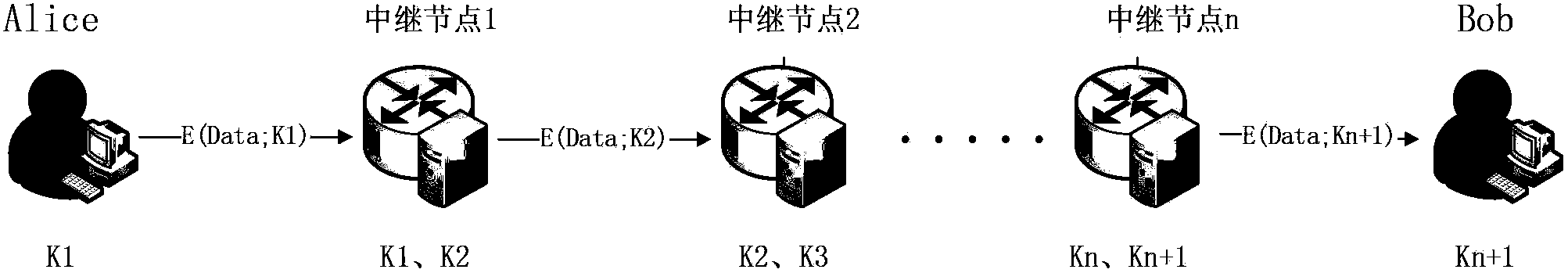
Quantum cryptography network dynamic routing method
ActiveCN103001875AConvenient for dynamic expansionFast convergenceKey distribution for secure communicationData switching networksRefresh cycleRoute server
The invention discloses a quantum cryptography network dynamic routing method. According to the method, dynamic routing selection of encryption communication is performed by utilizing quantum cryptography according to changes of the quantum key quantity between relay nodes of a quantum cryptography network. According to the method, a route server is arranged for the relay nodes of the whole quantum cryptography network, and topology refresh cycles of the quantum cryptography network are set; in each topology refresh cycle, each relay node collects and processes state information of the relay node and reports results to the route server. After the route server collects the topology state information of each relay node, quantum cryptography network topology state information of a next topology refresh cycle is generated and sent to all the relay nodes of the quantum cryptography network. According to the quantum cryptography network topology state information obtained from the route server, a target relay node is calculated and determined to be a next skip route of communication data of a random other relay node according to a shortest path law through each relay node.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF QUANTUM SCI & TECH +2
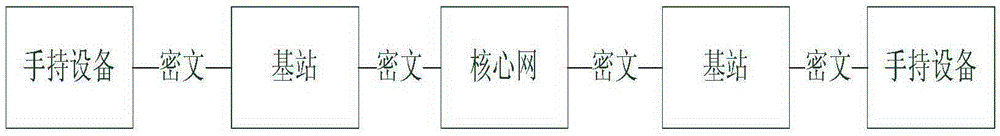
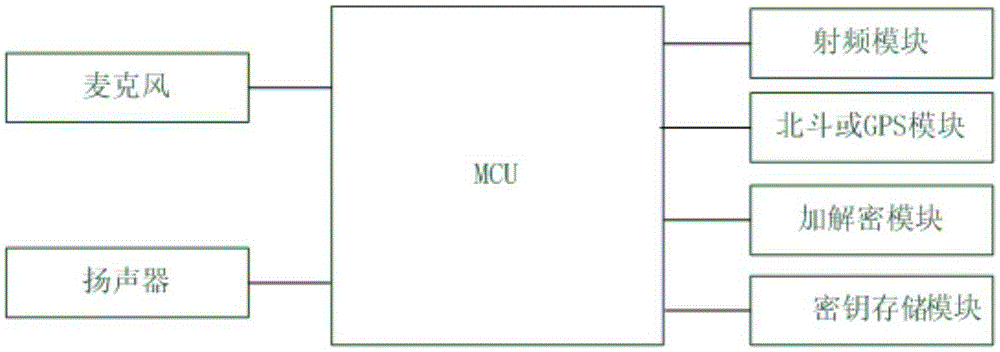
End-to-end hand-held device encryption method based on quantum cryptography and system
InactiveCN105337726AImprove securityIncrease independenceKey distribution for secure communicationHand heldHand held devices
The invention discloses an end-to-end hand-held device encryption method based on quantum cryptography and a system. The encryption method comprises following steps of storing quantum keys; initiating a call; synchronizing the quantum keys; performing synchronous confirmation; answering the call; and performing encryption communication. In the encryption communication, an MCU of a main calling end injects quantum communication keys Ksa into an encryption and decryption model; an MCU of a called end injects the quantum communication keys Ksa into the encryption and decryption model; the MCU of the called end using the quantum communication keys to encrypt the data; the encrypted data is sent out via a radio frequency module of the called end; a radio frequency module of the main calling end injects the received encrypted data into the encryption and decryption model for decryption; and after being decrypted, the data is played by a loudspeaker of the main calling end or displayed via a touch type display. The invention also discloses an end-to-end hand-held device encryption system based on quantum cryptography. The encryption method and system are highly safe, independent and easy, quick and simple to deploy.
Owner:ANHUI QASKY QUANTUM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Blockchain account processing method and apparatus, and storage medium
ActiveCN109716375AImprove securityResistance to crackingKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationPasswordSecurity level
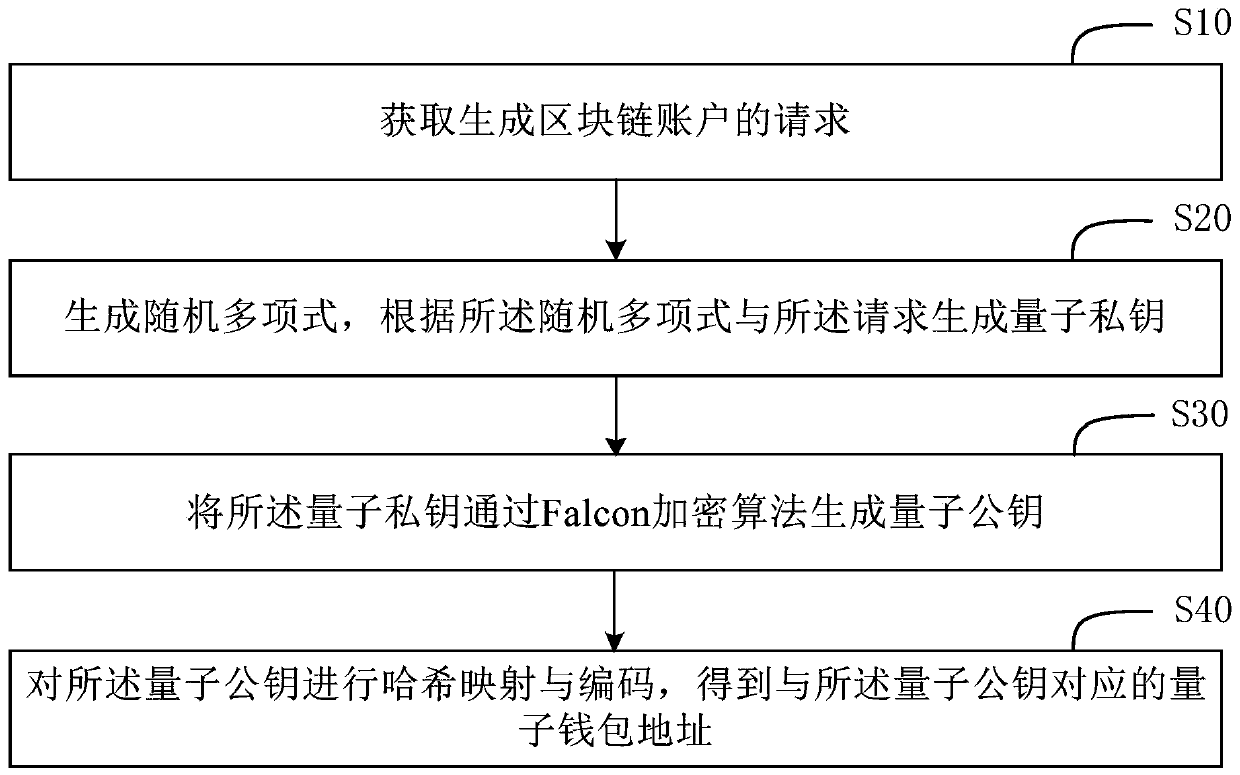
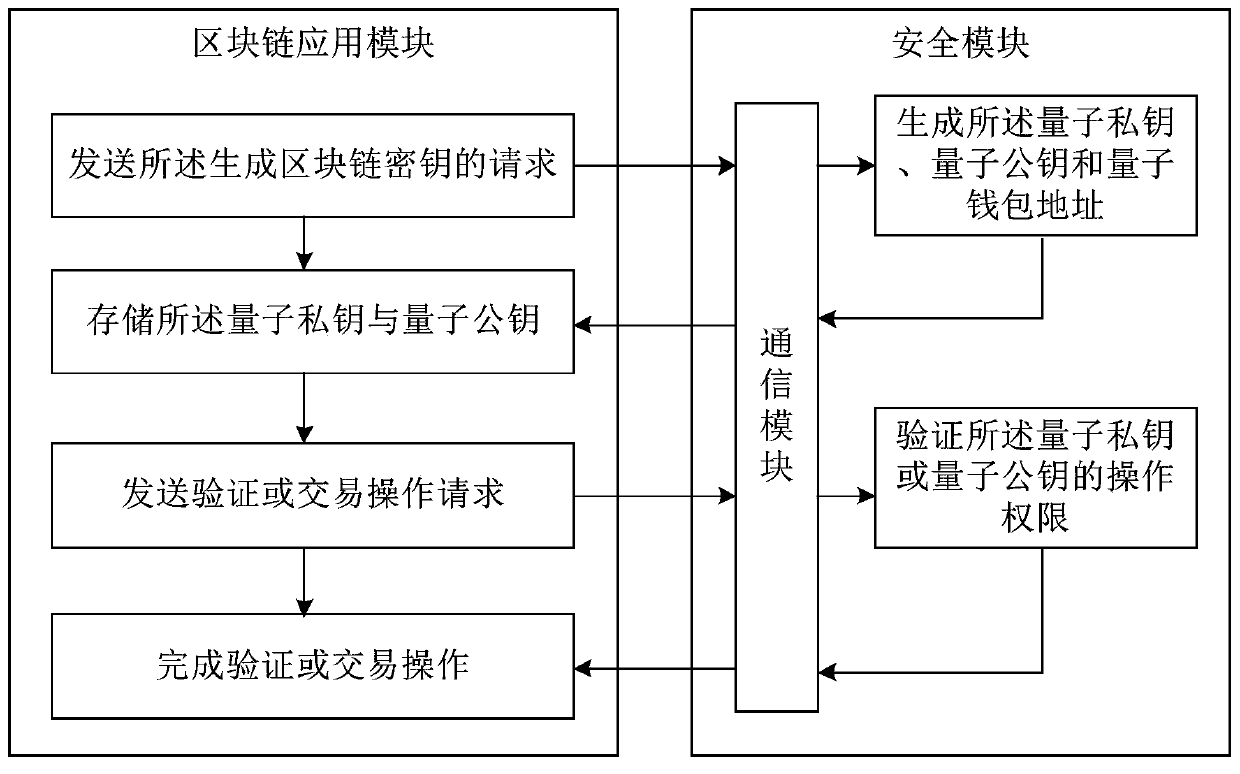
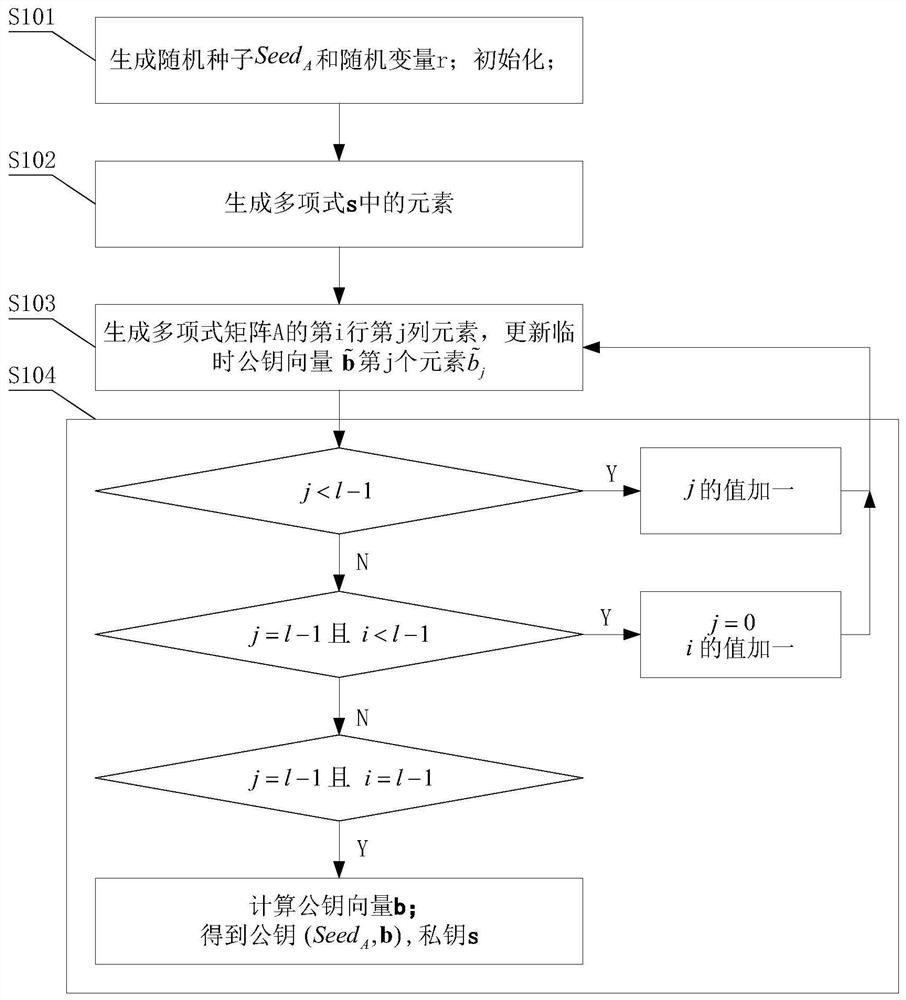
The invention provides a blockchain account processing method and apparatus, and a storage medium. The blockchain account processing method comprises the steps of obtaining a request for generating ablockchain account; generating a random polynomial, and generating a quantum private key according to the random polynomial and the request; generating a quantum public key from the quantum private key through a Falcon encryption algorithm; and performing Hash mapping and coding on the quantum public key to obtain a quantum wallet address corresponding to the quantum public key. The quantum publickey is generated through the Falcon encryption algorithm, the security level of the block chain account is improved, and cracking of an existing block chain account system by a quantum computer can be resisted; Compared with an existing secret key formed by a student with a later quantum password, the quantum private key and the quantum public key generated by the method are smaller in storage space and faster in signature and verification speed, and the operation burden caused to the block chain server is also reduced.
Owner:BCM SOCIAL CORP +1
Mobile device having quantum cryptographic security function for mobile commerce, and authentication method
ActiveUS20170324552A1Improve securityLow costKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageQuantum gateCommunication device
Disclosed herein are technologies regarding a communication device and server which are capable of cryptographic communication based on quantum cryptography. The communication device includes: a quantum signal generation unit configured to generate a series of first quantum signals by using a first quantum filter; an optical transmission unit configured to send the series of first quantum signals to a server; and a processor configured to select the first quantum filter based on a series of randomly generated first quantum states, and to control the quantum signal generation unit to generate the series of first quantum signals by using the first quantum filter.
Owner:FIRST QUANTUM INC
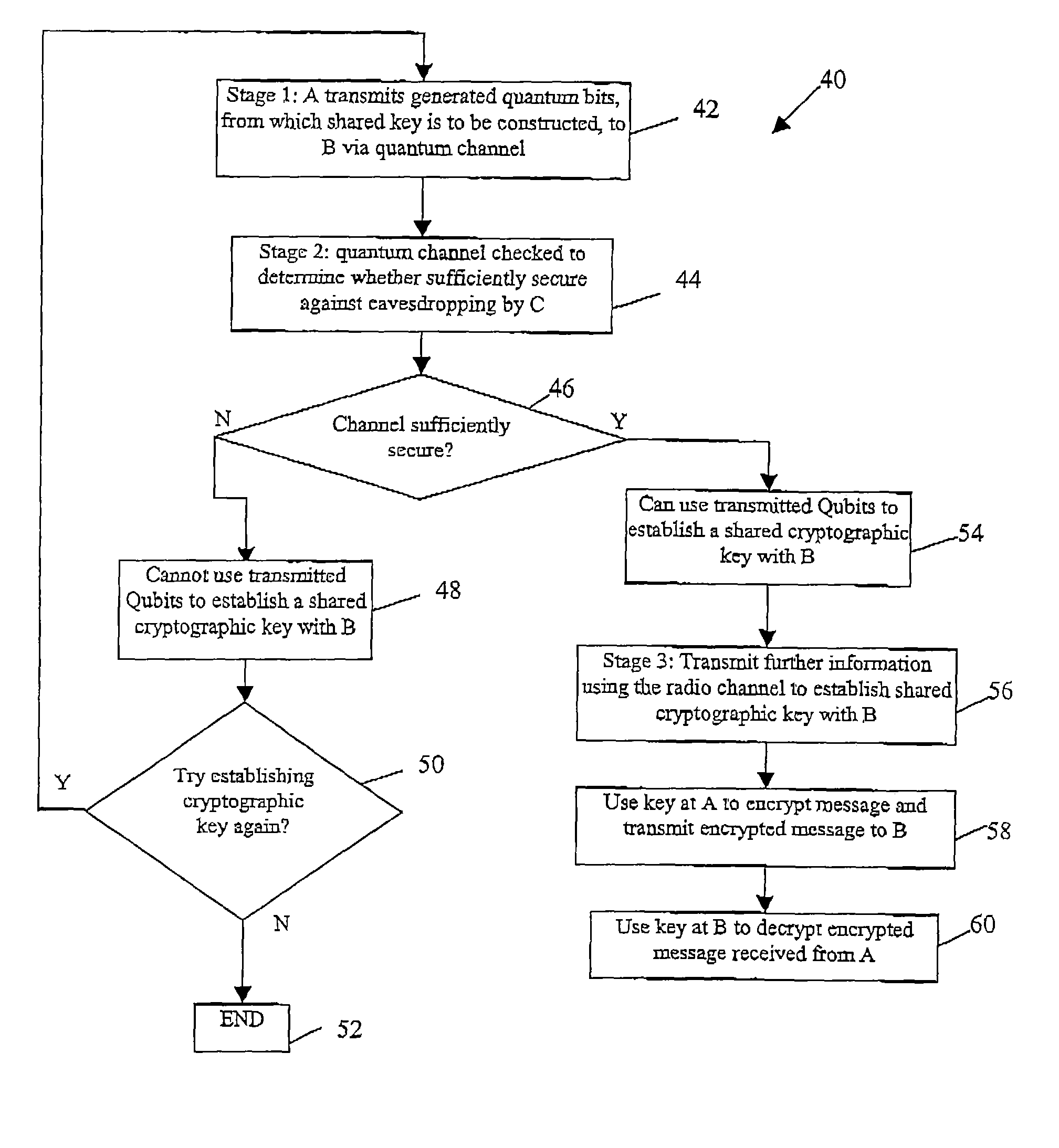
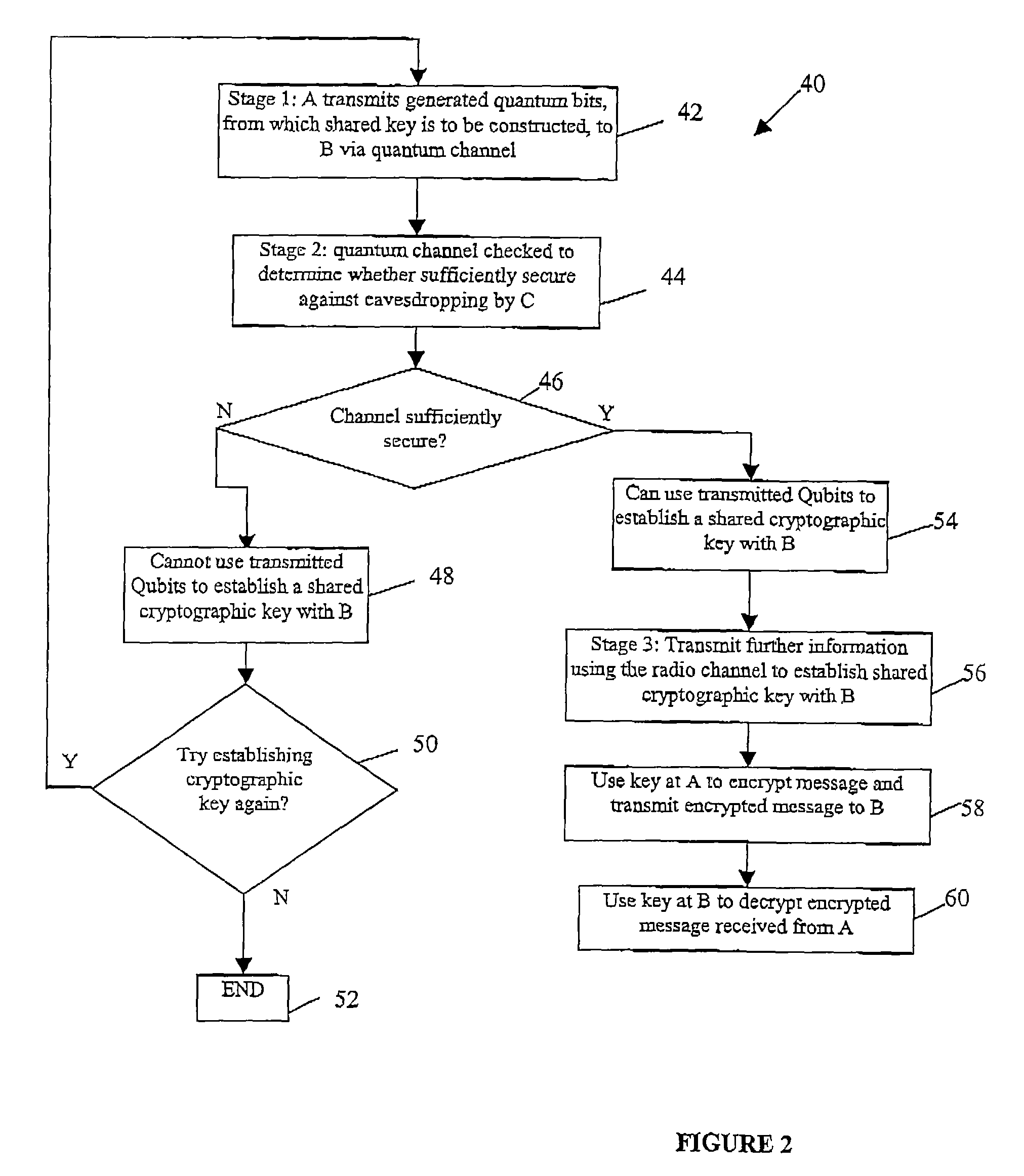
Method and system for using quantum cryptography in safe IP communication
ActiveCN103441839AImprove securityFix compatibility issuesKey distribution for secure communicationKey exchangeIPsec
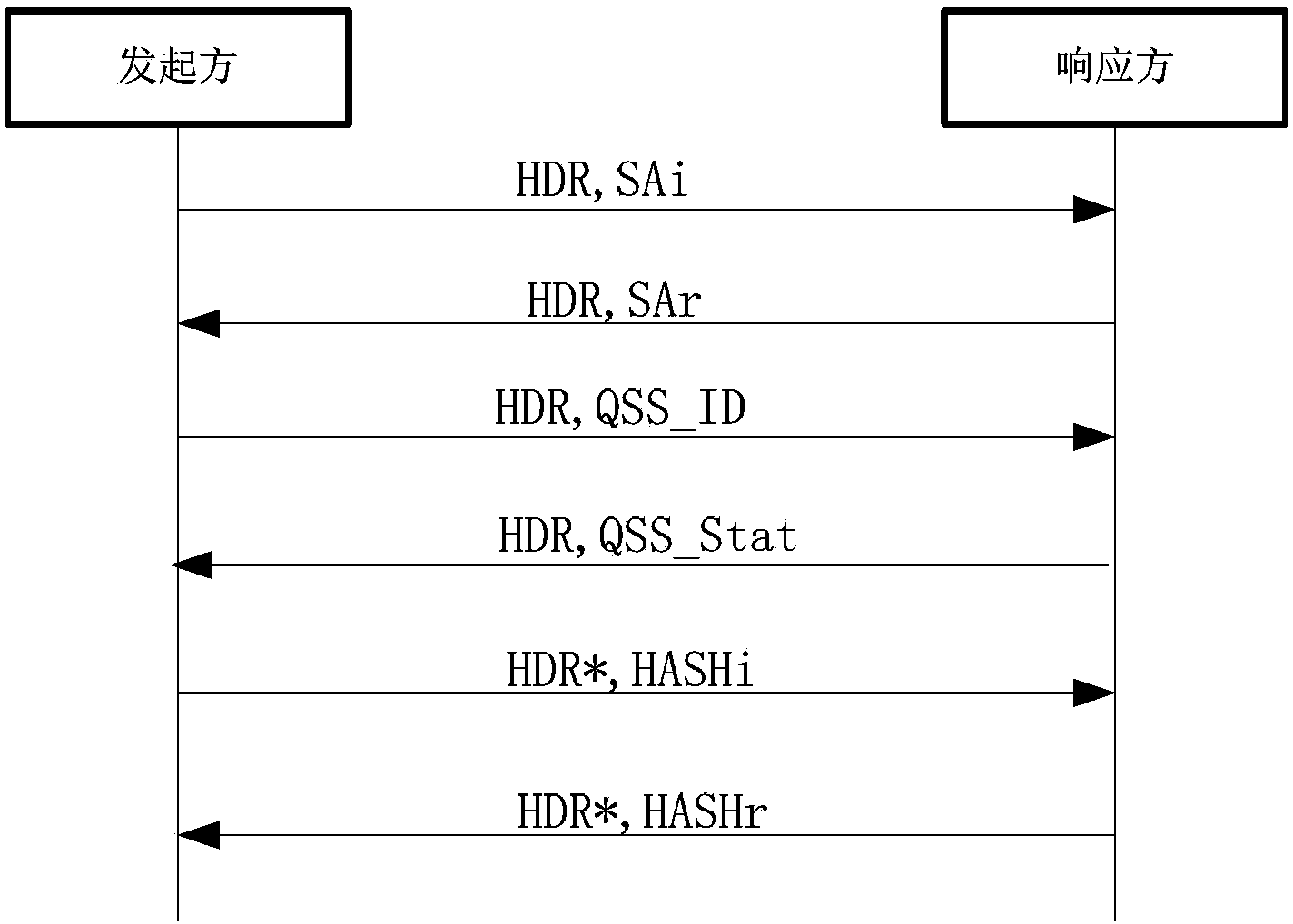
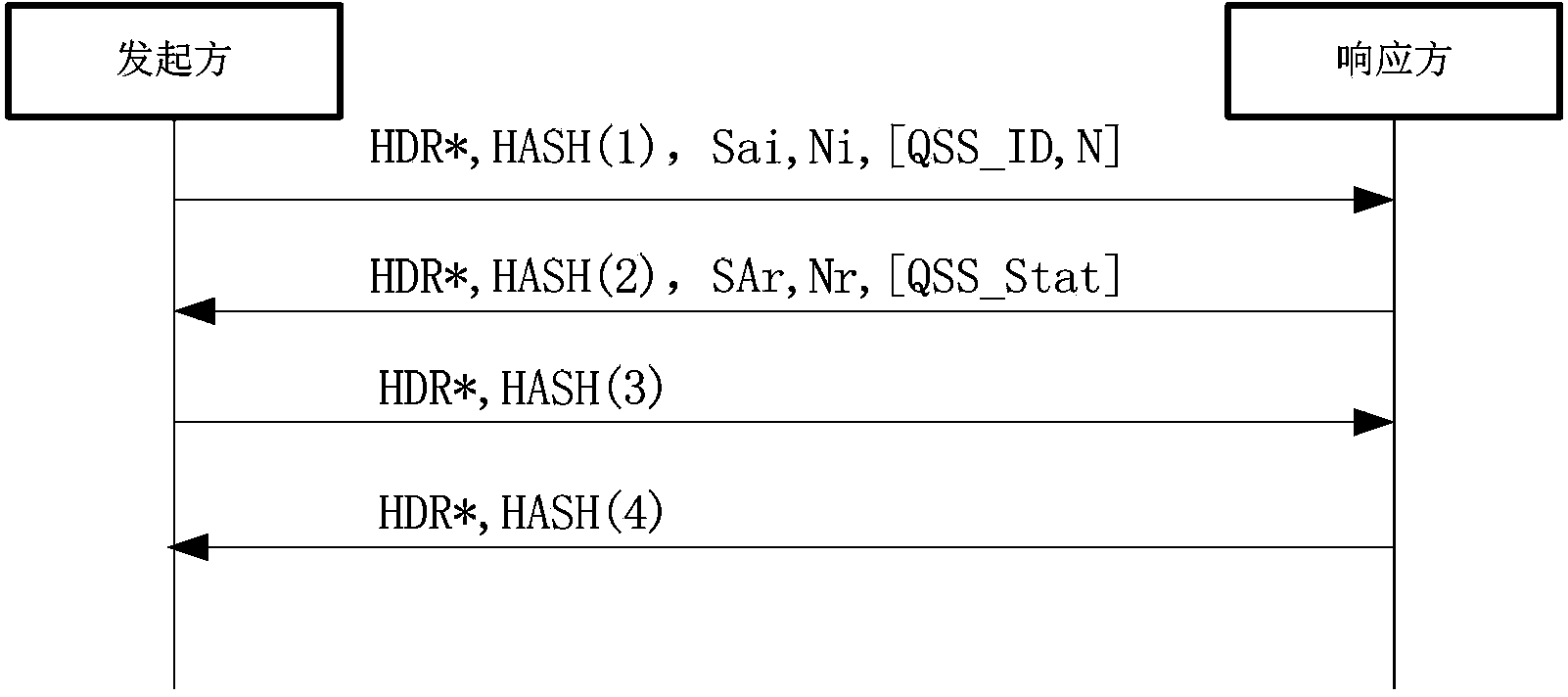
The invention provides a method and system for using the quantum cryptography in safe IP communication. The method is on the basis of a framework defined by an ISAKMP and comprises the following steps that quantum keys are distributed and a shared secret is established; IQKE SA negotiation is conducted; IPSec SA negotiation is conducted; session keys are generated. According to an IQKE protocol defined by the method and system, the framework defined by the ISAKMP is adopted and is independent of a standard IKE protocol, the problem existing in the compatibility of the standard IKE protocol and a QKD system can be avoided so that the safety of the quantum keys generated by the IPSec through the QKD system can be enhanced; in addition, according to the IQKE protocol, the quantum keys generated by the QKD system are adopted and serve as pre-shared keys, so that the adoption of the typical key exchange algorithm is not needed and the complexity of key negotiation is reduced. QIKE and QKD can be conducted in parallel; according to the QKD system with the low speed, the key storage technology is adopted; according to the QKD system with the high speed, OTP encryption can be achieved, so that the unconditional safety is achieved. The method and system are significant for improvement of the safety of IP communication.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
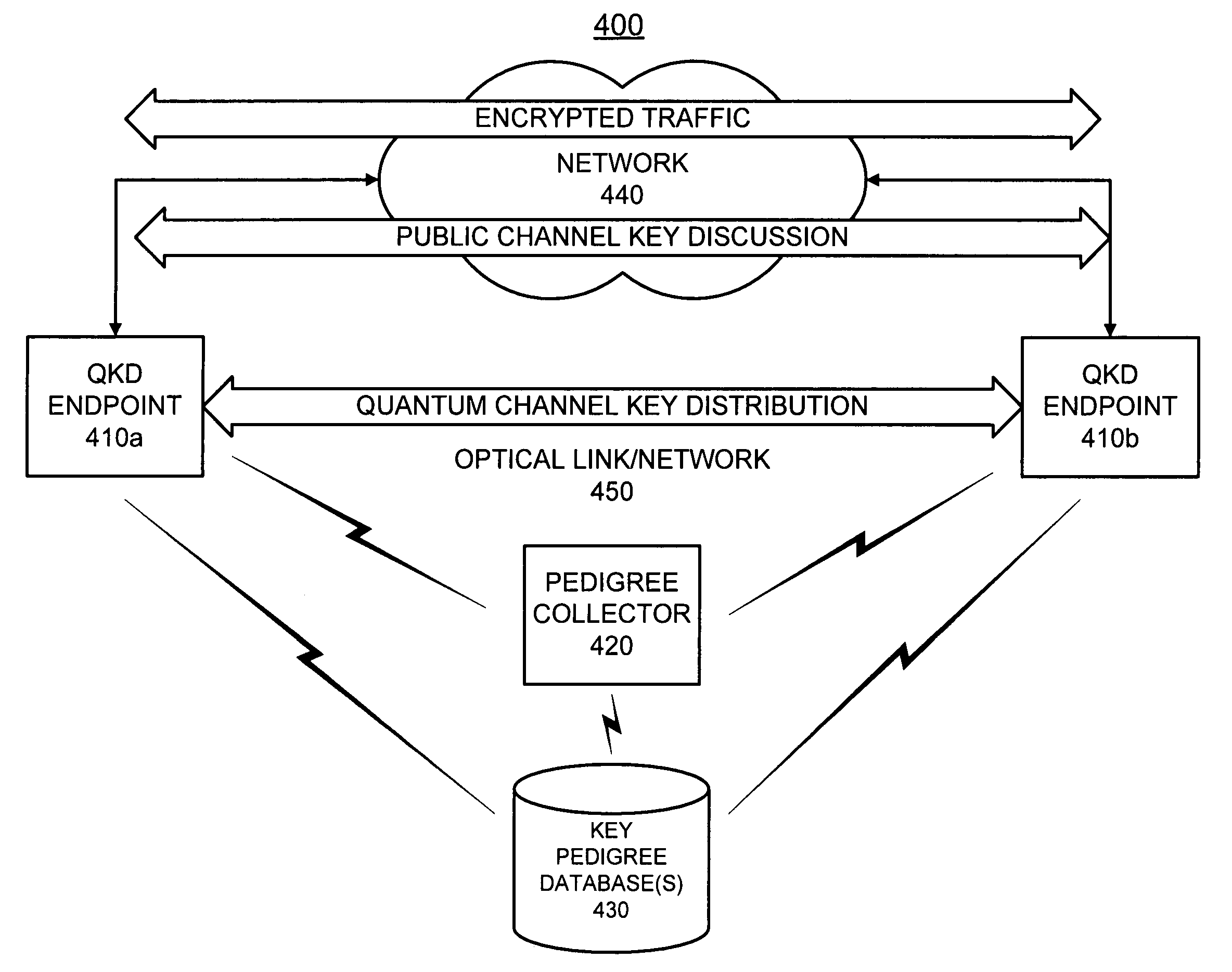
Pedigrees for quantum cryptography
ActiveUS8082443B2Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationMinutiaeQuantum
A system stores pedigrees that include details of how and when each of multiple blocks of encryption key material were distributed between two endpoints using quantum cryptographic techniques. The system receives an indication of a possible quantum cryptographic security violation and accesses the stored pedigrees to identify one or more of the multiple blocks of encryption key material that may have been compromised.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
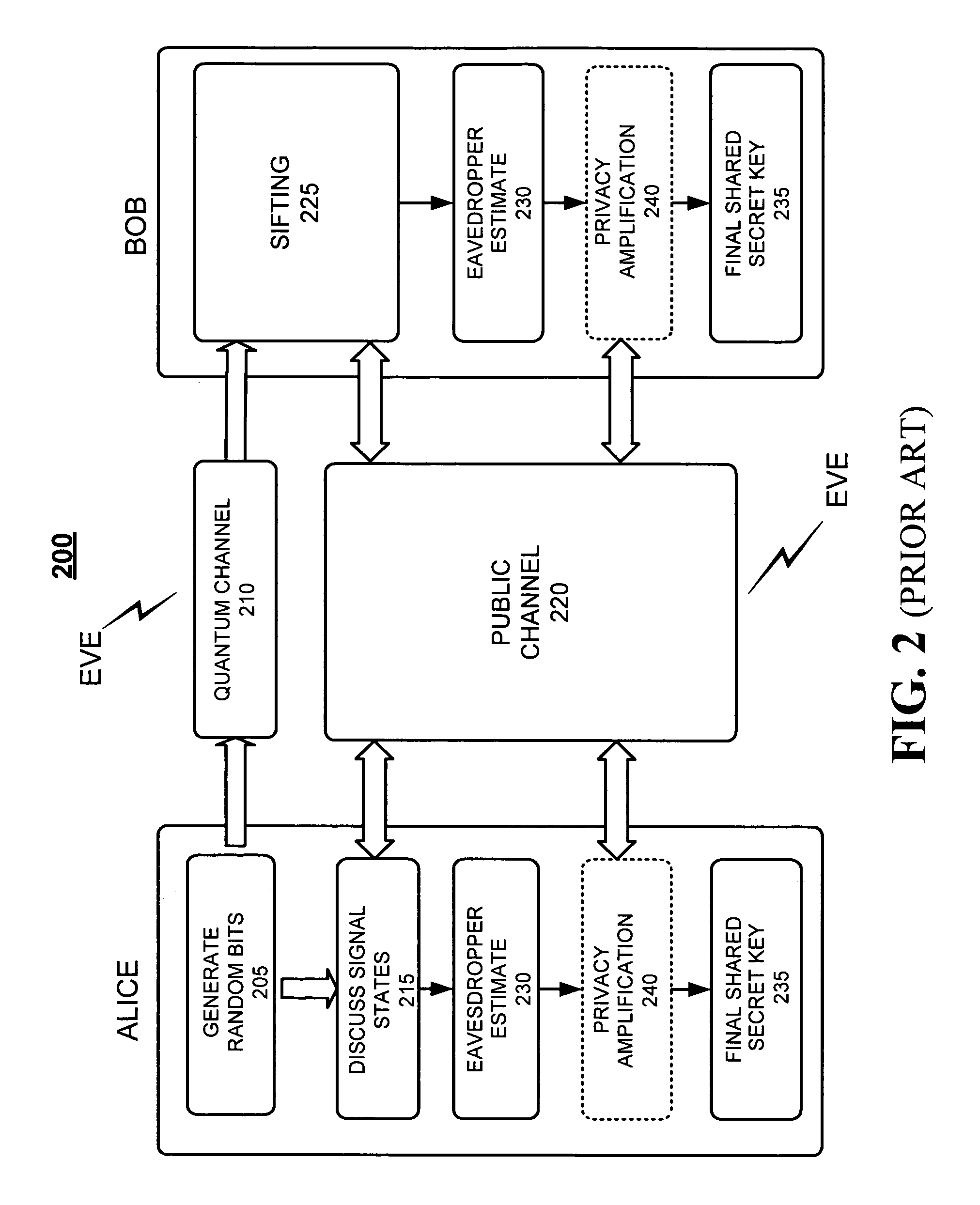
Quantum cryptography
ActiveUS7983422B2Reduce bitrateIncrease bitrateKey distribution for secure communicationQuantum channelHilbert space
A method of establishing a shared secret random cryptographic key between a sender and a recipient using a quantum communications channel is described. The method comprises: generating a plurality of random quantum states of a quantum entity, each random state being defined by a randomly selected one of a first plurality of bases in Hilbert space, transmitting the plurality of random quantum states of the quantum entity via the quantum channel to a recipient, measuring the quantum state of each of the received quantum states of the quantum entity with respect to a randomly selected one of a second plurality of bases in Hilbert space, transmitting to the recipient composition information describing a subset of the plurality of random quantum states, analysing the received composition information and the measured quantum states corresponding to the subset to derive a first statistical distribution describing the subset of transmitted quantum states and a second statistical distribution describing the corresponding measured quantum states, establishing the level of confidence in the validity of the plurality of transmitted random quantum states by verifying that the first and second statistical distributions are sufficiently similar, deriving a first binary sting and a second binary string, correlated to the first binary string, respectively from the transmitted and received plurality of quantum states not in the subset, and carrying out a reconciliation of the second binary string to the first binary string by using error correction techniques to establish the shared secret random cryptographic key from the first and second binary strings.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Secure payment and authentication system having security function enhanced by using quantum cryptography
ActiveUS20170324553A1Improve securityCost of device is highKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationUser authenticationCommunication device
Disclosed herein are a quantum cryptography-based cryptographic communication system and an authentication, payment and transaction system via a relay device between a communication device and a server. A relay device for quantum cryptography authentication includes an optical receiver unit, an optical transmission unit, and a processor. The processor includes a quantum signal control unit, a user authentication unit, and a random number generation unit. The optical receiver unit receives a series of second quantum signals generated in such a manner that a series of first quantum signals generated by a first quantum filter and sent from a communication device pass through the second quantum filter of the relay device or a reception side, and the optical transmission unit transfers the series of second quantum signals to a server.
Owner:FIRST QUANTUM INC
Interactive type zero-knowledge identity authentication method based on multivariate public-key cryptosystem
InactiveCN103259658AFix bugs that are no longer safeSafePublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPost-quantum cryptographyHybrid cryptosystem
An interactive type zero-knowledge identity authentication method based on a multivariate public-key cryptosystem comprises the steps of generating system parameters and repeatedly executing interactive steps t (t>=1) times. The interactive type zero-knowledge identity authentication method based on the multivariate public-key cryptosystem can solve the problem that an existing interactive type zero-knowledge identity certification method is no longer safe under quantum computing, has completeness, soundness and zero knowledgeability, and is still safe in a post quantum cryptography age.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
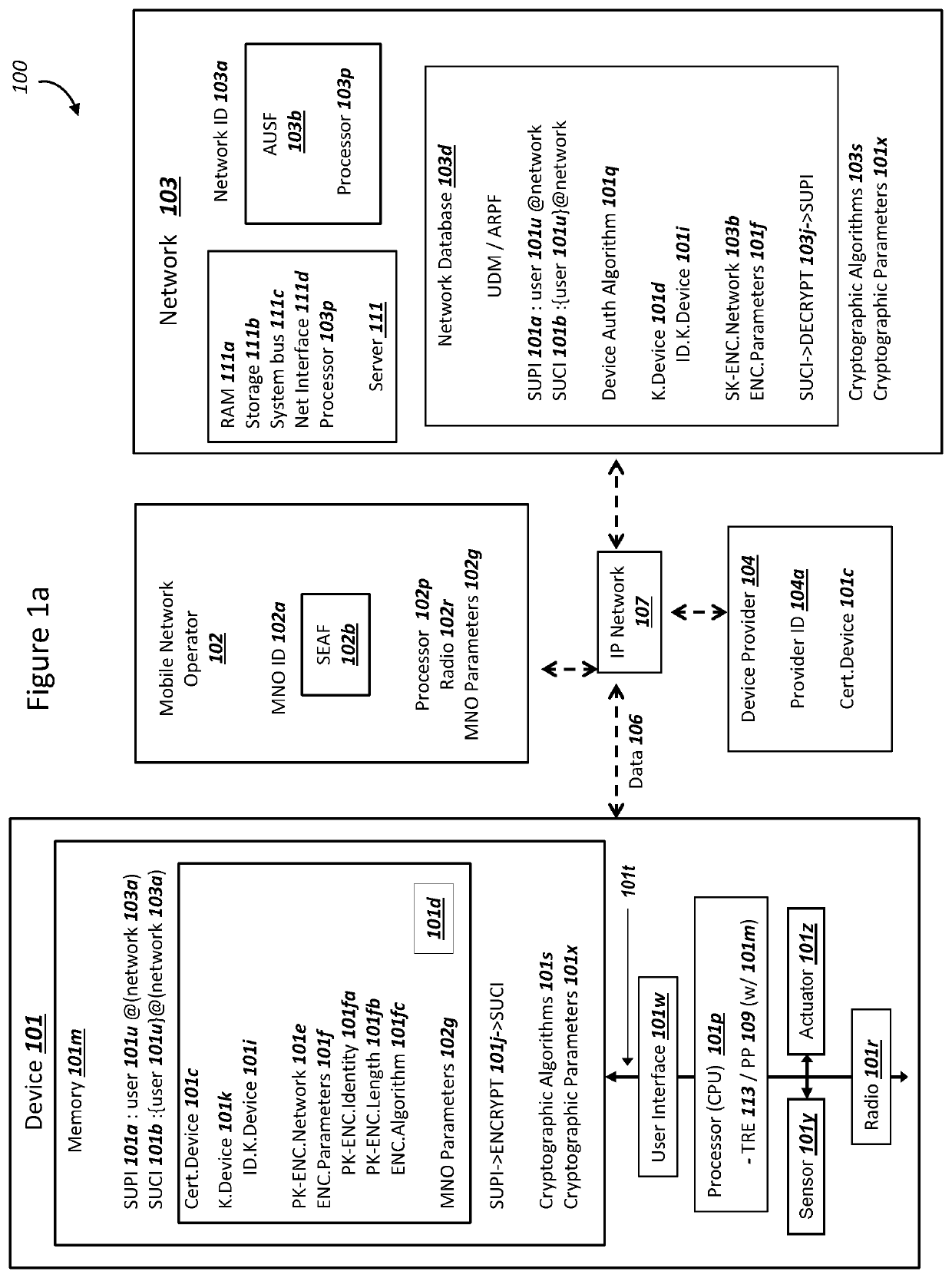
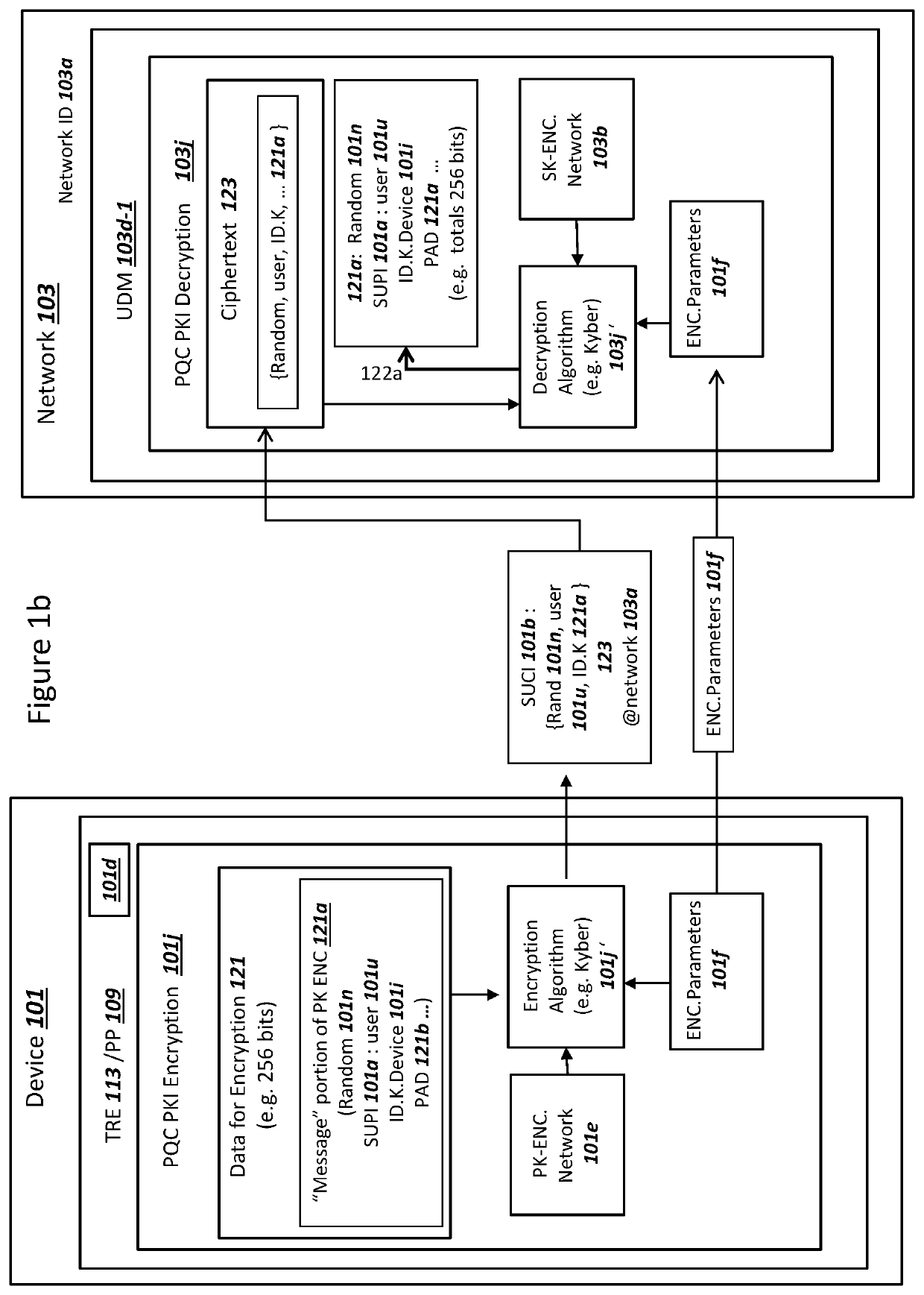
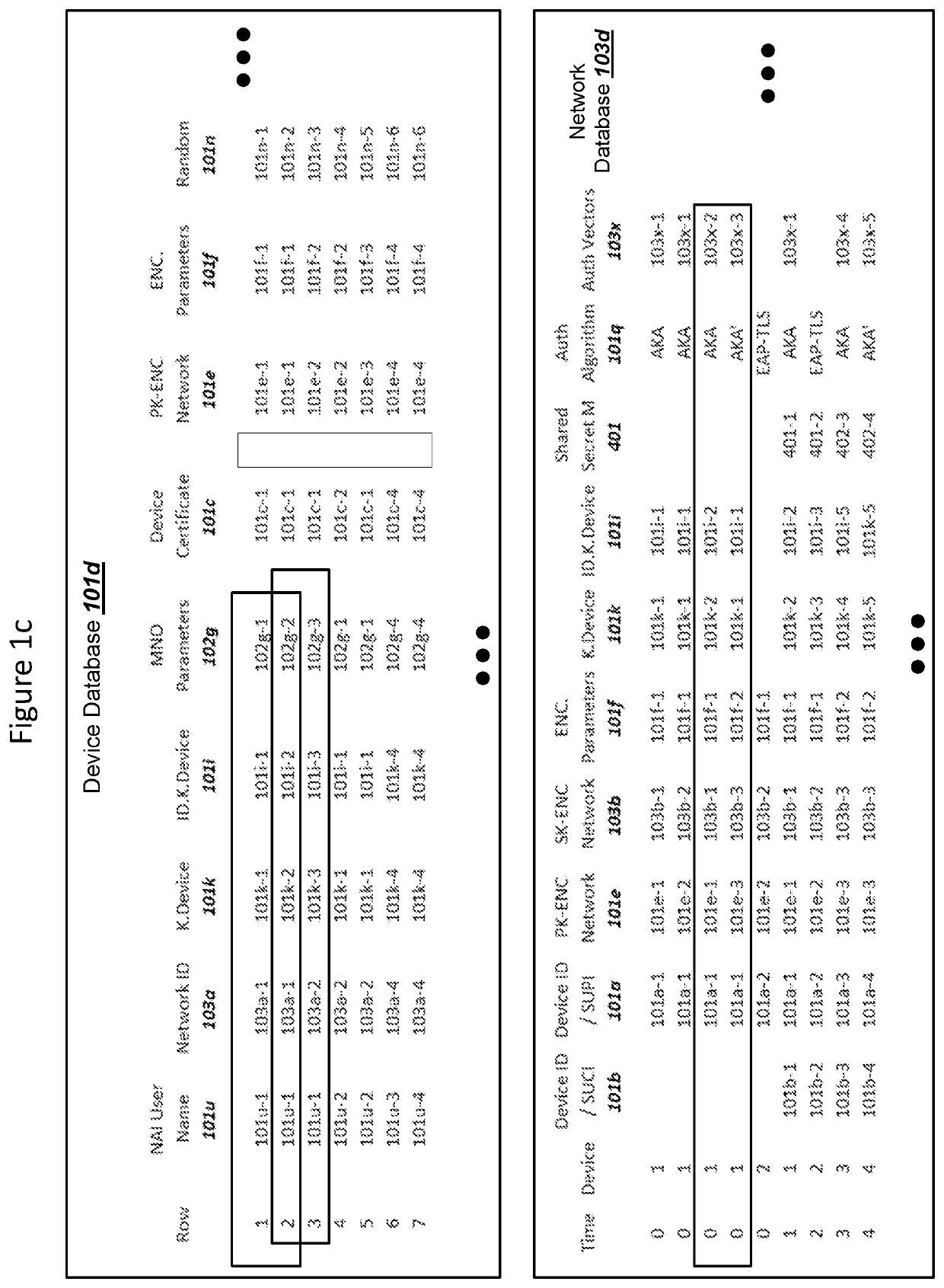
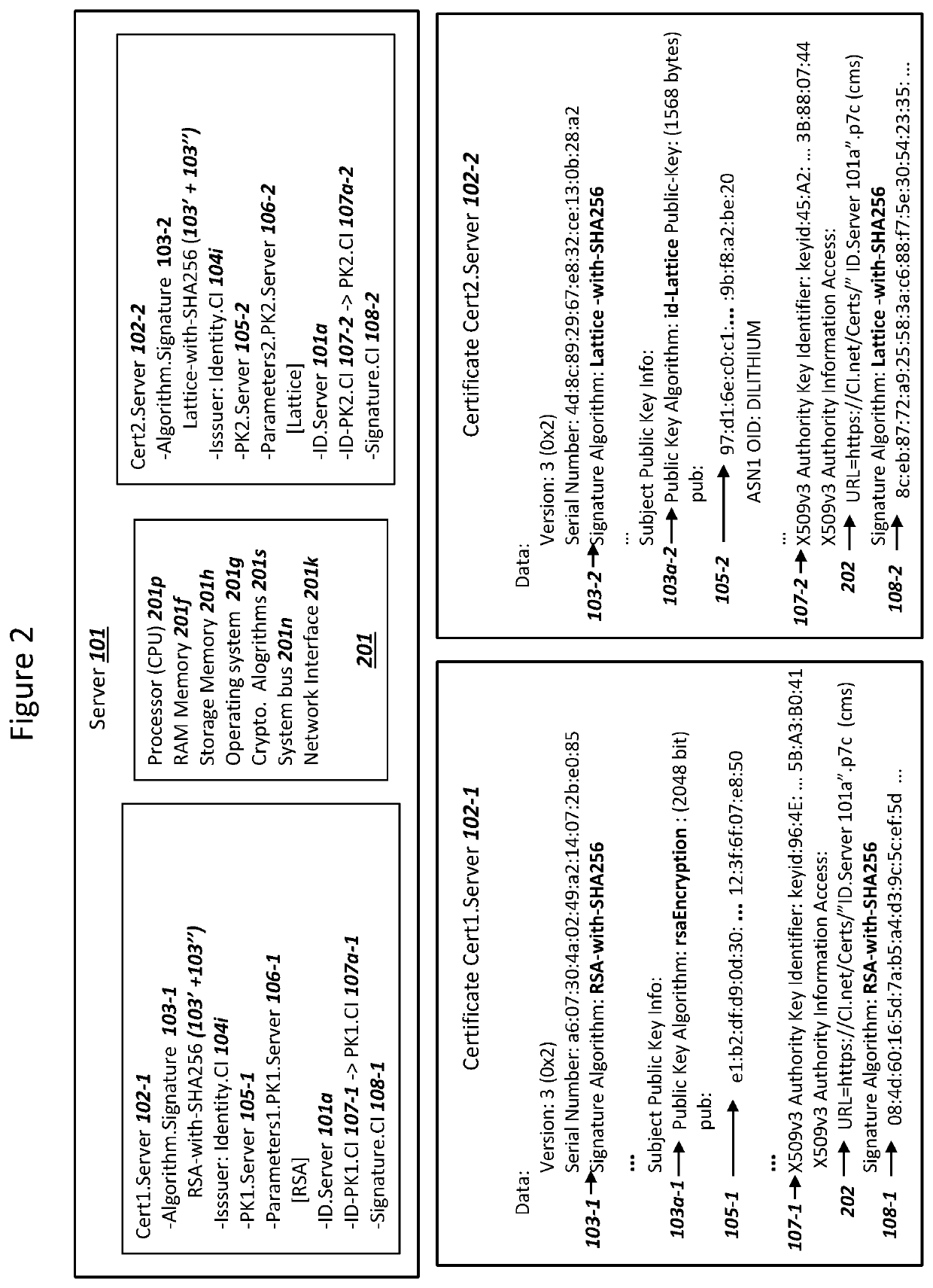
Subscription Concealed Identifier (SUCI) Supporting Post-Quantum Cryptography
PendingUS20210409214A1Key distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationKey (cryptography)Ciphertext
A device and a network can authenticate using a subscription concealed identifier (SUCI). The device can store (i) a plaintext subscription permanent identifier (SUPI) for the device, (ii) a network static public key, and (iii) a key encapsulation mechanism (KEM) for encryption using the network static public key. The network can store (i) a device database with the SUPI, (ii) a network static private key, and (iii) the KEM for decryption using the network static private key. The device can (i) combine a random number with the SUPI as input into the KEM to generate a ciphertext as the SUCI, and (ii) transmit the ciphertext / SUCI to the network. The network can (i) decrypt the ciphertext using the KEM to read the SUPI, (iii) select a key K from the device database using the SUPI, and (iv) conduct an Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA) with the selected key K.
Owner:NIX JOHN A
Post-quantum cryptography side chain
ActiveUS11223470B1Improve securitySafe storageQuantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationTheoretical computer scienceComputer engineering
A computing entity accesses one or more blocks of a blockchain, encrypts the content of the one or more blocks using a first cryptographic technique to generate one or more first encrypted block values, and writes a first side chain block comprising the one or more first encrypted block values and a first signature to a first side chain. The computing entity accesses at least one of (a) at least one block of a particular second set of one or more second sets of the plurality of blocks or (b) one or more first side chain blocks corresponding to blocks of the second set, encrypts the content of the accessed block(s) using a second cryptographic technique to generate at least one second encrypted block value, and writes a second side chain block comprising the at least one second encrypted block value and a second signature to a second side chain.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NA
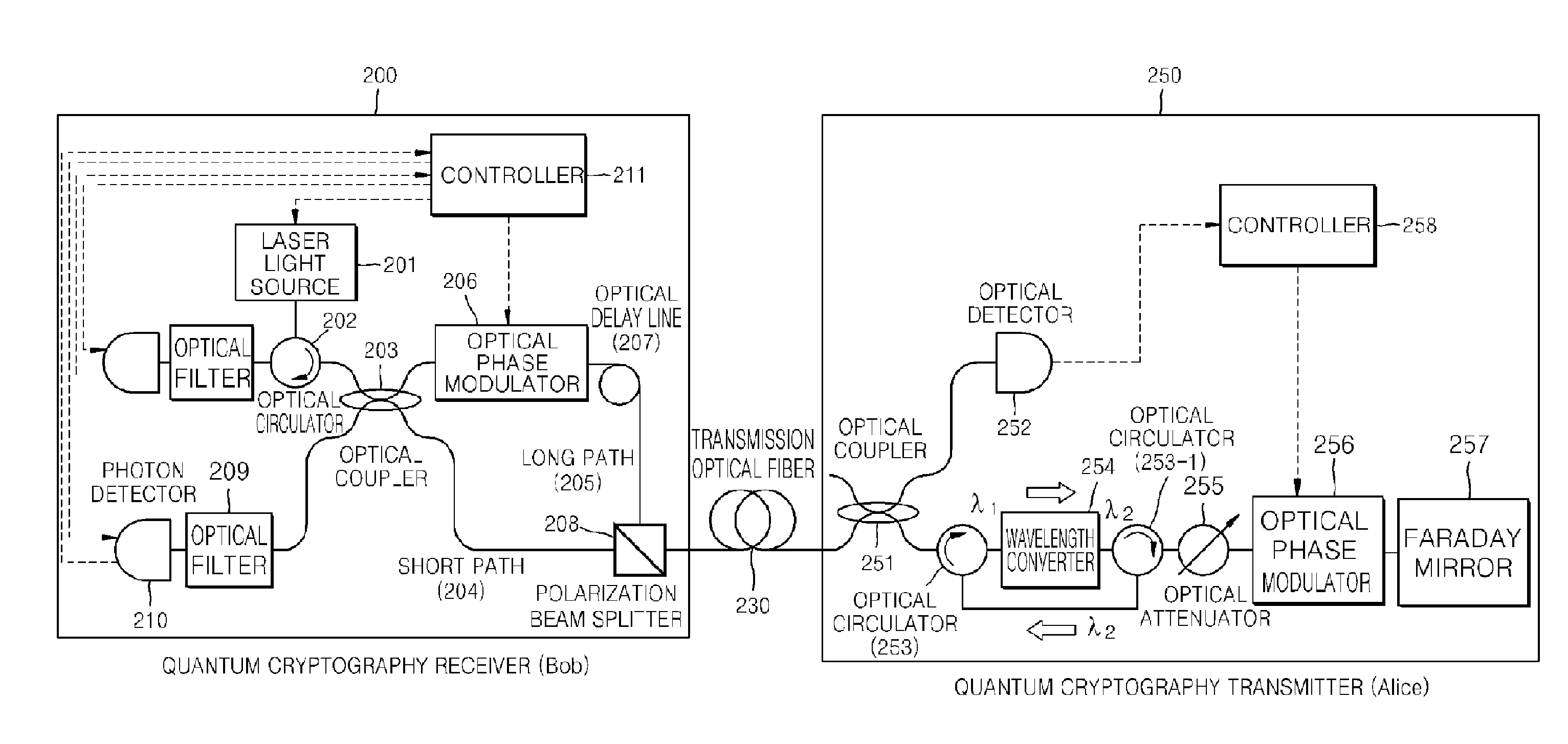
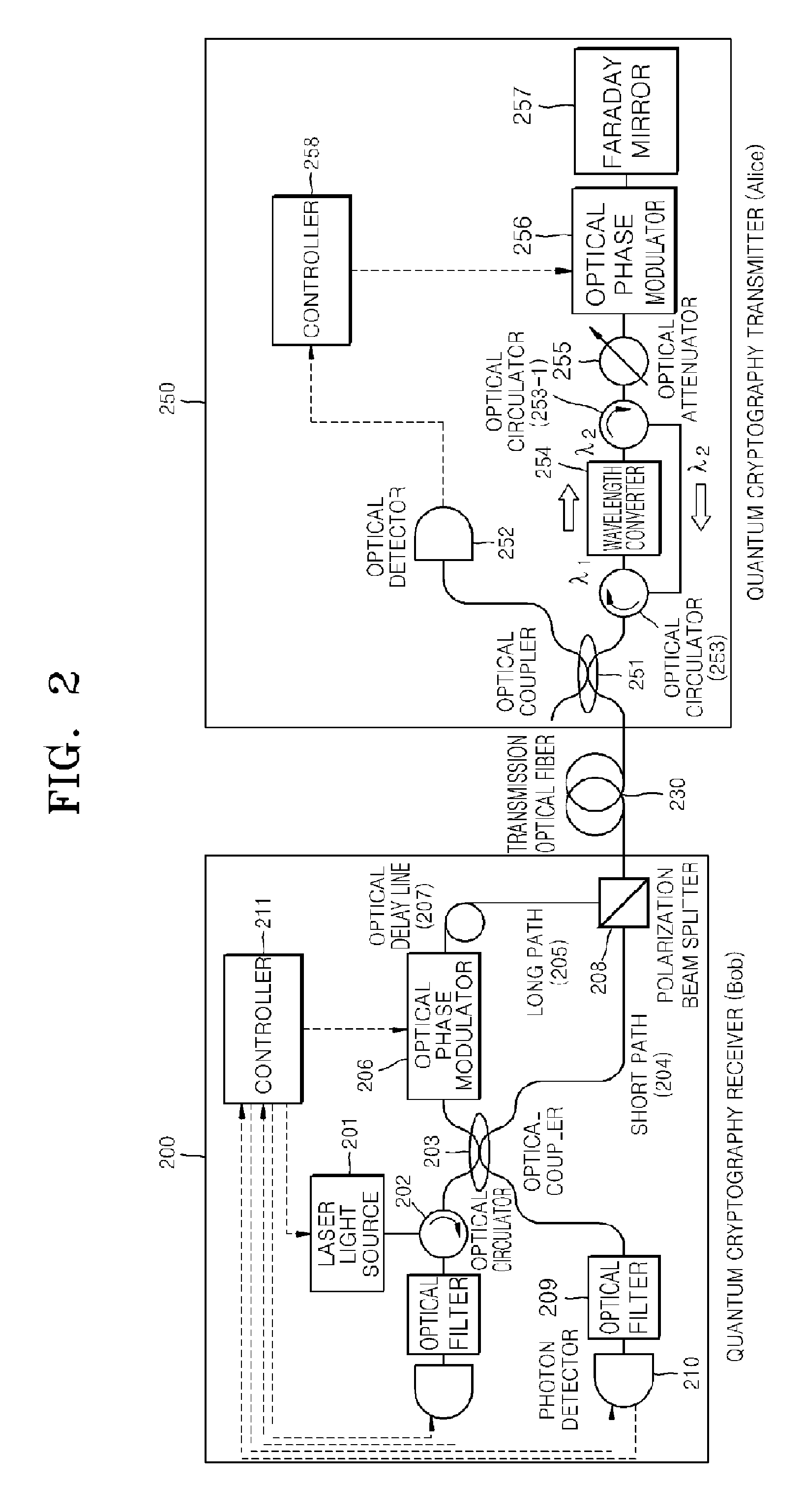
Transceiver and method for high-speed auto-compensating quantum cryptography
ActiveUS8116636B2Overcome limitationsDigital computer detailsElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsRayleigh scatteringTransceiver
Provided are an auto-compensating quantum cryptography transceiver and method of transmitting a quantum cryptography key at a high speed. A quantum cryptography transmitter includes a wavelength converter, an optical attenuator, an optical phase modulator, and a Faraday mirror. A quantum cryptography receiver includes a polarization beam splitter, an optical coupler, an optical filter, and a photon detector. Thus, a limit of a transmission rate caused by Rayleigh scattering of an optical fiber can be overcome.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
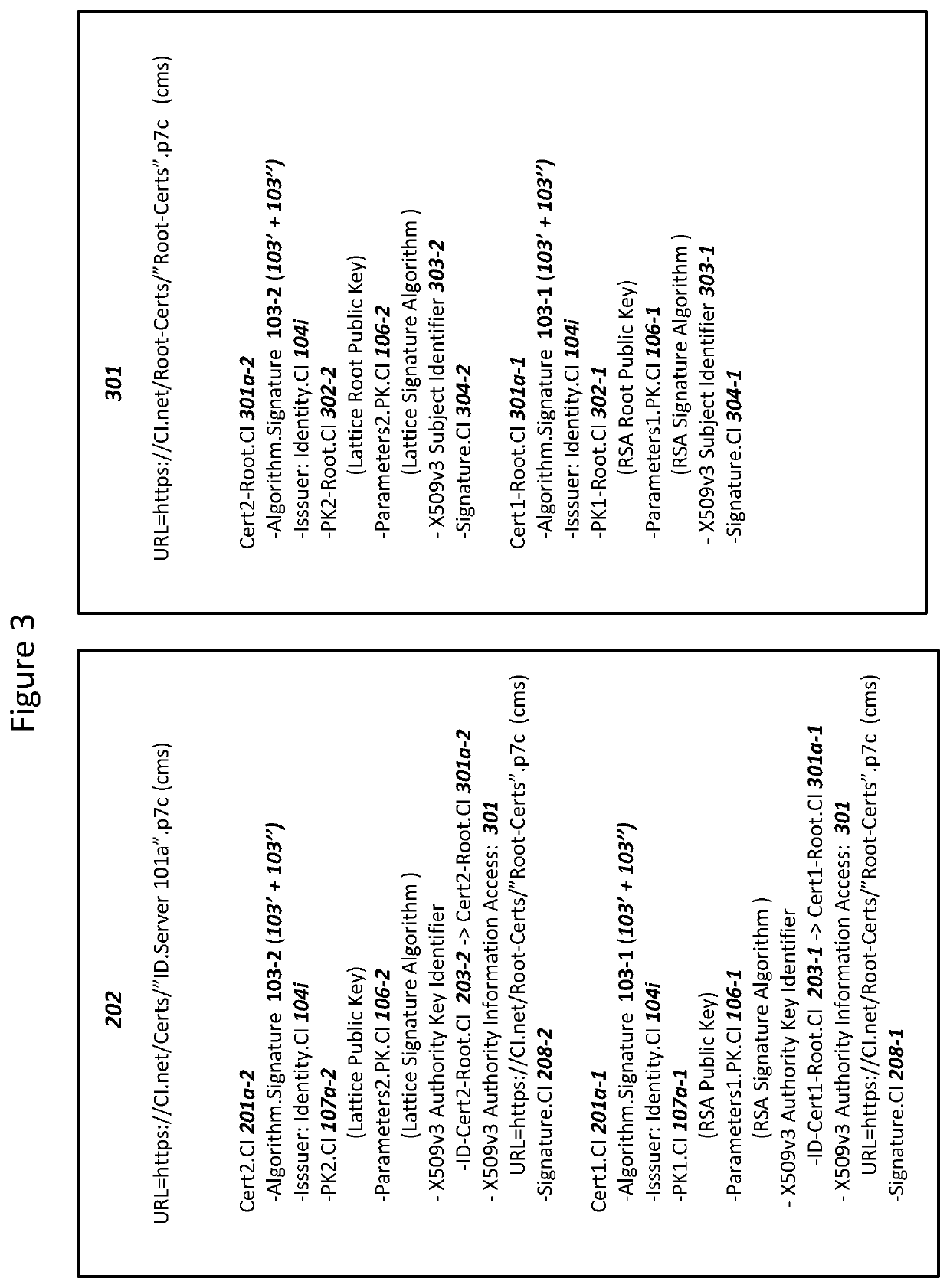
Combined Digital Signature Algorithms for Security Against Quantum Computers
ActiveUS20210377049A1Improve securityEasy to useKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageKey (cryptography)Theoretical computer science
A server can record (i) a first digital signature algorithm with a first certificate, and a corresponding first private key, and (ii) a second digital signature algorithm with a second certificate, and a corresponding second private key. The server can select first data to sign for the first algorithm and the first private key in order to generate a first digital signature. The server can select second data to sign, wherein the second data to sign includes at least the first digital signature. The server can generate a second digital signature for the second data to sign using the second algorithm and the second private key. The server can transmit a message comprising (i) the first and second certificates, and (ii) the first and second digital signatures to a client device. Systems and methods can concurrently support the use of both post-quantum and classical cryptography to enhance security.
Owner:NIX JOHN A
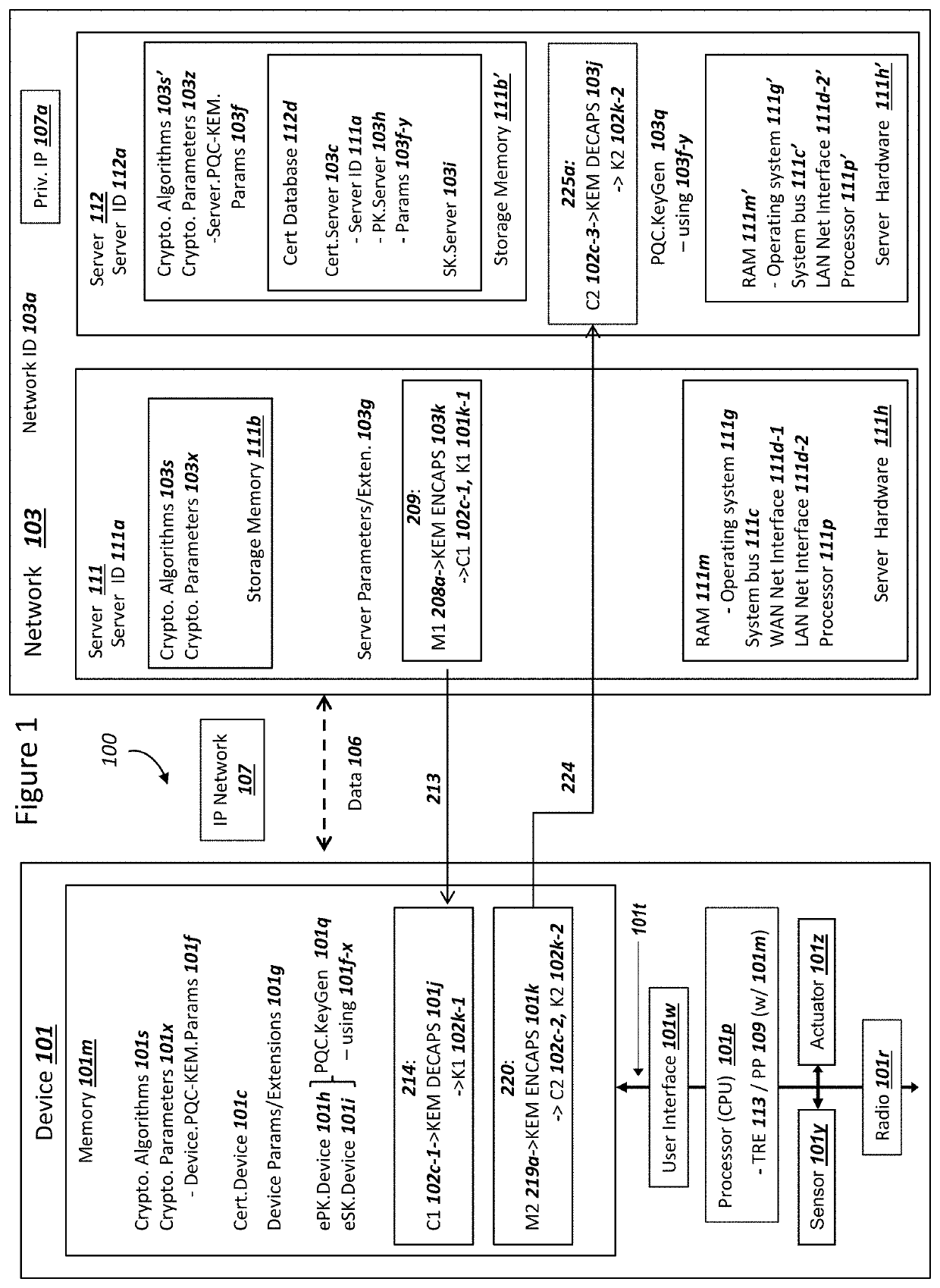
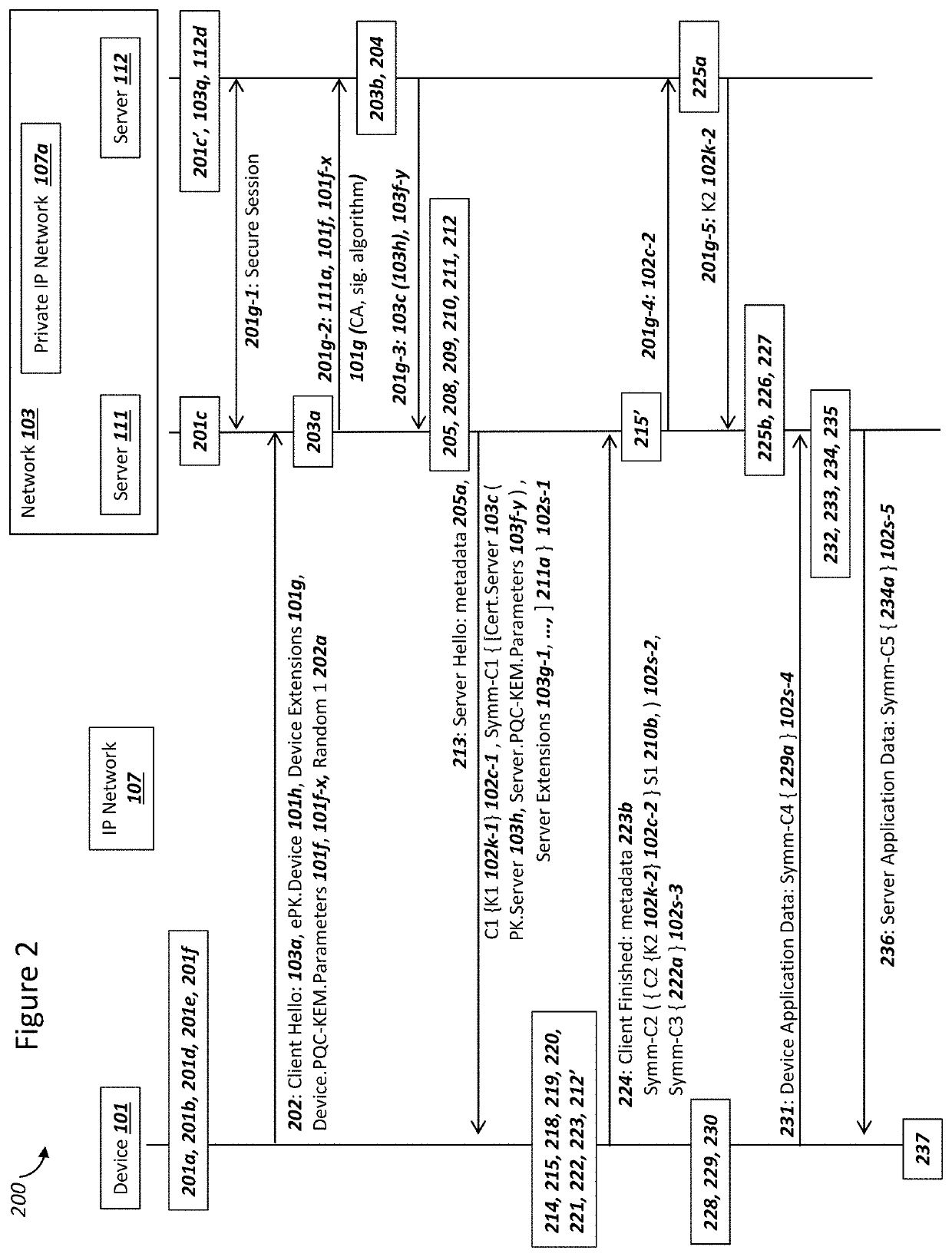
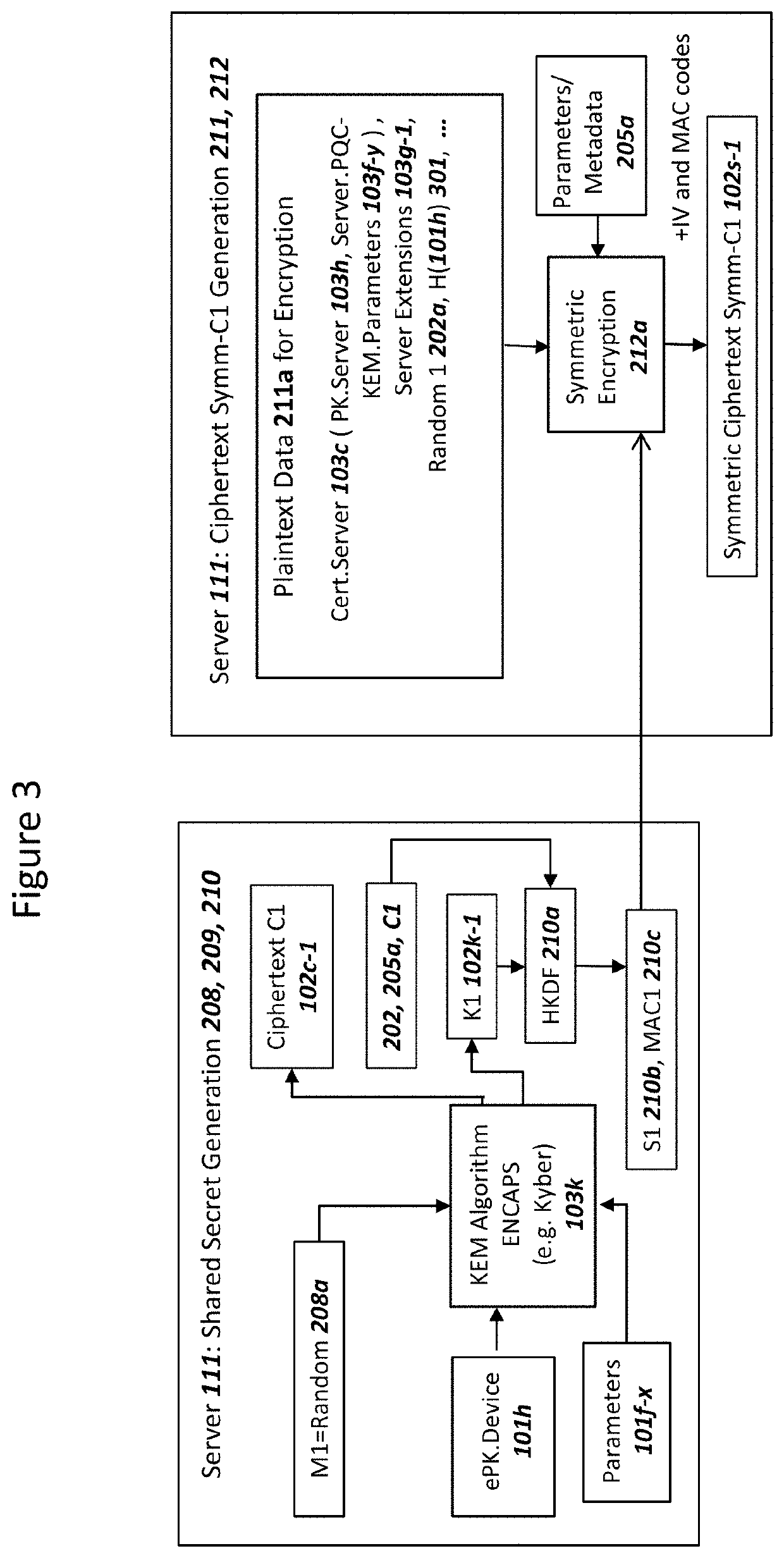
Device Securing Communications Using Two Post-Quantum Cryptography Key Encapsulation Mechanisms
ActiveUS20220038269A1Improve securityImprove security levelKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationKey (cryptography)Ciphertext
A network and a device can support secure sessions with both (i) a post-quantum cryptography (PQC) key encapsulation mechanism (KEM) and (ii) forward secrecy. The device can generate (i) an ephemeral public key (ePK.device) and private key (eSK.device) and (ii) send ePK.device with first KEM parameters to the network. The network can (i) conduct a first KEM with ePK.device to derive a first asymmetric ciphertext and first shared secret, and (ii) generate a first symmetric ciphertext for PK.server and second KEM parameters using the first shared secret. The network can send the first asymmetric ciphertext and the first symmetric ciphertext to the device. The network can receive (i) a second symmetric ciphertext comprising “double encrypted” second asymmetric ciphertext for a second KEM with SK.server, and (ii) a third symmetric ciphertext. The network can decrypt the third symmetric ciphertext using the second asymmetric ciphertext.
Owner:NIX JOHN A
Method of quantum cryptography using blind photon polarization quibits with multiple stages
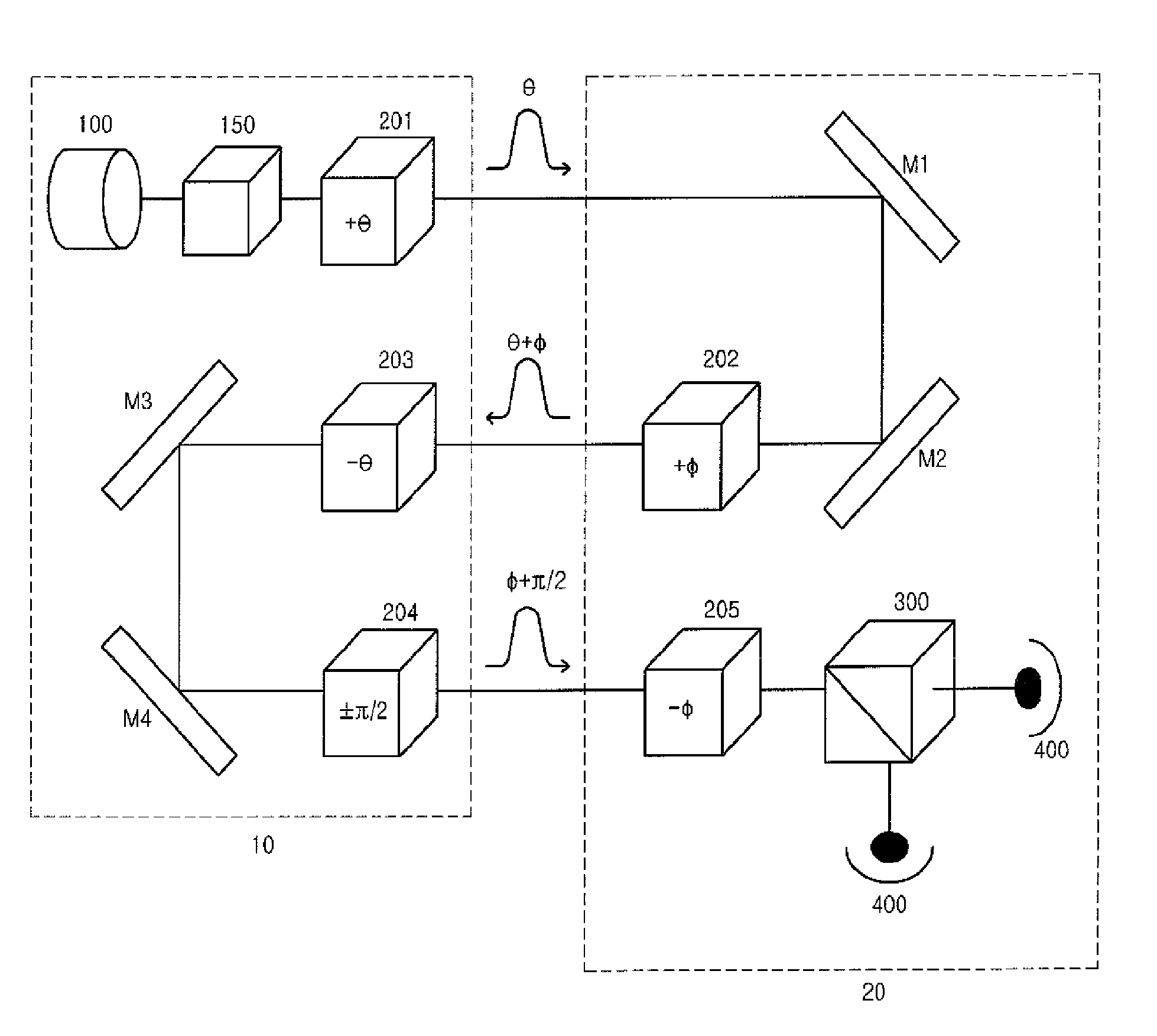
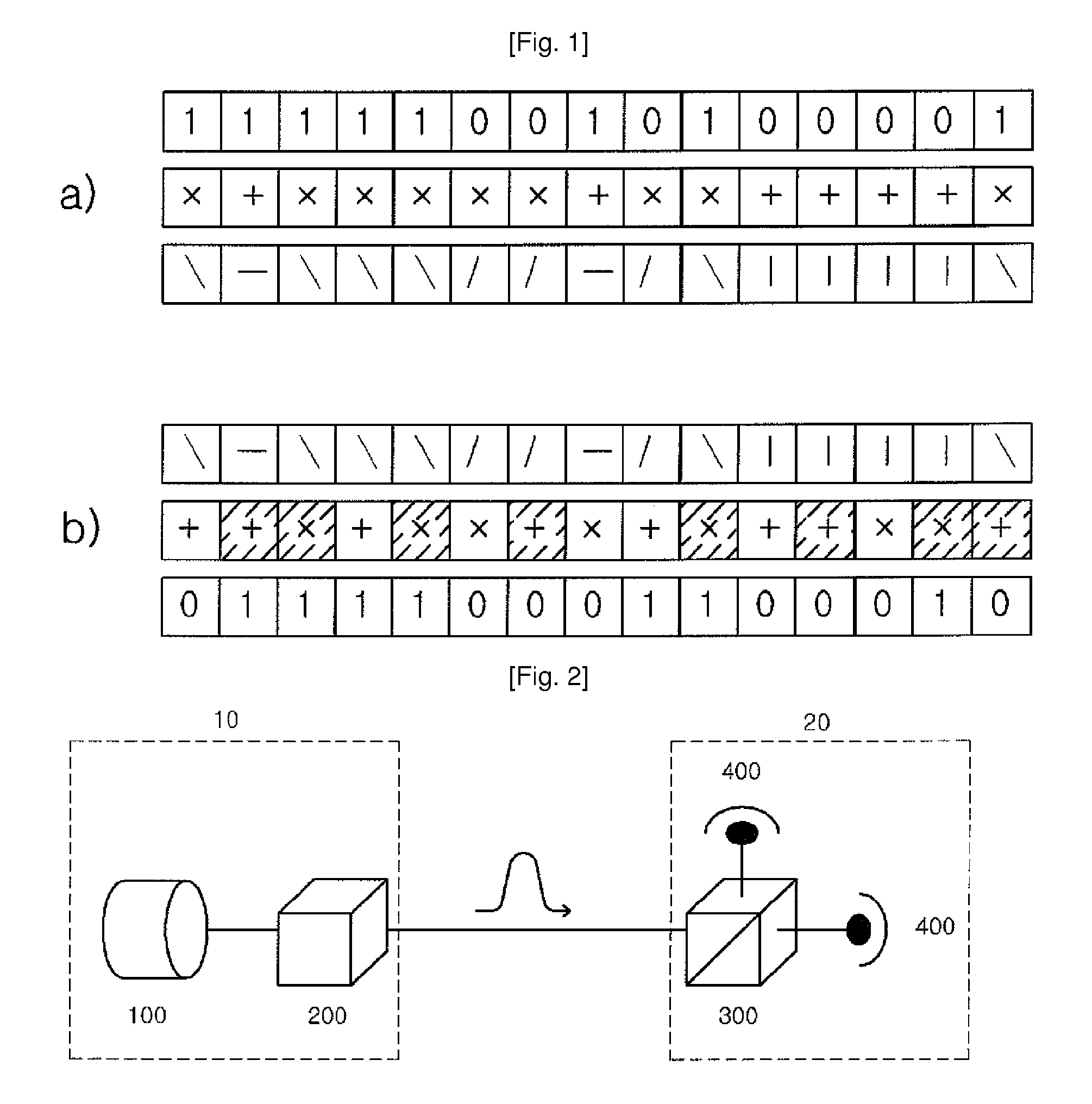
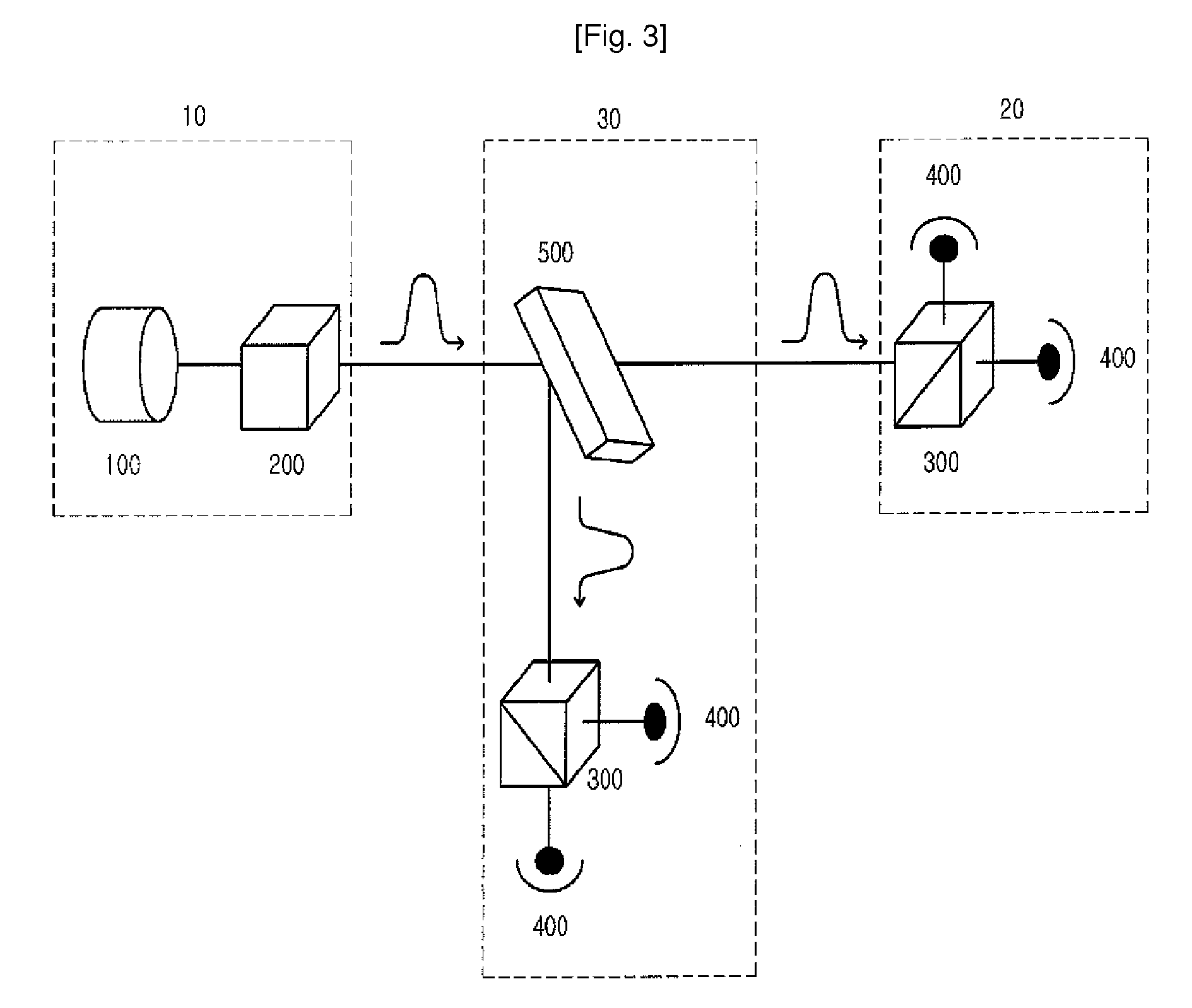
ActiveUS8126146B2Key distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationThird partyPhoton polarization
A cryptography method using a quantum phenomenon, which performs a multi-staged polarization process between a transmitter and a receiver to prevent a third party from knowing the polarization value of a photon. A transmitter rotates a photon flux by arbitrary angle θ and transmits it to a receiver. The receiver rotates the received photon flux by arbitrary angle φ and transmits it to the transmitter. The transmitter rotates the received photon flux by the reverse angle −θ of an angle, by which the transmitter 10 rotated it, then rotates it by polarization corresponding to an information bit, and transmits it to the receiver which rotates the received photon flux by the reverse angle −φ of an angle, and measures the polarization of the photon flux corresponding to the information bit, and recovers the information bit transmitted by the transmitter. Cryptography information may be transmitted using a plurality of photon fluxes.
Owner:PAICHAI UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
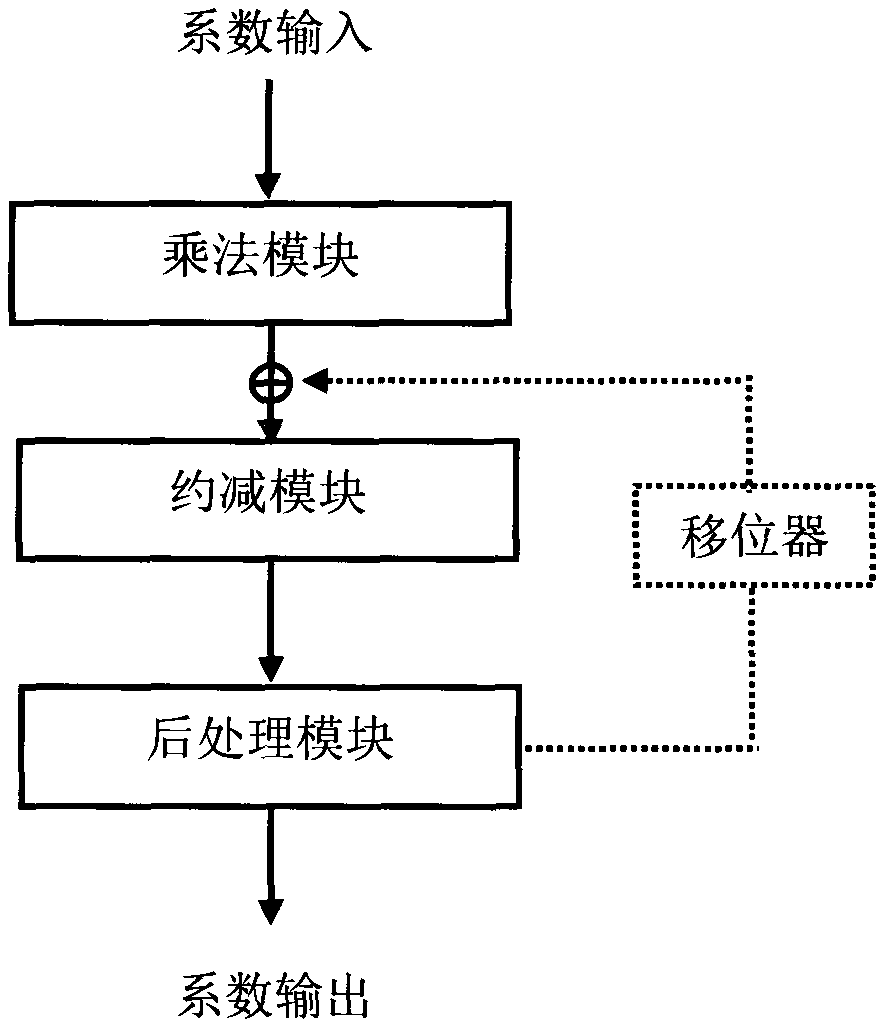
High-speed modular multiplier based on post-quantum cryptography of homologous curve and modular multiplication method of high-speed modular multiplier
PendingCN110908635ACalculation speedImprove throughputKey distribution for secure communicationComputations using residue arithmeticComputer hardwareComputer architecture
The invention discloses a high-throughput modular multiplier based on post-quantum cryptography of a homologous curve and a corresponding modular multiplication method thereof. The modular multipliermainly comprises a multiplication module, a reduction module and a post-processing module, wherein the multiplication module reduces the number of multipliers through methods such as Karatsuba and thelike. The reduction module uses a constant multiplier and a parallelization strategy with less resource consumption. And the post-processing module performs parallelization processing on the adder and calculates constant parameters in advance for optimization. Therefore, the modular multiplier disclosed by the invention has the characteristic of high throughput rate. Besides, the modular multiplication method disclosed by the invention is based on a prime number form of an unconventional cardinal number, and an optimized Barrett reduction method is used, so that the modular multiplication method has higher calculation speed than a traditional Montgomery representation method. In conclusion, the invention provides an effective modular multiplier architecture and a modular multiplication method for an existing encryption scheme of post-quantum cryptography based on a homologous curve.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Quantum cryptography network dynamic routing method
ActiveCN103001875BConvenient for dynamic expansionFast convergenceKey distribution for secure communicationData switching networksRefresh cycleRoute server
The invention discloses a quantum cryptography network dynamic routing method. According to the method, dynamic routing selection of encryption communication is performed by utilizing quantum cryptography according to changes of the quantum key quantity between relay nodes of a quantum cryptography network. According to the method, a route server is arranged for the relay nodes of the whole quantum cryptography network, and topology refresh cycles of the quantum cryptography network are set; in each topology refresh cycle, each relay node collects and processes state information of the relay node and reports results to the route server. After the route server collects the topology state information of each relay node, quantum cryptography network topology state information of a next topology refresh cycle is generated and sent to all the relay nodes of the quantum cryptography network. According to the quantum cryptography network topology state information obtained from the route server, a target relay node is calculated and determined to be a next skip route of communication data of a random other relay node according to a shortest path law through each relay node.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF QUANTUM SCI & TECH +2
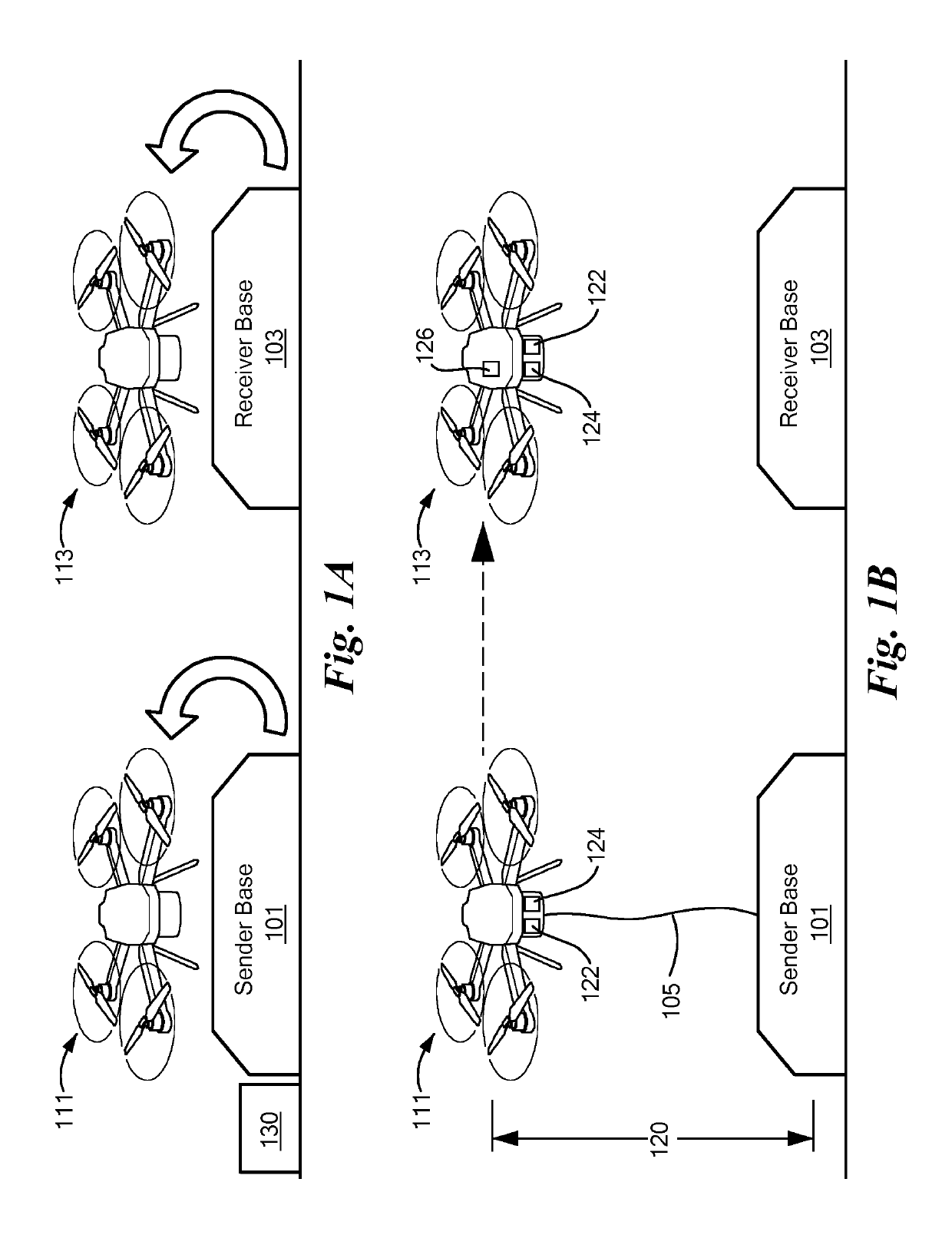
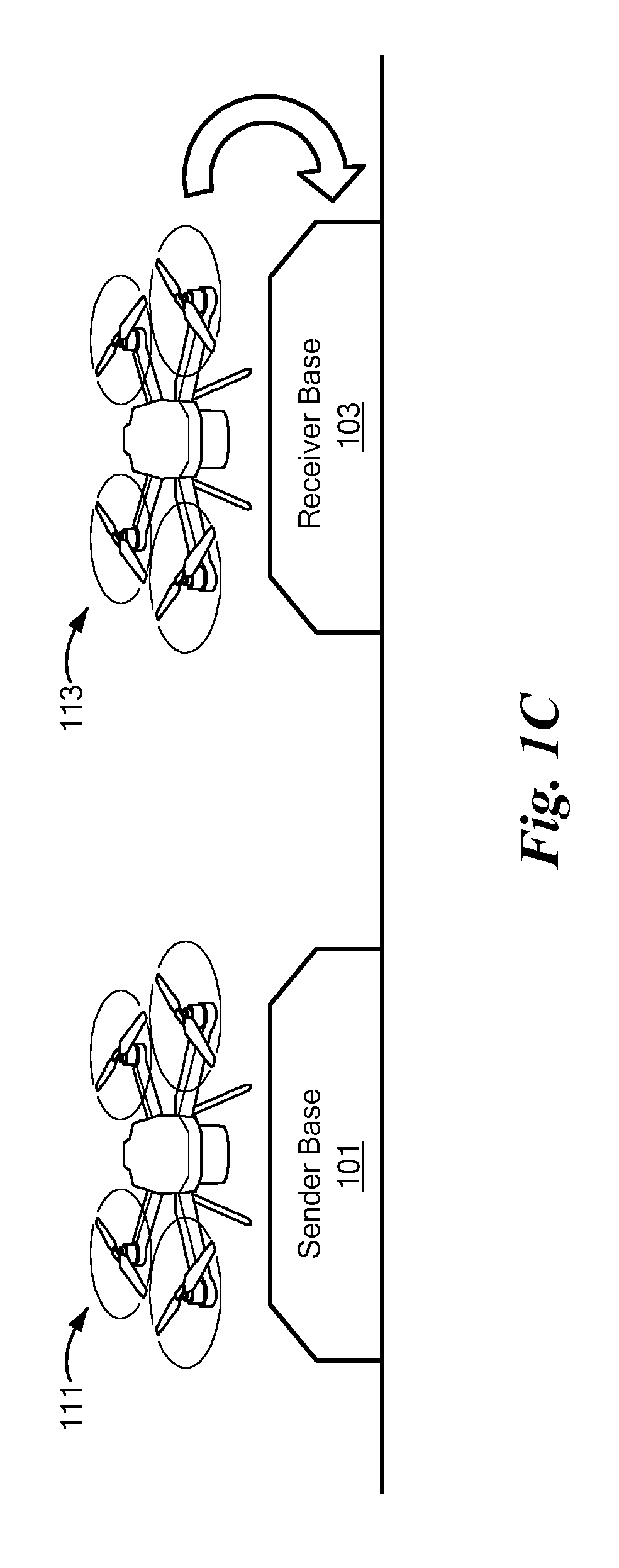
Reconfigurable free-space quantum cryptography system
ActiveUS10333701B2Key distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationTransmission protocolSecure communication
A system, and methods, for transmitting encrypted information as a quantum transmission between a first node and a second node, or among more than two nodes. Each node is characterized by an instantaneous spatial position, and the instantaneous spatial position of the second node is repositionable within a frame of reference associated with the first node. A hovering drone is adapted either for running a quantum key transmission protocol in secure communication with the first node, and / or for running a quantum key reception protocol in secure communication with the second node. Either drone may serve as a relay of optical data between a base station and another drone. Secure communication among more than two nodes may be reconfigured.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Processor for realizing post quantum cryptography Saber algorithm
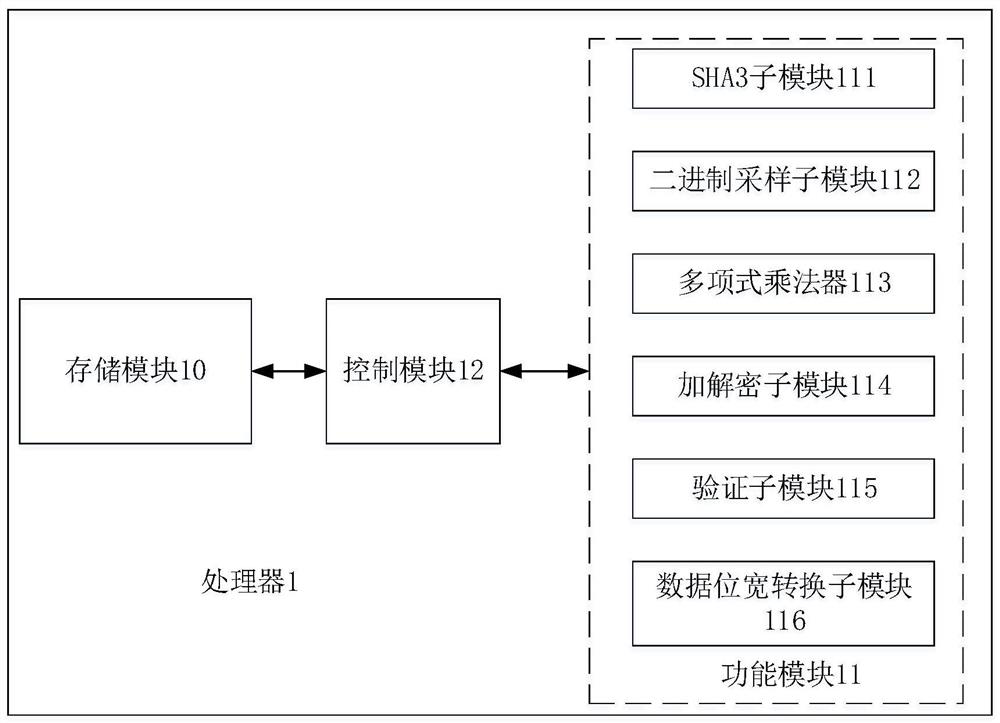
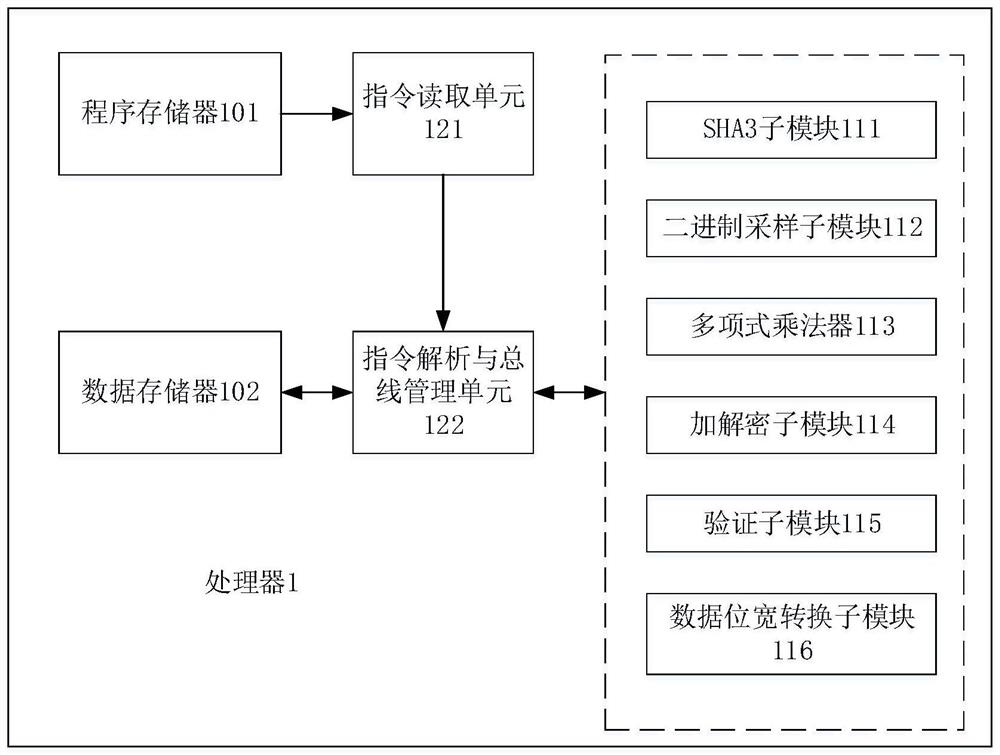
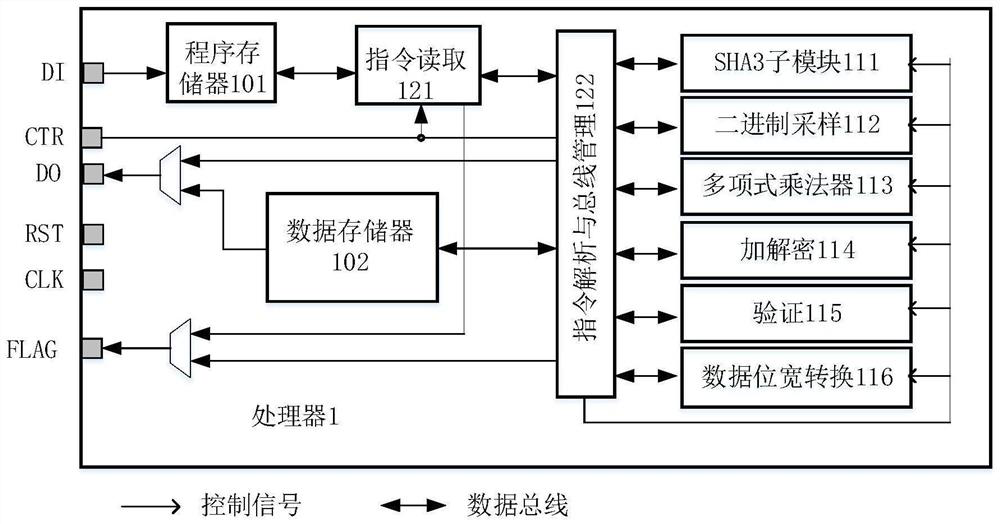
PendingCN114154640AReduce consumptionA large amountQuantum computersMachine execution arrangementsKey (cryptography)Algorithm
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of information security, and discloses a processor for implementing a post quantum cryptography Saber algorithm, the processor is implemented by hardware and comprises a storage module for storing data and instructions, the processor uses a customized reduced instruction set, and the instructions stored in the storage module are instructions in an instruction set; the function module is used for executing operations related to the post quantum cryptography Saber algorithm, and the function module comprises the following sub-modules: a third generation secure hash algorithm SHA3 sub-module, a binary sampling sub-module, a polynomial multiplier, an encryption and decryption sub-module, a verification sub-module and a data bit width conversion sub-module; and the control module is used for controlling each sub-module in the functional module to execute corresponding operation according to the instruction stored in the storage module so as to realize at least one of key generation, key encapsulation and key de-encapsulation in the post quantum cryptography Saber algorithm. According to the embodiment of the invention, the resource overhead can be saved while high efficiency is realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
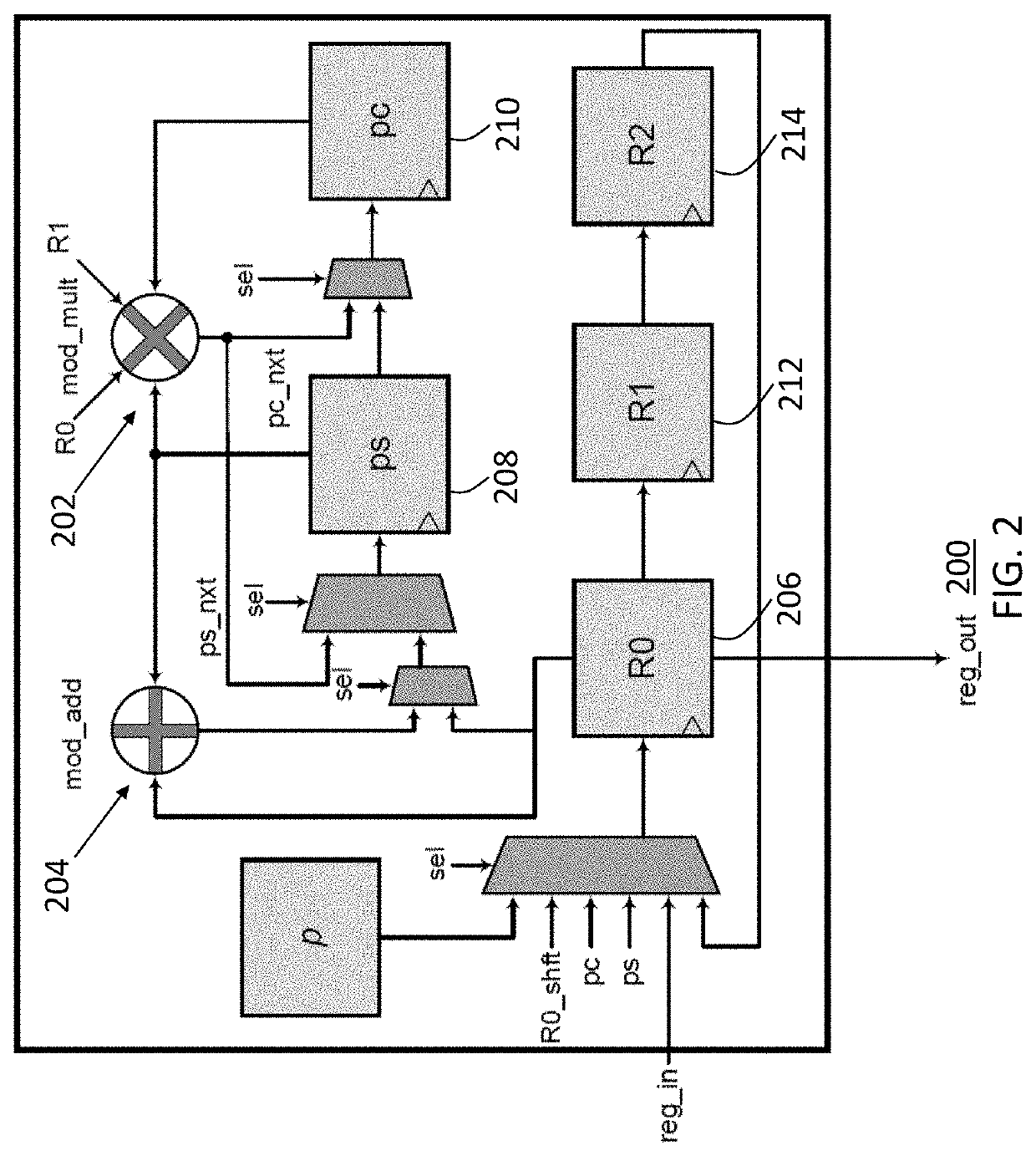
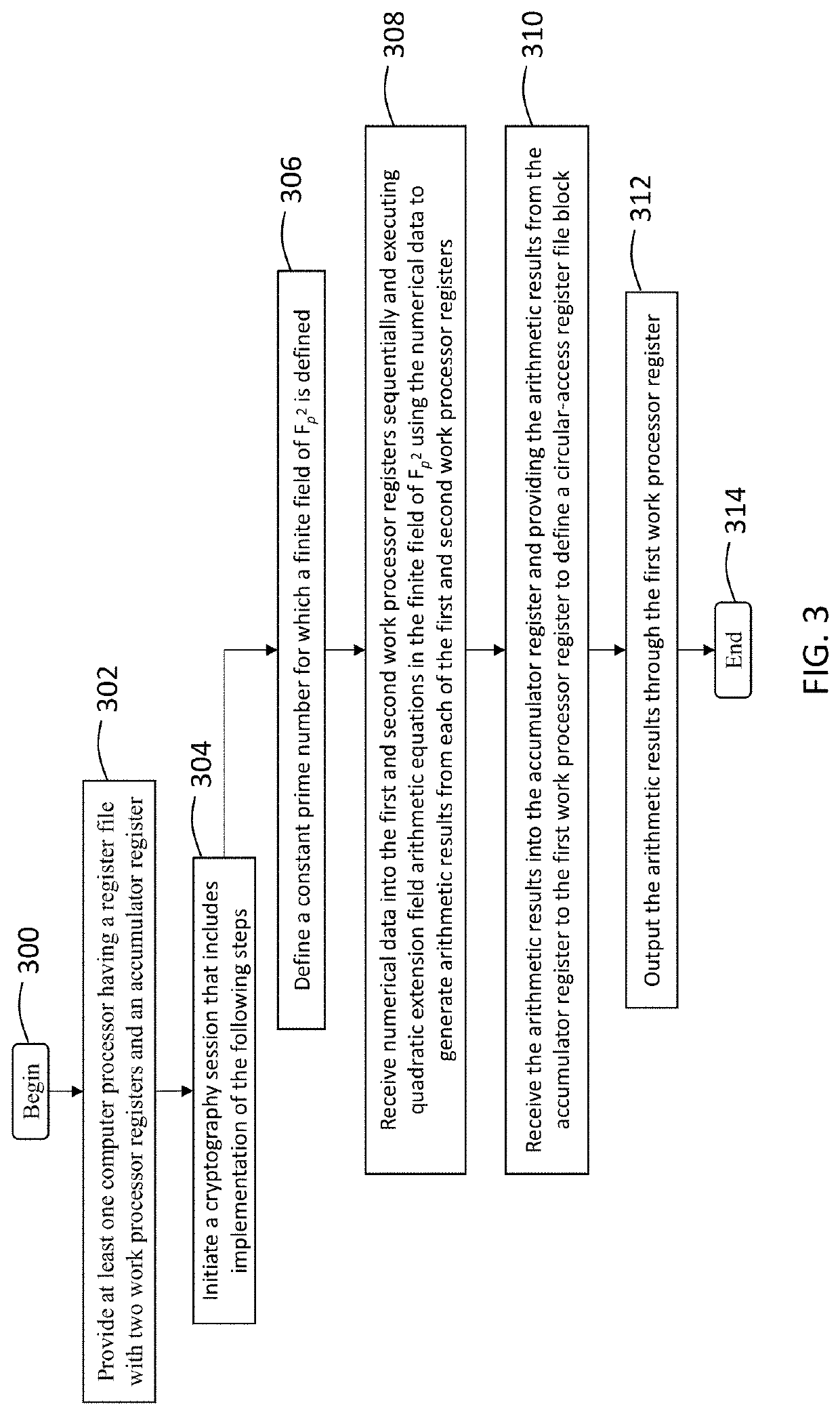
Efficient architecture and method for arithmetic computations in post-quantum cryptography
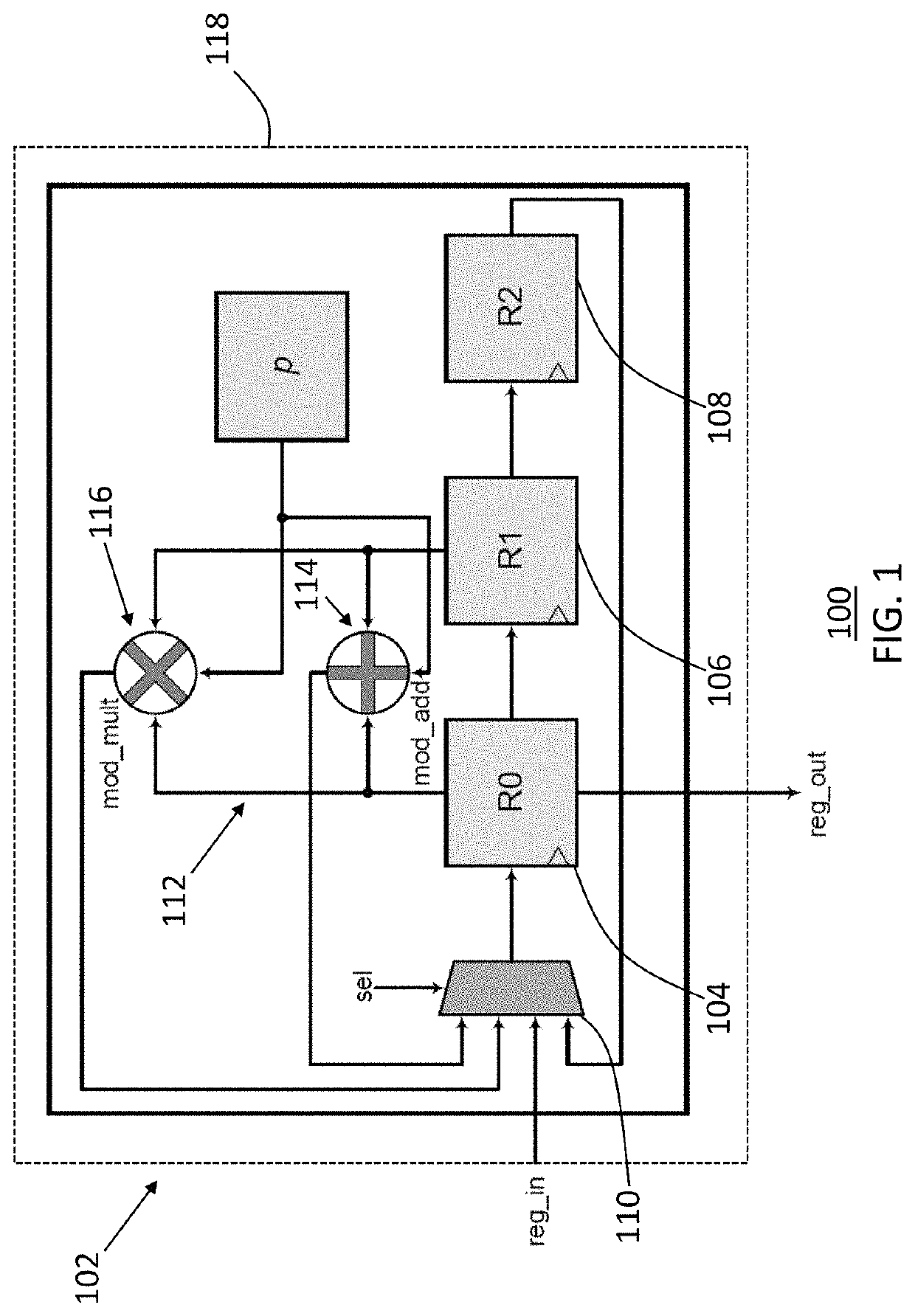
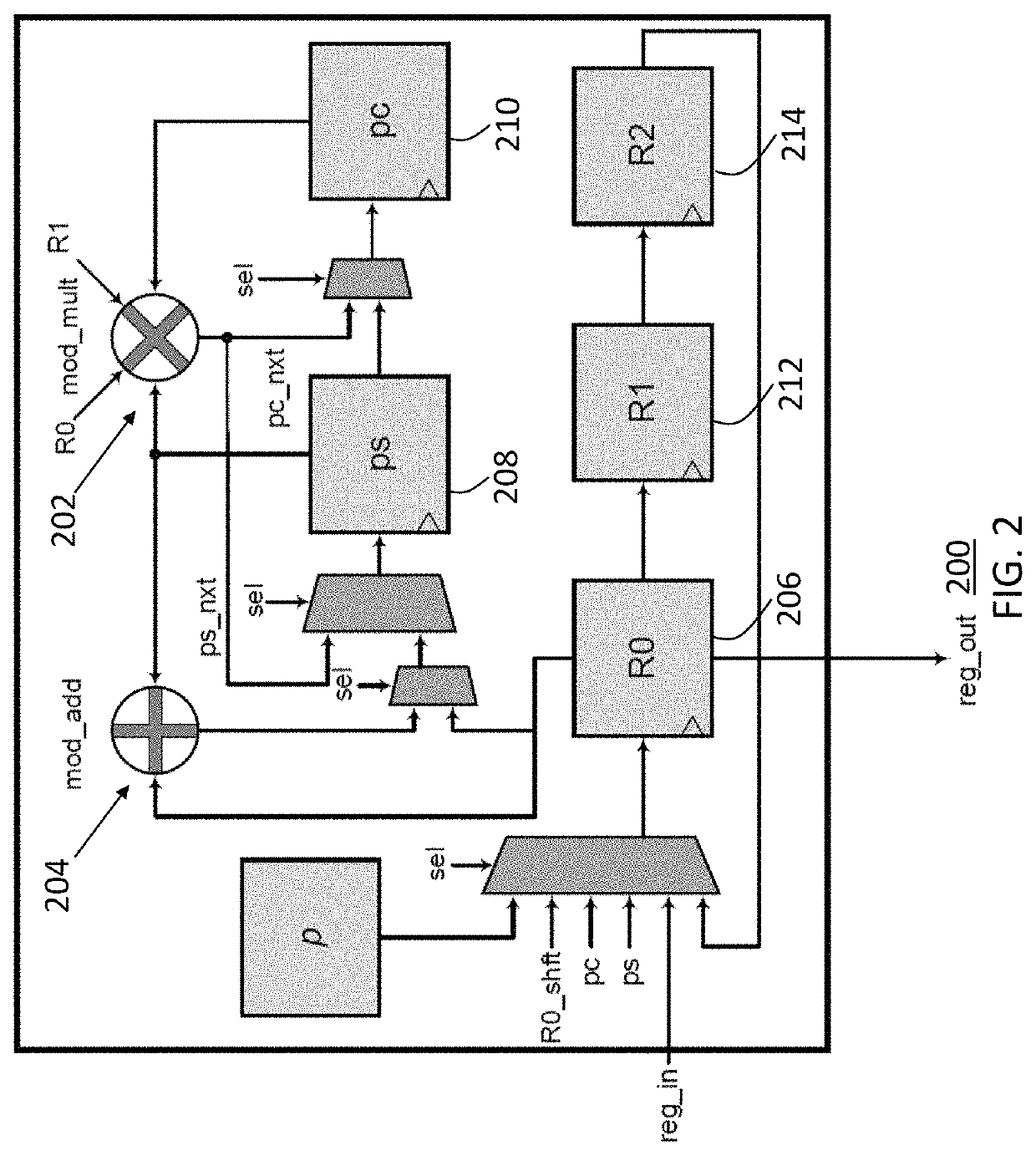
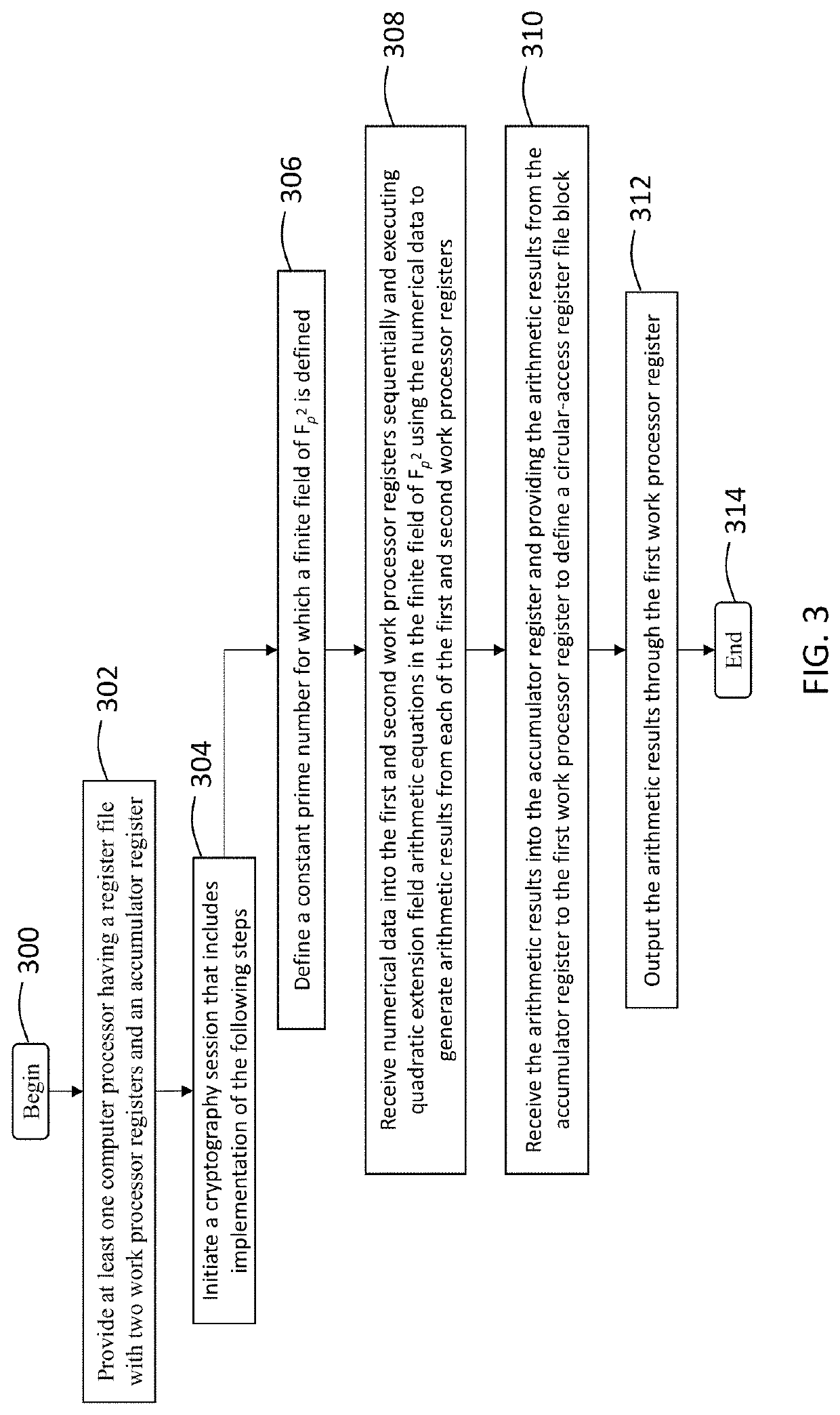
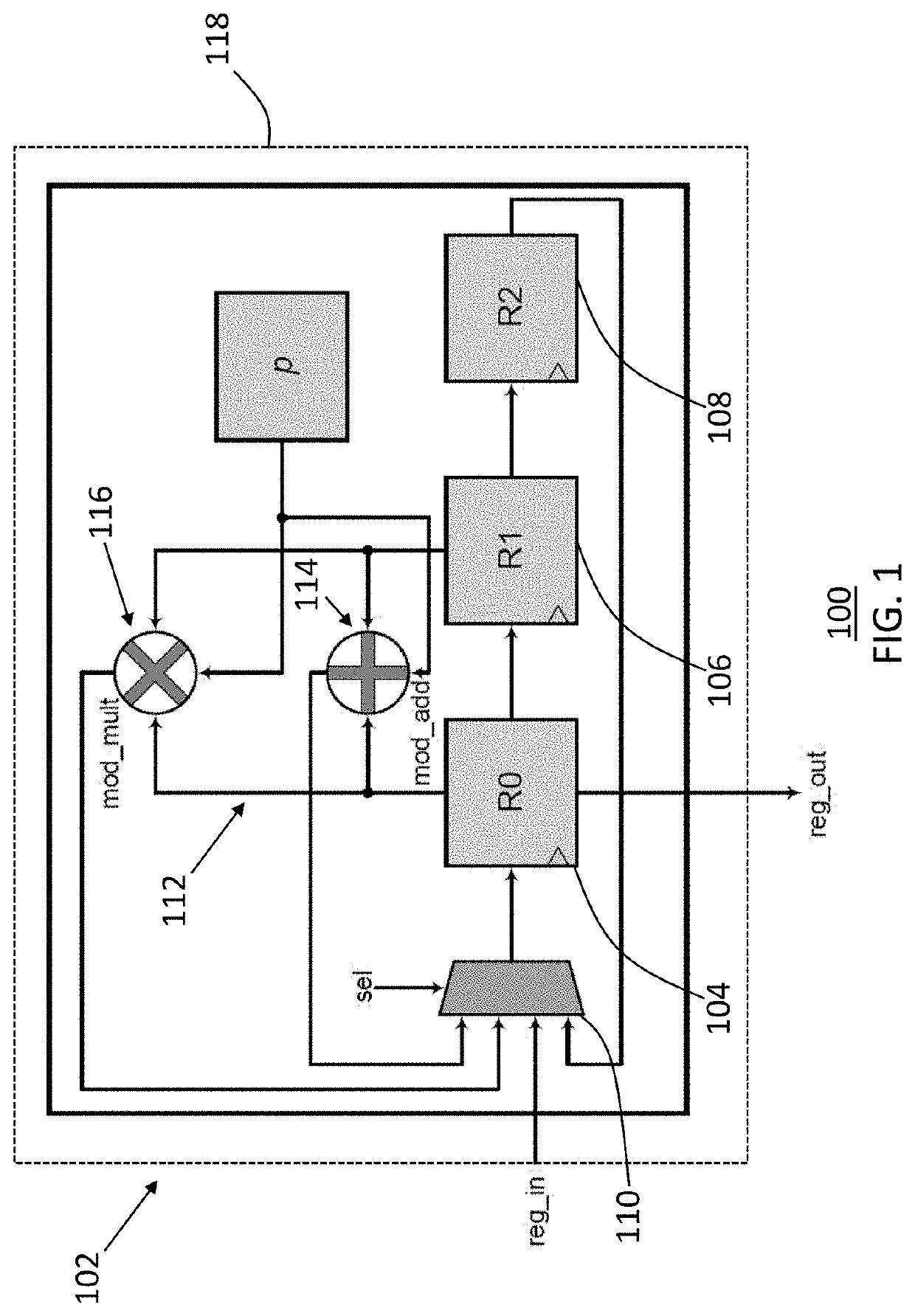
ActiveUS11165578B1Reducing processing footprintReduce necessary power and energyKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer architectureCryptosystem
A computer processing system for reducing a processing footprint in cryptosystems utilizing quadratic extension field arithmetic such as pairing-based cryptography, elliptic curve cryptography, code-based cryptography and post-quantum elliptic curve cryptography that includes at least one computer processor having a register file with three processor registers operably configured to implement quadratic extension field arithmetic equations in a finite field of Fp2 and a multiplexer operably configured to selectively shift from each of the three processor registers in sequential order to generate modular additional results and modular multiplication results from the three processor registers.
Owner:PQSECURE TECH LLC
Efficient architecture and method for arithmetic computations in post-quantum cryptography
ActiveUS20210320796A1Reducing processing footprintReduce necessary power and energyKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationComputer architectureCryptosystem
A computer processing system for reducing a processing footprint in cryptosystems utilizing quadratic extension field arithmetic such as pairing-based cryptography, elliptic curve cryptography, code-based cryptography and post-quantum elliptic curve cryptography that includes at least one computer processor having a register file with three processor registers operably configured to implement quadratic extension field arithmetic equations in a finite field of Fp2 and a multiplexer operably configured to selectively shift from each of the three processor registers in sequential order to generate modular additional results and modular multiplication results from the three processor registers.
Owner:PQSECURE TECH LLC
Low-memory-occupancy implementation technology based on post quantum cryptography Saber algorithm
ActiveCN113472525AReduce memory usageReduce the difficulty of deploymentKey distribution for secure communicationKey (cryptography)Algorithm
The invention discloses a low-memory-occupancy implementation technology based on a post quantum cryptography Saber algorithm. The low-memory-occupancy implementation technology comprises a key generation method and system, an encryption method and system and a decryption method and system. The vector multiplication of the polynomial matrix is calculated by adopting the immediate generation of the matrix, and the memory space occupied by the polynomial matrix is reduced to the memory size occupied by a single element, so that the memory occupation of the Saber scheme is remarkably reduced, and the deployment of the Saber scheme in the Internet of Things equipment is facilitated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Polarization coding quantum cryptography system
ActiveUS8265279B2Stable characteristicsKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationQuantum channelOptoelectronics
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
General software implementation method for round-off learning on ring in post quantum cryptography construction
ActiveCN113179151AWide applicabilityQuantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationGeneral purpose softwareAlgorithm
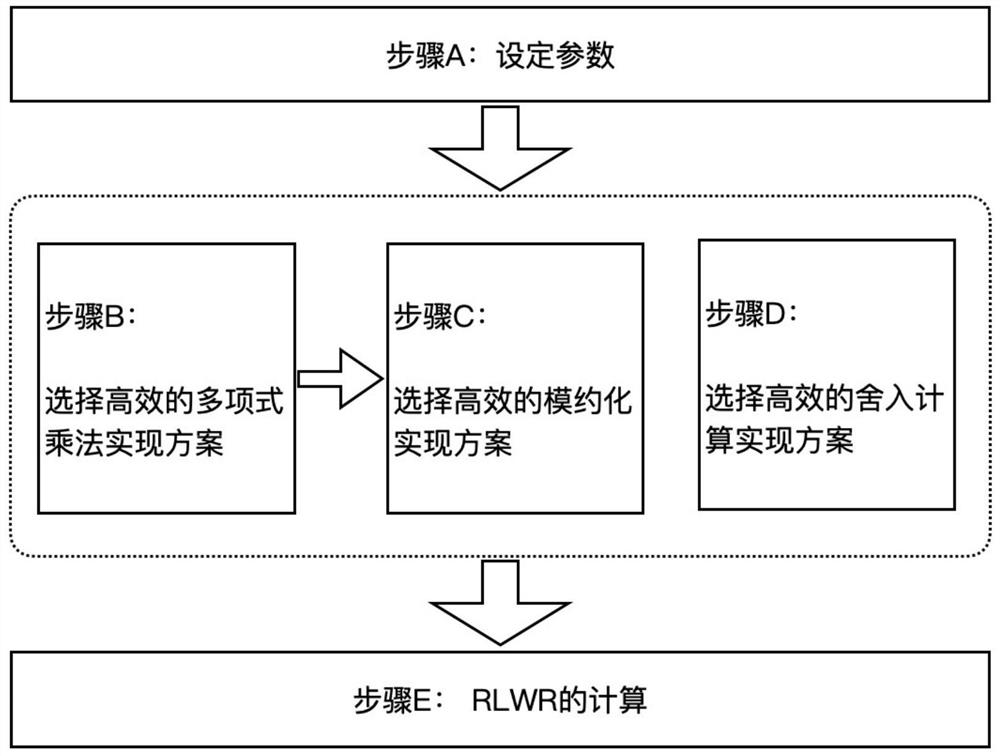
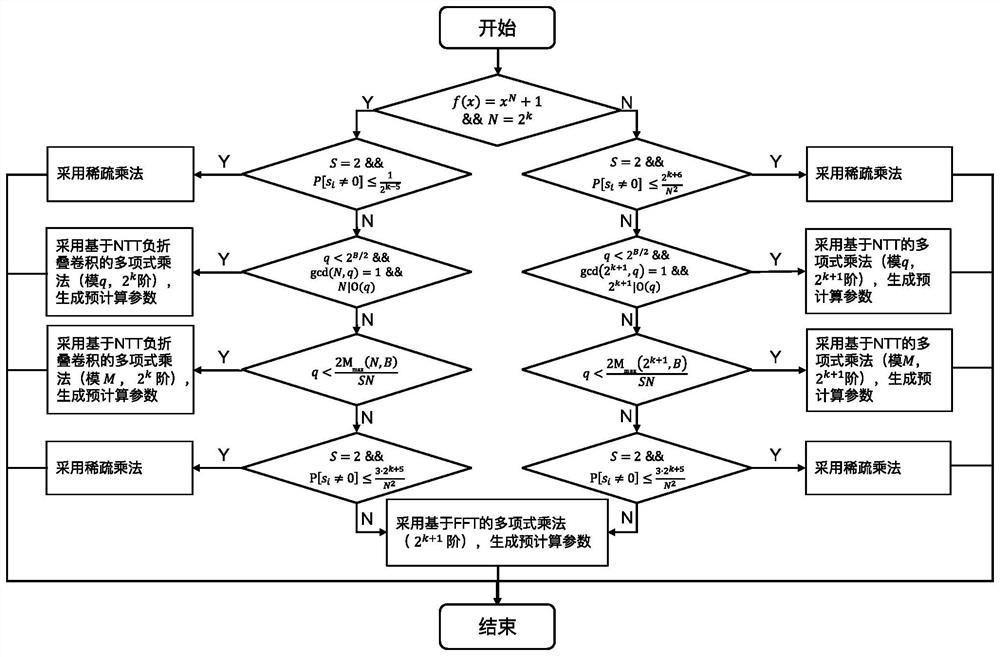
The invention discloses a general software implementation method for round-off learning on a ring in post quantum cryptography construction, which comprises the following steps of: A, setting RLWR parameters N, f, p, q and S and a CPU digit B of an actual operation platform; B, selecting a polynomial multiplication implementation algorithm according to the parameters N, f, q, S and B, recording the algorithm as PMA, and generating pre-computable parameters in the polynomial multiplication implementation scheme; C, selecting an available modular reduction method as a modular reduction implementation scheme according to the parameter q and the selected polynomial multiplication implementation scheme PMA, and recording as MRA; D, selecting a rounding calculation implementation method according to the parameters p and q, recording the rounding calculation implementation method as RA, and generating parameters which can be pre-calculated in the rounding calculation implementation scheme; and E, for the input polynomials a(x) and s(x), calculating and outputting a corresponding value b(x) in RLWR distribution.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CAS
Special processor, model verification method and device thereof, processing method and medium
PendingCN114764551AImprove verification efficiencyImprove development efficiencyQuantum computersCAD circuit designProcessor modelMachine instruction
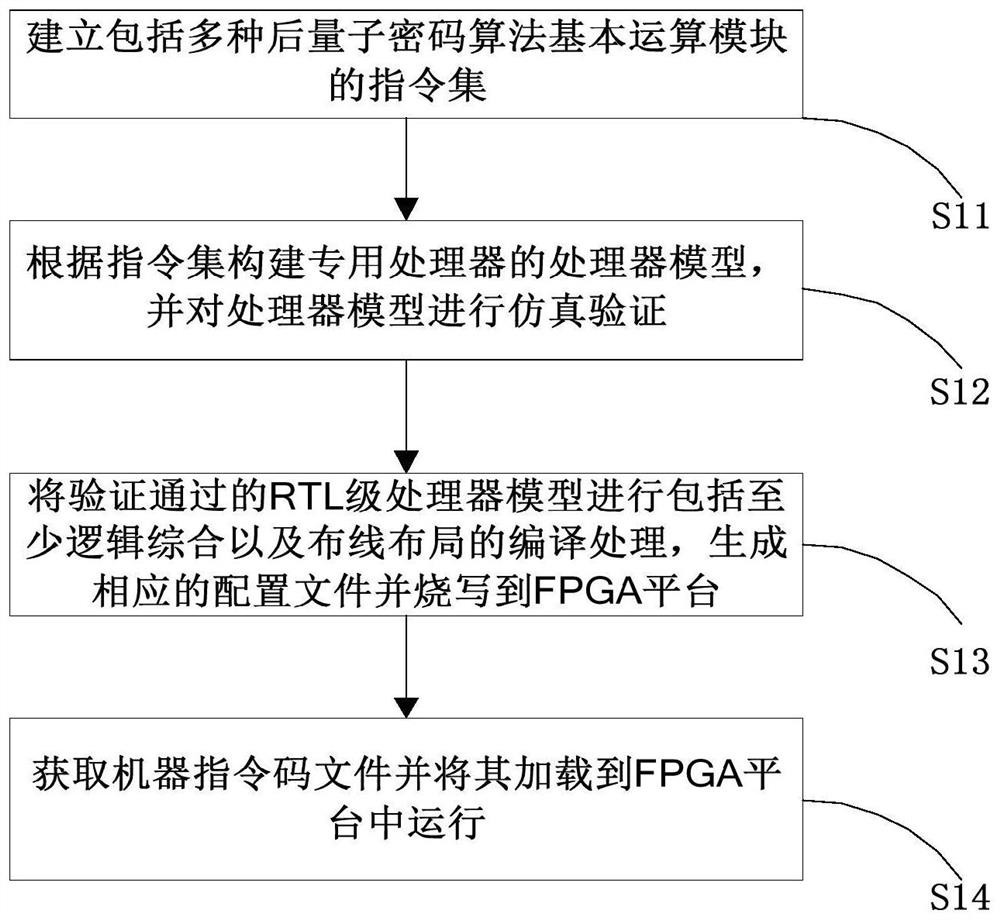
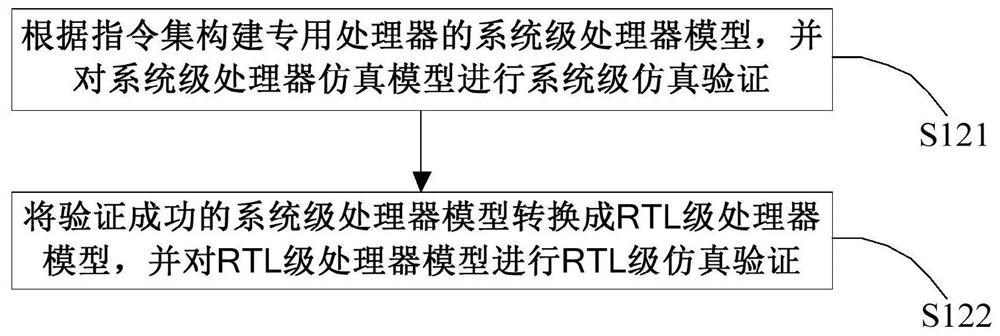
The invention discloses a special processor, a model verification method and device thereof, a processing method and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an instruction set comprising various post quantum cryptography algorithm basic operation modules; constructing a processor model of the special processor based on the instruction set, and performing simulation verification on the processor model; the processor model passing the simulation verification is subjected to compiling processing including at least logic synthesis and layout wiring so as to generate a corresponding configuration file, and the configuration file is programmed to an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) platform; obtaining a machine instruction code file and loading the file into the FPGA platform for operation to verify whether the special processor model can execute processing corresponding to the post quantum cryptography algorithm code corresponding to the machine instruction code file, and the post quantum cryptography algorithm code is realized based on the instruction set. And at least one basic operation module of the post-quantum cryptographic algorithm is called. In this way, the flexibility of processor design and development can be improved.
Owner:NATIONZ TECH INC
Quantum encryption communication device, quantum encryption communication method and quantum encryption communication system
InactiveCN102447557BKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesCommunications systemLength wave
Owner:SONY CORP
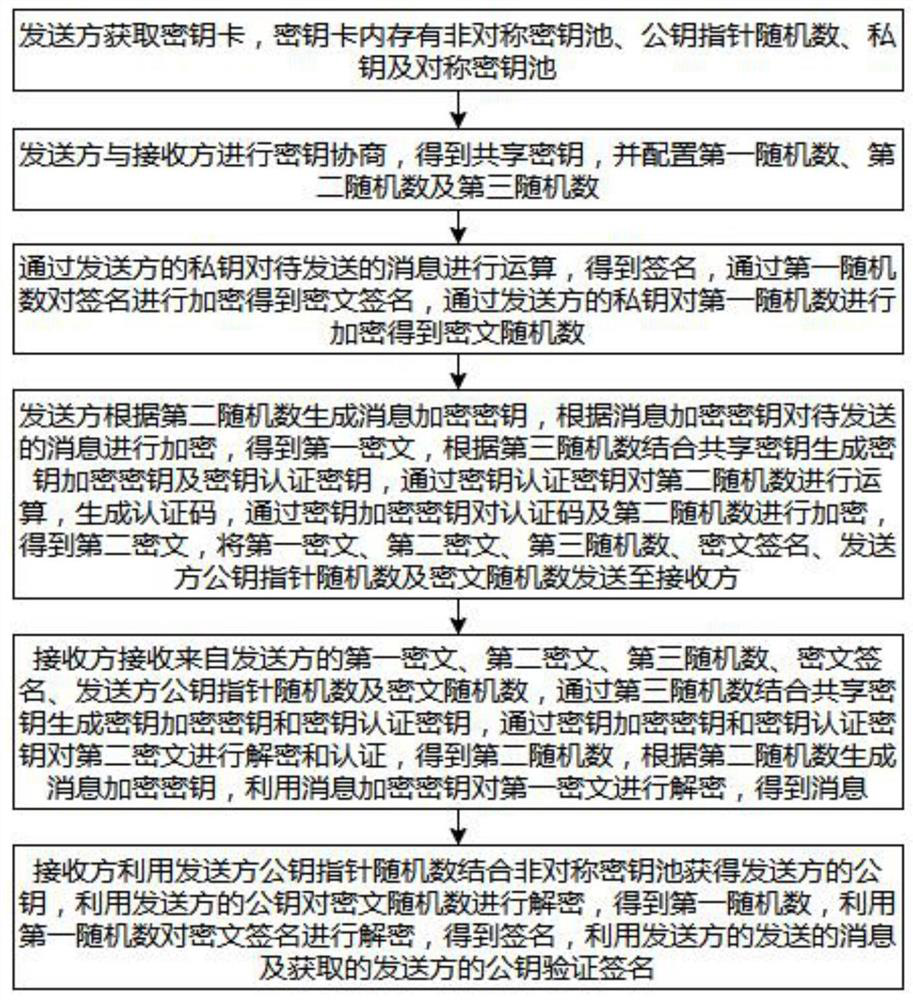
Post quantum cryptography communication method
PendingCN113468582ARandom number generatorsDigital data protectionKey (cryptography)Digital signature
The invention provides a post quantum cryptography communication method, which comprises the following steps that: a sender encrypts a signature through a first random number, encrypts the first random number through a private key of the sender, encrypts a message to be sent according to a message encryption key generated by a second random number, encrypts the second random number according to a key encryption key generated by the third random number, and sends the encrypted datato a receiver; and the receiver obtains the second random number through the key encryption key generated by the third random number, obtains a message through the second random number, obtains a public key of the sender through a public key pointer random number of the sender, obtains a first random number through the public key of the sender, obtains a signature through the first random number, and performs verification according to the message, the public key and the signature. According to the post quantum cryptography communication method provided by the invention, message transmission communication and digital signature authentication are realized, and the risk that a key is stolen or cracked by a quantum computer is reduced.
Owner:佳乔(深圳)投资有限公司
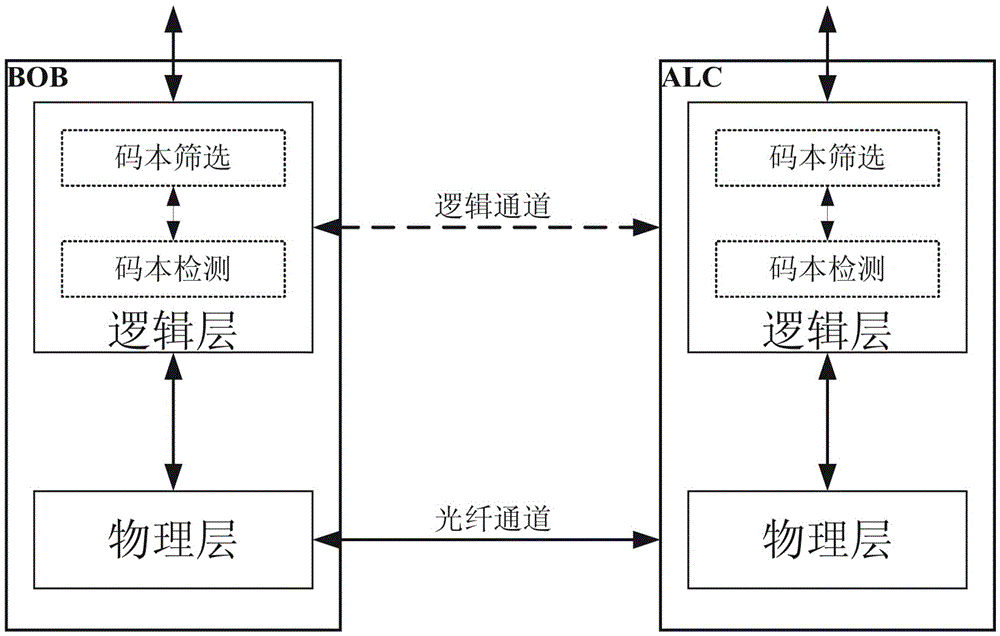
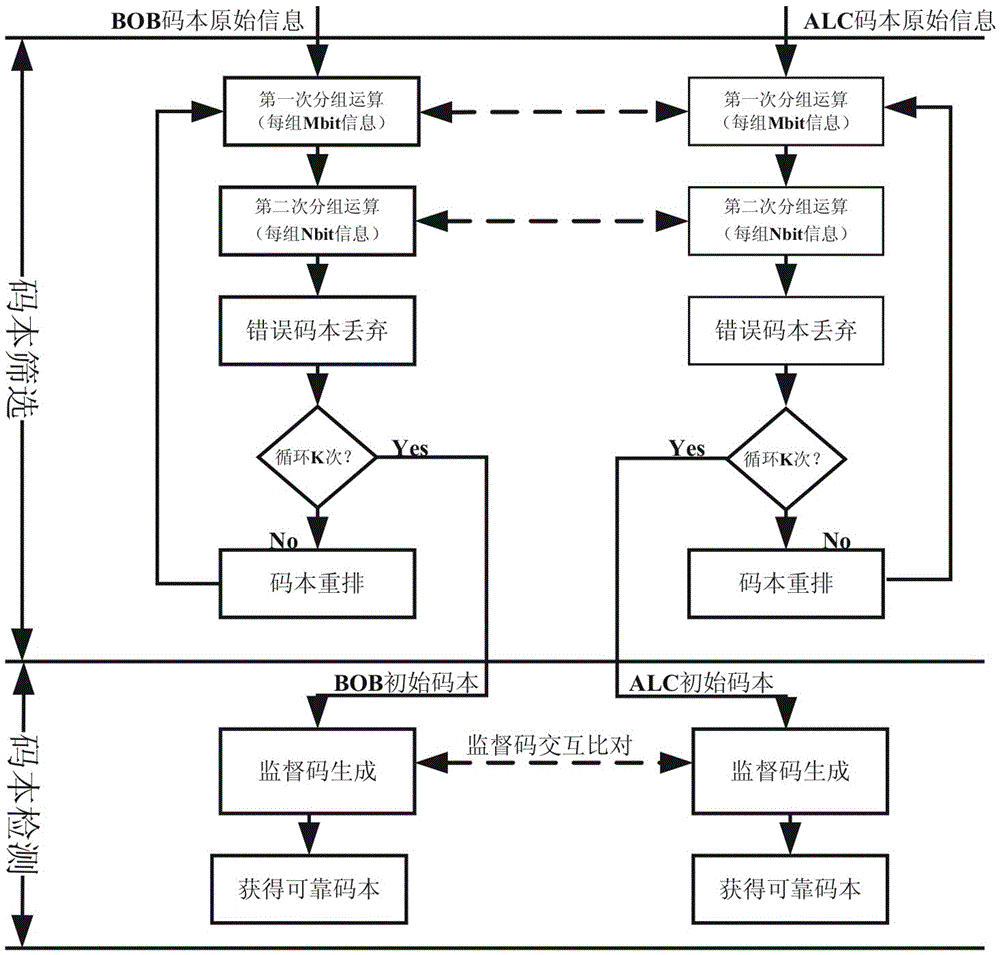
A codebook verification method for quantum secure communication
ActiveCN103532705BAddress riskAchieve exclusivityKey distribution for secure communicationCommunications systemReliable transmission
The invention discloses a codebook verifying method for quantum secret communication. The method comprises the following steps: a plurality of screening, comprising a plurality of grouping operation, comparison and rearrangement of codebooks, are implemented for original information of generated codebooks obtained through ALC and BOB to obtain the codebooks with higher credibility; then the obtained screened codebooks are integrally calculated to obtain one supervision code; if the supervision codes of two parties are consistent, the codebooks are reliable codebooks; otherwise, the codebooks are unreliable and directly discarded; the next group of codebooks is generated renewedly. Through using the codebook verifying method, the two parties for communication can obtain safe and reliable codebooks without disclosing one section of secret keys; the characteristics of stability and high efficiency are achieved. The codebook verifying method can be used for solving the problem for obtaining credible codebooks in the quantum secret communication, can improve the characteristics of secret reliable transmission of the quantum communication system, and has the characteristics of high efficiency and high stability.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAPU SCI INSTR CO LTD
Quantum Secure Dialogue Method Based on Quantum Encryption
To solve the information leakage problem is a research focus of a quantum dialogue. To solve the information leakage problem, a quantum encryption thought is first introduced to the field of quantum dialogues, and a novel method for privately sharing an initial quantum state between correspondents is provided, namely quantum encryption sharing is provided. The quantum encryption sharing is utilized to provide a quantum secure dialogue protocol based on quantum encryption. According to the protocol, an EPR serves as a quantum private key to encrypt and decode transmission photons, and the private key can be reused after rotating operation. Public announcement of the initial quantum state can be omitted due to the quantum encryption sharing, and accordingly the information leakage problem is solved. Information theory efficiency of the protocol is nearly 100% and is higher than that of a previous information leakage resisting quantum dialogue protocol. In addition, only single photon measurement is needed by the protocol, nearly only single photons are utilized to serve as quantum resources, and accordingly the protocol is easy to execute in practice.
Owner:浙江康奥思信息技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com