Patents
Literature
31 results about "Power line noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
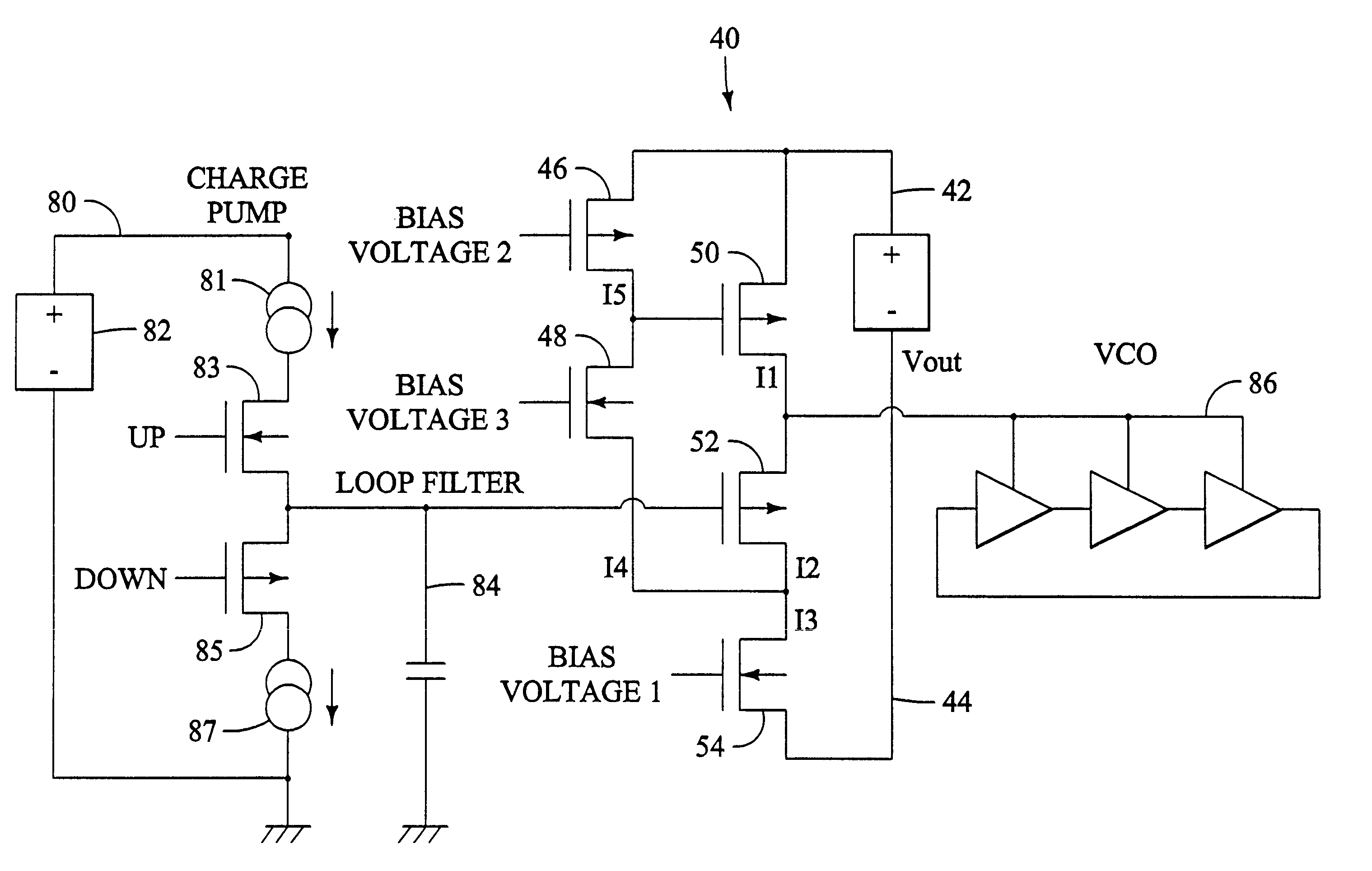
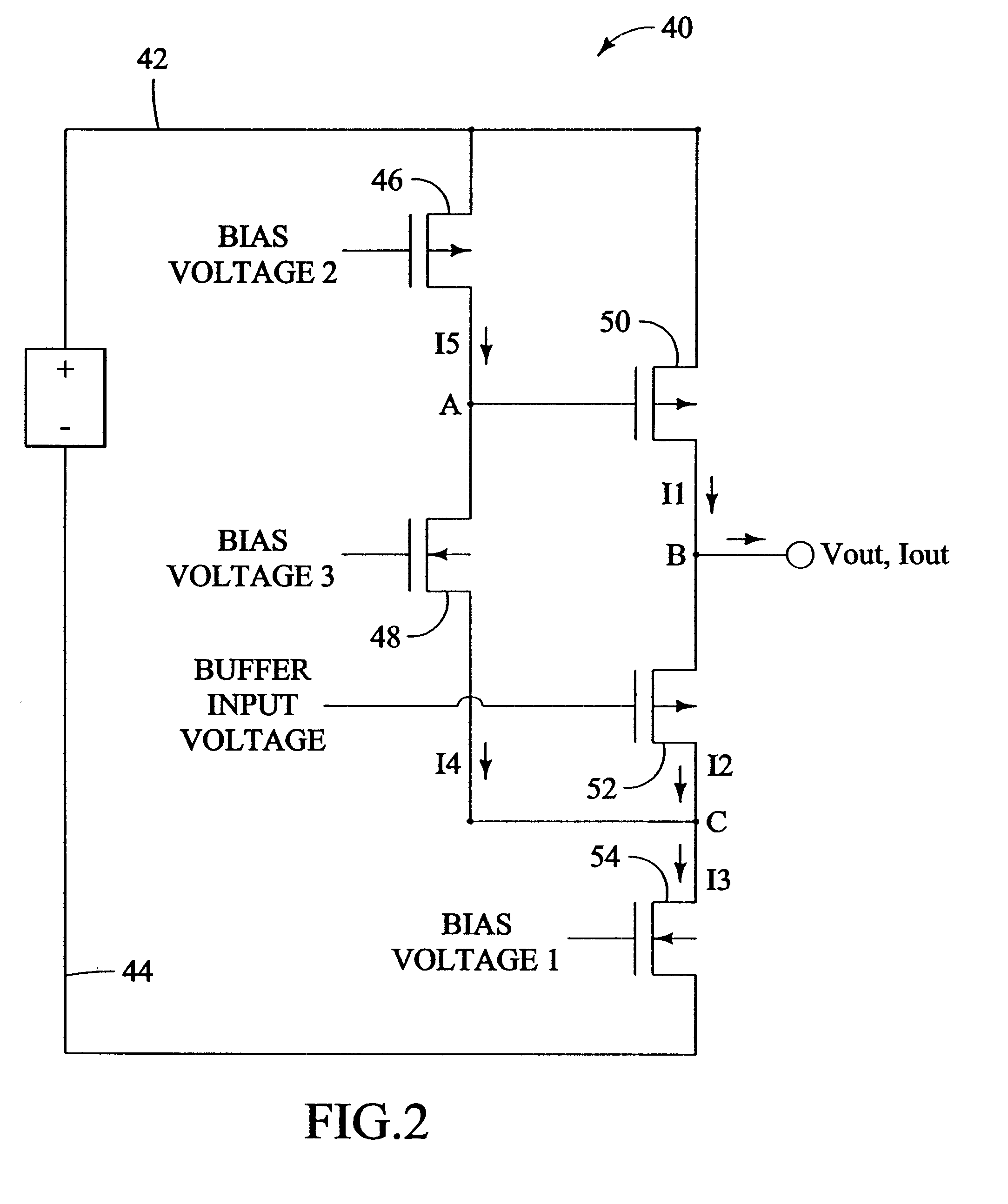
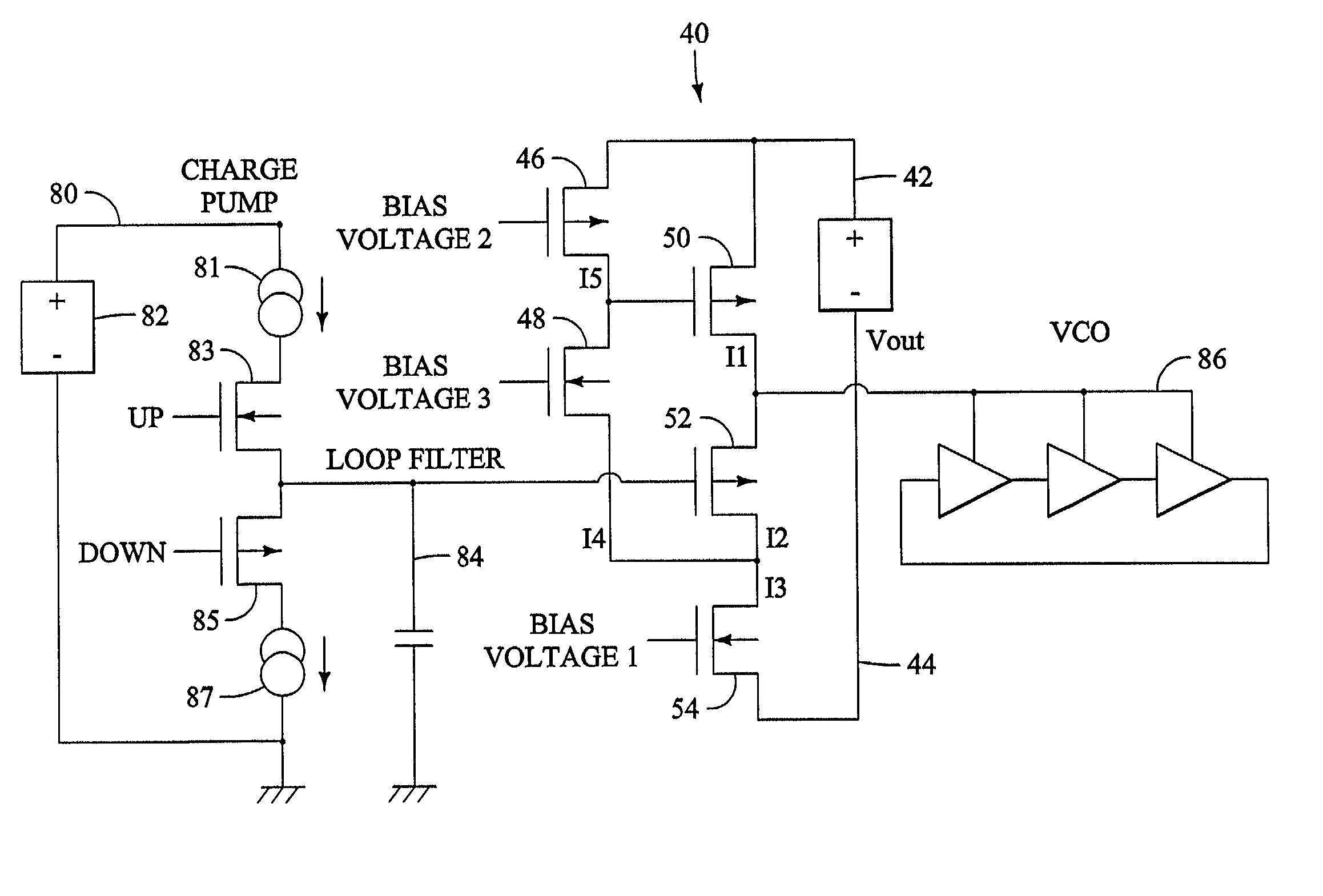
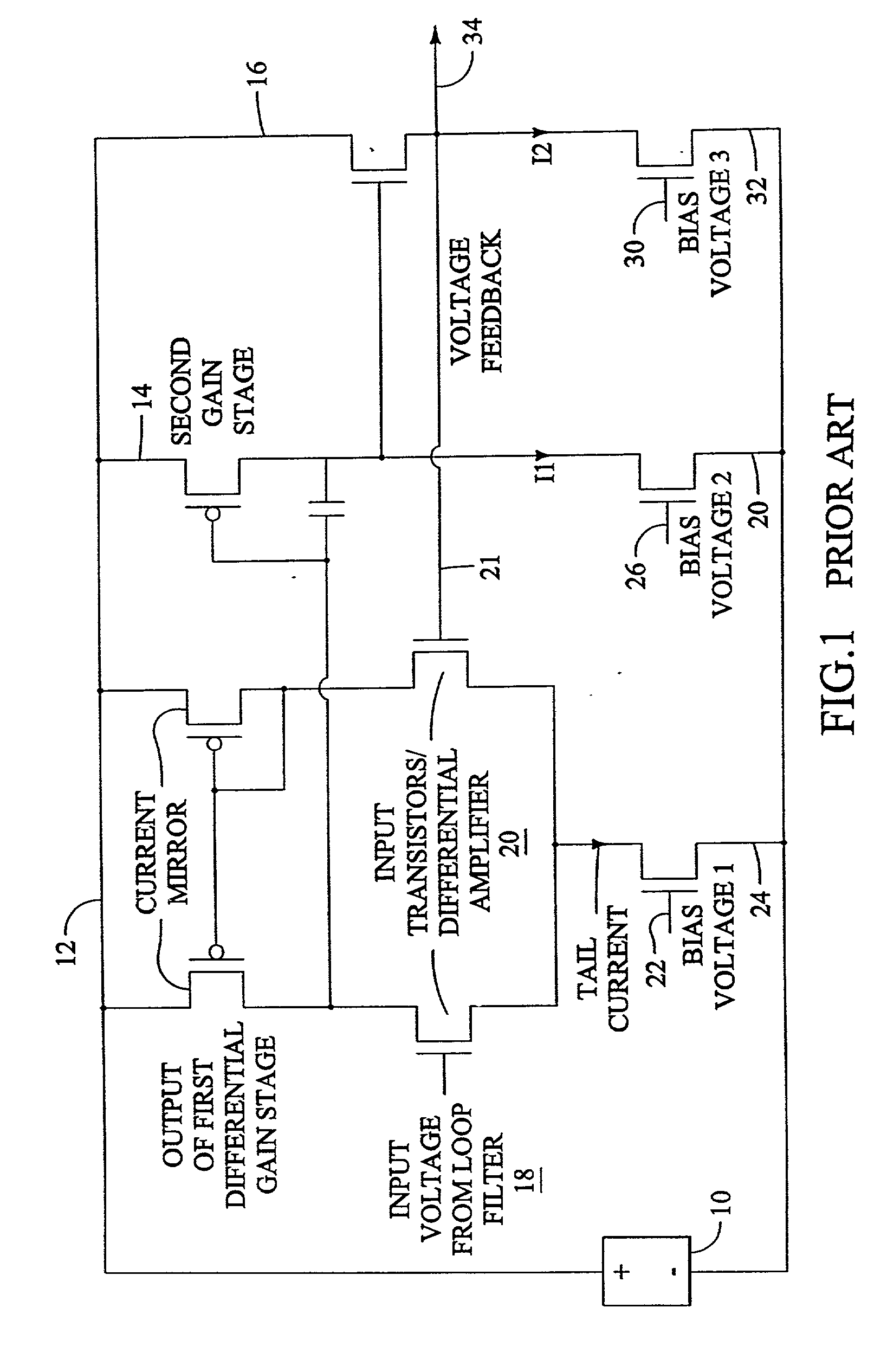
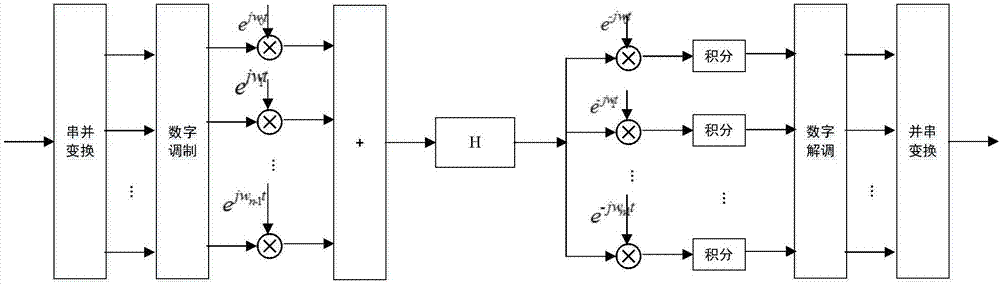
Efficient current feedback buffer
InactiveUS6525613B2Optimization rangeLimit its operationPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsDelay-locked loopFrequency synthesizer
An efficient current feedback buffer is revealed. The buffer is useful in power supplies for a number of analog and digital devices, including CMOS voltage controlled ring oscillators, frequency synthesizers, delay locked loops, phase accumulators, and phase locked loops. The power supply and buffer maintains a low impedance output to the load, regulates the voltage output of the supply, and rejects power line noise.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
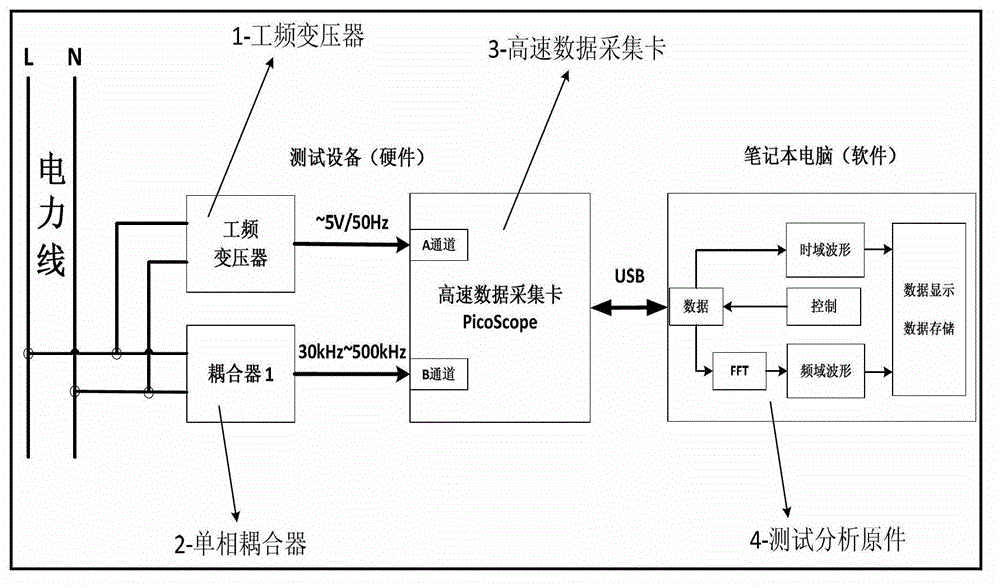
Spot low-voltage power line carrier channel noise testing system and method thereof
ActiveCN103063936AHigh utility valueSolve some difficult problems of noise field testingNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementLow voltageCarrier signal
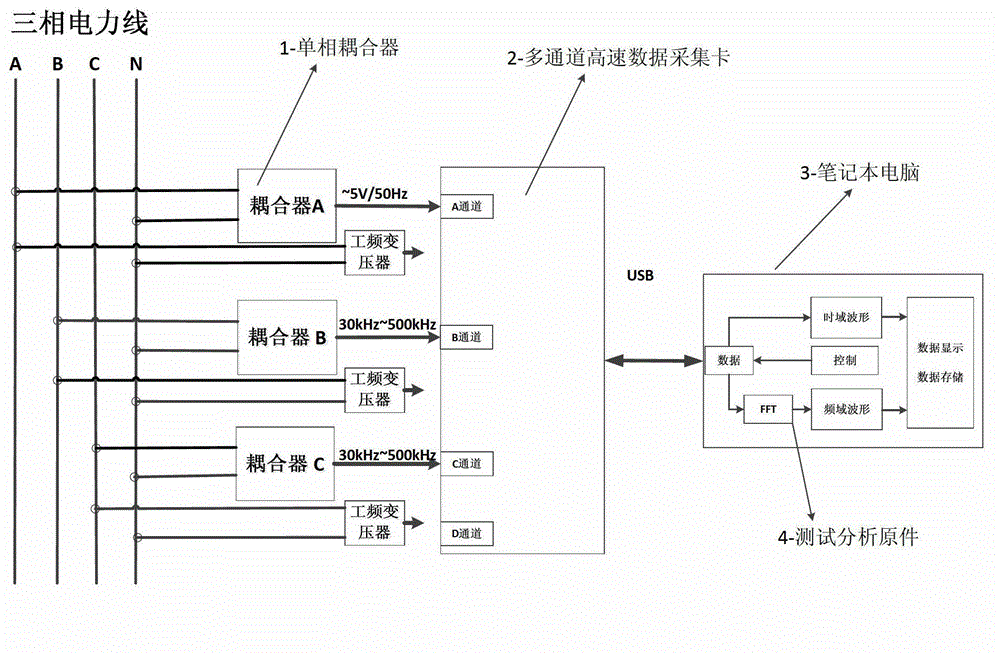
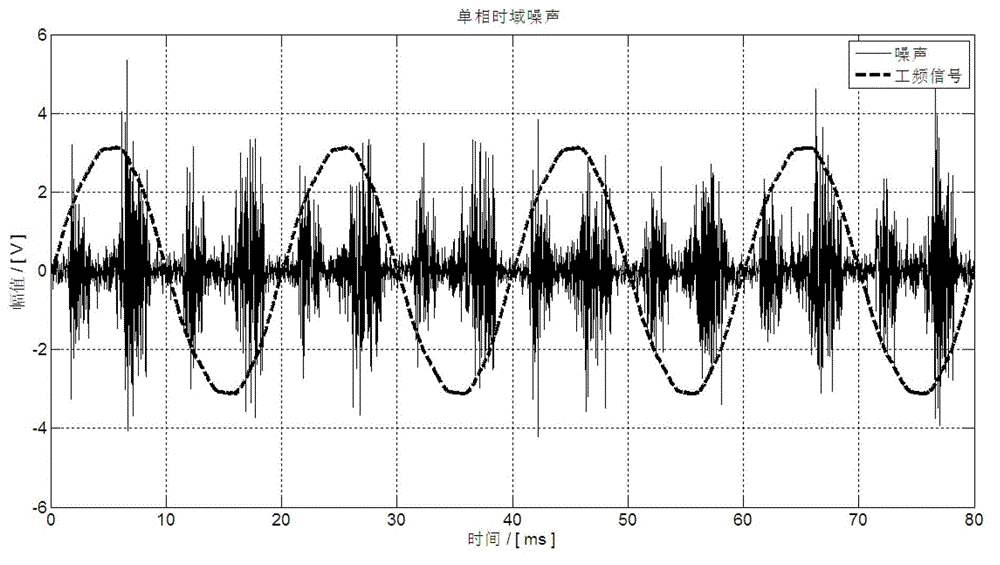
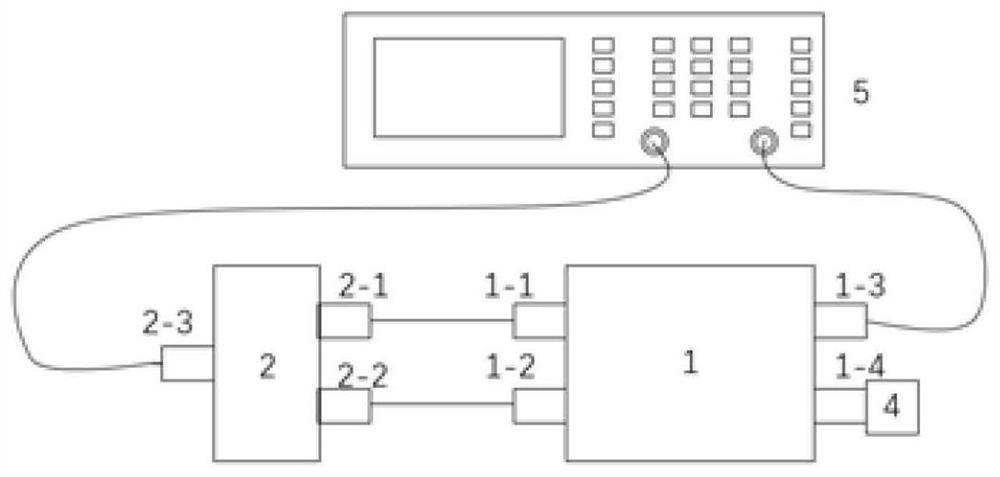
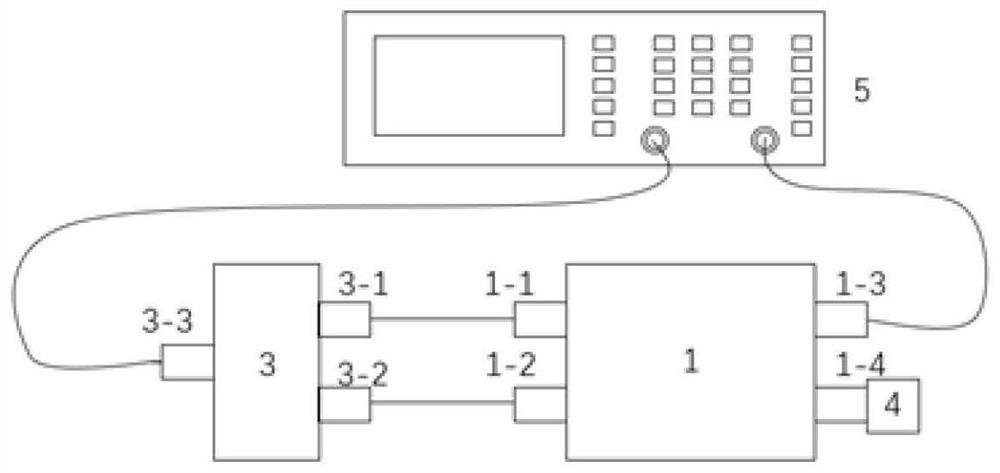
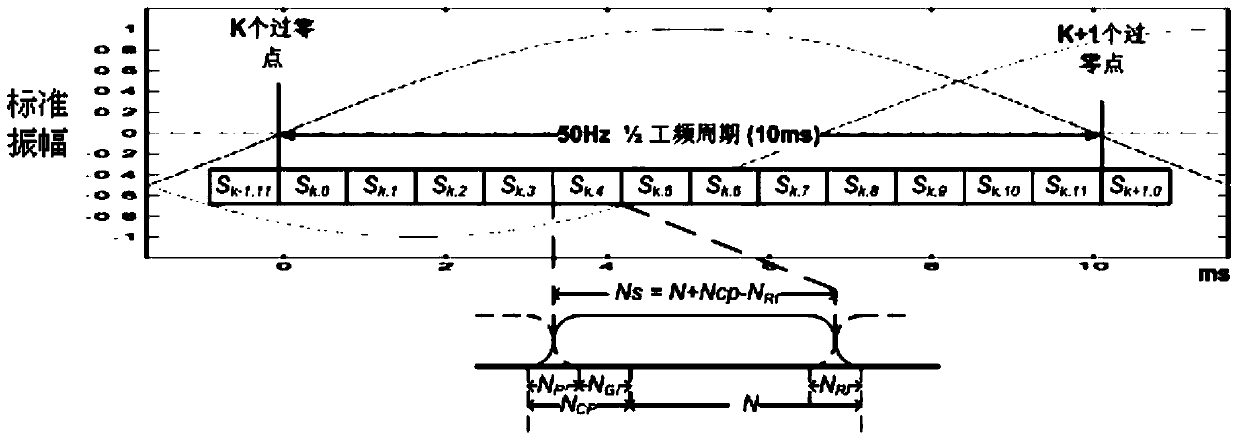
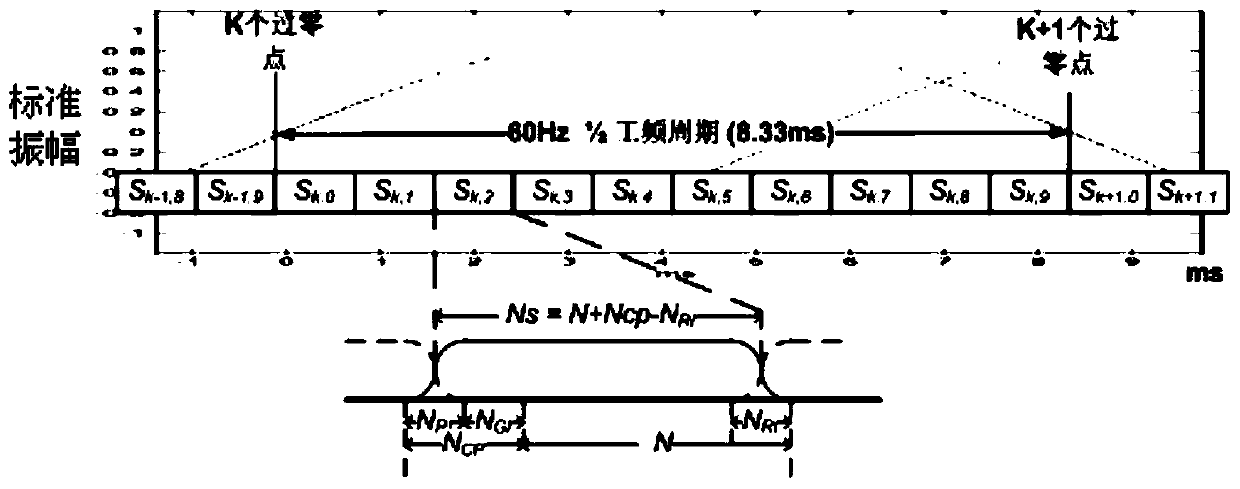
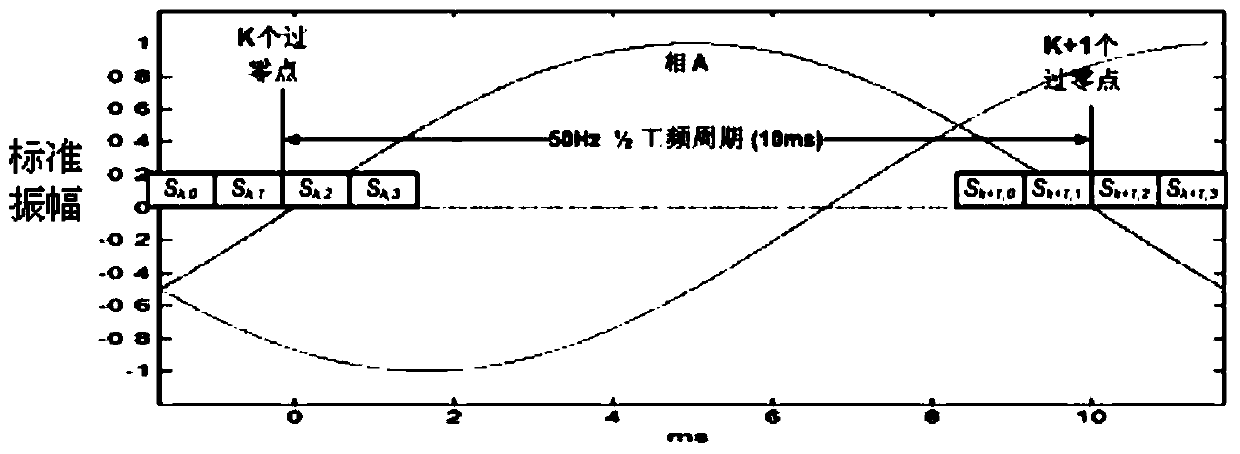
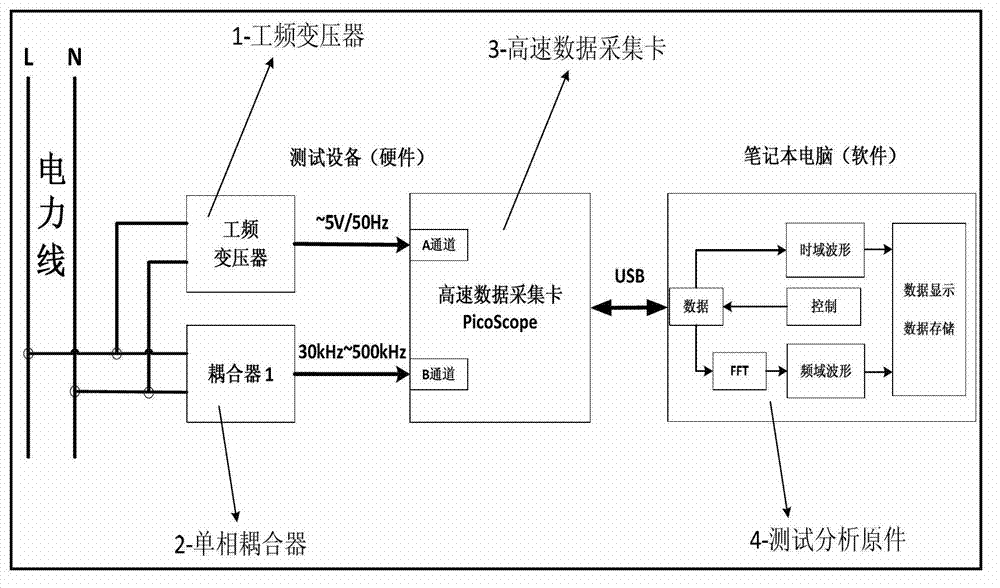
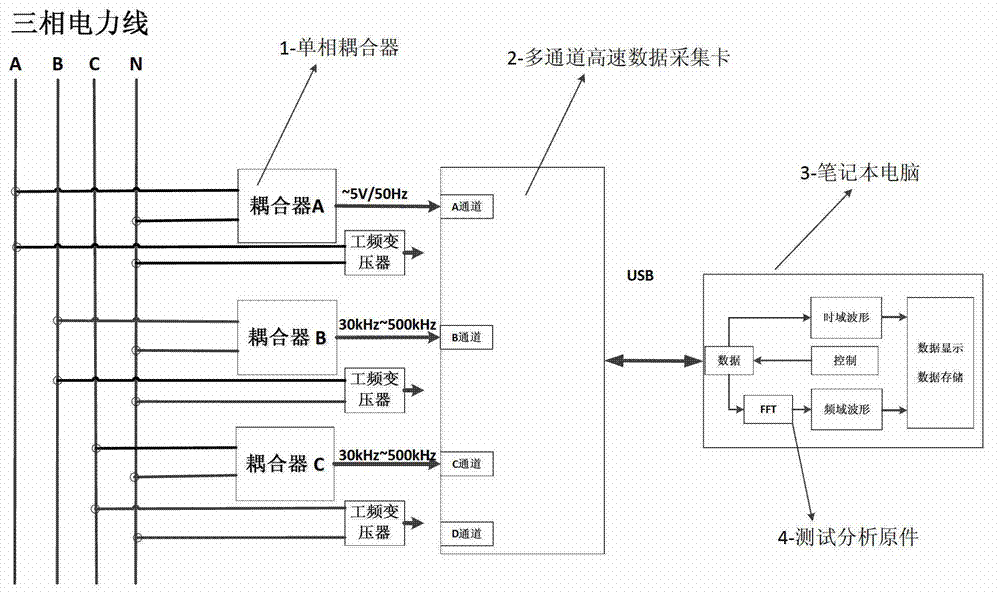
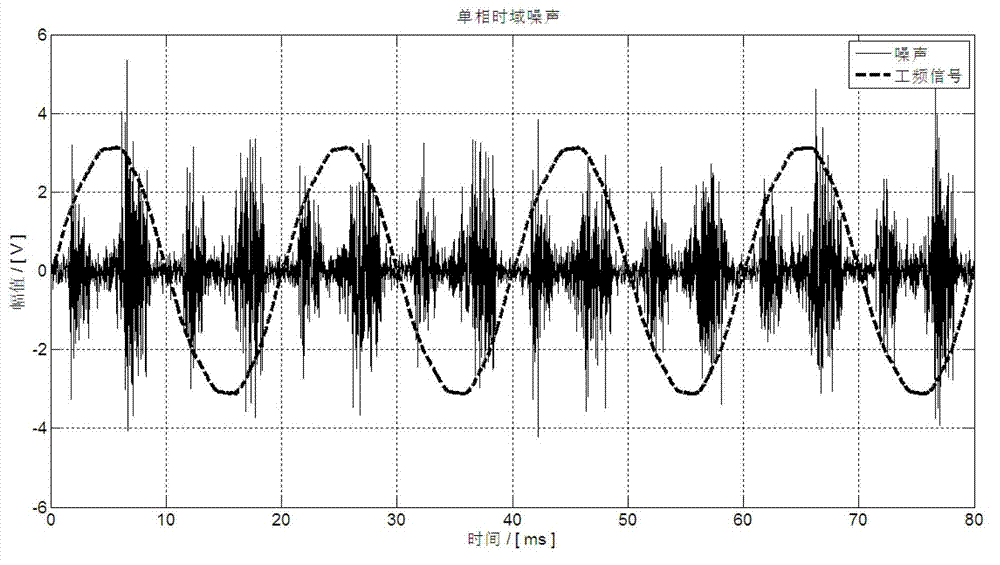
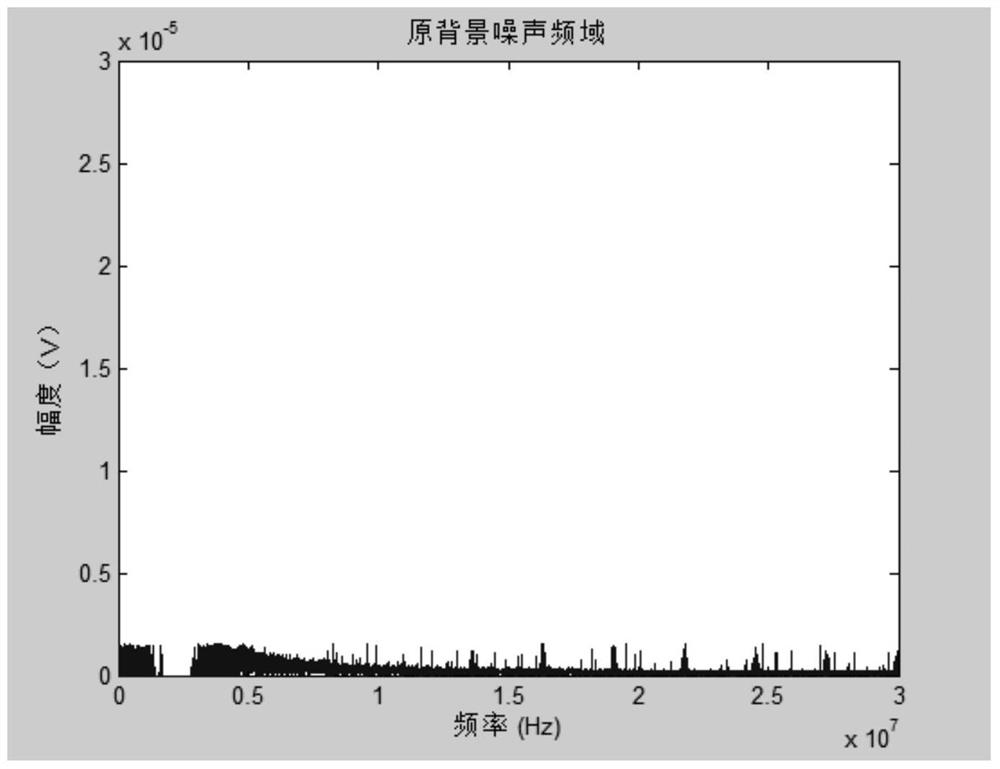
The invention discloses a spot low-voltage power line carrier channel noise testing system and a method thereof. Noise testing of a time domain and a frequency domain is carried out through a specially-designed coupler and a high-speed and multichannel data acquisition card, time domain waveform display of noise signals is achieved through testing software in a laptop, fast Fourier transform algorithm (FFT) is carried out on time domain data through the software, and noise frequency domain waveform (power spectral density) is obtained. When the waveform is observed, computer date storage resources can be used at the same time to carry out long-time data storage and monitoring so that recording, analyzing and assessing on low-voltage power line noise characteristics can be achieved. Meanwhile, the spot low-voltage power line carrier channel noise testing system and the method thereof have the advantages of being flexible, convenient and fast, and suitable for various low-voltage power line environments.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
OFDM power-frequency synchronous power carrier communication and physical layer coded modulation method
ActiveCN105991499AIncrease profitImprove reliabilityMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsCarrier signalEngineering
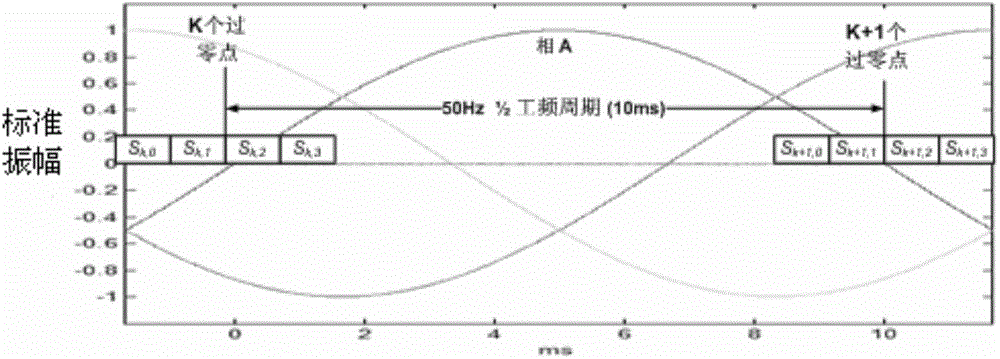
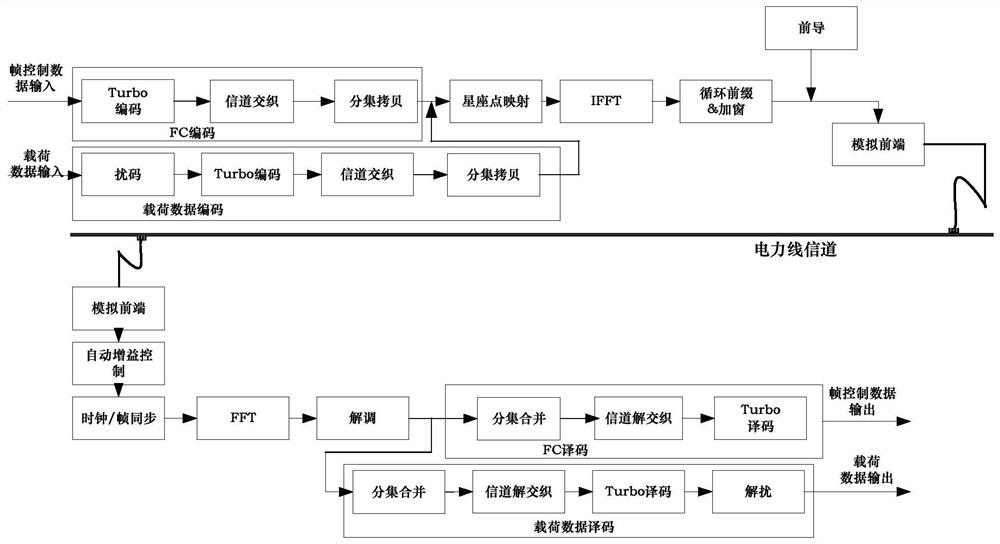
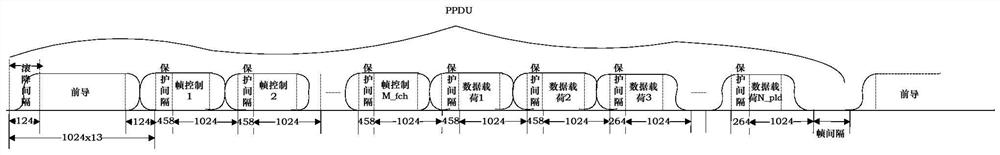
The invention discloses an OFDM power-frequency synchronous power carrier communication and physical layer coded modulation method. The communication method comprises that P OFDM symbols are sent within 1 / 2 AC power-frequency period, and P represents a positive integer; the SNR of each subcarrier and the corresponding OFDM symbol is measured repeatedly; and according to a measured SNR sequence, a bit loading table is generated via a time domain and frequency domain 2D ToneMap and sent to achieve the channel adaptability and improve the reliability and communication speed of the whole communication system. The method of the invention has the advantages that the sparsity of period static characteristic and noises in the time and frequency domains of power line noises is utilized fully, the utilization rate (speed) of a PLC channel is improved, the transmission reliability and the system throughput are improved, and coding efficiency is high. The method can support an OFDM power-frequency synchronous continuous sending mode as well as a discontinuous sending mode.
Owner:HI TREND TECH SHANGHAI
Method and apparatus for sensing noise signals in a wireline communications environment
InactiveUS20140177694A1Reduce the impactImprove featuresCross-talk reductionTransmission monitoringLine sensorWired communication
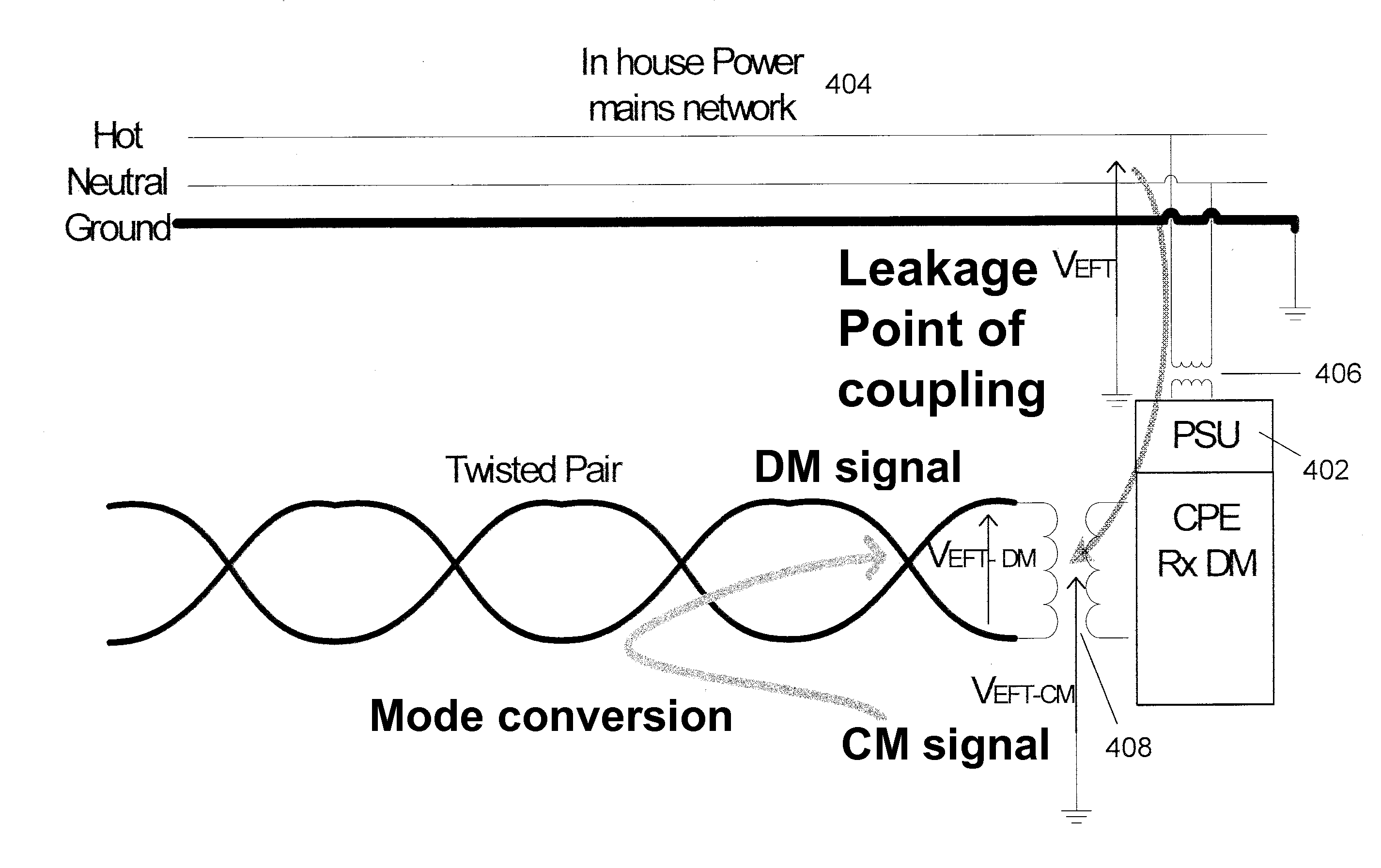
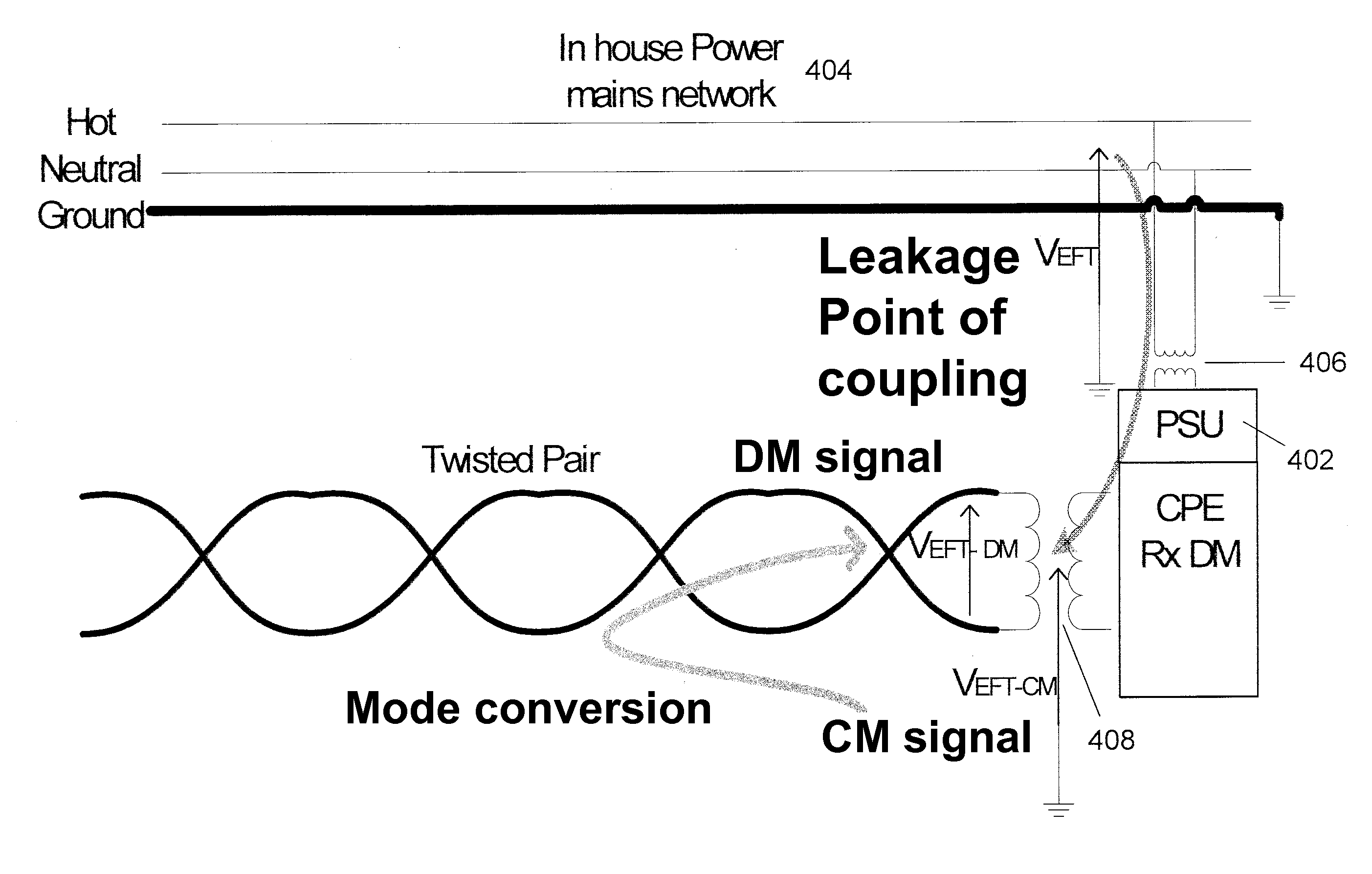
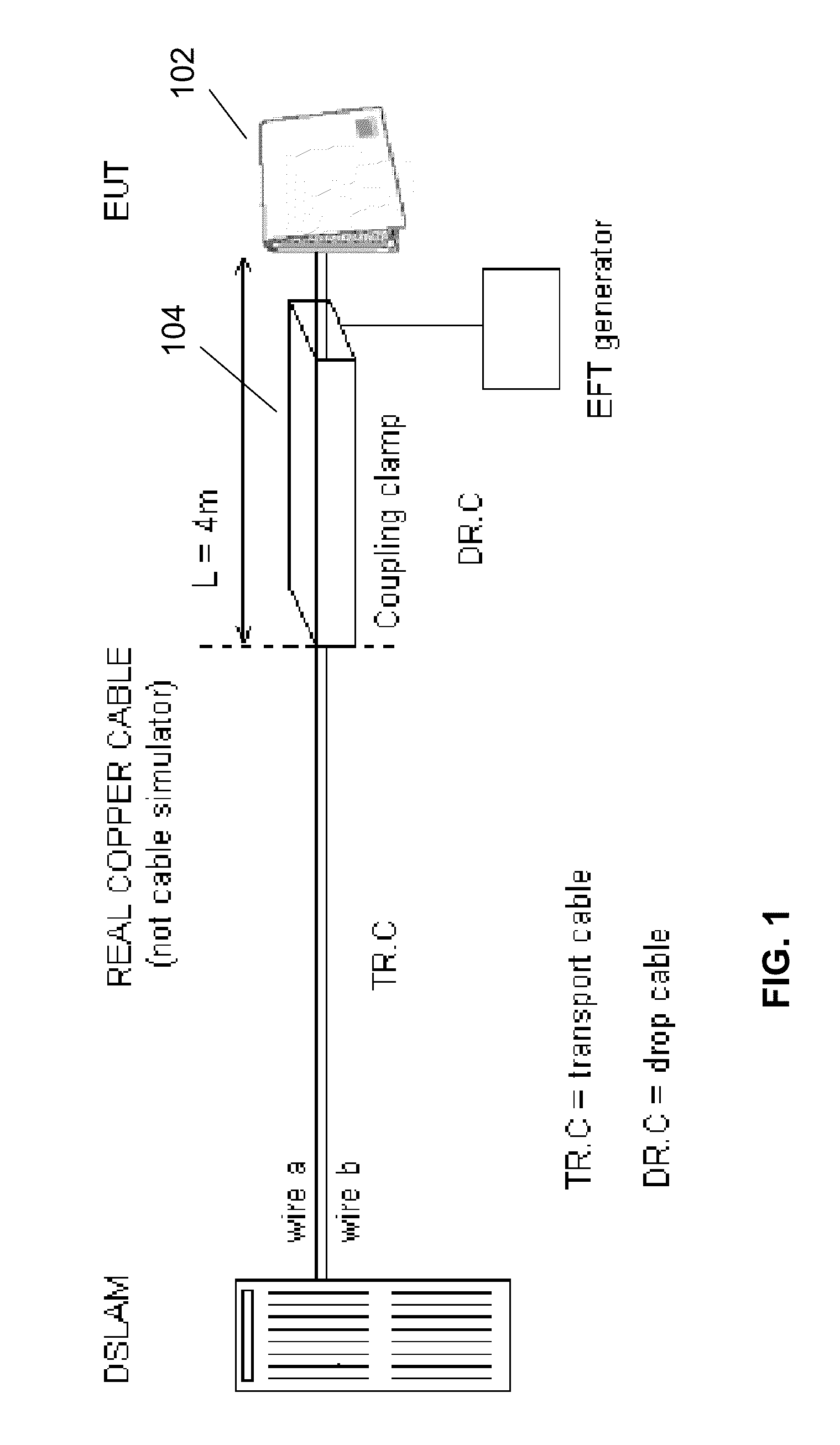
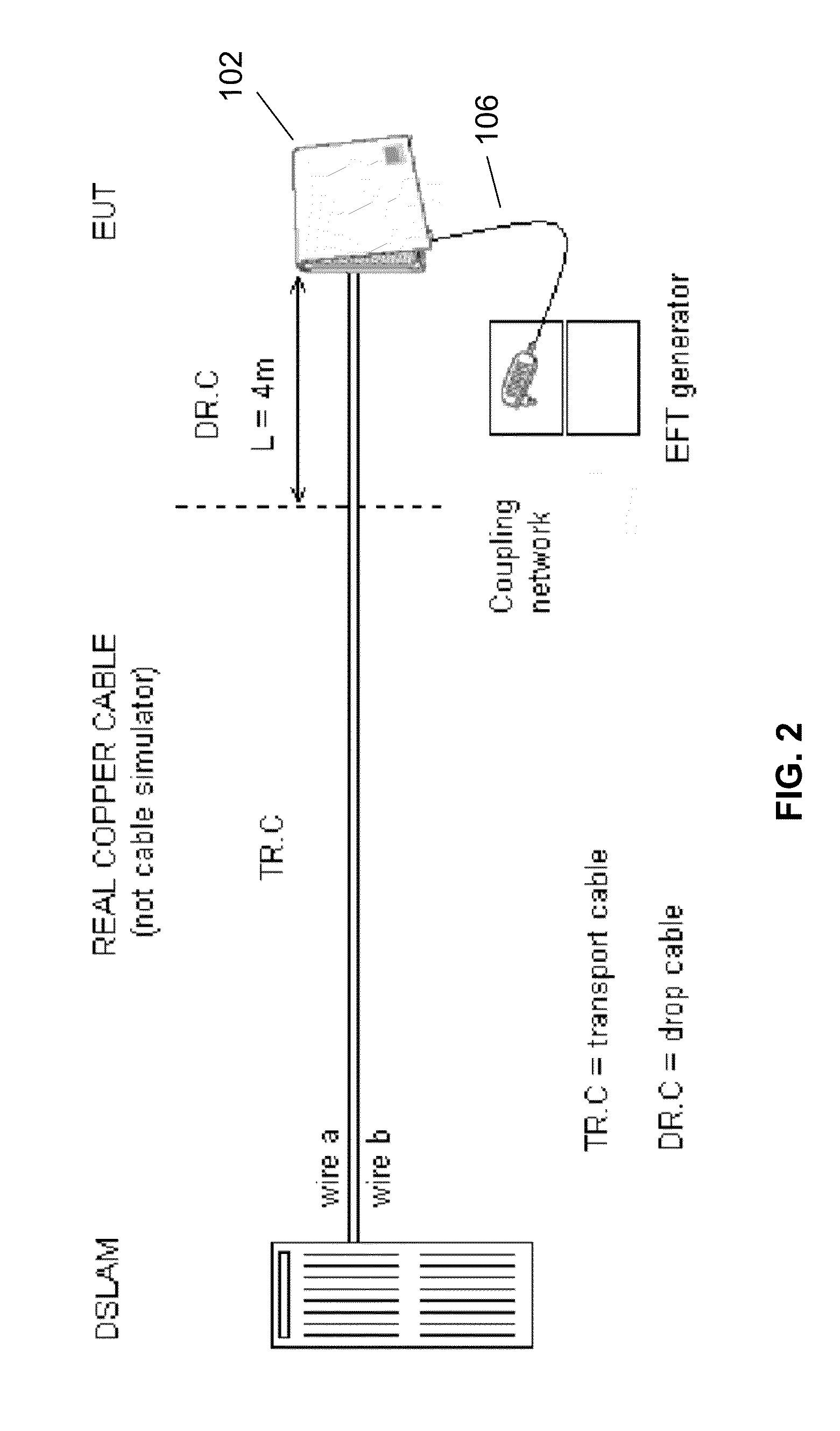
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for sensing noise sources in a wireline communications environment such as a customer premises environment in a DSL system. In embodiments, the invention includes an additional sensor that is connected to power mains in a DSL customer premises environment either to characterize, at their source, noises coupling into the DSL lines, and / or to mitigate their impact into the DSL lines. One objective is associated with diagnostics that help to better characterize the noise signals themselves and derive correlation of signals sensed from the power mains and their possible projection onto the DSL line. Another objective makes use of these power line sensor signals to mitigate or to eliminate power line noises that make their way onto the DSL line. Example embodiments further include and exploit signals from additional secondary sensors such as secondary common mode, differential mode and phantom mode sensors.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Power line noise compression method and device thereof based on compressive sensing
InactiveCN105356886AEfficient storageReduce data volumeCode conversionObservation matrixCompression device
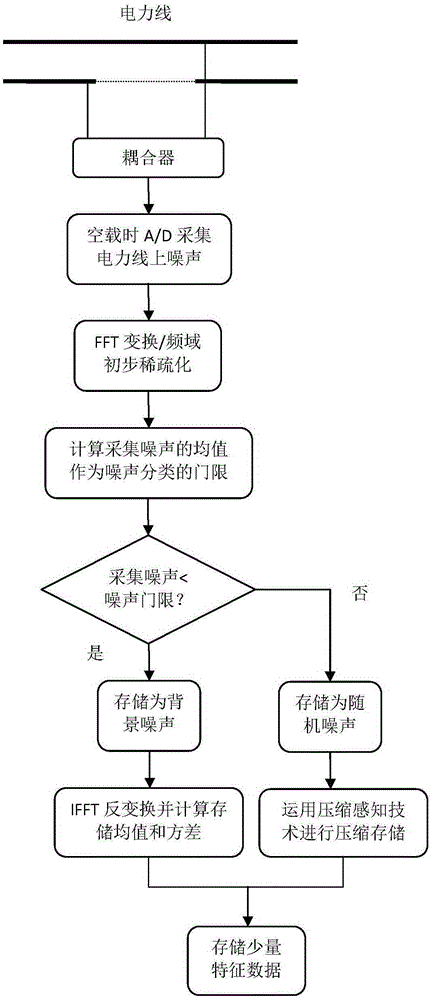
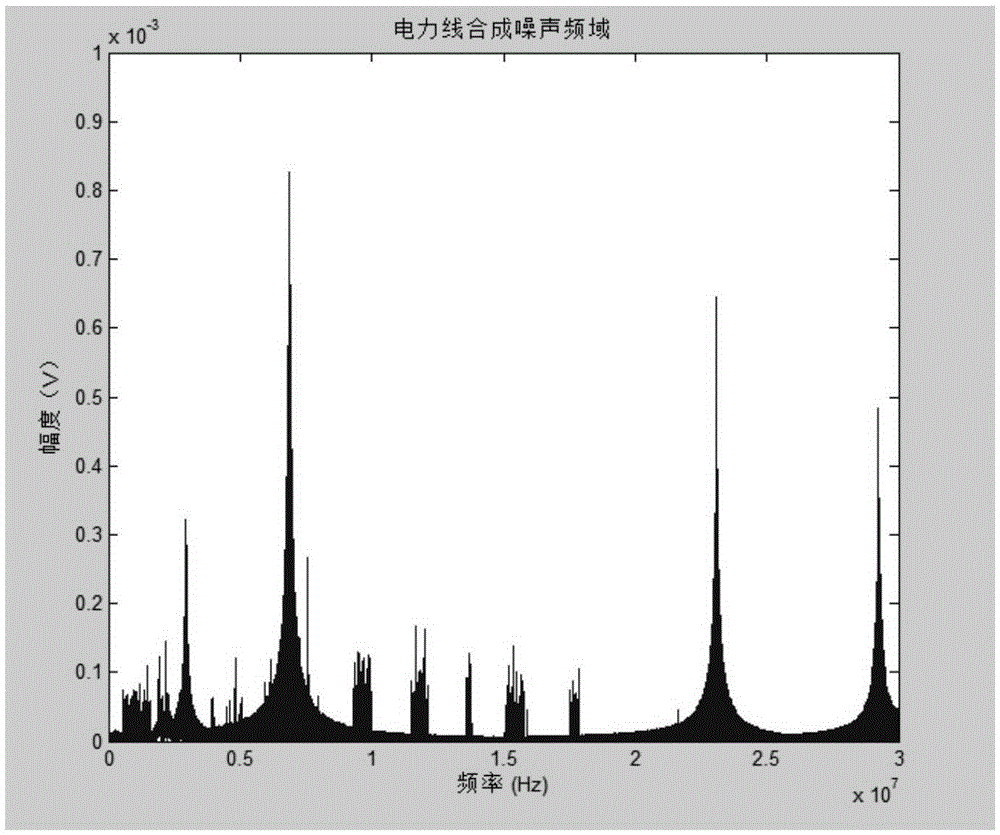
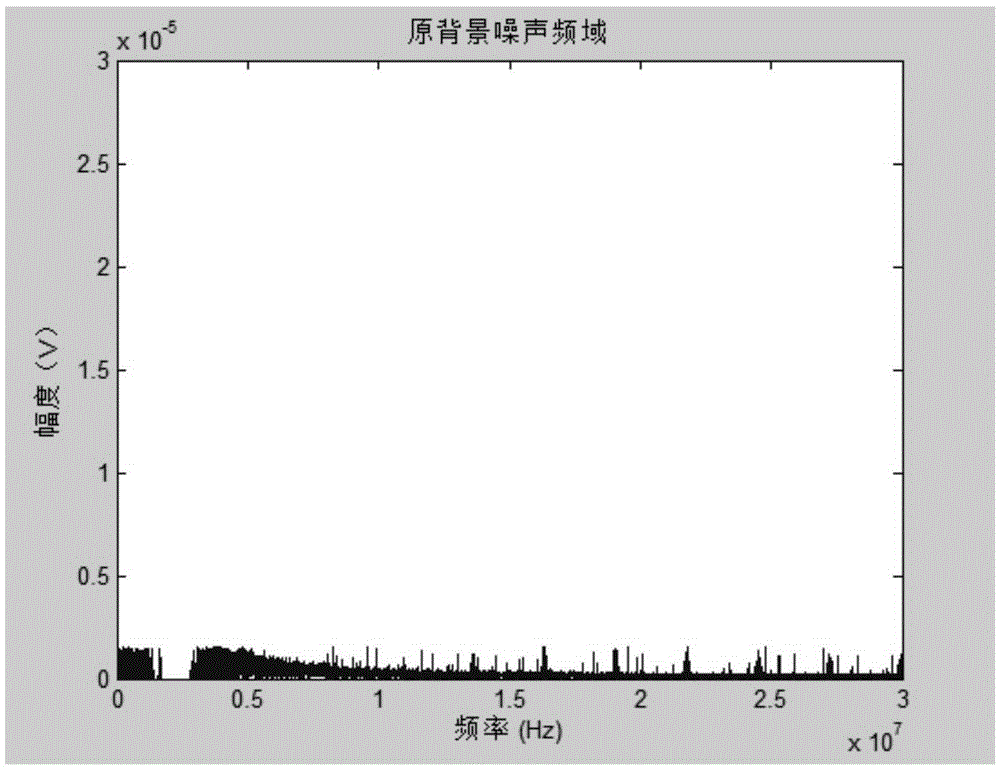
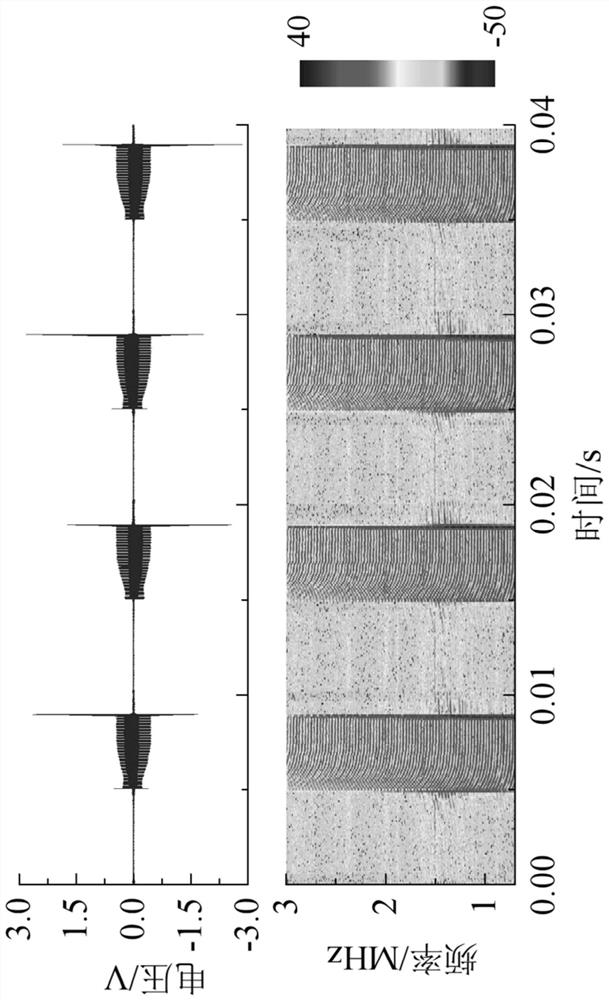
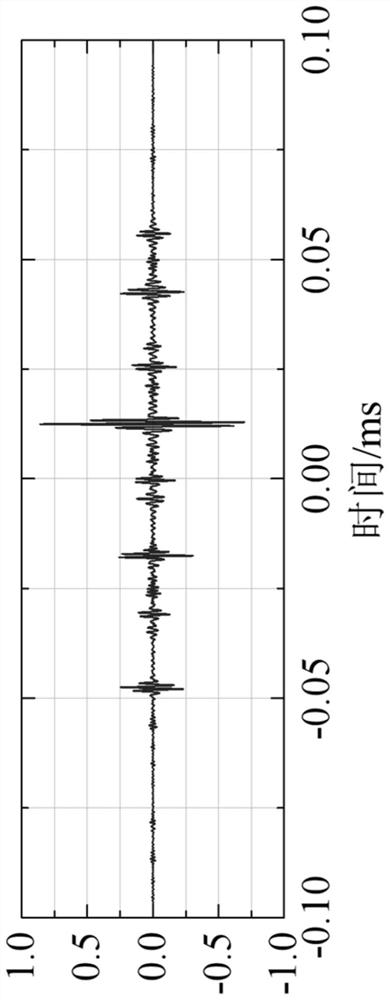
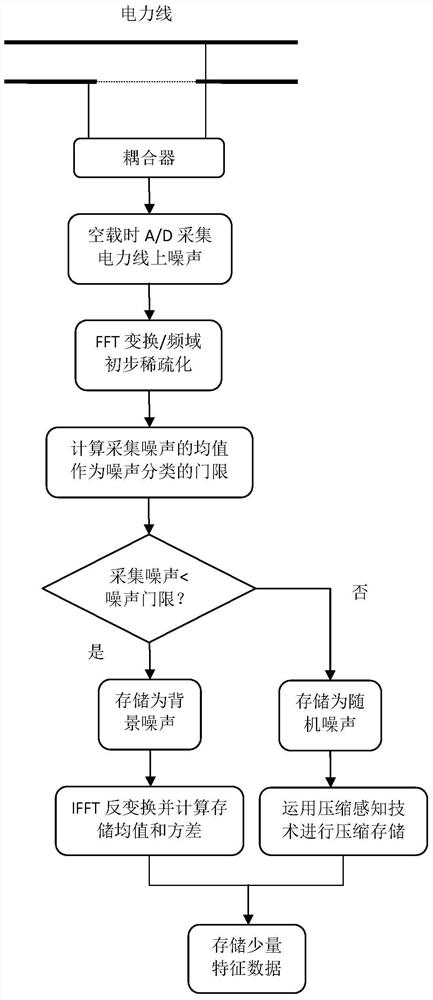
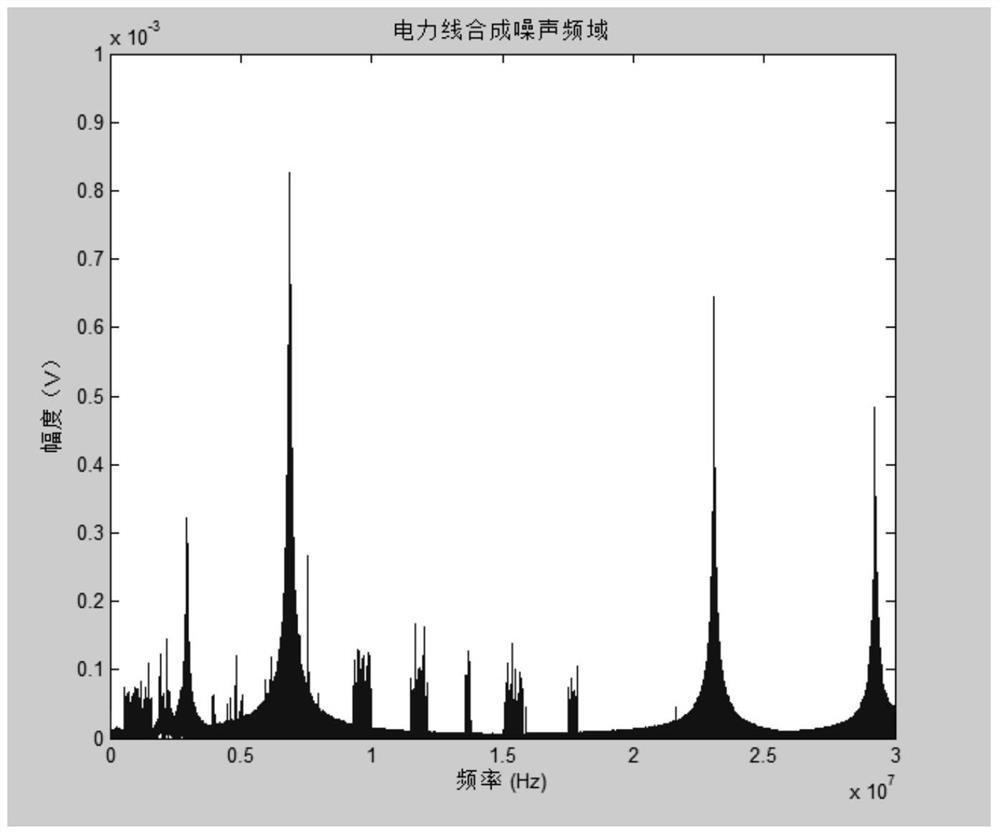
The invention discloses a power line noise compression method based on compressive sensing. When a power line is unloaded, noise on the power line is subjected to strong electrical isolation and attenuation through a coupler; then, noise of a power line channel is acquired through noise acquisition equipment; the acquired noise of the power line channel is divided into background noise and random noise; then, characteristic data of the background noise are extracted in a time domain and stored; the random noise is compressively sensed in a frequency domain according to an observation matrix; and furthermore, main information obtained after the random noise is processed is stored. The invention further discloses a power line noise compression device based on compressive sensing. By means of the invention, when the power line is unloaded, the power line noise acquired from the power line in a coupled manner is effectively compressed and stored; therefore, the volume of data in need of being stored can be effectively reduced; and the relatively high compression removal rate can be achieved.
Owner:CHINA GRIDCOM +2
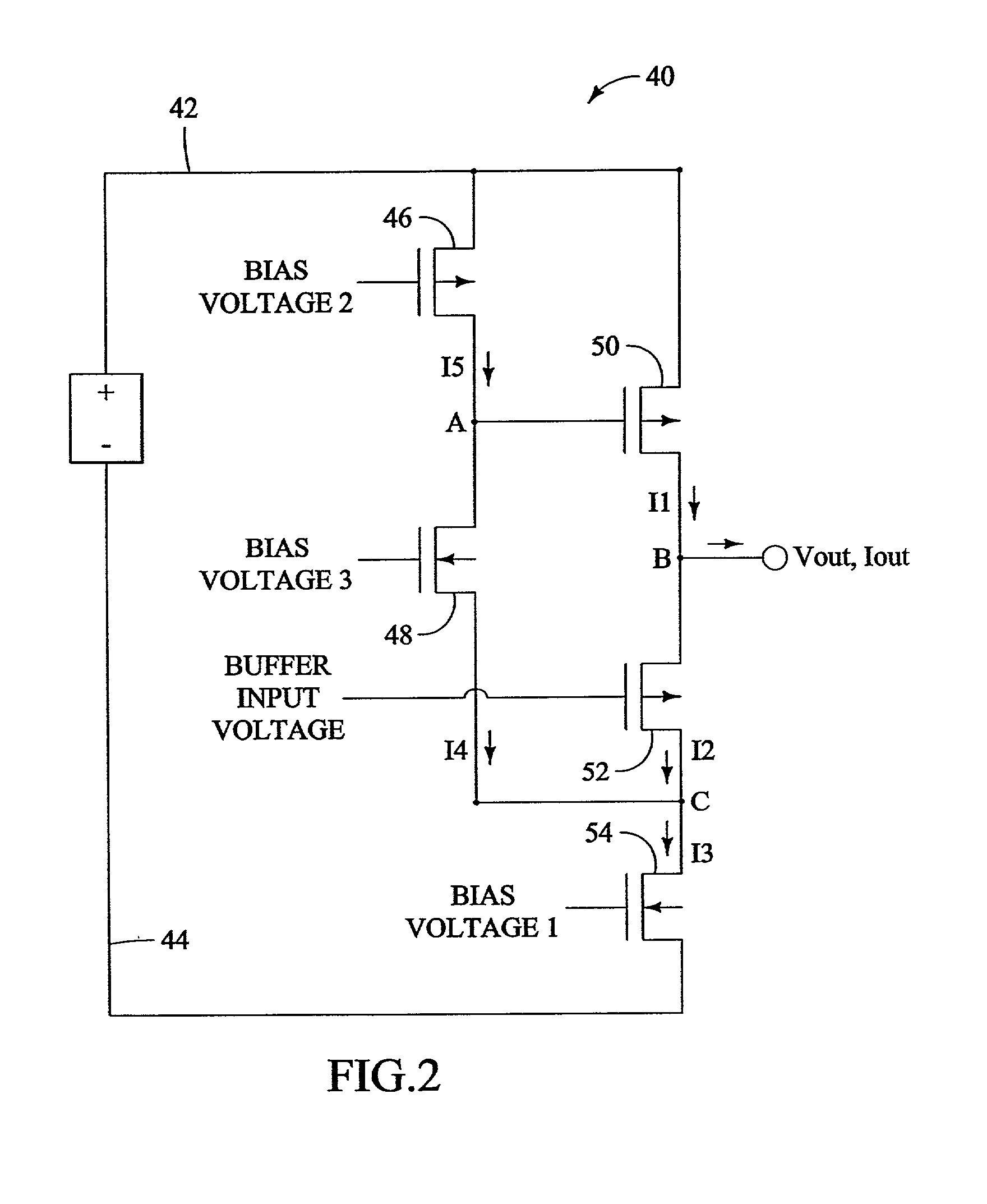
Efficient current feeback buffer
InactiveUS20020175770A1Great voltage rangeLimit its operationPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsDelay-locked loopFrequency synthesizer
An efficient current feedback buffer is revealed. The buffer is useful in power supplies for a number of analog and digital devices, including CMOS voltage controlled ring oscillators, frequency synthesizers, delay locked loops, phase accumulators, and phase locked loops. The power supply and buffer maintains a low impedance output to the load, regulates the voltage output of the supply, and rejects power line noise.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Power line anti-noise channel estimation method
InactiveCN106877907AOvercoming sensitivityReduce bit error rateBaseband system detailsPower distribution line transmissionViewpointsHigh energy
The invention discloses an interference noise elimination method suitable for a power line carrier (PLC) communication network, which is mainly used for solving the impulse interference noise which appears randomly and has high energy causes performance attenuation of the whole communication system in the PLC network. The method mainly comprises two parts of receiver-side signal amplitude pretreatment and robust channel estimation. The initial filtering of the impulse interference noise is performed according to the statistical characteristics of received signals by the receiver-side signal amplitude pretreatment, and the influence on the residual noise is further weakened by the robust channel estimation. Compared with other conventional power line noise elimination algorithms, the method provided by the present invention is characterized by a relatively low complexity and being insensitive to noise change. The method eliminates the power line noise from the viewpoint of practical feasibility and effectiveness, so that the bit error rate is reduced during the power line carrier transmission, and the system reliability can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
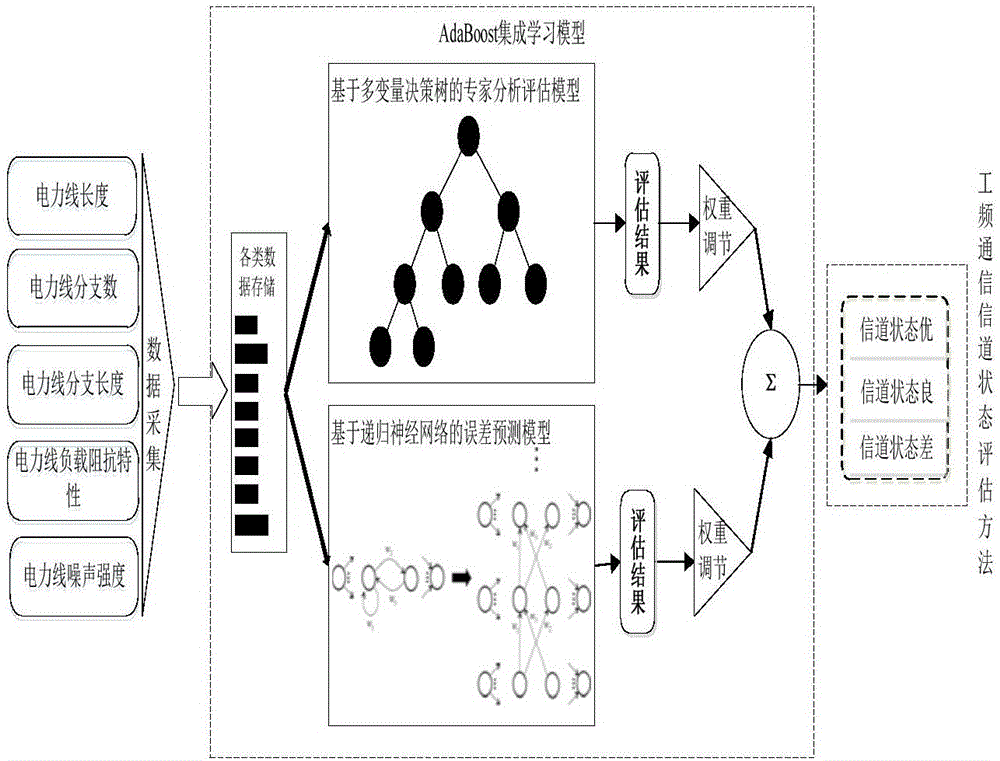
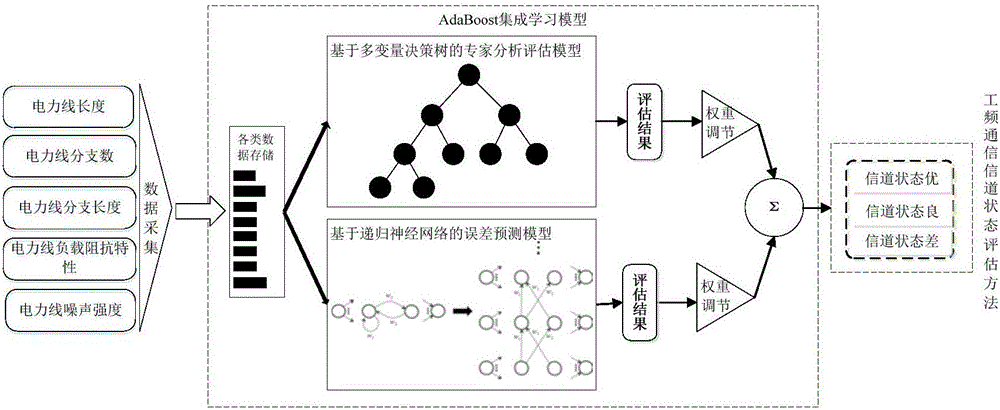
System and method of evaluating state of power frequency communication channel
ActiveCN106656357AImprove statusImprove accuracyBiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionEnsemble learningBranch length
The invention belongs to the technical field of power frequency communication channel state analysis algorithms, and particularly relates to a method of evaluating the state of a power frequency communication channel. The method comprises steps: through acquiring data influencing the quality of the power frequency communication channel such as lengths of different power lines, the power line branch number, a branch length, load impedance characteristics, power line types and power line noise, a power frequency communication channel quality evaluation data storage and sharing platform is built; on the basis, the data are mined and calculated; and an Adaboost ensemble learning algorithm is used, through an expert analysis system and a neural network algorithm based on deep learning, the state of the power frequency communication channel under multiple parameters is evaluated comprehensively. Compared with the traditional simplex and fixed channel state evaluation method, the method of the invention can continuously learn and optimize the evaluation model according to changes of influence factors, and a more accurate channel state is obtained.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD TAIZHOU POWER SUPPLY BRANCH +2
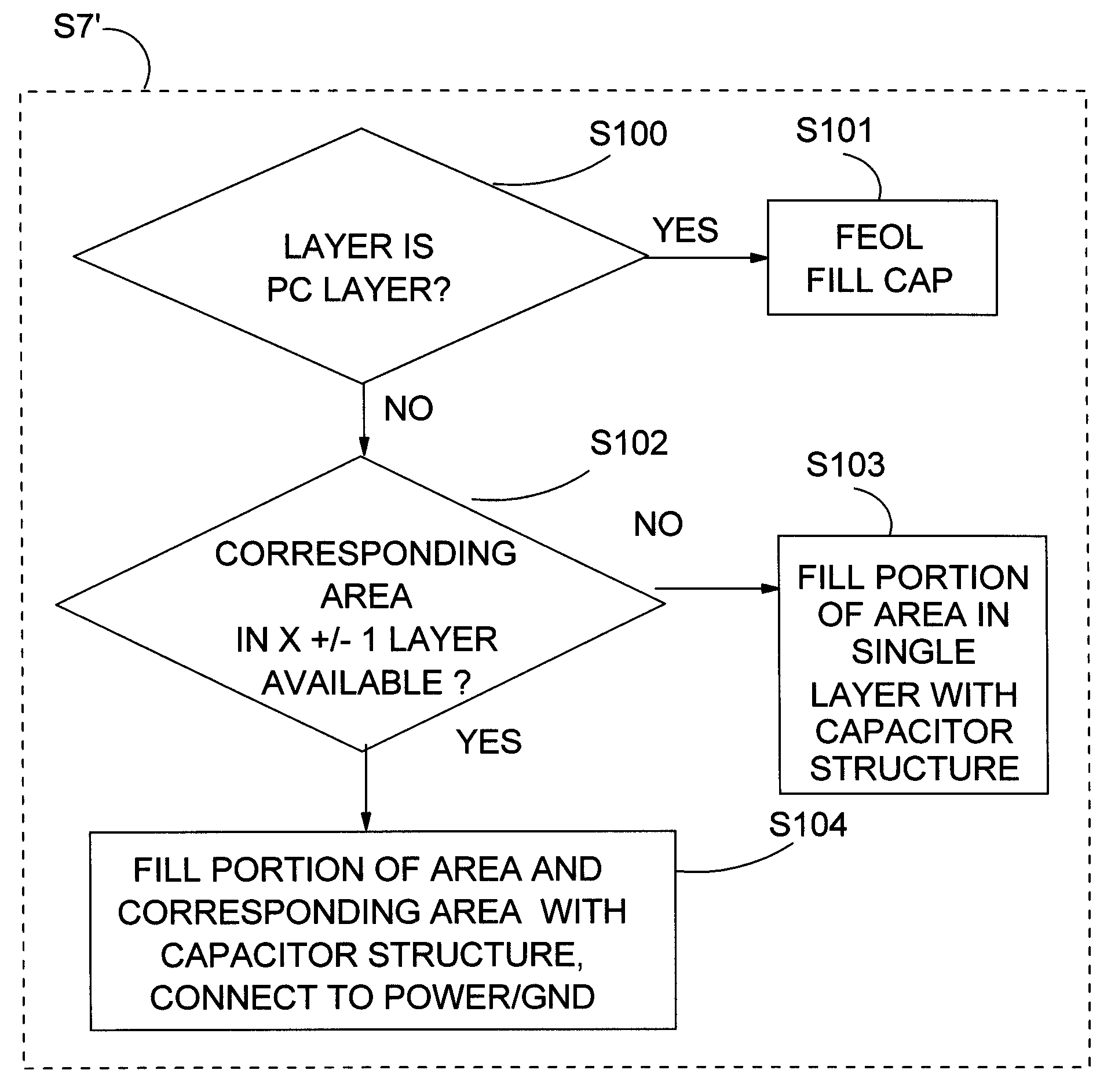
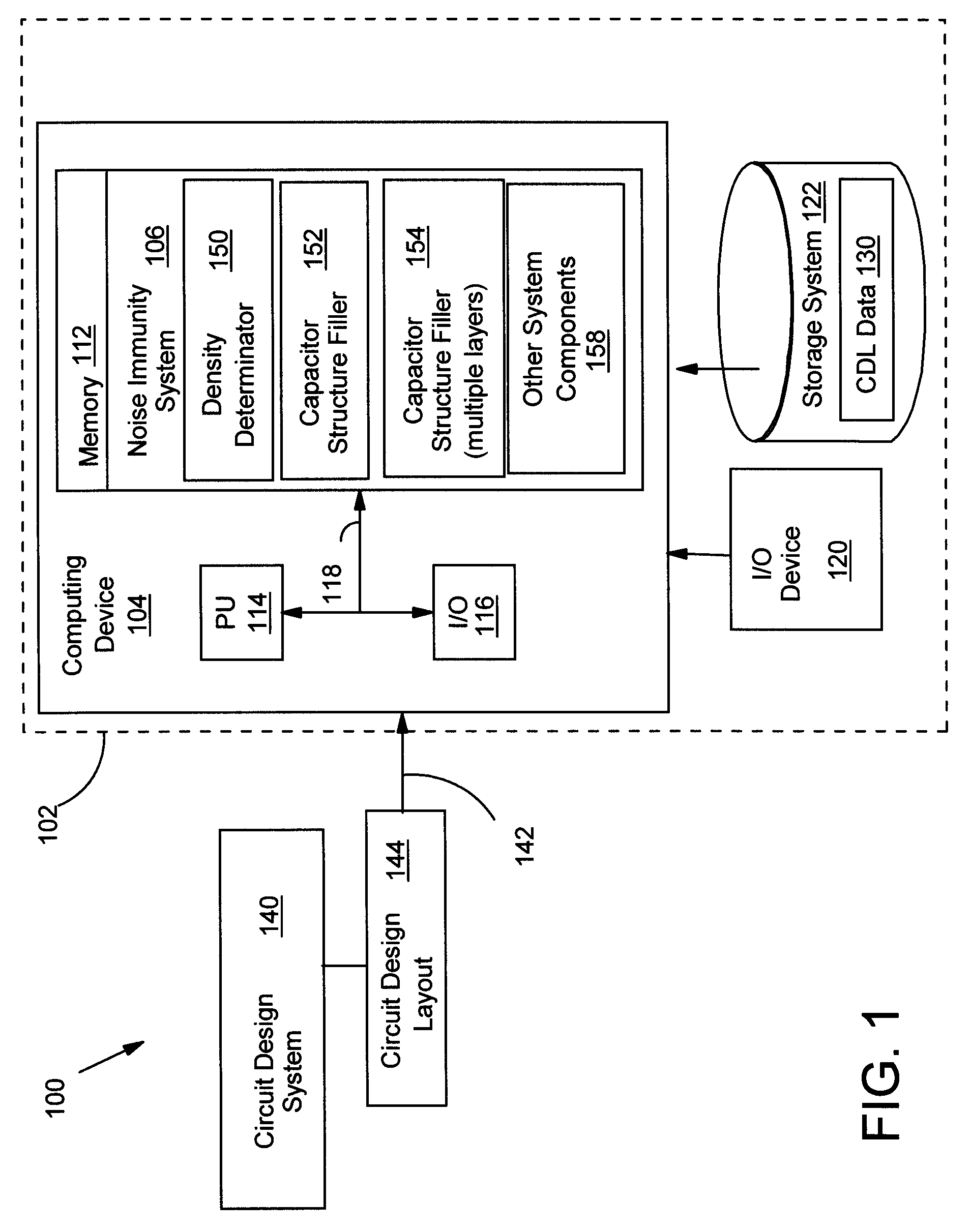
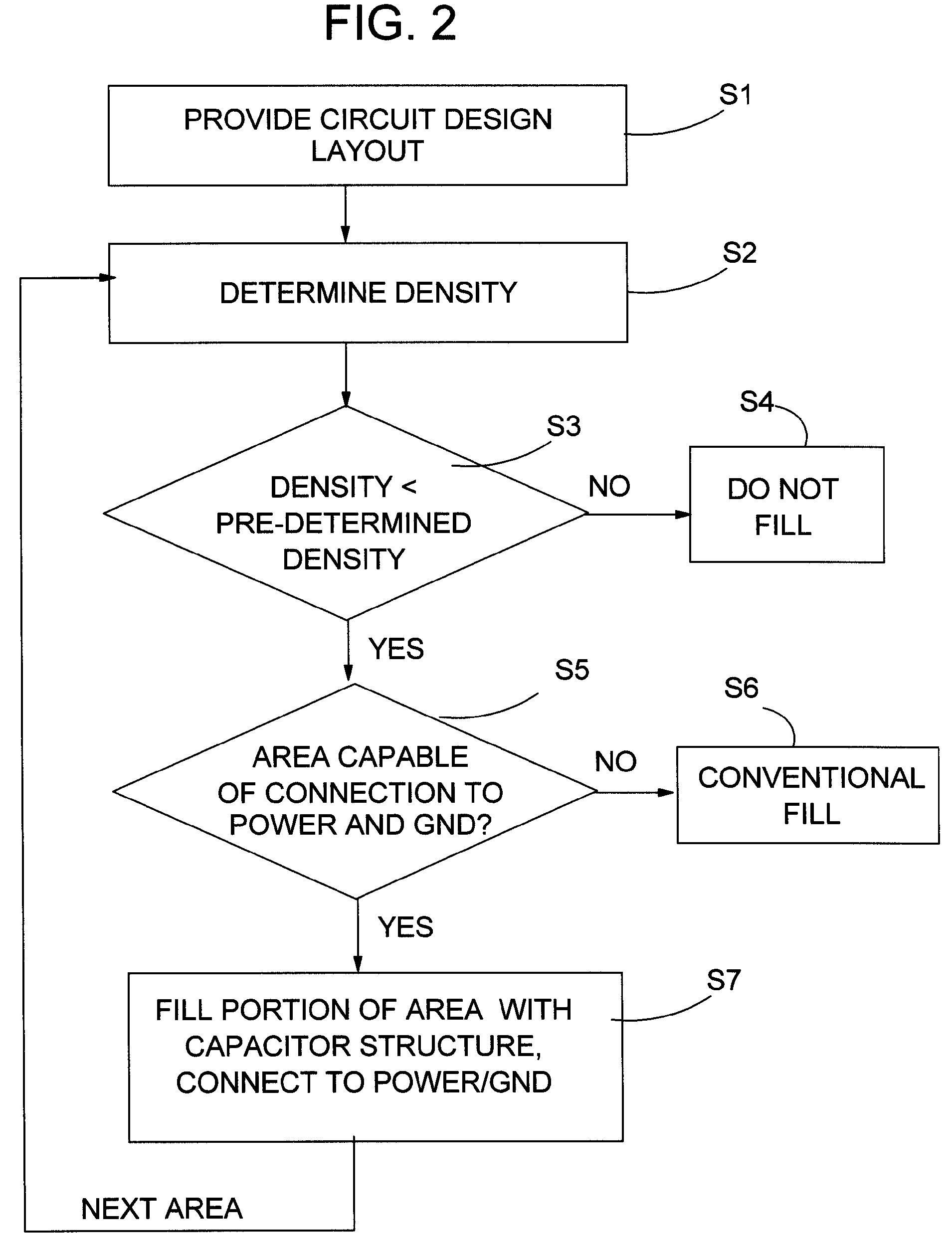
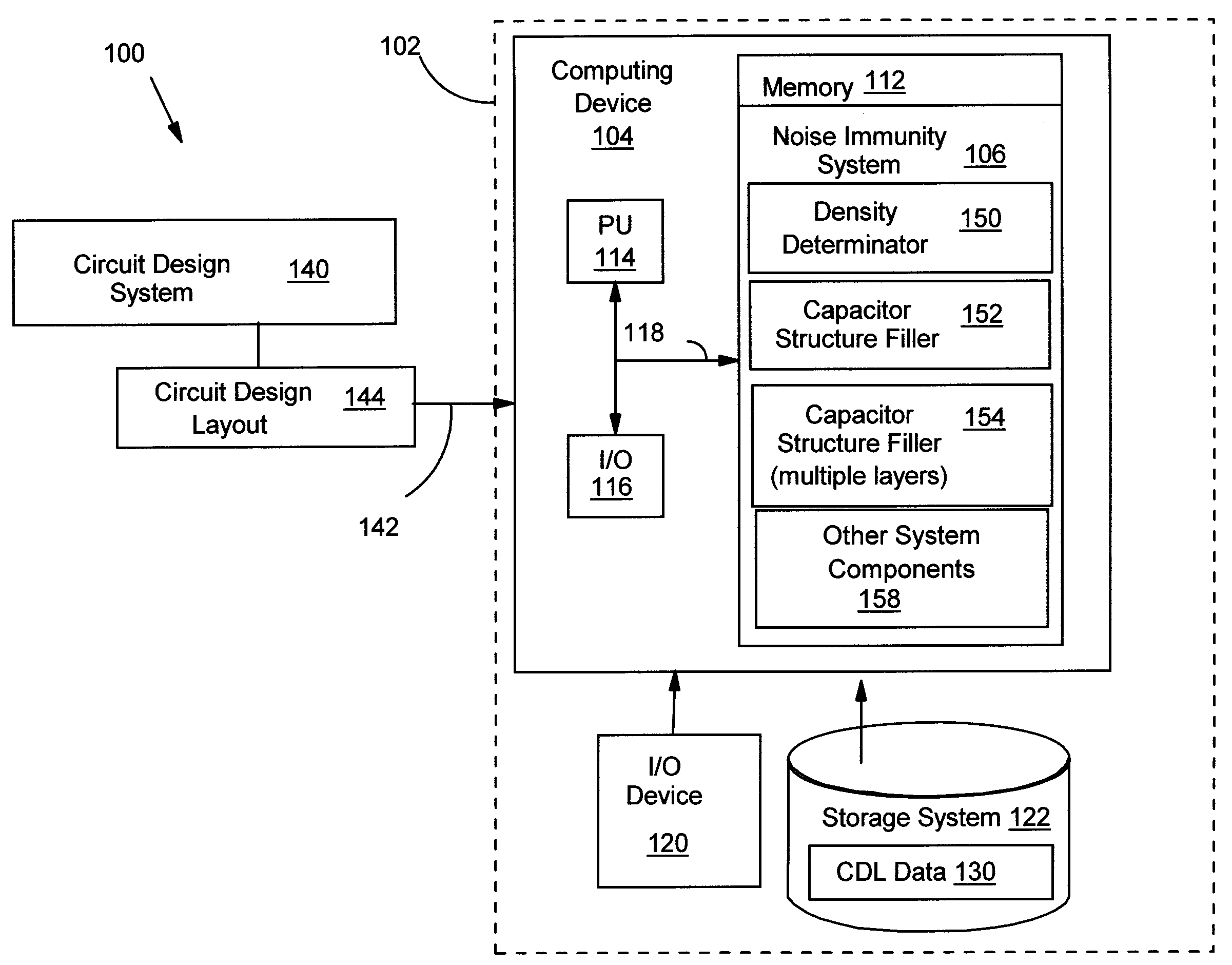
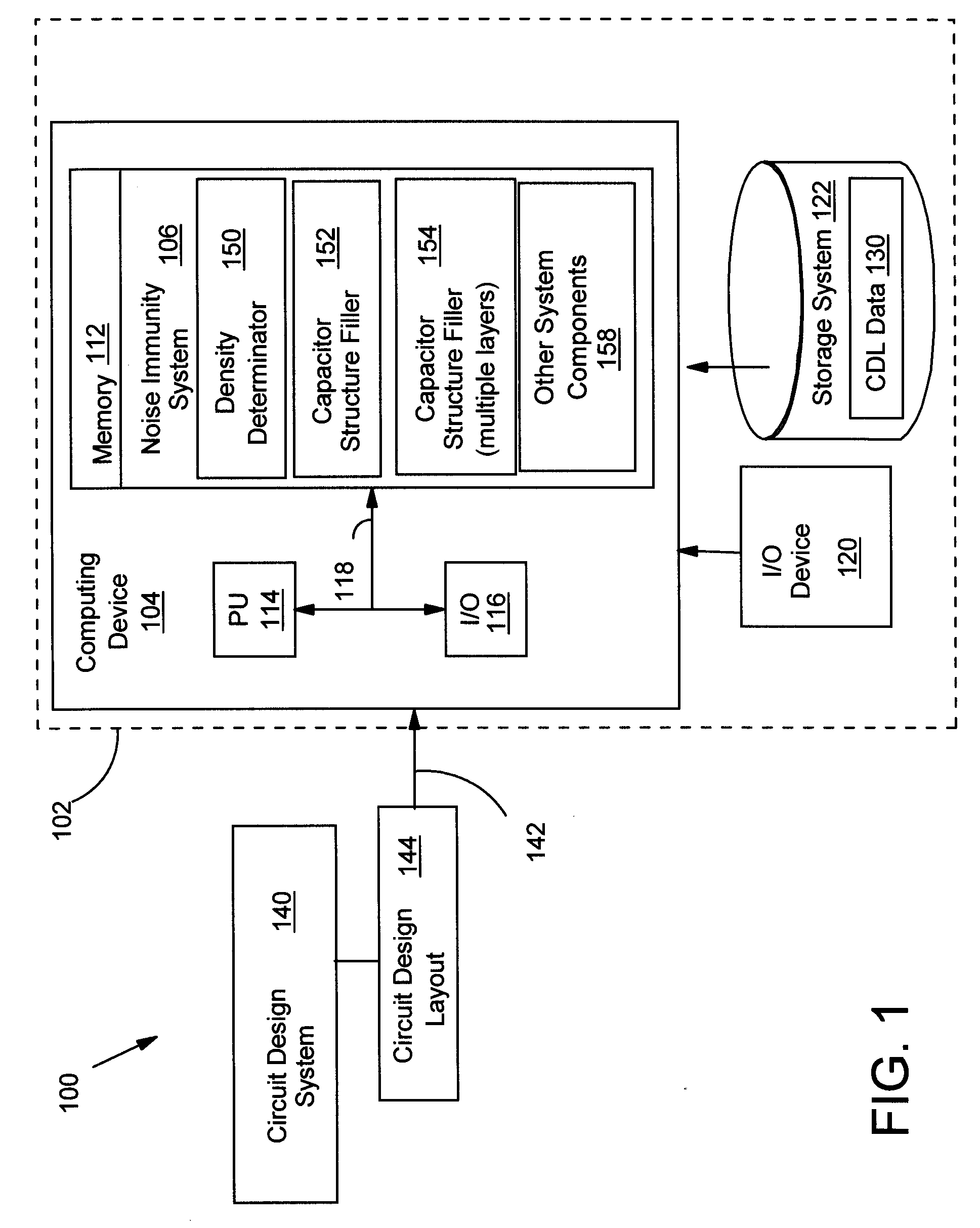
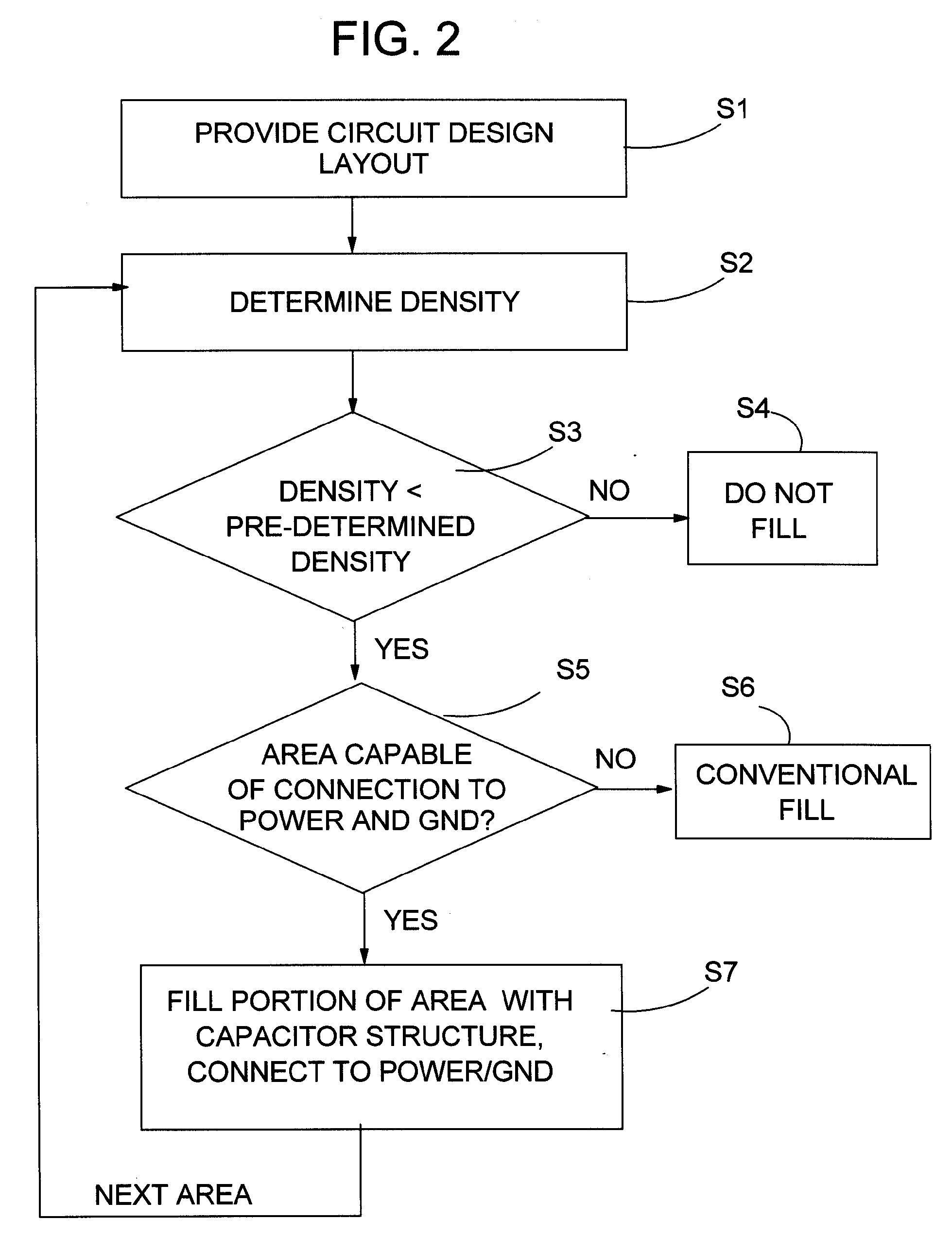
Increased power line noise immunity in IC using capacitor structure in fill area
InactiveUS7689961B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCapacitanceEngineering
Increase power line noise immunity in an IC is provided by using decoupling capacitor structure in an area of the IC that is typically not used for routing, but filled with unconnected and non-functional metal squares (fills). In one embodiment, a method includes providing a circuit design layout; determining a density of a structure in an area of the circuit design layout; and in response to the density being less than a pre-determined density for the structure in the area, filling in a portion of the area with at least one capacitor structure until a combined density of the structure and the at least one capacitor structure in the area is about equal to the pre-determined density. Power line noise immunity is increased by increasing decoupling capacitance without enlarging the IC's total size by using a (fill) area that would normally be filled with unconnected and non-functional metal shapes.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
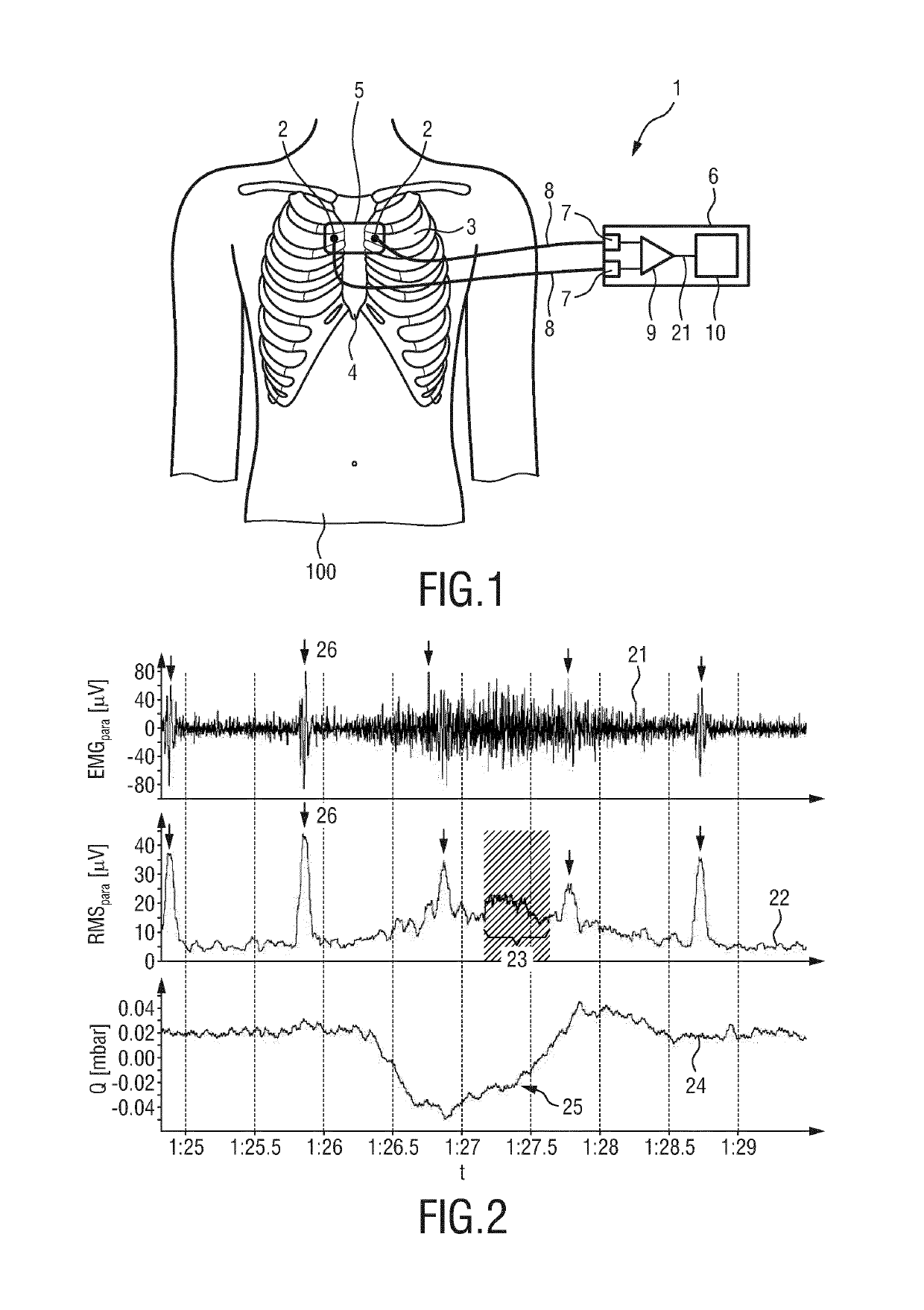
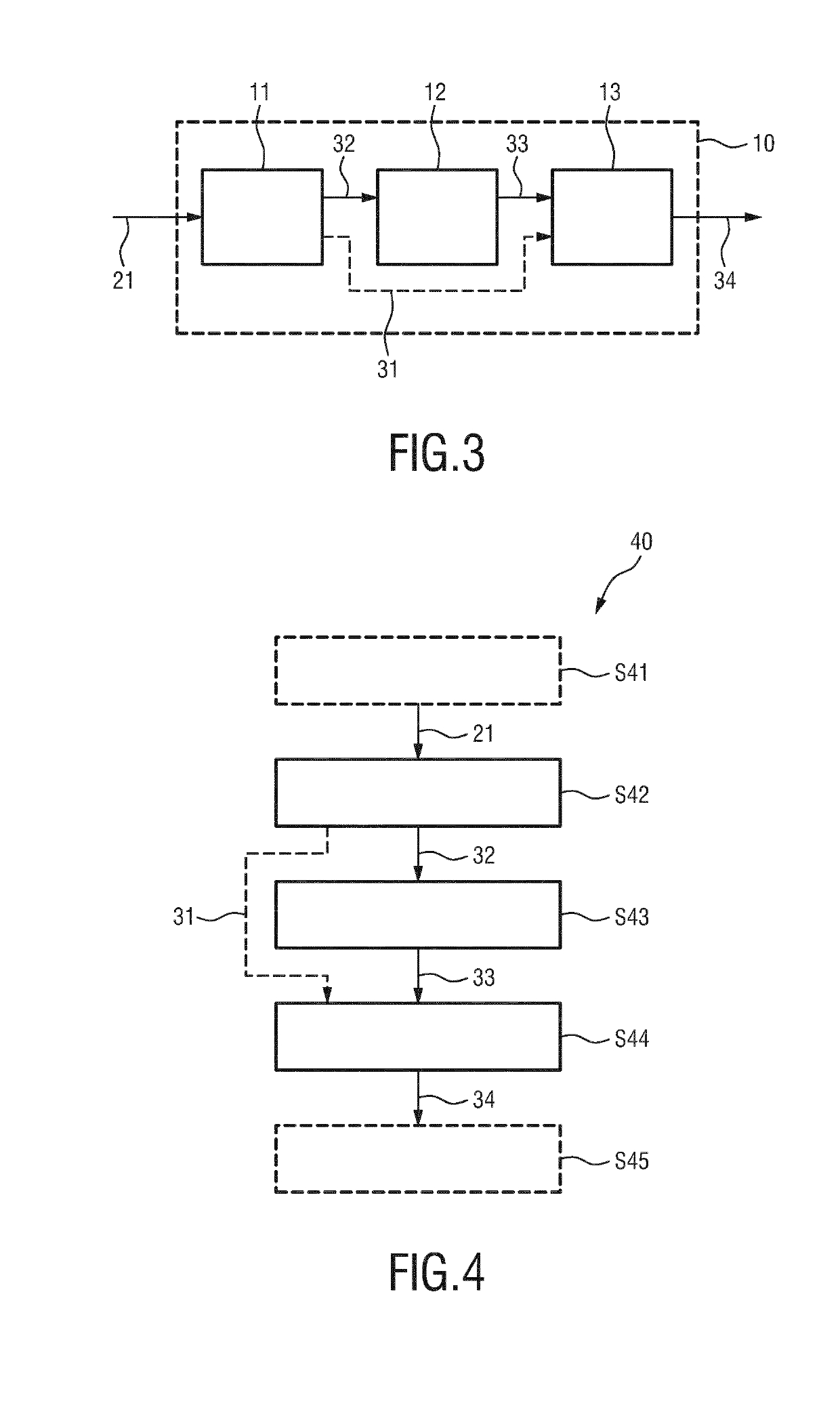
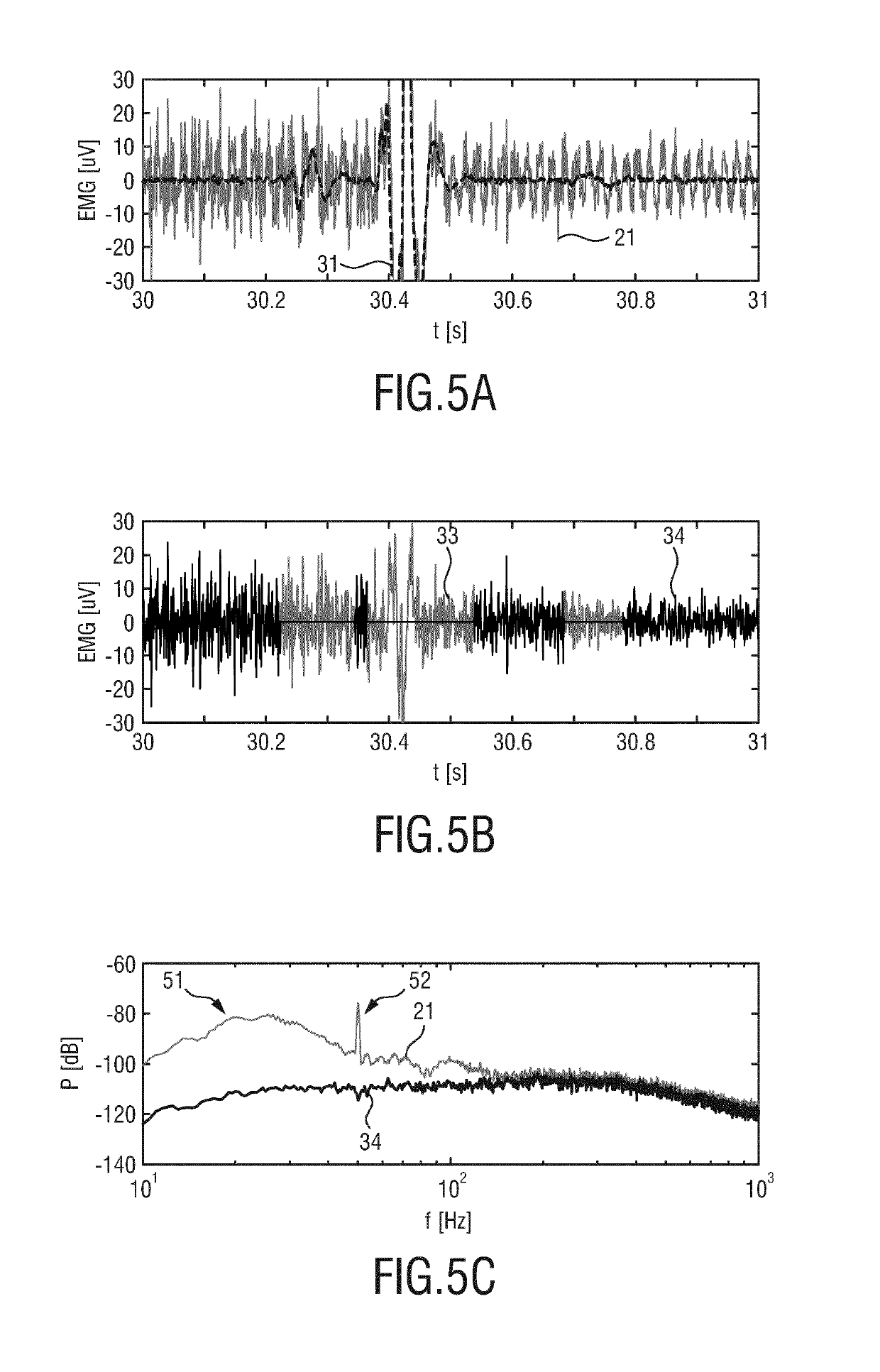
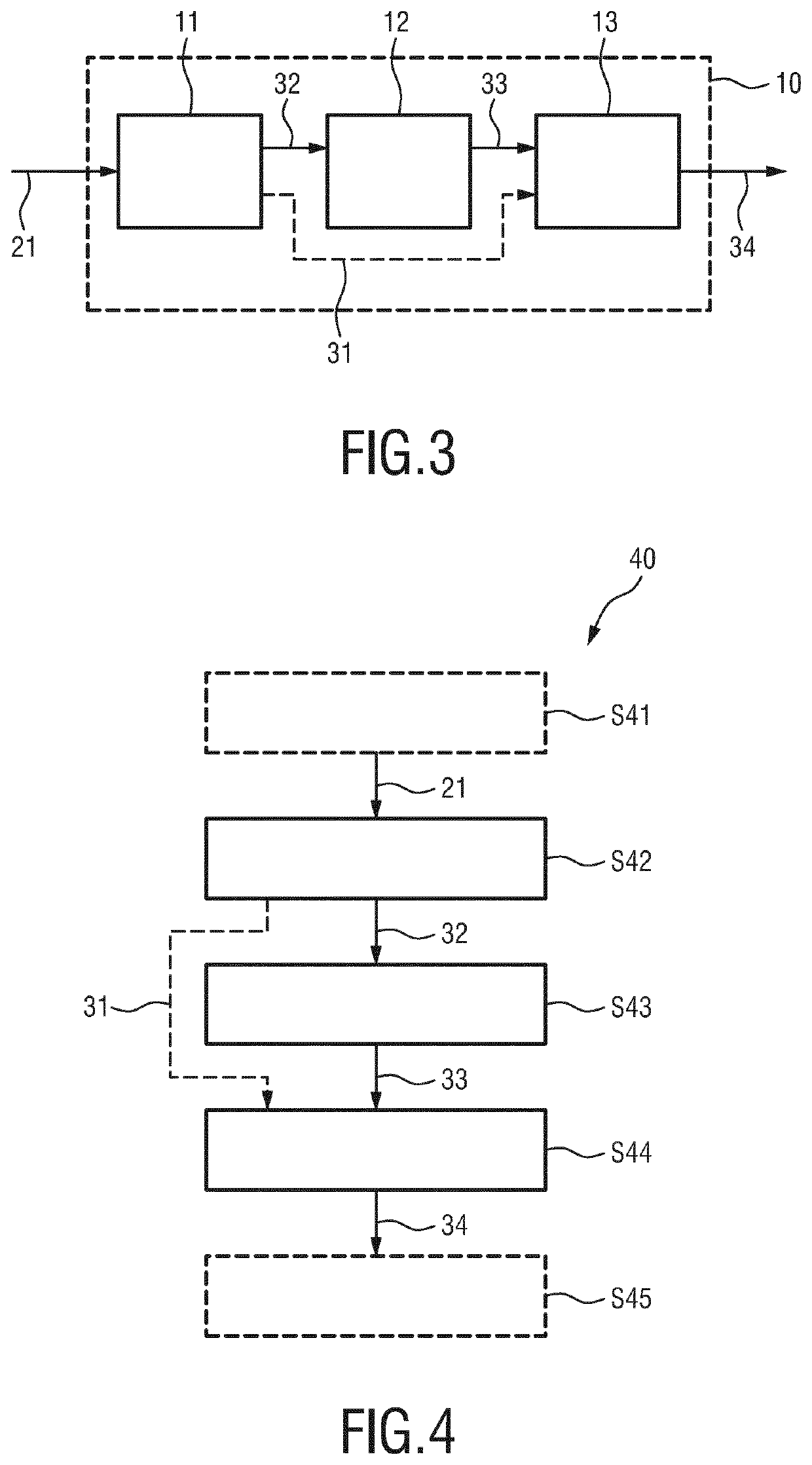
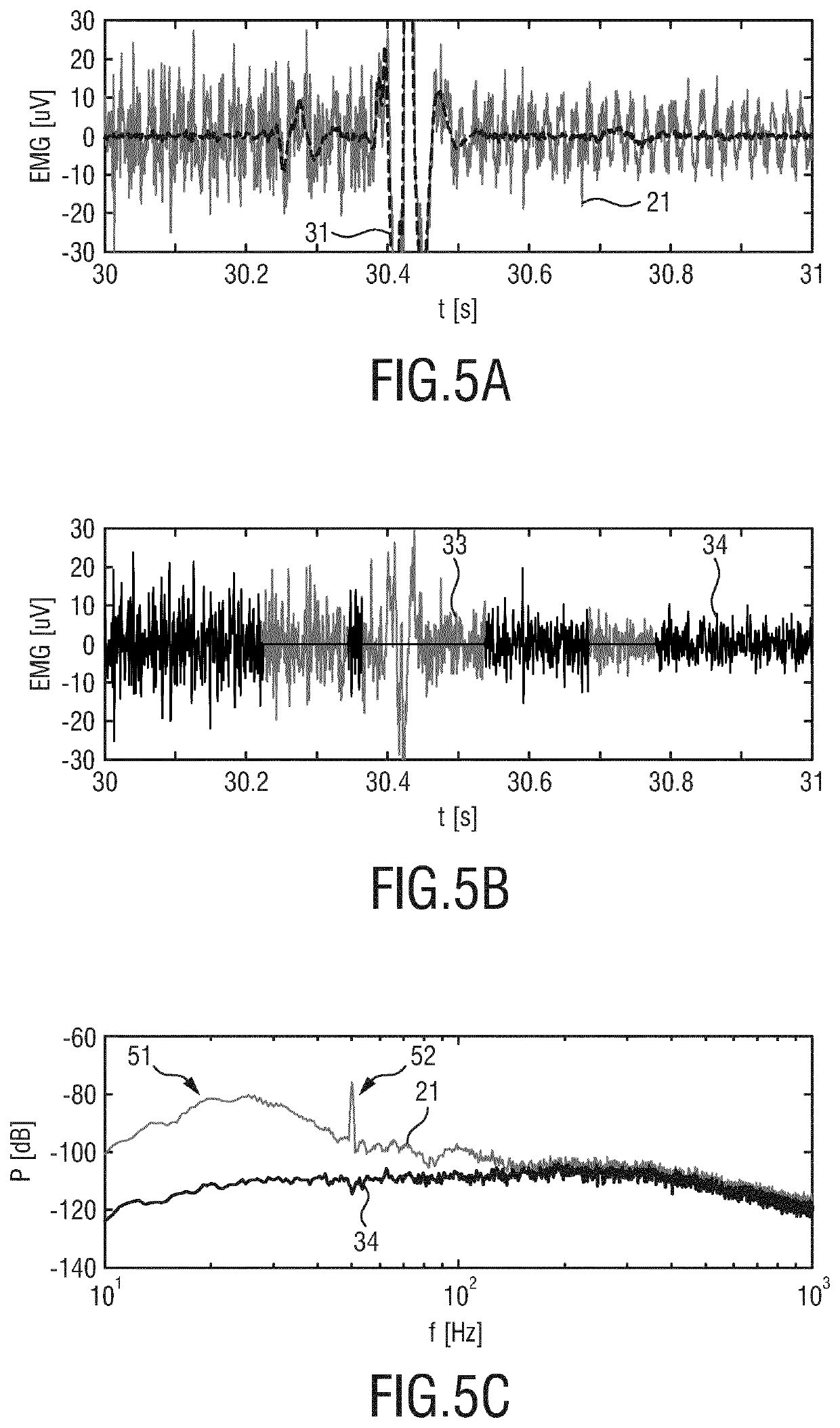
Processing apparatus for processing a physiological signal
ActiveUS20190320930A1Improve performanceReduce componentsElectromyographySensorsContaminationAND gate
The present invention relates to a processing apparatus (10) for processing a physiological signal (21) using model subtraction, notch filtering and gating. The processing apparatus comprises a model subtraction unit (11) configured to receive the physiological signal (21) and to reduce a first unwanted signal component, such as an ECG contamination, in the physiological signal by subtracting from the physiological signal a model (31) of the 5 first unwanted signal component to obtain a residual signal (32); a filter unit (12) configured to receive the residual signal (32) and to reduce a second unwanted signal component, such as power line noise, in the residual signal by applying a notch filter to obtain a filtered signal (33); and a gating unit (13) configured to receive the filtered signal (33) and to apply gating to the filtered signal to obtain a gated signal (34). The present invention further relates to a 10 corresponding electromyography system and a method for processing a physiological signal using model subtraction, notch filtering and gating.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Increased power line noise immunity in IC using capacitor structure in fill area
InactiveUS20070038968A1Improve noise immunityIncreased decoupling capacitanceCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCapacitanceEngineering
Increase power line noise immunity in an IC is provided by using decoupling capacitor structure in an area of the IC that is typically not used for routing, but filled with unconnected and non-functional metal squares (fills). In one embodiment, a method includes providing a circuit design layout; determining a density of a structure in an area of the circuit design layout; and in response to the density being less than a pre-determined density for the structure in the area, filling in a portion of the area with at least one capacitor structure until a combined density of the structure and the at least one capacitor structure in the area is about equal to the pre-determined density. Power line noise immunity is increased by increasing decoupling capacitance without enlarging the IC's total size by using a (fill) area that would normally be filled with unconnected and non-functional metal shapes.
Owner:IBM CORP
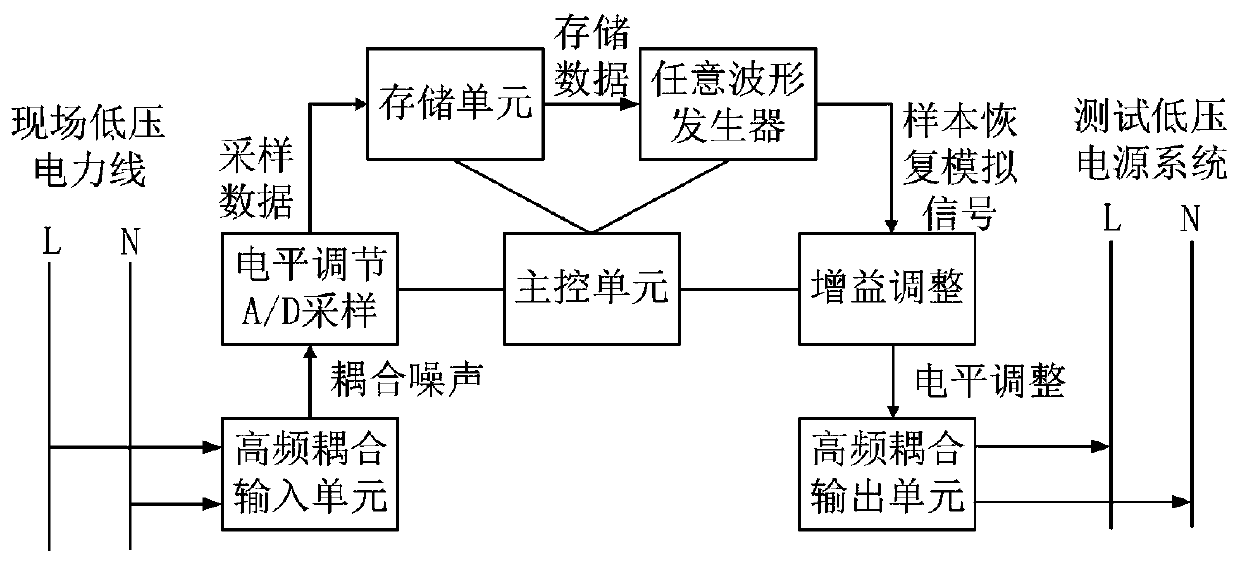
Low-voltage power line noise recording and injecting system
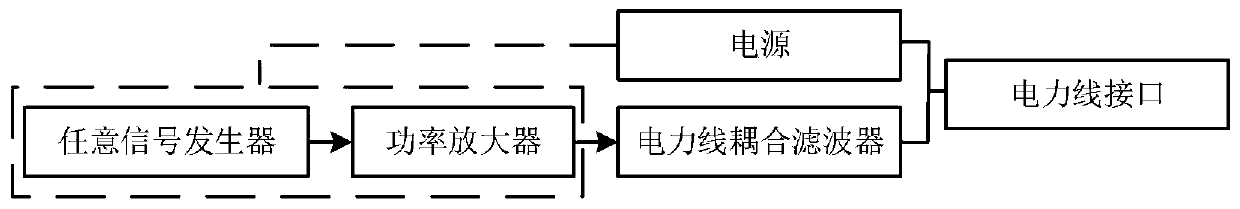
InactiveCN111030730AImplement testRealize the test of communication performancePower distribution line transmissionLine-transmission monitoring/testingInterference resistanceMeasuring instrument
The invention relates to a low-voltage power line noise recording and injecting system, and the system comprises a power line interface, a power module, a power line coupling filter, a power amplifier, an arbitrary waveform generator and a power line communication signal detecting and analyzing device. According to the system, on-site noise is recorded and stored, and on-site noise signals are restored through any signal generator in a laboratory, so that the working characteristics of the power line carrier communication module in an on-site noise environment are verified; high-voltage mainssupply is isolated through the power line coupling filter, so a measuring instrument is isolated from strong current, the safety of measuring equipment is ensured, noise outside a test frequency bandis filtered, useless signal interference is reduced, and the system provides a basis for an anti-interference test of the low-voltage carrier communication module.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCI & RES INST OF STATE GRID TIANJIN ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
Device for measuring impedance of power line access point
PendingCN108226647AEasy to calculateSolve collection problemsResistance/reactance/impedenceElectricityMeasurement device
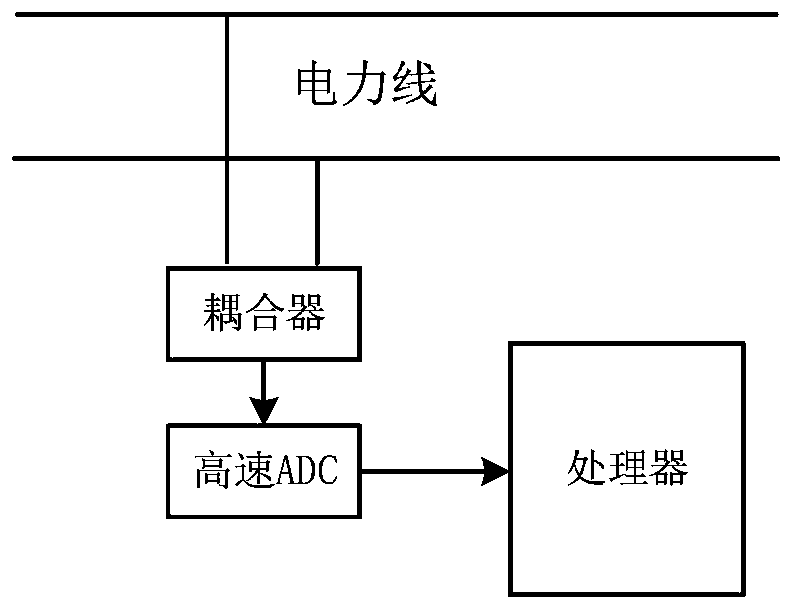
An embodiment of the invention discloses a device for measuring impedance of a power line access point. The device comprises a PCB (printed circuit board), a signal collector, a PC, a signal transmitter and a coupler, the signal collector, the PC, the signal transmitter and the coupler are fixedly arranged on the PCB, the output end of the signal collector is electrically connected with the inputend of the PC, the output end of the PC is electrically connected with the input end of the signal transmitter, the output end of the signal transmitter is electrically connected with the input end ofthe coupler, the output end of the coupler is electrically connected with a power line, and the input end of the signal collector is electrically connected with the power line. By the device, the technical problem that conventional oscilloscopes and spectrometers do not have a long-time signal storage function generally, which goes against long-time recording and playback of power line noise is solved.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD
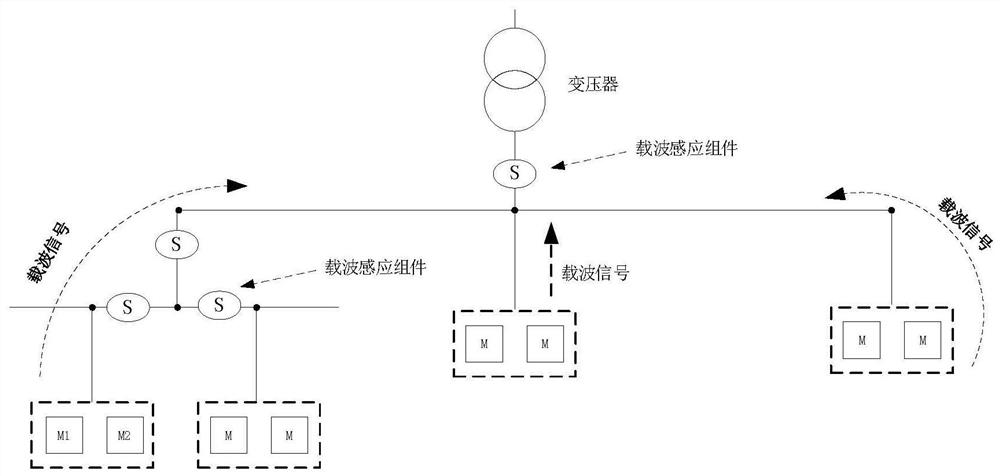
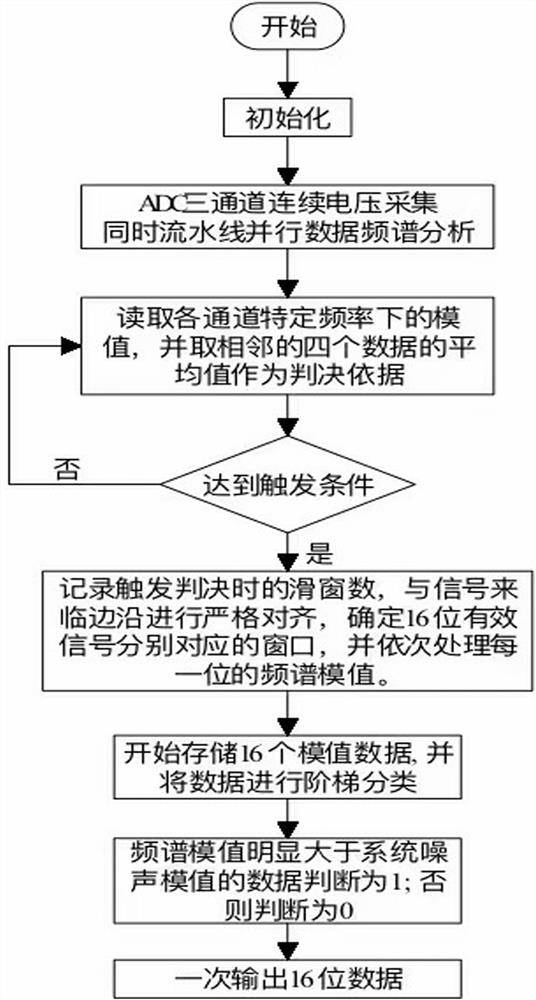
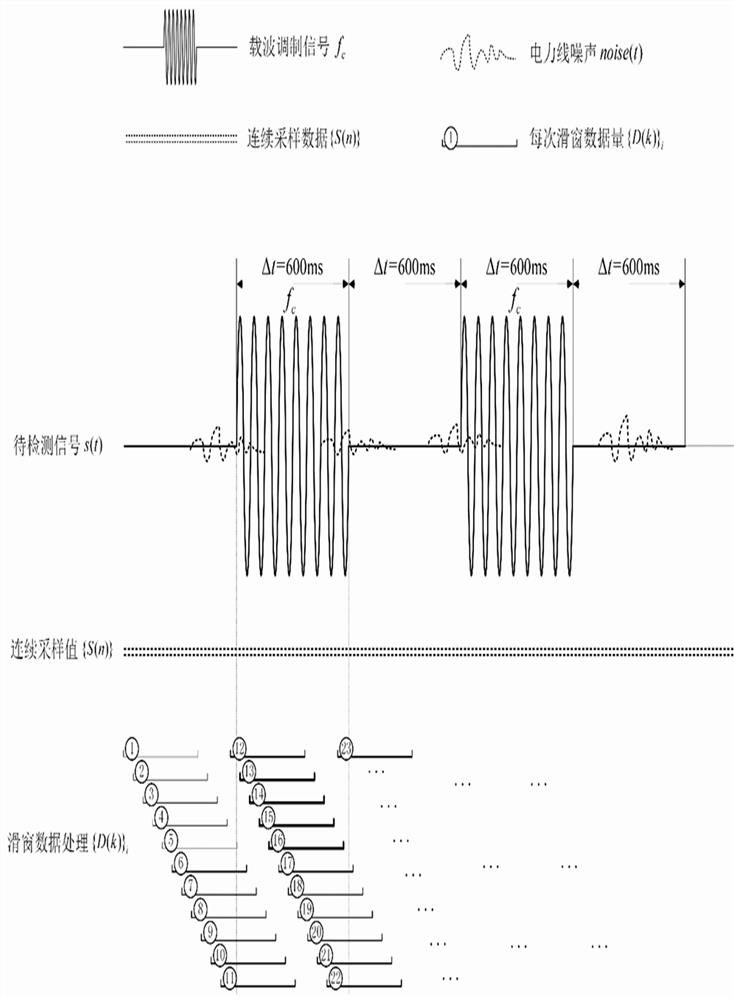
Low-frequency power line carrier topology identification method
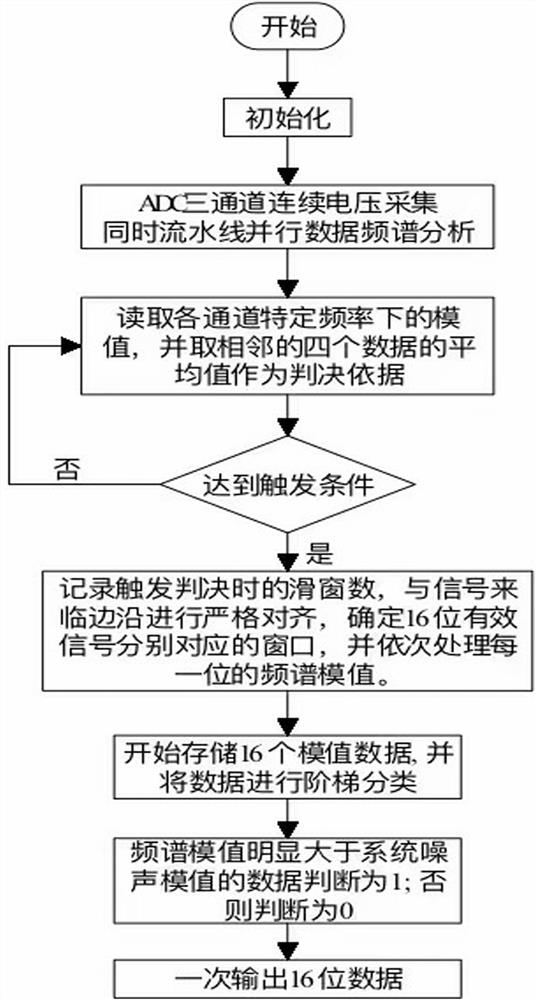
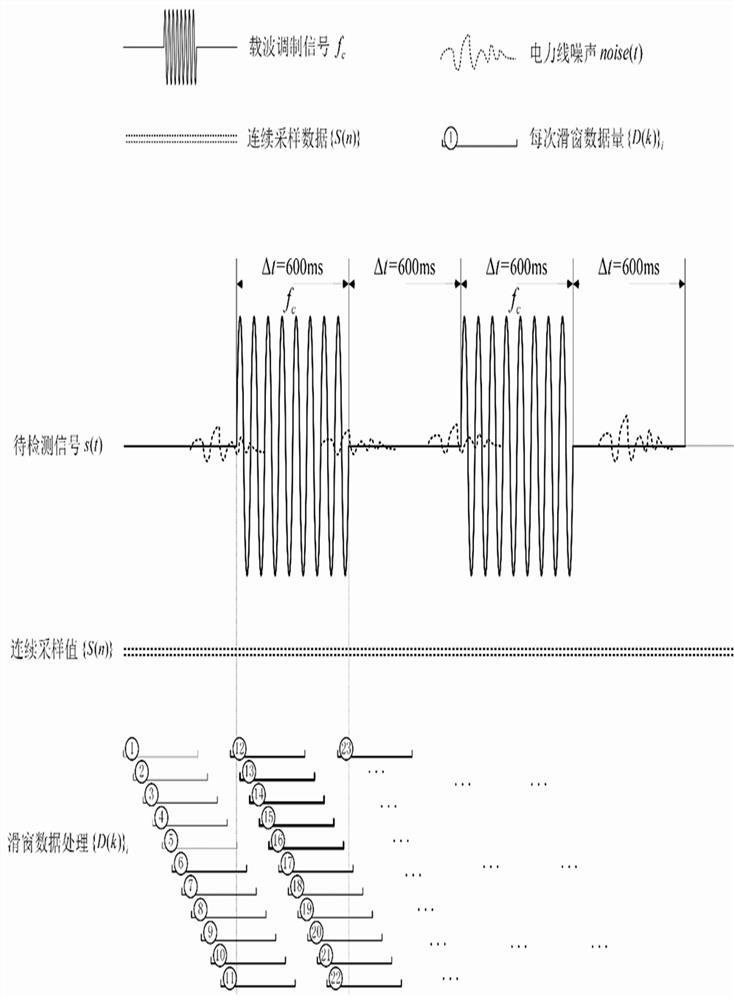
ActiveCN114374411AReduce distractionsImprove accuracyPower distribution line transmissionNeural architecturesTopology identificationFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a low-frequency power line carrier topology identification method, which comprises the following steps of: 1, continuously carrying out continuous voltage sampling, and simultaneously carrying out parallel processing on sampling data at a previous moment in an assembly line mode; 2, performing high-density data analysis on the sampled data by adopting a method based on an FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) convolutional neural network; 3, averaging analysis results of the multiple sliding window data, and taking an averaged frequency spectrum module value as a judgment basis of a carrier signal; 4, step classification is carried out according to the frequency spectrum module value amplitude of the signals, and 16-bit modulation signal codes are output; the signal detection mode based on the FFT convolutional neural network can utilize the effective duration of the modulation signal to the maximum extent, and the interference of the power line noise on the modulation signal is reduced and the topology identification monitoring accuracy is improved by using the mode of combining the digital filter and the multi-sliding window FFT average.
Owner:江苏米特物联网科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for sensing noise signals in a wireline communications environment
InactiveUS9166651B2Reduce impactImprove featuresCross-talk reductionLine-transmission monitoring/testingLine sensorWired communication
The present invention relates to methods and apparatuses for sensing noise sources in a wireline communications environment such as a customer premises environment in a DSL system. In embodiments, the invention includes an additional sensor that is connected to power mains in a DSL customer premises environment either to characterize, at their source, noises coupling into the DSL lines, and / or to mitigate their impact into the DSL lines. One objective is associated with diagnostics that help to better characterize the noise signals themselves and derive correlation of signals sensed from the power mains and their possible projection onto the DSL line. Another objective makes use of these power line sensor signals to mitigate or to eliminate power line noises that make their way onto the DSL line. Example embodiments further include and exploit signals from additional secondary sensors such as secondary common mode, differential mode and phantom mode sensors.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Device and method for testing performance of electromagnetic interference noise separator
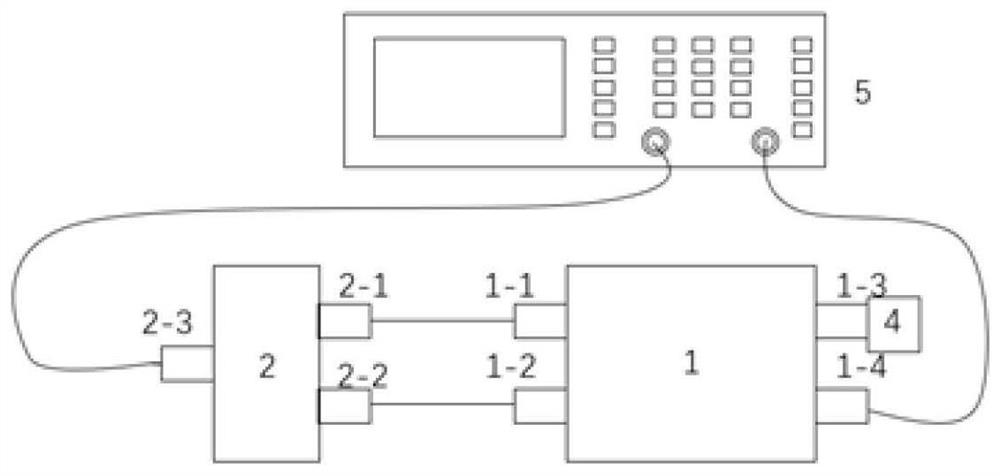
ActiveCN113092892AScientific targeted guidanceEffective targeted guidanceMeasuring interference from external sourcesEnvironmental/reliability testsTest performanceCoaxial line
The invention relates to a device and a method for testing the performance of an electromagnetic interference noise separator, and the device consists of a tested conducted noise separator, an in-phase power divider, an anti-phase power divider, a 50-ohm matching load and a dual-port network analyzer which are connected through a 50-ohm coaxial line. The tested conducted noise separator is provided with two input ports and two output ports and is used for inputting a power line noise signal and outputting a differential mode noise component and a common mode noise component, and the anti-phase power divider and the in-phase power divider are used for simulating the differential mode signal and the common mode signal. The method can be used for testing the performance of the conducted noise separator and also can be used for testing the performance of the filter, and carrying out common-mode and differential-mode separation and quantification on electromagnetic compatibility disturbance conducted noise in a product test process. Scientific and effective targeted guidance is provided for common-mode and differential-mode filter parameters designed for suppressing conducted noise in the electromagnetic compatibility rectification and optimization process.
Owner:FAW CAR CO LTD
Method for detecting noise signal power of power line
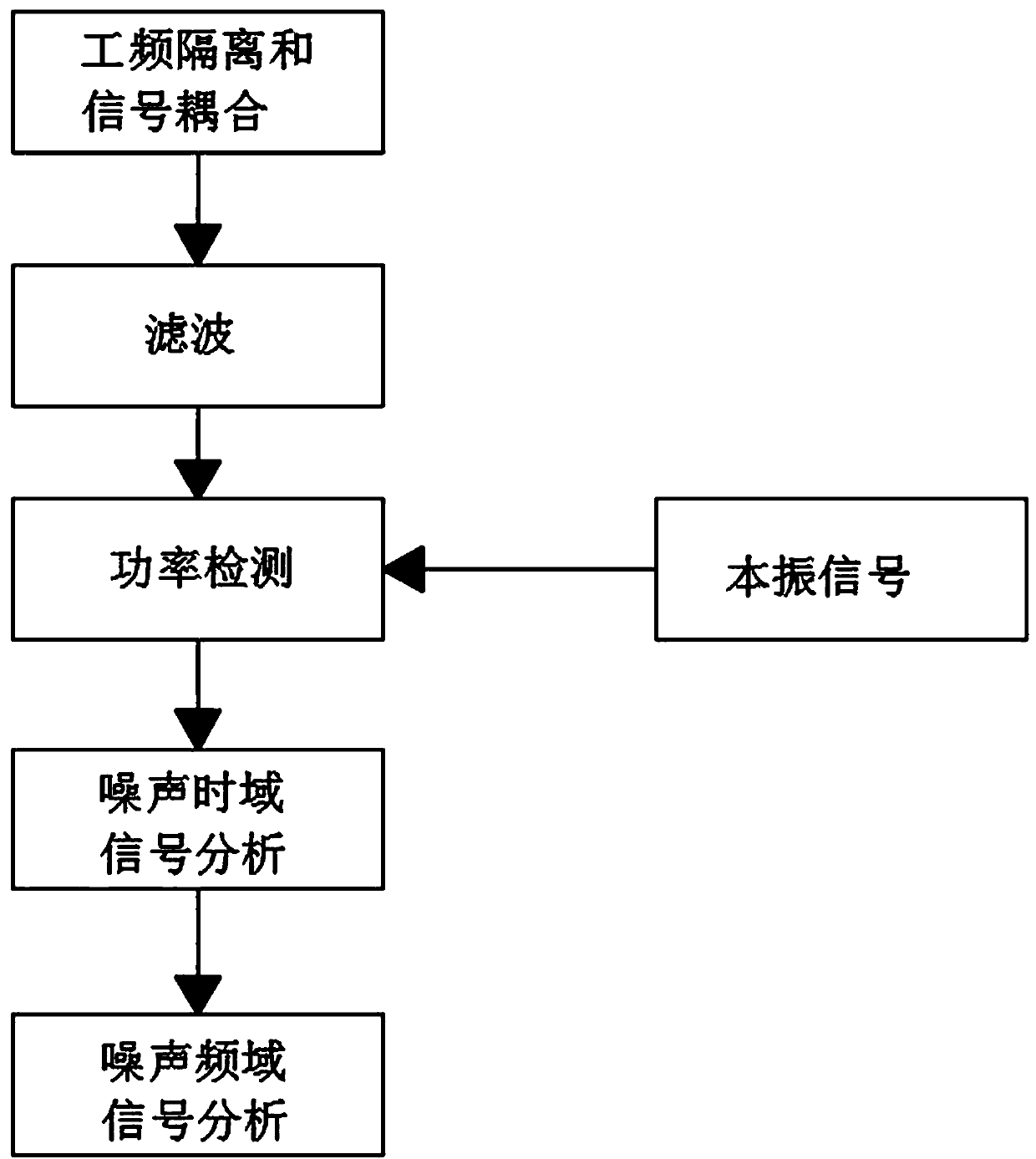
InactiveCN107645317ARealize graphic displayImprove accuracyPower distribution line transmissionLine-transmission monitoring/testingBandpass filteringLocal oscillator signal
The invention relates to a method for detecting a noise signal power of a power line. The method comprises the following steps: step a, on the basis of a frequency difference between a power frequencyand that of a carrier signal needing to be tested, carrying out coupling of a power frequency signal and a tested signal; step b, transmitting a coupled power line signal to a band-pass filtering unit; step c, processing the filtered signal by using a carrier signal power testing unit; step d, generating a local oscillator signal needed by a mixing unit in the carrier signal power testing unit byusing a program-controlled local oscillator unit; step e, transmitting a filtered intermediate-frequency signal to an AD sampling unit for detection; and step f, sending AD data generated by the AD sampling unit to a DSP unit for FFT operation. With the obtained power information, noise time domain information, and frequency domain information of the noise, graphic displaying of waveform data andspectrum data of the collected current power line signal is realized and the noise signal in the power line is analyzed deeply and conveniently, so that the accuracy of terminal communication is enhanced and reliability is improved; and targeted advice is provided for selection of a terminal product.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
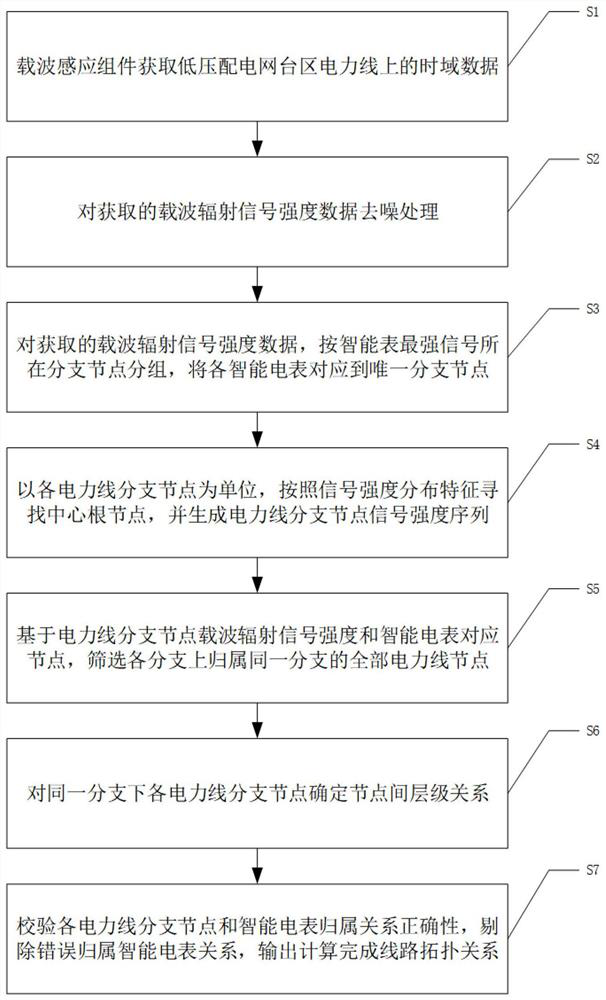
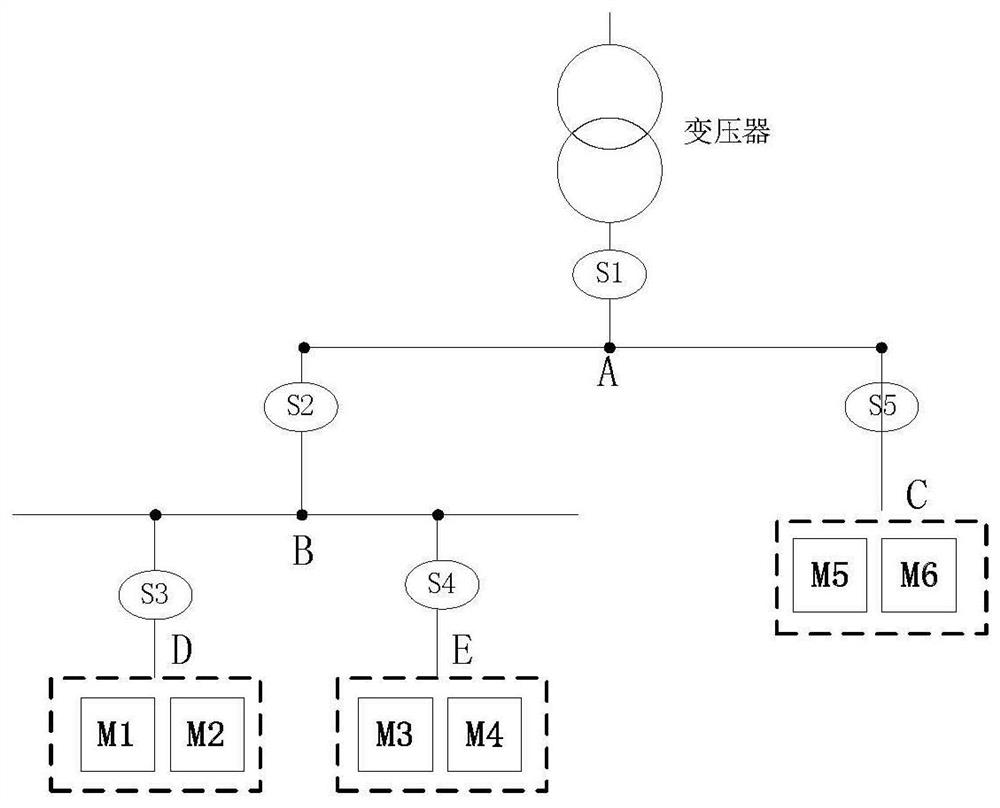
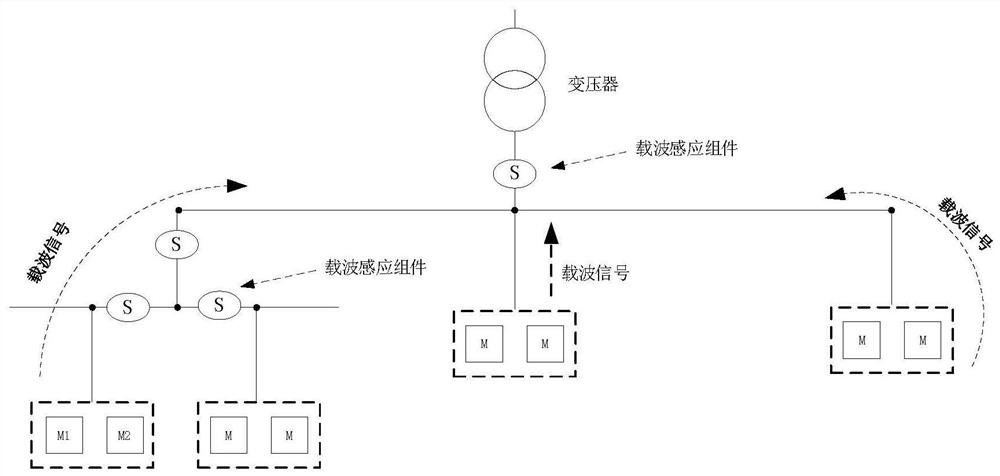
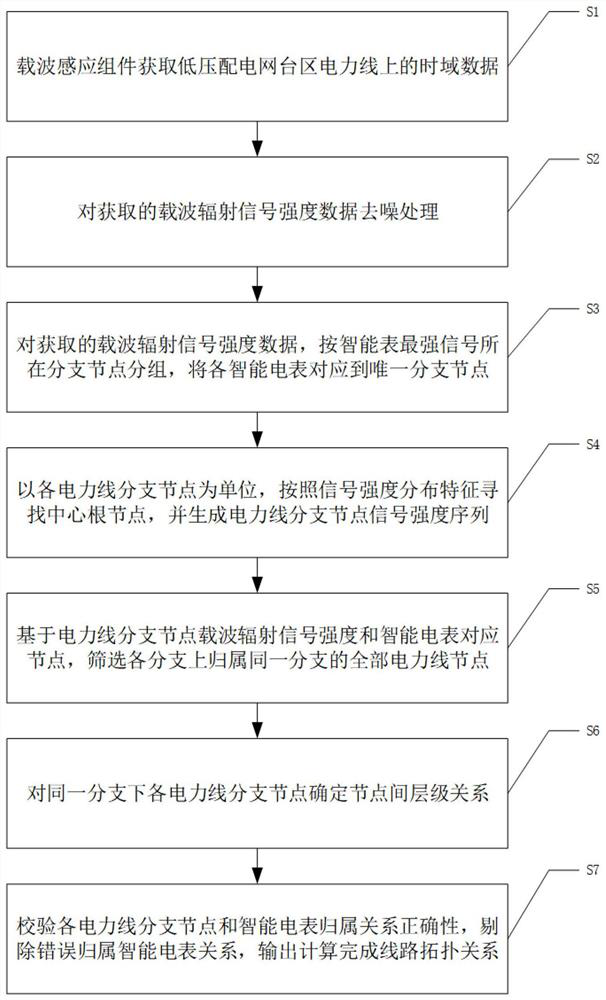
A Method for Calculating Line Topology Based on Distribution Characteristics of Power Carrier Radiated Signal Strength
ActiveCN112436866BLess investmentImprove investment benefit ratioPower distribution line transmissionTelecommunicationsLow voltage
The invention discloses a method for calculating the topological structure relationship of low-voltage power line branches based on the distribution characteristics of the radiation signal intensity of low-voltage power line carrier communication. The invention is based on the strength of the radiation signal intensity of low-voltage power line carrier communication collected by each branch node. Since the carrier signal attenuation characteristics of low-voltage power line carrier communication and power line noise characteristics interfere with the data of carrier communication radiation signals, it is impossible to use the method of carrier communication radiation signal strength to calculate the topological relationship. According to the characteristics, the method of accurately calculating the belonging branch of the terminal meter is given. According to the relationship between the carrier communication radiation signal strength between the branch nodes, the connection relationship between the calculation branch and the branch is given. Based on the relationship between the terminal smart meter and the branch and the relationship between the branches The connection relationship between them can accurately draw the topology relationship of low-voltage power line branches.
Owner:SICHUAN NENGXIN SCI & TECH
Method for calculating line topology based on power line carrier radiation signal intensity distribution characteristics
ActiveCN112436866ALess investmentImprove investment benefit ratioPower distribution line transmissionData switching networksInterference (communication)Telecommunications
The invention discloses a method for calculating a low-voltage power line branch topological structure relationship based on low-voltage power line carrier communication radiation signal intensity distribution characteristics, which is based on low-voltage power line carrier communication radiation signal intensity acquired by each branch node. The innovativeness of the method is to solve the problem that the topological relation cannot be calculated in a carrier communication radiation signal intensity mode due to interference of low-voltage power line carrier communication carrier signal attenuation characteristics and power line noise characteristics on carrier communication radiation signal data. The method for accurately calculating the affiliated branch of the tail-end electric meteris provided according to the radiation signal distribution characteristics of the intelligent electric meter at the tail end of each branch on each branch node, the connection relationship between the branches is calculated according to the carrier communication radiation signal intensity relationship between the branch nodes, and a low-voltage power line branch topological structure relationshipaccurately drawn based on the connection relationship between the tail-end intelligent electric meter and the branches and the connection relationship between the branches.
Owner:SICHUAN NENGXIN SCI & TECH
Improved electrocardiosignal noise reduction method based on singular spectrum analysis
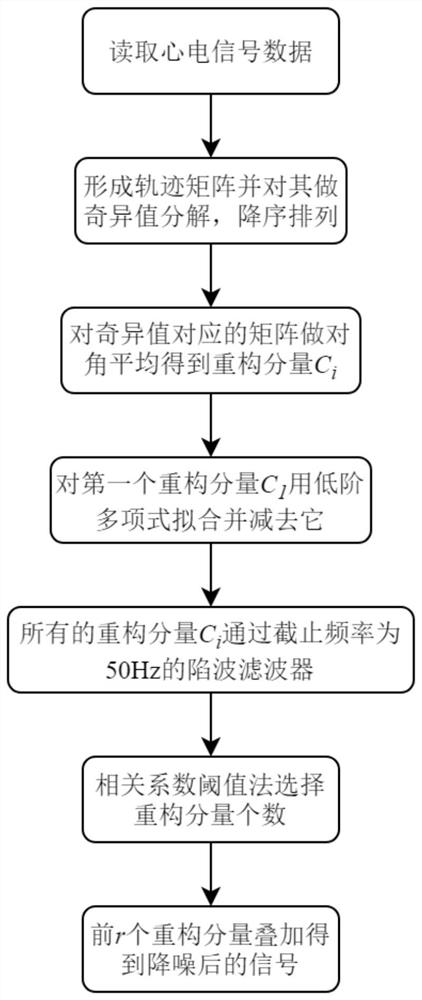
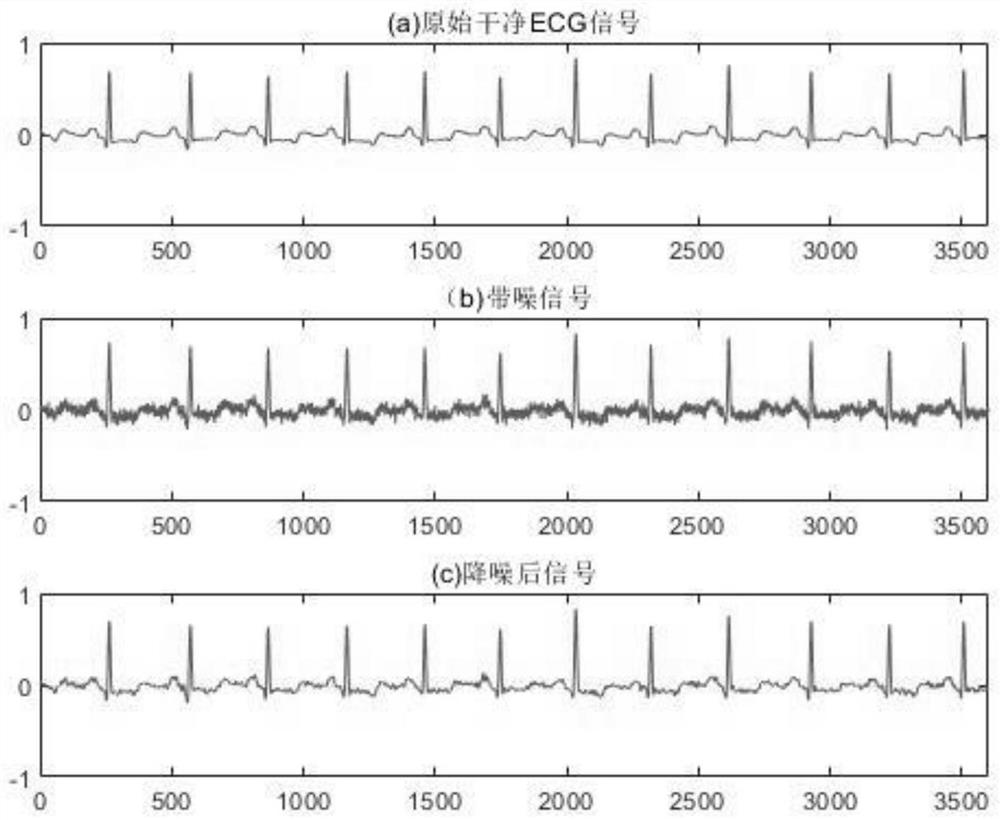
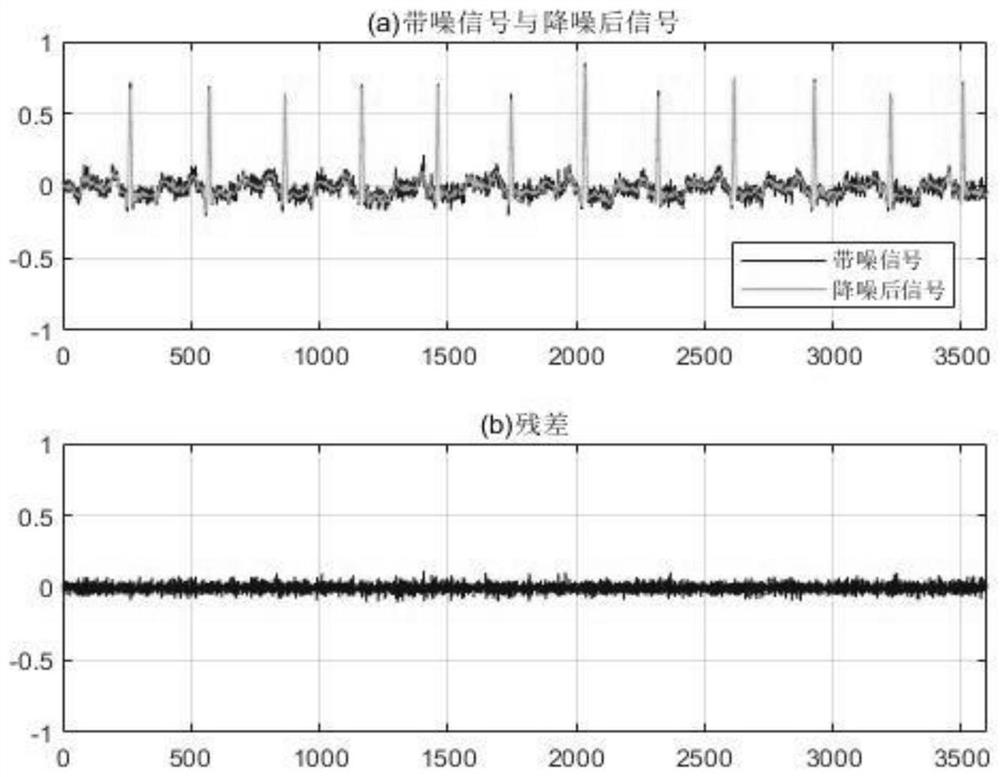
ActiveCN113180680AImprove analytical performanceEfficient removalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalSingular spectrum analysis
The invention relates to an improved electrocardiosignal noise reduction method based on singular spectrum analysis. The method specifically comprises the following steps: selecting a proper window length for electrocardiosignals to construct a track matrix, and carrying out singular value decomposition; calculating a signal reconstruction component corresponding to each singular value, and removing a trend term from the first reconstruction component by adopting a low-order polynomial fitting method; adopting a wave trap to remove power frequency interference in each reconstruction component; calculating an absolute value of a correlation coefficient between the reconstruction components and comparing the absolute value with a threshold value to select an effective signal component; and finally, superposing the effective signal components to obtain a denoised electrocardiosignal. The method is driven by data, does not need reference input, is suitable for removing Gaussian white noise, baseline drift, myoelectricity interference, power line noise and other noise, and can improve the subsequent signal analysis effect. According to the method, the signal distortion degree is small, noise reduction can be well achieved under the condition of the low signal-to-noise ratio, and the method can be popularized to noise reduction of one-way or multi-way other physiological signals.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
ofdm power frequency synchronous power carrier communication and physical layer coding and modulation method
ActiveCN105991499BIncrease profitImprove reliabilityMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsCarrier signalEngineering
The invention discloses an OFDM power-frequency synchronous power carrier communication and physical layer coded modulation method. The communication method comprises that P OFDM symbols are sent within 1 / 2 AC power-frequency period, and P represents a positive integer; the SNR of each subcarrier and the corresponding OFDM symbol is measured repeatedly; and according to a measured SNR sequence, a bit loading table is generated via a time domain and frequency domain 2D ToneMap and sent to achieve the channel adaptability and improve the reliability and communication speed of the whole communication system. The method of the invention has the advantages that the sparsity of period static characteristic and noises in the time and frequency domains of power line noises is utilized fully, the utilization rate (speed) of a PLC channel is improved, the transmission reliability and the system throughput are improved, and coding efficiency is high. The method can support an OFDM power-frequency synchronous continuous sending mode as well as a discontinuous sending mode.
Owner:HI TREND TECH SHANGHAI
A low-voltage power line carrier channel noise test system and method for field use
ActiveCN103063936BHigh utility valueSolve some difficult problems of noise field testingNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementLow voltageData acquisition
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Method for estimating power line system channel by using neural network
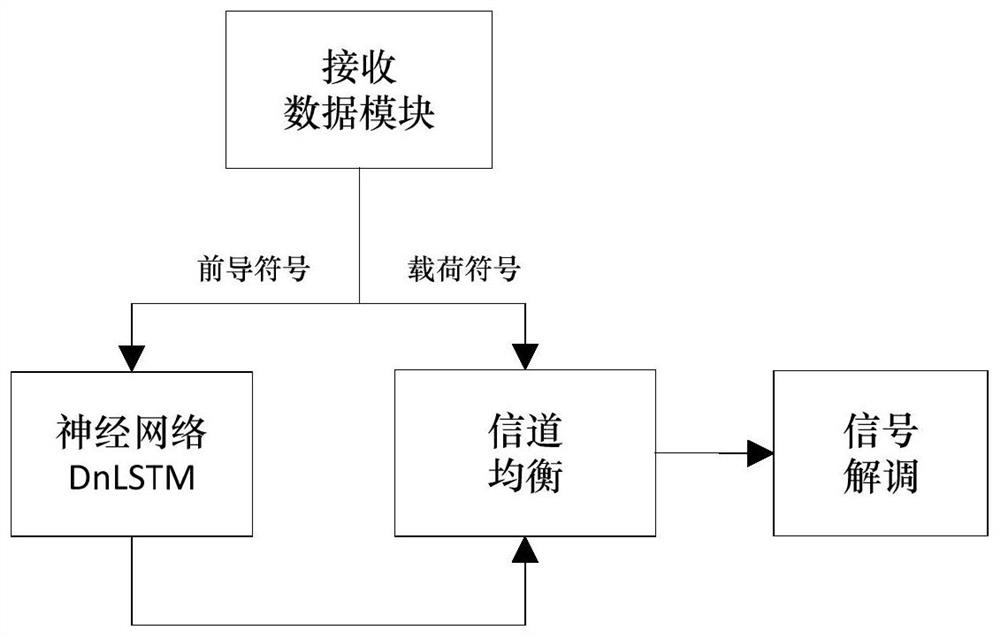
ActiveCN114884783AImprove robustnessSatisfy signal demodulation requirementsPower distribution line transmissionFrequency-modulated carrier systemsLogitEngineering
The invention relates to a method for estimating a power line system channel by using a neural network, and belongs to the technical field of communication. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, performing channel estimation in a neural network DnLSTM by using preamble orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) symbol data; then, a neural network DnLSTM is adopted to generate a channel characteristic matrix of each symbol in frame control and frame load, and the channel characteristic matrix is used for channel equalization; and carrying out signal demodulation on the frame control and frame load symbols after channel equalization to obtain a log likelihood estimation value LLR of data carried by each OFDM symbol. According to the method for demodulating the communication signal by adopting the deep neural network, the robustness is good, specific algorithm processing does not need to be carried out on specific noise on the power line, and different power line noise environments are self-adapted through a large amount of training.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
rc electronic arc extinguisher
InactiveCN102290271AExcellent anti-pulsation abilityEasy to use and installElectric switchesNumerical controlCapacitance
The invention discloses an RC electronic arc extinguisher. The RC arc extinguisher includes a capacitor and a resistor; the capacitor and the resistor are connected in series, and the capacitor and the resistor are packaged in a packaging body; a capacitor and a resistor The resonant circuit composed of it can effectively filter out interference and absorb quasi-waves, has a certain safety guarantee function and excellent anti-pulsation ability, integrated design, easy to use and install, and improves reliability; suitable for power cross-line noise reduction routes, CNC machine tools, AC and DC occasions such as audio equipment.
Owner:兴化市华宇电子有限公司
HPLC-oriented power line noise suppression method
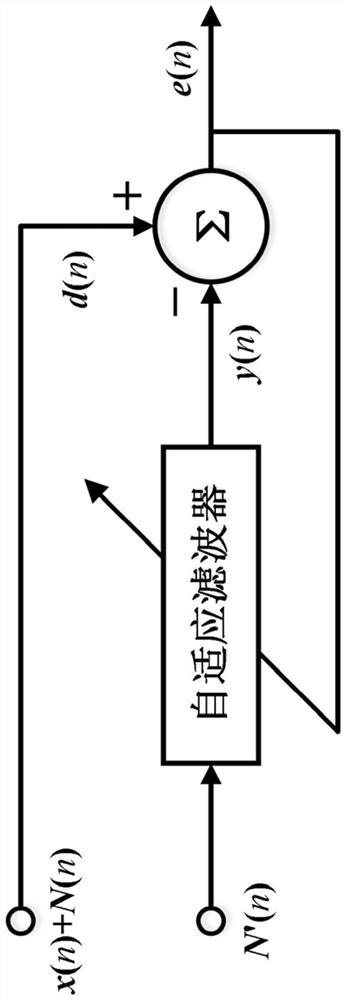
InactiveCN113067603AImprove work efficiencyGood effectPower distribution line transmissionTransmission noise suppressionTelecommunicationsAdaptive filter
The invention discloses an HPLC-oriented power line noise suppression method, and relates to the technical field of power communication. Based on a self-adaptive power line noise suppressor, pre-noise N'(n) is extracted from a power line according to preset pre-time, self-adaptive noise suppression is carried out on a power line signal d(n) through the pre-noise N'(n), a noise reduction signal e(n) is obtained, and the self-adaptive power line noise suppressor comprises a self-adaptive filter and a subtracter which are electrically connected with each other; and through the adaptive power line noise suppressor, pre-noise N'(n) is extracted to carry out adaptive noise suppression on a power line signal d (n), a noise reduction signal e(n) and the like are obtained, the working efficiency of power line noise suppression is high, and the effect is good.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Power line noise compression method and device based on compressed sensing
The invention discloses a power line noise compression method based on compressive sensing. When a power line is unloaded, noise on the power line is subjected to strong electrical isolation and attenuation through a coupler; then, noise of a power line channel is acquired through noise acquisition equipment; the acquired noise of the power line channel is divided into background noise and random noise; then, characteristic data of the background noise are extracted in a time domain and stored; the random noise is compressively sensed in a frequency domain according to an observation matrix; and furthermore, main information obtained after the random noise is processed is stored. The invention further discloses a power line noise compression device based on compressive sensing. By means of the invention, when the power line is unloaded, the power line noise acquired from the power line in a coupled manner is effectively compressed and stored; therefore, the volume of data in need of being stored can be effectively reduced; and the relatively high compression removal rate can be achieved.
Owner:CHINA GRIDCOM +2
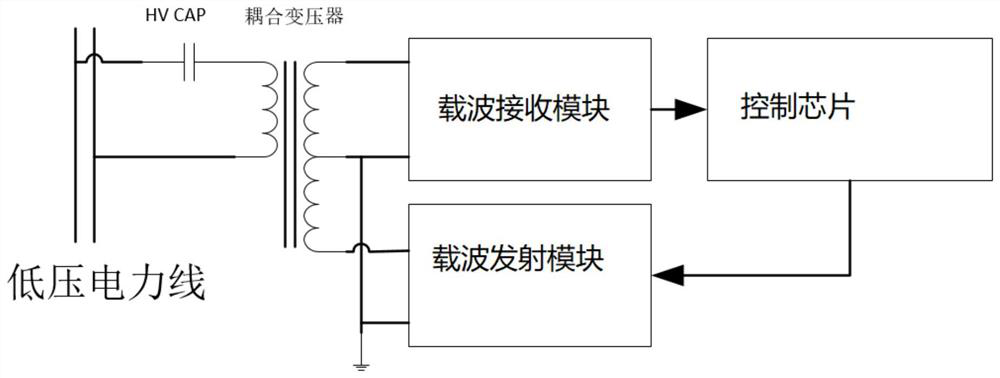
Power line carrier communication equipment and communication system
PendingCN112910507ARealize interactive data communicationNormal communicationPower distribution line transmissionCommunications systemElectric power system
The invention discloses power line carrier communication equipment, which comprises a carrier receiving module, a carrier transmitting module, a coupling transformer and a control chip, the input end of the carrier receiving module is connected with the power line through the coupling transformer, and the output end is connected with the control chip; the input end of the carrier transmitting module is connected with the control chip, and the output end is connected with the power line through the coupling transformer; and the control chip realizes data interaction with the power line through the carrier receiving module and the carrier transmitting module based on a G3-PLC standard. The invention further discloses a power line carrier communication system. By adopting a G3-PLC standard power line carrier communication mode, normal communication between the power system and the terminals is realized, interactive communication between the multiple terminals and the power system during charging is ensured, and the system has strong anti-interference capability and power line noise resistance, and interactive data communication across transformers can be realized.
Owner:北京中宸微电子有限公司
Pairing apparatus using secret key based on power line noise, method thereof
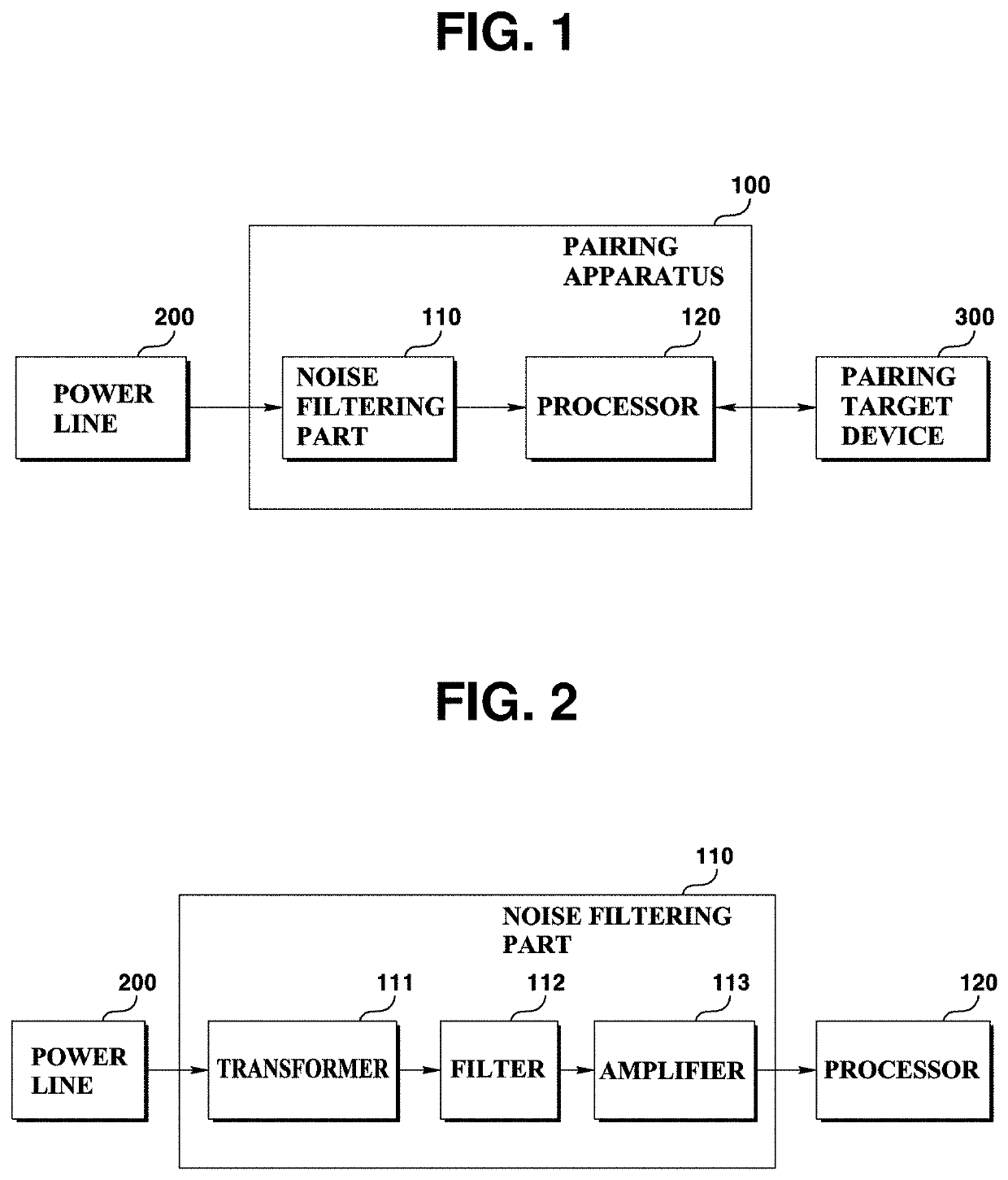
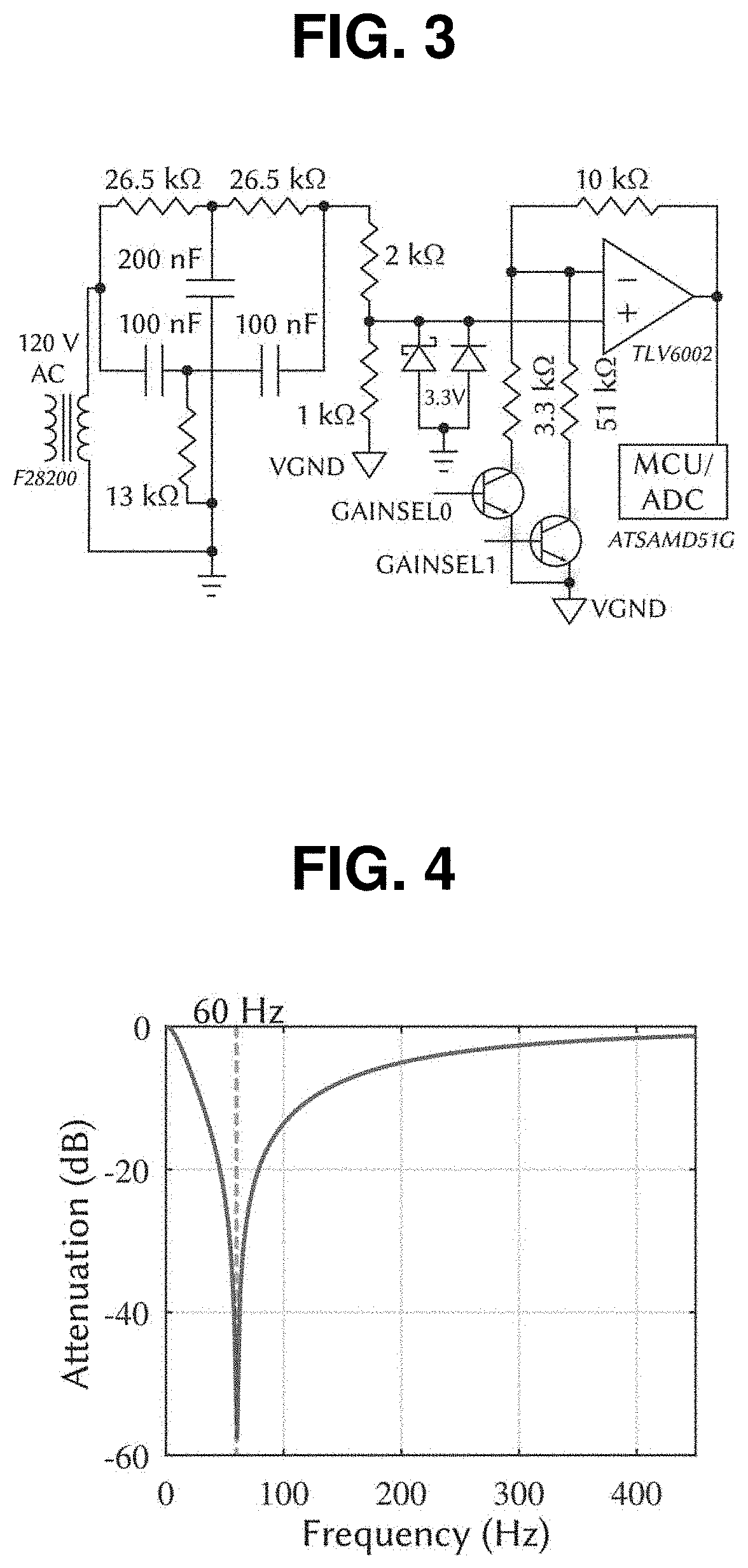
ActiveUS20220078013A1Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesTelecommunicationsAuthentication
A pairing apparatus according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes: a noise filtering part for filtering a noise on a power line; and a processor for pairing with a pairing target device and performing an authentication by generating a secret key using the filtered noise and by using the generated secret key.
Owner:LEE KYUIN +3
Processing apparatus for processing a physiological signal
ActiveUS11083404B2Improve performanceReduce componentsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHemt circuitsComputer science
A processing apparatus for processing a physiological signal using model subtraction, notch filtering and gating. The processing apparatus comprises a model subtraction circuit configured to receive the physiological signal and to reduce a first unwanted signal component, such as an ECG contamination, in the physiological signal by subtracting from the physiological signal a model of the first unwanted signal component to obtain a residual signal; a filter circuit configured to receive the residual signal and to reduce a second unwanted signal component, such as power line noise, in the residual signal by applying a notch filter to obtain a filtered signal; and a gating circuit configured to receive the filtered signal and to apply gating to the filtered signal to obtain a gated signal. The processing apparatus further relates to a corresponding electromyography system and a method for processing a physiological signal using model subtraction, notch filtering and gating.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
A low-frequency power line carrier topology identification method
ActiveCN114374411BReduce distractionsImprove accuracyPower distribution line transmissionNeural architecturesTopology identificationFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a low-frequency power line carrier topology identification method, which includes the following steps: Step 1: Continuously perform continuous voltage sampling, and simultaneously process the sampled data at the previous moment in parallel in a pipeline; Step 2: Use FFT-based convolution The neural network method performs high-density data analysis on the sampling data; step 3: average the analysis results of multiple sliding window data, and use the averaged spectrum modulus as the basis for judging the carrier signal; Stepwise classification of value and amplitude, and output 16-bit modulation signal code; the signal detection method based on FFT convolutional neural network in the present invention can maximize the effective duration of modulation signal, and use digital filter and multi-sliding window FFT average phase The combined method improves the accuracy of topology identification and monitoring while reducing the interference of power line noise on the modulation signal.
Owner:江苏米特物联网科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com