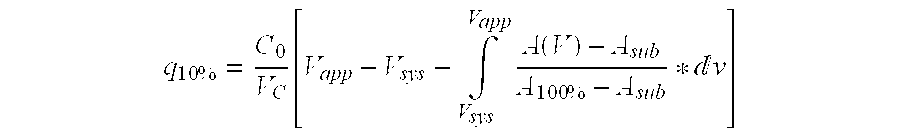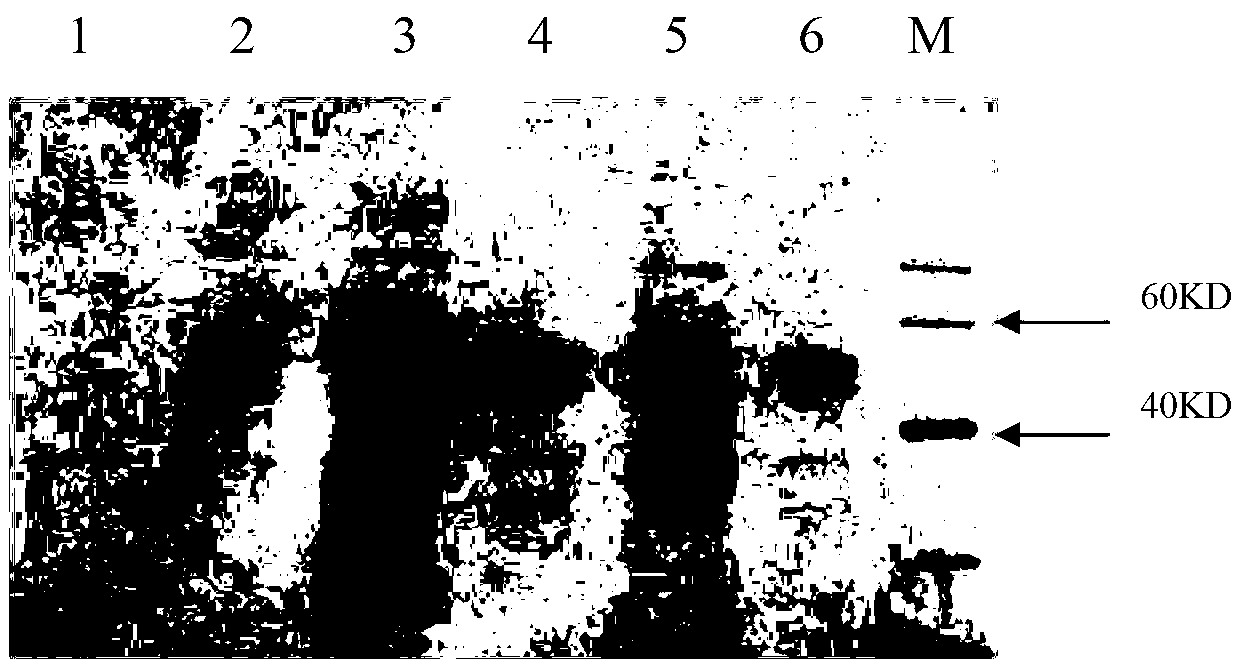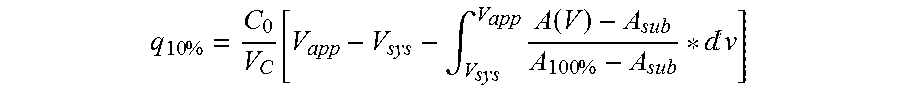Patents
Literature
34 results about "Protein Z" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein Z (PZ or PROZ) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PROZ gene. Protein Z is a member of the coagulation cascade, the group of blood proteins that leads to the formation of blood clots. It is a gla domain protein and thus vitamin K-dependent, and its functionality is therefore impaired in warfarin therapy. It is a glycoprotein.
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS20130274451A1Increased elution pHGuaranteed cost-effective operationSolid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsElutionA domain
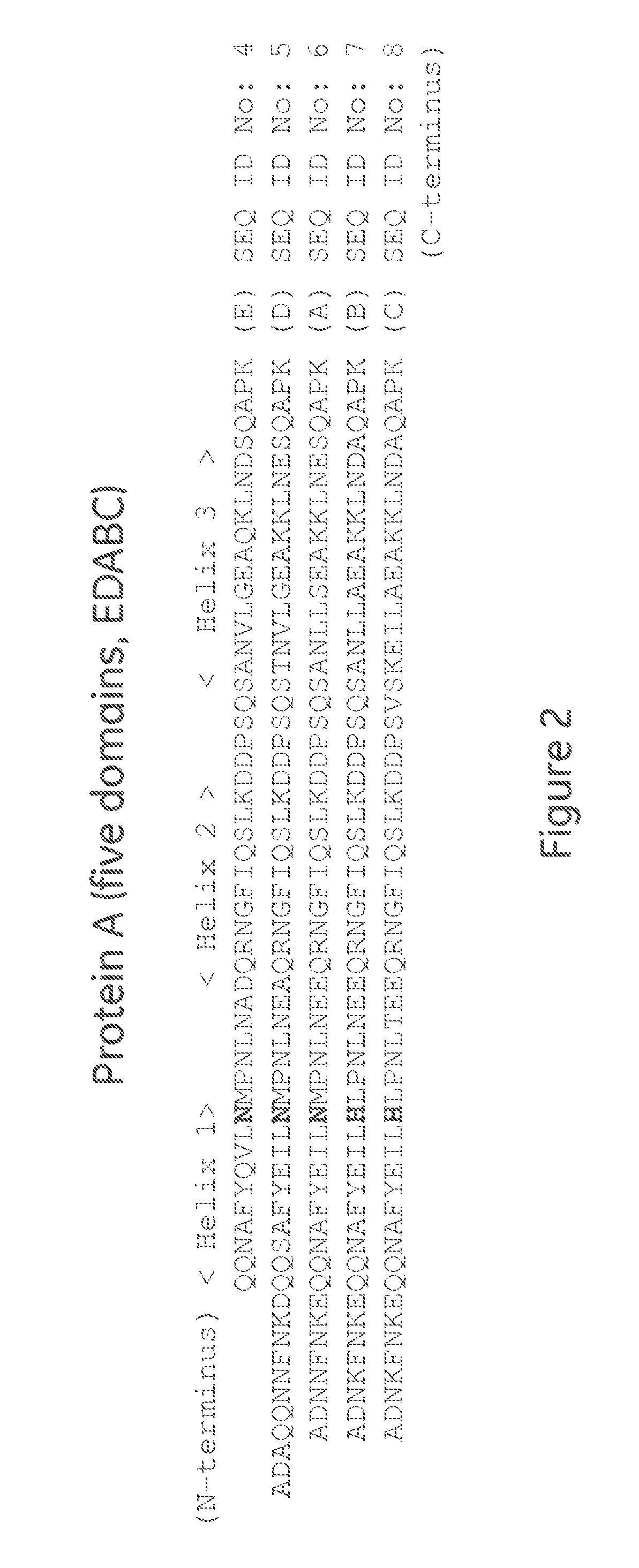
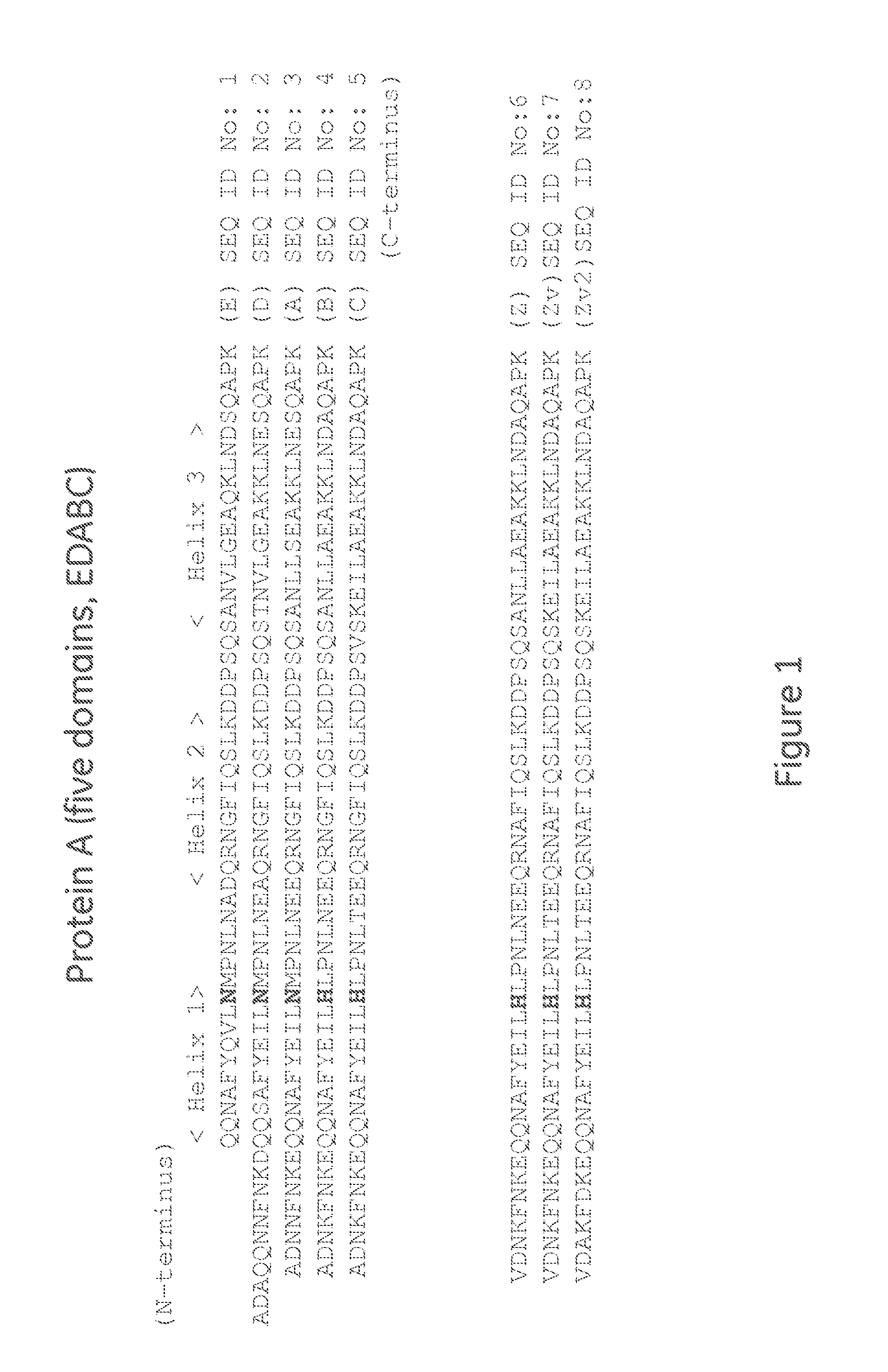
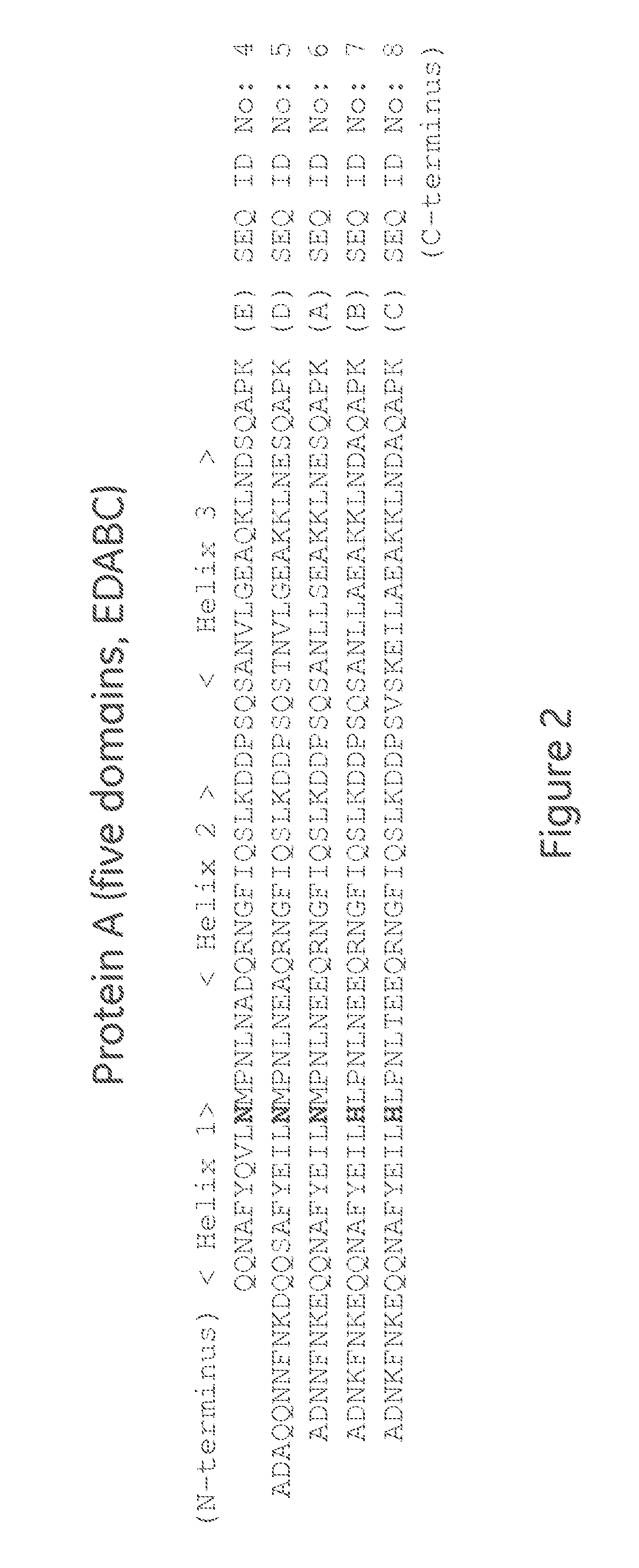
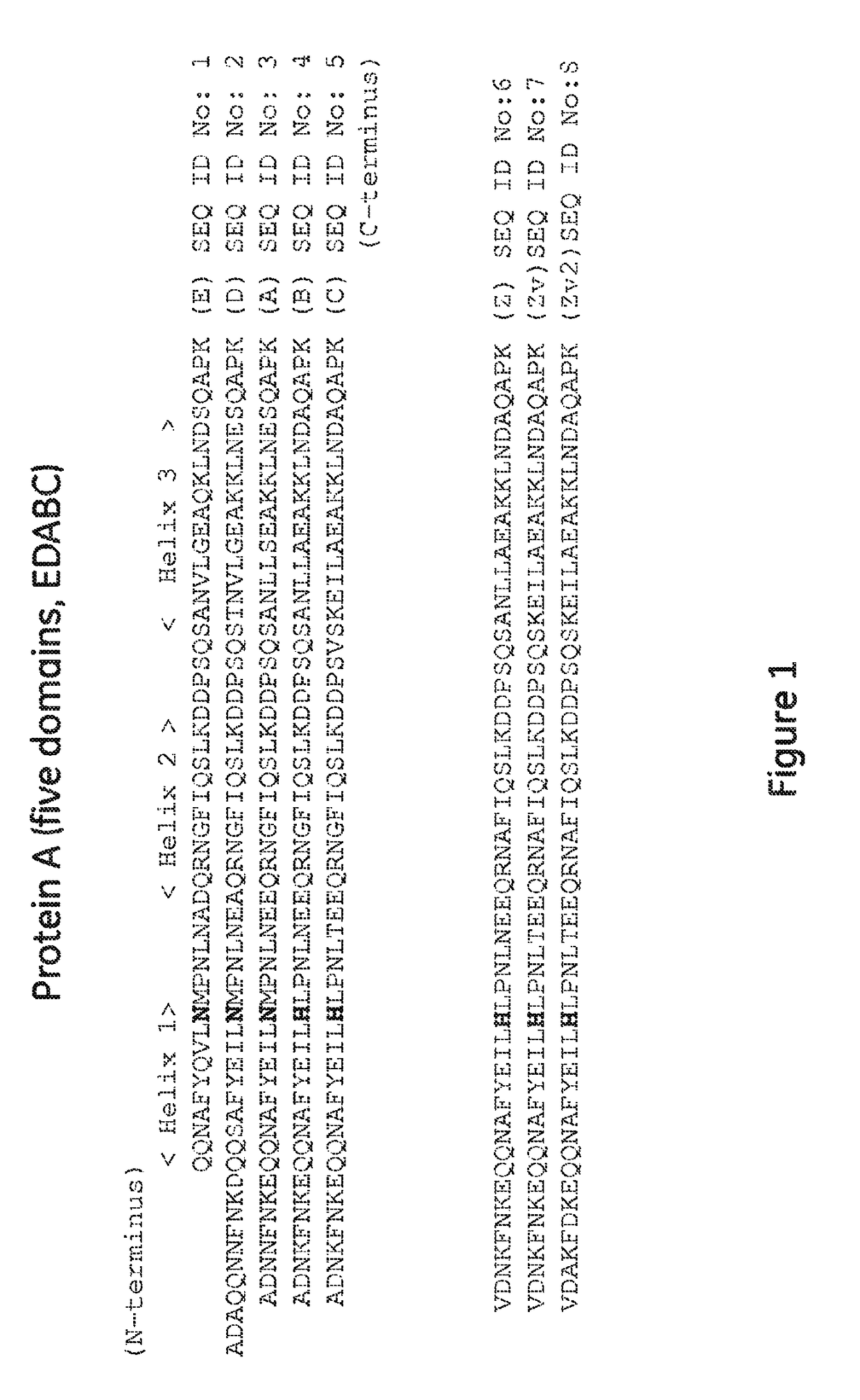
The present invention relates to a method of separating one or more immunoglobulin containing proteins from a liquid. The method includes first contacting the liquid with a separation matrix comprising ligands immobilised to a support; allowing the immunoglobulin containing proteins to adsorb to the matrix by interaction with the ligands; followed by an optional step of washing the matrix containing the immunoglobulin containing proteins adsorbed thereon; and recovering said immunoglobulin containing proteins by contacting the matrix with an eluent which releases the proteins. The method improves upon previous separation methods in that each of the ligands comprises one or more of a protein A domain (E, D, A, B, C), or protein Z, or a functional variant thereof, with at least one of the monomers having a substitution of the Asparagine at the position corresponding to N28 of B domain of Protein A or Protein Z, and wherein the ligand provides an increase in elution pH compared to non-substituted ligand.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Bone delivery conjugates and method of using same to target proteins to bone
ActiveUS7763712B2Success in targetingPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderProtein targetAmino acid
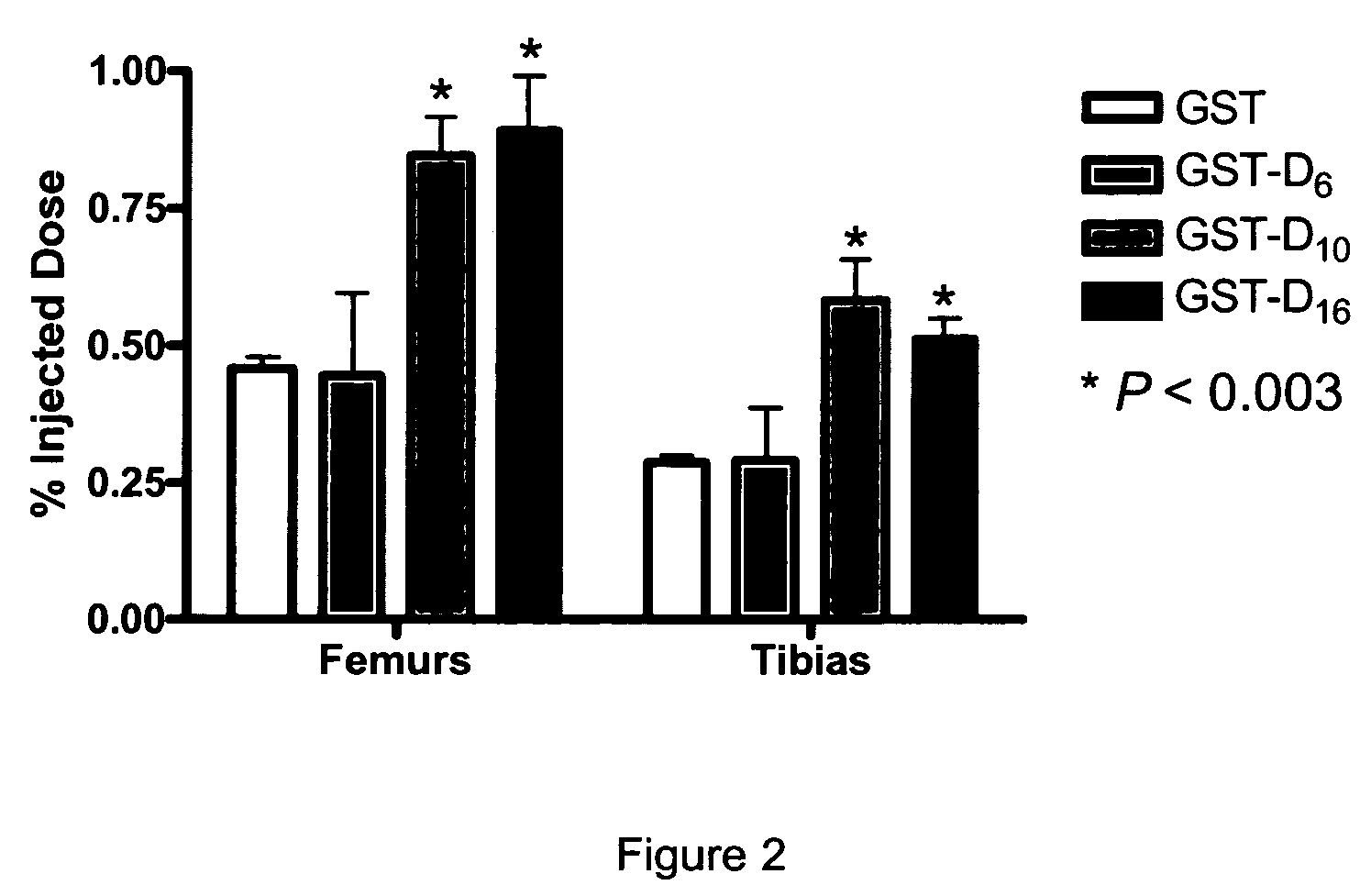
A bone delivery conjugate having a structure selected from the group consisting of: A) X-Dn-Y-protein-Z; and B) Z-protein-Y-Dn-X, wherein X is absent or is an amino acid sequence of at least one amino acid; Y is absent or is an amino acid sequence of at least one amino acid; Z is absent or is an amino acid sequence of at least one amino acid; and Dn is a poly aspartate wherein n=10 to 16. Compositions comprising same and methods of use thereof.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Replication-defective arenavirus vectors
ActiveUS20100297172A1Enhance protein expressionHigh expressionAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntigenDisease
The invention relates to an infectious arenavirus particle that is engineered to contain a genome with the ability to amplify and express its genetic information in infected cells but unable to produce further infectious progeny particles in normal, not genetically engineered cells. One or more of the four arenavirus open reading frames glycoprotein (GP), nucleoprotein (NP), matrix protein Z and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase L are removed or mutated to prevent replication in normal cells but still allowing gene expression in arenavirus vector-infected cells, and foreign genes coding for an antigen or other protein of interest or nucleic acids modulating host gene expression are expressed under control of the arenavirus promoters, internal ribosome entry sites or under control of regulatory elements that can be read by the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, cellular RNA polymerase I, RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III. The modified arenaviruses are useful as vaccines and therapeutic agents for a variety of diseases.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Mutated Immunoglobulin-Binding Polypeptides
ActiveUS20160159857A1Highly selective bindingImproved alkaline stabilitySolid sorbent liquid separationDepsipeptidesTryptophanMutant
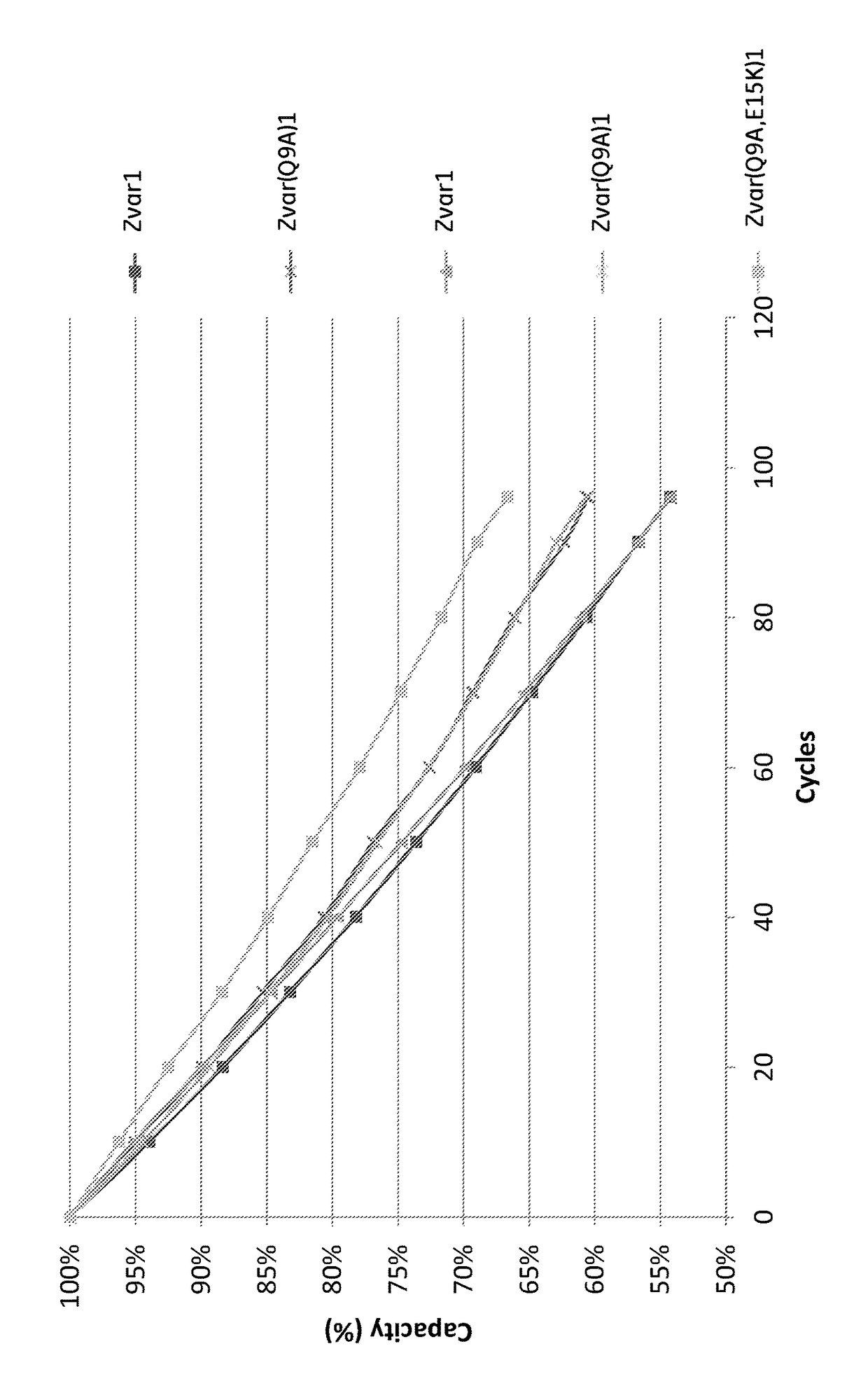
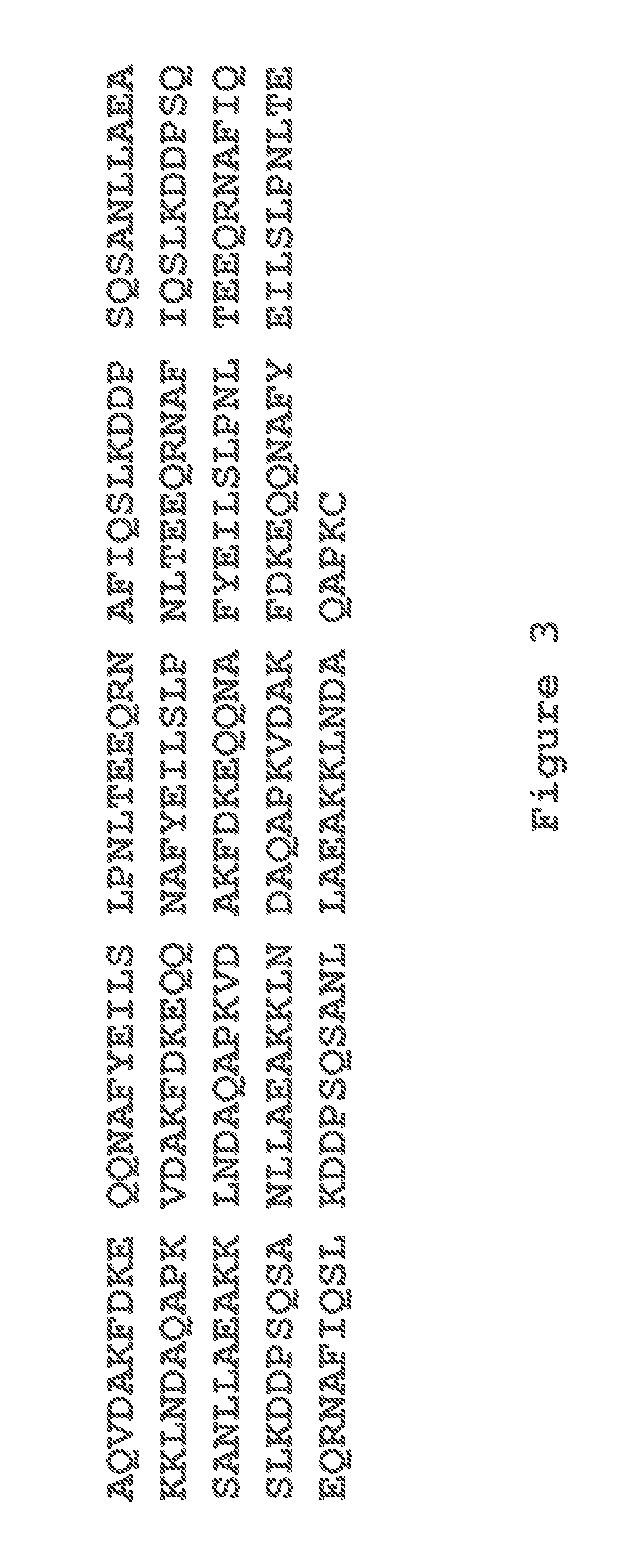
The invention discloses a polypeptide with improved alkaline stability, which polypeptide comprises a mutant of a B or C domain of Staphylococcus Protein A (SpA), as specified by SEQ ID NO 1 or SEQ ID NO 2, or of Protein Z, as specified by SEQ ID NO 3, comprising at least the mutation wherein the glutamine residue at position 9 has been mutated to a tryptophan, leucine, glutamic acid, valine or lysine. The invention also discloses multimers of the polypeptide, as well as separation matrices comprising the multimers or polypeptides.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Mutated immunoglobulin-binding polypeptides
ActiveUS20160159855A1Improved alkaline stabilityHighly selectiveSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulin IgEMutant
A polypeptide with improved alkaline stability, which polypeptide comprises a mutant of a B or C domain of Staphylococcus Protein A, as specified by SEQ ID NO 1 or SEQ ID NO 2, or of Protein Z, as specified by SEQ ID NO 3, wherein at least the glutamine residue at position 9 has been mutated to an amino acid other than asparagine. The invention also discloses multimers of said polypeptide, as well as separation matrices comprising the multimers or polypeptides.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Replication-defective arenavirus vectors
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS20140329995A1Improve bindingImprove stabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolid sorbent liquid separationAntibody Affinity ChromatographyProtein Z
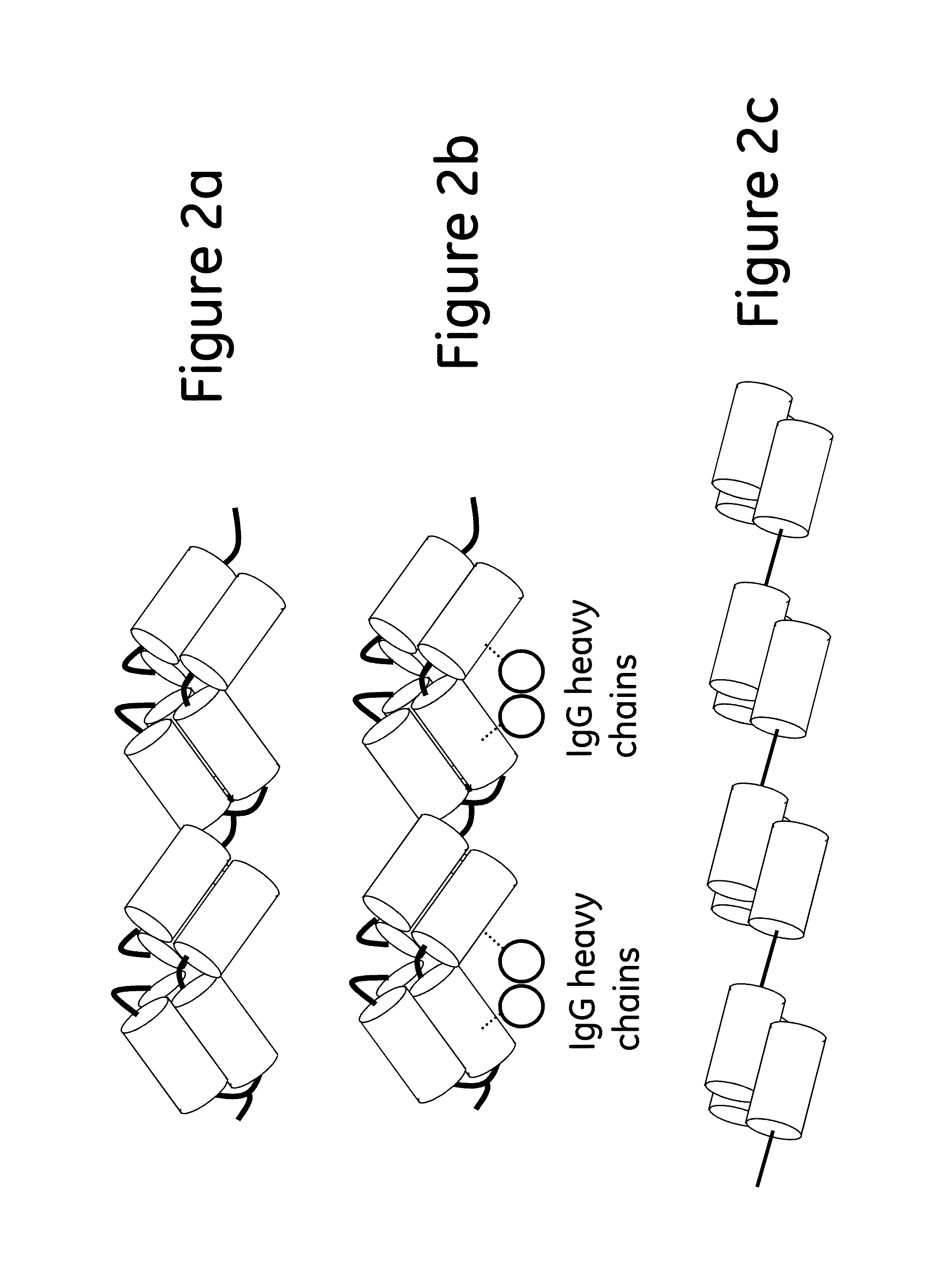
The invention discloses a polypeptide capable of binding immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin-containing proteins, which polypeptide comprises six or more domains of protein Z or the C domain of protein A or a functional variant thereof. It also discloses separation matrices comprising the polypeptide and methods of using the separation matrices for separation of immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin-containing proteins.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS9187555B2Easy to eluteGuaranteed cost-effective operationPeptide/protein ingredientsOther chemical processesElutionAsparagine
The present invention relates to a method of separating one or more immunoglobulin containing proteins from a liquid. The method includes first contacting the liquid with a separation matrix comprising ligands immobilized to a support; allowing the immunoglobulin containing proteins to adsorb to the matrix by interaction with the ligands; followed by an optional step of washing the matrix containing the immunoglobulin containing proteins adsorbed thereon; and recovering said immunoglobulin containing proteins by contacting the matrix with an eluent which releases the proteins. The method improves upon previous separation methods in that each of the ligands comprises one or more of a protein A domain (E, D, A, B, C), or protein Z, or a functional variant thereof, with at least one of the monomers having a substitution of the Asparagine or Histidine at the position corresponding to H18 of B domain of Protein A or Protein Z, and wherein the ligand provides an increase in elution pH compared to non-substituted ligand.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS8859726B2Increase capacityGuaranteed cost-effective operationPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum immunoglobulinsAlpha helixAntibody Affinity Chromatography
The present invention relates to a method of separating one or more immunoglobulin containing proteins from a liquid. The method includes first contacting the liquid with a separation matrix comprising ligands immobilised to a support; allowing the immunoglobulin containing proteins to adsorb to the matrix by interaction with the ligands; followed by an optional step of washing the adsorbed immunoglobulin containing proteins; and recovering said immunoglobulin containing proteins by contacting the matrix with an eluent which releases the proteins. The method improves upon previous separation methods in that each of the ligands comprises one or more of a protein A domain (E, D, A, B, C), or protein Z, or a functional variant thereof, with at least one of the monomers having a substitution of the C-terminal most proline residue after the third alpha-helix.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS20150080554A1Optimize purification stepsInhibition formationOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationThreonineHistidine
The invention discloses an immunoglobulin-binding protein comprising one or more mutated immunoglobulin-binding domains (monomers) of staphylococcal Protein A (E, D, A, B, C) or protein Z or a functional variant thereof, wherein in at least one of the one or more mutated monomers, the asparagine or histidine at the position corresponding to H18 of the B domain of Protein A or of Protein Z has been deleted or substituted with a first amino acid residue which is not proline or asparagine and wherein, if the amino acid residue at position 57 is proline and the amino acid residue at position 28 is asparagine, then the amino acid residue at the position corresponding to H18 of the B domain of protein A or of protein Z is not serine, threonine or lysine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
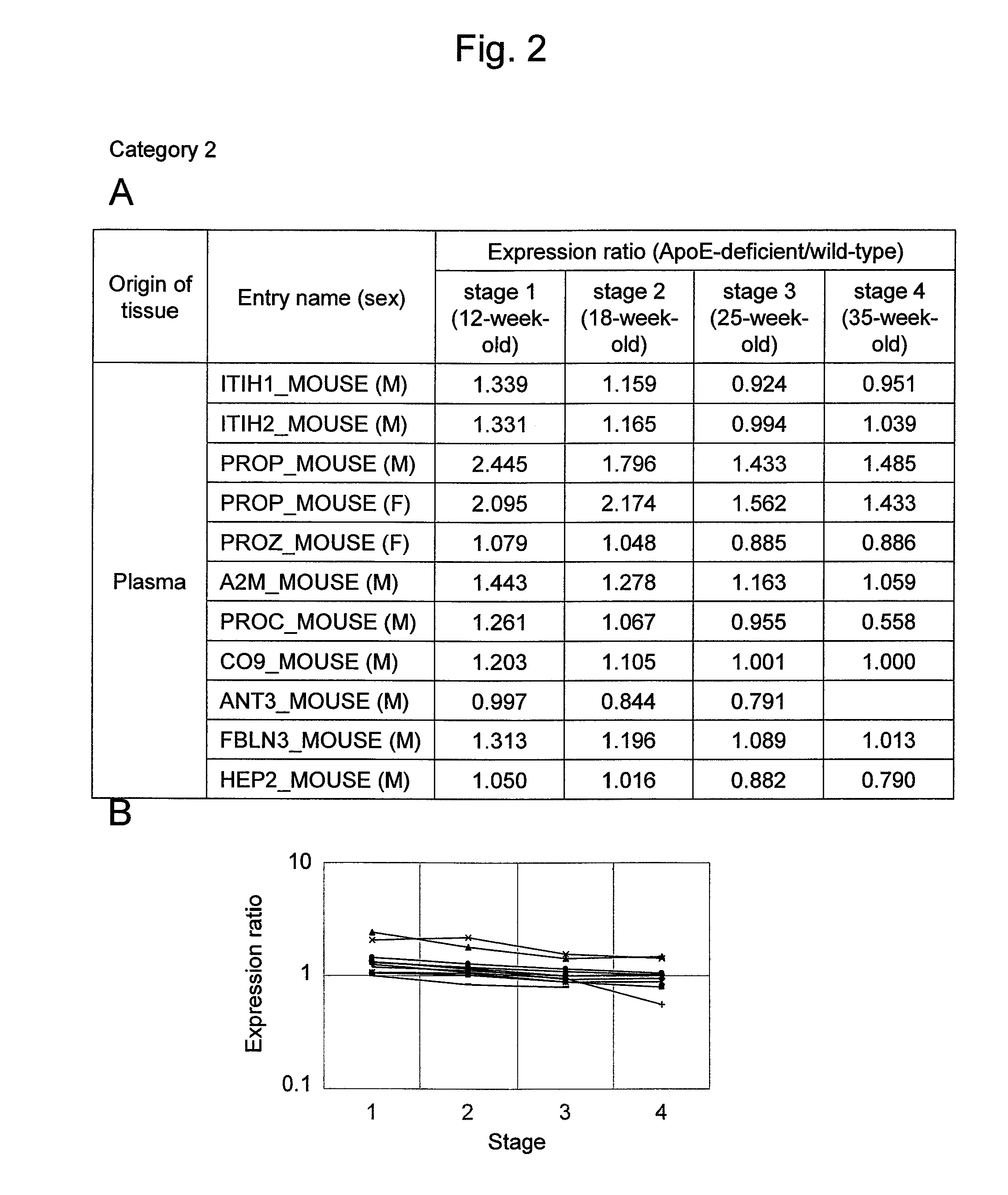
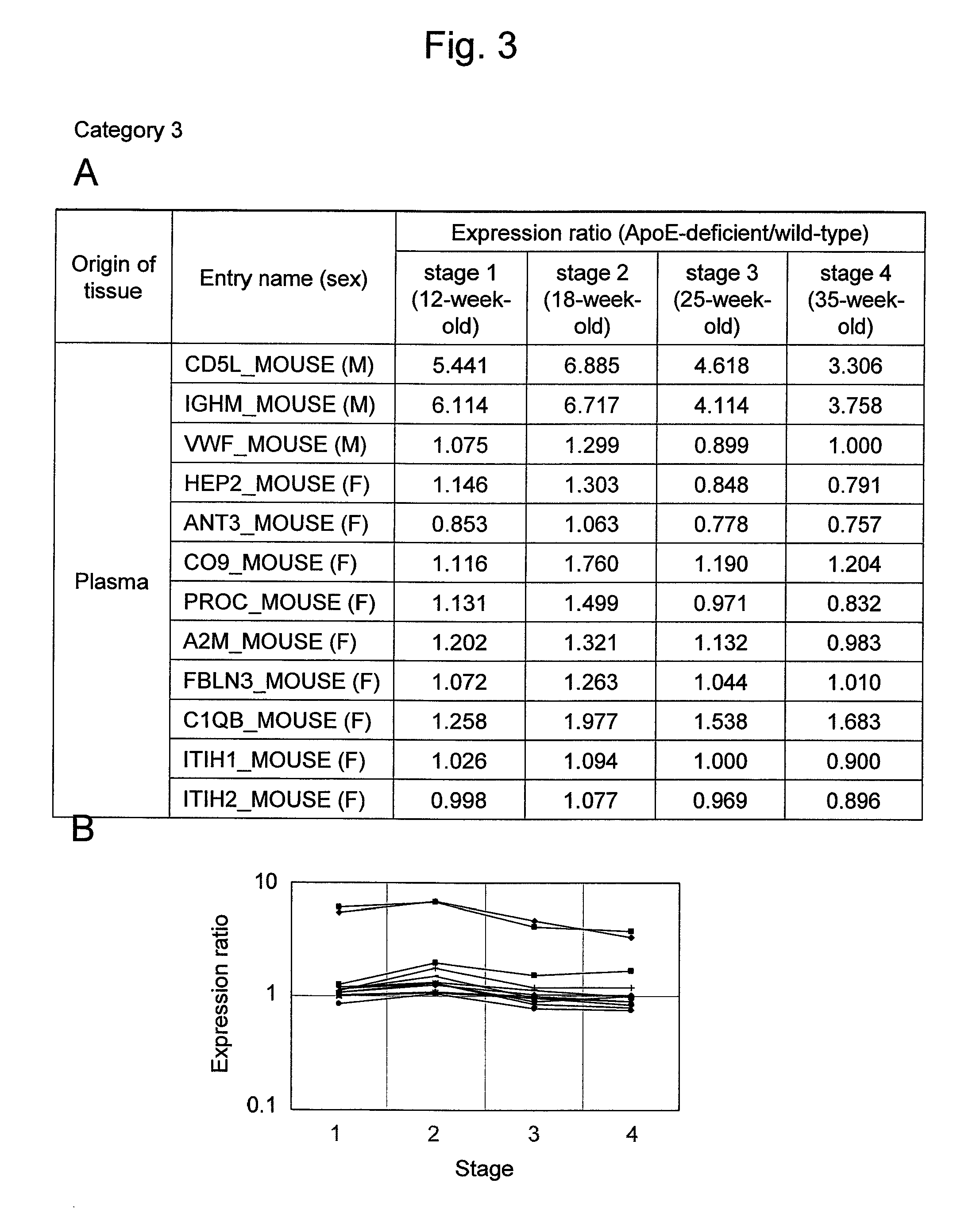
Evaluation Method for Arteriosclerosis
ActiveUS20130040851A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein markersVon Willebrand factor
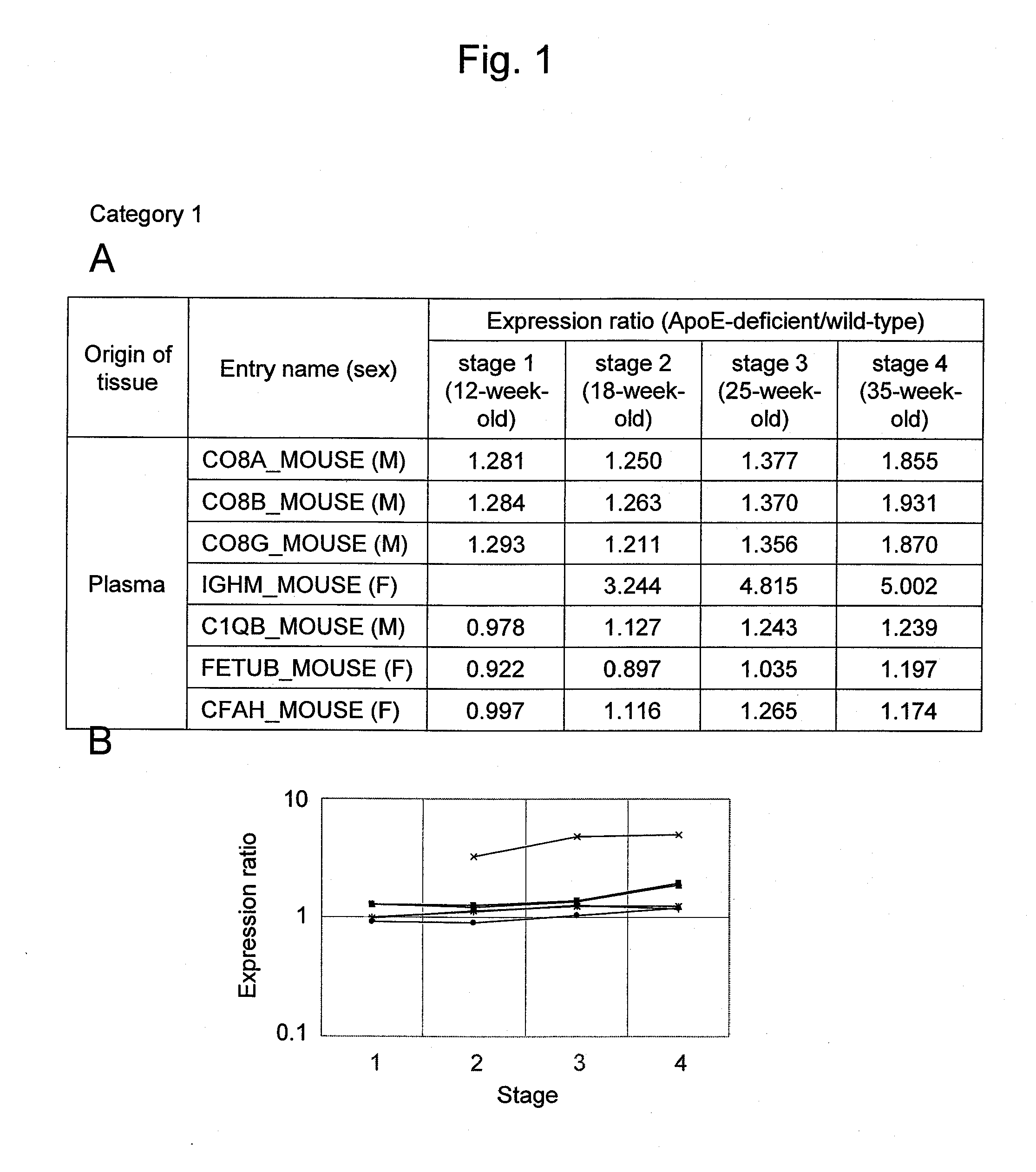
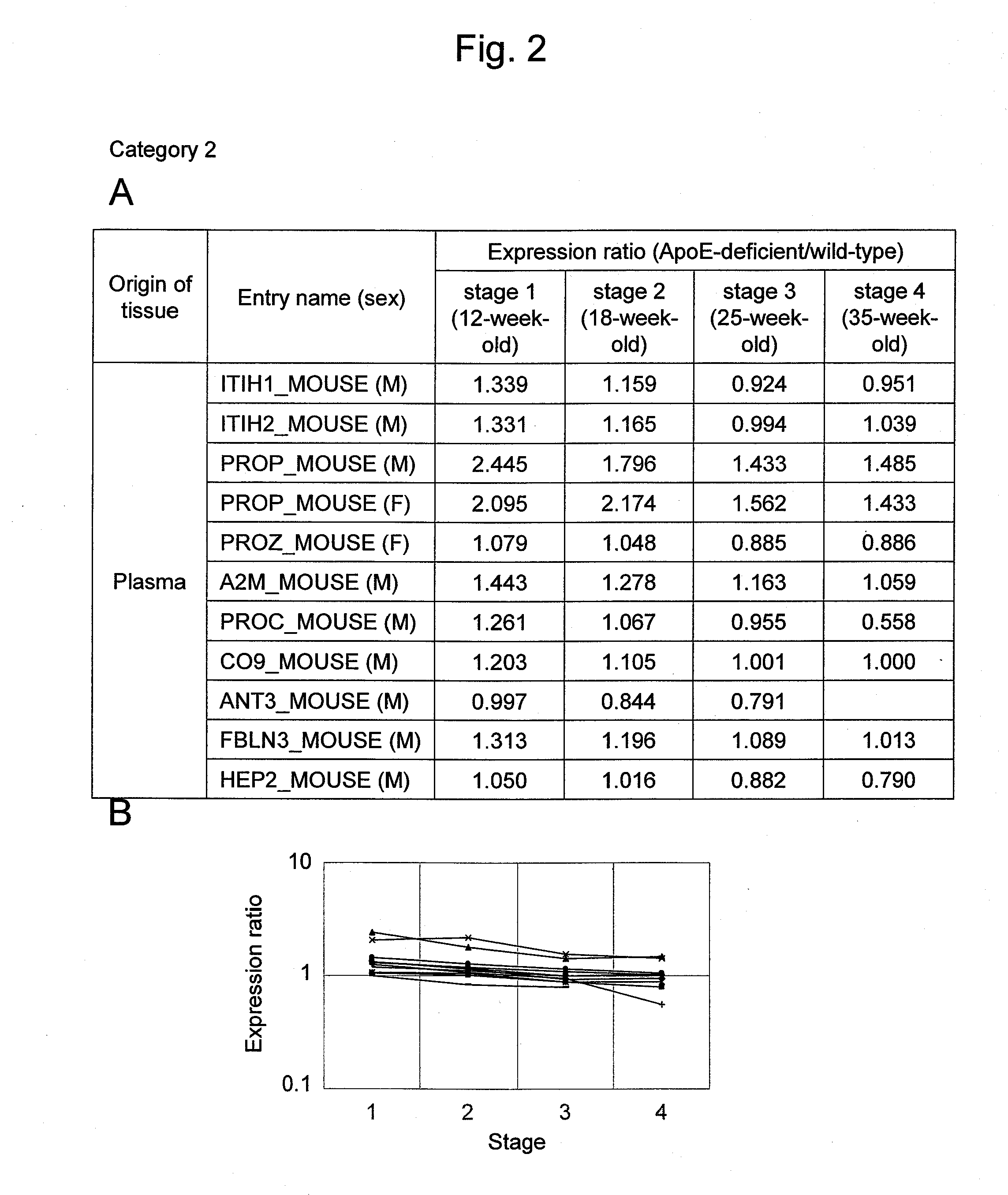
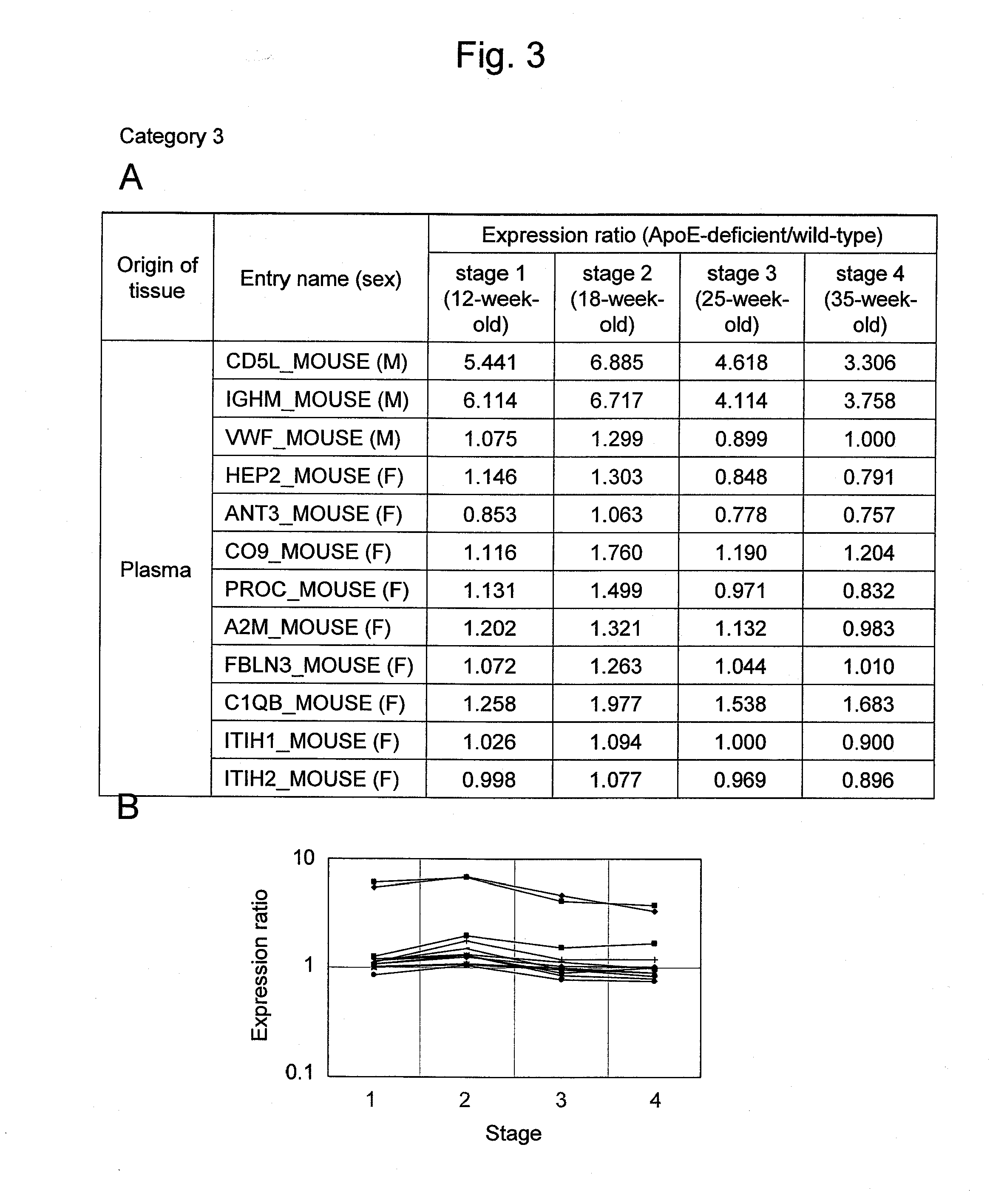
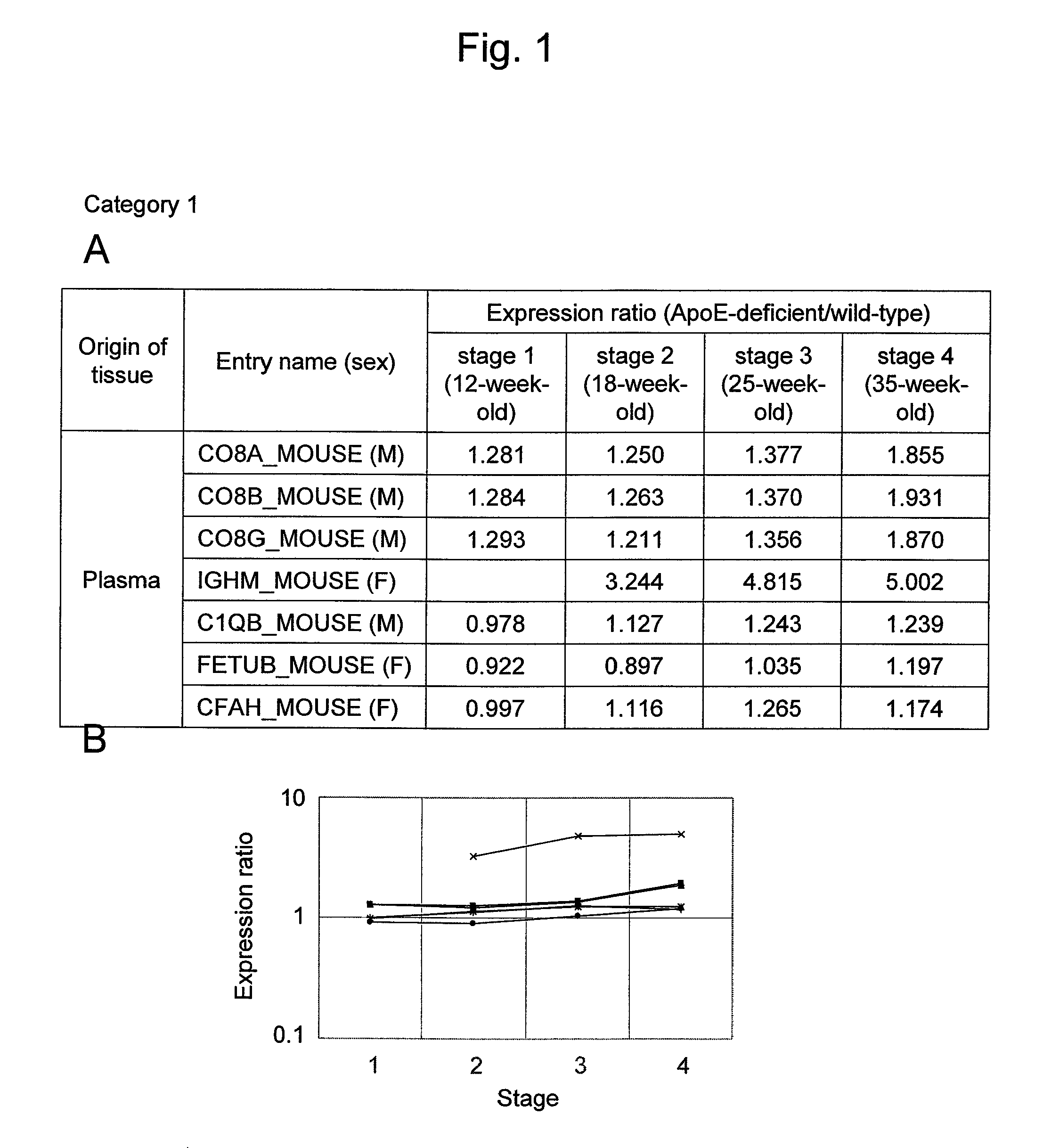
Arteriosclerosis induces cerebral infarction and myocardial infarction. A multi-marker (a group of protein markers) that assesses the accurate pathogenesis of arteriosclerosis and enables the selection of an adequate treatment method for arteriosclerosis and prediction of the progression of arteriosclerosis, and an evaluation method for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of arteriosclerosis that uses said marker group as an indicator have been sought. The present invention relates to A method for evaluation of arteriosclerosis comprising the steps of (a) measuring the expression of von Willebrand factor and / or complement factor D in a sample derived from a subject, (b) measuring the expression of complement component C8 and / or vitamin K-dependent protein Z in the sample derived from the subject, and (c) evaluating arteriosclerosis in the subject on the basis of the results from (a) and (b).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Mutated immunoglobulin-binding polypeptides
ActiveUS9663558B2Improve stabilityHighly selectiveOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationStaphylococcusImmunoglobulin IgE
A polypeptide with improved alkaline stability, which polypeptide comprises a mutant of a B or C domain of Staphylococcus Protein A, as specified by SEQ ID NO 1 or SEQ ID NO 2, or of Protein Z, as specified by SEQ ID NO 3, wherein at least the glutamine residue at position 15 has been mutated to an amino acid other than asparagine. The invention also discloses multimers of the polypeptide, as well as separation matrices comprising the multimers or polypeptides.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS9683013B2Easy to eluteGuaranteed cost-effective operationOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationElutionA domain
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
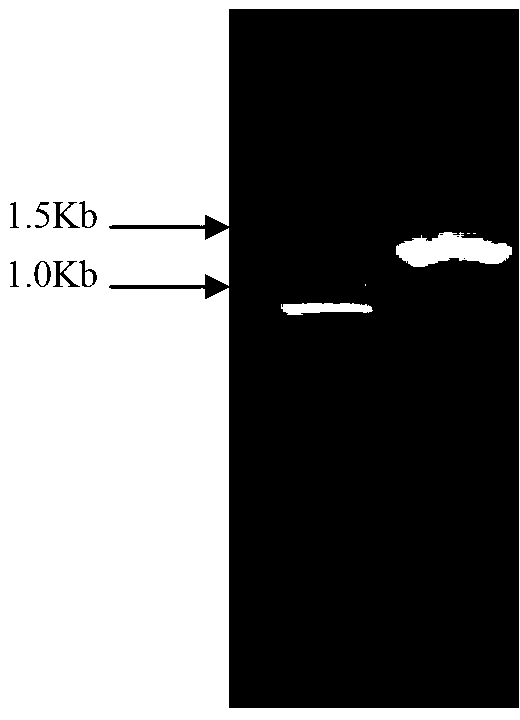
Aspergillus-versicolor-derived alpha-galactosidase Z-GALC, and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103320413AHas alpha-galactosidase activityIncrease enzyme activityFungiBacteriaAgricultural scienceAlpha-galactosidase activity
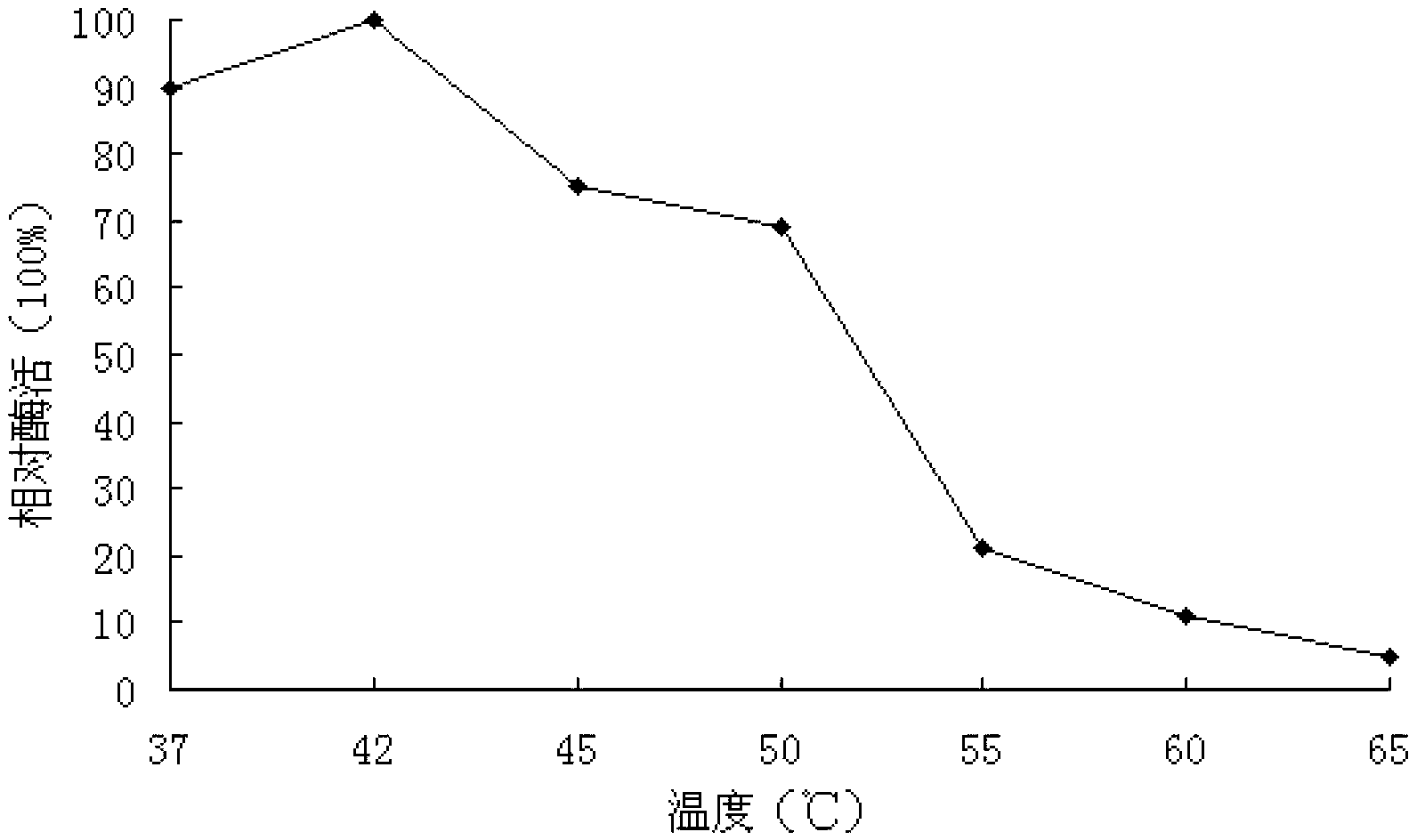
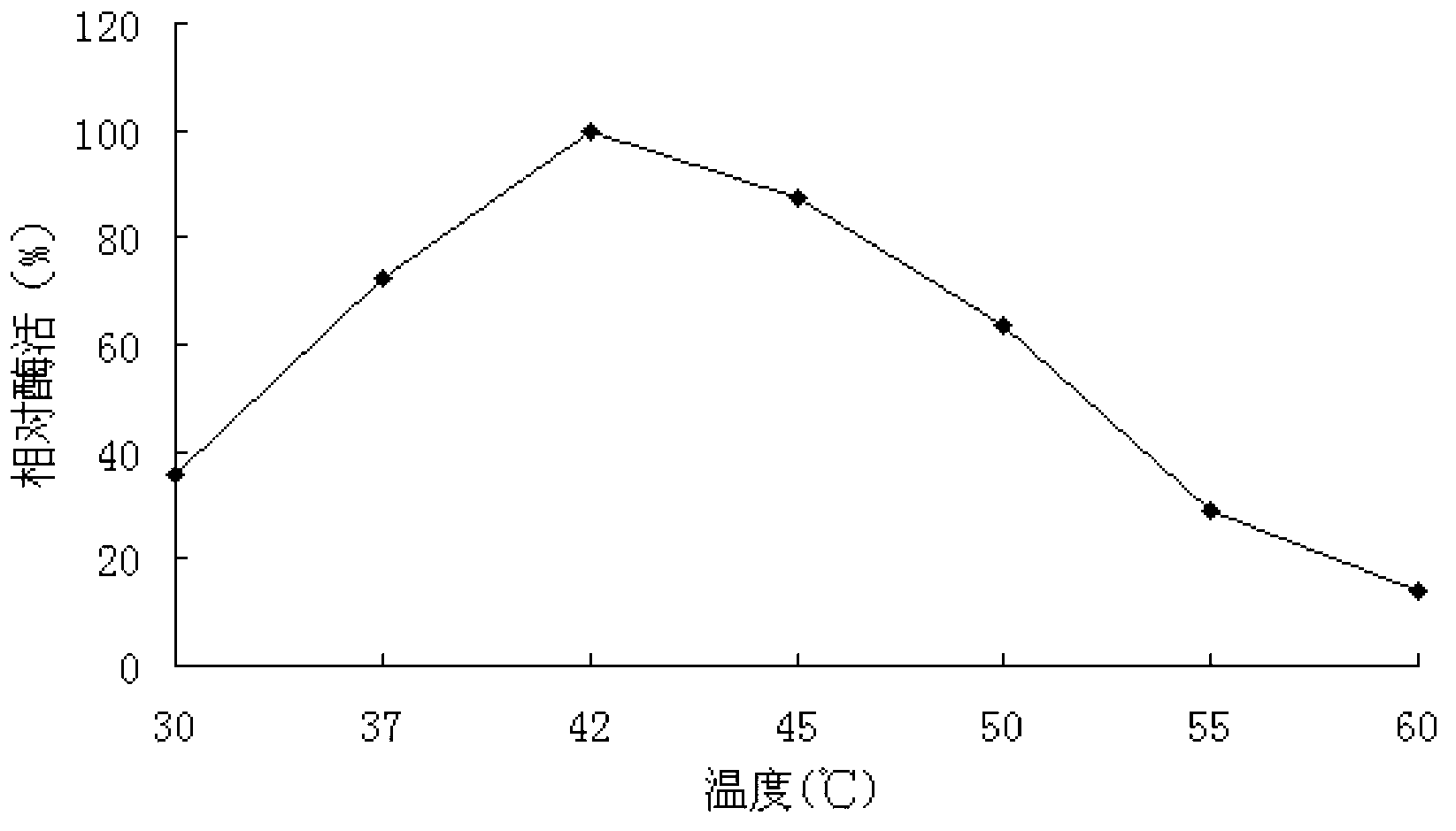
The invention discloses an Aspergillus-versicolor-derived alpha-galactosidase Z-GALC, and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein Z-GALC has alpha-galactosidase activity, is derived from Aspergillus versicolor, and is (a) or (b) as follows: (a) protein composed of amino acid sequence disclosed as Sequence 1 in the sequence table; or (b) protein derived from Sequence 1 in the sequence table with alpha-galactosidase activity, which is subjected to substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence disclosed as Sequence 1 in the sequence table. The specific activity of the protein Z-GALC disclosed by the invention as the alpha-galactosidase is 4.07U / mg; the optimum pH value is 7.0; the optimum temperature is 42 DEG C; and the protein Z-GALC has high enzyme activity at the temperature of 37-50 DEG C under the pH value of 6.0-8.0. The invention provides a new way for preparing alpha-galactosidase, and has important application value.
Owner:湖北佳洪生物饲料股份有限公司
Mutated immunoglobulin-binding polypeptides
ActiveUS20160207966A1Improve stabilityHighly selectivePeptide/protein ingredientsSolid sorbent liquid separationMutantGlutamine
A polypeptide with improved alkaline stability, which polypeptide comprises a mutant of a B or C domain of Staphylococcus Protein A, as specified by SEQ ID NO 1 or SEQ ID NO 2, or of Protein Z, as specified by SEQ ID NO 3, wherein at least the glutamine residue at position 15 has been mutated to an amino acid other than asparagine. The invention also discloses multimers of the polypeptide, as well as separation matrices comprising the multimers or polypeptides.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
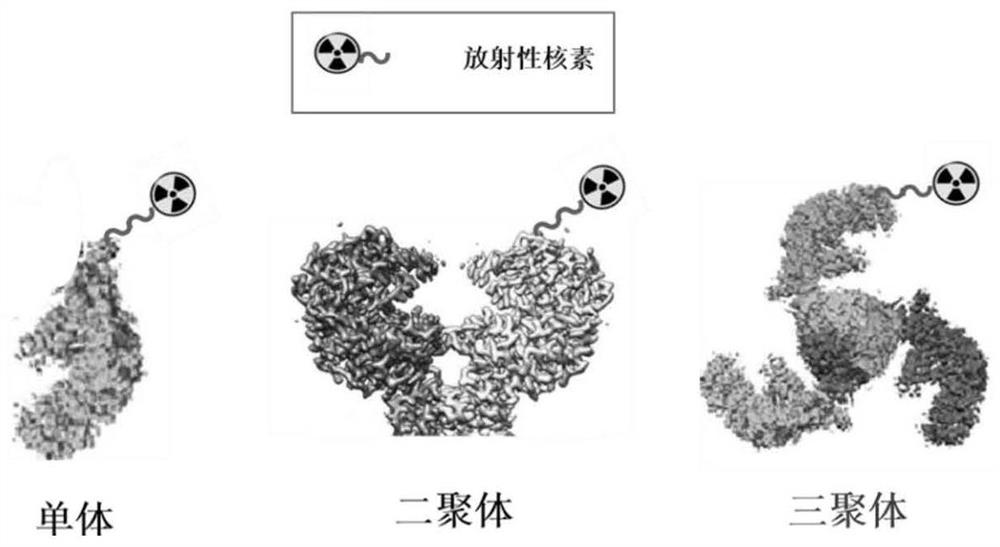
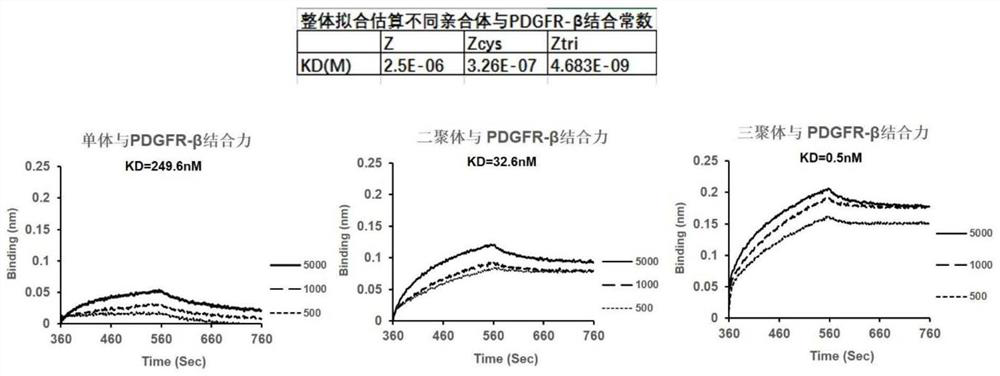
Gallium 68 labeled affinity protein PET imaging agent and application thereof
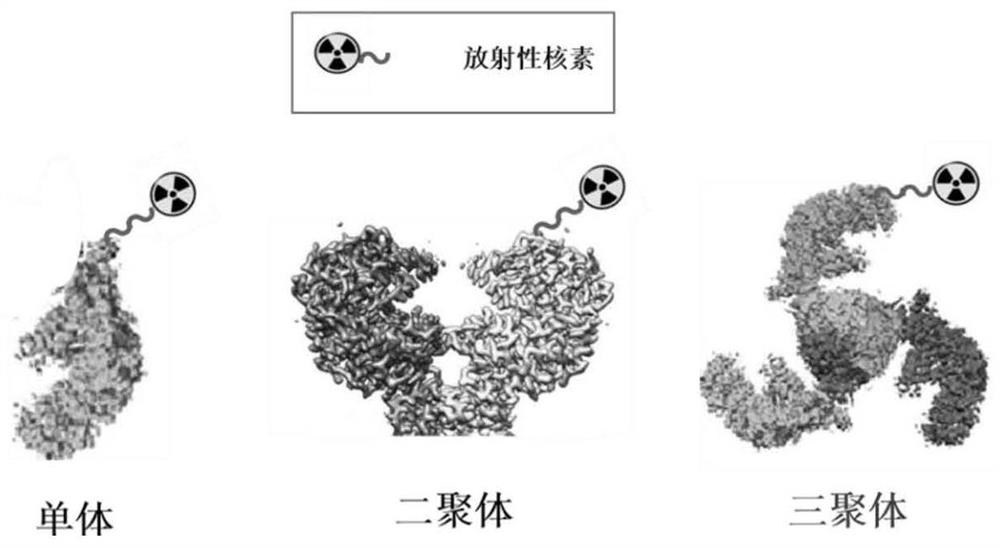
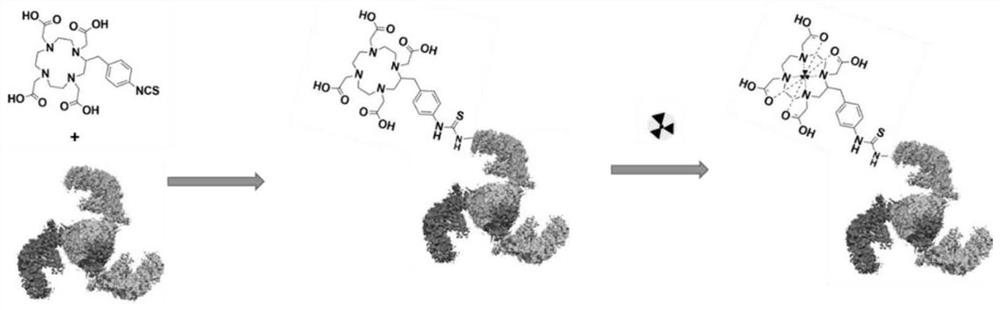
ActiveCN112870390APDGFR-β targeting affinityImprove stabilityRadioactive preparation carriersAntibody ingredientsDimerPet imaging
The invention discloses a gallium 68 labeled affinity protein PET (positron emission tomography) developer and the application thereof. The gallium 68 labeled affinity protein PET developer comprises 68Ga-Z-tri, the 68Ga-Z-tri is obtained by labeling affinity protein with gallium 68, the affinity protein comprises PDGFR-beta targeted trimerization affinity protein Z-tri, and the amino acid sequence table of the affinity Z-tri protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. According to the invention, a trimeric PDGFR-beta targeting affibody with a unique amino acid sequence is utilized. Compared with a monomer and a dimer affinity, the trimer PDGFR-beta targeting affinity with a unique amino acid sequence has the characteristics of high affinity and high stability, the labeling rate of nuclide can be greatly improved, and the effectiveness of the trimer PDGFR-beta targeting affinity as a PET imaging probe is realized.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS20130338339A1Increased elution pHGuaranteed cost-effective operationPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunglobulin eElution
The present invention relates to a method of separating one or more immunoglobulin containing proteins from a liquid. The method includes first contacting the liquid with a separation matrix comprising ligands immobilised to a support; allowing the immunoglobulin containing proteins to adsorb to the matrix by interaction with the ligands; followed by an optional step of washing the matrix containing the immunoglobulin containing proteins adsorbed thereon; and recovering said immunoglobulin containing proteins by contacting the matrix with an eluent which releases the proteins. The method improves upon previous separation methods in that each of the ligands comprises one or more of a protein A domain (E, D, A, B, C), or protein Z, or a functional variant thereof, with at least one of the monomers having a substitution of the Asparagine or Histidine at the position corresponding to H18 of B domain of Protein A or Protein Z, and wherein the ligand provides an increase in elution pH compared to non-substituted ligand.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
PDGFR beta targeted TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand) variant as well as preparation method and application thereof
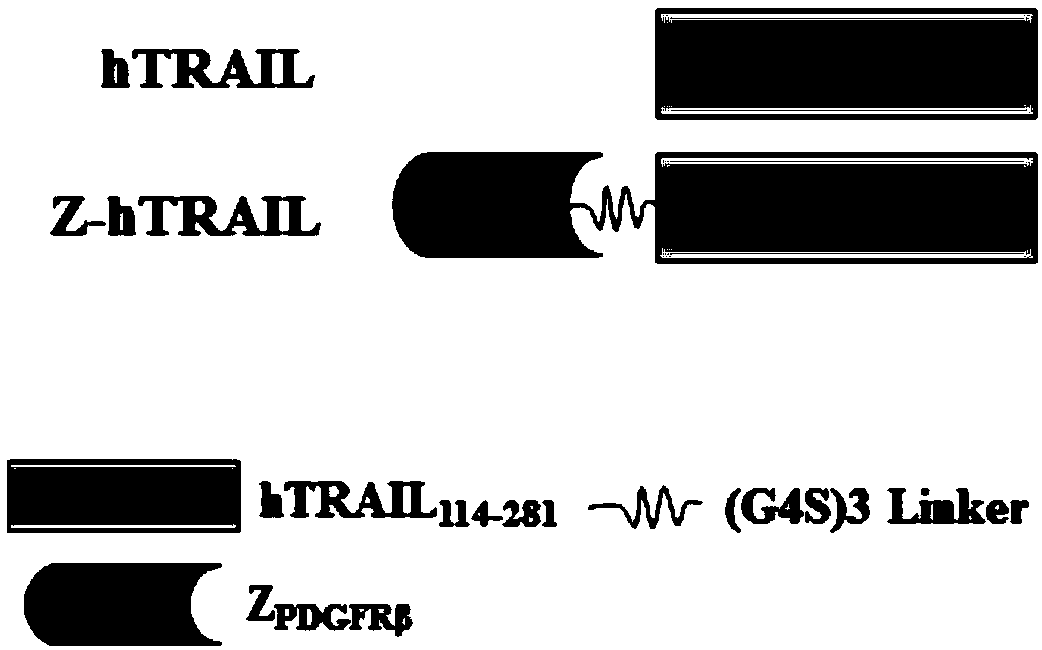
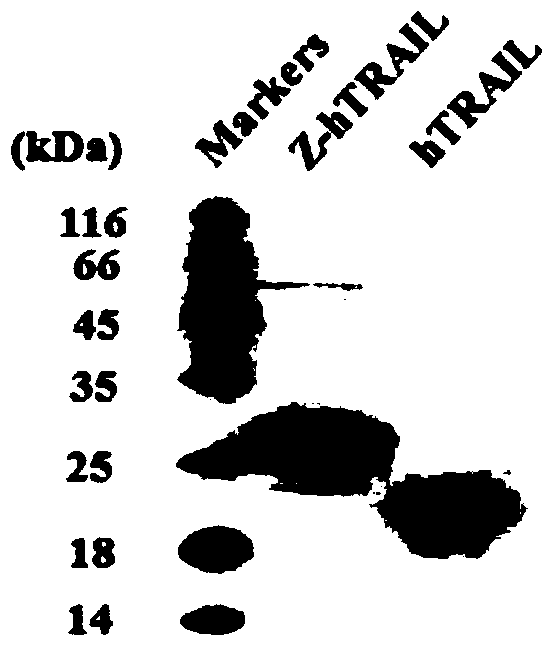
ActiveCN109400711APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaAbnormal tissue growthNucleotide
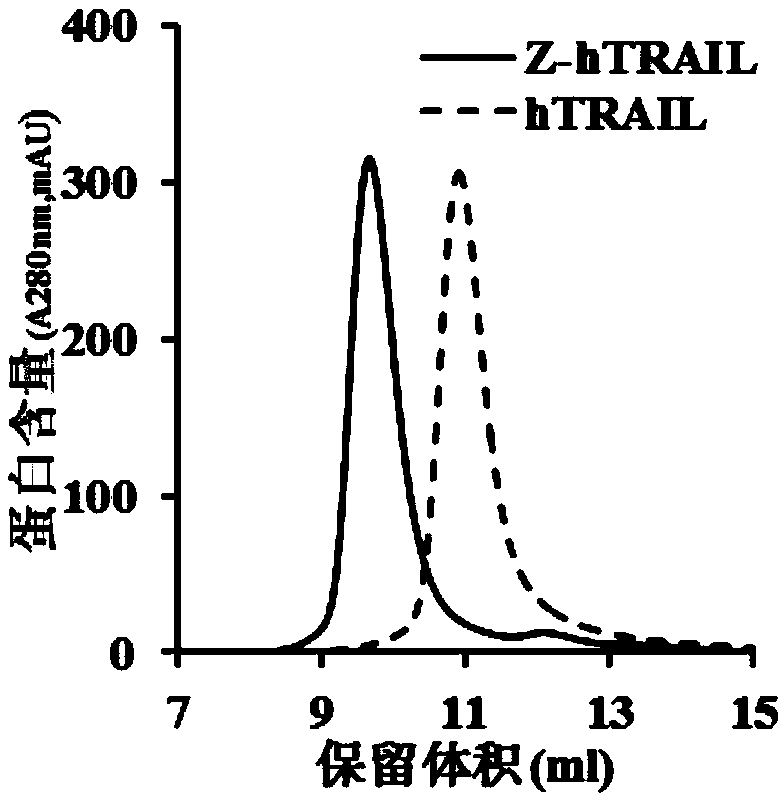
The invention discloses a TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand) variant. The variant is fusion protein of TRAIL and ZPDGFR beta, wherein ZPDGFR beta is linked to the N end or the C end of theTRAIL through a linker. The invention further discloses a nucleotide sequence as well as a recombinant vector and a recombinant bacterium which comprise the nucleotide sequence, and further disclosesa preparation method and an application of the variant. The TRAIL variant protein Z-hTRAIL has good tumor killing activity and definite curative effect on hepatic fibrosis-renal tubular ectasia syndrome, and has good clinical application prospects.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS9657055B2Improve bindingImprove stabilityOther chemical processesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAffinity chromatographyProtein Z
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Evaluation method for arteriosclerosis
ActiveUS9175346B2Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningProtein markersComplement factor I
Arteriosclerosis induces cerebral infarction and myocardial infarction. A multi-marker (a group of protein markers) that assesses the accurate pathogenesis of arteriosclerosis and enables the selection of an adequate treatment method for arteriosclerosis and prediction of the progression of arteriosclerosis, and an evaluation method for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of arteriosclerosis that uses said marker group as an indicator have been sought. The present invention relates to A method for evaluation of arteriosclerosis comprising the steps of (a) measuring the expression of von Willebrand factor and / or complement factor D in a sample derived from a subject, (b) measuring the expression of complement component C8 and / or vitamin K-dependent protein Z in the sample derived from the subject, and (c) evaluating arteriosclerosis in the subject on the basis of the results from (a) and (b).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Neutral alpha-galactosidase M-GALC, and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103320414AIncrease enzyme activityFungiBacteriaAgricultural scienceAlpha-galactosidase activity
The invention discloses a neutral alpha-galactosidase M-GALC, and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein M-GALC has alpha-galactosidase activity, is derived from chaetomium globosum, and is (a) or (b) as follows: (a) protein composed of amino acid sequence disclosed as Sequence 1 in the sequence table; or (b) protein derived from Sequence 1 in the sequence table with alpha-galactosidase activity, which is subjected to substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence disclosed as Sequence 1 in the sequence table. The specific activity of the protein M-GALC disclosed by the invention as the alpha-galactosidase is 1.91U / mg; the optimum pH value is 7.0; the optimum temperature is 42 DEG C; and the protein Z-GALC has high enzyme activity at the temperature of 37-50 DEG C under the pH value of 6.0-9.0. The invention provides a new way for preparing alpha-galactosidase, and has important application value.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOFEED TECH CO LTD
Affinity chromatography matrix
InactiveUS20170247407A1Improve bindingImprove stabilityOther chemical processesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAffinity chromatographyProtein Z
The invention discloses a polypeptide capable of binding immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin-containing proteins, which polypeptide comprises six or more domains of protein Z or the C domain of protein A or a functional variant thereof. It also discloses separation matrices comprising the polypeptide and methods of using the separation matrices for separation of immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin-containing proteins.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Purification process of chlorogenic acid in corn vinasse
InactiveCN109369398AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyReduce dosageOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationPentagalacturonic acidChlorogenic acid
The invention relates to the technical field of chlorogenic acid purification, in particular to a purification process of chlorogenic acid in corn vinasse. The purification process comprises the stepsthat under the action of ultrasonic dispersion, cellulose, polygalacturonase and a protein Zeah can all be evenly dispersed in a mixed component, the contact probability between the cellulose, the polygalacturonase as well as a the protein Zeah and corn cell walls is increased to the great extent, and thus the enzymolysis efficiency on the corn cell walls is improved; the permeability of corn cells is increased under the action of calcium ions, and through cooperative use of an ultrasonic cell crusher, the crushing efficiency of the corn cells is improved greatly; under cooperative use actionof complex enzymes, ultrasonic dispersion, a calcium ion solution and the ultrasonic cell crusher, the chlorogenic acid flows out to the maximum limit; and then the chlorogenic acid is preliminarilypurified, namely lixiviated, through an ethanol solution, a crude chlorogenic acid product is prepared, then the crude chlorogenic acid product is eluted through ethyl acetate, finally, the chlorogenic acid is recrystallized through an organic solvent, and thus the purity of the prepared chlorogenic acid is improved, and yield of the prepared chlorogenic acid is increasedpurity and yield of the prepared chlorogenic acid are increased.
Owner:JILIN AGRI SCI & TECH COLLEGE
Affinity chromatography matrix
ActiveUS10189891B2Optimize purification stepsInhibition formationOther chemical processesSolid sorbent liquid separationThreonineHistidine
The invention discloses an immunoglobulin-binding protein comprising one or more mutated immunoglobulin-binding domains (monomers) of staphylococcal Protein A (E, D, A, B, C) or protein Z or a functional variant thereof, wherein in at least one of the one or more mutated monomers, the asparagine or histidine at the position corresponding to H18 of the B domain of Protein A or of Protein Z has been deleted or substituted with a first amino acid residue which is not proline or asparagine and wherein, if the amino acid residue at position 57 is proline and the amino acid residue at position 28 is asparagine, then the amino acid residue at the position corresponding to H18 of the B domain of protein A or of protein Z is not serine, threonine or lysine.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
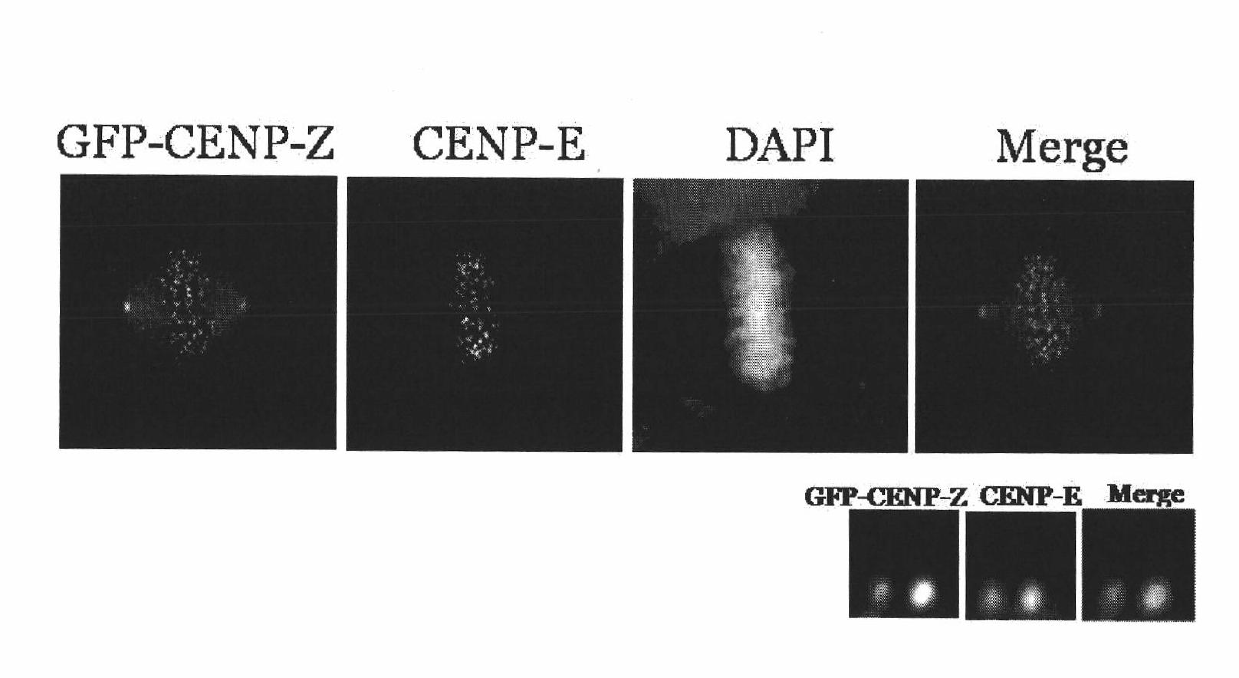
Spindle centromere associated protein Z (CENP-Z) and encoded gene as well as application thereof
The invention discloses a centromere associated protein and encoded gene as well as application thereof, and aims to provide the centromere associated protein and the encoded gene as well as the application in preparing drug for inhibiting tumor proliferation. The protein is one of the following amino acid sequences: 1) the amino acid sequence indicated in SEQ ID NO.1; or 2) the amino acid residue sequence of the SEQ ID NO.1 is replaced by one or multiple amino acid residues, lost and added so as to be the amino acid sequence that is derived from the SEQ ID NO.1 and has the regulating and controlling functions to the process of the cell mitosis as combined with the CENP-E protein. The protein participates in the spindle checkpoint signal transduction route of the cell mitosis through the mutual function with the CENP-E, and the active ingredient of the protein can be taken as the drug target for developing the drug for inhibiting tumor proliferation. The protein and the encoded gene thereof play a significant role in the field of medicine and pharmacy, and have a wide application range.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
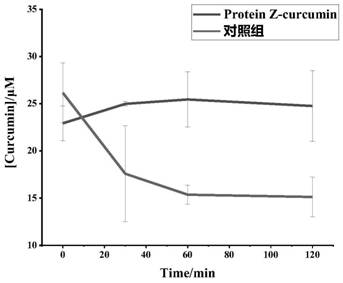
Method for improving water solubility and small intestine digestion stability of curcumin
PendingCN113907353ANo pollution in the processSimple stepsAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsSmall intestineDigestion
The invention provides a method for improving water solubility and small intestine digestion stability of curcumin. The method comprises the following steps that (a), Protein Z is separated and purified from malt, and dissolved in a buffer solution to obtain a Protein Z solution of 2-10 [mu]M; (b), excessive curcumin is added into the Protein Z solution and oscillated, and the obtained mixture of Protein Z and curcumin pass through a water-based filter membrane; and (c), an aqueous solution of Protein Z-curcumin obtained by filtration and the trypsin solution are mixed according to the Protein Z / trypsin molar ratio of 1: 1-1: 10, and the mixture is added into an in-vitro simulated small intestine digestion system. Protein Z in natural malt is used as a main raw material, and is used for improving the solubility and digestion stability of the curcumin. The curcumin and Protein Z interact with each other, so that the curcumin is effectively protected, and the bioavailability of the curcumin is further improved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A gallium 68-labeled affimer protein pet imaging agent and its application
The invention discloses a gallium 68-labeled affimer protein PET imaging agent and its application, including 68 Ga‑Z‑tri, the 68 Ga-Z-tri is obtained by labeling the affibody protein with gallium 68. The affibody protein includes PDGFR-β targeting trimeric affibody protein Z-tri. The amino acid sequence of the affibody Z-tri protein is SEQ ID NO.1 shown. The present invention utilizes a trimeric PDGFR-β targeting affibody with a unique amino acid sequence, which has the characteristics of high affinity and high stability compared with monomer and dimeric affibody, can greatly improve the labeling rate of nuclides, and realize The effectiveness of its use as a PET imaging probe.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Neutral alpha-galactosidase M-GALC, and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103320414BIncrease enzyme activityFungiBacteriaAgricultural scienceAlpha-galactosidase activity
The invention discloses a neutral alpha-galactosidase M-GALC, and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein M-GALC has alpha-galactosidase activity, is derived from chaetomium globosum, and is (a) or (b) as follows: (a) protein composed of amino acid sequence disclosed as Sequence 1 in the sequence table; or (b) protein derived from Sequence 1 in the sequence table with alpha-galactosidase activity, which is subjected to substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence disclosed as Sequence 1 in the sequence table. The specific activity of the protein M-GALC disclosed by the invention as the alpha-galactosidase is 1.91U / mg; the optimum pH value is 7.0; the optimum temperature is 42 DEG C; and the protein Z-GALC has high enzyme activity at the temperature of 37-50 DEG C under the pH value of 6.0-9.0. The invention provides a new way for preparing alpha-galactosidase, and has important application value.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOFEED TECH CO LTD
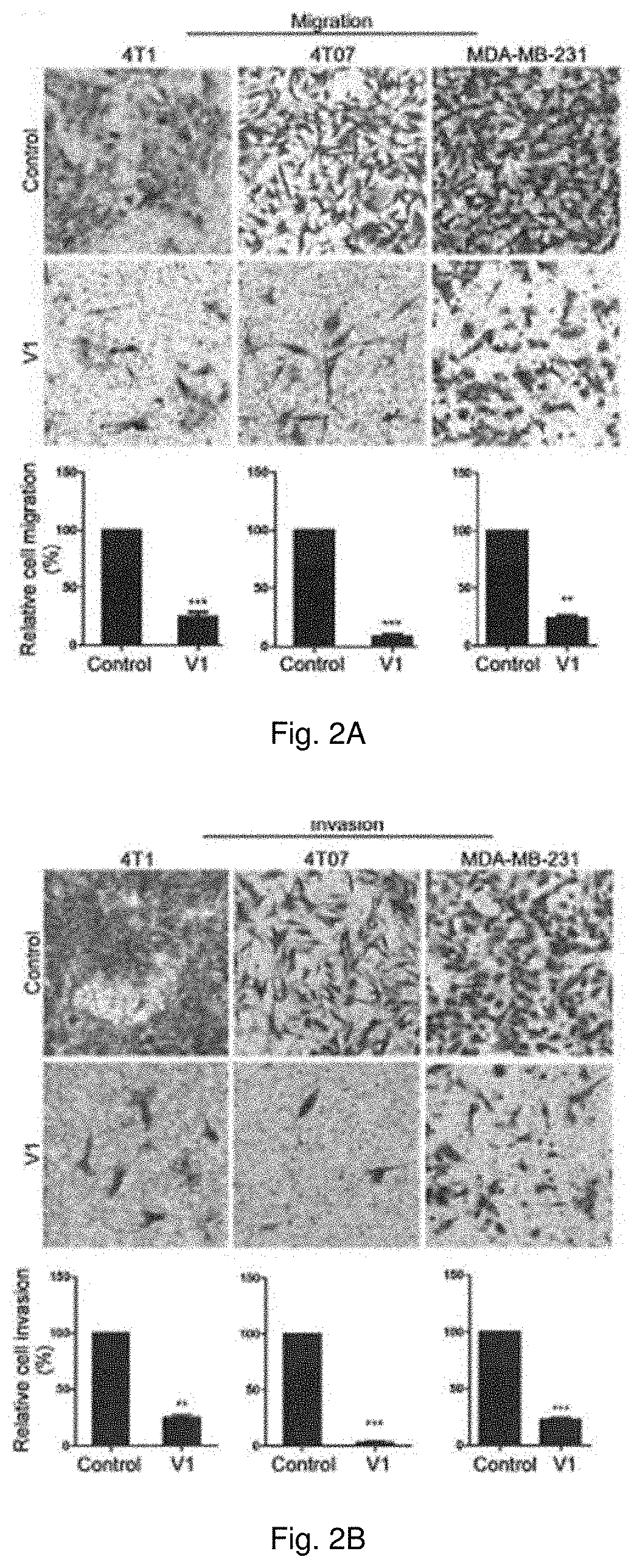
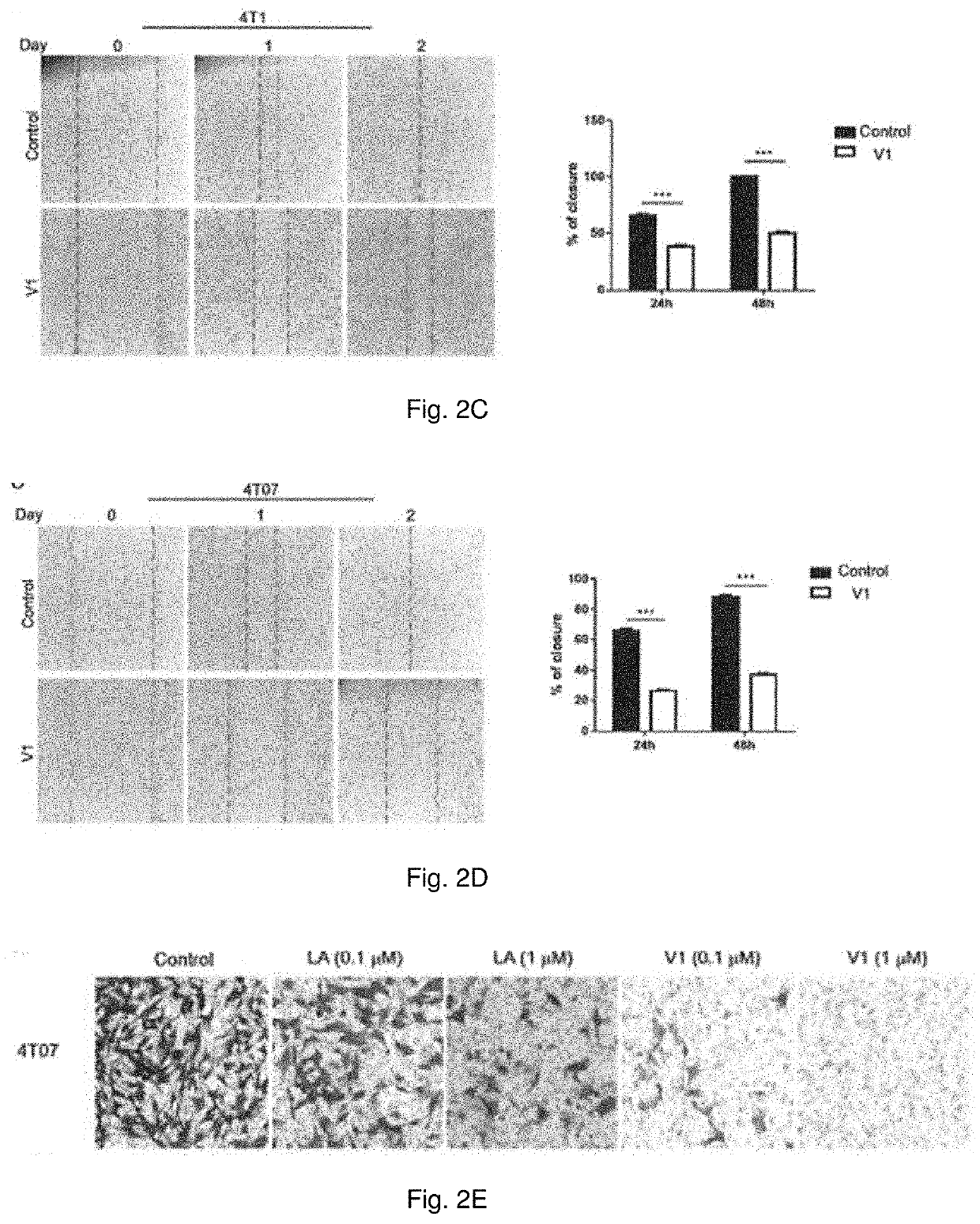
Method of treating metastatic cancer in a subject with a protein inhibitor
ActiveUS20220023307A1Improve concentrationUseful in treatmentOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellOncology
A method of treating metastatic cancer in a subject in need thereof including administering an effective amount of a capping protein Z inhibitor to the subject. A method of inhibiting metastasis of cancer cells including administering an effective amount of a capping protein Z inhibitor.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG +1
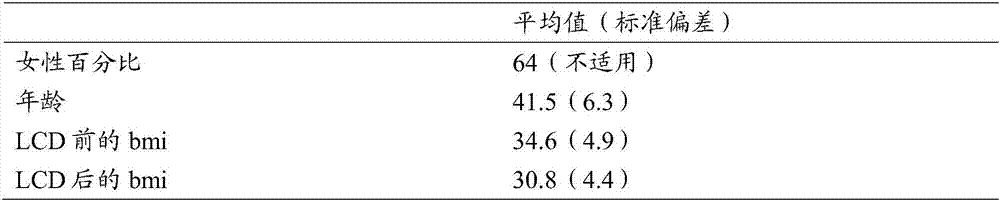
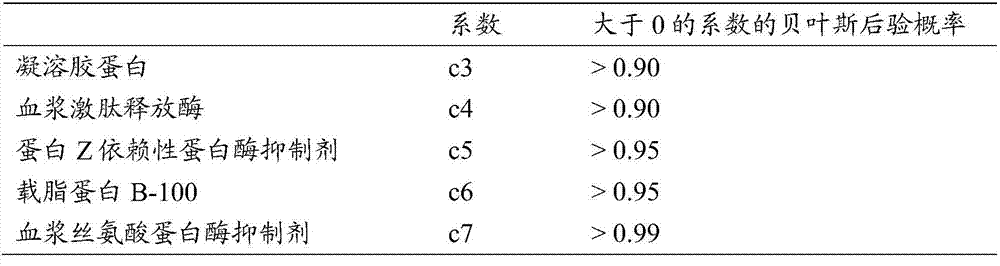
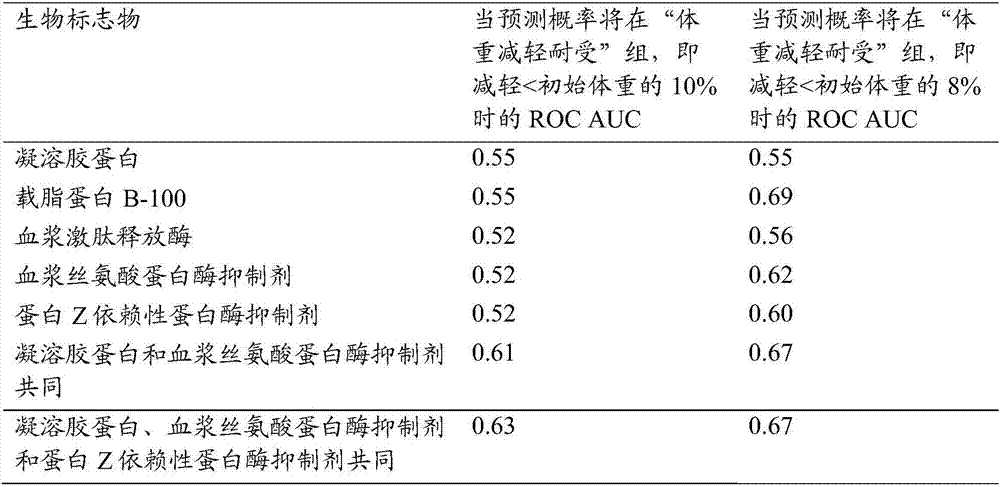
Biomarkers for predicting degree of weight loss in female subjects
A method for predicting the degree of weight loss in a female subject attainable by applying one or more dietary interventions to a subject, said method comprising; determining the level of one or more biomarkers in one or more samples obtained from the subject, wherein the biomarkers are selected from gelsolin, apolipoprotein B-100, plasma kallikrein, protein Z- dependent protease inhibitor and plasma serine protease inhibitor.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com