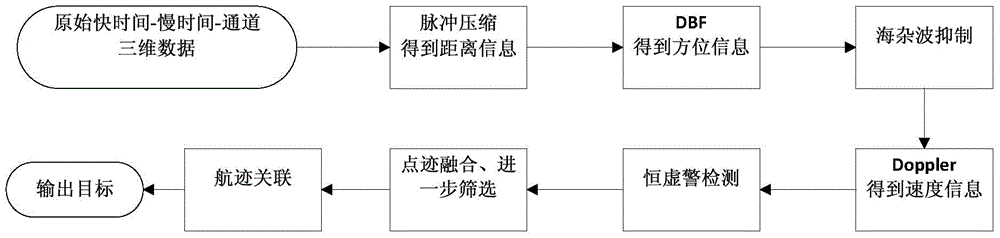
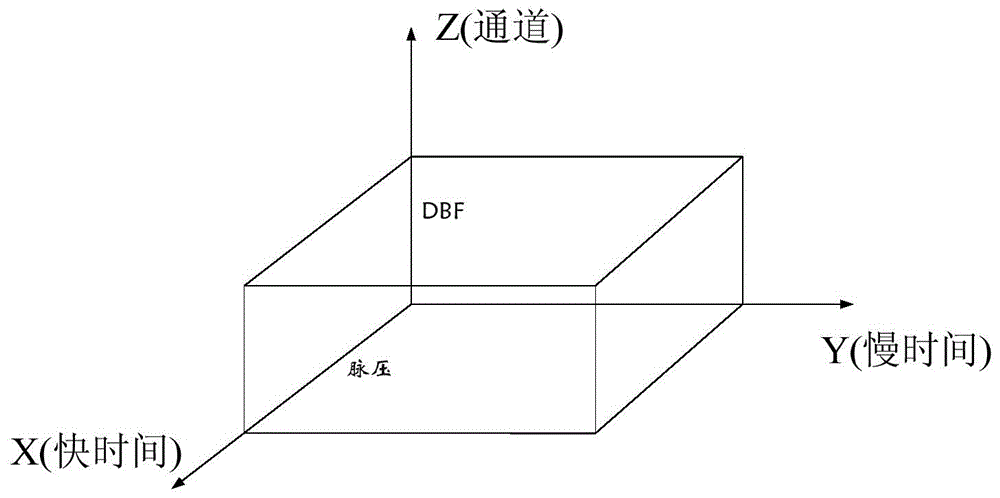
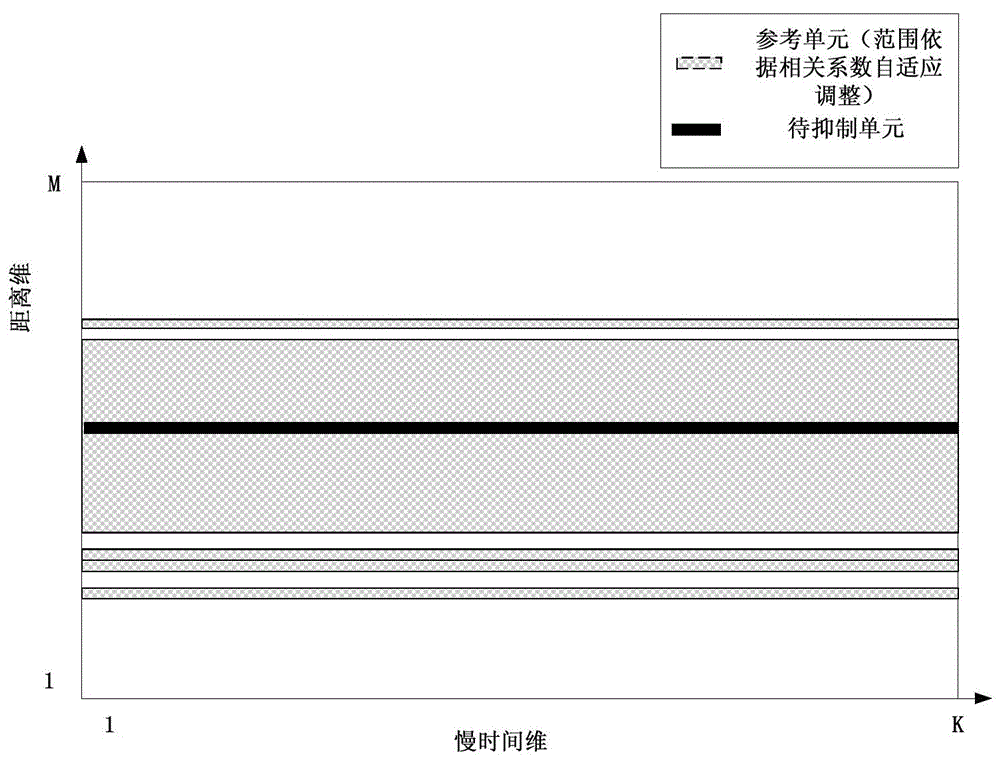
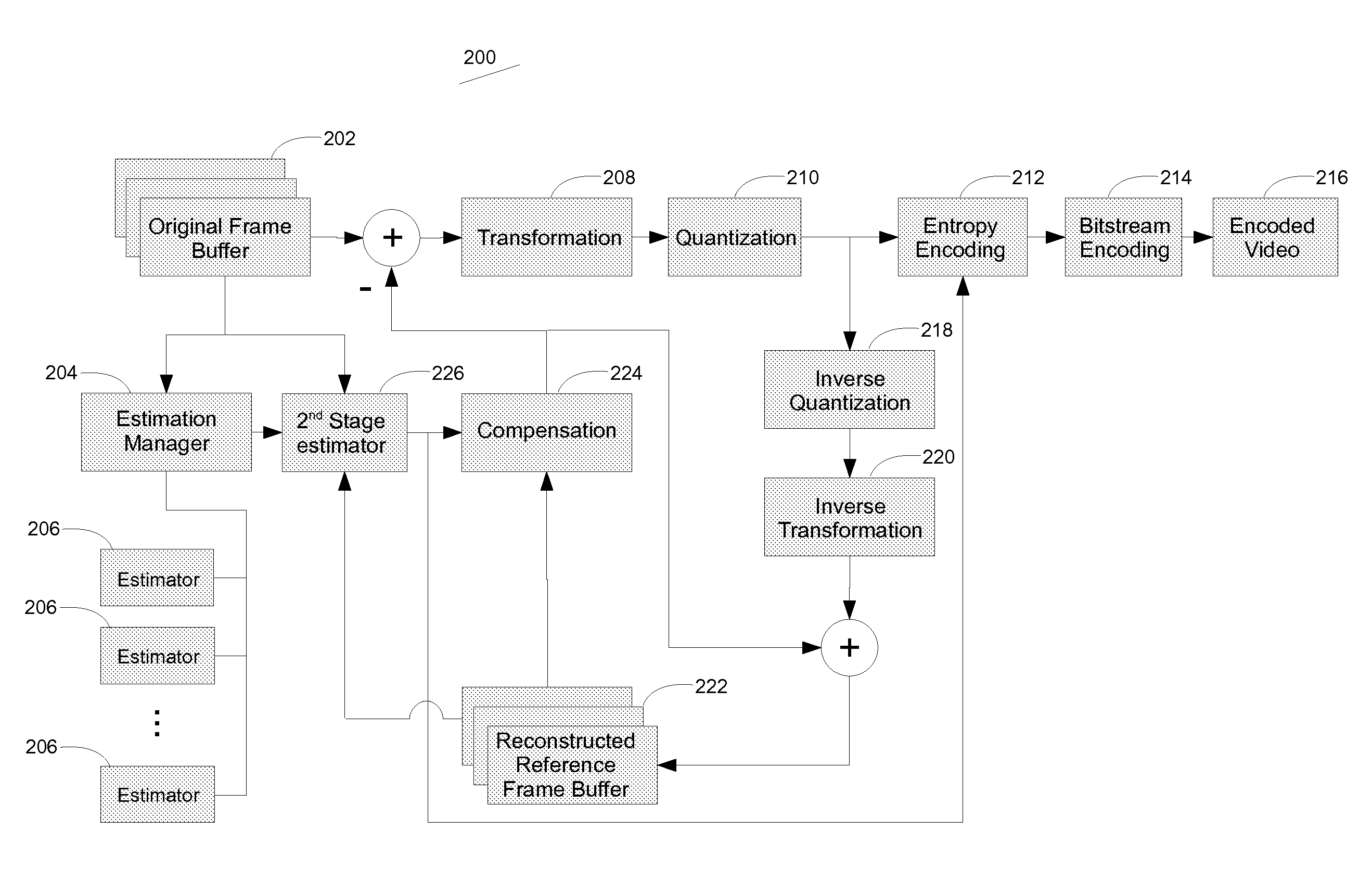
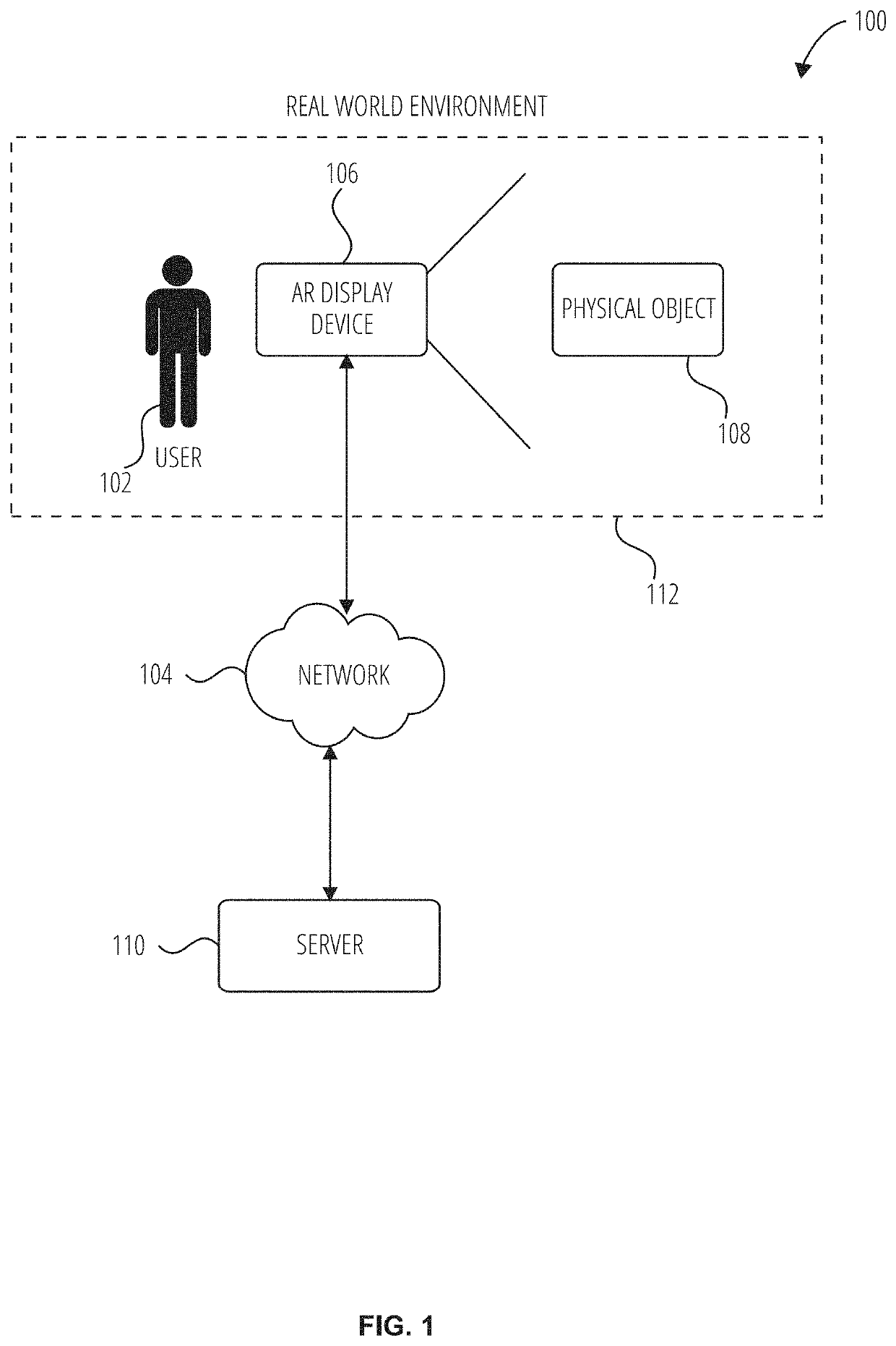
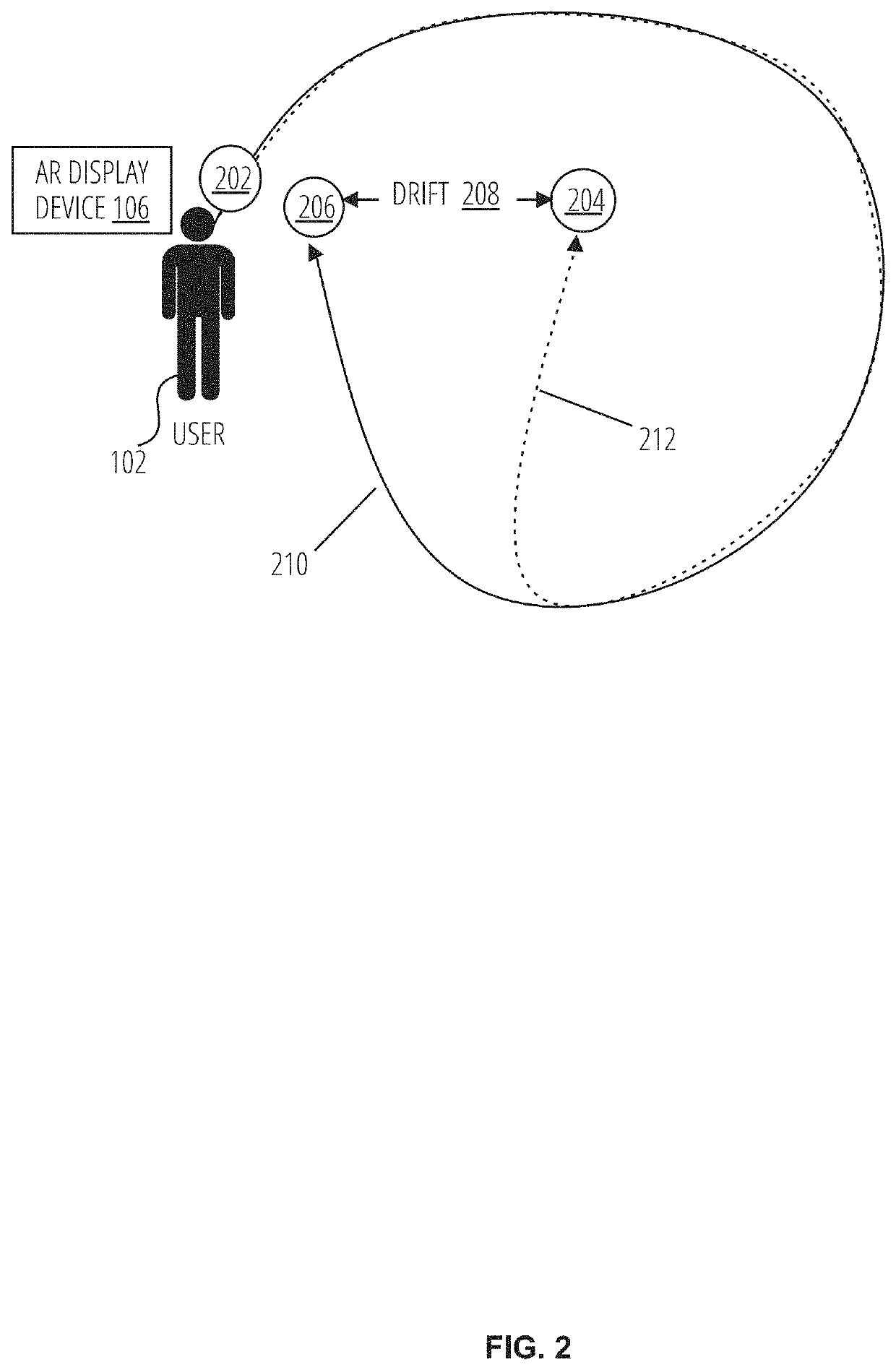
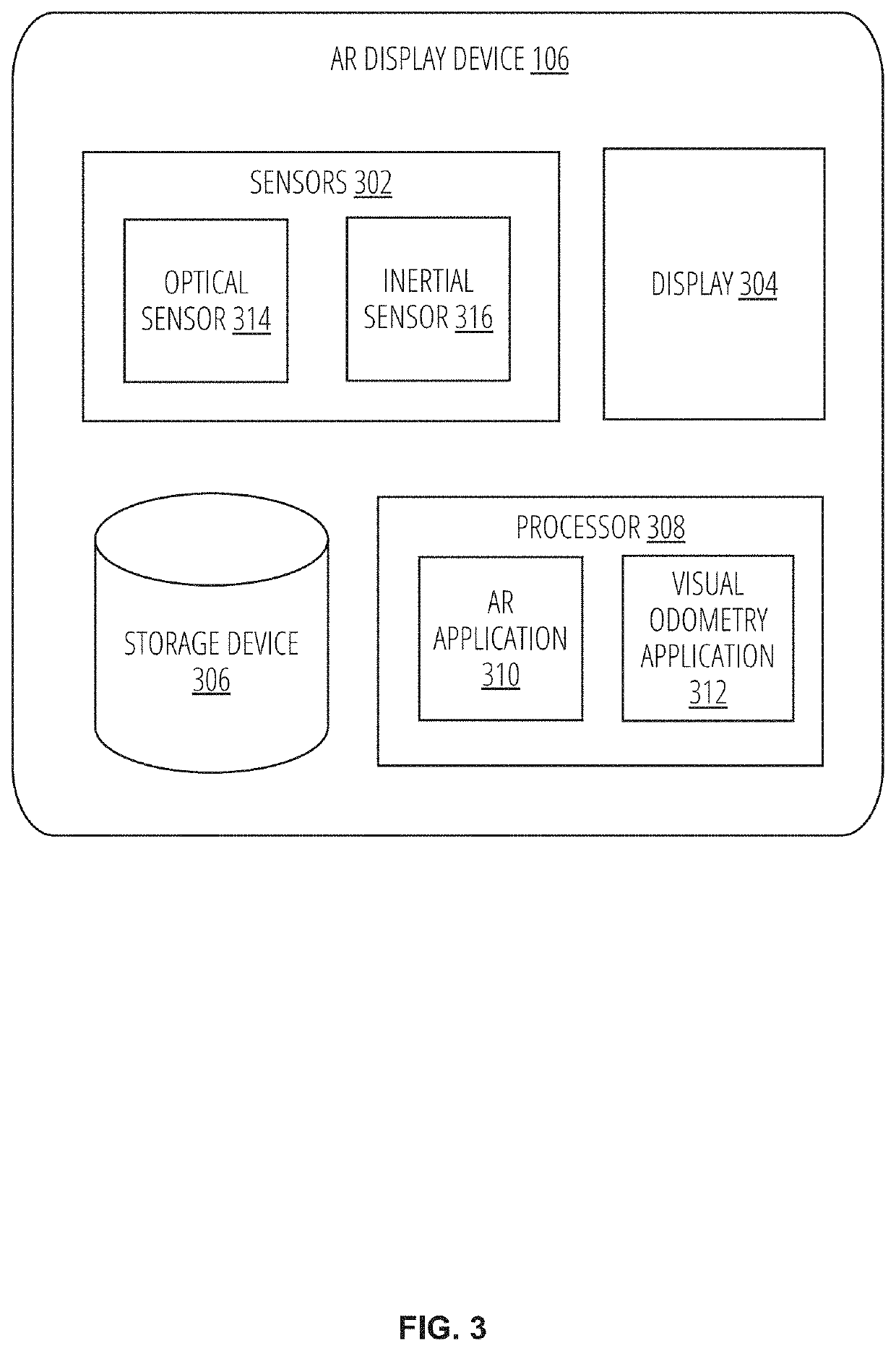
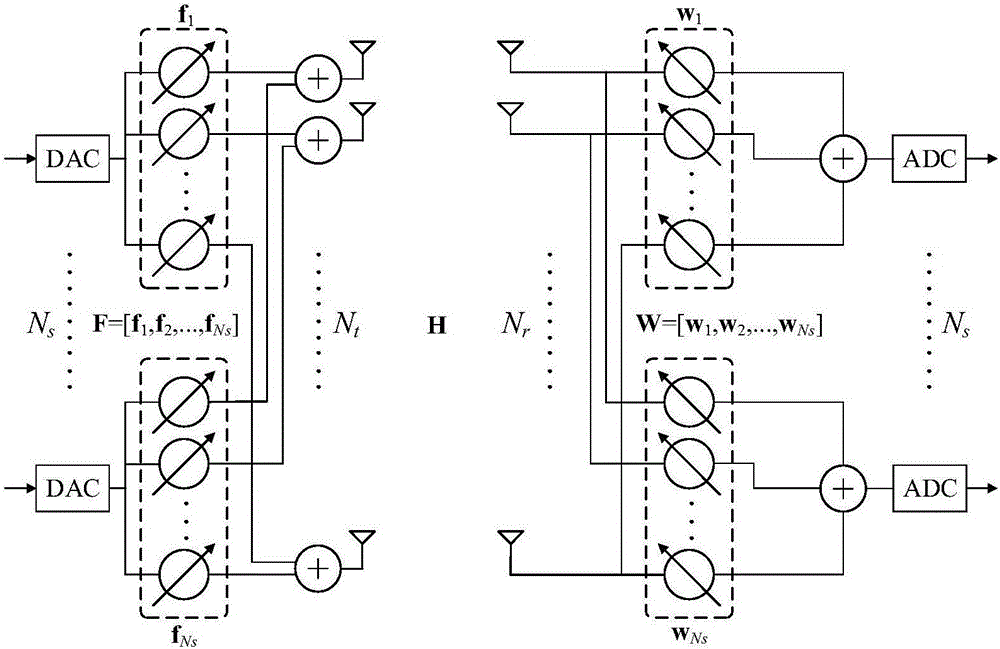
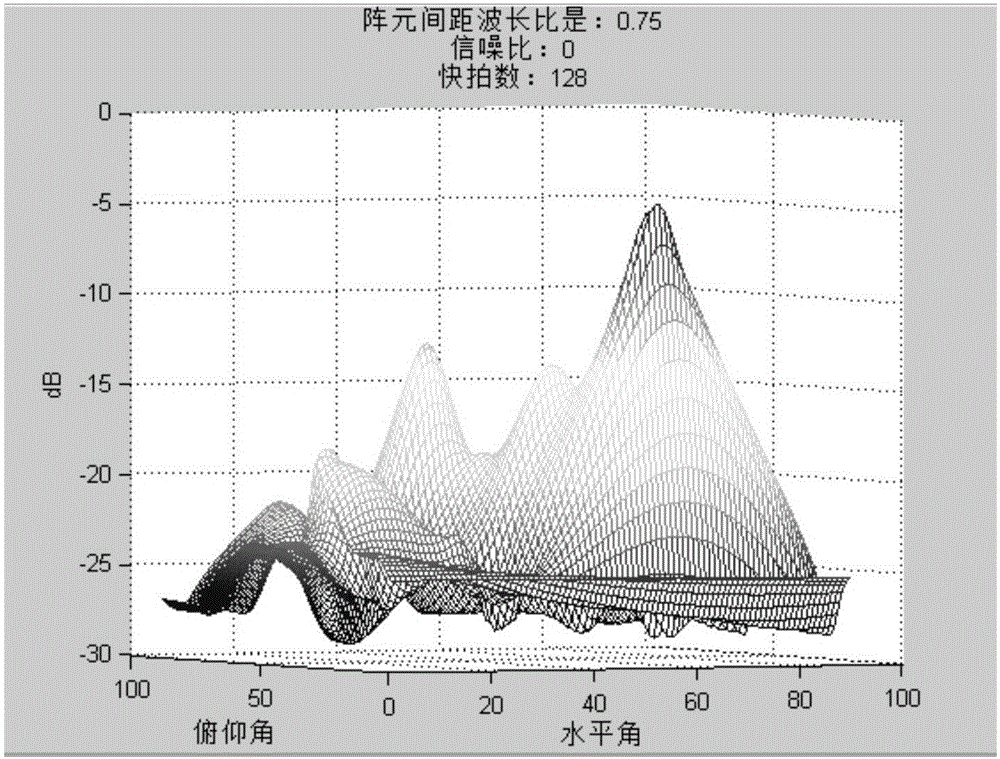
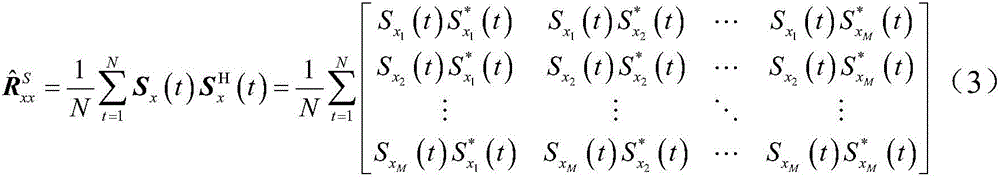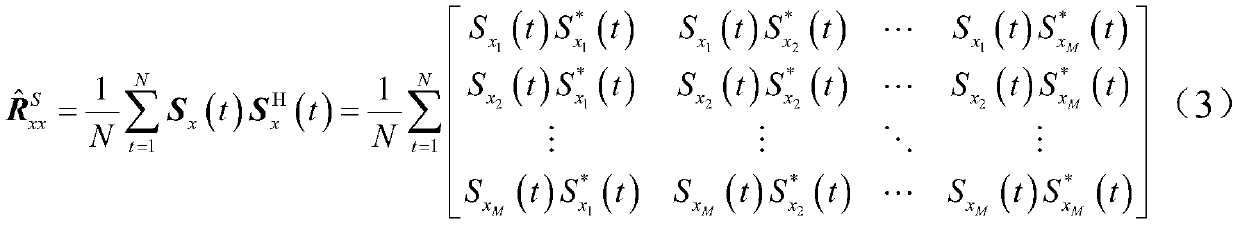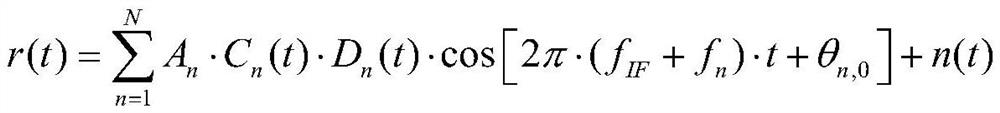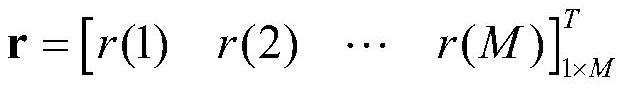Patents
Literature
40 results about "Spatial estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Improved subspace sea clutter suppression method based on local correlation
InactiveCN104155632AAids in target detectionImprove signal to noise ratioRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSingular value decompositionSpatial estimation
The invention discloses an improved subspace sea clutter suppression method based on local correlation. Suppression of sea clutter can improve the signal to clutter ratio of targets and is conductive to improving the vessel target detection performance of high frequency surface wave radar (HFSWR). The original subspace method leads to identical covariance matrix of all distance unit structures during sea clutter suppression, so that a poor suppression effect caused by inaccurate clutter space estimation is brought about, which is reflected on the distance Doppler spectrum that the suppression effects of sea clutter in different distances are similar. According to the invention, the related coefficient between a distance unit to be detected and adjacent distance units is calculated, the reference unit of the covariance matrix is determined and formed in a self-adaptive manner, the formed covariance matrix is subjected to singular value decomposition (SVD) to obtain subspaces of the sea clutter, and finally, suppression is realized. The method can simultaneously suppress first-order and high-order sea clutter, improves the signal to clutter ratio of the targets and has a relatively ideal suppression effect on all distance units.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
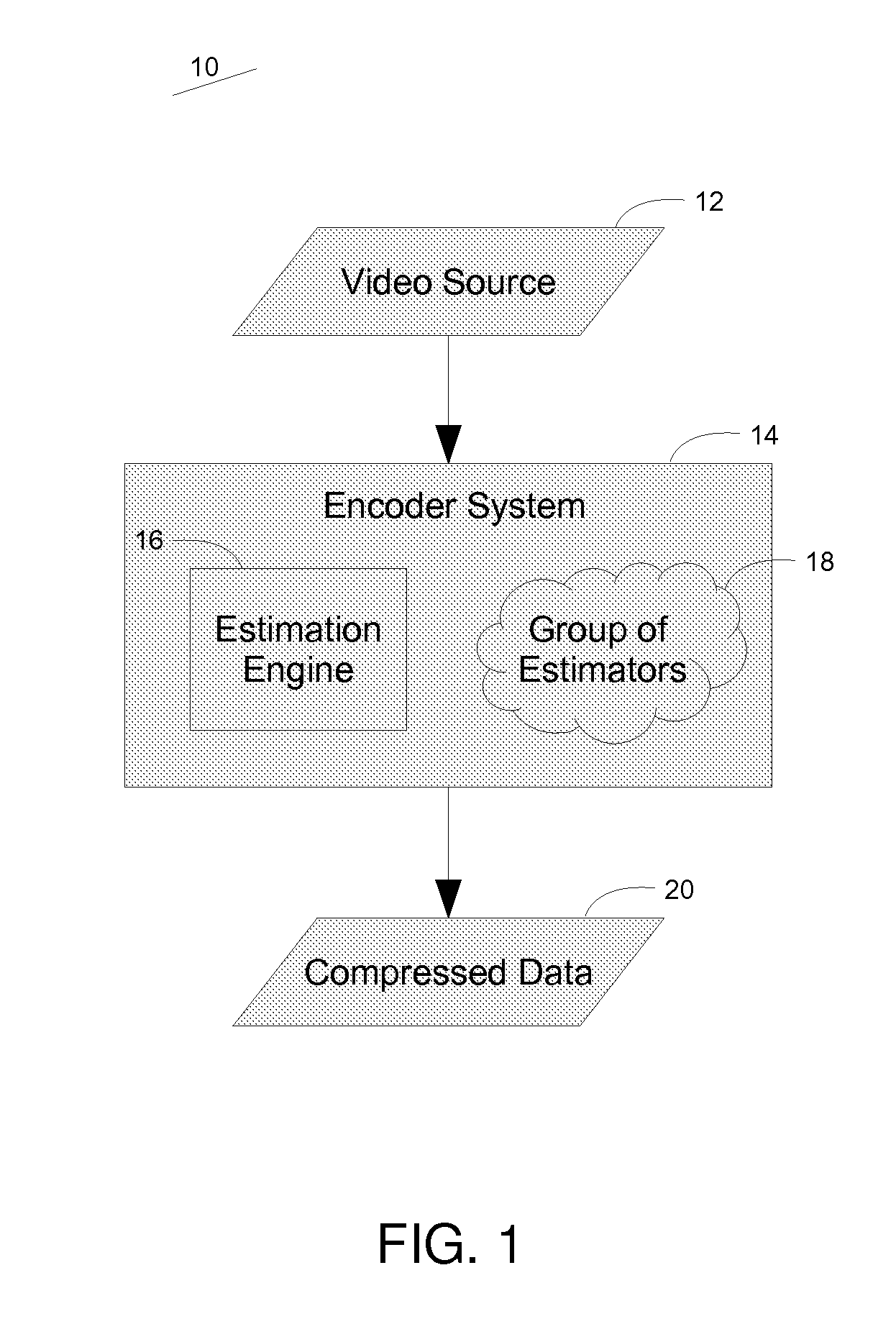
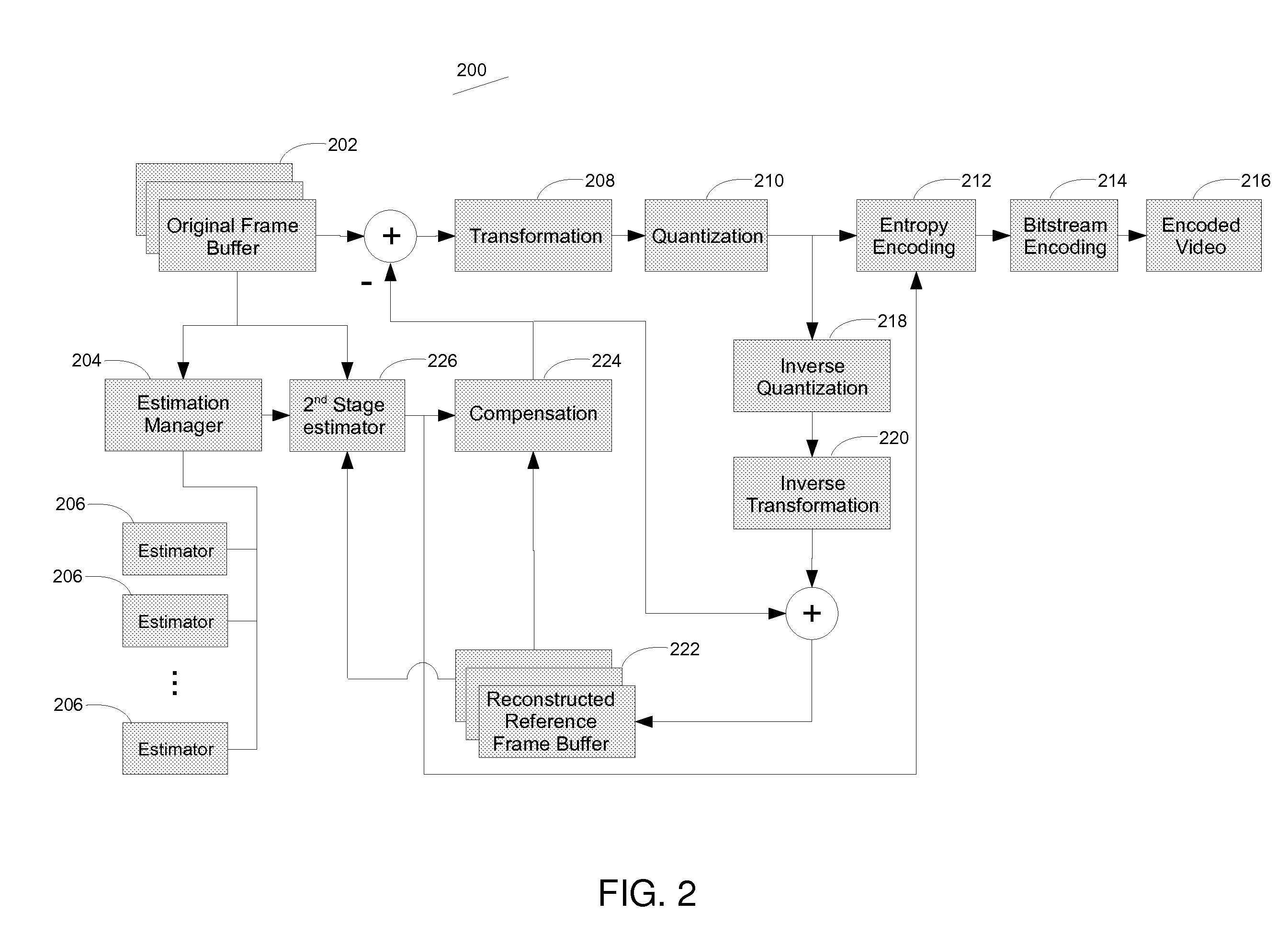
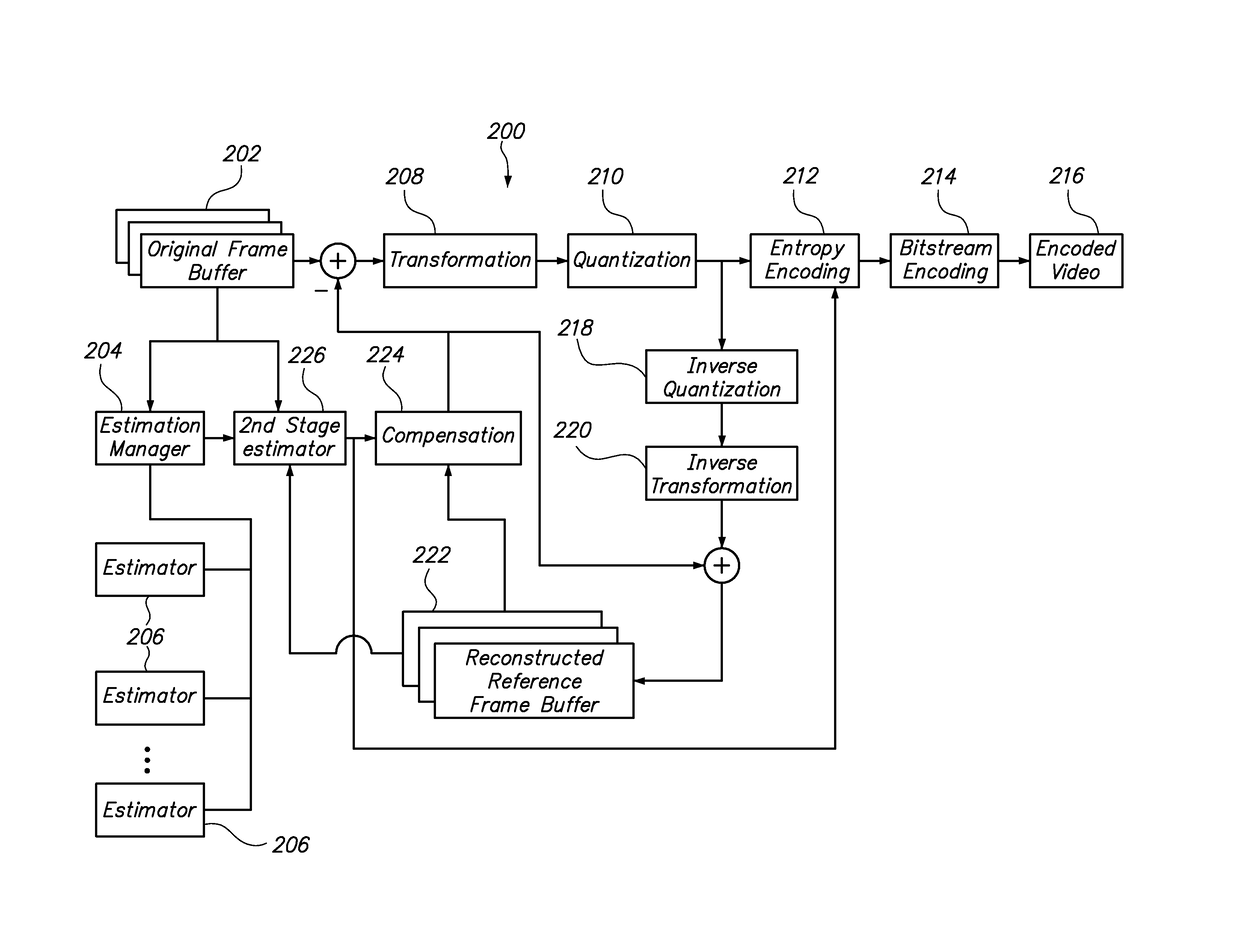
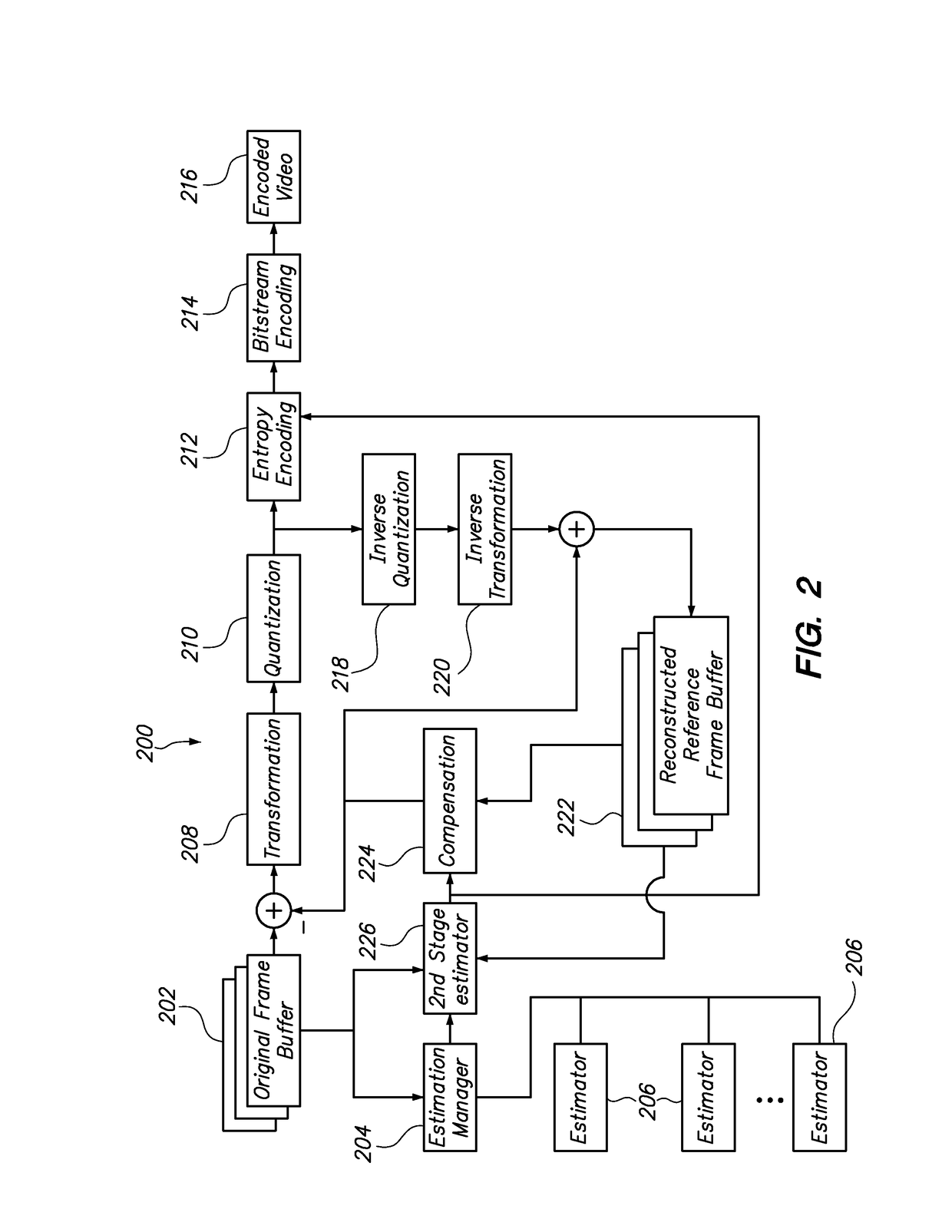
Method and system for parallelizing video compression
ActiveUS20110188577A1Shorten the timeQuality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData compressionPattern recognition
Video data compression performance is improved through the use of multiple processors operating in parallel. The parallel processors perform motion or spatial estimation, where portions of a video frame are found to be similar to portions in reference frames. Because this estimation operation can be very time consuming, the use of multiple processors can reduce the overall time required, or they can enable higher-performing algorithms that might otherwise require a prohibitively long processing time. The motion or spatial estimation results are applied to reconstructed versions of the video frame data to enable high levels of video data compression.
Owner:COMPRESSION LABS
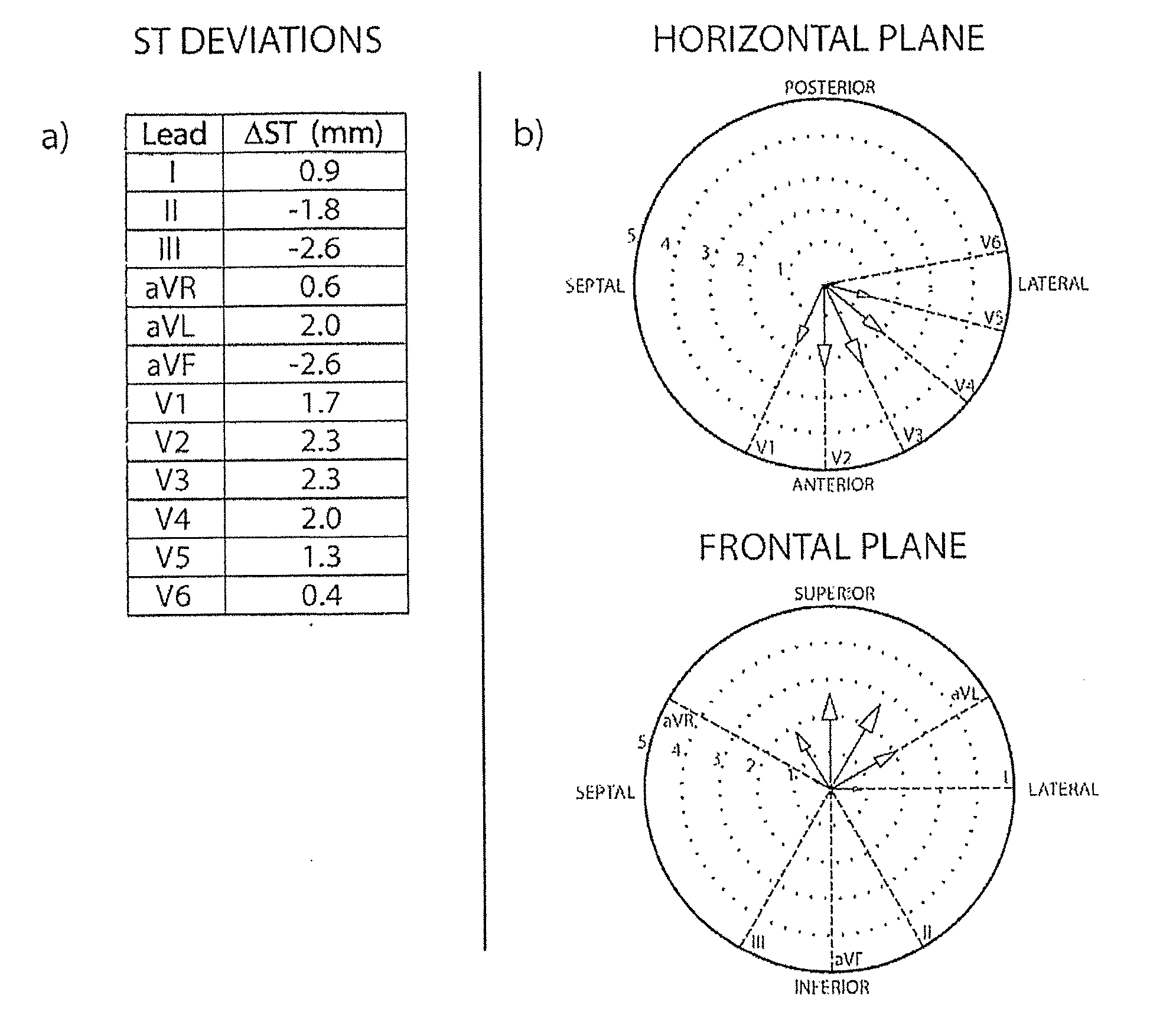
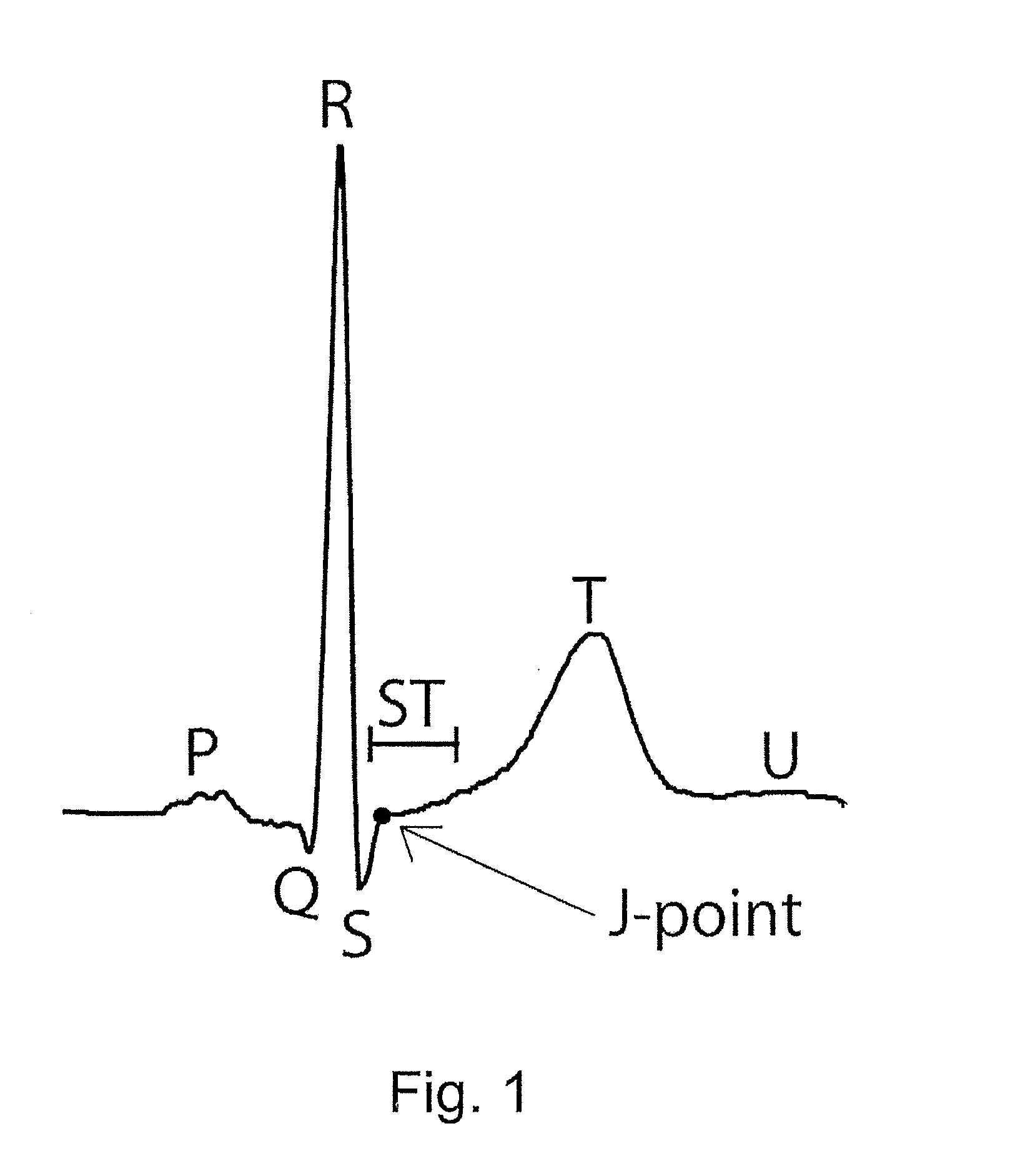
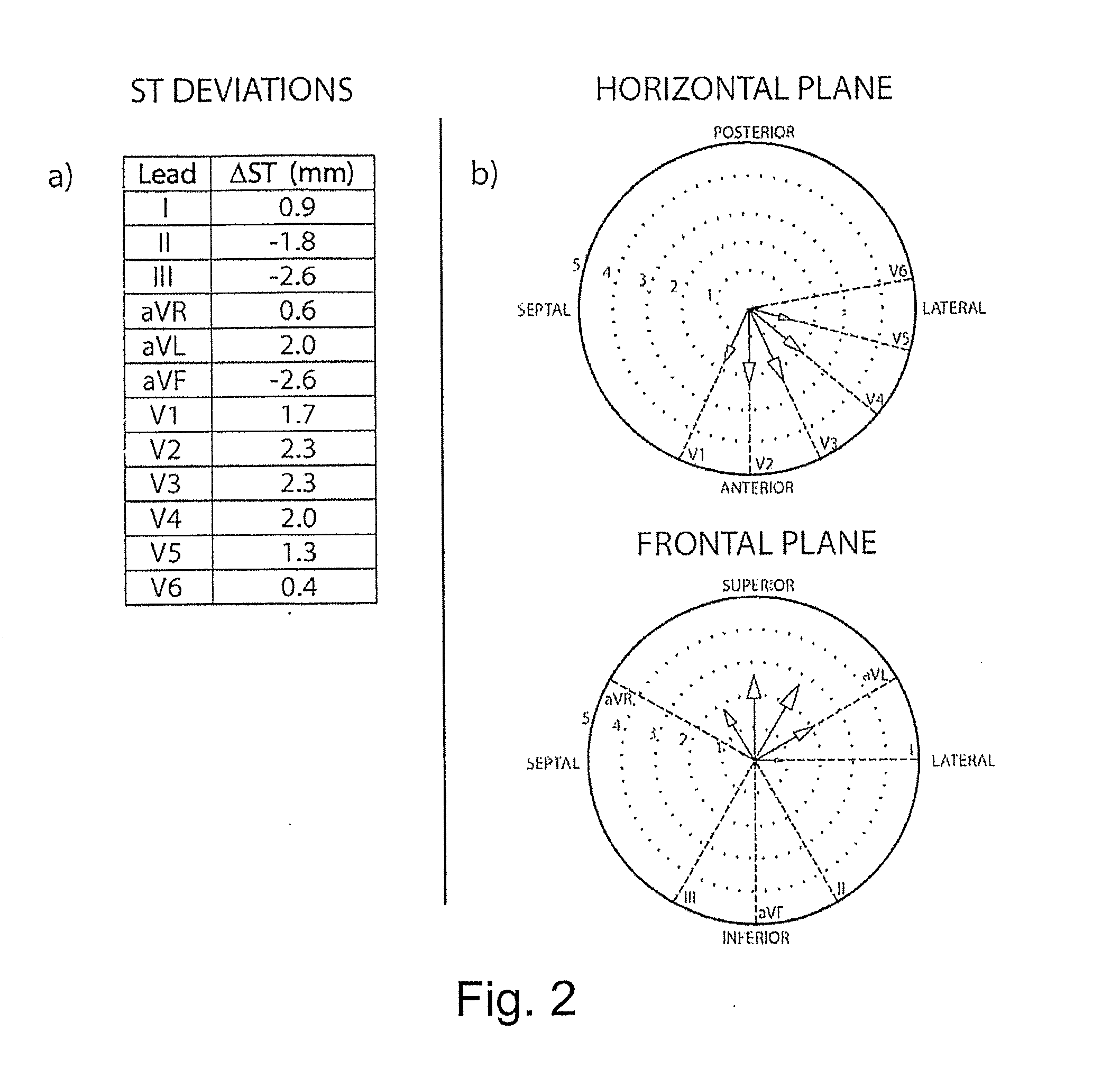
System and a method for spatial estimation and visualization of multi-lead electrocardiographic st deviations
InactiveUS20110184692A1Fast and easy and accurate diagnosisPrecision therapyElectrocardiographyDigital computer detailsEcg signalSpatial estimation
A system and a method for spatially ordered estimation and visualization of multi-lead electrocardiographic ST deviations induced by myocardial ischemia, in which system a plurality of ECG signals are recorded from a ECG source, which signals are stored by a processor in a memory, which processor processes the signals to obtain ST deviation, which processor performs measurement of ST deviation from each lead where the processor performs a multi-dimensional estimation of an vector representing of the spatial direction and magnitude of the underlying cardiac injury-current giving rise to the measured ST deviations, which processor hereby estimates the spatial location and severity of myocardial ischemia.
Owner:AALBORG UNIV
Signal arrival direction self-correction method for sensor array
ActiveCN106980104AImprove performanceStrong ability to suppress interferenceRadio wave finder detailsRadio wave finder monitoring/testingSensor arrayMultiple signal classification
The invention relates to an arrival direction self-correction method for a sensor array. According to the method, a noise subspace estimated value is determined; an array phase error of the sensor array is initialized, and an initial value of the signal arrival direction is estimated through utilizing an MUSIC algorithm; based on the calculation value of the signal arrival direction, a Hermitian positive definite matrix is calculated, and the Hermitian positive definite matrix satisfies a first equation; an array element phase error is made to satisfy the first limit condition, and the array phase error is converted to satisfy a second equation; the first equation and the second equation are solved through utilizing a Lagrangian multiplier method to acquire a vector estimated value of the array phase error; a correction value of the signal arrival direction is acquired through utilizing the MUSIC algorithm or a high resolution subspace algorithm; and iteration of the previous steps is repeatedly carried out till iteration stop conditions are satisfied. The method is advantaged in that dependence on special structure characteristics of an array output covariance matrix is avoided, excellent performance is realized under the condition of limited sampling data, and influence of the sensor array error on the arrival direction can be effectively reduced.
Owner:CHINA UNIONPAY
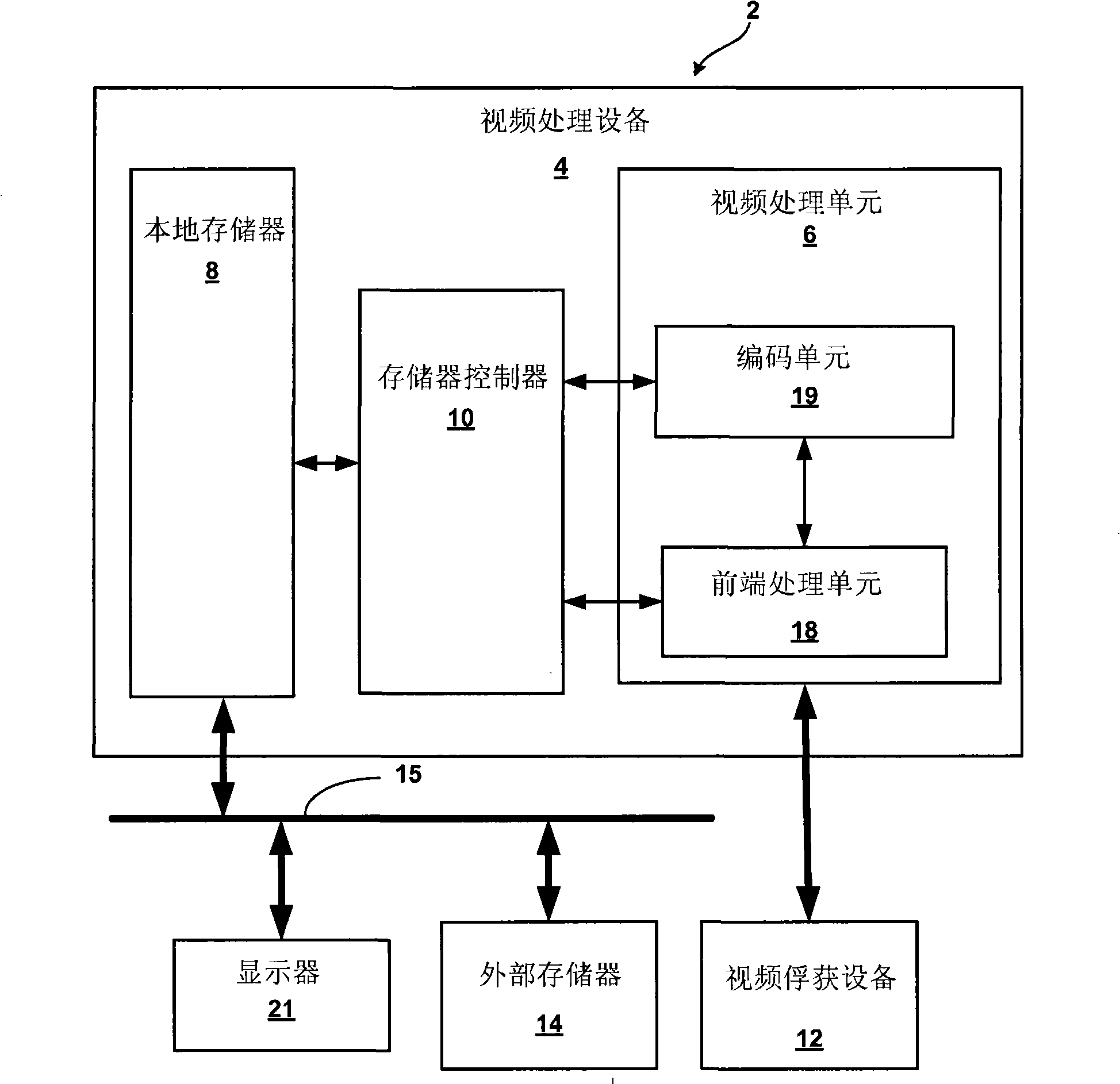
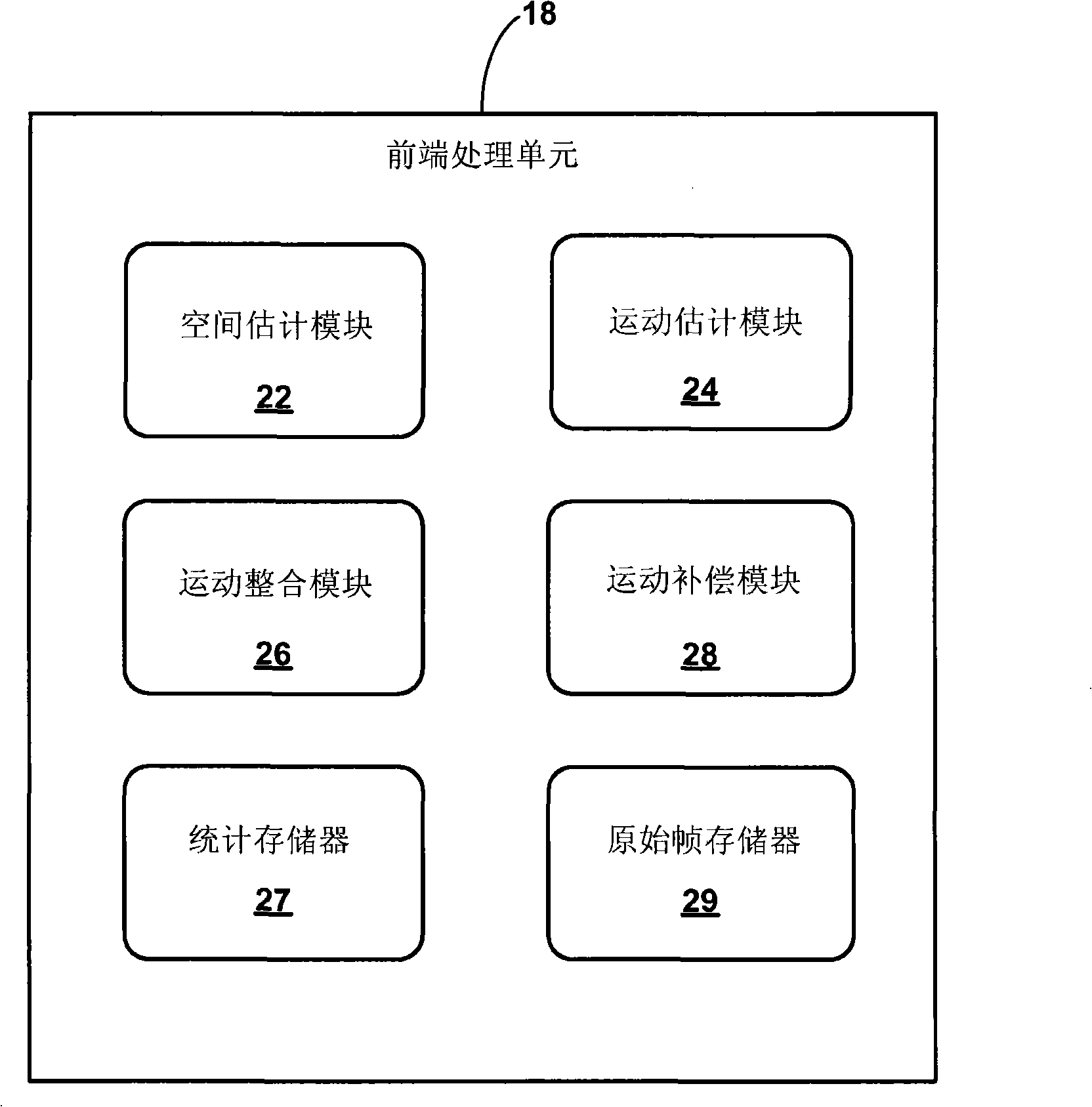
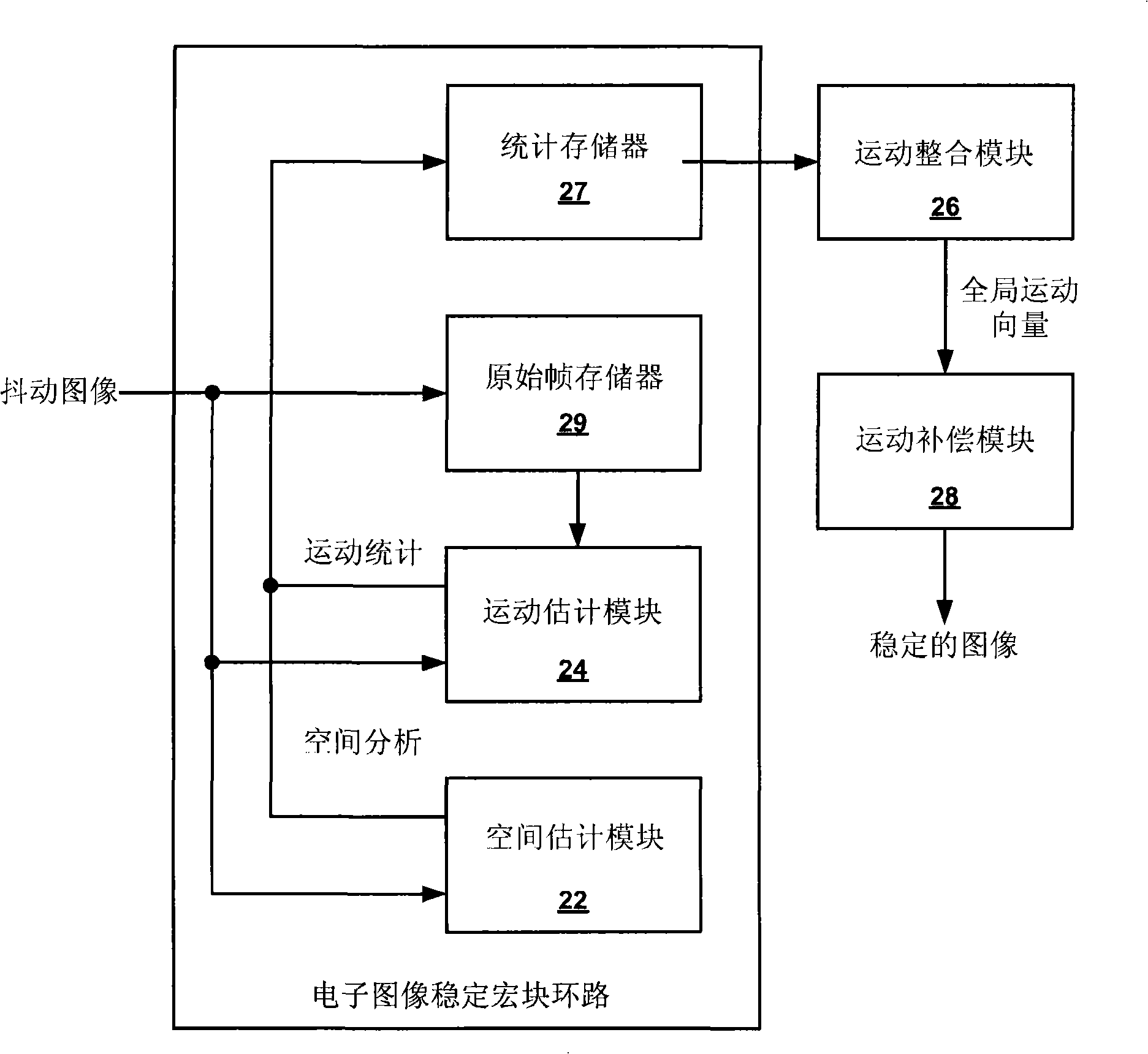
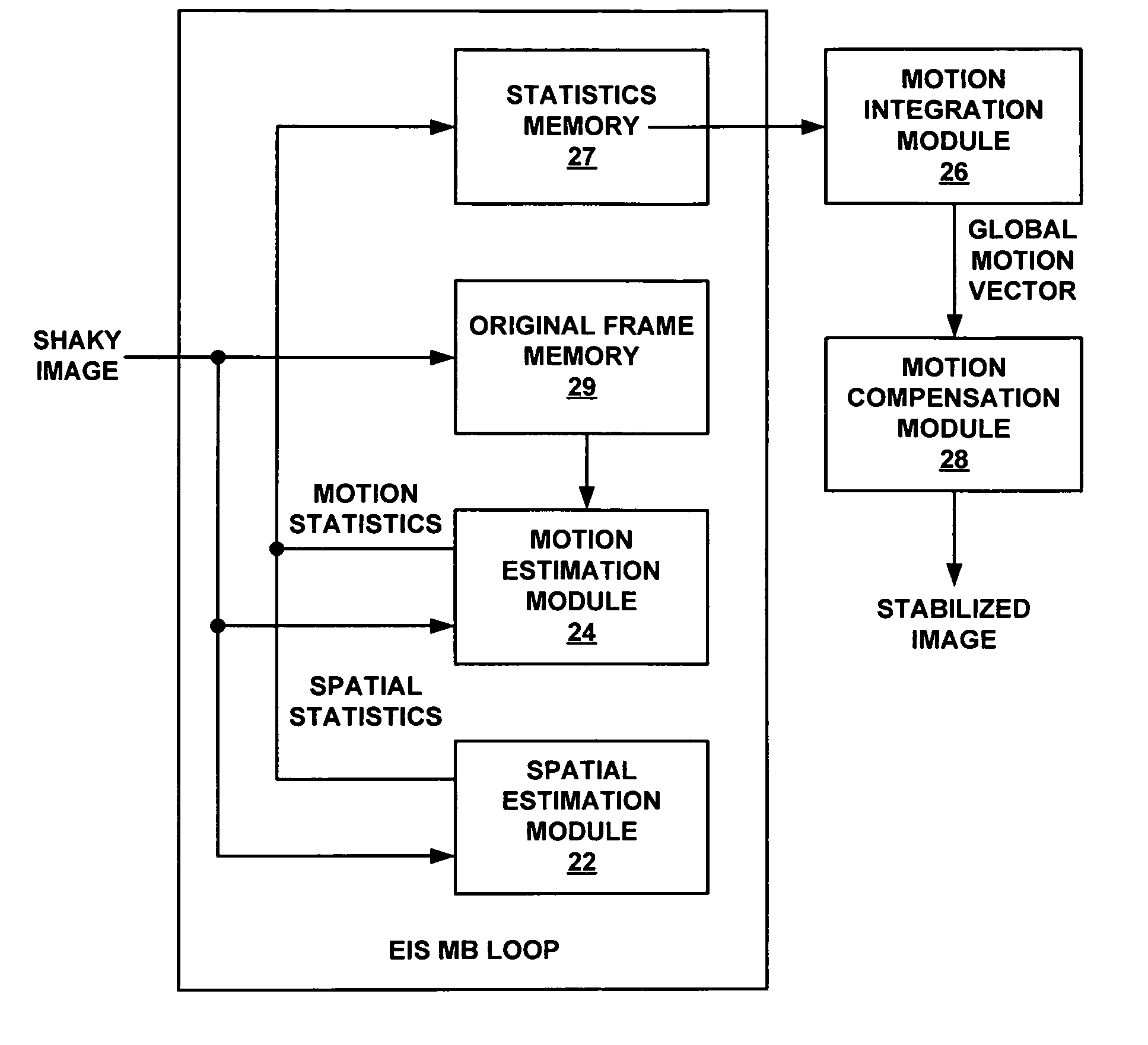
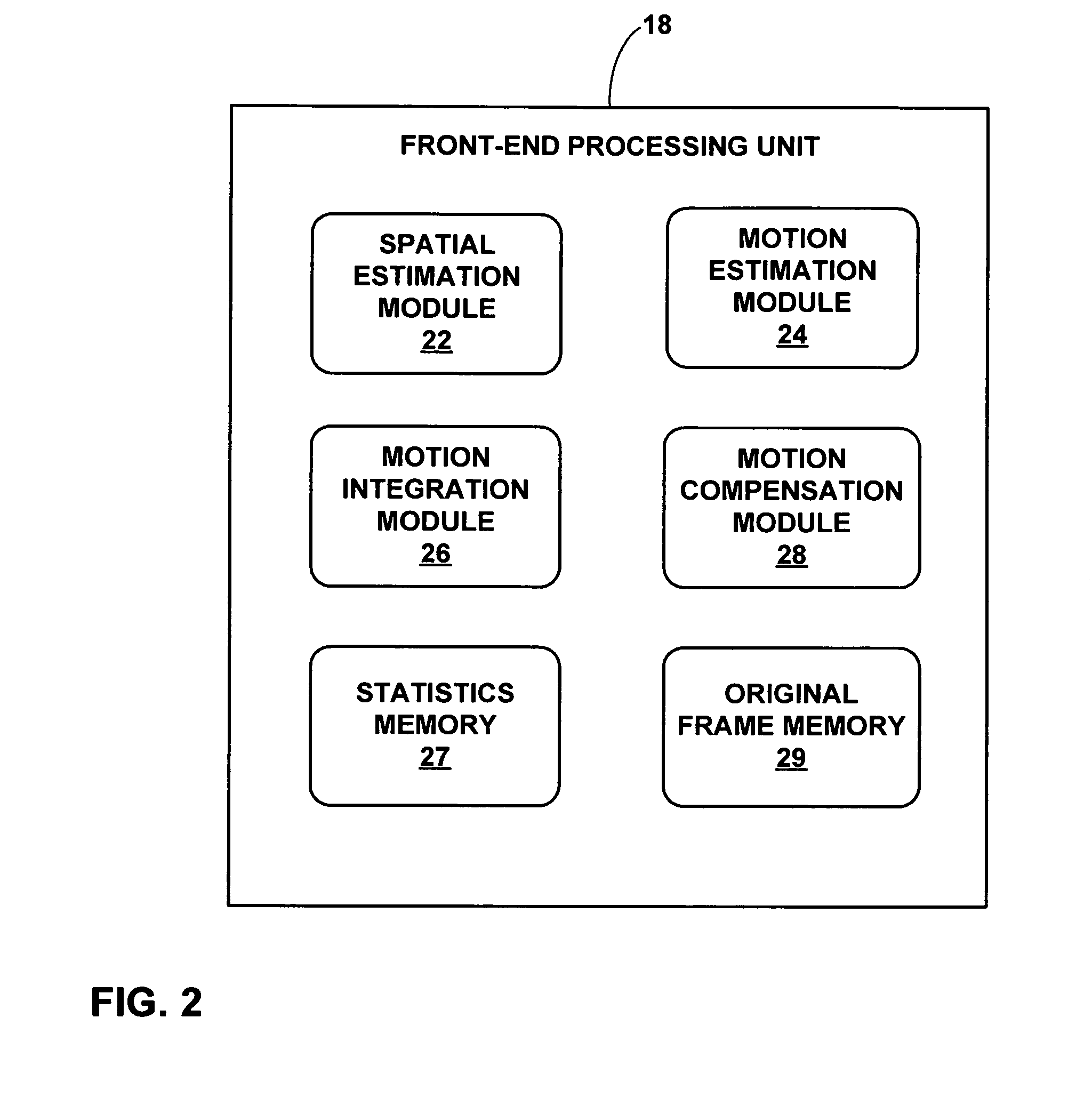
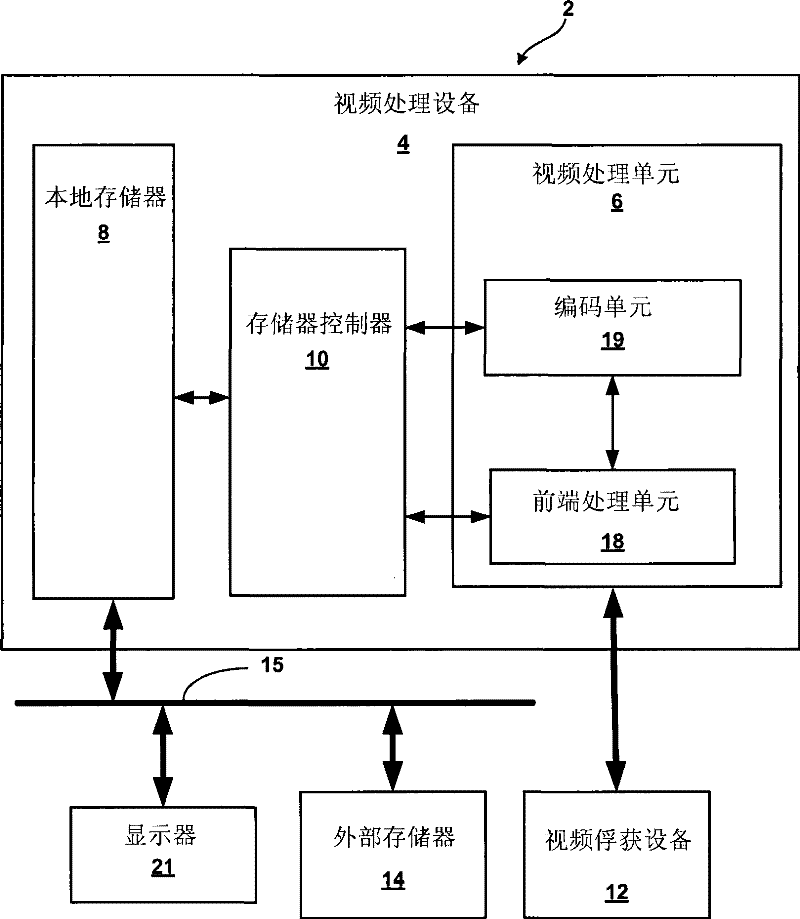
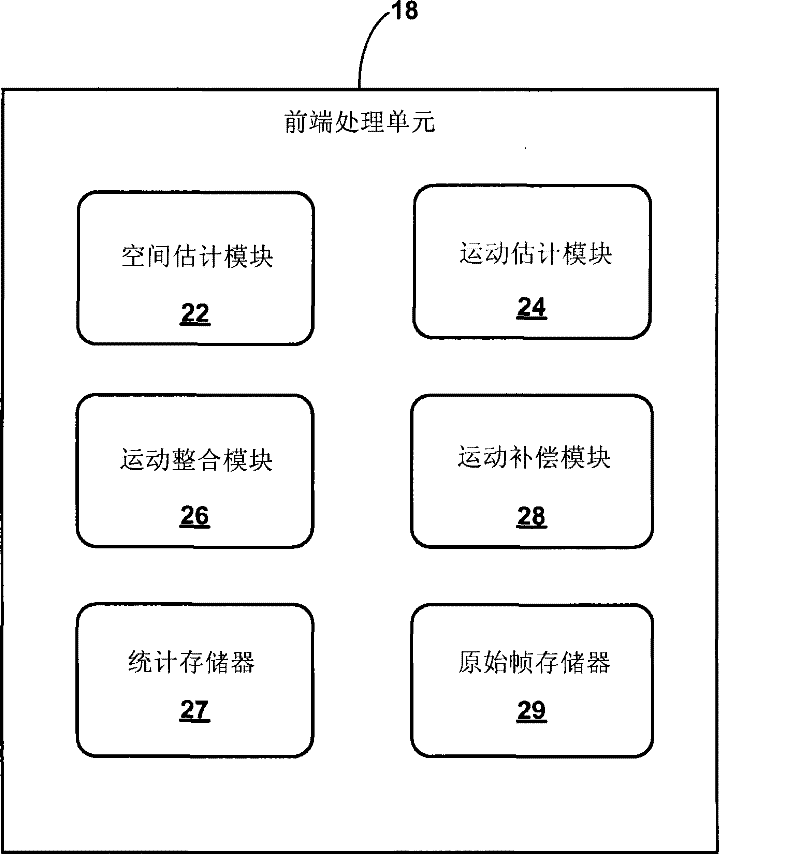
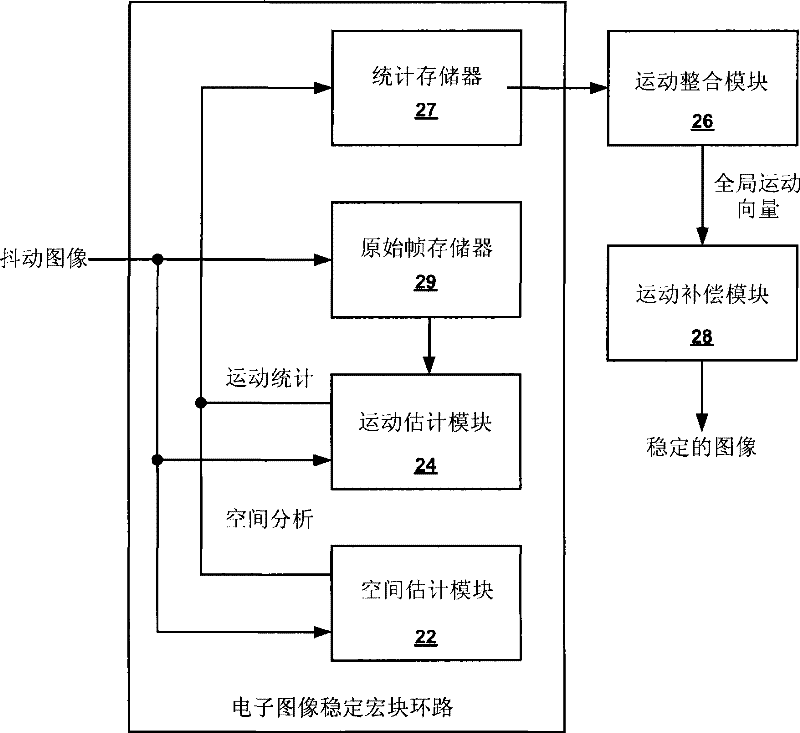
Electronic video image stabilization
This disclosure describes electronic video image stabilization techniques for imaging and video devices. The techniques involve determining motion and spatial statistics for individual macroblocks of a frame, and determining a global motion vector for the frame based on the statistics of each of the macroblocks. In one embodiment, a method of performing electronic image stabilization includes performing spatial estimation on each of a plurality of macroblocks within a frame of an image to obtain spatial statistics for each of the macroblocks, performing motion estimation on each of the plurality of macroblocks to obtain motion statistics for each of the macroblocks, integrating the spatial statistics and the motion statistics of each of the macroblocks to determine a global motion vector for the frame, and offsetting the image with respect to a reference window according to the global motion vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for large scale, non-reverting and distributed spatial estimation
Described herein is a system and a method of spatial field estimation from input data from a domain of interest. The method comprises defining a spatial mesh of positions over the domain of interest (802) and defining a smoothness information model (804) which is defined with respect to the spatial mesh to form an information matrix Y1 and vector y1. The method further comprises defining an information representation of the input data, the information representation comprising an information matrix Yobs and vector y, both defined relative to the spatial mesh. The method further comprises through an additive function fusing (806) the smoothness information model with the information representation of the input data to form an information matrix Y and vector y. The method then comprises, in a computational system, solving for x in Yx=y (808), wherein x represents the spatial field estimation.
Owner:SYDNEY THE UNIV OF
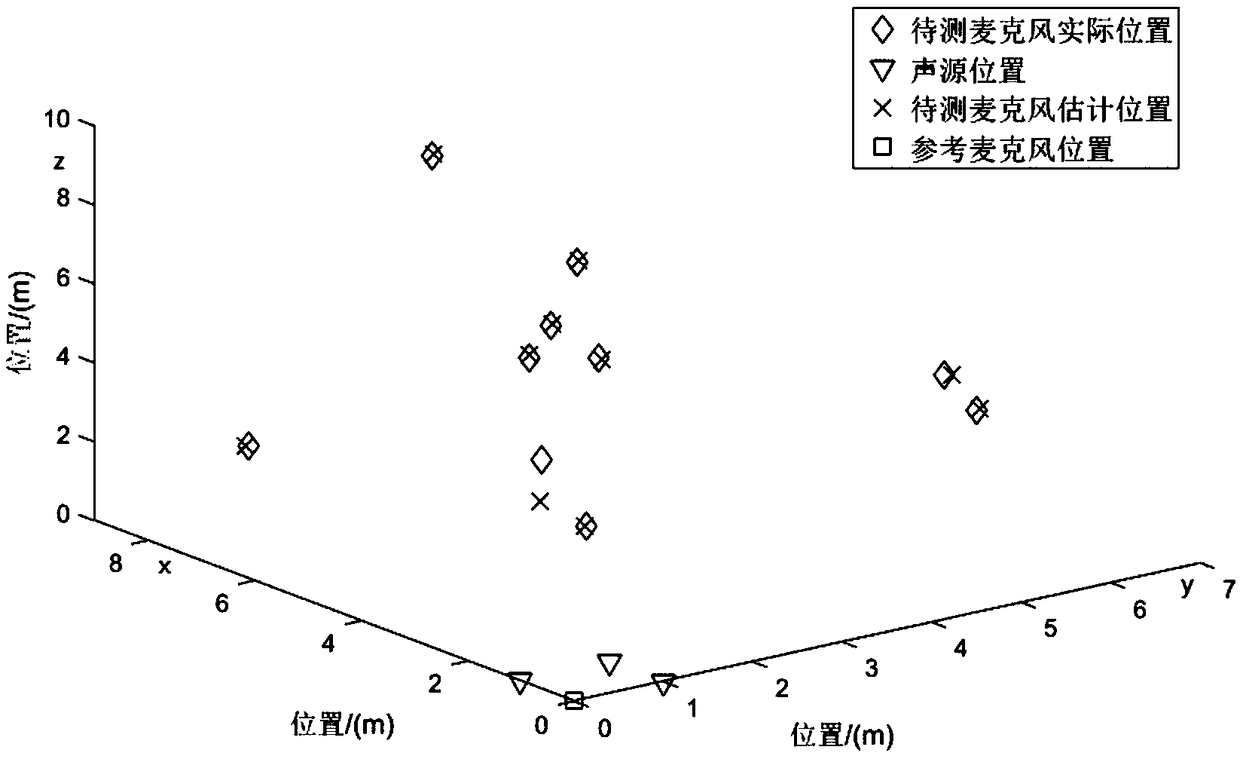
Spatial microphone positioning method based on sound source array
ActiveCN108646221AOutstanding FeaturesHighlight significant progressPosition fixationSpatial estimationSound sources
The invention provides a spatial microphone positioning method based on a sound source array and relates to the field of indoor positioning. According to the method, a device composed of a sound source distribution unit, a reference microphone, a to-be-positioned microphone and a microphone signal processing unit is used, three sound signals different in frequency band are selected and used as sound production signals of three sound sources to achieve spatial estimation of the microphone position, and the three sound signals different in frequency band are received by the to-be-positioned microphone and the reference microphone; by calculating the distance between the to-be-positioned microphone and the sound sources, the spatial position of the to-be-positioned microphone is calculated; through a mode of sodar time difference and geometric volume solution, spatial microphone positioning based on the sound source array is achieved. The defects in the prior art are overcome that the operation is cumbersome, the efficiency is low, installation is inconvenient, only offline calculation can be conducted, and online estimation of the microphone position and position estimation of the spatially distributed microphones cannot be achieved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Electronic video image stabilization
ActiveUS7840085B2Effectively lead to differentiationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFrame basedSpatial estimation
This disclosure describes electronic video image stabilization techniques for imaging and video devices. The techniques involve determining motion and spatial statistics for individual macroblocks of a frame, and determining a global motion vector for the frame based on the statistics of each of the macroblocks. In one embodiment, a method of performing electronic image stabilization includes performing spatial estimation on each of a plurality of macroblocks within a frame of an image to obtain spatial statistics for each of the macroblocks, performing motion estimation on each of the plurality of macroblocks to obtain motion statistics for each of the macroblocks, integrating the spatial statistics and the motion statistics of each of the macroblocks to determine a global motion vector for the frame, and offsetting the image with respect to a reference window according to the global motion vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
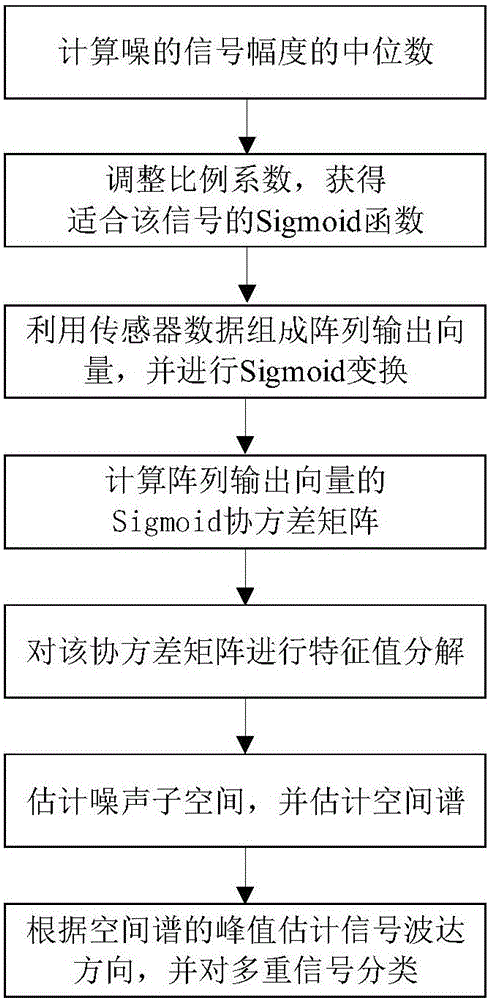
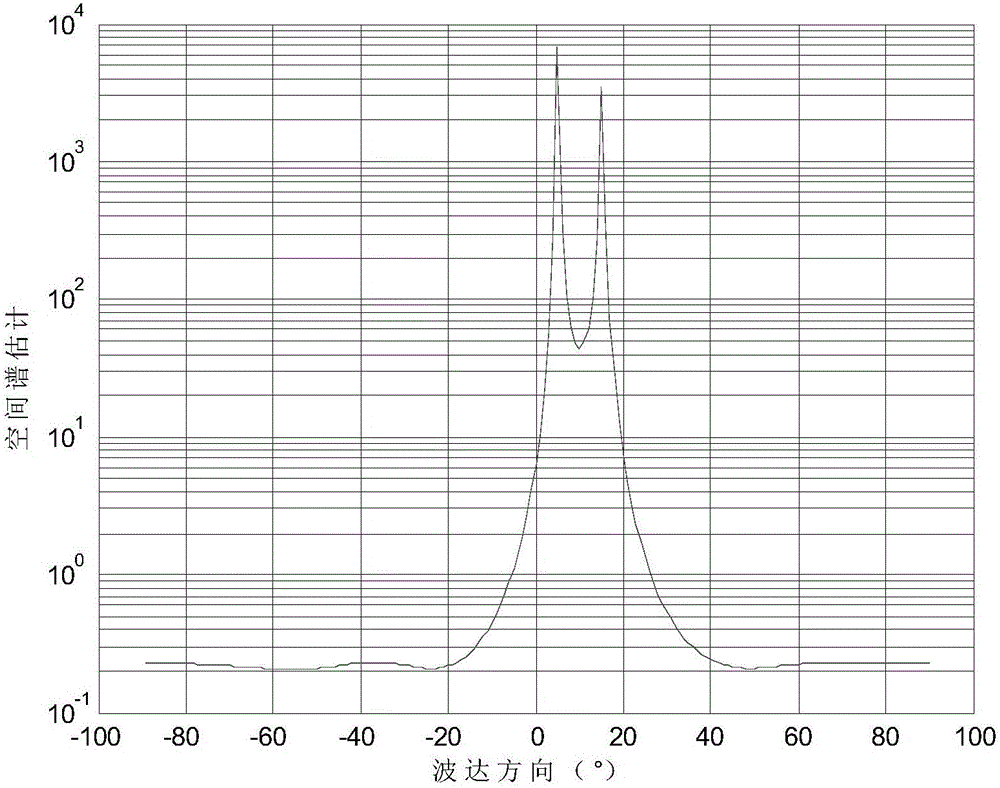
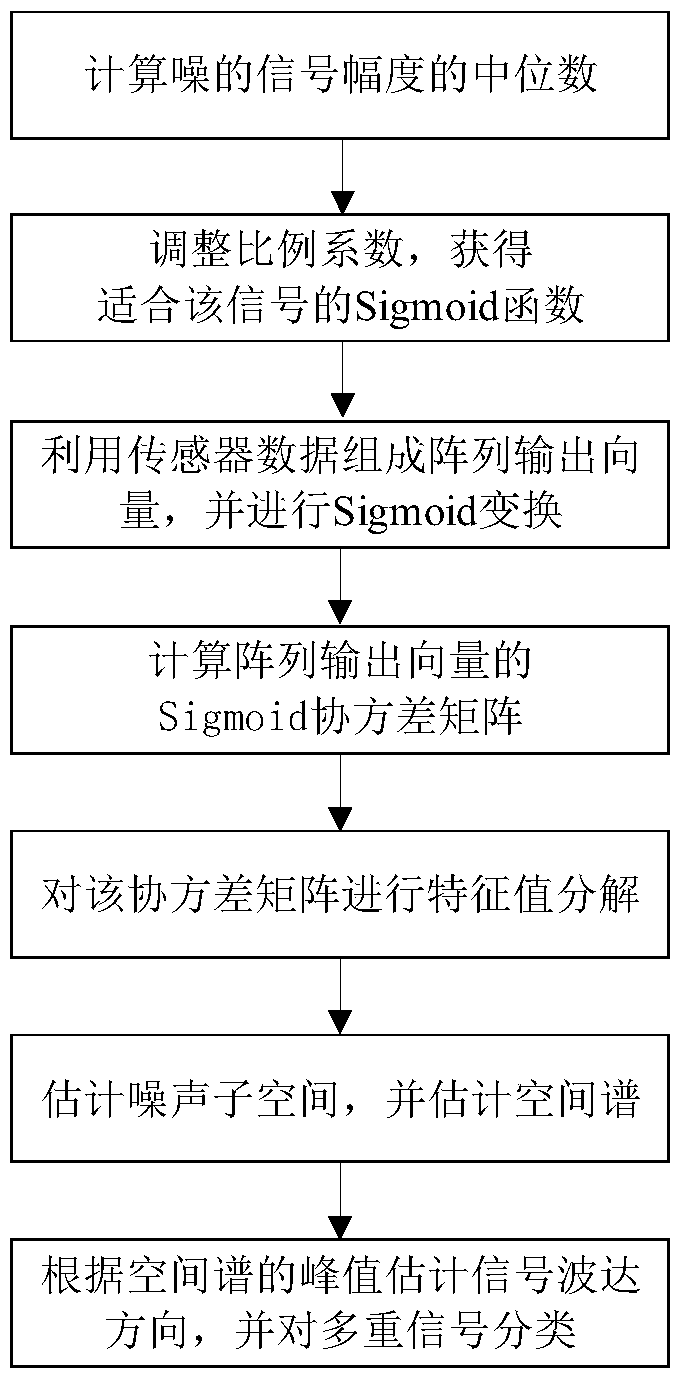
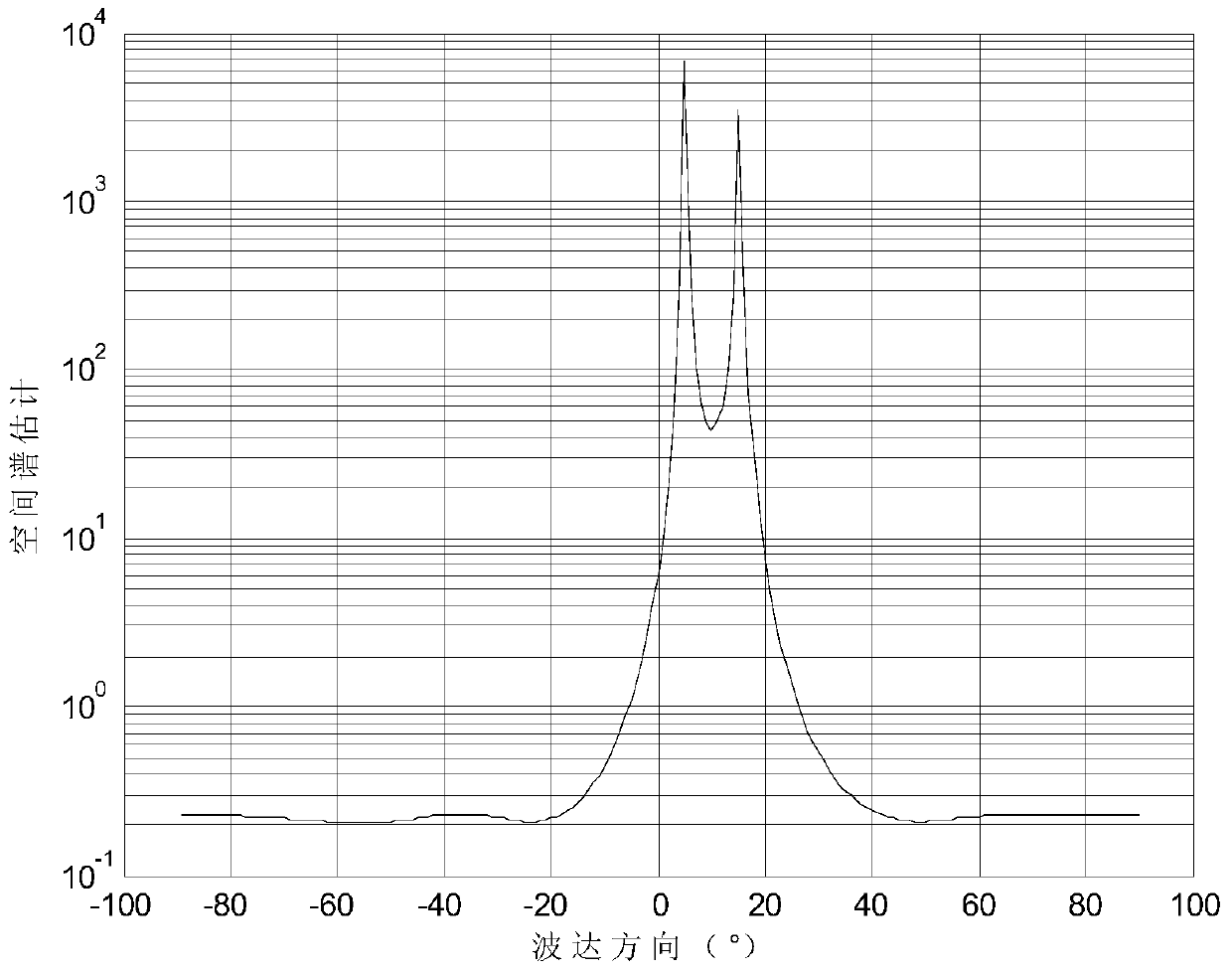
Multiple signal classification method based on Sigmoid covariance matrix
The present invention belongs to the field of the array signal processing technology, and provides a multiple signal classification method based on a Sigmoid covariance matrix. The method has high inhibition capability for the pulse noise obeying the non-Gaussian distribution, and is able to realize the multiple signal classification in the condition of the pulse noise and estimate the wave reaching direction of each signal. The method comprises: 1) estimating the parameters of a Sigmoid function according to the median including the signal amplitude of noise; 2) estimating the Sigmoid covariance matrix outputted by the array through adaption of the Sigmoid function and the output vector of an uniform linear array; 3) performing characteristic constant decomposition of the Sigmoid covariance matrix and obtaining the estimation of the noise subspace; and 4) employing the noise subspace estimation for the space spectrum of the multiple signal classification, and estimating the wave reaching direction angle through adaption of the estimated value of the space spectrum. The multiple signal classification method based on a Sigmoid covariance matrix has good algorithm performance, and has a good application prospect in the real engineering application.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Radio environment map field intensity parameter estimation algorithm
InactiveCN106707035AConform to spatial correlationGood prediction accuracyElectromagentic field characteristicsComplex mathematical operationsSpatial estimationRadio propagation
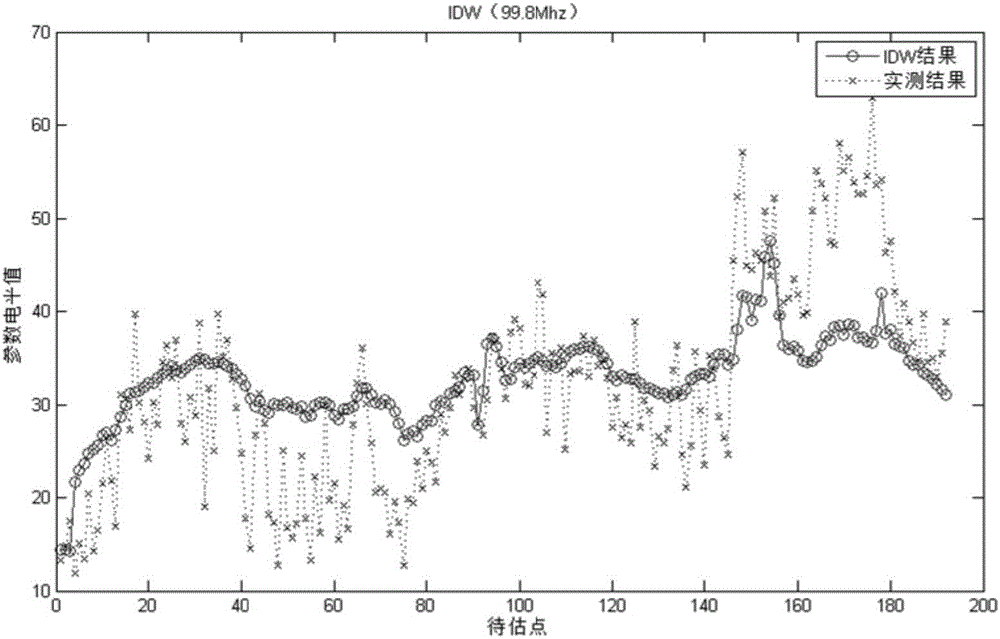
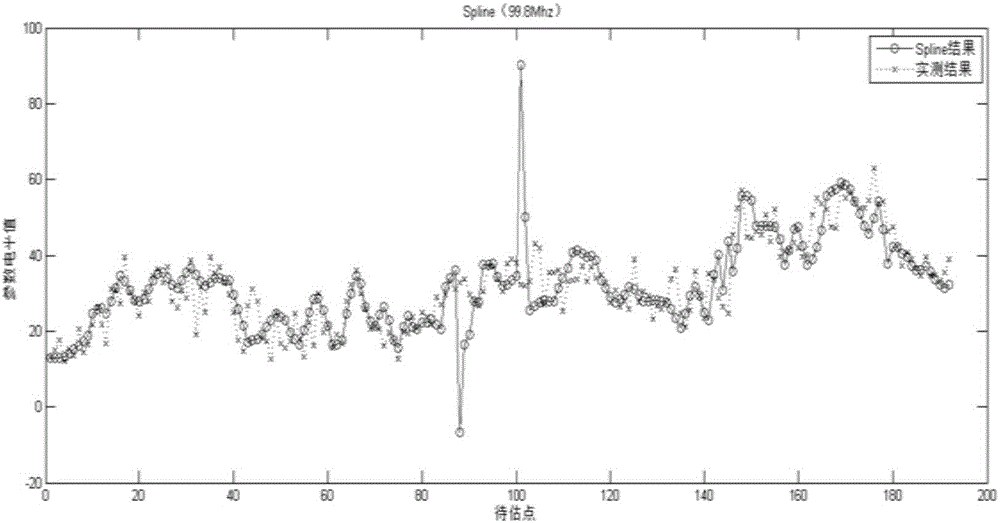
The invention discloses a radio environment map field intensity parameter estimation algorithm. Based on a radio environment map parameter space estimation method used for monitoring node perception data, through combining a radio propagation signal intensity loss rule, a theory variation function model based on propagation model improvement is provided. An improved theory variation function accords with a radio signal propagation attenuation change rule. And through combining a field intensity parameter estimation characteristic, a weighted theory variation function fitting method is provided. In the method of the invention, a physical characteristic of an electromagnetic environment map parameter is tightly combined and a variation function and a fitting method are designed so as to accord with an electromagnetic environment map parameter space distribution change rule.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
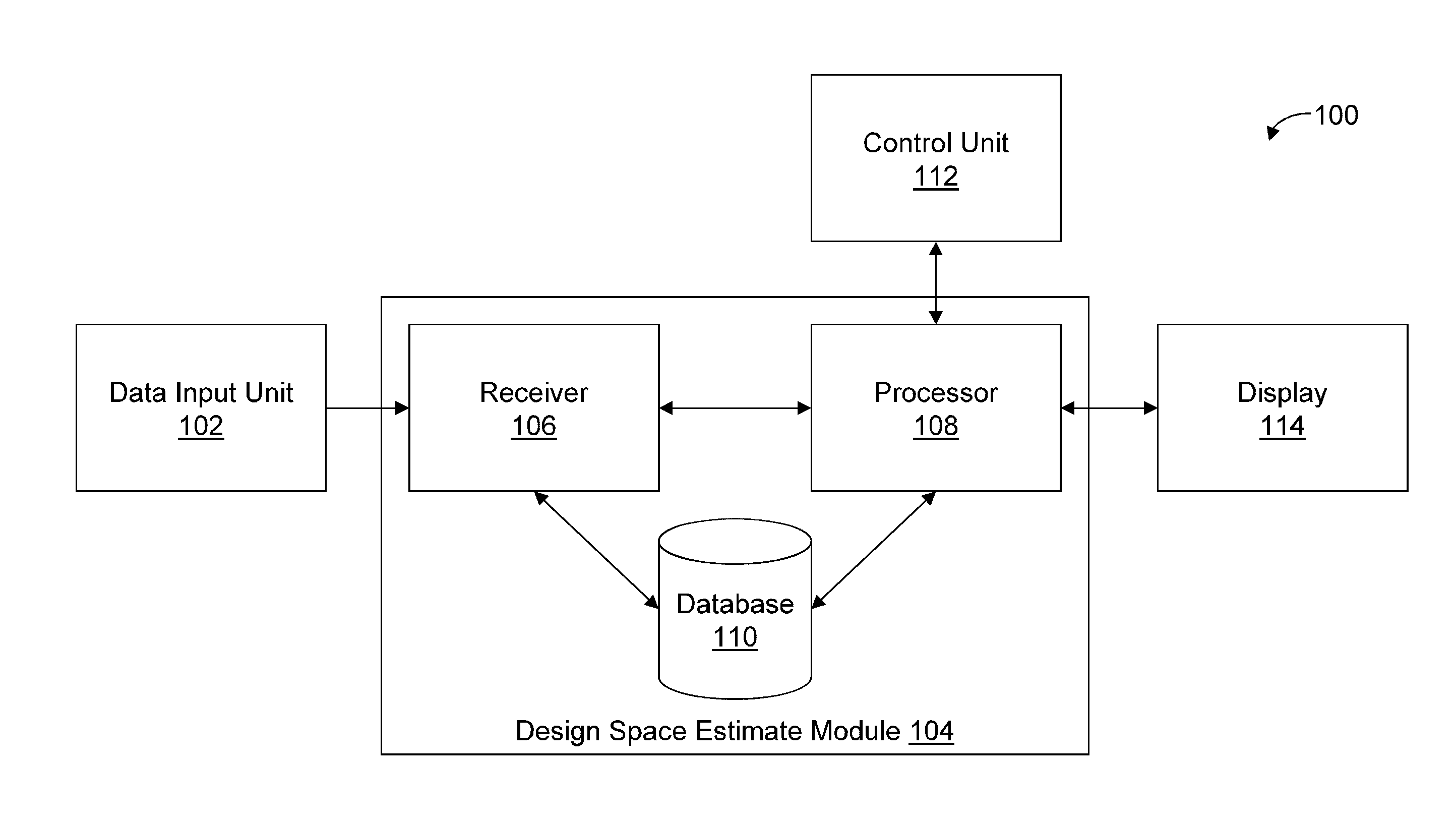
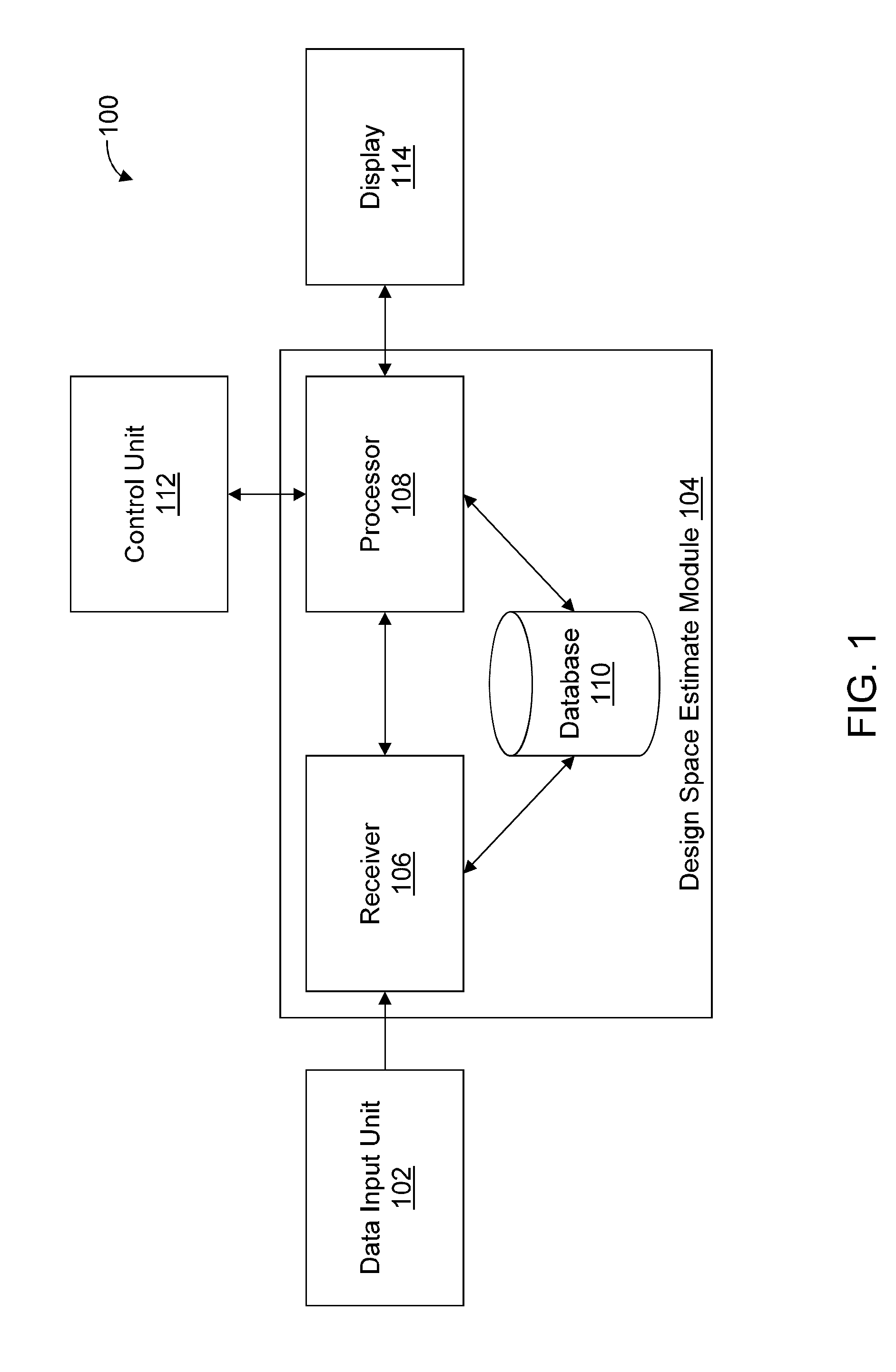
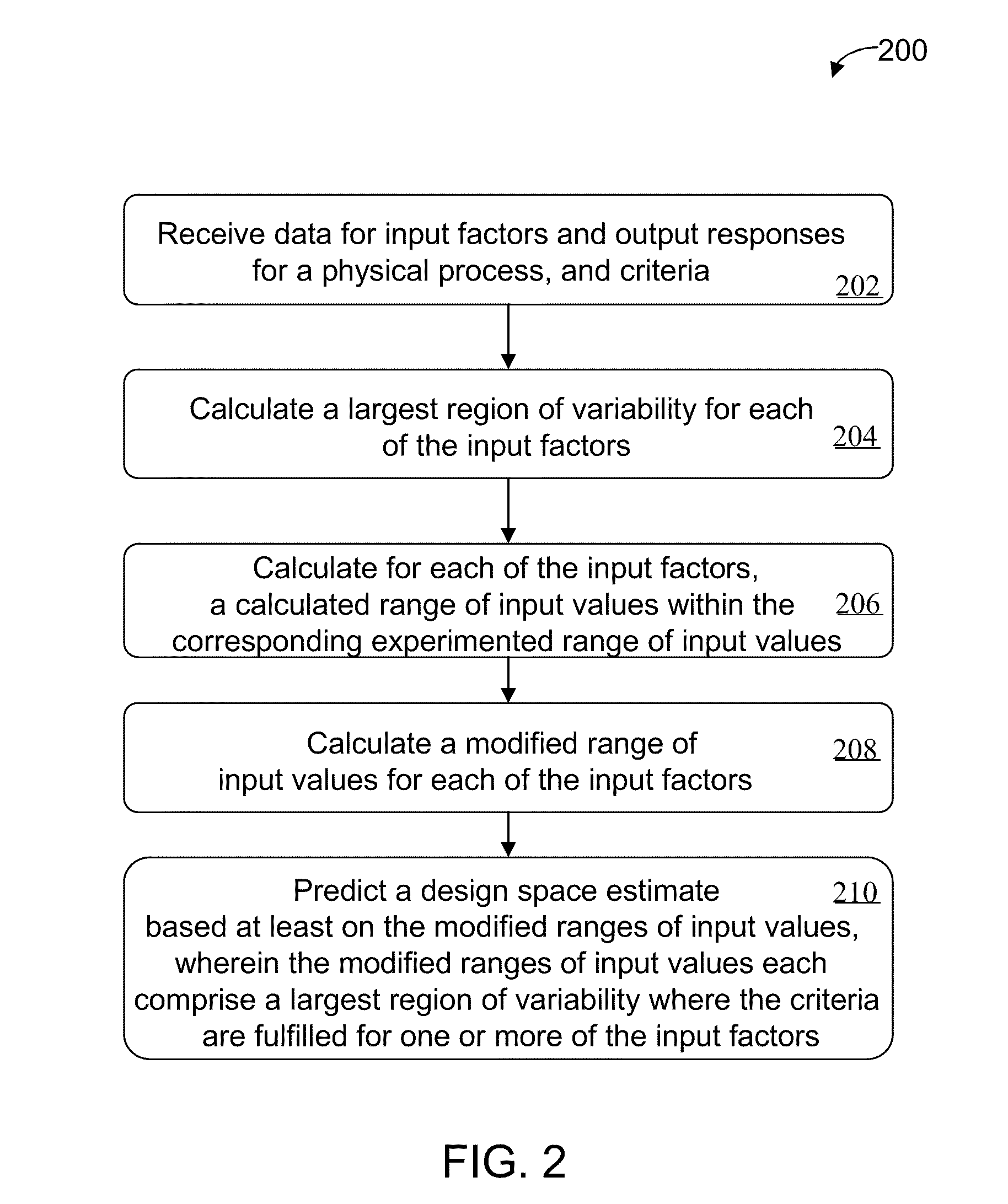
Methods and apparatus for automated predictive design space estimation
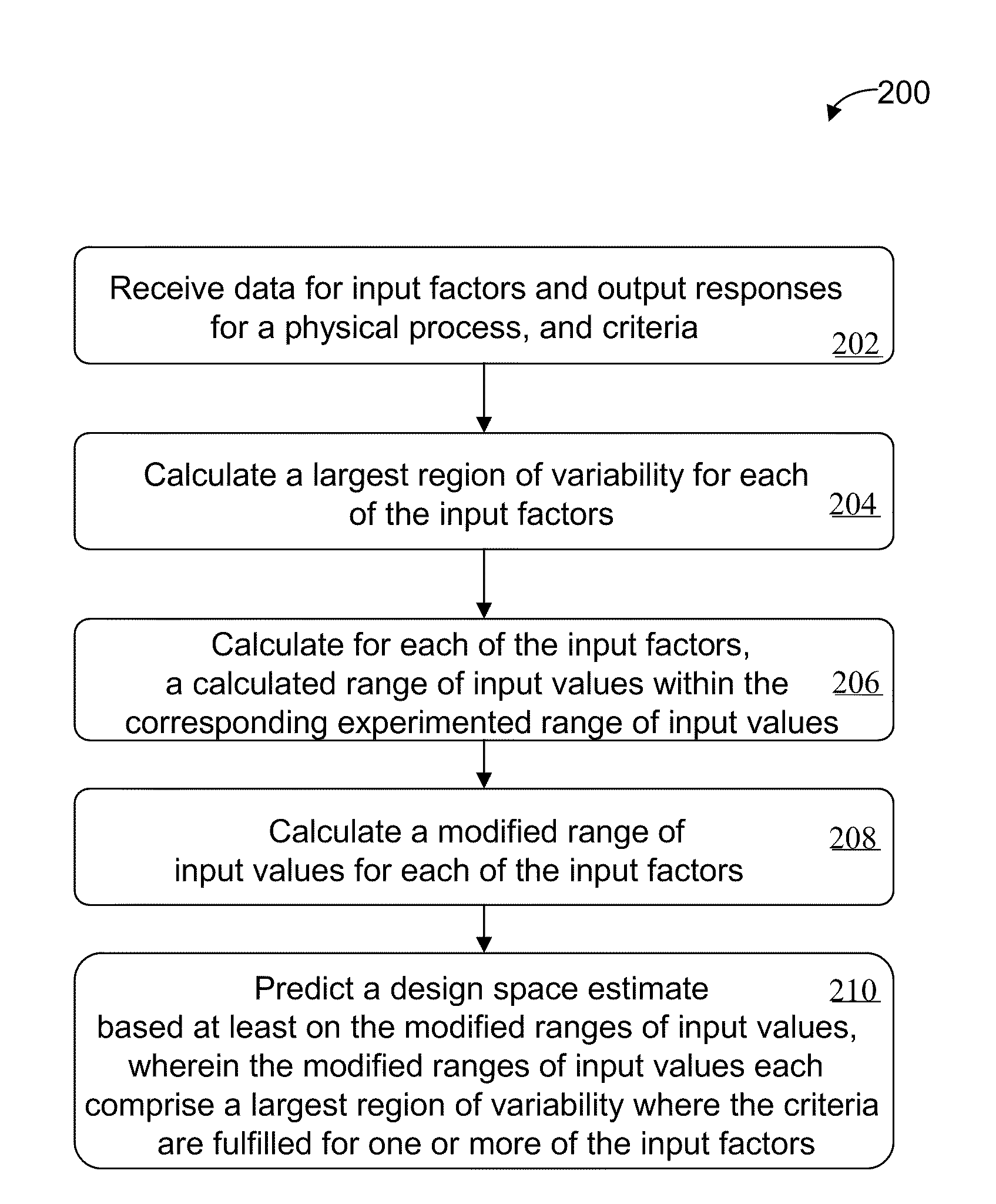
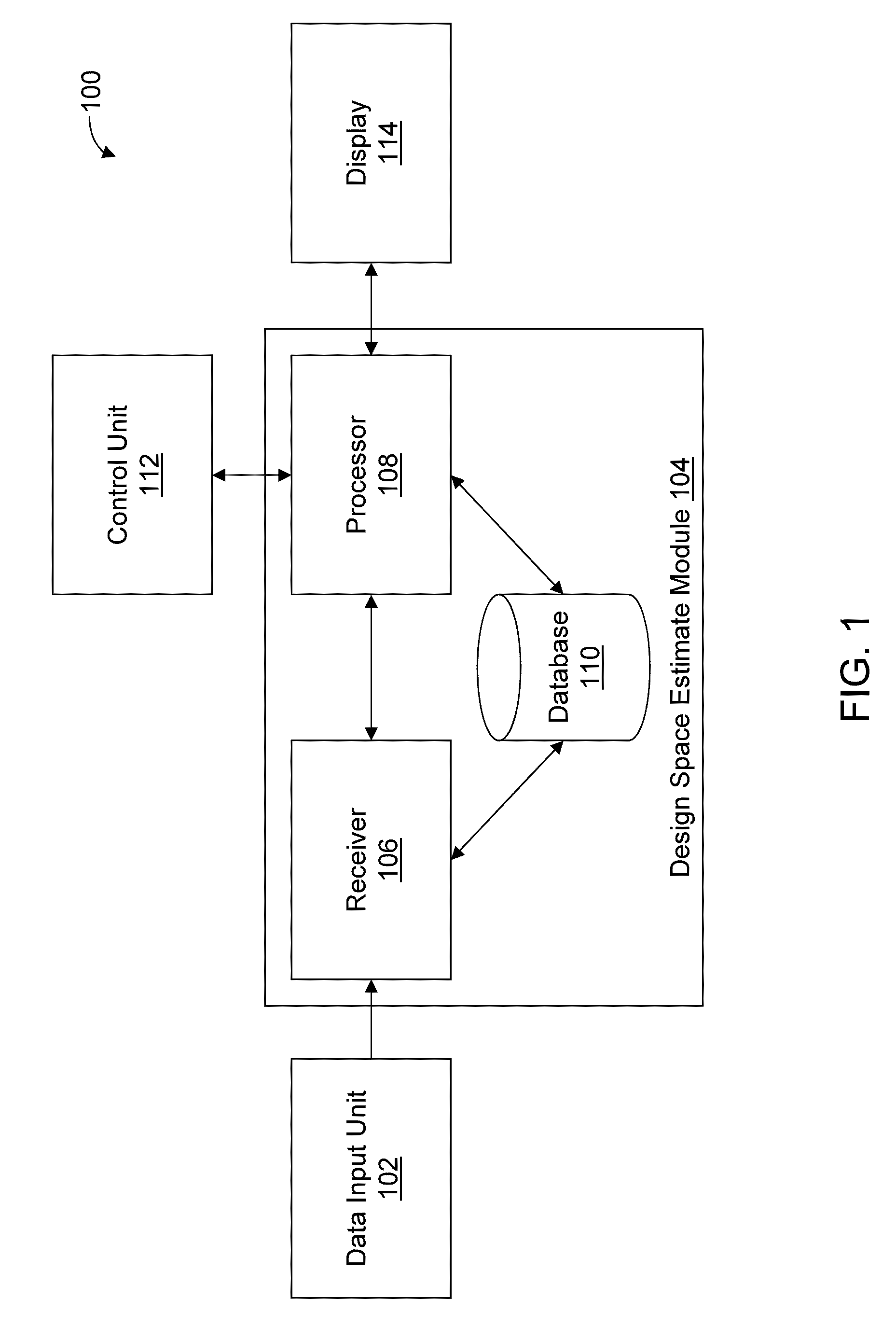
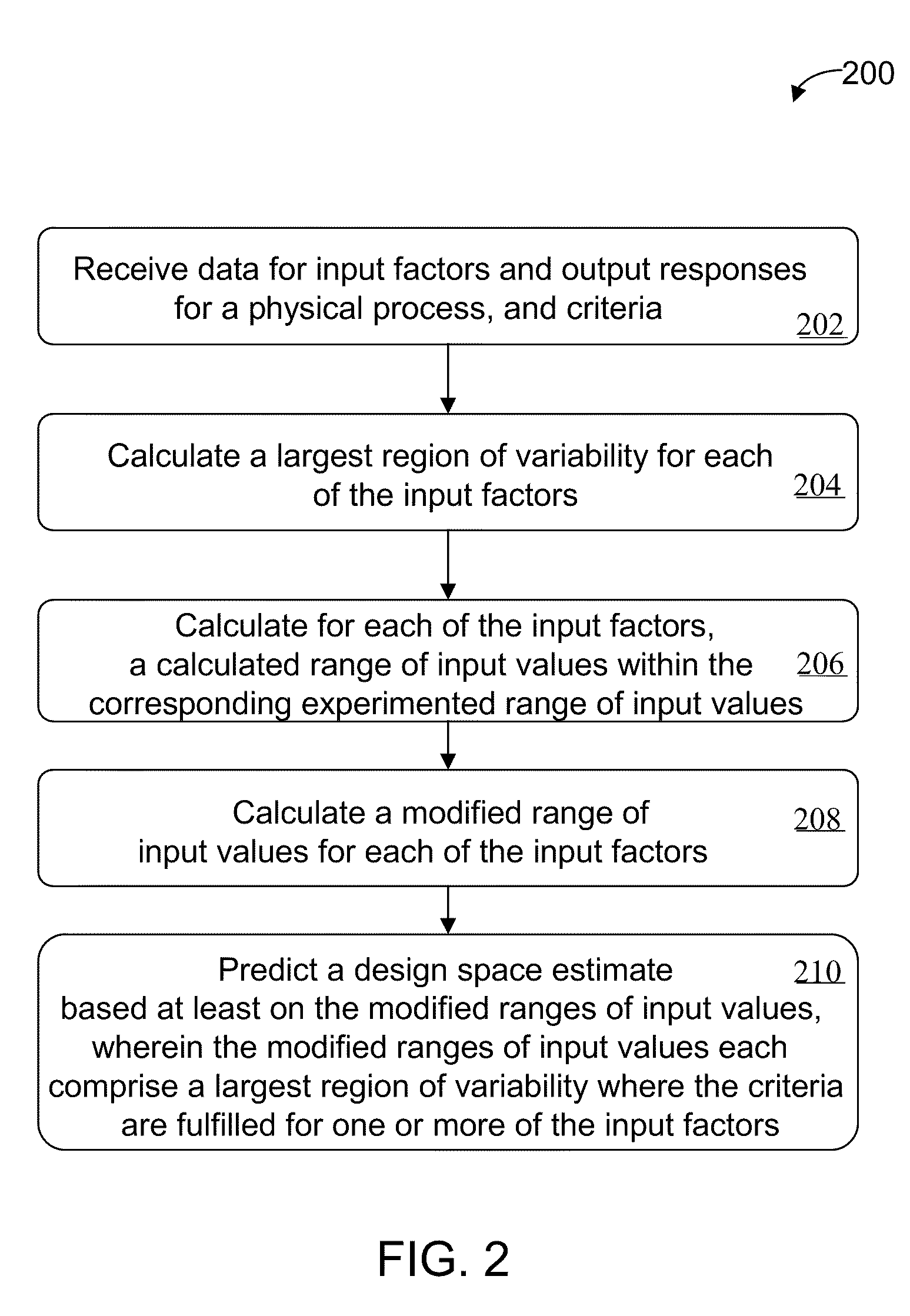
Described are computer-based methods and apparatuses, including computer program products, for automated predictive design space estimation. A design space of input factors and output responses is estimated for a physical process. Data is received for one or more input factors for a physical process, one or more output responses for the process, and criteria. For each of the one or more input factors, a calculated range of input values within the corresponding experimented range of input values is calculated. A modified range of input values is calculated for each of the one or more input factors. A design space estimate is predicted based at least on the modified ranges of input values, wherein the modified ranges of input values each comprise a largest region of variability for one or more of the input factors where the criteria are fulfilled.
Owner:SARTORIUS STEDIM DATA ANALYTICS AB
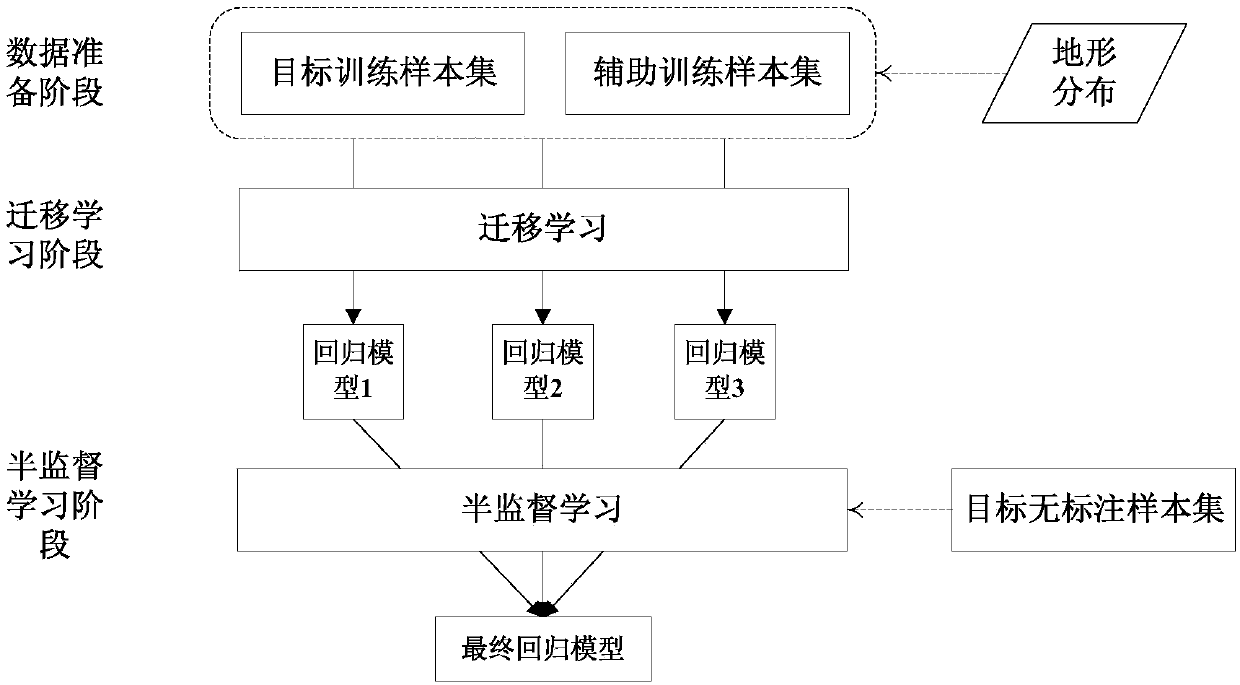
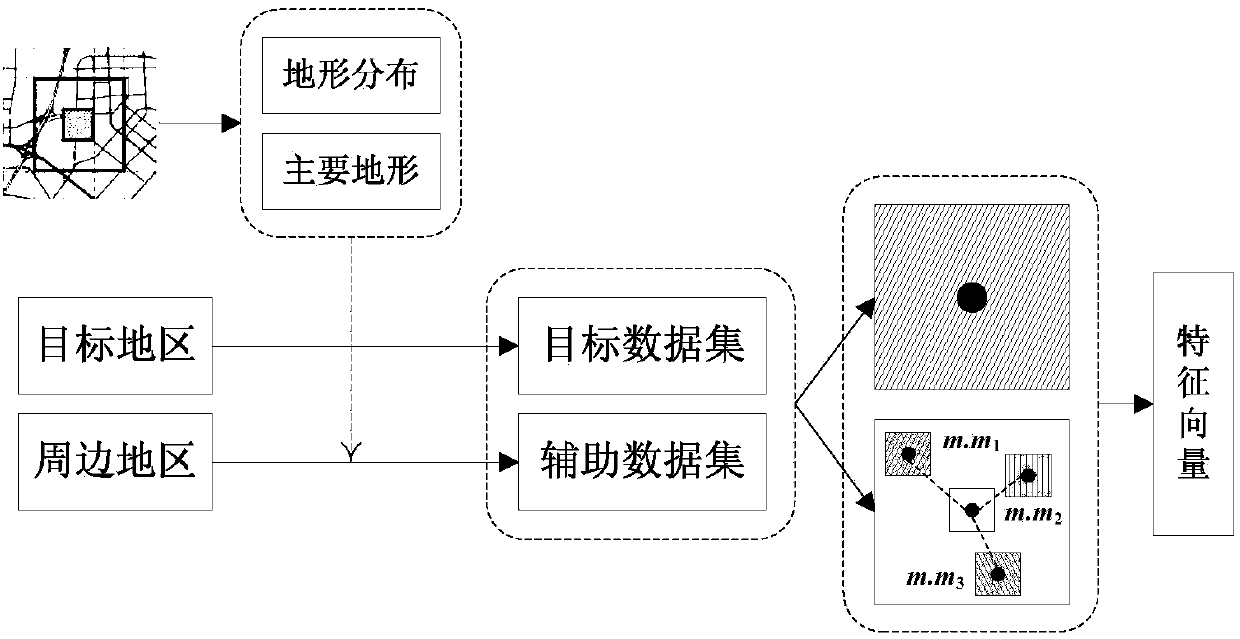
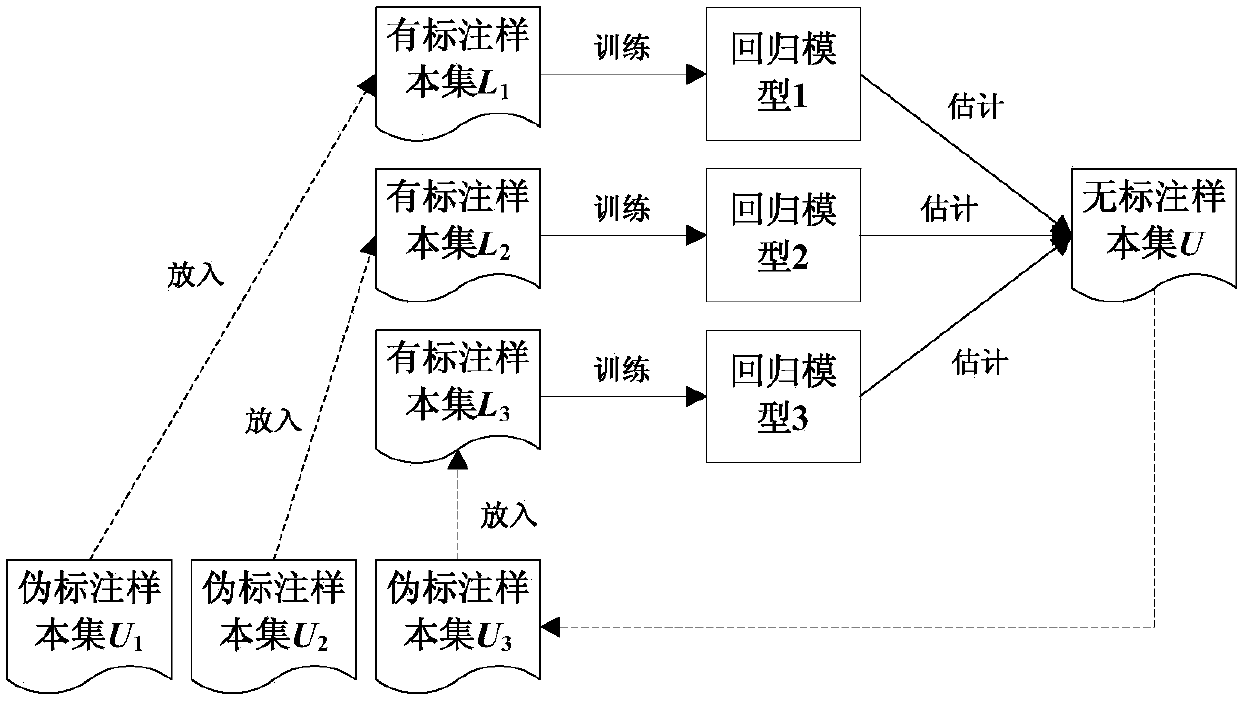
Transfer and semi-supervised learning-based spatial estimation method for air quality index of non-city region
ActiveCN108509565AEfficient use ofComputing modelsSpecial data processing applicationsSpatial estimationSupervised learning
The invention discloses a transfer and semi-supervised learning-based spatial estimation method for an air quality index of a non-city region. The method comprises the following steps of (1) based onterrain distribution and air quality monitoring station deployment situations, looking for an auxiliary region around a target region, and constructing an auxiliary sample set; (2) based on a transferlearning technology, and in combination with a tagged sample set of the target region and the auxiliary sample set, training multiple regression models; and (3) based on a semi-supervised learning technology, and by utilizing an untagged sample set of the target region, enhancing and fusing the multiple regression models to obtain a final air quality index spatial estimation model. The method isbased on the transfer and semi-supervised learning technologies, and effectively utilizes tagged data generated by air quality monitoring stations of the non-city region of the auxiliary region and untagged data of the non-city region of the target region, thereby solving the problem that the target region lacks of the air quality monitoring stations deployed in the non-city region.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Voting space-based loop closure detection
A method for detecting a loop closure is described. A device accesses pose information and a three-dimensional map of feature points generated by a visual inertia system of the device. The device splits the pose information into a translational part and a rotational part. The device limits the translational part to two-dimensional coordinates and estimates two-dimensional information of the limited translational part based on an accumulator voting space. The device determines an updated pose of the device based on the estimated two-dimensional information, the rotational part, and the three-dimensional map. The pose information is updated with the updated pose.
Owner:RPX CORP
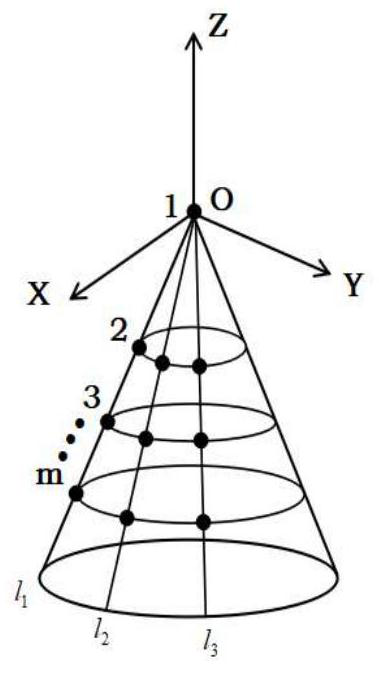
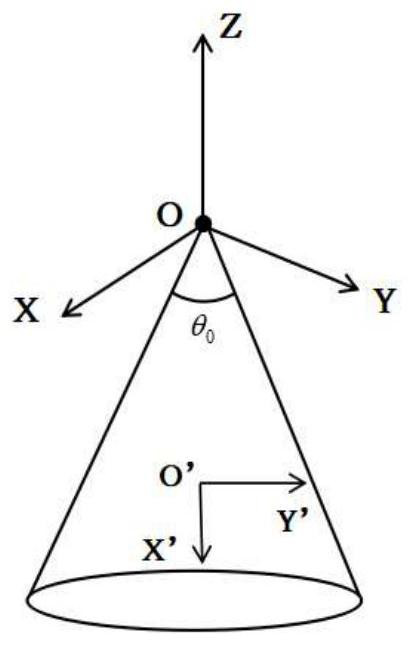
Conical surface conformal array blind polarization direction of arrival estimation method
PendingCN113419209AGuaranteed estimation accuracyReduce complexityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsICT adaptationSpatial estimationData modeling
The invention provides a conical surface conformal array blind polarization direction-of-arrival estimation method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, performing of data modeling on a conical surface conformal array antenna snapshot; and 2, a real-valued blind polarization direction-of-arrival estimation method. According to the new algorithm, the subspace estimation process is subjected to real-valued processing, the problem of mirror image blur caused by covariance matrix splitting is solved through subarray segmentation design, the Cramer-Rao bound of parameter estimation is deduced, and the algorithm complexity is reduced on the premise that DOA estimation precision is guaranteed.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Method and system for parallelizing video compression
ActiveUS9762898B2Improve scalabilityExtended processing timePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionData compression
Video data compression performance is improved through the use of multiple processors operating in parallel. The parallel processors perform motion or spatial estimation, where portions of a video frame are found to be similar to portions in reference frames. Because this estimation operation can be very time consuming, the use of multiple processors can reduce the overall time required, or they can enable higher-performing algorithms that might otherwise require a prohibitively long processing time. The motion or spatial estimation results are applied to reconstructed versions of the video frame data to enable high levels of video data compression.
Owner:COMPRESSION LABS
Voting space-based loop closure detection
A method for detecting a loop closure is described. A device accesses pose information and a three-dimensional map of feature points generated by a visual inertia system of the device. The device splits the pose information into a translational part and a rotational part. The device limits the translational part to two-dimensional coordinates and estimates two-dimensional information of the limited translational part based on an accumulator voting space. The device determines an updated pose of the device based on the estimated two-dimensional information, the rotational part, and the three-dimensional map. The pose information is updated with the updated pose.
Owner:RPX CORP
Methods and apparatus for automated predictive design space estimation
Described are computer-based methods and apparatuses, including computer program products, for automated predictive design space estimation. A design space of input factors and output responses is estimated for a physical process. Data is received for one or more input factors for a physical process, one or more output responses for the process, and criteria. For each of the one or more input factors, a calculated range of input values within the corresponding experimented range of input values is calculated. A modified range of input values is calculated for each of the one or more input factors. A design space estimate is predicted based at least on the modified ranges of input values, wherein the modified ranges of input values each comprise a largest region of variability for one or more of the input factors where the criteria are fulfilled.
Owner:SARTORIUS STEDIM DATA ANALYTICS AB
Rapid MUSIC spectrum decomposition method, device and equipment for large-scale antenna
PendingCN111859272AQuick estimateAccuracy is not affectedWave based measurement systemsComplex mathematical operationsComputation complexitySpatial estimation
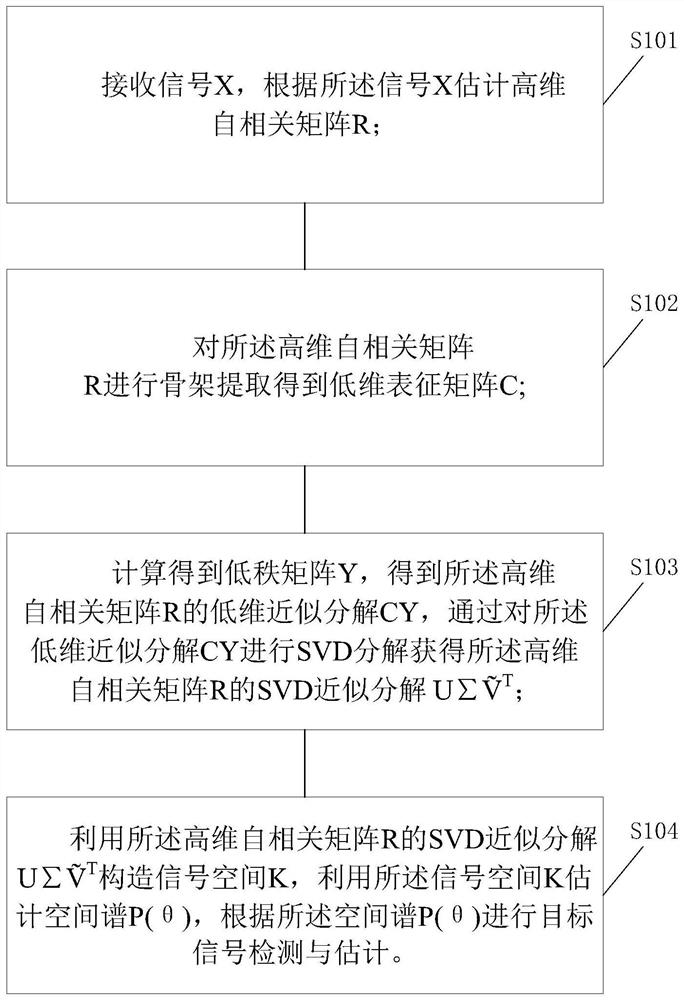
The invention discloses a rapid MUSIC spectrum decomposition method, device and equipment for a large-scale antenna, and the method comprises the steps: receiving a signal X, and estimating a high-dimensional autocorrelation matrix R according to the signal X; performing skeleton extraction on the high-dimensional autocorrelation matrix R to obtain a low-dimensional representation matrix C; calculating to obtain a low-rank matrix Y and obtaining a low-dimensional approximate decomposition CY of the high-dimensional autocorrelation matrix R; obtaining an SVD approximate decomposition (shown inthe description) of the high-dimensional autocorrelation matrix R is obtained by conducting SVD decomposition on the low-dimensional approximate decomposition CY; constructing a signal space K by means of the SVD approximate decomposition (shown in the description) of the high-dimensional autocorrelation matrix R, estimating a spatial spectrum P (theta) by means of the signal space K, and conducting target signal detection and estimation according to the spatial spectrum P (theta). According to the invention, while estimating the MUSIC spatial spectrum accurately, the calculation complexity ofSVD is reduced from cubic growth to square and even linear growth rate, high-precision and low-complexity MUSIC spatial spectrum estimation is realized, matrix norm minimization is used as an optimization criterion, and the approximate error precision of a high-dimensional autocorrelation matrix is ensured.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
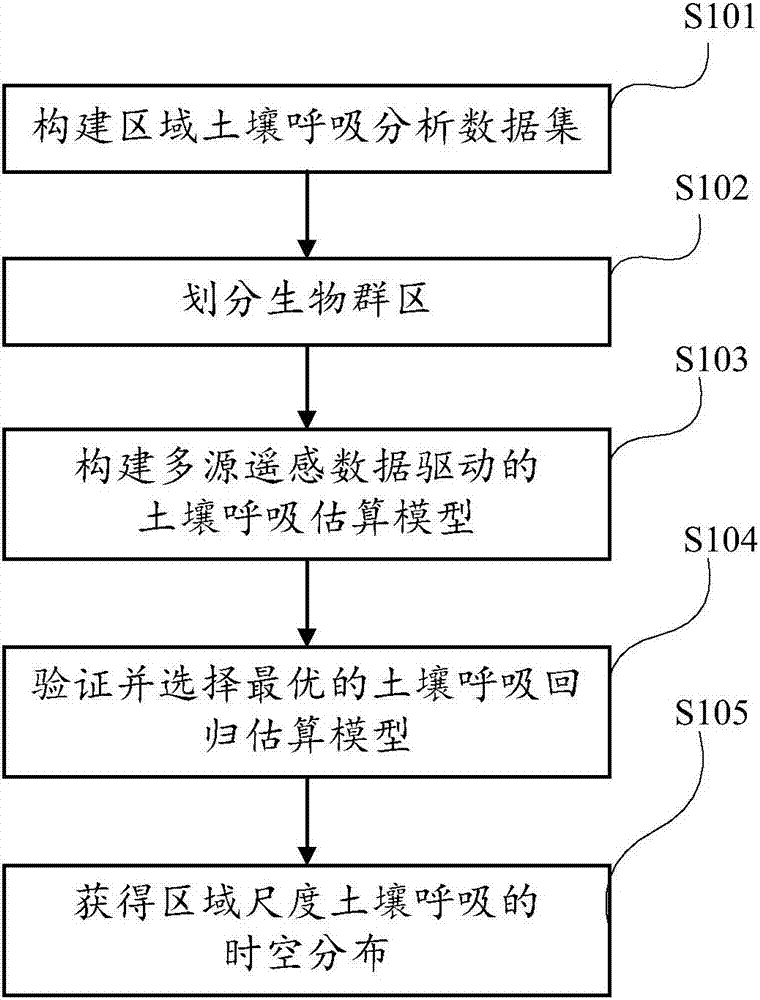
Estimation method for soil respiration on basis of remote sensing data
The invention discloses an estimation method for soil respiration on basis of remote sensing data. According to the estimation method, spatial estimation accuracy of the soil respiration on large-area scale can be improved and the uncertainty of a soil respiration space is reduced. The estimation method comprises the following steps: constructing a regional soil respiration analysis data set; dividing biomes; constructing a soil respiration estimation model driven by multi-source remote sensing data; verifying and selecting an optimal soil respiration estimation model, so as to obtain regional-scale spatial-temporal distribution of the soil respiration by using spatial remote sensing data as driving data.
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION RES INST CAS
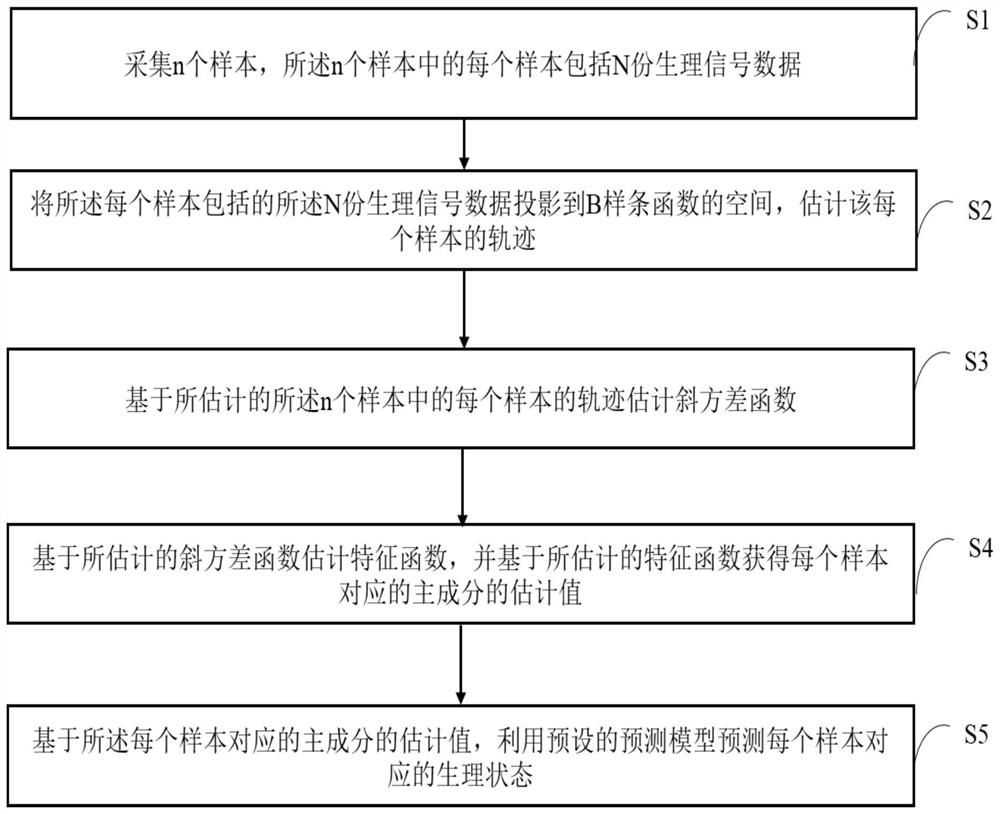
Physiological state prediction method, computer device and storage medium
ActiveCN112837816ASimplify the computational burdenImprove accuracyHealth-index calculationForecastingState predictionSpatial estimation
The invention provides a physiological state prediction method, which comprises the following steps that: collecting n samples, wherein each sample in the n samples comprises N parts of physiological signal data; projecting the N parts of physiological signal data included in each sample to a space of a B-spline function, and estimating a track of each sample; estimating a slope variance function based on the estimated trajectory of each of the n samples; estimating a characteristic function based on the estimated oblique variance function, and obtaining an estimated value of a principal component corresponding to each sample based on the estimated characteristic function; and based on the estimated value of the principal component corresponding to each sample, utilizing a preset prediction model to predict the physiological state corresponding to each sample. The invention further provides a computer device and a storage medium for implementing the physiological state prediction method. The method can improve the prediction accuracy while simplifying the calculation burden.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A method for spatial feature extraction of ionospheric total electron content using conditional generative adversarial network
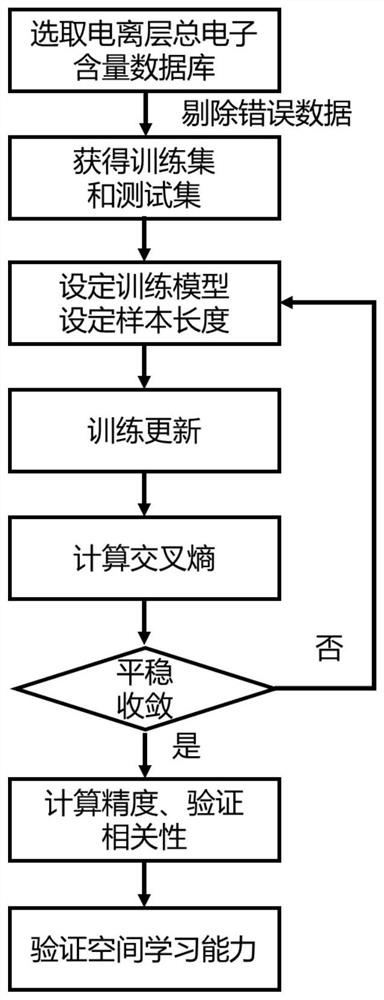
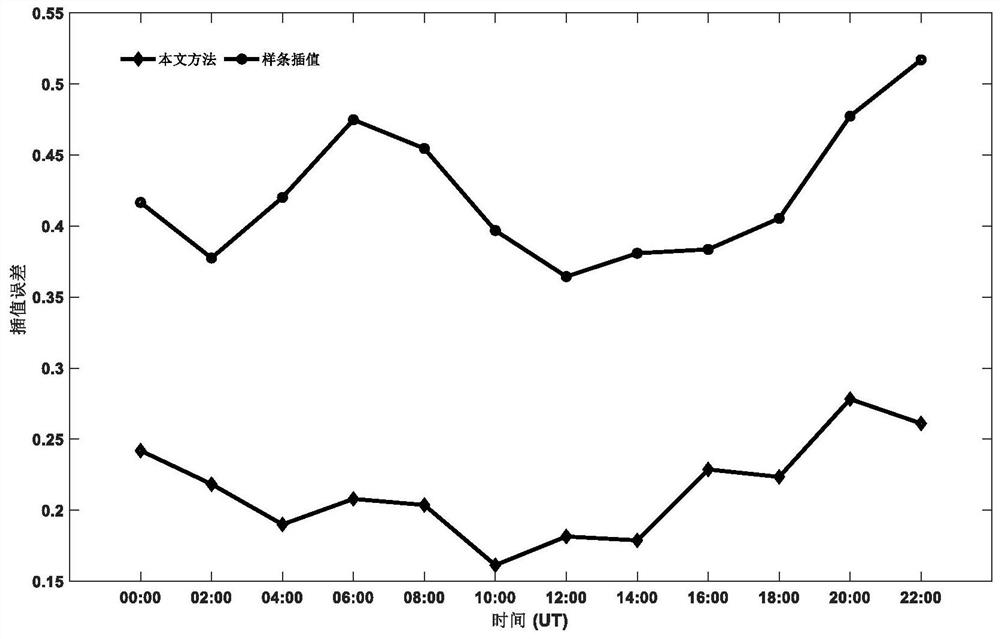
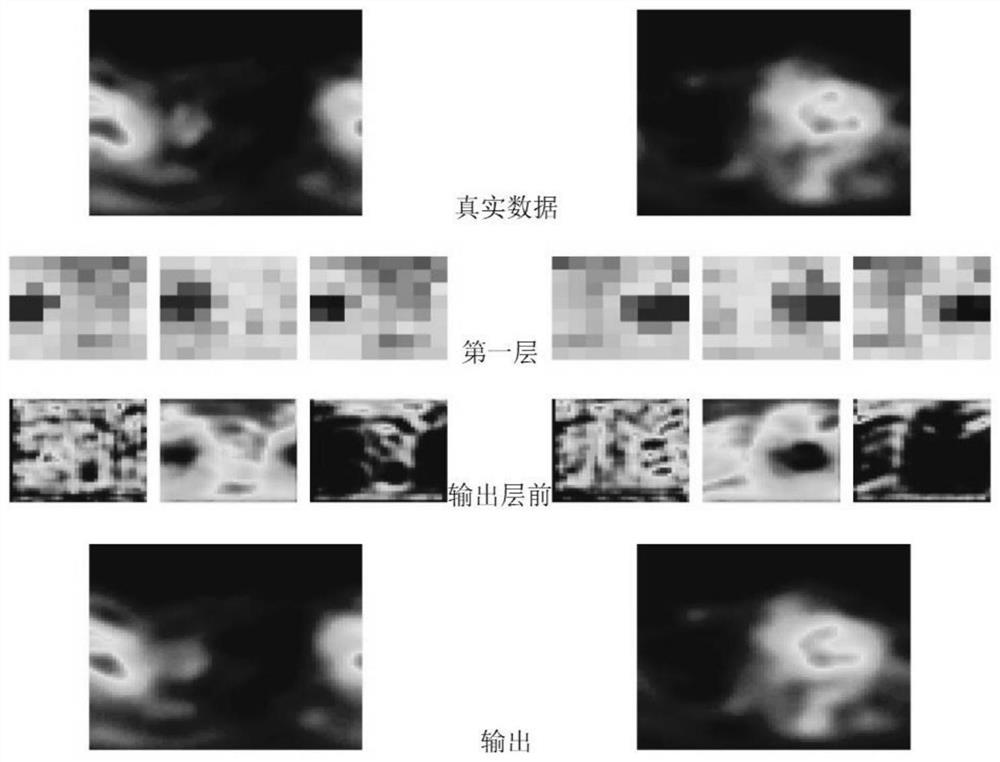
ActiveCN111428746BSpatial distribution characteristics of high ionosphereHigh precision ionospheric spatial distribution characteristicsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsEncoder decoderFeature extraction
The invention discloses a method for realizing spatial feature extraction of ionospheric total electron content by using conditional generative adversarial network. In the method, a deep learning model of conditional encoding and decoding generative adversarial neural network with space considerations is firstly designed. The designed model Incorporating an encoder-decoder structure with the idea of adversarial learning, the deep features of the input ionospheric total electron content sampling spatial data and their complex interactions with local structural patterns can be learned. The validity of the method is proved by the example analysis. Compared with the traditional method, this method successfully completes the extraction and restoration of the spatial characteristics of the ionospheric total electron content when faced with complex ionospheric spatial distribution characteristics, and has higher accuracy in realizing the spatial estimation of the ionospheric total electron content and a smaller mean square error.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
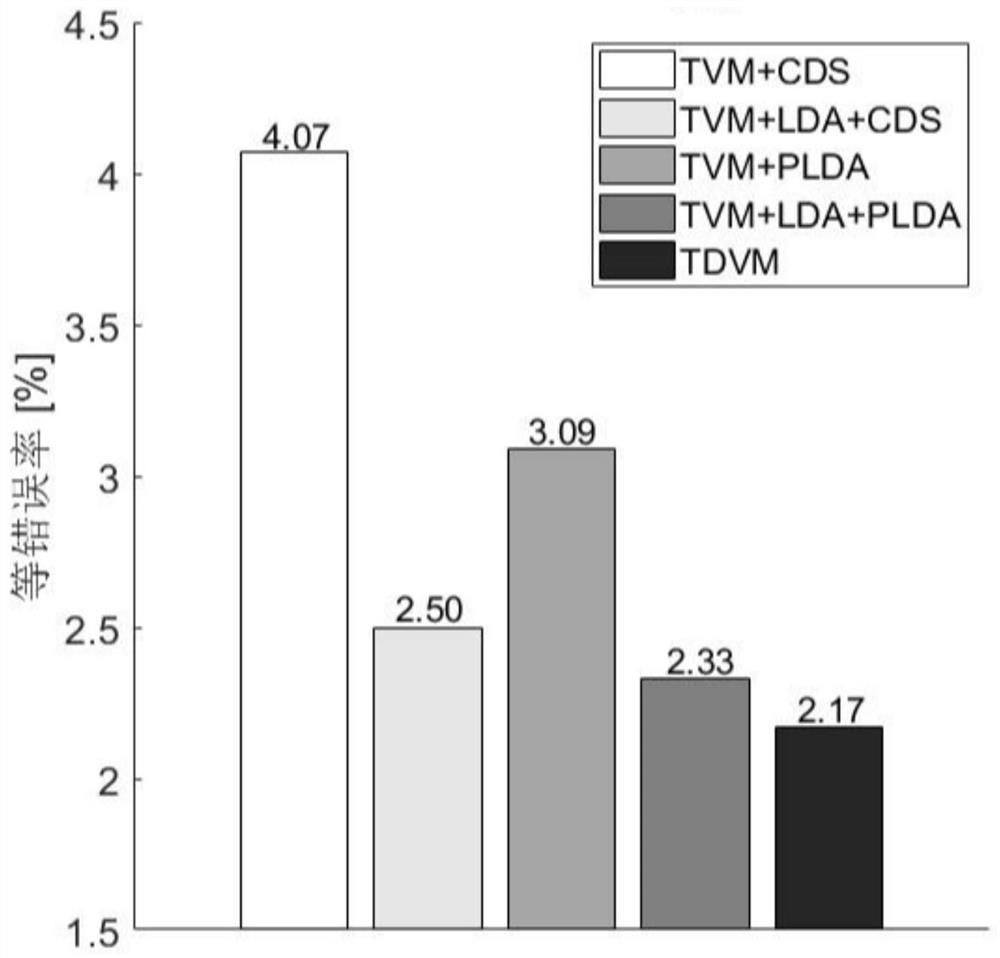
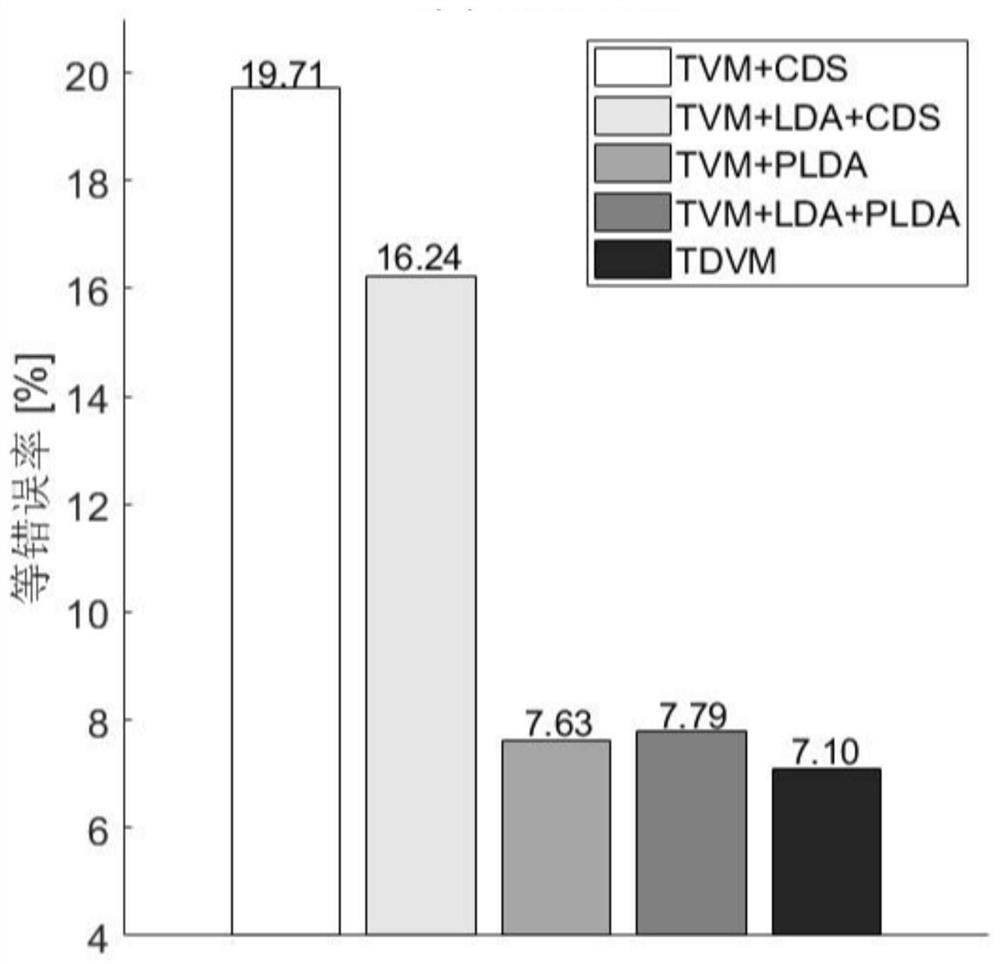
Speaker identification method based on joint optimization of total variation space and classifier
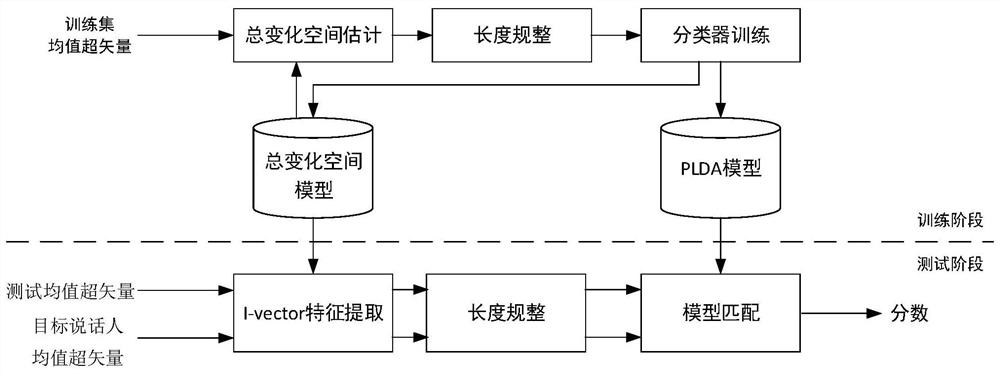
ActiveCN110148417BImprove performanceReduce error rateSpeech analysisSpatial estimationIdentity recognition
The invention discloses a speaker identity recognition method based on combined optimization of a total change space and a classifier, and belongs to the technical field of speaker identity recognition. The speaker identity recognition method solves the problem that a current total change space estimation method is high in equal error rate for speaker identity recognition. The speaker identity recognition method comprises the steps that firstly, the representation of a training set mean value hyper vector in an initial total change space is obtained; then the length of the representation is normalized and input to the classifier PLDA; then, under the supervision of the classifier PLDA, the parameters of the classifier and parameters of the total change space are updated, the steps are repeated until the set maximum number of iterations is reached, and the final classifier parameters and the total change space parameters are obtained; and during the test, the mean hyper vector of a testspeech and the mean hyper vector of a target speaker are used for calculating the representation of the mean hyper vectors in the total change space, then the length of the representation is normalized, and the joint probability density of the mean hyper vectors on the classifier is calculated as the basis for final classification. The speaker identity recognition method can be applied to the technical field of speaker identification.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
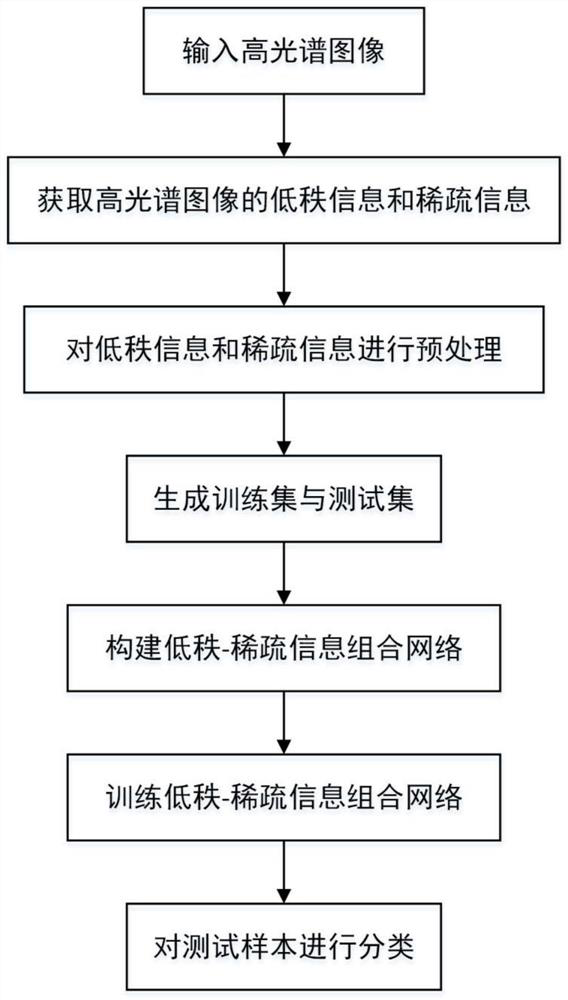
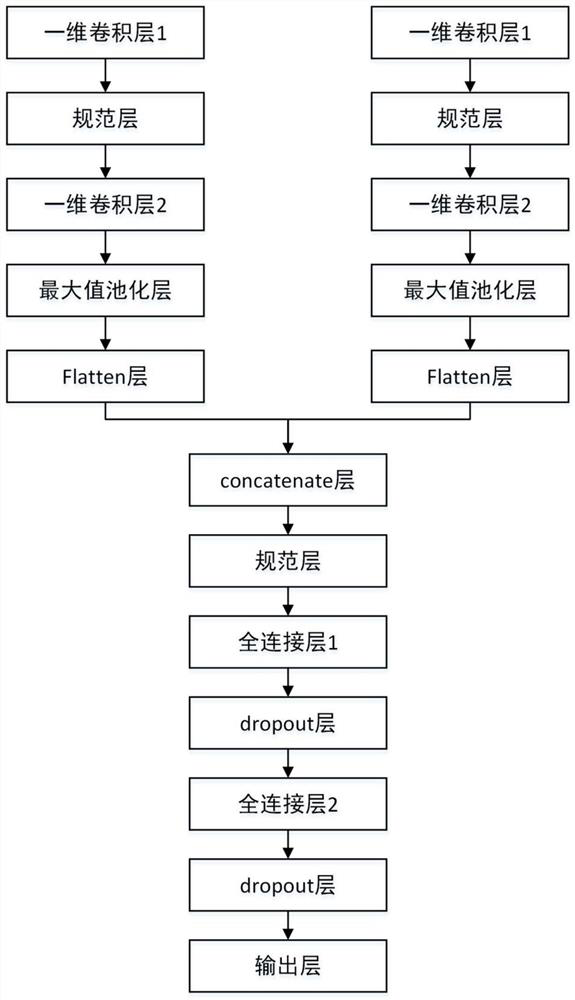
Hyperspectral Image Classification Method Based on Low Rank-Sparse Information Combination Network
ActiveCN109460788BHigh precisionOvercoming low-rank recovery classification methodsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial estimationTest sample
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on a low-rank-sparse information combination network, the implementation steps of which are: (1) inputting hyperspectral images; (2) obtaining low-rank information and sparse information of hyperspectral images; 3) Preprocess low-rank information and sparse information; (4) generate training set and test set; (5) construct low-rank-sparse information combination network; (6) train low-rank-sparse information combination network; (7) Classify the test samples. The invention can effectively solve the problem that the traditional low-rank recovery classification algorithm has a classification accuracy drop caused by inaccurate low-rank subspace estimation, avoids complex low-rank recovery operations, and can maintain a small number of samples while achieving high classification accuracy. recognition ability and stable classification performance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Electronic video image stabilization device and method
This disclosure describes electronic video image stabilization techniques for imaging and video devices. The techniques involve determining motion and spatial statistics for individual macroblocks of a frame, and determining a global motion vector for the frame based on the statistics of each of the macroblocks. In one embodiment, a method of performing electronic image stabilization includes performing spatial estimation on each of a plurality of macroblocks within a frame of an image to obtain spatial statistics for each of the macroblocks, performing motion estimation on each of the plurality of macroblocks to obtain motion statistics for each of the macroblocks, integrating the spatial statistics and the motion statistics of each of the macroblocks to determine a global motion vector for the frame, and offsetting the image with respect to a reference window according to the global motion vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
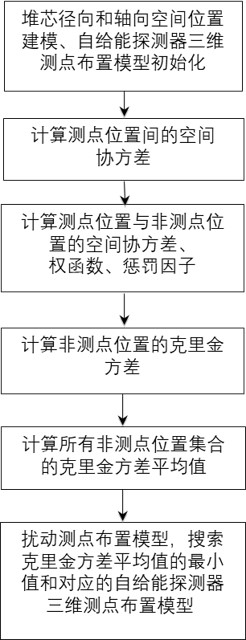
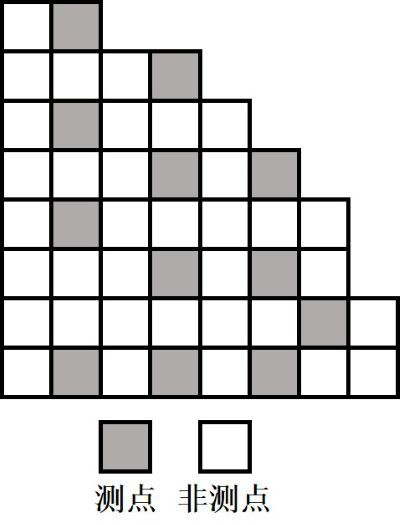
Self-powered detector three-dimensional measuring point arrangement optimization method based on Kriging model
ActiveCN114722646AImprove stabilityGood modelingNuclear energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationNuclear reactorSpatial estimation
The invention discloses a self-powered detector three-dimensional measuring point arrangement optimization method based on a Kriging model, and the method comprises the steps: considering the influence of a self-powered detector measuring point position set in a nuclear reactor monitoring system on a spatial estimation value of a non-measuring point position, and calculating a spatial covariance between specific positions of the monitoring system; calculating a weight function, a penalty factor and a Kriging variance of a non-measuring point position according to the spatial covariance; on the basis of a simulated annealing process, searching a minimum value which takes a Kriging variance average value of a non-measuring-point position set as an objective function, and optimizing an arrangement scheme of the self-powered detector according to the minimum value; the measuring point arrangement optimization method can effectively reduce uncertainty of estimated parameters, is high in universality, is suitable for various nuclear reactor monitoring systems, can be used for evaluating a current self-powered detector measuring point arrangement scheme and recommending measuring point optimization design, and provides a new method for reactor core design of the self-powered detector.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
An audio localization method based on emission angle estimation
ActiveCN113099405BReduce time synchronization requirementsAvoid interferenceParticular environment based servicesSound sourcesSpatial estimation
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Single-base FDA-MIMO radar distance angle joint estimation method based on real value order reduction
PendingCN114545349AImprove estimation performanceReduce computational complexityWave based measurement systemsComputation complexitySpatial estimation
The invention relates to a monostatic FDA-MIMO radar distance angle joint estimation method based on real value order reduction, and belongs to the technical field of FDA-MIMO radar research. On the basis of a real value order reduction method, a complex value receiving model is converted into a real value receiving model by utilizing forward and reverse average and unitary transformation technologies, original complex operation is converted into real value operation, the calculation complexity is reduced compared with other methods, then a covariance matrix of a real value receiving signal is calculated according to a maximum likelihood estimation criterion, and the real value receiving signal is obtained. And carrying out eigenvalue decomposition on the real-value covariance matrix by adopting EVD, selecting eigenvectors corresponding to smaller eigenvalues to form a real-value noise subspace, and estimating the angle and the distance by utilizing the real-value noise subspace. According to the angle and distance estimation method, the two-dimensional search cost function of the angle and the distance is decomposed into two one-dimensional searches by using the property of the Kronecker product, and the calculation amount is greatly reduced on the premise of ensuring the search precision.
Owner:SOUTH WEST INST OF TECHN PHYSICS
A Multiple Signal Classification Method Based on Sigmoid Covariance Matrix
The invention belongs to the technical field of array signal processing and provides a multiple signal classification method based on a Sigmoid covariance matrix. This method has a strong ability to suppress impulsive noise that obeys non-Gaussian distribution, and can realize multiple signal classification under the impulsive noise condition, and estimate the direction of arrival of each signal; including: 1) According to the noise-containing The median of the signal amplitude estimates the parameters of the Sigmoid function; 2) uses the Sigmoid function and the output vector of the uniform linear array to estimate the Sigmoid covariance matrix output by the array; 3) performs eigenvalue decomposition on the Sigmoid covariance matrix to obtain the noise sub- Space estimation: use the noise subspace to estimate the spatial spectrum for multiple signal classification, and use the estimated value of the spatial spectrum to estimate the direction of arrival angle. The algorithm of the invention has good performance and has good application prospect in real engineering applications.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
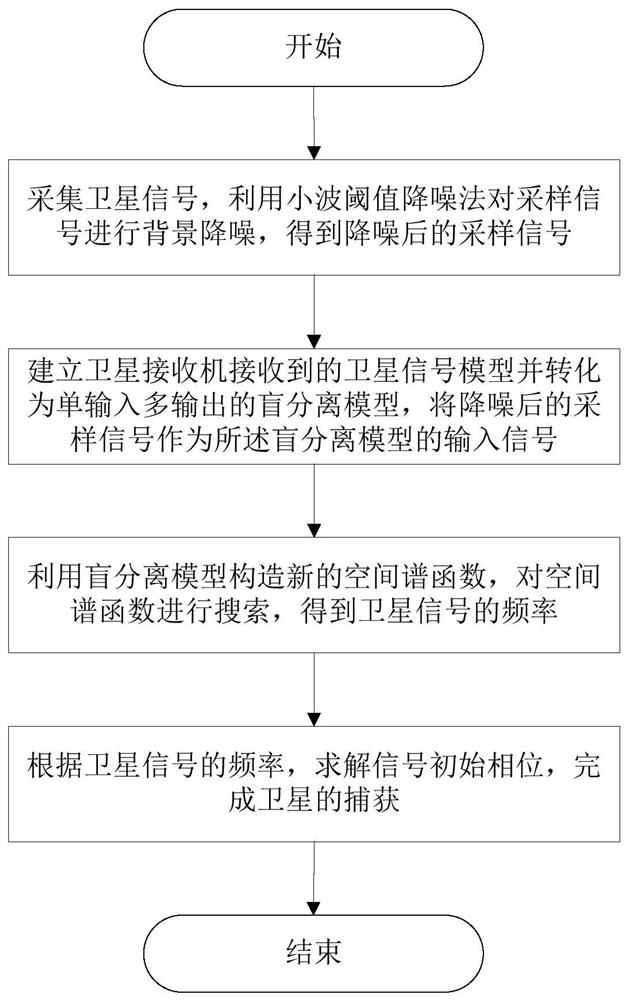
A High-precision Blind Acquisition Method of Beidou Satellite Signal Based on Wavelet Transform
ActiveCN109975842BImprove noise immunityImprove performanceSatellite radio beaconingSpatial estimationWavelet thresholding
The invention discloses a Beidou satellite signal high-precision blind capture method based on wavelet transform. The method comprises the steps that S1 a satellite signal is collected, and backgroundnoise reduction is carried out on a sampled signal through a wavelet threshold noise reduction method to acquire a noise-reduced sampled signal; S2 a model is established for the satellite signal received by a satellite receiver, and the model is converted into a single-input and multiple-output blind disjunctive model, and the noise-reduced sampled signal is used as the input signal of the blinddisjunctive model; S3 the blind disjunctive model is used to construct a new spatial spectral function, and the spatial spectral function is searched to acquire the frequency of the satellite signal;and S4 the initial phase of the signal is solved according to the frequency of the satellite signal to complete satellite capture. According to the invention, the blind disjunctive model and the wavelet transform theory are combined; a satellite signal blind separation method based on a subspace estimation algorithm is used to solve the Doppler effect frequency and phase of the Beidou satellite signal; and the method has the advantages of strong anti-noise ability, stable performance and high precision.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
DOA estimation method based on circular array of noise power
InactiveCN106169941AImprove performanceSpatial transmit diversityChannel estimationCommunications systemSpatial estimation
The invention belongs to the wireless communication technology field, especially relates to an algorithm of estimating a signal real sub-space by using noises in a wireless multiple input multiple output (MIMO) communication system. The invention provides a DOA estimation method based on a circular array of noise power. By using a white Gaussian noise invariability characteristic, a sub-space DOA estimation method is changed from a way of purely separating a signal sub-space from a noise sub-space into a way of providing the signal sub-space and the noise sub-space after a separation process by using the existence of the noises, and therefore performance is increased by 50% under a condition of a weak channel by using related theories of a matrix theory.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com