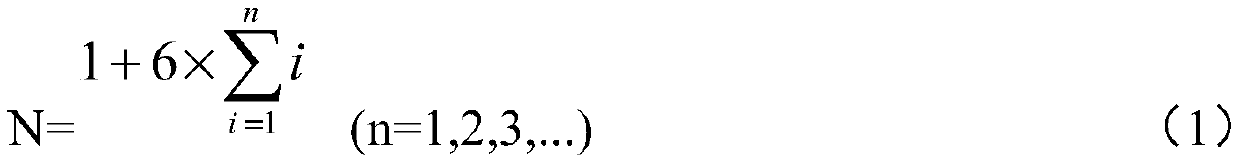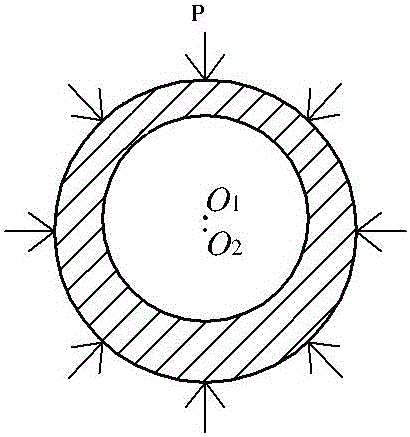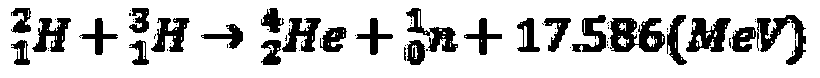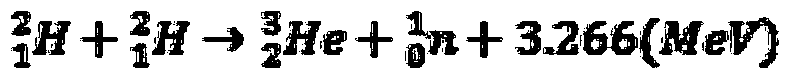Patents
Literature
31 results about "Subcritical reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A subcritical reactor is a nuclear fission reactor concept that produces fission without achieving criticality. Instead of a sustaining chain reaction, a subcritical reactor uses additional neutrons from an outside source. There are two general classes of such devices. One uses neutrons provided by a nuclear fusion machine, a concept known as a fusion-fission hybrid. The other uses neutrons created through spallation of heavy nuclei by charged particles such as protons accelerated by a particle accelerator, a concept known as an accelerator-driven system (ADS) or accelerator-driven sub-critical reactor.
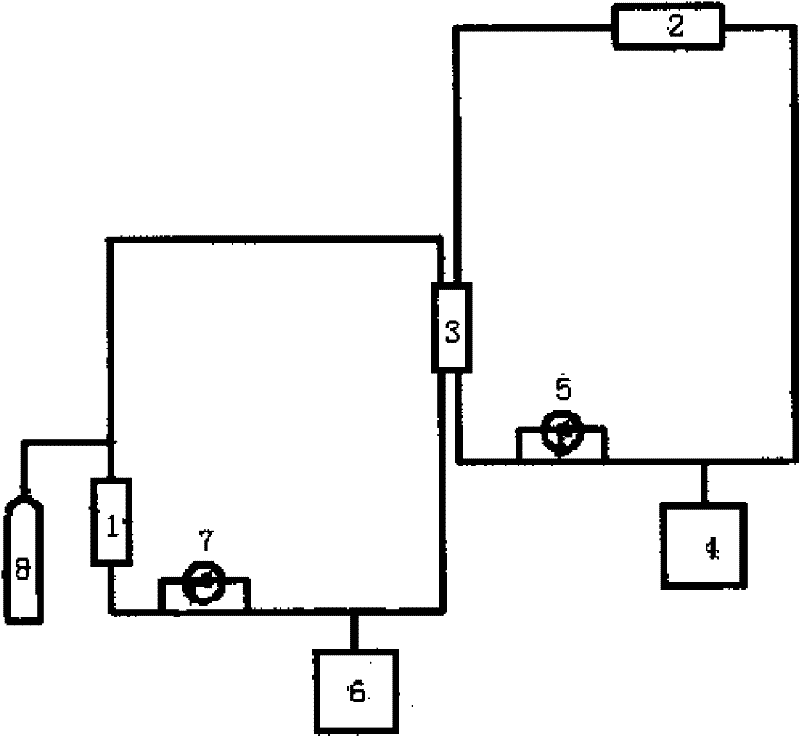
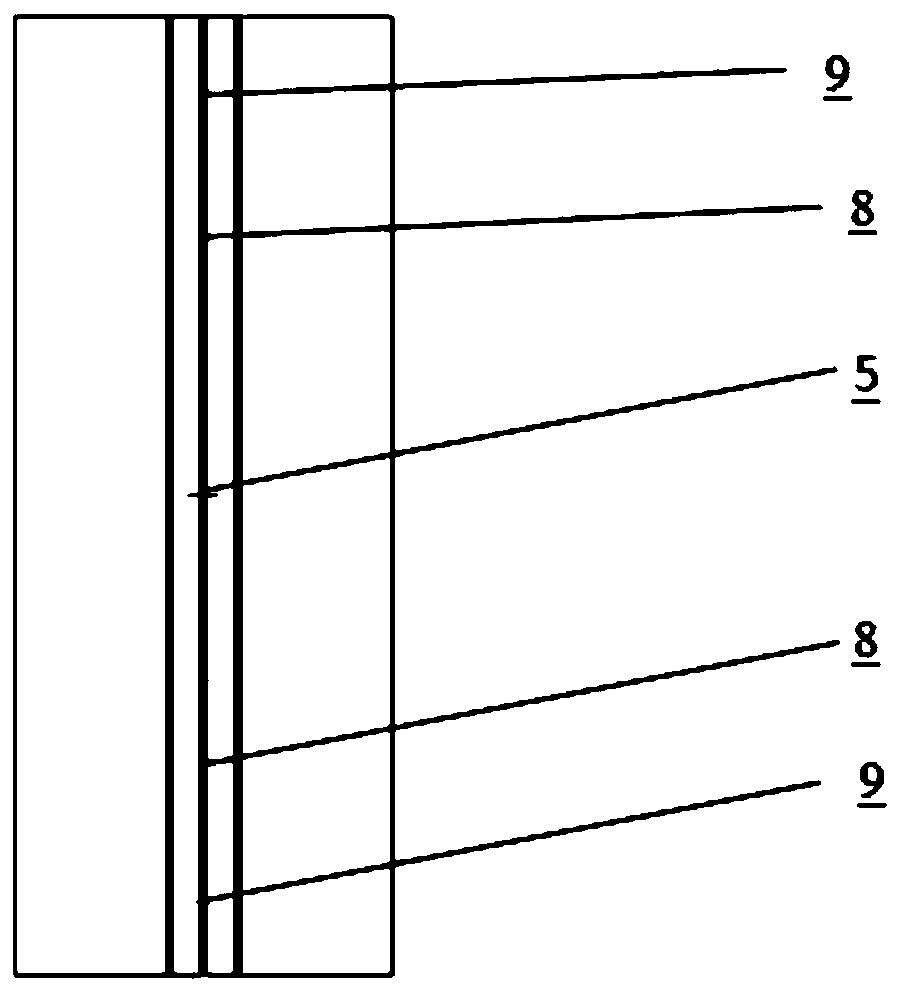
Passive natural-circulation lead bismuth heat exchange device and method for discharging heat out of reactor core
InactiveCN102446564AImprove securityImprove reliabilityNuclear energy generationStationary tubular conduit assembliesLead bismuthNuclear engineering
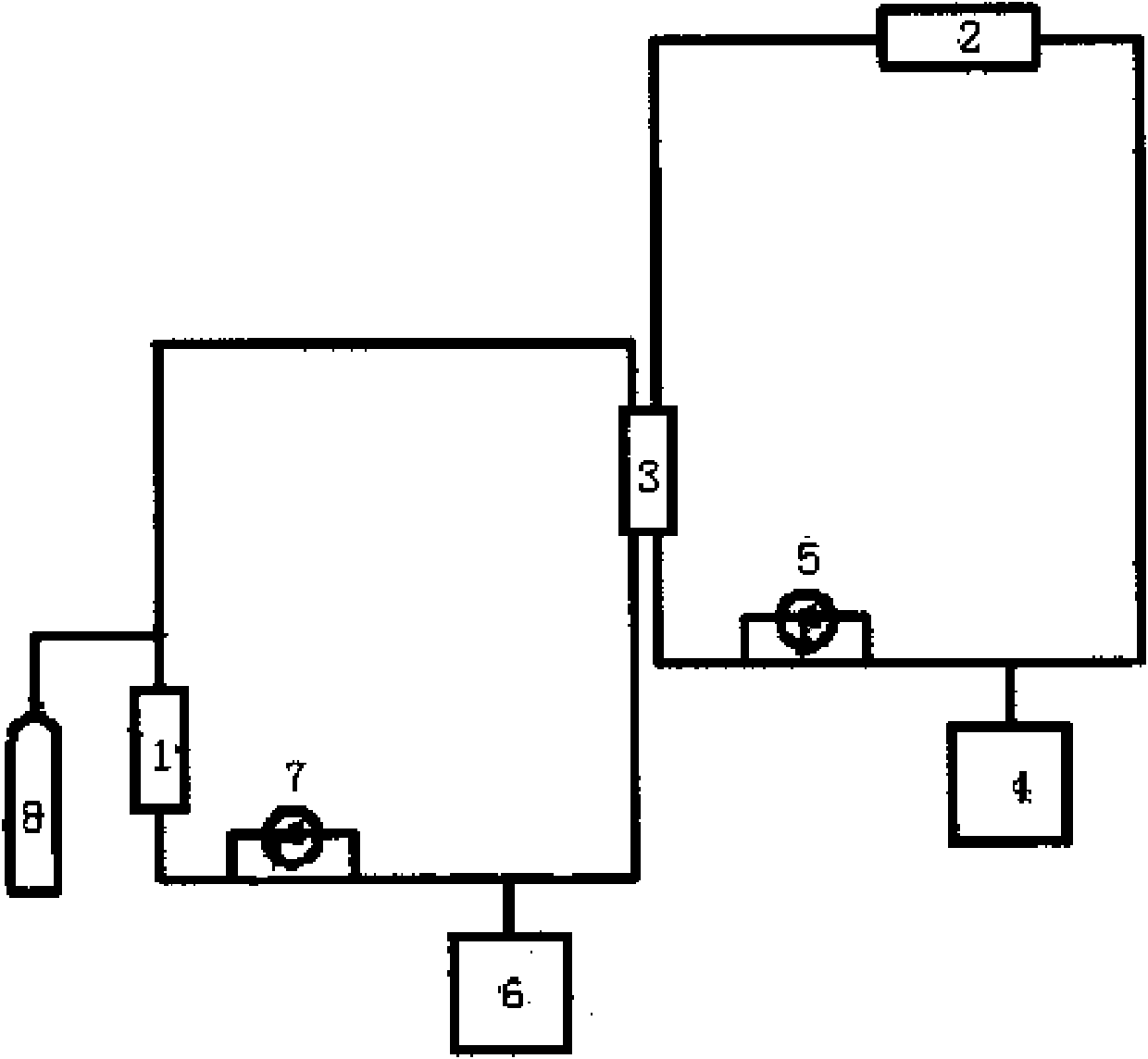
The invention discloses a passive natural-circulation lead bismuth heat exchange device for heat transfer by a lead bismuth fluid and a method for discharging heat out of reactor core, belonging to the field of nuclear energy heat exchange equipment. The heat exchange device particularly comprises two natural-circulation heat transfer loop structures, namely a round loop and a square loop, and is a device which realizes natural-circulation heat transfer at two sides. The inner ring of an inner ring pipe is a primary side lead bismuth alloy fluid passage, and a secondary side fluid passage is arranged between the outer ring of the inner ring pipe and the inner wall of an outer ring pipe. Heat generated by a subcritical reactor of an ADS (accelerator driven system) is transferred to coolants of the two loops by the liquid lead bismuth alloy through the inner ring pipe of the device, the lead bismuth alloy flows through the device to exchange heat with a secondary side fluid. The primary side heat exchange fluid and the secondary side heat exchange fluid form natural circulation under the driving of a density difference, and the high-efficiency, energy-saving, safe and reliable passive characteristic is achieved. The device is simple and easy to operate, is free of a complicated lead bismuth pump, is in no need of a power source and has the characteristics of energy conservation, high safety and high reliability. The passive natural-circulation lead bismuth heat exchange device and the method for discharging heat out of the reactor core comply with the current policy of energy conservation and emission reduction and are easy in market promotion.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
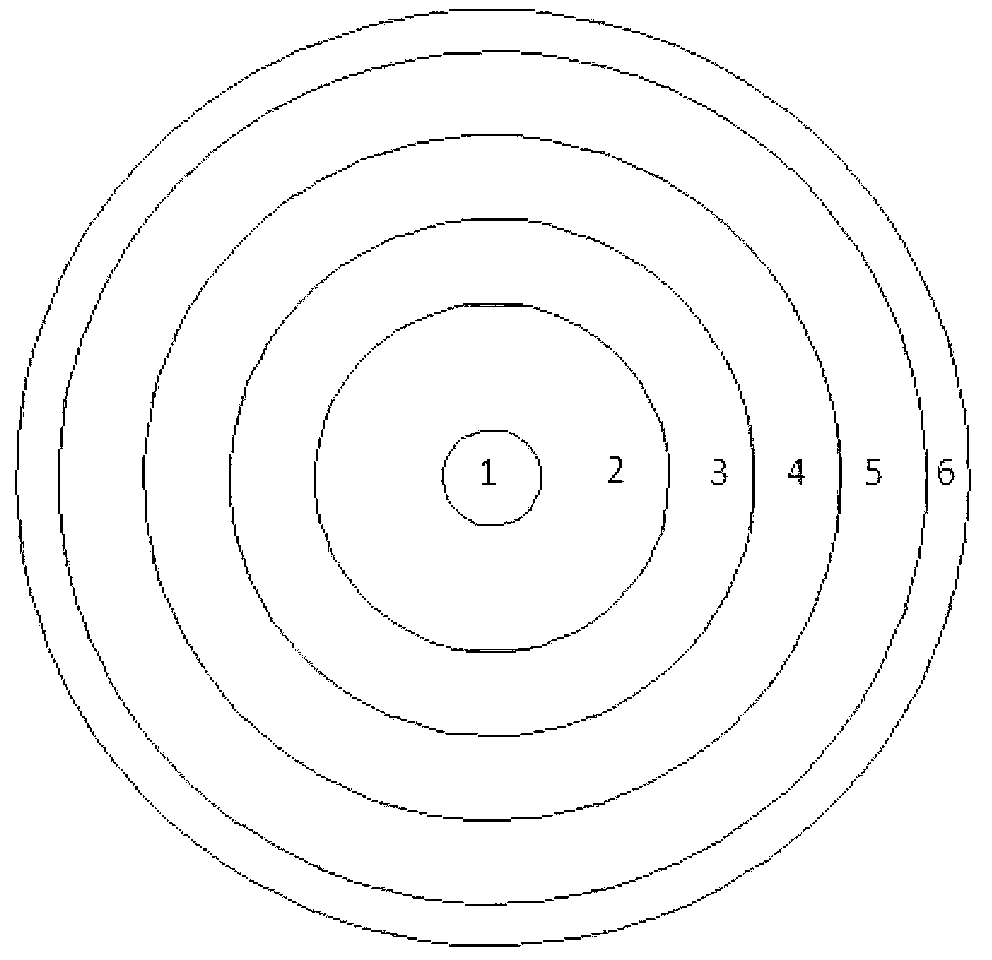
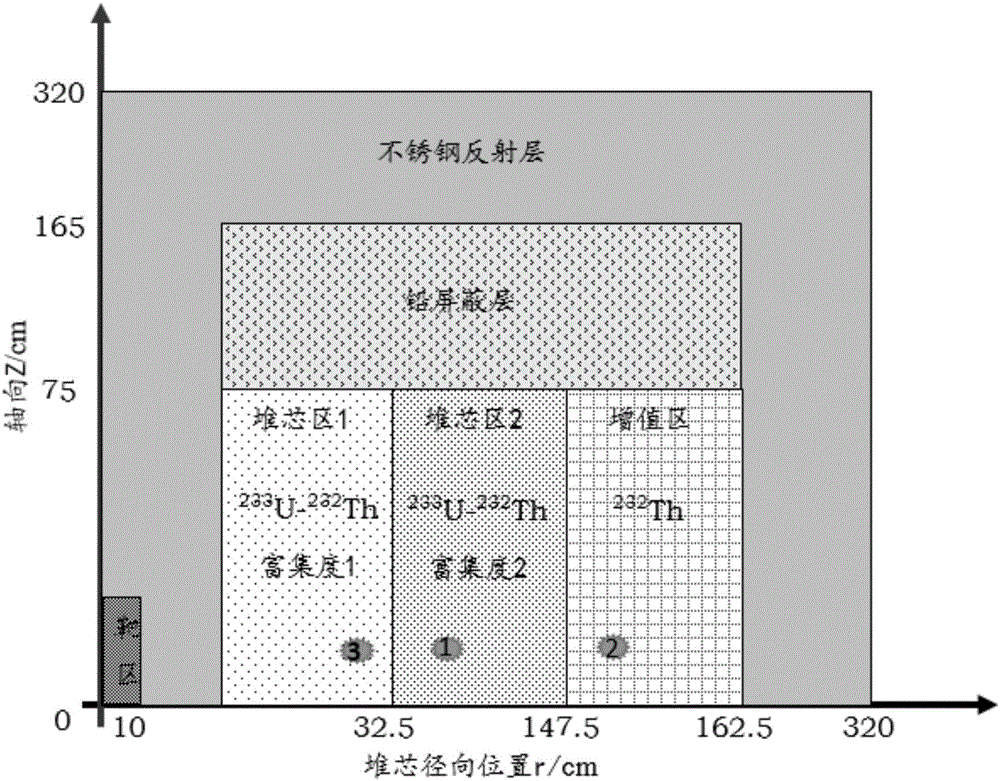
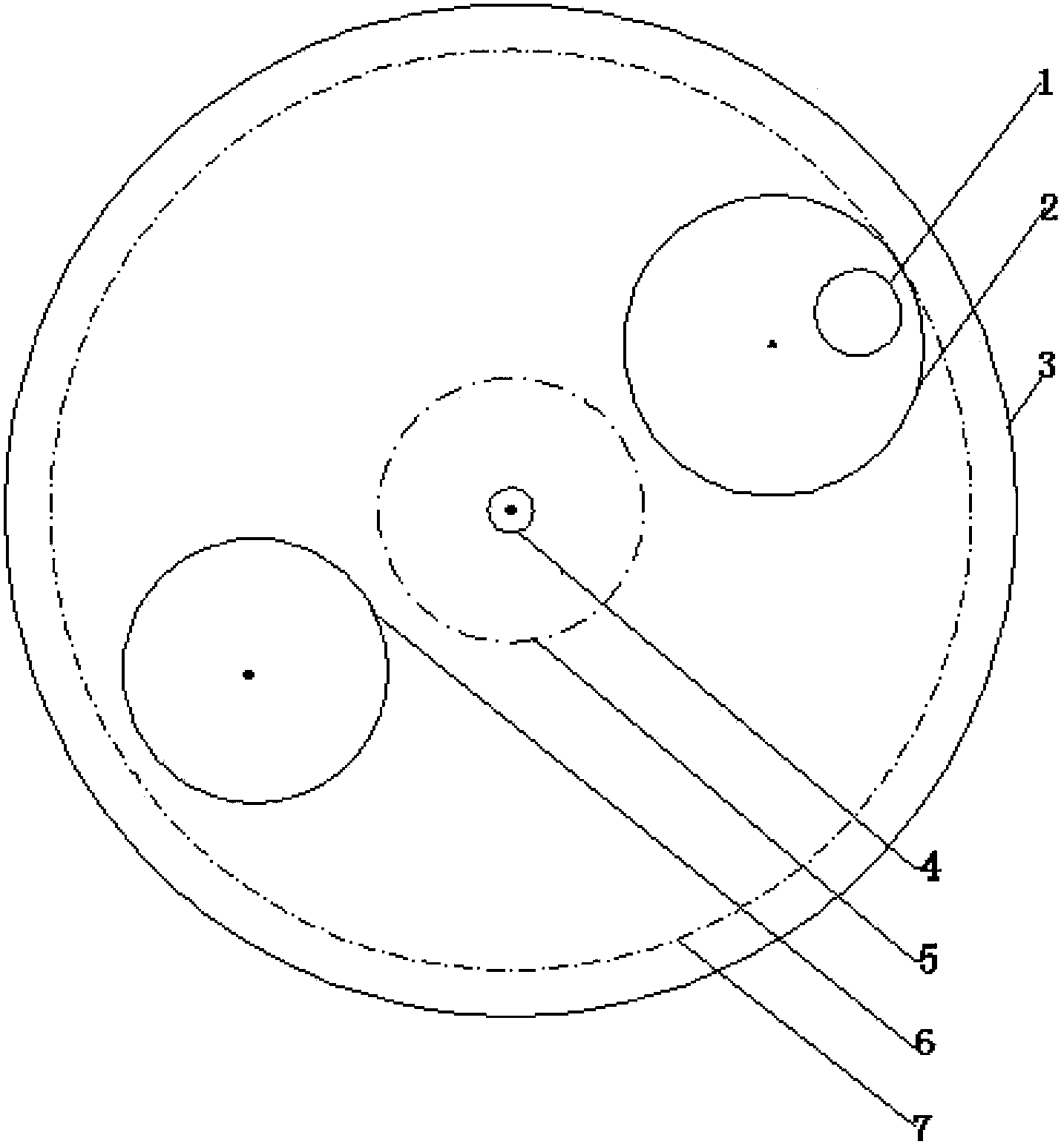
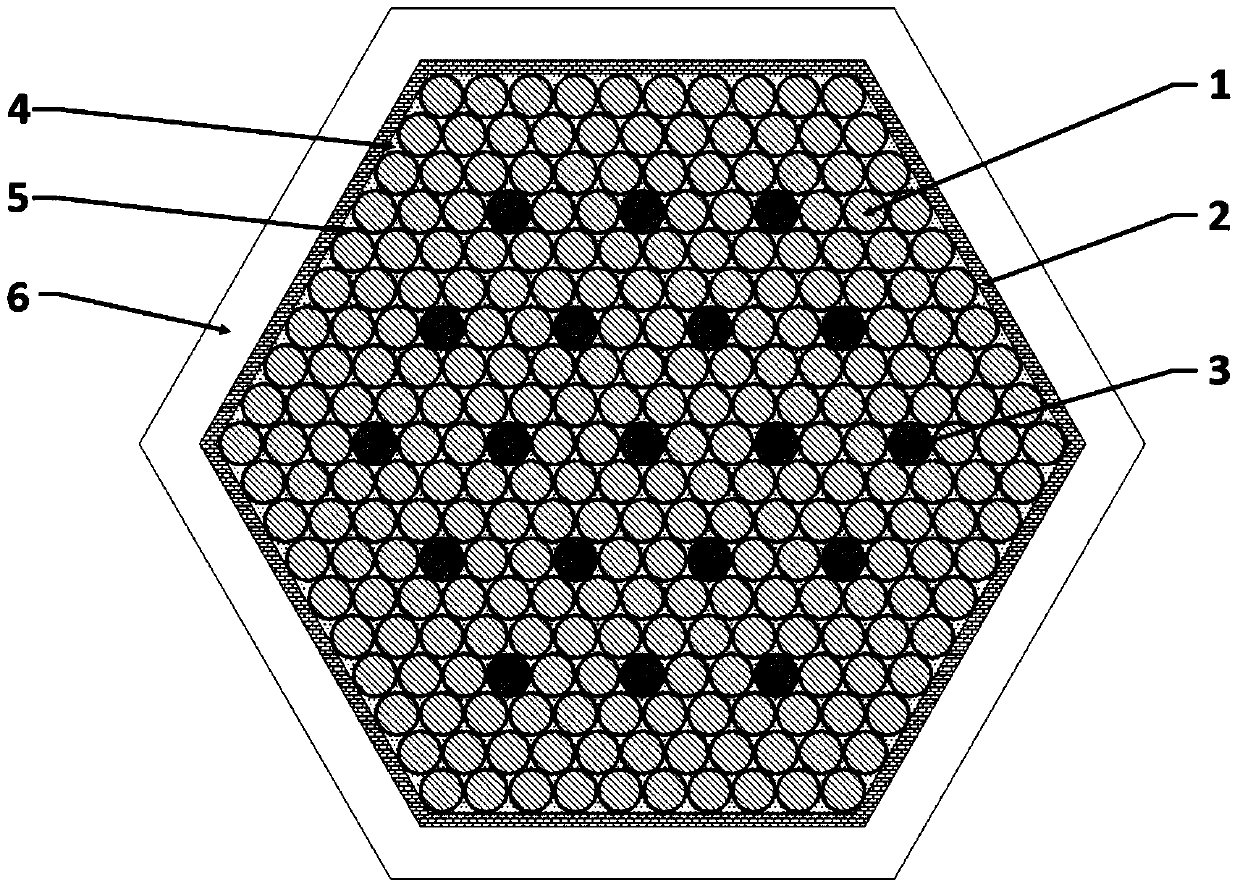
Radial-power-flattened efficient nuclear waste transmutation subcritical core and design method thereof
InactiveCN103077758AEfficient transmutationImprove power generation efficiencyNuclear energy generationReactors manufactureNuclear engineeringSubcritical reactor
The invention relates to a radial-power-flattened efficient nuclear waste transmutation subcritical reactor core and a design method thereof. The reactor core sequentially comprises an outer neutron source region (1), a first transmutation fuel zone (2), a second transmutation fuel zone (3), a third transmutation fuel zone (4), a reflective area (5) and a shielded area (6) from the center outwards. The transmutation fuel zones of the reactor core are arranged in three zones; the reactor core is arranged in a triangular shape, and is subjected to principle design and analysis by analyzing coupled neutronics and thermal-hydraulic principles and using mathematical methods; and aiming at each transmutation zone, specific geometry layer arrangement is performed from inside to outside based on the design principles, so that the power distribution of the transmutation fuel zones can be flattened in the radial direction. The reactor core can utilize fast neutron transmutation TRU (Transuranic) generated by exogenous neutron, is high in neutron utilization, good in radial power flattening, high in power generation efficiency and simple in structure, and has the functions of safety and high efficiency in nuclear waste disposal and economy.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Subcritical degree reverse dynamic measuring method free of space effect
ActiveCN106297920ALow powerIncrease powerNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringInverse dynamicsDelayed neutron
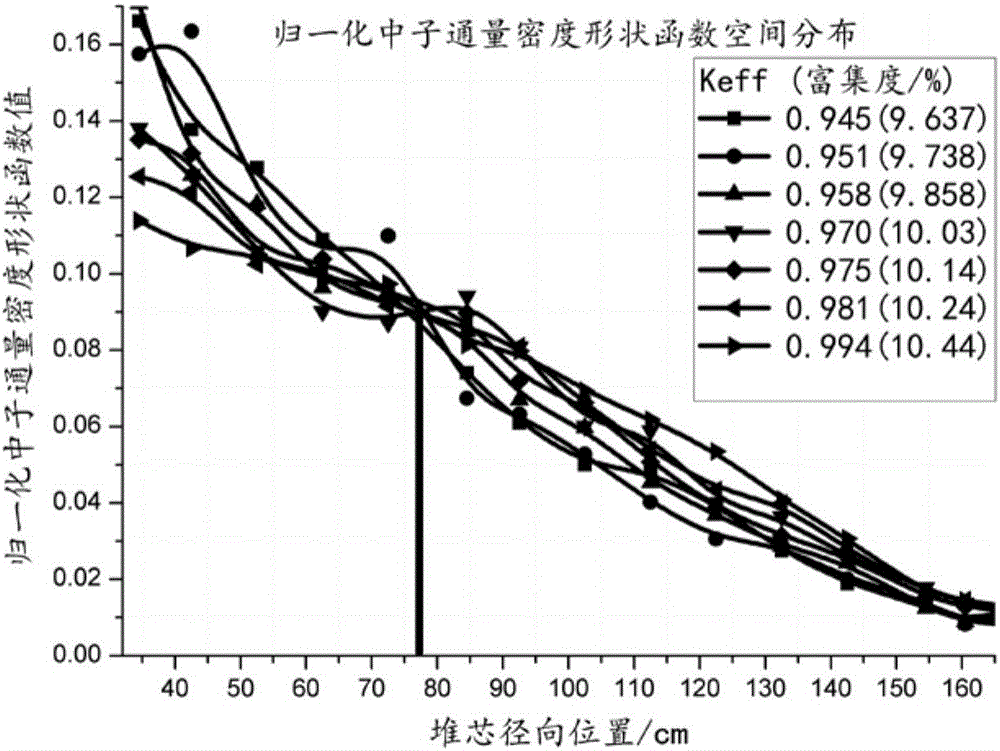
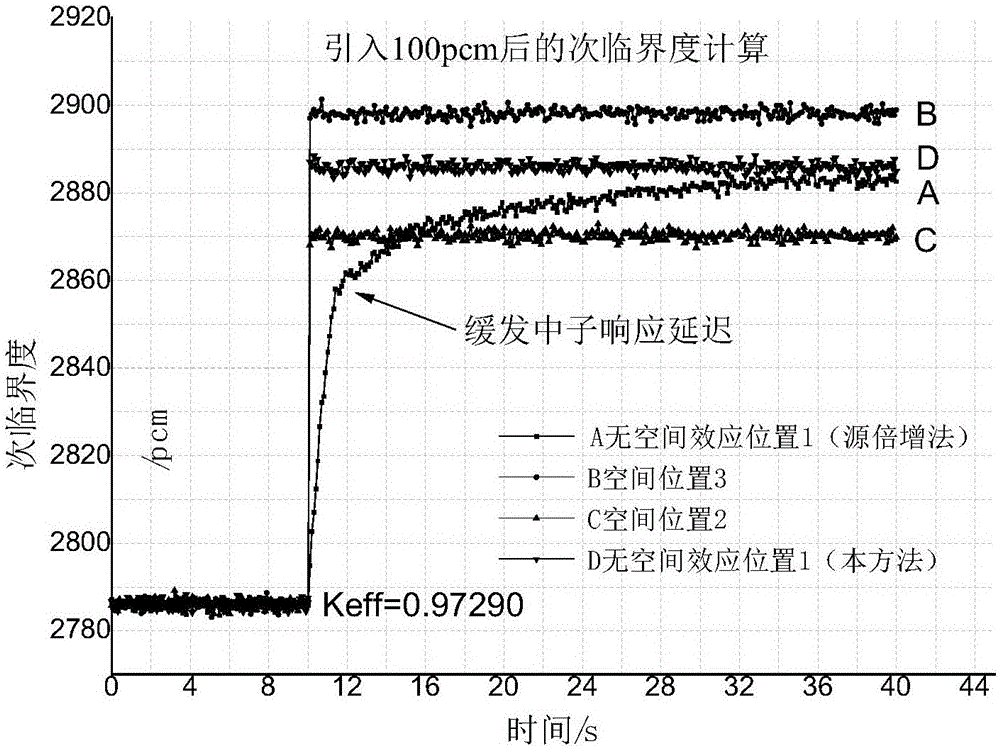
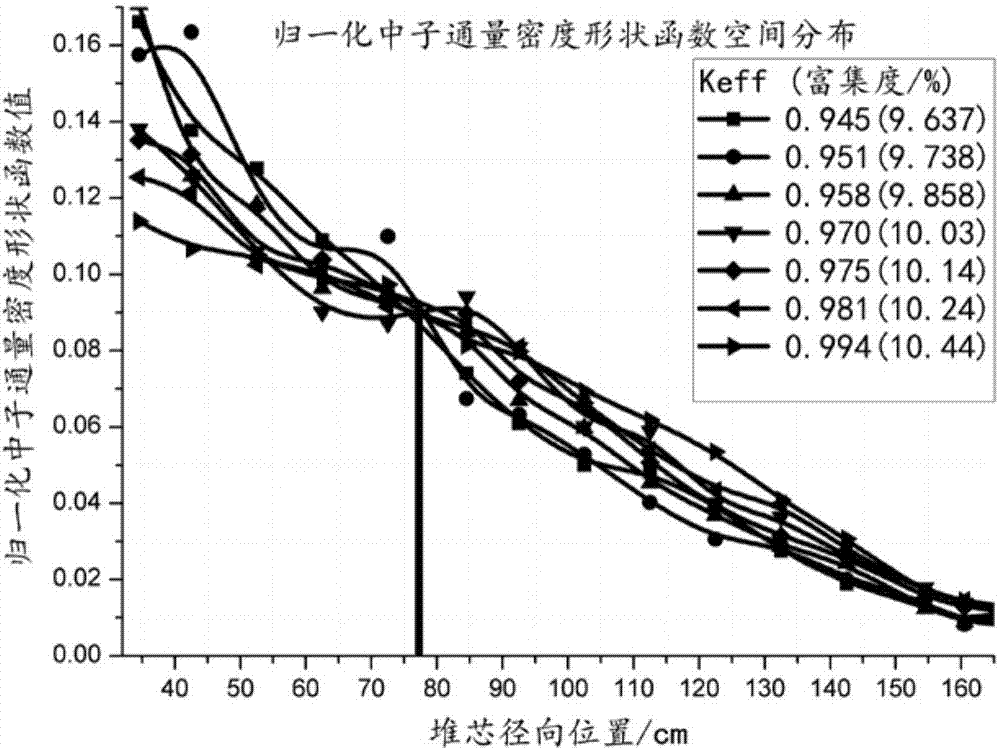
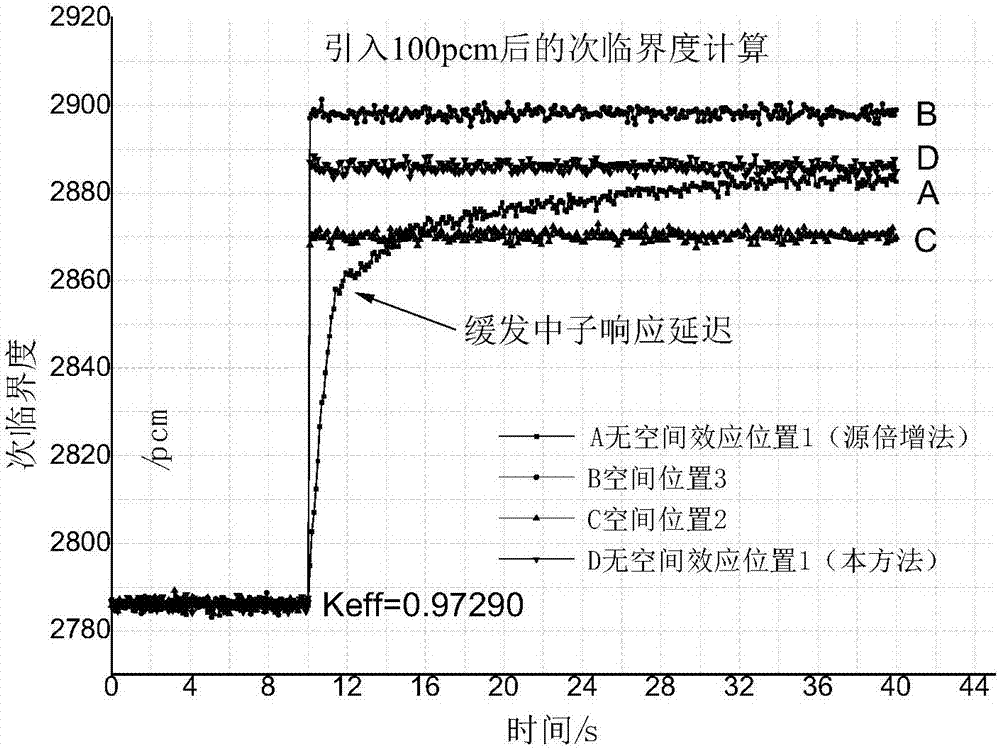
The invention provides a subcritical degree reverse dynamic measuring method free of a space effect. Compared with other methods, the method is characterized in that subcritical degree online measurement free of the influence of the space effect is achieved, wherein a stationary source mode is selected to work out space positions with the neutron-flux density normalization shape function unchanged after the state of a reactor is changed to arrange detectors; the reference subcritical degree of a subcritical reactor and the neutron-flux density under the condition that a stable external source is available are measured based on a pulse neutron source method or a source jerk method, and an external neutron source item is scaled with a subcritical inverse dynamic formula; the subcritical degree is calculated on line according to time-sequence data read at the positions of the detectors. The method has the advantages that the influence of redistribution of the neutron-flux shape space is avoided when the subcritical degree is measured; the delay effect of delayed neutrons can be responded to; the subcritical degree can be measured online in real time regardless of low power or high power.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
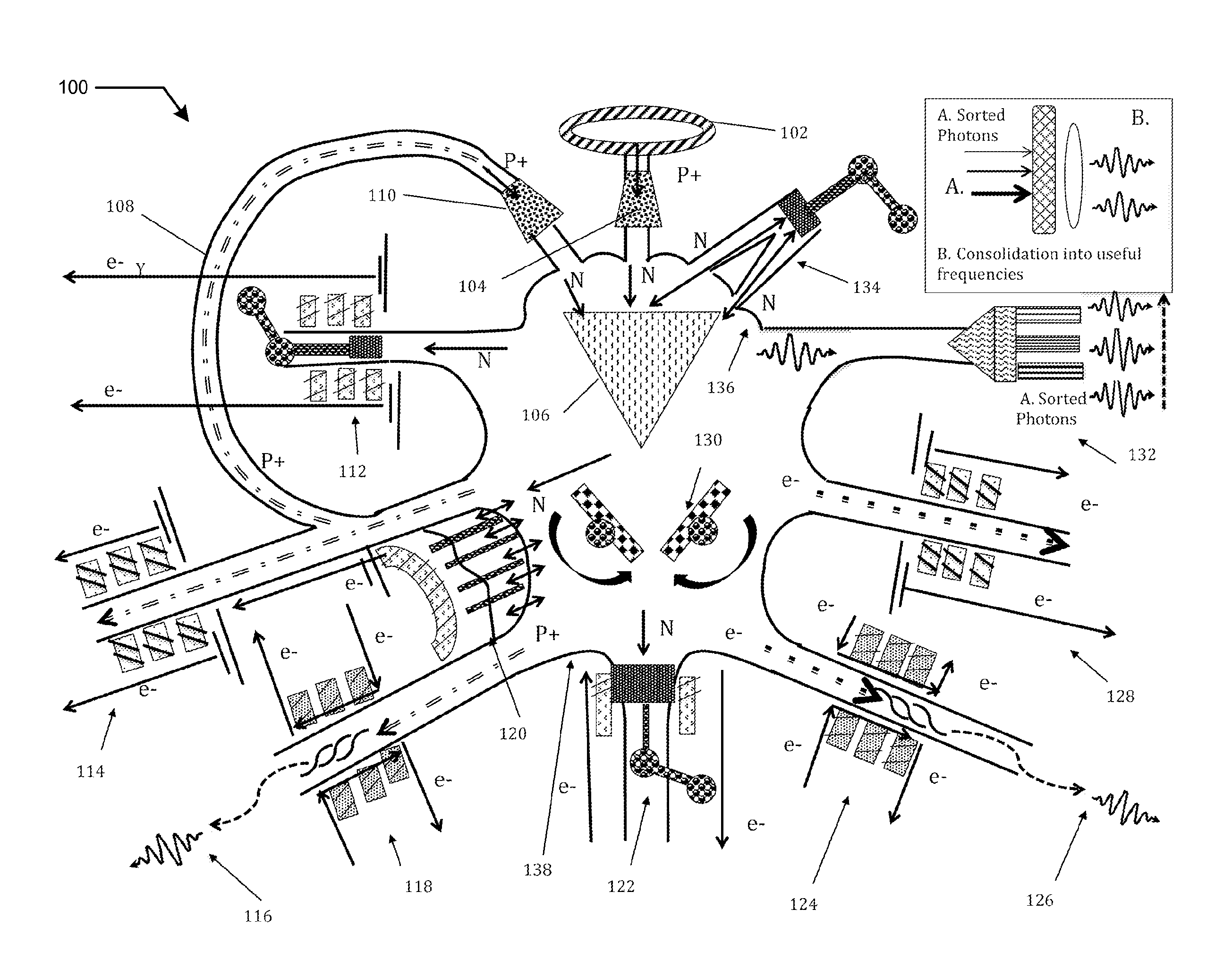
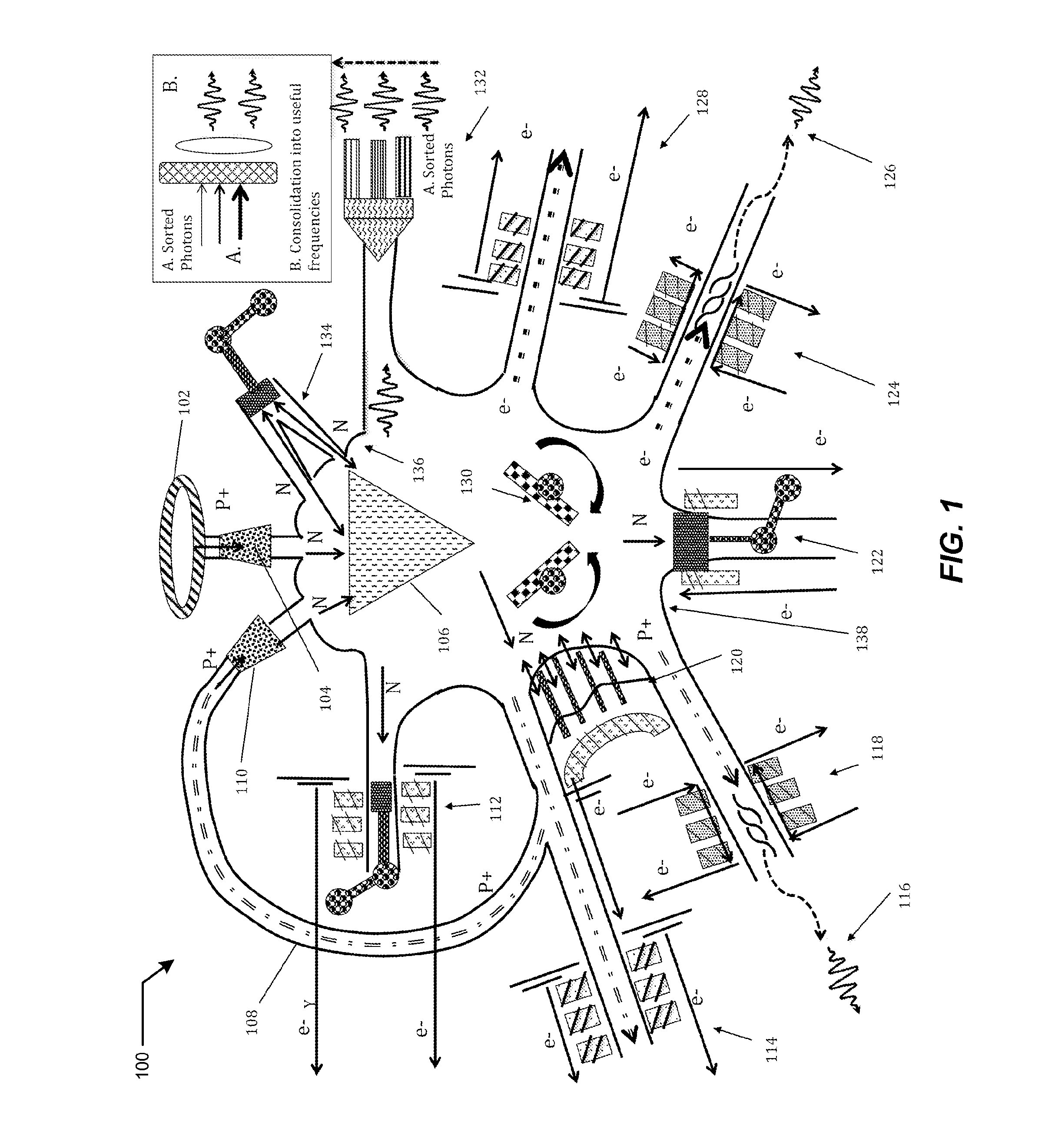
Accelerator driven power generation
InactiveUS20110286564A1Producing wasteEasy to useConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationControl systemNuclear engineering
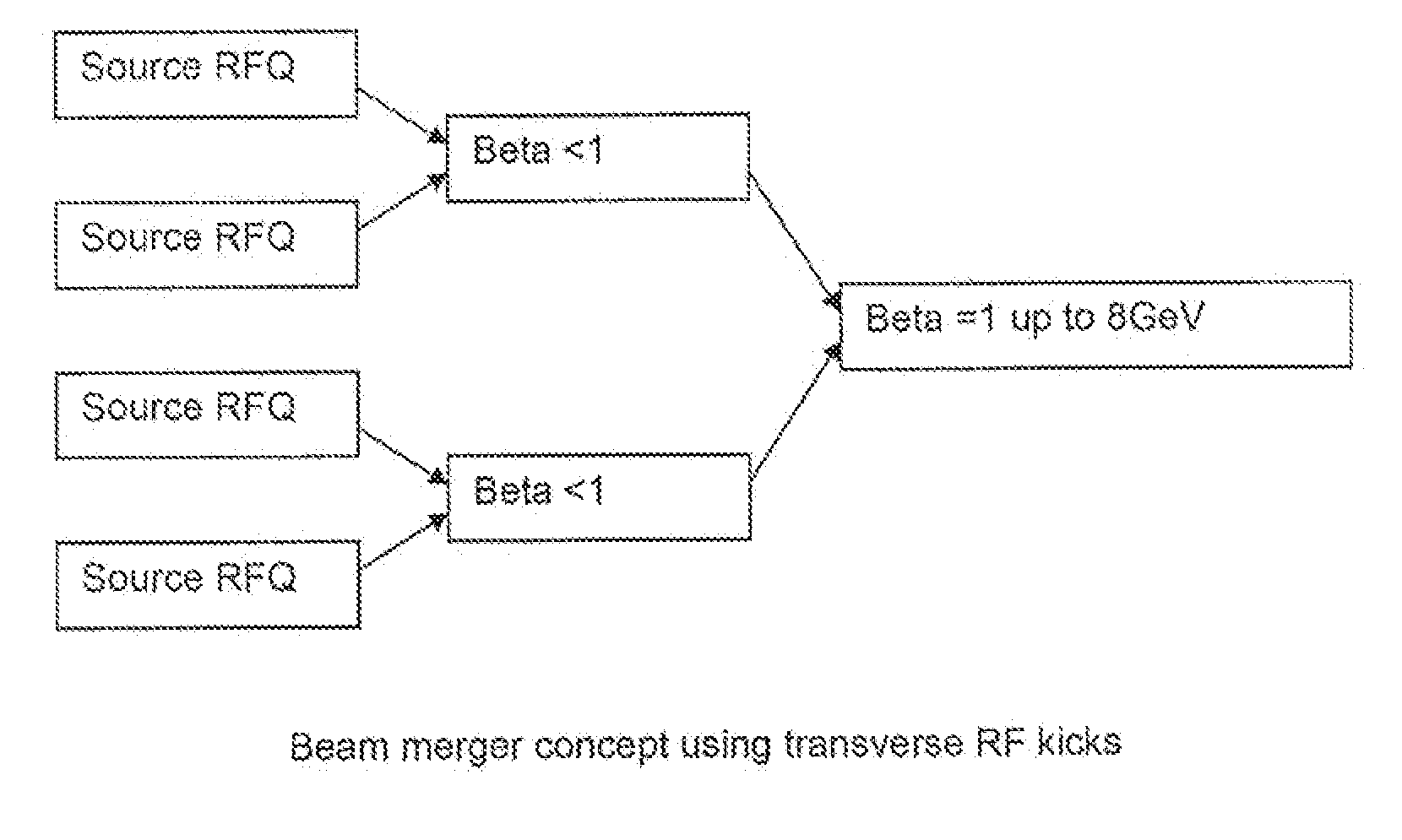
A redundant, low cost accelerator driven system for power generation or waste treatment. The system generates fission from fertile nuclear materials and includes multiple charged particle sources, nested redundancy of low energy accelerator sections for reliability, and multiple subcritical reactors. Merging and splitting devices based on radiofrequency transverse kickers enable the nested redundancy. A control system provides RF buckets with identifiers, enabling the control of charged particles on an RF bucket basis through the accelerator, for the delivery to a desired subcritical reactor of a desired number of RF buckets of such predetermined characteristics to generate a desired reactor power. Consequently, the power level of each reactor may be controlled independently even though a large part of the high power accelerator system is used to feed multiple reactors simultaneously.
Owner:ACCELERATOR TECH
Method for monitoring sub-critical reactor reactivity
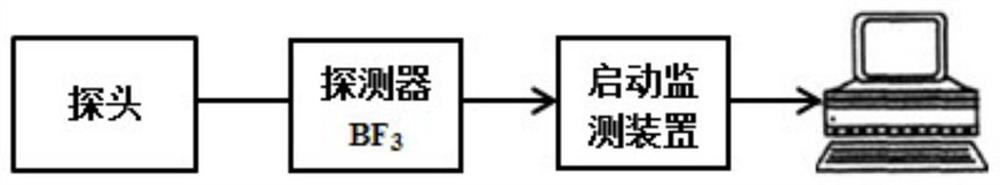
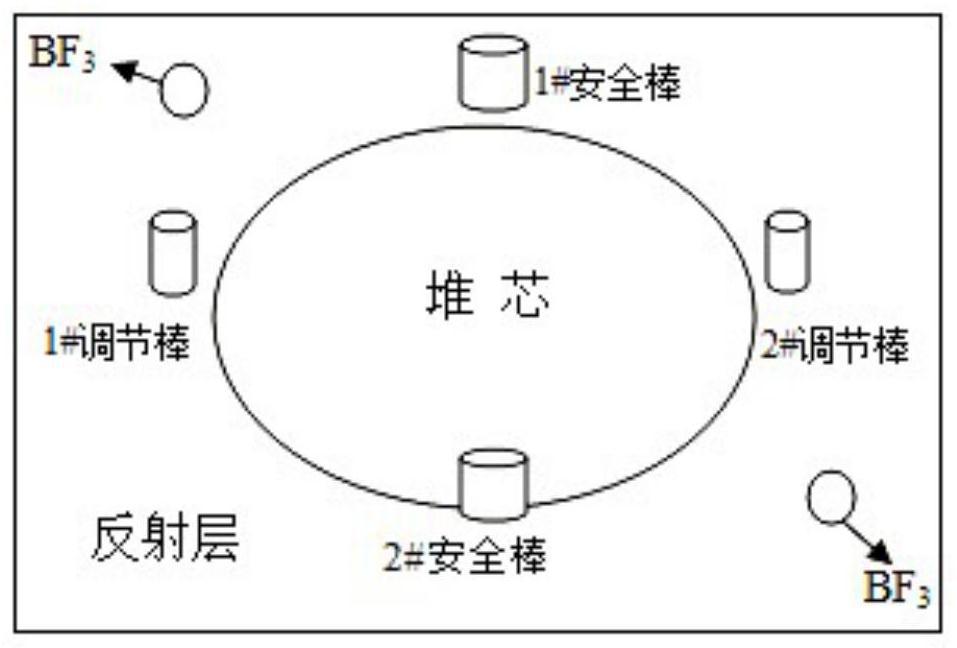
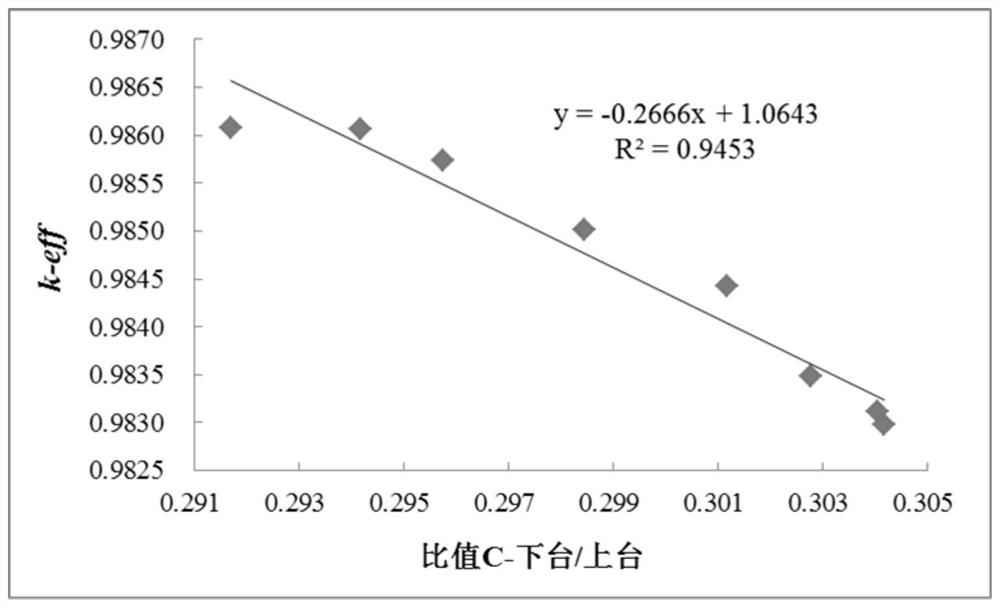
ActiveCN109903866AMonitor reactive changes in real timeNot affected by external strengthNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringCounting rateNeutron count
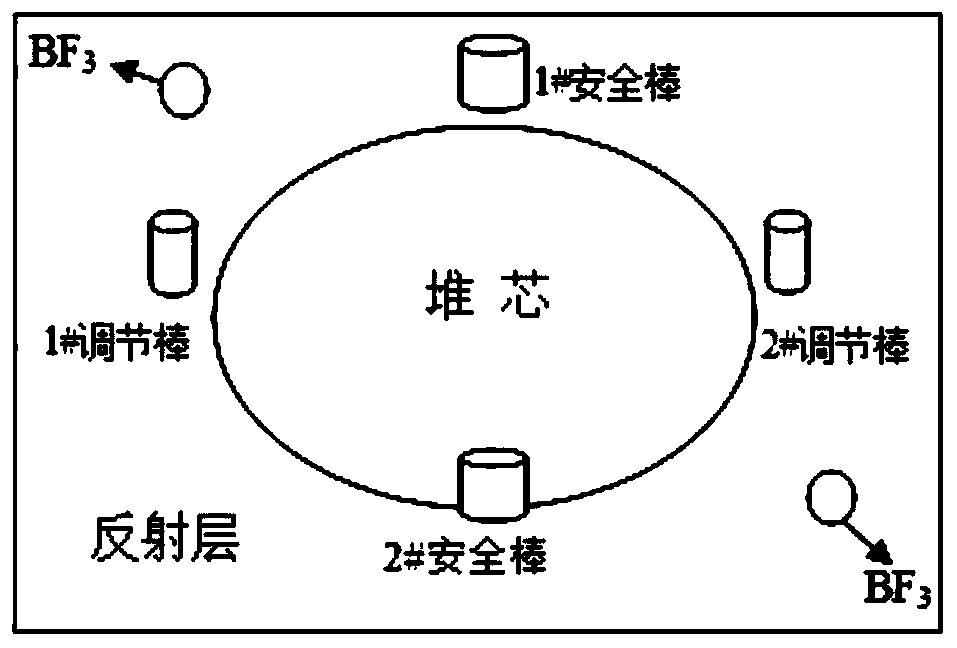
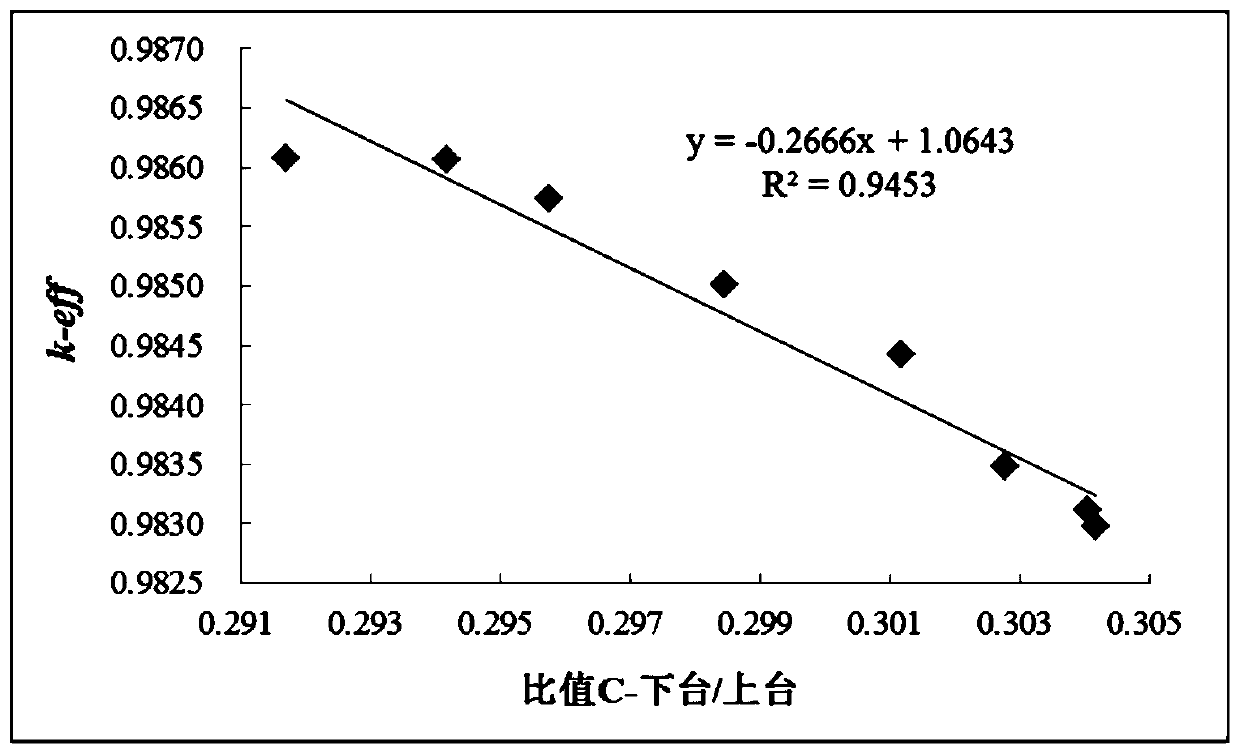
The invention relates to a method for monitoring sub-critical reactor reactivity. The method includes the steps: placing neutron detectors at two different positions of a reactor; effective multiplication constant gradually changing the reactor reactivity, and recording a specific value C and an effective multiplication constant keff of neutron counting rate at the same moment; fitting calibratingcurve graphs of the specific values C and the effective multiplication constants keff of the neutron counting rate of various moments; recording neutron counting rates of the two neutron detectors inreal time to obtain specific values of the two neutron counting rates, and substituting the specific values into the calibrating curve graphs to obtain effective multiplication constants of the effective multiplication constant when reactor reactivity is practically monitored. The neutron detectors are used for acquiring neutron counting rates, and the specific values C of the neutron counting rates recorded by two detectors represent characteristic parameters of neutron flux density space distribution shapes. Compared with a traditional method, the method is more visual, simple and convenient, on-line real-time monitoring of the reactivity change can be achieved, effects of external source intensity are omitted, and space effect correction of the traditional method under a deep sub-critical condition is avoided.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
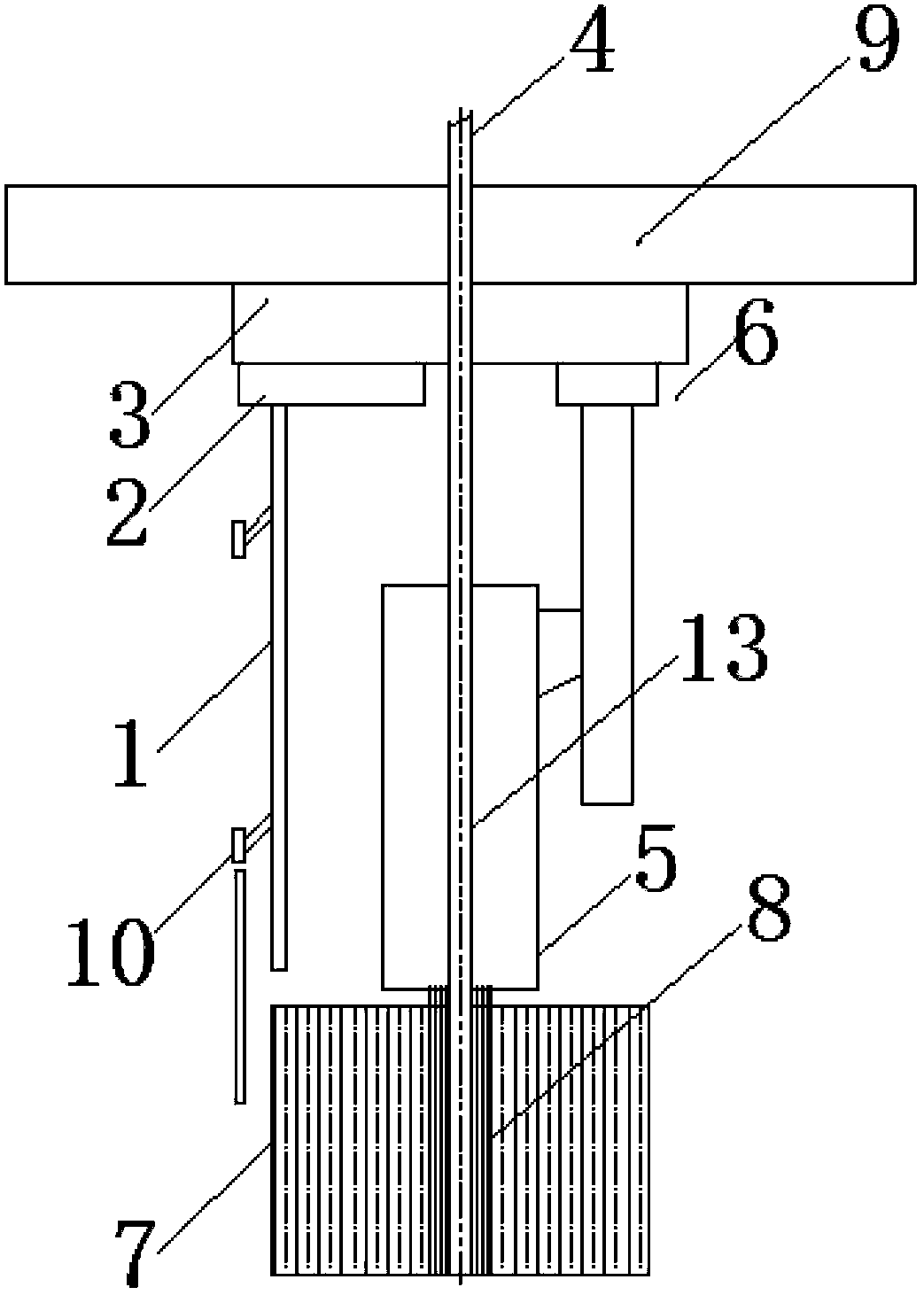
Material changing system and accelerator driving subcritical reactor with material changing system
InactiveCN107154277ASimple structureCompact structureNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsEngineeringSubcritical reactor
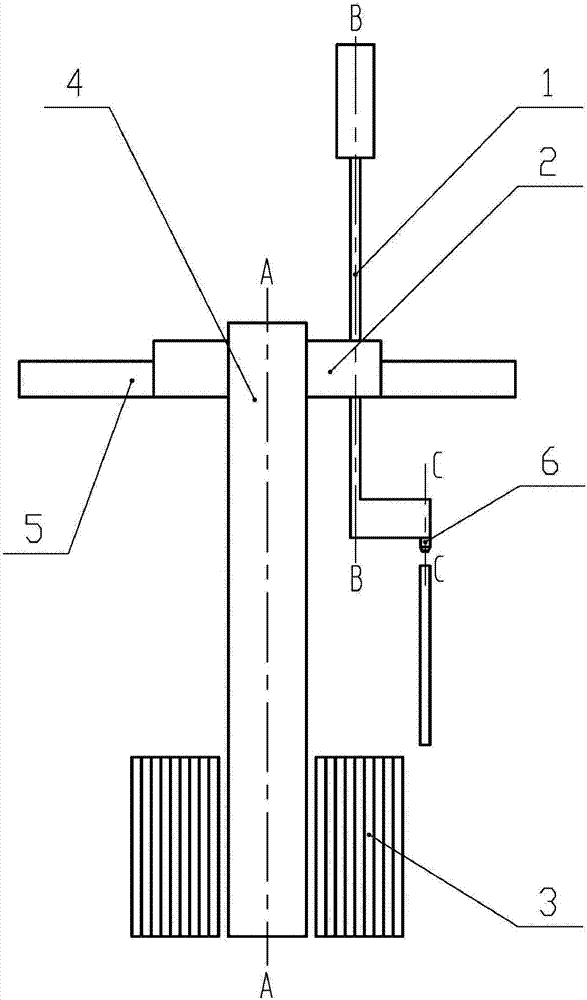
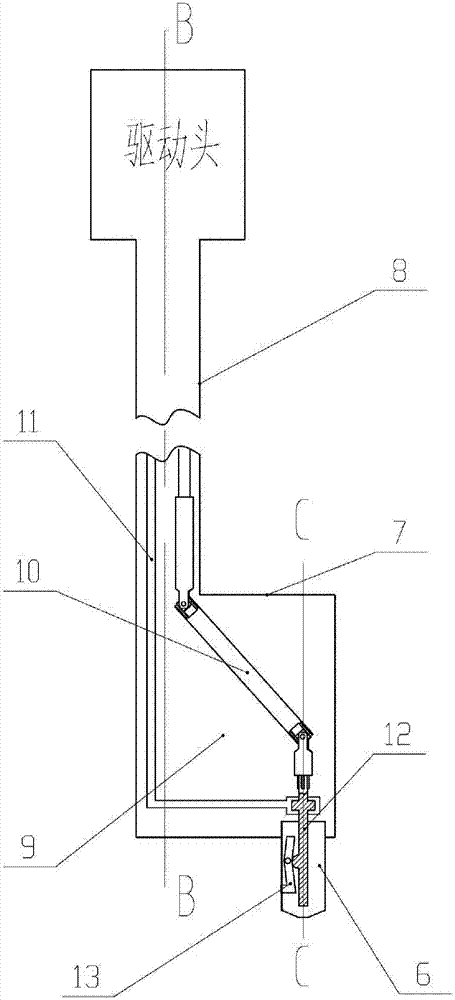
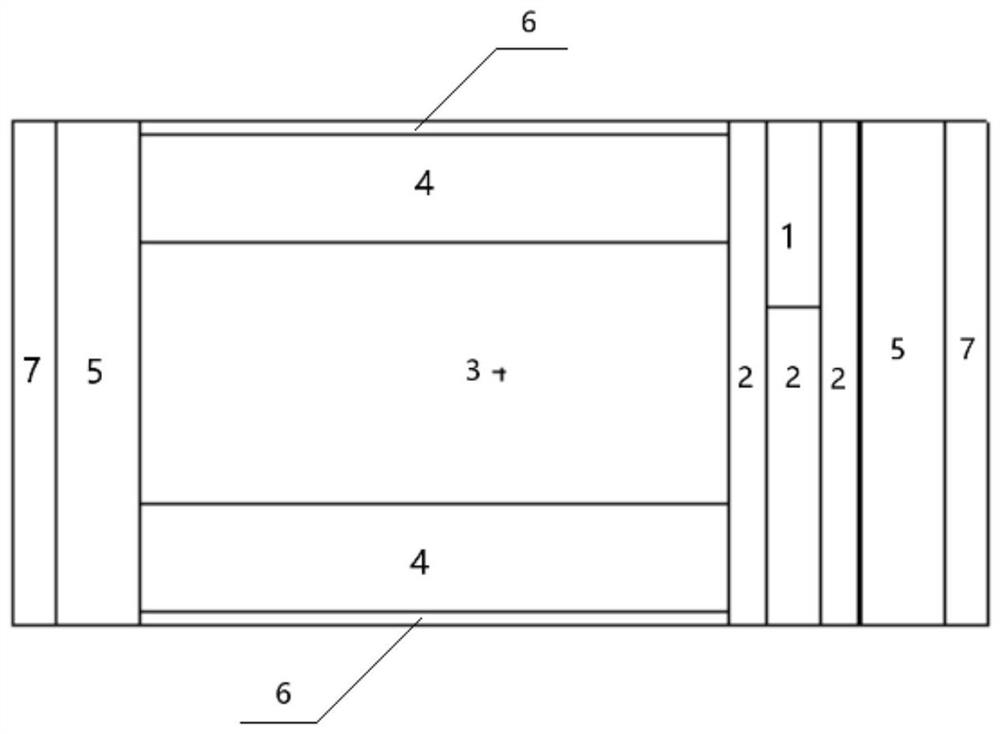
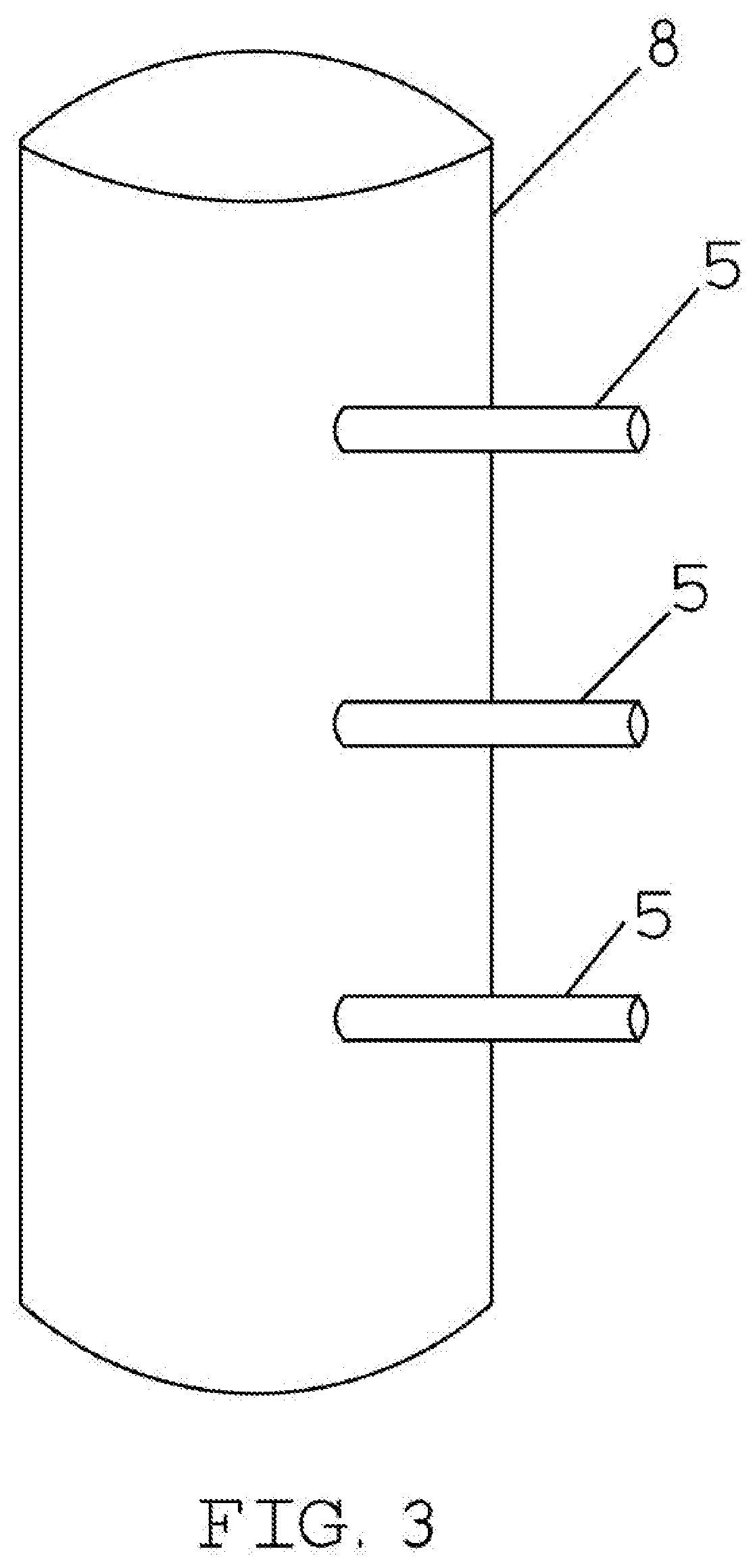
The embodiment of the invention provides a material changing system for an accelerator driving subcritical reactor and the accelerator driving subcritical reactor with the material changing system. The material changing system comprises a rotatable rotating plug (2) and a material changing machine (1), wherein the rotating plug (2) is arranged on a top cover of a reactor; the material changing machine (1) comprises a rotating rod (8), a cantilever (7) and a material changing grasping head (6); the cantilever (7) is connected with the lower end of the rotating rod (8); the material changing grasping head (6) is connected with the end part, far away from the rotating rod (8), of the cantilever (7); the rotating rod (8) is arranged on the rotating plug (2), can rotate around the self axial line and can vertically move. The material changing system according to the embodiment of the invention has the advantages that the structure is simple and compact; the material changing operation is simple and convenient after the material changing system according to the embodiment of the invention is used.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
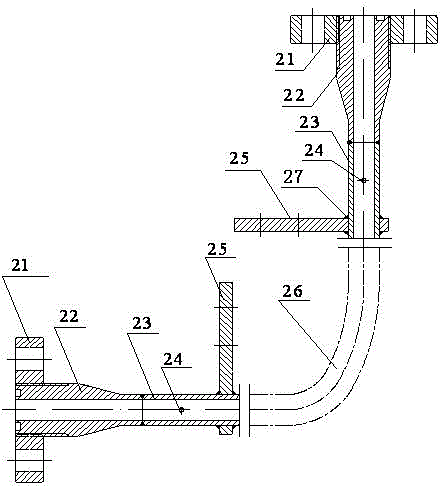
Experimental device for flow and heat transfer characteristics of curved single passage of subcritical energy reactor coolant
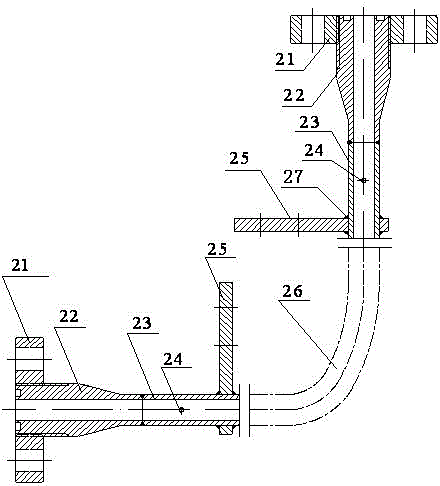
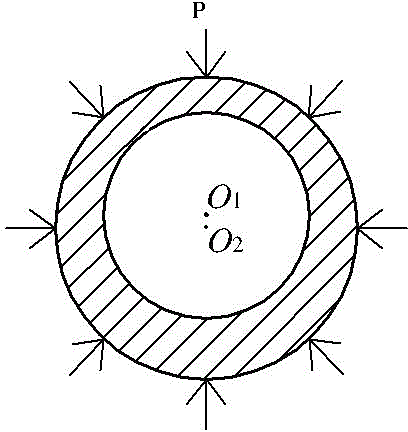
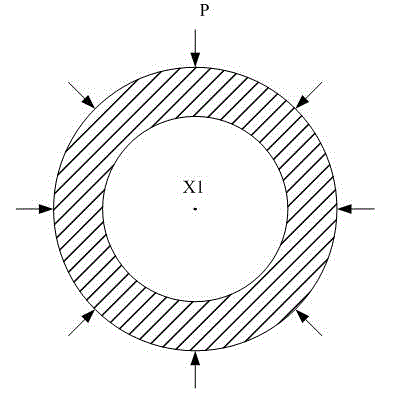
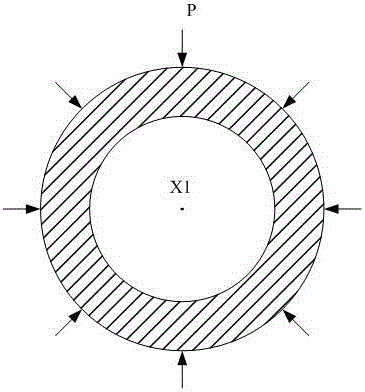
The invention discloses an experimental device for flow and heat transfer characteristics of a curved single passage of a subcritical energy reactor coolant. The experimental device comprises a curved heating single tube, wherein the two ends of the heating single tube are communicated with stabilizing straight tubes, and the stabilizing straight tubes are communicated with threaded joints, the threaded joint are sleeved with threaded flanges; the stabilizing straight tubes are welded with powered copper bars, and pressure diversion holes are formed in the stabilizing straight tubes; the heating single tube is an eccentric curved tube or a concentric curved tube; the center of an inside diameter circle of the eccentric curved tube is O1, the center of an outside diameter circle of the eccentric curved tube is O2, the distance between the O1 to the O2 is larger than zero, and a line segment for connecting the O1 to the O2 is O1O2; the eccentric curved tube is welded with a thermocouple, and a heat insulation protection structure is arranged on the outer wall of the eccentric curved tube; the center of an inside diameter circle of the concentric curved tube and the center of an outside diameter circle of the concentric curved tube are overlaid at a point X1, a plurality of thermocouples are welded on the outer wall of the concentric curved tube, and a heat insulation protection structure is arranged on the outer wall of the concentric curved tube. The experimental device can provide experiment support for the feasibility study on a thermo-hydraulic design of the subcritical reactor coolant.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Fused-salt fuel multi-reactor system
ActiveCN109273121AIncrease production capacityAchieve multiplicationNuclear energy generationNuclear plant auxillary equipmentReactor systemNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a fused-salt fuel multi-reactor system. The fused-salt fuel multi-reactor system comprises a reactor module, a heat exchange module, a pump module and a fuel processing module,wherein the reactor module comprises a type I reactor module and a type II reactor module, which adopt the same kind of fused-salt fuel flowing therein; and the type I reactor module and the type IIreactor module are serially and / or parallelly arranged. The type I reactor module operates in an overmoderated region or near the optimal grid point, is used for realizing productivity and multiplication, and comprises a set of reactivity control system which is used for controlling reactivity variation of the rectors. The type II reactor module operates in an undermoderated region and non-moderated region, is used for multiplication and transmutation, belongs to a subcritical reactor, and comprises a set of neutron source systems for driving the reactors. The fused-salt fuel multi-reactor system disclosed by the invention fully utilizes the fluidity of the liquid fuel, and can realize the functions of productivity, multiplication, transmutation and the like in the same system.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
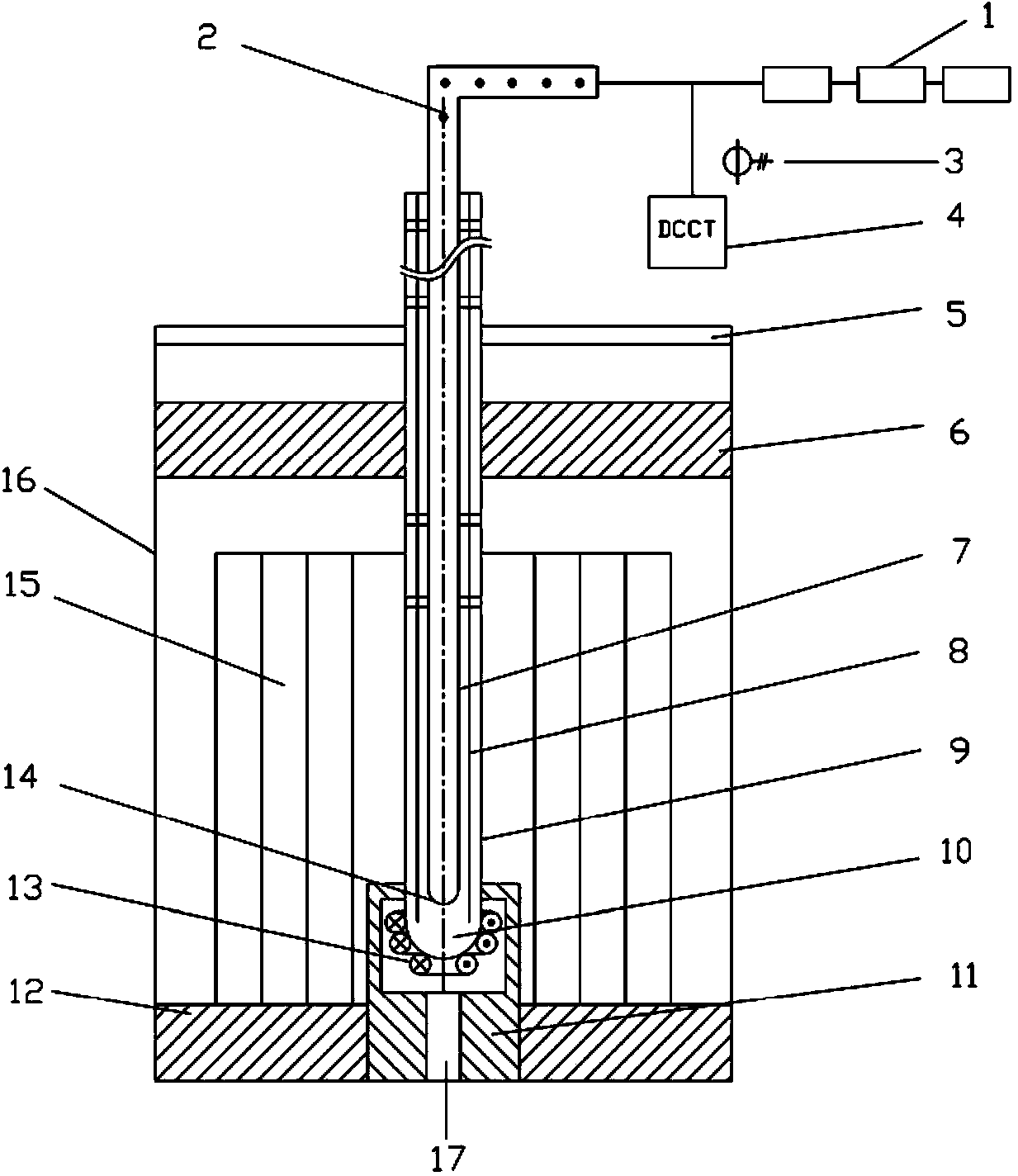
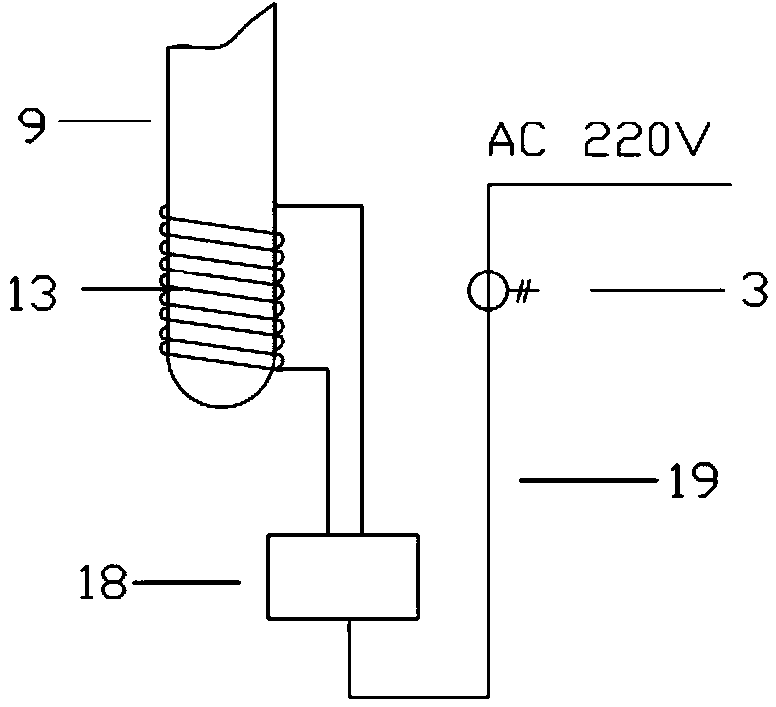
System for keeping constant temperature of target window of accelerator driven sub-critical reactor
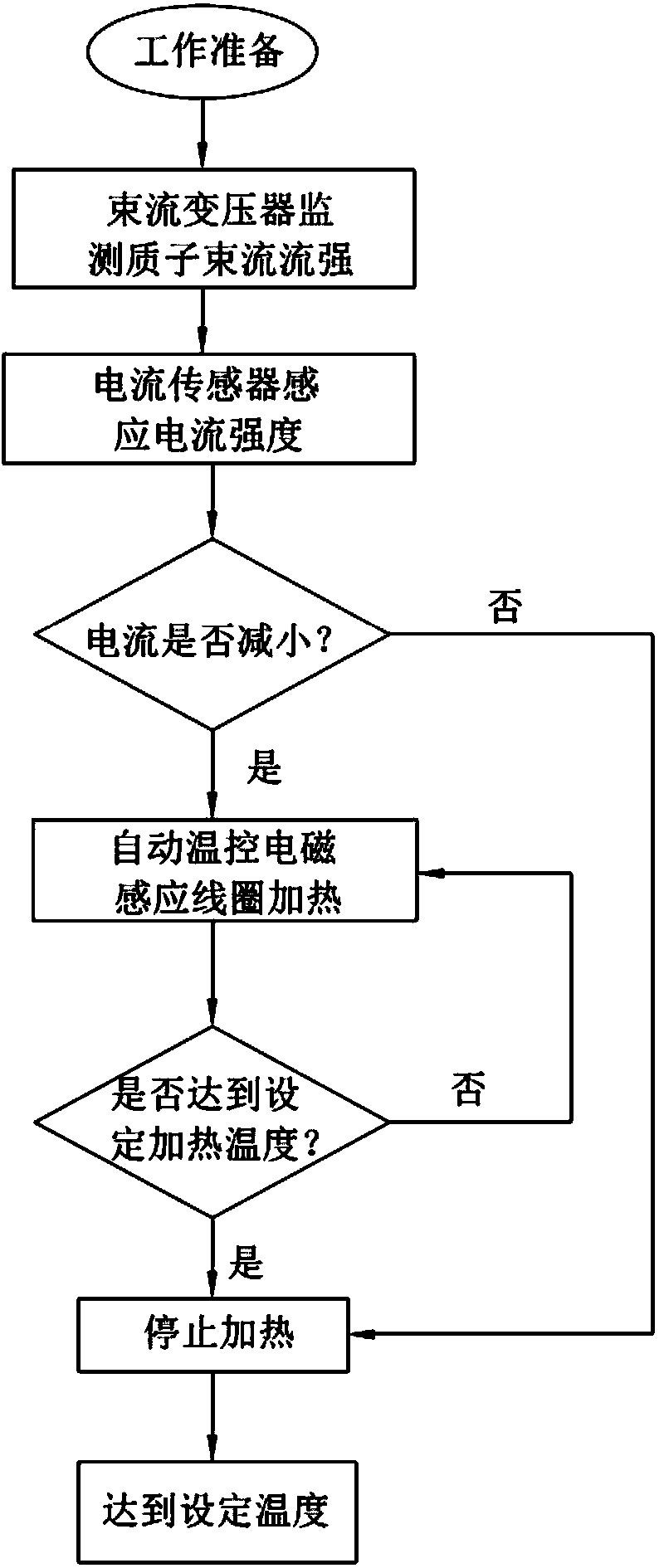
ActiveCN104282345AThermal stress remains constantStable temperatureConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationCurrent sensorBeam tube
The invention discloses a system for keeping the constant temperature of a target window of an accelerator driven sub-critical reactor. The system is composed of a current sensor, a DCCT, a target loop rack, a cock, a proton beam tube, a guide tube, an outer sleeve, a target fixing plug, an automatic temperature control electromagnetic induction coil, the target window, a sub-critical reactor core, a reactor container and a reactor-core lower grid tray. The system has the advantages that after proton beam currents of an accelerator suddenly disappear, as the beam current strength is reduced, working signals of the electromagnetic coil are triggered through current changes, the electromagnetic coil rapidly works, the bottom of the outer sleeve is heated, coolants located in the outer sleeve and below the target window are further heated, the temperature of the target window after the proton beam currents disappear is kept constant, it is guaranteed that after the proton beam currents of the accelerator disappear, the temperature of the target window can not drop obviously, heat stress changes, caused by beam disappearing, of the target window are greatly reduced, and the target window material fatigue fracture risk caused by the fact that the heat stress cycle of the target window is generated due to the proton beam currents of the accelerator frequently disappear is further lowered.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
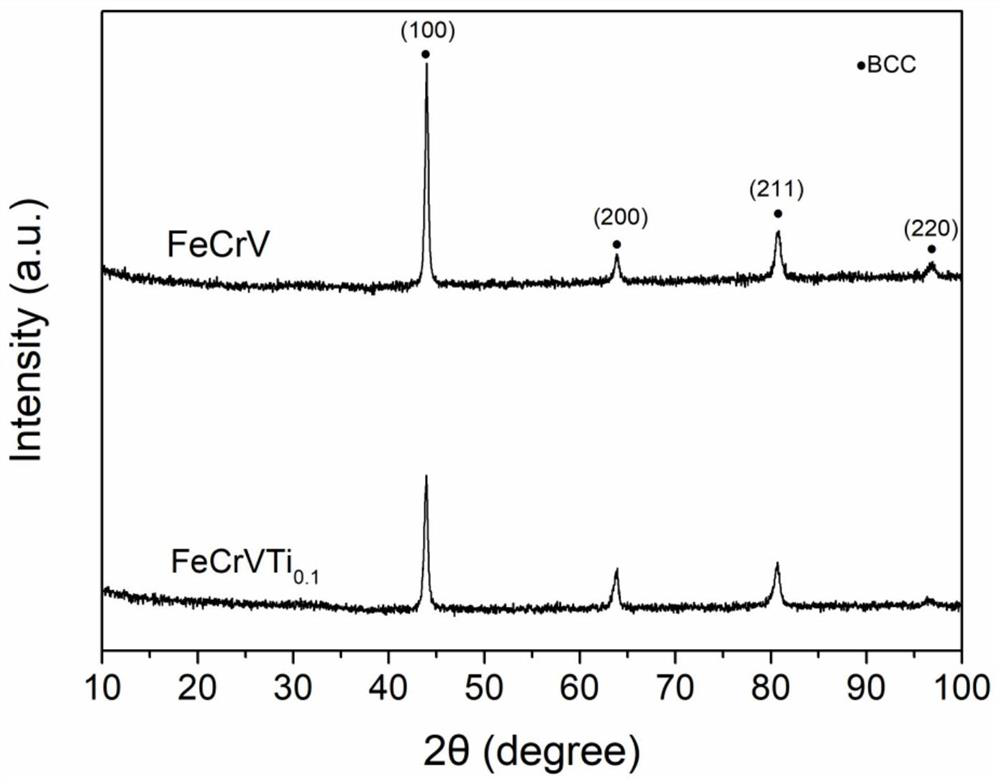
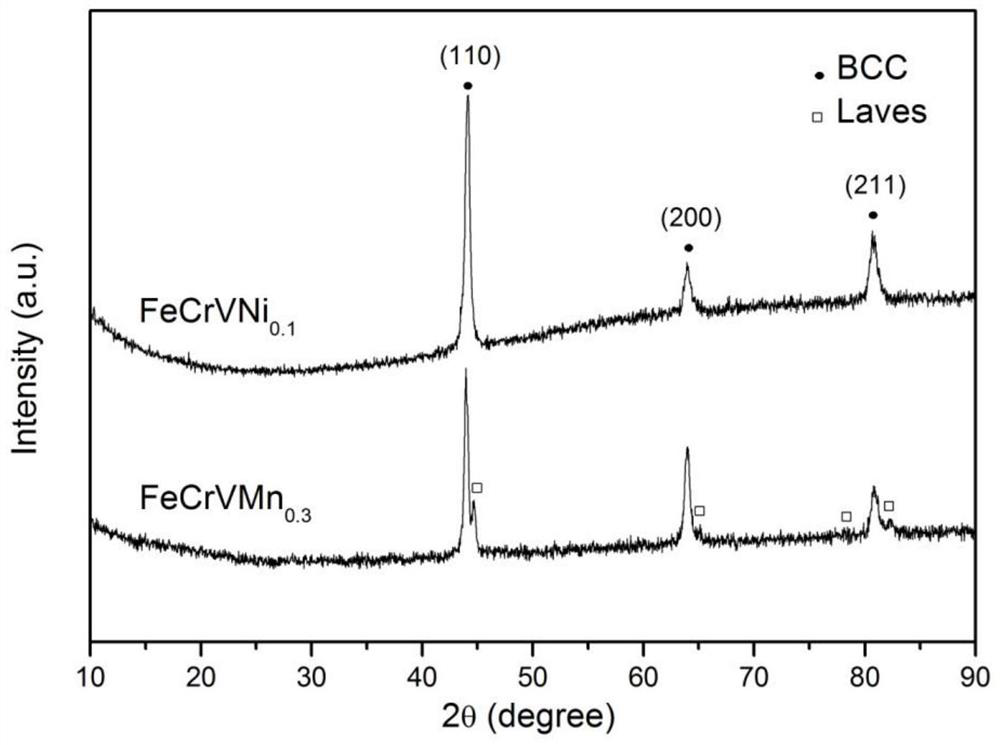
Medium-entropy alloy system for nuclear use and preparation method and application thereof
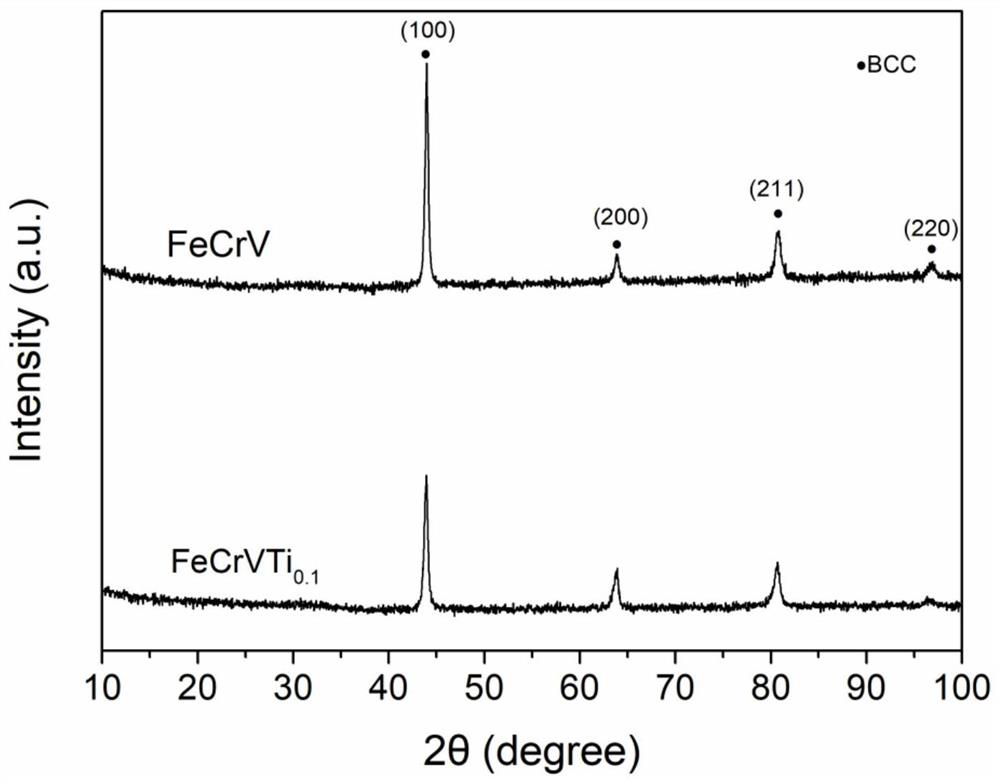
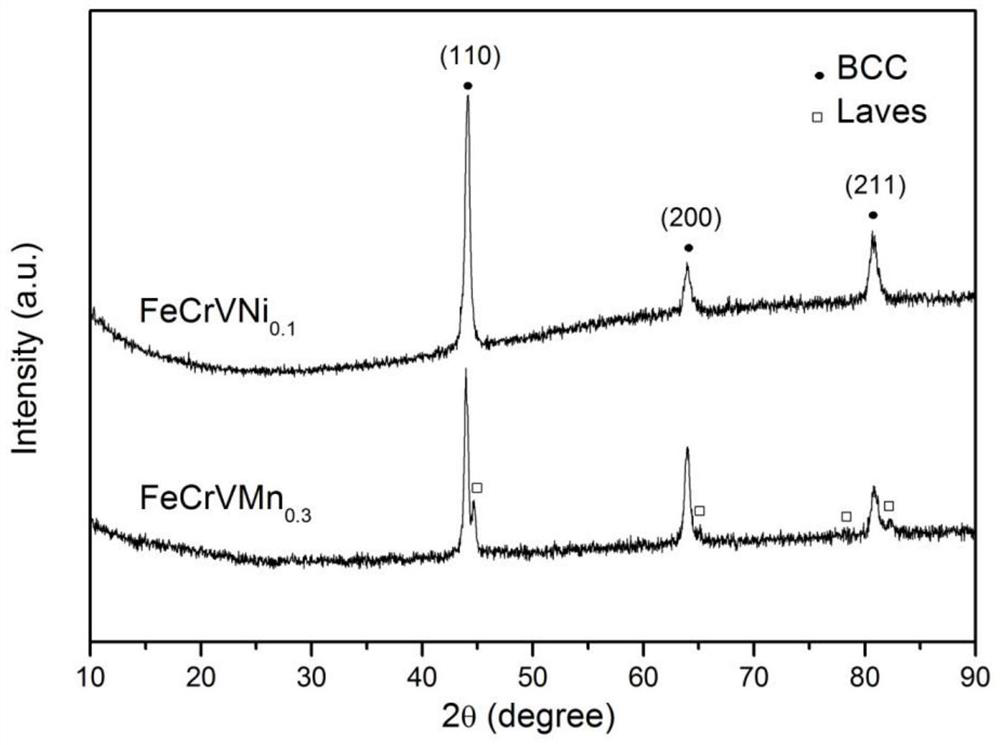
ActiveCN112981210ANuclear reaction cross section is smallReduced induced radioactivityOptical rangefindersNuclear energy generationHeat stabilityLiquid metal
The invention discloses a medium-entropy alloy system for nuclear use and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medium-entropy alloy materials and preparation thereof. According to the medium-entropy alloy system for nuclear use and the preparation method and application thereof, the FeCrV series is composed of four low-activation elements of Fe, Cr, V and M (one of Ti, Mn, Ni and Zn), the atom molar ratio of Fe to Cr to V to M is 1: 1: 1: x, and x is larger than or equal to 0 and smaller than or equal to 0.5; the low-activation, high-temperature-resistant, high-strength and high-toughness FeCrV-series medium-entropy alloy material for nuclear use is prepared by adopting a magnetic suspension (metal raw material samples are not in contact with a crucible) electric arc melting mode and annealing heat treatment through raw material treatment and material weighing and proportioning; the low-activation FeCrV-series medium-entropy alloy material disclosed by the invention shows excellent high-temperature thermal stability, high strength and high toughness; and the medium-entropy alloy is expected to be applied to ADS spallation target windows and subcritical reactor cores, fusion reactors and the fourth-generation nuclear fission type reactor cores, and structural materials or coating materials in a strong acid environment or a liquid metal environment.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Accelerator-driven subcritical reactor system
InactiveUS20160027534A1Reducing and eliminating thermal lossImprove efficiencyNuclear energy generationDirect voltage acceleratorsReactor systemNuclear engineering
An accelerator-driven sub-critical reactor providing: 1) a significantly more efficient Thorium-cycle system, in one configuration, 2) a more energy-productive nuclear waste reduction system, 3) accelerator driven systems for other fertile-fission candidate elements, and 4) which may be applied to fusion systems (substituting the fission unit in the proposed system class and category) in a way that may lower the break-even point for such systems and thus make the advent of practical fusion sooner than otherwise possible. 5) In addition and importantly, an optical-power processing and distribution is also enabled by the proposed, providing both optical power as base power for telecom, process energy for industrial uses, and lighting and other wavelengths for consumer and general business use.
Owner:ELLWOOD SUTHERLAND COOK
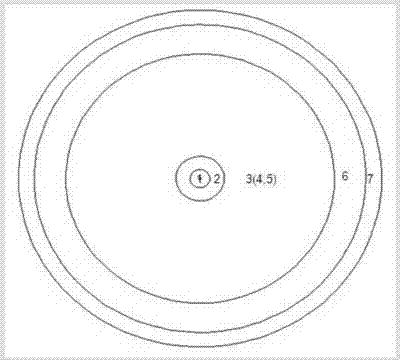
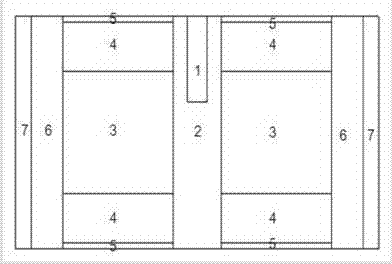
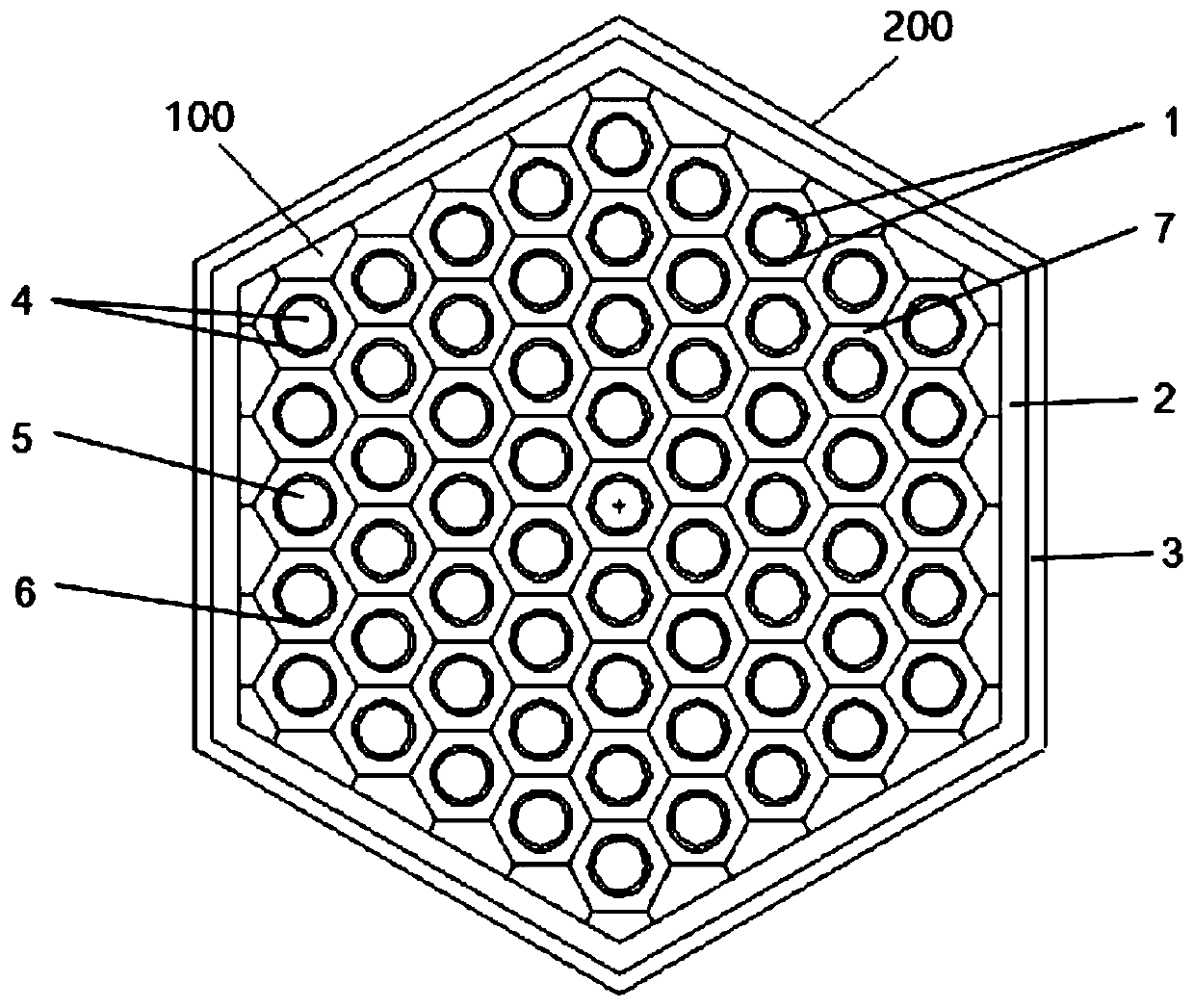
Spallation target of accelerator drive sub-critical reactor of low proton beam intensity efficient transmutation nuclear waste
InactiveCN104302088AEfficient transmutationReduce beam current intensityDirect voltage acceleratorsNuclear targetsLiquid stateProton
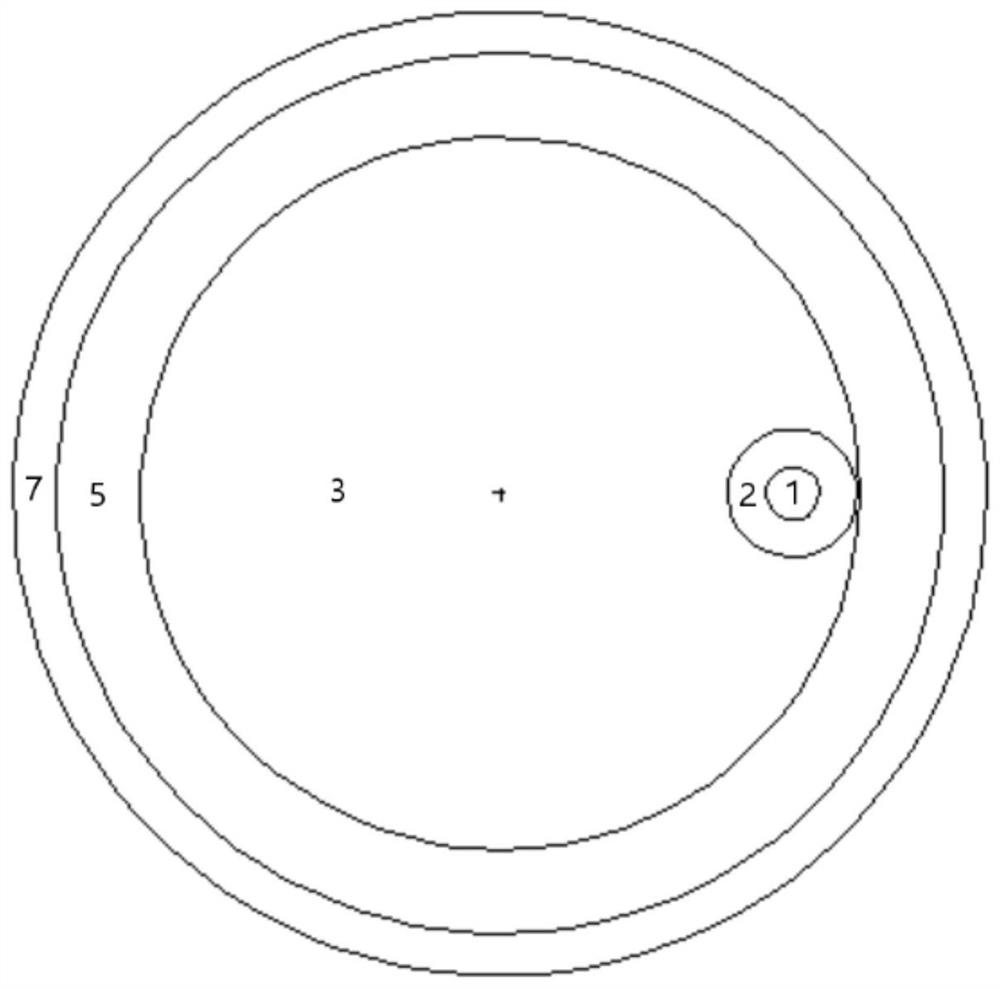
The invention discloses a spallation target of an accelerator drive sub-critical reactor of low proton beam intensity efficient transmutation nuclear waste, and relates to the technical field of nuclear energy. The spallation target is characterized in that reactor cores of the spallation target are arranged in a shape of a triangular grid, a proton beam (1), a liquid state heavy metal spallation target (2), a fission fuel region (3), an axial reflecting region (4), an axial shielding region (5), a radial reflecting region (6) and a radial shielding region (7) are sequentially arranged from center to outside. Based on the reactor cores adopting TRU dispersion metal fuels, the reactor physics principle and the spallation target physics principle are applied, and spallation target geometrical optimizing is carried out with the transmutation performance as evaluation indexes. Based on the optimized spallation target, in the state that structures and material component distribution of the reactor cores are not changed, the reactor cores of the spallation target can have the functions that the same transmutation performance is obtained in the fixed power operation mode, the proton beam intensity is reduced, energy gain factors of the reactor are improved, and the higher MA transmutation performance is obtained in the fixed proton beam intensity mode.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
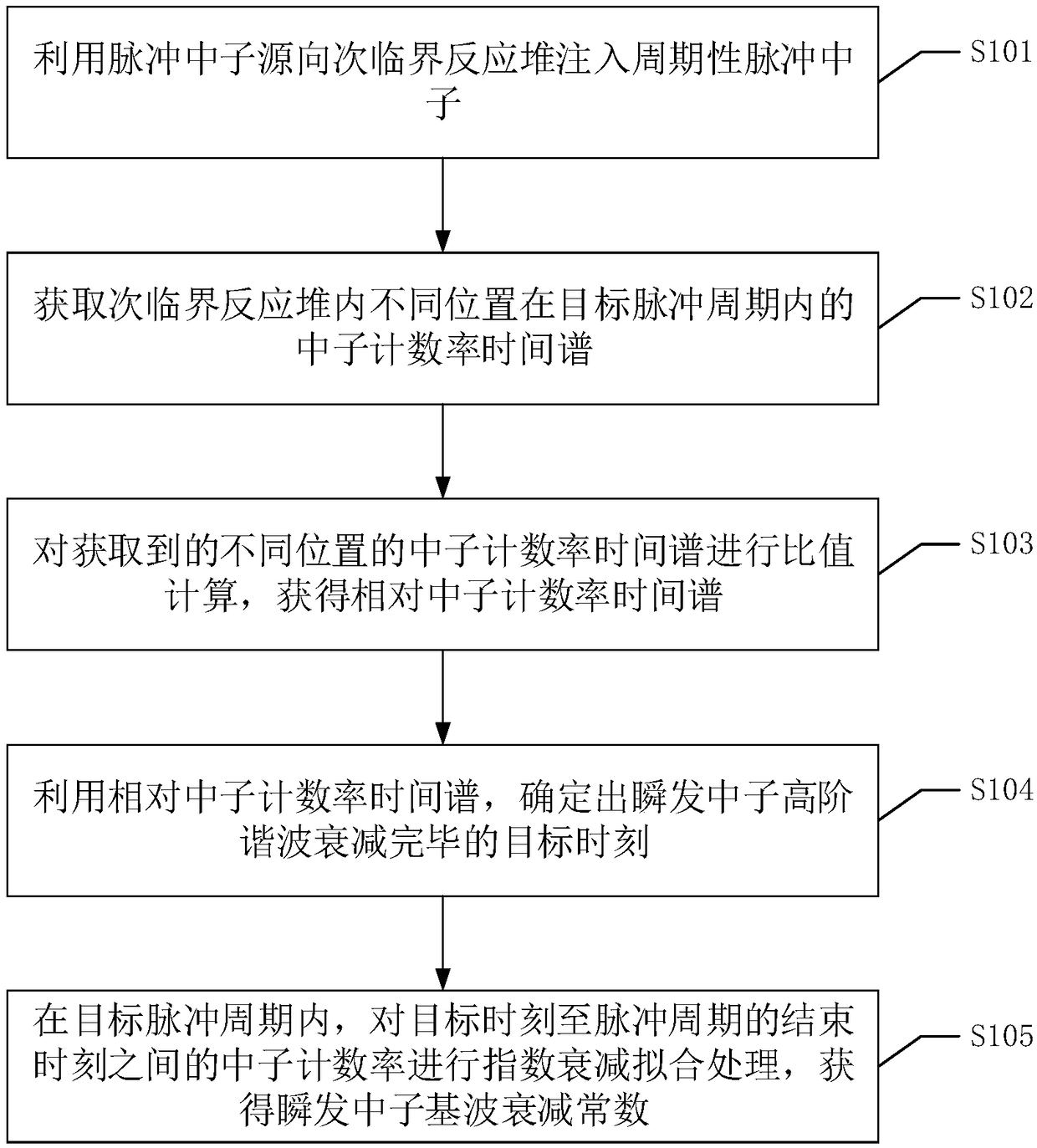
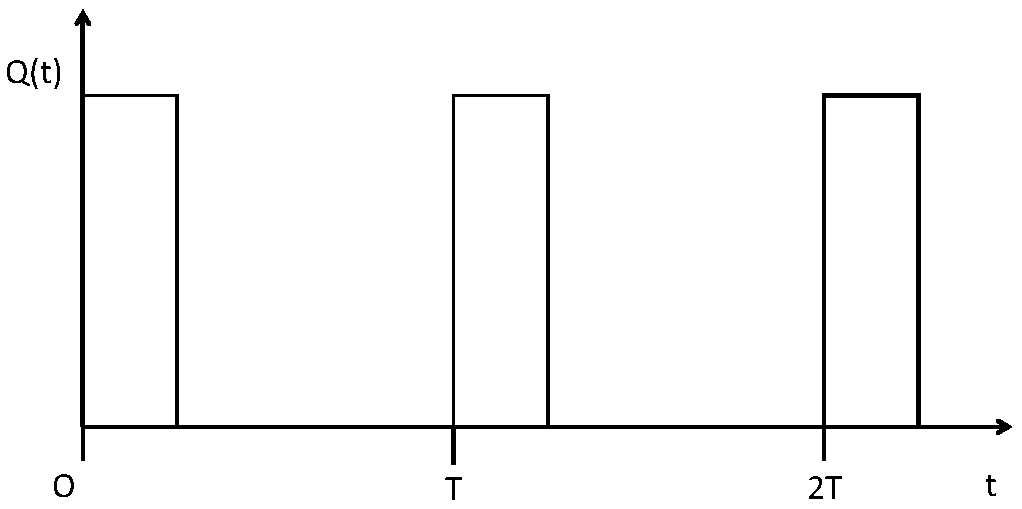
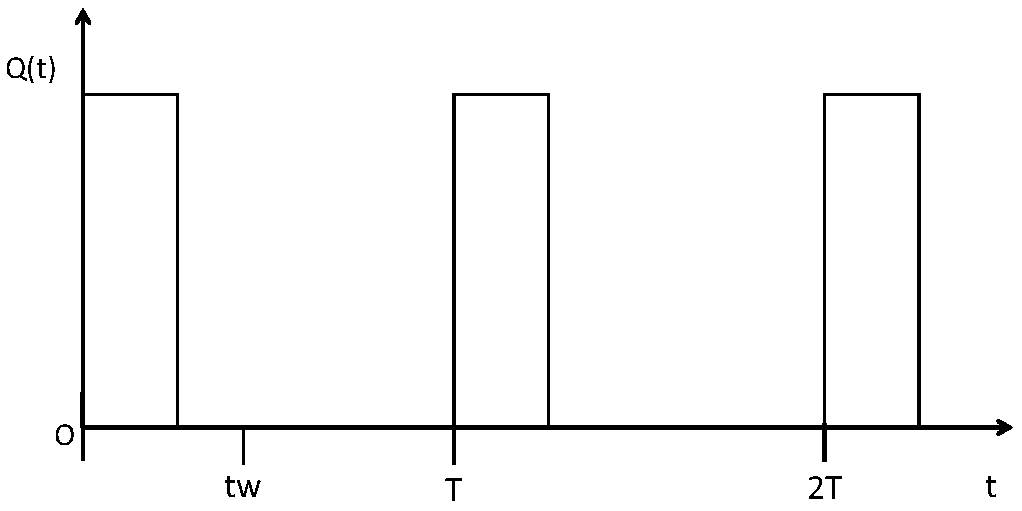
Prompt-neutron-attenuation-constant obtaining method, device, equipment and system
PendingCN109490945AHigh precisionAccurate fundamental decay constantNeutron radiation measurementCounting rateUltrasound attenuation
The invention discloses a prompt-neutron-attenuation-constant obtaining method. The prompt-neutron-attenuation-constant obtaining method includes the following steps that periodic pulse neutrons are injected into a subcritical reactor through a pulse neutron source; in a target pulse period, neutron counting rate time spectrums of different positions in the subcritical reactor are obtained; specific values of the obtained neutron counting rate time spectrums of the different positions are computed, and relative neutron counting rate time spectrums are obtained; through the relative neutron counting rate time spectrums, a target moment when prompt-neutron higher-order harmonic attenuation is completed is determined; in the target pulse period, the neutron counting rate between the target moment and an ending moment of the pulse period is subjected to exponential attenuation fitting processing, and a prompt-neutron fundamental-wave attenuation constant is obtained. The more-accurate prompt-neutron fundamental-wave attenuation constant under the condition that interference of prompt-neutron higher-order harmonic waves does not exist can be obtained. The invention also discloses a prompt-neutron-attenuation-constant obtaining device, equipment and system and a readable storage medium, and the prompt-neutron-attenuation-constant obtaining device, equipment and system and the readable storage medium have corresponding technical effects.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
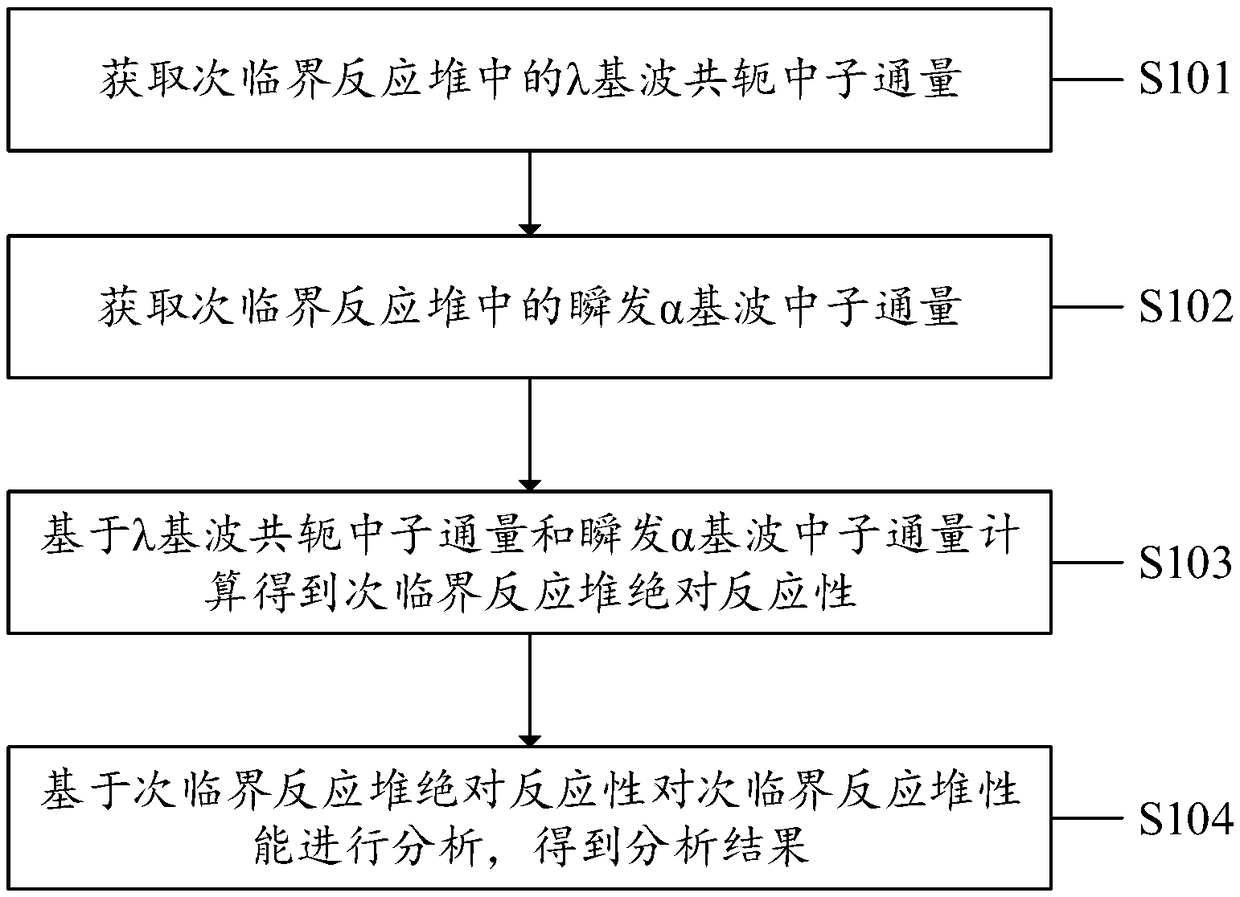
Subcritical reactor performance analysis method, system, apparatus and computer medium
ActiveCN109376457AAbsolute Reactivity AccurateThe analysis result is accurateNuclear energy generationDesign optimisation/simulationSubcritical reactorAnalysis method
Subcritical reactor performance analysis method, system, apparatus and computer medium are disclosed. That method include: obtaining lambda fundamental conjugate neutron flux in a subcritical reactor;Obtaining the neutron flux of the instantaneous alpha fundamental wave in the subcritical reactor; calculating The absolute reactivity of subcritical reactor based on lambda-fundamental conjugate neutron flux and alfa-fundamental neutron flux. Based on the absolute reactivity of subcritical reactor, analyzing and acquiring the performance of subcritical reactor and the results. In a subcritical reactor performance analysis method disclosed herein, The absolute reactivity of subcritical reactor is calculated based on Lambda-fundamental conjugate neutron flux and alfa-fundamental neutron flux.It is proved that the analysis results of subcritical reactor performance based on absolute reactivity of subcritical reactor are more accurate. The invention discloses a subcritical reactor performance analysis system, a device and a computer-readable storage medium, which also solve the corresponding technical problems.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
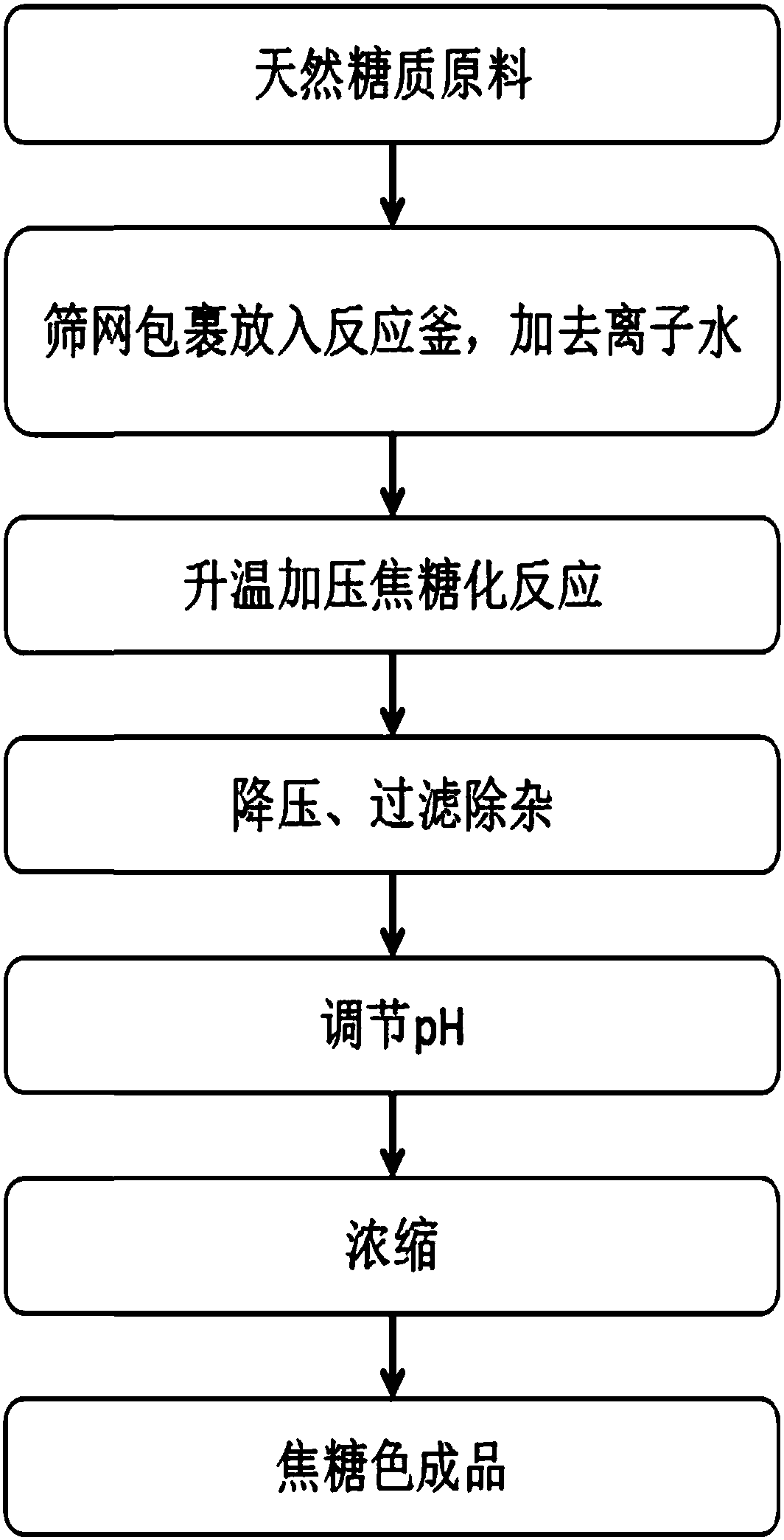
Method of using subcritical water to prepare caramel color and application thereof
ActiveCN108410207ANo pollution in the processSimple processNatural dyesFood scienceReaction temperatureCaramel Flavor
The invention discloses a method of using subcritical water to prepare caramel color and application thereof. The method comprises the steps (1) crushing sugar material into raw powder, and wrapping the powder in nylon cloth; (2) adding the raw powder in nylon cloth, into a subcritical reactor, with deionized water serving as a solvent, and heating to reaction temperature performing caramelization, wherein the reaction temperature is 150-210 DEG C; (3) after caramelization ends, adjusting to normal pressure, and filtering the mixture to remove impurities; (4) adjusting pH of filtrate in the step (3) to 5.0-6.0 shop; (5) concentrating the solution of step (4) to 0.2-0.6 times by mass so that caramel is obtained. The method is free of pollution and environmentally friendly, has a simple process flow and low equipment requirement, and is easy to use to implement industrial application and production.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Accelerator-driven subcritical reactor system
InactiveUS20150364221A1Reducing and eliminating thermal lossImprove cost efficiencyNuclear energy generationSubcritical reactorsNuclear engineeringFuel type
Now disclosing previously undisclosed aspects of the original accelerator-driven sub-critical reactor, whose since-then familiar parts and operation was first disclosed publicly starting in 1990: a more efficient accelerator-driven system is proposed which fully and completely implements the fundamental insights of the original invention and which realizes then a completely next-generation and practical and wave energy processing system, departing fundamentally from thermal-conversion / turbine based systems and moving much more completely to a fusion-like paradigm, as was originally conceived. Departing fundamentally from the conventional energy processing paradigm, proposed are more efficient energy collection and conversion systems “directly” collecting particle flows and wave radiation, converting them more efficiently to usably power for distribution, and recycling flows required for the accelerator-driven system. Thus, by those greater net efficiencies, thereby enabling a wider range of feedstock / fuel types and cycles generalized, while also providing: 1) a significantly more efficient Thorium-cycle system, in one configuration, 2) a more energy-productive nuclear waste reduction system, in another configuration, 3) accelerator driven systems for other fertile-fission candidate elements, and 4) which may be applied to fusion systems (substituting the fission unit in the proposed system class and category) in a way that may lower the break-even point for such systems and thus make the advent of practical fusion sooner than otherwise possible. 5) In addition and importantly, an optical-power processing and distribution is also enabled by the proposed, providing both optical power as base power for telecom, process energy for industrial uses, and lighting and other wavelengths for consumer and general business use.
Owner:ELLWOOD JR SUTHERLAND COOK
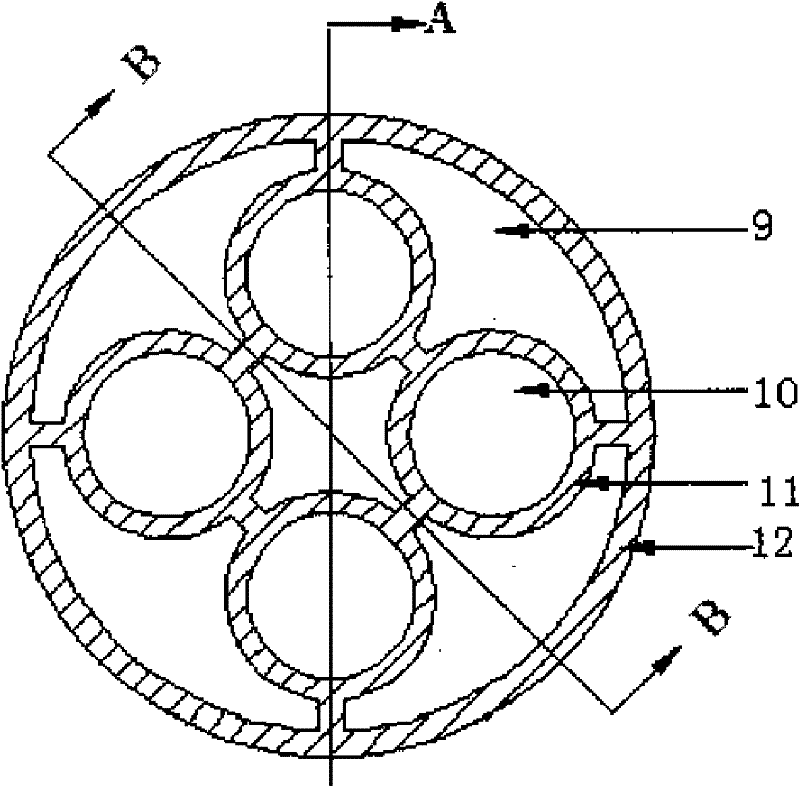
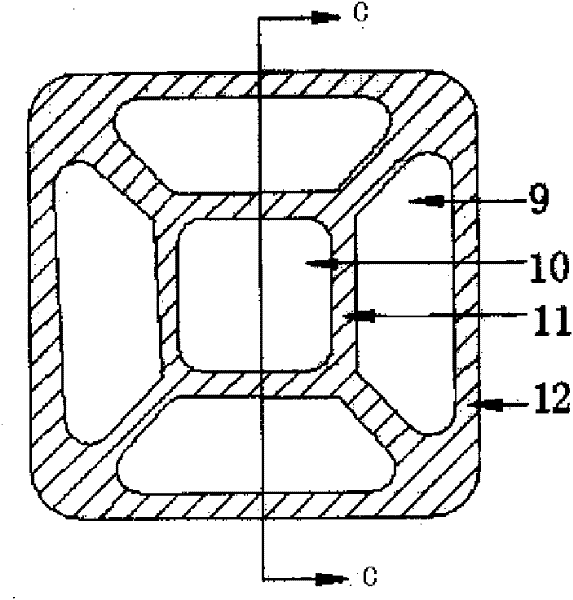
A Design Method for Hexagonal Accelerator-Driven Subcritical Reactor Fuel Assembly
ActiveCN109559835BImprove economyHigh neutron multiplication capacityFuel elementsNuclear energy generationSubcritical reactorNeutron multiplication
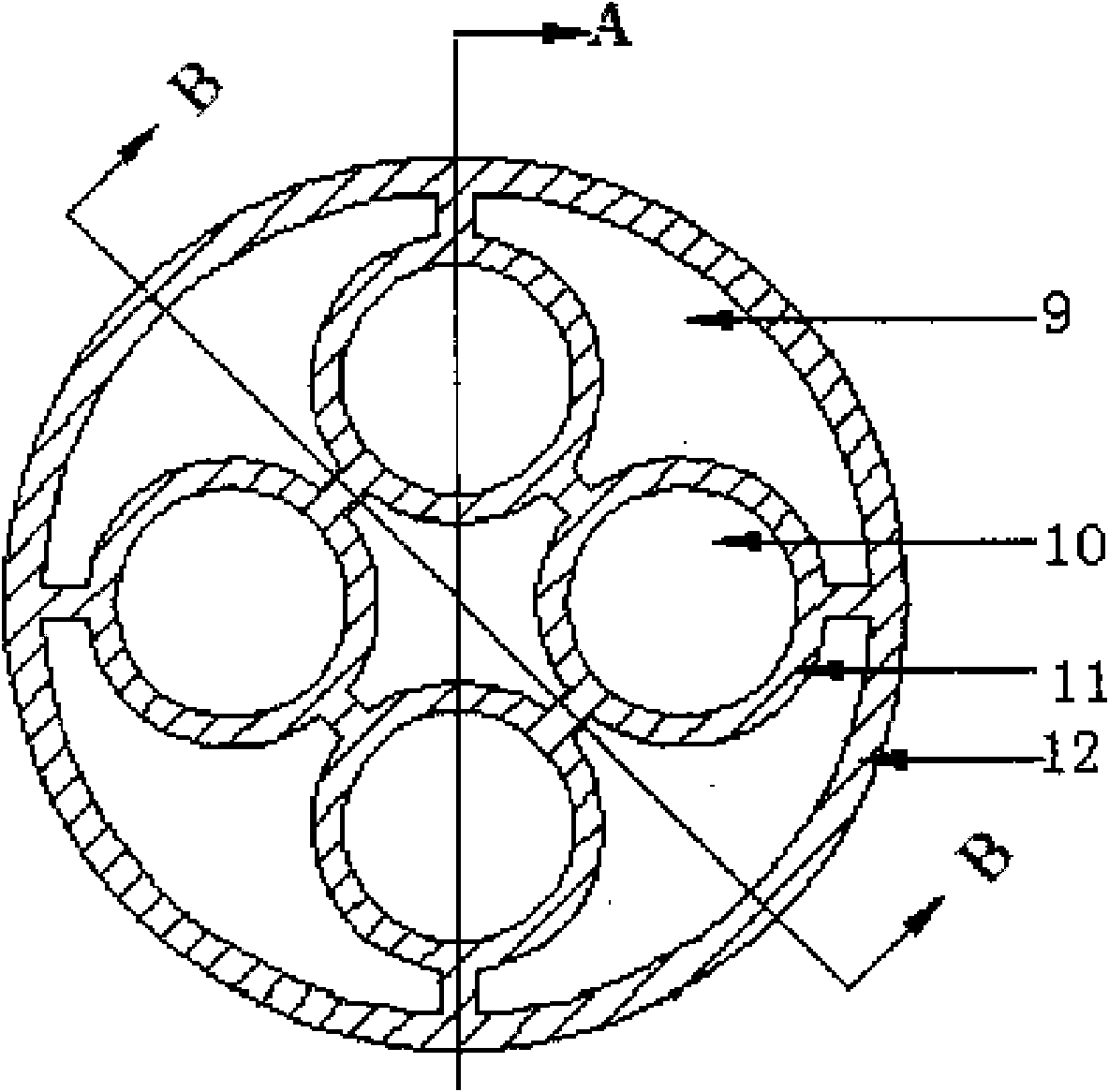
A hexagon accelerator driven subcritical reactor fuel assembly and a design method thereof are disclosed. The assembly includes a hexagon base the top surface of which is provided with a plurality ofbase units for fuel rod mounting, with one of the base units being at the center of the base, other base units surrounding the center base unit and being arranged in an annular array manner, distancesbetween adjacent base units being equal; a shell including a prismatic sleeve the cross section of which adapts to the shape of the base and the bottom of which is mounted on the base; an inner sleeve including a prismatic sleeve, disposed inside the shell with a gap between the inner sleeve and the shell, with the bottom of the inner sleeve being mounted on the base; and a plurality of fuel rods, wherein each fuel rod includes a cylindric casing and a core rod in the casing and made of fuel, the bottom of each casing is mounted in one base unit, and the number of the fuel rods is equal to the number of the base units. The assembly and the method are used for solving a problem that neutron performance is poor, and technical effects that economic performance and neutron performance are high are achieved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
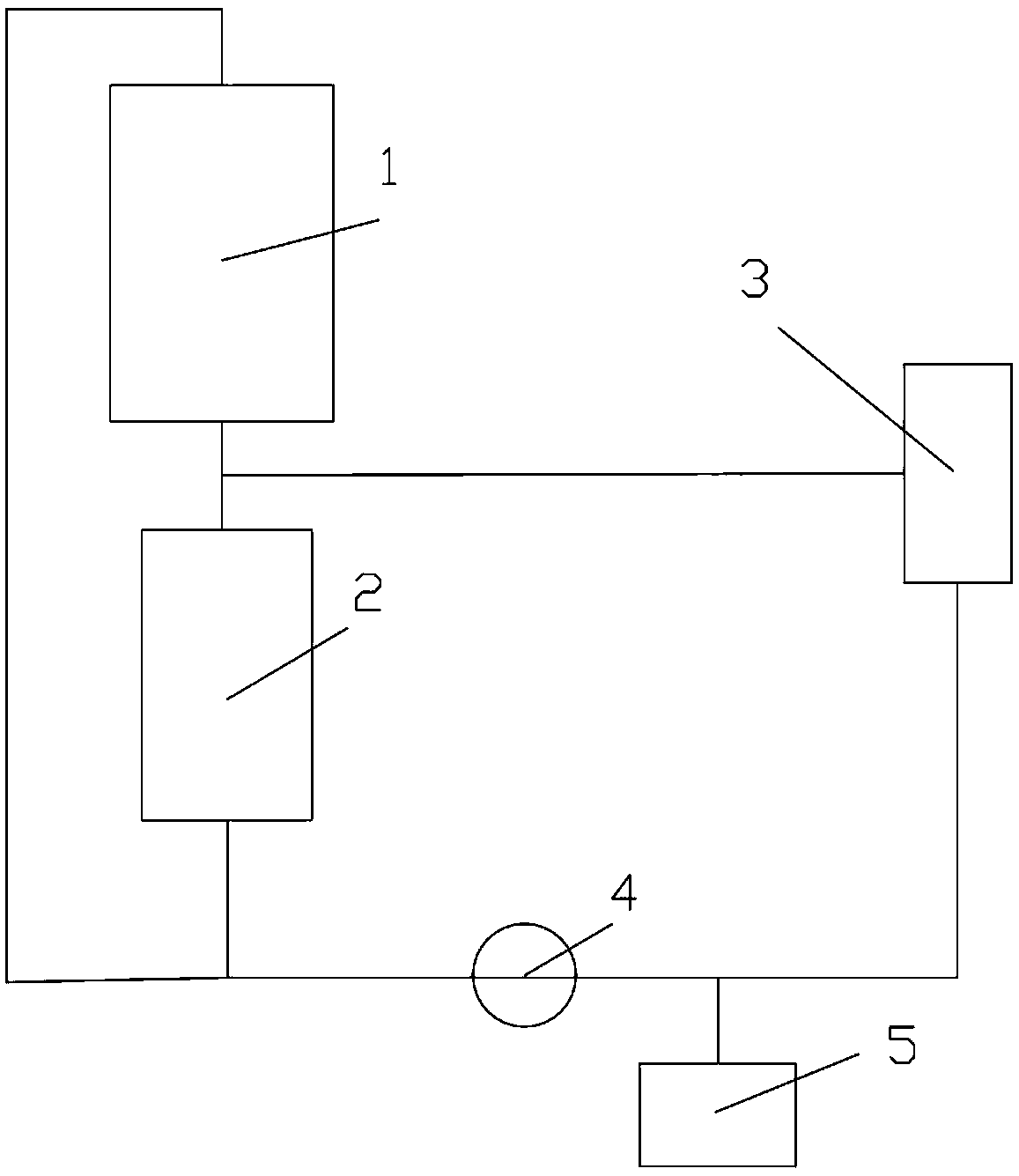
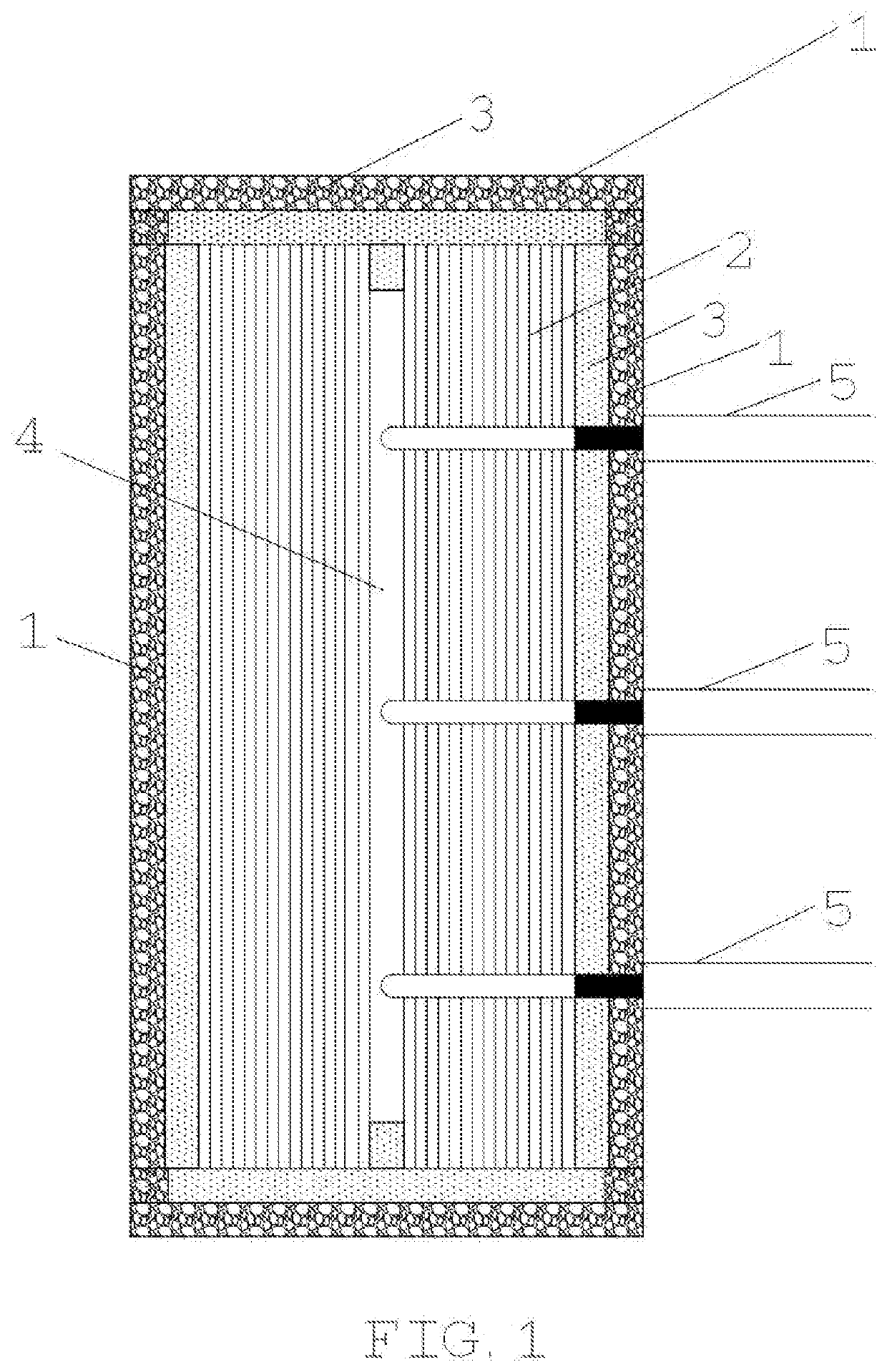
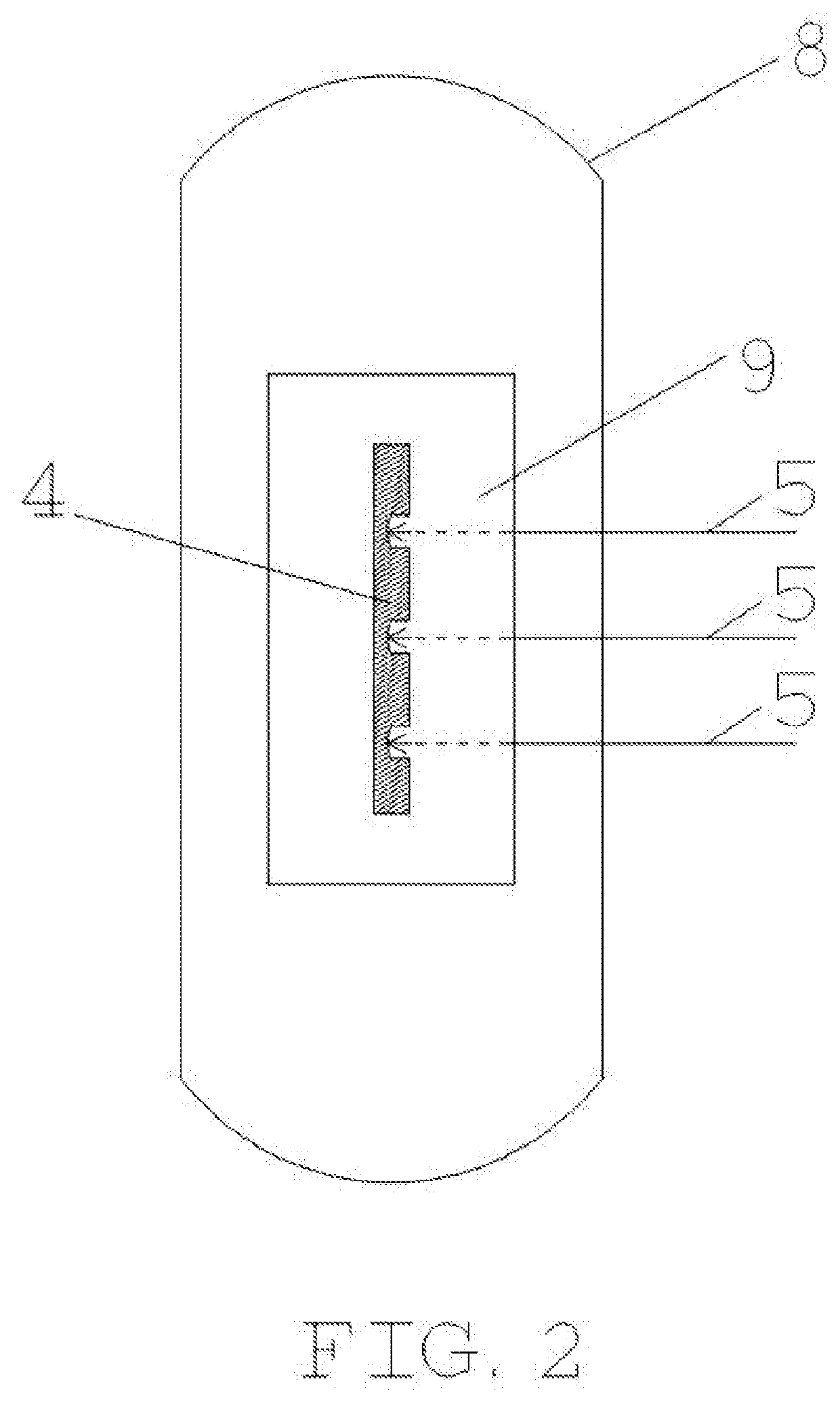
A Multi-Cock System for Accelerator-Driven Subcritical Stack Refueling
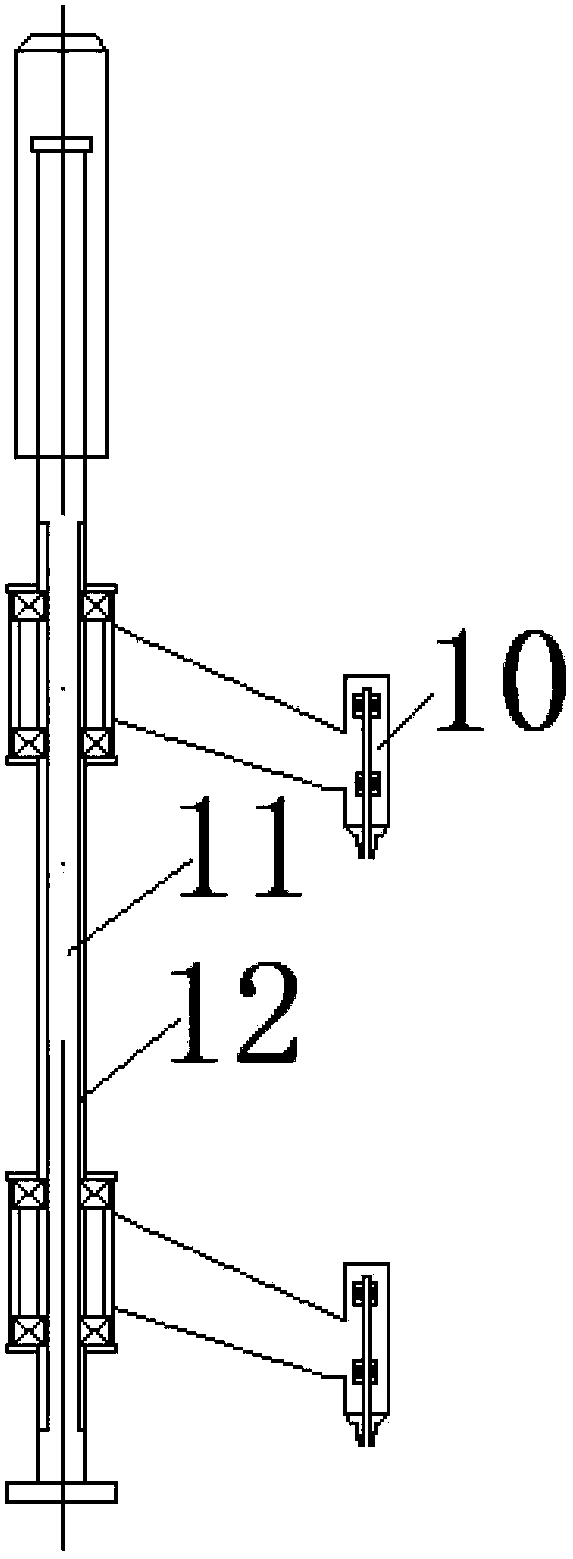
InactiveCN102708936BLittle room for movementEasy to separateNuclear energy generationReactor fuel elementsNuclear engineeringProton
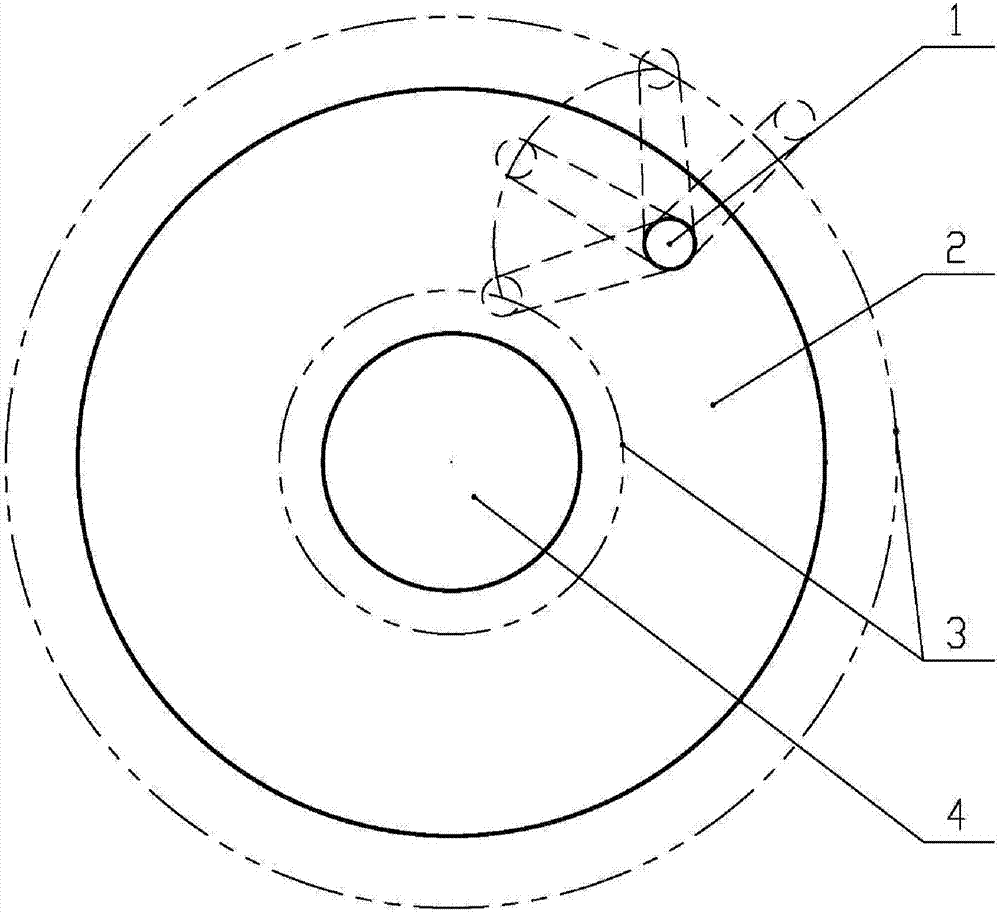
A multi-cock system for an accelerator to drive a subcritical reactor to refuel comprises a large cock, a first small cock, a second small cock, a control deflection barrel and a refueling machine, wherein the large cock is installed on a reactor top cover to be concentric with the reactor top cover, the first small cock and the second small cock are installed on the large cock and are eccentric to the large cock, the refueling machine is installed on the first small cock and is eccentric to the first small cock, the control deflection barrel is connected onto the second small cock, the control deflection barrel is a cylindrical mechanism carrying a control bar system, and the control deflection barrel is provided with a curved through groove from the axis to the outside and from top to bottom, which is used for detaching an accelerator proton beam tube. When the reactor runs, the control deflection barrel is positioned right above a reactor core. Fusible alloy at the sealed position of the cock is molten in refueling operation, the second small cock firstly translates the control deflection barrel to the position which is away from the reactor core so as to reserve a space for the refueling operation, and then a crankshaft connecting rod mechanism consisting of the large cock, the first small cock and the refueling machine can align the refueling machine to any refueling position on the reactor core through the reciprocating movement. Due to the adoption of the multi-cock system, the refueling circulation of an accelerator drive system (ADS) reactor can be well completed, and the normal work of other systems of the ADS is not influenced.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
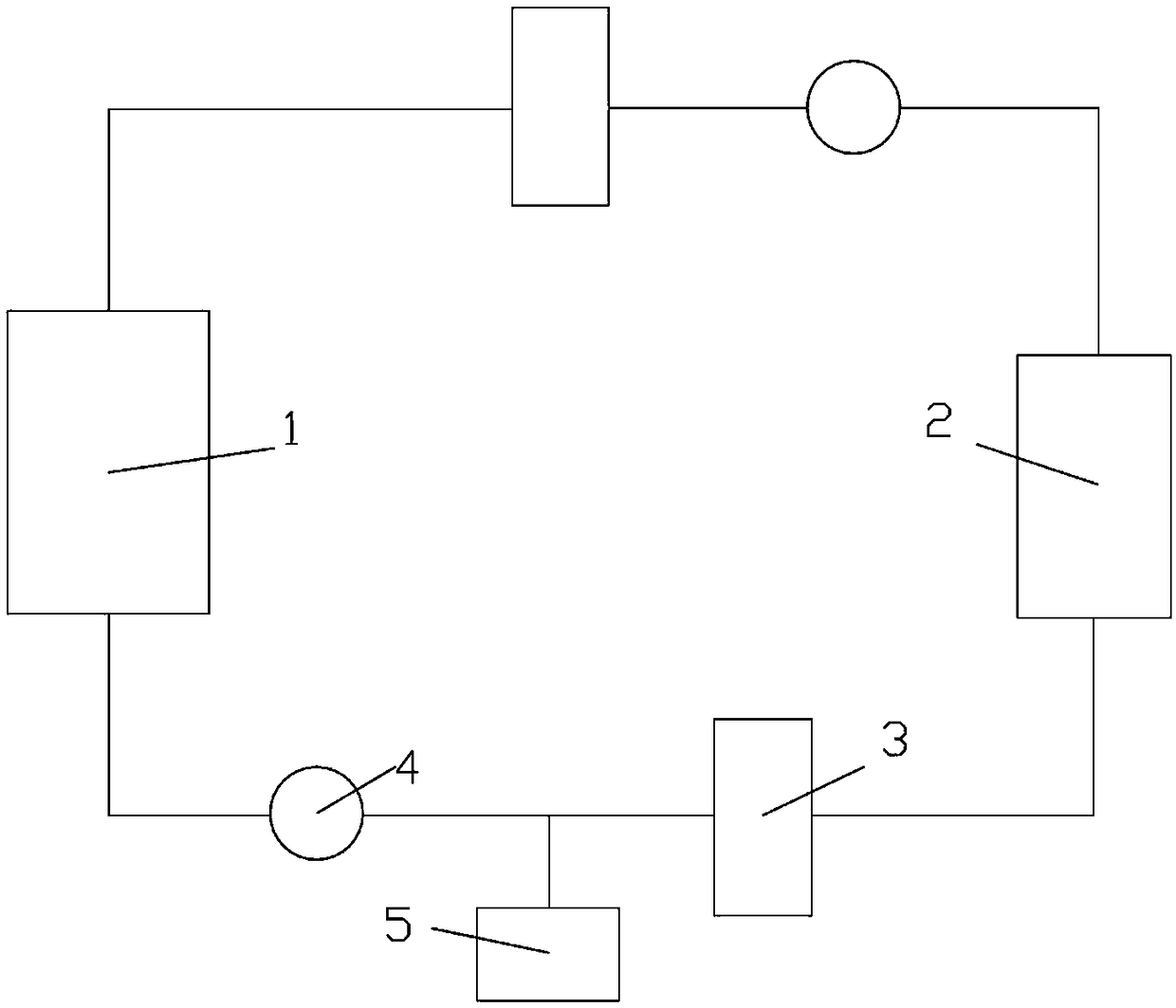
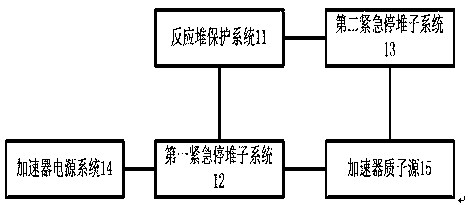
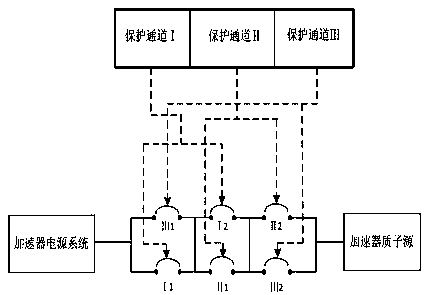
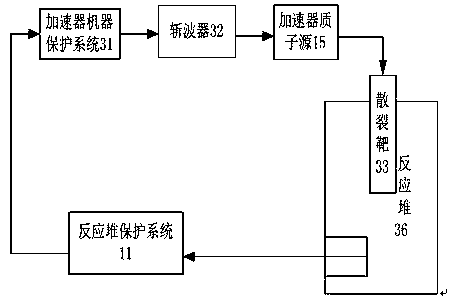
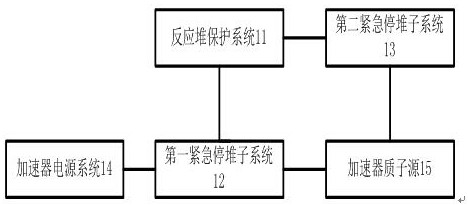
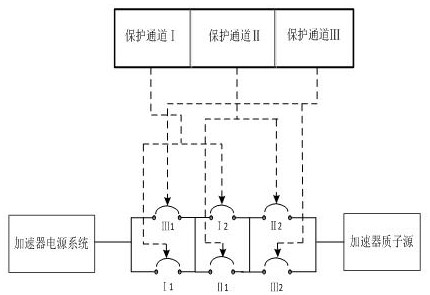
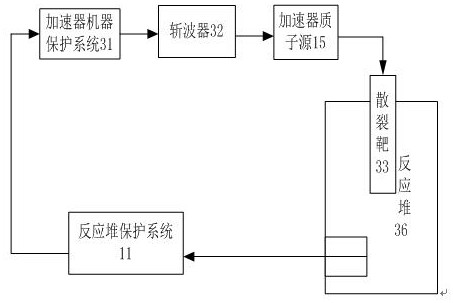
Emergency reactor-shutdown system and method for sub-critical reactor system
ActiveCN108831570ARealize emergency shutdownThe chain reaction cannot be maintainedNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsReactor systemNuclear engineering
The invention provides an emergency reactor-shutdown system and method suitable for accelerator driving for a sub-critical reactor system. The emergency reactor-shutdown system includes a first emergency reactor-shutdown subsystem used for controlling a reactor-shutdown circuit breaker to cut off a path between an accelerator proton source and an accelerator power source system according to an emergency reactor-shutdown signal emitted by a reactor protection system, and a second emergency reactor-shutdown subsystem used for controlling an accelerator chopper to set an accelerator proton beam current pulse duty ratio to a minimum value according to a transient signal which cannot realize emergency reactor shutdown emitted by the reactor protection system. The system and method provided by the invention can realize the emergency reactor shutdown by adopting the second emergency reactor-shutdown subsystem in the case that the first emergency reactor-shutdown subsystem fails to realize theemergency reactor shutdown, thereby greatly improving safety of a reactor.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +2
Non-centrosymmetric single-beam accelerator driven subcritical reactor
PendingCN112837830AImprove energy efficiencyHigh economic advantageNuclear energy generationSubcritical reactorsNuclear engineeringProton
The invention discloses a non-centrosymmetric single-beam accelerator driven subcritical reactor. The single-beam accelerator driven subcritical reactor comprises a proton beam, a spallation target, a fuel area and a radiation shielding layer, the radiation shielding layer wraps the periphery of the fuel area, the spallation target is located at a non-central position in the fuel area, and is inserted into the fuel area in a penetrating manner along the axial direction, and a proton beam is inserted into the spallation target along one axial end of the spallation target. According to the single-beam accelerator driven subcritical reactor provided by the invention, the proton beam and the spallation target are arranged at the non-central position of the fuel area, and under the same parameters, the neutron multiplication factor of the single-beam accelerator driven subcritical reactor provided by the invention is improved by 0.02399 compared with that of a centrosymmetric ADS; and the integral energy efficiency of the reactor is improved under the condition that the charging amount is not increased, high economic advantages are achieved, the refueling operation of the refueling mechanism is obviously simplified, engineering implementation is simpler, more convenient and safer, and the economical efficiency is better.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method for inverse dynamic measurement of subcriticality without space effect
ActiveCN106297920BLow powerIncrease powerNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringInverse dynamicsDelayed neutron
The invention provides a subcritical degree reverse dynamic measuring method free of a space effect. Compared with other methods, the method is characterized in that subcritical degree online measurement free of the influence of the space effect is achieved, wherein a stationary source mode is selected to work out space positions with the neutron-flux density normalization shape function unchanged after the state of a reactor is changed to arrange detectors; the reference subcritical degree of a subcritical reactor and the neutron-flux density under the condition that a stable external source is available are measured based on a pulse neutron source method or a source jerk method, and an external neutron source item is scaled with a subcritical inverse dynamic formula; the subcritical degree is calculated on line according to time-sequence data read at the positions of the detectors. The method has the advantages that the influence of redistribution of the neutron-flux shape space is avoided when the subcritical degree is measured; the delay effect of delayed neutrons can be responded to; the subcritical degree can be measured online in real time regardless of low power or high power.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Experimental device for heat transfer characteristics of curved single-channel flow of subcritical energy reactor coolant
The invention discloses an experimental device for flow and heat transfer characteristics of a curved single passage of a subcritical energy reactor coolant. The experimental device comprises a curved heating single tube, wherein the two ends of the heating single tube are communicated with stabilizing straight tubes, and the stabilizing straight tubes are communicated with threaded joints, the threaded joint are sleeved with threaded flanges; the stabilizing straight tubes are welded with powered copper bars, and pressure diversion holes are formed in the stabilizing straight tubes; the heating single tube is an eccentric curved tube or a concentric curved tube; the center of an inside diameter circle of the eccentric curved tube is O1, the center of an outside diameter circle of the eccentric curved tube is O2, the distance between the O1 to the O2 is larger than zero, and a line segment for connecting the O1 to the O2 is O1O2; the eccentric curved tube is welded with a thermocouple, and a heat insulation protection structure is arranged on the outer wall of the eccentric curved tube; the center of an inside diameter circle of the concentric curved tube and the center of an outside diameter circle of the concentric curved tube are overlaid at a point X1, a plurality of thermocouples are welded on the outer wall of the concentric curved tube, and a heat insulation protection structure is arranged on the outer wall of the concentric curved tube. The experimental device can provide experiment support for the feasibility study on a thermo-hydraulic design of the subcritical reactor coolant.
Owner:NUCLEAR POWER INSTITUTE OF CHINA
Passive natural-circulation lead bismuth heat exchange device and method for discharging heat out of reactor core
InactiveCN102446564BImprove securityImprove reliabilityNuclear energy generationStationary tubular conduit assembliesLead bismuthNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a passive natural-circulation lead bismuth heat exchange device for heat transfer by a lead bismuth fluid and a method for discharging heat out of reactor core, belonging to the field of nuclear energy heat exchange equipment. The heat exchange device particularly comprises two natural-circulation heat transfer loop structures, namely a round loop and a square loop, and is a device which realizes natural-circulation heat transfer at two sides. The inner ring of an inner ring pipe is a primary side lead bismuth alloy fluid passage, and a secondary side fluid passage is arranged between the outer ring of the inner ring pipe and the inner wall of an outer ring pipe. Heat generated by a subcritical reactor of an ADS (accelerator driven system) is transferred to coolants of the two loops by the liquid lead bismuth alloy through the inner ring pipe of the device, the lead bismuth alloy flows through the device to exchange heat with a secondary side fluid. The primary side heat exchange fluid and the secondary side heat exchange fluid form natural circulation under the driving of a density difference, and the high-efficiency, energy-saving, safe and reliable passive characteristic is achieved. The device is simple and easy to operate, is free of a complicated lead bismuth pump, is in no need of a power source and has the characteristics of energy conservation, high safety and high reliability. The passive natural-circulation lead bismuth heat exchange device and the method for discharging heat out of the reactor core comply with the current policy of energy conservation and emission reduction and are easy in market promotion.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method and equipment for simultaneously removing VOCs and PM2.5
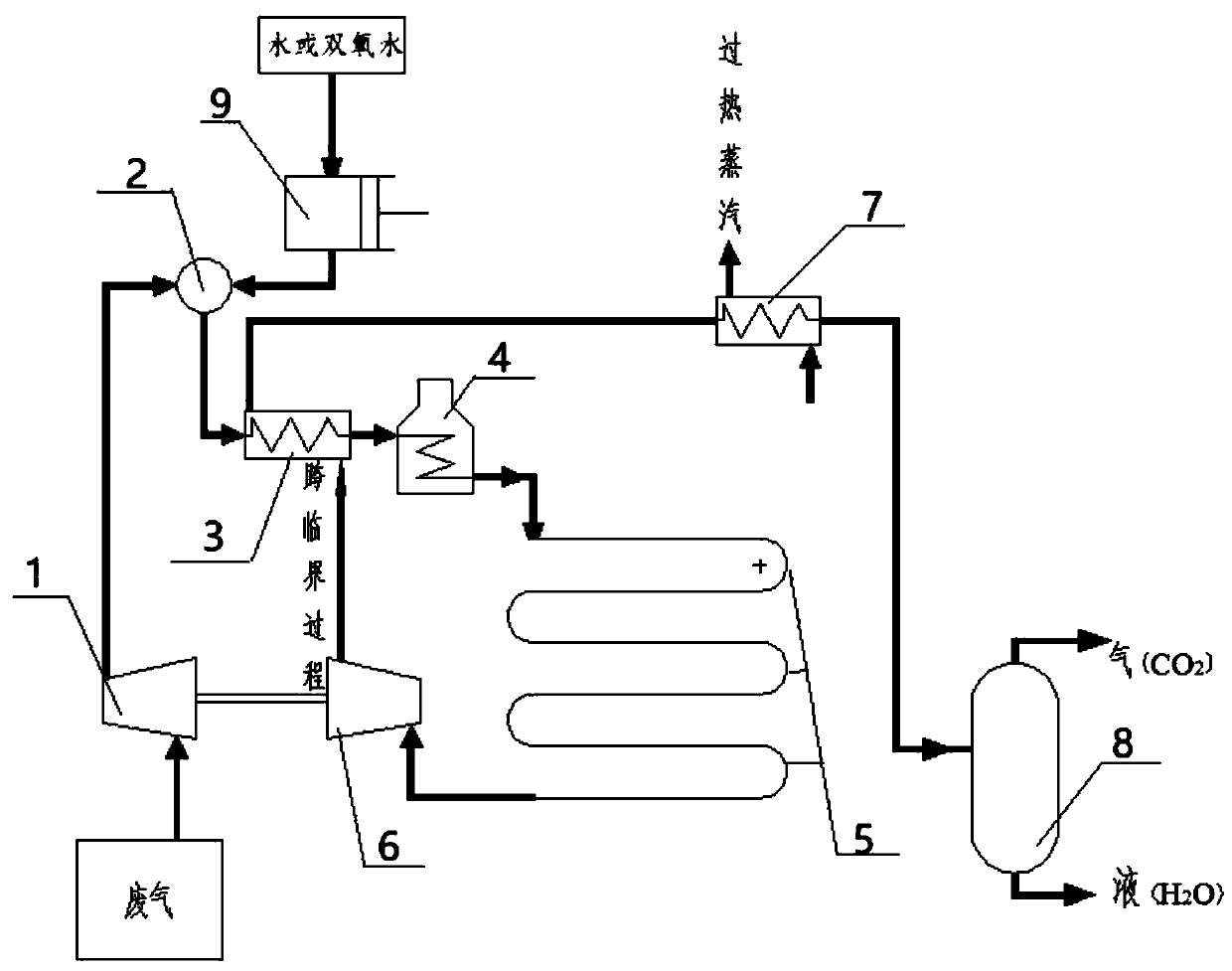
PendingCN111346483AEfficient governanceNo secondary pollutionGas treatmentDispersed particle separationSorbentExhaust fumes
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously removing VOCs and PM2.5. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pressurizing waste gas containing VOCs and / or PM2.5 by a compressor and thenconveying the waste gas to a mixer; (2) pressurizing water or hydrogen peroxide through a pressurizing pump, conveying the pressurized water or hydrogen peroxide to a mixer for mixing, and conveying an obtained mixture to a preheating-cooling device and a high-temperature preheater for heating; (3) performing water oxidation reaction in a supercritical / subcritical reactor to remove VOCs and PM2.5;(4) conveying high-temperature and high-pressure fluid flowing out of a turbo expander into a preheating-cooling device to heat the materials; (5) taking high-temperature and high-pressure fluid flowing out of the preheating-cooling device as a heat source of a waste heat boiler to generate superheated steam; and (6) conveying fluid flowing out of the waste heat boiler into a gas-liquid separatorafter pressure reduction, and carrying out separation of gas and liquid. The method provided by the invention does not need any adsorbent, flocculant or catalytic combustion, and the device is simpleto operate, energy-saving, environment-friendly and easy to implement.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
A molten salt fuel multi-stack system
ActiveCN109273121BIncrease production capacityAchieve multiplicationNuclear energy generationNuclear plant auxillary equipmentReactor systemControl system
The invention discloses a fused-salt fuel multi-reactor system. The fused-salt fuel multi-reactor system comprises a reactor module, a heat exchange module, a pump module and a fuel processing module,wherein the reactor module comprises a type I reactor module and a type II reactor module, which adopt the same kind of fused-salt fuel flowing therein; and the type I reactor module and the type IIreactor module are serially and / or parallelly arranged. The type I reactor module operates in an overmoderated region or near the optimal grid point, is used for realizing productivity and multiplication, and comprises a set of reactivity control system which is used for controlling reactivity variation of the rectors. The type II reactor module operates in an undermoderated region and non-moderated region, is used for multiplication and transmutation, belongs to a subcritical reactor, and comprises a set of neutron source systems for driving the reactors. The fused-salt fuel multi-reactor system disclosed by the invention fully utilizes the fluidity of the liquid fuel, and can realize the functions of productivity, multiplication, transmutation and the like in the same system.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of nuclear entropy alloy system and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112981210BNuclear reaction cross section is smallReduced induced radioactivityOptical rangefindersNuclear energy generationHeat stabilityLiquid metal
The invention discloses a nuclear medium-entropy alloy system and its preparation method and application, and belongs to the technical field of medium-entropy alloy materials and their preparation. The FeCrV system of the present invention is composed of four low activation elements Fe, Cr, V and M (one of Ti, Mn, Ni, Zn), wherein the atomic molar ratio of Fe, Cr, V and M is 1:1: 1:x, 0≤x≤0.5. FeCrV medium entropy alloy materials with low activation, high temperature resistance, high strength and high toughness for nuclear use were prepared by using magnetic levitation (no contact between metal raw material samples and crucible) arc melting method and annealing heat treatment after raw material treatment and weighing ratio. The low-activation FeCrV-based medium-entropy alloy material of the invention exhibits excellent high-temperature thermal stability, high strength and high toughness. The medium entropy alloy is expected to be used in ADS spallation target window and subcritical reactor core, fusion reactor and fourth generation nuclear fission reactor core, as well as structural material or coating material in strong acid environment or liquid metal environment.
Owner:INST OF MODERN PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Utilizing Multiple Proton Injection Ports in Accelerator Driven Subcritical Reactor for Direct Adopting Spent Fuels from Light Water Reactors
PendingUS20210391094A1Simple materialLow costConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsNuclear energy generationFuel reprocessingProton implantation
The new features of an accelerator driven subcritical reactor disclosed by this invention include the multiple intake ports connected to the reactor vessel for delivering protons from one or more accelerators to accommodate the full length LWR spent fuels for furnishing the desirable neutron distribution in a subcritical core to incinerate nuclear wastes. This is based on the notion of adopting the spent fuels in intact form to feed directly to the newly designed subcritical core. External modulators in the proton intake ports have the ability of splitting the fluxes and adjusting their energy from one or more accelerators to form multiple proton streams arriving at different axial locations in the spallation target for creating multiple neutron sources. The new design could combine the cycles of reprocessing spent fuels, manufacturing fuels for reuse, and incinerating minor actinides into one single cycle.
Owner:CHAO JIATSONG JASON
An emergency shutdown system and method for a subcritical reactor system
ActiveCN108831570BRealize emergency shutdownThe chain reaction cannot be maintainedNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsReactor systemNuclear engineering
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER TECH RES INST CO LTD +2
A method of monitoring the reactivity of a subcritical reactor
ActiveCN109903866BMonitor reactive changes in real timeNot affected by external strengthNuclear energy generationNuclear monitoringCritical conditionNuclear engineering
The invention relates to a method for monitoring sub-critical reactor reactivity. The method includes the steps: placing neutron detectors at two different positions of a reactor; effective multiplication constant gradually changing the reactor reactivity, and recording a specific value C and an effective multiplication constant keff of neutron counting rate at the same moment; fitting calibratingcurve graphs of the specific values C and the effective multiplication constants keff of the neutron counting rate of various moments; recording neutron counting rates of the two neutron detectors inreal time to obtain specific values of the two neutron counting rates, and substituting the specific values into the calibrating curve graphs to obtain effective multiplication constants of the effective multiplication constant when reactor reactivity is practically monitored. The neutron detectors are used for acquiring neutron counting rates, and the specific values C of the neutron counting rates recorded by two detectors represent characteristic parameters of neutron flux density space distribution shapes. Compared with a traditional method, the method is more visual, simple and convenient, on-line real-time monitoring of the reactivity change can be achieved, effects of external source intensity are omitted, and space effect correction of the traditional method under a deep sub-critical condition is avoided.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
A subcritical microreactor driven by a neutron tube
ActiveCN105590658BGood spectral monochromaticityStable outputNuclear energy generationSubcritical reactorsNuclear engineeringDensity distribution
The invention discloses a sub-critical miniature reactor driven by neutron tubes. The sub-critical miniature reactor comprises fuel rods, the neutron tubes, a coolant, cladding tubes, a reflecting layer, a shielding layer and other ingredients, wherein the neutron tubes are taken as neutron sources for operation of a sub-critical miniature reactor and are uniformly dispersed and distributed in a sub-critical reactor core, and the neutron-flux density distribution of the reactor core is initiatively flattened in design. The quantity of neutrons output by each neutron tube in the reactor core in unit time can be continuously adjusted, so that power in each position in the reactor can be continuously adjusted, and the output power in each position of the reactor core is actively controlled. Under the accident condition, a power supply for the neutron tubes can be turned off at any time as required, reactor shutdown is completed, and serious accidents are completely eradicated. Due to the advantages, the reactor has high safety and economic performance and has great significance in improvement of geometric dimension miniaturization and maneuverability of the reactor.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com