Patents
Literature
37 results about "Terabit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A terabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The terabit has the unit symbol Tbit or Tb. The terabit is closely related to the tebibit, a unit multiple derived from the binary prefix tebi of the same order of magnitude, which is equal to 2⁴⁰bits = 1099511627776bits, or approximately 10% larger than the terabit.
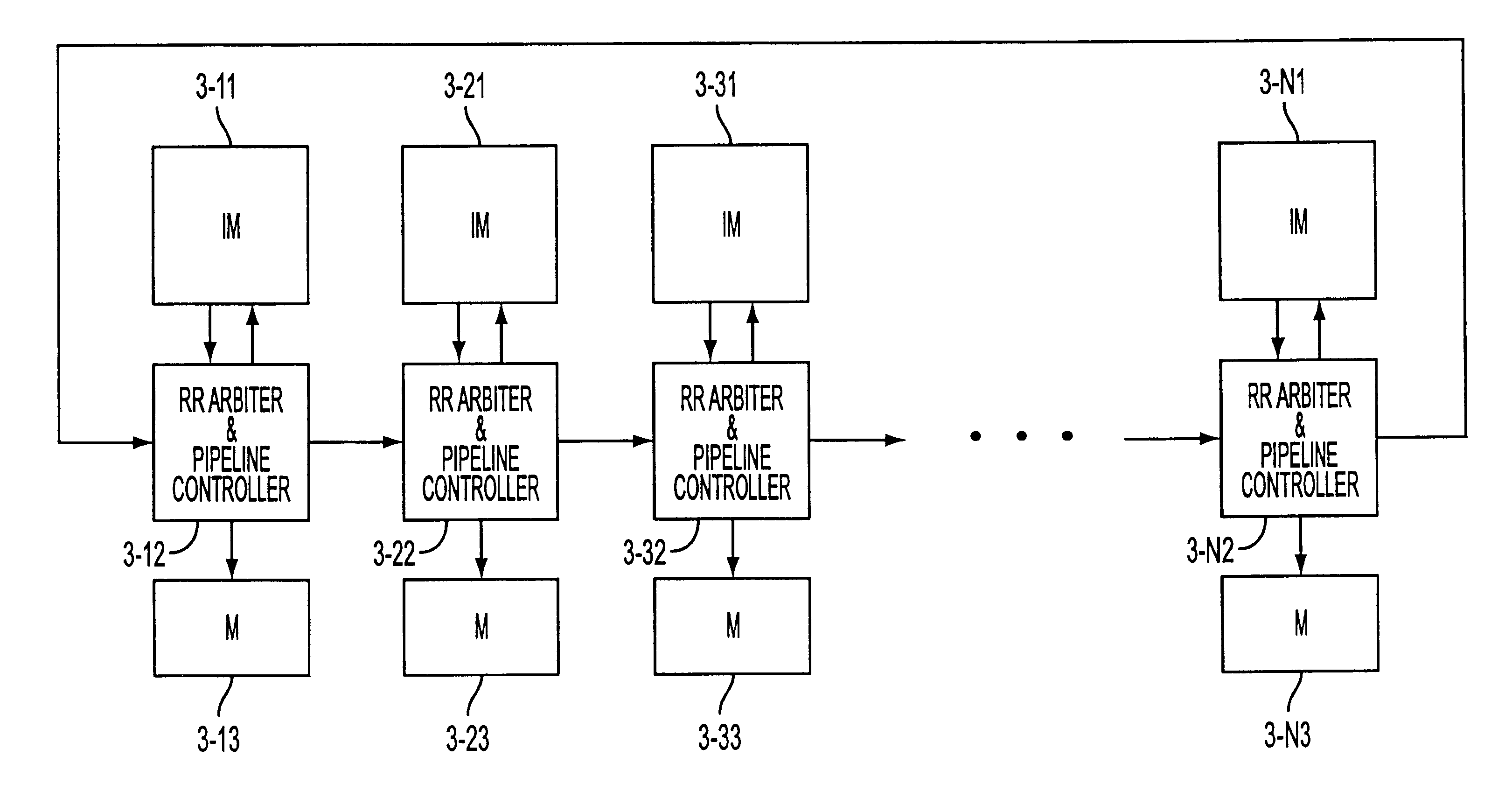
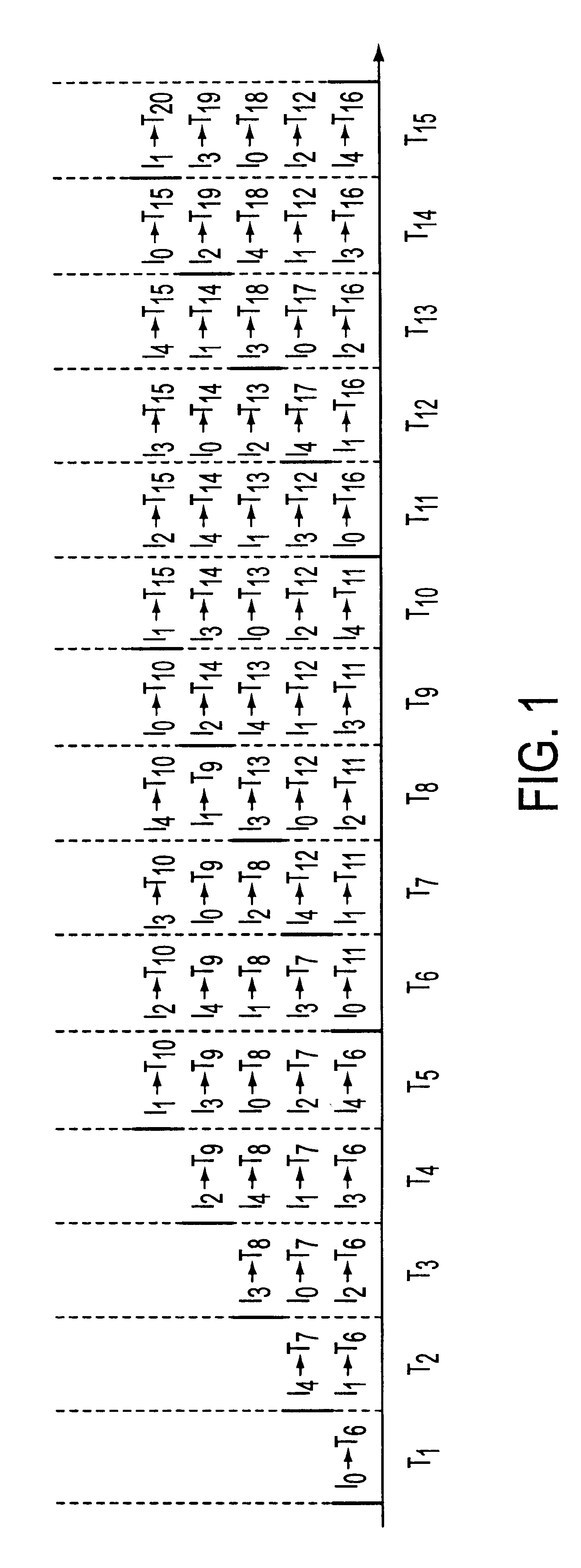
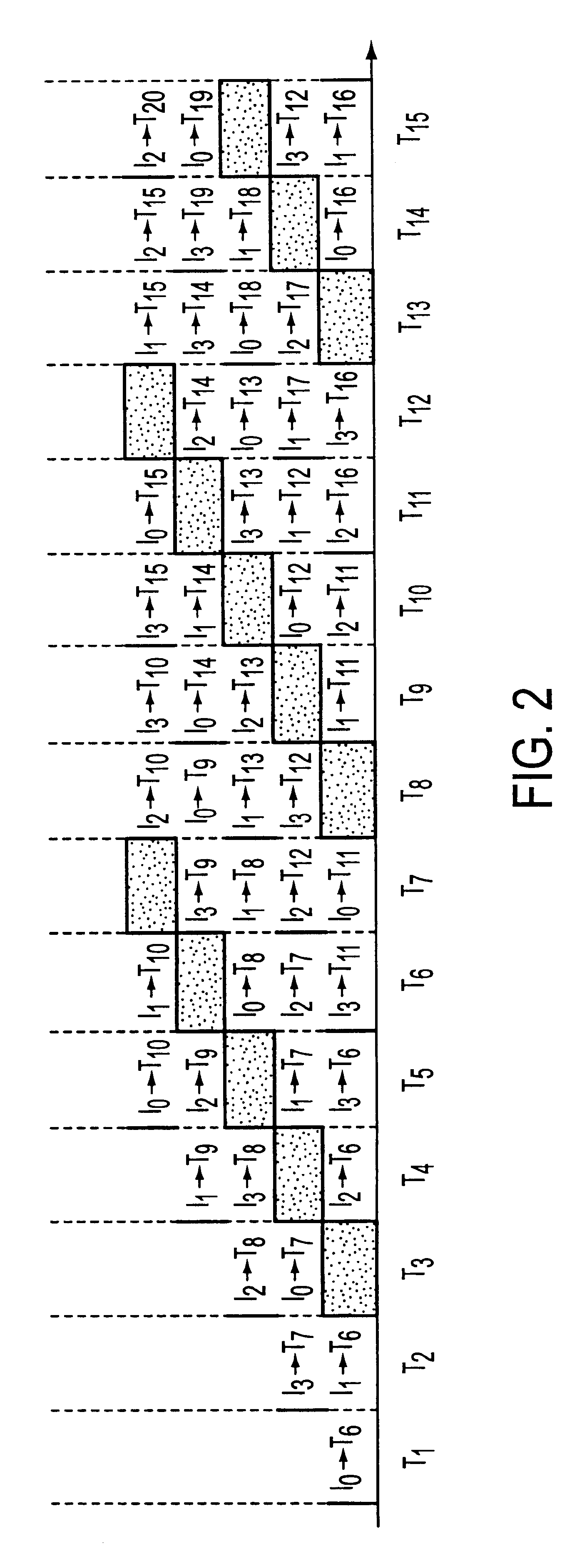
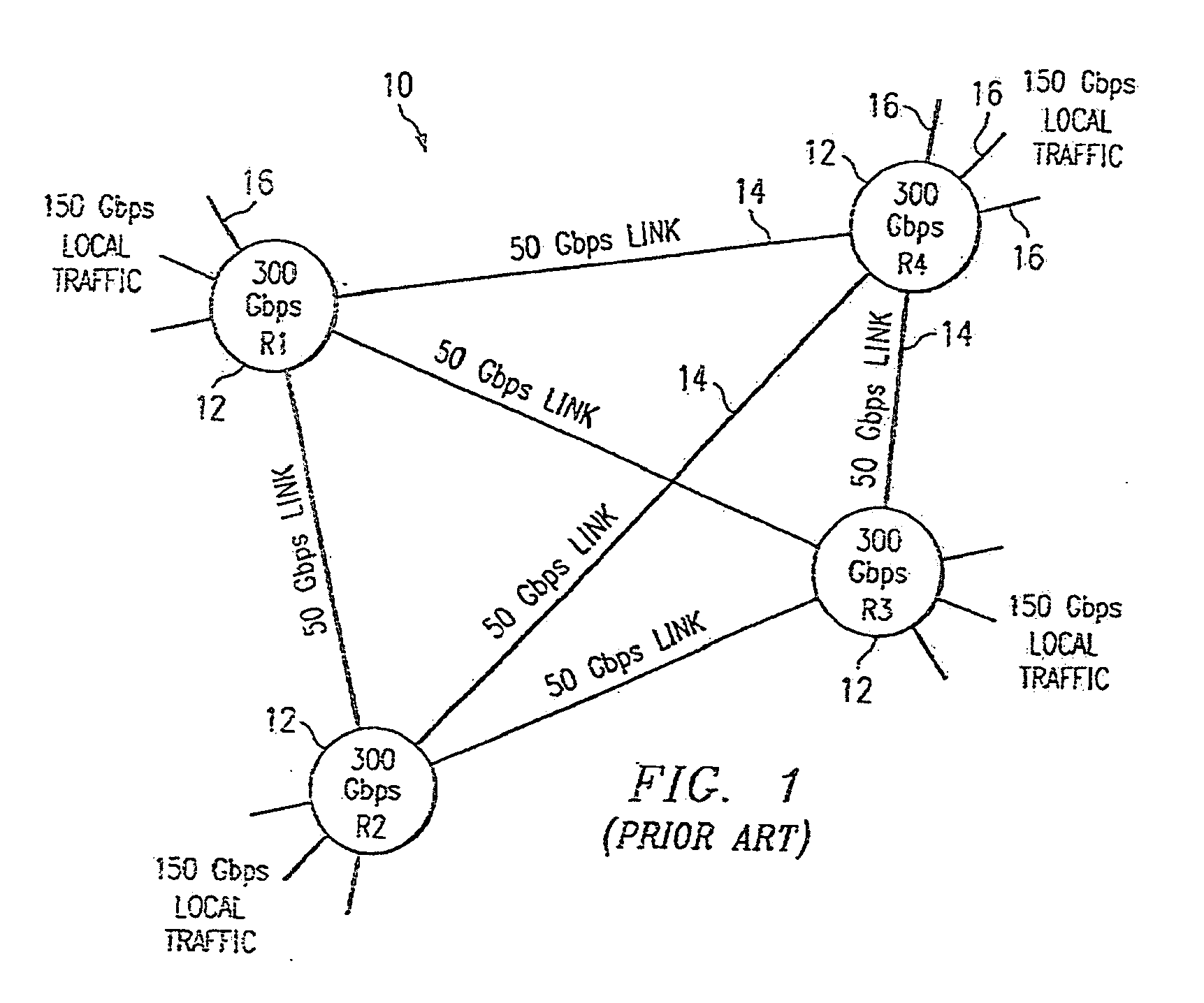
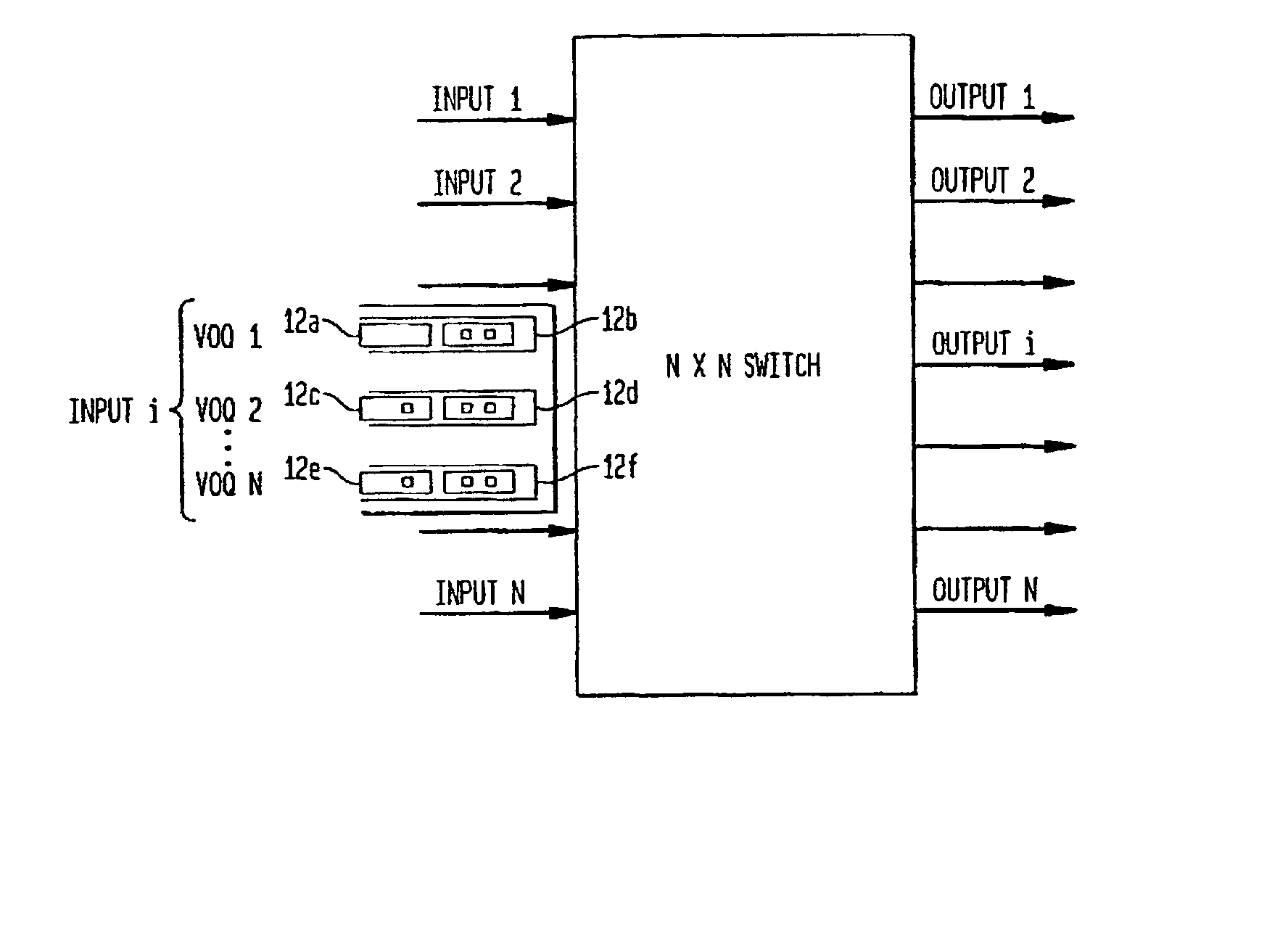
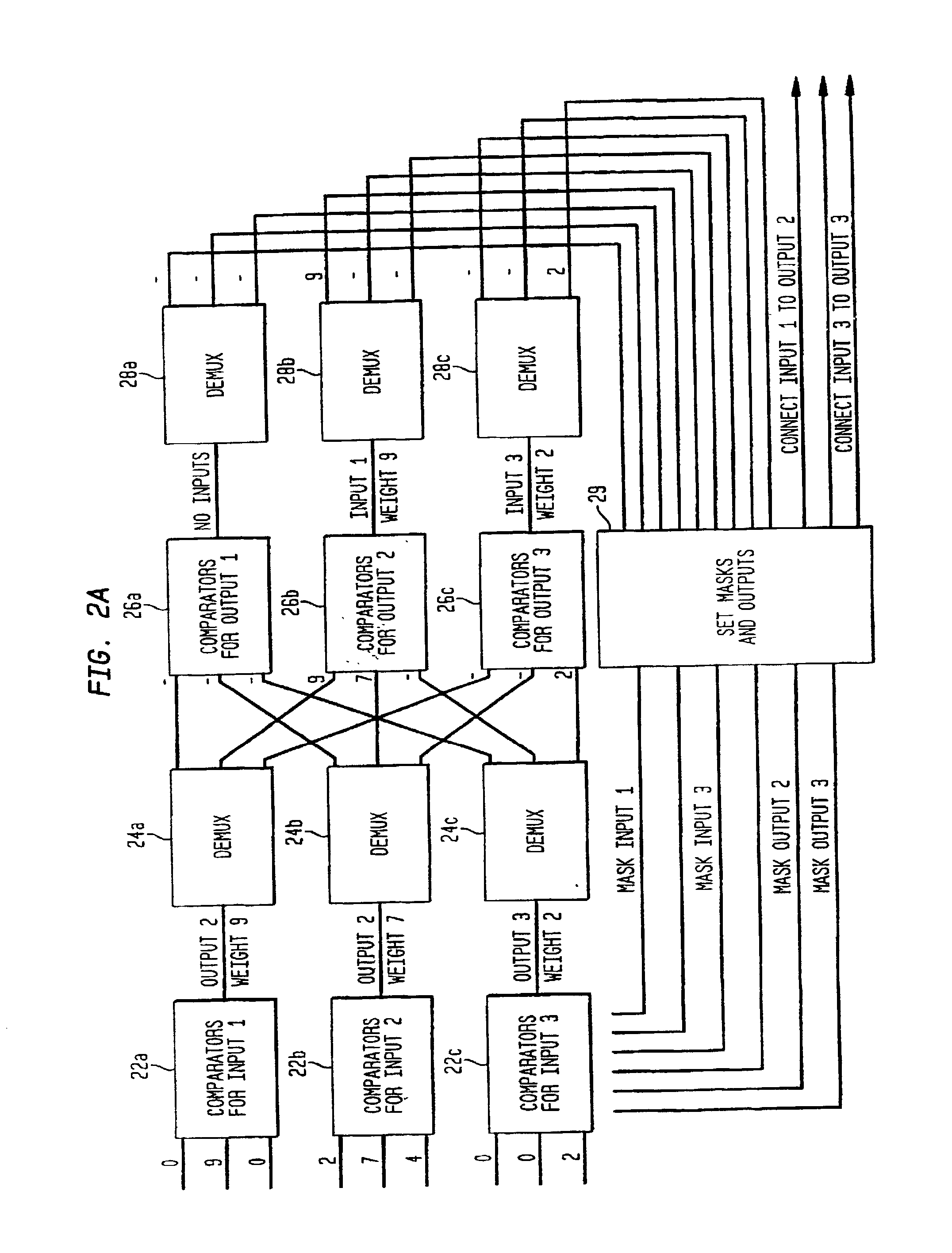
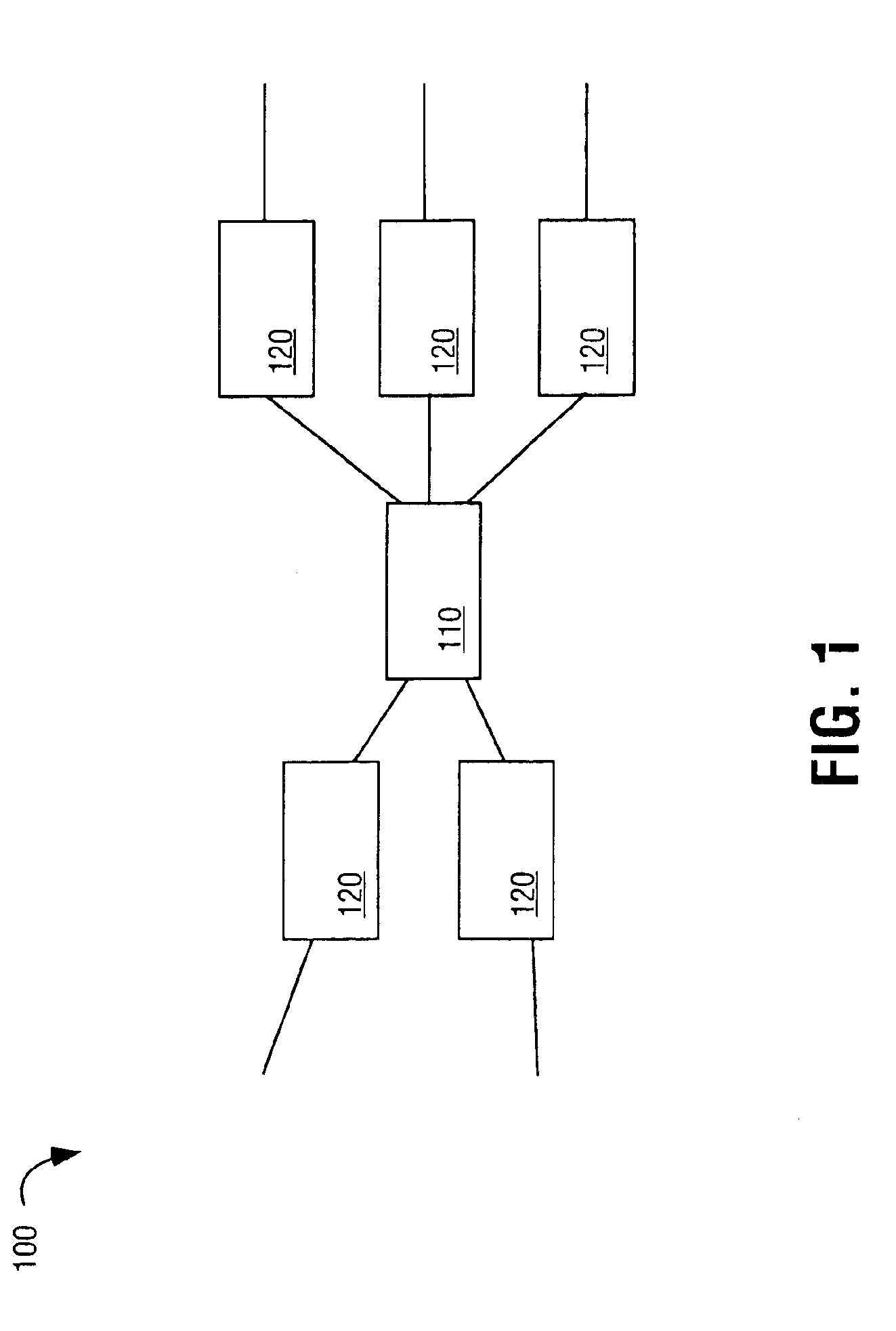
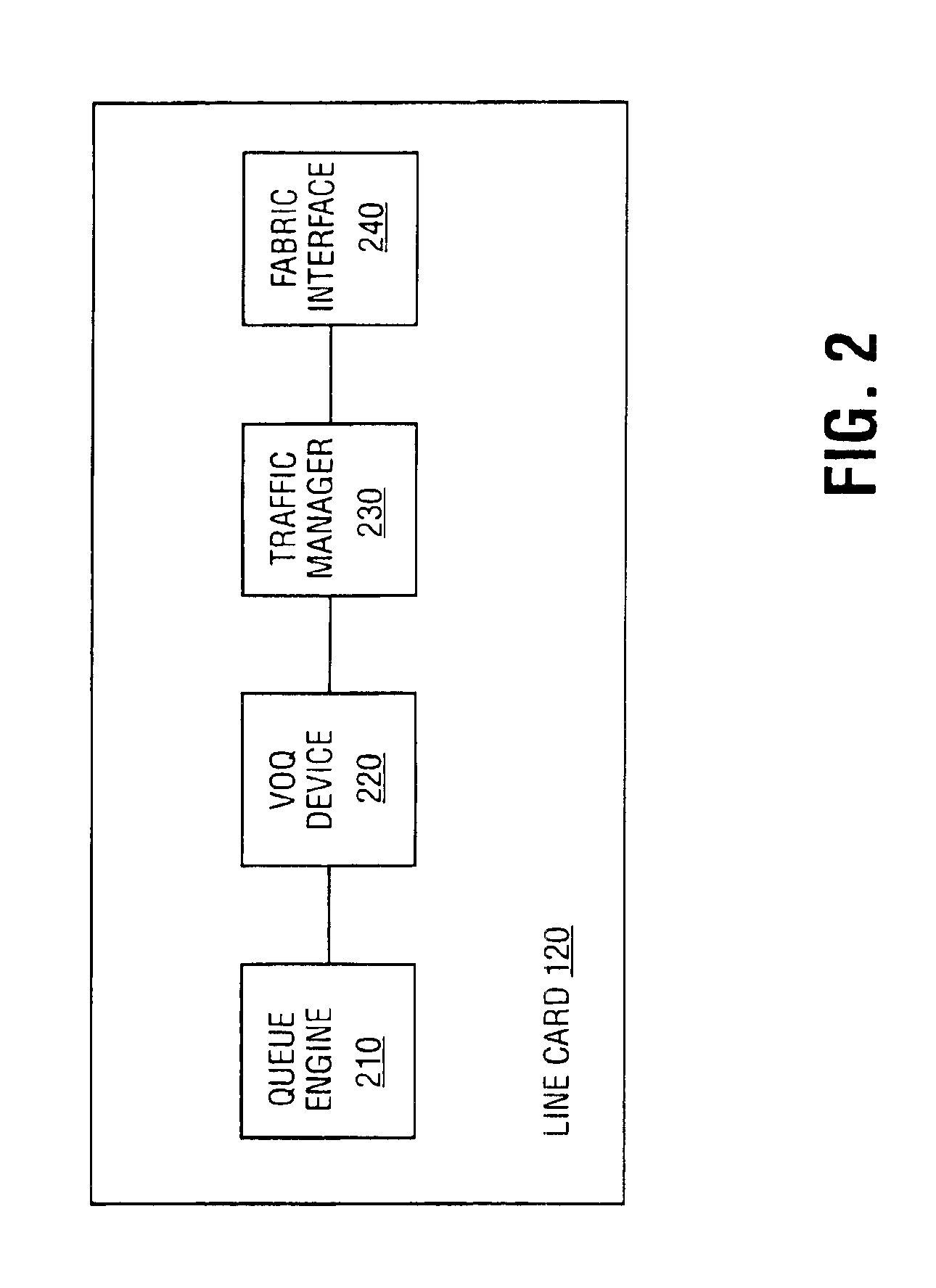
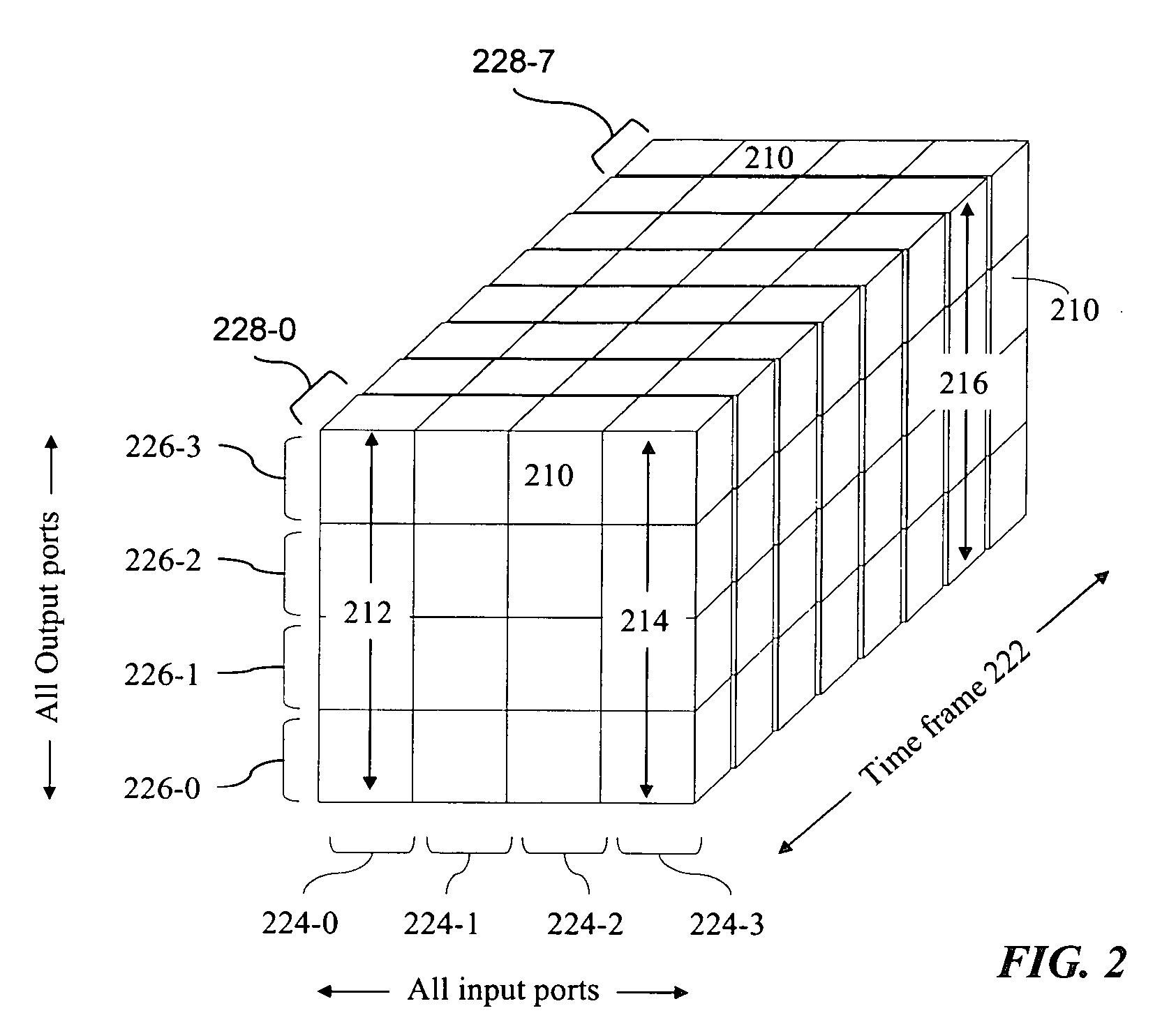
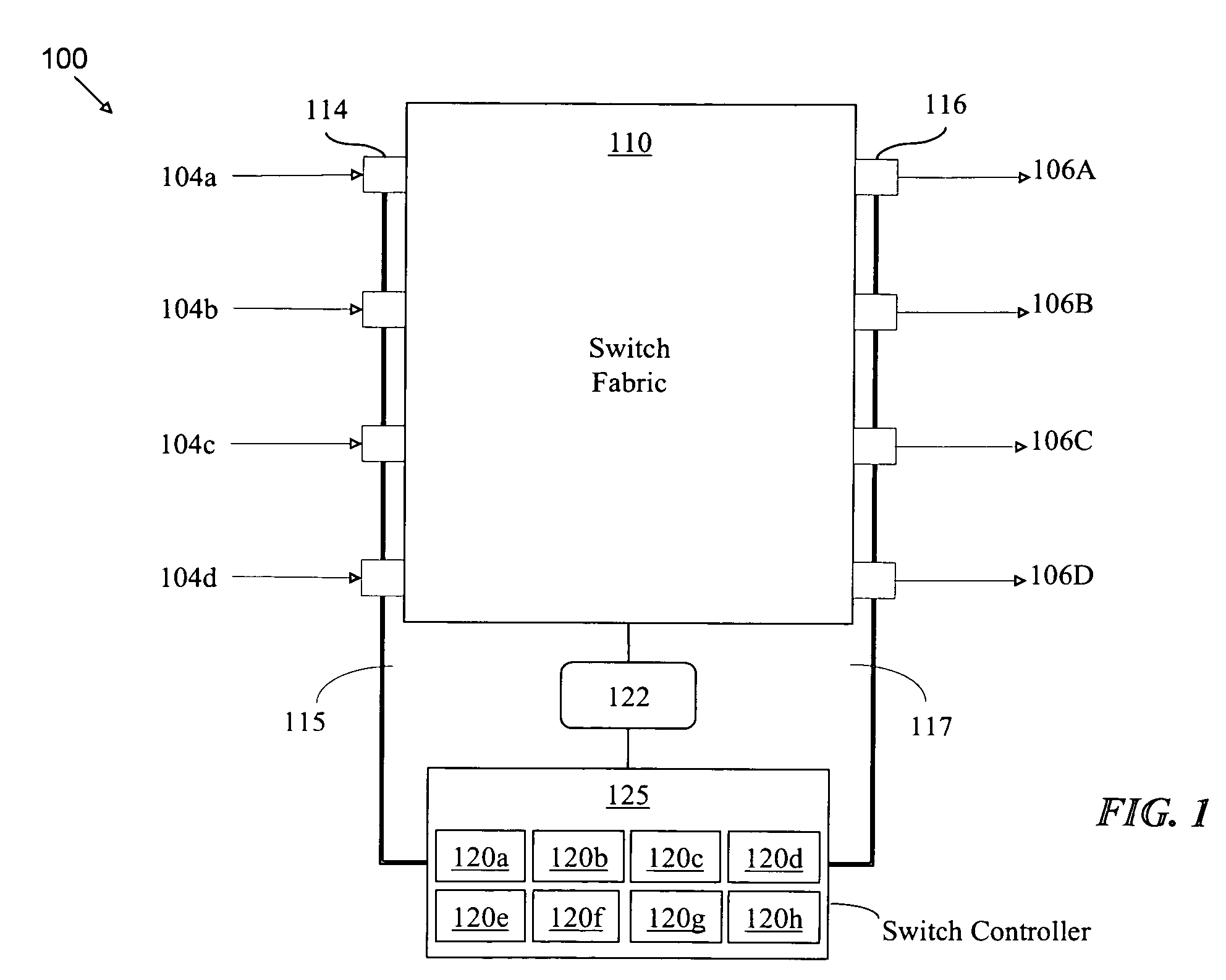
RRGS-round-robin greedy scheduling for input/output terabit switches
InactiveUS6618379B1Easy to useImprove performanceTime-division multiplexLoop networksCrossbar switchOptimal scheduling
A novel protocol for scheduling of packets in high-speed cell based switches is provided. The switch is assumed to use a logical cross-bar fabric with input buffers. The scheduler may be used in optical as well as electronic switches with terabit capacity. The proposed round-robin greedy scheduling (RRGS) achieves optimal scheduling at terabit throughput, using a pipeline technique. The pipeline approach avoids the need for internal speedup of the switching fabric to achieve high utilization. A method for determining a time slot in a NxN crossbar switch for a round robin greedy scheduling protocol, comprising N logical queues corresponding to N output ports, the input for the protocol being a state of all the input-output queues, output of the protocol being a schedule, the method comprising: choosing input corresponding to i=(constant-k-1)mod N, stopping if there are no more inputs, otherwise choosing the next input in a round robin fashion determined by i=(i+1)mod N; choosing an output j such that a pair (i,j) to a set C={(i,j)| there is at least one packet from I to j}, if the pair (i,j) exists; removing i from a set of inputs and repeating the steps if the pair (i,j) does not exist; removing i from the set of inputs and j from a set of outputs; and adding the pair (i,j) to the schedule and repeating the steps.
Owner:NEC CORP
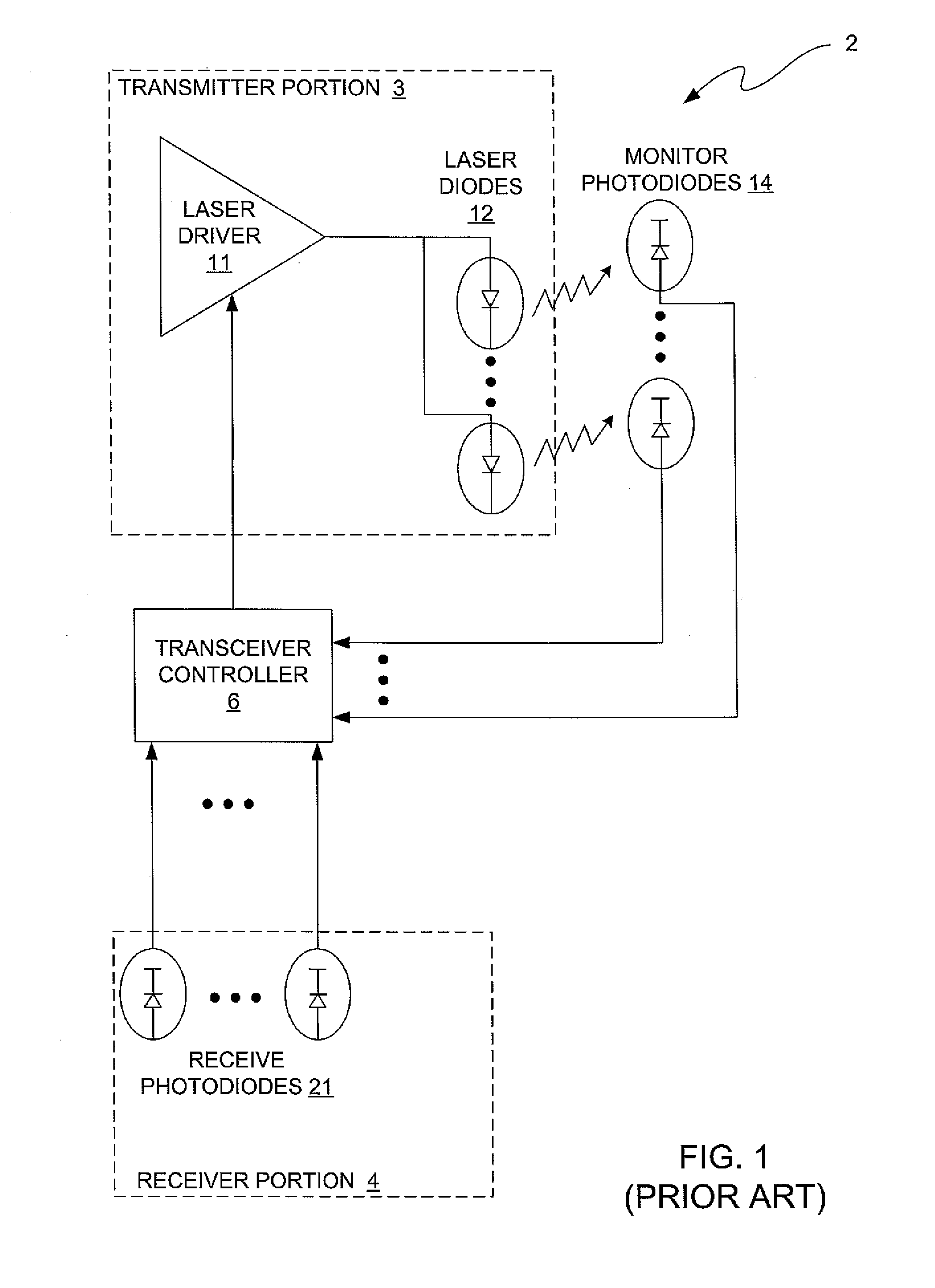
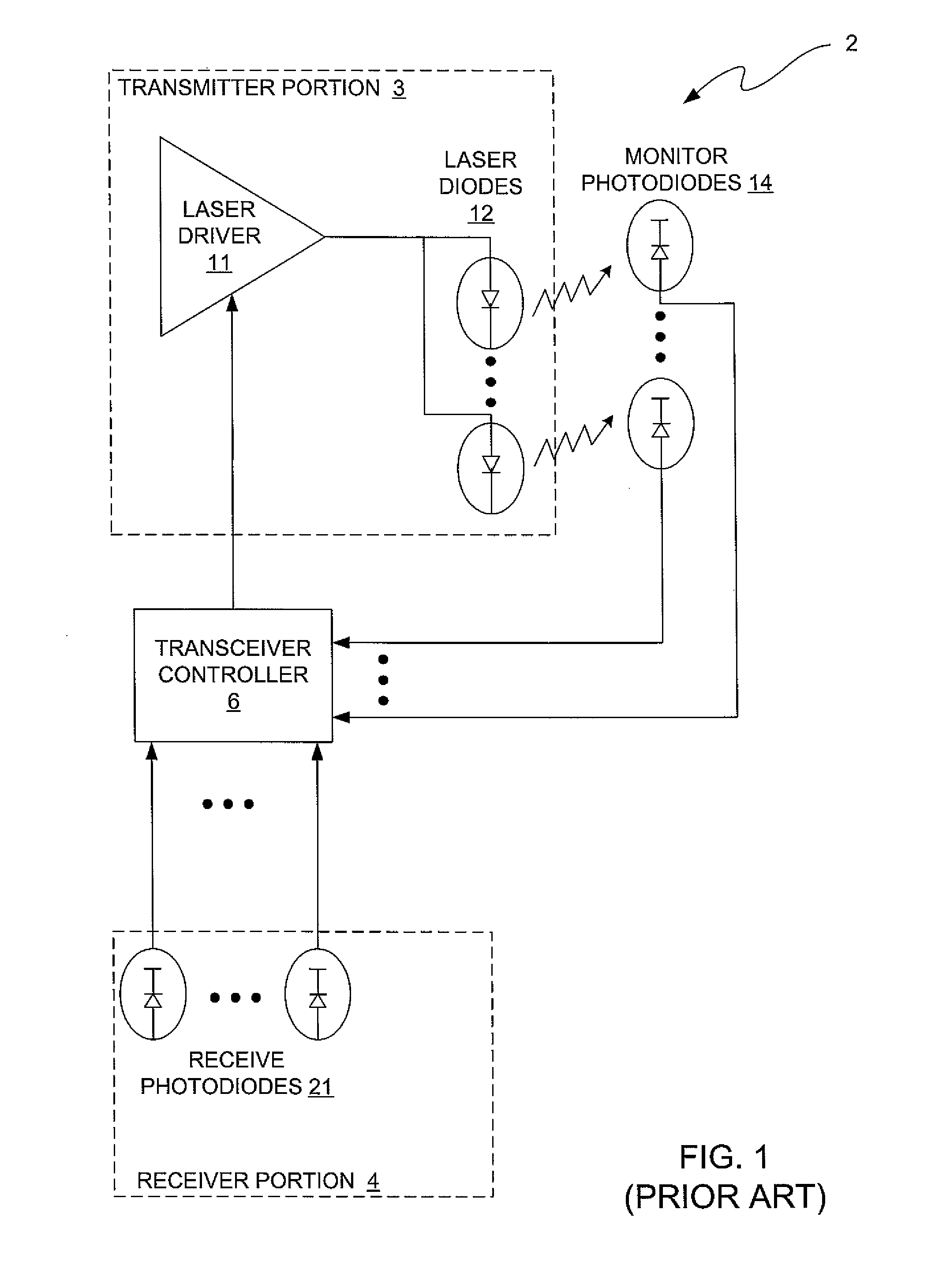
Transceiver system on a card for simultaneously transmitting and receiving information at a rate equal to or greater than approximately one terabit per second
An optical transceiver system is provided that comprises multiple parallel transceiver modules that are mounted on a card. The transceiver card is small in terms of spatial dimensions, has very good heat dissipation characteristics, and is capable of simultaneously transmitting and receiving data at a rate equal to or greater than approximately one Tb per second (1 Tb / s). A plurality of the transceiver systems may be interconnected to achieve a communications hub system having even higher bandwidths. In addition, the transceiver system may be configured such that each card has a routing controller mounted thereon for performing router functions. The router functions include, for example: causing signals received by one transceiver module on the card to be routed to and transmitted by another of the transceiver modules; causing signals received by one transceiver module on the card to be retransmitted by the same transceiver module over one of it's optical transmit channels; and causing signals received by one transceiver module on the card to be routed to and transmitted by a transceiver module on a different card.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
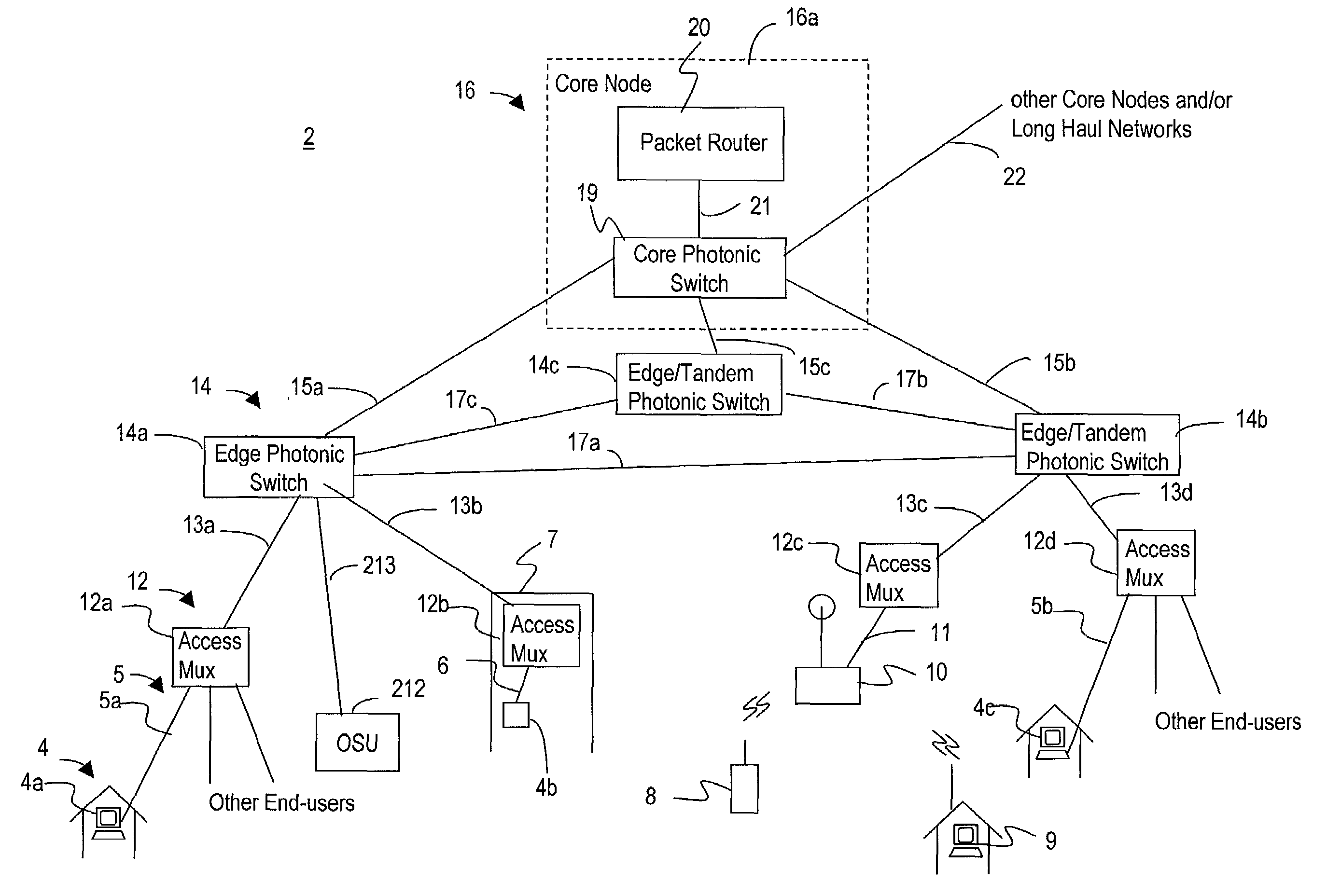
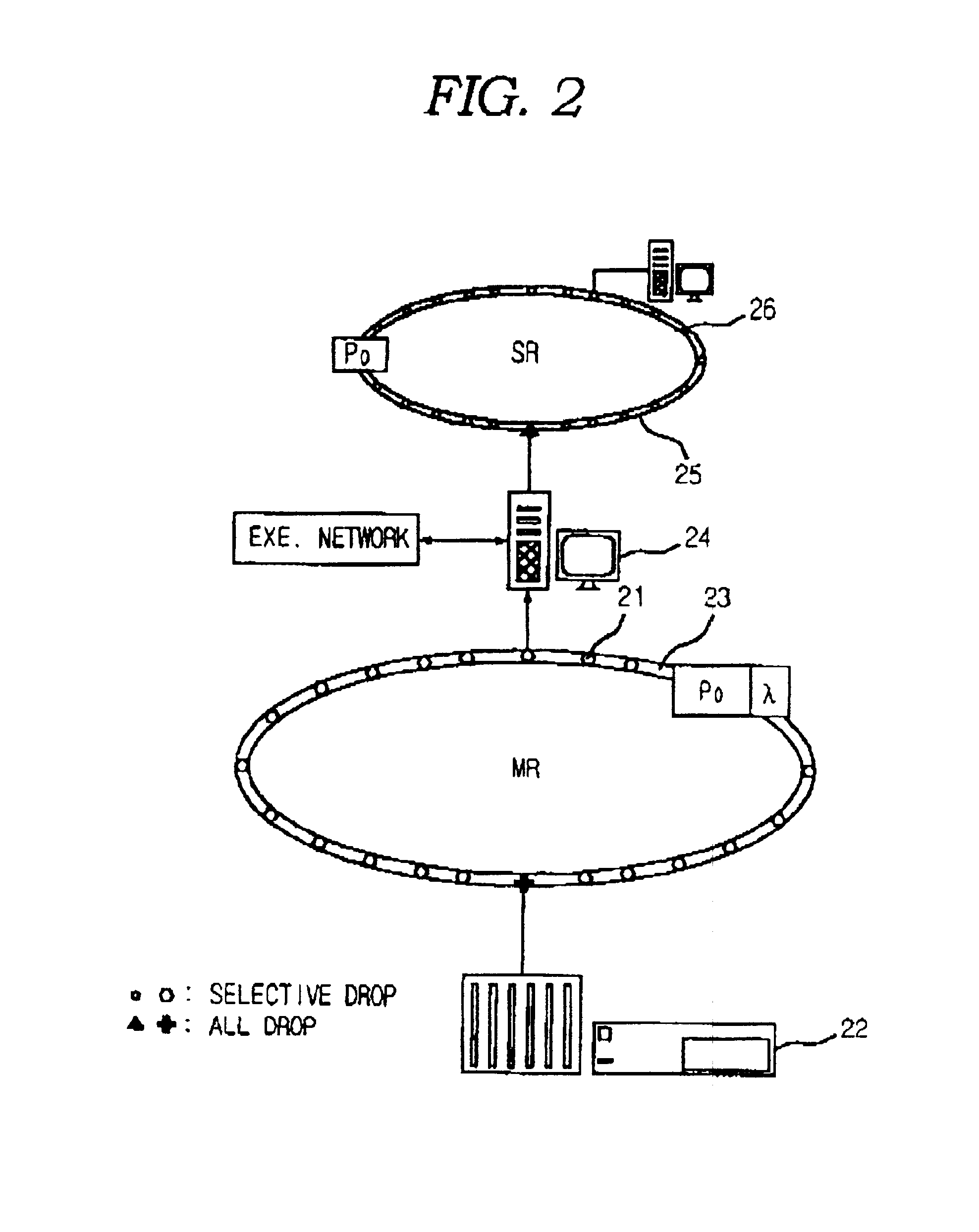
Communications network for a metropolitan area
InactiveUS7599620B2Improved communication networkReduce in quantityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberPhotonics
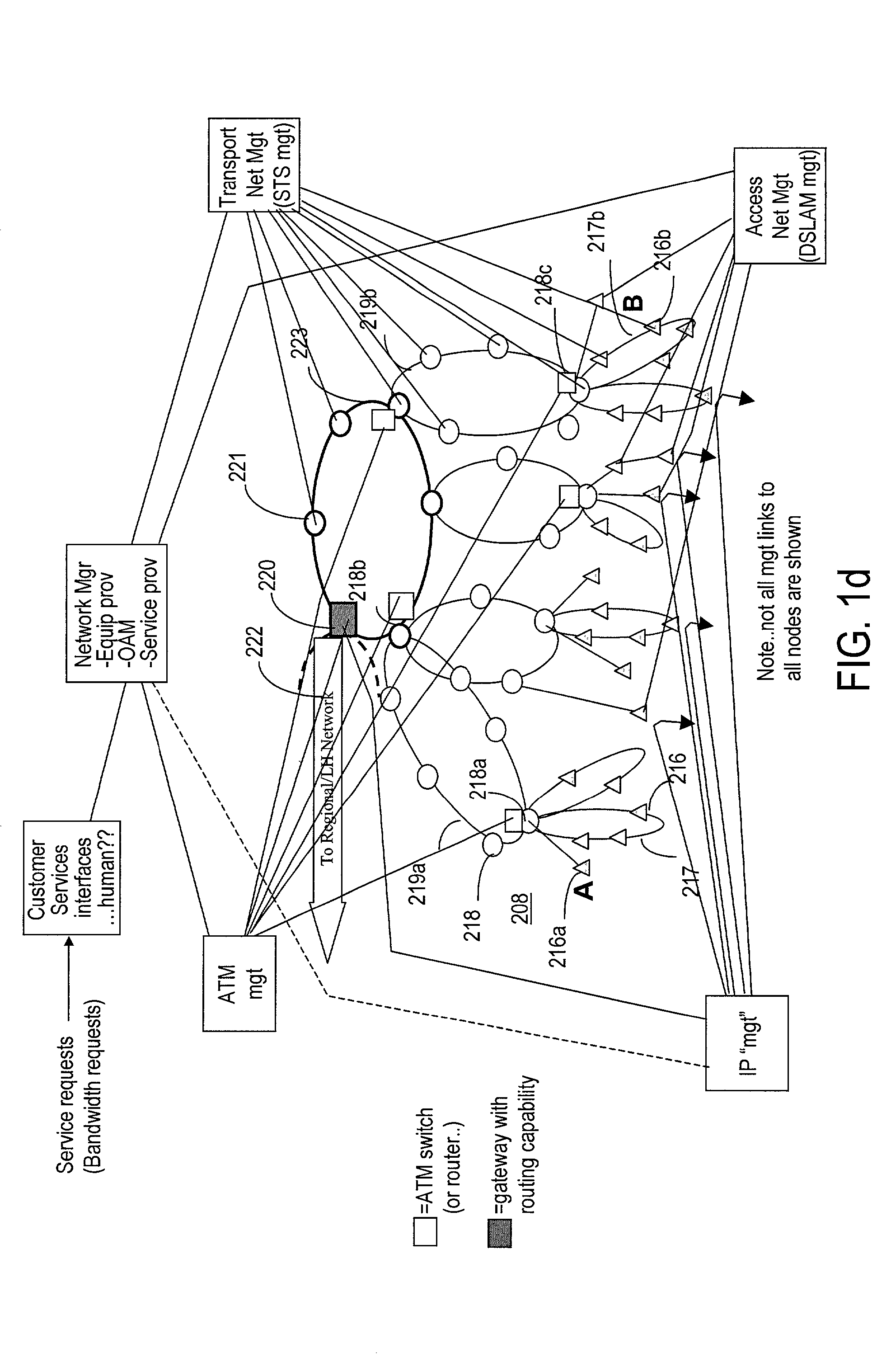
A communications network for a metropolitan area is disclosed. The network is comprised of three basic types of nodes: an access multiplexer, a photonic switch, and a core node. The access multiplexer provides multiplexing of data packets from end-users onto at least one sparse wavelength division multiplexed (SWDM) wavelength. The SWDM wavelengths are carried over fiber cable to the photonic switches, which consolidate these wavelengths into dense wavelength division multiplexed (DWDM) wavelengths for transmission to the core node. The core nodes include a photonic switch (PSX) and a service-aware terabit router core for routing packets within the metropolitan area via the network or out to a long haul network. The photonic switches and core nodes are capable of switching at the wavelength, group of wavelength, and fiber levels.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Port-to-port, non-blocking, scalable optical router architecture and method for routing optical traffic
InactiveUS20090074414A1Maximize throughputMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCross connectionStructure of Management Information
Owner:MIND FUSION LLC
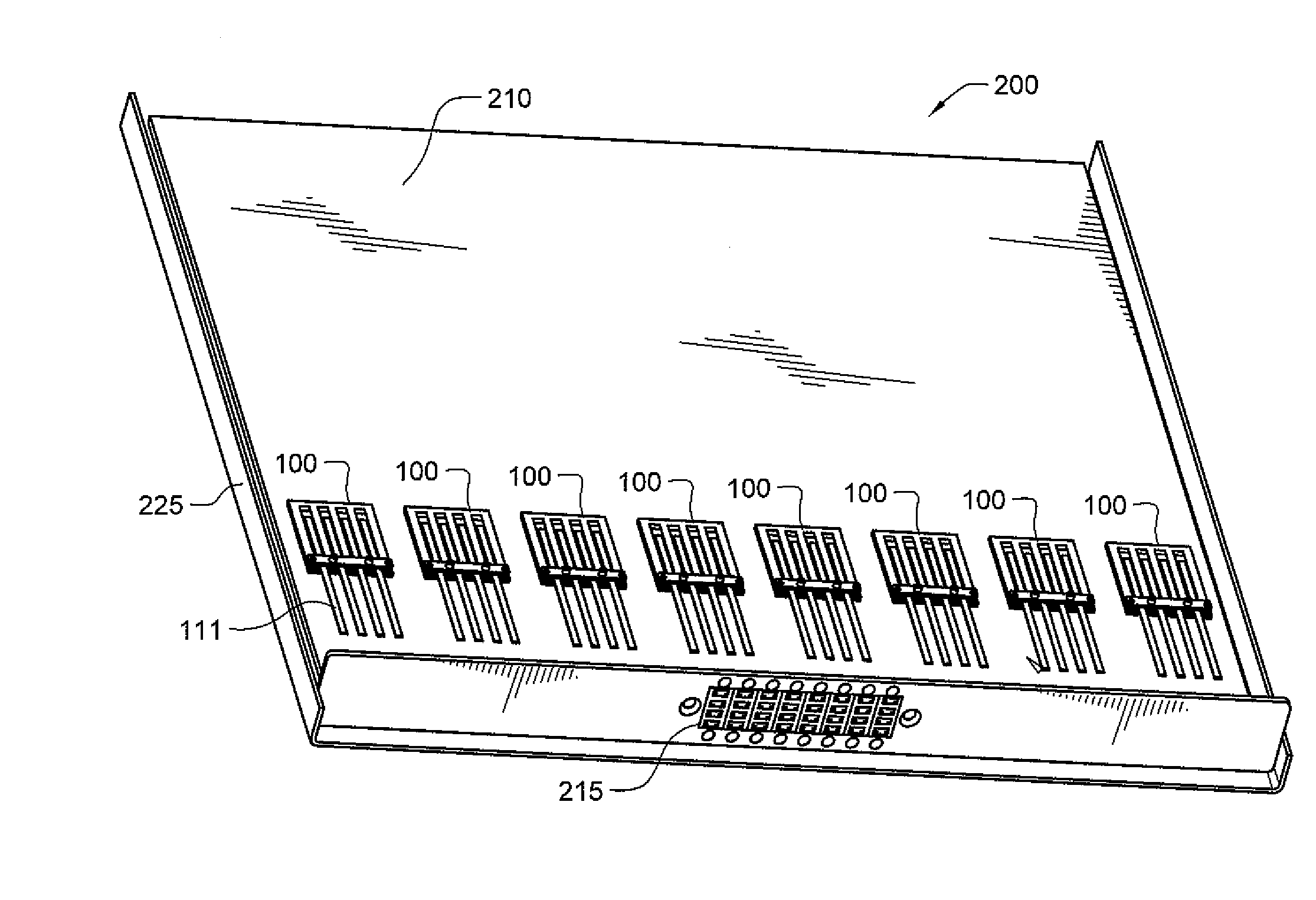
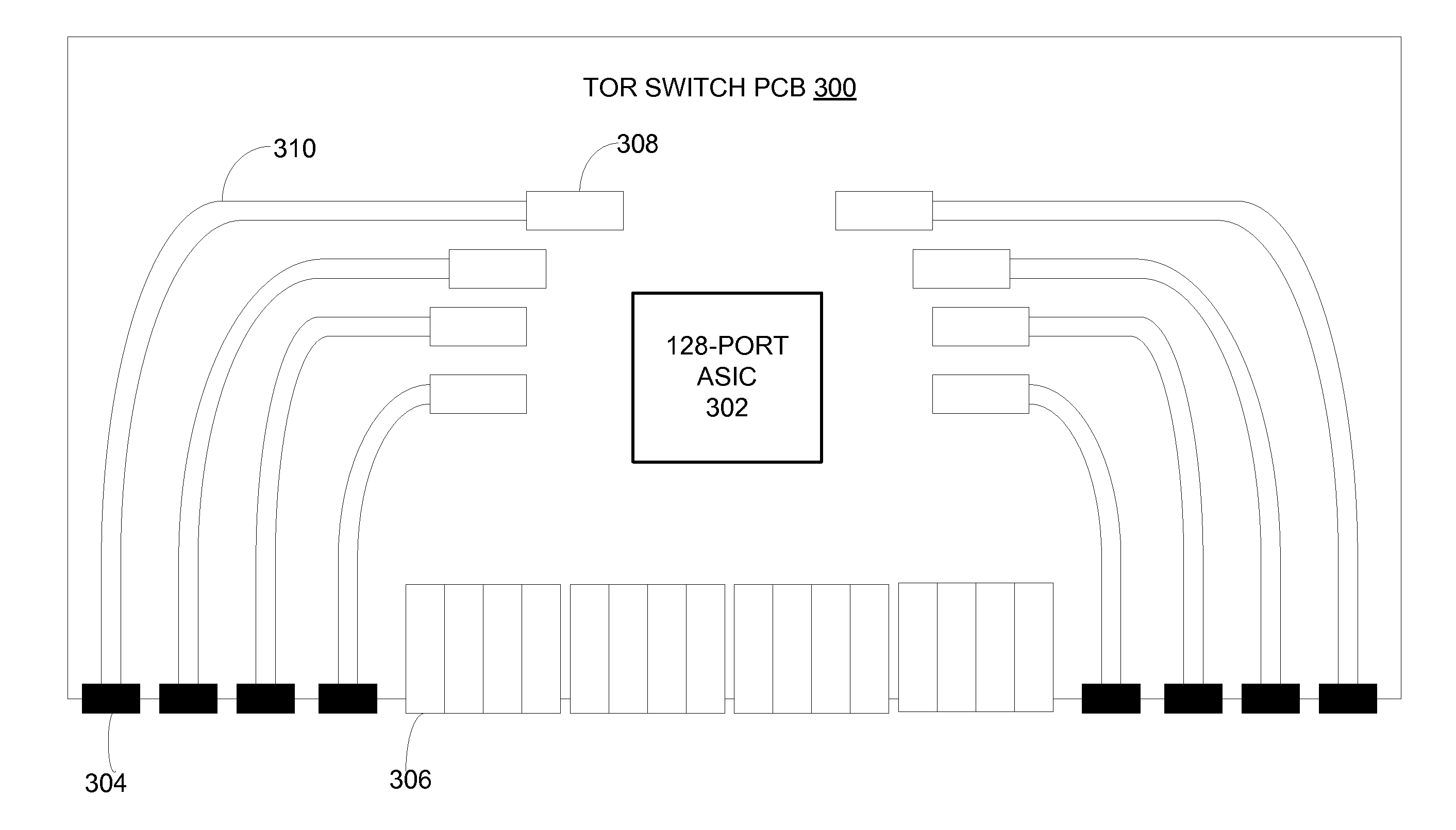
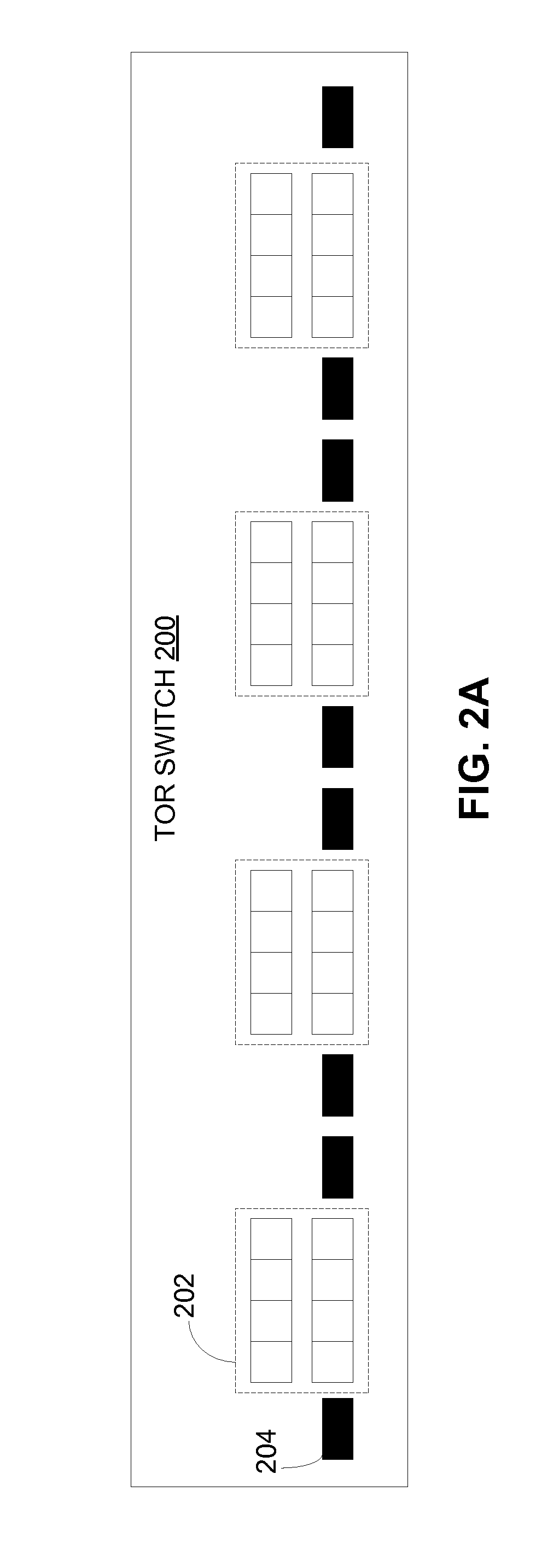
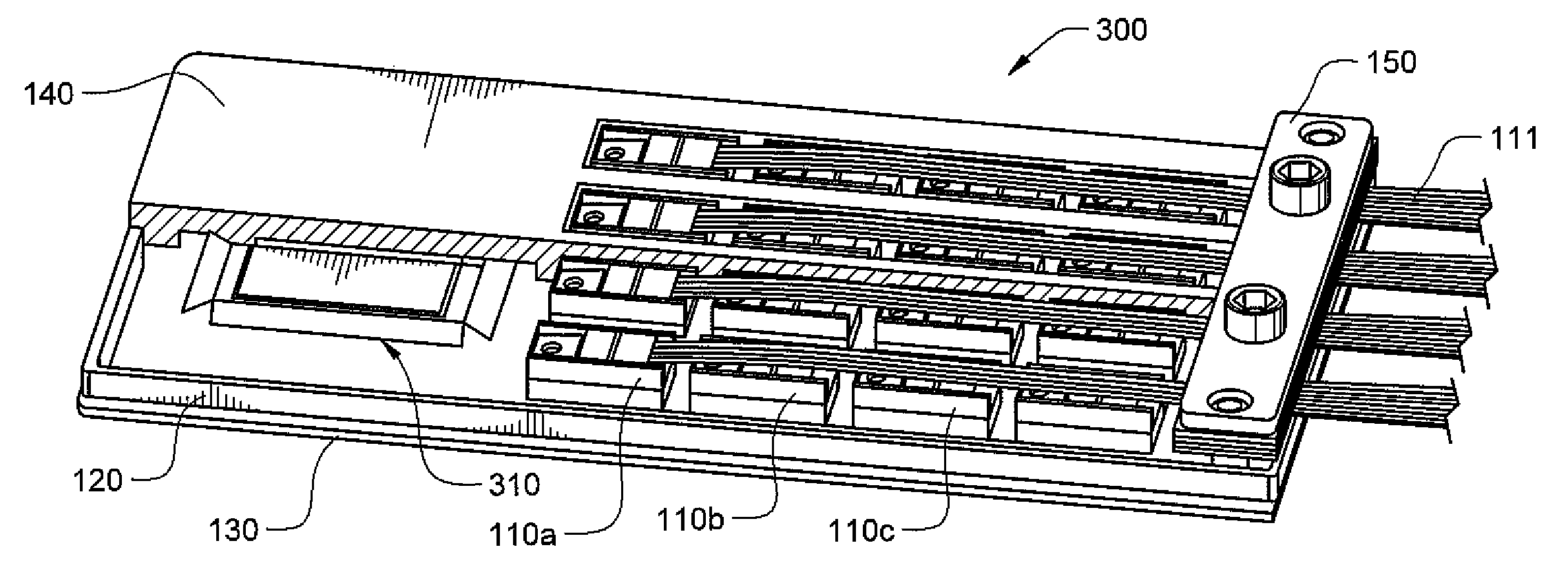
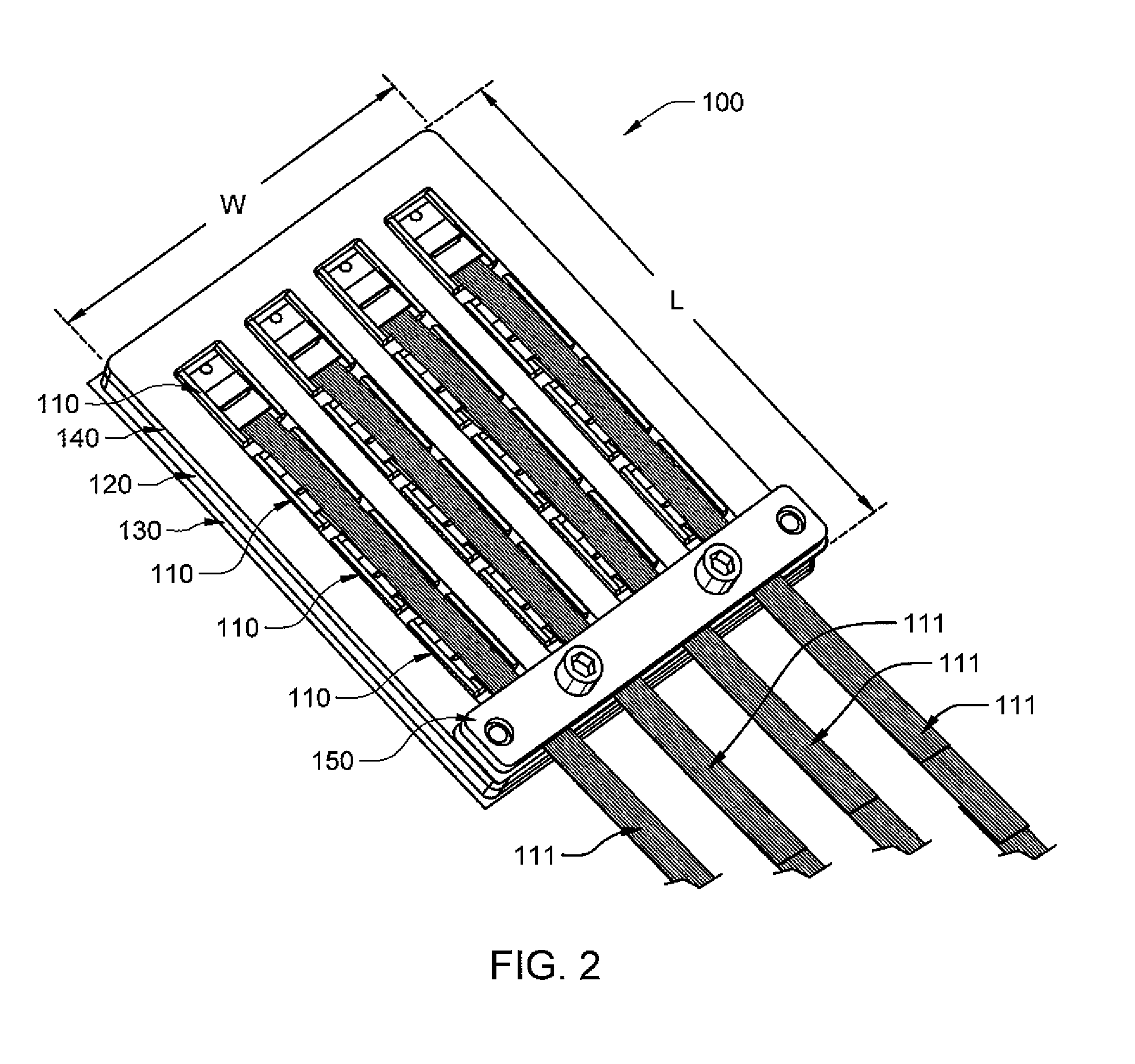
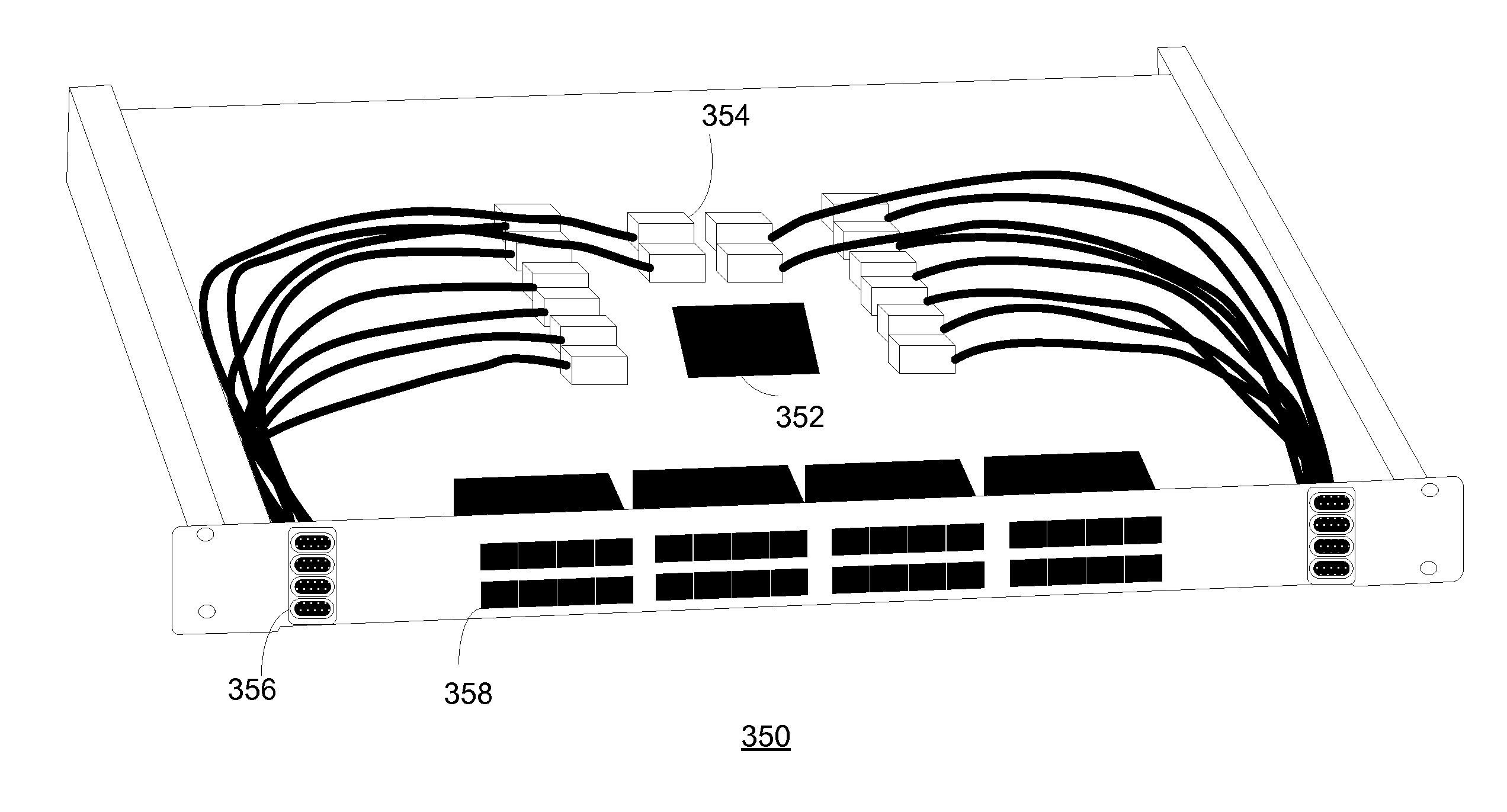
Terabit top-of-rack switch
ActiveUS20130315586A1Small interfaceMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexTransceiverEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention provides a switch. The switch includes a printed circuit board (PCB), a number of multi-channel optical transceivers mounted on the PCB, and a number of switch ports accessible from a front panel of the switch. The switch ports include a number of electrical interfaces that are electrically coupled to a switch chip mounted on the PCB, and a number of optical interfaces that are coupled to the switch chip via the multi-channel optical transceivers.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
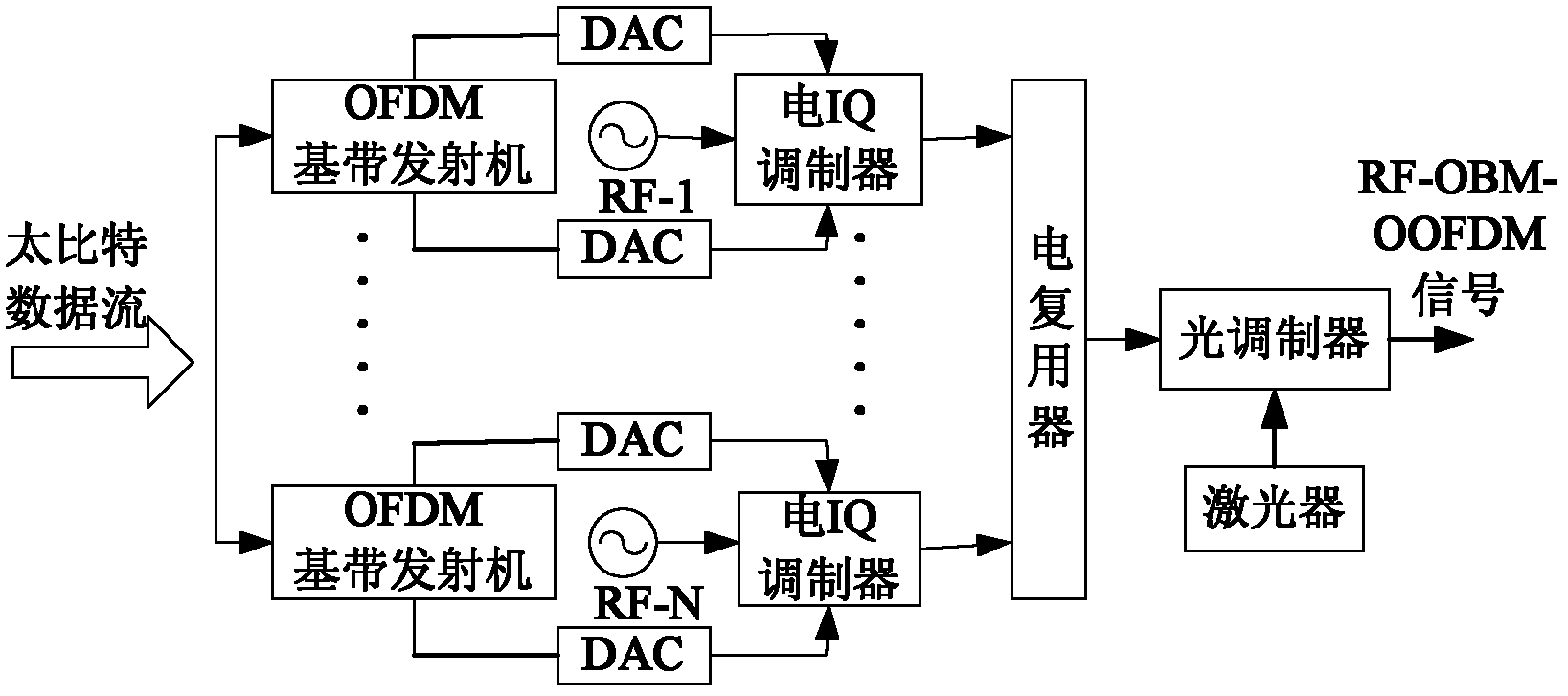
Terabit transmission rate coherent light orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system based on optical comb
InactiveCN102223340AGood hardware availabilityIncreased complexityMulti-frequency code systemsElectromagnetic transmissionTransceiverFrequency comb
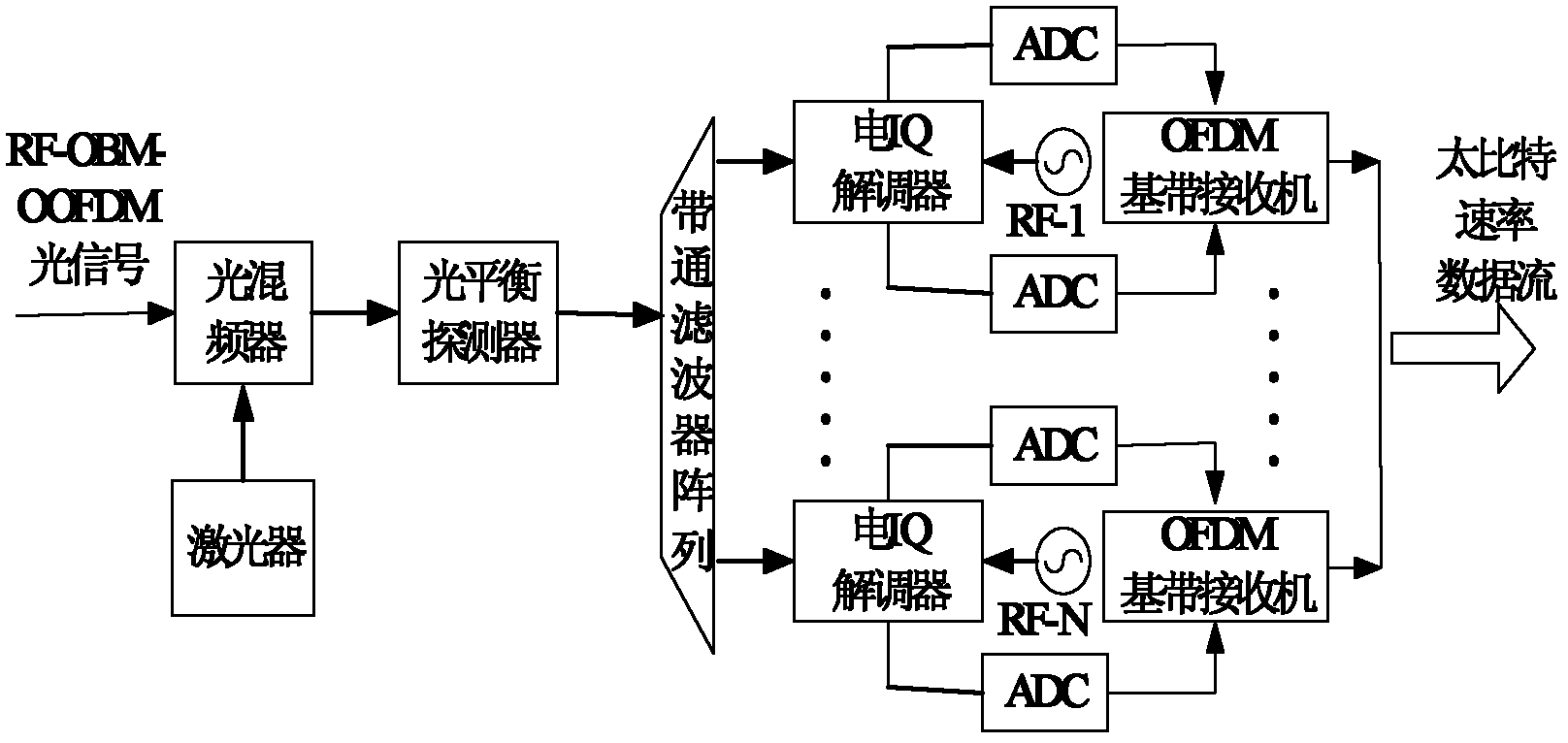
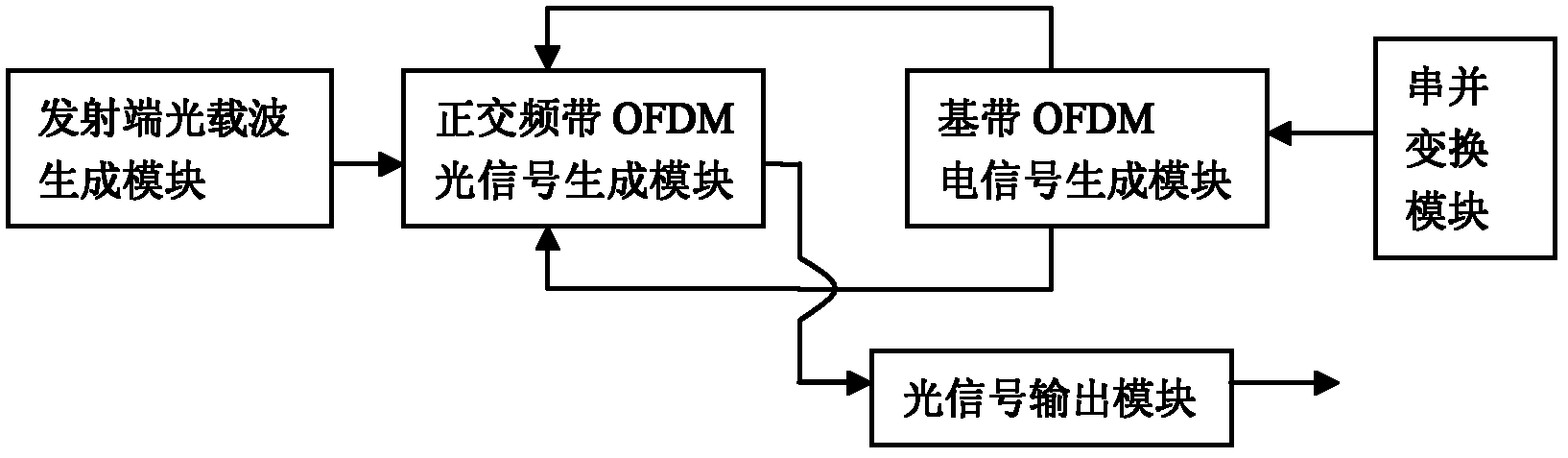
The invention provides a feasible Terabit transmission rate coherent light orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system which is of simpler system structure, and comprises a transmitting end and a receiving end, wherein, the transmitting end comprises a transmitting end optical carrier generation module which comprises a transmitting end laser, an optical comb generator and an optical demultiplexer. In the system, on the basis of single light source, the optical comb generator is utilized to obtain light frequency combs with multiple wavelengths, which are used as optical carriers of base band OFDM signals, and mutually orthogonal OFDM frequency bands are generated on an optical domain, thus a plurality of radio frequency (RF) oscillation sources with complex structures are not need in the prior art. By utilizing the system, an OBM-COOFDM (orthogonal-band-multiplexed-coherent optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing) optical signal is obtained under the condition of not using the RF oscillation sources, thus greatly reducing the complexity and cost of a transmitter; and the system has better feasibility of the OBM-COOFDM hardware, thus reducing the higher sampling rate requirements of the traditional COOFDM Terabit transceiver on a digital to analog converter (DAC) and an analog to digital converter (ADC).
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
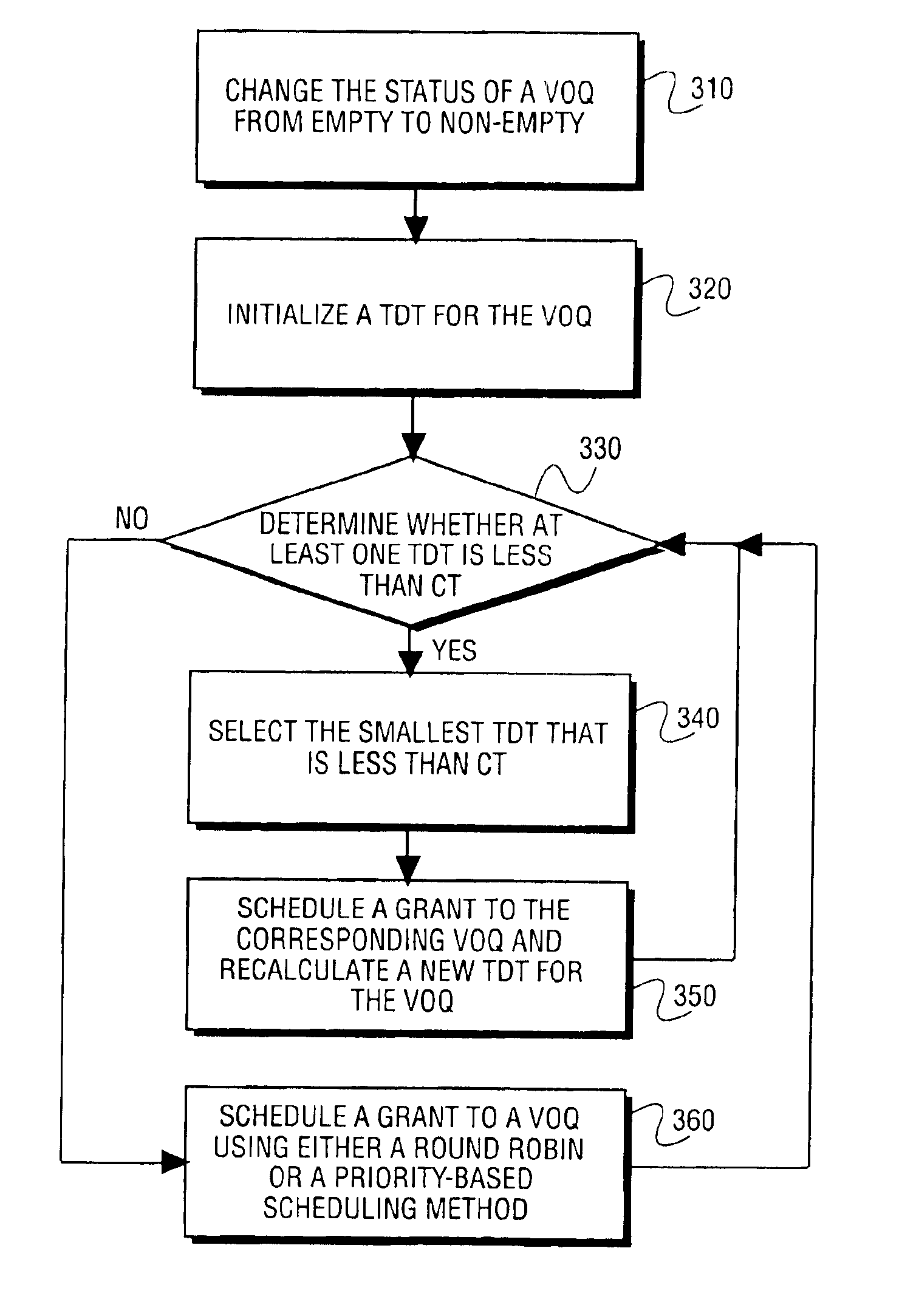
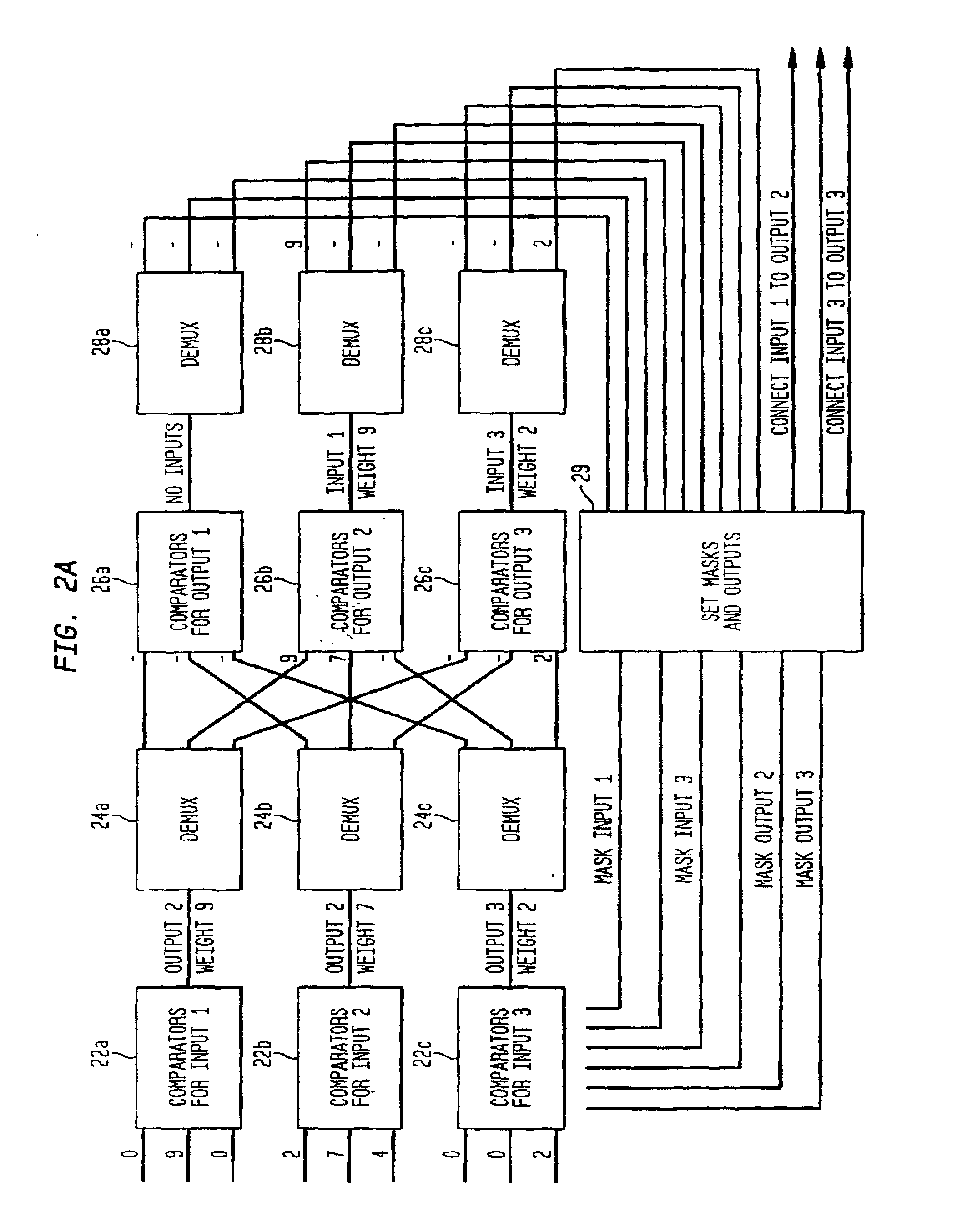
Scalable weight-based terabit switch scheduling method
InactiveUS20030031193A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQos quality of serviceParallel computing
A method and apparatus are disclosed for scheduling arriving data packets for input to a switch having a plurality of input channels, and a plurality of output channels, the scheduling method is performed in successive scheduling phases where each scheduling phase further comprises at least log N scheduling iterations. The method is a parallelized weight-driven input queued switch scheduling algorithm which possesses good bandwidth and delay properties, is stable, and can be configured to offer various delay and quality of service (QoS) guarantees. The scheduling method utilizes envelope scheduling techniques and considers partially filled envelopes for scheduling.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
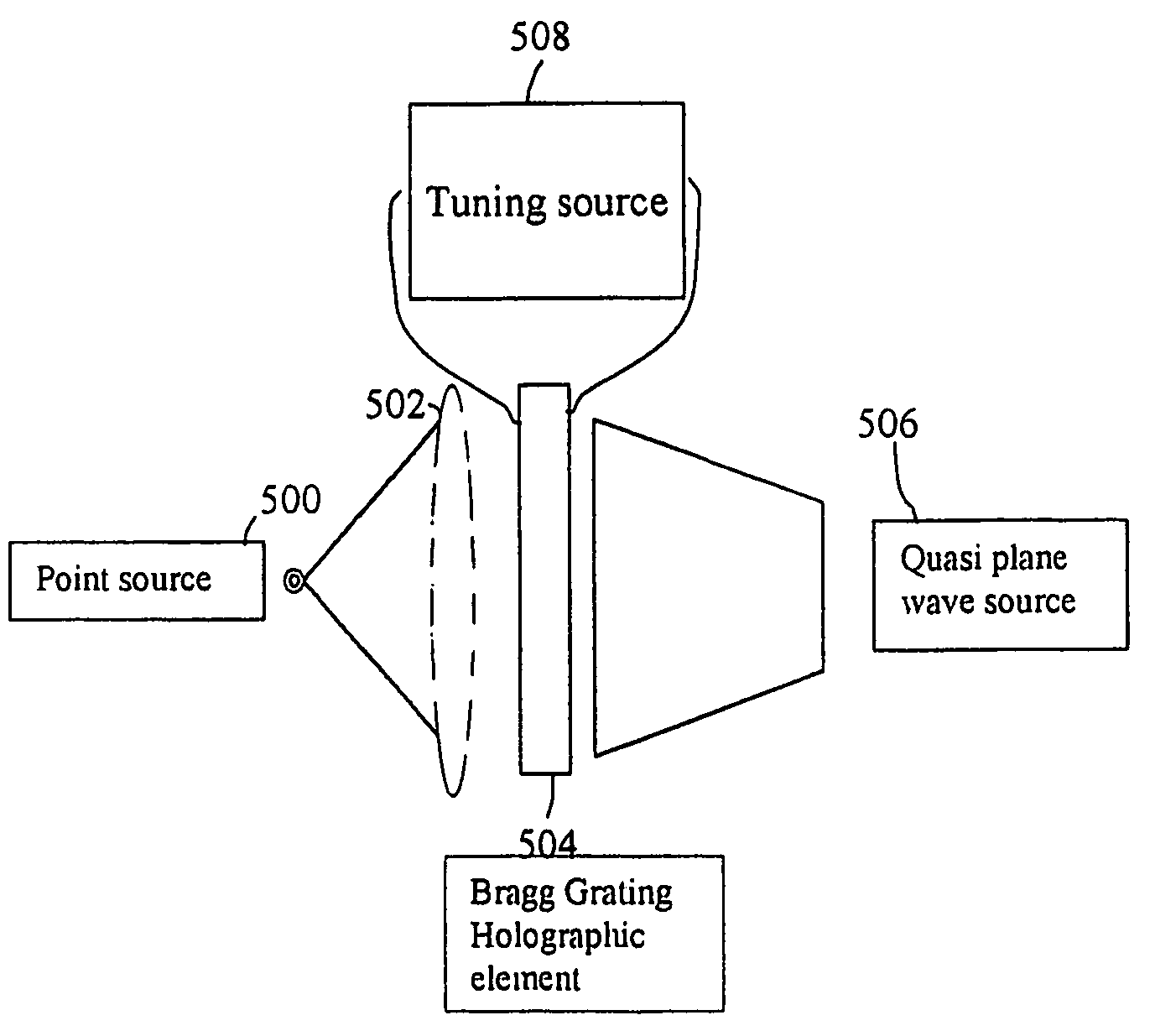
Nano-scale resolution holographic lens and pickup device
InactiveUS7376068B1Record information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsImage resolutionLight beam
An extremely high resolution holographic lens is provided, comprising an interference pattern between light emitted from at least one tiny point source of light such as the tip of an optical fiber, having a diameter in the nanoscale region, and at least one plane or quasi-plane broad light beam. The holographic lens is employed for example in pickups for reading data off of, and writing data upon terabit optical storage mediums and nanoscale resolution microscopic media.
Owner:KHOURY JEHAD
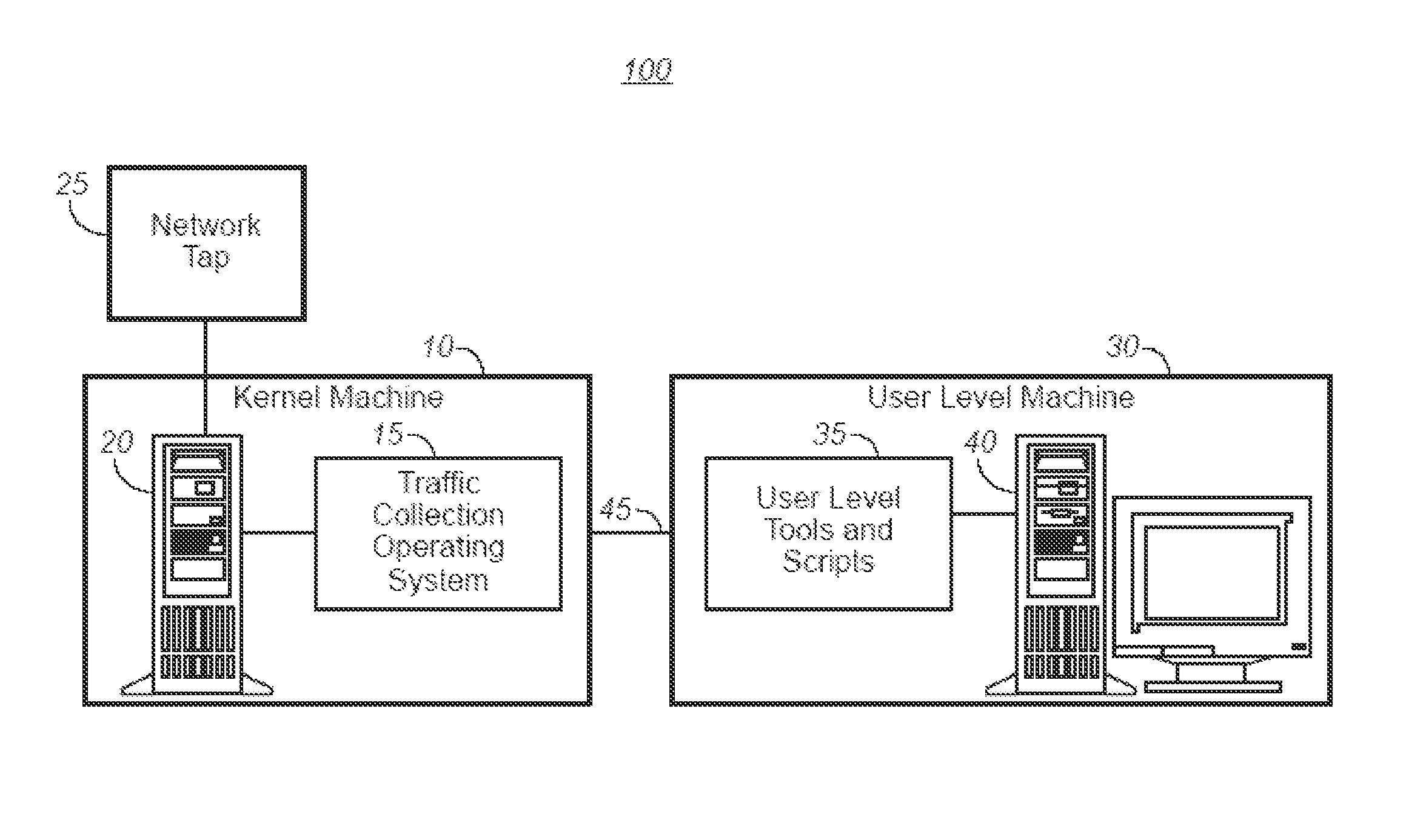
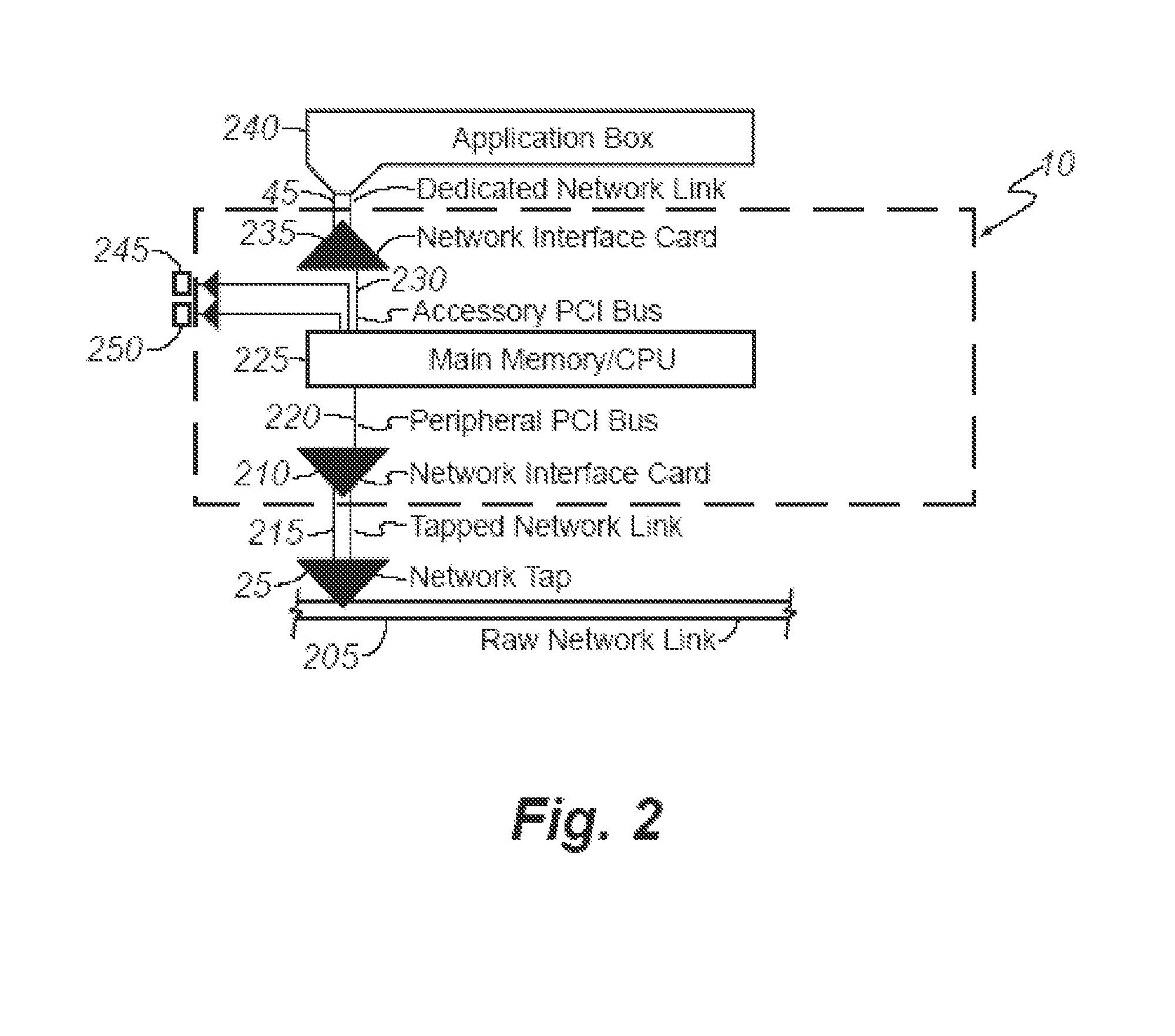
High-speed and high-fidelity system and method for collecting network traffic
ActiveUS7783739B1Increase traffic-monitoring rateReduce speedError preventionTransmission systemsOperational systemResearch purpose
A system is provided for the high-speed and high-fidelity collection of network traffic. The system can collect traffic at gigabit-per-second (Gbps) speeds, scale to terabit-per-second (Tbps) speeds, and support additional functions such as real-time network intrusion detection. The present system uses a dedicated operating system for traffic collection to maximize efficiency, scalability, and performance. A scalable infrastructure and apparatus for the present system is provided by splitting the work performed on one host onto multiple hosts. The present system simultaneously addresses the issues of scalability, performance, cost, and adaptability with respect to network monitoring, collection, and other network tasks. In addition to high-speed and high-fidelity network collection, the present system provides a flexible infrastructure to perform virtually any function at high speeds such as real-time network intrusion detection and wide-area network emulation for research purposes.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
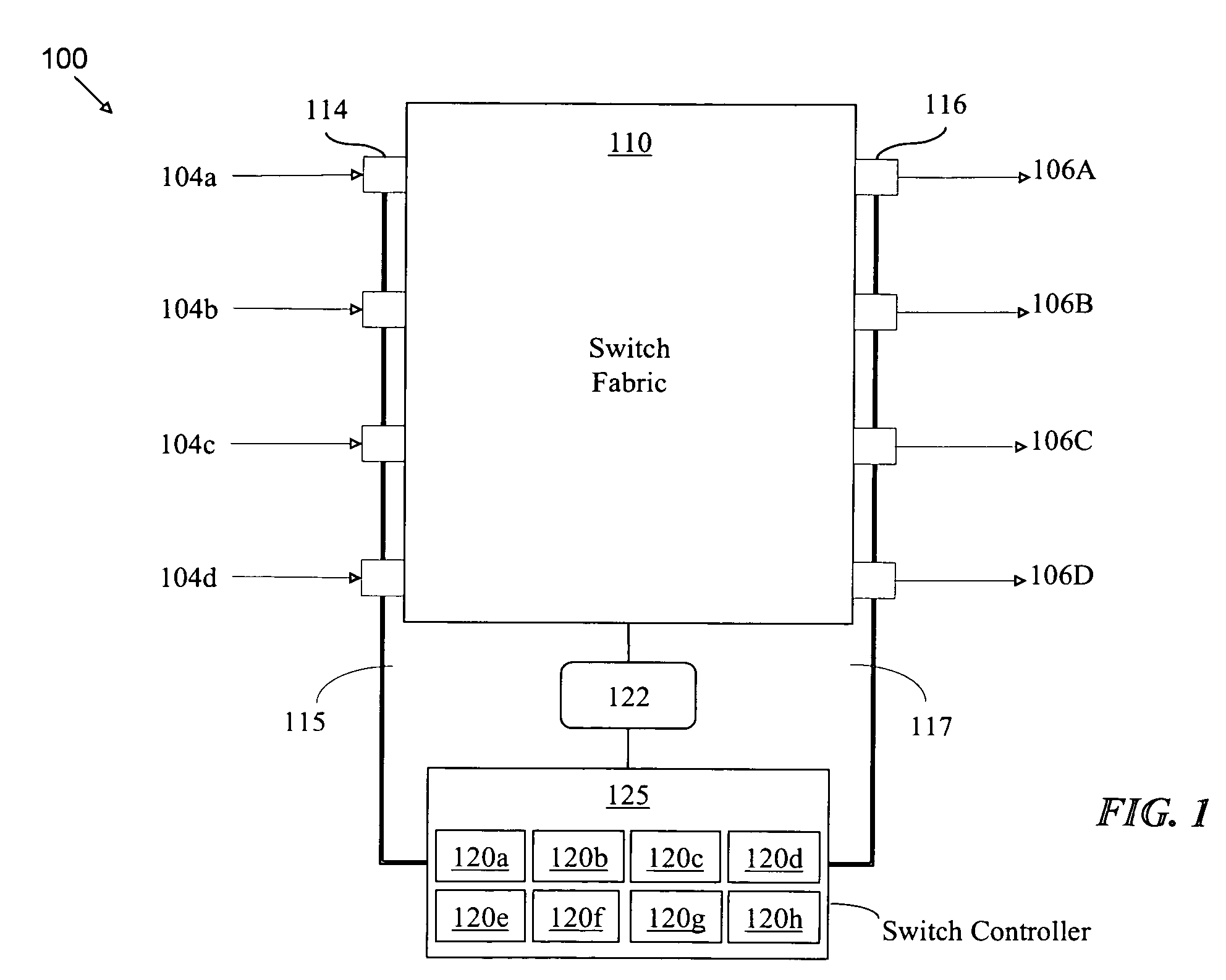
Guaranteed bandwidth mechanism for a terabit multiservice switch
A method to guarantee bandwidth for a terabit multiservice switch including receiving control cells indicating that a destination port of an asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network is congested, and reducing incoming traffic to the congested port to a guaranteed bandwidth of traffic until the destination port is uncongested, is disclosed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
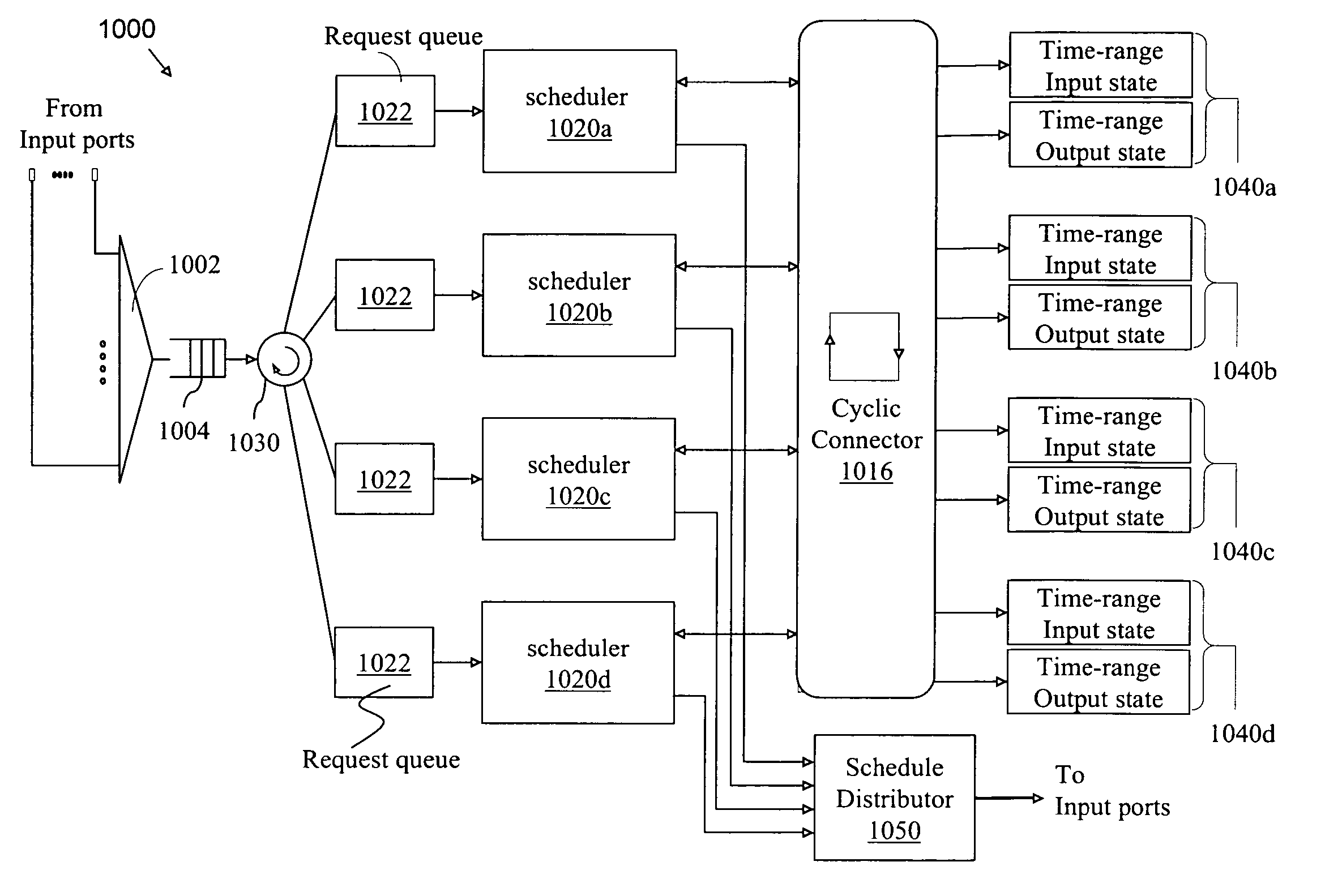
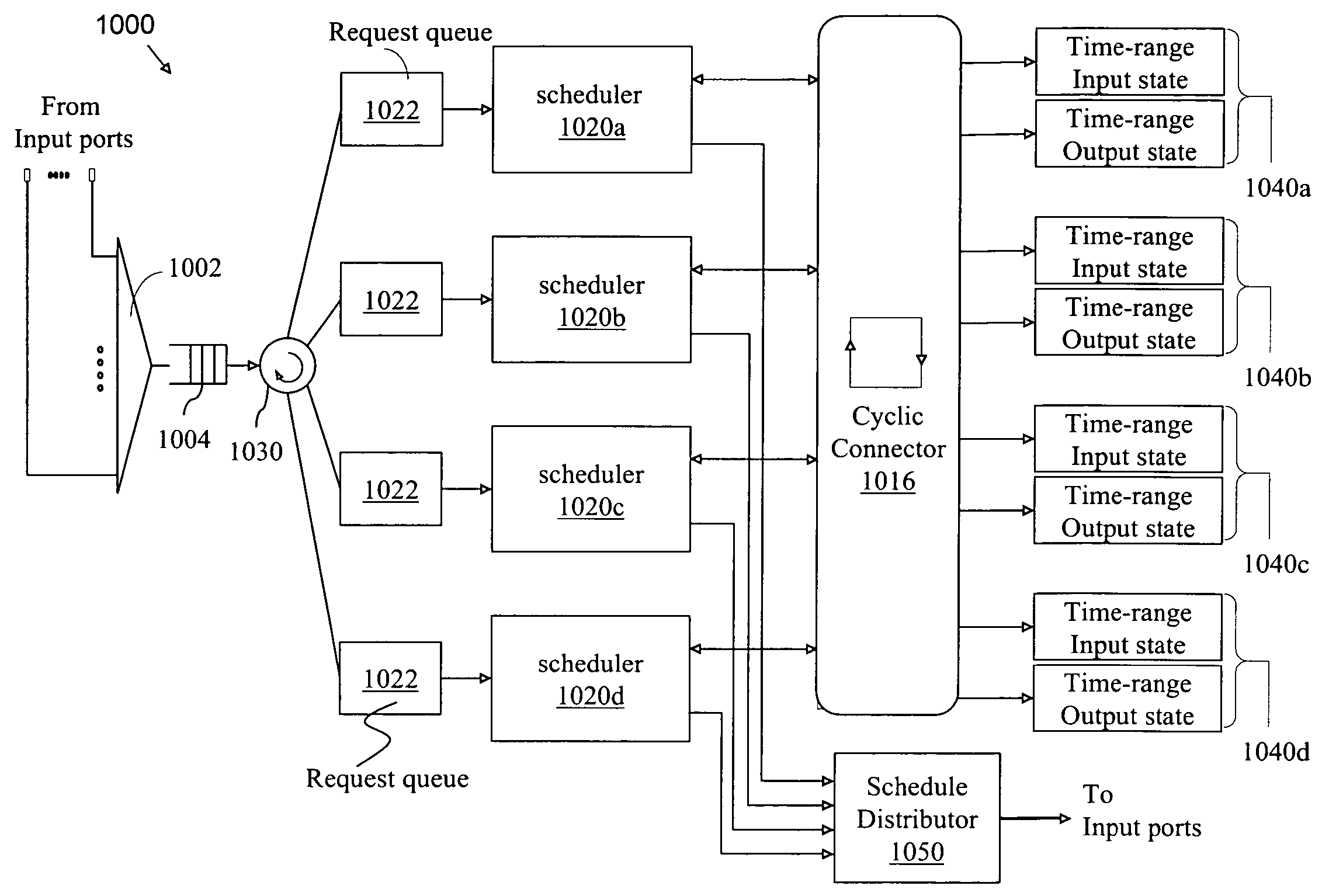
High-speed scheduling apparatus for a switching node
InactiveUS20060120379A1High per-scheduler capacity increaseEasy to set upData switching by path configurationGranularityDistributed computing
A scheduling apparatus for a switch includes multiple schedulers which are assigned in a variety of ways to non-intersecting control domains for establishing connections through the switch. The control domains are defined by spatial and temporal aspects. The control domains may be dynamically selected and assigned to schedulers in a manner that achieves a high throughput gain. Control domains may be considered in a cyclic and / or a pipeline discipline for accommodating connection requests. The invention enables the realization of a highly scalable controller of a switching node of fine granularity that scales to capacities of the order of hundreds of terabits per second.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Routing and rate control in a universal transfer mode network
InactiveUS7310349B2Improves connection setup rateImprove connectivityError preventionTransmission systemsData formatPacket routing
A method and a network for a universal transfer mode (UTM) of transferring data packets at a regulated bit rate are disclosed. The method defines a protocol that uses an adaptive packet header to simplify packet routing and increase transfer speed. The protocol supports a plurality of data formats. The network includes a plurality of modules that provide interfaces to various data sources. The modules are interconnected by an optic core with adequate inter-module links. The adaptive packet header is used for both signaling and payload transfer. The header is parsed to determine its function. Rate regulation is accomplished using each module control element and egress port controllers to regulate packet transfer. The protocol enables the modules to behave as a single distributed switch capable of multi-terabit transfer rates. The advantage is a high speed distributed switch capable of serving as a transfer backbone for substantially any telecommunications service.
Owner:APPLE INC
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and manufacturing method of the same
InactiveCN102385871AHigh degree of orderSmall crystal particle sizeRecord information storageRecord carriers manufactureAlloyNon magnetic
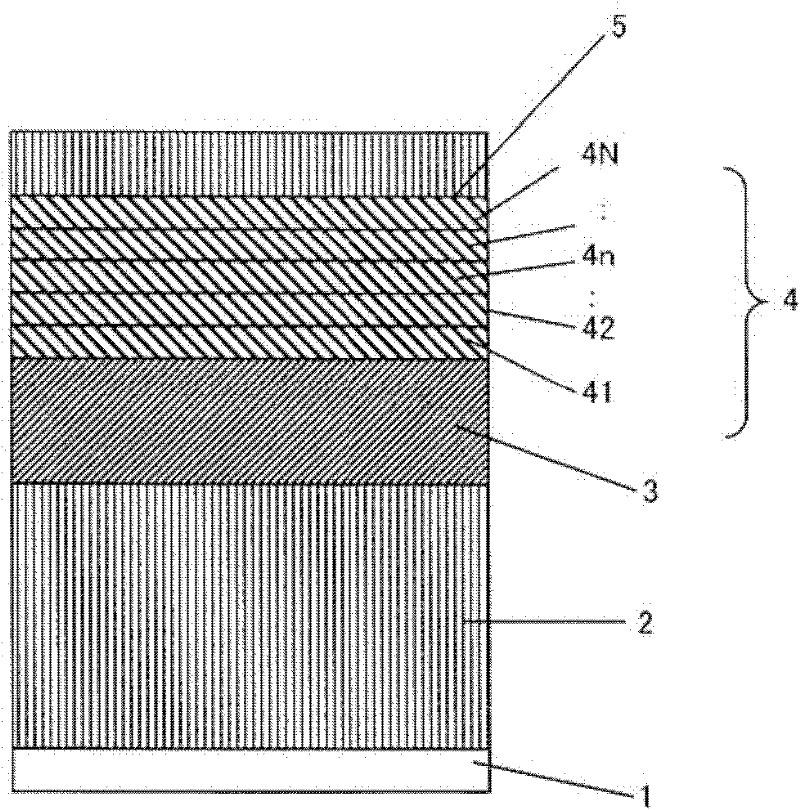
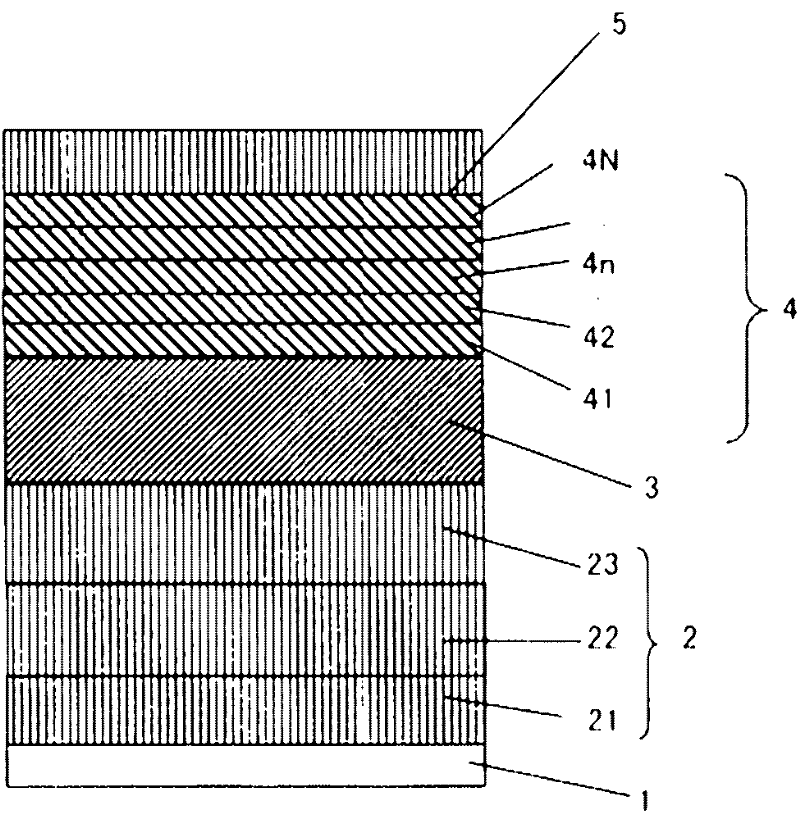
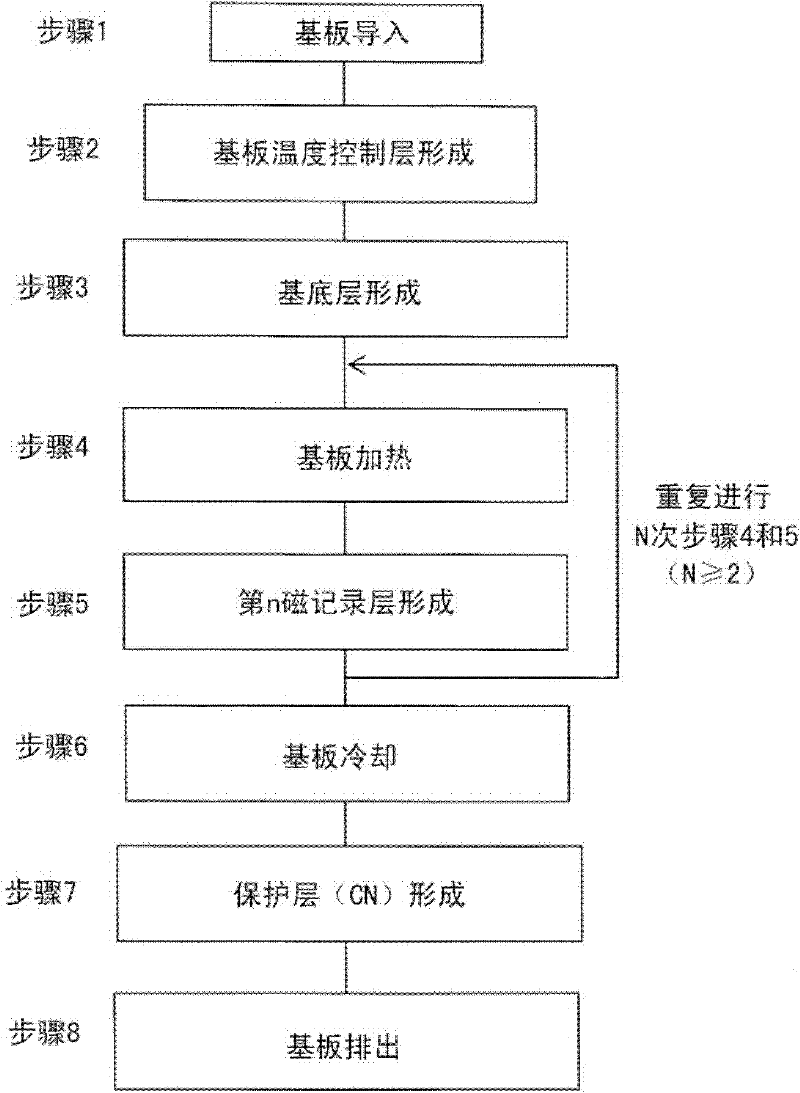
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium having sufficient perpendicular uniaxial magnetic anisotropy energy and a crystal grain size for realizing an areal recording density of one terabit or more per one square centimeter, and excellent in mass productivity, and a manufacturing method of the same are provided. On a substrate, a substrate-temperature control layer, an underlayer and a magnetic recording layer are sequentially formed. The magnetic recording layer is formed by repeating a magnetic layer stacking step N times (N>=2), which includes a first step of heating the substrate in a heat process chamber, and a second step of depositing, in a deposition process chamber, the magnetic recording layer constituted of an alloy mainly composed of FePt to which at least one kind of non-magnetic material selected from a group constituted of C and an Si oxide is added.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
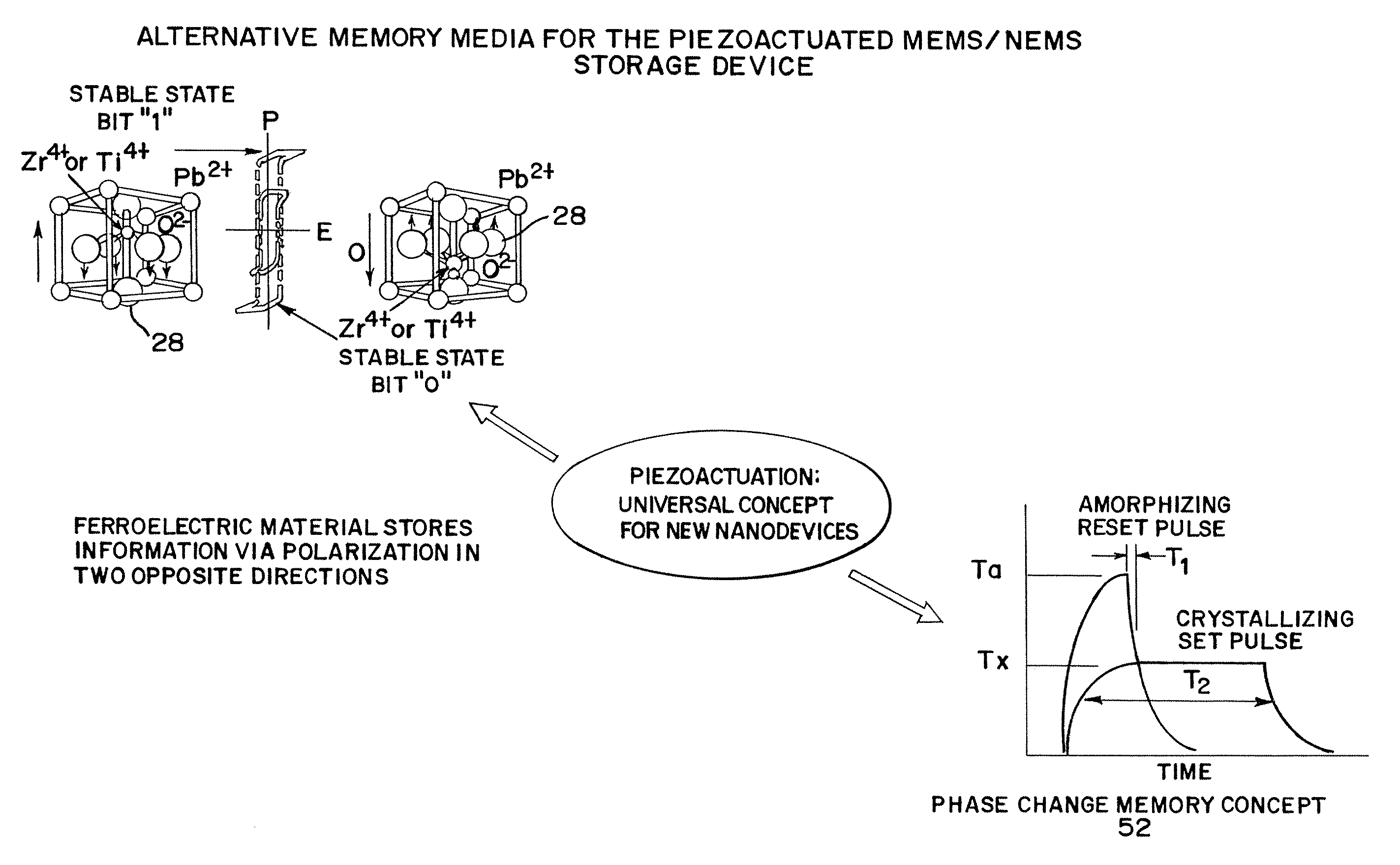
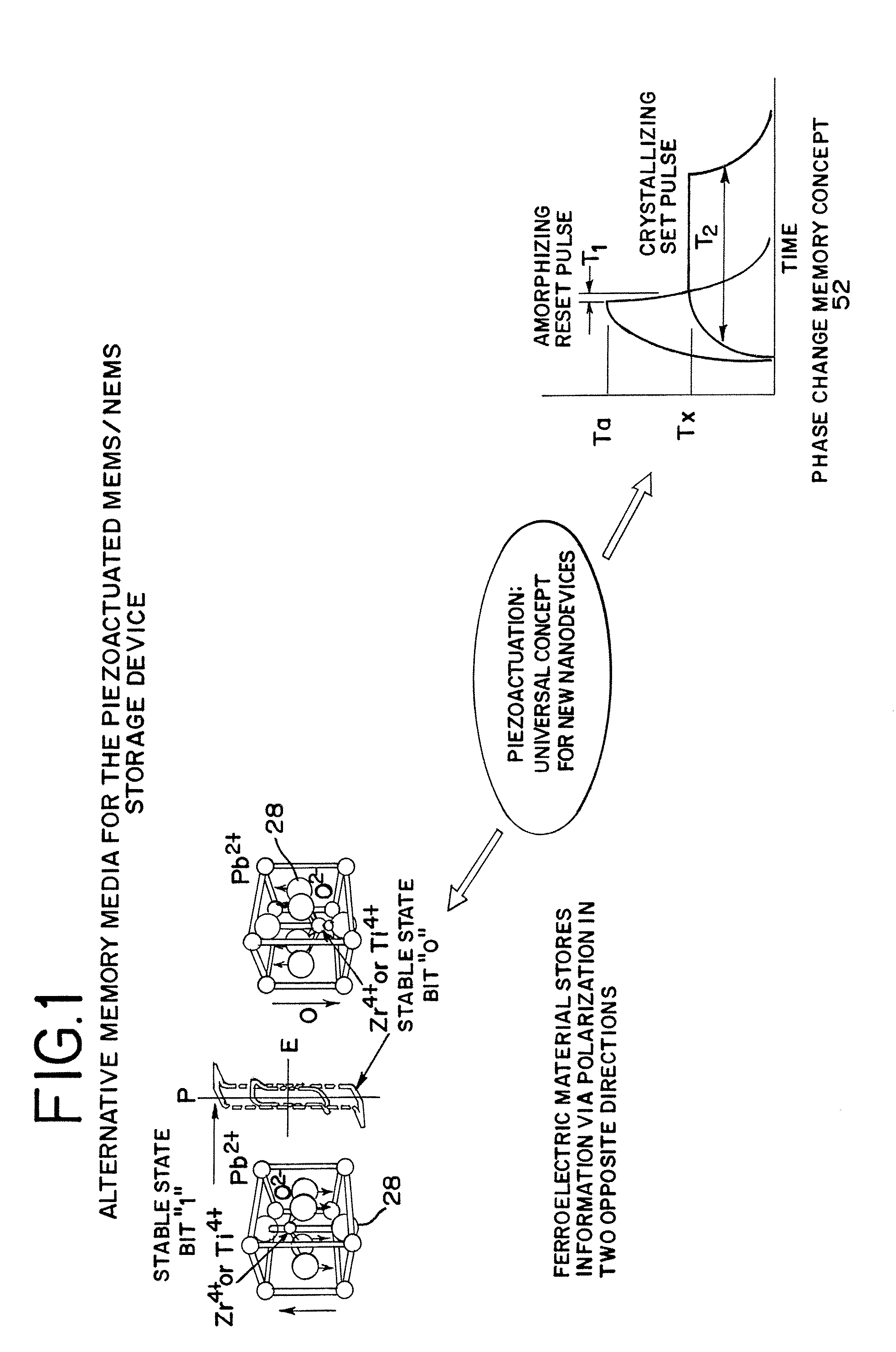
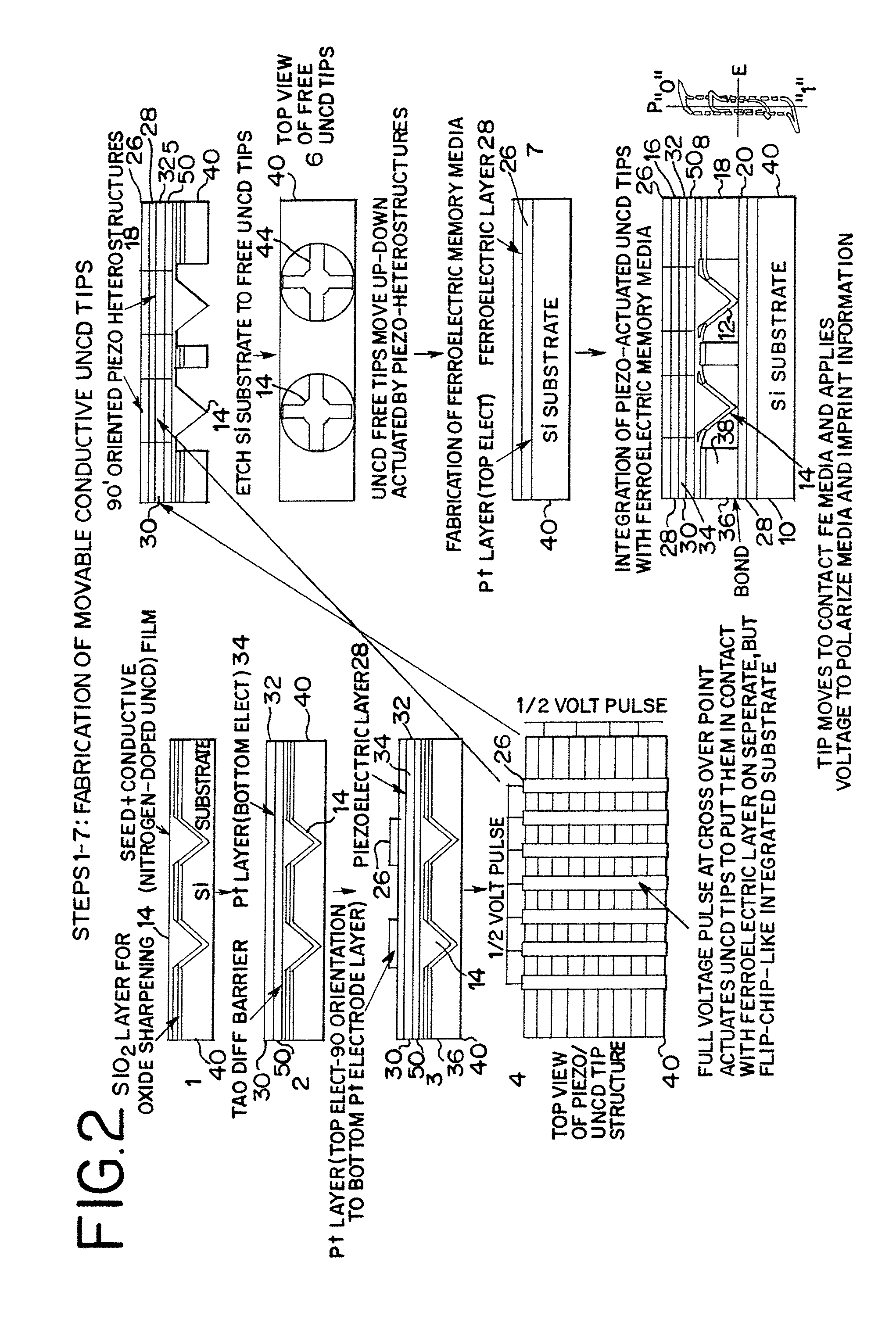
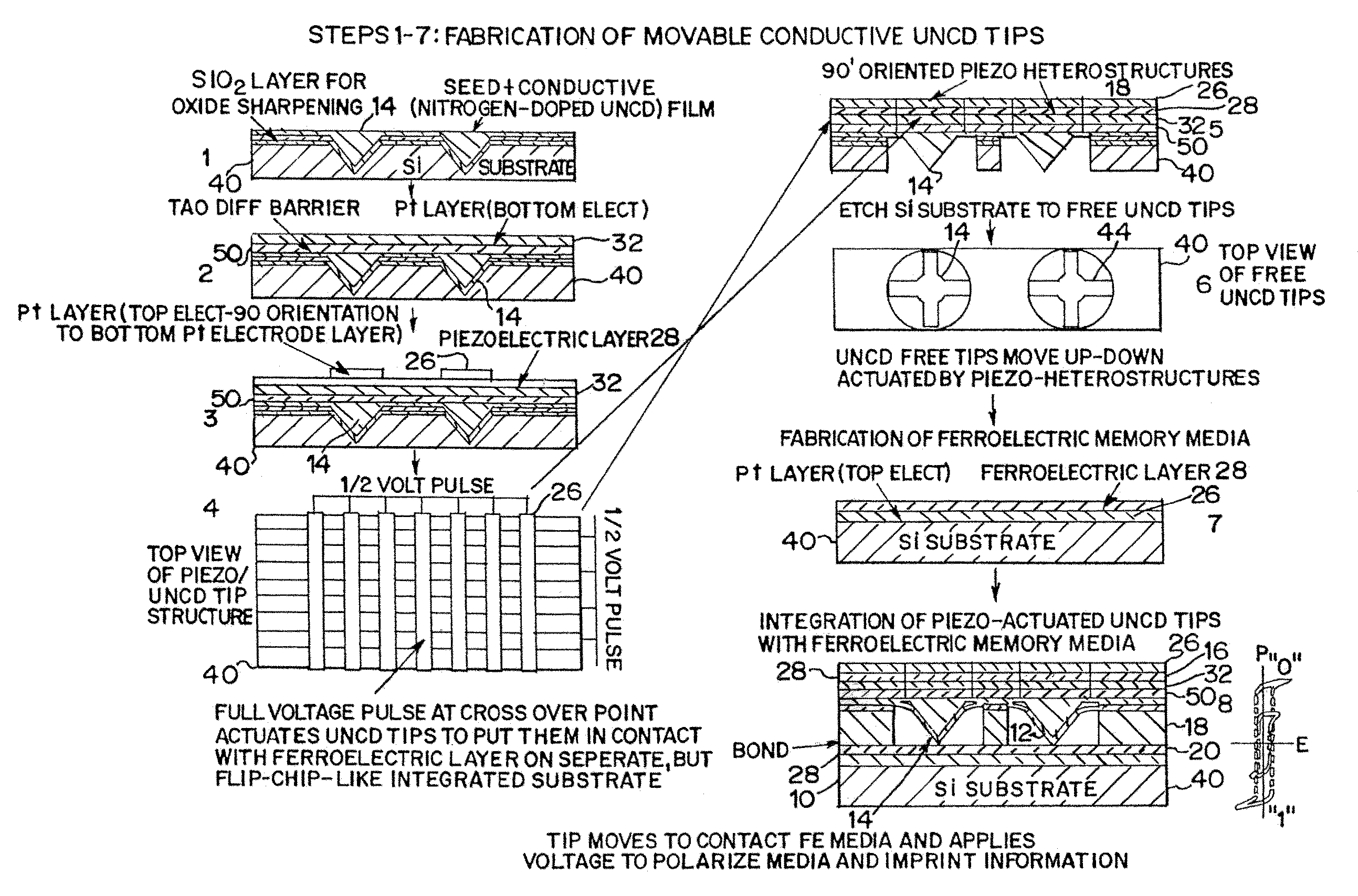
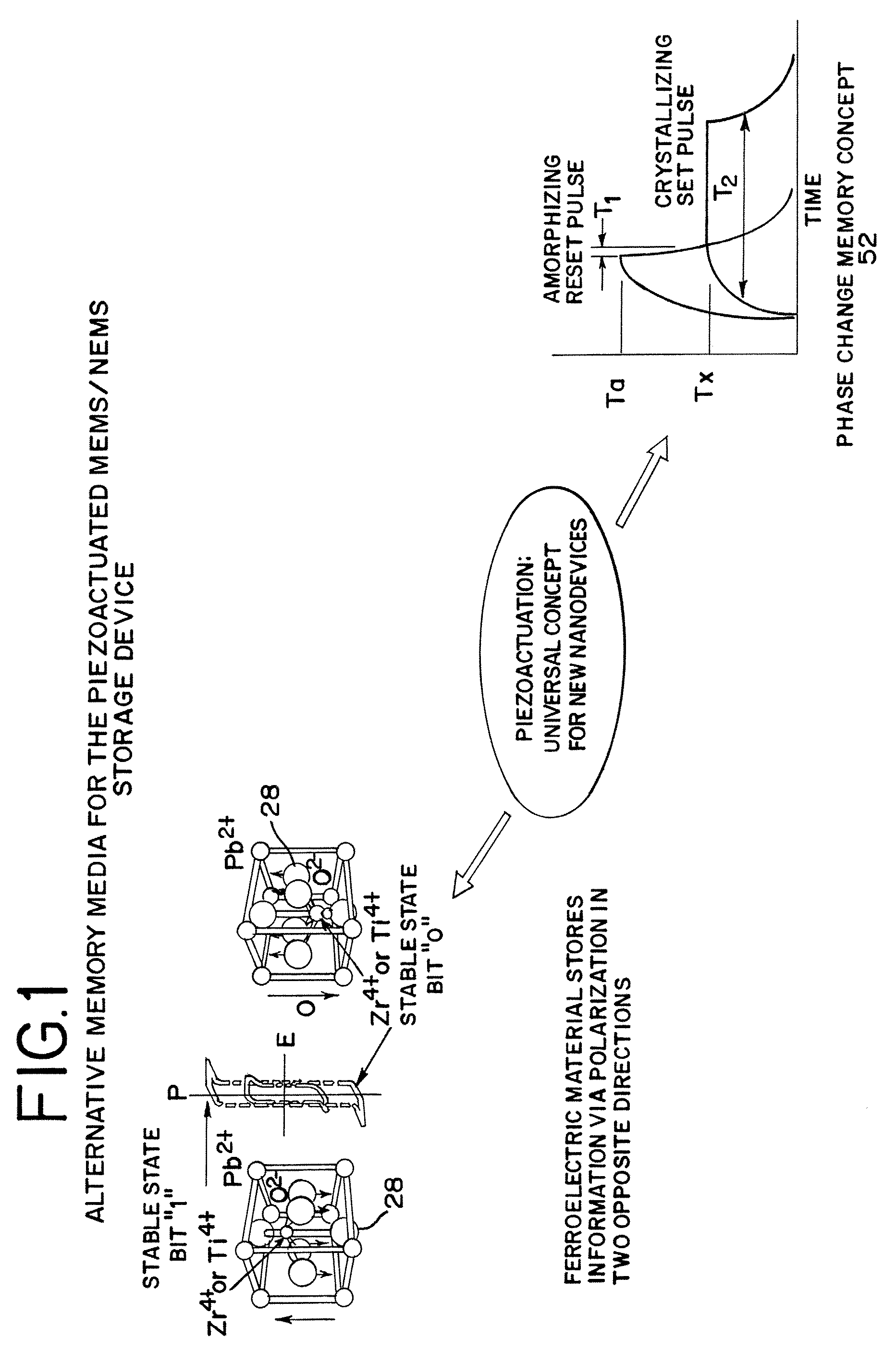
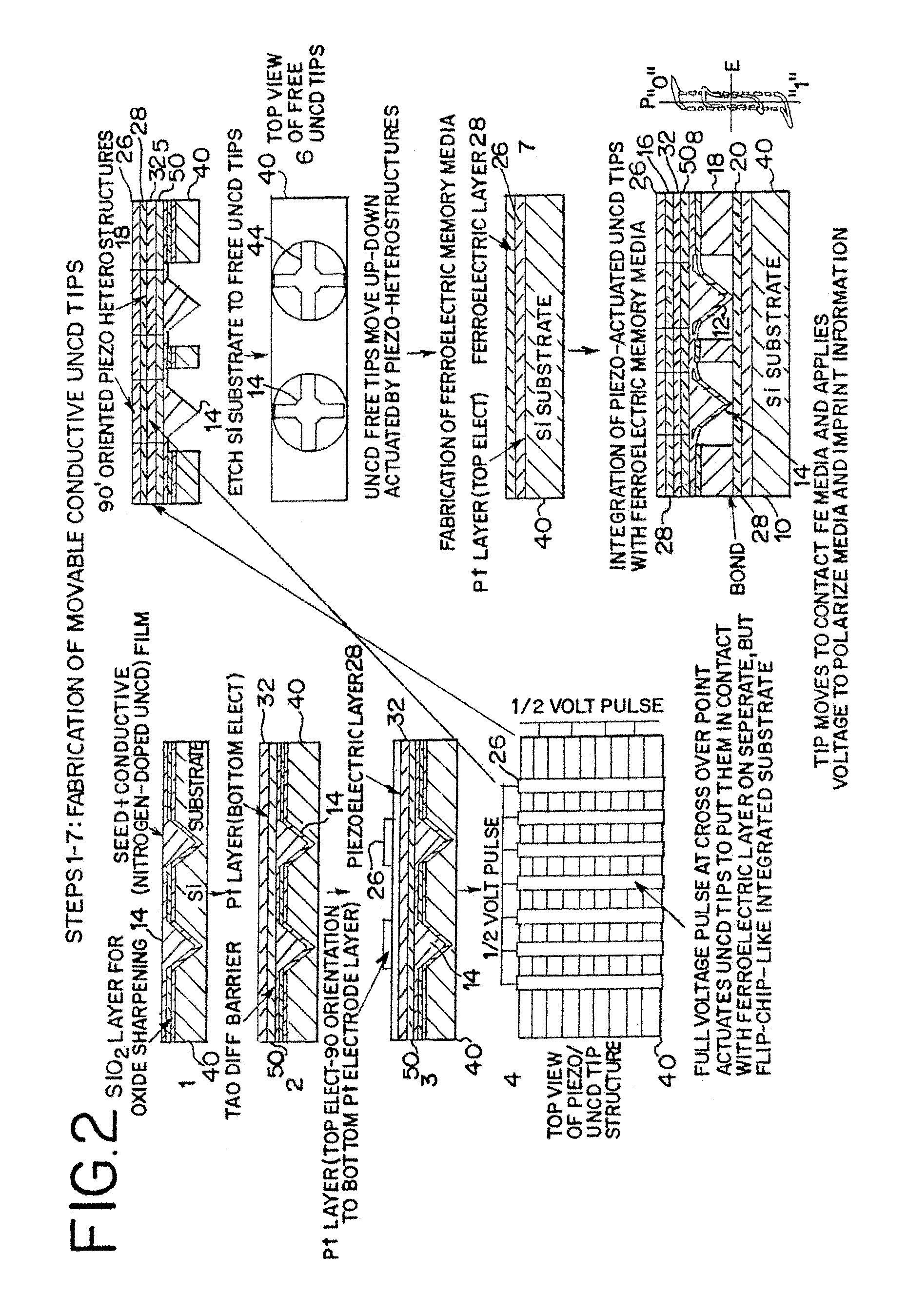
Piezoelectrically actuated ultrananocrystalline diamond tip array integrated with ferroelectric or phase change media for high-density memory
A compact large density memory piezoactuated storage device and process for its fabrication provides an integrated microelectromechanical (MEMS) and / or nanoelectromechanical (NEMS) system and structure that features an integrated large density array of nanotips made of wear-resistant conductive ultrananocrystalline diamond (UNCD) in which the tips are actuated via a piezoelectric thin film integrated with the UNCD tips. The tips of the special piezoactuated storage device effectively contact an underlying metal layer (top electrode) deposited on a polarizable ferroelectric layer that is grown on top of another metal layer (bottom electrode) to form a ferroelectric capacitor. Information is imprinted in the ferroelectric layer by the polarization induced by the application of a voltage pulse between the top and bottom electrodes through the conductive UNCD tips. This integrated microelectromechanical (MEMS) and / or nanoelectromechanical (NEMS) system and structure can be efficiently used to imprint data in the ferroelectric layer for memory storage with high density in the gigabit (Gb) to terabit (Tb) range. An alternative memory media to the ferroelectric layer can be a phase change material that exhibits two orders of magnitude difference in electrical resistance between amorphous and crystalline phases.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Scalable weight-based terabit switch scheduling method
InactiveUS7065046B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of servicePartial filling
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
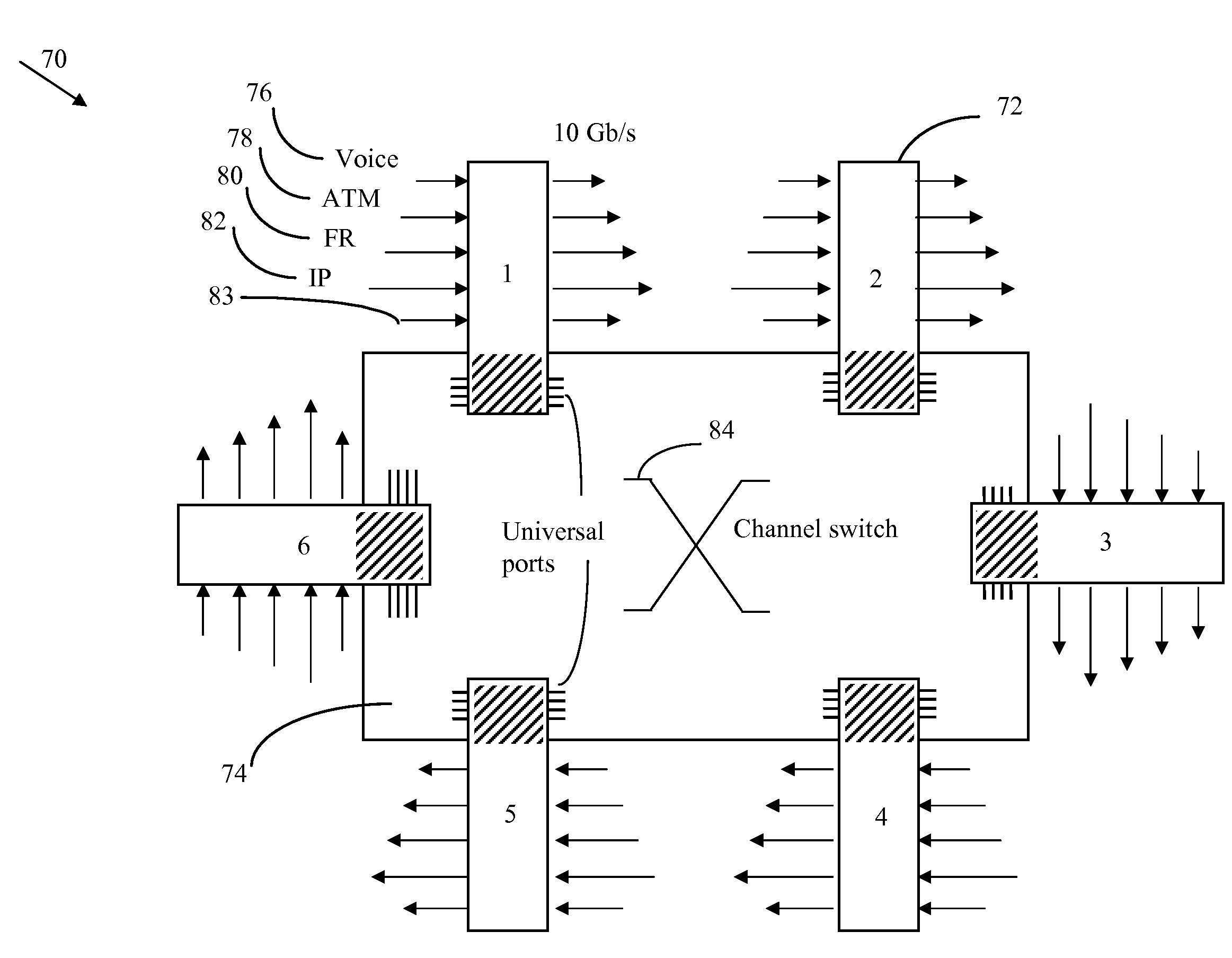
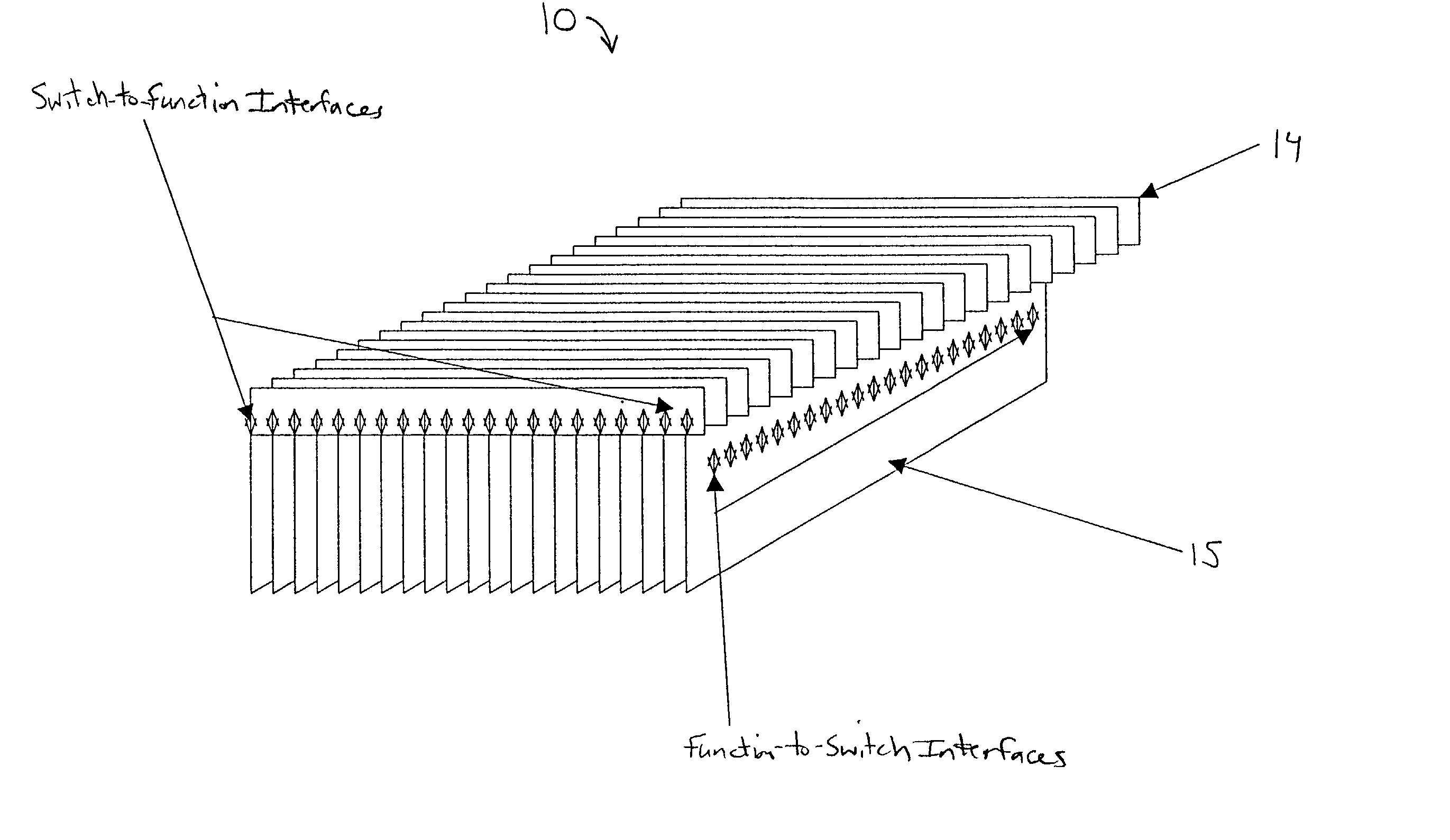
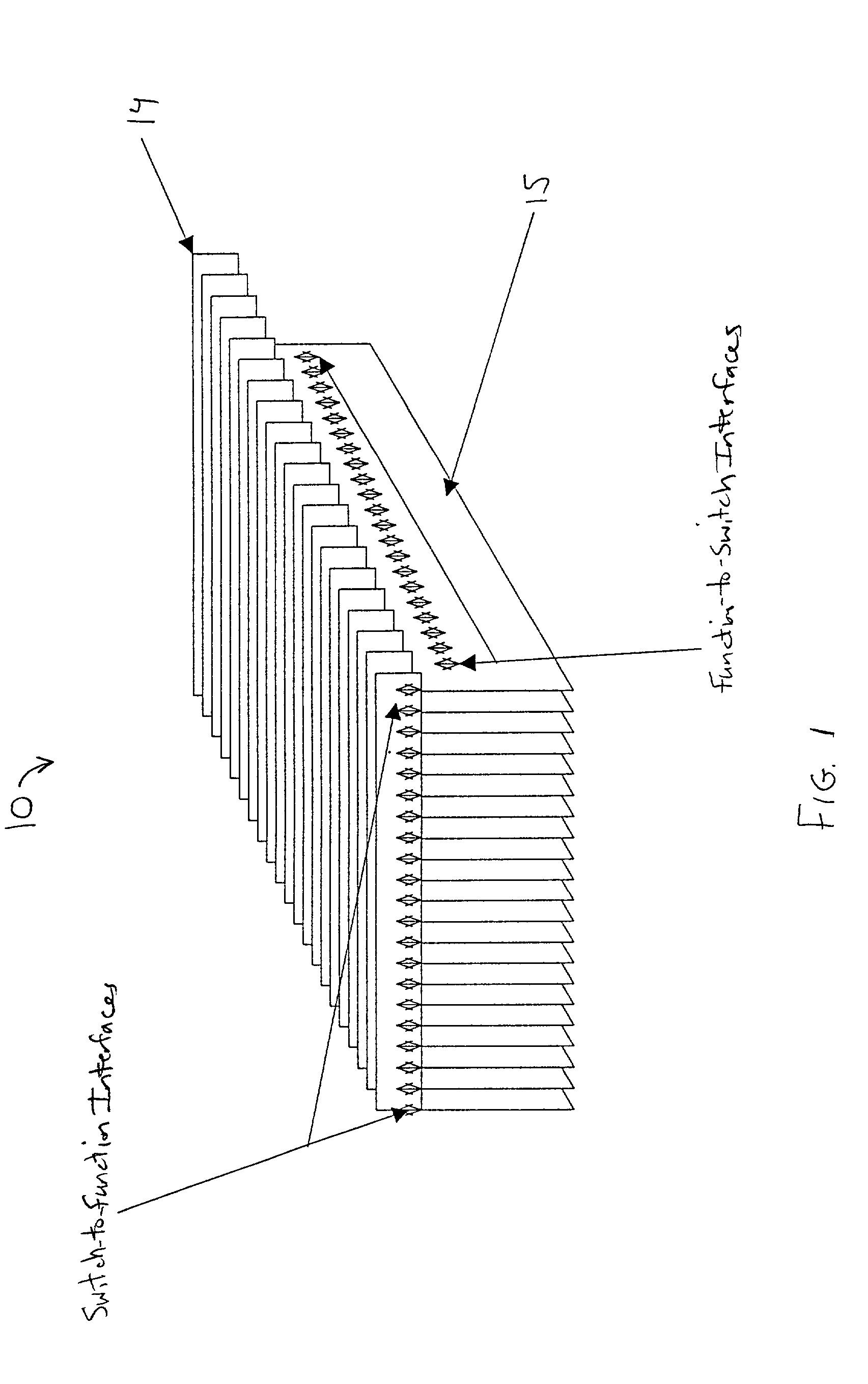
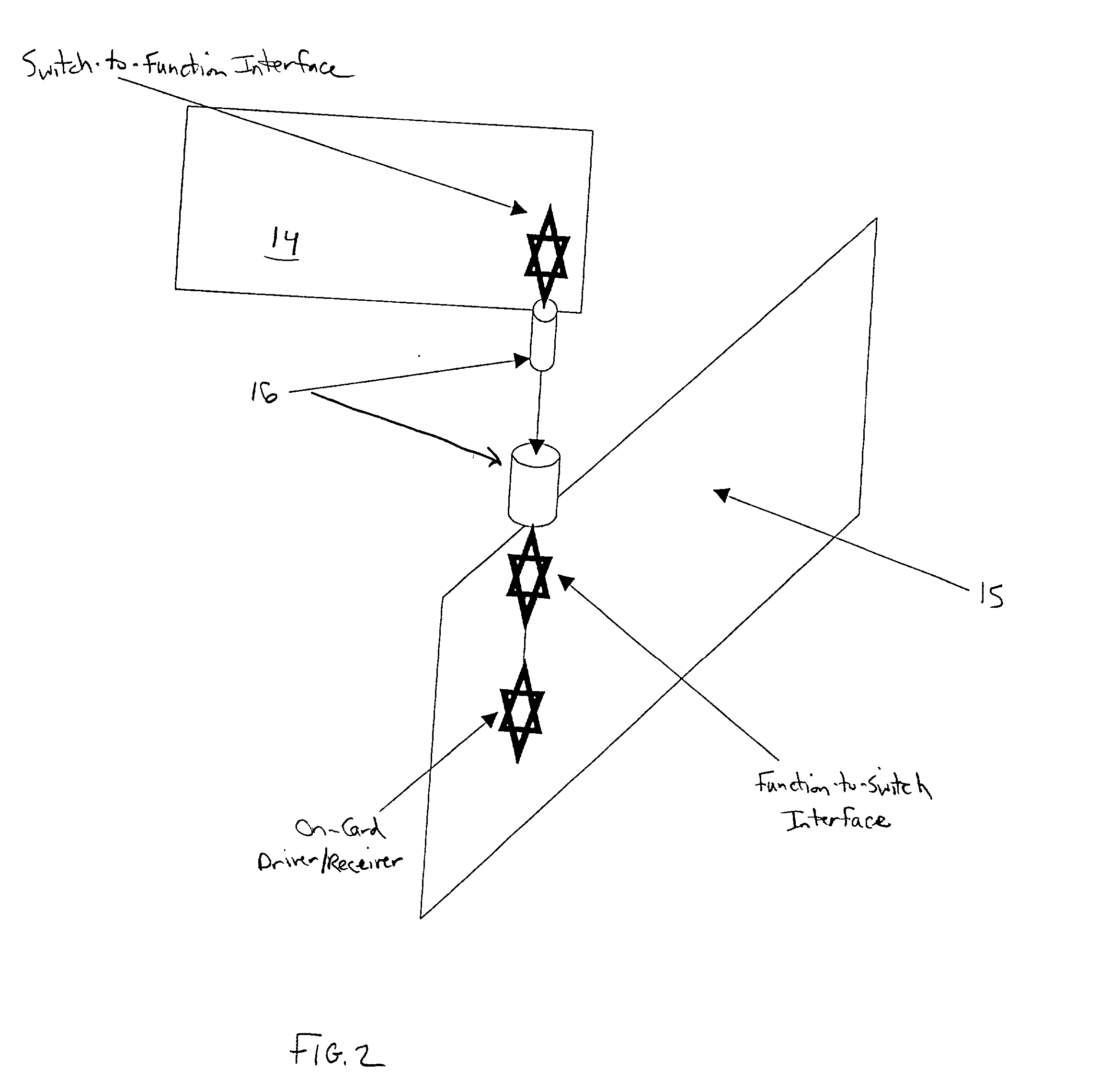
Mid-connect architecture with point-to-point connections for high speed data transfer
InactiveUS20020162083A1Maximize throughputElectrically conductive connectionsSupport structure mountingTransceiverLine card
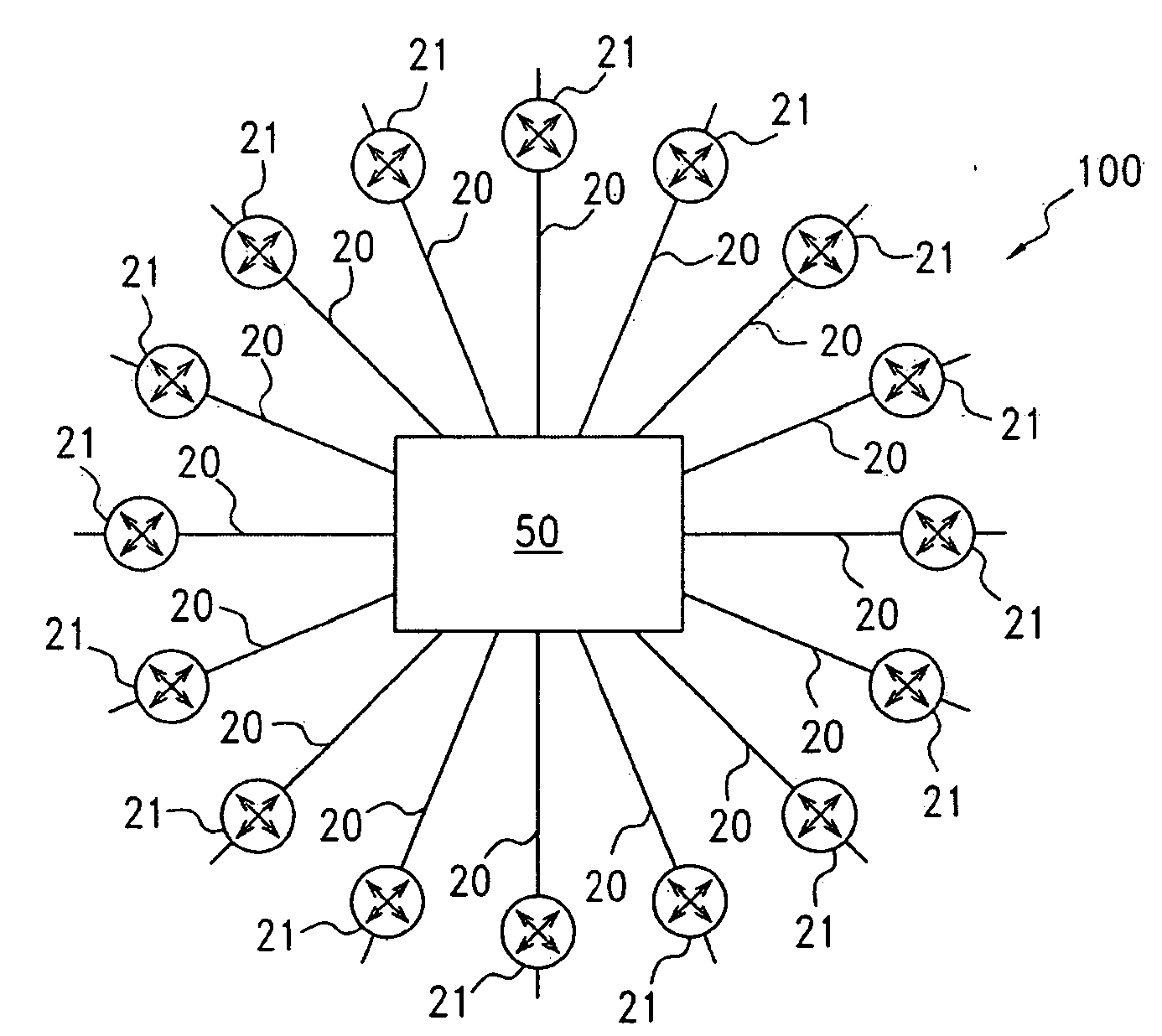
A mid-connect interconnection system for coupling a plurality of function cards to one another via a plurality of switch cards. The connection may be established using direct connectors of very short length to provide high-speed transmission with little to no reflection concerns. The connectors are arranged such that the function cards are not connected in parallel with the switch cards. The mid-connect arrangement provides connector access points or locations corresponding in number to the number of switch cards multiplied by the number of line cards. The connectors are formed as one or more pairs of connectors, attached to the switch and function cards, to enable multi-channel point-to-point connections for full input and output among function cards. Each of the switch cards and each of the function cards includes a transceiver driver to enable high speed switching. The arrangement of cards provides broadband throughput on the order of Terabits per second.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Piezoelectrically actuated ultrananocrystalline diamond tip array integrated with ferroelectric or phase change media for high-density memory
InactiveUS7602105B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesNanoinformaticsVoltage pulseWear resistant
A compact large density memory piezoactuated storage device and process for its fabrication provides an integrated microelectromechanical (MEMS) and / or nanoelectromechanical (NEMS) system and structure that features an integrated large density array of nanotips made of wear-resistant conductive ultrananocrystalline diamond (UNCD) in which the tips are actuated via a piezoelectric thin film integrated with the UNCD tips. The tips of the special piezoactuated storage device effectively contact an underlying metal layer (top electrode) deposited on a polarizable ferroelectric layer that is grown on top of another metal layer (bottom electrode) to form a ferroelectric capacitor. Information is imprinted in the ferroelectric layer by the polarization induced by the application of a voltage pulse between the top and bottom electrodes through the conductive UNCD tips. This integrated microelectromechanical (MEMS) and / or nanoelectromechanical (NEMS) system and structure can be efficiently used to imprint data in the ferroelectric layer for memory storage with high density in the gigabit (Gb) to terabit (Tb) range. An alternative memory media to the ferroelectric layer can be a phase change material that exhibits two orders of magnitude difference in electrical resistance between amorphous and crystalline phases.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Wavelength tunable optical sources, filters and detectors
ActiveUS20180348507A1Reduce restrictionsTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTransceiverEngineering
Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) has enabled telecommunication service providers to fully exploit the transmission capacity of optical fibers. State of the art systems in long-haul networks now have aggregated capacities of terabits per second. Moreover, by providing multiple independent multi-gigabit channels, WDM technologies offer service providers with a straight forward way to build networks and expand networks to support multiple clients with different requirements. In order to reduce costs, enhance network flexibility, reduce spares, and provide re-configurability many service providers have migrated away from fixed wavelength transmitters, receivers, and transceivers, to wavelength tunable transmitters, receivers, and transceivers as well as wavelength dependent add-drop multiplexer, space switches etc. However, to meet the competing demands for improved performance, increased integration, reduced footprint, reduced power consumption, increased flexibility, re-configurability, and lower cost it is desirable to exploit / adopt monolithic optical circuit technologies, hybrid optoelectronic integration, and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
Owner:VALORBEC PARTNERSHIP
Internet protocol over WDM network, and packet communication system and method in the IPOW network
InactiveUS6952533B2Increase speedDiversity of efficiencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPacket communicationTransport system
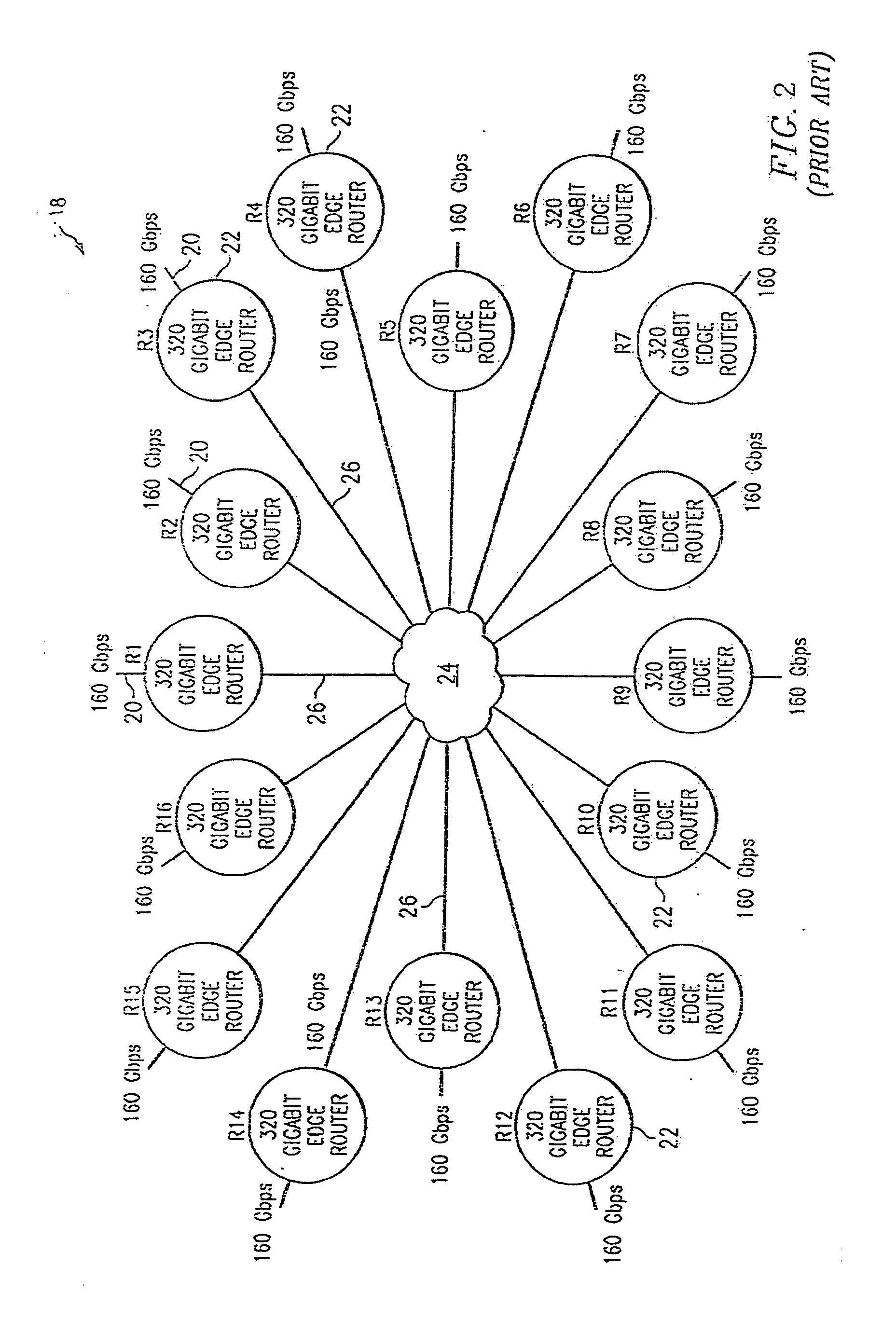
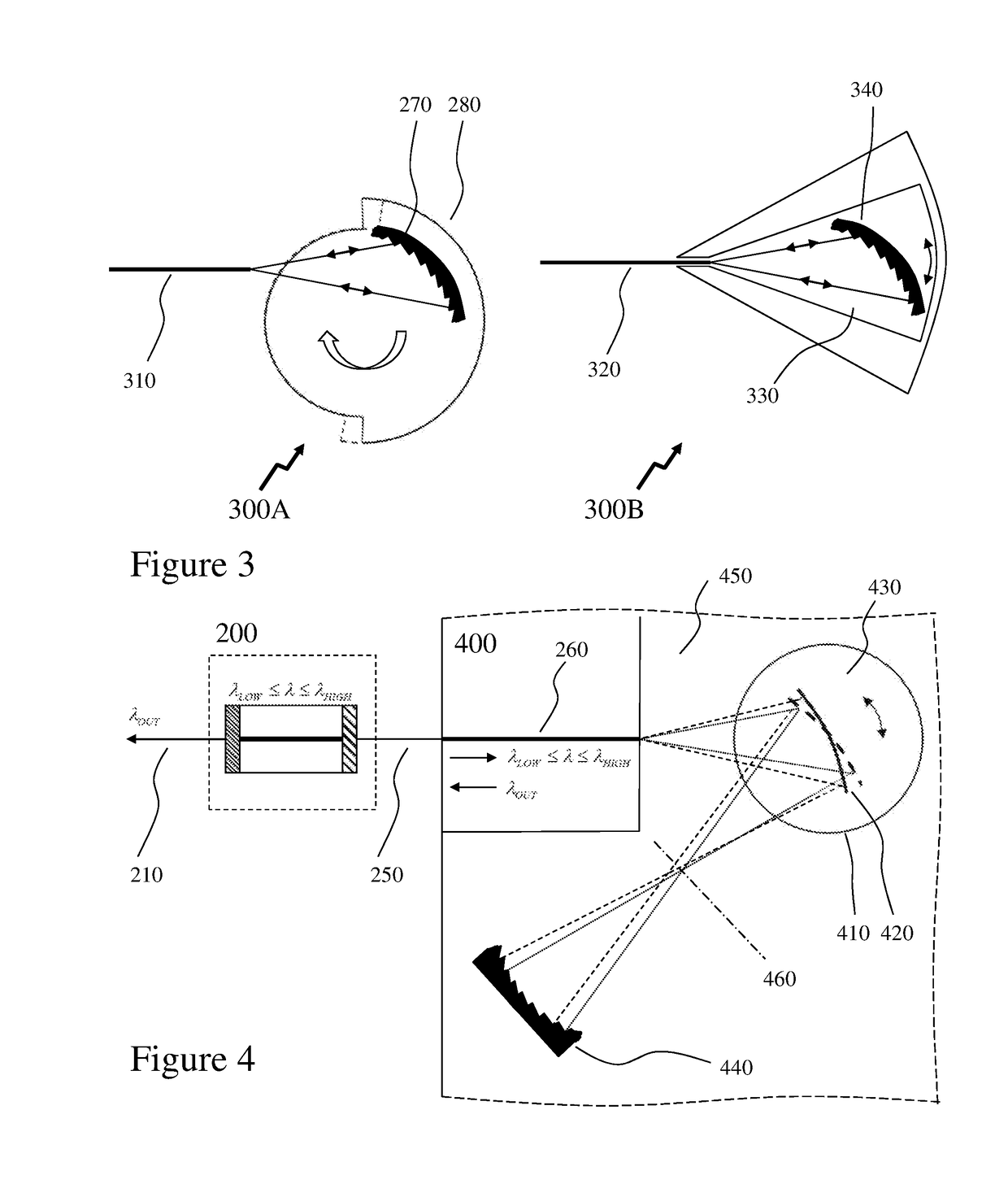
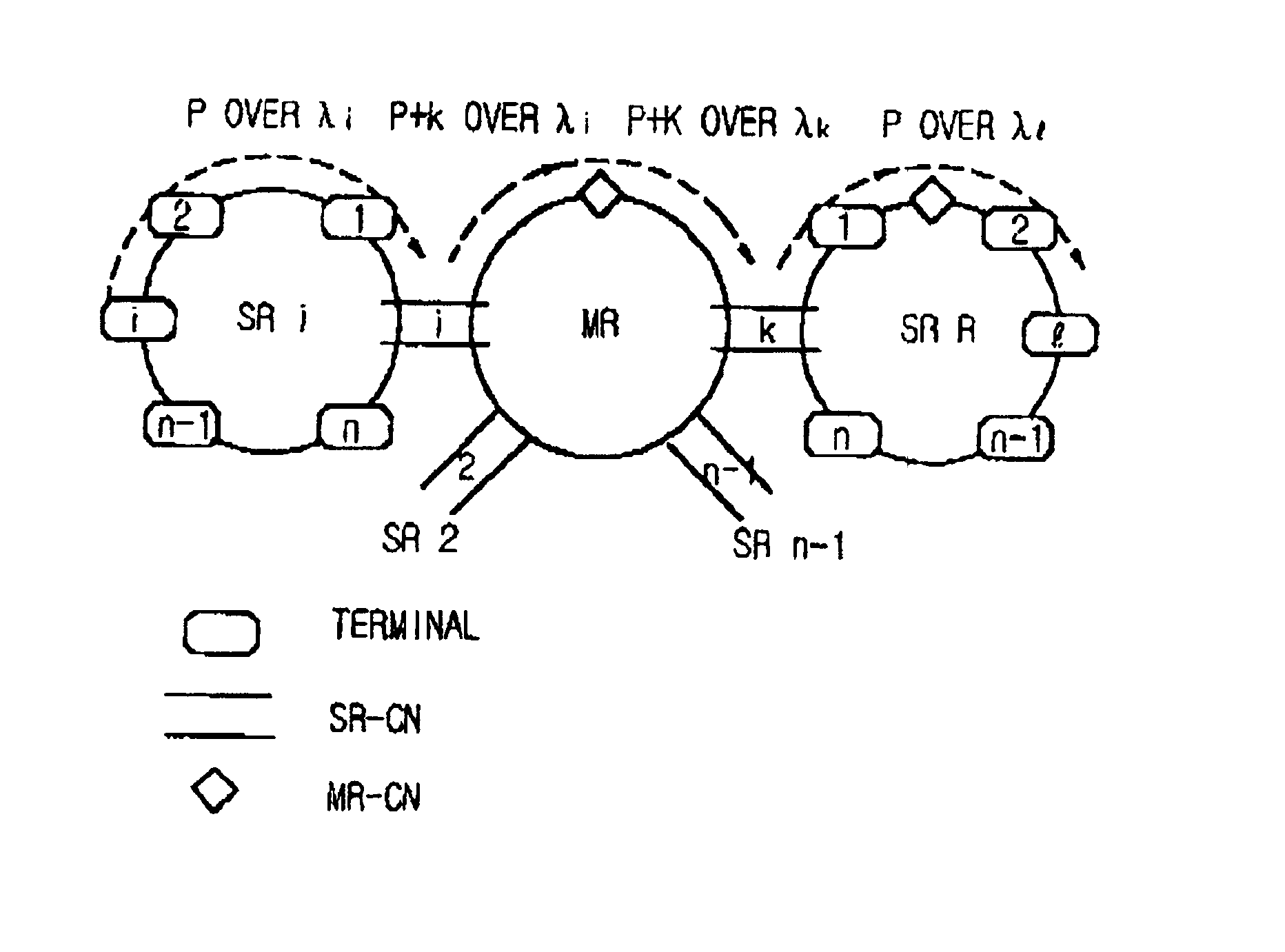
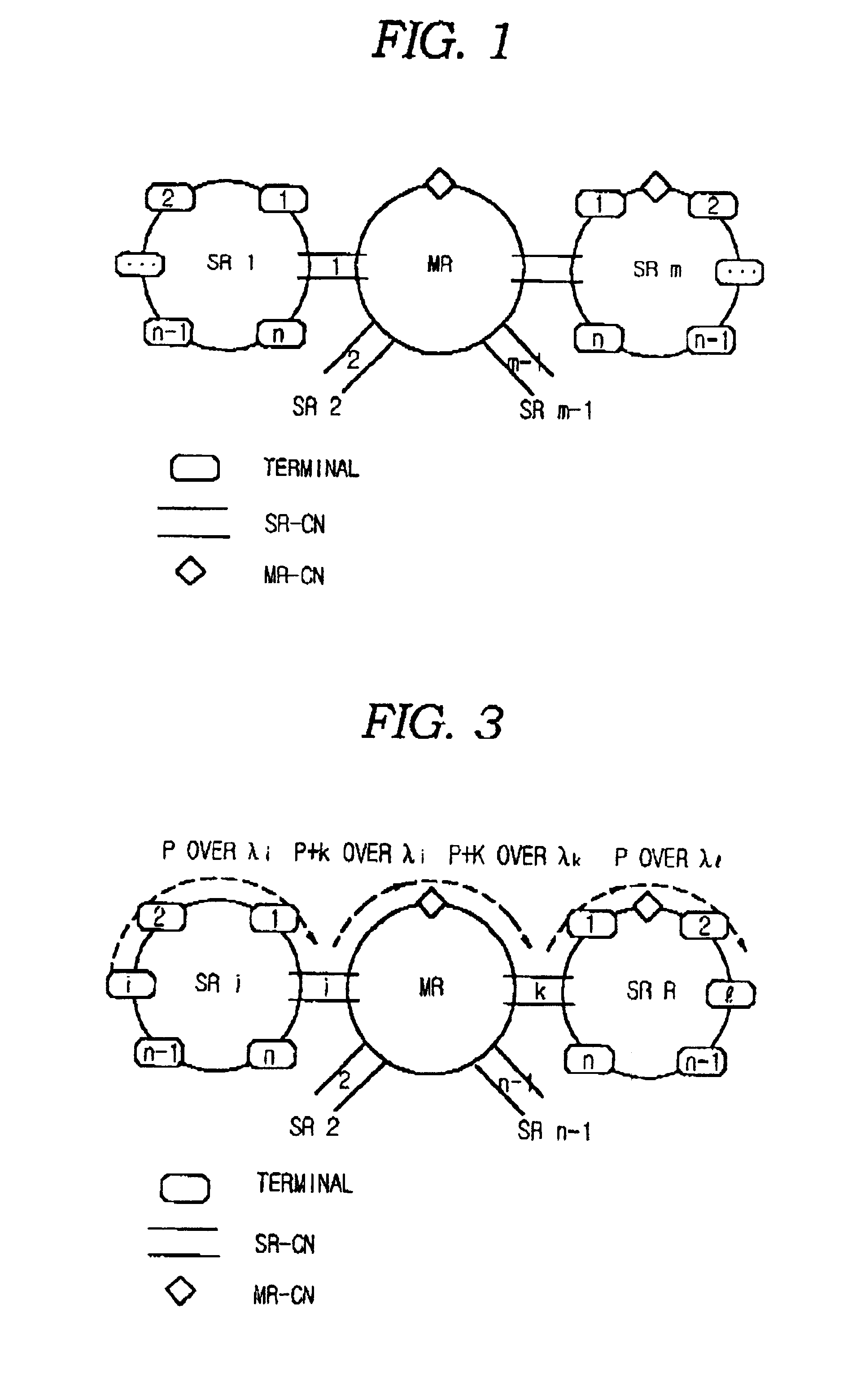
There is disclosed an internet protocol over WDM (IPOW) network structure which can directly route / transmit packets via a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) optical communication network, and a packet transmission system in the network structure and method using the network structure. The internet protocol over wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) network structure comprising: a plurality of sub-ring for connecting n number of terminals (where n is a positive integer) to which unique user wave lengths are respectively allocated; a main ring for connecting n number of connection nodes connecting sub-rings to which unique user wave lengths are respectively allocated; a single sub-ring controller for controlling the flows of a packet transmitted / received inside the sub-ring and a packet transmitted / received between the sub-ring and the main ring; and a main ring controller connected to the single sub-ring and the main ring, and controlling the flow of a packet transmitted / received inside the main ring, wherein the terminals and connection nodes each add / drop only their own unique wavelength signals, the sub-ring controller and main ring controller drop all the wavelength division multiplexed signals to de-multiplex the signals, load each of the signals on their unique user wavelengths in their destination terminals, and then multiplex again the signals to transmit to the sub-ring and main ring, the sub-ring controller adds the identifying code (which is called a λ tag) of the sub-ring having a destination terminal, to the transmitted packet, and then transmits it to the main ring. The present invention has an advantage that it can route the packet at high speed, and also significantly simplifies a network structure. In addition, the present invention can process several tens of terabit traffic, expensive optical elements or optical systems, and a high-performance traffic routing apparatus such as a terra-bit level controller, etc.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
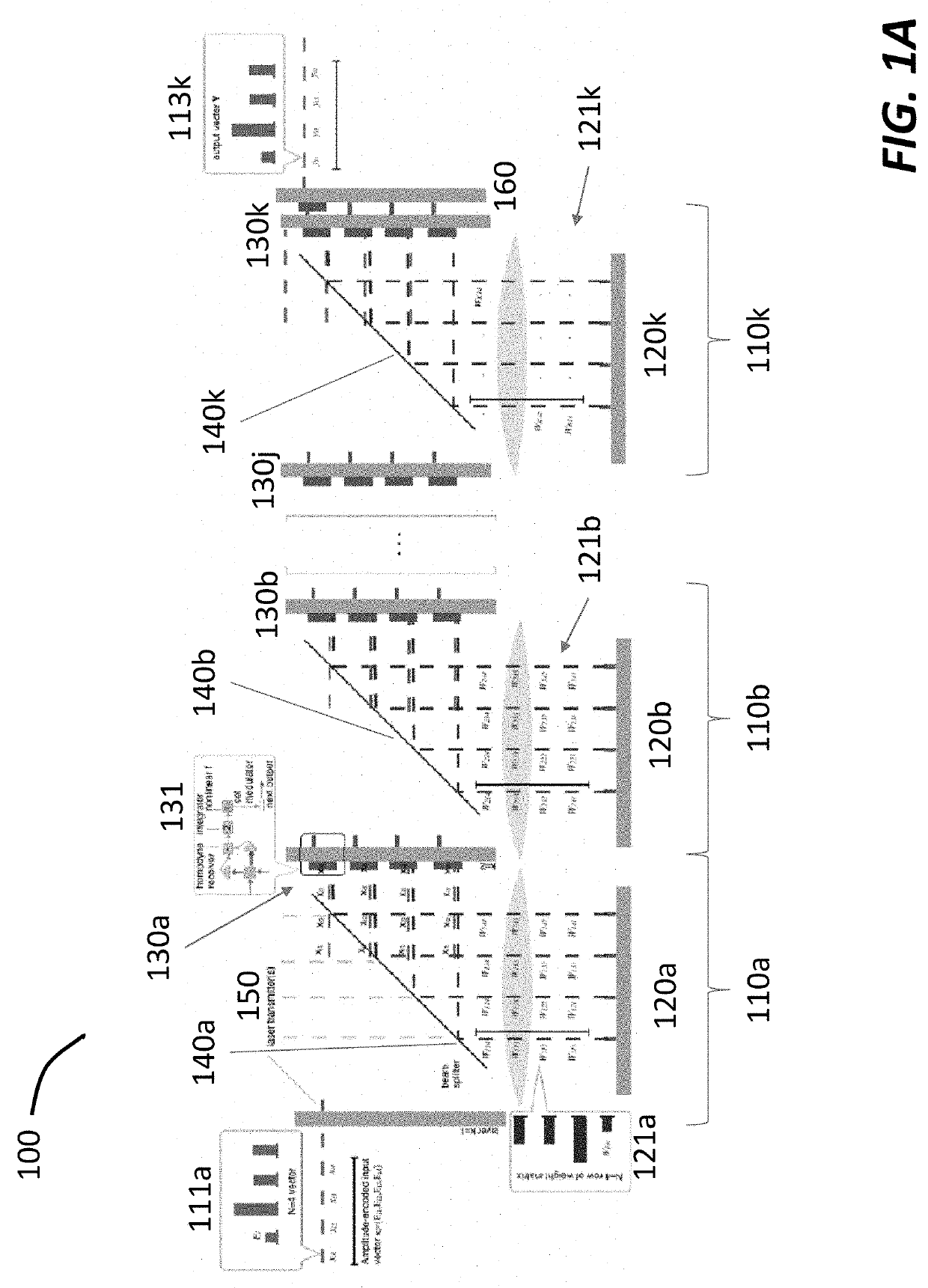
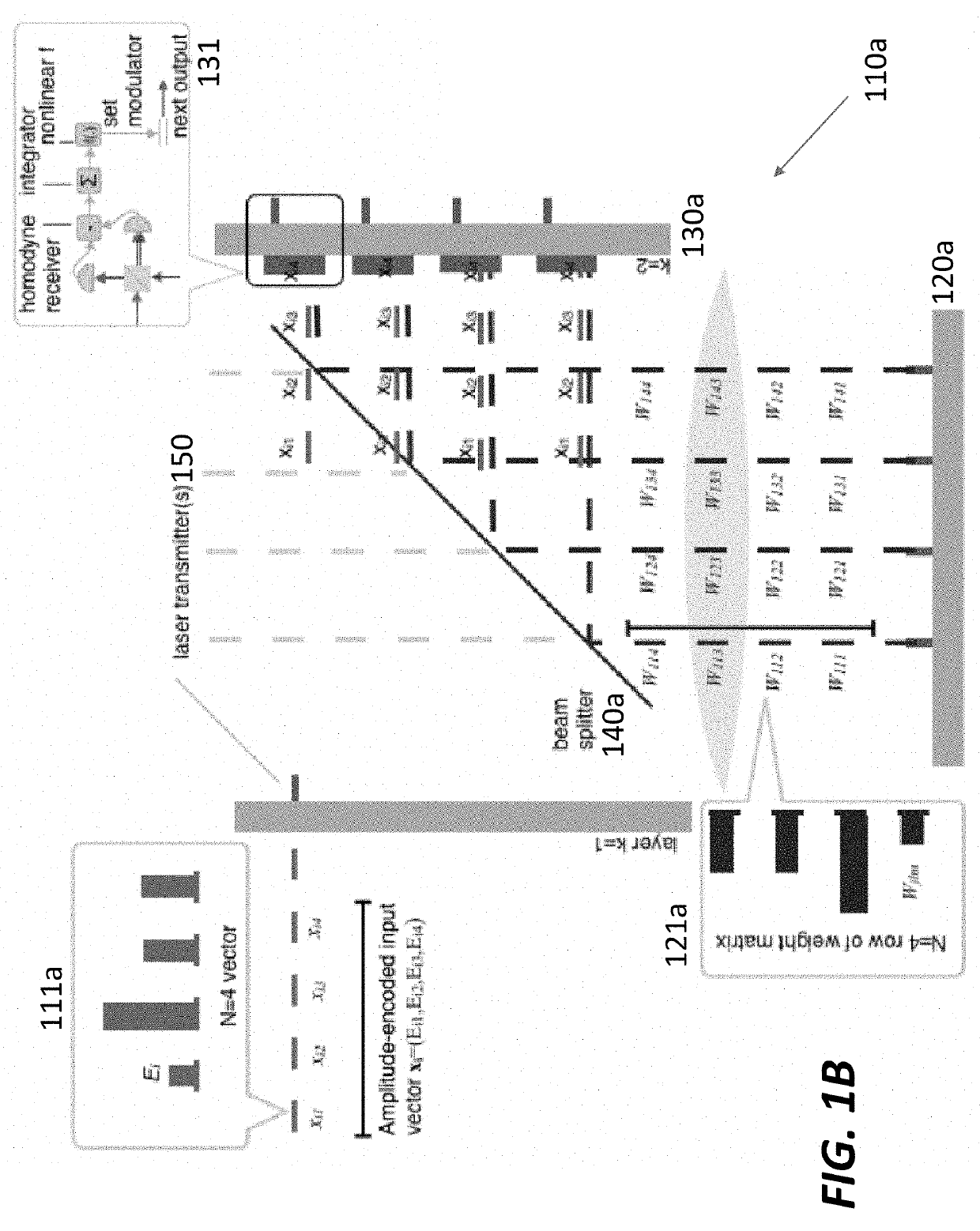
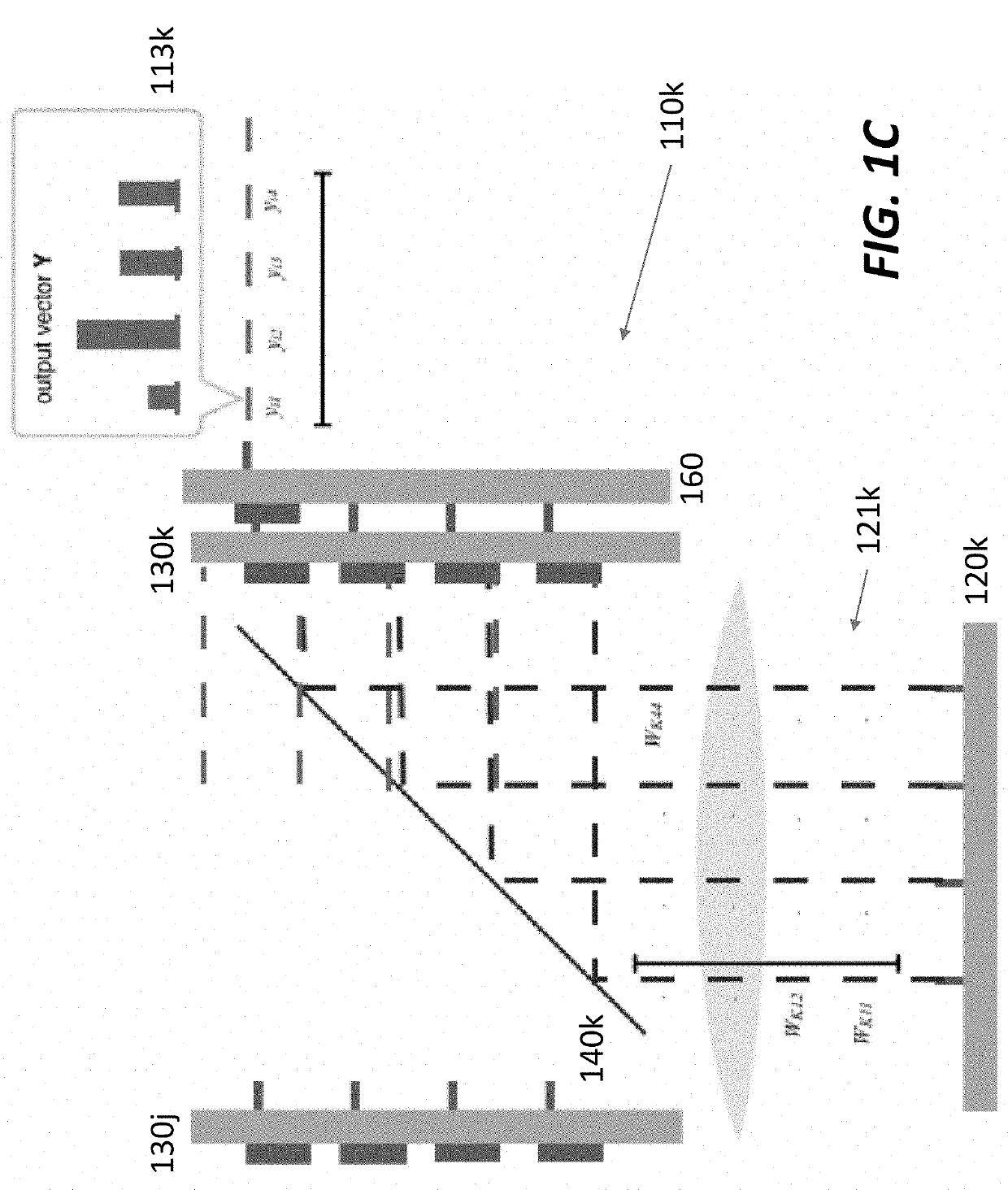
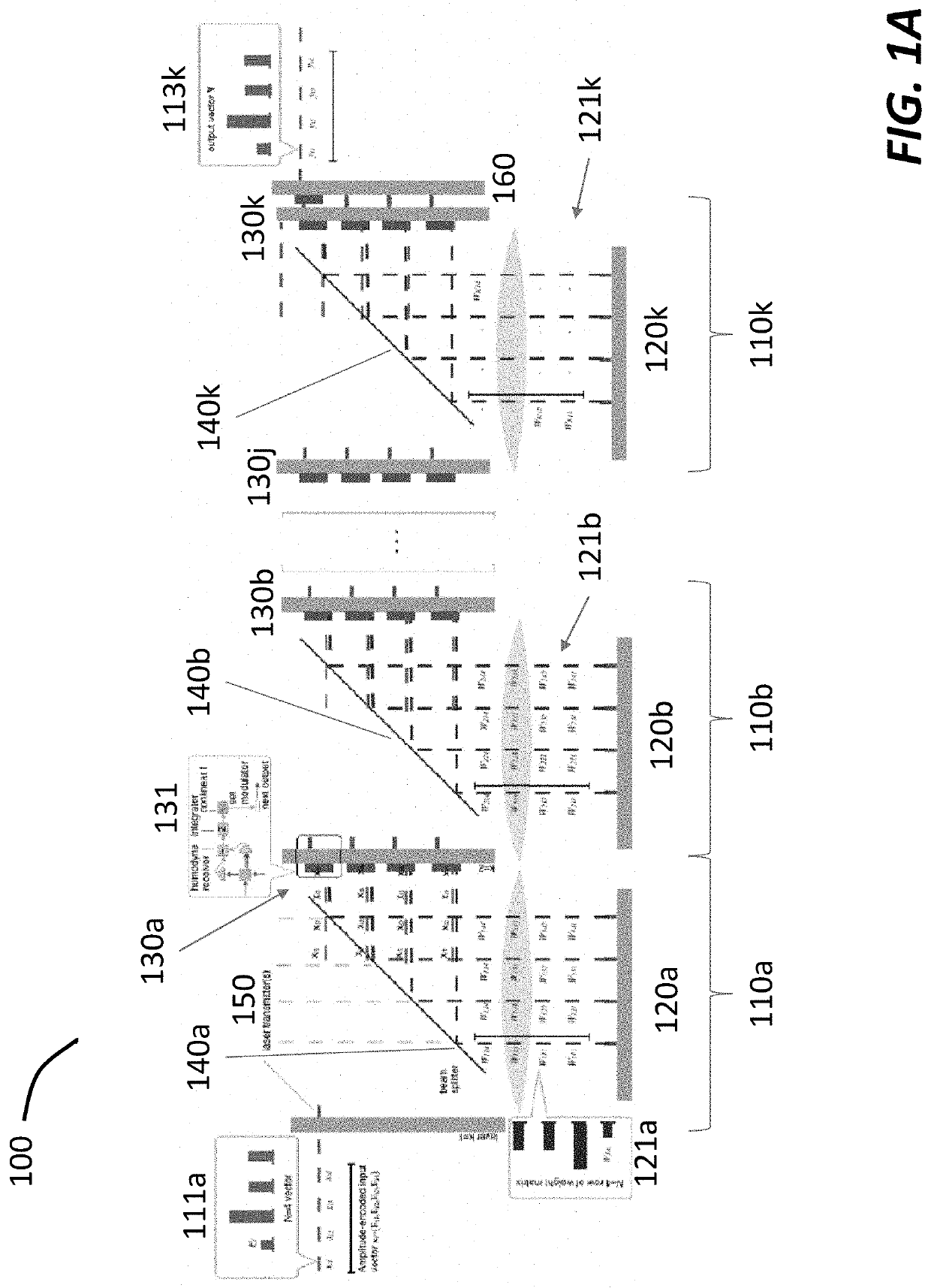
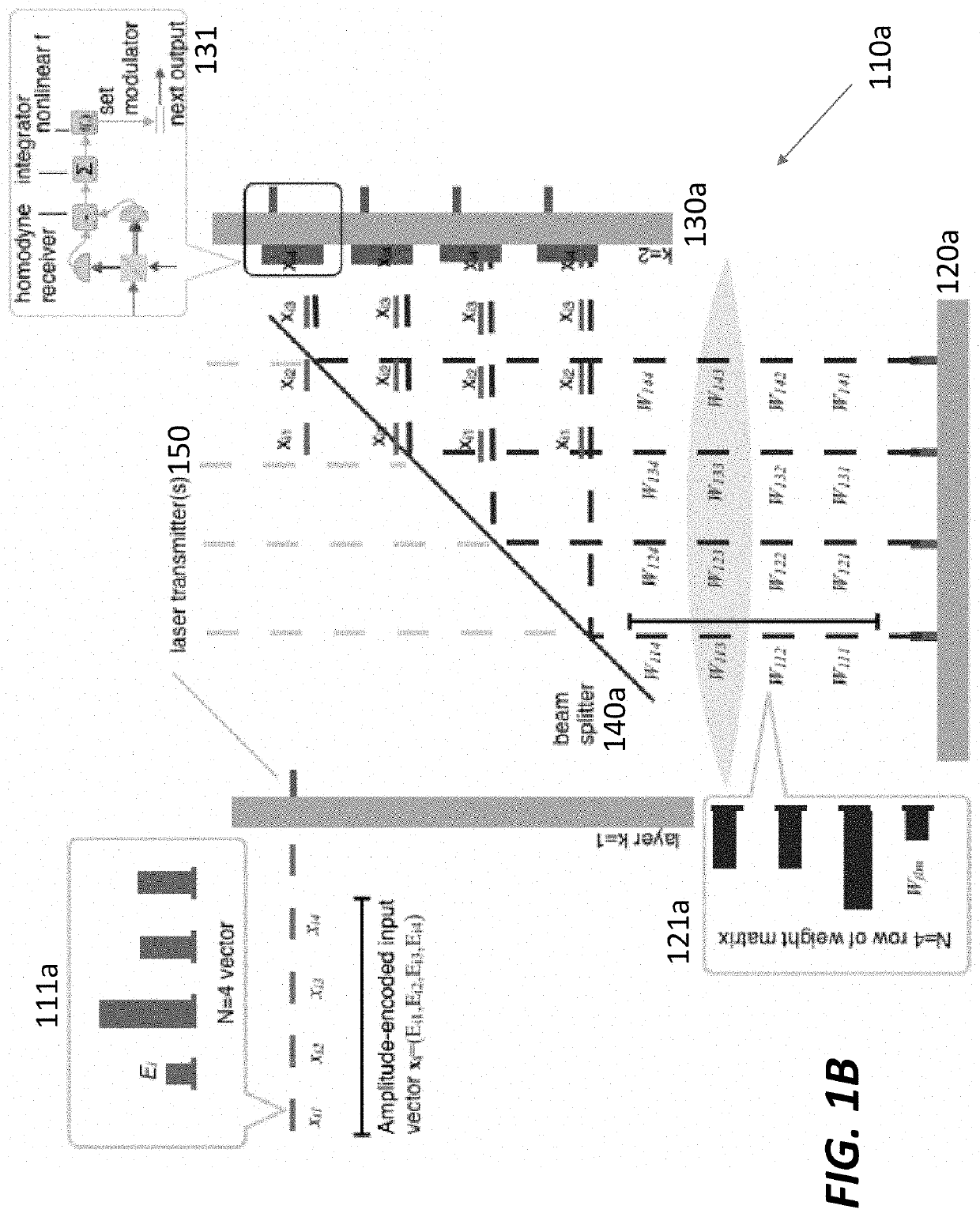
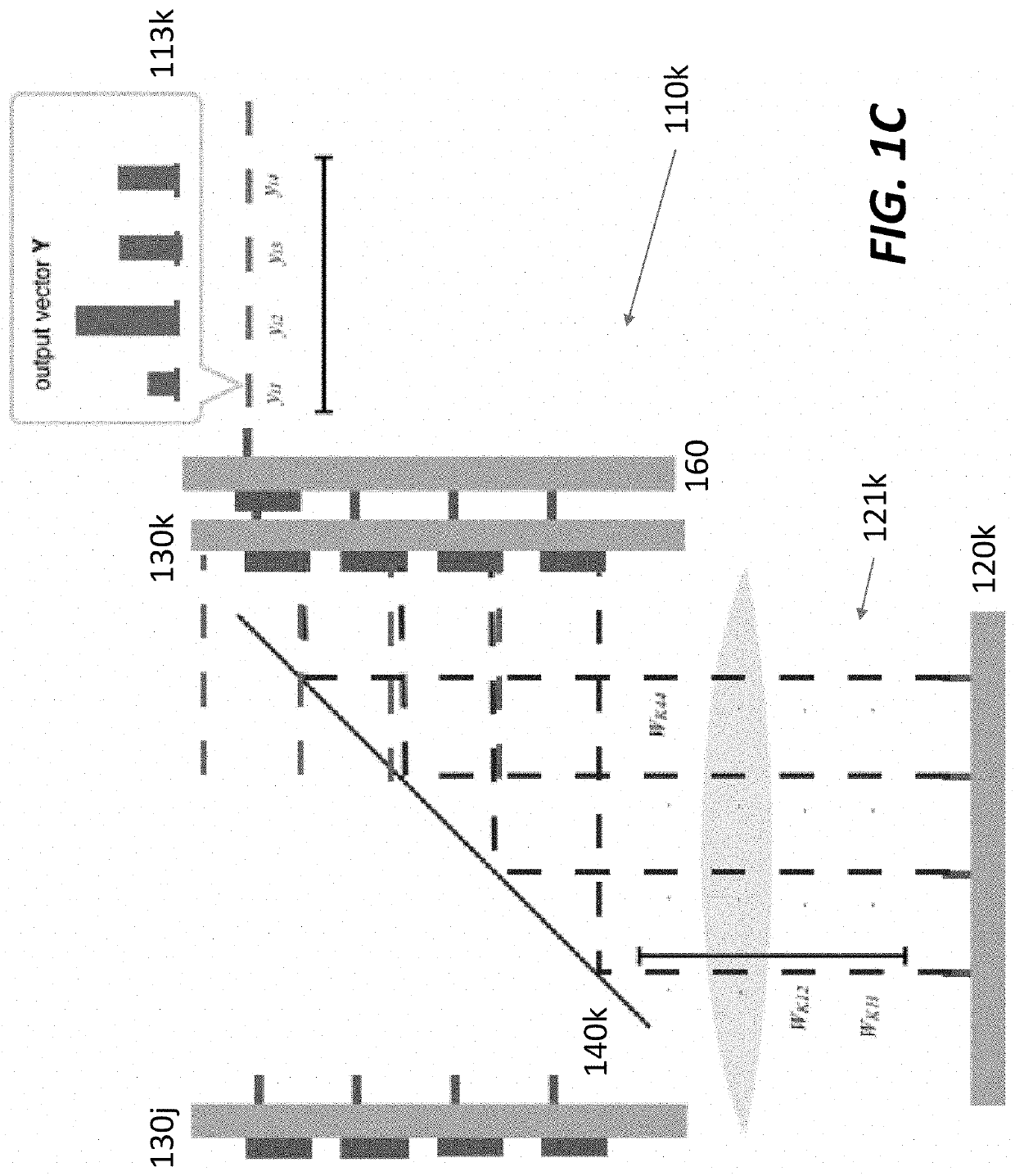
Serialized electro-optic neural network using optical weights encoding
Most artificial neural networks are implemented electronically using graphical processing units to compute products of input signals and predetermined weights. The number of weights scales as the square of the number of neurons in the neural network, causing the power and bandwidth associated with retrieving and distributing the weights in an electronic architecture to scale poorly. Switching from an electronic architecture to an optical architecture for storing and distributing weights alleviates the communications bottleneck and reduces the power per transaction for much better scaling. The weights can be distributed at terabits per second at a power cost of picojoules per bit (versus gigabits per second and femtojoules per bit for electronic architectures). The bandwidth and power advantages are even better when distributing the same weights to many optical neural networks running simultaneously.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
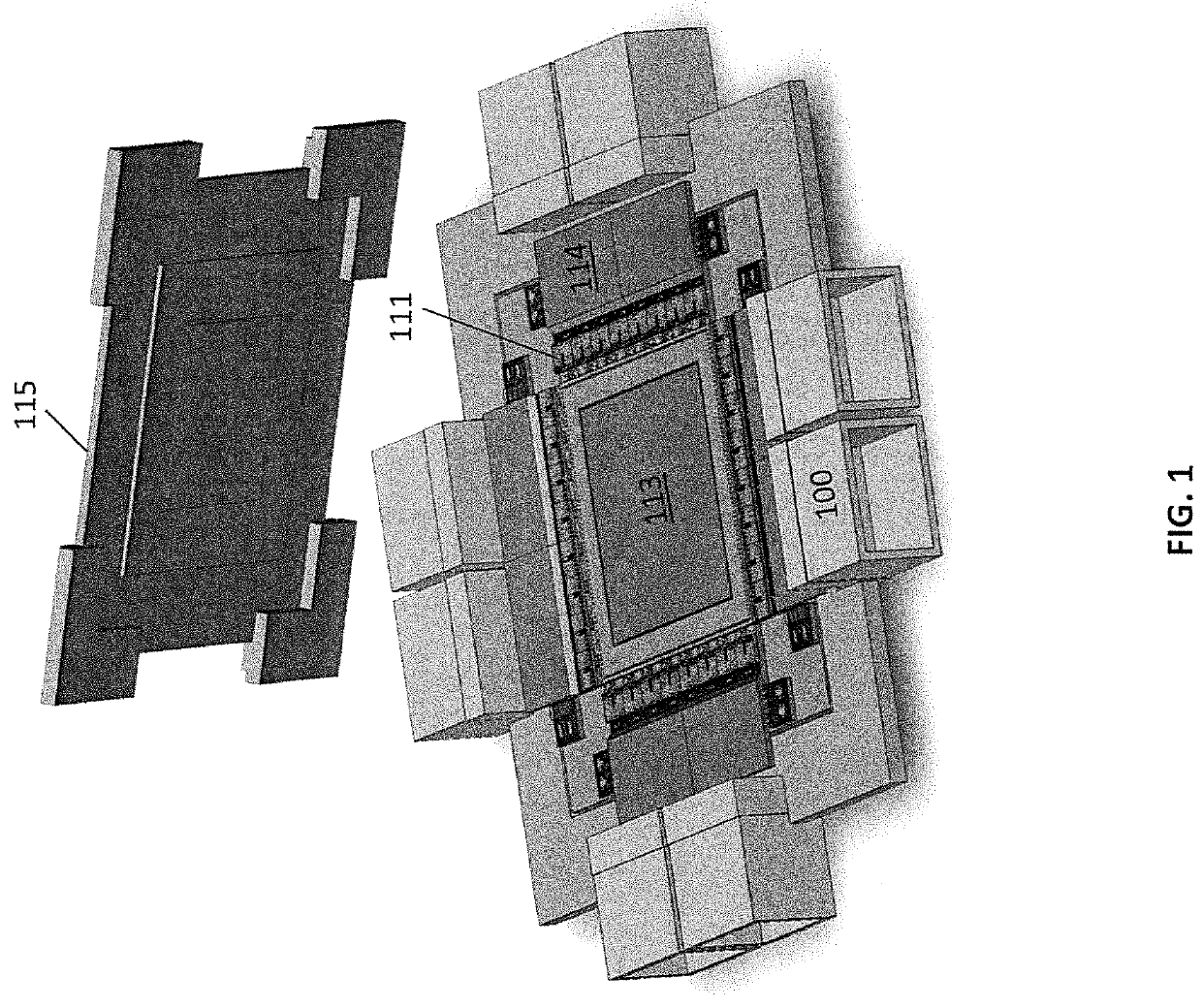
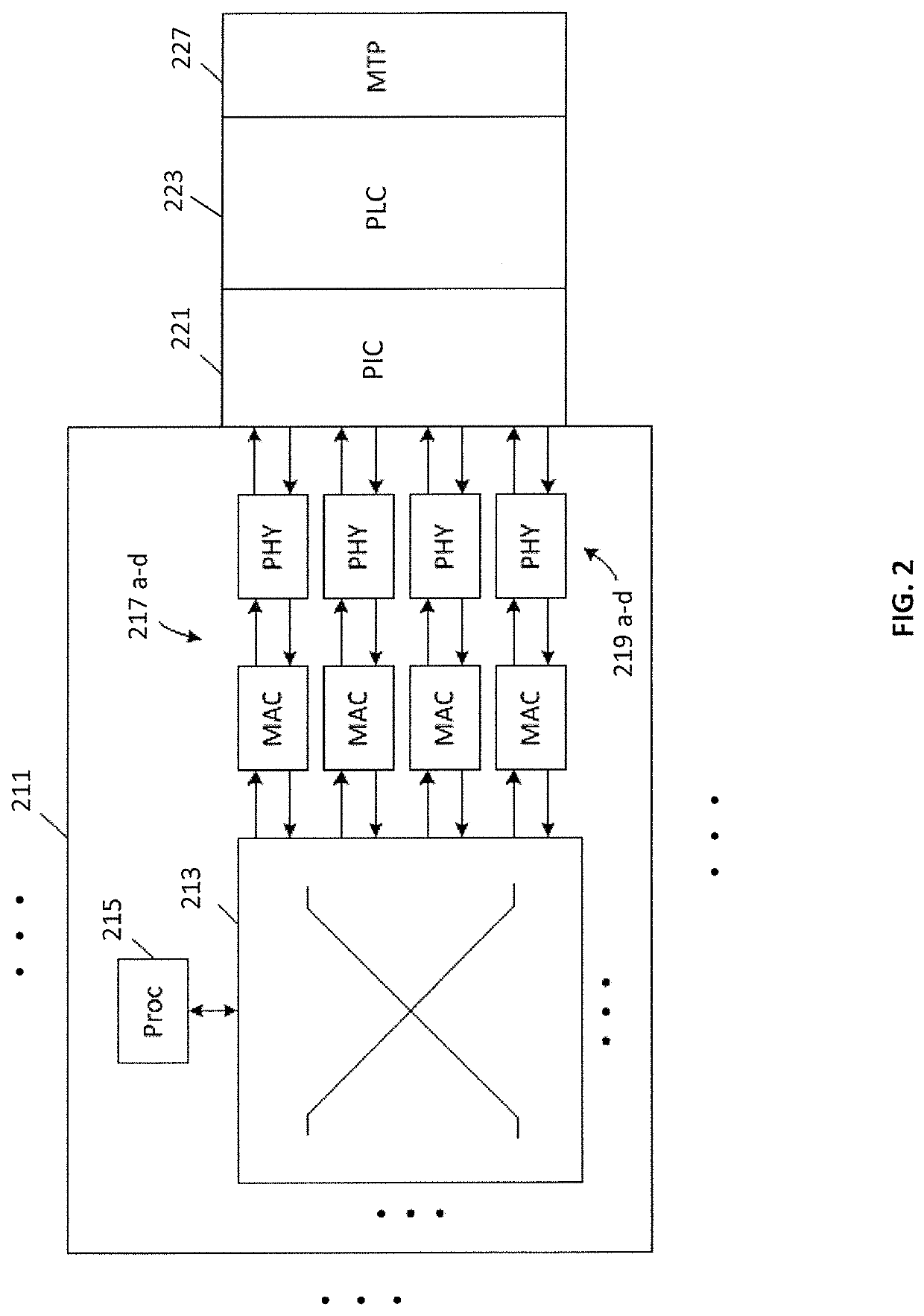
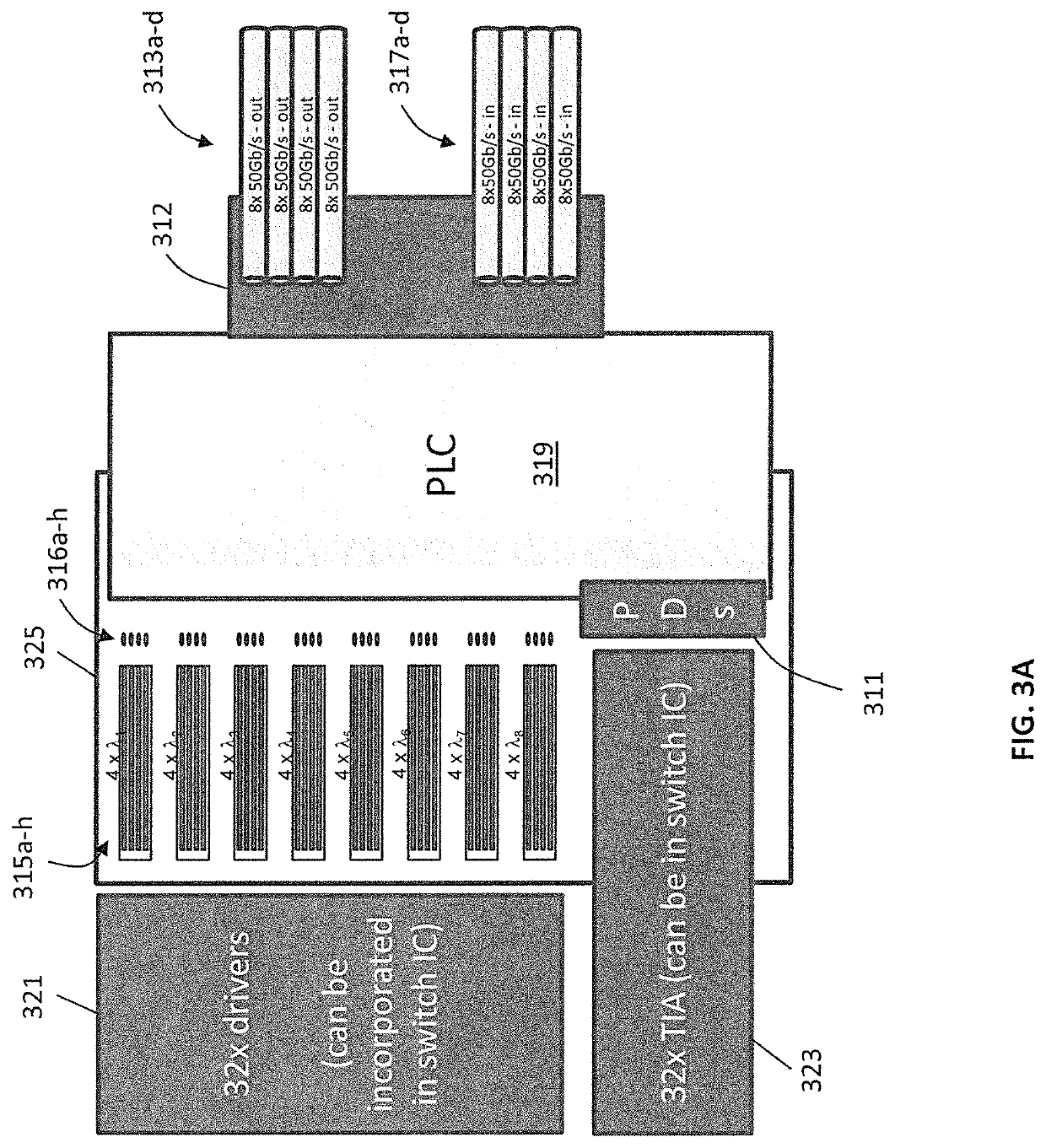
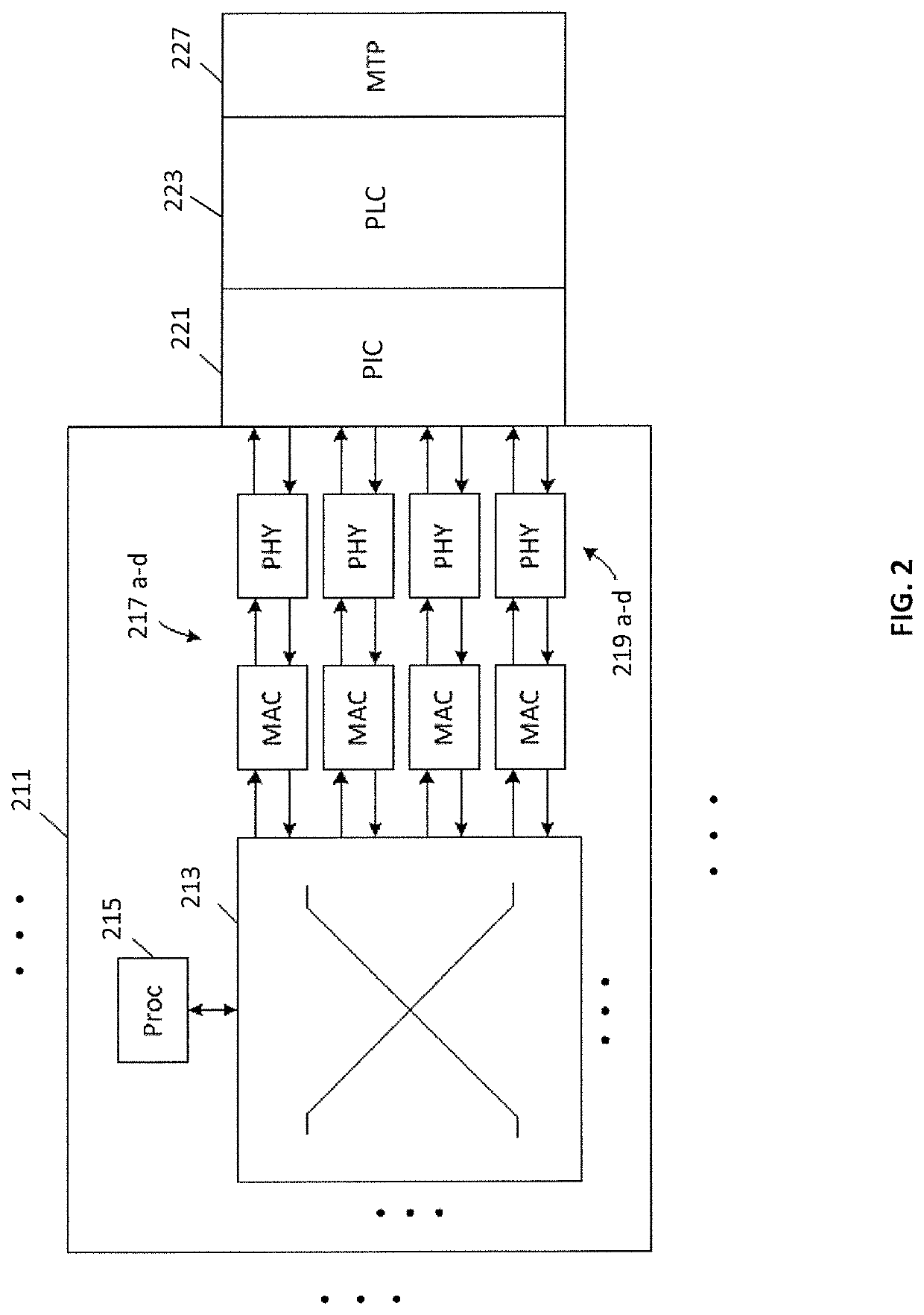
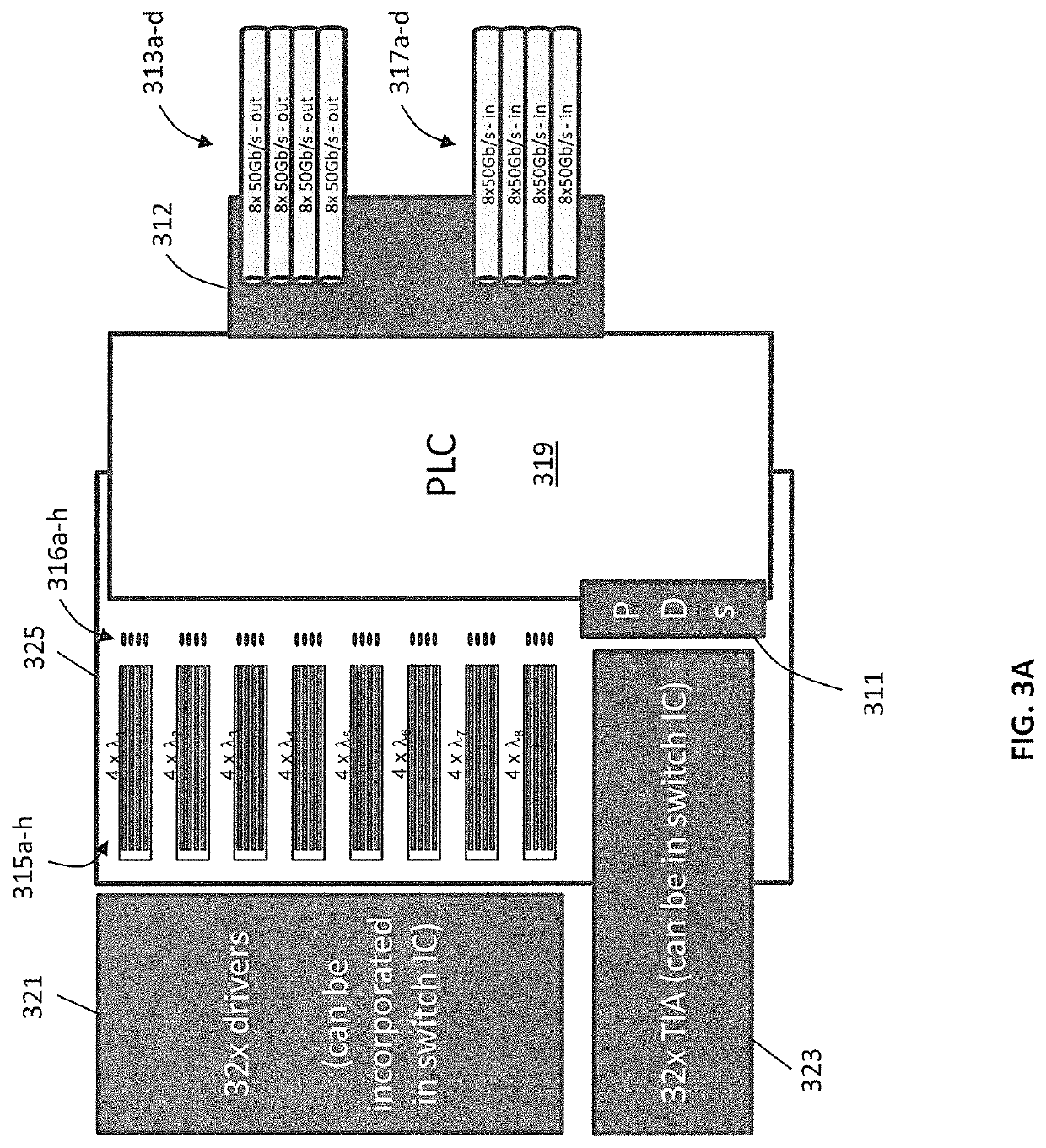
Optical module for terabit switch
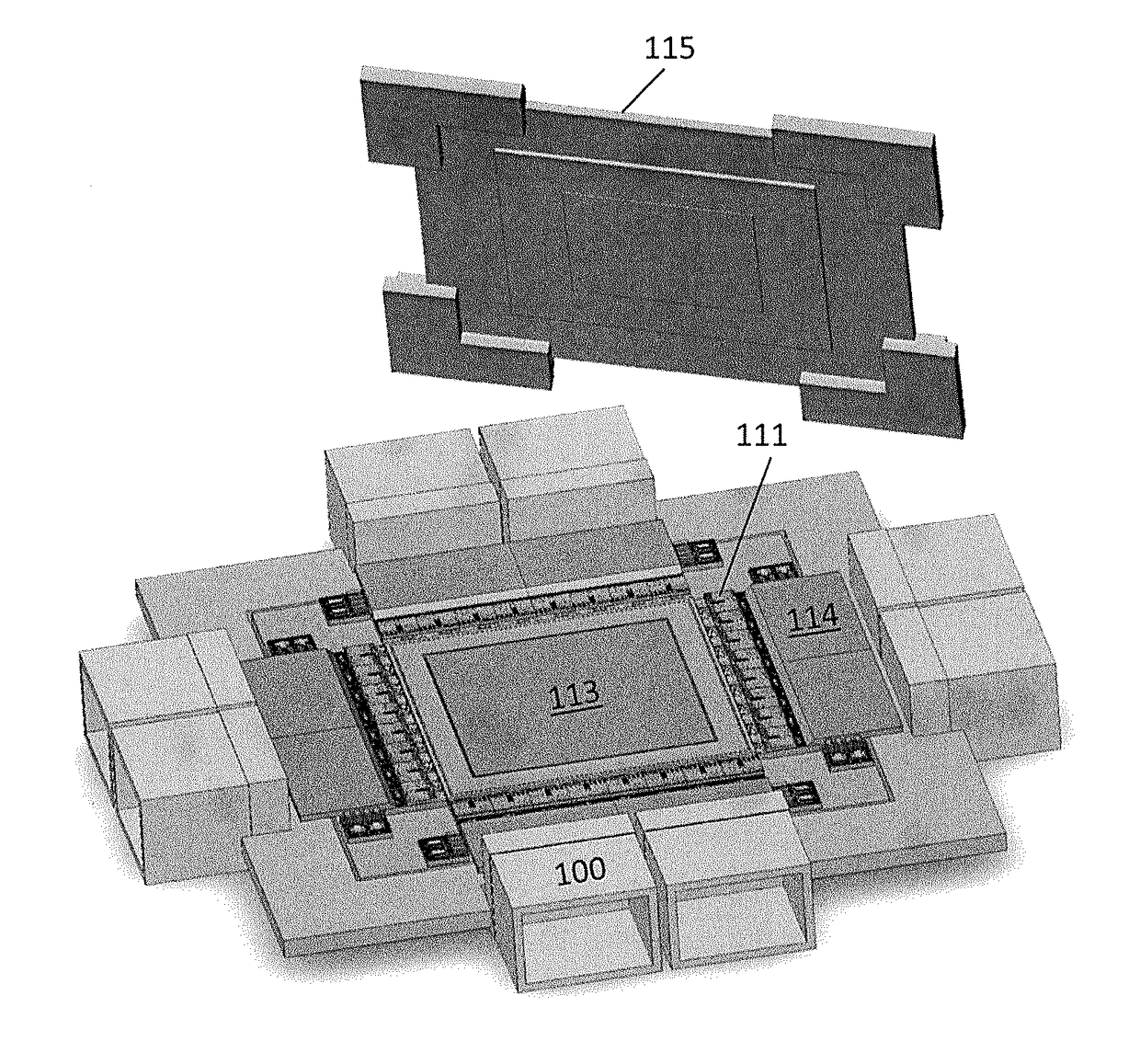
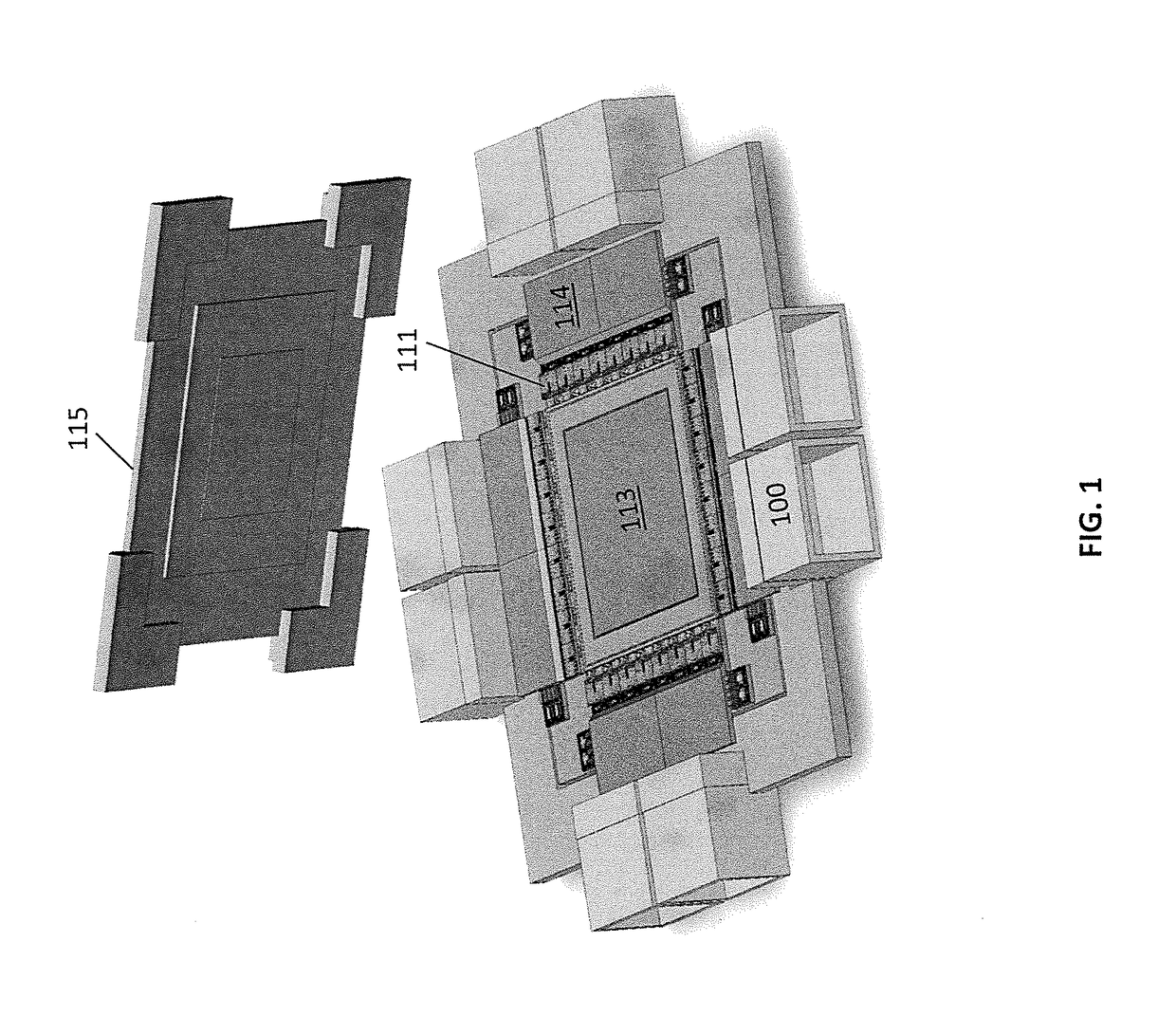
InactiveUS20180083417A1Fully comprehendedSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser arrangementsOptical ModuleComputer module
A switch module includes a switch integrated circuit (IC), a photonic integrated circuit (PIC), and a planar lightwave circuit (PLC). The PIC may include a plurality of light sources, an optical splitter, and a plurality of modulators. A dual MEMS may be used to align lens arrays, which may be used to couple light from the PIC to the PLC.
Owner:BROADEX TECH UK LTD
High-speed scheduling apparatus for a switching node
InactiveUS7542473B2Large capacityFirmly connectedData switching by path configurationGranularityDistributed computing
A scheduling apparatus for a switch includes multiple schedulers which are assigned in a variety of ways to non-intersecting control domains for establishing connections through the switch. The control domains are defined by spatial and temporal aspects. The control domains may be dynamically selected and assigned to schedulers in a manner that achieves a high throughput gain. Control domains may be considered in a cyclic and / or a pipeline discipline for accommodating connection requests. The invention enables the realization of a highly scalable controller of a switching node of fine granularity that scales to capacities of the order of hundreds of terabits per second.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Magnetooptic element exploiting spin chirality
InactiveUS6985276B2Guaranteed detection effectGigantic effective magnetic fieldConductive materialRecord information storageRare-earth elementAlkaline earth metal
A magnetooptic element whose size is essentially that of a lattice, namely several angstroms in size of magnetic material and which at the same time has its exhibiting magnetooptic effect detectable is provided along with a magnetooptic disk, a memory device and a magnetooptical picture or image display with a storage capacity of several terabits per square inch or more, each using such a magnetooptic element. The magnetooptic element utilizes a gigantic effective magnetic filed based on a spin chirality formed by geometrically configuring the spin orientation and crystallographic structure of a certain solid material. The solid material exhibiting the spin chirality may be such as a pyrochlore type oxide compound whose chemical composition is represented by chemical formula: A2B2O7 where A is a rare-earth element and B is a transition metal, or a pyrochlore type oxide compound whose chemical composition is represented by chemical formula: (A1-xCx)2B2O7 where A is a rare-earth element, C is an alkali-earth metallic element and B is a transition metal and where 0<x<1.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Serialized electro-optic neural network using optical weights encoding
Most artificial neural networks are implemented electronically using graphical processing units to compute products of input signals and predetermined weights. The number of weights scales as the square of the number of neurons in the neural network, causing the power and bandwidth associated with retrieving and distributing the weights in an electronic architecture to scale poorly. Switching from an electronic architecture to an optical architecture for storing and distributing weights alleviates the communications bottleneck and reduces the power per transaction for much better scaling. The weights can be distributed at terabits per second at a power cost of picojoules per bit (versus gigabits per second and femtojoules per bit for electronic architectures). The bandwidth and power advantages are even better when distributing the same weights to many optical neural networks running simultaneously.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Transceiver system on a card for simultaneously transmitting and receiving information at a rate equal to or greater than approximately one terabit per second
ActiveUS9112616B2Coupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsHigh bandwidthComputer module
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
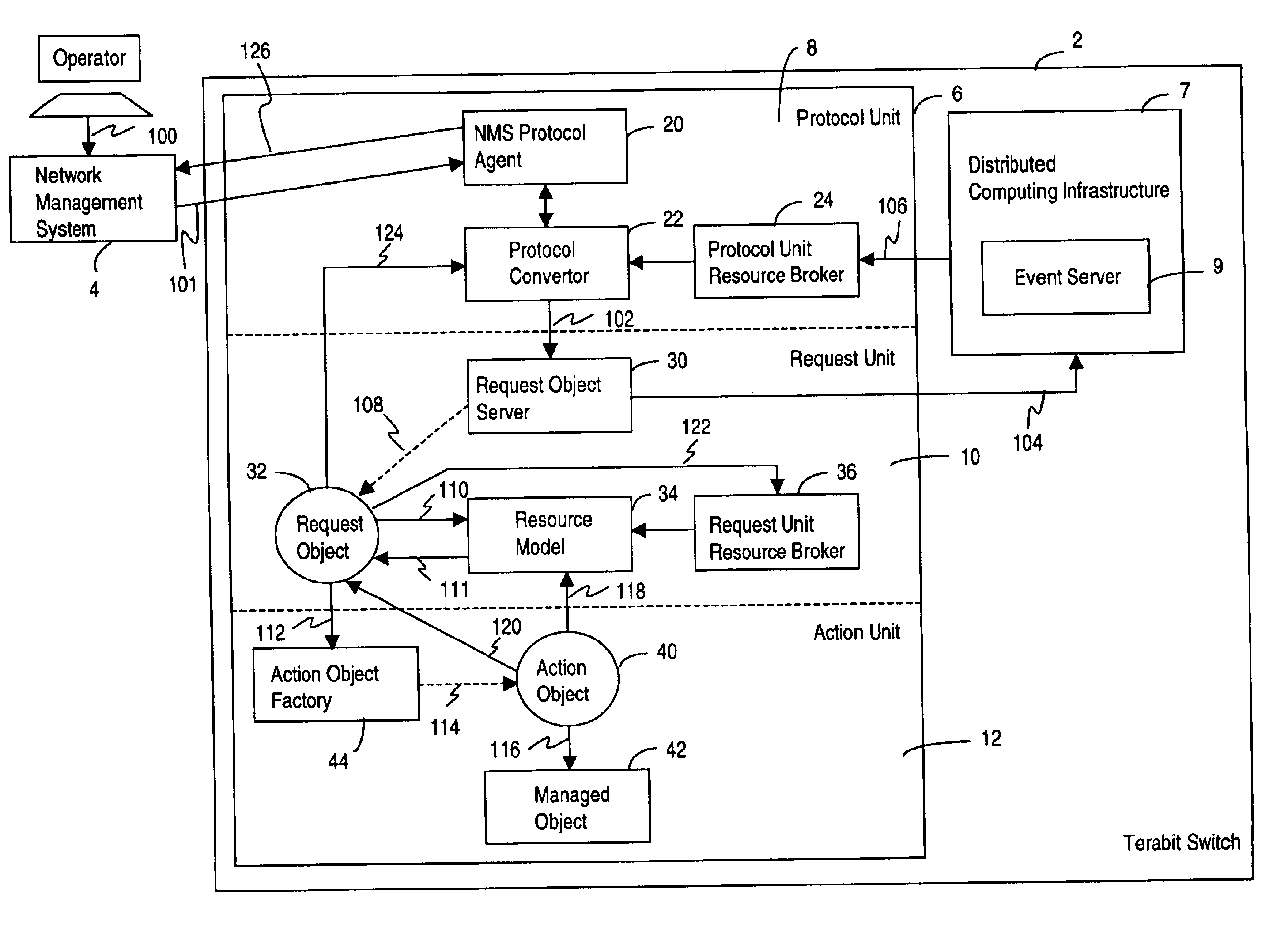
Management system for a telecommunications switch
InactiveUS6947547B2Easy to manageLow production costInterconnection arrangementsError preventionTraffic capacityTelecommunications link
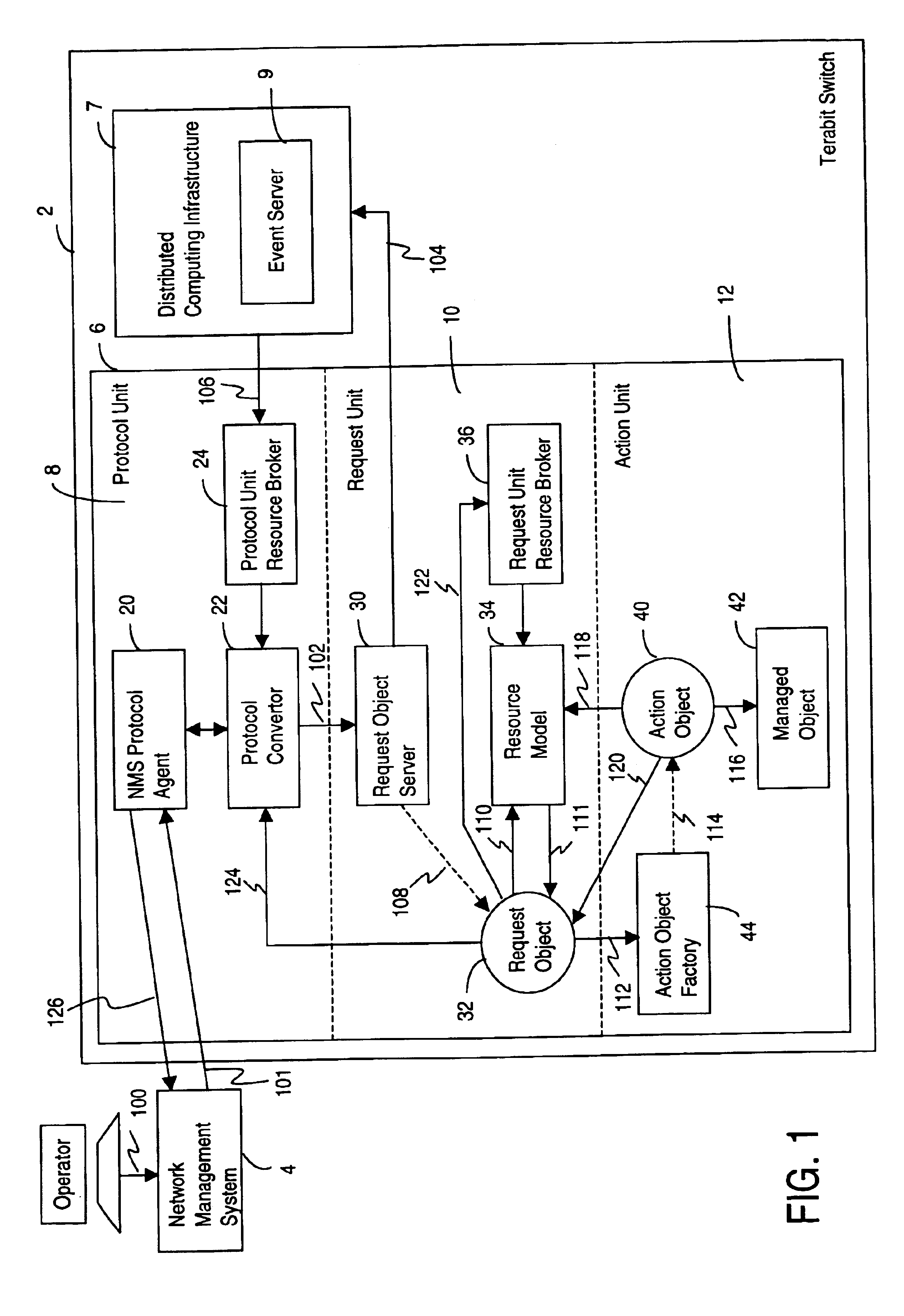
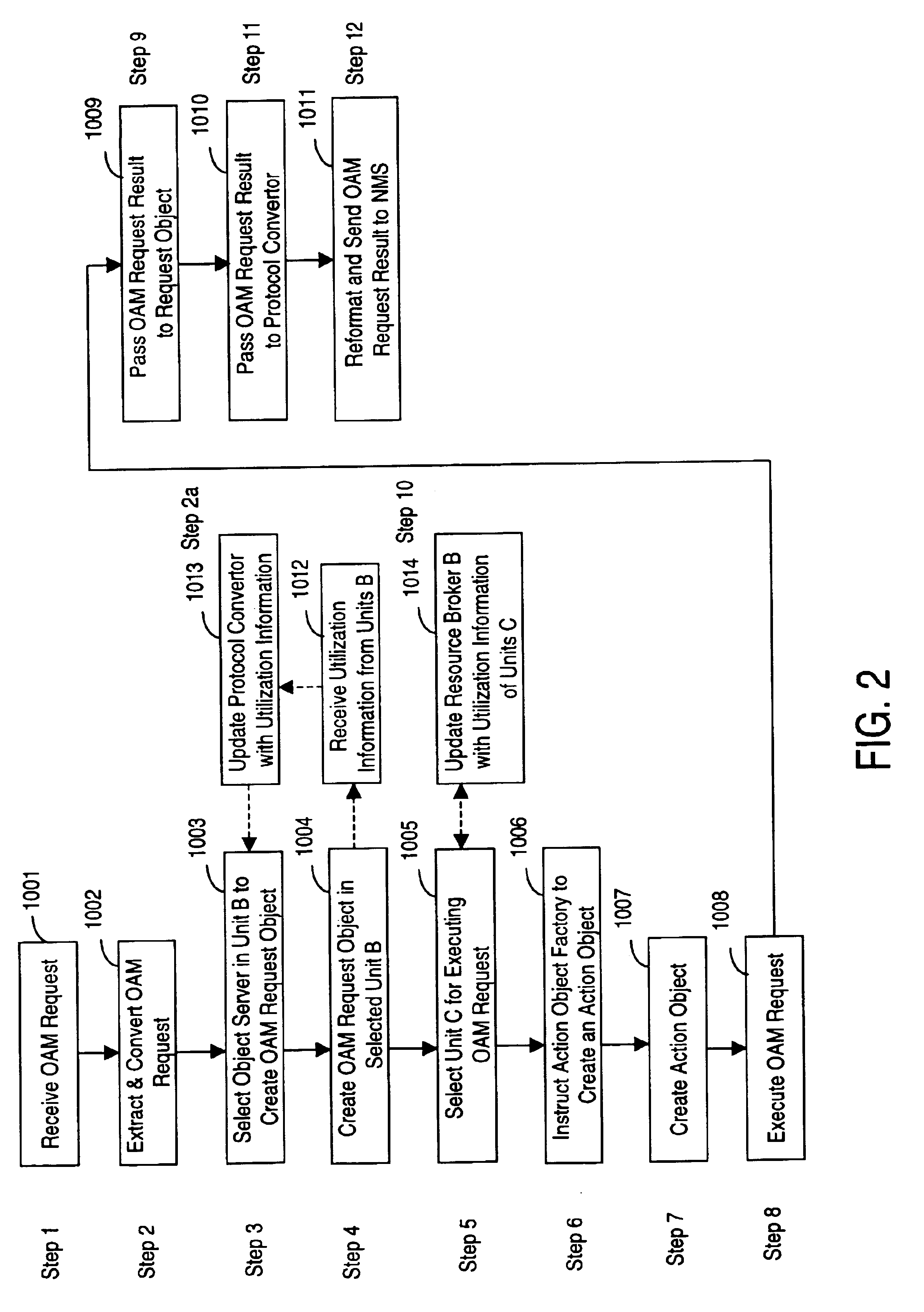
A management system for telecommunication switch is described. The management system is useful for providing operations, administration and maintenance (OAM) functions in a terabit switch. The management system is a scalable management system, whereby processing of large amounts of network management traffic from carrier operators and virtual private network (VPN) customers in a terabit switch is enabled. The management system is efficiently implemented by utilizing surplus processing resources in the network interface cards of the switch. The management system includes a protocol unit residing on a first processor card of the switch for receiving a management request, a first request unit residing on the first processor card for creating a request object in response to the received management request, and a first action unit residing on a first network interface card of the switch for executing the received management request in response to an instruction from the request object.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Optical module for terabit switch
A switch module includes a switch integrated circuit (IC), a photonic integrated circuit (PIC), and a planar lightwave circuit (PLC). The PIC may include a plurality of light sources, an optical splitter, and a plurality of modulators. A dual MEMS may be used to align lens arrays, which may be used to couple light from the PIC to the PLC.
Owner:BROADEX TECH UK LTD
Micromechanically actuated deformable optical beam steering for wavelength tunable optical sources, filters and detectors
Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) has enabled telecommunication service providers to fully exploit the transmission capacity of optical fibers. State of the art systems in long-haul networks now have aggregated capacities of terabits per second. Moreover, by providing multiple independent multi-gigabit channels, WDM technologies offer service providers with a straight forward way to build networks and expand networks to support multiple clients with different requirements. In order to reduce costs, enhance network flexibility, reduce spares, and provide re-configurability many service providers have migrated away from fixed wavelength transmitters, receivers, and transceivers, to wavelength tunable transmitters, receivers, and transceivers as well as wavelength dependent add-drop multiplexer, space switches etc. However, to meet the competing demands for improved performance, increased integration, reduced footprint, reduced power consumption, increased flexibility, re-configurability, and lower cost it is desirable to exploit / adopt monolithic optical circuit technologies, hybrid optoelectronic integration, and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
Owner:VALORBEC PARTNERSHIP
Terabit top-of-rack switch
ActiveUS9461768B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexTransceiverPrinted circuit board
One embodiment of the present invention provides a switch. The switch includes a printed circuit board (PCB), a number of multi-channel optical transceivers mounted on the PCB, and a number of switch ports accessible from a front panel of the switch. The switch ports include a number of electrical interfaces that are electrically coupled to a switch chip mounted on the PCB, and a number of optical interfaces that are coupled to the switch chip via the multi-channel optical transceivers.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Optical module for terabit switch
Owner:BROADEX TECH UK LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com