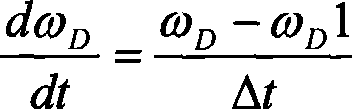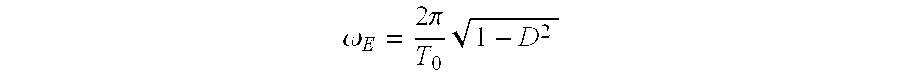Patents
Literature
136results about "Generator control of frequency and voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
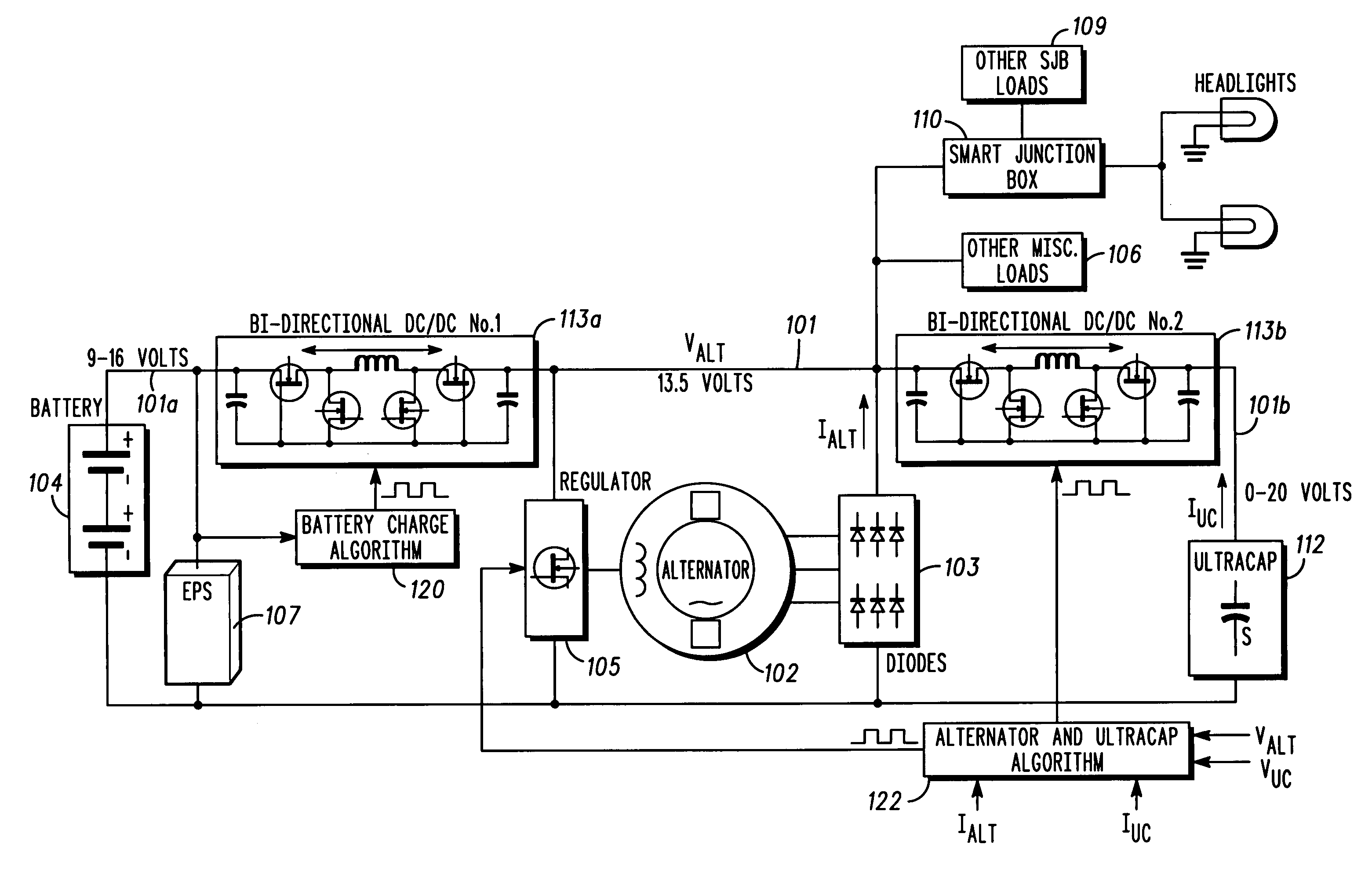
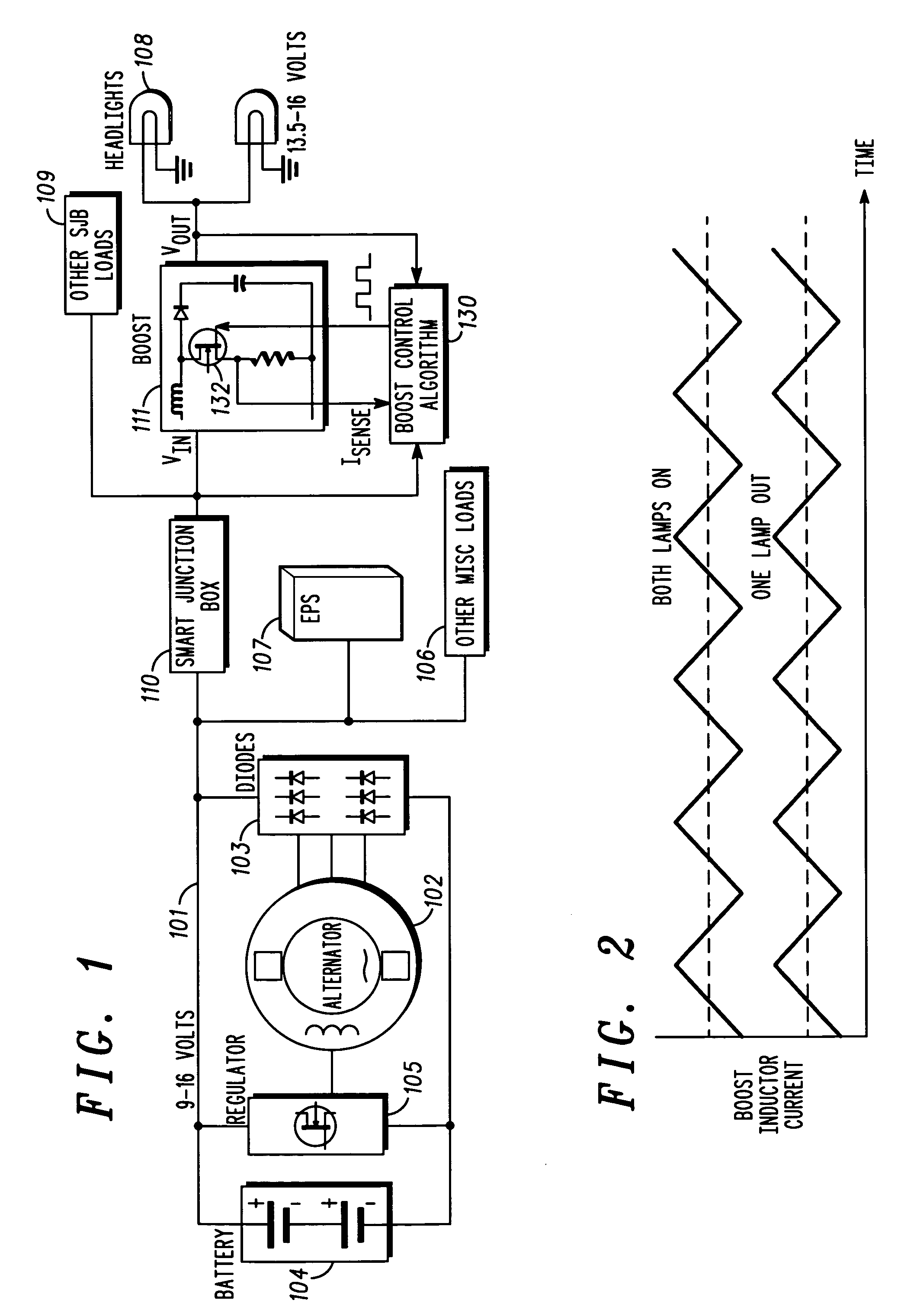
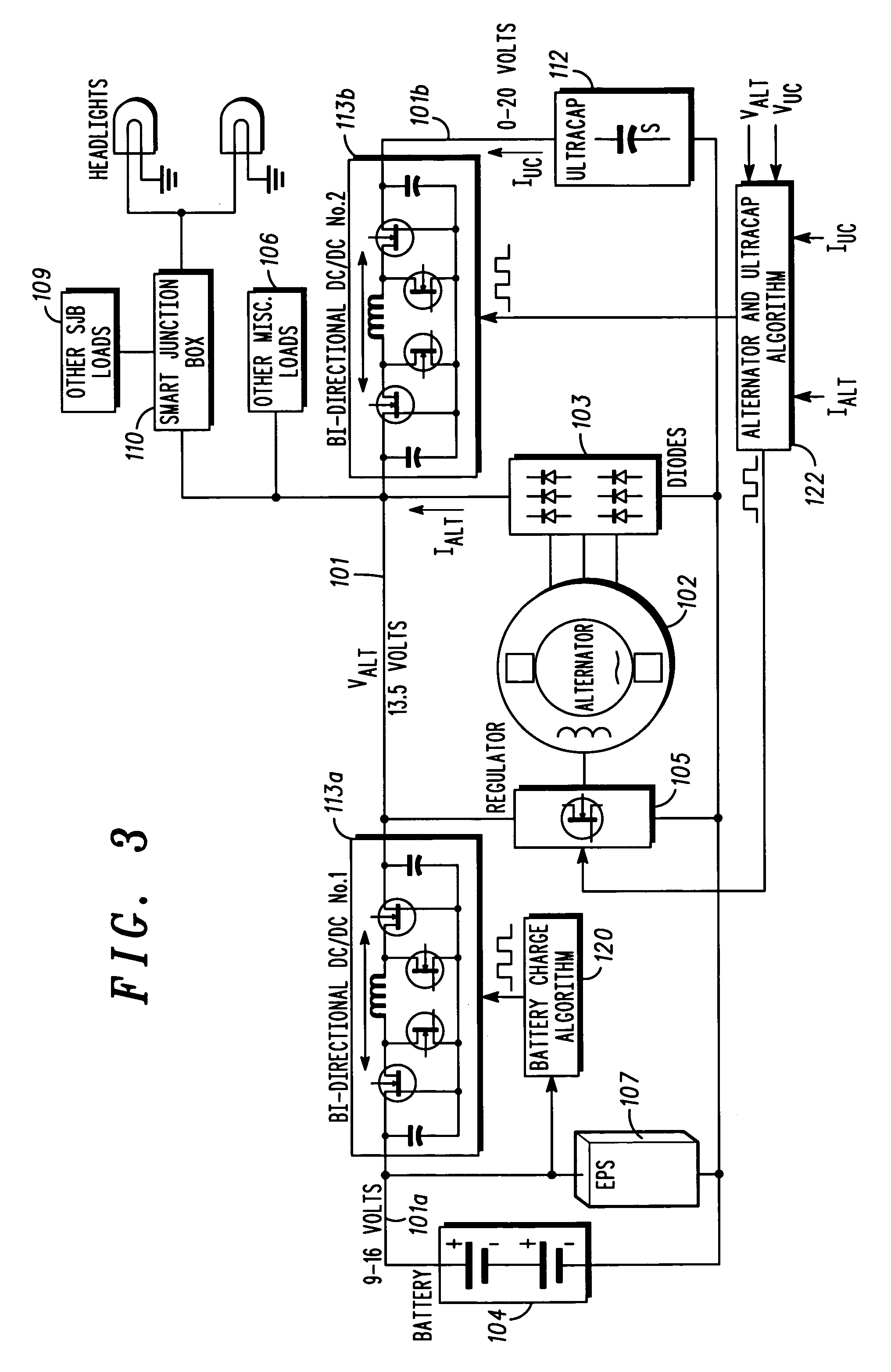
Automotive electrical system configuration using a two bus structure
InactiveUS7075273B2Batteries circuit arrangementsLoad balancing in dc networkAlternatorCritical load
Disclosed herein are a variety of different electrical system topologies intended to mitigate the impact of large intermittent loads on a 12 volt vehicle power distribution system. In some embodiments the intermittent load is disconnected from the remainder of the system and the voltage supplied to this load is allowed to fluctuate. In other embodiments, the voltage to critical loads is regulated independently of the voltage supplied to the remainder of the system. The different topologies described can be grouped into three categories, each corresponding to a different solution technique. One approach is to regulate the voltage to the critical loads. A second approach is to isolate the intermittent load that causes the drop in system voltage. The third approach is to use a different type of alternator that has a faster response than the conventional Lundell wound field machine.
Owner:TEMIC AUTOMOTIVE OF NORTH AMERICA
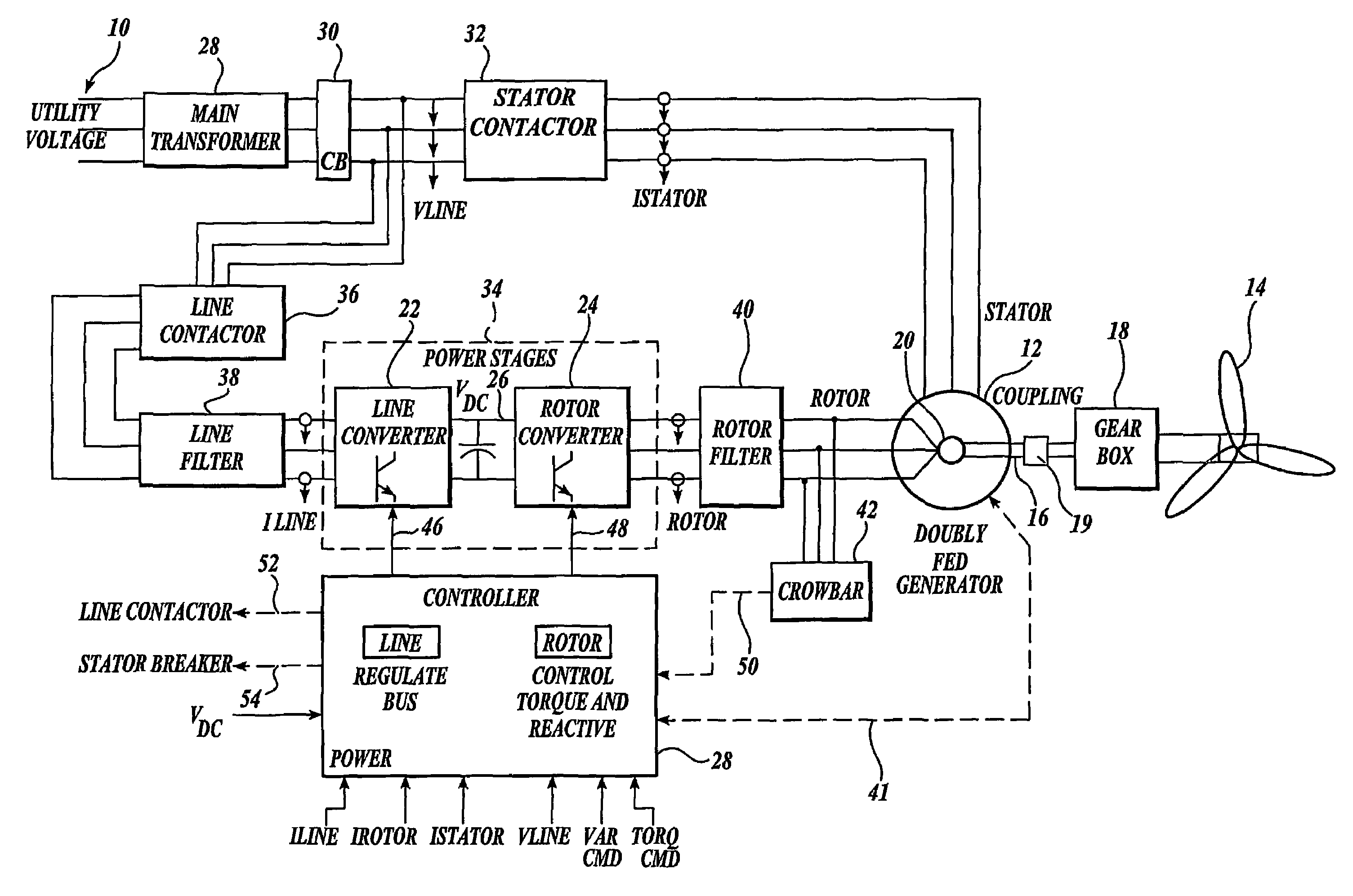
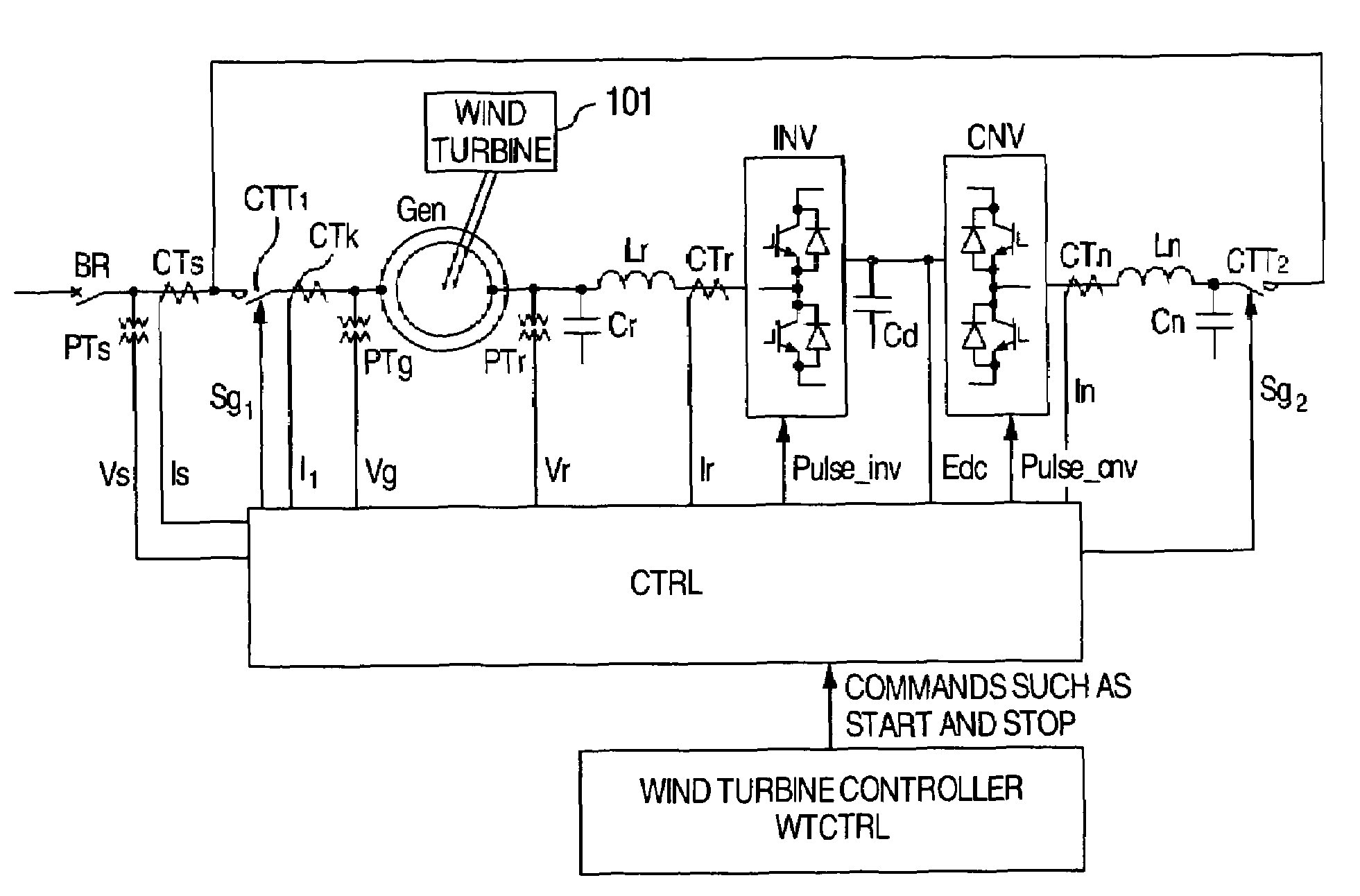
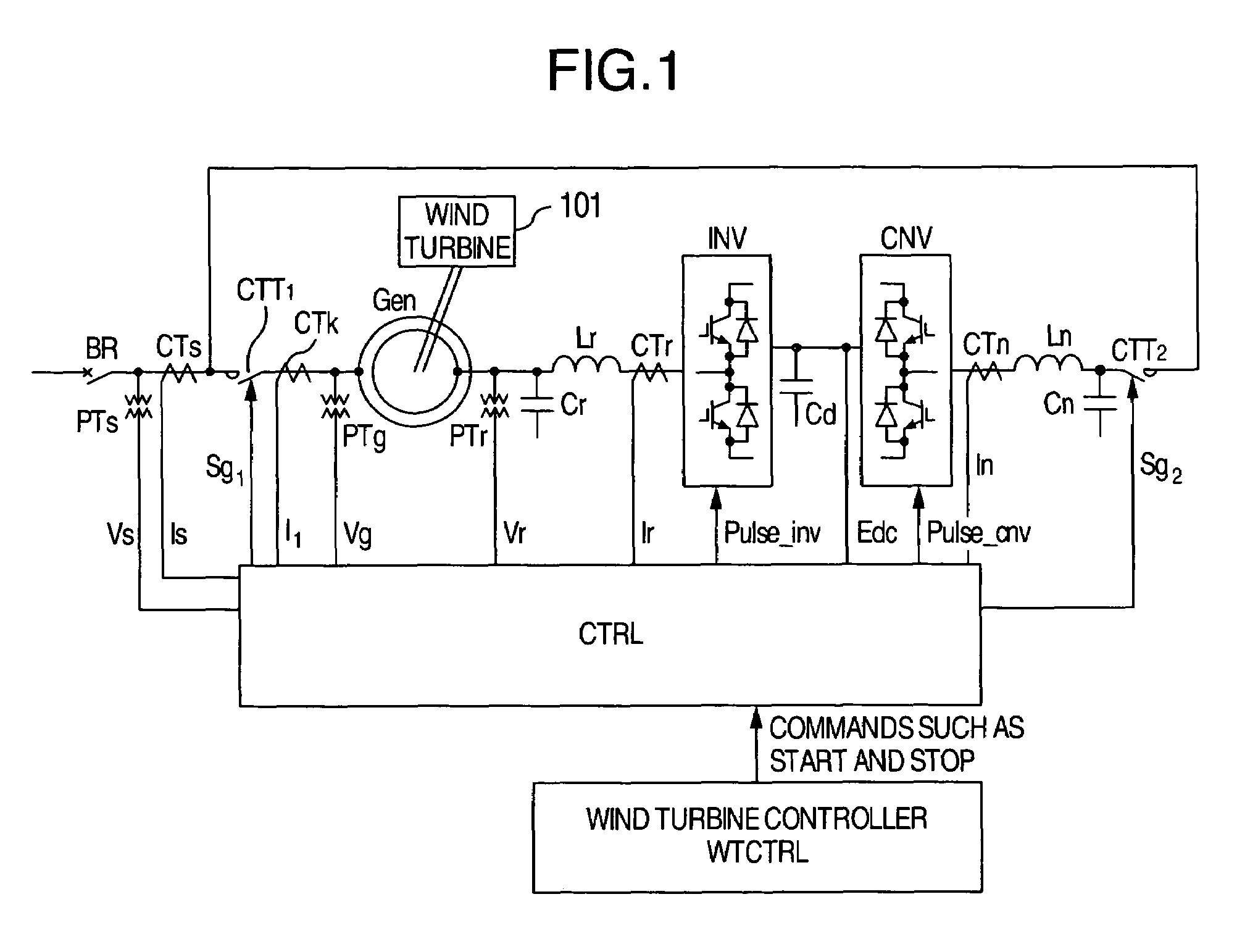
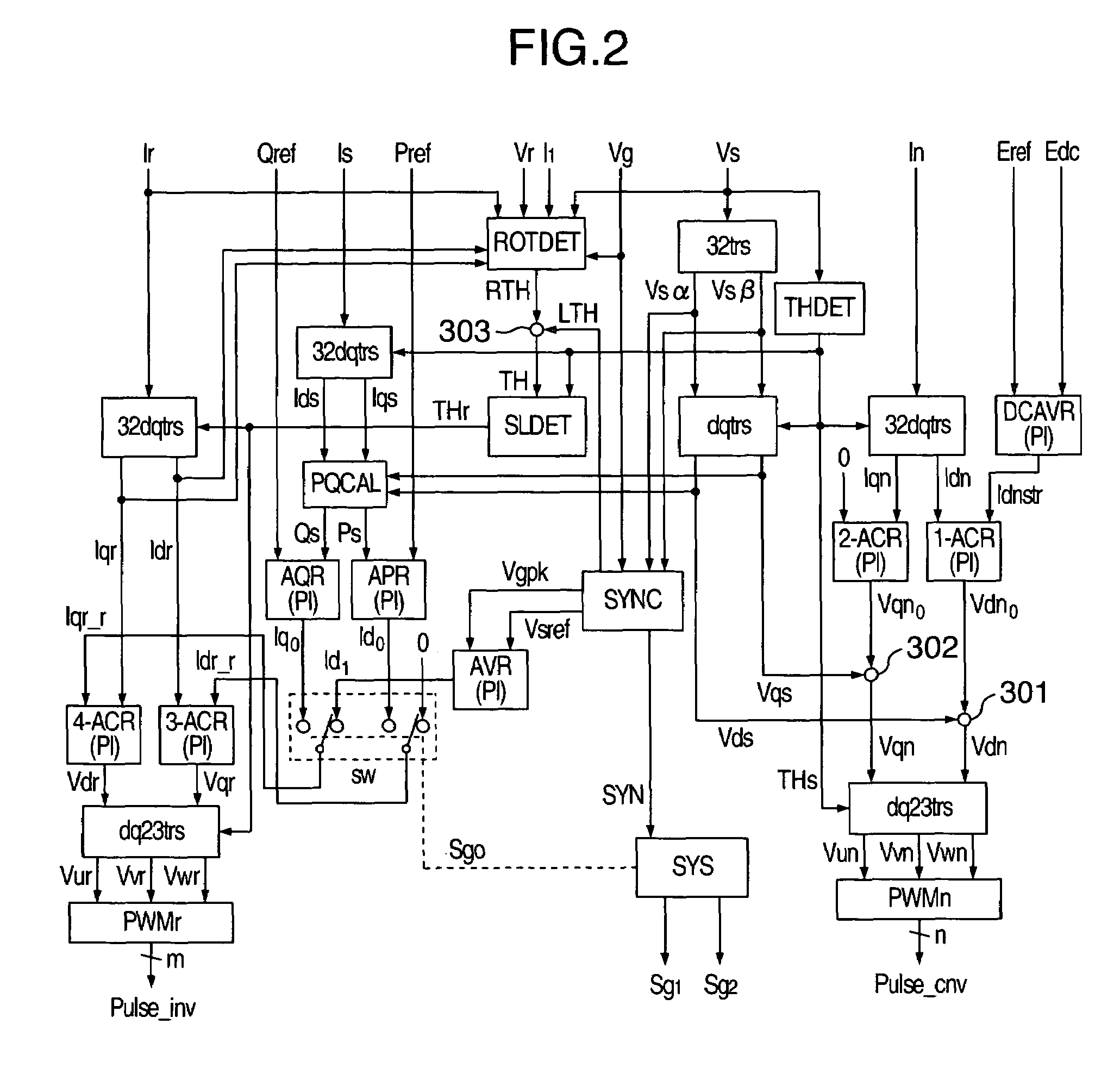
Control system for doubly fed induction generator
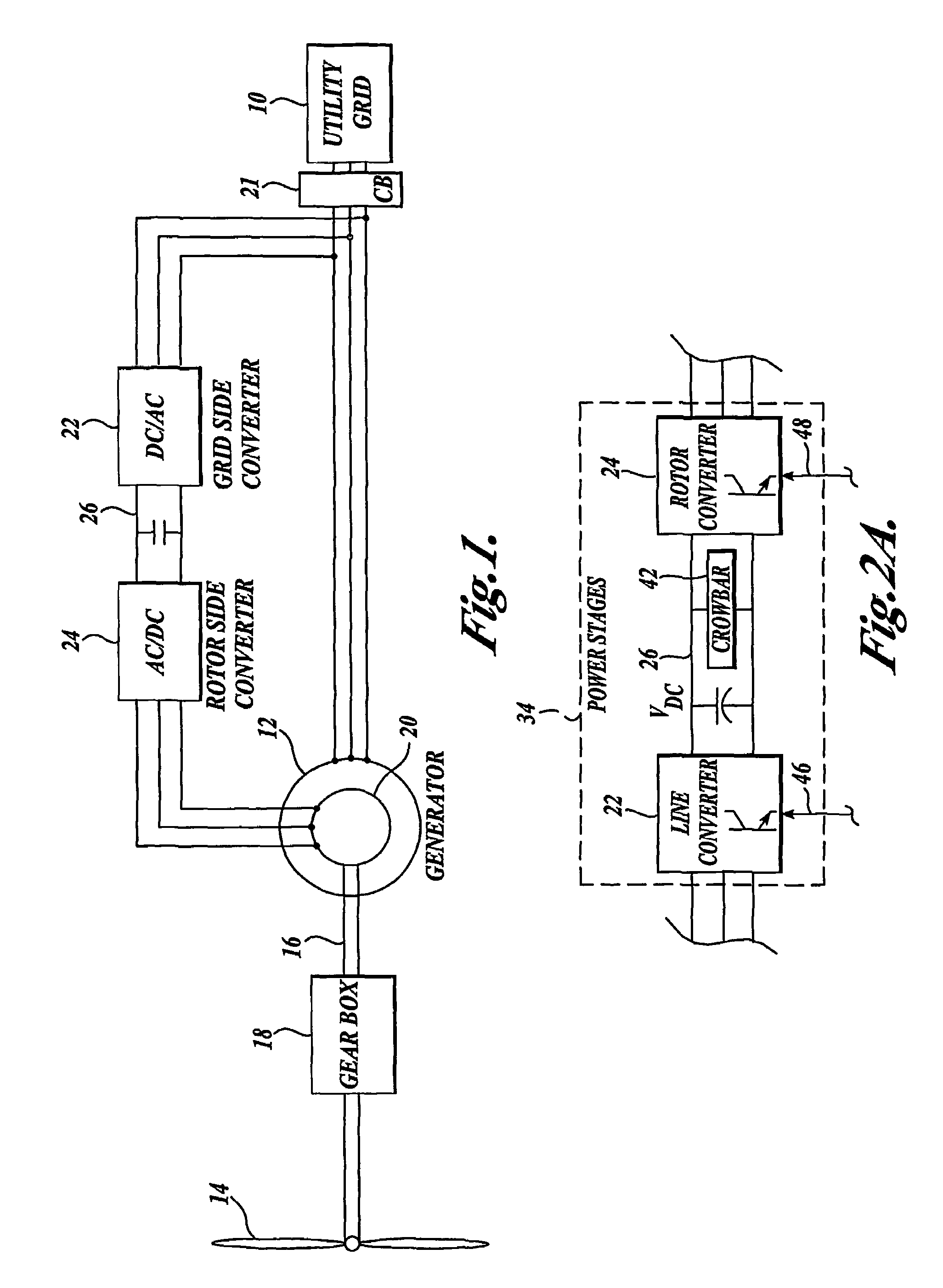
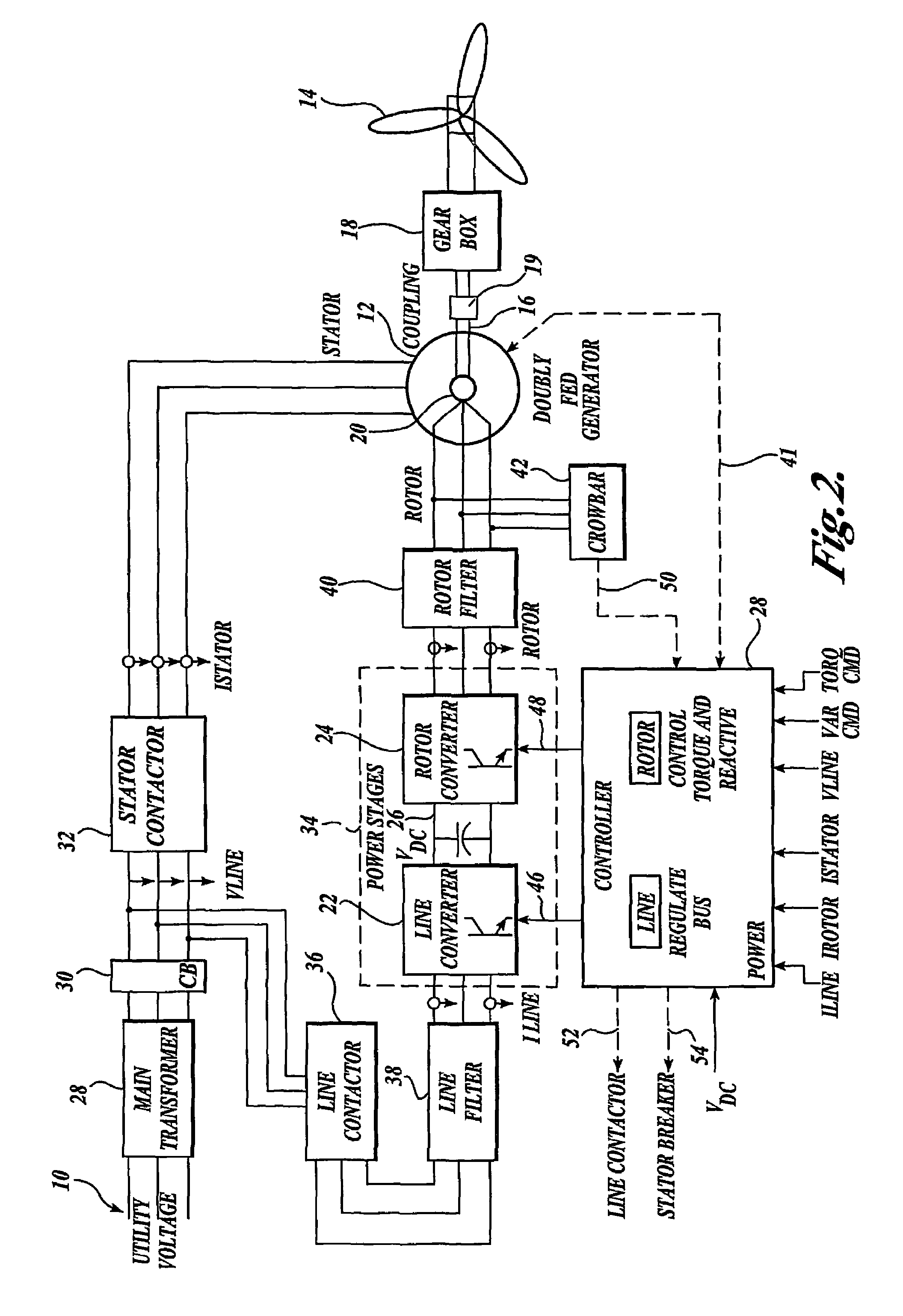
ActiveUS7411309B2Total current dropGuaranteed uptimeGenerator control circuitsAC motor controlControl systemControl signal
A controller (28) for a doubly fed induction generator (12,20) adjusts control signals to a rotor side converter (24) and line side converter (22) to adjust rotor current when a voltage transient on a utility grid (10) occurs, so that the doubly fed induction generator can ride through the transient. The controller can also turn off the transistors of the rotor side converter (24) to reduce rotor current and / or activate a crowbar (42) to reduce the voltage of the DC link (26) connecting the converters (22, 24) when significant voltage transients occur on the grid (10). This permits continued operation of the DFIG system without disconnecting from the grid.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SOLAR INVERTERS USA
Frequency converter for high-speed generators
InactiveUS7180270B2Simple and flexibleReduce switching lossesAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFrequency changerPower grid
The present invention relates to a method and to a device for adapting the alternating current generated by a generator (1) and the alternating voltage generated by a generator (1) to a grid (8), whereby the generator (1) has at least one excitation coil (2). The power fed into the grid (8) can be flexibly adapted while entailing low switching losses in that a static frequency converter (9) is employed for the adaptation between the generator (1) and the grid (8), and in that, in order to control the power fed into the grid (8), means (3) are provided with which, on the one hand, the strength of the excitation field generated by the at least one excitation coil (2) is regulated and, on the other hand, the phase angle between the frequency converter voltage and the generator or grid voltage is appropriately controlled.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Power generating system including a high-frequency alternator, a rectifier module, and an auxiliary power supply
ActiveUS7053590B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAlternatorComputer module
A power generating system includes a high-frequency alternator, a rectifier, a capacitor in each phase line extending between an output terminal of the alternator and the rectifier, and an auxiliary power supply, providing auxiliary power for use within the power generating system, which is also connected to the output terminals of the alternator.
Owner:CAPSTONE GREEN ENERGY CORP +1
Power generation apparatus using AC energization synchronous generator and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS7332894B2Short timeGenerator control circuitsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsStator voltagePhase difference
In a power generation apparatus equipped with an AC energization synchronous generator, when energization of a secondary winding starts to conduct connecting to the network of the AC energization synchronous generator to a network voltage, energization of the secondary winding starts at a fixed frequency and a slip frequency is calculated from a difference between a frequency of the network voltage and a resultant stator voltage frequency. Thereafter, energization starts at the calculated slip frequency and a voltage having a frequency generally coincident with the network frequency is output to the stator to incorporate the generator to the network. A phase is adjusted to make zero a phase difference when the rotation speed changes or the phases become different.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
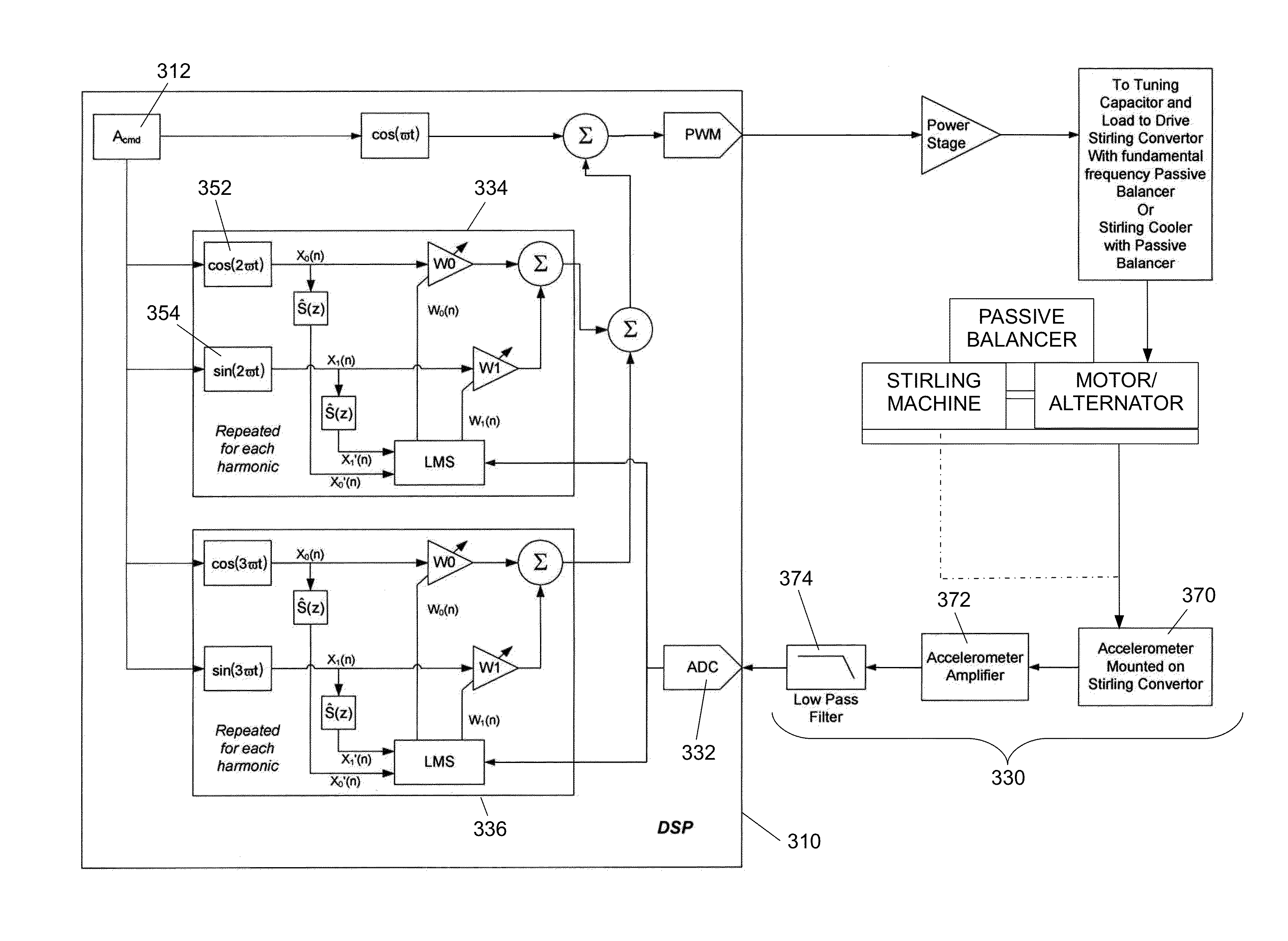
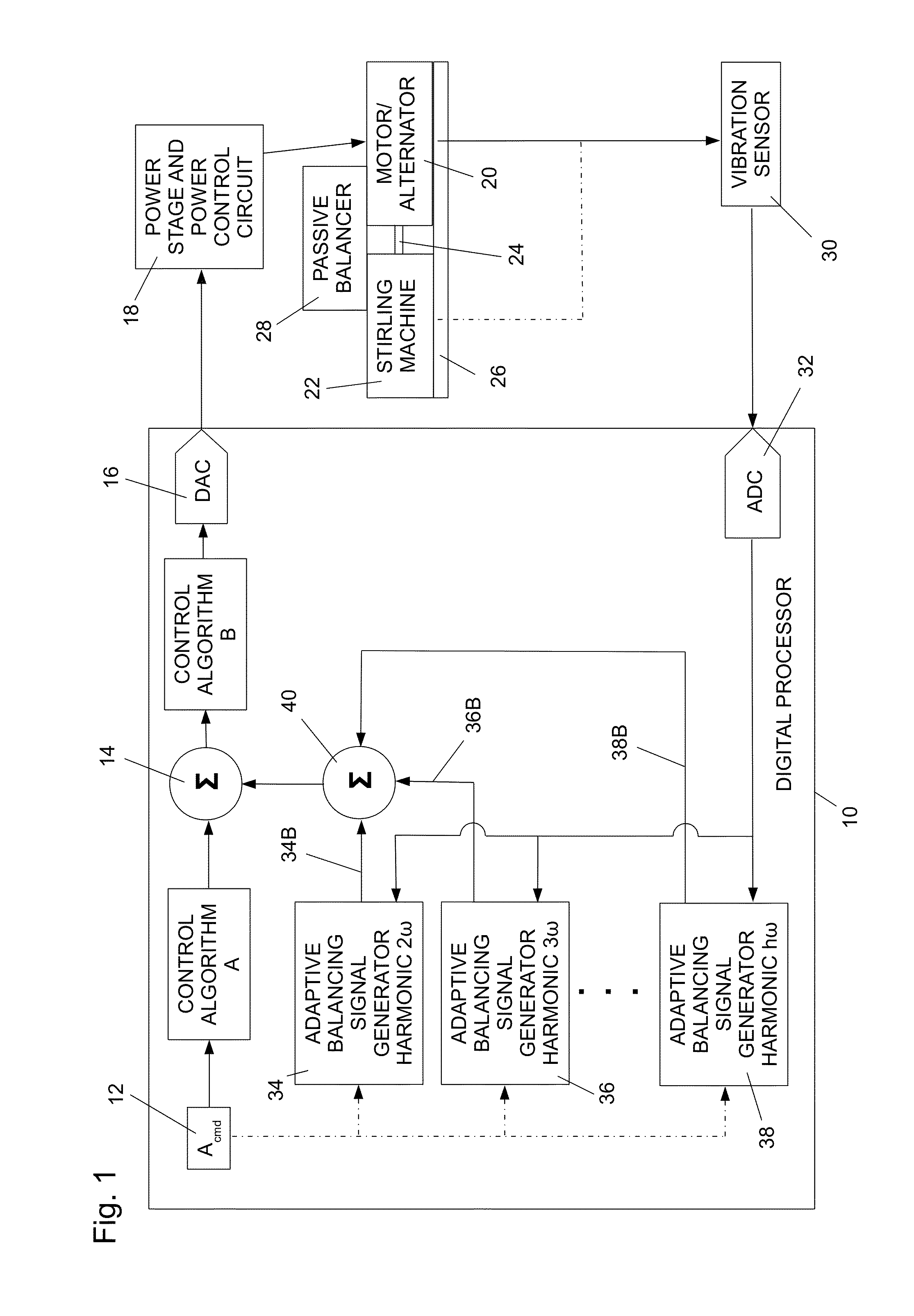
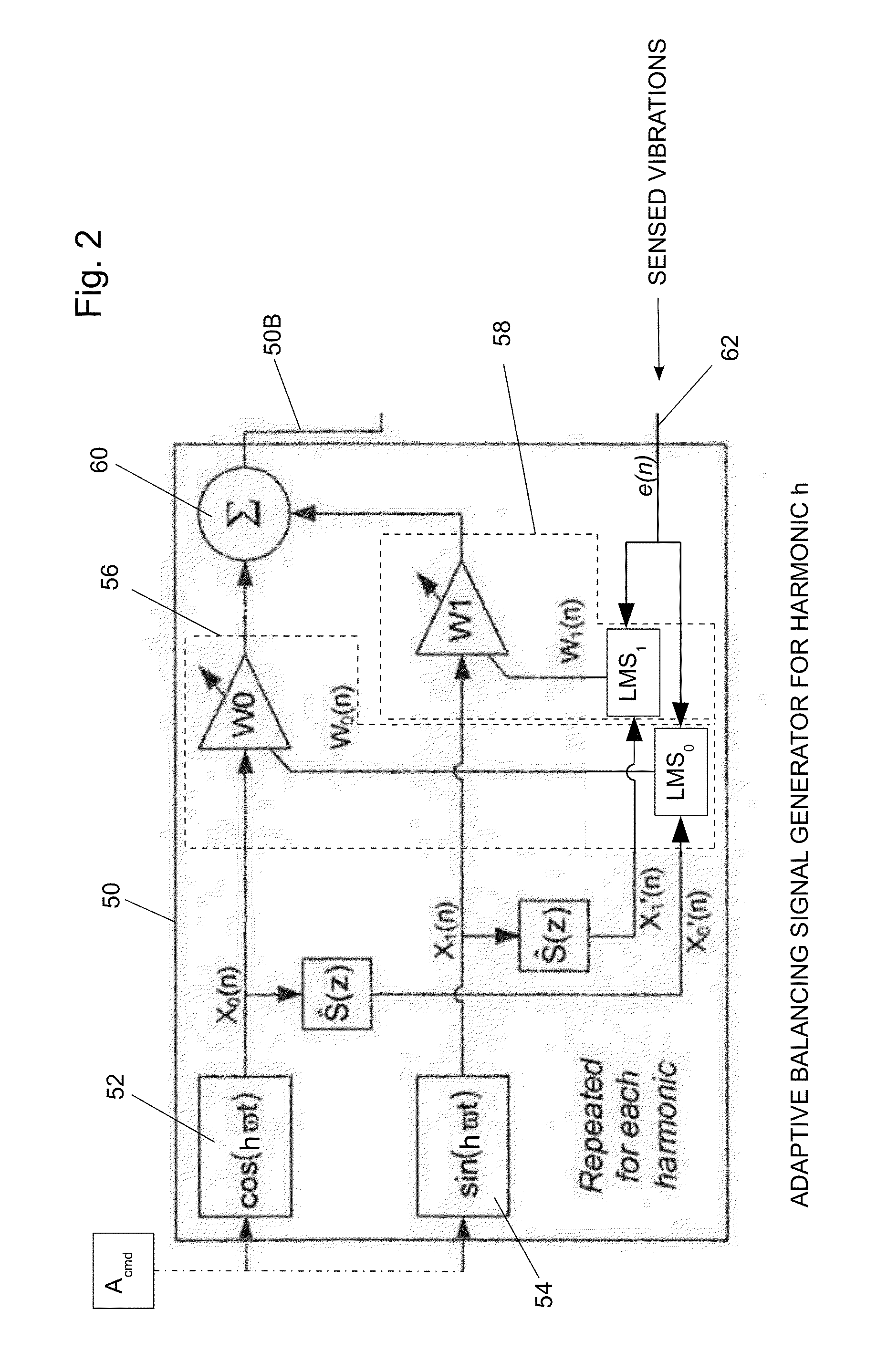
Balancing Vibrations At Harmonic Frequencies By Injecting Harmonic Balancing Signals Into The Armature Of A Linear Motor/Alternator Coupled To A Stirling Machine
ActiveUS20140015497A1Vibration minimizationMechanical oscillations controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAdaptive filtering algorithmMachining vibrations
Vibrations at harmonic frequencies are reduced by injecting harmonic balancing signals into the armature of a linear motor / alternator coupled to a Stirling machine. The vibrations are sensed to provide a signal representing the mechanical vibrations. A harmonic balancing signal is generated for selected harmonics of the operating frequency by processing the sensed vibration signal with adaptive filter algorithms of adaptive filters for each harmonic. Reference inputs for each harmonic are applied to the adaptive filter algorithms at the frequency of the selected harmonic. The harmonic balancing signals for all of the harmonics are summed with a principal control signal. The harmonic balancing signals modify the principal electrical drive voltage and drive the motor / alternator with a drive voltage component in opposition to the vibration at each harmonic.
Owner:SUNPOWER
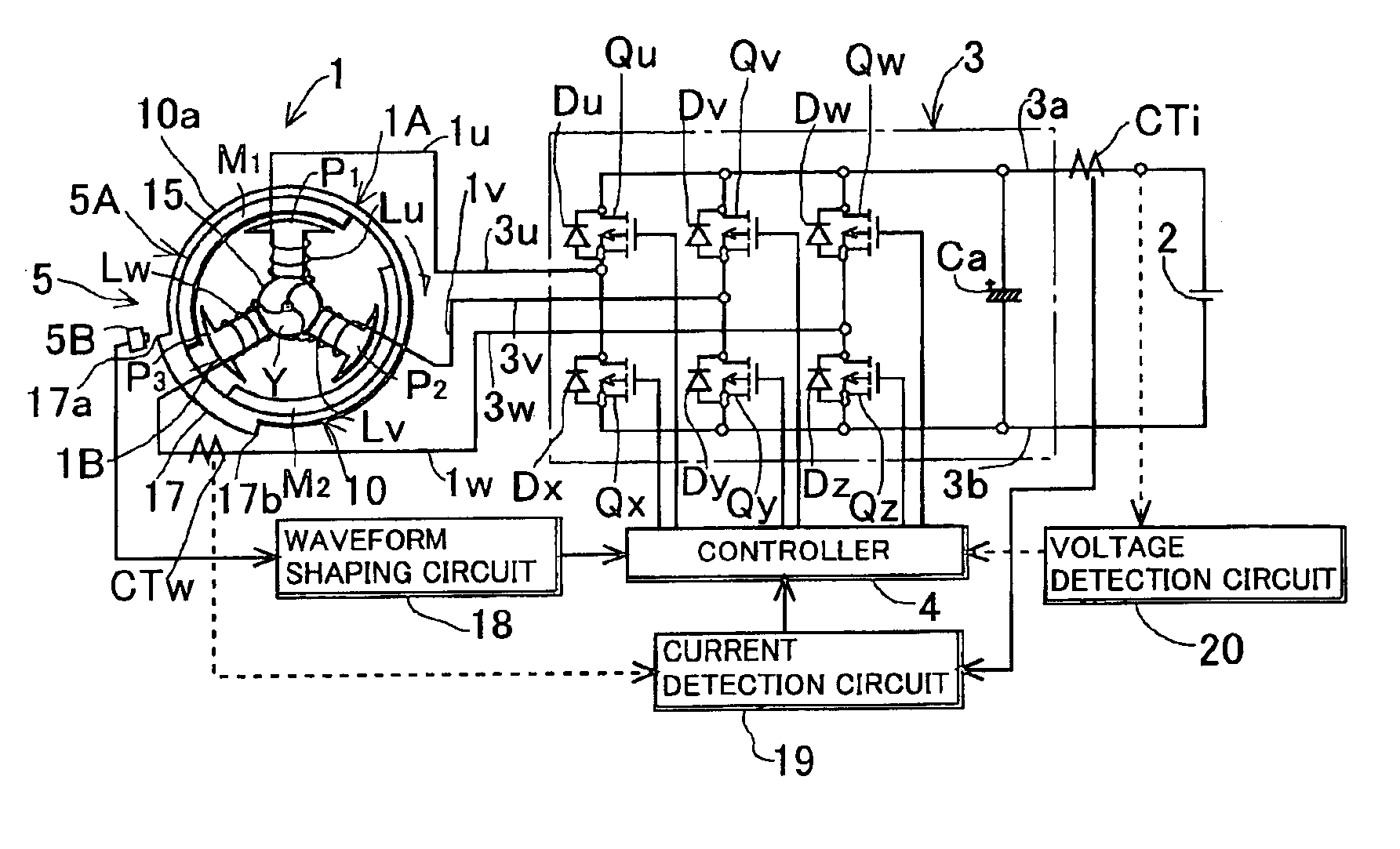
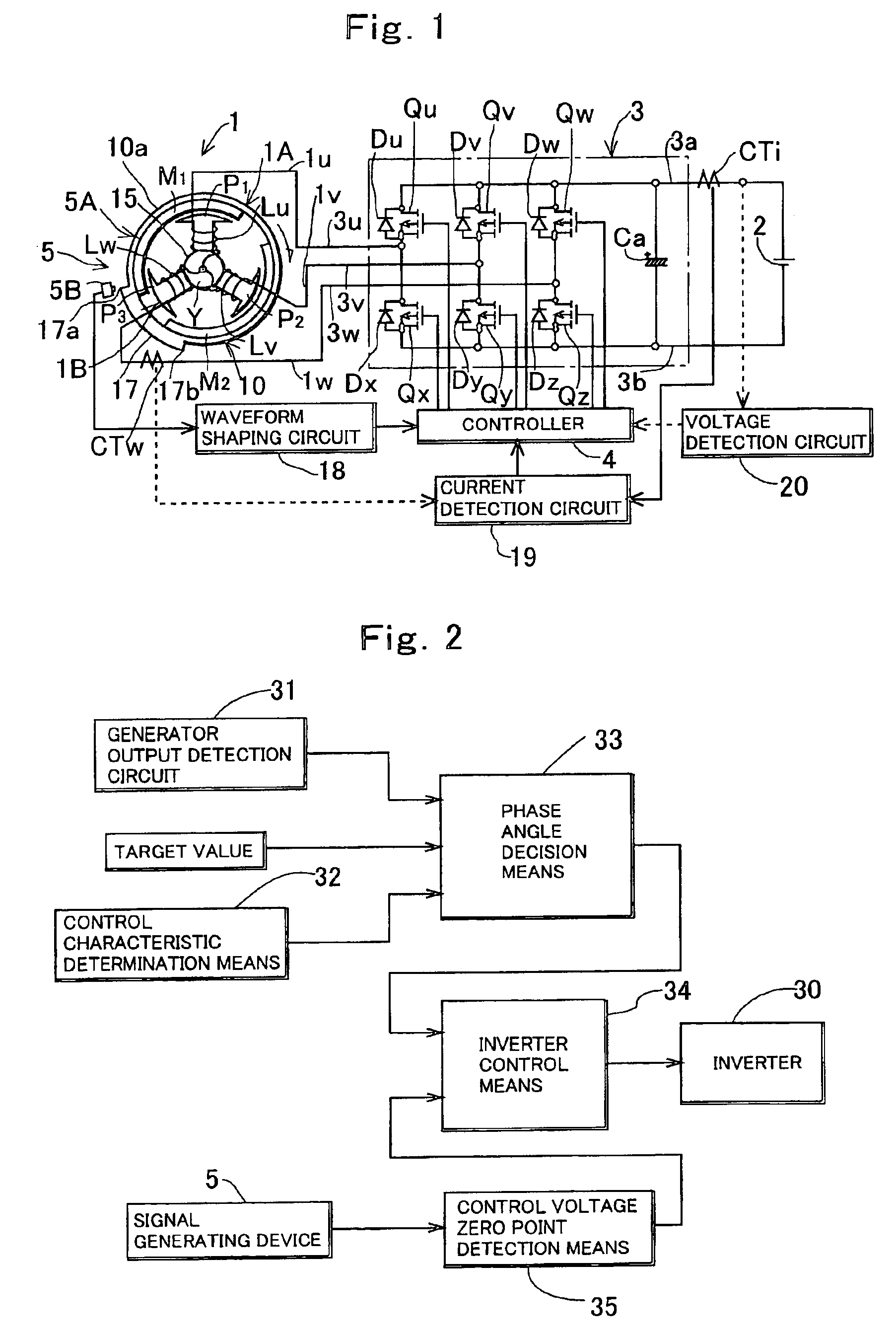
Generating device including magneto generator
InactiveUS6940259B2Easy to controlAvoid convergenceEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlControl theoryPhase angle
A generating device including a magneto generator, wherein: an AC control voltage is applied to an armature coil of the magneto generator from a battery via an inverter to change a phase angle of the AC control voltage, thus increase / reduce an output of the magneto generator and match the output of the generator with a target value; it is determined that a characteristic, in which the output of the magneto generator increases when the phase angle of the AC control voltage is delayed, is a normal control characteristic, and a characteristic, in which the output of the magneto generator decreases when the phase angle of the AC control voltage is delayed, is a reciprocal control characteristic; and it is determined whether a present control characteristic of the output of the generator relative to the phase angle of the AC control voltage is the normal control characteristic or the reciprocal control characteristic to decide, based on a determination result, a changing direction of the phase angle of the AC control voltage when the output of the generator is controlled and brought close to the target value.
Owner:KOKUSAN DENKI CO LTD
Control system for a sputtering system
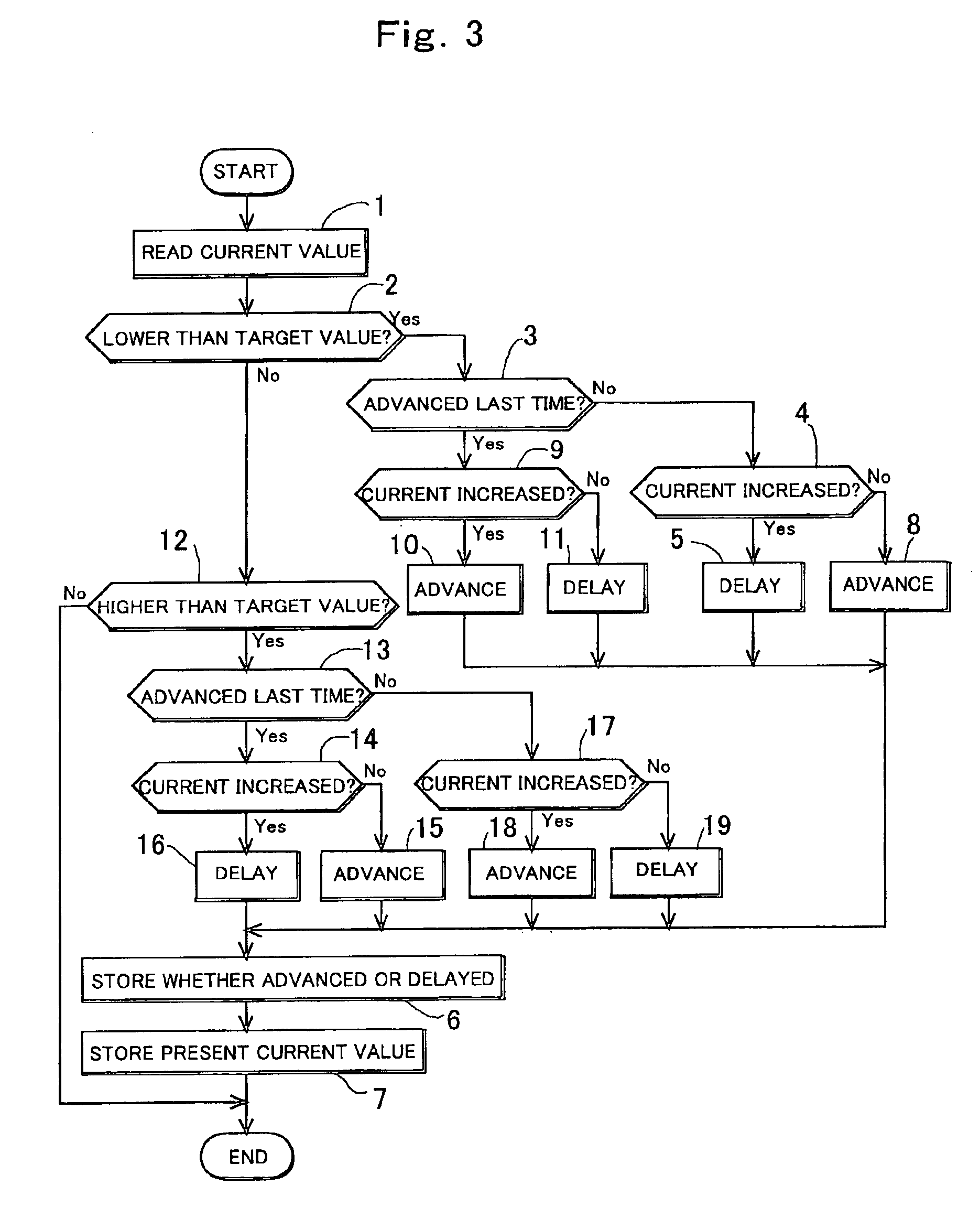
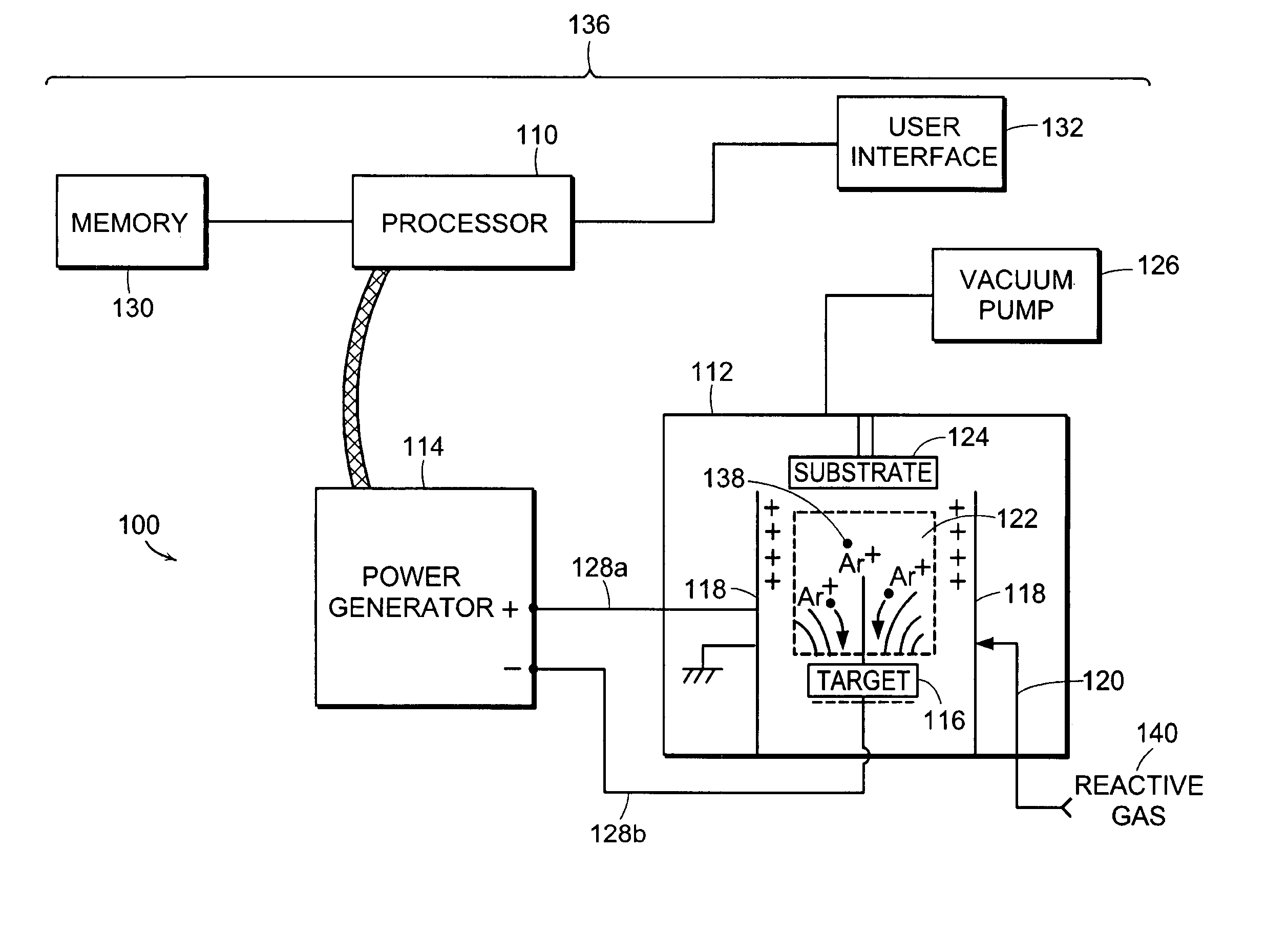
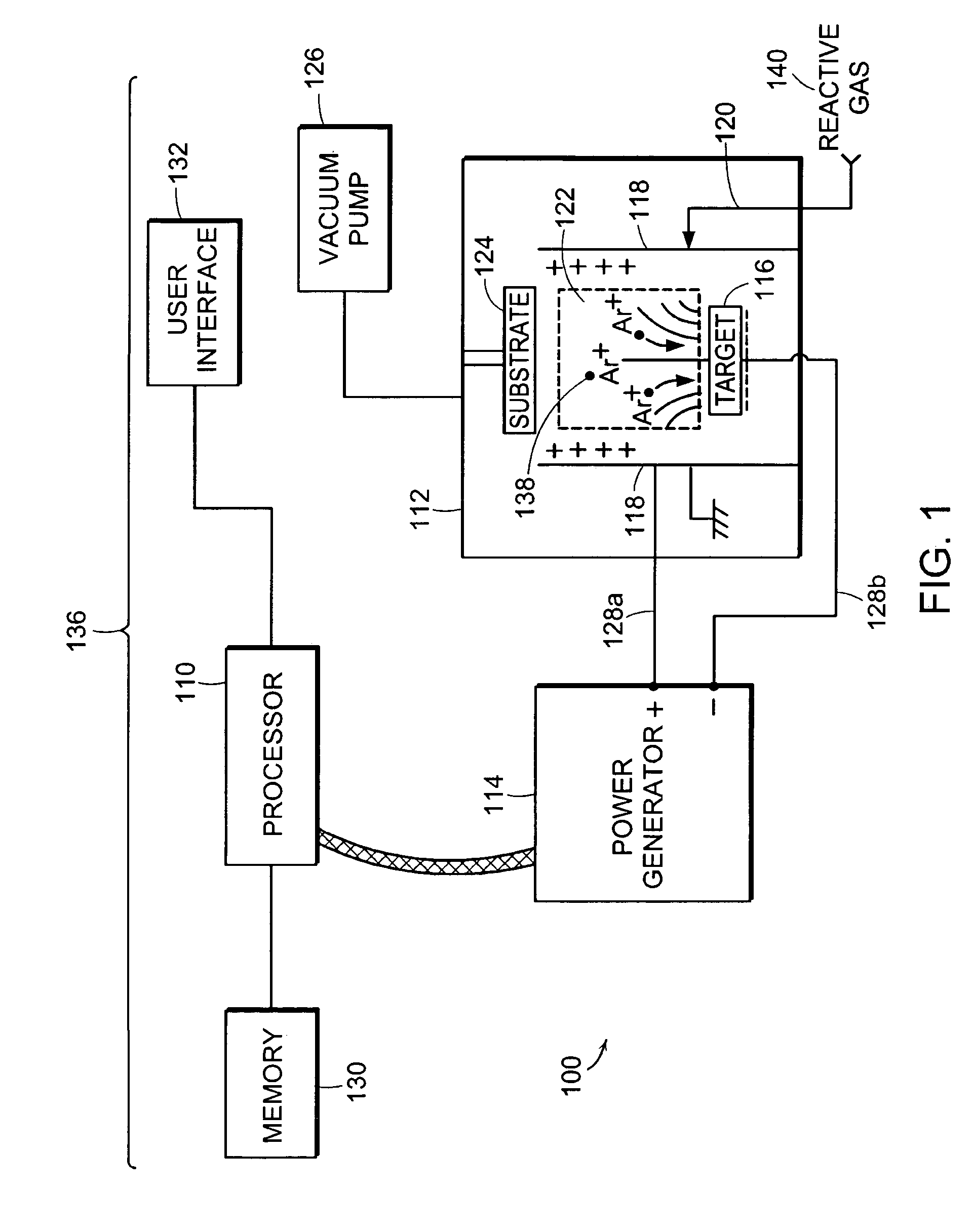
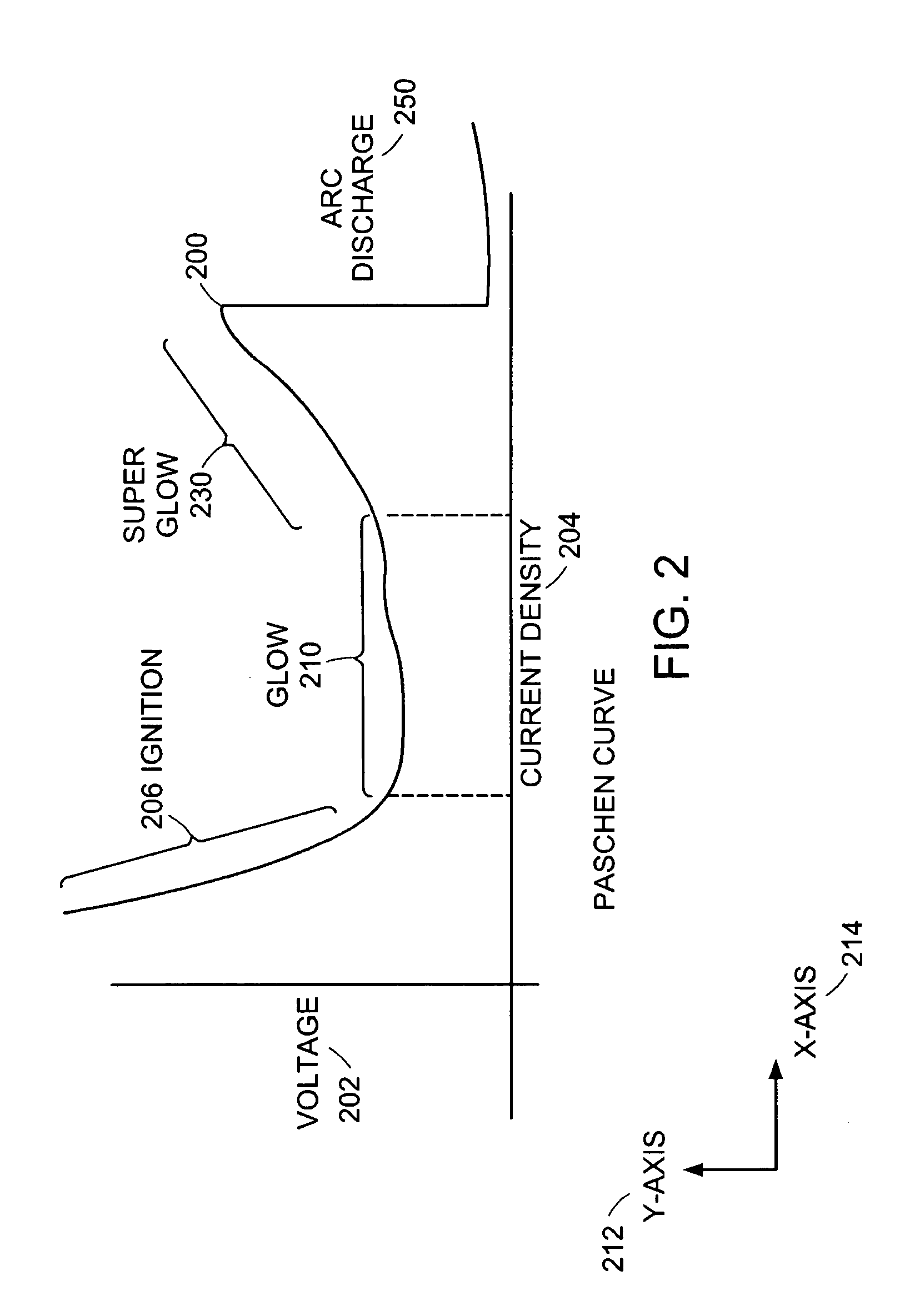
ActiveUS6995545B2Electric discharge tubesEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSputteringControl system
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
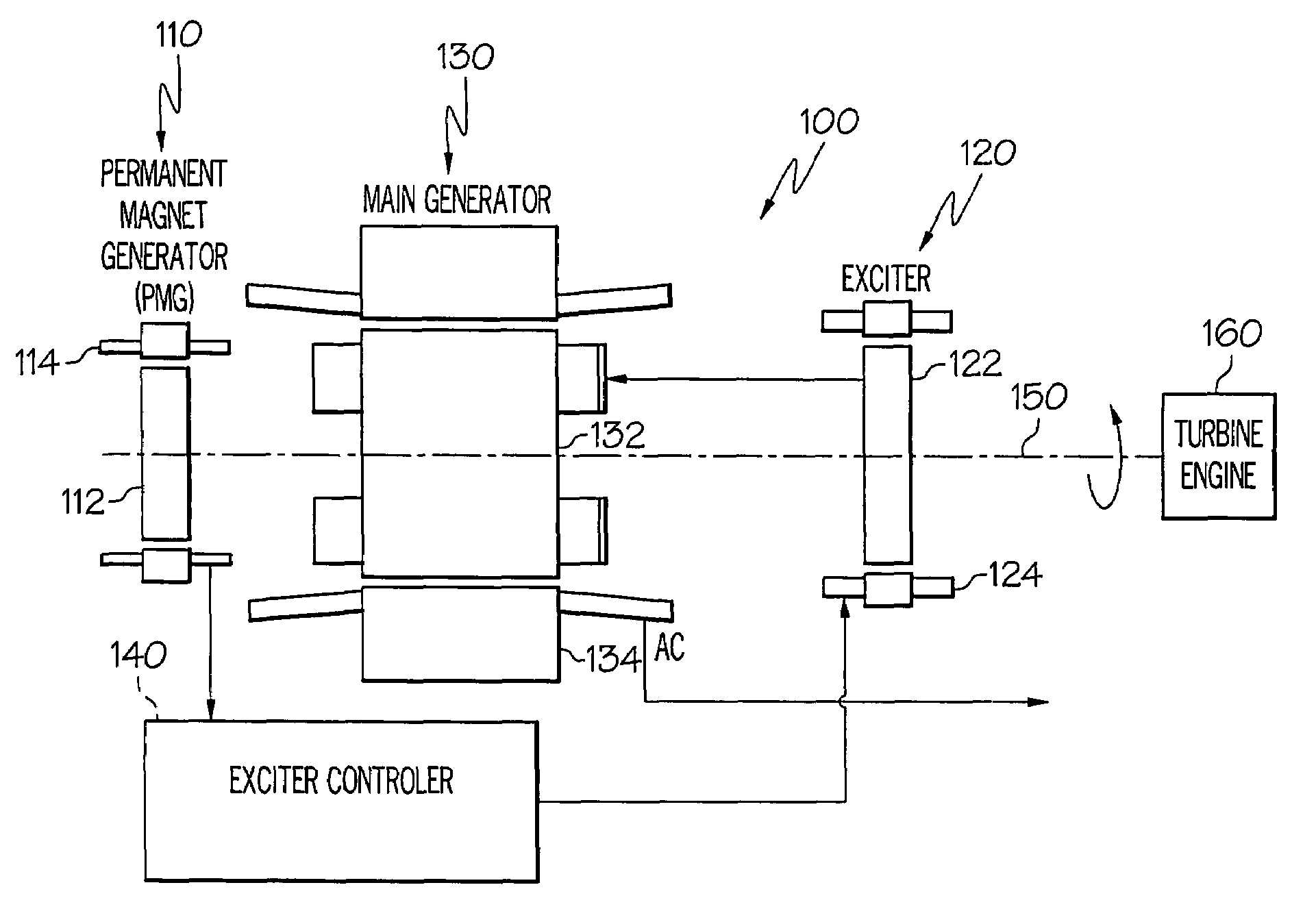
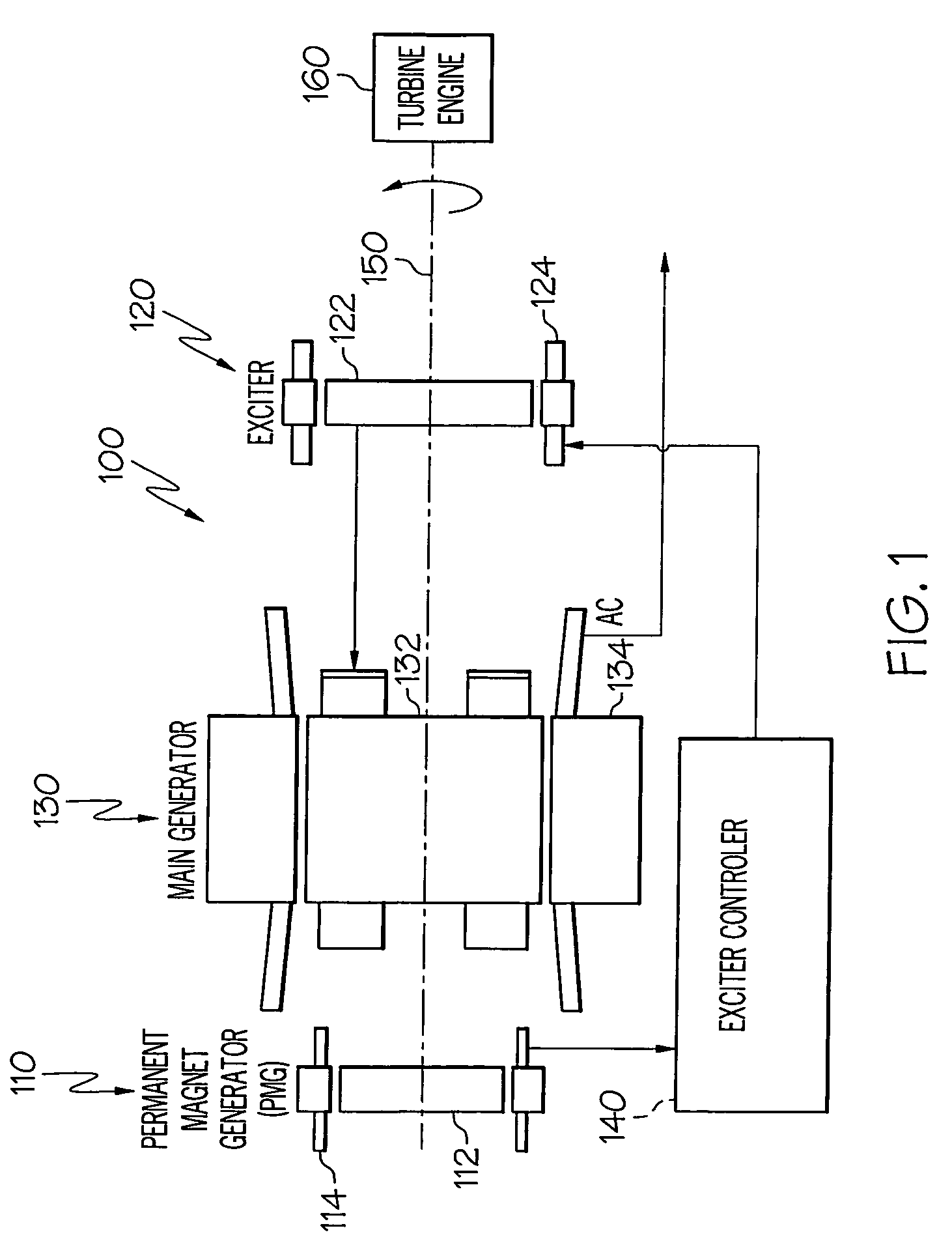
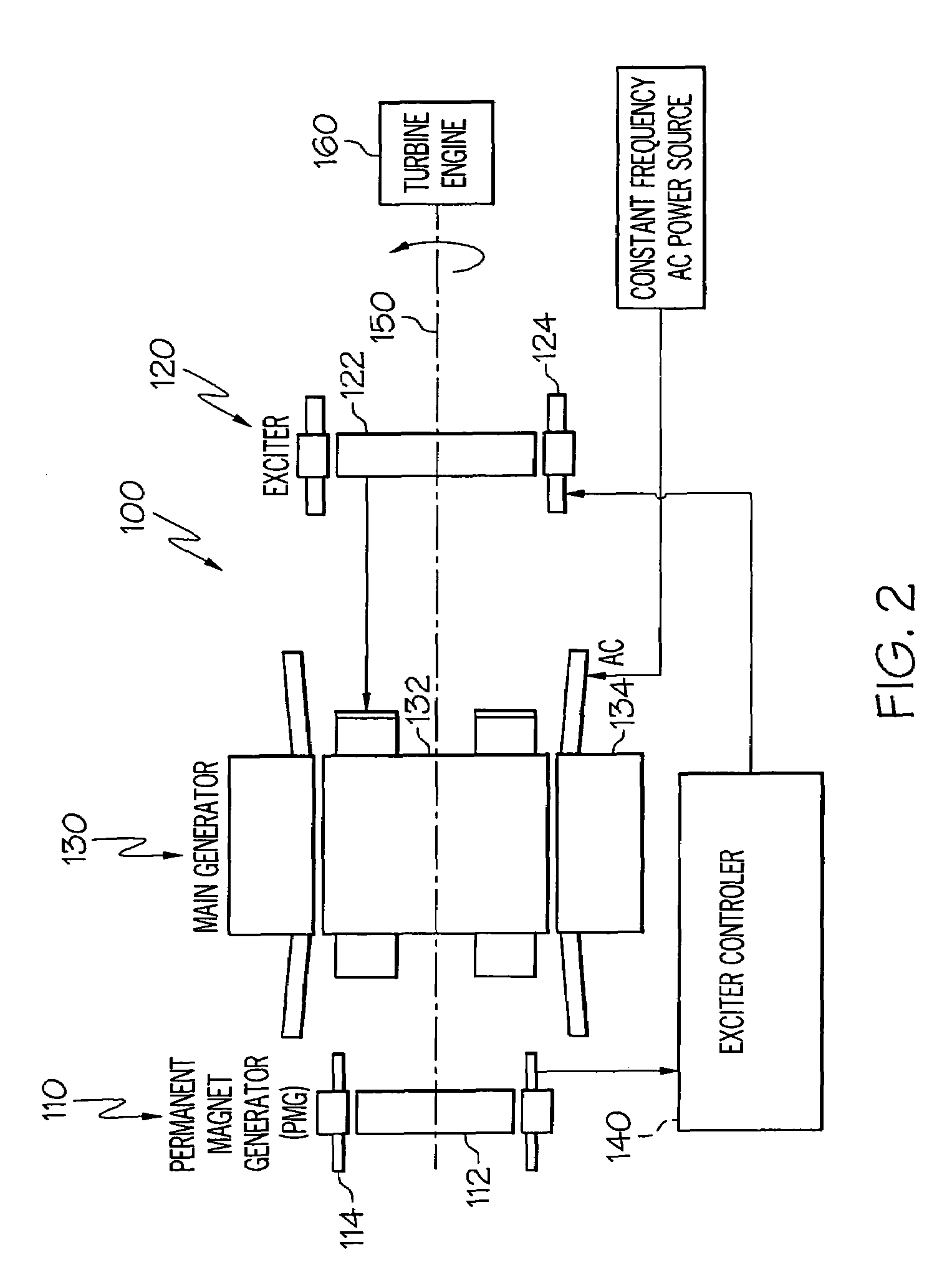
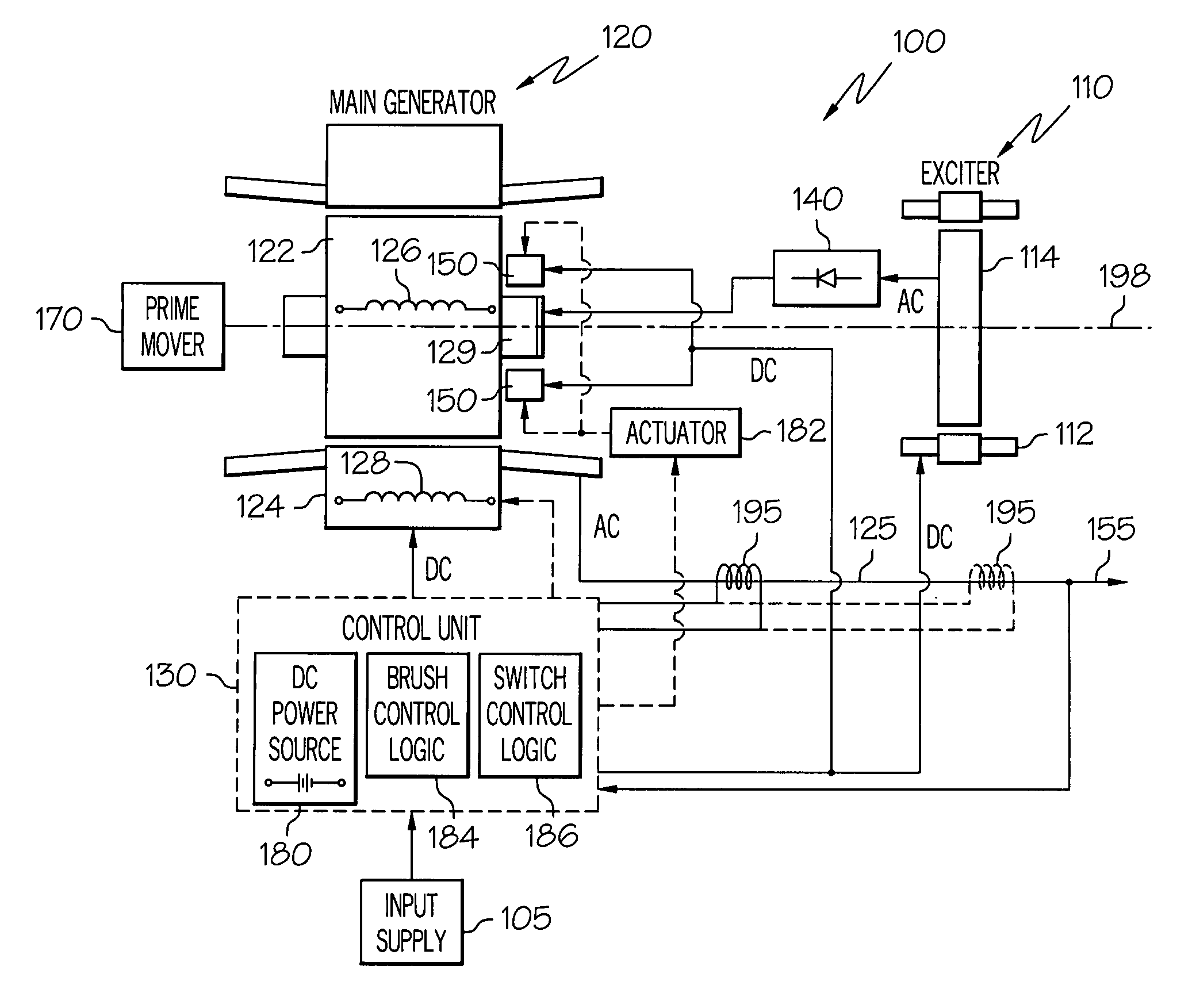
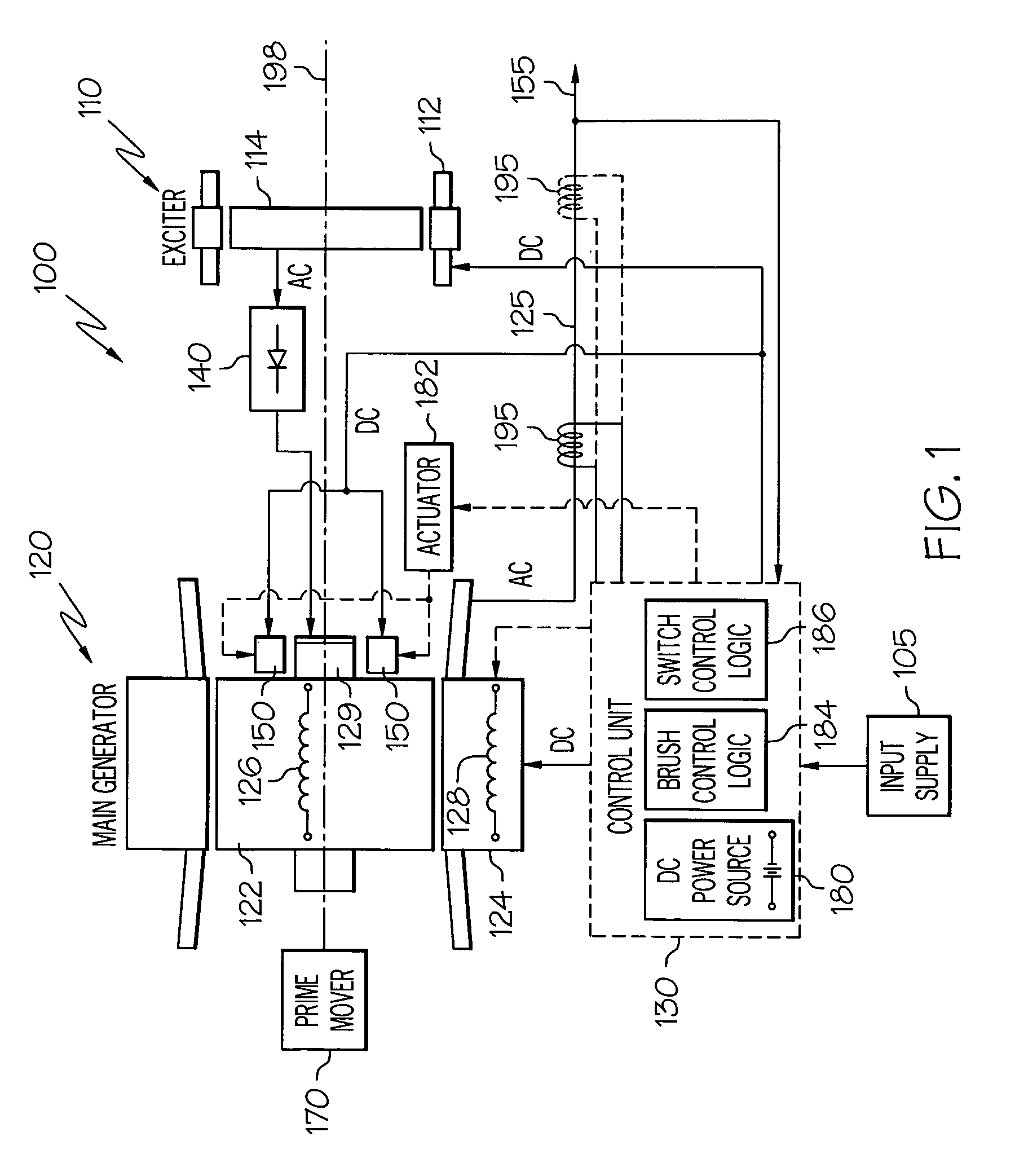
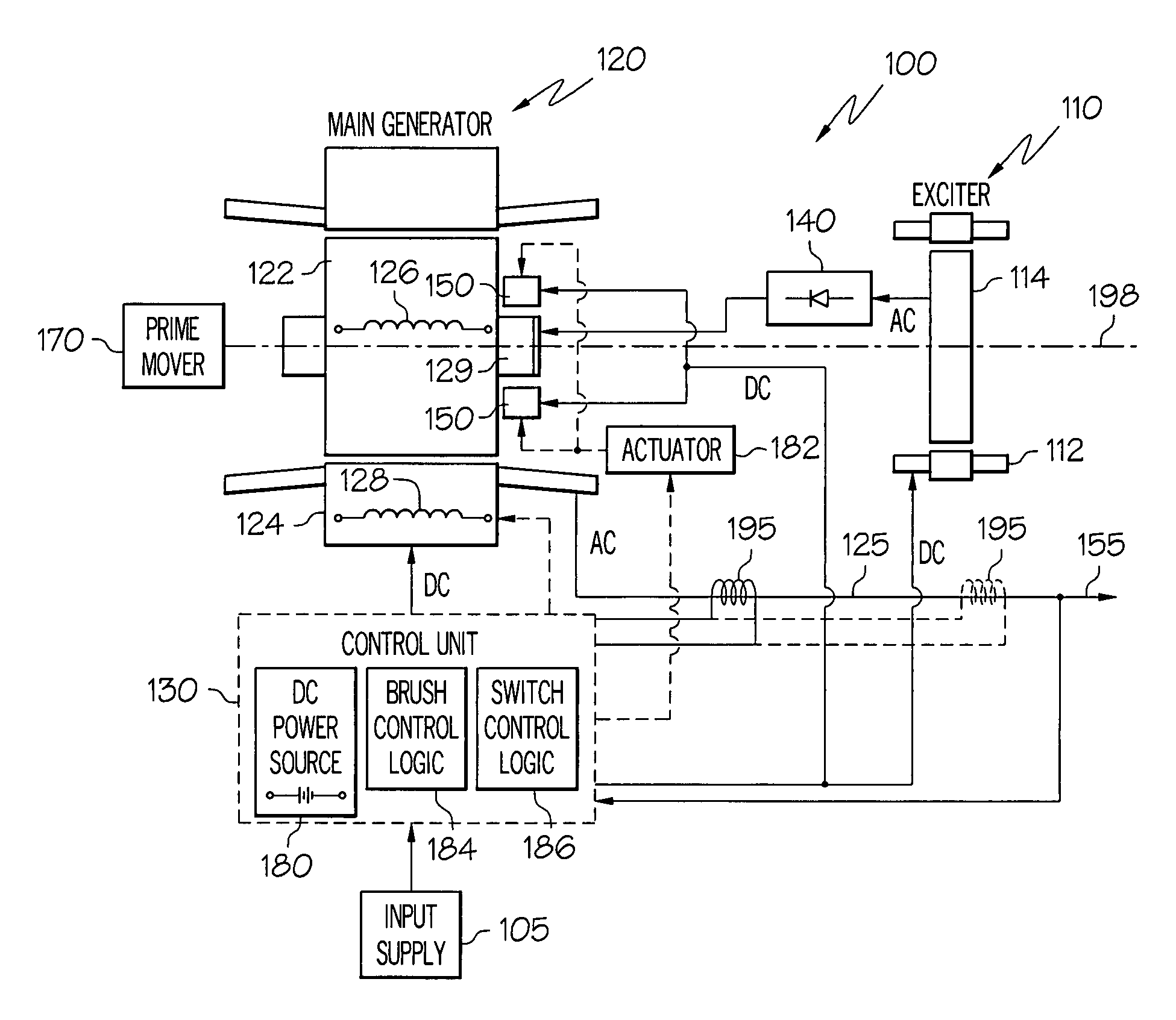
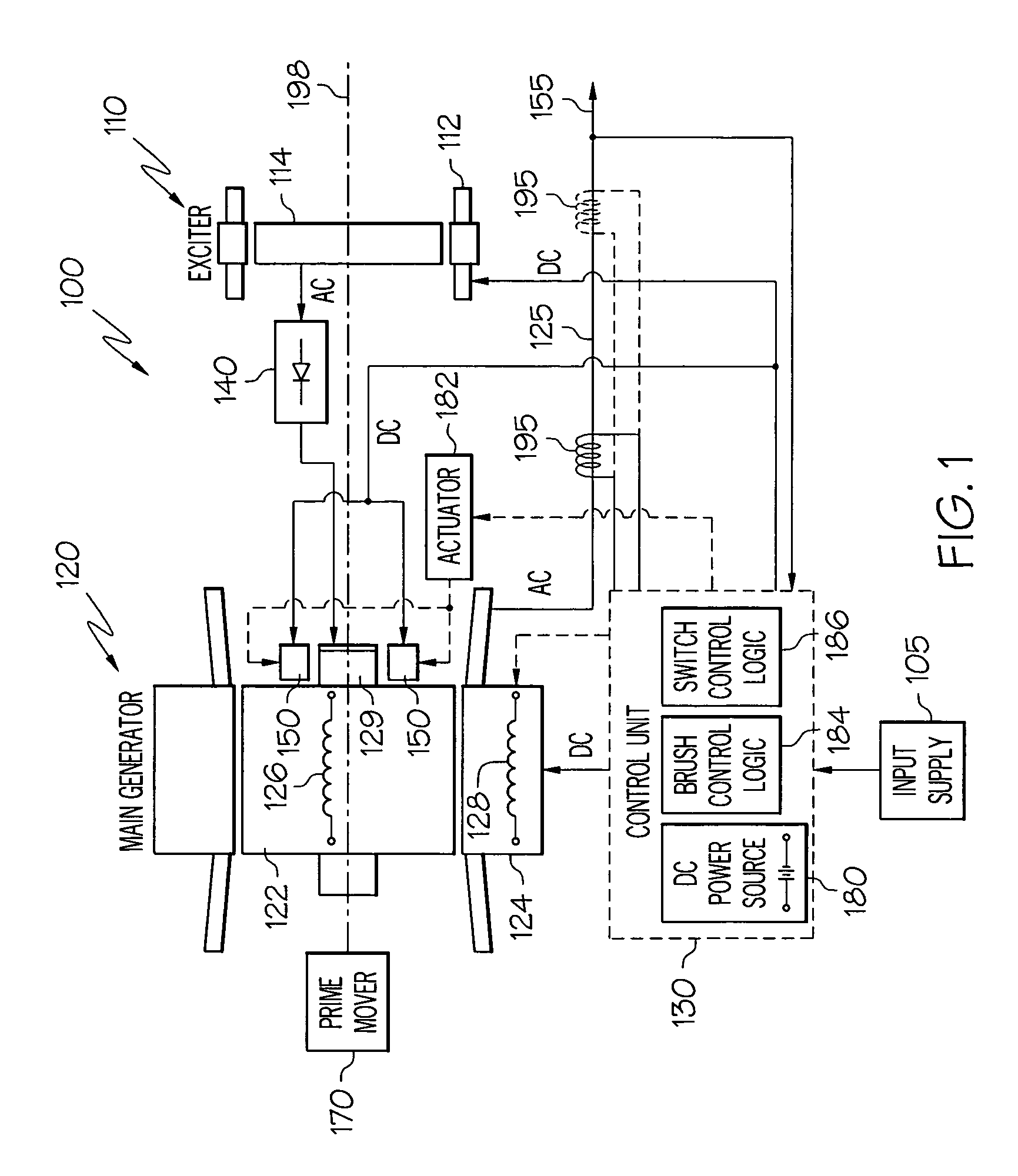
Brushless starter-generator with independently controllable exciter field
A starter-generator system supplies a controllable torque to a gas turbine engine, to thereby assist in starting the gas turbine engine, by independently controlling excitation frequency and / or voltage magnitude. The starter-generator includes a multi-phase exciter stator, a rotationally mounted multi-phase exciter rotor, a multi-phase main stator, a rotationally mounted multi-phase main rotor, and an exciter controller. The rotationally mounted multi-phase exciter rotor has a plurality of exciter rotor windings wound thereon that, upon excitation thereof with a rotating electromagnetic exciter flux generated by the exciter stator, have non-rectified excitation currents induced therein. The rotationally mounted multi-phase main rotor has a plurality of main rotor windings wound thereon that are electrically connected to receive the non-rectified excitation currents induced in the exciter rotor windings and that, upon excitation thereof with a rotating electromagnetic flux and in response to the non-rectified excitation currents supplied thereto, have currents induced therein that generate a main rotor torque to thereby cause the multi-phase main rotor and the multi-phase exciter rotor to rotate. The exciter controller is electrically coupled to at least the exciter stator and is configured to selectively supply the electrical excitation thereto, to thereby selectively control the generated main rotor torque.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Hybrid gas turbine engine starter-generator
InactiveUS7078826B2Improve wear lifeLow costSynchronous generatorsAC motor controlElectricityStarter generator
A rotating electrical machine, such as an aircraft starter-generator, that may be operated in either a DC motor mode or an AC generator mode. The machine includes a conventionally wound main stator that is selectively configurable as a multi-pole AC stator and a multi-pole DC stator. The machine also includes rotor windings that are configured to be selectively coupled to either an exciter or a plurality of commutator segments, and DC brushes that are selectively moveable into, and out of, electrical contact with the commutator segments, to thereby electrically couple and decouple a DC power source to and from, respectively, the rotor windings.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
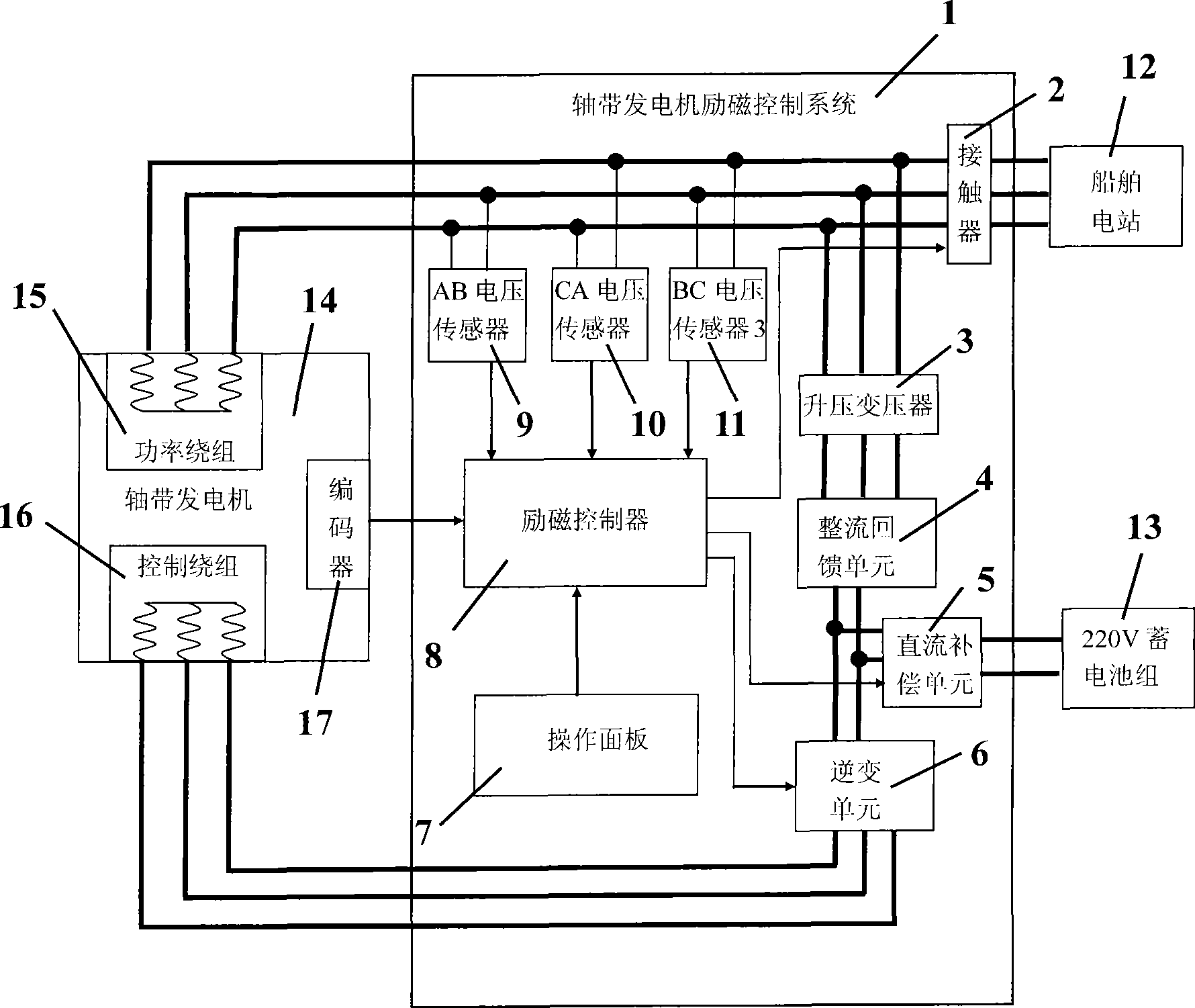
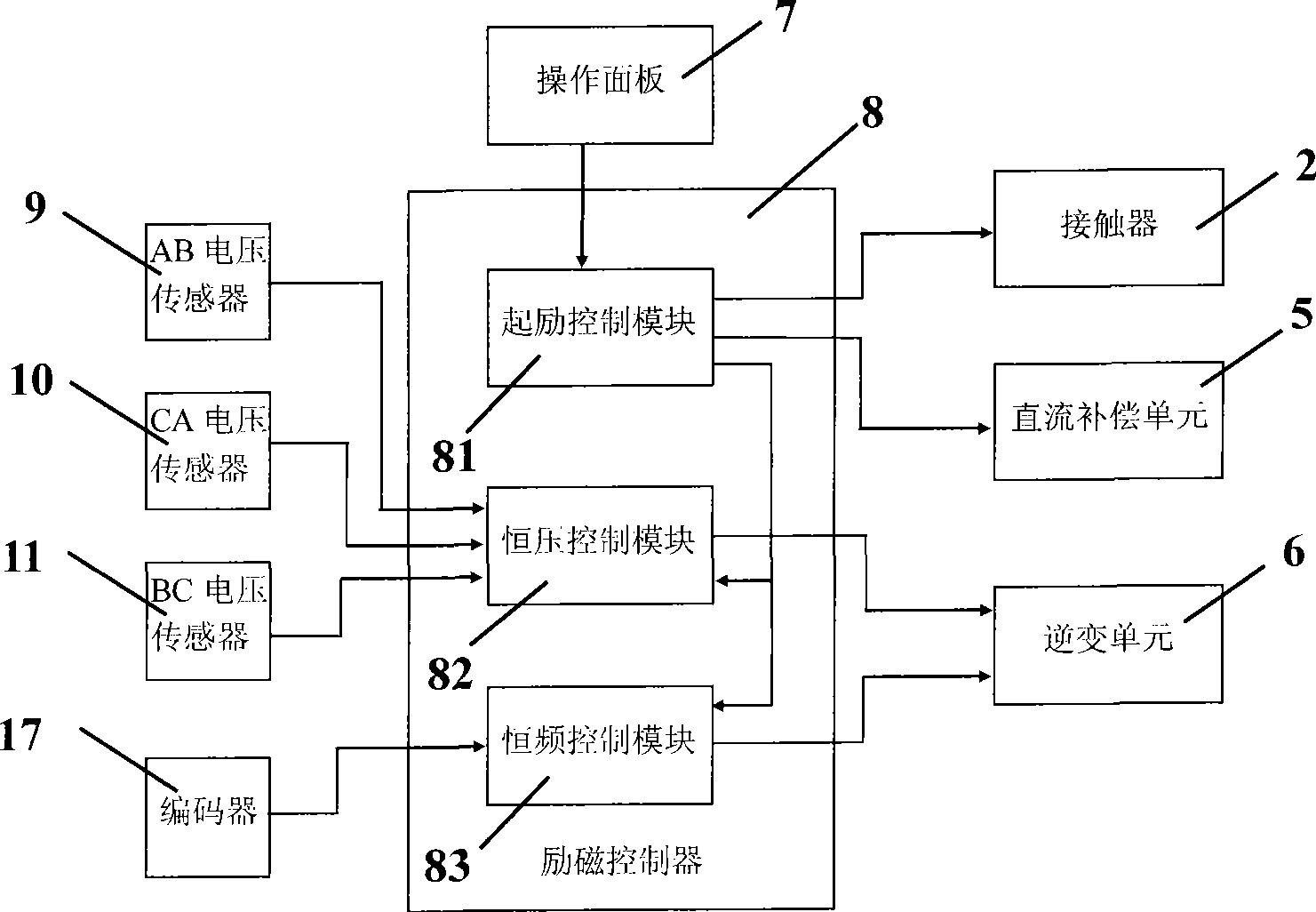
Excitation control system architecture and control method for marine diesel brushless double fed shaft generator
InactiveCN101510747AImprove operational efficiencyImprove reliabilityGenerator control circuitsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsConstant frequencyTransformer
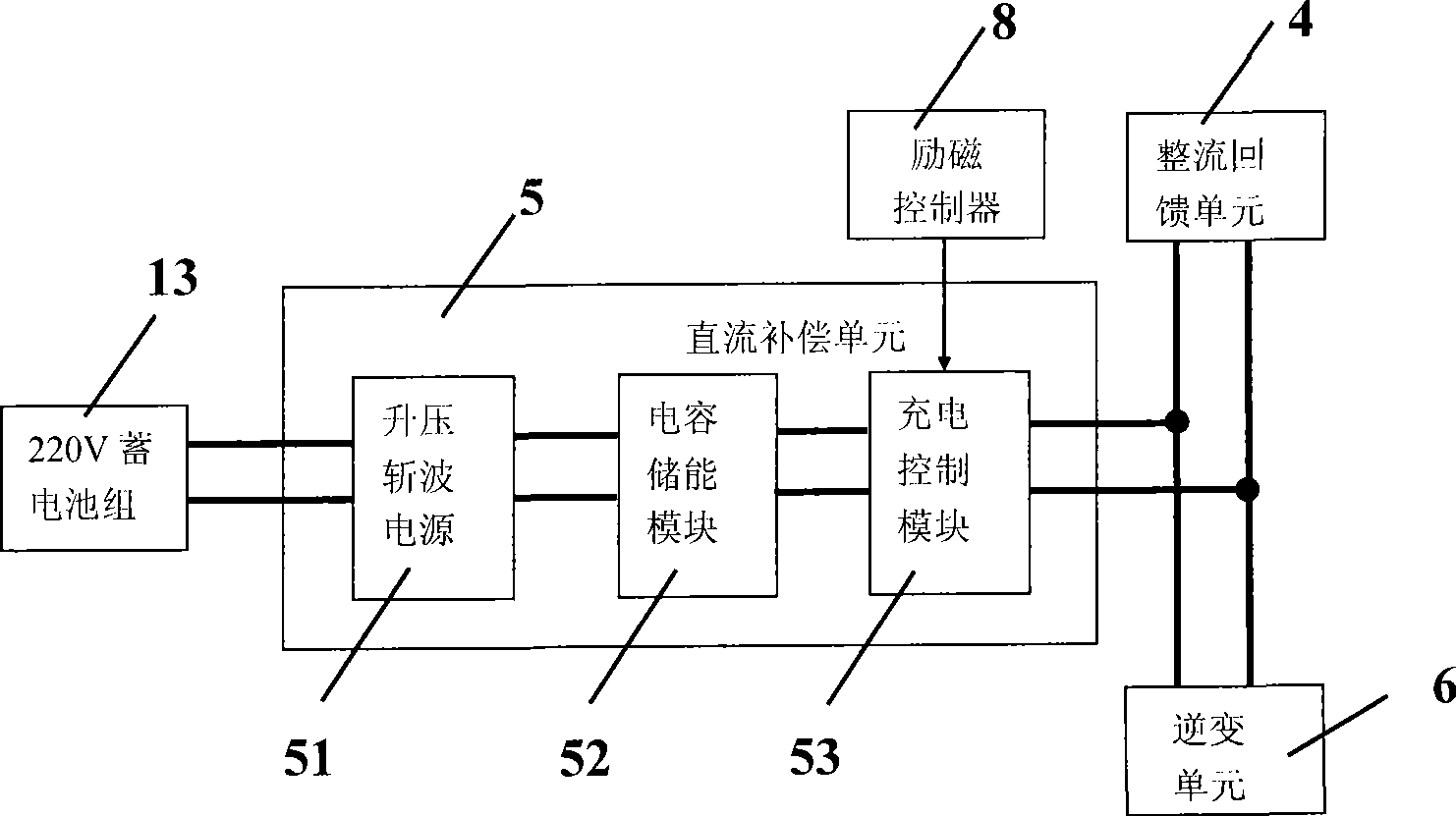
The invention relates to a structure of an excitation control system of a brushless doubly-fed shaft generator used for a marine diesel and a control method thereof. The structure comprises a contactor, a step-up transformer, a rectification feedback unit, a direct current compensation unit, a inverter unit, an operation panel, an excitation controller, an AB phase voltage sensor, a CA phase voltage sensor, and a BC phase voltage sensor; the method based on the control system structure can realize the excitation, constant-voltage control, constant-frequency control, under-voltage protection and over-voltage protection of the brushless doubly-fed shaft generator of the marine diesel.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Procedure to connect an asynchronous generator on an alternating current and an electrical connecting for use at this procedure
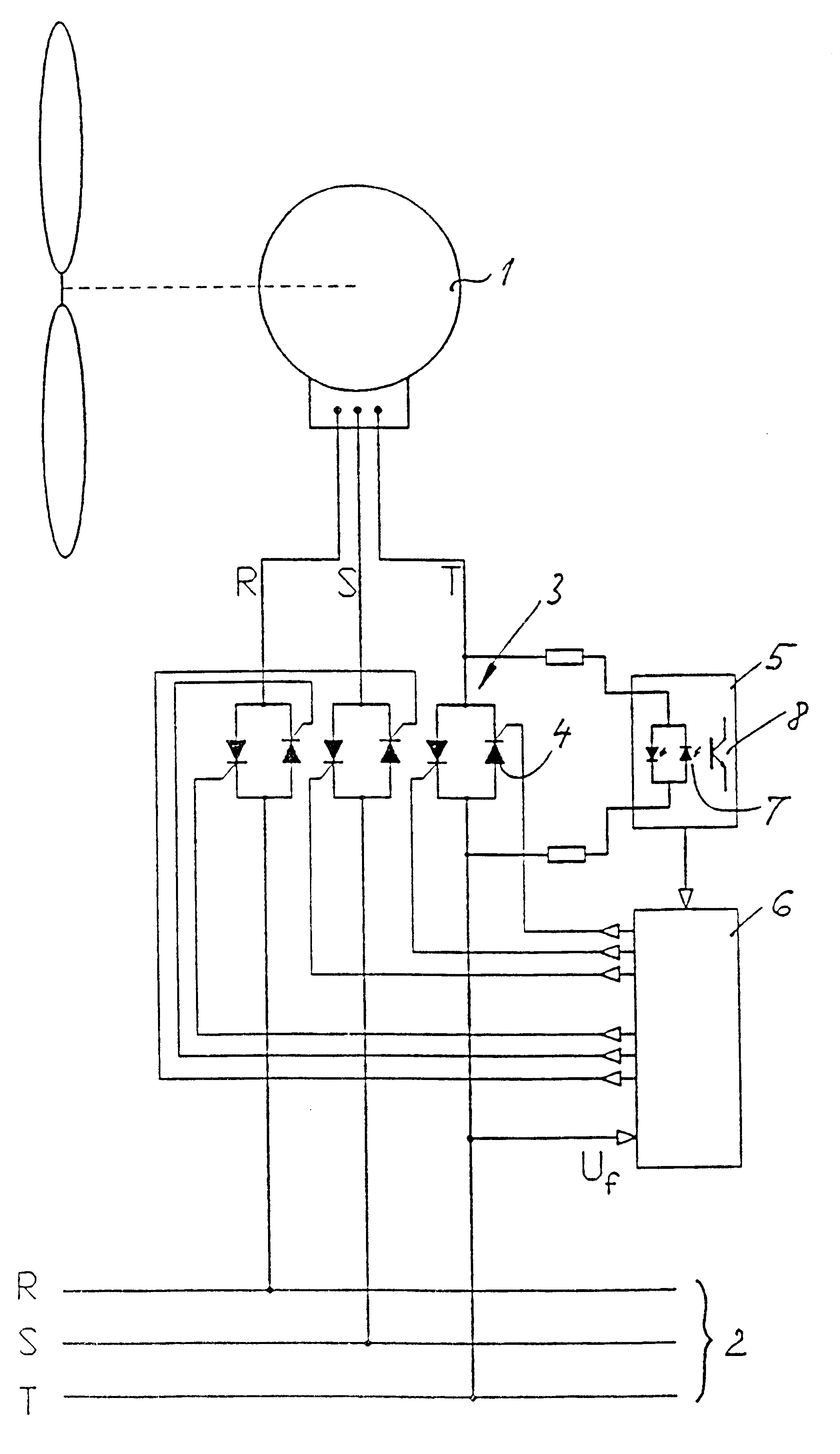
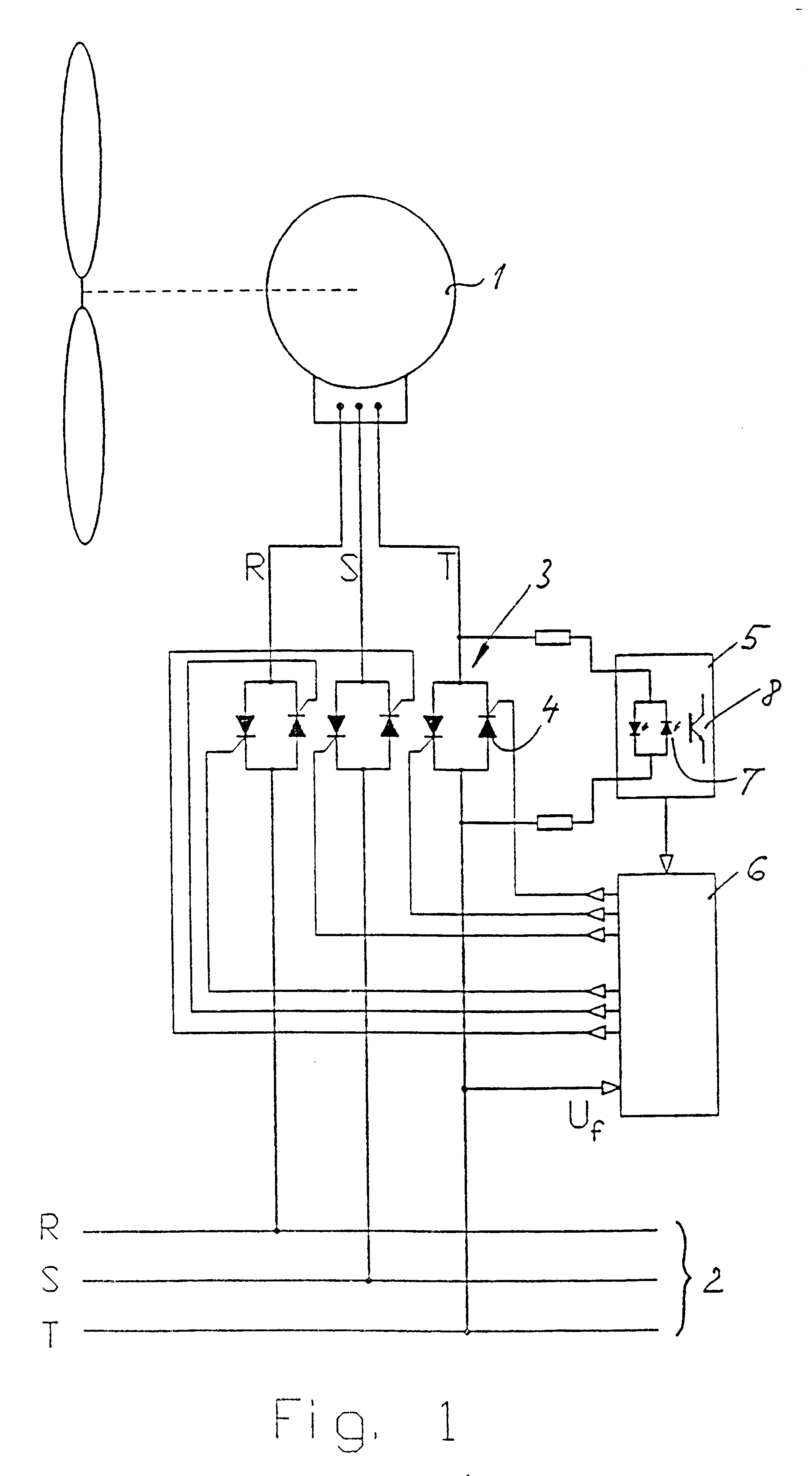
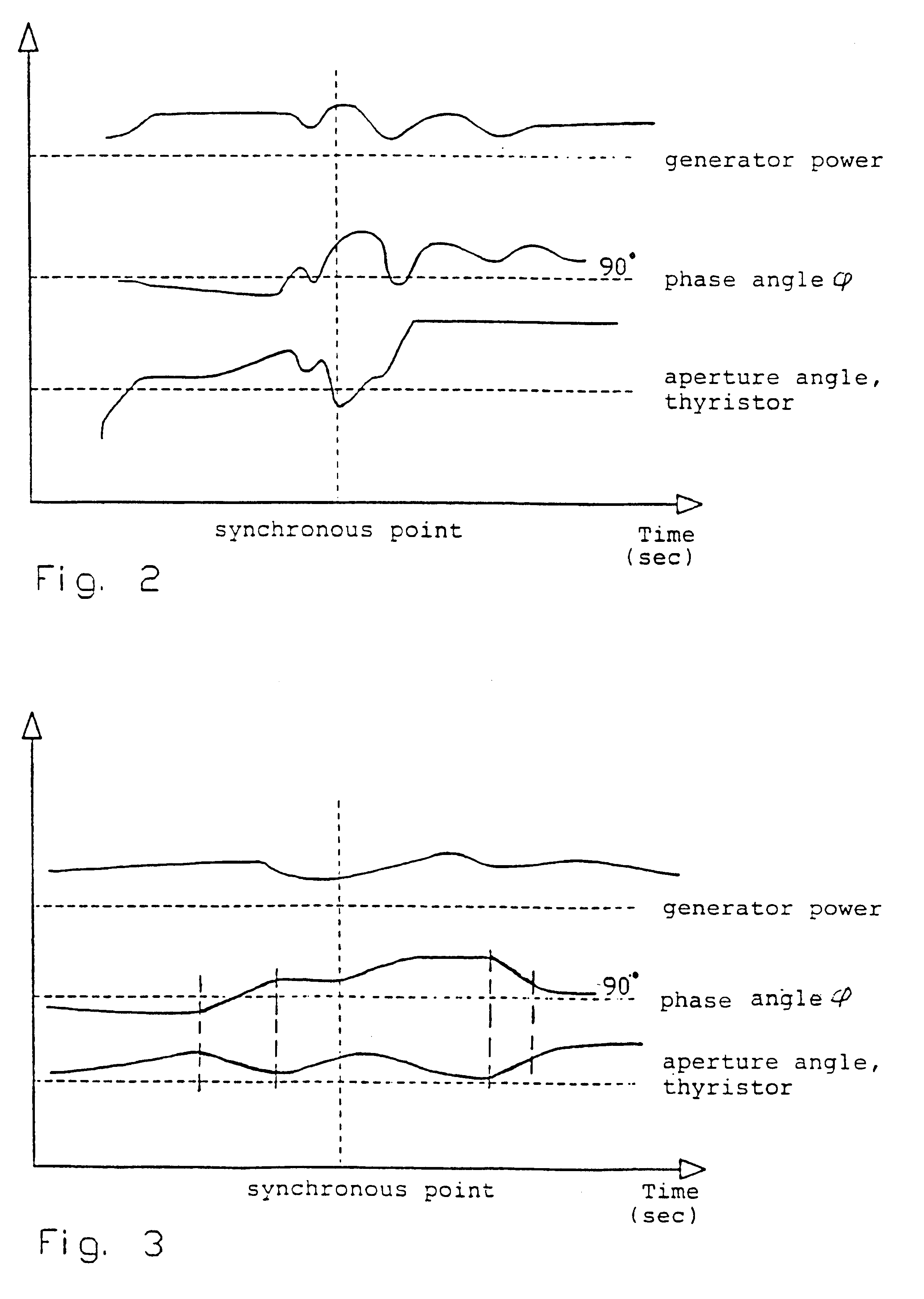
InactiveUS6323624B1Thyristor aperture angle is reducedHigh degreeEmergency protective circuit arrangementsConversion without intermediate conversion to dcThyratronEngineering
The invention relates to a procedure of connecting a polyphased asynchronous generator on a polyphased alternating voltage network. The connecting is carried out by means of an adjustable, electronic connecting based on thyristors or similar variable (adjustable) connecting items, the connecting degree of which is varied during a controlled connecting course, which is controlled in consideration of the wish of a "soft" connecting on the network and a limitation of the maximum amperage during the connecting course. During the whole connecting course a continuous determination of the generator phase angle phi is carried out, and on basis of this determination a continuous adjustment of thyristors-the aperture angle is carried out, thus the aimed, successive load connection of the generator on the network (soft-connecting) is obtained. Furthermore the procedure include a new method to determine the generator phase angle phi by registering the time of zero circulation on the phase voltage, and at the same time detection of the respective thyristor voltage zero circulation point at a measuring method based on measuring of the thyristor voltage. The novelty of the invention consists in adjusting the ignition point of the thyristors successively to the phase angle phi, thus the connecting degree resulted to the thyristors is increased in a controlled speed regardless of the variations registered in the phase angle during the connecting course, i.e. in the principle the thyristor aperture angle is reduced, when phi increases and so on.
Owner:MITA TEKNIK
Method and apparatus for monitoring turbine parameters of turbine/alternator on common shaft
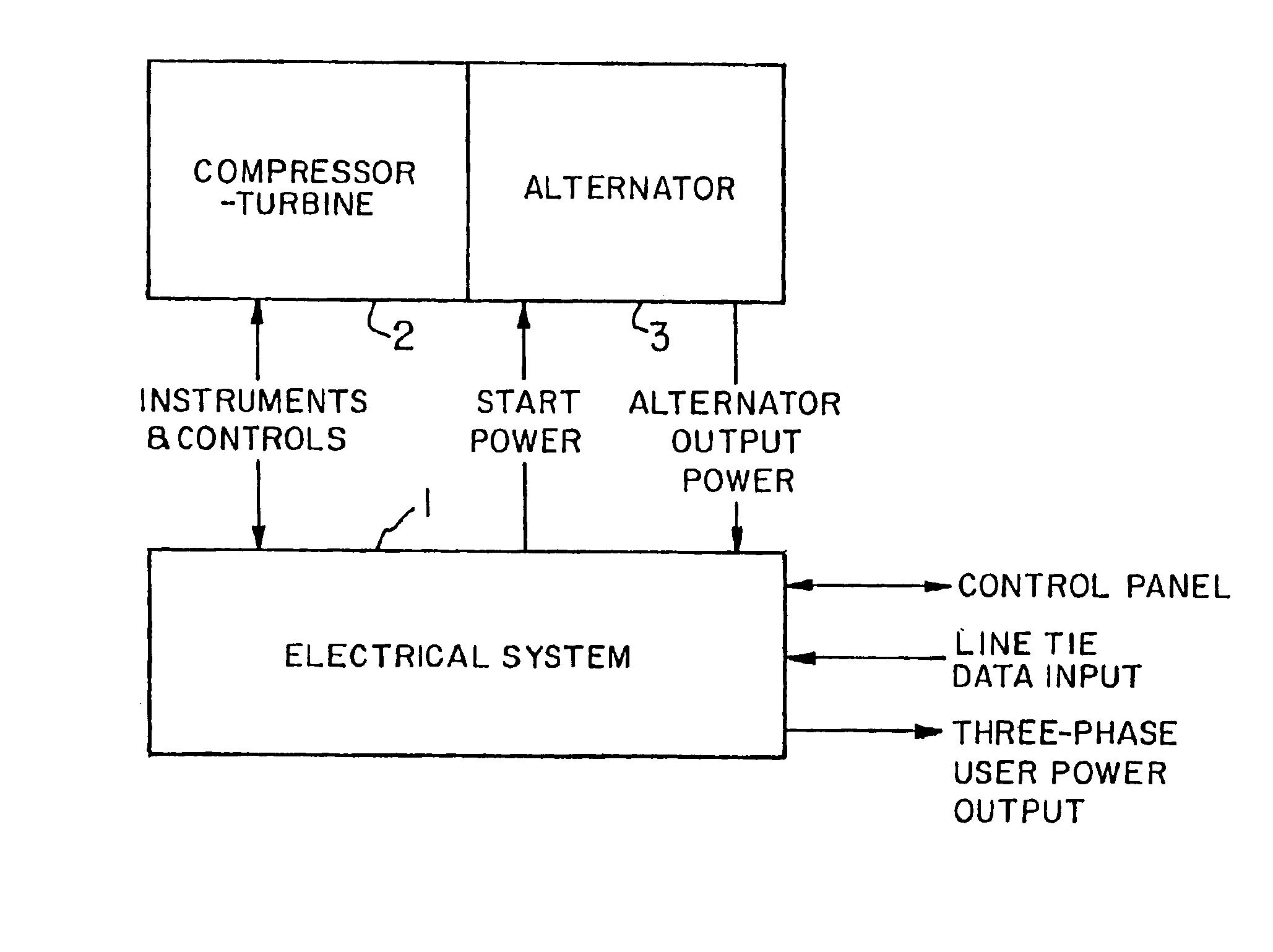
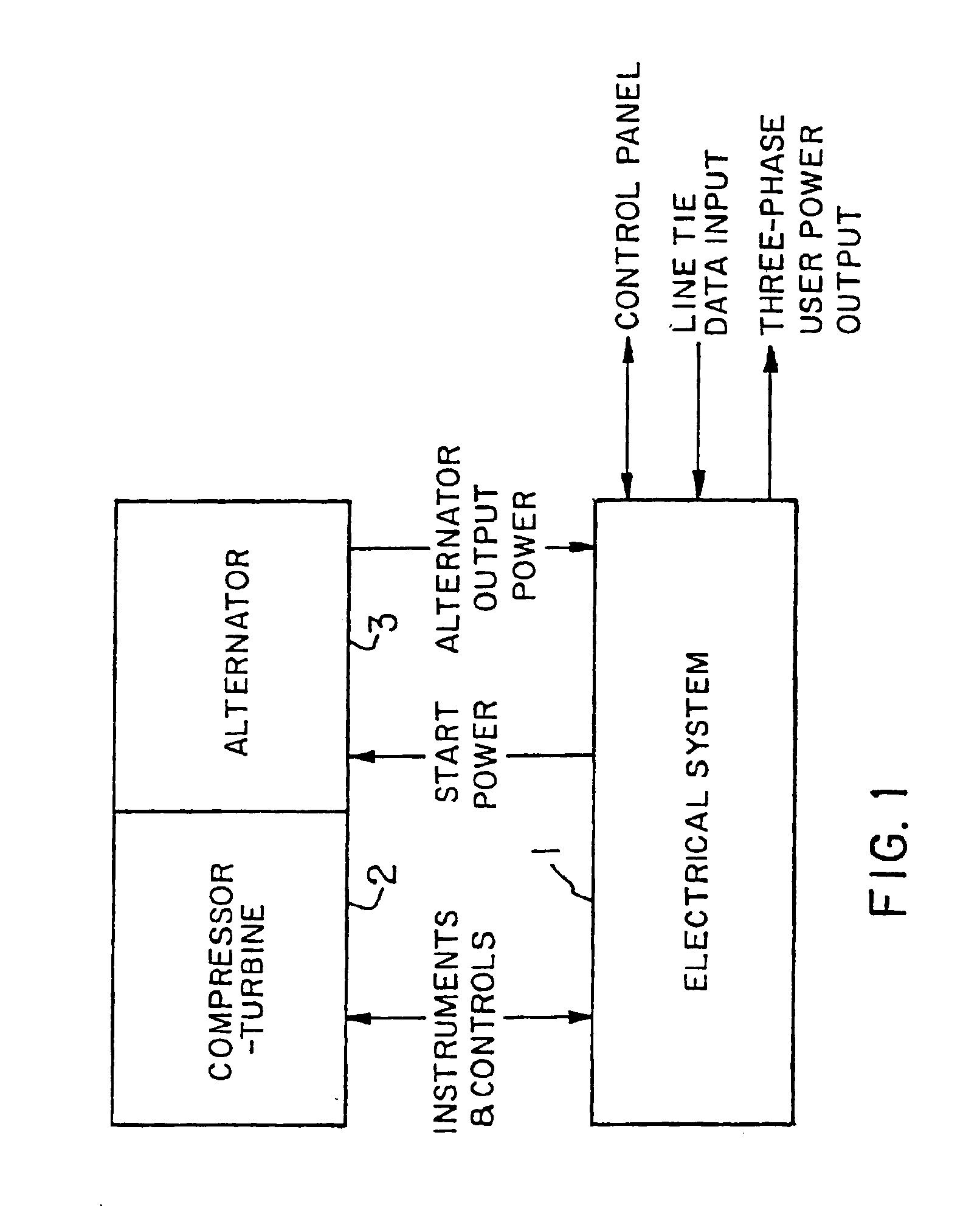
InactiveUS6891282B2Starting is possibleTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionTurbine/propulsion engine startersPower inverterAlternator
An electrical system and apparatus for a turbine / alternator comprising a gas driven turbine and a permanent magnet alternator rotating on a common shaft includes an inverter circuit connectable either to an output circuit or the stator winding of the alternator. A control circuit during a start-up mode switches the inverter circuit to the stator winding of the alternator and during a power out mode switches the inverter circuit to the output circuit. The operating parameters of the turbine are monitored during start-up and / or the power out mode.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC
Synthetic regulating apparatus for digital hydro-turbo generator set and control method thereof
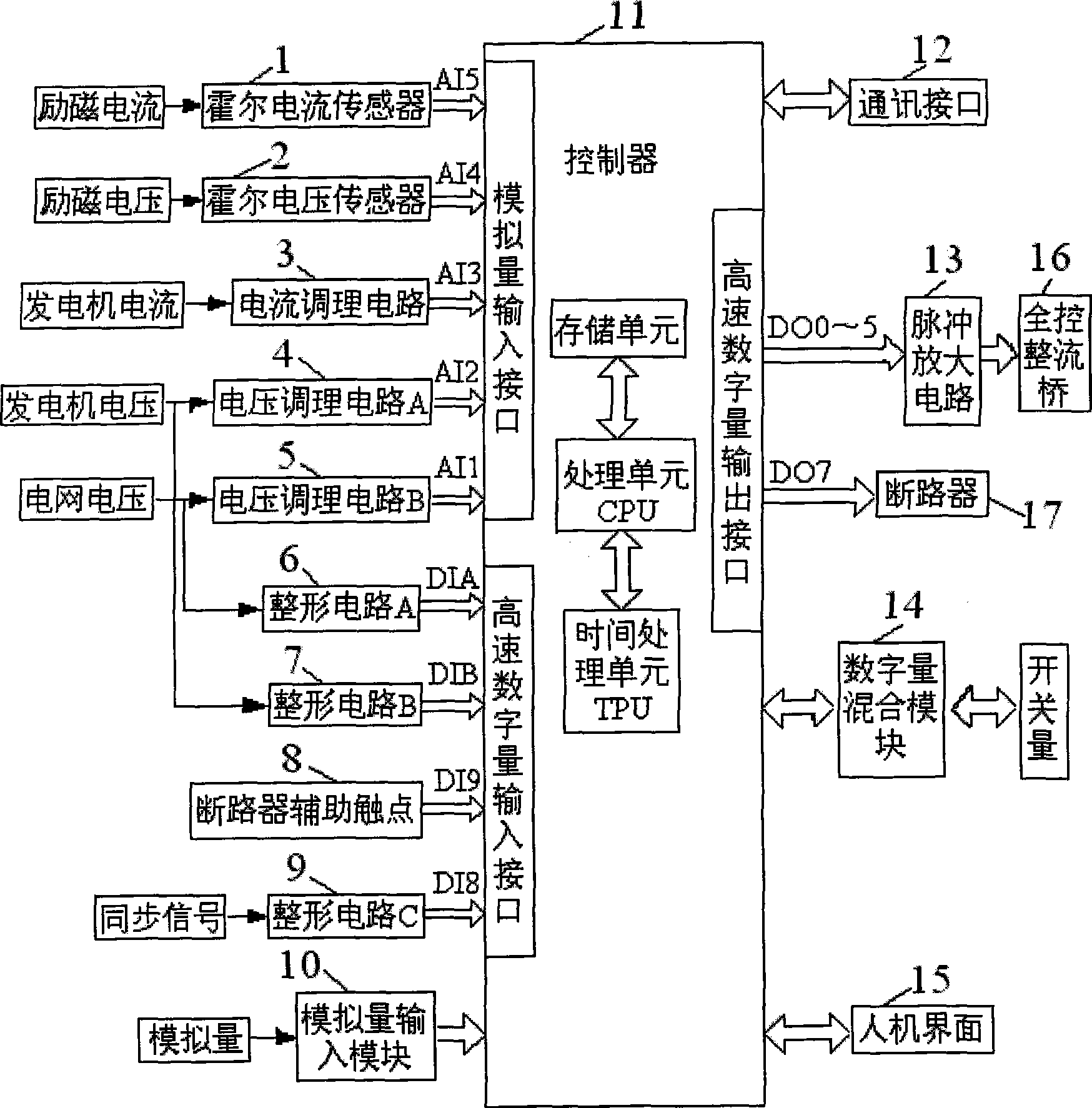
InactiveCN101505129AIncrease the level of automationImprove reliabilitySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsGenerator control of frequency and voltagePower gridEngineering
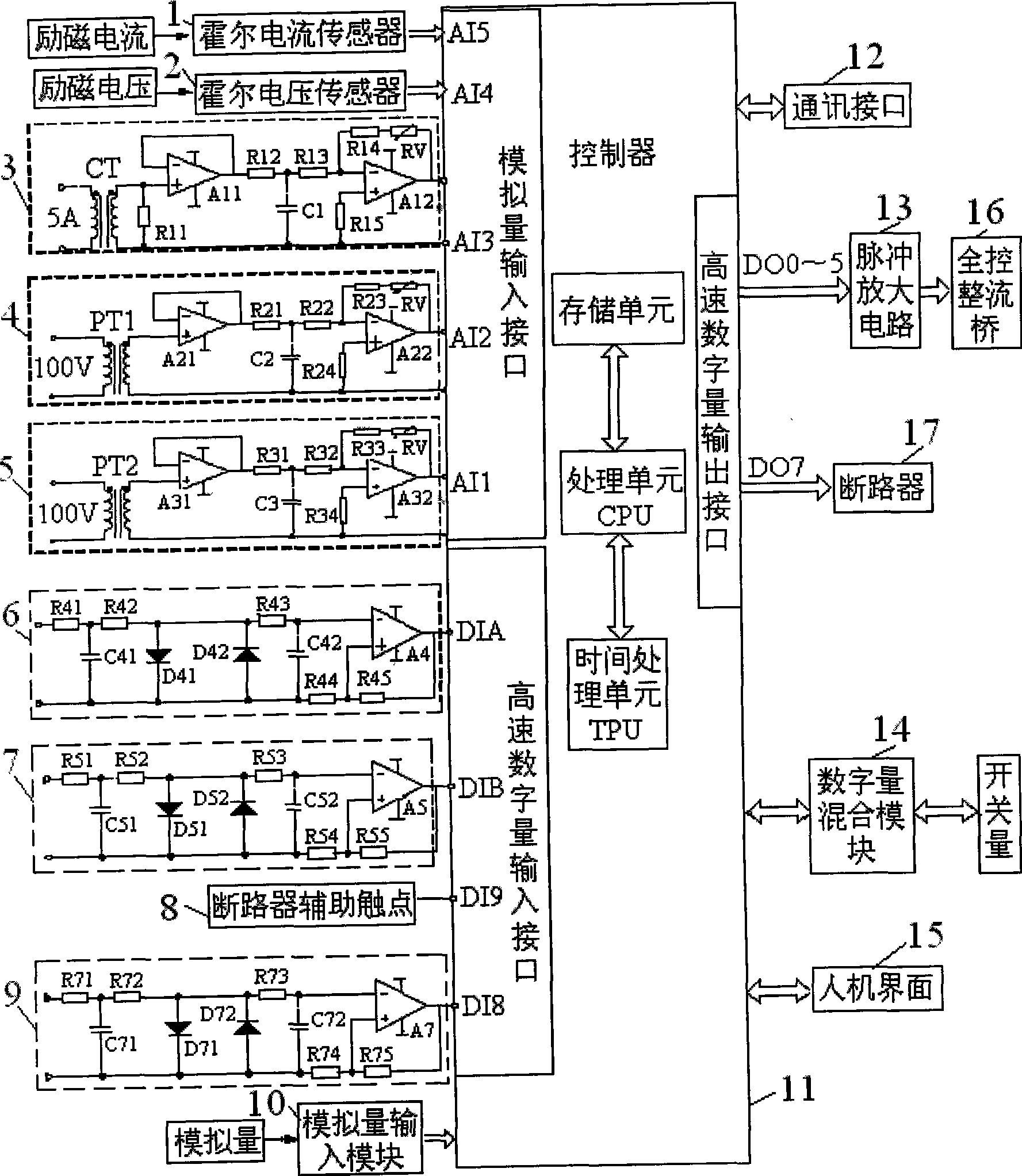
The invention provides a digital comprehensive regulation device for hydroelectric generating sets, and a control method thereof. The device comprises a controller, wherein the controller is respectively connected with a Hall current sensor, a Hall voltage sensor, a current conditioning circuit, a voltage conditioning circuit A and a voltage conditioning circuit B through analog input interfaces, and is respectively connected with a shaping circuit A, a shaping circuit B, a circuit-breaker auxiliary contact and a shaping circuit C through high-speed digital input interface; the controller is respectively connected with a pulse amplification circuit and a circuit breaker through high-speed digital output interfaces; and the controller is also respectively connected with a digital mixing module and an analog input module. The device can control and regulate the dynamic performances of generating sets by measuring and calculating the parameters of power networks and generators. The device integrates synchronization, speed regulation and excitation, has the characteristics of high control performance, short response time, programming easiness, debugging convenience, high execution speed and the like, and is particularly applicable to the comprehensive control over medium / small-size hydroelectric generating sets.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for operation of a power station
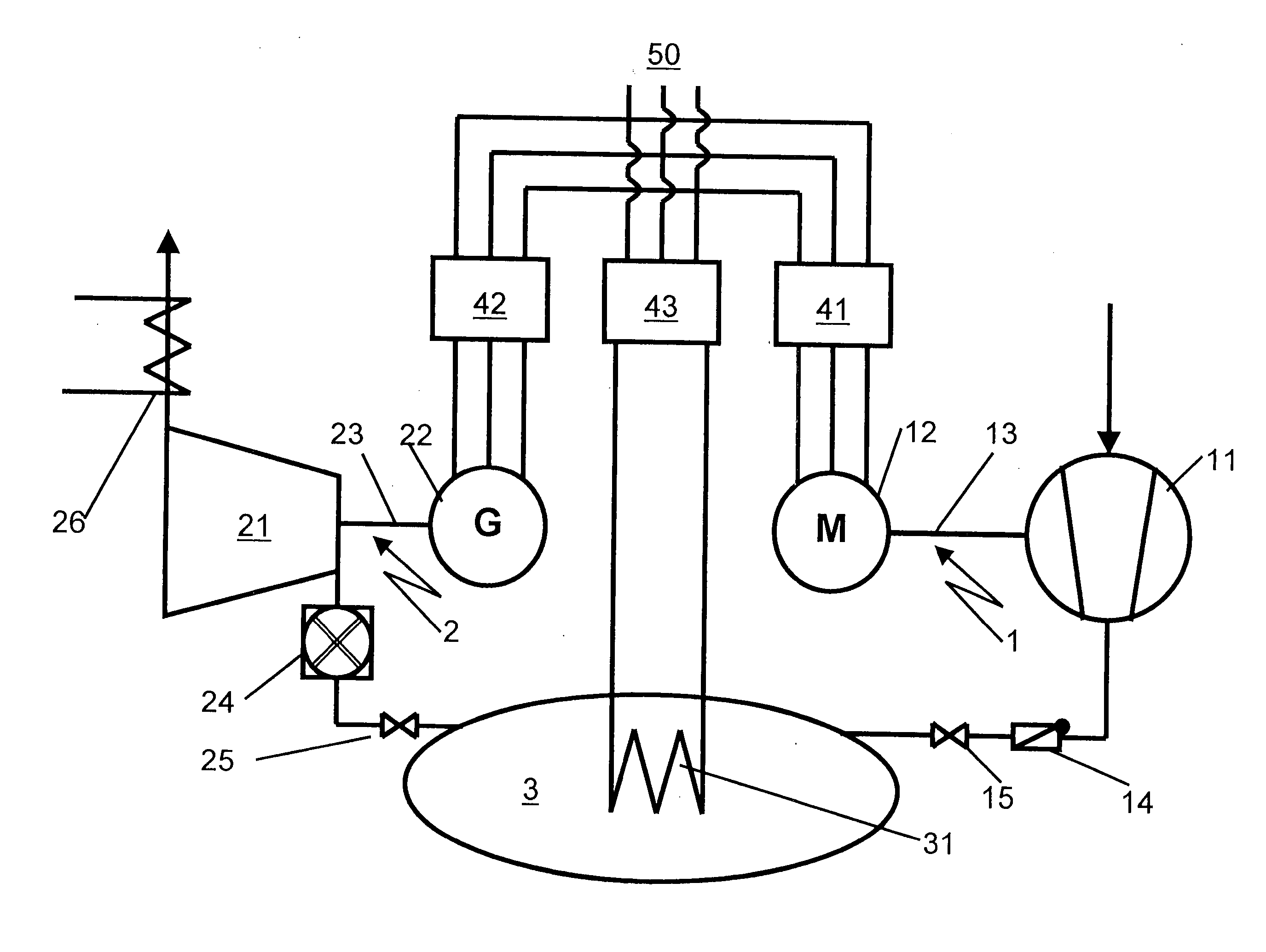
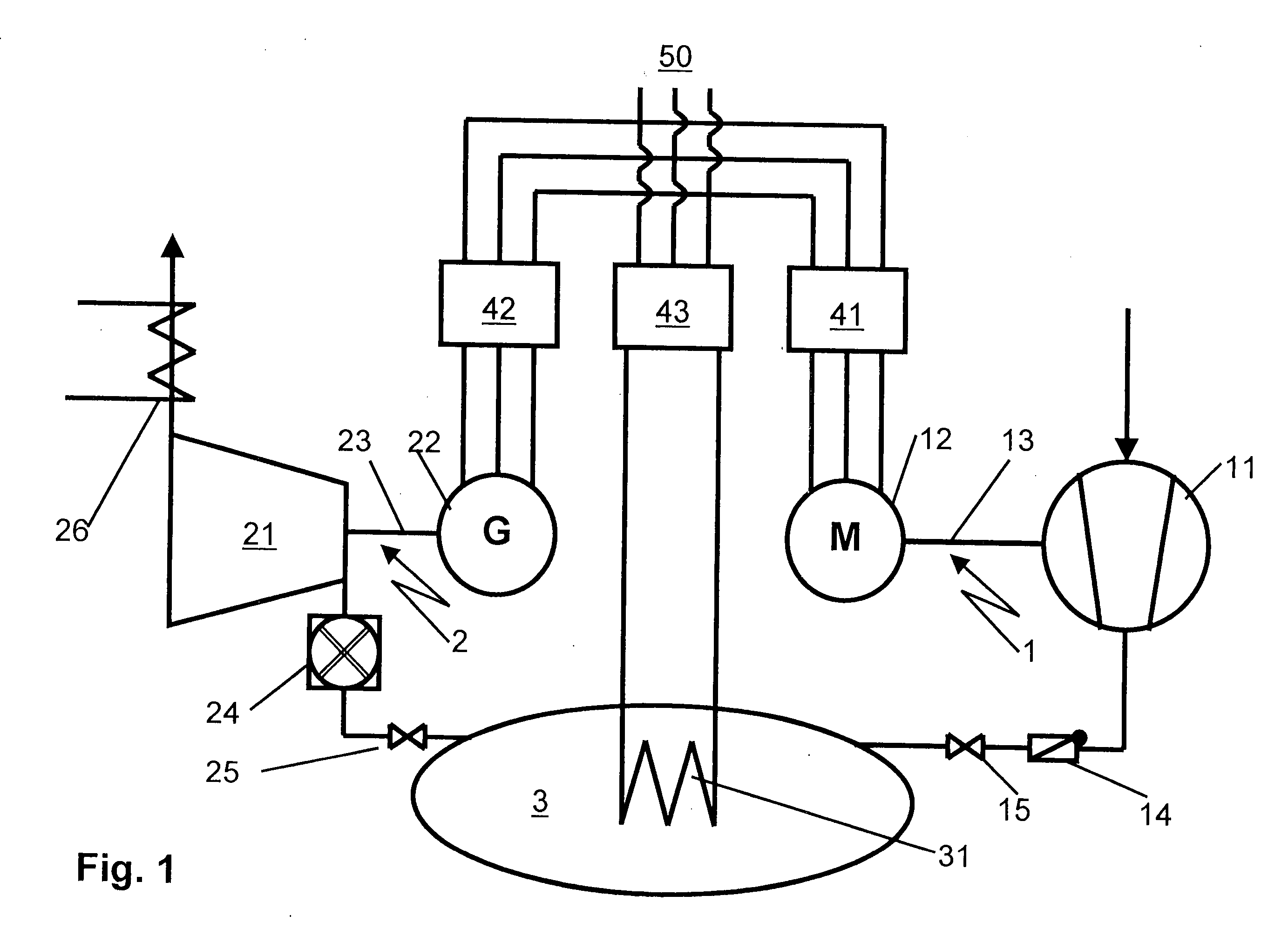
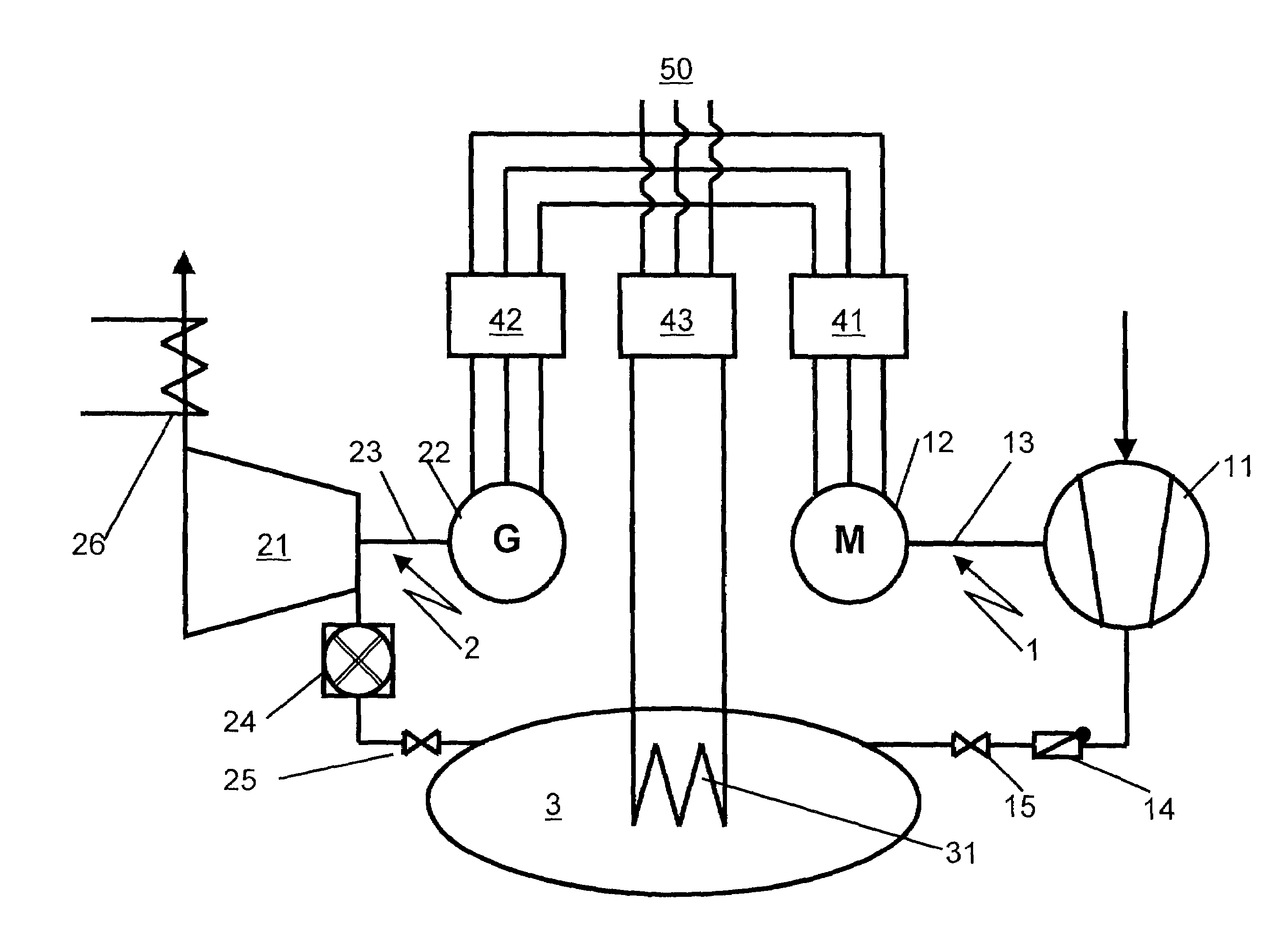
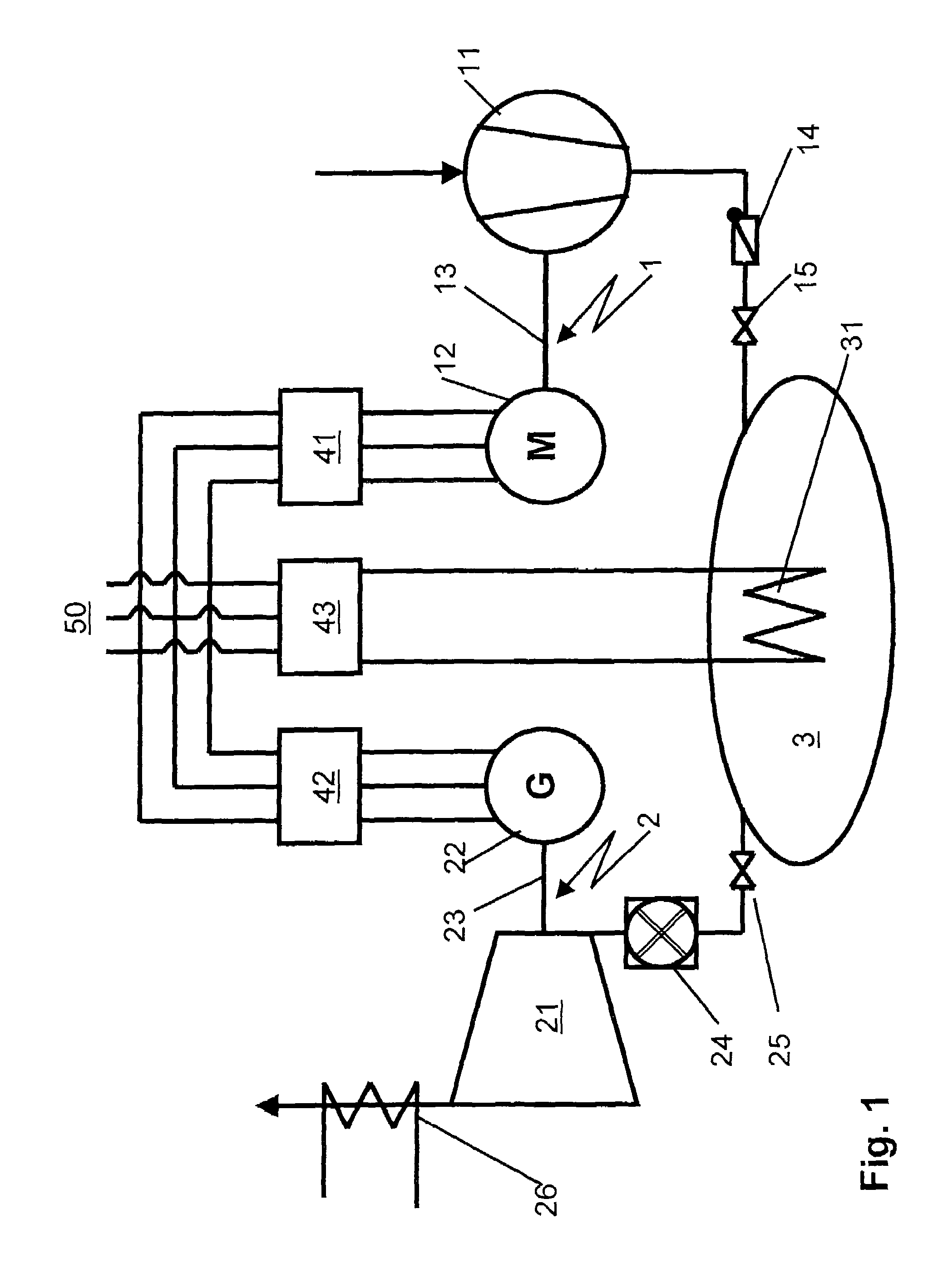
ActiveUS20070255459A1Valid matchEffective supervisionLevel controlSpeed/accelaration controlFrequency changerPower station
A power station comprises a power-consuming shaft run on which a motor and a compressor are arranged, as well as a power-emitting shaft run on which a generator and an expansion machine are arranged. The compressor feeds a compressed fluid into a storage volume. The compressed storage fluid is expanded in the expansion machine, producing work. The generator and the motor are connected to the electrical grid system via frequency converters. This makes it possible to operate the electrical machines at a rotation speed which is asynchronous with respect to the grid system. A method and apparatus is disclosed that allows the net power output of the power station to be matched to the demands of the electrical grid system by varying the rotation speed of at least one of the shaft runs.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Method and apparatus for operation of a power station
ActiveUS7566992B2Valid matchEffective supervisionLevel controlSupport structure mountingFrequency changerPower station
A power station comprises a power-consuming shaft run on which a motor and a compressor are arranged, as well as a power-emitting shaft run on which a generator and an expansion machine are arranged. The compressor feeds a compressed fluid into a storage volume. The compressed storage fluid is expanded in the expansion machine, producing work. The generator and the motor are connected to the electrical grid system via frequency converters. This makes it possible to operate the electrical machines at a rotation speed which is asynchronous with respect to the grid system. A method and apparatus is disclosed that allows the net power output of the power station to be matched to the demands of the electrical grid system by varying the rotation speed of at least one of the shaft runs.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Turbine starter-generator
The invention consists of a ring motor, in which a first ring forms a toroidally wound stator and a second ring forms the rotor. A turbine is fixed to the rotor ring. The invention is specifically targeted towards the environment inside a gas turbine, in which hot gases may permeate the space between rotor and stator.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
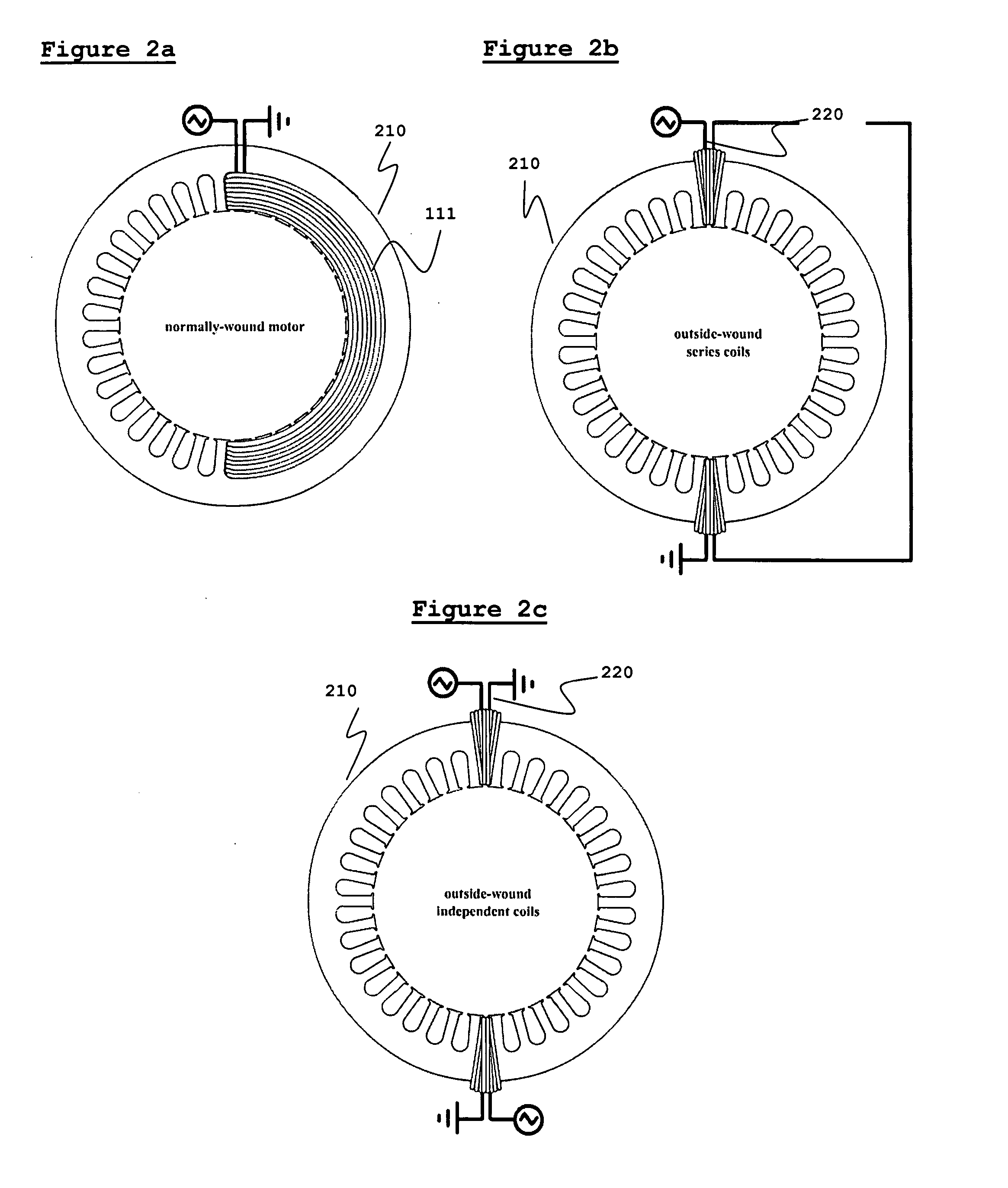
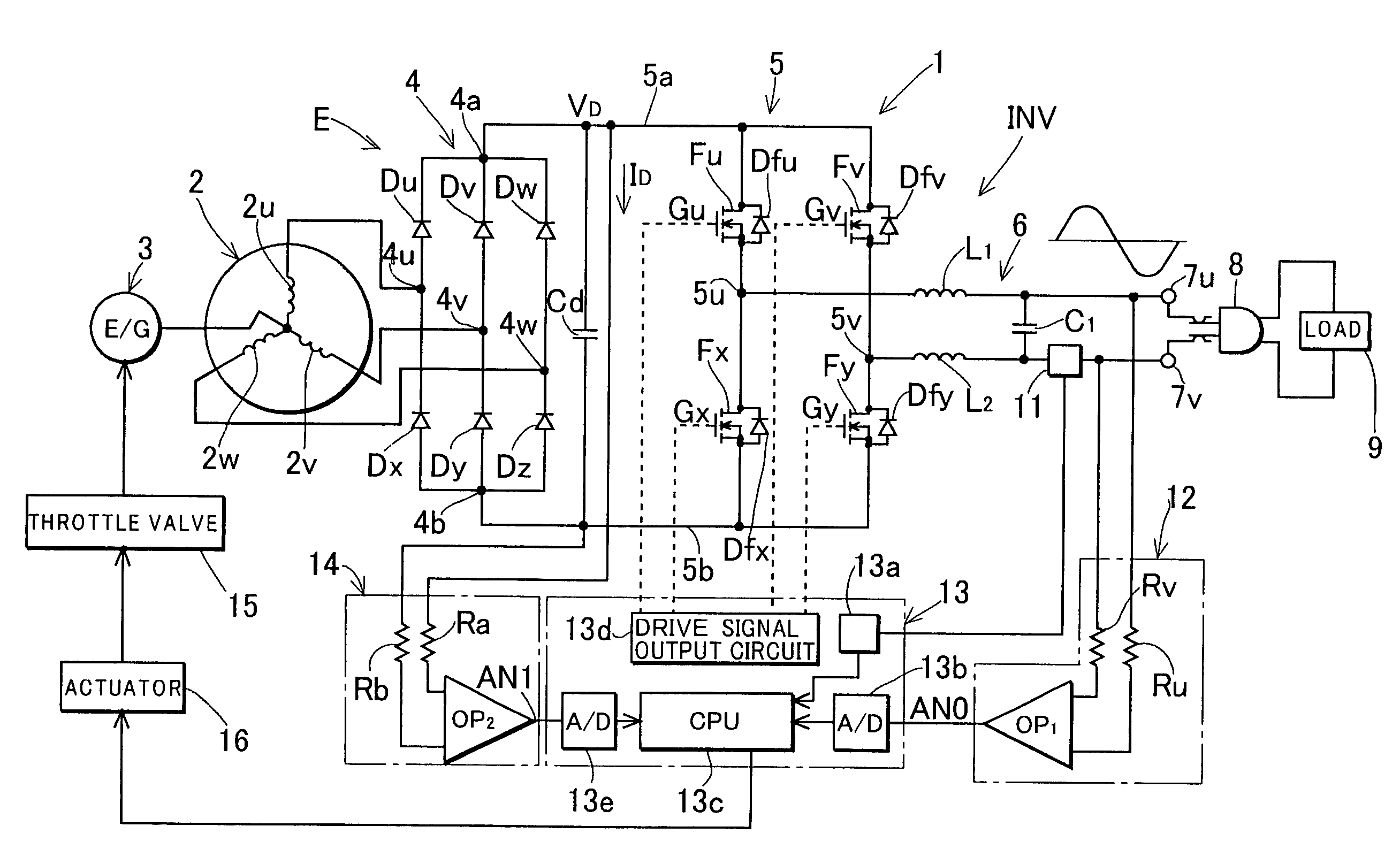
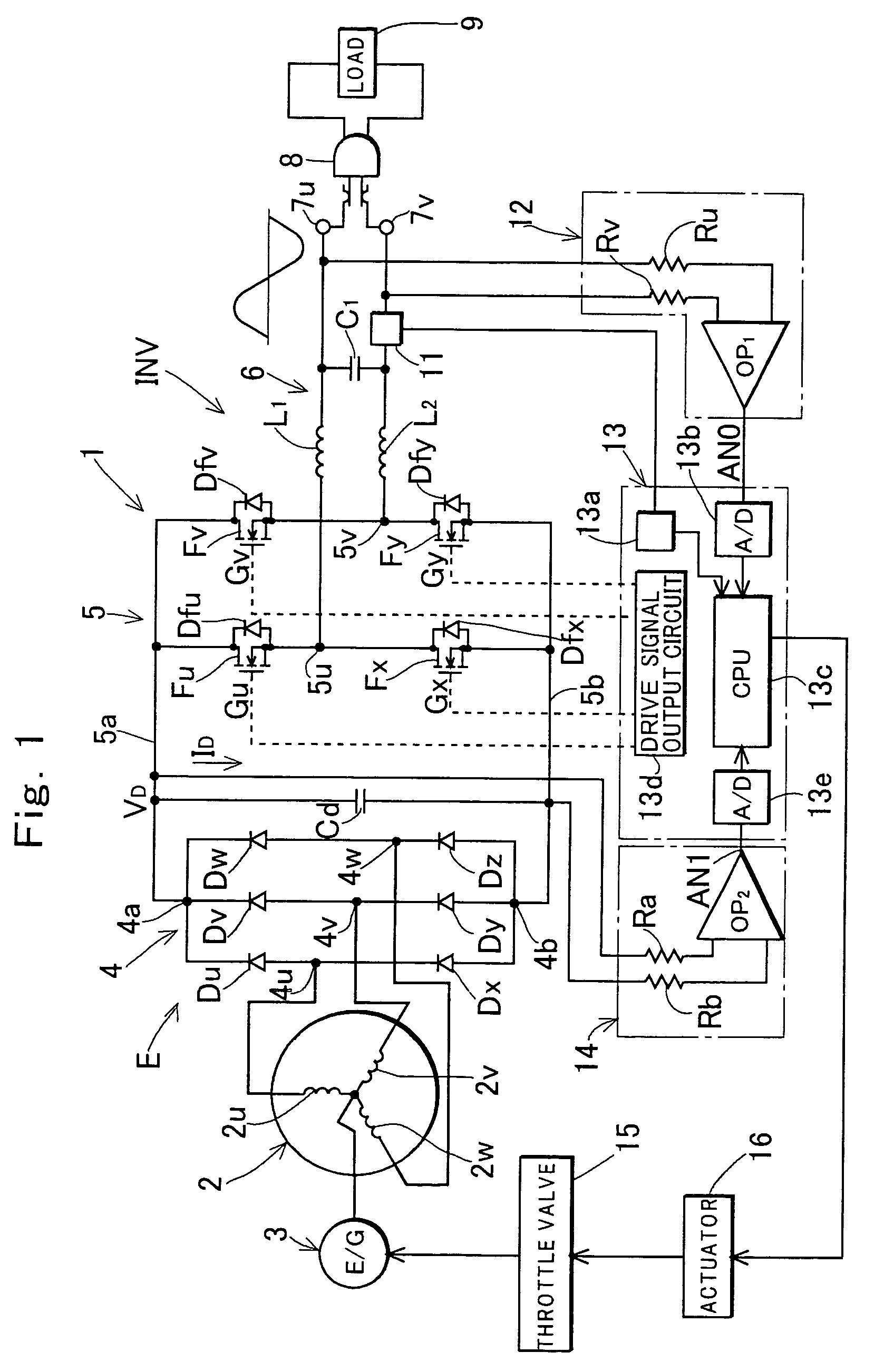
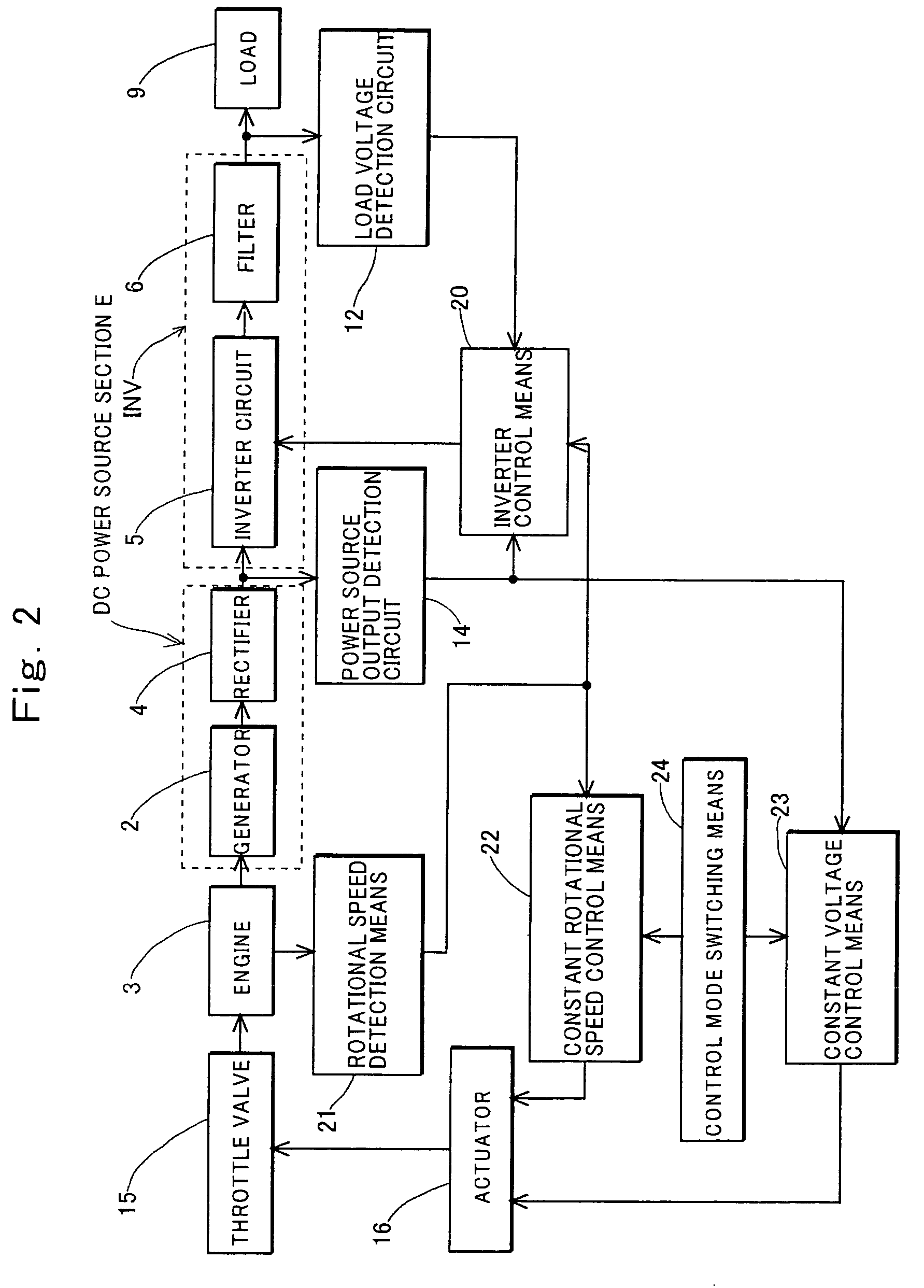
Inverter controlled generator set and method for controlling the same
InactiveUS7157885B2Drive stabilityIncrease rotation speedMotor/generator/converter stoppersBatteries circuit arrangementsFrequency changerMode control
A method for controlling an inverter controlled generator set which comprises a DC power source section having as a power source a generator driven by an engine and an inverter which converts an output of said DC power source section into an AC output, the method comprising a step of controlling a rotational speed of the engine so that the AC output suitable for driving a load is output from the inverter; wherein, after the engine is started, the rotational speed of the engine is controlled by a constant speed control mode for maintaining the rotational speed of the engine at a set rotational speed, and the rotational speed of the engine is increased to the set rotational speed; and wherein an operation of the inverter is started after the rotational speed of the engine reaches the set rotational speed.
Owner:KOKUSAN DENKI CO LTD
Output control device of generation device
InactiveUS7253590B2Easy to controlAccurately determineEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlPhase currentsConductor Coil
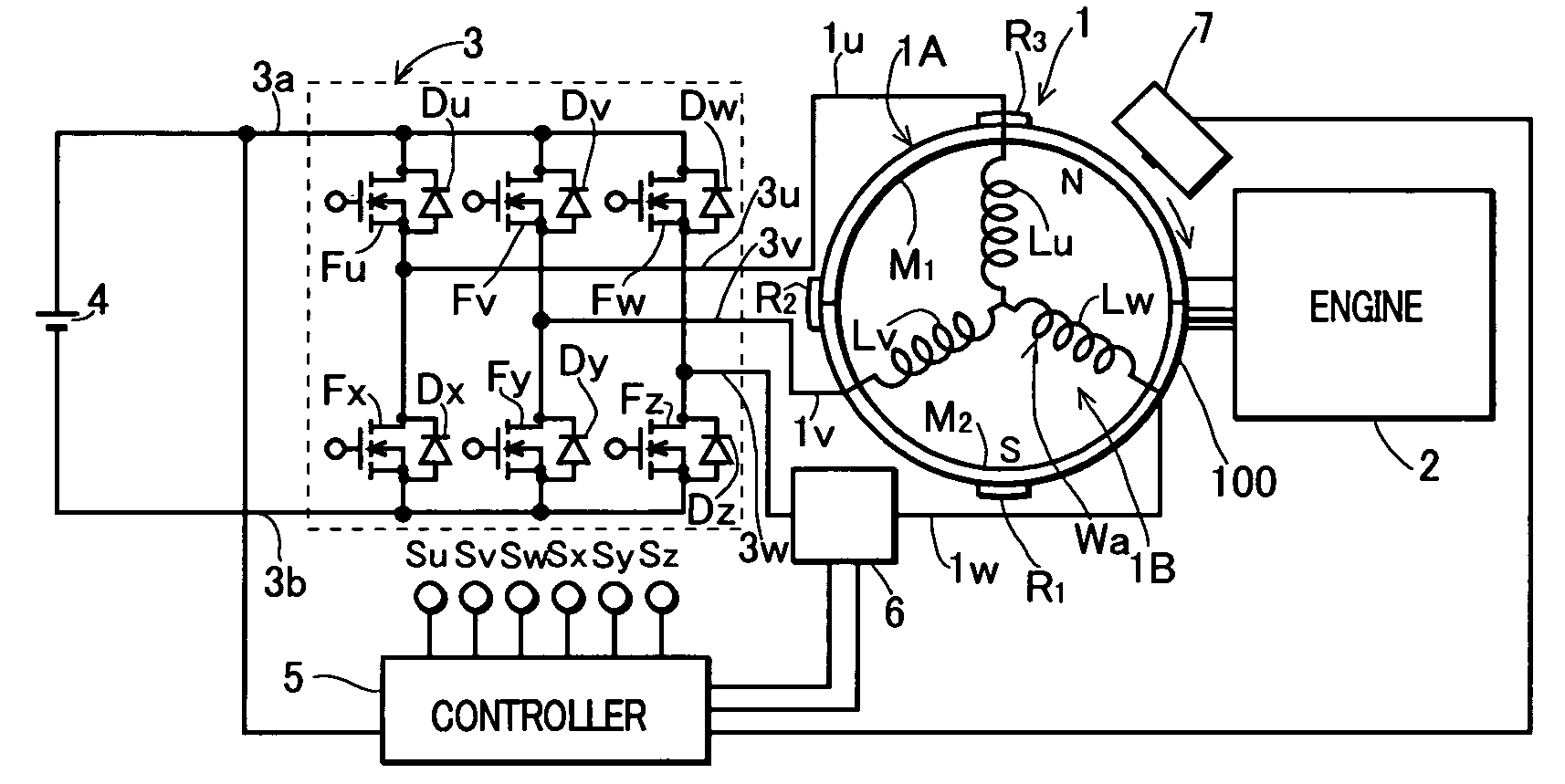
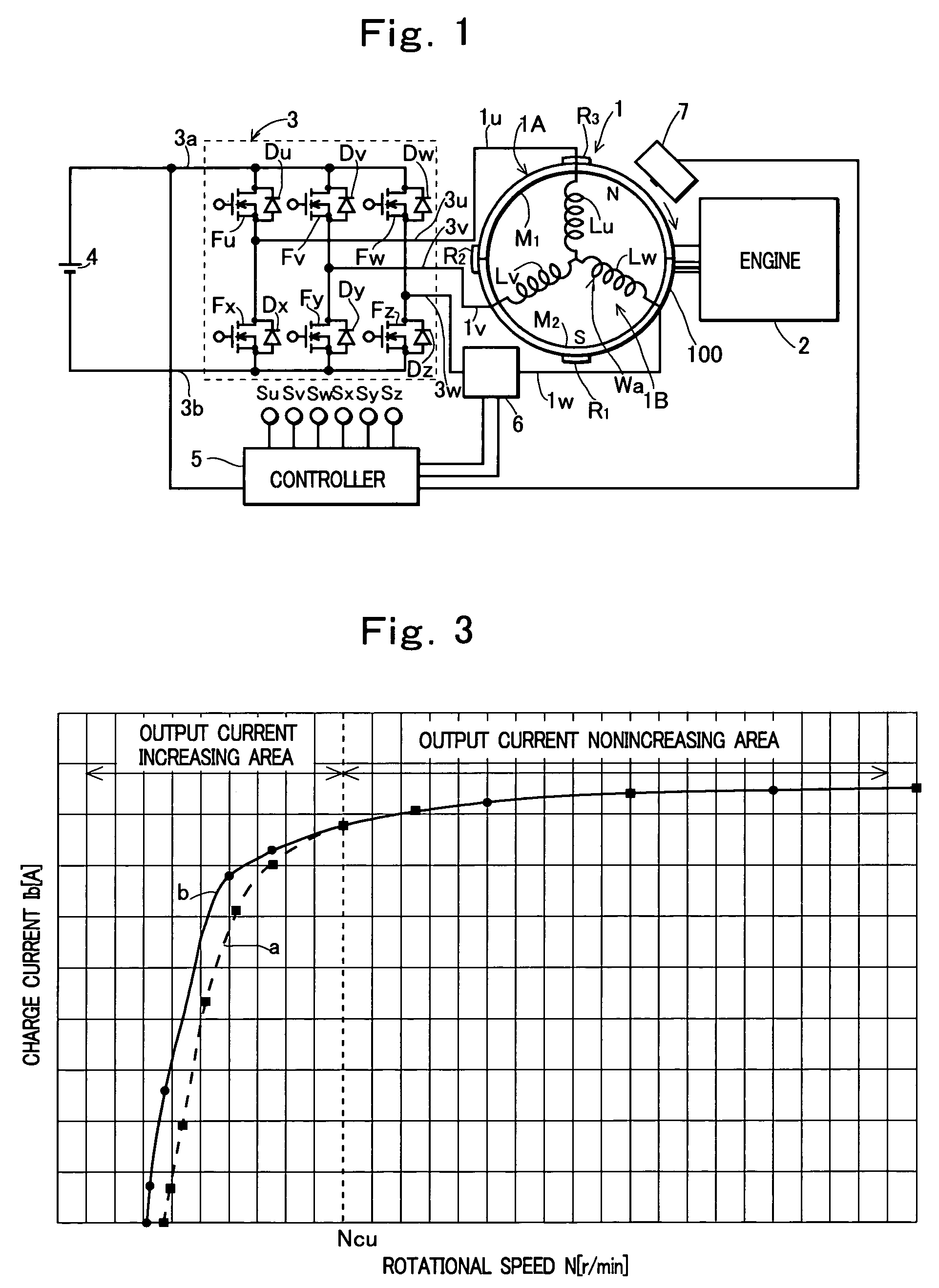
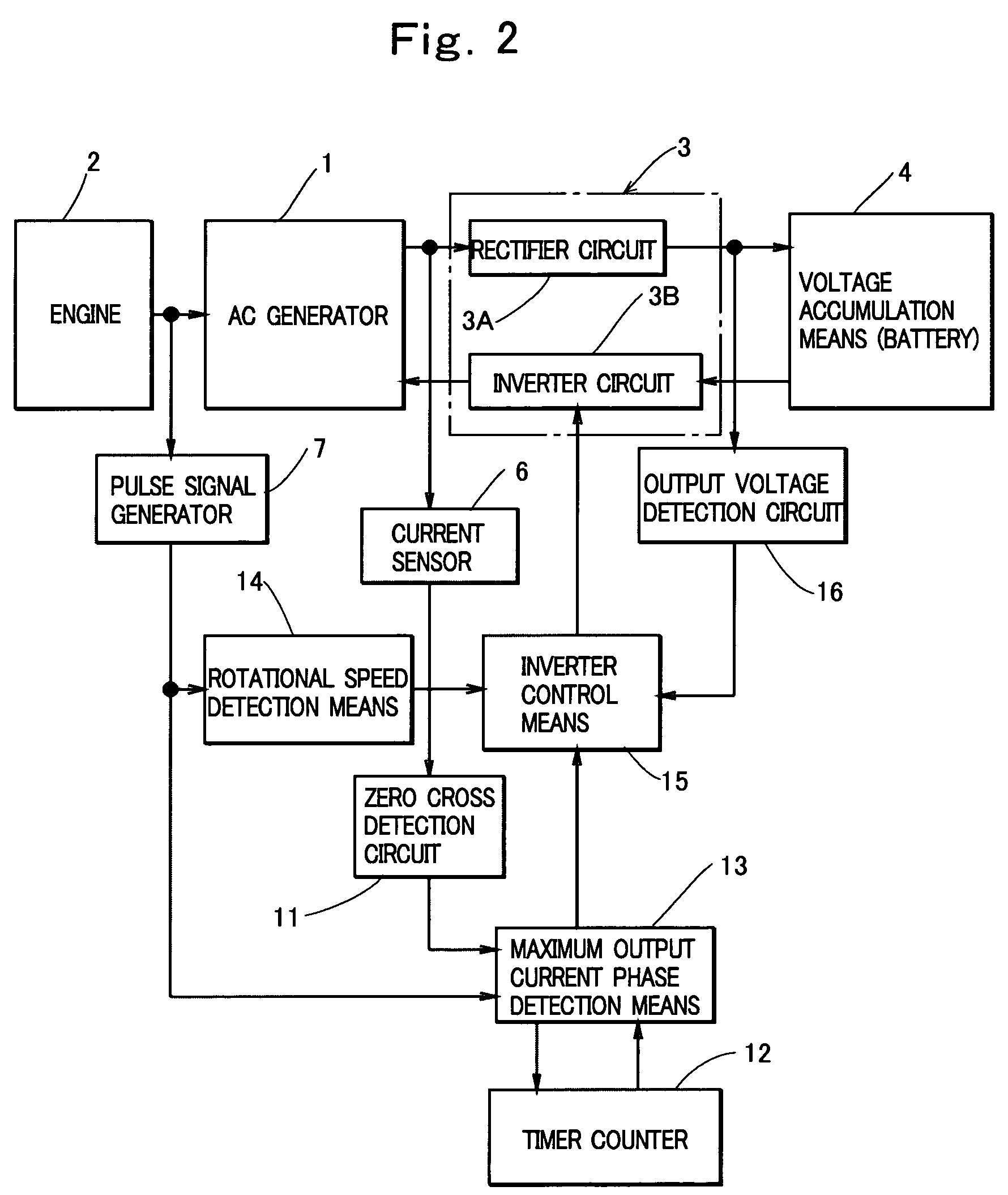
An output control device of a generation device including: a rectifier circuit that rectifies an output of an AC generator and applies the output across a battery; an inverter circuit provided between the battery and the generator; inverter control means for controlling the inverter circuit to convert a voltage across the battery into an AC control voltage and apply the voltage to an armature winding of the generator; and phase detection means for detecting a phase of a phase current flowing through the armature winding of the generator as a maximum output current phase, wherein the inverter control means is comprised to control a phase of the AC control voltage so as not to be delayed with respect to the maximum output current phase, and thus prevent a reduction in the output of the generator caused by an excessive delay of the phase of the AC control voltage.
Owner:KOKUSAN DENKI CO LTD
Controller for controlling actuator device installed on vehicle so as to maintain silence and comfort in vehicle
ActiveUS20050218856A1Improves silence and comfortNoise minimizationAnalogue computers for vehiclesAC motor controlIn vehicleMotor control
A controller for controlling an actuator device which is installed on a vehicle and operated by a motor. The controller includes: a motor control portion operable to control the motor on the basis of a target value; and a target-value determining portion operable to determine the target value on the basis of a wave intensity characteristic. The wave intensity characteristic is represented by a relationship between (A) a propagated wave intensity indicative of an intensity of a wave which is generated as a result of activation of the actuator device and which is propagated to occupant of the vehicle, and (B) an output index indicative of an amount of an output of the motor. Also disclosed is a wave-intensity-characteristic obtainer for obtaining the wave intensity characteristic by measuring the intensity of the wave.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Gas turbine engine starter generator that selectively changes the number of rotor poles
InactiveUS6995478B2Improve wear lifeLow costSynchronous generatorsGas turbine plantsStarter generatorGas turbines
A rotating electrical machine, such as an aircraft starter-generator, that may be operated in either a motor mode or an generator mode. The machine includes a main rotor that is selectively configurable as an M-pole rotor or an N-pole rotor. The machine can also include DC brushes that are selectively moveable into, and out of, electrical contact the main rotor, to thereby electrically couple and decouple a DC power source to and from, respectively, the rotor windings.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and apparatus for regulating excitation of an alternator
ActiveCN102150357APropulsion using engine-driven generatorsGenerator control of frequency and voltageElectricityAlternator
Owner:KOHLER CO
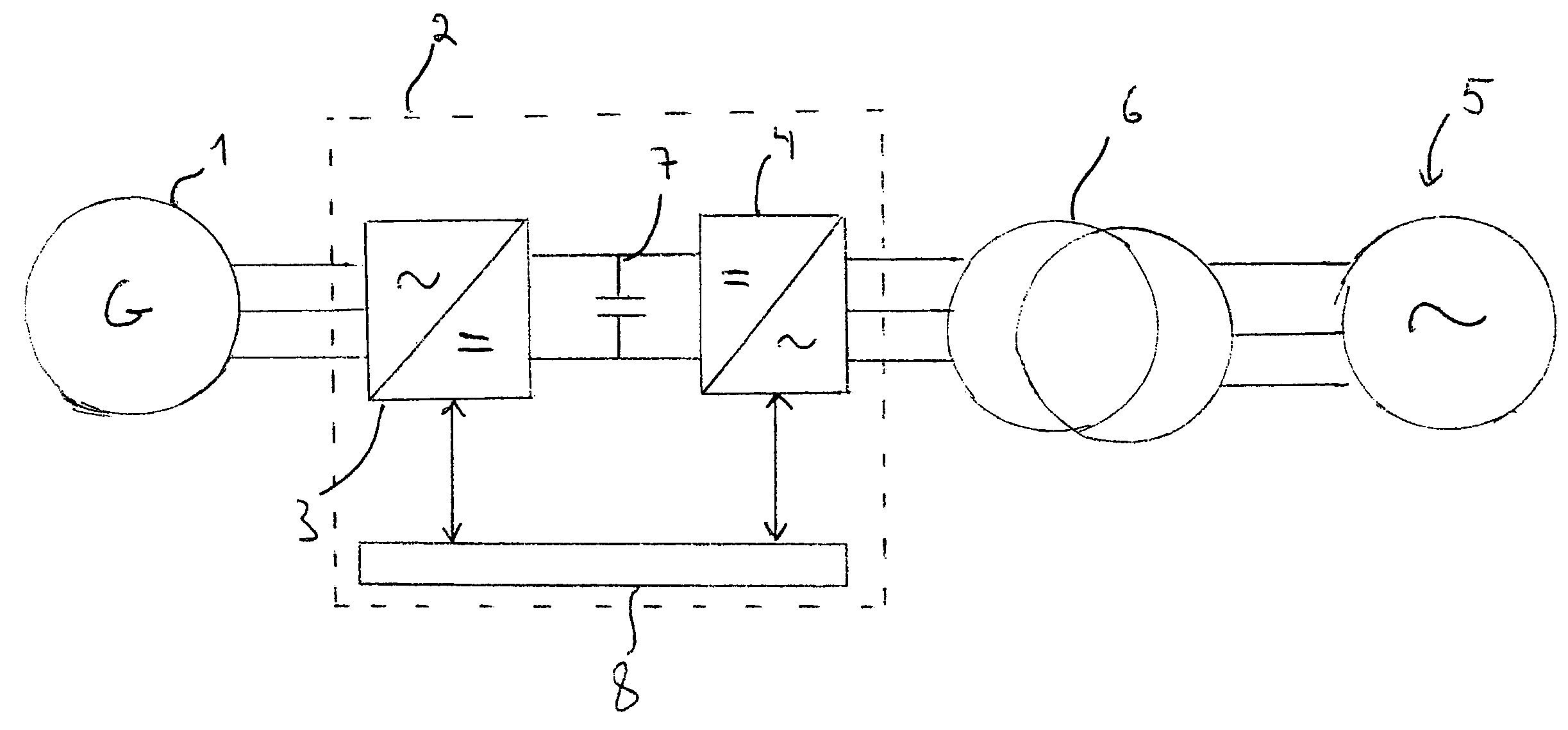
Method in frequency converter provided with voltage intermediate circuit, and frequency converter
ActiveUS7215099B2Reduce the amount requiredAC motor controlAc-dc conversionFrequency changerEngineering
A method in a frequency converter provided with a voltage intermediate circuit in connection with interference in a network (5) to be supplied and a frequency converter (2), which comprises a network converter part (4) and an inverter part (3) and a DC intermediate circuit (7) between them. The method comprises steps of controlling the intermediate circuit voltage at the beginning of network interference by limiting the torque on the inverter side, detecting interference in the network voltage, setting a torque reference to a predetermined value in response to the network interference, detecting network voltage recovery, and controlling the torque reference to a normal value in response to the network voltage recovery.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
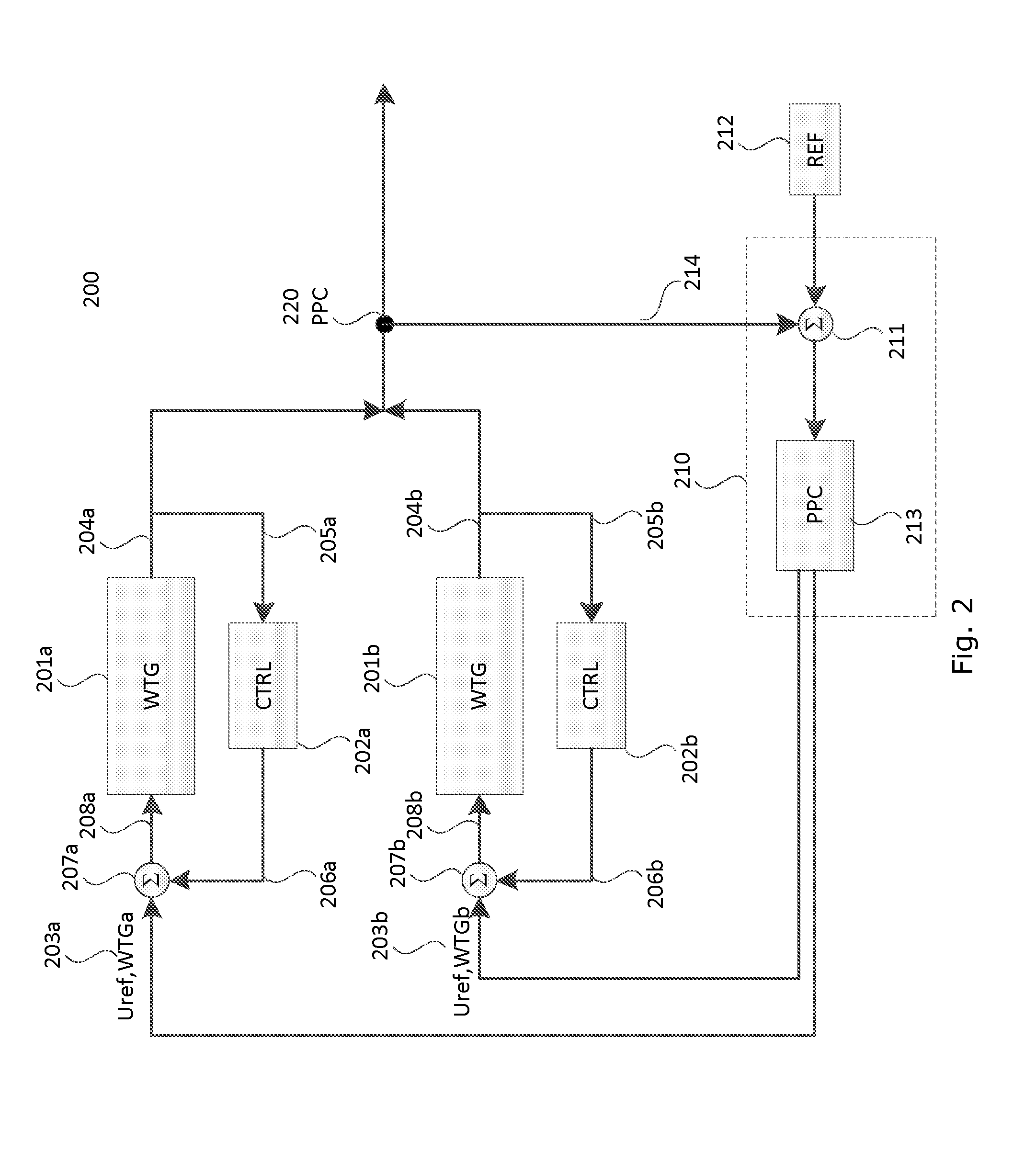
Multi bandwidth voltage controllers for a wind power plant
The present invention relates to a wind power plant, with at least one wind turbine generator, where each of the at least one wind turbine generator has a first voltage controller with a first bandwidth, arranged for controlling a voltage level, and where the wind power plant has a power plant controller with a second voltage controller with a second bandwidth also arranged for controlling the voltage level, the first bandwidth is larger than the second bandwidth. The invention also relates to a method for controlling the voltage level of a wind power plant, by using multi bandwidth voltage controllers.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Small wind power generation power controller
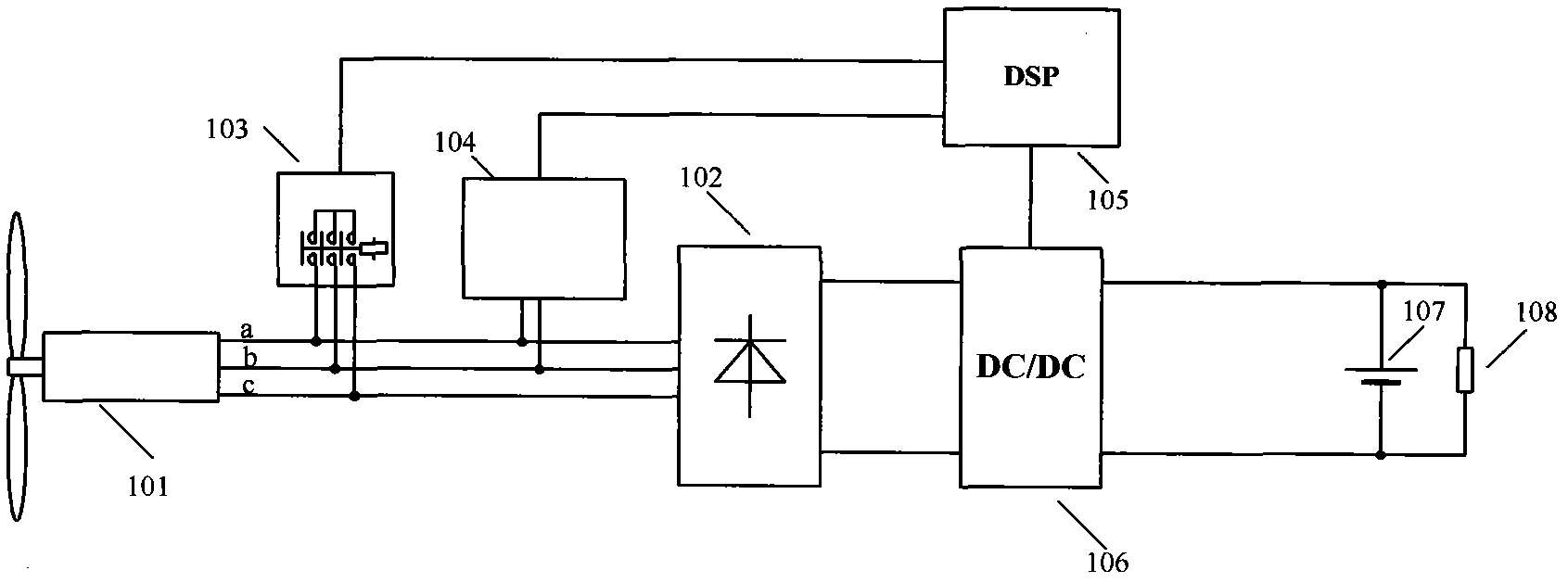
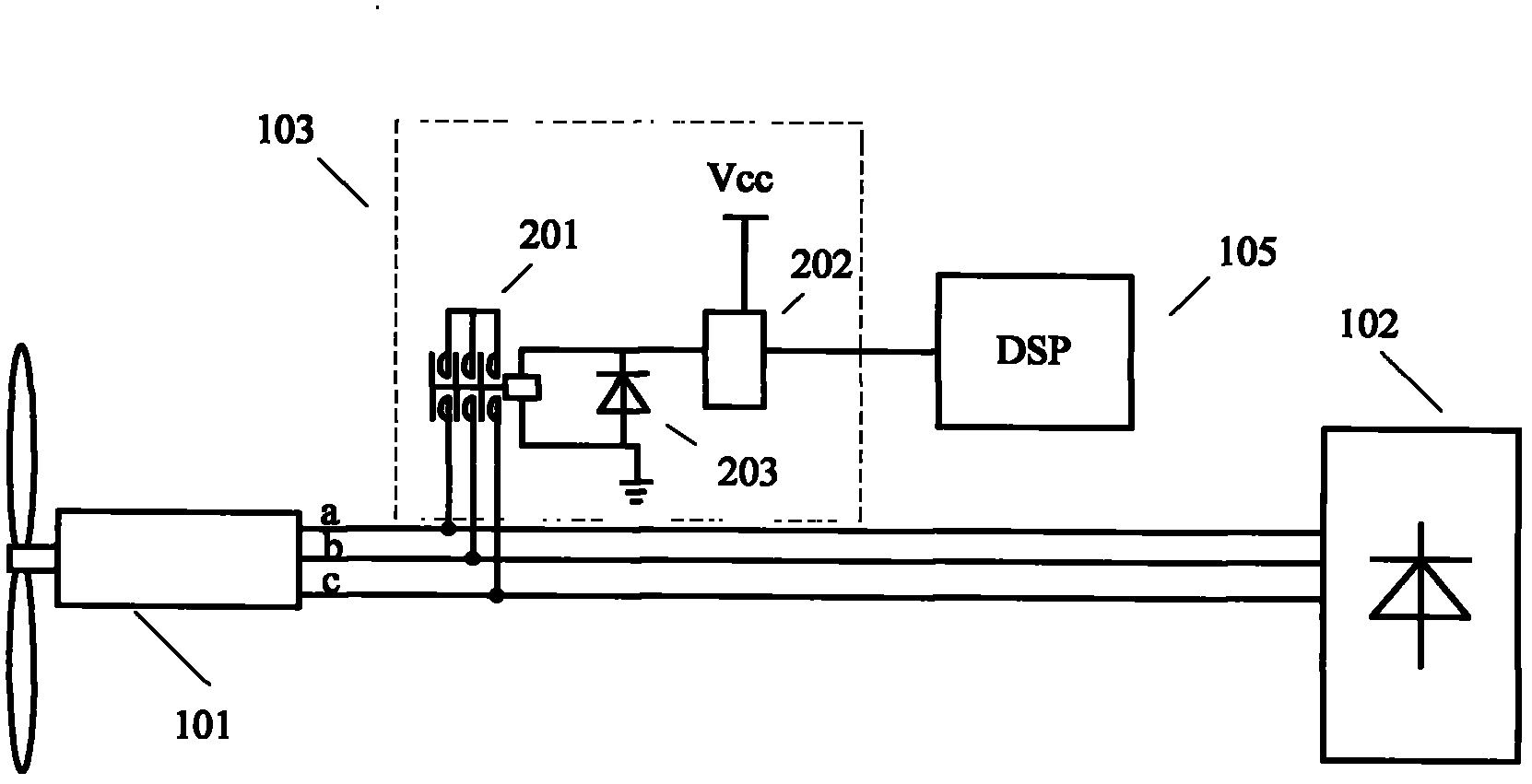
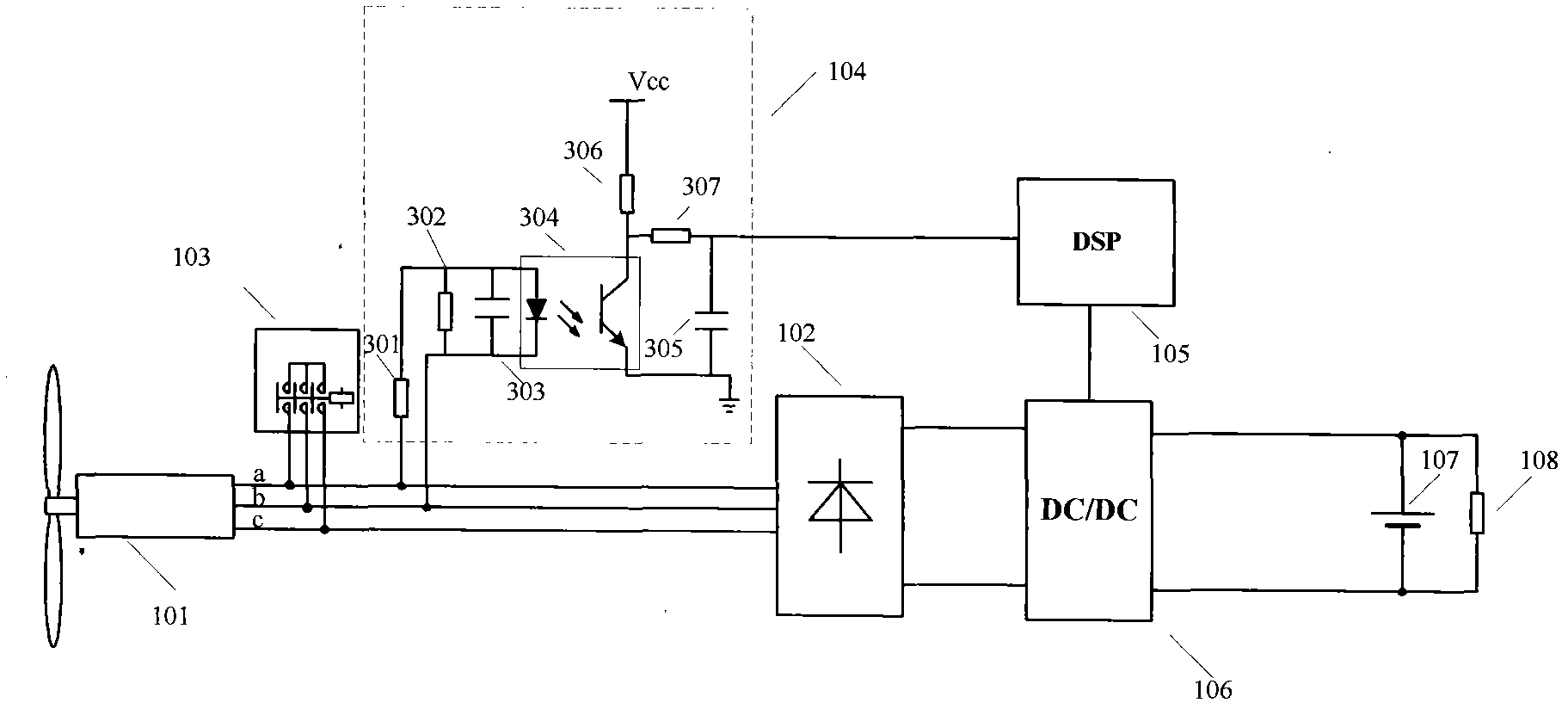
InactiveCN103166557ALow costImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsMachines/enginesCurrent loadPower controller
The invention discloses a controller of a small wind-driven generator, and belongs to the technical field of controllers of clean energy. A small wind power generation power controller comprises the wind-driven generator, a rectifying module, a boosting step-down direct current (DC) / direct current (DC) convertor, a rotating speed detection module, an all-digital controller, a storage battery and a direct-current load. The small wind power generation power controller achieves a speed detection function by detecting a line voltage frequency of the wind-driven generator, and is low in cost, high in reliability, and free from an extra speed sensor which is added to the wind-driven generator, thereby being capable of accurately conducting tracking and controlling of a maximum power spot. The small wind power generation power controller utilizes a target power curve to calculate the maximum power spot, and is high in accuracy, fast in response, free from generating oscillation, and beneficial to improvement of generating efficiency of a system.
Owner:RES INST OF BIT & ZHONGSHAN +1
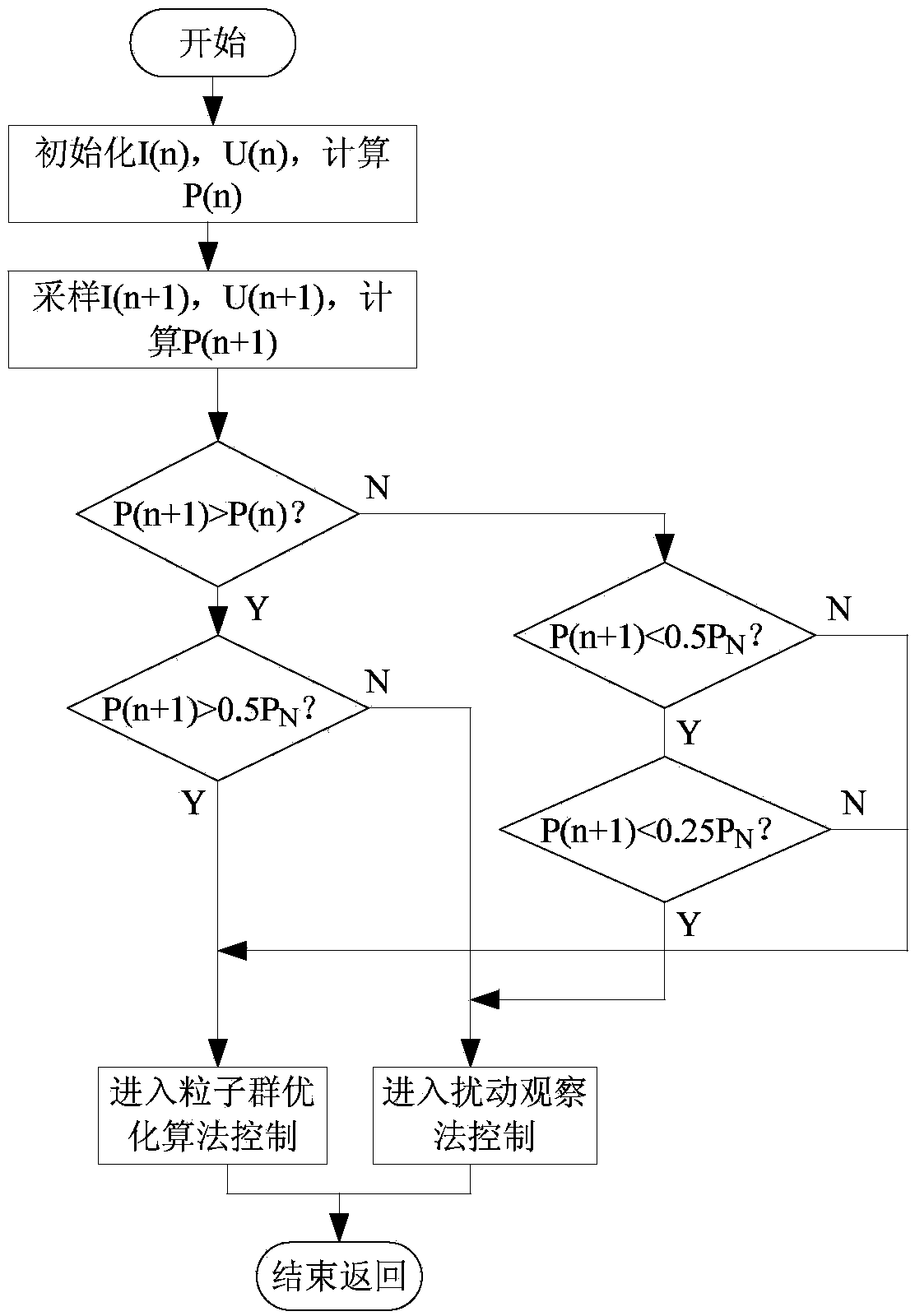
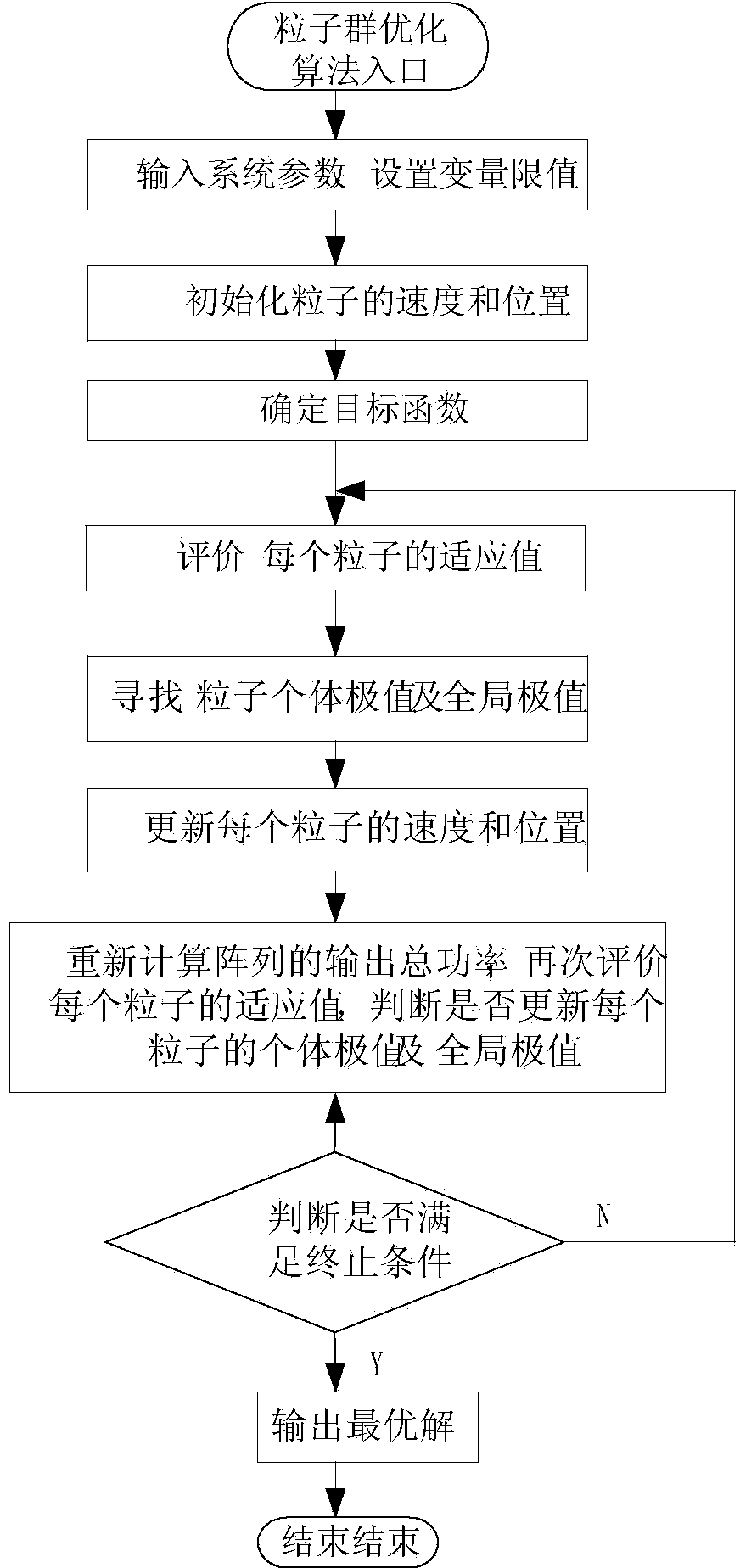
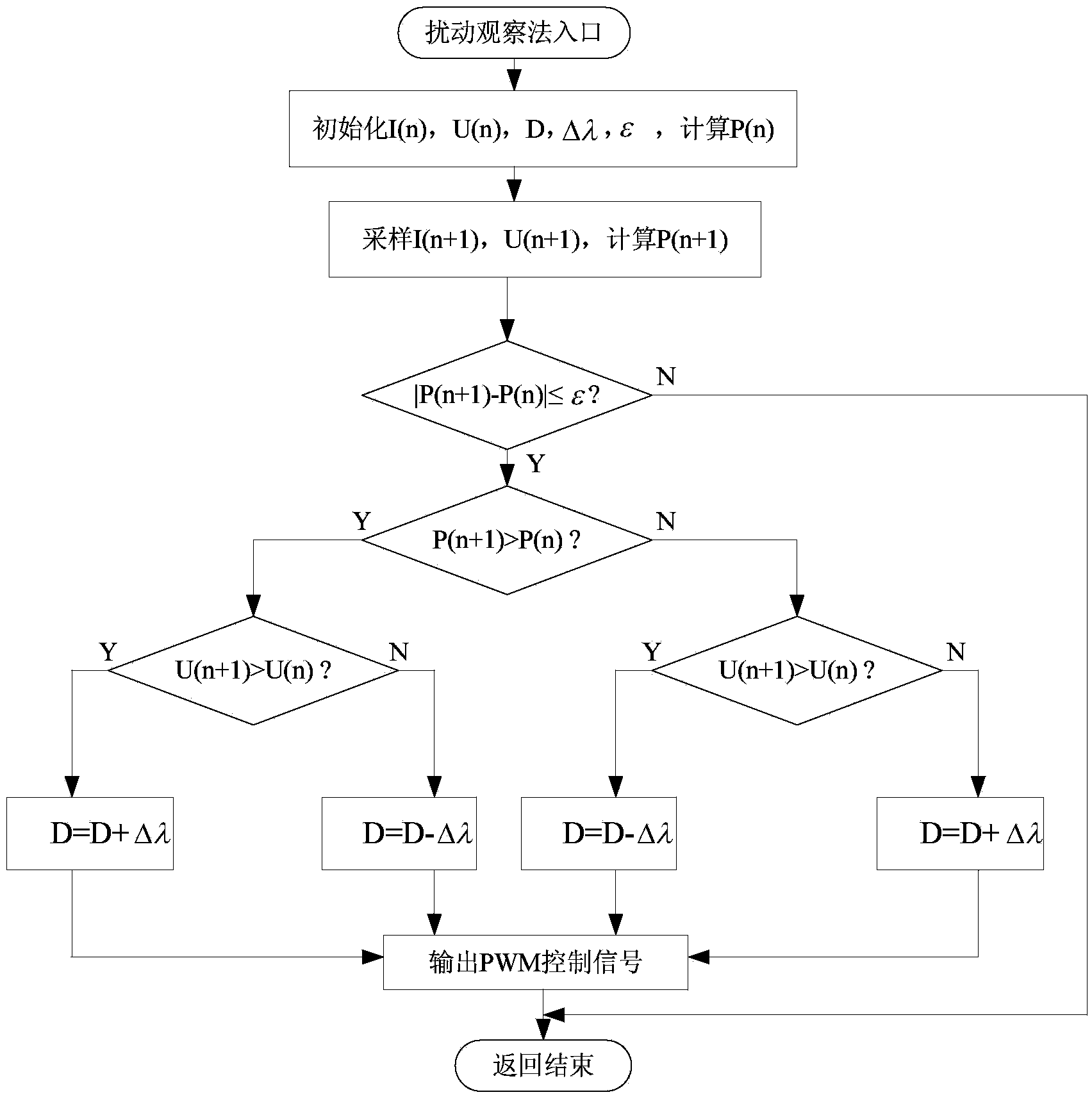
Maximum power point tracking method of wind power generation system under condition of variable wind speed
InactiveCN103414414AImprove tracking speedImprove output efficiencyGenerator control of frequency and voltageElectric variable regulationPower qualityAutomatic control
The invention discloses a maximum power point tracking method of a wind power generation system under the condition of a variable wind speed, and relates to the technical field of natural wind power generation automatic control. According to the method, when a draught fan is started or at the stage of a low wind speed, if output power of the draught fan is less than one half of rated power at the moment, a disturbance observation method is adopted; when the draught fan is at an operating stage and the wind speed becomes higher and rapidly changes, if the output power is higher than one half of the rated power and continues to rise at the moment, a particle swarm optimization algorithm is adopted; if the wind speed begins to reduce during operation, the output power of the draught fan is lower than one half of the rated power but still larger than a quarter of the rated power, the particle swarm optimization algorithm is still adopted until the output power is lower than a quarter of the rated power, and then the disturbance observation method is adopted. The method has the advantages that wind energy maximum power point tracking control can be well achieved, the tracking speed and the output power of the system are effectively improved, an output curve is relatively smooth, output vibration is reduced, and quality of electric energy is improved.
Owner:XUZHOU COLLEGE OF INDAL TECH
Method for the active damping of the drive train in a wind energy plant
InactiveUS7501798B2High componentsHigh trainWind motor controlEngine fuctionsControl theoryWind power
A method for the active damping of a drive train in wind energy plant, with the following steps: the actual value of the generator rotational speed is acquired and amplified via an oscillatory delay element, the oscillatory delay element has a predetermined natural oscillation frequency (ωE), which is smaller than the smallest natural frequency of the drive train, and a difference between the actual value of the rotational speed and the amplified value for the rotational speed is connected to a controller as actuating variable, which determines a correction moment for a generator control.
Owner:NORDEX ENERGY
Generation device
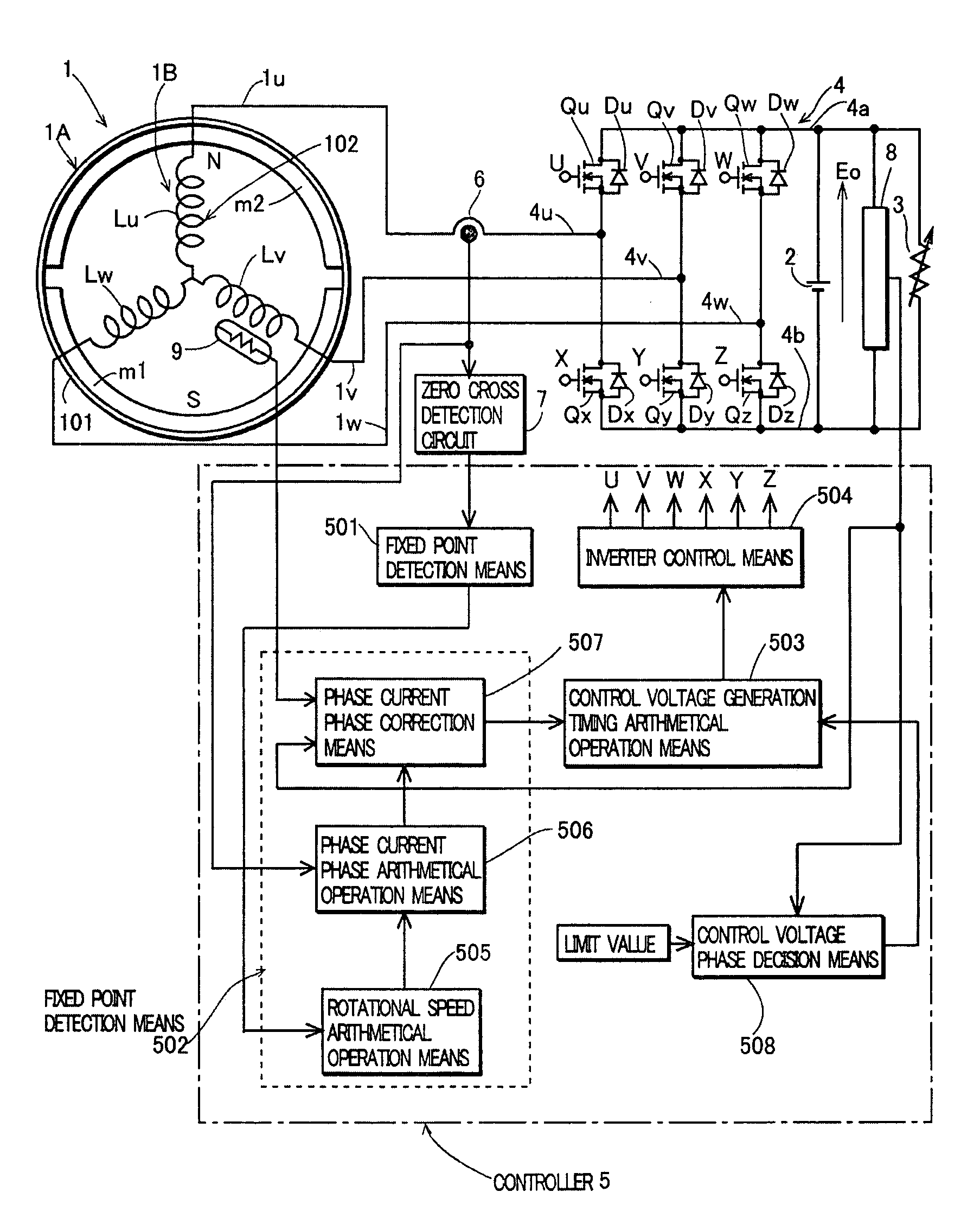
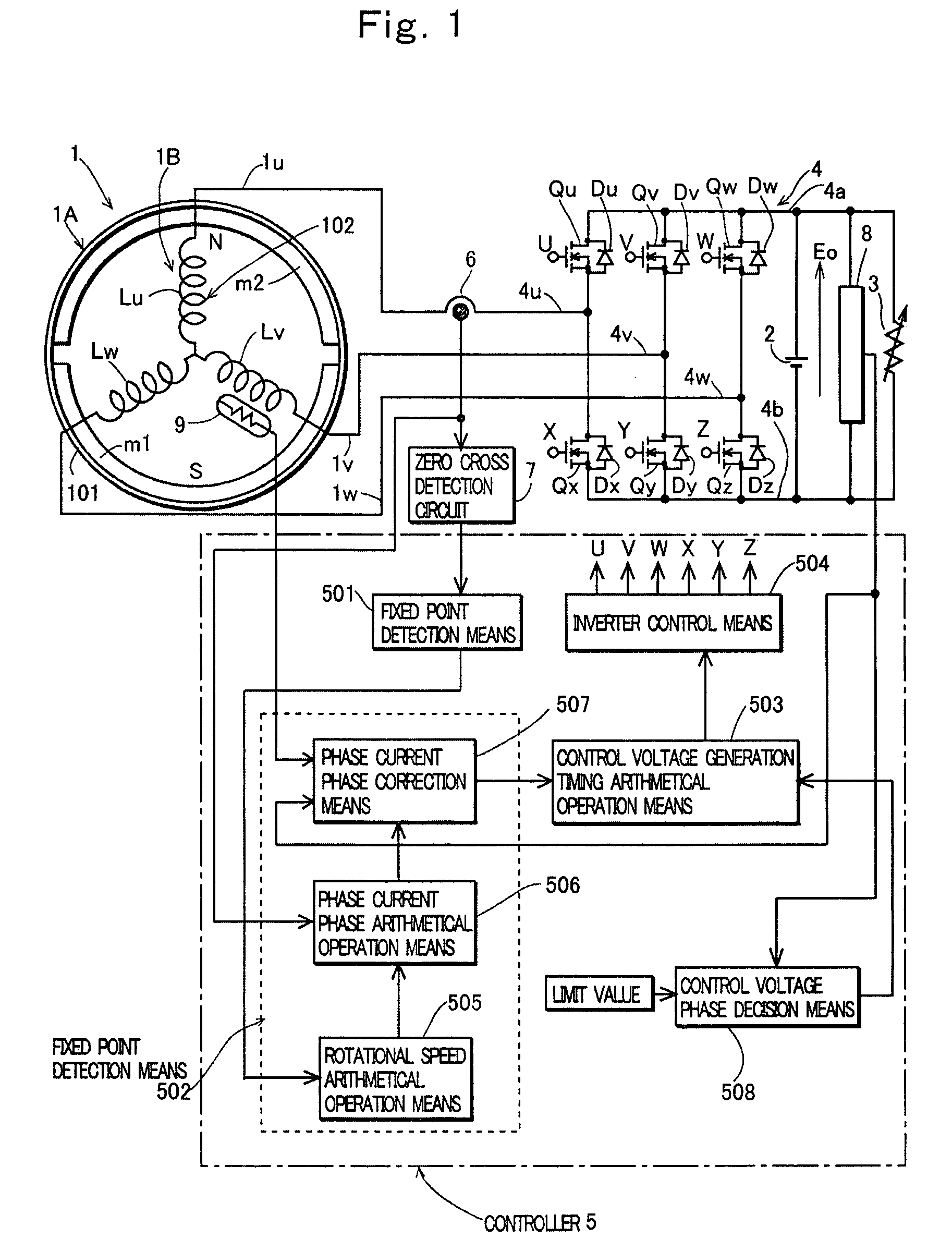
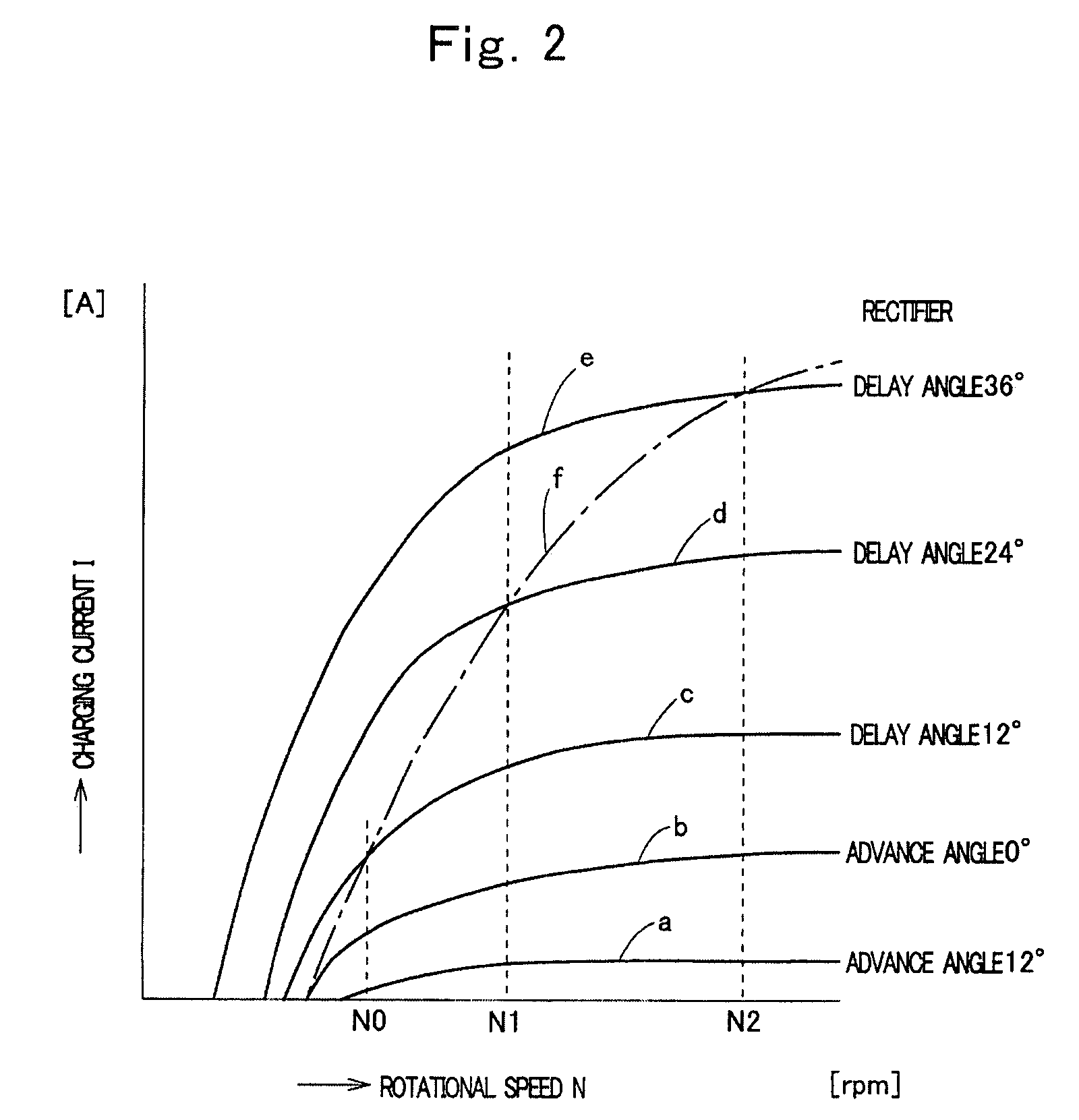
InactiveUS7683587B2Low costEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlPhase currentsBattery charge
A generation device, having a magneto generator, in which an AC control voltage is applied from a battery charged with a rectified output of the magneto generator to an armature winding of the generator through an inverter to control a battery voltage to a limit value or less, comprising: fixed point detection means for detecting a fixed point on a waveform of a phase current of the generator; phase current phase detection means for detecting a phase angle of the fixed point in relation to a reference phase; arithmetical operation means for arithmetically operating timing for generating the AC control voltage with reference to the phase of the fixed point; and inverter control means for controlling switch elements of the inverter so as to generate the AC control voltage at the timing arithmetically operated by the arithmetical operation means.
Owner:KOKUSAN DENKI CO LTD
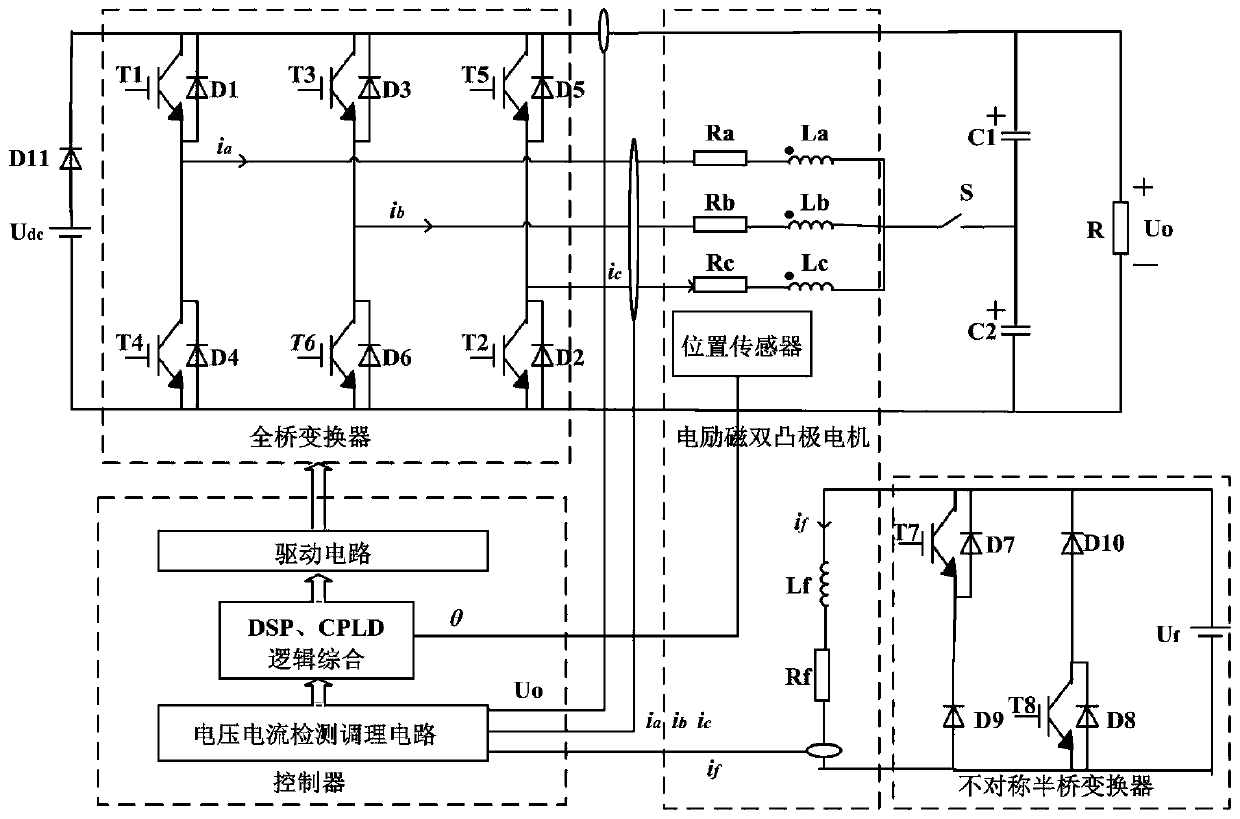
Electric excitation double-salient pole motor loss-of-magnetic fault fault-tolerant power generation system and control method thereof
ActiveCN110247597AReduce in quantityLow costGenerator control of frequency and voltageCapacitanceFull bridge
The invention discloses an electric excitation double-salient pole motor loss-of-magnetic fault fault-tolerant power generation system and a control method thereof. The system is characterized in that two capacitors are introduced based on an original three-phase full-bridge topology to form a split capacitor type topology, moreover, the two capacitors further act as storage capacitors, before an excitation fault occurs, the power is generated in a traditional uncontrolled rectifier power generation mode through the three-phase full-bridge topology, after the excitation fault occurs, switching to a fault-tolerant power generation mode is performed to achieve fault-tolerant power generation through the split capacitor type topology. The system is advantaged in that the system realizes fault-tolerant power generation after the loss-of-magnetic fault of the electric excitation double-salient pole motor, improves the fault-tolerant capability of the system and is suitable for aerospace and other fields with high reliability requirements.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
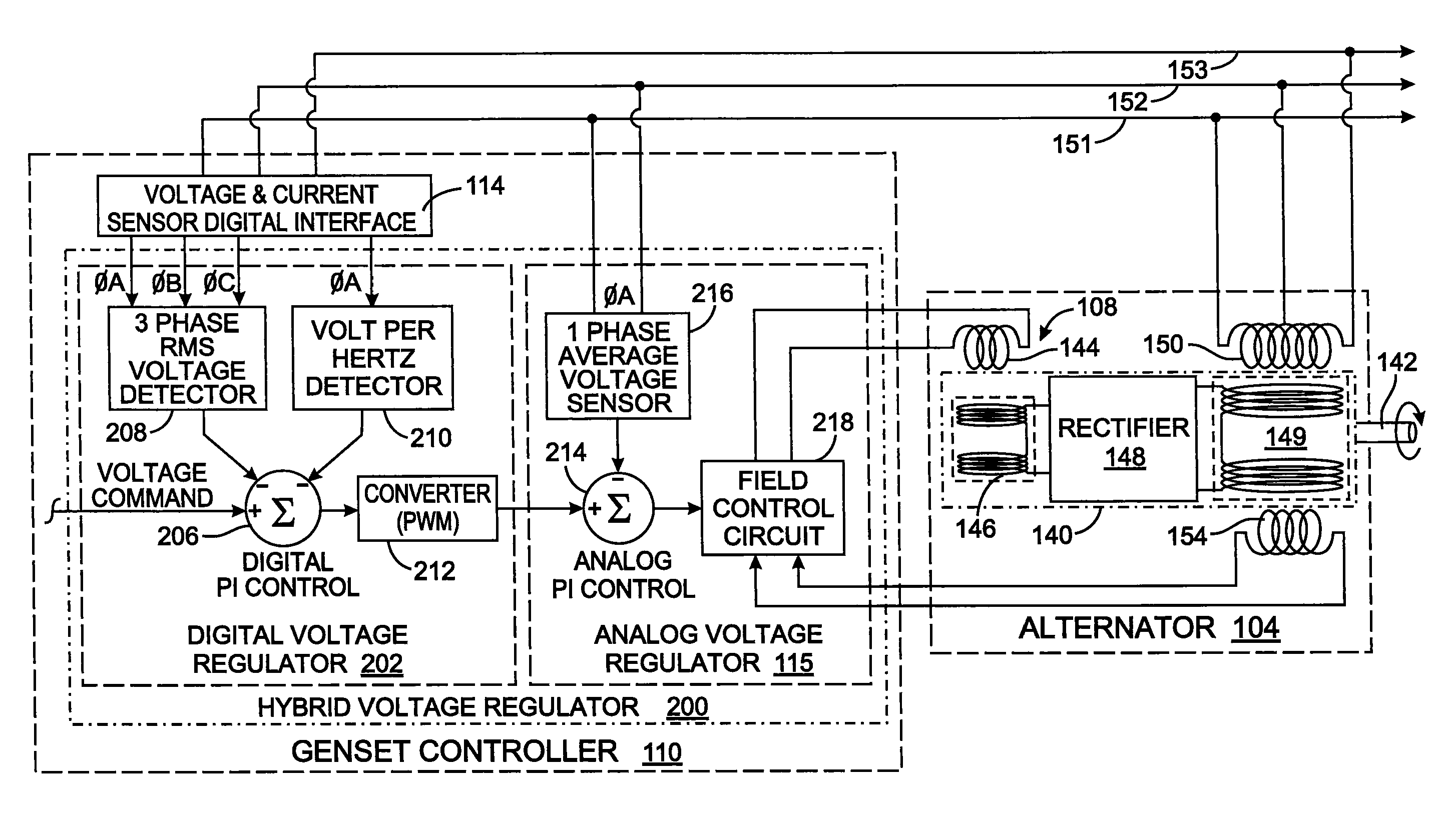
Method and apparatus for regulating excitation of an alternator
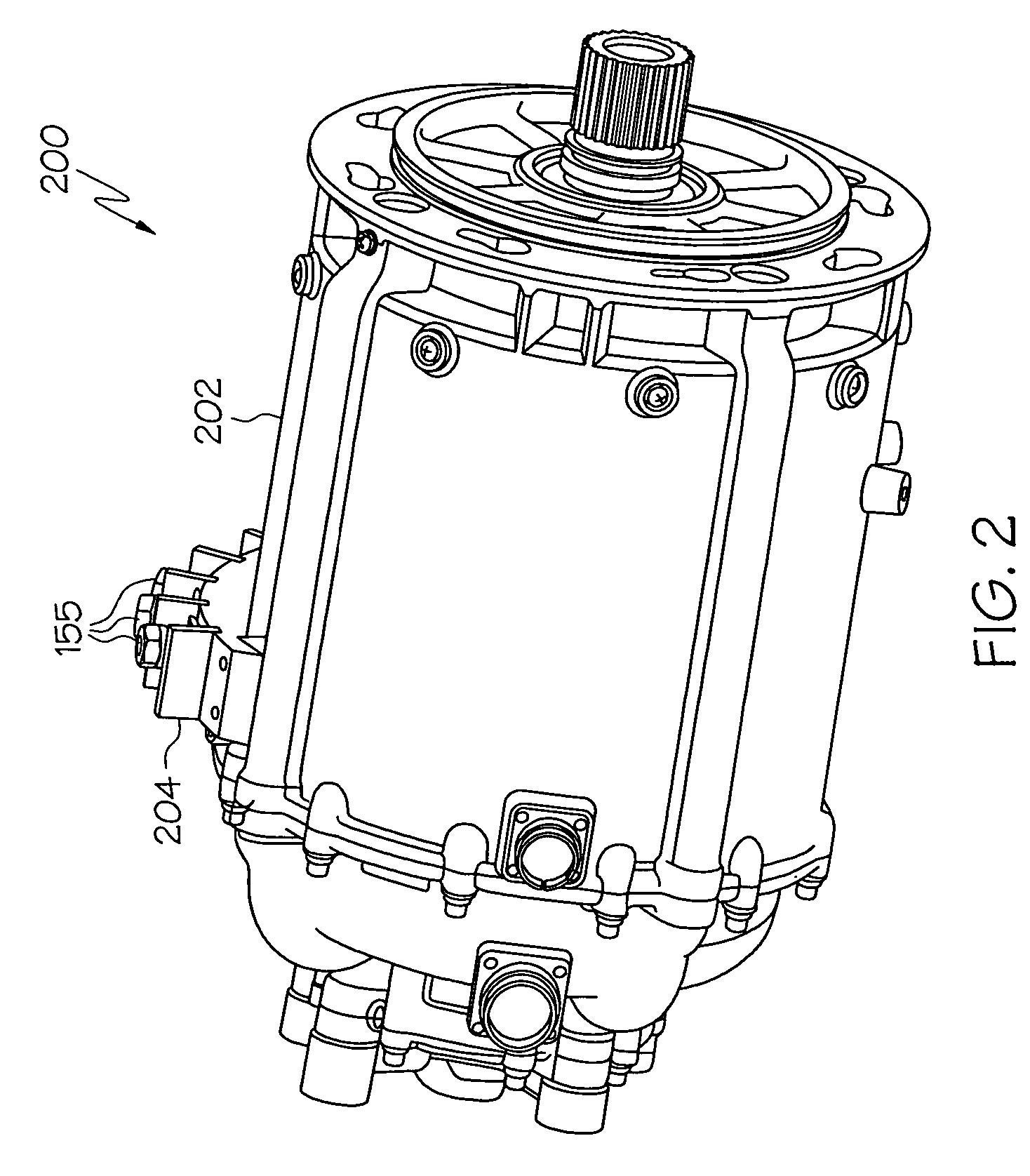
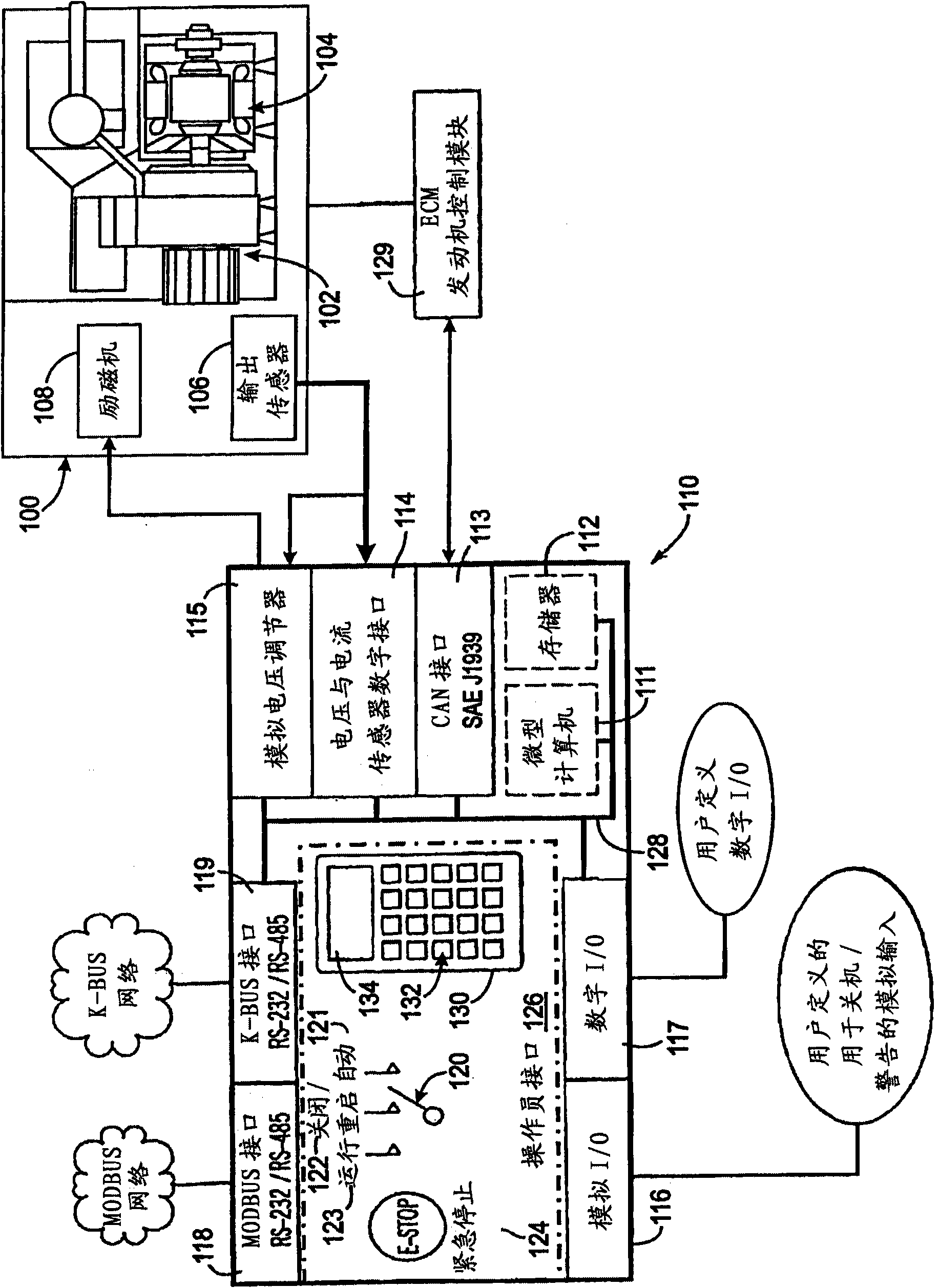
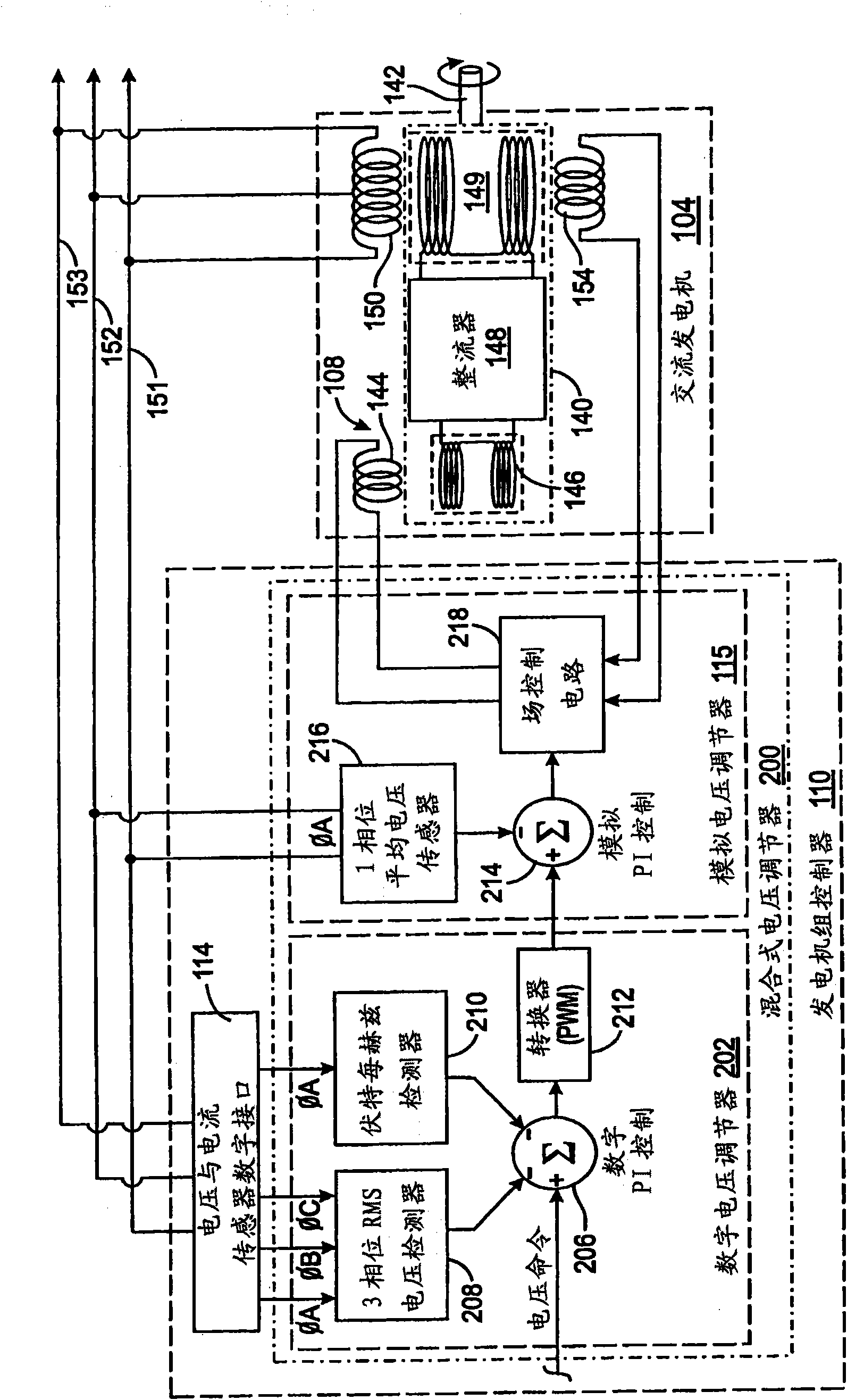
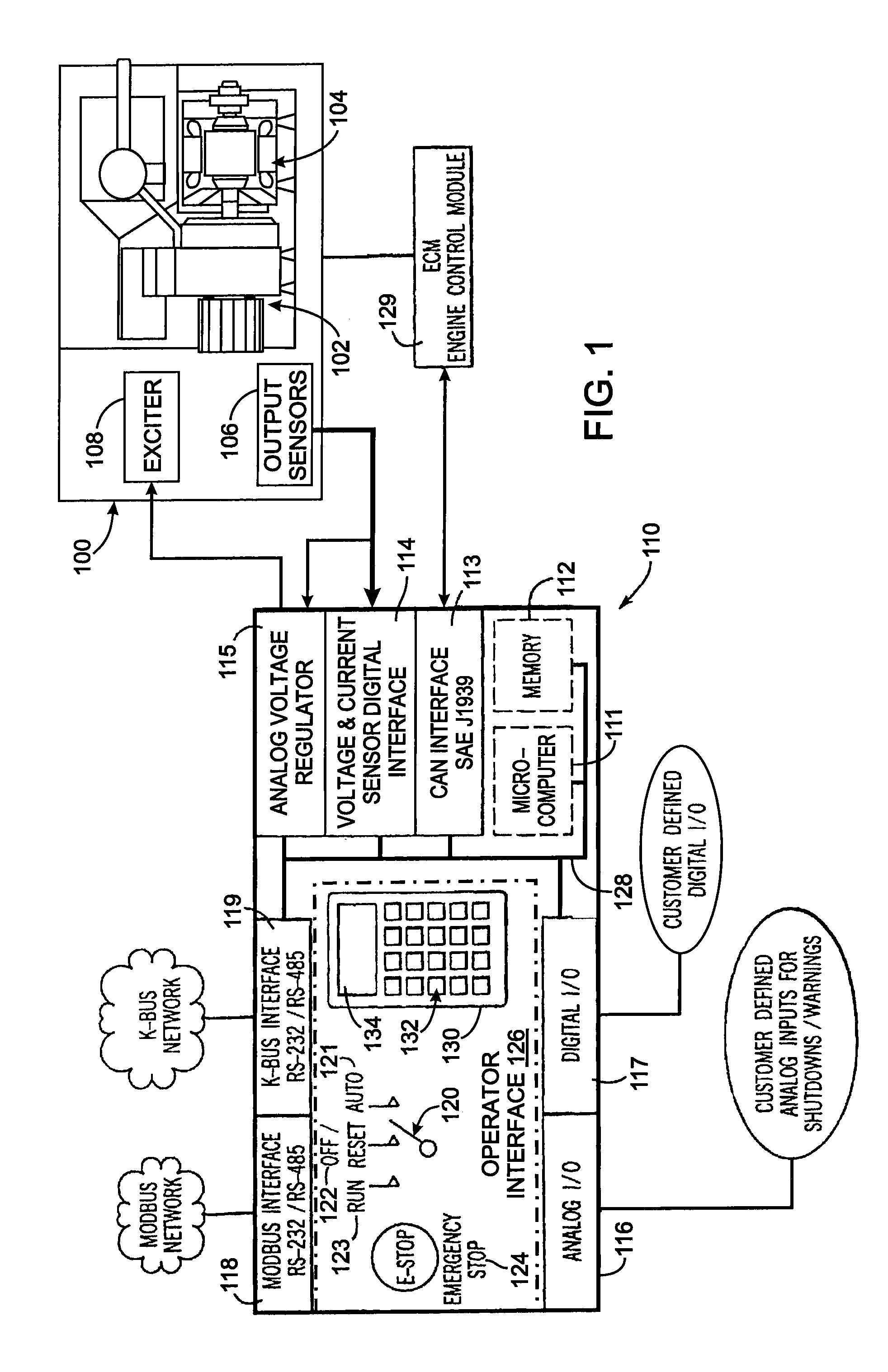
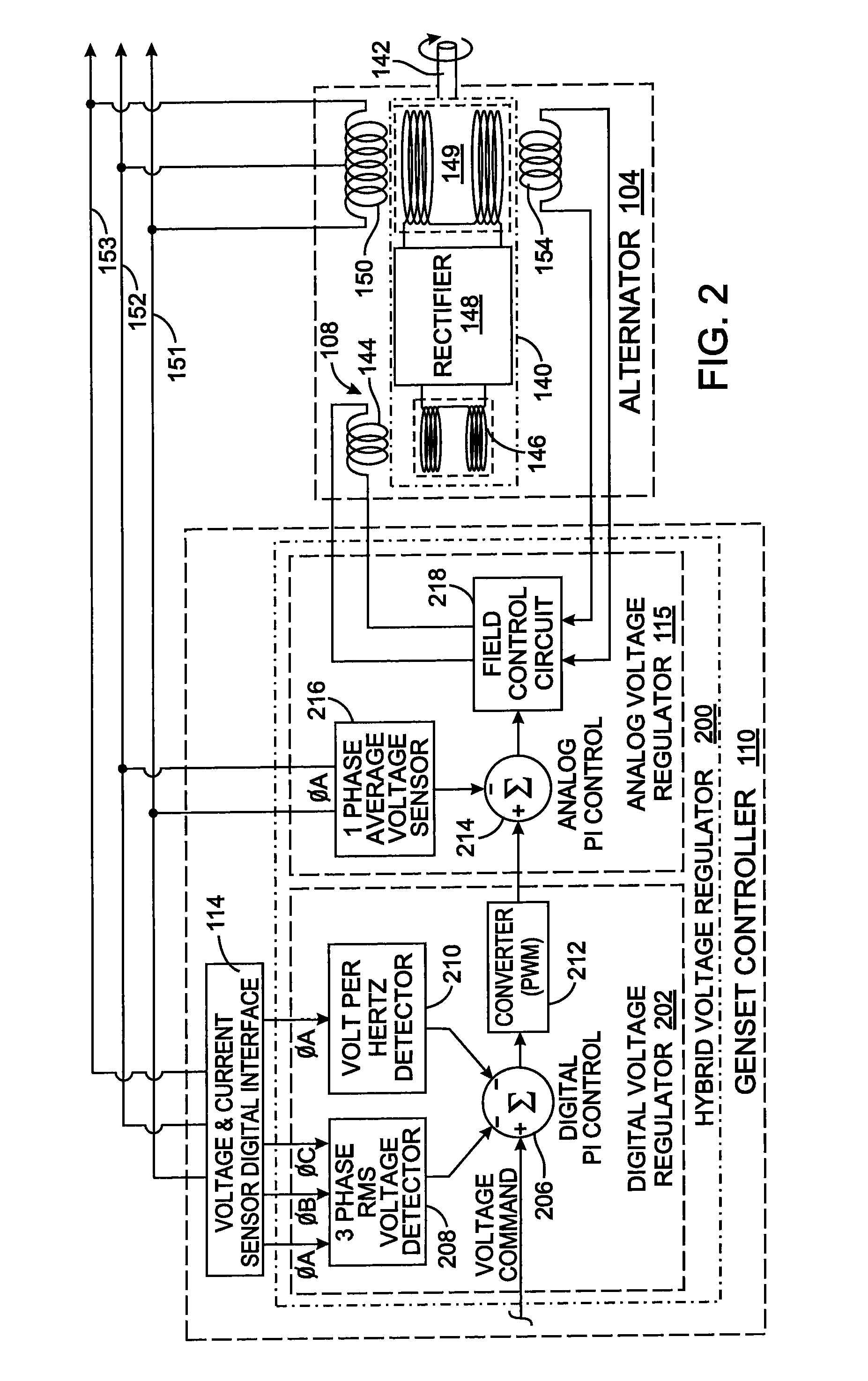
ActiveUS20090218991A1Rapid responseEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsElectricityAlternator
A hybrid voltage regulator controls the voltage of three phases of alternating electricity produced by an alternator. A digital voltage regulator produces an average of the RMS voltage for each phase and produces an error value based on a ratio of the voltage to the frequency of the alternating electricity. The RMS voltage average and the error value are used to modify a voltage command designating a desired voltage level. The modified voltage command is processed by an analog voltage regulator that rectifies the alternator output voltage which then is averaged over an period of time. The resultant average voltage value is utilized to modify the voltage command to produce a regulated voltage command that determines a level of current to apply to excite the alternator.
Owner:KOHLER CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com