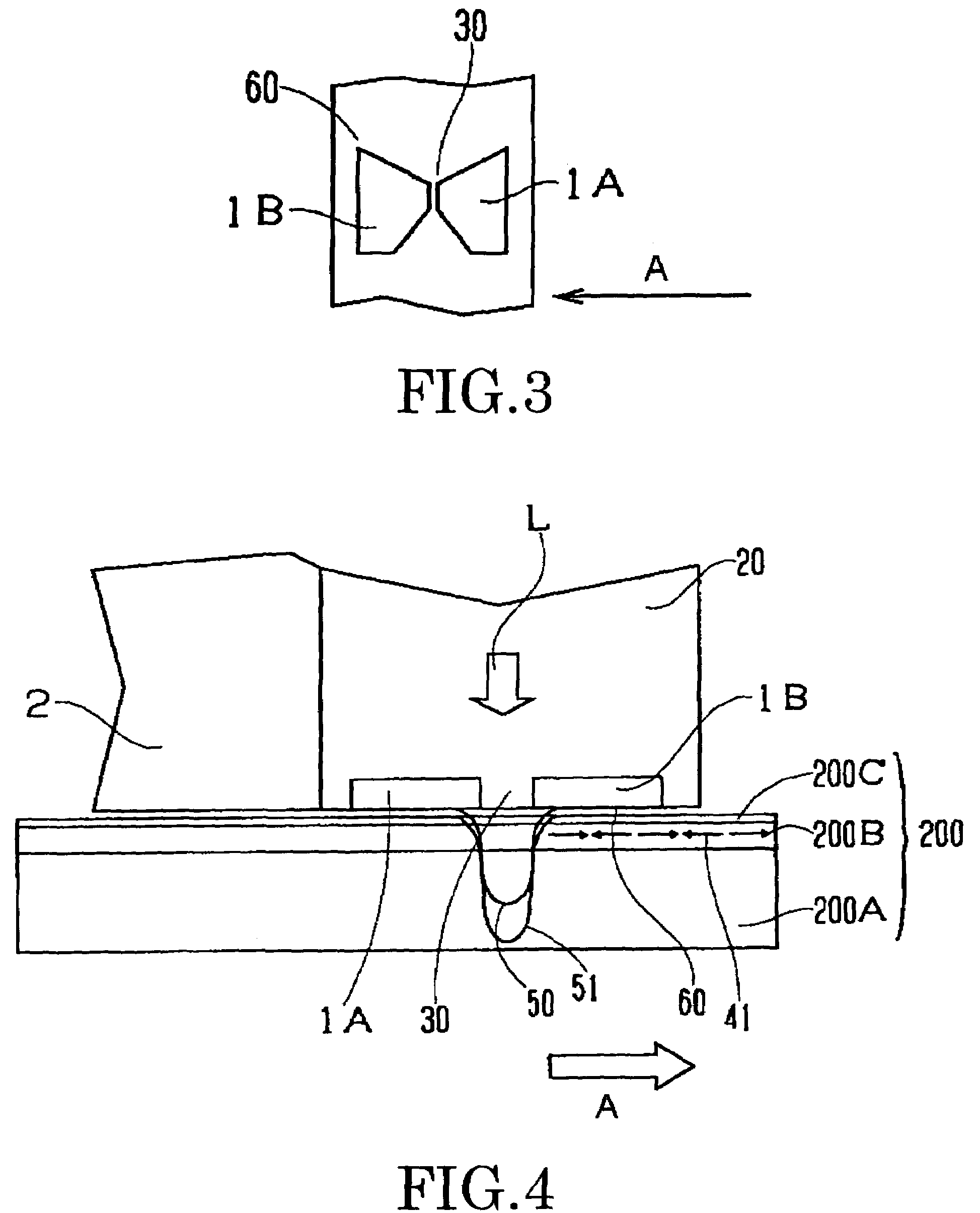
Patents
Literature
176results about "Magnetic and optical recordings" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
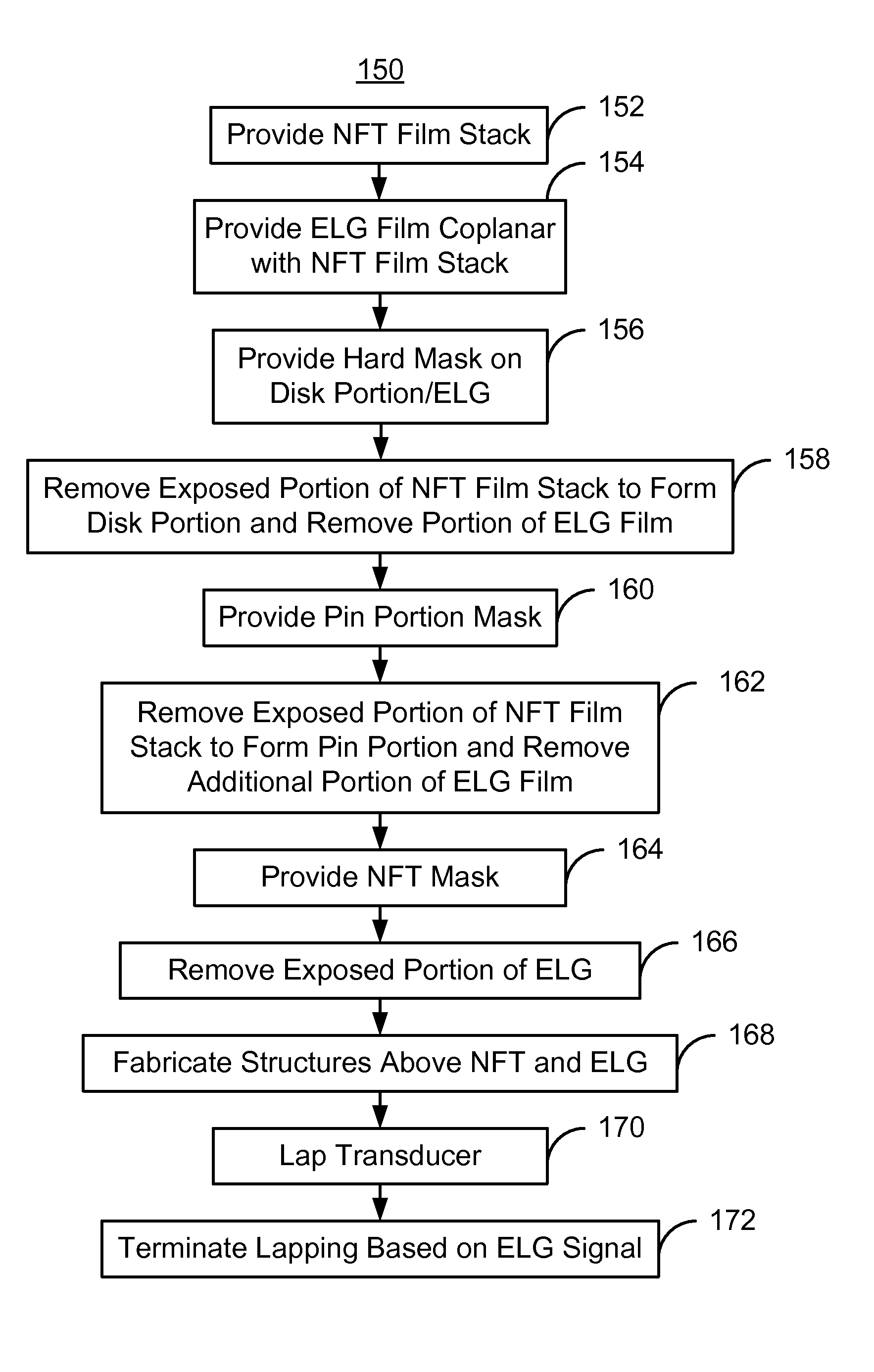
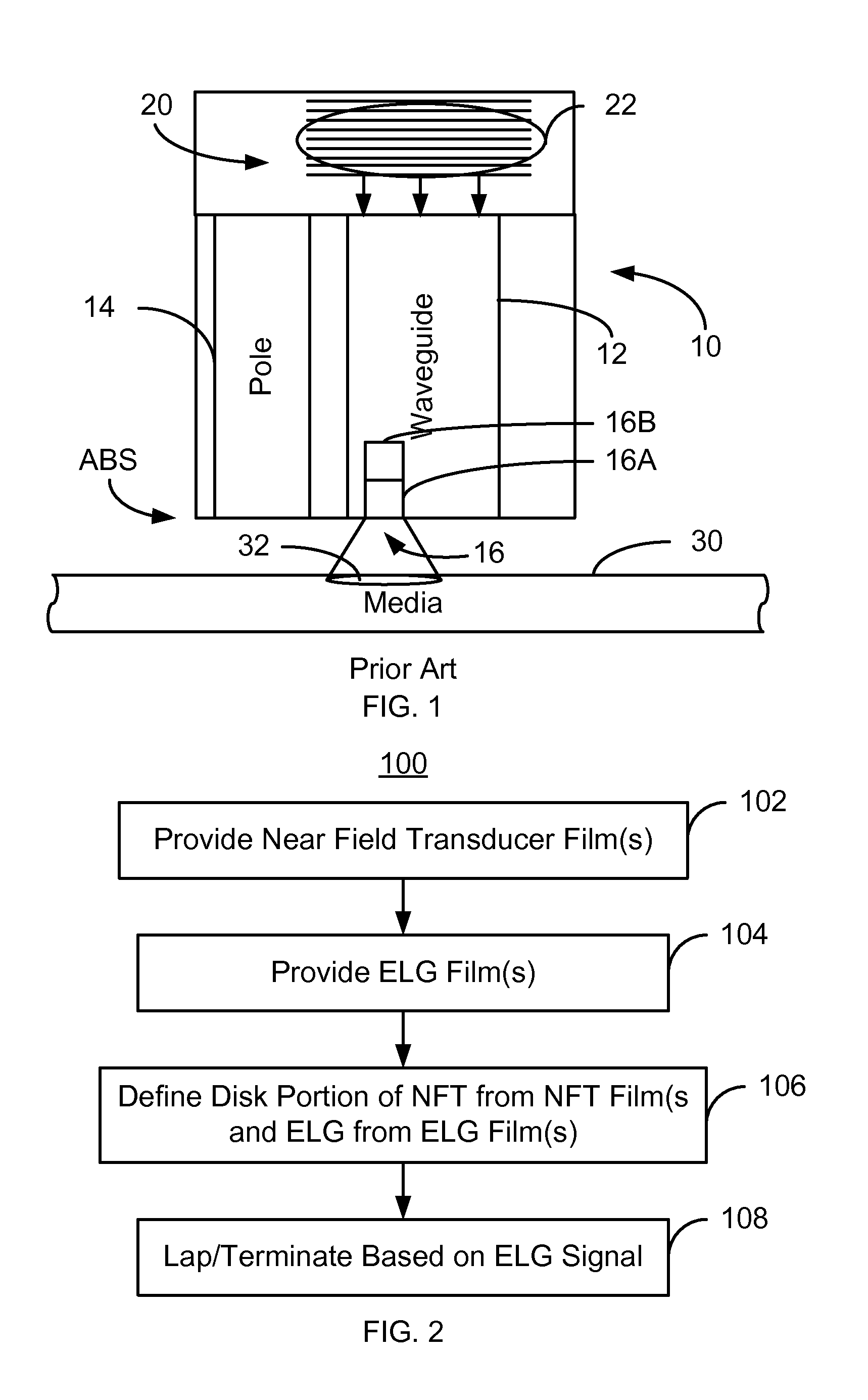
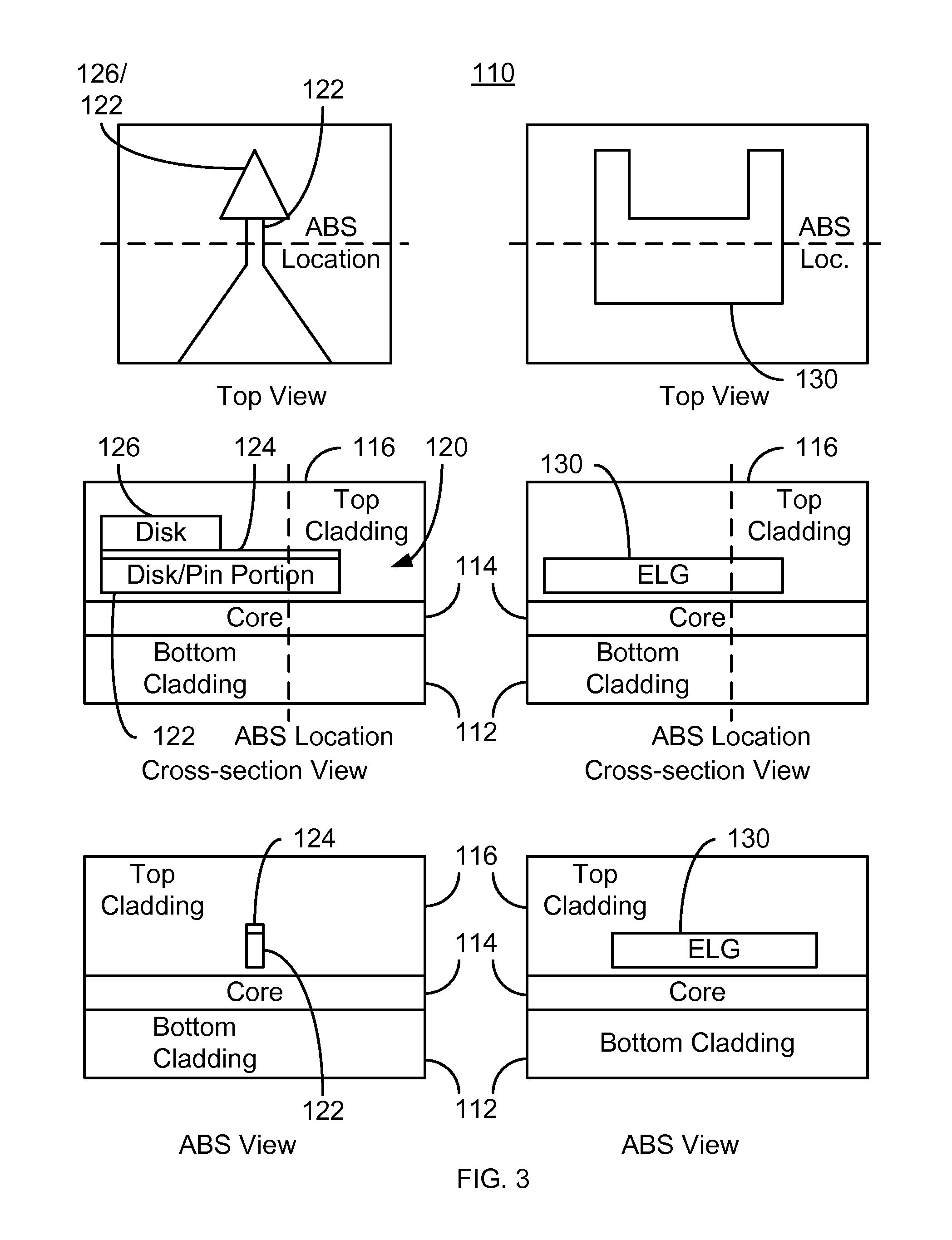
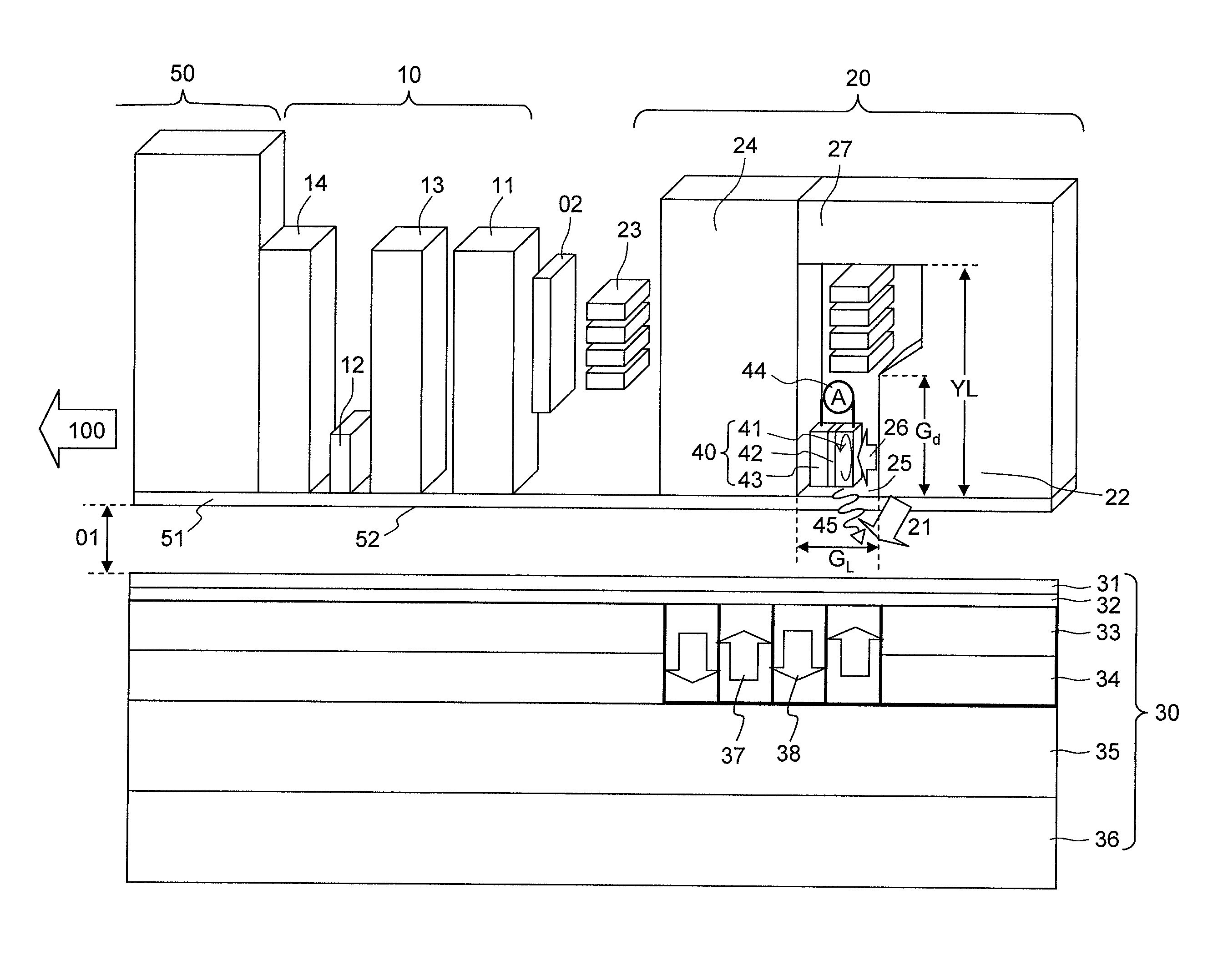
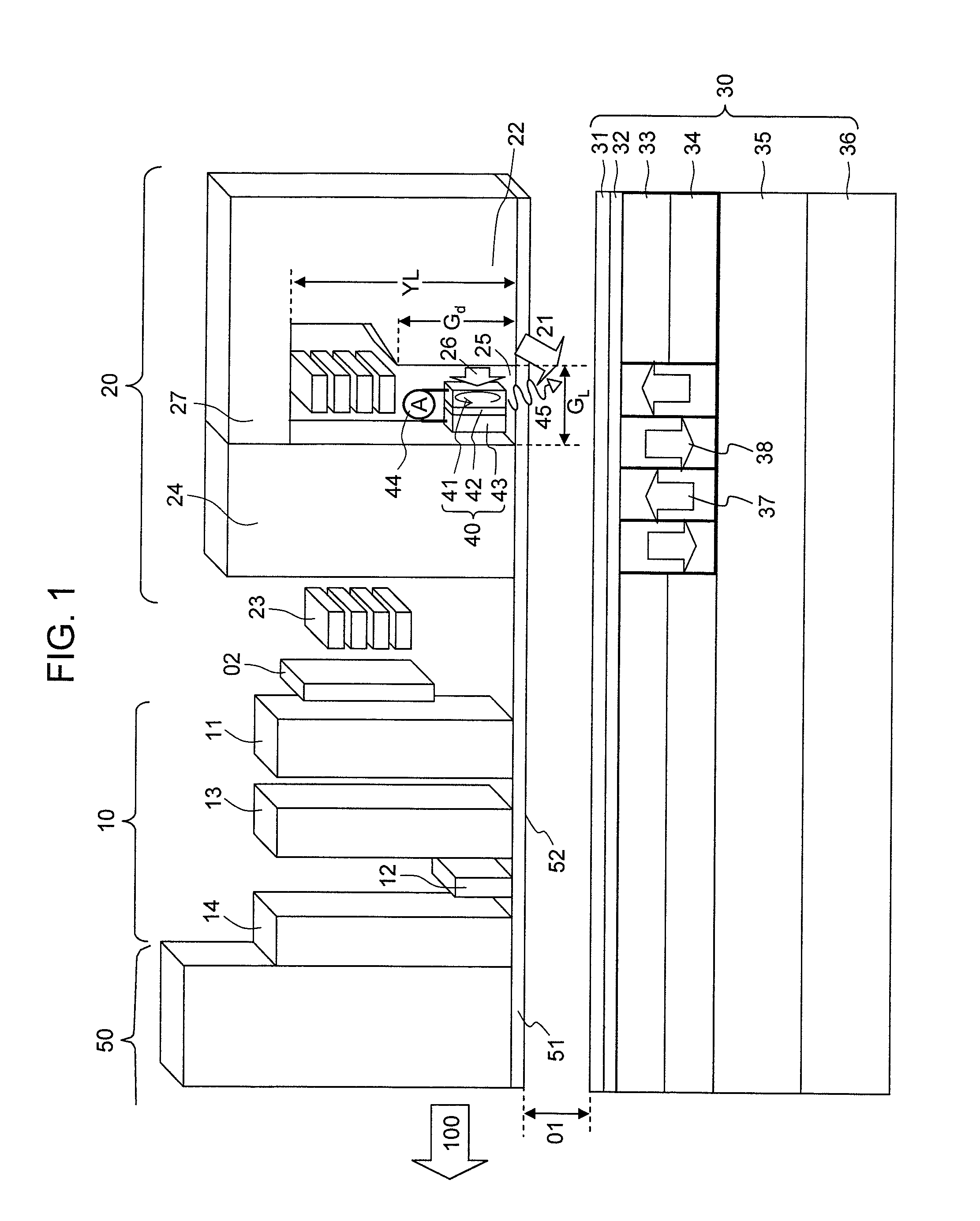
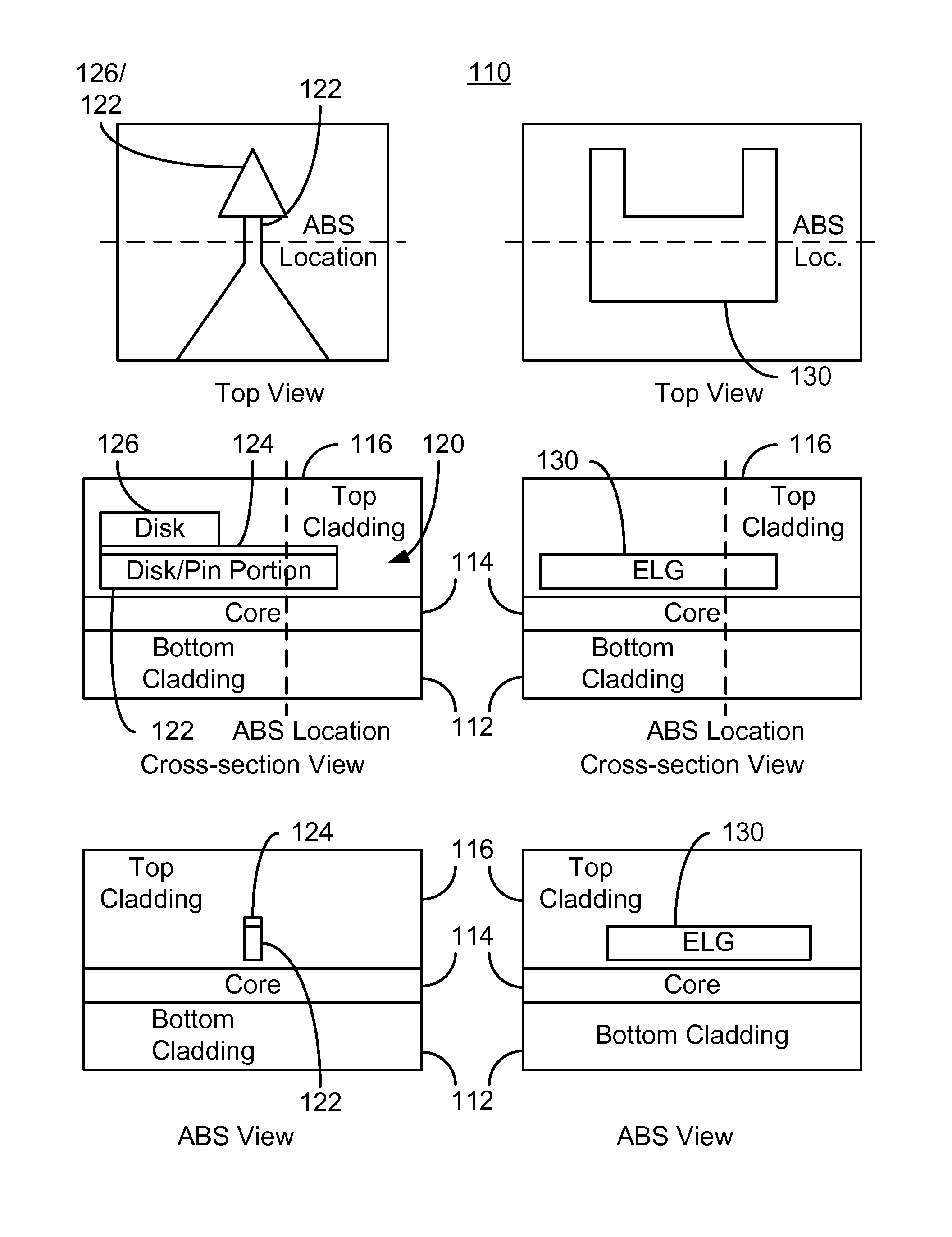
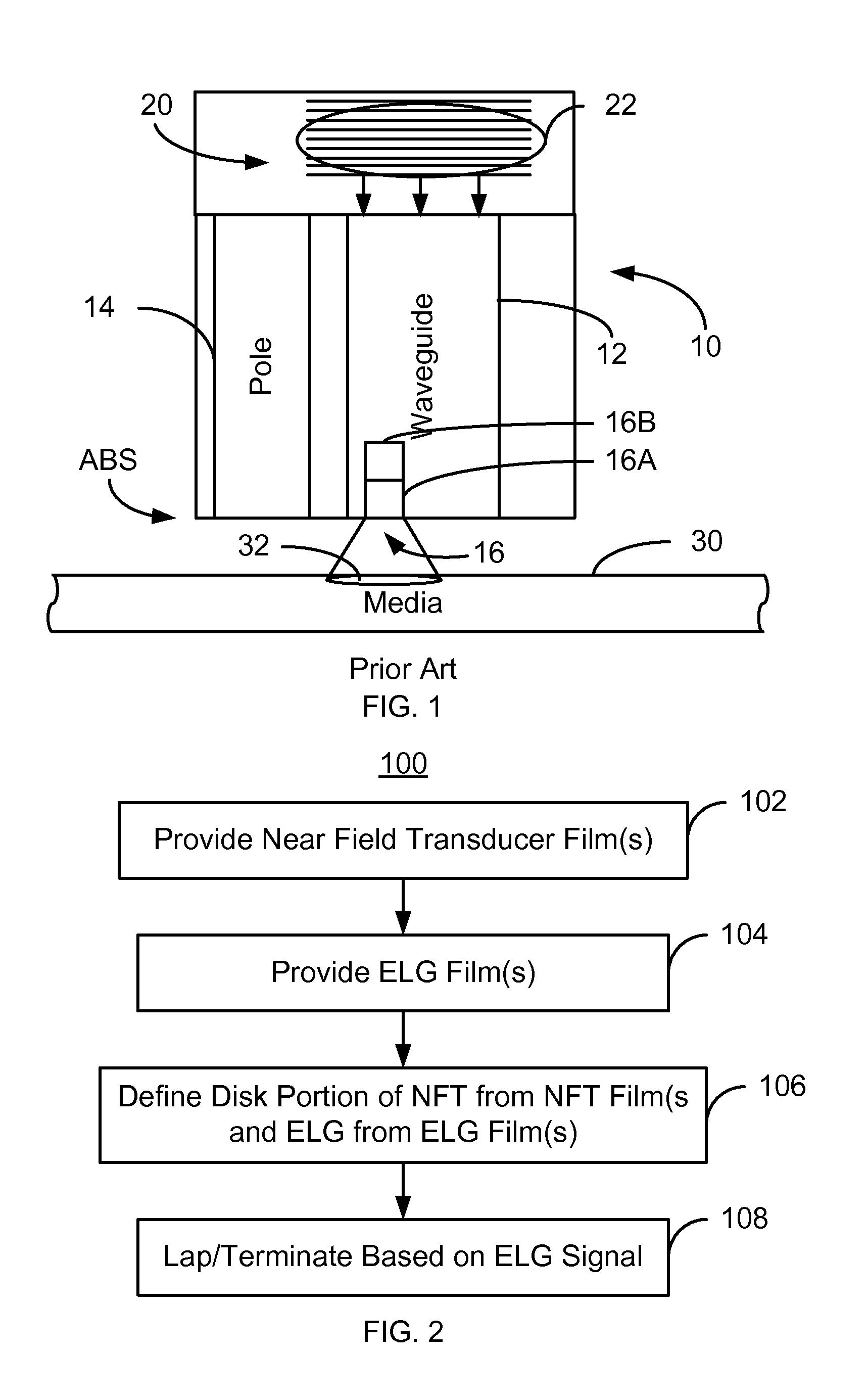
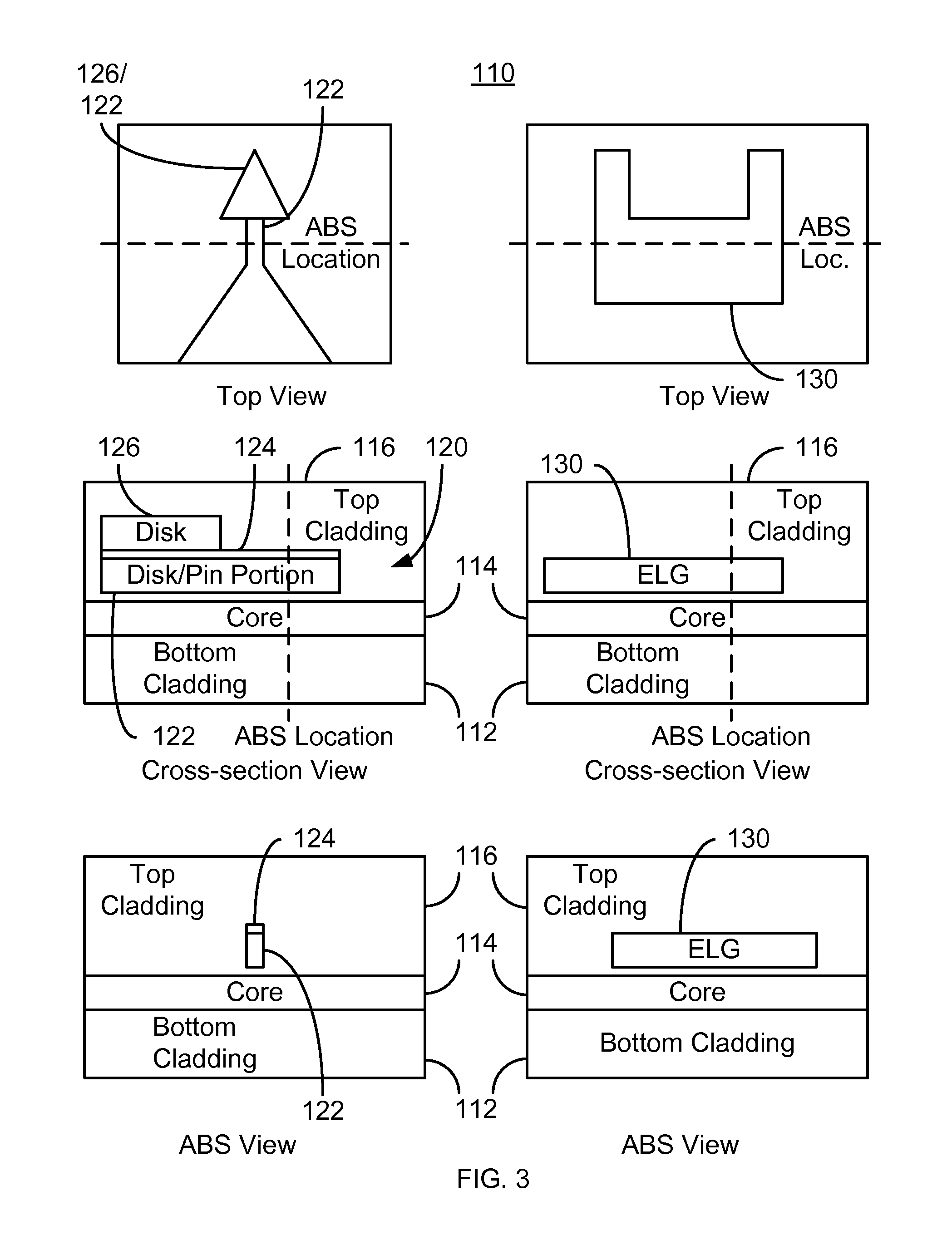
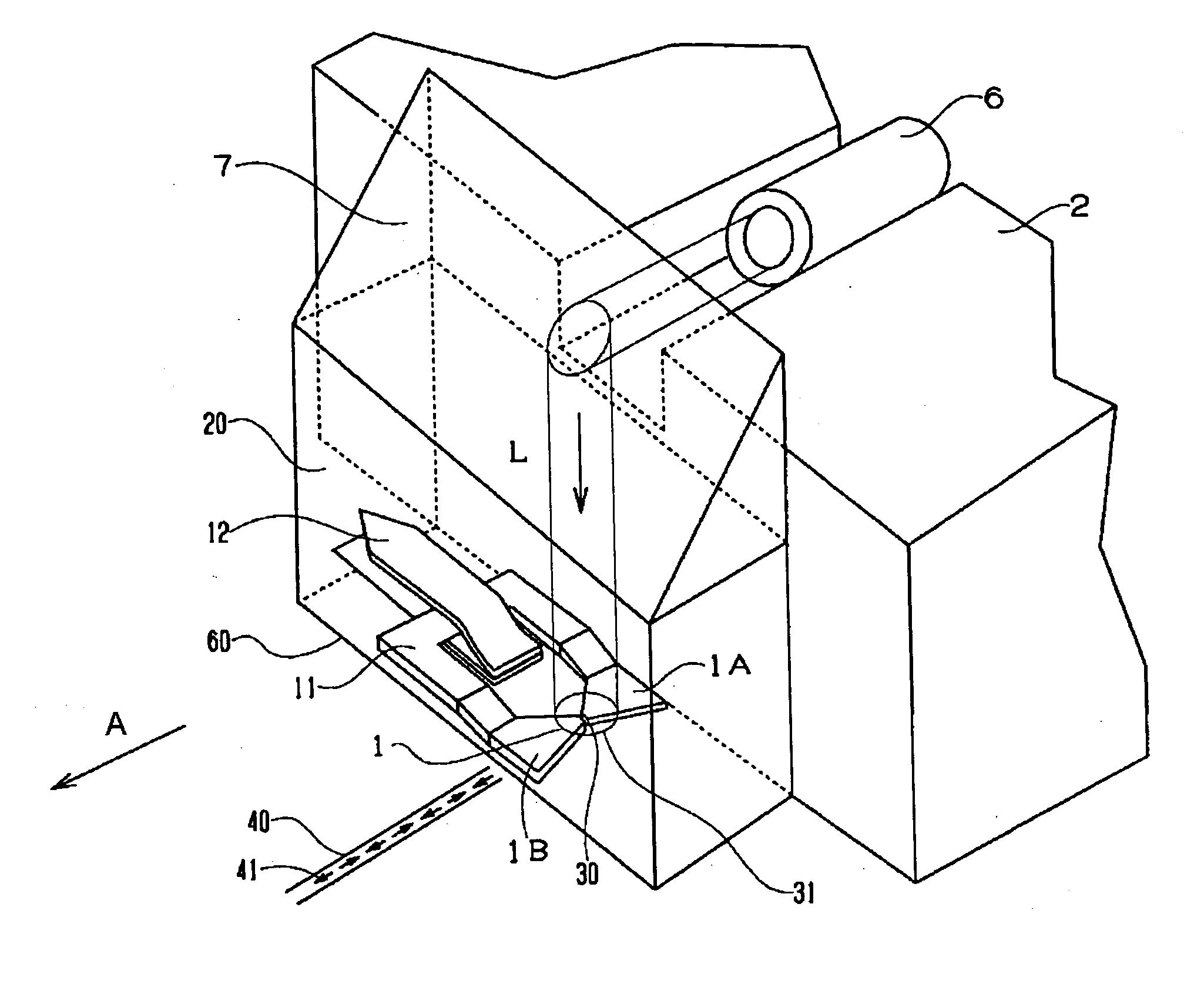
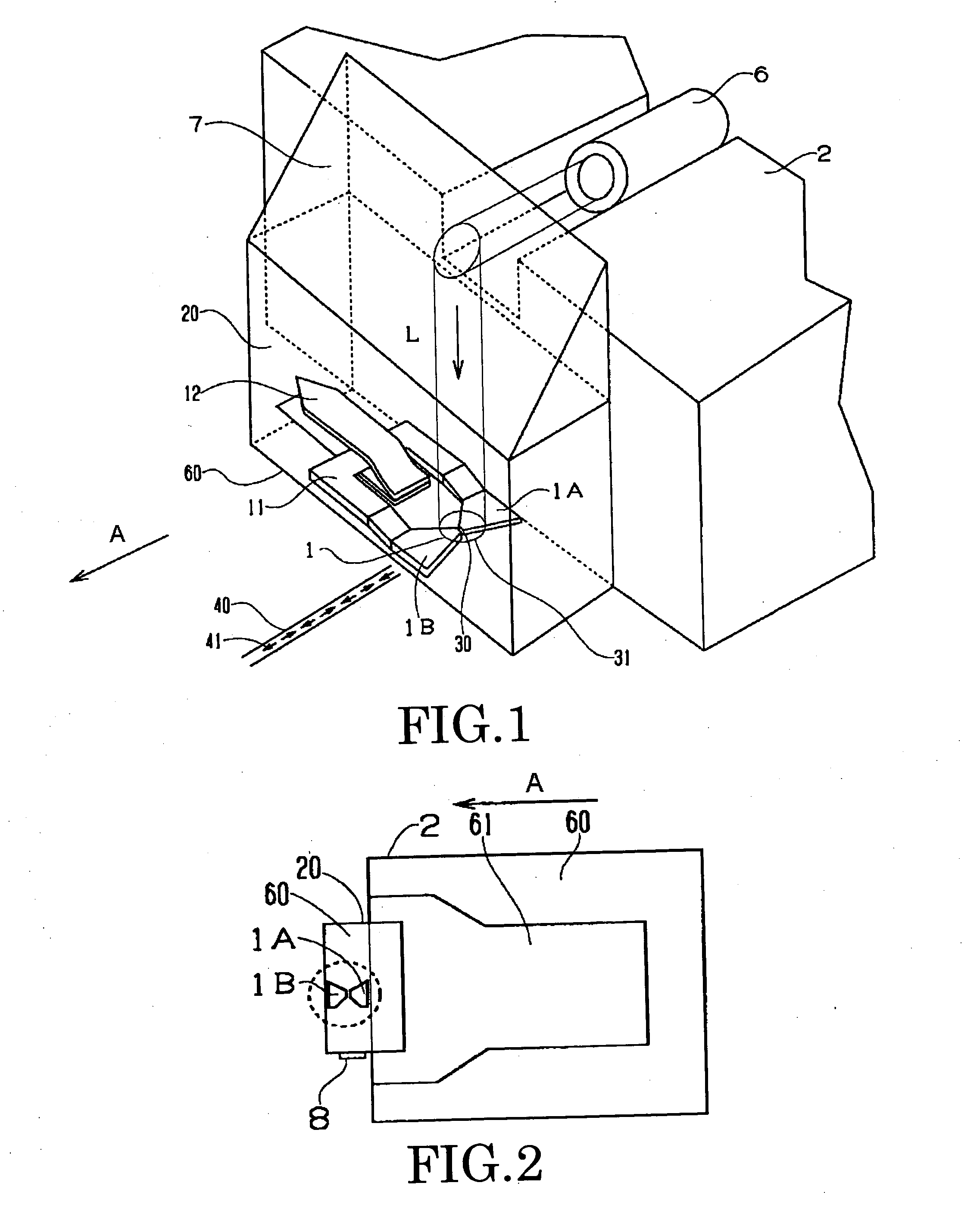
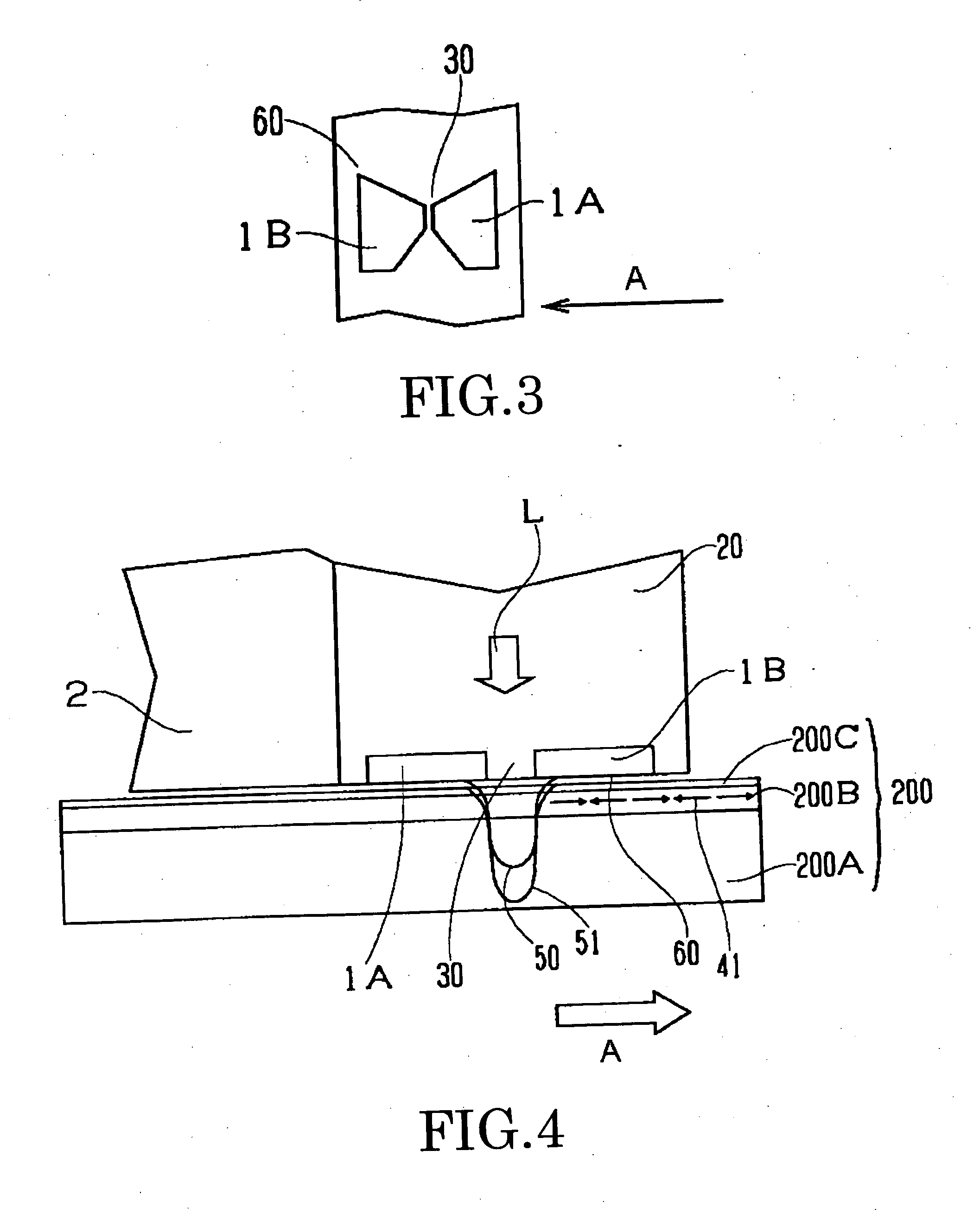
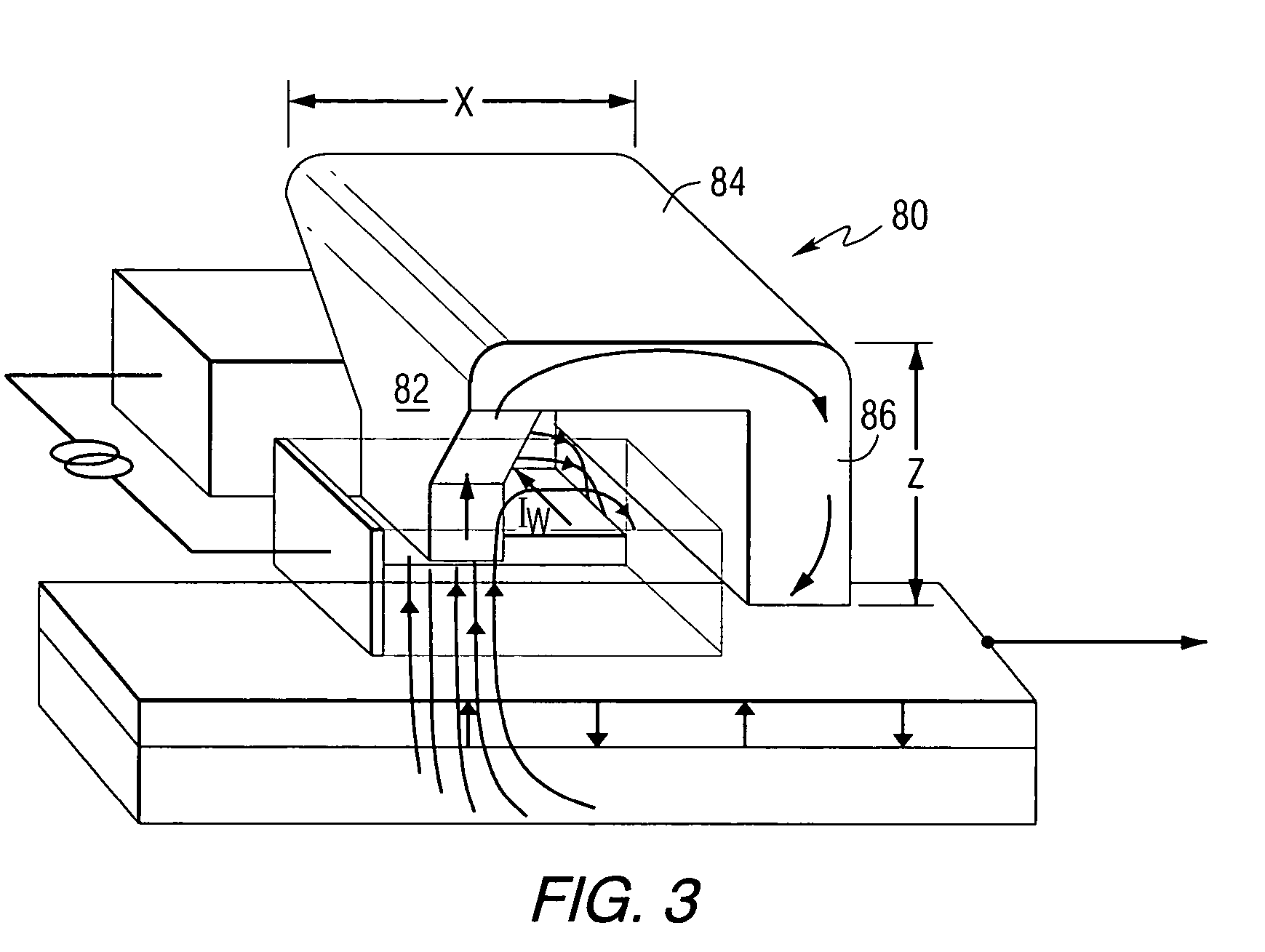
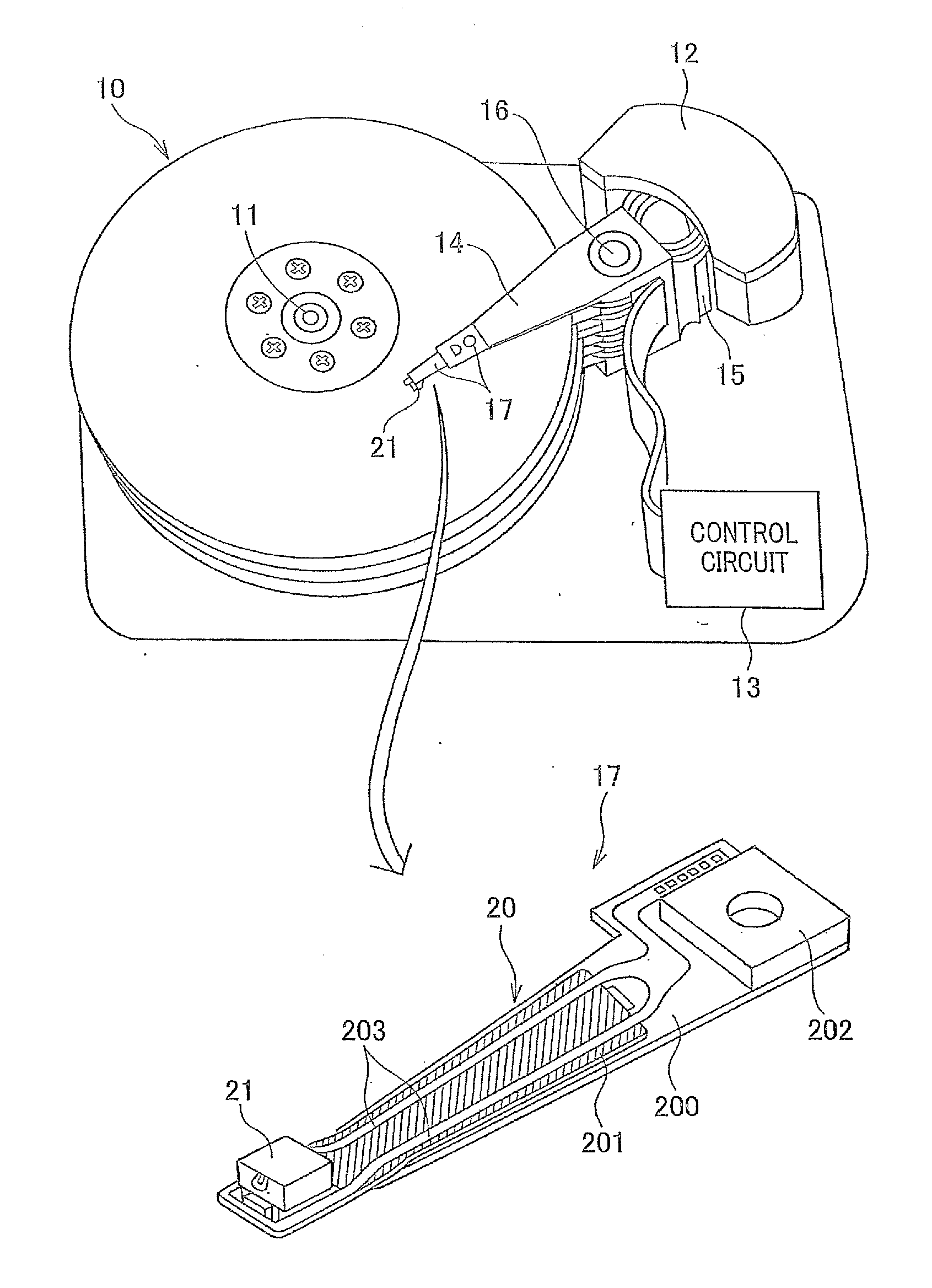
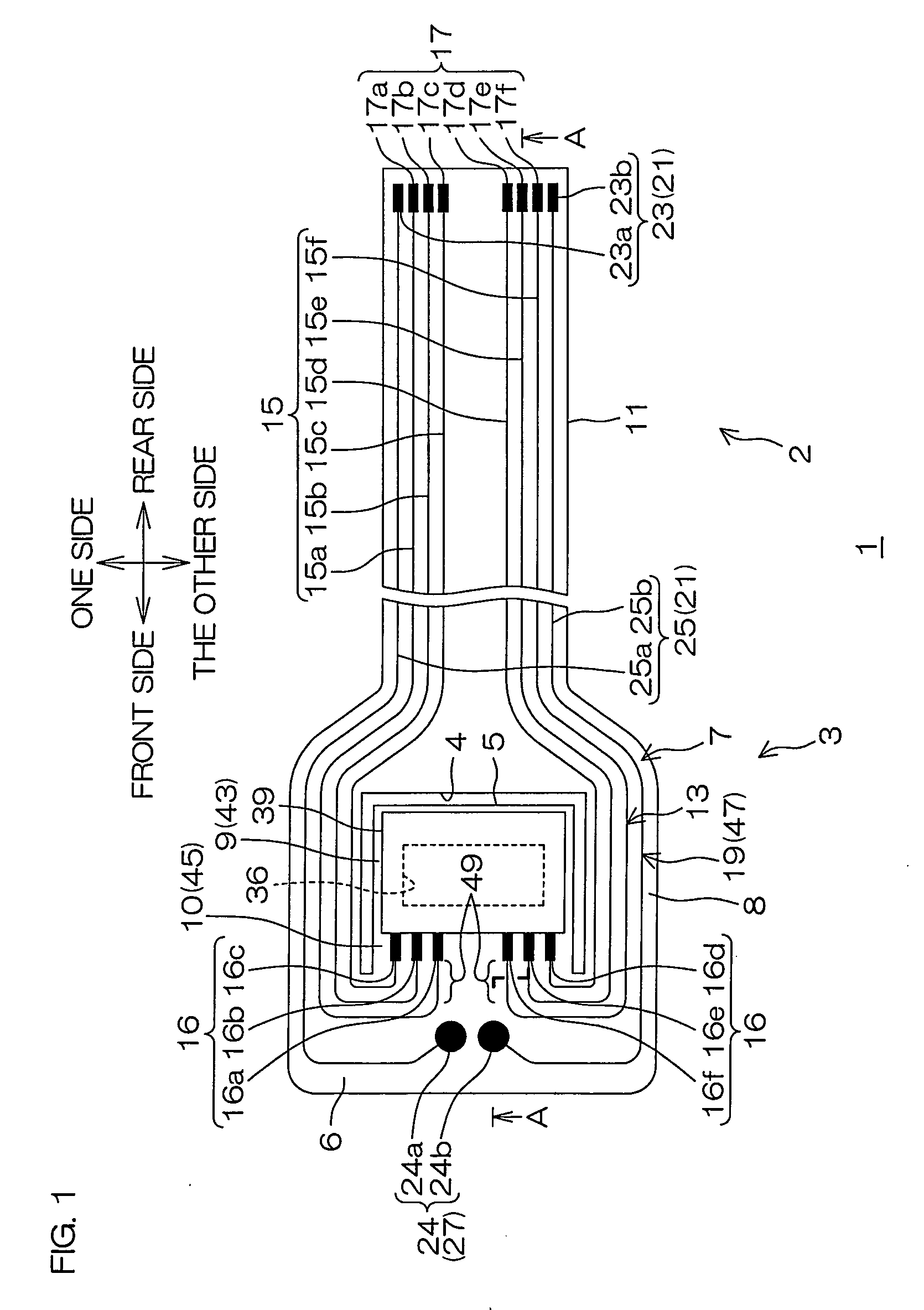
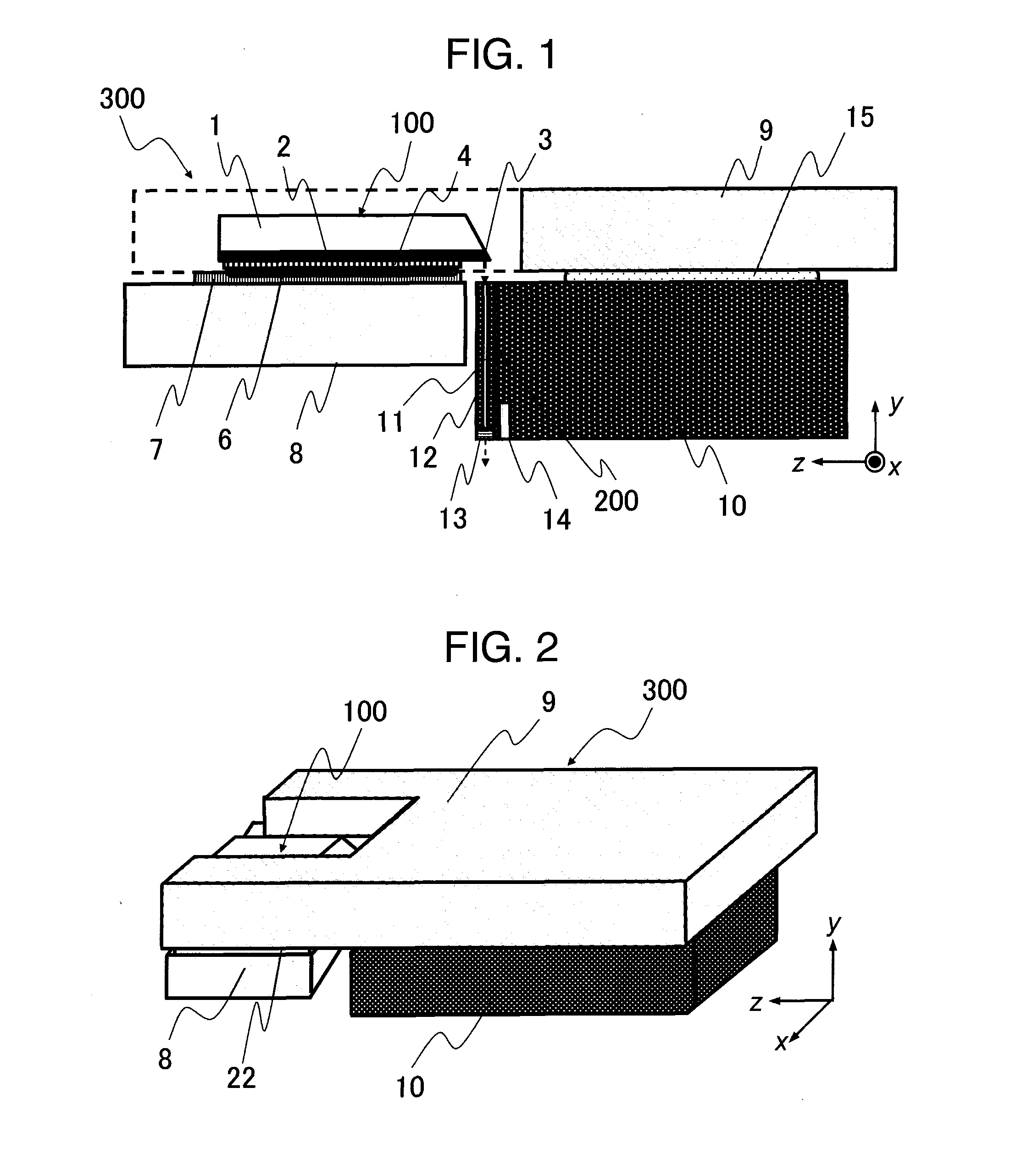
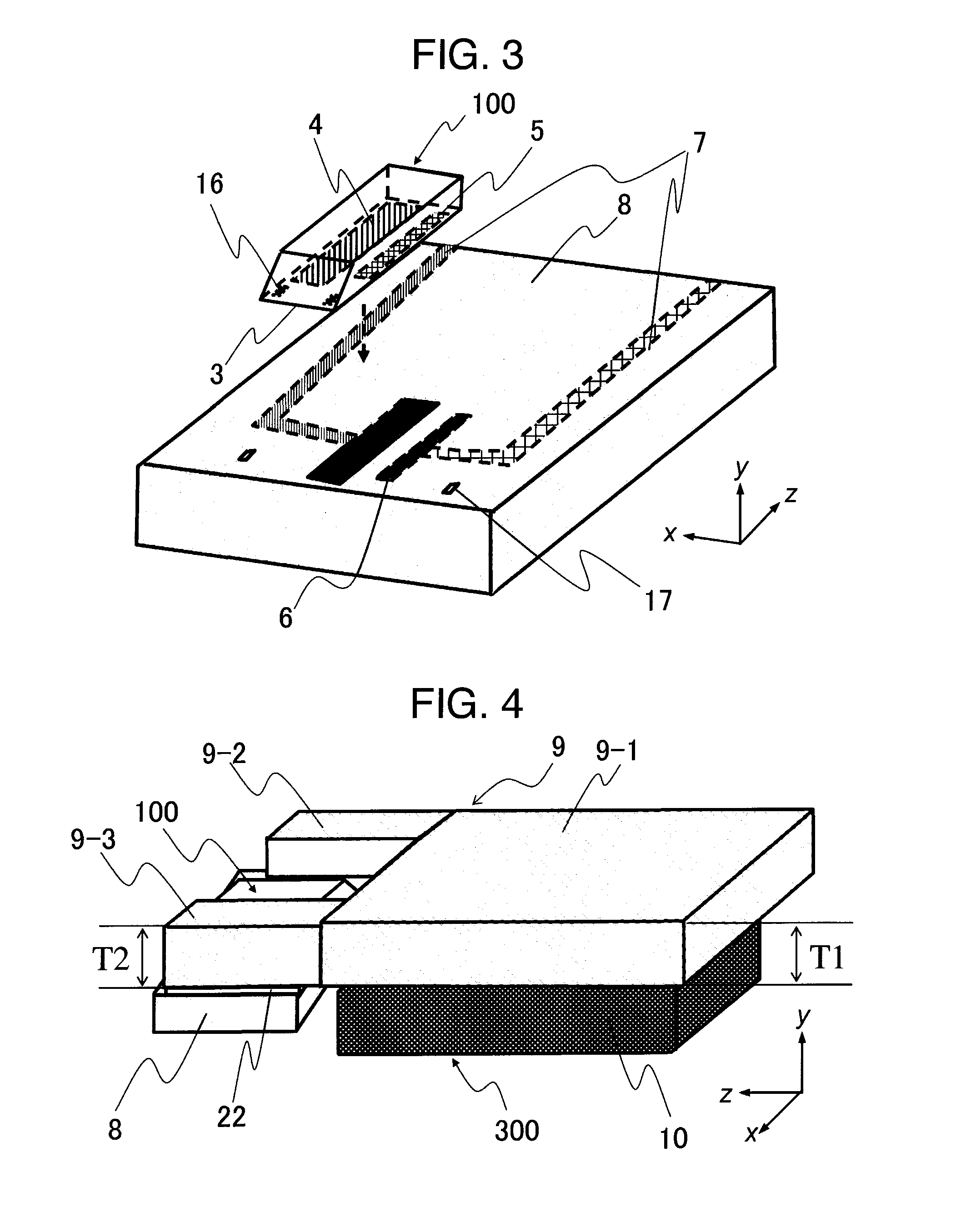
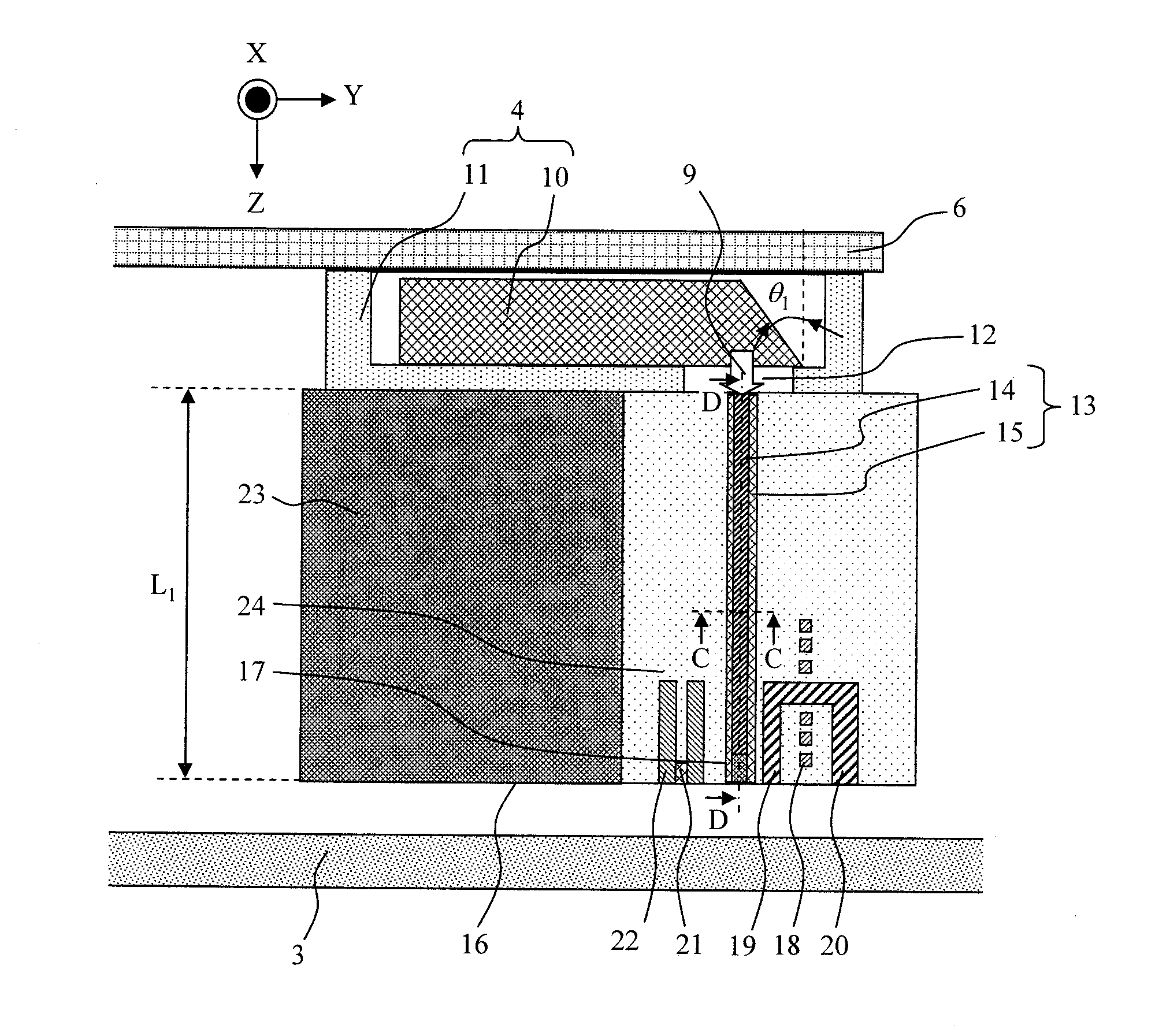
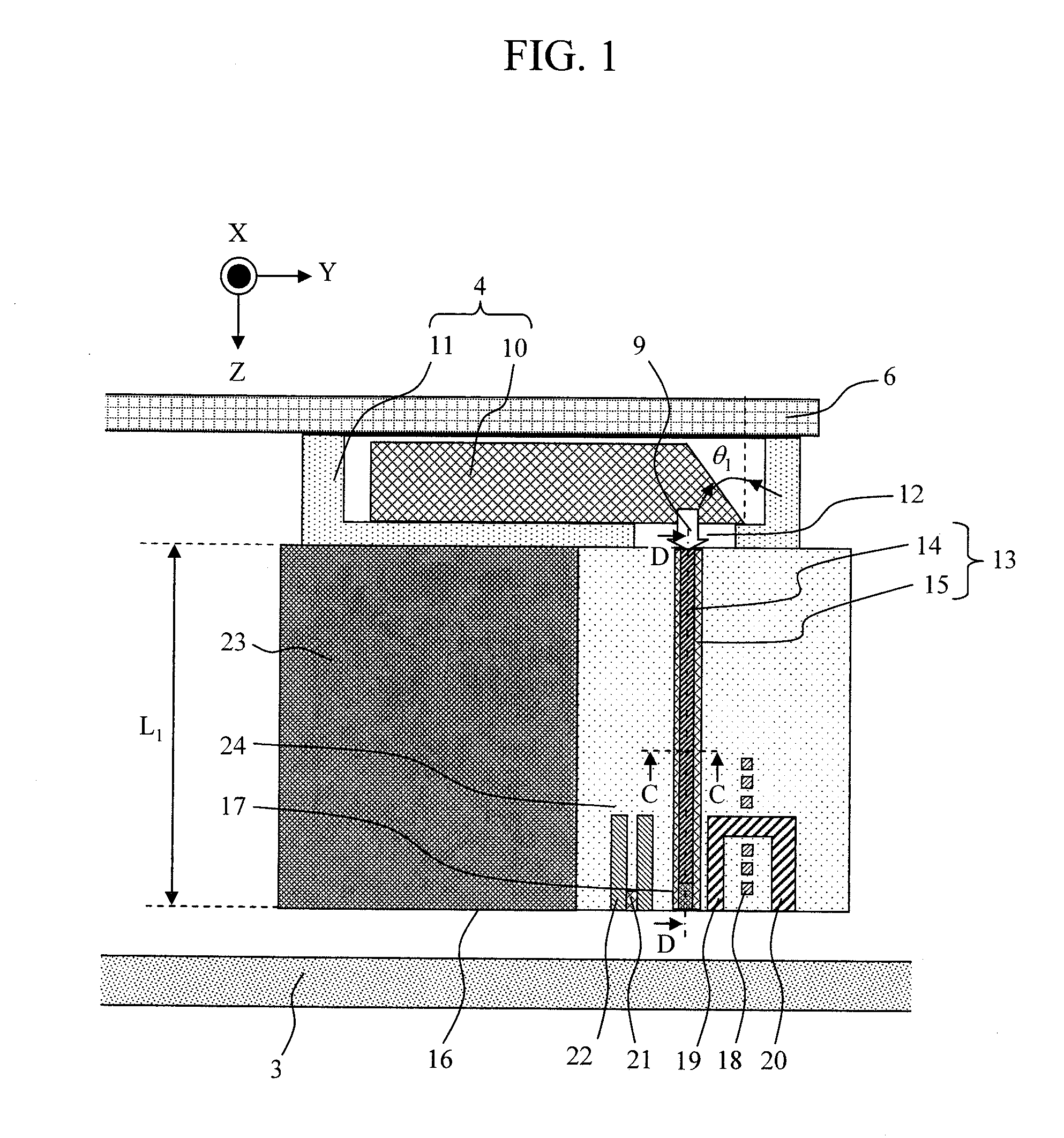
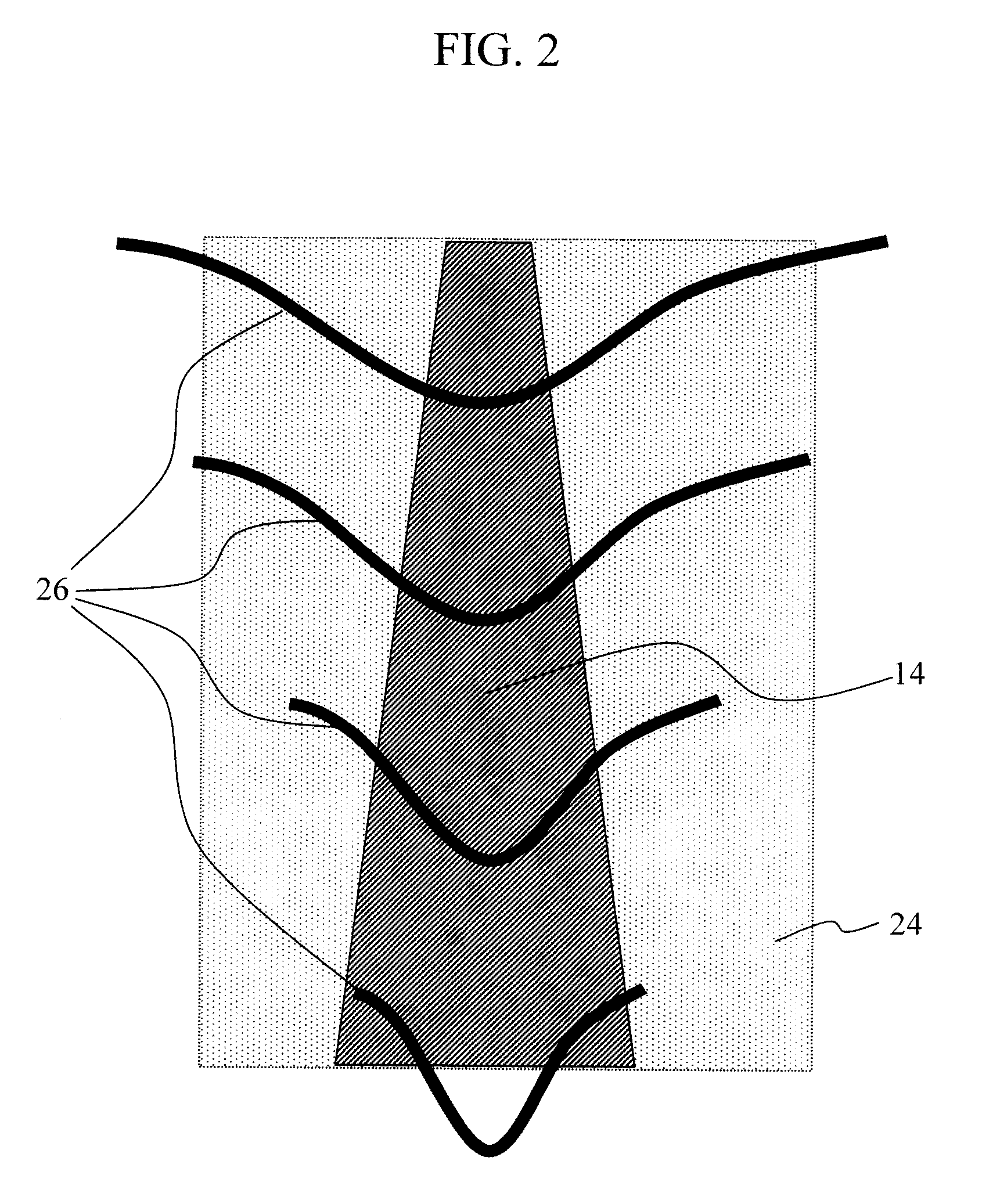
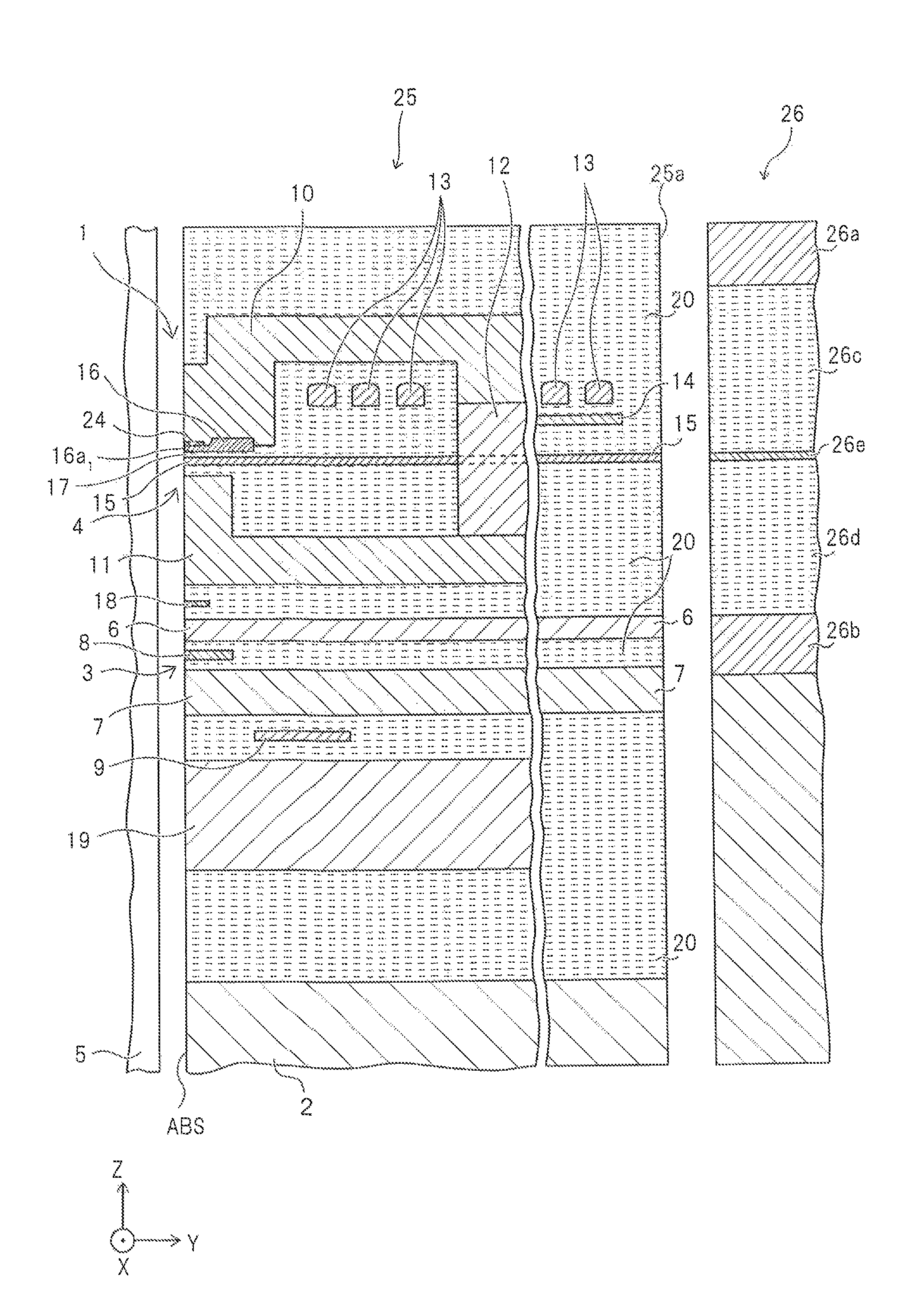
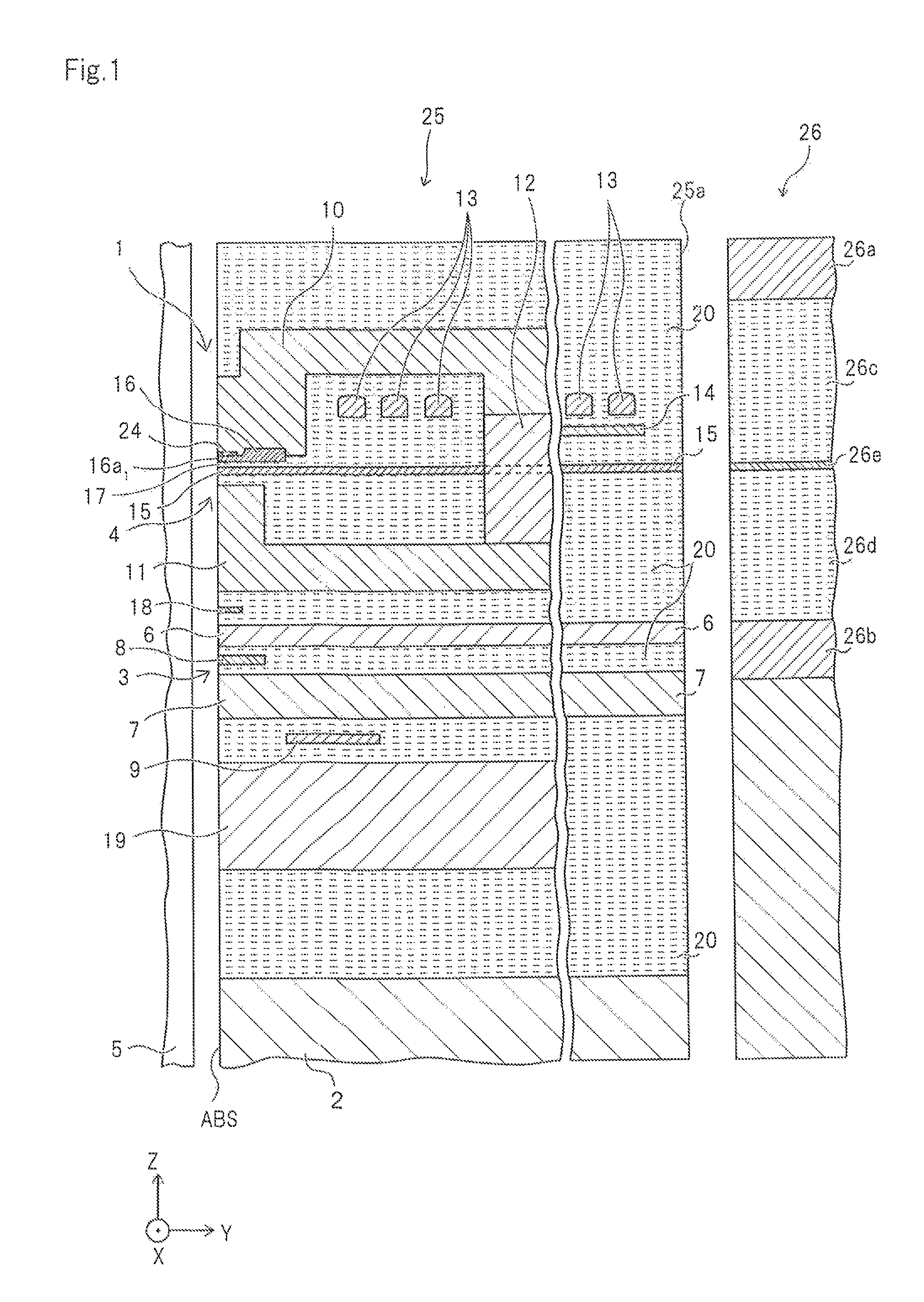
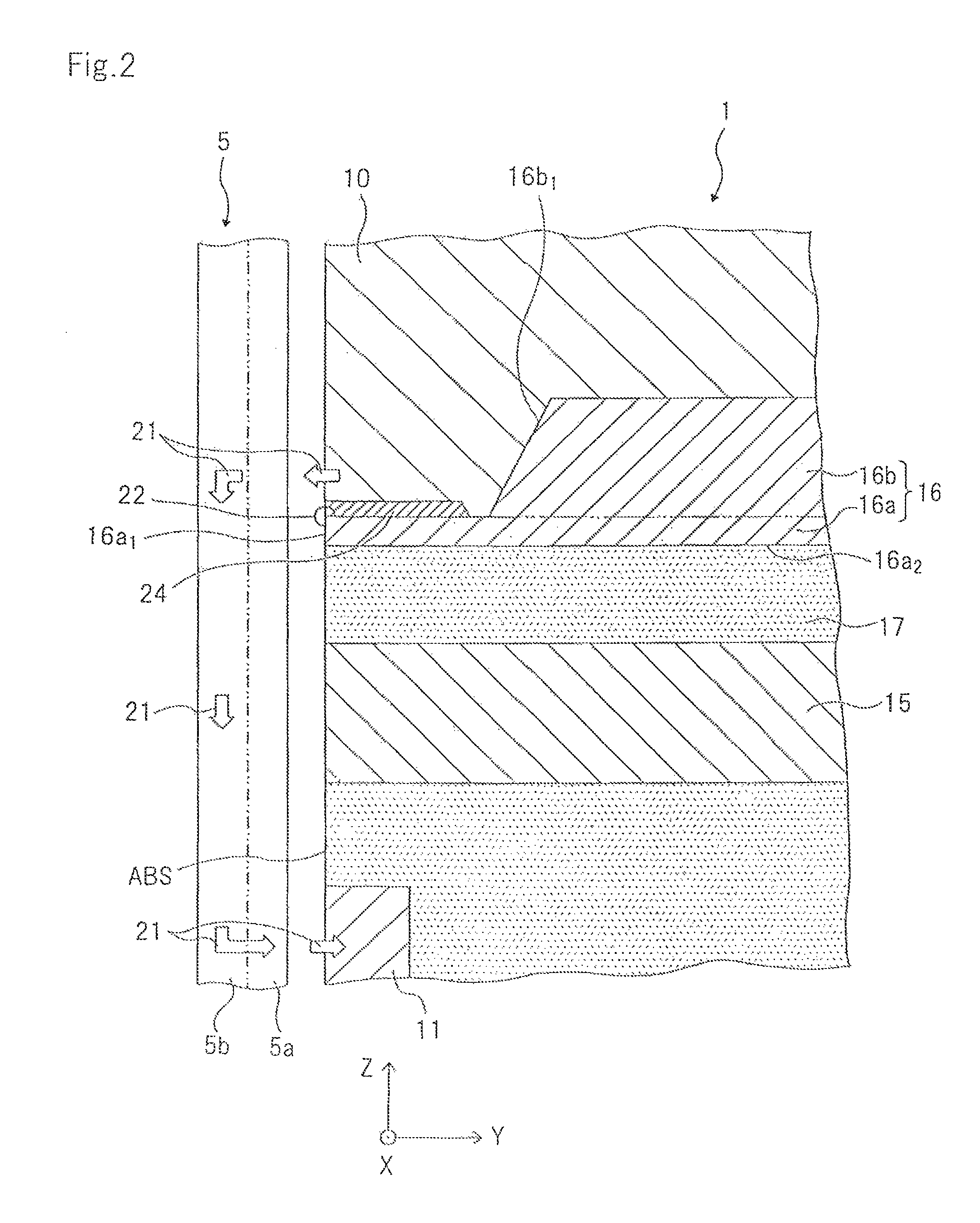
Method for providing an electronic lapping guide corresponding to a near-field transducer of an energy assisted magnetic recording transducer
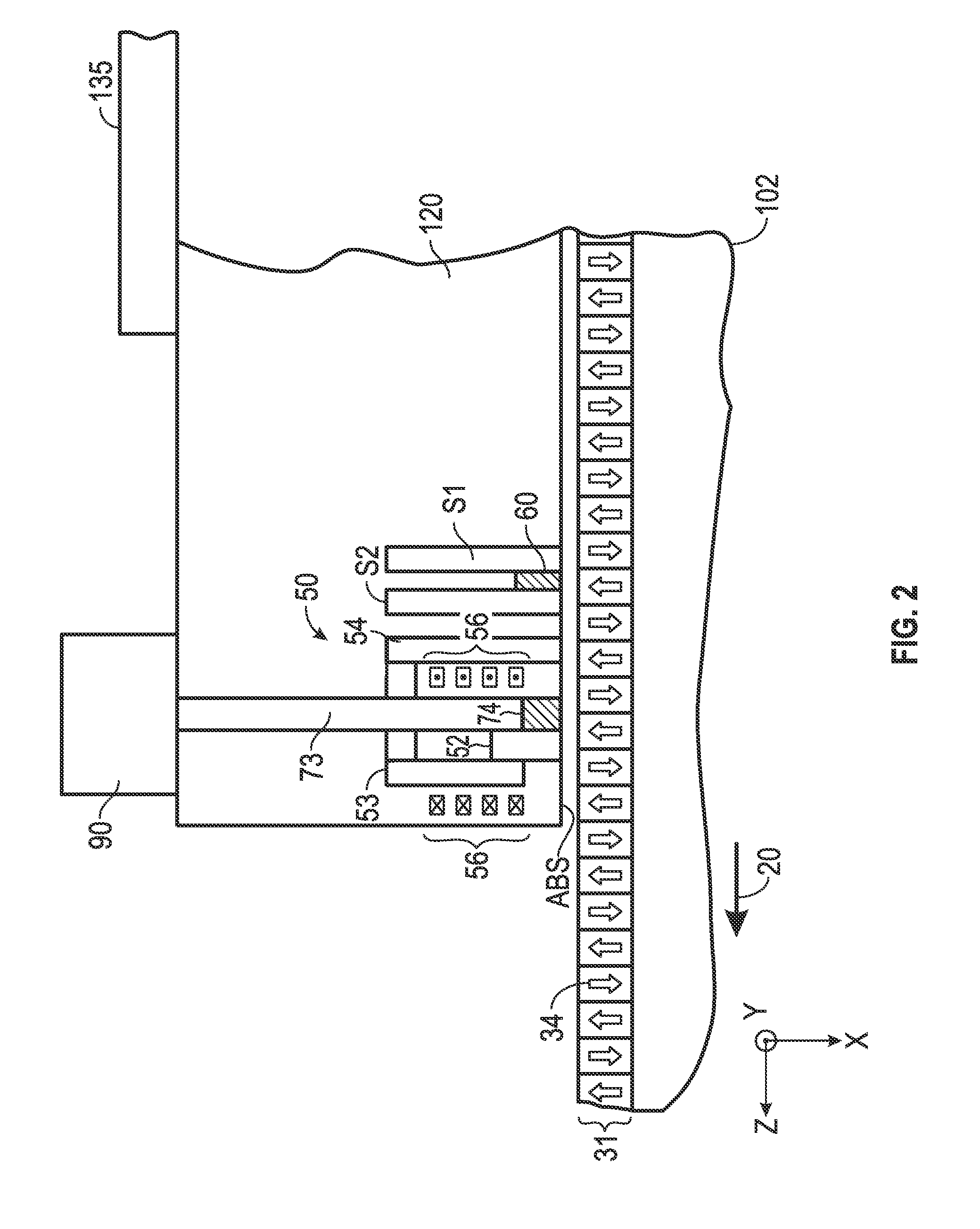
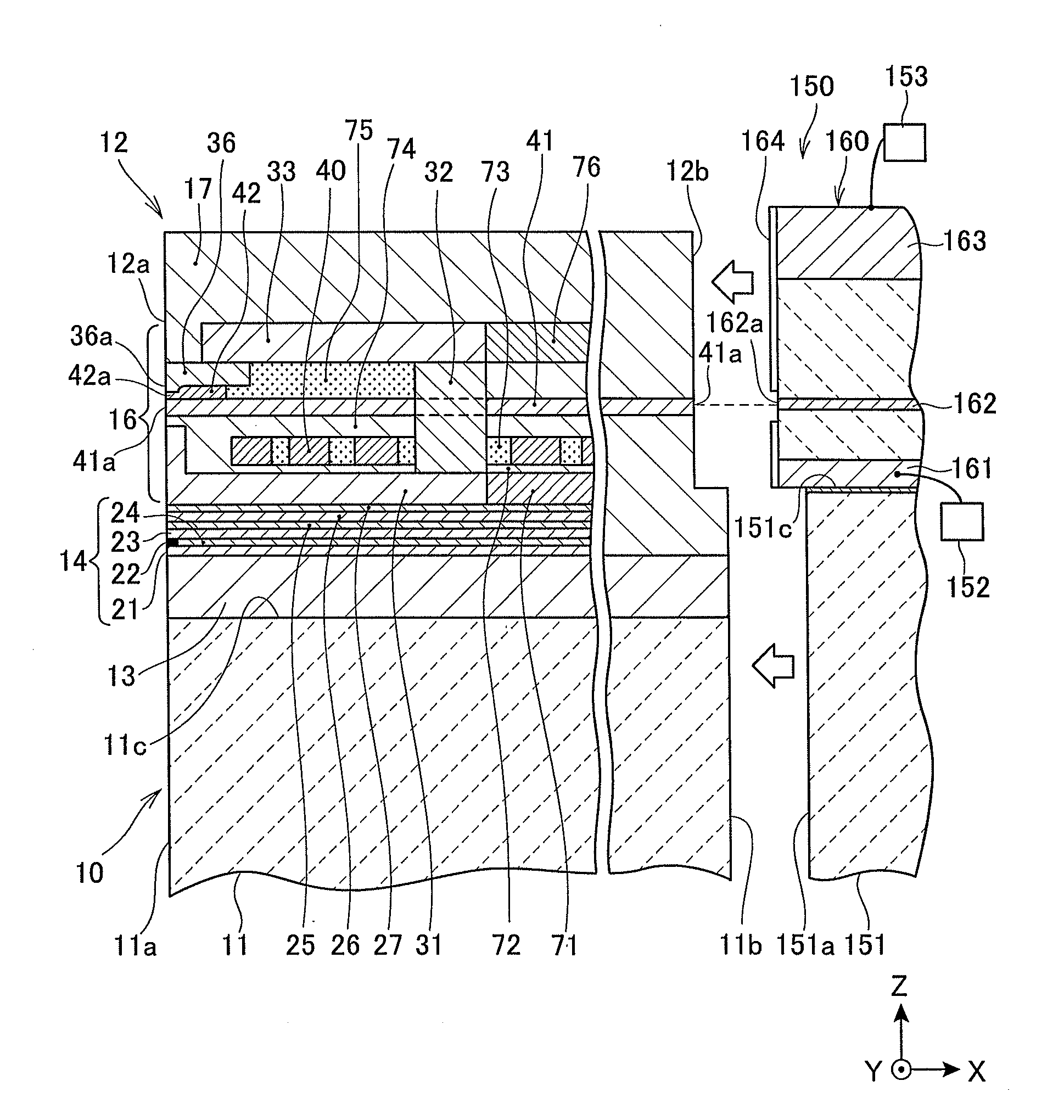
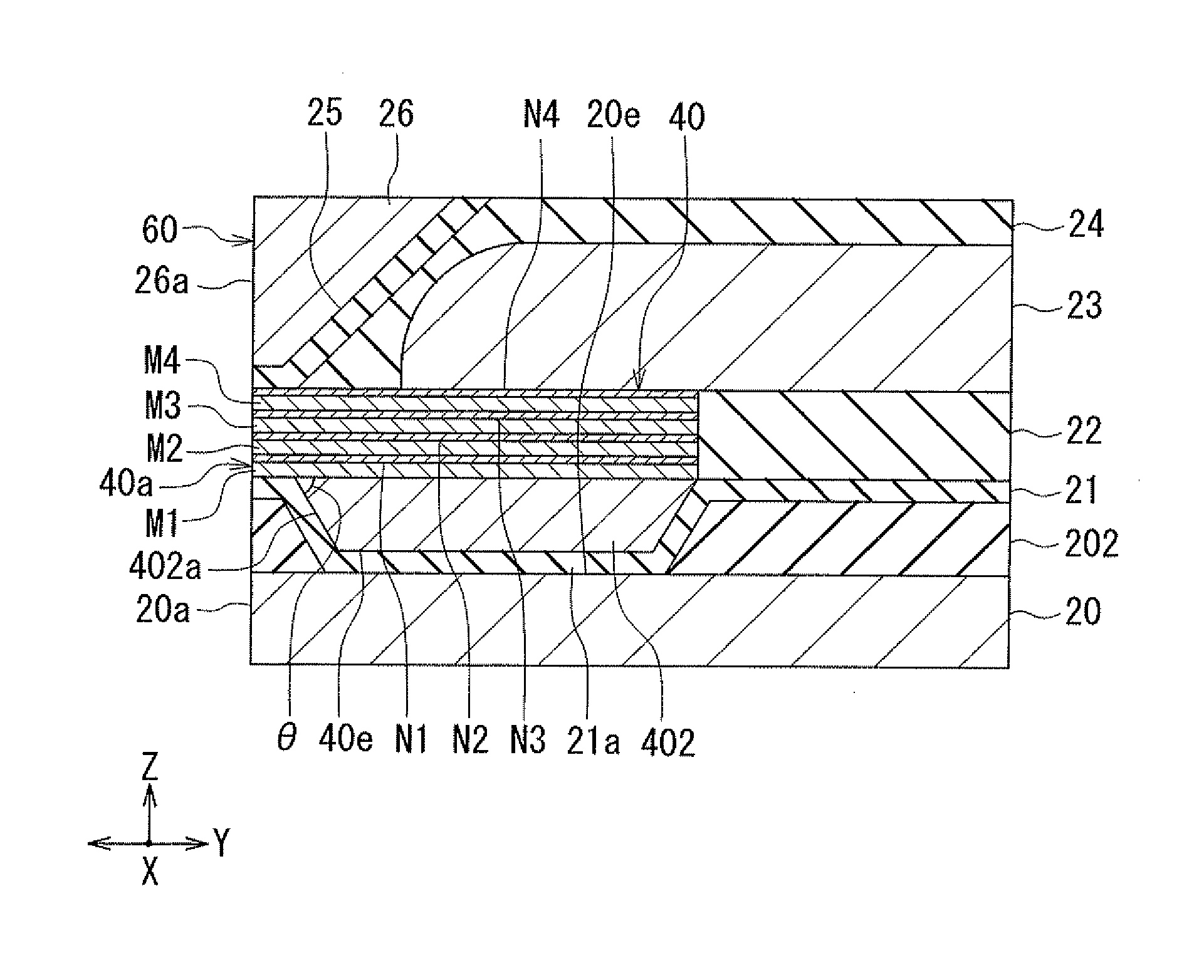
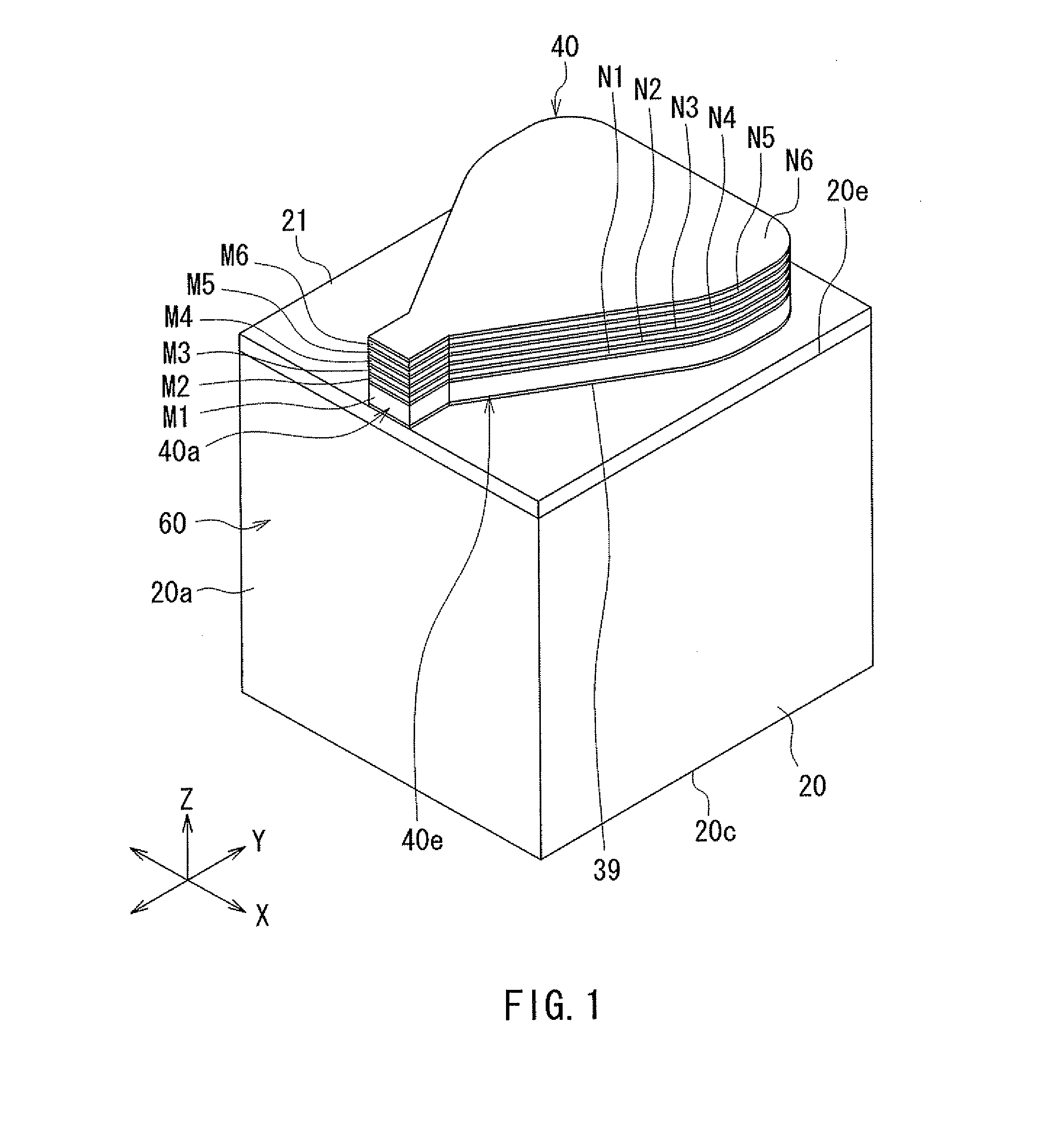
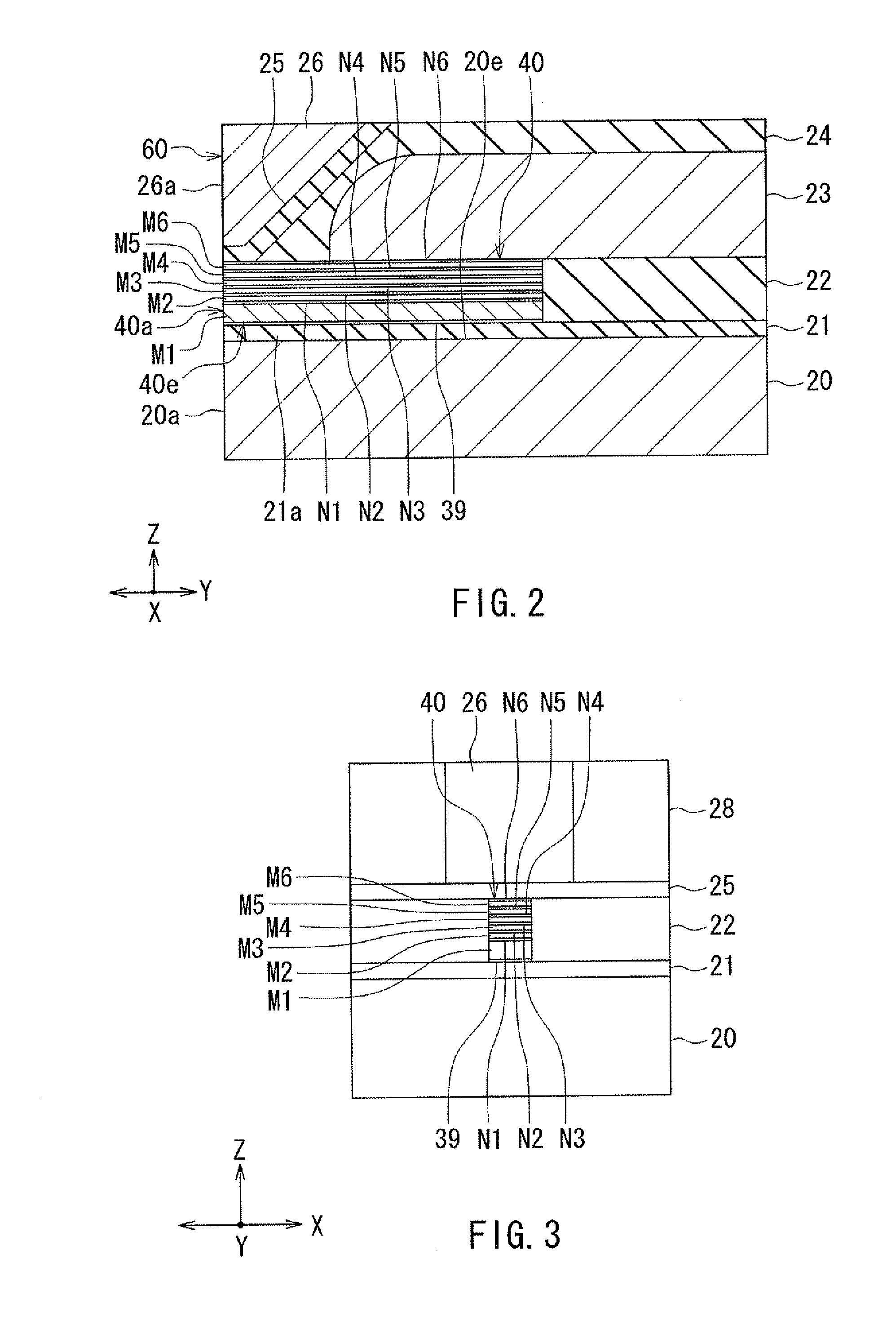
A method fabricates a transducer having an air-bearing surface (ABS). The method includes providing at least one near-field transducer (NFT) film and providing an electronic lapping guide (ELG) film substantially coplanar with a portion of the at least one NFT film. The method also includes defining a disk portion of an NFT from the portion of the at least one NFT film and at least one ELG from the ELG film. The disk portion corresponds to a critical dimension of the NFT from an ABS location. The method also includes lapping the at least one transducer. The lapping is terminated based on a signal from the ELG.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
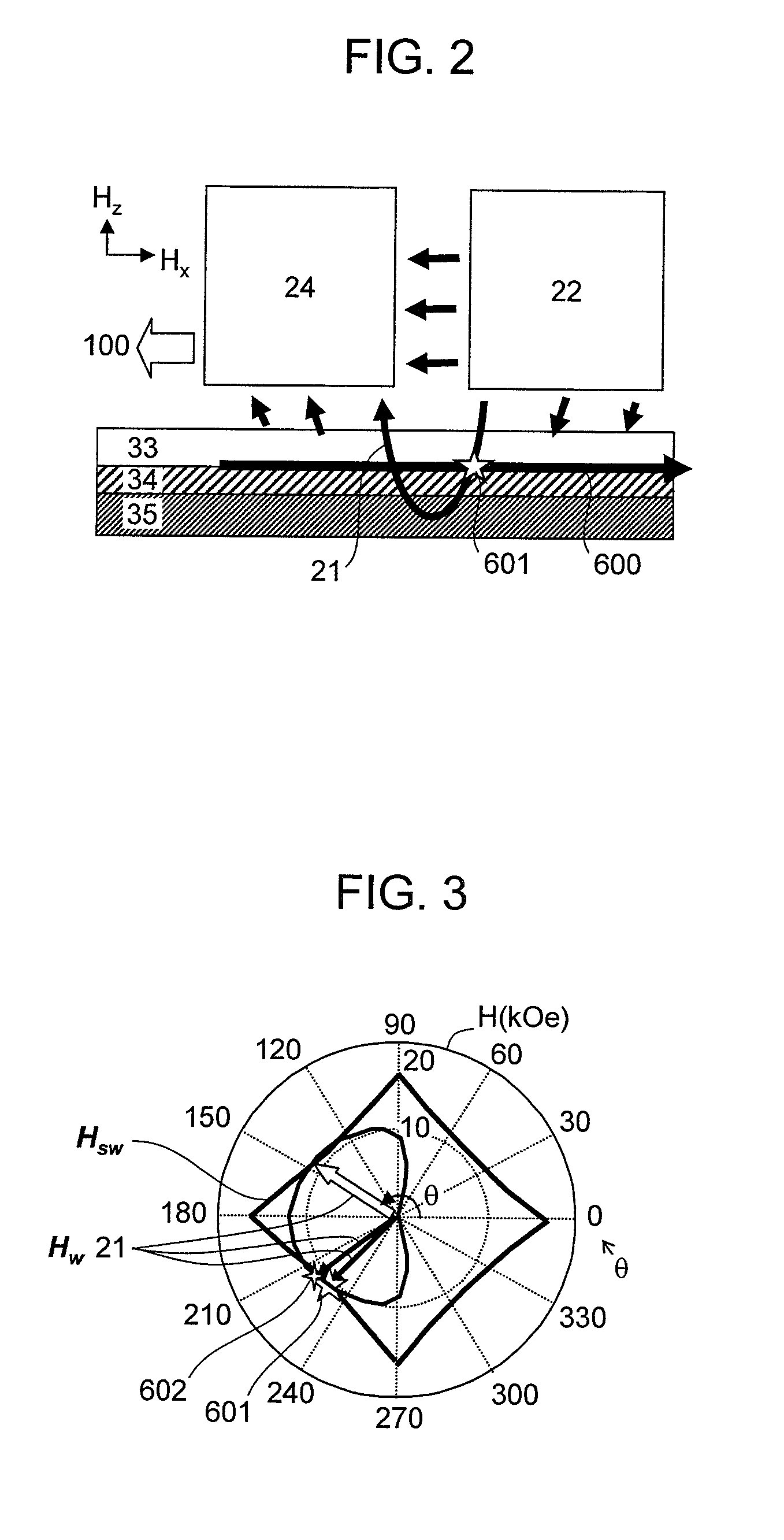
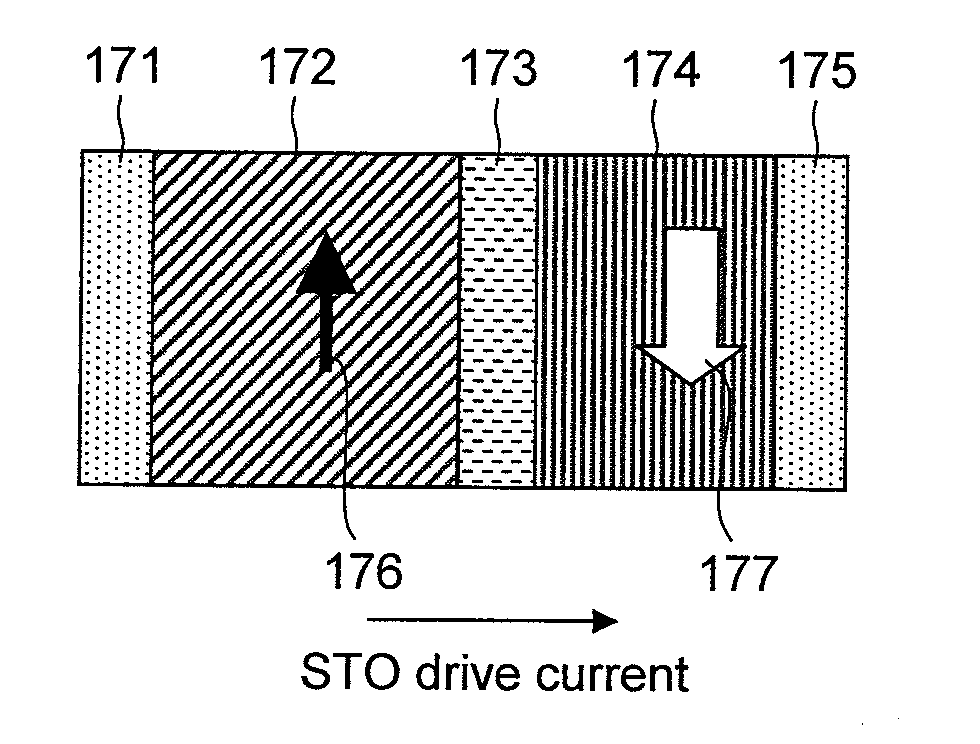
Magnetic head, magnetic recording method and apparatus for controlling magnetic head with spin torque oscillator in a disk drive
ActiveUS9275672B2Improve recording densityHigh densityManufacture head surfaceDriving/moving recording headsSpin torque oscillatorsMagnetic poles
A microwave assisted magnetic recording head includes a recording magnetic pole unit that produces a recording field for writing to a perpendicular magnetic recording medium, and a high-frequency magnetic field oscillator that produces a high-frequency magnetic field. The recording magnetic pole unit includes a magnetic core with a write gap portion at which a main recording field component is concentrated, and the high-frequency magnetic field oscillator is disposed in the write gap.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
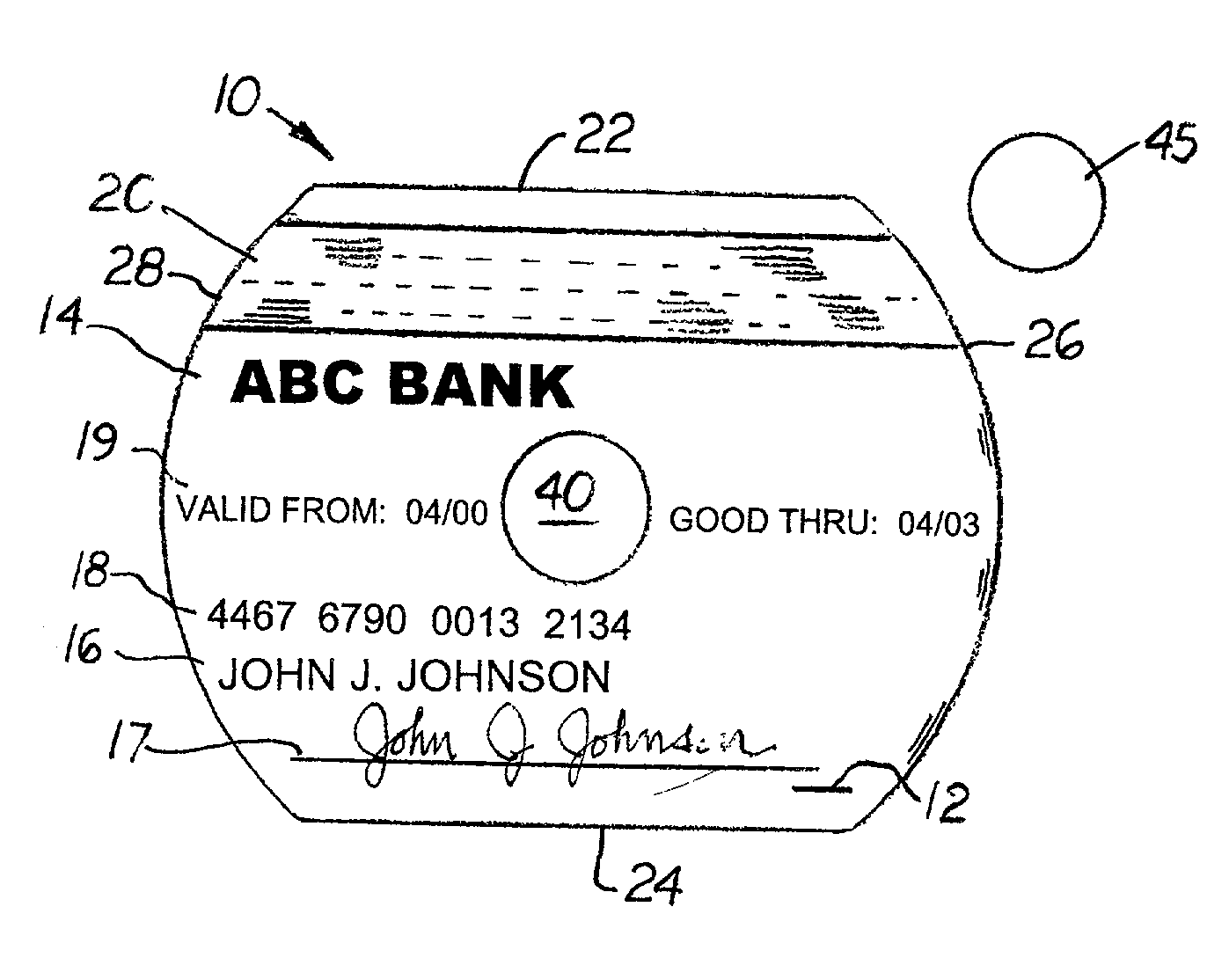
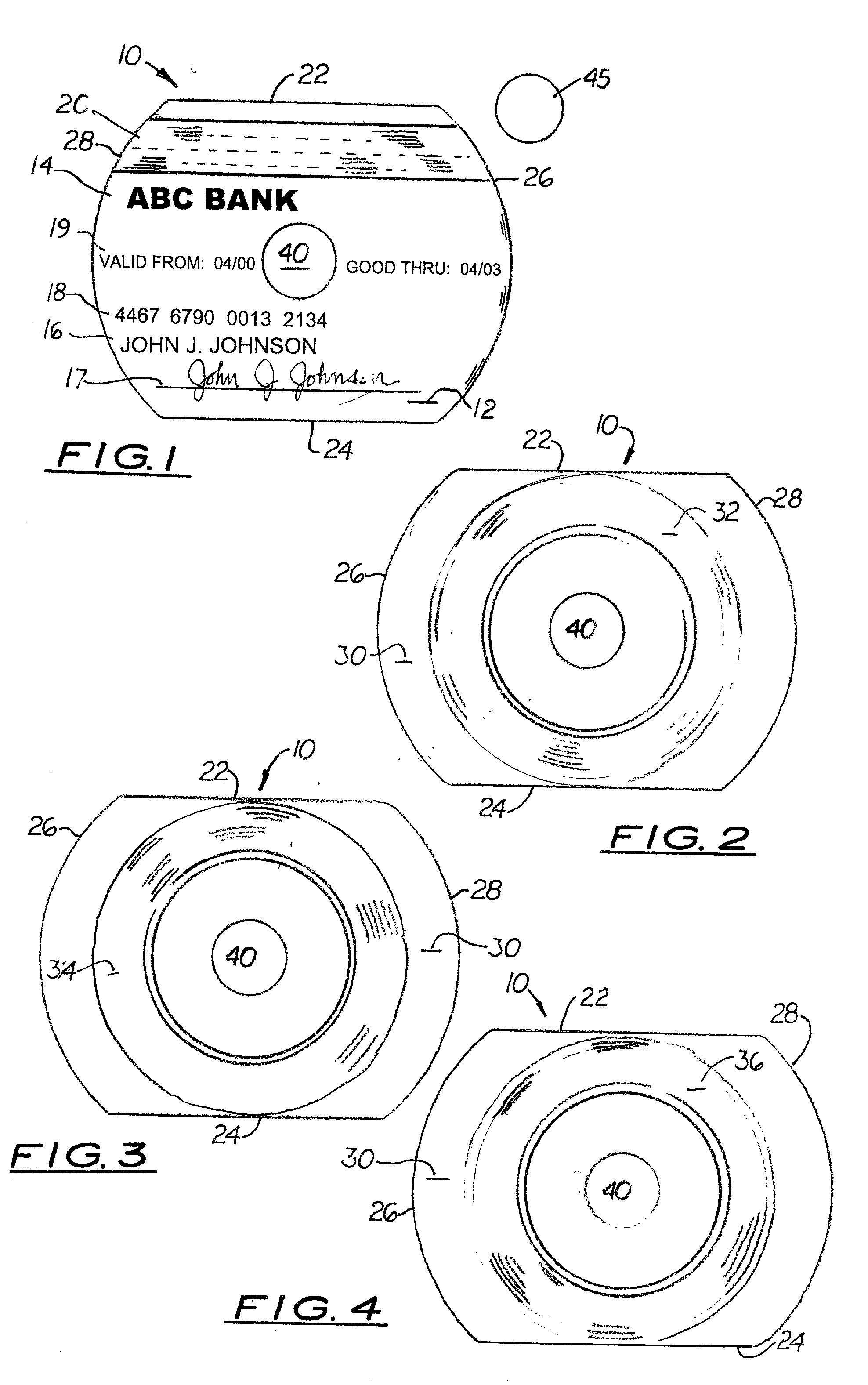
Rewritable CD credit card
InactiveUS20020027837A1Credit registering devices actuationRecord information storageCredit cardRecordable CD
The CD credit card includes vendor and cardholder information and a magnetic strip attached to the front surface designed to be used with a standard reading terminal. Formed on the rear surface is a CD media surface capable of being read in a standard CD-ROM player. In one embodiment, the CD media surface is a "multiple write and read" media surface capable of being produced by a CD-RW device. In a second embodiment, the CD media surface is in "write once, read many" media surface capable of being produced by a CD-R device. Formed centrally on the disc body is a spindle hole which enables the disc to be placed in a CD player. An optional plug may be inserted into the spindle hole.
Owner:WEBER WARREN D
Thermally-assisted magnetic recording head, method of manufacturing the same, and thermally-assisted magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS7042810B2Optimize timingEfficient and stable recordingElectron beam carrier recordingNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic poles
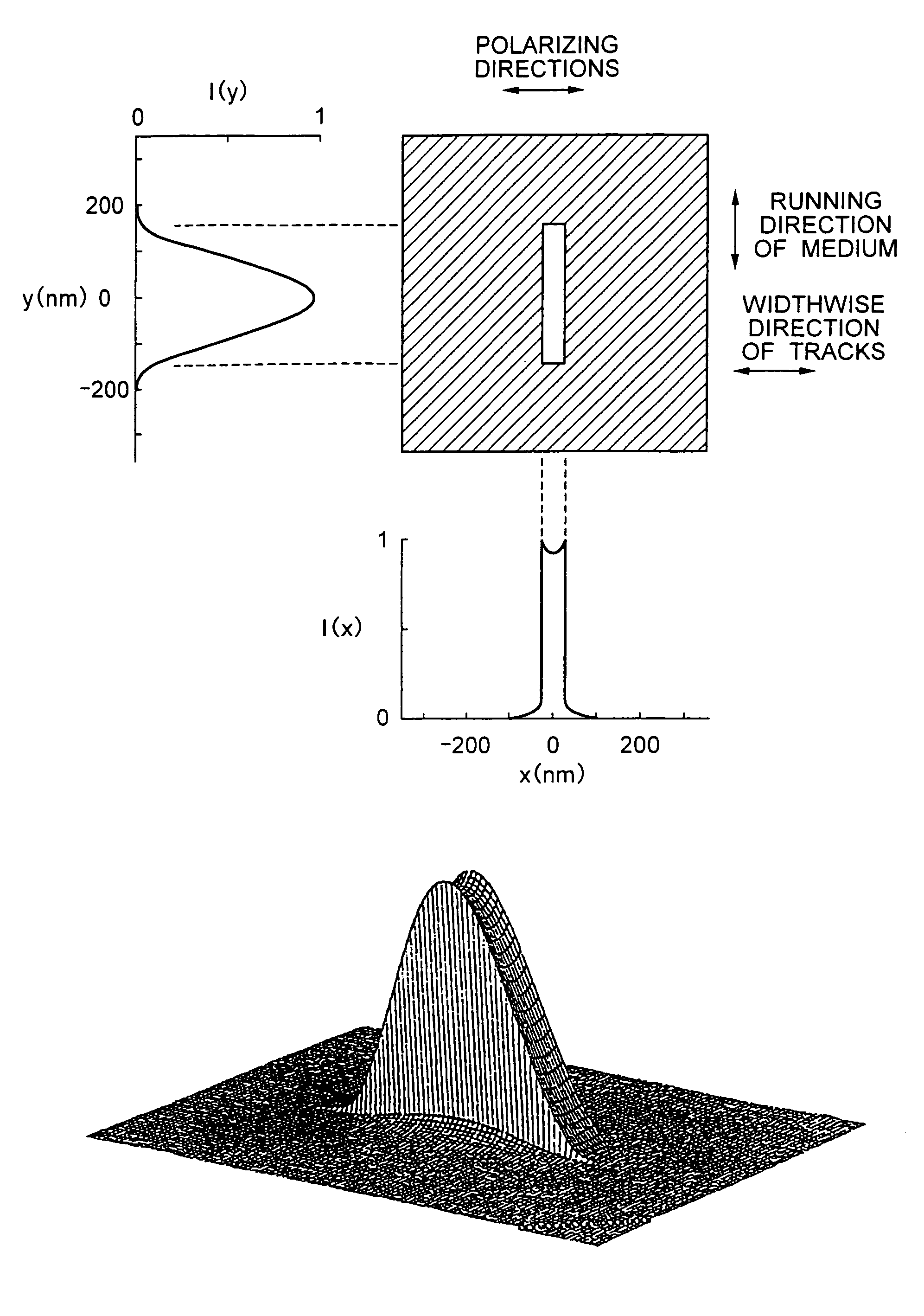
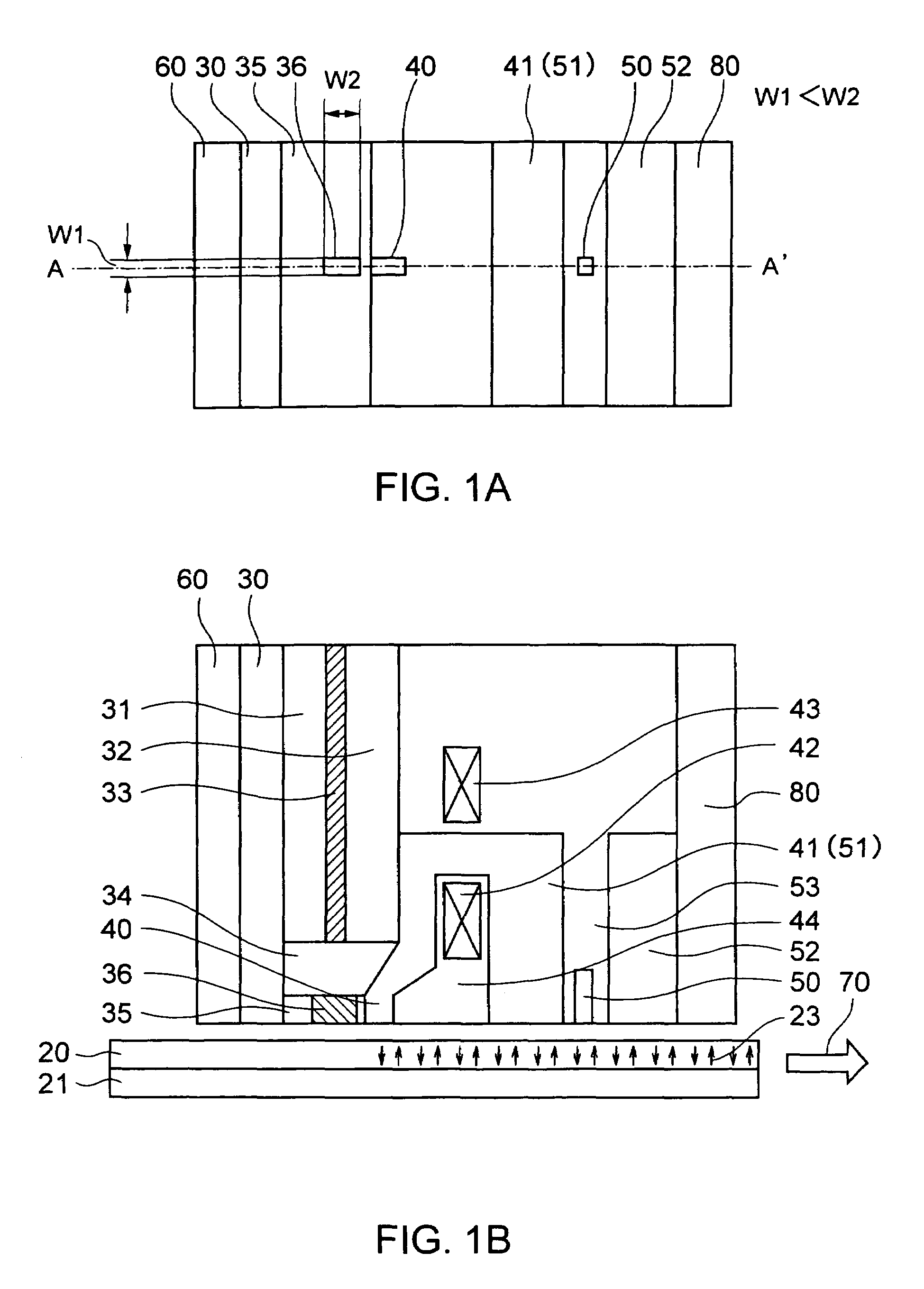
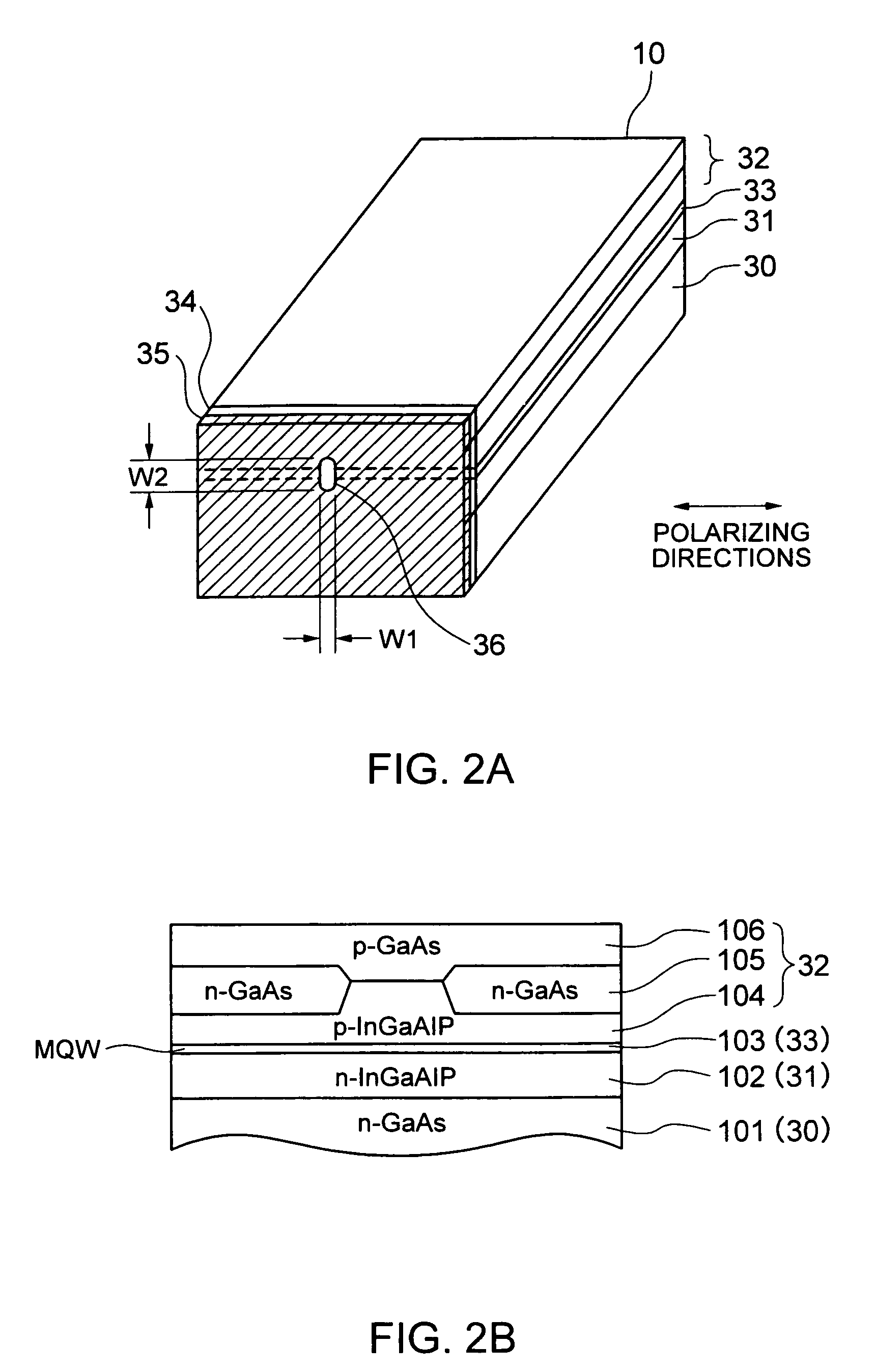
A thermally-assisted magnetic recording head and a magnetic recording apparatus having the magnetic recording head built in are disclosed. The magnetic recording head is capable of recording magnetic information by heating a recording unit of a recording medium and raising its temperature to reduce magnetic coercive force and then applying recording magnetic field to the recording unit having the reduced coercive force. The magnetic recording head has a light absorbing film having an aperture, a laser device emitting and directing light through the aperture to the recording medium to head the recording unit and raise its temperature, and a recording magnetic pole for applying the recording magnetic field to the recording unit. In the aperture, an aperture width W1 is along a polarizing direction of the light emitted from the laser device while an aperture width W2 is approximately perpendicular to the polarizing direction of the aperture width W1, and the aperture width W1 is shorter than the aperture width W2. The heating source such as a laser device recedes from the medium to provide a unique configuration where a tip of the recording magnetic pole protrudes ahead of the heating source, and hence, heating beam and the recording magnetic pole can be located close to each other without losing sufficient energy density to heat the medium.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
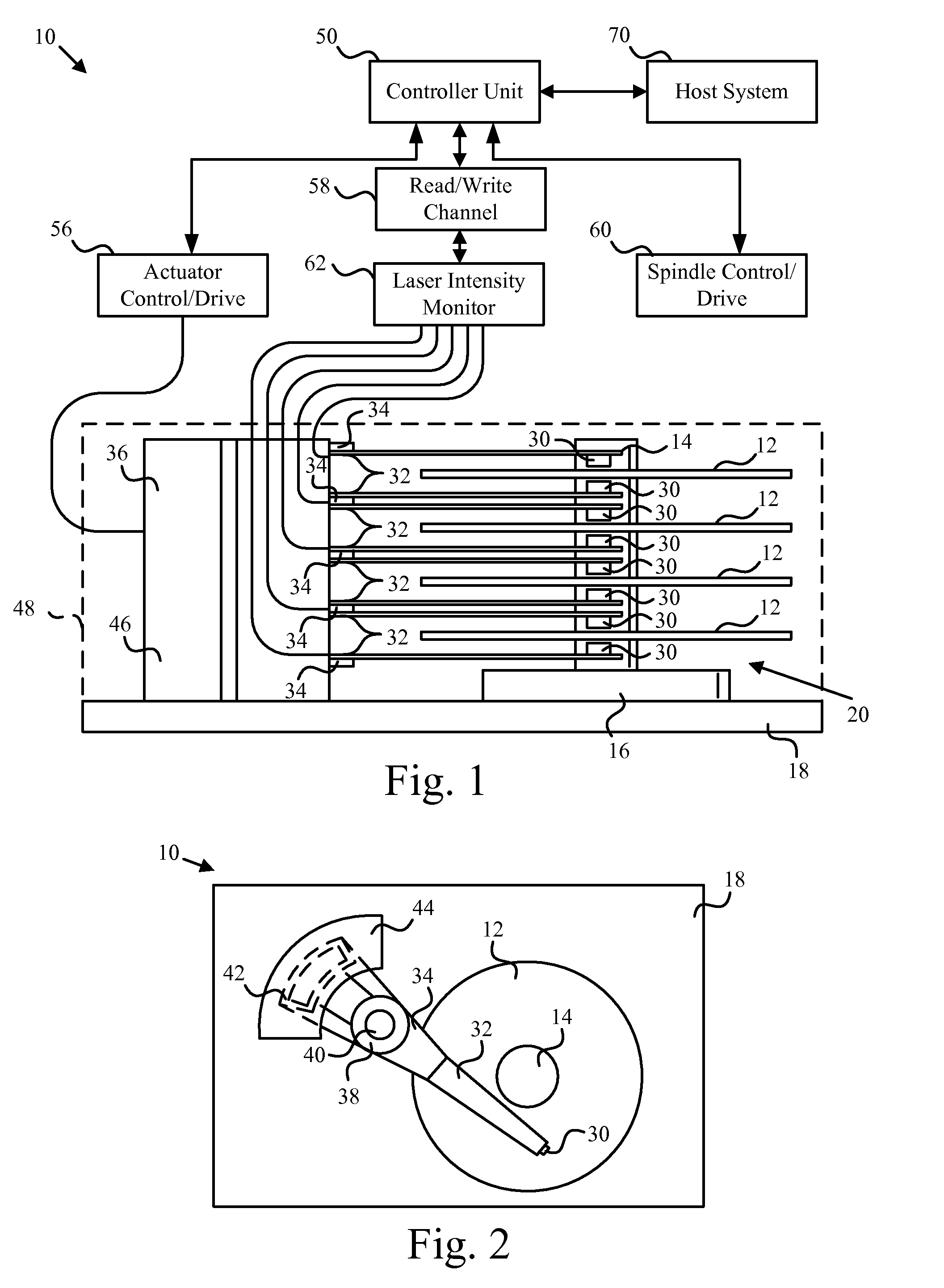
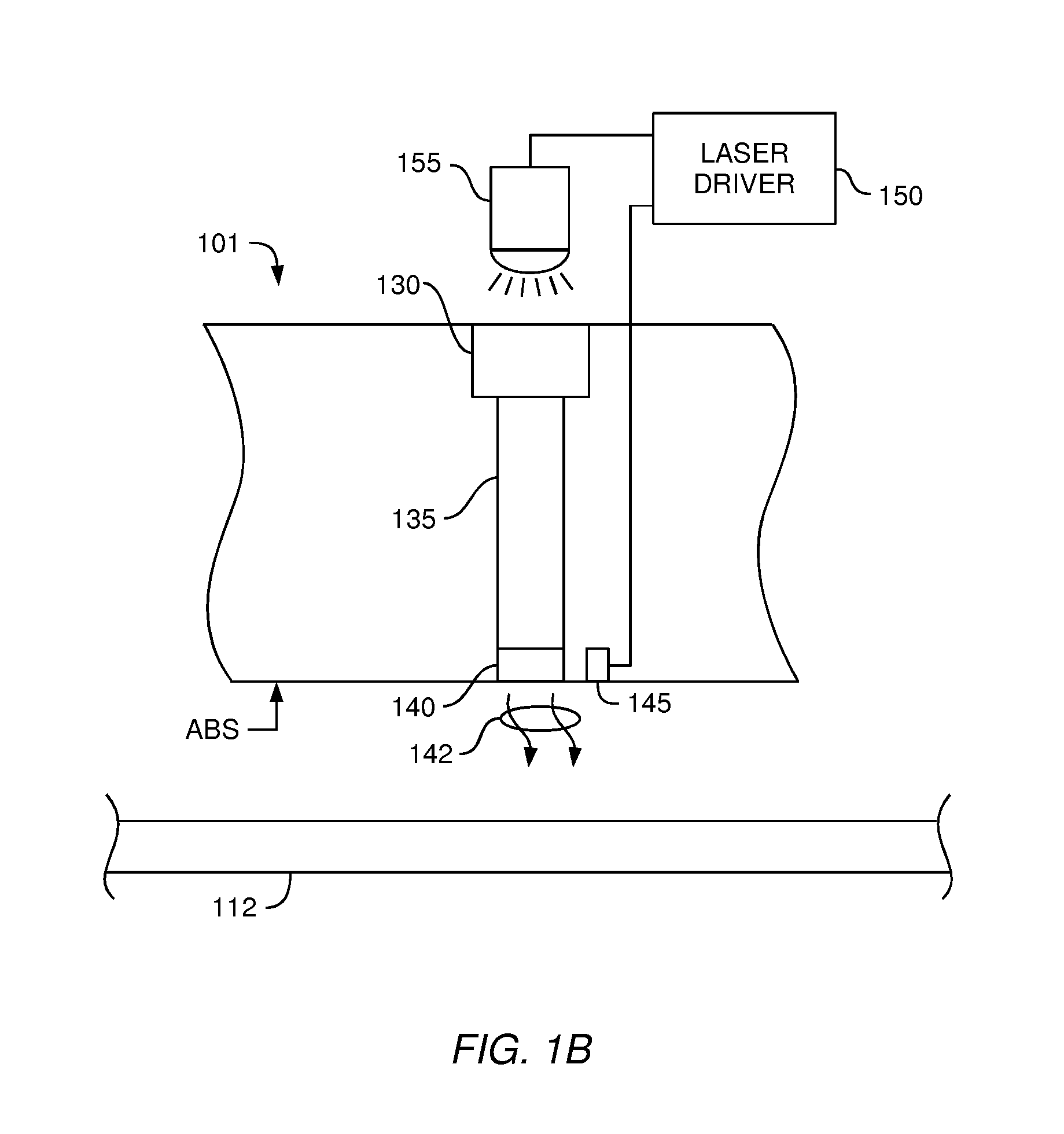
Laser power sensor for thermally assisted magnetic recording
ActiveUS20090225464A1Record information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsPower sensorHeat-assisted magnetic recording
An apparatus, system, and method for measuring thermally induced electric resistance changes in thermally assisted magnetic recording are disclosed for monitoring laser light output in thermally assisted magnetic recording disk drives. An electrical lead is coupled to a read / write head element. A first electrical resistance in the read / write head element is measured. The read / write head is heated by a laser and a second electrical resistance in the read / write head element is measured. The electrical resistance may be monitored at regular intervals when the read / write head element is on the ramp or the electrical resistance measurements may be continuously monitored as the read / write head flies over the magnetic media.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) head with diffusion barrier between waveguide core and write pole lip
ActiveUS20140313872A1Arm with optical waveguideRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingDiffusion barrier
A heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR) head in which the core of the optical waveguide has an end face that abuts the NFT and the write pole lip has a diffusion barrier between the end face of the waveguide core and the write pole lip. The diffusion barrier layer may also be located between the waveguide core end face and the NFT, in which case it is formed of an optically transparent material, like TaNx, TiNx, ZrNx, HfNX, NbNx, CrNx, VNx, TiC, TaC, WC, SiC or SiNx, or a layer of Au, Ru, Rh or Ir with a thickness less than 5 nm. In addition to being located between both the NFT and the write pole lip and the waveguide core end face, the diffusion barrier layer may also be located between the waveguide core and the lower waveguide cladding layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
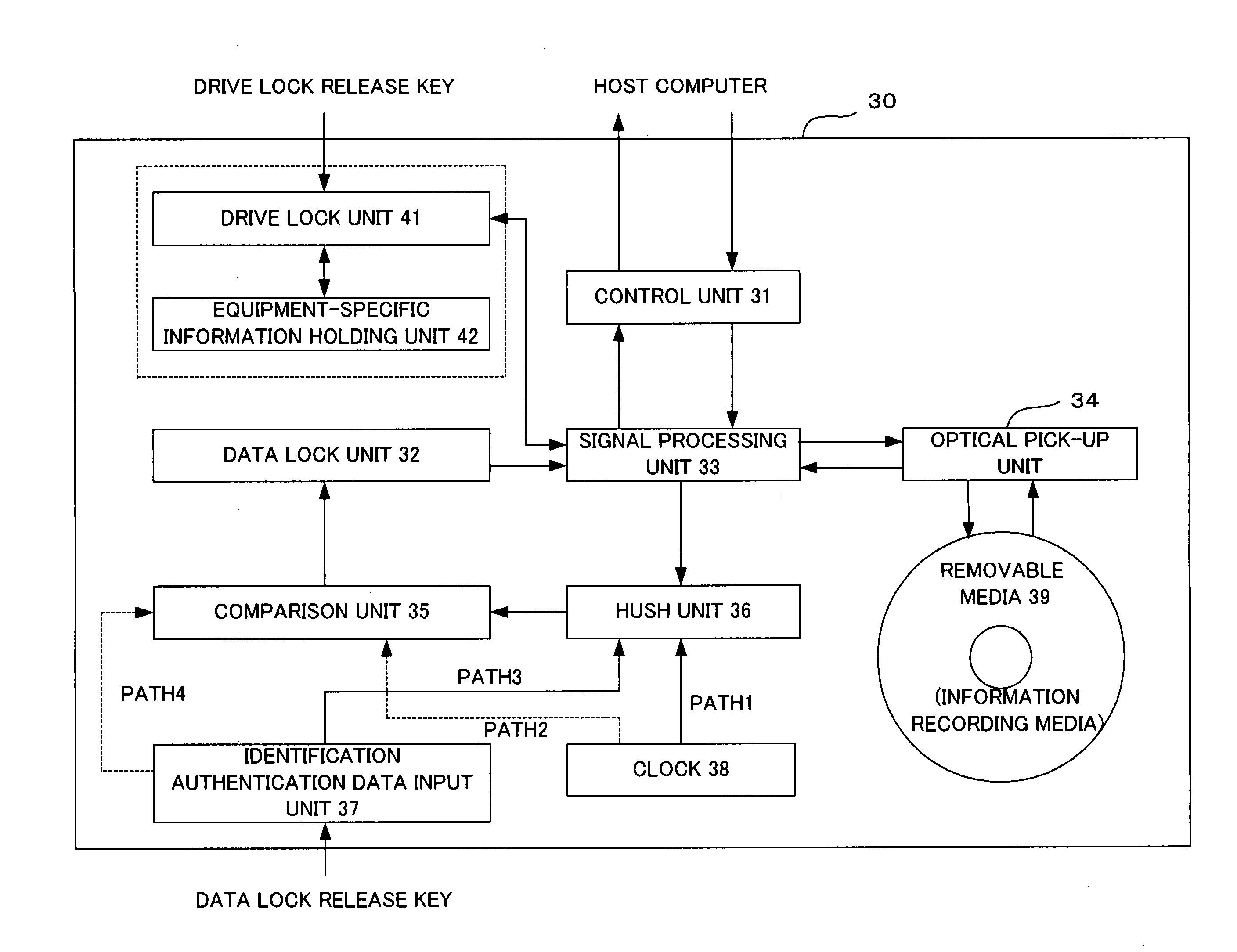
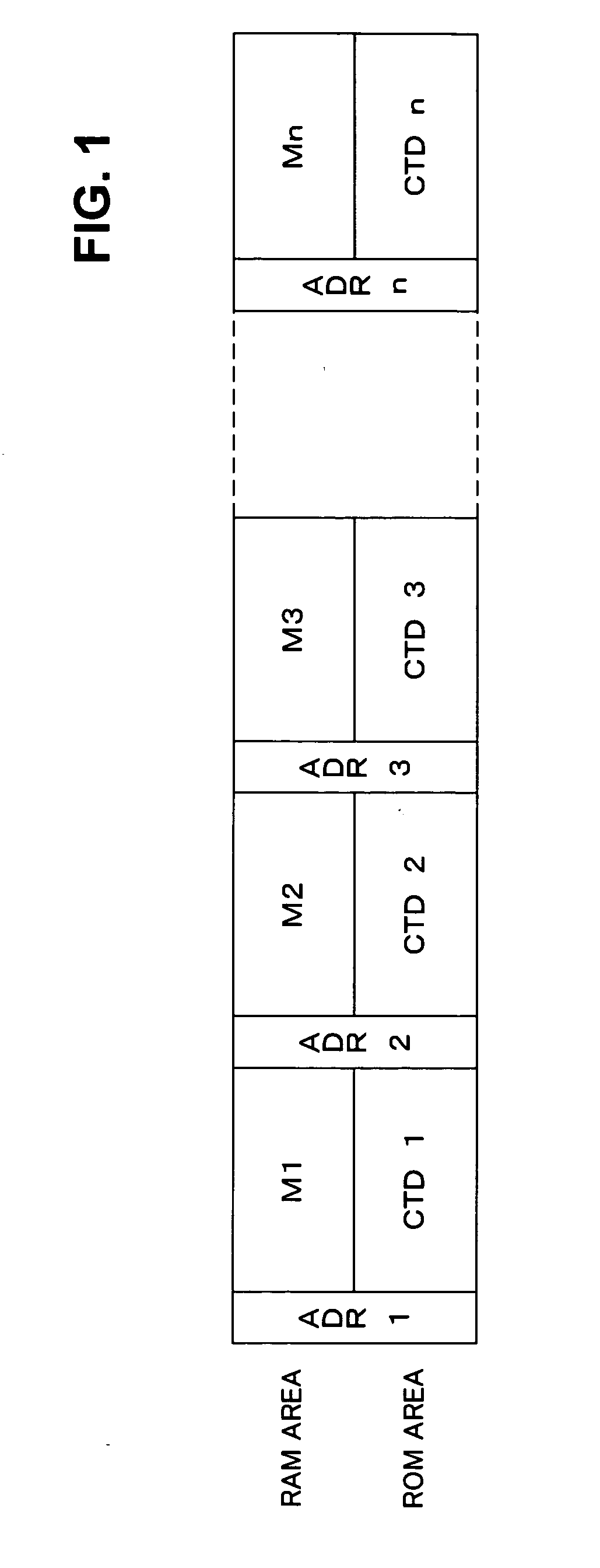
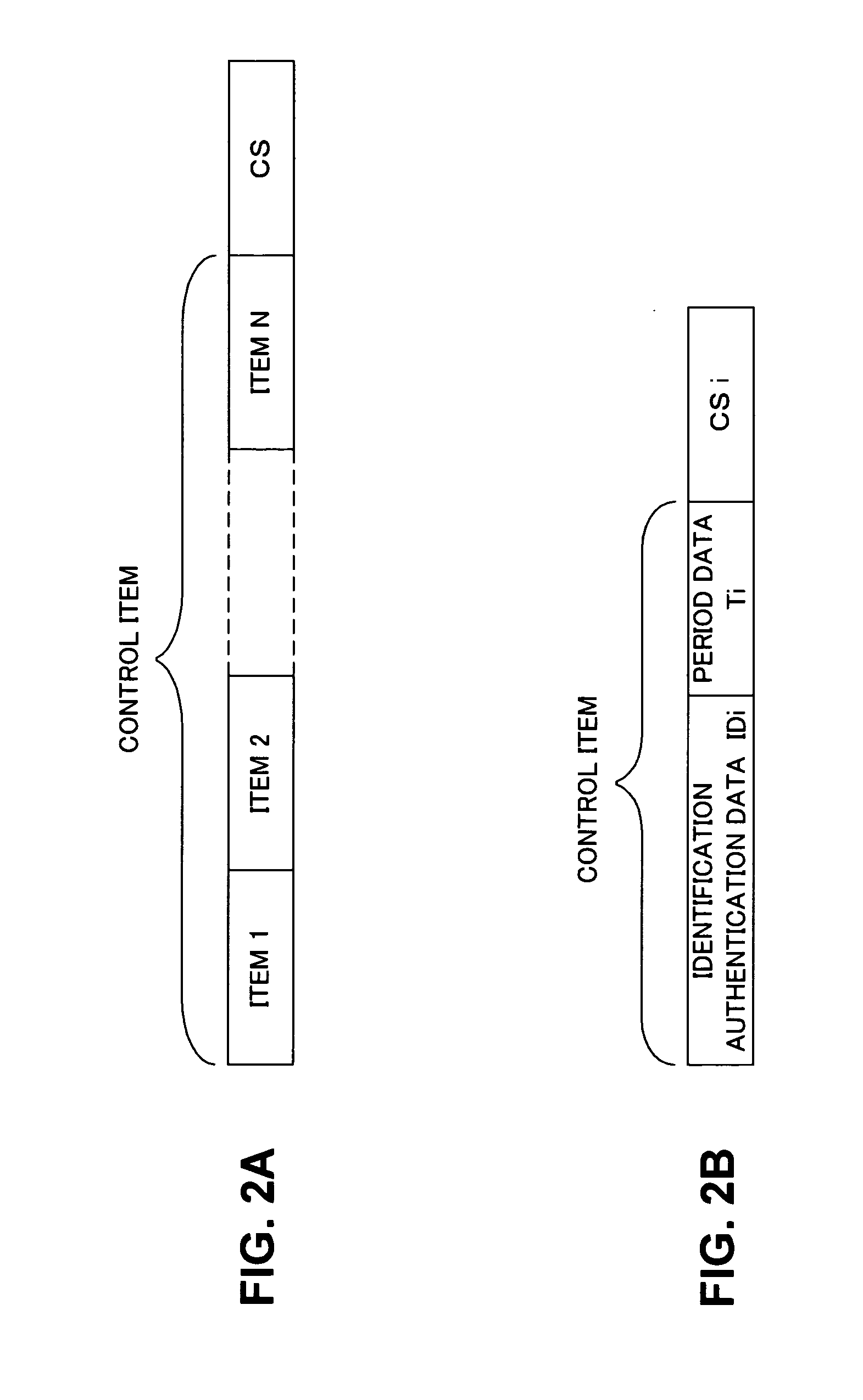
Information record medium and information writing/reading apparatus
InactiveUS20050094516A1Ensuring validityPreventing rewrite (interpolation)Record information storageDigital recordingComputer hardwareInformation control
An information writing / reading apparatus is disclosed that cooperates with an information record medium including a ROM area and a RAM area, either the RAM area or the ROM area having in advance control information recorded thereon used to limit reading and / or writing of information, the information writing / reading apparatus comprising an optical pick-up unit for reading information stored on the information record medium; and a control unit for, based on the control information read by the optical pick-up unit, limiting reading and / or writing of information from / to the other area on which the control information is not recorded and outputting a signal which notifies of presence of the other area only out of the ROM area and the RAM area on the information record medium.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Magnetic head, magnetic recording method and apparatus for controlling magnetic head with spin torque oscillator in a disk drive
ActiveUS20130229895A1Improve recording densityThe implementation process is simpleManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageSpin torque oscillatorsMagnetic poles
A microwave assisted magnetic recording head includes a recording magnetic pole unit that produces a recording field for writing to a perpendicular magnetic recording medium, and a high-frequency magnetic field oscillator that produces a high-frequency magnetic field. The recording magnetic pole unit includes a magnetic core with a write gap portion at which a main recording field component is concentrated, and the high-frequency magnetic field oscillator is disposed in the write gap.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
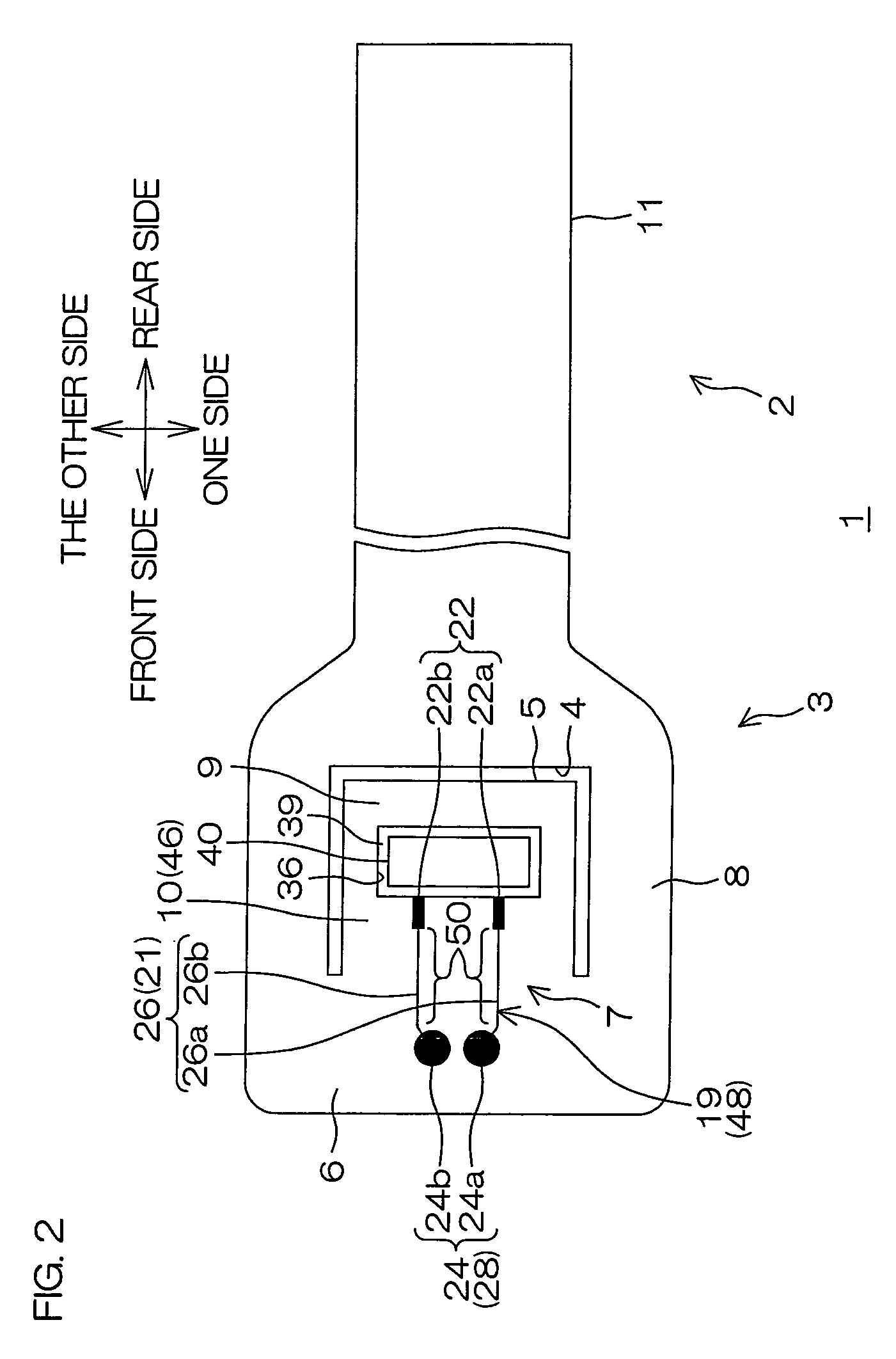
Method and system for providing an electronic lapping guide corresponding to a near-field transducer of an energy assisted magnetic recording transducer
A method and system for fabricating transducer having an air-bearing surface (ABS) is described. The method and system include providing at least one near-field transducer (NFT) film and providing an electronic lapping guide (ELG) film substantially coplanar with a portion of the at least one NFT film. The method and system also include defining a disk portion of an NFT from the portion of the at least one NFT film and at least one ELG from the ELG film. The disk portion corresponds to a critical dimension of the NFT from an ABS location. The method and system also include lapping the at least one transducer. The lapping is terminated based on a signal from the ELG.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
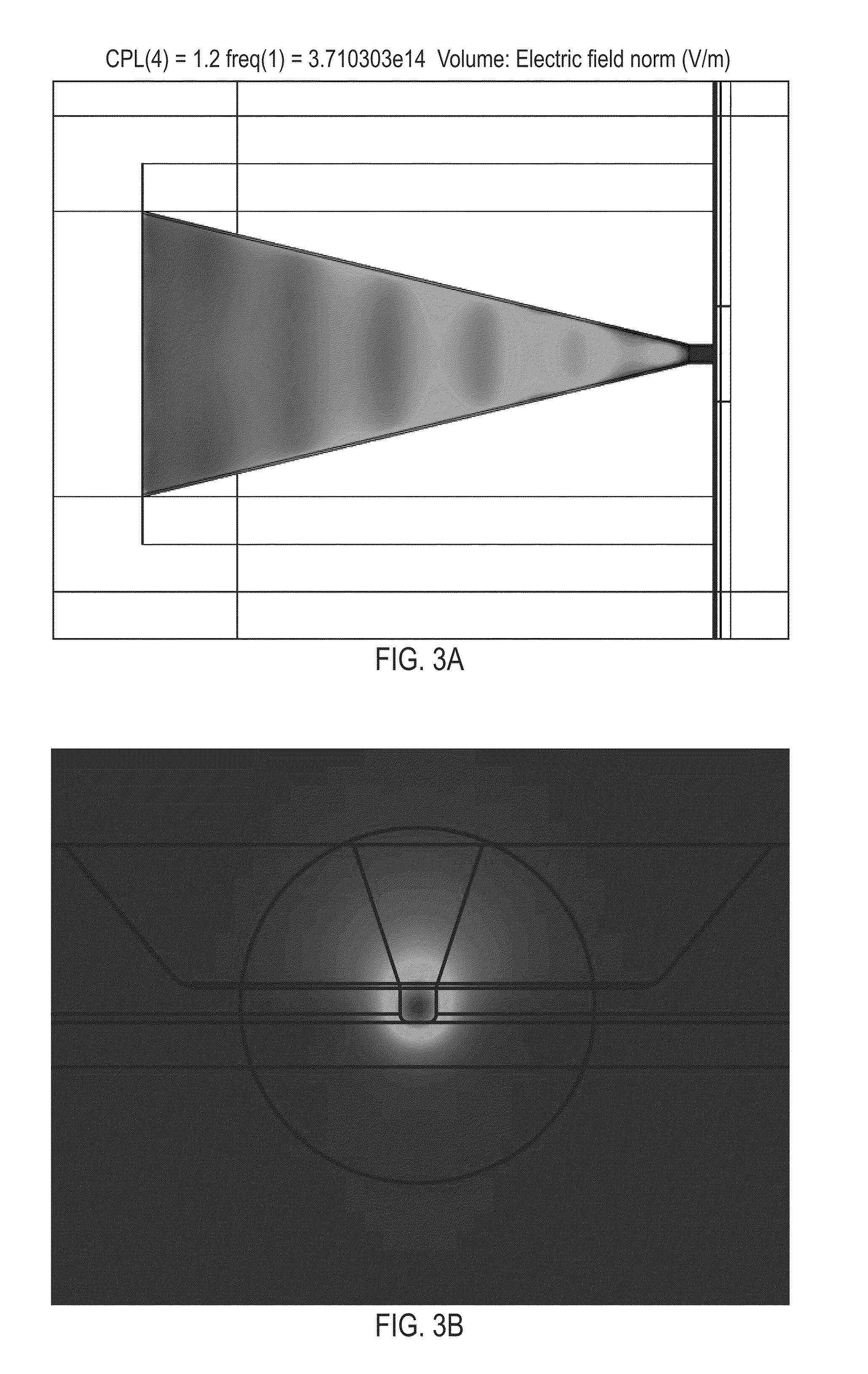
Planar Plasmon Generator with a Scalable Feature for TAMR
ActiveUS20130148485A1Reduce spot sizeReduce widthRecord information storageMagnetic recordingMagnetic anisotropyHeat-assisted magnetic recording
A TAMR (Thermal Assisted Magnetic Recording) write head uses the energy of optical-laser excited surface plasmons in a scalable planar plasmon generator to locally heat a magnetic recording medium and reduce its coercivity and magnetic anisotropy. The planar plasmon generator is formed as a multi-layered structure in which one planar layer supports a propagating surface plasmon mode that is excited by evanescent coupling to an optical mode in an adjacent waveguide. A peg, which can be a free-standing element or an integral projection from one of the layers, is positioned between the ABS end of the generator and the surface of the recording medium, confines and concentrates the near field of the plasmon mode immediately around and beneath it.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Plasmon generator and thermally-assisted magnetic recording head having the same
ActiveUS20140043948A1Laser detailsRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingPlasma generator
A plasmon-generator of the invention is configured to include a first configuration member including a near-field light generating end surface; and a second configuration member joined and integrated with the first configuration member and not including the near-field light generating end surface. The first configuration member is configured to contain Au as a primary component and to contain any one or more elements selected from a group of Co, Fe, Sb, Nb, Zr, Ti, Hf, and Ta, and is configured so that a content percentage X1 of the contained element is within a range between 0.2 at % or more and 2.0 at % or less. Thereby, thermostability, optical characteristic, and the process stability are satisfied. Also, heat dissipation and heat generation suppression effect are extremely superior.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
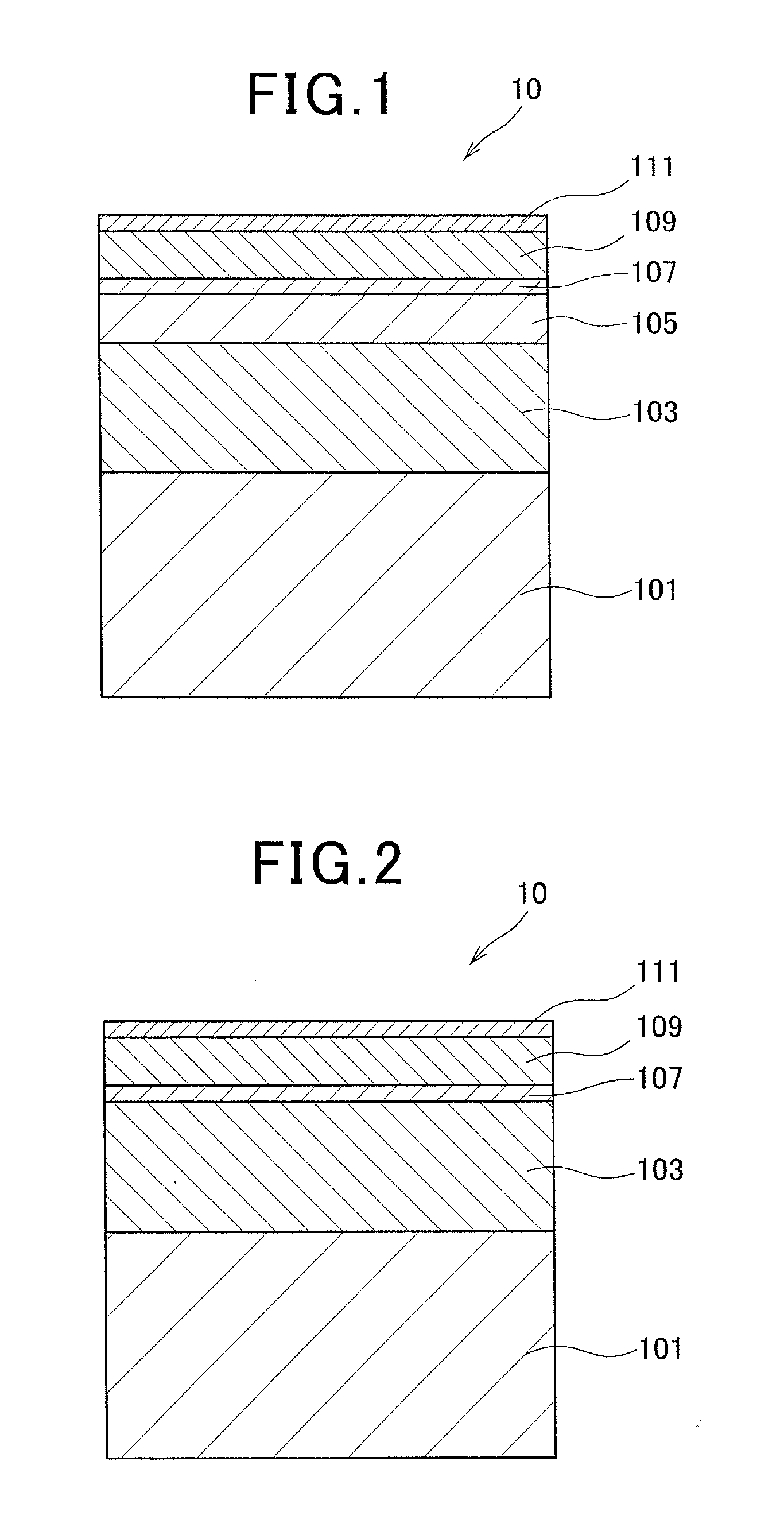
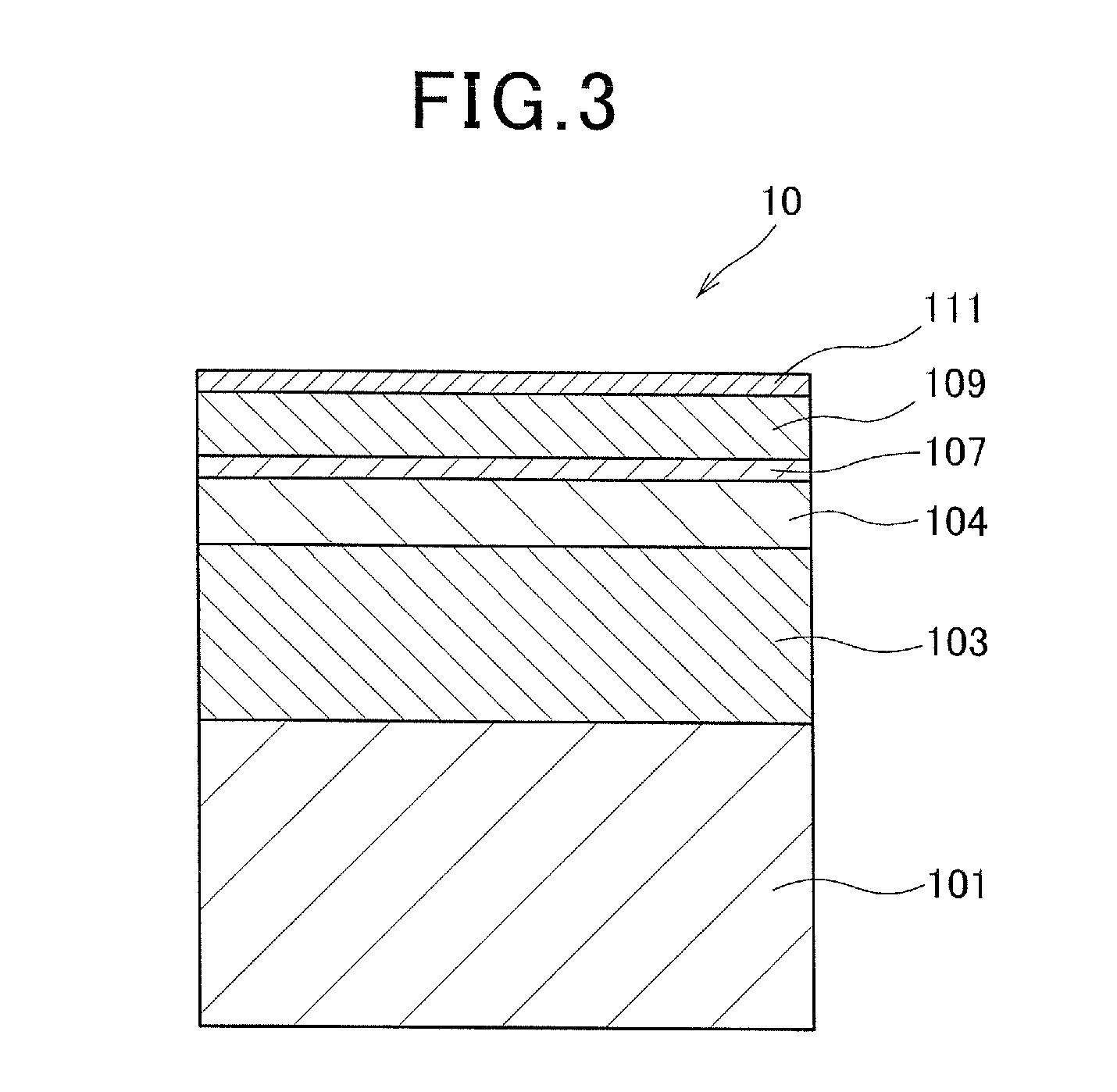
Heat-assisted magnetic recording medium and magnetic storage device
ActiveUS20120113768A1Reduce couplingReduce magnetic cluster sizeMechanical record carriersRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetic storage
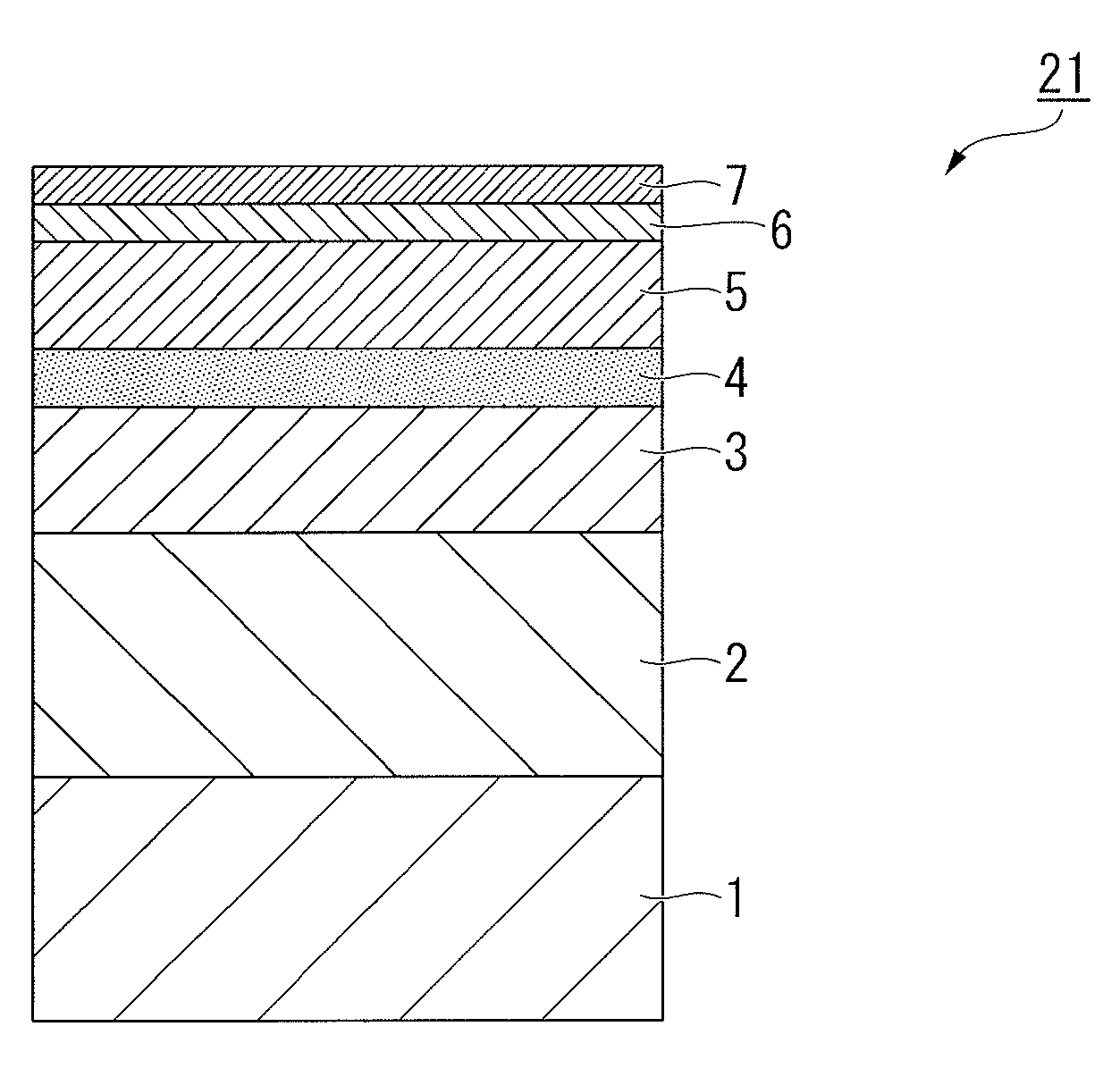
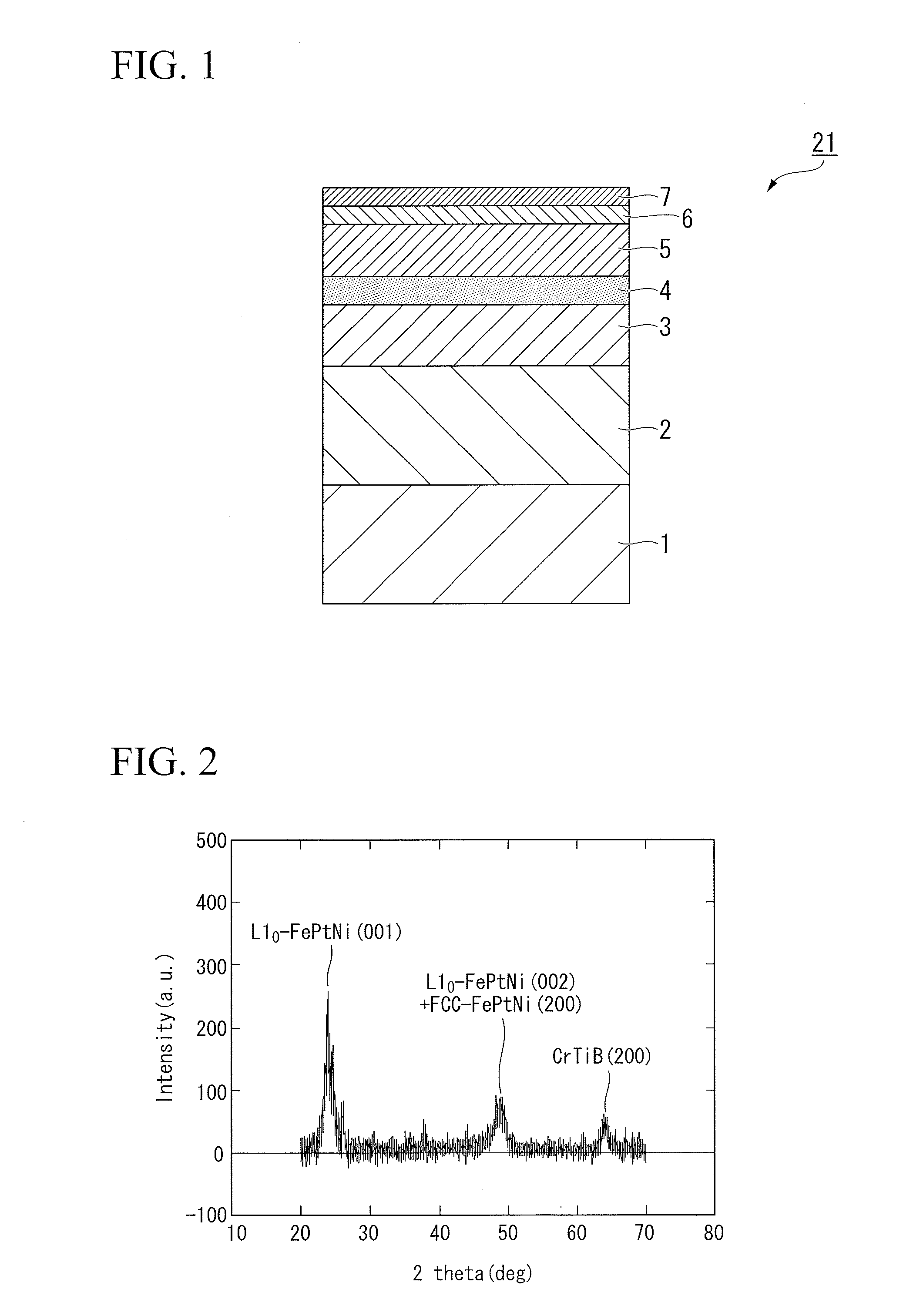
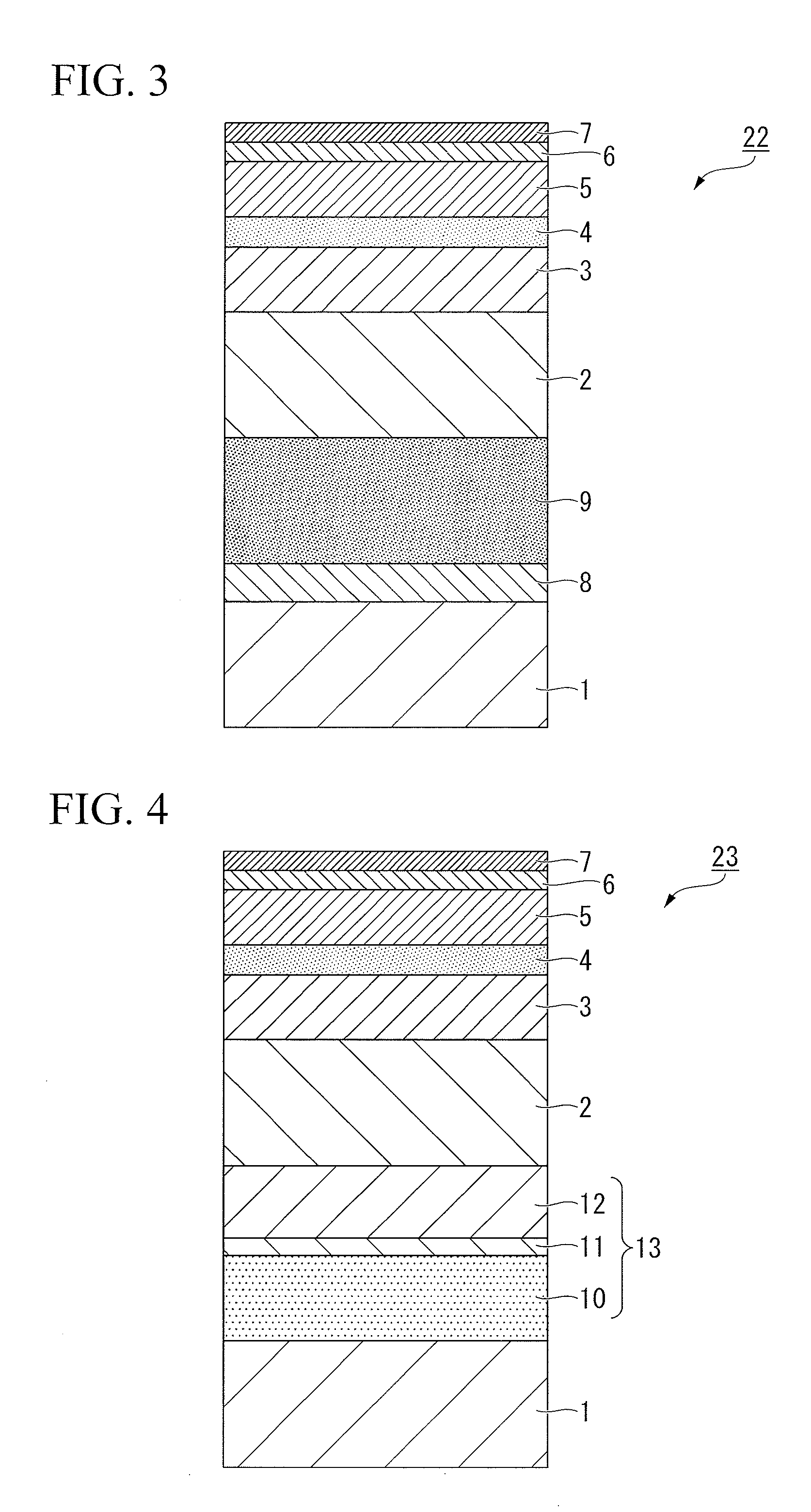
A heat-assisted magnetic recording medium that includes a substrate 1, underlayers formed on the substrate 1, and a magnetic layer 5 which is formed on the underlayers and contains either an FePt alloy having an L10 structure or a CoPt alloy having an L10 structure as a main component, wherein the underlayers include a first underlayer 2 formed from an amorphous alloy, a second underlayer 3 formed from an alloy having a BCC structure containing Cr as a main component and also containing at least one element selected from among Ti, Mo, W, V, Mn and Ru, and a third underlayer 4 formed from MgO. Also, a magnetic storage device that uses the heat-assisted magnetic recording medium.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
Recording/reproducing head and recording/reproducing apparatus incorporating the same
InactiveUS6982932B2Smooth rotationNanomagnetismManufacture head surfaceMagnetic reluctanceRecording media
A magnetic head for reproducing a signal recorded on a recording medium, includes a substrate, a magnetic head core provided on the substrate, having a magnetic gap, and a magnetoresistance device provided on the magnetic head core. The magnetic head core is provided in such a manner that a thickness direction of the magnetic head core around the magnetic gap is substantially the same as a track width direction of the recording medium.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Recordable optical disk including an auxiliary information presence indicator
InactiveUS6885629B2Copyright protectionPrevent the software from being illegally installedAccessories for auxillary signalsDigital data processing detailsRecordable compact discComputer science
An optical disk having a first recording area for recording information; and a second recording area having auxiliary information including disk identification information unique to that optical disk recorded therein, wherein the second recording area including circumferentially arranged multiple stripe patterns each strip extending along a radius of the disk; and indicator indicating the presence of auxiliary information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optically-assisted magnetic recording head and optically-assisted magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20050018547A1Stable magnetic recordingUltra-high densityRecording by magnetic meansHeads using thin filmsHigh intensityLength wave
A pair of members opposed to each other via a gap are commonly used as an evanescent light probe and a writing magnetic head. When the spacing and width of the gap are smaller than the wavelength λ of injected light, highly intensive evanescent light is generated from the gap position of the opposite surface. Magnetic writing is carried out by applying a recording magnetic field from the pair of members to a medium heated by the evanescent light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
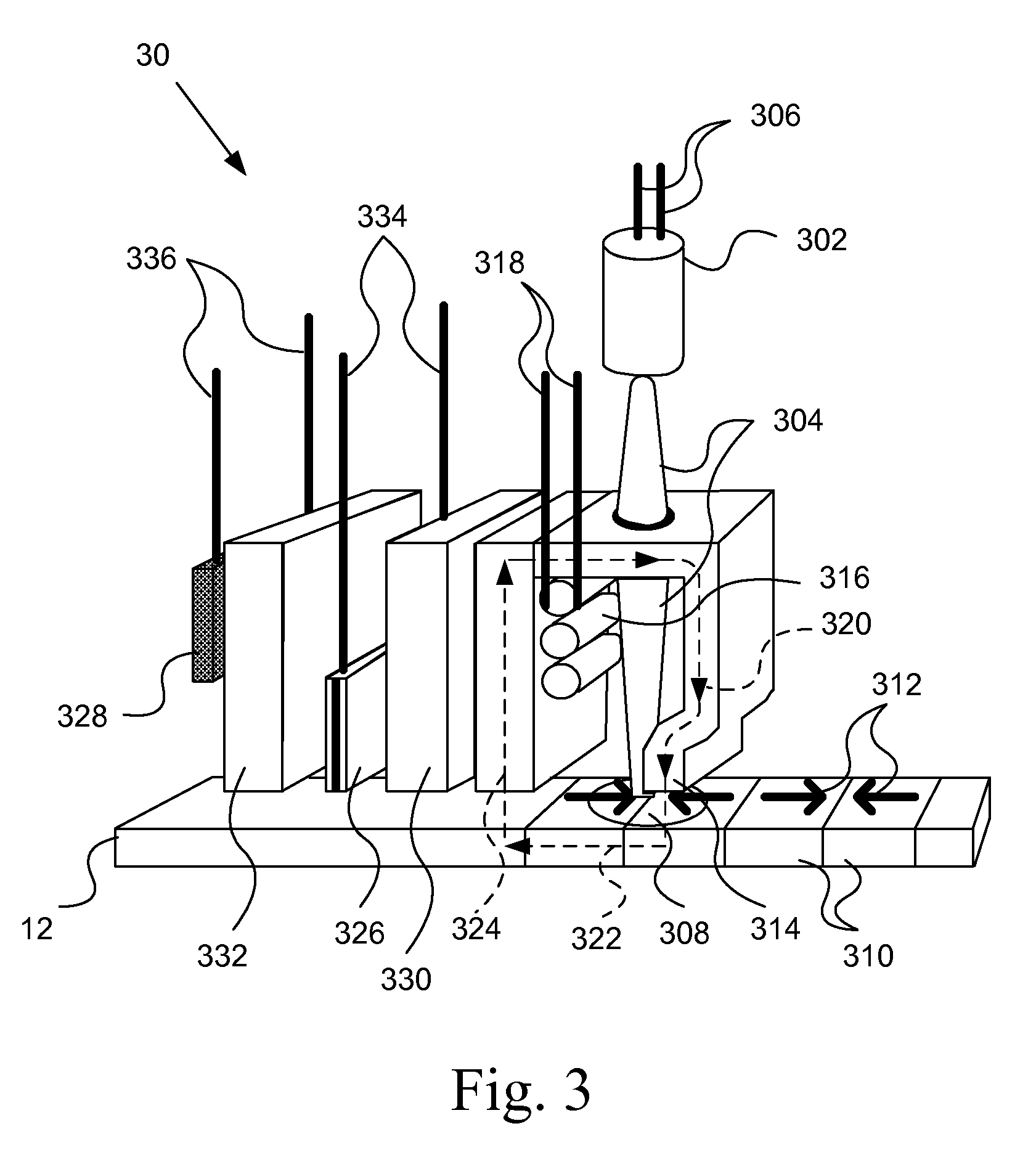
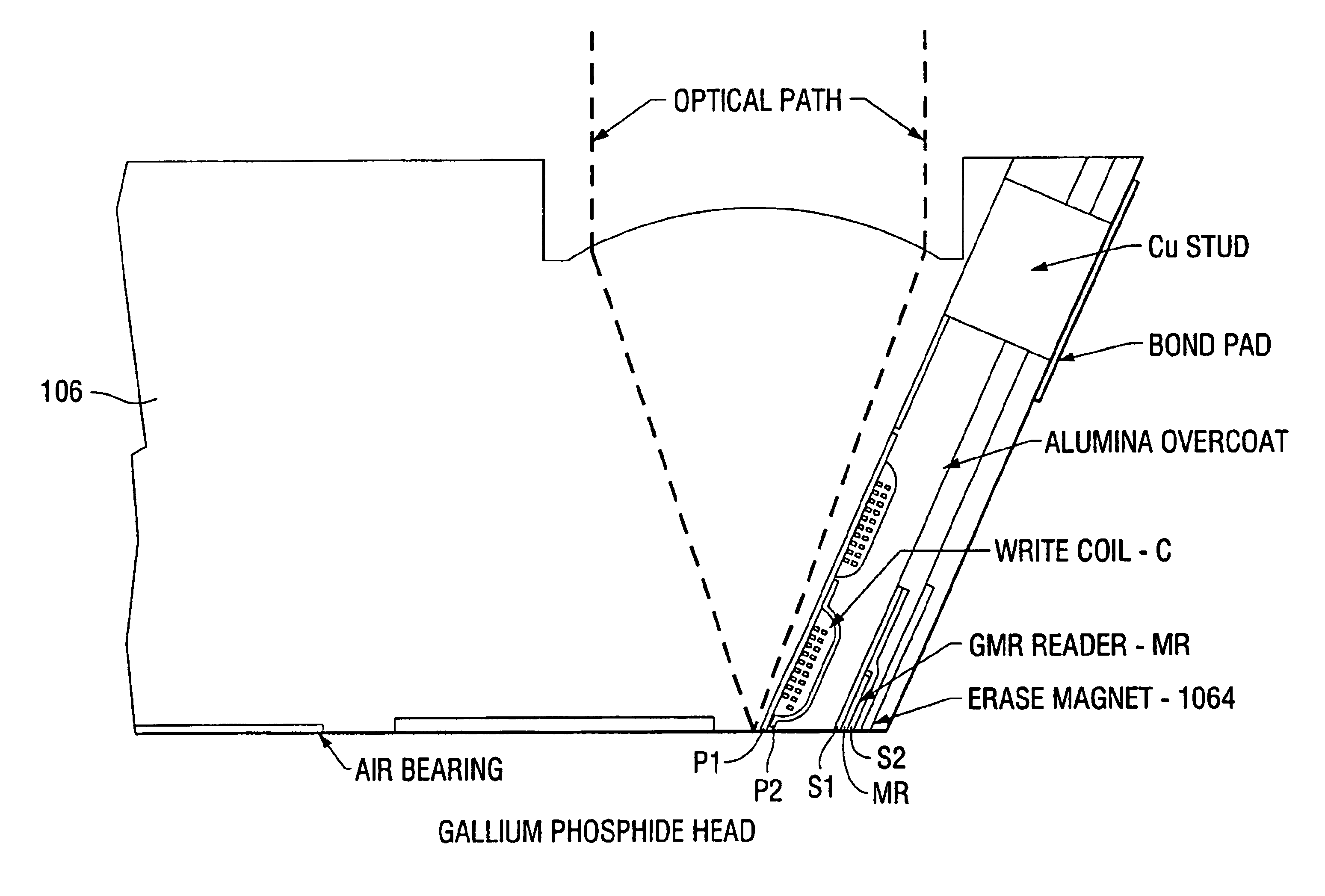
TAR temperature sensor having faster response time
ActiveUS8705323B2Record information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic media
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Inductive write head driven only by an ampere wire
InactiveUS7149055B2Efficient executionDifficult to magnetizeConstruction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceElectrical conductorEngineering
A magnetic recording head comprises a write pole having a tip adjacent to an air bearing surface of the recording head, a return pole magnetically coupled to the write pole, a conductor positioned adjacent to at least one edge of the write pole at the air bearing surface for carrying current to produce a magnetic field that saturates at least a portion of the write pole and augments a write field, a first conductive heat sink connected to a first end of the conductor, and a second conductive heat sink connected to a second end of the conductor. Disc drives that include the recording head are also included.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Tar temperature sensor having faster response time
ActiveUS20130107680A1Record information storageProtective measures for recording headsElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic media
TAR enable write heads may use a plasmonic device (e.g., an optical transducer) which uses electromagnetic energy generated from a laser to heat the magnetic media. However, as the temperature of the plasmonic device rises, the likelihood of stressing the material of the device or other materials of the head near the plasmonic device increases. Accordingly, the write head may include a temperature sensor proximate to the plasmonic device. In one embodiment, the resistance of the temperature sensor may change according to the temperature of the plasmonic device. Based on the measured resistance of the temperature sensor, a sensing circuit may adjust the power of the laser, and thus, prevent the stressing of the materials. Moreover, the thermal coupling between the temperature sensor and a heat sink connected to the plasmonic device may be improved by moving elements associated with the sensing circuit closer to a heat sink.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Thermally-assisted magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording/reproducing device using the same
ActiveUS20130016591A1Magnetic materials for record carriersMechanical record carriersHeat-assisted magnetic recordingMagnetization
A thermally-assisted magnetic recording (TAMR) medium of the present invention includes: a magnetization direction arrangement layer on a substrate; and a magnetic recording layer on the magnetization direction arrangement layer, wherein the magnetization direction arrangement layer is made of at least one selected from a group consisting of Co, Zr, CoZr, CoTaZr, CoFeTaZrCr, CoNbZr, CoNiZr, FeCoZrBCu, NiFe, FeCo, FeAlN, (FeCo)N, FeAlSi, and FeTaC so that a spreading of the heating spot applied from the magnetic head for thermally-assisted recording to the film surface of the magnetic recording medium is suppressed, and that an SN is improved by arranging the magnetization direction of the perpendicularly written recording magnetization to become identical to a perpendicular direction, and realizing the higher recording density.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
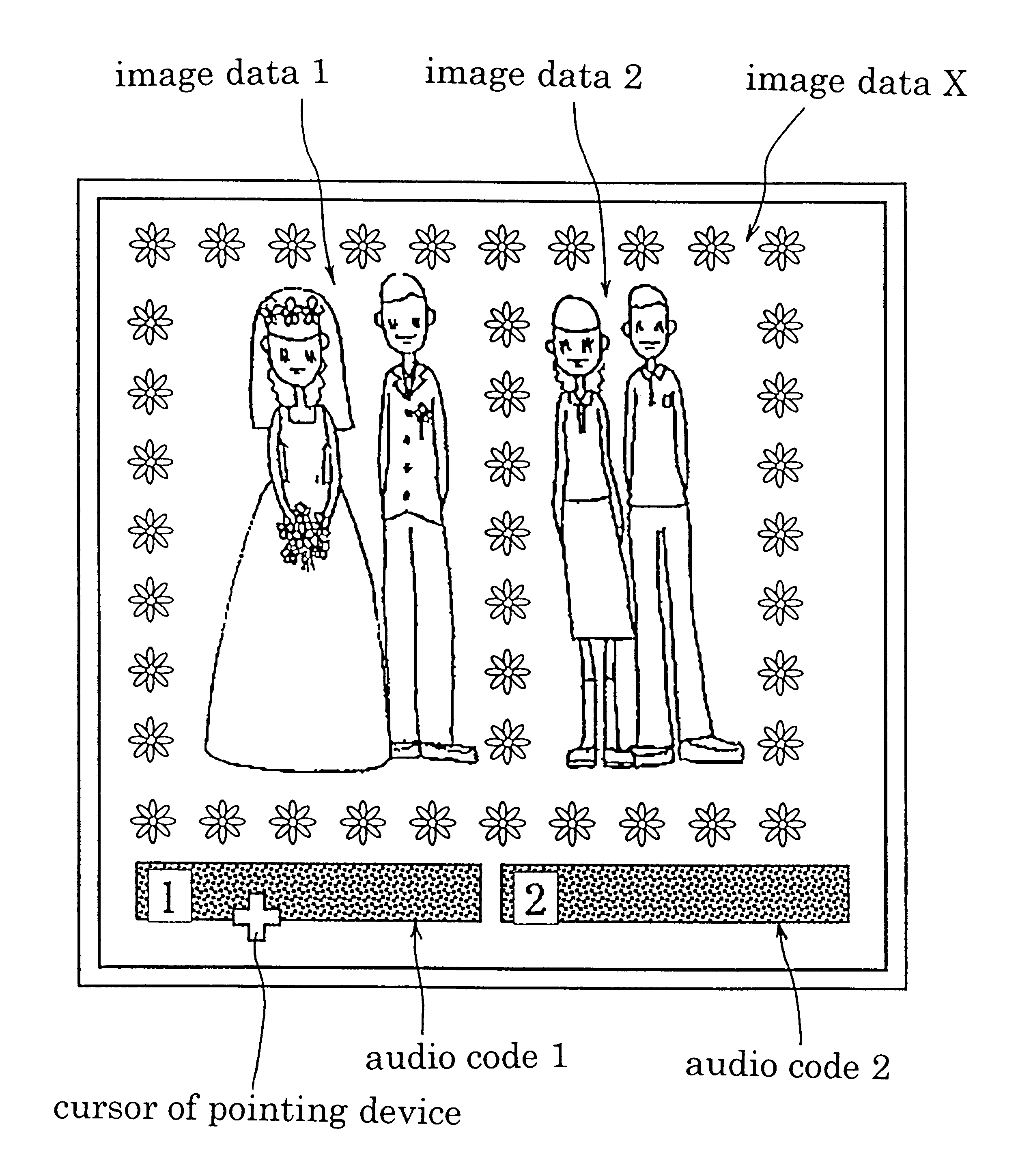
Apparatus for making recording media with audio code images
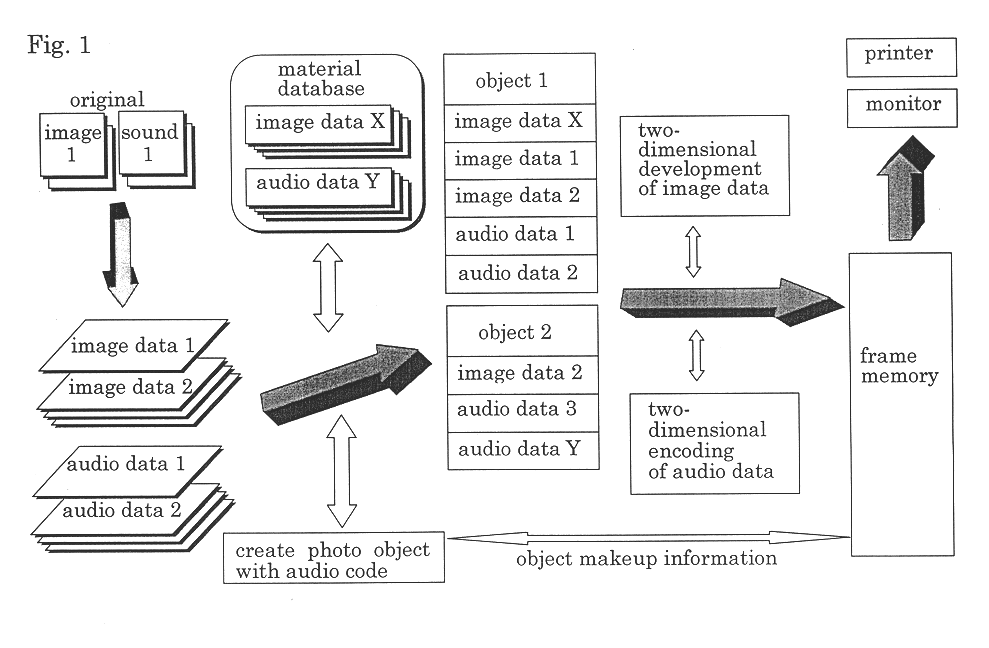
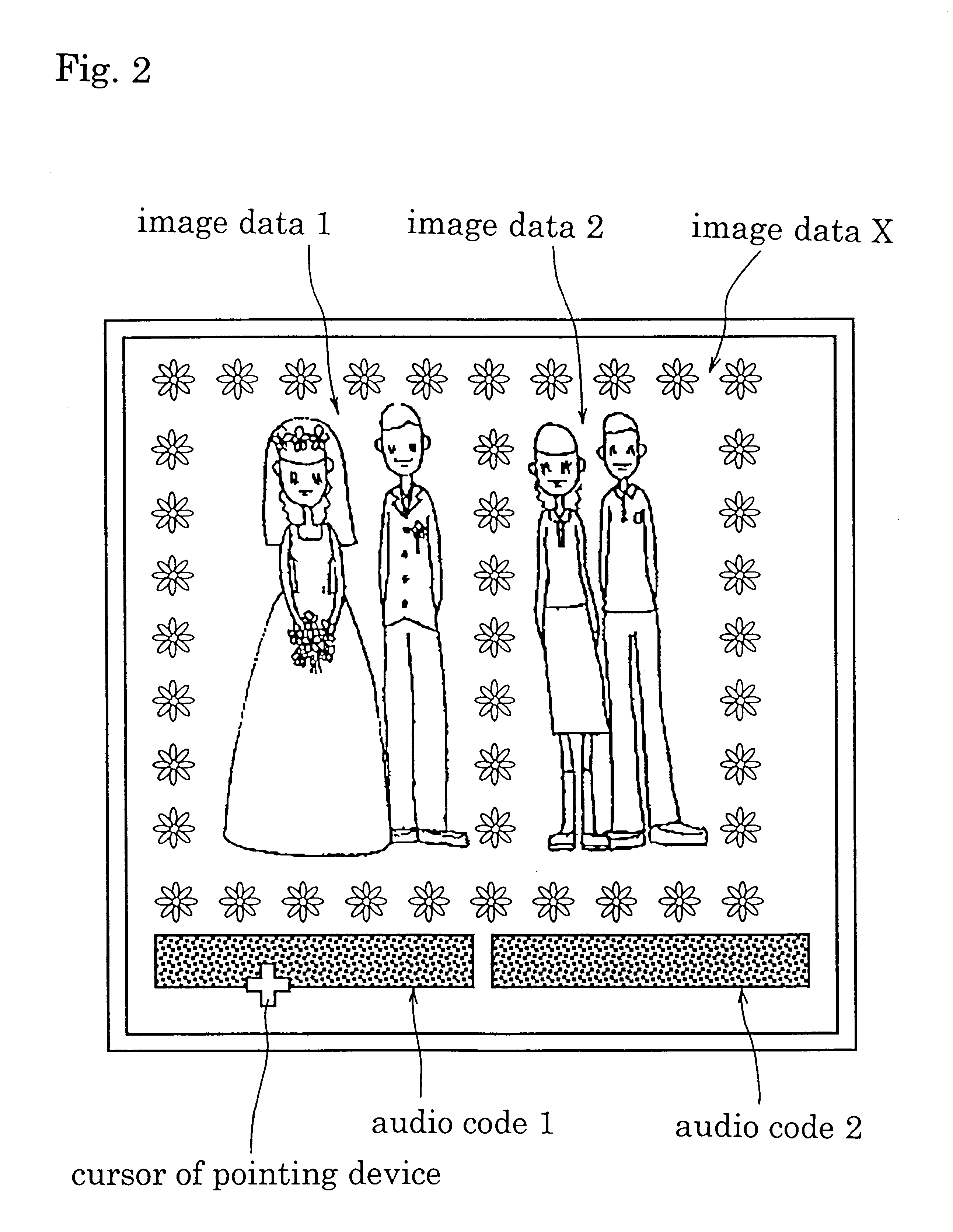
InactiveUS6388681B1Easy to checkEasy to changeProjectorsRecord information storageReverse converterImage Inspection
An apparatus for making recording media with audio code images by combining visual images converted from image information and audio code images encoded to be optically readable from audio information relating to the image information. This apparatus includes a monitor 60 for displaying composite images of visual images and audio code images. To transmit to a speaker audio signals corresponding to the audio code images displayed on the monitor 60, the apparatus has a first audio code image checking function including a pointing device 81 or keyboard 86, an audio data retriever 82, an audio reproducer 83, a speaker 84 and a controller 100, and a second audio code image checking function including the pointing device 81 or keyboard 86, audio reproducer 83, speaker 84, a reverse converter 85 and controller 100.
Owner:NORITZ CORP +1
Laser assisted track width definition and radial control with magnetic recording
InactiveUS6775100B1Increase data capacityReduce the total massTrack finding/aligningNanomagnetismComputer architectureLaser assisted
The present invention provides for the enhancement of the storage capacity of a data disk drive while reducing optical path optics, electronics and / or the mass and complexity of associated read / write heads. The system utilizes light transmitted by optical elements to servo track a data disk and to heat the data disk during reading and writing of data, and magnetic elements for actual reading and writing.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Disk drive media access system
Owner:APPLE INC
Multilayer plasmon generator
ActiveUS20140269237A1Improve reliabilityEfficient disseminationArc welding apparatusRecord information storageSurface plasmonMetallic materials
A plasmon generator has a front end face, a first metal layer, a second metal layer, and an intermediate layer. The front end face generates near-field light based on a surface plasmon. The intermediate layer is interposed between the first metal layer and the second metal layer. Each of the first metal layer, the second metal layer and the intermediate layer has an end located in the front end face. Each of the first and second metal layers is formed of a metal material. The intermediate layer is formed of a material higher in Vickers hardness than the metal material used to form the first metal layer and the metal material used to form the second metal layer.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC +1
Suspension board with circuit
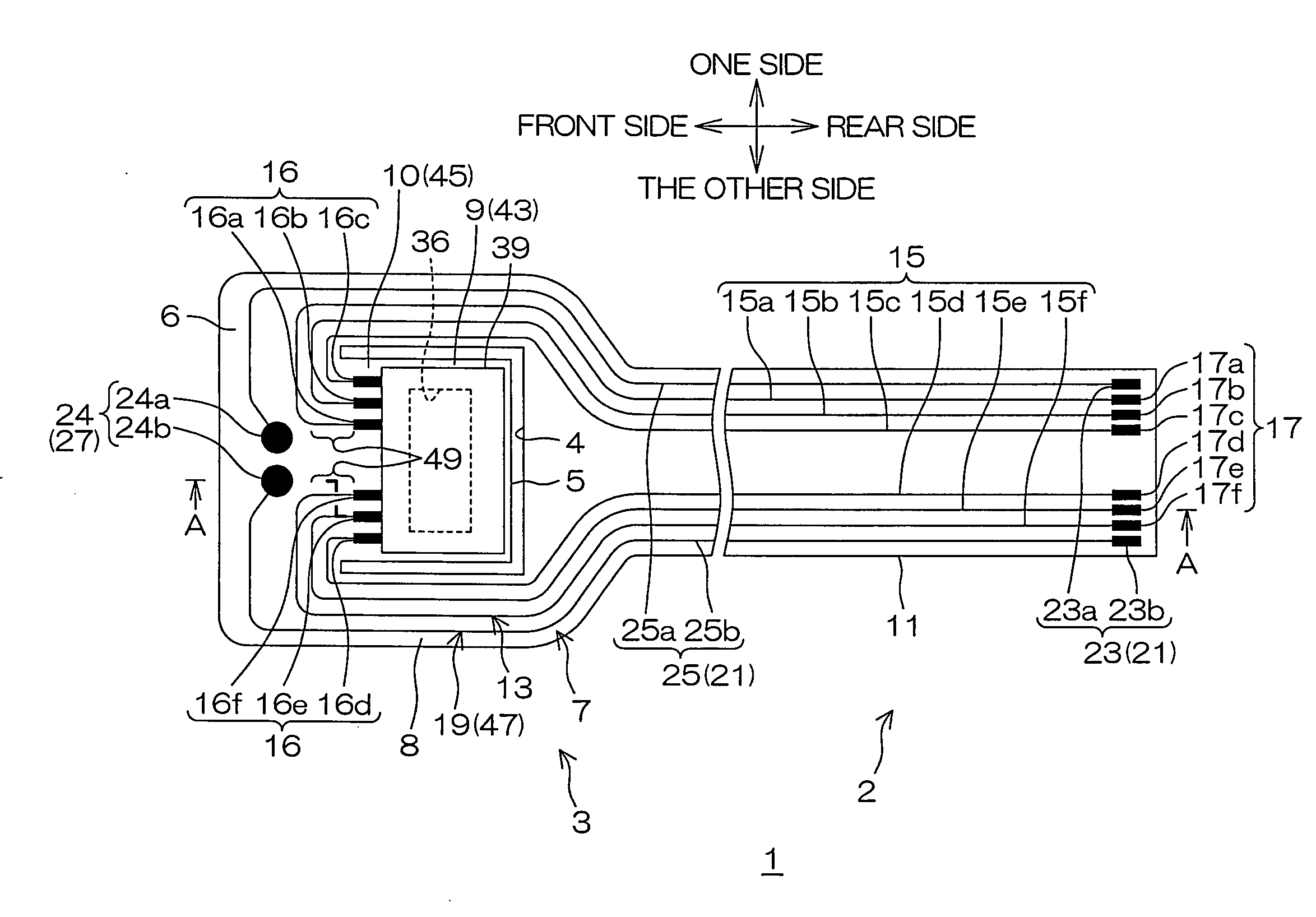
InactiveUS20100110590A1Improve design flexibilityEasily causedElectrical connection between head and armPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringLight emitting device
A suspension board with circuit includes a conductive pattern, including a slider arranged on a surface side of the suspension board with circuit and mounted with a magnetic head, the magnetic head being electrically connected with the conductive pattern; and a light emitting device arranged on the back surface side of the suspension board with circuit and electrically connected with the conductive pattern, in which the conductive pattern includes a first terminal provided on a surface of the suspension board with circuit and electrically connected with the magnetic head; and a second terminal provided on the back surface of the suspension board with circuit and electrically connected with the light emitting device.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Optically-assisted magnetic recording head and optically-assisted magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS7372648B2Stable magnetic recordingUltra-high densityRecording by magnetic meansHeads using thin filmsHigh intensityLength wave
A pair of members opposed to each other via a gap are commonly used as an evanescent light probe and a writing magnetic head. When the spacing and width of the gap are smaller than the wavelength λ of injected light, highly intensive evanescent light is generated from the gap position of the opposite surface. Magnetic writing is carried out by applying a recording magnetic field from the pair of members to a medium heated by the evanescent light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Hard disk drive apparatus with thermally assisted head
ActiveUS20120134246A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioExcessive increase in track width is preventedArm with optical waveguideRecord information storageHard disc driveDriving current
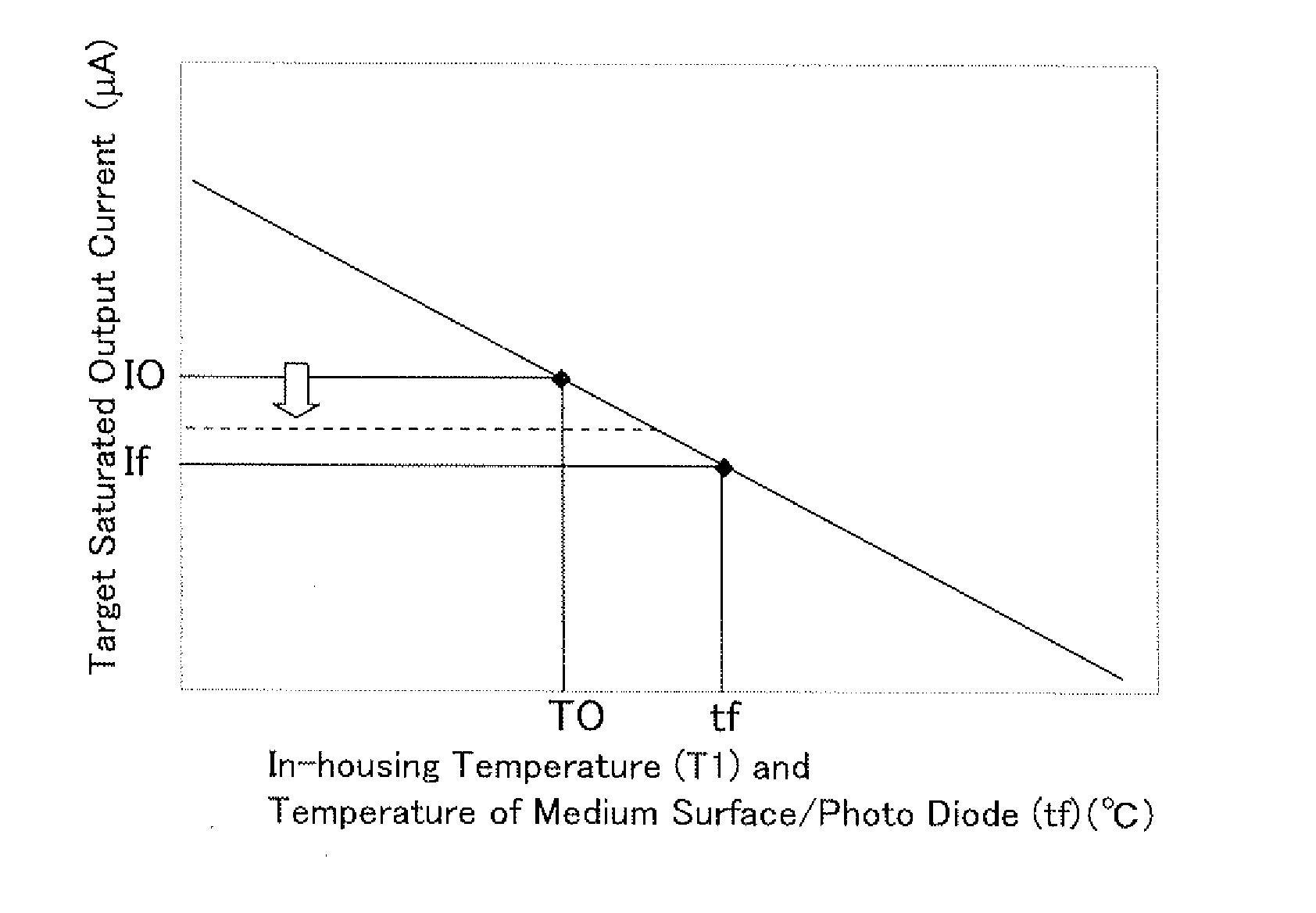
A hard disk drive includes a recording medium and a thermally assisted type magnetic head. The controller determines one output current of a photodiode as a first saturated output current, the one output current being defined where temperature measured by a temperature sensor is a first temperature and where signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) of the reproducing signal current of the reproducing element is saturated with respect to an increase in output current of the photodiode, and another output current of the photodiode as a second saturated output current, the another output current being defined where temperature measured by the temperature sensor is a second temperature, which is different from the first temperature, and where SNR of the reproducing signal current of the reproducing element is saturated with respect to an increase in the output current of the photodiode. A target saturated output current at operation temperature is estimated from operation temperature measured by the temperature sensor during the hard disk device operation, the first and second temperatures, and the first and second saturated output currents; and the driving current of the laser diode is controlled in order to obtain the estimated target saturated output current.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Systems and Methods for Laser Write Control
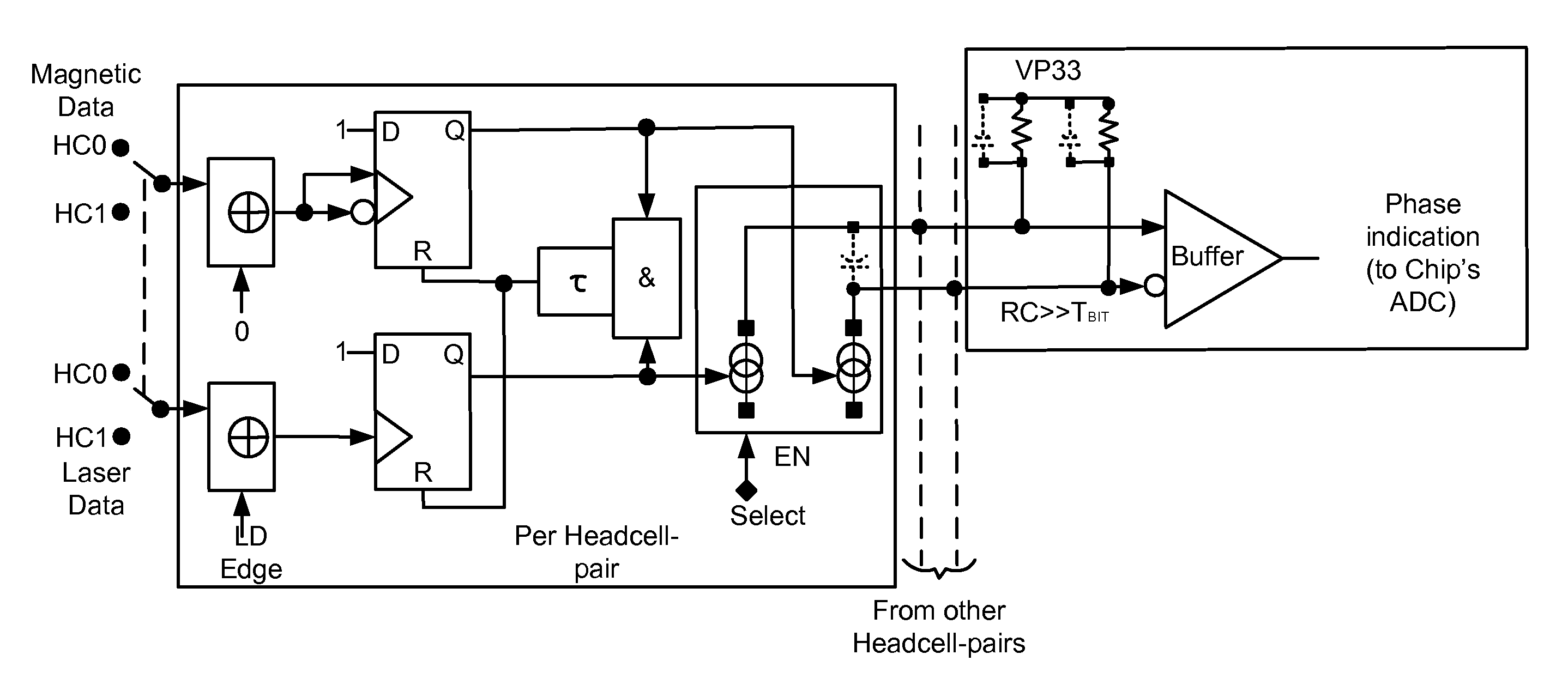
InactiveUS20120275279A1Phase offset is reducedModification of read/write signalsRecord information storagePhase shiftedRelative phase
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for data writing. As an example, a heat assisted data write circuit is discussed that includes a heat write output, a magnetic write output, and a variable phase shift circuit operable to modify a relative phase of the heat write output to the magnetic write output.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
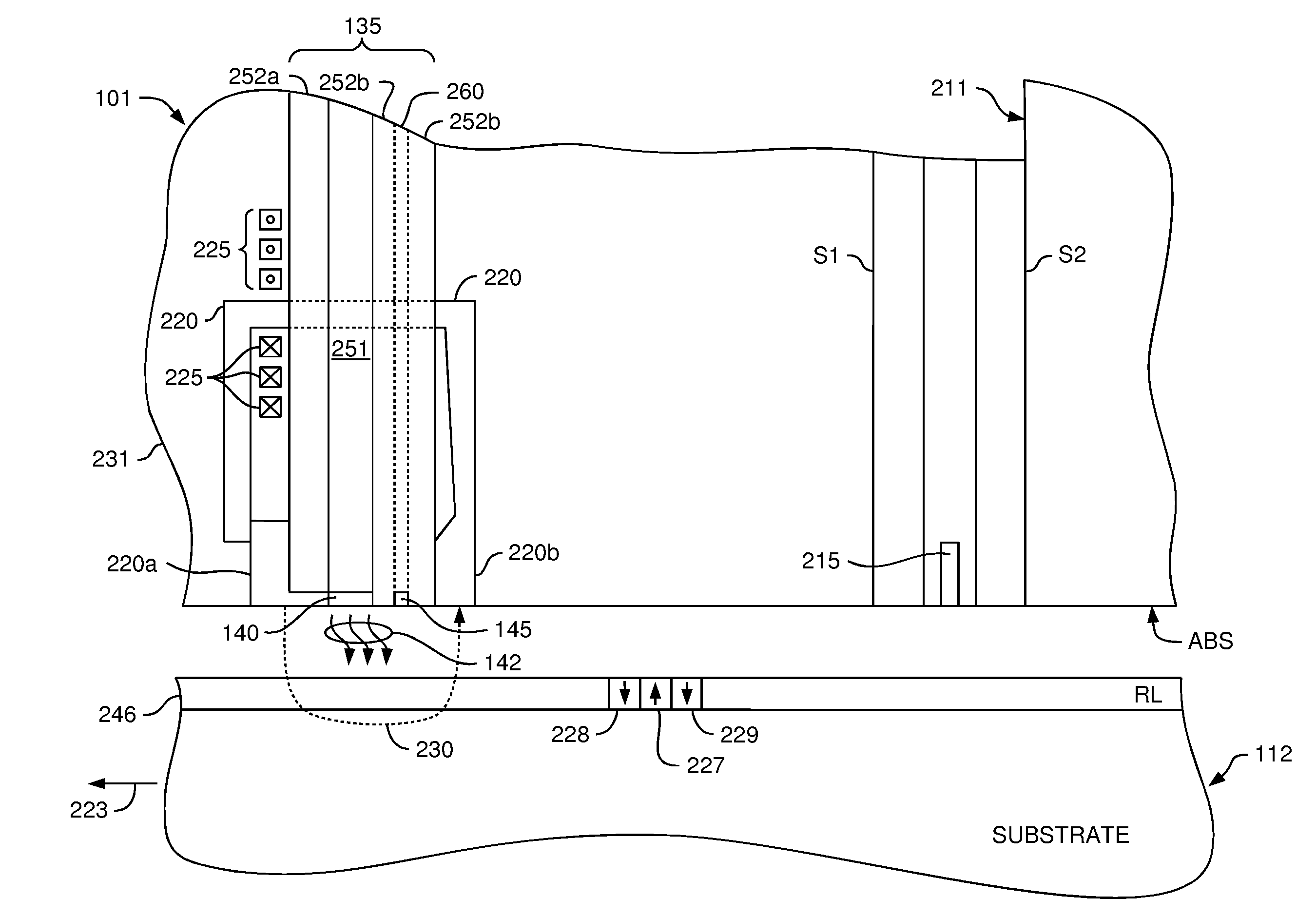
Thermally-Assisted Magnetic Recording Head
InactiveUS20110141862A1Arm with optical waveguideRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingOptical axis
In a thermally assisted magnetic recording head having a light source and a waveguide to lead a laser beam radiated from the light source to a front end of the magnetic head, while blocking an adverse effect of heat generated in the light source and securing a good floating characteristic, the light source and the magnetic head are optically coupled with high efficiency and the magnetic head itself is reduced in size. This invention provides a reflection mirror that is formed of a part or whole of one inclined end surface of the semiconductor laser mounted on the first submount. Near one end surface of the slider is provided the optical waveguide that pierces through the slider in a direction of the thickness thereof. The slider is mounted on the second submount and the positions of the first submount and the second submount are adjusted to practically align the light axis of the beam emitted from the mirror with the light axis of the optical waveguide, thereby realizing a novel thermally assisted magnetic recording head.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Thermal-assisted-magnetic-recording head and magnetic recording system equipped with the same
InactiveUS20120182842A1High total optical propagation efficiencyImprove efficiencyRecord information storageMagnetic and optical recordingsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingRefractive index
Provided is a thermal-assisted-magnetic-recording head capable of irradiating a magnetic recording medium with light with a spot size reduced on the submicron order with high utilization efficiency. A spot size converter 13 for guiding light emitted from an optical source 4 into a magnetic head is provided at a position adjacent to a magnetic main pole 19 in the magnetic head. In the spot size converter 13, a cover layer 15 having a lower refractive index than those of a core 14 and a clad material 24 is formed between the core 14 and the clad 15 and has a shape composed of a shape substantially rectangular in a light traveling direction and a taper shape having a width increasing toward the bottom surface of the magnetic head.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic head comprising recording part, reading part, heater for expansion of the recording part, and heater for expansion of the reading part
ActiveUS8811127B1Increase heightInhibit the influence of heatRecord information storageMagnetic recordingThermal expansionComputer science
A magnetic head includes a reading part, a recording part that is laminated on the reading part in a planer view, a recording part expansion heater, a reading part expansion heater, and a thermal expansion promoting layer that is prepared at a position closer to the reading part than to the recording part and extends to an air bearing surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com