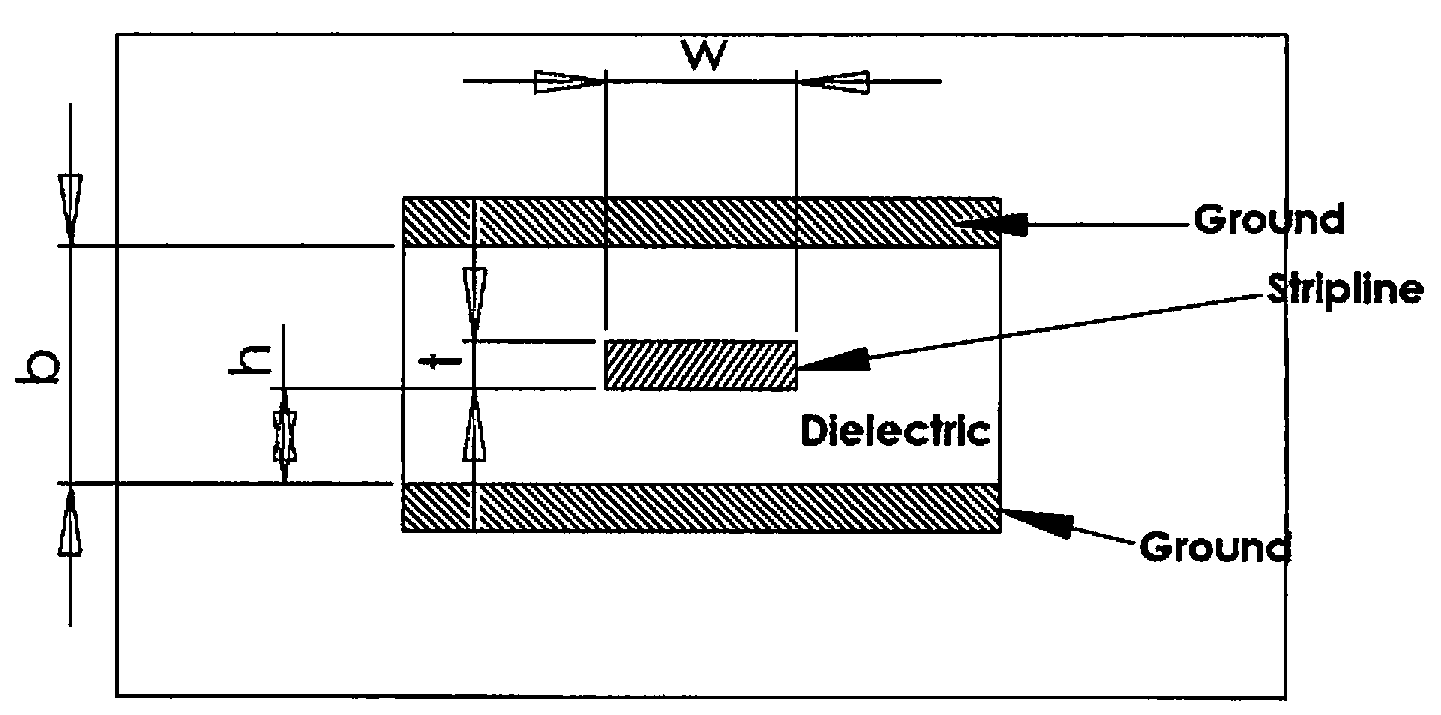
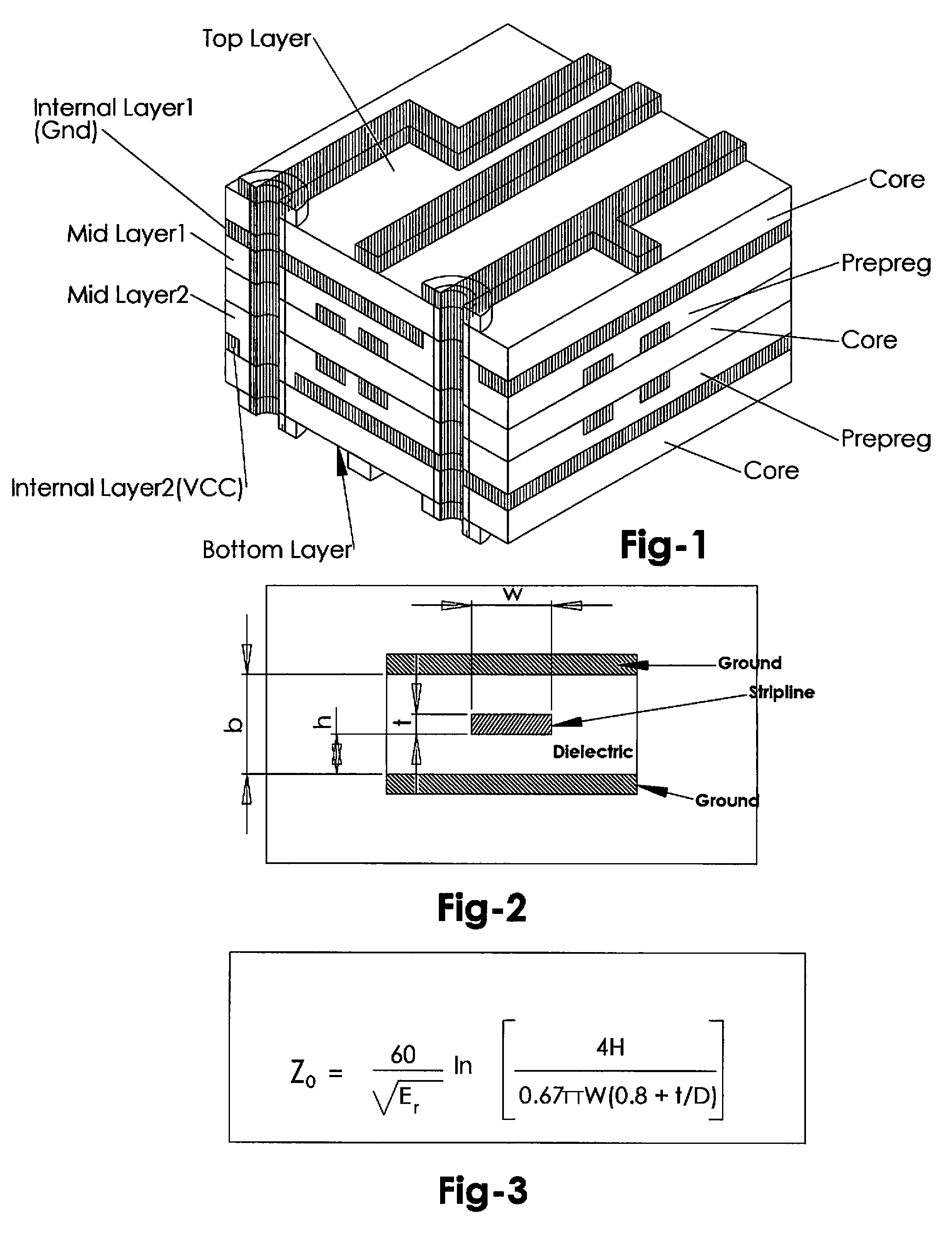
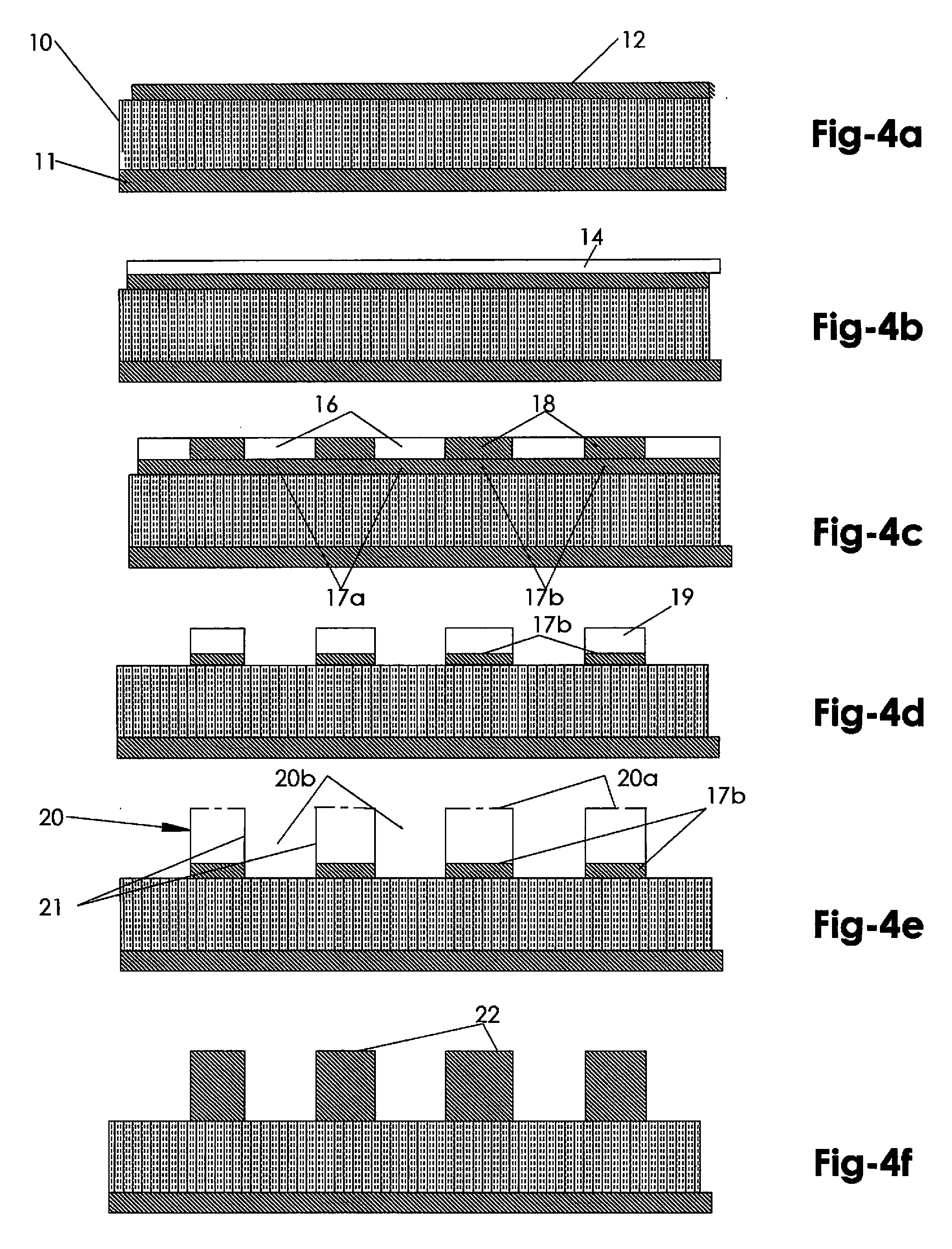
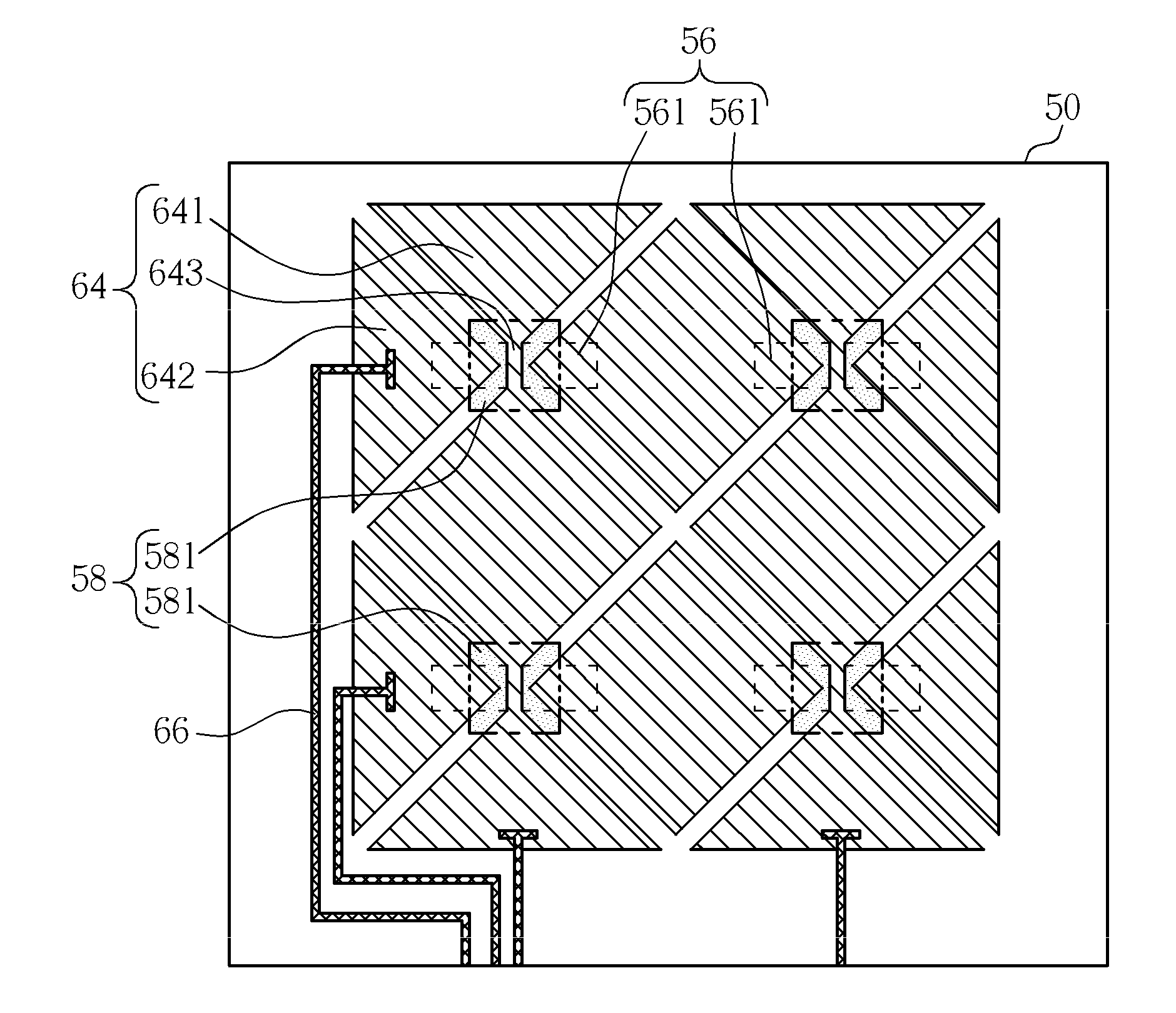
Patents
Literature
160results about "Paste/ink/powder application resist" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
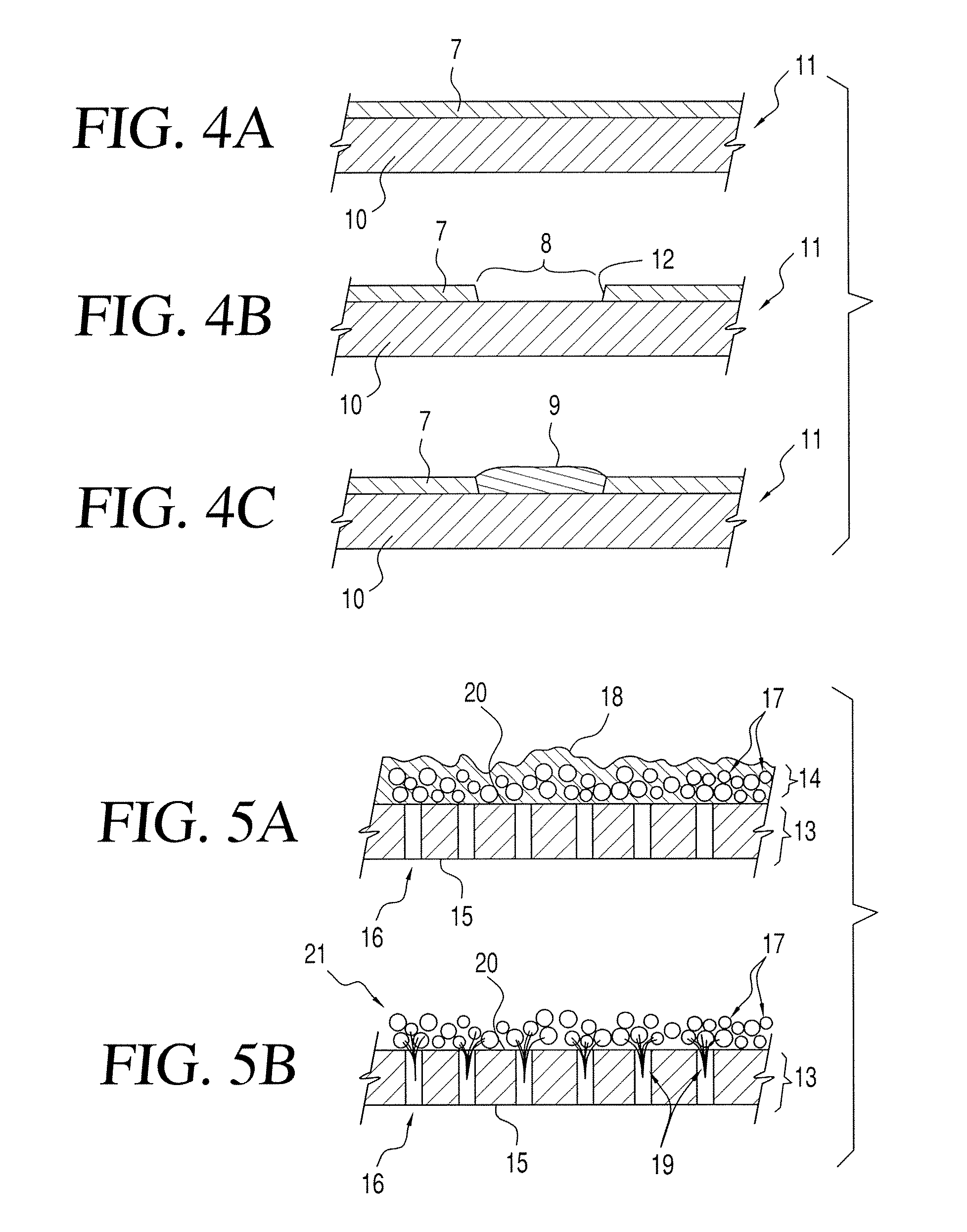
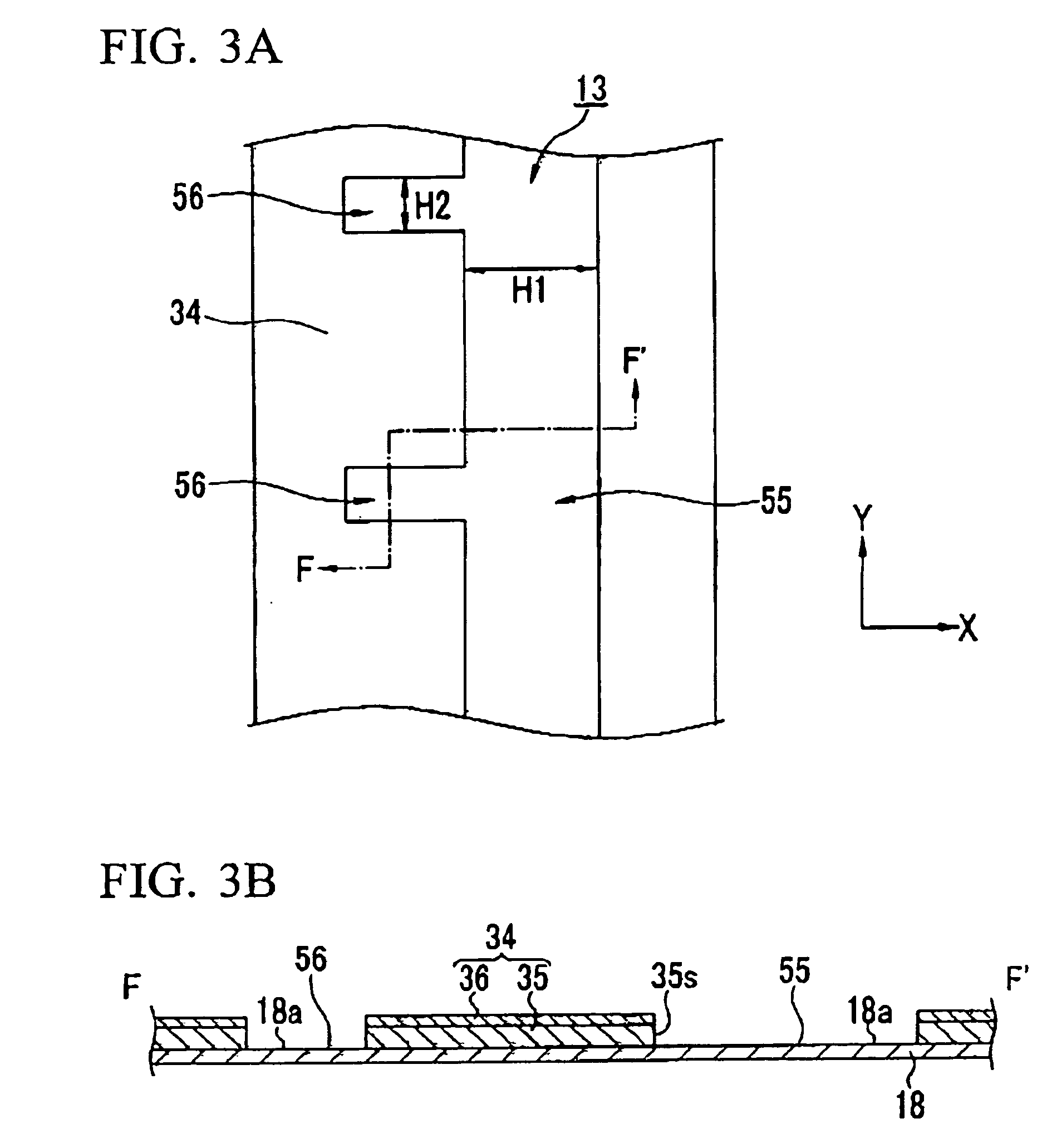
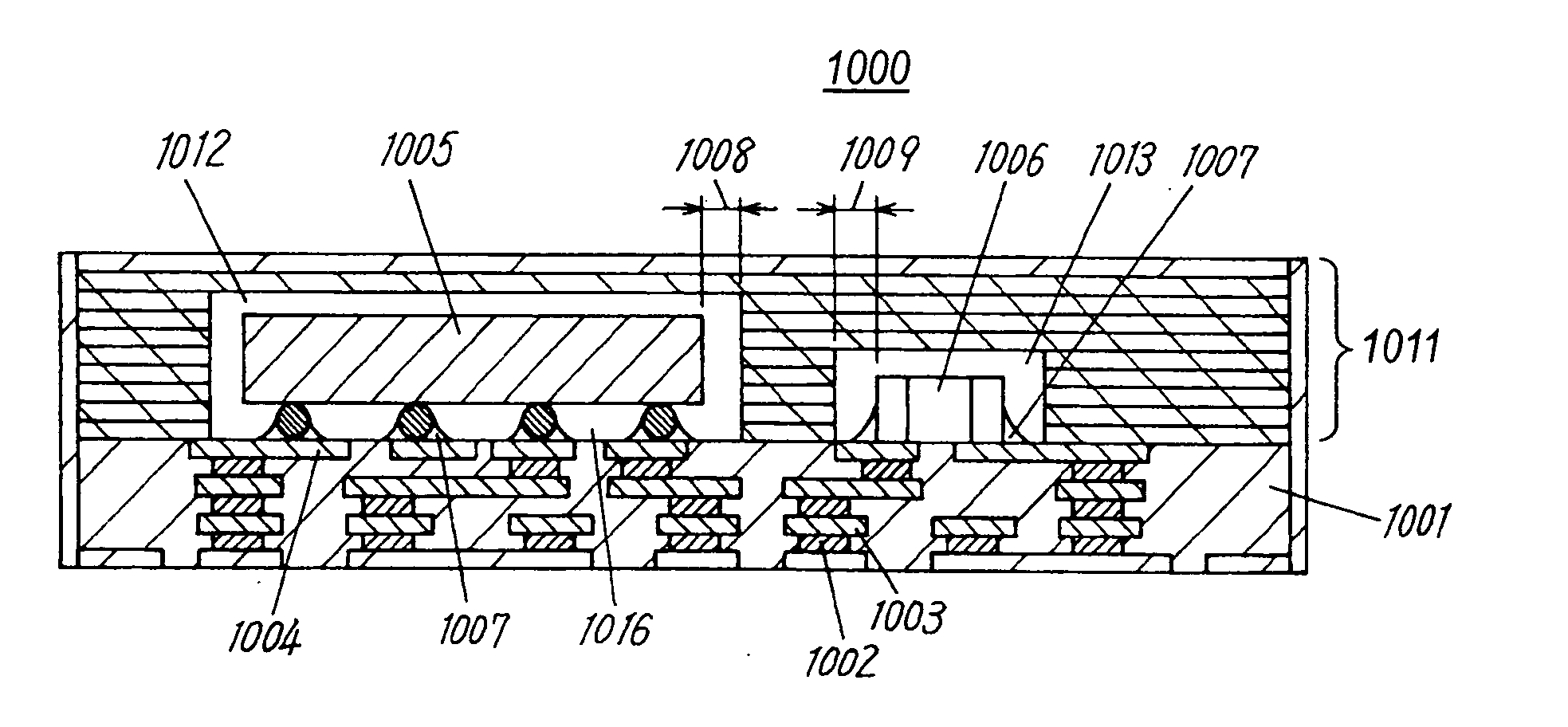
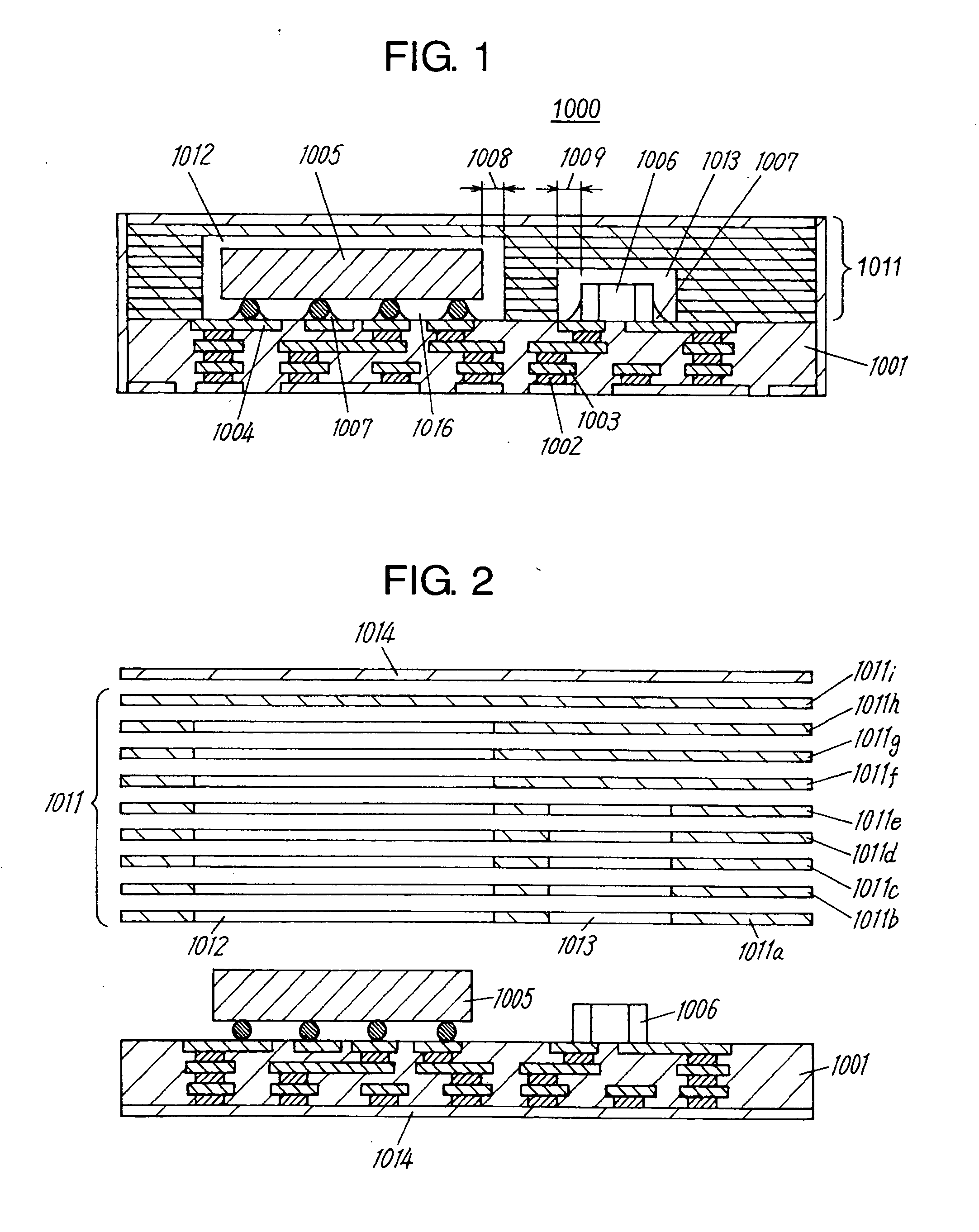
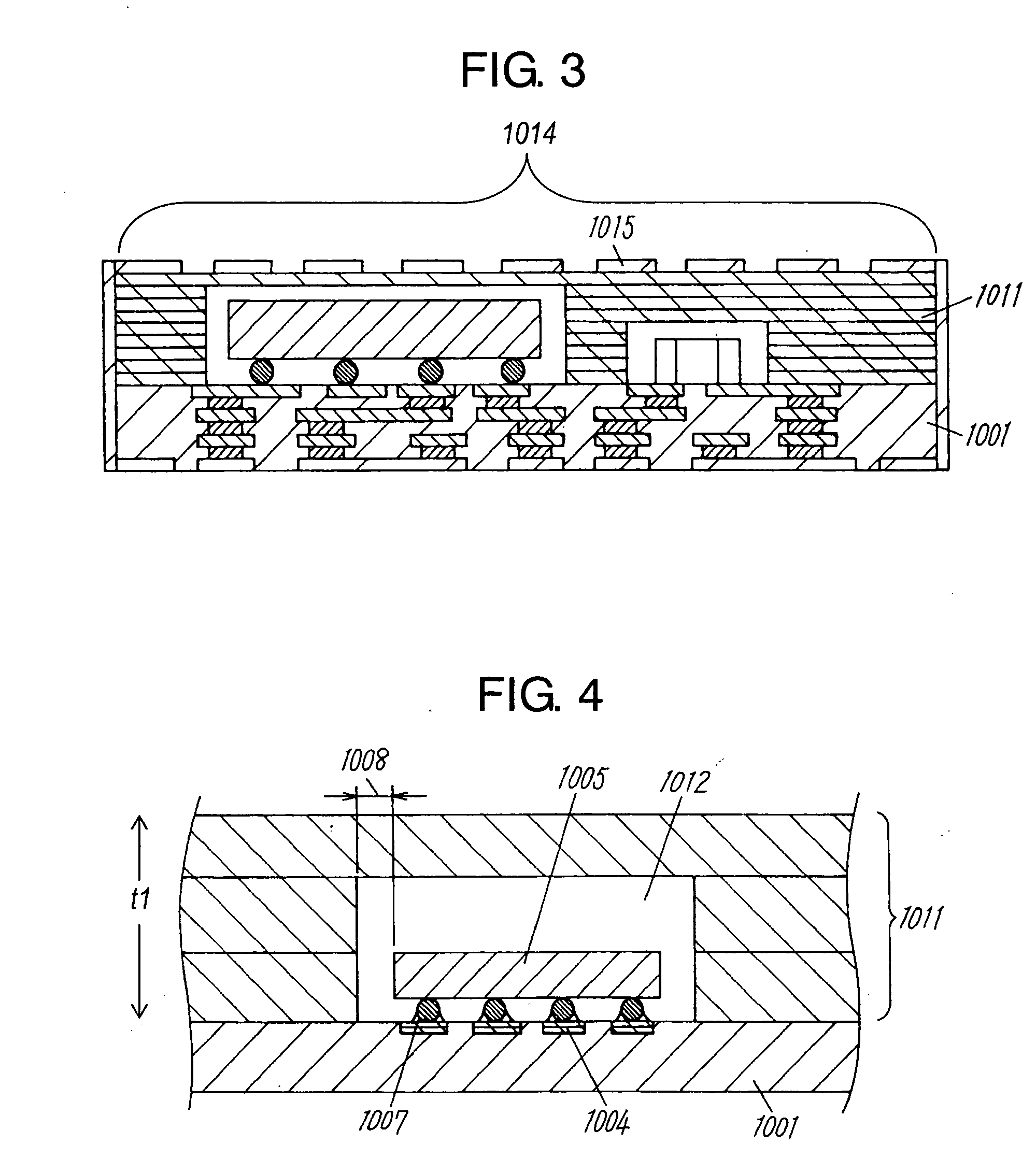
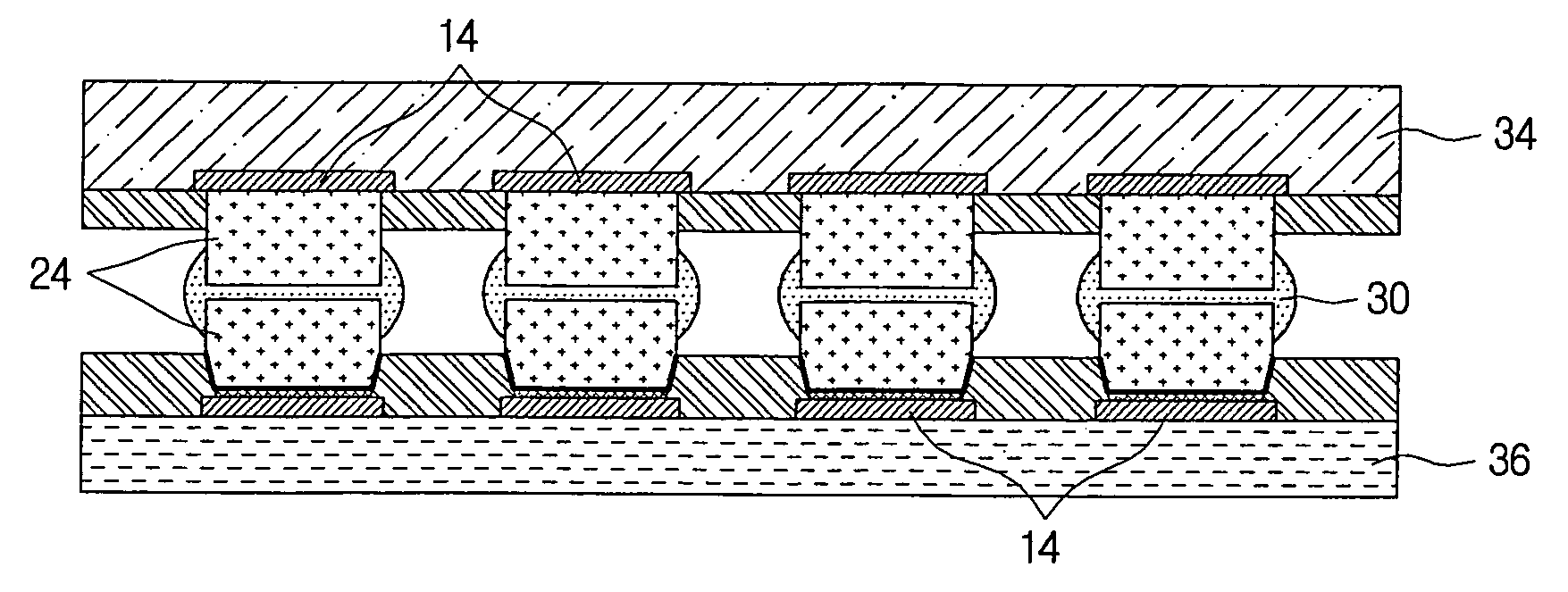
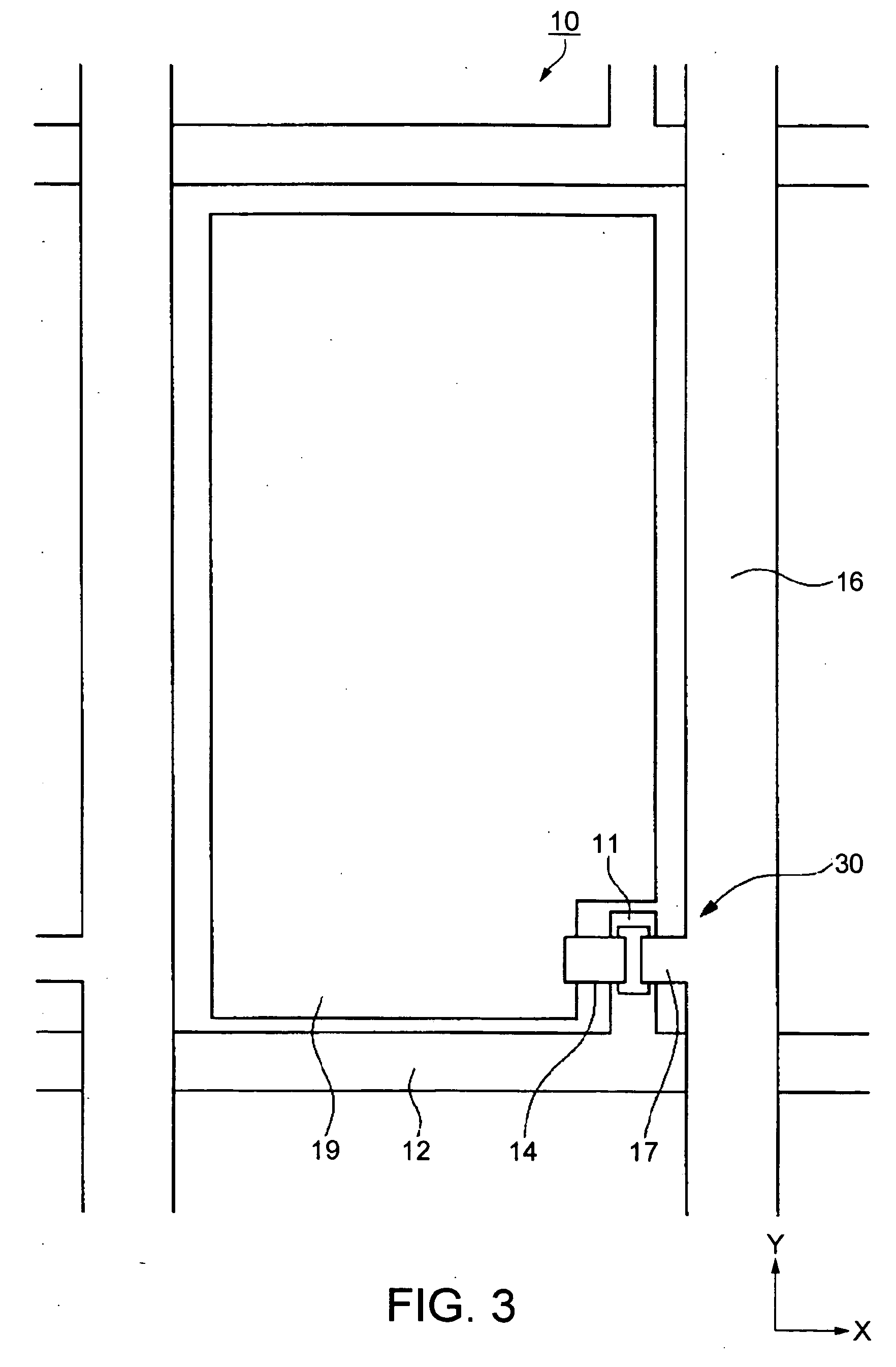
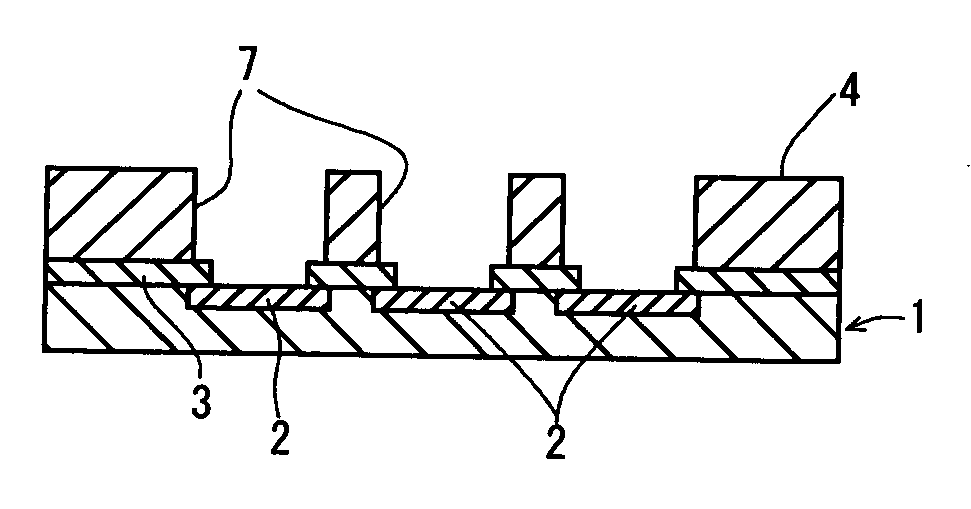
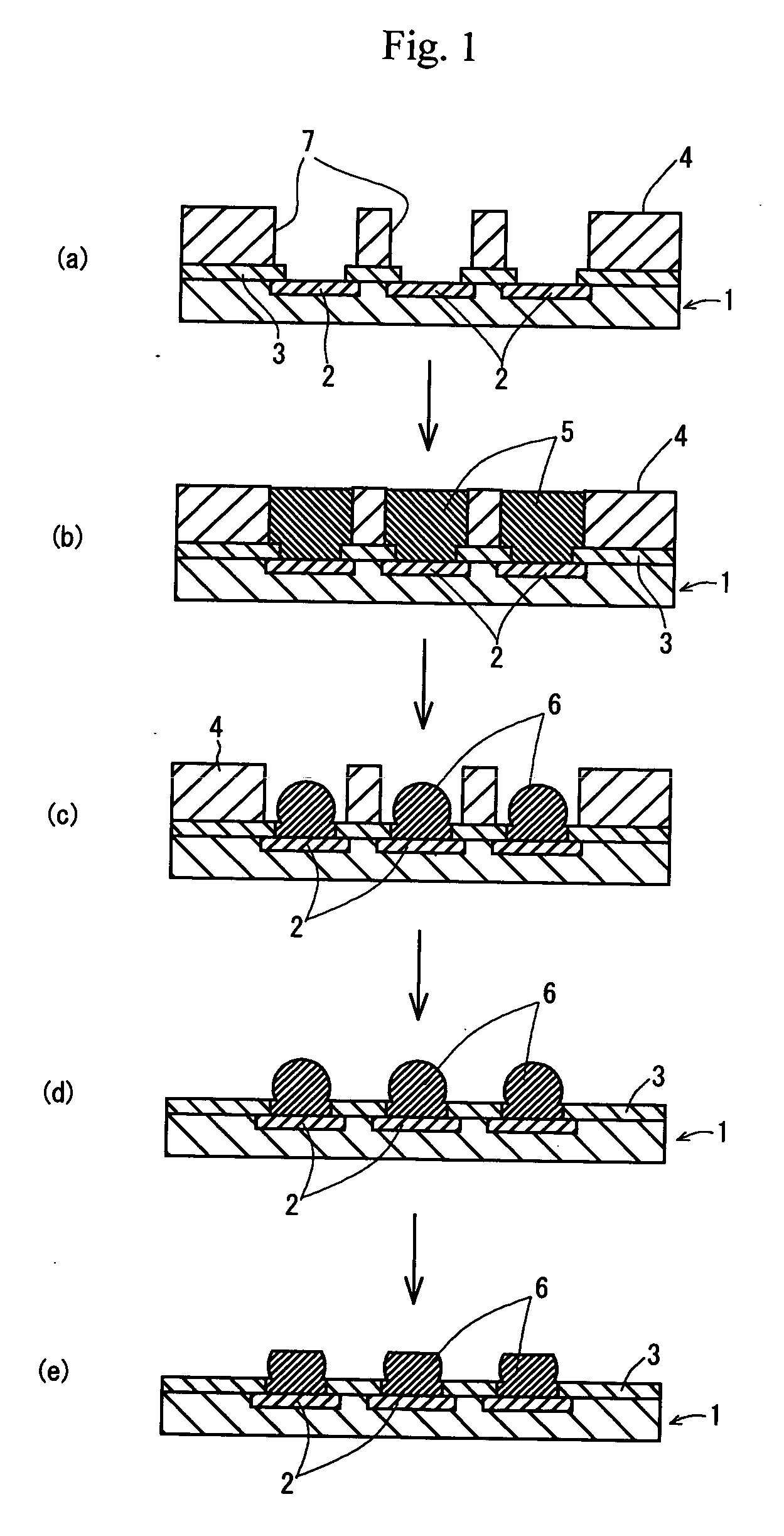
Component connections using bumps and wells
InactiveUS6881609B2Conveniently formedAccurate locationPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureHigh densityInterconnection
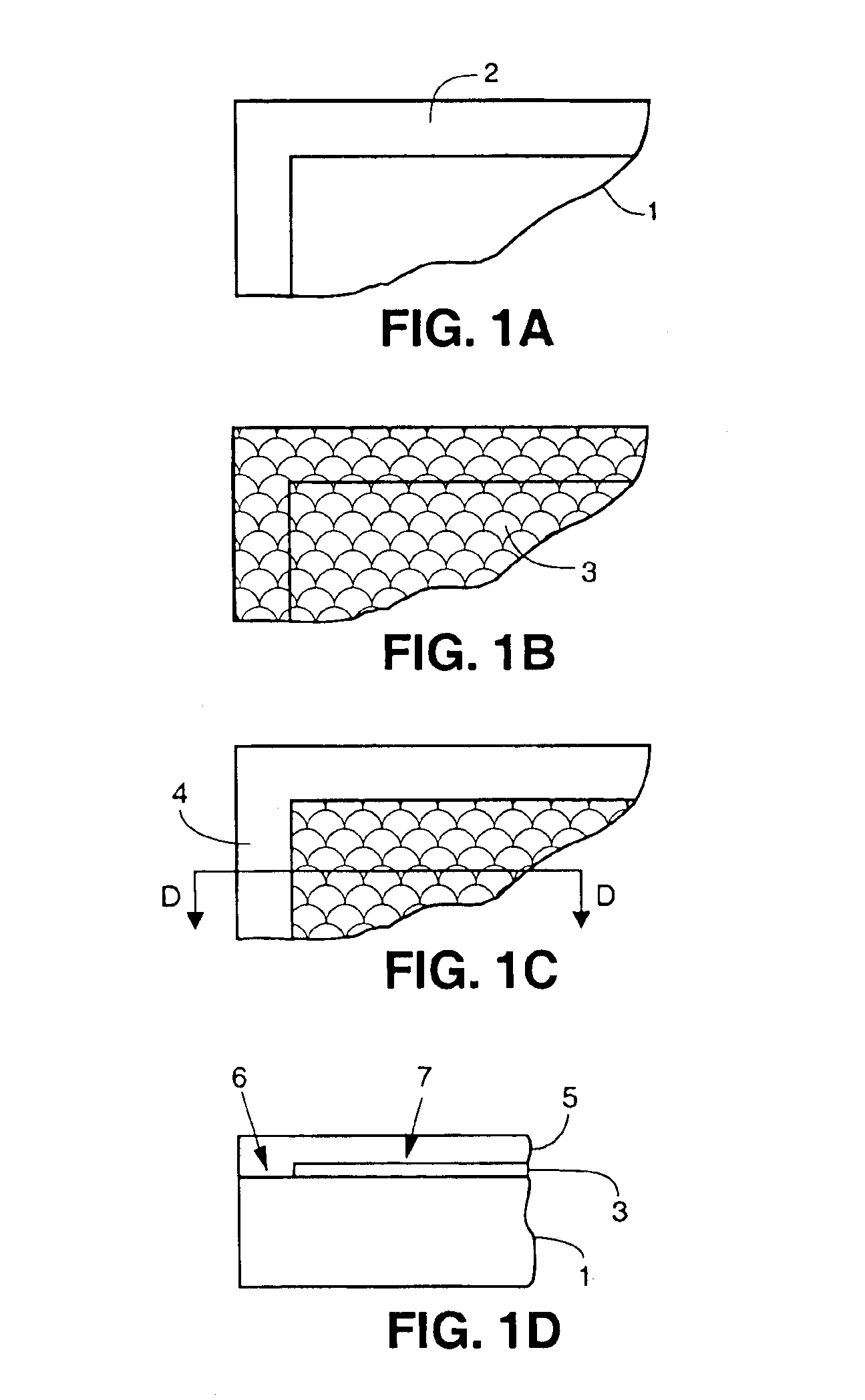
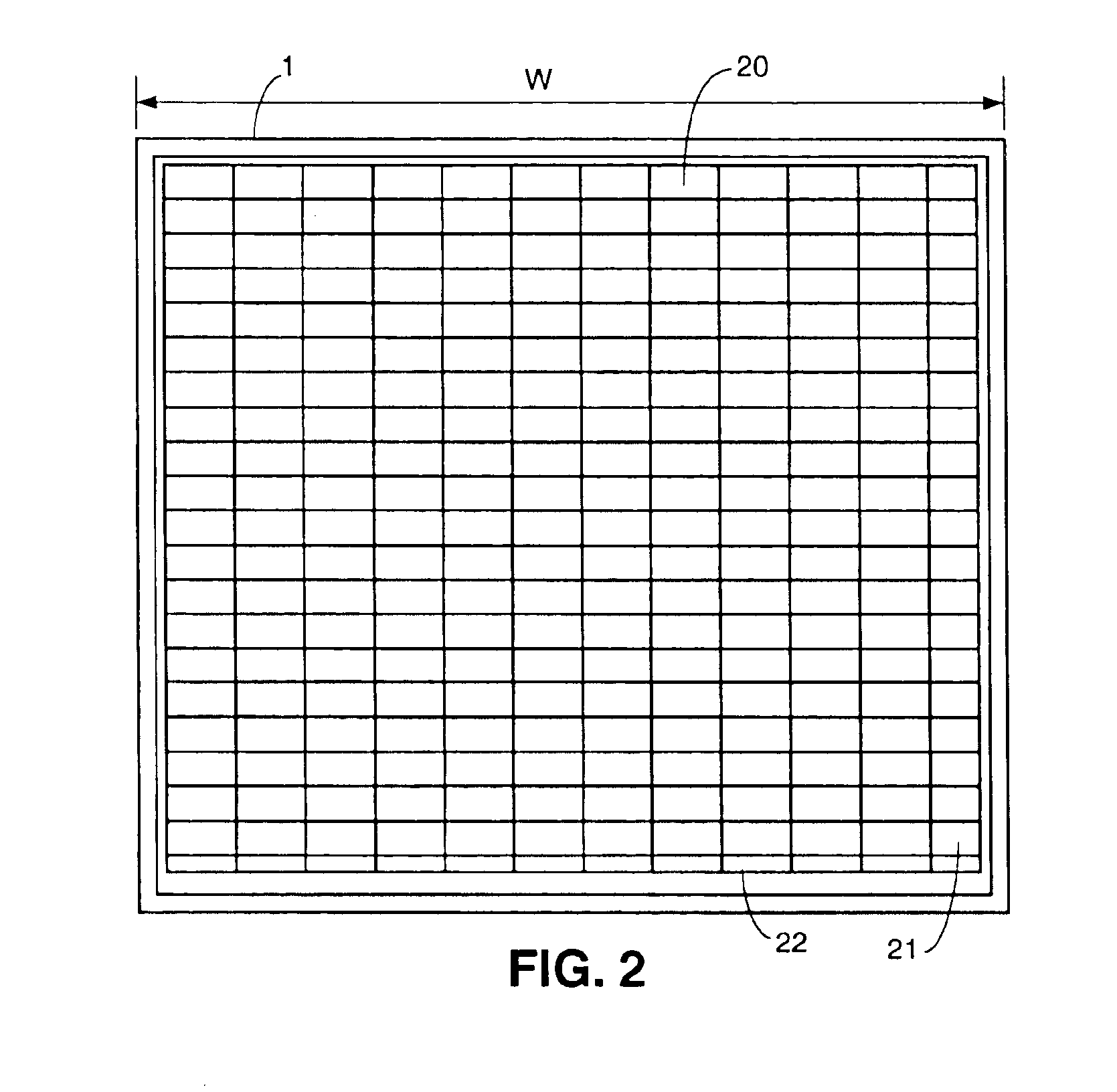
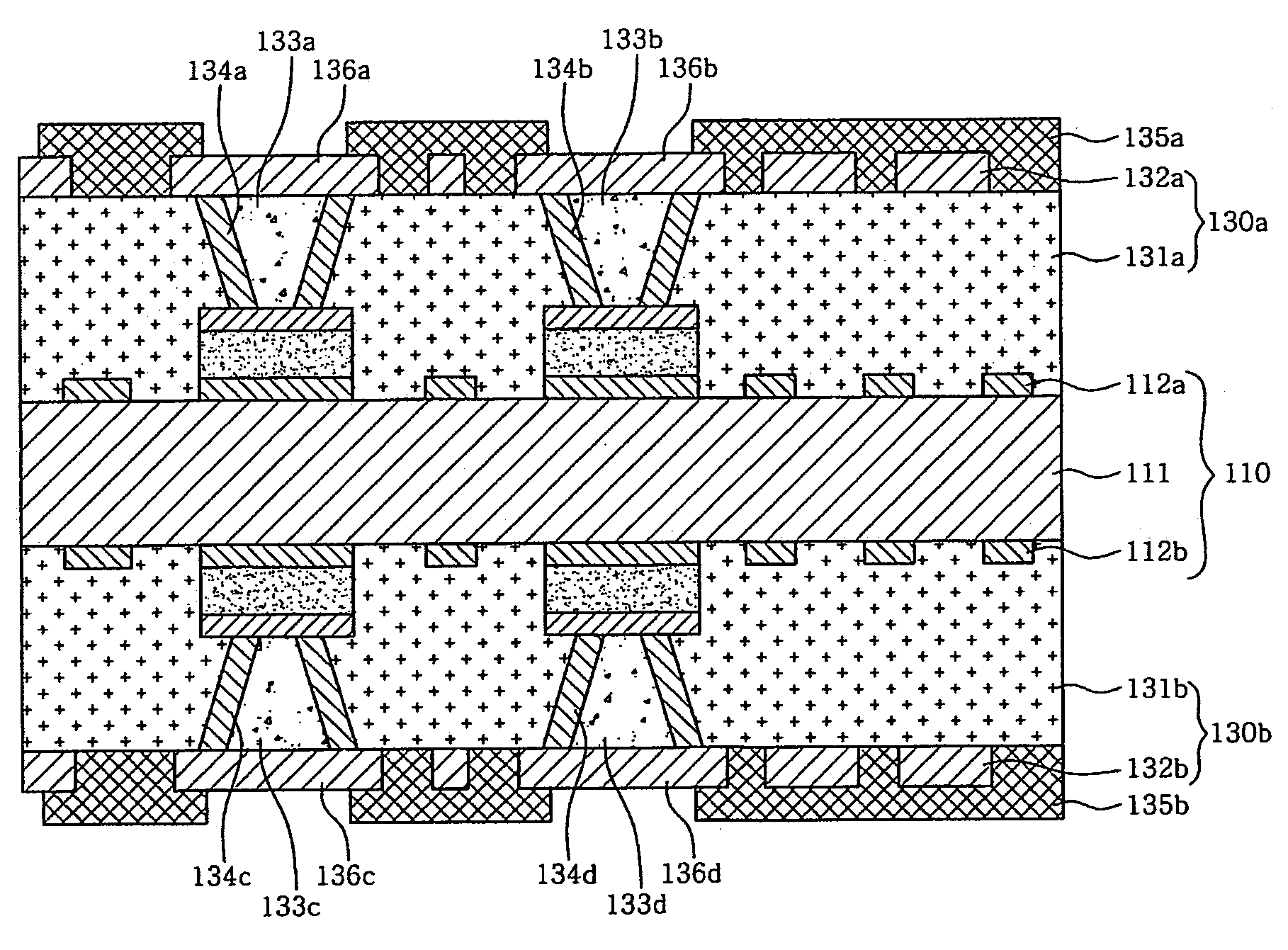
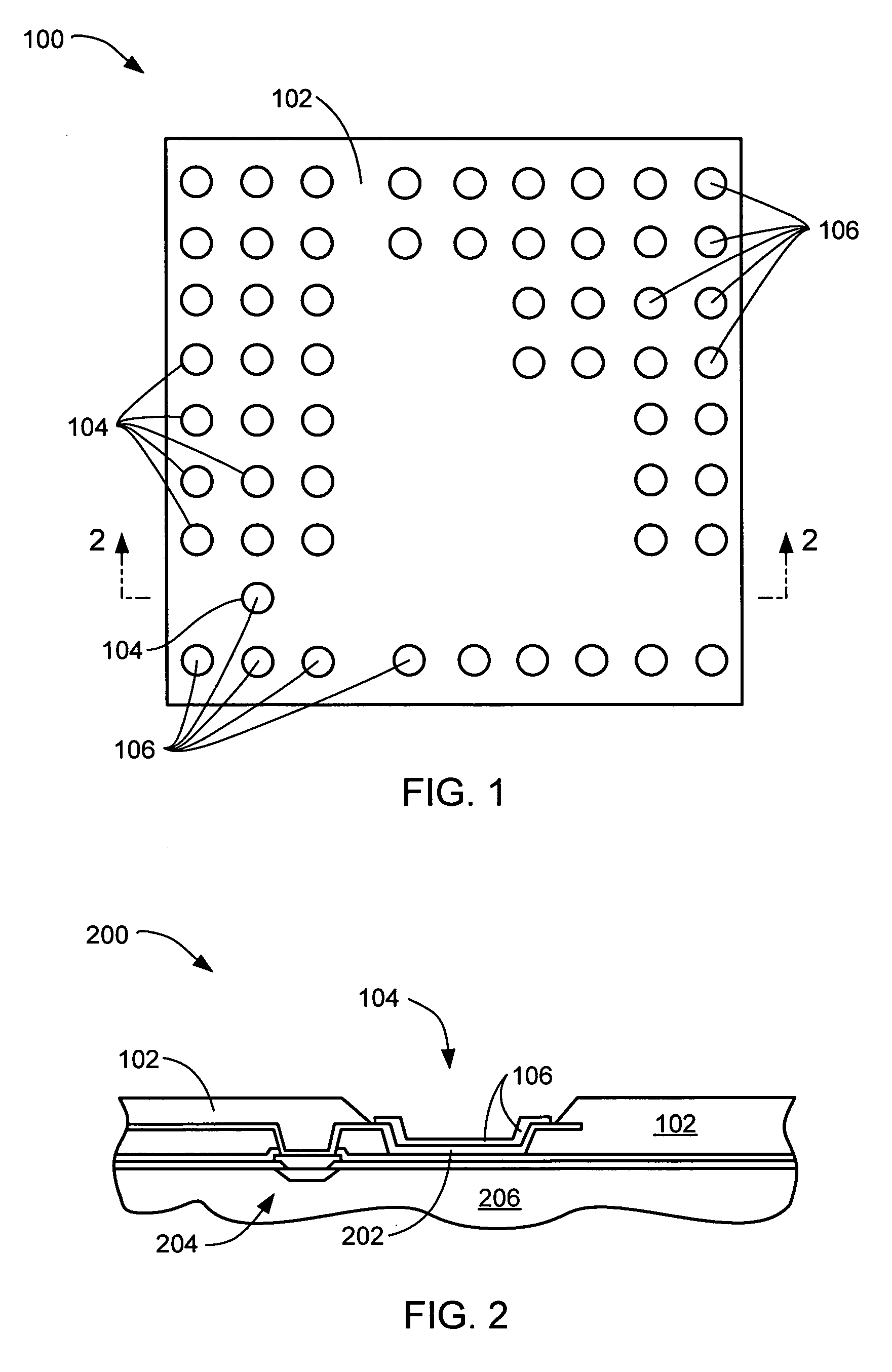
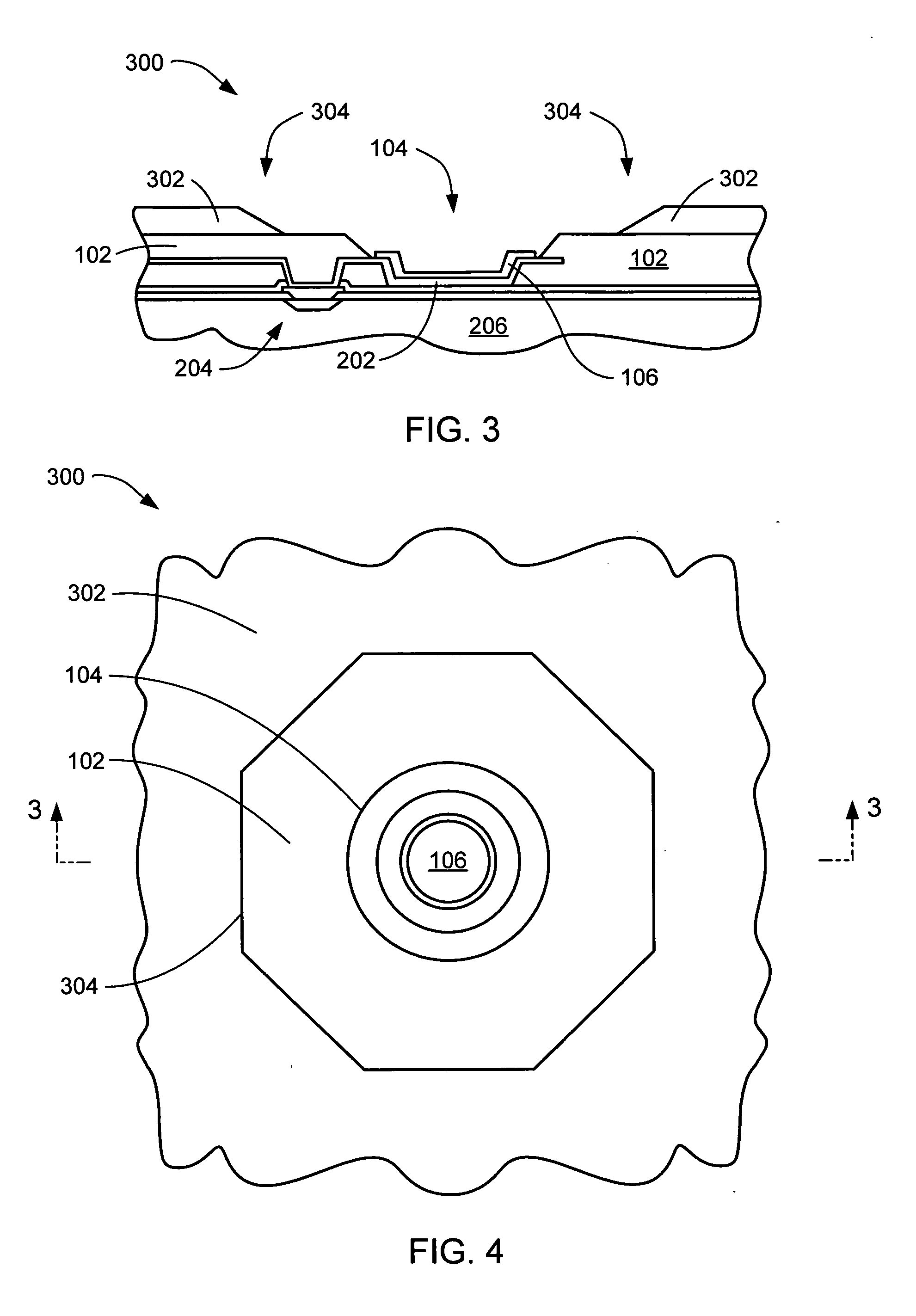
This specification describes techniques for fabricating connections between pairs of components. Each connection includes an array of bumps on a male component, and a matching array of wells filled with bonding material on a female component. The bump / well connections can be spaced with a pitch of less than 100 microns. One application of the invention is the attachment of electronic components to interconnection circuits or circuit assemblies to form electronic modules. The electronic components may be IC chips or high-density interconnect cables. Another application is alignment of optical components. The direct chip attachment techniques are described in the context of fabrication, assembly, test, rework, and cooling of electronic modules employing flip chip components. The preferred method is to fabricate the module on a glass carrier using a release layer so that the carrier can be removed after most of the processing is done.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
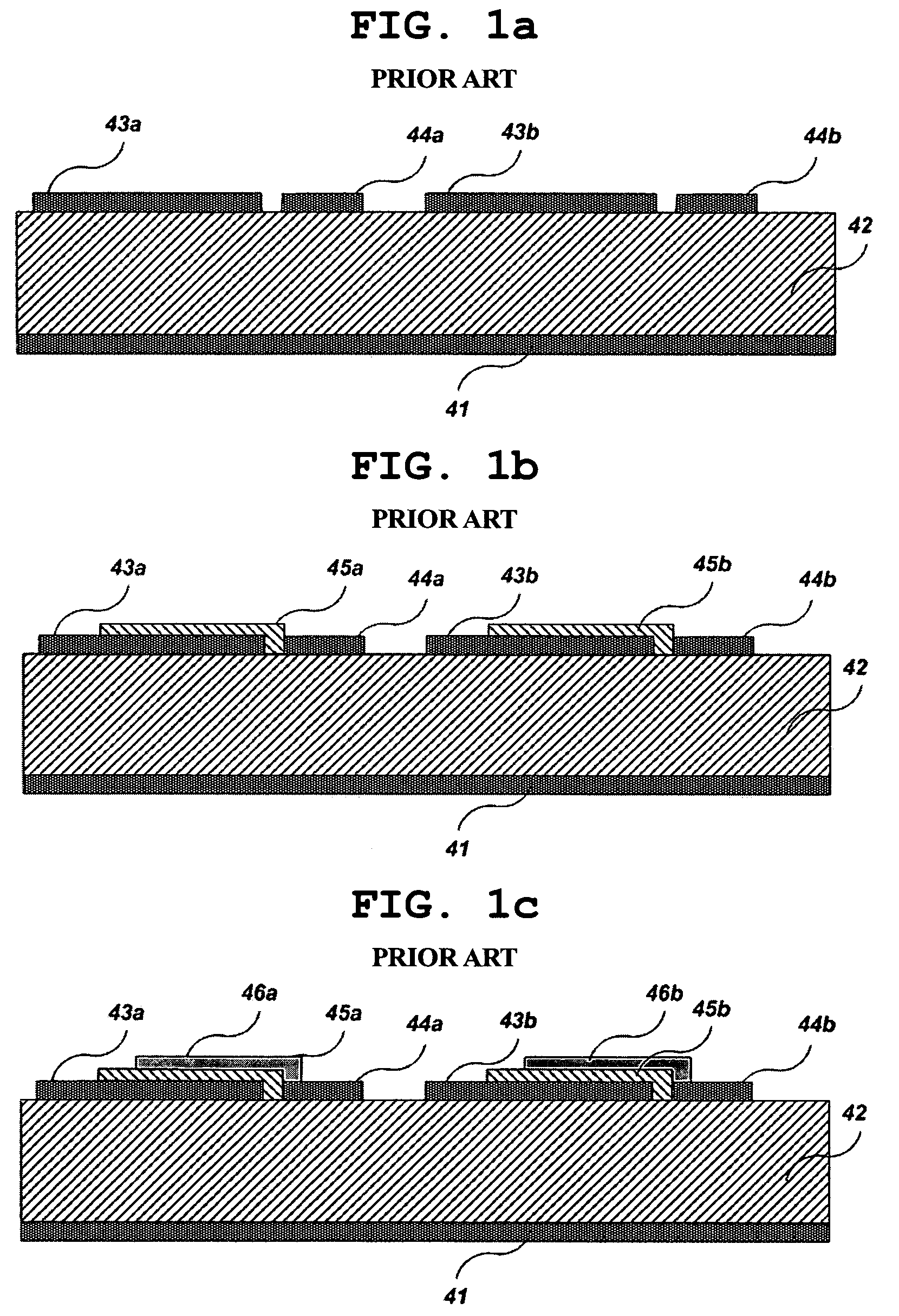
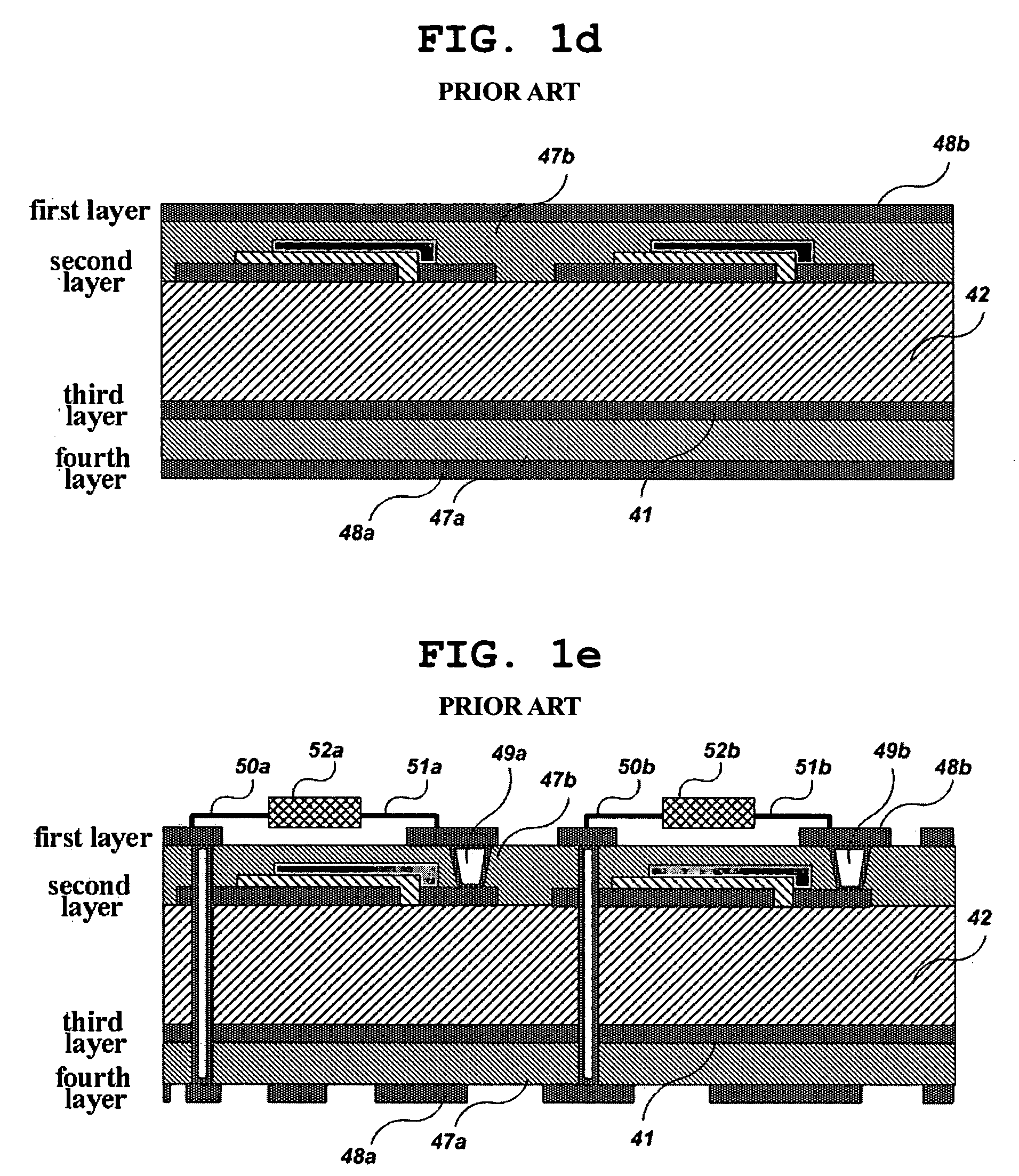
Electronic system modules and method of fabrication
InactiveUS6927471B2Good dimensional stabilityLow costPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureDielectricEngineering
This specification describes techniques for manufacturing an electronic system module. The module includes flexible multi-layer interconnection circuits with trace widths of 5 microns or less. A glass panel manufacturing facility, similar to those employed for making liquid crystal display, LCD, panels is used to fabricate the interconnection circuits. A polymer base layer is formed on a glass carrier with an intermediate release layer. Alternate layers of metal and dielectric are formed on the base layer, and patterned to create an array of multi-layer interconnection circuits on the glass panel. A thick layer of polymer is deposited on the interconnection circuit, and openings formed at input / output (I / O) pad locations. Solder paste is deposited in the openings to form wells filled with solder. After dicing the glass carrier to form separated interconnection circuits, IC chips are stud bumped and assembled using flip chip bonding, wherein the stud bumps on the components are inserted into corresponding wells on the interconnection circuits. The IC chips are tested and reworked to form tested circuit assemblies. Methods for connecting to testers and to other modules and electronic systems are described. Module packaging layers are provided for hermetic sealing and for electromagnetic shielding. A blade server embodiment is also described.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Process for Making a Multilayer Circuit Device Having Electrically Isolated Tightly Spaced Electrical Current Carrying Traces
A process for making a multilayer circuit device having electrically isolated tightly spaced electrical current carrying traces, comprising of providing an insulative substrate having a first side coated with a layer of conductive metal intended to form a ground plane; providing a plurality of seed layer traces of a predetermined width of approximately 25 microns or less separated from each other by a predetermined distance of approximately 25 microns or less on a second side of the insulative substrate, the narrowness of such separation being essentially limited only by characteristics of the photoresist material to be deposited and developed therebetween and to withstand subsequent processing; developing ribs or barriers of photoresist forming vertical walls rising above the spaces separating the seed layer traces and defining valleys or channels thereover; depositing a desired thickness of conductive material over the seed layer traces and in the valleys or channels between the vertical walls; stripping away the resist ribs or barriers to leave conductive traces to be variously used as ground lines, signal lines and power lines; repeating the previous steps to develop a plurality of circuit boards; stacking the several circuit boards and joining them together with layers of insulative material; identifying particular ones of the traces as signal lines and other traces as power lines and / or ground lines; interconnecting at least some of the ground lines on one board to ground lines and / or ground planes on other boards by conductors extending through vias; interconnecting signal lines to signal input and output terminals; and perhaps to signal lines on other boards through vias; and interconnecting power lines to power input and output terminals, and perhaps to power lines on other boards through vias.
Owner:VERTICALTEST
Touch panel and fabricating method thereof
ActiveUS20110148780A1Reduce manufacturing costPrinted circuit aspectsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingScreen printingEngineering
A method of fabricating touch panel includes the following steps. A base is provided. A first transparent conductive layer is formed on the base. A first screen printing process is performed to form a first patterned sacrificial layer on the first transparent conductive layer, and the first patterned sacrificial layer is used to pattern the first transparent conductive layer to form a patterned sensing pad layer. A second screen printing process is carried out to form a patterned insulating layer. A second transparent conductive layer is formed on the base. A third screen printing process is performed to form a second patterned sacrificial layer, and the second patterned sacrificial layer is used to pattern the second transparent conductive layer to form a patterned bridge line layer.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Forming method for film pattern, device, electro-optical apparatus, electronic apparatus, and manufacturing method for active matrix substrate
InactiveUS20070020899A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive matrixSide chain
A forming method for a film pattern, includes: forming a first bank layer on a substrate; forming a second bank layer on the first bank layer; patterning the first bank layer and the second bank layer thereby forming a bank having a pattern formation region including a first pattern formation region and a second pattern formation region which is connected to the first pattern formation region and has a width which is wider than that of the first pattern formation region; and forming the film pattern by depositing a functional liquid onto the pattern formation region which has been demarcated by the bank, wherein a first bank formation material and a second bank formation material are both materials including a siloxane bonds as a main chain, and the second bank formation material is a material including a fluorine bonds as a side chain.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
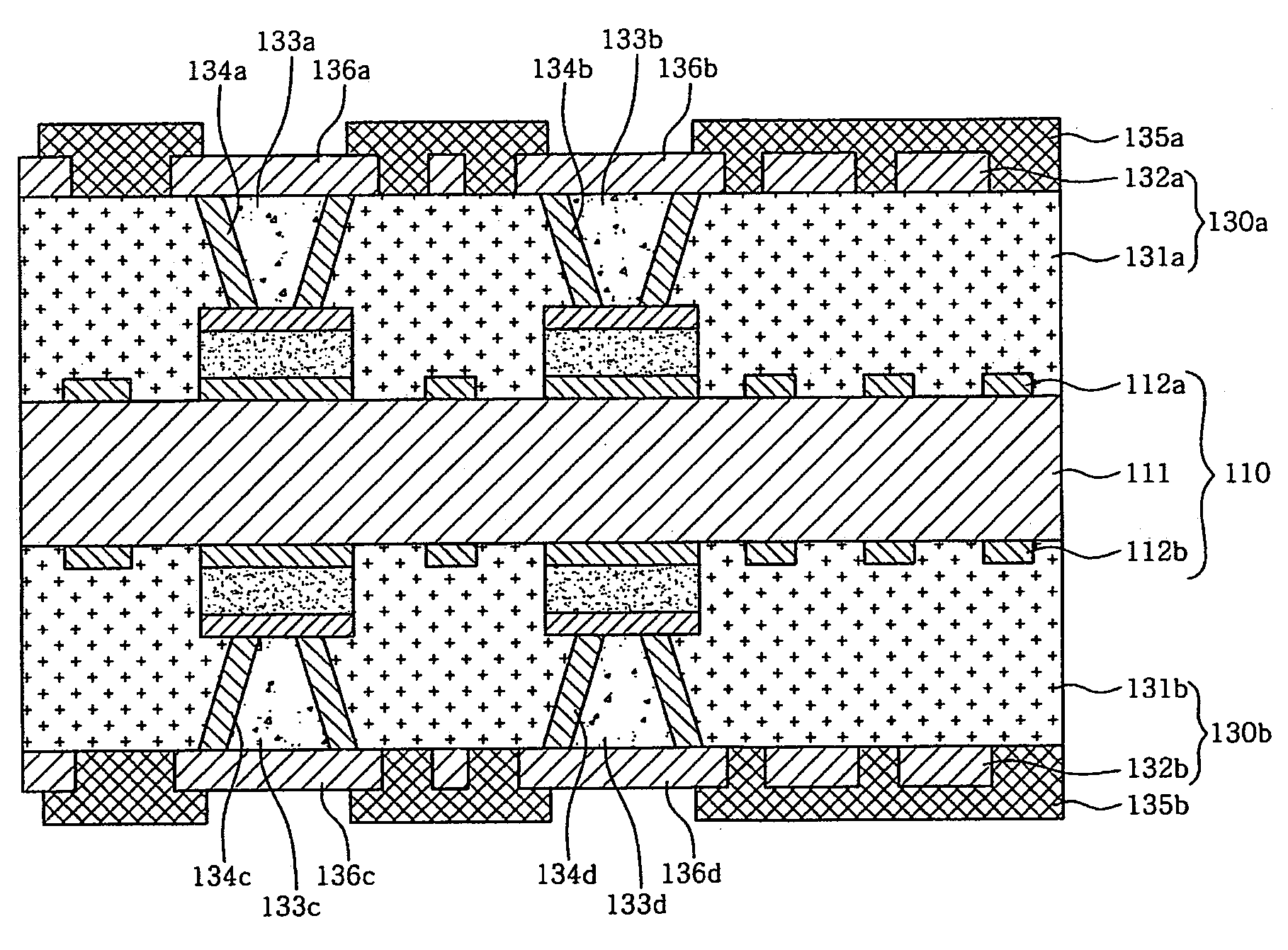
Printed circuit board including embedded capacitor having high dielectric constant and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS20060044734A1Raw material is expensiveReduce material costsThin/thick film capacitorFixed capacitor dielectricCapacitanceHigh capacitance
Disclosed is a PCB including embedded capacitors and a method of fabricating the same. A dielectric layer is formed using a ceramic material having a high capacitance, thereby assuring that the capacitors each have a high dielectric constant corresponding to the capacitance of a decoupling chip capacitor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method of forming pattern, film structure, electrooptical device and electronic equipment
InactiveUS20070099396A1Alignment precision is highLow transparencyPrinted circuit aspectsSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsFilm structure
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method of embedding tamper proof layers and
ActiveUS20060086534A1Enhance layeringCircuit security detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringDielectric layer
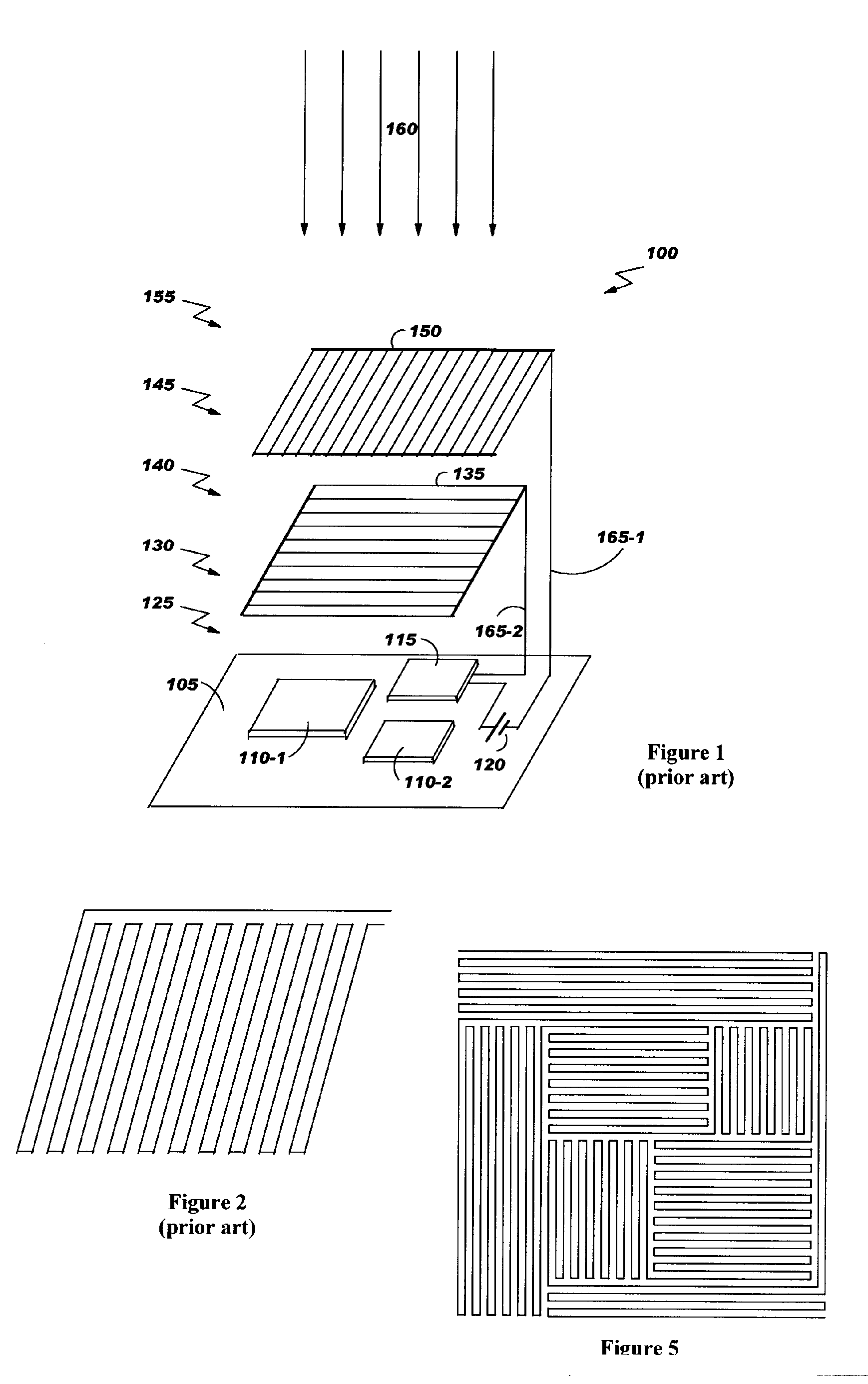
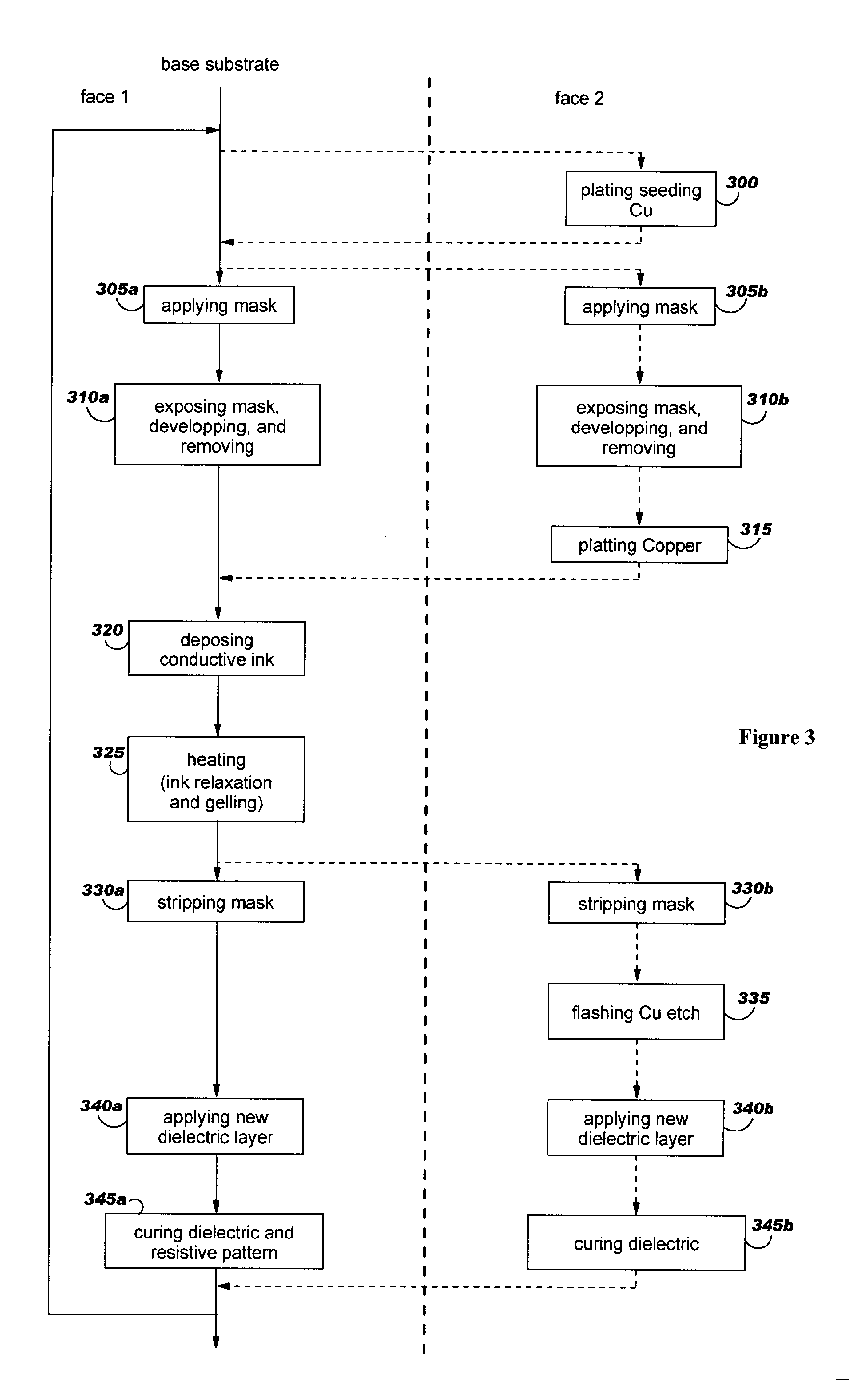
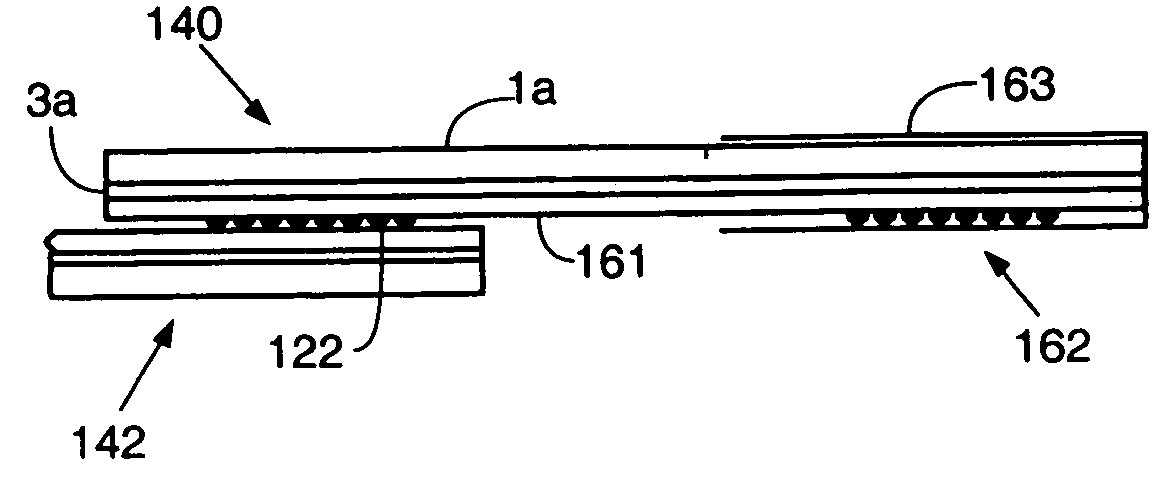
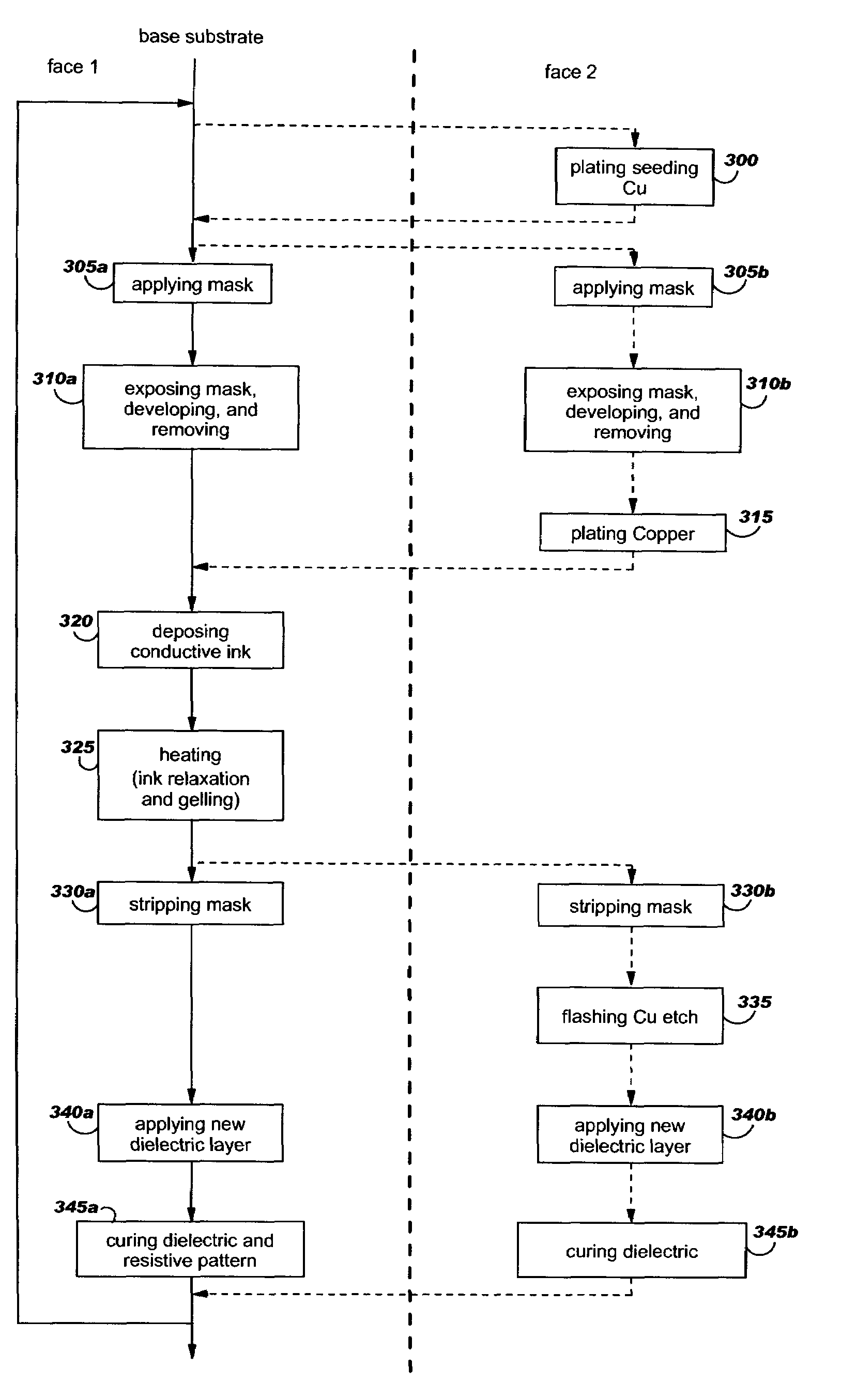
A method for embedding tamper proof layers and discrete components into a printed circuit board stack-up is disclosed. According to this method, a plating mask is applied on a base substrate to cover partially one of its faces. Conductive ink is then spread on this face so as to fill the gap formed by the plating mask. To obtain a uniform distribution of the conductive ink and then gel it, the conductive ink is preferably heated. A dielectric layer is applied on the conductive ink layer and the polymerization process is ended to obtain a strong adhesion between these two layers. In a preferred embodiment, conductive tracks are simultaneously designed on the other face of the base substrate to reduce thermo-mechanical strains and deformations.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Printed circuit board including embedded capacitor having high dielectric constant and method of fabricating same
InactiveUS7351915B2Raw material is expensiveReduce material costsThin/thick film capacitorPrinted circuit aspectsCapacitanceHigh capacitance
A printed circuit board (PCB) having at least one embedded capacitor and a method of fabricating the same is provided. A dielectric layer is formed using a ceramic material having a high capacitance, thereby assuring that the capacitors each have a high dielectric constant corresponding to the capacitance of a decoupling chip capacitor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method of making a capacitive substrate for use as part of a larger circuitized substrate, method of making said circuitized substrate and method of making an information handling system including said circuitized substrate
InactiveUS20070010065A1Enhance the circuitized substrate artLow costPrinted circuit aspectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A method of forming a capacitive substrate in which at least one capacitive dielectric layer of material is screen or ink jet printed onto a conductor and the substrate is thereafter processed further, including the addition of thru-holes to couple selected elements within the substrate to form at least two capacitors as internal elements of the substrate. The capacitive substrate may be incorporated within a larger circuitized substrate, e.g., to form an electrical assembly. A method of making an information handling system including such substrates is also provided.
Owner:TTM TECH NORTH AMERICA LLC
Fabrication methods for electronic system modules
InactiveUS20050140026A1Good dimensional stabilityRobust processingPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureDielectricElectromagnetic shielding
This specification describes techniques for manufacturing an electronic system module. The module includes flexible multi-layer interconnection circuits with trace widths of 5 microns or less. A glass panel manufacturing facility, similar to those employed for making liquid crystal display, LCD, panels is used to fabricate the interconnection circuits. A polymer base layer is formed on a glass carrier with an intermediate release layer. Alternate layers of metal and dielectric are formed on the base layer, and patterned to create an array of multi-layer interconnection circuits on the glass panel. A thick layer of polymer is deposited on the interconnection circuit, and openings formed at input / output (I / O) pad locations. Solder paste is deposited in the openings to form wells filled with solder. After dicing the glass carrier to form separated interconnection circuits, IC chips are stud bumped and assembled using flip chip bonding, wherein the stud bumps on the components are inserted into corresponding wells on the interconnection circuits. The IC chips are tested and reworked to form tested circuit assemblies. Methods for connecting to testers and to other modules and electronic systems are described. Module packaging layers are provided for hermetic sealing and for electromagnetic shielding. A blade server embodiment is also described.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method of embedding tamper proof layers and discrete components into printed circuit board stack-up
A method for embedding tamper proof layers and discrete components into a printed circuit board stack-up is disclosed. According to this method, a plating mask is applied on a base substrate to cover partially one of its faces. Conductive ink is then spread on this face so as to fill the gap formed by the plating mask. To obtain a uniform distribution of the conductive ink and then gel it, the conductive ink is preferably heated. A dielectric layer is applied on the conductive ink layer and the polymerization process is ended to obtain a strong adhesion between these two layers. In a preferred embodiment, conductive tracks are simultaneously designed on the other face of the base substrate to reduce thermo-mechanical strains and deformations.
Owner:TWITTER INC
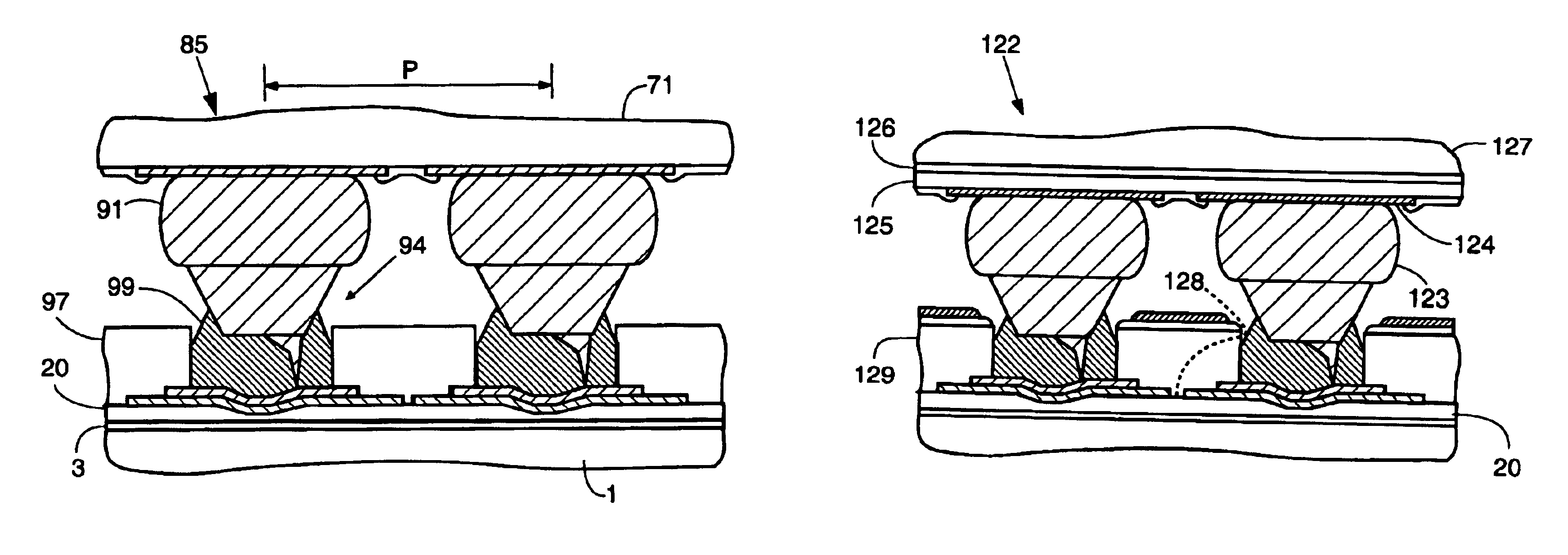
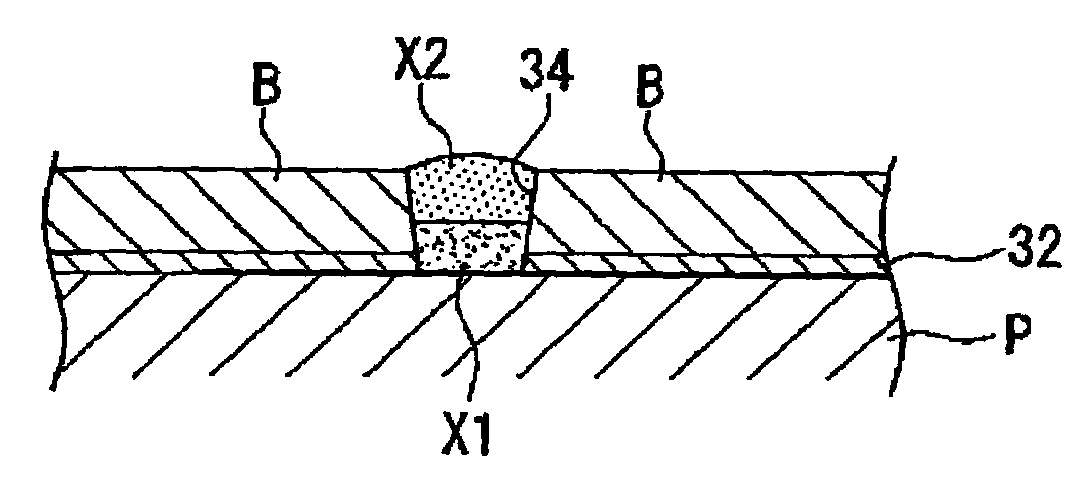
Electronic component with bump electrodes, and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7189927B2Reduce generationAvoid insufficient thicknessFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringElectronic component
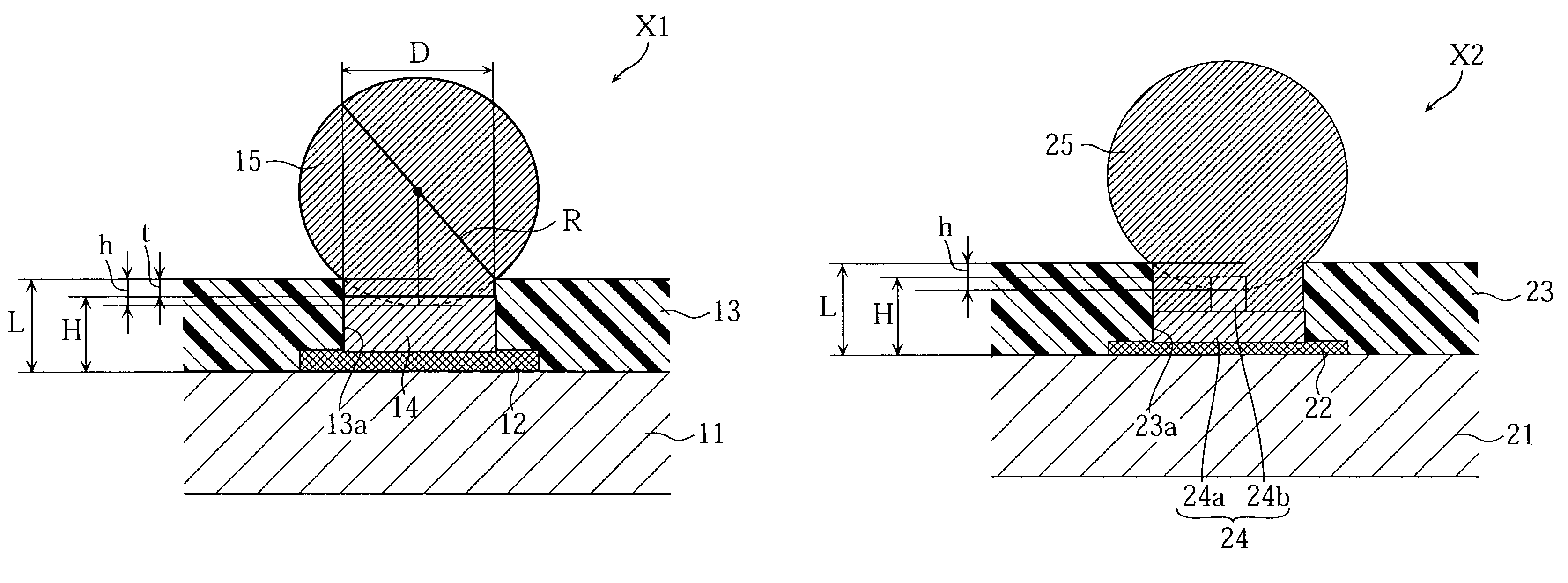
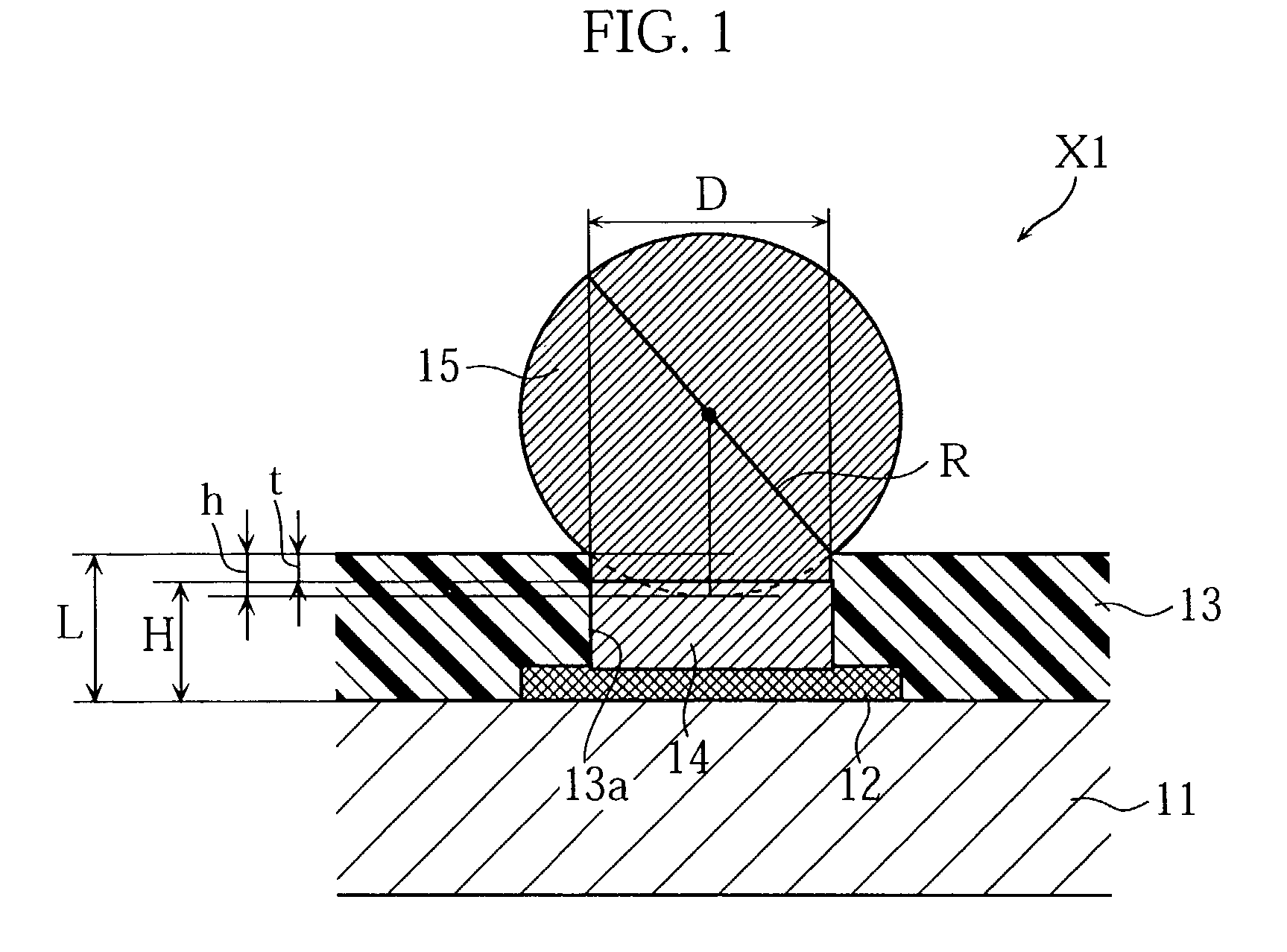
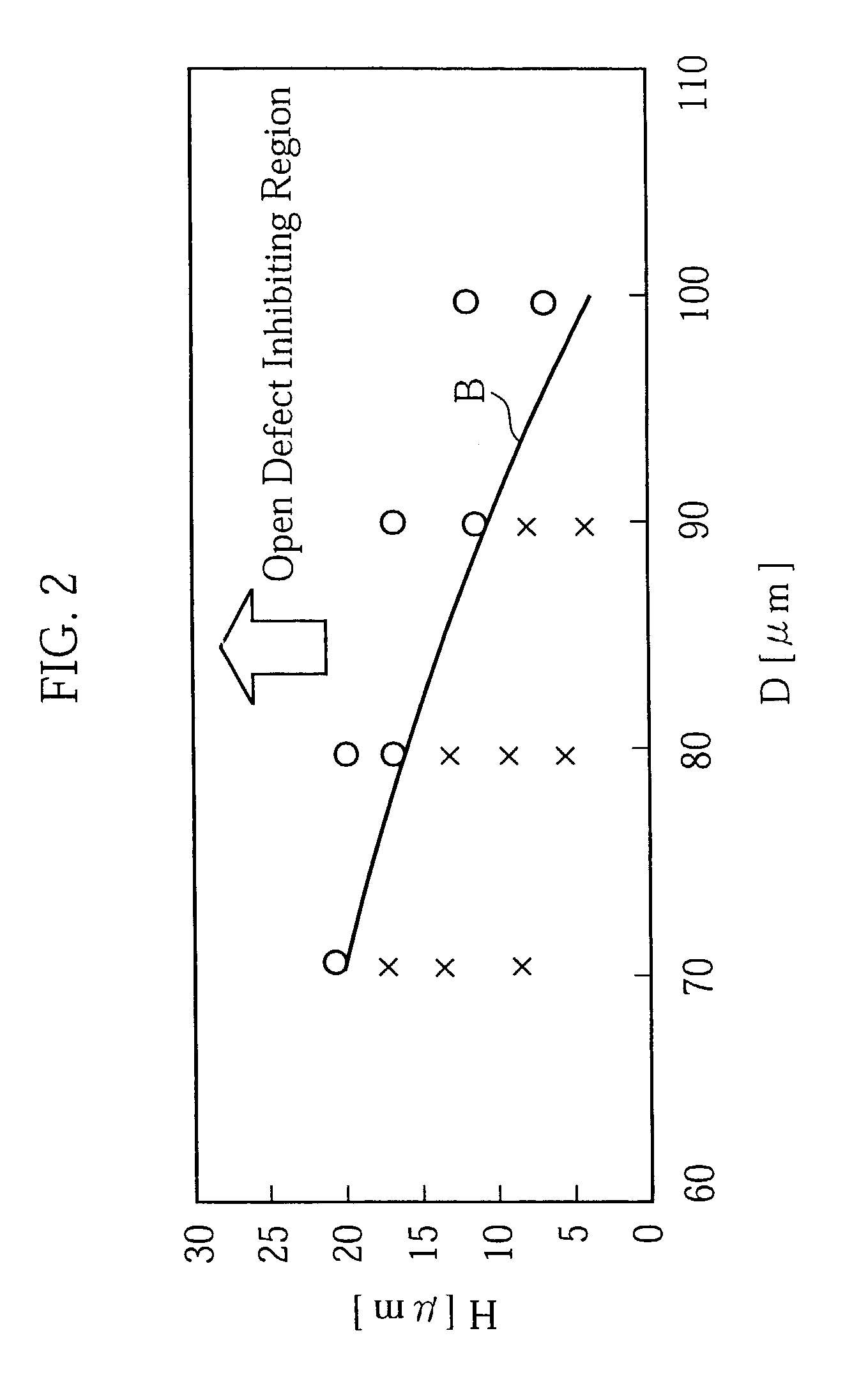
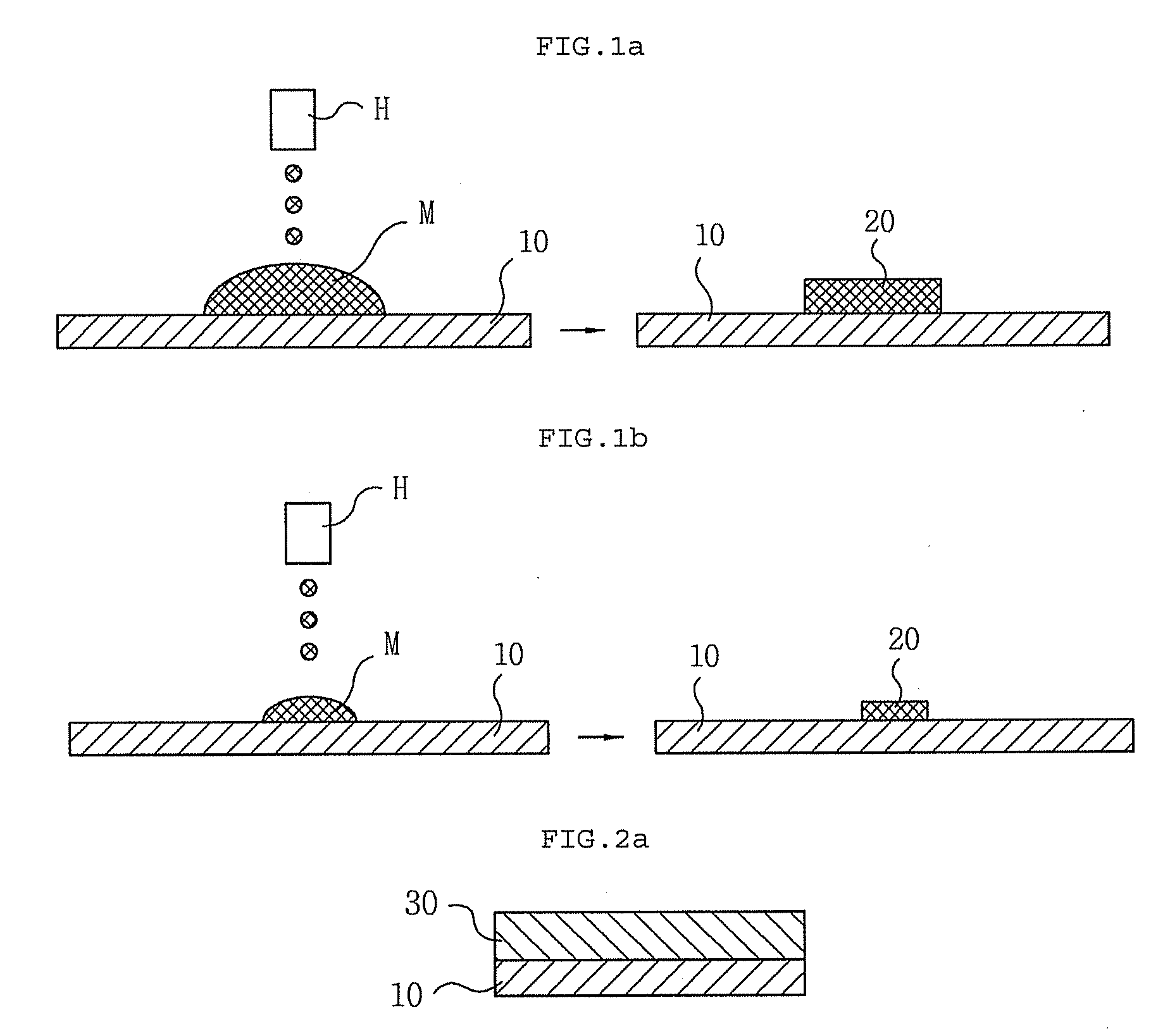
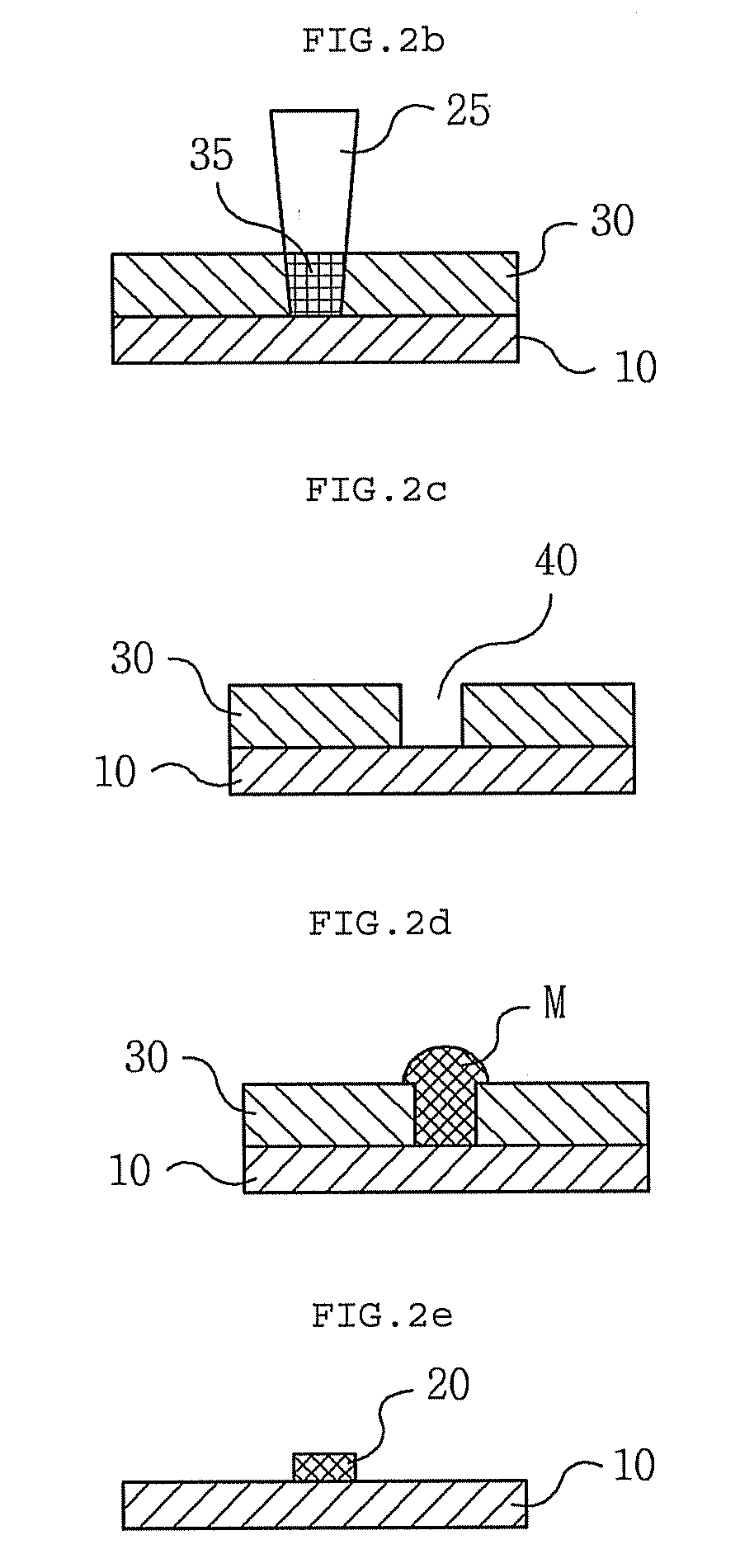
An electronic component with bump electrodes includes a surface-protecting insulating film of adequate thickness and bump elements of adequate height, and allows the occurrence of open defects in the manufacturing process to be appropriately reduced. An electronic component with bump electrodes (X1) includes a substrate (11), electrode pads (12) provided on the substrate (11), an insulating film (13) that has openings (13a) in correspondence with the electrode pads (12) and is laminated and formed on the substrate (11), electroconductive connecting elements (14) provided on the electrode pads (12) in the openings (13a), and bump elements (15) that are in direct contact with the electroconductive connecting elements (14) and project from the openings (13a).
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for forming high-resolution pattern having desired thickness or high aspect ratio using dry film resist
InactiveUS20070259293A1Reduce thicknessHigh-resolution patterningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistSemi solid
Disclosed herein is a method for forming a pattern, comprising: attaching a single-layer or multi-layer dry film resist made of a semi-solid or solid material to part or all of the surface of a substrate; exposing the dry film resist to light either by irradiating a focusable energy beam directly onto the resist or by projecting a specific wavelength range of light onto the resist, to form a region to be filled with a functional material; charging the functional material into the formed region using a method such as inkjetting; drying the functional material; and removing the dry film resist, thus obtaining the desired pattern.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MASCH & MATERIALS
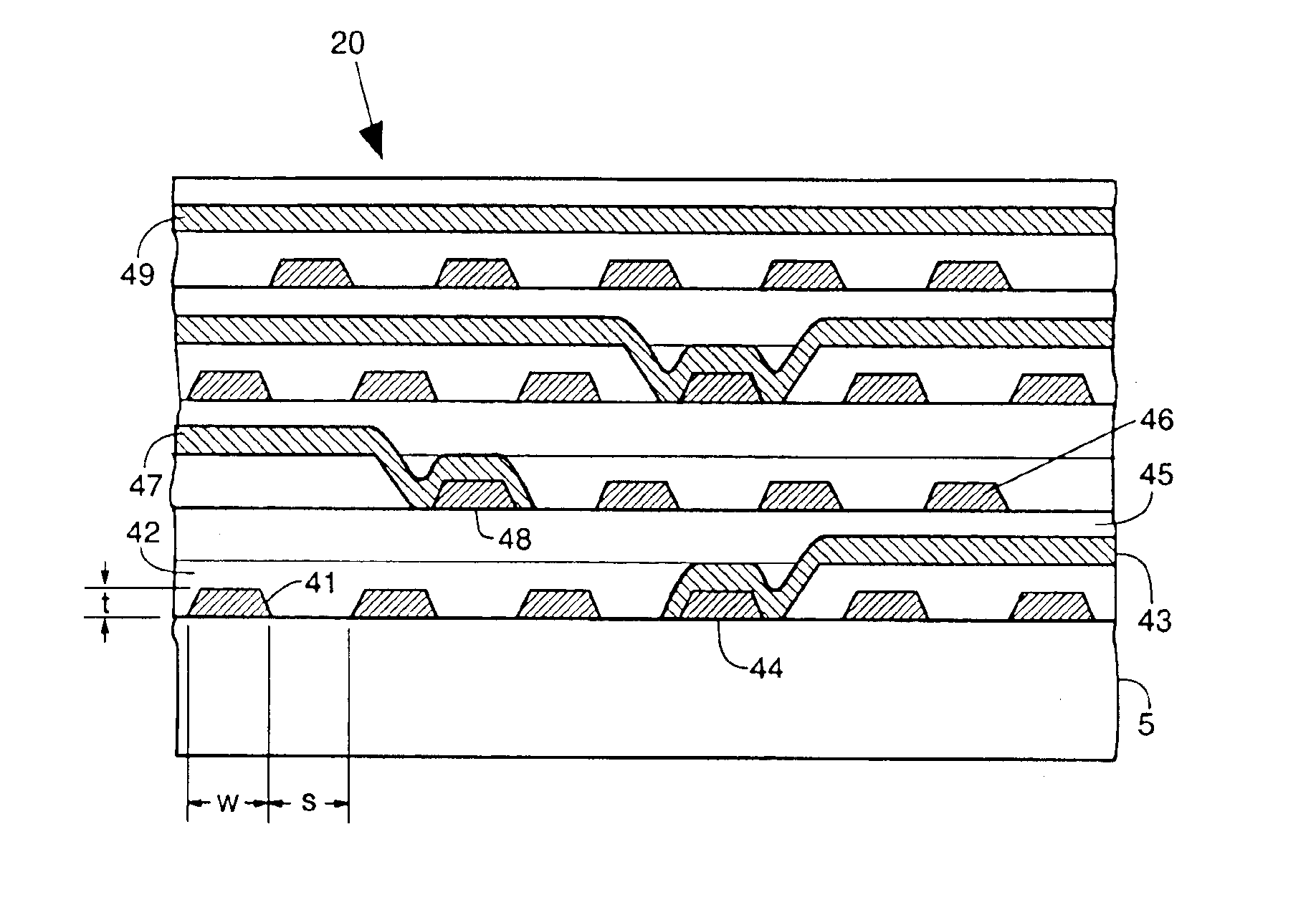
Laminated circuit board and its manufacturing method, and manufacturing method for module using the laminated circuit board and its manufacturing apparatus
InactiveUS20050117312A1High reliability in electrical connectionImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectronic component
A laminated circuit board with electronic components buried therein comprises a substrate on which a land disposed on one main surface thereof is connected and fixed by solder to an integrated circuit (or the like). A sheet is laminated on the upper surface of the substrate. A filling portion by fluid resin is formed by clearance at the outer periphery of the integrated circuit (or the like). The sheet maintains its shape by woven or non-woven cloth having a hole in which the integrated circuit (or the like) is buried. The woven or non-woven cloth is impregnated with resin having heat fluidity and is thermally compressed. Thus, the electrical and mechanical connections between the laminated circuit board and electronic component can be enhanced in reliability.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
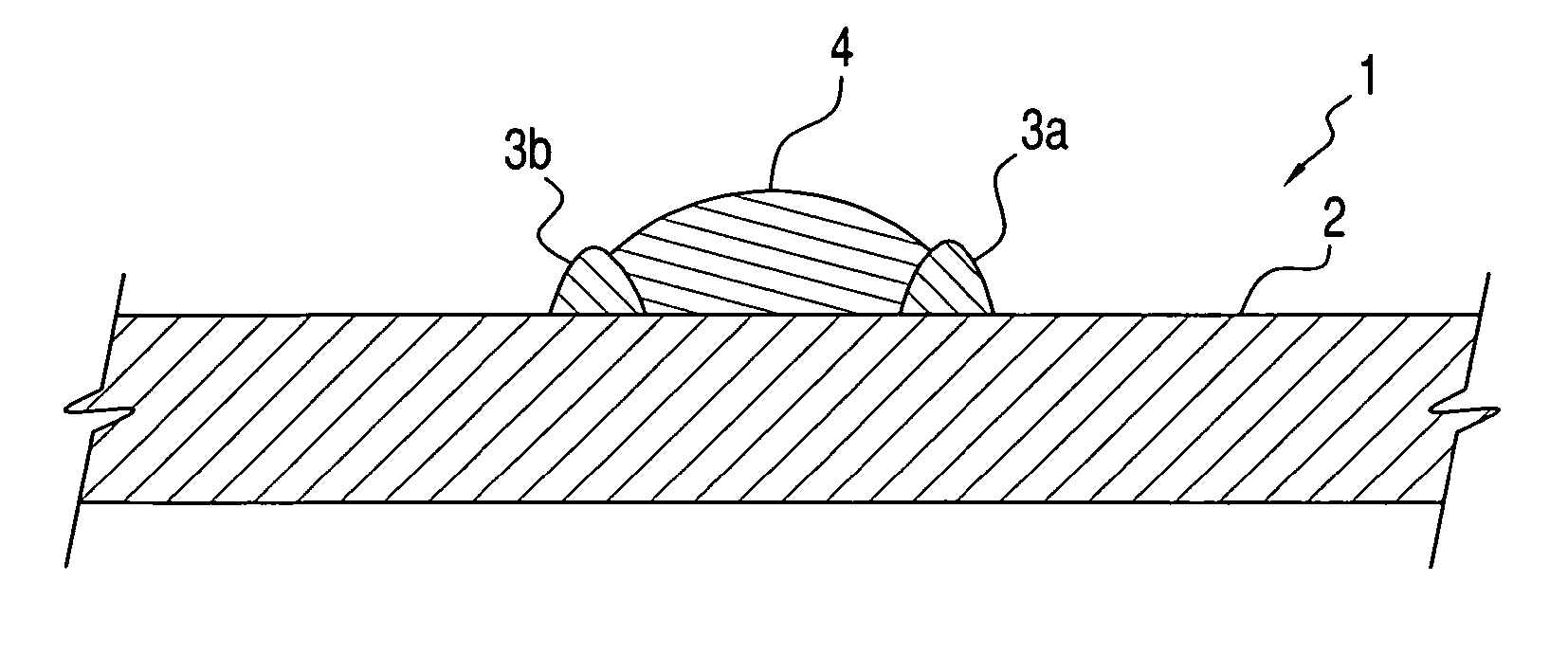
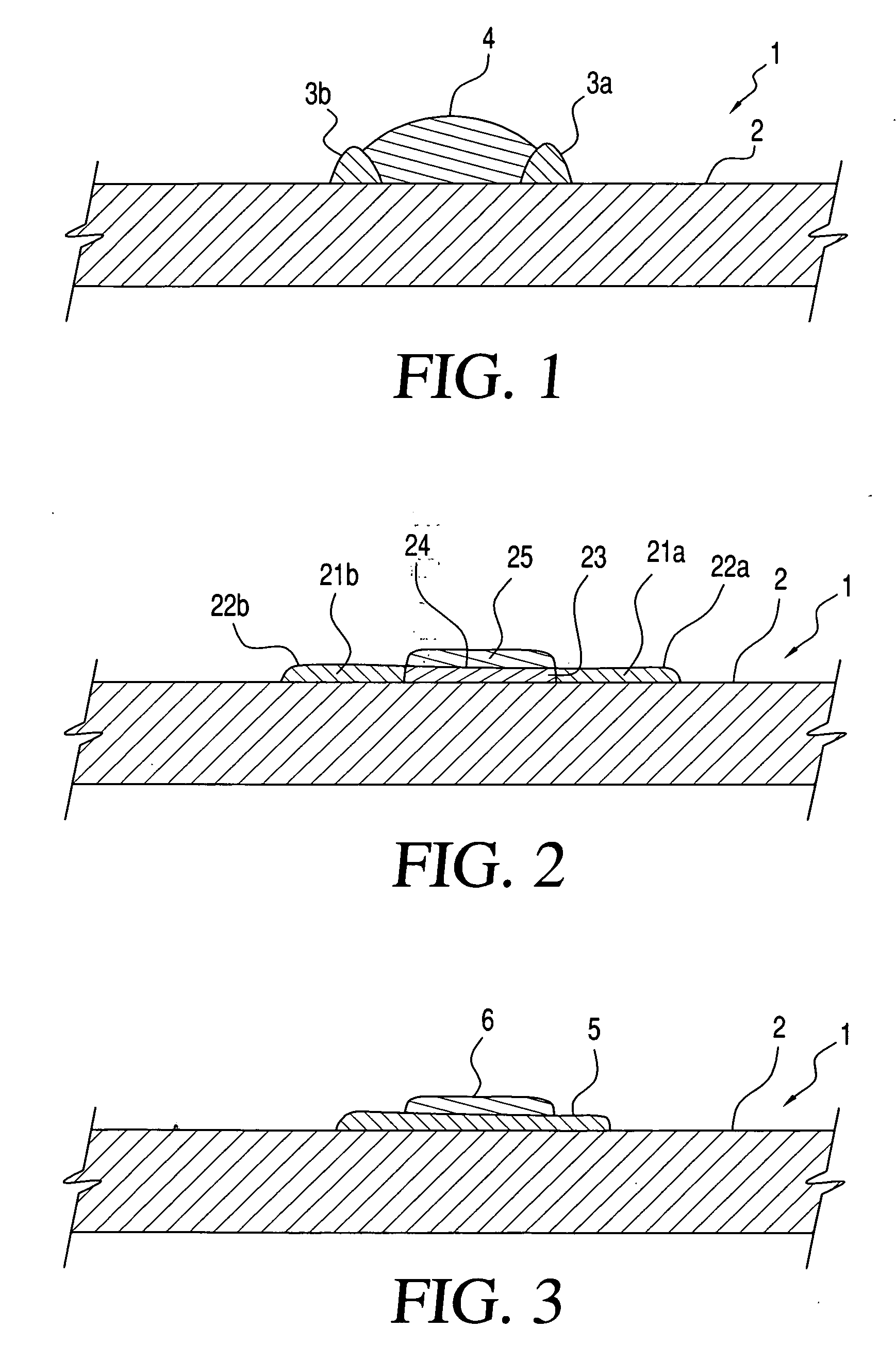
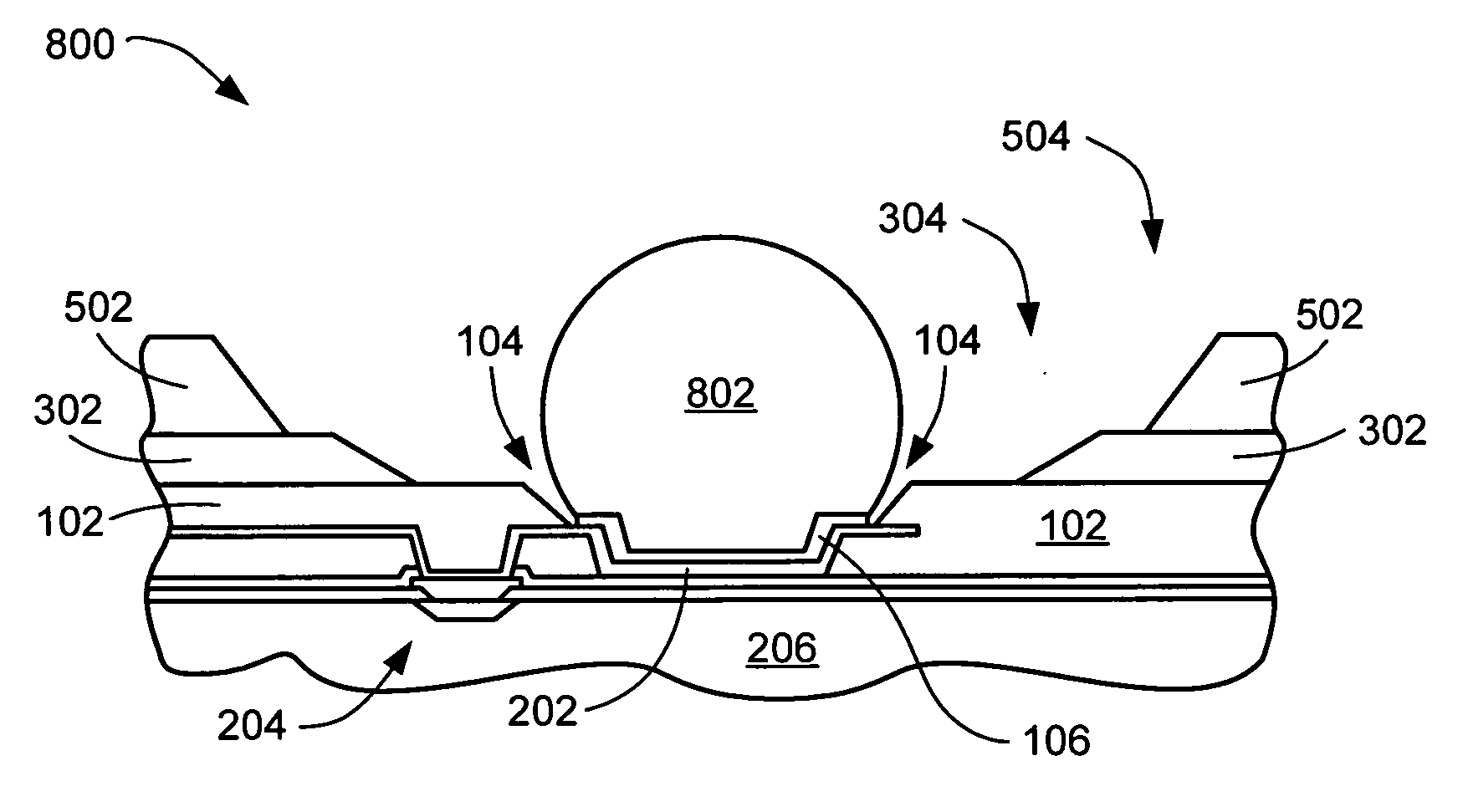
Post bump and method of forming the same
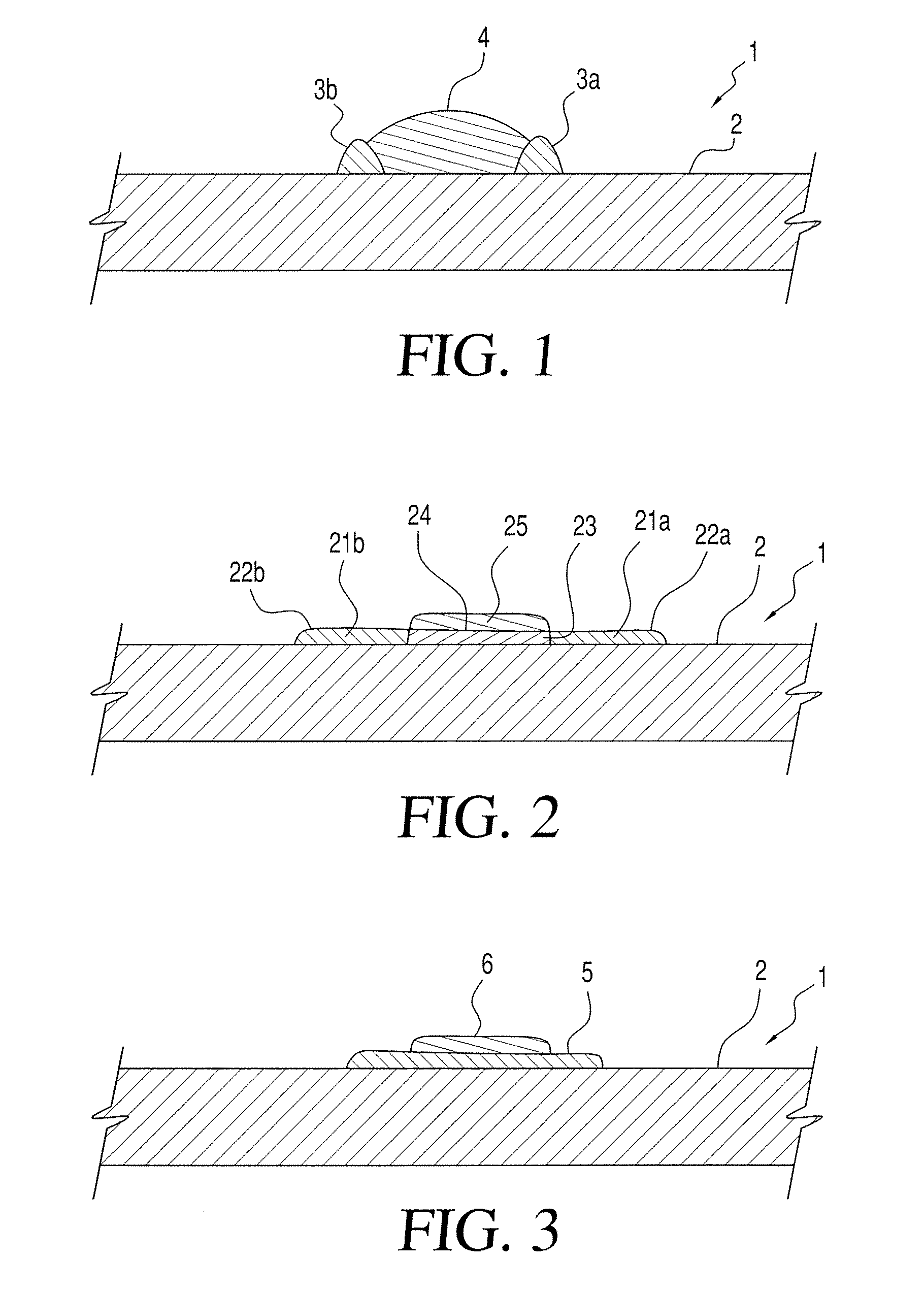
InactiveUS20110012261A1Prevent deviationAvoid flowSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringSolder form
A post bump formed over an electrode pad of a substrate for electrically connecting to an external device, the post bump including a metal post formed over the electrode pad; and a solder formed over the metal post and shaped as a dome, the dome occupying a space defined by imaginary lines extending from a perimeter of the metal post along an axial direction of the metal post.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Fabrication method for electronic system modules
InactiveUS7297572B2Good dimensional stabilityLow costPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureSupercomputerElectromagnetic shielding
This specification describes techniques for manufacturing an electronic system module. The module includes flexible multi-layer interconnection circuits with trace widths as narrow as 5 microns or less. A glass panel manufacturing facility, similar to those employed for making liquid crystal display, LCD, panels is preferably used to fabricate the interconnection circuits. A multi-layer interconnection circuit is fabricated on the glass panel using a release layer. A special assembly layer is formed over the interconnection circuit comprising a thick dielectric layer with openings formed at input / output (I / O) pad locations. Solder paste is deposited in the openings using a squeegee to form wells filled with solder. IC chips are provided with gold stud bumps at I / O pad locations, and these bumps are inserted in the wells to form flip chip connections. The IC chips are tested and reworked. The same bump / well connections can be used to attach fine-pitch cables. Module packaging layers are provided for hermetic sealing and for electromagnetic shielding. A blade server or supercomputer embodiment is also described.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Polymer-based integrated thin film capacitors, packages containing same and methods related thereto
Some embodiments include thin film capacitors (TFC) formed on a package substrate of an integrated circuit package. The TFC include a polymer-based dielectric layer deposited directly on the package substrate. At least one of the TFC includes a first electrode layer, a second electrode layer, with the polymer-based dielectric layer located between the first and second electrode layers. Each of the first and second electrode layers is also formed individually and directly on the package substrate. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for forming high-resolution pattern with direct writing means
ActiveUS20060281333A1High resolutionAvoid huge wasteSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionLine width
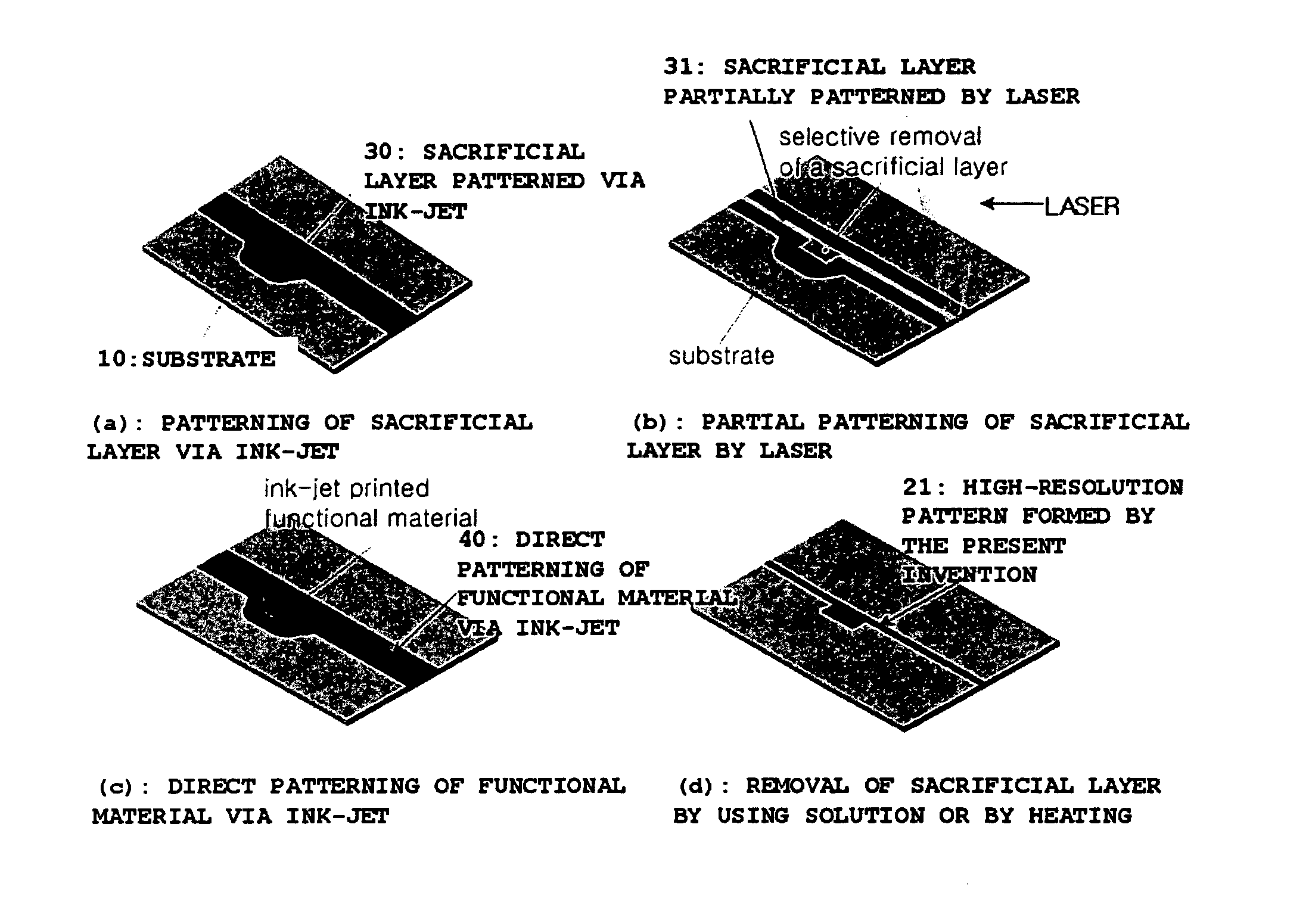
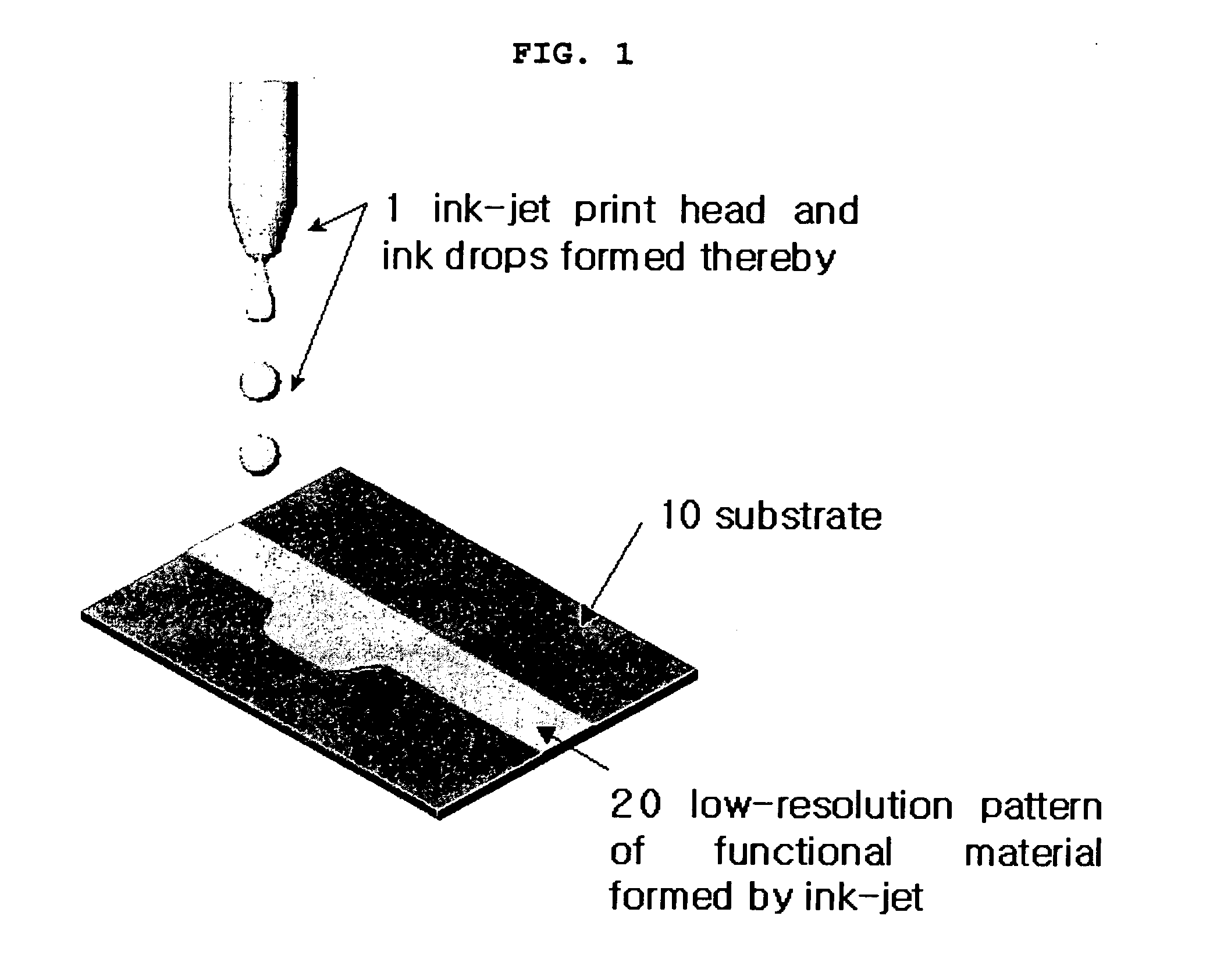
Disclosed is a method for forming a pattern which comprises the steps of: (a) providing a substrate having a sacrificial layer made of a first material, partially or totally formed on the substrate; (b) forming pattern grooves, which are free from the first material and have a line width of a first resolution or lower, on the sacrificial layer by using a first means, by which the sacrificial layer is directly processed to form a line; (c) filling the pattern grooves with a second material to a second resolution by using a second means, to form a pattern of the second material on the substrate. A substrate having a pre-pattern formed by the method is also disclosed. The method for forming a pattern provides a high-resolution pattern with little or no waste of the second material, thereby reducing production costs. The method includes use of the first means with a high resolution, such as focused energy beams of laser, combined with the second means with a low resolution, such as ink-jet, and provides a high-resolution pattern with high processing efficiency.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Method for solder bumping, and solder-bumping structures produced thereby
ActiveUS20060125110A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSolder ballSolder paste
A method for solder bumping provides a substrate and forms a film on the substrate. The film has openings therethrough. A stencil is aligned on the film. The stencil has openings therethrough over the openings through the film. Solder paste is printed onto the substrate and into the openings through the stencil and the openings through the film. The solder paste is reflowed to form solder balls therefrom. The stencil and the film are then removed.
Owner:JCET SEMICON (SHAOXING) CO LTD
Thin-film pattern forming method, semiconductor device, electro-optic device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20060084206A1Increase the areaSufficient film thicknessPrinted circuit aspectsSolid-state devicesDevice materialFilm material
A thin-film pattern forming method that deposits a plurality of thin films on a substrate to form a thin-film pattern, includes: forming a second thin film on the substrate, the second thin film having an affinity for a functional liquid containing a thin-film material that makes up a first thin film; providing lyophobic treatment that makes a surface of the second thin film repellent to the functional liquid; forming a concave portion that defines a pattern shape of the first thin film by removing part of the second thin film; discharging the functional liquid to the concave portion; and forming the first thin film by drying the functional liquid discharged to the concave portion.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Pattern and fabricating method therefor, device and fabricating method therefor, electro-optical apparatus, electronic apparatus, and method for fabricating active matrix substrate
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for removing resin mask layer and method for manufacturing solder bumped substrate
ActiveUS20060110907A1Easy to disassembleShort timeDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesResistHeat treated
Owner:HARIMA CHEM INC
Pattern and fabricating method therefor, device and fabricating method therefor, electro-optical apparatus, electronic apparatus, and method for fabricating active matrix substrate
InactiveUS7220682B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMulti materialActive matrix
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
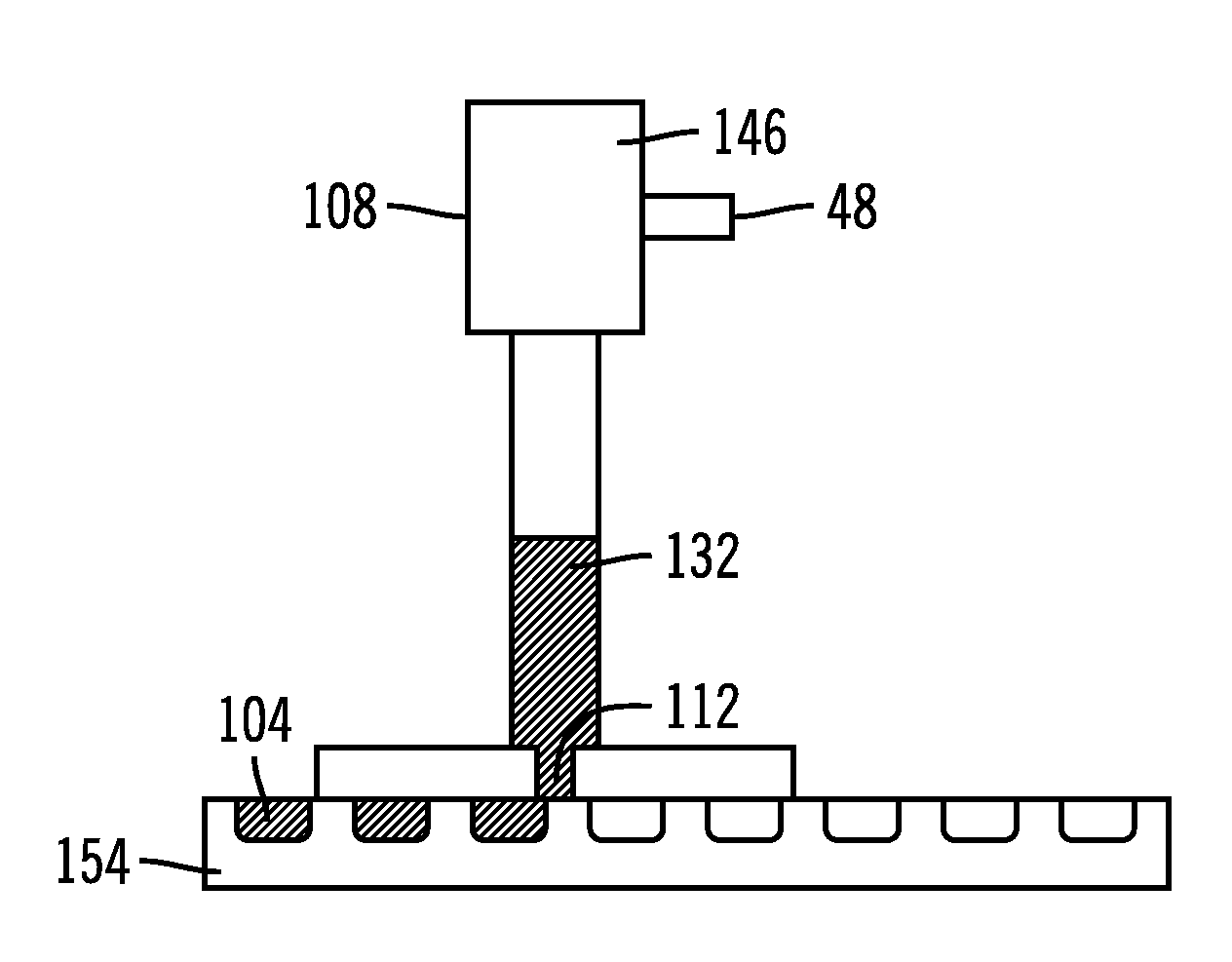
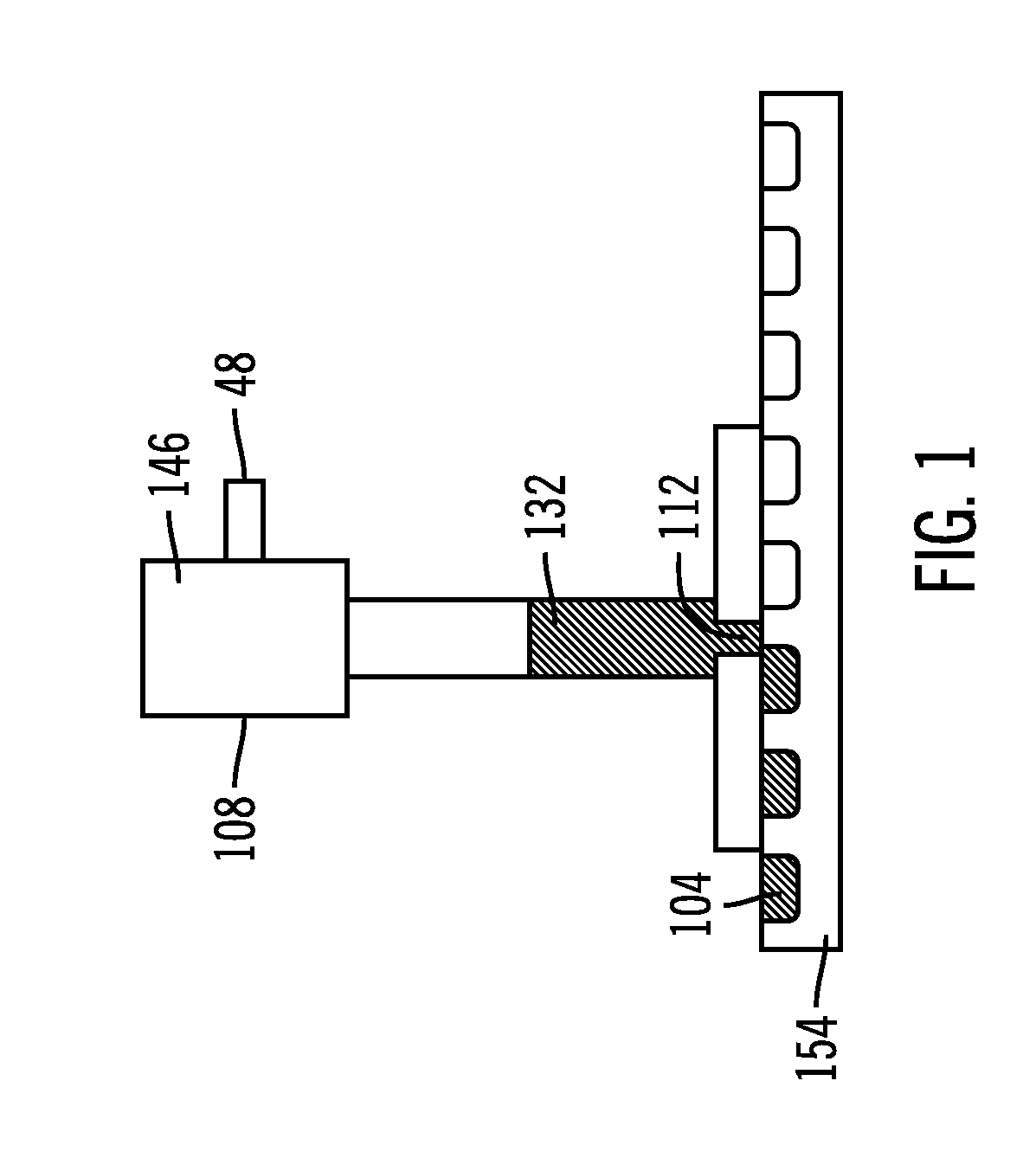
Conductive bonding material fill techniques
InactiveUS20080272177A1Cost of delayDelay materialPrinted circuit aspectsWelding/cutting auxillary devicesLinear motionElectrical and Electronics engineering
A system provides solder into cavities in a circuit supporting substrate. The system places a fill head in substantial contact with a circuit supporting substrate. The circuit supporting substrate includes at least one cavity. A linear motion or a rotational motion is provided to at least one of the circuit supporting substrate and the fill head while the fill head is in substantial contact with the circuit supporting substrate. Solder is forced out of the fill head toward the circuit supporting substrate. The solder is provided into the at least one cavity contemporaneous with the at least one cavity being in proximity to the fill head. The system brings a second circuit supporting substrate in close proximity to the circuit supporting substrate, at least one receiving pad on the second circuit supporting substrate substantially contacts the conductive bonding material of the at least one cavity.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
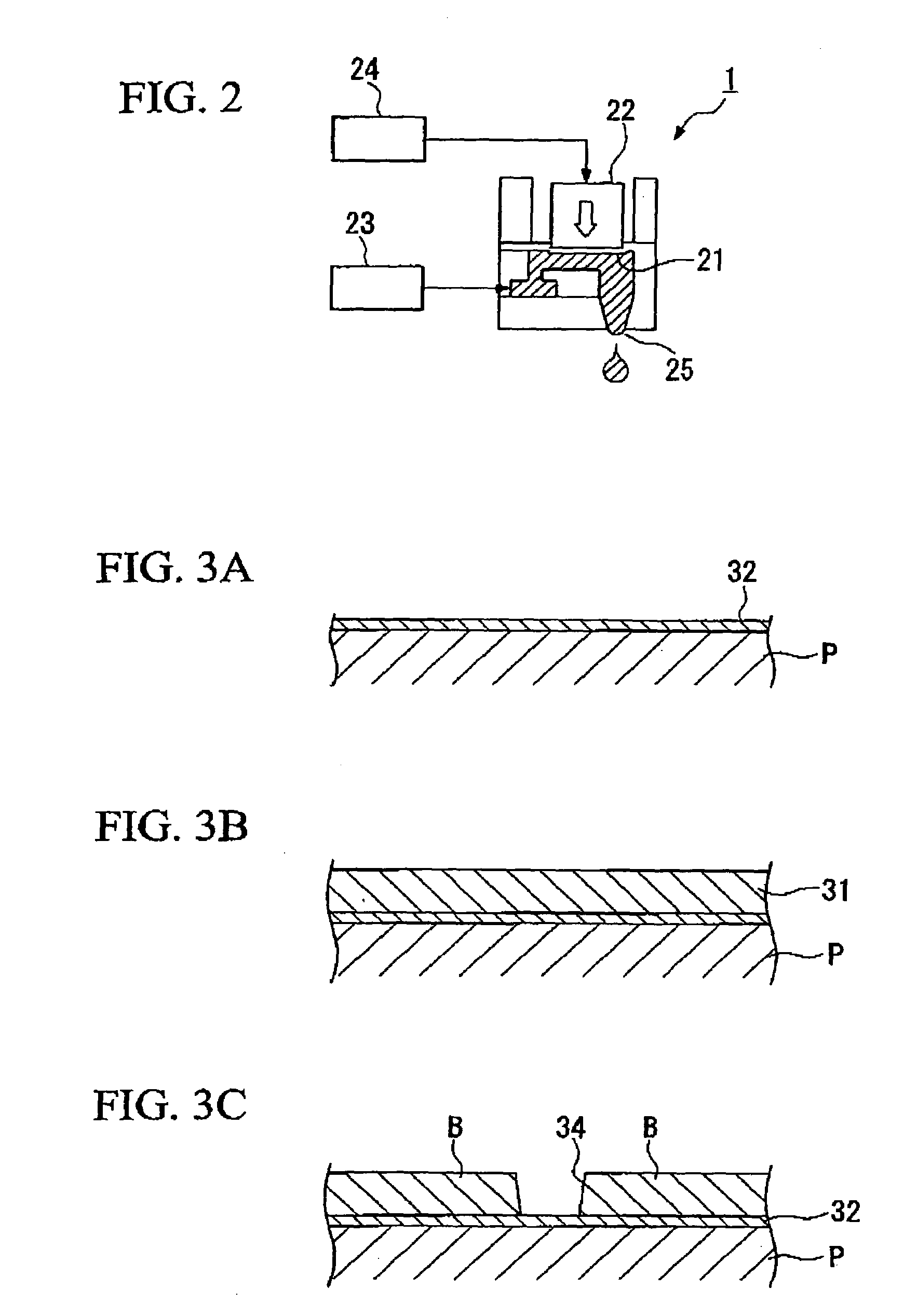
Manufacture of solid-solder-deposit PCB utilizing electrically heated wire mesh
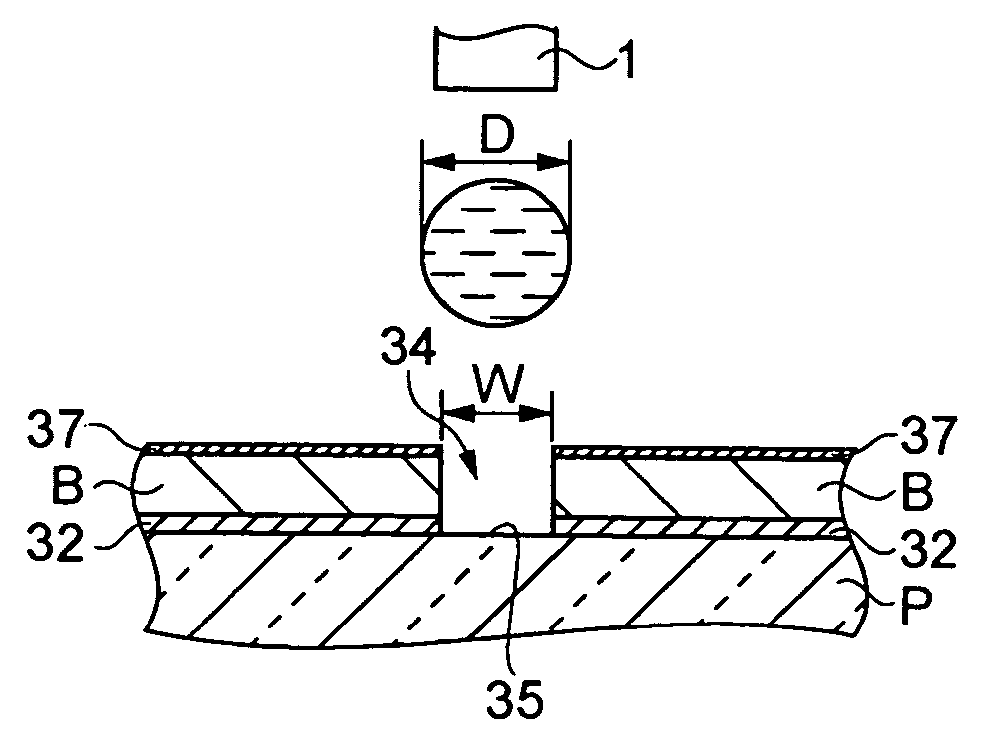
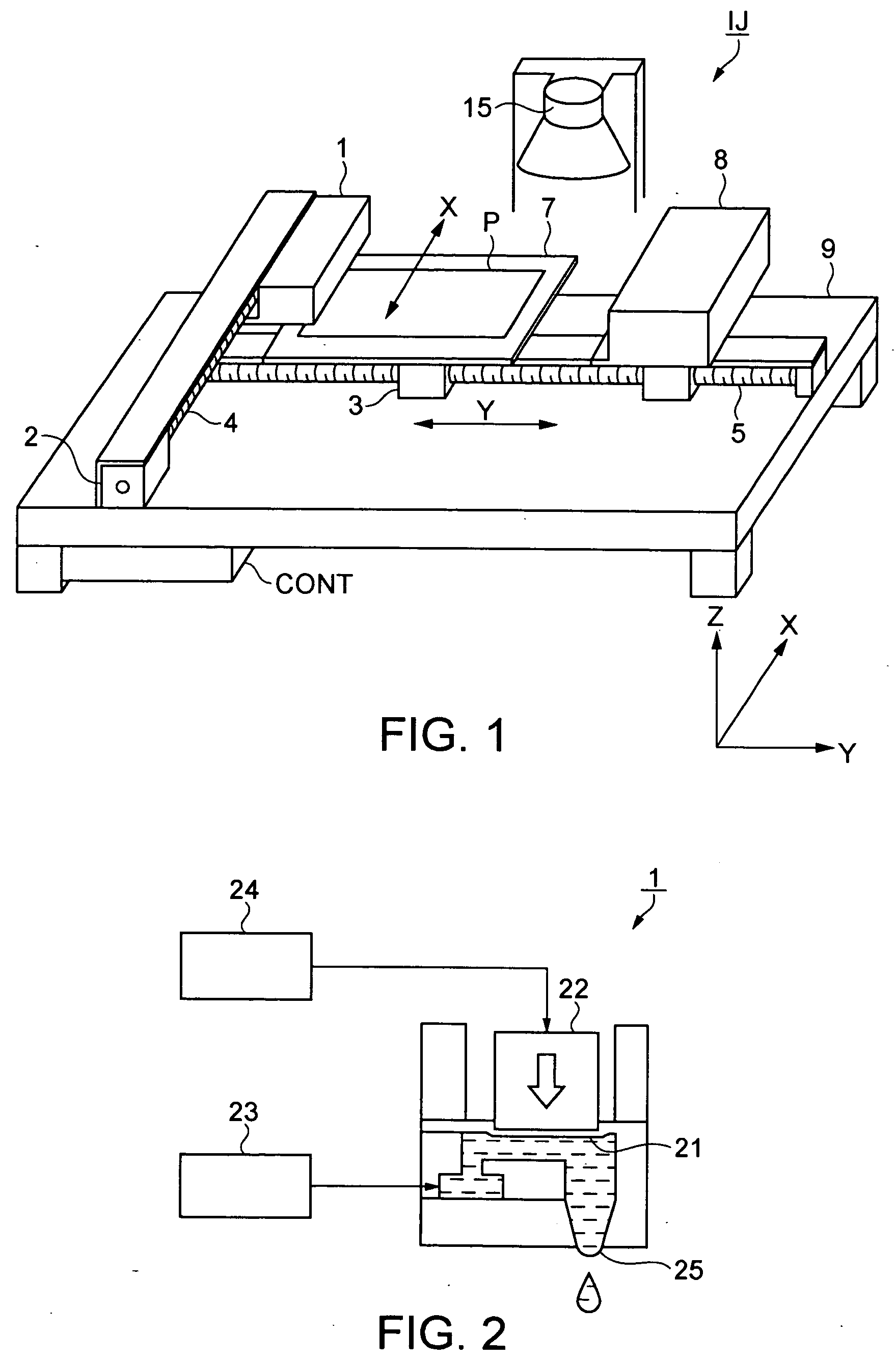
InactiveUS20040178251A1Reduce present cost for SSD-PCBsImprove reliabilityPrinted circuit assemblingPrinted circuit aspectsAssembly lineSolder paste
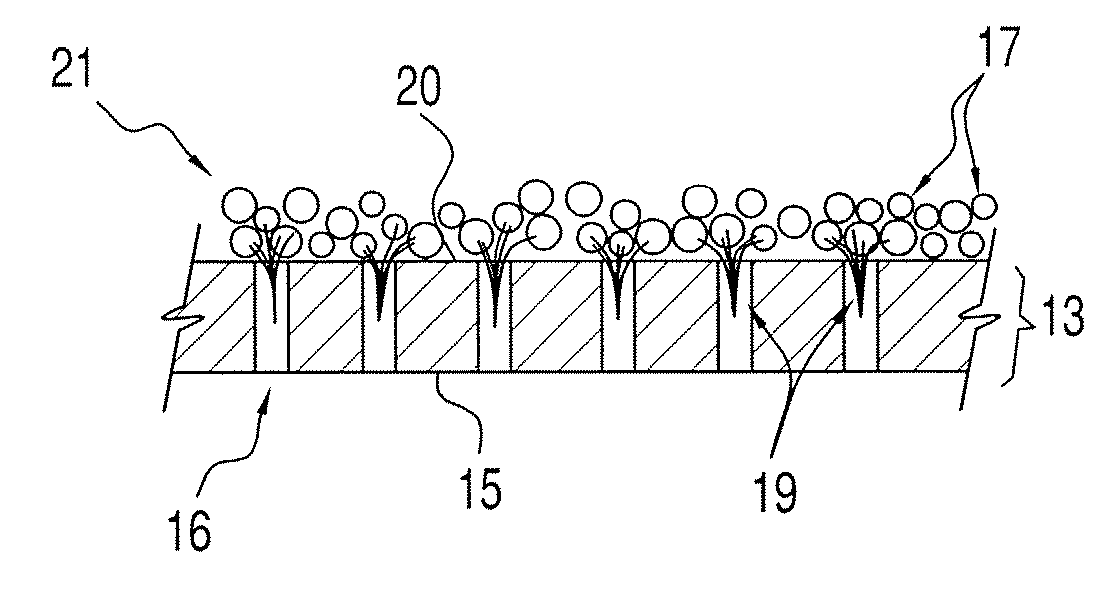
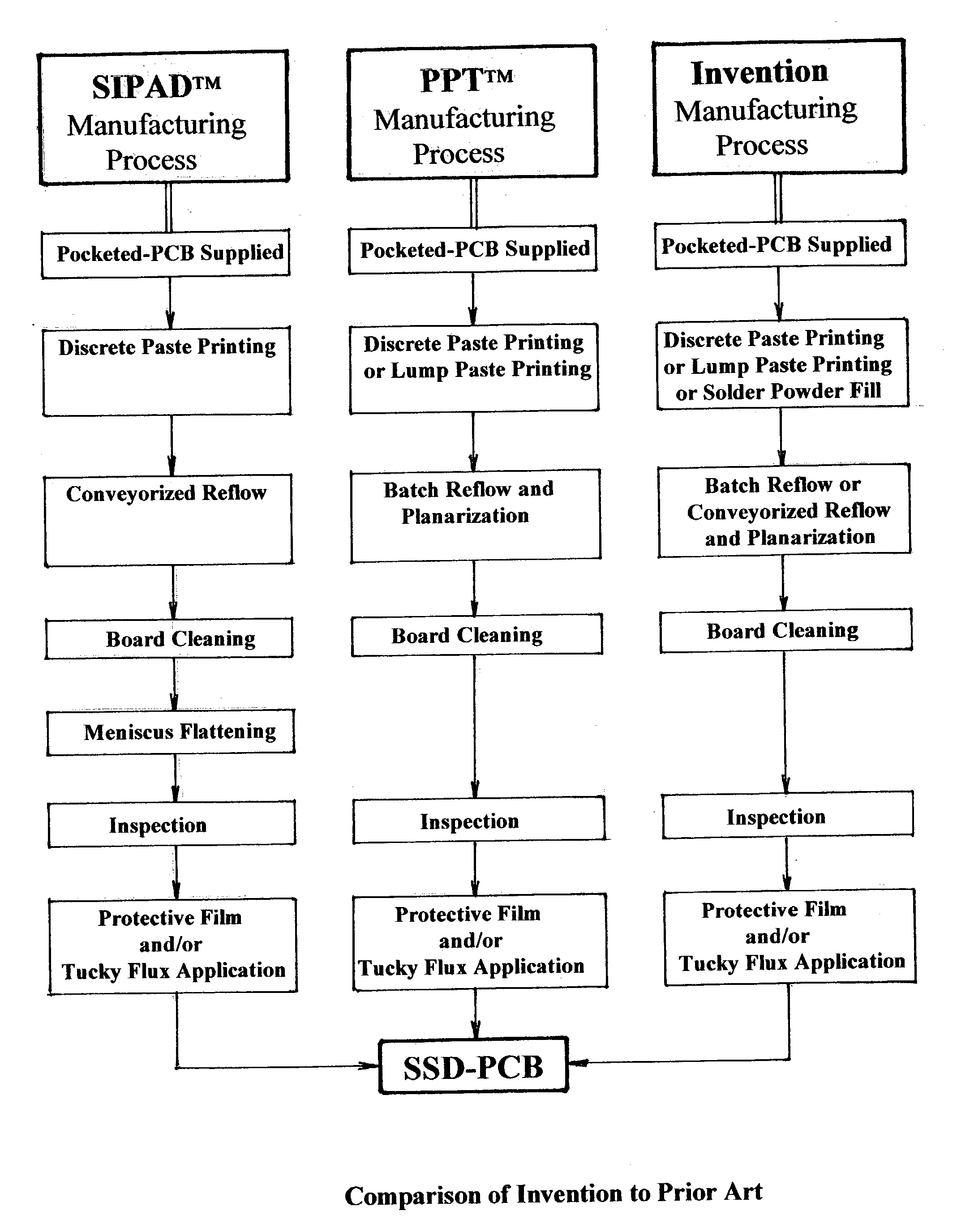
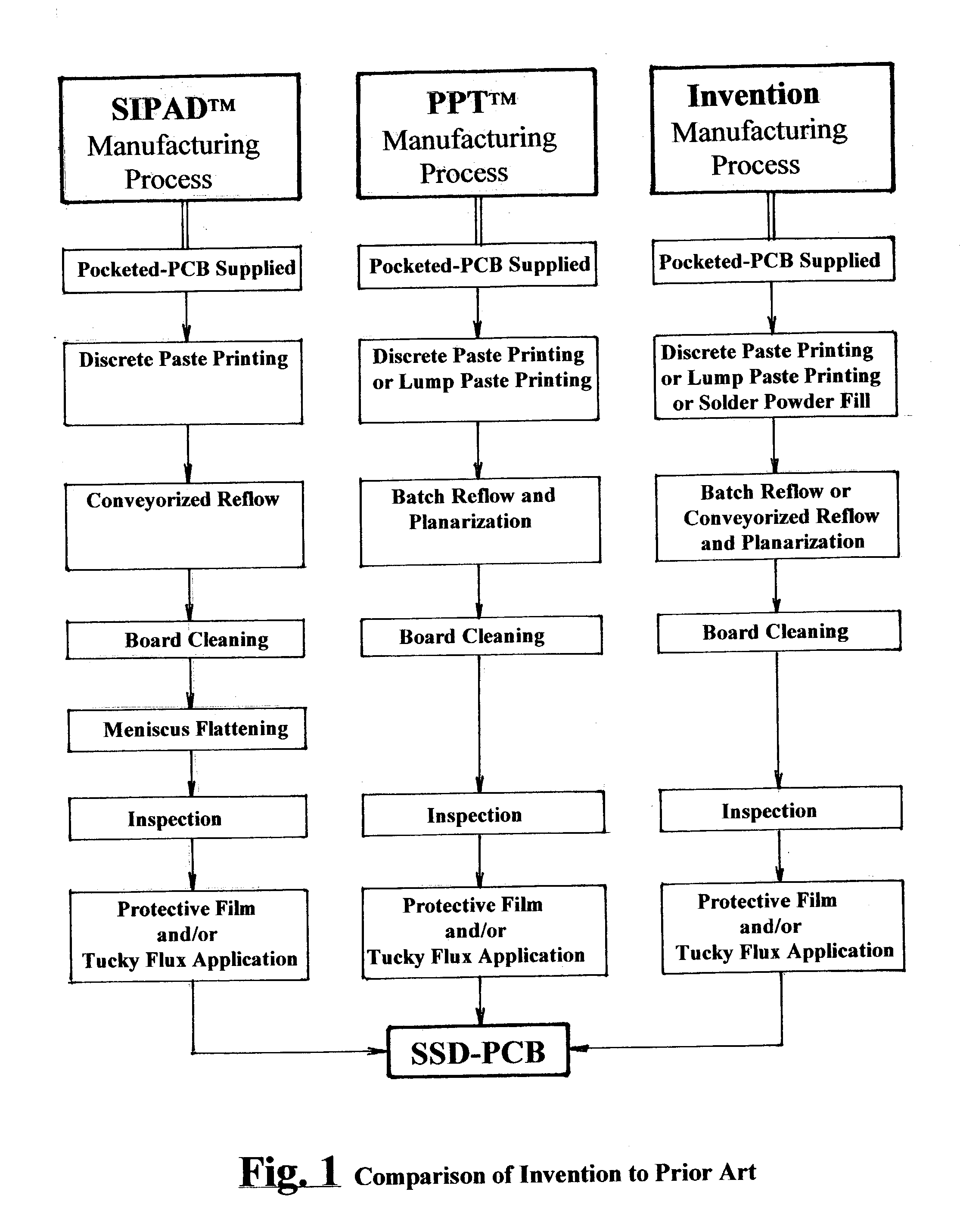
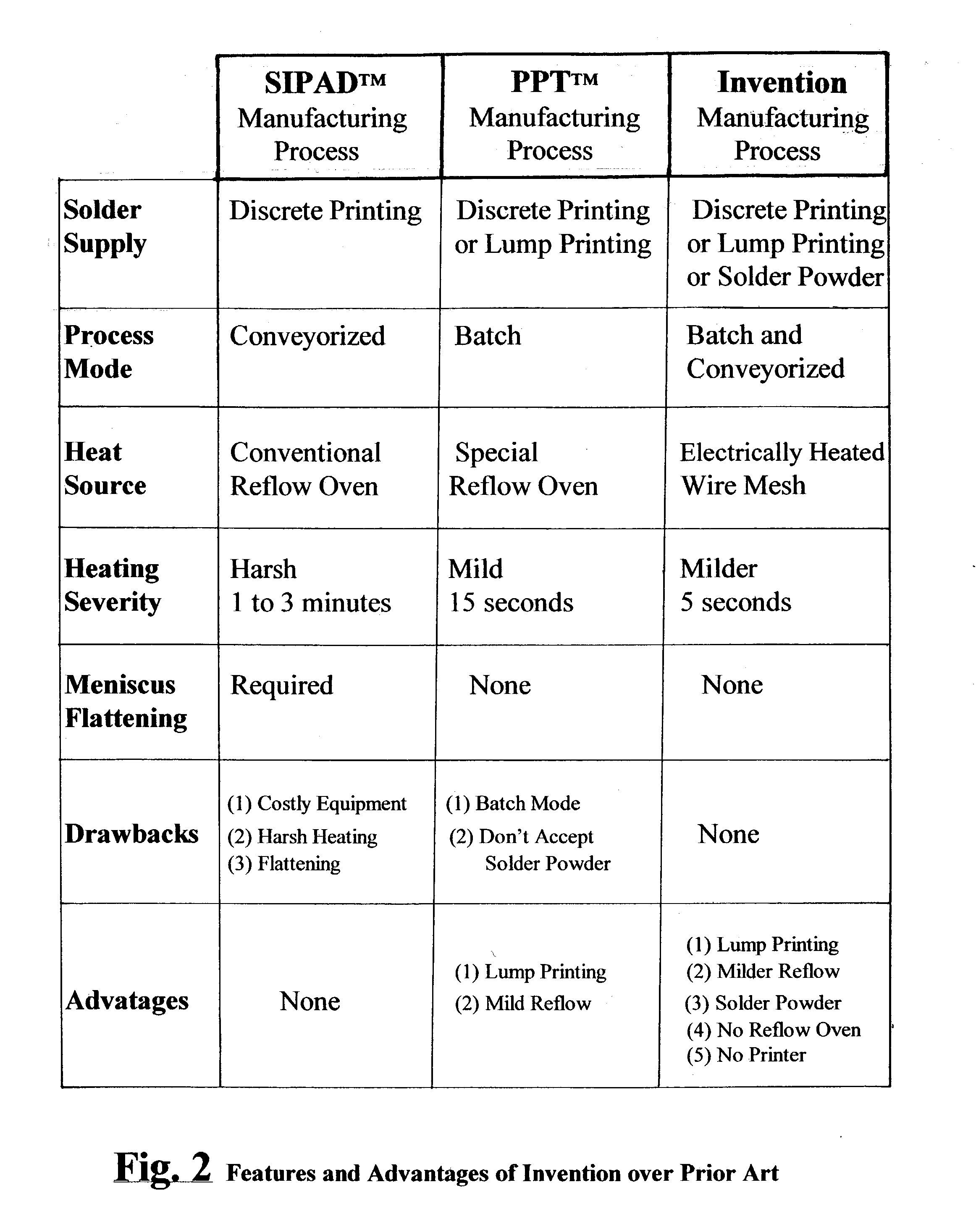
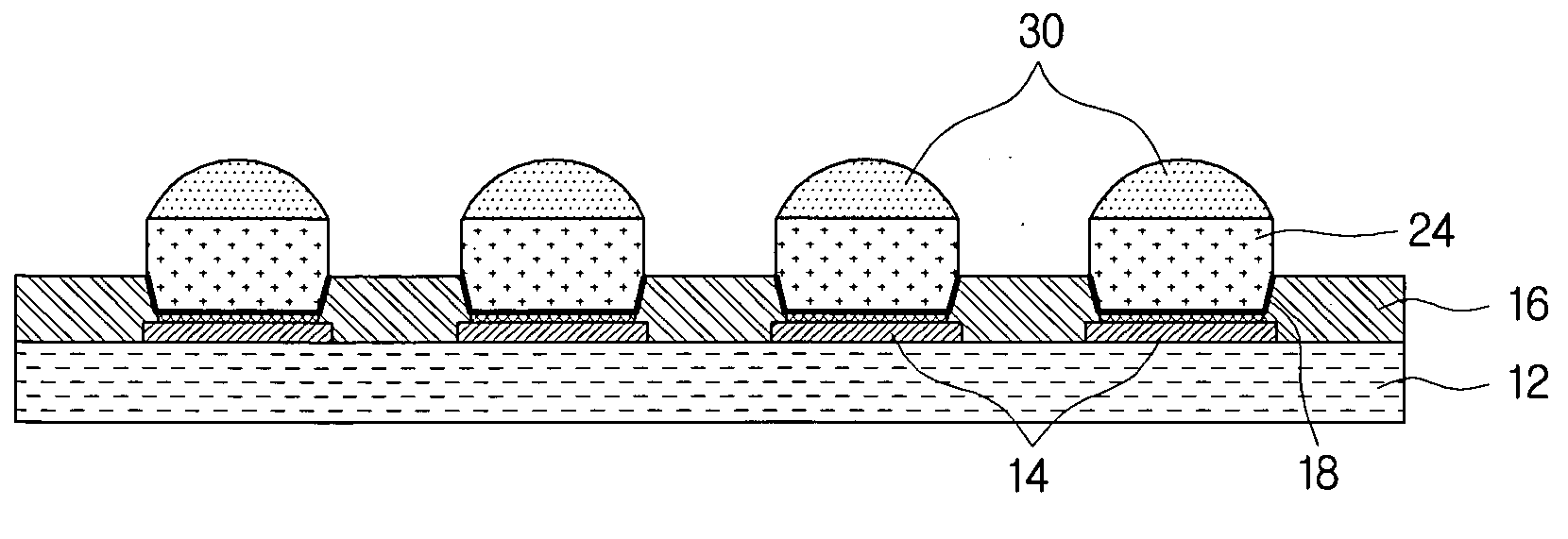
A novel process and apparatus for manufacturing Solid Solder Deposit-Printed Circuit Board (SSD-PCB) by either melting solder paste or dry solder powder previously deposited on a pocketed-PCB 20. Said process and apparatus, unlike the prior art, utilize as heat source an electrically heated conveyor wire mesh 76 instead of a reflow oven. Relatively thick flat-shaped SSDs 44 metallurgically bonded over each soldering pad 24 of said pocketed-PCB 20 are formed. By itself, SSD-PCB technology provides the electronic assembly industry with ready-to-solder PCBs consequently eliminating the need to use solder paste at the assembly line. This invention, unlike the prior art for producing SSD-PCBs, can utilize dry solder powder piles 38 in conjunction with flux layers 116 deposited on top of said conveyor wire mesh 76 thereby excluding, all together, the use of paste printing equipment. Specifically my invention reduces the manufacturing cost, shortens manufacturing time, reduces manufacturing energy consumption and improves SSD-PCB's quality and reliability while requiring less manufacturing equipment than the prior art.
Owner:TRUCCO HORACIO ANDRES
Post bump and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20090184420A1Avoid flowPrevent deviationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsResistMetallic materials
A post bump and a method of forming the post bump are disclosed. The method of forming the post bump can include: forming a resist layer, in which an aperture is formed in correspondence to a position of an electrode pad, over a substrate, on which the electrode pad is formed; forming a metal post by filling a part of the aperture with a metallic material; filling a remaining part of the aperture with solder; reflowing the solder by applying heat; and removing the resist layer. This method can be utilized to prevent deviations in the plated solder and prevent the unnecessary flowing of the solder over the sides of the metal post during reflowing, so that the amount of solder used can be minimized.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method for Fabricating Blackened Conductive Patterns
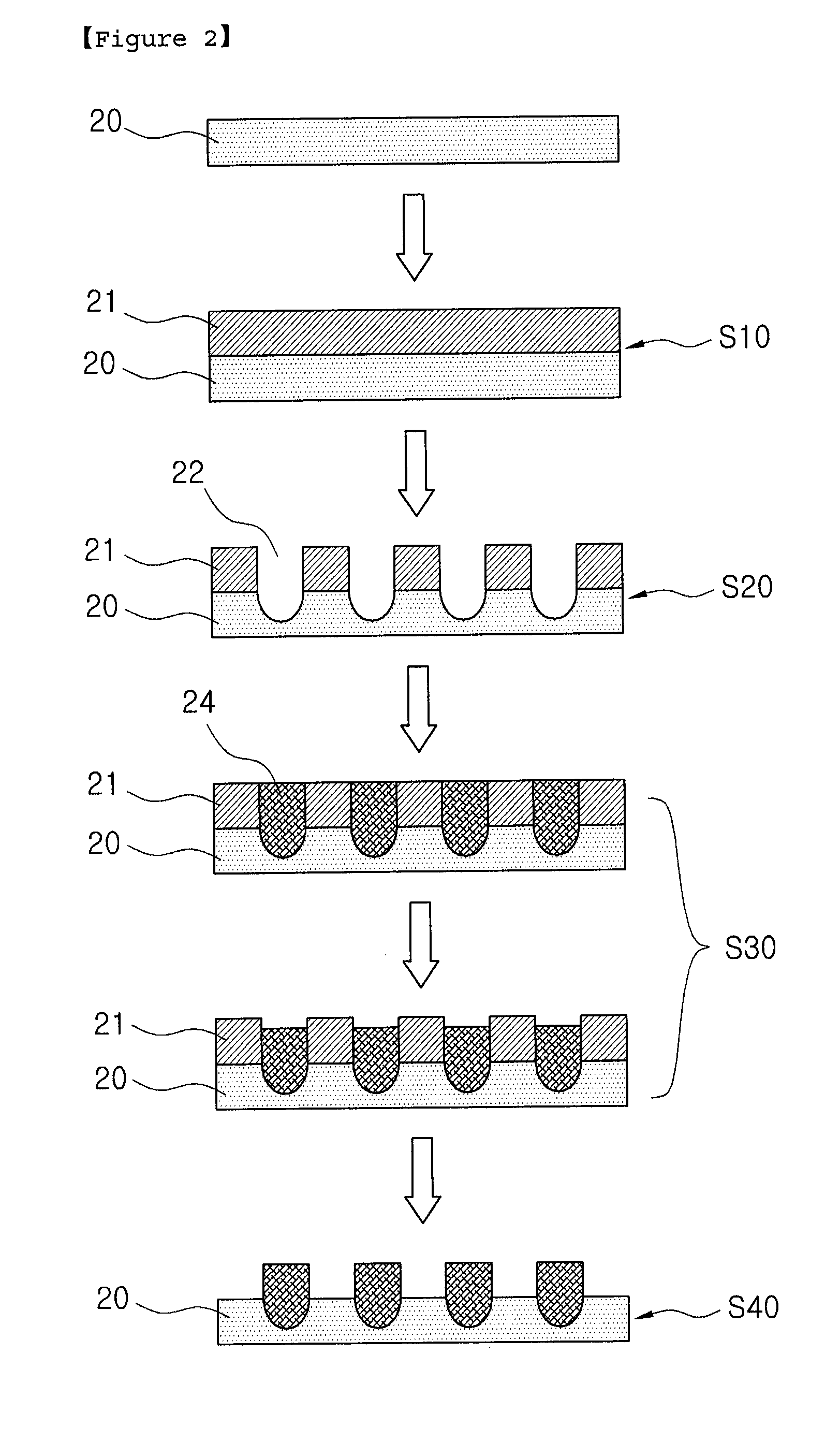
ActiveUS20110003086A1High resolutionImprove conductivityLight absorption dielectricsRadiation applicationsResistConductive materials
The present invention relates to a method for fabricating blackened conductive patterns, which includes (i) forming a resist layer on a non-conductive substrate; (ii) forming fine pattern grooves in the resist layer using a laser beam; (iii) forming a mixture layer containing a conductive material and a blackening material in the fine pattern grooves; and (iv) removing the resist layer remained on the non-conductive substrate.
Owner:INKTEC CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com