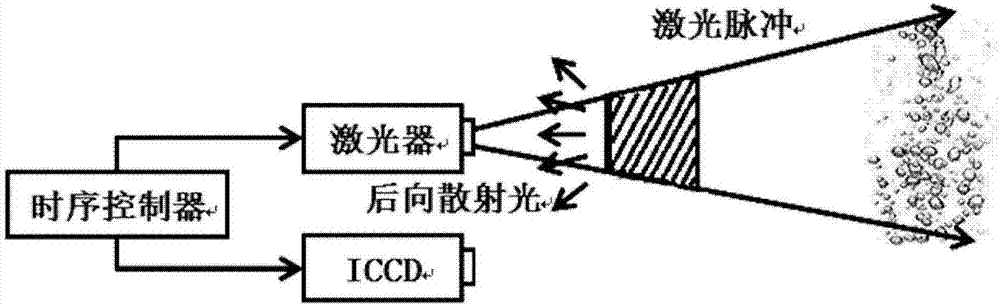
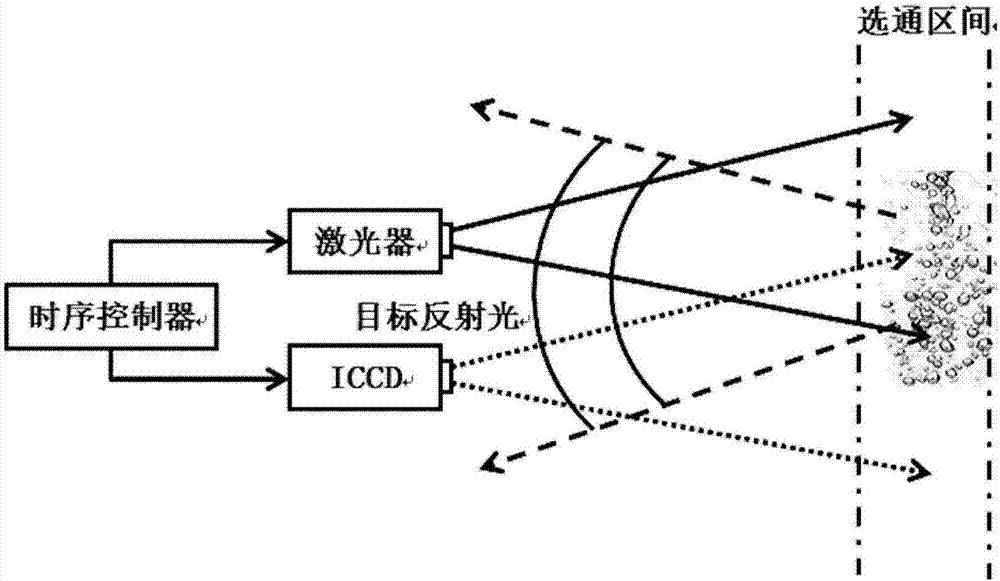
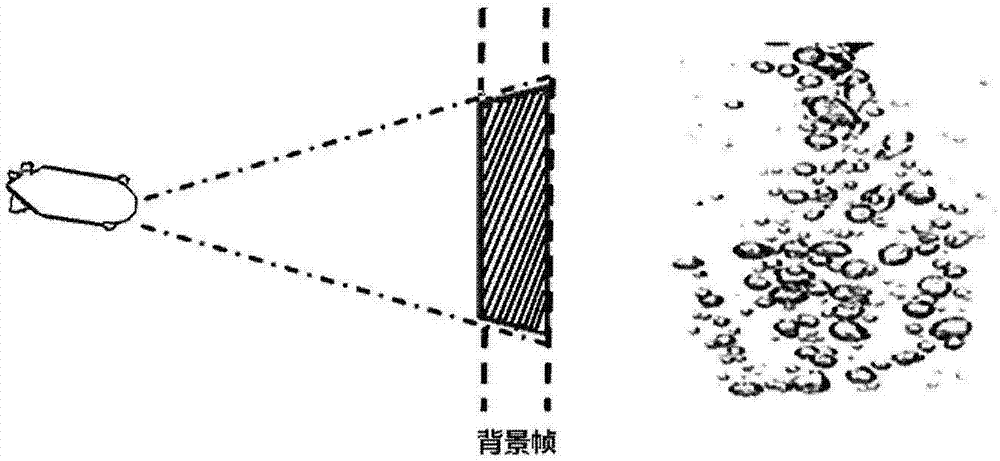
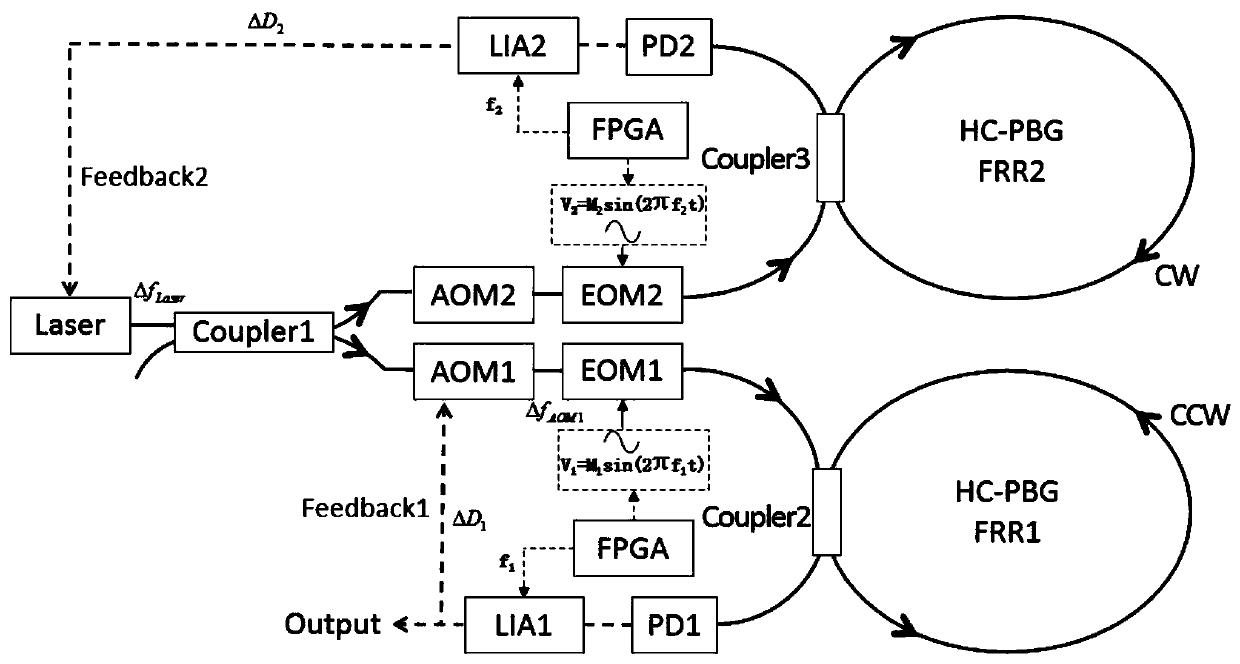
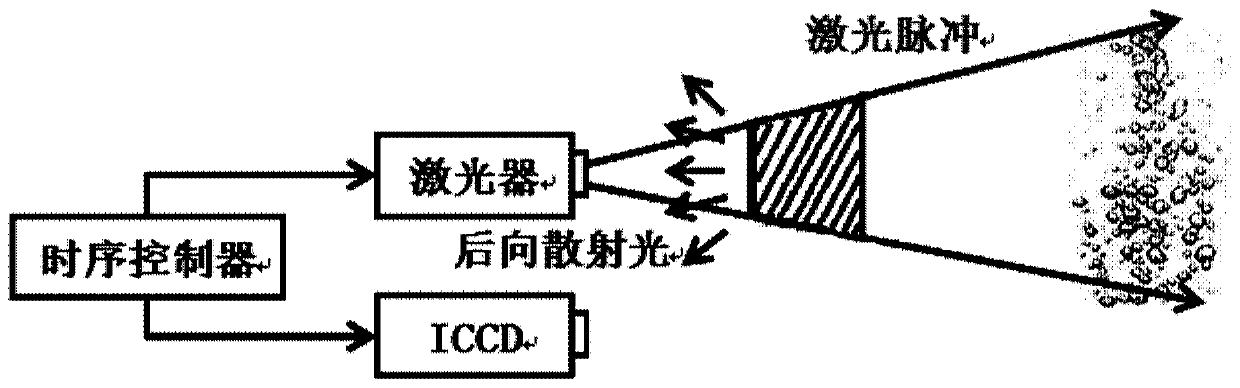
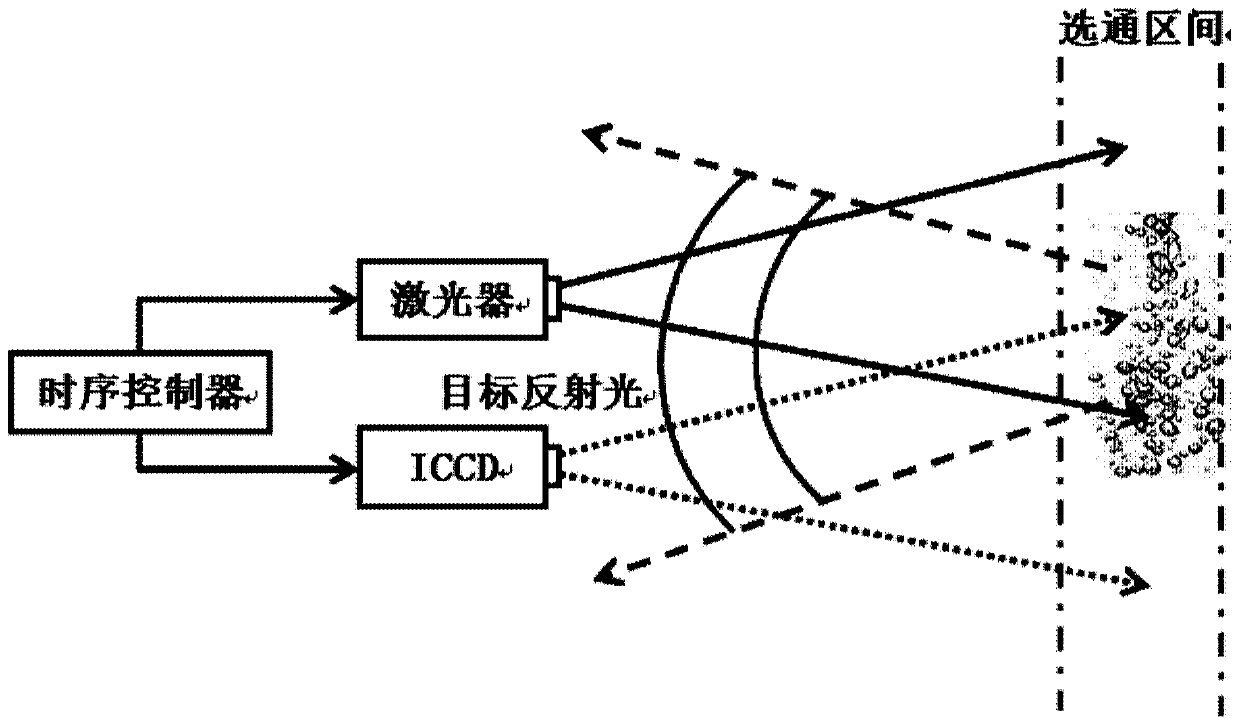
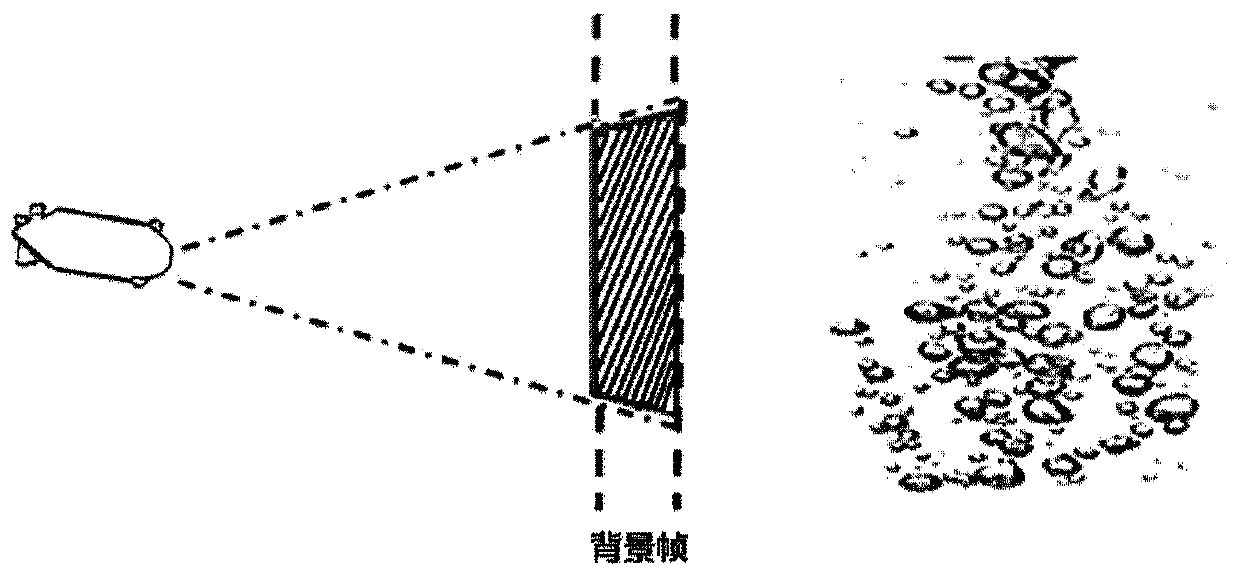
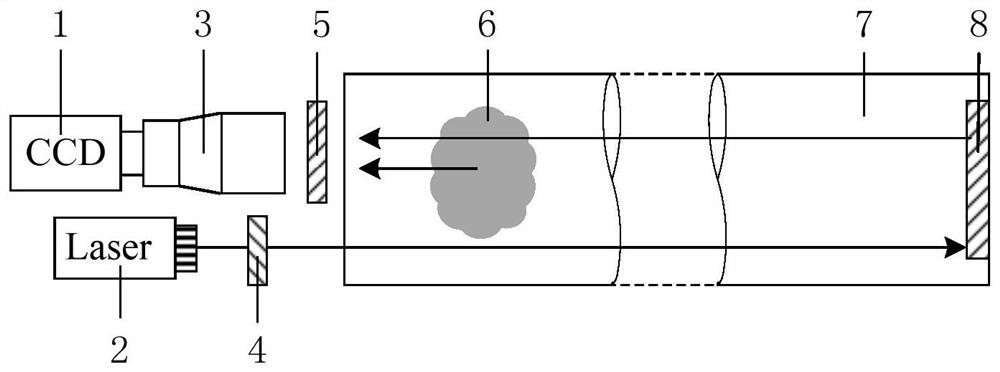
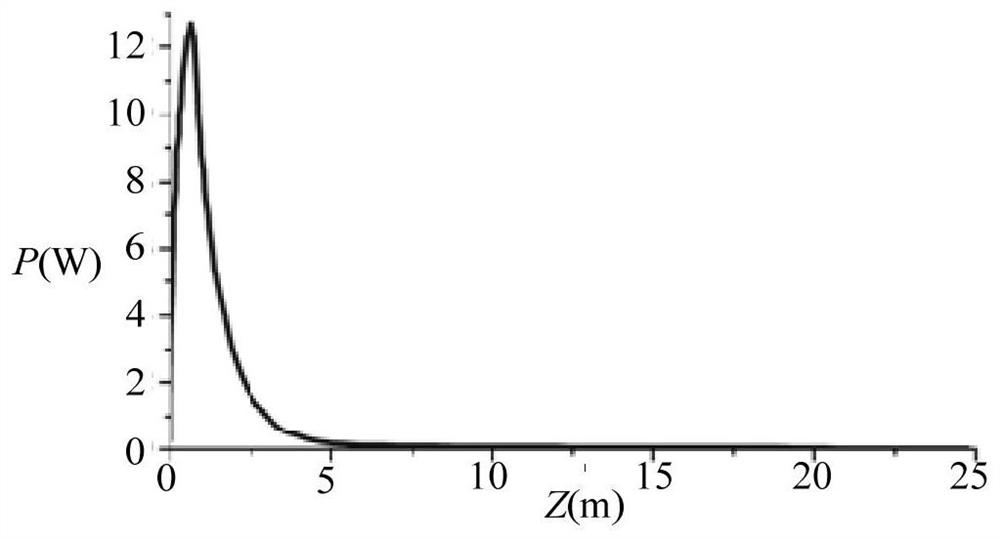
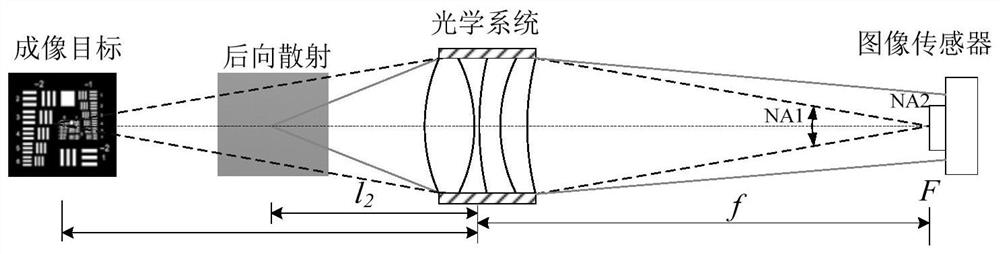
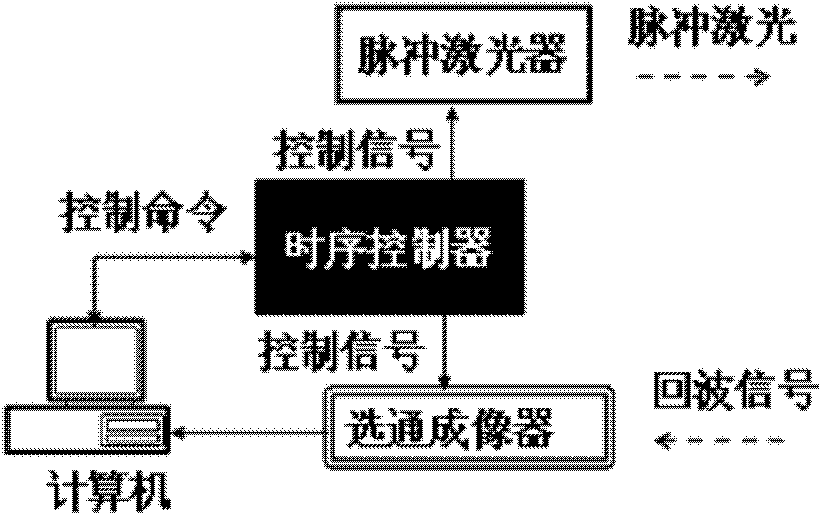
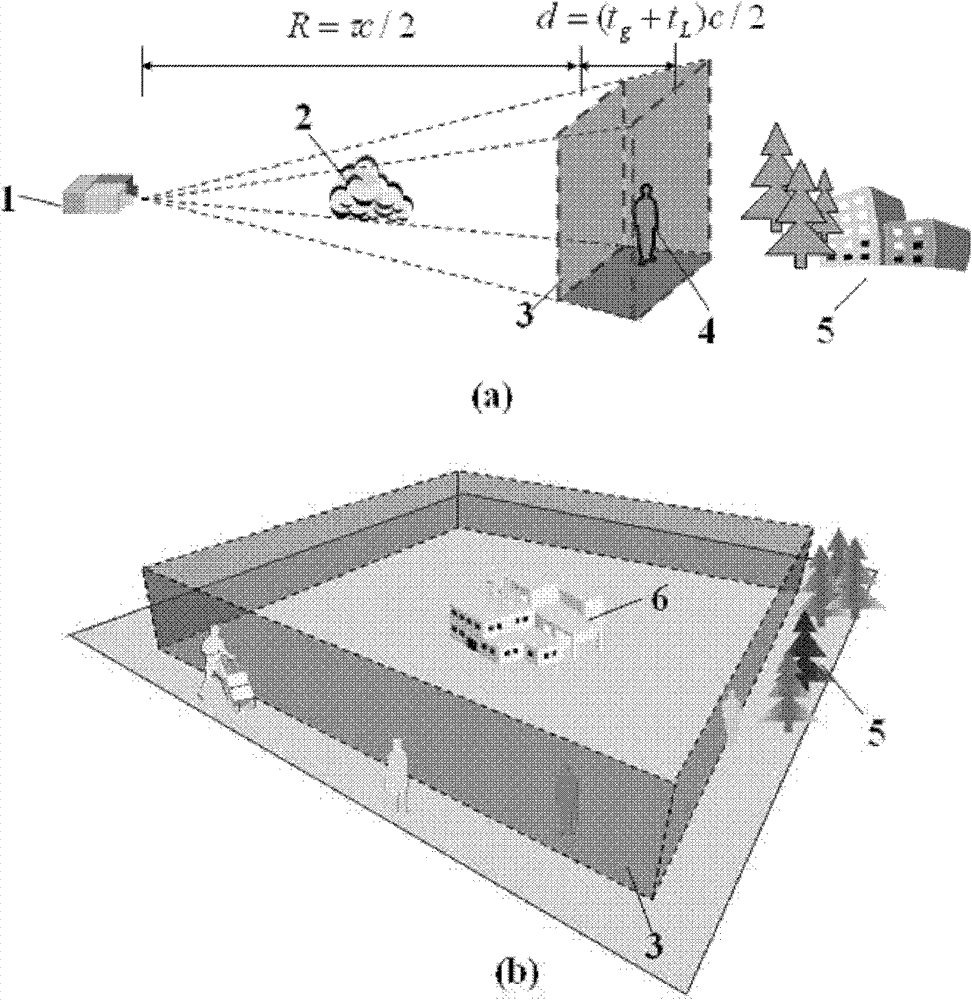
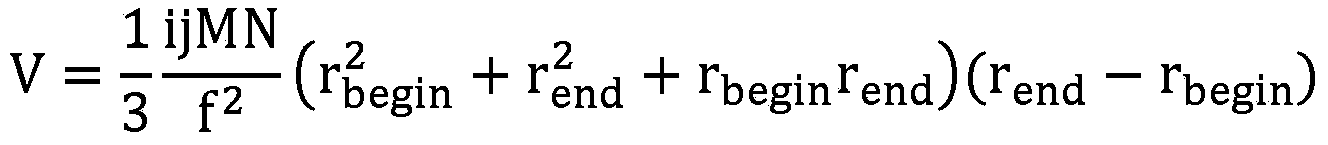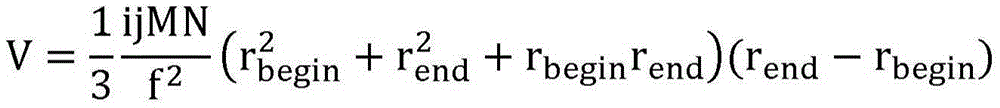Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Suppress backscatter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
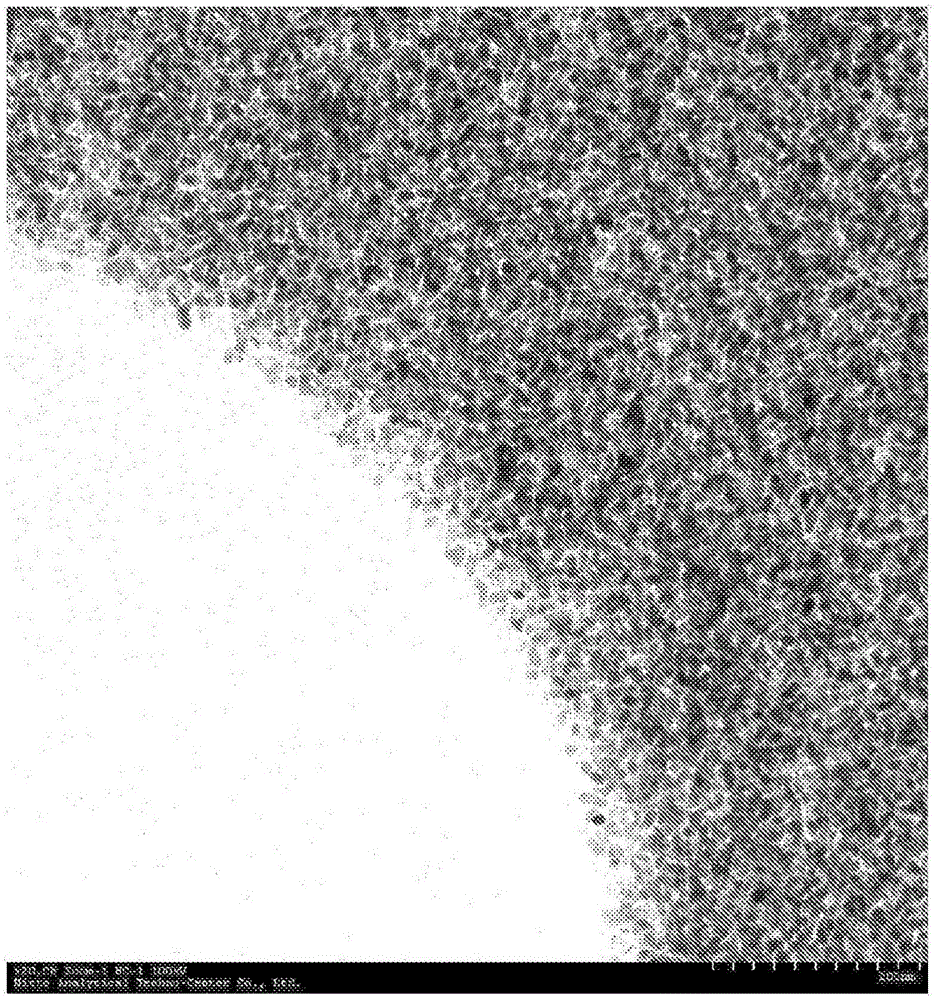
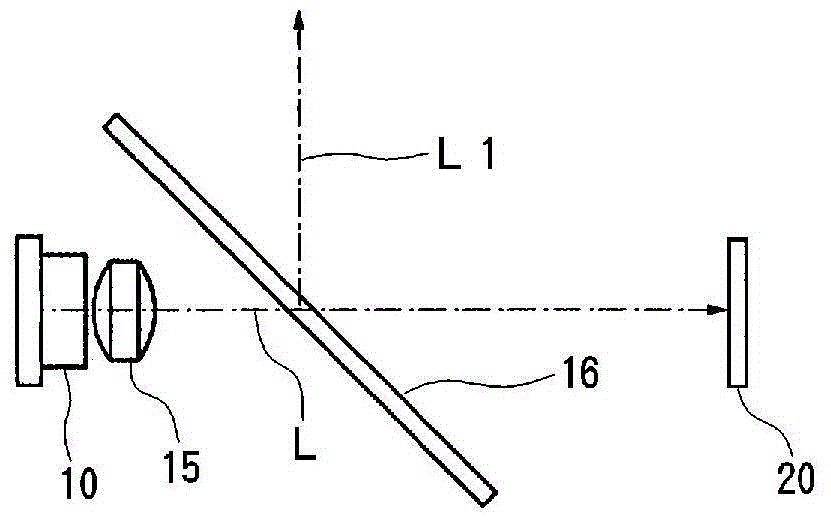
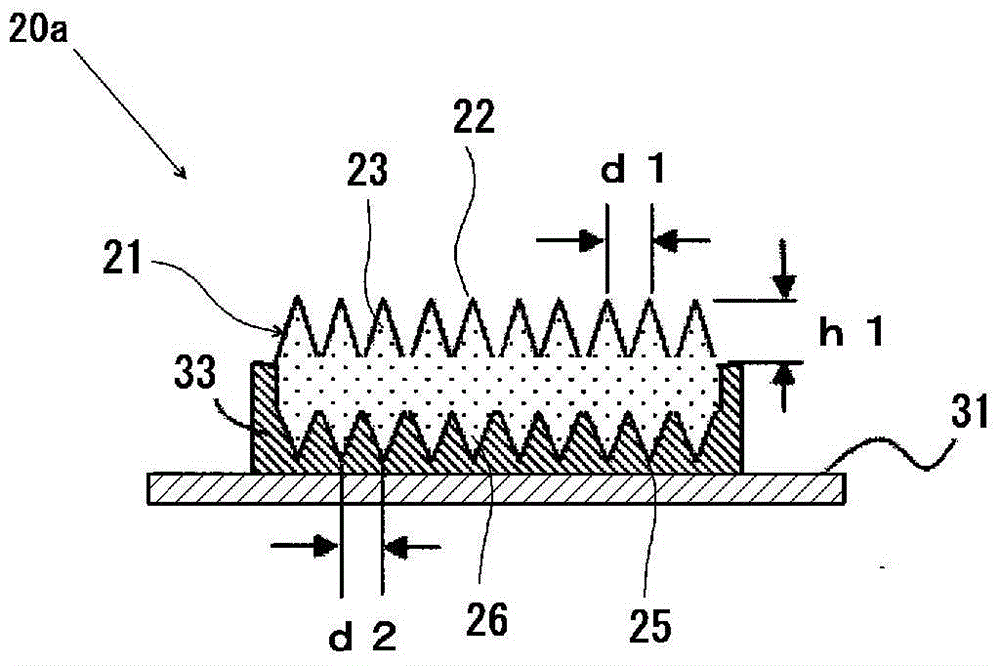
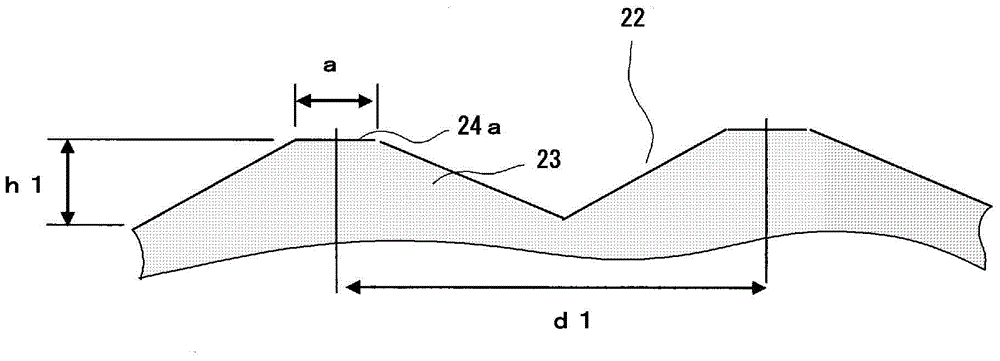
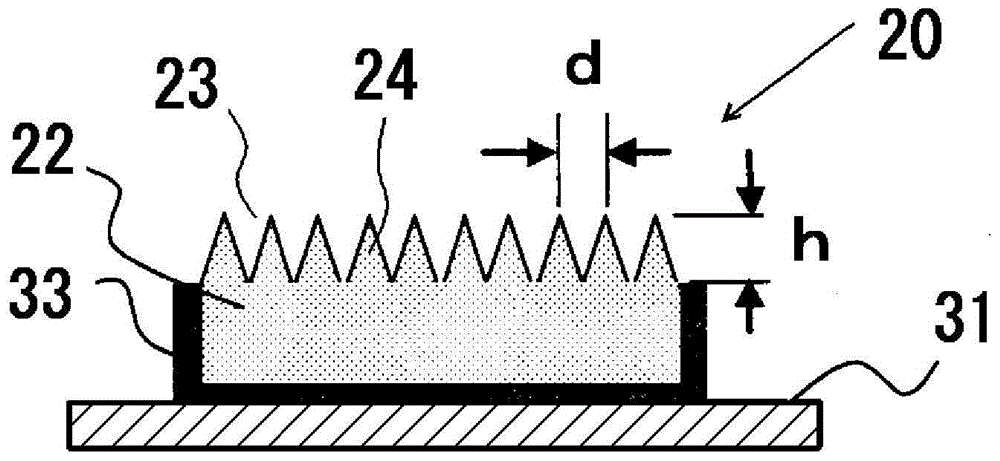
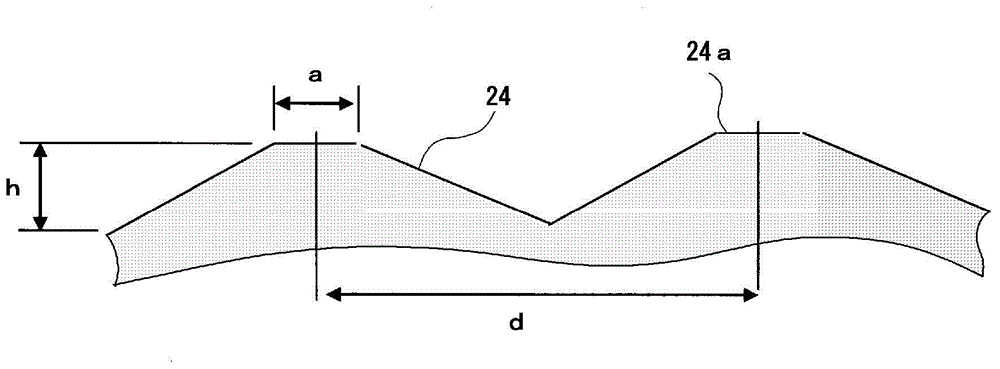
Fluorescent light source device
ActiveCN104968995ASuppress backscatterFull accessVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourcePhosphorLight reflection
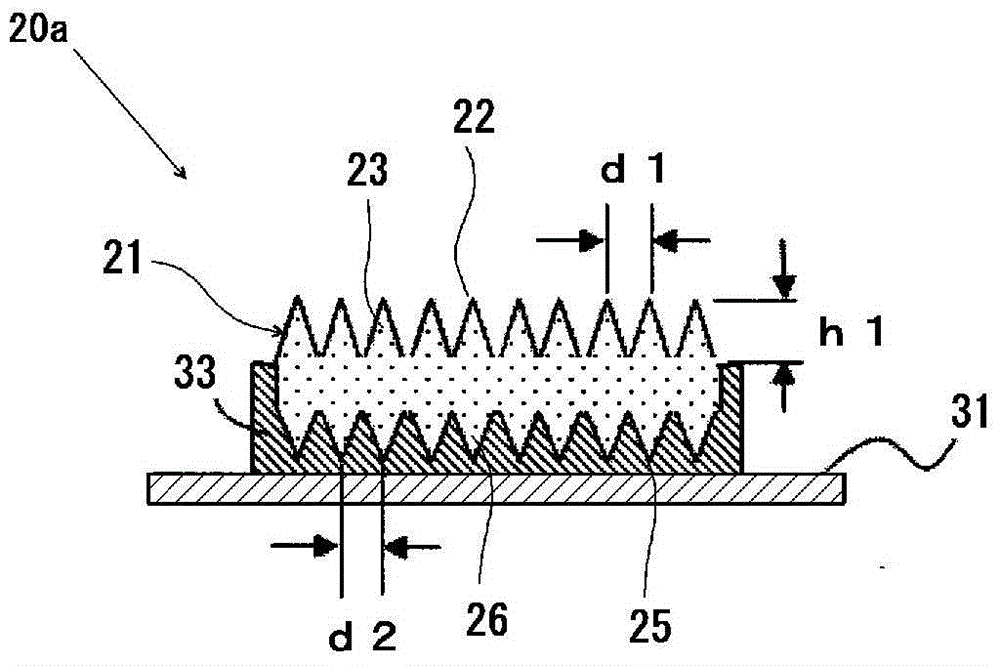
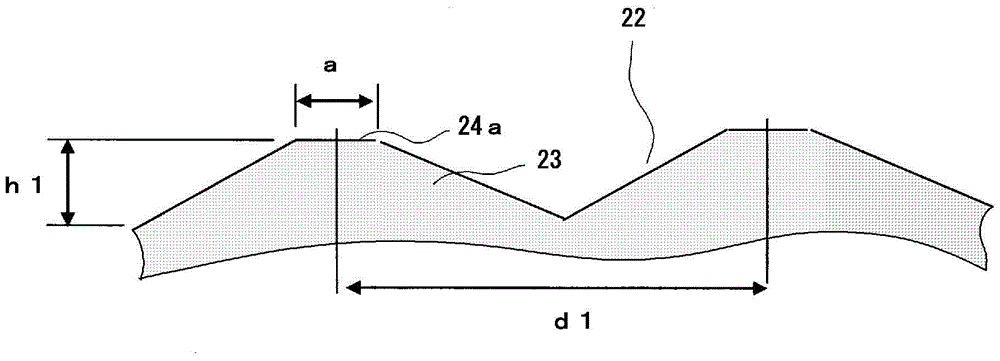
Provided is a fluorescent light source device with which, when excitation light is emitted to a wavelength conversion member, rearward scattering of the excitation light is controlled and fluorescence generated inside the wavelength conversion member can be emitted to the outside with high efficiency, and with which high light-emitting efficiency can be obtained. The fluorescent light source device comprises a wavelength conversion member which uses phosphors that are excited by excitation light, and is characterized in that the wavelength conversion member has formed on a front surface thereof serving as an excitation light receiving surface a front-surface-side periodic structure, has formed on a rear surface thereof a rear-surface-side periodic structure, and has a light reflecting surface disposed on the outside of the rear surface.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Image target seeking laser imaging distance measurement method and device
ActiveCN102736085AGuaranteed to workSuppress backscatterElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadiologyLaser imaging
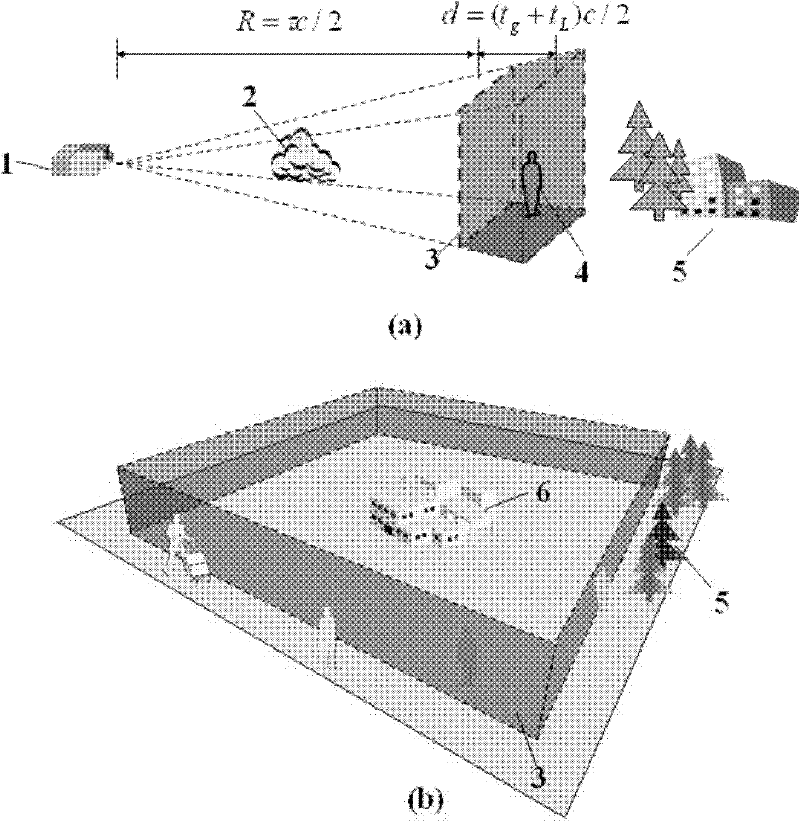
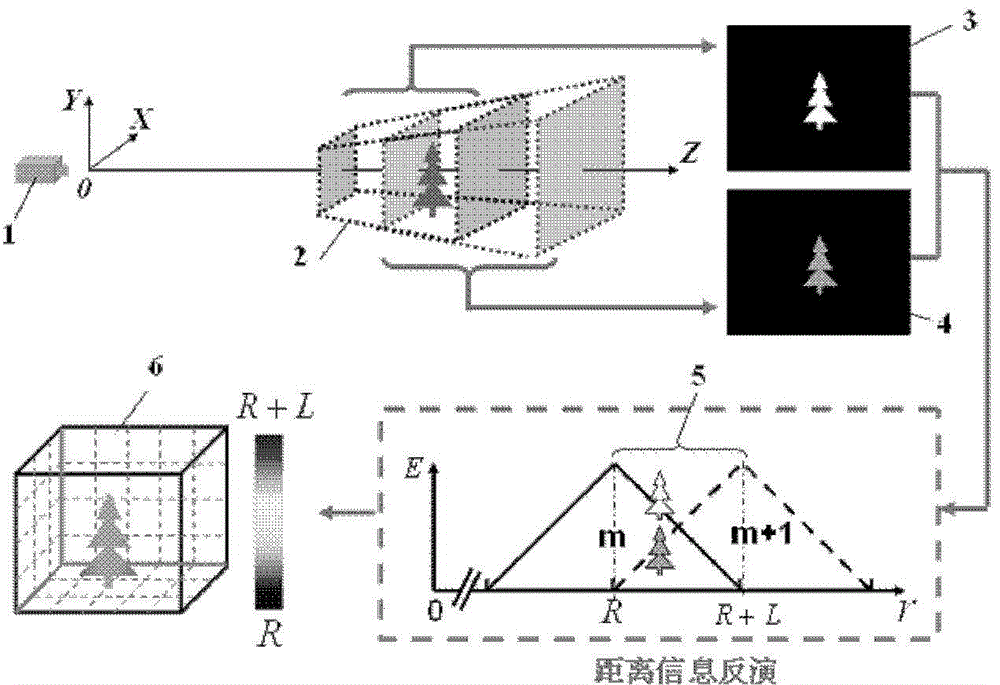
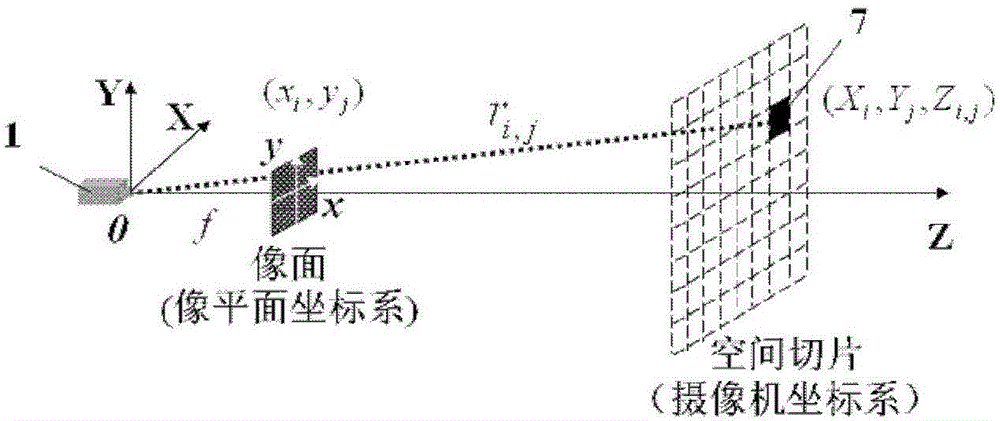
The invention discloses an image target seeking laser imaging distance measurement method and an image target seeking laser imaging distance measurement device. The method comprises the following steps of: imaging environment where a target is positioned in a non-gating imaging mode, and outputting a digital panorama to realize image target seeking; opening a distance measurement function, outputting a target-containing panoramic frame, selecting the target by a user, and opening the distance measurement function; obtaining a background frame in a distance measurement timing mode, constructing spatial slices with triangular distance energy envelope through distance gating imaging, performing slice scanning on a foresight field, and outputting slice frames; and when a target distance is subjected to inversion, performing differential processing on all the slice frames and the background frame to obtain new slice frames in which background influence is eliminated, and automatically calculating distance information of the target based on a mapping relation between the image gray scale ratio of a main window area among adjacent new slice frames and a distance energy ratio, which is established according to a distance gating echo broadening effect, by using a system, so that target distance measurement is finished. The method and the device are high in adaptability and easy to operate, target distance measurement is easy to realize, and particularly the problem that the distance of a small target is difficult to measure can be solved.
Owner:北京中科盛视科技有限责任公司
Light diffusing element, polarizing plate with light diffusing element, liquid crystal display using both, and manufacturing method for light diffusing element
InactiveCN102356334AInhibition reflexIncrease the refractive index differenceDiffusing elementsProjectorsDiffusionProduction rate
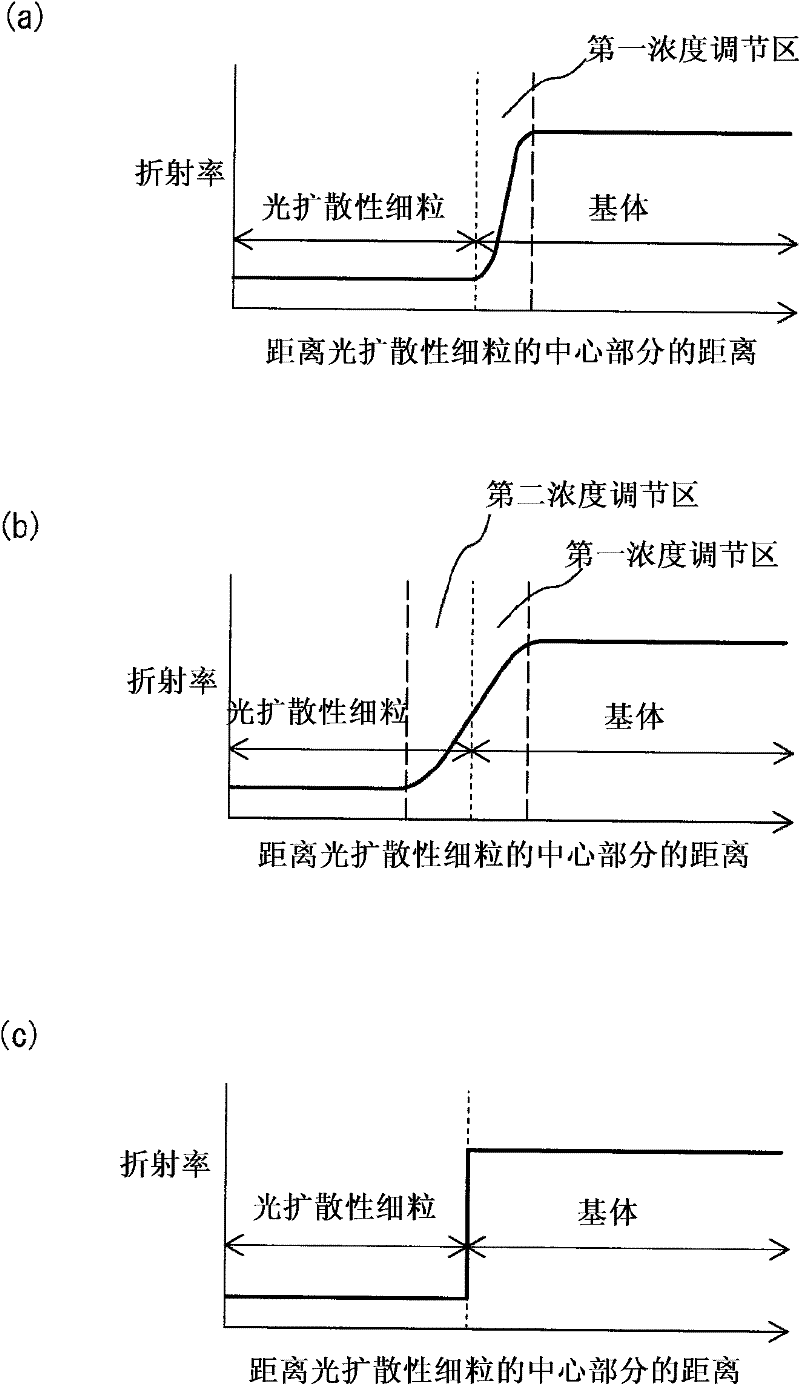
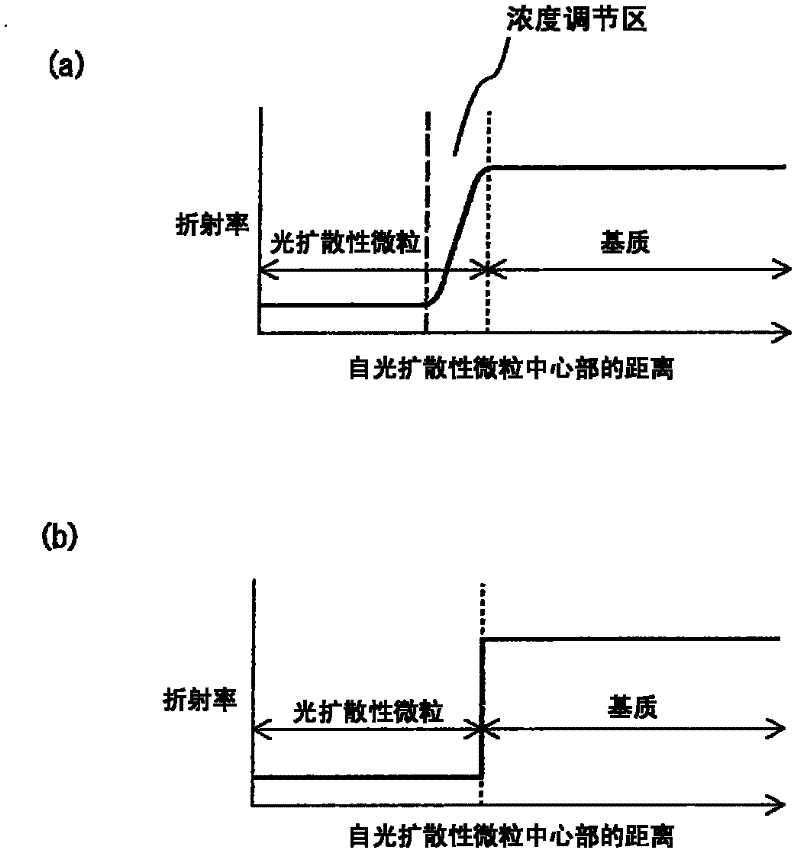
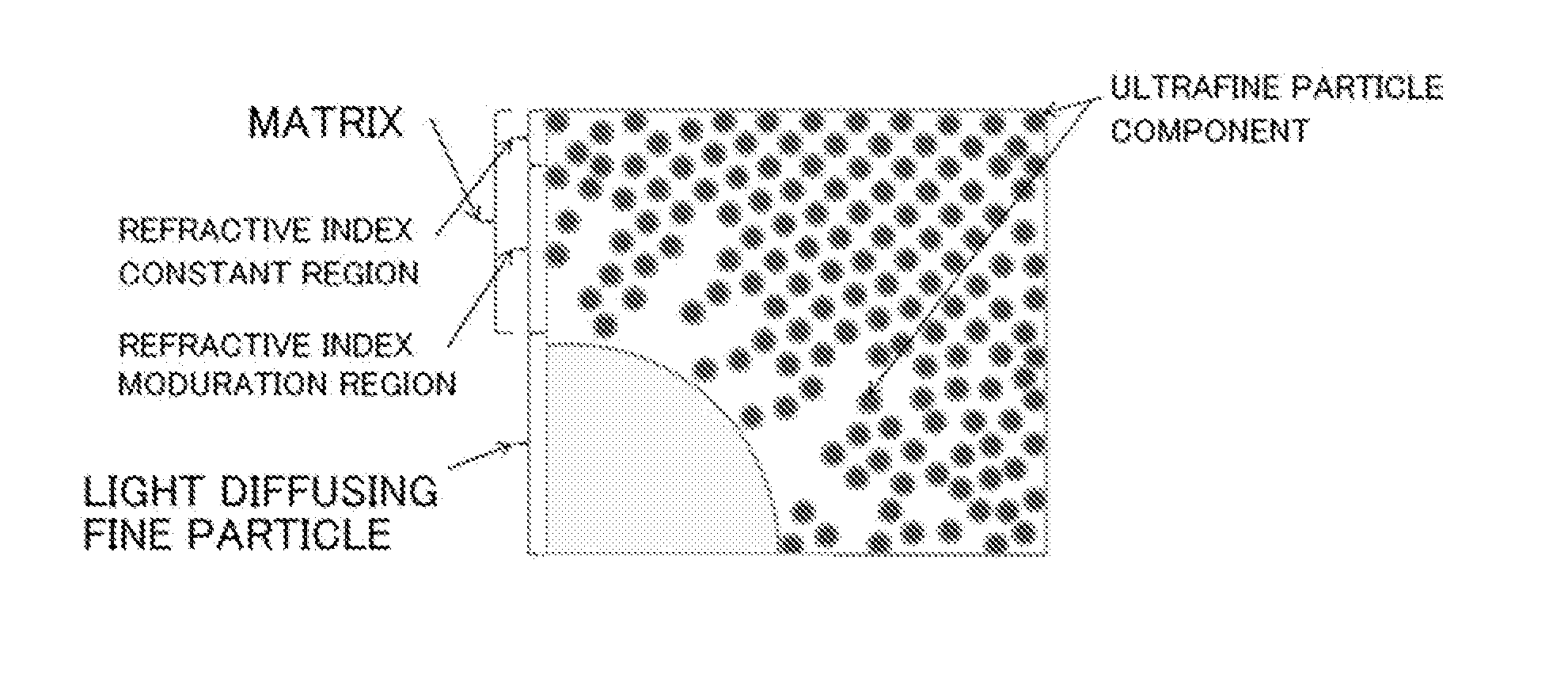
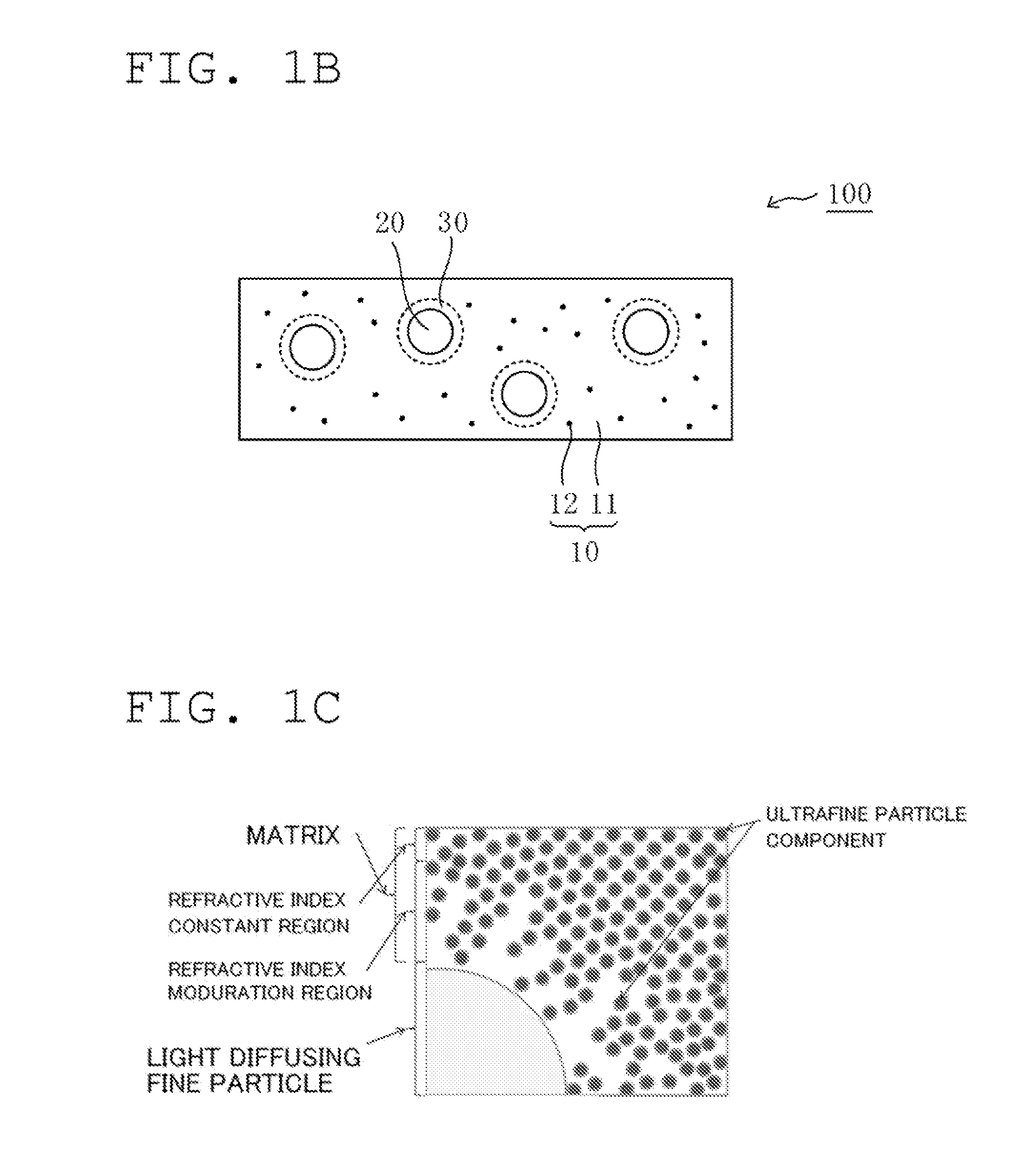
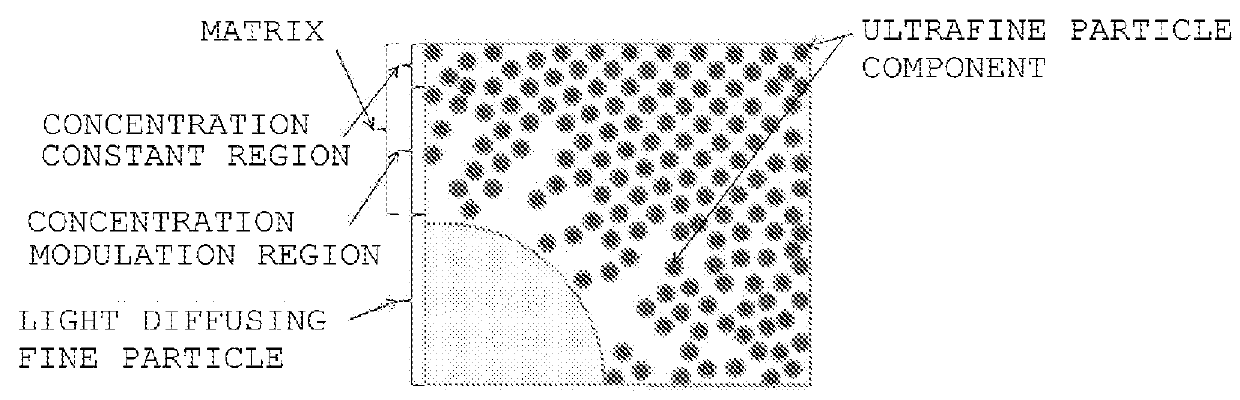
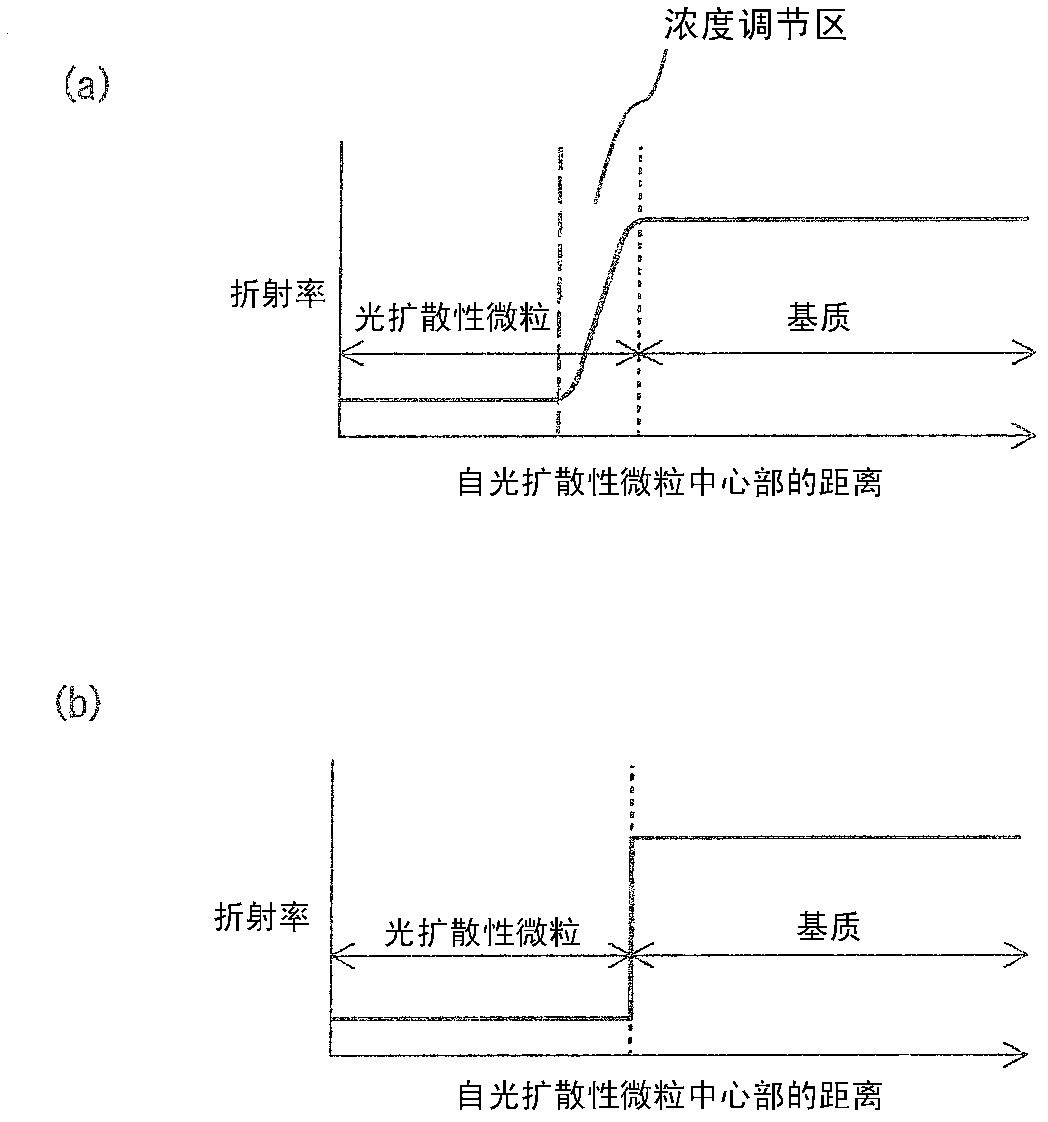
Provided is a light diffusing element that has a high haze value and strong diffusion characteristics with limited backscatter, and can be produced at a low cost. The light diffusing element has a matrix that includes a resin component and an ultra-fine particle component, and light diffusing micro particles dispersed within said matrix, wherein said resin component, said ultra-fine particle component, and said light diffusing micro particles fulfill the conditions of a formula (1) below, and has a concentration adjusted area that is formed near the interface of said matrix and said light diffusing micro particles wherein the weight concentration of said resin component becomes progressively lower and the weight concentration of said ultra-fine particle component becomes progressively higher with distance from said light diffusing particles. (1) |nP-nA|P-nB| In formula (1), nA represents the refractive index of the resin component in the matrix, nB represents the refractive index of the ultra-fine particle component in the matrix, and nP represents the refractive index of the light diffusing micro particles.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Photon fence system for perimeter security monitoring at night
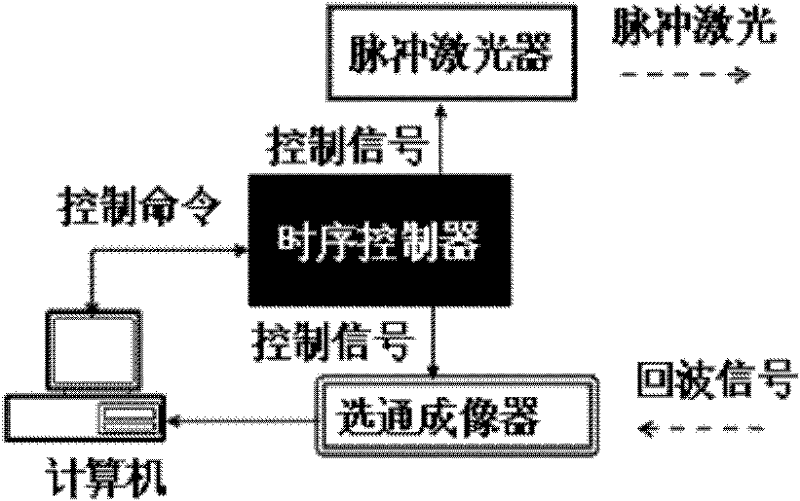
The invention discloses a photon fence system for monitoring on security protection of perimeter at night. The system comprises: a pulsing laser, which is used for emitting a laser pulse to carry out illumination on an object; a gated imaging device, which is used for controlling exposure time by a pulse width of a gated pulse; a time schedule controller, which is used for controlling time delay between the gated pulse and the laser pulse; and a computer, which is used for carry out controlling, image processing and displaying on the pulsing laser, the gated imaging device and the time schedule controller. According to the system provided in the invention, a pulsing laser is utilized as a light source and a gated imaging device is employed as a detector; time delay between a gated pulse and a laser pulse is controlled so as to establish a photon fence in space, wherein the photon fence is invisible for human eyes; therefore, when an invading object passed through the photon fence, image information of the invading object is collected and background outside the photon fence and a non-invading object are removed by filtering, so that non-background extraction on the invading object is realized.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
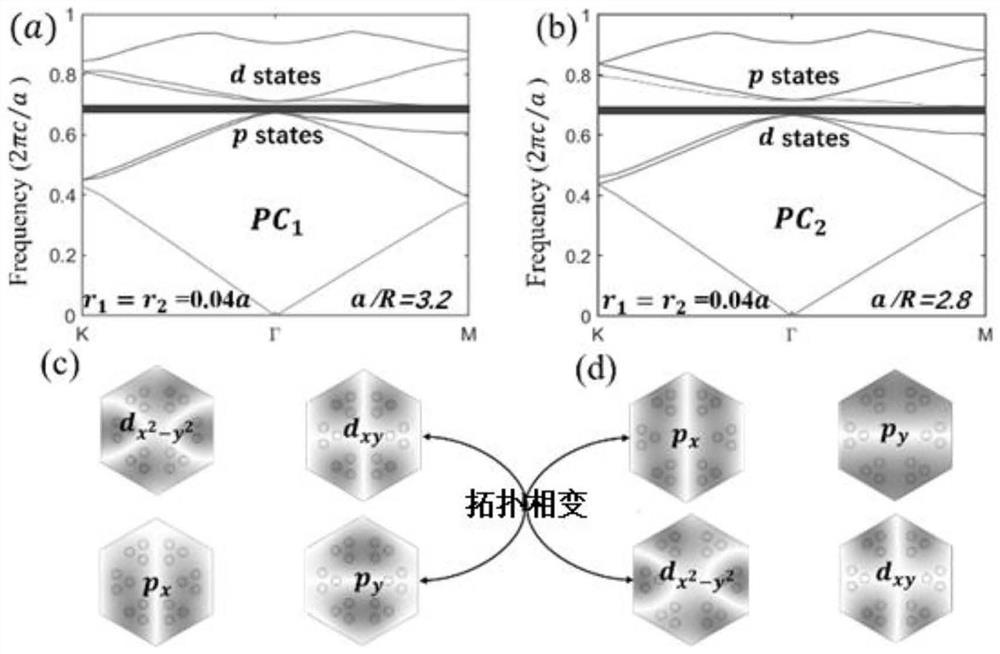
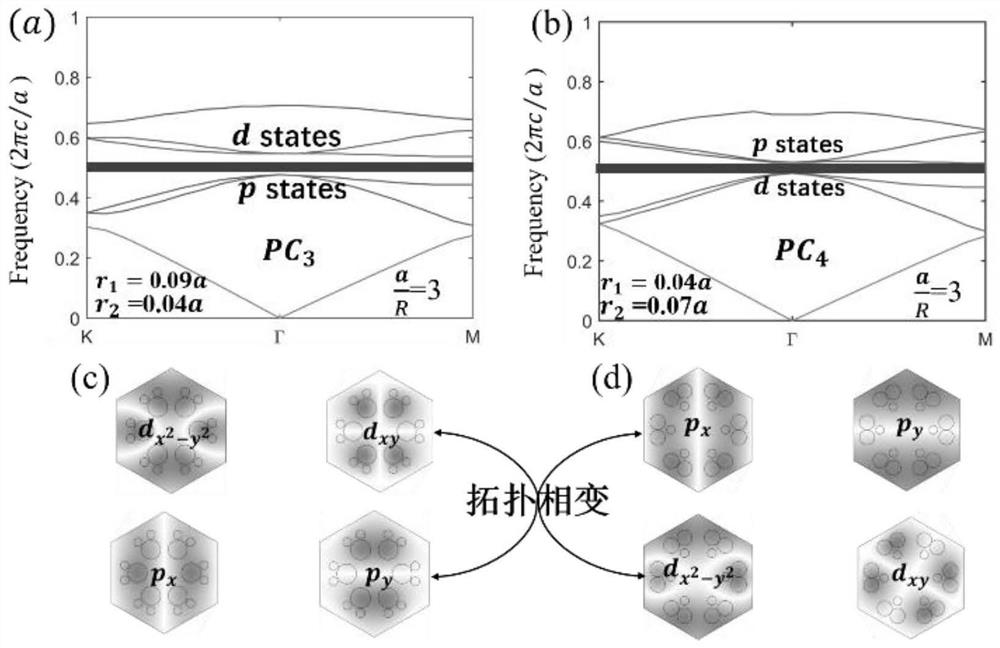
Novel topological photonic crystal structure and optical waveguide
ActiveCN112596154AHas rotational symmetryAchieving a topological phase transitionOptical light guidesPhotonic bandgapDielectric cylinder
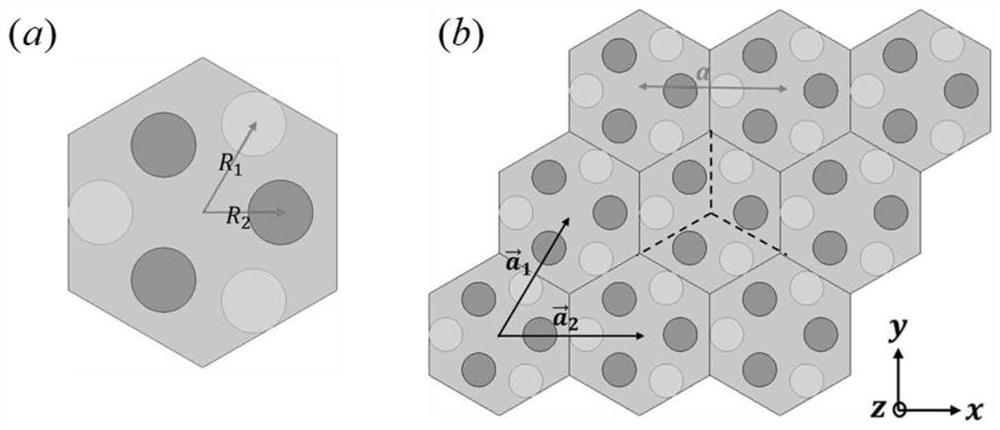
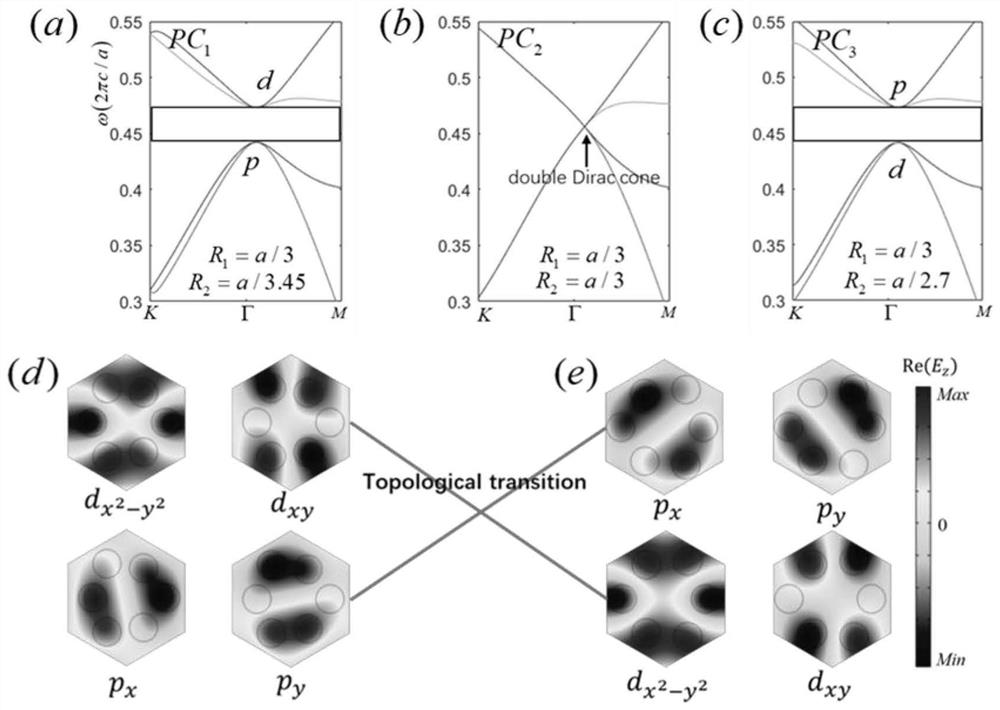
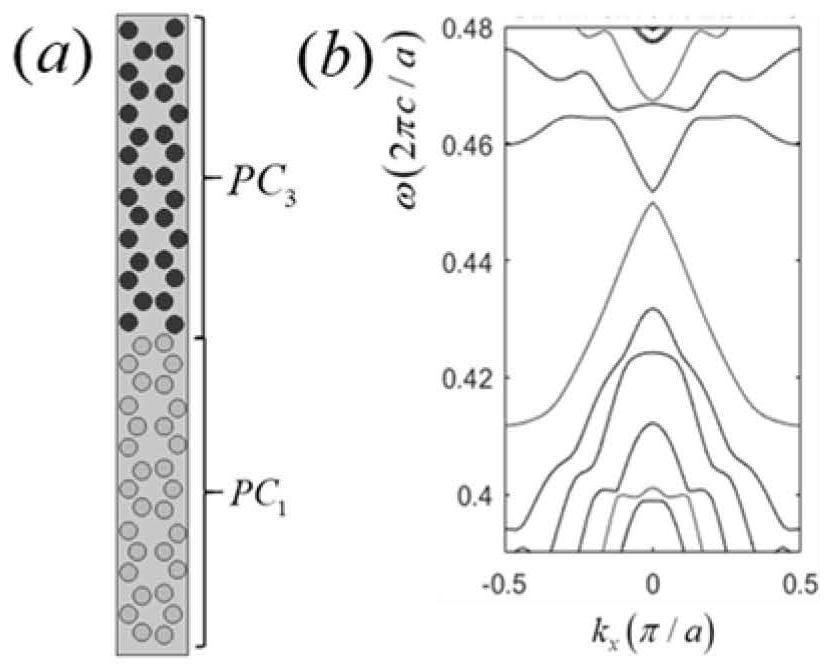
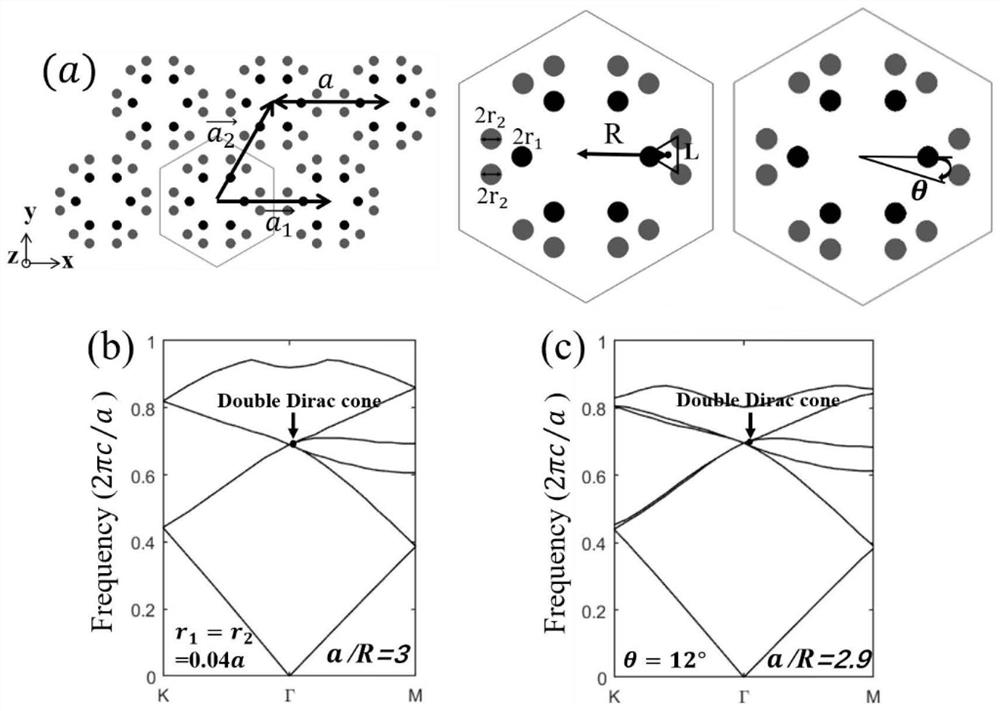
The invention discloses a novel topological photonic crystal structure and an optical waveguide, and a unit cell of the novel topological photonic crystal structure is formed by arranging six identical dielectric cylinders into two independent regular triangle units and has C3 rotational symmetry. A plurality of structural states of the crystal structure all have a dual Dirac cone cell, and energyband inversion and topological phase transition are achieved by stretching and compressing at least one of the two triangular units on the basis of each cell state having a dual Dirac cone, and a large topological non-mediocre photonic band gap is opened. An optical waveguide is also constructed based on the crystal structure, the topological non-mediocre photonic crystal (PC3) and the topological mediocre photonic crystal (PC1) are combined to support optical unidirectional transmission at the interface to inhibit backscattering, the transmission efficiency is extremely high, the immunity tostructural defects is strong, and three different structural defects can be perfectly passed.
Owner:江阴多高自动化科技有限公司
Fluorescent-light-source device
InactiveCN104969370ASuppress backscatterFull accessLaser detailsPoint-like light sourceFluorescenceWavelength conversion
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a fluorescent-light-source device in which, when a wavelength conversion member is exposed to excitation light, backscattering of said excitation light is minimized and fluorescent light generated inside the wavelength conversion member is utilized effectively and emitted to the outside with high efficiency, yielding a high light-emission efficiency. This fluorescent-light-source device is characterized by the provision of a wavelength conversion member in the form of a florescent material that is excited by excitation light. This fluorescent-light-source device is further characterized in that: a periodic structure comprising substantially cone-shaped protrusions arrayed in a periodic fashion is formed on an excitation-light-receiving surface on the wavelength conversion member; the aspect ratio of said periodic structure, namely the quotient of the heights of the protrusions and the period of the periodic structure, is at least 0.2; and said period falls within a range within which fluorescent light emitted by the florescent material is diffracted.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Optical waveguide structure capable of regulating and controlling boundary state of topological photonic crystal
ActiveCN112147805AReduce scatterGood photon localityStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsPhotonic crystalDielectric cylinder
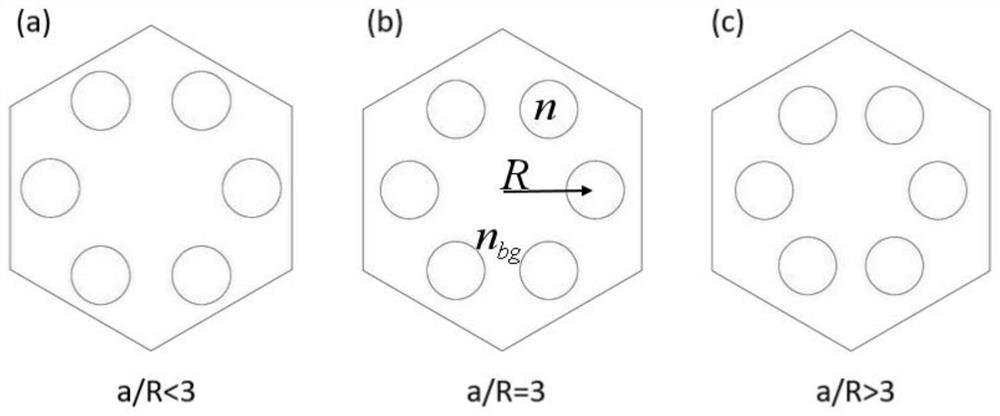
The invention provides an optical waveguide structure capable of regulating and controlling the boundary state of a topological photonic crystal. The optical waveguide structure comprises an upper metal plate, a lower metal plate, a waveguide, a background material and a shell, wherein the upper metal plate and the lower metal plate are arranged in the shell, the waveguide is arranged between theupper metal plate and the lower metal plate, the waveguide is composed of a part A and a part B, the part A is formed by arranging unit cells with moderate topological properties, the part B is formedby arranging unit cells with non-moderate topological properties, each unit cell is formed by arranging six cylindrical dielectric cylinders with the radius of 0.12a, the cross section of each unit cell is in a regular hexagon shape, the distance radius from the center of each unit cell to the corresponding cylindrical dielectric cylinder in the unit cell is R, the distance between the centers ofevery two adjacent unit cells is a lattice constant a, the unit cells with the moderate topological property meet a / R=3.36, and the unit cells with the non-moderate topological property meet a / R=2.8.The problems that a traditional waveguide photon is weak in locality and low in transmission efficiency, and the frequency cannot be regulated and controlled are solved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Process for producing light-diffusing element, light-diffusing element, and processes for producing polarizing plate with light-diffusing element and liquid-crystal display device
InactiveCN102356335ALow costImprove productivityDiffusing elementsOptical articlesProduction rateLiquid-crystal display
A process for producing a light-diffusing element is provided by which a light-diffusing element having a high haze and high diffusing properties and reduced in backward scattering can be produced at low cost with high productivity. The process for producing a light-diffusing element comprises a step in which a matrix-forming material comprising a resin-ingredient precursor and an ultrafine-particle ingredient is brought into contact with fine light-diffusing particles, a step in which at least some of the precursor is infiltrated into an inner part of the fine light-diffusing particles, and a step in which the precursor that has infiltrated into the inner part of the fine light-diffusing particles and the precursor that has not infiltrated into the fine light-diffusing particles are simultaneously polymerized to form a matrix comprising the resin ingredient and the ultrafine-particle ingredient and simultaneously form a concentration gradation region in the vicinity of the inner side of the surface of the fine light-diffusing particles.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Silicon nanosphere trimer-based unidirectional optical nano antenna structure
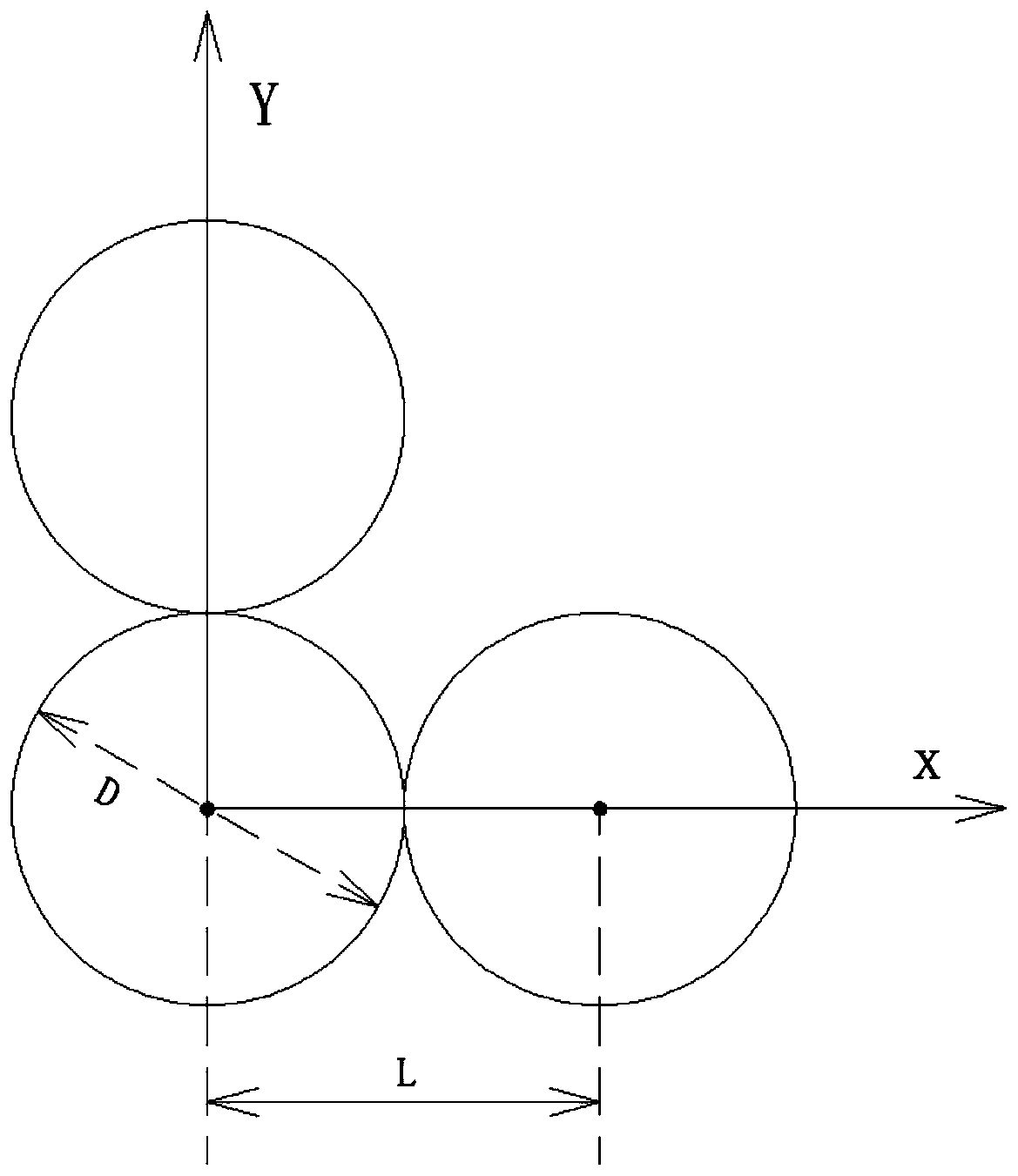
ActiveCN110161598AAchieve unidirectional scatteringSuppress backscatterOptical waveguide light guideDielectricResonance
The invention relates to an optical nano antenna, in particular to a silicon nanosphere trimer-based unidirectional optical nano antenna structure. The antenna structure is formed by three nanospheresin an X=Y axis symmetric form; the diameters D of the three nanospheres are 200-280 nm; the distances between the nanospheres located on the two sides of the symmetric axis and the nanosphere locatedat the center of the symmetric axis are 0; and the material of the nanospheres is a high dielectric material silicon. The structure can be used for adjusting the far-field direction characteristics;the wave vectors of incident waves are parallel to the x axis direction; and the polarization is parallel to the y axis direction. By utilizing a multistage decomposition method for analysis, the structure not only supports electric dipole and magnetic dipole resonance, but also supports electric quadrupole and annular dipole resonance; and through the coupling of the resonance modes, the far-field unidirectional scattering of the high dielectric material silicon nanosphere trimer structure is realized. Solid theoretical foundation is provided for realizing far-field unidirectional controllable nano antennas.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Light diffusing film, polarizing plate with light diffusing film, liquid crystal display device, and lighting equipment
ActiveUS20130242241A1Good light diffusion effectImprove production efficiencyDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsProduction rateDiffusion
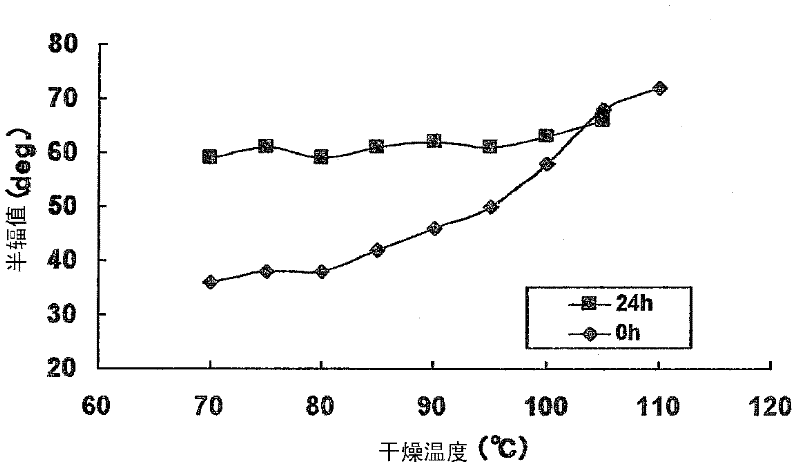
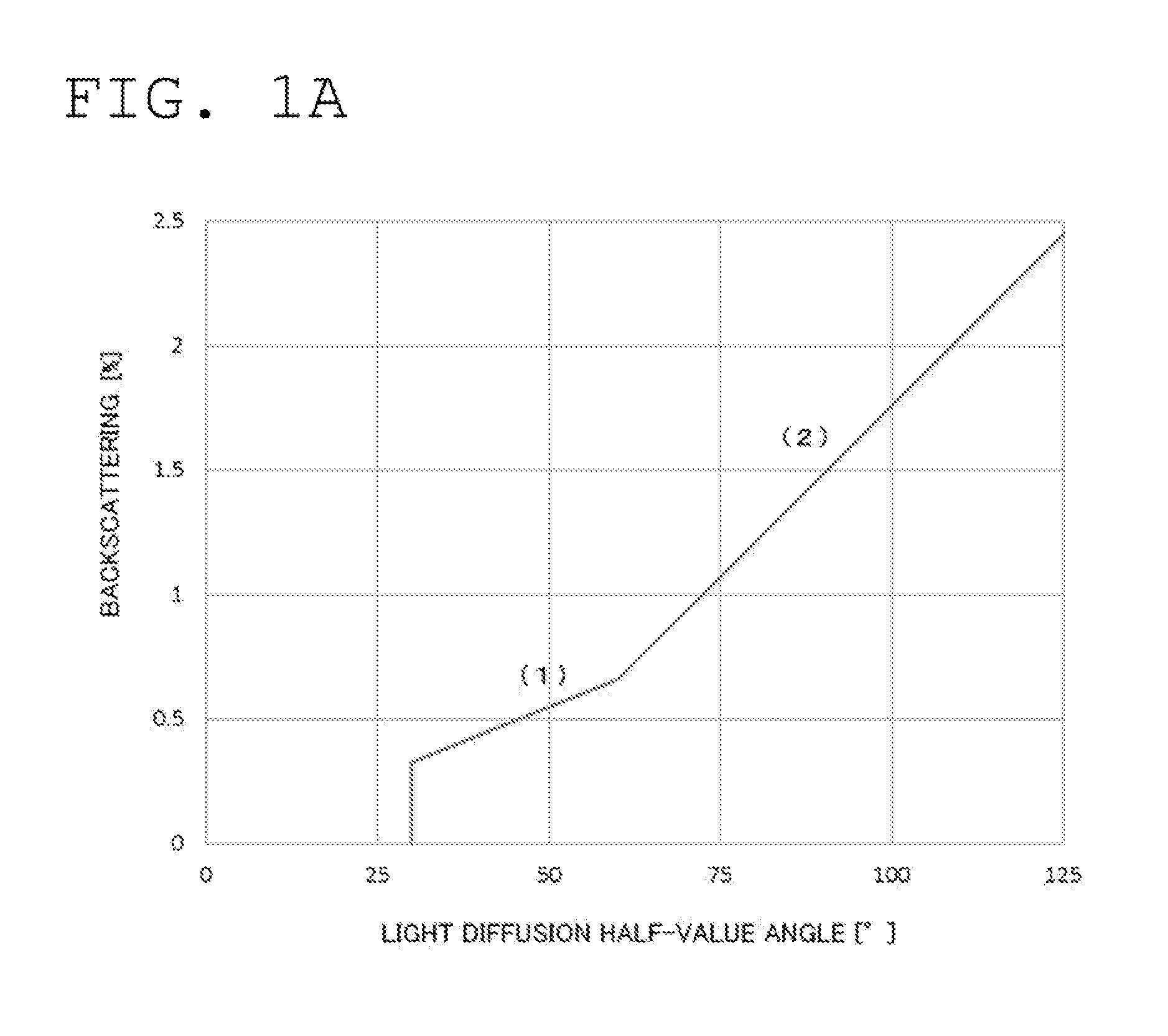
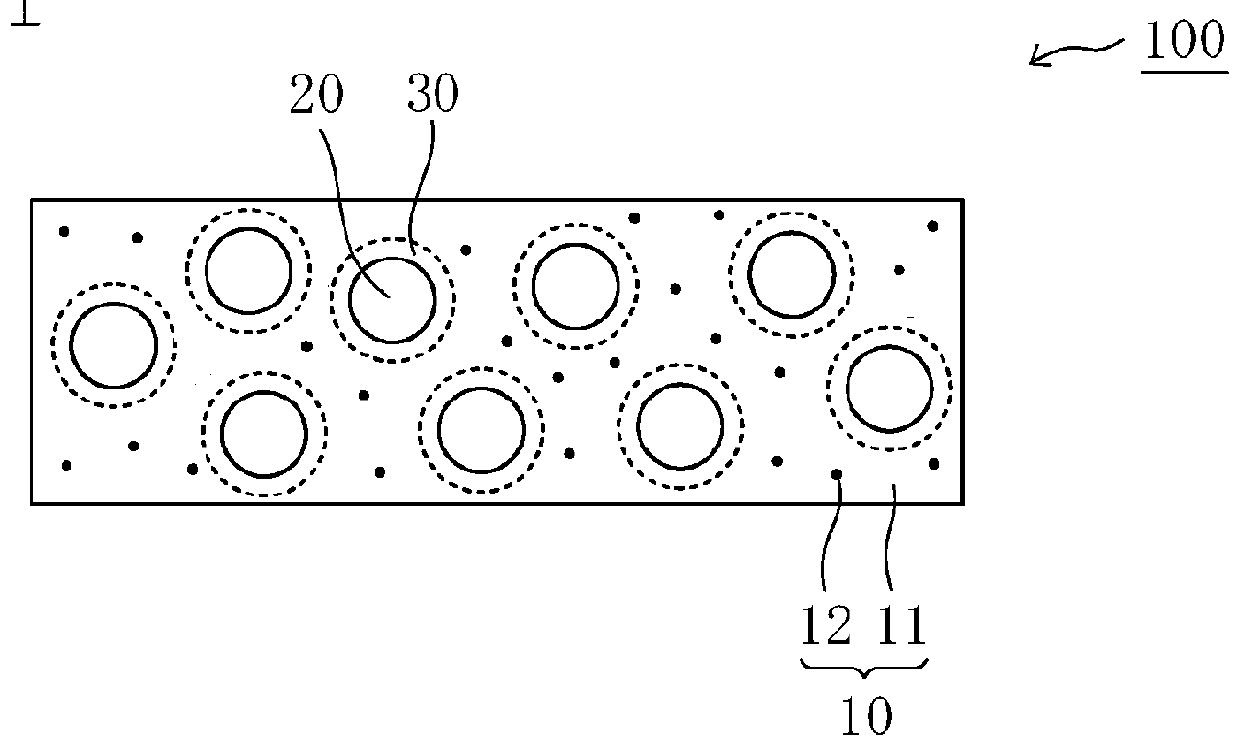
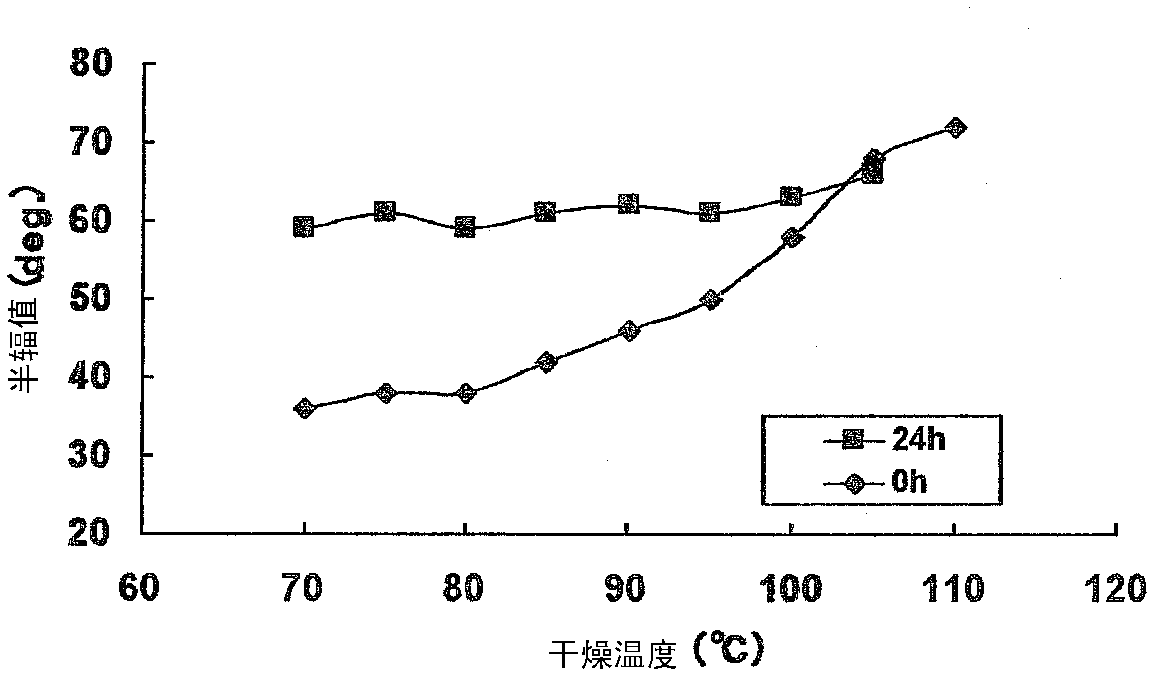
There is provided an extremely thin light diffusing film, which has strong light diffusibility, has suppressed backscattering, and is excellent in productivity. The light diffusing film includes: a first region having a first refractive index; a substantially spherical shell-shaped refractive index modulation region surrounding the first region; and a second region having a second refractive index, the region being positioned on a side of the refractive index modulation region opposite to the first region. The light diffusing film has a light diffusion half-value angle of 30° or more and a thickness of 4 μm to 25 μm, and satisfies the following expressions (1) and (2):y≦0.011x (30≦x≦60) (1)y≦0.0275x−0.99 (60<x) (2)where x represents the light diffusion half-value angle (°) and y represents a backscattering ratio (%), the expressions (1) and (2) each representing a relationship between a numerical value for the light diffusion half-value angle and a numerical value for the backscattering ratio.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Optical stereo sampling in-situ detection method capable of acquiring zooplankton information
ActiveCN103901438ASolve the problem of low contrast and poor qualitySuppress backscatterElectromagnetic wave reradiationZooplanktonNon invasive
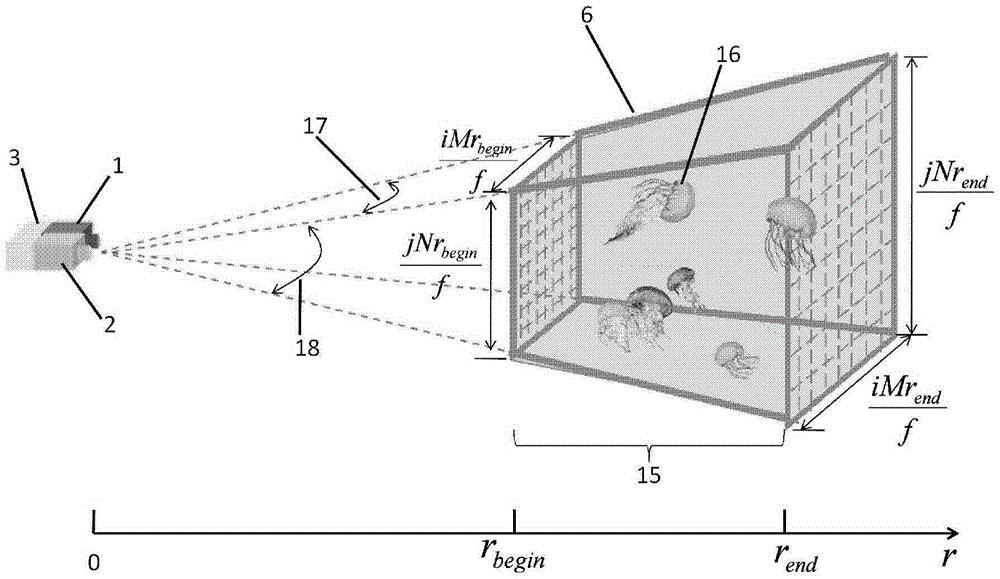
The invention discloses an optical stereo sampling in-situ detection method capable of acquiring zooplankton information. The method comprises the steps that laser pulse is transmitted by a pulsed laser and is reflected through zooplankton in a stereo sampling area, and a target echo signal is returned; when the target echo signal reaches a gating imaging device, a gating door of the gating imaging device is opened to receive the target echo signal, in-situ detection imaging is conducted on the zooplankton in the stereo sampling area, and an underwater two-dimensional strength image acquired by sampling is output; abundance information of the zooplankton is acquired according to the acquired behavior information, quantity information, size information of the zooplankton in the stereo sampling area through combining the underwater two-dimensional strength image and the volume of the stereo sampling area. By means of the method, the problems that in an existing in-situ detection imaging method, the real non-invasive and non-disruptive in-situ detection can not be achieved and the sampling area is uncertain are solved, the quantifiable optical stereo sampling area can be formed, and the acquisition of the non-disruptive stereo data of the zooplankton is achieved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Short coherent illumination and polarization combined underwater long-distance optical imaging device and method
ActiveCN111123619AEasy to separateGaze Imaging RealizedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight beamPolarizer
The invention discloses a short coherent illumination and polarization combined underwater long-distance optical imaging device and method. The system comprises a short coherent laser, an optical imaging system, a polarizer and an analyzer, wherein a polarizer is arranged at the image side end of the short coherent laser, the analyzer is arranged at the object side end of the optical imaging system, a laser emitted by the short coherent laser enters an imaging target through the polarizer, the imaging target is arranged in a water body environment, and a reflected light beam of the imaging target is transmitted to the optical imaging system through the analyzer.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Laser difference imaging detection method and device for same
ActiveCN106872468AAccurate measurementAdaptableMaterial analysis by optical meansTime delaysRange gate
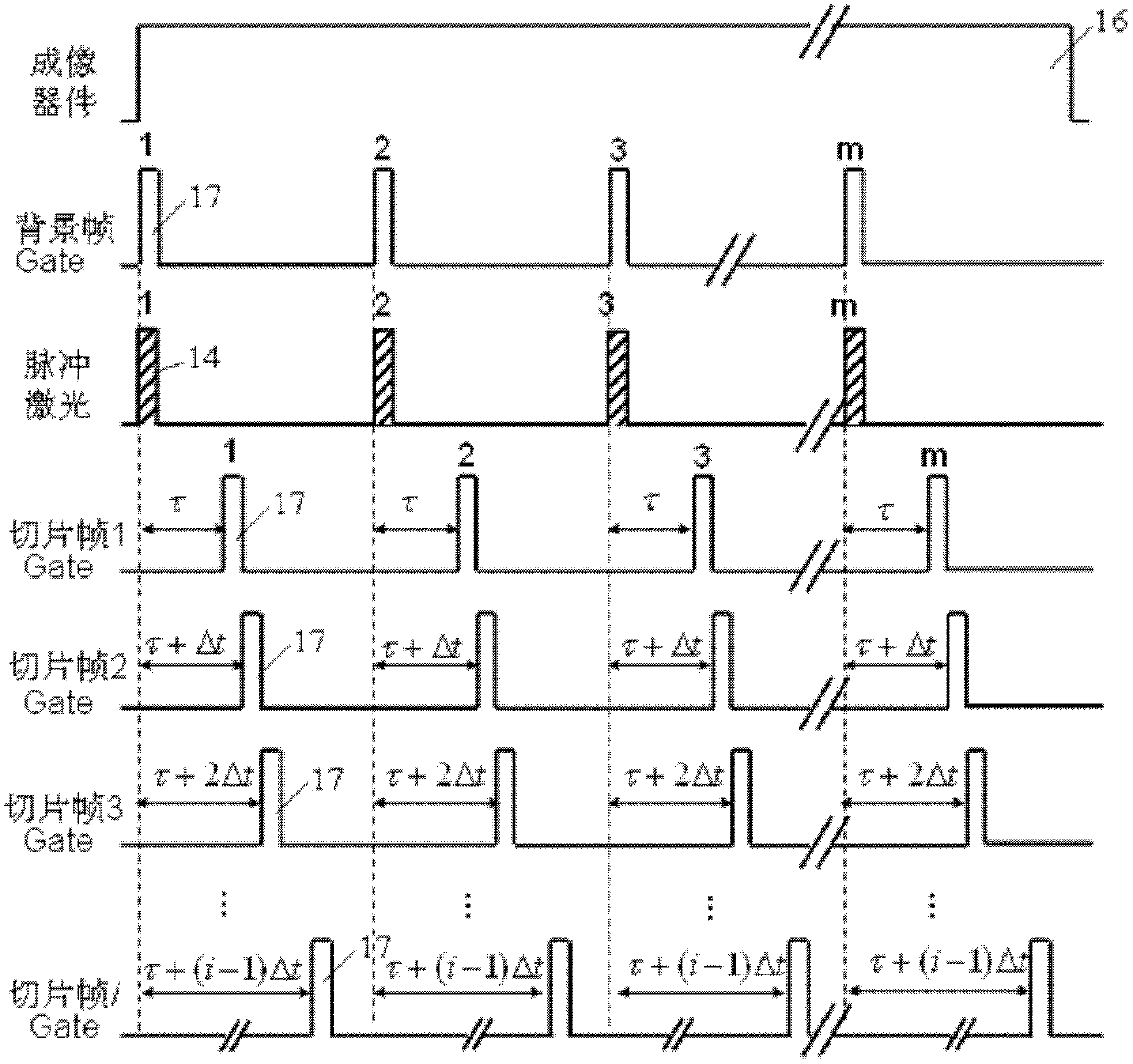
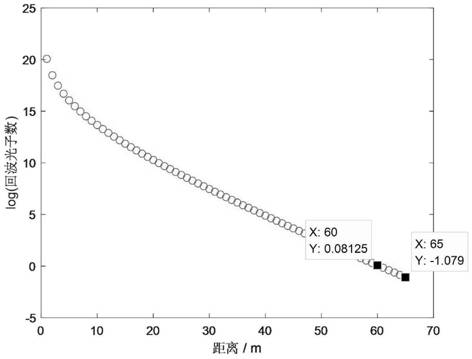
The invention discloses a laser difference imaging detection method and a device for the same. The method comprises the following steps: performing range-gated imaging to obtain n frames of retroreflected images of n slices of a region to be detected in a one-frame one-pulse one-gate exposure manner; dividing the n frames of retroreflected images into m information frames and n-m background frames according to a grayscale threshold value; calculating differences of the m information frames and the background frames to obtain m enhanced information frames of the m information frames, and dividing the m enhanced information frames into k bubble information frames and m-k pseudo information frames by adopting a trained classifier; calculating a grayscale mean value and modulation time delays of the k bubble information frames respectively, and performing fitting to obtain a spatial distribution curve of bubbles along with the time delay; obtaining a range of a bubble region and yield of the bubbles according to the spatial distribution curve, wherein m, n and k are all natural numbers not smaller than 1. According to the method and the device, the range and the yield of the bubble region can be accurately detected, and the method and the device have the characteristics of high accuracy, high adaptability and high flexibility, and is significant for underwater bubble detection and analysis.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Double-ring parallel resonant gyro system and double-closed-loop digital demodulation method thereof
ActiveCN111536960AImprove environmental temperature adaptabilityLittle effect of temperature changeSagnac effect gyrometersOptical frequenciesPhotonic bandgap
The invention discloses a double-ring parallel resonant gyro system and a double-closed-loop digital demodulation method thereof. The system comprises a tunable laser, outgoing light of the tunable laser is split into clockwise light and anticlockwise light through a signal beam splitter, the clockwise light and the anticlockwise light sequentially enter an acousto-optic frequency shifter, an electro-optic modulator, an optical fiber coupler, a hollow photonic band gap optical fiber resonant cavity, a photoelectric detector and a digital lock-in amplifier respectively, and frequency closed-loop feedback is formed through the tunable laser and the acousto-optic frequency shifter respectively. According to the double-ring hollow photonic band gap optical fiber structure, clockwise and anticlockwise light waves are respectively propagated in the independent resonant cavities without mutual influence, so that the temperature stability is improved, and nonreciprocal effect noises such as anoptical Kerr effect, Rayleigh backscattering and the like are effectively inhibited. According to the double-closed-loop digital demodulation method, optical frequencies in a clockwise optical path and an anticlockwise optical path are locked at respective transmission resonant frequencies, so that the system works in a linear region, and the linear range of angular velocity detection of the system and the linearity of a scale factor are effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Laser strobe active night vision method for remote night monitoring
ActiveCN101794057BHigh single pulse energyLower requirementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVisibilityNight vision
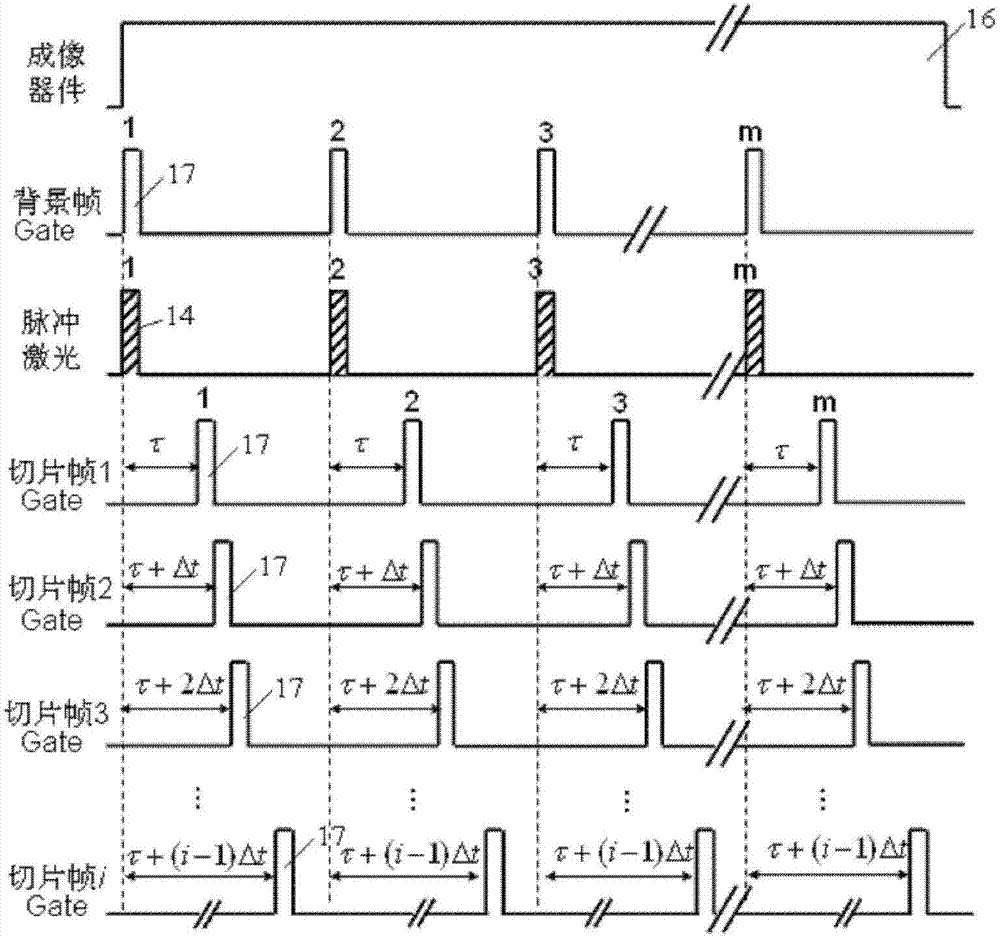
The invention discloses a laser strobe active night vision method for remote night monitoring. In the method, a one-frame multi-pulse and multi-door working mode is adopted, in one frame time of exposure of an imaging device, a pulse laser emits a laser pulse sequence, a strobing gate works according to a preset strobing pulse sequence, and the imaging device receives a plurality of target echo signals from a target, therefore, the purpose of light accumulation and signal enhancement is achieved. The invention has good working environmental suitability, and can normally work under the condition of low visibility. Since a long-distance target can be observed at night by using the low-power pulse laser, the cost of the system is greatly reduced, the laser security of the system is improved,and especially the security of eyes is improved.
Owner:北京中科盛视科技有限责任公司
Wake flow detection device for time correlation single photon counting and operation method of wake flow detection device
ActiveCN113447232ANo distortionImprove uniformityAerodynamic testingInformation processingPhoton counter
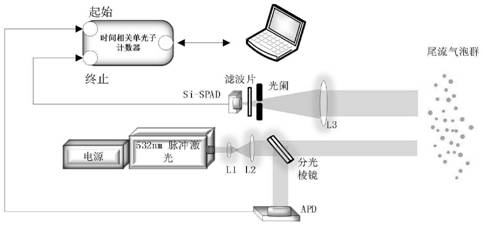
The invention discloses a wake flow detection device based on time-dependent single photon counting and an operation method of the wake flow detection device, and belongs to the field of laser underwater wake flow target detection. The device includes a laser emitting assembly, a laser receiving assembly and an information processing assembly, wherein the laser emitting assembly and the laser receiving assembly are both electrically connected with the information processing assembly, and the laser emitting assembly is used for irradiating bubbles in wake flow with laser and synchronously transmitting an initial electric signal to the information processing assembly; the laser receiving assembly is used for receiving reflected light reflected by the bubbles in the wake flow and synchronously transmitting a termination electric signal to the information processing assembly; and the information processing assembly is used for receiving the initial electric signal transmitted by the laser transmitting assembly and the termination electric signal transmitted by the laser receiving assembly, completing photon flight time interval measurement and time-dependent single photon counter analysis, and finally calculating to obtain a target distance. According to the invention, detection of underwater weak wake flow echo signals can be realized, and the technical limitation of low sensitivity in the prior art is overcome.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Light-diffusing element and method for manufacturing light-diffusing element
InactiveUS20160054485A1High haze valueImprove diffusivityDiffusing elementsSpecial surfacesSurface roughnessPermeation
An object of the present invention is to provide a light diffusing element having a high haze value, strong diffusibility, a smooth surface, and suppressed backscattering. The light diffusing element of the present invention includes: a matrix including a resin component and ultrafine particle components; and light diffusing fine particles dispersed in the matrix, in which part of the resin component permeates the light diffusing fine particles, and a permeation range of the resin component in the light diffusing fine particles is 90% or more with respect to an average particle diameter of the light diffusing fine particles in the light diffusing element, and in which the light diffusing element has an arithmetic average surface roughness Ra of 0.04 μm or less.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Photonic crystal structure with complex unit cells and optical waveguide
PendingCN114660719AIncrease freedomAchieving a topological phase transitionOptical light guidesDielectric cylinderPhotonic crystal structure
The invention provides a photonic crystal structure with a complex unit cell and an optical waveguide. The complex unit cell is formed by arranging six subcells according to a C6 structure, and the section of the complex unit cell is of a regular hexagon structure. The multiple complex unit cells are adjacent in edge-to-edge mode and are arranged in an array mode to form the photonic crystal structure. According to the invention, energy band inversion and topological phase change are realized through three different modes, i.e., compression and stretching of unit cells, change of section diameters of dielectric cylinders and rotation of sub-cells, so that a topological trivialness to topological non-trivialness crystal structure is constructed. An optical waveguide constructed by the crystal structure is larger in photonic band gap and high in photon localization performance, electromagnetic waves in the working bandwidth can be transmitted in a one-way mode along topological common and non-common interfaces, the optical localization is enhanced, backscattering is restrained, and the crystal structure has high immunity to sharp turns and defects.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Light-diffusing element and method for manufacturing light-diffusing element
InactiveCN105164557AIncrease the refractive index differenceImprove diffusivityDiffusing elementsSurface roughnessChemistry
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a light-diffusing element that has a high haze value, is strongly diffusing, and has a smooth surface, reducing backscatter. This light-diffusing element has the following: a matrix that contains a resin component and an ultrafine-particle component; and light-diffusing fine particles dispersed within said matrix. Some of the resin component osmoses into the light-diffusing fine particles, and the distance to which the resin component osmoses into the light-diffusing fine particles is at least 90% of the mean diameter of the light-diffusing fine particles in this light-diffusing element. The arithmetic-mean surface roughness (Ra) is less than or equal to 0.04 mum.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Laser differential imaging detection method and device thereof
ActiveCN106872468BAccurate measurementAdaptableMaterial analysis by optical meansRange gateComputer vision
The invention discloses a laser difference imaging detection method and a device for the same. The method comprises the following steps: performing range-gated imaging to obtain n frames of retroreflected images of n slices of a region to be detected in a one-frame one-pulse one-gate exposure manner; dividing the n frames of retroreflected images into m information frames and n-m background frames according to a grayscale threshold value; calculating differences of the m information frames and the background frames to obtain m enhanced information frames of the m information frames, and dividing the m enhanced information frames into k bubble information frames and m-k pseudo information frames by adopting a trained classifier; calculating a grayscale mean value and modulation time delays of the k bubble information frames respectively, and performing fitting to obtain a spatial distribution curve of bubbles along with the time delay; obtaining a range of a bubble region and yield of the bubbles according to the spatial distribution curve, wherein m, n and k are all natural numbers not smaller than 1. According to the method and the device, the range and the yield of the bubble region can be accurately detected, and the method and the device have the characteristics of high accuracy, high adaptability and high flexibility, and is significant for underwater bubble detection and analysis.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Underwater long-distance optical imaging device and method combining short coherent illumination and polarization
ActiveCN111123619BEasy to separateGaze Imaging RealizedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight beamEngineering
The invention discloses an underwater long-distance optical imaging device and method combining short-coherent illumination and polarization, including a short-coherent laser, an optical imaging system, a polarizer and an analyzer, and polarizers are set at the image side of the short-coherent laser An analyzer is installed at the object side of the optical imaging system. The laser light emitted by the short coherent laser is incident on the imaging target through the polarizer. The imaging target is placed in the water body environment, and the reflected beam of the imaging target is transmitted to the optical imaging system through the analyzer.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Photon fence system for monitoring on security protection of perimeter at night
The invention discloses a photon fence system for monitoring on security protection of perimeter at night. The system comprises: a pulsing laser, which is used for emitting a laser pulse to carry out illumination on an object; a gated imaging device, which is used for controlling exposure time by a pulse width of a gated pulse; a time schedule controller, which is used for controlling time delay between the gated pulse and the laser pulse; and a computer, which is used for carry out controlling, image processing and displaying on the pulsing laser, the gated imaging device and the time schedule controller. According to the system provided in the invention, a pulsing laser is utilized as a light source and a gated imaging device is employed as a detector; time delay between a gated pulse and a laser pulse is controlled so as to establish a photon fence in space, wherein the photon fence is invisible for human eyes; therefore, when an invading object passed through the photon fence, image information of the invading object is collected and background outside the photon fence and a non-invading object are removed by filtering, so that non-background extraction on the invading object is realized.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
An underwater optical imaging device with axial multi-sensors
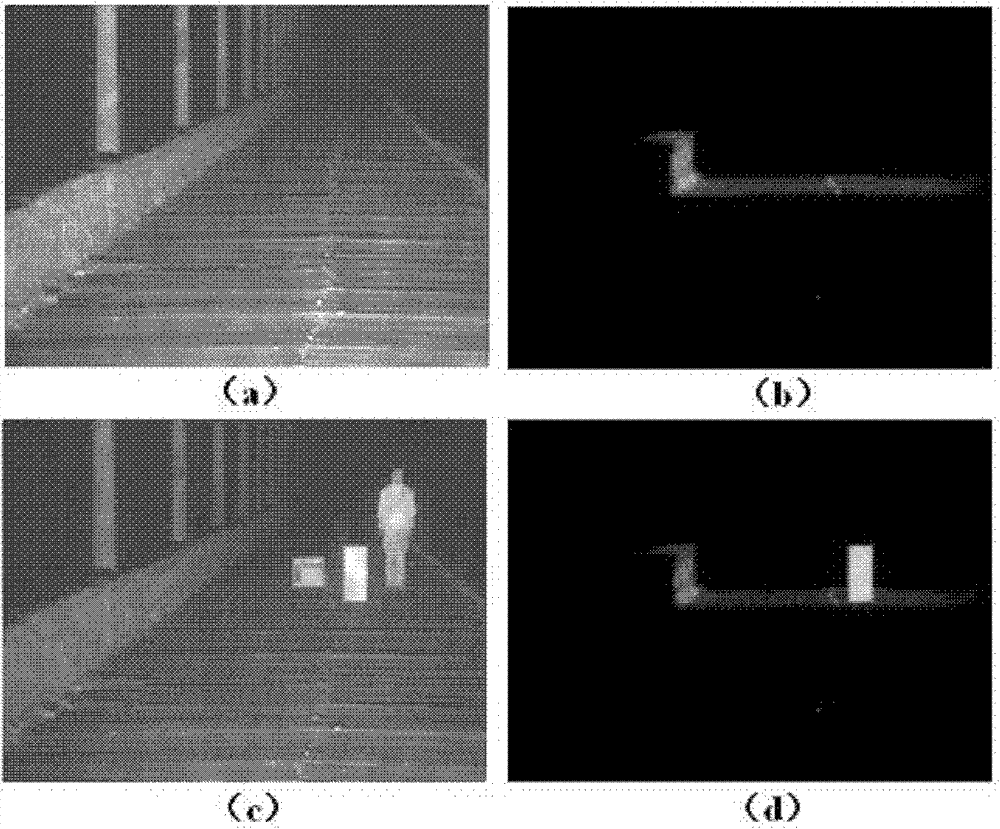
ActiveCN107147829BSuppress backscatterLow costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSuspended particlesDiffusion function
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
A range-gated super-resolution three-dimensional imaging device and method
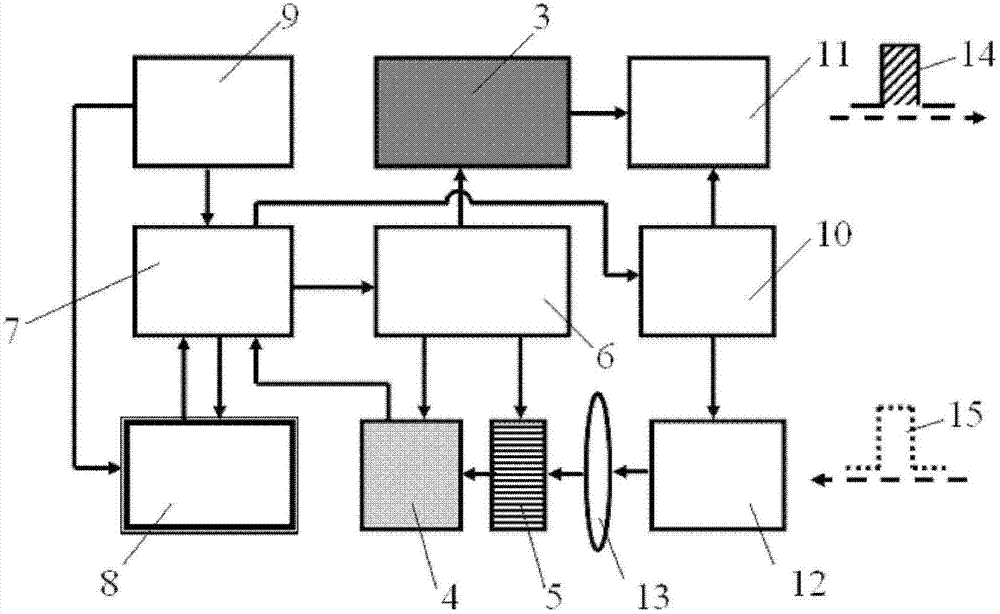
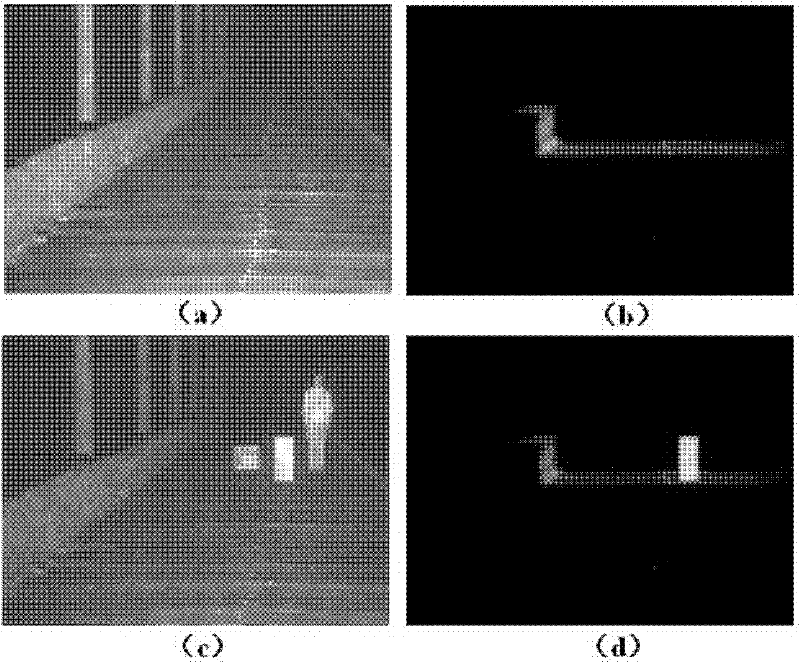
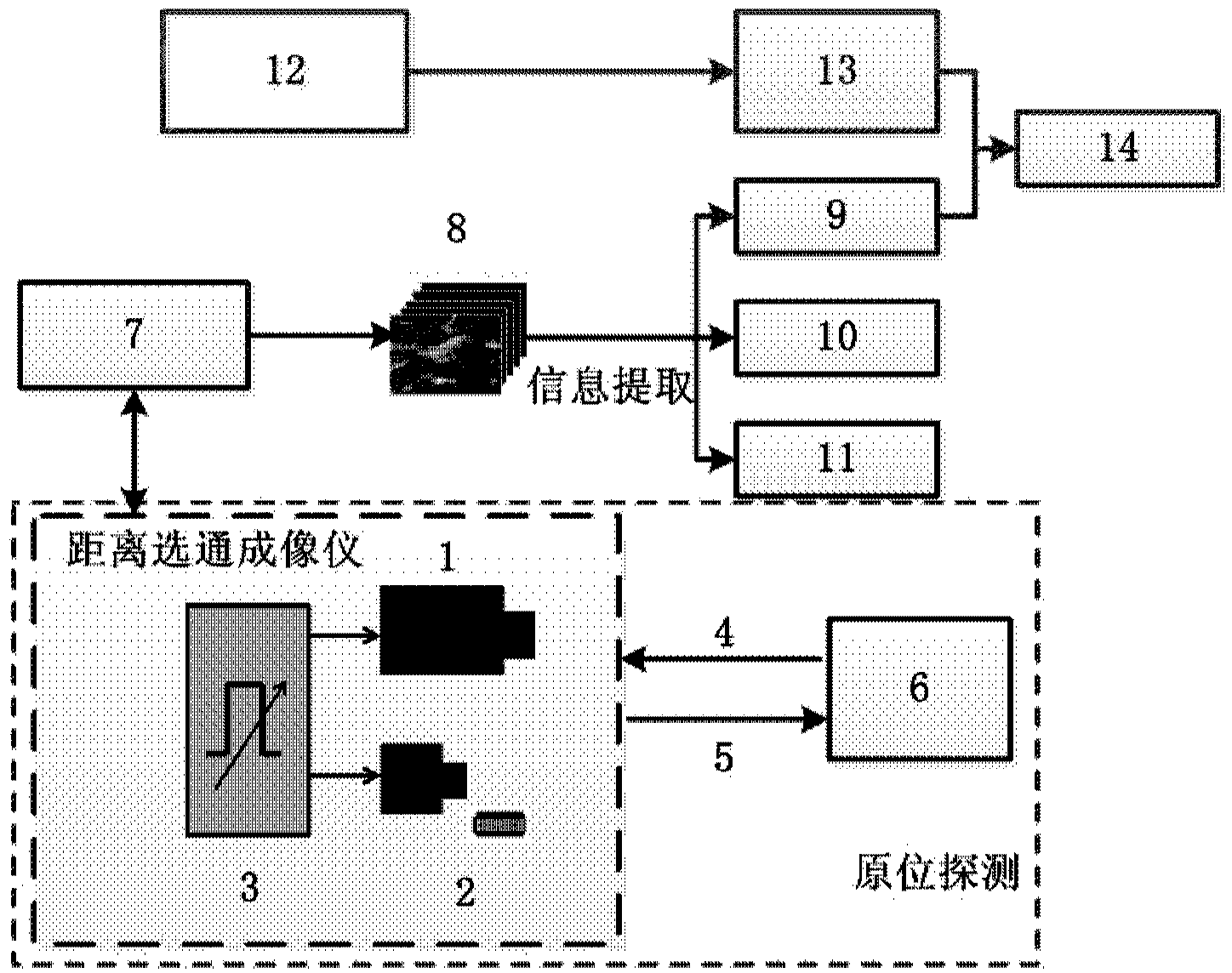
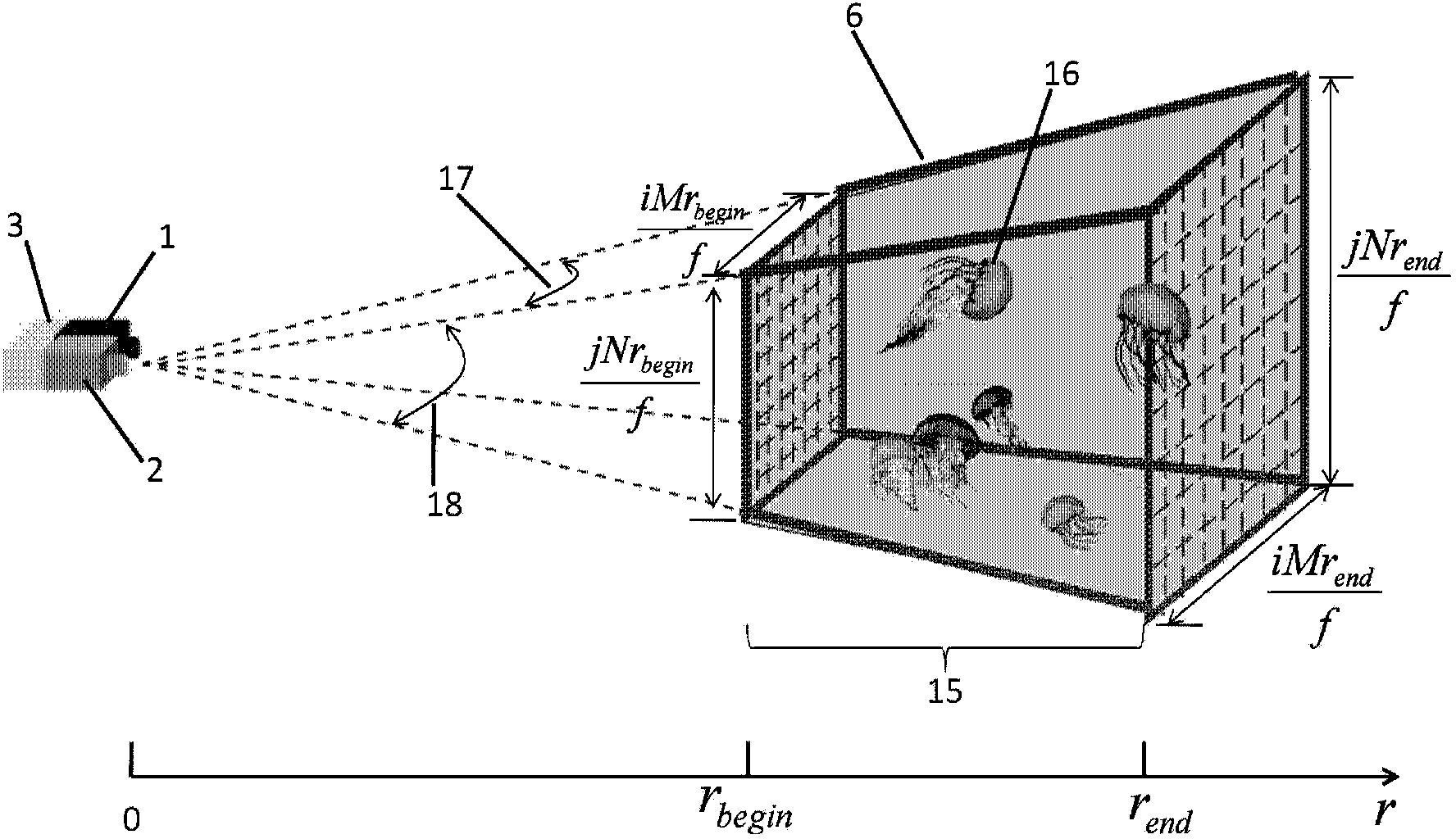
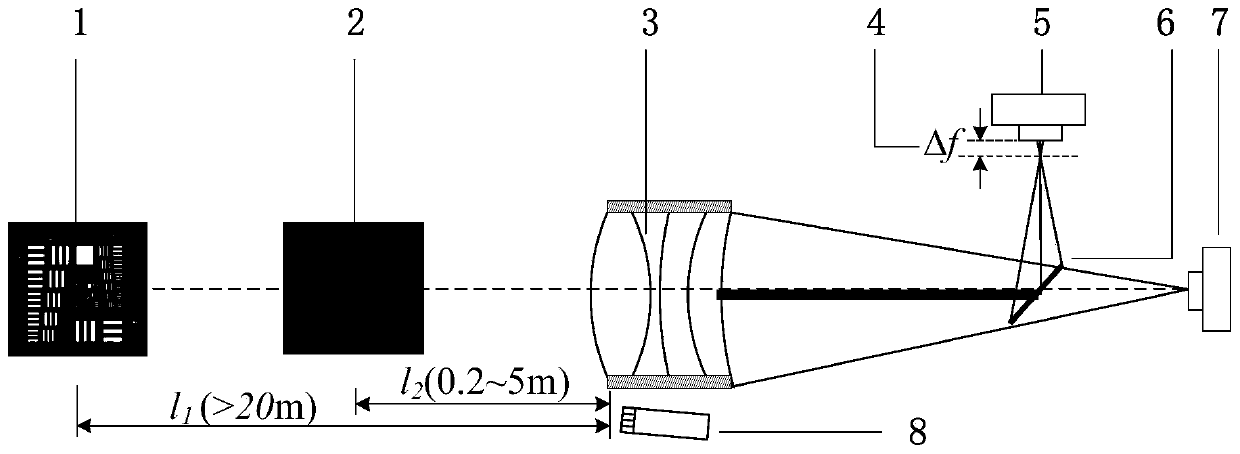
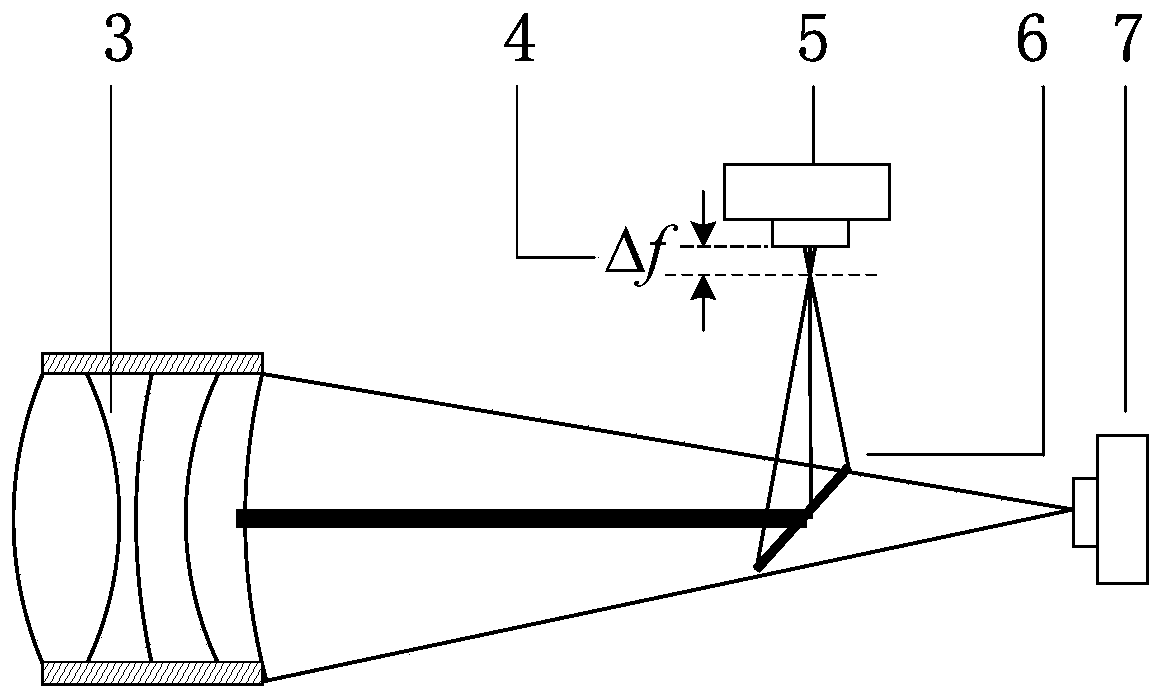
ActiveCN102927972BReduce raw data volumeEasy to handlePhotogrammetry/videogrammetryTime scheduleDisplay device
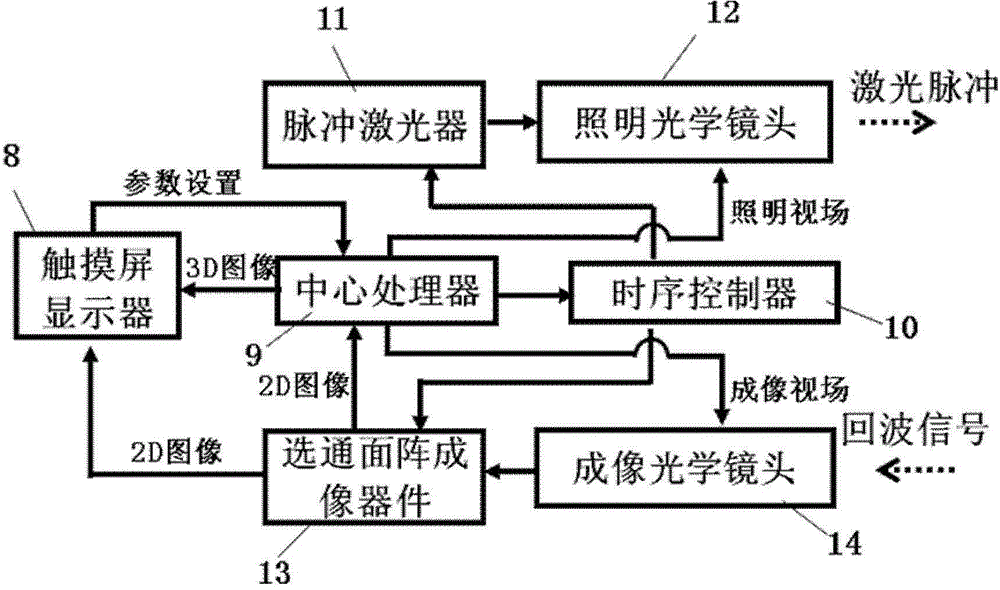
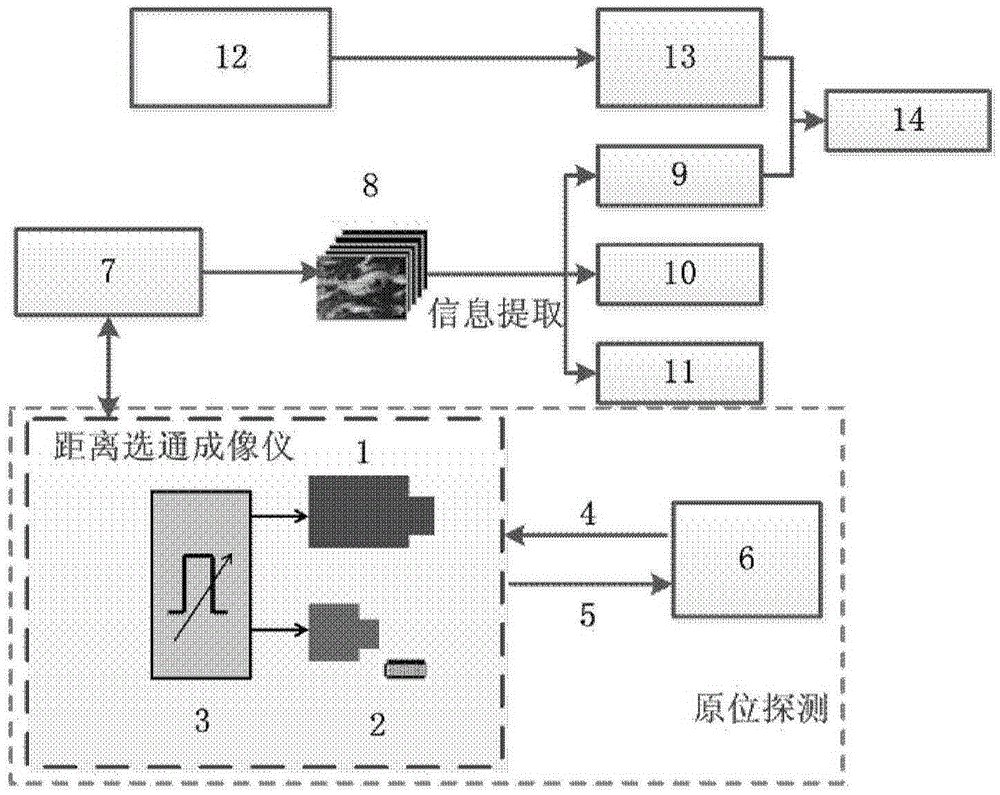
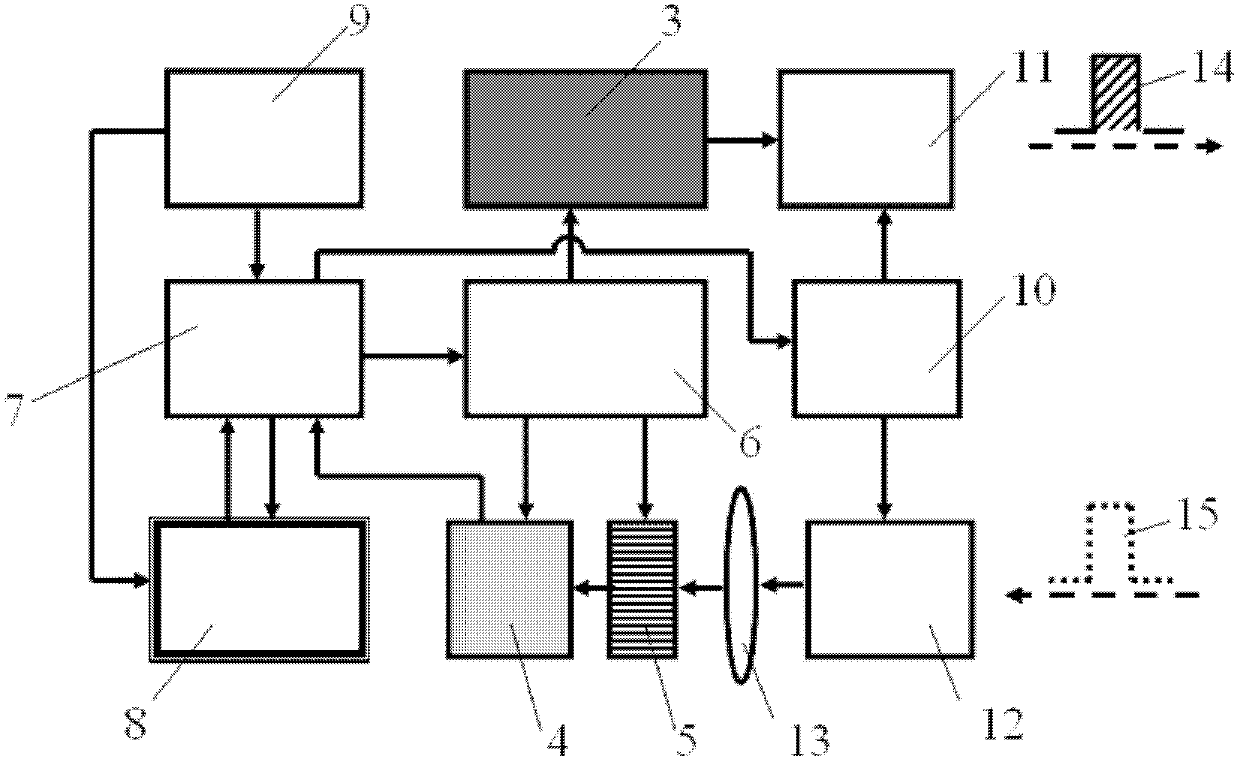
The invention discloses a range gating super-resolution three-dimensional imaging device and method. The range gating super-resolution three-dimensional imaging device comprises a touch screen display (8), a central processor (9), a time schedule controller (10), a pulse laser (11), an illuminating optical lens (12), a gating area array imaging device (13) and an imaging optical lens (14), wherein the pulse laser (11) and the illuminating optical lens (12) are connected to form an illuminating unit; the gating area array imaging device (13) and the imaging optical lens (14) are connected to from an imaging unit; and the touch screen display (8), the central processor (9) and the time schedule controller (10) are connected to form a system control and display unit. According to the invention, the problems of poor instantaneity and sensitive noise disturbance of the traditional range gating three-dimensional imaging are solved; and the range gating super-resolution three-dimensional imaging device and method disclosed by the invention have the advantages of good adaptability and high flexibility and can be used for realizing the fast high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of a target.
Owner:北京中科盛视科技有限责任公司
Fluorescent light source device
ActiveCN104968995BSuppress backscatterFull accessVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourceFluorescencePhosphor
The present invention provides a fluorescent light source device that suppresses the backscattering of the excitation light when the wavelength conversion member is irradiated with excitation light, and at the same time can emit the fluorescence generated inside the wavelength conversion member to the outside with high efficiency, thereby enabling Obtain high luminous efficiency. This fluorescent light source device is a fluorescent light source device provided with a wavelength conversion member composed of a phosphor excited by excitation light, wherein the wavelength conversion member forms a surface-side periodic structure on a surface serving as an excitation light receiving surface, A rear side periodic structure is formed on the rear surface, and a light reflection surface is provided on the outside of the rear surface.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Process for producing light-diffusing element, light-diffusing element, and processes for producing polarizing plate with light-diffusing element and liquid-crystal display device
InactiveCN102356335BLow costImprove productivityDiffusing elementsPolarising elementsProduction rateLiquid-crystal display
A process for producing a light-diffusing element is provided by which a light-diffusing element having a high haze and high diffusing properties and reduced in backward scattering can be produced at low cost with high productivity. The process for producing a light-diffusing element comprises a step in which a matrix-forming material comprising a resin-ingredient precursor and an ultrafine-particle ingredient is brought into contact with fine light-diffusing particles, a step in which at least some of the precursor is infiltrated into an inner part of the fine light-diffusing particles, and a step in which the precursor that has infiltrated into the inner part of the fine light-diffusing particles and the precursor that has not infiltrated into the fine light-diffusing particles are simultaneously polymerized to form a matrix comprising the resin ingredient and the ultrafine-particle ingredient and simultaneously form a concentration gradation region in the vicinity of the inner side of the surface of the fine light-diffusing particles.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
An in-situ detection method of optical stereo sampling to realize zooplankton information acquisition
ActiveCN103901438BSolve the problem of low contrast and poor qualitySuppress backscatterElectromagnetic wave reradiationZooplanktonNon invasive
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A double-loop parallel resonant gyroscope system and its double-closed-loop digital demodulation method
ActiveCN111536960BImprove environmental temperature adaptabilityLittle effect of temperature changeSagnac effect gyrometersOptical frequenciesAcousto-optics
The invention discloses a double-loop parallel resonant gyroscope system and a double-closed-loop digital demodulation method thereof, including a tunable laser Laser, and the output light of the tunable laser is split into two paths of clockwise and counterclockwise light by a signal beam splitter. Enter the acousto-optic frequency shifter, electro-optic modulator, fiber coupler, hollow photonic bandgap fiber resonator, photodetector, digital lock-in amplifier in sequence, and form a frequency closed-loop feedback through the tunable laser and the acousto-optic frequency shifter respectively . The double-ring hollow-core photonic bandgap fiber structure allows clockwise and counterclockwise light waves to propagate independently in independent resonant cavities, which can improve temperature stability and effectively suppress non-reciprocal effects such as optical Kerr effect and Rayleigh backscattering noise. The double-closed-loop digital demodulation method locks the optical frequencies in the forward and counterclockwise optical paths at their respective transmission resonant frequencies, making the system work in the linear region, effectively improving the linear range of angular velocity detection and the linearity of the scale factor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Image target seeking laser imaging distance measurement method and device
ActiveCN102736085BGuaranteed to workSuppress backscatterElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadiologyLaser imaging
The invention discloses an image target seeking laser imaging distance measurement method and an image target seeking laser imaging distance measurement device. The method comprises the following steps of: imaging environment where a target is positioned in a non-gating imaging mode, and outputting a digital panorama to realize image target seeking; opening a distance measurement function, outputting a target-containing panoramic frame, selecting the target by a user, and opening the distance measurement function; obtaining a background frame in a distance measurement timing mode, constructing spatial slices with triangular distance energy envelope through distance gating imaging, performing slice scanning on a foresight field, and outputting slice frames; and when a target distance is subjected to inversion, performing differential processing on all the slice frames and the background frame to obtain new slice frames in which background influence is eliminated, and automatically calculating distance information of the target based on a mapping relation between the image gray scale ratio of a main window area among adjacent new slice frames and a distance energy ratio, which is established according to a distance gating echo broadening effect, by using a system, so that target distance measurement is finished. The method and the device are high in adaptability and easy to operate, target distance measurement is easy to realize, and particularly the problem that the distance of a small target is difficult to measure can be solved.
Owner:北京中科盛视科技有限责任公司
A time-correlated single photon counting wake detection device and its operating method
ActiveCN113447232BNo distortionImprove uniformityAerodynamic testingInformation processingEngineering
The invention discloses a time-correlated single photon counting wake detection device and an operation method thereof, belonging to the field of laser underwater wake target detection. It includes a laser emitting component, a laser receiving component and an information processing component. Both the laser emitting component and the laser receiving component are electrically connected to the information processing component. The component transmits the start electrical signal; the laser receiving component is used to receive the reflected light reflected by the bubbles in the wake, and transmits the termination electrical signal to the information processing component synchronously; the information processing component is used to receive the light from the laser emitting component The start electrical signal and the termination electrical signal from the laser receiving component complete the measurement of the photon flight time interval and the analysis of the time-correlated single photon counter, and finally calculate the target distance. The invention can realize the detection of underwater weak wake echo signals, and overcomes the technical limitation of low sensitivity existing in the traditional technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com