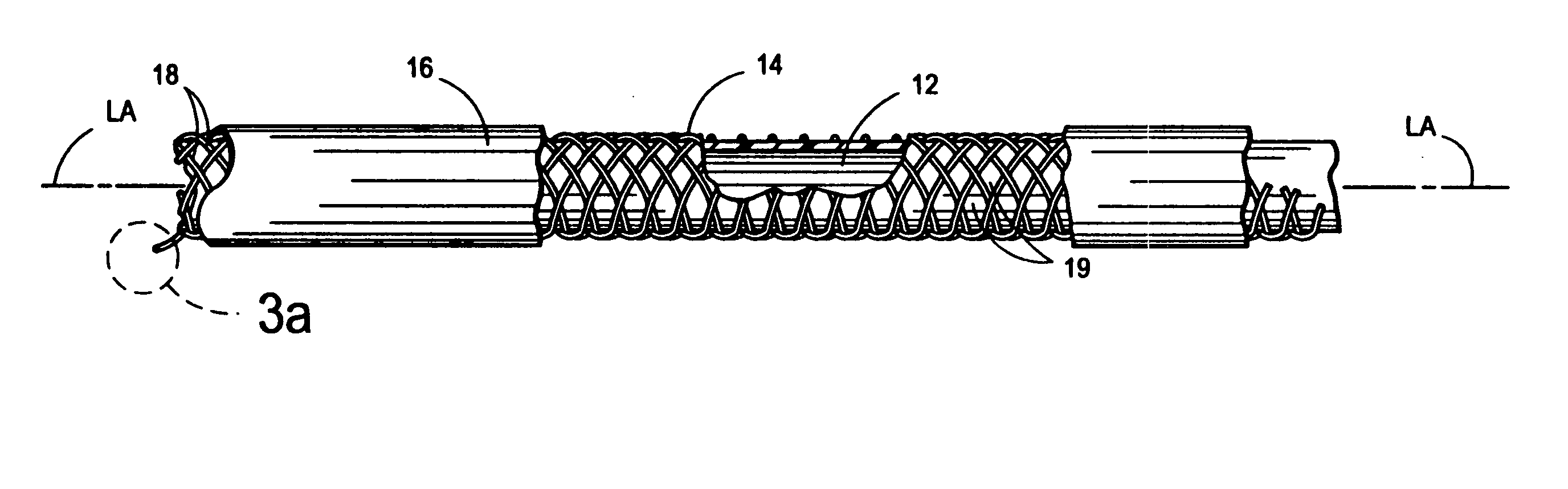
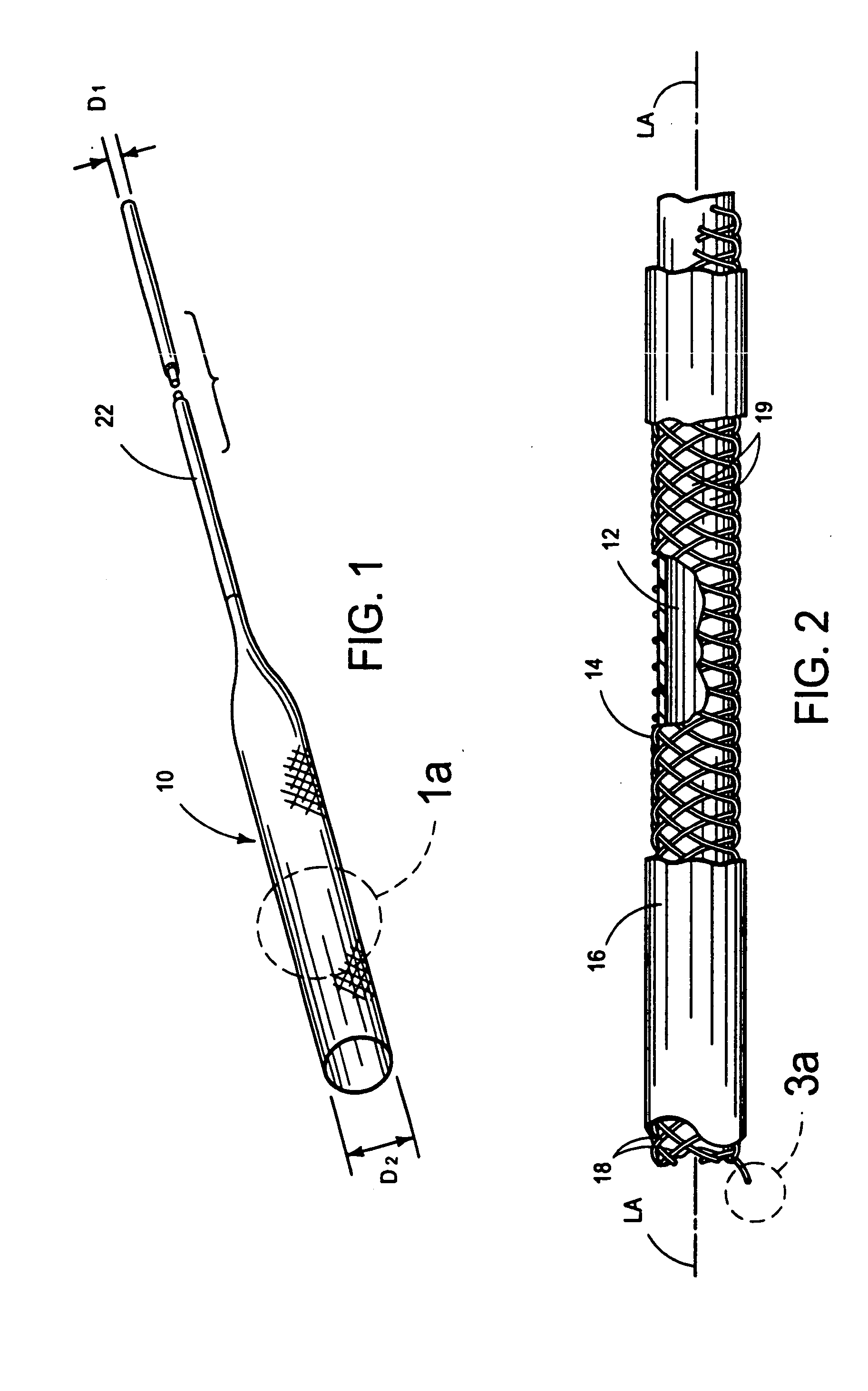
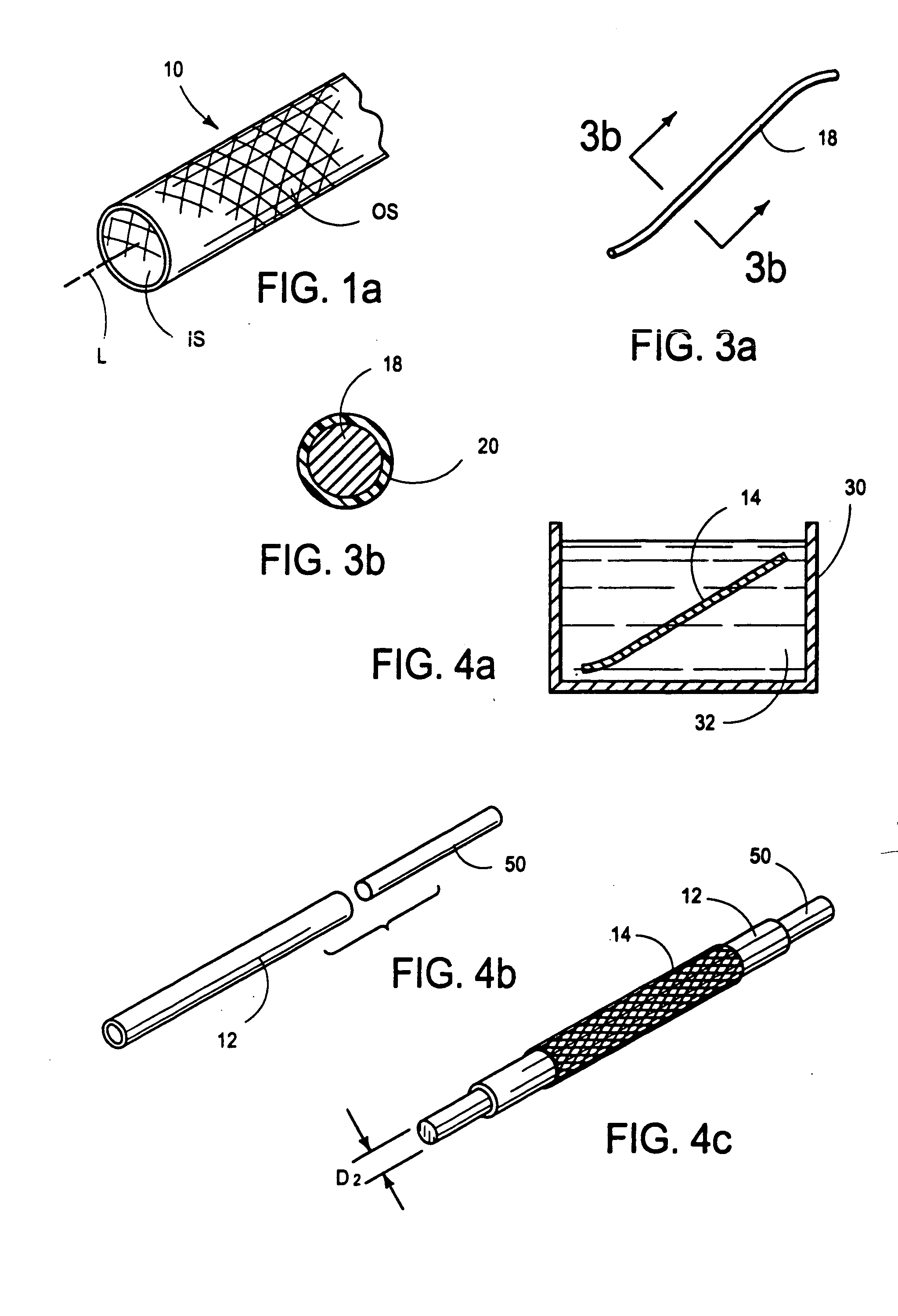
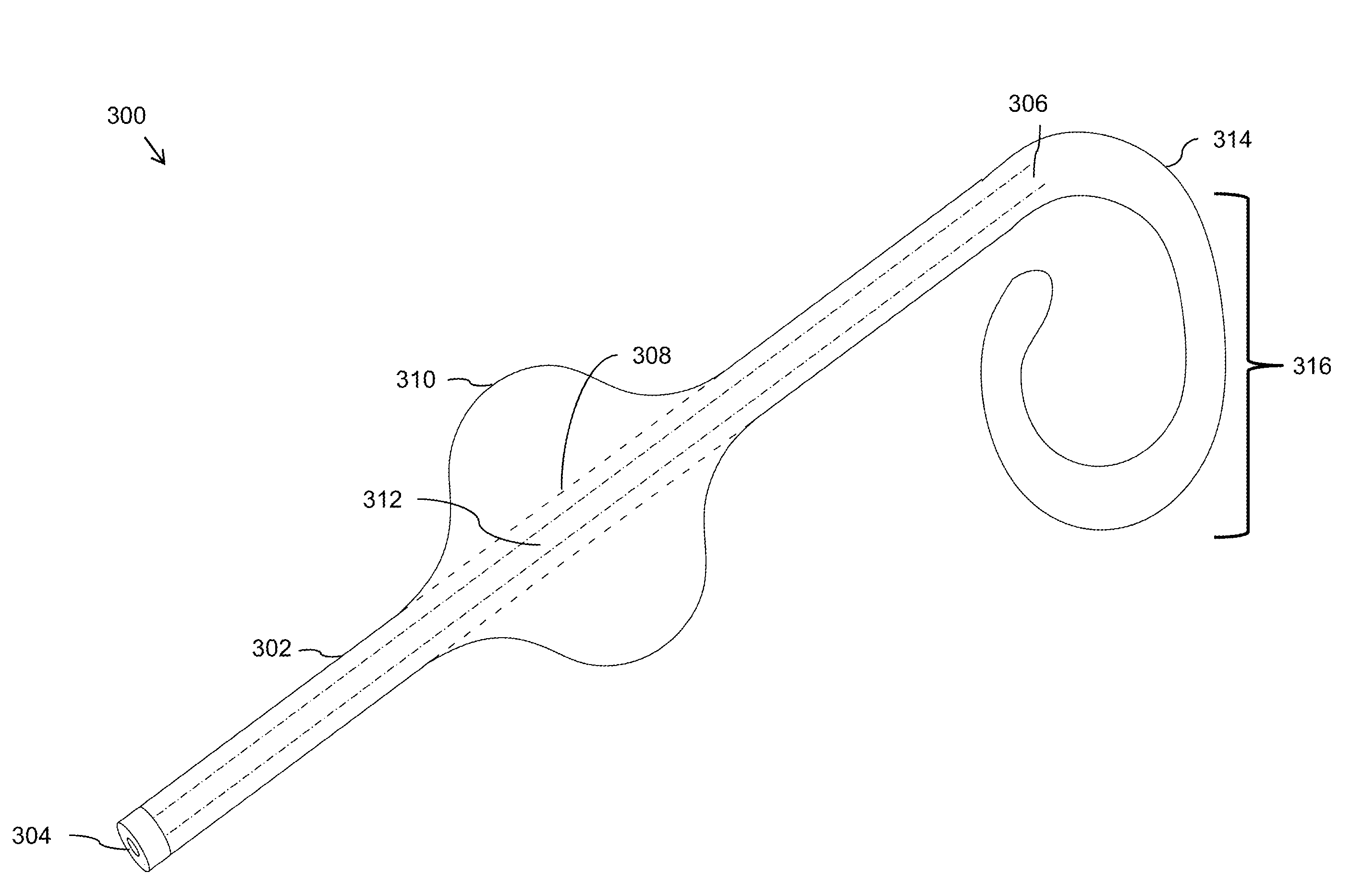
Patents
Literature
87 results about "Balloon expandable stent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quick-connect prosthetic heart valve and methods
ActiveUS8308798B2Quickly and easily replacingUse minimizedBalloon catheterHeart valvesCouplingInsertion stent
A heart valve prosthesis that can be quickly and easily implanted during a surgical procedure is provided. The prosthetic valve has a base stent that is deployed at a treatment site, and a valve component configured to quickly connect to the base stent. The base stent may take the form of a self- or balloon-expandable stent that expands outward against the native valve with or without leaflet excision. The valve component has a non-expandable prosthetic valve and a self- or balloon-expandable coupling stent for attachment to the base stent, thereby fixing the position of the valve component relative to the base stent. The prosthetic valve may be a commercially available to valve with a sewing ring and the coupling stent attaches to the sewing ring. The system is particularly suited for rapid deployment of heart valves in a conventional open-heart surgical environment. A catheter-based system and method for deployment is provided.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Quick-connect prosthetic heart valve and methods
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Methods of using an intravascular balloon catheter in combination with an angioscope
A method of performing a medical procedure is disclosed which involves the use of a balloon catheter in combination with an angioscope to monitor an intravascular stent before, during or after deploying the stent. Specifically, the method may include the steps of (1) delivering an intravascular stent into the vasculature of a patient, (2) positioning a balloon catheter in the vasculature such that the inflatable balloon is adjacent the stent, (3) inserting an angioscope into the balloon catheter such that the distal end of the angioscope is adjacent an optically-transparent tube traversing the interior of the balloon, and (4) visually monitoring the stent before, during or after deploying the intravascular stent. The optically-transparent tube may define a guide wire lumen for use with a guide wire and the angioscope may be inserted into the guide wire lumen. The intravascular stent may be a balloon-expandable stent, a self-expanding stent, or a stent made of a photo-responsive polymer.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
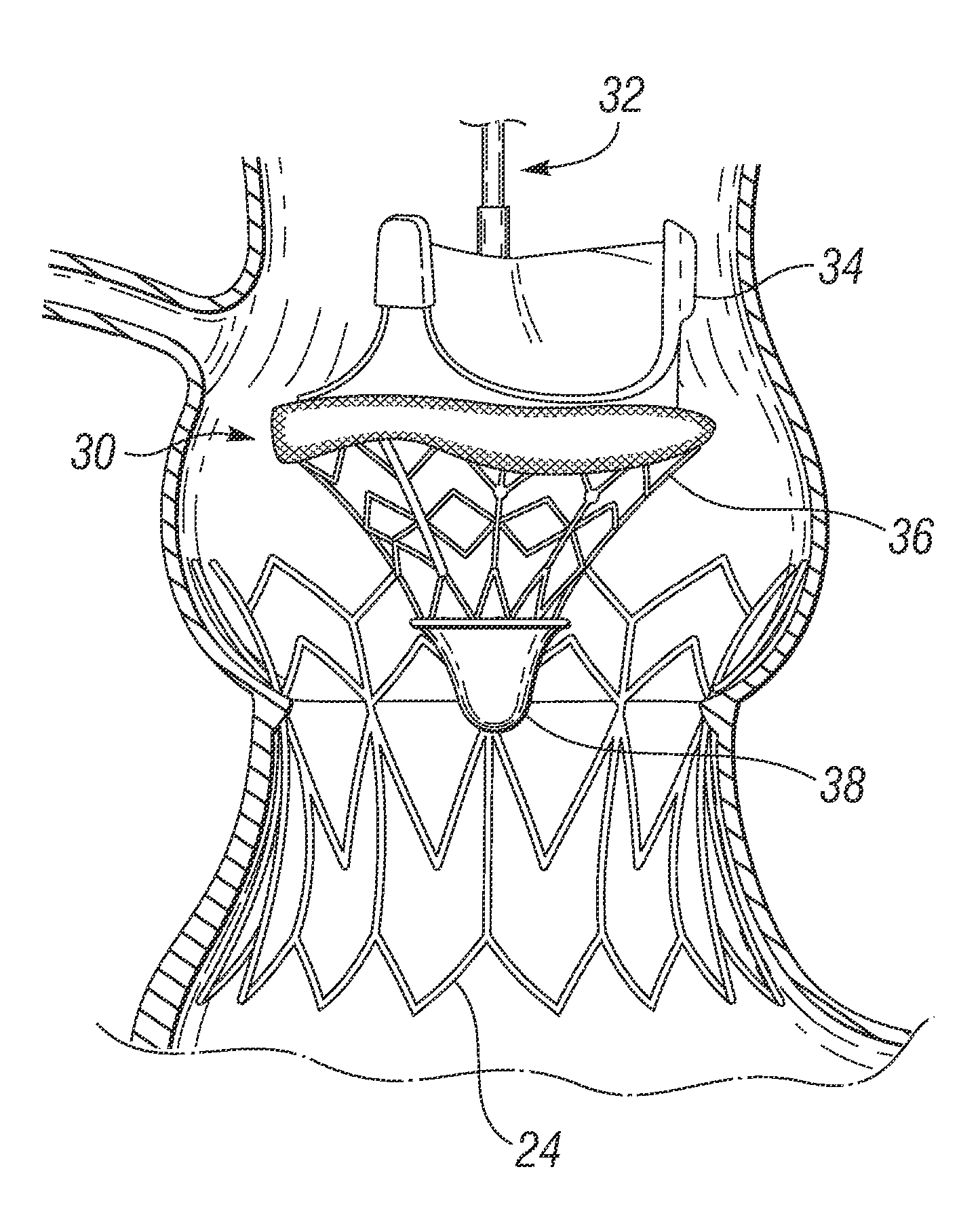
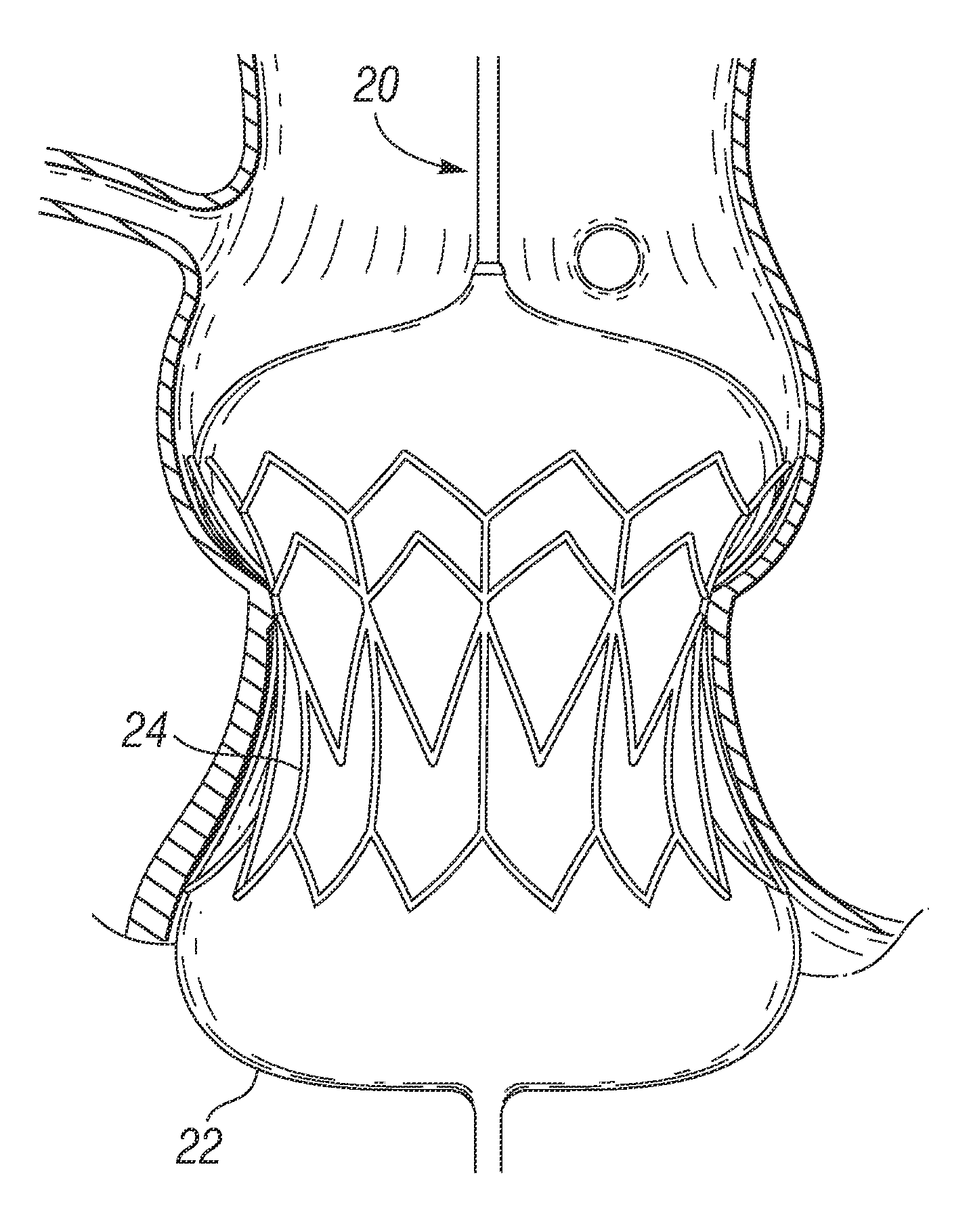
Prosthetic Valve Delivery System
A prosthetic valve delivery system for percutaneously delivering and deploying a prosthetic valve within an existing valve is disclosed. The delivery system includes a stented prosthetic valve having a balloon-expandable stent portion with a prosthetic valve disposed therein and at least one self-expanding stent portion. The delivery system further includes a dual balloon catheter having a first balloon on which the stented prosthetic valve is disposed during delivery and a second balloon. Upon delivery within the existing valve, the self-expanding stent portion contacts the existing valve and the first balloon expands the balloon-expandable stent portion to a first diameter such that the stented prosthetic valve is in a first stage deployment configuration. The second balloon then expands the balloon-expandable stent portion to a second diameter, greater than the first diameter, such that the stented prosthetic valve is in a second stage deployment configuration being fully deployed within the existing valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Apparatus and methods for delivery of multiple distributed stents
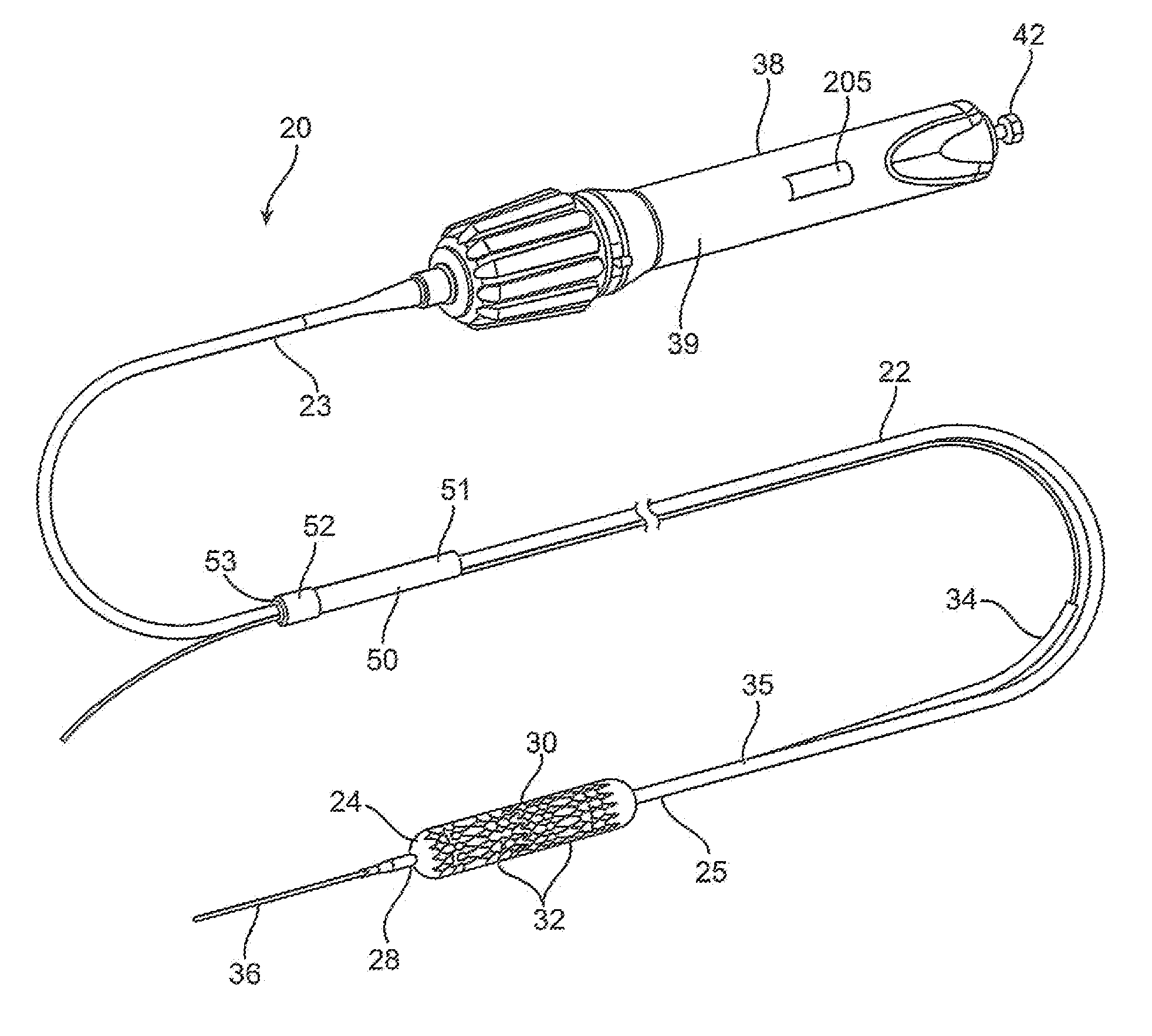
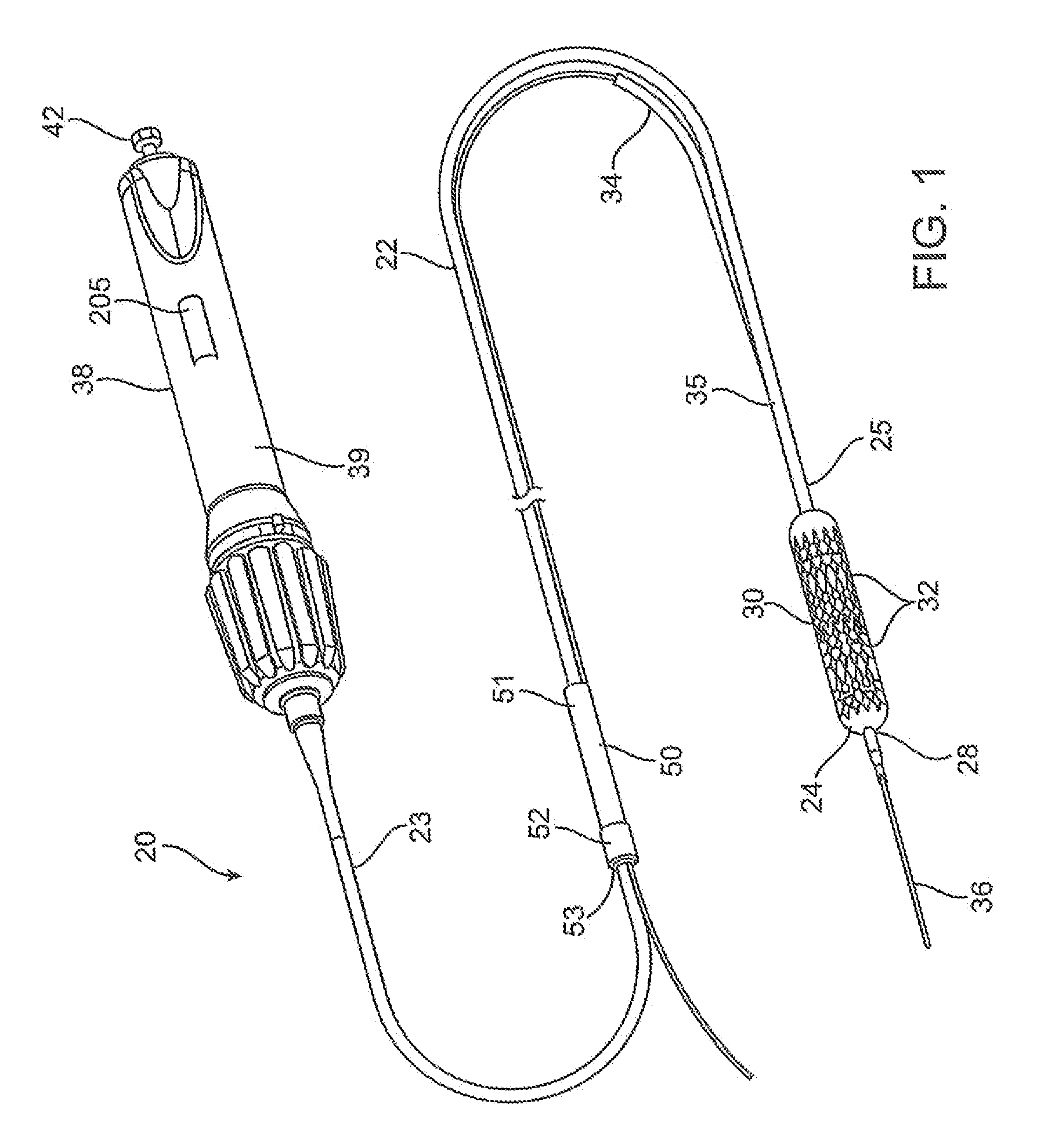
Delivery catheters and systems are adapted for delivering multiple discreet prostheses in body lumens. An exemplary delivery catheter comprises a sheath, a pusher for moving the prostheses relative to the sheath, and a valve member for selectively retaining the prostheses in the sheath. For balloon expandable stents, an elongated shaft and an expandable member are slidably disposed in the sheath, and the prostheses are positionable on the expandable member for deployment in the body lumen. The valve member allows a selected number of prostheses to be deployed from the sheath while retaining other prostheses within the sheath.
Owner:JW MEDICAL SYSTEMS LTD
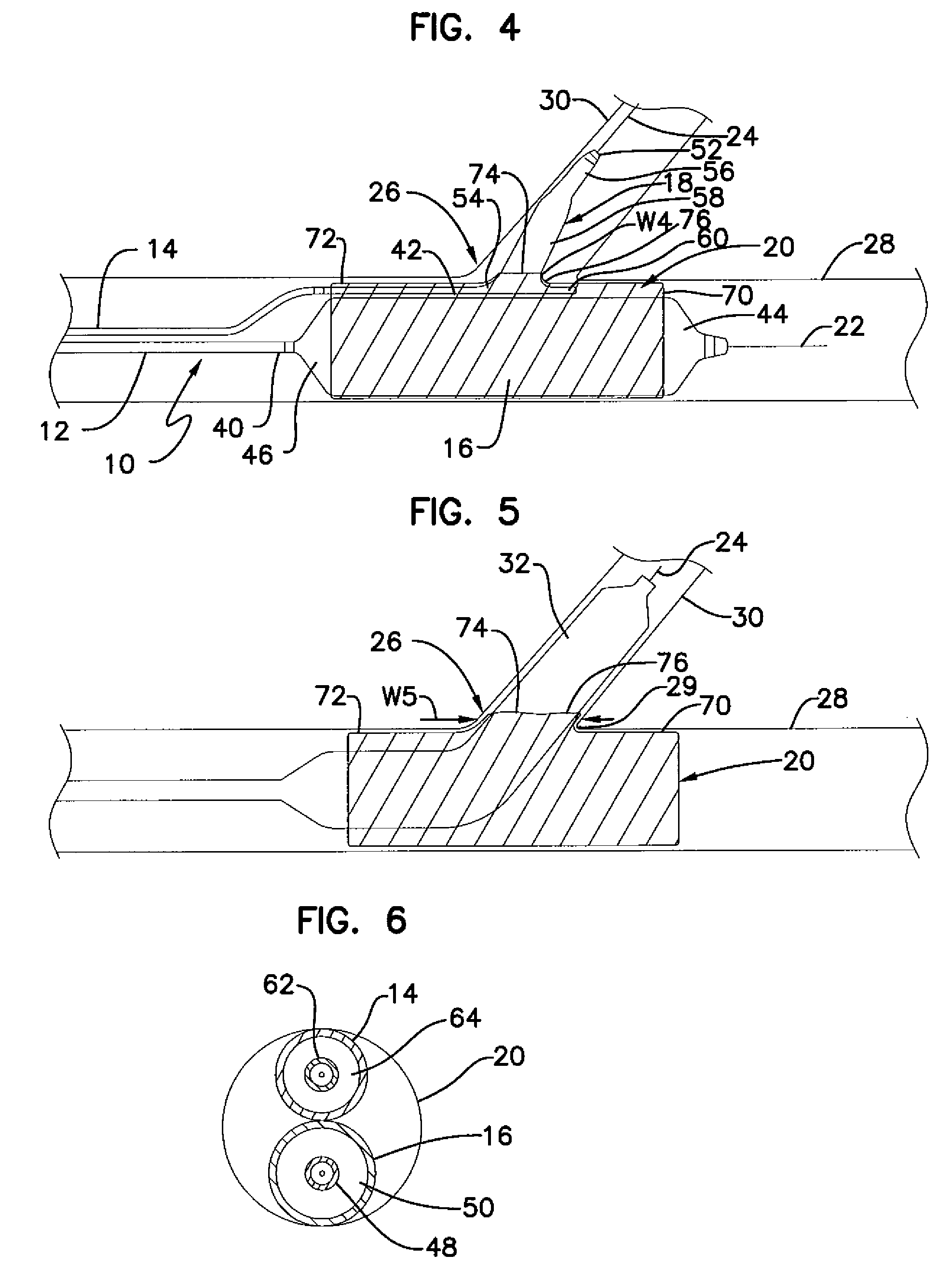
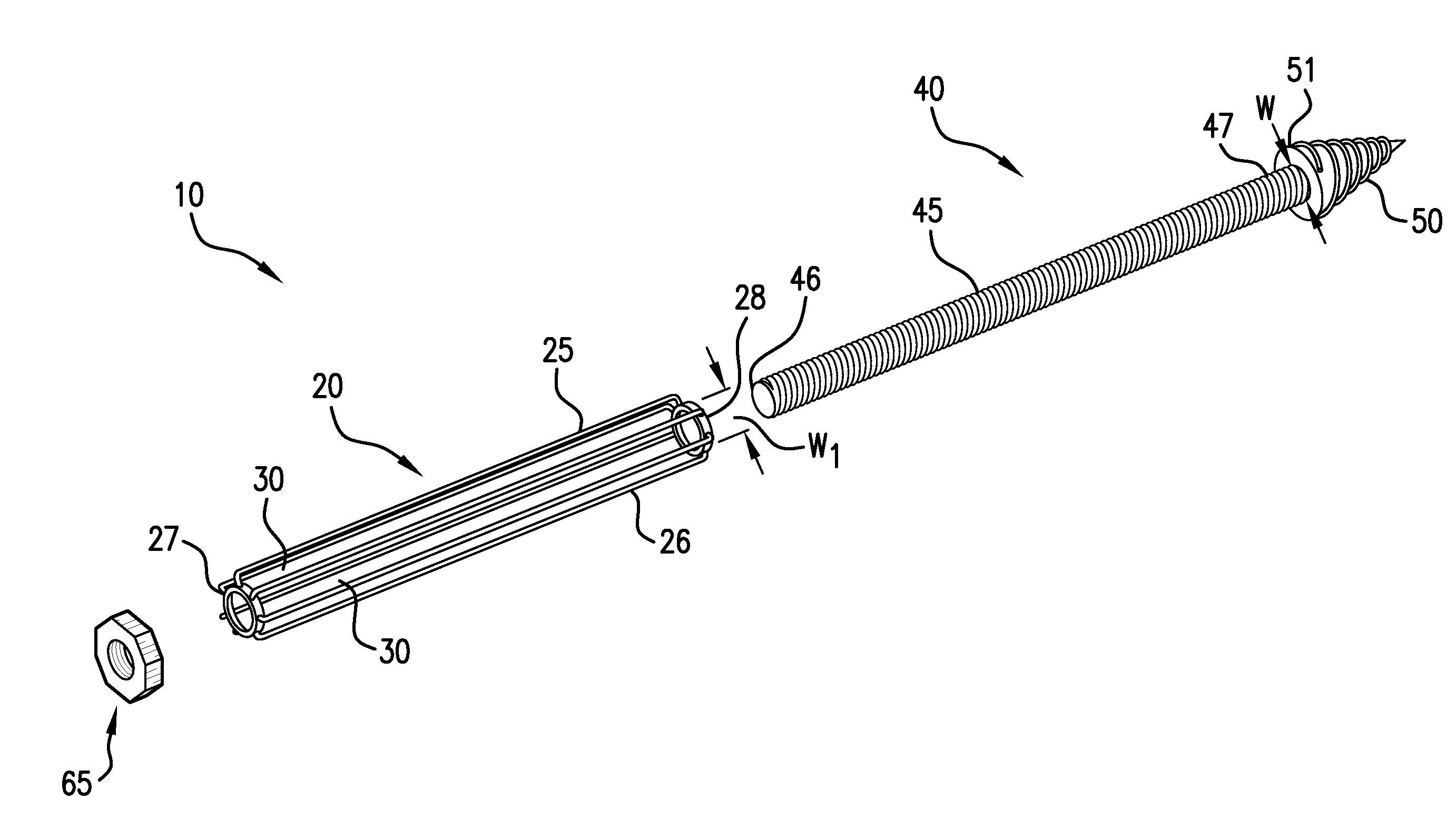
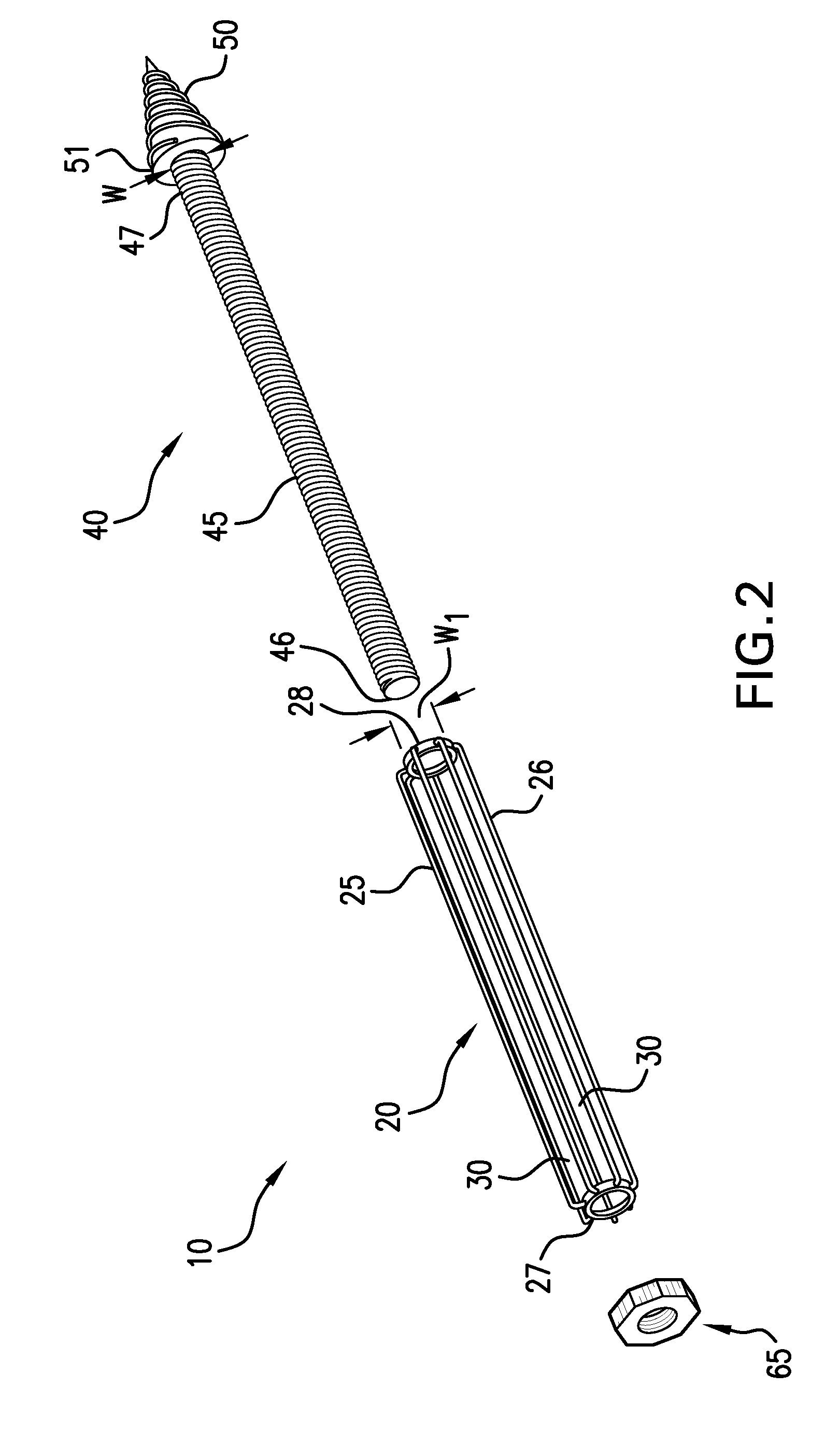
Methods of stabilizing the sacroiliac joint
ActiveUS20090099610A1Not easy to relative displacementPermit fusionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSacrum boneSacro-iliac joint
Methods of stabilizing the sacroiliac joint by placing an expandable device in the joint to generate laterally opposing forces against the iliac and sacral surfaces of the SI joint to securely seat the device in a plane generally parallel to the SI joint. The expandable device is coated with or otherwise contains a bone material to promote fusion of the joint. The expandable device used in methods of the present invention can be, for example, an expandable cage, a balloon, a balloon-expandable stent or a self-expanding stent.
Owner:SPINAL INNOVATIONS +1
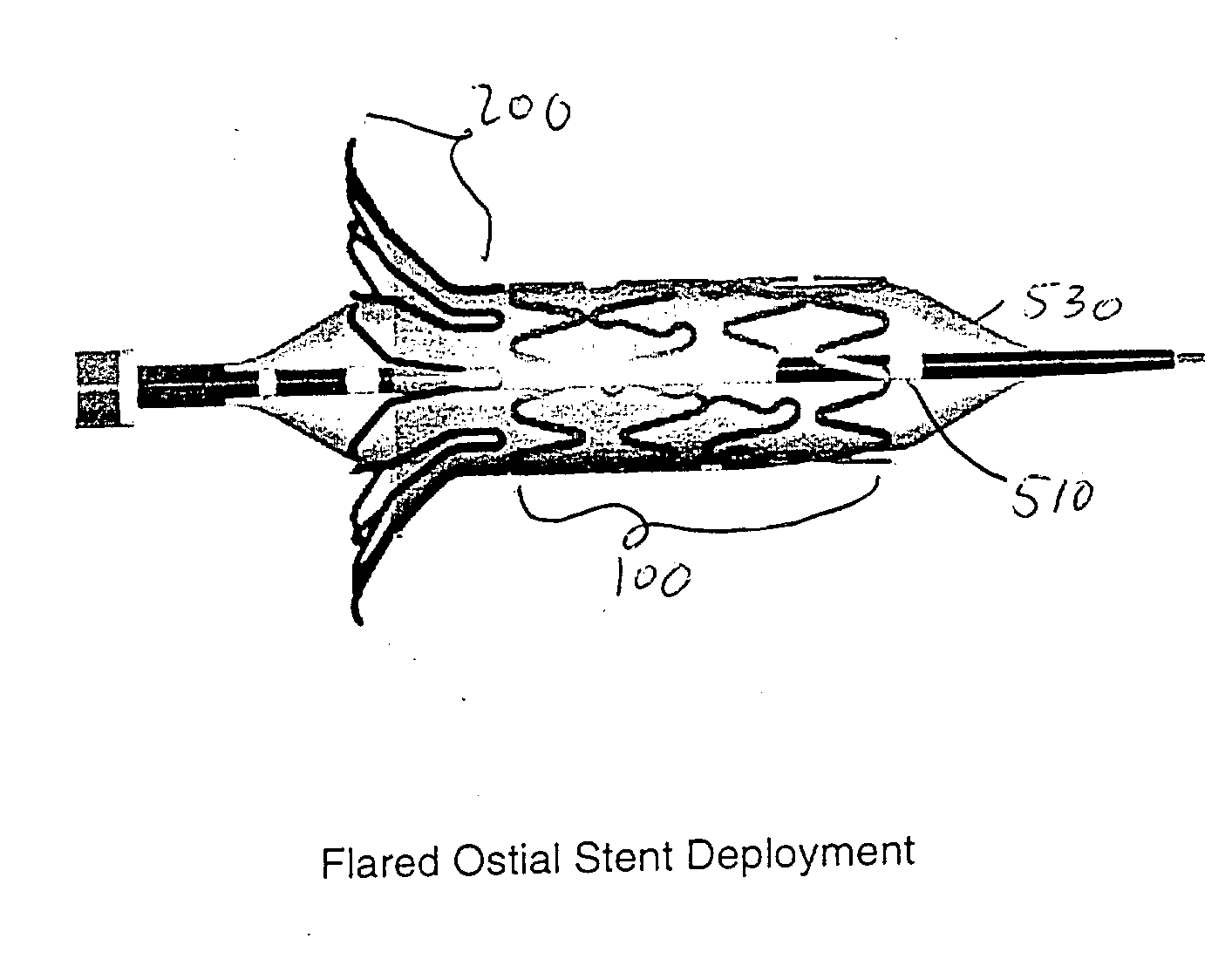
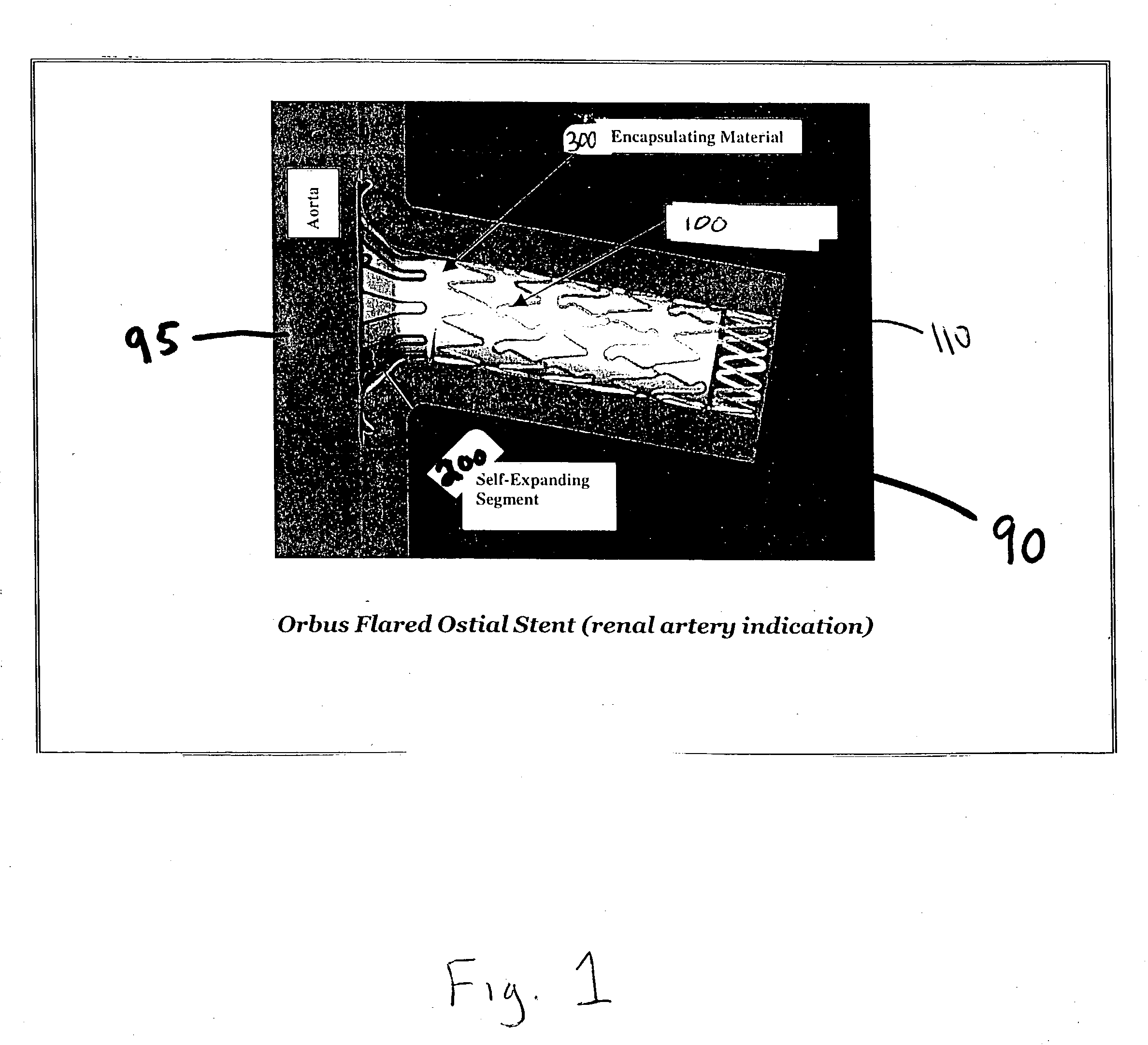
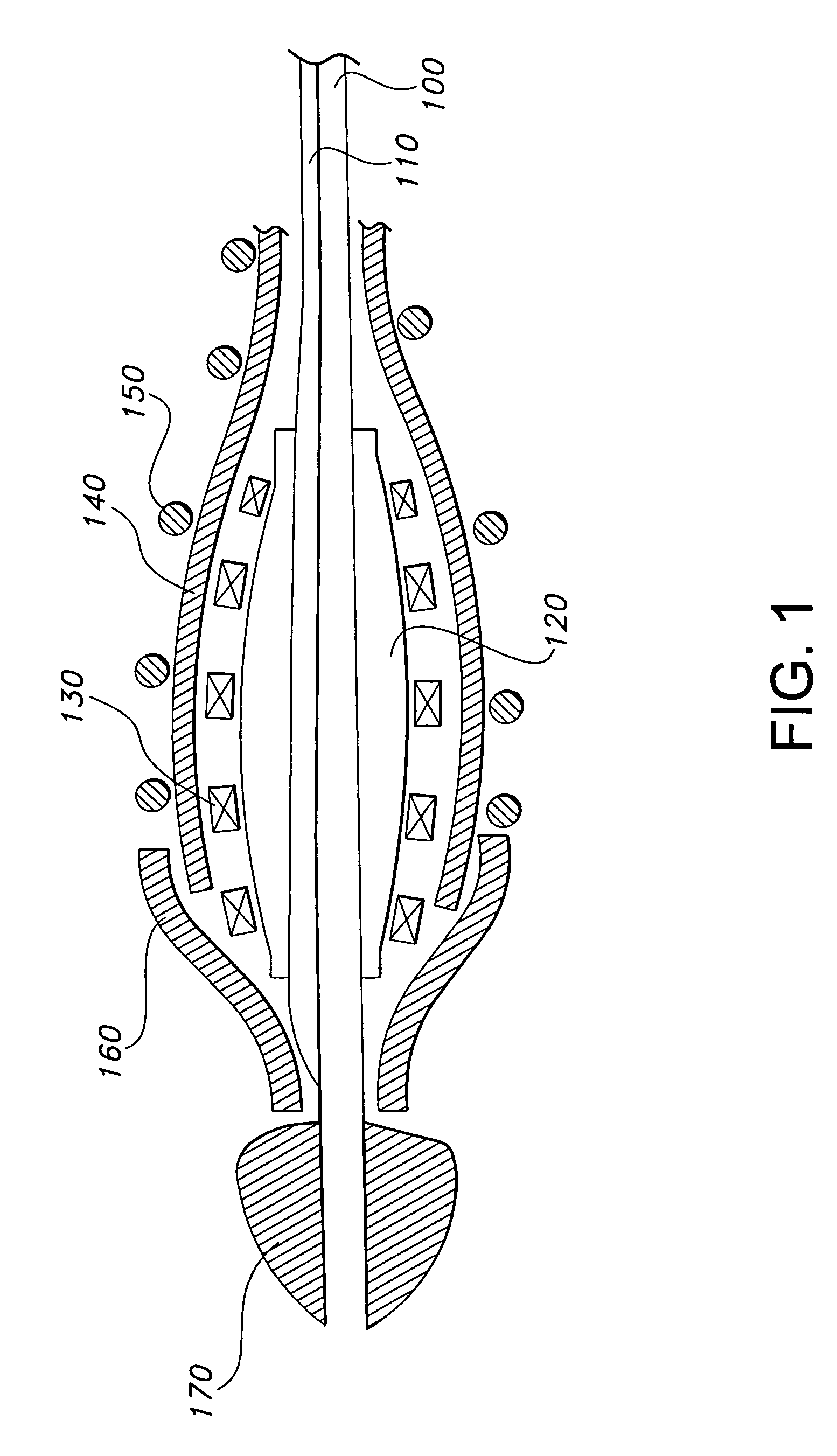
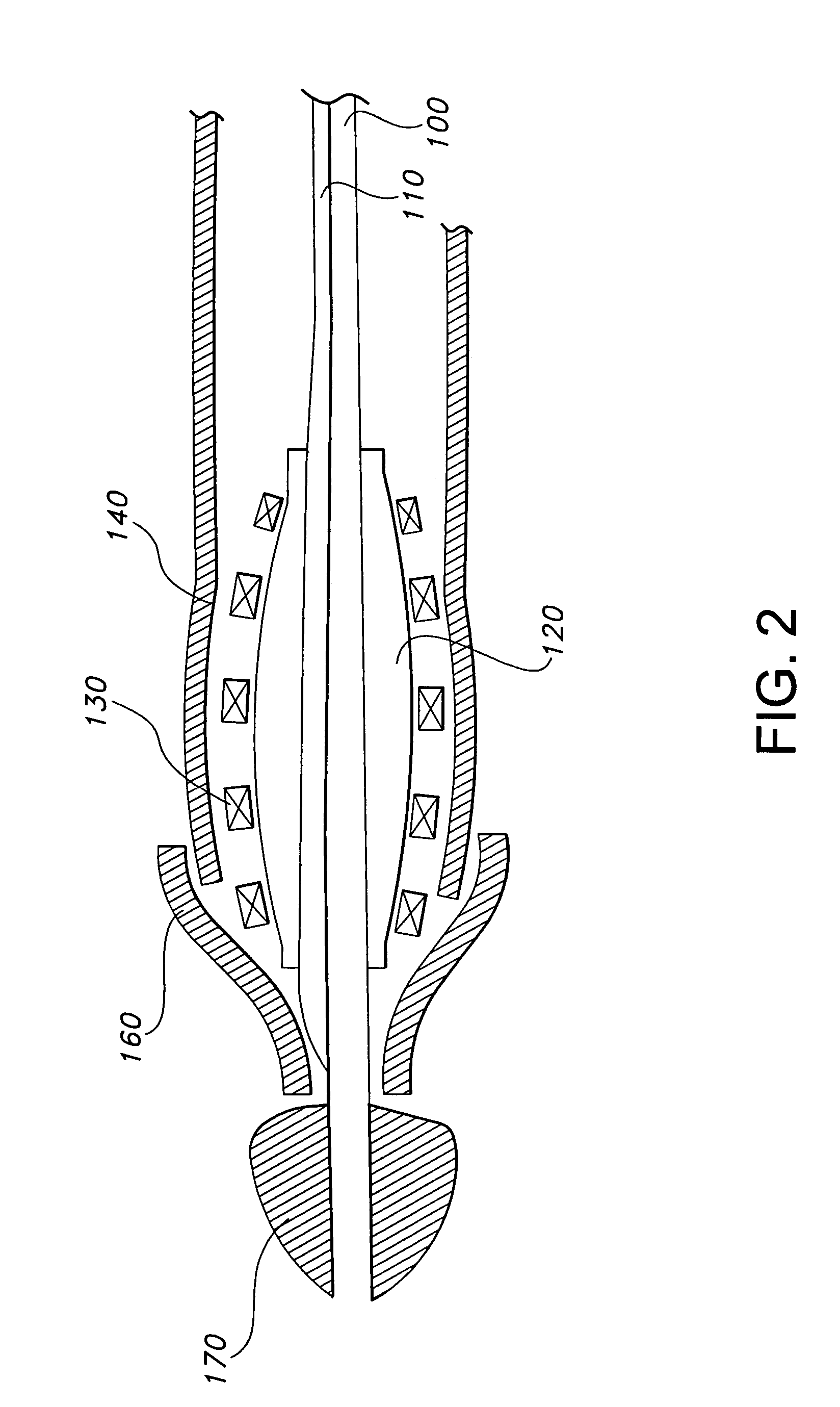
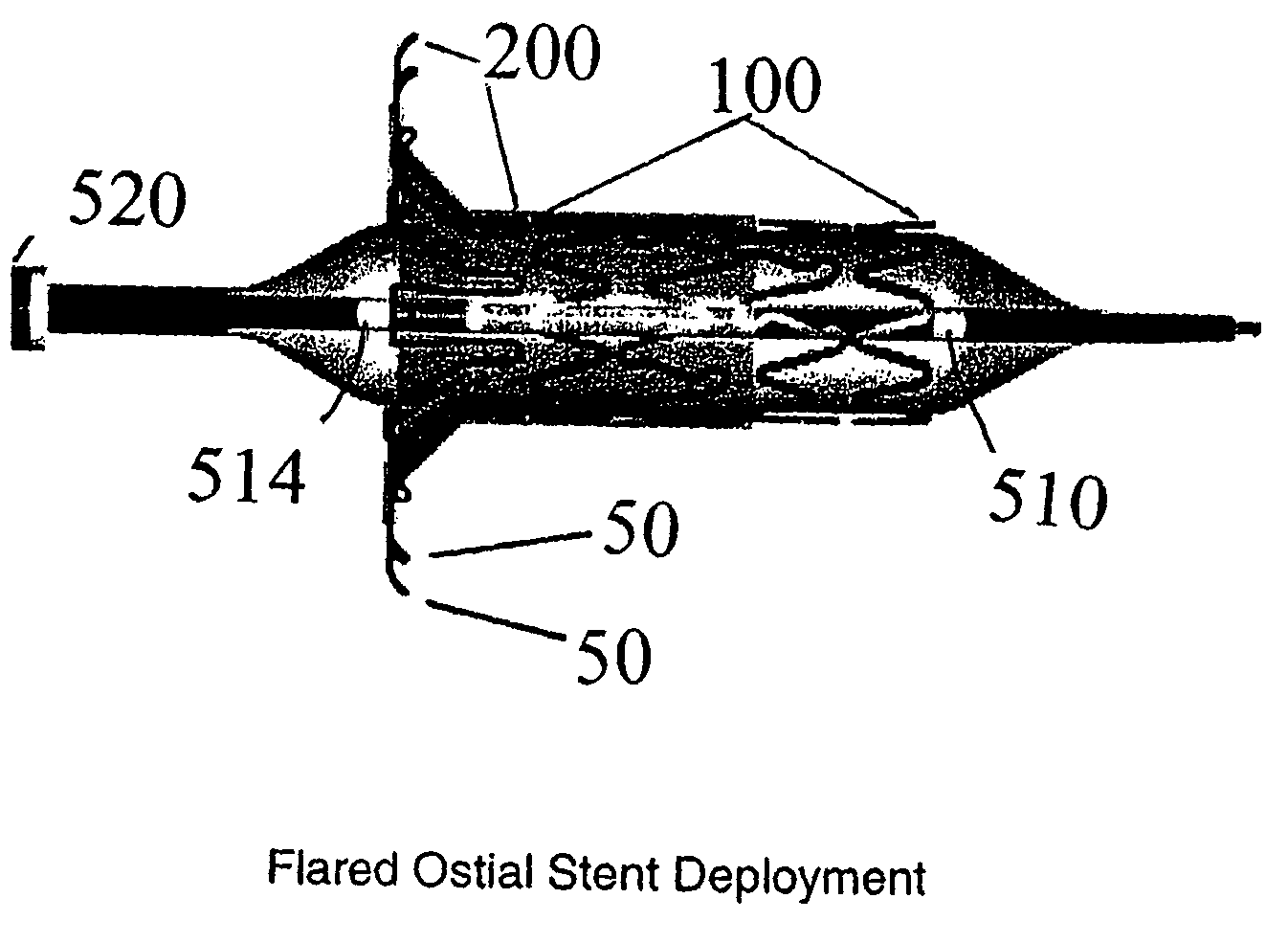
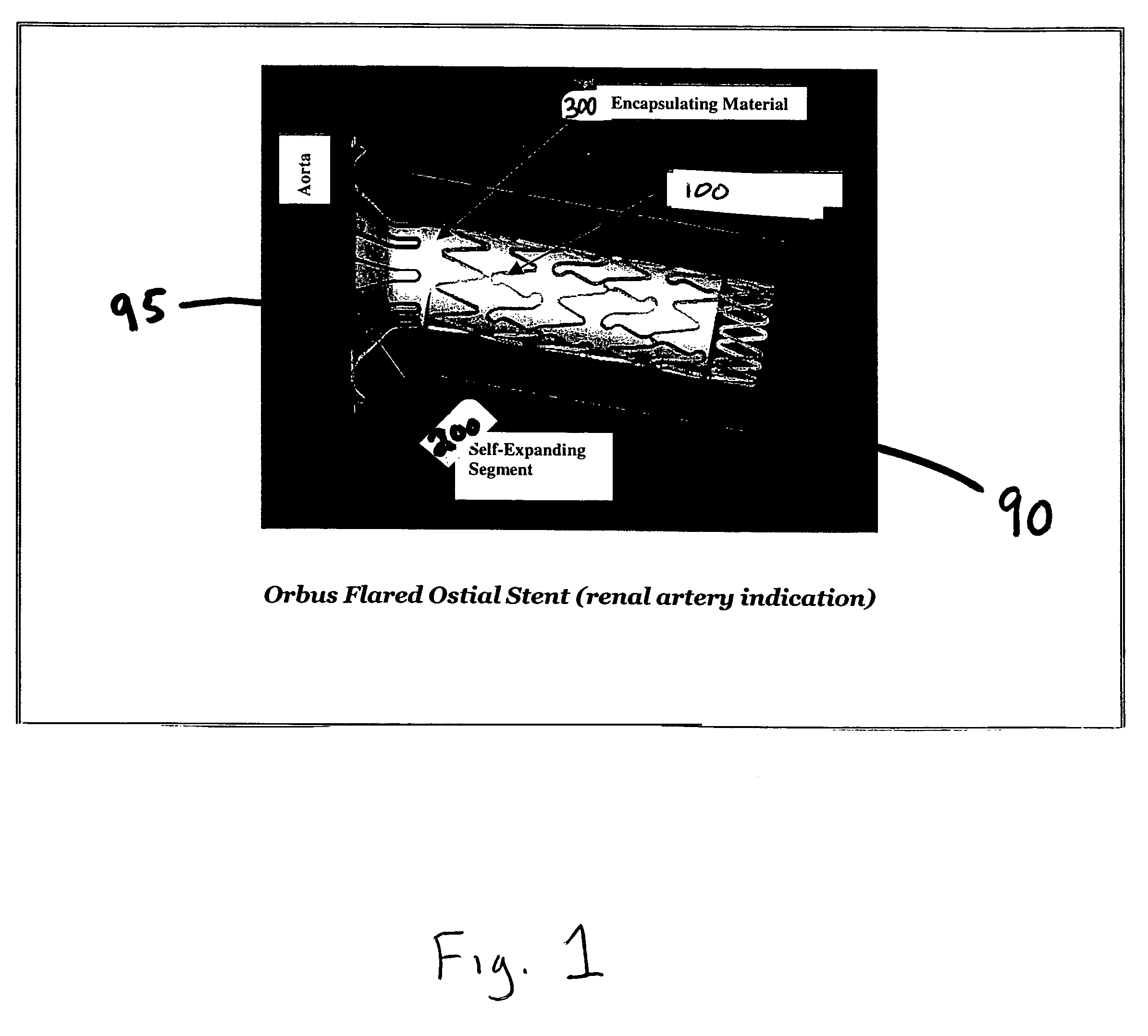
Flared ostial endoprosthesis and delivery system
An intraluminal endoprosthesis having a conically shaped first end and a tubular shaped balloon-expandable stent for a main body is disclosed. The conically shaped first end may form a flare to the main body and is particularly well suited for in ostium use. The first end is preferably self-expanding and the main body is preferably balloon-expandable. Also disclosed is a delivery device for delivering intraluminal ostial endoprosthetic devices, especially those disclosed herein, to a site for deployment. The delivery device may comprise an over-the-wire system or may comprise a rapid-exchange shuttle system. The self-expanding portion of the endoprosthesis is encapsulated in a sheath or other restraining apparatus on the delivery device. The balloon-expandable stent portion of the endoprosthesis is crimped onto a balloon delivery device. The delivery system and endoprosthesis of the present invention allow the endoprosthesis to be partially expanded and relocated if it is determined that it is not located in the proper location. To aid in positioning, the delivery device may comprise marker bands.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Delivery catheter having active engagement mechanism for prosthesis
Delivery catheters and systems are adapted for delivering multiple discreet prostheses in body lumens. An exemplary delivery catheter comprises a sheath, a pusher for moving the prostheses relative to the sheath, and a valve member for selectively retaining the prostheses in the sheath. For balloon expandable stents, an elongated shaft and an expandable member are slidably disposed in the sheath, and the prostheses are positionable on the expandable member for deployment in the body lumen. The valve member allows a selected number of prostheses to be deployed from the sheath while retaining other prostheses within the sheath.
Owner:JW MEDICAL SYSTEMS LTD
Prosthetic valve delivery system
A prosthetic valve delivery system for percutaneously delivering and deploying a prosthetic valve within an existing valve is disclosed. The delivery system includes a stented prosthetic valve having a balloon-expandable stent portion with a prosthetic valve disposed therein and at least one self-expanding stent portion. The delivery system further includes a dual balloon catheter having a first balloon on which the stented prosthetic valve is disposed during delivery and a second balloon. Upon delivery within the existing valve, the self-expanding stent portion contacts the existing valve and the first balloon expands the balloon-expandable stent portion to a first diameter such that the stented prosthetic valve is in a first stage deployment configuration. The second balloon then expands the balloon-expandable stent portion to a second diameter, greater than the first diameter, such that the stented prosthetic valve is in a second stage deployment configuration being fully deployed within the existing valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Balloon expandable crush-recoverable stent device
InactiveUS20060020324A1Improve radial strengthKeep openStentsBlood vesselsLocking mechanismInsertion stent
An intraluminal, balloon expandable stent for implantation in a body lumen is disclosed. The present invention provides a lumen support stent with an unobstructed through-lumen for use in a blood vessel. A constraining mechanism is provided for securely maintaining the stent in the collapsed condition during delivery. The stent is preferably formed with a series of interconnected slide and lock mechanisms for permitting movement from a collapsed condition to an expanded condition and inhibiting radial recoil from the expanded condition. The stent may be formed from a shape memory alloy for providing crush-recovery after deployment.
Owner:REVA MEDICAL
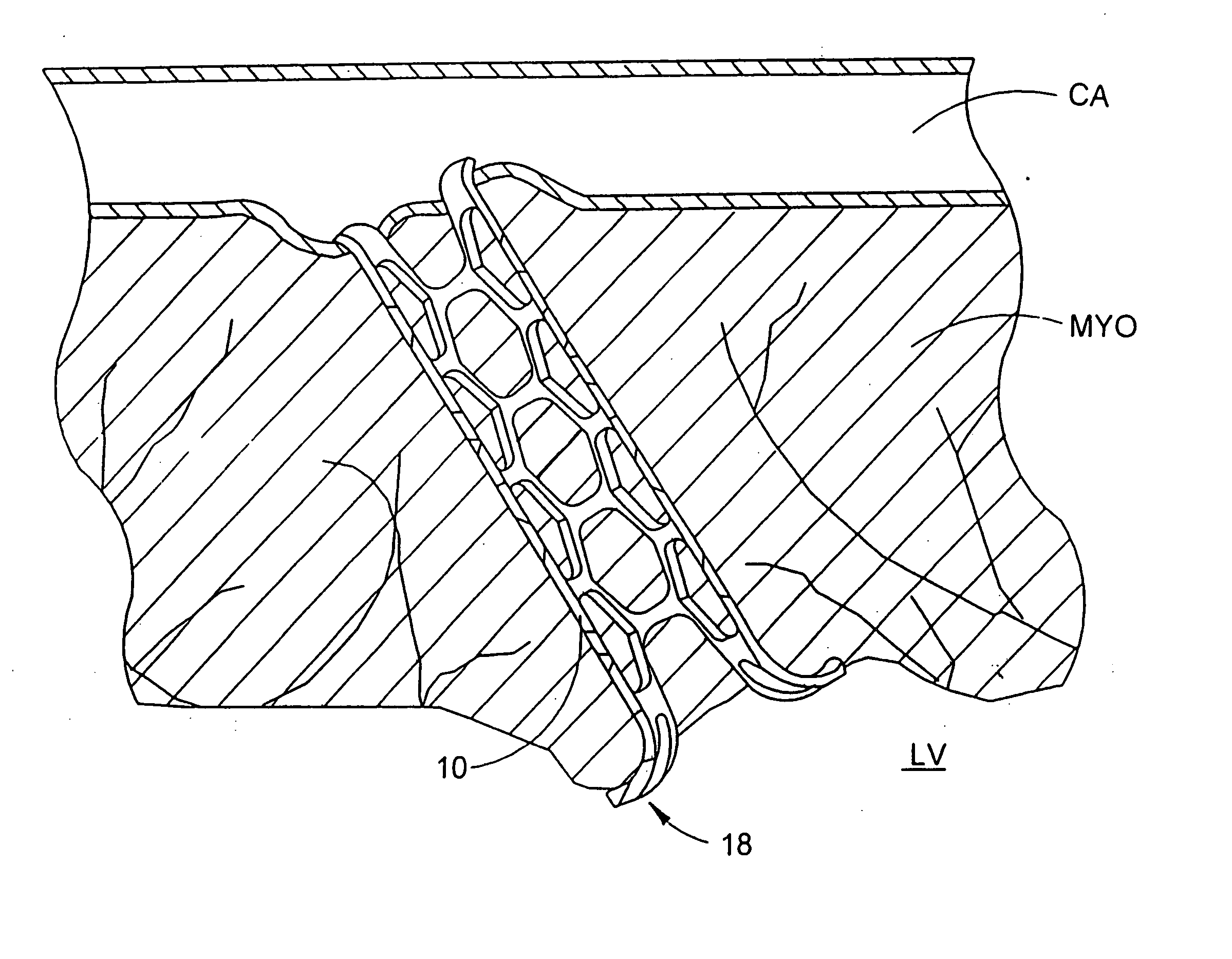
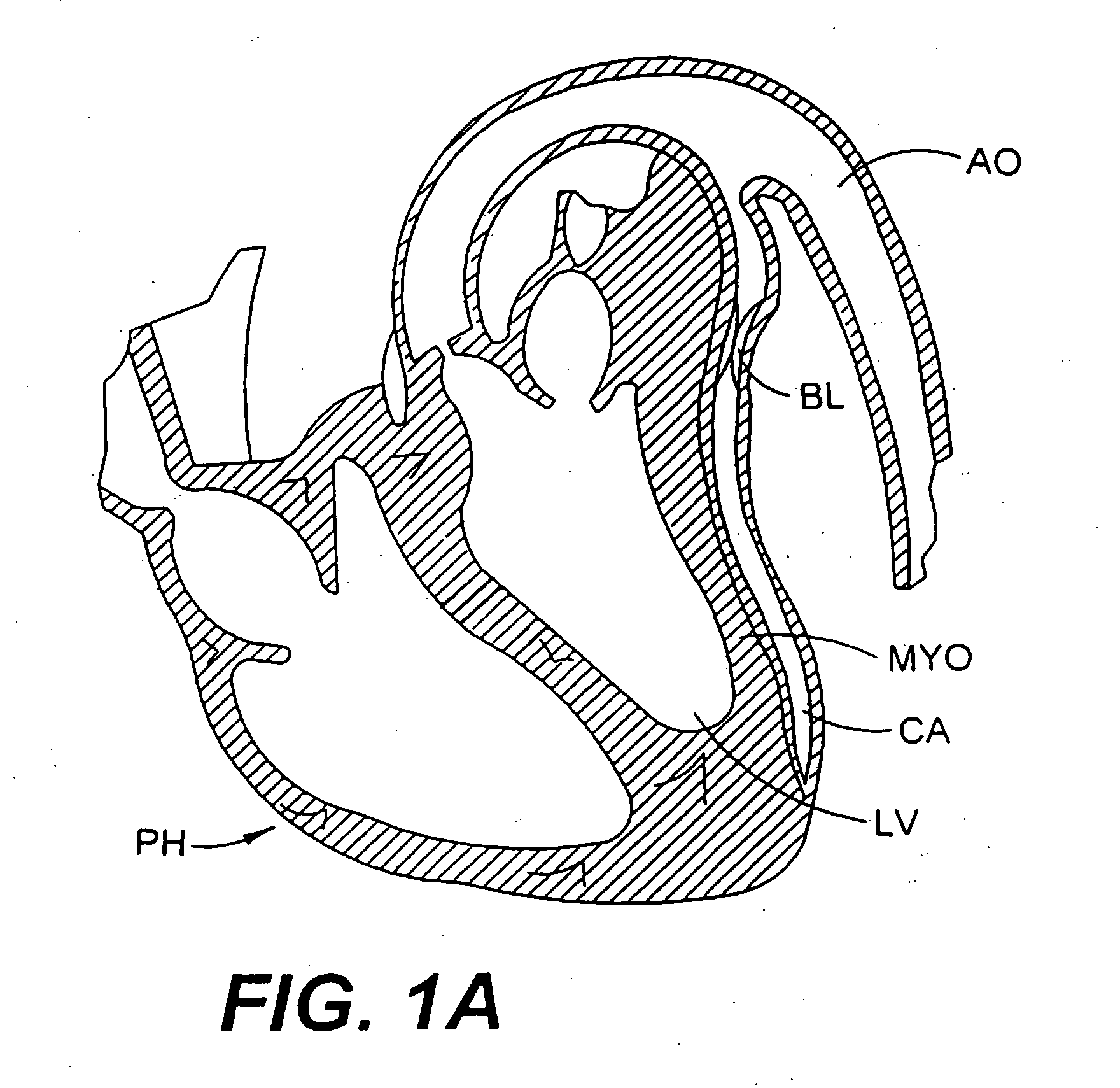
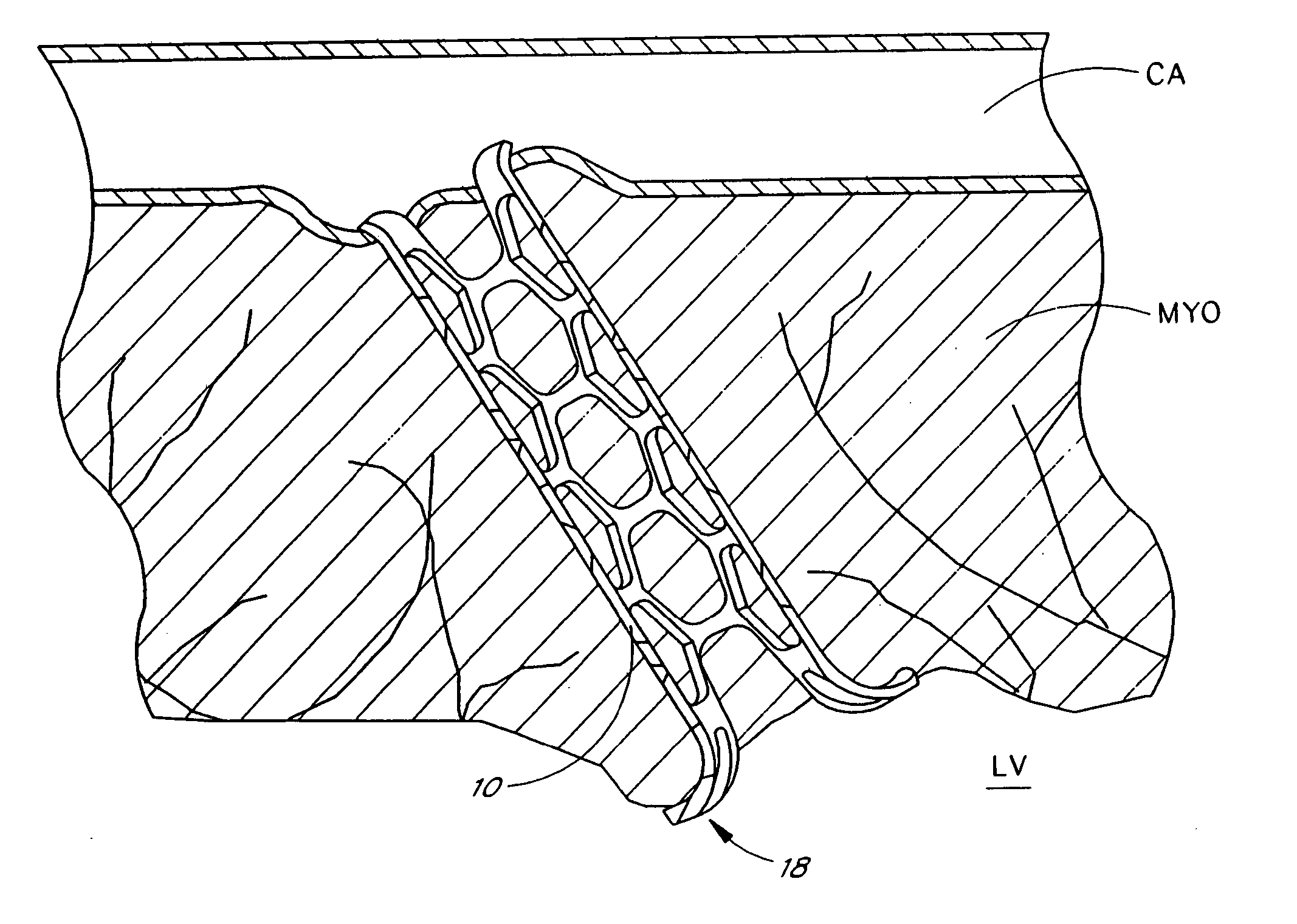
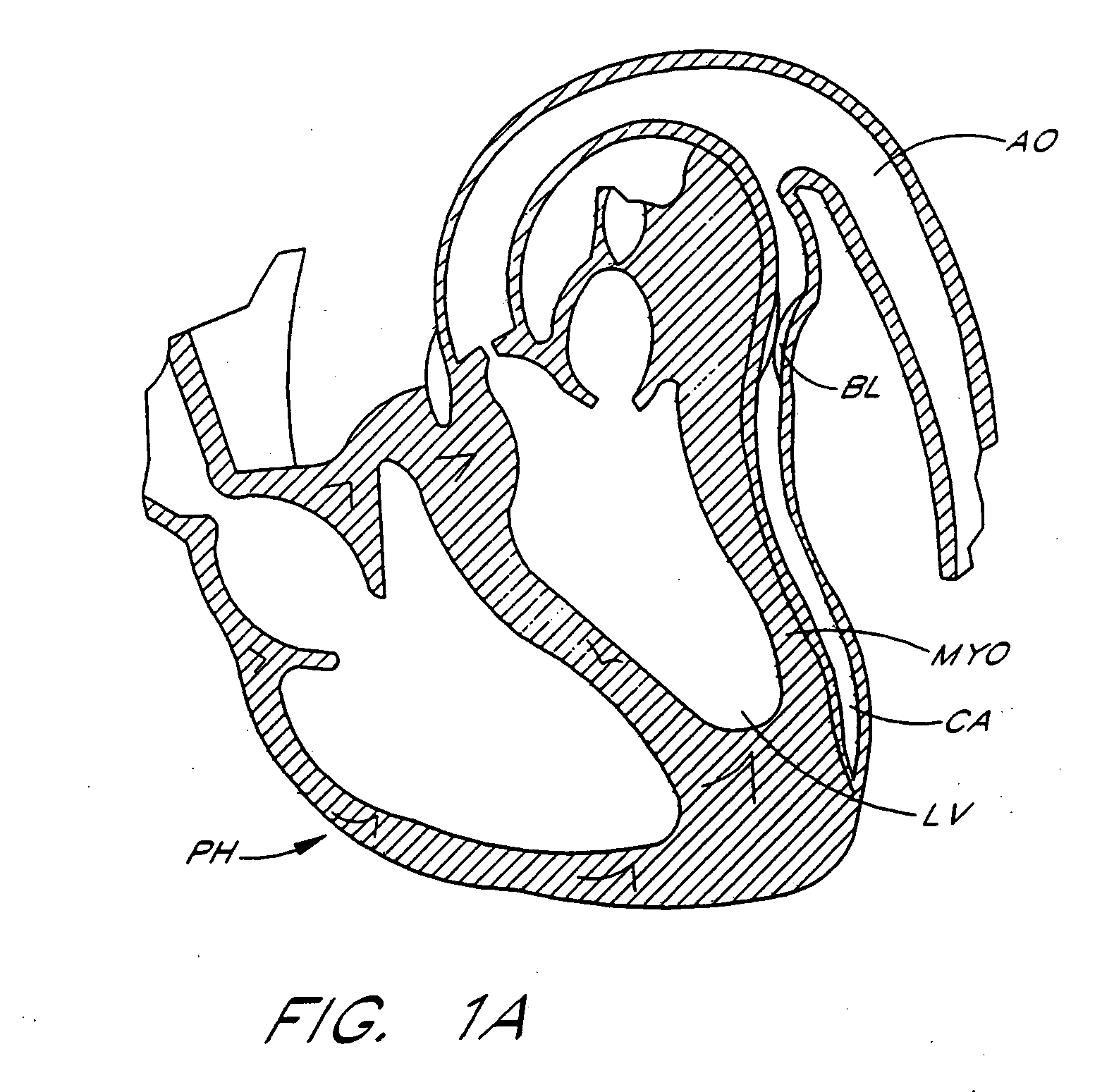
TMR shunt
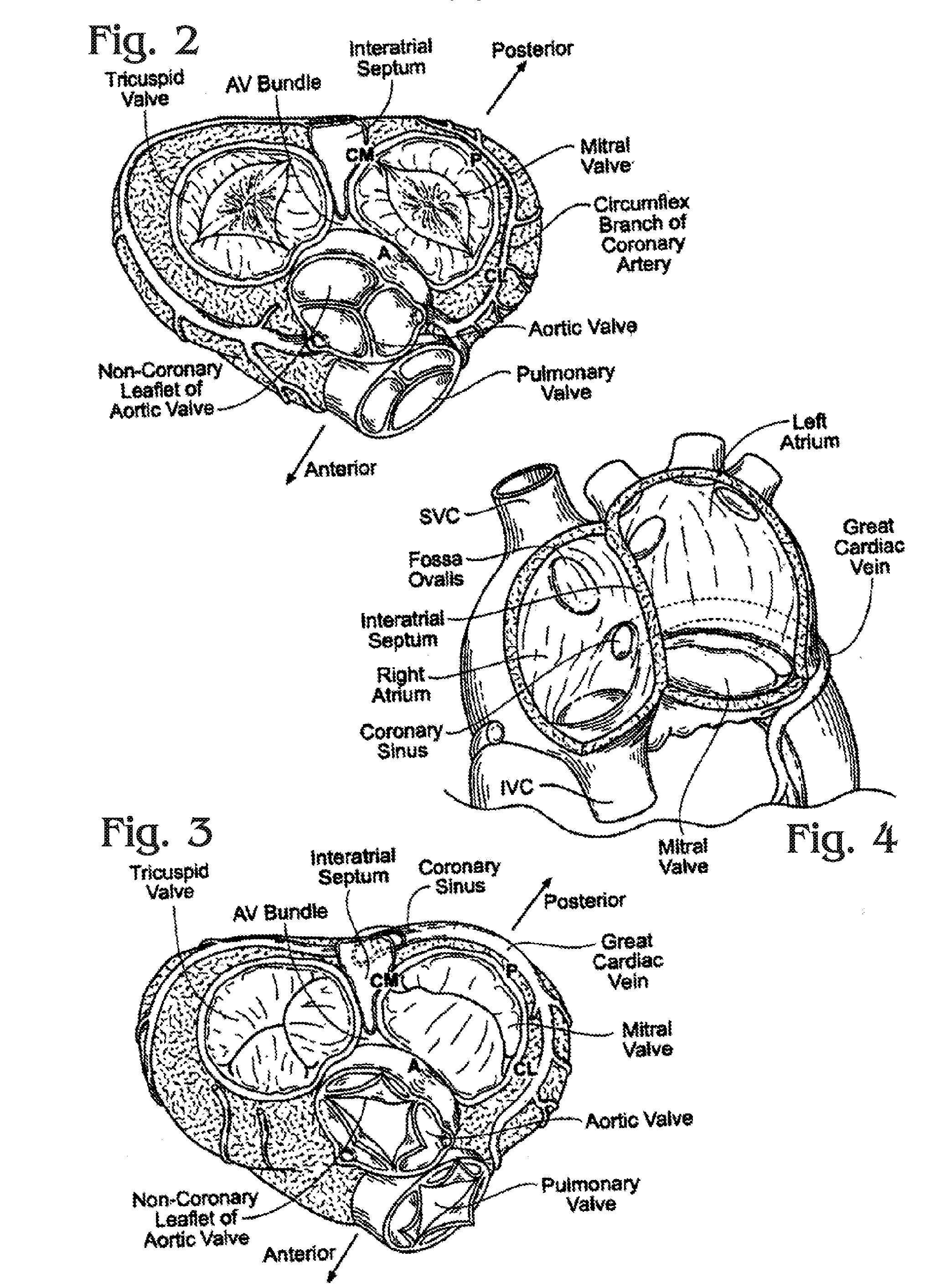
A conduit is provided to provide a bypass around a blockage in the coronary artery. The conduit is adapted to be positioned in the myocardium or heart wall to provide a passage for blood to flow between a chamber of the heart such as the left ventricle and the coronary artery, distal to the blockage. The stent is self-expanding or uses a balloon to expand the stent in the heart wall. Various attachment means are provided to anchor the stent and prevent its migration. In one embodiment, a conduit is provided having a distal top which is more preferably a ball top, wire top, flare top or flip-down top. These top configurations anchor the shunt at one end in the coronary artery.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC +1
Delivery catheter having active engagement mechanism for prosthesis
Delivery catheters and systems are adapted for delivering multiple discreet prostheses in body lumens. An exemplary delivery catheter comprises a sheath, a pusher for moving the prostheses relative to the sheath, and a valve member for selectively retaining the prostheses in the sheath. For balloon expandable stents, an elongated shaft and an expandable member are slidably disposed in the sheath, and the prostheses are positionable on the expandable member for deployment in the body lumen. The valve member allows a selected number of prostheses to be deployed from the sheath while retaining other prostheses within the sheath.
Owner:JW MEDICAL SYSTEMS LTD
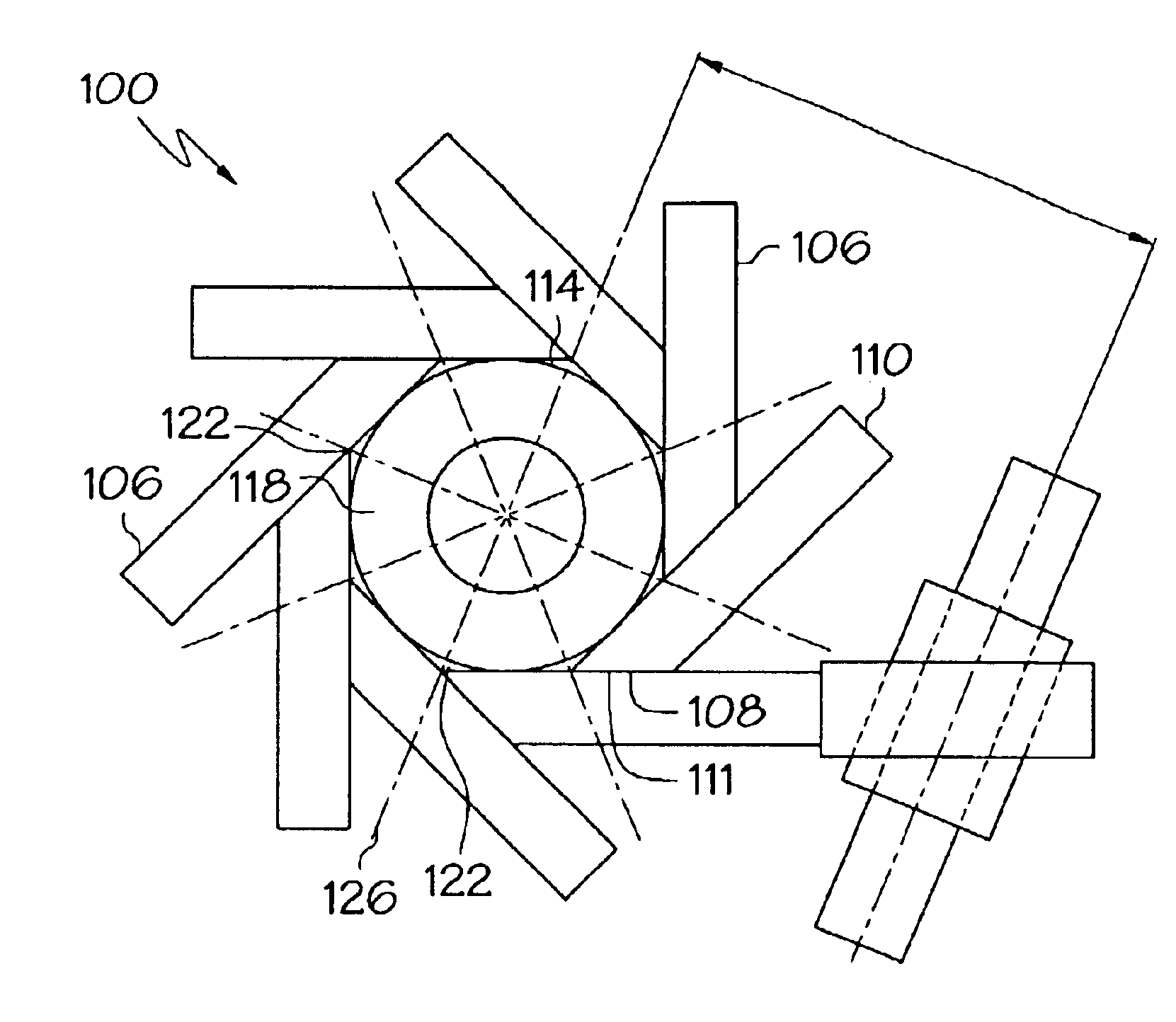
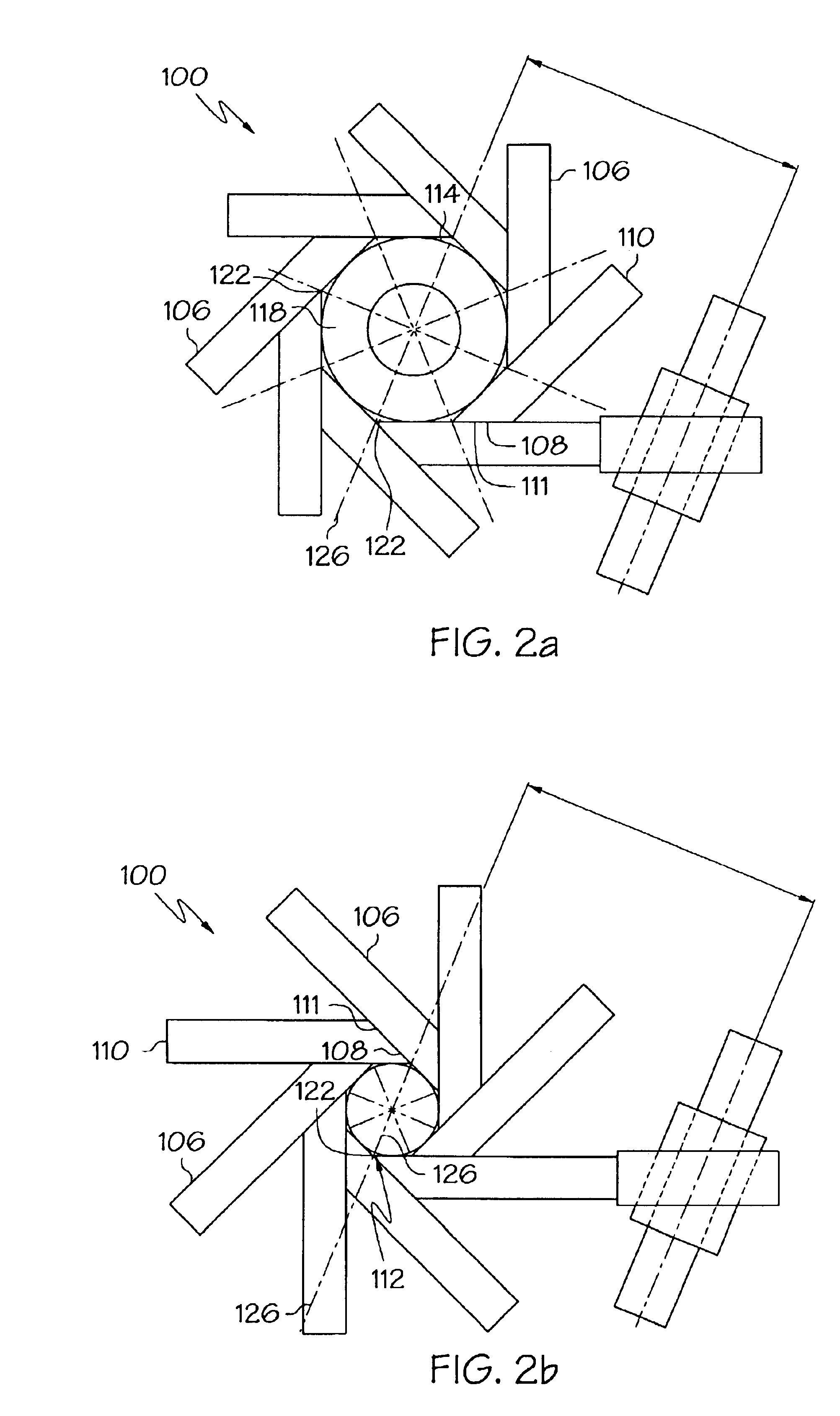
Apparatus for contracting, loading or crimping self-expanding and balloon expandable stent devices
InactiveUS6915560B2Minimizing distortion of and scoringReduce the overall diameterStentsAutomatic control devicesEngineeringKnife blades
An apparatus for manipulating a medical device is formed of at least three coupled movable blades which are disposed about a reference circle to form an aperture whose size may be varied. The aperture capable of being sized to contain a medical device. Each blade is in communication with an actuation device which is capable of moving the blade to alter the size of the aperture. Each blade includes a single radial point which a) lies on the circumference of the reference circle prior to movement of the blade, and b) may be moved only along a radius of the reference circle on movement of the blade.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC +2
Balloon expandable crush-recoverable stent device
InactiveUS7763065B2Improve radial strengthKeep openStentsBlood vesselsLocking mechanismShape-memory alloy
Owner:REVA MEDICAL
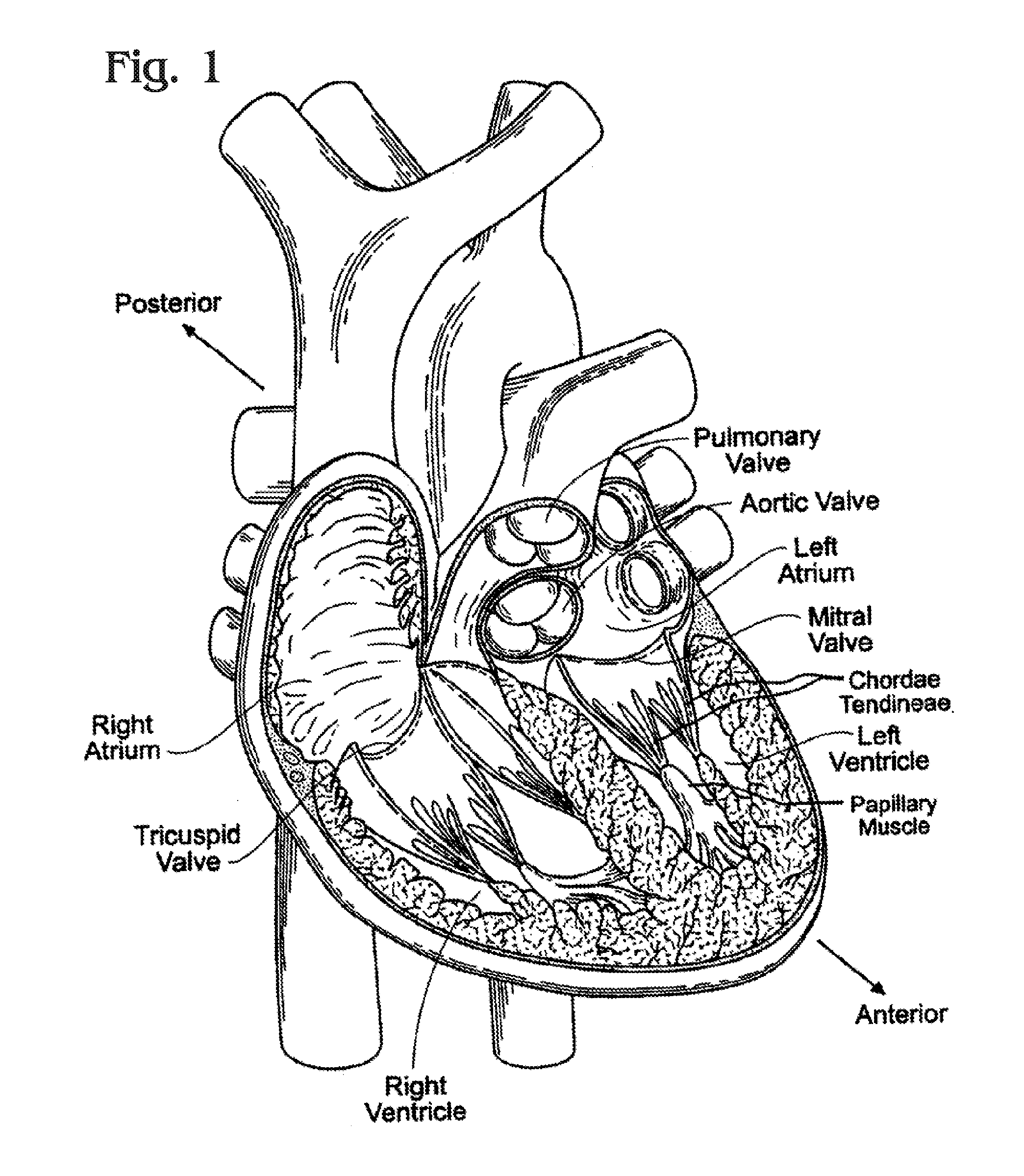
Methods of delivery of flexible heart valves
ActiveUS20140364943A1Fast implantIncreased durabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthesisProsthetic heart
A prosthetic heart valve can include a valve frame having a wireform portion and a stent portion. The wireform and stent portions can be undetachably coupled together via a plurality of upright struts so as to form a one-piece prosthetic heart valve frame. Alternatively, a self-expanding wireform portion and a balloon-expandable stent portion can be coupled together via one or more leaflets and a subassembly having a flexible leaflet support stent and a sealing ring. The wireform portion can include cusps and commissures configured to support a plurality of leaflets. The prosthetic valve can be radially collapsible for minimally invasive and / or transcatheter delivery techniques. Disclosed embodiments can also provide flexion of the wireform portion (e.g., of the commissures) in response to physiologic pulsatile loading when the valve is implanted in a patient's native valve annulus. Methods of making and using prosthetic heart valves are also disclosed.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
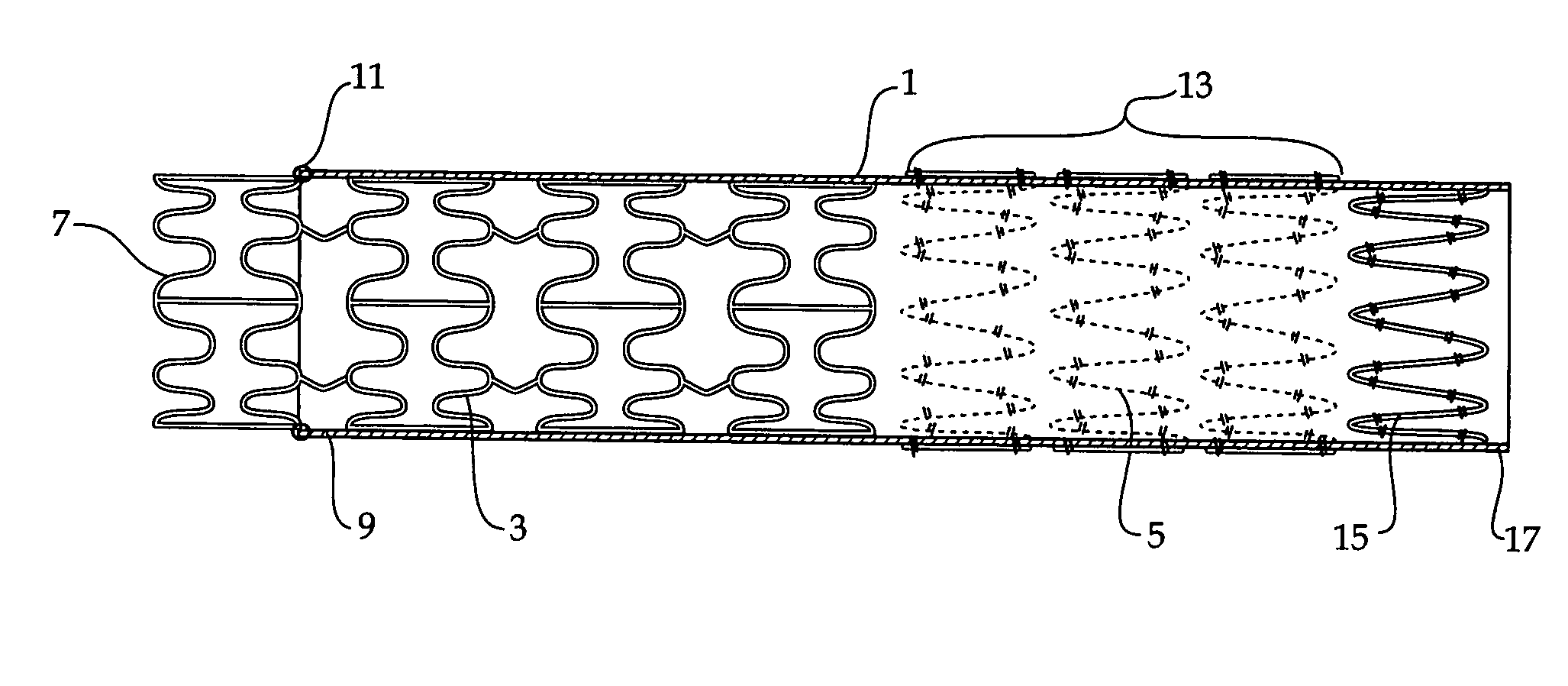
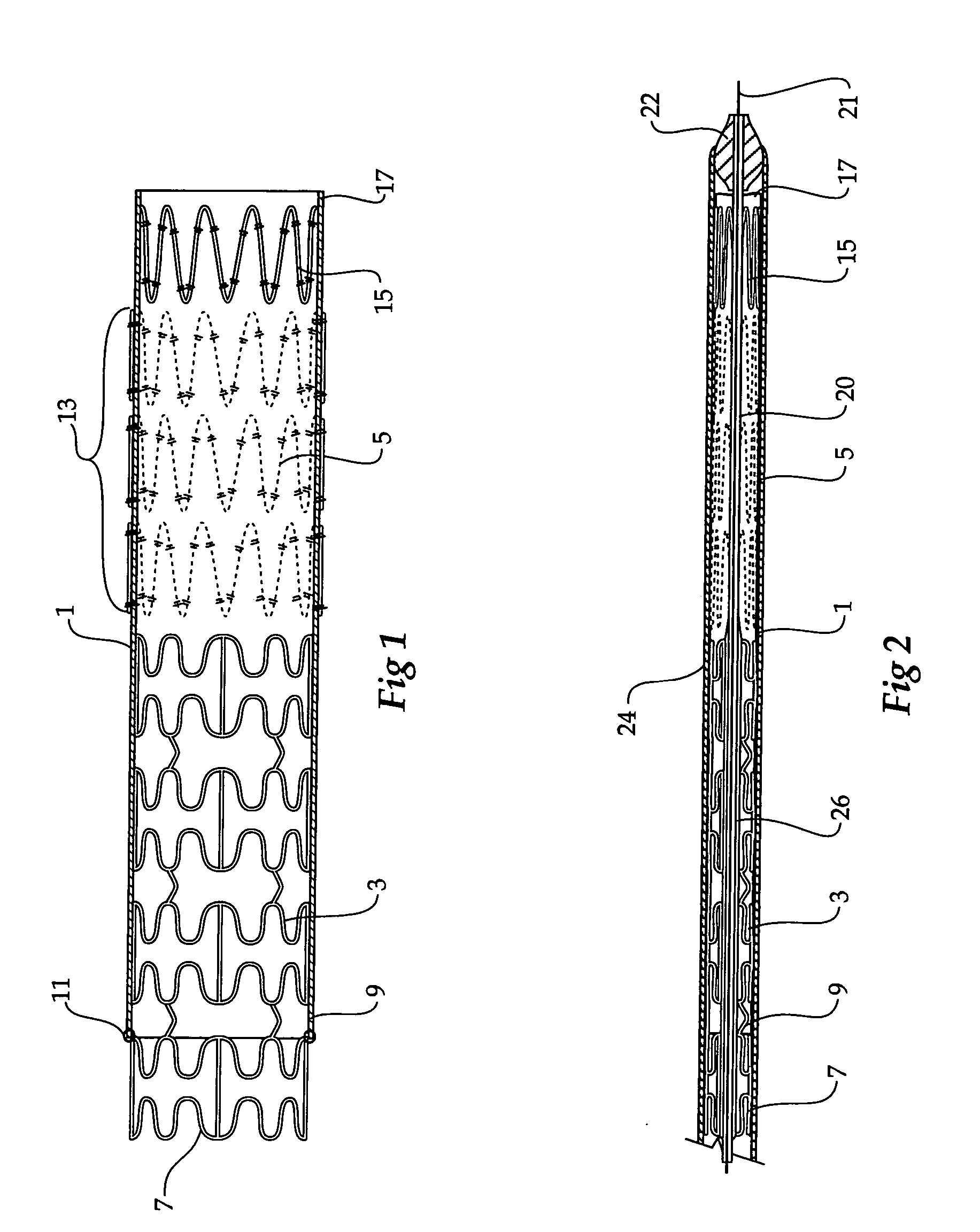
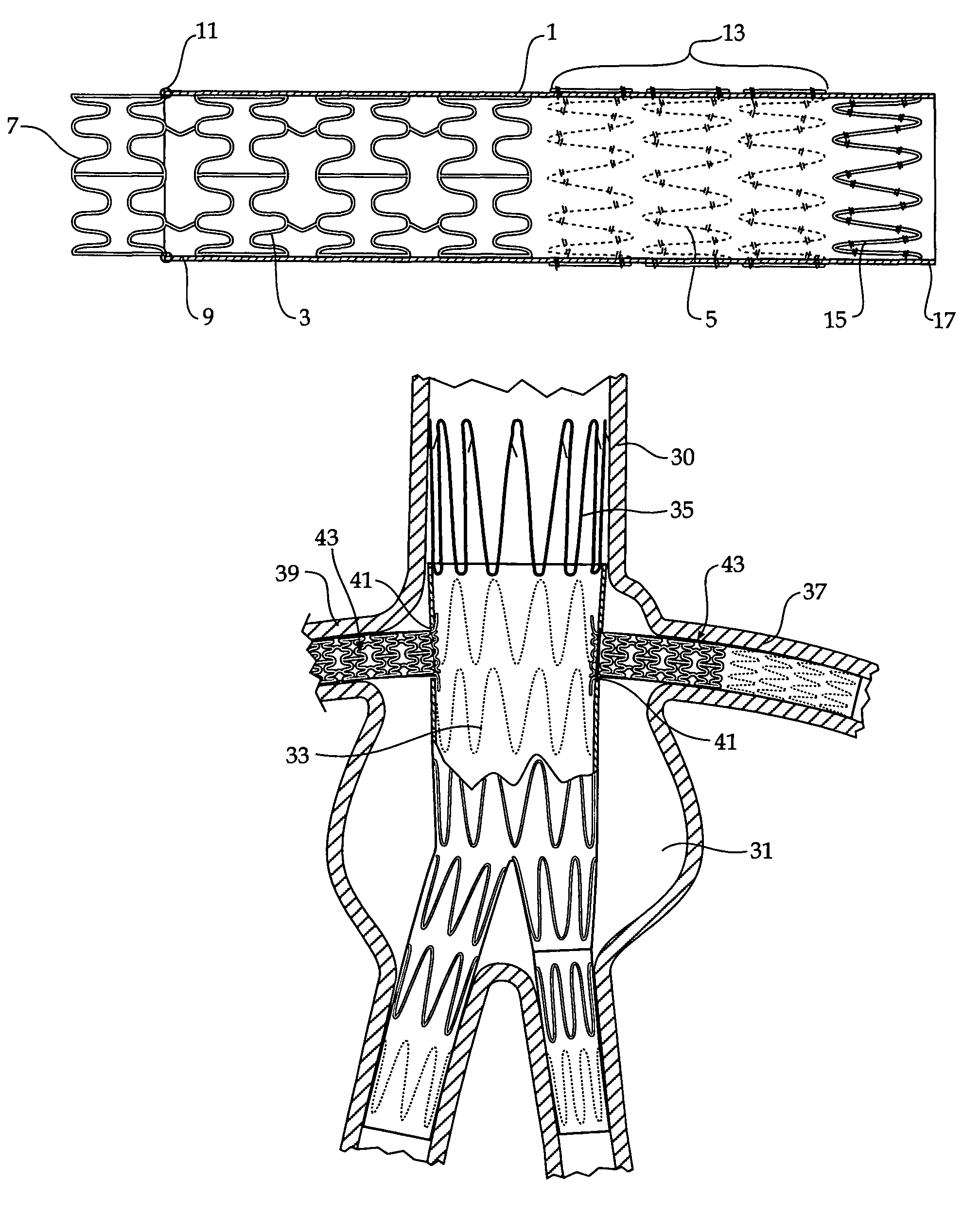
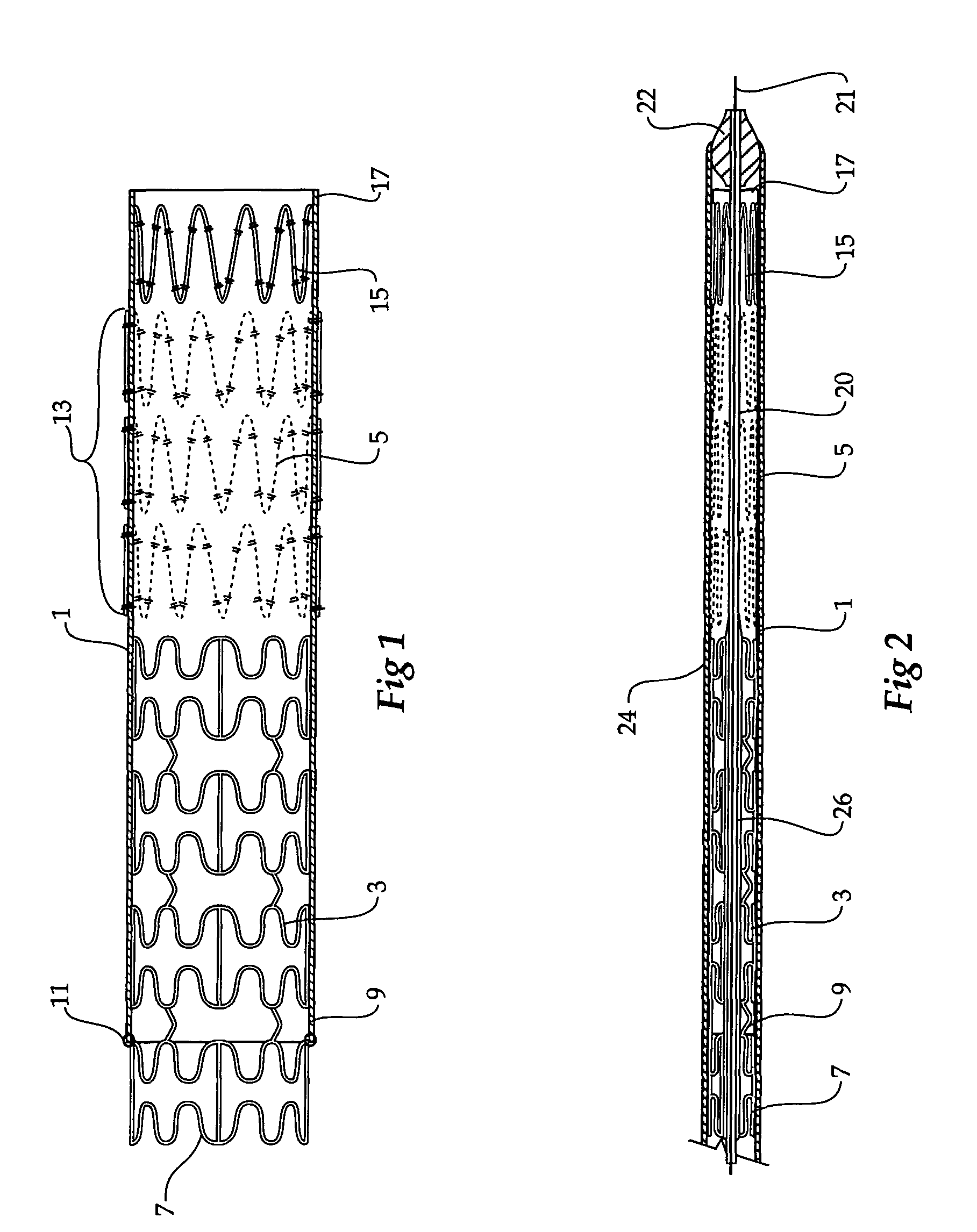
Composite stent graft
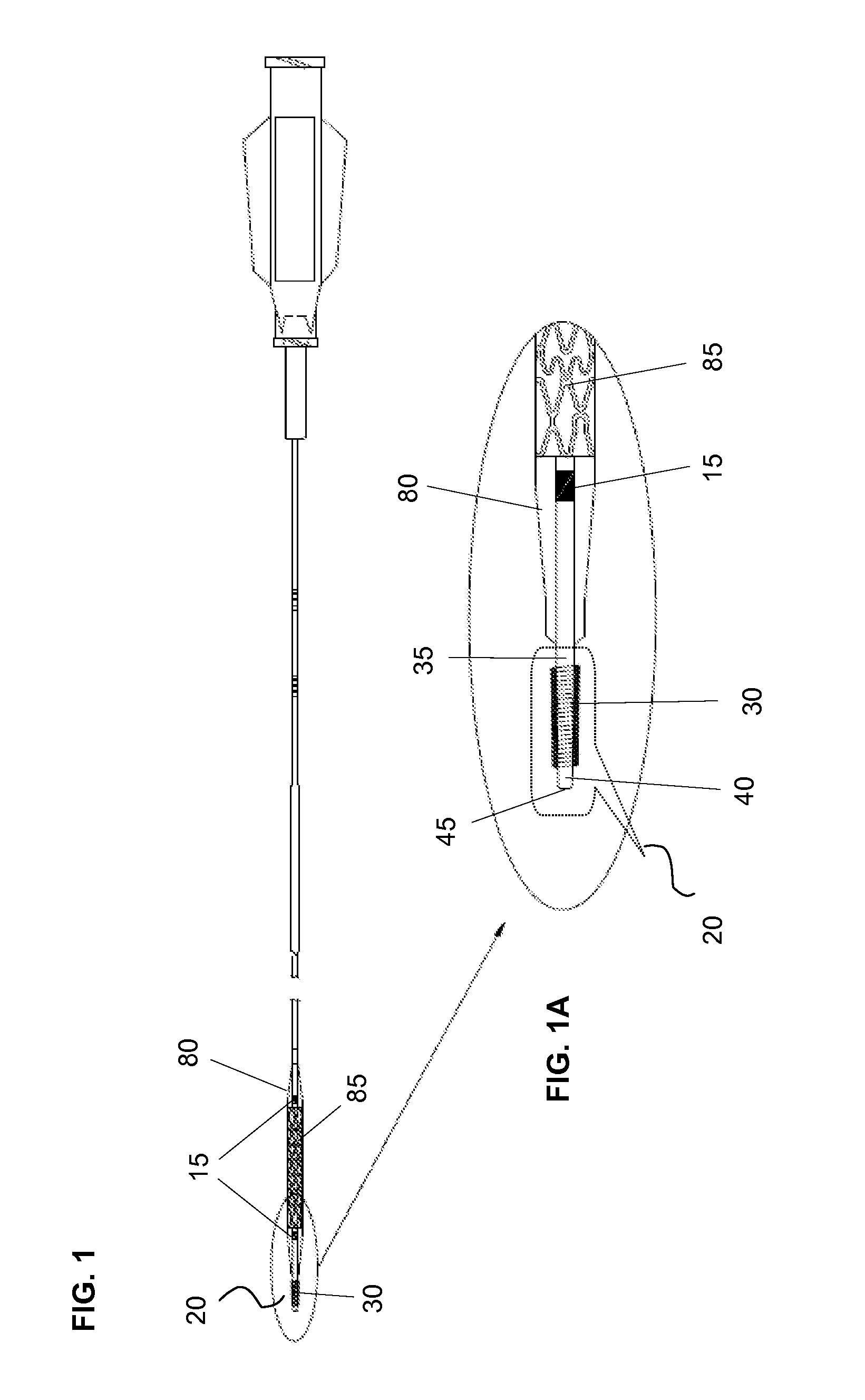
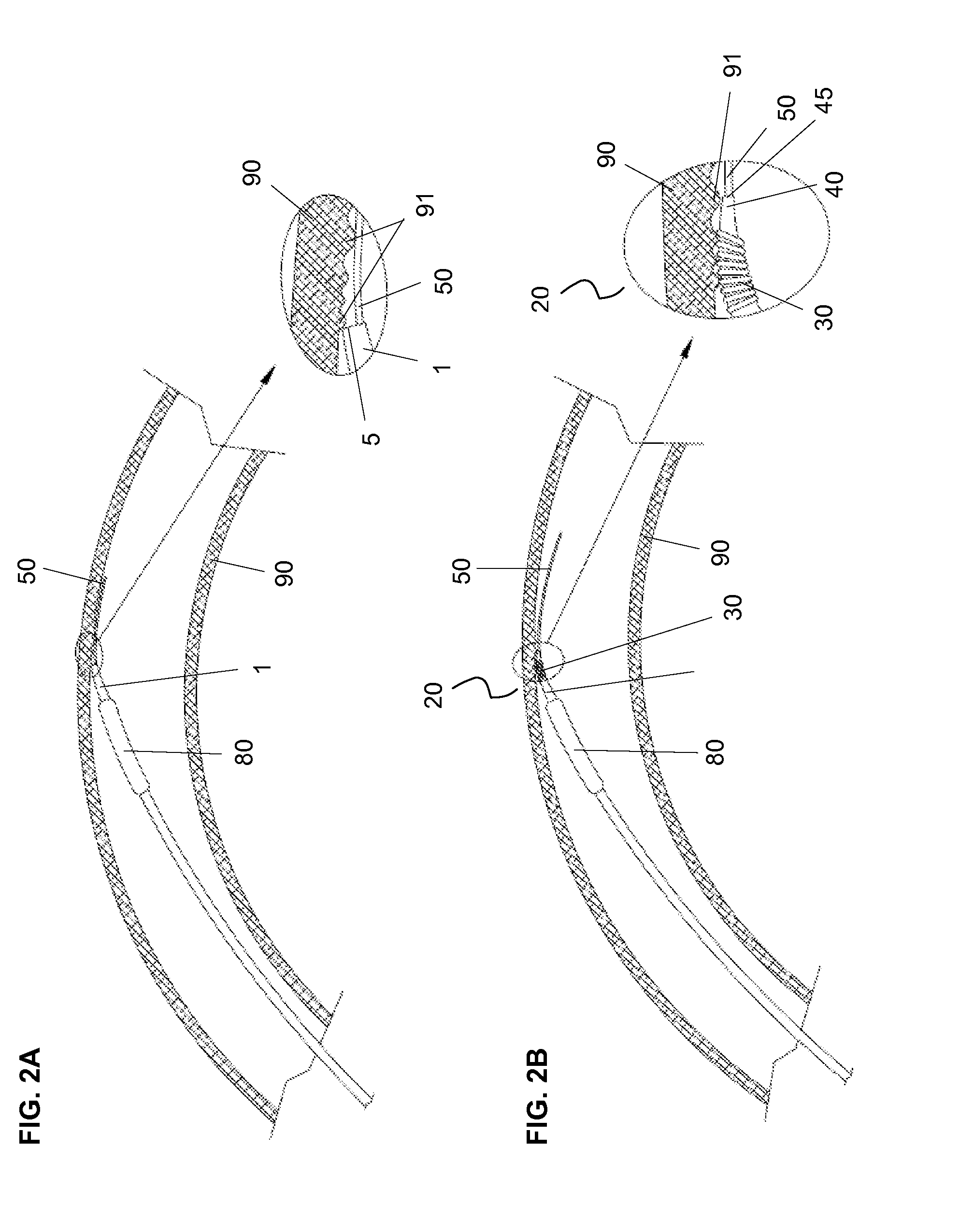
A composite stent graft has a balloon expandable stent portion ( 3 ), a tubular graft material portion ( 1 ) inside or outside of the balloon expandable stent portion and self expanding stents ( 5 ) associated with the tubular graft material portion. Part ( 7 ) of the balloon expandable stent portion can extend beyond the proximal end ( 9 ) of the tubular graft material portion. The tubular graft material can be polytetrafluoroethylene, Dacron, Thoralon(TM), polyamide, small intestine submucosa, collagenous extracellular matrix material, or any other suitable biocompatible material. A method of deploying which includes flaring a part ( 7 ) of the balloon expandable stent portion is also discussed.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
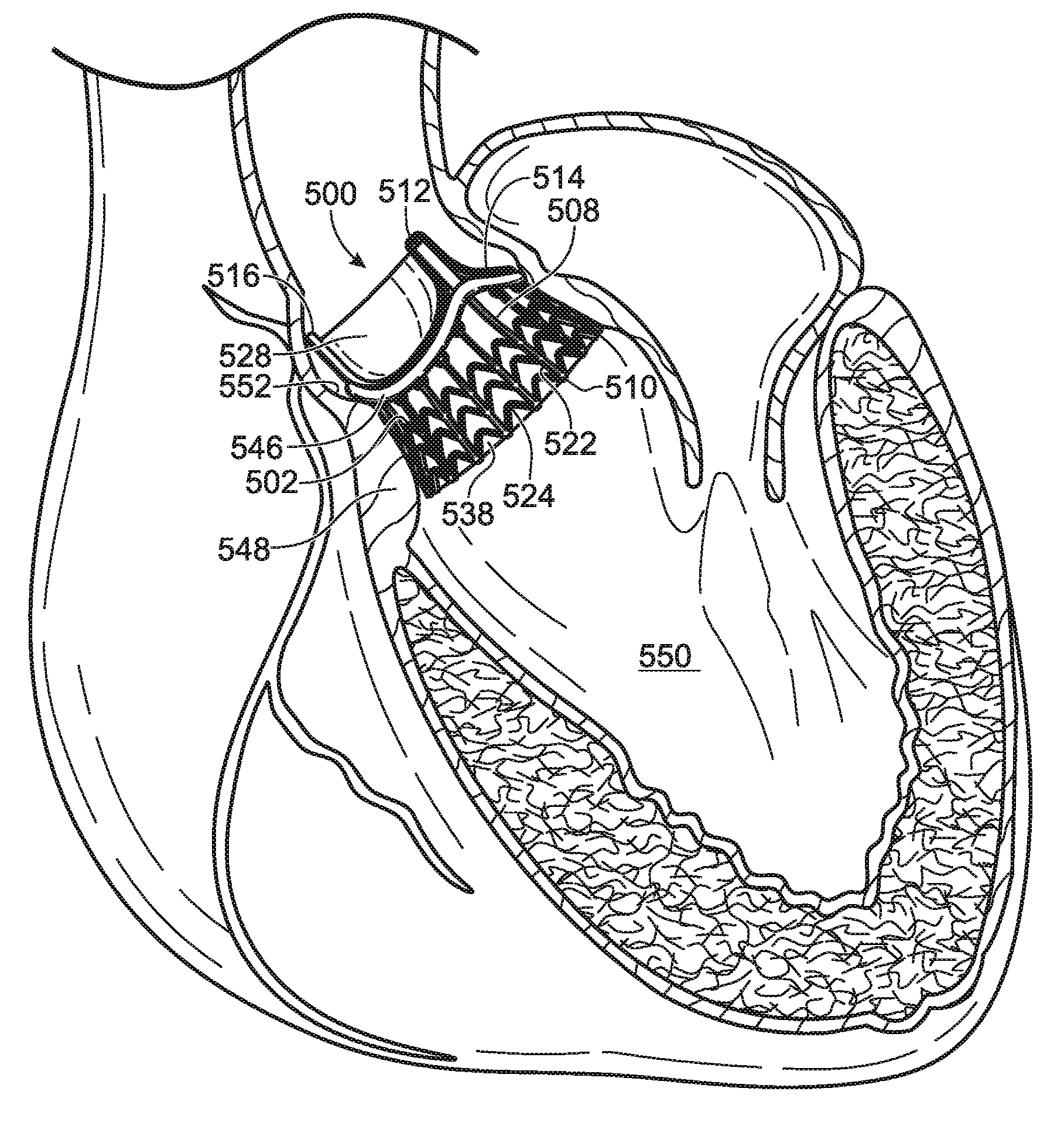
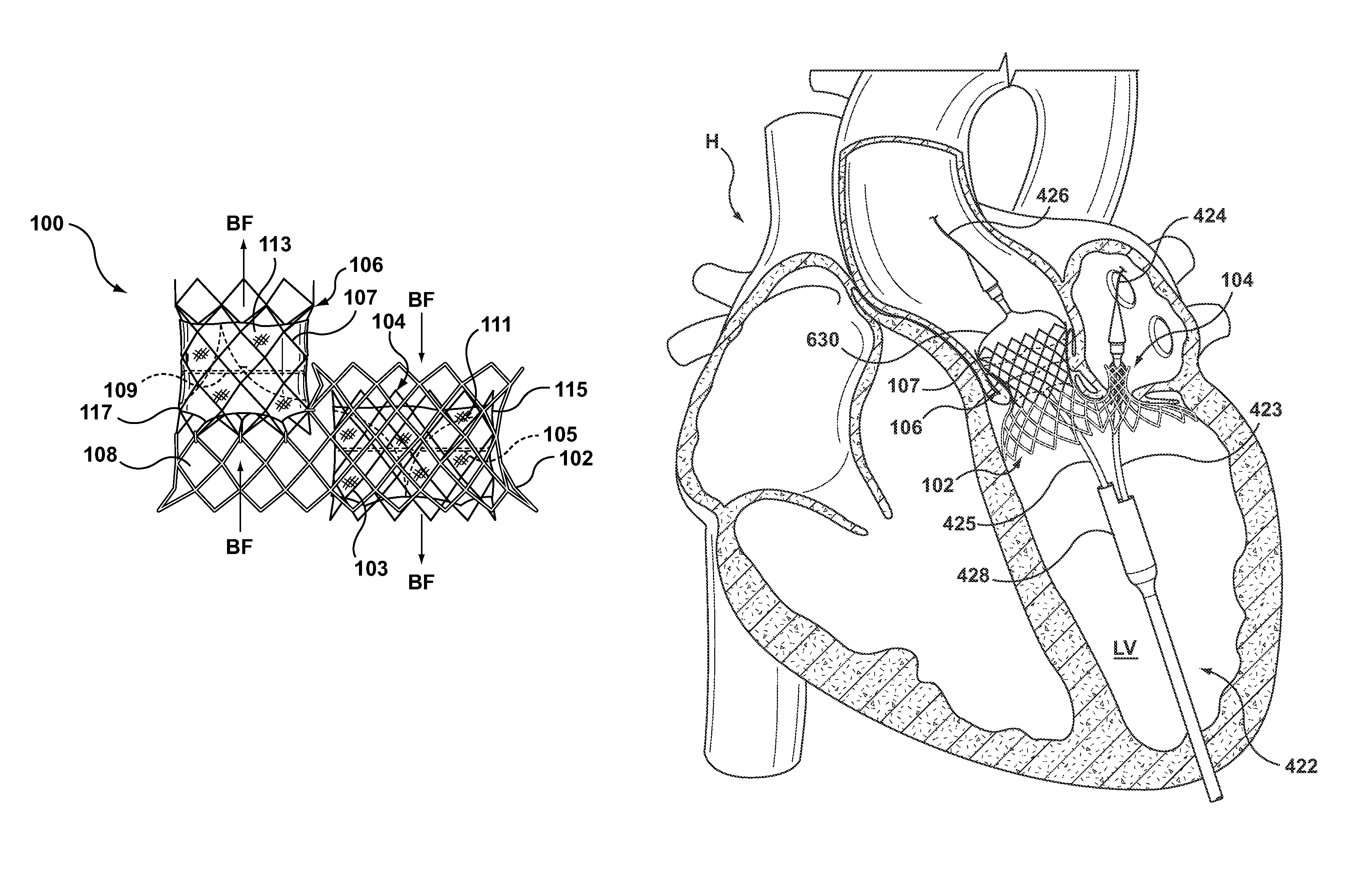
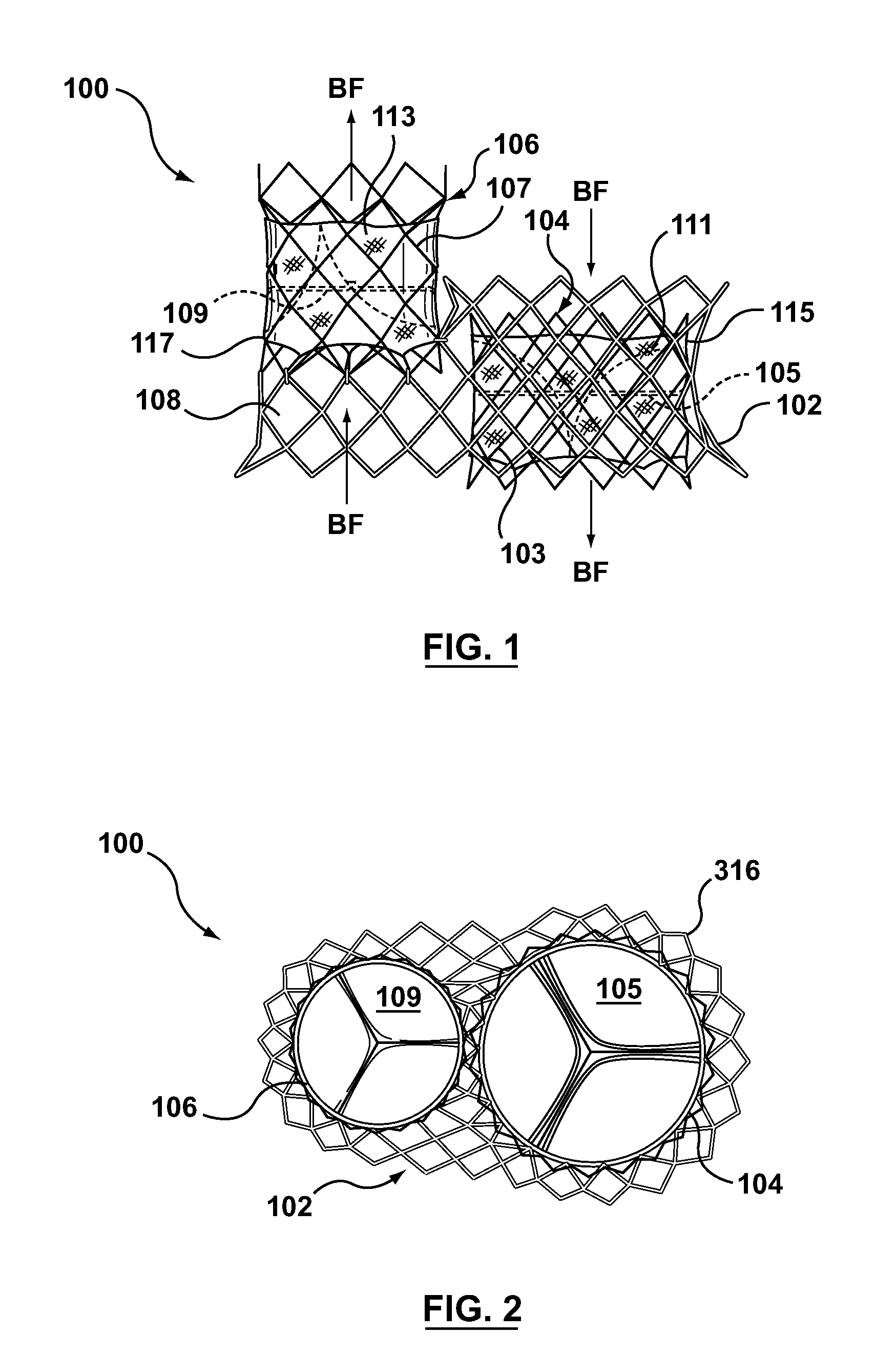
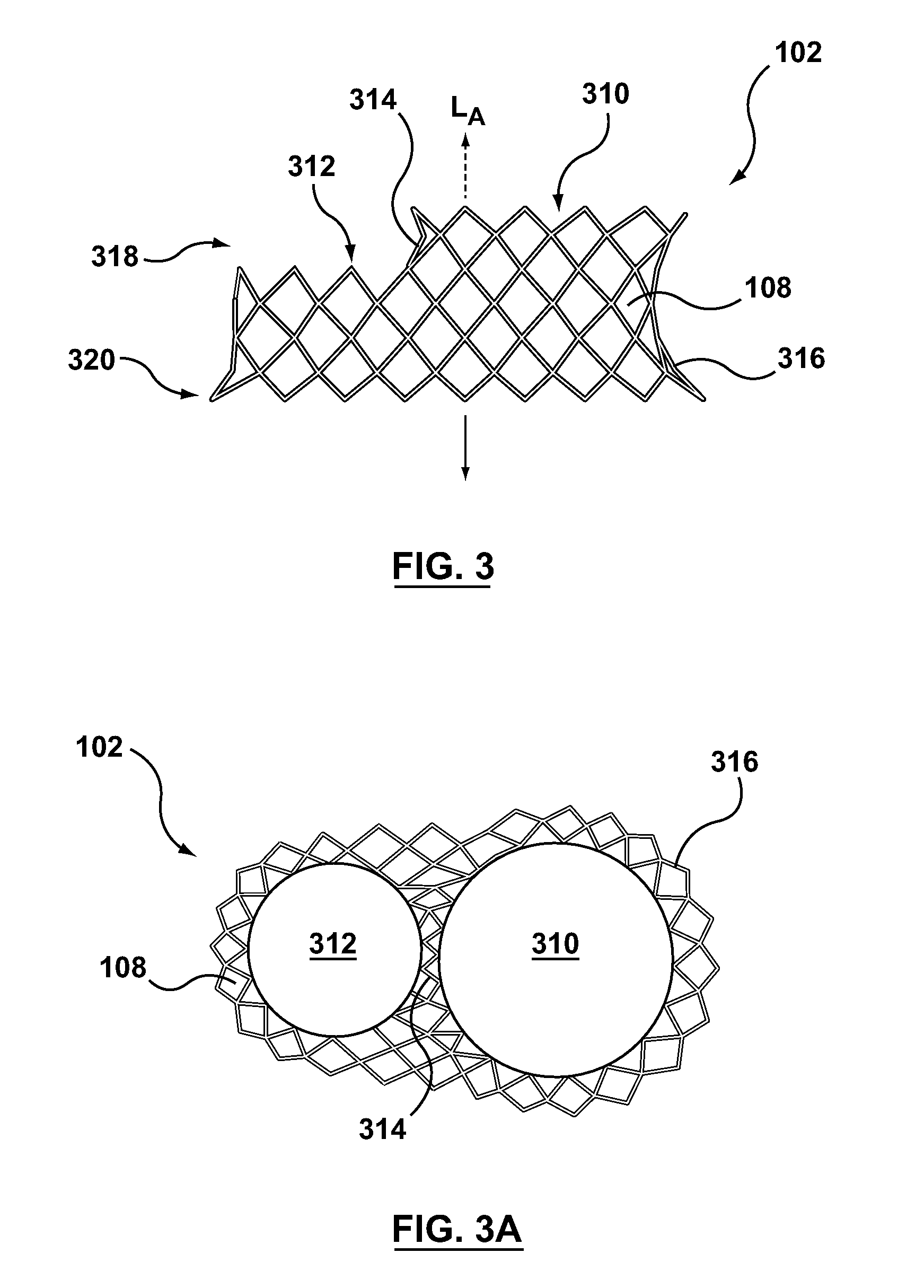
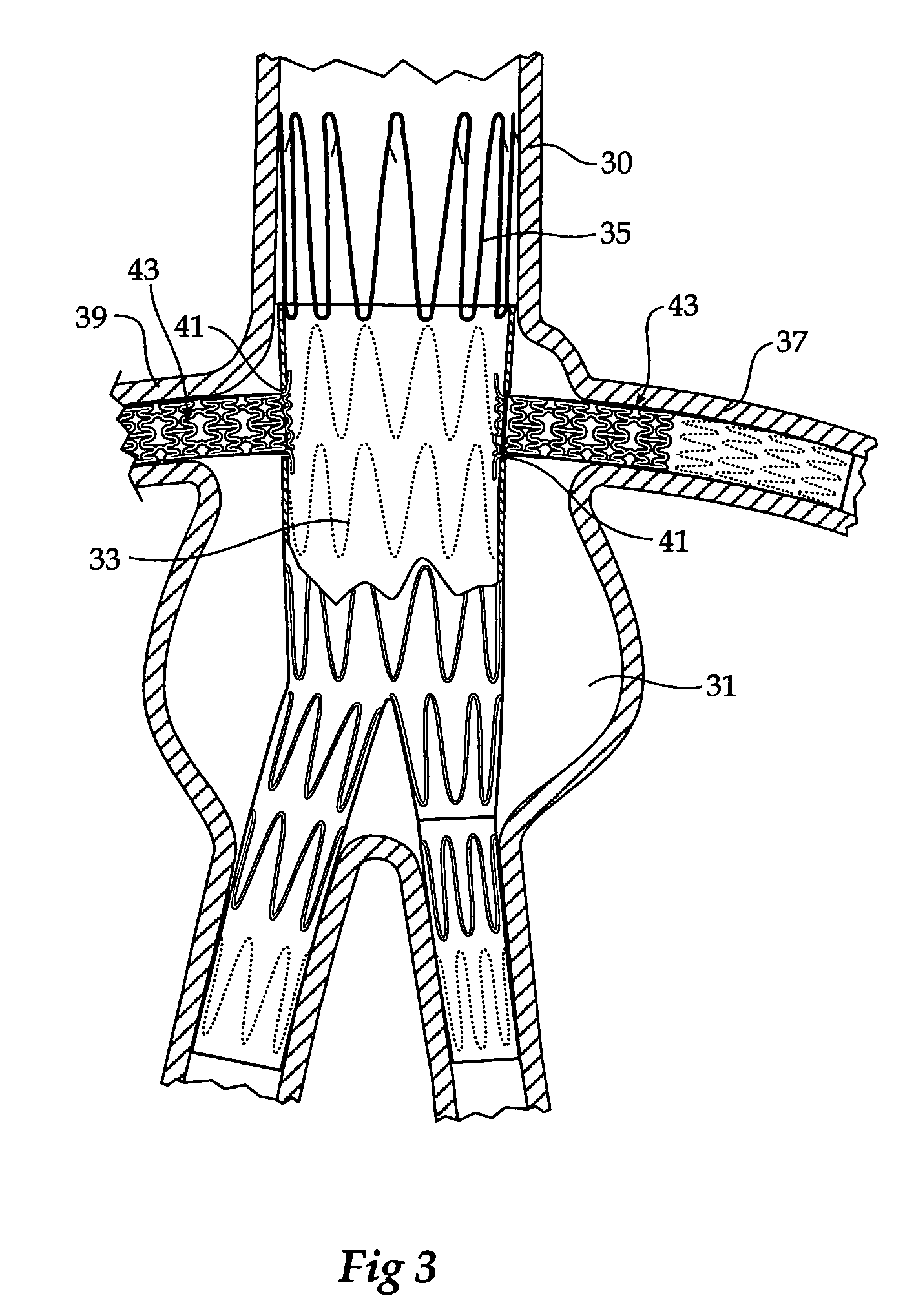
Dual valve prosthesis for transcatheter valve implantation
A dual valve prosthesis having a self-expanding anchoring frame with first and second prosthetic valve assemblies attached to the anchoring frame is disclosed. Each of the first and second prosthetic valve assemblies includes a balloon-expandable stent structure with a prosthetic valve secured therein. In a disclosed method, the first and second prosthetic valve assemblies include prosthetic mitral and aortic valves, respectively, and the dual heart valve prosthesis is configured to replace both the native mitral and aortic valves of the heart in a single transcatheter heart valve implantation procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Catheter tip assembled with a spring
ActiveUS20110196315A1Enhanced deliverability parameterImprove radiopacityBalloon catheterIntravenous devicesCatheterBlood vessel
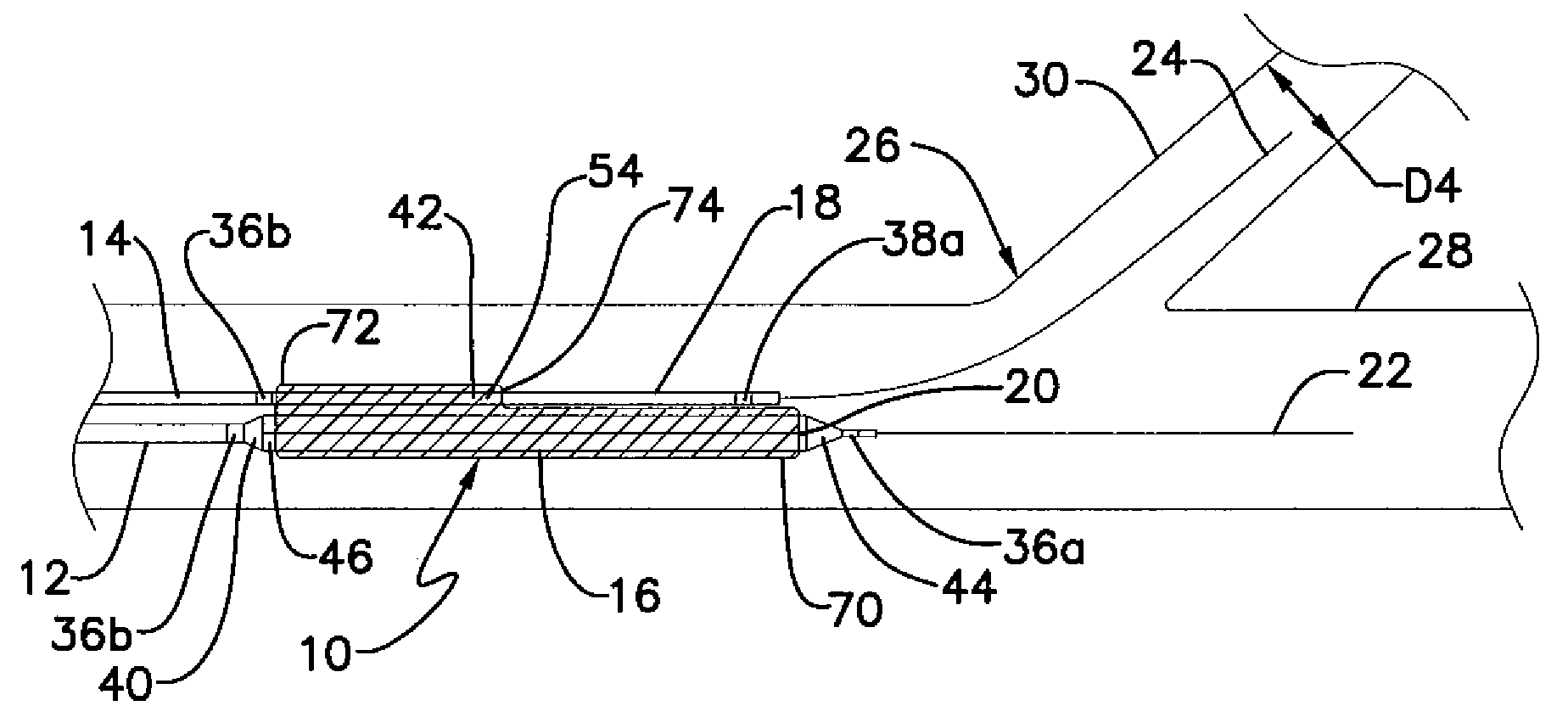
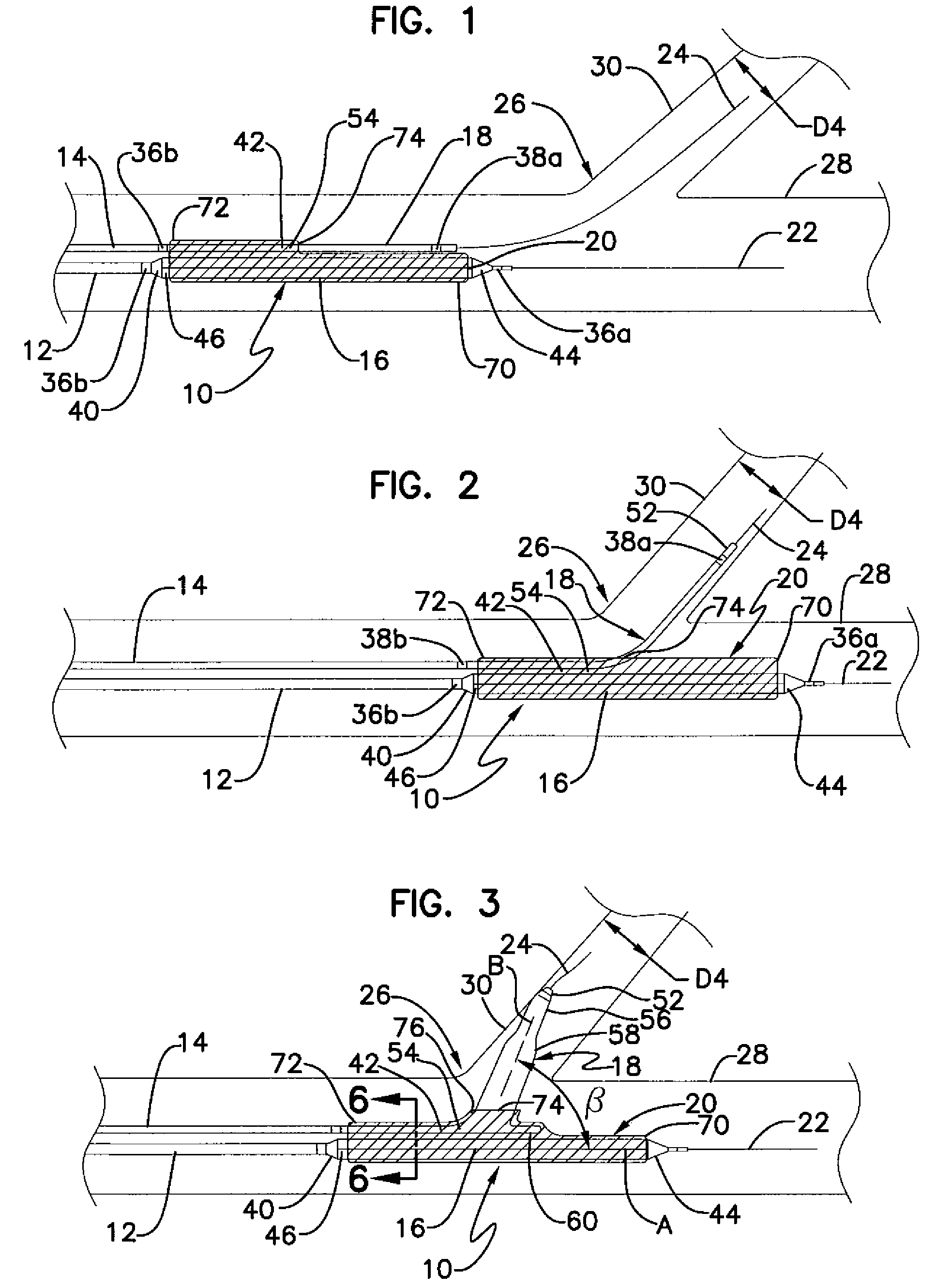
A catheter tip that provides longitudinal flexibility, pushability and radial rigidity thereby improving deliverability is provided. The catheter tip includes a spring-like element to provide longitudinal flexibility and pushability to the catheter tip. The spring-like element may also provide radial support to the distal edge of the catheter tip. Alternatively, a radially rigid distal end may also be included distal of the spring-like element. The apparatus may be used with any interventional catheter system, but is particularly suitable for use with balloon-expandable stent systems and balloon-angioplasty systems, where flexibility of the catheter tip and minimal flaring of the distal edge of the catheter tip is desirable.
Owner:MEDINOL LTD
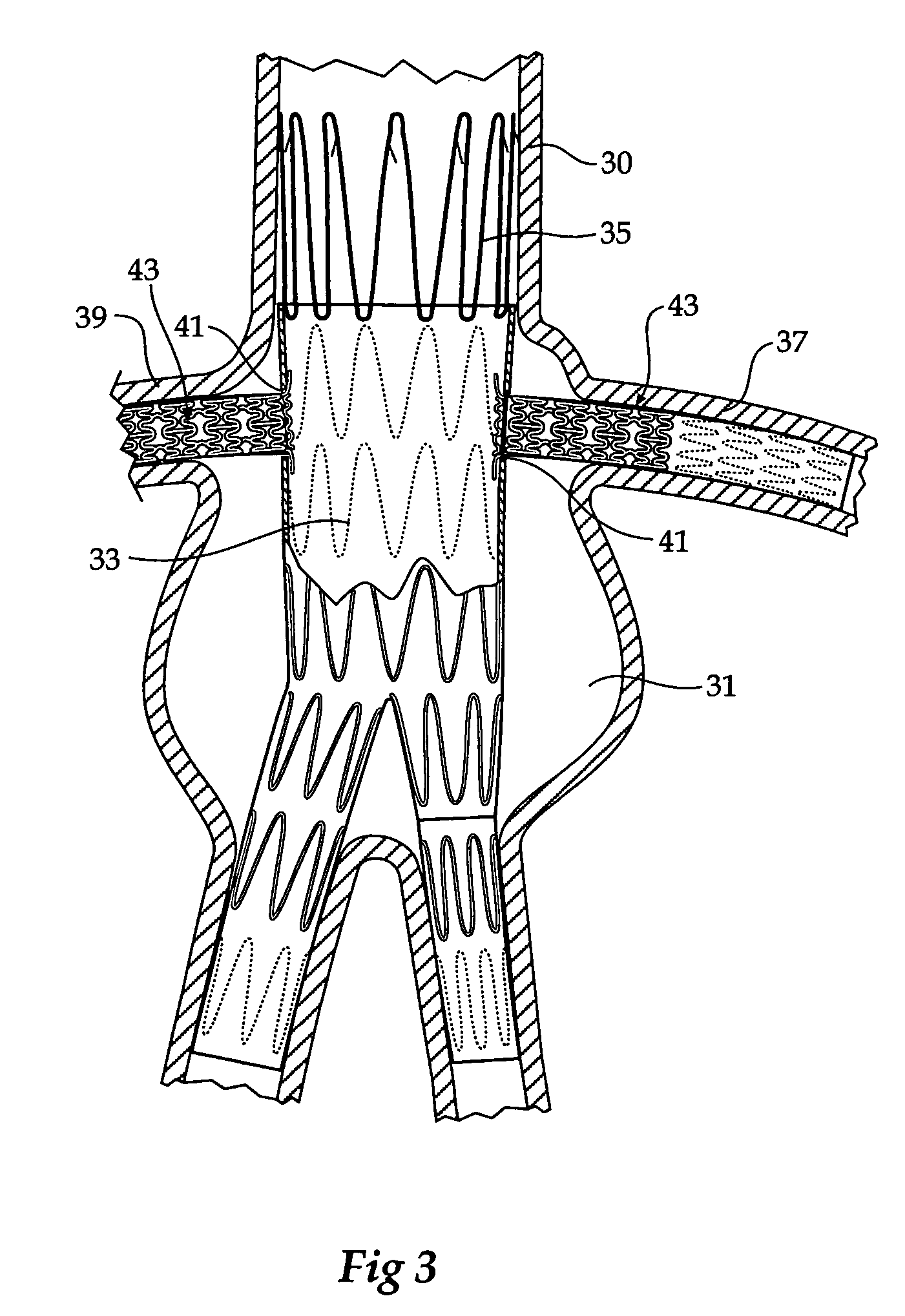
Bifurcation stent delivery system and methods
A catheter assembly may include a main balloon arranged to reside within the main vessel, and a branch balloon configured to extend from the main vessel into the branch vessel. A stent may be situated around the main balloon and may include a branch aperture at a location between proximal and distal open ends of the stent. The branch balloon may extend from within the stent, through the branch aperture, and into the branch vessel. The branch balloon, when inflated, may extend into the branch vessel. The main balloon, when inflated, may also expand the stent within the main vessel. In some arrangements, the branch balloon, when inflated, can function as an anchor within the branch vessel that resists radial and axial movement of the stent relative to the branch vessel and main vessel during expansion of the stent by the main balloon.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods of stabilizing the sacroiliac joint
ActiveUS8551171B2Stability in the SI jointResistance to and loadingSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSacrum boneSacro-iliac joint
Methods of stabilizing the sacroiliac joint by placing an expandable device in the joint to generate laterally opposing forces against the iliac and sacral surfaces of the SI joint to securely seat the device in a plane generally parallel to the SI joint. The expandable device is coated with or otherwise contains a bone material to promote fusion of the joint. The expandable device used in methods of the present invention can be, for example, an expandable cage, a balloon, a balloon-expandable stent or a self-expanding stent.
Owner:SPINAL INNOVATIONS +1
Composite stent graft
A composite stent graft has a balloon expandable stent portion (3), a tubular graft material portion (1) inside or outside of the balloon expandable stent portion and self expanding stents (5) associated with the tubular graft material portion. Part (7) of the balloon expandable stent portion can extend beyond the proximal end (9) of the tubular graft material portion. The tubular graft material can be polytetrafluoroethylene, Dacron, Thoralon™, polyamide, small intestine submucosa, collagenous extracellular matrix material, or any other suitable biocompatible material. A method of deploying which includes flaring a part (7) of the balloon expandable stent portion is also discussed.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
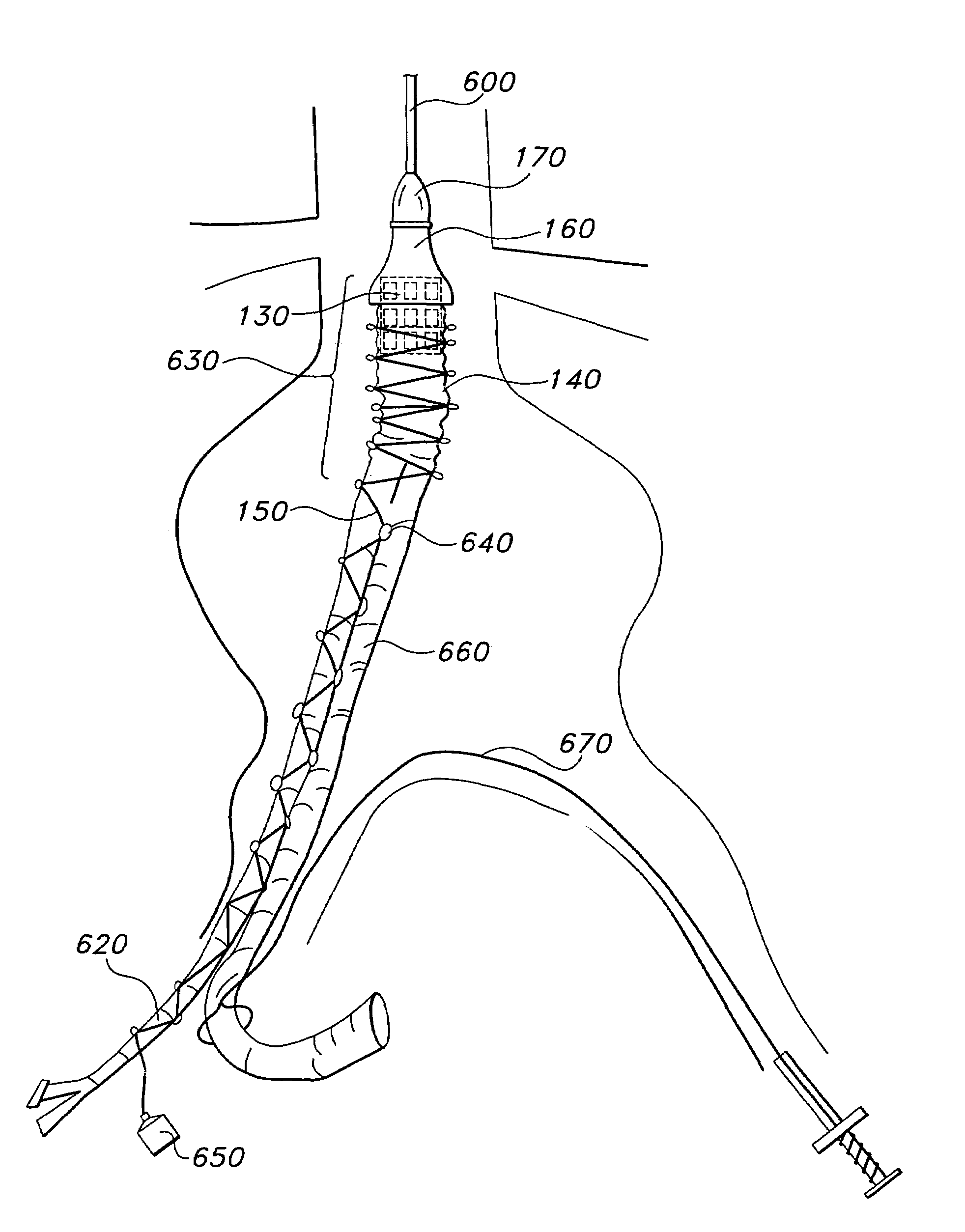
Method for inserting a prosthesis
A graft system for intraluminal delivery in a vessel in need of repair comprising a graft, anchoring means, and a strippable sheath around at least part of the graft. A preferred anchoring means is a balloon-expandable stent. Also included in the invention is a method of using the device to treat a body lumen. The strippable sheath is removable by pulling on a drawstring to remove it which permits expansion of the graft. The positioning of the device may then be adjusted prior to stent dilation. A preferred embodiment of the invention includes a bifurcated graft system for intraluminal delivery in an aortic aneurysm comprising a bifurcated graft having a distal region and two legs, an expandable stent disposed in part of the distal region, and a strippable crocheted sheath around the distal region and one of the two legs. The strippable crocheted sheath is removable by untying it to permit expansion of the graft after initial placement within the aneurysm.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Flared ostial endoprosthesis and delivery system
An intraluminal endoprosthesis having a conically shaped first end and a tubular shaped balloon-expandable stent for a main body is disclosed. The conically shaped first end may form a flare to the main body and is particularly well suited for in ostium use. The first end is preferably self-expanding and the main body is preferably balloon-expandable. Also disclosed is a delivery device for delivering intraluminal ostial endoprosthetic devices, especially those disclosed herein, to a site for deployment. The delivery device may comprise an over-the-wire system or may comprise a rapid-exchange shuttle system. The self-expanding portion of the endoprosthesis is encapsulated in a sheath or other restraining apparatus on the delivery device. The balloon-expandable stent portion of the endoprosthesis is crimped onto a balloon delivery device. The delivery system and endoprosthesis of the present invention allow the endoprosthesis to be partially expanded and relocated if it is determined that it is not located in the proper location. To aid in positioning, the delivery device may comprise marker bands.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
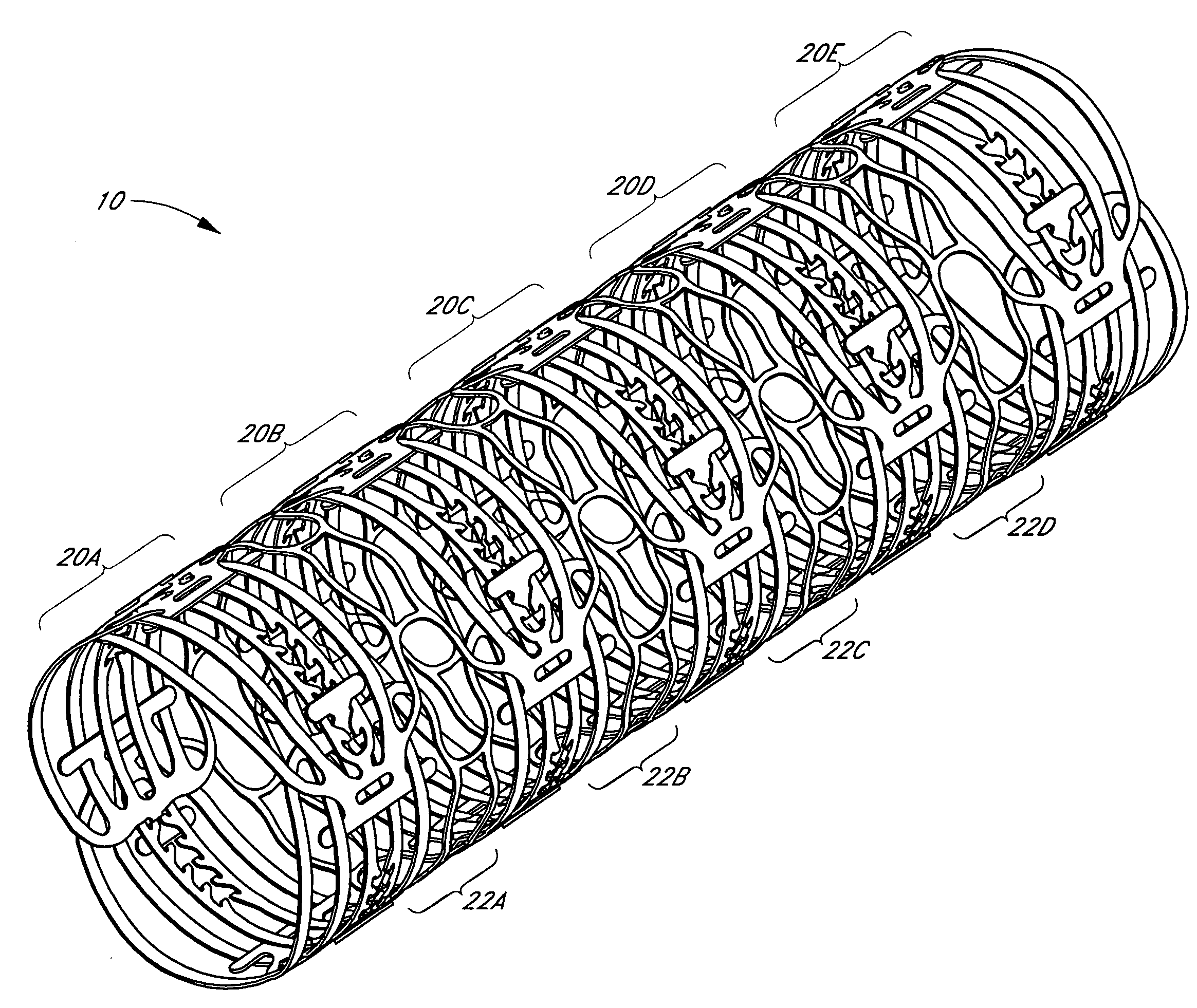
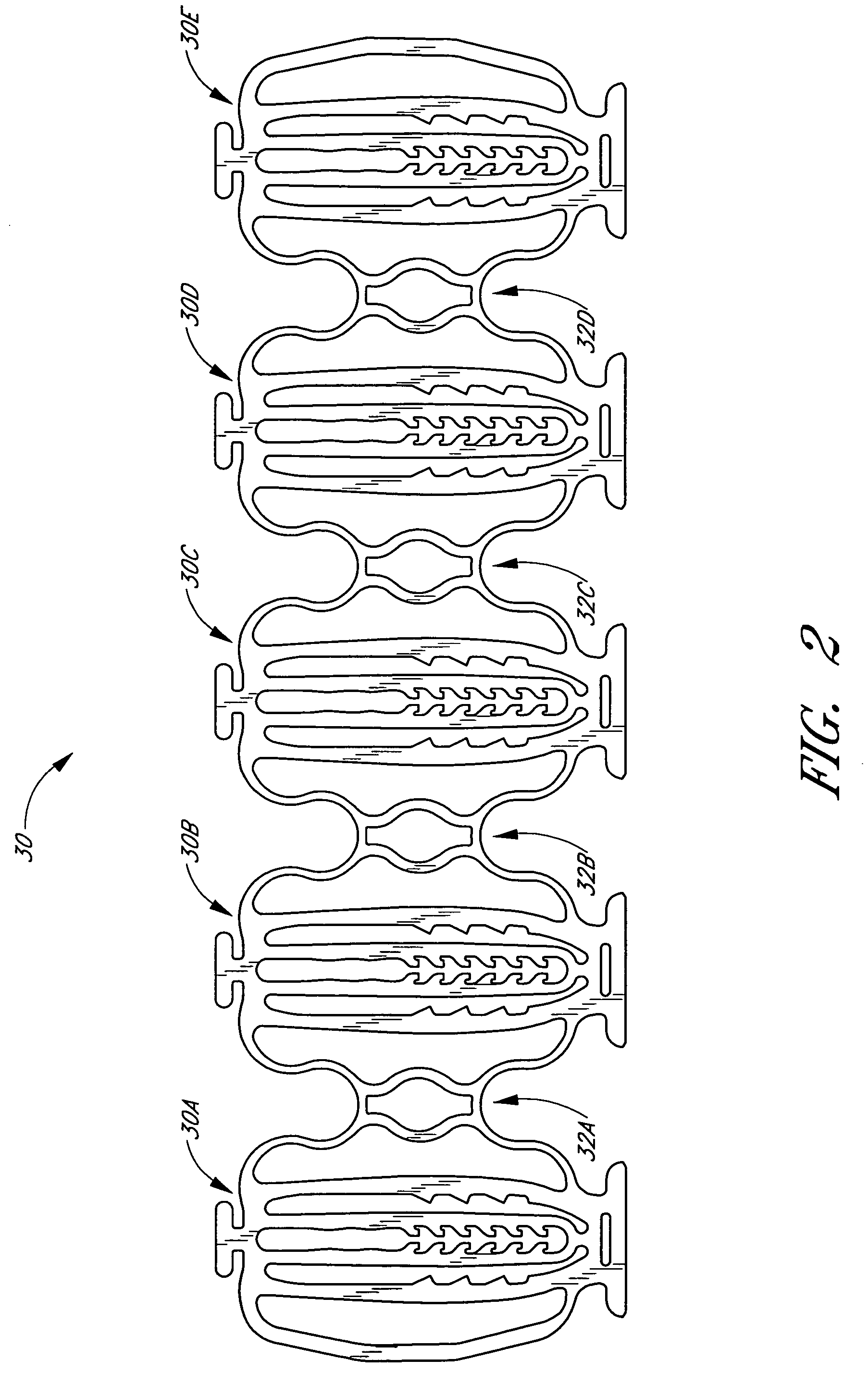
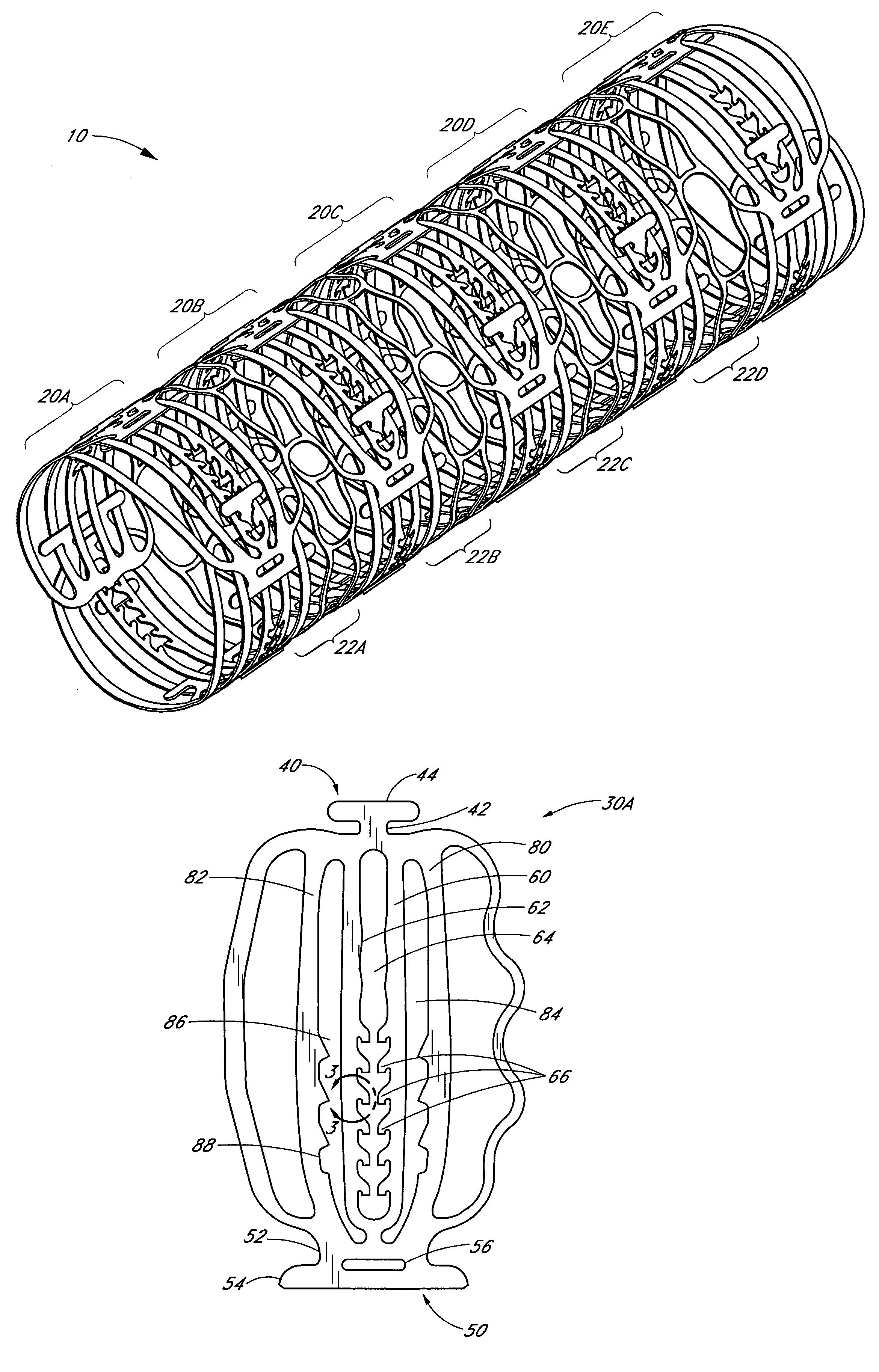
Intraluminal medical device with nested interlocking segments
An intraluminal medical device having nested interlocking axially adjacent segments that remain interlocked during delivery to an intended treatment site. The medical device is preferably a stent in which the nested interlocked axially adjacent segments provide increased control and stability of the stent during delivery and increased vessel support when full deployment is effected. The stent may be a self-expanding stent or a balloon expandable stent. In either case, a series of repeating cells comprise a segment. Each cell comprises a protrusion and a radially and circumferentially adjacent receptacle. The protrusion from at least one cell in a segment interlocks with the receptacle of an axially adjacent segment to form the stent. The protrusions remain coupled with a corresponding receptacle during delivery of the stent to the intended treatment site, and can remain engaged thereafter, or can disengage from the corresponding receptacle after full deployment of the stent is effected. An LID ratio of the expanded length of the stent segment relative to the expanded diameter of the stent is preferably greater than one to enhance stent delivery and maximize fatigue durability of the structure. Radiaopaque markers may be inserted within, integral therewith, or coated thereon ends of the protrusions.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Medicine eluted cardiovascular frame and its preparing process
InactiveCN1355005AContinuous and stable releasePromote healingStentsCoatingsCardiovascular stentEthylene Homopolymers
A medicine eluted cardiovascular frame is composed of expandible support and the medicine coated biodegradable layer coated on the said frame. The said biodegradable material contains one of the homopolymer and copolymer of glycollide, L-lactide or epsilon-caprolactone, and the copolymer of multi-group amino acids. The medicine can resist the cardiovascular narrowness. The process for preparing the said support includes such steps as preparing the said expandible support, immersing it in the mixture of the said medicine, biodegradable material and solvent, and drying. It can prevent thrombosis.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
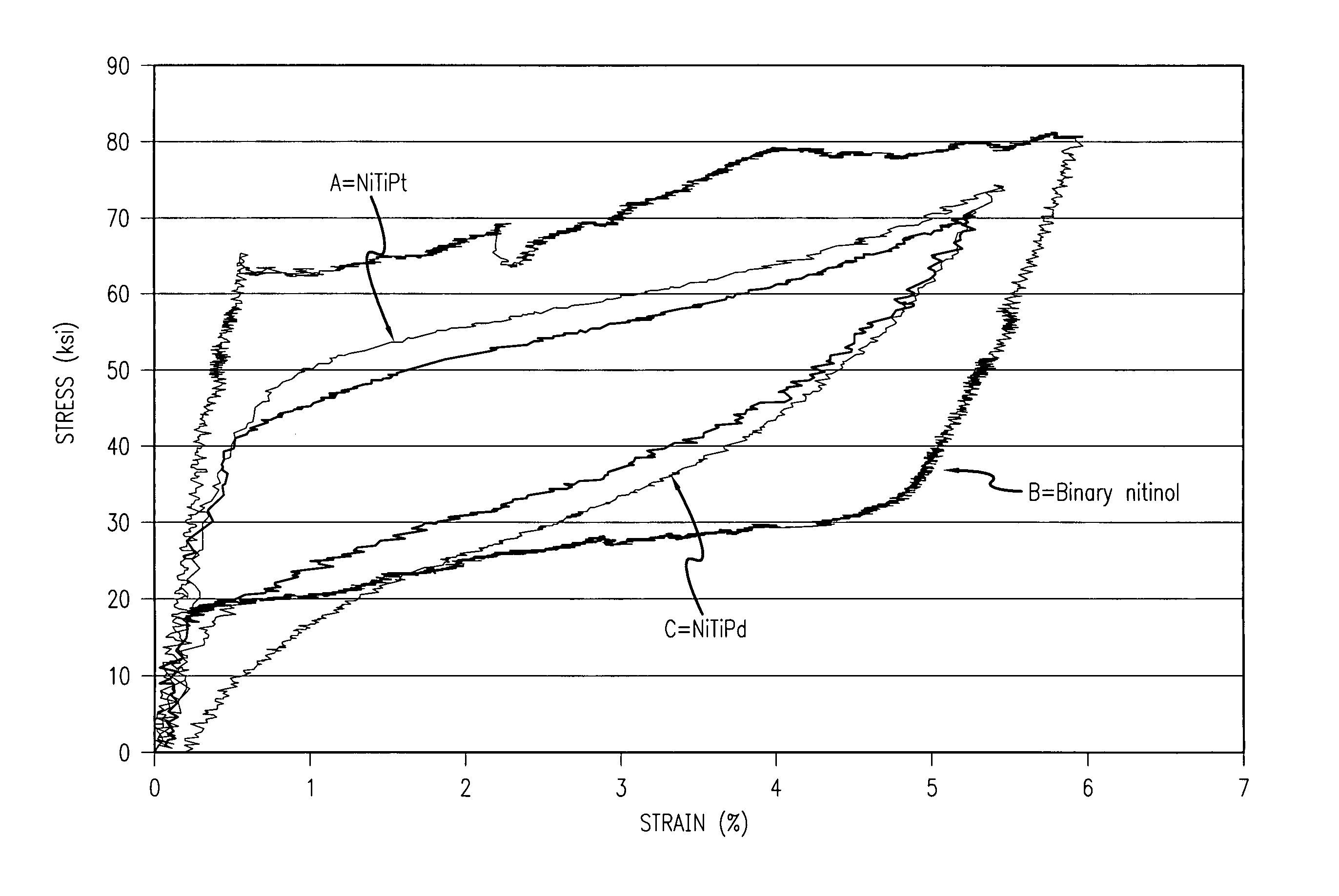
Radiopaque and MRI compatible nitinol alloys for medical devices
A radiopaque nitinol medical device such as a stent for use with or implantation in a body lumen is disclosed. The stent is made from a superelastic alloy such as nickel-titanium or nitinol, and includes a ternary element selected from the group of chemical elements consisting of iridium, platinum, gold, rhenium, tungsten, palladium, rhodium, tantalum, silver, ruthenium, or hafnium. The nitinol stent has improved radiopacity yet retains its superelastic and shape memory behavior and further maintains a thin strut / wall thickness for high flexibility. Another embodiment includes a balloon expandable stent made from a radiopaque and MRI compatible alloy such as nitinol and includes a ternary element selected from the group of chemical elements consisting of iridium, platinum, gold, rhenium, tungsten, palladium, rhodium, tantalum, silver, ruthenium, hafnium, osmium, zirconium, niobium, or molybdenum.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Polymer coated stents
InactiveUS20050113909A1Increase flexibilitySmoothly inserted into region of convolutionStentsSurgeryMedicineInsertion stent
A polymer coated stent is disclosed. The stent may be a self-expanding stent or a balloon-expandable stent. The metal surface of the stent is coated with a polymer for enhanced biocompatibility. Amongst the various polymers that can comprise the coating of the stent are fluorine-containing polymers such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Methods are also disclosed for depositing the coating on the surface of the stent.
Owner:SHANNON DONALD T +2
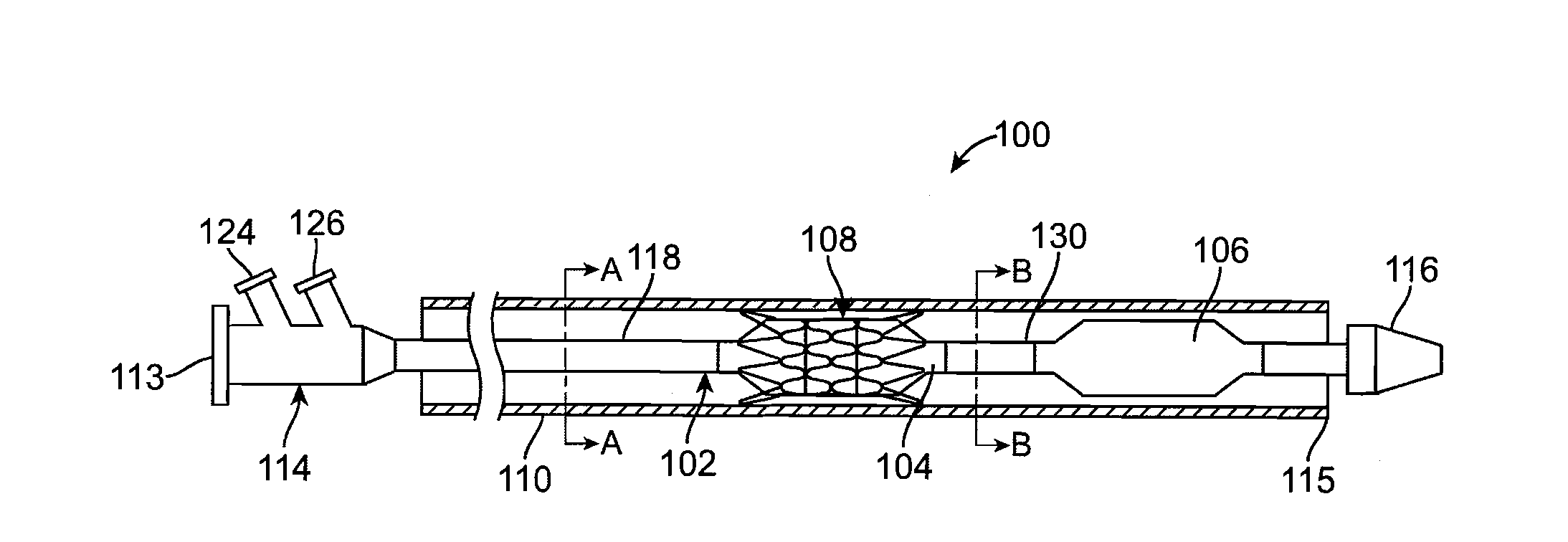
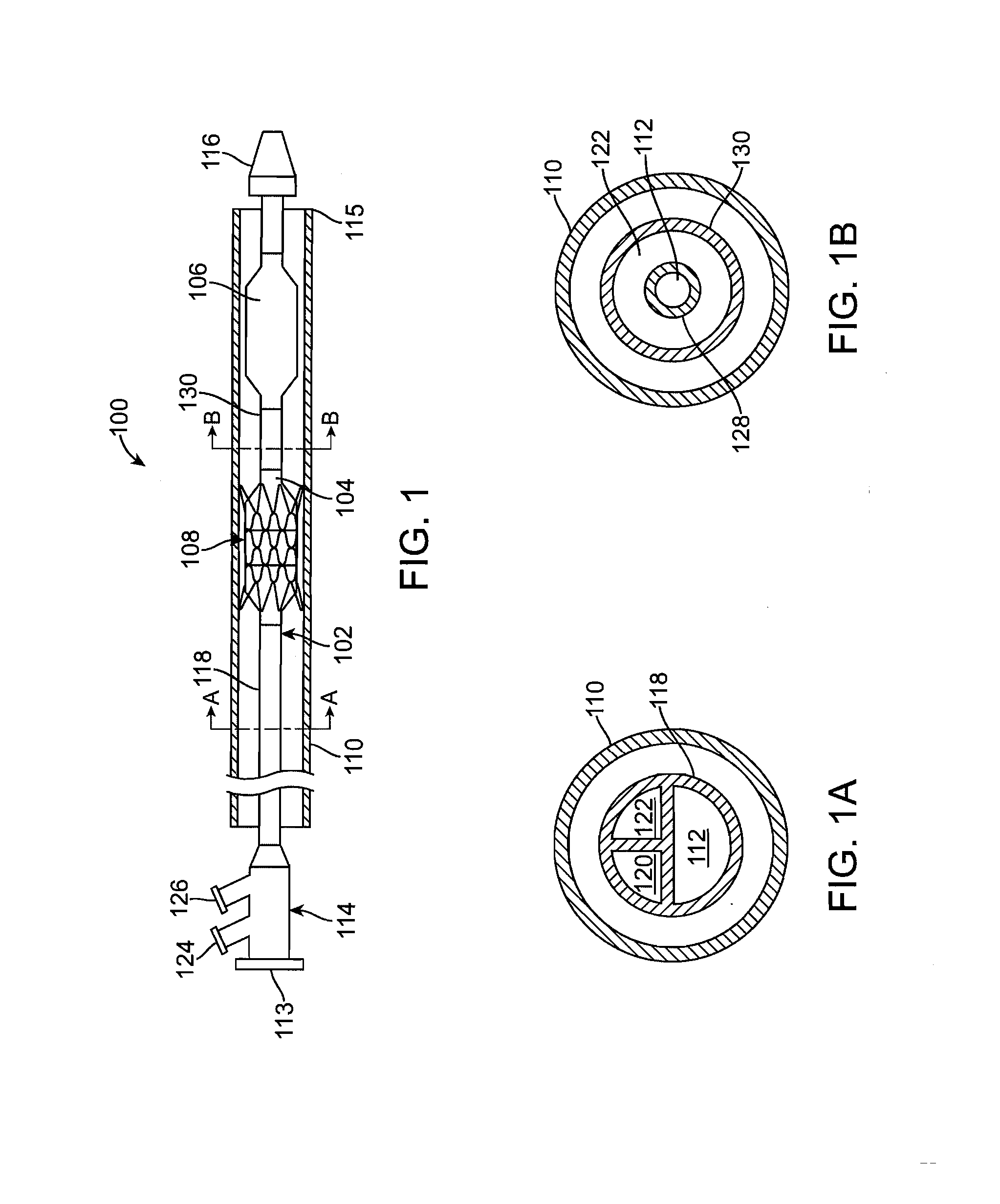
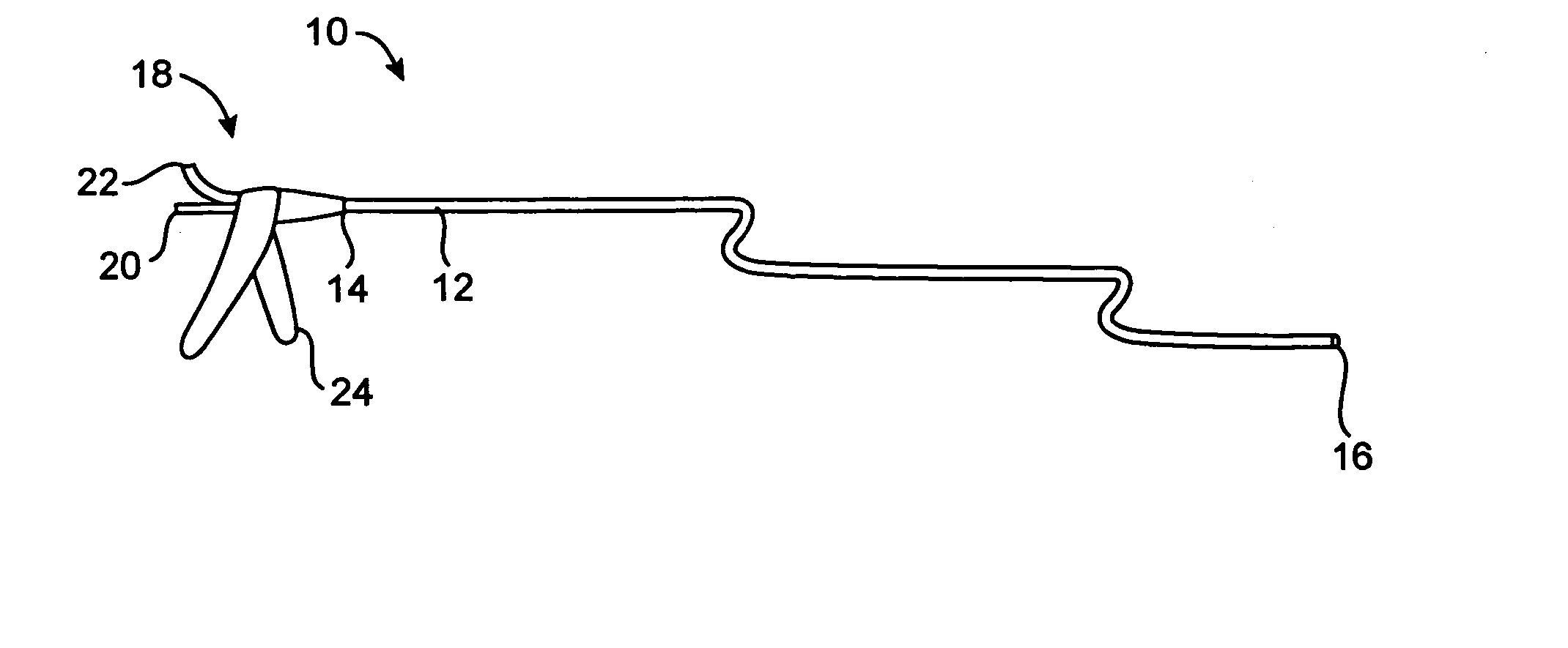
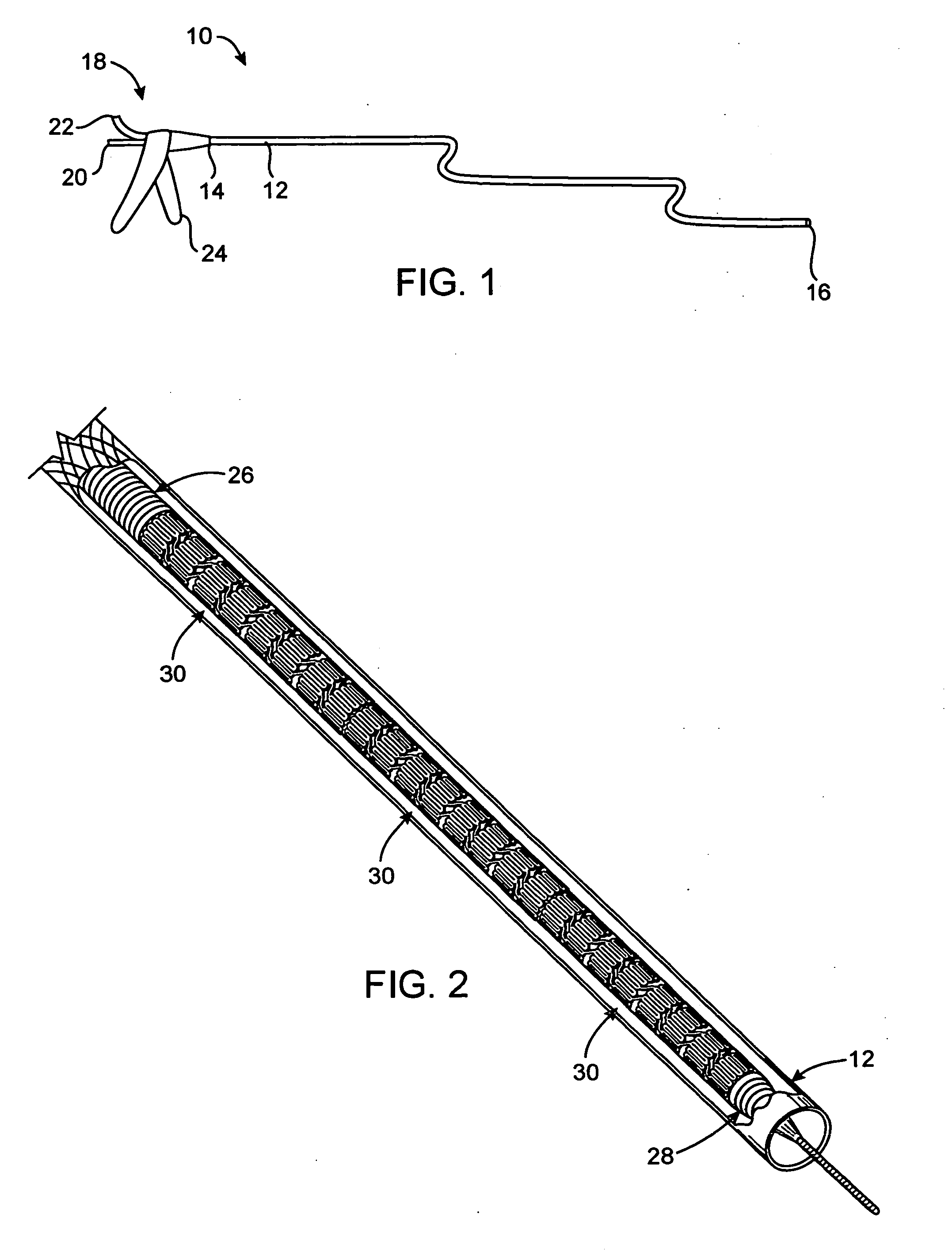
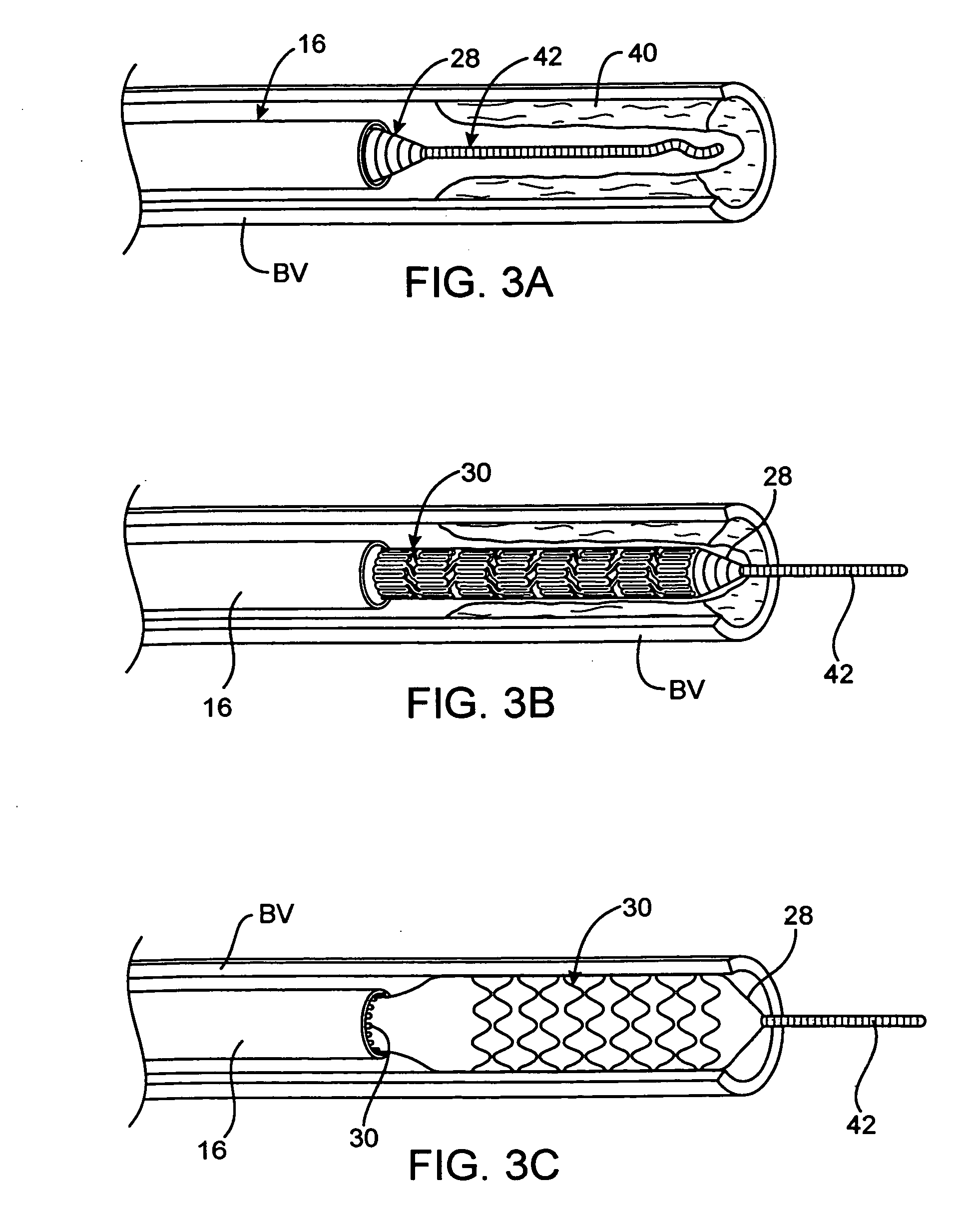
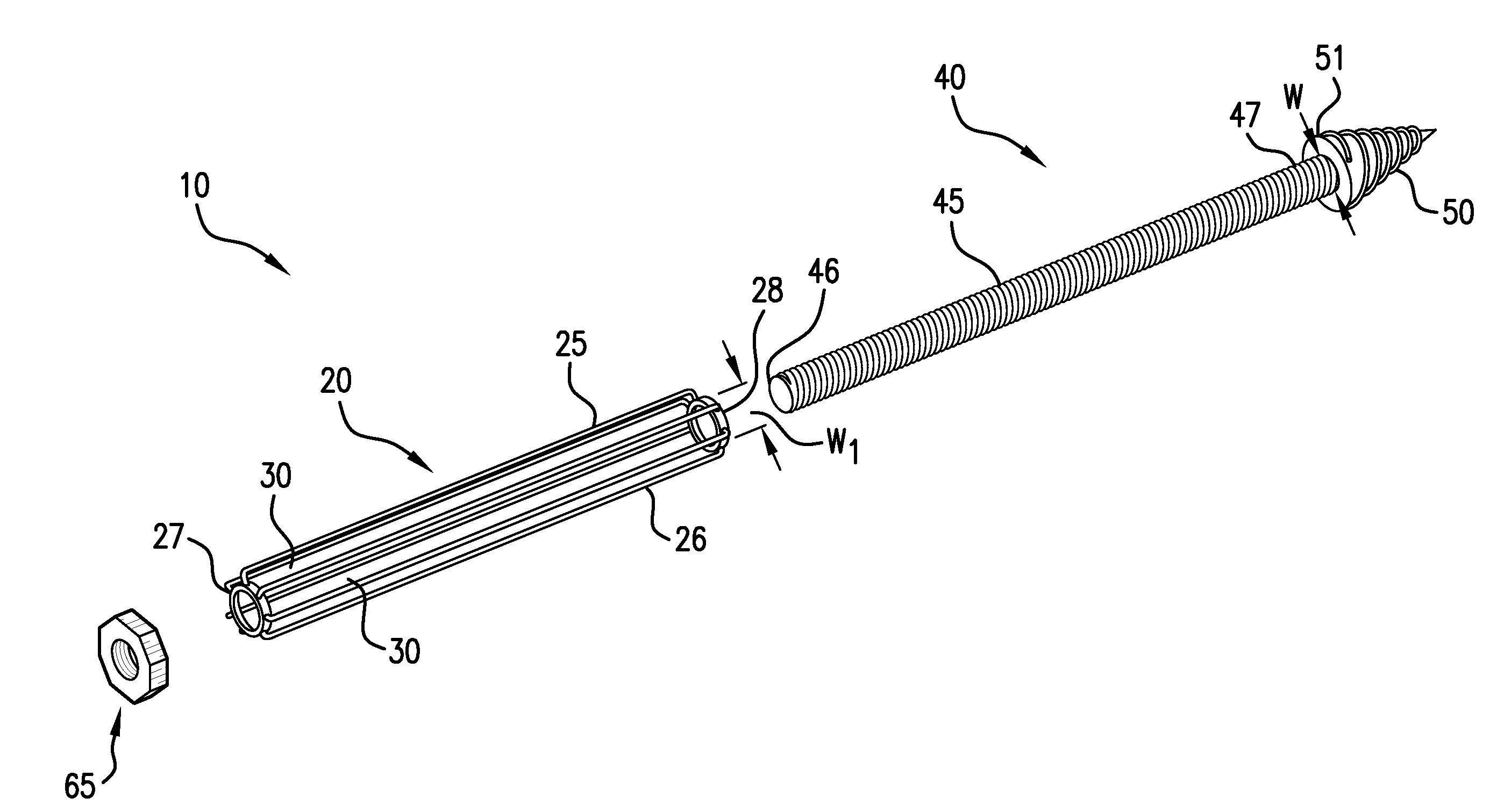
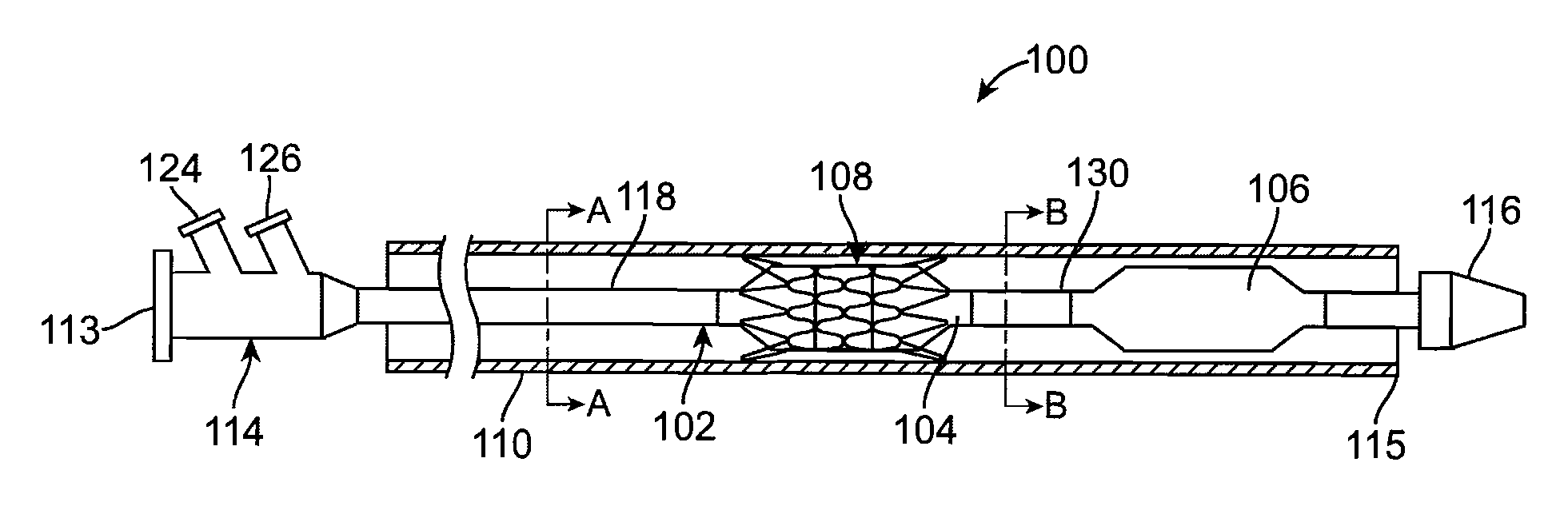
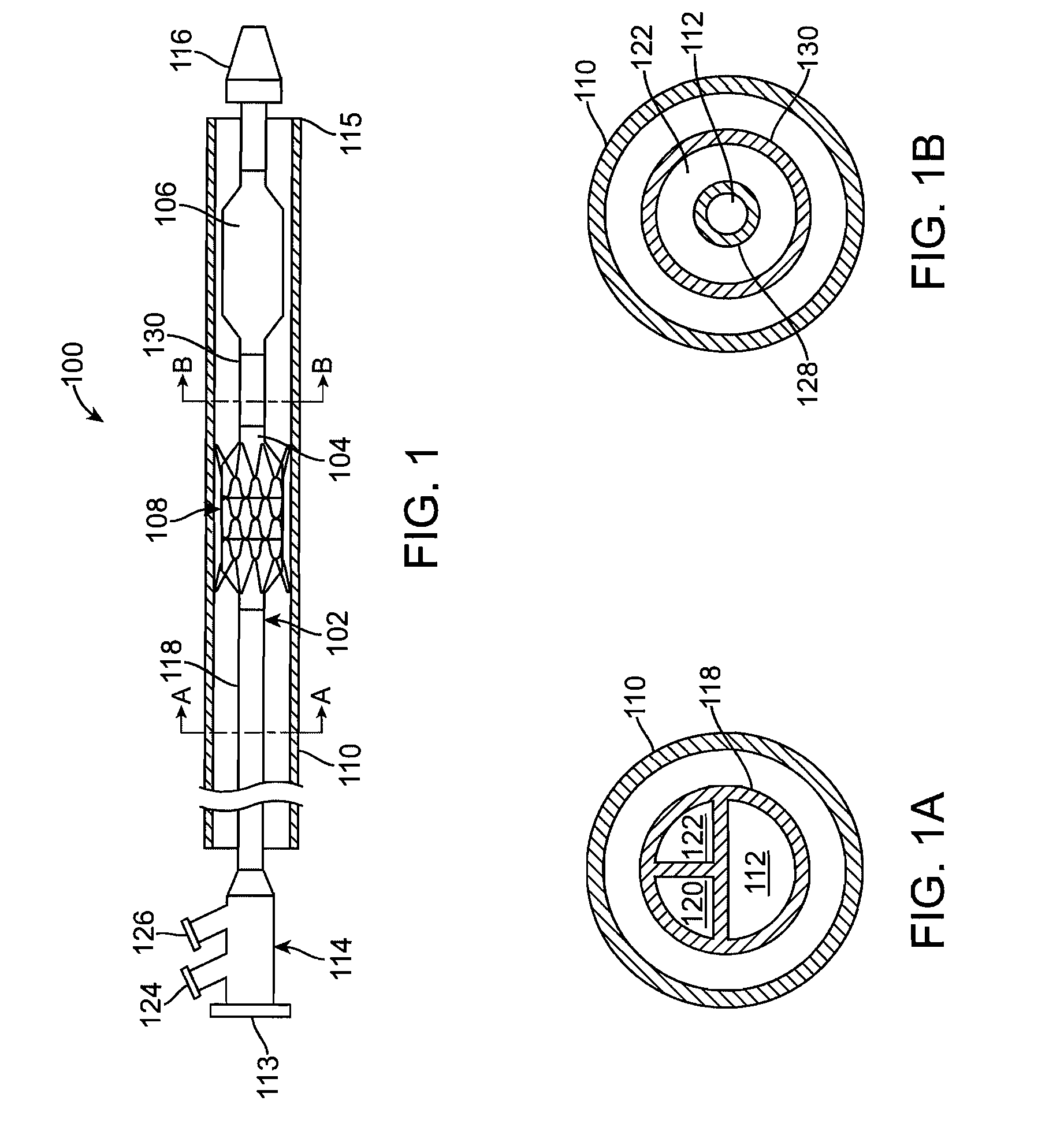
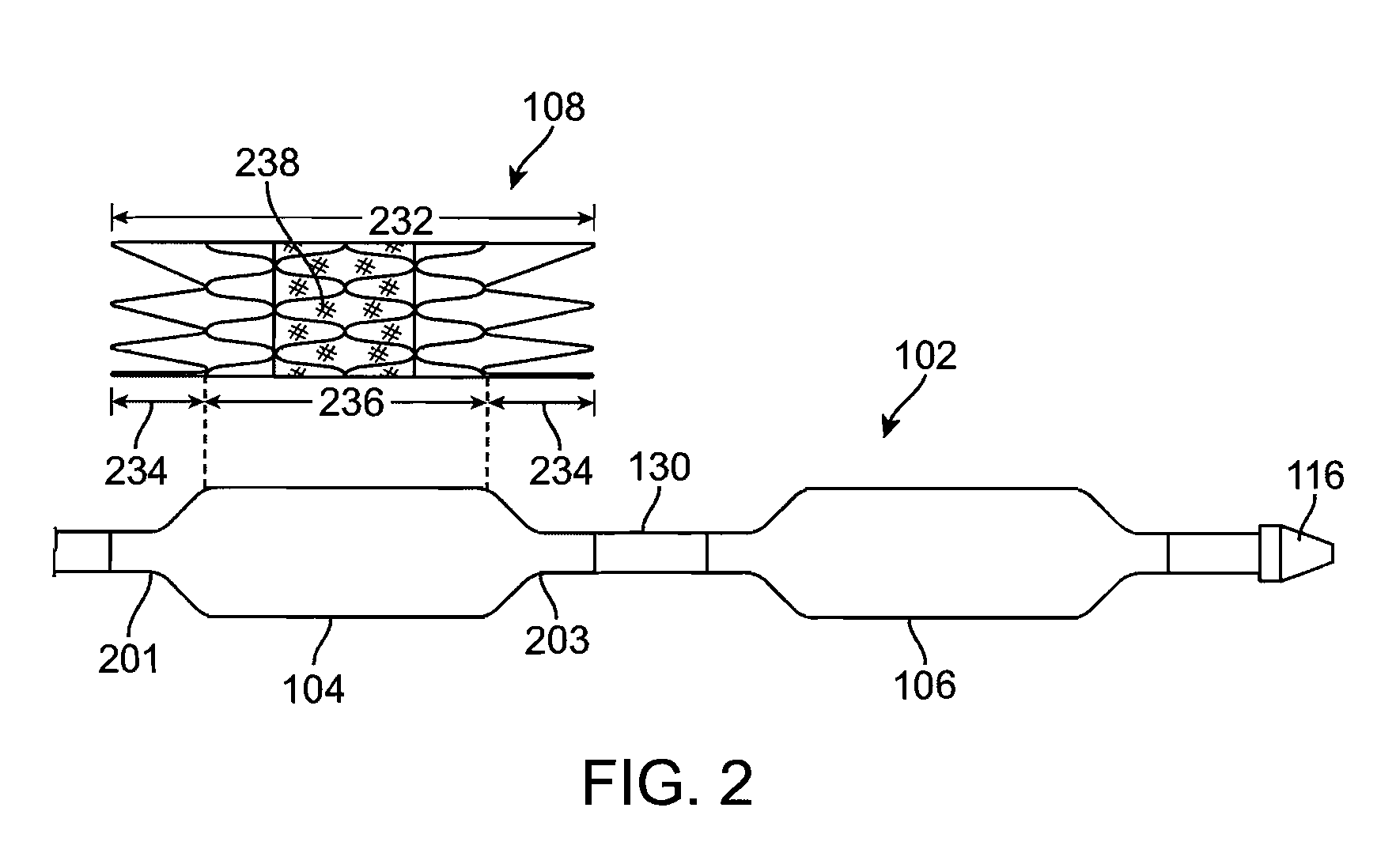
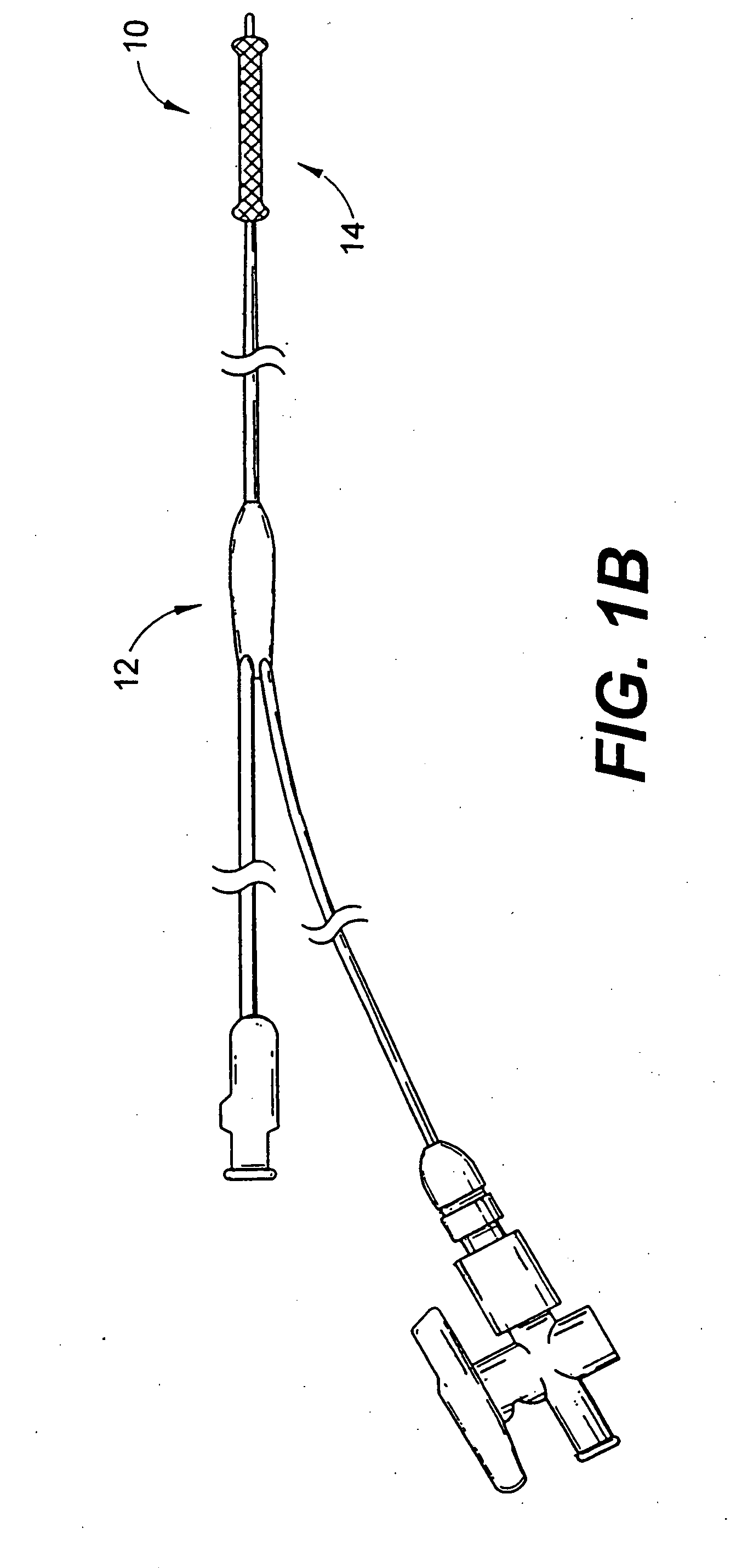
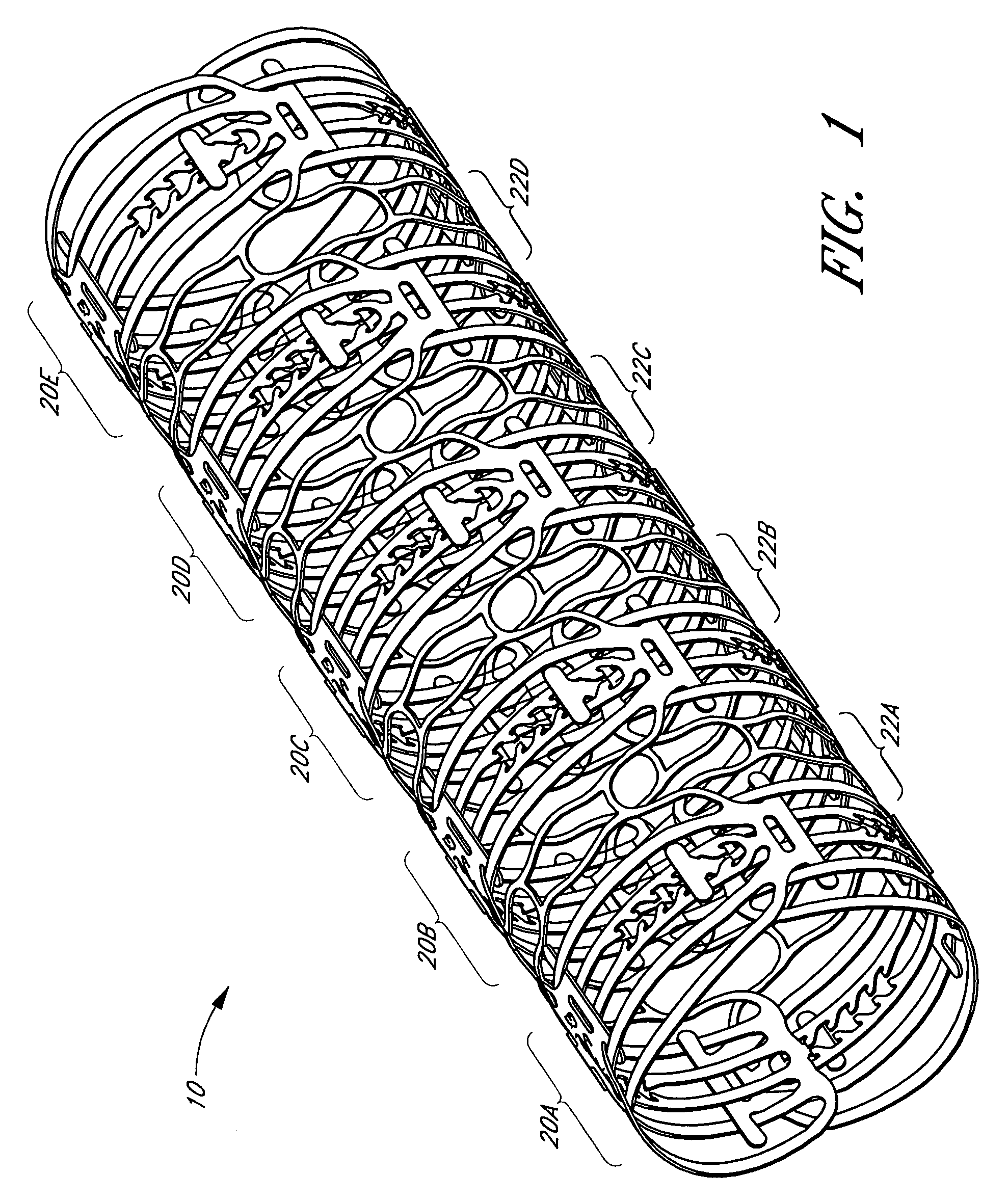
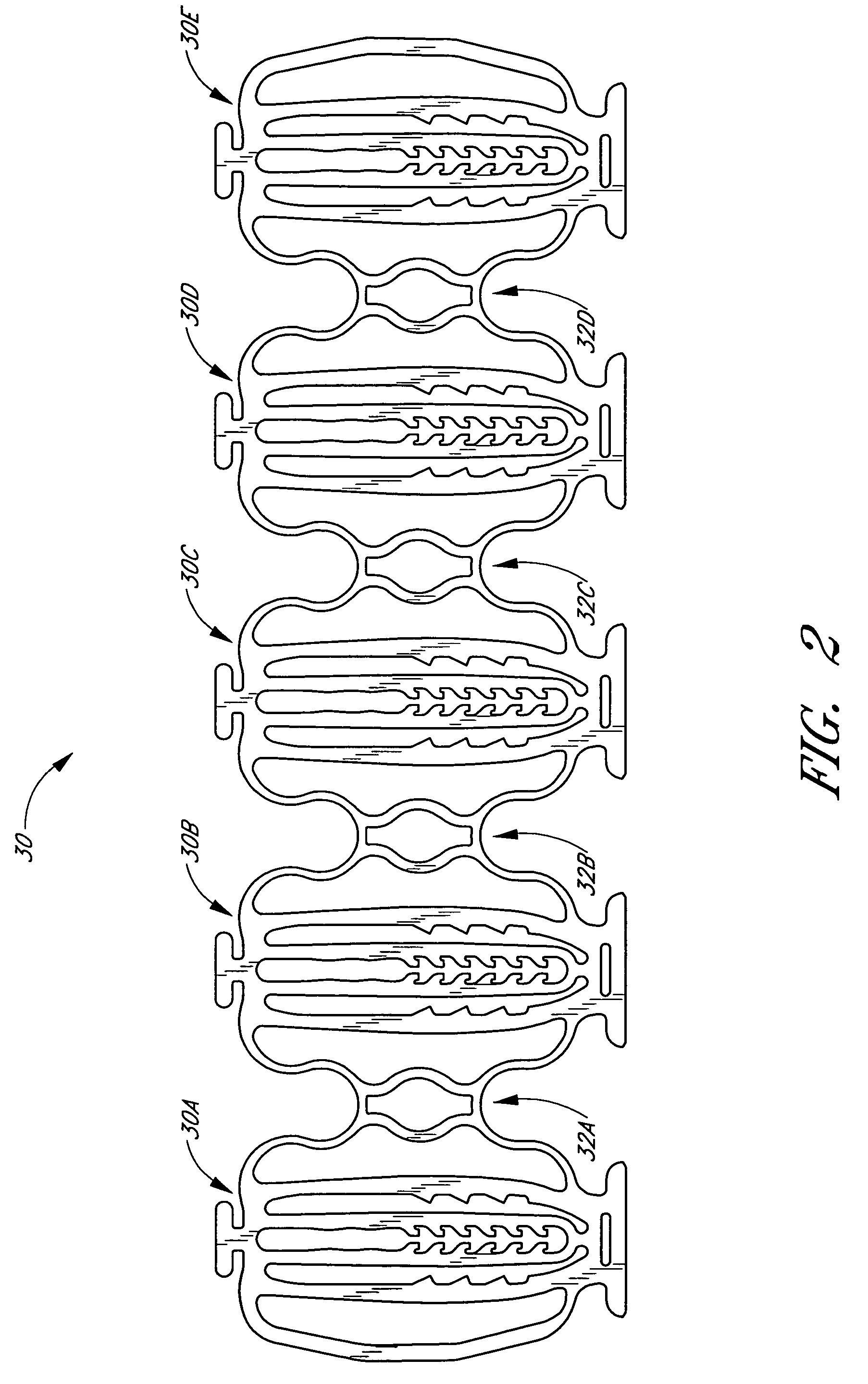
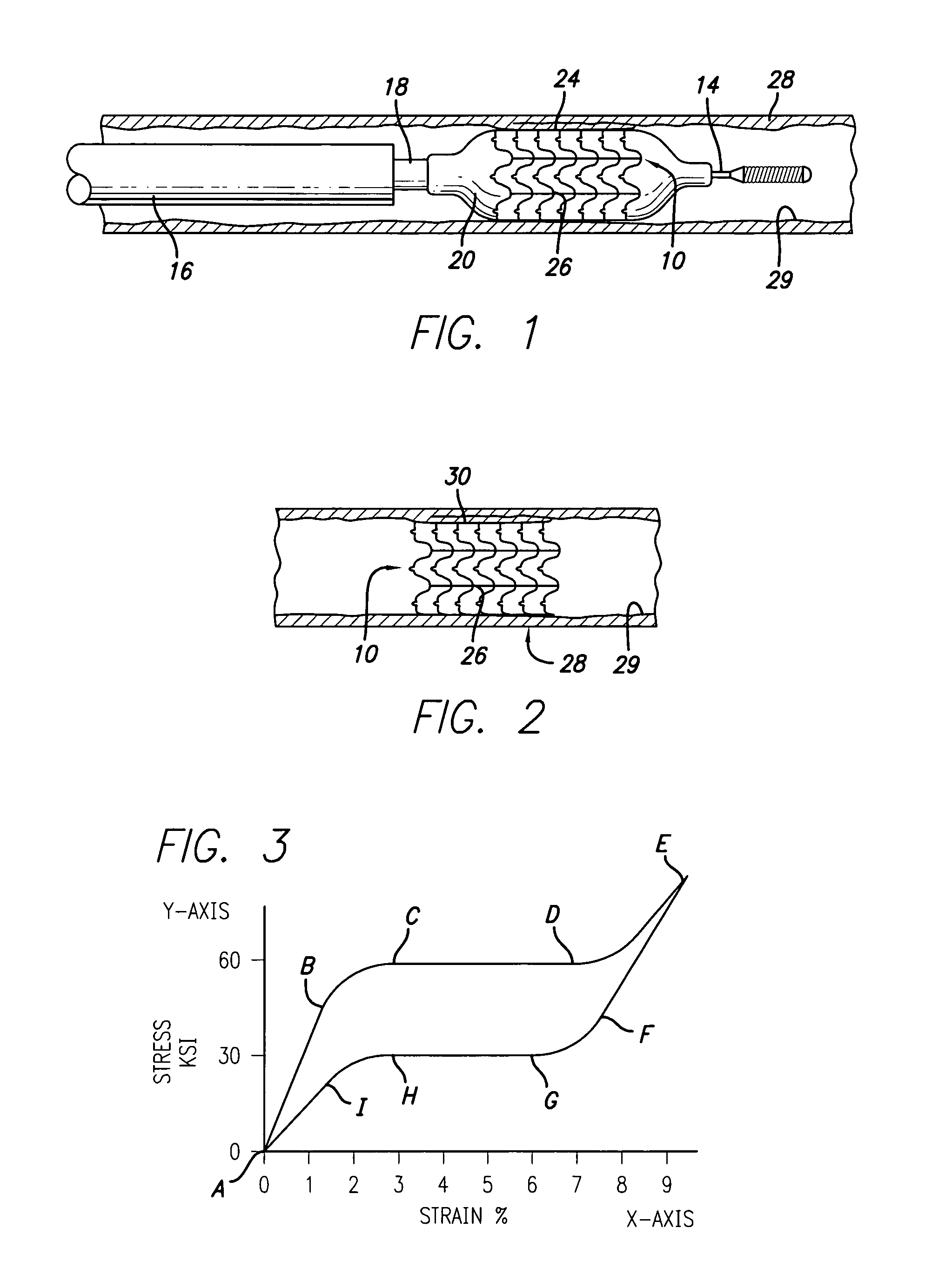
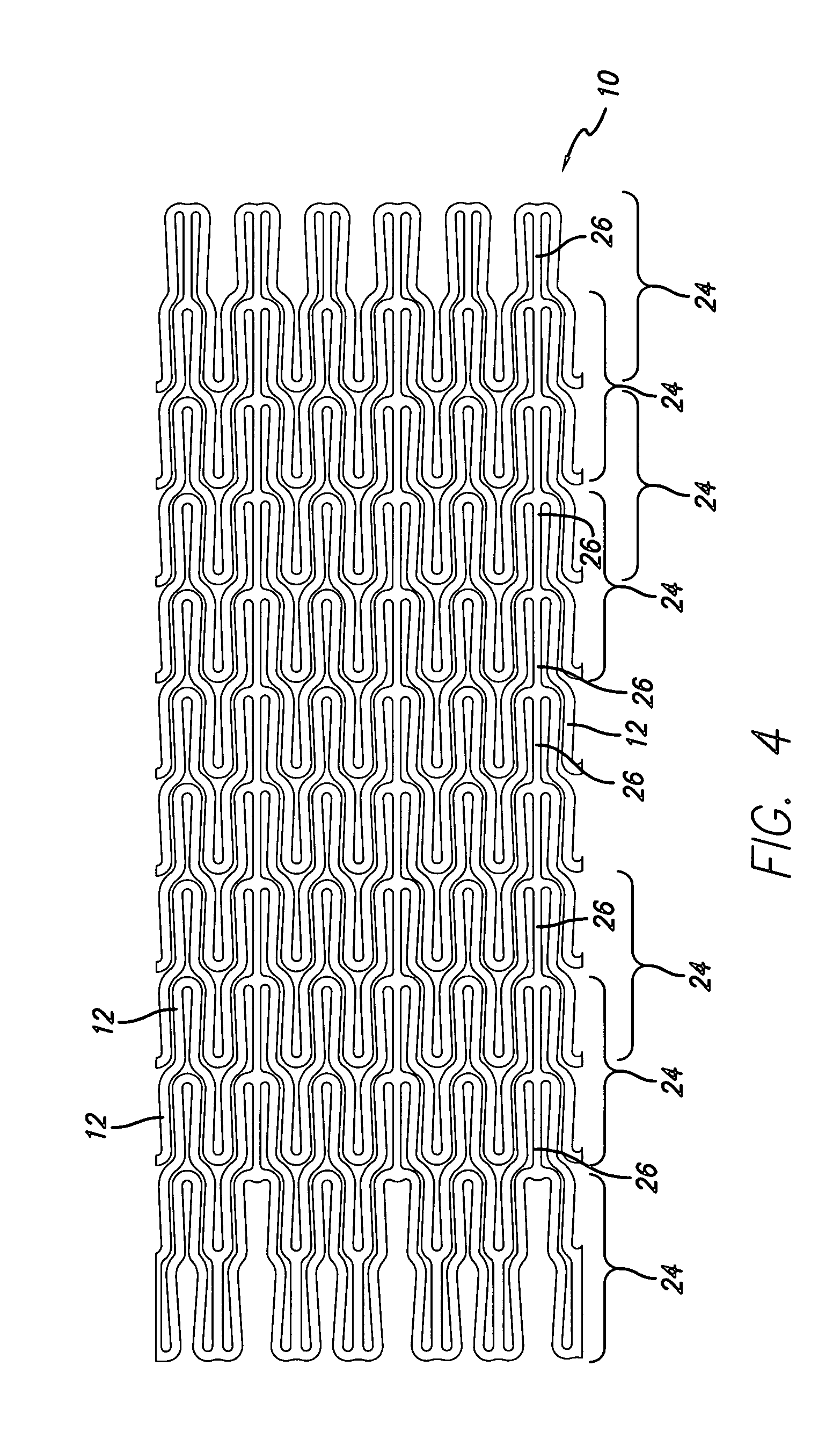
Balloon expandable stent
An apparatus is provided that includes an elongate member having a distal end portion, a proximal end portion, and a medial portion that is disposed between the distal end portion and the proximal end portion. The medial portion is configured to be disposed in a ureter of a patient. The apparatus further includes an expandable member that is coupled to the elongate member. The expandable member has an expanded configuration and a collapsed configuration. The expandable member is further configured to be inserted into the ureter of the patient and configured to contact the ureter to help retain the elongate member in place within the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Selectively light curable support members for medical devices
Methods of forming support layers for use in catheters using having a support layer included, and stents incorporating coatings of photosensitive polymerizable resins and stents including fibers coated with photosensitive polymerizable resins. A fiber is coated with a PPC resin and incorporated into a support structure for a catheter. Portions of the PPC are polymerized by exposure to light of a desired wavelength, causing increased rigidity and strength to the polymerized portions. As the PPC is polymerized, the fibers coated by the PPC resins become stronger and change the flexibility of devices incorporating such fibers. Additional embodiments include stents incorporating PPC coatings and methods of using such stents, including polymerizing a PPC coating after inserting a self-expanding or balloon-expandable stent.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
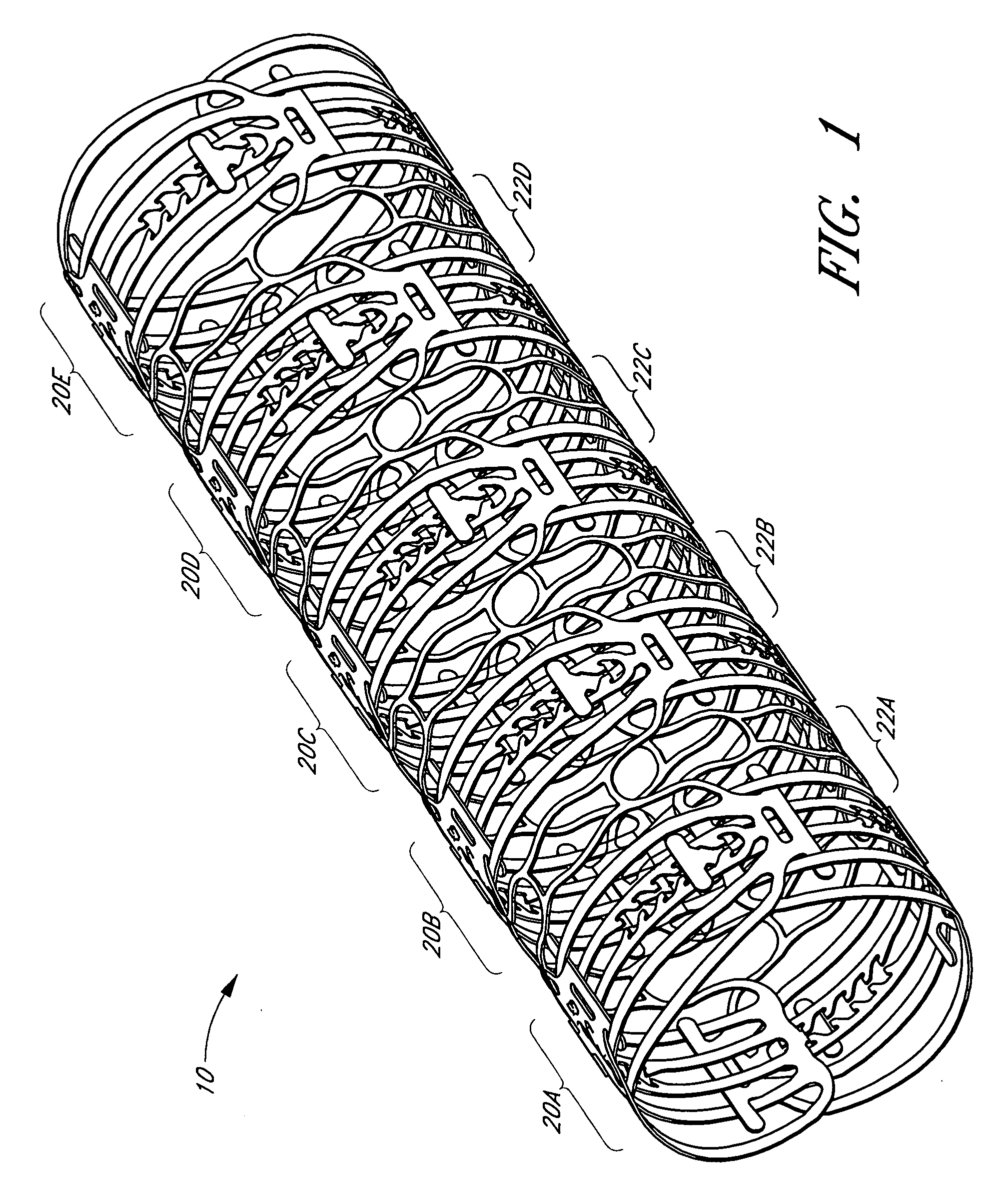
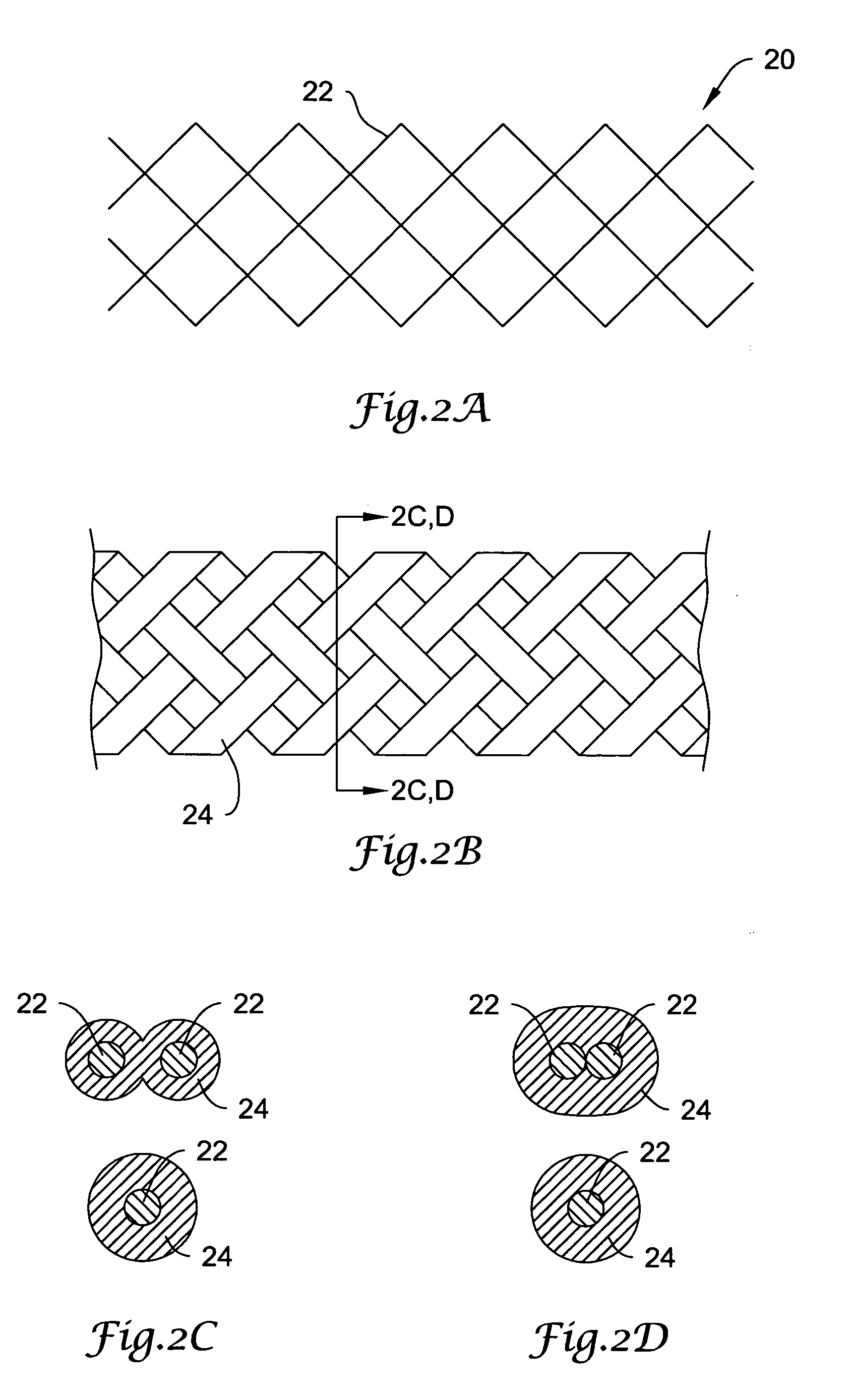
Designs for left ventricular conduit
A conduit is provided to provide a bypass around a blockage in the coronary artery. The conduit is adapted to be positioned in the myocardium or heart wall to provide a passage for blood to flow between a chamber of the heart such as the left ventricle and the coronary artery, distal to the blockage. The stent is self-expanding or uses a balloon to expand the stent in the heart wall. Various attachment means are provided to anchor the stent and prevent its migration.
Owner:HORIZON TECH FUNDING CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com