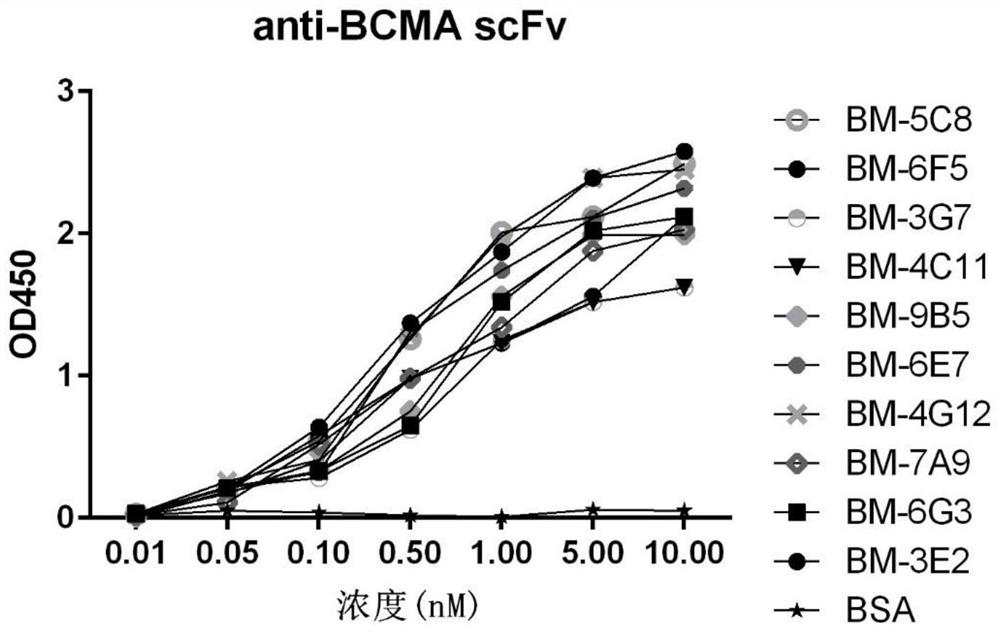
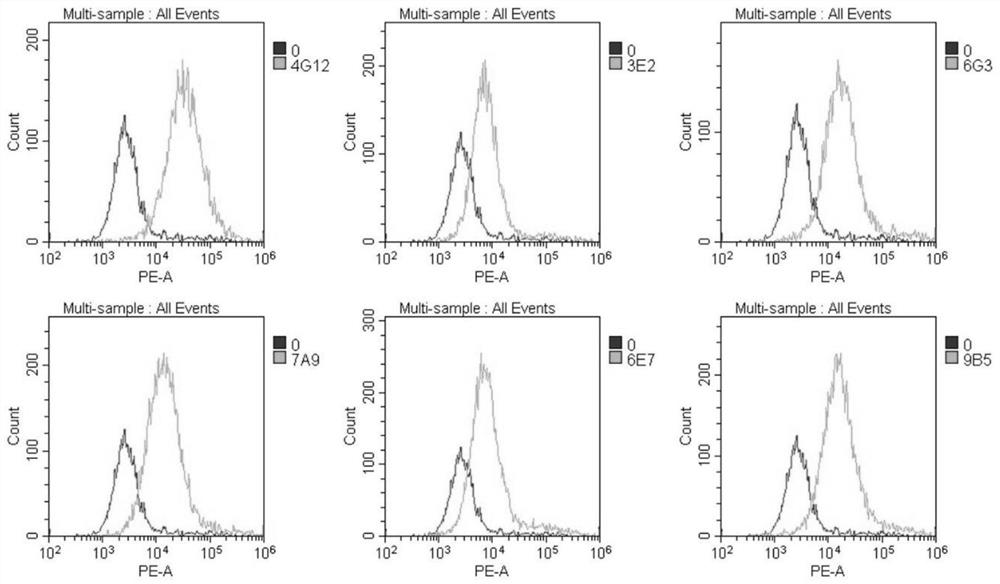
Patents
Literature
30 results about "CD46" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
CD46 complement regulatory protein also known as CD46 (cluster of differentiation 46) and Membrane Cofactor Protein is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CD46 gene. CD46 is an inhibitory complement receptor.
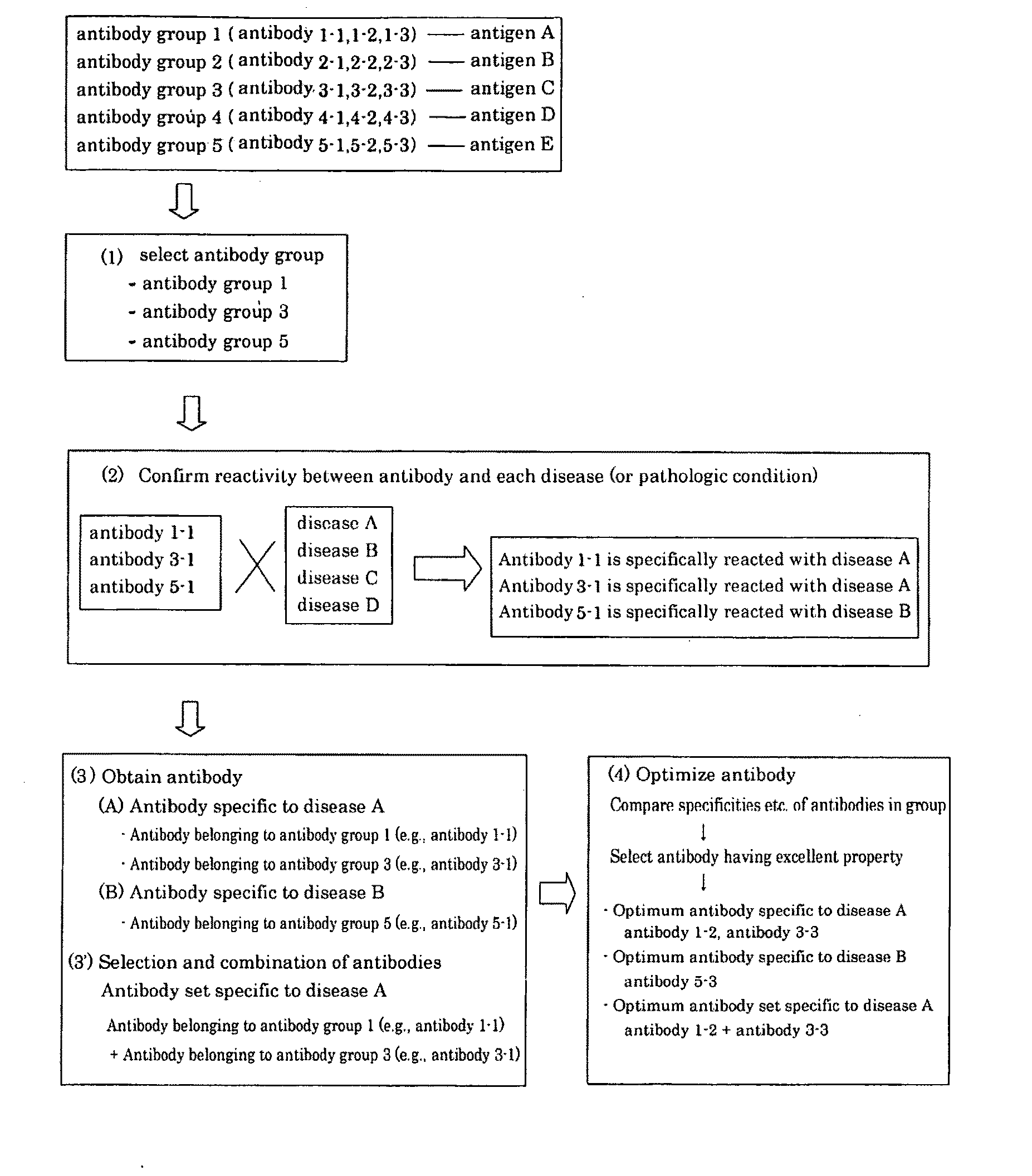
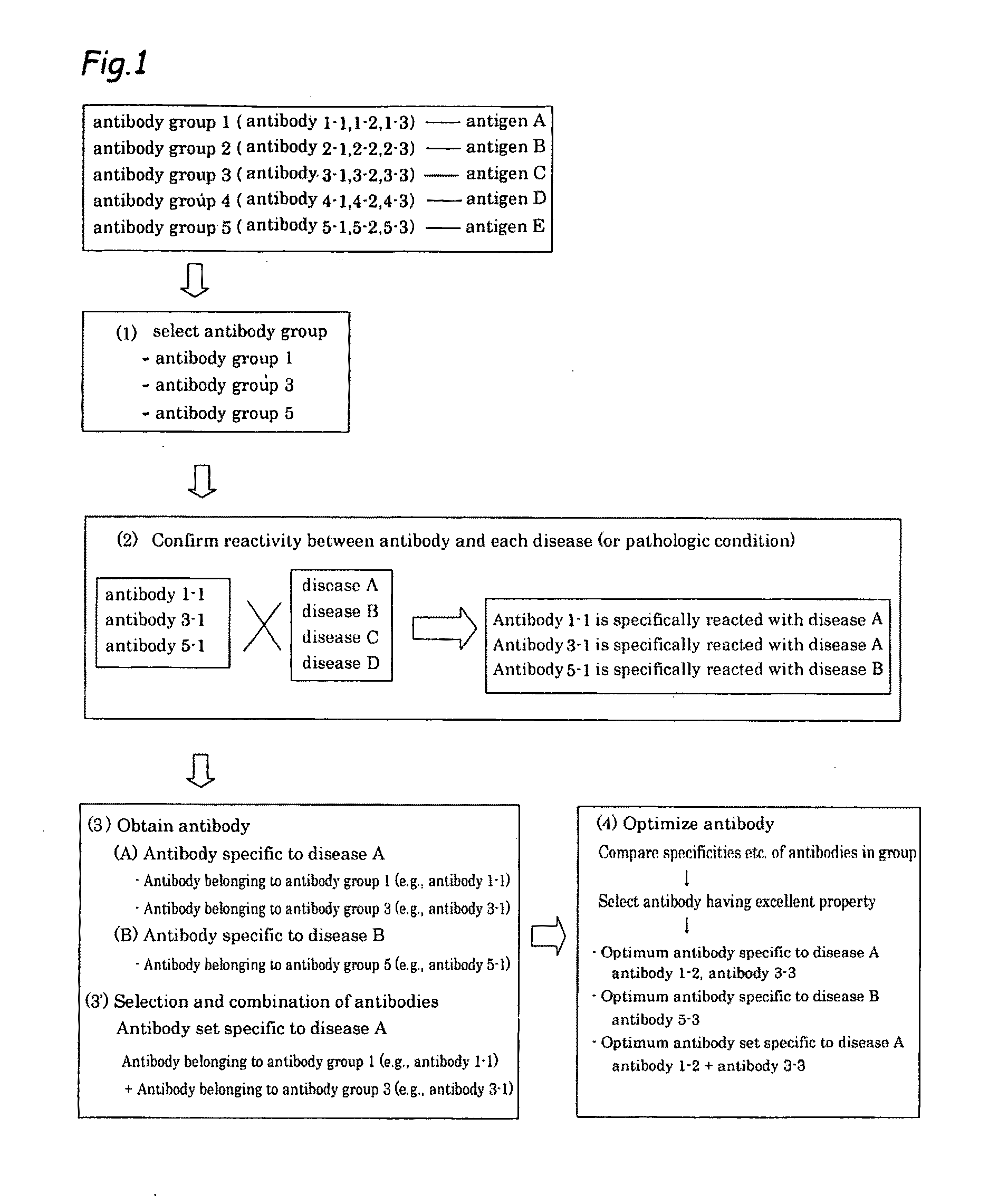
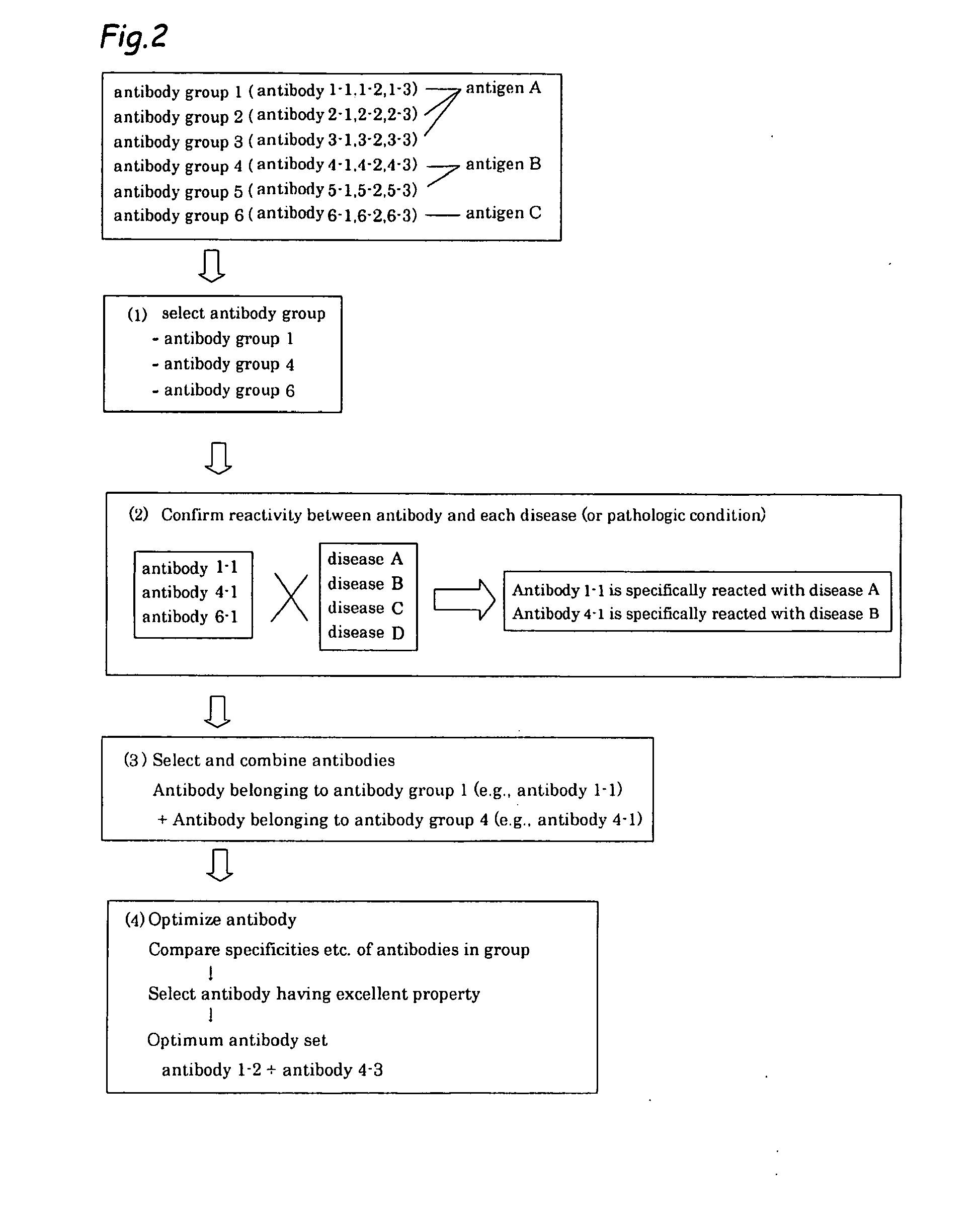
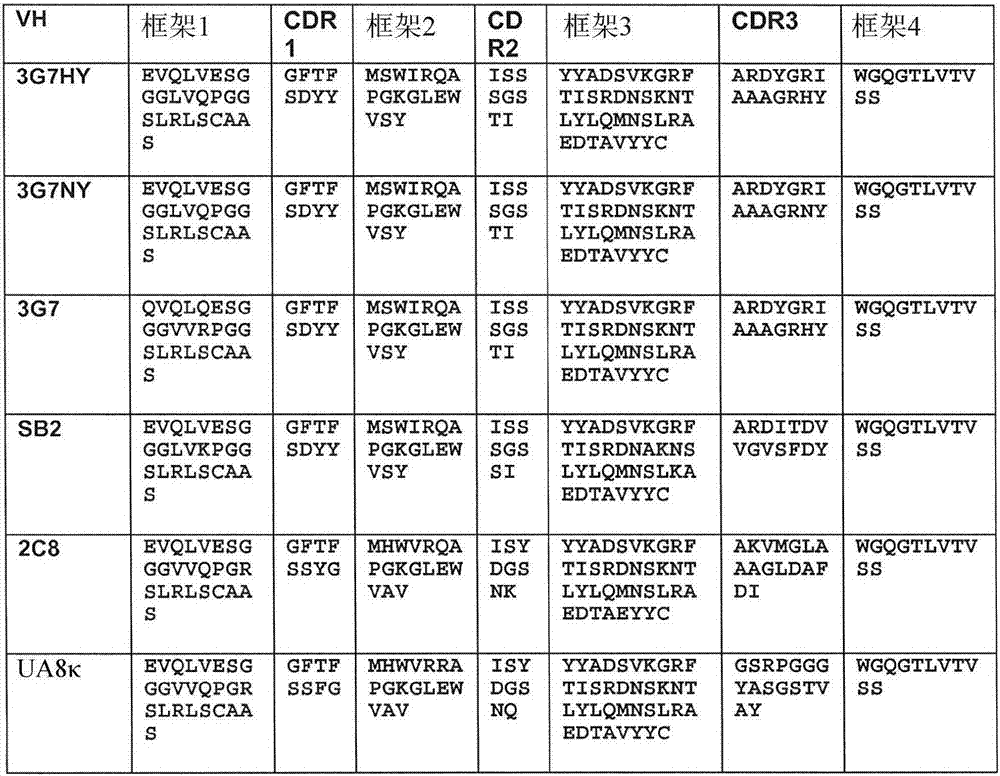
Method of classifying antibody, method of identifying antigen, method of obtaining antibody or antibody set, method of constructing antibody panel and antibody or antibody set and use of the same
InactiveUS20090203538A1Labor moreMany timesPeptide librariesLibrary screeningAntigenCell Surface Antigens
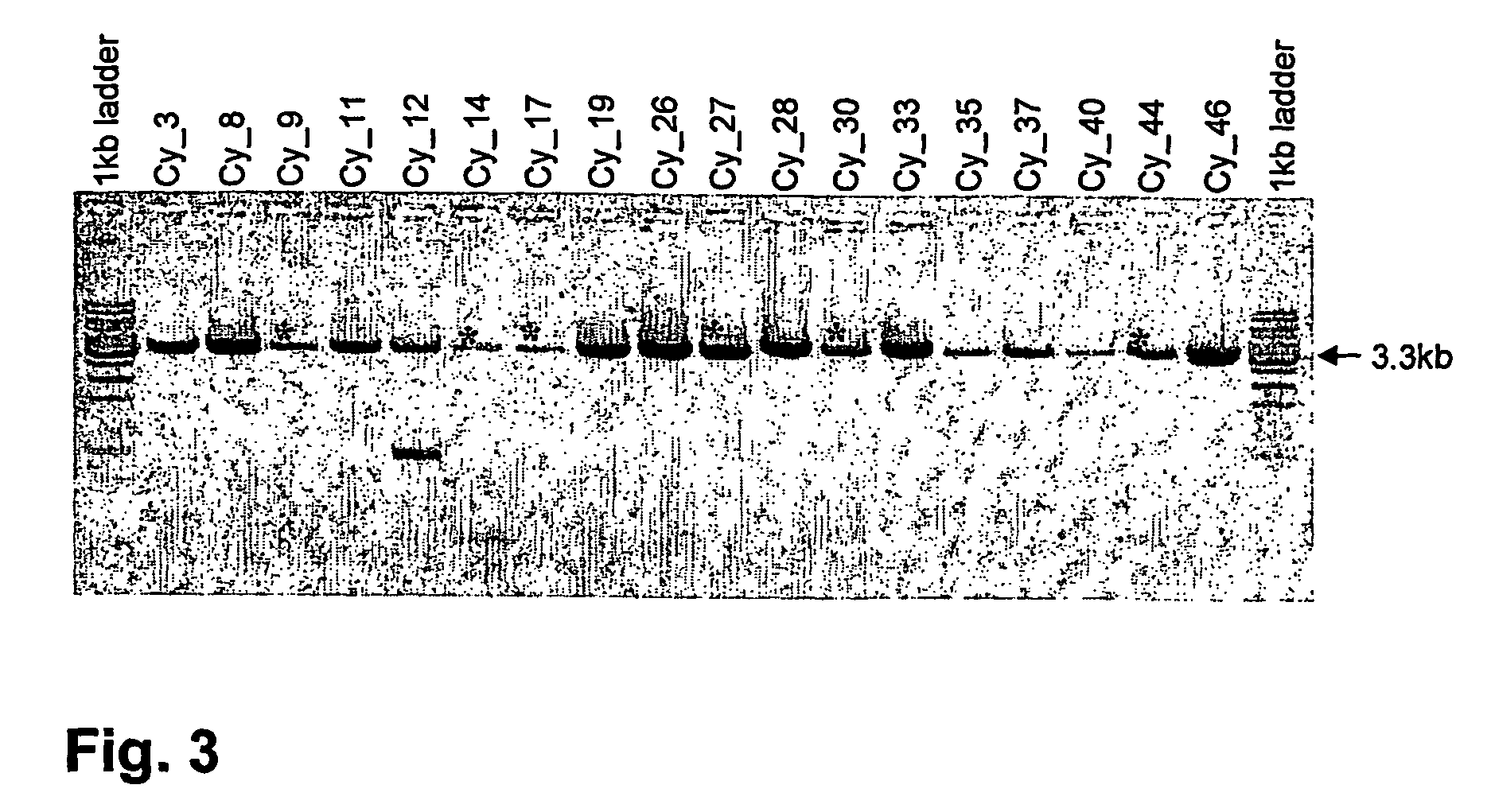
It is intended to provide a method whereby a plural number of antibodies against cell surface antigens are quickly classified and to provide a method whereby antigens of the thus classified antibodies are quickly identified. Further, it is intended to provide a method of promoting the utilization of the useful data obtained by the above methods. Furthermore, it is intended to provide an antibody which is effective in treating or diagnosing cancer. Namely, a method of classifying antibodies which comprises: (1) the step of preparing a plural number of antibodies respectively recognizing cell surface antigens; (2) the step of bringing each of these antibodies into contact with a cell of the same species; (3) the step of analyzing each of the cells having been treated in the step (2) by flow cytometry and thus obtaining data indicating the reactivity of each antibody with its cell surface antigen; and (4) the step of comparing the thus obtained data and classifying the individual antibodies depending on the similarity. A method of identifying antigens which further comprises: (5) the step of selecting one to several antibodies from each antibody group formed in the step (4) and identifying antigens thereof; and (6) on the assumption that antigens of the antibodies belonging to a single antibody group are the same or highly related to one another, making relations between the antigens having been identified in the step (5) and the antibody groups to thereby identify the antigens. An antibody against HER1, an antibody against HER2, an antibody against CD46, an antibody against ITGA3, an antibody against ICAM1, an antibody against ALCAM, an antibody against CD147, an antibody against C1qR, an antibody against CD44, an antibody against CD73, an antibody against EpCAM and an antibody against HGFR, each obtained by using the above methods.
Owner:FUJITA HEALTH UNIVERSITY
Animal model systems for viral pathogenesis of neurodegeneration, autoimmune demyelination, and diabetes
InactiveUS20060130161A1Nervous disorderPeptidesProgressive multifocal leukoencephalopathyAutoimmune disease
Provided are non-human animal model systems for viral pathogenesis of neurodegeneration, autoimmune demyelination, and autoimmune diseases such as diseases of the central nervous system, including multiple sclerosis (MS), and diabetes. Such non-human animal model systems may be suitably employed for the study of diseases such as MS and diabetes and for the identification and characterization of candidate therapeutic compounds and compositions for the treatment of such diseases. Also provided herein are markers and methods for the detection, in patients susceptible to autoimmune disease, of autoimmune diseases of the central nervous system such as progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) following treatment with one or more therapeutic agent as exemplified herein by the therapeutic agent natalizumab. Exemplary animal model systems comprise marmosets infected with a herpesvirus such as HHV6-A and HHV6-B, transgenic mouse and zebrafish animal model systems wherein the transgene encodes CD46, and methods for monitoring the risks of patients having MS, diabetes and other auto-immune disorders treated with anti-adhesion molecules such as natalizumab.
Owner:CARANTECH
Methods and materials for reducing cardiac xenograft rejection
ActiveUS20130111614A1Reducing cardiac xenograft rejectionIncreased durabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenGlycan
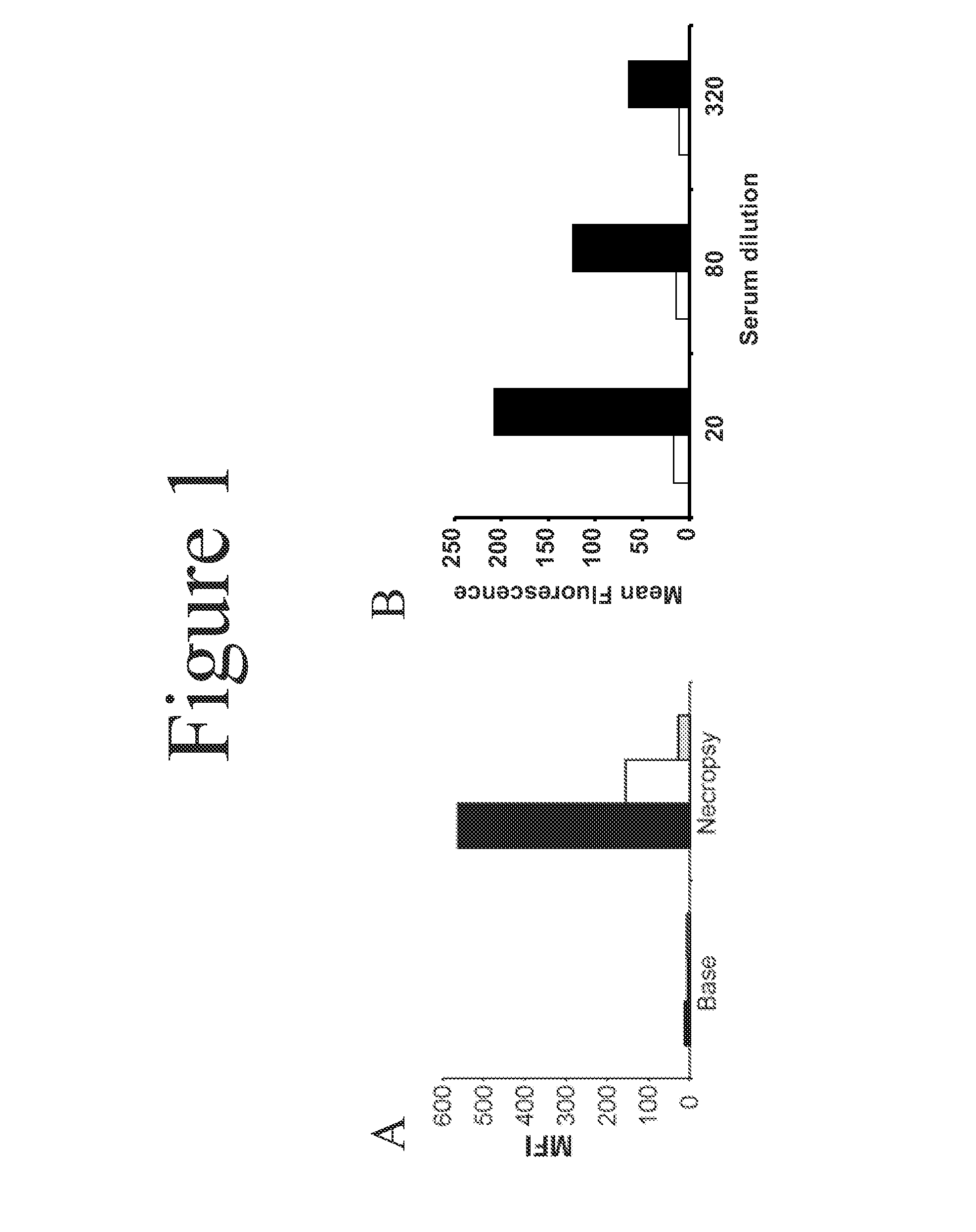
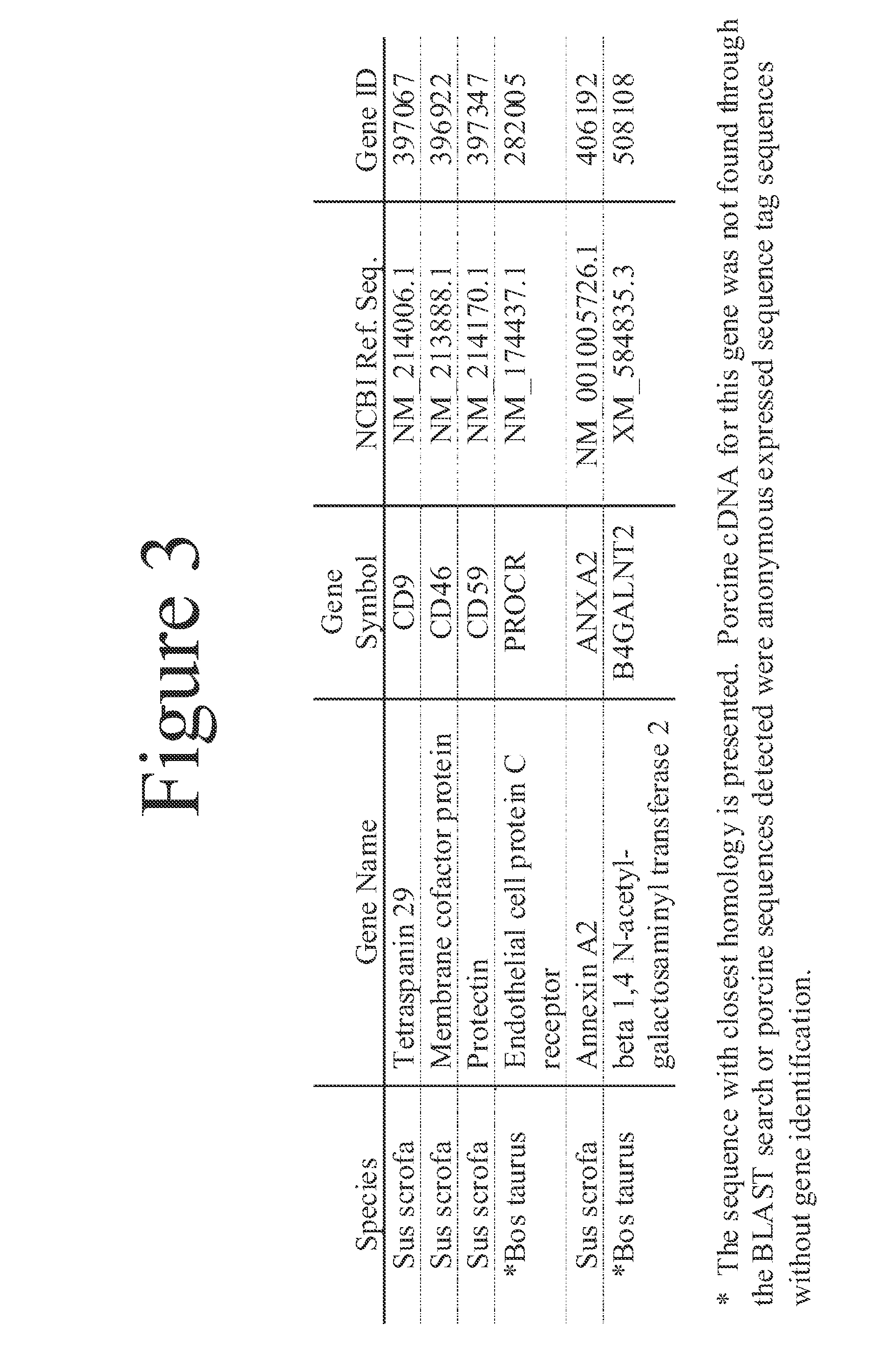
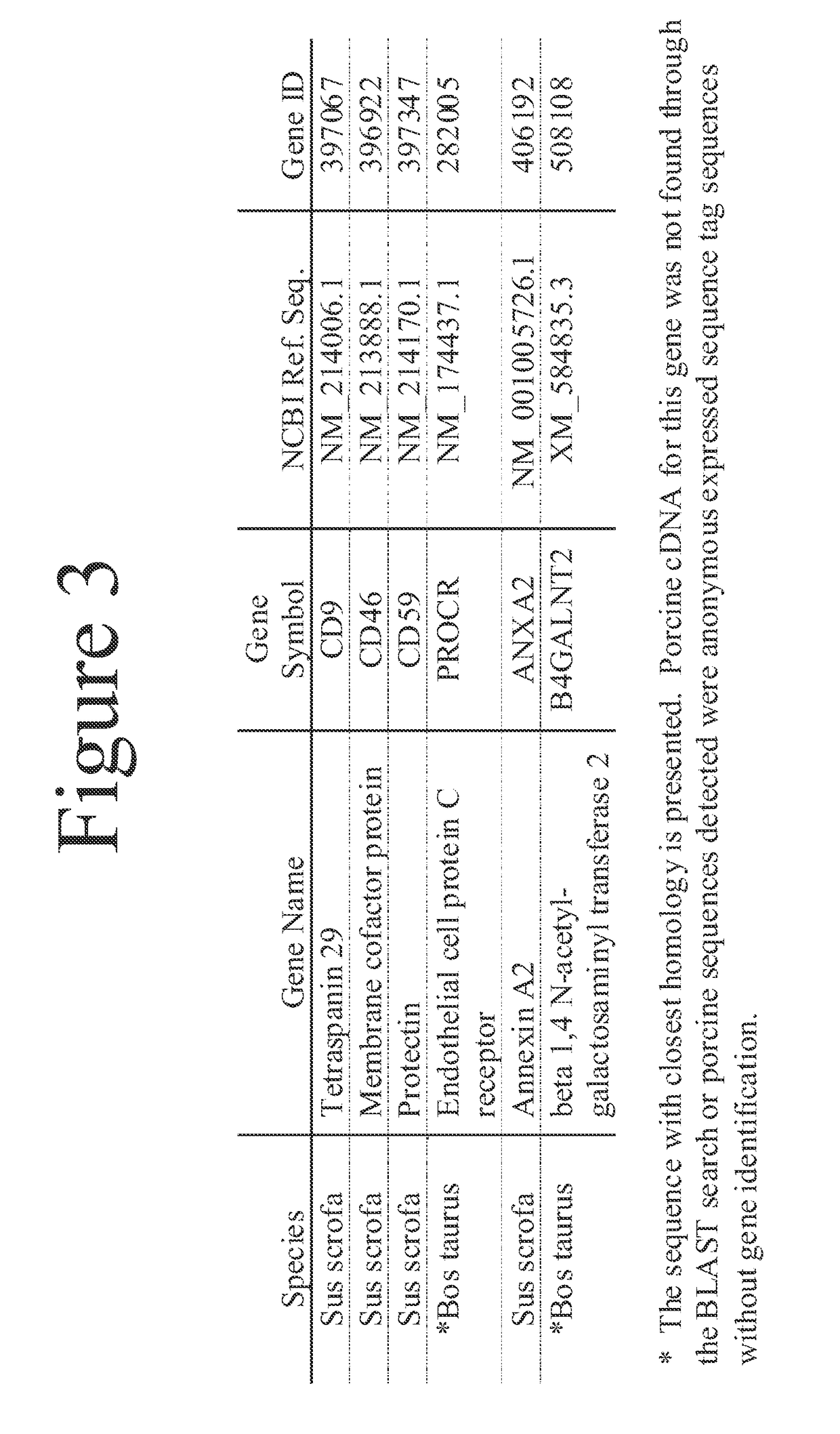
This document provides methods and materials involved in reducing cardiac xenograft rejection. For example, methods and materials for preparing transgenic pigs expressing reduced or no endogenous Sda or SDa-like glycans derived from the porcine β1,4 N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 2 (B4GALNT2) glycosyltransferase and / or reduced or no endogenous α-Gal antigens, methods and materials for modifying the xenograft recipient's immunological response to non-Gal antigens (e.g. CD46, CD59, CD9, PROCR, and ANXA2) to reduce cardiac xenograft rejection, and methods and materials for monitoring the progress of xenotransplant immunologic rejection are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Duplex-specific chimeric antigen receptor molecule and application thereof to tumor therapy
ActiveCN109503716AIncreased persistenceImprove targetingPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsSequence signalCD20
Owner:CELLYAN THERAPEUTICS WUHAN CO LTD
Fiber-modified adenoviral vectors for enhanced transduction of tumor cells
InactiveCN101068933AReduced amount of vectorEnhanced transductionBiocideViral antigen ingredientsPrimary tumorSerotype
Adenoviral vectors which effectively transduce primary tumor cells are provided. The adenoviral vectors comprise a chimeric adenovirus fiber protein which includes at least a portion of a Subgroup C adenovirus fiber shaft and at least a portion of a Subgroup B adenovirus or serotype 37 adenovirus head, wherein the head region binds CD46.
Owner:细胞基因系统有限公司
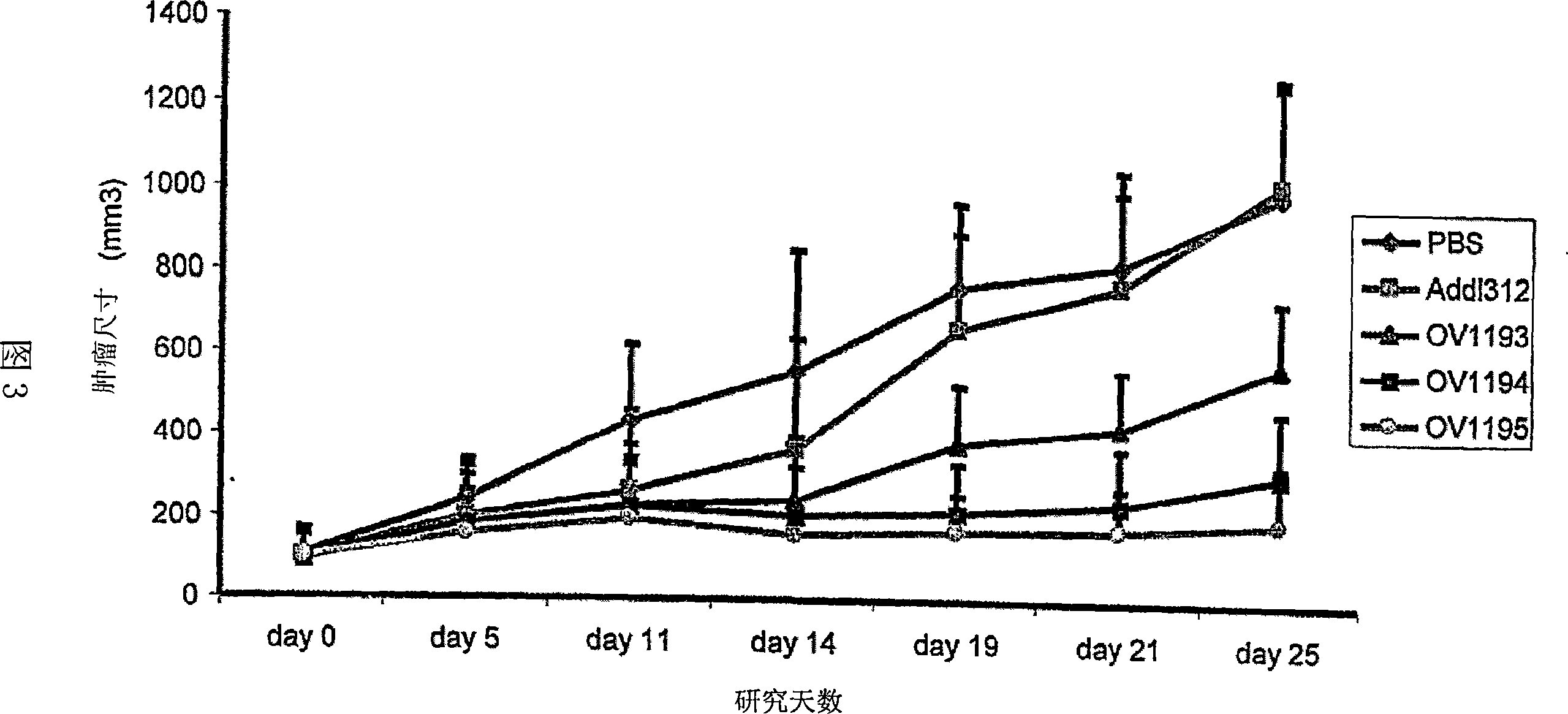
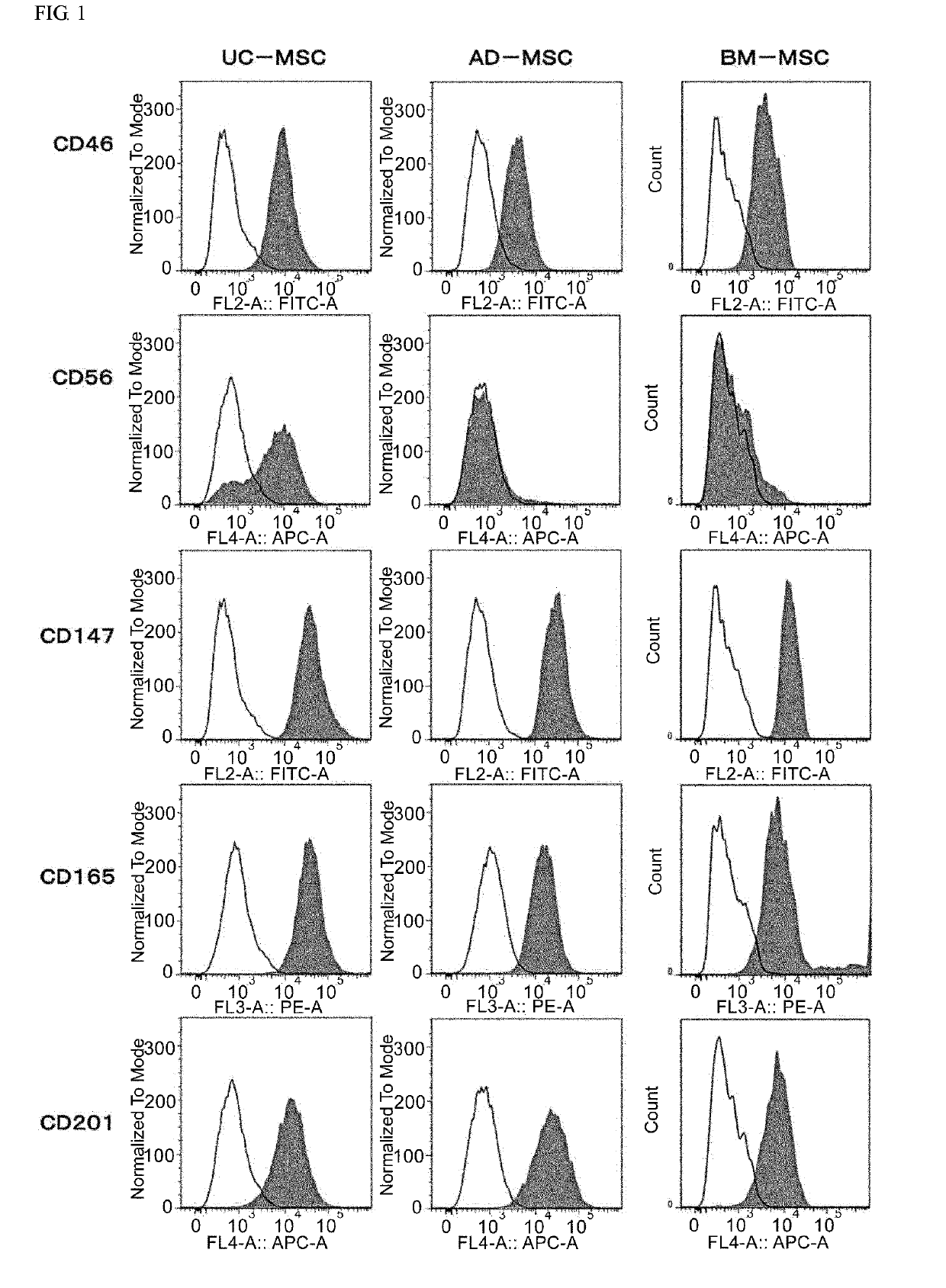
Mesenchymal stem cell expressing at least one cell surface marker selected from the group consisting of cd201, cd46, cd56, cd147, and cd165, method for preparing the same, pharmaceutical composition containing the mesenchymal stem cells, and method for preparing the same
An object of the present invention is to provide novel mesenchymal stem cells demonstrating superior therapeutic effects for various diseases, a novel pharmaceutical composition containing the mesenchymal stem cells, and methods for preparing these. The present invention provides mesenchymal stem cells expressing at least one cell surface marker selected from the group consisting of CD201, CD46, CD56, CD147 and CD165. The mesenchymal stem cells expressing such a specific marker are positive for CD29, CD73, CD90, CD105 and CD166, and maintain an undifferentiated state.
Owner:ROHTO PHARM CO LTD
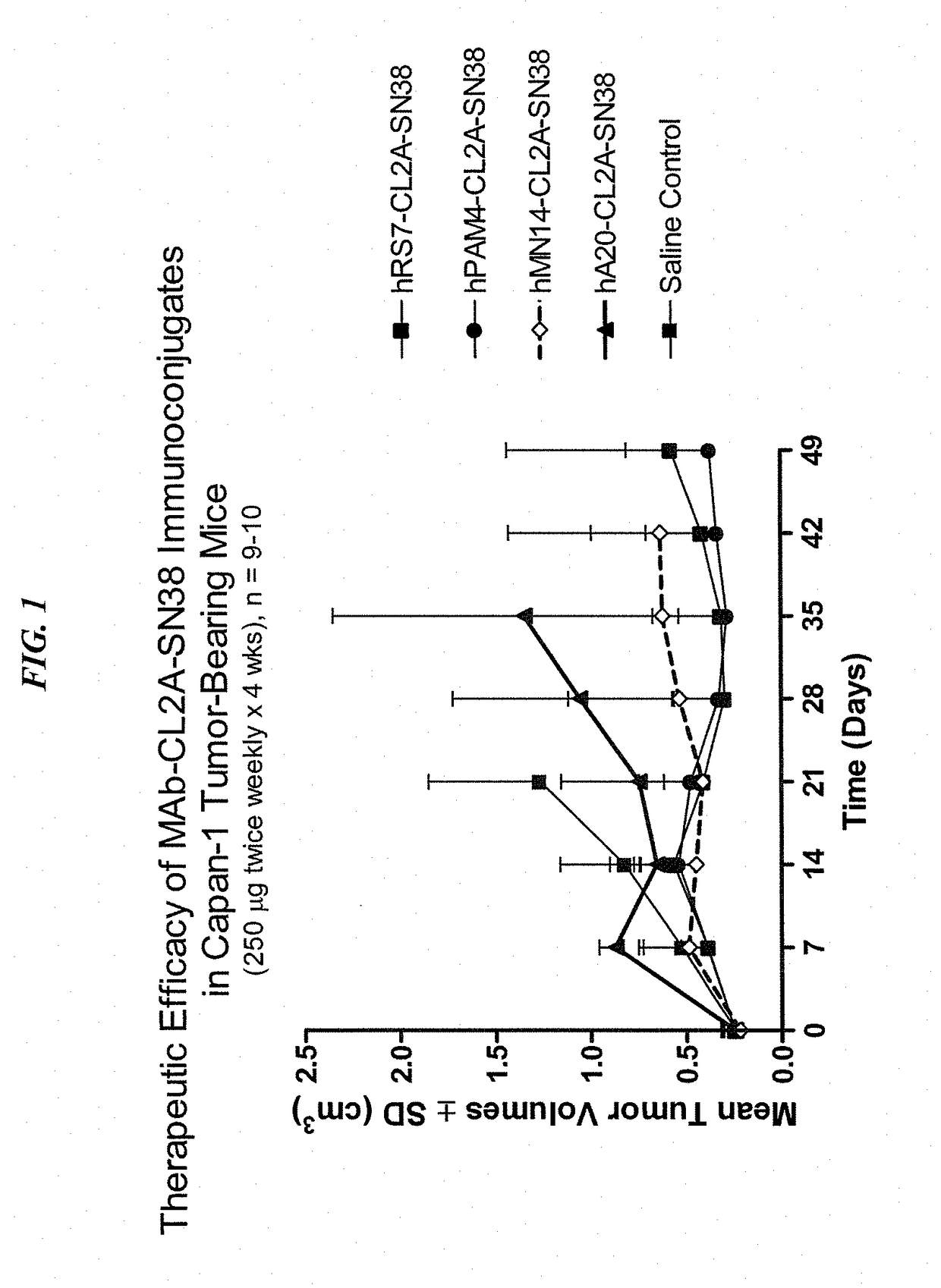
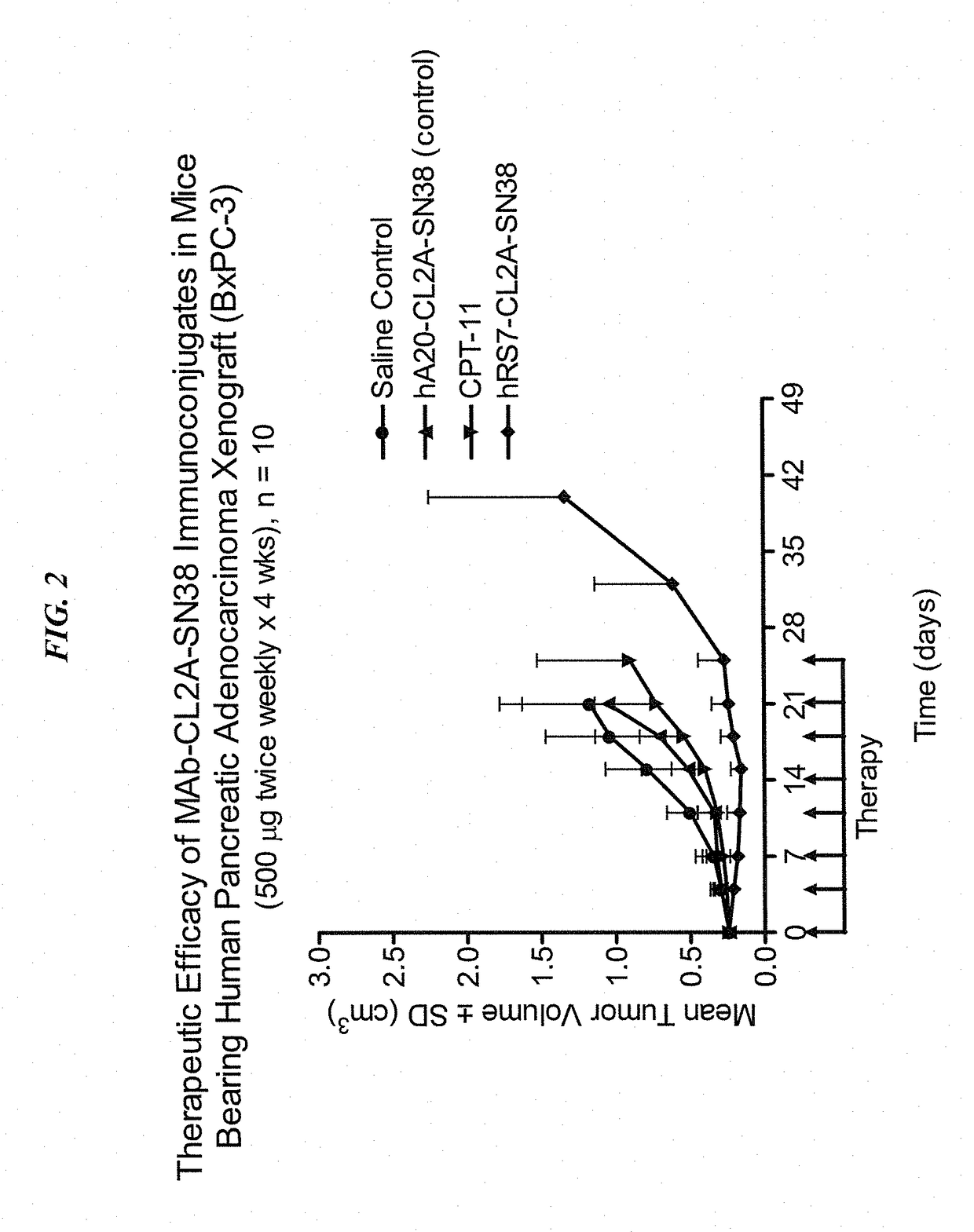
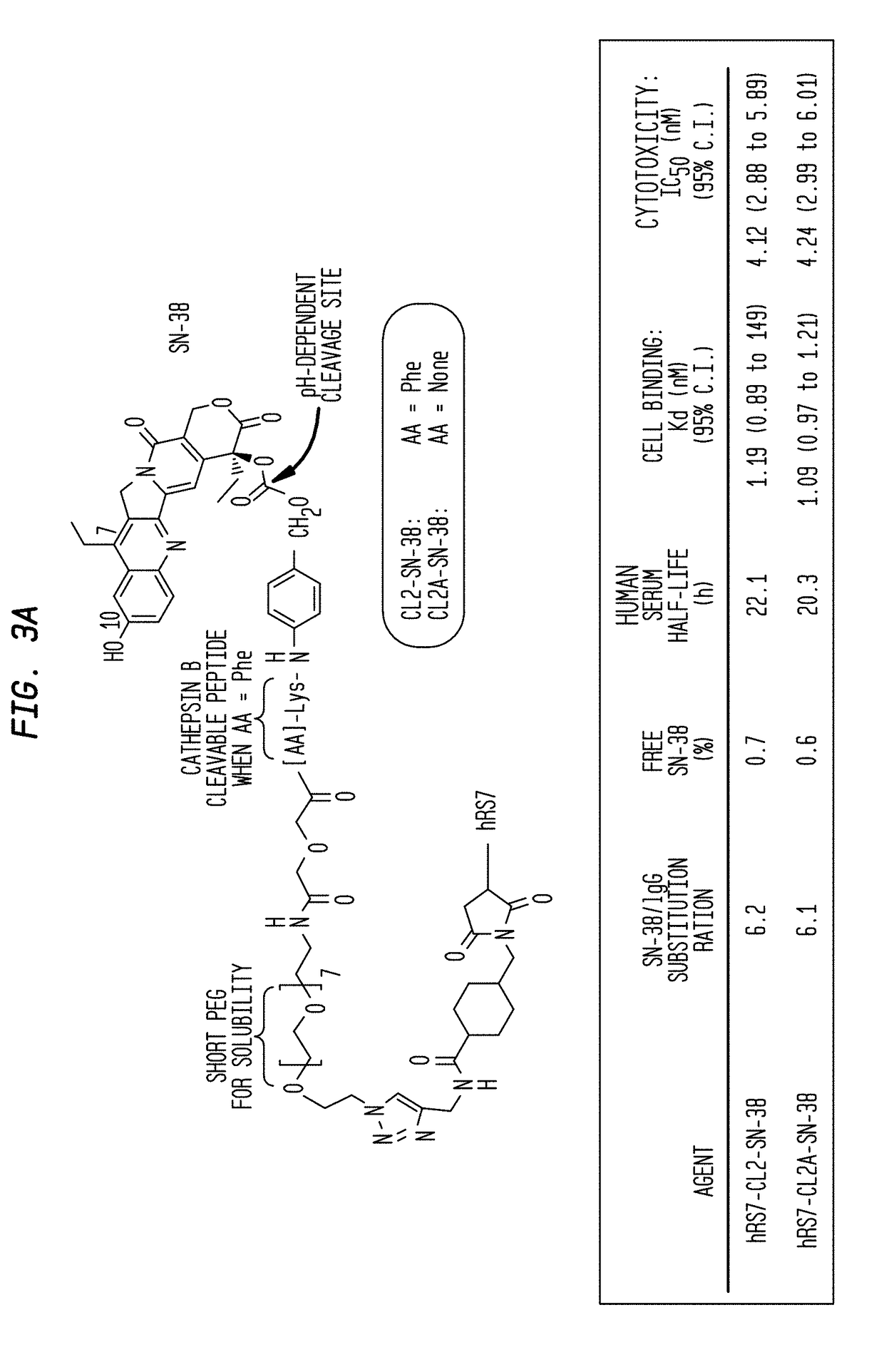
Subcutaneous administration of antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy
ActiveUS20180280532A1Good effectLow toxicityInorganic non-active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCD20Lymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to methods of cancer therapy using subcutaneous administration of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Preferably, the ADC comprises an antibody that binds to Trop-2, CEACAM5, CEACAM6, CD20, CD22, CD30, CD46, CD74, Her-2, folate receptor, or HLA-DR. More preferably, the drug is SN-38. Subcutaneous administration is at least as effective as intravenous administration of the same ADC. Surprisingly, subcutaneous administration can be used without inducing unmanageable adverse local toxicity at the injection site. Subcutaneous administration is advantageous in requiring less frequent administration, substantially reducing the amount of time required for intravenous administration, and reducing the levels of systemic toxicities observed with intravenous administration. When administered at specified dosages and schedules, the ADCs can reduce solid tumors in size, reduce or eliminate metastases and are effective to treat cancers resistant to standard therapies, such as radiation therapy, chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
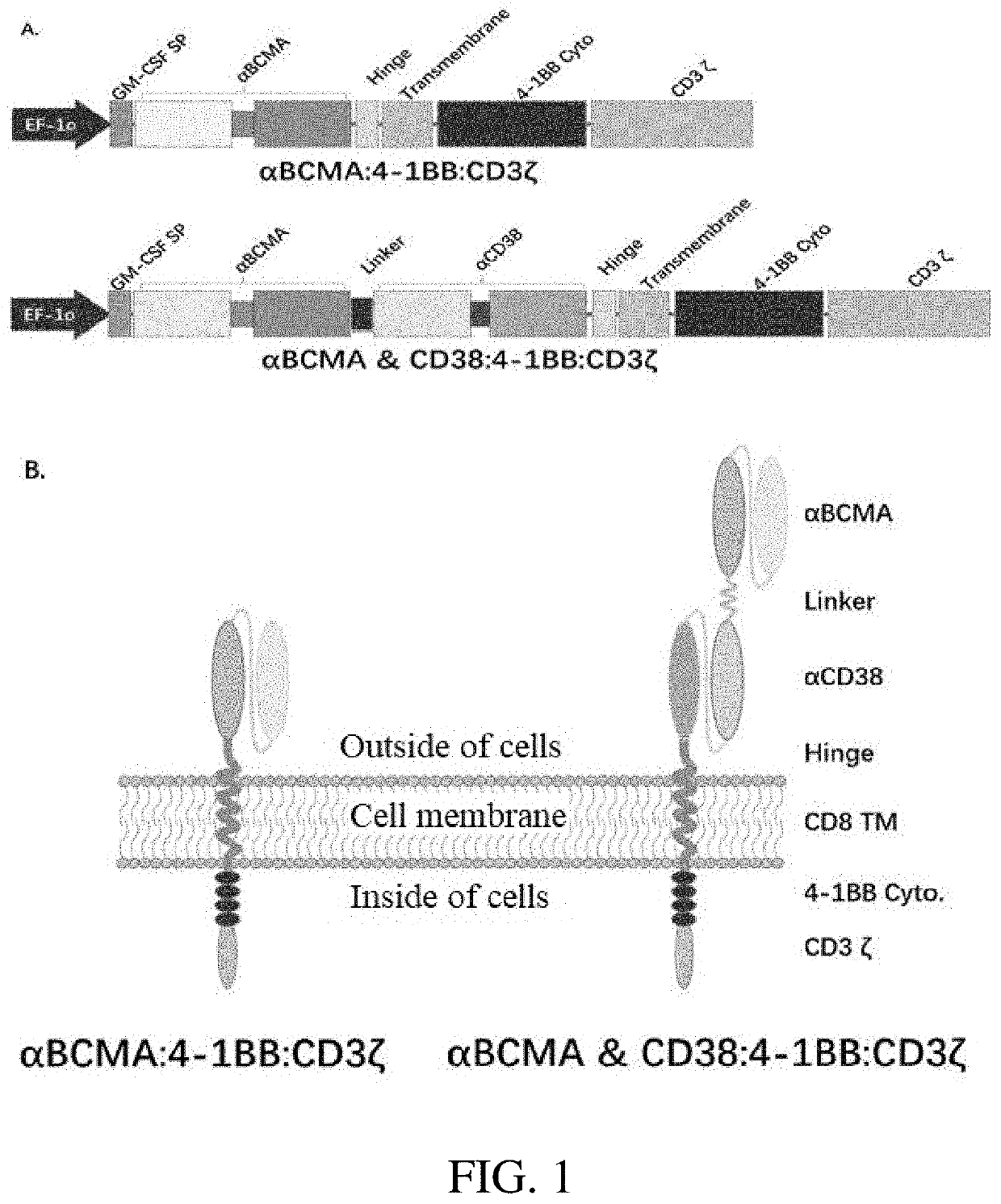
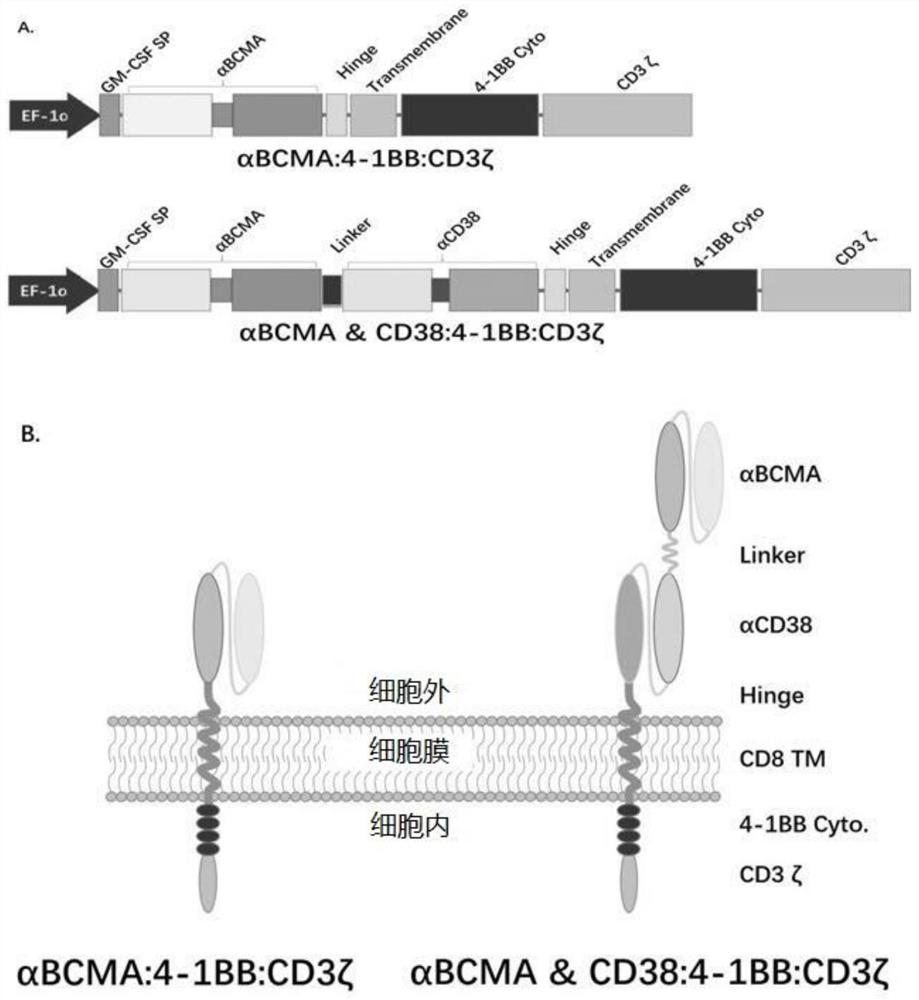
Bispecific chimeric antigen receptors and their application in the treatment of tumor
PendingUS20210000870A1Improve targetingAvoid it happening againPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCD20CD79A
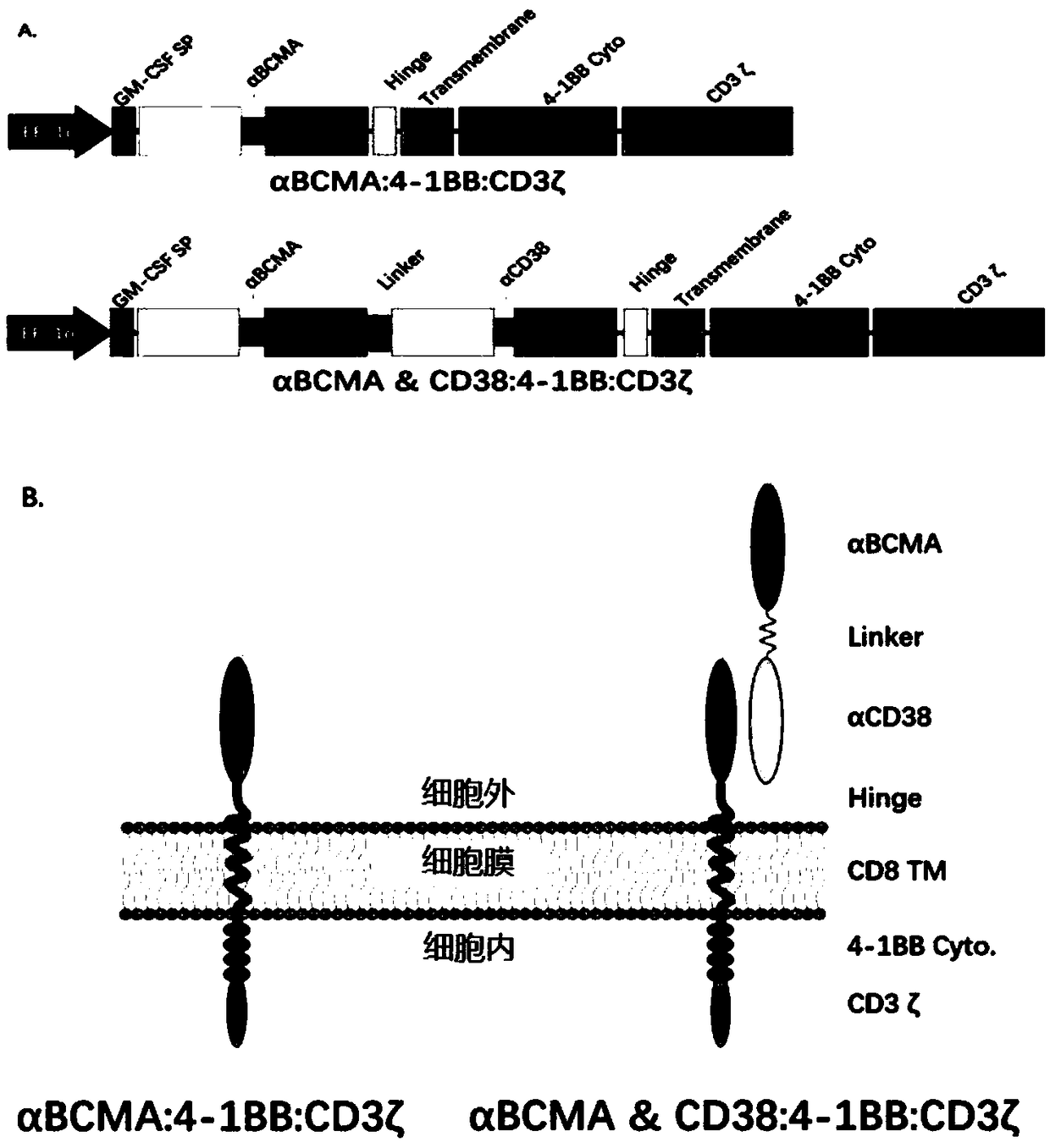
The embodiments of the present invention provide a bispecific chimeric antigen receptor, consisting of a signal peptide, two specific antigen-binding fragments, an extracellular spacer region, a transmembrane region, an intracellular co-stimulatory signaling domain, the first antigen that is recognized and bound by the specific antigen-binding fragments is a member selected from the group consisting of CD19, CD20, CD22, CD33, CD269, CD138, CD79a, CD79b, CD23, ROR1, CD30, B cell surface antibody light chain, CD44, CD123, Lewis Y, CD7 and CD46; the second antigen that is recognized and bound by the specific antigen-binding fragments is CD38, the two specific antigen-binding fragments is linked by a linker peptide, the bispecific chimeric antigen receptor can recognize respectively two kinds of tumor-associated antigens by constructing low affinity chimeric antigen receptors and high affinity chimeric antigen receptors and have very strong specificity. In addition, the embodiments of the present invention also provide a use of the bispecific chimeric antigen receptor in the treatment of tumors.
Owner:CELLYAN THERAPEUTICS WUHAN CO LTD
Implantation of a cardiac xenograft from a B4GALNT2KO and GTKO transgenic pig to reduce immunogenicity
ActiveUS9642899B2Low immunogenicityIncreased durabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenGlycan
This document provides methods and materials involved in reducing cardiac xenograft rejection. For example, methods and materials for preparing transgenic pigs expressing reduced or no endogenous Sda or SDa-like glycans derived from the porcine β1,4 N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase 2 (B4GALNT2) glycosyltransferase and / or reduced or no endogenous α-Gal antigens, methods and materials for modifying the xenograft recipient's immunological response to non-Gal antigens (e.g. CD46, CD59, CD9, PROCR, and ANXA2) to reduce cardiac xenograft rejection, and methods and materials for monitoring the progress of xenotransplant immunologic rejection are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Genetically engineered bacterium capable of expressing cell-penetrating peptide fusion protein and application
InactiveCN104530241AHigh expressionEase of mass productionBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsClassical swine fever virus CSFVCell membrane
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium capable of expressing cell-penetrating peptide fusion protein and application. The genetically engineered bacterium E.coli BL21 / pET-32a-CSFR with CCTCC NO: M2014631. The strain can be used for expressing protein transduction domain polypeptide (PEP-1) and hog cholera virus acceptor (CD46) genetically engineered fusion protein PEP-1-CD46. The genetically engineered bacterium has the advantages of large expression amount, soluble protein, low cost and high safety. The expressed PEP-1-CD46 protein can be used as mediated protein of hog cholera virus penetrating a cell membrane, so that the virus titer of hog cholera virus can be improved, and the defect that the virus content in a current hog cholera virus cell vaccine is low and cannot achieve the standard of vaccine preparation can be overcome.
Owner:武汉市畜牧兽医科学研究所
Novel markers for dopaminergic neuron progenitor cells
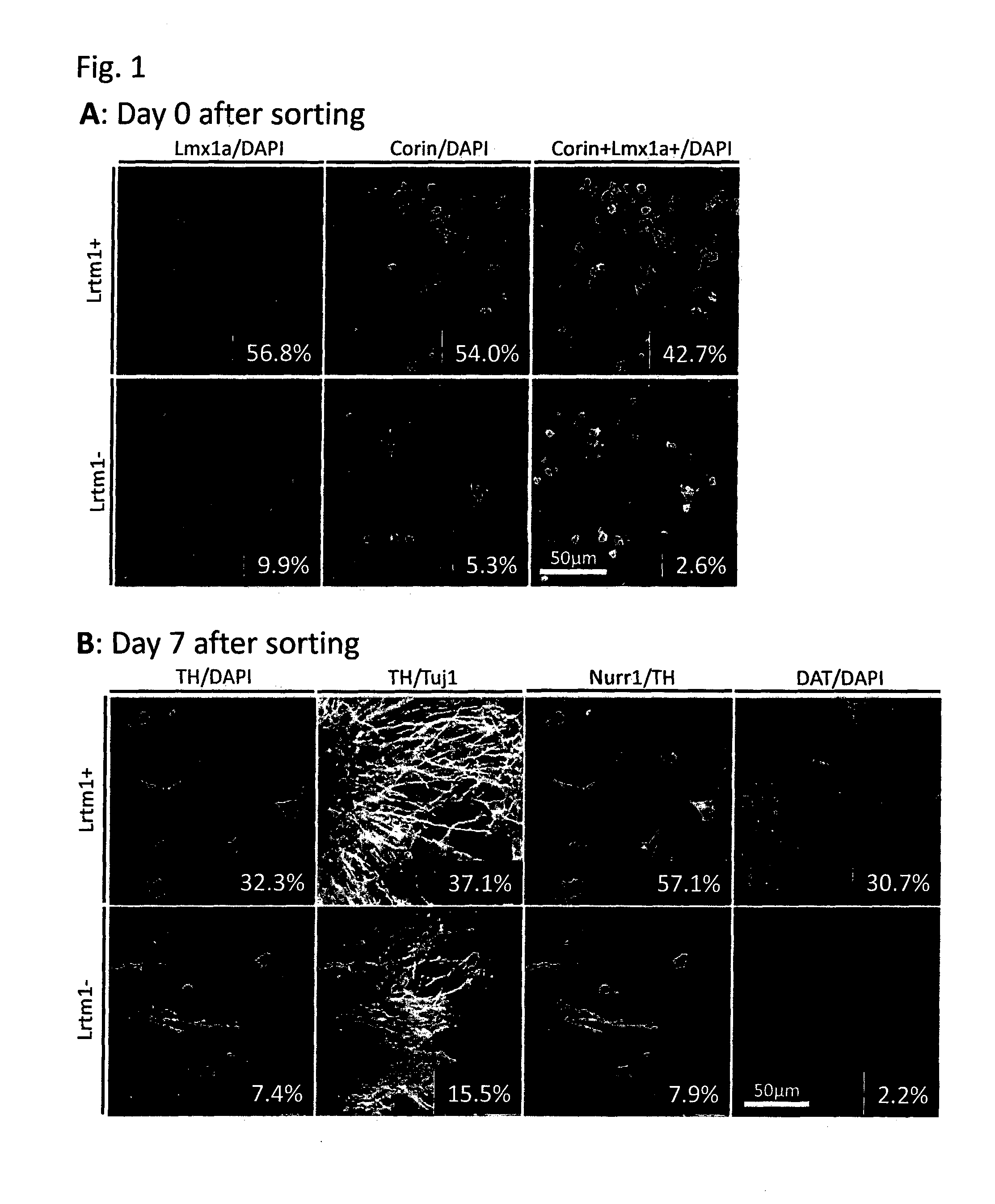
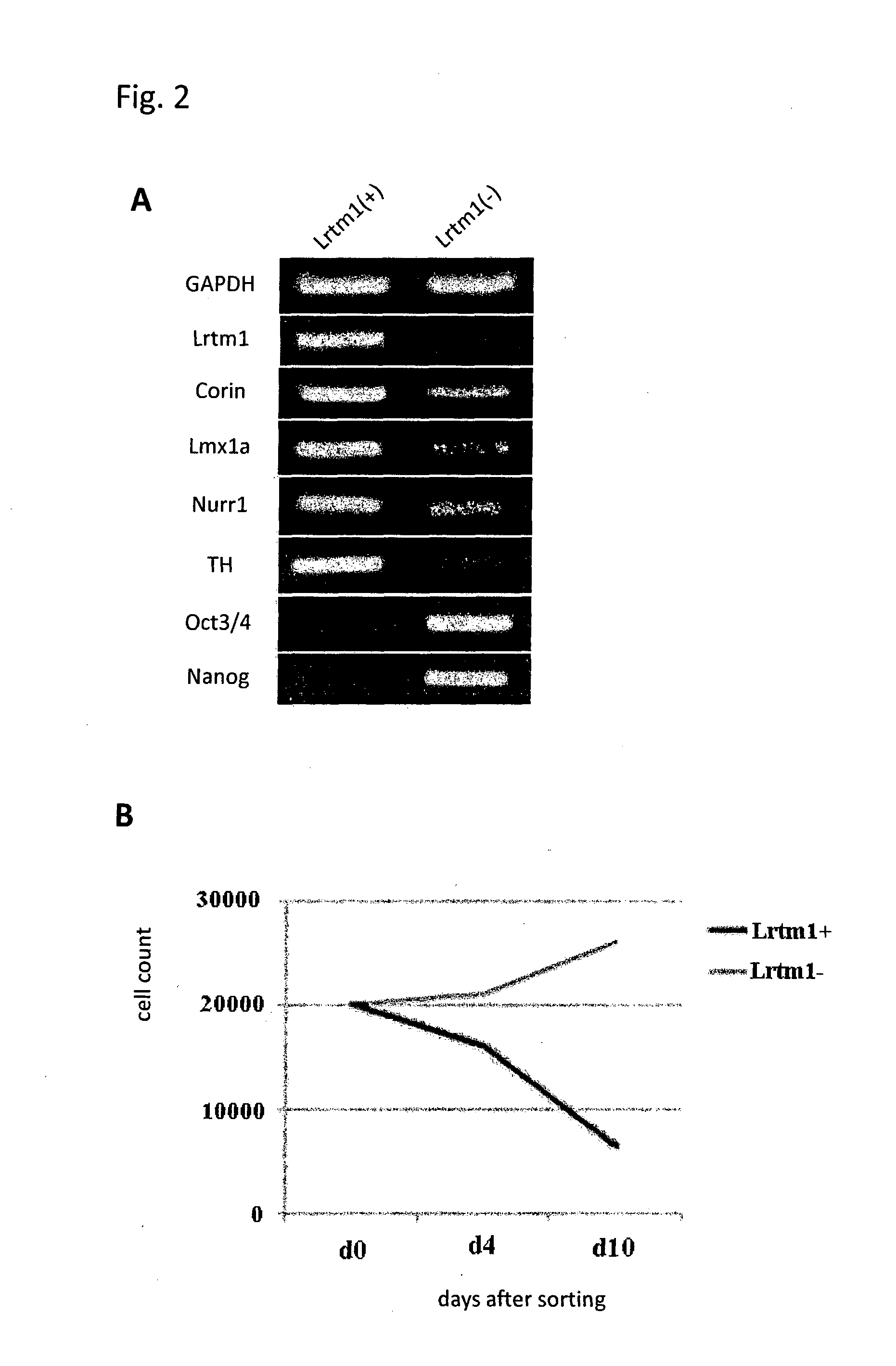
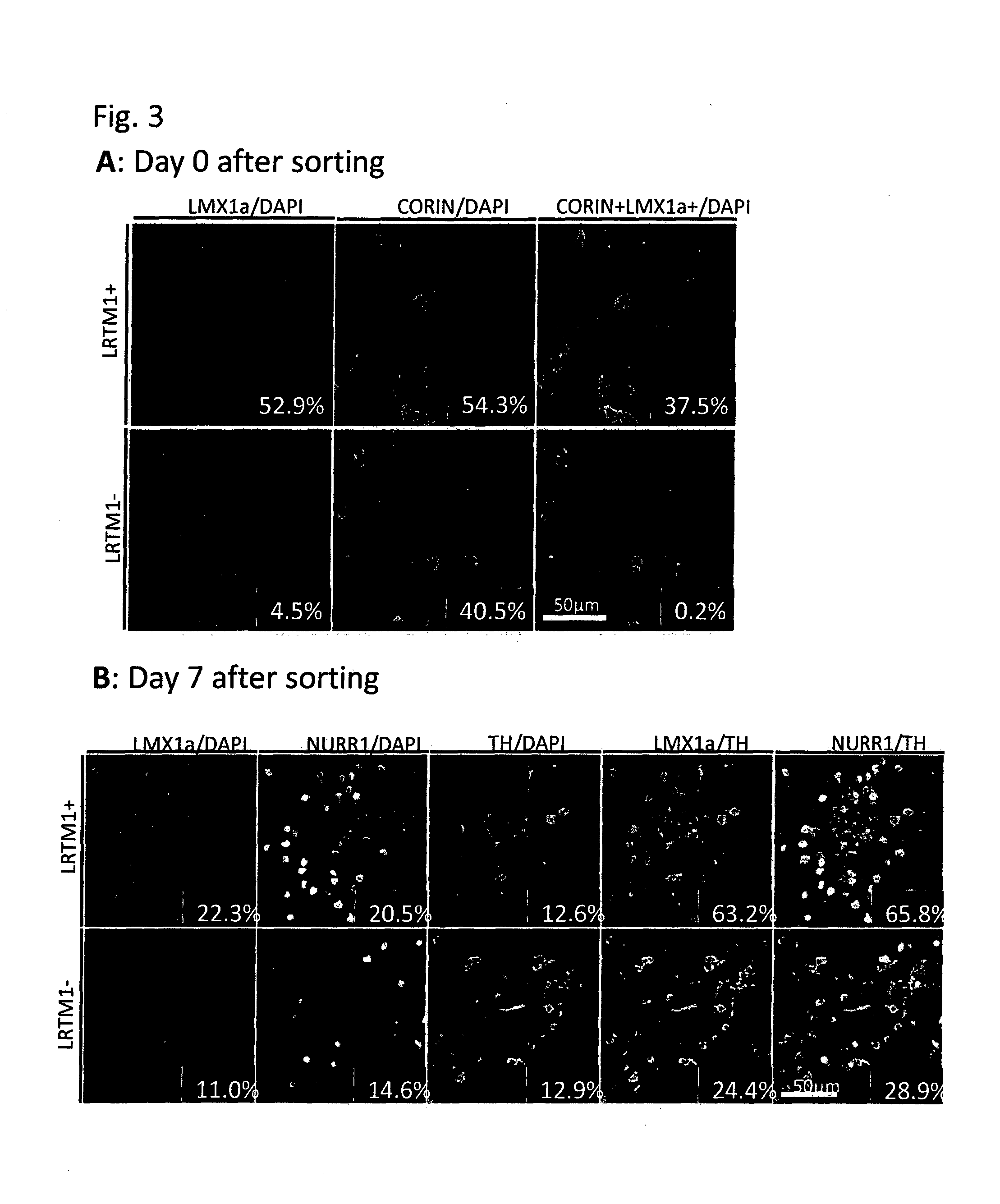
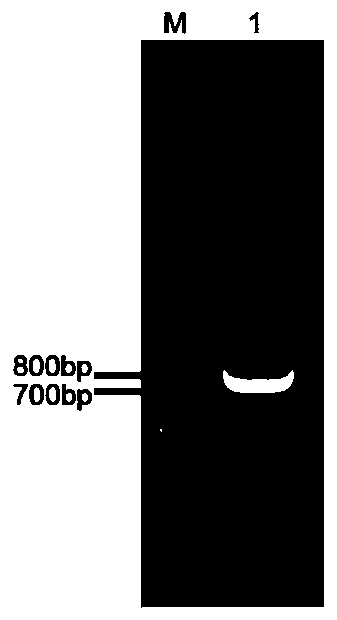
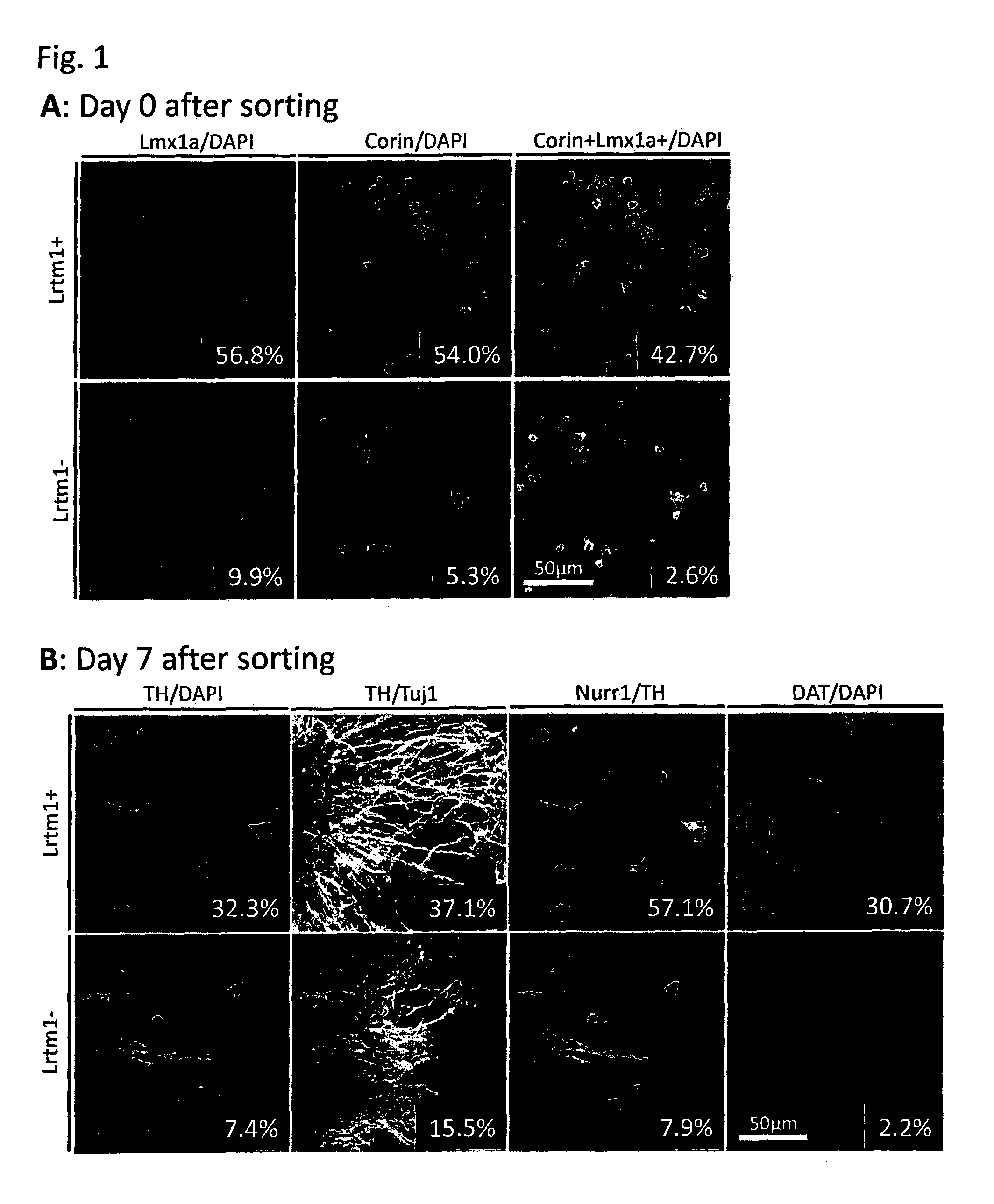
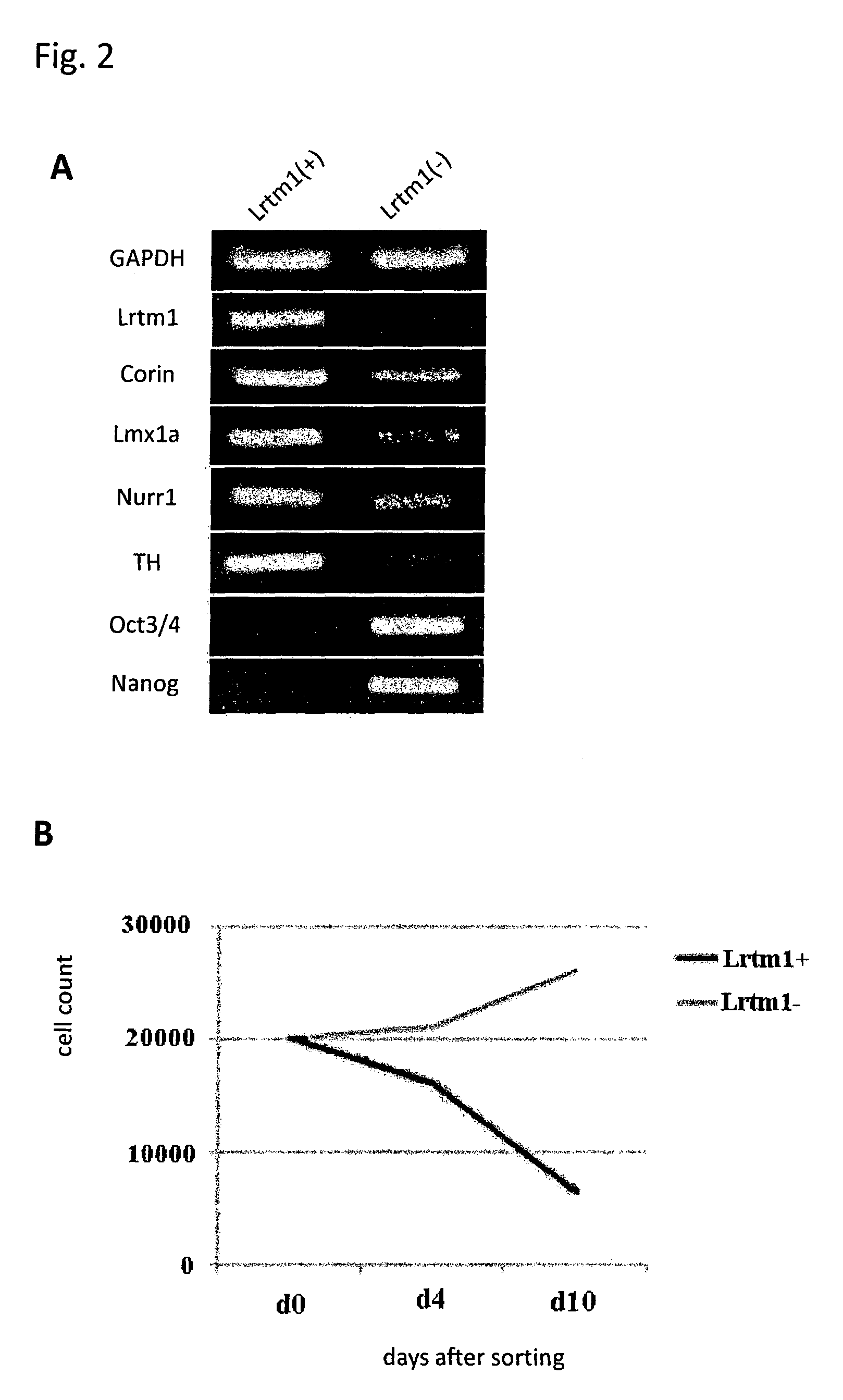
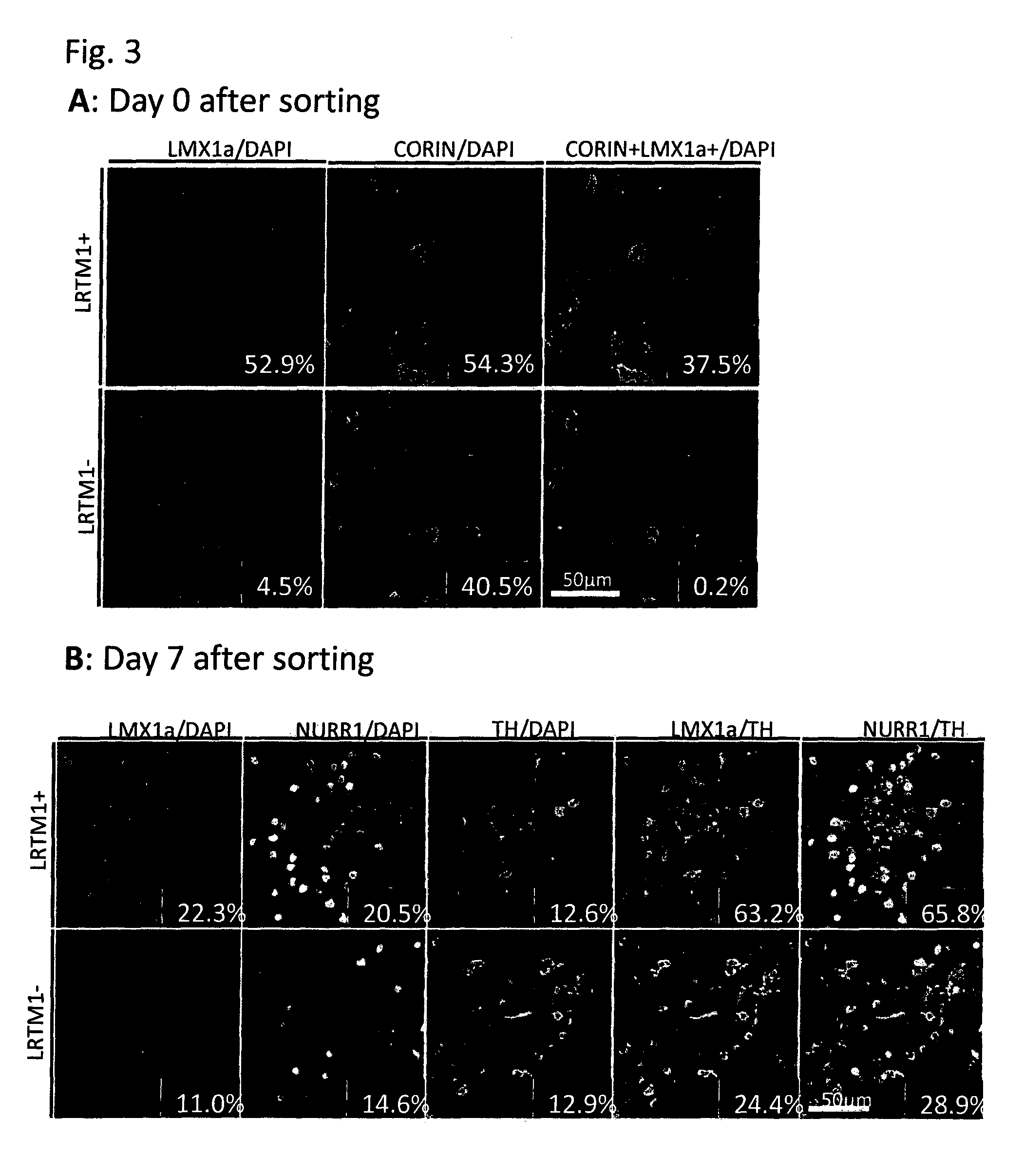
The present invention provides a method for selecting dopaminergic neuron progenitor cells, which comprises detecting any one or more of markers selected from the group consisting of CD15 (SSEA-1), CD24, CD46, CD47, CD49b, CD57, CD58, CD59, CD81, CD90, CD98, CD147, CD184, Disalogangliosid GD2, SSEA-4, CD49f, SERINC4, CCR9, PHEX, TMPRSS11E, HTR1E, SLC25A2, Ctxn3, Cc17, Chrnb4, Chrna3, Kcnv2, Grm2, Syt2, Lim2, Mboat1, St3ga16, Slc39a12, Tacr1, Lrtm1, Dscam and CD201.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Novel pseudotyped lentiviral particles and their use in the in vitro targeted transduction of undifferentiated pluripotent human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20150291979A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHemagglutininGerm layer
The inventors developed novel pseudotyped lentiviral vector particles comprising a morbillivirus fusion (F) protein and a mutated hemagglutinin (H) protein of the measles virus (MeV) or the Edmonton strain of the measles virus (MeVEdm), wherein the cytoplasmic portions of the F and the H protein are truncated, and wherein the amino acids necessary for receptor recognition in the H protein are mutated that it does not interact with CD46, SLAM and / or nectin-4 and further has a single chain antibody to a cell surface marker of hESCs and iPSCs at its ectodomain. In this invention, the single chain variable fragment (scFv) anti-cell surface marker coding sequence of the single chain antibody is fused to the coding sequence at the ectodomain of the H protein, wherein the single chain antibody is selected from the group consisting of CD30, EpCAM (CD326), CD9, Thy-1 (CD90), SSEA-3, SSEA-4, TRA-1-60 or TRA-1-81. The transduction according to the present invention does not interfere with the pluripotency, i.e. present transduced hESCs and iPSCs remain undifferentiated, i.e. are able differentiate into all germ layer lineages.
Owner:PAUL EHRLICH INST - FEDERAL OFFICE FOR SERA & VACCINE
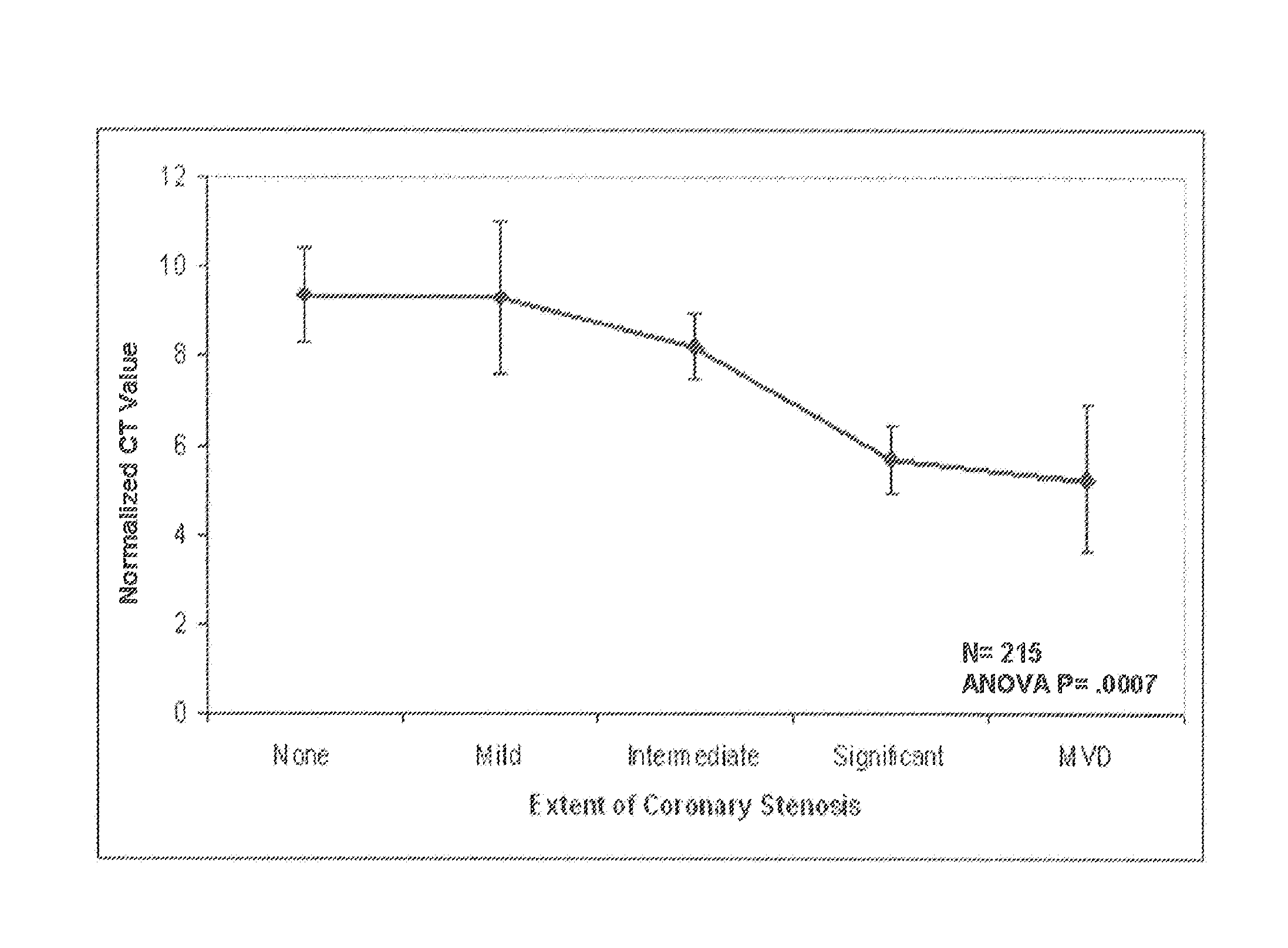
Predictive models and methods for diagnosing and assessing coronary artery disease
InactiveUS20110184712A1Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesOLIG2Coronary artery disease
Biomarkers useful for diagnosing and assessing the extent of coronary artery disease (CAD) are provided, along with kits for measuring their expression. The invention also provides predictive models, based on the biomarkers, as well as computer systems, and software embodiments of the models for scoring and optionally classifying samples. In a preferred embodiment, the biomarkers are organized into clustered groups. The expression level of the biomarkers within a group are highly correlated to each other in normal and disease states. Expression values of genes chosen from each of two, three, four or five of the clustered gene groups, A, B, C, D, E may be used. Alternatively, expression values of genes chosen from the groups are combined into a metagene. Preferred biomarkers include S100A12, S100A8, S100A9, BCL2A1, and F5 (group A); XK, P62, and FECH (group B); TUBB2 (group C); IFNG, PDGFB, VSIG4, and TNF (group D); CSF3R, TLR5, CD46, and NCF1 (group E); S100A12, S100A9, BCL2A1, TXN and CSTA (group I); OLIG1, OLIG2, ADORA3, CLC, and SLC29A1 (group II); and CBS and ARG1 (group IV).
Owner:CARDIODX
Methods for detecting and treating cancers having adenosine pathway activation
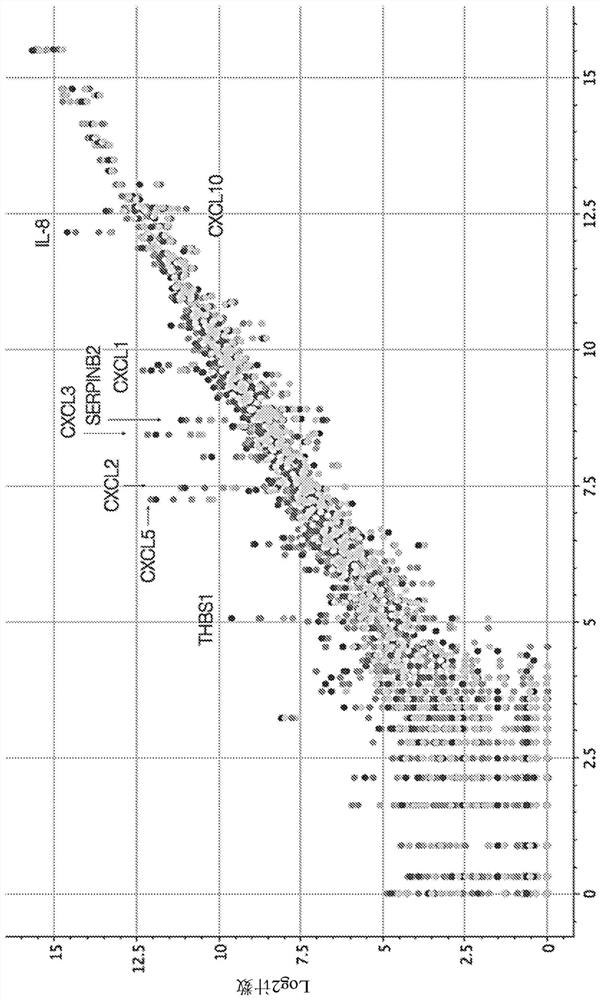
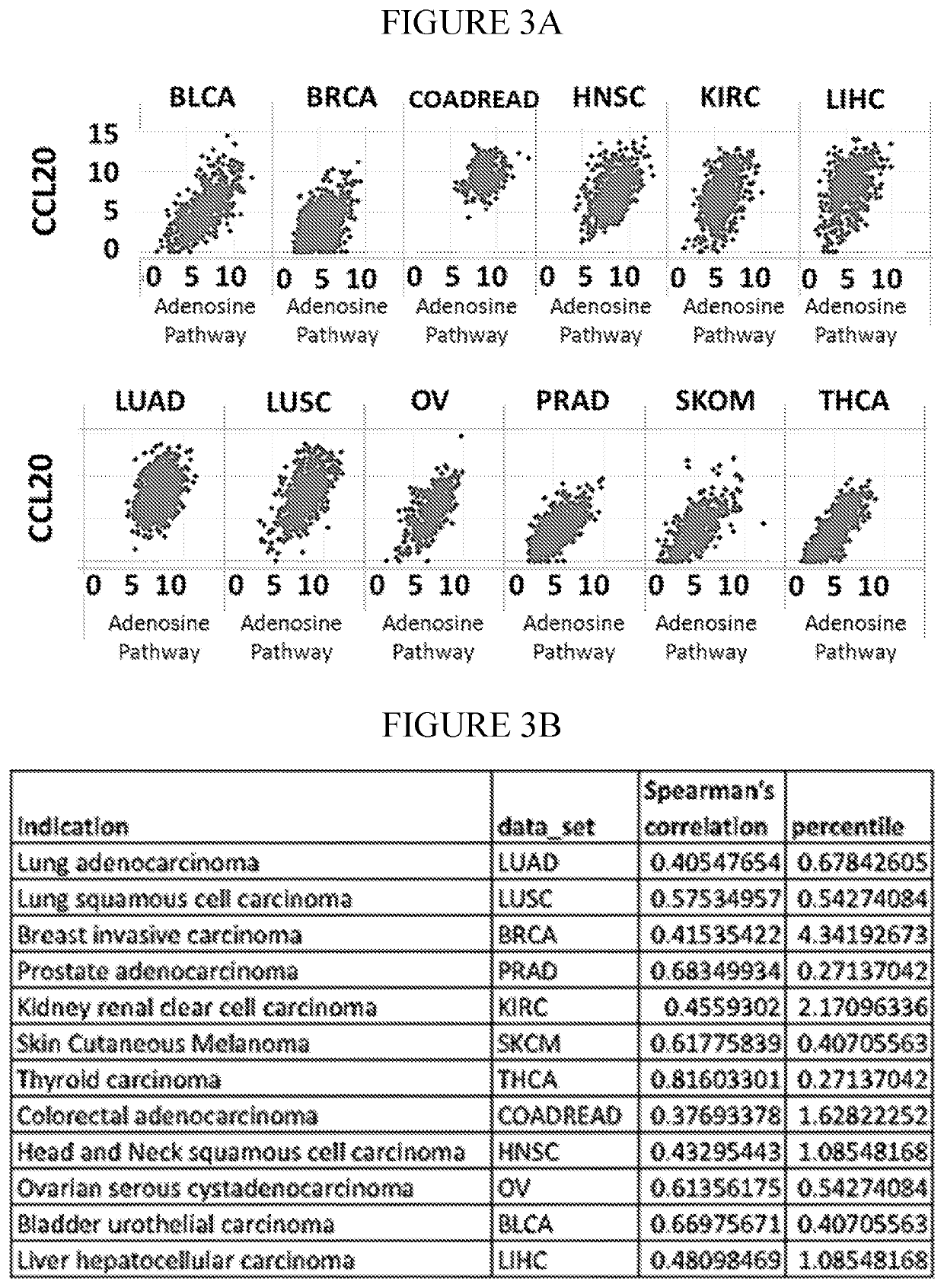
InactiveCN112601552AOrganic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsRHCGCCL7
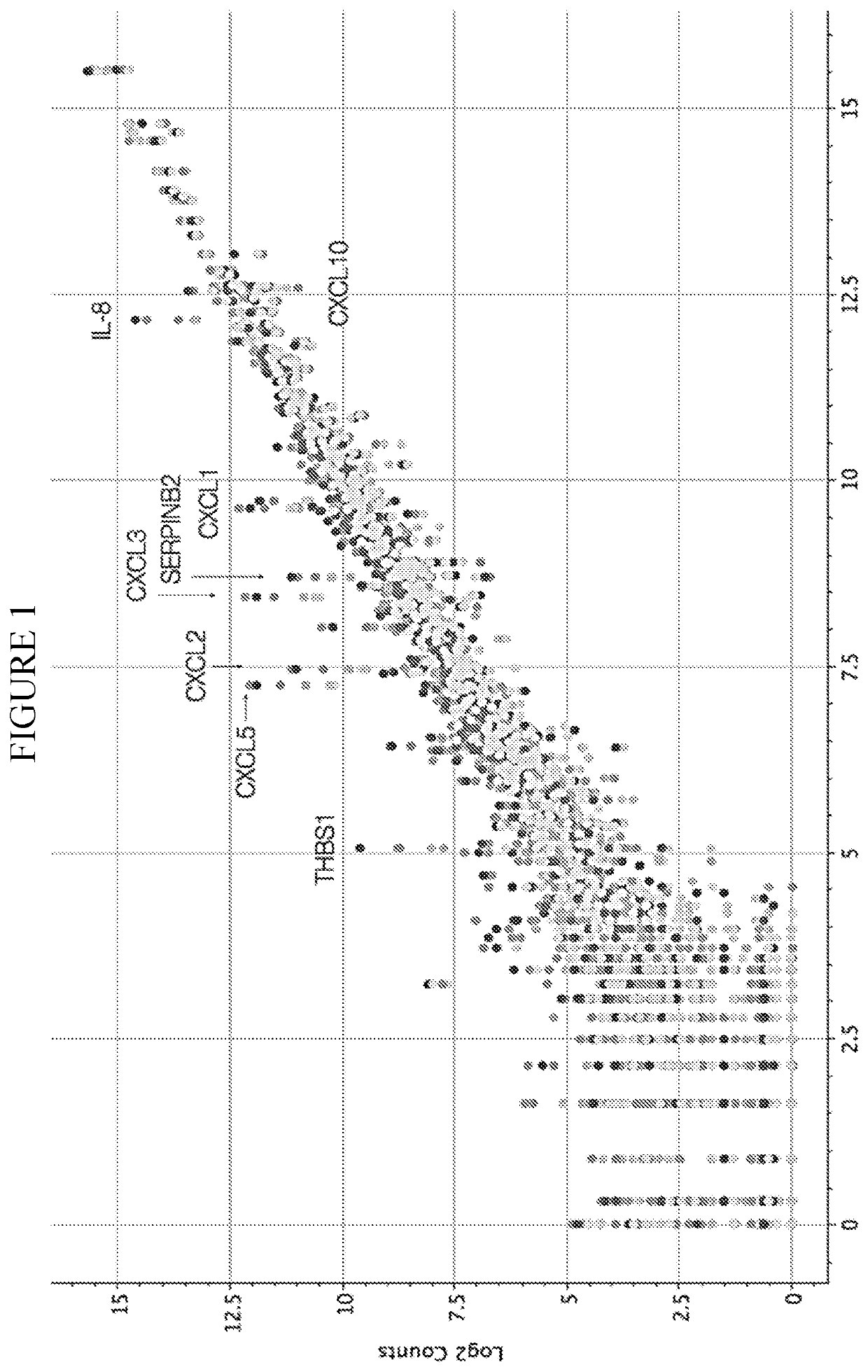
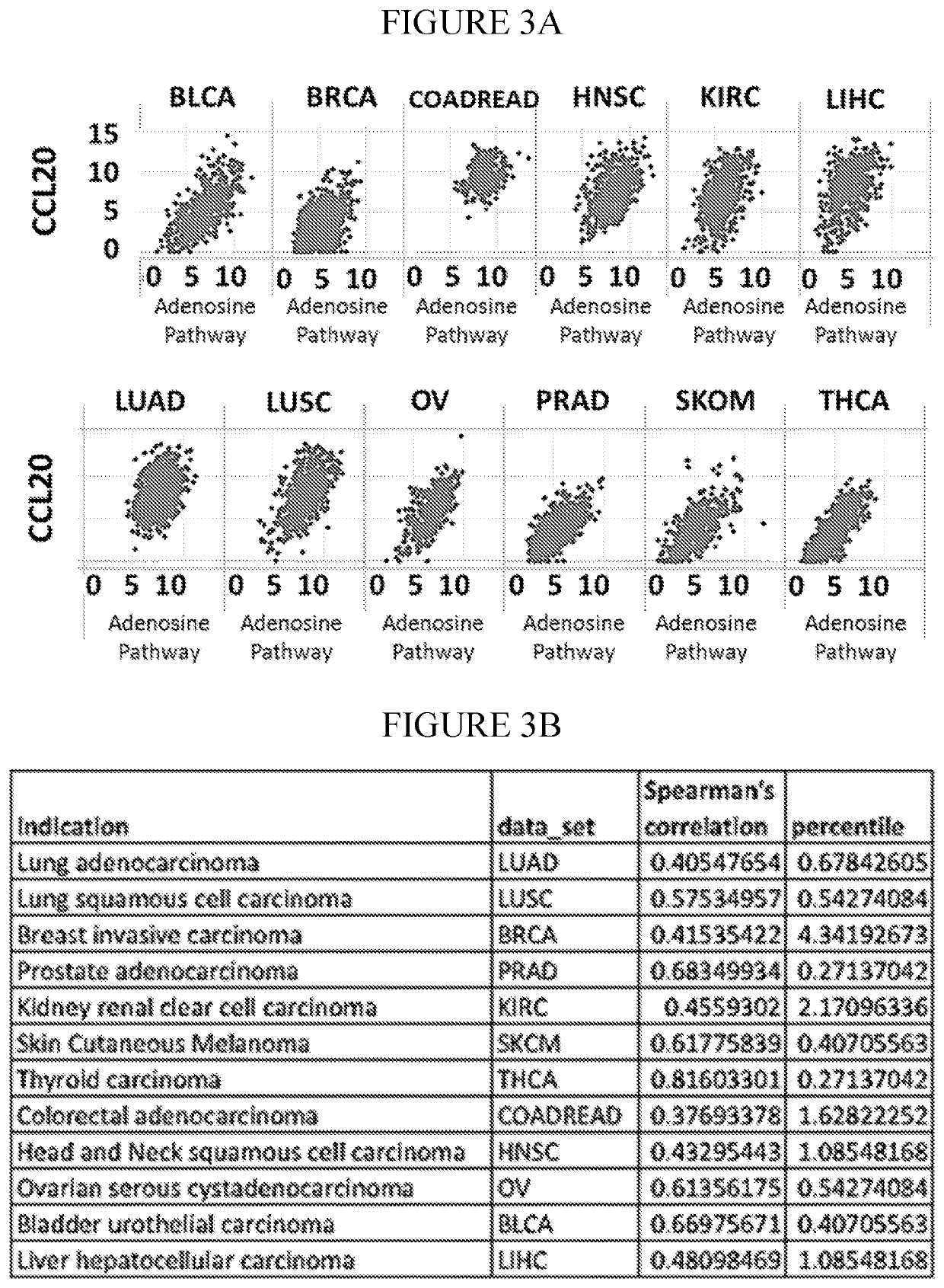
This disclosure relates to methods for detecting a level of expression of one or more genes (or proteins) in a subject having or suspected of having cancer, and optionally treating the subject with anadenosine pathway antagonist, for example an adenosine A2A receptor (ADORA2A) antagonist, to treat the cancer. The genes (or proteins) include, without limitation, CD68, CD163, LBP, CCL2, CCL3, CCL7,CCL24, CCNE1, CD 14, CD300E, CD86, CD93, CLEC5A, CSF3, CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL5, CXCL6, CXCL8, DFNA5, ECEL1, EPB41L3, EHF, FUT7, GALM, GBP6, GPR157, HAS1, IL1A, IL-1[beta], IL23, IL24, IL5, IL6, IL8, INHBA, LAP3, LAYN, LOC100505585, MRPL11, NID1, OST4, PADI2, PID1, PLAUR, PPBP, PTGS2, RHCG, SERPINB2, SLC11A1, SLC7A7, SPON1, ST6GALNAC2, TBX21, THBS1, C1R, C1S, C4BPA, CCL11, CCL20, CXCL16, CXCL2,HAMP, HSD11B1, ITGAM, LIF, SAA1, TFRC, TLR5, TNFSF14, TREM2, APP, ATG10, BCL2, CCL15, CD24, CD46, CD59, CREB5, CX3CL1, CXCL14, CYFIP2, DEFB1, DPP4, ECSIT, EPCAM, IFIT1, IGF1R, ITGA6, ITGB3, MAP2K4, MAPK1, MASP1, PPARG, RORC, SPA17, STAT5B, TOLLIP, AKT3, BMI1, CD 164, CD34, CDH5, CREB1, DOCK9, ENG, HMGB1, ITGA1, JAM3, MAF, MAPK3, MAPK8, MCAM, MFGE8, NOTCH1, NRP1, PRKCE, SMAD2, TAL1, THY1, TNFSF12,TRAF6, TXNIP, VEGFA, S100A8, and / or WDR83OS.
Owner:CORVUS PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Macropinocytosis of human anti-CD46 antibody and targeted cancer therapy
ActiveCN107135654BIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer targetingAntiendomysial antibodies
In various embodiments, human anti-CD46 antibodies internalized via the macropinocytic pathway and into tumor cells are provided, as well as antibody-drug conjugates developed from these antibodies for diagnostic and / or therapeutic targeting of CD46 overexpressing tumors Object ADC.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
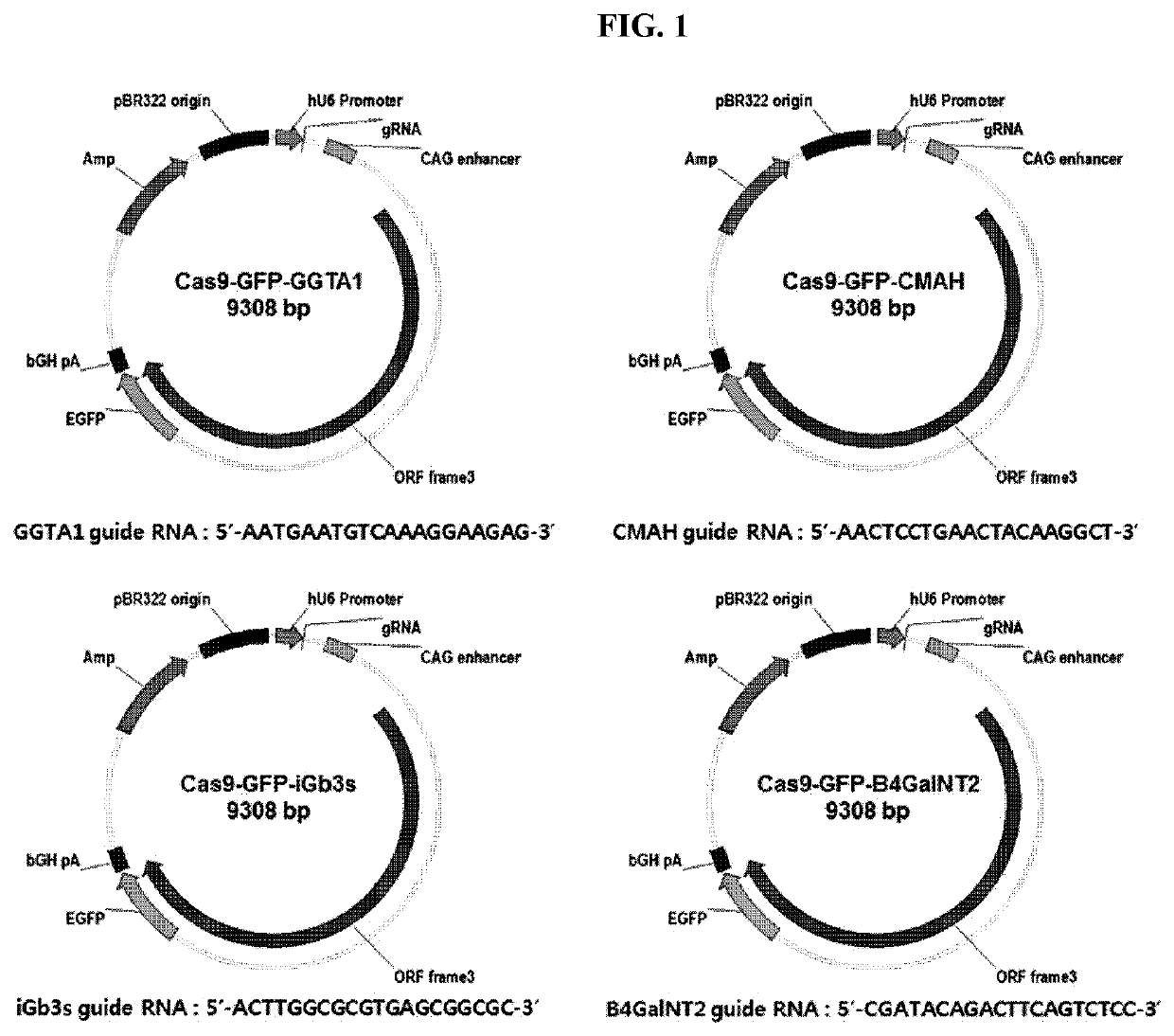
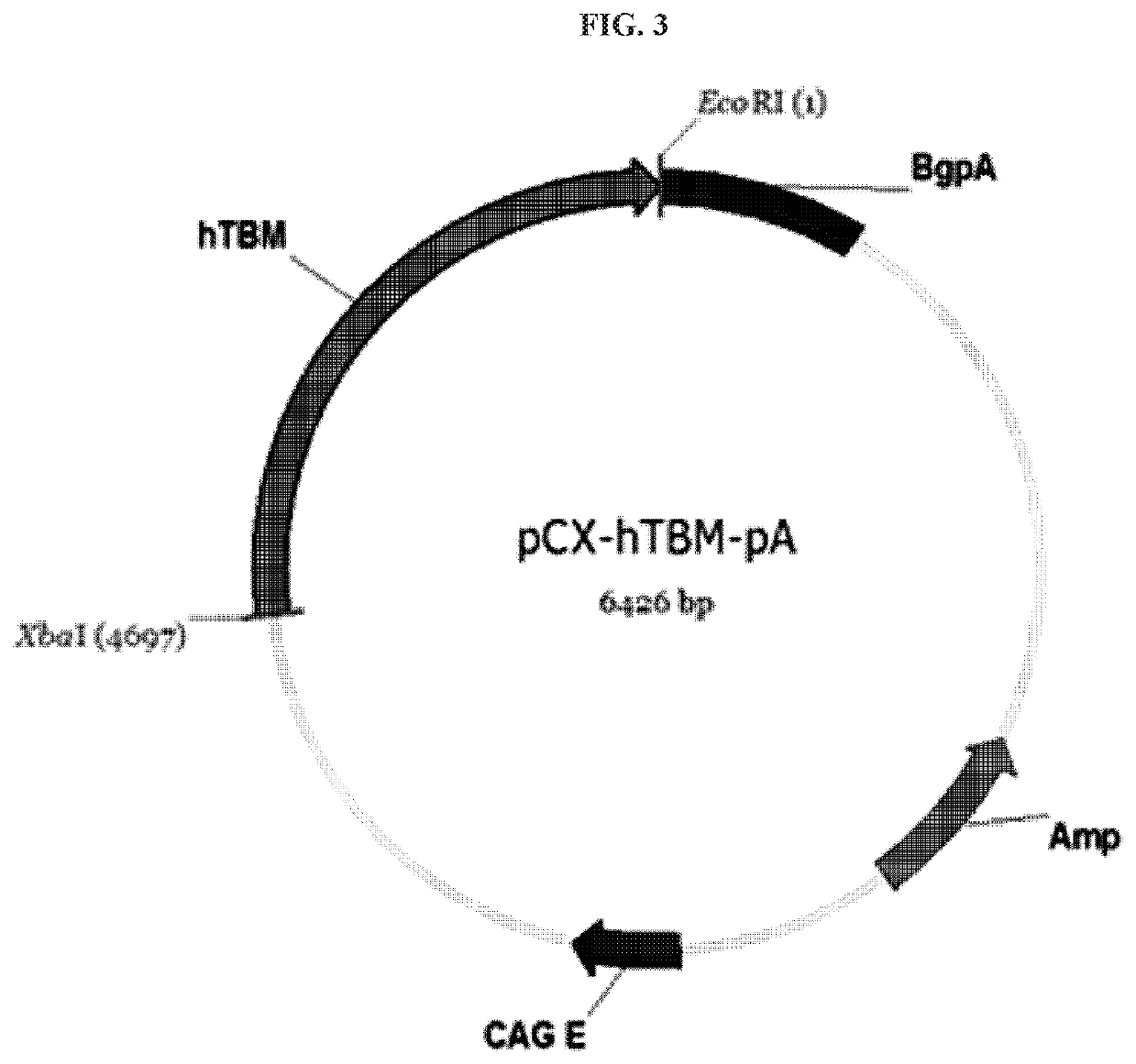
TRANSGENIC CLONED PIG FOR XENOTRANSPLANTATION EXPRESSING HUMAN CD46 AND TBM GENES, IN WHICH PORCINE ENDOGENOUS RETROVIRUS ENVELOPE C IS NEGATIVE AND GGTA1, CMAH, iGb3s AND ß4GalNT2 GENES ARE KNOCKED OUT, AND METHOD FOR PREPARING SAME
PendingUS20220248647A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsThrombomodulinAntigenPig endogenous retrovirus
The present invention relates to a transgenic cloned pig for xenotransplantation in which porcine endogenous retrovirus (RUN) EnvC is negative, α1,3-galactosyltransferase (GGTA1), CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase (CMAH), isoglobotrihexosylceramide synthase (iGb3s), and beta-I,4-N-acetyl-galactosaminyl transferase2 (β4GalNT2) are knocked out, and human CD46 and thrombomodulin (TBM) genes are expressed, and to a method of preparing the transgenic cloned pig. The transgenic cloned pig according to the present invention may overcome hyperacute and antigen-antibody mediated immune rejection reaction, immune rejection reaction due to blood coagulation, and immune rejection reaction due to complement activity, without causing transfer of porcine endogenous retrovirus that occurs in xenotransplantation. Therefore, the transgenic cloned pig according to the present invention may be usefully utilized as a donor animal for xenotransplantation of organs and cells.
Owner:OPTIPHARM
A kind of genetically engineered bacteria expressing membrane-penetrating peptide fusion protein and its application
InactiveCN104530241BHigh expressionEase of mass productionBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsFusion Protein ExpressionCell membrane
The present invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium expressing a membrane-penetrating peptide fusion protein and its application. The present invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium, E. coli BL21 / pET‑32a-CSFR, CCTCC NO: M2014631. The strain can express protein transduction domain polypeptide (PEP‑1) and classical swine fever virus receptor (CD46) genetically engineered fusion protein PEP‑1‑CD46. Its advantages are large expression, soluble protein, low cost and good safety. The expressed PEP‑1‑CD46 protein can be used as a mediating protein for CSFV to cross the cell membrane, improve the virus titer of CSFV in cell culture, and solve the problem that the current CSFV cell vaccine has a low virus content and cannot meet the vaccine standard Shortcomings.
Owner:武汉市畜牧兽医科学研究所
Macropinocytosing human anti-CD46 antibodies and targeted cancer therapeutics
ActiveCN107135654AIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug conjugationCancer targeting
In various embodiments human anti-CD46 antibodies that are internalizing and enter tumor cells via the macropinocytosis pathway are provided, as well as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) developed from these antibodies for diagnostic and / or therapeutic targeting of CD46-overexpressing tumors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Modified polypeptides for targeting cell-entry of the adenoviruses of subtype b
InactiveUS20070065408A1High densityAvoid interactionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousDisease
This invention relates to modified polypeptides comprising two functional components: first, a polypeptide derived from the extracellular region of CD46 as a specific binding site for adenoviruses of the subgroup B, and second, a component capable of binding to a cell surface molecule. Such modified polypeptides are able to direct adenovirus infection specifically to cells having said cell surface molecule on their surface. The invention relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding fusion proteins comprising a) a polypeptide derived from the extracellular domain of CD46 and b) a heterologous polypeptide, methods for the production of the modified polypeptides and suitable recombinant expression vectors and host cells. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the modified polypeptide of the invention are useful together with recombinant, genetically engineered adenovirus of subtype B for the treatment and prophylaxis of disorders and diseases, like cancer.
Owner:CYTOS BIOTECHNOLOGY AG
A bispecific chimeric antigen receptor molecule and its application in tumor therapy
ActiveCN109503716BIncreased persistenceImprove targetingPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsCD20CD79A
Owner:CELLYAN THERAPEUTICS WUHAN CO LTD
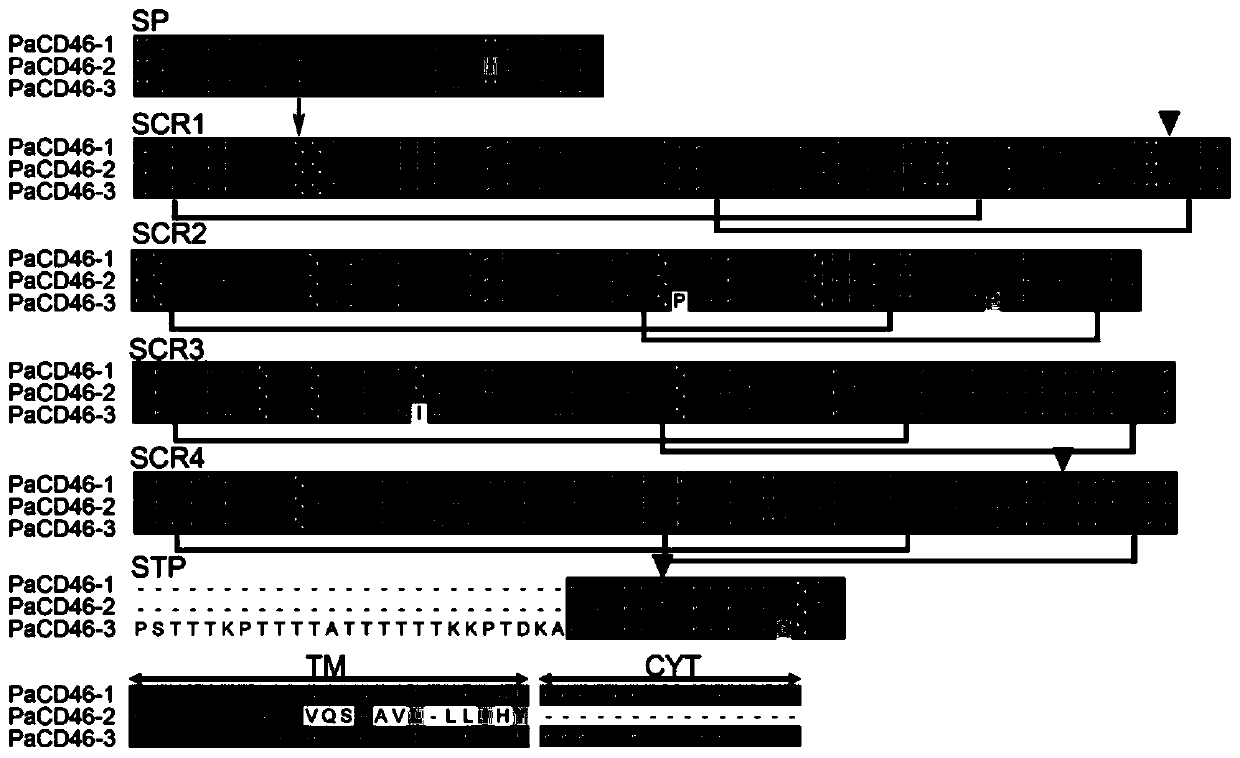
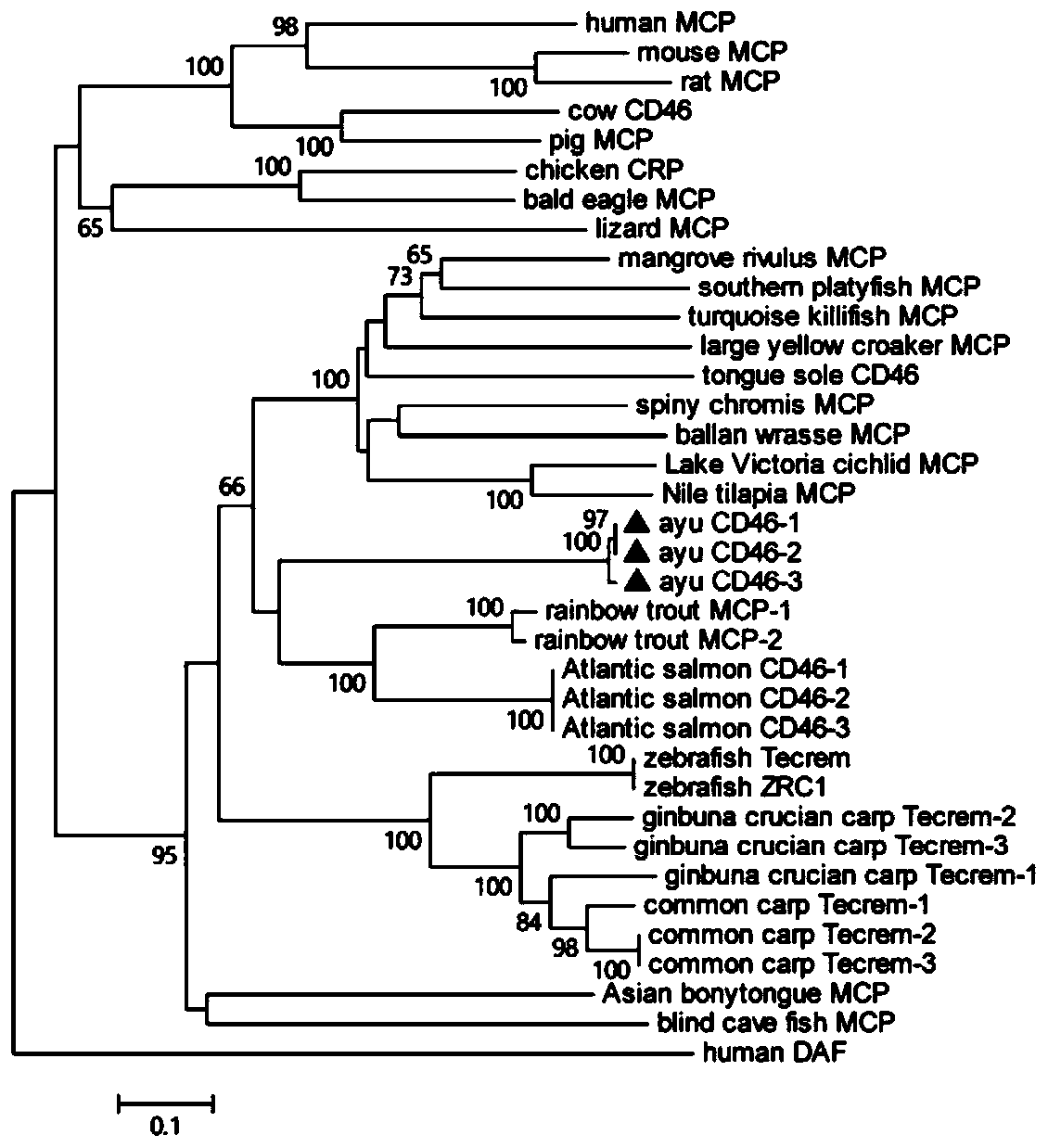
Plecoglossus altivelis CD46 gene, recombinant engineering bacterium and preparation method of polyclonal antibody of CD46 gene
ActiveCN111004806AFungiCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPichia pastorisMicrobiology
The invention discloses a plecoglossus altivelis CD46 gene, a recombinant engineering bacterium and a preparation method of a polyclonal antibody of the CD46 gene. The plecoglossus altivelis CD46 geneis characterized in that the plecoglossus altivelis CD46 gene comprises plecoglossus altivelis CD46-1, CD46-2 and CD46-3 genes, and the cDNA sequences are shown as SEQID NO.1, SEQID NO.3 and SEQID NO.5 correspondingly. The preparation method of the recombinant plecoglossus altivelis CD46 gene engineering bacterium comprises the following steps: constructing a recombinant plecoglossus altivelis CD46 protein extracellular region pichia pastoris expression plasmid; screening a high-expression recombinant engineering strain; culturing the high-expression yeast strain in a fermentation tank; purifying the recombinant plecoglossus altivelis CD46 extracellular region protein to obtain a recombinant plecoglossus altivelis CD46 gene engineering bacterium; and preparing a rabbit anti-plecoglossus altivelis CD46 protein polyclonal antibody through a rabbit immunization method. The advantage is that a plecoglossus altivelis CD46 protein isomer can be specifically recognized.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Markers for dopaminergic neuron progenitor cells
The present invention provides a method for selecting dopaminergic neuron progenitor cells, which comprises detecting any one or more of markers selected from the group consisting of CD15 (SSEA-1), CD24, CD46, CD47, CD49b, CD57, CD58, CD59, CD81, CD90, CD98, CD147, CD184, Disalogangliosid GD2, SSEA-4, CD49f, SERINC4, CCR9, PHEX, TMPRSS11E, HTR1E, SLC25A2, Ctxn3, Ccl7, Chrnb4, Chrna3, Kcnv2, Grm2, Syt2, Lim2, Mboat1, St3gal6, Slc39a12, Tacr1, Lrtm1, Dscam and CD201.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Macropinocytosis human anti-CD46 antibodies and targeted cancer therapies
PendingCN114106179AOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCancer targetingAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to macropinocytosis human anti-CD46 antibodies and targeted cancer therapies. In various embodiments, provided are human anti-CD46 antibodies that internalize via the macropinocytosis pathway and enter tumor cells, as well as antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) developed from these antibodies for diagnostic and / or therapeutic targeting of CD46 over-expressing tumors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for detecting and treating cancers having adenosine pathway activation
InactiveCN112654365AOrganic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsRHCGCCL7
The present disclosure relates to methods for detecting expression levels of one or more genes in a subject having or suspected of having a cancer and optionally treating the subject with an adenosine pathway antagonist (e.g., an adenosine A2A receptor (ADORA2A) antagonist) in combination with a PD-1 inhibitor and / or a PD-L1 inhibitor to treat the cancer. The genes comprise, but are not limited to, CD68, CD163, LBP, CCL2, CCL3,CCL7,CCL24,CCNE1,CD14,CD300E,CD86,CD93,CLEC5A, CSF3,CXCL1,CXCL2,CXCL3,CXCL5,CXCL6,CXCL8,DFNA5,ECEL1,EPB41L3,EHF,FUT7,GALM,GBP6,GPR157,HAS1,IL1A,IL-1beta,IL23,IL24,IL5,IL6,IL8,INHBA,LAP3,LAYN,LOC100505585,MRPL11,NID1,OST4,PADI2,PID1,PLAUR,PPBP,PTGS2,RHCG,SERPINB2,SLC11A1,SLC7A7,SPON1,ST6GALNAC2,TBX21,THBS1,C1R,C1S,C4BPA,CCL11,CCL20,CXCL16,CXCL2,HAMP,HSD11B1,ITGAM,LIF,SAA1,TFRC,TLR5,TNFSF14,TREM2,APP,ATG10,BCL2,CCL15,CD24,CD46,CD59,CREB5,CX3CL1,CXCL14,CYFIP2,DEFB1,DPP4,ECSIT,EPCAM,IFIT1,IGF1R,ITGA6,ITGB3,MAP2K4,MAPK1,MASP1,PPARG,RORC,SPA17,STAT5B,TOLLIP,AKT3,BMI1,CD164,CD34,CDH5,CREB1,DOCK9,ENG,HMGB1,ITGA1,JAM3,MAF,MAPK3,MAPK8,MCAM,MFGE8,NOTCH1,NRP1,PRKCE,SMAD2,TAL1, THY1, TNFSF12,TRAF6, TXNIP,VEGFA,S100A8 and / or WDR83OS.
Owner:CORVUS PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Fusion protein
InactiveCN110003341ASimple structureEasy to manufactureAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHybrid peptidesBiophysicsFusion protein
The invention discloses a fusion protein, and belongs to the biopharmaceutical technical field. The fusion protein is a fusion protein obtained by fusion of a regulatory protein CD46 and a regulatoryprotein CD55.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for detecting and treating cancers having adenosine pathway activation
PendingUS20210255190A1Improve expression levelTreat cancerOrganic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsOST4RHCG
This disclosure relates to methods for detecting a level of expression of one or more genes (or proteins) in a subject having or suspected of having cancer, and optionally treating the subject with an adenosine pathway antagonist, for example an adenosine A2A receptor (ADORA2A) antagonist, to treat the cancer. The genes (or proteins) include, without limitation, CD68, CD163, LBP, CCL2, CCL3, CCL7, CCL24, CCNE1, CD 14, CD300E, CD86, CD93, CLEC5A, CSF3, CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL5, CXCL6, CXCL8, DFNA5, ECEL1, EPB41L3, EHF, FUT7, GALM, GBP6, GPR157, HAS1, IL1A, IE-1β, 1L23, 1L24, IL5, 1L6, 1L8, INHBA, LAP3, LAYN, LOC100505585, MRPL11, NID1, OST4, PADI2, PID1, PLAUR, PPBP, PTGS2, RHCG, SERPINB2, SLC11A1, SLC7A7, SPON1, ST6GALNAC2, TBX21, THBS1, C1R, C1S, C4BPA, CCL11, CCL20, CXCL16, CXCL2, HAMP, HSD11B1, IT GAM, LIF, SAA1, TFRC, TLR5, TNFSF14, TREM2, APP, ATG10, BCL2, CCL15, CD24, CD46, CD59, CREB5, CX3CL1, CXCL14, CYFIP2, DZ, EC, EE, EG, ES, FI, GB, GD, GE, GH, GM, GT, HN, HR, HU, ID, IL, IN, IR, IS, JO, JP, KE, KG, KH, KN, KP, KR, KW, KZ, LA, LC, LK, LR, LS, LU, LY, MA, MD, ME, MG, MK, MN, MW, MX, MY, MZ, NA, NG, NI, NO, NZ, OM, PA, PE, PG, PH, PL, PT, QA, RO, RS, RU, RW, SA, SC, SD, SE, SG, SK, SL, SM, ST, SV, SY, TH, TJ, TM, TN, TR, TT, TZ, UA, UG, US, UZ, VC, VN, ZA, ZM, ZW.
Owner:CORVUS PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Substance for improving lethality of immune cells as well as preparation and application of substance
PendingCN112618718AIncrease lethalityHydroxy compound active ingredientsDigestive systemBenzoic acidChlorogenic acid
The invention discloses a substance for improving the lethality of immune cells as well as a preparation and application of the substance. The substance for improving the lethality of immune cells comprises one or more of berberine, benzoyloxypaeoniflorin, methylophiopogonone A, canadin(tetrahydroberberine), leucoside(kaempferol 3-O-sambubioside), cheilanthifoline, bucuculline, sibirioside A, harpagide, dendrobine, coptisine hydrochloride, coptisine, norisoboldine, ginsenoside Rg3, 3,5-Dicaffeoyl quinic acid, L-arginine, 3-O-feruloylquinic acid, lucidone, atractyloside A, ginsenoside Rh3, Cholan-24-oic acid, oleuropein, parishin A, parishin B, p-hydroxyphenylethyl trans-ferulate, Palbinone, pseudo-ginsenoside RT1, pimpinellin, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, Eburicoic acid, alismoxide and alpha-cyperone. According to the substance disclosed by the invention, immunity-related genes such as CD46, MUC16, TGF-beta and the like and GAST and SS18 are selected as direct or indirect regulation and control target genes from genes of which the expression quantity is obviously changed in transcriptome analysis data.
Owner:HANDAN PHARMA
Real-time fluorescence LAMP detection method for specific expression human CD46 transgenic pigs and kit
ActiveCN106191242AReduce the risk of contaminationAvoid opening the lidMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceBiology
The invention provides a real-time fluorescence LAMP detection method for specific expression human CD46 transgenic pigs and a kit. Real-time fluorescence LAMP detection is carried out on specific expression human CD46 transgenic pigs by screening six specific primers, and a detection system and reaction conditions are optimized. The method is applicable to on-site rapid screening, closed tube detection is carried out fluorescence amplification signals, cover opening operation after the reaction is avoided, the aerosol pollution risk is lowered, and false positive occurrence possibility is greatly reduced; meanwhile, reaction time is shortened, and a judgment result can be obtained within 45 min.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Methods for detecting and treating cancers having adenosine pathway activation
PendingUS20210254178A1Organic active ingredientsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsCCL7TREM2
This disclosure relates to methods for detecting a level of expression of one or more genes in a subject having or suspected of having cancer, and optionally treating the subject with an adenosine pathway antagonist, for example an adenosine A2A receptor (ADORA2A) antagonist in combination with a PD-1 inhibitor and / or a PD-L1 inhibitor, to treat the cancer. The genes include, without limitation, CD68, CD 163, EBP, CCL2, CCL3, CCL7, CCL24, CCNE1, CD 14, CD300E, CD86, CD93, CLEC5A, CSF3, CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL5, CXCL6, CXCL8, DFNA5, ECEL1, EPB41L3, EHF, FUT7, GALM, GBP6, GPR157, HAS1, IL1A, IE-1β, IL23, IL24, IL5, IL6, IL8, INHBA, LAP3, LAYN, LOC100505585, MRPL11, NID1, OST4, PADI2, PID1, PLAUR, PPBP, PTGS2, NRHCG, SERPINB32, SLC11A1, SLC7A7, SPON1, ST6GALNAC2, TBX21, THBS1, C1R, C1S, C4B3PA, CCL11, CCL20, CXCL16, CXCL2, HAMP, HSD11B1, IT GAM, LIF, SAA1, TFRC, TLR5, TNFSF14, TREM2, APP, ATG10, BCL2, CCL15, CD24, CD46, CD59, CREB5, CX3CL1, CXCL14, CYFIP2, DEFB1, DPP4, EC SIT, EPCAM, IFIT1, IGF1R, ITGA6, ITGB3, MAP2K4, MAPK1, MASP1, PPARG, RORC, SPA17, STAT5B, TOLLIP, AKT3, BMI1, CD 164, CD34, CDH5, CREB1, DOCK9, ENG, HMGB1, ITGA1, JAM3, MAF, MAPK3, MAPK8, MCAM, MFGE8, NOTCH1, NRP1, PRKCE, SMAD2, TAL1, THY1, TNFSF12, TRAF6, TXNIP, VEGFA, S100A8, and / or WDR83 OS.
Owner:CORVUS PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Real-time fluorescent lamp detection method and kit for transgenic pigs specifically expressing human cd46
ActiveCN106191242BReduce the risk of contaminationAvoid opening the lidMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceTransgenesis
The invention provides a real-time fluorescence LAMP detection method for specific expression human CD46 transgenic pigs and a kit. Real-time fluorescence LAMP detection is carried out on specific expression human CD46 transgenic pigs by screening six specific primers, and a detection system and reaction conditions are optimized. The method is applicable to on-site rapid screening, closed tube detection is carried out fluorescence amplification signals, cover opening operation after the reaction is avoided, the aerosol pollution risk is lowered, and false positive occurrence possibility is greatly reduced; meanwhile, reaction time is shortened, and a judgment result can be obtained within 45 min.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com