Patents
Literature
209 results about "Decreased diameter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
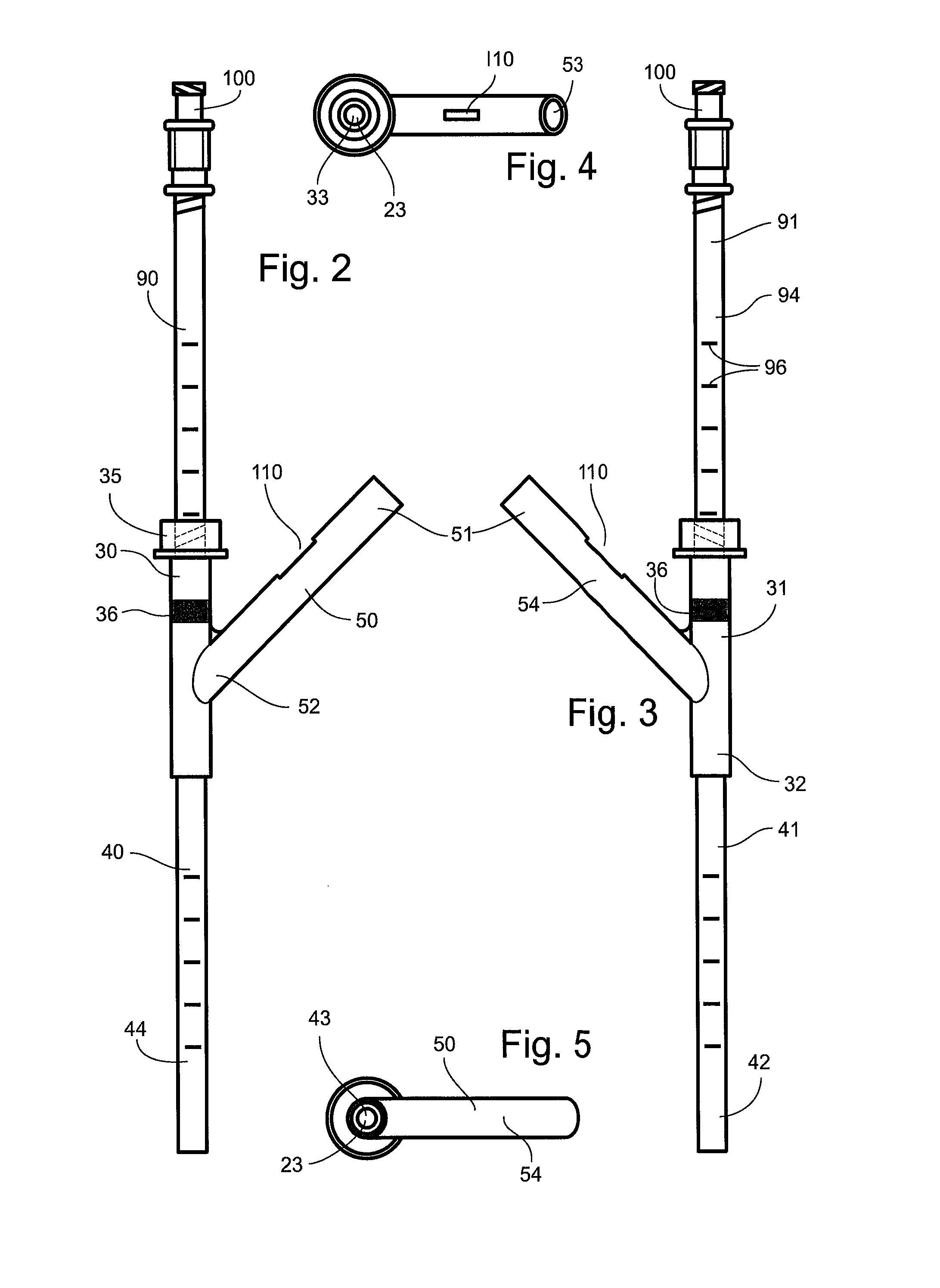
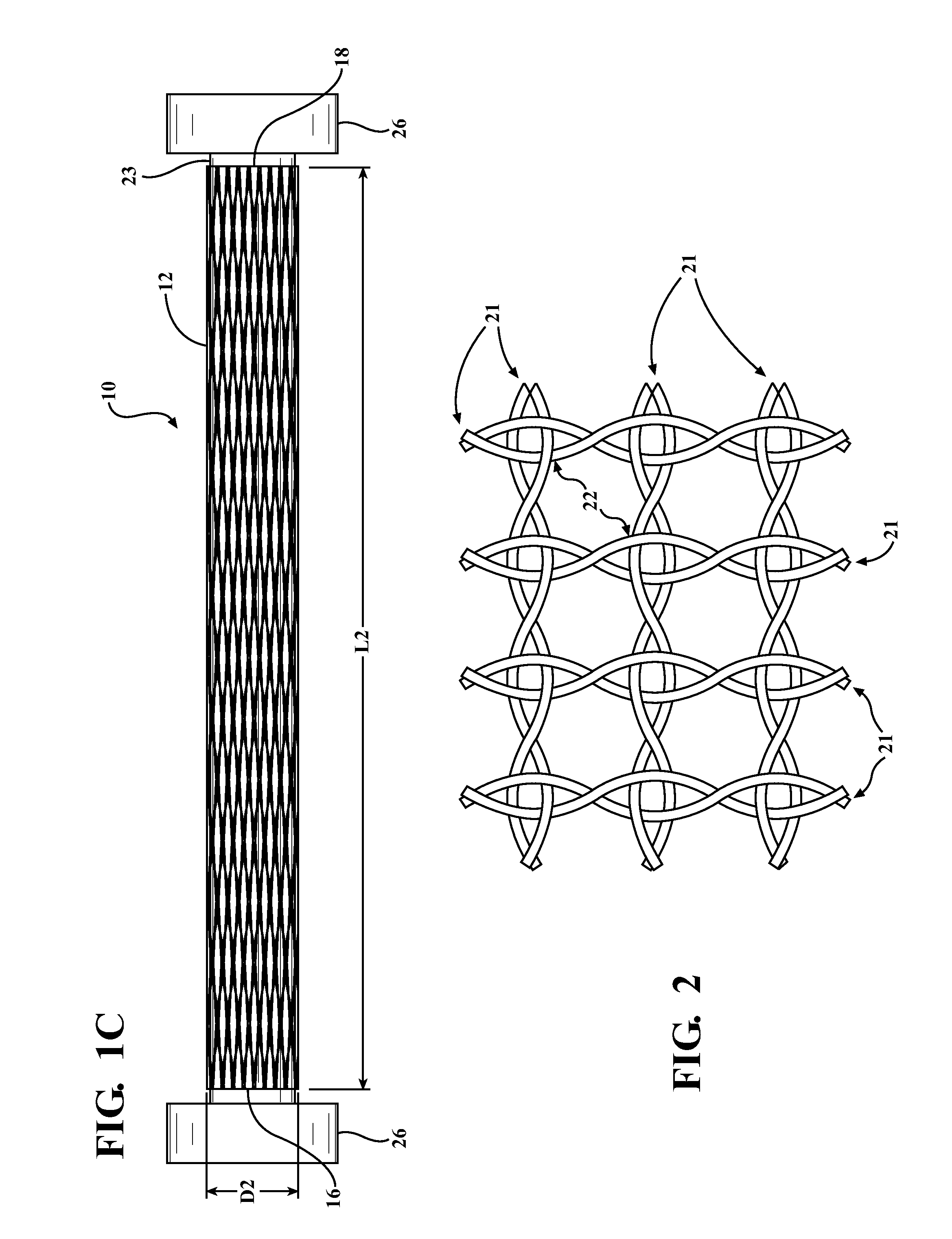
Distraction screw
InactiveUS20050038438A1Simple and safe processRelieve stressSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisDistractionDistal portion
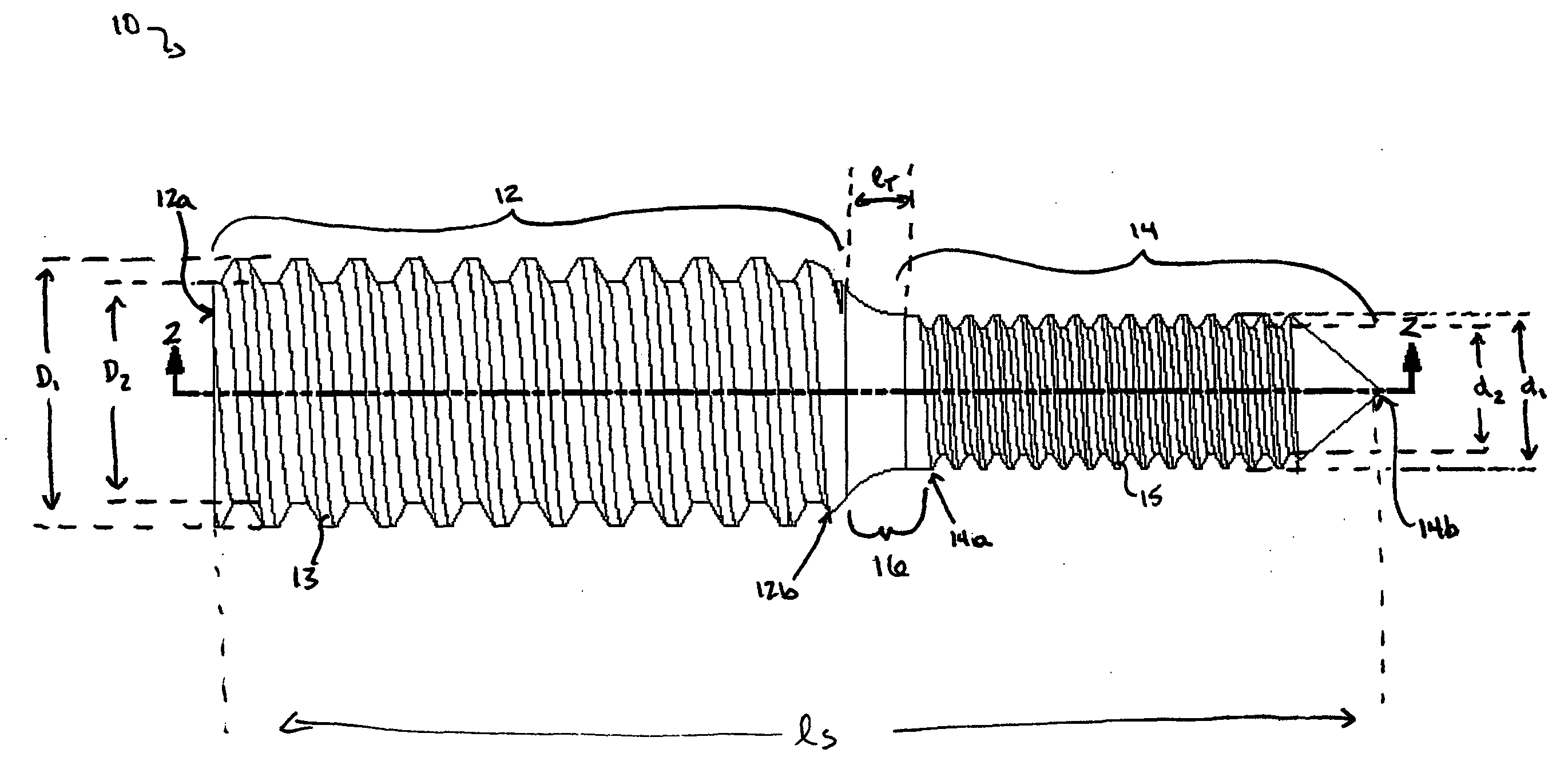
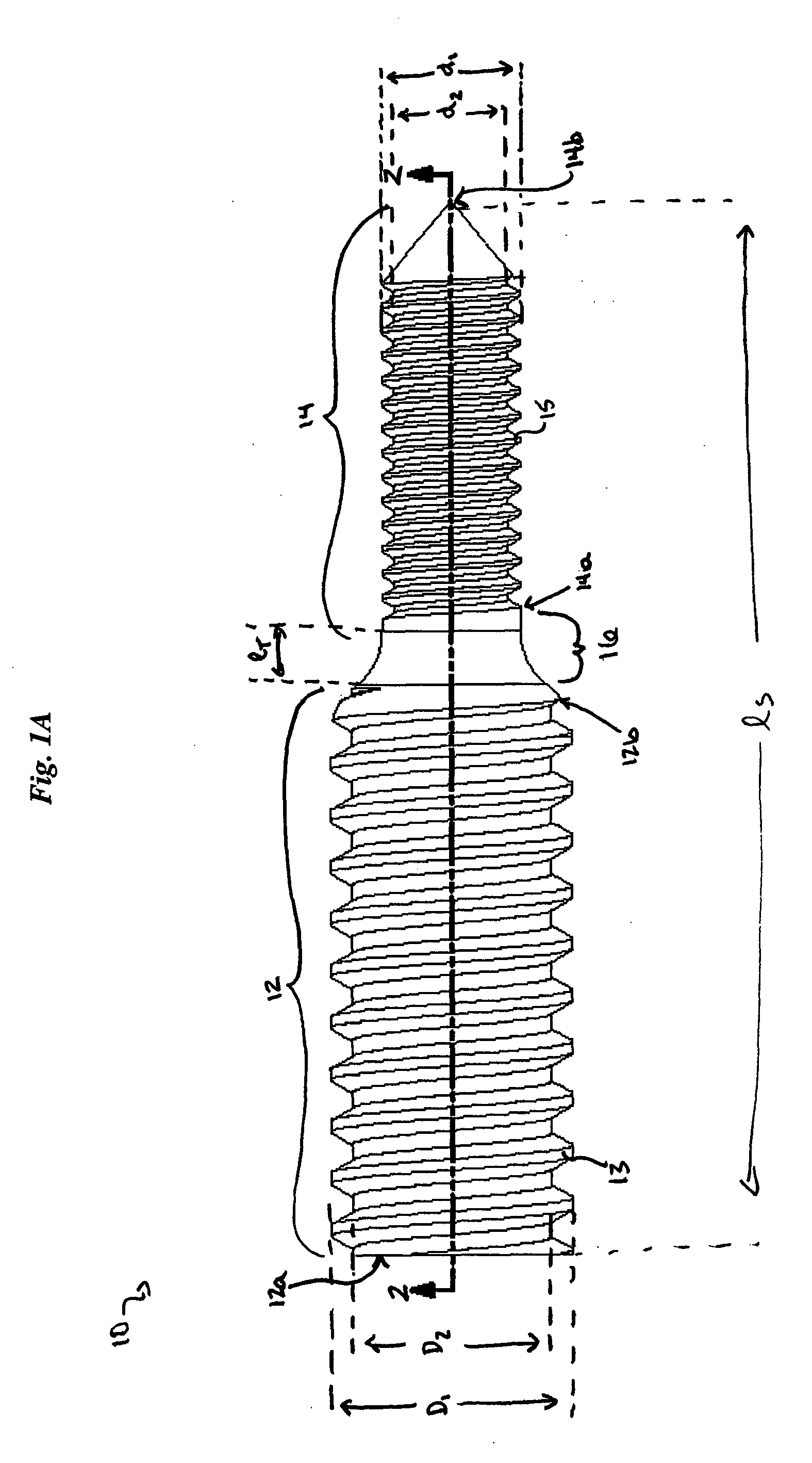
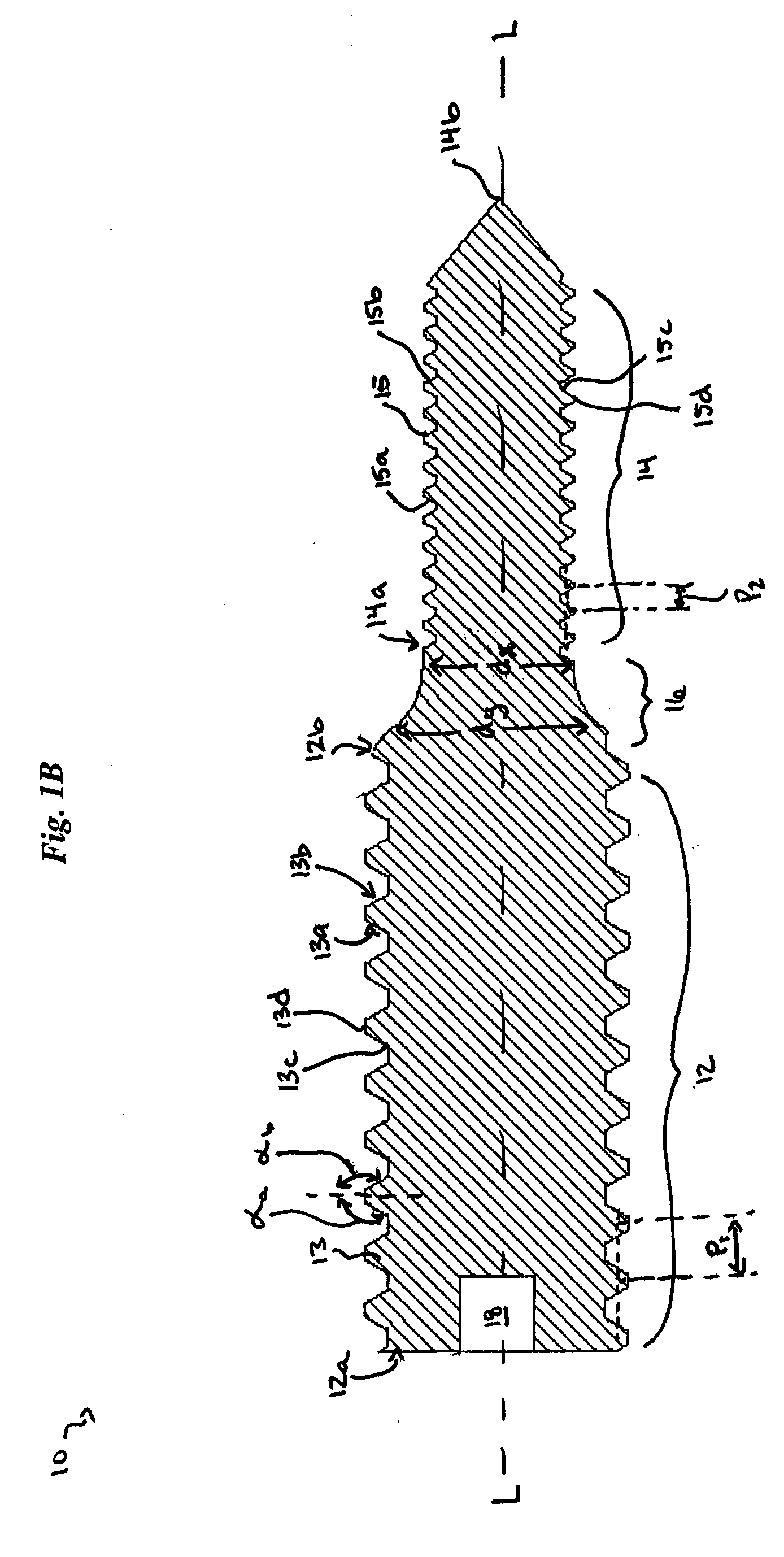
A simple, safe implantable bone screw, and a method for distracting two bone segments, is provided. In general, the bone screw includes a shank having a threaded proximal portion and a distal portion with a major diameter that is less than a minor diameter of the threaded proximal portion. A transitional region of decreasing diameter can be disposed between the threaded proximal portion and the distal portion, and a driver receiving element is preferably disposed on a proximal end of the bone screw. In use, the proximal and distal portions of the bone screw are adapted to engage two segments of bone, and to create a distraction force between the two segments of bone.
Owner:DEPUY ACROMED INC
Leak resistant lid assembly for a beverage container
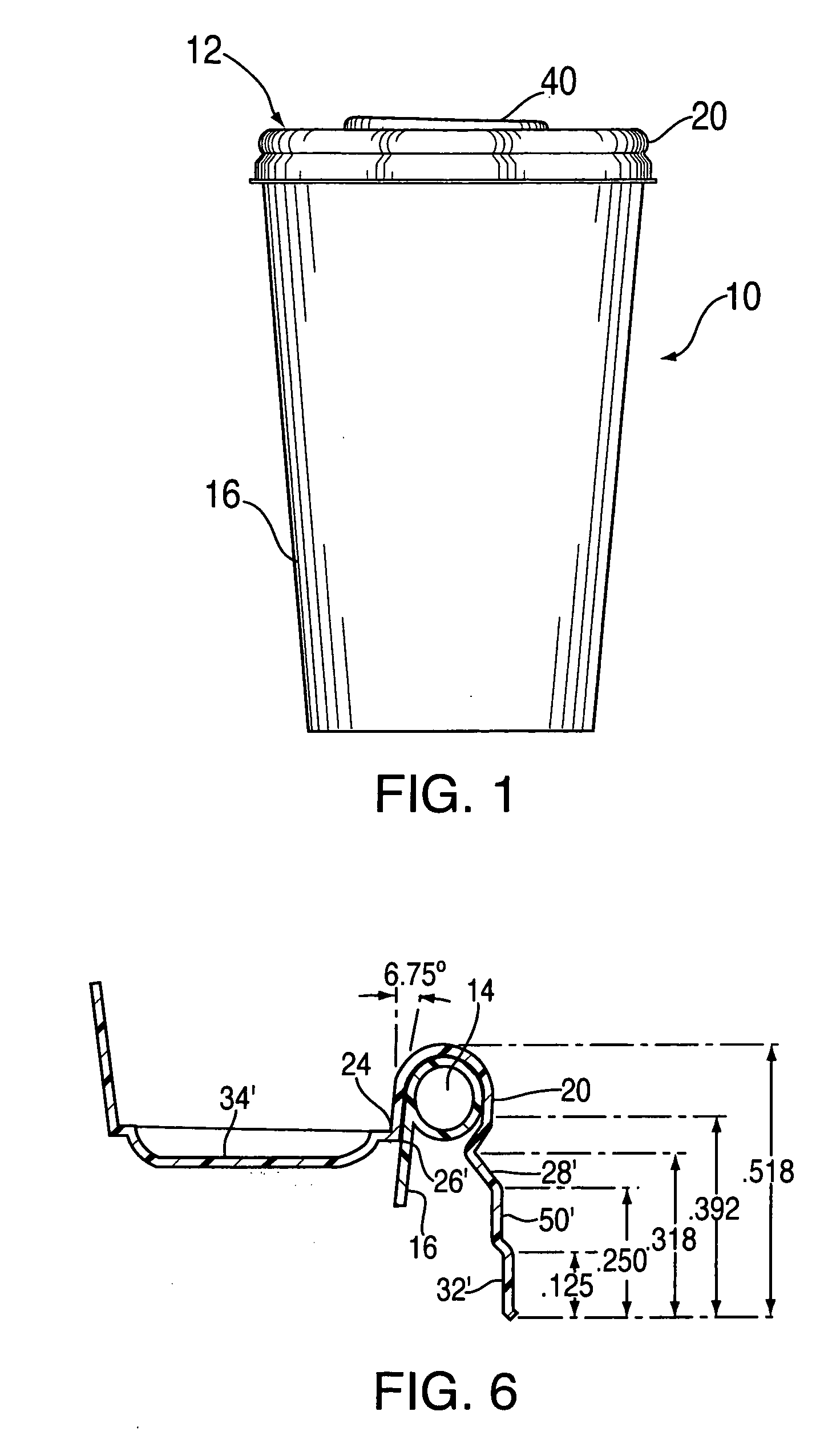
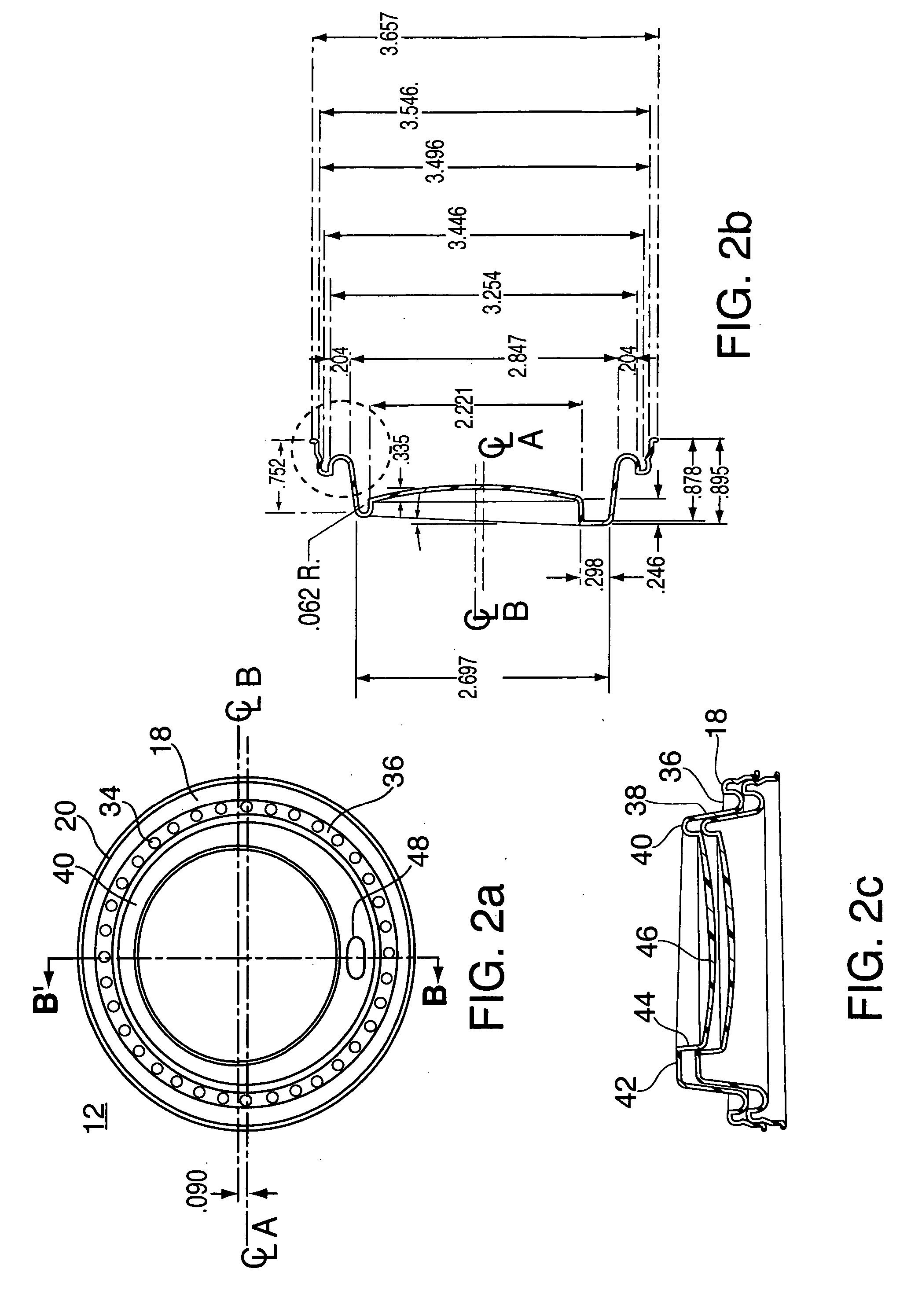
InactiveUS20050224505A1Highly leak resistant “sipperPrevent leakageCapsClosure using stoppersFlangeDecreased diameter
A leak resistant lid for a beverage container is formed with a depending skirt portion having one or more progressively decreasing diameter rings between a lower extremity and a sealing channel adapted to fit over the rim bead of the container. An inner wall of the channel extends downwardly inside the inner surface of the side wall of the container in a plug fit relationship. The relatively deep inside plug fit provides added surface area contact for sealing the interface between the lid and the container. An elevated and rigid central plateau supports a drinking orifice and is connected to the inner wall of the channel by a reinforced, rigid flange or web which maintains the channel and its inner wall in leak resistant relationship with the rim bead and container wall.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Suction evacuation device
A method for removing a stone from a patient comprising the steps of: providing a suction evacuation assembly which includes a sheath and one or more side arms; inserting and positioning a distal end of the sheath into a lumen or cavity of a patient's body containing a stones; connecting a tube to one of the side arms and to a collection bottle; connecting another tube to the collection bottle and a negative pressure system; visualizing the stone or foreign body using a scope inserted through the assembly; activating the negative pressure system in order to remove the stone from the cavity if the diameter of the stone is narrower than an inside diameter of the sheath and the side arm, or performing a lithotripsy on the stone to create fragments with a decreased diameter which allow the passage through the assembly; and collecting the stone in the collection bottle.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WELLLEAD MEDICAL EQUIP CO LTD
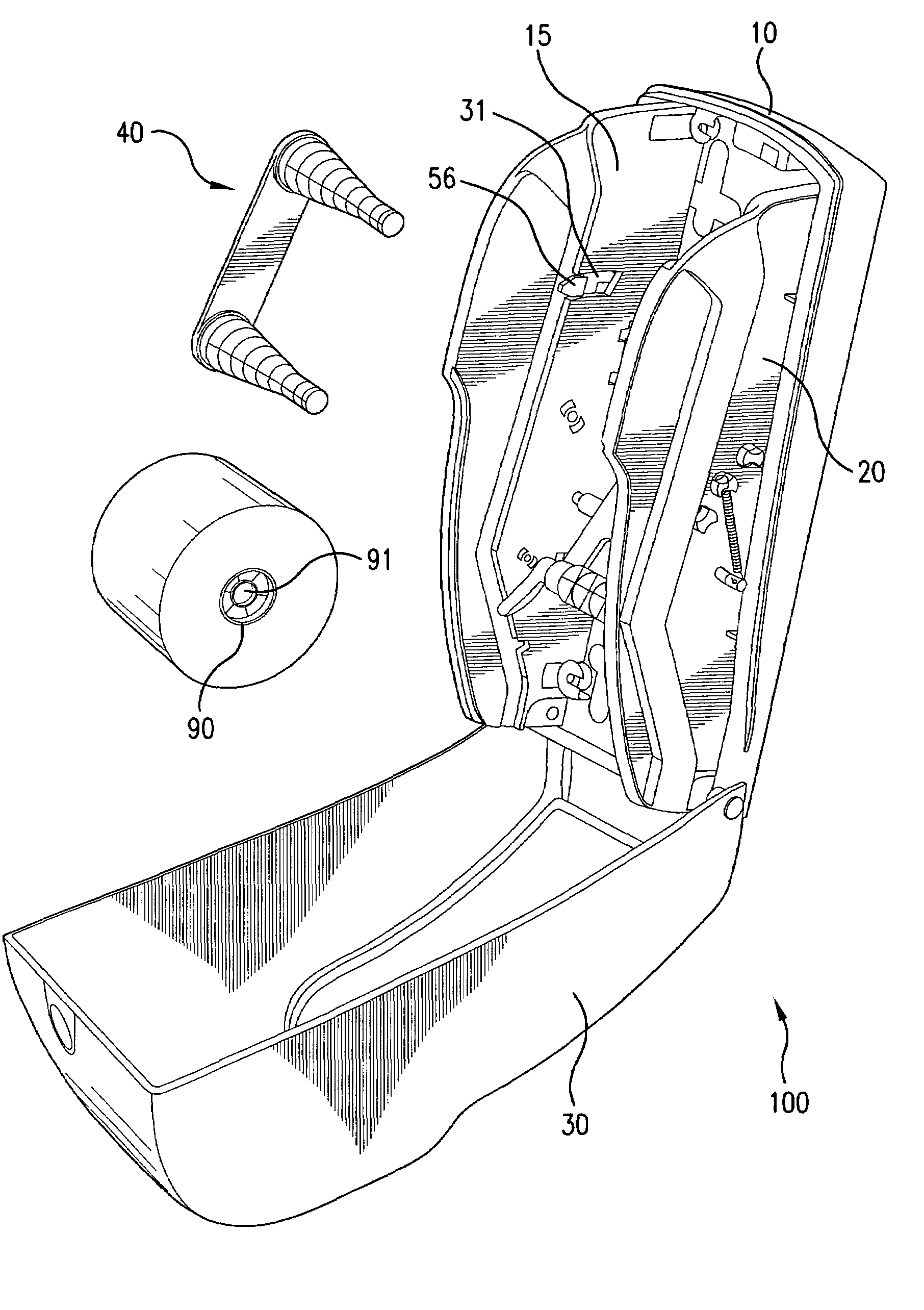
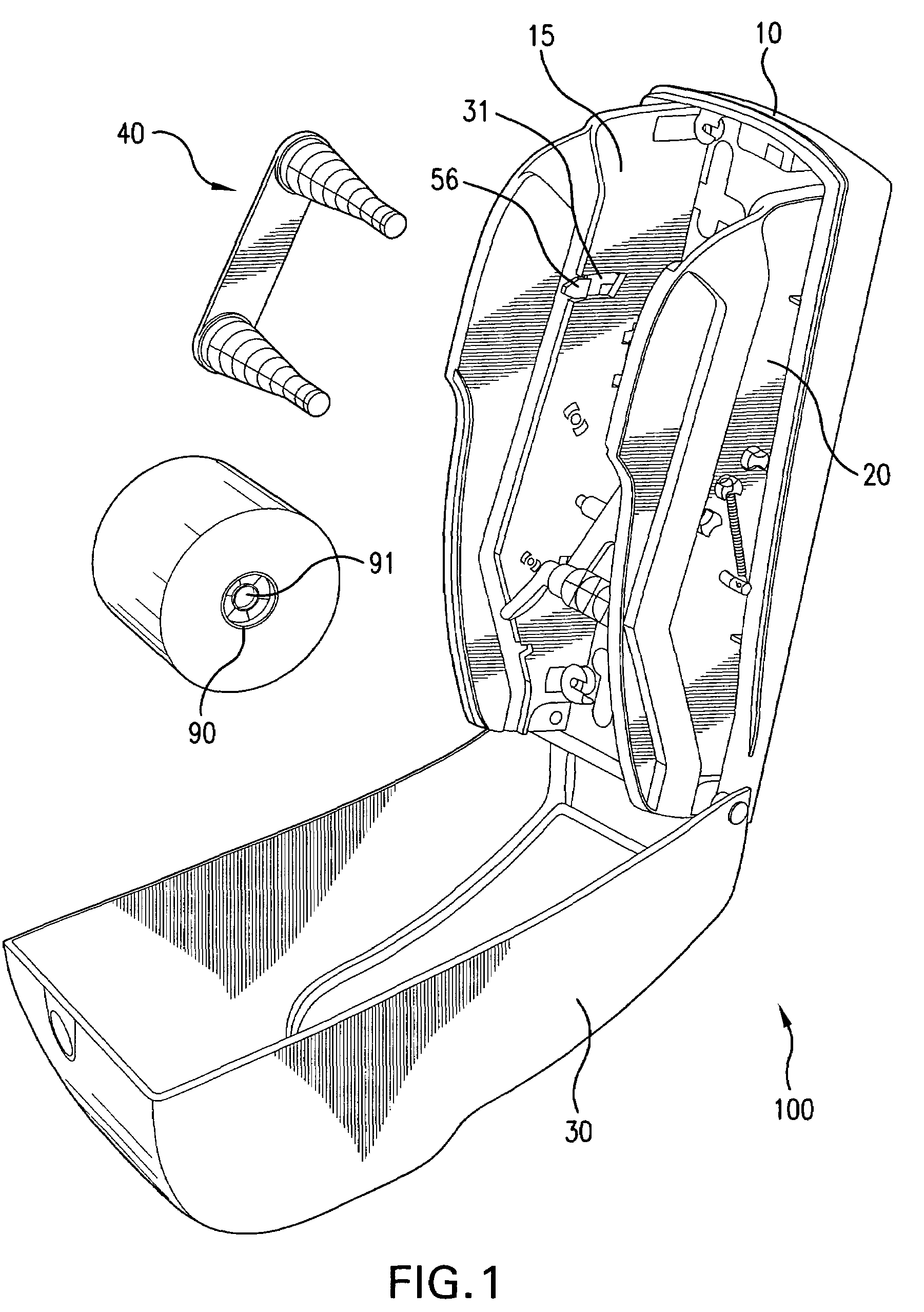
Dispenser that automatically transfers rolls of absorbent material, method of reloading same, and rolls of absorbent material for use in same
ActiveUS7967235B2Simple equipmentSimple technologyFilament handlingDomestic applicationsAbsorbent materialMechanical engineering
A two-roll toilet paper dispenser automatically transfers a new roll into dispensing position once the previous roll is spent or nearly spent. A spring-loaded plate senses the decreasing diameter of the first roll, and once it reaches a predetermined minimum, actuates a linkage that permits a mandrel carrying the two rolls to drop down within the dispenser body and position the second roll for dispensing. The mandrel and track structure permits reloading the dispenser without removing the mandrel. The rolls of toilet paper have adapter plugs in one end only, to ensure that the rolls are placed in the correct orientation within the dispenser.
Owner:ESSITY PROFESSIONAL HYGIENE NORTH AMERICA LLC
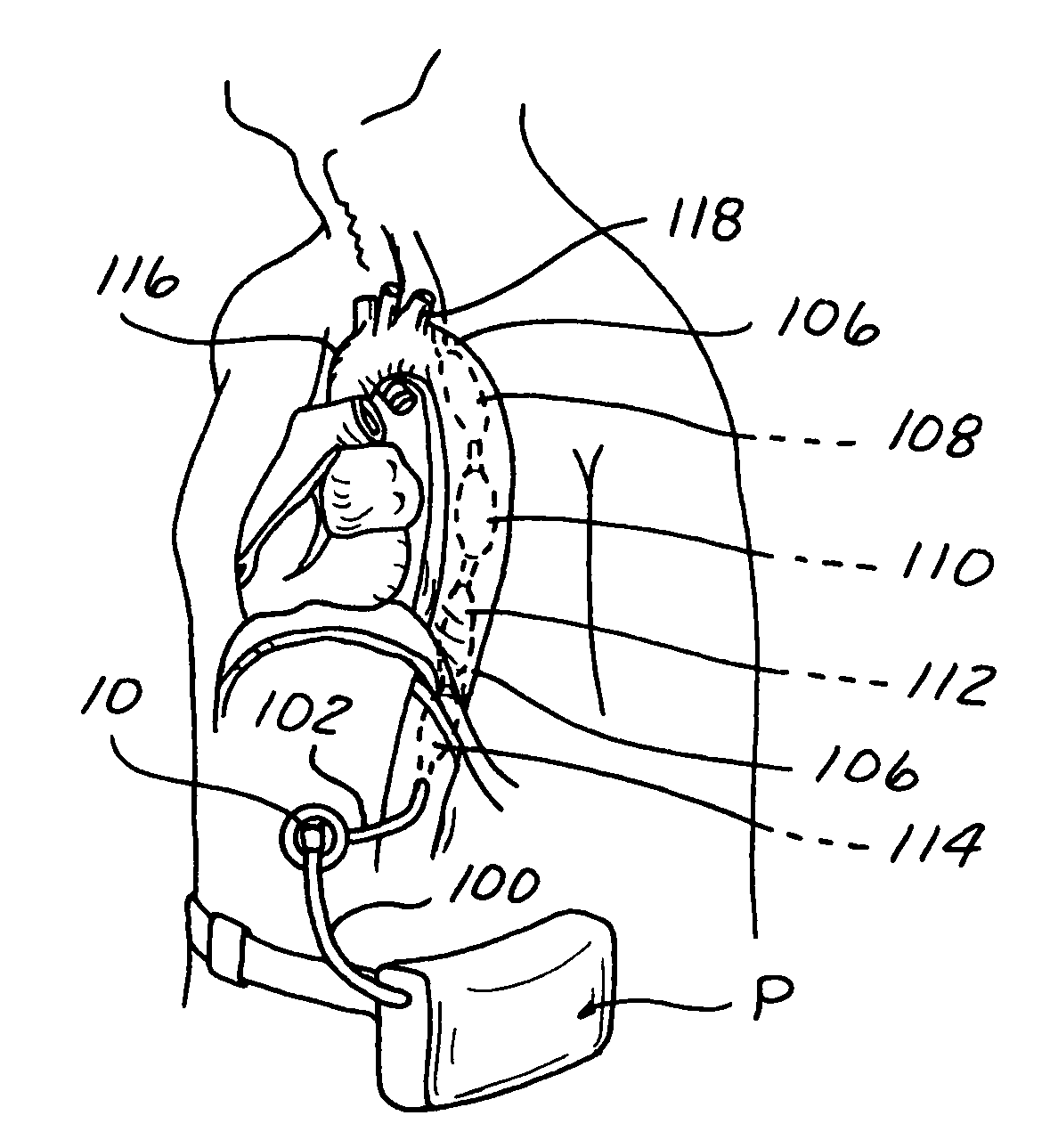
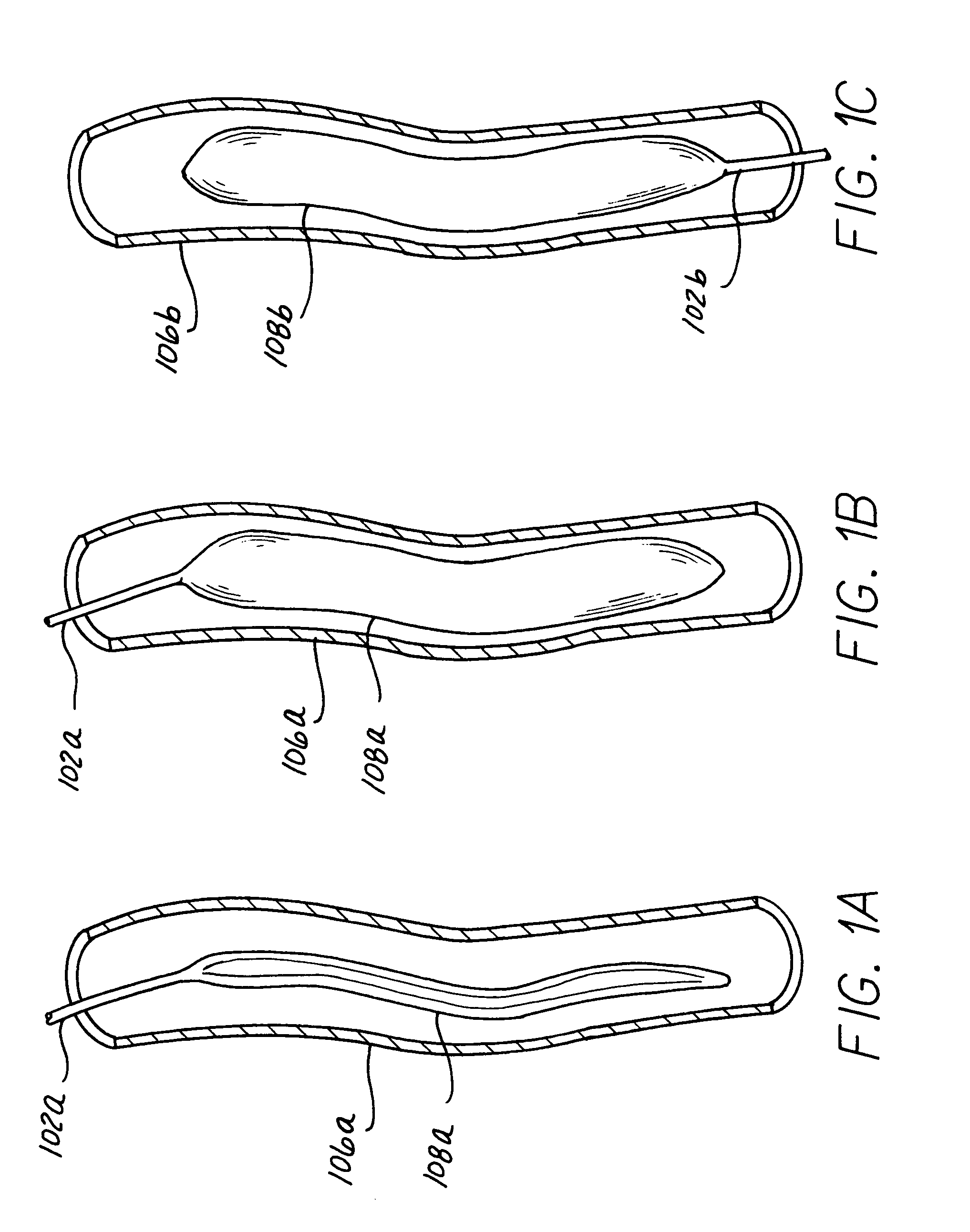
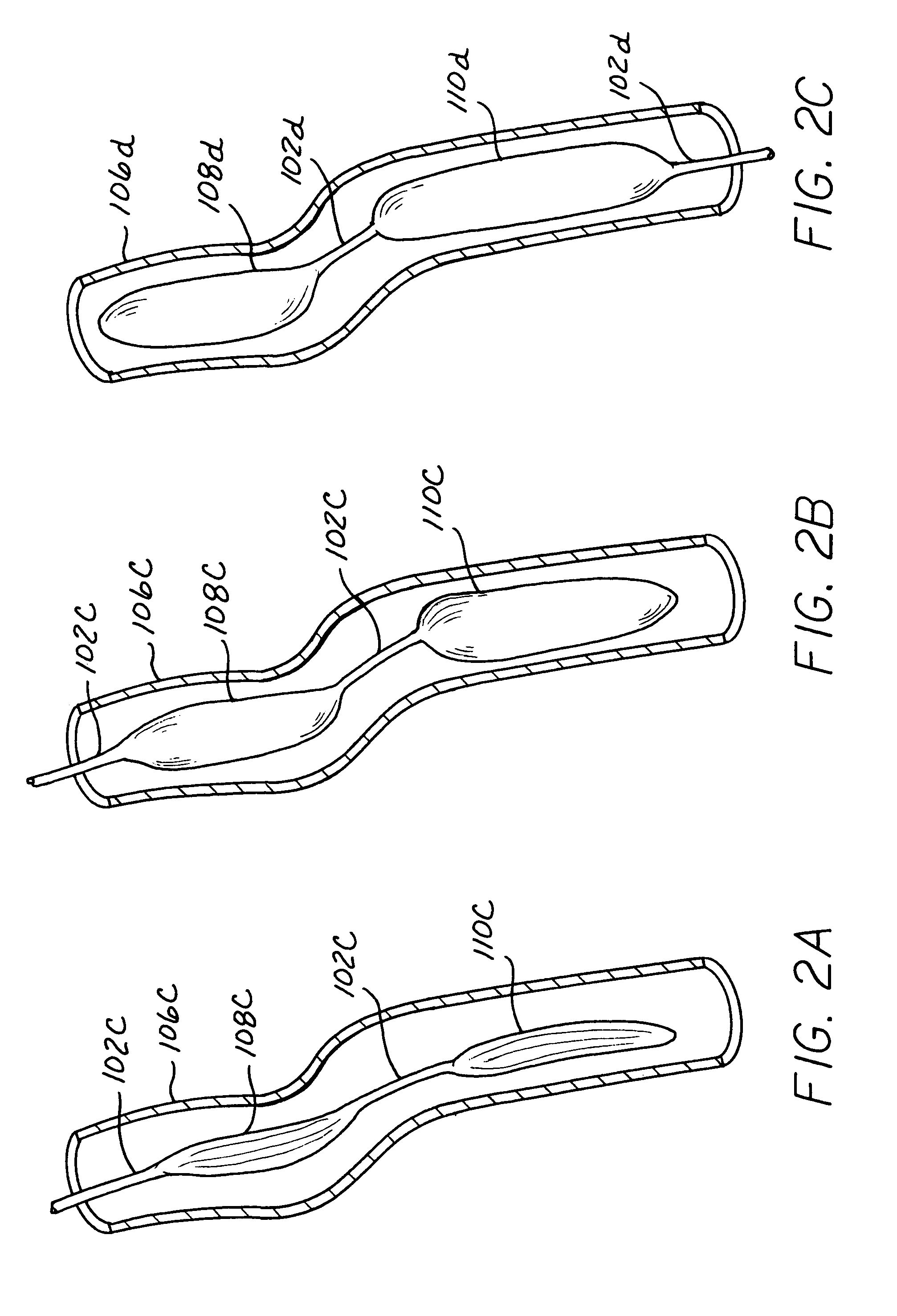
Long term ambulatory intra-aortic balloon pump
ActiveUS7468050B1Increase pump volumeIncrease the diameterElectrocardiographySurgeryAmbulatoryAortic balloon pump
A long term intra-aortic balloon pump (LTIABP) includes an enlarged pumping chamber on the order of 50 cc to 65 cc, inclusive. The pumping chamber is an intra luminal, large volume, long term balloon pump. The balloon pump can include tapered longitudinal ends and / or be segmented into a plurality of pumping chamber segments, each pumping chamber subsegment separated by a flexible power conduit link, where the diameter of the pumping chamber subsegments are independent of one another such as decreasing in size as the subsegments are further from the heart to accommodate the decreasing diameter of the aorta. The LTIABP can be used with any skin connector, or can be used with a percutaneous access device (PAD). The PAD can be sized and shaped to be surgically implanted in any desired location of the patient corresponding to the particular entry selected for implantation of a temporary IABP or LTIABP.
Owner:L VAD TECH
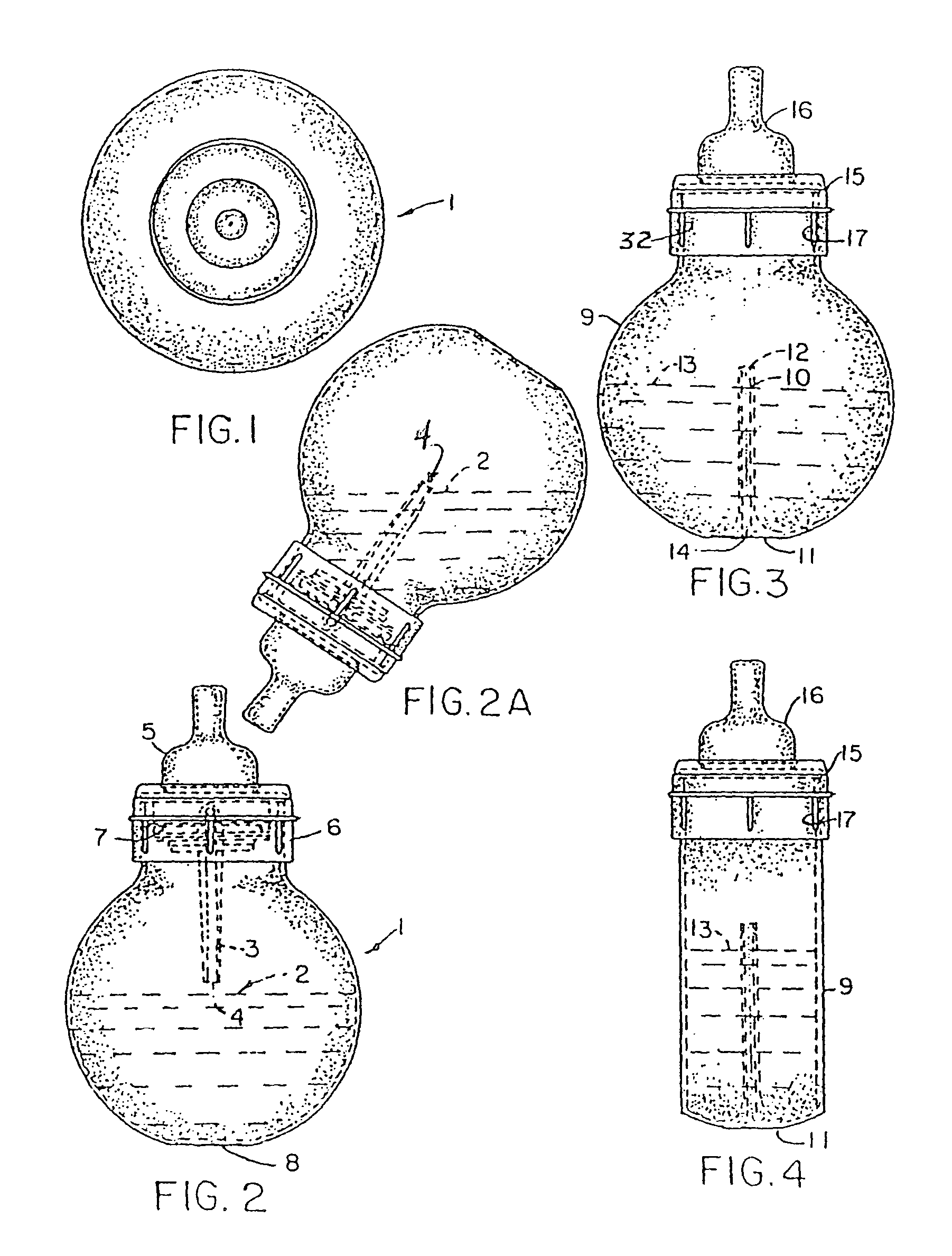
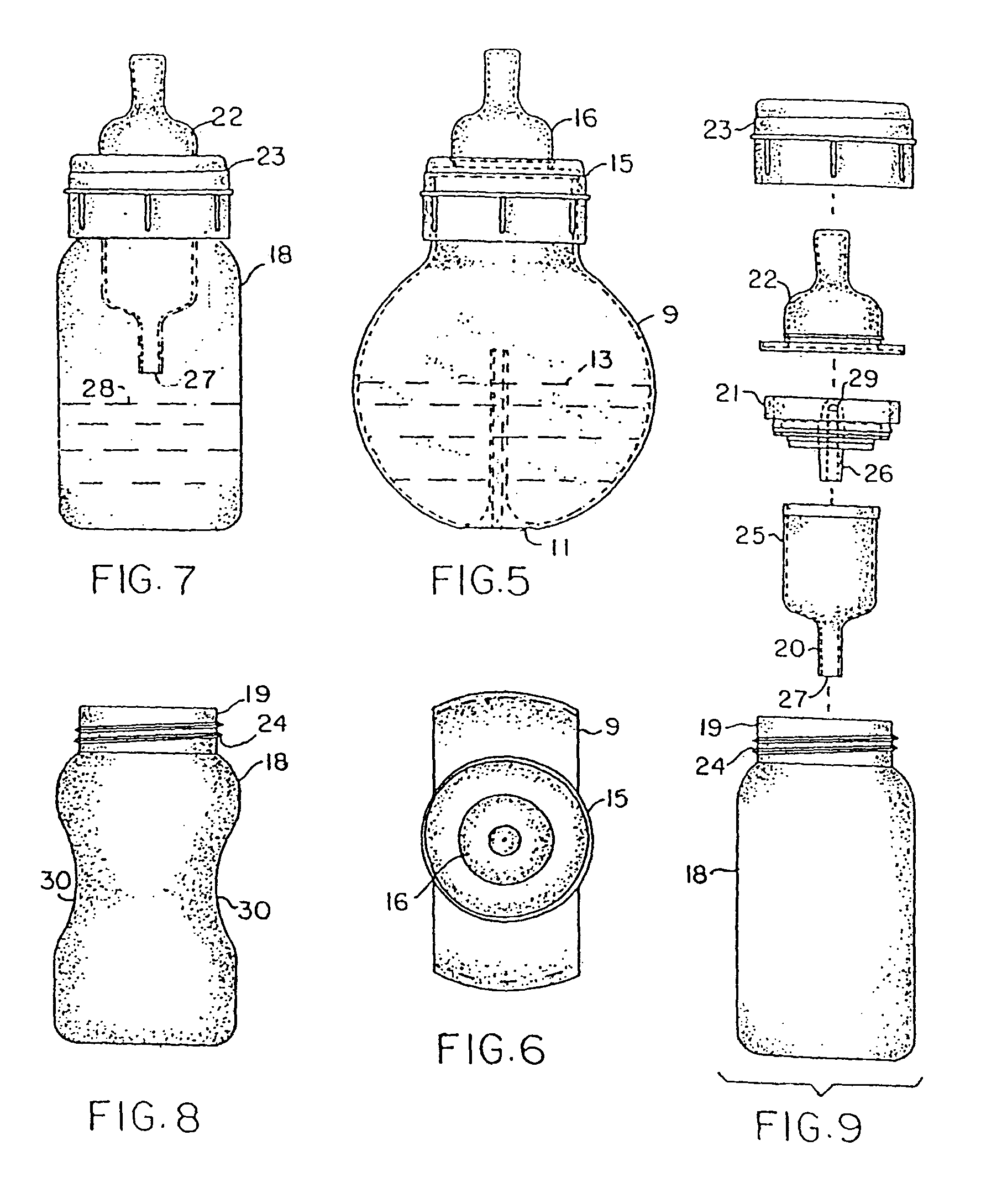
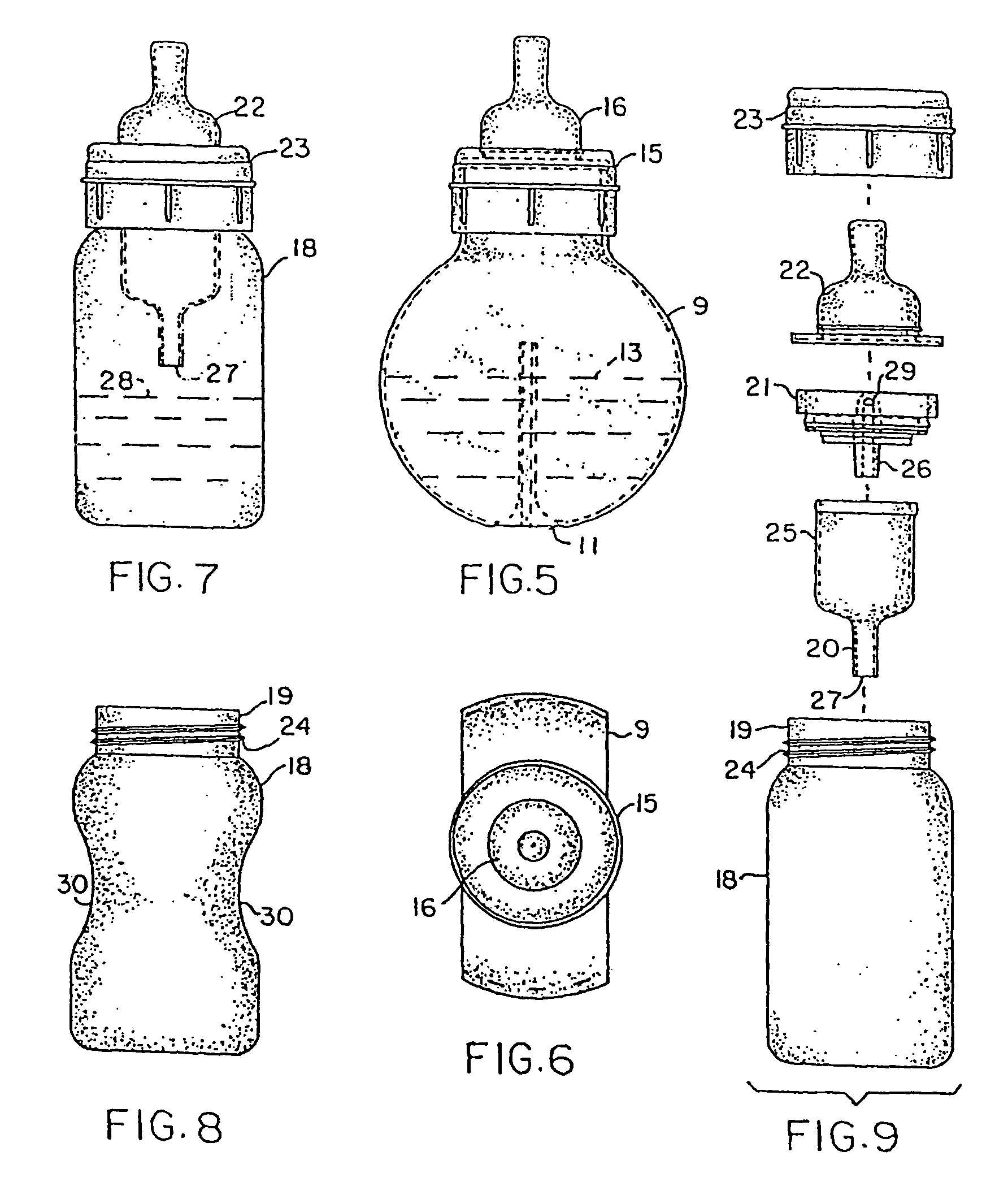
Fully vented nursing bottle with single piece vent tube
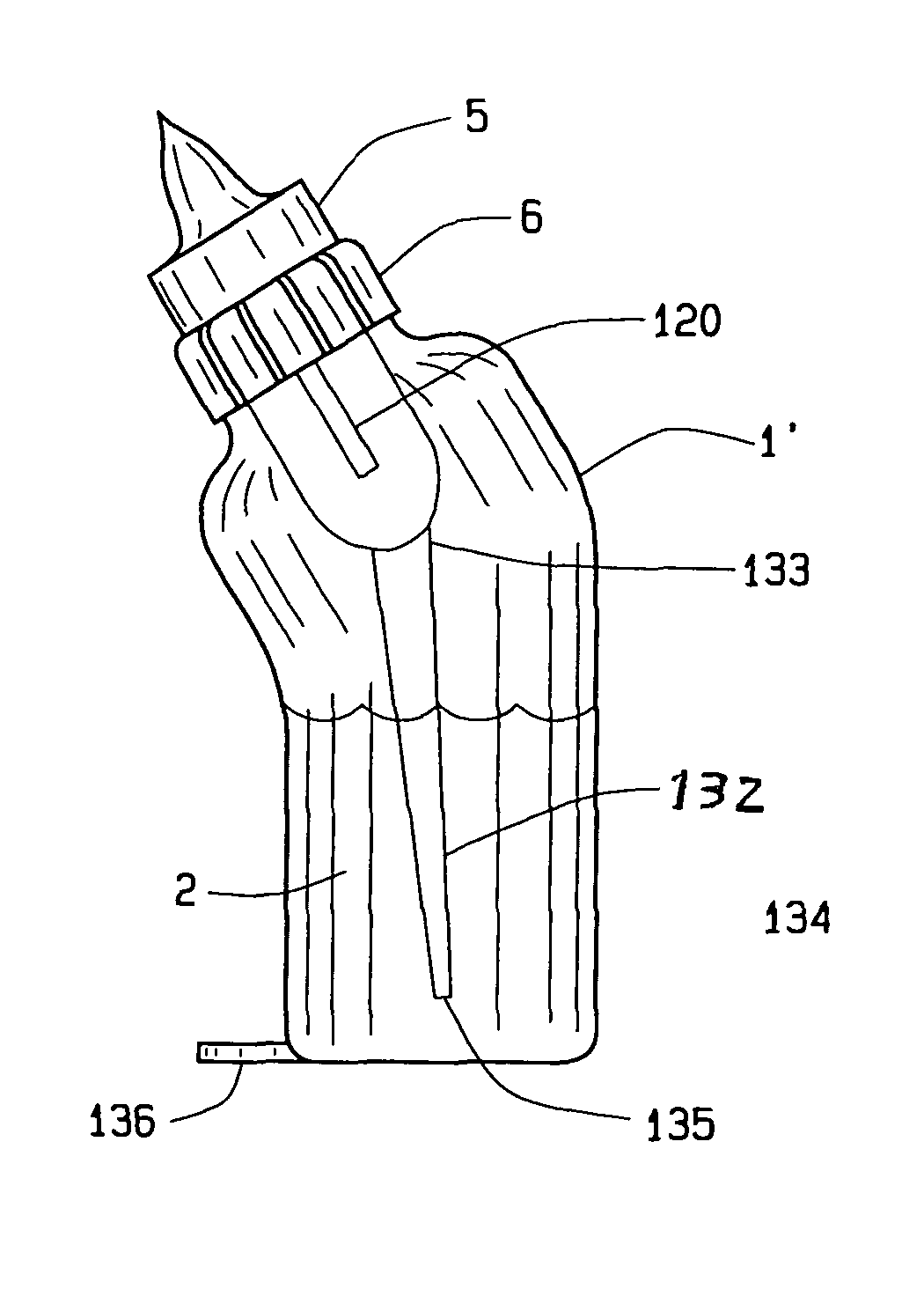
ActiveUS8113365B2Eliminates formation of vacuumFosters normal oral, ear, respiratory, and digestive physiologyBottlesFeeding-bottlesEngineeringBottle
A nursing bottle formed of a small volume container, incorporating a venting tube that extends to dissipate pressure at all times. The nursing bottle may have a cylindrical shape or other configuration that prevents formula placed therein from blocking the venting tube when held at any angle. The venting tube extends distally from the insert portion, operatively associated with a collar that holds the vent structures and the nipple to the neck of the container. The vent opens at the volumetric center of the reservoir above the venting tube. Alternatively, the venting tube has a conical shape of decreasing diameter distally toward the center of the bottom to dissipate the pressure that may cause leakage from the bottle.
Owner:NYUU BENTO DEZAINZU
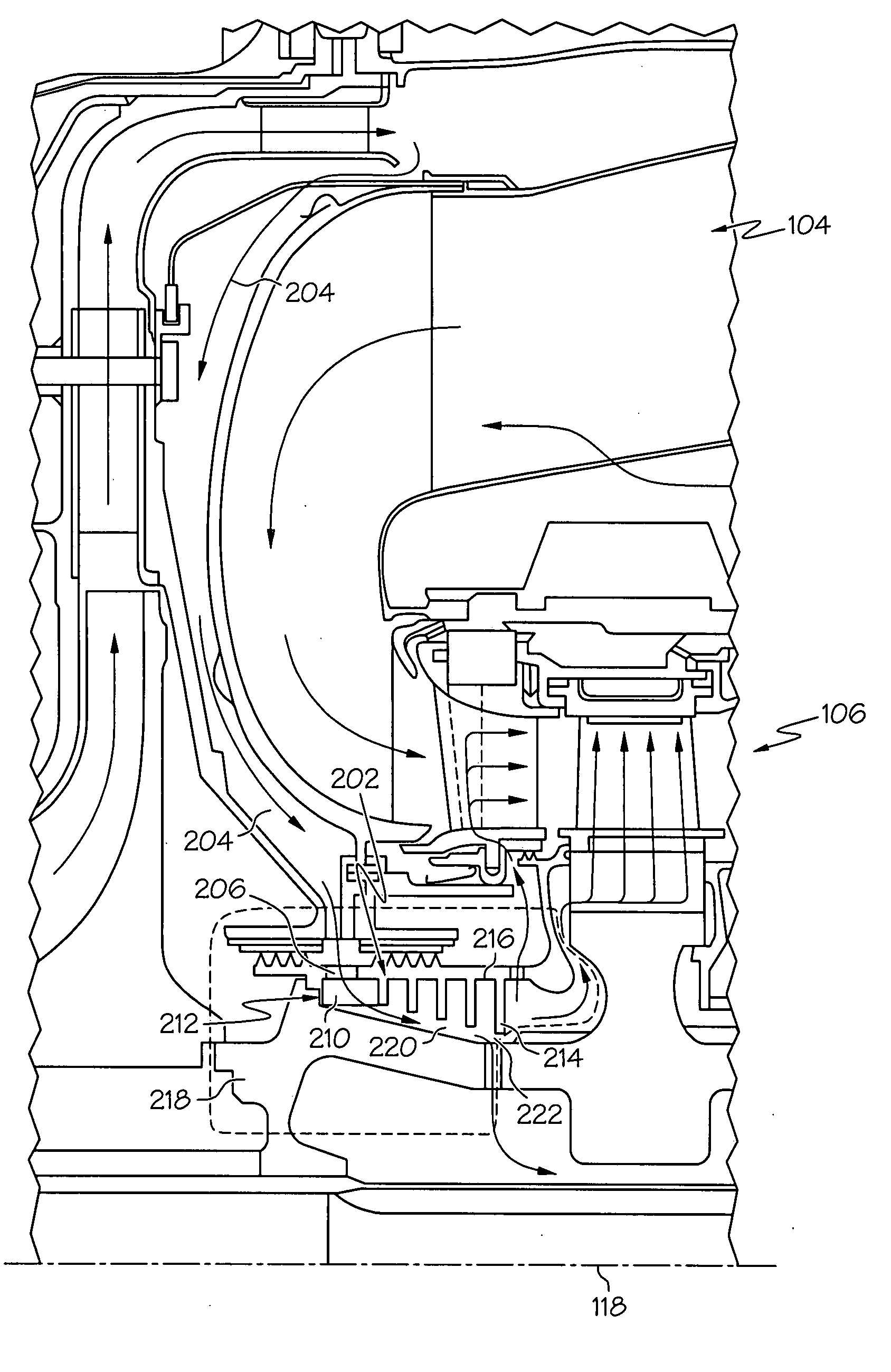
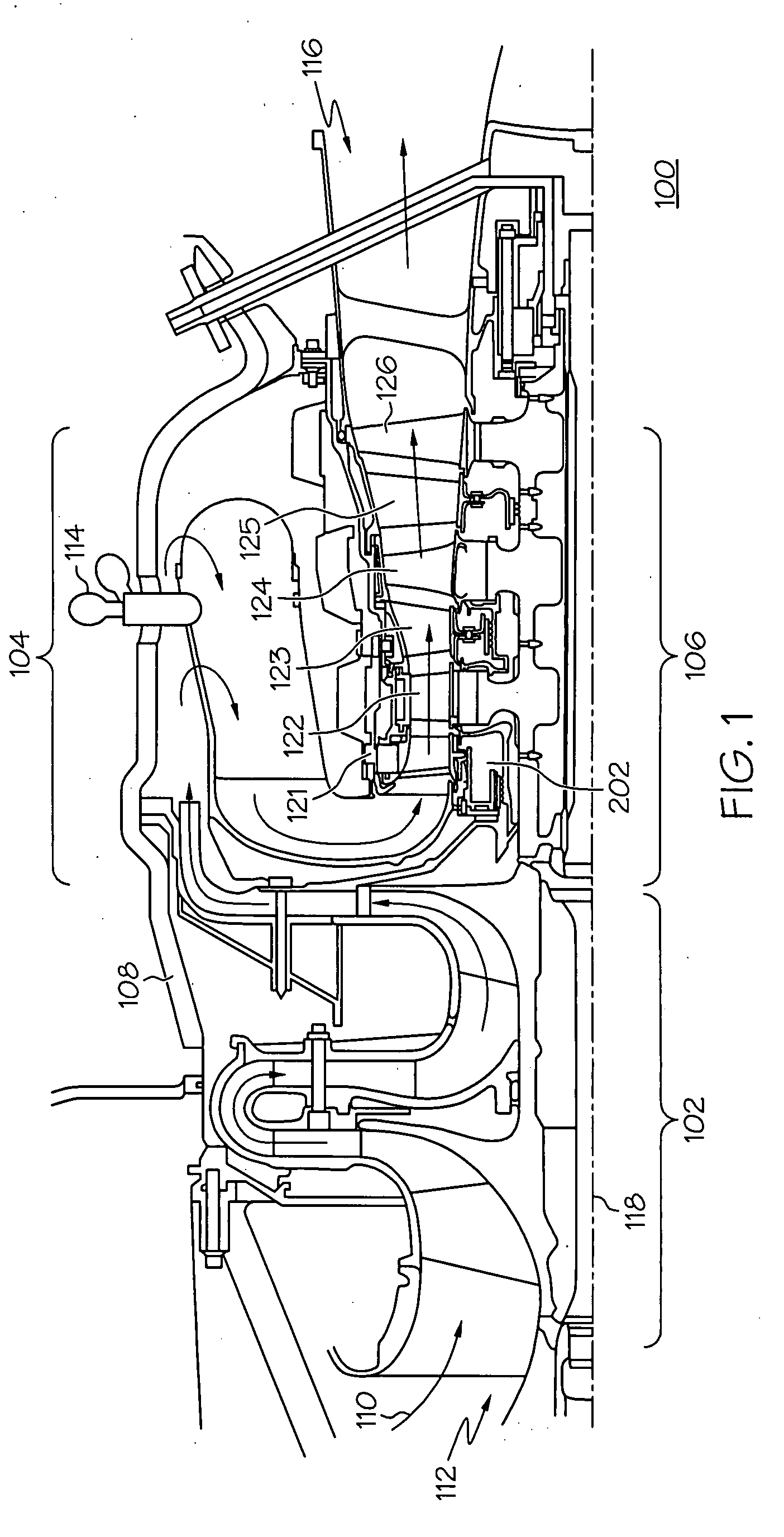
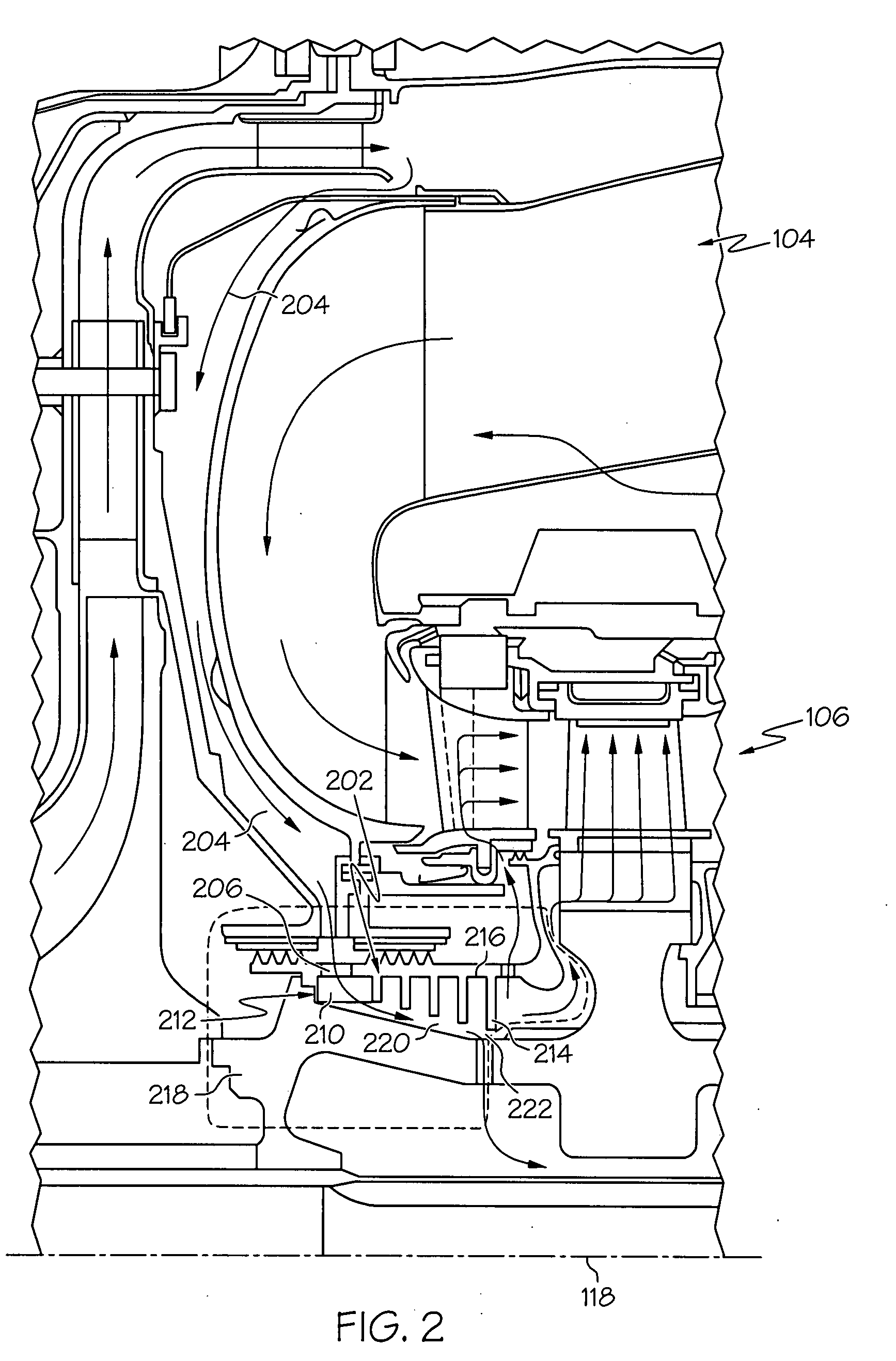
Turbine cooling air centrifugal particle separator
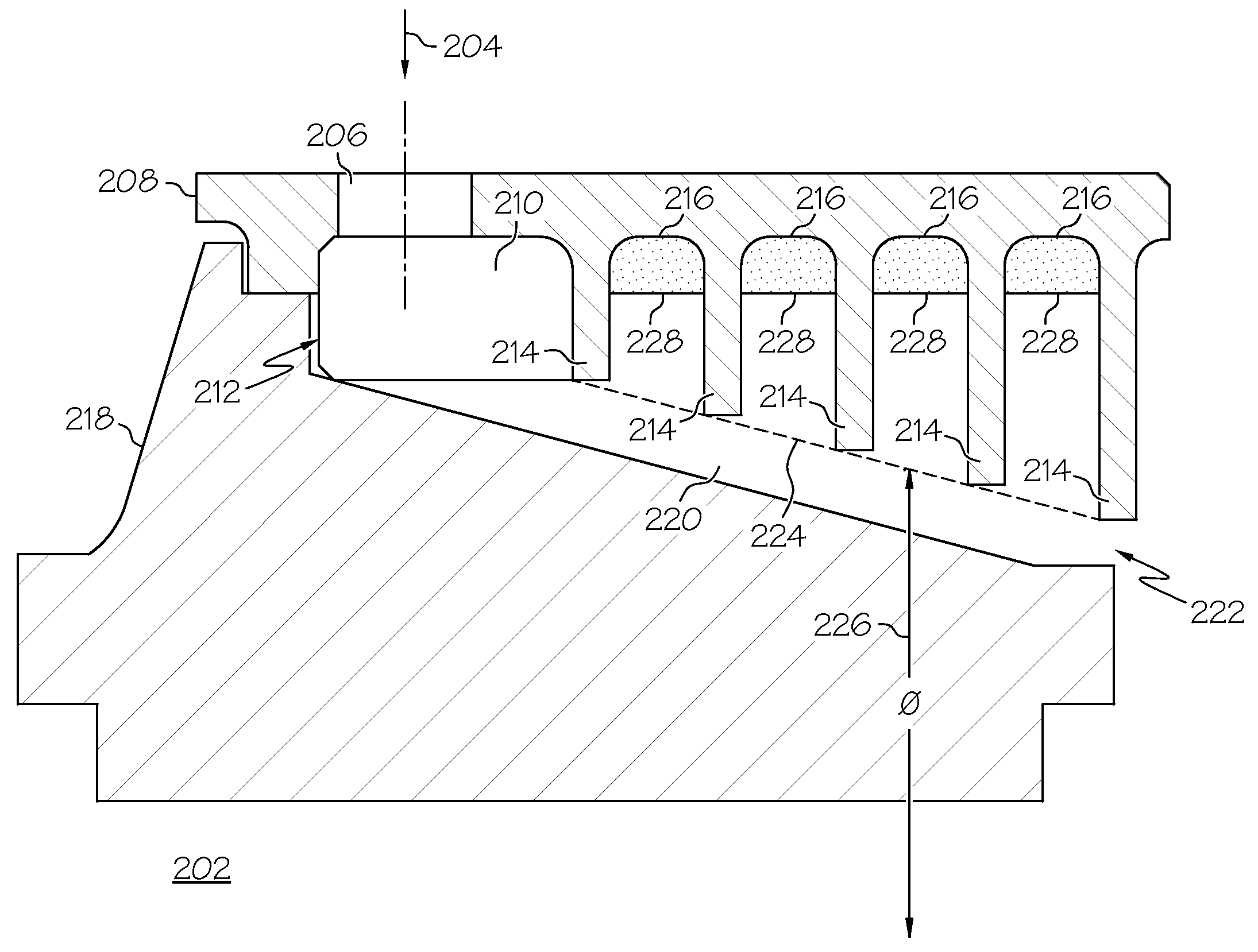
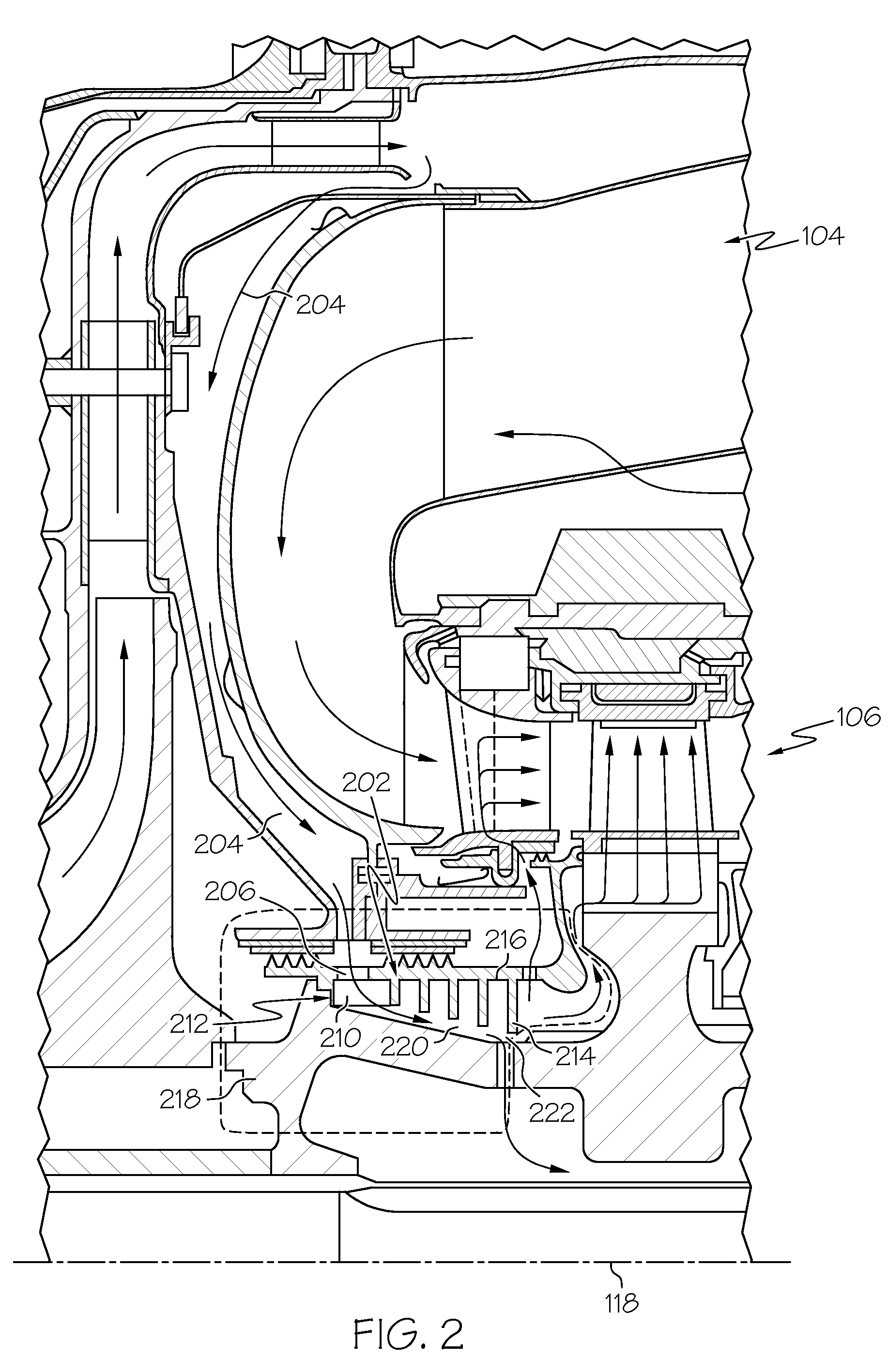
InactiveUS20080310951A1Efficient removalReduce the overall diameterPump componentsEngine fuctionsTurbine bladeCoupling
A centrifugal particle separator (202) is provided for removing particles such as dust particles from the compressed airflow (110) prior to reaching and cooling the turbine blades (122, 124, 126) of a turbine engine (100). A particle separator structure (208) has a side facing the axis (118) about which it rotates, the side including a plurality of pocket dividers (214) defining a plurality of pockets (216), and further defining an entrance cavity (206) for receiving the compressed air (110) containing particles. An inner flowpath coupling (218) includes a side opposed to the axis (118) that is positioned adjacent the particle separator structure (208) to define an airflow path (220) having an entrance communicating with the entrance cavity (212) and an exit (222), wherein the diameter (226) of the airflow outer flowpath (224) decreases from the entrance to the exit, and wherein a centrifugal force created by the centrifugal particle separator assembly (202) rotating around the axis (118) and the decreasing diameter (226) of the airflow path (224) which accelerates the rotational velocity of the air, forces the particles (228) to collect within the plurality of pockets (216) and the remaining compressed air is provided to cool turbine blades (122, 124, 126). A plurality of optional air accelerator fins (210) may be positioned within the entrance cavity (212). The combination of quickly accelerating air from non-rotating to rotating velocity, for example, by accelerator fins (210), and further subjecting the air and entrained particles to increasing rotational velocity resulting in an increasing centrifugal force field as particles (228) progress from the entrance (212) to the exit (222) of the separator assembly (202), efficiently removes the particles (228) from the air.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
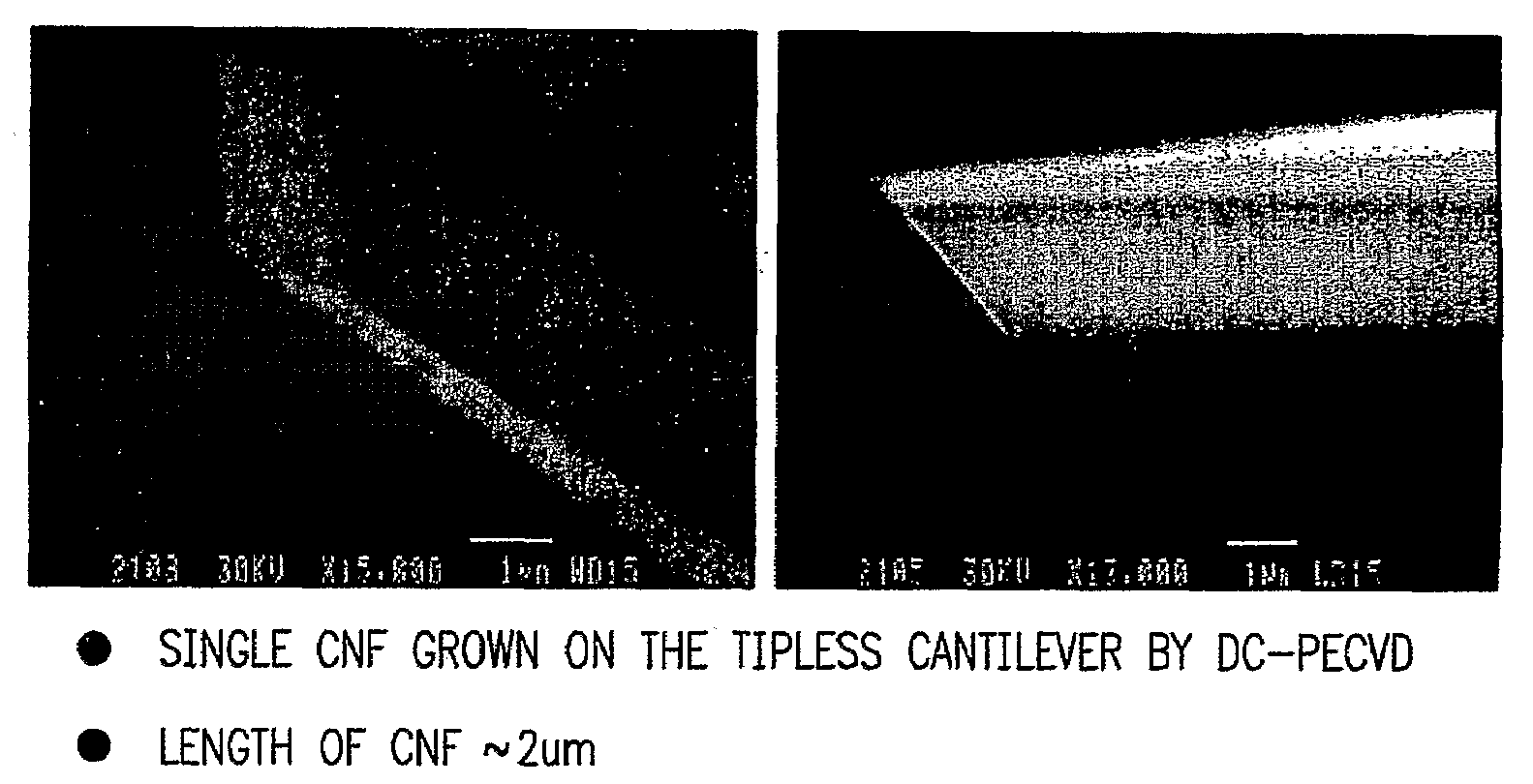
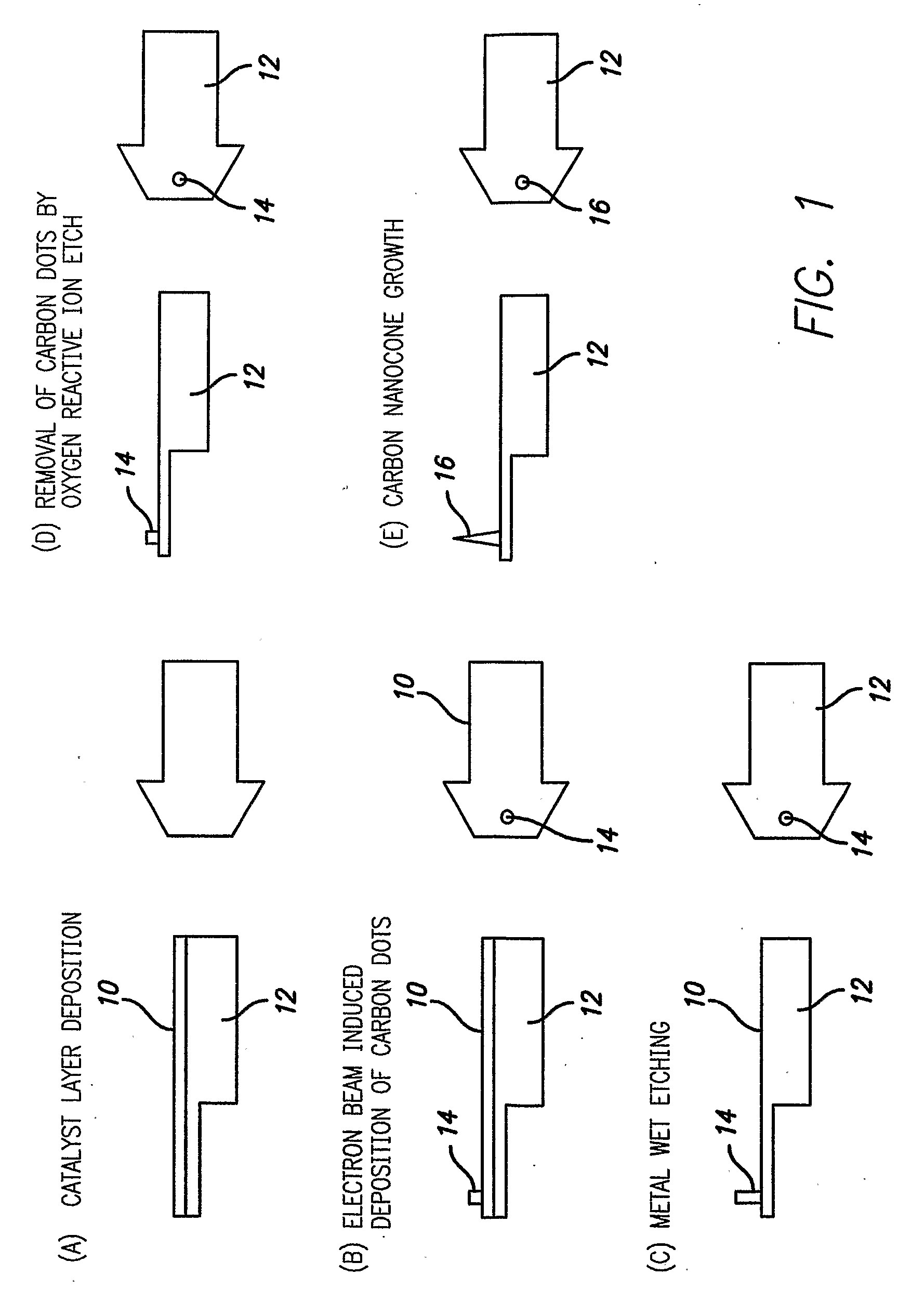
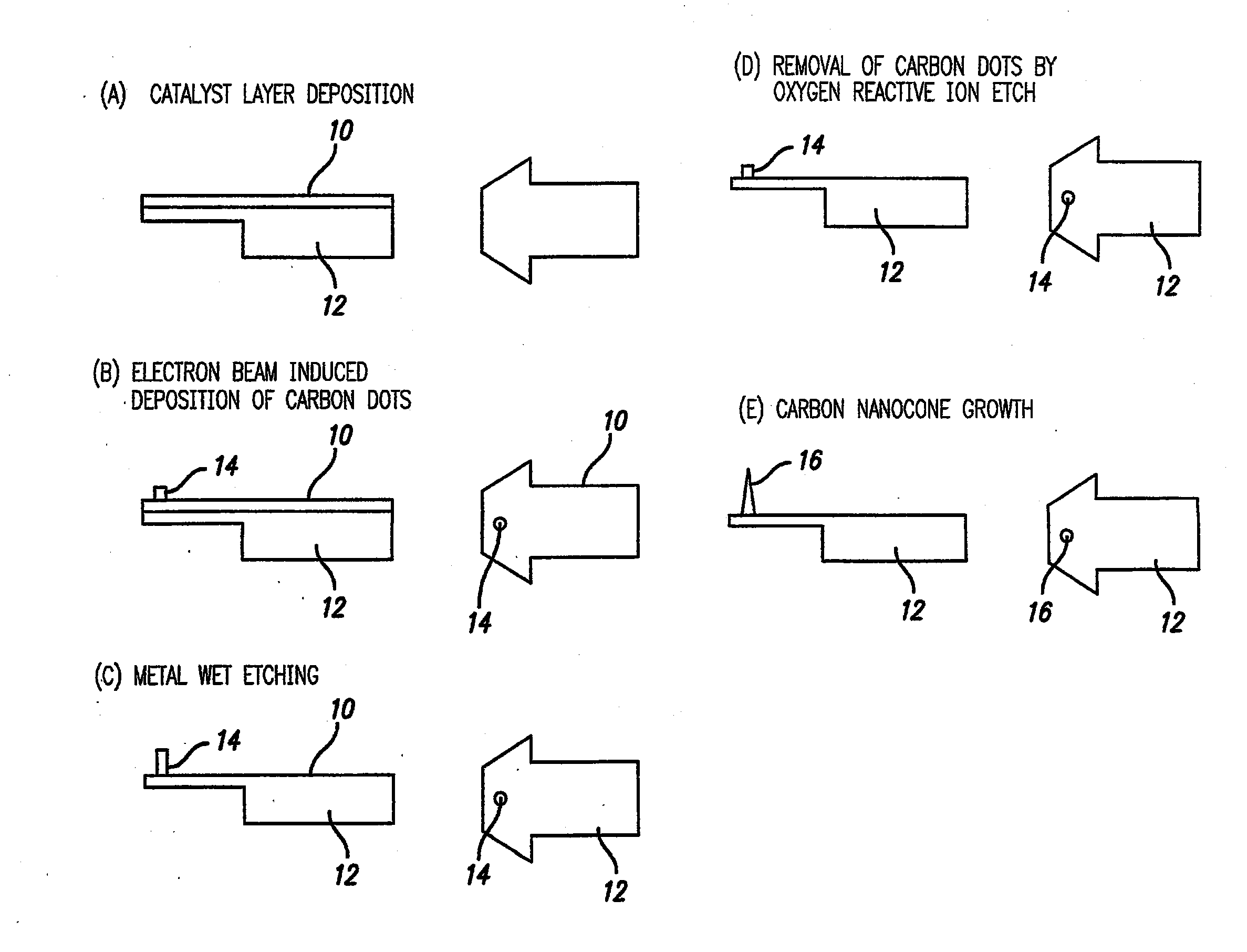
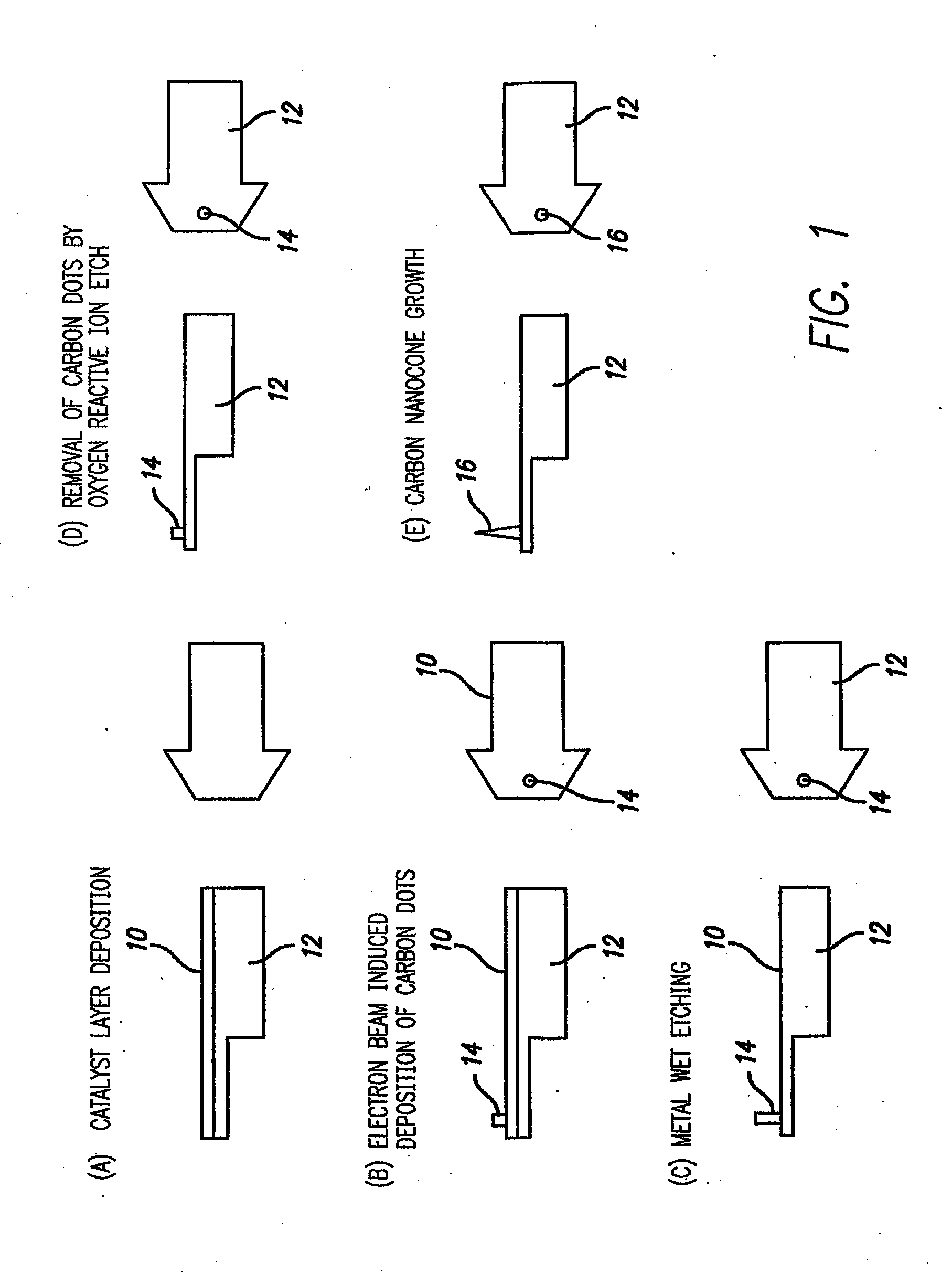
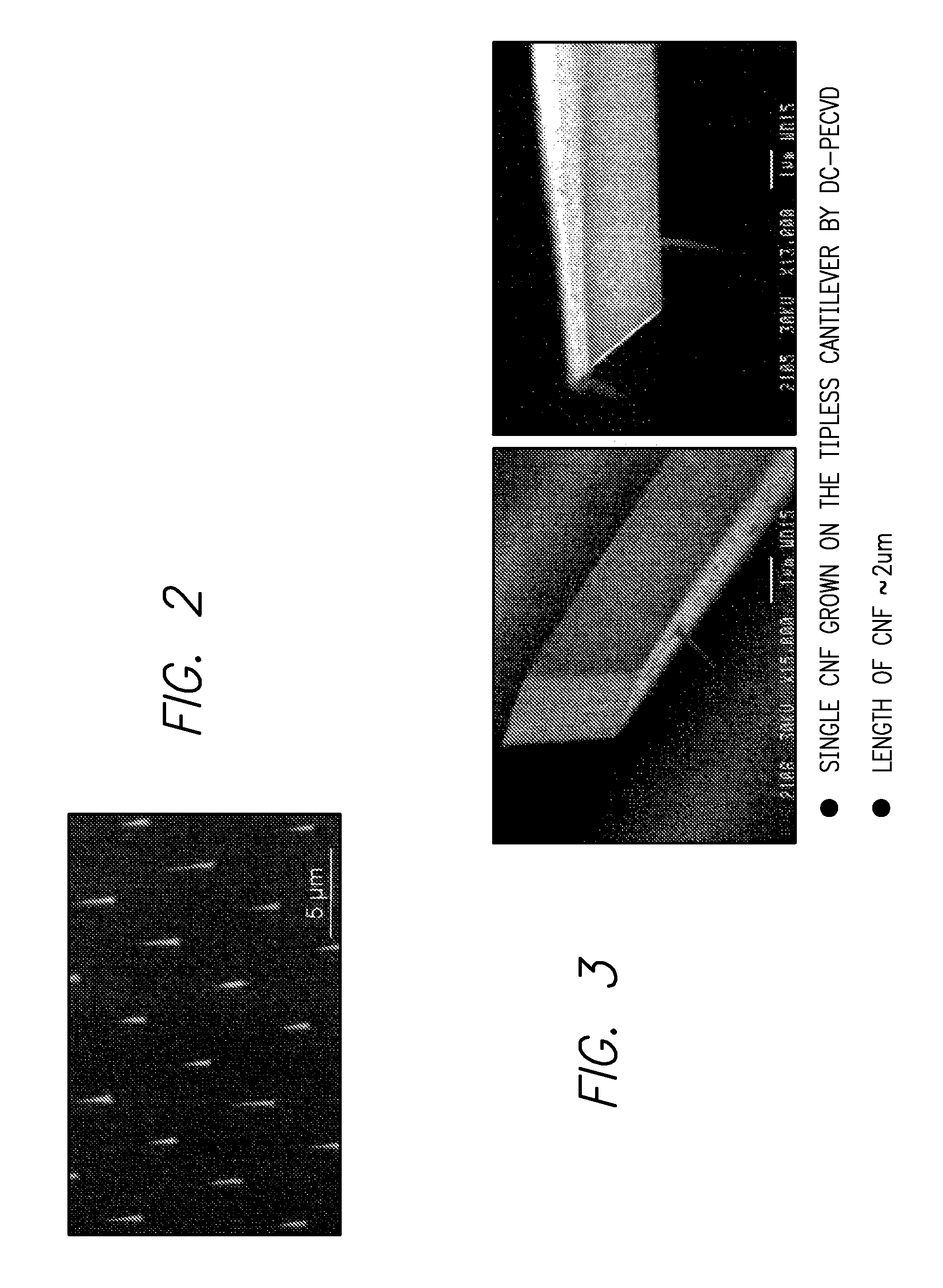
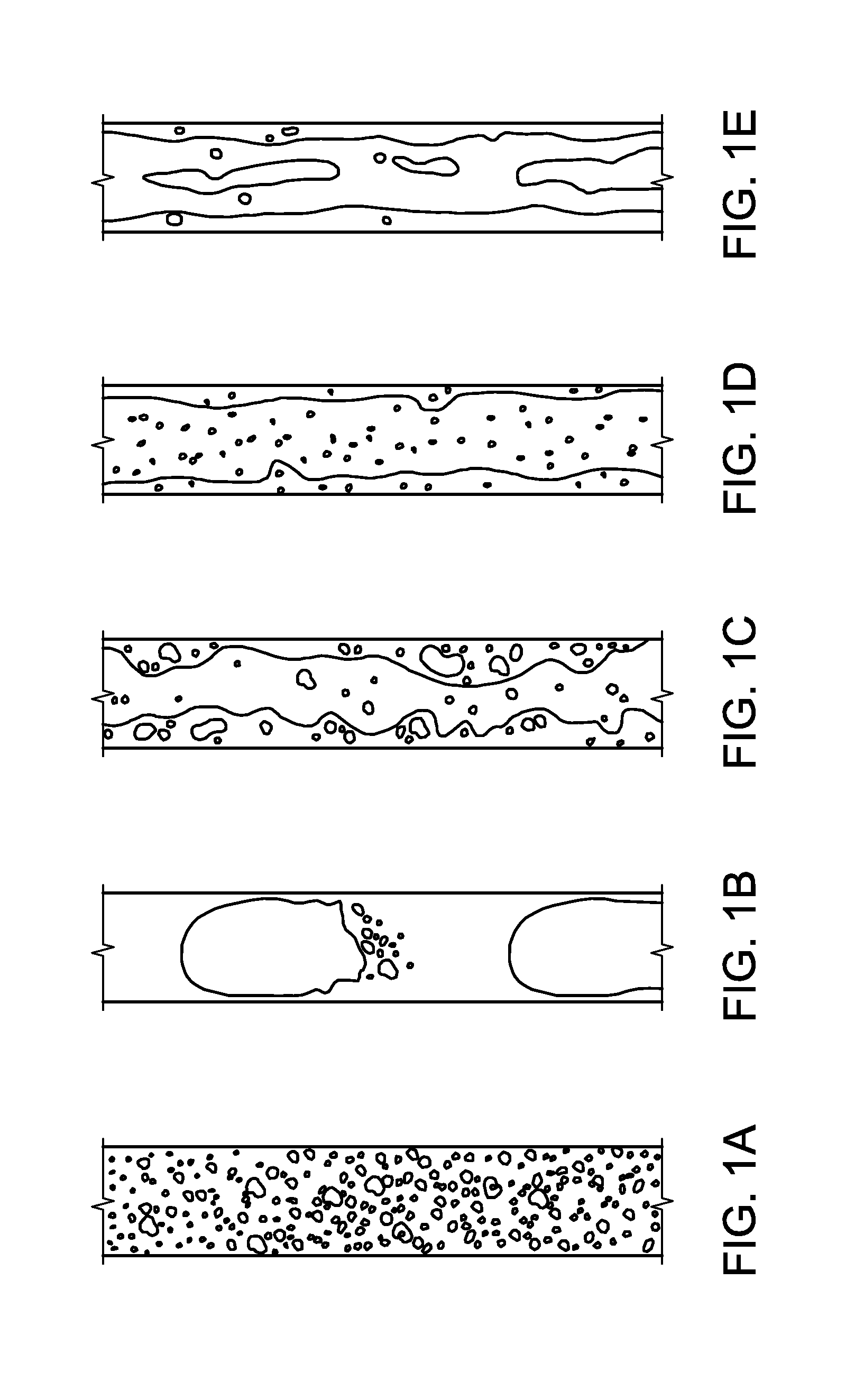
Probe System Comprising an Electric-Field-Aligned Probe Tip and Method for Fabricating the Same
A mechanically stable and oriented scanning probe tip comprising a carbon nanotube having a base with gradually decreasing diameter, with a sharp tip at the probe tip. Such a tip or an array of tips is produced by depositing a catalyst metal film on a substrate (10 & 12 in FIG. 1(a)), depositing a carbon dot (14 in FIG. 1(b)) on the catalyst metal film, etching away the catalyst metal film (FIG. 1(c)) not masked by the carbon dot, removing the carbon dot from the catalyst metal film to expose the catalyst metal film (FIG. 1(d)), and growing a carbon nanotube probe tip on the catalyst film (16 in FIG. 1(e)). The carbon probe tips can be straight, angled, or sharply bent and have various technical applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Fully vented wide rim nursing bottle with contoured vent tube
Owner:NYUU BENTO DEZAINZU
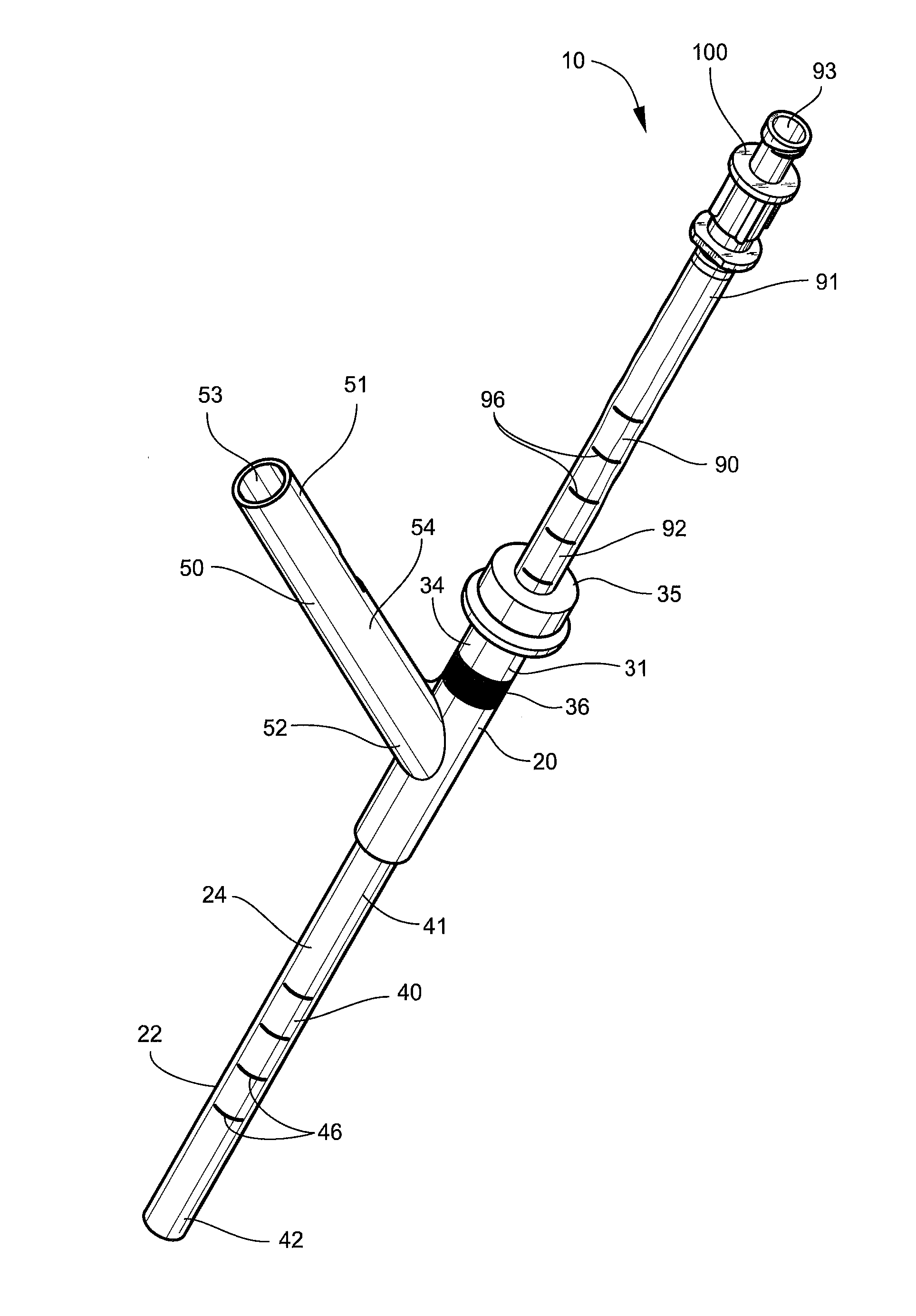
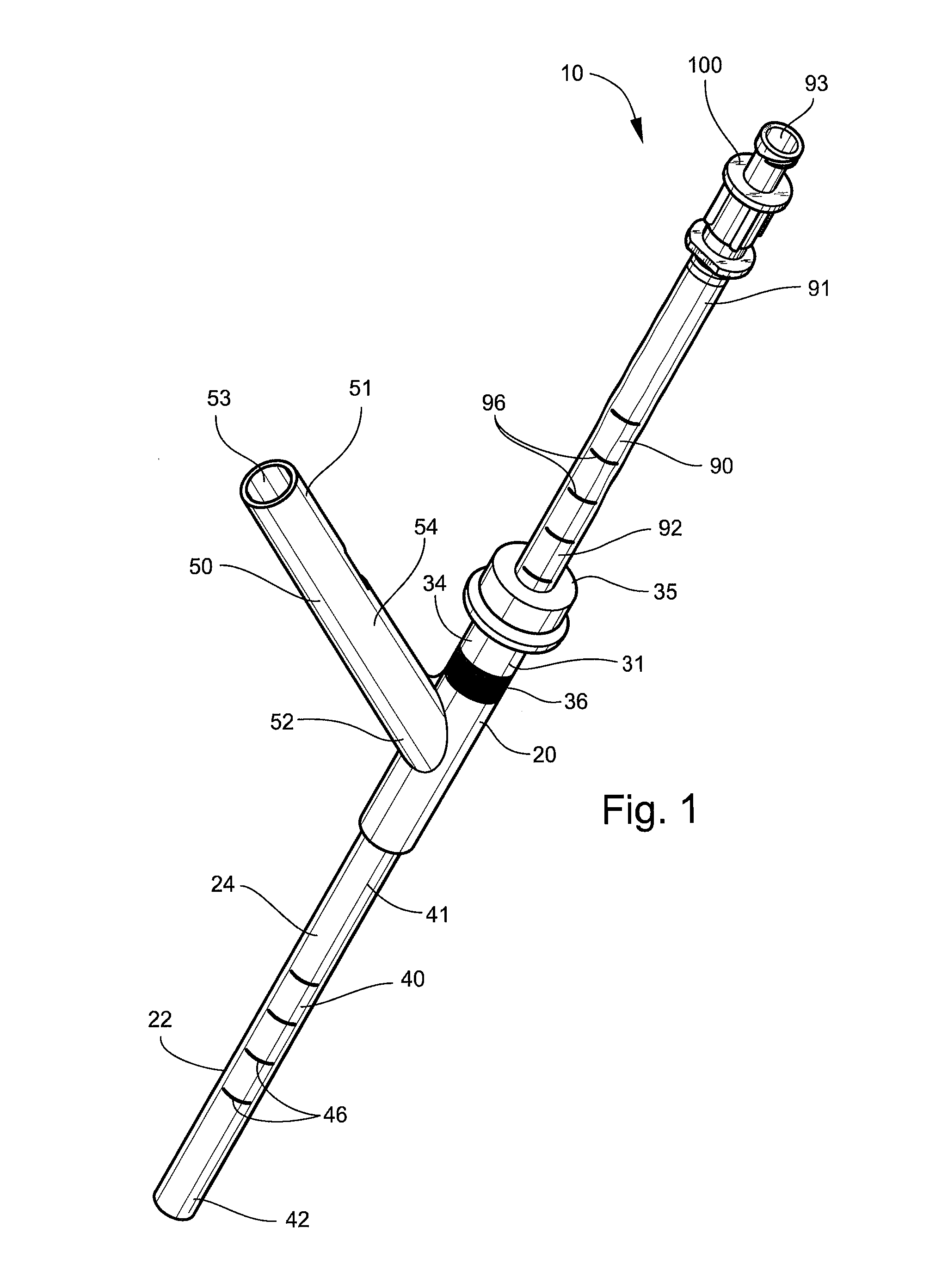
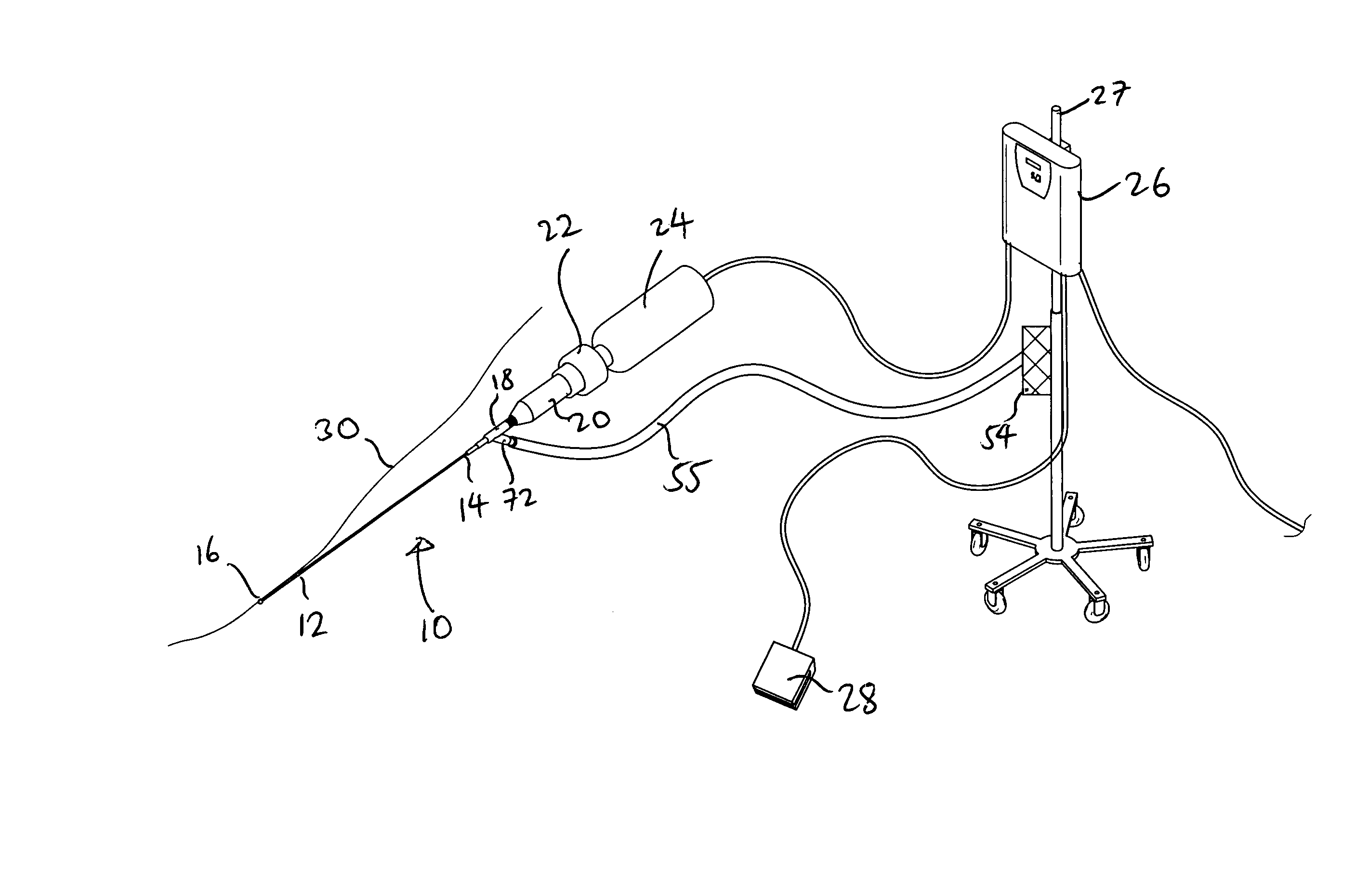
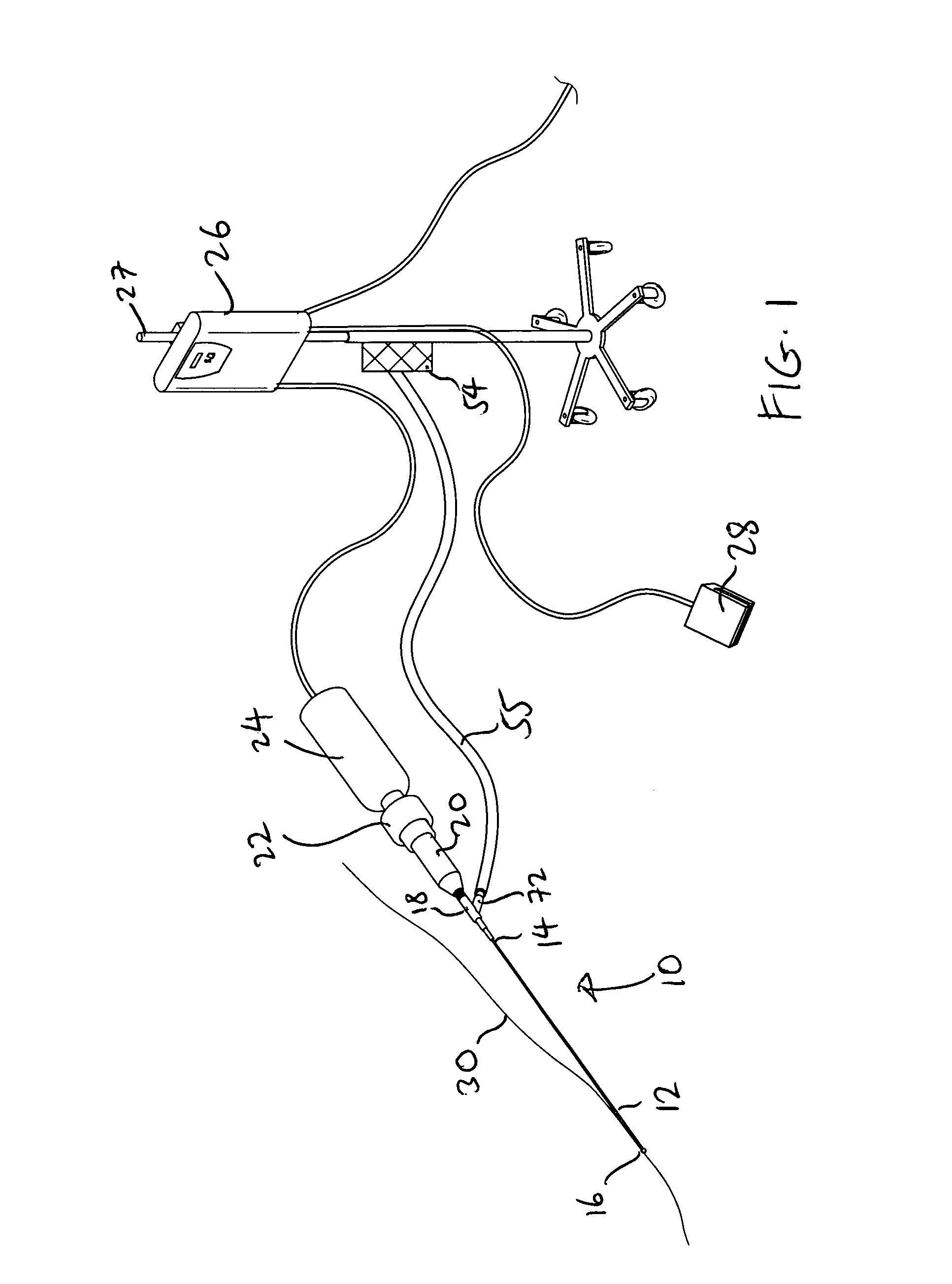
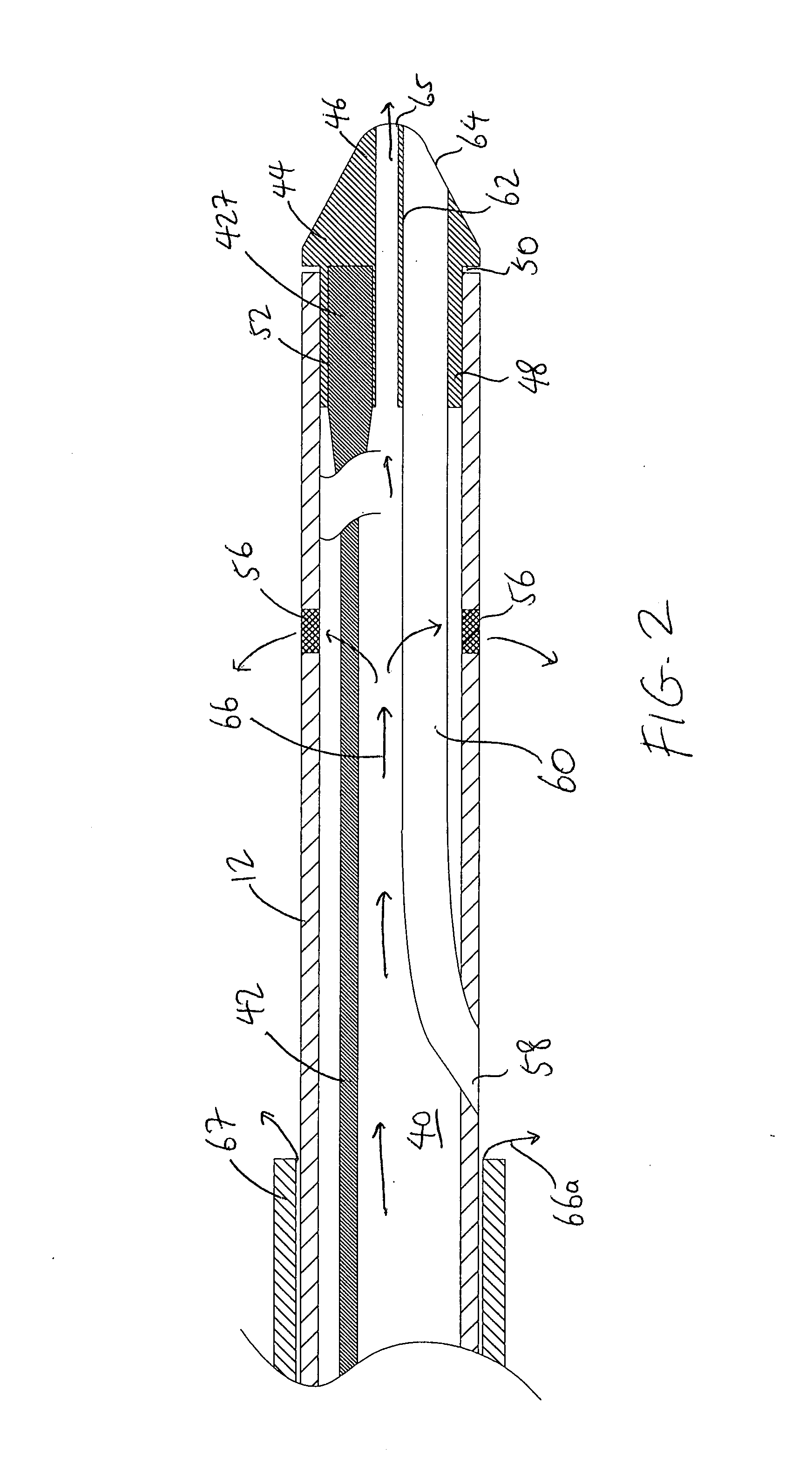
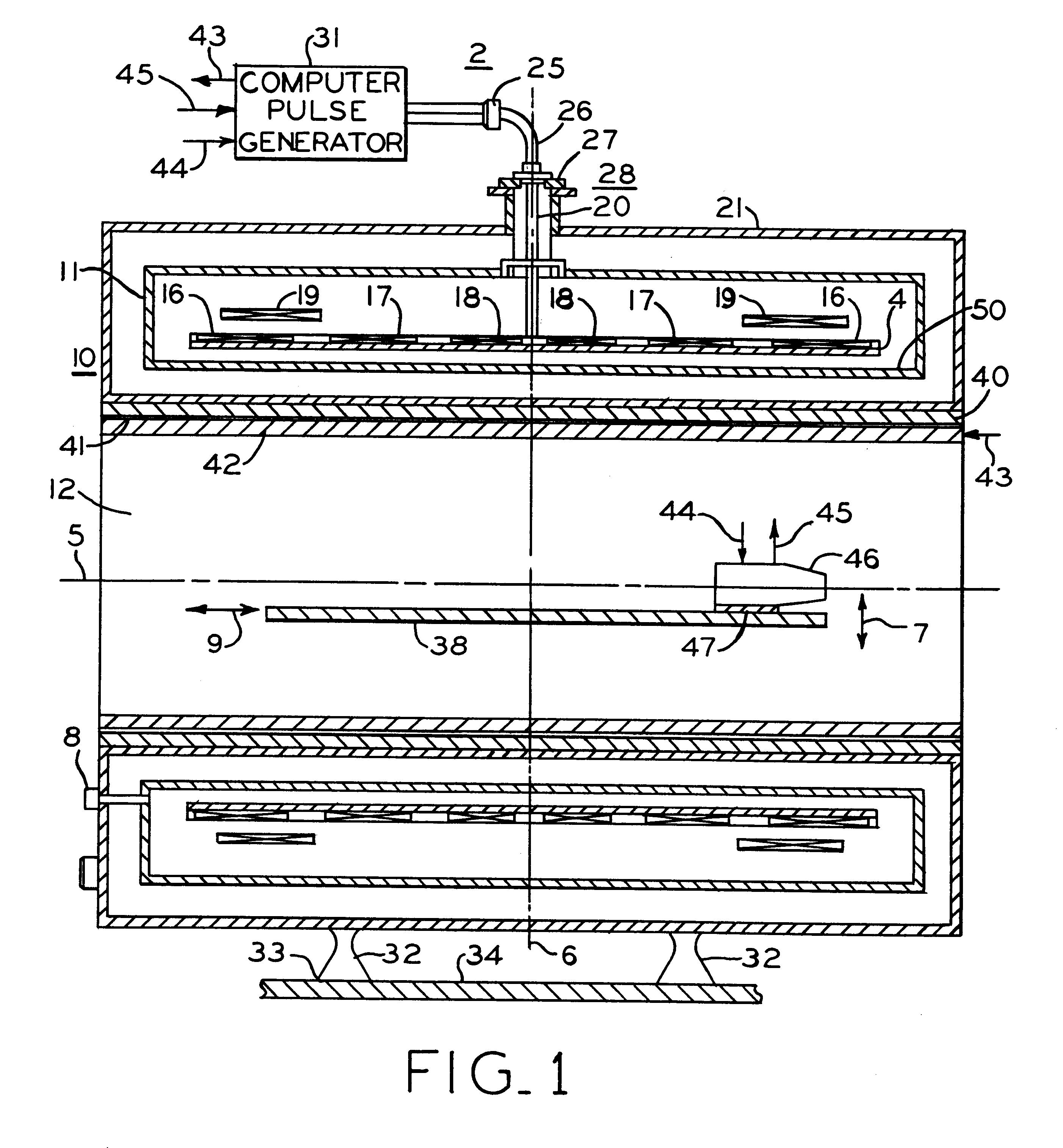
Therapeutic ultrasound system
ActiveUS20070239027A1Way of increaseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryAcoustic transmission lineTherapeutic ultrasound
An ultrasound system has a catheter including an elongate flexible catheter body having at least one lumen extending longitudinally therethrough. An ultrasound transmission wire extends longitudinally through the lumen of the catheter body, and has a proximal region, a distal region, and an intermediate region between the proximal region and the distal region. A sonic connector is connected to the proximal region of the ultrasound transmission wire, and a distal head is positioned at the distal end of the catheter body and coupled to the distal region of the ultrasound transmission wire. The proximal region of the ultrasound transmission wire has a larger diameter than the intermediate region, the intermediate region is continuously tapered with a progressively decreasing diameter from its proximal end to its distal end, and the distal region has a greater diameter than the distal end of the intermediate region.
Owner:FLOWCARDIA
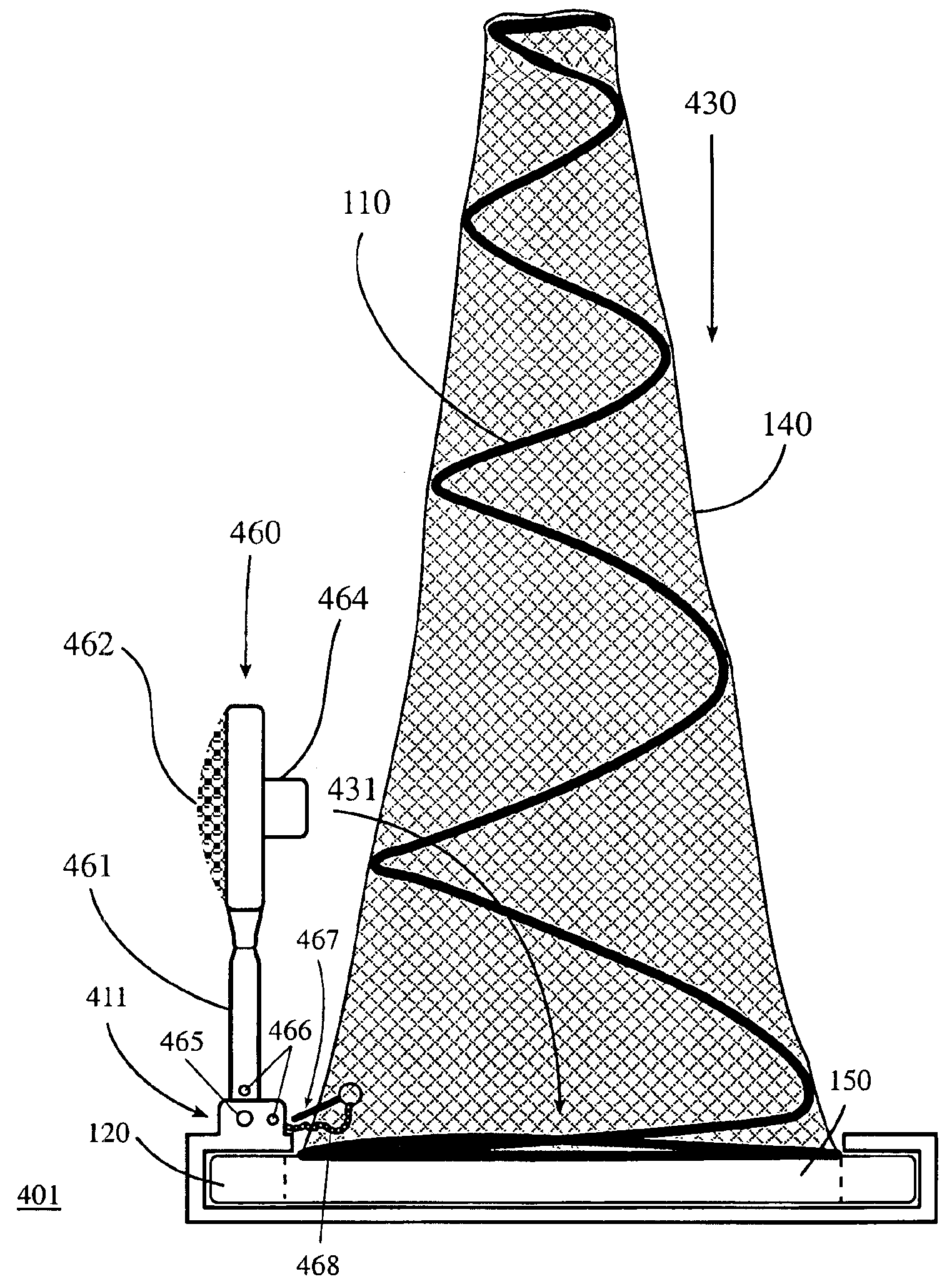
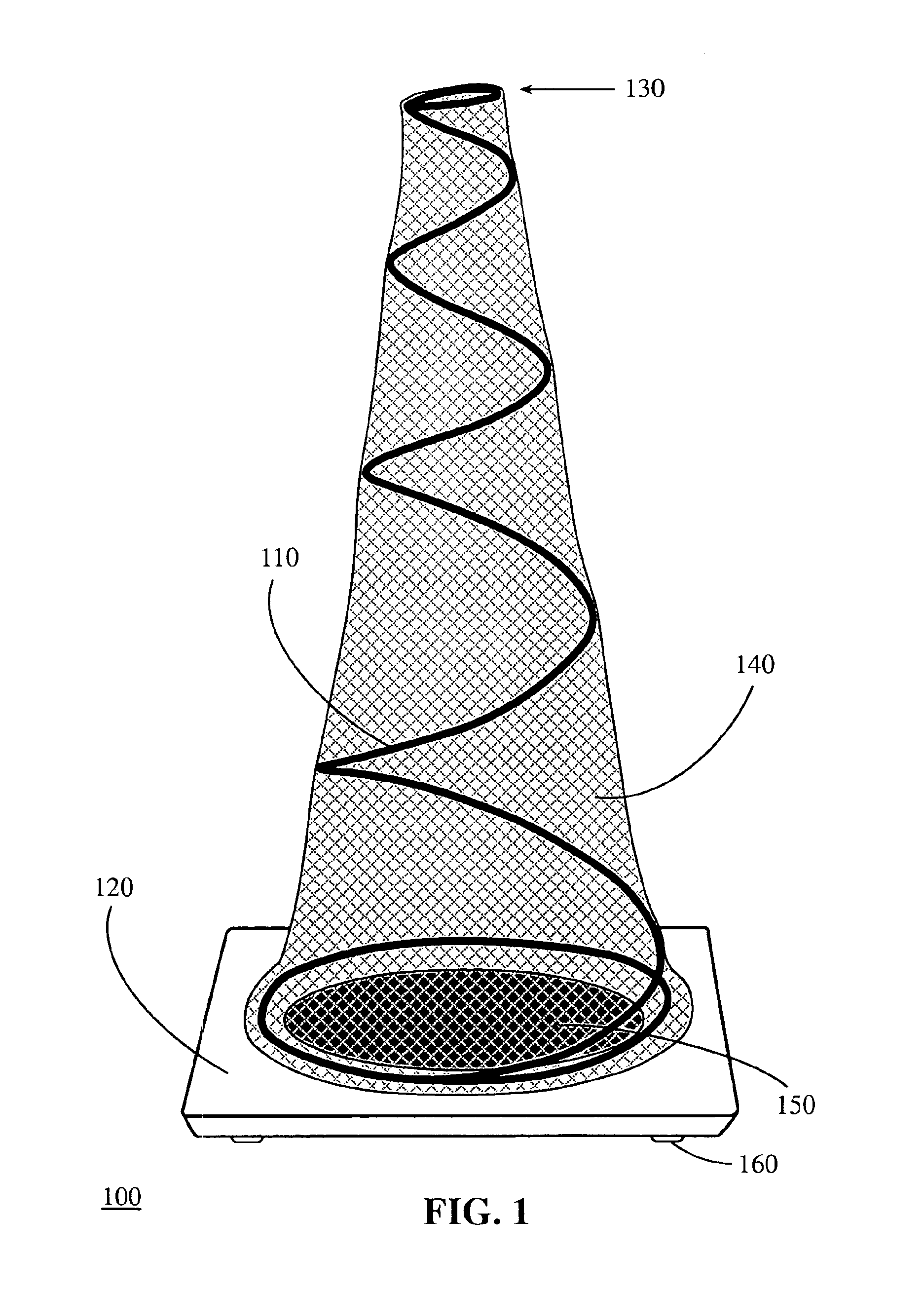
Compact safety cone
InactiveUS6928952B2Easy to carryEasy to storeTraffic signalsRoad signsFinite impulse responseCompact Pattern
A compact safety cone that can self-right when in use and be reduced to a compact size when not. The compact safety cone has a base, flexible means, and cover. The spring flexible means coils around the center of the base in decreasing diameters without overlapping. The compact safety cone has a substantially low center of gravity due to the weight distribution among its components. By design, the compact safety cone has a fast impulse response to direct (contact) and indirect (no-contact) perturbations and is capable of being run over or hit by a vehicle and “self-right” substantially immediately after the impact. When not in use, an integrated holding means conveniently and securely keeps the flexible means to the base. The holding means can be, e.g., a cover, lid, light, sign, mirror, box, case, hook, latch, strap, Velcro, pin, lock, etc. In some cases, an optional handle may be included.
Owner:RAMSTAR MILLS INC
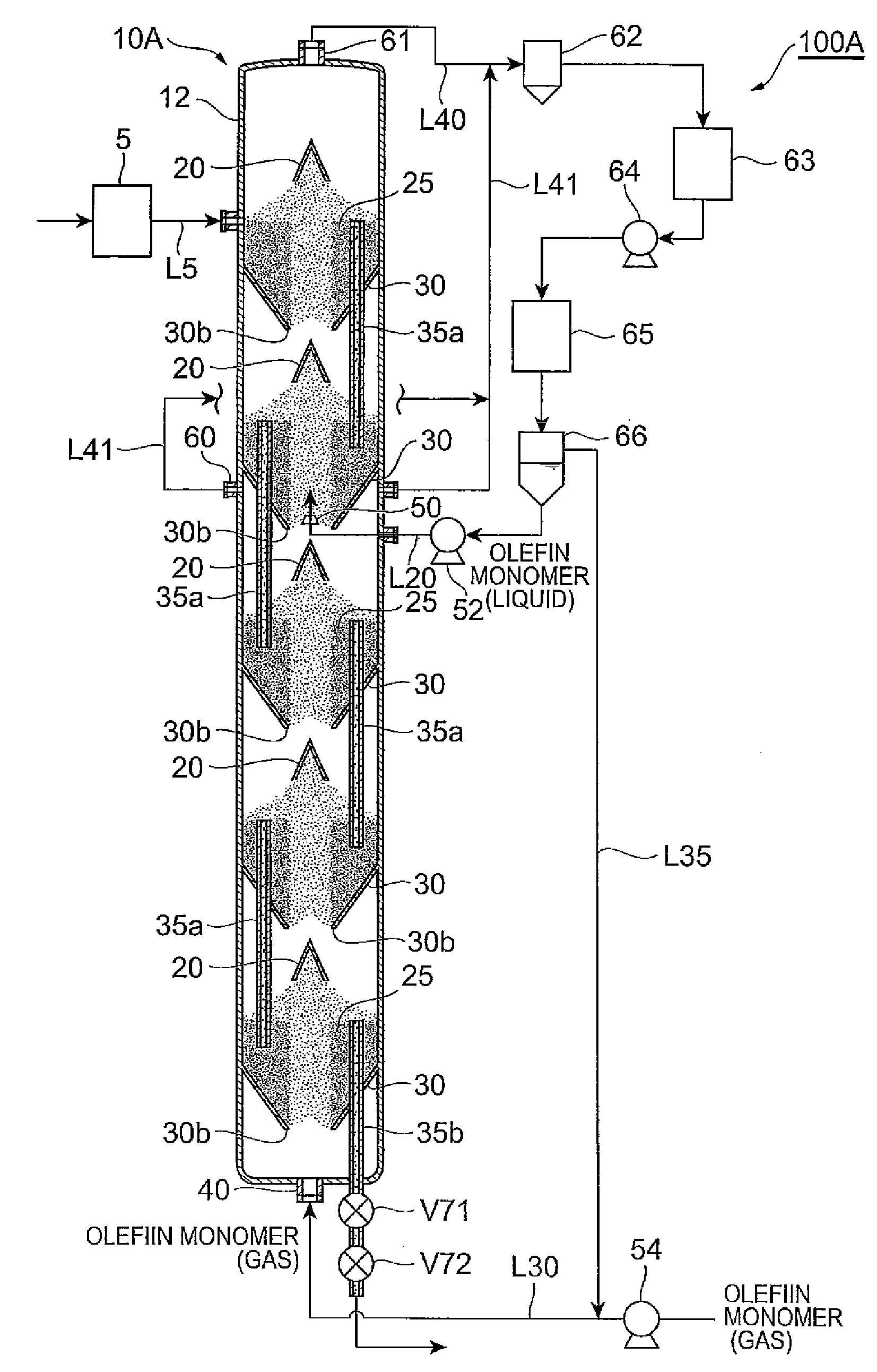
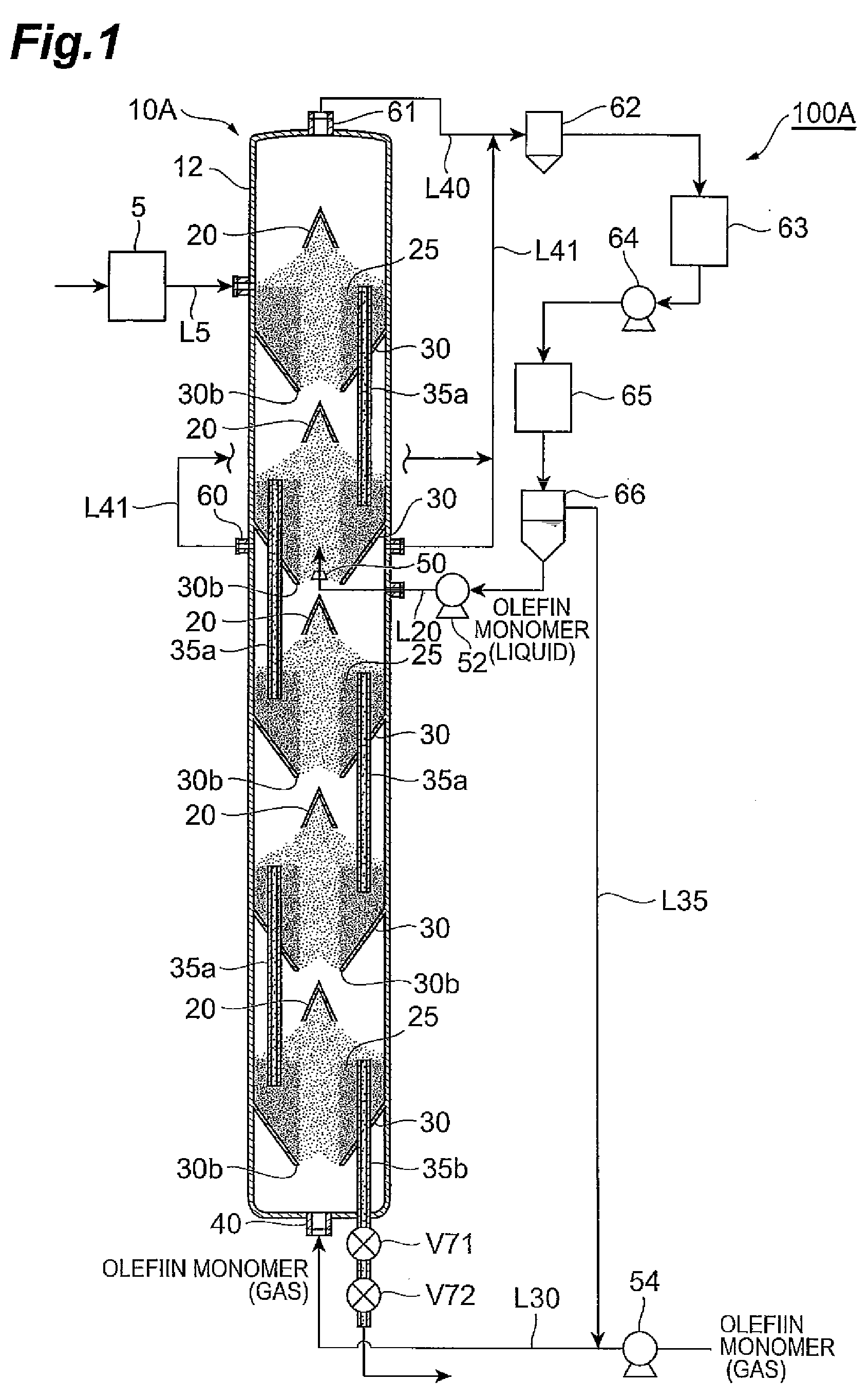
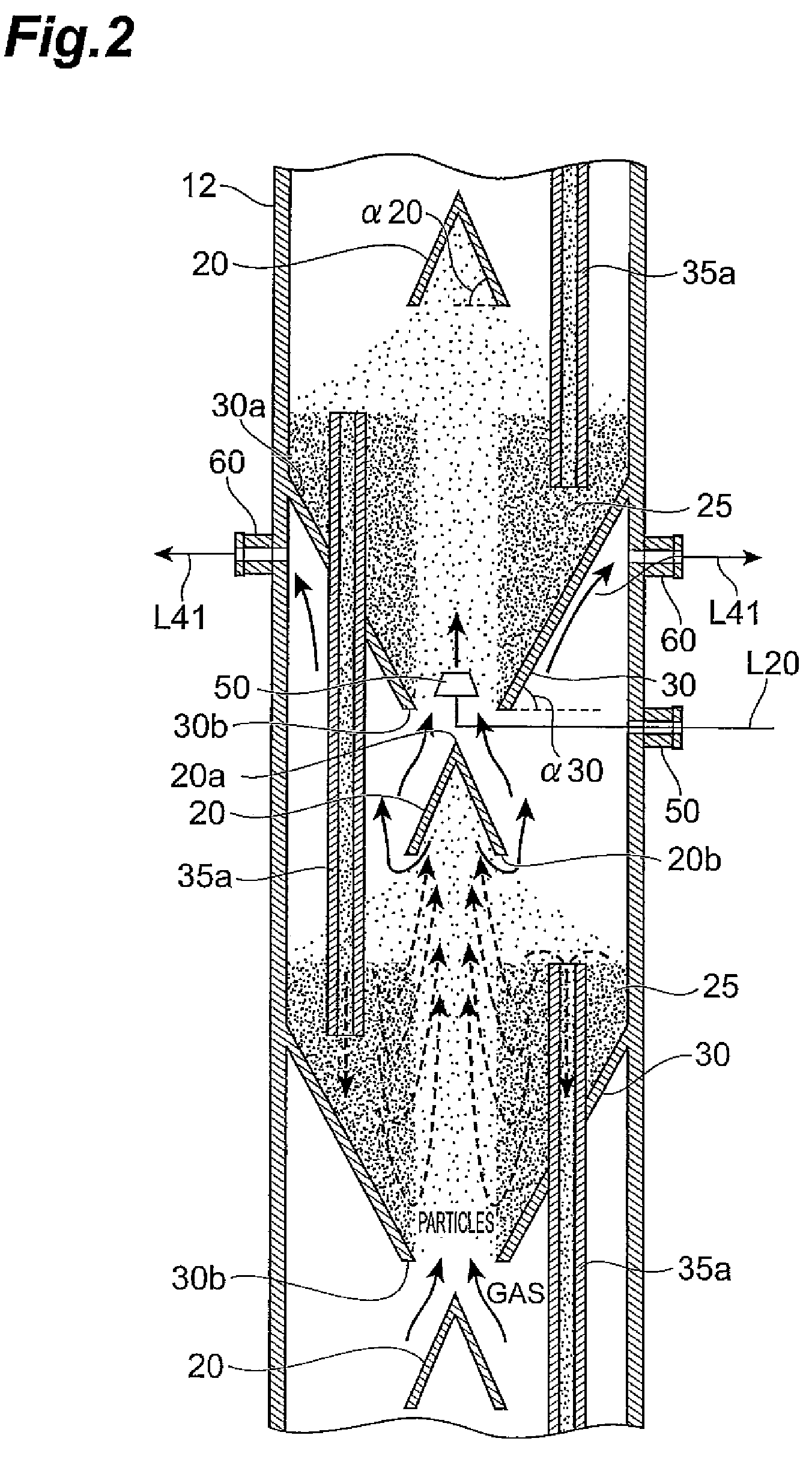
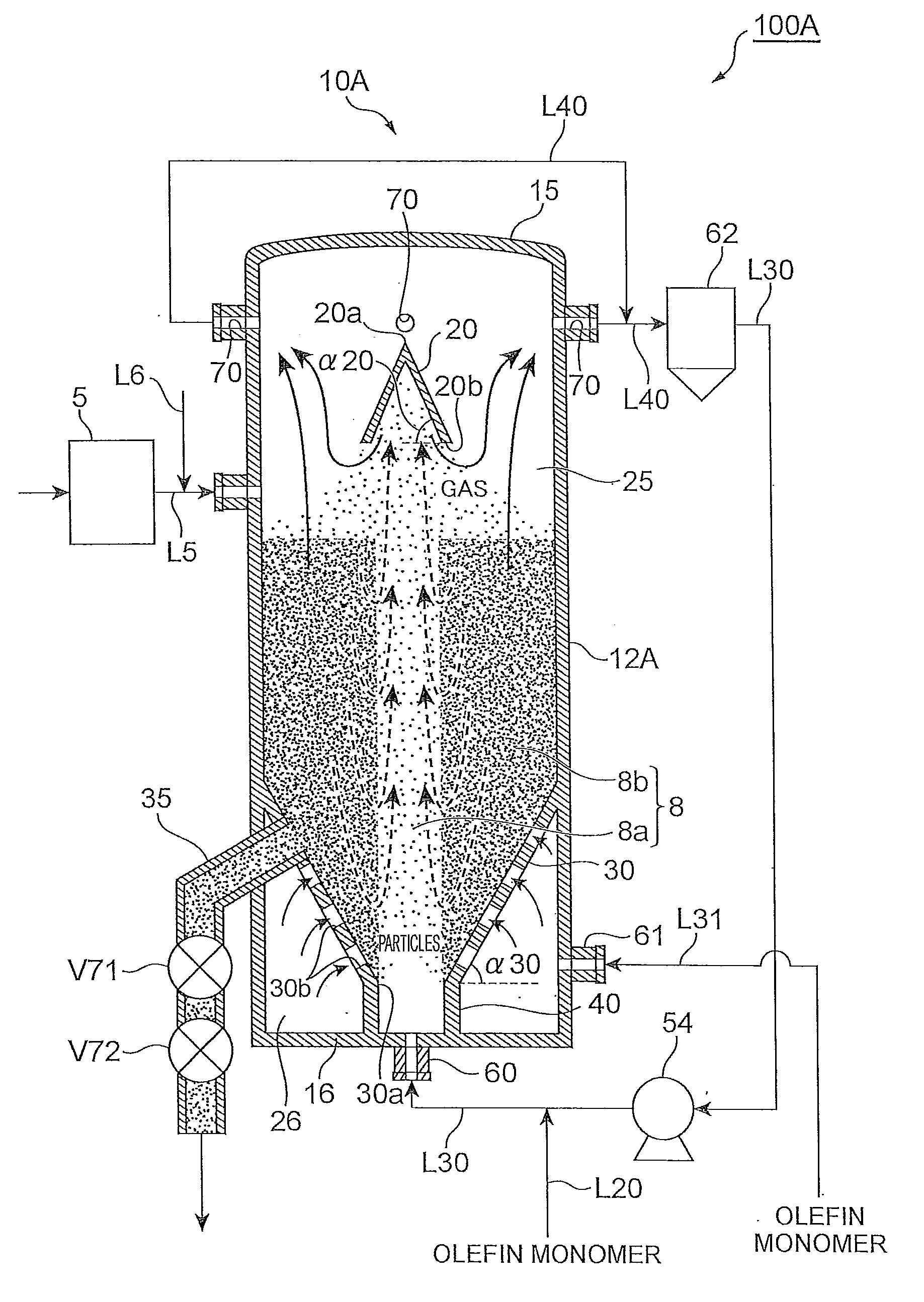
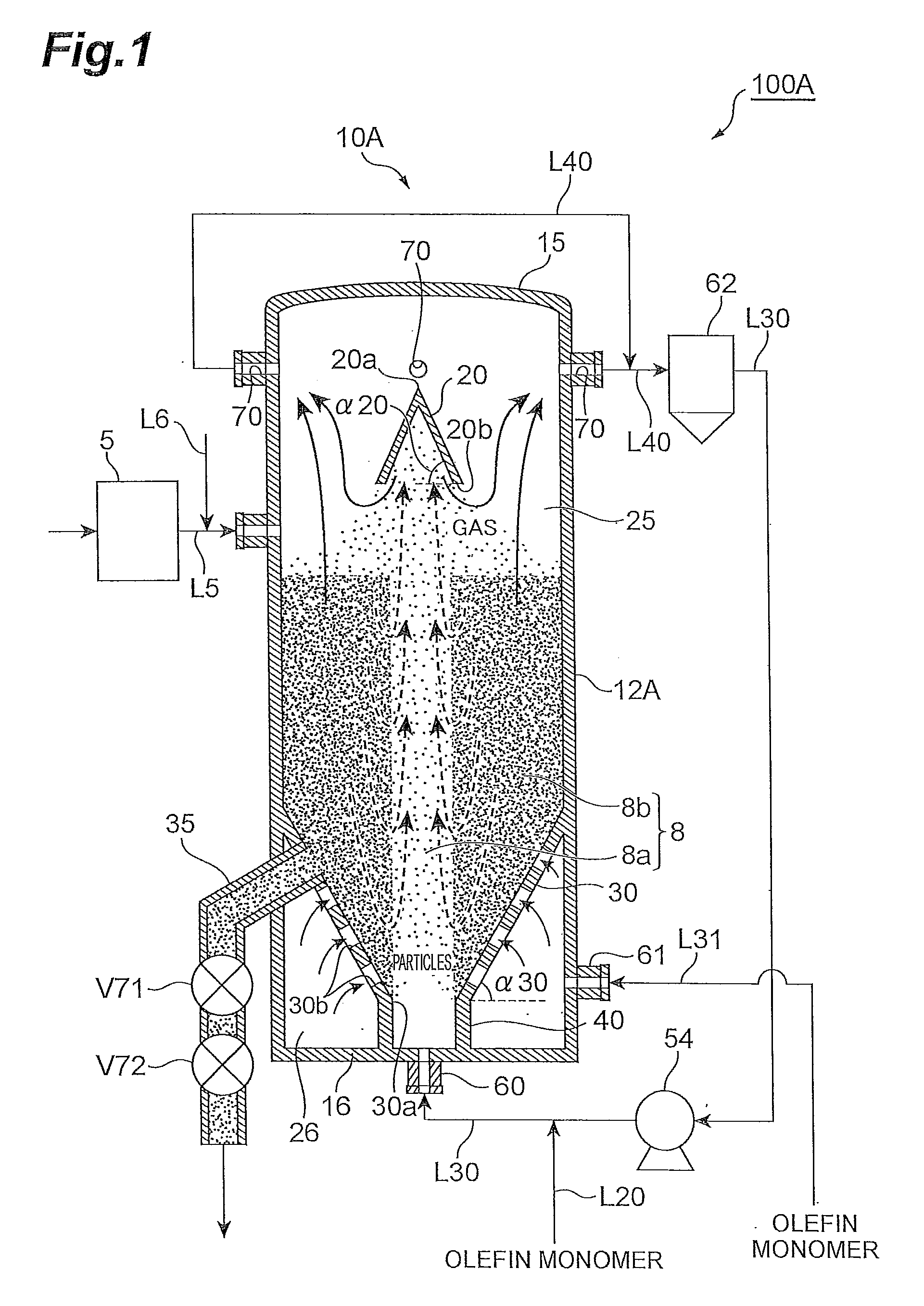
Olefin polymerization reactor, polyolefin production system, and polyolefin production process
ActiveUS20090149610A1Improve structural uniformityNarrow residence time distributionChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPolyolefinReaction zone
An olefin polymerization reactor of the present invention includes a cylinder which extends vertically, and a decreasing diameter member which is formed on the cylinder, has an inside diameter that decreases progressively downward and has a gas inlet orifice at a bottom end thereof. A spouted bed is formed inside a reaction zone enclosed by an inside surface of the decreasing diameter member and an inside surface of the cylinder above the decreasing diameter member.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
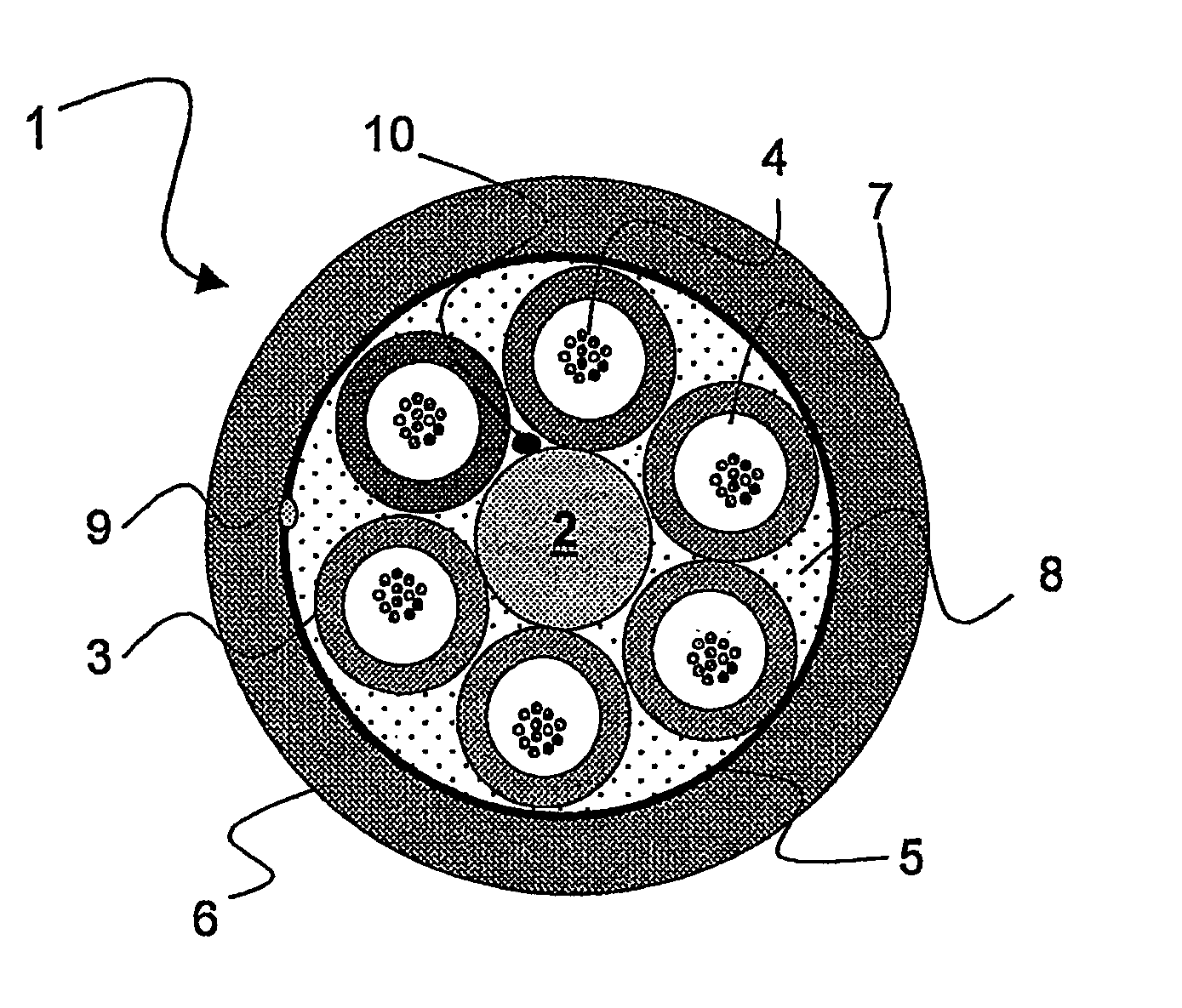
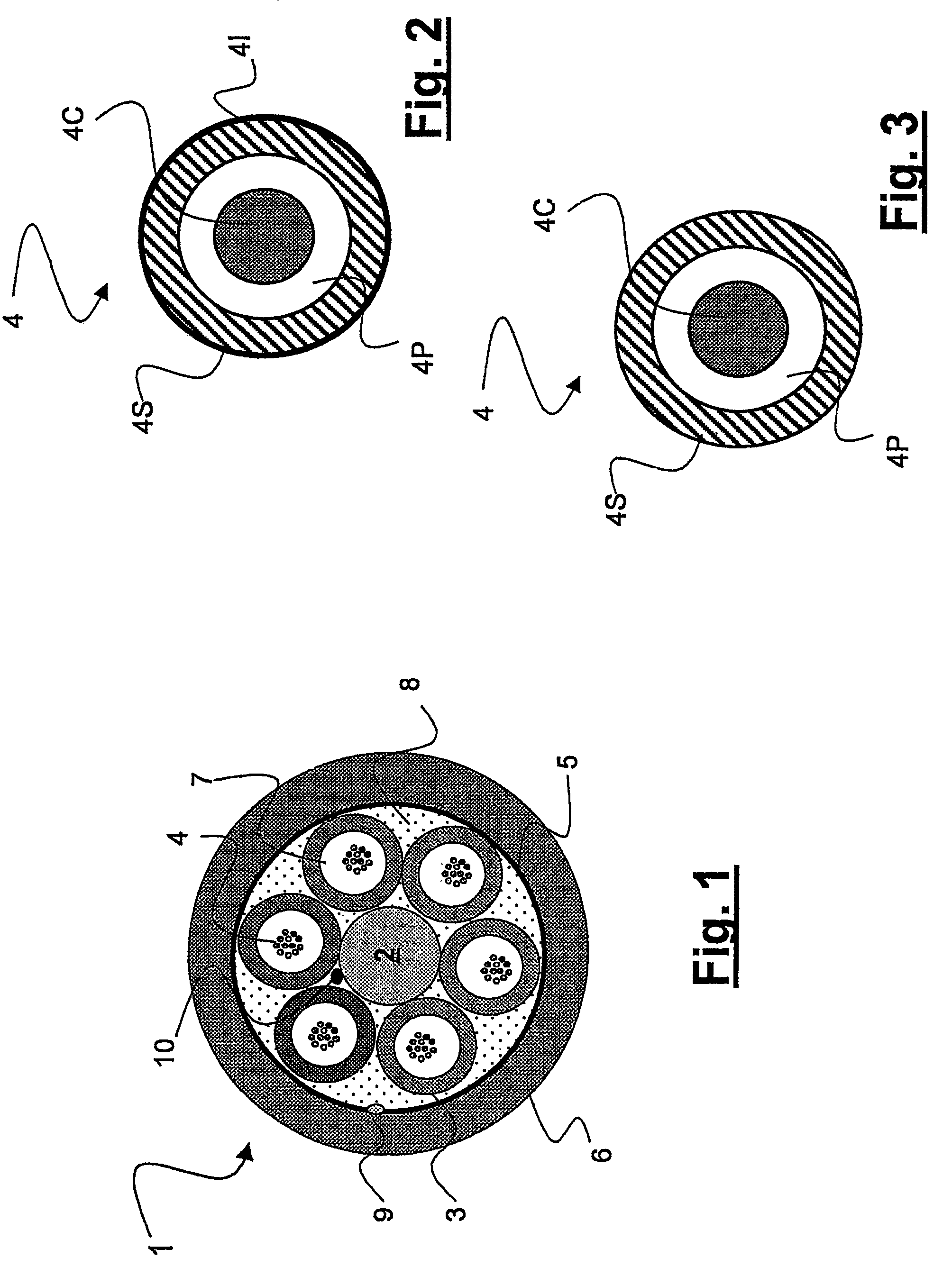
Telecommunication loose tube optical cable with reduced diameter
ActiveUS7373057B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFibre mechanical structuresFiberEngineering
An optical fiber cable has a highly reduced diameter. The cable has a central strength member; a number of tubes containing loosely arranged optical fibers, each tube having a thickness, and each optical fiber having a coating; and a protective outer jacket, wherein the filling coefficient of optical fibers in at least one loose tube is ≧45° / 0. The tubes are made of a material having an elasticity modulus ≧700 MPa; and the optical fibers are SM-R fibers having a microbending sensitivity ≦4.0 dB·km−1 / g·mm−1 at a temperature of about −30° C. to +60° C. at about 1550 nm.
Owner:PRYSMIAN CAVI E SISTEMI ENERGIA
Therapeutic ultrasound system
ActiveUS9282984B2Way of increaseUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryTherapeutic ultrasoundGreatest Diameter
An ultrasound system has a catheter including an elongate flexible catheter body having at least one lumen extending longitudinally therethrough. An ultrasound transmission wire extends longitudinally through the lumen of the catheter body, and has a proximal region, a distal region, and an intermediate region between the proximal region and the distal region. A sonic connector is connected to the proximal region of the ultrasound transmission wire, and a distal head is positioned at the distal end of the catheter body and coupled to the distal region of the ultrasound transmission wire. The proximal region of the ultrasound transmission wire has a larger diameter than the intermediate region, the intermediate region is continuously tapered with a progressively decreasing diameter from its proximal end to its distal end, and the distal region has a greater diameter than the distal end of the intermediate region.
Owner:FLOWCARDIA
Turbine cooling air centrifugal particle separator
InactiveUS7967554B2Efficient removalReduce the overall diameterPump componentsEngine fuctionsMomentumTurbine blade
A centrifugal particle separator removes particles such as dust particles from a compressed airflow prior to reaching and cooling the turbine blades of a turbine engine. A particle separator structure defines a plurality of inward-facing pockets which are separated by pocket dividers defining an airflow path having a diameter that decreases from the entrance to the exit. A centrifugal force created by the rotating centrifugal particle separator assembly causes particles to collect within the plurality of pockets and the remaining compressed air is provided to cool the turbine blades. The decreasing diameter of the airflow path forces the airflow with particles to accelerate to a rotational velocity greater than that of the rotating particle separator by conservation of momentum.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
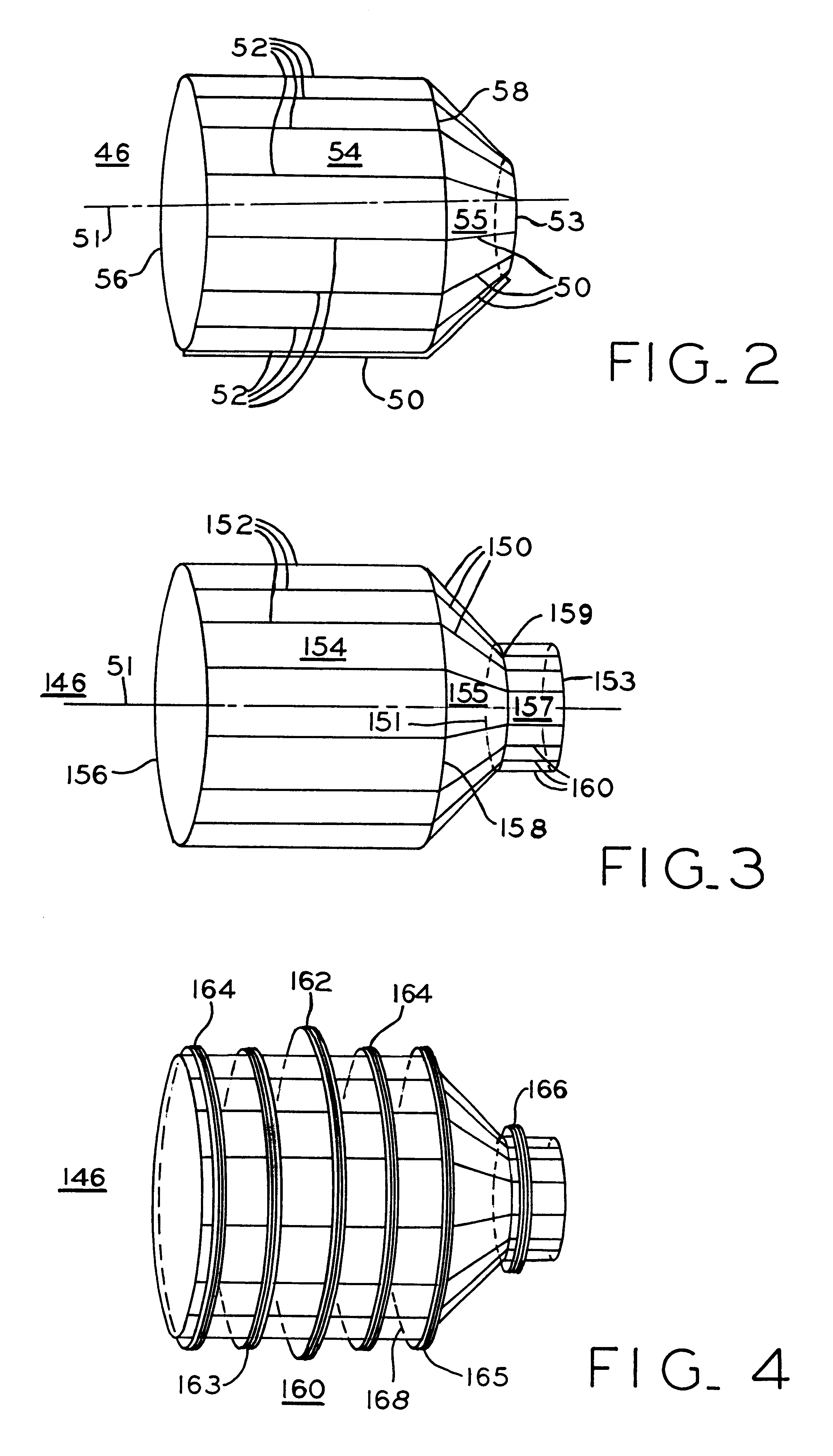
Magnetic resonance imaging head coil
InactiveUS6313633B1Improve homogeneityImprove image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrical conductorHomogeneous magnetic field
A short radio frequency coil for magnetic resonance imaging of the head to provide a homogeneous magnetic field including parallel conductors forming a first cylindrical portion with end rings supporting the conductors which then continue at an angle to form the frustum of a cone and further continuing to form a reduced diameter second cylindrical portion. A third conductive end ring of reduced diameter positioned at the open end of the second cylindrical portion supports the end of the conductors and provides a reduced diameter opening. An asymmetrical coil surrounds portions of the radio frequency coil including the first cylindrical and frustum of a cone portions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
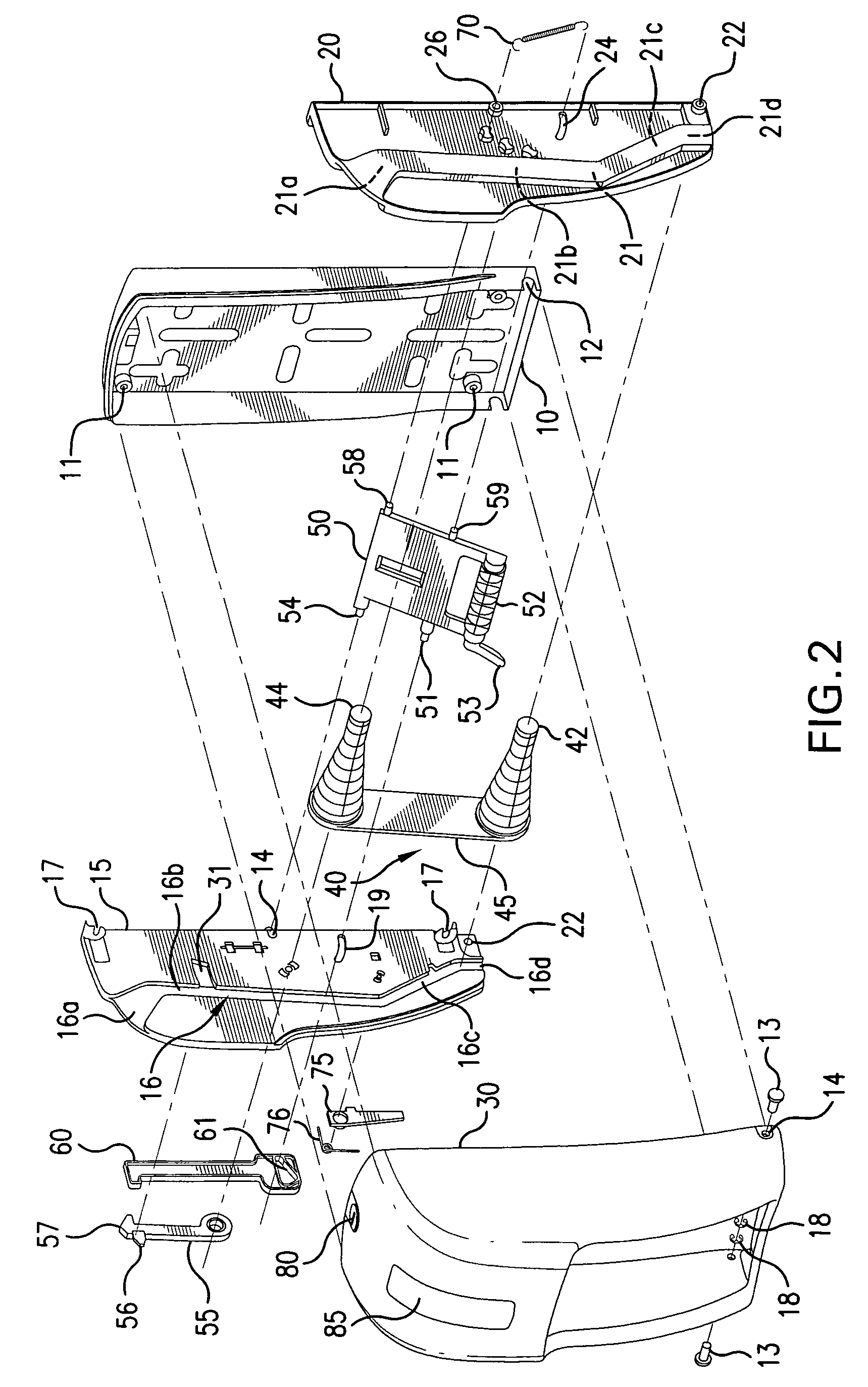
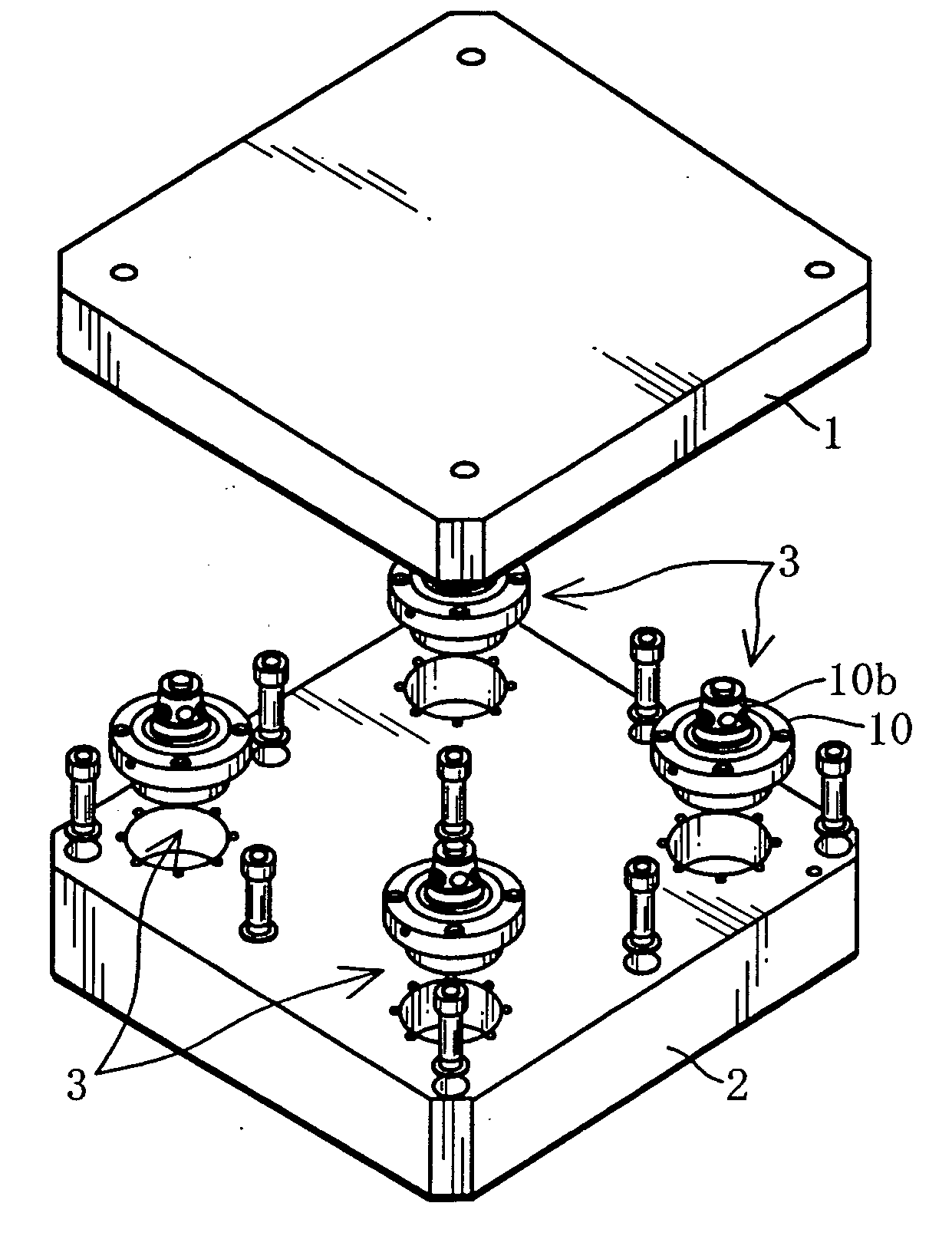
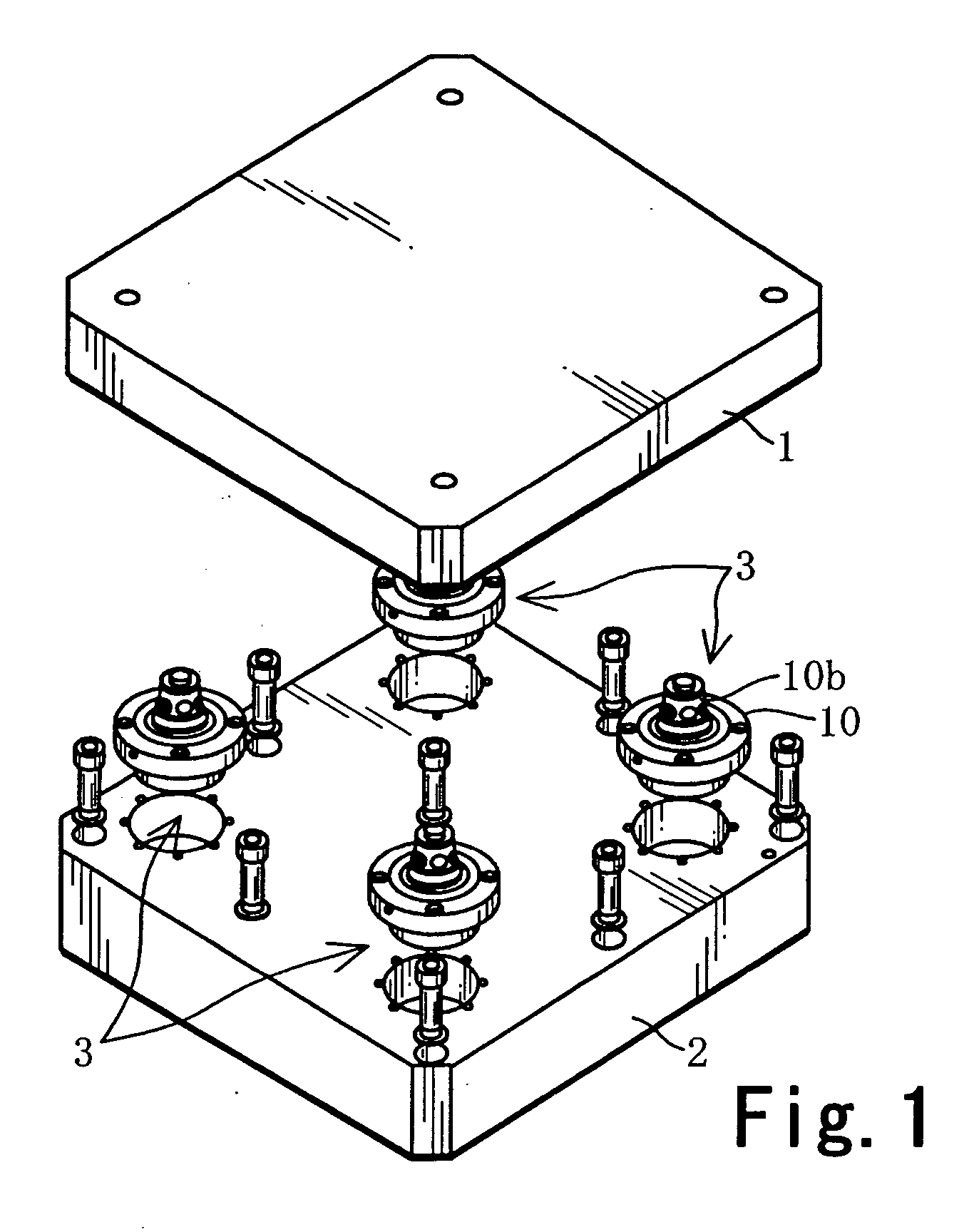
Positioning and Clamping Device and Positioning Device
ActiveUS20080061486A1Improve elastic deformation abilityAppropriate stiffnessShaping toolsLarge fixed membersMechanical engineeringDecreased diameter
In the positioning and clamping device (3), a positioning mechanism (13) has an annular tapered surface (40) that is formed on the outer periphery of a cylindrical shaft (10b) for positioning a pallet (1) in the horizontal direction, and has a decreasing diameter toward the axial tip of the cylindrical shaft (10b), and an annular engaging mechanism (41), which is formed on the inner periphery side portion of an annular engagement member (11), to engage with the annular tapered surface (40), and is elastically deformed in the radial direction, as a result of engagement with the annular tapered surface(40), and the engaging mechanism (41) has a tapered ring portion (50), which makes a face contact with the annular tapered surface (40), and multiple ribs (51) extending outward, radially, from the tapered ring portion (50).
Owner:PASCAL ENG
Probe system comprising an electric-field-aligned probe tip and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20100229265A1Improve spatial resolutionMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeMetal
A mechanically stable and oriented scanning probe tip comprising a carbon nanotube having a base with a gradually decreasing diameter, with a sharp tip at the probe tip. Such a tip or an array of tips is produced by depositing a catalyst metal film on a substrate, depositing a carbon dot on the catalyst metal film, etching away the catalyst metal film not masked by the carbon dot, removing the carbon dot from the catalyst metal film to expose the catalyst metal film and growing a carbon nanotube probe tip on the catalyst metal film. The carbon probe tips can be straight, angled, or sharply bent and have various technical applications.
Owner:JIN SUNGHO +2
Dispenser that automatically transfers rolls of absorbent material, method of reloading same, and rolls of absorbent material for use in same
ActiveUS20080078855A1Simple equipmentSimple technologyFilament handlingDomestic applicationsAbsorbent materialEngineering
A two-roll toilet paper dispenser automatically transfers a new roll into dispensing position once the previous roll is spent or nearly spent. A spring-loaded plate senses the decreasing diameter of the first roll, and once it reaches a predetermined minimum, actuates a linkage that permits a mandrel carrying the two rolls to drop down within the dispenser body and position the second roll for dispensing. The mandrel and track structure permits reloading the dispenser without removing the mandrel. The rolls of toilet paper have adapter plugs in one end only, to ensure that the rolls are placed in the correct orientation within the dispenser.
Owner:ESSITY PROFESSIONAL HYGIENE NORTH AMERICA LLC
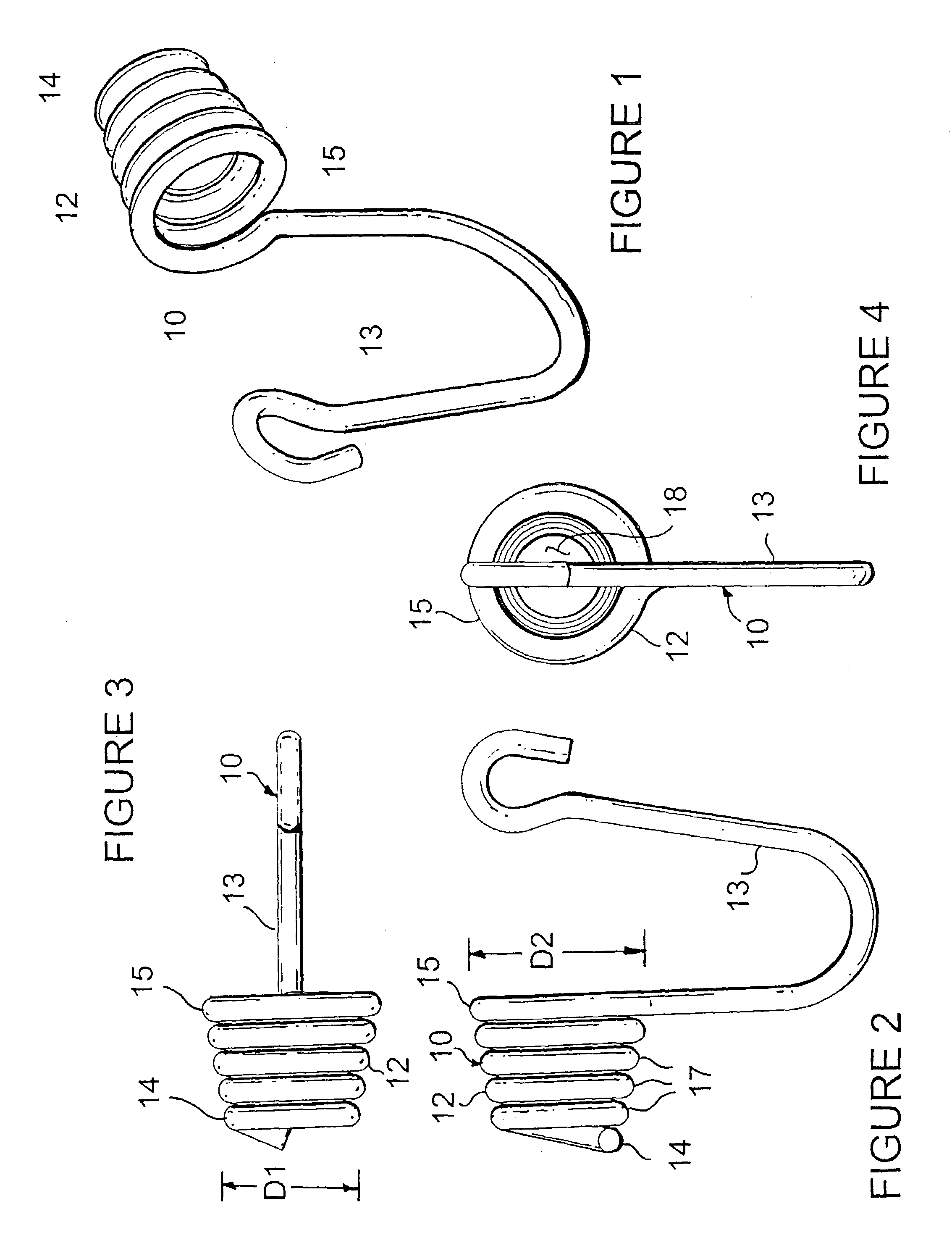
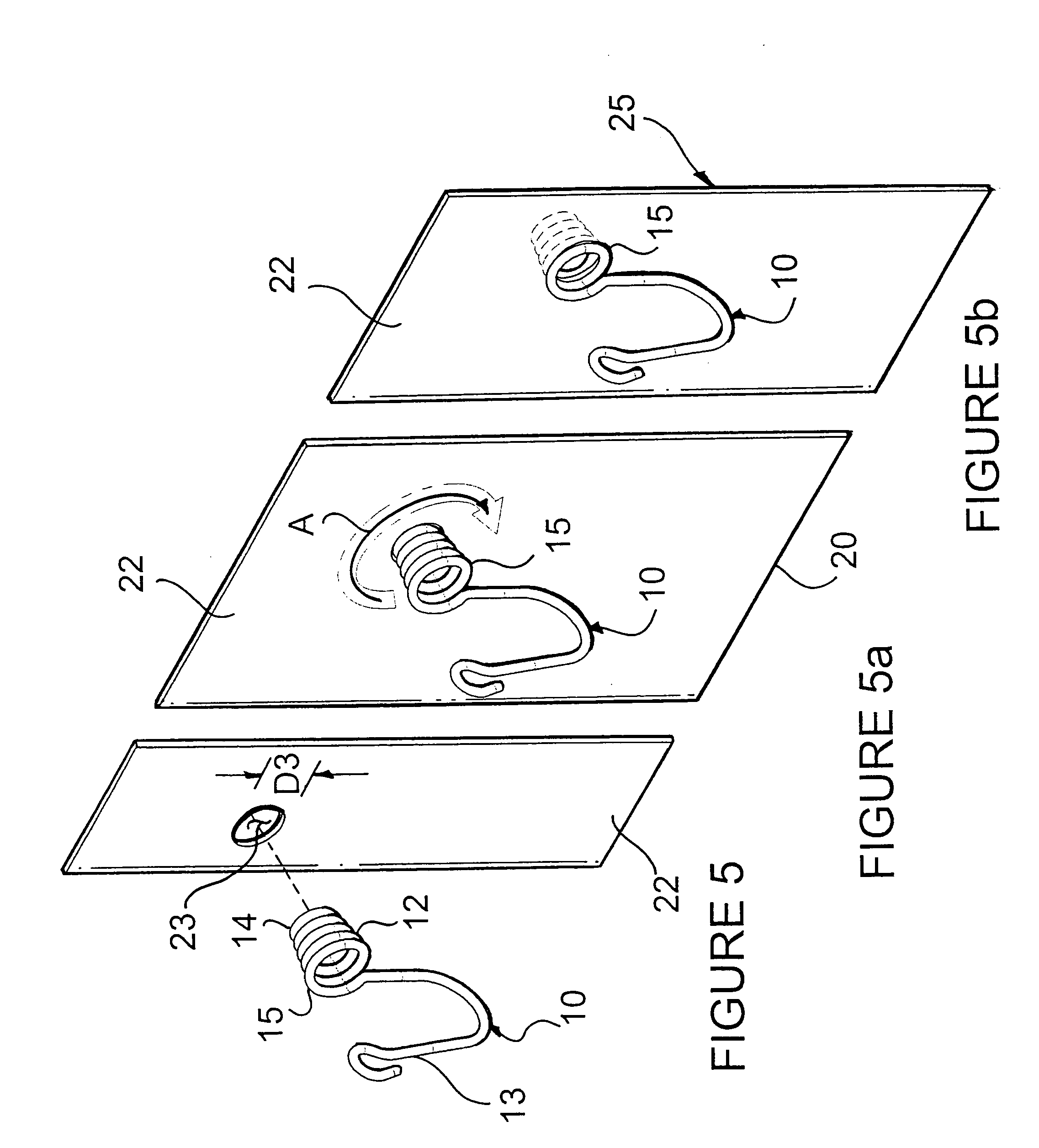
Hanger apparatus
A hanger apparatus is fabricated of a strand of material that is formed into a plurality of coils of incrementally decreasing diameter to fabricate a tapered, hollow helix. A hook or other engagement means is integrally formed at one end of the helix. The helix is compressively or frictionally engaged with an opening in a selected substrate to provide a hanger assembly for receiving and holding a selected object.
Owner:BABJAK JAMES
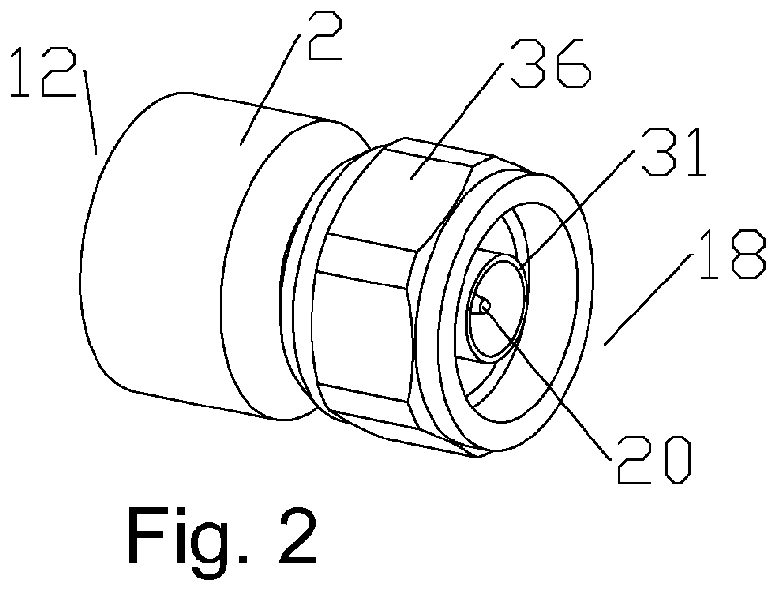
Method and aparatus for radial ultrasonic welding interconnected coaxial connector
ActiveUS20120129384A1Cost-effectiveLower potentialContact member manufacturingElectrically conductive connectionsCoaxial cableElectrical conductor
A coaxial connector assembly for interconnection with a coaxial cable with a solid outer conductor is provided with a monolithic connector body with a bore. A mating surface with a decreasing diameter toward a connector end is provided on an outer diameter of the connector body proximate the connector end. An overbody may be provided overmolded upon a cable end of the connector body. An interface end may be seated upon the mating surface, the interface end provided with a desired connection interface. The interface end may be permanently coupled to the mating surface by a molecular bond interconnection. In a method of interconnection, the interface end is coupled to the mating surface by application of radial ultrasonic welding.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
Seal head heat insulating layer forming method and mold of filament winding engine heat insulating structure
ActiveCN105437521AOvercome stabilityOvercome the defect of low bonding strengthDomestic articlesVulcanizationEngineering
The invention discloses a seal head heat insulating layer forming method of a filament winding engine heat insulating structure. A cover layer and a bottom layer of a seal head heat insulating layer are firstly and independently formed in a vulcanization and compression manner and then overall formed in a vulcanization and compression manner, and the defect that the forming quality stability and consistency of manual SMT technology products are low is overcome. A release agent is sprayed or release cloth is pasted in the direction with the decreasing diameter at the crack arrest point, a proper tackiness agent is adopted in other lining layers, and the releasing effect of the cover layer and the bottom layer of the manufactured seal head heat insulating layer is good. In addition, when the seal head heat insulating layer is a rear seal head heat insulating layer, an EPDM heat insulating material wrapping structure is adopted in a T-1 anti-elation layer, and therefore the seal head heat insulating layer is isolated from a high-strength aluminum alloy connector. According to a provided integral forming mold, two sets of tools of the integral forming mold and a bottom layer forming mold can be achieved only by replacing an upper integral mold and an upper bottom layer mold, the structure is simple, and cost is low. Meanwhile, locating and mold releasing can be achieved well, and mold stripping of products is facilitated.
Owner:湖北三江航天江北机械工程有限公司
Fully vented wide rim nursing bottle with canted vent tube
A nursing bottle formed of a large volume container, incorporating a vent tube that extends to vent pressure at all times. The nursing bottle may have a cylindrical shape or other configuration that prevents formula placed therein from blocking the vent tube regardless of its angular disposition. The vent tube extends distally from the vent insert, operatively associated with a collar, that holds the vent structures and the nipple to the wide rimmed opening. In addition, the vent tube has a conical shape of decreasing diameter distally toward the center of the bottom to dissipate the pressure that may cause leakage from the bottle. Further, the vent insert has a major and minor seal that prevents leaks out of the collar and onto an infant.
Owner:NYUU BENTO DEZAINZU
Medical guide wire
ActiveUS20070282225A1High steerable propertyGuide wiresDiagnostic recording/measuringDiameter ratioHelical coil
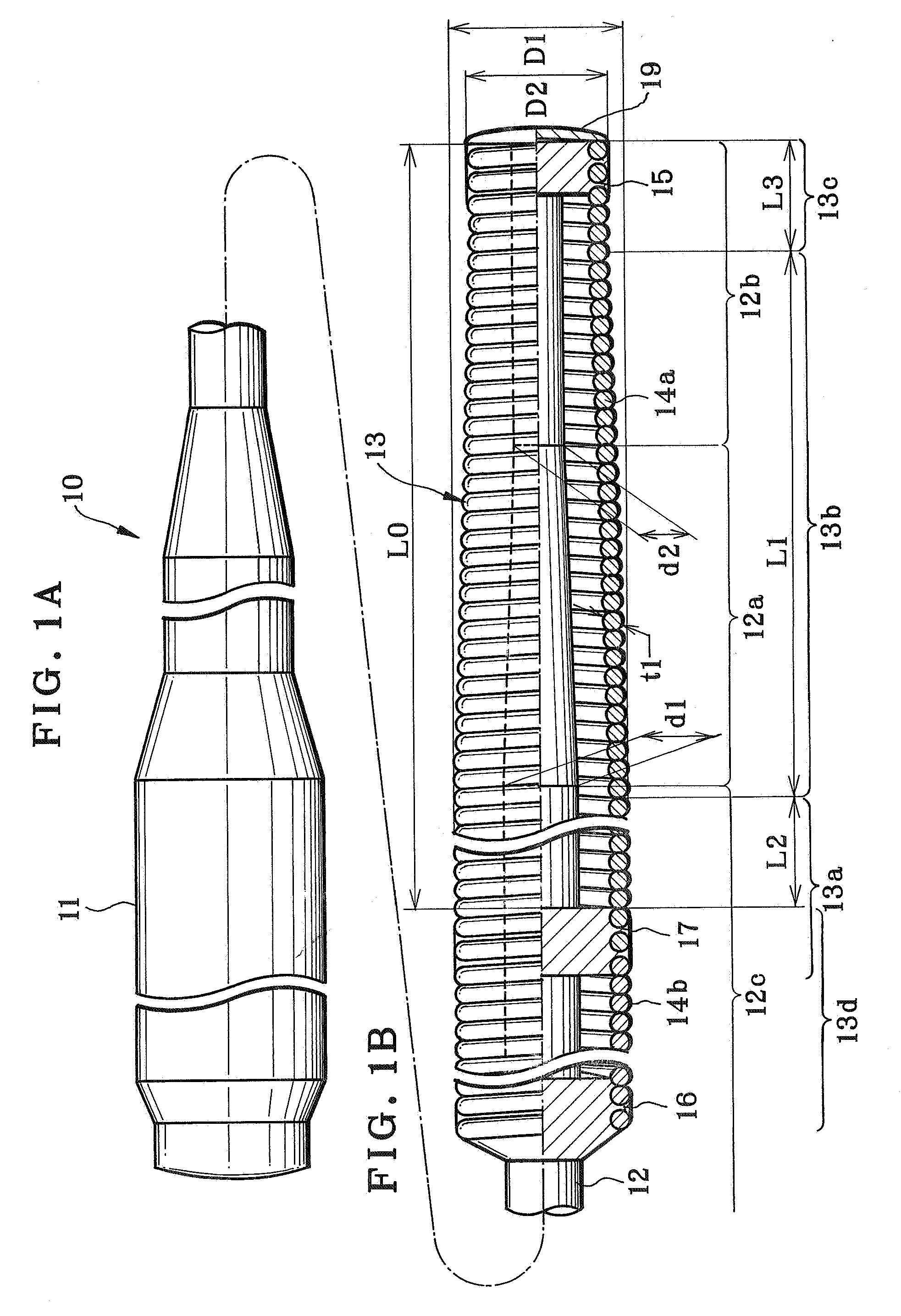
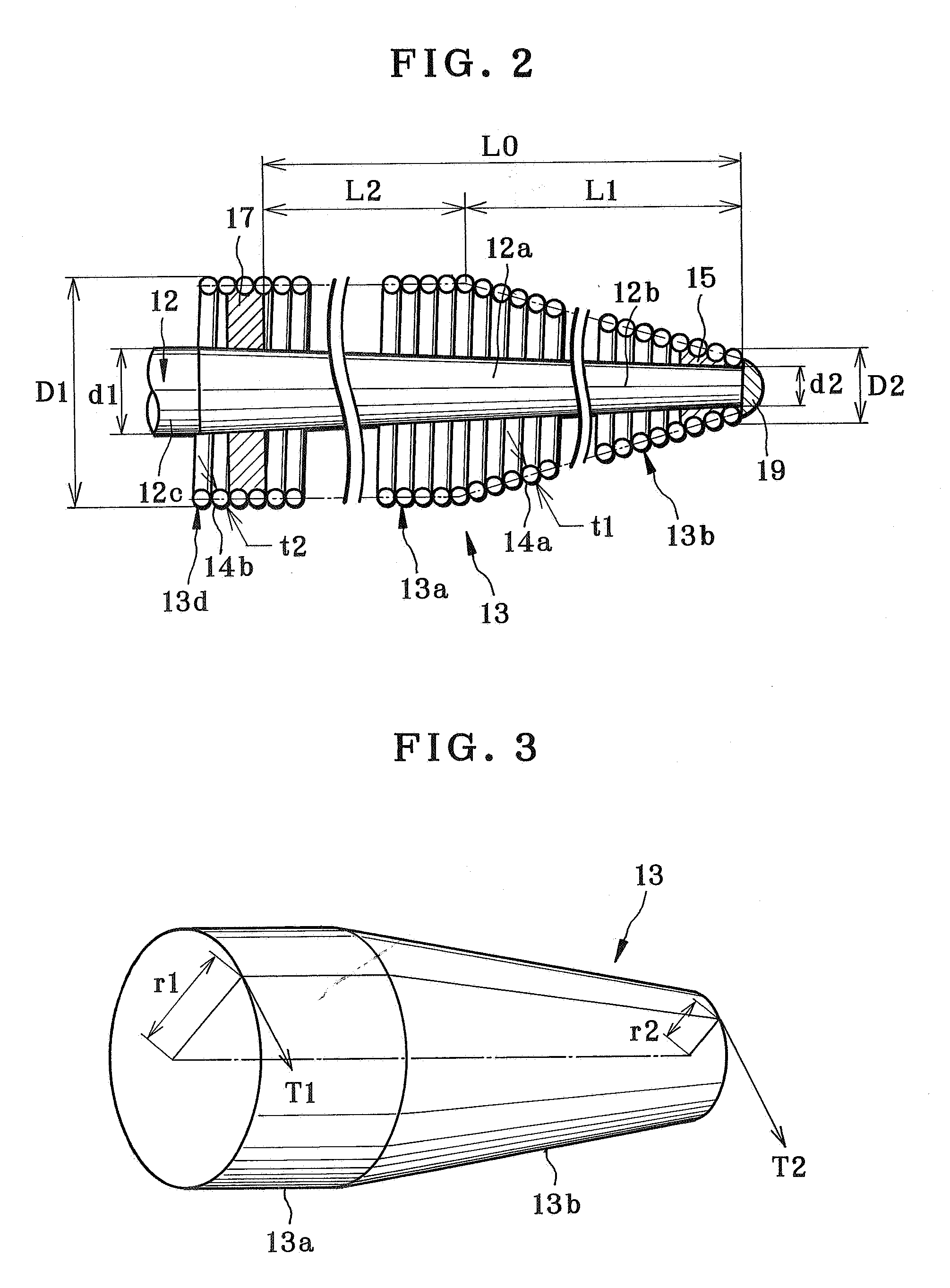
A medical guide wire includes a flexible long core. A core elongated component is disposed to extend forwards from the core, and has a tapered shape. A helical coil is disposed about the core elongated component, secured by attachment of a coil distal end and a coil proximal end to the core elongated component. The helical coil includes an equiradial coil portion having the coil proximal end, disposed at a portion of the core elongated component on a side of the core. A diameter decreasing coil portion has the coil distal end, extends forwards from the equiradial coil portion, has a decreasing diameter, and has a length 25 mm or more. A diameter ratio D1 / D2 of the diameter decreasing coil portion is 1.22-2.31, where D1 is a proximal end diameter of the diameter decreasing coil portion, and D2 is a distal end diameter of the diameter decreasing coil portion.
Owner:FMD
Braided textile sleeve with self-sustaining expanded and contracted states and method of construction thereof
ActiveUS20160122915A1Shorten the lengthIncrease the diameterLayered productsDomestic netsYarnDecreased diameter
A protective textile sleeve includes a braided, tubular wall extending lengthwise along a central longitudinal axis between opposite ends. The wall has a decreased length, increased diameter first state and an increased length, decreased diameter second state. Heat-set, braided yarns within the wall impart a bias on the wall, wherein the bias causes the first and second states to be bi-stable and self-sustaining.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL POWERTAIN LLC
Spouted-fluidized bed-type olefin polymerization reactor
ActiveUS20100311923A1Low blowing amountLow blowing rateChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsFluidized bedEngineering
An olefin polymerization reactor according to the present invention comprises: a vertically extending cylinder; a decreasing diameter portion on the cylinder, having an inside diameter that decreases progressively downward, and having a gas inlet orifice at a bottom end thereof; and a plurality of through holes passing through from an outside surface towards an inside surface of the decreasing diameter portion. Inside a reaction zone enclosed by an inside surface of the decreasing diameter portion and an inside surface above the decreasing diameter portion of the cylinder, a spouted-fluidized bed or a spouted bed is formed.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Surgical obturator
InactiveUS8057502B2Facilitates delicate insertionReduce the risk of injurySurgical needlesTrocarEngineeringDecreased diameter
In a surgical obturator for piercing a body wall, comprising a tubular housing that at one end forms an introduction tip with a continuously decreasing diameter, and comprising a blade projecting from the introduction tip for making an incision in the body wall, in order to reduce the risk of injury during piercing of the body wall it is proposed that the introduction tip comprises a central protective cap, which is displaceable in longitudinal direction relative to the introduction tip between an advanced inoperative position and a retracted working position, that the blade in the housing is displaceable in longitudinal direction between an advanced cutting position and a retracted protected position, that disposed in the housing is a retraction device that displaces the blade from the cutting position into the protected position, and that the retraction device may be activated by a displacement of the protective cap from the working position into the inoperative position.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Mounting structure for in-wheel motor system
ActiveUS8863874B2Avoid damageFirmly connectedElectric propulsion mountingMotor depositionStileMotor system
A mounting structure for an in-wheel motor system is provided. The mounting structure includes the in-wheel motor system installed in a wheel of the vehicle, and a torsion beam axle (TBA) assembly to fix the in-wheel motor system to a vehicle body, wherein a rear portion of a motor housing includes a step portion formed in a stepped manner to have a decreased diameter, and a ring-shaped fastening face vertically arranged from the step portion, and the TBA assembly includes a trailing arm provided with a through hole to surround the step portion of the motor housing, a mount integrated with the trailing arm to fix the trailing arm to a vehicle body, and a plurality of fastening bolts to fix the motor housing to the trailing arm, wherein, when the step portion is fitted and coupled into the through hole, the fastening face closely contacts the trailing arm.
Owner:HL MANDO CORP
Dowel connection system and method
An embodiment of the connection system is for connecting a plurality of components together. One embodiment of a method of the system provides a dowel having first and second portions. Each of the portions has first and second ends, the first and second portions being connected to one another at their second ends. At least one portion of the first and second portions has at least three dowel sections of successively decreasing diameters. One of these dowel sections has a side wall and an end wall that forms the first end of the at least one portion and each of the other dowel sections has a side wall and step wall. A first component has a first opening configured to substantially fit the first portion, and a second component has a second opening configured to substantially fit the second portion. An adhesive material is then applied on at least part of the first portion, and the first portion is inserted into the first opening in the first component. Adhesive material is then also applied on at least a part of the second portion, and the second portion is inserted into the second opening in the second component, thereby connecting together the two components.
Owner:MILLER DOWEL
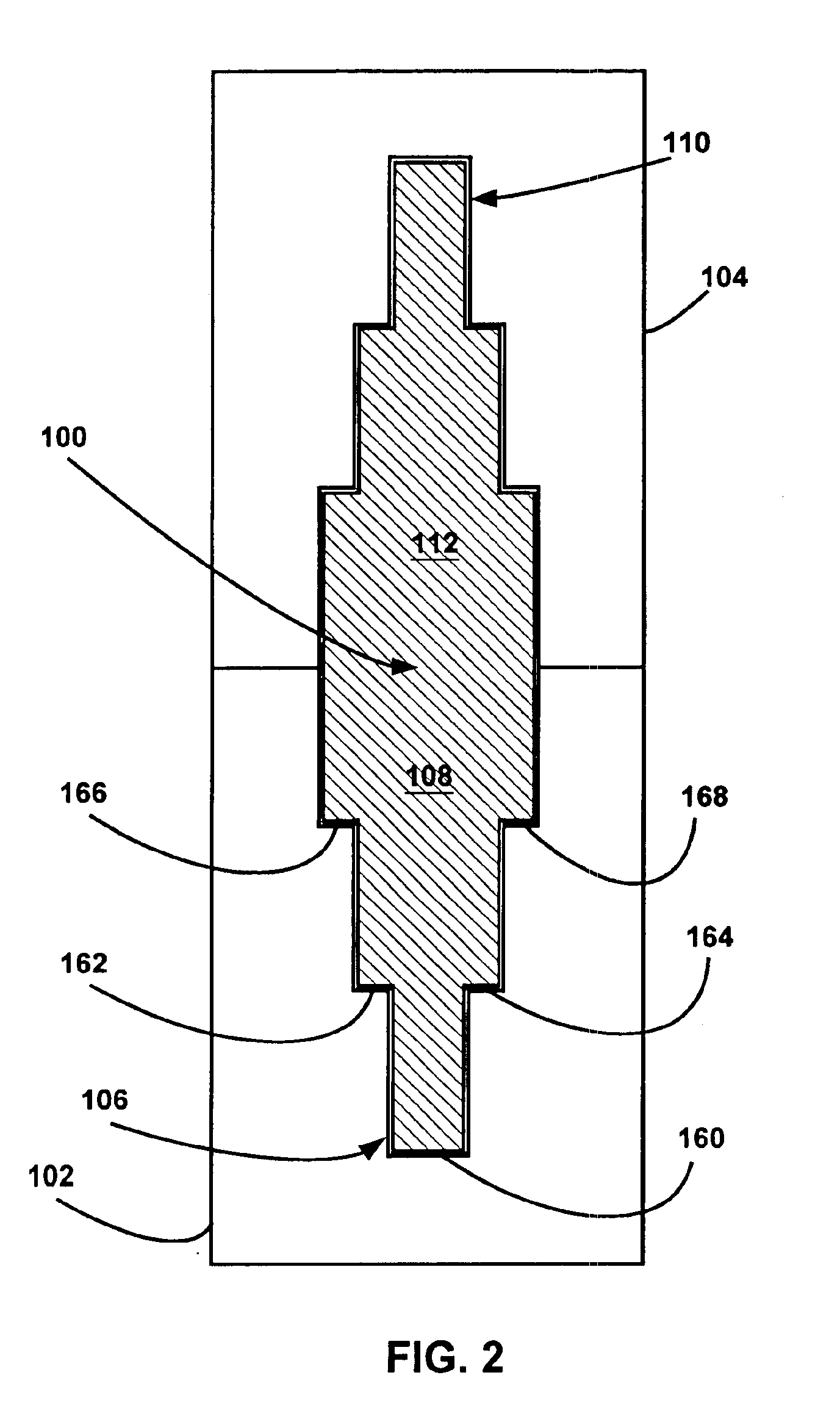
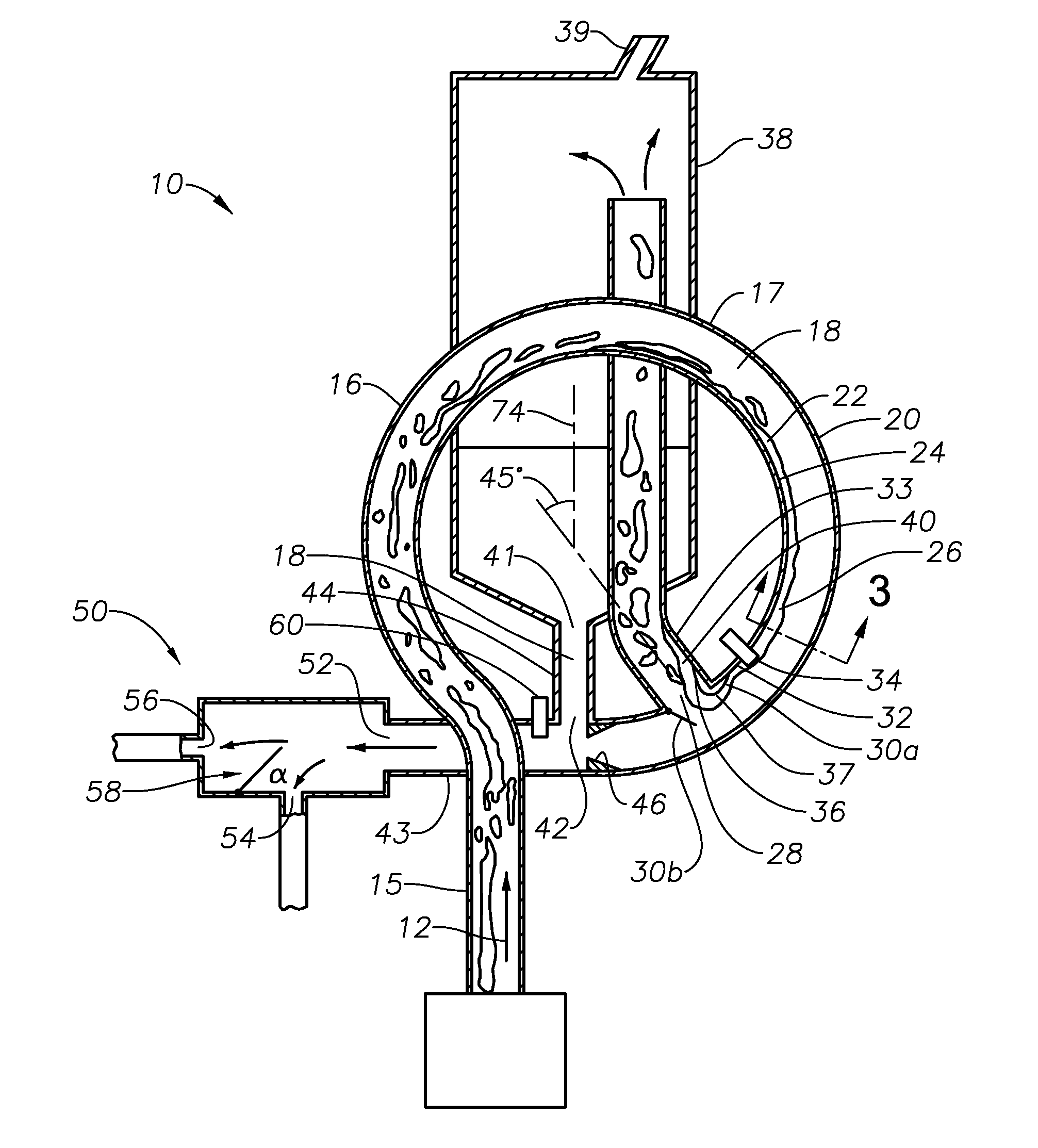
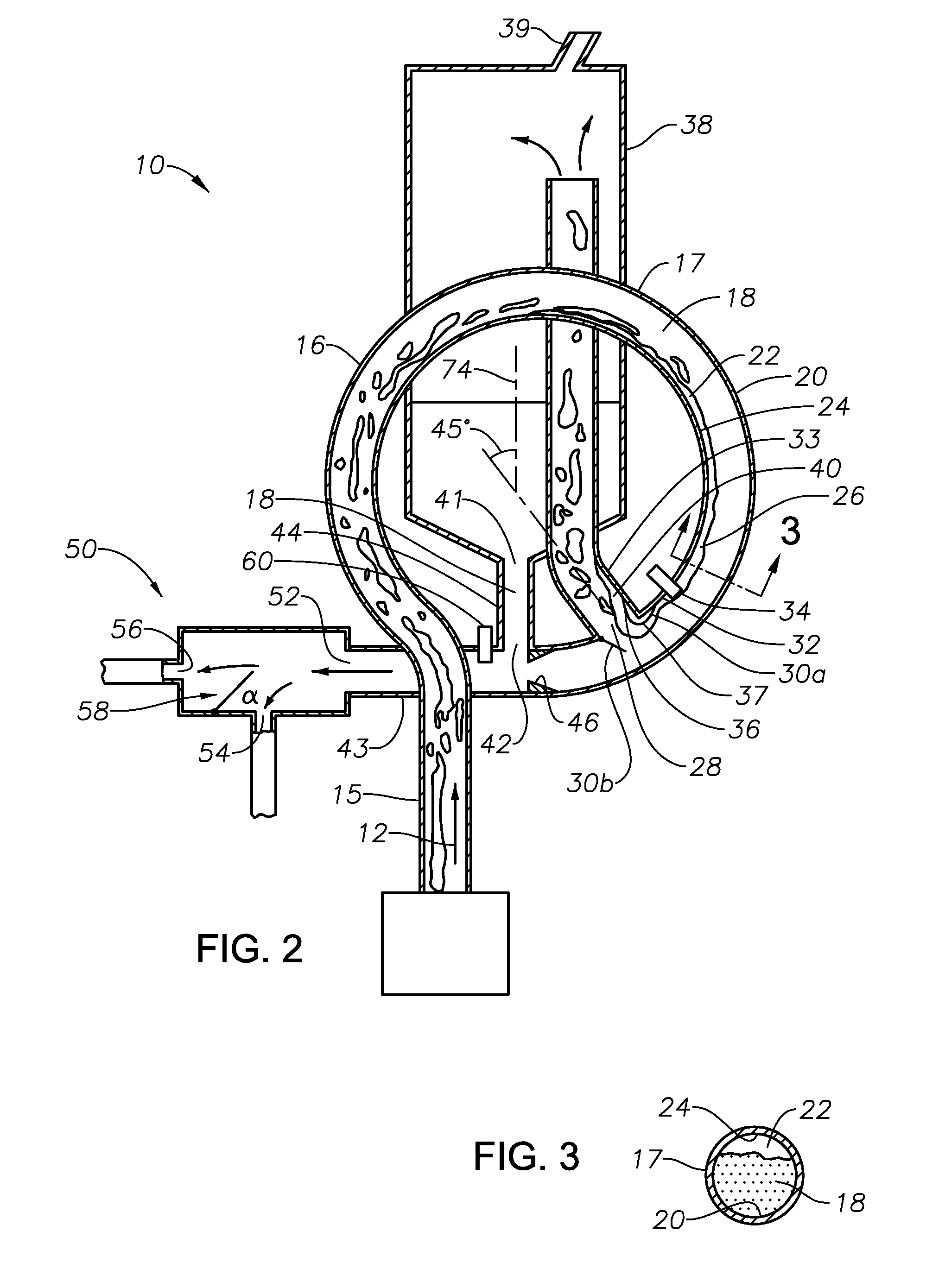
Apparatus and method for gas-liquid separation
ActiveUS20140260993A1Raise the ratioEfficient separationCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentVapor–liquid separatorPhase splitter
A multi-phase separation apparatus shapes fluid flow in a flow shaping line preferably shaped to have a plurality of loops with consecutively decreasing diameters. Shaping the two-phase flow drives the heavier, denser fluids to the outside wall of the flow shaping line and allows the lighter, less dense fluids such as gas to occupy the inner wall of the flow shaping line. With the gas positioned on the inner wall, an exit port on the inner wall permits a majority, if not all, of the gas, along with a minimal amount of liquid, to be diverted to a conventional gas-liquid separator at a flow rate much lower than the total flow rate within the flow shaping line. The remaining liquid flow in the flow shaping line is subsequently introduced into an adjustable phase splitter to separate different liquid components from one another.
Owner:HAVEN TECH SOLUTIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com