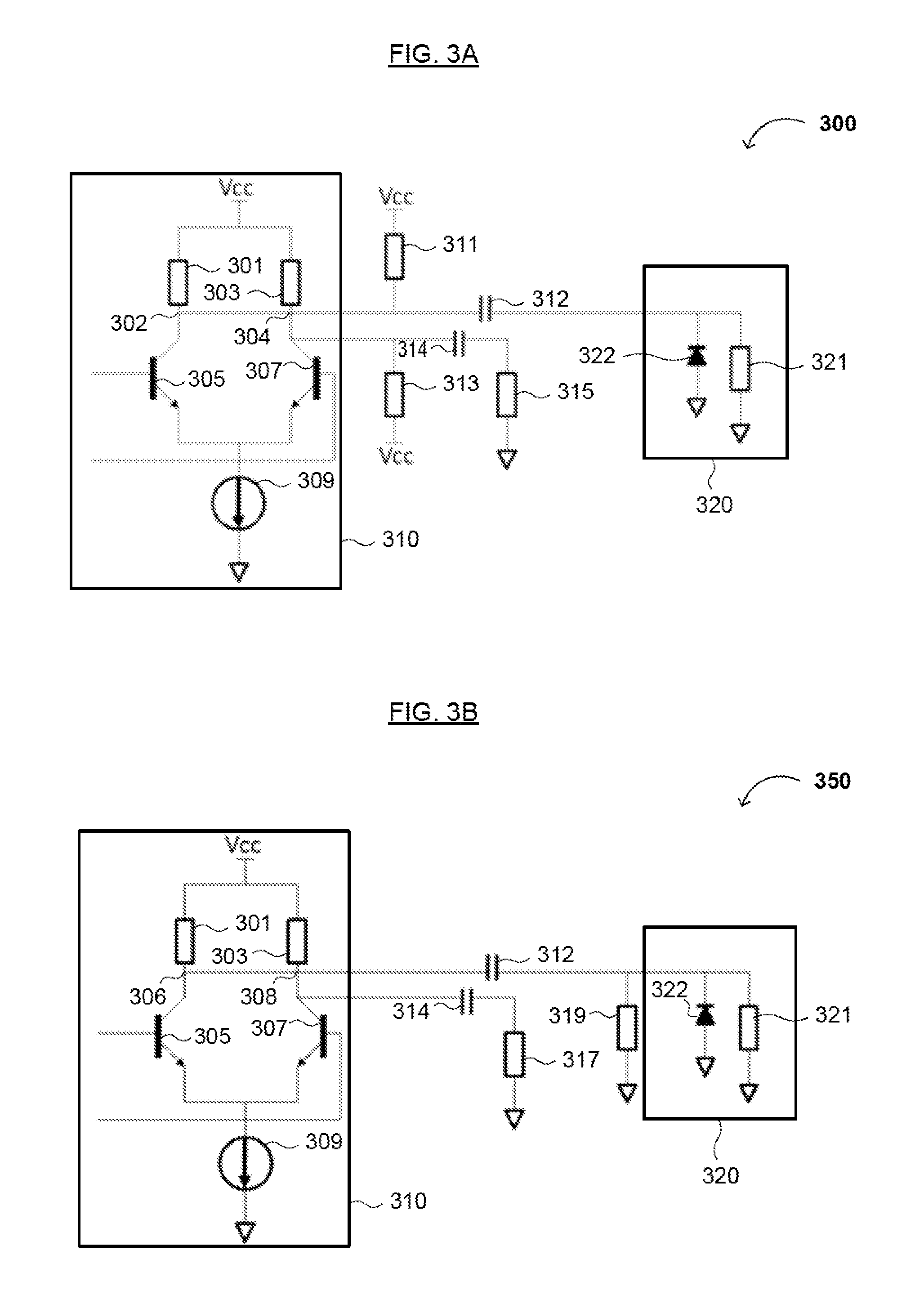
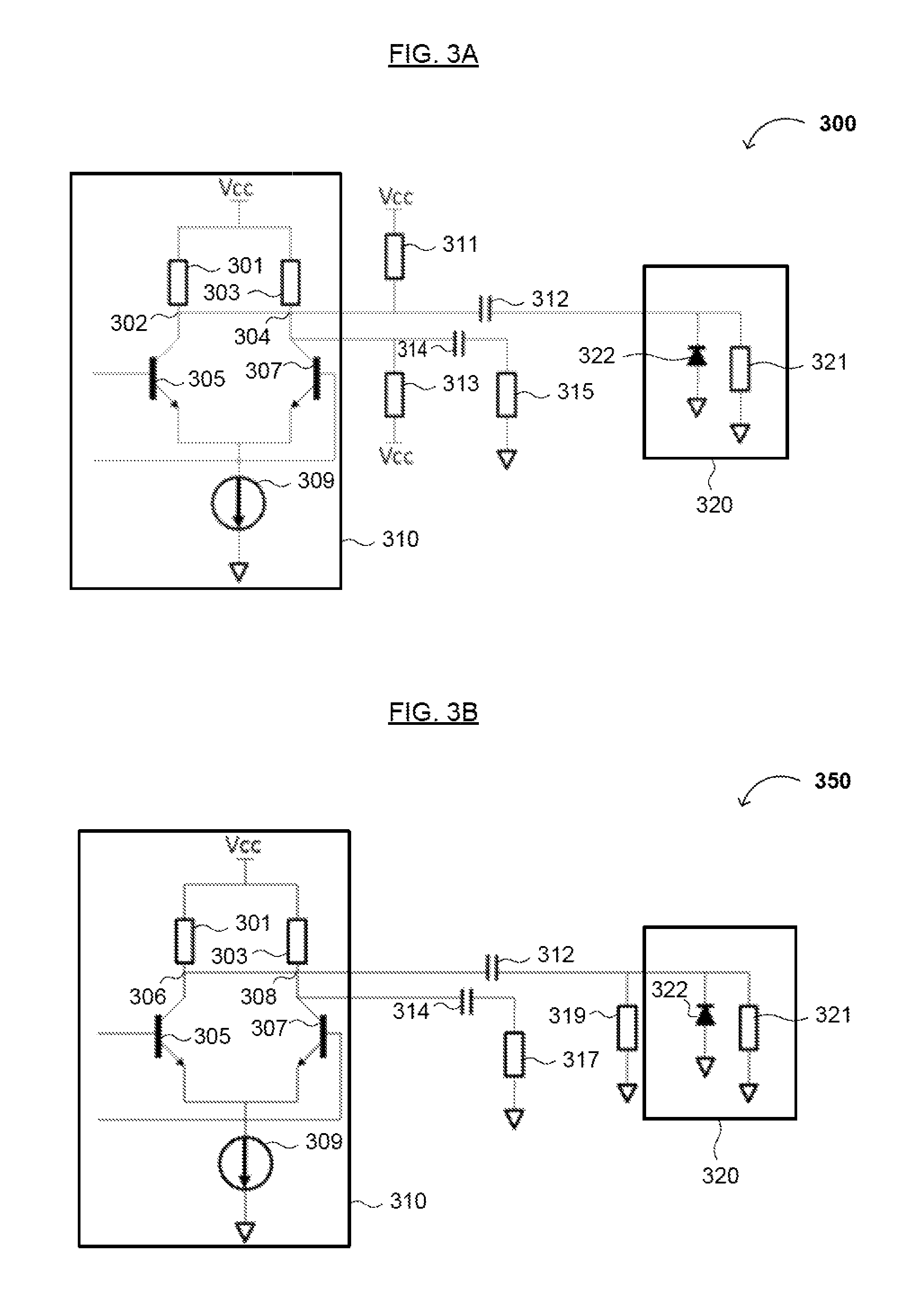
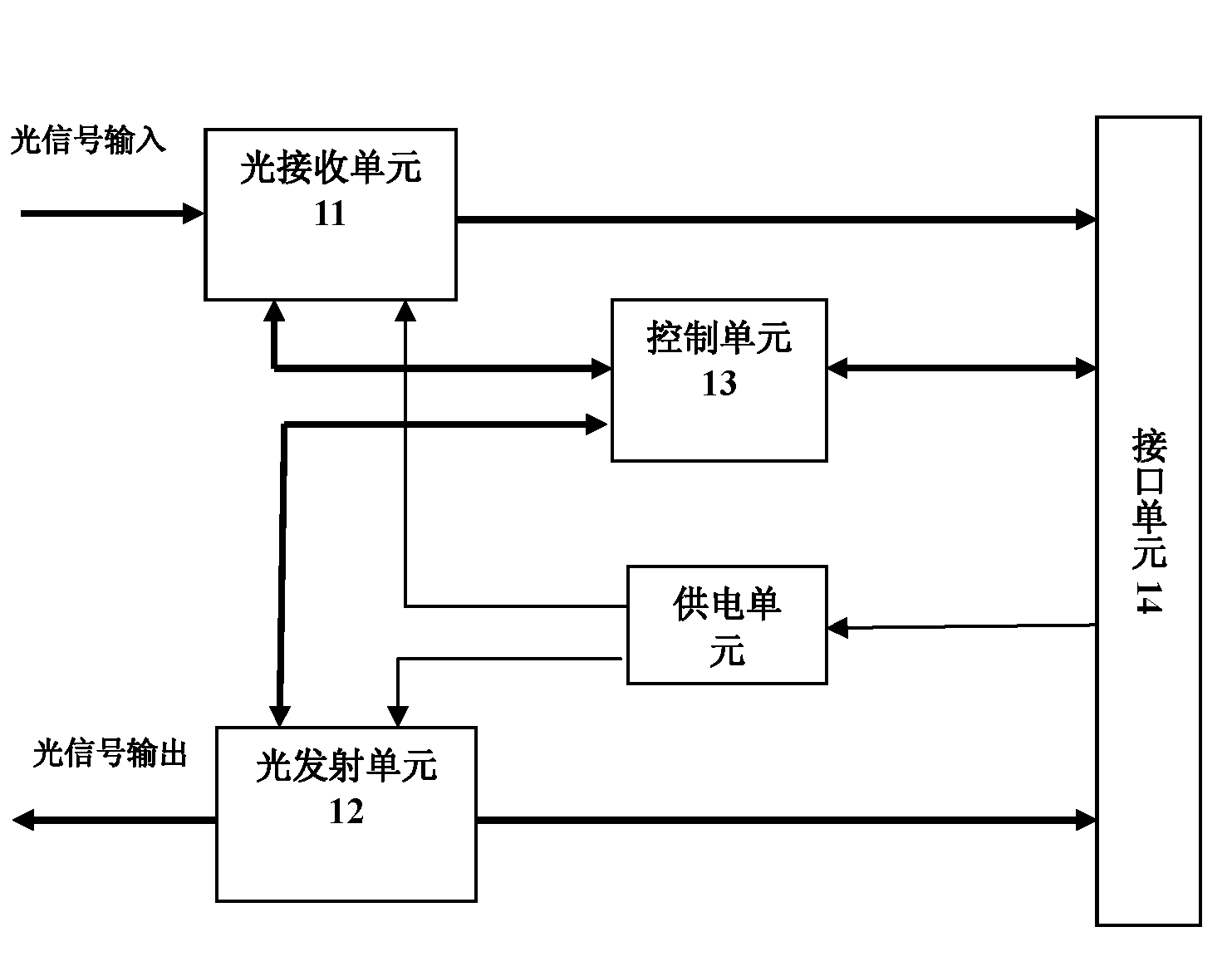
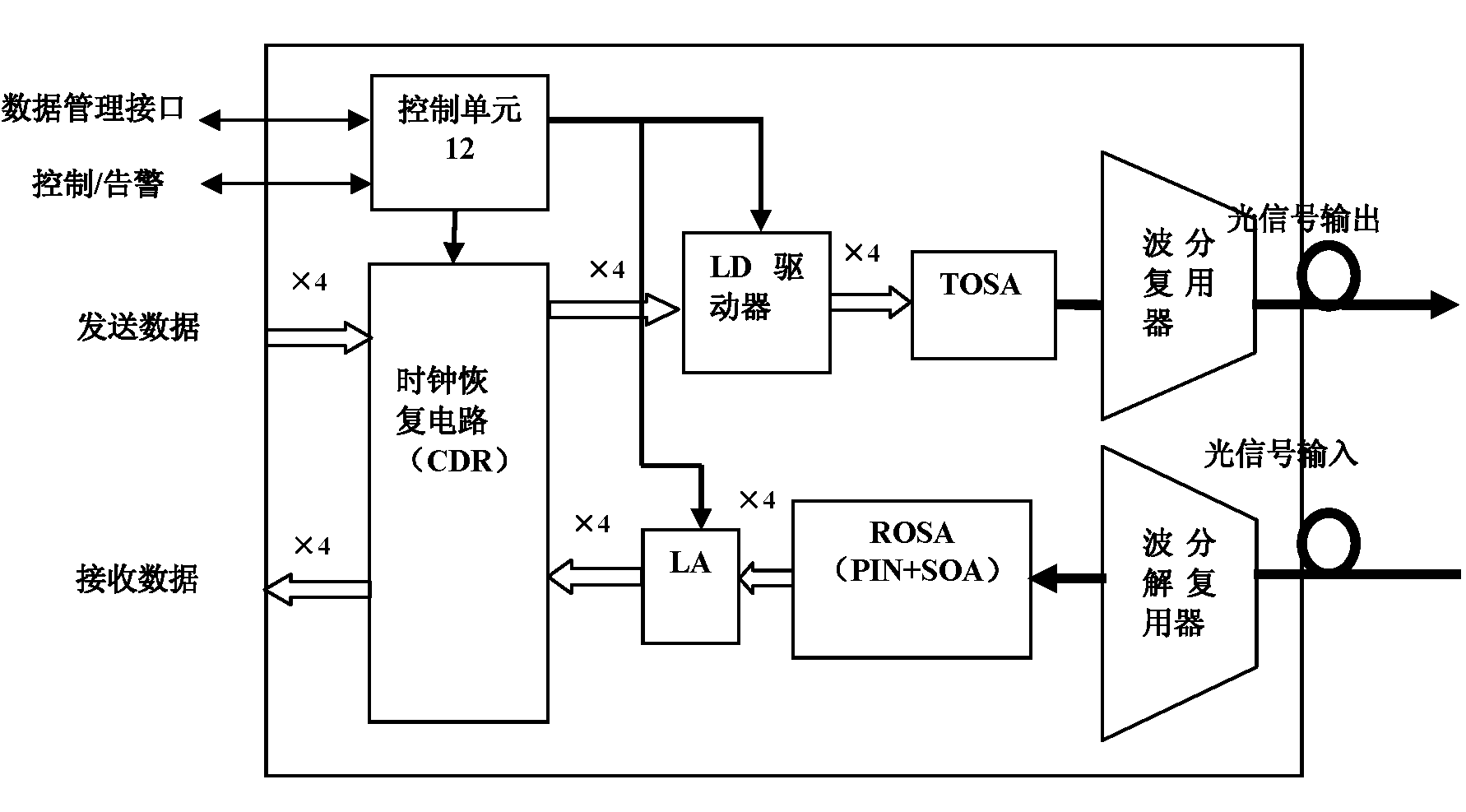
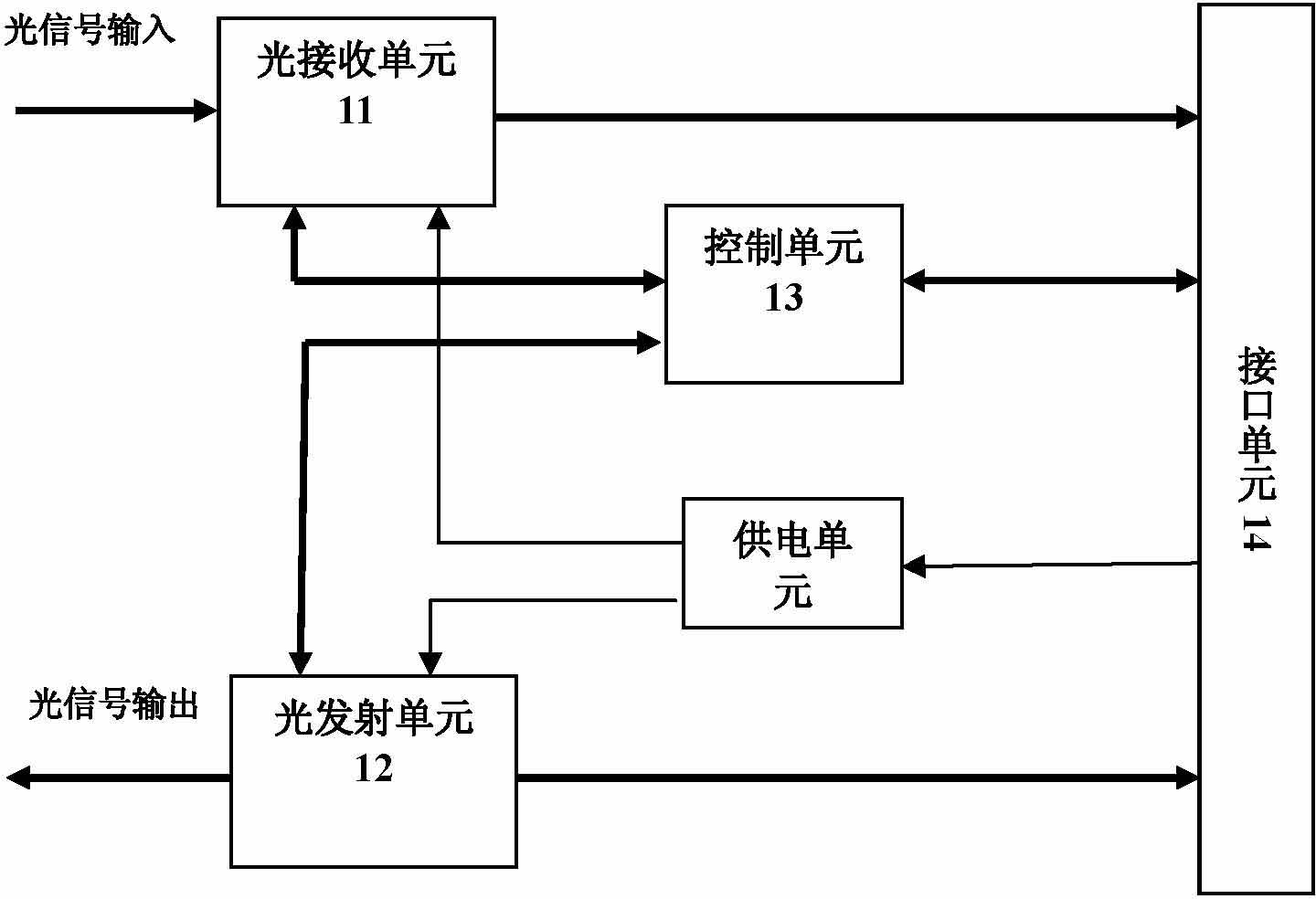
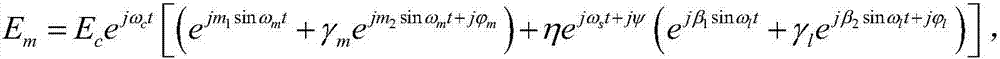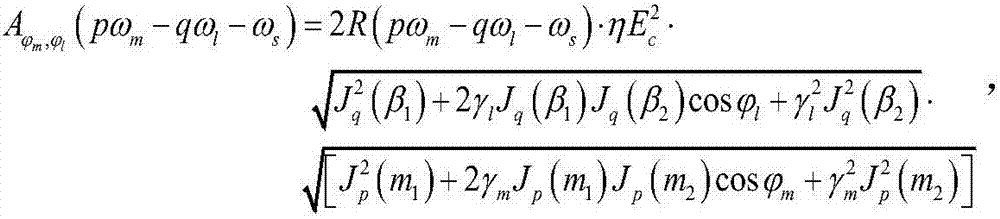Patents
Literature
139 results about "Directly modulated laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
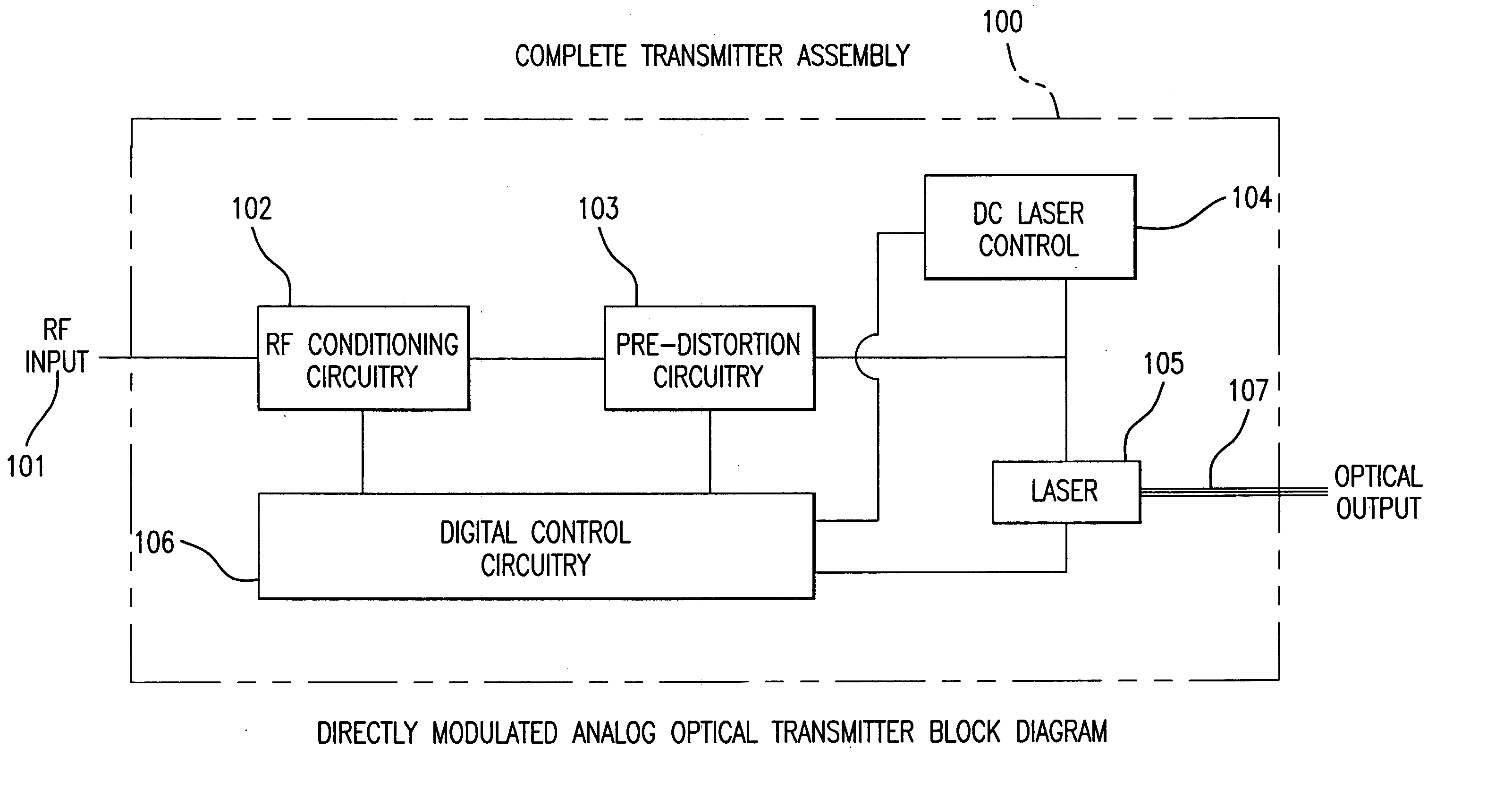
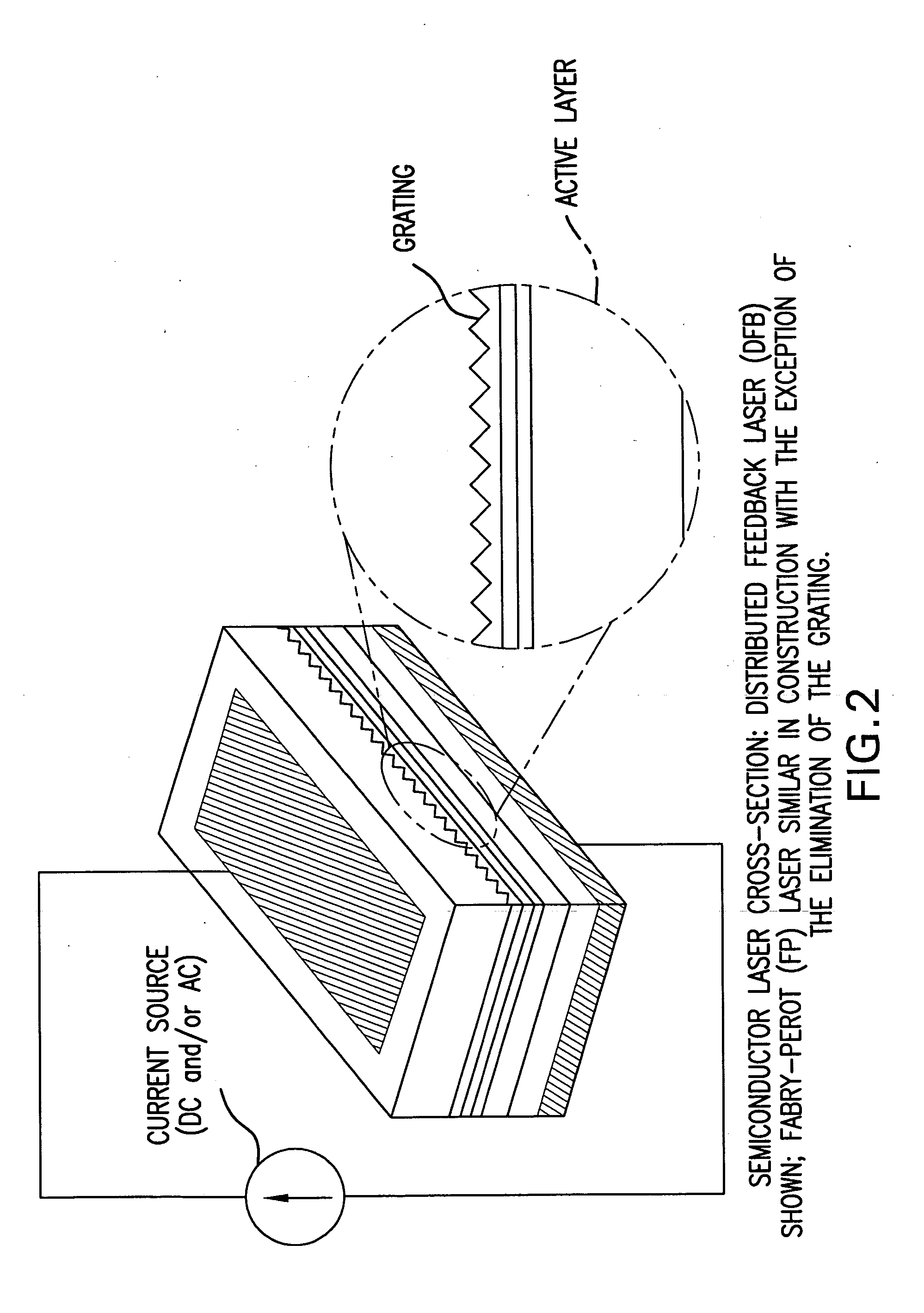
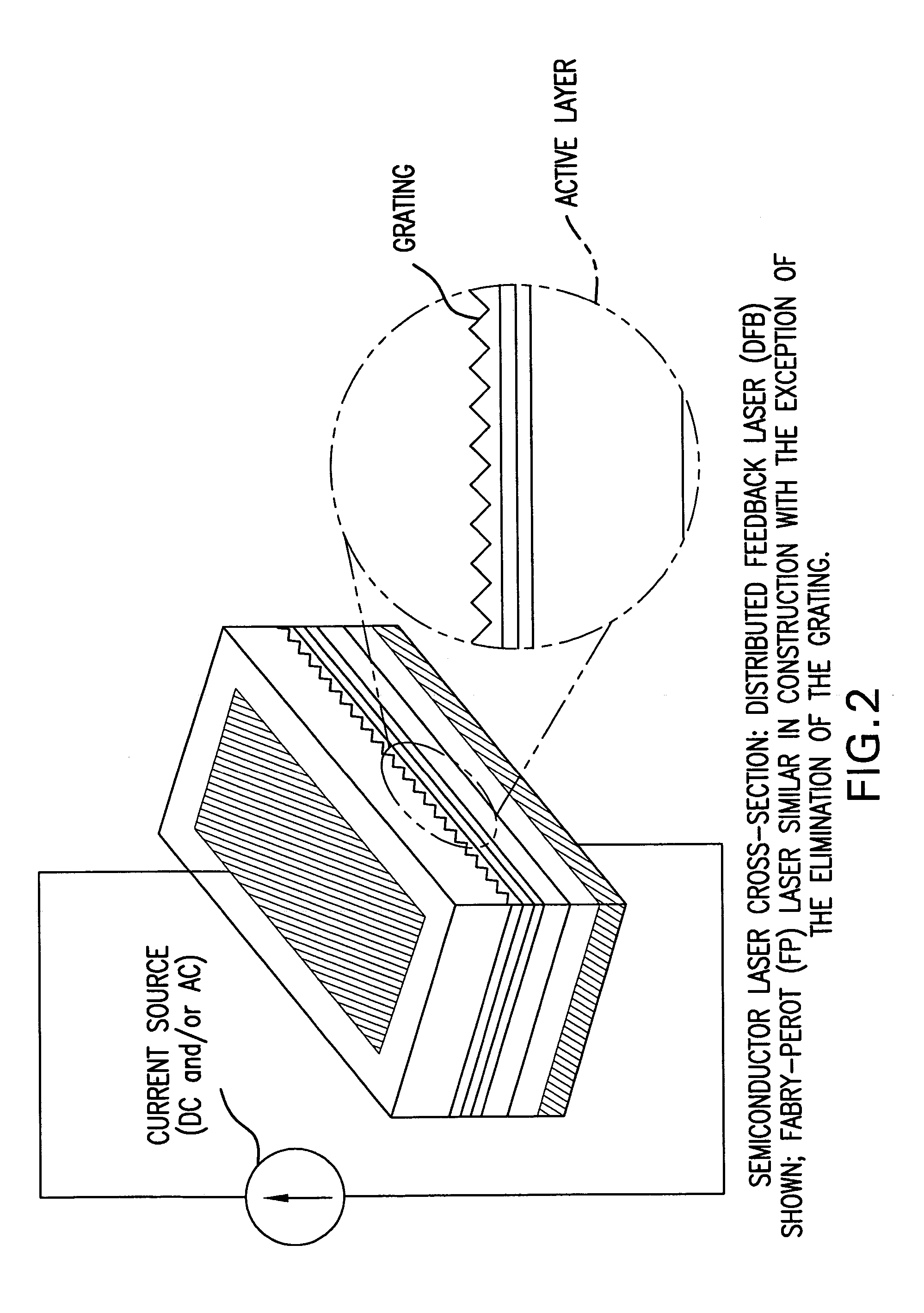
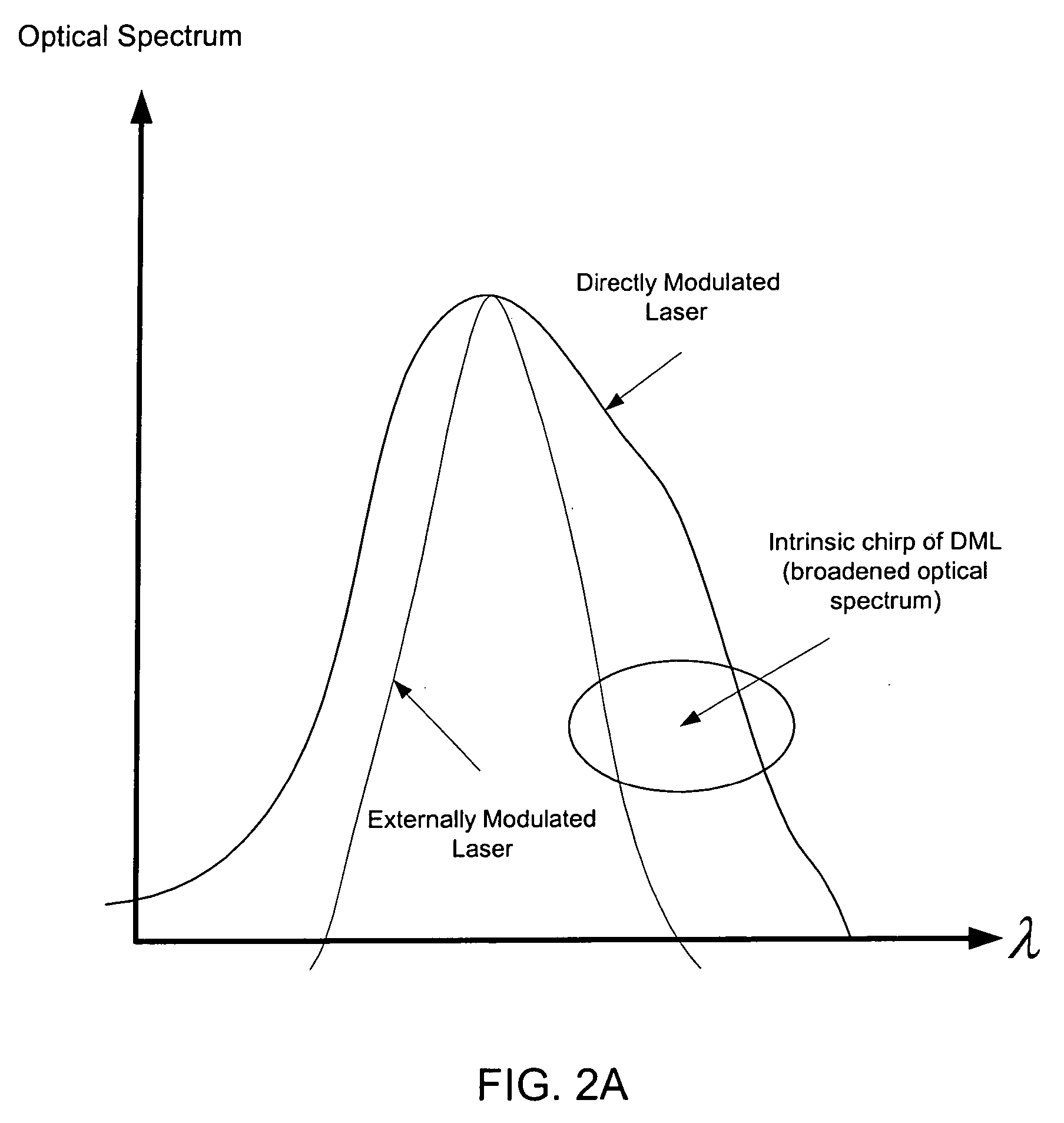
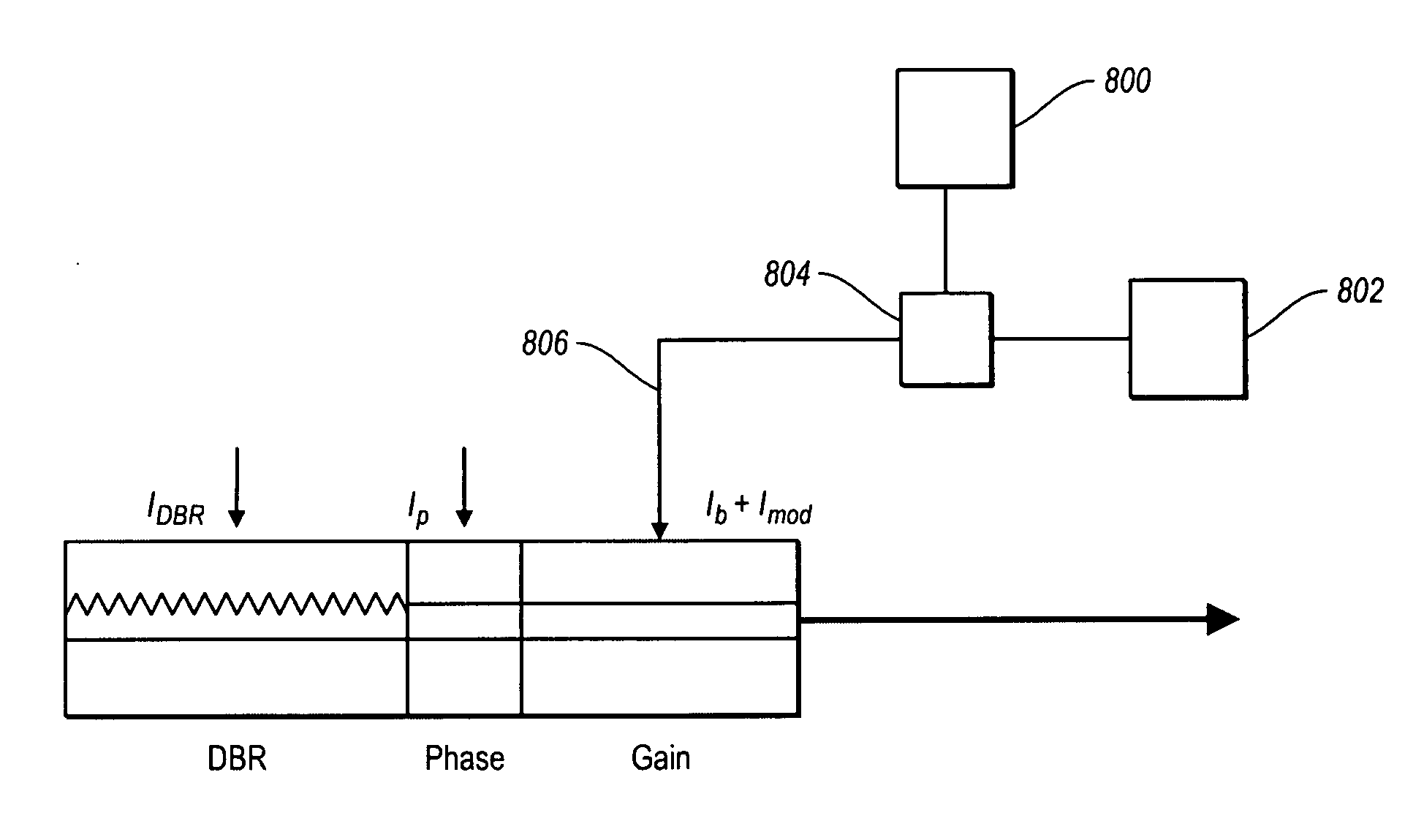
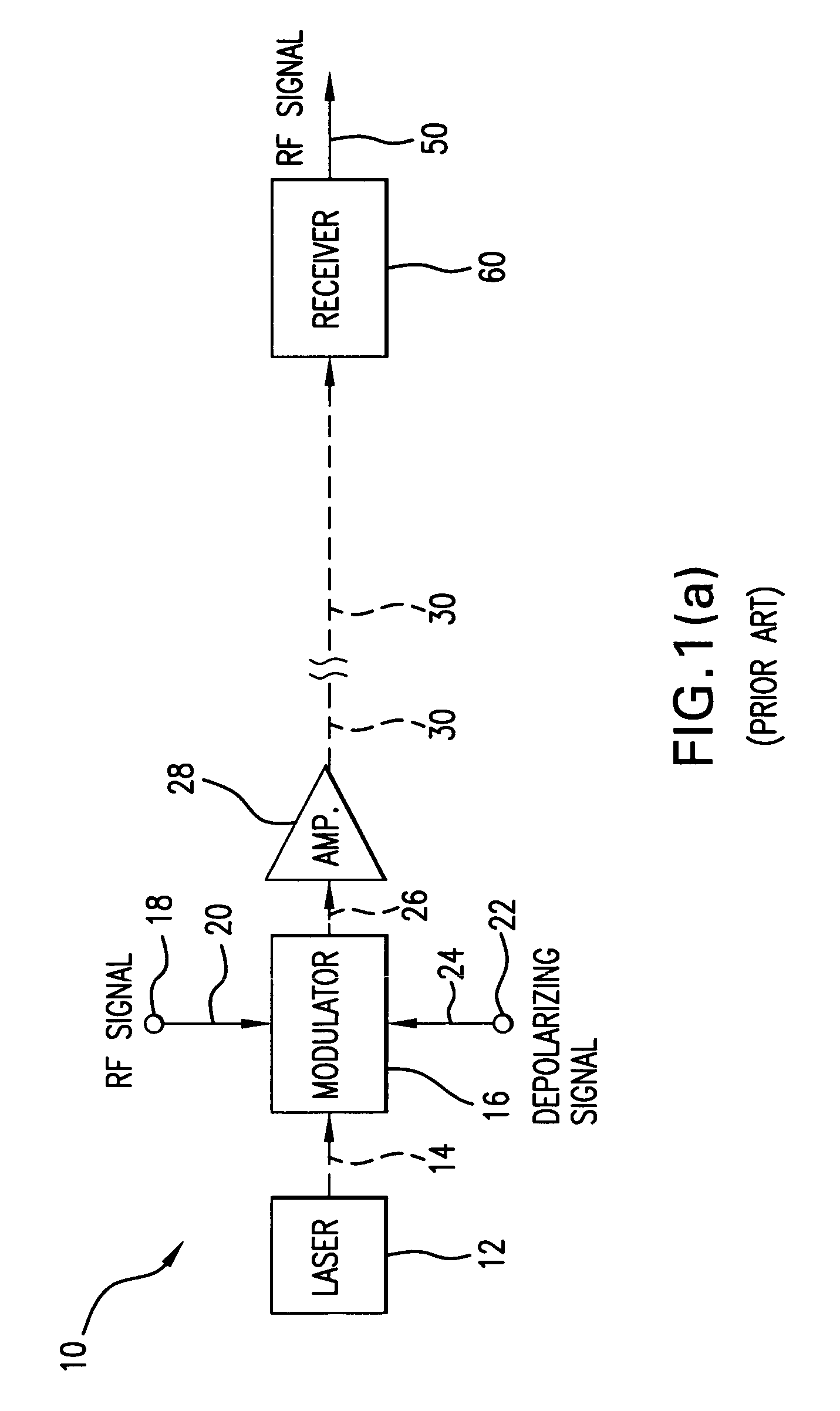
Directly Modulated Laser diode (DML) DMLs generally use distributed feedback structure with a diffraction grating in the waveguide for stable operation for direct modulation, and so this laser is also called a “DFB” (Distributed-Feedback laser diode).
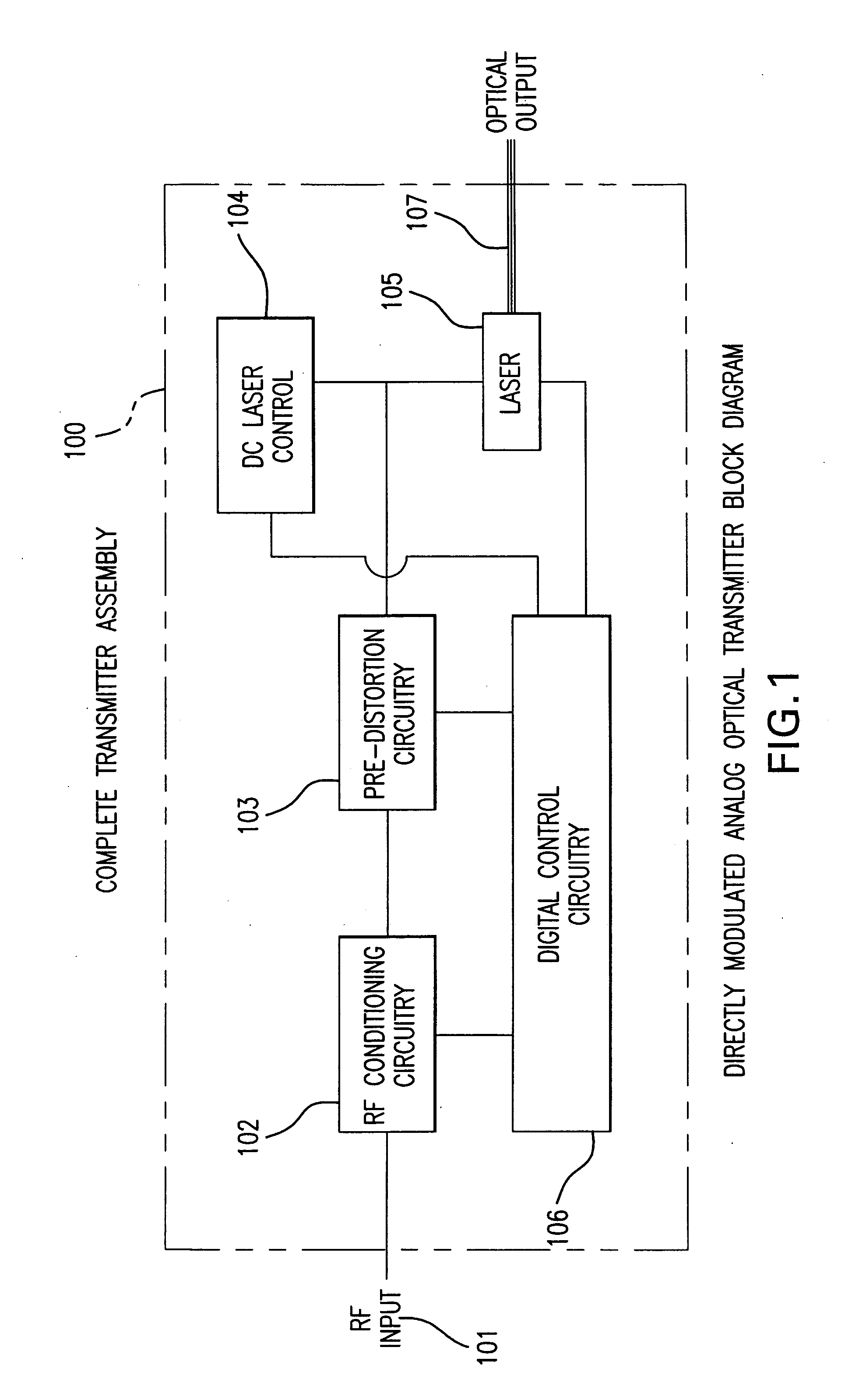
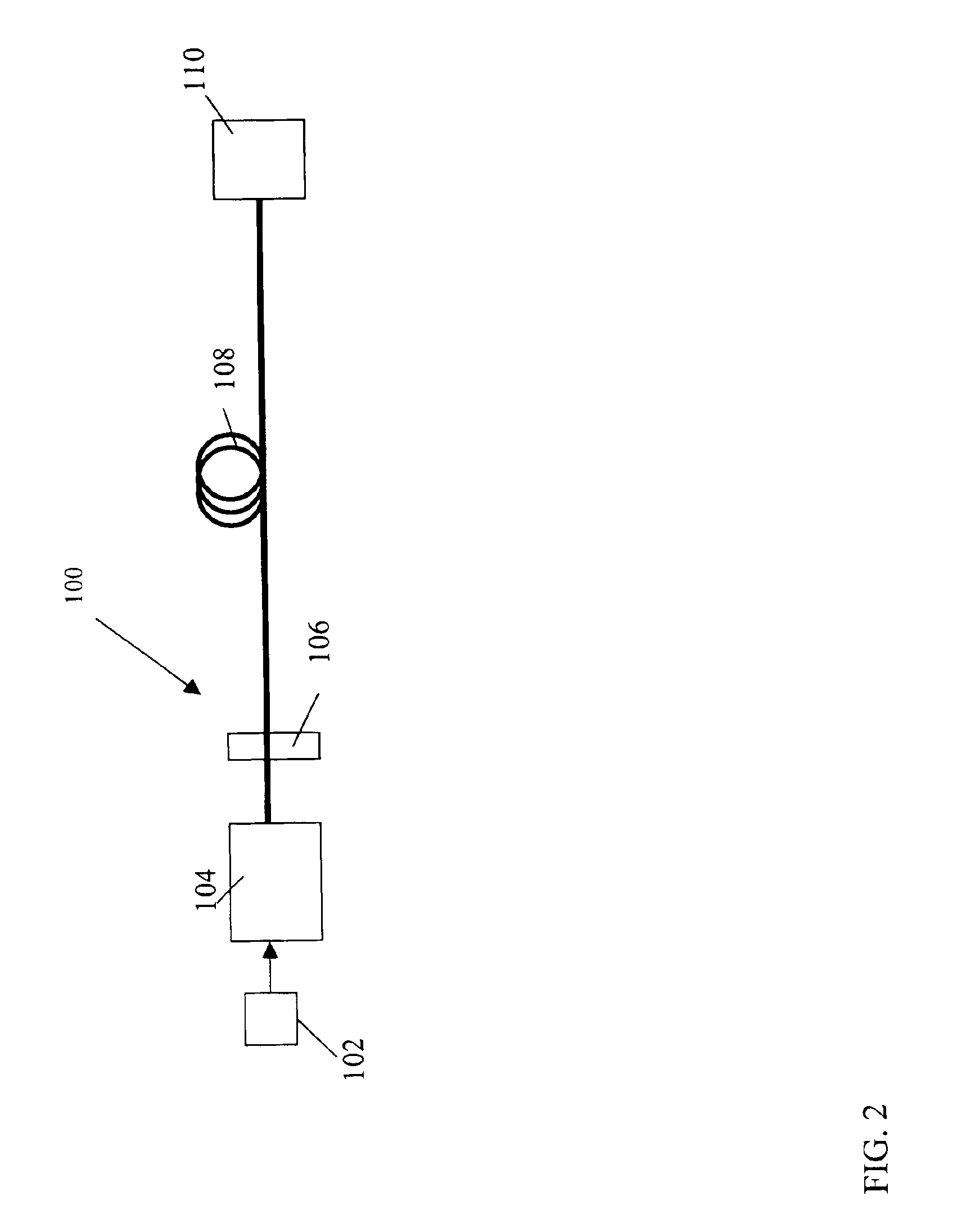
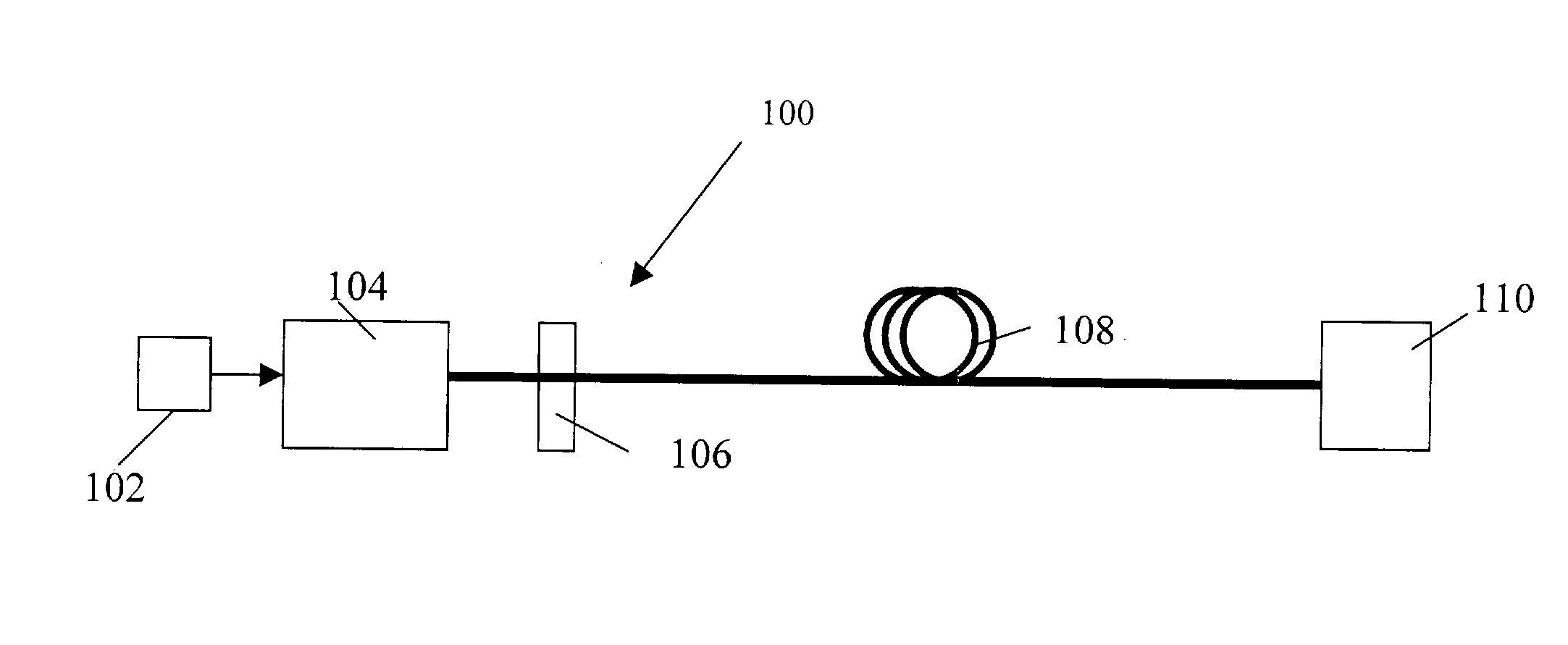
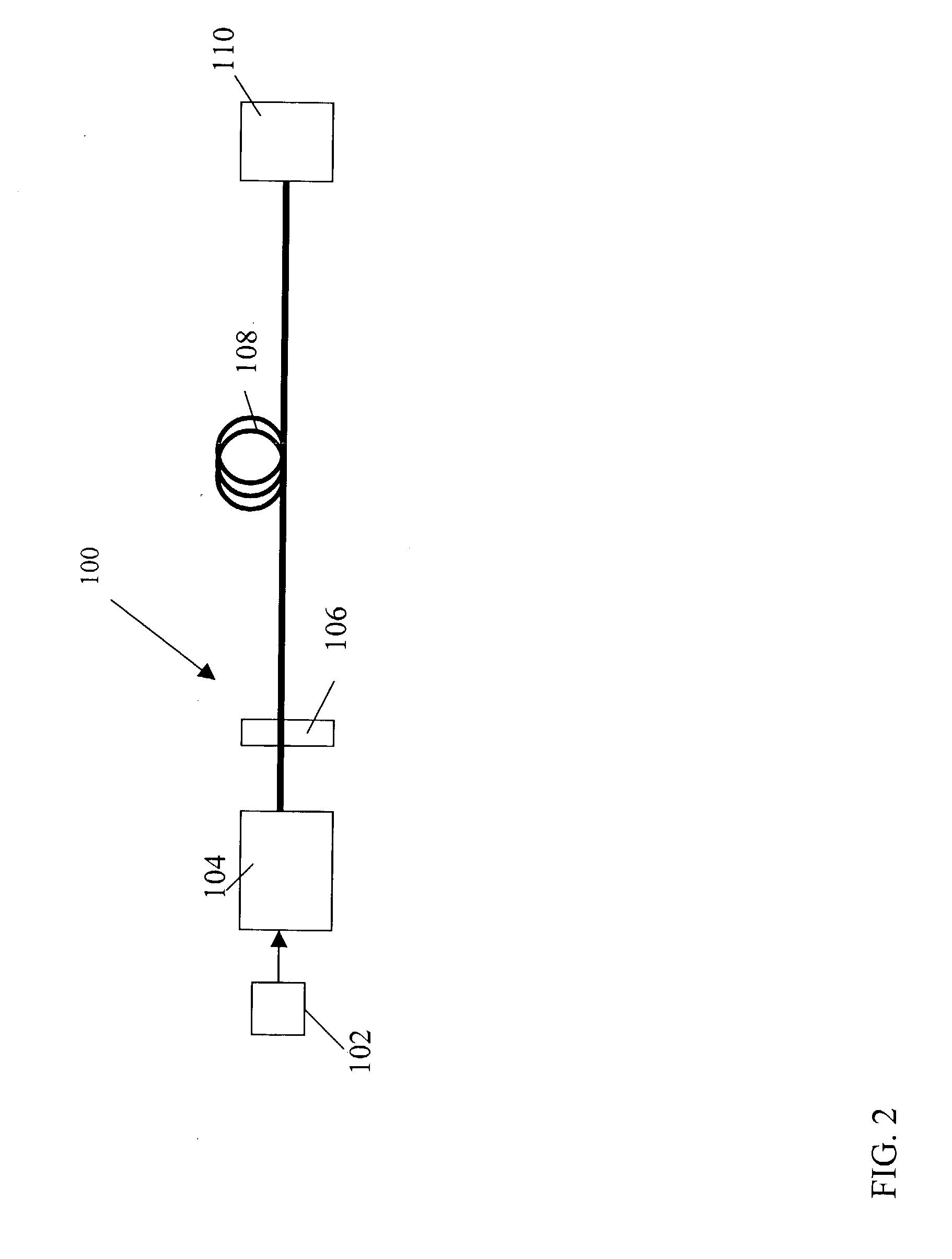
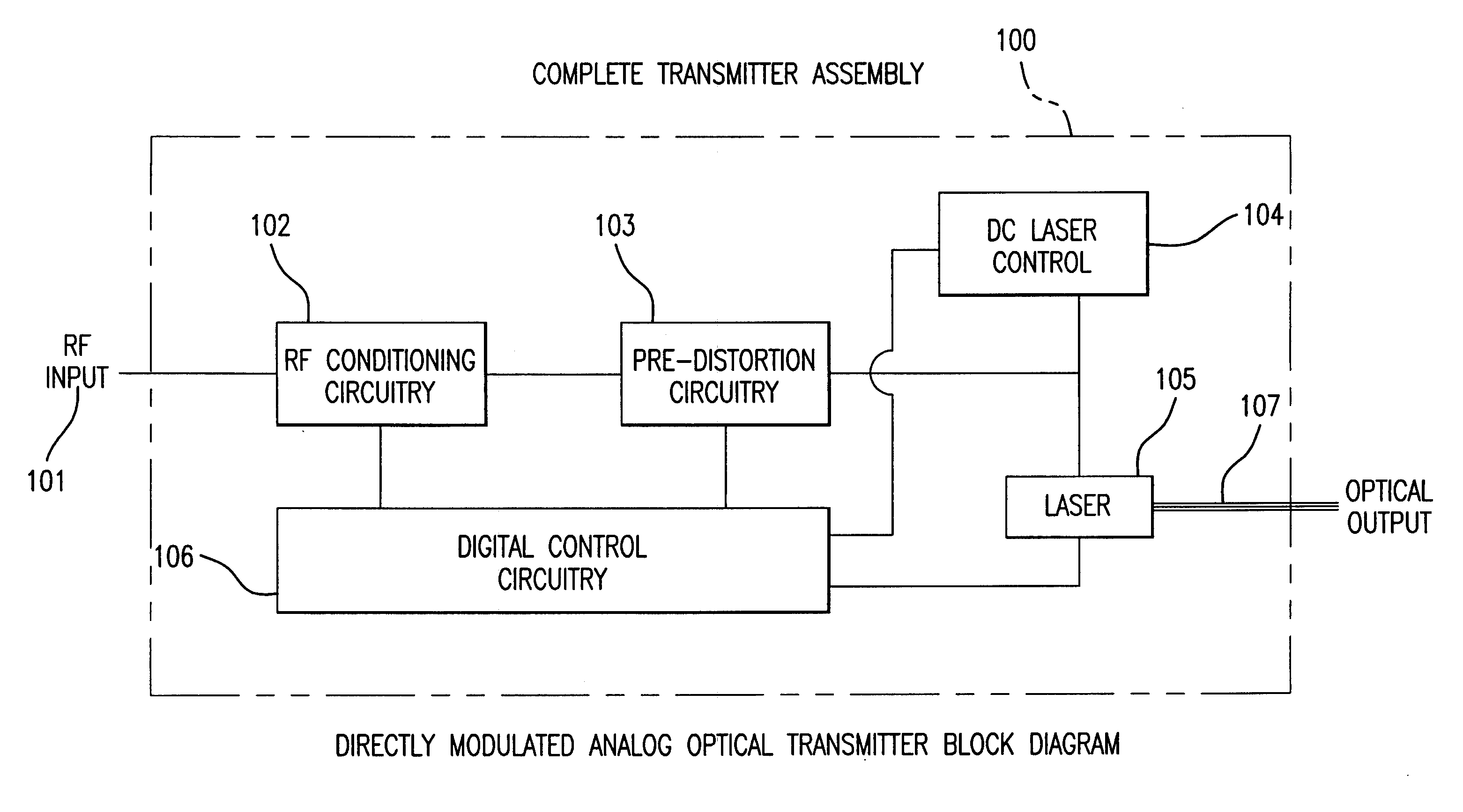
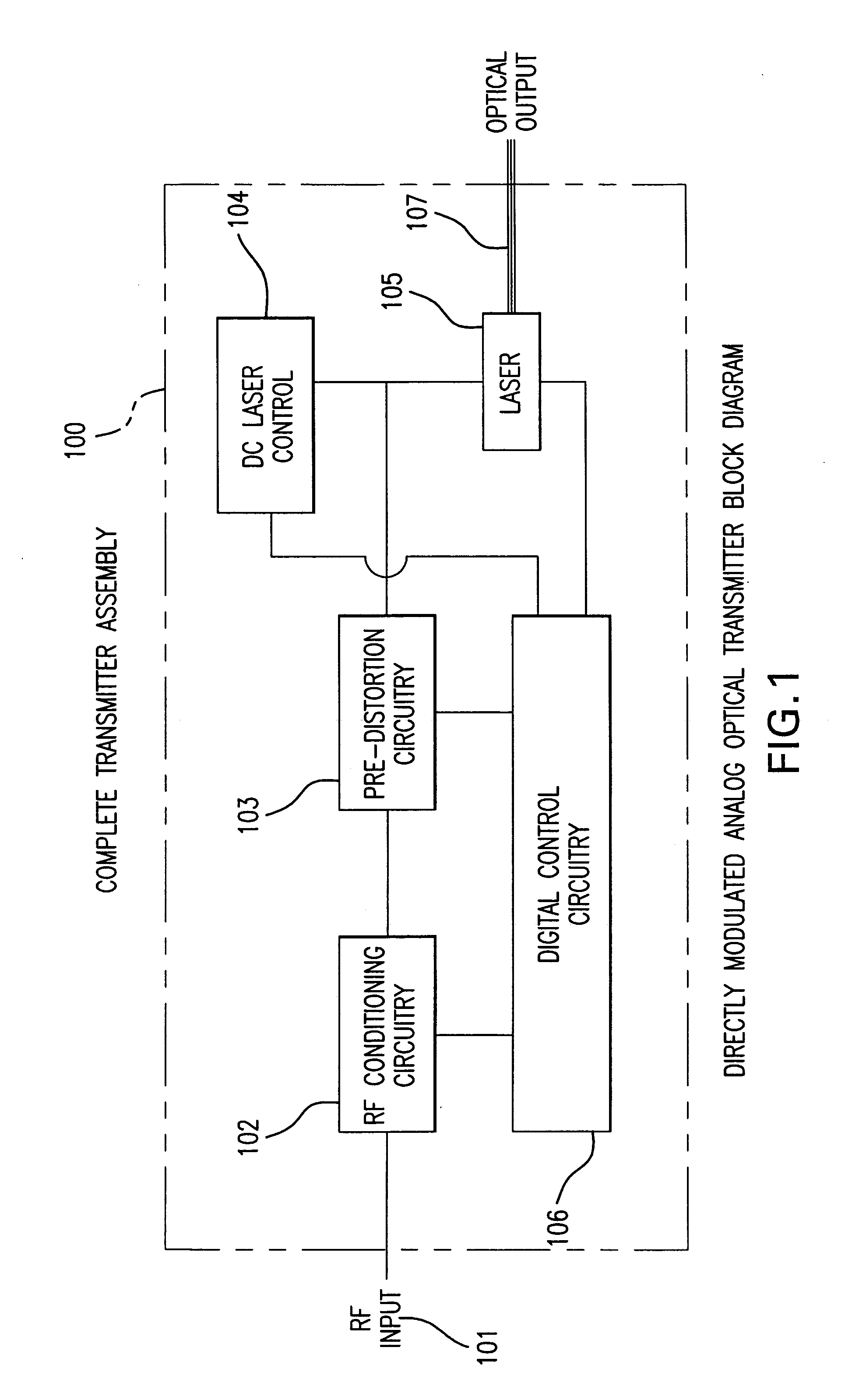
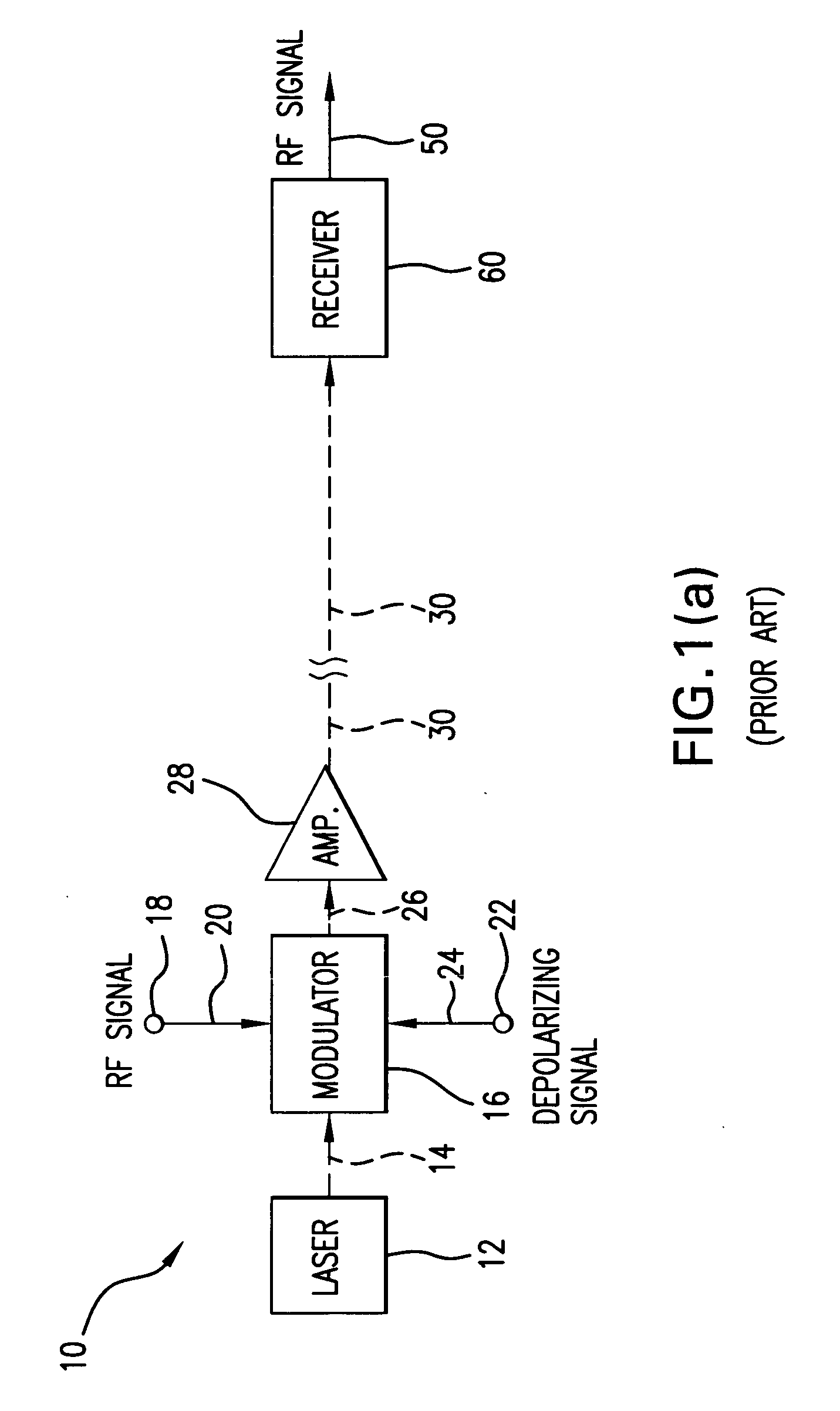
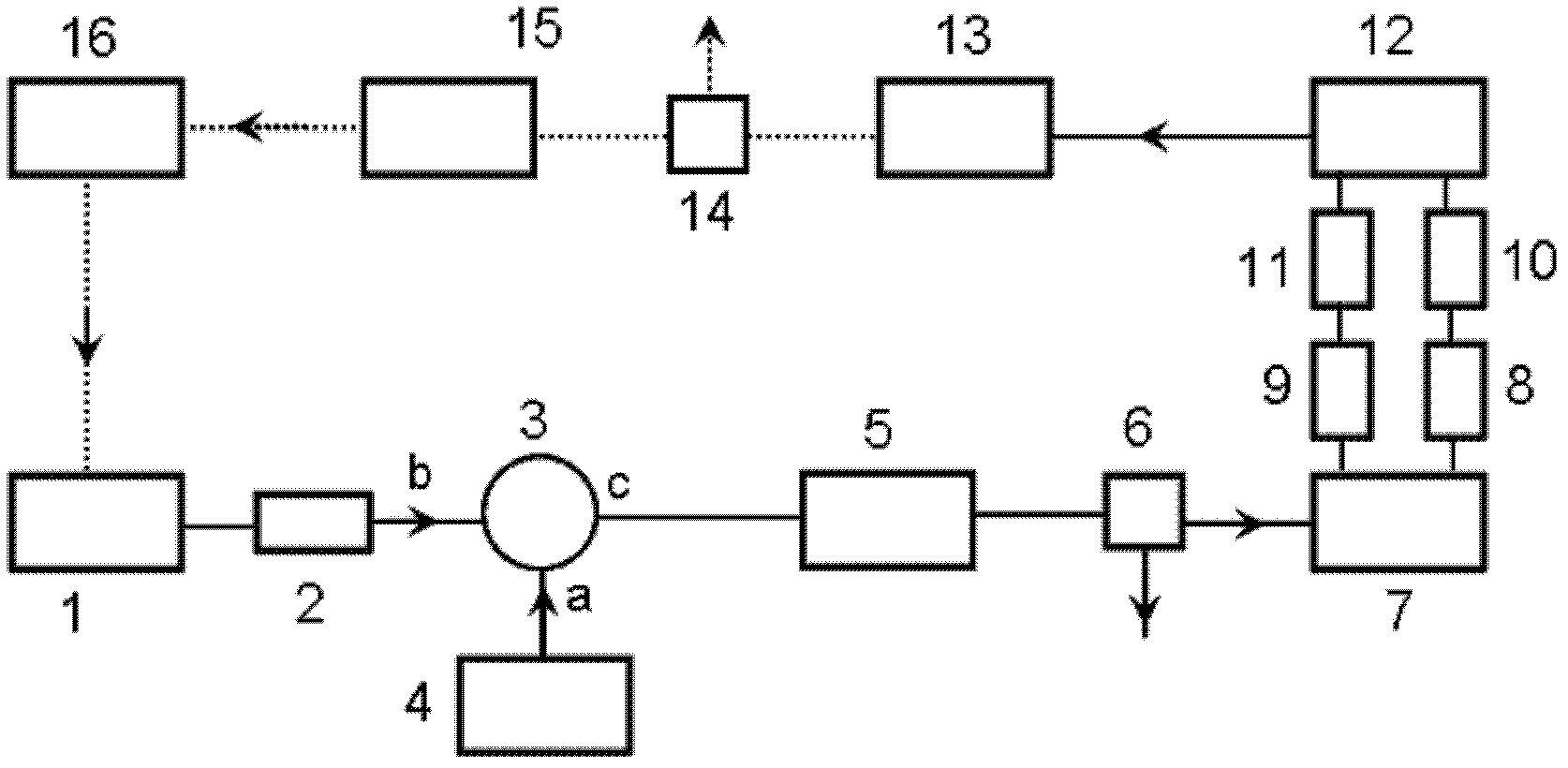
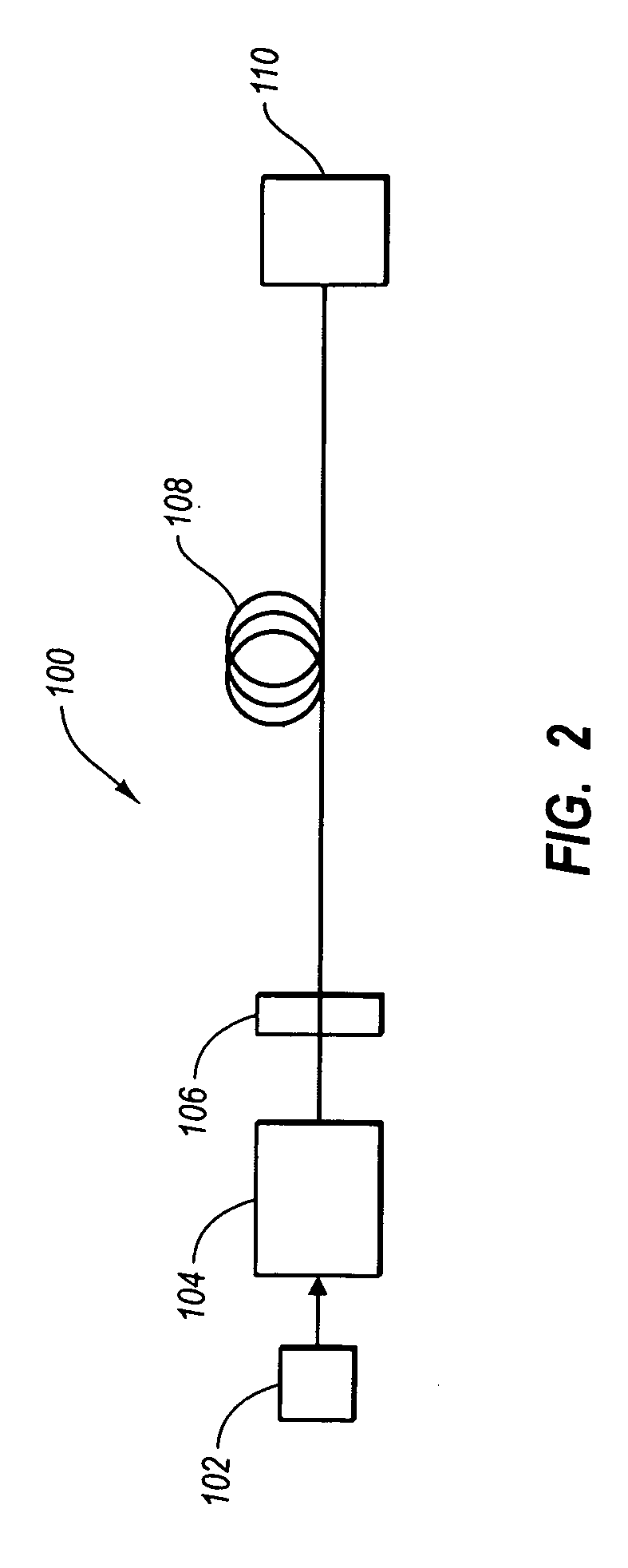
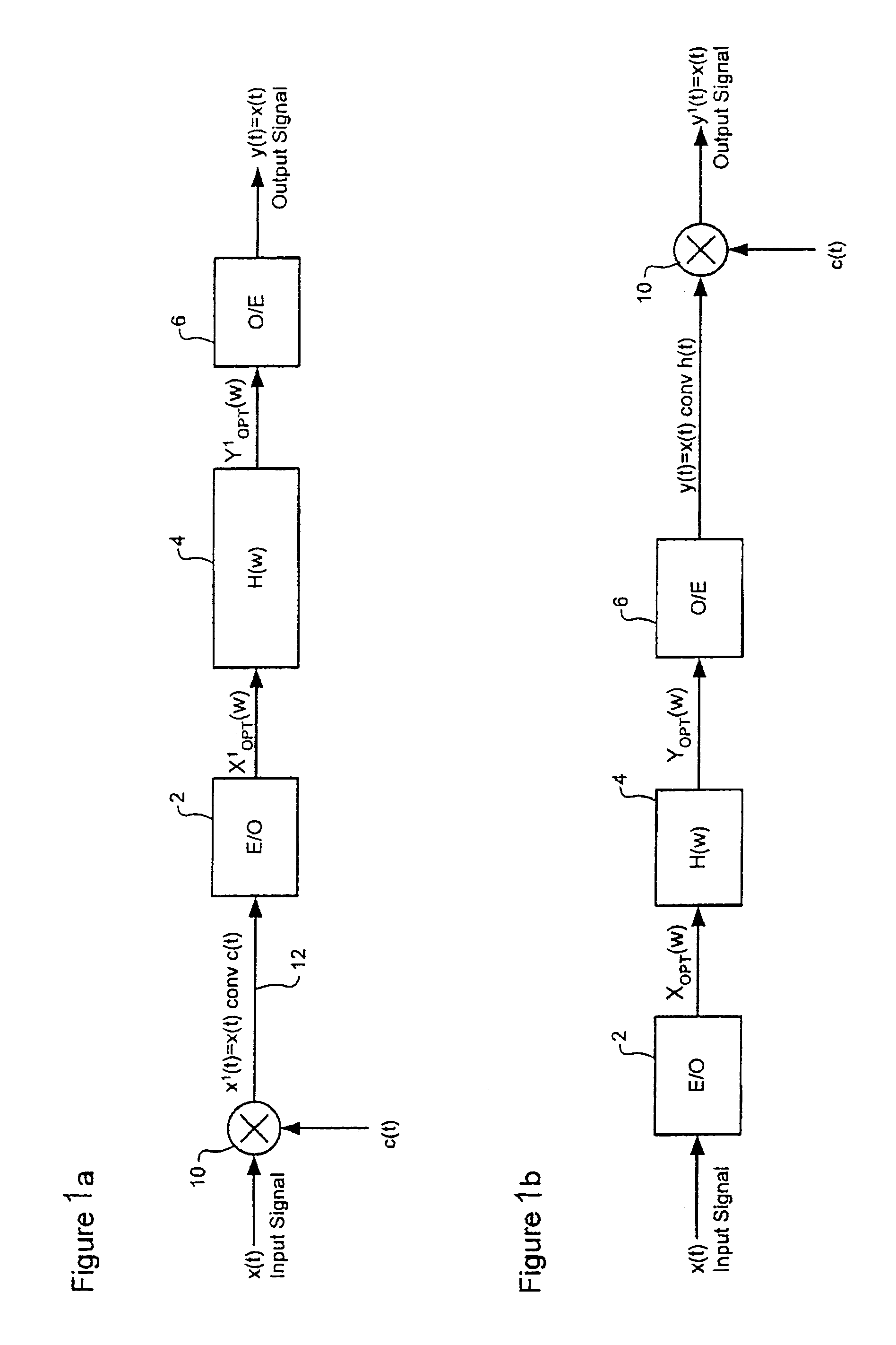
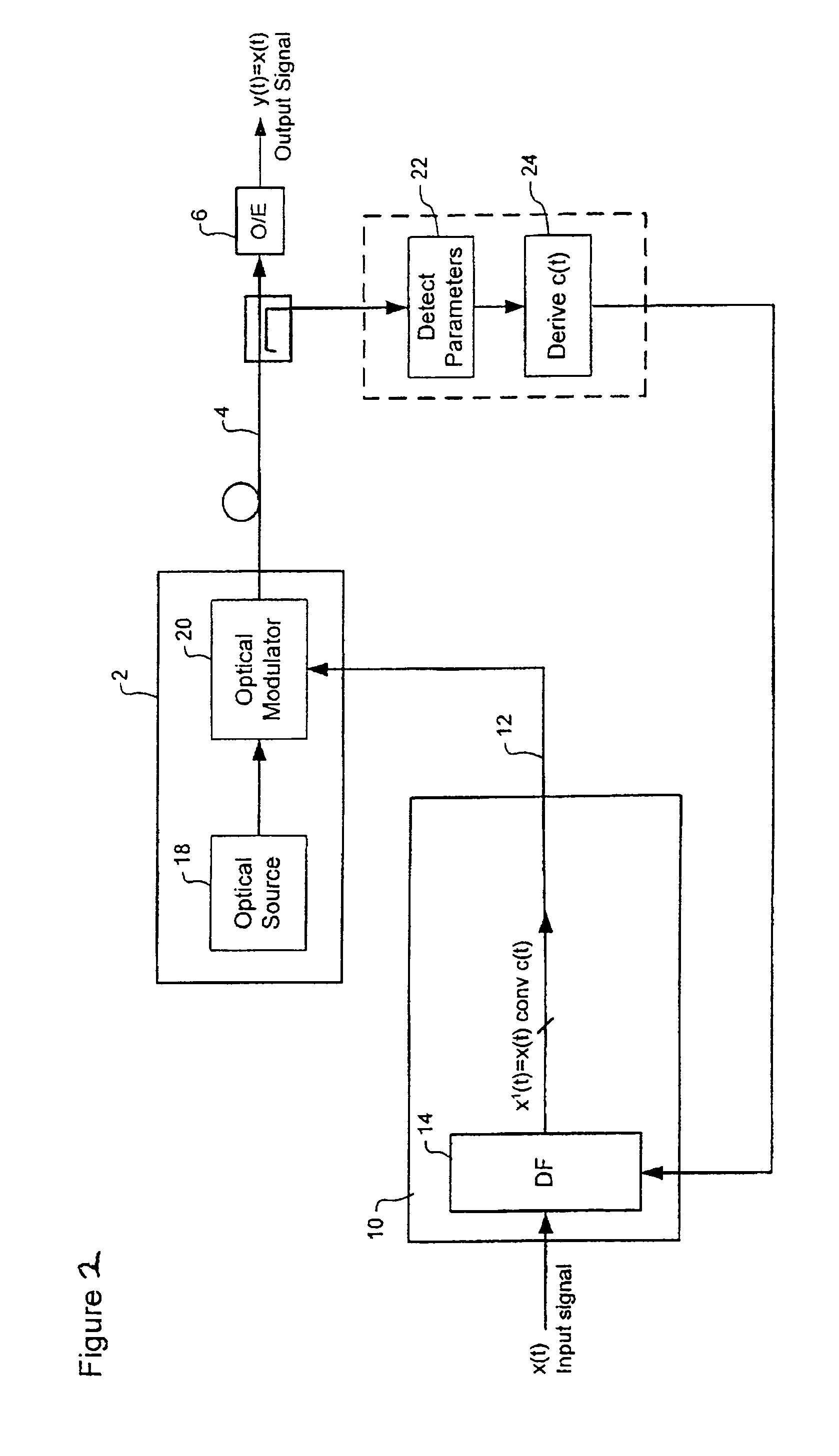
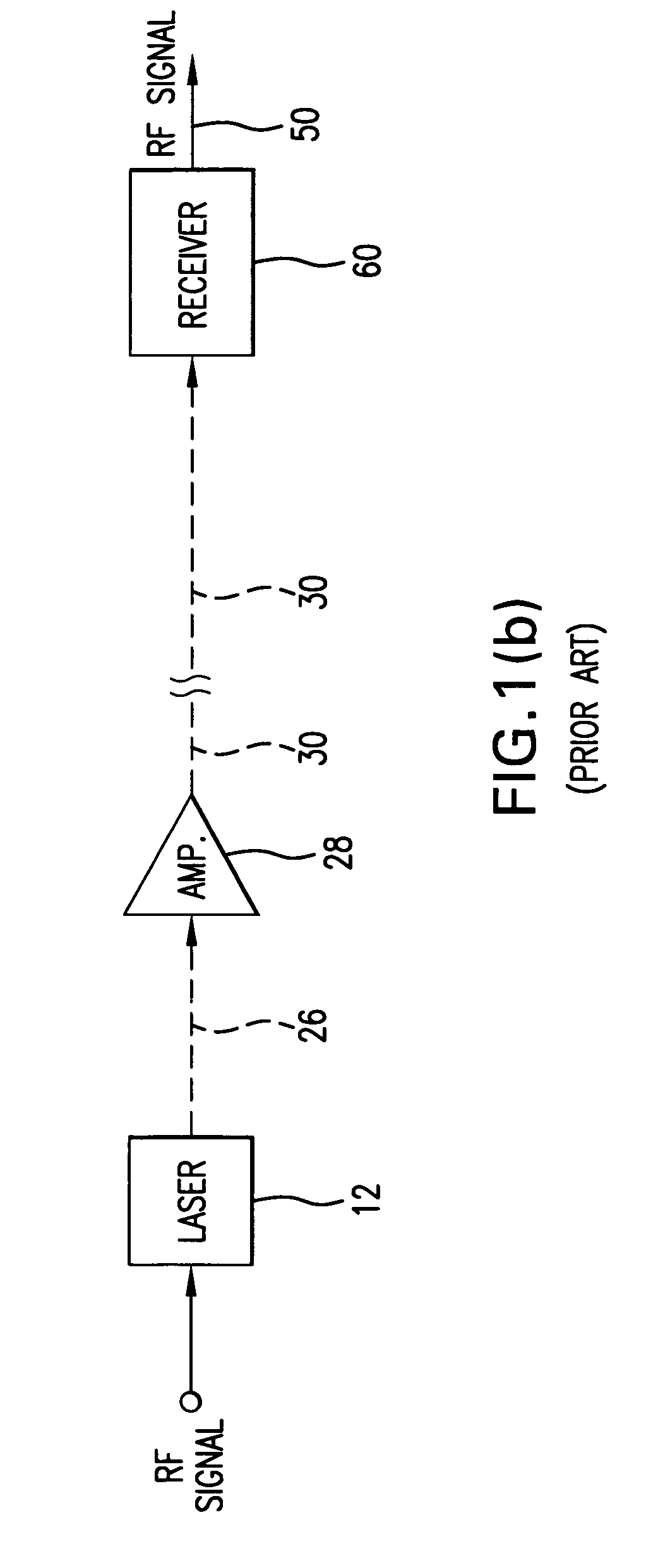
Directly modulated laser optical transmission system
InactiveUS20050271396A1Reduce signal distortionReducing frequency independent componentLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFiberEngineering
An optical transmitter for generating a modulated optical signal for transmission over dispersive fiber optic links in which a broadband analog radio frequency signal input is applied to a modulation circuit for directly modulating a semiconductor laser with the analog signal input. The transmitter may further include a temperature sensor in proximity to the laser and a negative feedback control circuit coupled to the temperature sensor for adjusting the temperature of the laser in response to an output characteristic of the laser, such as linearity.
Owner:EMCORE INC
Power source for a dispersion compensation fiber optic system
InactiveUS6963685B2Minimize signalingIncrease bitrateCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency modulationDispersion compensation
Owner:OPTICAL HORIZONS CORP +1
High-speed transmission system comprising a coupled multi-cavity optical discriminator
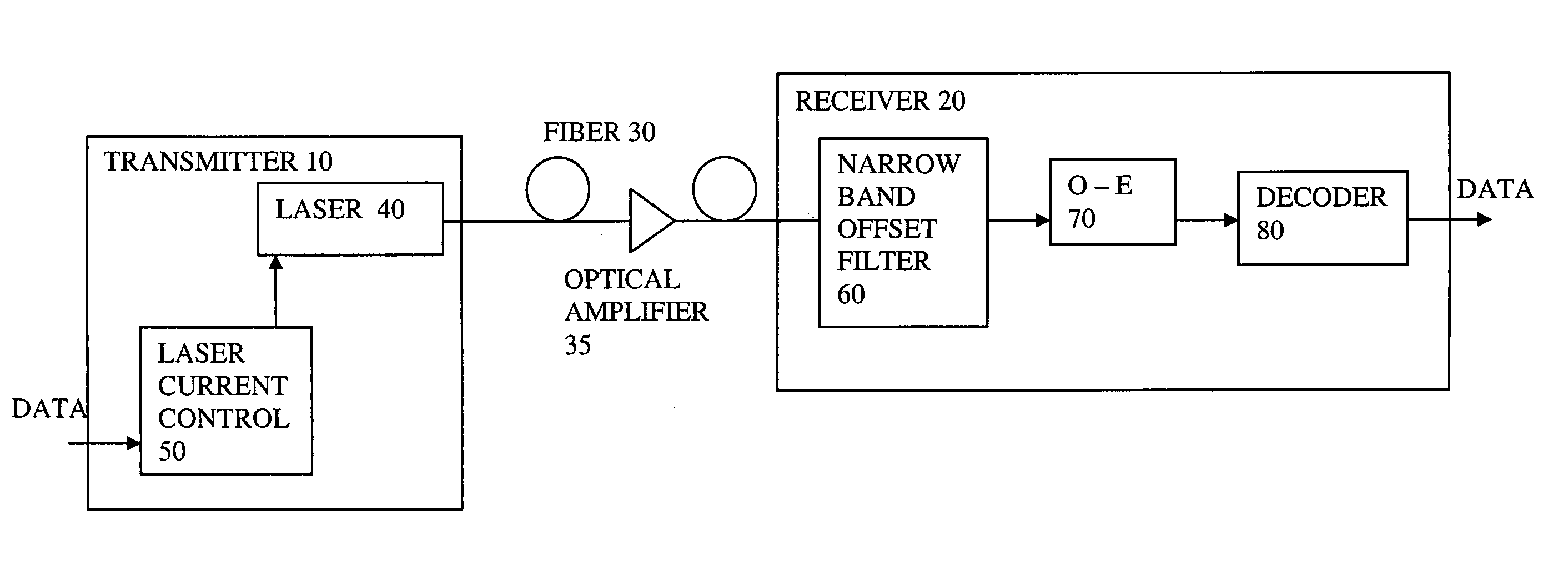
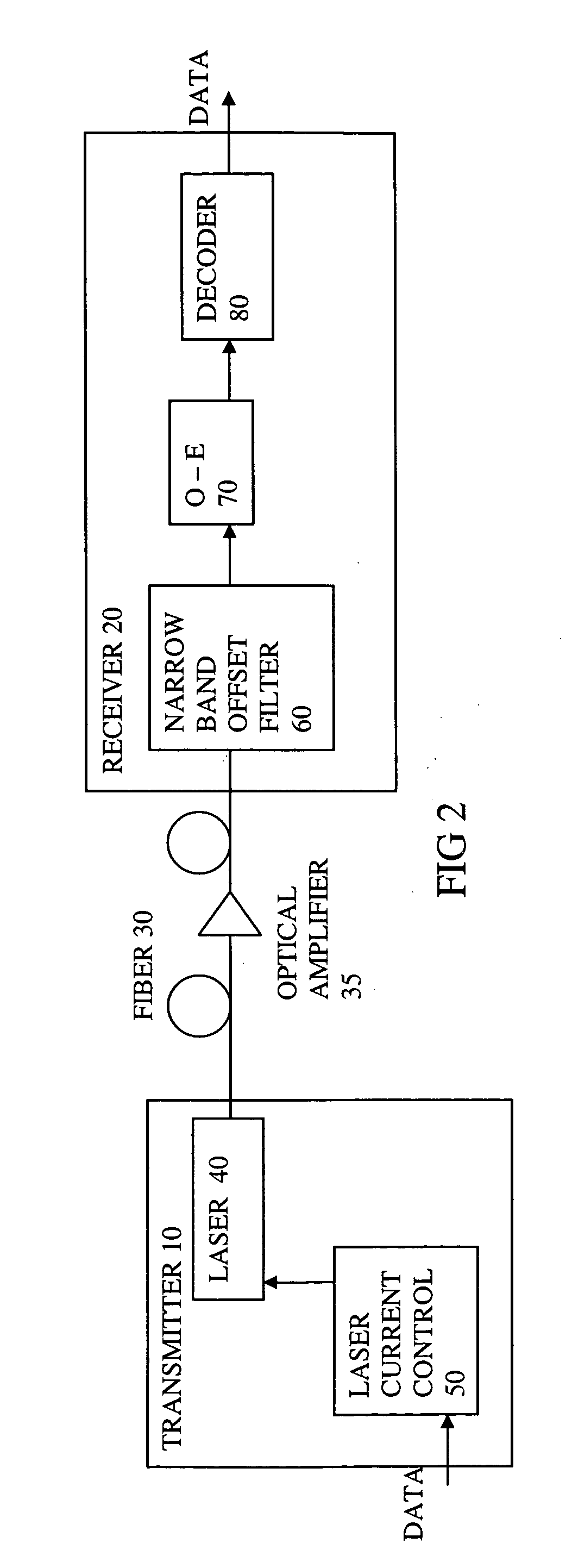
This invention generally relates to an optical filter for a fiber optic communication system. A coupled multi-cavity optical filter may be used, following a directly modulated laser source, and converts a partially frequency modulated signal into a substantially amplitude modulated signal. The optical filter may compensate for the dispersion in the fiber optic transmission medium and may also lock the wavelength of the laser source.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Directly modulated laser optical transmission system
InactiveUS7466925B2Reduce signal distortionReducing frequency independent componentLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFiberEngineering
An optical transmitter for generating a modulated optical signal for transmission over dispersive fiber optic links in which a broadband analog radio frequency signal input is applied to a modulation circuit for directly modulating a semiconductor laser with the analog signal input. The transmitter may further include a temperature sensor in proximity to the laser and a negative feedback control circuit coupled to the temperature sensor for adjusting the temperature of the laser in response to an output characteristic of the laser, such as linearity.
Owner:EMCORE INC
Filter to improve dispersion tolerance for optical transmission
InactiveUS20050271394A1Reduce phase differenceInexpensive optical filteringElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency spectrumPhase difference
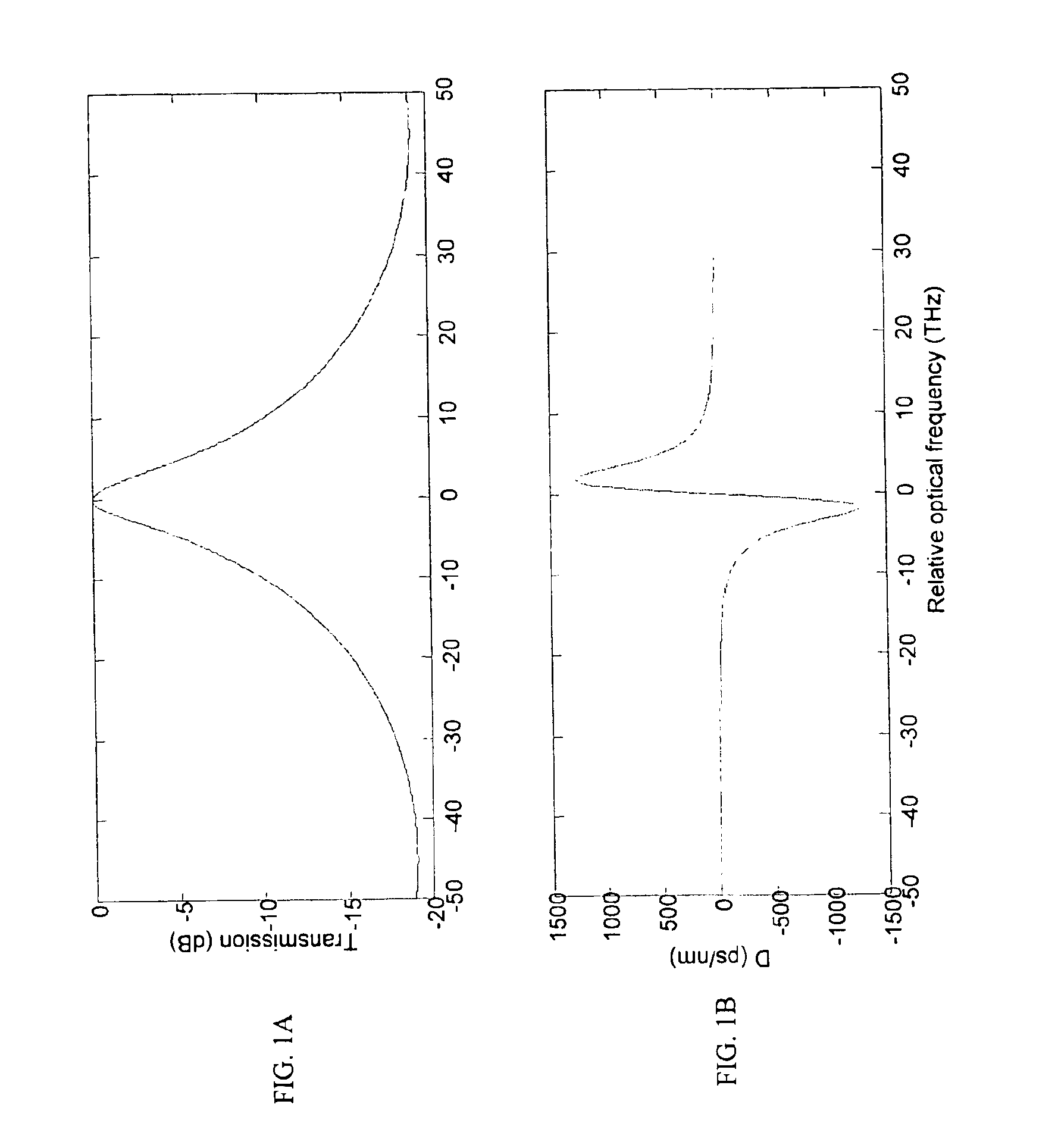
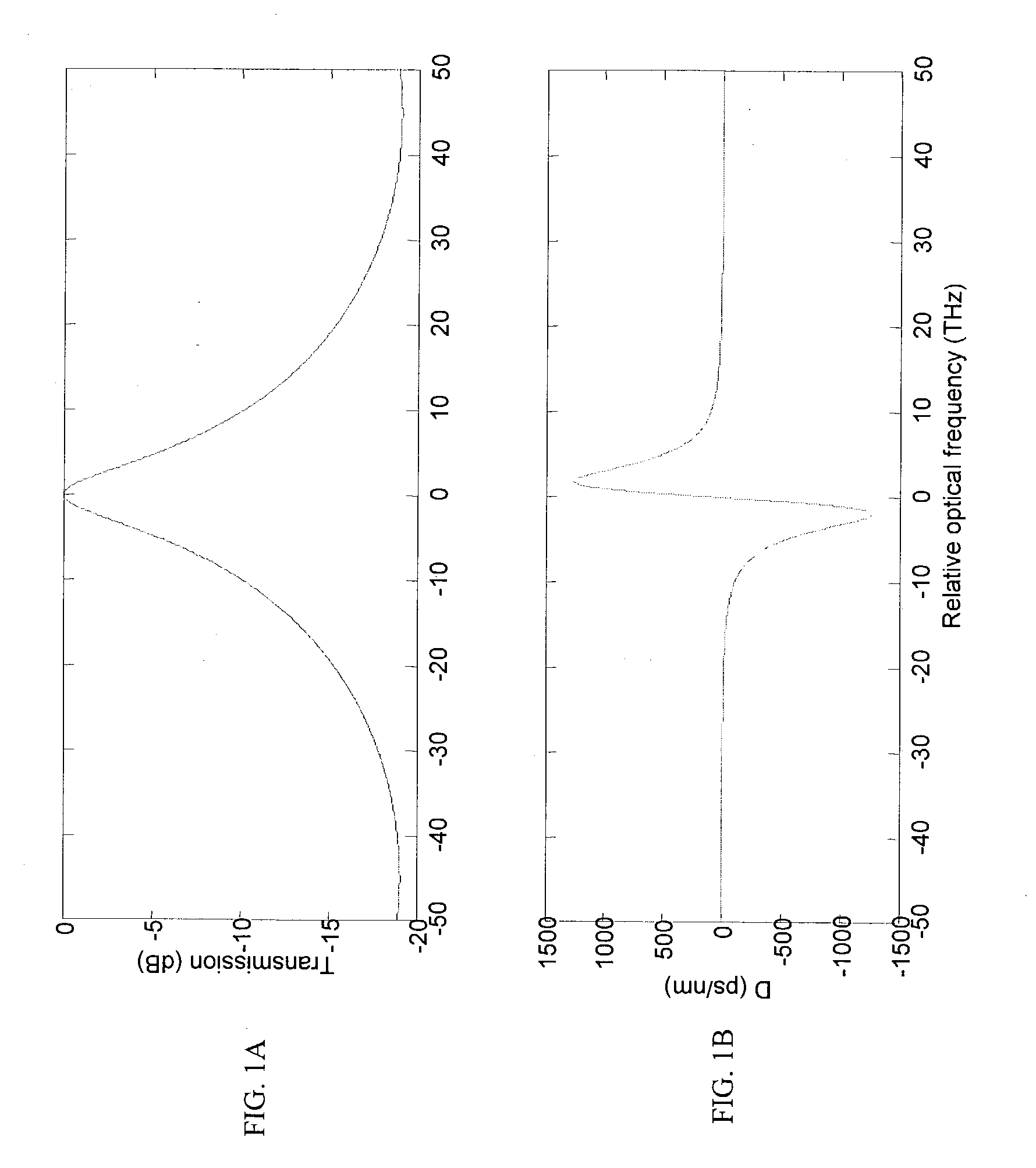
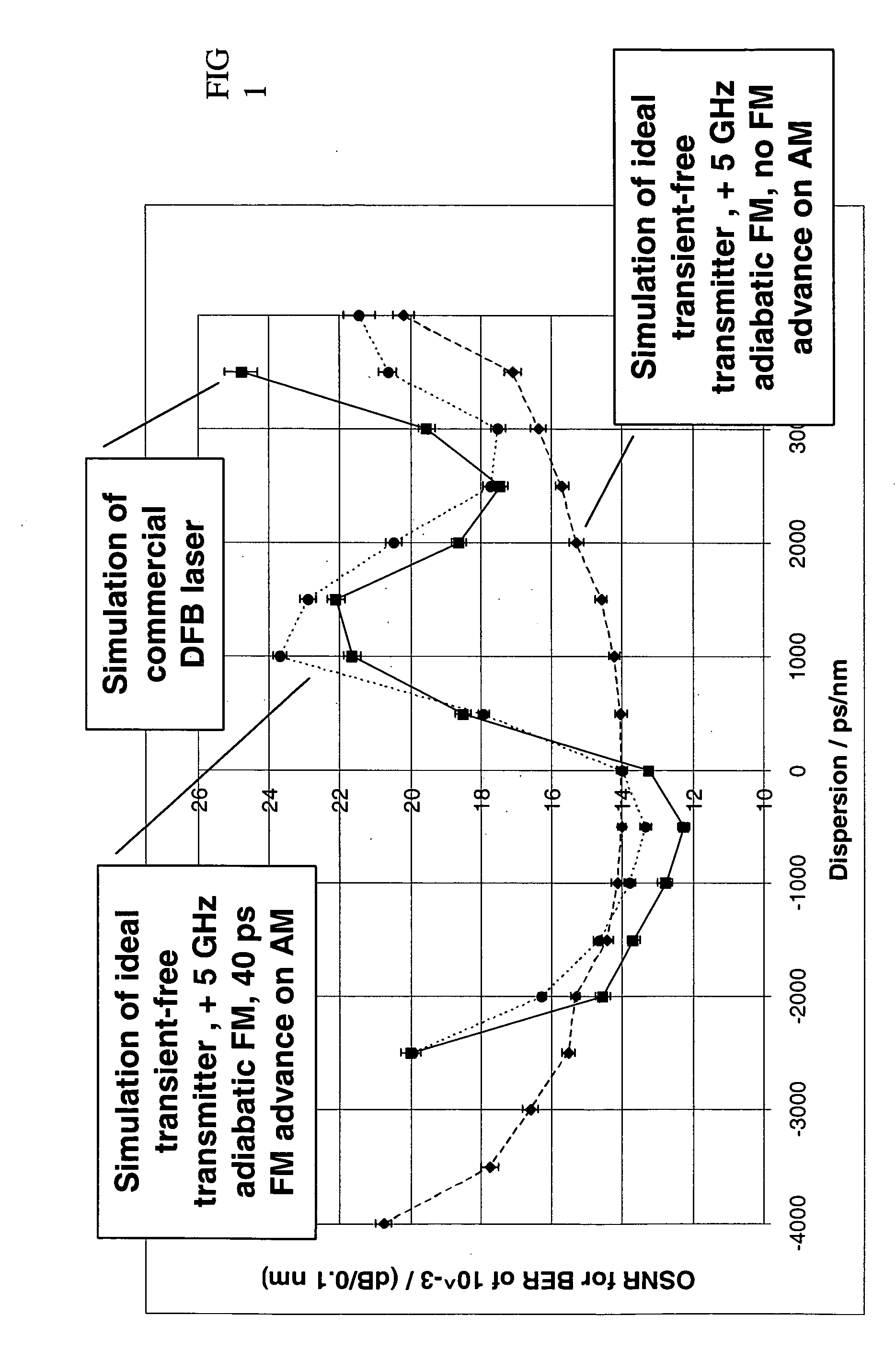
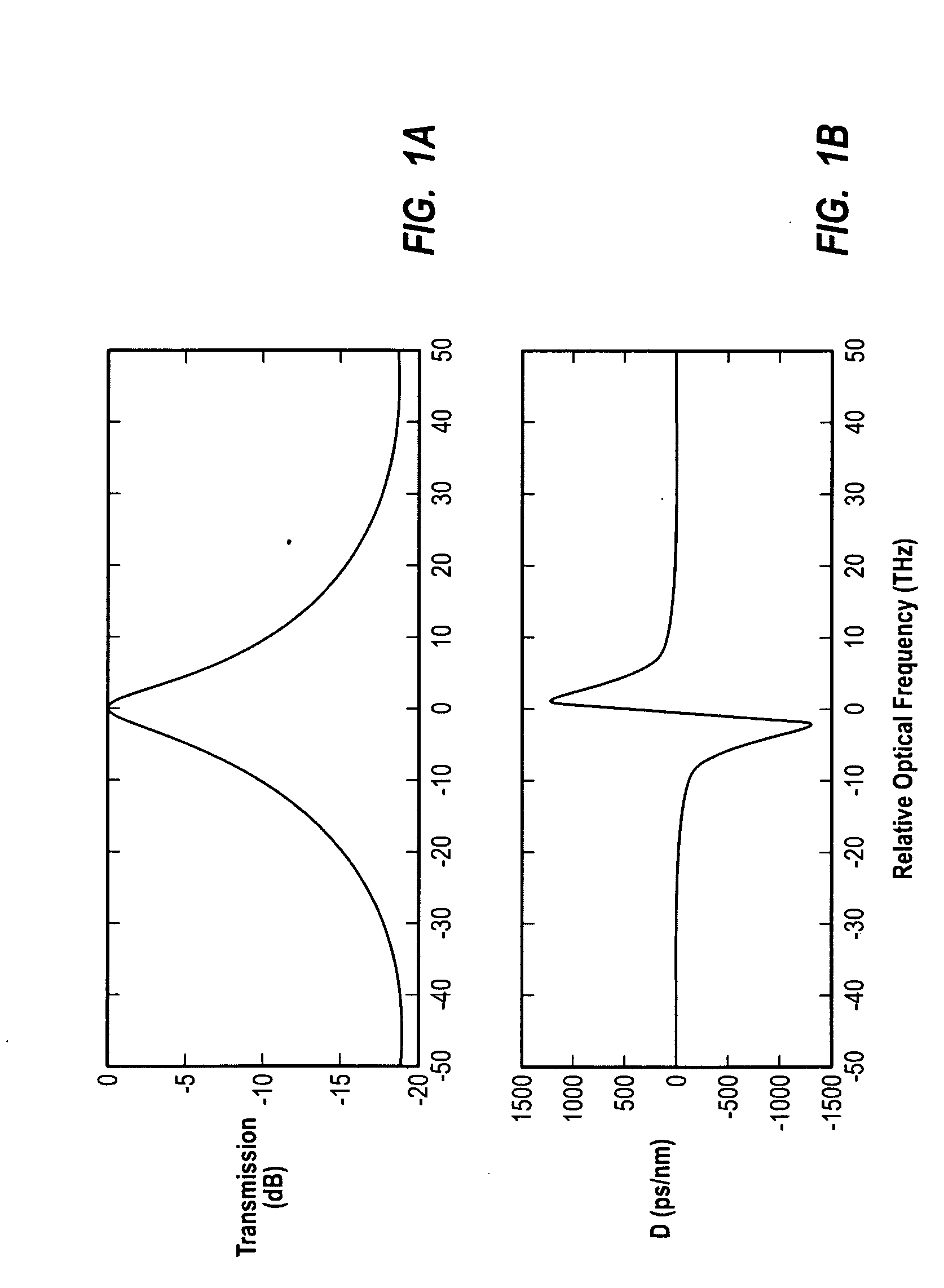
An optical transmission system has a directly modulated laser for modulating data directly on an optical signal, and a narrow band optical filter having a band center frequency offset from a central optical frequency of the optical signal, to reduce the phase difference between FM and AM of the modulated optical signal, the filter having a bandwidth sufficiently narrow to substantially remove frequencies outside a spectrum of adiabatic frequency chirp resulting from the modulation, combined with Fourier broadening caused by the data modulation. This is a cost effective way of improving the dispersion tolerance to give greatly improved system reach and to make it practical to use directly modulated lasers with existing NDSF. The narrow band filter can be located at the transmitter or the receiver, and can have a center frequency locked to a feature in the frequency spectrum of the laser.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
Directly modulated laser optical transmission system with phase modulation
ActiveUS20060210282A1Reduce distortion problemsComponent distortionFibre transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersFiberTransfer system
An optical transmitter for generating a modulated optical signal for transmission over a fiber optic link to a remote receiver including a laser; a modulator for directly amplitude modulating the laser with an analog RF signal to produce an optical signal including an amplitude modulated information-containing component; and a phase modulated component and a phase modulator coupled to the output of the laser for reducing the distortion present in the received optical signal at the remote receiver.
Owner:EMCORE INC
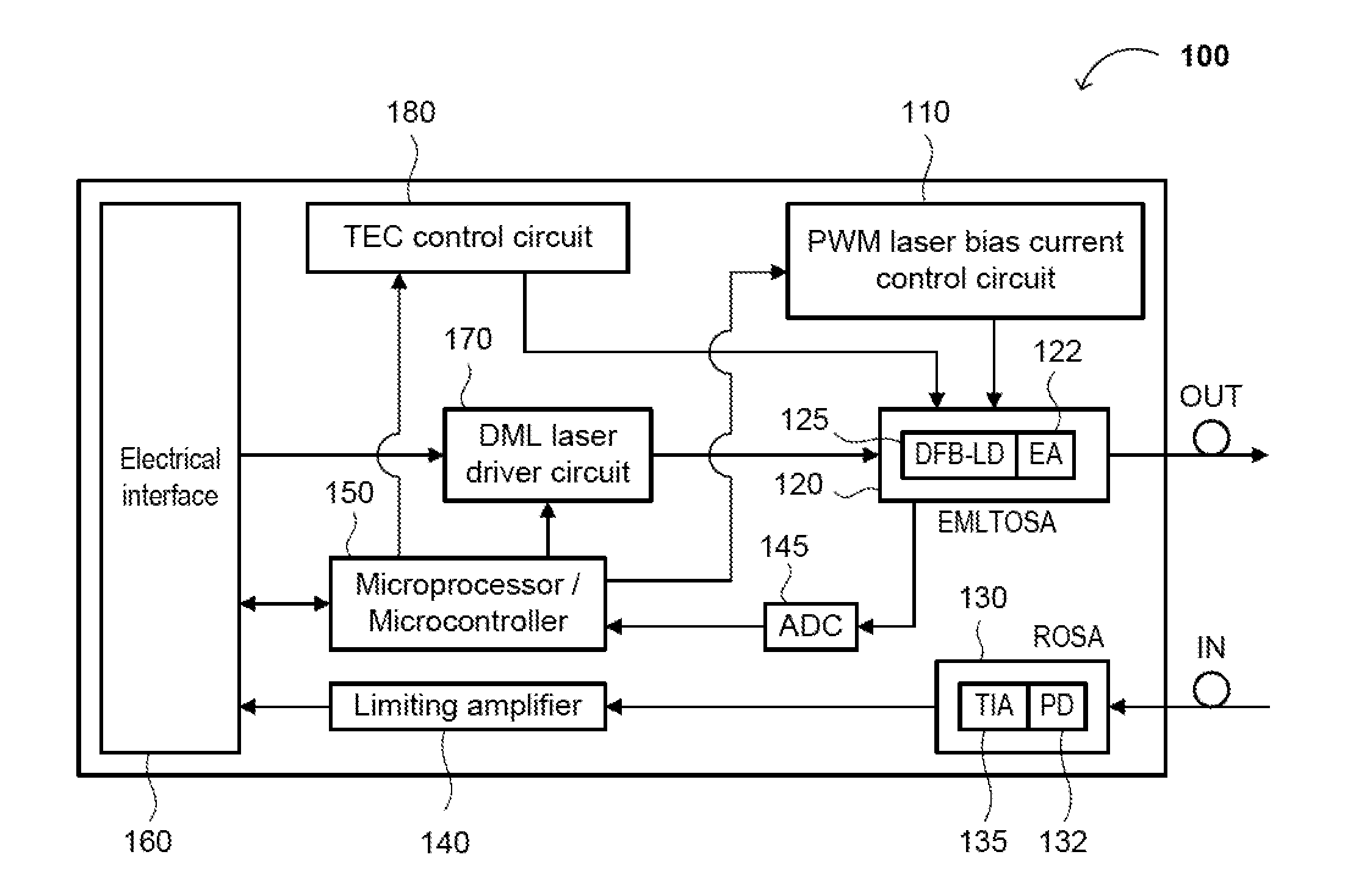
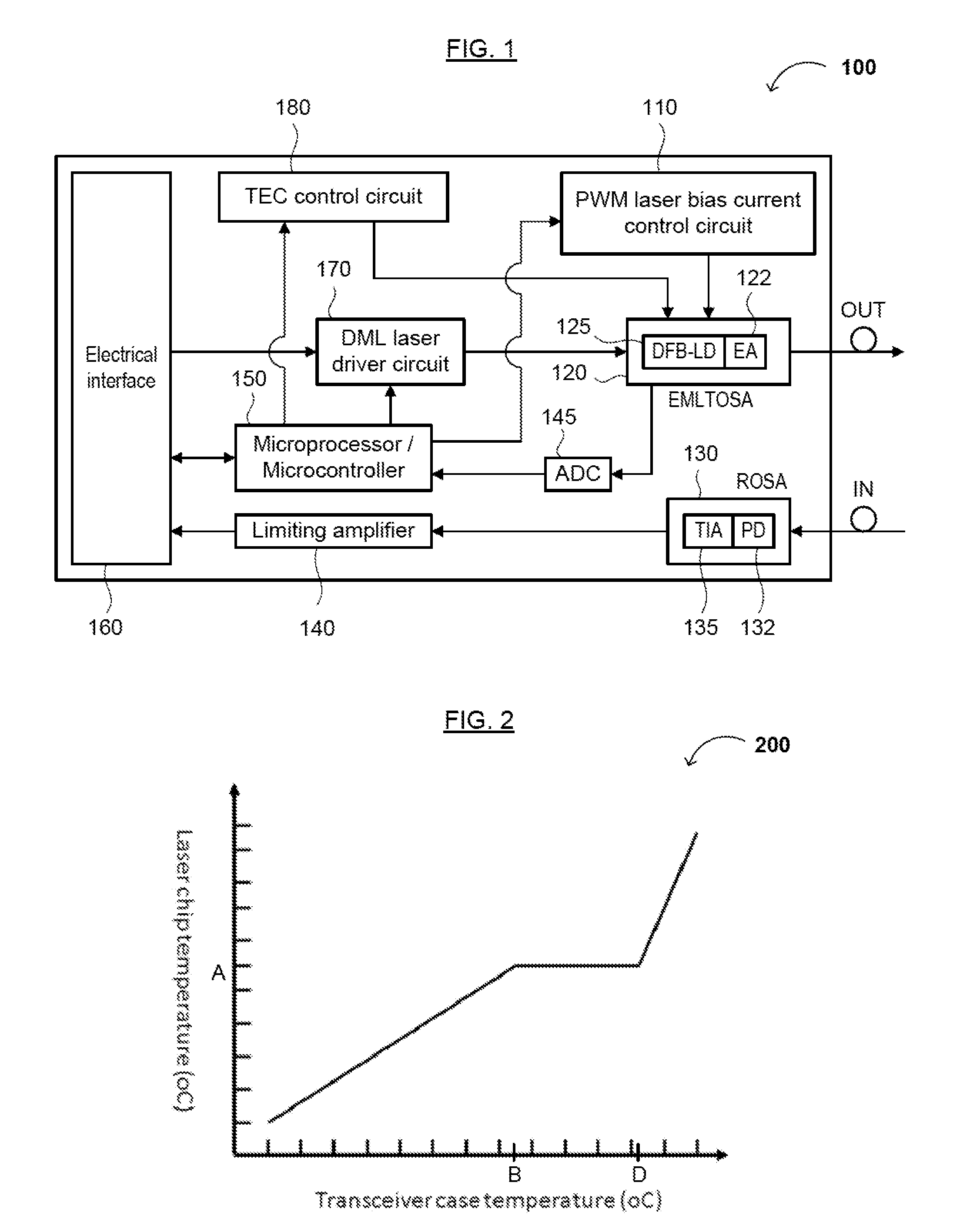
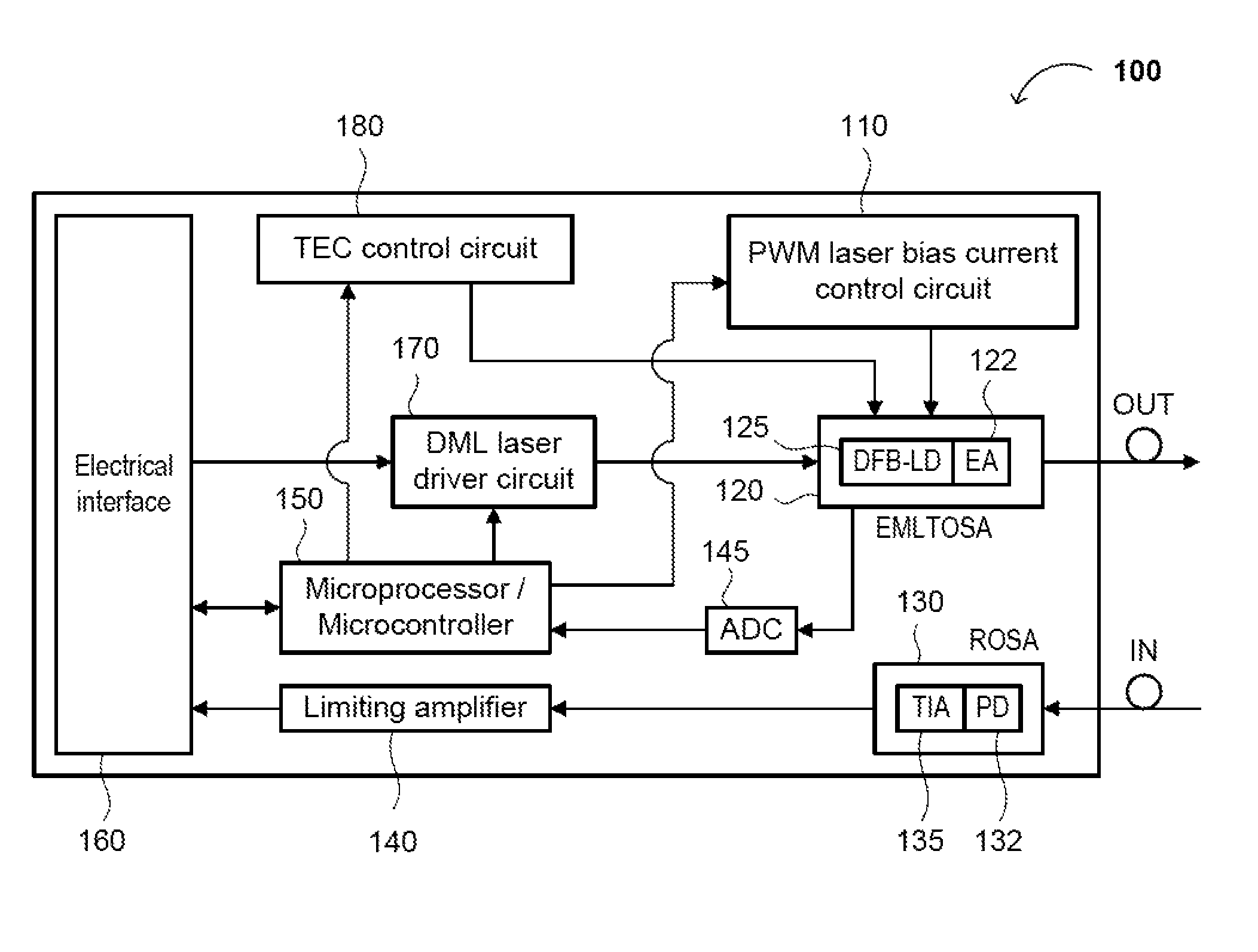
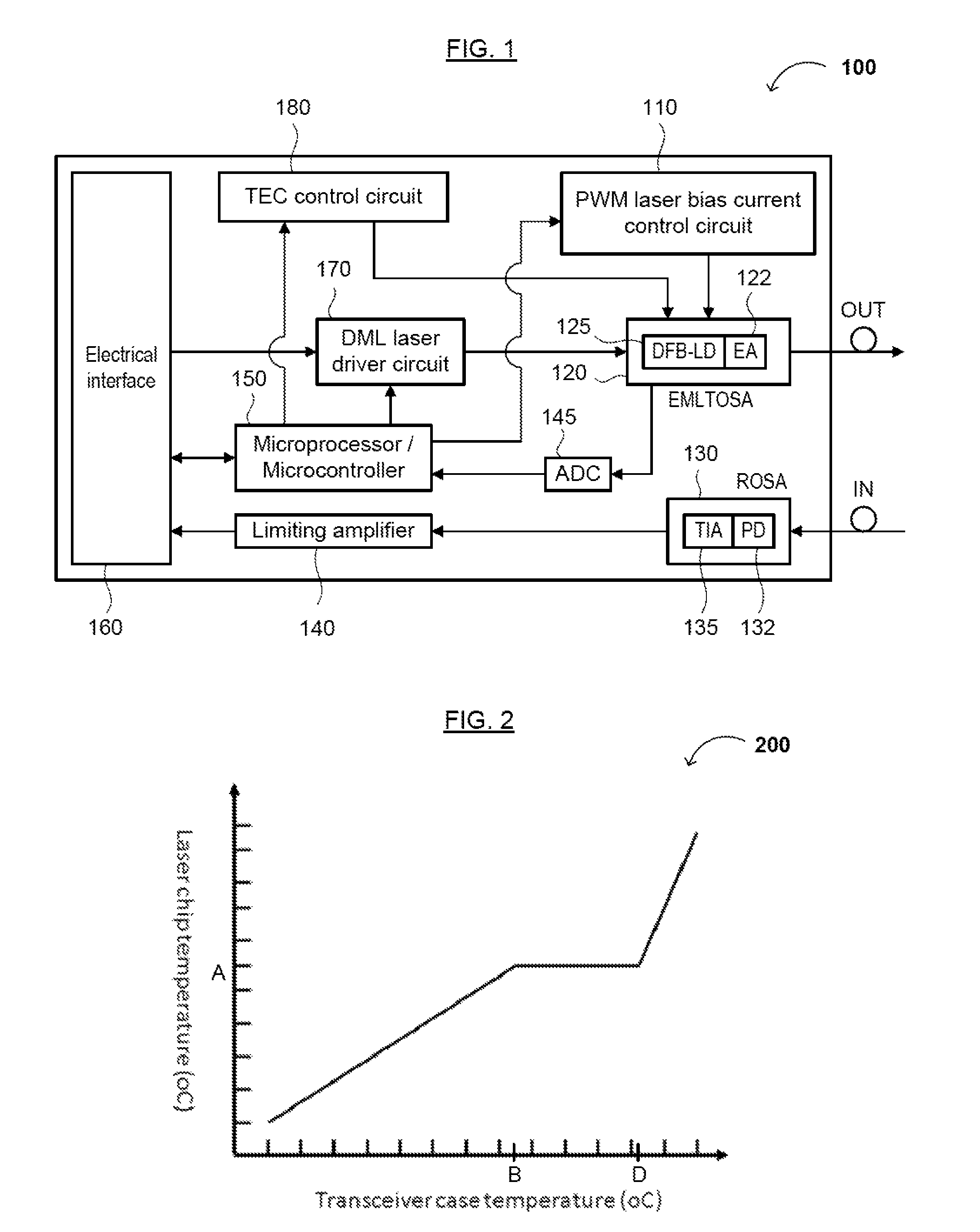
Low Power Consumption, Long Range, Pluggable Transceiver, Circuits and Devices Therefor, and Method(s) of Using the Same
ActiveUS20120301151A1Reduce power consumptionMaximize efficiencyElectromagnetic transmittersSolid cathode detailsTransceiverTransimpedance amplifier
The present disclosure relates to an optical transceiver for use in optical fiber communications and / or telecommunications systems and, more specifically, a low power consumption, long range pluggable transceiver. The transceiver generally comprises a photodiode with a transimpedance amplifier (PIN-TIA); an electro-absorption modulated laser (EML); an optical detector; and a directly modulated laser (DML) driving module connected between the PIN-TIA and EML laser configured to drive the EML laser. A low power-consumption DML driving module is utilized to drive the EML laser, so as to further reduce power consumption. An impedance matching circuit can be applied to modulate an electro-absorption (EA) modulator of the EML laser with maximum efficiency.
Owner:SOURCE PHOTONICS
Multi-pulse star signal simulator
InactiveCN101644580AMeet the data requirements of the simulationHigh precisionInstruments for comonautical navigationCelestial navigationData reliability
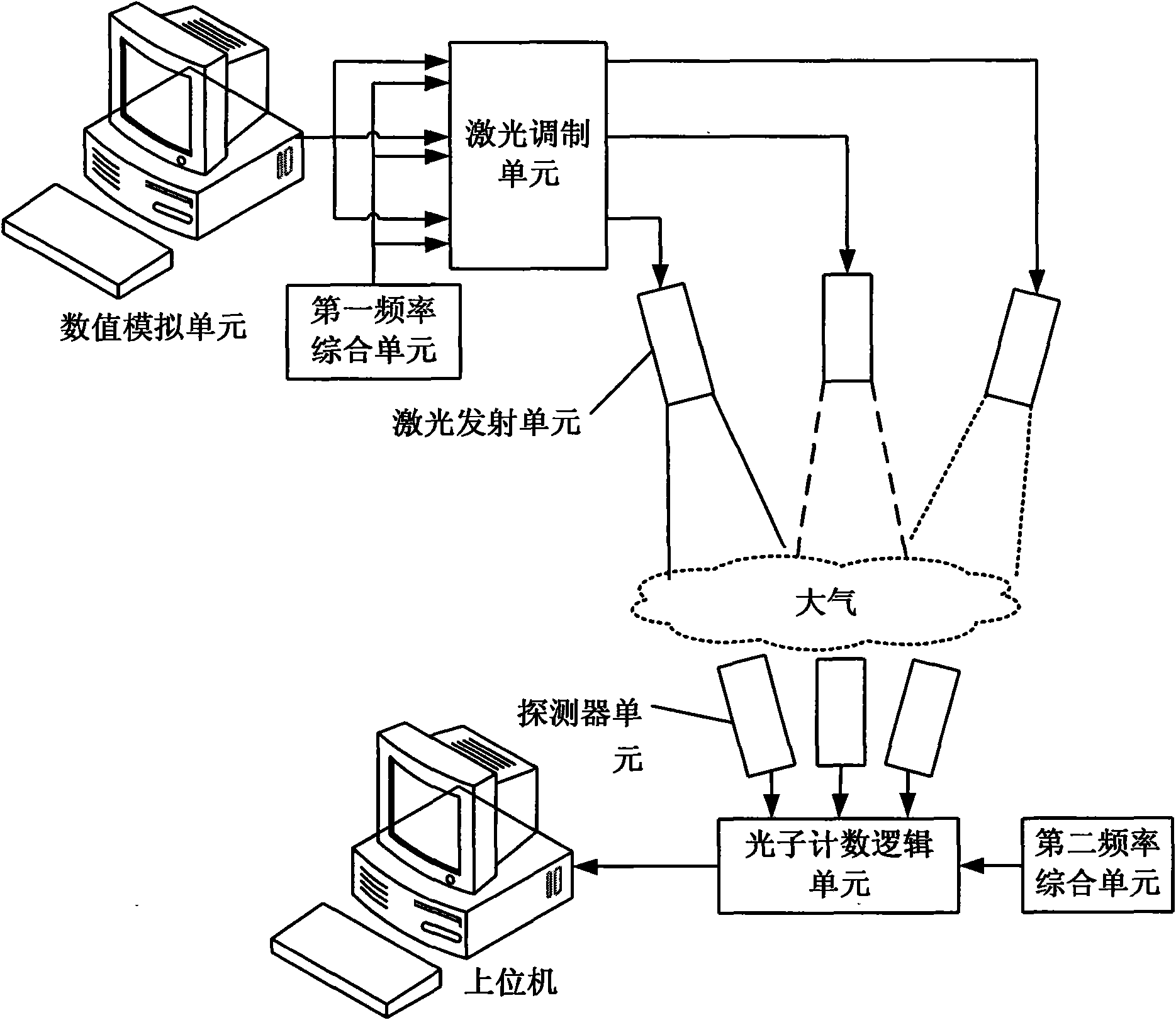
The invention discloses a multi-pulse star signal simulator comprising a numerical value simulation unit, a first frequency integration unit, a laser modulation unit, a laser emission unit, a detectorunit, a second frequency integration unit and a photon counting logical unit, wherein the numerical value simulation unit generates radiation signal data of a plurality of pulse stars by using a clock of the first frequency integration unit according to a signal numerical value model and sends the radiation signal data to the laser modulation unit; the laser modulation unit generates a current signal which can directly modulate a laser according to the clock of the first frequency integration unit; the laser emission unit converts the current signal of a laser modulator into a laser intensitysignal; the detector unit receives the laser signal, generates pulses and sends the pulses into the photon counting logical unit; and the photon counting logical unit counts the pulses according to aclock of the second frequency integration unit and sends a counting result to an upper computer. The invention has the advantages of high data reliability and coincidence of a signal generation and detection mechanism with the actual condition and is used for providing simulated data to the independent celestial navigation simulation of a spacecraft.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Optical transmitter
InactiveUS20070110453A1Low costSmall sizeWavelength-division multiplex systemsFibre transmissionWavelength filterPeak value
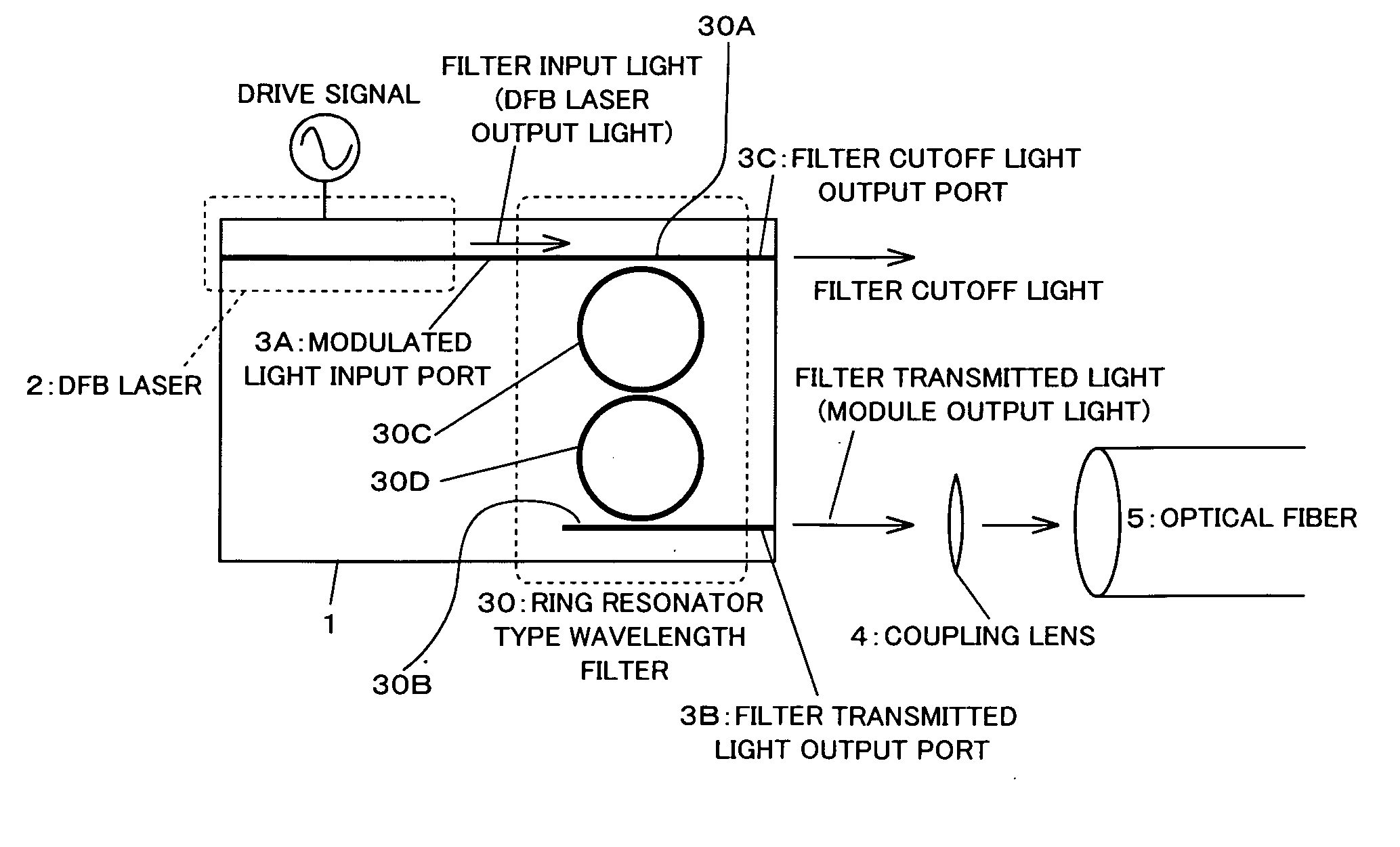
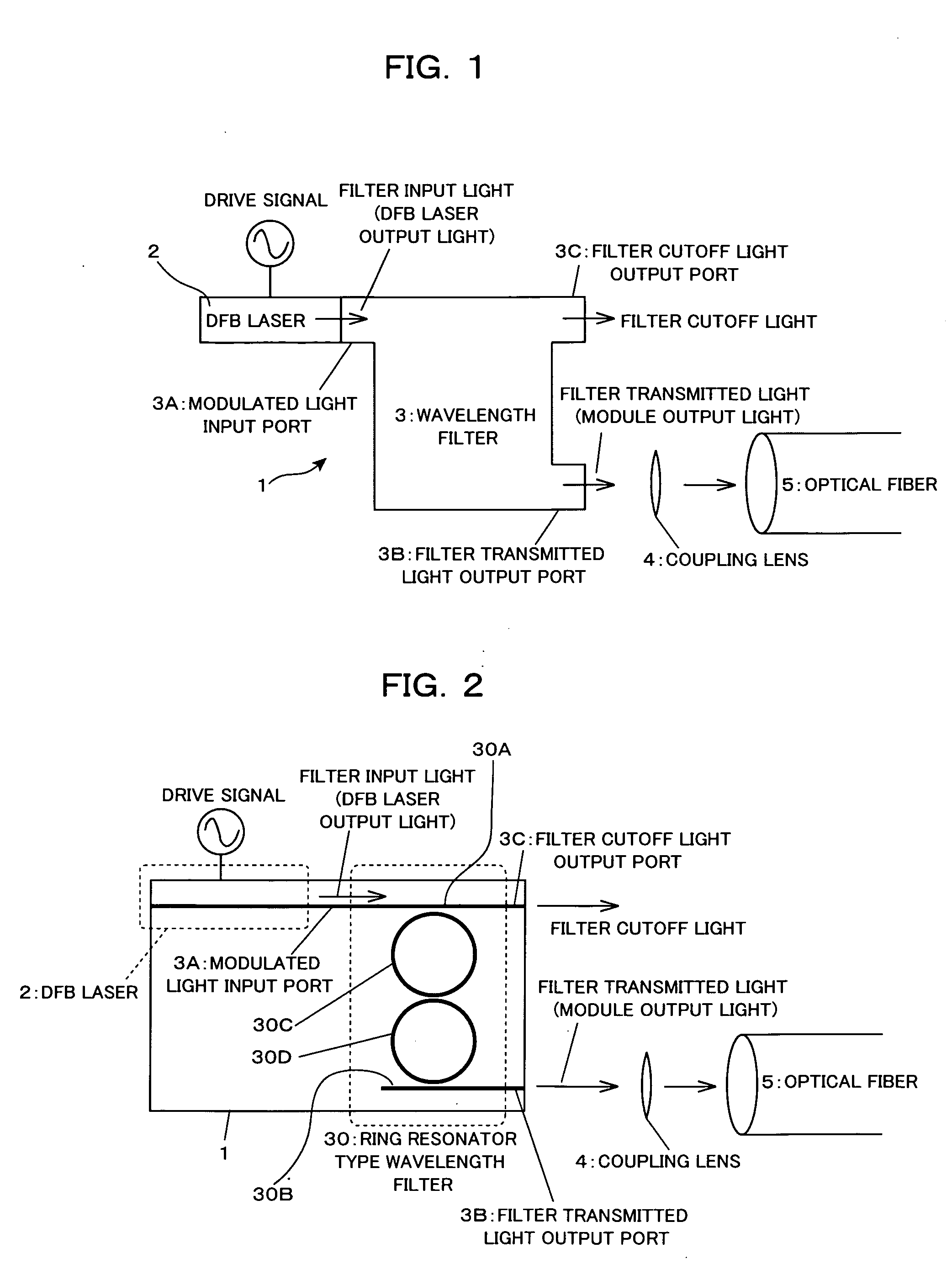
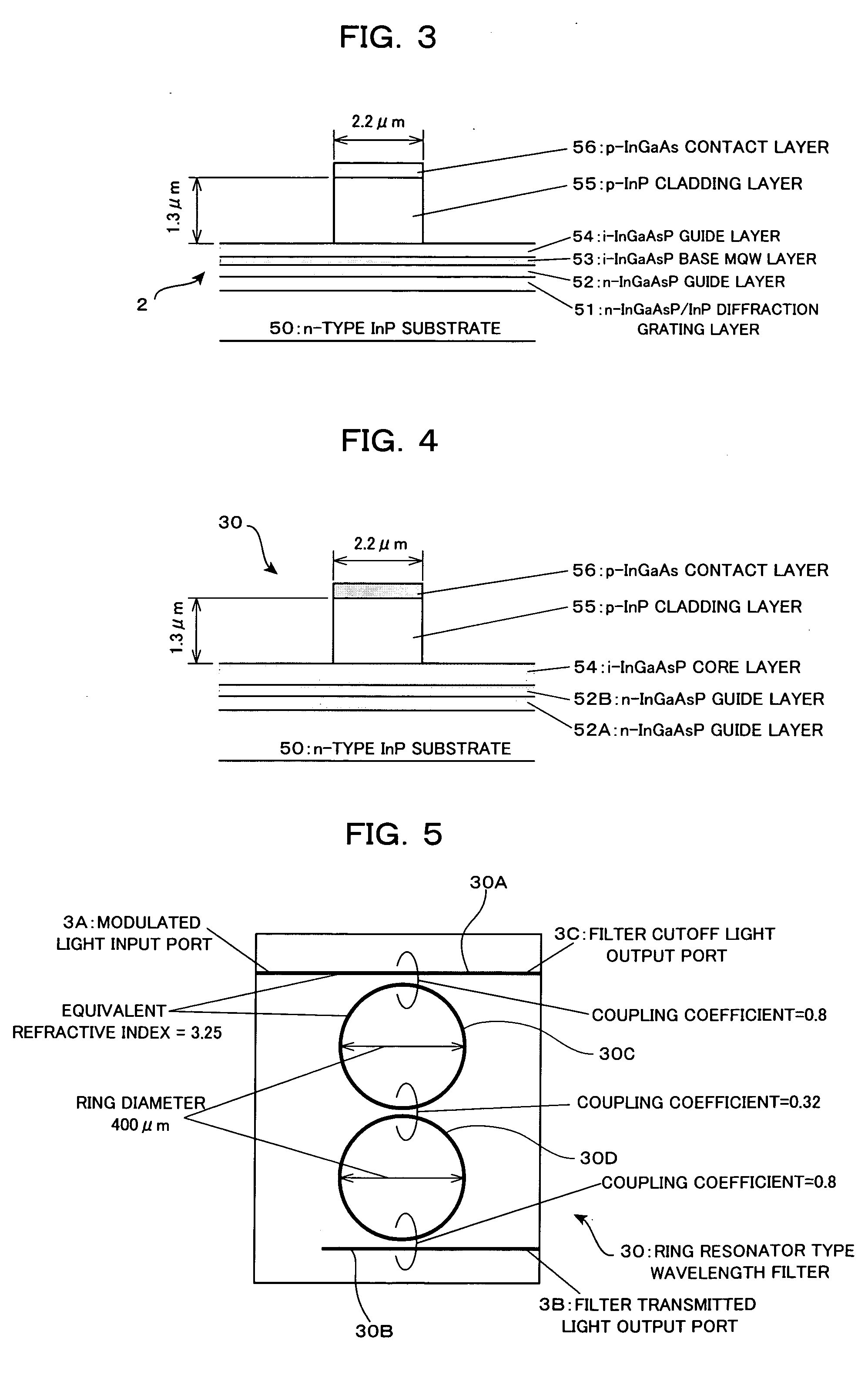
In an optical transmitter comprising a directly modulated laser and a wavelength filter provided on a post-stage of the directly modulated laser, the wavelength filter has a modulated light input port for inputting modulated light output from the directly modulated laser, a filter transmitted light output port for outputting light having a wavelength included in a filter transmission band among the modulated light as filter transmitted light, and a filter cutoff light output port provided separately from the modulated light input port and the filter transmitted light output port and outputting light having a wavelength included in a filter cutoff band among the modulated light as filter cutoff light, and the peak of the filter transmission band is set on a shorter-wave side from the peak of the spectrum of modulated light output from the directly modulated laser.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
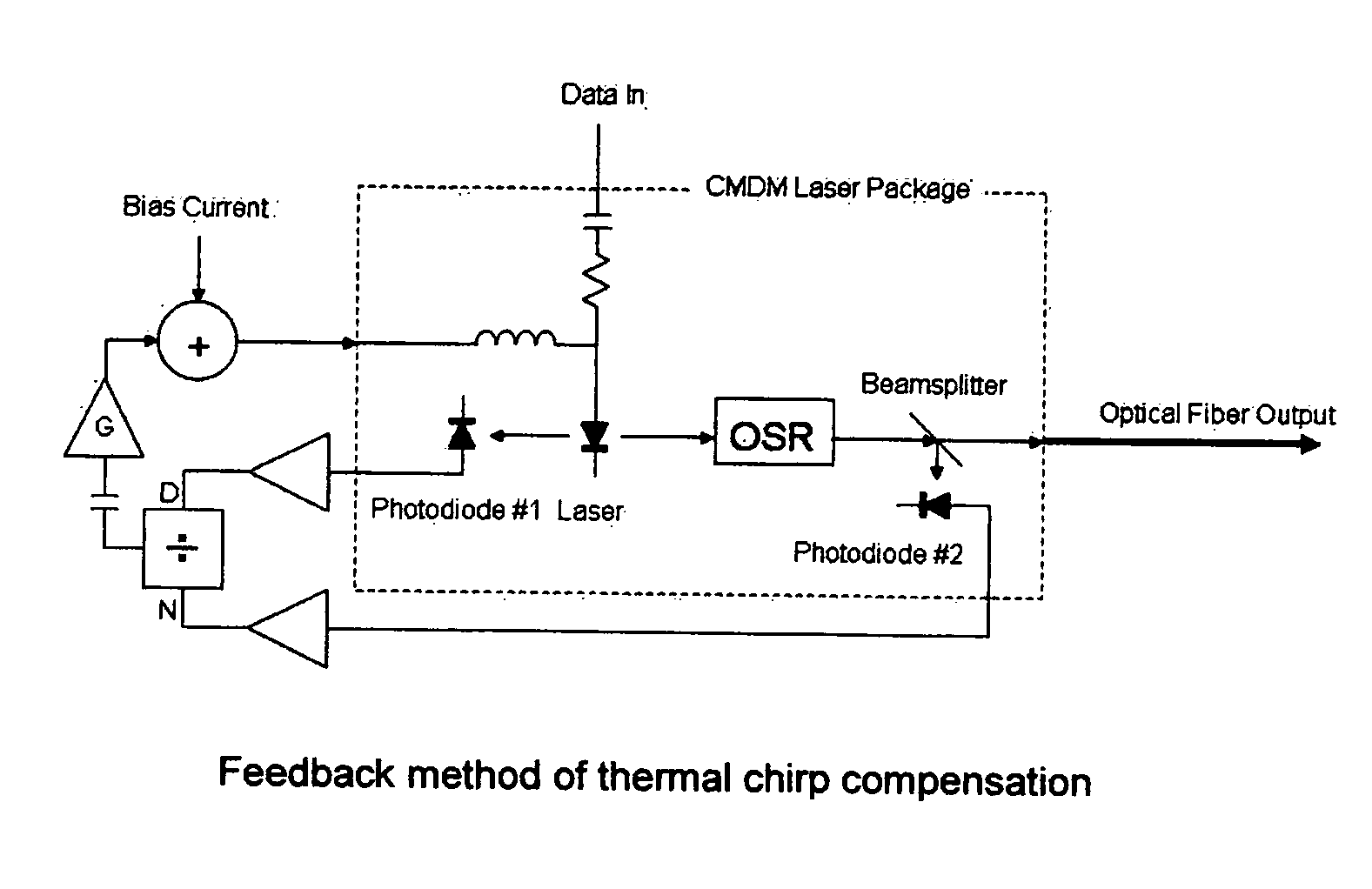
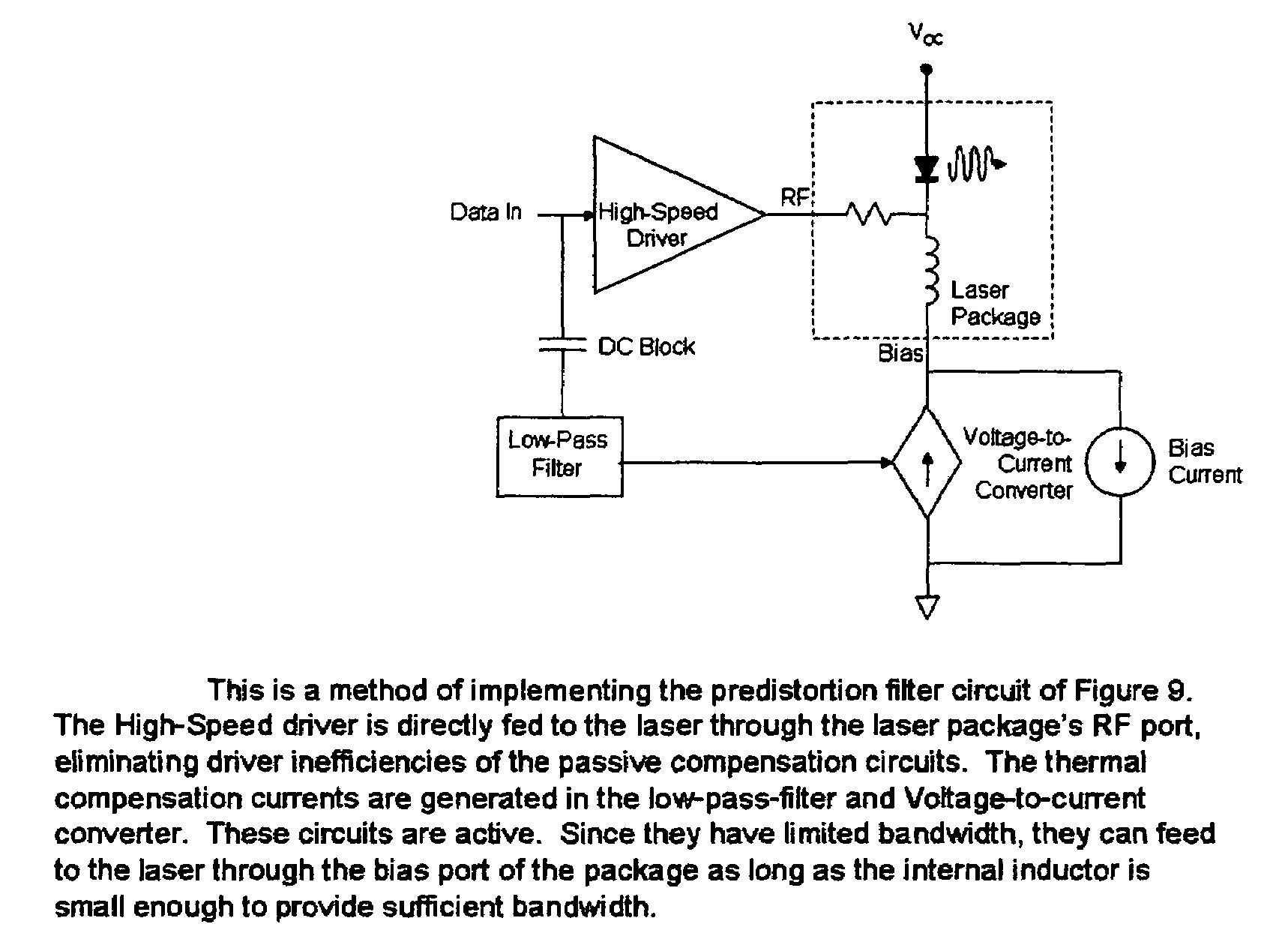
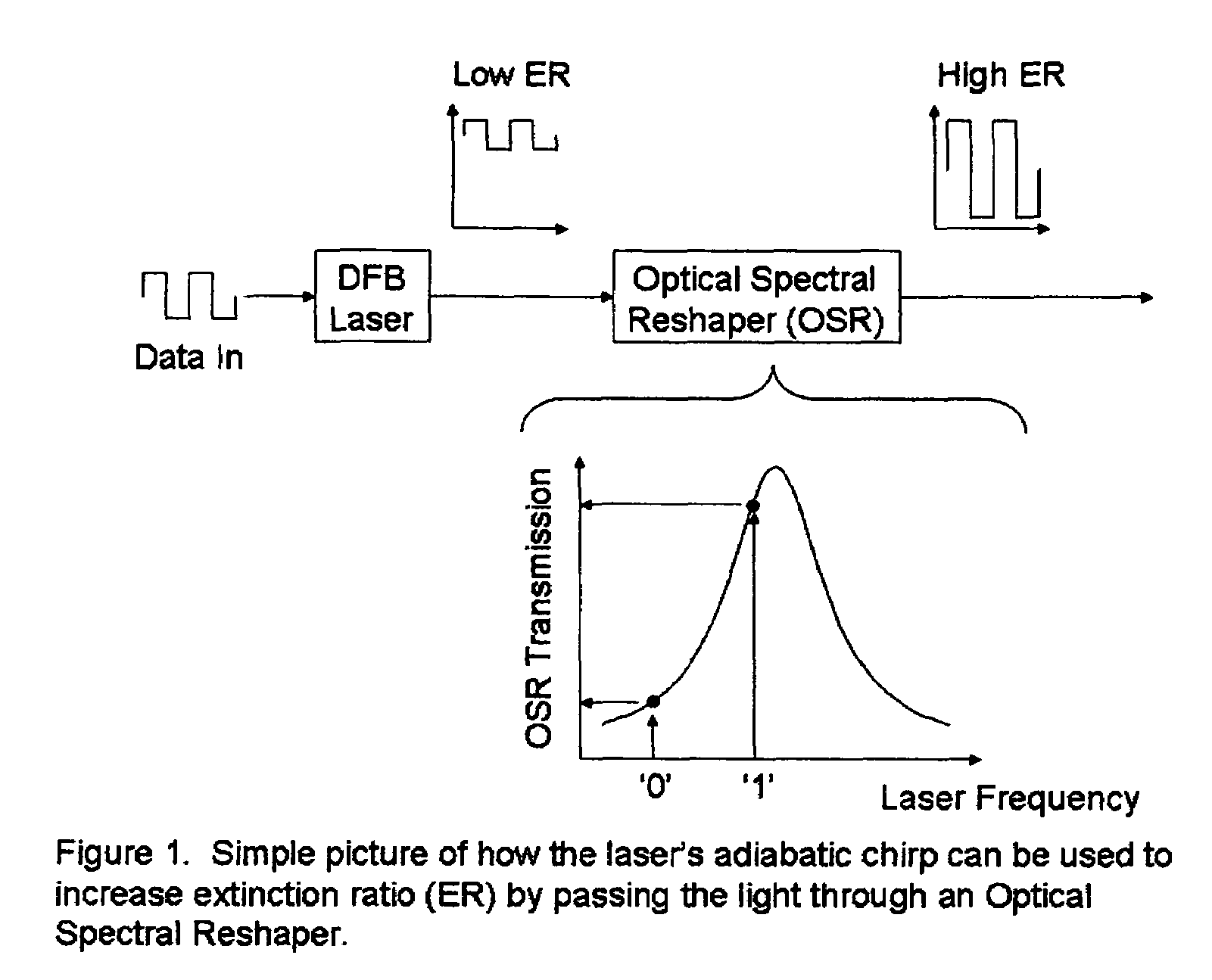
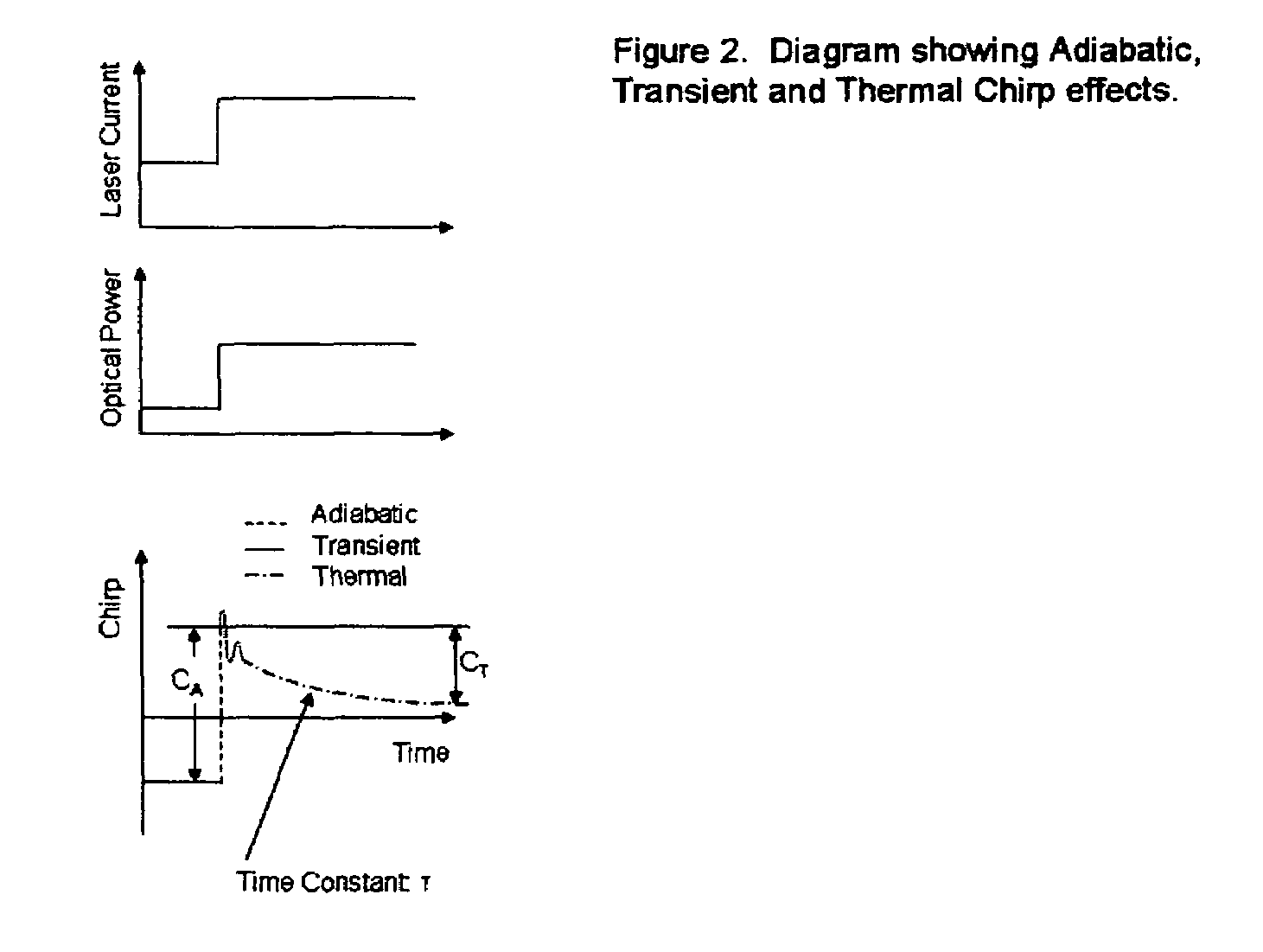
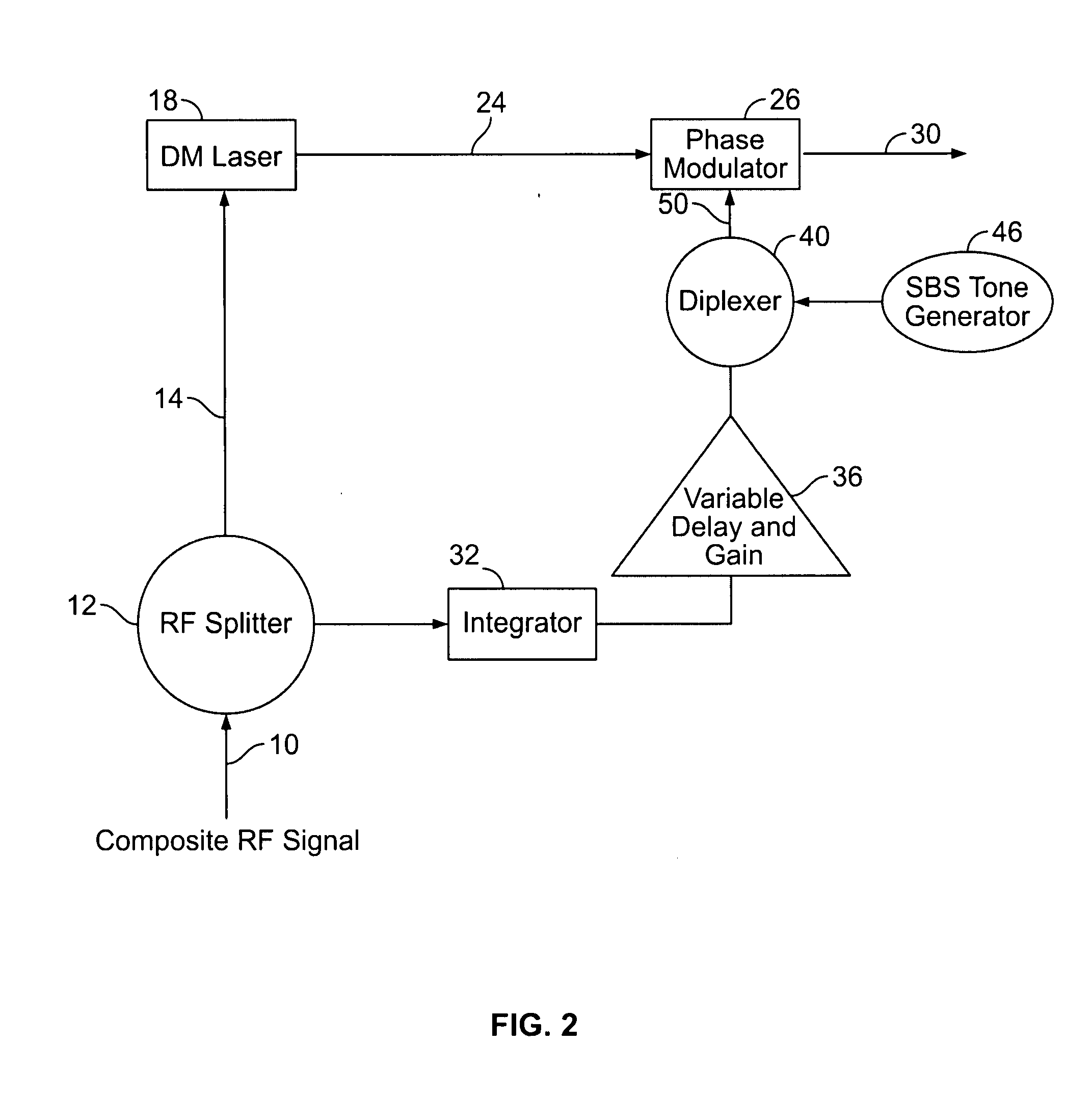
Thermal chirp compensation systems for a chirp managed directly modulated laser (CML(TM)) data Link
ActiveUS20060078338A1Reduce the impactReduce the amplitudeElectromagnetic transmittersSemiconductor lasersDigital dataFrequency modulation
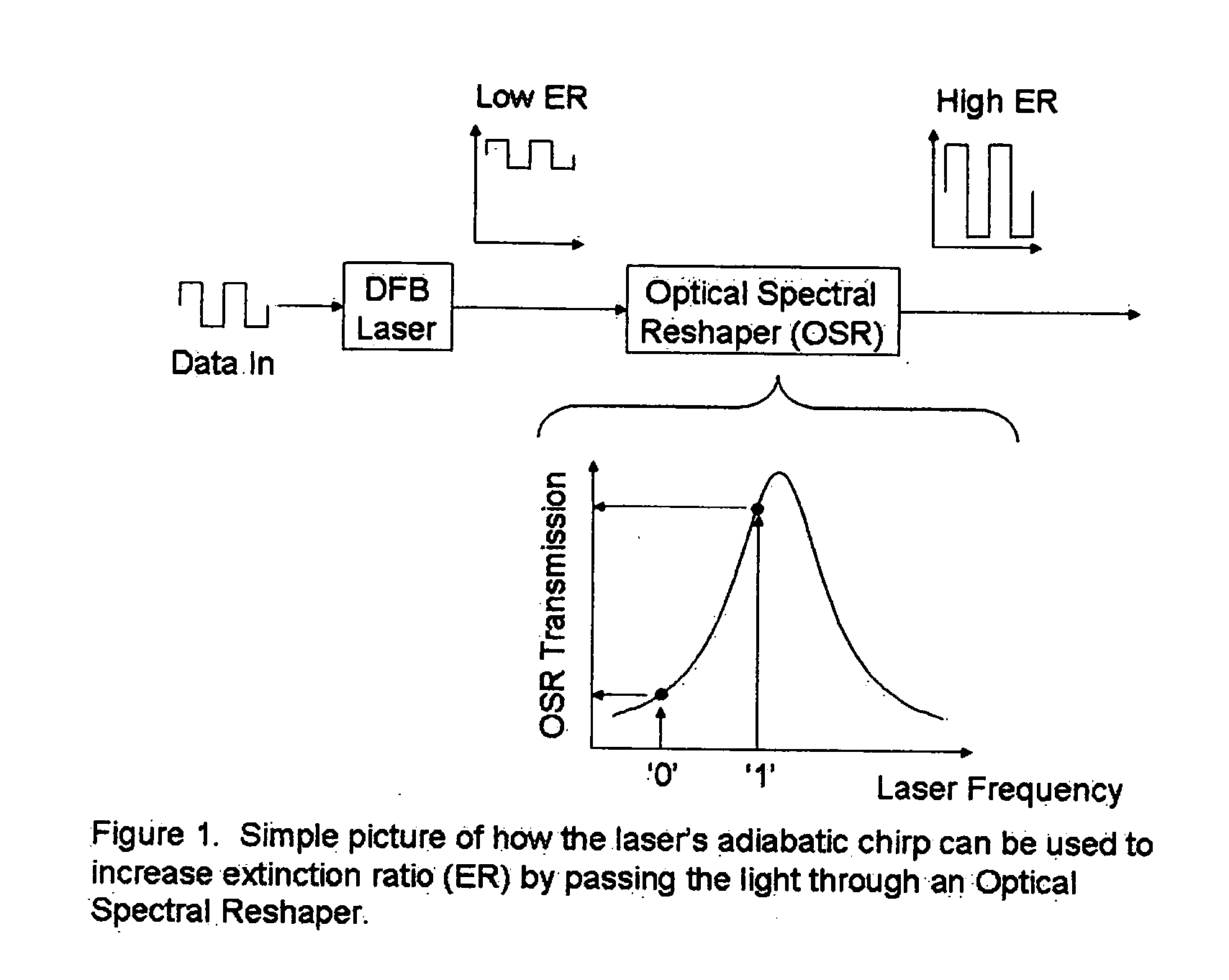
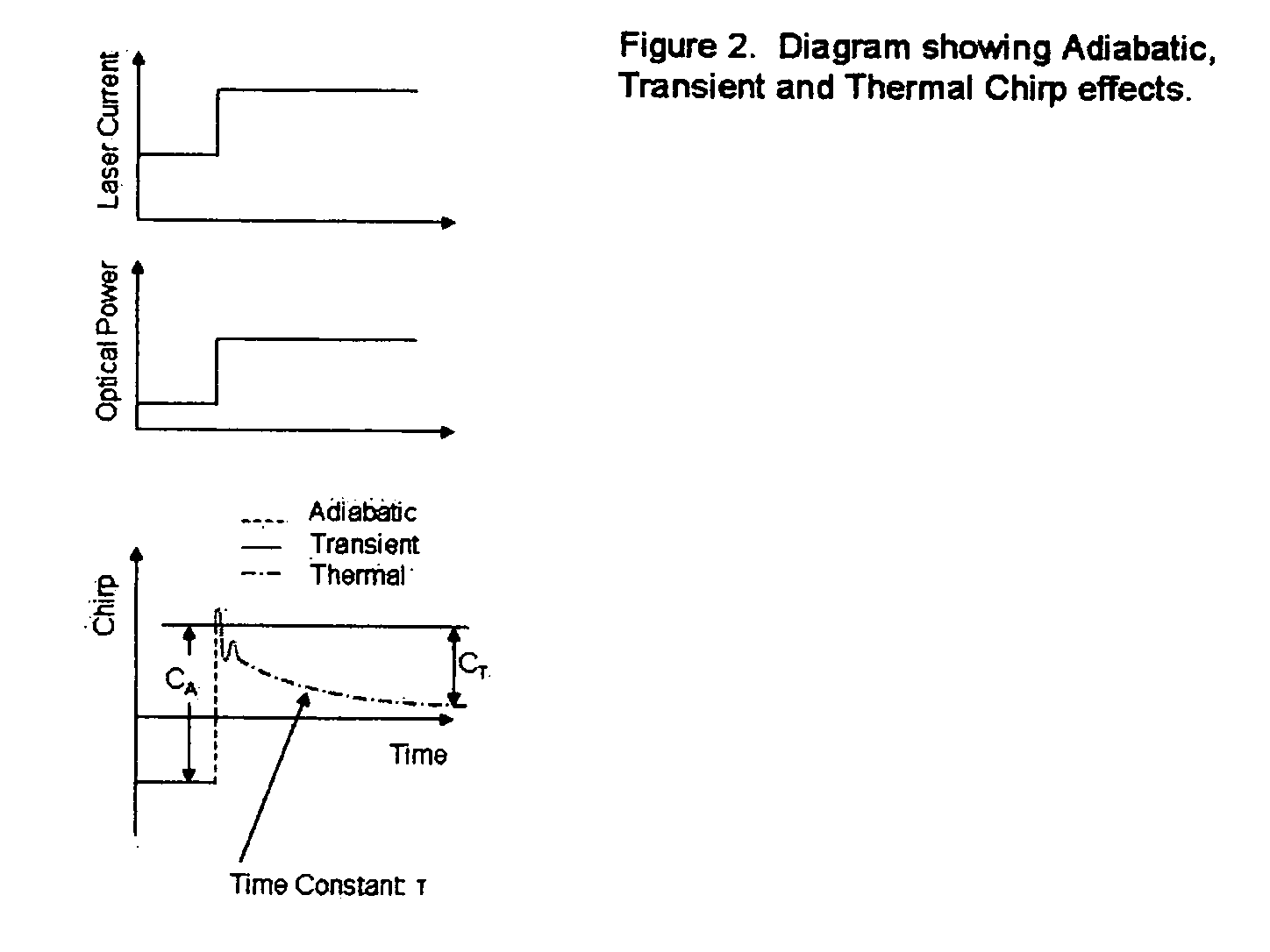
A fiber optic communication system for receiving an electronic digital data signal and transmitting the same, comprising an optical signal source adapted to receive the digital data signal and to produce a frequency modulated optical signal from a directly modulated semiconductor laser; an optical spectrum reshaper adapted to convert the frequency modulated optical signal into an amplitude modulated optical signal; and compensation apparatus for compensating for the adverse effects of the thermal chirp normally induced in the frequency modulated optical signal by modulating the semiconductor laser with the electronic digital data signal.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Sideband filtering of directly modulated lasers with feedback loops in optical networks
InactiveUS20060177225A1Minimizing chirpMonitor qualityWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTemperature controlPeak value
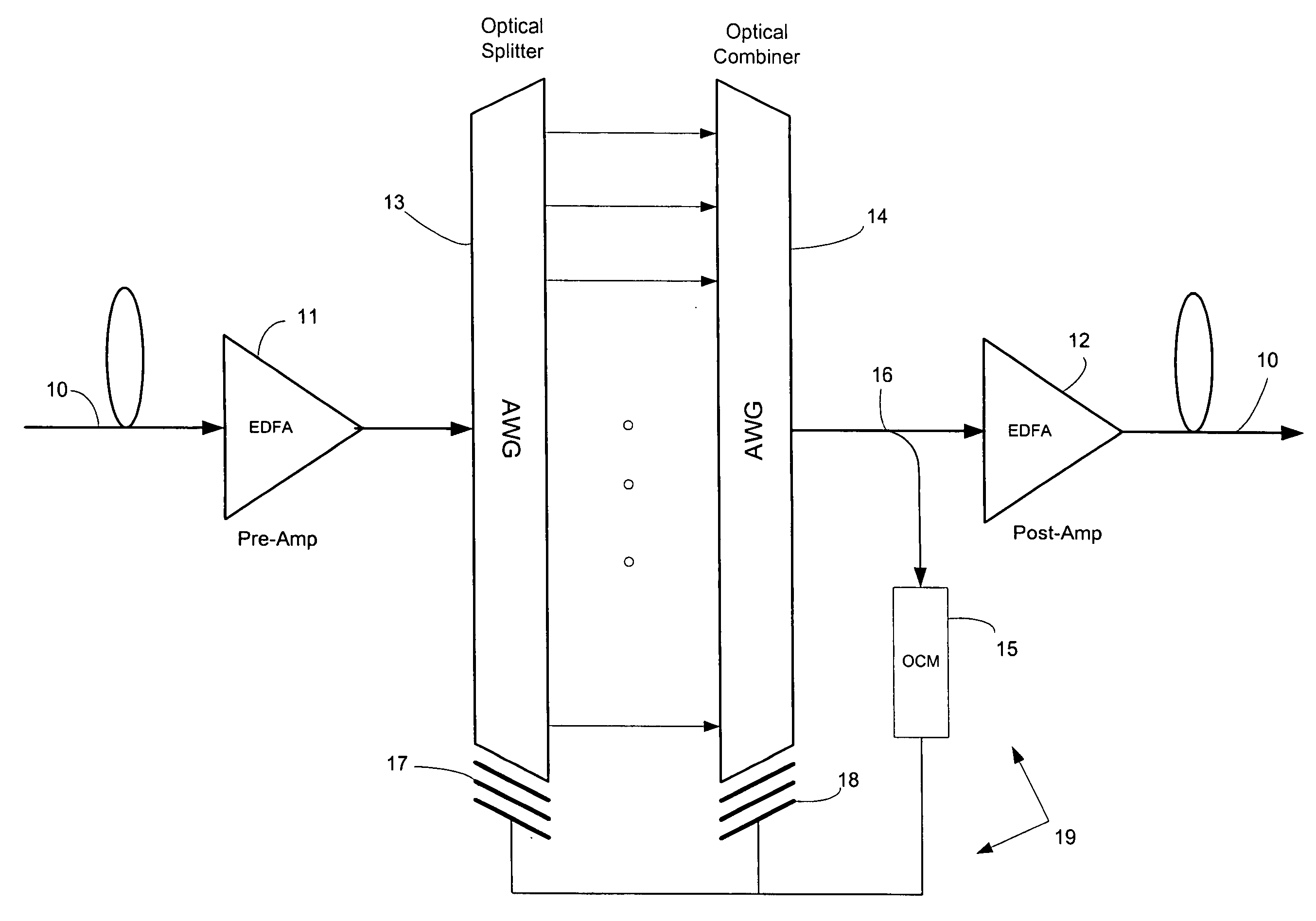
In a WDM optical network DML signals are sideband filtered to compensate for chirp with a feedback loop carrying signals from a monitor unit which helps maintain the sideband filter offset from a peak output of the DMLs. Network components with filtering characteristics, such as AWGs, can be used as the sideband filters. The monitor units monitor the Q-factors or BERs of the filtered signals and the sideband offset is maintained by temperature control of the sideband filters with respect to the DMLs.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Thermal chirp compensation systems for a chirp managed directly modulated laser (CML(TM)) data link
ActiveUS7505694B2Reduce the amplitudeLower Level RequirementsElectromagnetic transmittersSemiconductor lasersDigital dataData signal
A fiber optic communication system for receiving an electronic digital data signal and transmitting the same, comprising an optical signal source adapted to receive the digital data signal and to produce a frequency modulated optical signal from a directly modulated semiconductor laser; an optical spectrum reshaper adapted to convert the frequency modulated optical signal into an amplitude modulated optical signal; and compensation apparatus for compensating for the adverse effects of the thermal chirp normally induced in the frequency modulated optical signal by modulating the semiconductor laser with the electronic digital data signal.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Production method of optical microwave signal with tunable broadband frequency
InactiveCN102545042AEnables tunabilityLow microwave frequencyLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsInjection lockedContinuous light
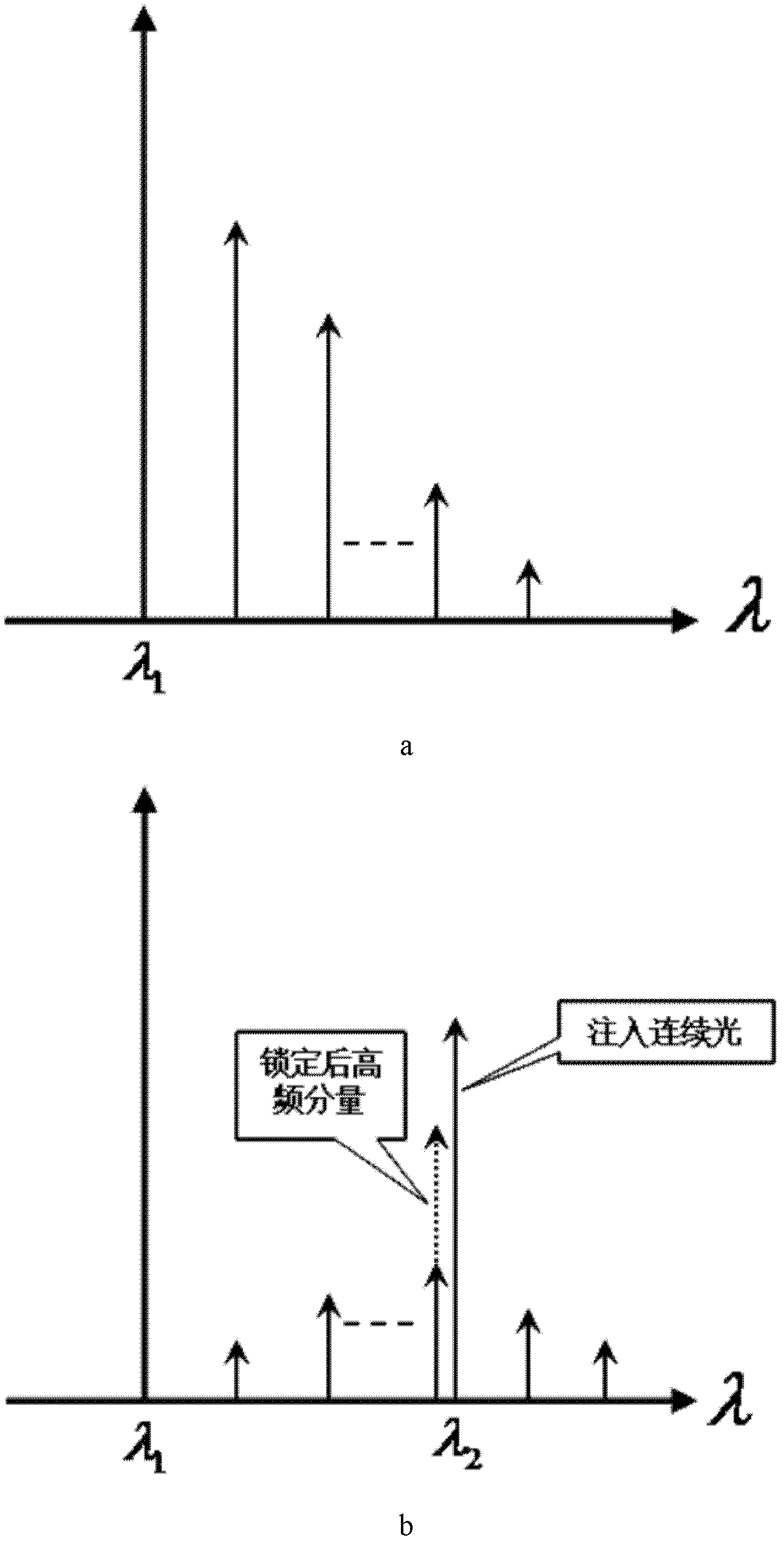
The invention discloses a production method of an optical microwave signal with tunable broadband frequency. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a stable dual-loop low-frequency optoelectronic oscillator; injecting an external continuous lights into the optoelectronic oscillator, implementing the injection locking in a directly modulated laser of a core component of the optoelectronic oscillator to finish the up-conversion process of the optical microwave so as to generate a high-frequency optical microwave signal; implementing the tunability of the optoelectronic oscillator by adjusting the wavelength, optical power and polarization state of the external continuous lights so as to generate the optical microwave signal with needed frequency. By injecting the external continuous lights into the directly modulated laser in the optoelectronic oscillator and then locking an optical carrier wave after the up-conversion is generated under a high-order mode, the high-quality optical microwave signal is produced. The method provided by the invention can be used for producing any high-frequency optical microwave signal based on an injection locking technology by using the lower-frequency electric signal, and the tunability of the microwave frequency can be realized by only controlling the wavelength, polarization state and optical power of the injected continuous lights.
Owner:SHANXI DATONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for low chirp transmitter for optical fiber communications
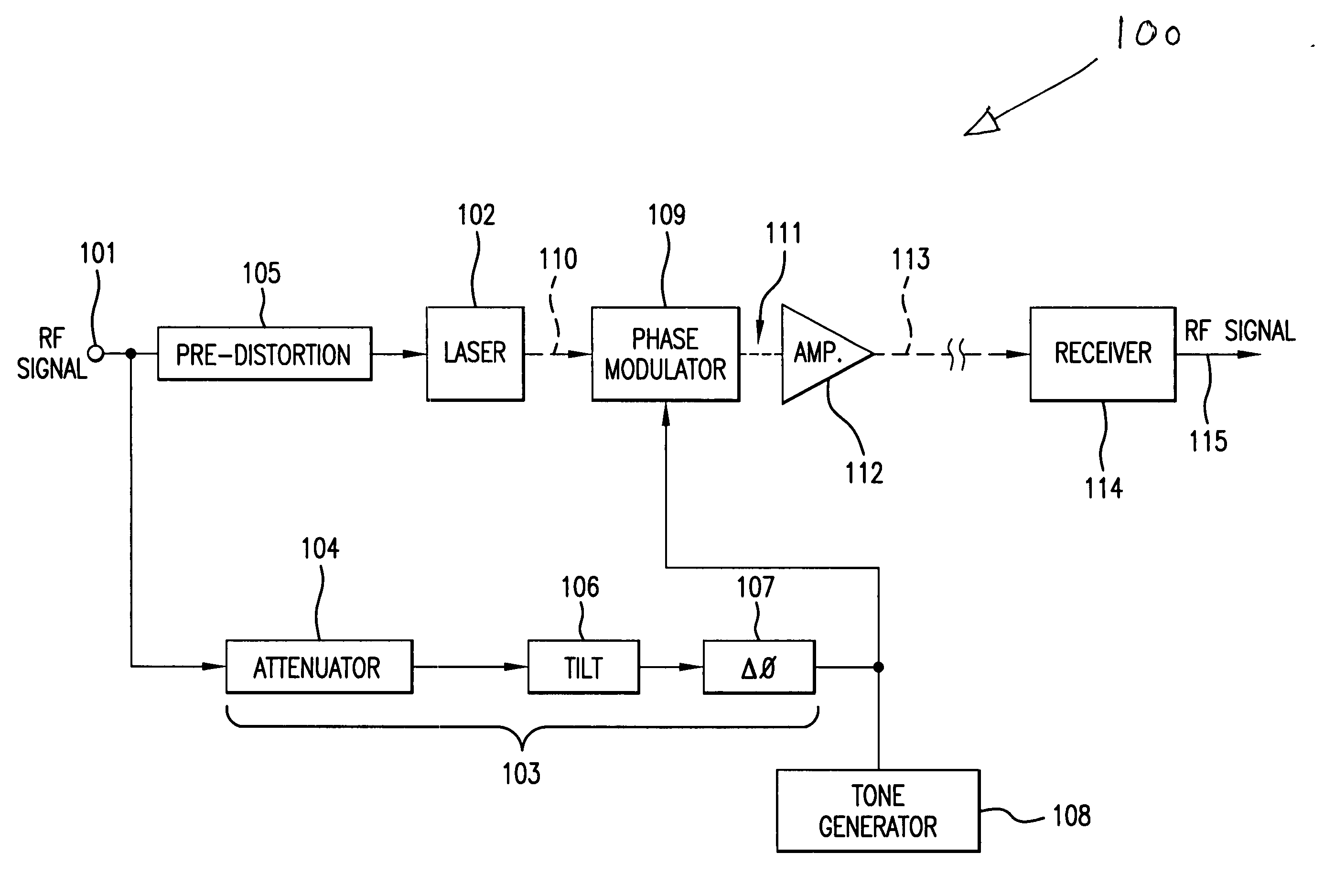
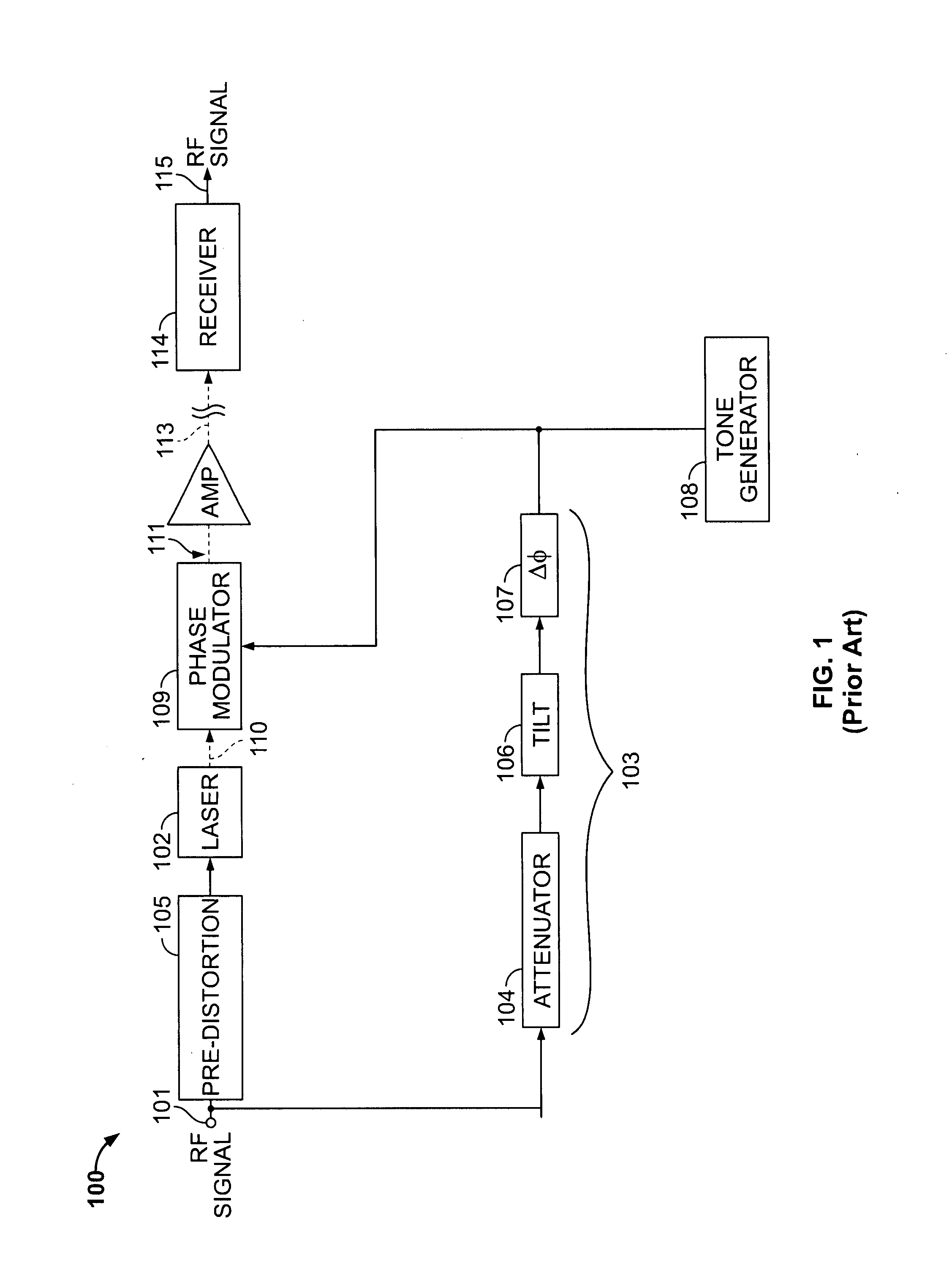
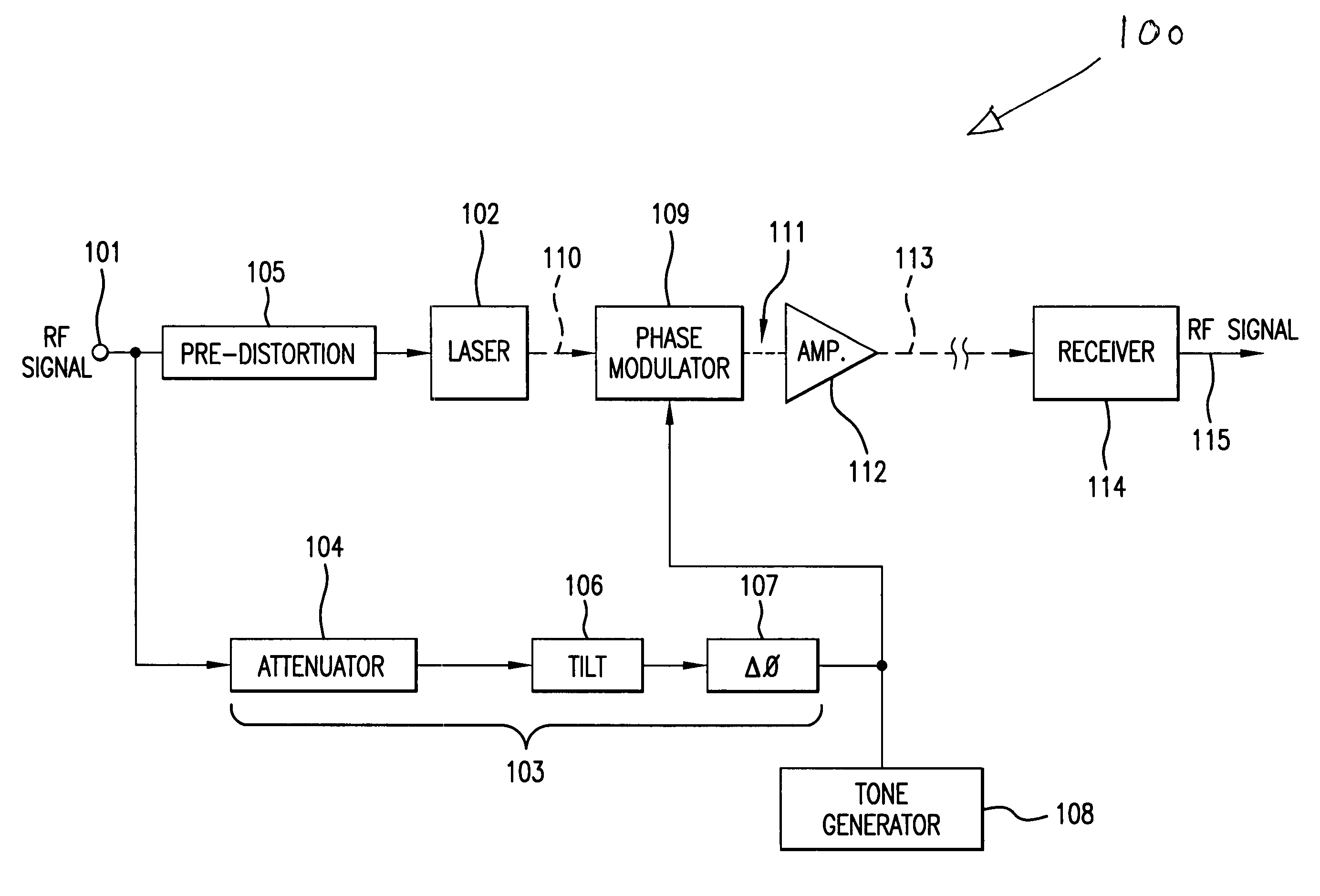
A directly modulated optical transmitter for use with a fiber optical communications system operating in the 1550 nm wavelength band exhibits very low chirp. The chirp inherently present in a directly modulated laser is cancelled by a phase modulator which optically modulates the directly modulated laser light beam by applying a 180° phase delay to a split-off portion of the input radio frequency signal. This provides a low cost transmitter capable of operating in the 1550 nm band and with laser chirp effectively cancelled or substantially reduced, thereby avoiding distortions due to laser chirp interactions with the downstream optical fiber.
Owner:ATX NETWORKS (TORONTO) CORP
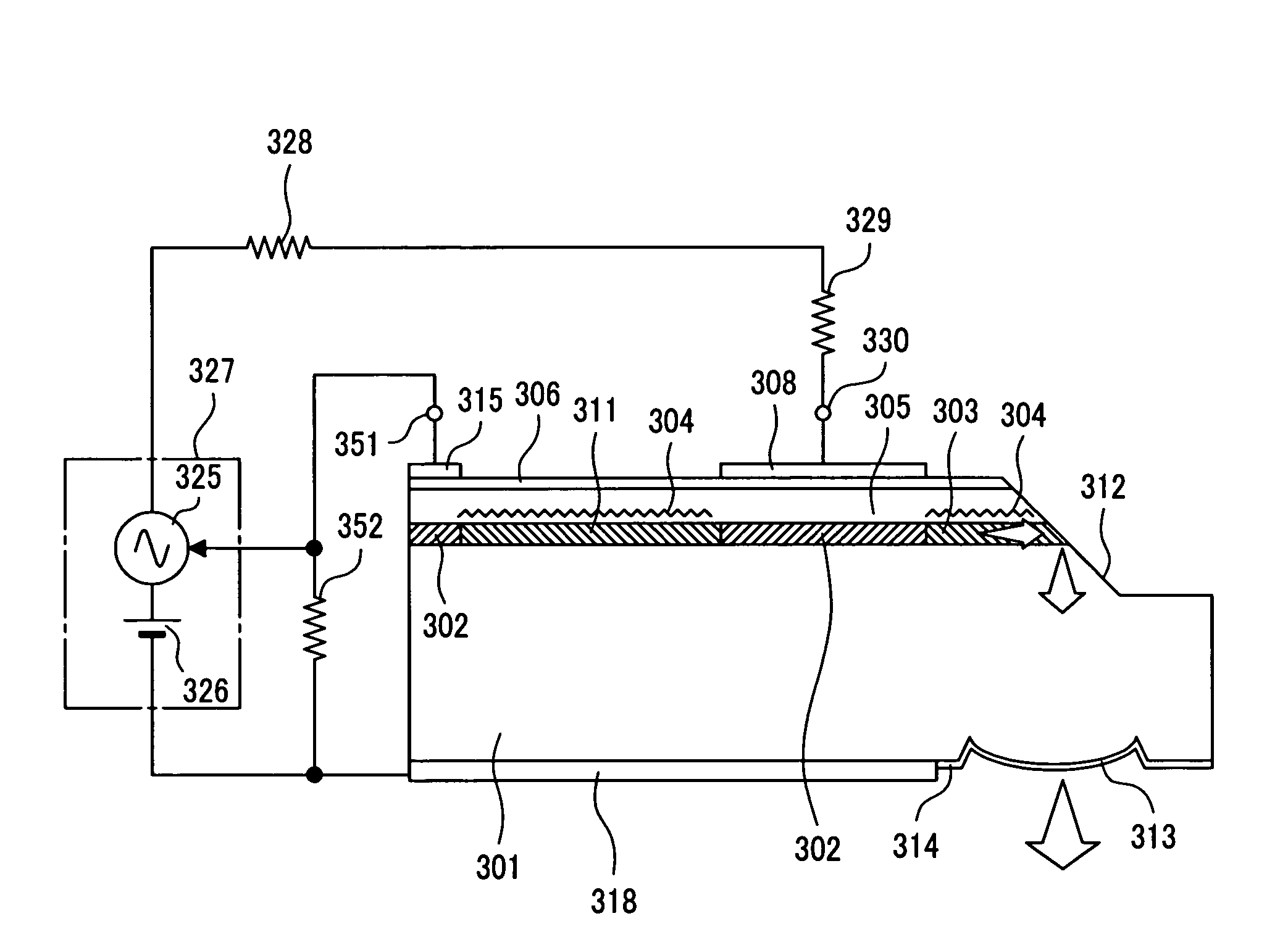
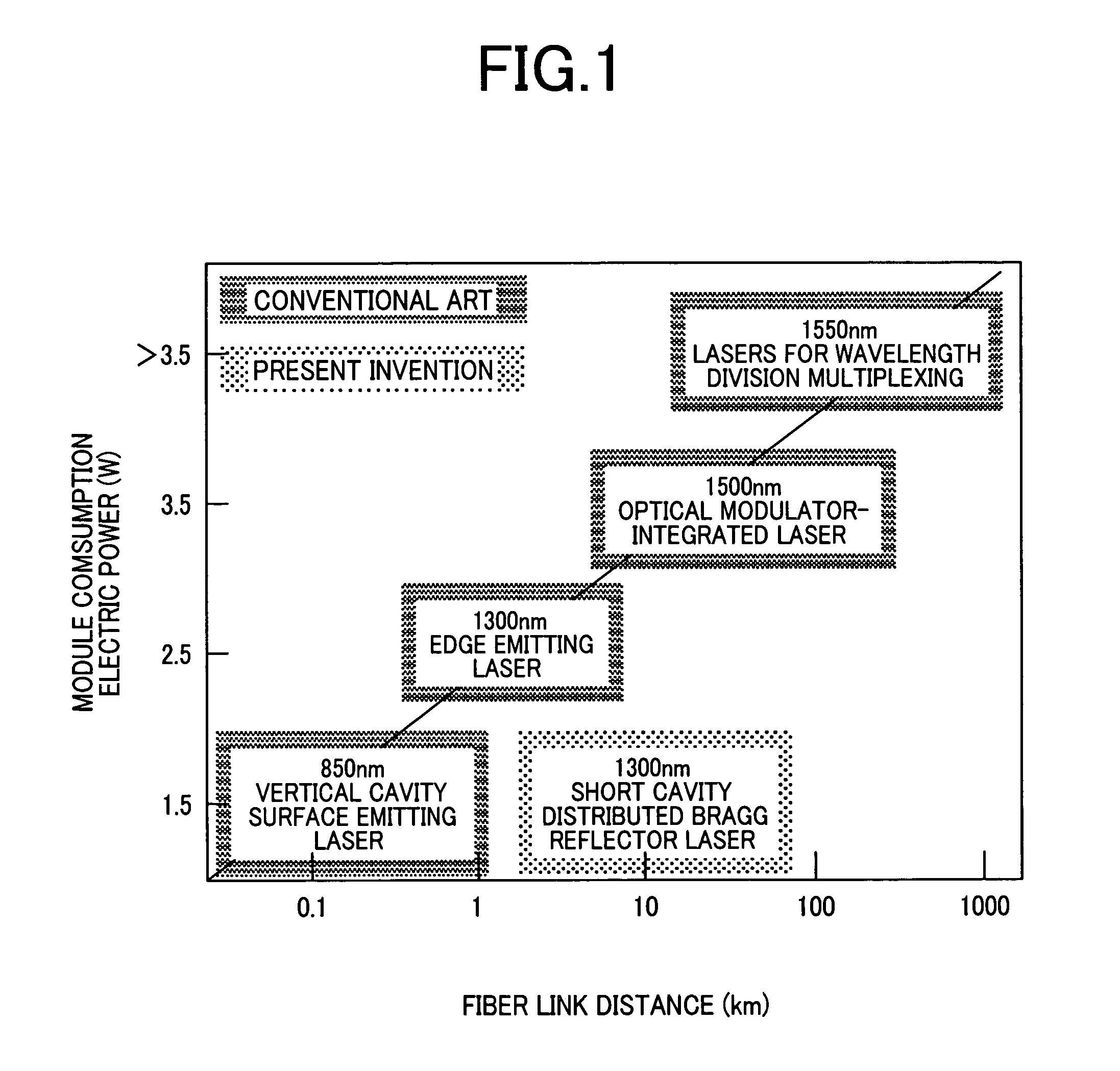
Optical semiconductor device and optical module using thereof
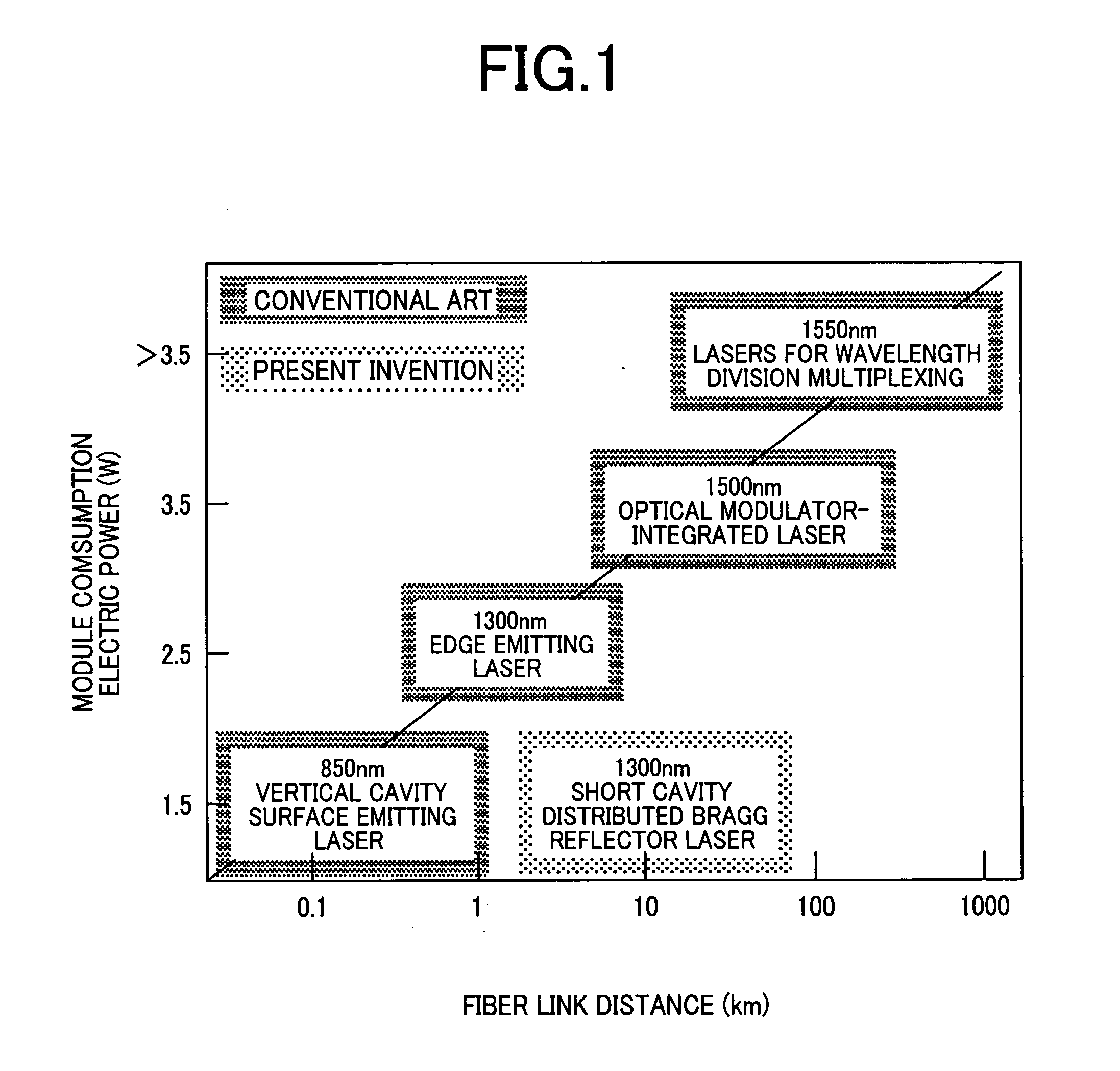
ActiveUS20060291516A1Economic efficiency is excellentLess power consumptionOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersOptical ModuleDistributed Bragg reflector laser
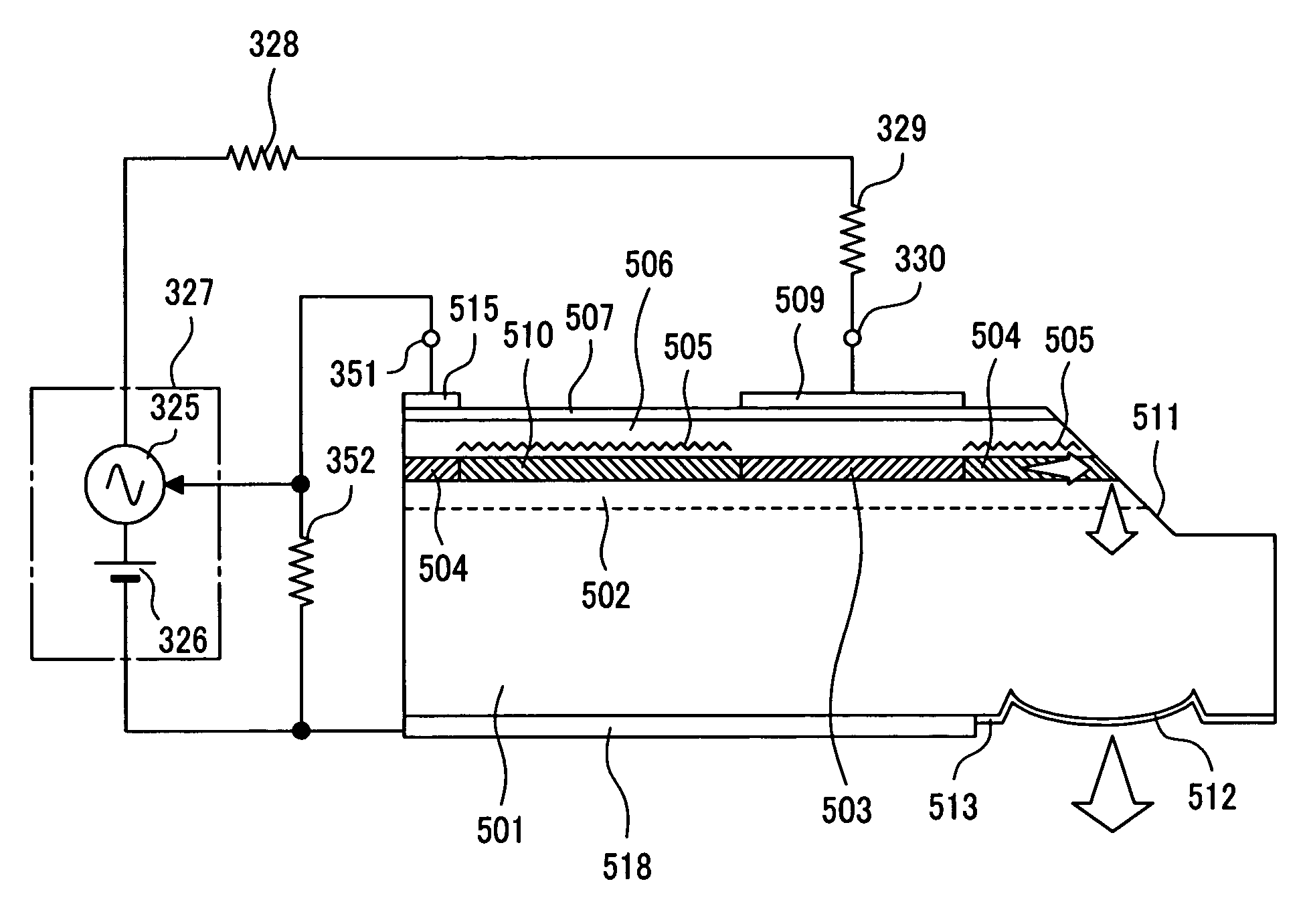
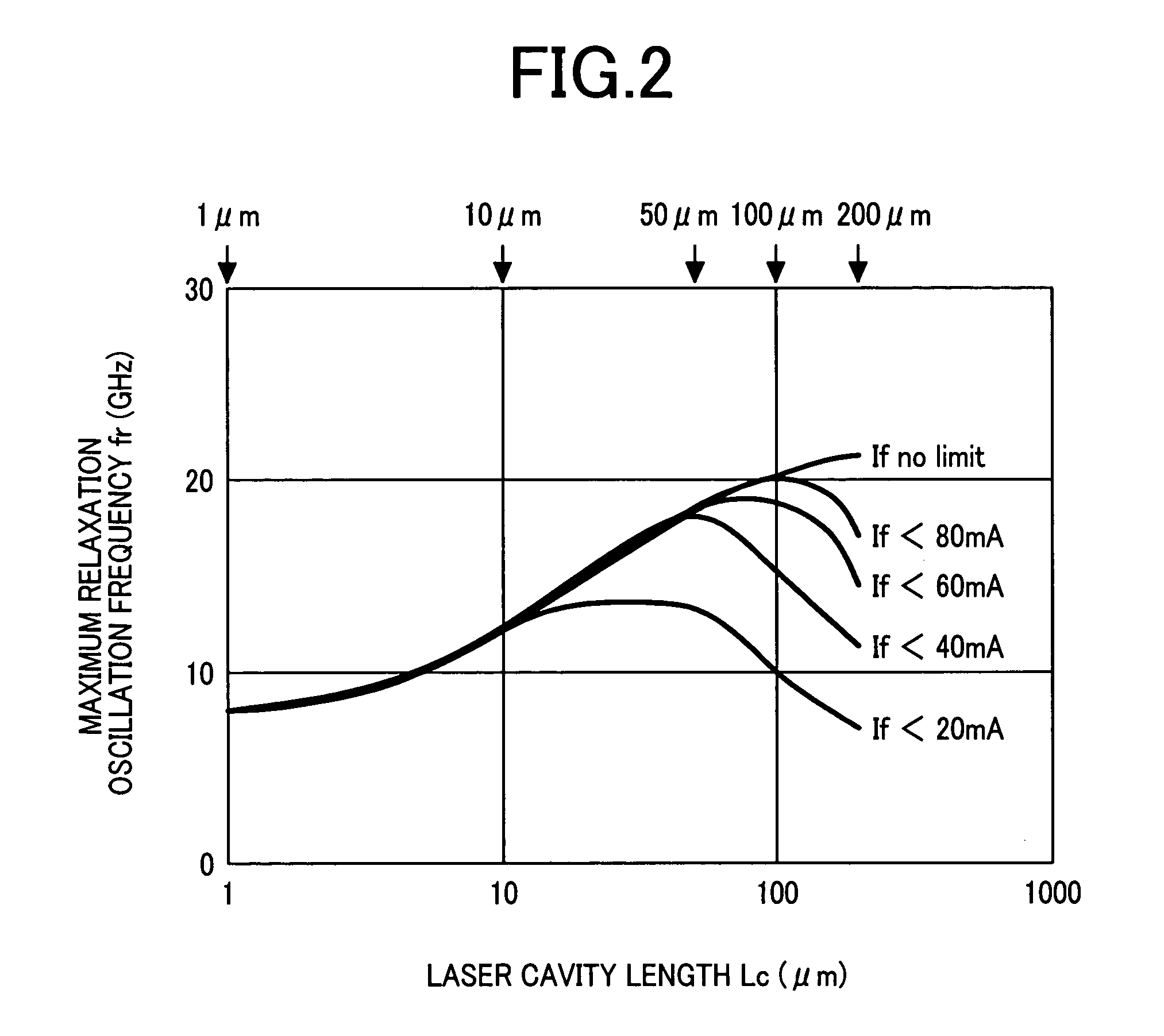
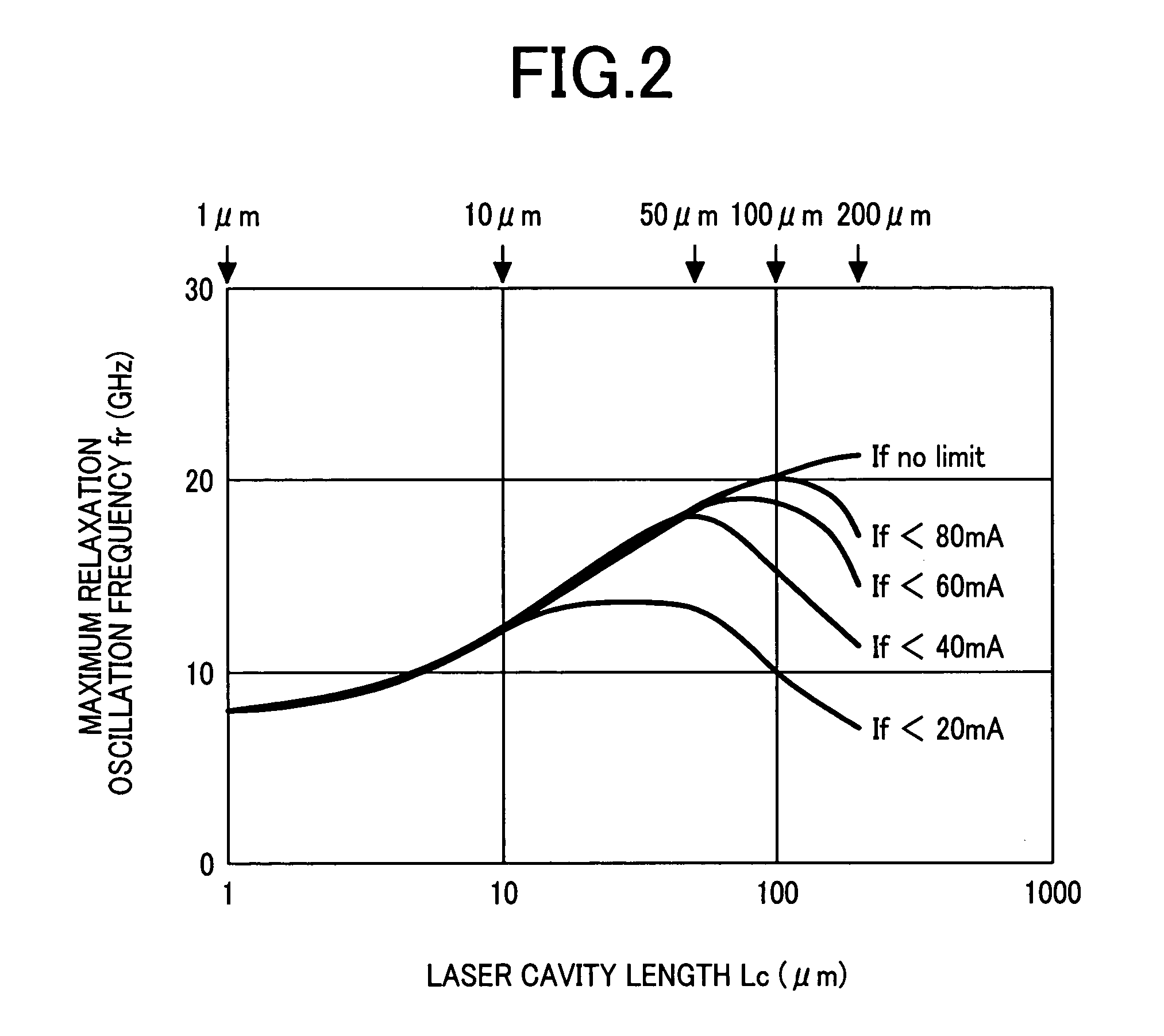
The invention aims at realizing a 1300-nm-band direct modulation laser, having a single lateral mode, in which a chip light power of several milliwatts and a low current operation are simultaneously realized. Also, the invention aims at realizing a laser light source excellent in economy as well by realizing output characteristics of a vertical cavity surface light emitting laser. A distributed Bragg reflector laser is constructed in the form of a semiconductor laser having a multilayer structure formed on a predetermined semiconductor substrate. The multilayer structure includes an active region for emitting a laser beam, and a distributed Bragg reflector layer. A length of the active region falls within the range of 10 to 100 μm, and a laser light beam is generated in accordance with ON / OFF of current injection to the active region.
Owner:LUMENTUM JAPAN INC
Power source for a dispersion compensation fiber optic system
InactiveUS20050152702A1Minimize signalingIncrease bitrateCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency modulationDispersion compensation
This invention generally relates to an optical filter for a fiber optic communication system. An optical filter may be used, following a directly modulated laser source, and converts a partially frequency modulated signal into a substantially amplitude modulated signal. The optical filter may compensate for the dispersion in the fiber optic transmission medium and may also lock the wavelength of the laser source.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Power source for a dispersion compensation fiber optic system
InactiveUS20080247765A1Minimize signalingIncrease bitrateCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency modulationDispersion compensation
This invention generally relates to an optical filter for a fiber optic communication system. An optical filter may be used, following a directly modulated laser source, and converts a partially frequency modulated signal into a substantially amplitude modulated signal. The optical filter may compensate for the dispersion in the fiber optic transmission medium and may also lock the wavelength of the laser source.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Optical laser control for optical communications systems
ActiveUS7805082B1Increase data rateElectromagnetic transmittersFiber chromatic dispersionTelecommunications link
An optical communications system comprises a transmitter, a receiver and an optical communications link between the transmitter and receiver. The transmitter comprises a current-driven directly modulated laser for providing a modulated optical signal and a current controller for controlling the current waveform applied to the laser. The current waveform applied to the laser is determined to compensate for the effects of the laser non-linearities and the fiber chromatic dispersion. This system applies pre-compensation to the directly modulated laser input current waveform to provide both pre-compensation for chromatic dispersion and compensation for the non-linearities of the directly modulated laser. These are two of the main limiting factors in providing a low cost high data rate and long reach optical communications system.
Owner:CIENA
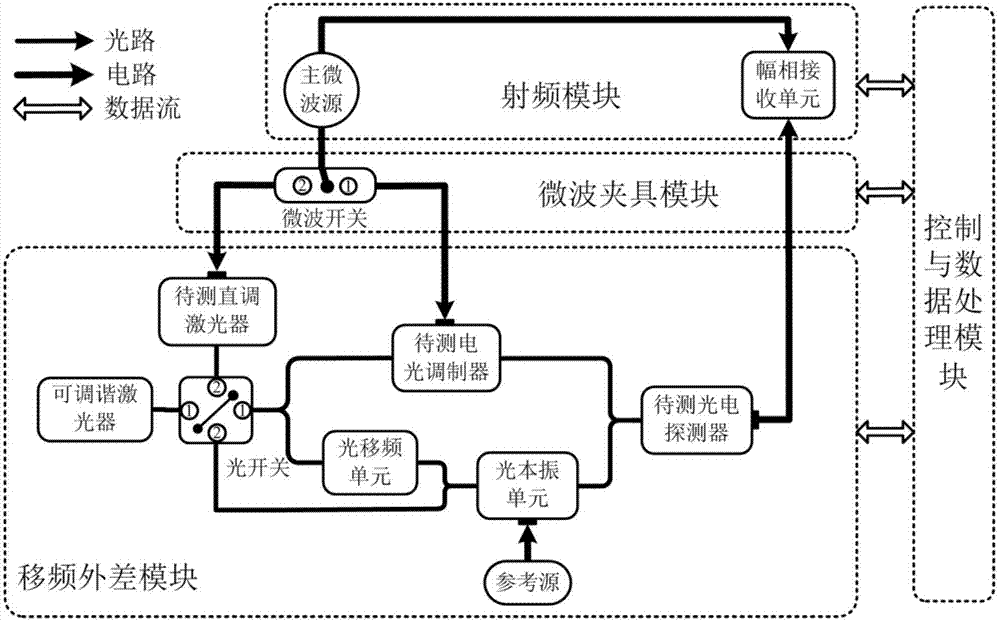
Photoelectric frequency response tester and test method thereof
ActiveCN107085143AEnables self-calibrating measurementsReduce cost of measurementHeterodyning/beat-frequency comparisonFrequency spectrumEngineering
The invention relates to a photoelectric frequency response tester and a test method thereof. The photoelectric frequency response tester is composed of a frequency shift heterodyne module, a microwave clamp module, a radio frequency module and a control and data processing module. The frequency shift heterodyne module is composed of a directly modulated laser to be tested, a tunable laser, an optical switch, an electro-optic modulator to be tested, an optical frequency shift unit, an optical local oscillation unit, a reference source and a photoelectric detector to be tested. The microwave clamp module provides a microwave switch and different radio frequency port use scenes. The radio frequency module is composed of a main microwave source and an amplitude phase receiving unit. The optical switch and the microwave switch are controlled, the frequency relation of the sinusoidal microwave signals outputted by the main microwave source and the reference source is set, and the required spectrum sideband is analyzed through cooperation of the amplitude phase receiving unit so that the frequency response characteristic parameters of the directly modulated laser to be tested, the electro-optic modulator to be tested and the photoelectric detector to be tested can be acquired, additional calibration test of the conventional method can be eliminated, the test cost of the photoelectronic device can be reduced, and the test accuracy and the flexibility and the reliability of the device can be enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
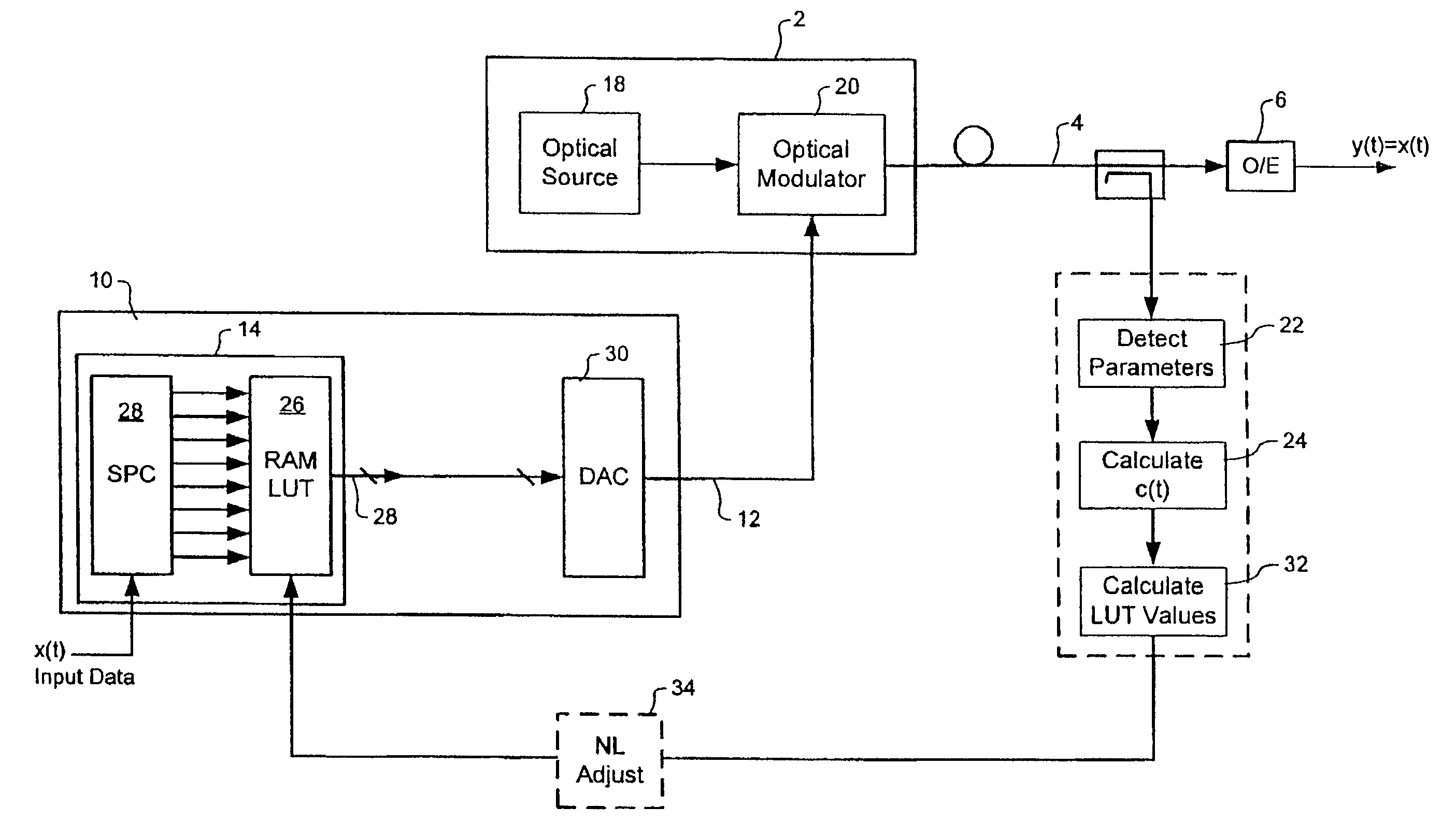
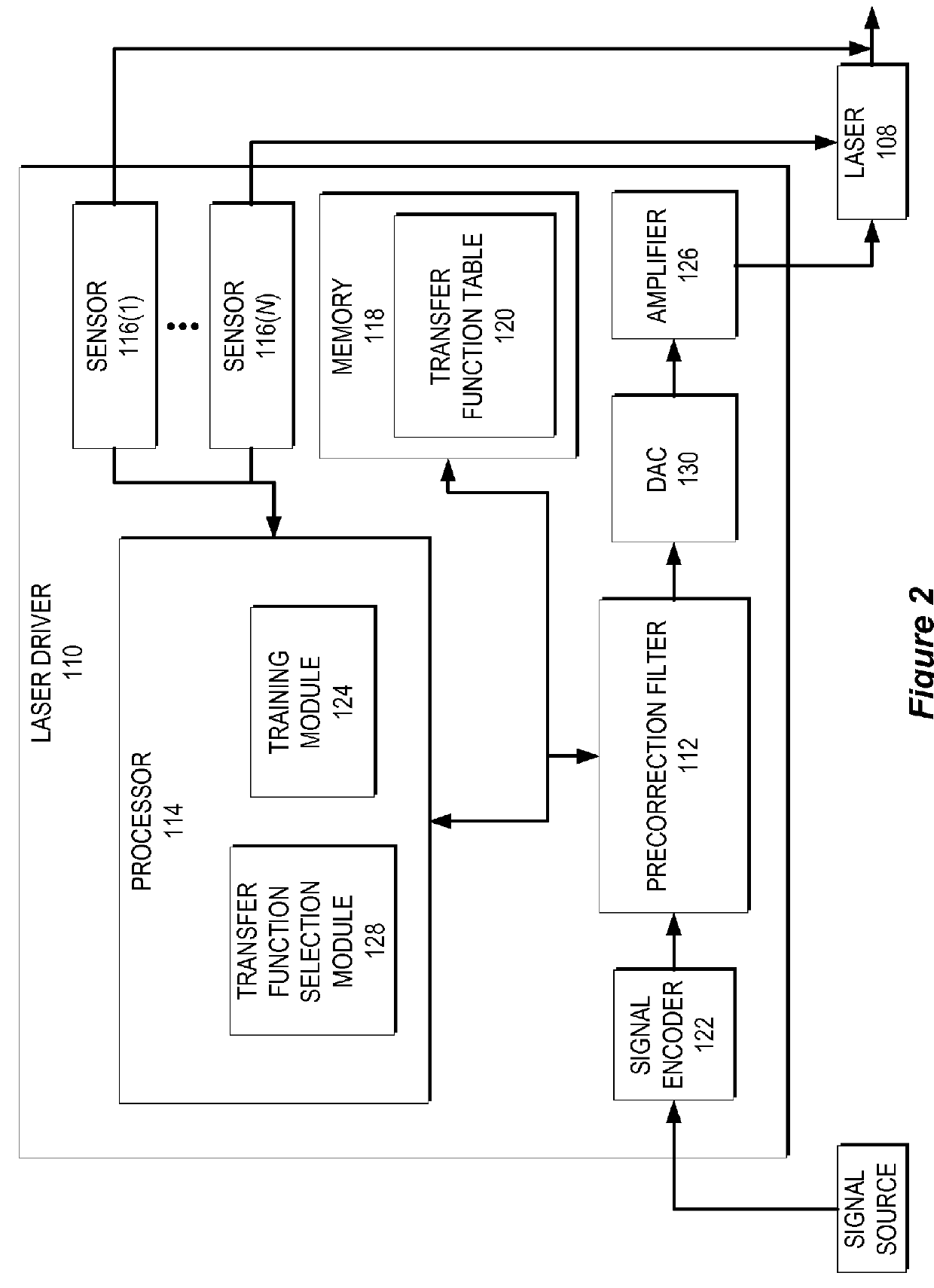
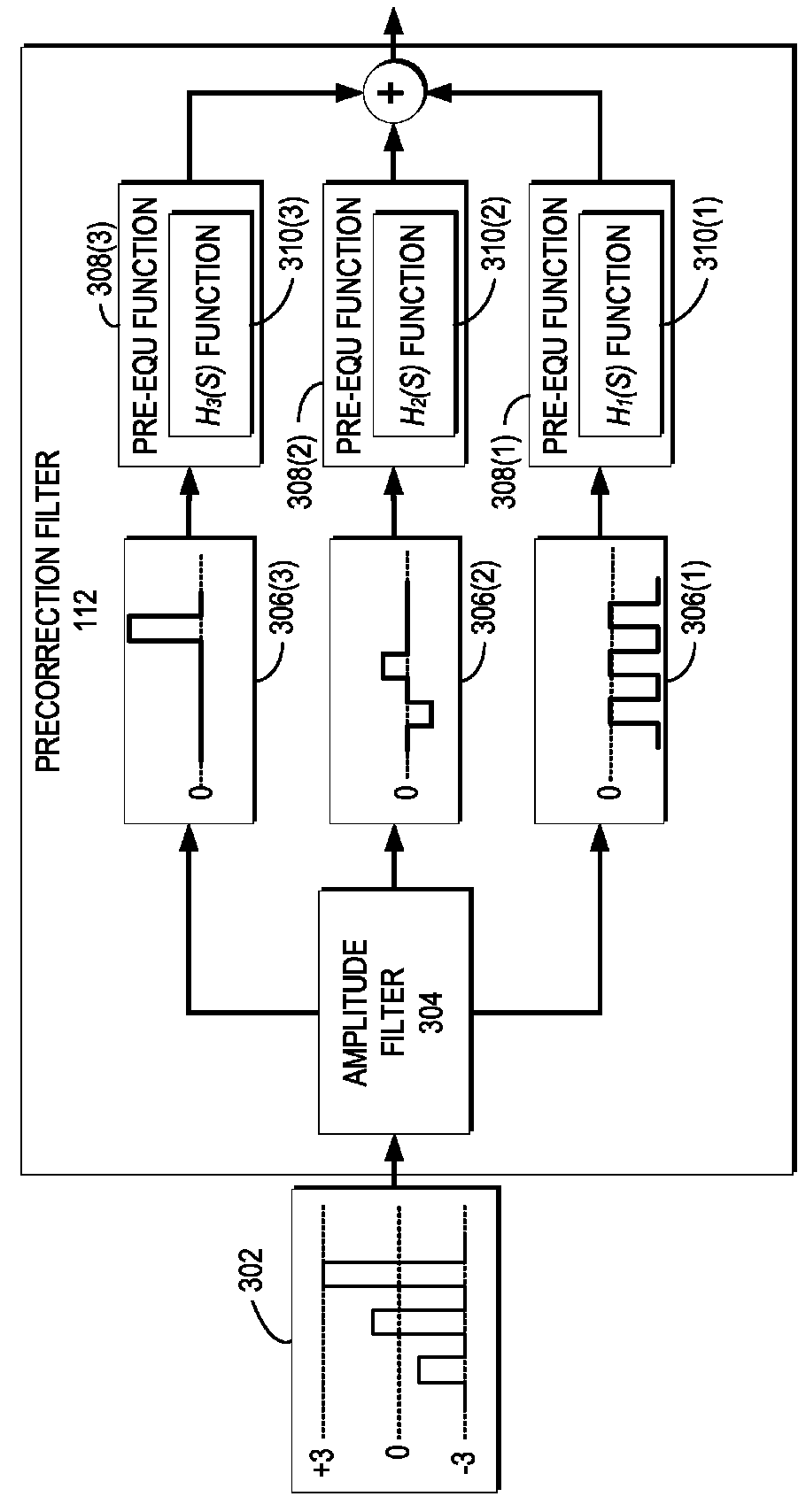
Electrical mitigation of DML nonlinearity for high-speed optical interconnection
In some implementations, the output of a directly modulated laser (DML) includes nonlinearities with respect to the input signal driving the DML. When the DML is transmitting an amplitude modulated signal, the nonlinearities can induce noise into the signal, which makes it difficult for a receiving node to correctly decode the received signal. The system and methods described herein pre-correct the error caused by the nonlinearities of the DML by filtering (or pre-correcting) the data signal that drives the DML.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Measuring method based on dispersion optical fiber dispersion coefficient measuring system
The invention relates to a measuring method based on a dispersion optical fiber dispersion coefficient measuring system, mainly in order to solve the problem that the existing measuring system has the disadvantages of low measuring speed, low measuring accuracy and poor anti-environmental-interference performance. A dispersion optical fiber dispersion coefficient measuring system includes a signal source. A high-frequency microwave signal output by the signal source is divided into two microwave signals after passing through a power divider. One microwave signal of the power divider enters a directly modulated laser. The laser loads the microwave signal to the optical domain to get an optical microwave signal. The optical microwave signal passes through a dispersion optical fiber to be measured, is incident on a high-speed photoelectric detector, and then enters the radio frequency input end of an IQ frequency mixer. The other microwave signal of the power divider enters the local oscillation input end of the IQ frequency mixer, passes through a low-pass filter, and then sequentially passes through a signal amplification circuit, a data acquisition circuit and a signal processing and display module. Through the technical scheme, the problem is well solved. The measuring method can be used to measure a dispersion optical fiber.
Owner:西安华兴搏发光电科技股份有限公司
Low power consumption, long range, pluggable transceiver, circuits and devices therefor, and method(s) of using the same
ActiveUS8903254B2Reduce power consumptionMaximize efficiencyOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsTransceiverImpedance matching
The present disclosure relates to an optical transceiver for use in optical fiber communications and / or telecommunications systems and, more specifically, a low power consumption, long range pluggable transceiver. The transceiver generally comprises a photodiode with a transimpedance amplifier (PIN-TIA); an electro-absorption modulated laser (EML); an optical detector; and a directly modulated laser (DML) driving module connected between the PIN-TIA and EML laser configured to drive the EML laser. A low power-consumption DML driving module is utilized to drive the EML laser, so as to further reduce power consumption. An impedance matching circuit can be applied to modulate an electro-absorption (EA) modulator of the EML laser with maximum efficiency.
Owner:SOURCE PHOTONICS
40G CFP optical module for long-distance transmission
InactiveCN102710334AHighly integratedImprove performanceElectromagnetic transceiversOptical ModuleEngineering
The invention discloses a 40G CFP optical module for long-distance transmission, which mainly comprises an optical receiving unit, an optical transmission unit, a control unit and a power supplying unit, wherein the optical receiving unit is for converting the received optical signal into an electrical signal through a detector and outputting the electrical signal; the optical transmission unit is for converting the electrical signal at an interface unit into the optical signal to output through a modulation laser DML; the control unit is connected with the optical transmission unit, the optical receiving unit and the interface unit respectively for communicating with a host computer, intelligently controlling parameters and reporting the monitoring information; and the power supplying unit is for supplying power to the optical transmission unit, the optical receiving unit and the control unit, and controlling on / off of each unit. Through the optical module, the application requirement on long-distance (more than 40km) transmission of the CFP optical module at present can be well met.
Owner:WUHAN TELECOMM DEVICES
Modulator-free optical millimeter wave generating method and full-duplex optical fiber wireless communication system
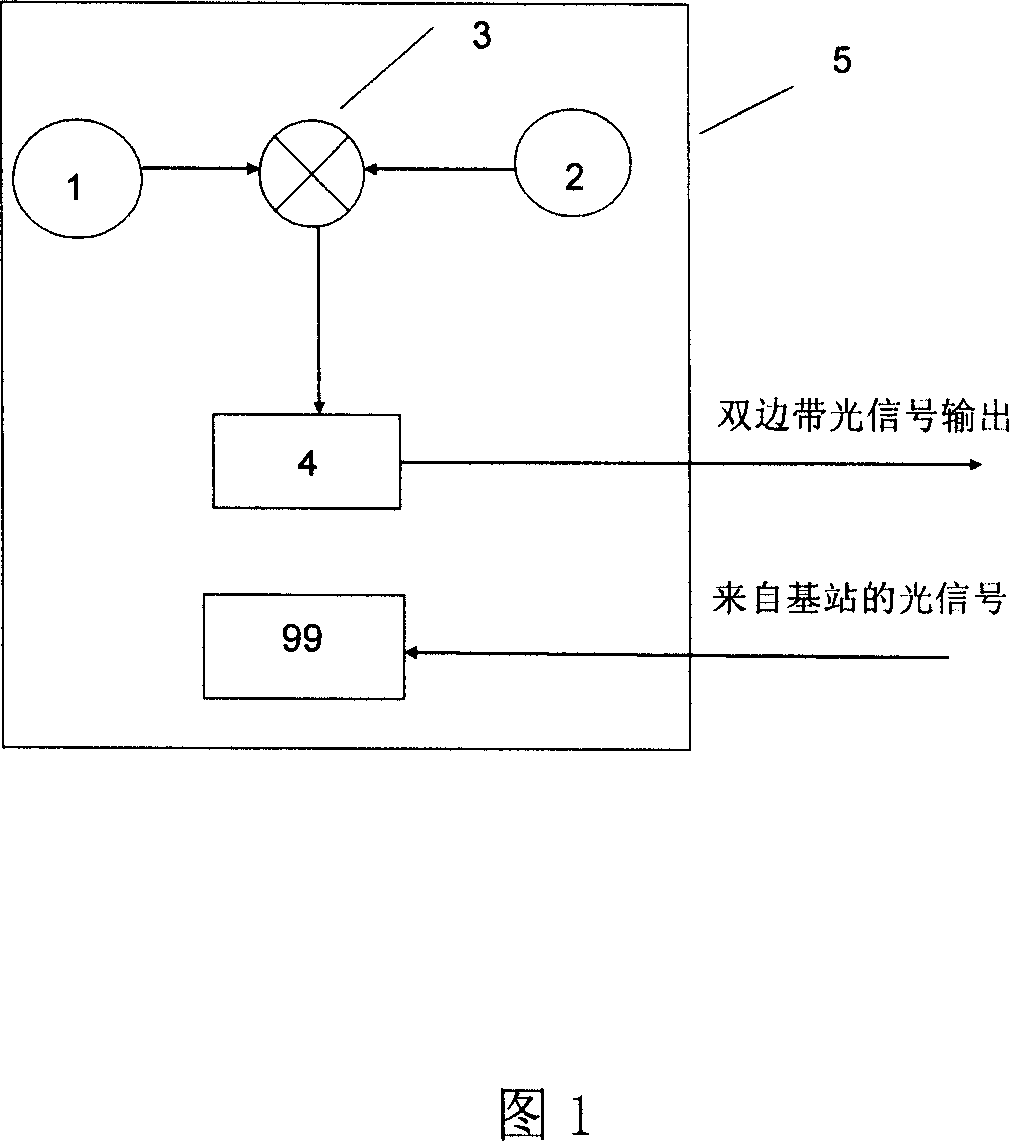
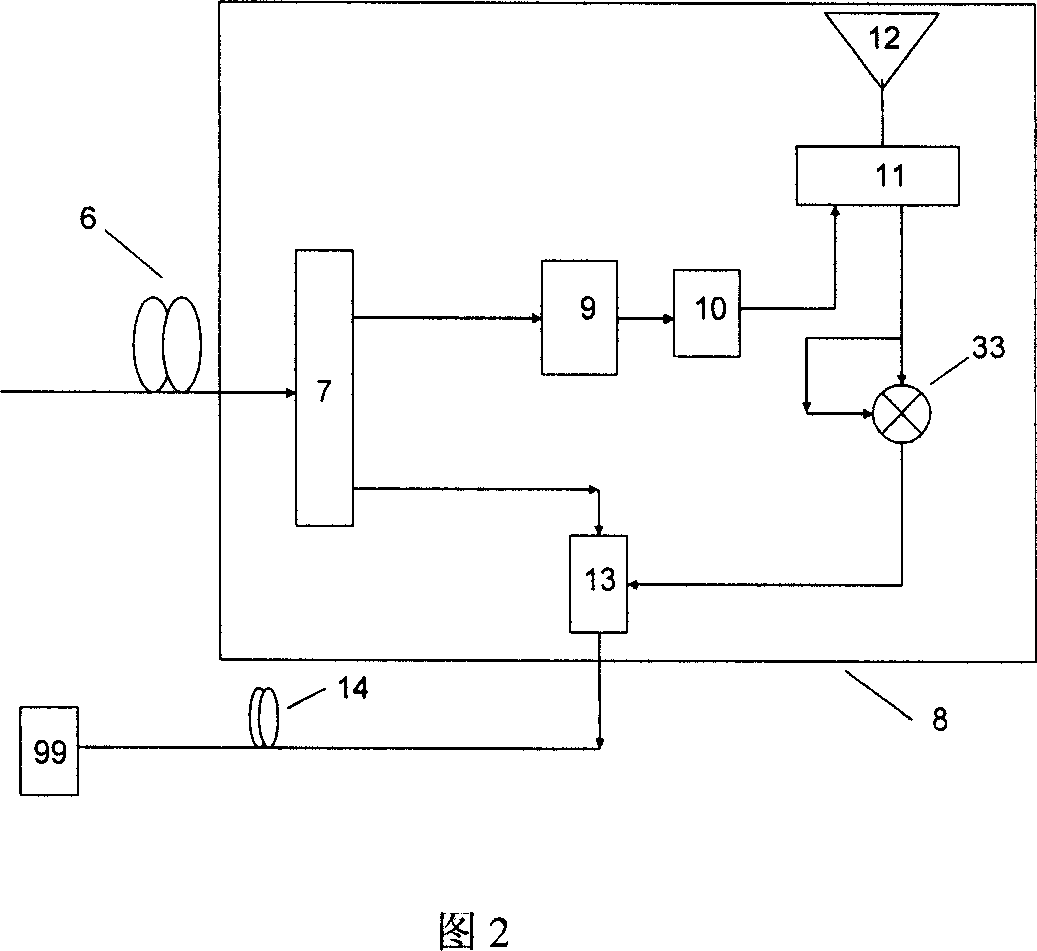
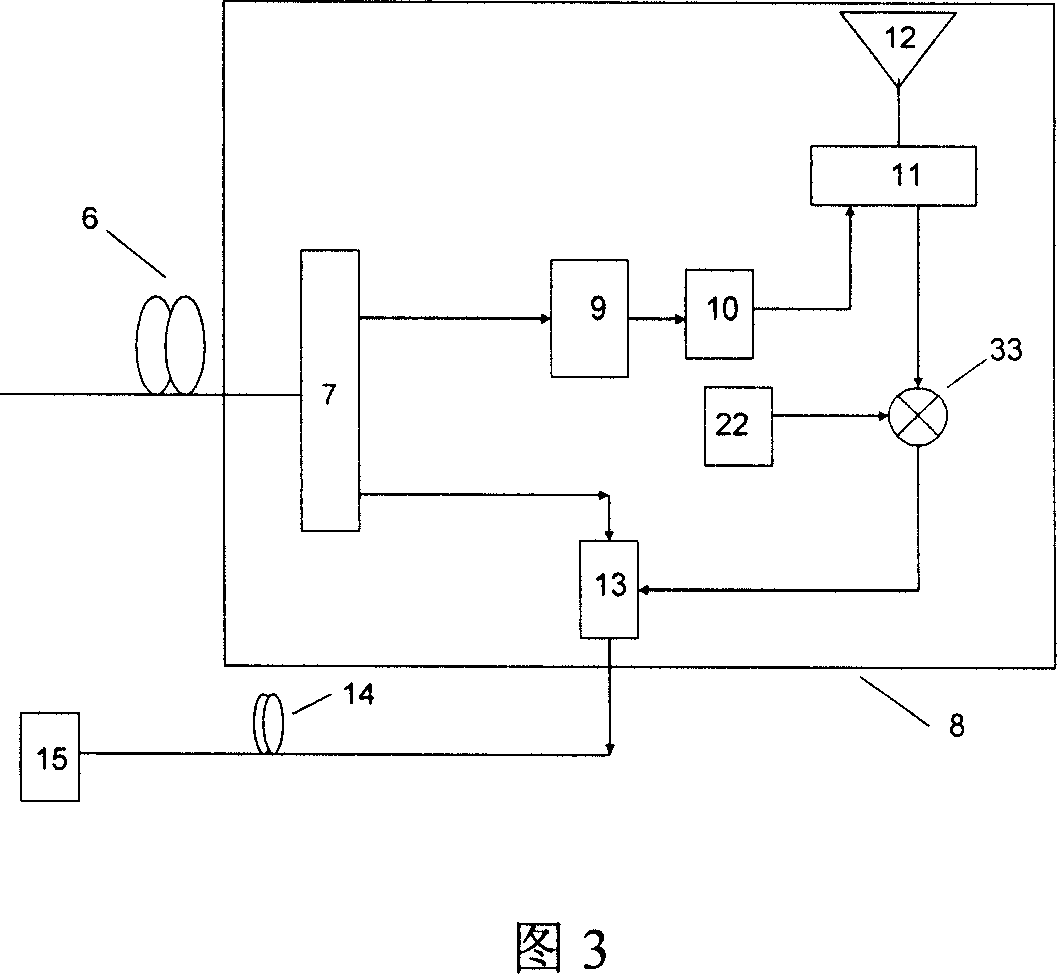
The invention discloses a method of generating light millimeter wave without light modulator and full duplex fiber wireless communication system which belongs to fields of Radio-on-Fiber (ROF) communication system. The base band data signal and radio frequency sine wave are mixed to drive the direct modulating laser to generate double-side-band signal, then transmitted to the base station via optical fiber, the base station adopts filter to separate first order side-band signal and center carrier wave. The first order side-band forms light millimeter wave whose repetition frequency is two times of radio frequency signal. The full duplex fiber wireless communication system of the invention provides five realization schemes of up-bound link and two schemes of receiver. Said method of generating light millimeter wave and full duplex fiber wireless communication system decrease the amount of light elements used, and economic effect can be obtained.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
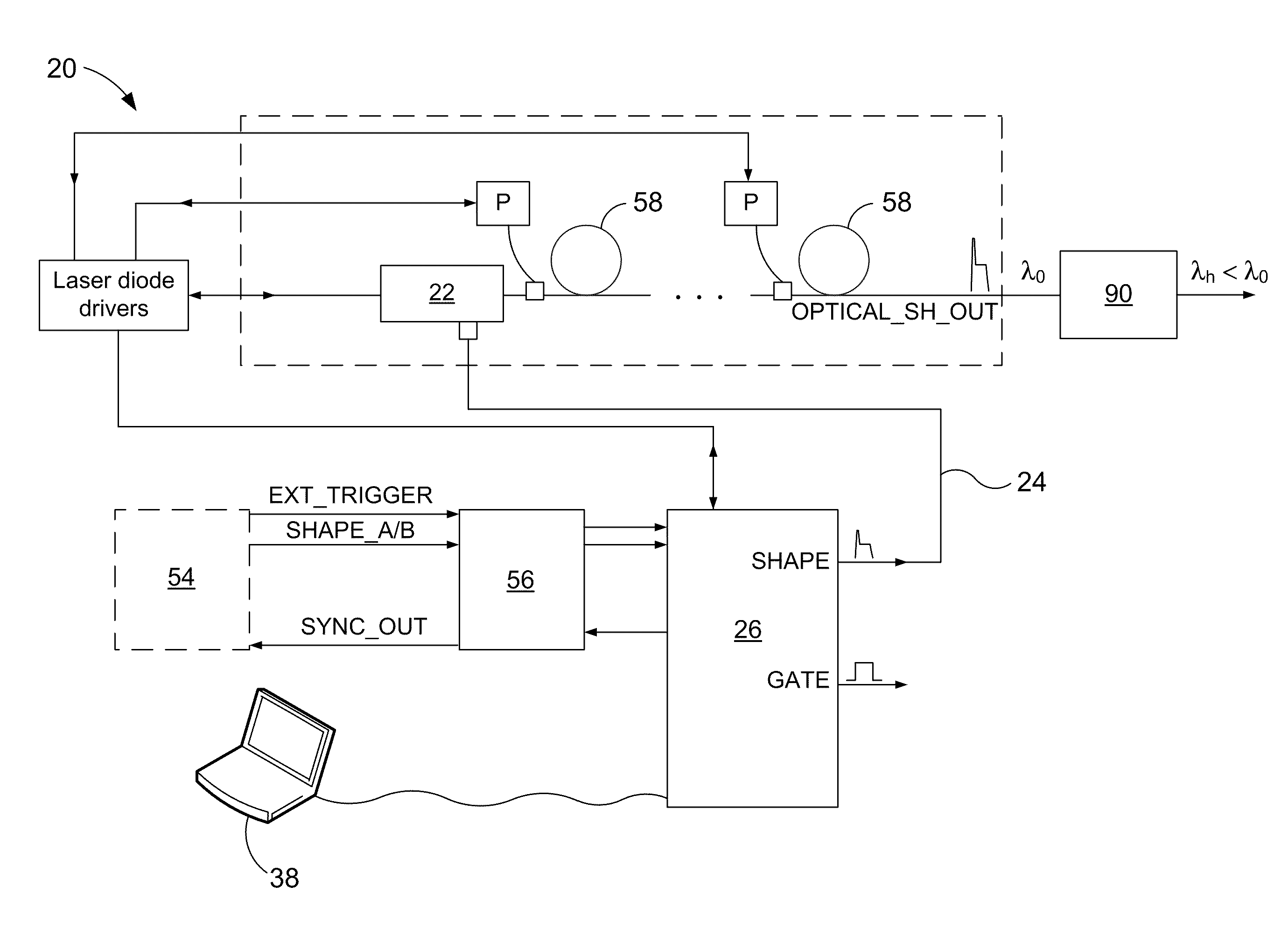
Method for stablizing an output of a pulsed laser system using pulse shaping
ActiveUS20110284507A1Improve output stabilityImprove stabilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersDriving currentPower flow
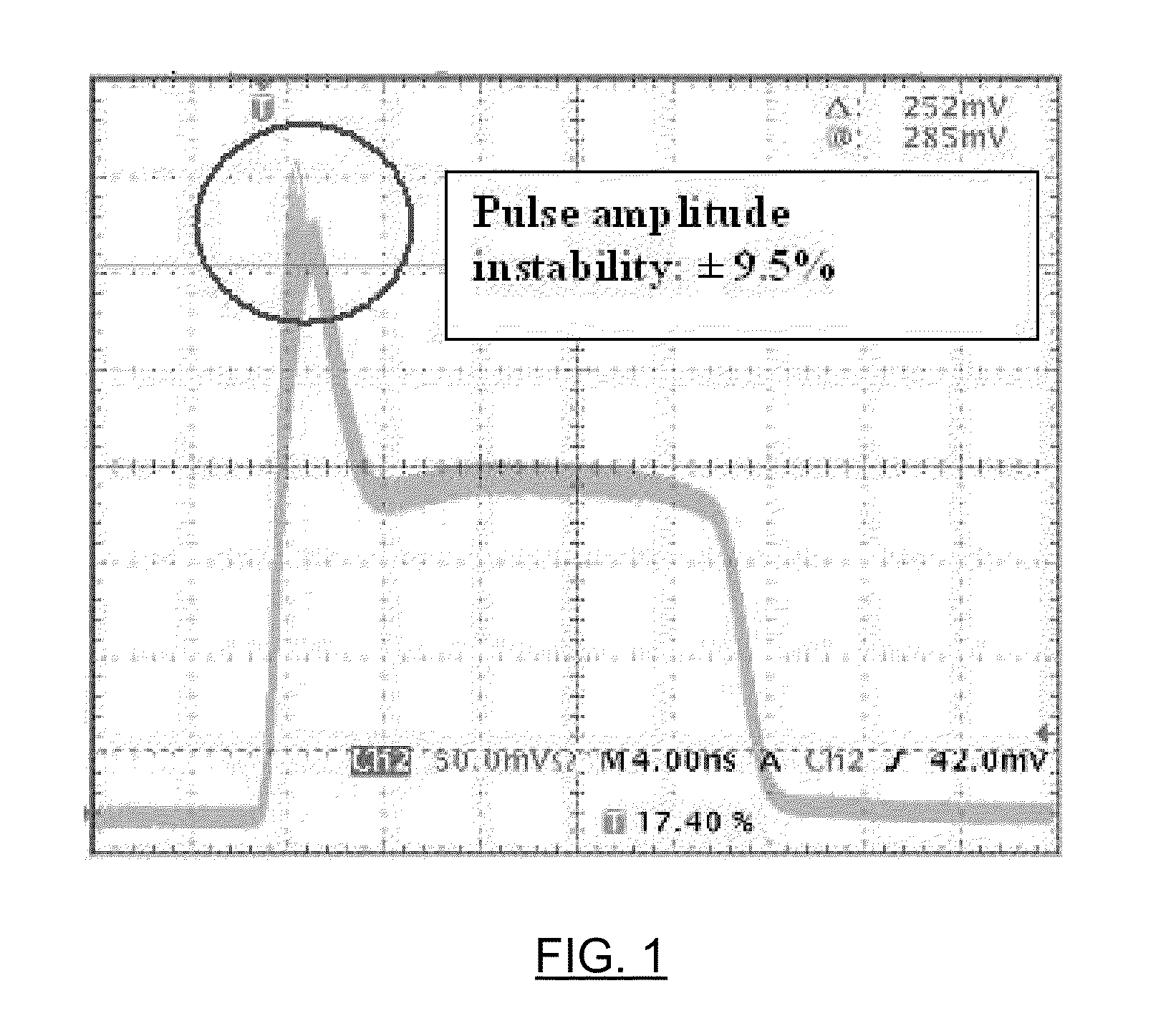
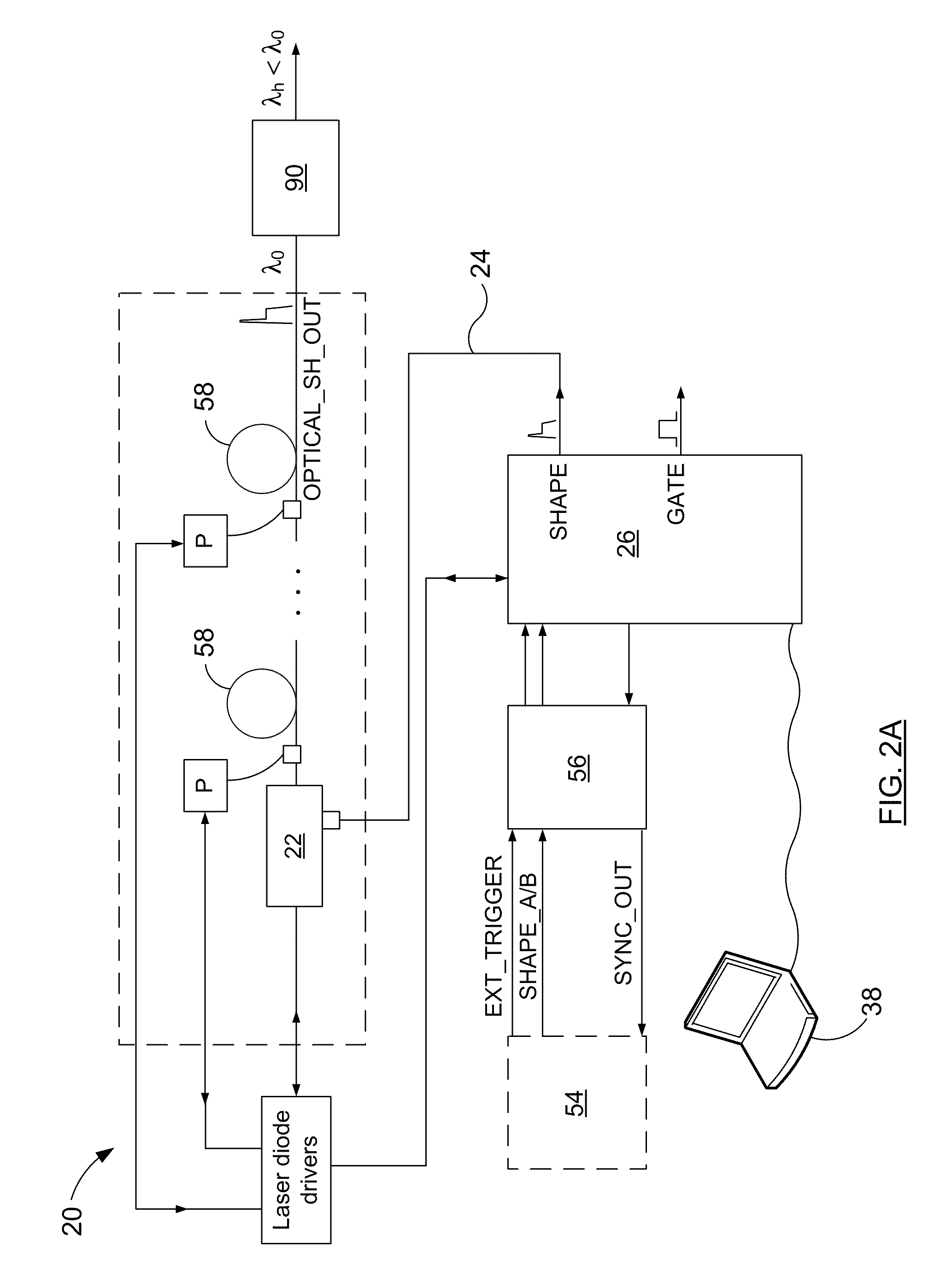
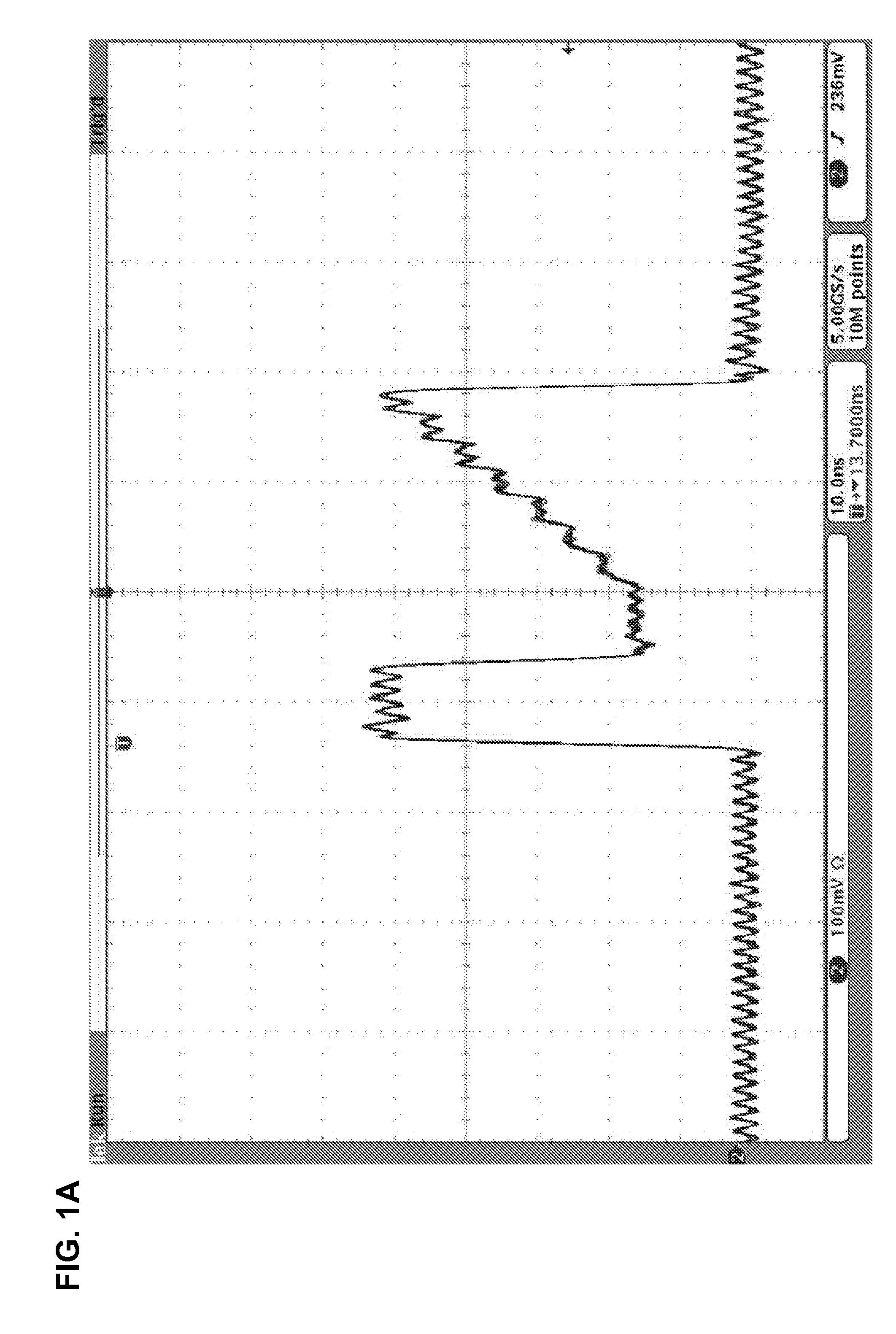
A method for stabilizing an output of a pulsed laser system includes a directly modulated laser diode by mitigating the effect of switching transients on the temporal shape of the outputted pulses. The method includes controlling a pulse shaping signal to define, over time, processing and conditioning periods. During the processing periods, the pulse shaping signal has an amplitude profile tailored to produce the desired temporal shape of the output. Each conditioning period either immediately precedes or follows a processing period. During a given processing period, the amplitude profile of the pulse shaping signal is tailored so that the drive current of the laser diode is lower than its maximum value during the corresponding processing period, and is of the same order of magnitude as the laser threshold current of the laser diode. In this manner, the stability of the output during the corresponding processing period is improved.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Driver circuit for the direct modulation of a laser diode
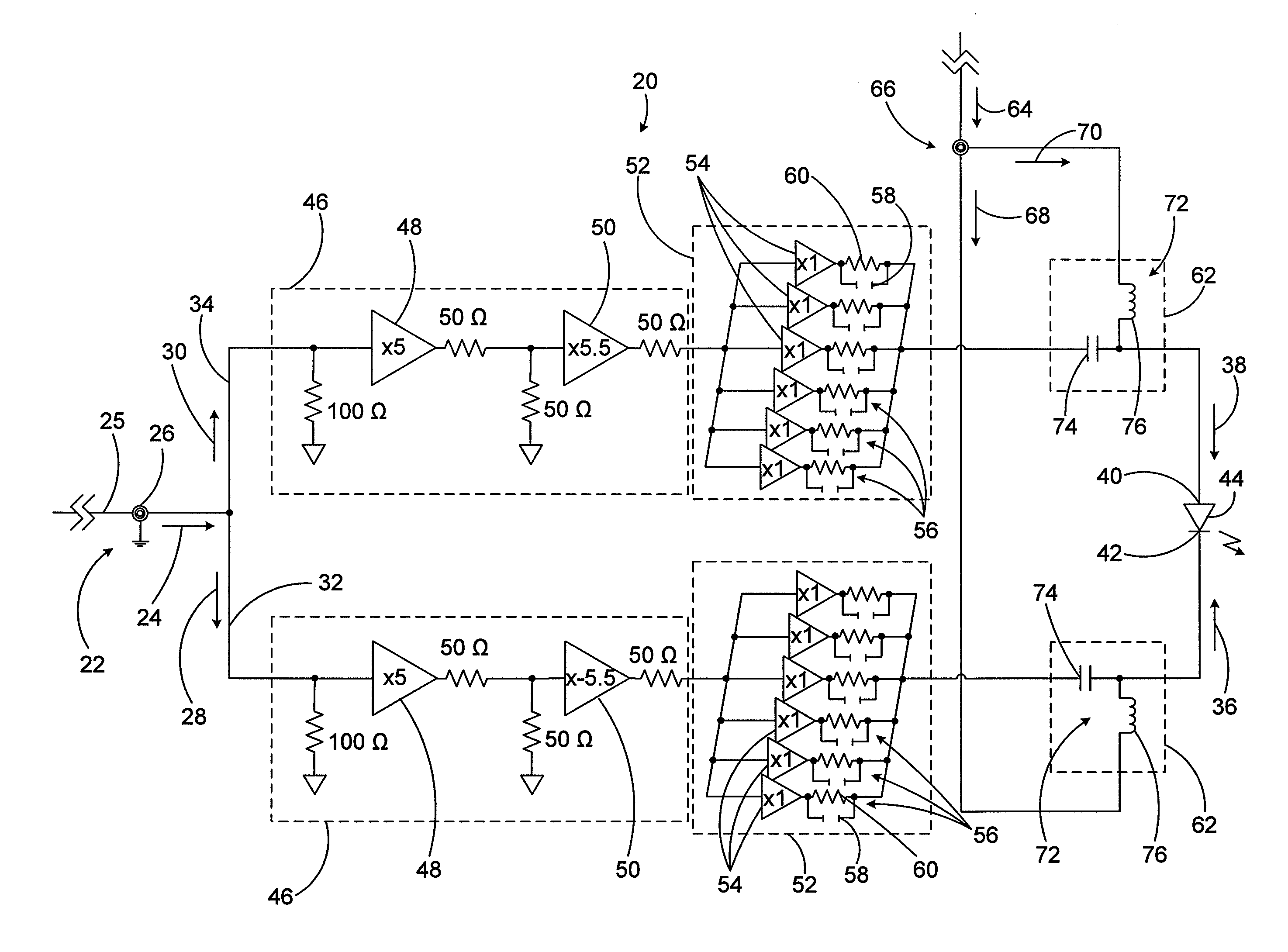
InactiveUS20110280265A1Improve fidelityLow amplitude noiseLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
A driver circuit for a laser diode provides drive signals to the electrodes of the laser diode based on a pulsed input signal. An input receives the pulsed input signal and launches it into an amplification stage which preferably includes dual amplifiers, a buffering stage and a biasing stage. The output of the laser diode is an optical signal that reproduces the pulsed input signal with high fidelity and low amplitude noise. In one embodiment, the input separates the pulsed input signal into two signal components, launched in respective inverting and non-inverting branches which each include successive amplification, buffering and biasing stages.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Radio frequency self-interference eliminating system applied to same-time and same-frequency full-duplex system
InactiveCN105634540AGood interference suppression effectPrecisely adjust the amplitudeDuplex signal operationSelf interferenceTime delays
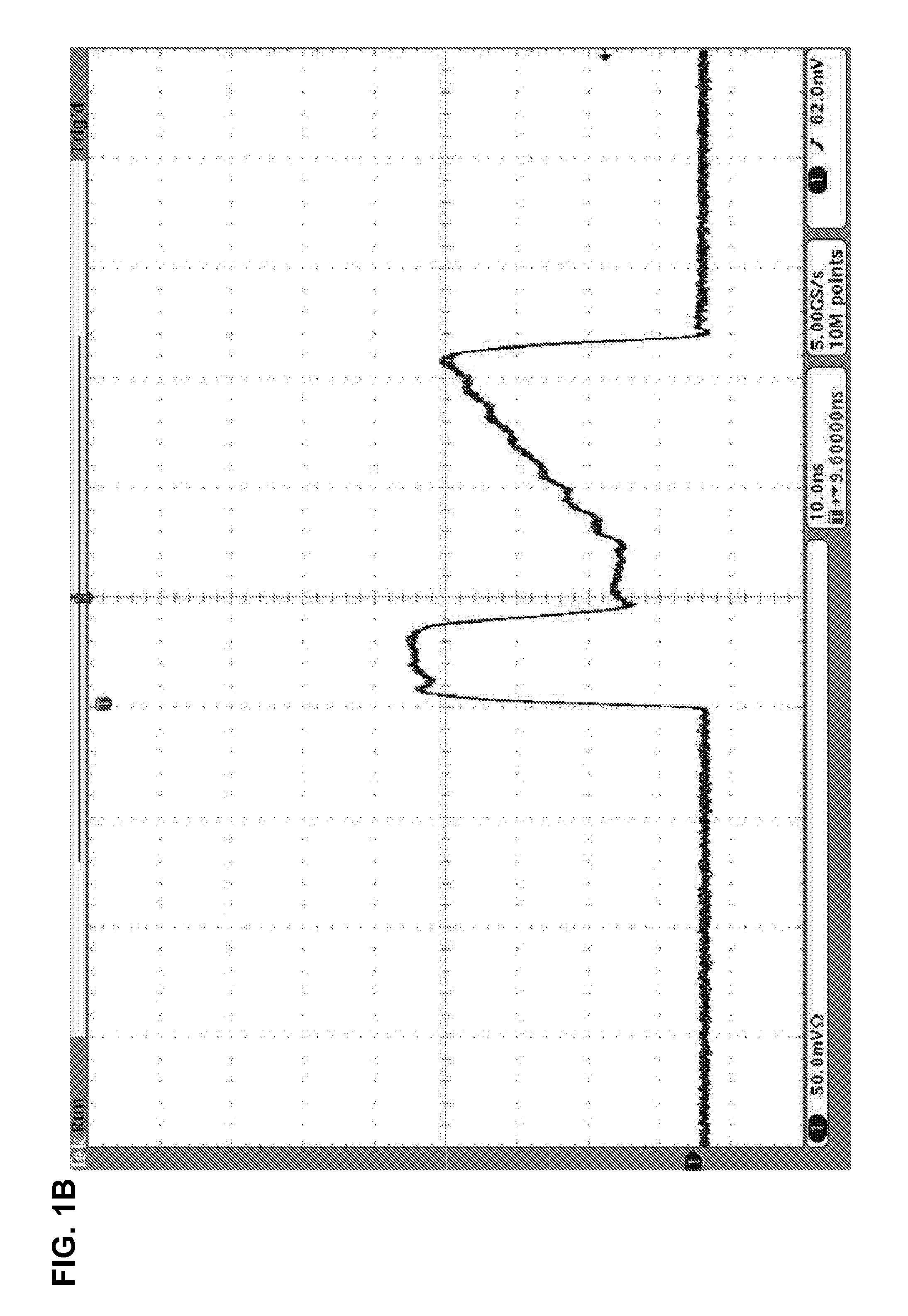
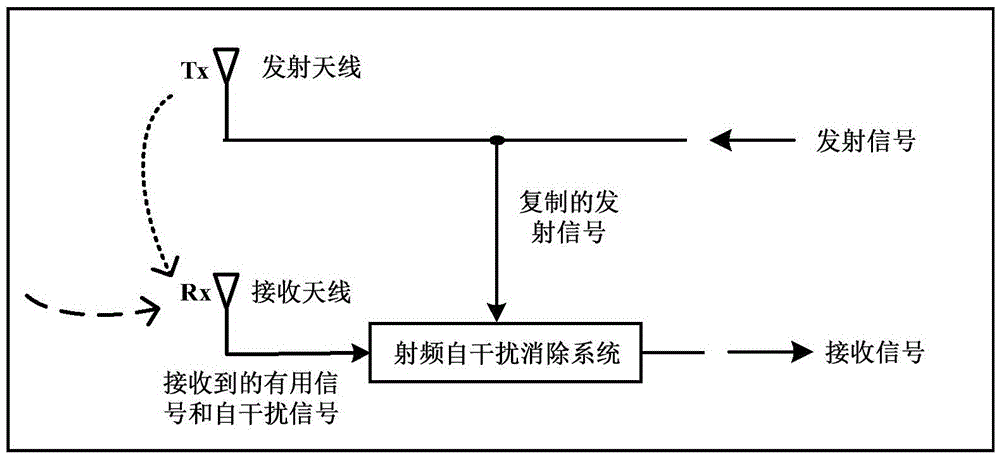
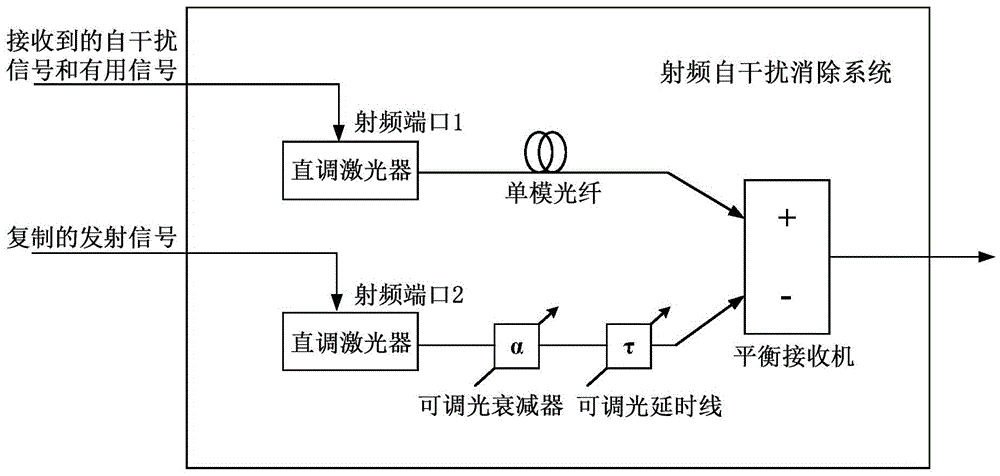
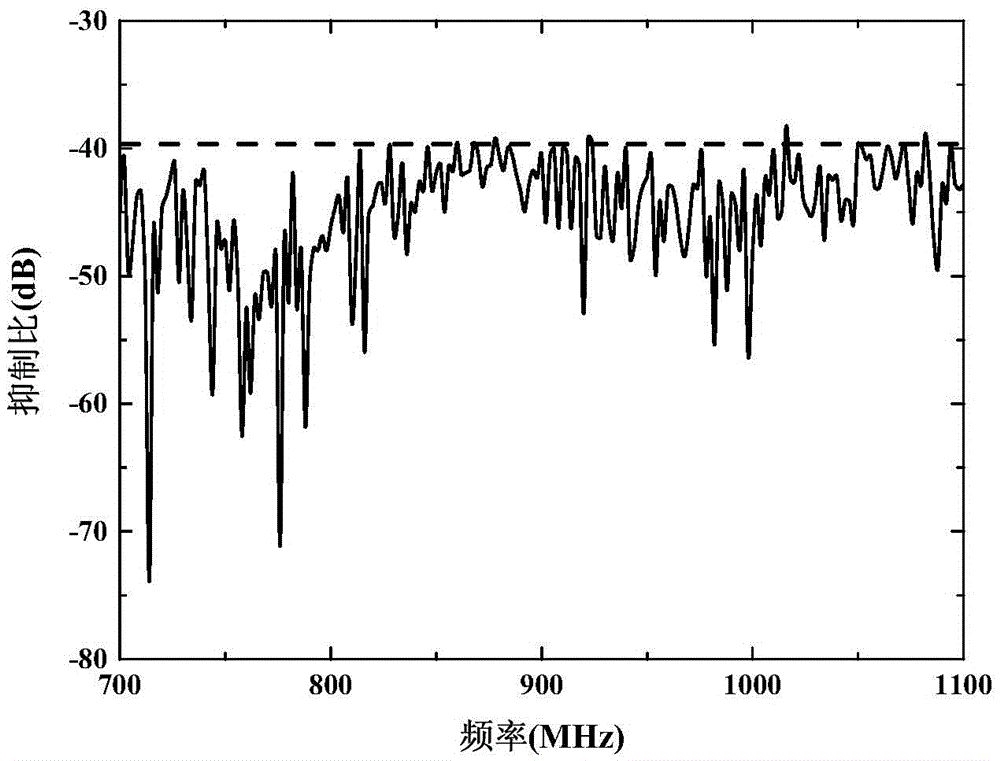
The invention provides a radio frequency self-interference eliminating system applied to a same-time and same-frequency full-duplex system. The radio frequency self-interference eliminating system comprises a direct modulation laser device, a variable optical delay line, a variable optical attenuator, and a balanced receiver, wherein the upper branch of the direct modulation laser device is connected with the first input end of the balanced receiver, while the lower branch of the direct modulation laser device is connected with the second input end of the balanced receiver via the variable optical attenuator and the variable optical delay line in sequence; the variable optical delay line is used for matching time delays generated by a self-interference signal passing through different paths; the variable optical attenuator is used for matching the magnitude of the self-interference signal; and the balanced receiver is used for receiving two optical signals from the upper branch and lower branch of the direct modulation laser device, performing subtraction, obtaining the available optical signals and then converting into corresponding electrical signals to output. According to the system, the radio frequency signal is modulated by using the direct modulation laser device with low cost, the self-interference signal is eliminated by the balanced receiver, and the good interference eliminating performance and inhibiting performance are obtained in a relatively wide frequency band range.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Light pulse generator and optical time domain reflectometer using the same
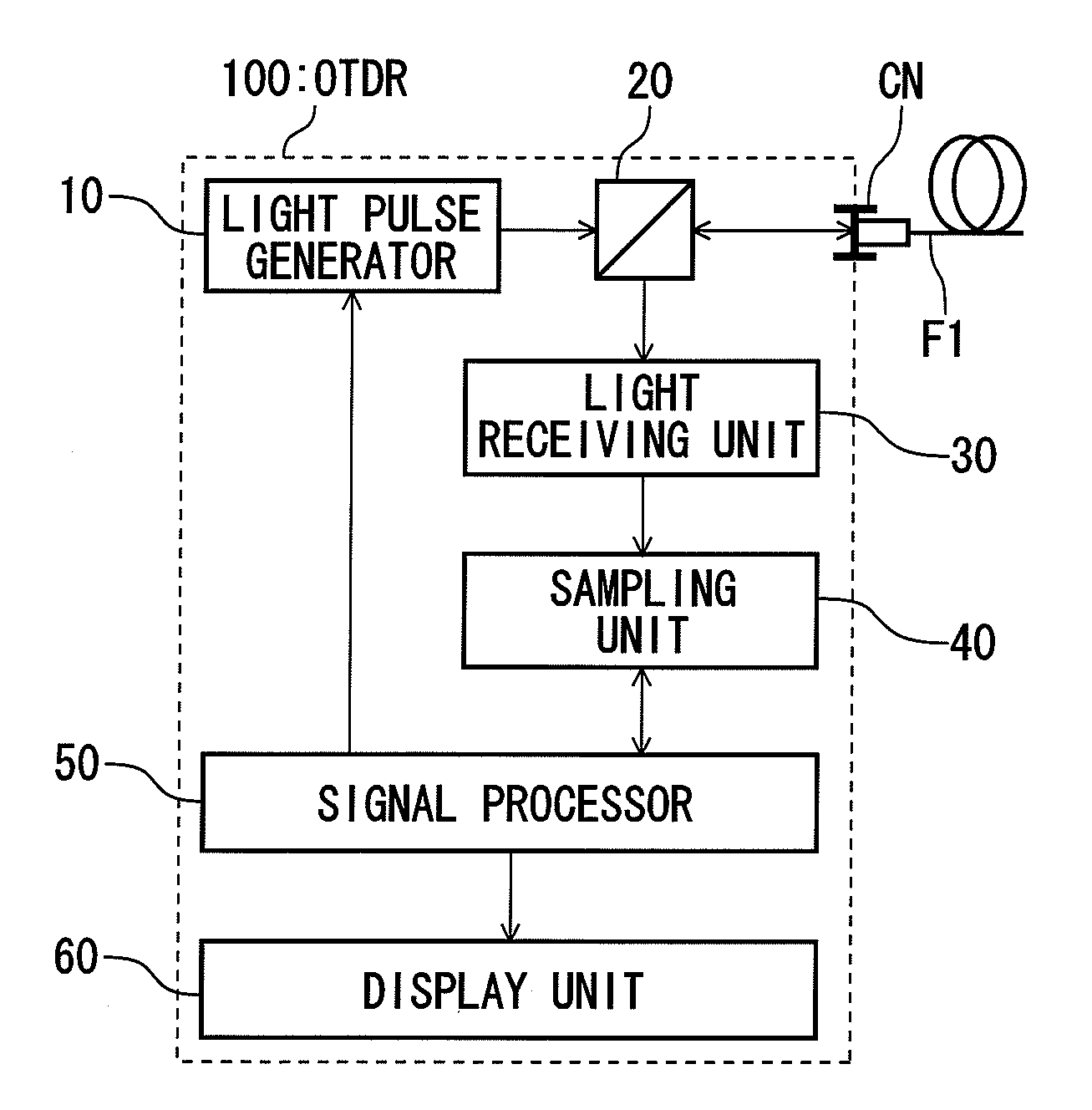
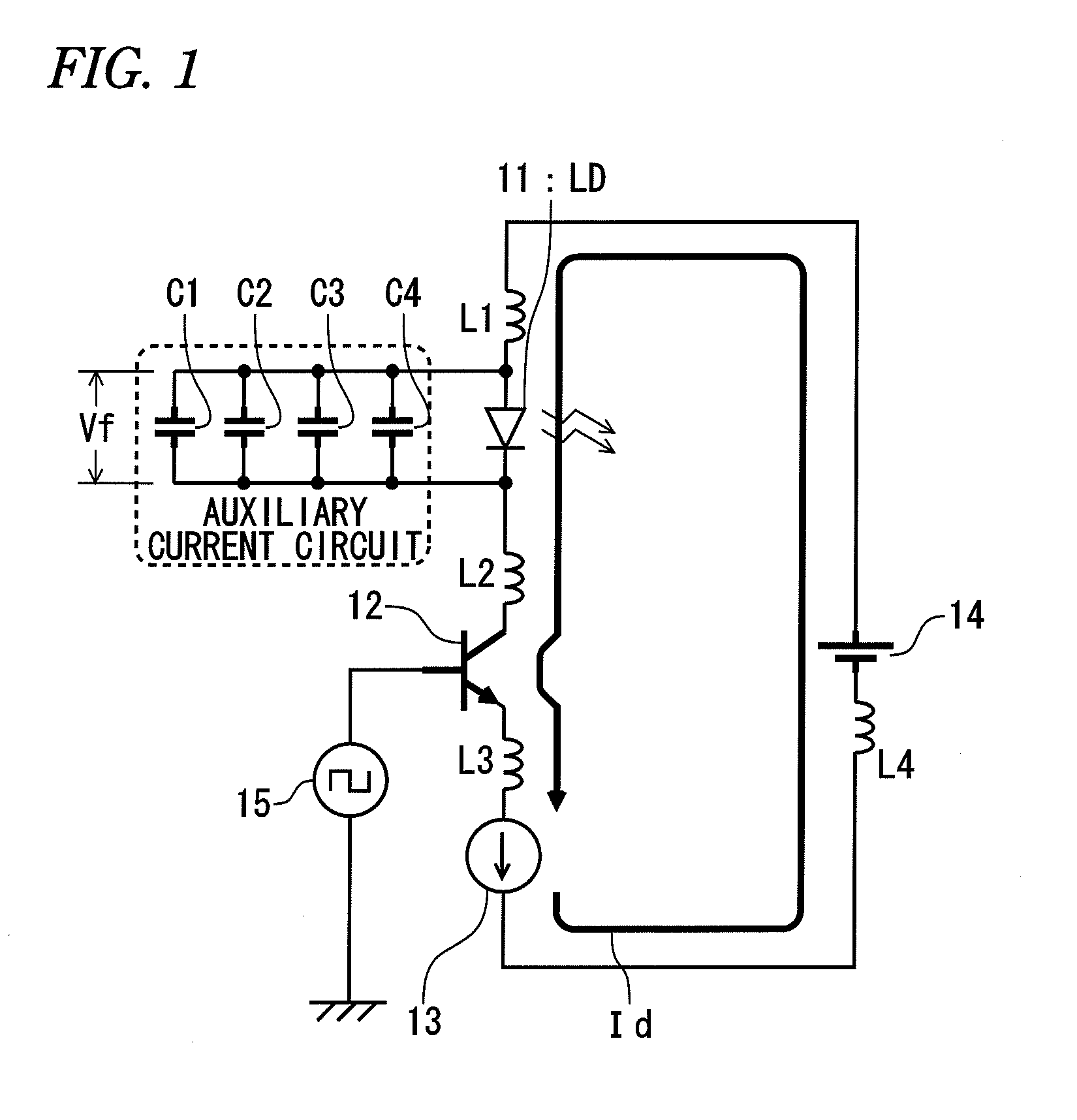
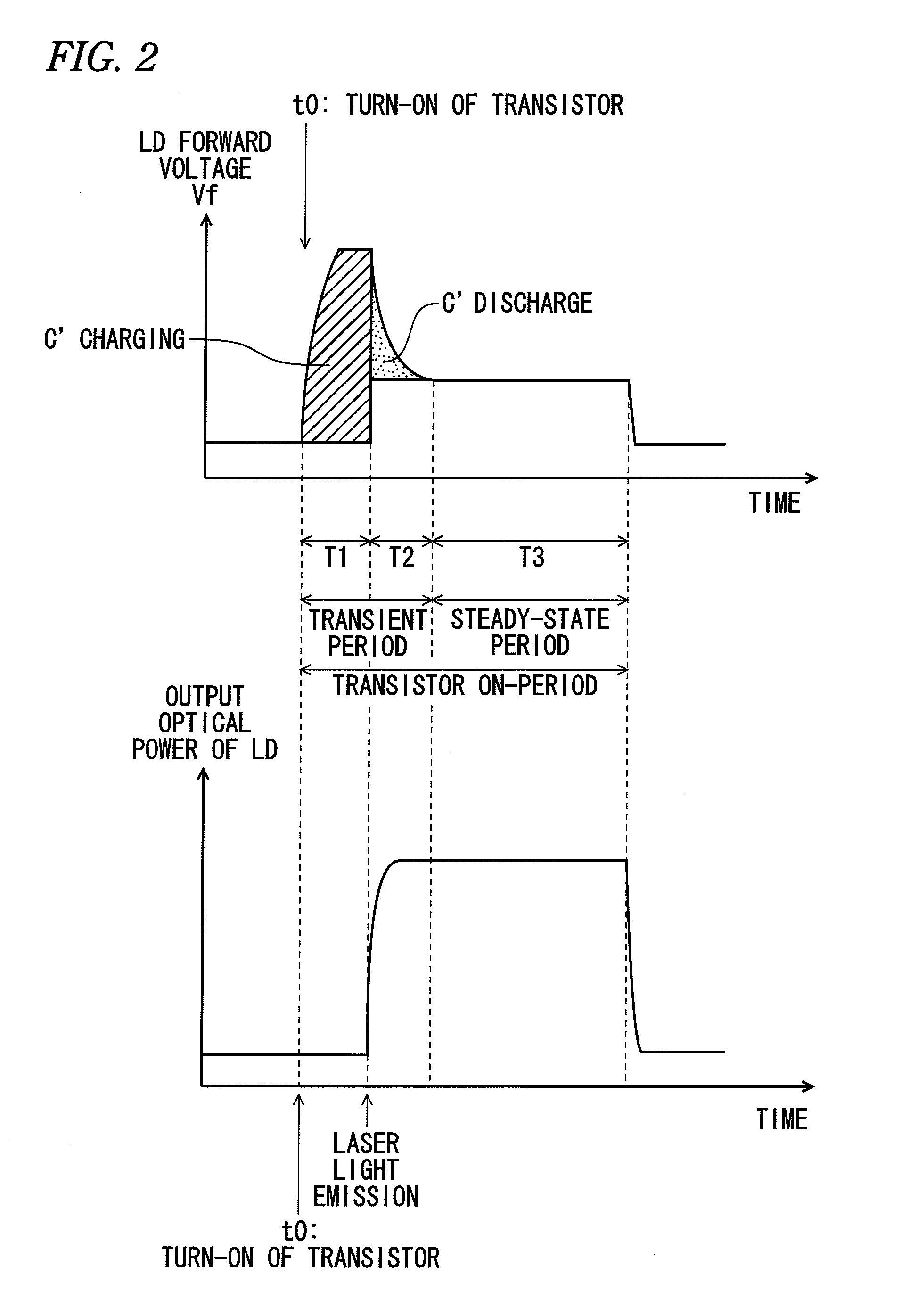
There is provided a light pulse generator. The light pulse generator includes: a laser diode; a voltage source that provides a bias voltage to the laser diode; a switching element that causes the laser diode to emit a light pulse by directly modulating the laser diode; and an auxiliary current circuit which starts to charge immediately after turn-on of the switching element and which starts to discharge after a forward current flows through the laser diode so as to provide a auxiliary current to the laser diode in the same direction as the forward current.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Directly modulated laser optical transmission system with phase modulation
ActiveUS7848661B2Improve noiseReduce signal distortionFibre transmissionElectromagnetic transmittersFiberAnalog signal
An optical transmitter for generating a modulated optical signal for transmission over a fiber optic link to a remote receiver including a laser; an input coupled to the laser for directly amplitude modulating the laser with an analog RF signal to produce an output optical signal including an amplitude modulated information-containing component; and a phase modulator coupled to the output of the laser for reducing the distortion present in the received optical signal at the remote receiver.
Owner:EMCORE INC
Distributed bragg reflector type directly modulated laser and distributed feed back type directly modulated laser
ActiveUS7760782B2Economic efficiency is excellentLess power consumptionOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersDistributed Bragg reflector laserLaser light
The invention aims at realizing a 1300-nm-band direct modulation laser, having a single lateral mode, in which a chip light power of several milliwatts and a low current operation are simultaneously realized. Also, the invention aims at realizing a laser light source excellent in economy as well by realizing output characteristics of a vertical cavity surface light emitting laser. A distributed Bragg reflector laser is constructed in the form of a semiconductor laser having a multilayer structure formed on a predetermined semiconductor substrate. The multilayer structure includes an active region for emitting a laser beam, and a distributed Bragg reflector layer. A length of the active region falls within the range of 10 to 100 μm, and a laser light beam is generated in accordance with ON / OFF of current injection to the active region.
Owner:LUMENTUM JAPAN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com