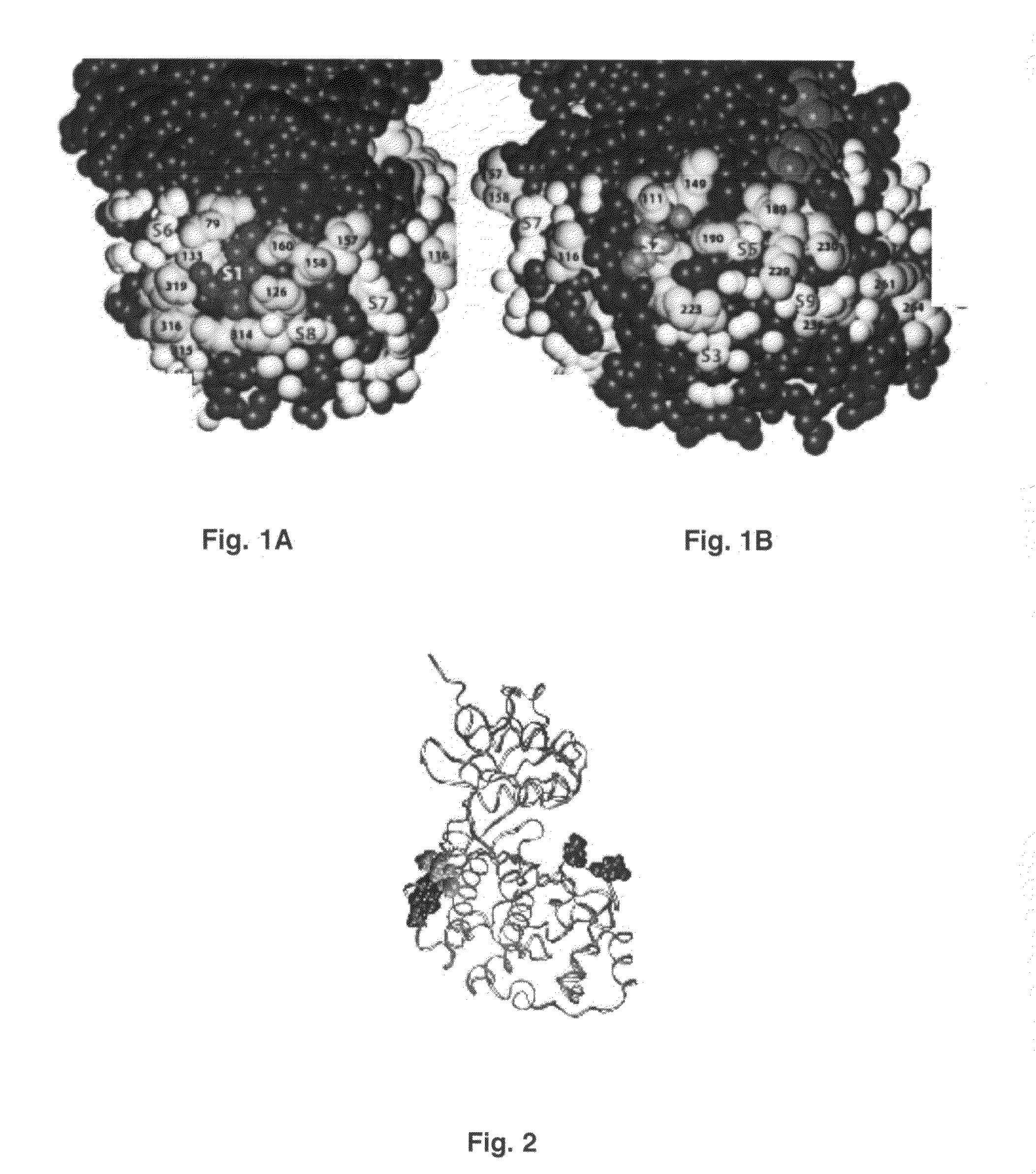
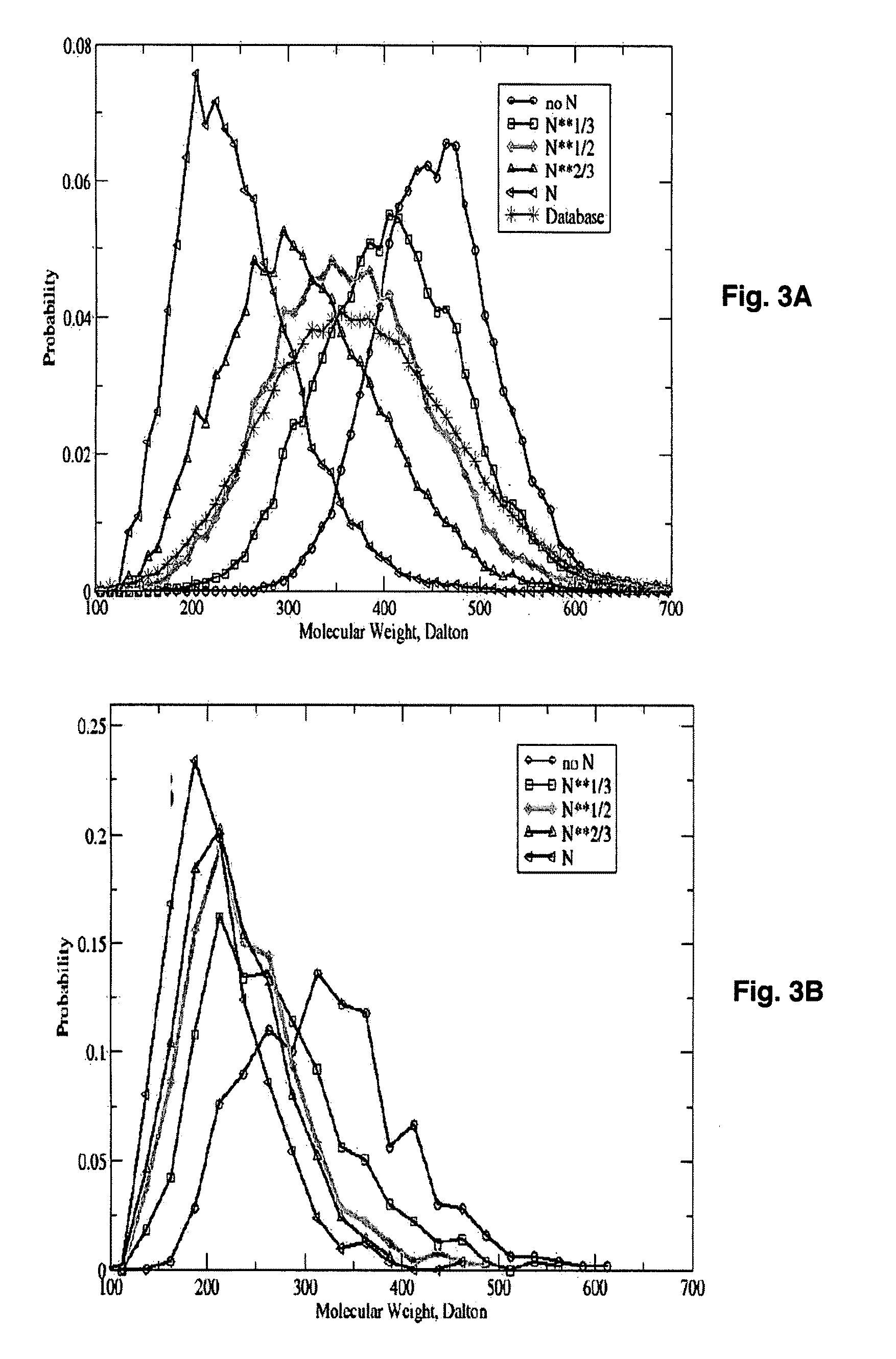
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Extracellular signal-regulated kinases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
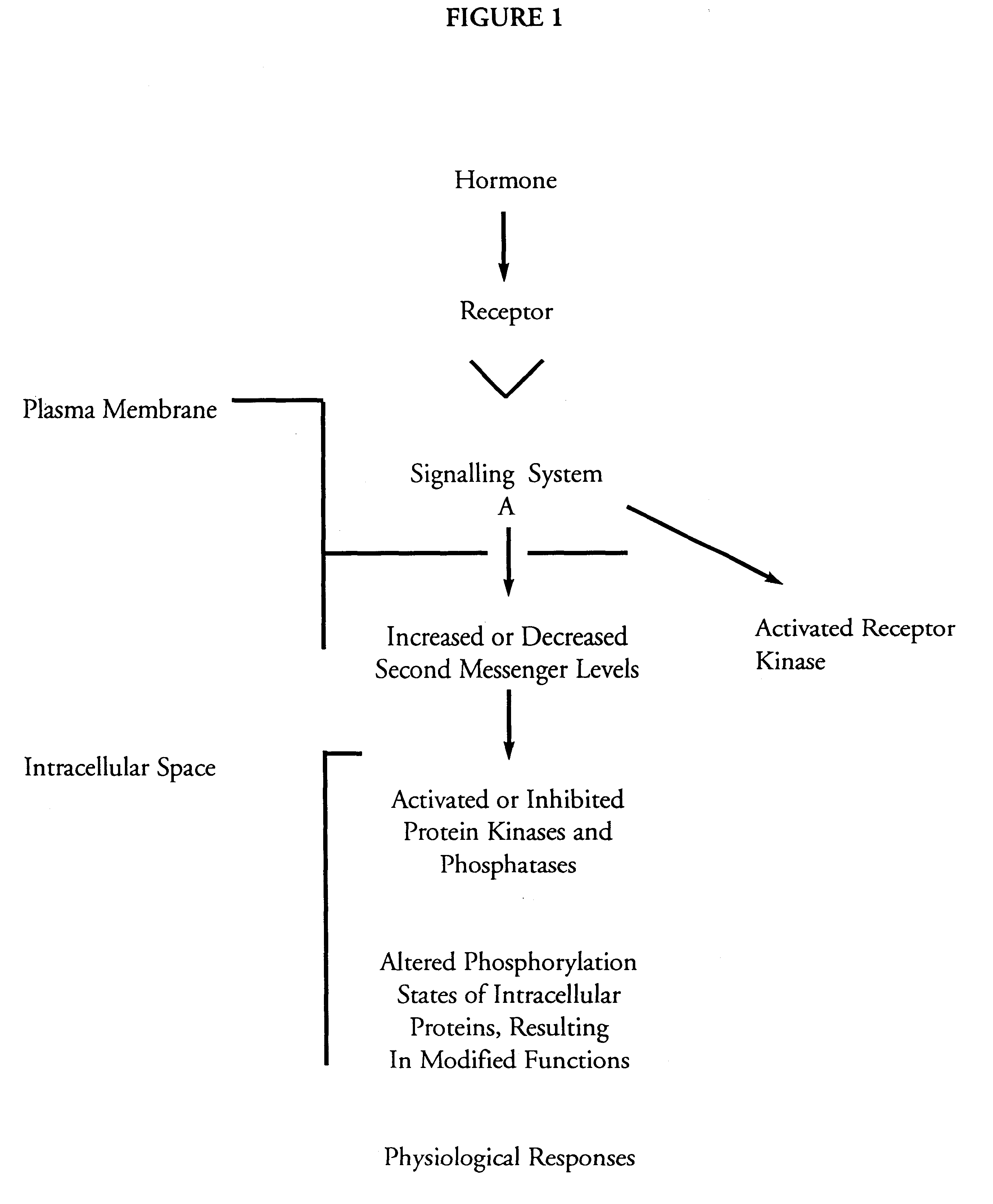
In molecular biology, extracellular signal–regulated kinases (ERKs) or classical MAP kinases are widely expressed protein kinase intracellular signalling molecules that are involved in functions including the regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells. Many different stimuli, including growth factors, cytokines, virus infection, ligands for heterotrimeric G protein-coupled receptors, transforming agents, and carcinogens, activate the ERK pathway.
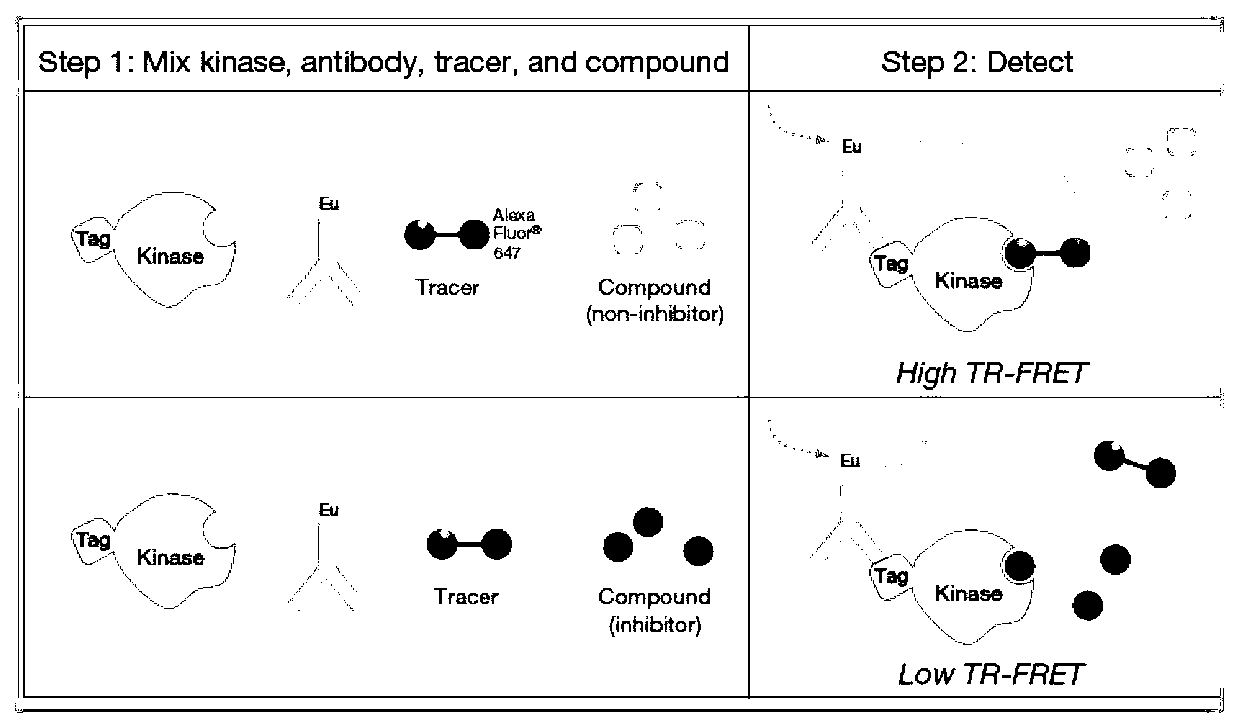
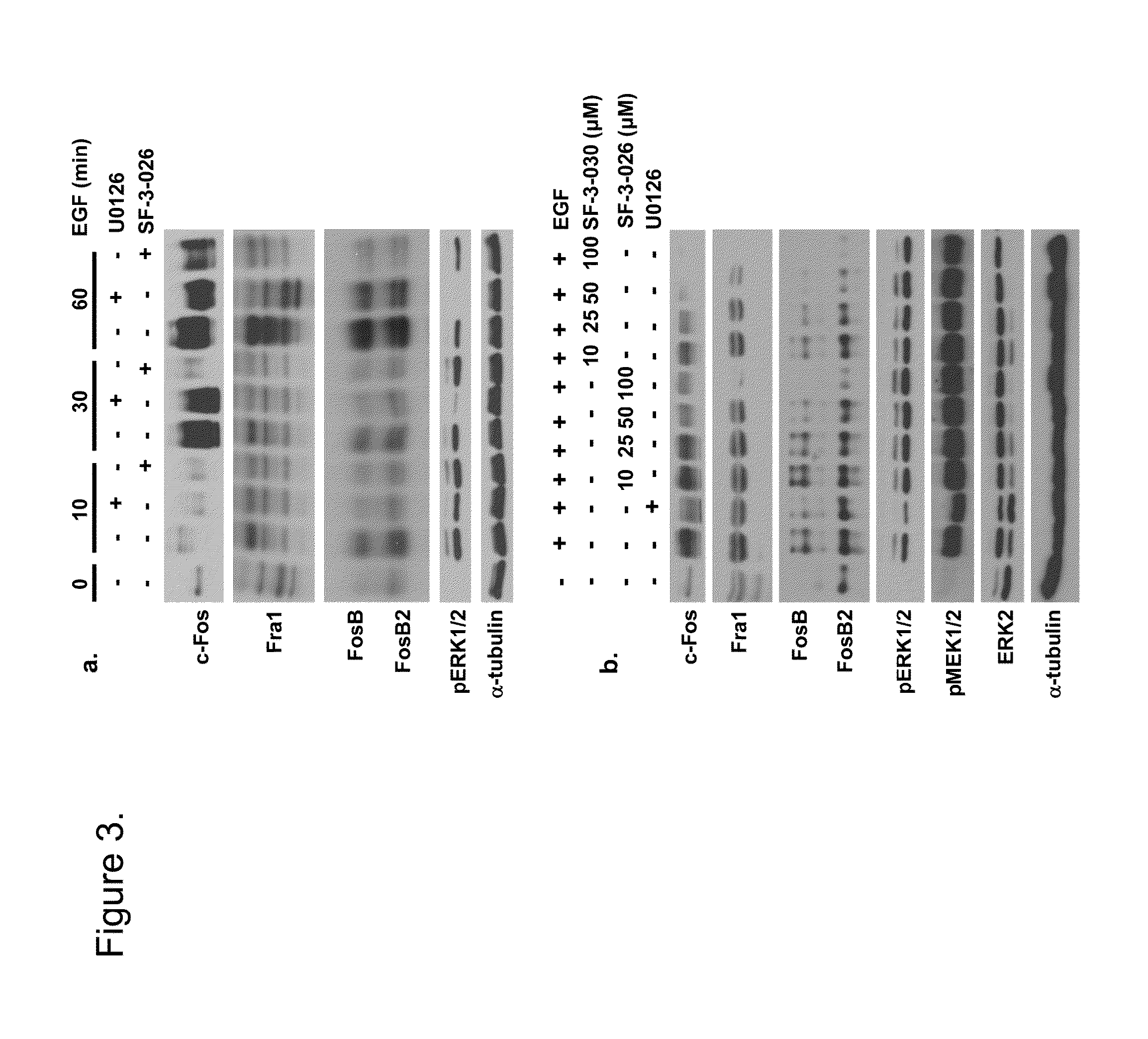
Inhibitors for extracellular signal-regulated kinase docking domains and uses therefor
InactiveUS20070066616A1Inhibit cell proliferationReduce cell proliferationBiocideAnimal repellantsExtracellular signalComputer aid
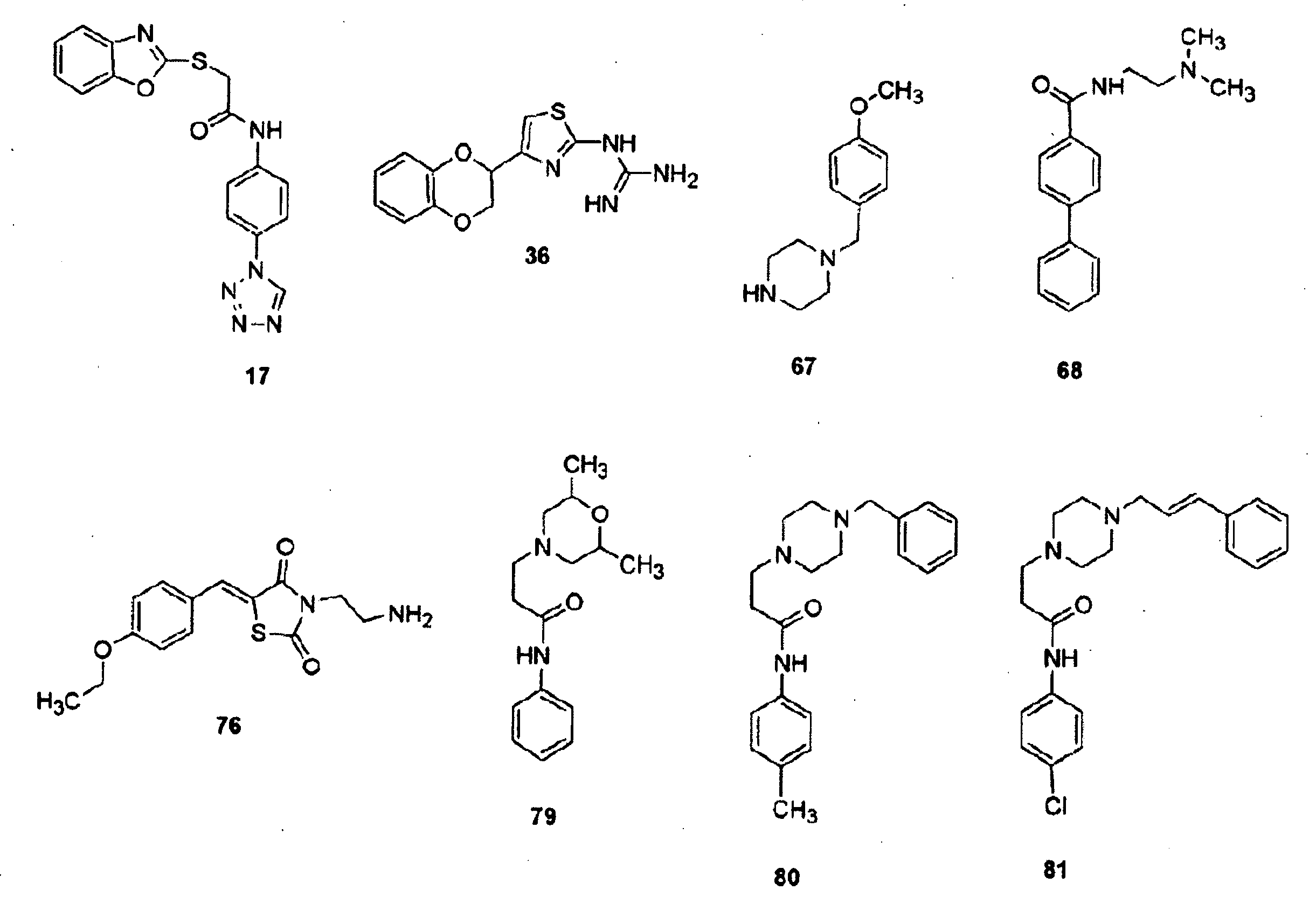
Provided herein are compounds and methods of using compounds that selectively inhibit binding to one or more docking domain regions of an extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) to inhibit in a cell having an extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity. Such methods may be used to inhibit cell proliferation of a neoplastic cell, to treat a cancer and further may be used in conjunction with administration of an anticancer drug at a reduced dosage to treat a cancer with a concomitant reduction in toxicity to an individual receiving the treatment. Also provided is a method to design and screen for compounds to inhibit binding within the extracellular signal-regulated kinase docking domain region, using at least in part computer-aided drug design modeling.
Owner:SHAPIRO PAUL +1
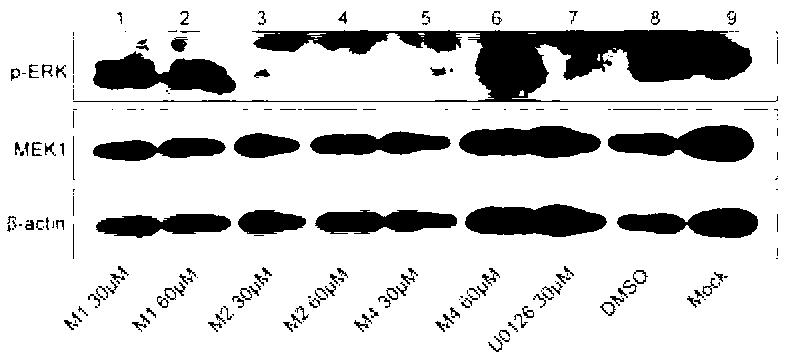
Compound with MEK (Mitogen-activated and Extracellular signal-regulated Kinase) inhibiting function as well as preparation method and application of compound
The invention discloses a compound with an MEK (Mitogen-activated and Extracellular signal-regulated Kinase) inhibiting function as well as a preparation method and application of the compound. The structure of the compound disclosed by the invention is as shown in a formula (I). The preparation method of the compound disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of forming a coumarin ring by adopting a Pechmann reaction mainly and carrying out structural modification of different sites. In the binding experiment of the compound disclosed by the invention and MEK, the binding activity is up to 54.57nM; the anti-proliferation effect IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration) value on the melanoma cell A375 is up to 1.23 micrometers; the anti-proliferation effect IC50 value on the colon cancer cell HT-29 is up to 2.13 micrometers; and the activity is higher than that of a positive control U0126. The novel structure type coumarins compound with the MEK inhibiting function shows good MEK binding activity, MEK inhibiting activity, ERK (Extracellular signal Regulated Kinase) pathway inhibiting activity, anti-tumor effect and antiviral effect and has broad application value. The formula (I) is as shown in the specification.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
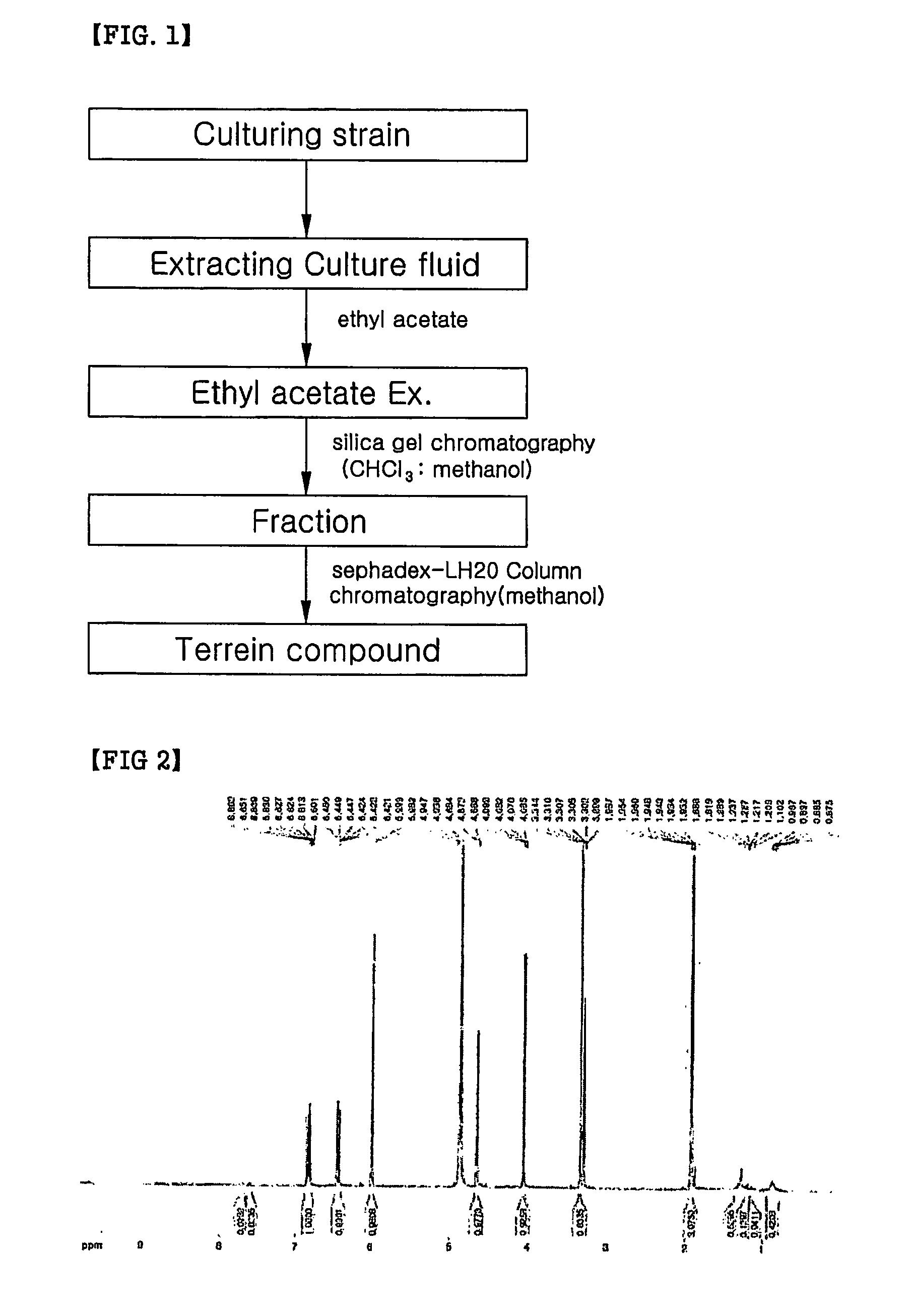
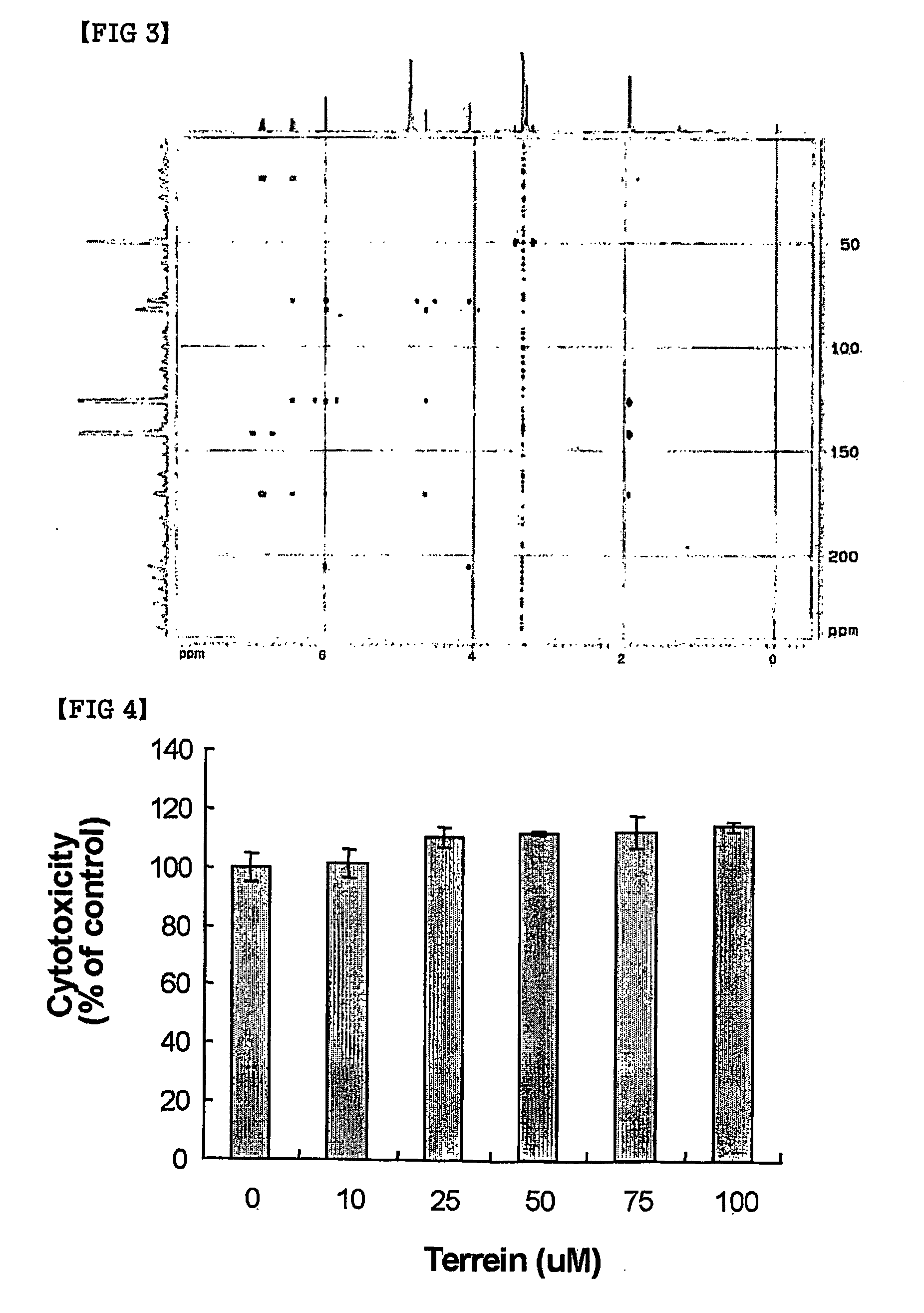
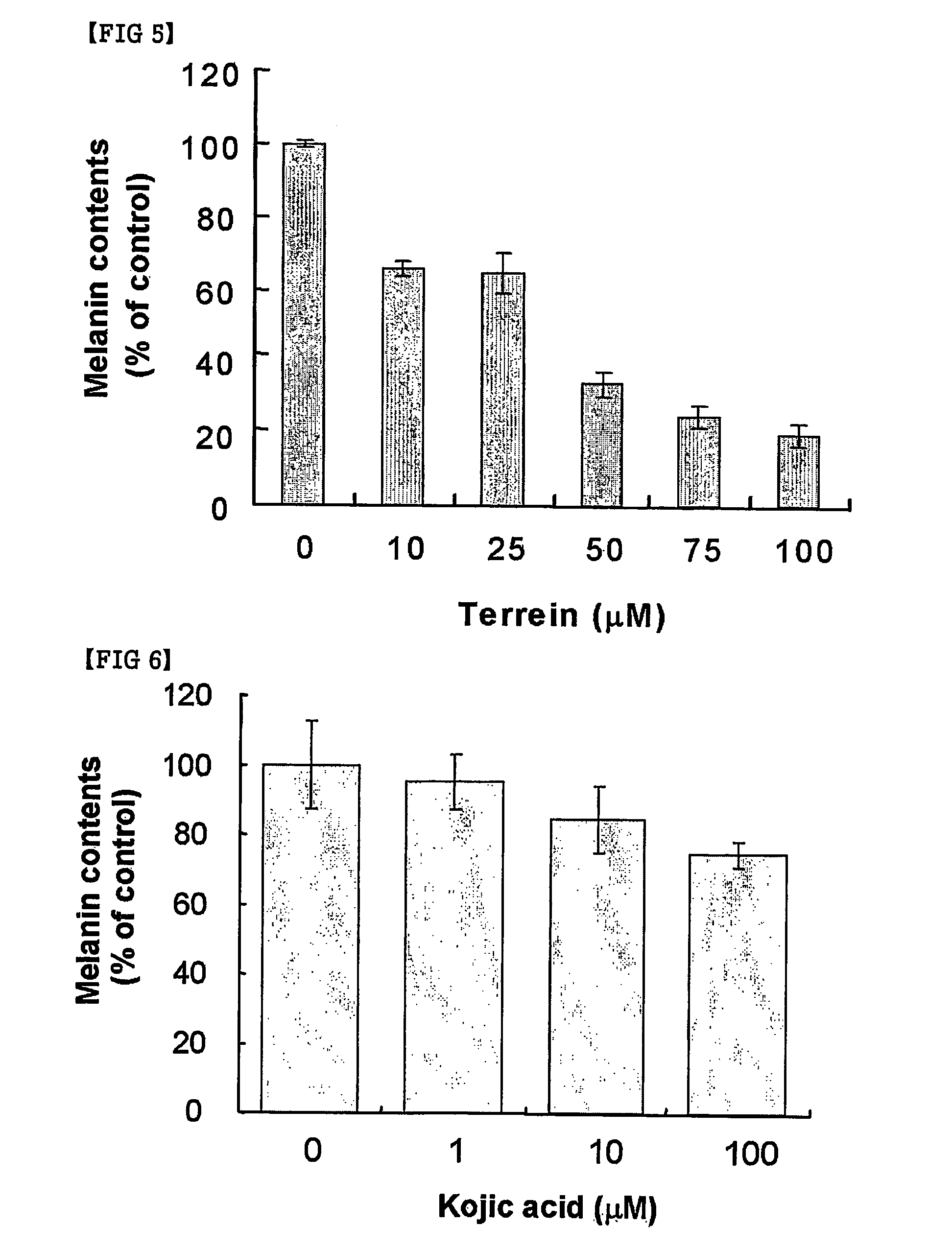
Terrein compound having melanin biosynthesis inhibitors and its preparation
InactiveCN1925848ANon-cytotoxicNo side effectsOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsExtracellular signalWhitening Agents
The present invention relates to a melanin biosynthesis inhibitor containing terrein compound as an effective ingredient. The terrein compound can be easily separated from Penicillium sp KCTC 26245, a fungal strain inhabited in domestic soil. It does not directly inhibit tyrosinase but inhibits the expression of MITF (microphthalmia-associated transcription factor) by activating ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) in melanin chromatocytes to give whitening effect. So, the melanin biosynthesis inhibiting effect of the compound is much greater than that of any other conventional inhibitors, and further the effect can be raised when the compound is used together with other inhibitors, owing to their different mechanisms. Thus, the compound of the present invention can be effectively used as a skin trouble treating agent, a skin whitening agent and a browning inhibitor.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH +1
Extracellular-signal-regulated-kinase (ERK) heteropolyligand polypeptide
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Sorafenib tosylate-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin clathrate compound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102145175APharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsExtracellular signalCancer cell
The invention relates to a sorafenib tosylate-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin clathrate compound and a preparation method thereof. Sorafenib plays the role of anticancer by inhibiting RAS / RAF / MEK (methyl ethyl ketone) / ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) signal conducting channels and inhibiting tumor angiogenesis, and is directed to cancer cells instead of normal cells. The sorafenib is almost insoluble in water, and the average relative bioavailability of oral administration is 38% to 49%. According to the preparation method of the invention, the sorafenib tosylate-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin clathrate compound is prepared based on the clathrate compound-forming property of hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin, thereby increasing medicine dissolvability, improving medicine dissolution and raising medicine bioavailability.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Terrein compound having melanin biosynthesis inhibitors and its preparation
InactiveUS20070128136A1Inhibit expressionInhibits the synthesis of melaninCosmetic preparationsBiocideExtracellular signalAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to a melanin biosynthesis inhibitor containing terrein compound as an effective ingredient. The terrein compound can be easily separated from Penicillium sp KCTC 26245, a fungal strain inhabited in domestic soil. It does not directly inhibit tyrosinase but inhibits the expression of MITF (microphthalmia-associated transcription factor) by activating ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) in melanin chromatocytes to give whitening effect. So, the melanin biosynthesis inhibiting effect of the compound is much greater than that of any other conventional inhibitors, and further the effect can be raised when the compound is used together with other inhibitors, owing to their different mechanisms. Thus, the compound of the present invention can be effectively used as a skin trouble treating agent, a skin whitening agent and a browning inhibitor.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH +1
Non-atp dependent inhibitors of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
JAK/STAT inhibitors and MAPK/ERK inhibitors for RSV infection
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
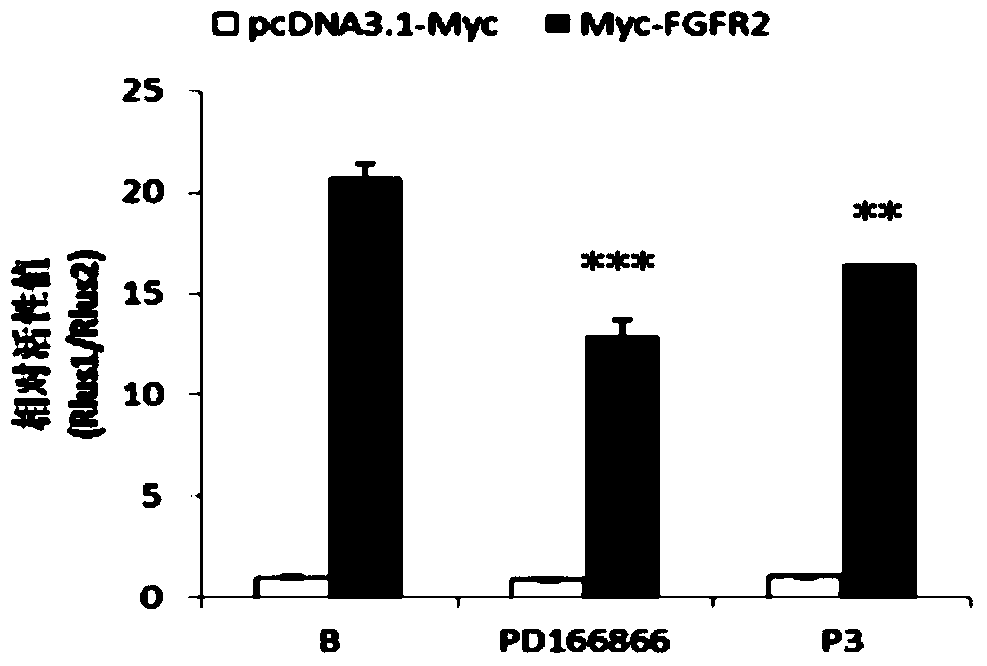
Polypeptide capable of regulating activity of FGFR2 (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2)
ActiveCN103980349AInhibitory activityEasy to adjustPeptidesExtracellular signalFibroblast growth factor receptor 2
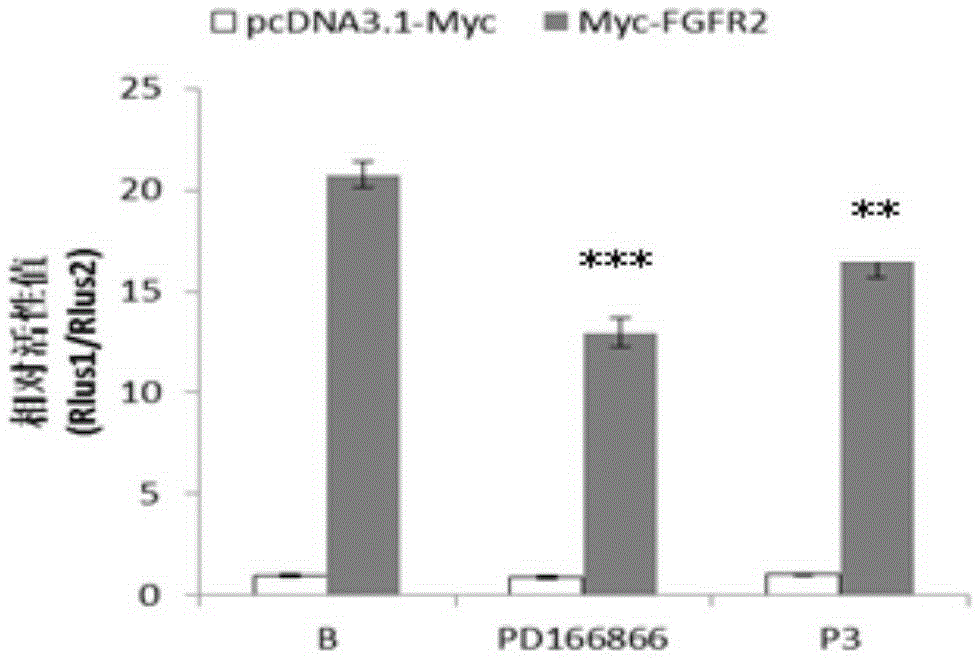
The invention discloses a polypeptide capable of regulating the activity of FGFR2 (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2). The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is Asn-Leu-Gly-Gln-Glu-Leu-Ala-Phe-Arg-Val-Pro-Asn. The polypeptide disclosed by the invention can be specifically combined with the FGFR2, plays an obviously regulating role on the activity of the FGFR2, can outstanding inhibit the activity of p-ERK (Phospho-Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase) contained in the main downstream signal channel MAPK (Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase) of the FGFR2, has the advantages of low molecular weight, easiness for preparation, controllability in quality, low immunogenicity and the like and has good potential application value in the field of medicines.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Non-ATP dependent inhibitors of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)
ActiveUS9115122B2Organic chemistryHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsExtracellular signalKinase
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
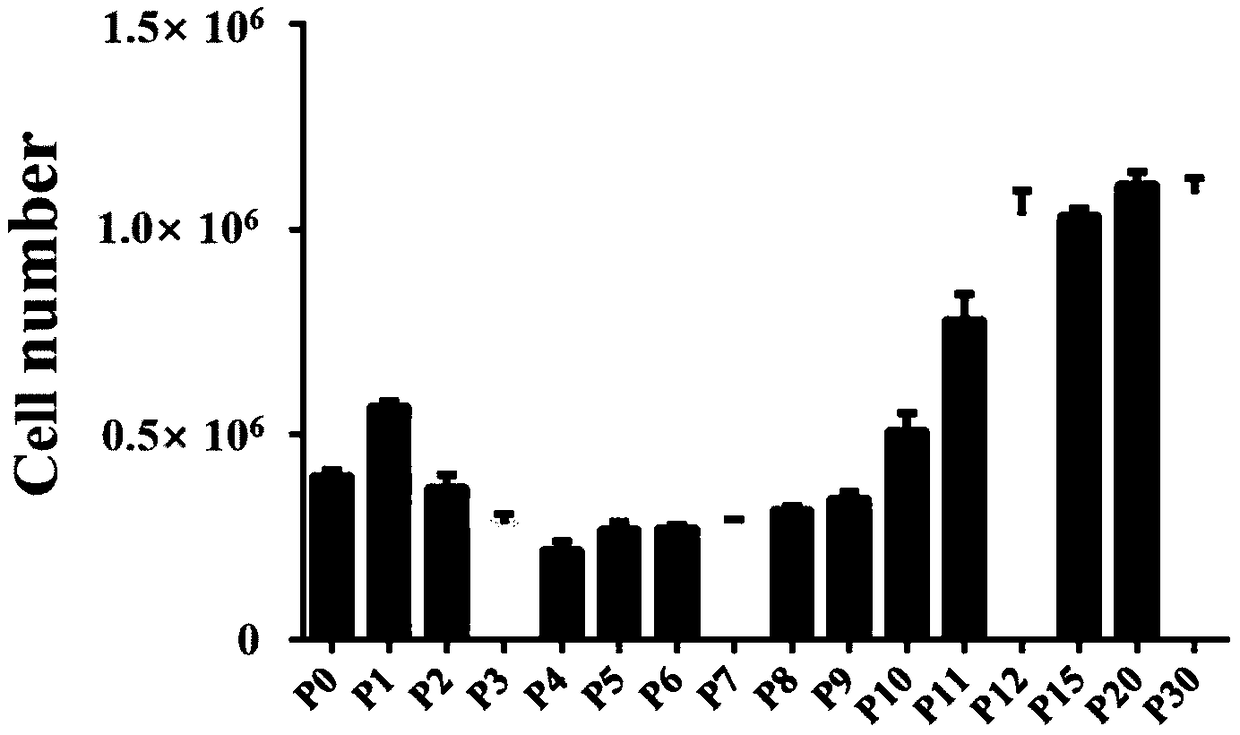
Lacrimal gland stem cell as well as culture system and culture method for lacrimal gland stem cell
ActiveCN109486766AA large amountOvercoming the defect that lacrimal gland stem cells cannot be effectively culturedCulture processNervous system cellsMatrigelL-alanyl-l-glutamine
The invention relates to a lacrimal gland stem cell as well as a culture system and a culture method for the lacrimal gland stem cell and relates to the field of cell engineering. According to the culture system for the lacrimal gland stem cell, disclosed by the invention, DMEM / F12 serves as a basal culture medium, and the following components are added to form a culture liquid: a cell culture additive, non-essential amino acids, L-alanyl-L-glutamine, mitogen activeated protein kinase / extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway ligand, fibroblast growth factors, a Wnt signaling pathway ligand, and a composition of ROCK signaling pathway inhibitors; and matrigel serves as a stereoscopic support. The culture method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: digesting lacrimal gland tissues of mice into single cells to be inoculated into matrigel, adding the cells into a lacrimal gland stem cell culture liquid after solidification, and performing primary culture. The lacrimal gland stem cells cultured by the method disclosed by the invention are high in quantity and capable of realizing stable and continuous passage, have an effect of restoring the lacrimalgland secretion effect, and can be used for effectively treating xerophthalmia.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
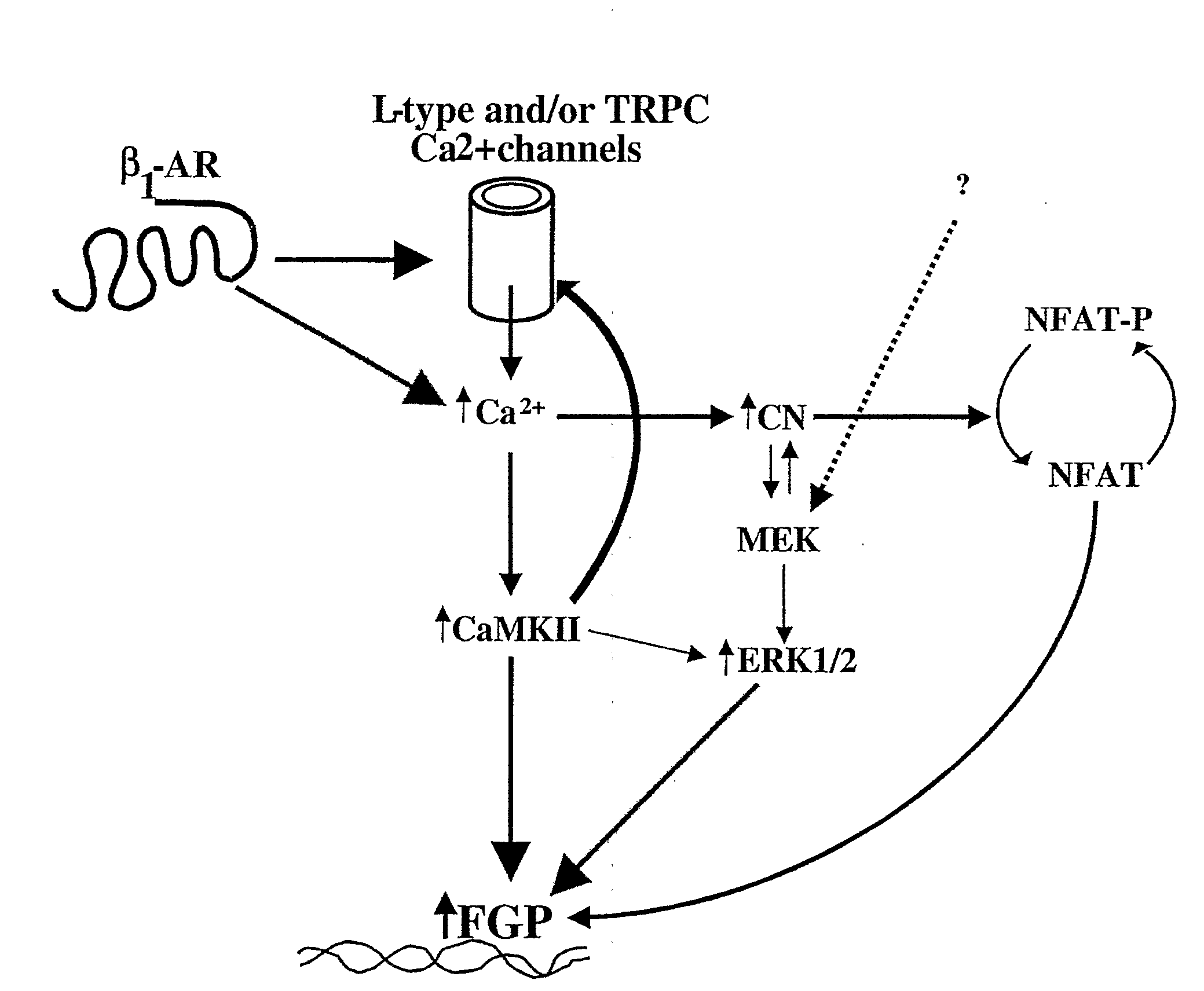
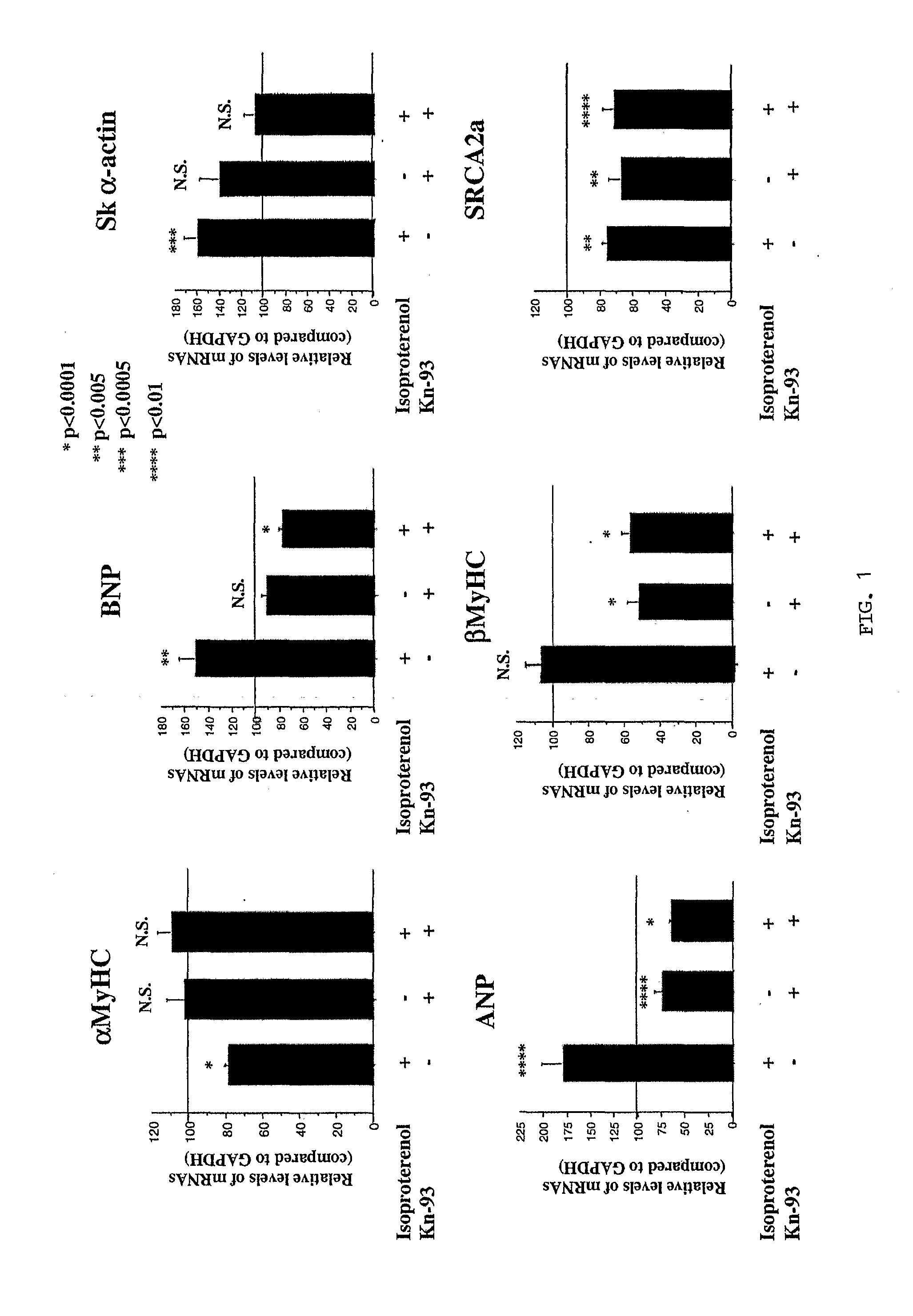
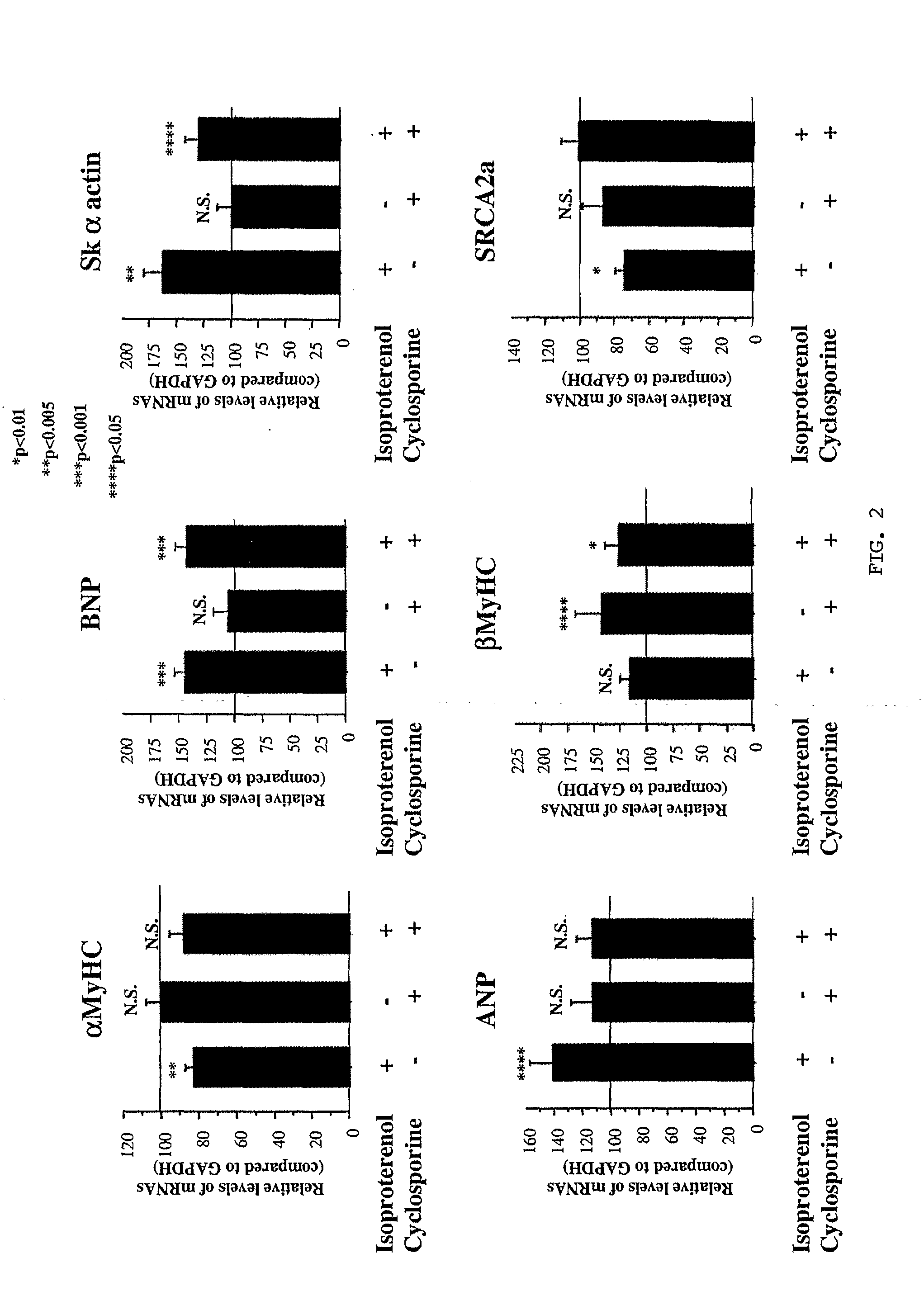
Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 as a treatment for cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure
InactiveUS20090220507A1Improve athletic abilityIncrease injection volumeCompound screeningApoptosis detectionExtracellular signalManagement of heart failure
The present invention provides for methods of treating and preventing cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. The present invention provides the link between ERK1 / 2 and calcineurin and CamKII. The present invention further demonstrates that inhibitors of ERK1 / 2 inhibit cardiac hypertrophy and heart disease by inhibiting, in part, the fetal cardiac gene expression that occurs when Ca2+-dependent signalling occurs in the heart.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
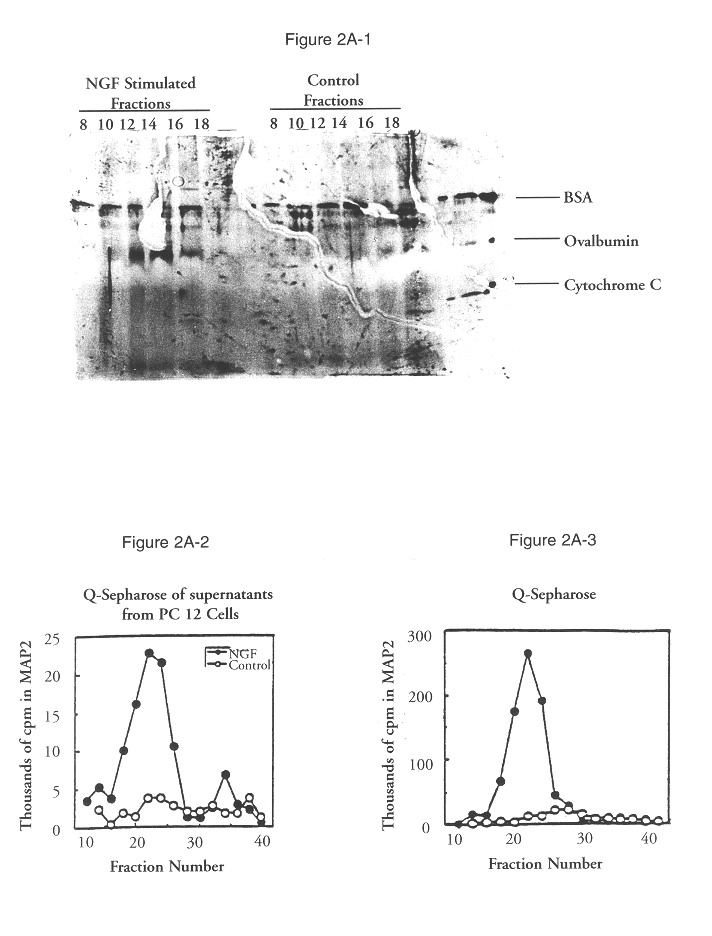
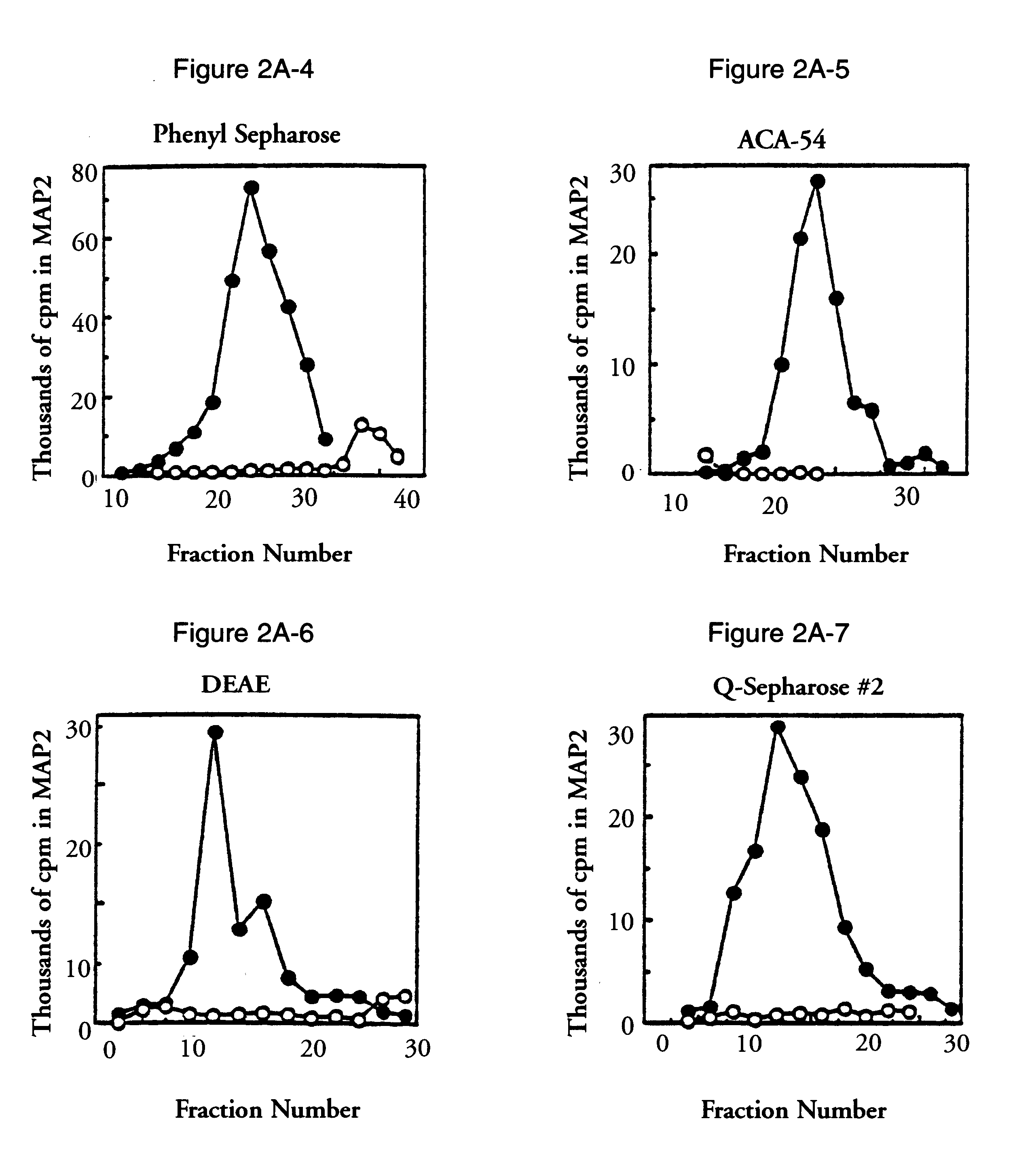
Antibodies directed toward extracellular signal-related kinases
The present invention relates to a newly identified family of protein serine / threonine kinases which phosphorylate microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2). It is based, in part, on the cloning and characterization of novel MAP2 kinases designated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, 2, and 3 (ERK1, ERK2, ERK3) which are expressed in the central nervous system, and on the identification of another ERK family member, ERK4, with antisera. The present invention provides for recombinant nucleic acid molecules and proteins representing members of the MAP2 kinase family, and also for microorganisms, transgenic animals, and cell lines comprising recombinant MAP2 kinase molecules. In additional embodiments of the invention, the present invention provides for methods for assaying cellular factor activity, including, but not limited to, nerve growth factor activity, in which the activation of MAP2 kinase serves as an indicator of cellular factor activity. These methods may be extremely useful in screening compounds for the presence of a desired cellular factor activity. In specific embodiments, compounds which may be useful in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, peripheral neuropathies, and diabetes may be identified using the methods of the invention.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC +1
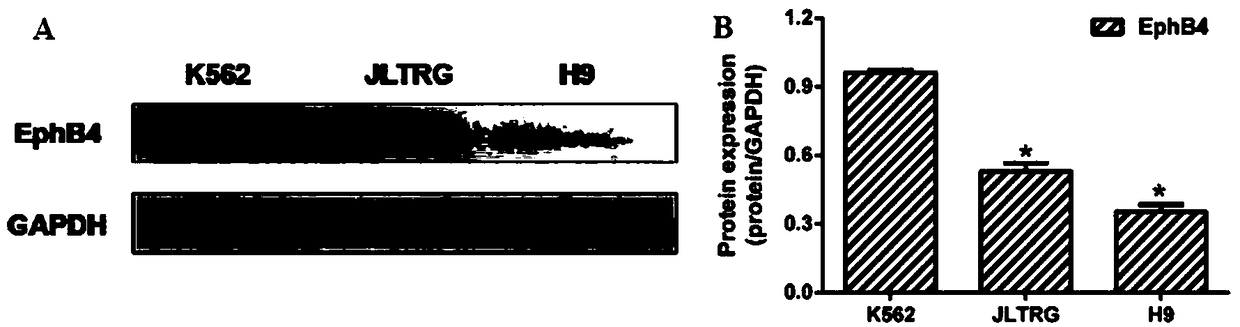
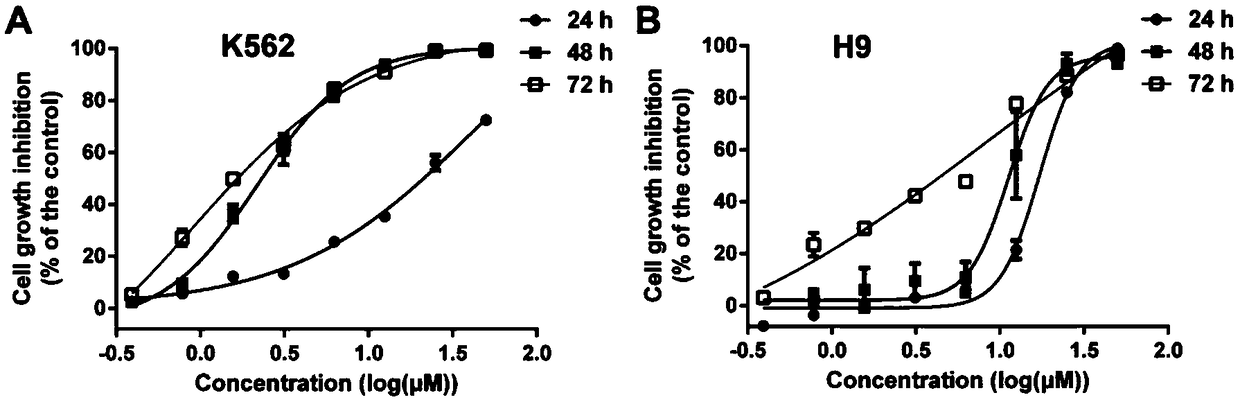
Application of Vandetanib to preparation of targeted EphB4 anti-tumor drug
InactiveCN108785310AInhibits kinase activityPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAntileukemic agentExtracellular signal
The invention discloses an application of Vandetanib to preparation of a targeted EphB4 anti-tumor drug, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. Experiments verify the application of the Vandetanib, and a molecular docking method, an SPR (surface plasmon resonance) method and MST (modulated scatterer technique) experiment results indicate that the Vandetanib can interact with EphB4. EphB4kinase experiments display that the Vandetanib can obviously inhibit EphB4 kinase activity. Proliferation of leukemic cells K562, JLTRG and H9 is remarkably inhibited. Besides, the Vandetanib remarkably inhibits expression of signal molecules p-PI3K p85 / p55 and PI3K p85 at the downstream of the EphB4, and the phosphorylation level of MEK (methyl ethyl ketone) and ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) is reduced. Therefore, the experiment results sufficiently support the application of the Vandetanib to an anti-leukemia drug and the targeted EphB4 anti-tumor drug.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
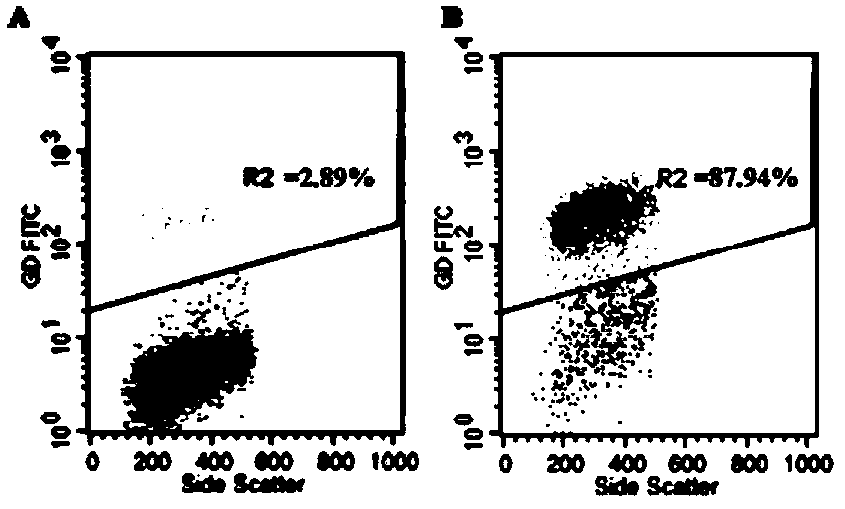
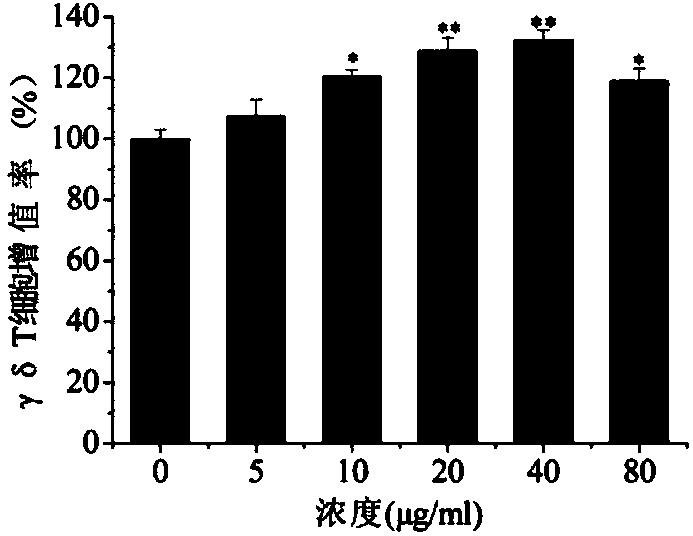
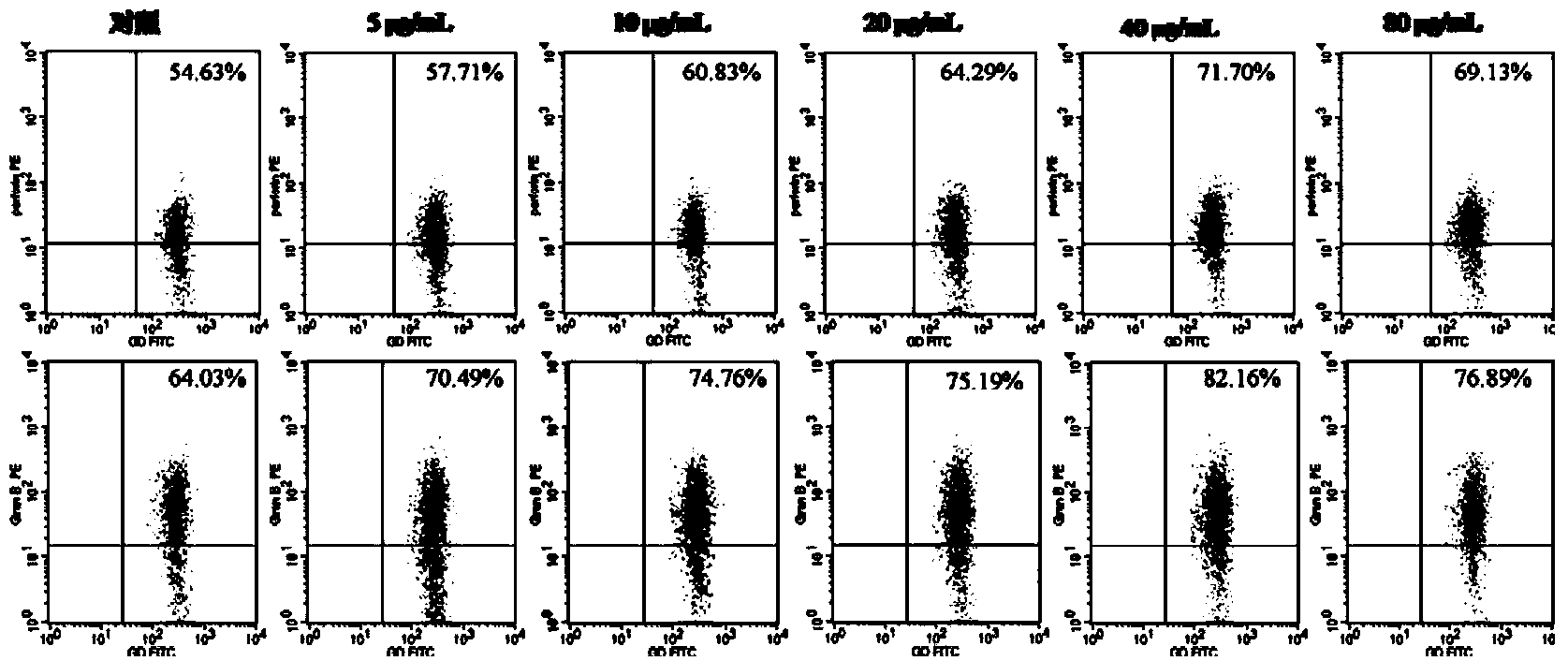
Application of quercitrin in preparation of human gamma delta T cell proliferator
InactiveCN103860574APromote proliferationHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersQuercitrinT cell
The invention discloses an application of quercitrin in preparation of a human gamma delta T cell proliferator, and relates to the technical field of medicines. Quercitrin can remarkably promote proliferation of human gamma delta T cells and promote expression of perforin and granzyme B, so that the quercitrin is of certain dose dependency. The gamma delta T cell treated by the quercitrin can promote expression of p-ERK (Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase)1 / 2 and p-Akt in active form and promote expression of an anti-apoptoasis protein Bcl-2, so that the gamma delta T cell is of certain dose dependency. The invention discovers the novel medical use of quercitrin and provides experimental references to development of tumor immunotherapy medicines.
Owner:NO 97 HOSPITAL OF PLA
Methods of treating inflammatory bowel disease
InactiveUS20060088533A1Increase gene expressionInhibition of activationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsExtracellular signalClostridium difficile
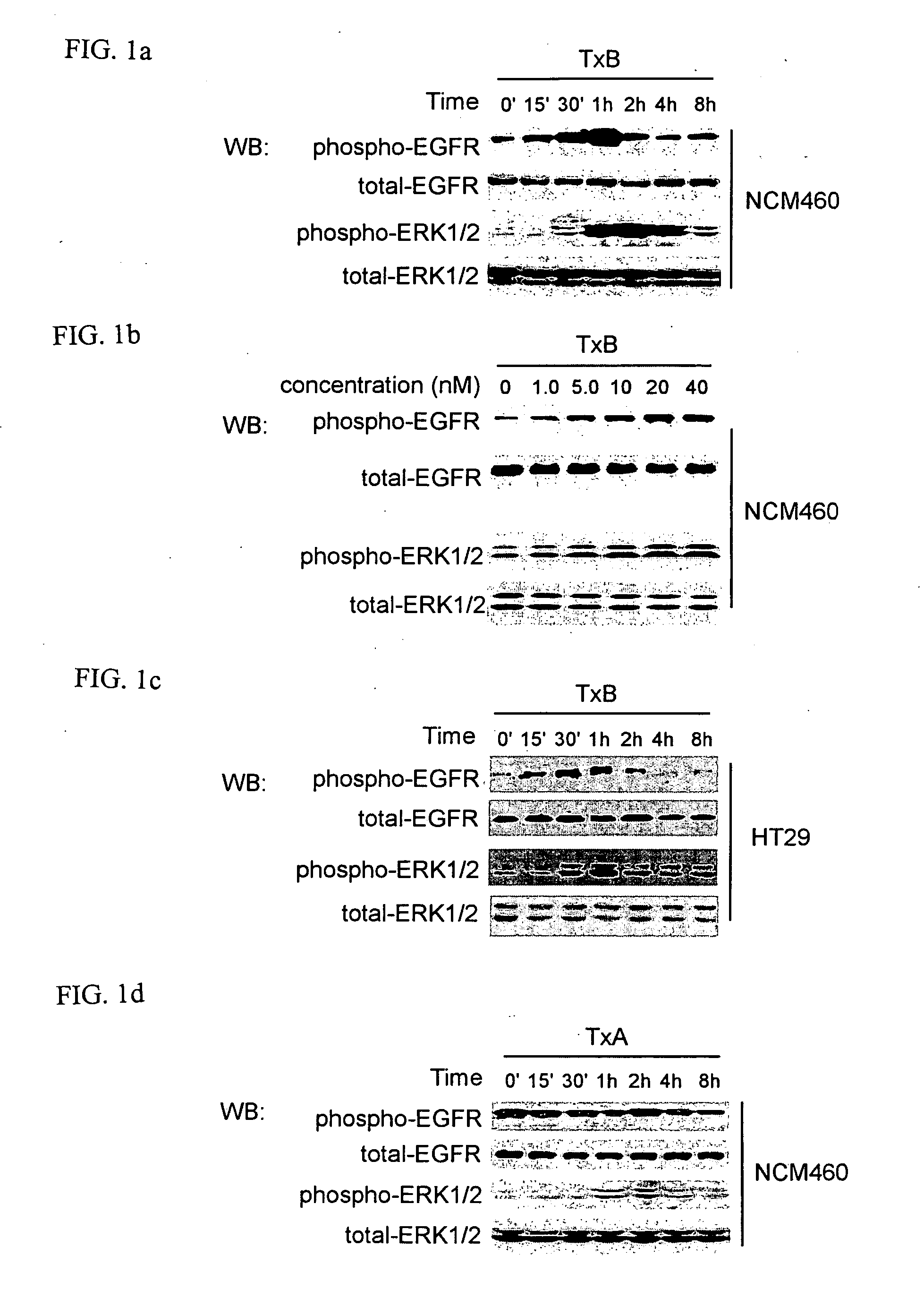
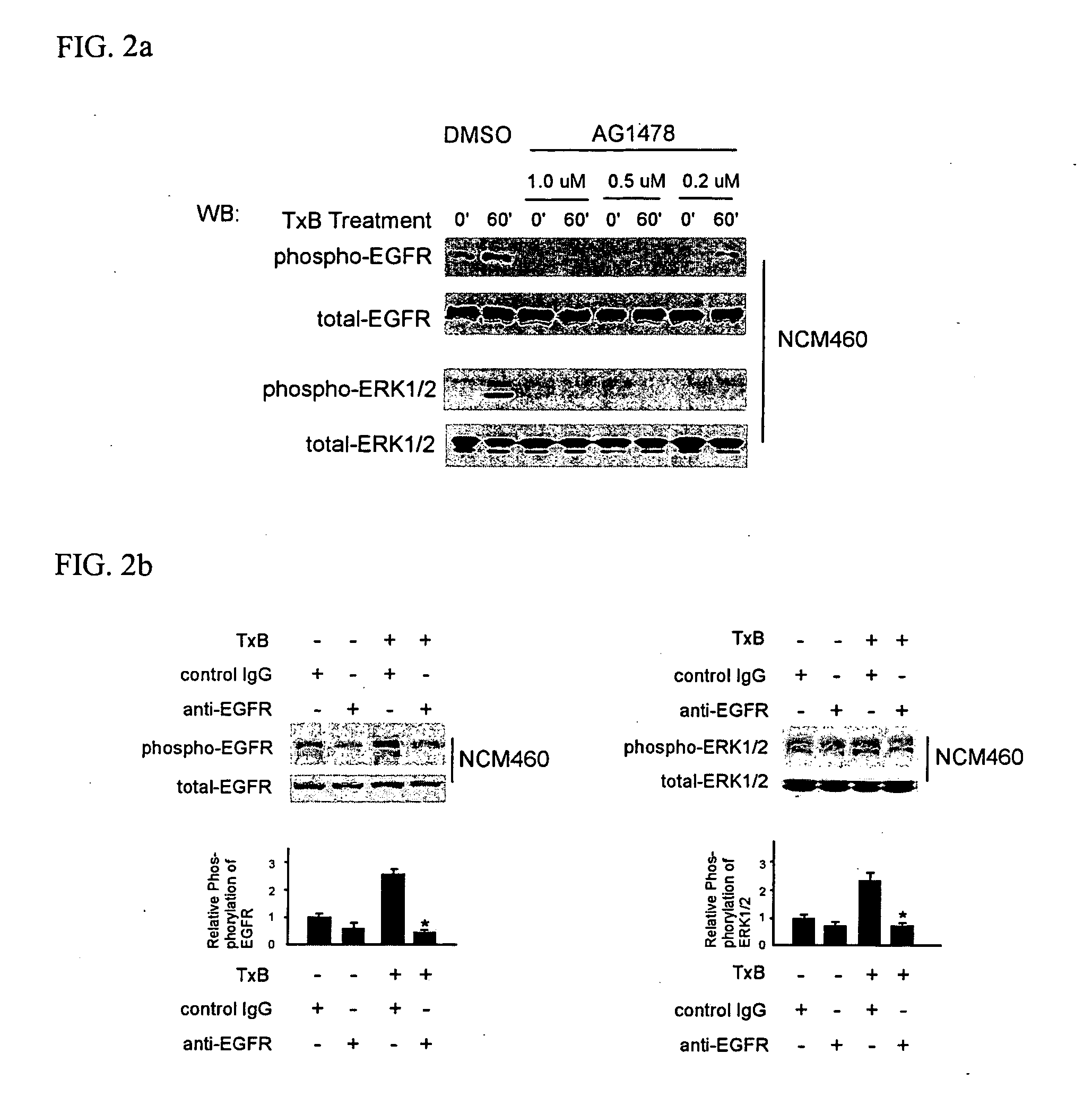
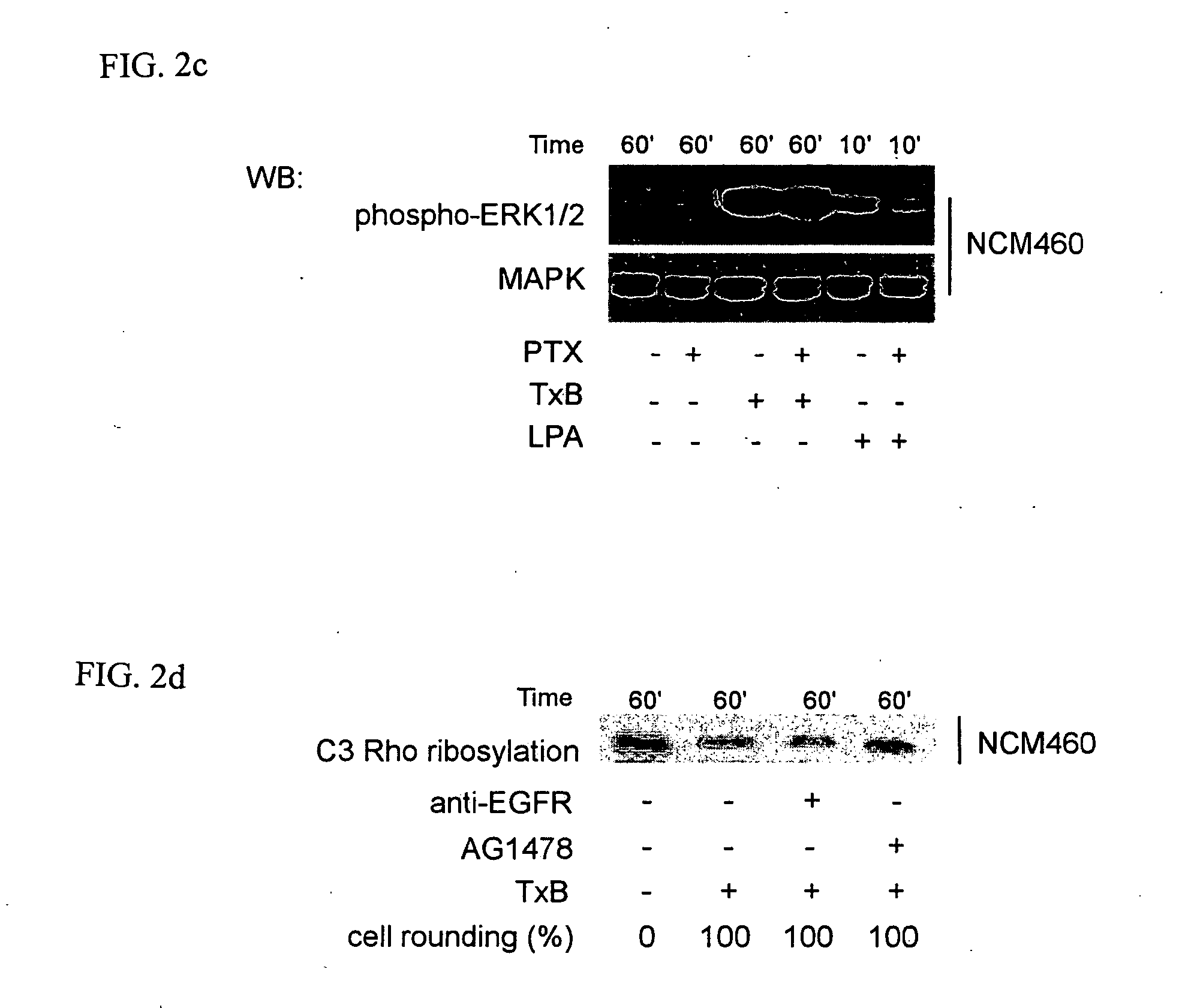
Methods for treating intestinal inflammation by inhibiting Clostridium difficile toxin B-mediated activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor or by inhibiting Clostridium difficile toxin B-mediated activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 / 2 are described.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
ERK1 MAP2 protein kinase
The present invention relates to a newly identified family of protein serine / threonine kinases which phosphorylate microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2). It is based, in part, on the cloning and characterization of novel MAP2 kinases designated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, 2, and 3 (ERK1, ERK2, ERK3) which are expressed in the central nervous system, and on the identification of another ERK family member, ERK4, with antisera. The present invention provides for recombinant nucleic acid molecules and proteins representing members of the MAP2 kinase family, and also for microorganisms, transgenic animals, and cell lines comprising recombinant MAP2 kinase molecules. In additional embodiments of the invention, the present invention provides for methods for assaying cellular factor activity, including, but not limited to, nerve growth factor activity, in which the activation of MAP2 kinase serves as an indicator of cellular factor activity. These methods may be extremely useful in screening compounds for the presence of a desired cellular factor activity. In specific embodiments, compounds which may be useful in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, peripheral neuropathies, and diabetes may be identified using the methods of the invention.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC +1
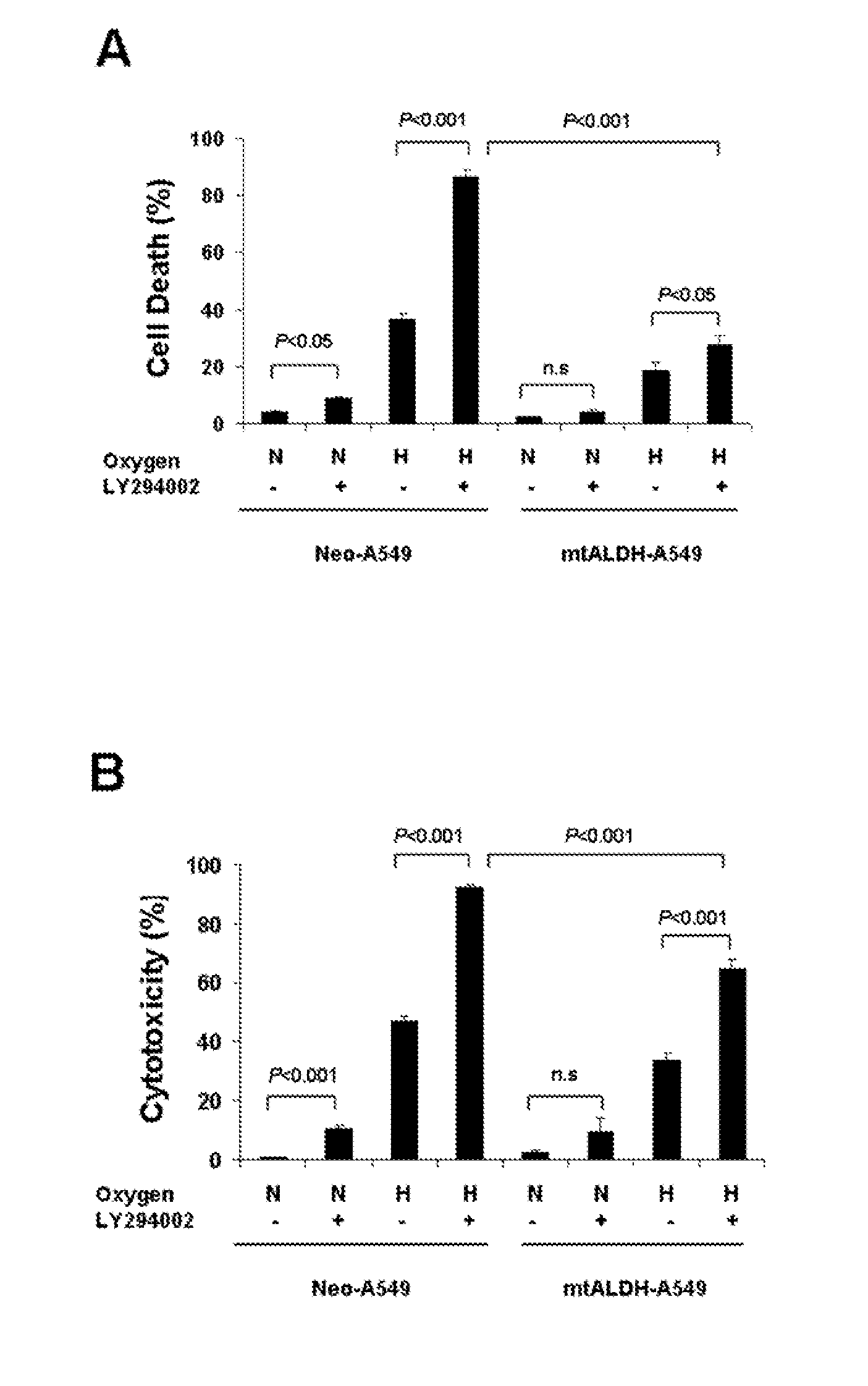
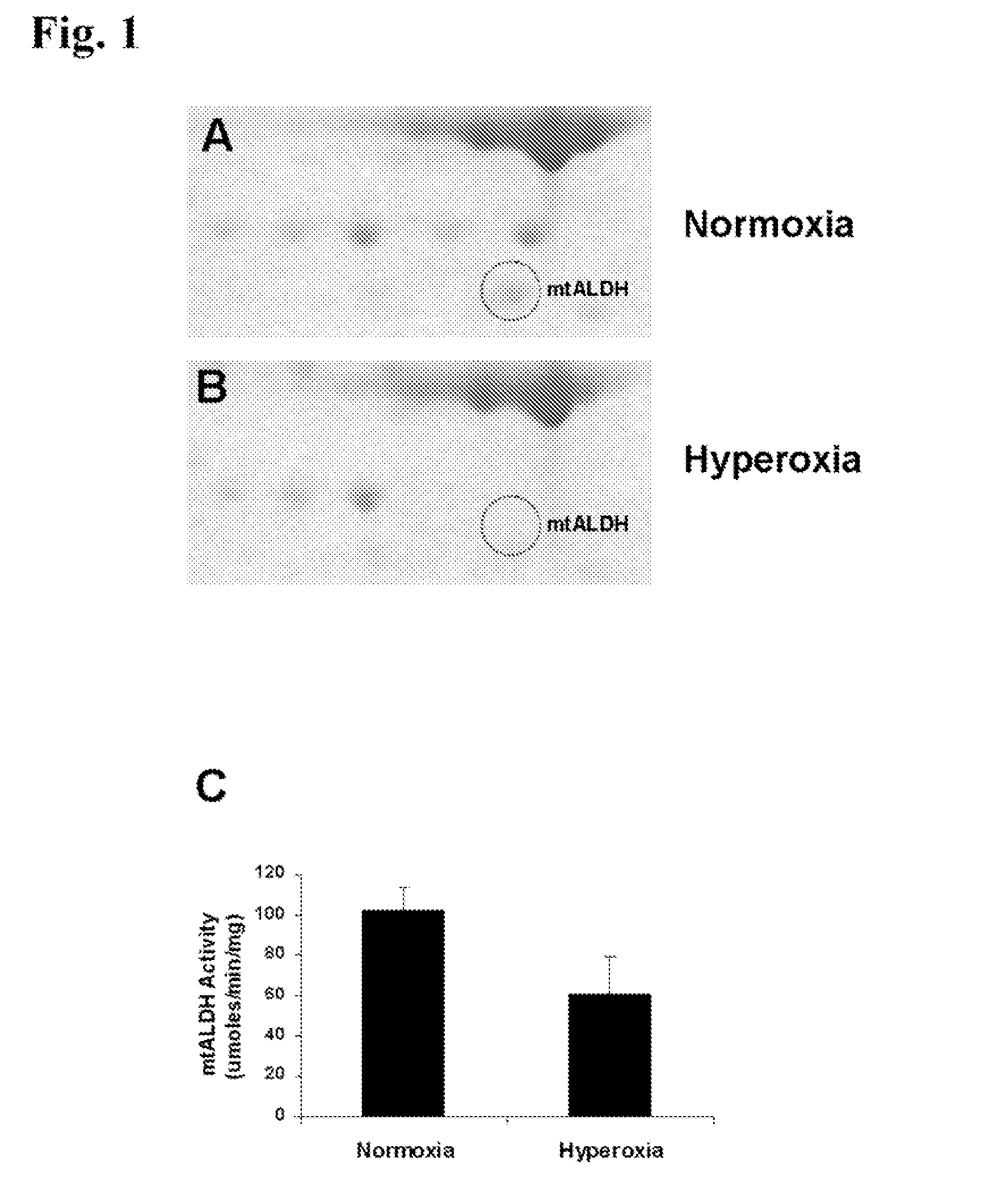
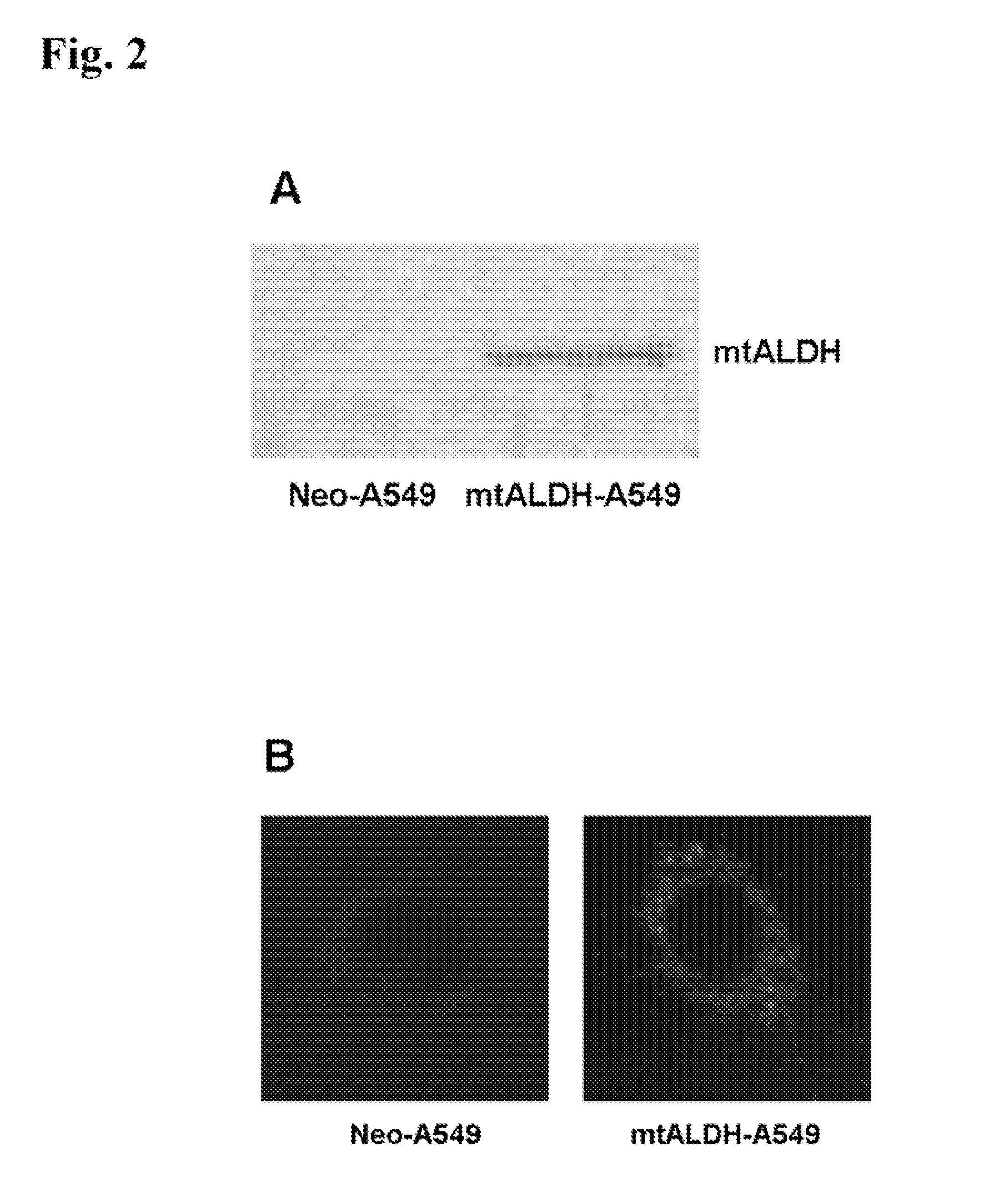
Attenuation of hyperoxia-induced cell death with mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase
InactiveUS20080058278A1Reducing and eliminating generationPrevent and reduce incidenceGenetic material ingredientsGenetically modified cellsExtracellular signalPhosphorylation
Oxygen toxicity is one of the major risk factors in the development of the chronic lung disease or bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature infants. Using proteomic analysis, we discovered mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (mtALDH or ALDH2) was down-regulated in neonatal rat lung after hyperoxic exposure. To study the role of mtALDH in hyperoxic lung injury, we overexpressed mtALDH in human lung epithelial cells (A549) and found that mtALDH significantly reduced hyperoxia-induced cell death. Compared to control cells (Neo-A549), the necrotic cell death in mtALDH overexpressing cells (mtALDH-A549) decreased from 25.3% to 6.5%, 50.5% to 9.1% and 52.4% to 15.06% after 24-, 48- and 72-hour hyperoxic exposure, respectively. The levels of intracellular and mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) in mtALDH-A549 cells after hyperoxic exposure were significantly lowered compared to Neo-A549 cells. mtALDH overexpression significantly stimulated extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation under normoxic and hyperoxic conditions. Inhibition of ERK phosphorylation partially eliminated the protective effect of mtALDH in hyperoxia-induced cell death, suggesting ERK activation by mtALDH conferred cellular resistance to hyperoxia. mtALDH overexpression augmented Akt phosphorylation and maintained the total Akt level in mtALDH-A549 cells under normoxic and hyperoxic conditions. Inhibition of PI3K activation by LY294002 in mtALDH-A549 cells significantly increased necrotic cell death after hyperoxic exposure, indicating that PI3K / Akt activation by mtALDH played an important role in cell survival after hyperoxia. Taken together, these data demonstrate that mtALDH overexpression attenuates hyperoxia-induced cell death in lung epithelial cells through reduction of ROS, activation of ERK / MAPK and PI3K / Akt cell survival signaling pathways.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
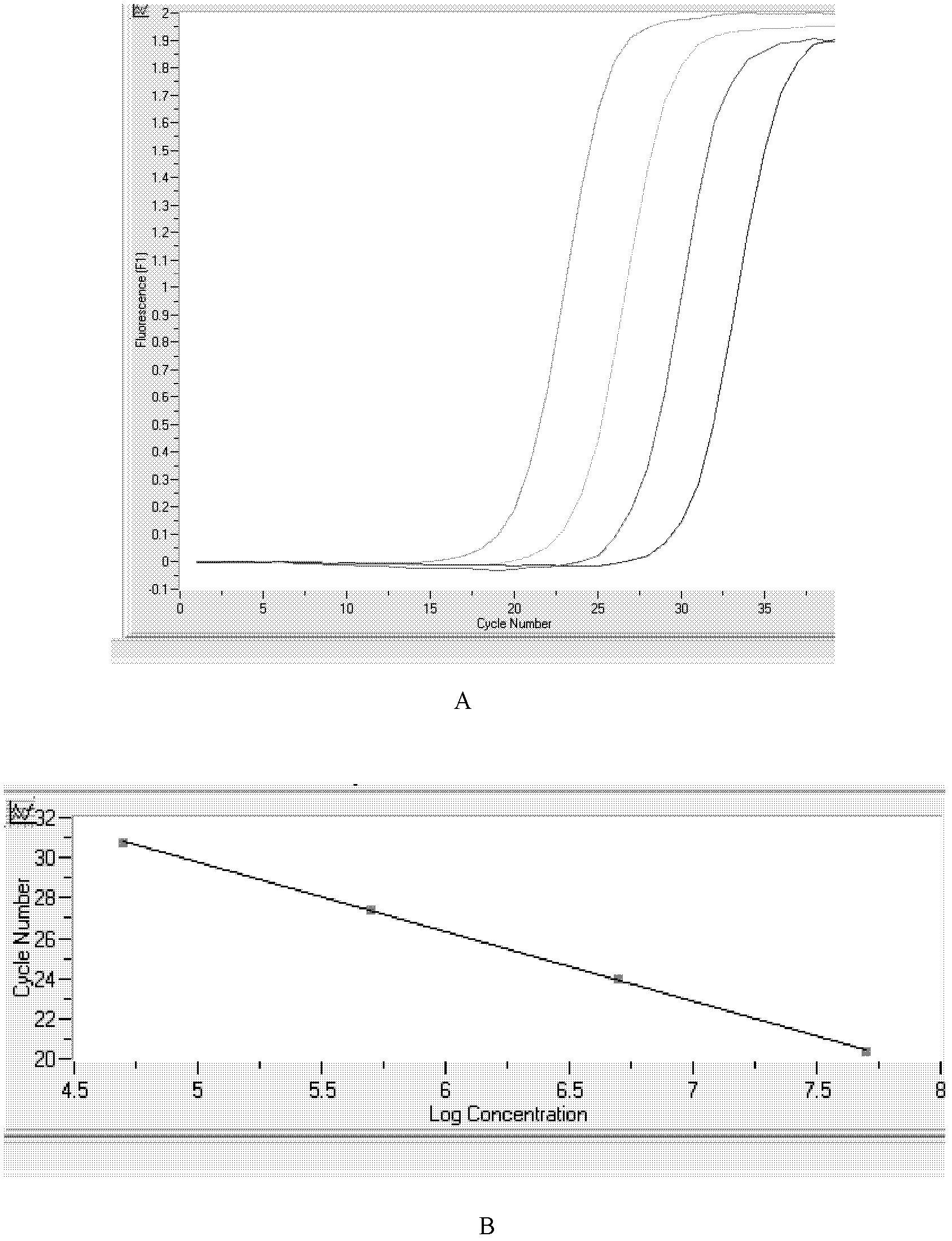
Kit for quickly detecting expression quantities of related genes of sorafenib chemotherapeutic medicament
InactiveCN102618656AImprove accuracyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceExtracellular signalTumor vessel
The invention relates to the technical field of biology. High expression of kinase insert domain receptors (KDR) and platelet-derived growth factor receptors alpha (PDGFRA) can be viewed in multiple tumor tissues; and sorafenib directly inhibits tumor growth by inhibiting the activities of the KDR and the PDGFR and inhibiting a recombinant activated factor / methyl ethyl ketone / extracellular signal-regulated kinase (RAF / MEK / ERK) signal transduction pathway, and blocks the formation of new tumor vessels by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF), so that the sorafenib achieves double inhibiting and multi-target blocking anti-hepatic cell carcinoma (HCC) effects. Detection of KDR and PDGFR mRNA levels can assist doctors in forecasting the curative effect of medicaments and the clinical outcome of patients, and has important clinical significance. The invention aims to provide a kit capable of quickly, conveniently, sensitively and specifically detecting expression quantities of related genes KDR and PDGFRA of a sorafenib chemotherapeutic medicament. According to the kit, the KDR and PDGFR mRNA levels are detected by adopting a fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology with high sensitivity and specificity, so that the sensitivity and the specificity are remarkably improved; and the kit is quick in detection and high in flux, and can finish the detection in 3 to 4 hours.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Inhibitors for Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Docking Domains and Uses Therefor
InactiveUS20090299063A1Low toxicityInhibit cell proliferationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryExtracellular signalMedicine
Provided herein are compounds and methods of using compounds that selectively inhibit binding to one or more docking domain regions of an extracellular signal-recognition kinase to inhibit in a cell having an extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity. Such methods may be used to inhibit cell proliferation of a neoplastic cell, to treat a cancer and further may be used in conjunction with administration of an anticancer drug at a reduced dosage to treat a cancer with a concomitant reduction in toxicity to an individual receiving the treatment. Also provided is a method to design and screen for compounds to inhibit binding within the extracellular signal-regulated kinase docking domain region, using at least in part computer-aided drug design modeling.
Owner:SHAPIRO PAUL +1
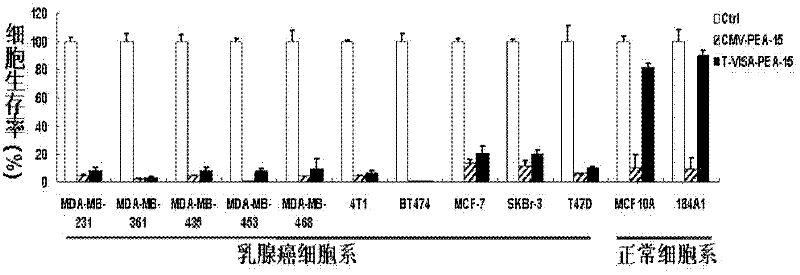
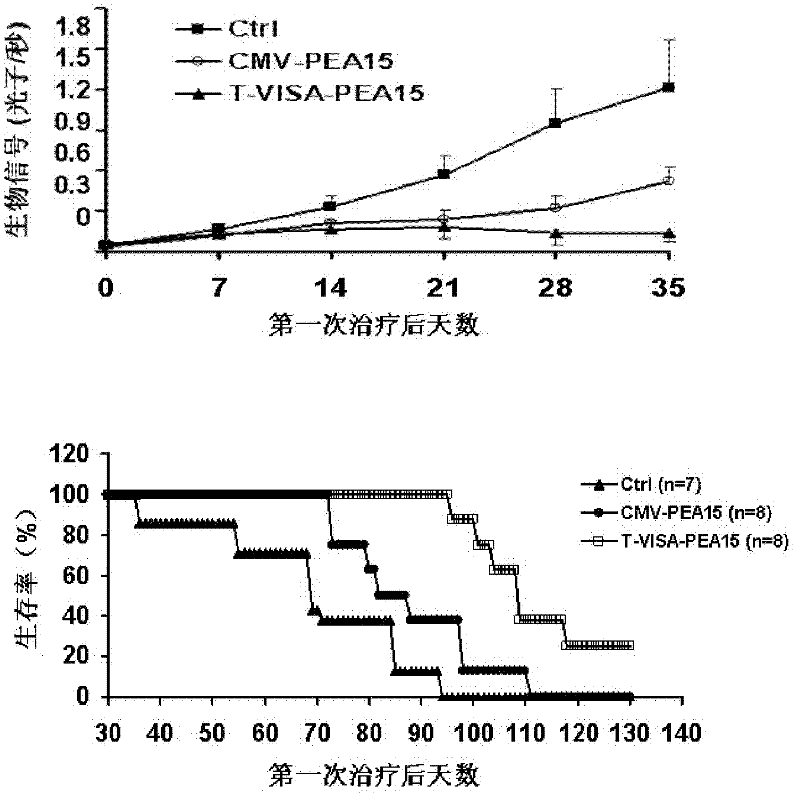
Medicine T-VISA-PEA15 capable of effectively and specifically killing breast cancer cells
ActiveCN102634531AGrowth inhibitionNo killing effectGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsExtracellular signalSide effect
The invention discloses a medicine T-VISA-PEA15 capable of effectively and specifically killing breast cancer cells. The sequence of a T-VISA-PEA15 therapy vector capable of effectively and specifically killing the breast cancer cells is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. A liposome of the medicine T-VISA-PEA15 liposome capable of effectively and specifically killing the breast cancer cells comprises a liposome and the T-VISA-PEA15 therapy vector coated by the liposome, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the T-VISA-PEA15 therapy vector is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. After being coated by the liposome and transferred, the T-VISA-PEA15 therapy vector is enriched on the breast cancer part, so as to effectively target the breast cancer ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) target point and inhibit the breast cancer ERK target point from entering the nucleus, thereby promoting the apoptosis of tumor cells, but not killing the normal cells. The medicine T-VISA-PEA15 can be applied to a whole body and has of the advantages of high gene expression amount, long gene expression time, high gene expression efficiency, definite efficacy, low toxicity and side effect, no toxicity to liver and kidneys and wide prospect in the treatment of the breast cancer.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
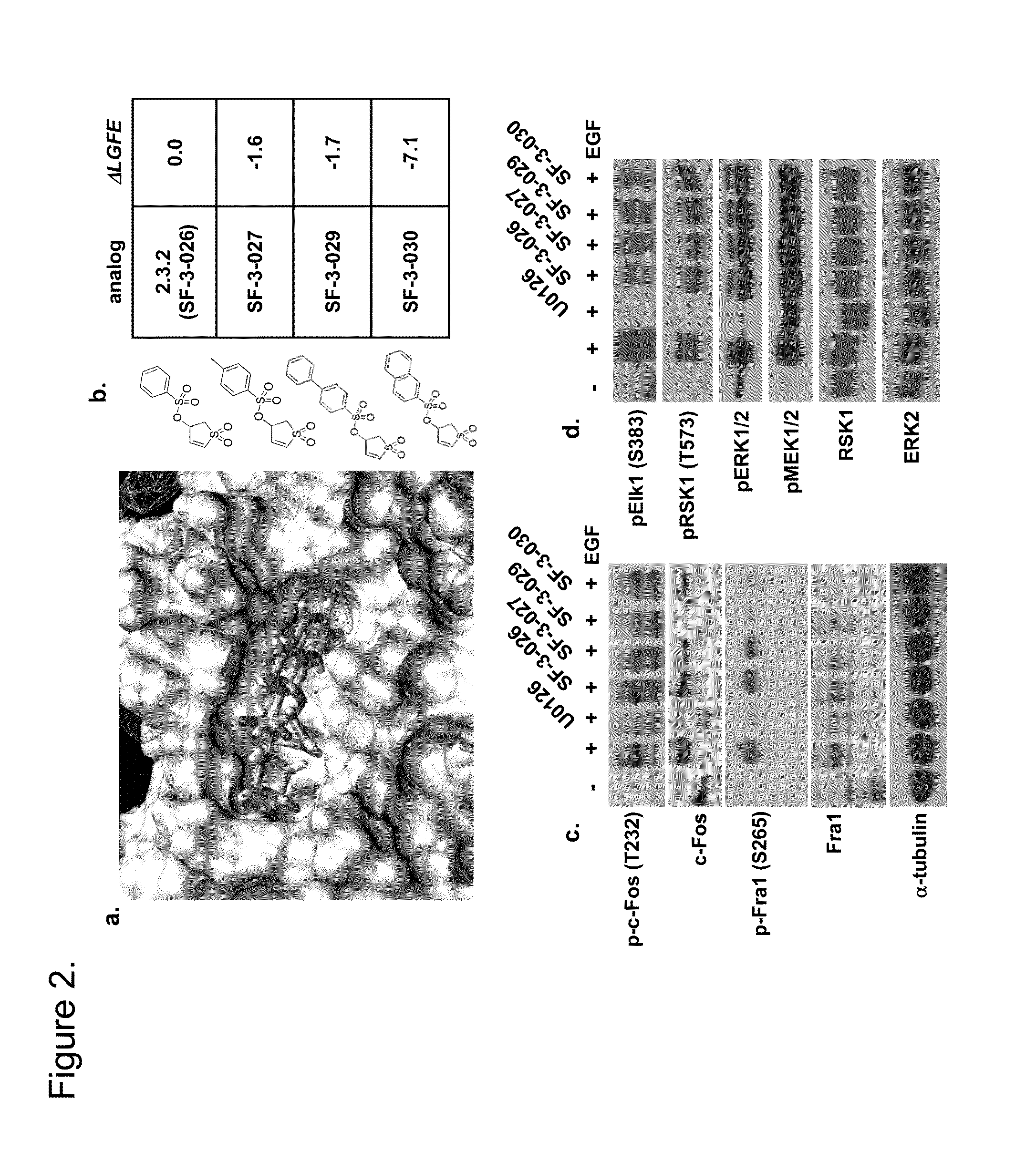
Substituted pyrimidines, pharmaceutical compositions and therapeutic methods thereof
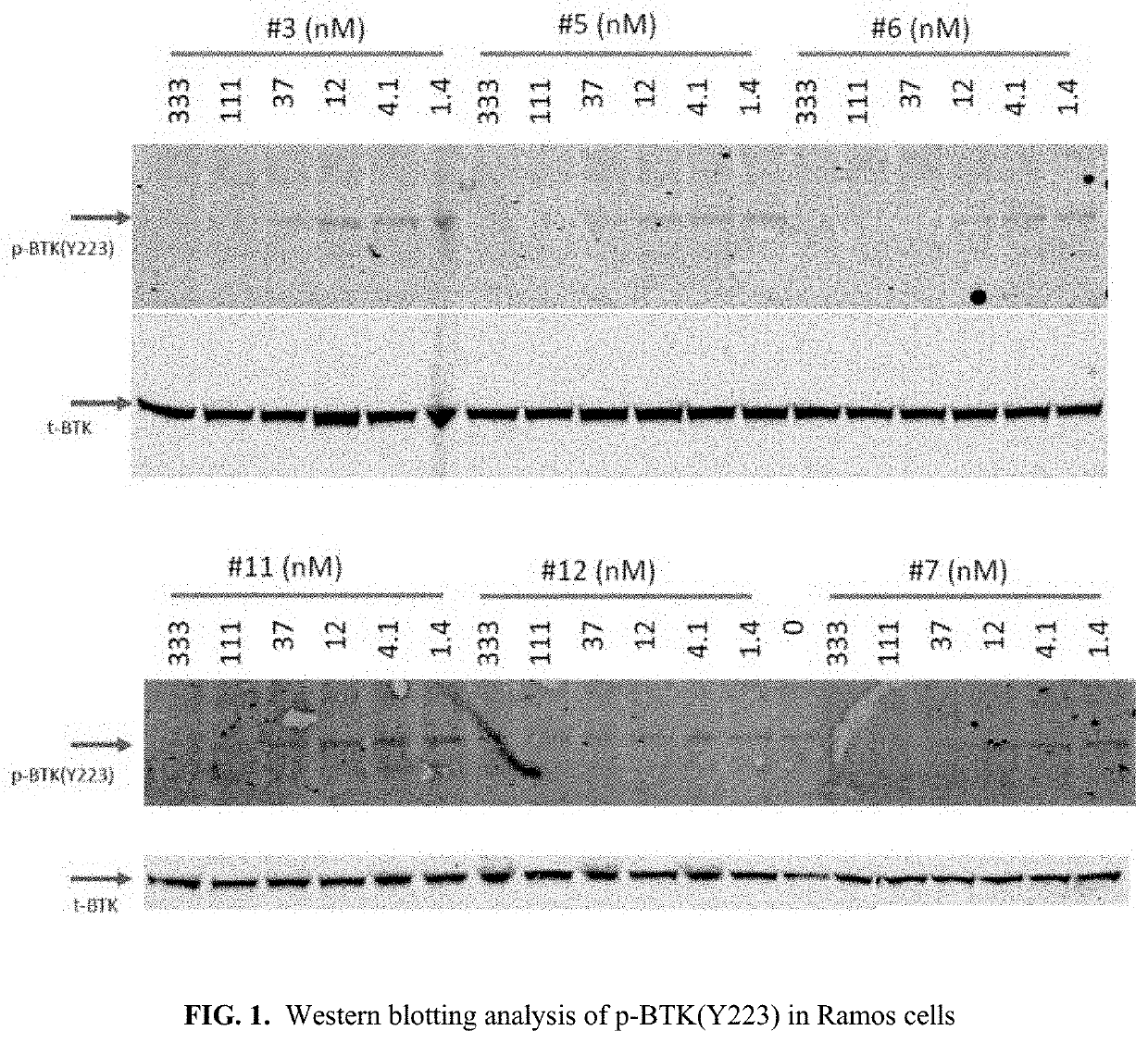
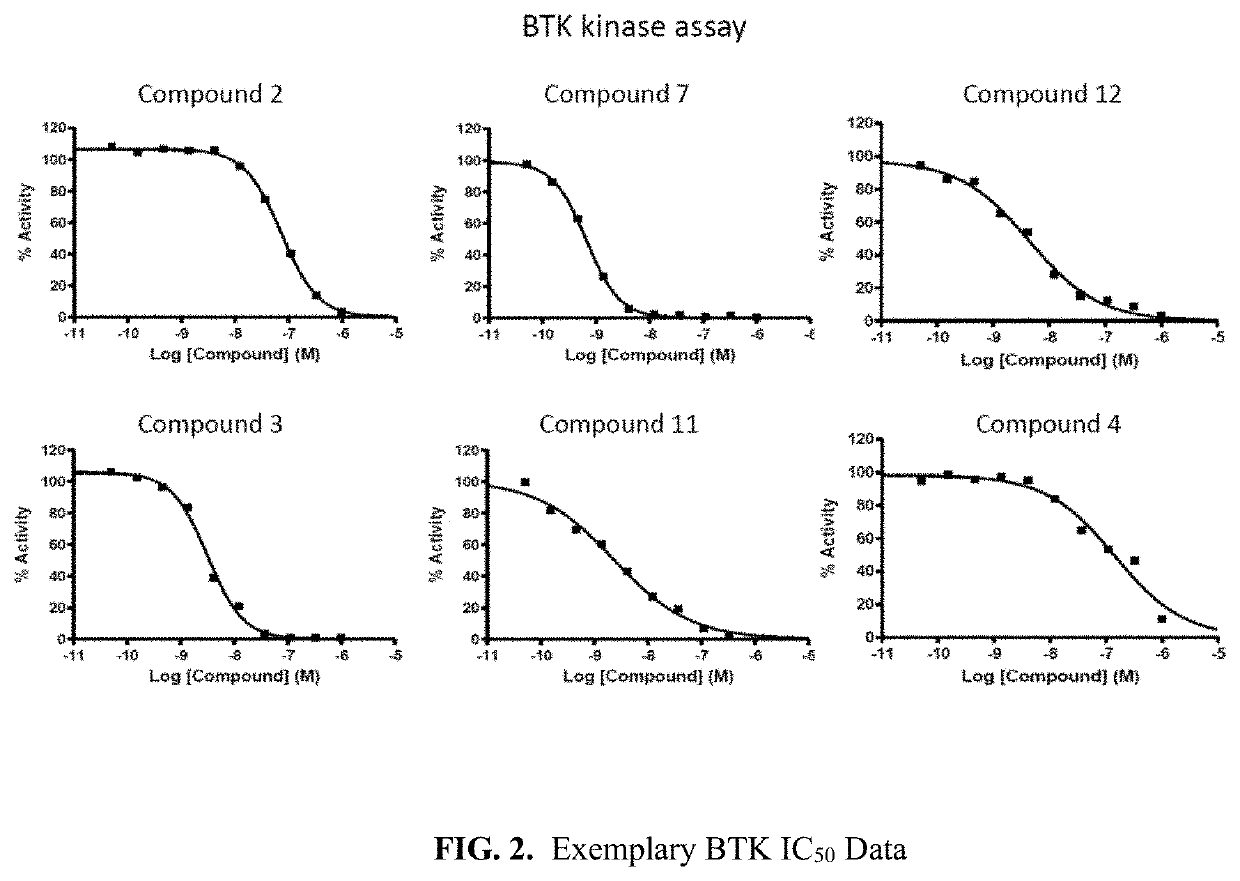
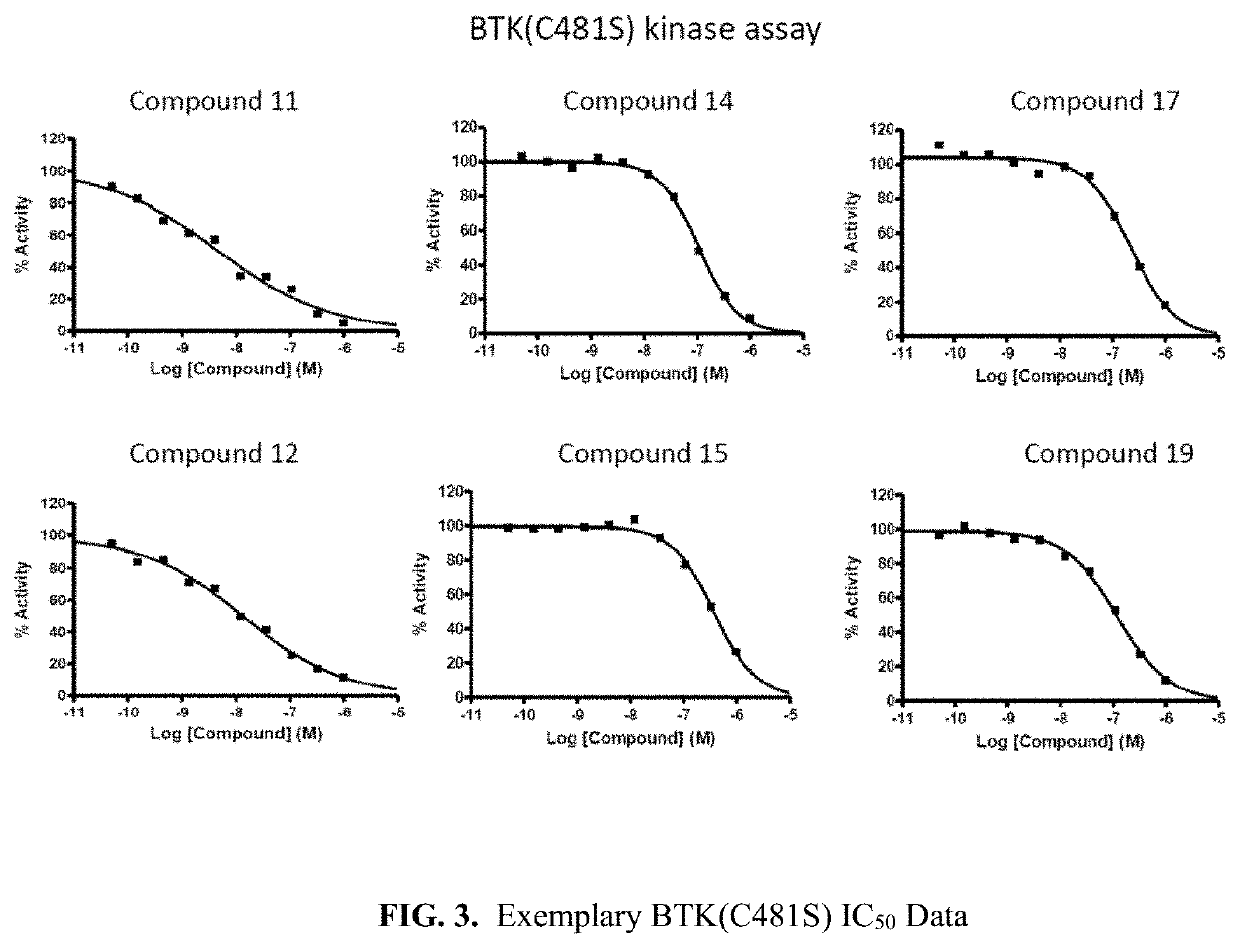
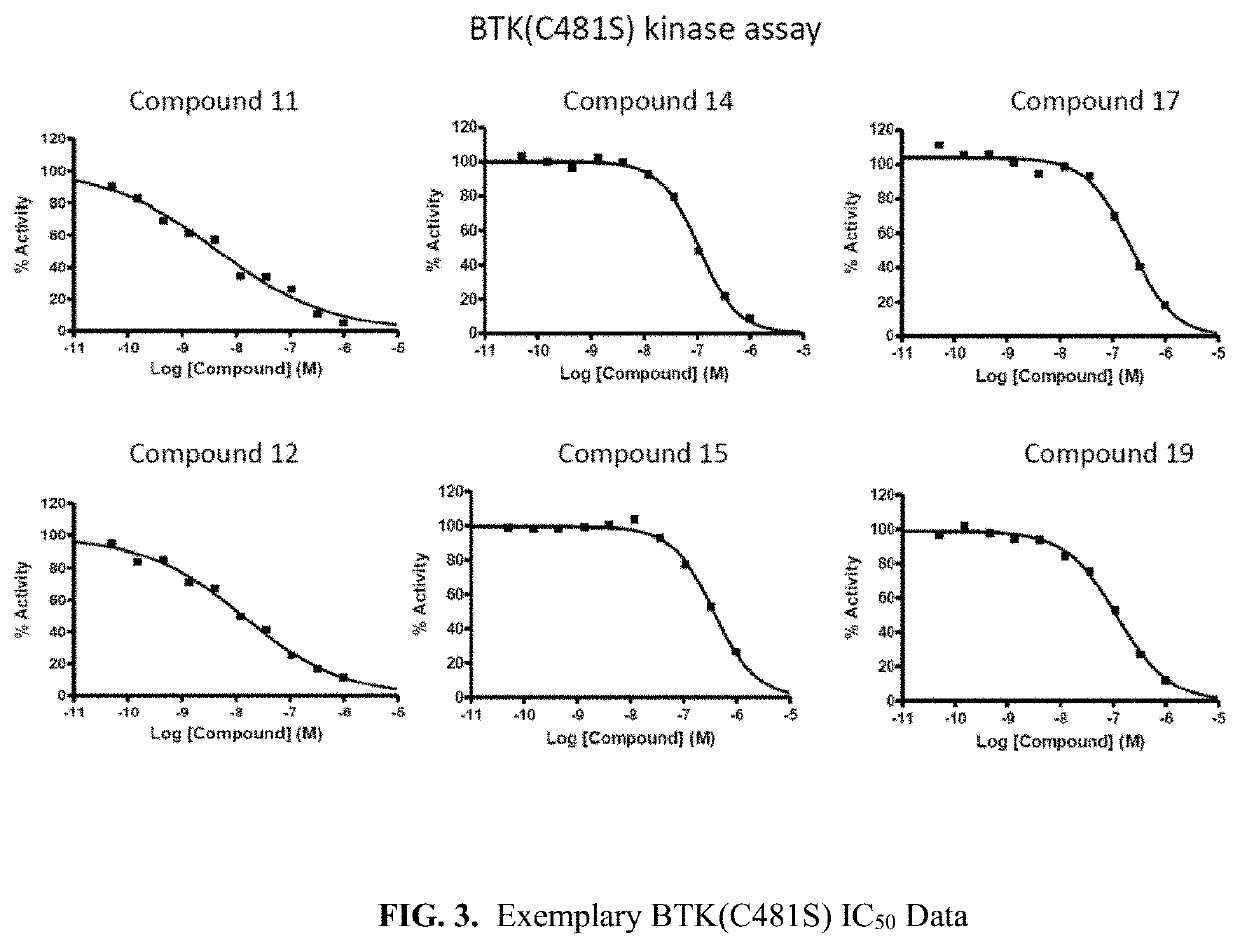
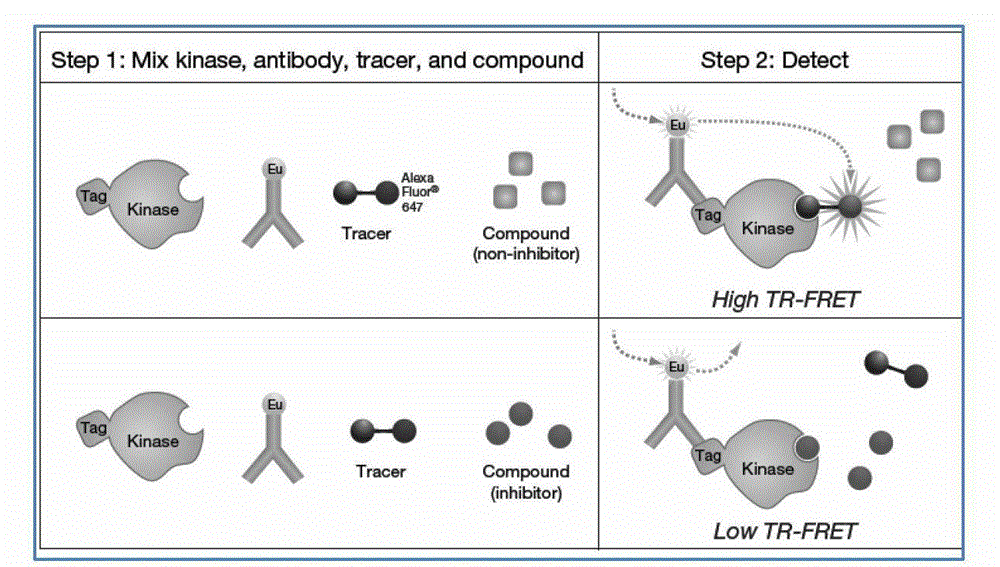
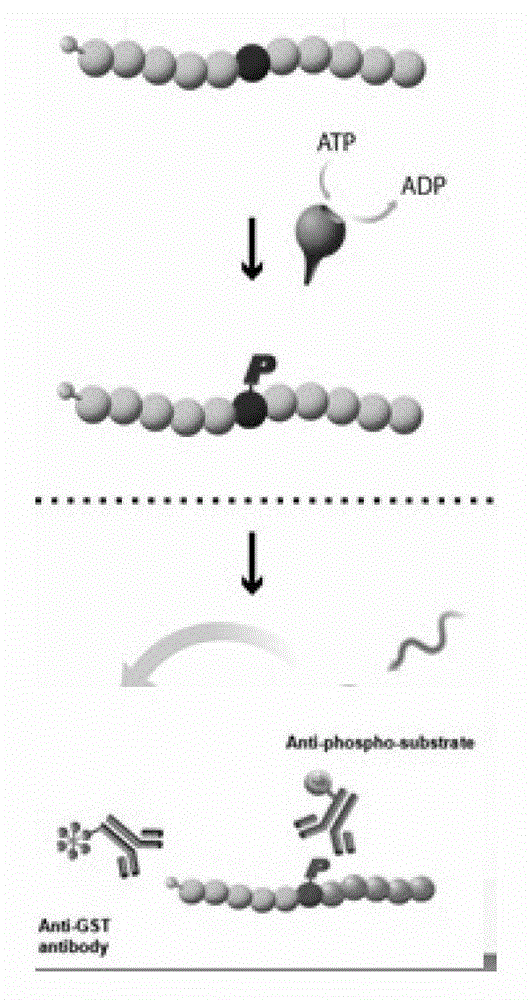
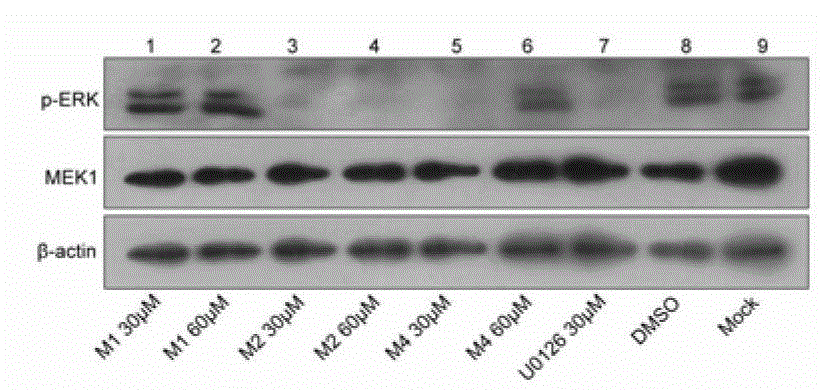
The invention provide novel pyrimidine derivatives and analogs having inhibitory activities towards certain tyrosine kinases, e.g., Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) and / or Focal adhesion kinase (FAK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treatment, reduction or prevention of certain diseases or conditions mediated by such by tyrosine kinases, e.g., cancers, tumors, fibrosis, inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, diabetes, or immunologically mediated diseases.
Owner:CHEN ZHIHONG
A kind of culture system and culture method of lacrimal gland stem cells and lacrimal gland stem cells
ActiveCN109486766BA large amountContinuous passageCulture processNervous system cellsExtracellular signalMatrigel
The invention relates to a lacrimal gland stem cell, a culture system and a culture method of the lacrimal gland stem cell, and relates to the field of cell engineering. The culture system of lacrimal gland stem cells of the present invention uses DMEM / F12 as the base medium, and adds the following components to form the culture medium: cell culture additives, non-essential amino acids, L-alanyl-L-glutamine, mitogen-activated protein Kinase / extracellular signal regulates the composition of kinase signaling pathway ligand, fibroblast growth factor, Wnt signaling pathway ligand and ROCK signaling pathway inhibitor, and uses matrigel as a three-dimensional culture support. The culture method of the present invention is as follows: the mouse lacrimal gland tissue is digested into single cells and inoculated into Matrigel, and after solidification, the lacrimal gland stem cell culture medium is added to carry out primary culture. The mouse lacrimal gland stem cells cultured by the method of the present invention have a relatively large number, are stable enough for continuous passage, and have the function of restoring lacrimal gland secretion function, and can effectively treat dry eye.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
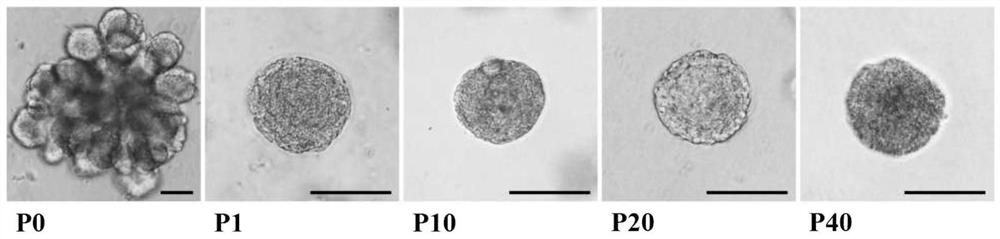
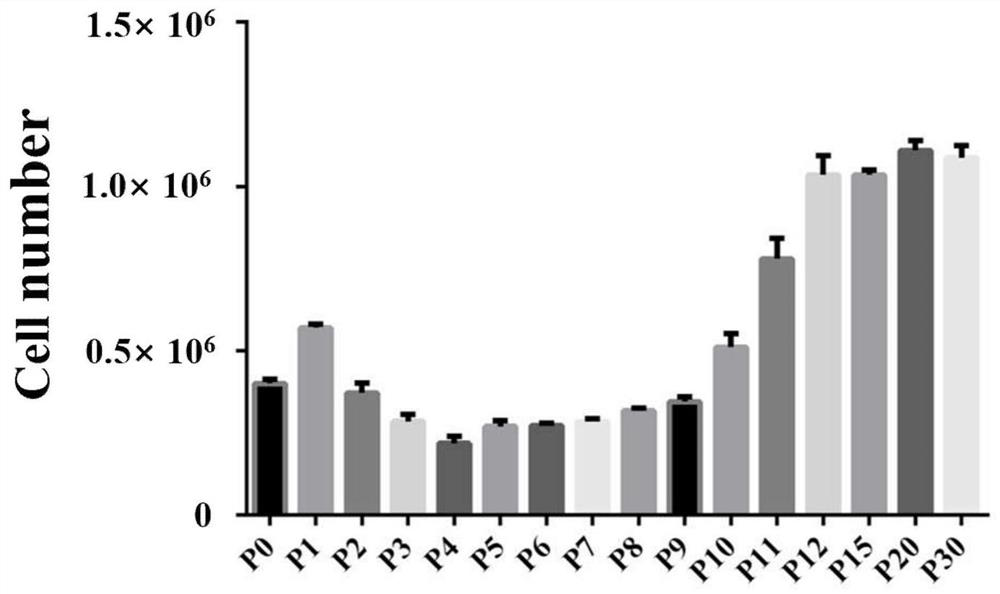
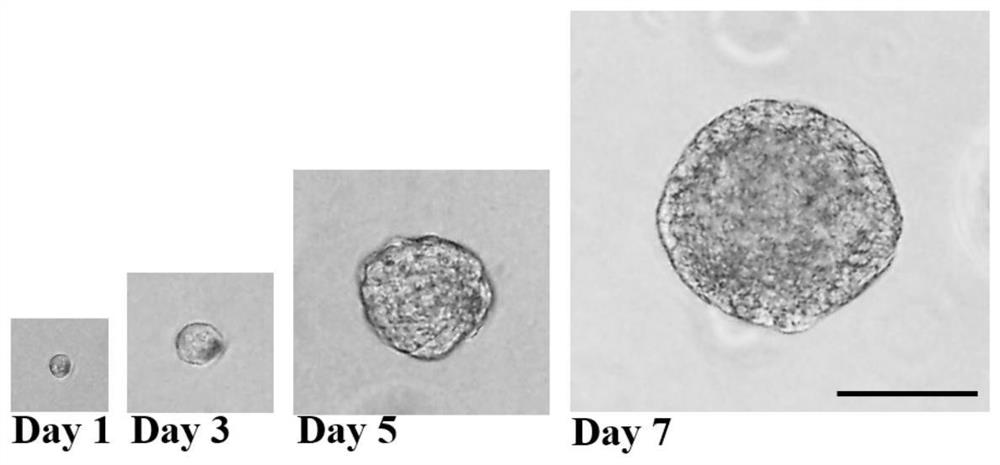
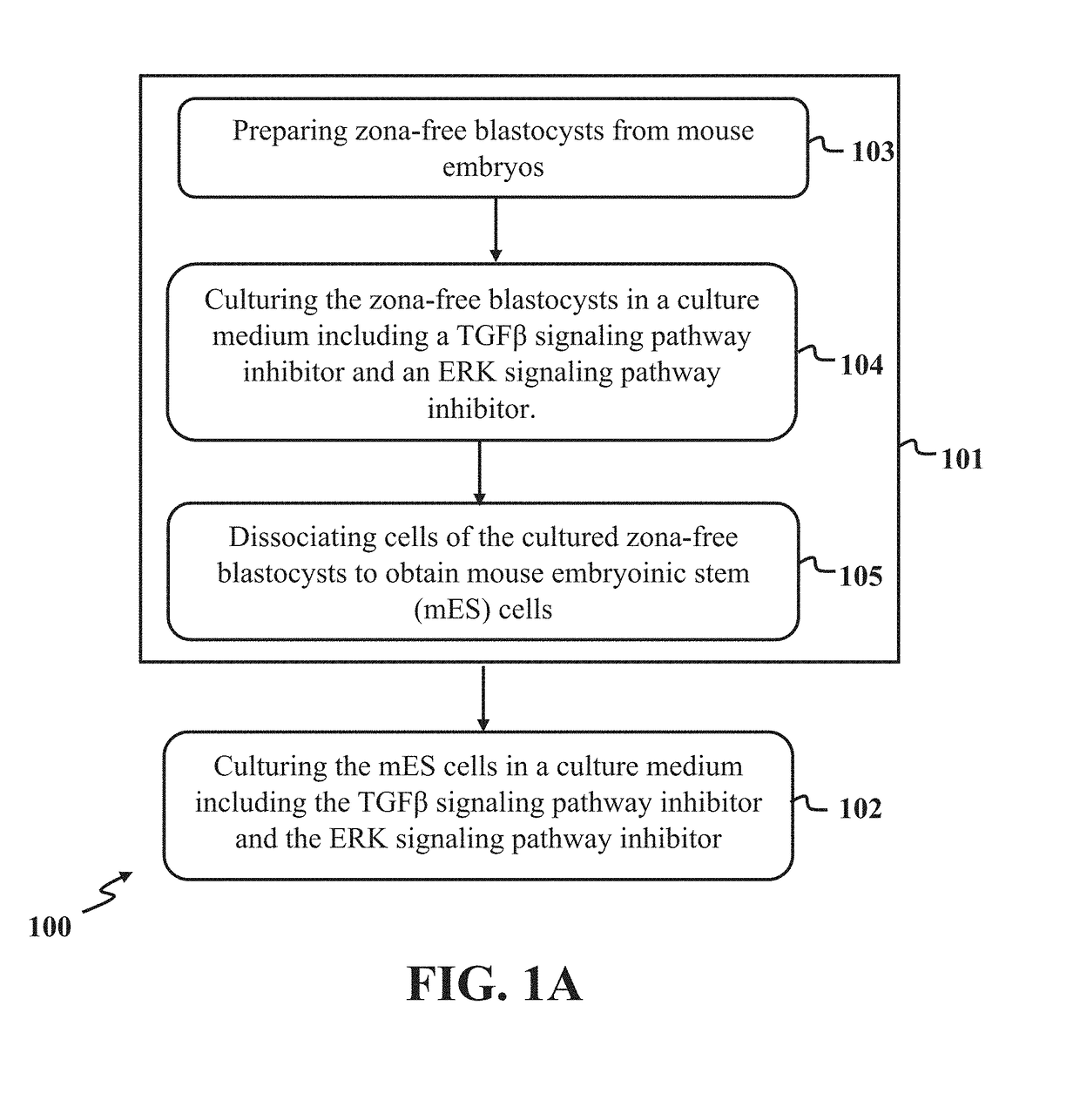
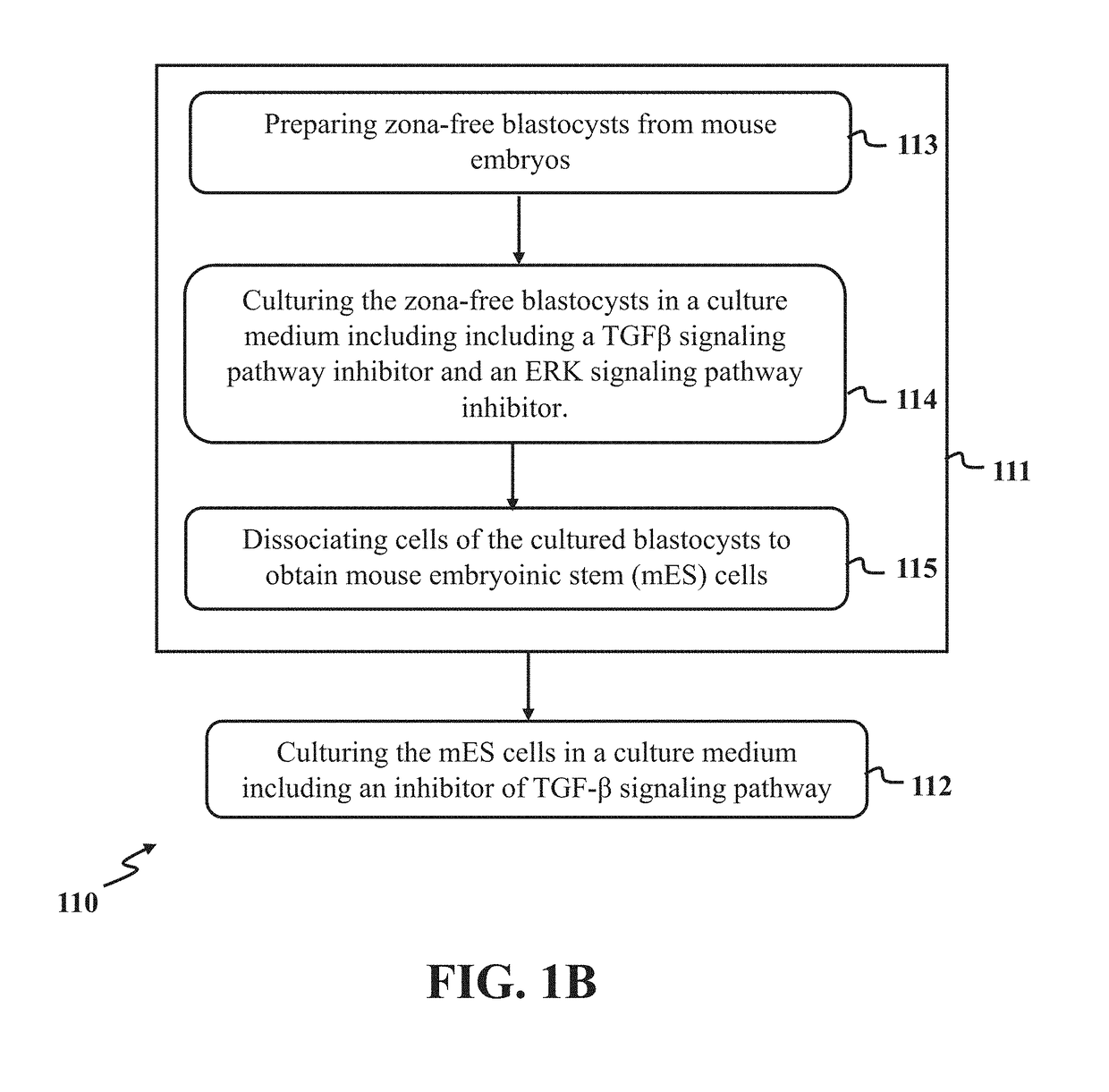
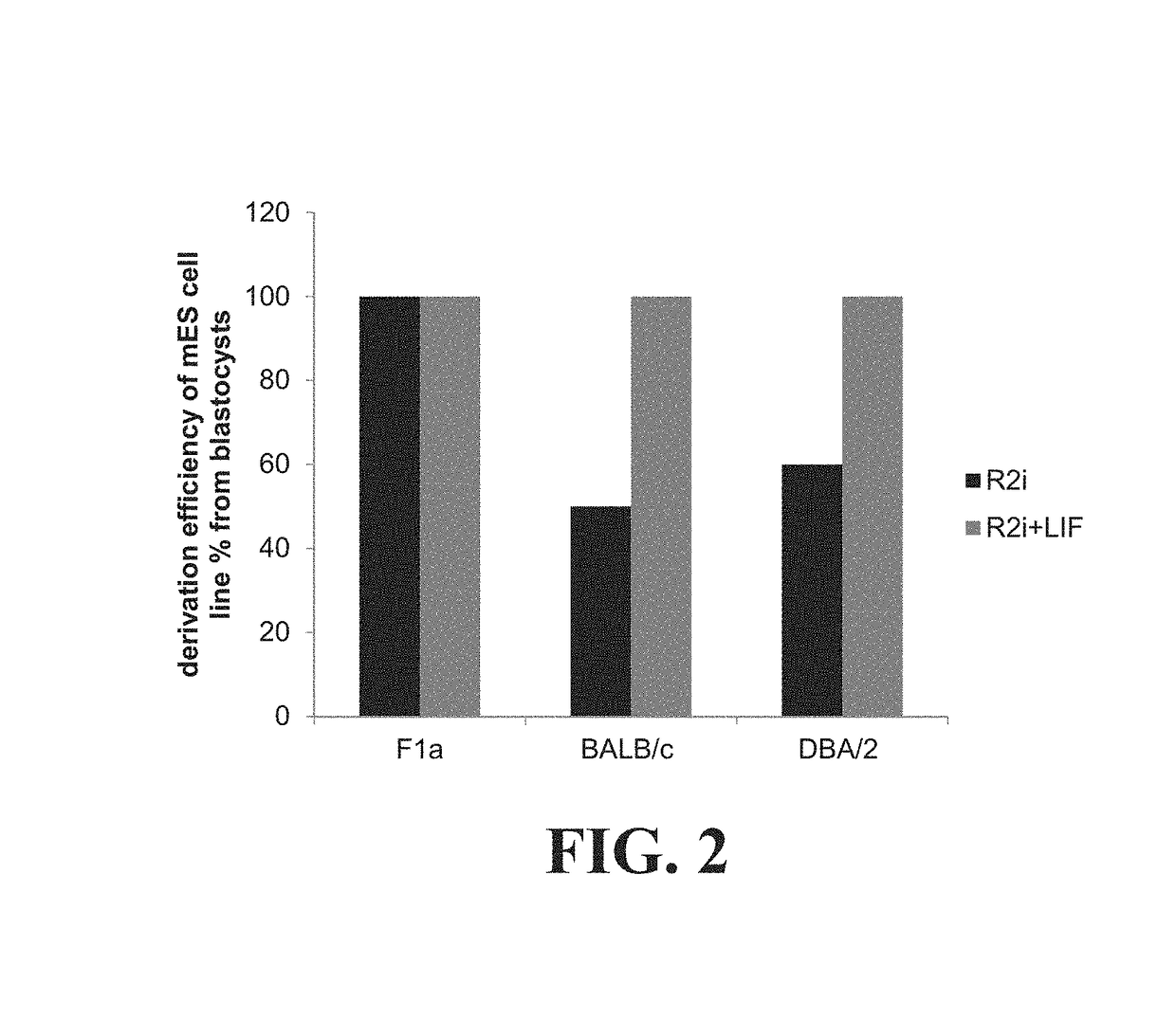
Establishing pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells
A method for derivation and maintenance of pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem (mES) cells is disclosed. The method includes isolating mES cells from mouse embryos in a culture medium including an R2i compound, and culturing the mES cells in a medium including the R2i compound or a transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway inhibitor. The R2i compound includes combination of a transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway inhibitor and an extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) signaling pathway inhibitor. This method can facilitate the homogeneous expression of pluripotency factors in embryonic stem cells.
Owner:ROYAN INST
Substituted pyrimidines, pharmaceutical compositions and therapeutic methods thereof
The invention provide novel pyrimidine derivatives and analogs having inhibitory activities towards certain tyrosine kinases, e.g., Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) and / or Focal adhesion kinase (FAK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treatment, reduction or prevention of certain diseases or conditions mediated by such by tyrosine kinases, e.g., cancers, tumors, fibrosis, inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, diabetes, or immunologically mediated diseases.
Owner:CHEN ZHIHONG
Compounds with MEK inhibitory function and their preparation methods and applications
The invention discloses a compound with an MEK (Mitogen-activated and Extracellular signal-regulated Kinase) inhibiting function as well as a preparation method and application of the compound. The structure of the compound disclosed by the invention is as shown in a formula (I). The preparation method of the compound disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of forming a coumarin ring by adopting a Pechmann reaction mainly and carrying out structural modification of different sites. In the binding experiment of the compound disclosed by the invention and MEK, the binding activity is up to 54.57nM; the anti-proliferation effect IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration) value on the melanoma cell A375 is up to 1.23 micrometers; the anti-proliferation effect IC50 value on the colon cancer cell HT-29 is up to 2.13 micrometers; and the activity is higher than that of a positive control U0126. The novel structure type coumarins compound with the MEK inhibiting function shows good MEK binding activity, MEK inhibiting activity, ERK (Extracellular signal Regulated Kinase) pathway inhibiting activity, anti-tumor effect and antiviral effect and has broad application value. The formula (I) is as shown in the specification.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
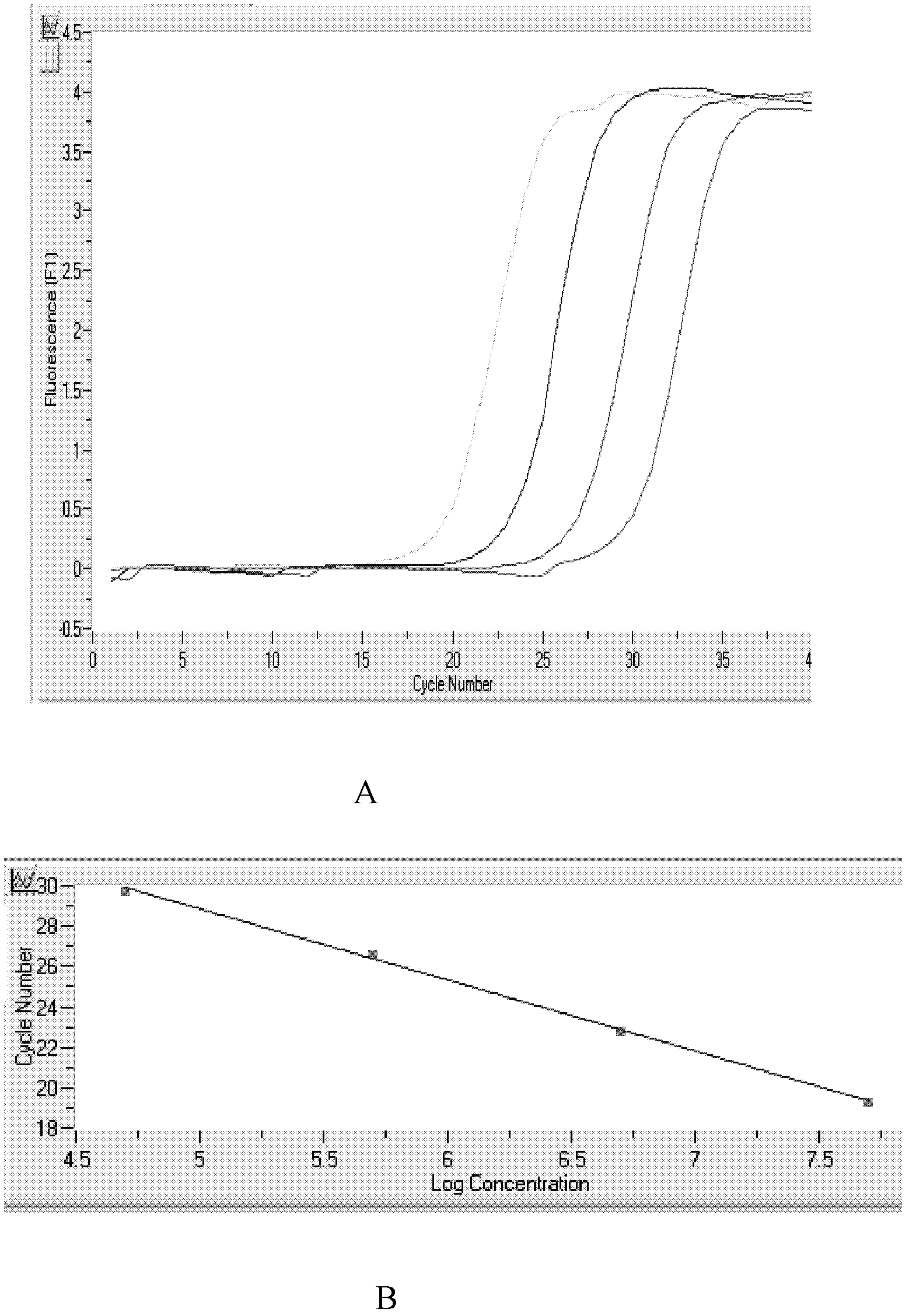
Kit for quickly detecting expression quantities of related genes of sorafenib chemotherapeutic medicament
InactiveCN102618656BHigh detection sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceExtracellular signalTumor vessel
The invention relates to the technical field of biology. High expression of kinase insert domain receptors (KDR) and platelet-derived growth factor receptors alpha (PDGFRA) can be viewed in multiple tumor tissues; and sorafenib directly inhibits tumor growth by inhibiting the activities of the KDR and the PDGFR and inhibiting a recombinant activated factor / methyl ethyl ketone / extracellular signal-regulated kinase (RAF / MEK / ERK) signal transduction pathway, and blocks the formation of new tumor vessels by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF), so that the sorafenib achieves double inhibiting and multi-target blocking anti-hepatic cell carcinoma (HCC) effects. Detection of KDR and PDGFR mRNA levels can assist doctors in forecasting the curative effect of medicaments and the clinical outcome of patients, and has important clinical significance. The invention aims to provide a kit capable of quickly, conveniently, sensitively and specifically detecting expression quantities of related genes KDR and PDGFRA of a sorafenib chemotherapeutic medicament. According to the kit, the KDR and PDGFR mRNA levels are detected by adopting a fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology with high sensitivity and specificity, so that the sensitivity and the specificity are remarkably improved; and the kit is quick in detection and high in flux, and can finish the detection in 3 to 4 hours.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
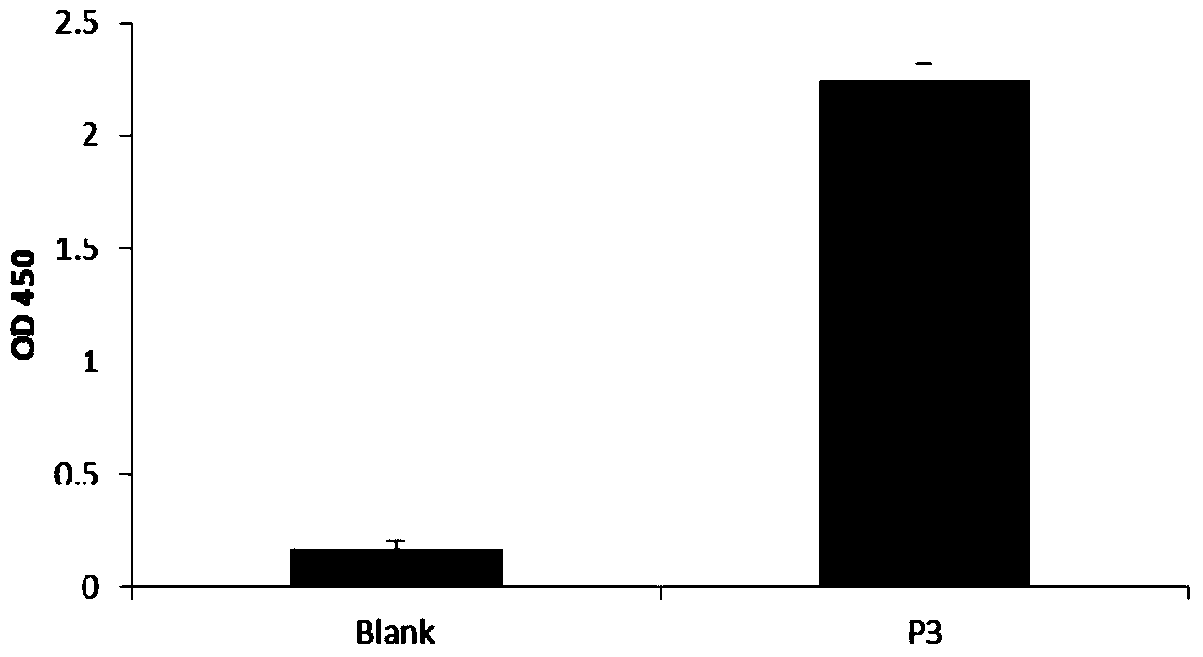
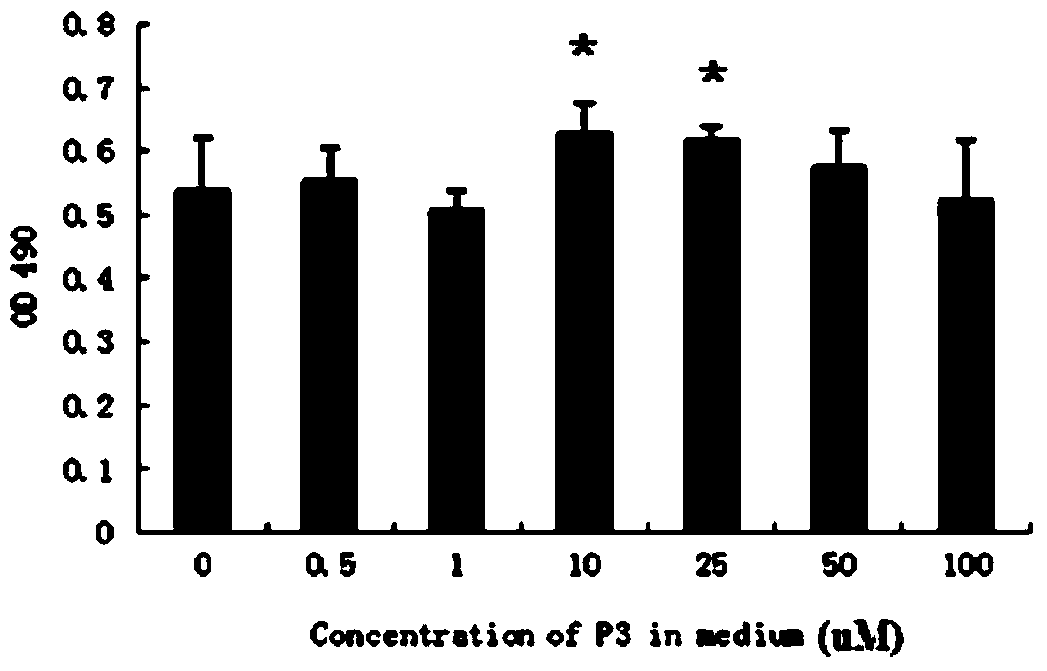
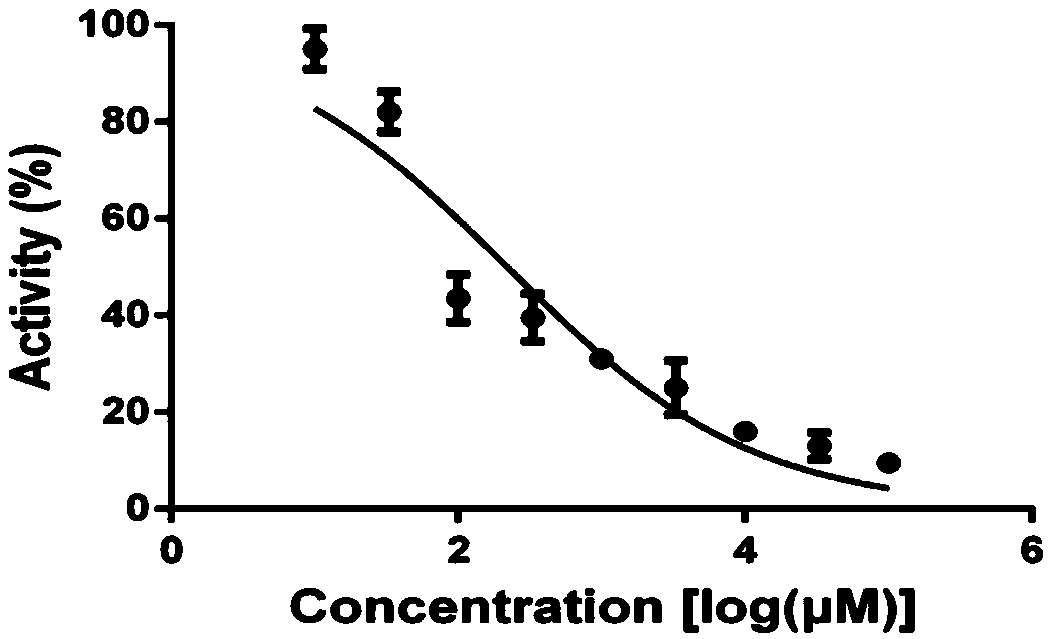
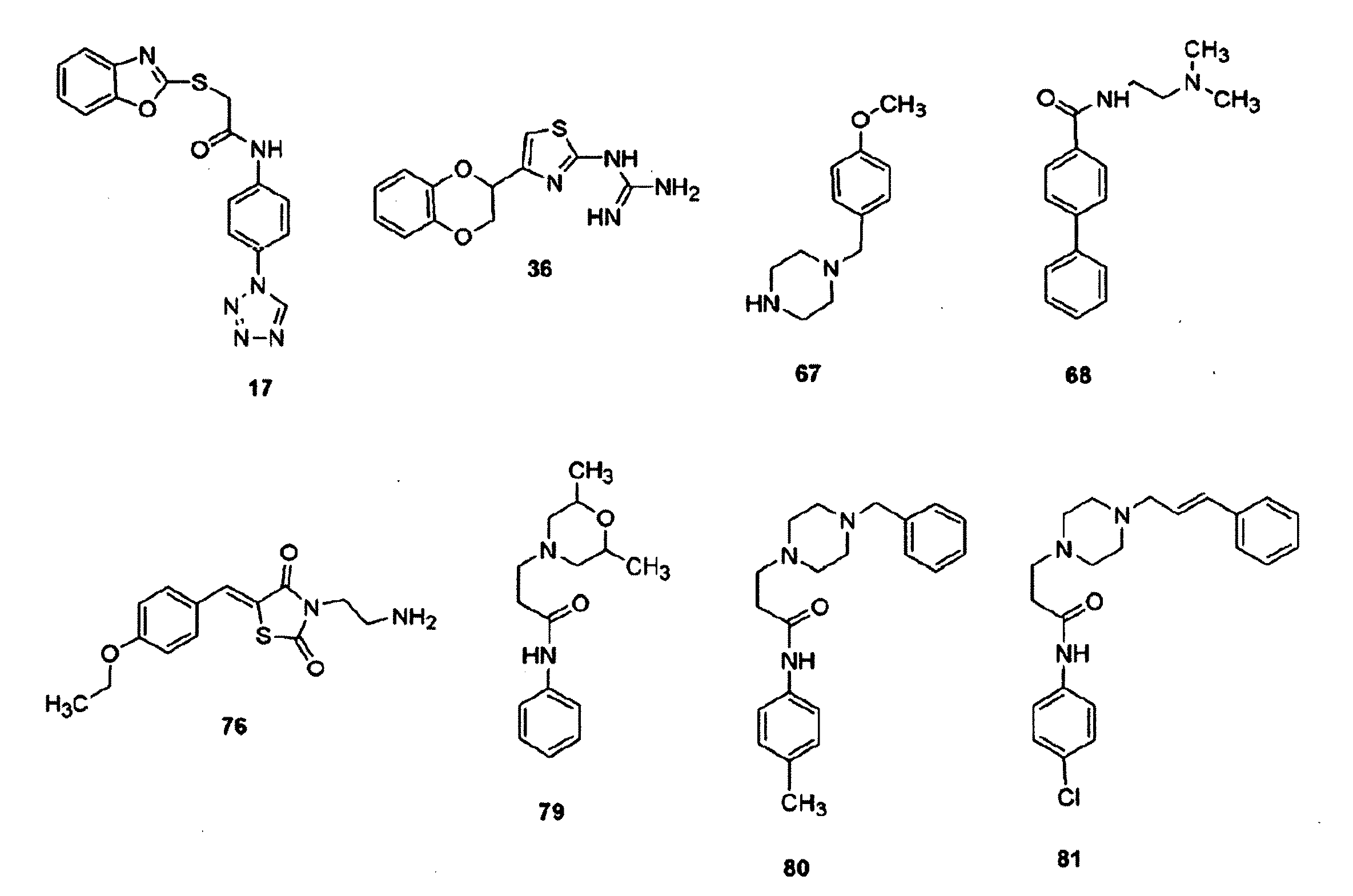
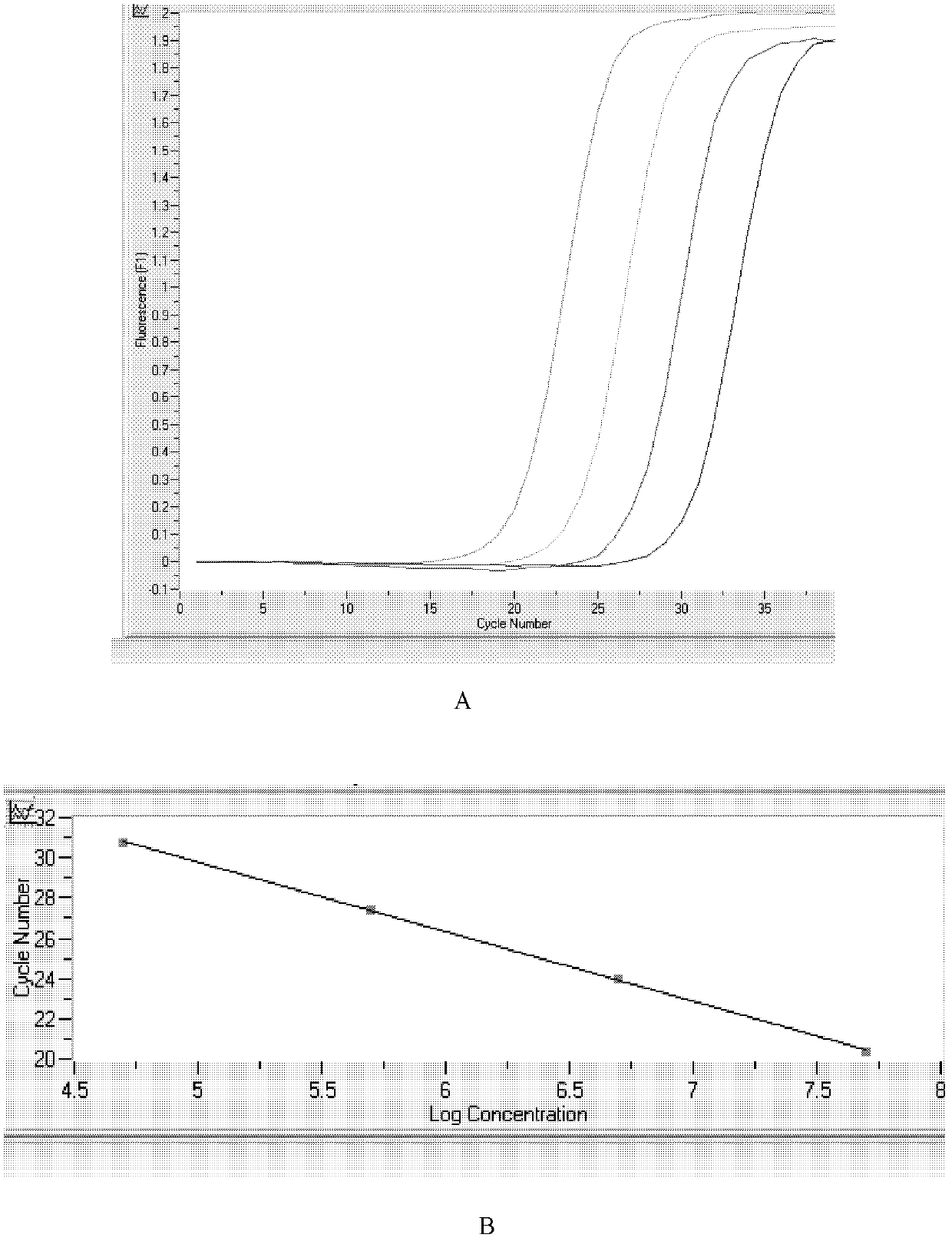
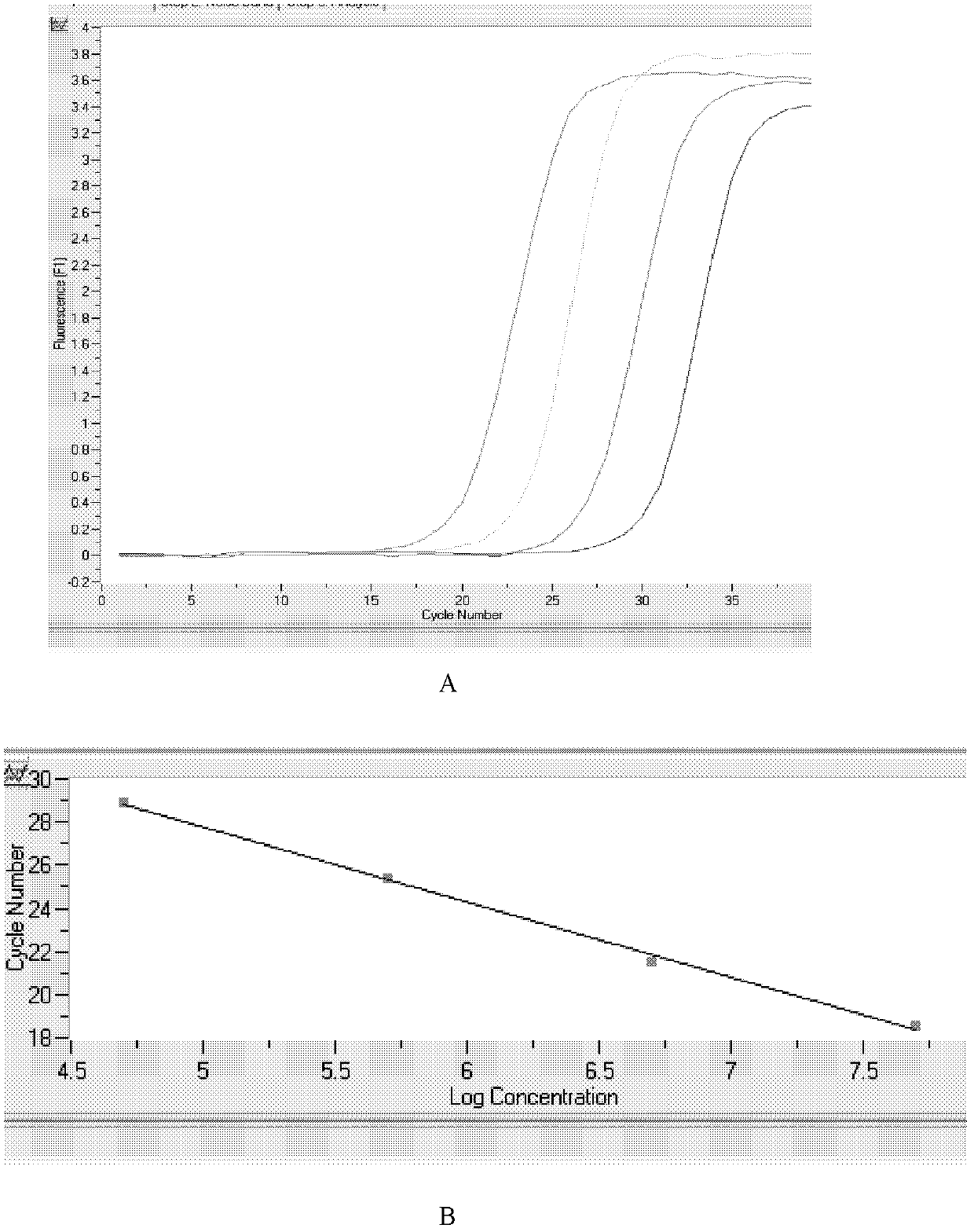
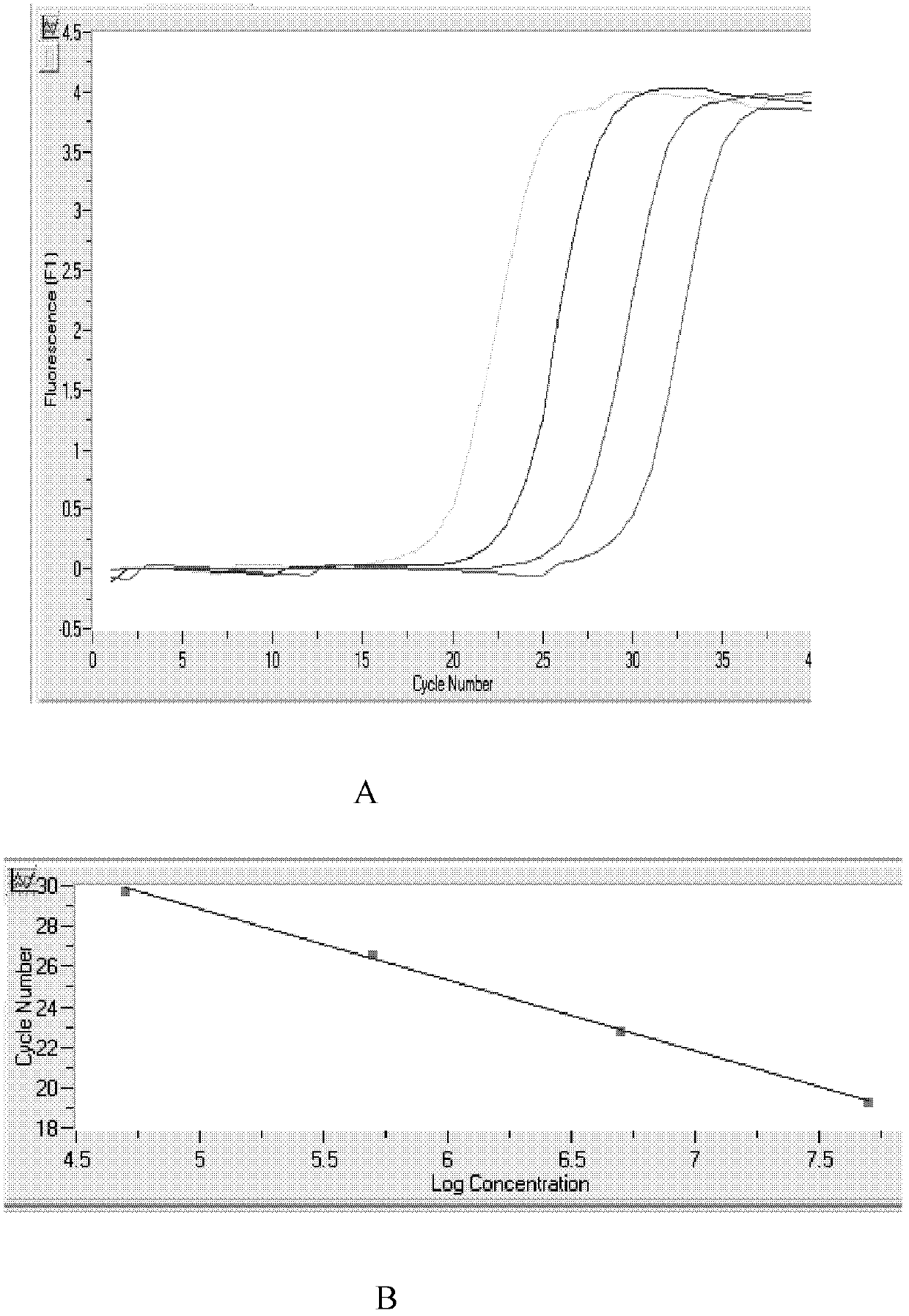
Novel application of 2-(4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-2-bromo-6-methoxyphenoxyl) acetic acid
InactiveCN105030768AGood inhibitory effectEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsInflammatory factorsMacrophage migration inhibition
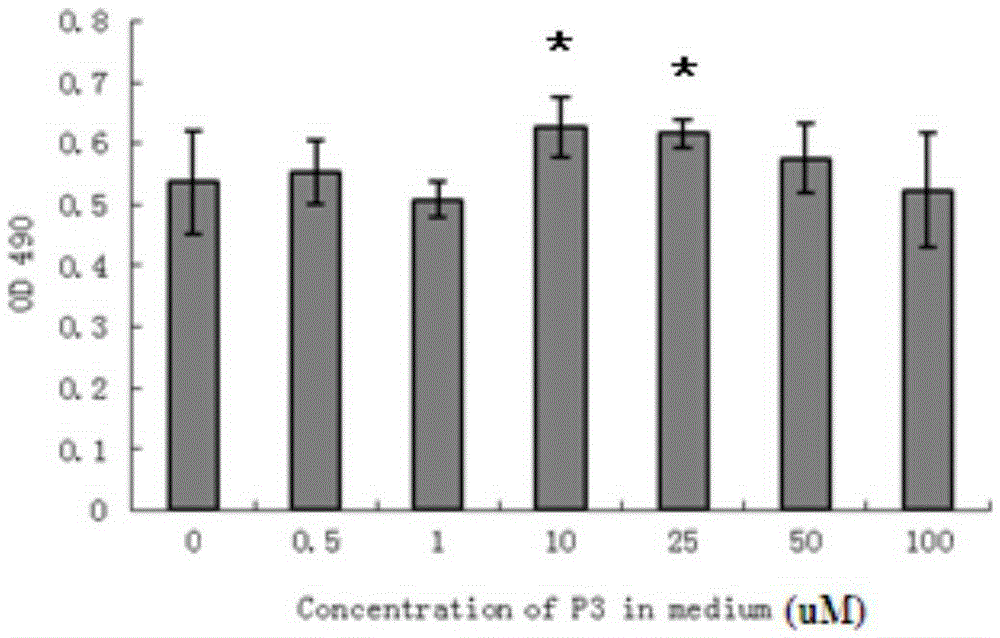
The invention discloses a novel application of 2-(4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-2-bromo-6-methoxyphenoxyl) acetic acid. Specifically speaking, the 2-(4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-2-bromo-6-methoxyphenoxyl) acetic acid in the novel application has a function of an MIF (macrophage migration inhibition factor) inhibitor and can be used for remarkably inhibiting release of inflammatory factors (TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor)-alpha and NO) induced by LPS (Lipopolysaccharide), inhibiting chemotactic migration of macrophage caused by MIF, inhibiting phosphorylation of ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) 1 / 2 and preparing MIF-related anti-inflammatory medicaments.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG INST OF IND TECH SOOCHOW UNIV
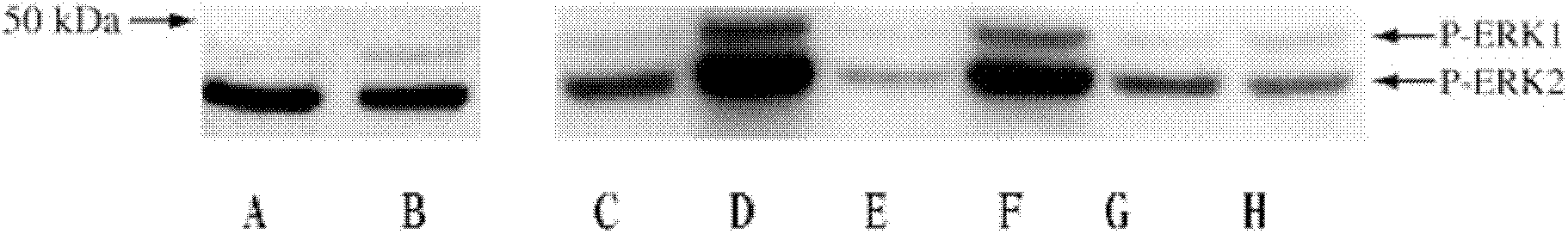
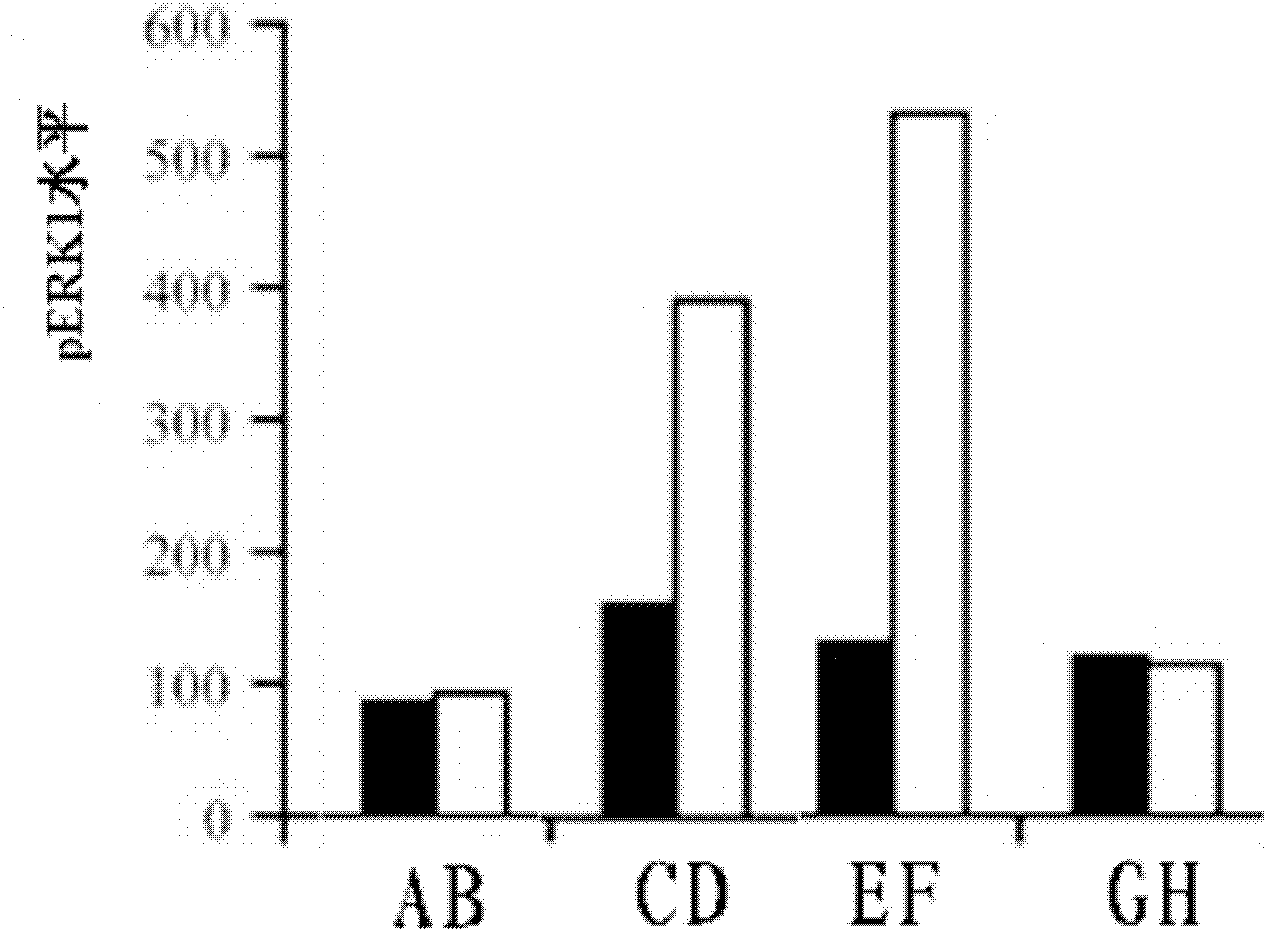
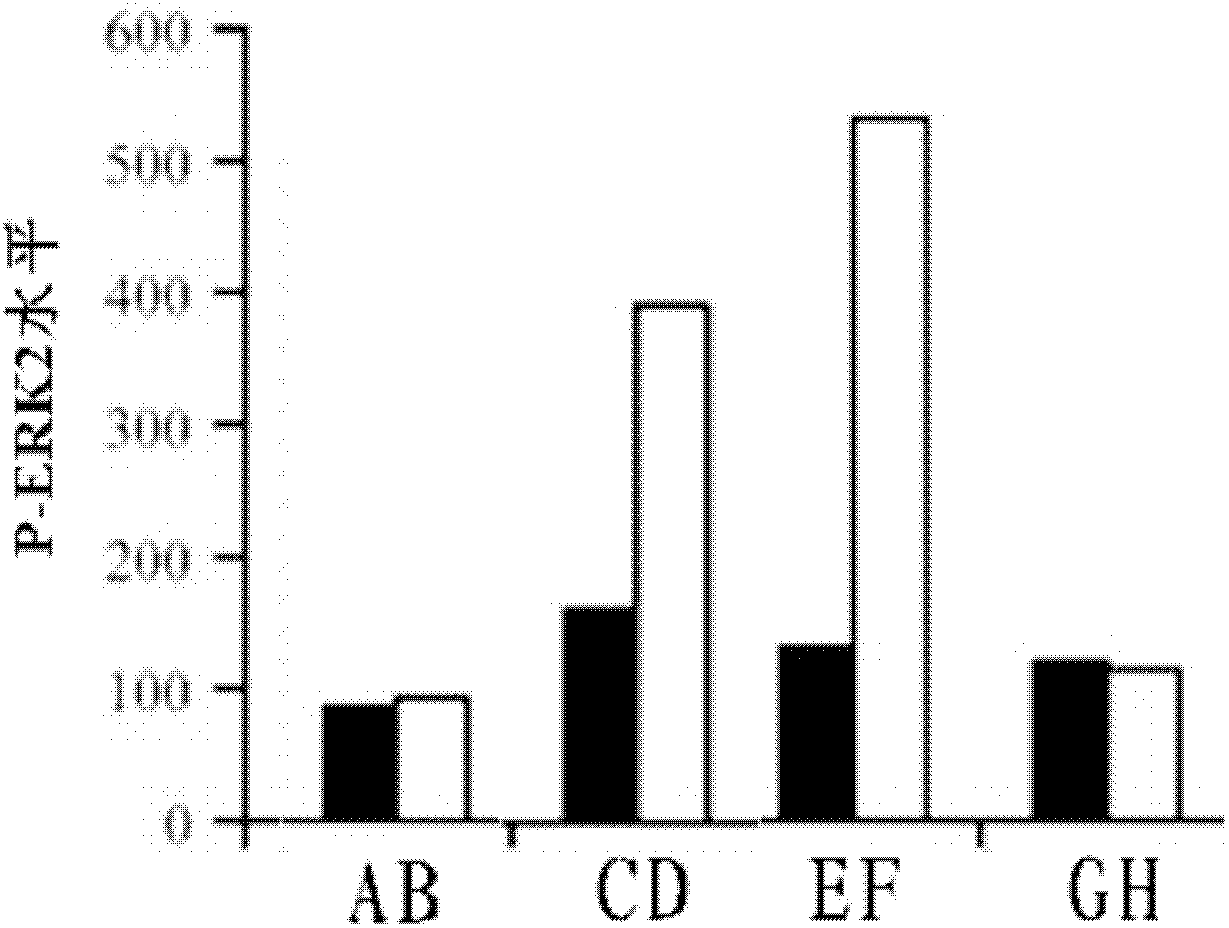
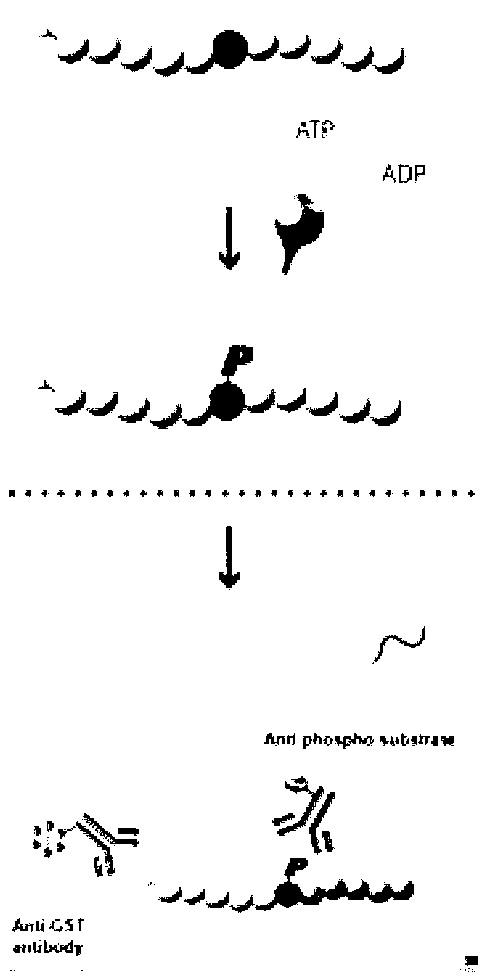
Method for determining retinal cell death process
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology analysis and detection, and discloses a method for determining a retinal cell death process. Firstly, a total protein sample except nucleoprotein is separated from a diseased retinal tissue, and antigen protein which has immunoreaction with an anti-phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 / 2 (P-ERK1 / 2) specific antibody in the extranuclear total protein sample is detected by a western blot method for quantitative analysis; comparison is performed with a retinal cell death process detected by immunohistochemistry so as to determine the retinal cell death process. The invention can determine a cell death process in genetic retinal degeneration process according to the level change of the phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, 2, and can provide critical and important information for the illustration of genetic disease tissue cell death and the discussion of prevention and treatment means.
Owner:刘军 +2
Polypeptides that regulate FGFR2 activity
ActiveCN103980349BInhibitory activityEasy to adjustPeptidesExtracellular signalFibroblast growth factor receptor 2
The invention discloses a polypeptide capable of regulating the activity of FGFR2 (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 2). The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is Asn-Leu-Gly-Gln-Glu-Leu-Ala-Phe-Arg-Val-Pro-Asn. The polypeptide disclosed by the invention can be specifically combined with the FGFR2, plays an obviously regulating role on the activity of the FGFR2, can outstanding inhibit the activity of p-ERK (Phospho-Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase) contained in the main downstream signal channel MAPK (Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase) of the FGFR2, has the advantages of low molecular weight, easiness for preparation, controllability in quality, low immunogenicity and the like and has good potential application value in the field of medicines.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com









![Novel application of 2-(4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-2-bromo-6-methoxyphenoxyl) acetic acid Novel application of 2-(4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-2-bromo-6-methoxyphenoxyl) acetic acid](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/41366faf-0a6d-4886-aa3a-0816c11d3961/150630124921.PNG)
![Novel application of 2-(4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-2-bromo-6-methoxyphenoxyl) acetic acid Novel application of 2-(4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-2-bromo-6-methoxyphenoxyl) acetic acid](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/41366faf-0a6d-4886-aa3a-0816c11d3961/150630124927.PNG)
![Novel application of 2-(4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-2-bromo-6-methoxyphenoxyl) acetic acid Novel application of 2-(4-(benzo[d]thiazole-2-yl)-2-bromo-6-methoxyphenoxyl) acetic acid](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/41366faf-0a6d-4886-aa3a-0816c11d3961/150630124932.PNG)