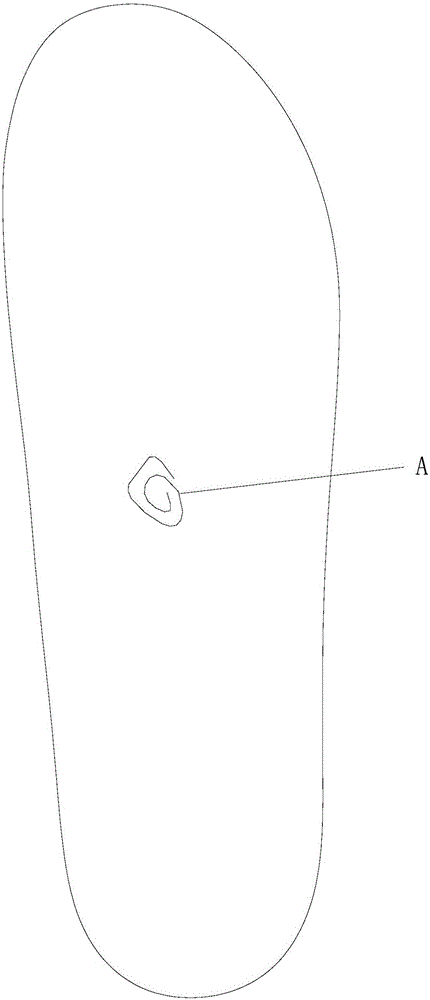
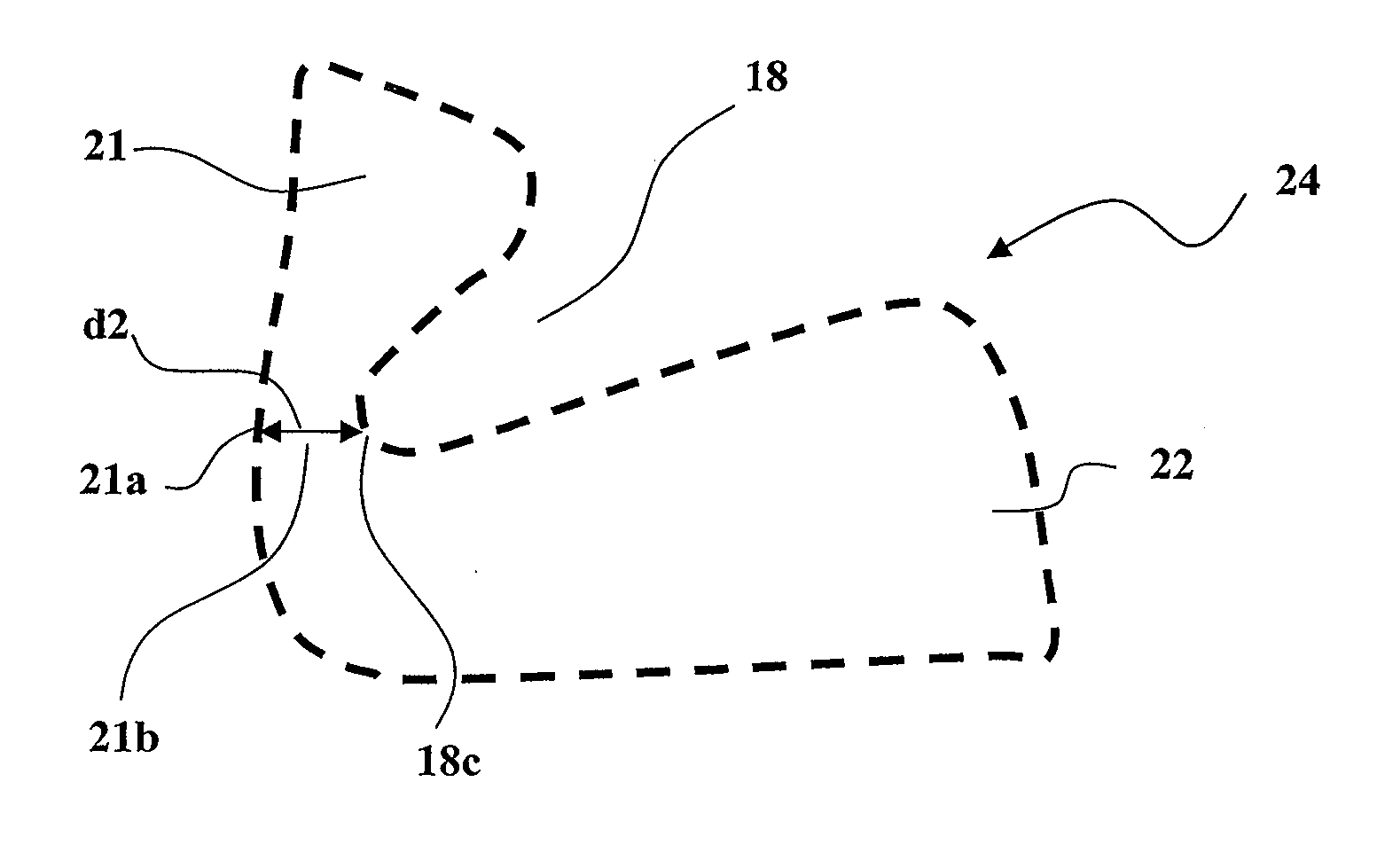
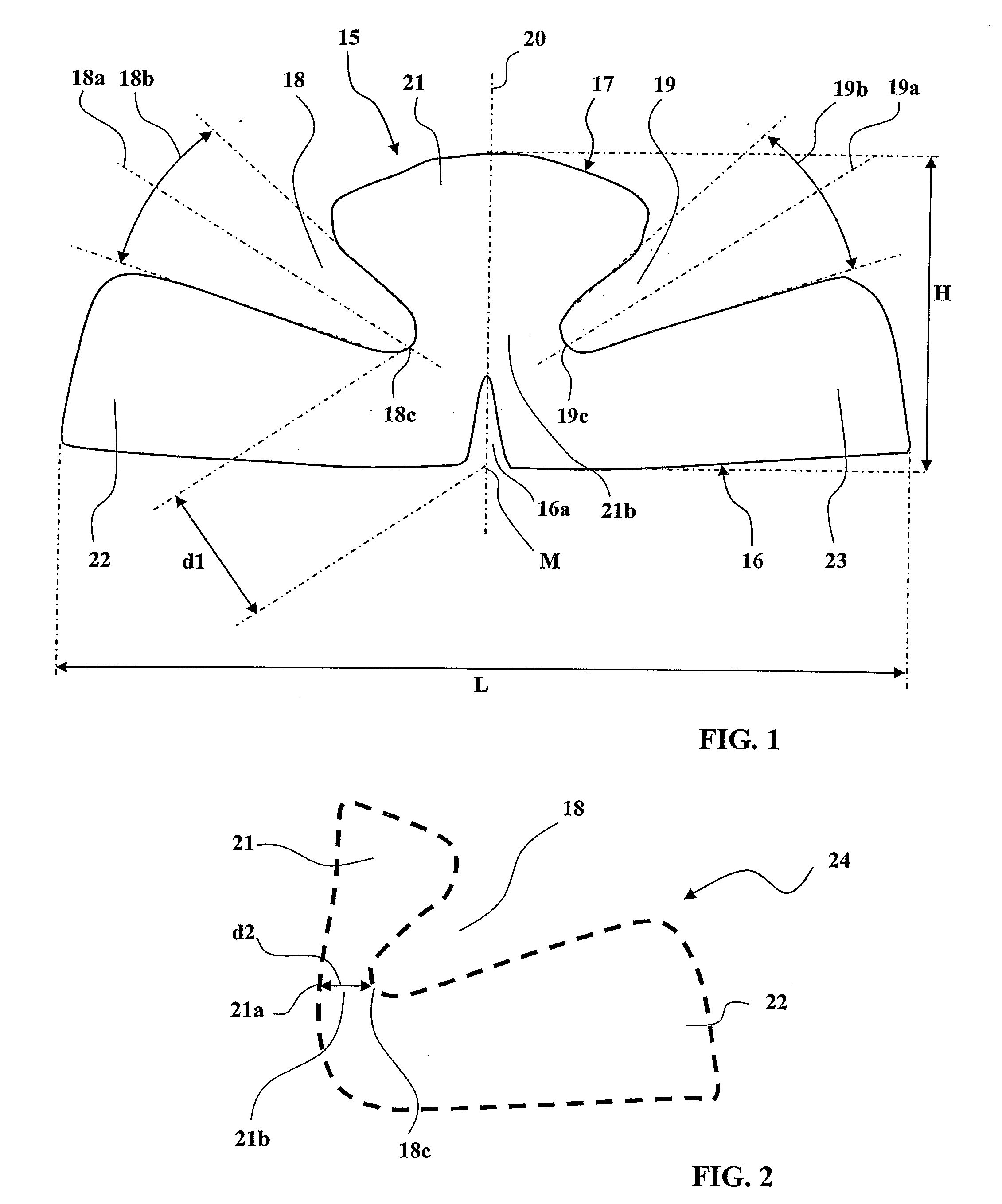
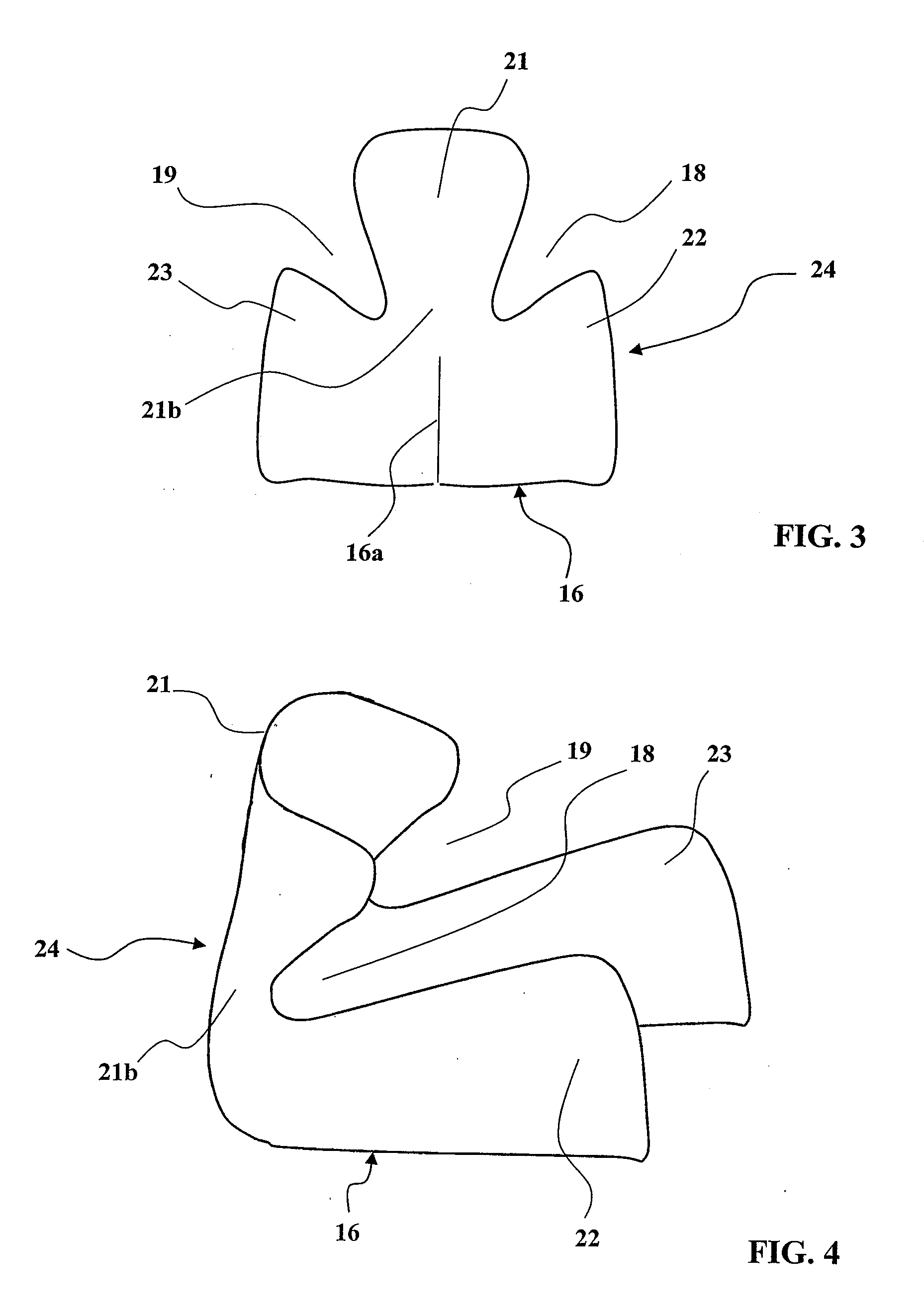
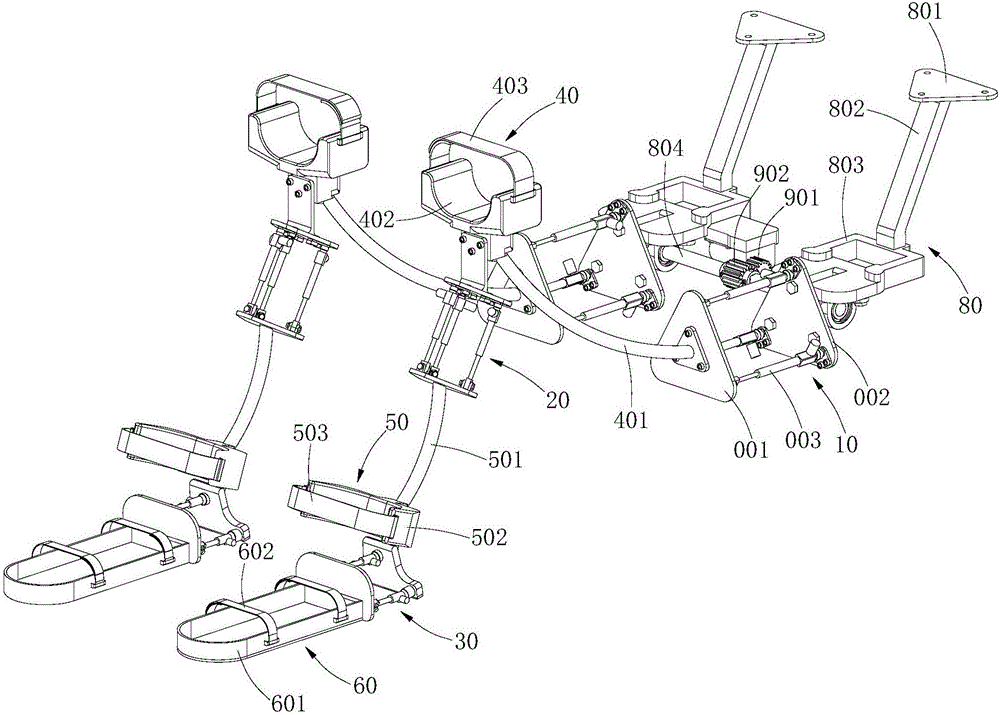
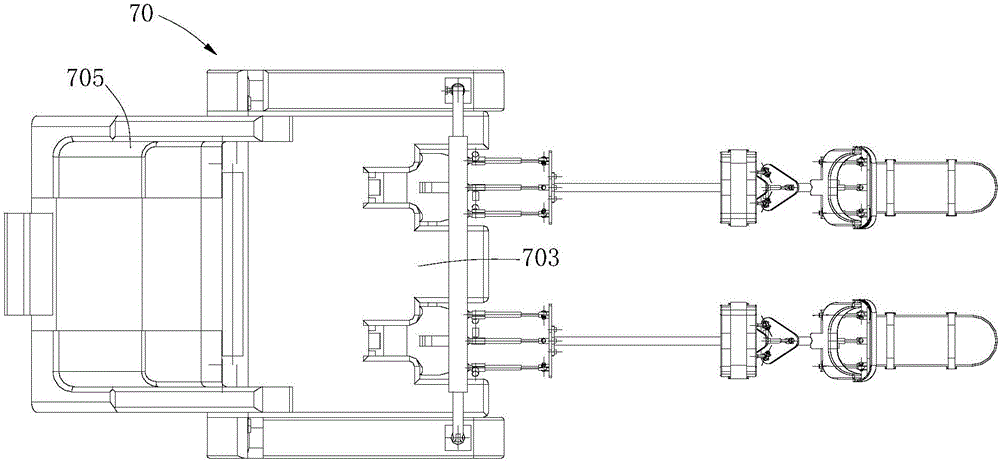
Patents
Literature
205 results about "Foot movements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
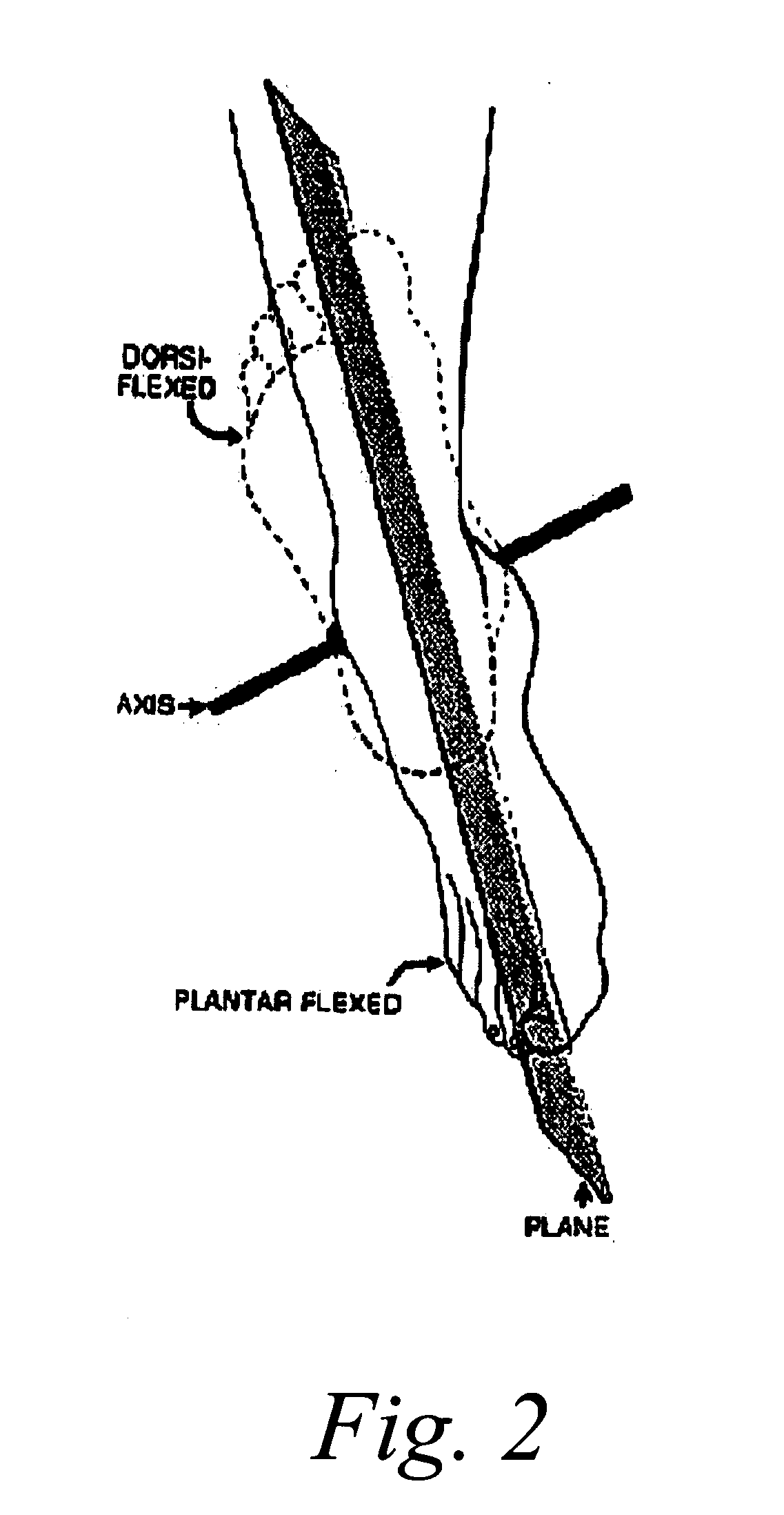
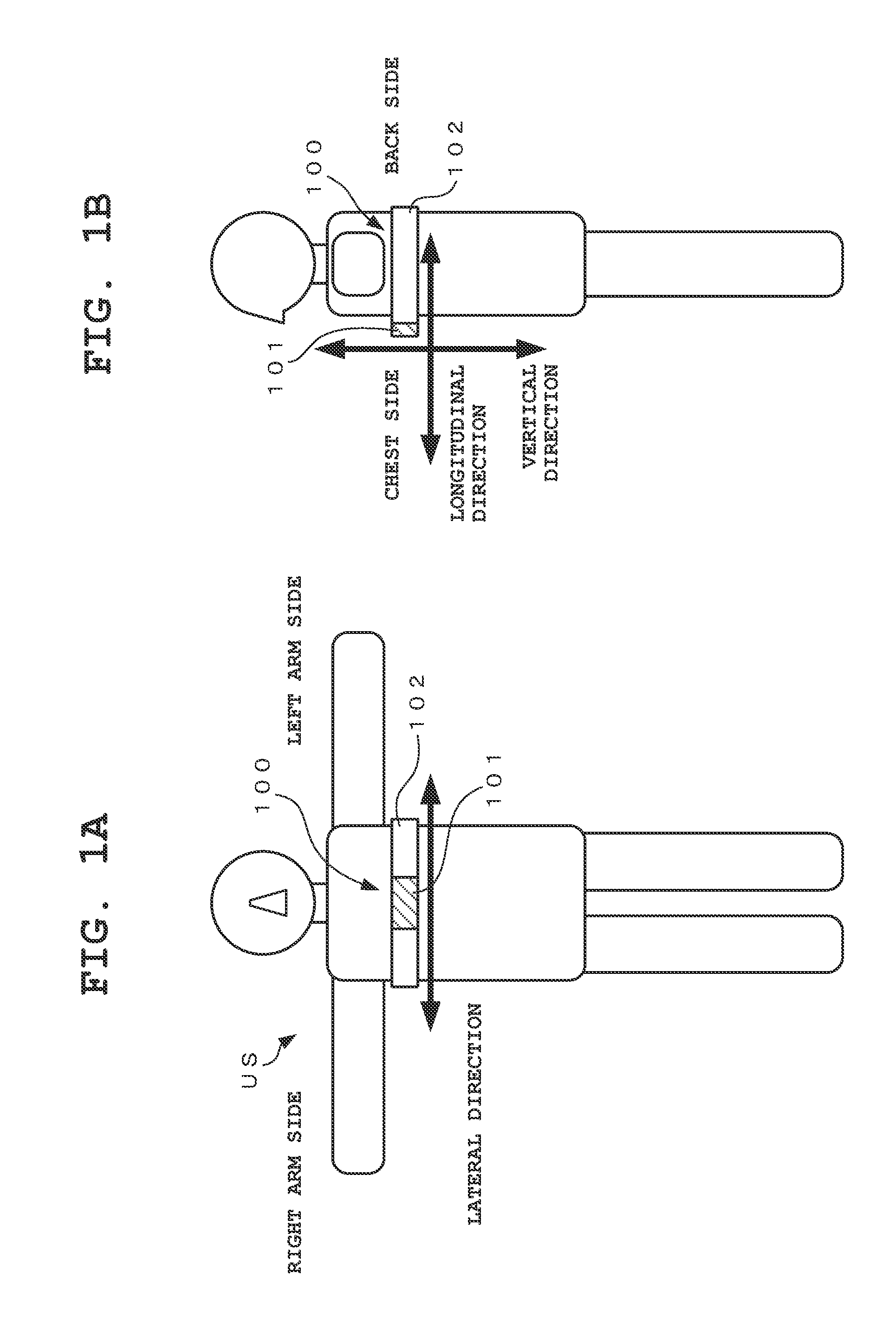
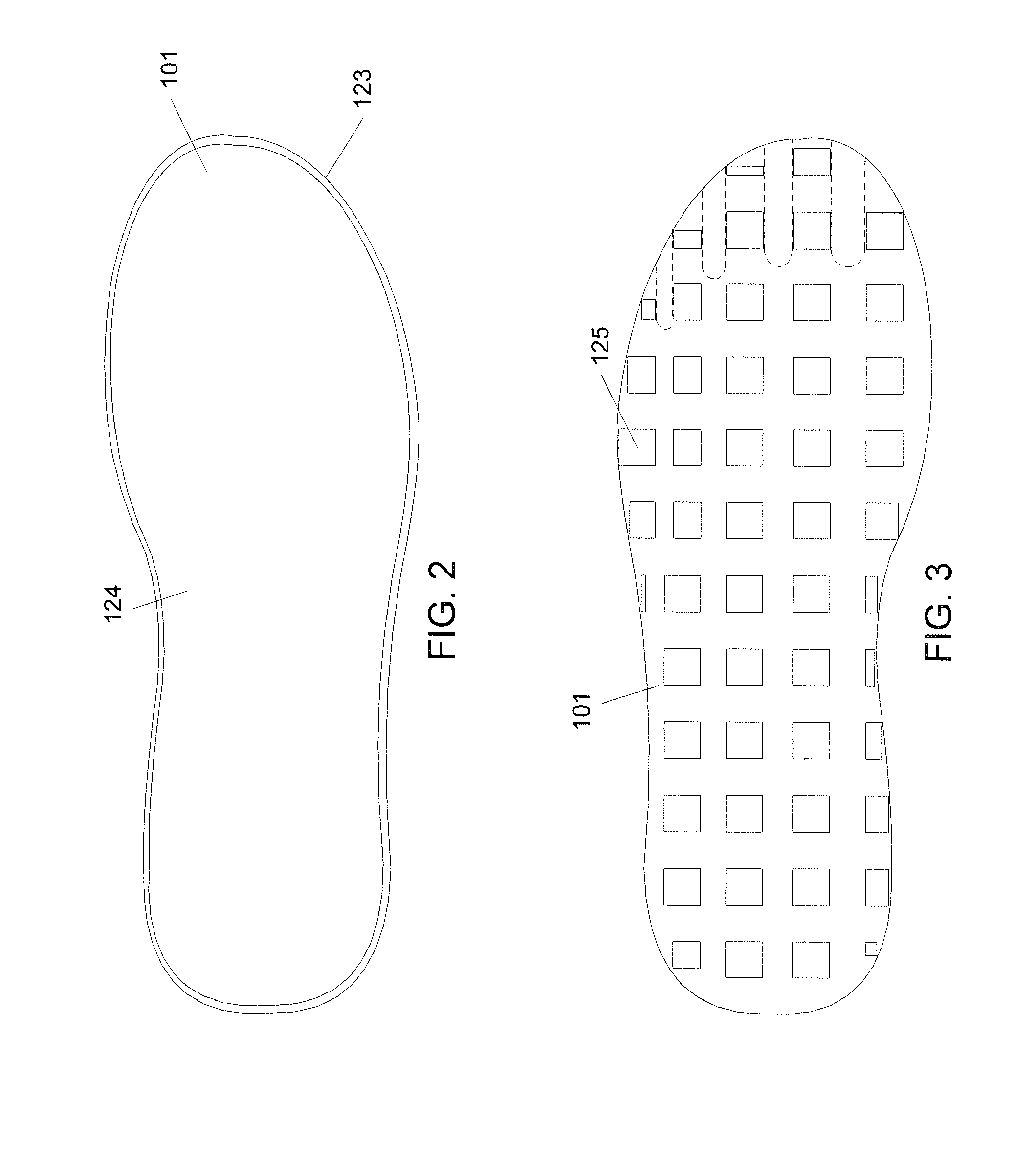
The triplanar movements of the foot are as follows, transverse plane adduction/abduction, frontal plane inversion/eversion, and sagittal plane dorsiflexion/plantarflexion. These movements can further compound into the positions of supination/pronation.
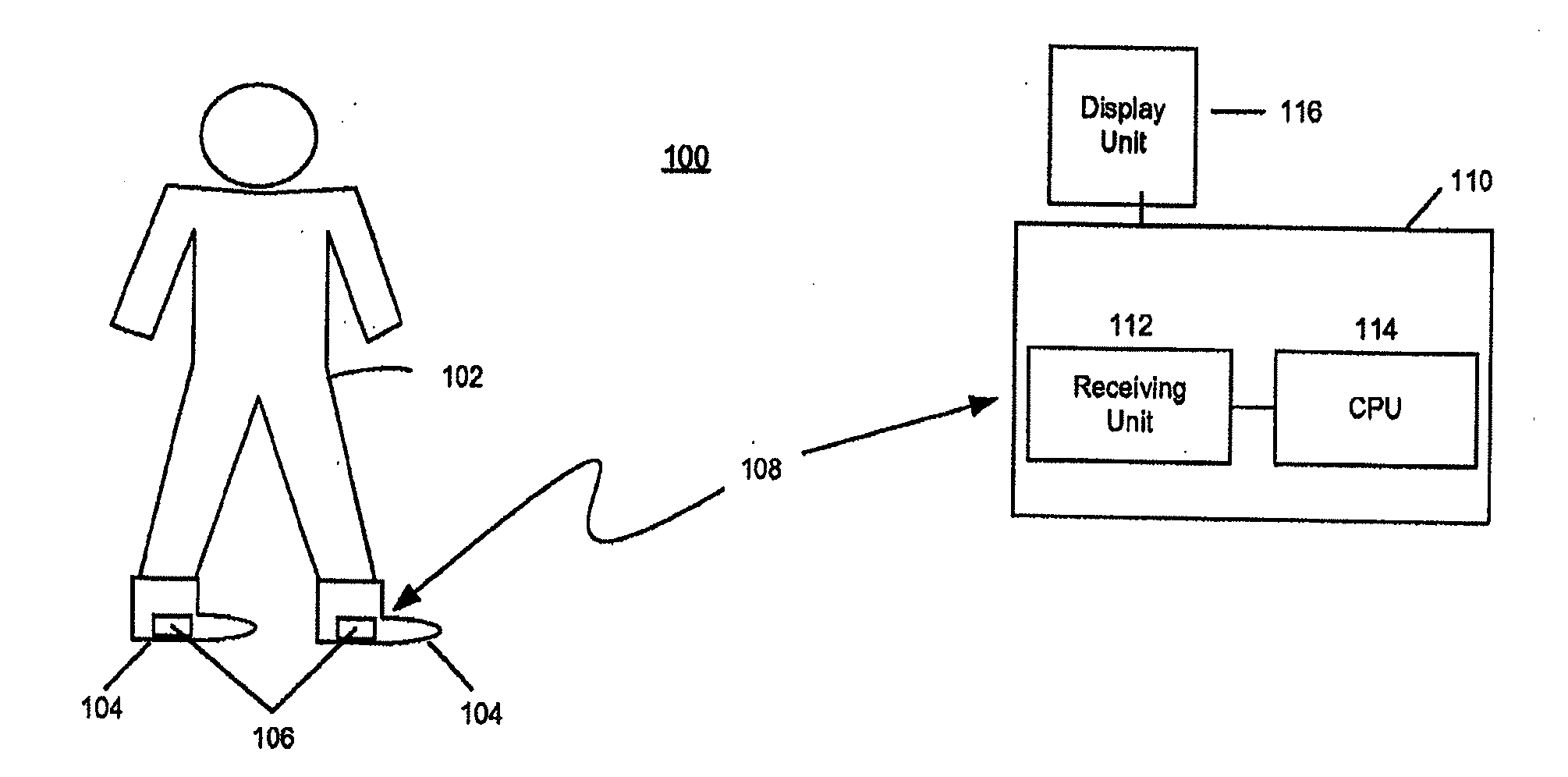
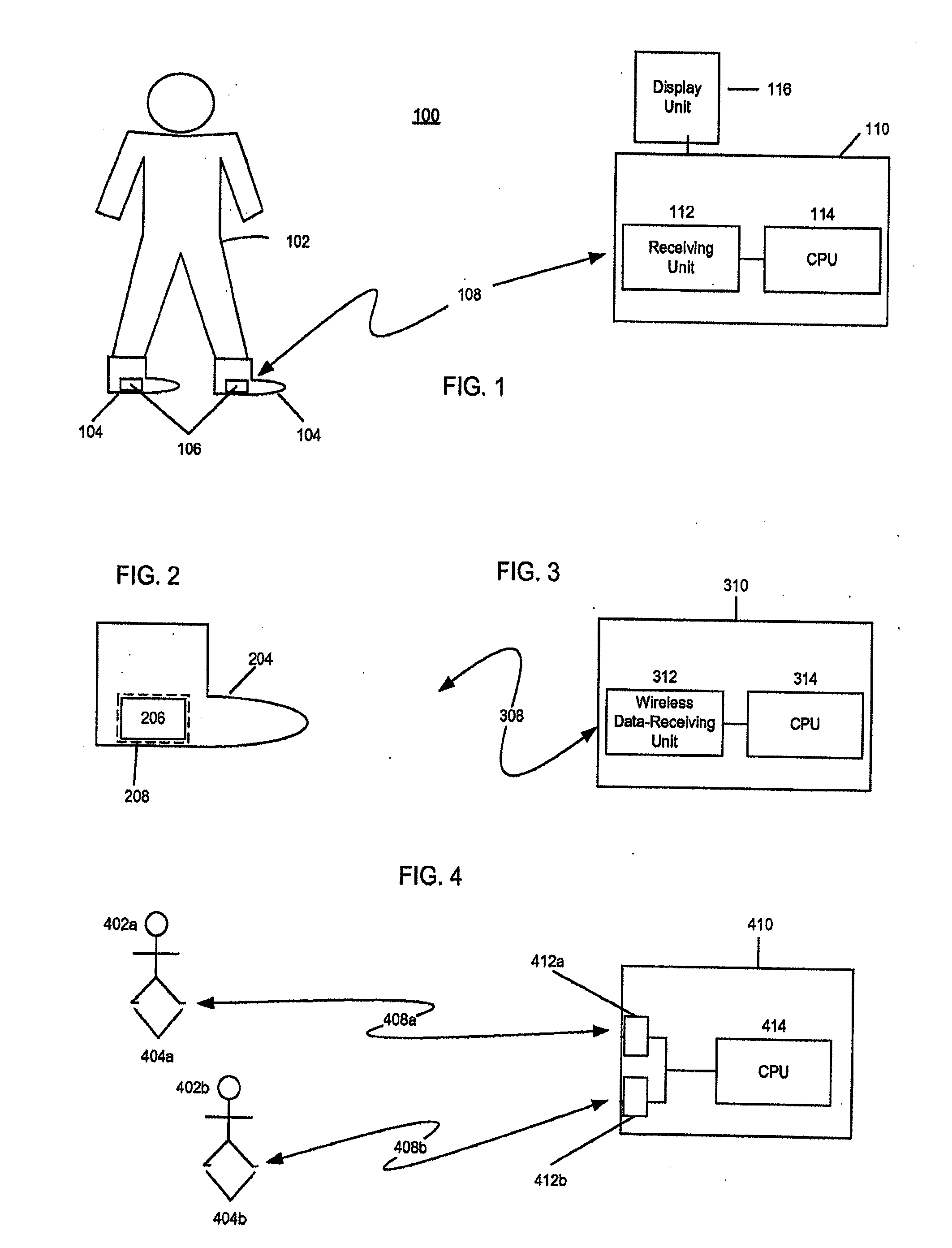
Electronic Game That Detects and Incorporates a User's Foot Movement
InactiveUS20100035688A1Beacon systems using electromagnetic wavesVideo gamesPhysical therapyReal-time computing
An electronic video system incorporates the foot movements of a user into a video program. The system includes a receiver and a computer processor. The receiver is configured to wirelessly receive signals transmitted from footwear worn by a user. The signals correspond to a series of foot movements of the user. The computer processor is operatively connected to the receiver and is configured to run the video program, which utilizes the signals received by the receiver as input data. The processor processes the input data to recognize the series of foot movements of the user, and outputs video signals simulating the series of foot movements.
Owner:HARMONIX MUSIC SYSTEMS
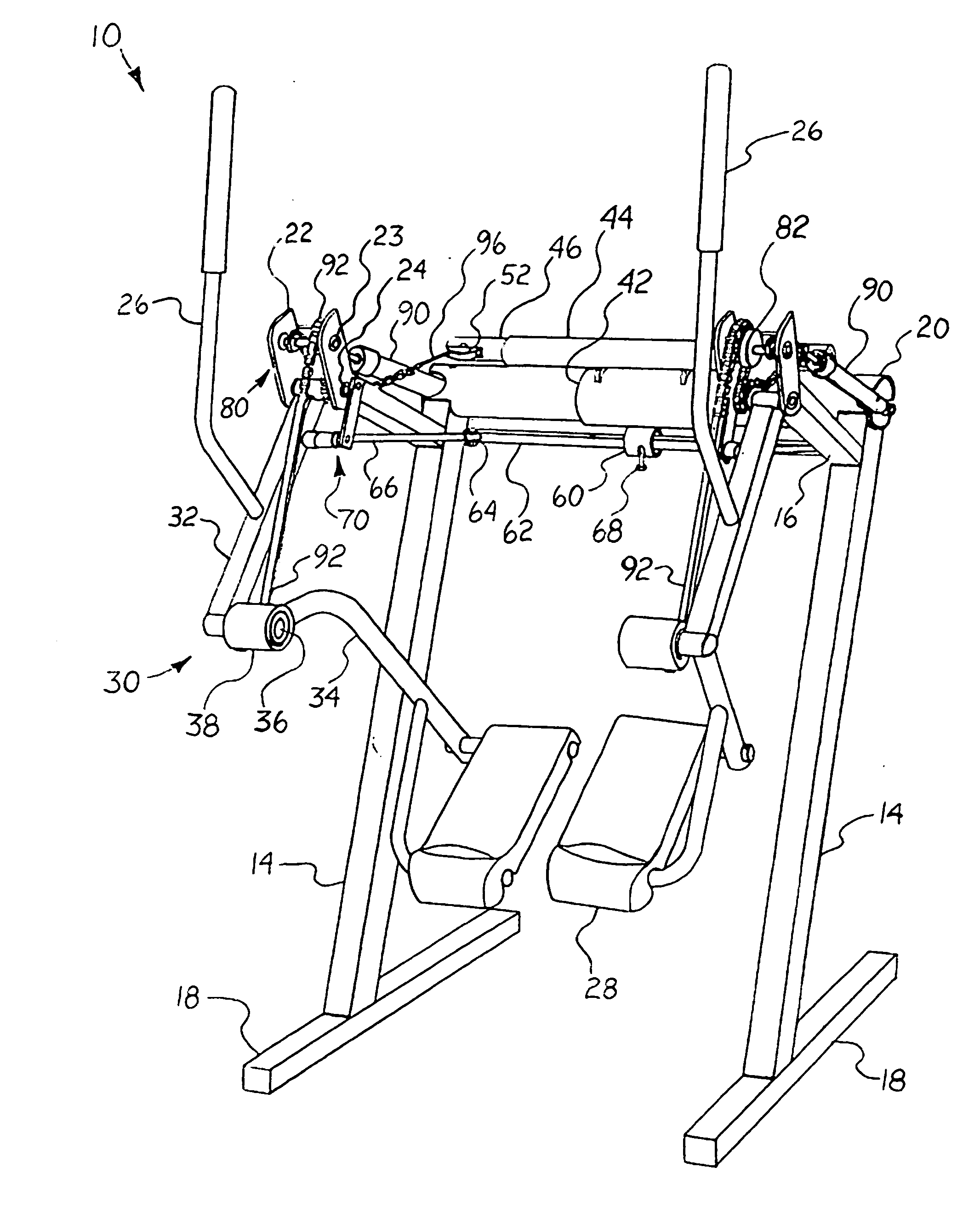
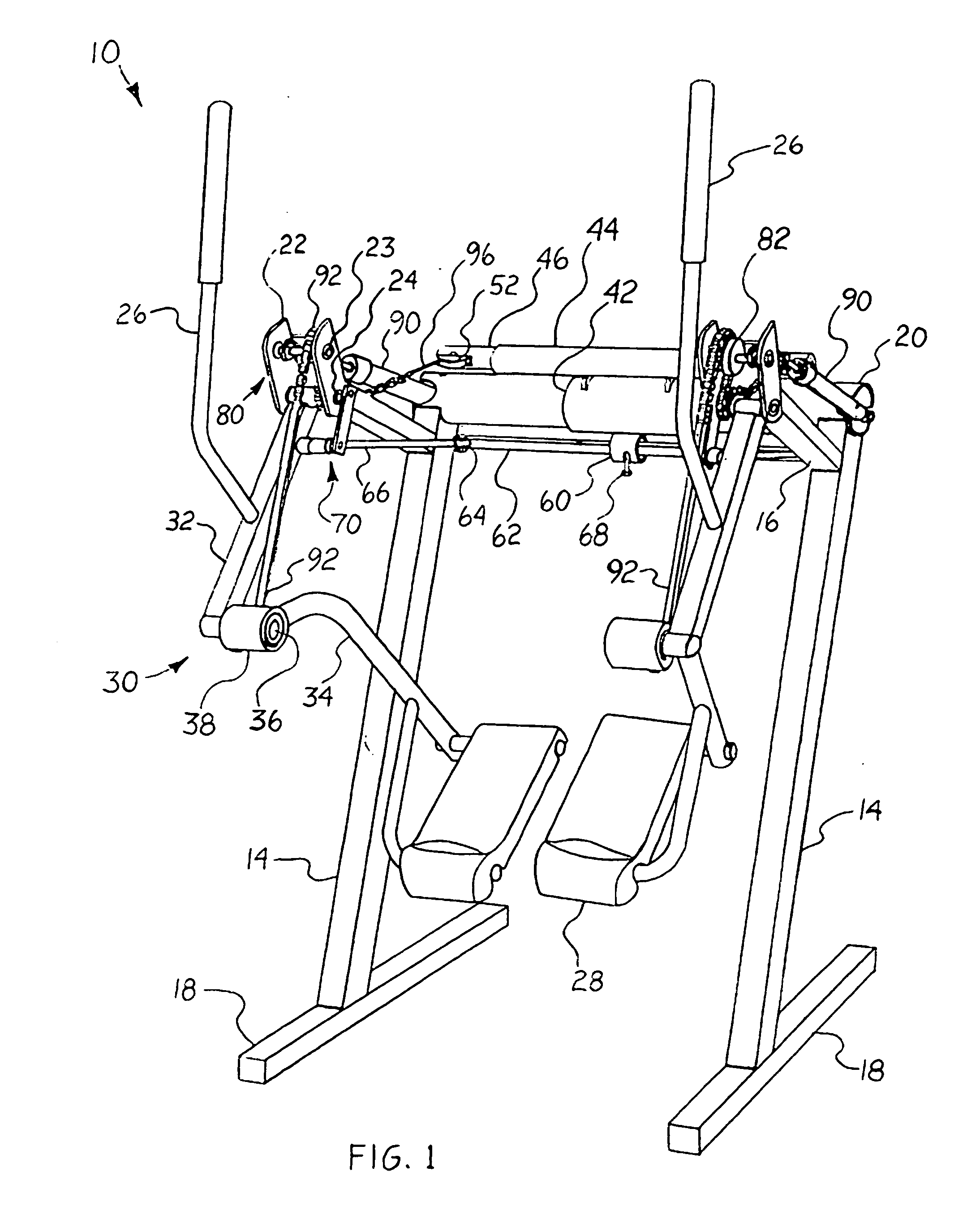
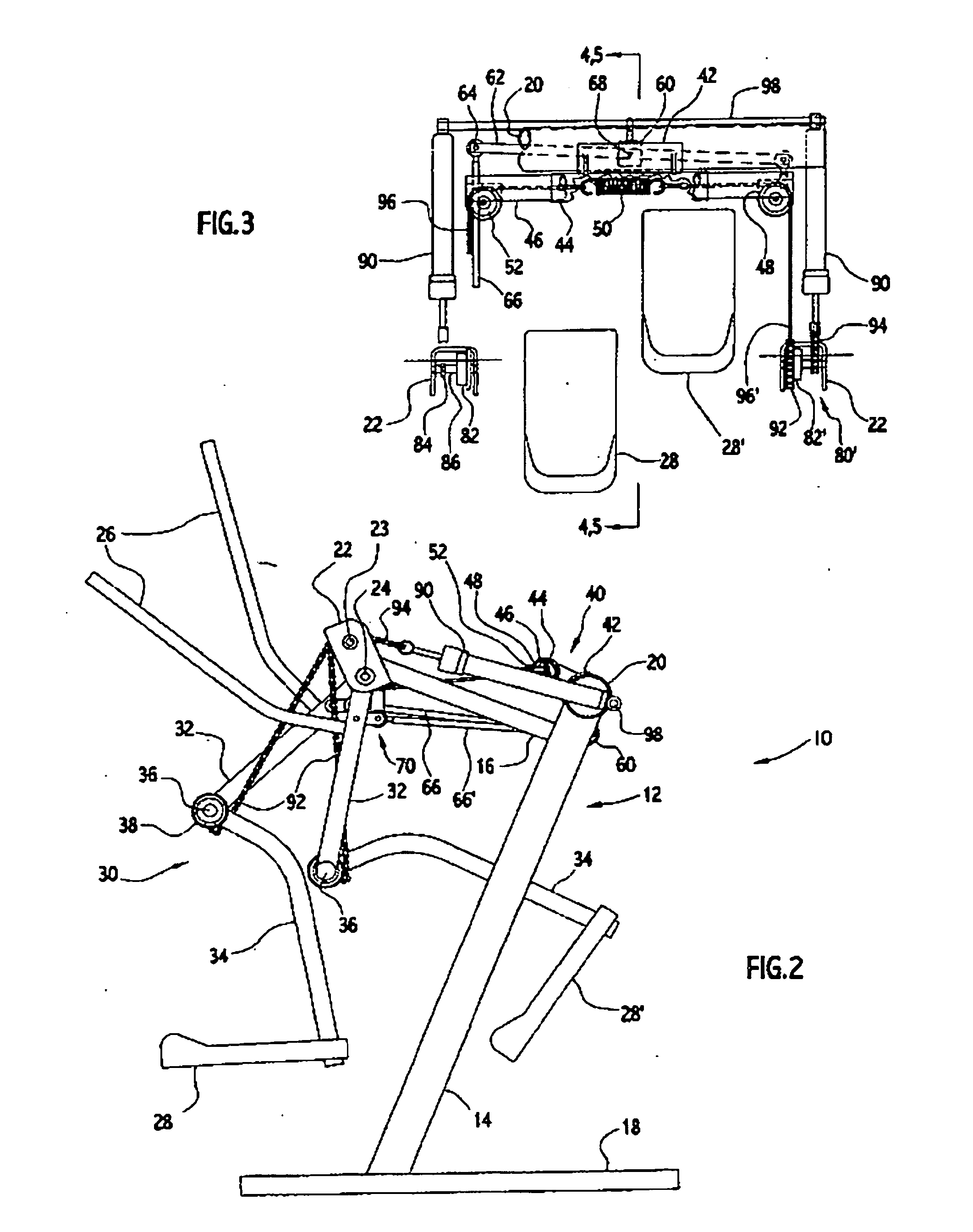
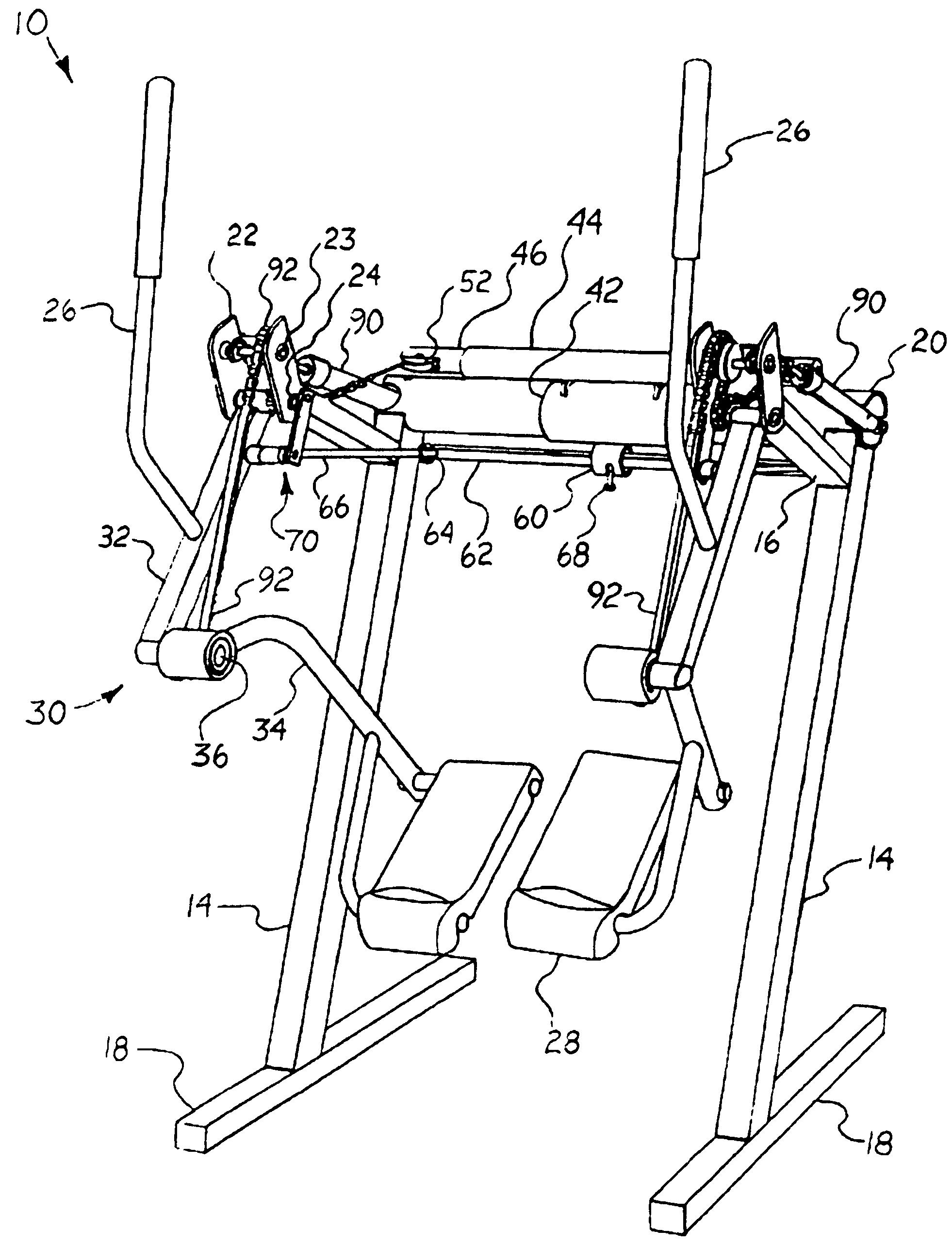
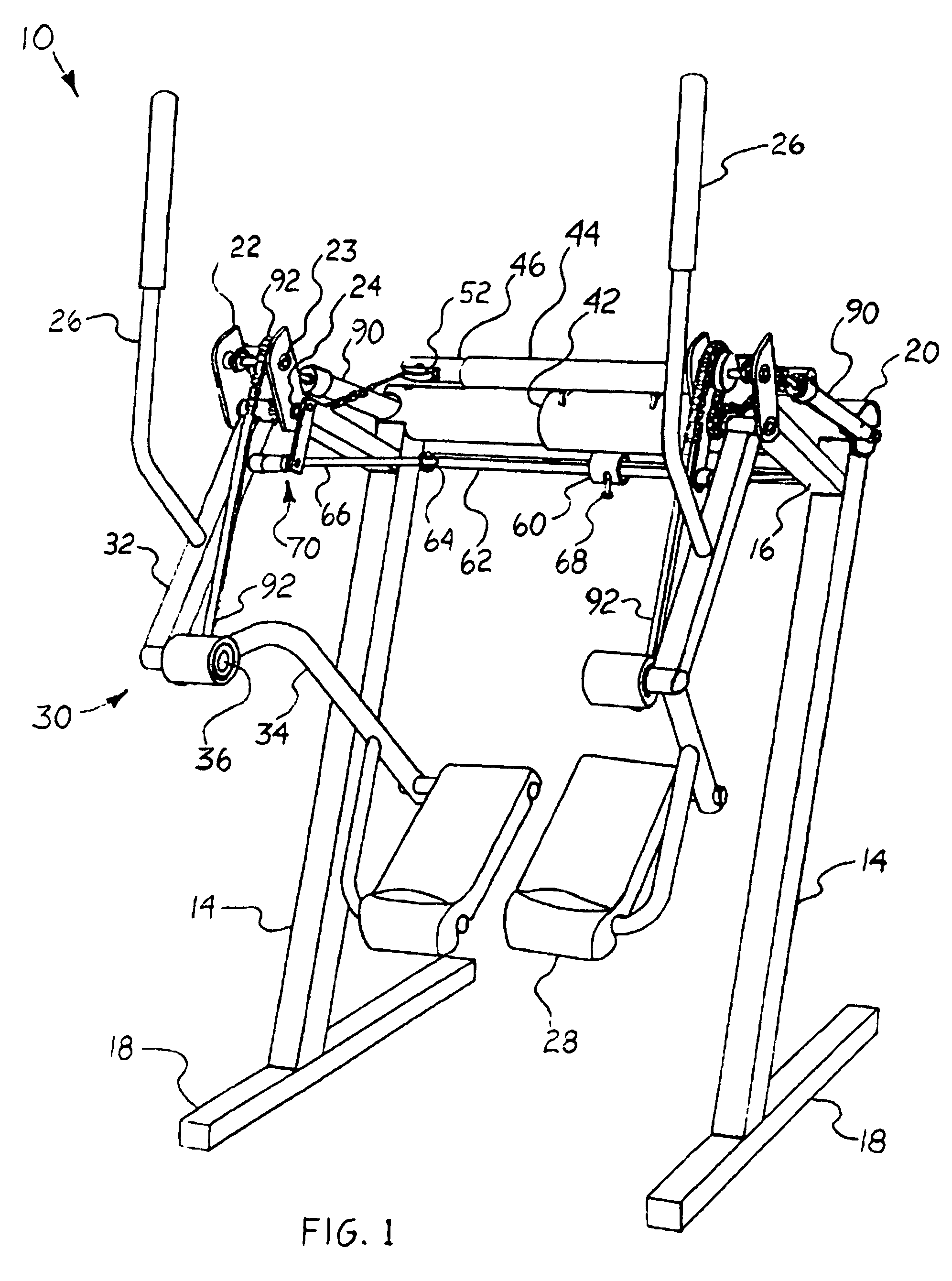
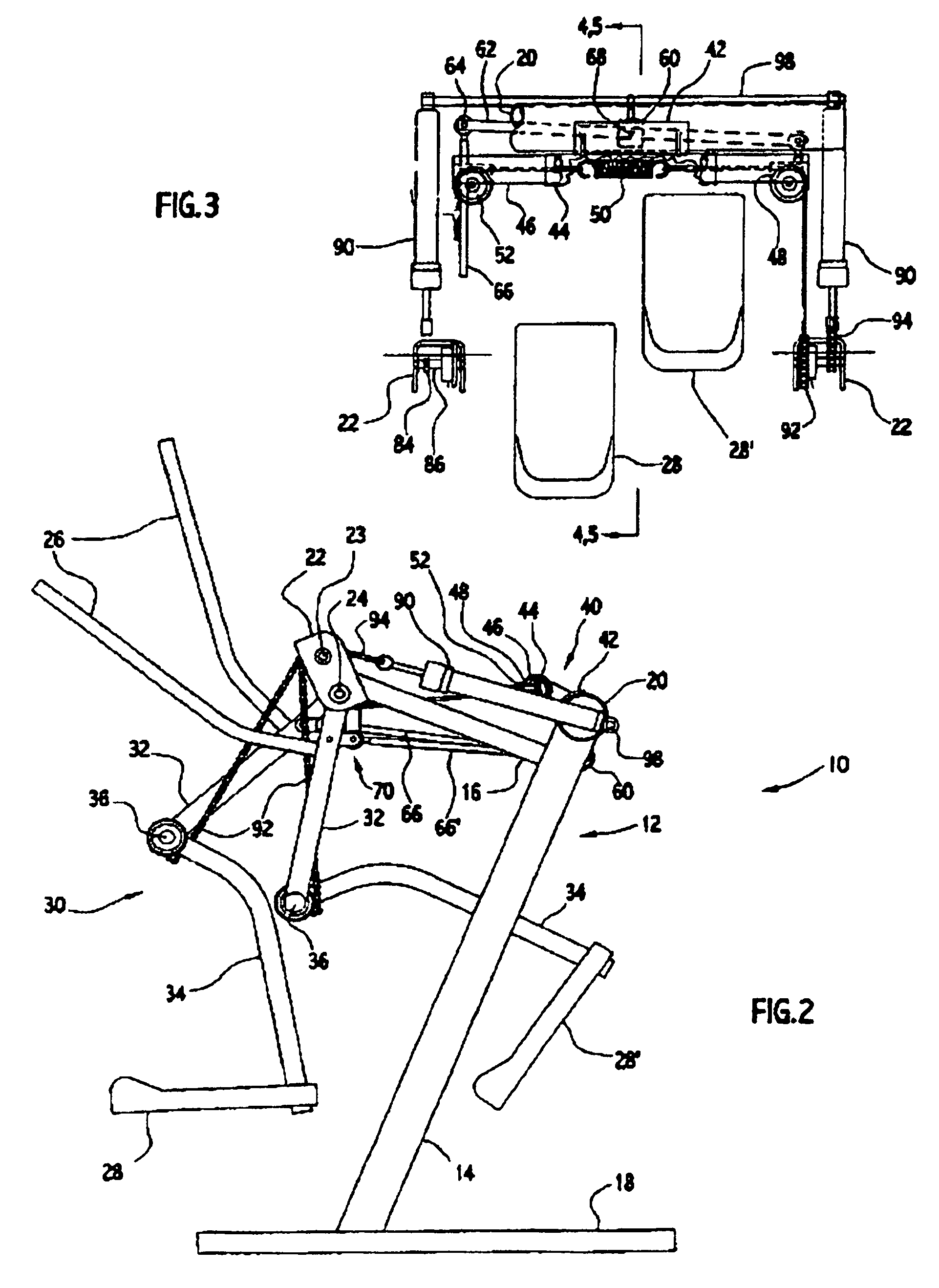
Exercise device
InactiveUS20070037667A1Great degreeHigh simulationRider propulsionMuscle exercising devicesVertical planeLeg exercise
An exercise device upon which a user generally standing upright supported by foot platforms suspended from a frame via linkages in which the linkage lengths and pivot points correspond generally to the users upper and lower legs and hip and knee joints. This device not only allows natural free and spontaneous leg movement, able to simulate such exercises as walking, jogging, running, stepping, skiing or gliding, bicycling, climbing, reverse action and various isolated leg exercises, where the exercises can be performed at random generally without the need to reconfigure the device. This device preferably includes an isolation system capable of simulating natural forces throughout the entire range of movement in the horizontal and / or vertical plane. A safety / suspension system can be provided, alone or in combination with the isolation system, to resist sudden foot movement in the same direction, yet allows a slow and controlled tilting of the linkages whereby the user may simulate uphill and downhill travel.
Owner:EXERCITING
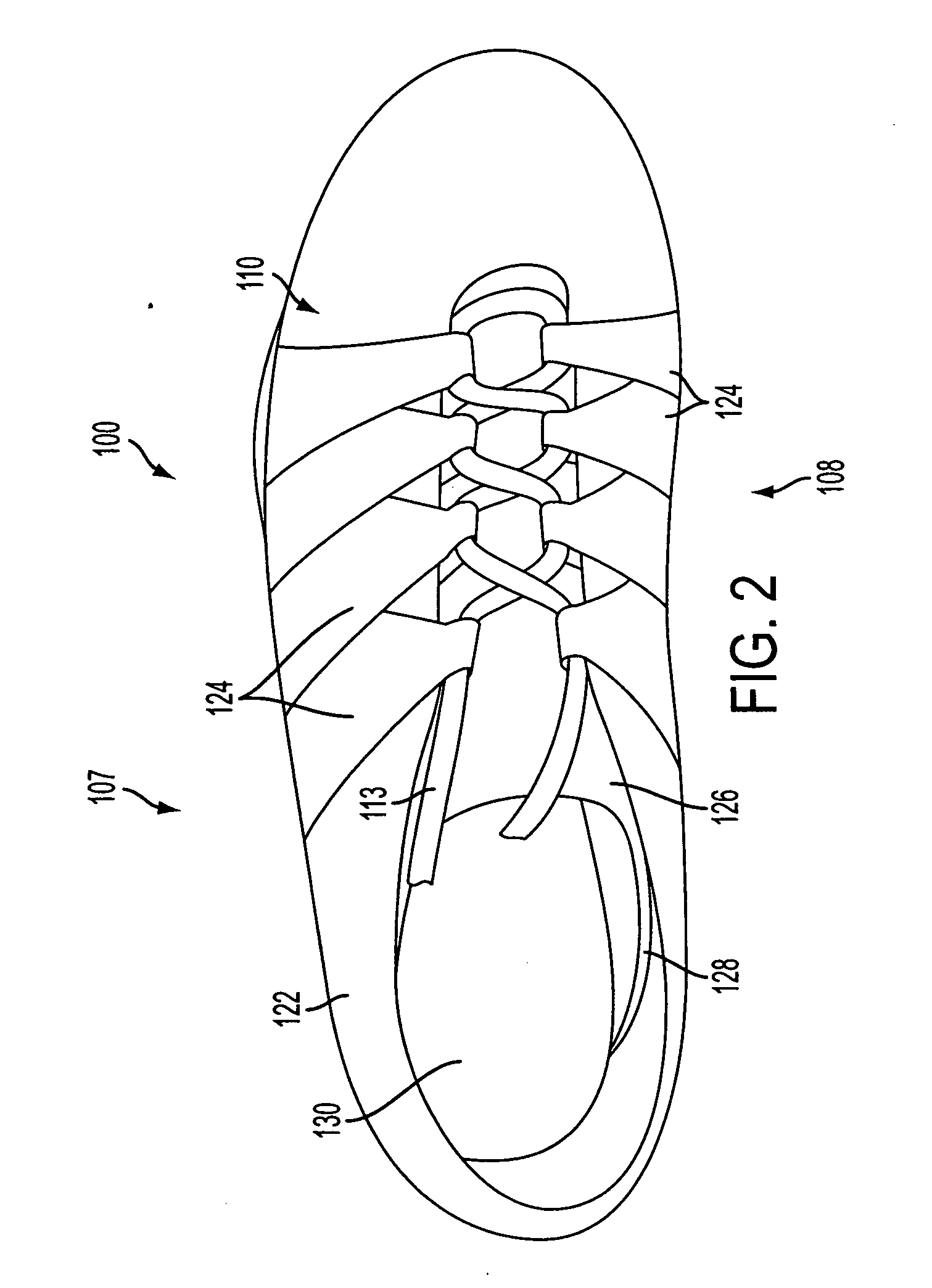
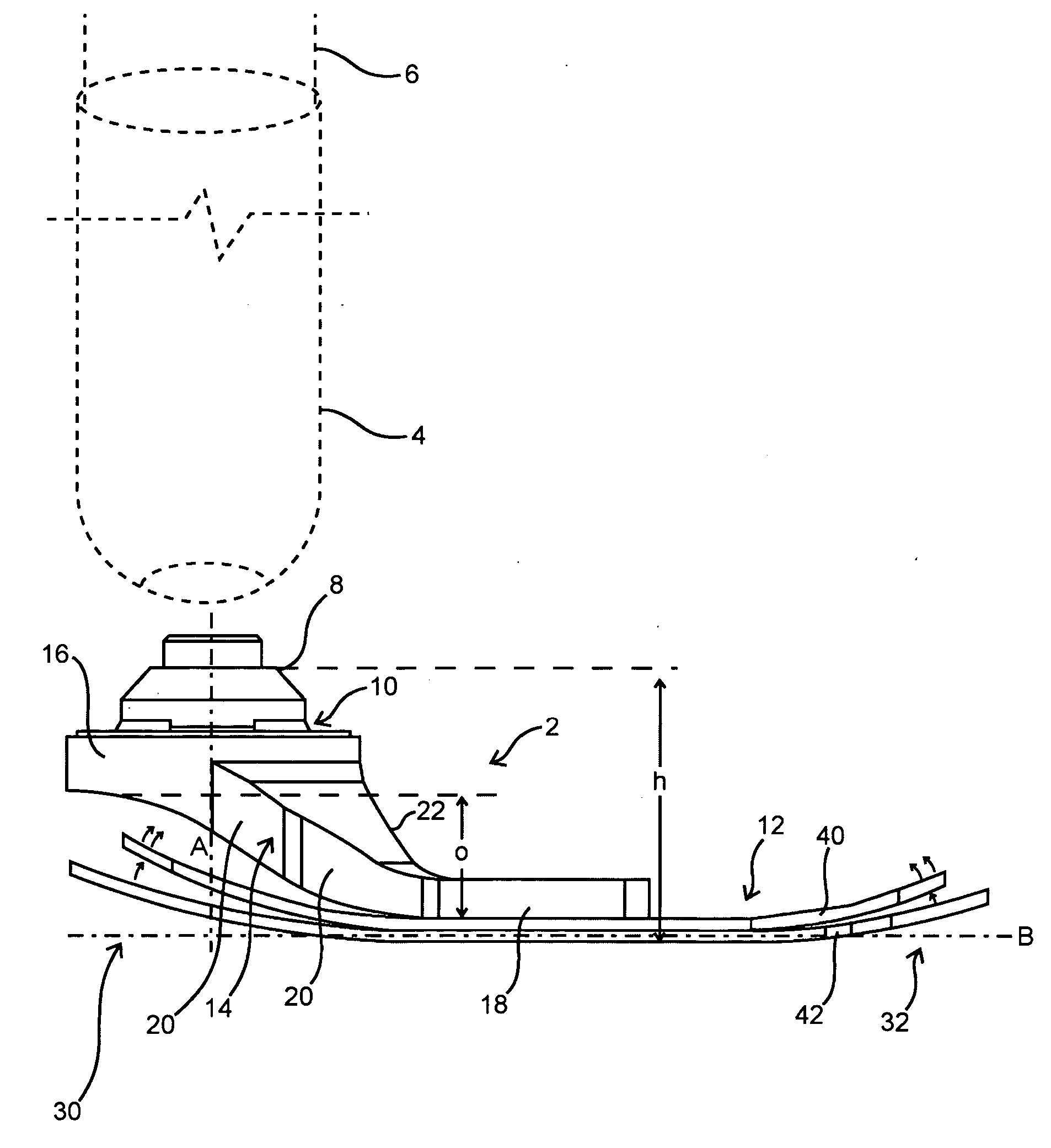
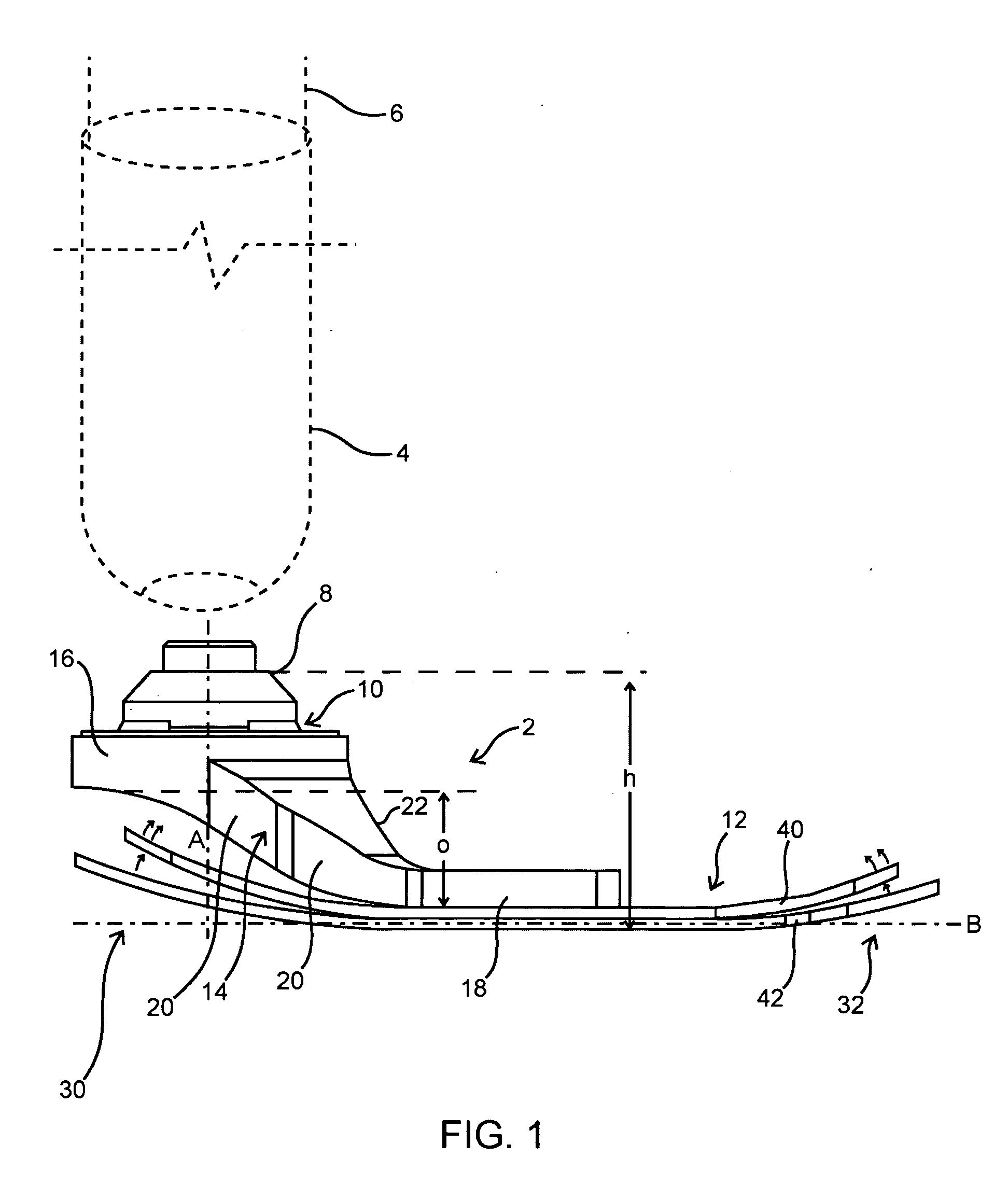
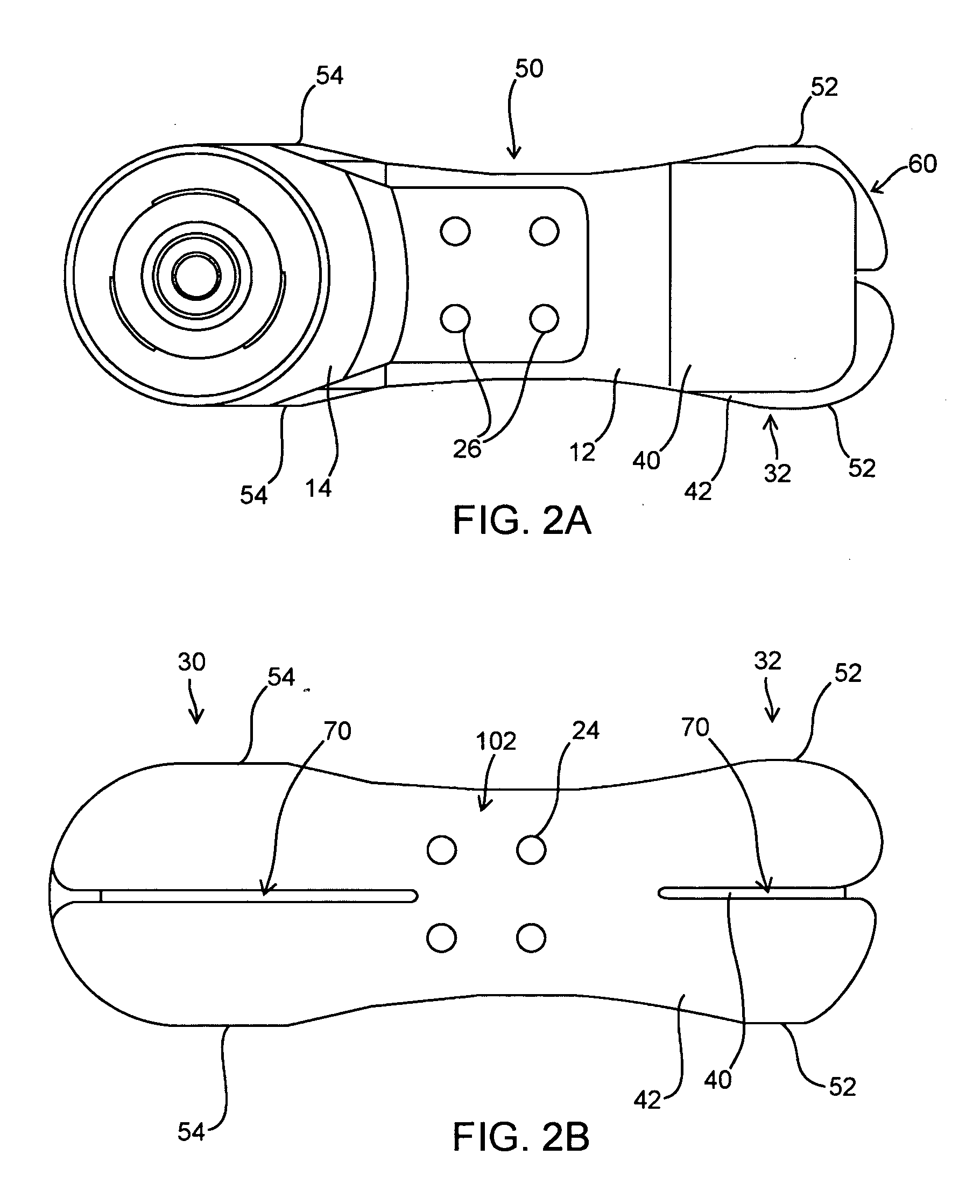
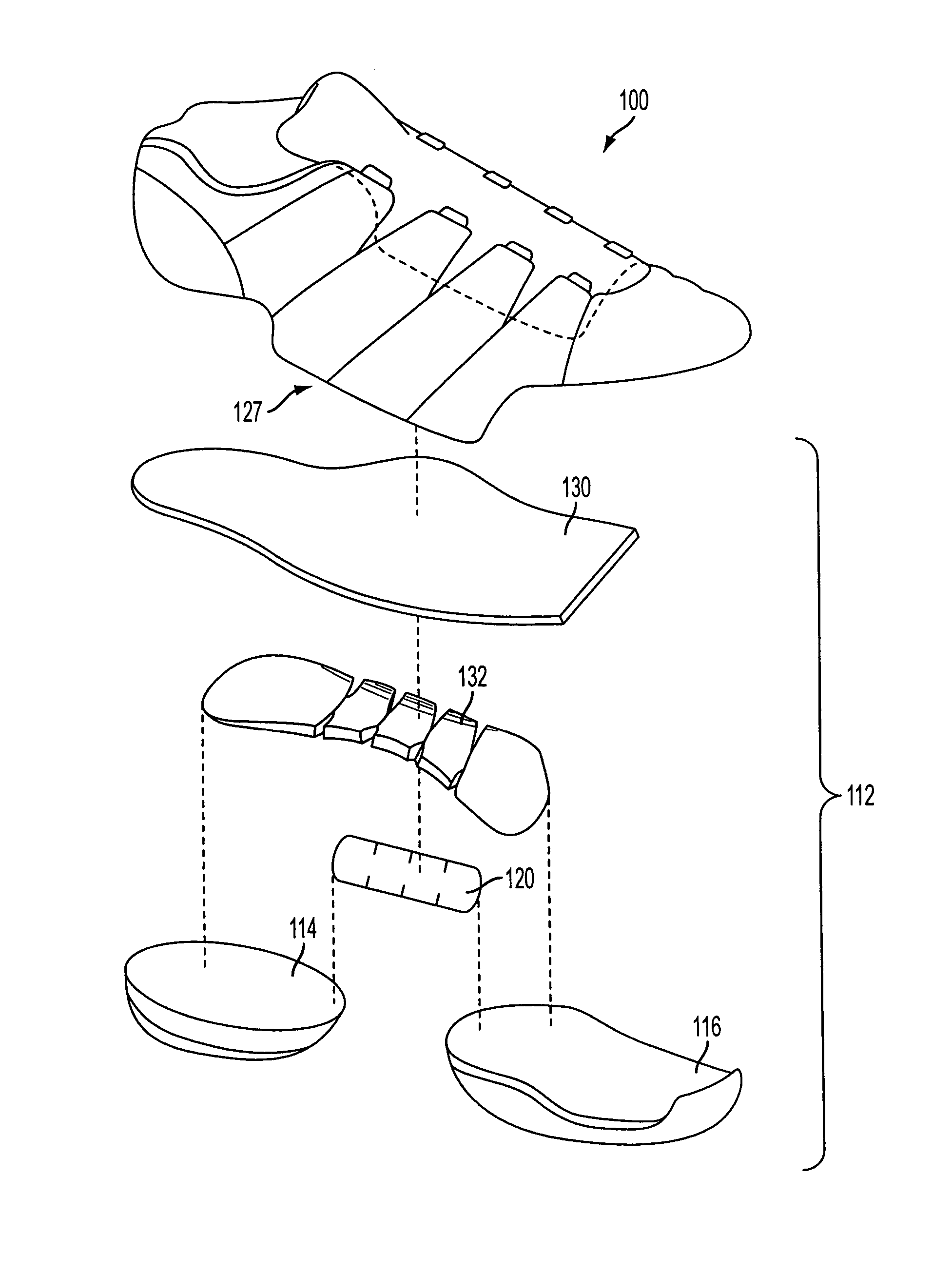
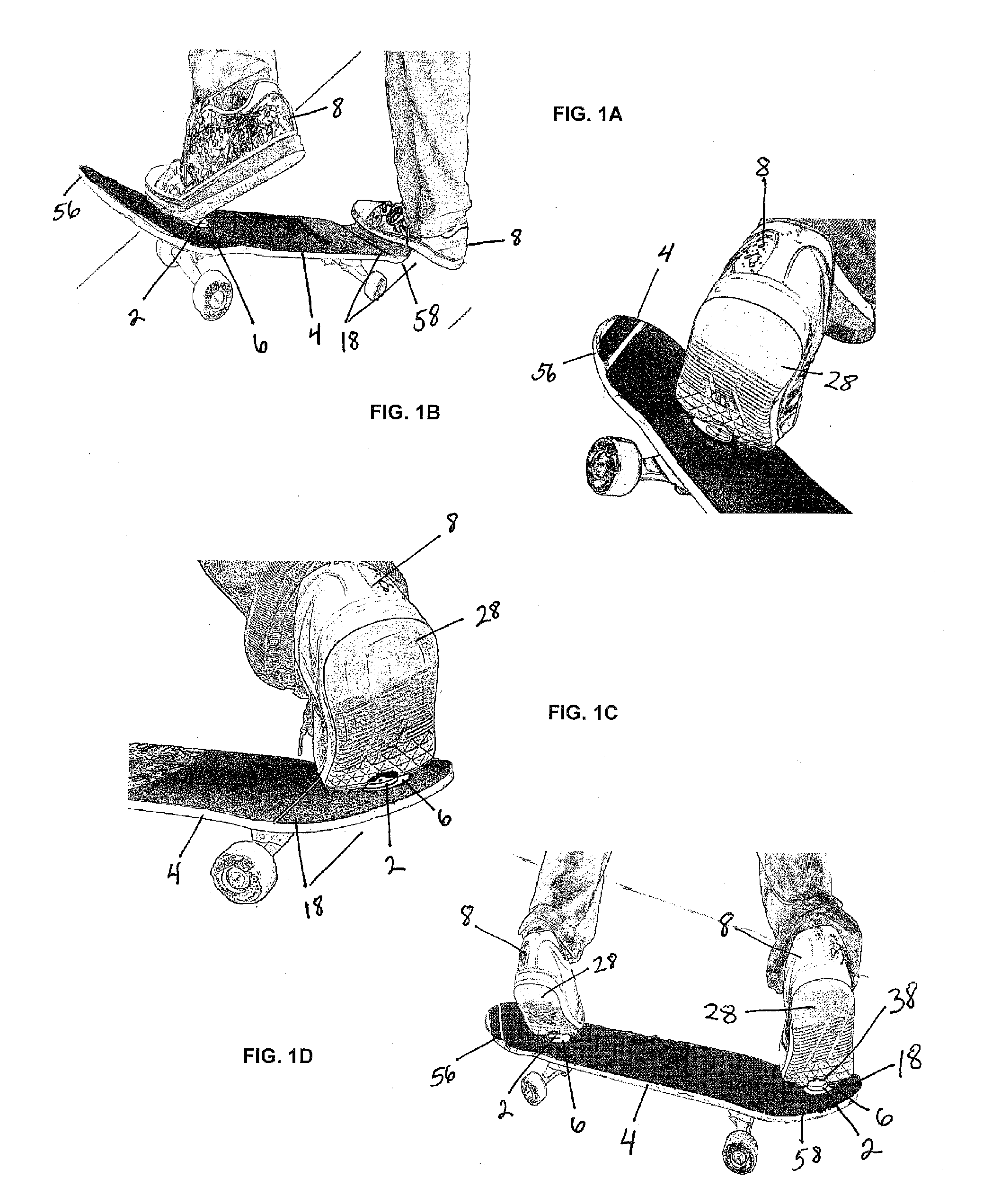
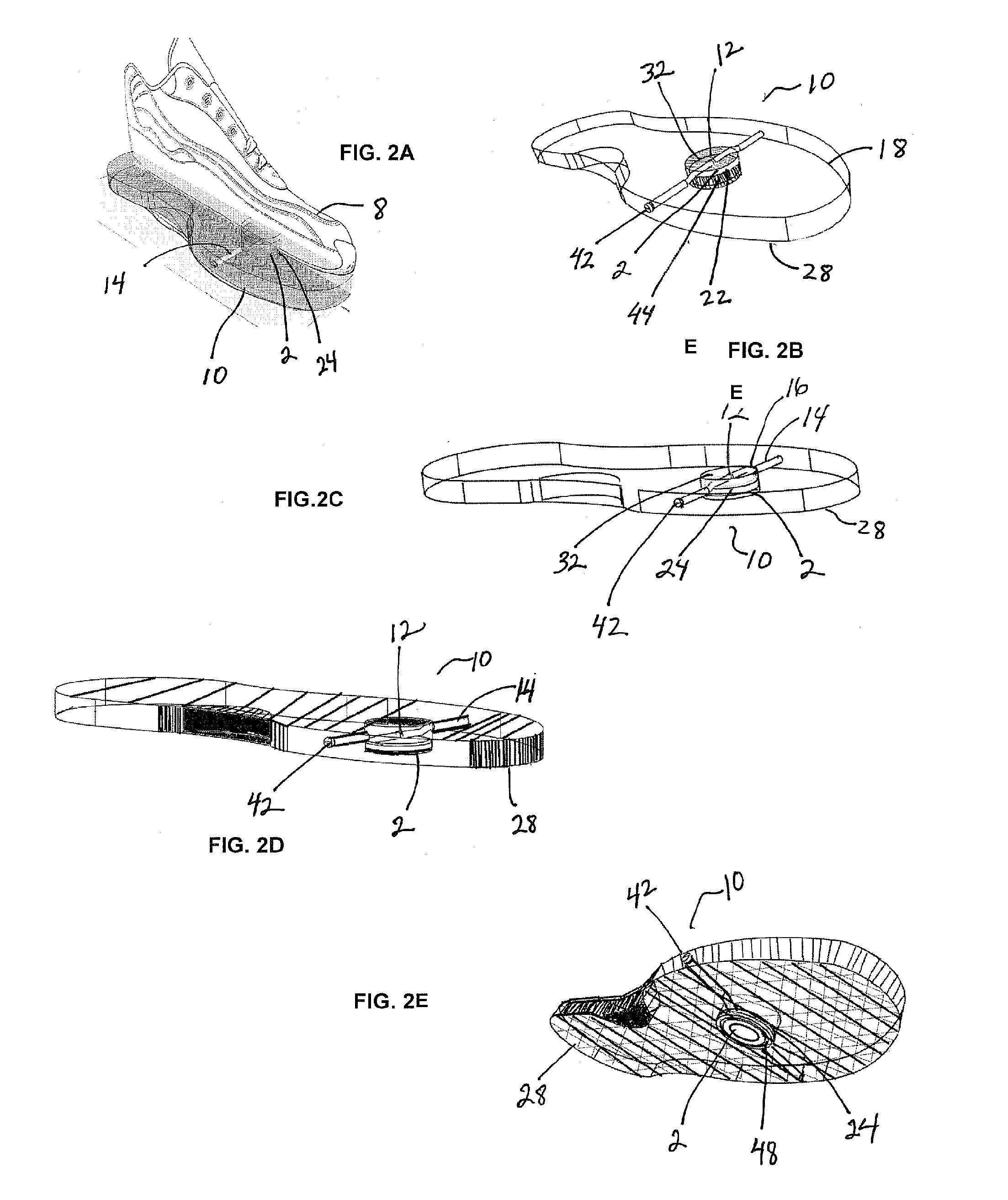
Flexible shank for an article of footwear
A directionally flexible shank for an article of footwear is disclosed, which provides support to the bottom of a user's foot while providing flexibility for foot movements in one or more particular directions. The directionally flexible shank may also support the arch of the foot. The directionally flexible shank may include a plurality of articulatable segments that can easily rotate with respect to each other in a first direction and thereby permit the directionally flexible shank to flex away from the foot, while limiting articulation in an opposite direction. The articulatable segments are connected to each other via hinge structures, which may include living hinges formed of a thermoplastic material. The hinge structures may also be formed from a flexible sheet attached to a bottom portion of the directionally flexible shank. Methods are also disclosed for manufacturing the directionally flexible shank.
Owner:NIKE INC
Exercise device
InactiveUS7645215B2Great degreeHigh simulationRider propulsionMovement coordination devicesVertical planeLeg exercise
An exercise device upon which a user generally standing upright supported by foot platforms suspended from a frame via linkages in which the linkage lengths and pivot points correspond generally to the users upper and lower legs and hip and knee joints. This device not only allows natural free and spontaneous leg movement, able to simulate such exercises as walking, jogging, running, stepping, skiing or gliding, bicycling, climbing, reverse action and various isolated leg exercises, where the exercises can be performed at random generally without the need to reconfigure the device. This device preferably includes an isolation system capable of simulating natural forces throughout the entire range of movement in the horizontal and / or vertical plane. A safety / suspension system can be provided, alone or in combination with the isolation system, to resist sudden foot movement in the same direction, yet allows a slow and controlled tilting of the linkages whereby the user may simulate uphill and downhill travel.
Owner:EXERCITING
Prosthetic foot
InactiveUS20050033451A1Facilitates iterative tuningNatural appearanceArtificial legsFeature completeEngineering
Features for a high performance prosthetic foot are provided in a package suitable for use with Symes and reverse-Symes amputees. The foot has a very low profile despite incorporating ankle-type torsional features complete with biasing. Other optional features are presented by way of a dual-rate padding spring system, that convincingly allow for both walking and running (together with related tasks like jumping) by way of a single prosthetic setup. Additional features may be provided in the padding springs directed toward more natural foot movement and response. The foot may be provided alone, in connection with a prosthetic socket and be bare or encased in order to appear more natural.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
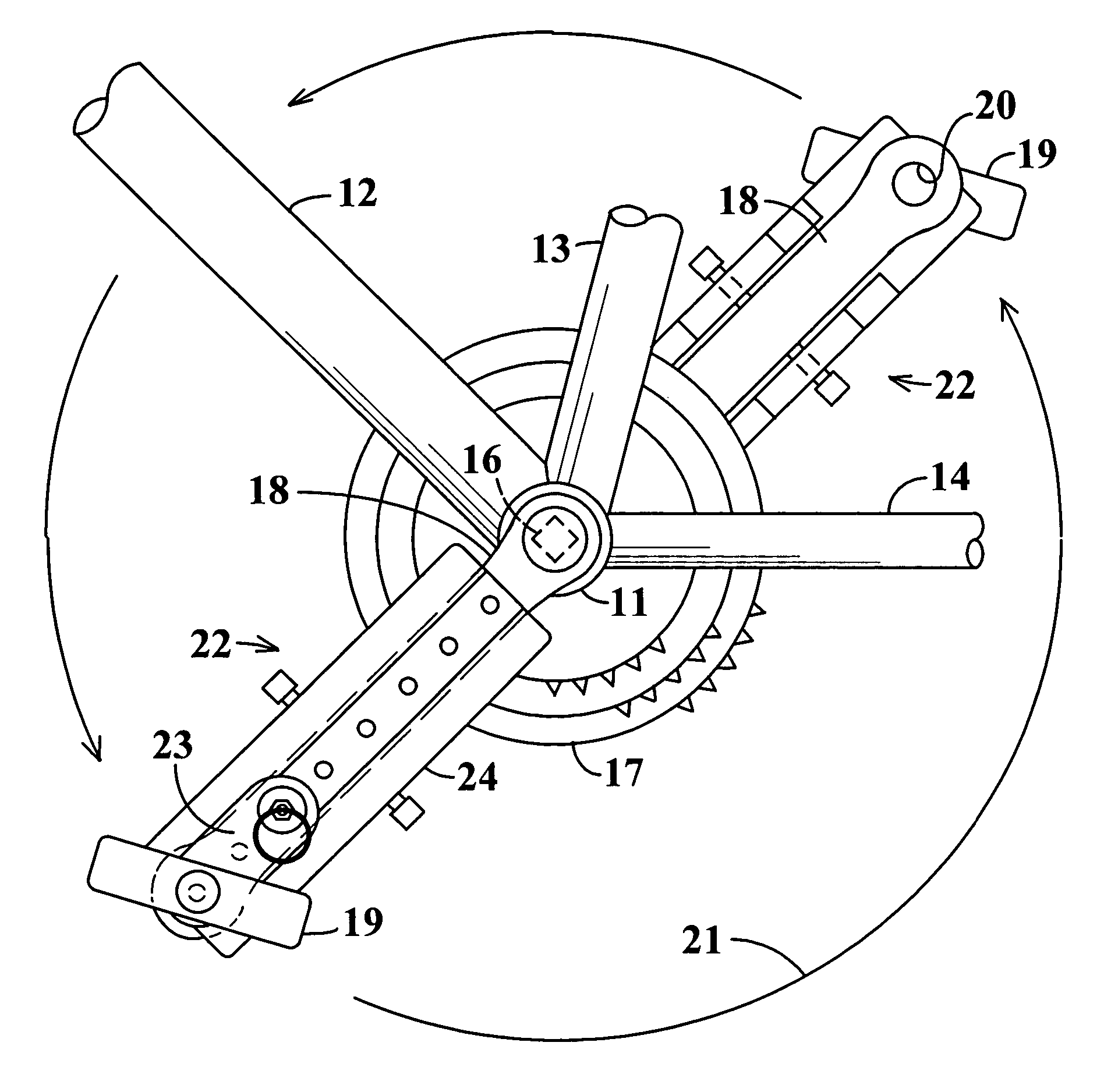
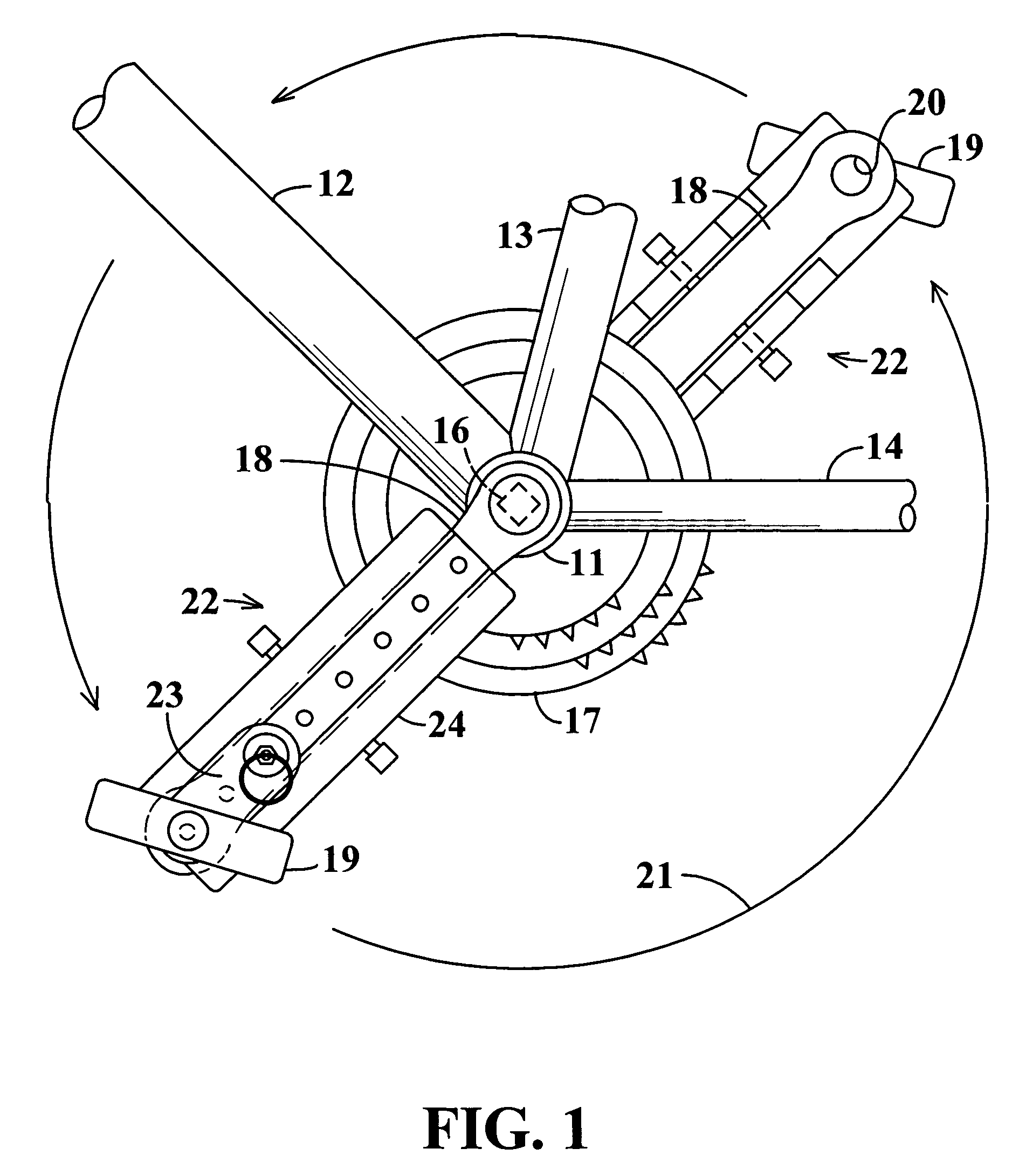
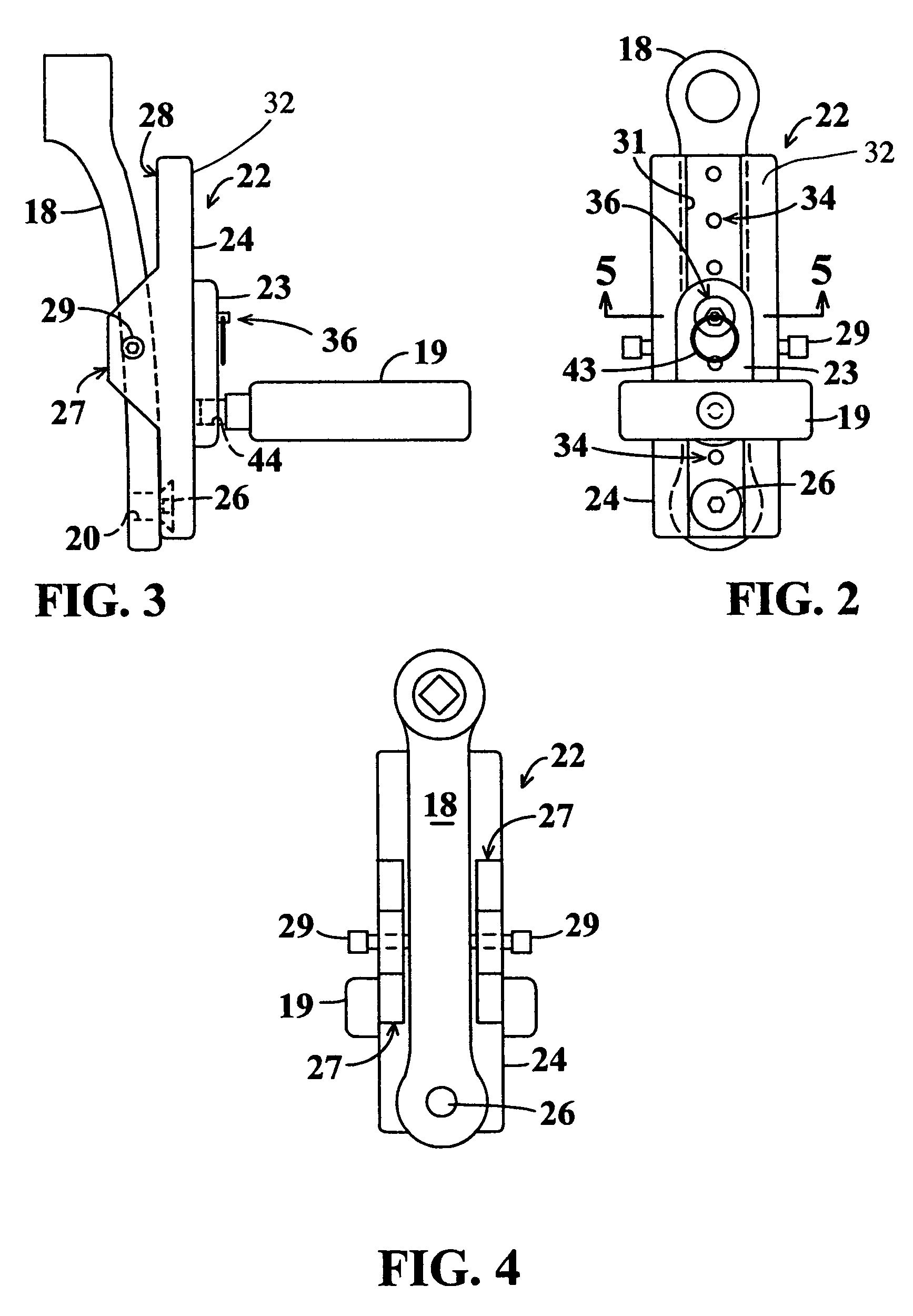
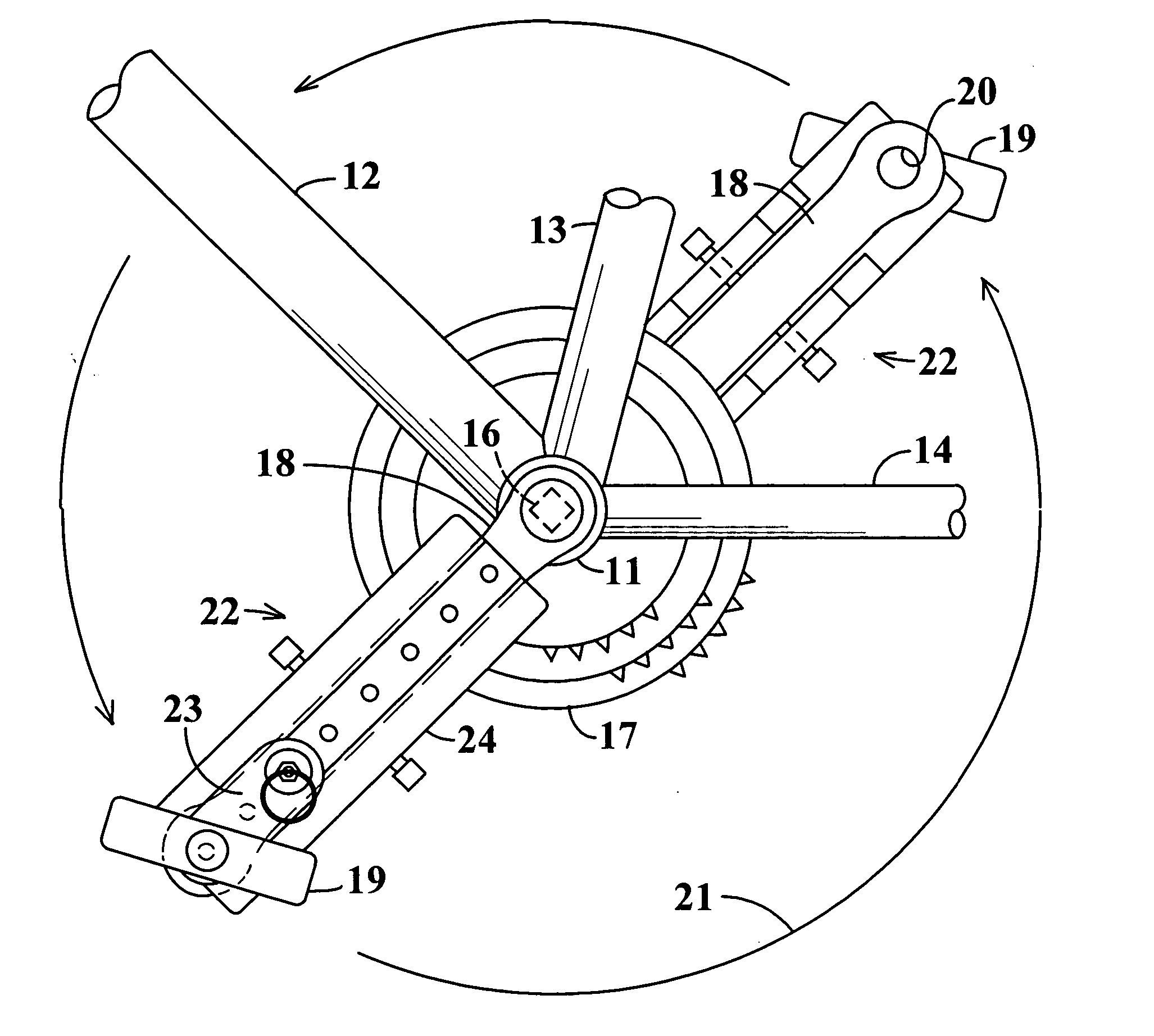
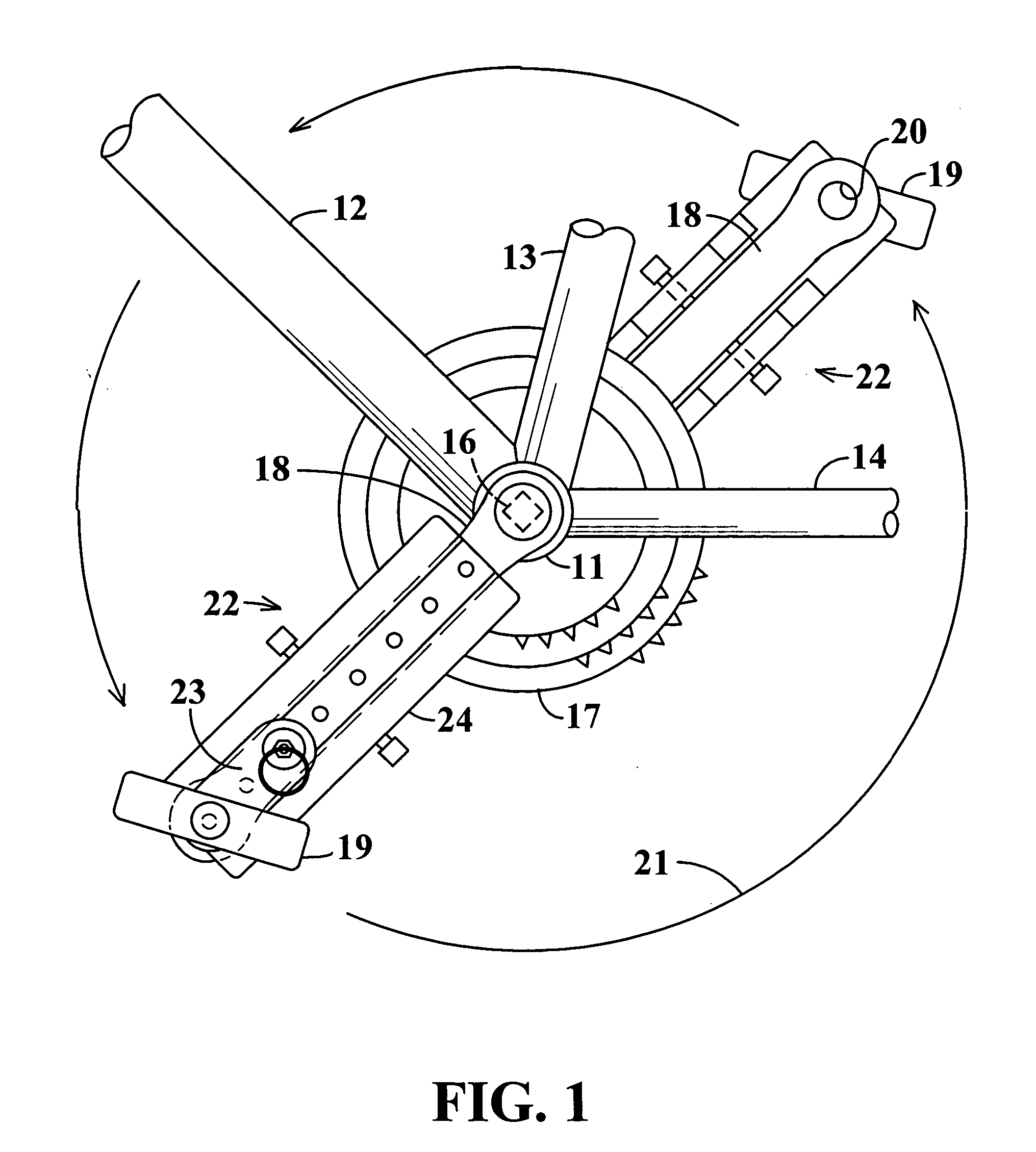
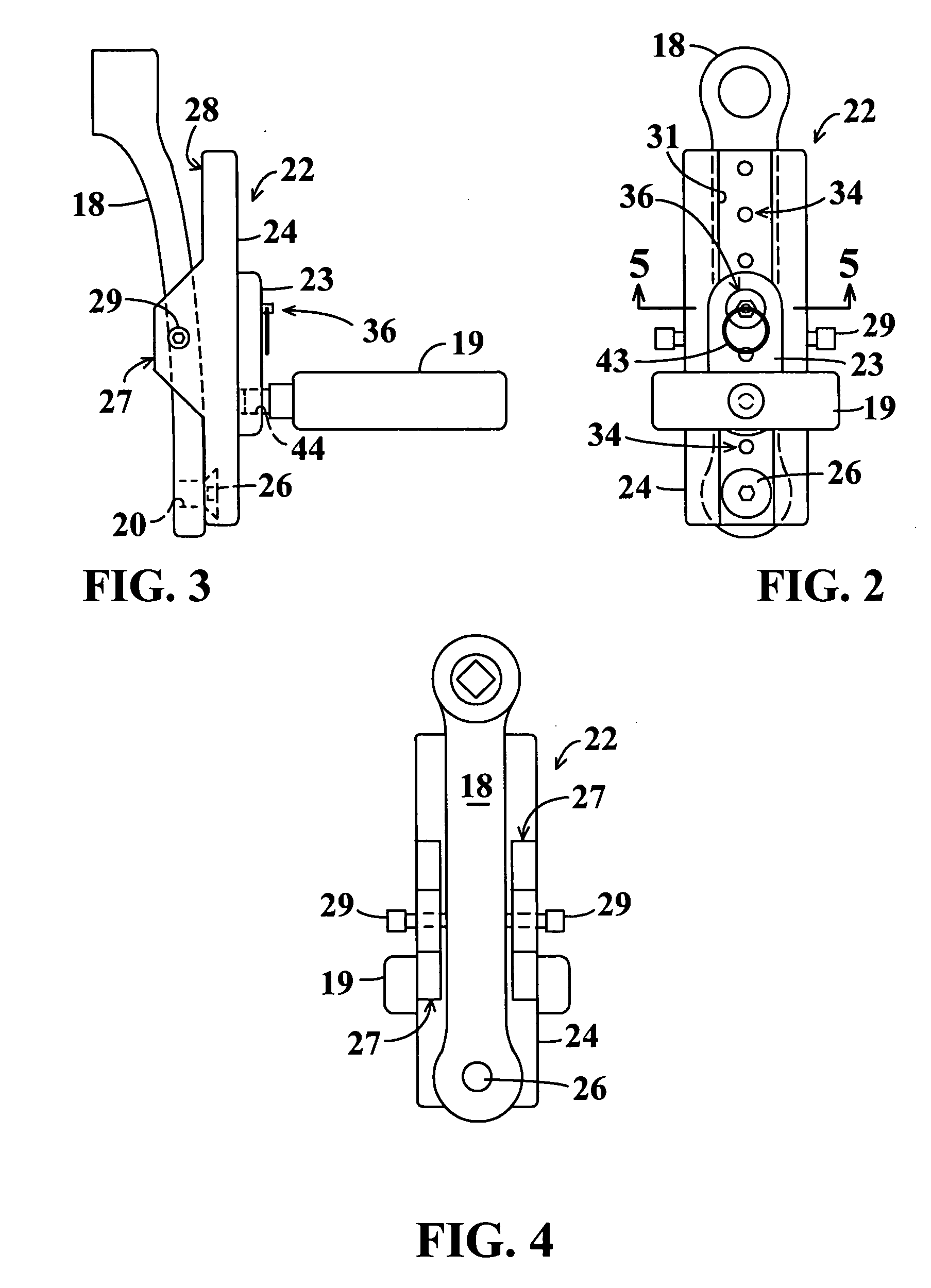
Pedal stroke adjuster for bicycles or the like
InactiveUS7204788B2Easy to processImprove distributionControlling membersMechanical apparatusLeg lengthEngineering
Owner:ANDREWS RONALD A
Snow removal device
InactiveUS6922920B1Much of exertionMuch of strainWeed uprootersLifting devicesSnow removalEngineering
A snow removal apparatus in the form of a shovel in which a leveraged arrangement is used to lift snow gathered on the shovel blade by lateral movement of such blade while supported by a handle adjustably secured upon the blade and the shovel handle is rested upon an underlying surface while snow is being lifted and moved to a dumping area by leveraged foot movement upon a pivot arm pivoted upon the handle and attached to the blade thus avoiding strain on a shovelers arms and spine while shoveling.
Owner:STRATZ ANTHONY
Flexible shank for an article of footwear
ActiveUS8549774B2Smooth rotationProvide flexibilitySolesUpperArches of the footMechanical engineering
A directionally flexible shank for an article of footwear is disclosed, which provides support to the bottom of a user's foot while providing flexibility for foot movements in one or more particular directions. The directionally flexible shank may also support the arch of the foot. The directionally flexible shank may include a plurality of articulatable segments that can easily rotate with respect to each other in a first direction and thereby permit the directionally flexible shank to flex away from the foot, while limiting articulation in an opposite direction. The articulatable segments are connected to each other via hinge structures, which may include living hinges formed of a thermoplastic material. The hinge structures may also be formed from a flexible sheet attached to a bottom portion of the directionally flexible shank. Methods are also disclosed for manufacturing the directionally flexible shank.
Owner:NIKE INC
Pedal stroke adjuster for bicyles or the like
InactiveUS20050020411A1Easy to processImprove distributionControlling membersMechanical apparatusLeg lengthEngineering
A stroke adjusting attachment for bicycles or the like enables selective changing of the diameter of the orbit which is traveled by a foot pedal to adapt a particular bicycle to persons having different leg lengths or who may have physical impairments which limit foot movement. The pedal is fastened to the attachment rather than being directly secured to a crank arm of the bicycle in the conventional manner. A track member is secured to the bicycle crank arm and the pedal is fastened to a slider which is travelable to any of a plurality of different locations along the track member. Blades extend from the track member adjacent to opposite surfaces of the crank arm thereby maintaining the attachment in a fixed orientation relative to the crank arm. A particular attachment of this form can be fitted onto a variety of crank arms of different sizes and shapes.
Owner:ANDREWS RONALD A
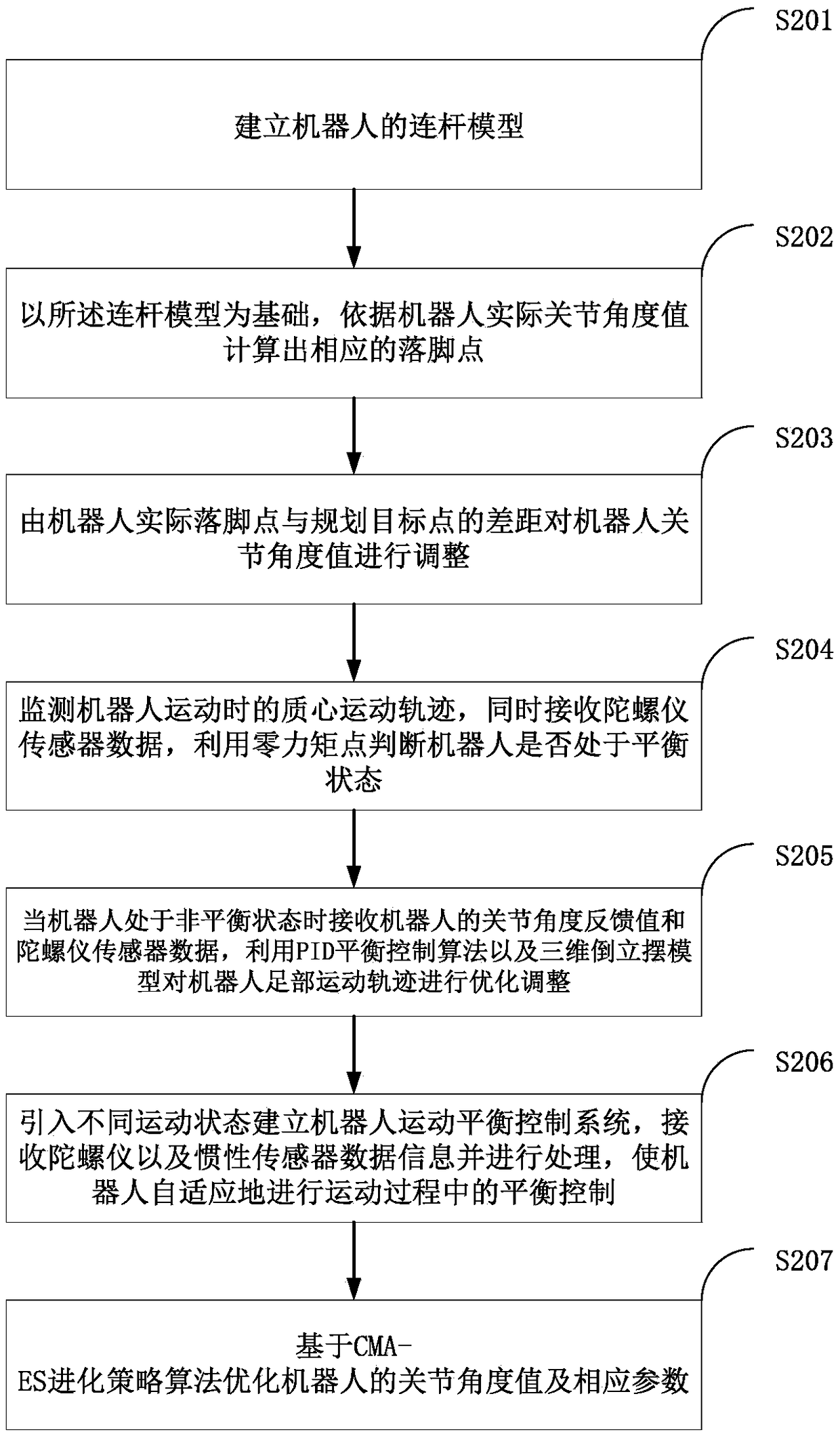
Method, device and system for self-adaption balance control of humanoid robot in complex terrain
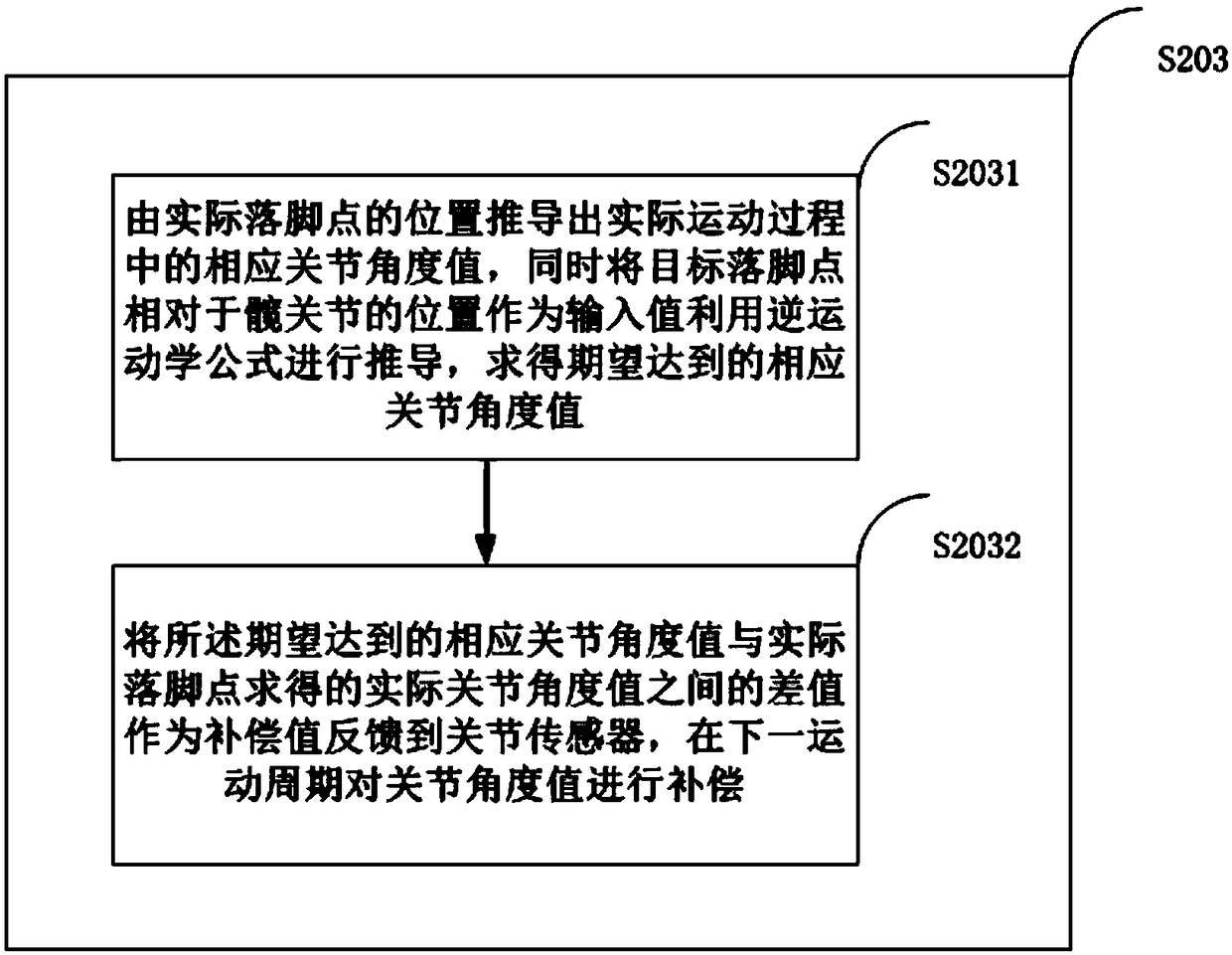
The invention relates to the field of robot control, in particular to a method, device and system for self-adaption balance control of a humanoid robot in a complex terrain. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a connecting rod model of a robot; calculating a corresponding foothold; adjusting the joint angle value of the robot; monitoring the mass center curve of the robot, receiving gyroscope sensor data, and judging whether the robot is in a balanced state; receiving a joint angle feedback value and the gyroscope sensor data when the robot is in an unbalanced state, and optimizing and adjusting the foot movement curve of the robot; enabling the robot to be self-adaptively subjected to balance control in the movement process; optimizing the joint angle value and relevant parameters of the robot. The robot can be applied to movement balance control of biped and quadruped robots and the like, the application range is wide, the self-adaptive capacity of the robot to an application environment can be greatly enhanced, and the hardware loss can be effectively reduced in the actual application process.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Prostration type crawl exercising machine
InactiveCN103055472AMake up for the shortcomings of inconsistent lengthReduce restrictionsChiropractic devicesFrictional force resistorsMotor driveTransmission belt
The invention discloses a prostration type crawl exercising machine. The prostration type crawl exercising machine comprises a main frame, an angle uplift mechanism, a hand movement mechanism, a waist and abdomen support device and a foot movement mechanism, the hand movement mechanism, the waist and abdomen support device and the foot movement mechanism are arranged on the main frame sequentially according to a front, middle and rear sequence, and the angle uplift mechanism is arranged at the position, corresponding to the hand movement mechanism, bellow the front end of the main frame. The hand movement mechanism comprises a motor, a transmission belt, a roller, a left woven belt and a right woven belt, the motor drives the transmission belt to drive the roller to rotate, and the woven belts are arranged on the roller. The foot movement mechanism comprises a left slider and a right slider, a left slide rail and a right slide rail are arranged on the main frame, and the sliders are mounted on the slide rails respectively. The prostration type crawl exercising machine is capable of enabling a person to achieve multiple crawl exercising modes on the exercising machine so as to achieve exercise and fitness effects.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
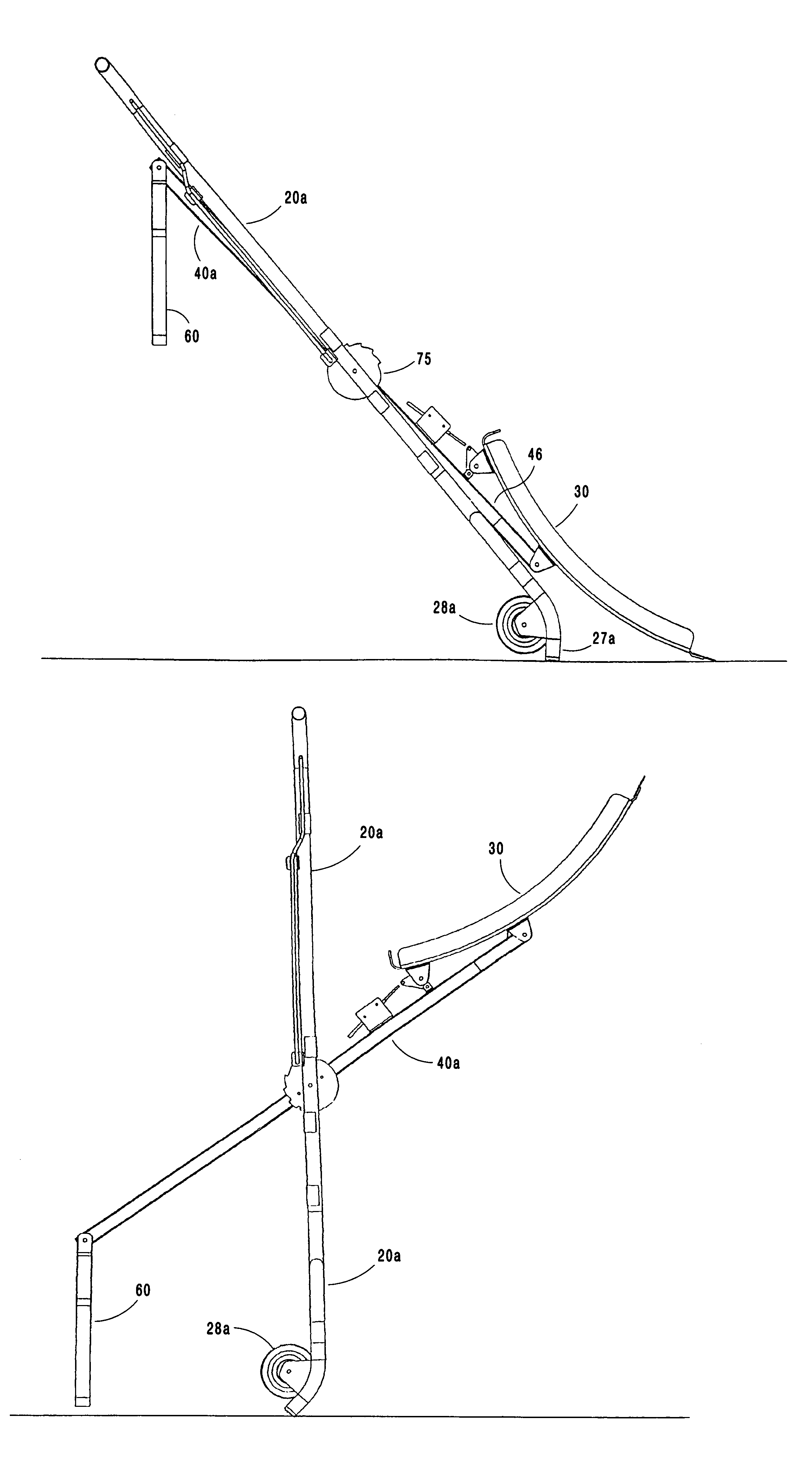
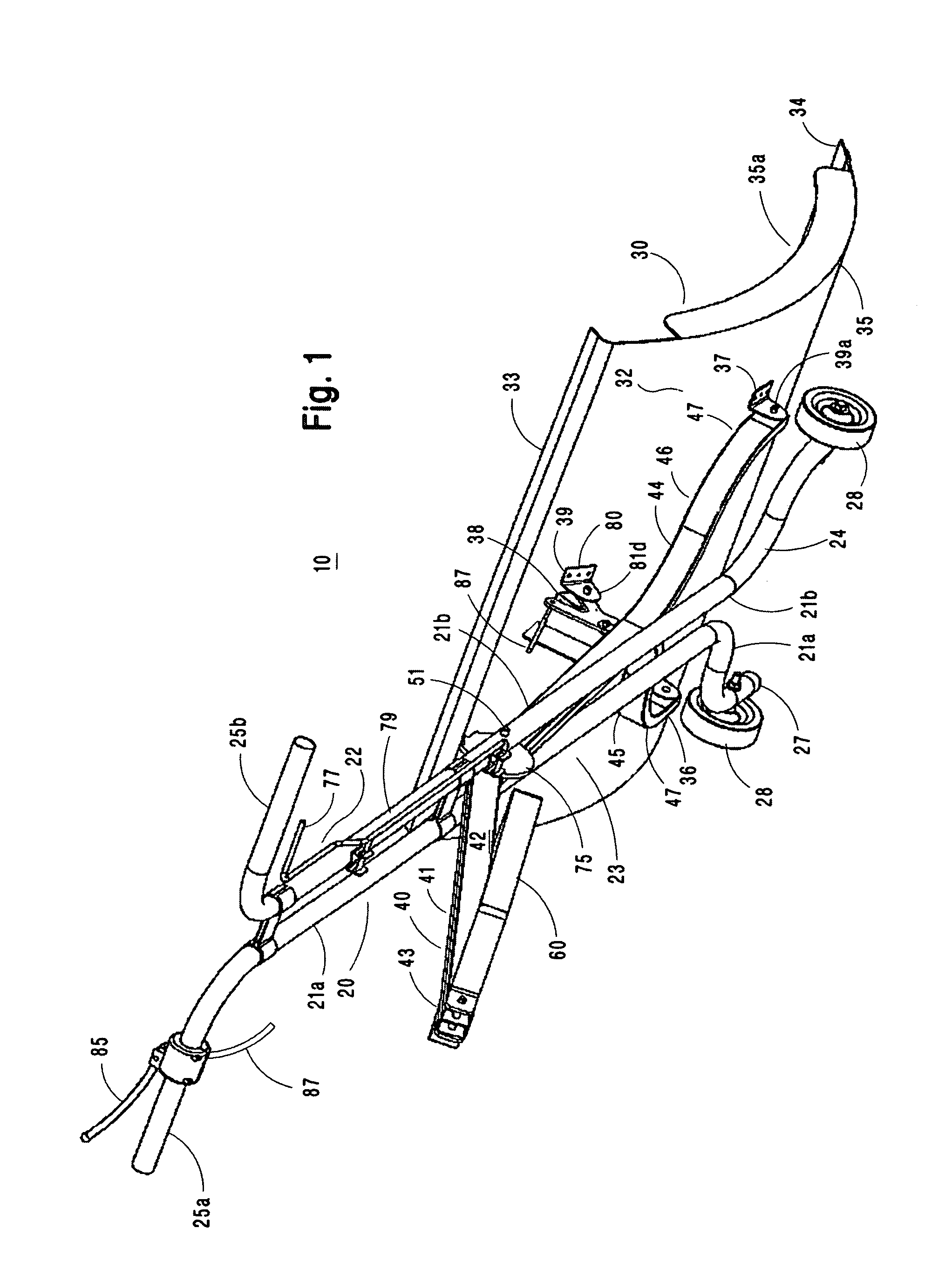
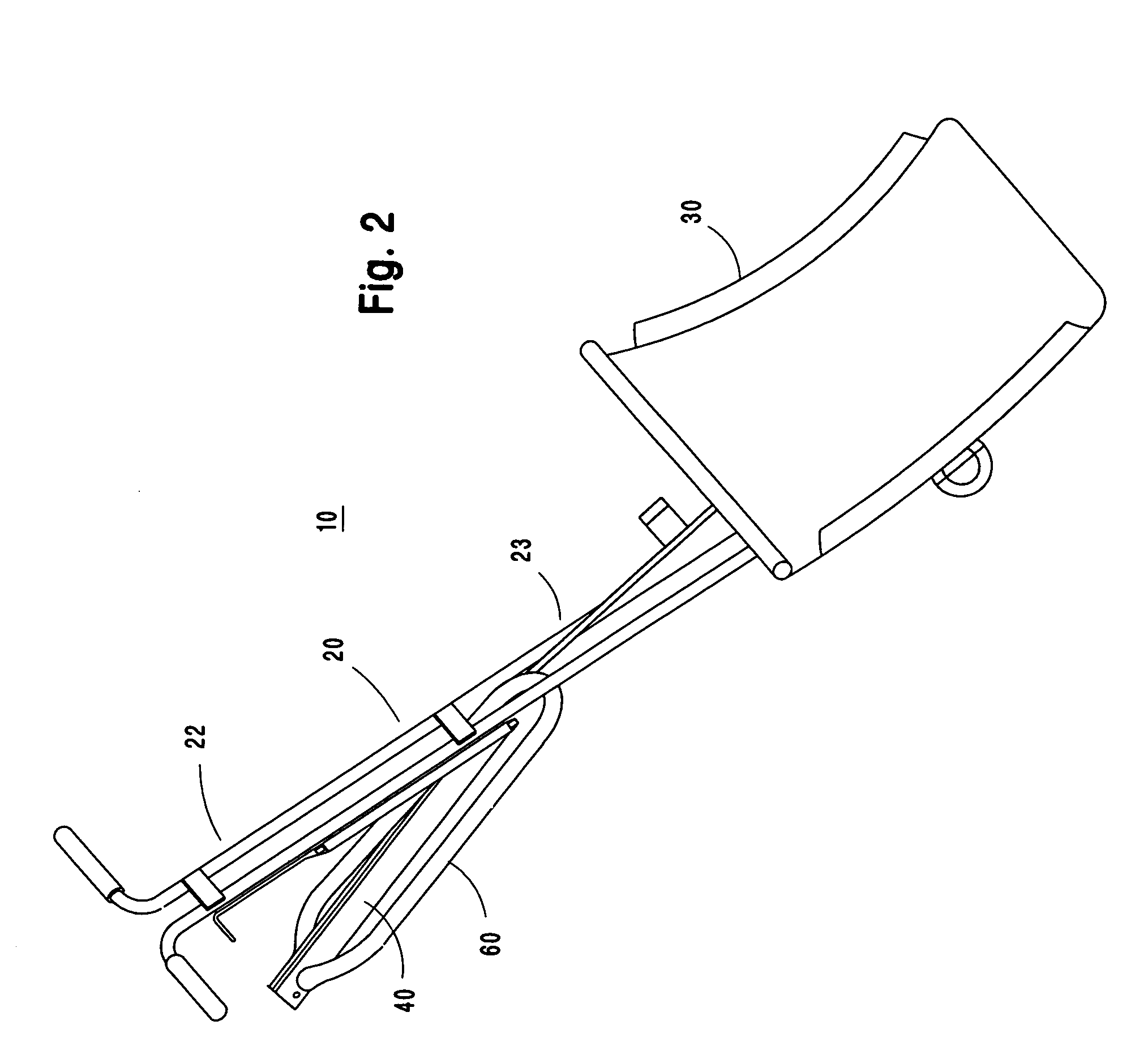
Crutch stroller
InactiveUS20080174084A1Solve the lack of durabilityWalking sticksChildren furnitureEngineeringAids walking
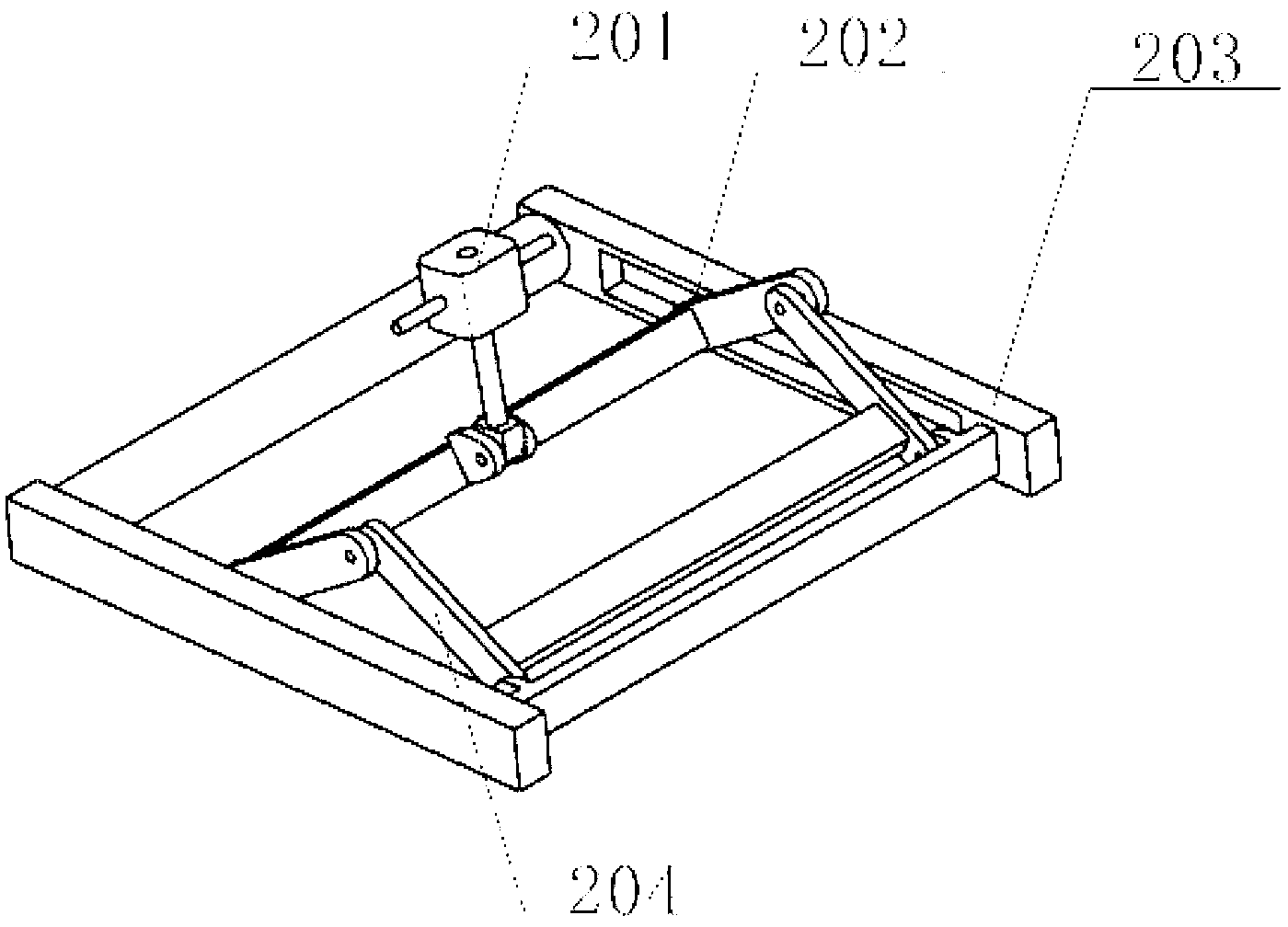
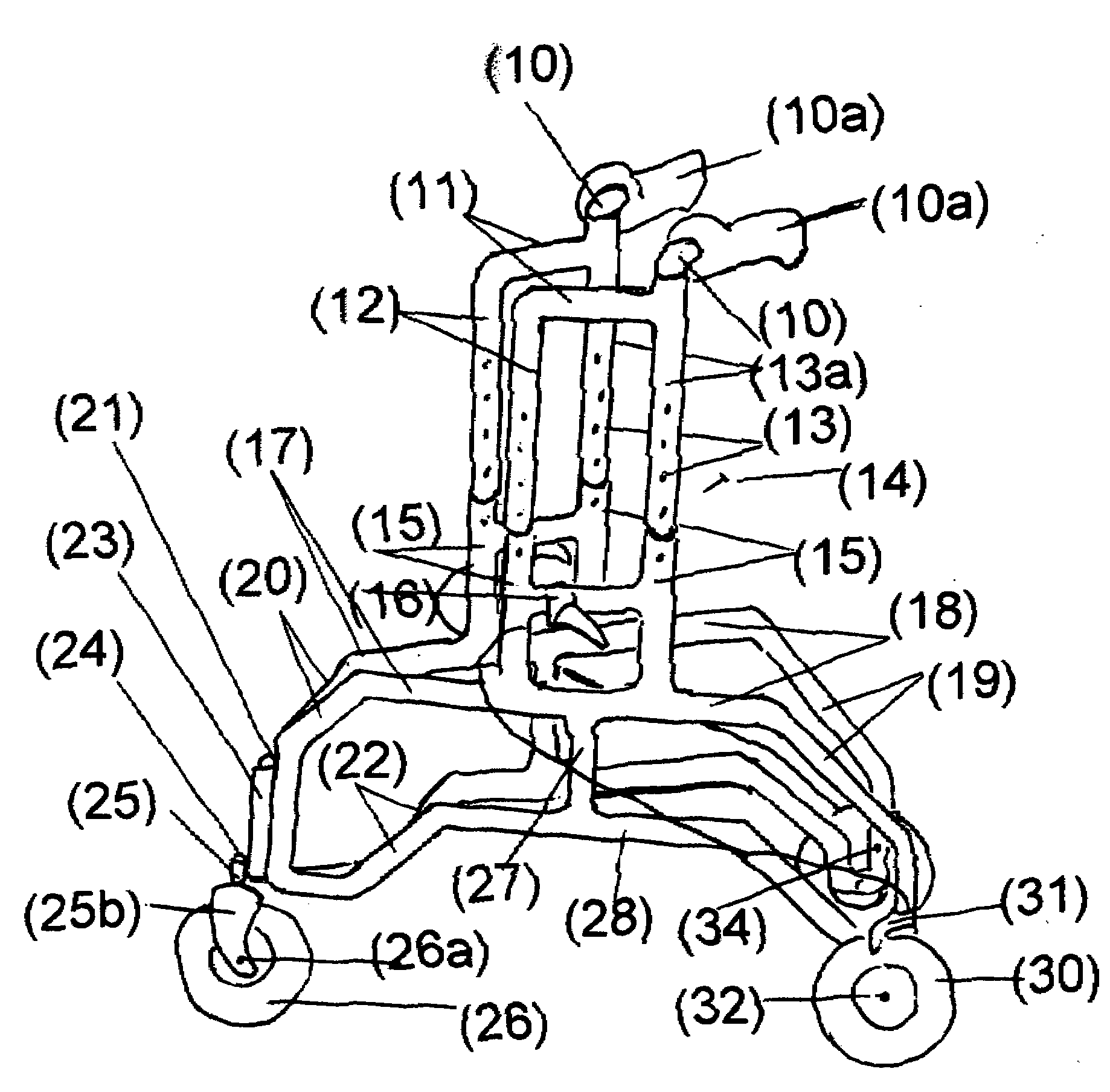
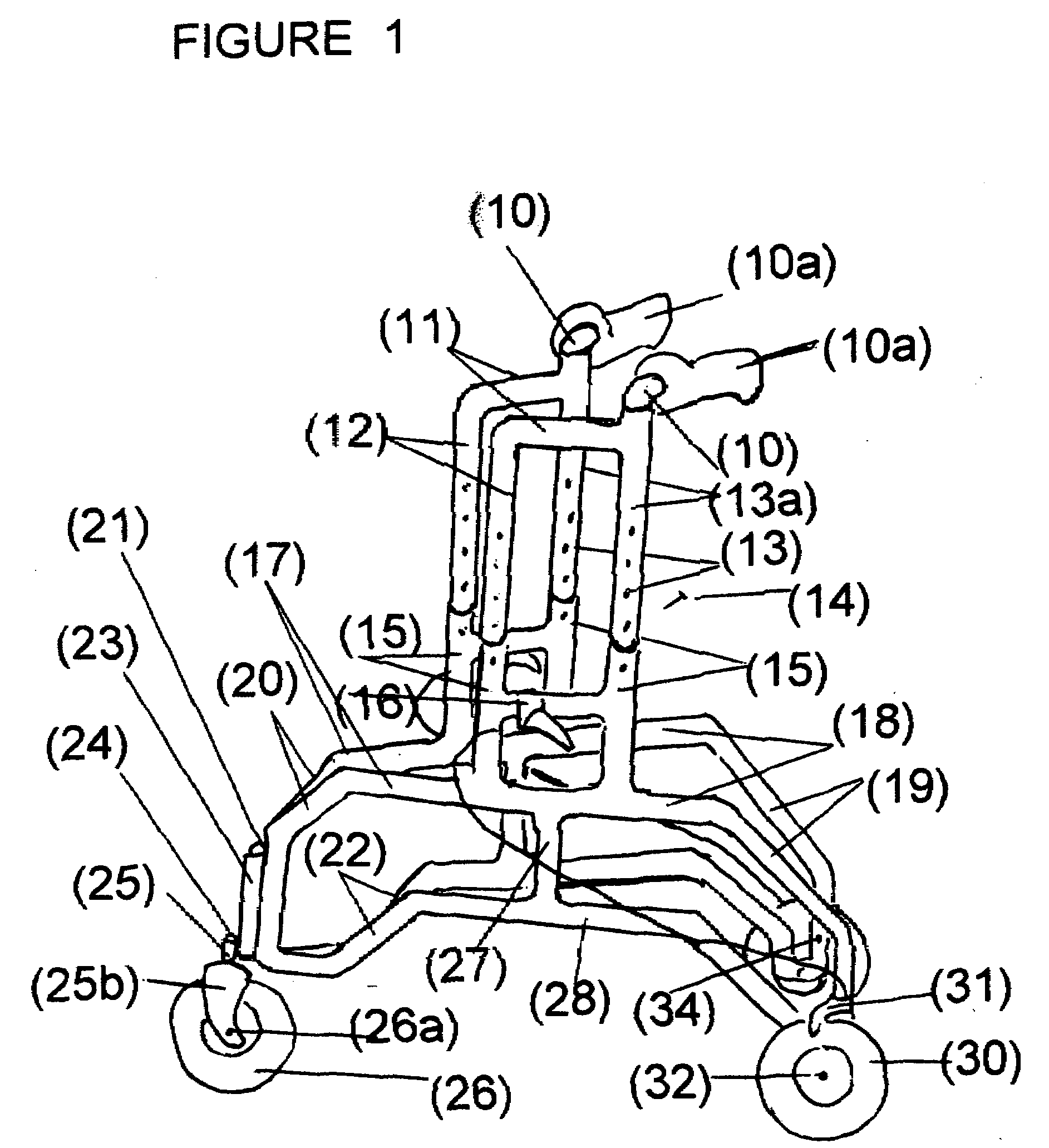
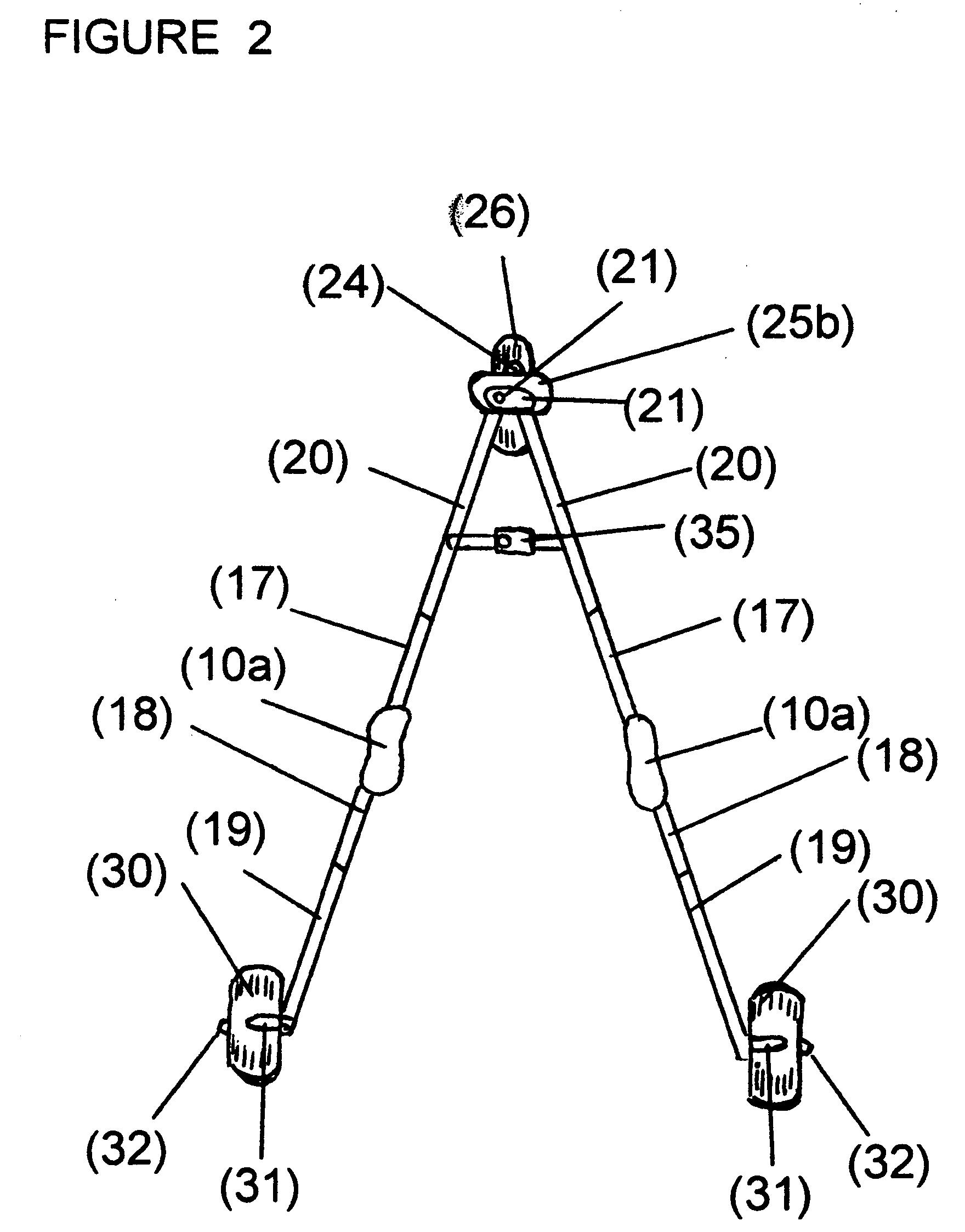
A mobility aid (FIG. 1) design for providing stabilized mobility support by the practical use of a two sided vertically supported rigid frame comprising front and rear bilaterally double support members (12), (12a), (13), (13a), (15), and (15a), and not limited to but preferably of aluminum construction to include a plurality of upper and lower substantially identical bilaterally horizontal and vertical tubular main frame members (17), (18), (19), (20), (22), (27), (28), and (29), supported on a plurality of sufficiently sized wheels (26), and (30), attached to the underside of the main frame (26), and (30), with predetermined spacing. Base members (22), (28), and (29), are sufficiently elevated-providing for unhindered foot movement during mobilization. A guide wheel assembly (23), (25), (25b), (26), and (26a), is vertically attached at a contiguously anterior junction surface of the two sided main frame assembly (20), and (23), thereby providing selective directional steering. Hand brake controls (16), secure by clamps to riser connectors (15), activate brakes (31).
Owner:GEE SR LARRY ELLIS
Ankle Derotation and Subtalar Stabilization Orthosis
ActiveUS20080082034A1Prevent reversalEffective in inversionFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesKnee orthosisFrenulum
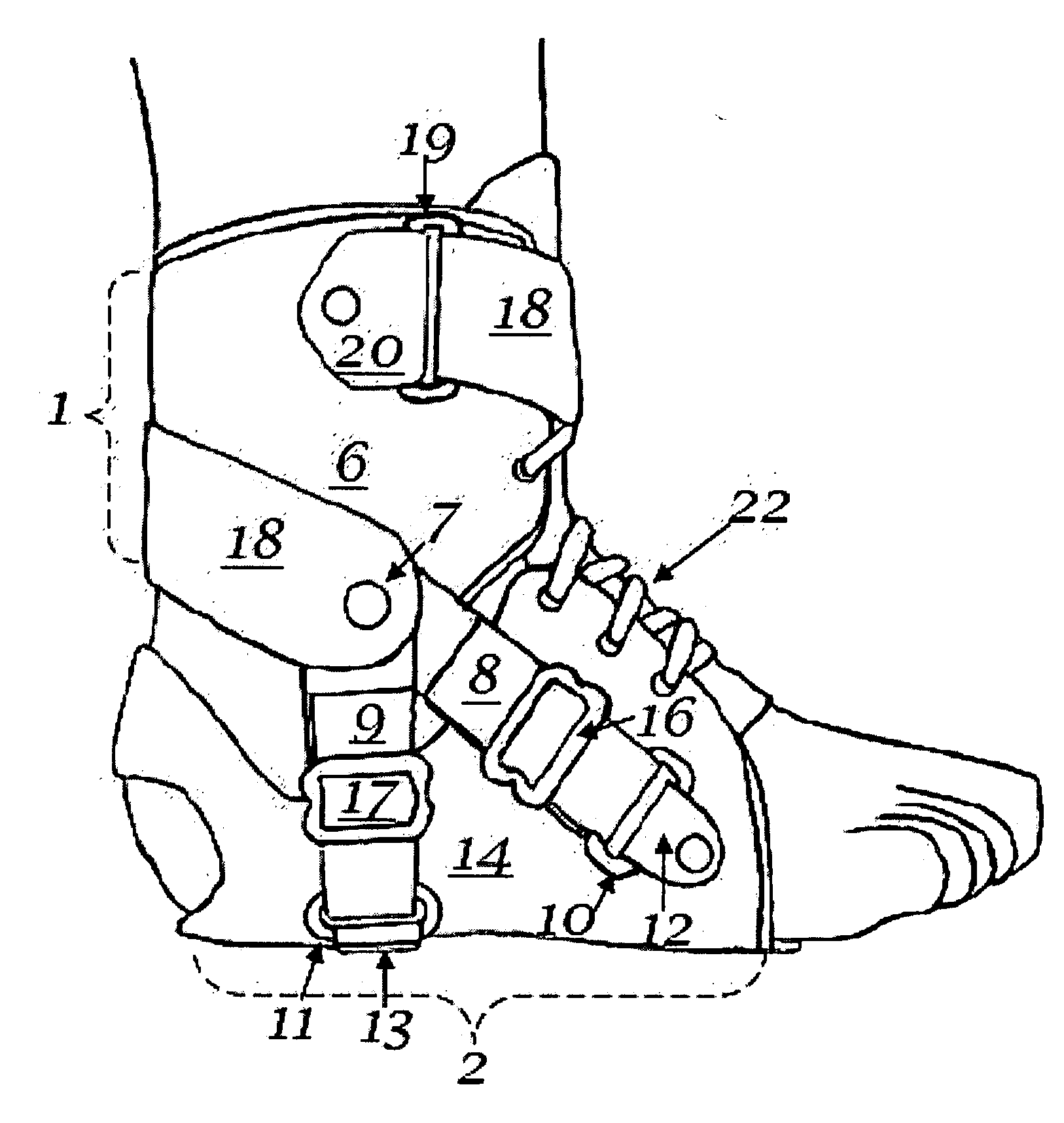
The invention is an ankle derotation and subtalar stabilization system that incorporates a pivoting adjustable-tension oblique tether strap that is anchored to both a forefoot component and leg component, and that is contiguous with pivoting adjustable-tension derotation strap that passes behind the leg and that is secured to a leg component. The system restrains oppositely directed rotation between the foot and the leg, and can actually after the normal biochemical relationship in a manner that produces foot rotation in a direction opposite to that which is normally coupled with leg rotation, without restriction of upward and downward foot movement. The primary application for the system is restraint of excessive subtalar joint inversion, leg external rotation, and anterolateral rotary displacement of the talus, but it can also be configured to restrain subtalar eversion and leg internal rotation through its incorporation into the structure of an ankle orthosis or shoe.
Owner:WILKERSON GARY BLAINE
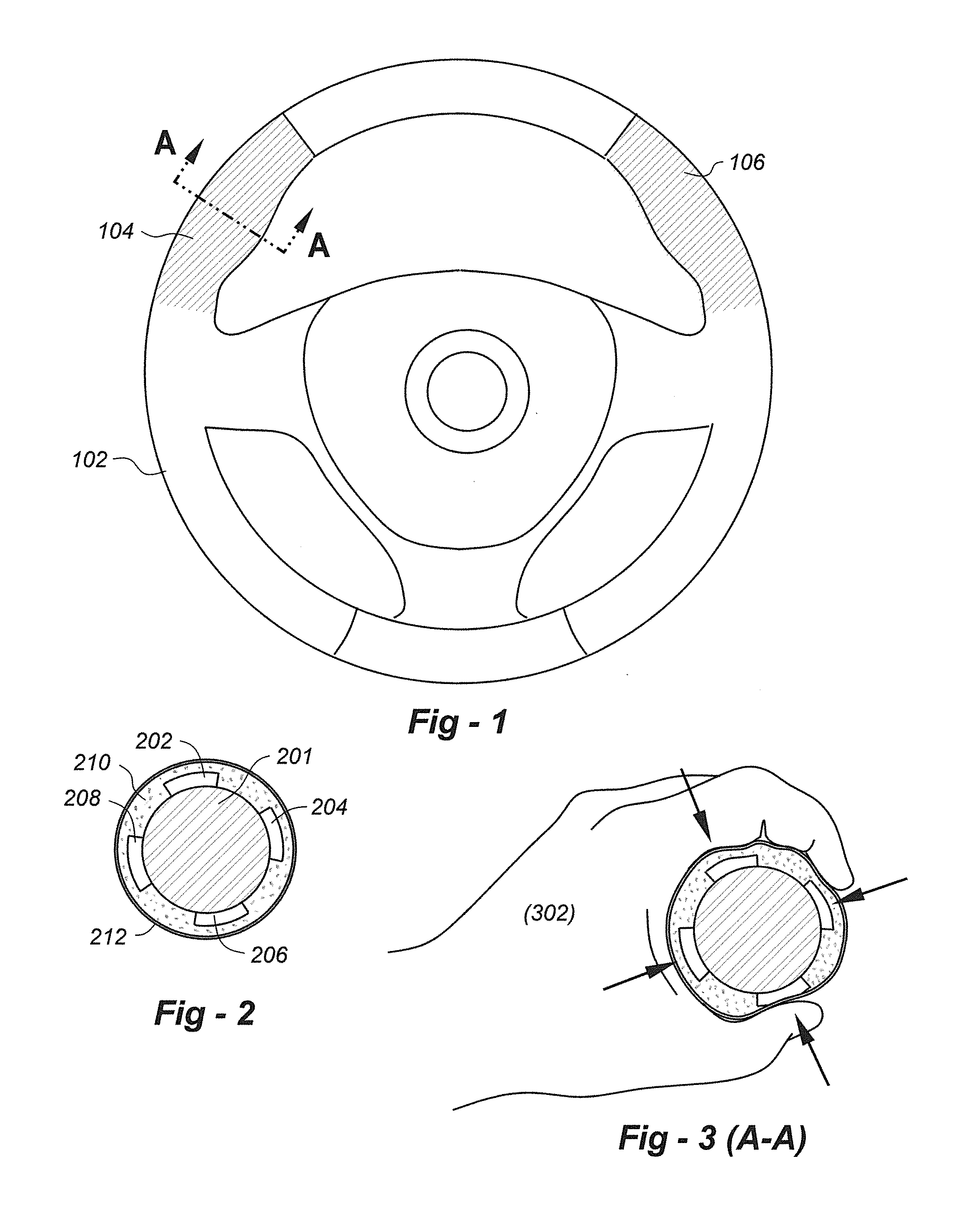
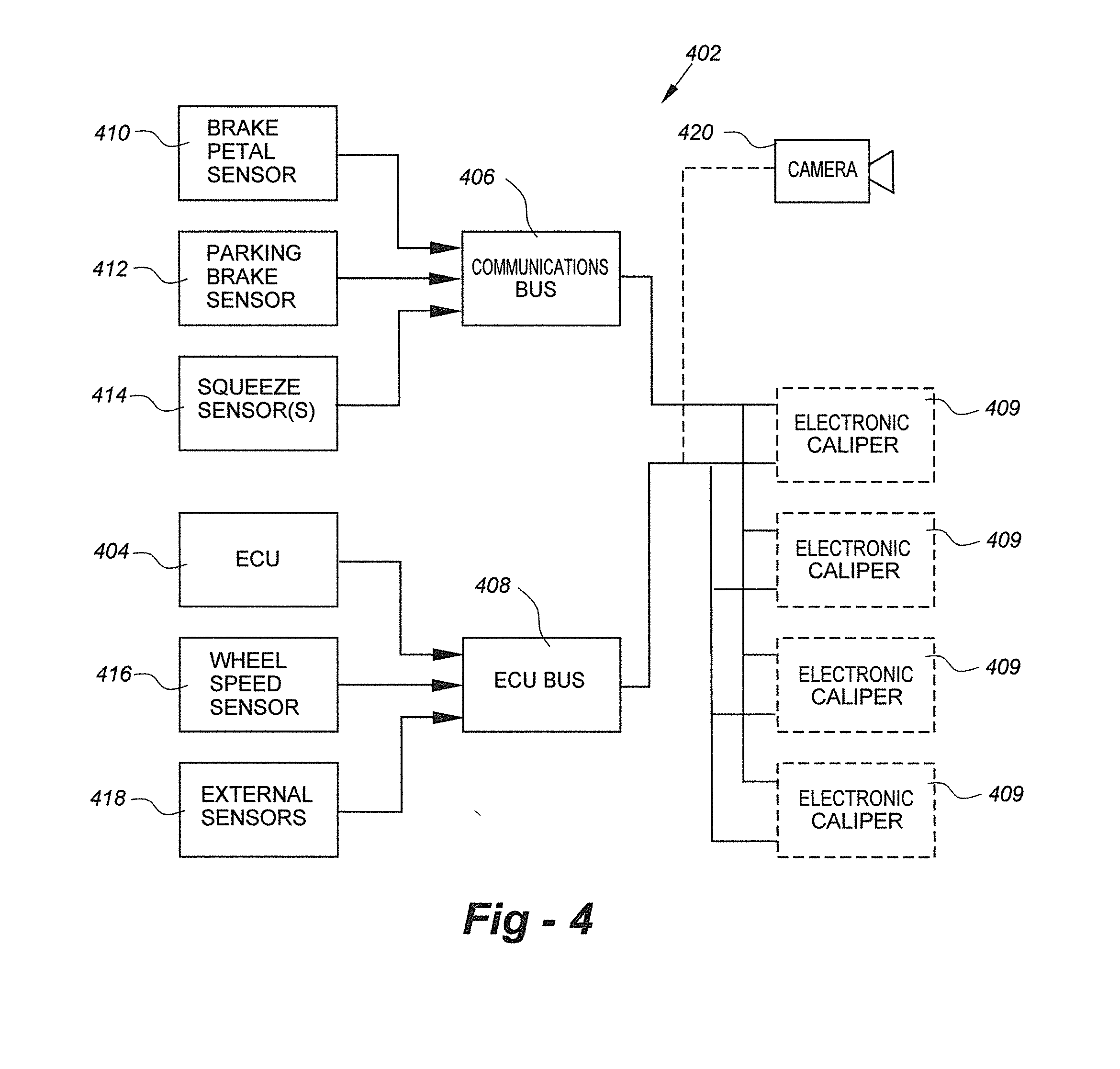
Steering wheel squeeze-activated vehicle braking system
ActiveUS20140224600A1Stop his or her vehicle more quicklyFaster vehicle stopBraking action transmissionElectrodynamic brake systemsLow speedDriver/operator
A brake-by-wire vehicle braking system is augmented with “squeeze” sensors placed in the steering wheel of the vehicle enabling a vehicle operator to stop the vehicle more quickly in an emergency situation by eliminating the significant times that it takes to move a driver's foot from the accelerator to the brake pedal and then depress the brake pedal. An important objective is to achieve a faster vehicle stop by allowing the driver to optionally eliminate foot movement from the accelerator pedal to the brake pedal and also the depression of the brake pedal. This invention also potentially allows a driver to squeeze a steering wheel to slow a vehicle, perhaps to comply with a lower speed limit, or accomplish the fastest possible “hard-stop” in an emergency situation.
Owner:REDEVEX
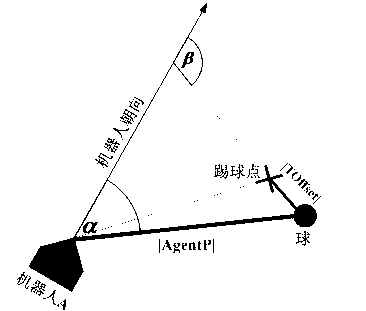
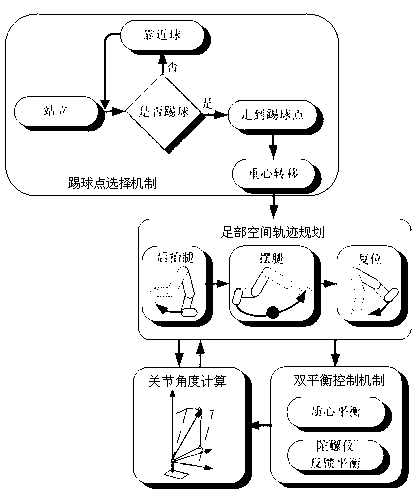
Method for kicking ball at all directions by humanoid soccer robot based on double-balance control mechanism
The invention provides a method for kicking a ball at all directions by a humanoid soccer robot based on a double-balance control mechanism. The method comprises the following steps of determining a ball kicking point with a minimum cost according to a distance cost value and an angle cost value, and controlling the robot to walk to the ball kicking point; transferring the center of gravity of the robot, and using a cubic spline interpolation method to plan feet space trajectory, namely obtaining the reference gesture of the feet movement of the robot at each moment; calculating the angle of each joint of the robot according to the obtained reference gesture by using inverse kinematics knowledge; and maintaining the stability of the robot in the ball kicking process through the double-balance control mechanism fed back by a centroid and a gyroscope. The invention provides a method for kicking a ball at all directions by a humanoid soccer robot based on a double-balance control mechanism; in the ball kicking process of the humanoid robot, kicking the ball at all directions by the robot can be realized through the double-balance mechanism fed back by the centroid and the gyroscope. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of high stability and high execution efficiency.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Sock shoes and production process thereof
The invention discloses a pair of sock shoes. Each sock shoe comprises a vamp, wherein the shape of the vamp is identical to the curve shape of the foot of the human body; the bottom of the vamp is provided with a shoe sole; the vamp is a sock obtained by using one or more than one weaving materials of cotton yarns, synthetic fiber and the like as basic yarns, adding heating fuse silks and performing weaving by a knitting sock machine; the vamp is subjected to heat shaping after being sleeved on a shoe tree; after the heat shaping, the vamp has the shape similar to the foot, and better conforms to the human engineering; meanwhile, the deformation quantity of the sock shoes can be greatly reduced; the telescopic quantity of the sock shoes is reduced, so that the great deformation cannot occur along with the foot movement in the sports doing and body building exercise taking processes; and the movement of the foot relative to the shoe sole can be effectively limited. A plastic layer is directly formed on the bottom of each vamp through injection molding to be used as the shoe sole, so that the bonding of the vamp and the sole is firmer; and stripping disconnection cannot easily occur.
Owner:陈雪源
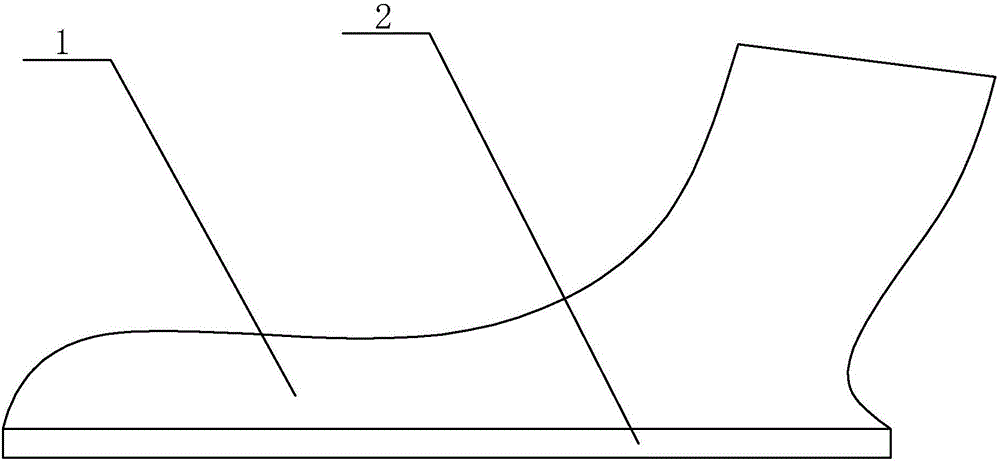
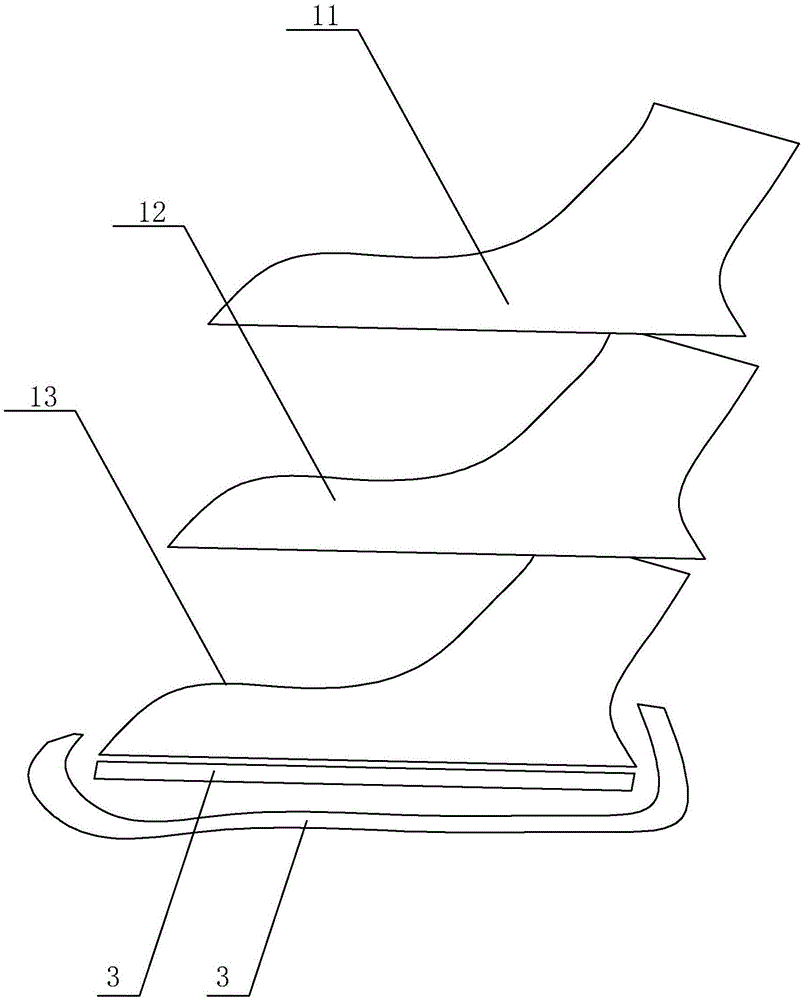
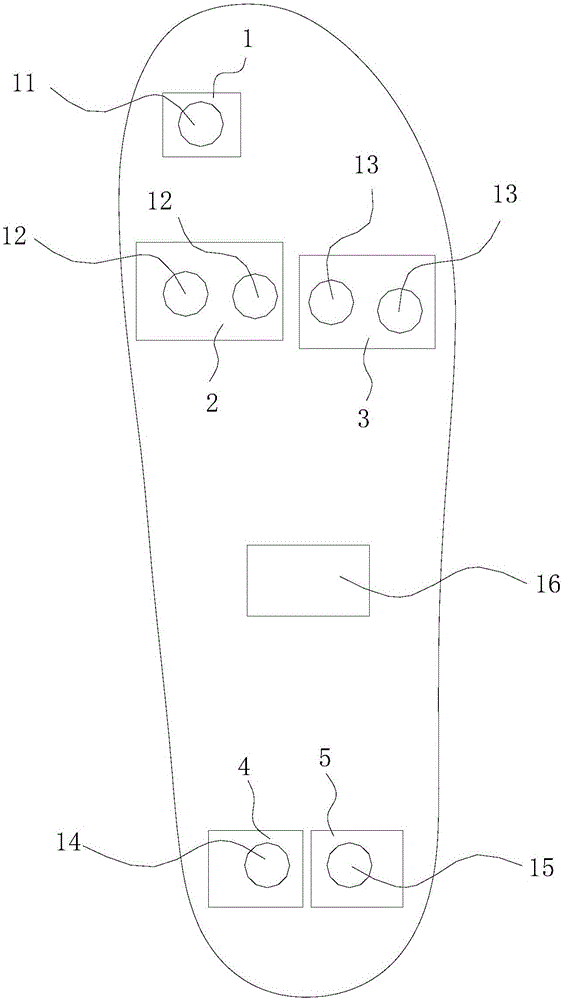
Foot movement posture judging device and method
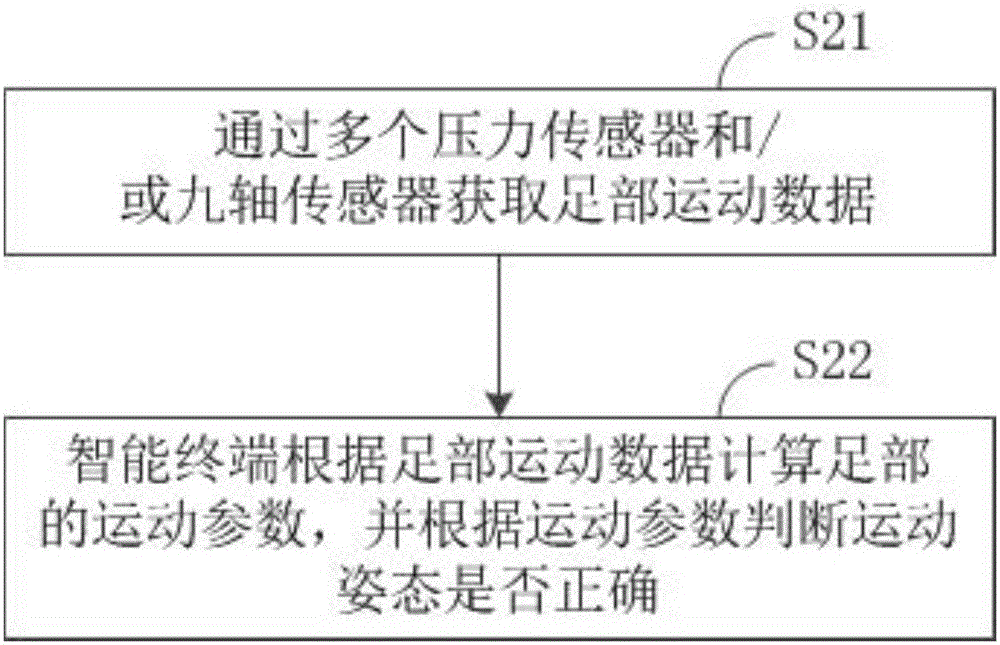
InactiveCN107174252AAvoid damageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsComputer sciencePlantar pressure
The invention discloses a foot movement posture judging device and method. The foot movement posture judging device comprises an intelligent insole and an intelligent terminal, wherein the intelligent insole is in communication connection with the intelligent terminal; the intelligent insole is used for acquiring foot movement data of a human body; the intelligent terminal is used for analyzing and storing the foot movement data acquired by using the intelligent insole; and the intelligent insole comprises a nine-shaft sensor and a plurality of pressure sensors. The foot movement posture judging method is implemented by the judging device and comprises the following steps: acquiring the foot movement data of the human body through the plurality of the pressure sensors and / or the nine-shaft sensor; and calculating movement parameters of the human body by the intelligent terminal according to the foot movement data, and judging whether the human body is in a correct movement posture or not according to the movement parameters. Due to adoption of the intelligent insole and the intelligent terminal in communication connection, foot pressure of human bodies is acquired and analyzed, so that whether the movement postures of feet of users are correct or nor is judged, the users can modify the movement postures according to judgment results, and body injuries can be reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG COROS SPORTS TECH JOINT CO
Shoe Heel Cup and Shoe Equipped with One Such Heel Cup
InactiveUS20080034616A1Improve securityWithout compromising comfortMedical scienceUpperCalcaneusEngineering
A heel cup can be inserted into a shoe in order to define a posterior upward projection and lateral wings which surround the posterior and lateral faces of the calcaneum and which, through lateral notches, define a preferential deformation zone at, and in the direction of, the subtalar cone of the tibiotarsal joint. Moreover, a sufficiently-rigid connecting zone connects the posterior upward projection and the lateral wings, thus providing the shoe with good stability while enabling inversion and eversion foot movements. In this way, comfort is increased considerably, while the risk of articular injuries is reduced since the subtalar articulation is contained correctly upon reaching the limit thereof.
Owner:RHENTER JEAN LUC
Gait assessment system, gait meter, gait assessment program and recording medium
InactiveCN101327125AEasy to operateEasy to masterChiropractic devicesInertial sensorsMeasuring instrumentUSB
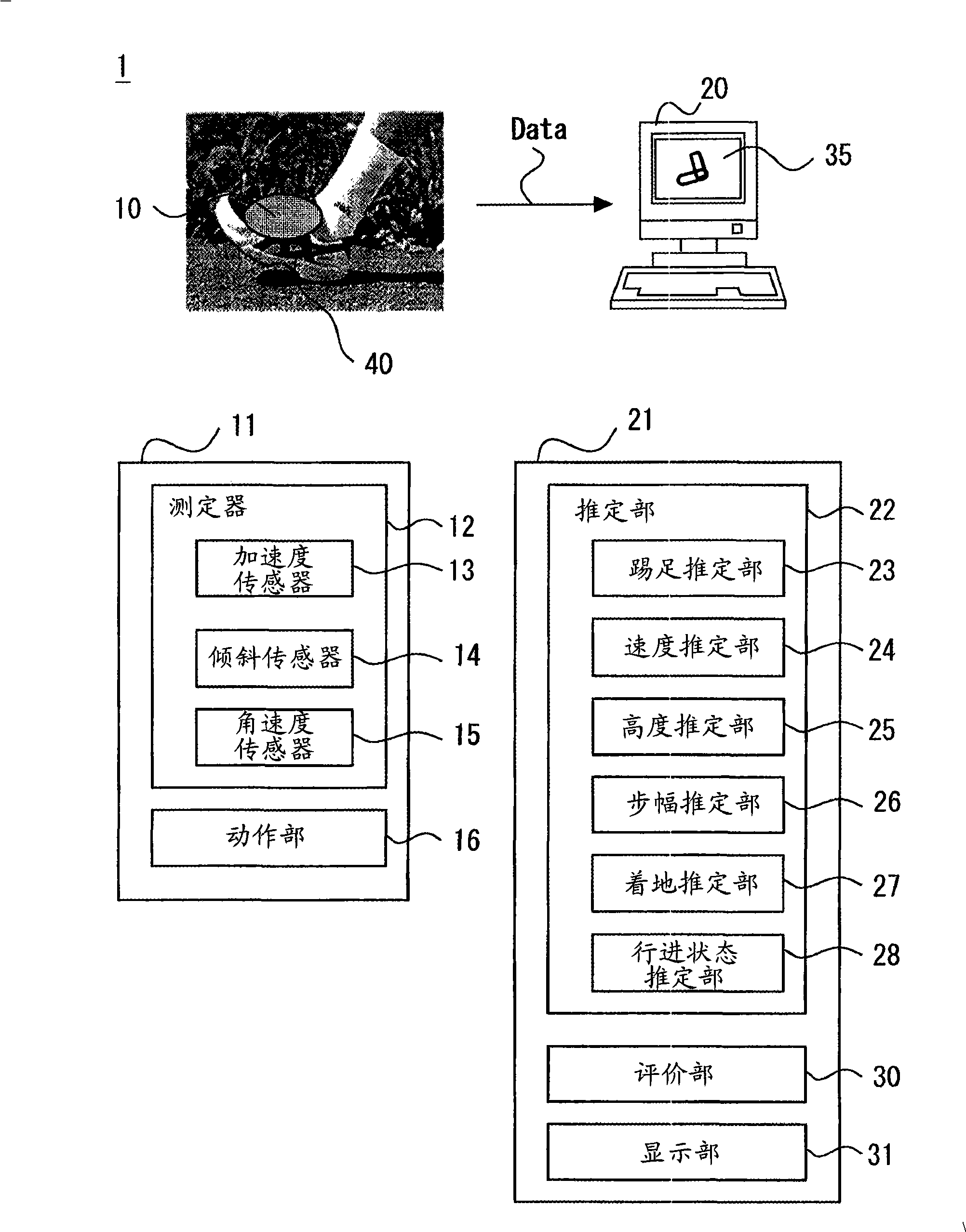
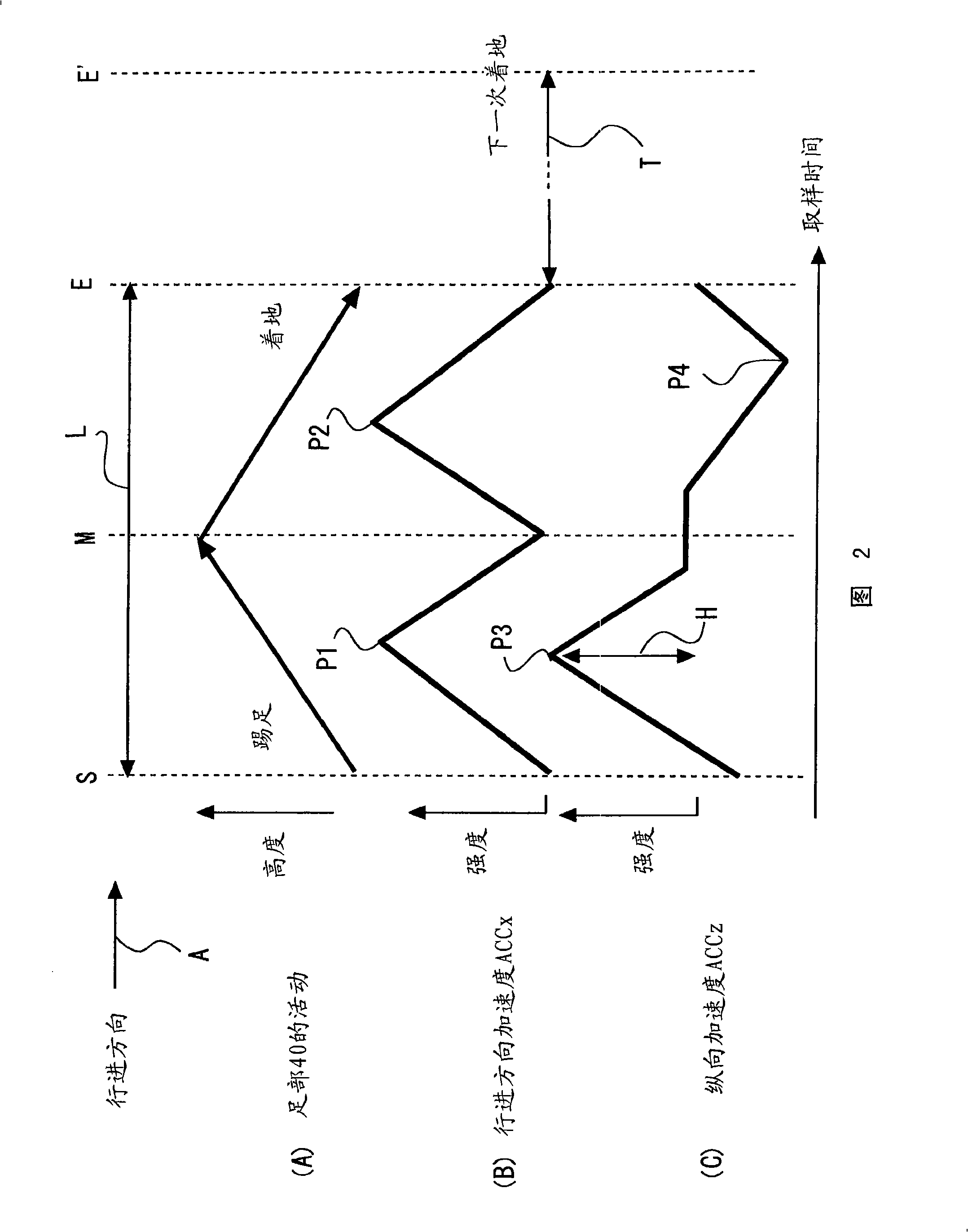
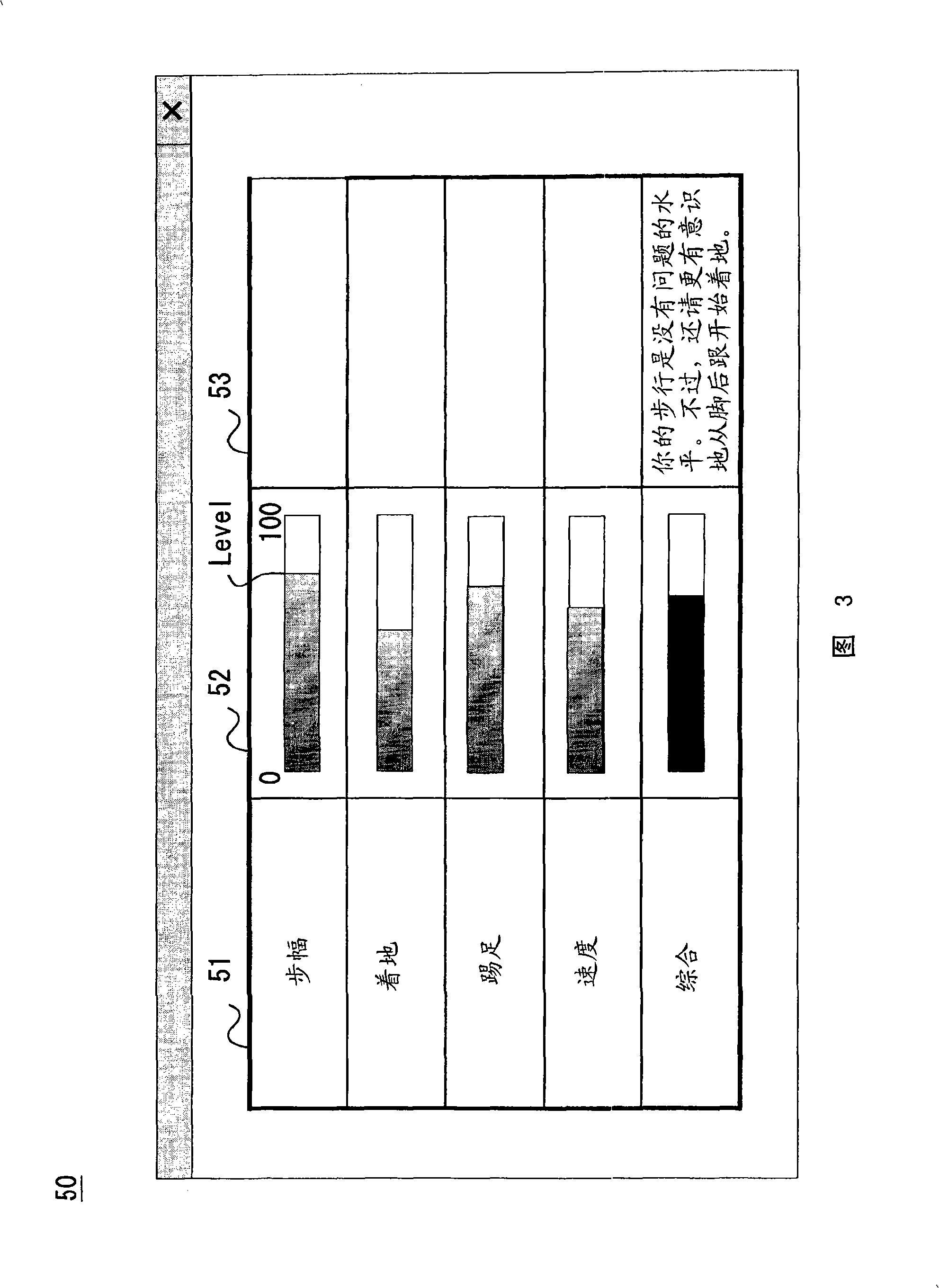
To provide a compact and inexpensive gait assessment system, including a basograph, which can be readily handled by, for example, trainers, and can eliminate the necessity to select any specialized measurement space to detect foot movement during walking. A basograph (10) is equipped with a measuring instrument (12), including, for example, an acceleration sensor (13), for measuring data related to gait of a subject, and a PC (20) receives the data via a USB interface or suchlike, so that an estimating section (22) estimates the gait status of the subject based on the received data. The estimating section (22) includes at least one of the following elements for performing estimation based on predetermined-direction acceleration ACC of the subject's foot (40) at each sampling time: a push-off estimating part (23) for estimating the intensity of the subject's push-off; a tempo estimating part (24) for estimating gait tempo; an elevation estimating part (25) for estimating foot elevation; and a stride estimating part (26). An assessing section (30) assesses the gait status of the subject based on the estimation of the estimating section (22), and a presentation section (31) presents the assessment result by the assessing section (30) in a predetermined form.
Owner:TANITA CORP
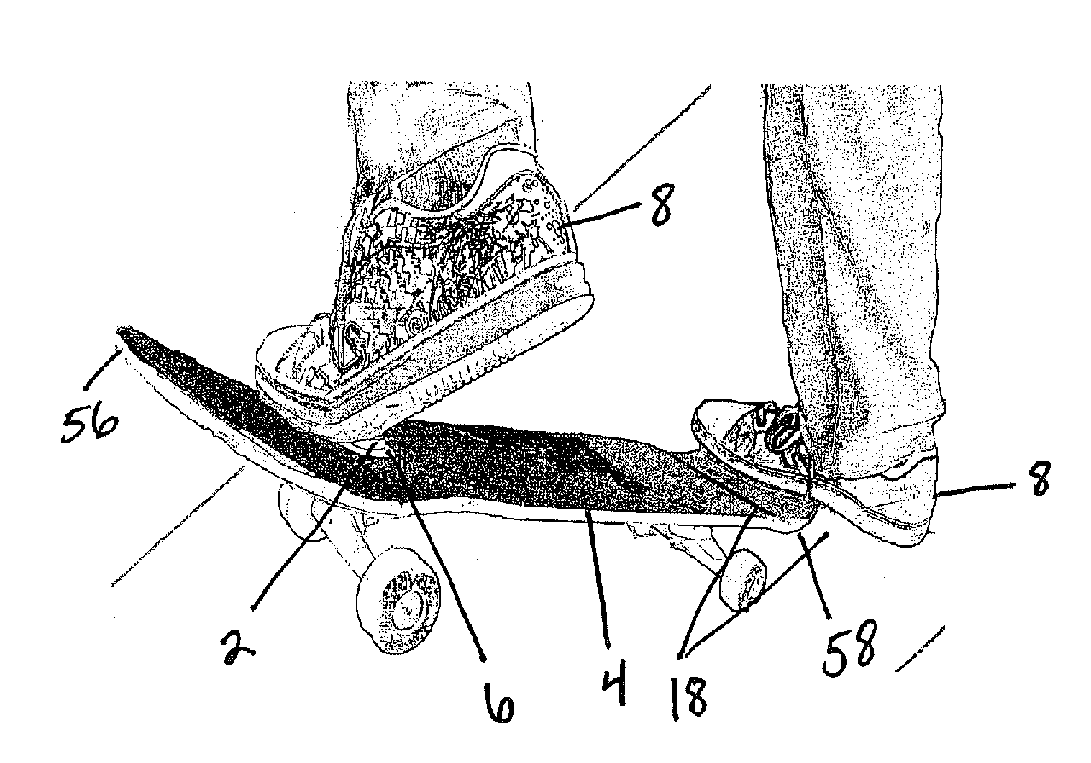
Magnetic attachment for board sports
InactiveUS20100237599A1Enhance rather than inhibit performanceImprove performanceSki bindingsSki-brakesEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
A magnetic device comprises a magnet adapted to suspend free-floating from a hole in a bottom of a shoe, the magnet capable of attaching the shoe to magnetized metal on a sports board. The magnet can be raised and lowered in the shoe and is “on” when in a down position and “off” when in an up position. Switching between “on” and “off” by moving the magnet up or down in the shoe is accomplished manually. When the magnet is up or off the space in the shoe can be occupied with a plug. The design of the attachment system allows a rider optimal freedom of foot movement for doing tricks while attached to the board. The small surface area of the magnet relative to its significant strength, the round contour of the magnet's face, the magnet's suspended free-floating configuration from the support, the position of the magnets on the shoe, and the position of the magnetized metal on the sports board are all factors that contribute to increased maneuverability for the board rider using the invention. Release of the shoe from the board is facilitated by the rider lifting or swiveling a heel to an angle greater than that which allows the magnet to remain attached. The magnetic device and system, provides ideal training for any board sport, and also provides skilled board riders new opportunities to be creative. Tricks thought to be impossible (along with newer undiscovered tricks) become possible with the aid of the invention.
Owner:BIANCHI STEVEN B
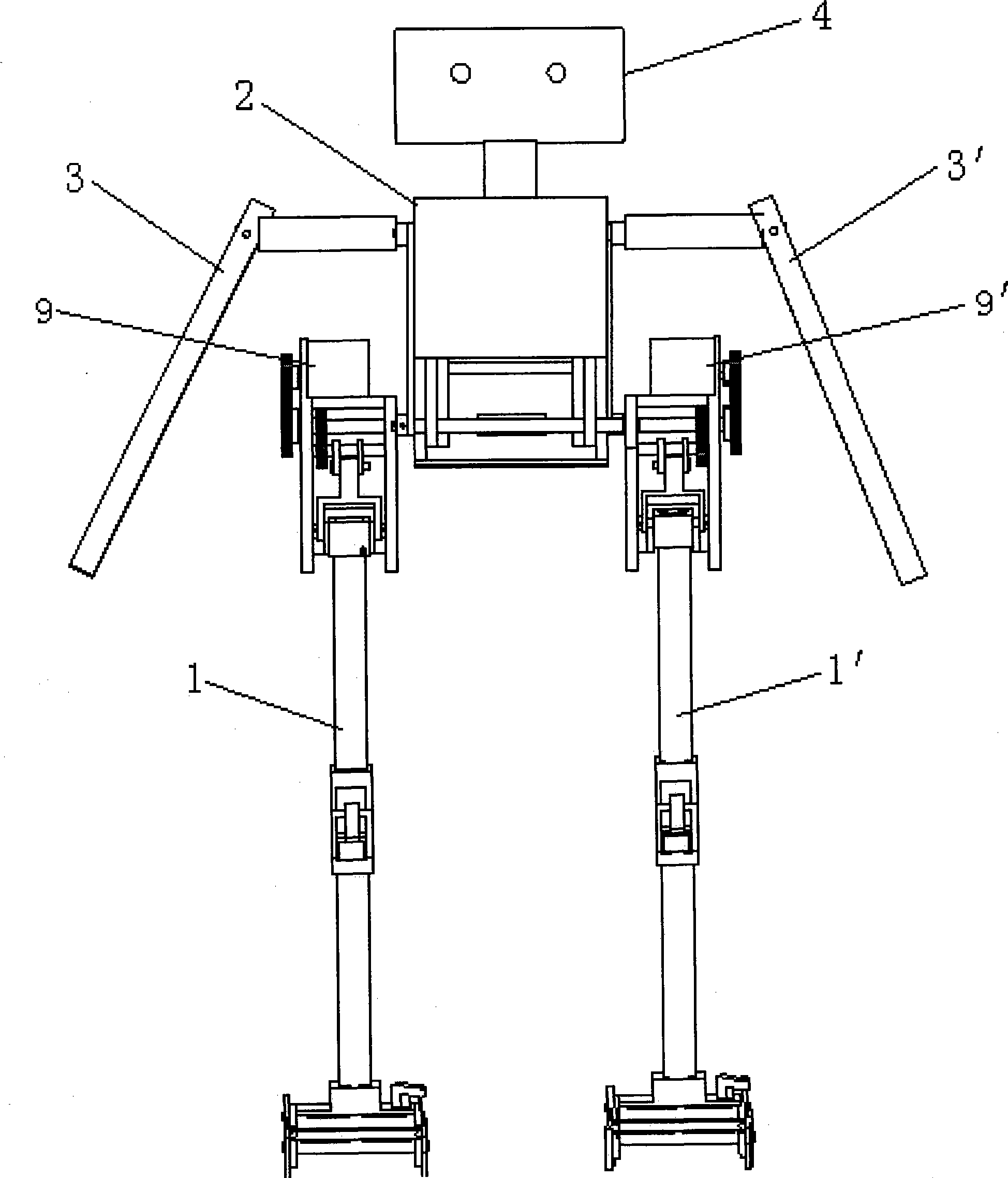
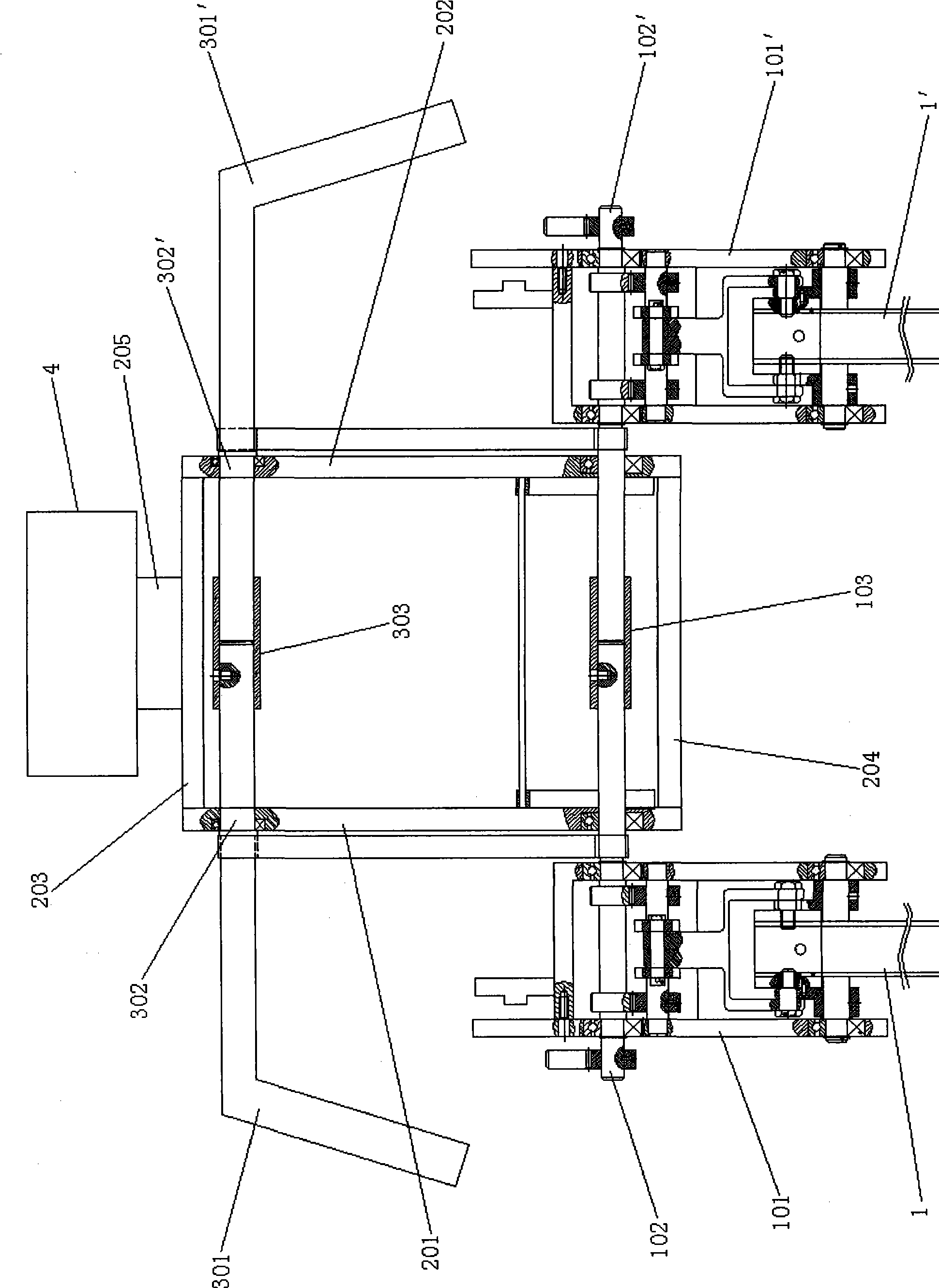
Both feet humanoid robot based on passive movement mode
InactiveCN101391417AReasonable exerciseSports rationalityProgramme-controlled manipulatorVehiclesRobotic armDrive shaft
The invention relates to a double-foot human-like robot based on a passive movement style, which is characterized in that: the robot includes a bionic elastic mechanical legs, a transmission trunk, mechanical drive arms; two convex arms are arranged respectively at the front and the back of the hip shell of the two mechanical legs, two extending sections of the convex arms are respectively and fixedly connected with one end of a driving shaft of the upper limb. The other end of driving shaft of the upper limb is connected with one end of a connecting rod, one end of which is fixedly connected with one end of a rocker. And the other end of rocker is fixedly connected with a limb half shaft arranged on the transmission trunk lateral side. The mechanical arm includes an upper limb; one end of the upper limb half shaft is connected with the upper limb with the other end respectively threaded through the upper part of the transmission trunk and is in butt joint. The butt joint position of the upper limb half shaft is provided with a connecting tube, wherein, the upper limb half shaft is fixed with the connecting tube through a screw with the other upper limb half shat loosely matched with the connecting tube. The invention adopts an active and passive combination movement style and realizes an energy optimization of the double-foot movement through a passive mechanical structural linkage limb, is wildly applicable to the research of footed robots and the development of service robots and the medical and health fields.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Quadruped robot with parallel waist structure
ActiveCN104924294AImprove passabilityDurable and stable explosive powerProgramme-controlled manipulatorTerrainMain branch
The invention discloses a quadruped robot with a parallel waist structure. The robot comprises a machine frame, the parallel waist structure and four parallel mechanical legs, wherein the machine frame comprises a front machine frame part and a rear machine frame part which are connected through the parallel waist structure, and the parallel waist structure has four freedom degrees; the four parallel mechanical legs are evenly installed on the two sides of the front machine frame part and the rear machine frame part, each parallel mechanical leg has three freedom degrees relative to the machine frame, and the front machine frame part and the rear machine frame part each have six freedom degrees for three-dimensional parallel motion and three-dimensional rotation under the cooperation of the parallel waist structure and the four parallel mechanical legs; the parallel waist structure comprises an auxiliary branch chain and four main branch chains with the same structure evenly distributed around the auxiliary branch chain. The body posture of the foot movement robot is changeable, movement is quick and flexible, terrain adaptability is high, obstacle crossing ability is high, and the robot is suitable for high-speed work under the complicated non-structural topographic condition.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Exercise support device, exercise support method, and exercise support program
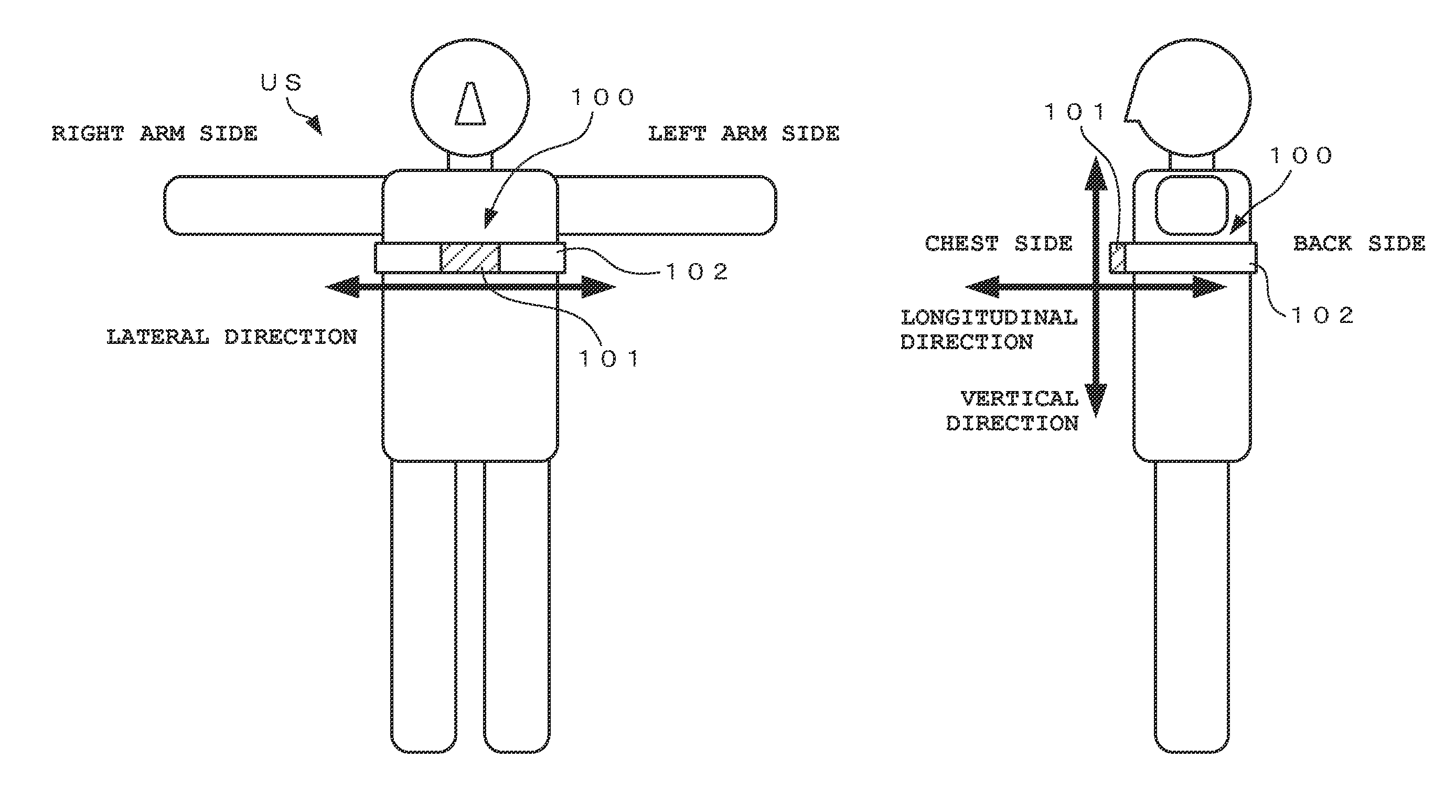
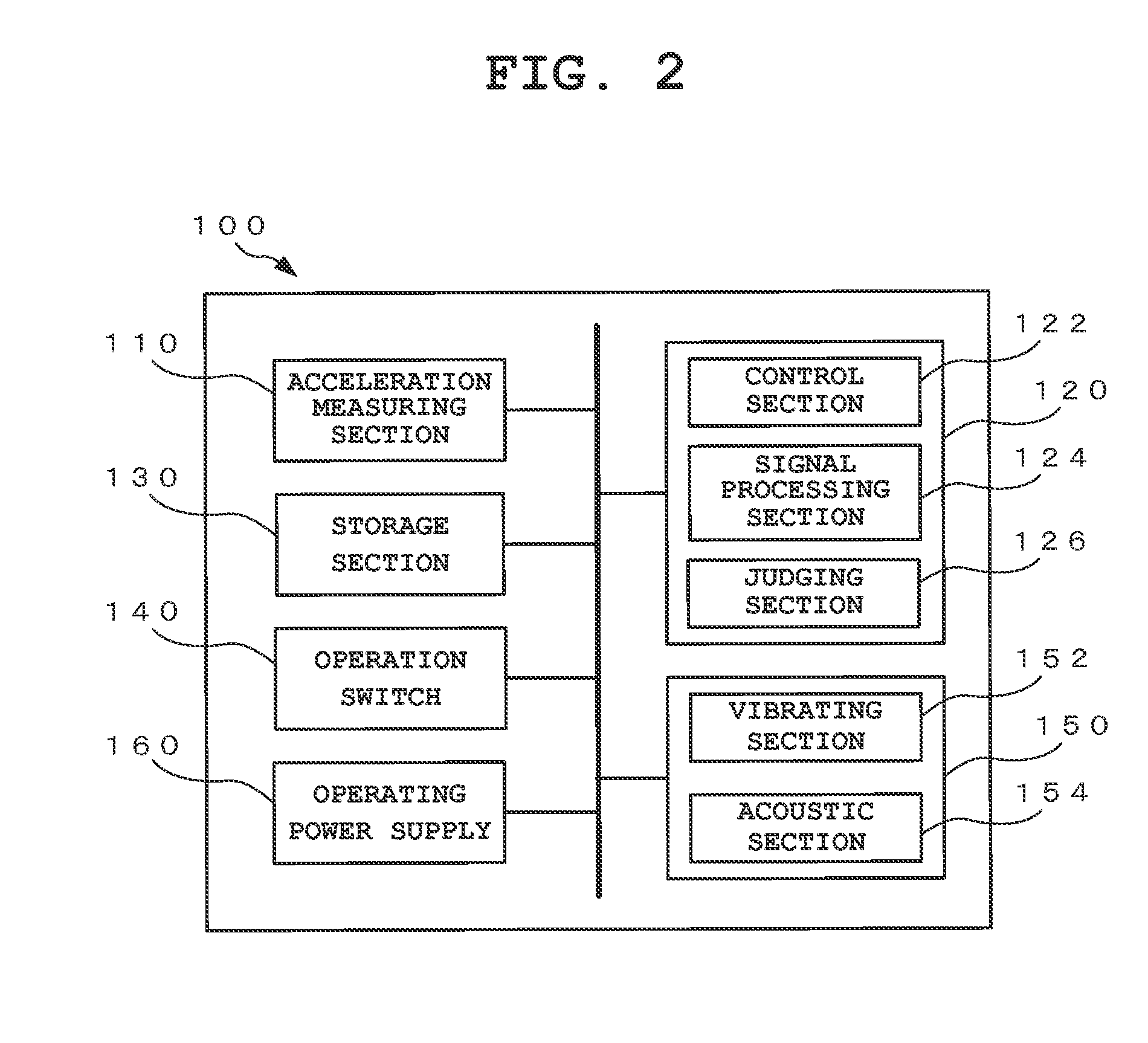
ActiveUS20150081245A1Simple structureAccurate estimatePhysical therapies and activitiesAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTime segmentEngineering
In an exercise support device of the present invention, acceleration signals in three axis directions including vertical, longitudinal, and lateral directions corresponding to the motion of a user performing exercise of cyclically moving feet are obtained, and a first maximum value in one cycle of a foot movement in the vertical acceleration signal is obtained. Subsequently, a search is made for first and second change points related to foot landing and takeoff motions in a composite acceleration signal obtained by combining acceleration signals in at least two axis directions, in forward and backward directions of the time point of a second maximum value of the composite acceleration signal, within the cycle. Then, a time period between the first and second change points is obtained as a change point interval, and a foot landing period while exercising is calculated based on the first maximum value and the change point interval.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Apparatus for shielding process chamber port
ActiveUS7685965B1Improve protectionImprove reliabilityElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingElectric fieldElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:LAM RES CORP
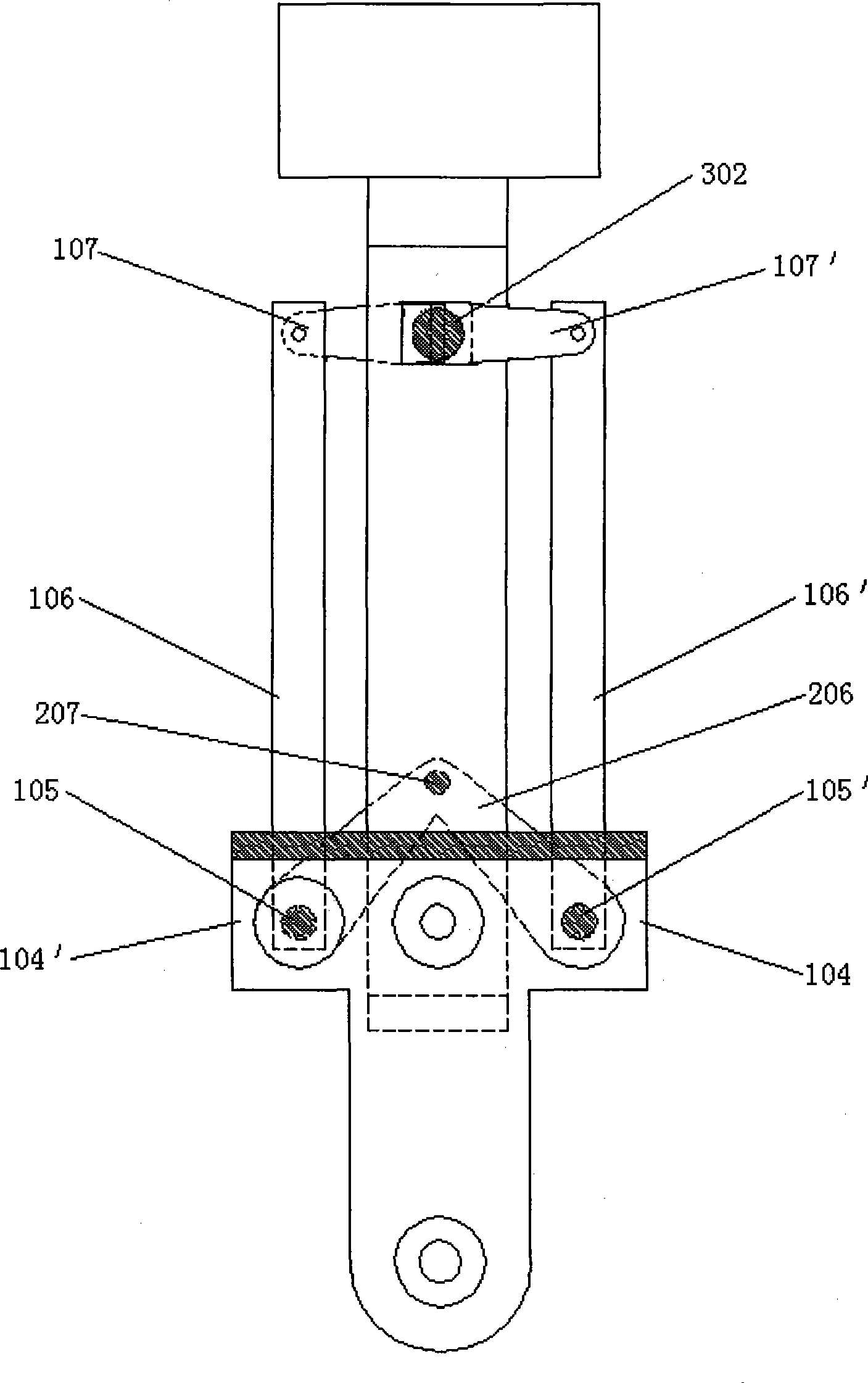
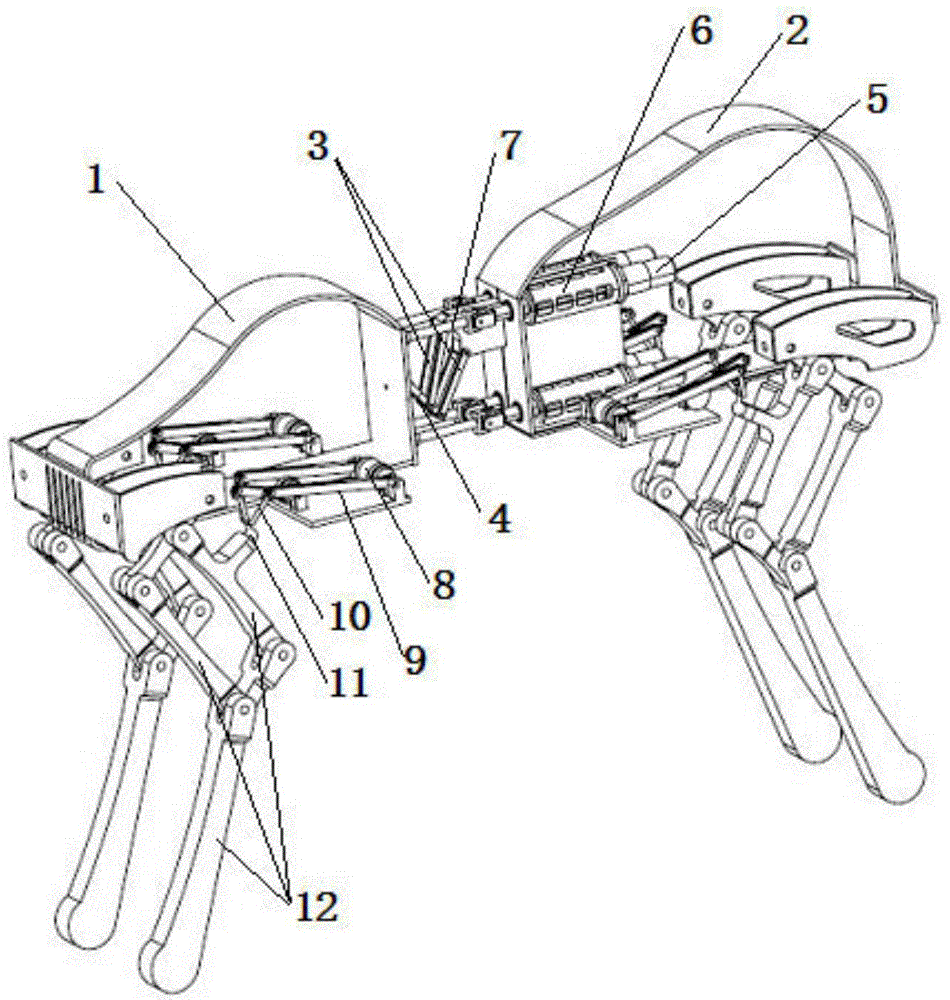
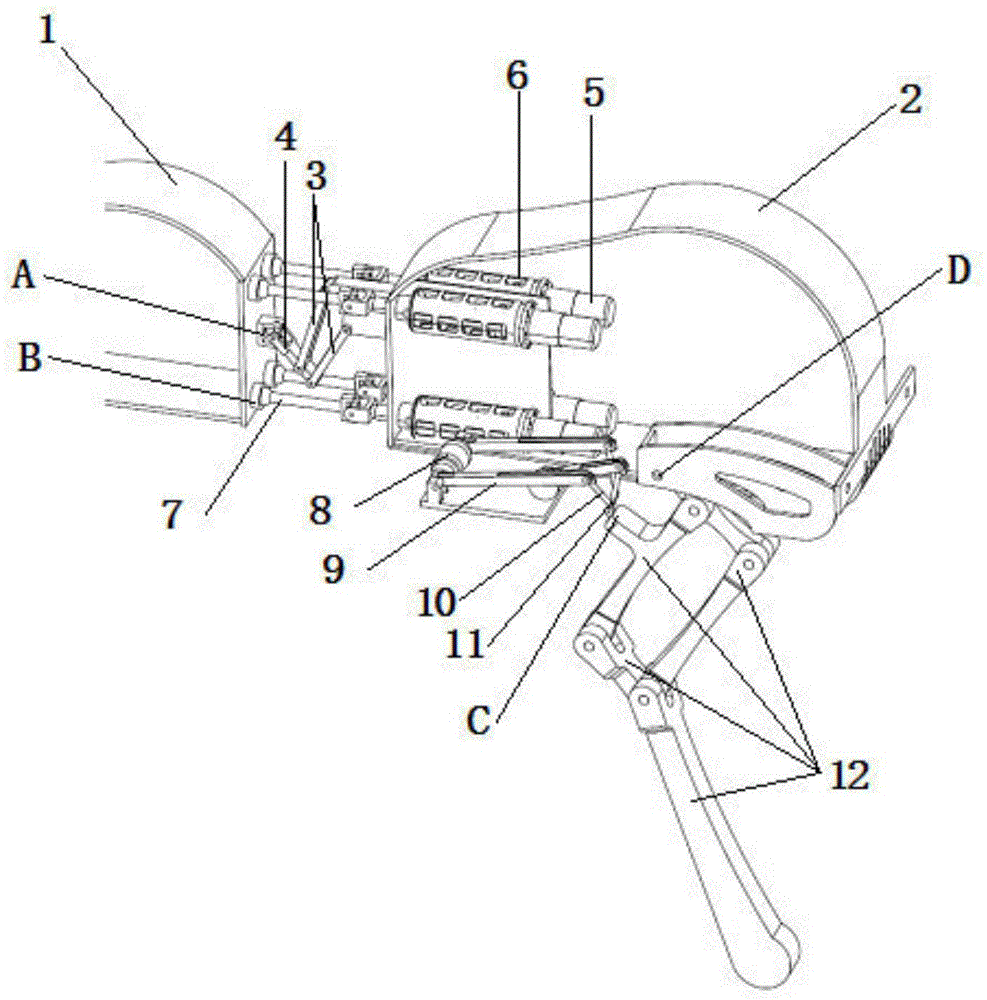
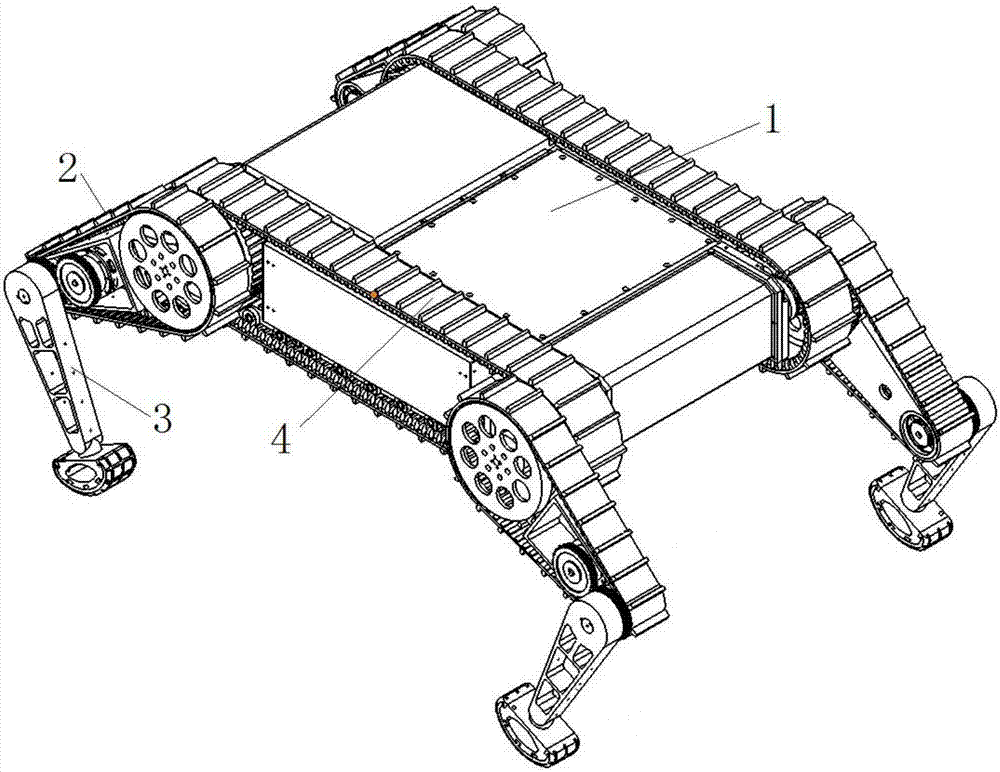
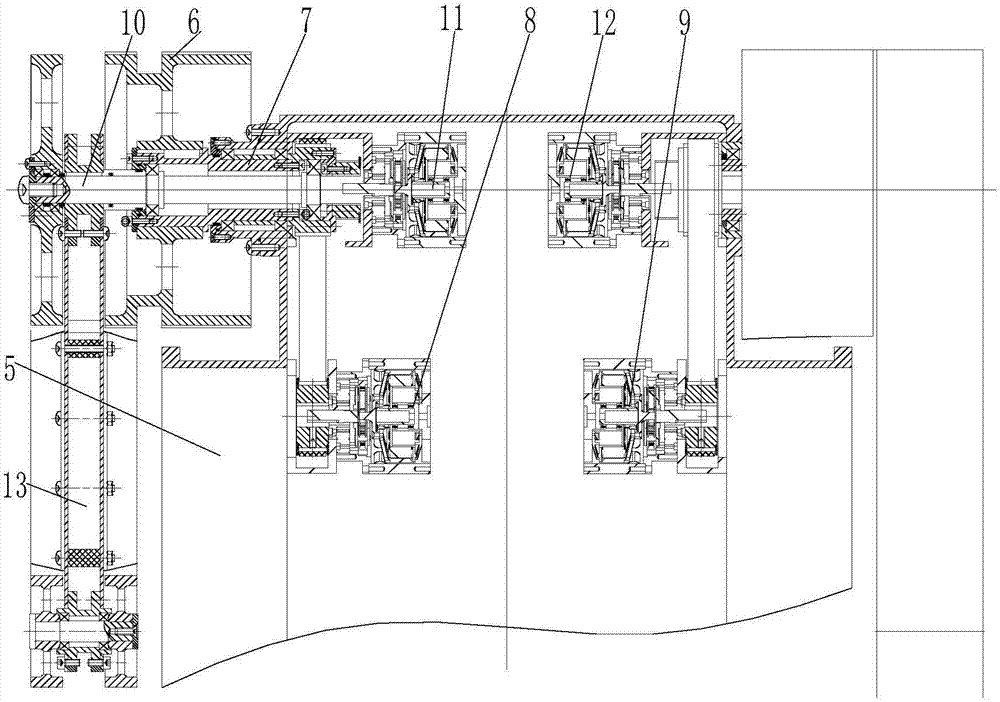
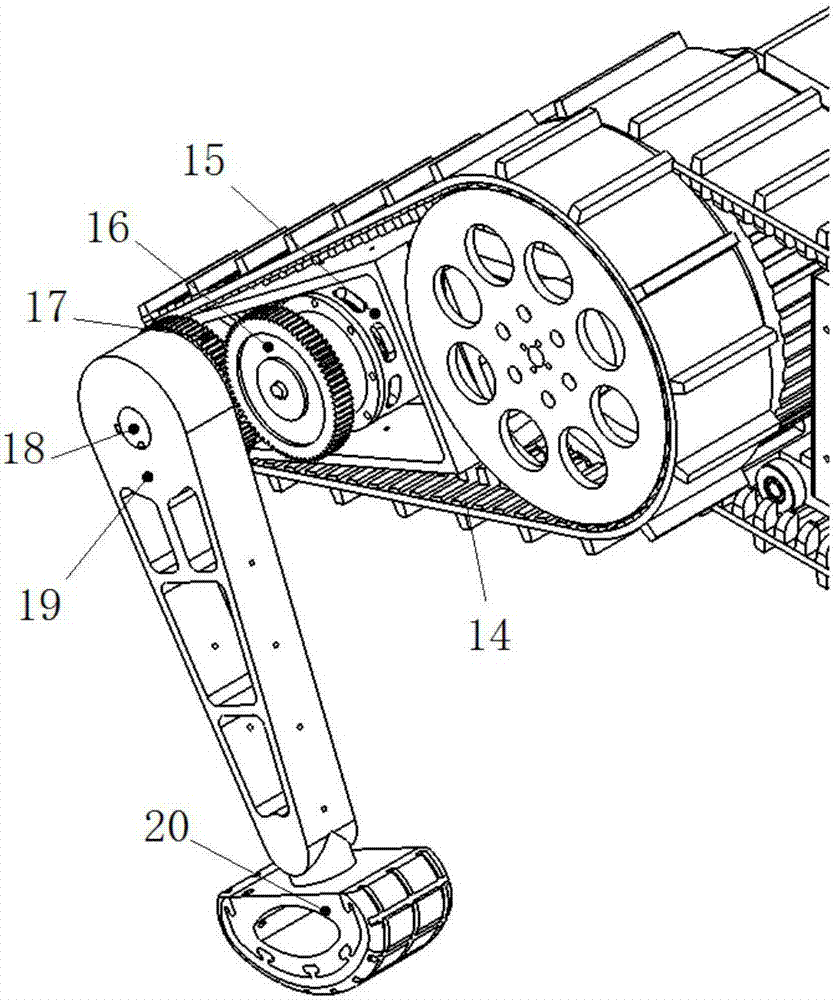
Track-leg and foot hybrid mobile robot
A track-leg and foot hybrid mobile robot comprises a track traveling unit, auxiliary thigh obstacle-crossing units are mounted on two sides of the front and the rear of the track traveling unit respectively, and an auxiliary shank obstacle-crossing unit is connected to every auxiliary thigh obstacle-crossing unit. In a conventional track traveling mode, thighs can assist in obstacle crossing and are extended to cross low obstacles but shanks can be put away through contraction; a shank participation mode can be changed into a four-foot movement mode. Both the thighs and the shanks on two sides are driven by independent power systems and can swing independently under control of a control system so as to assist in obstacle crossing or traveling like four feet. The track-leg and foot hybrid mobile robot has the advantages that the thighs and the shanks are added on the basis of a conventional tracked robot, and the track-leg and foot hybrid mobile robot can travel in a traditional track mode and can cross the obstacles with the aid of the four-foot mode, so that a steady traveling speed and energy efficiency of the tracked robot are maintained, and high trafficability of a footed robot is enhanced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Horizontal lower limb rehabilitation robot capable of contracting and moving in an ICU ward
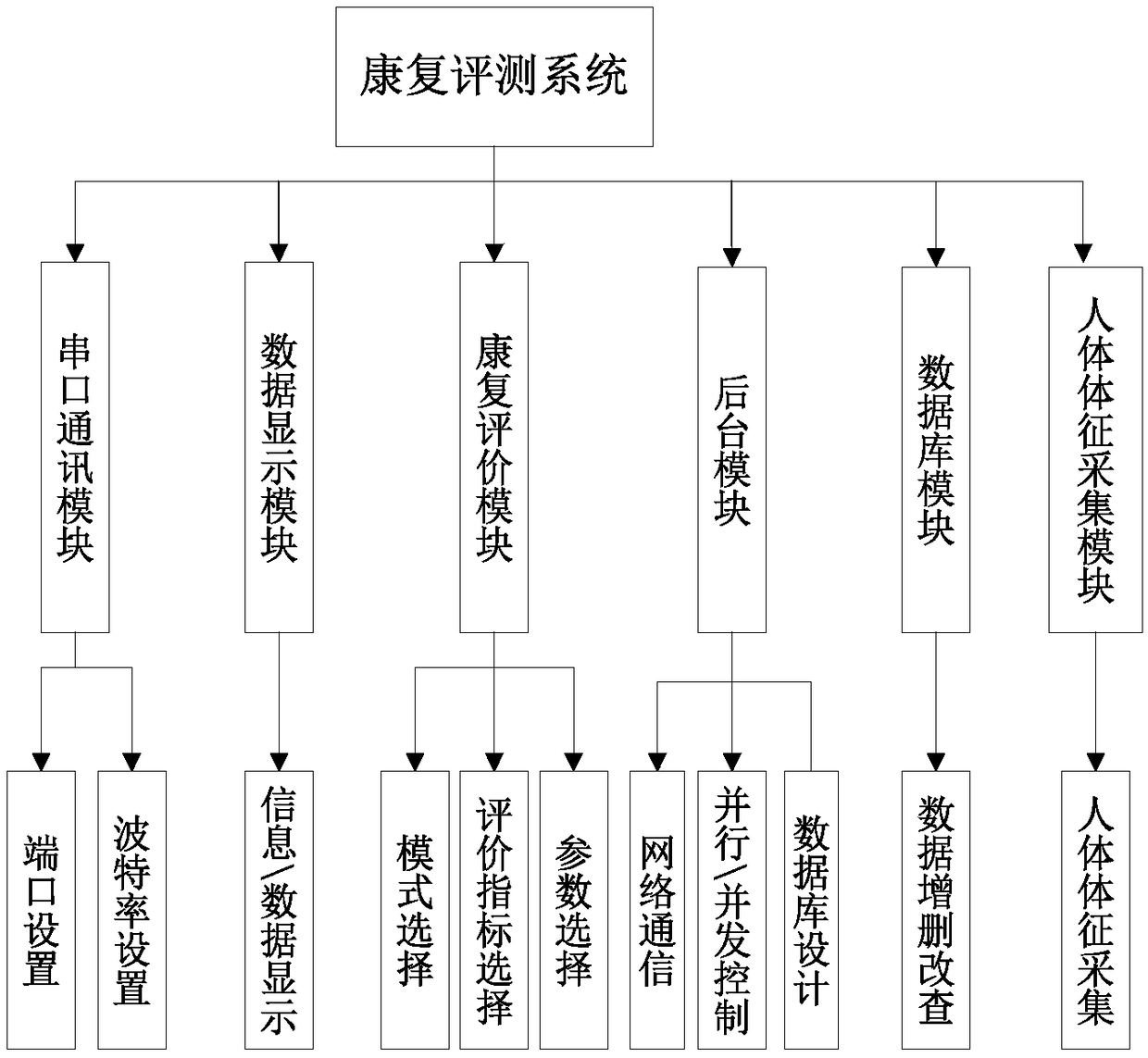
InactiveCN109157376AAvoid painAvoid secondary damageGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesPatient's roomEngineering
The invention discloses a horizontal lower limb rehabilitation robot capable of contracting and moving in an ICU ward. The device comprises a human body sign acquisition module, a base module, a lowerlimb exoskeleton, a control module and a rehabilitation evaluation system. Based on modular design, the rehabilitation evaluation and training of different joints of human lower limbs can be realizedaccording to the characteristics of different patients. Design reset command switch to achieve structural shrinkage and deformation, easy to carry and use in small space of intensive care unit. Emergency stop switch, alarm lamp, leg exoskeleton limit block and foot movement limit block are designed to ensure the safe and reliable operation of lower limb rehabilitation training process. Through serial port and network communication, parallel and concurrent processing and database design, the lower limb rehabilitation evaluation process is well managed, and the real-time intelligent evaluationand training of different joint movements of lower limb with multi-mode and multi-parameter is realized. The results can also be visualized highly, which provides data and reference for doctors to make lower limb rehabilitation training program.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
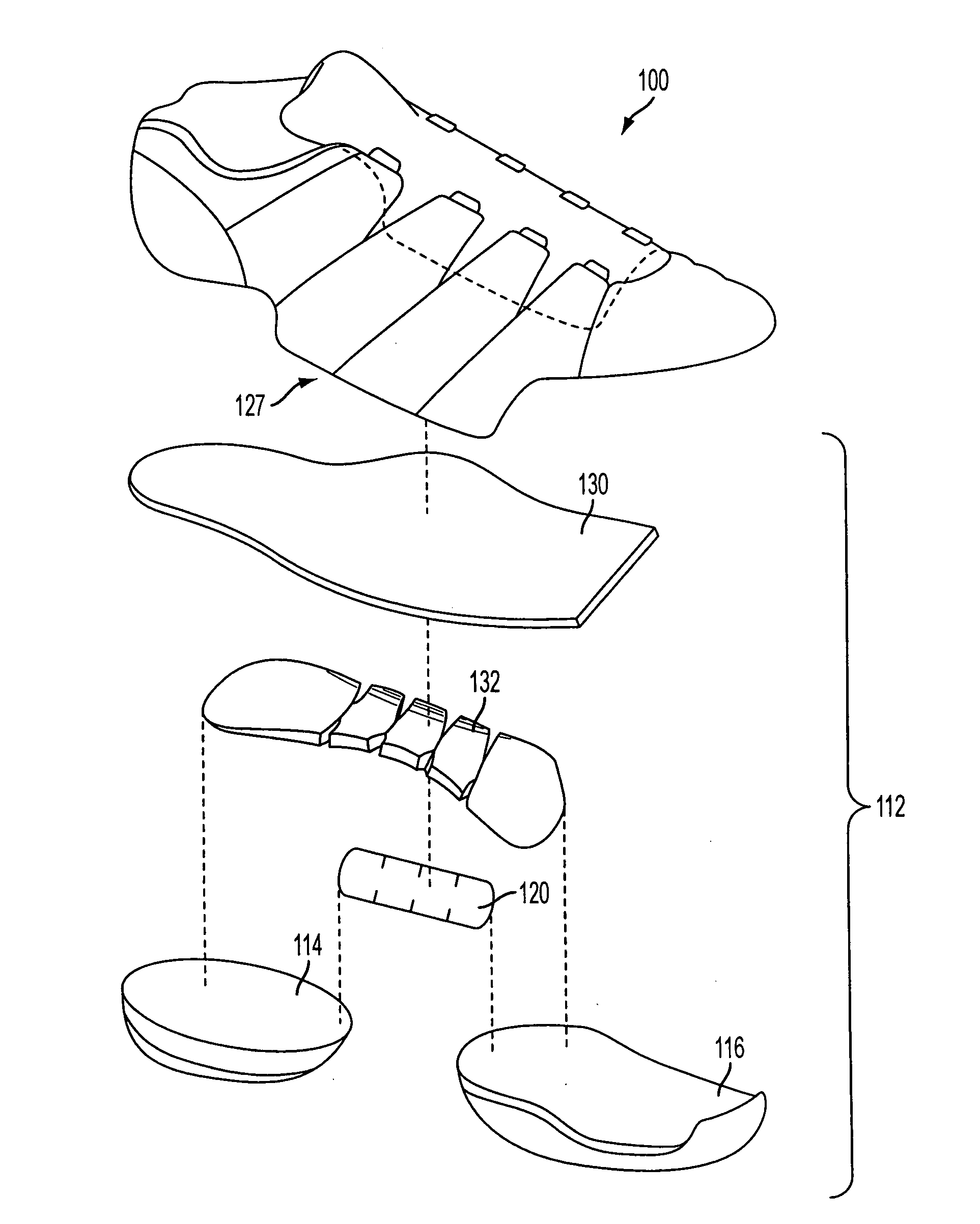
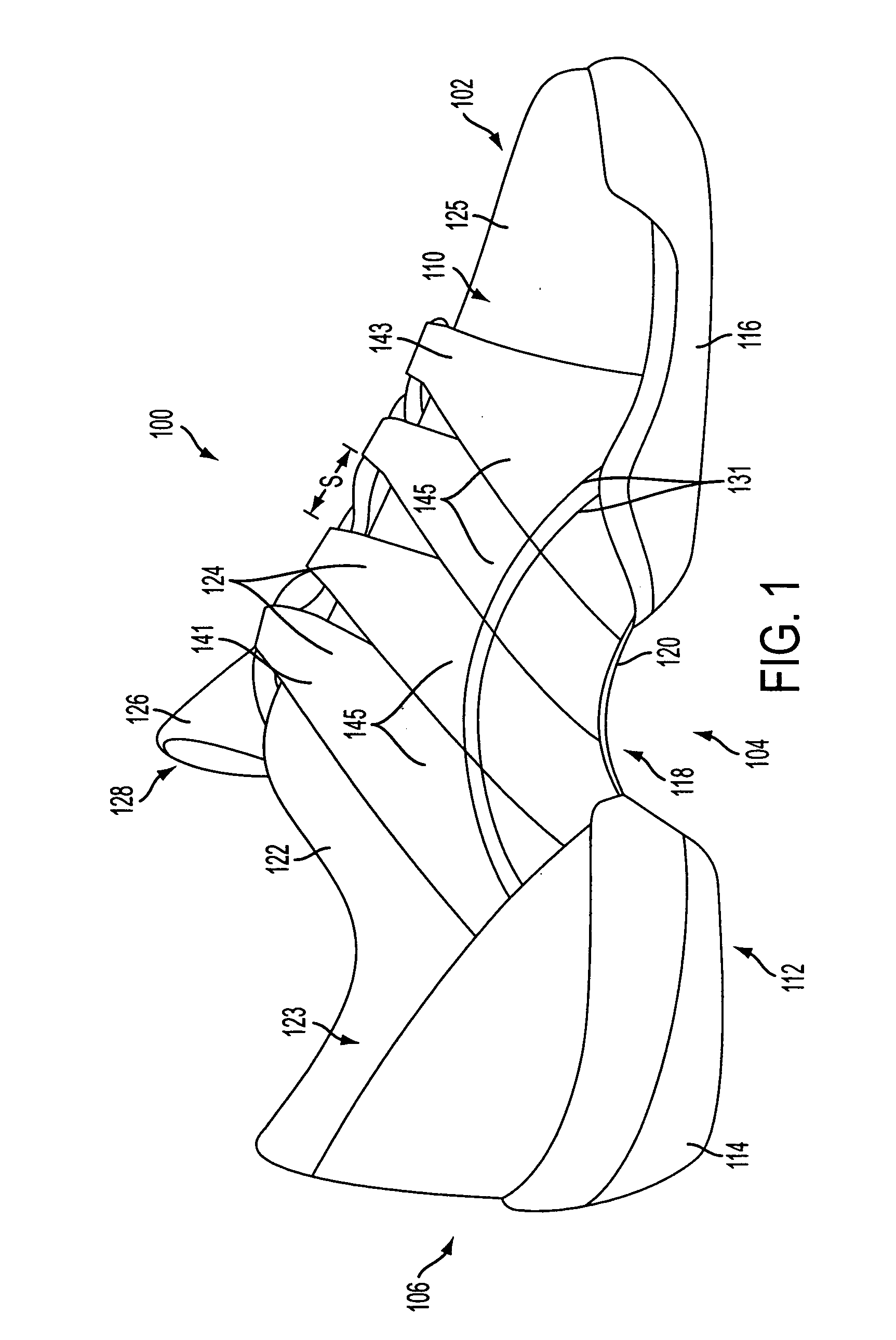
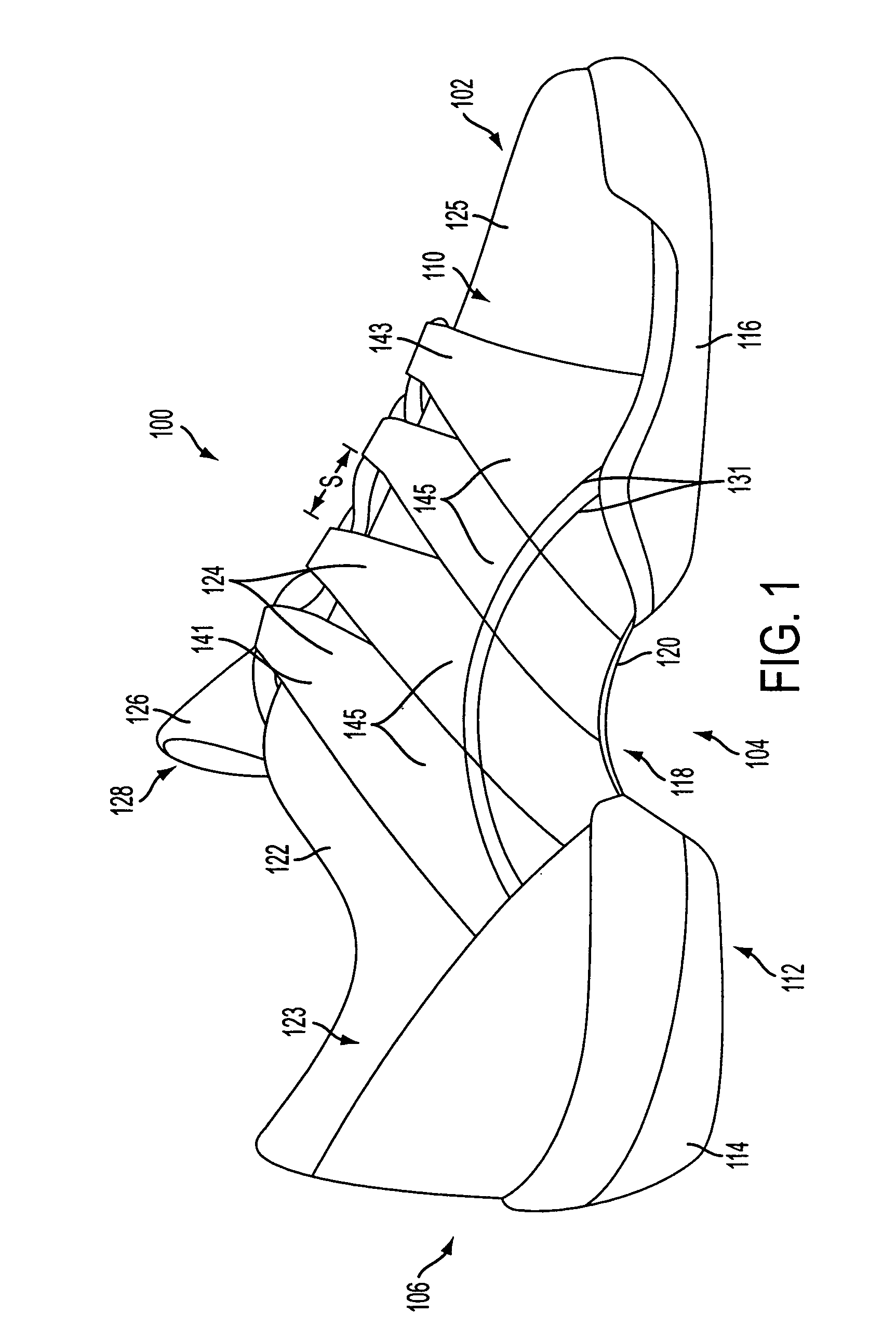
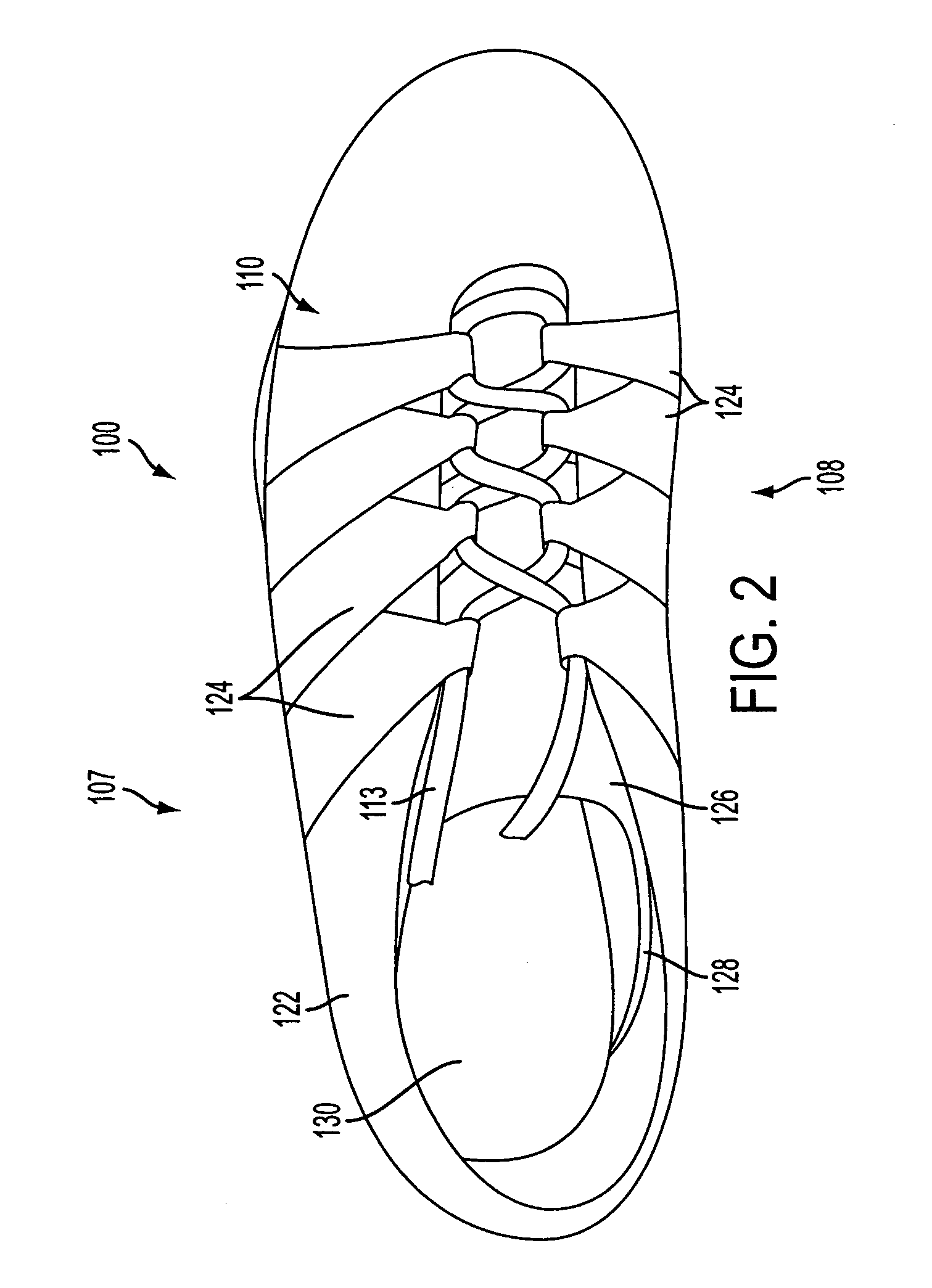
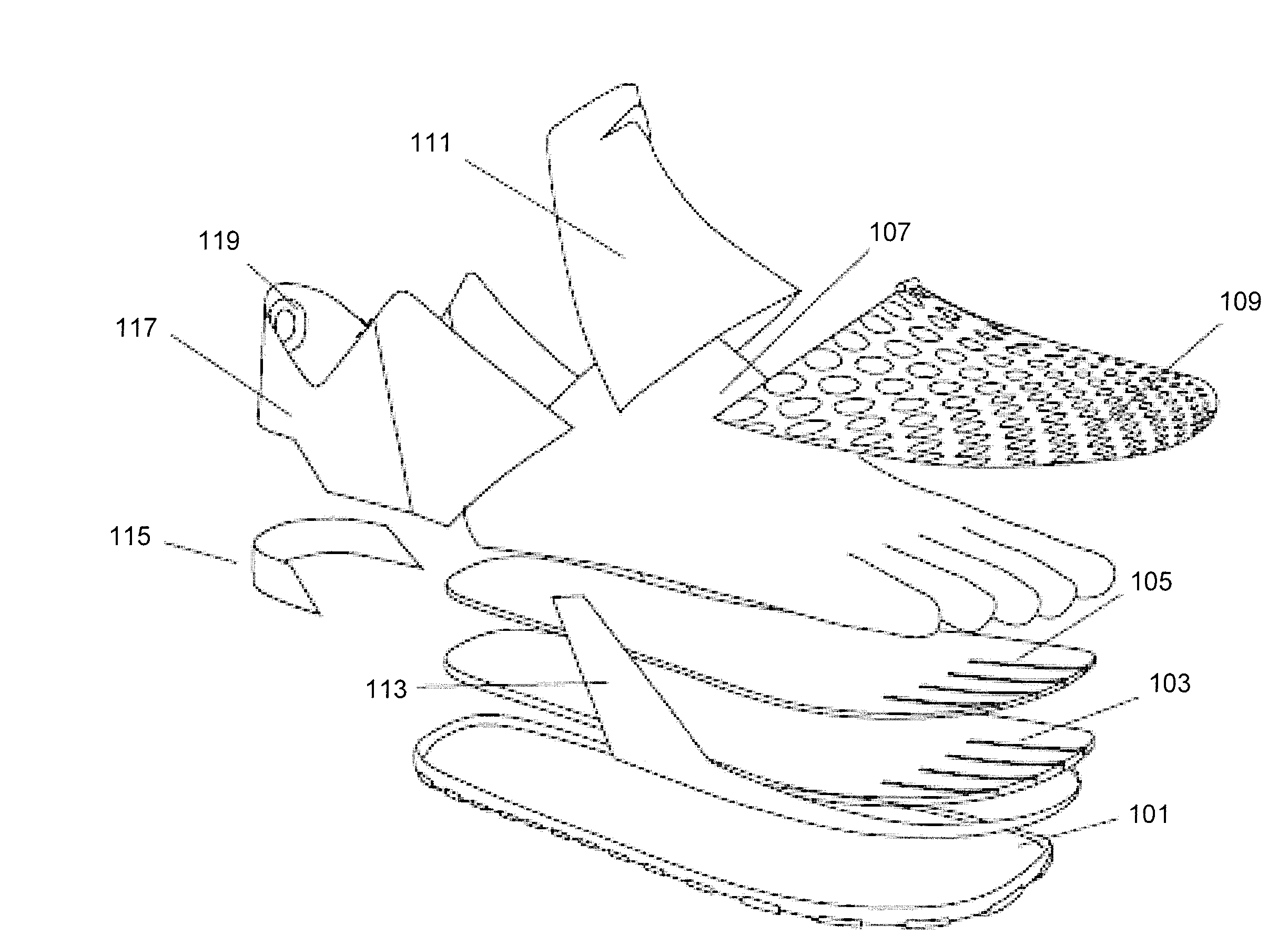
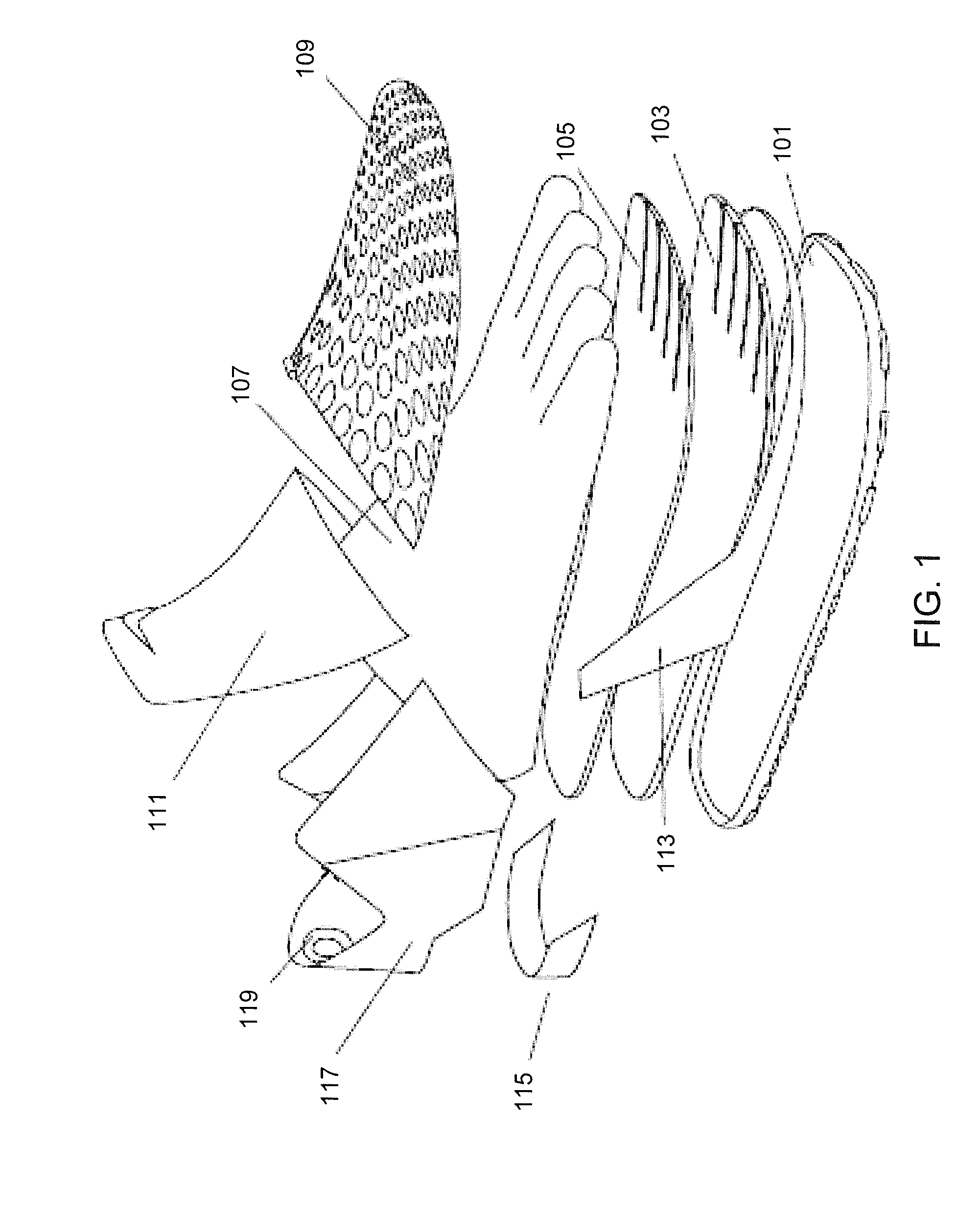
Athletic performance shoes
An athletic shoe includes an outsole, a midsole, an insole, a bootie, a cage surrounding the upper front of the bootie, a tongue, a quarter, a heel counter and wings. The bootie can have one, two, three, four or five individual toe sections which allow the toes of the foot to move independently. The bootie may be removable or adhesively attached to the midsole and the innersole. Both the midsole and the innersole can have slots cut between the toe portions which further allows for independent movement of the toes. The cage and outsole surround the front toe portions of the bootie, insole and midsole. The cage and outsole prevent all large particles from falling between the toes. The individual toe sections in the inventive shoe increase natural foot movement, haptic response and improve stability / balance, footstrike biomechanics and foot strength.
Owner:SAMUEL TAYLOR +1
Novel intelligent omni-directional treadmill
InactiveCN105617605ABasic structure is simpleIngenious designMovement coordination devicesCardiovascular exercising devicesEngineeringOmni directional
The invention discloses a novel intelligent omni-directional treadmill, belonging to the field of treadmills. The novel intelligent omni-directional treadmill comprises a driving unit with a universal transmission function and a support platform for supporting a user, wherein a control panel is arranged above the support platform; a detection unit for detecting the foot movement of a runner is arranged on the edge of the support platform; multiple power output holes are formed in the support platform; a driven unit is arranged in the support platform and comprises a support frame and support rods arranged on the support frame; and the top ends of the support rods are positioned in the power output holes. In the invention, the power of the driving unit is transferred to the support platform through the driven unit, and the user can freely change the running direction and increase / reduce the running speed.
Owner:深圳市盖范教育科技有限公司
Bionic six-foot robotic exploration ant
InactiveCN108818551ASimple structureImprove reliabilityManipulatorVehiclesMulti degree of freedomEngineering
The invention provides a bionic six-foot robotic exploration ant, and belongs to the technical field of multi-degree-of-freedom moving robotic explorers. The bionic six-foot robotic exploration ant comprises three left feet, three right feet and a host body. The left feet and the right feet are completely identical in the connection mode, and are in mirror symmetry during assembly. According to the left feet and the right feet, multi-degree-of-freedom movement of a single leg is simplified into two-degree-of-freedom movement which is realized by two steering gears in each group, and the groupof the steering gears of each single leg include a linear action steering gear and a rotating action steering gear which drive two-phase movement of swinging and lifting legs, so that decoupling of leg movement is realized, control schemes are simplified, and control stability is improved. Six-foot tread control laws are designed to achieve movement of the robotic exploration ant on different grounds, a camera on the host body is used for acquiring more environmental information, and accordingly, the exploration effect is good. The bionic six-foot robotic exploration ant has the advantages ofdiversity in movement mode, rapidness in multi-foot movement switching, efficiency in tread and step pitch adjustment, accuracy and rapidness in movement direction adjustment and multi-directional movement.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Lower limb rehabilitation training device for lying, sitting and standing postures
ActiveCN106236508ARealize rehabilitation trainingAchieve exerciseGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesThighLower limb exercises
The invention discloses a lower limb rehabilitation training device for lying, sitting and standing postures. The lower limb rehabilitation training device comprises a seat and a lower limb rehabilitation trainer, wherein the lower limb rehabilitation trainer comprises thigh movement mechanisms, calf movement mechanisms and foot movement mechanisms which are serially connected sequentially; the thigh movement mechanisms, the calf movement mechanisms and the foot movement mechanisms, which are identical in structure, are three-freedom-degree parallel mechanisms; a thigh supporting and fixing part is connected between each thigh movement mechanism and the corresponding calf movement mechanism; a calf supporting and fixing part is connected between each calf movement mechanism and the corresponding foot movement mechanism; and a pedaling and fixing part is connected to the front end of each foot movement mechanism. According to the lower limb rehabilitation training device disclosed by the invention, the lower limb of a user, sitting on the seat, can be bound by virtue of the various supporting and fixing parts and the lower limb rehabilitation trainer, and then lower limb exercises can be conducted comfortably by virtue of the lower limb rehabilitation trainer. The lower limb rehabilitation training device disclosed by the invention is broad in application scope; and lower limb rehabilitation training and exercises in a mode of three-dimensional spatial motions can be achieved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com