Patents
Literature
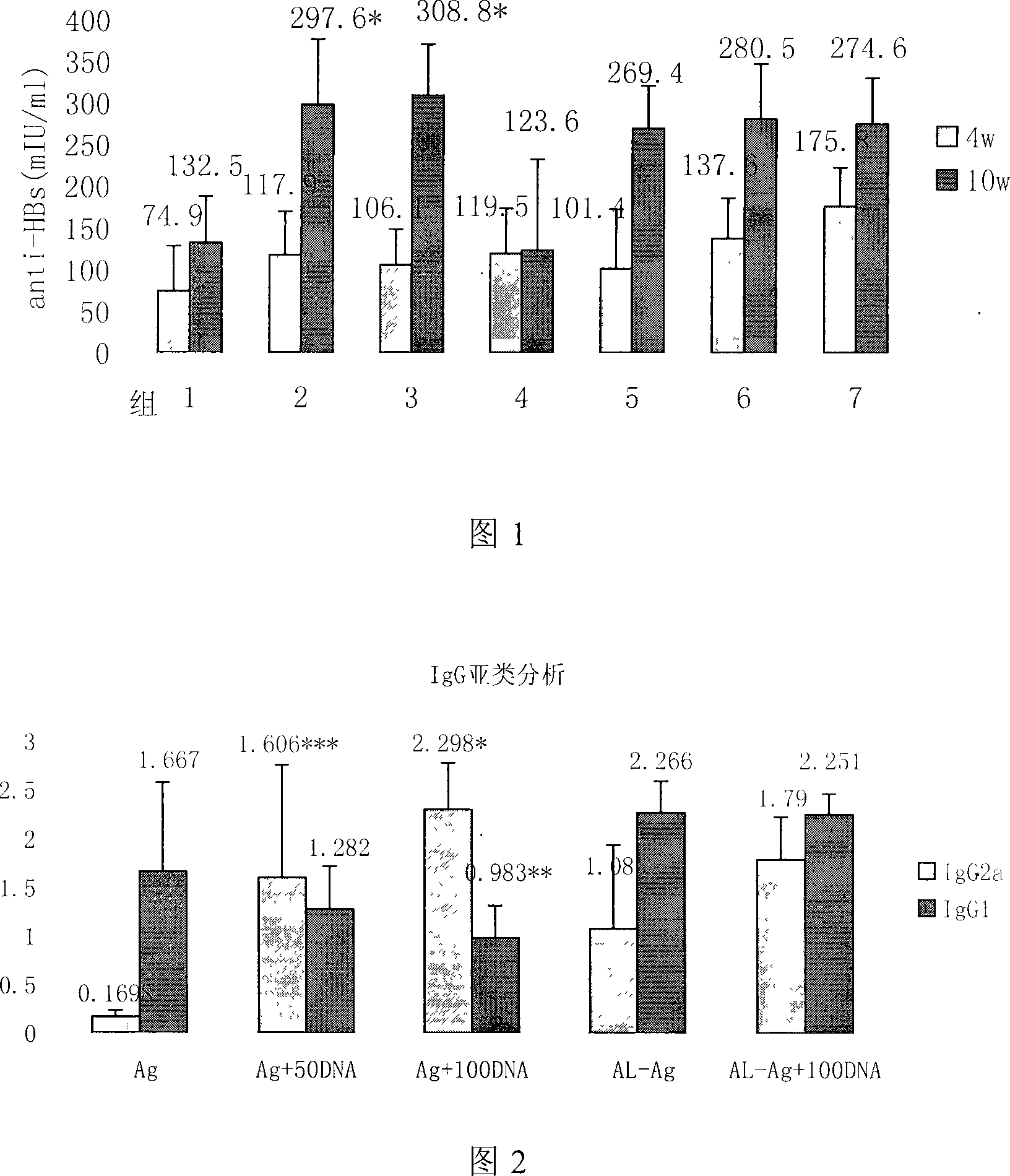
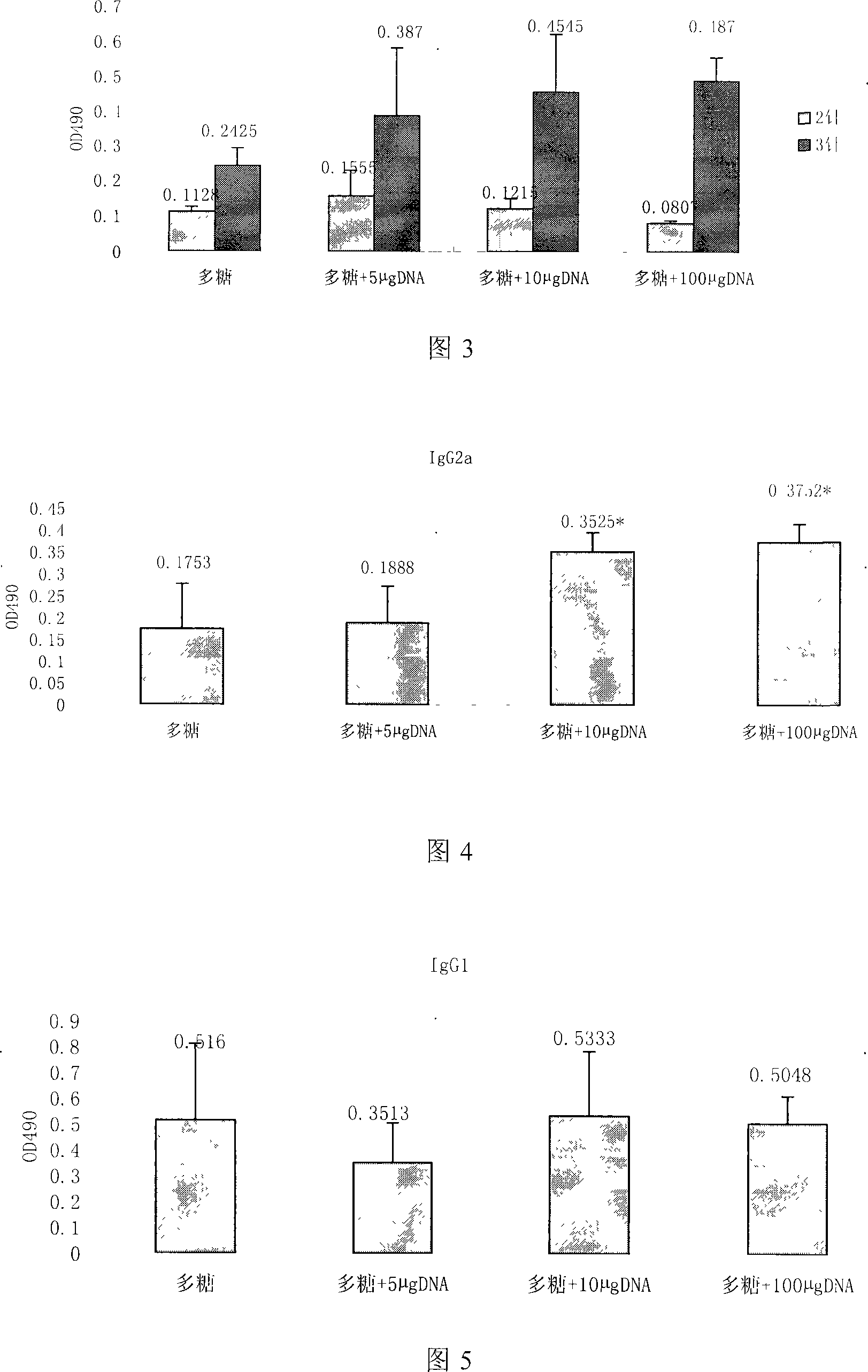
115 results about "Methyl cytosine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
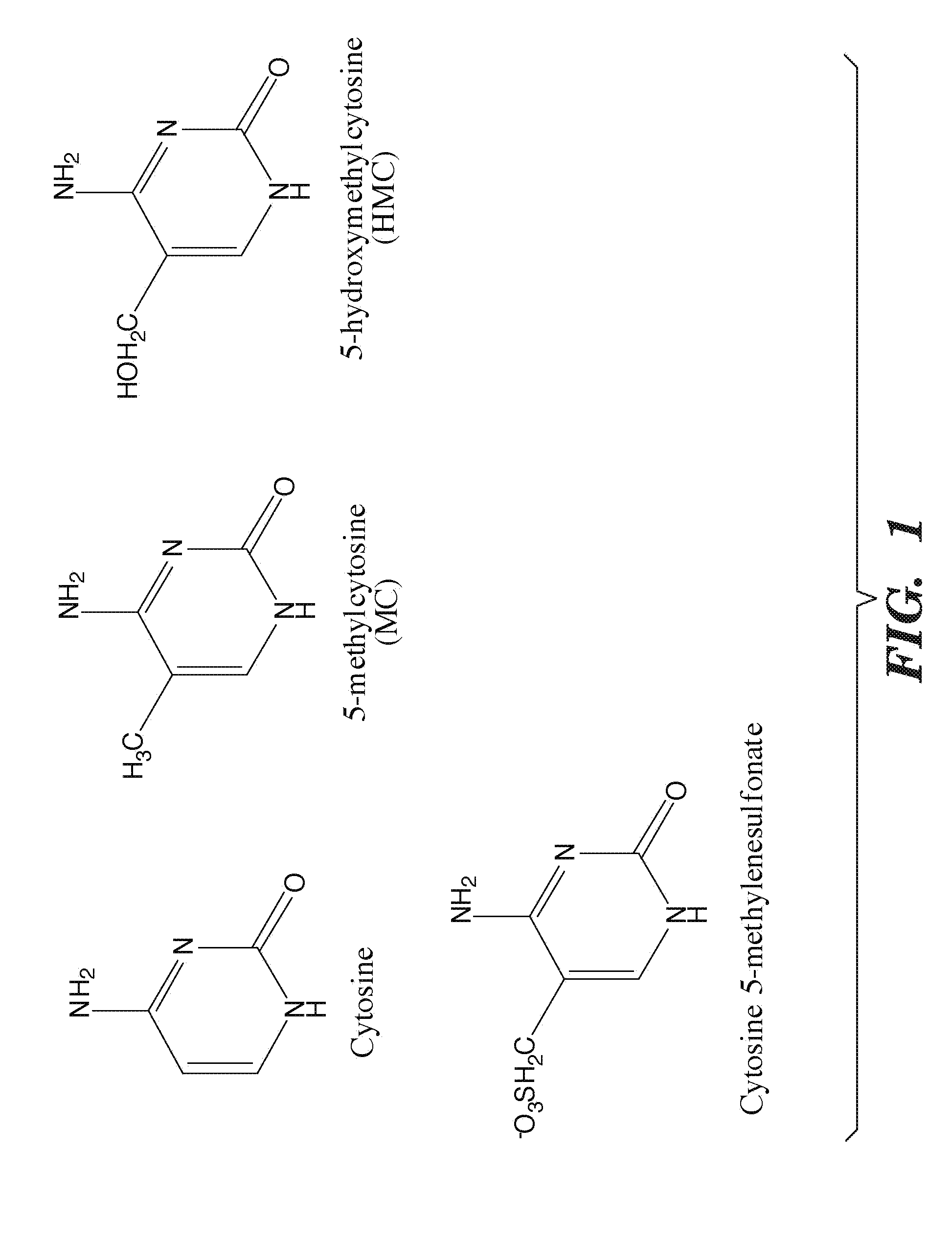
Methylation of cytosine is a covalent modification of DNA, in which hydrogen H5 of cytosine is replaced by a methyl group.
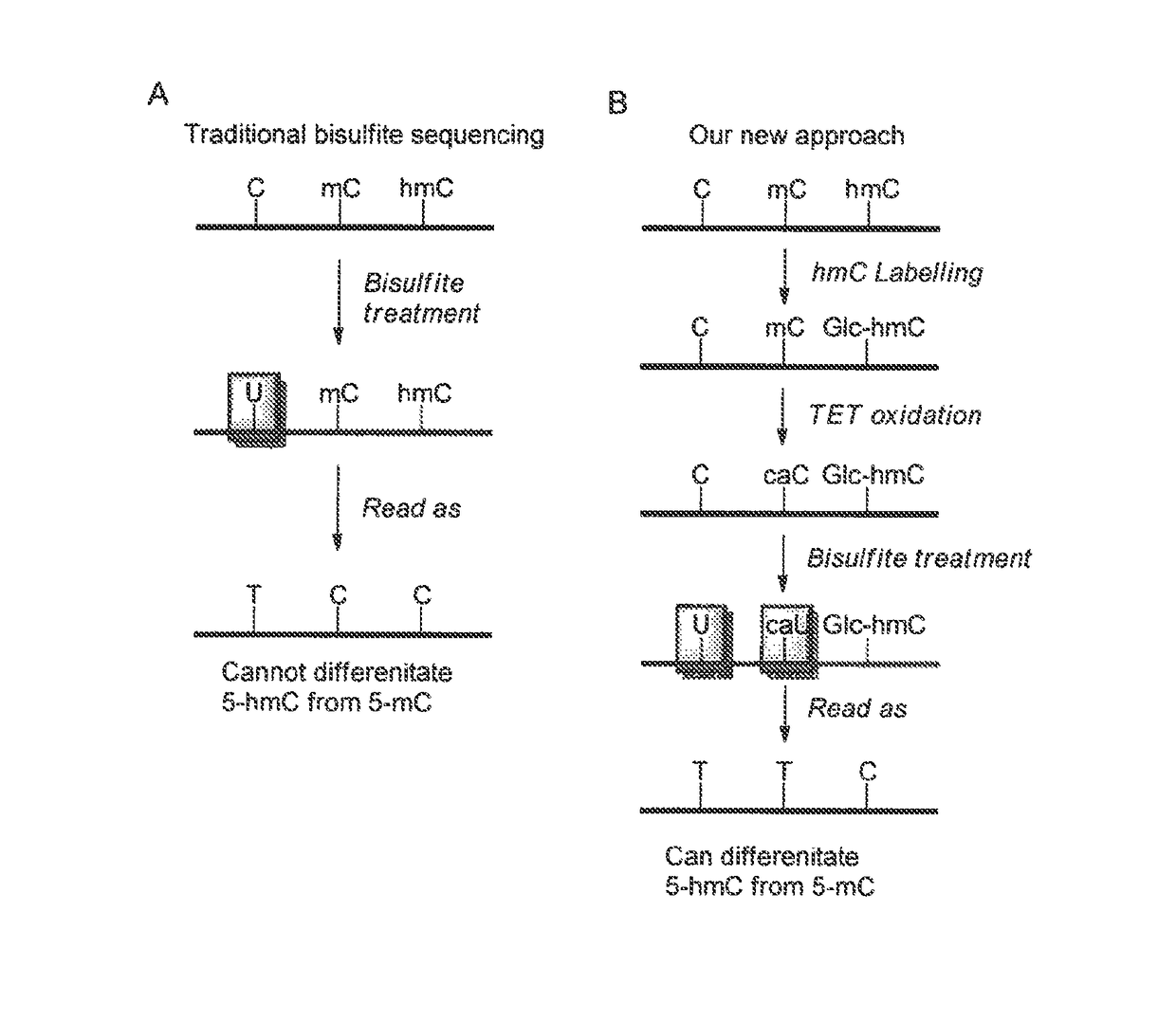
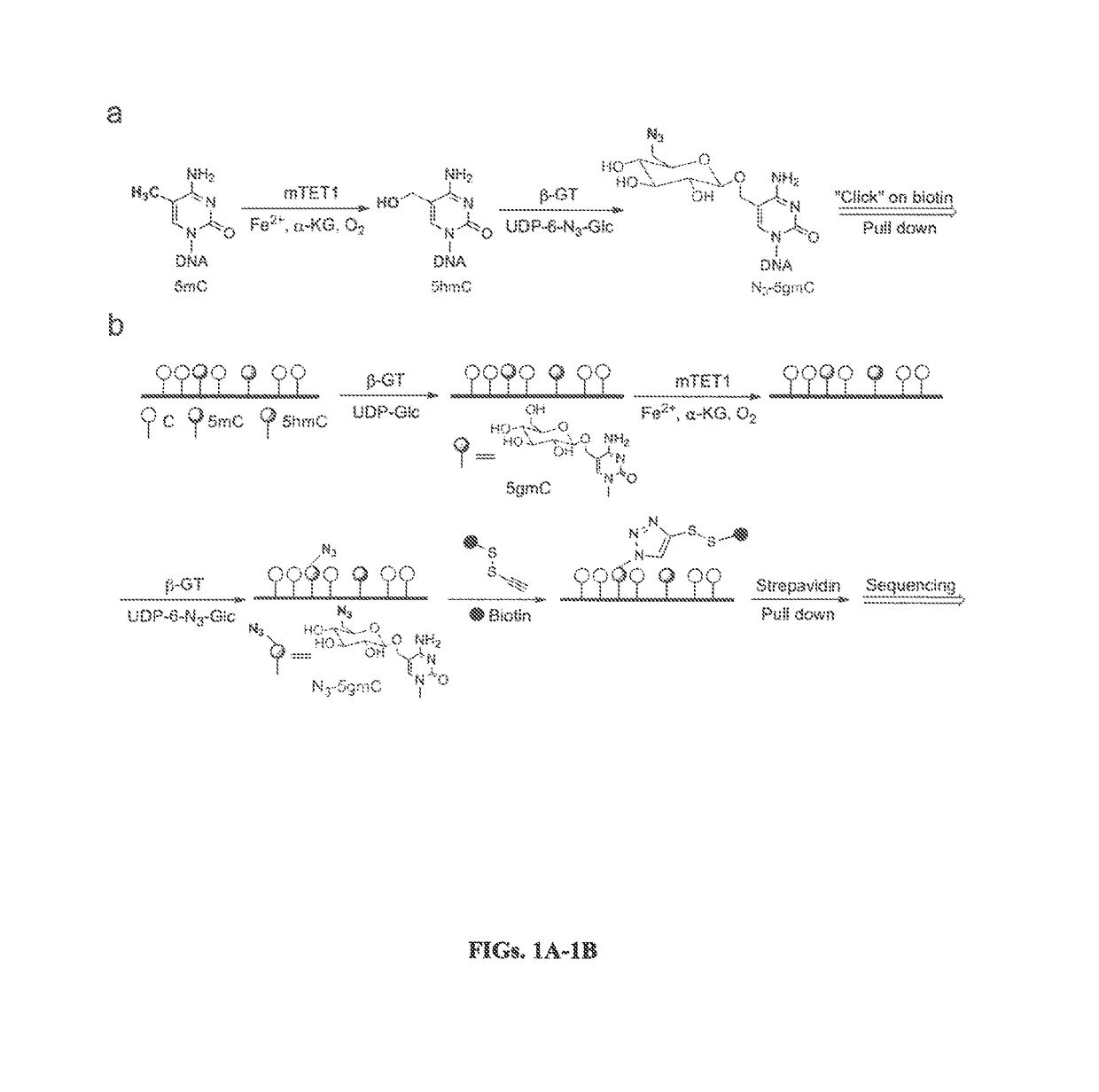
COMPOSITION AND METHODS RELATED TO MODIFICATION OF 5-METHYLCYTOSINE (5-mC)
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for detecting, evaluating, and / or mapping 5-methyl-modified and / or 5-hydroxylmethyl-modified cytosine bases within a nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
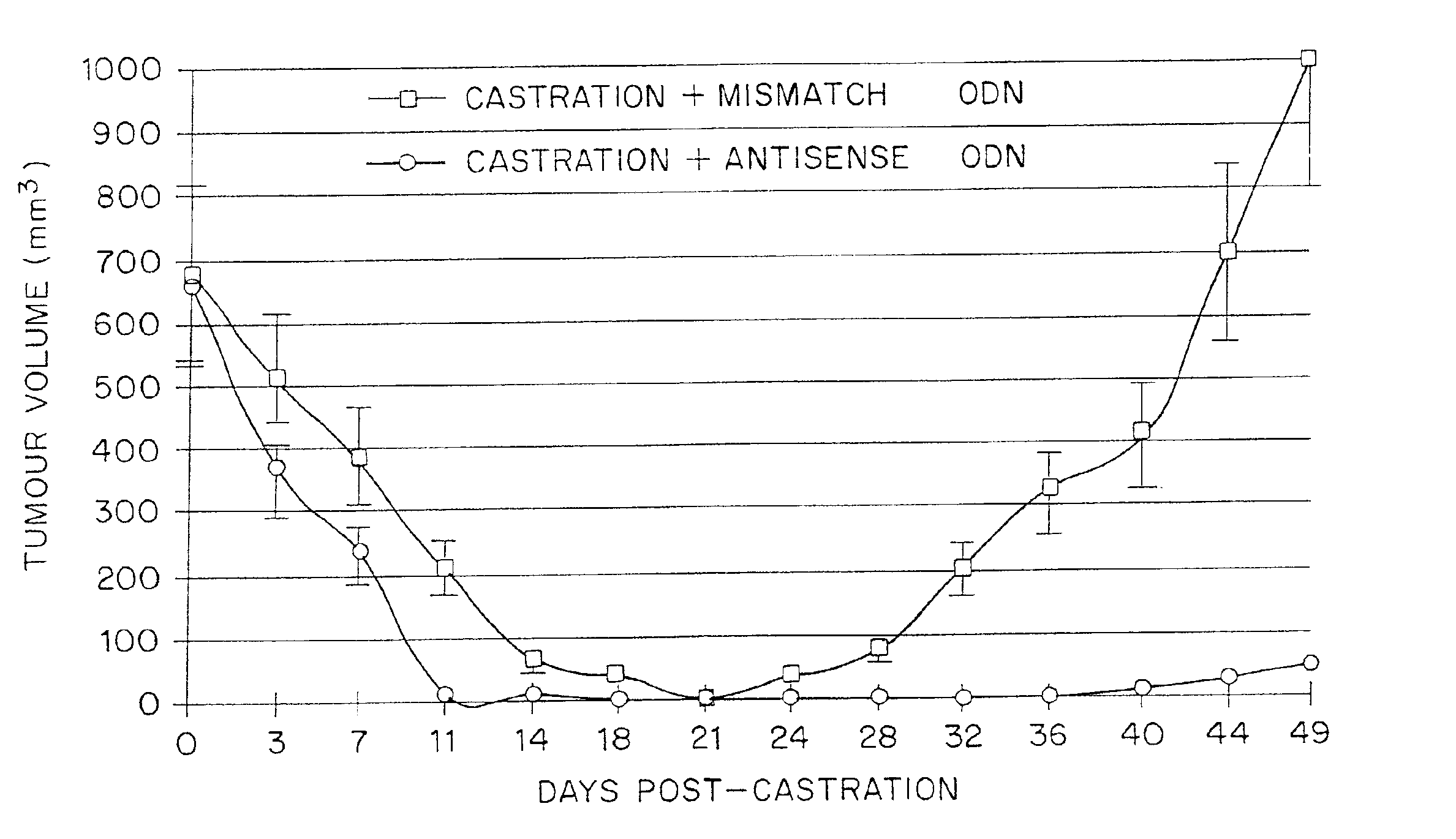
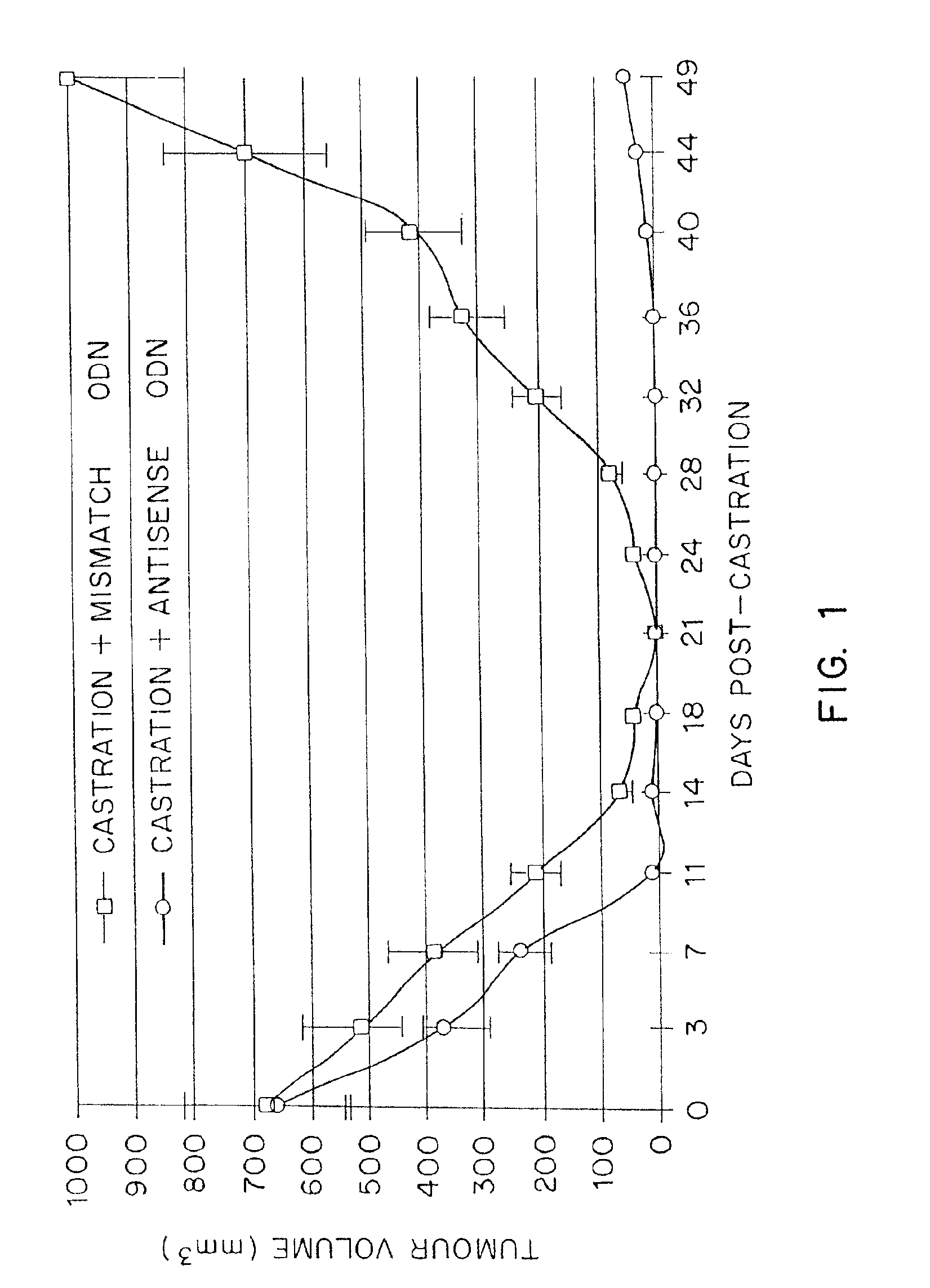
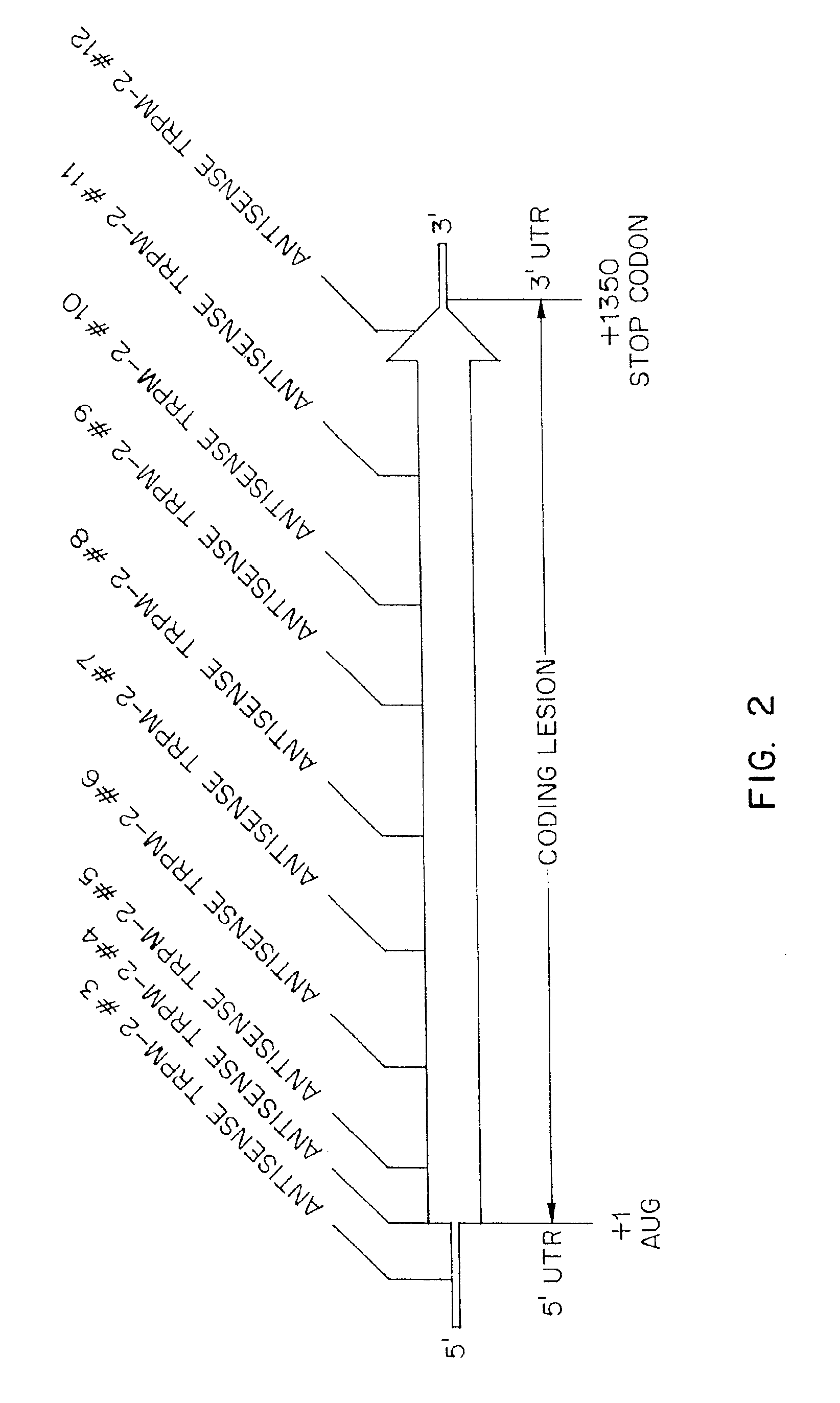
TRPM-2 antisense therapy using an oligonucleotide having 2′-O-(2-methoxy)ethyl modifications
InactiveUS6900187B2Improve in vivo stabilityImproved in vitroPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsIn vivoOligonucleotide
A compound consisting of an oligonucleotide of sequence CAGCAGCAGAGTCTTCATCAT, where the oligonucleotide has a phosphorothioate backbone throughout, the sugar moieties of nucleotides 1-4 and 18-21 bear 2′-O-methoxyethyl modifications, and the remaining nucleotides (nucleotides 5-17) are 2′-deoxynucleotides, and where the cytosines of nucleotides 1, 4 and 19 are 5-methylcytosines. The compound has increased stability in vivo and improved in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
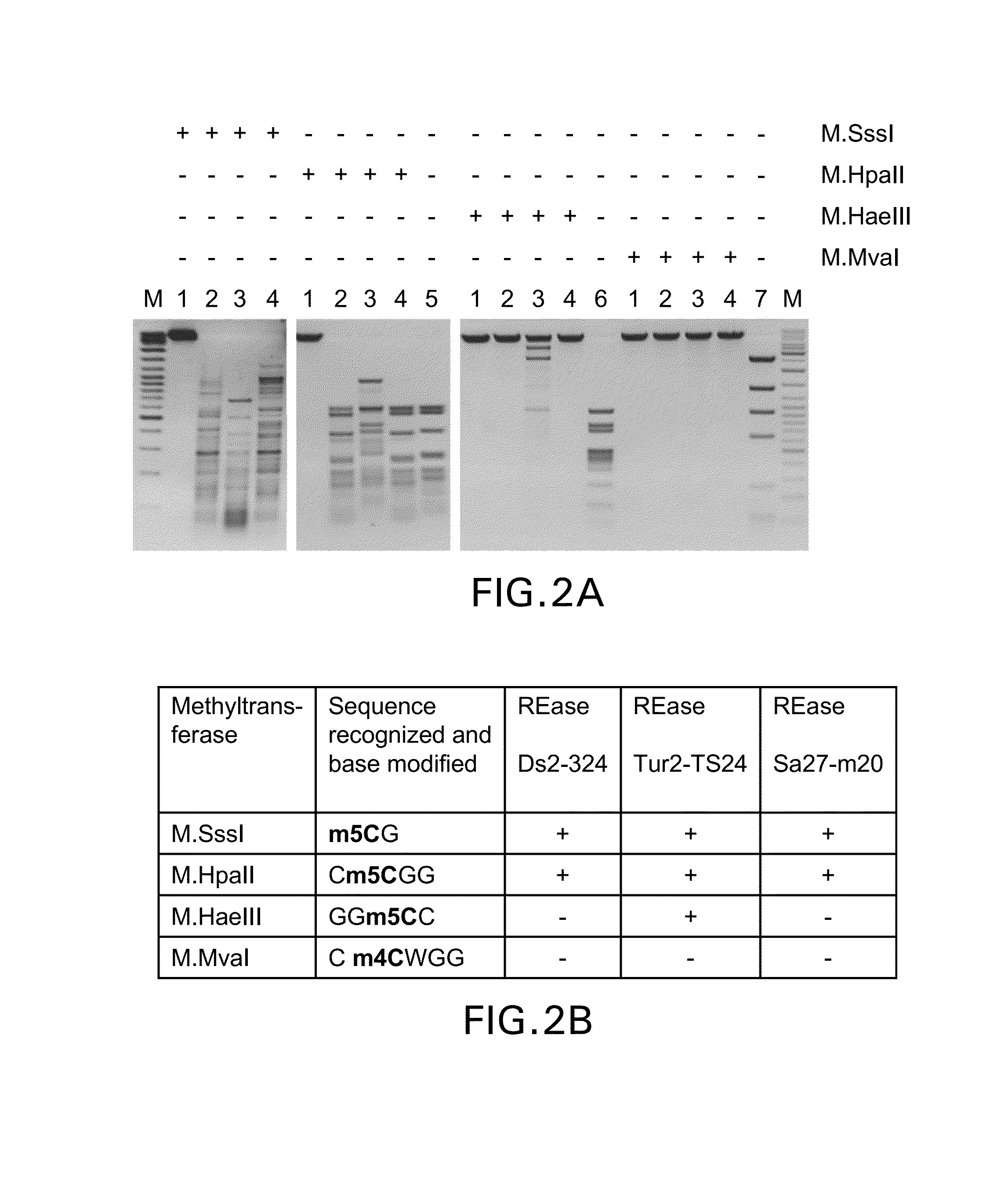
Restriction endonucleases and their applications
Provided is a methylation-specific restriction endonuclease for a DNA duplex substrate, which endonuclease recognizes in a strand of the duplex a 2 to 6 nucleotide recognition sequence comprising a 5-methylcytosine, and cleaves each strand of the duplex at a fixed position outside the recognition sequence.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BALTICS UAB
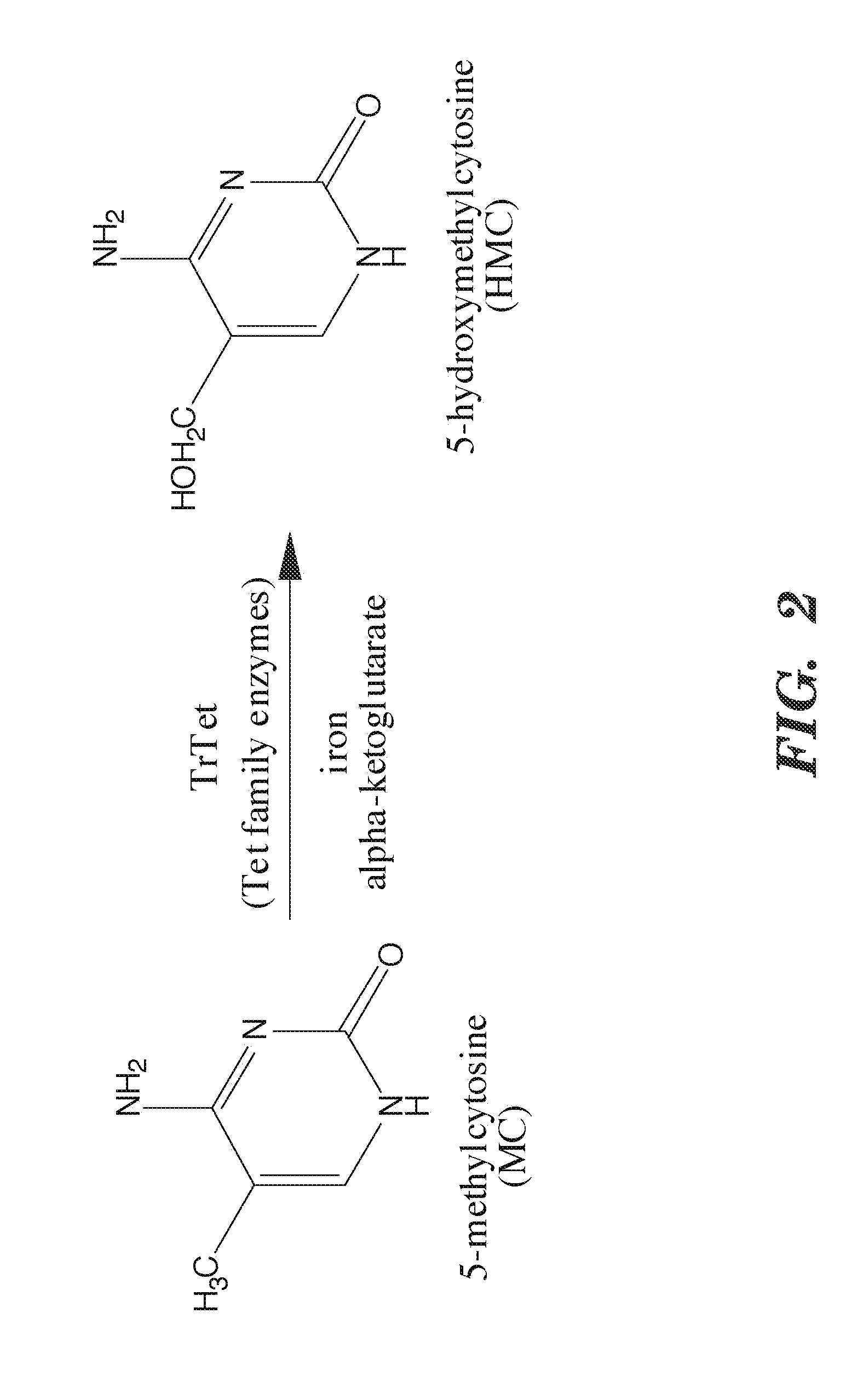
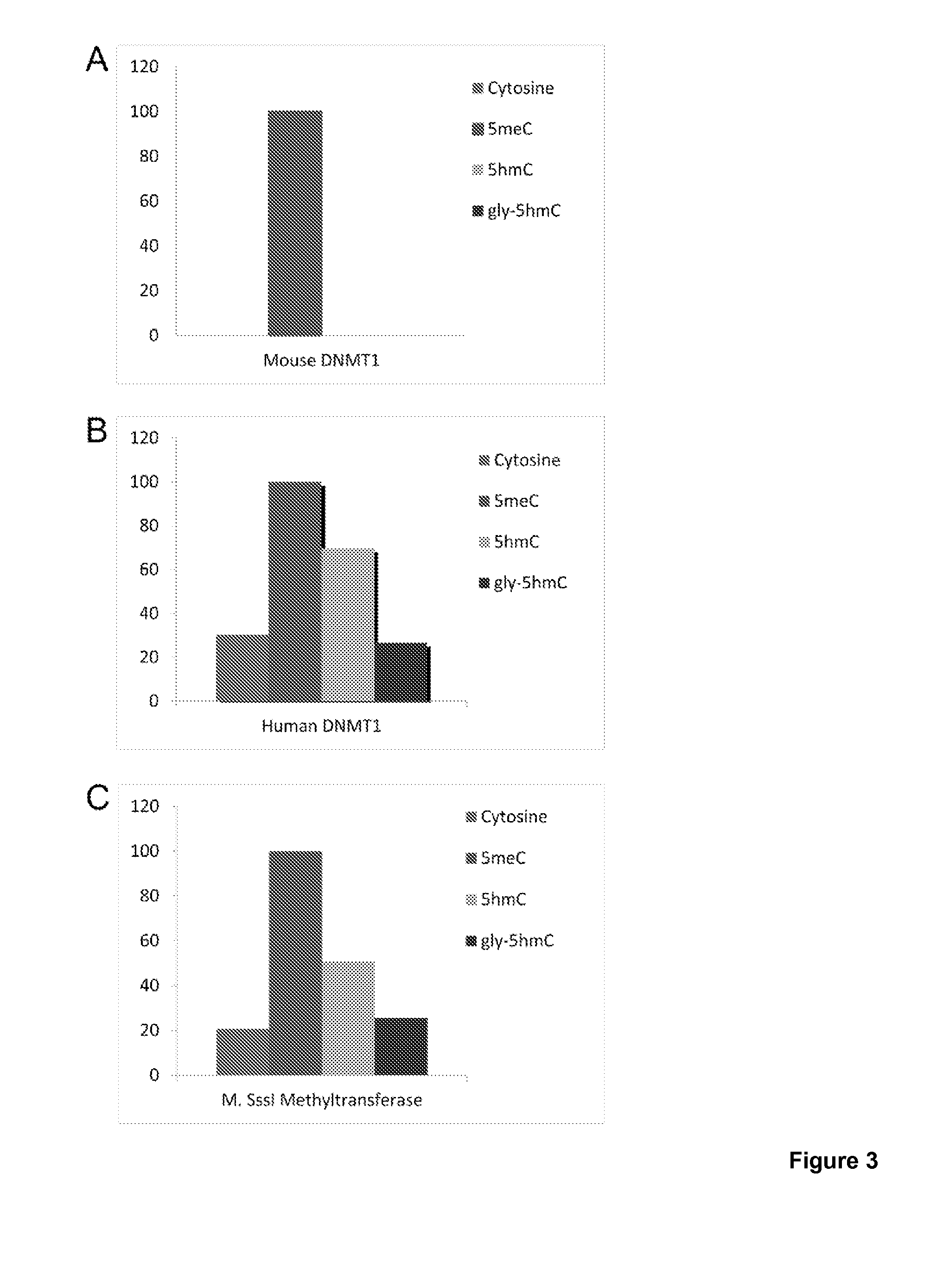
Selective oxidation of 5-methylcytosine by TET-family proteins
ActiveUS9115386B2Promotes reprogrammingImprove efficiencyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHydroxymethylMethyl cytosine
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Self-repairing polyurethane coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104356338ARepair damageGood physical and mechanical propertiesPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyesterPolyol
The invention discloses a self-repairing polyurethane coating and a preparation method thereof. The polyurethane coating comprises the following raw materials in parts by mass: 15-20 parts of polyisocyanates, 40-60 parts of hydrophilic polyester polyol or polyether polyol, 2-3 parts of a chain extender and 7-15 parts of methylcystein. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a hydrophilic polyurethane prepolymer from hydrophilic polyester polyol or polyether polyol and the chain extender, and reacting the isocyanate group in the hydrophilic polyurethane prepolymer with methylcystein, so as to obtain a polyurethane material of which the tail end or the main chain contains 2-urea-4-pyrimidone units; spraying or coating the polyurethane material on the surface of a substrate, thereby obtaining the self-repairing polyurethane coating. The self-repairing of the self-repairing polyurethane coating disclosed by the invention can be completed without external repairing agent or requirements of special environment, the coating is good in transparency, high in strength, good in filming property, simple in process and low in cost, and the function of repeated repairing in same positions can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Nucleic acid detection assay
A method for determining the methylation status of a potential methylation site in genomic nucleic acid comprising treating genomic nucleic acid with an agent which modifies cytosine bases but does not modify 5methyl-cytosine bases under conditions to form a. modified nucleic acid template containing a potential methylation site; providing a first clamp containing a first capture sequence complementary to a region flanking one side of the potential methylation site in the modified nucleic acid template, providing a second clamp containing a second capture sequence complementary to a region flanking the other side of the potential methylation site in the modified nucleic acid template; allowing the first clamp and the second clamp to hybridise to the modified nucleic acid template; ligating the hybridised first and second clamps to form a probe spanning the potential methylation site in the modified nucleic acid template; digesting the modified nucleic acid template to obtain the probe; and detecting the probe and determining the methylation status of the potential methylation site in the modified genomic nucleic acid.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
Methods and kits for detection of methylation status
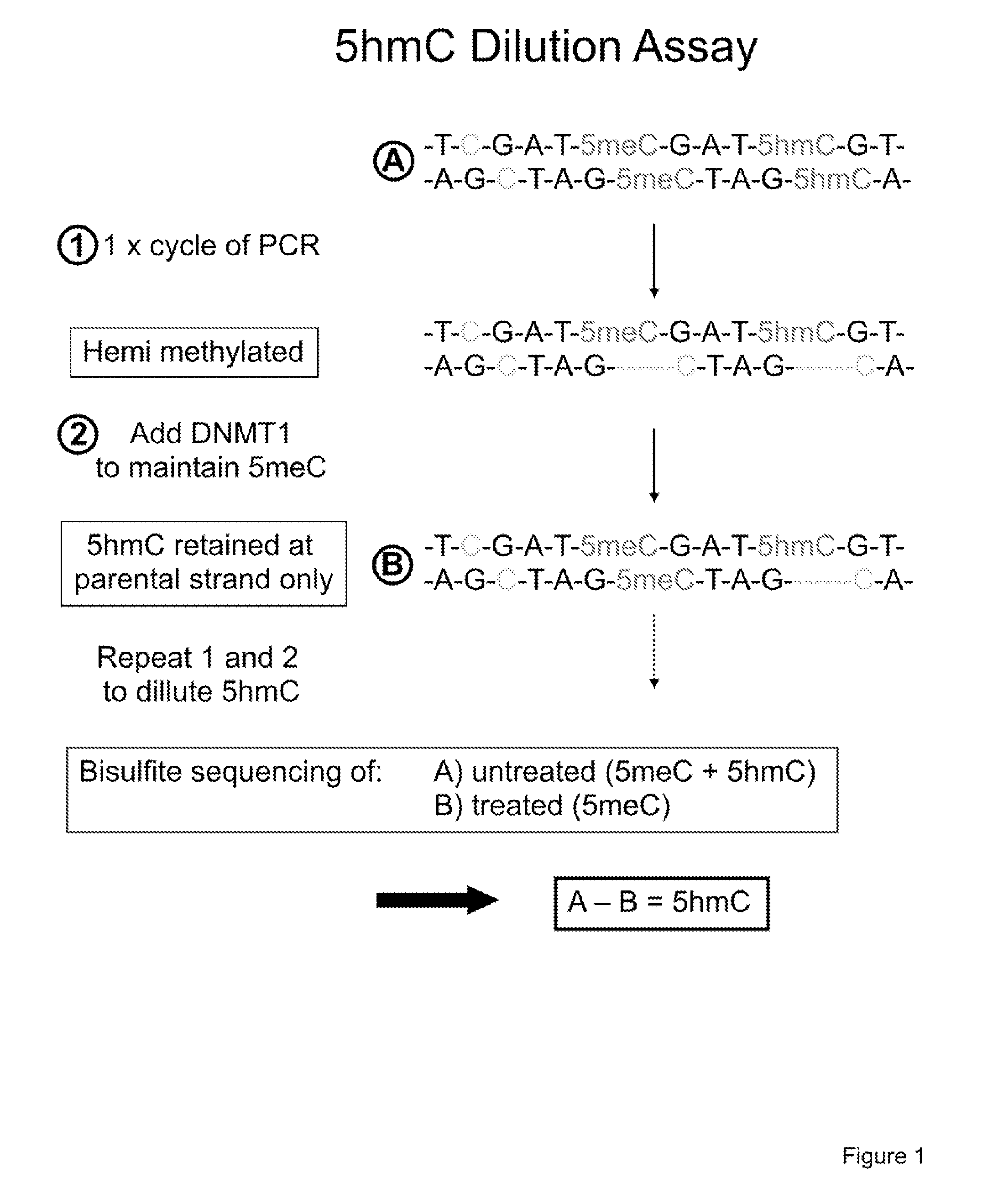
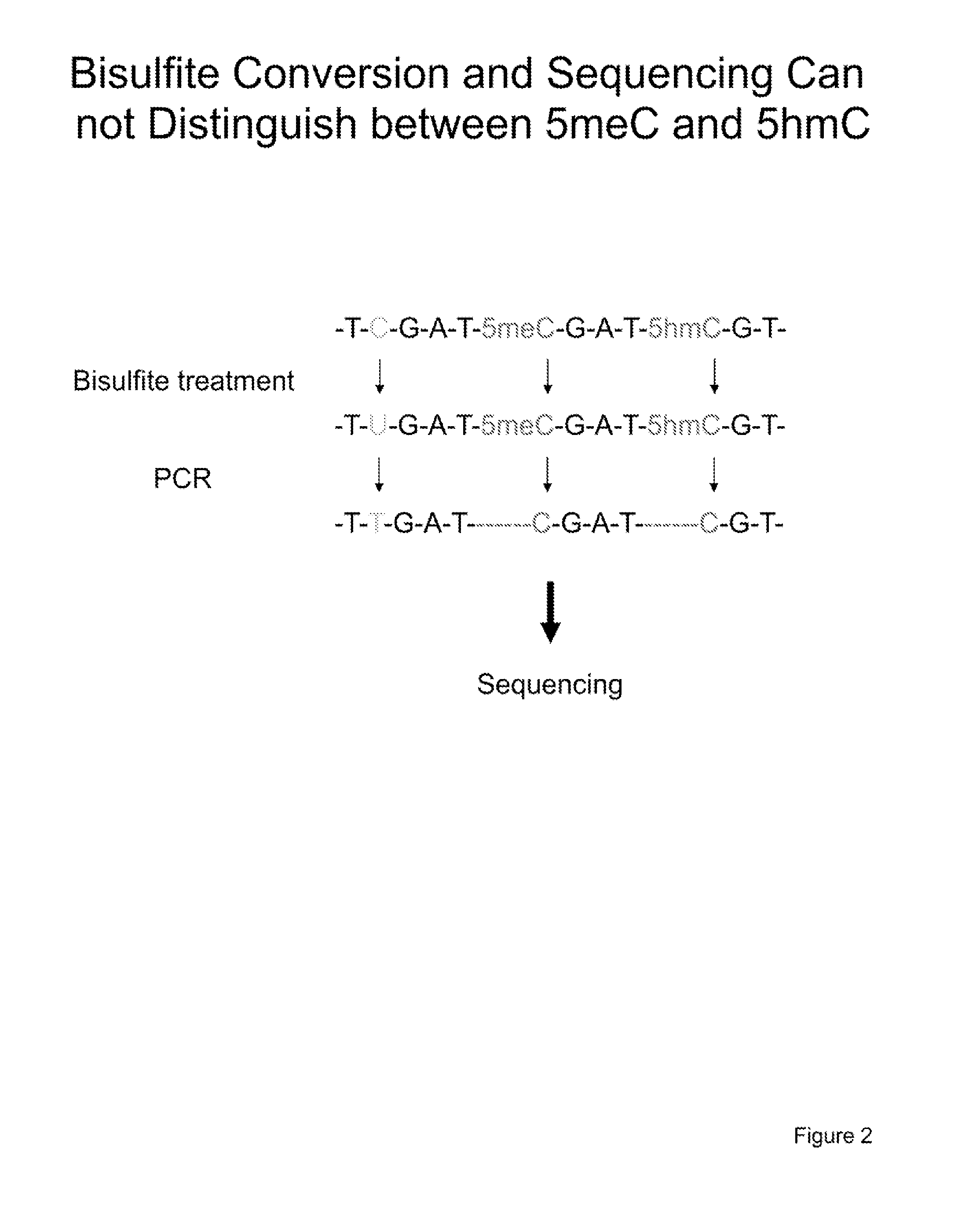
The present invention relates to methods and kits for the detection of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) and / or 5-methylcytosine (5meC). In some embodiments, the present invention relates to methods and kits for detection of 5hmC and / or 5meC in nucleic acid (e.g., DNA, RNA). In some embodiments, the present invention relates to detection of 5hmC in genomic DNA, e.g., mammalian genomic DNA
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
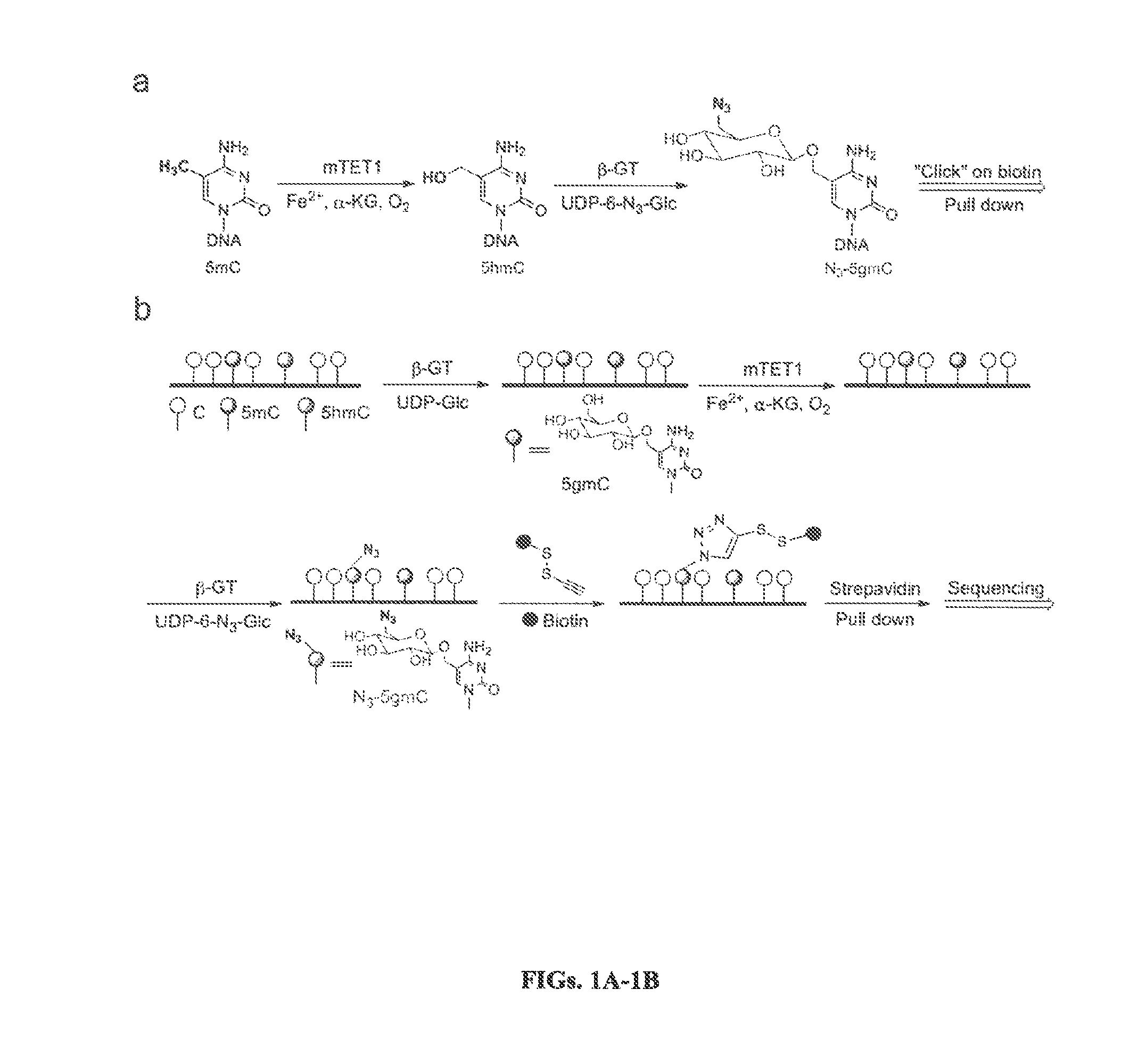
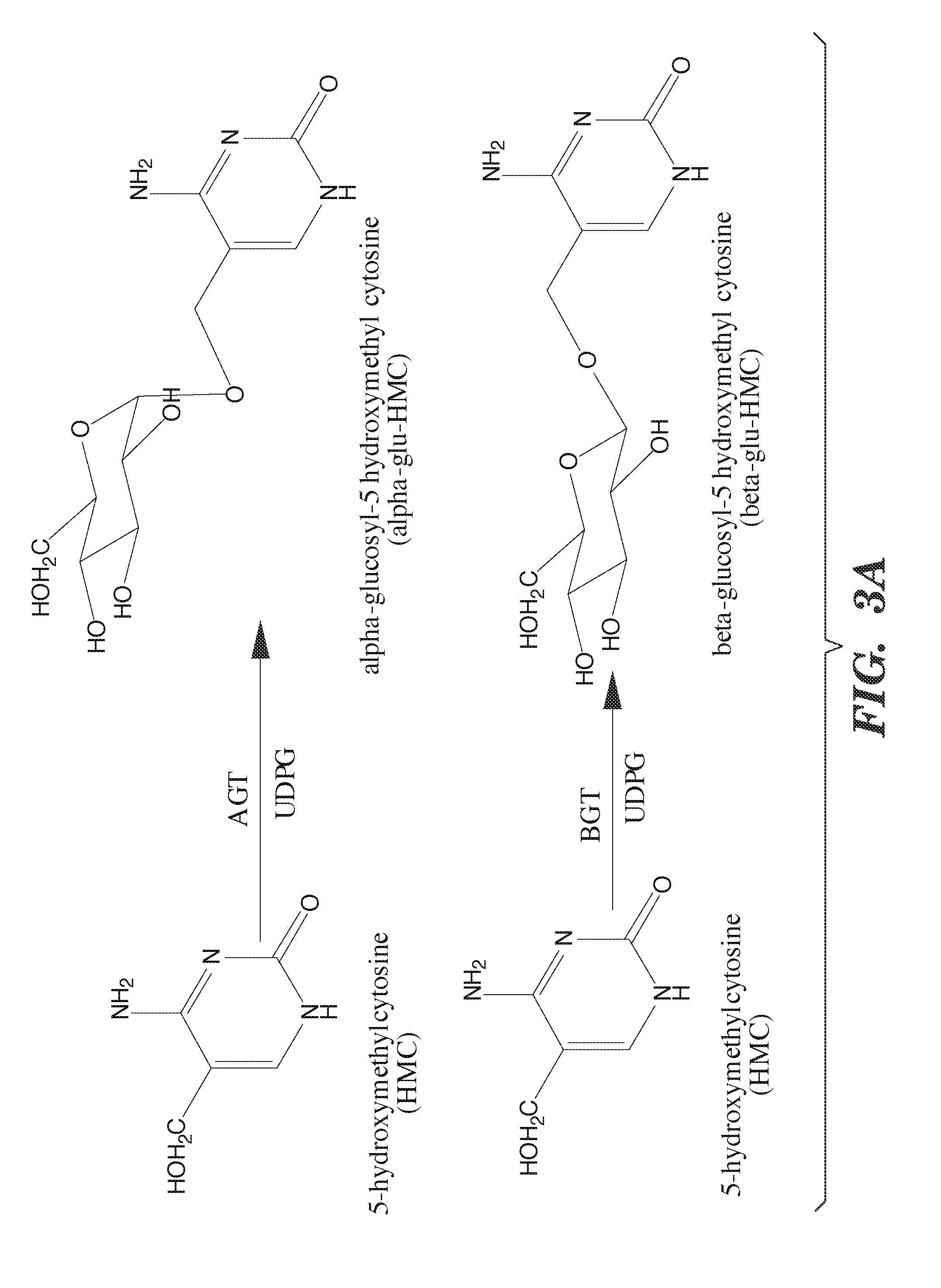
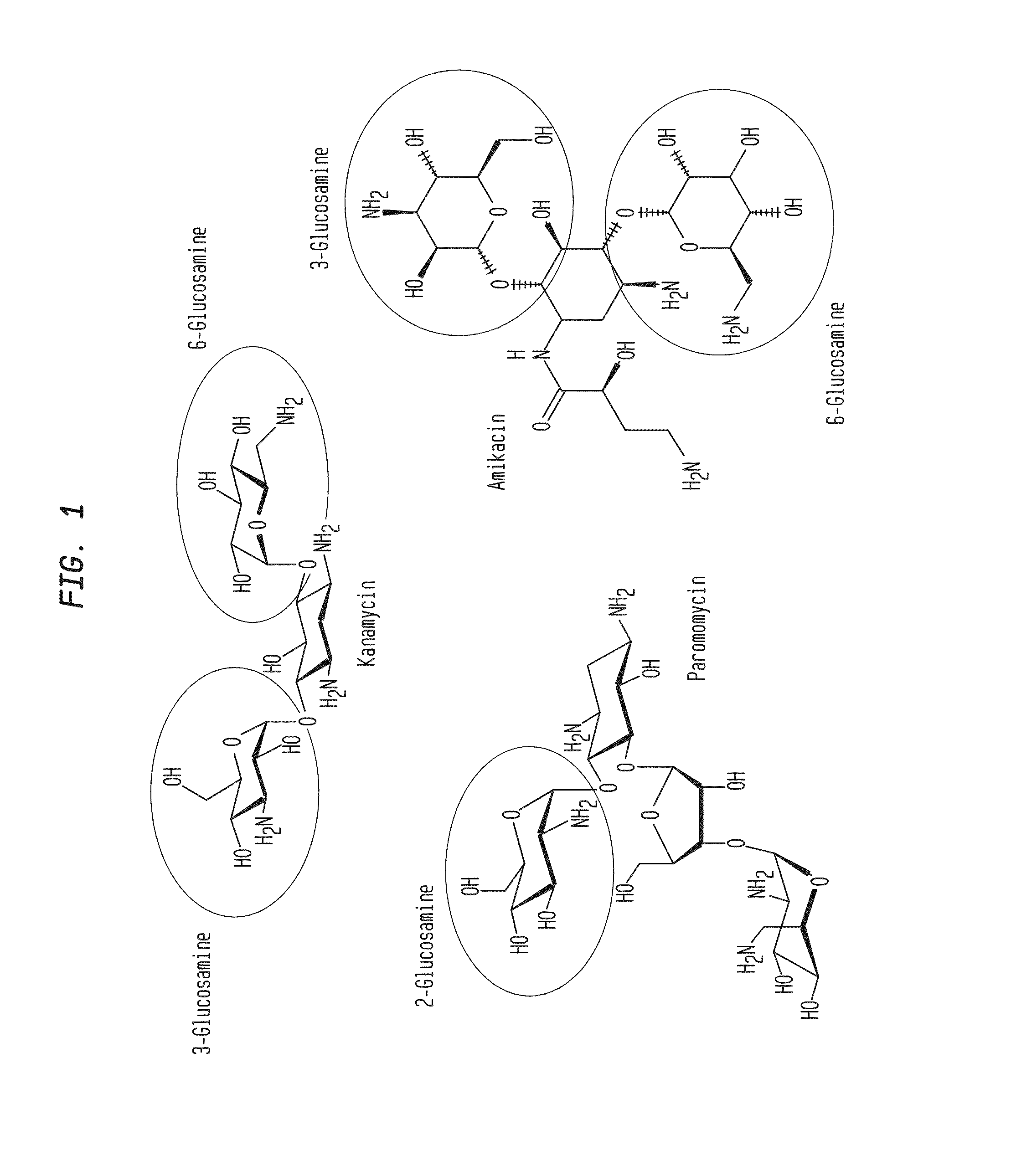
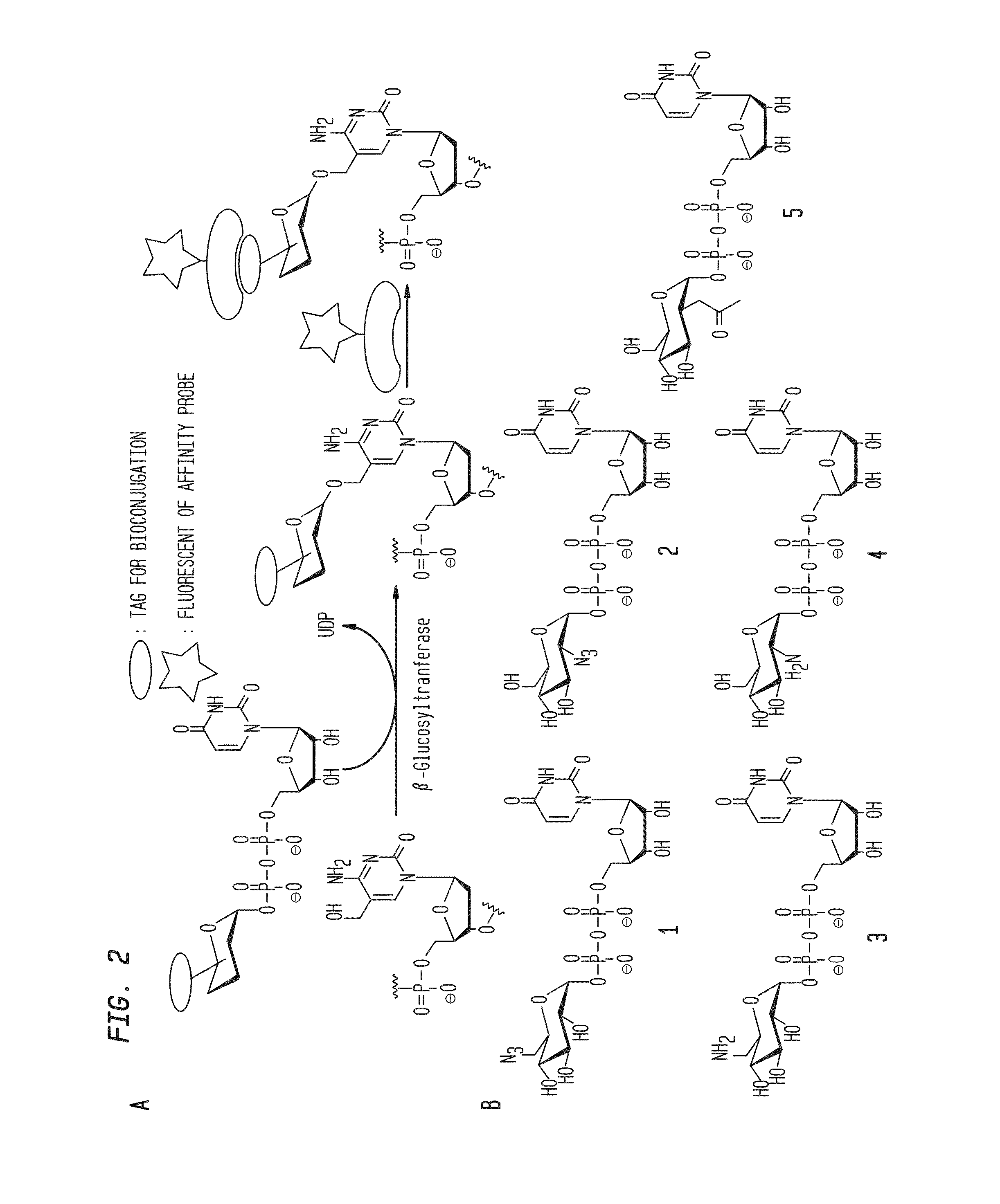
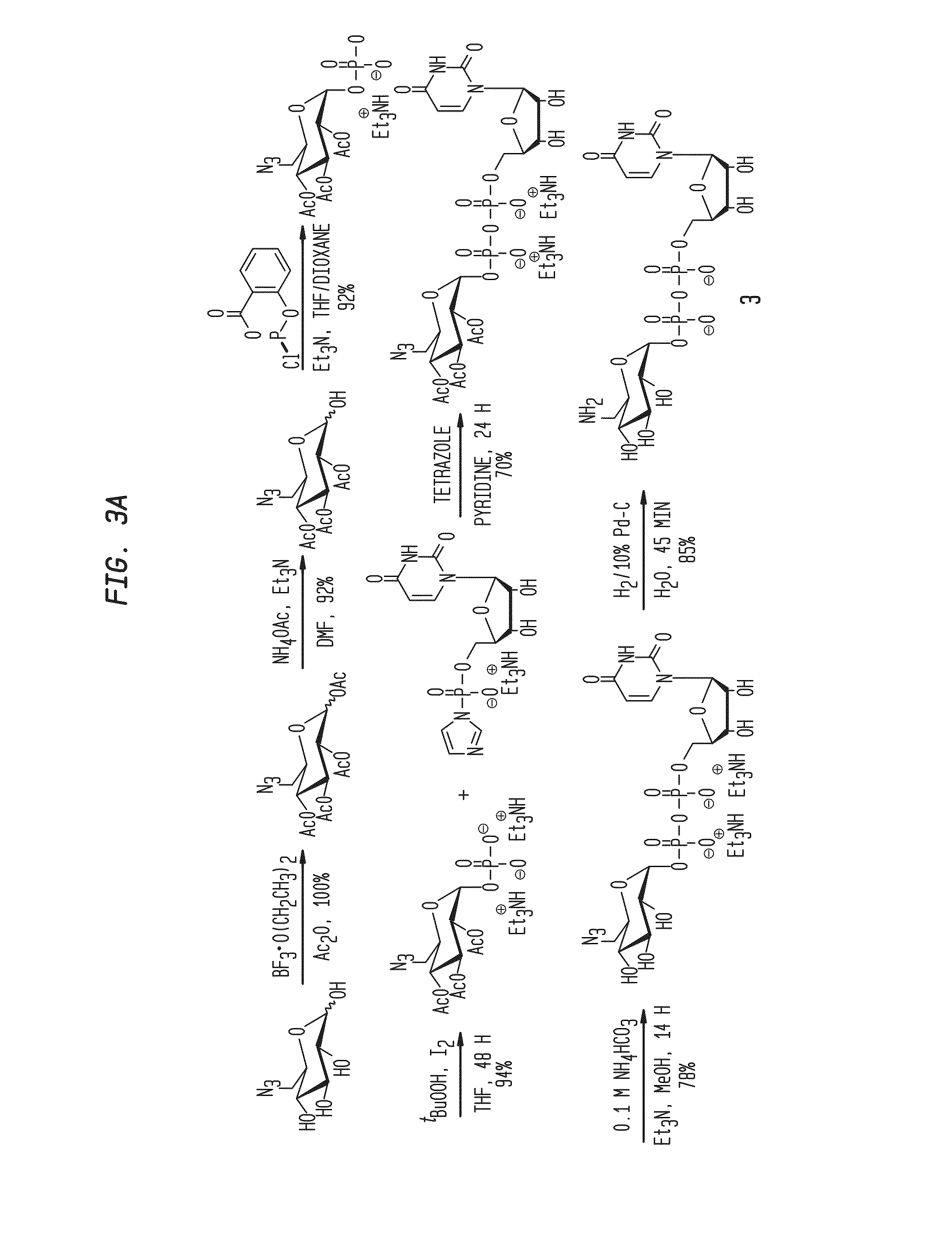
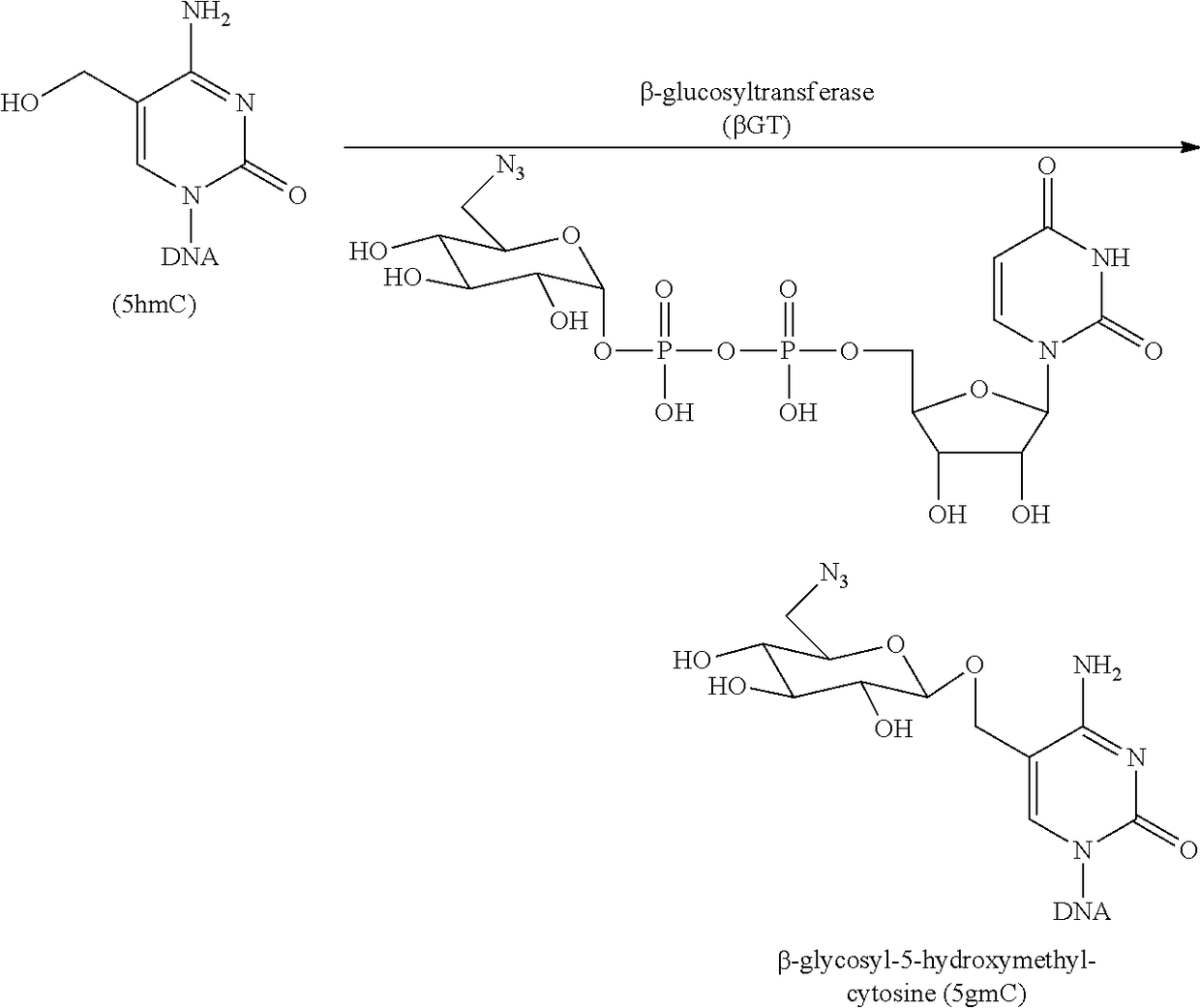
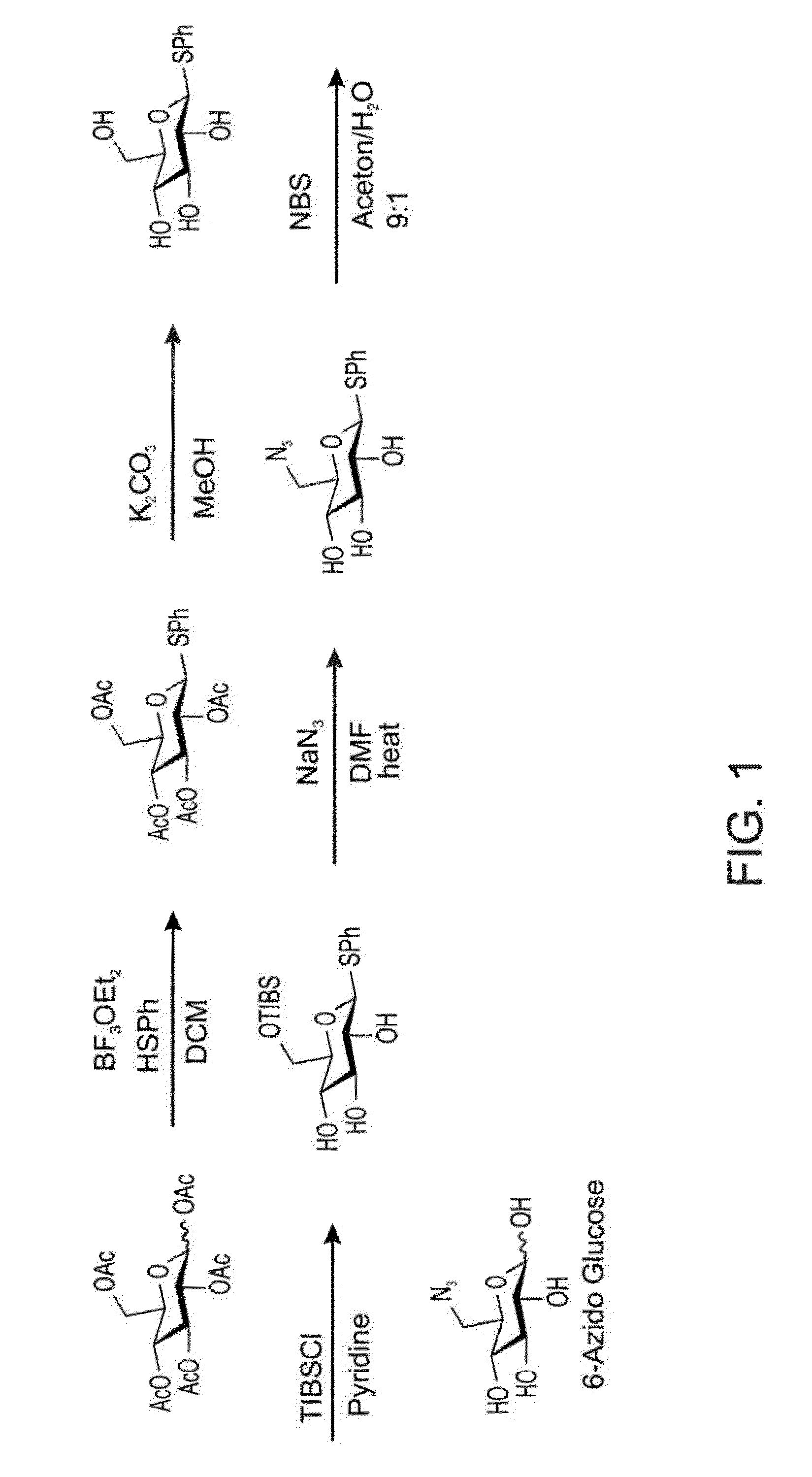
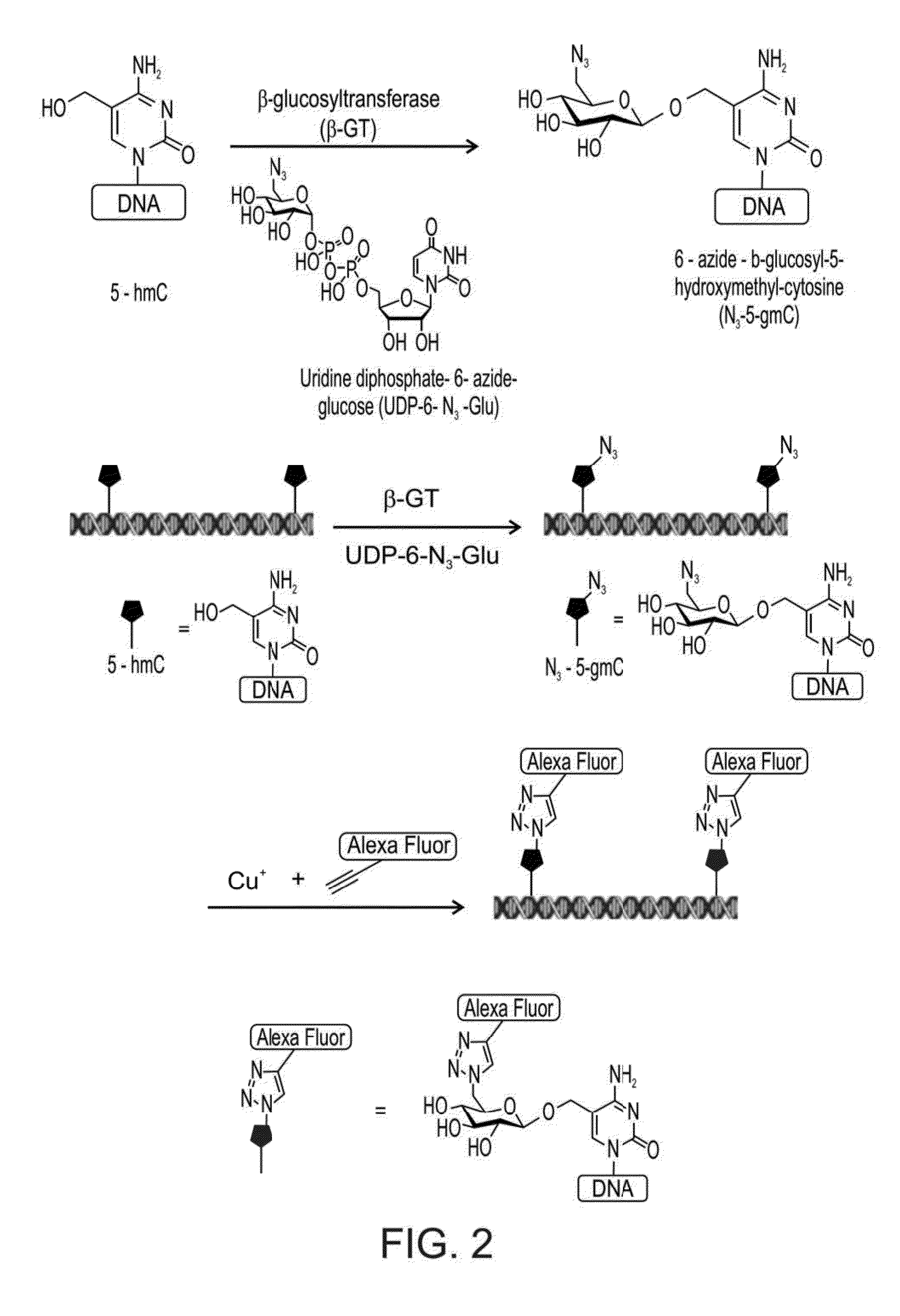
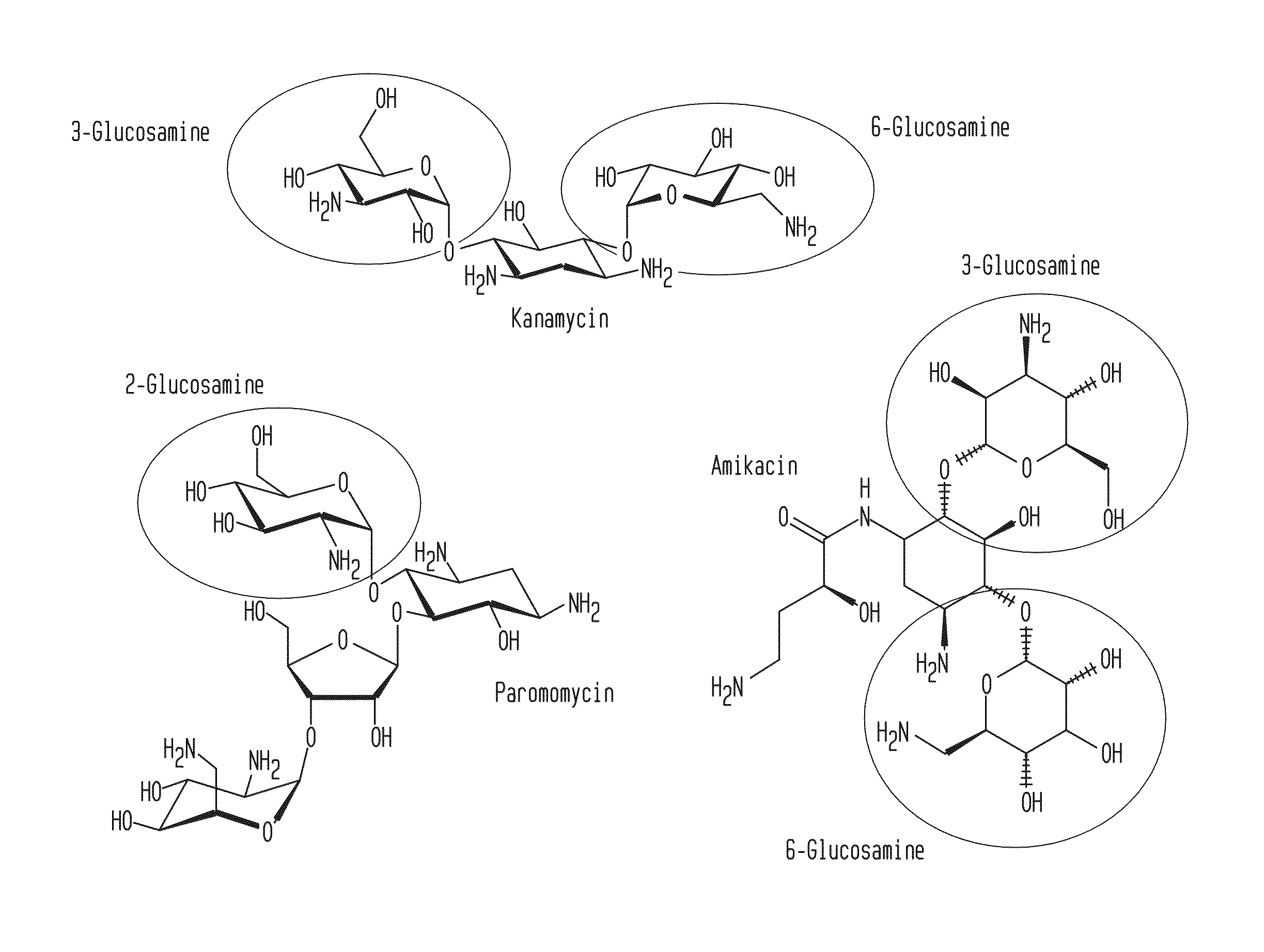
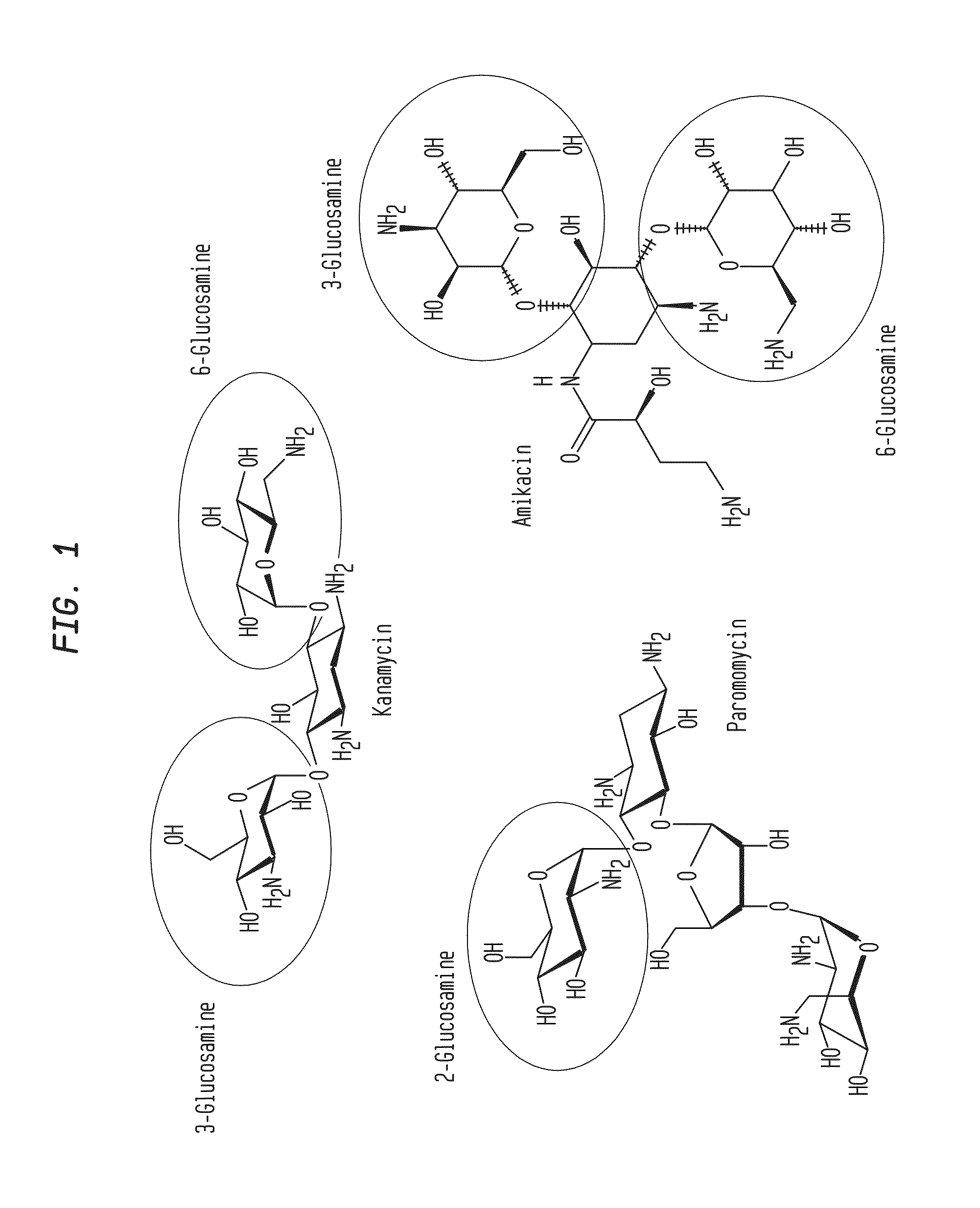
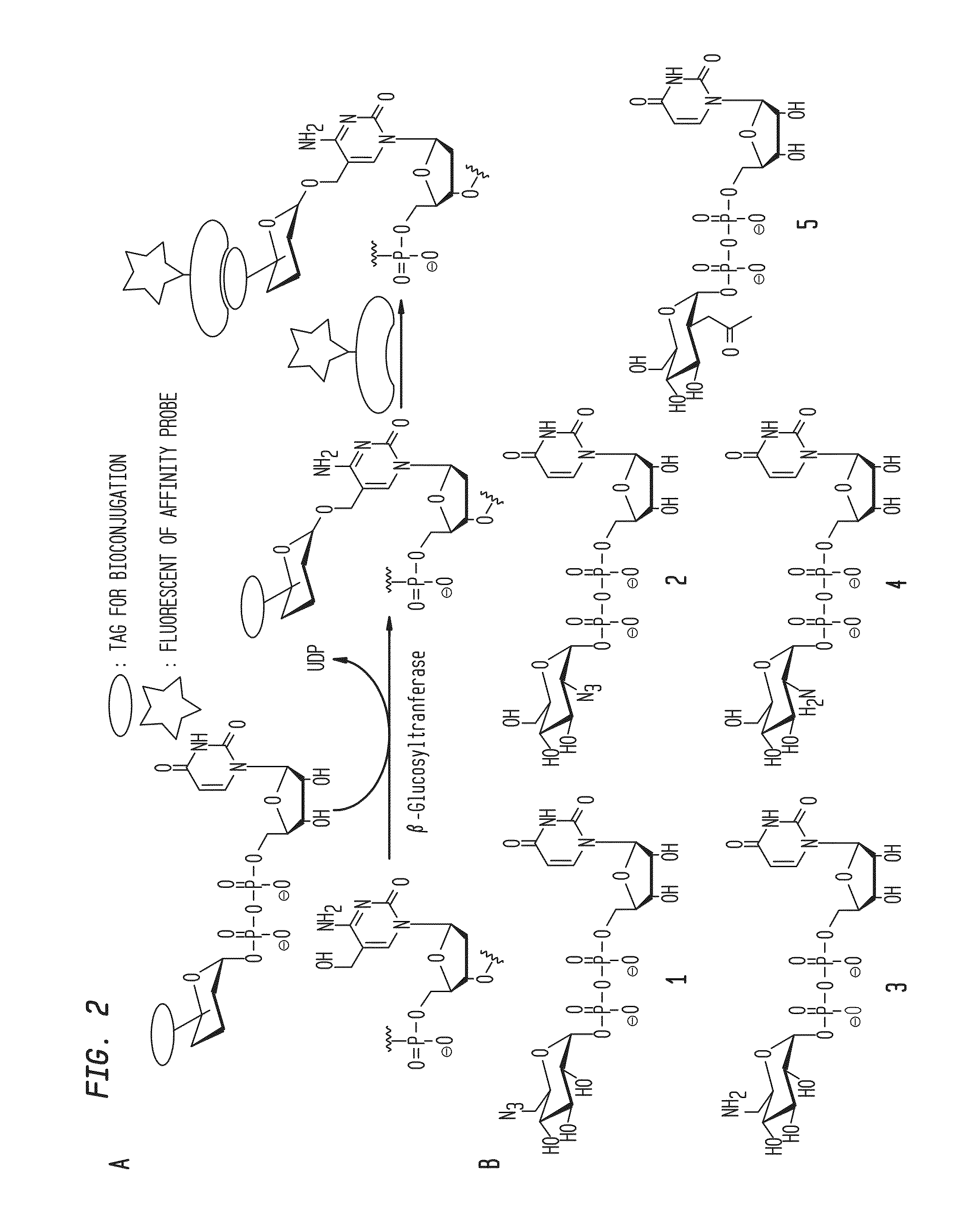
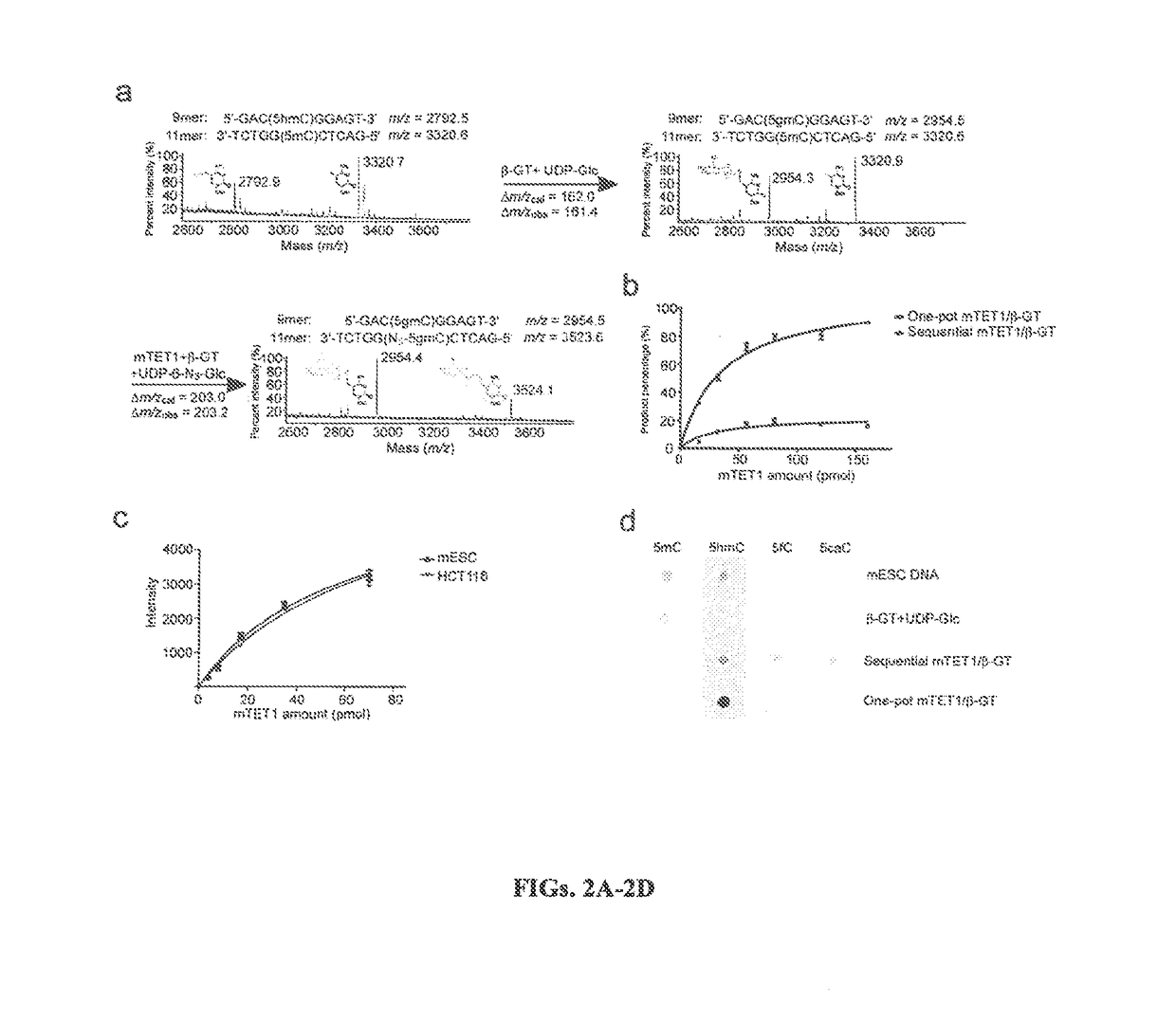
Compositions and Methods for the Transfer of a Hexosamine to a Modified Nucleotide in a Nucleic Acid
ActiveUS20140127677A1Well representedSelective control over cleavage of the nucleic acidFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesNucleotideHexosamines
Nucleic acids comprising β-glucosaminyloxy-5-methylcytosine; compositions, kits and methods of producing the nucleic acids using a glycosyltransferase; and methods of using the nucleic acids are described.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
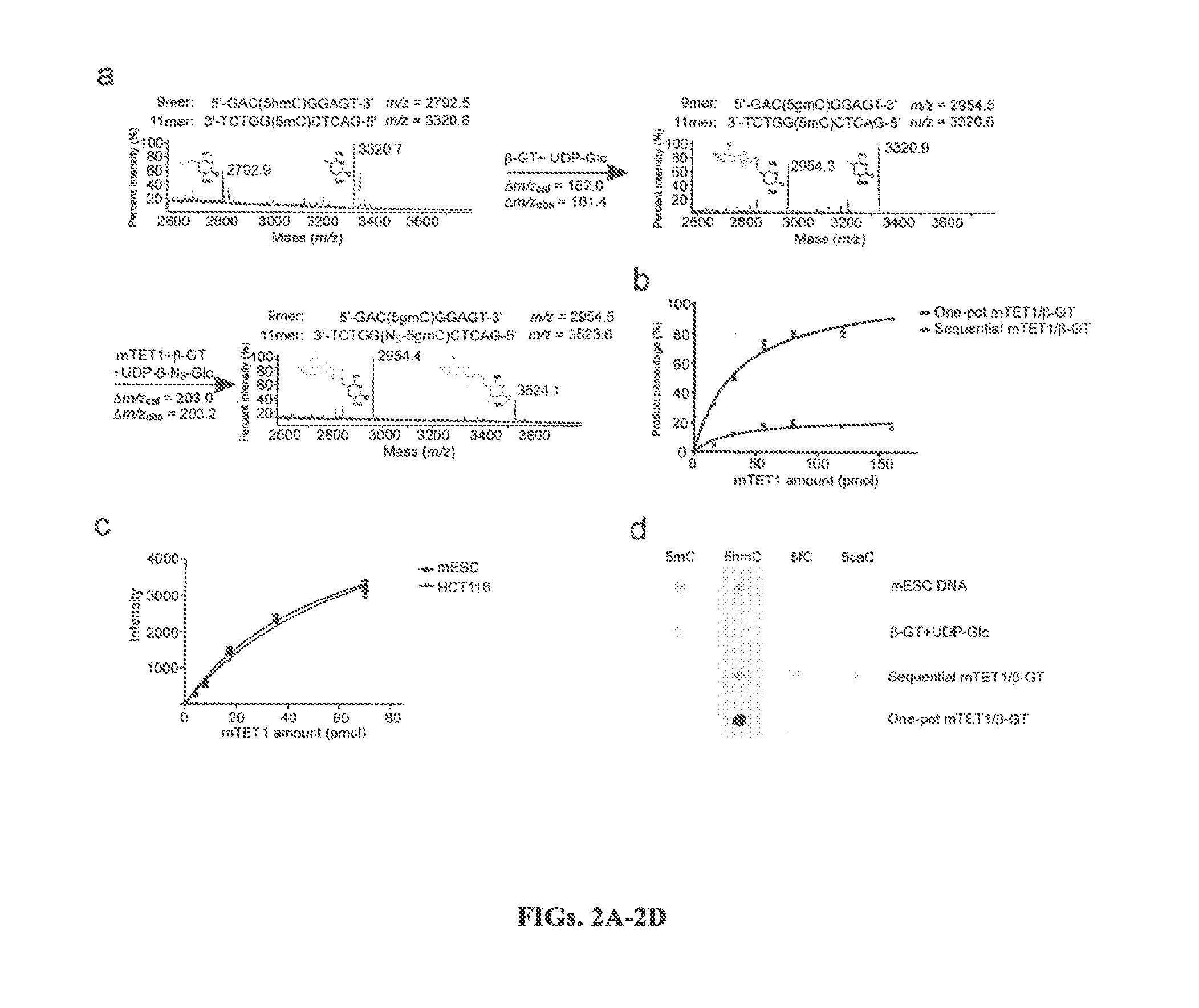
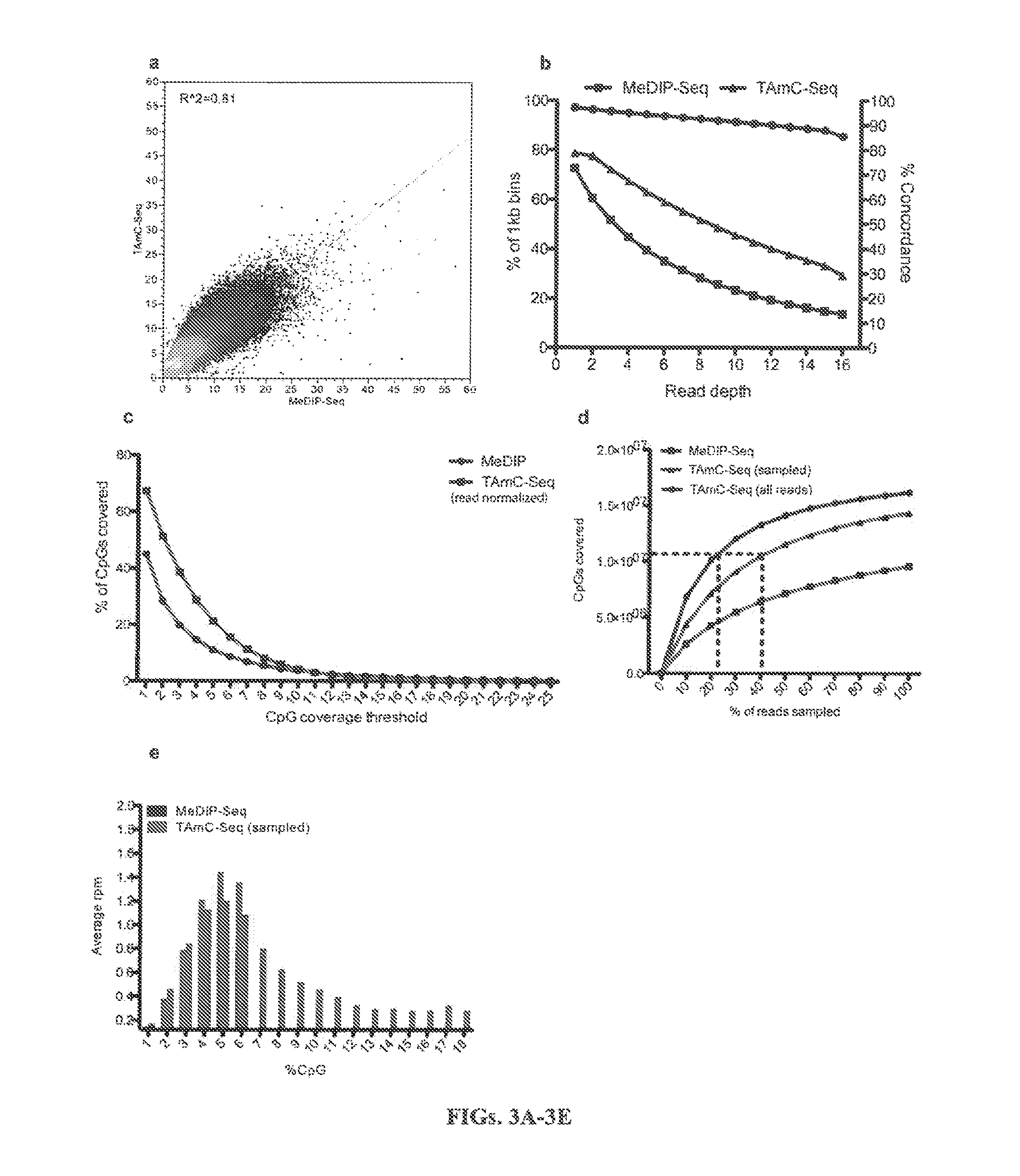
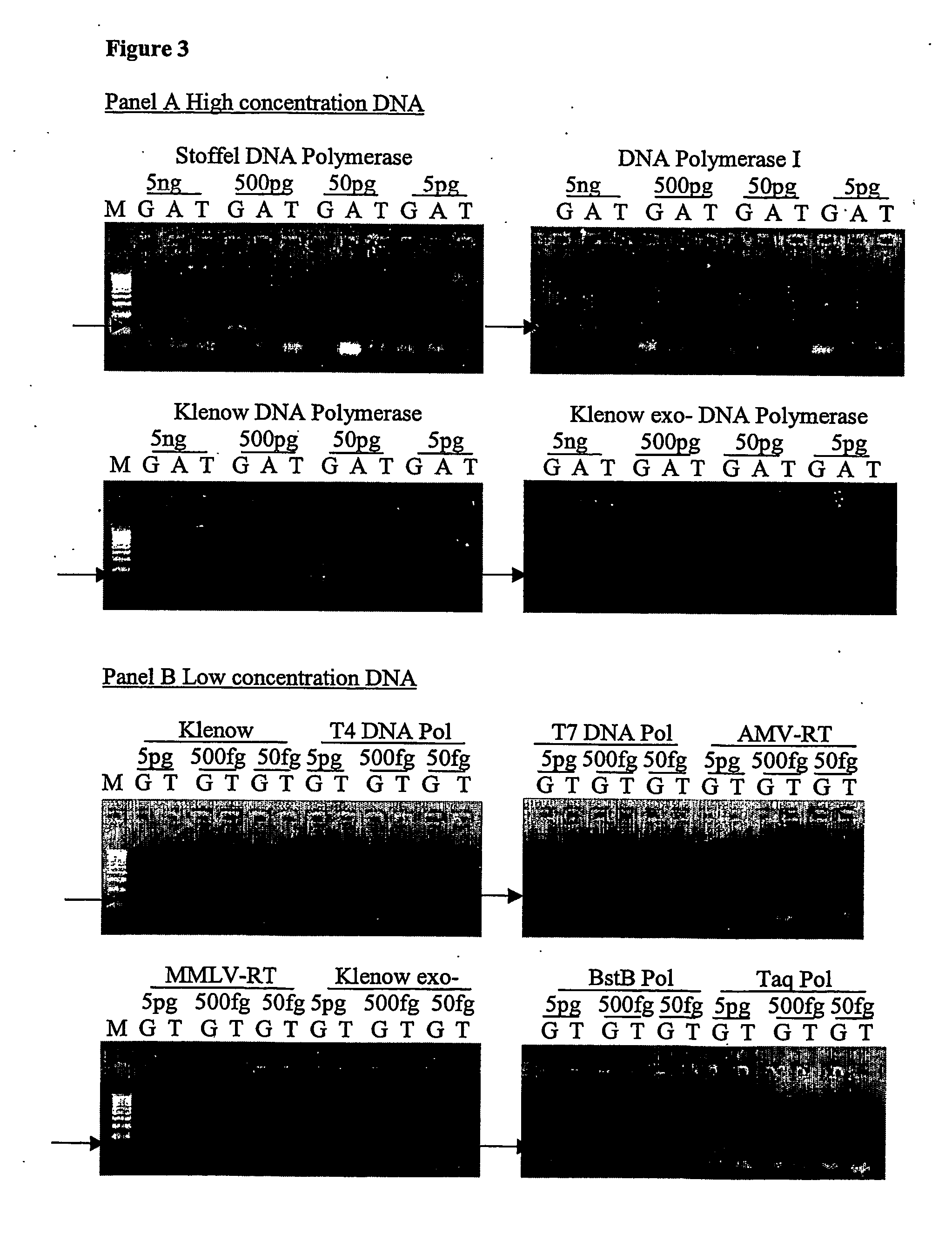
Method for genomic profiling of DNA 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine
ActiveUS20170253924A1Improve sequencing efficiencySufficient selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideDNA fragmentation
The present invention provides a method for genomic profiling of DNA 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, comprising the following steps: (1) DNA purification and fragmentation pretreatment: the target DNA is extracted and then broken to an average of 50 nucleotides to 10,000 nucleotides in length; (2) the repair of trace amount of DNA and the ligation thereof to the adaptor: the pre-treated DNA fragments are repaired and ligated with the sequencing adaptor required for the second-generation sequencing, (3) covalently labeling 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, (4) solid-phase enrichment of the labeled DNA fragments having cytosine with 5-position modification; (5) the PCR amplification of the solid-phase enriched DNA fragments, the PCR product is obtained and purified to obtain a library for the second-generation sequencing, after mapping the sequencing reads to the genome, the distribution map of the cytosine with 5-position modification in the DNA sample could be generated. The present invention greatly enhances the selectivity and efficiency of binding of the solid-phase surface with the DNA modified base.
Owner:BEIJING XUANNIAO FEIXUN TECH CO LTD
Highly sensitive method for the detection of cytosine methylation patterns
InactiveUS7229759B2Inhibit bindingSolution value is not highSugar derivativesComponent separationChemical treatmentPolymerase L
The present invention concerns a method for the detection of cytosine methylation in DNA samples, wherein the following steps are conducted: (a) a genomic DNA sample, which comprises the DNA to be investigated and background DNA, is chemically treated in such a way that all of the unmethylated cytosine bases are converted to uracil, whereas the 5-methylcytosine bases remain unchanged; (b) the chemically treated DNA sample is amplified with the use of at least 1 primer oligonucleotide as well as a polymerase, whereby the DNA to be investigated is preferred as the template over the background DNA, and (c) the amplified products are analyzed and the methylation status in the DNA to be investigated is concluded from the presence of an amplified product and / or from the analysis of additional positions.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Detection of hydroxymethylcytosine bases
ActiveUS20160115525A1High sensitivityReduce resolutionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNAMethyl cytosine
Methodologies for labeling the epigenetic modification 5-hydroxymethyl-cytosine (5hmC) along a DNA molecule, and for imaging this epigenetic modification along a DNA molecule are disclosed. Related compositions and reagents, and methods of preparing same are also disclosed.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Methods for genome amplification
A method for whole genome amplification comprising (a) treating genomic DNA with a modifying agent which modifies cytosine bases but does not modify 5′-methyl-cytosine bases under conditions to form single stranded modified DNA; (b) providing a population of random X-mers of exonuclease-resistant primers capable of binding to at least one strand of the modified DNA, wherein X is an integer 3 or greater; (c) providing polymerase capable of amplifying double stranded DNA, together with nucleotides and optionally any suitable buffers or diluents to the modified DNA; and (d) allowing the polymerase to amplify the modified DNA.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
Method for the quantification of methylated DNA
InactiveUS20050287553A1Reliable valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseProbe type
Particular aspects of the present invention provide a method for quantification of two different variations of a DNA sequence. Particularly, the invention relates to a quantification of methylated DNA, and for this purpose, the test DNA is converted so that cytosine is converted to uracil, while 5-methylcytosine remains unchanged. The converted DNA is amplified by means of a real-time PCR, wherein two labeled real-time probe types are utilized: one specific for methylated DNA; and one for unmethylated DNA. Preferably, the degree of methylation of the test DNA is calculated from the ratio of the signal intensities of the probes or from the Ct values. The inventive methods have substantial utility for diagnosis and prognosis of cancer and other disorders associated with altered or characteristic DNA methylation status, as well as having substantial utility for analysis of SNPs, allelic expression, and prediction of drug response, drug interactions, among other uses.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Determination of methylation of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20080207460A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementRe sequencingSingle strand
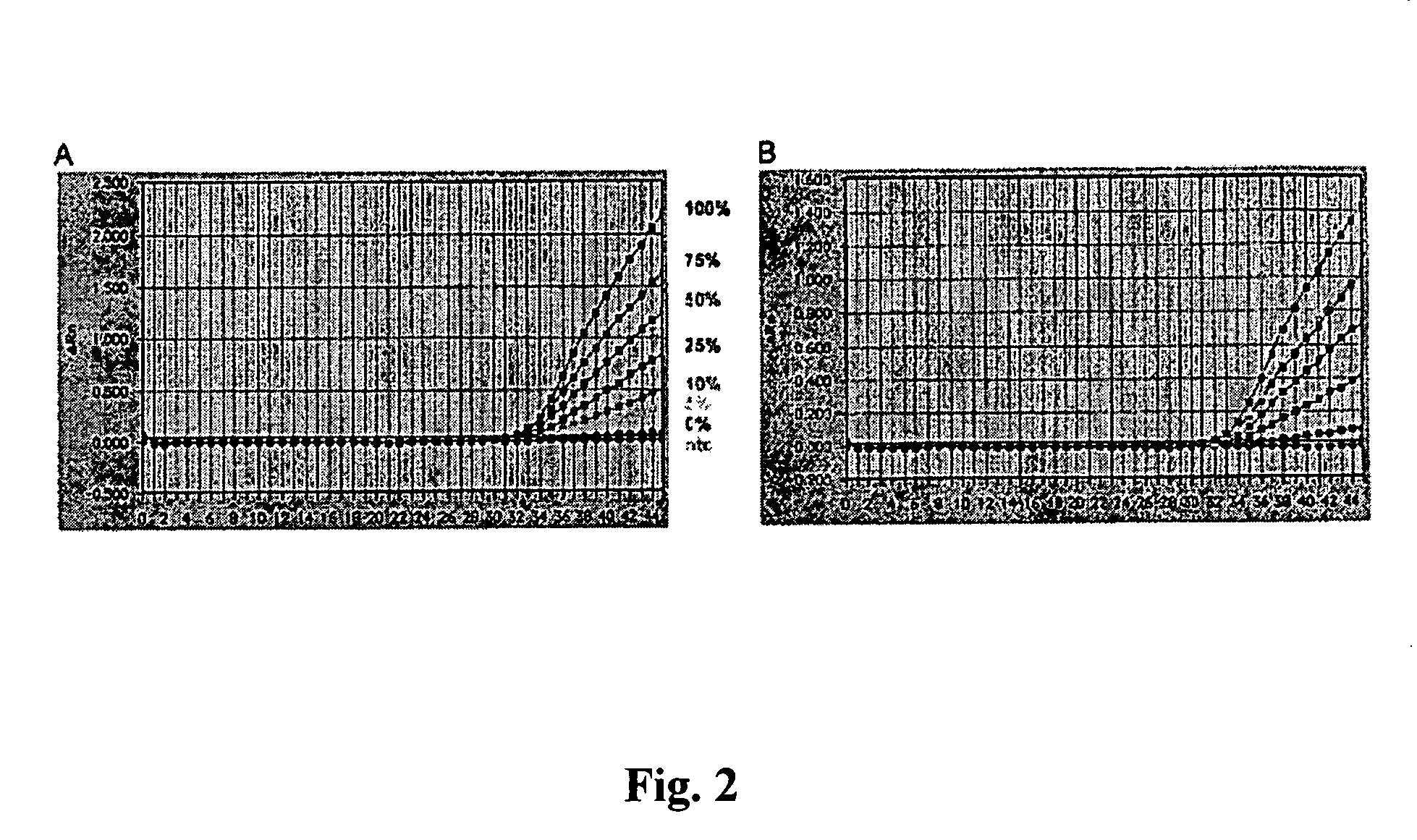
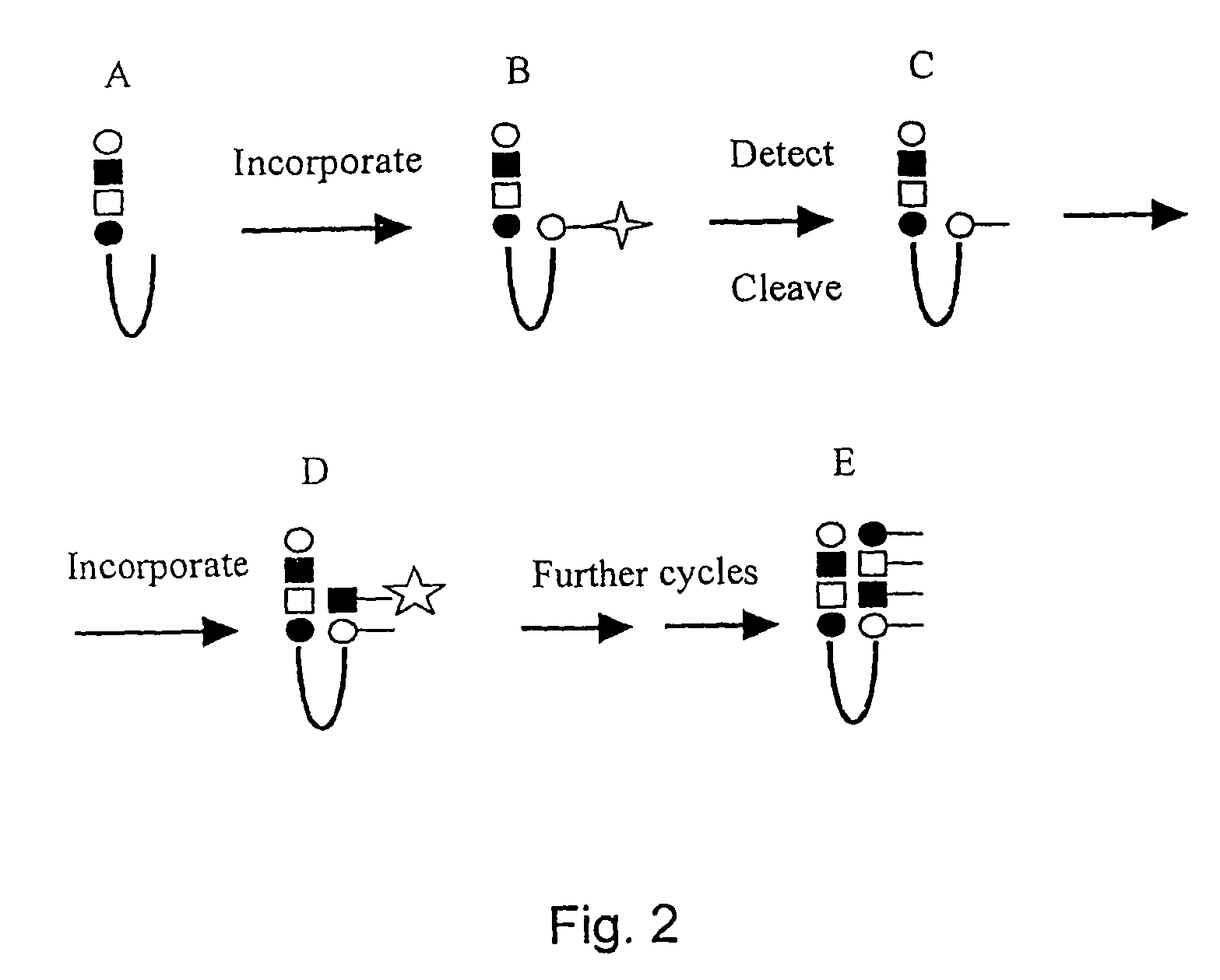
The invention relates to a method of detecting the precise locations of methyl-cytosines in a given nucleic acid sequence. In particular, the invention features a method which includes sequencing a template nucleic acid that is attached to a hairpin nucleic acid or double-stranded nucleic acid anchor, which contain specifically-designed sites for nicking or other endonucleases. The template nucleic acid is then regenerated to single-stranded form via methods described herein, and then treated to convert either the methylated cytosines, or non-methylated cytosines, and the template nucleic acid is then re-sequenced The results of the first and second sequencing reactions are then compared.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Method for the detection of cytosine methylations in dna with the aid of scorpion
The invention relates to a method for analyzing cytosine methylations in DNA sequences, according to which non-methylated cytosines are first converted into uracil while 5-methylcytosine remains unmodified. The DNA is then amplified by means of a polymerase and at least one primer whose 5 end is connected to a probe via a linker. The probe is intramolecularly hybridized onto the amplified products in accordance with the methylation state of the DNA, hybridization being detectable via different detection systems. The inventive method is particularly suitable for diagnosing and predicting cancer diseases and other diseases associated with a modification of the methylation state as well as for predicting undesired effects of medicaments.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Compositions and methods for the transfer of a hexosamine to a modified nucleotide in a nucleic acid
ActiveUS9200260B2Selective control over cleavage of the nucleic acidFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesNucleotideHexosamines
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Composition and methods related to modification of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC)
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for detecting, evaluating, and / or mapping 5-methyl-modified and / or 5-hydroxylmethyl-modified cytosine bases within a nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
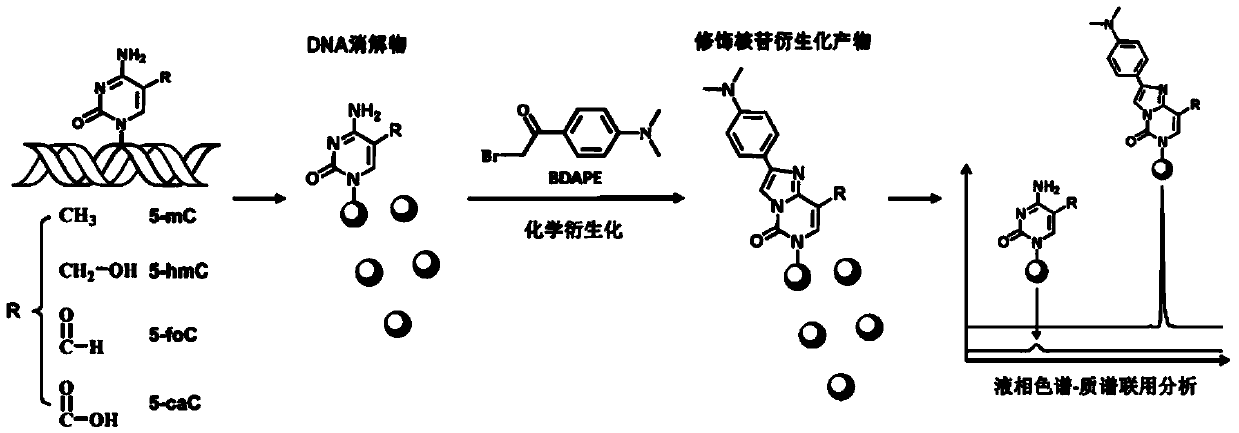
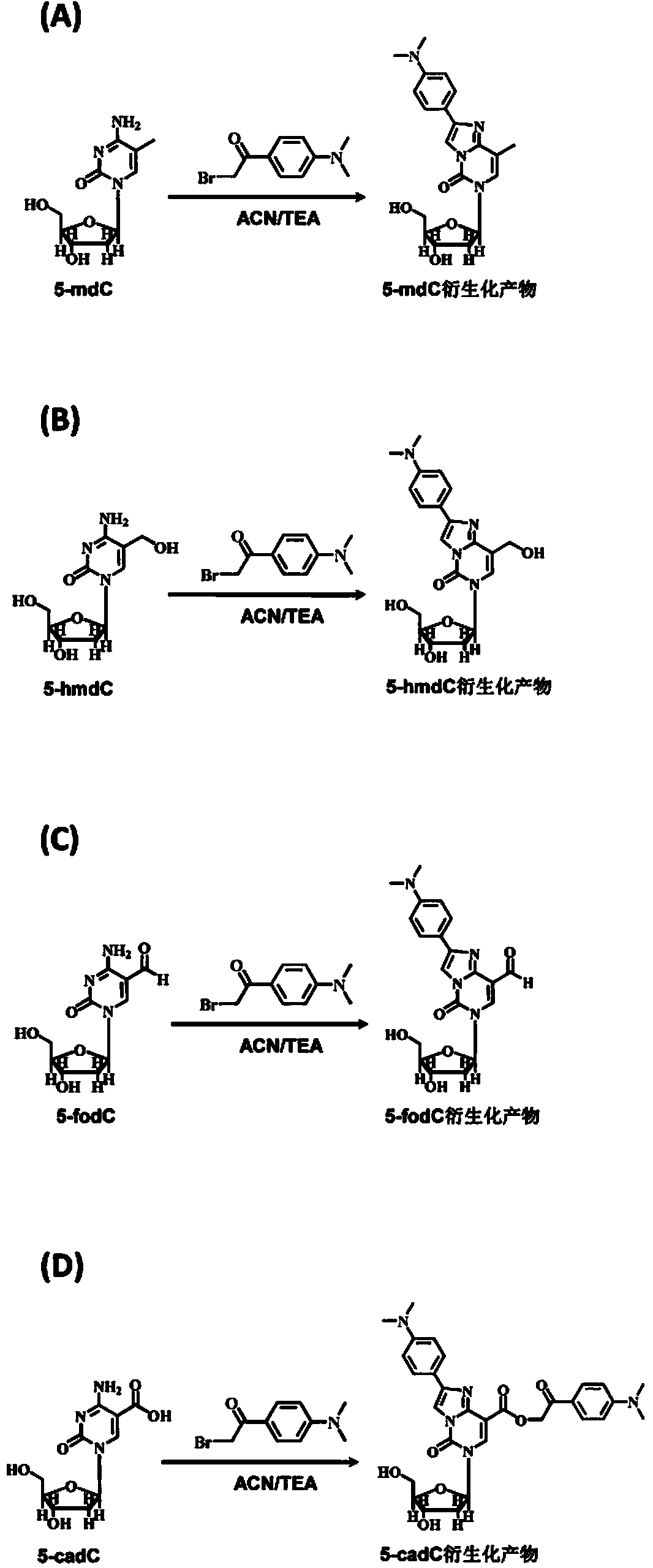
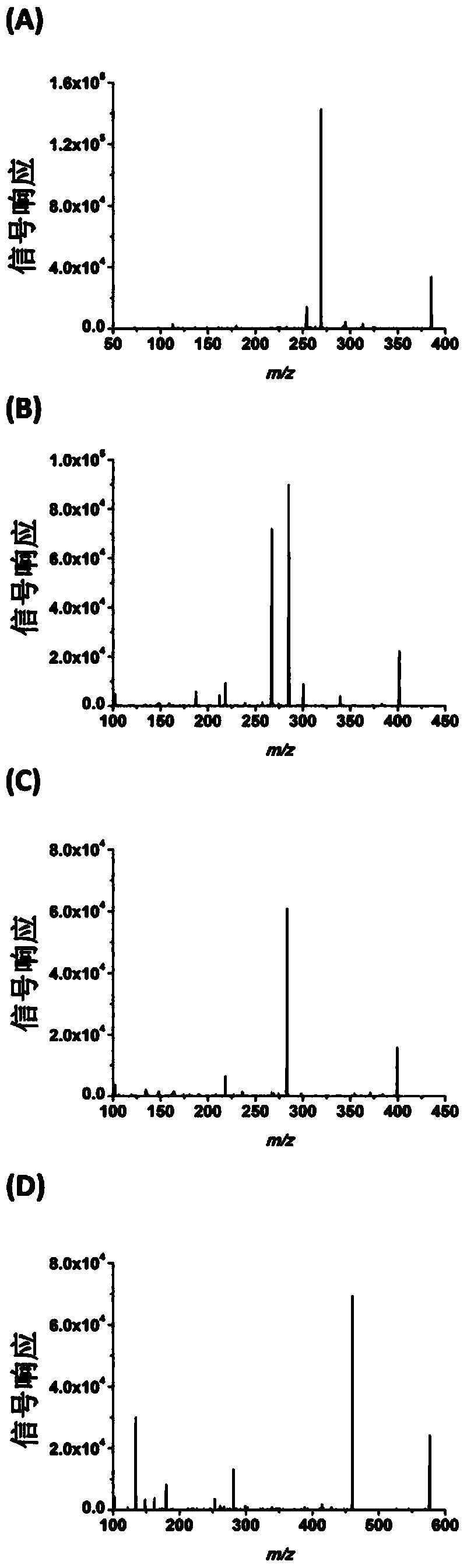
Chemical derivatization method and application thereof to nucleic acid modification detection by liquid chromatogram-mass spectrometer (LC-MS) method
InactiveCN104502492AThe method is easy to operateEasy to separateComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementReversed-Phase Liquid ChromatographyKetone
The invention discloses a chemical derivatization method and an application thereof to nucleic acid modification detection by a liquid chromatogram-mass spectrometer (LC-MS) method. A derivatization strategy is performed on 5-methylcystein, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, 5-aldehyde cytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) by means of 2-bromo-1-(4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-ethyl ketone (BDAPE). Retention behaviors of modified nucleosides in reversed phase liquid chromatography are remarkably improved, and meanwhile, the detection sensitivity of the modified nucleosides in mass spectra is greatly improved. The chemical derivatization method has the advantages that the sensitivity and the selectivity are high, the operation is simple and convenient, quantitative detection of cytosine modification with extremely low abundance in the DNA can be achieved without complicated sample pretreatment, and the method can be applied to analysis of diseases and study on mutual relation among the 5-methylcystein, the 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, the 5-aldehyde cytosine and the 5-carboxylcytosine.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
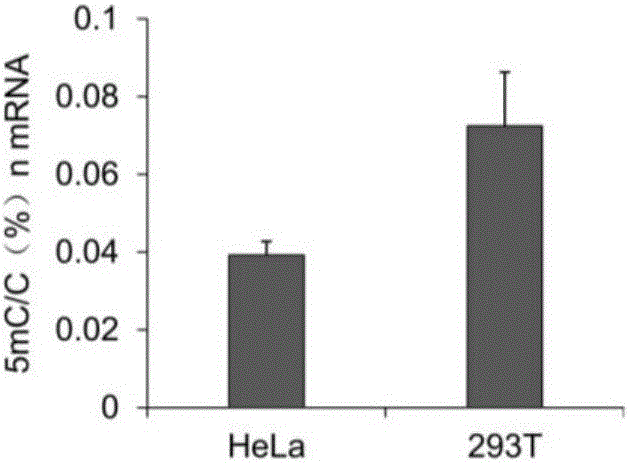
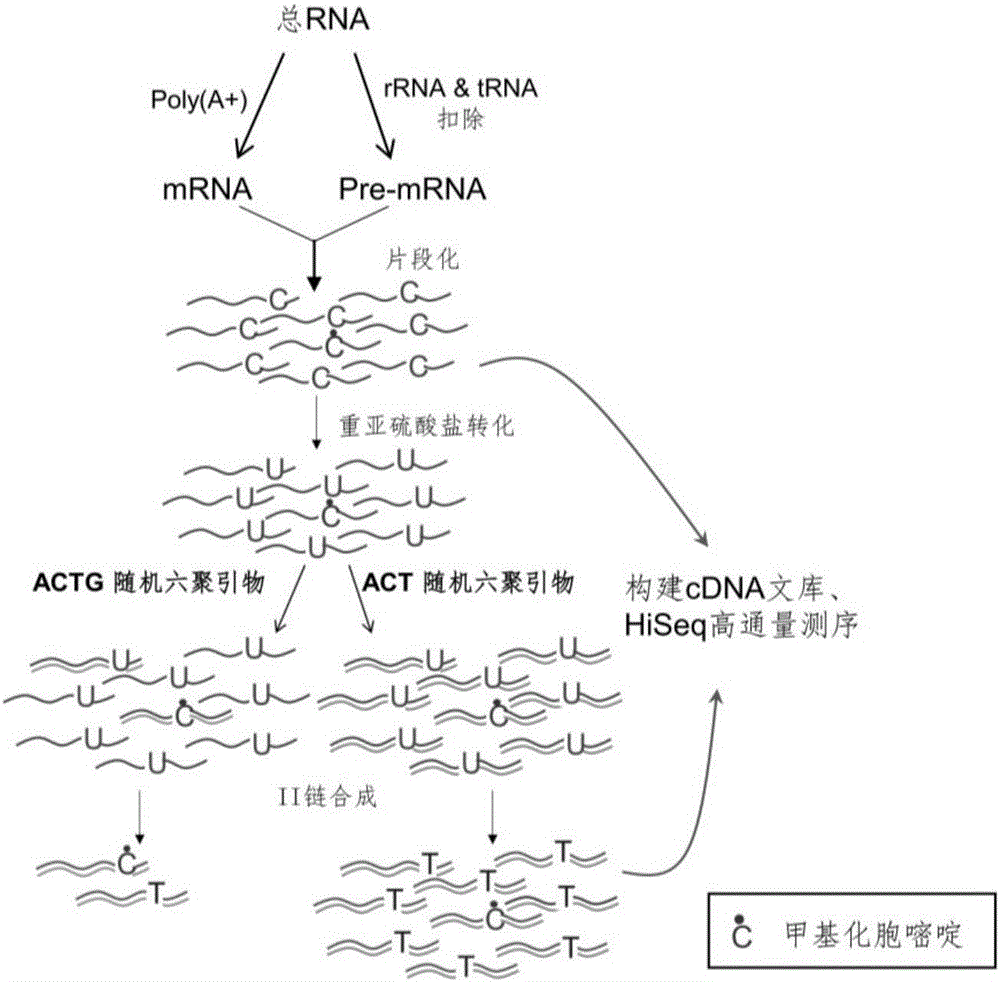
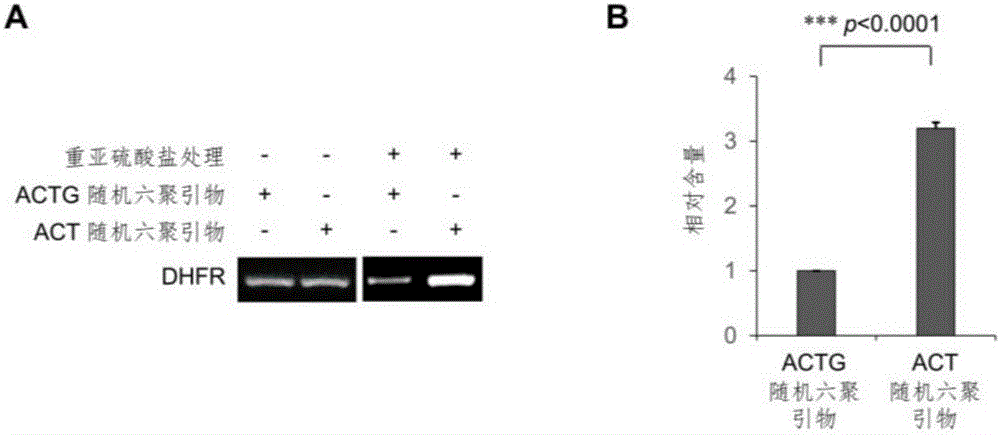
Library construction method for RNA 5mC bisulfite sequencing and application of library
ActiveCN105132409AEfficient matchingHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBisulfite sequencingRandom hexamer
The invention relates to a library construction method, a sequencing method and a methylation detection method for sequencing 5-methylcytosine (5mC) modified bisulfite on RNA molecule. By designing and using triplet base random hexamers which contain ACT only, RNA fragment reverse transcription, PCR amplification efficiency and 5mC site detection efficiency after bisulfite treatment can be significantly improved, which is conducive to high-throughput sequencing of the 5mC site.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Method for relative quantification of methylation of cytosine bases in DNA samples
InactiveUS7153671B2Overcome disadvantagesMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyAmplification dnaGenomic DNA
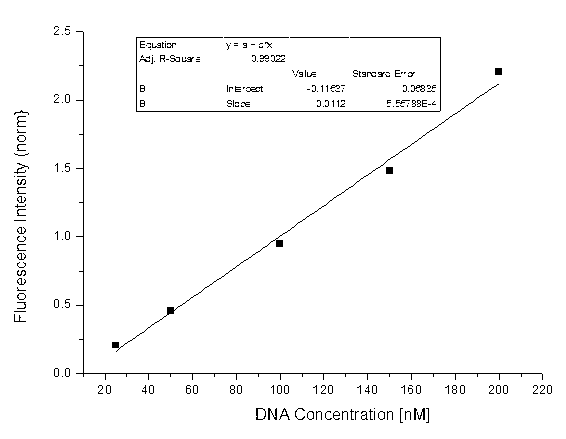
A method is described for the relative quantification of the methylation of cytosine bases in DNA samples, wherein the following method steps are conducted:a) a genomic DNA sample is chemically converted with a reagent, wherein 5-methylcytosine and cytosine react differently and show a different base pairing behavior in the DNA duplex after the reaction;b) the DNA sample is amplified, whereby a fluorescently labeled dCTP or dGTP derivative is added;c) the amplified products are separated spatially from each other; andd) the fluorescence of the separated amplified products is measured quantitatively.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Fluorescent method of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine based on FRET (Forster Resonance Energy Transfer) principle
InactiveCN103305621ARemove fluorescent backgroundThe detection method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescence5-hydroxylmethylcytosineBODIPY
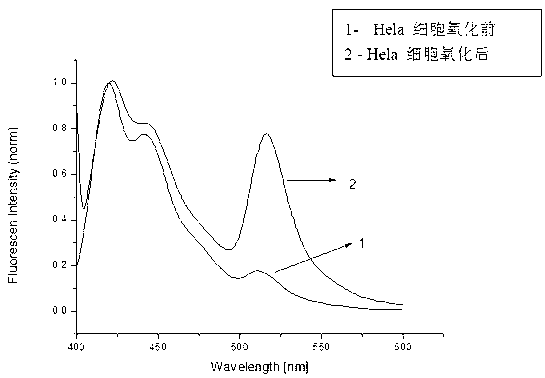
The invention provides a fluorescent detection method of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine based on FRET (Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer) principle with non-diagnostic purposes. The fluorescent detection method comprises the following steps of: firstly, oxidizing the 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in a DNA into 5-aldehyde cytosine by using potassium perruthenate; secondly, reacting a BODIPY (Boron Trifluoride Complex Dipyrromethene) compound with fluorescence with the 5-aldehyde cytosine in the DNA; and finally, adding a cationic fluorescent polymer, and measuring the content of the 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the DNA through fluorescent detection. The detection method has the advantages of simpleness and rapidity, and low cost.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Methods for genome amplification
A method for whole genome amplification comprising (a) treating genomic DNA with a modifying agent which modifies cytosine bases but does not modify 5′-methyl-cytosine bases under conditions to form single stranded modified DNA; (b) providing a population of random X-mers of exonuclease-resistant primers capable of binding to at least one strand of the modified DNA, wherein X is an integer 3 or greater; (c) providing polymerase capable of amplifying double stranded DNA, together with nucleotides and optionally any suitable buffers or diluents to the modified DNA; and (d) allowing the polymerase to amplify the modified DNA.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
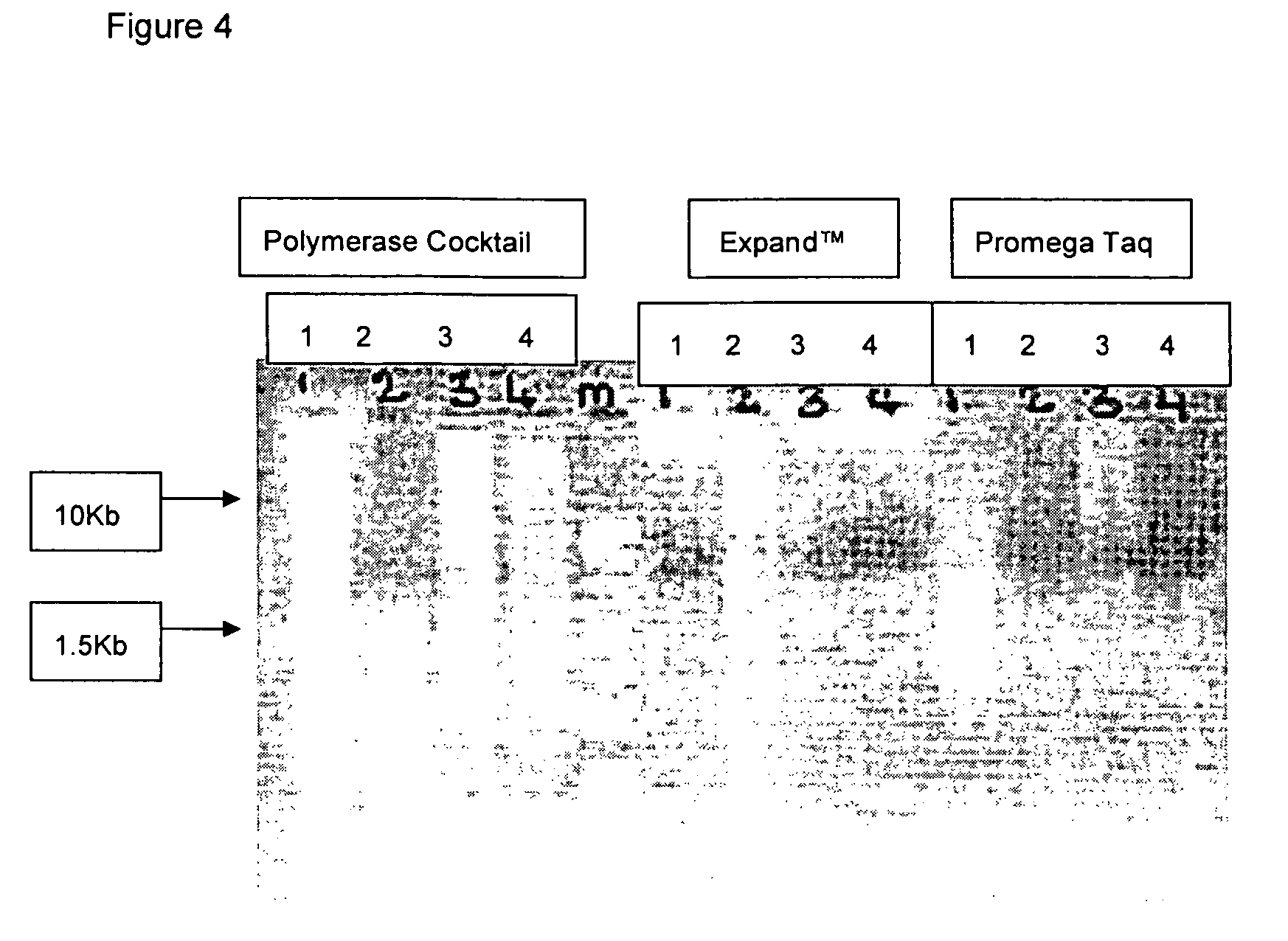
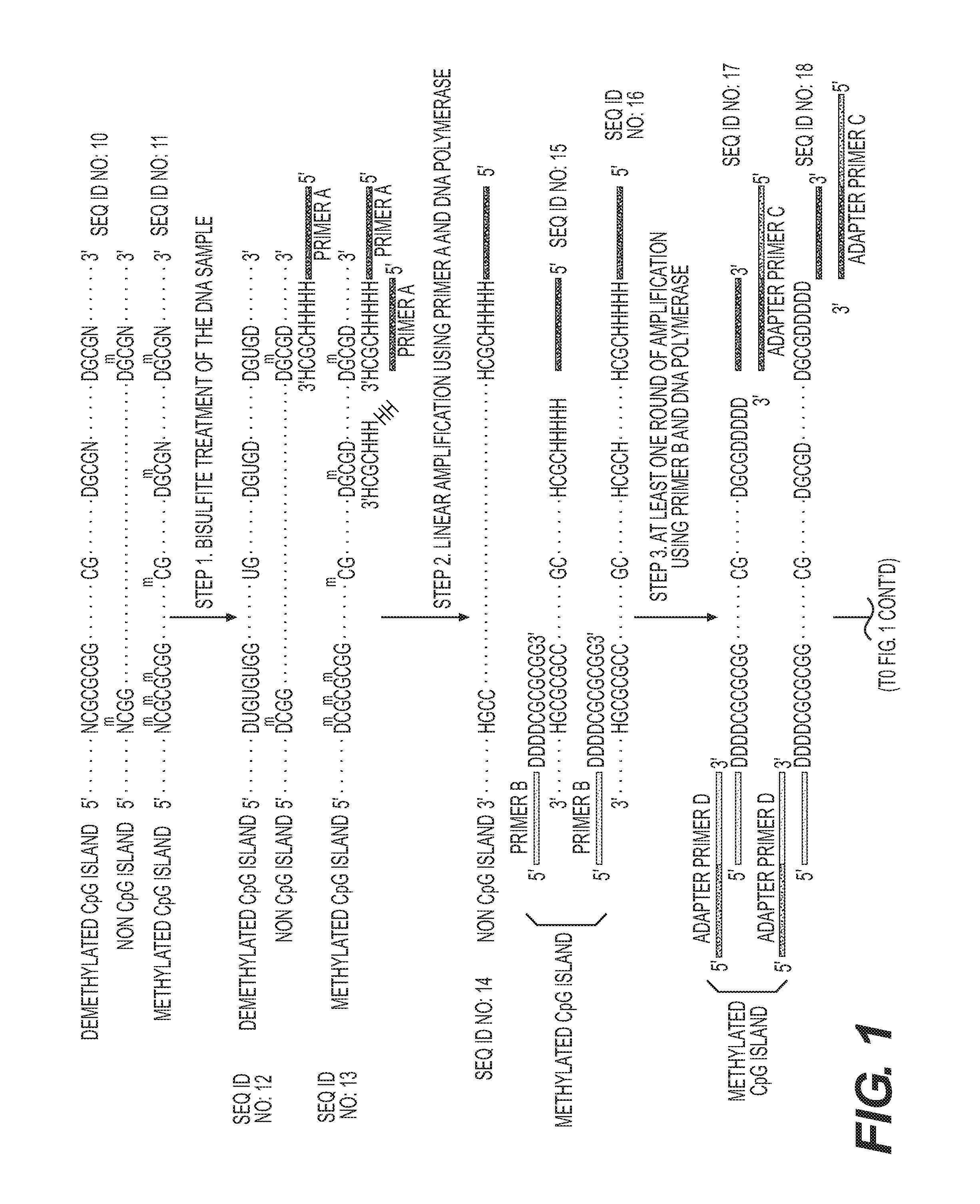
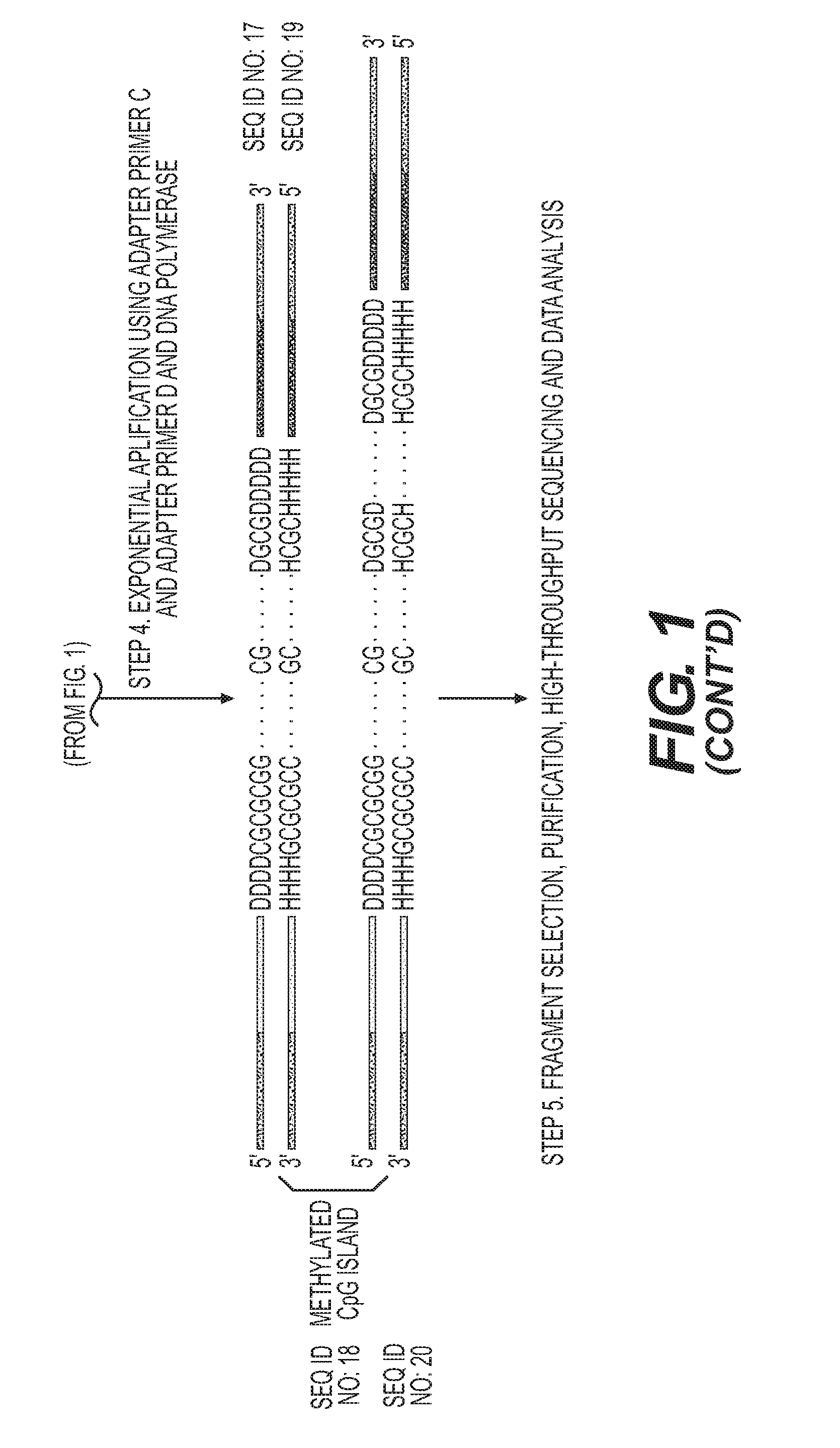
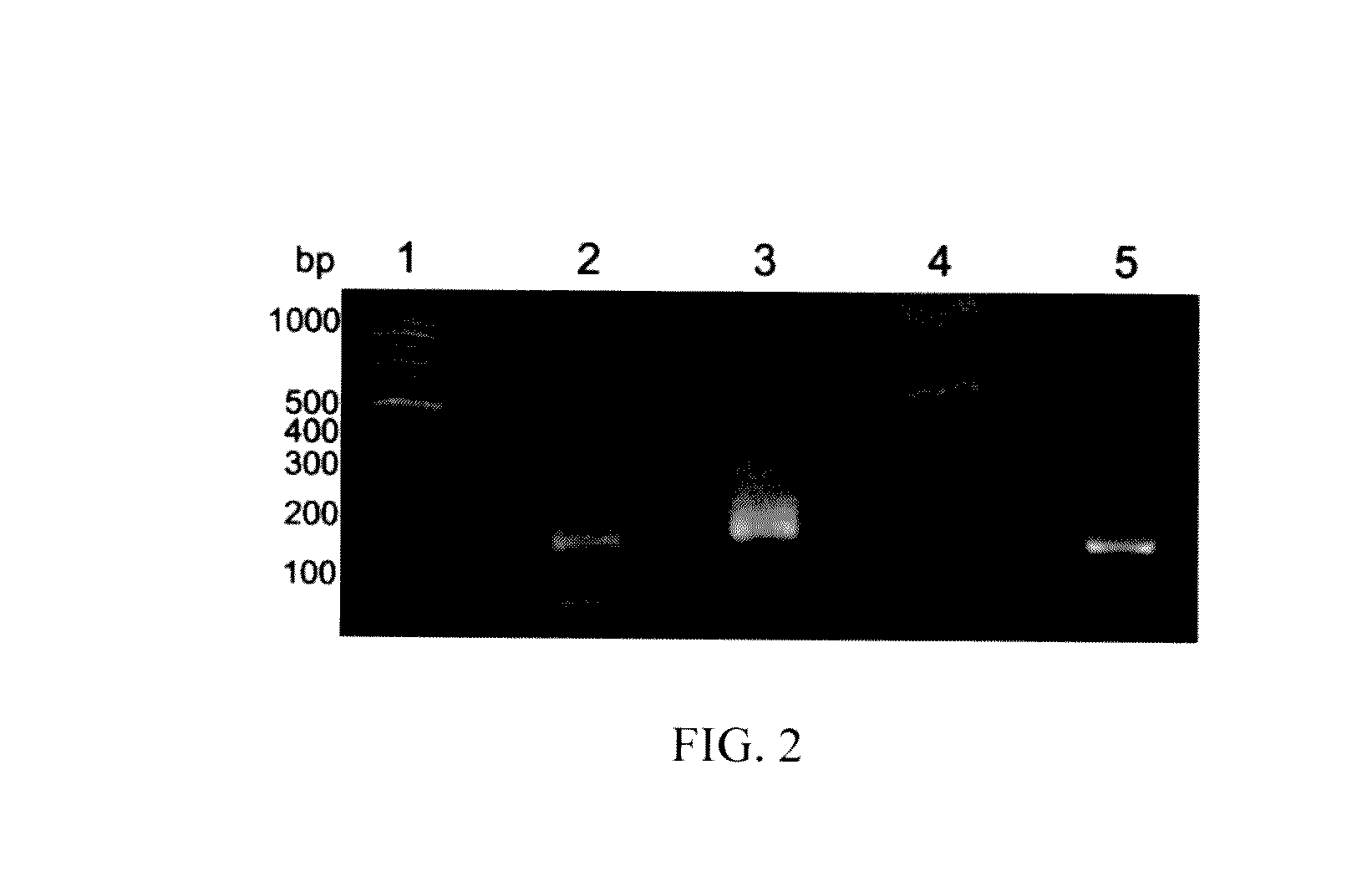
High-throughput sequencing detection method for methylated cpg islands
ActiveUS20160298183A1Efficient enrichmentCost-effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementDna polymerasenA-DNA
A high-throughput sequencing method for detecting methylated CpG islands includes: processing a DNA sample by using a modifier, and converting cytosine in the DNA sample into uracil, and keeping 5′methylcytosine unchanged; amplifying the obtained segment by using a primer A and DNA polymerase, to obtain a segment having one end being capable of anchoring a junction primer C; amplifying the obtained segment by using a primer B and DNA polymerase, to obtain a segment gathering methylated CpG islands and having two ends being capable of separately anchoring junction primers C and D; amplifying the obtained segment at a PCR exponent by using the junction primers C and D and the DNA polymerase, to obtain the amplified product; and separating and purifying the amplified product, to form a high-throughput sequencing library and perform computer sequencing, and data analysis.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Restriction endonucleases and their applications
ActiveUS20110207139A1Well representedHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideGenetics
Provided is a methylation-specific restriction endonuclease for a DNA duplex substrate, which endonuclease recognizes in a strand of the duplex a 2 to 6 nucleotide recognition sequence comprising a 5-methylcytosine, and cleaves each strand of the duplex at a fixed position outside the recognition sequence.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BALTICS UAB
Nucleic acid methylation detection process using an internal reference sample
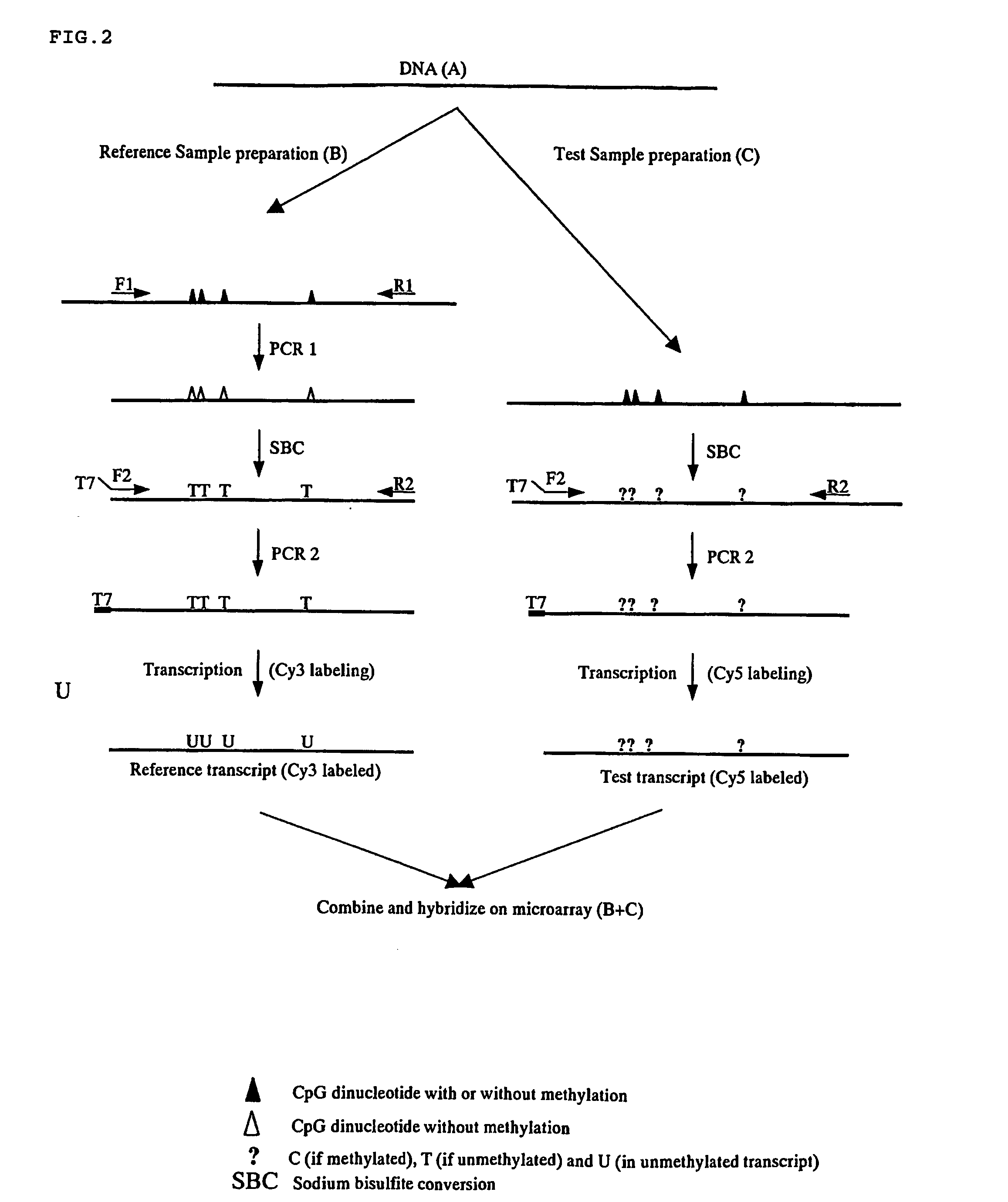
InactiveUS20060110741A1Rapidly and effectively screenNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementReference sampleFluorescence
There is disclosed a process for detection of DNA methylation at CpG sites using nucleic acid arrays and preferably microarrays. Specifically, there is disclosed a process for directly generating a reference sample from the sample to be tested and detecting methylation at large numbers of CpG island sites simultaneously. More specifically, the inventive process comprises dividing a DNA sample into two samples (a first sample and a second sample), amplifying the first DNA sample by a nucleic acid amplification process such that any methylcytosine residues are amplified as unmethylated cytosine residues, treating the amplified first sample and the (unamplified) second sample with bisulfite to convert unmethylated cytosine residues in both samples to deoxyuracil residues, labeling the bisulfite-converted second sample with a second fluorescent marker and the bisulfite-converted first sample with a first fluorescent marker, wherein the first and second fluorescent markers have non-overlapping fluorescent excitation and emission spectra; and hybridizing the first sample and the second sample onto a microarray device having a plurality of oligonucleotide capture probes designed to hybridize to CpG island sites of the DNA sample as converted and non-converted by bisulfite.
Owner:COMBIMATRIX CORP +1
Method for high performance liquid chromatography(HPLC)-mass spectrometry (MS) detection of DNA oxidation and DNA methylation
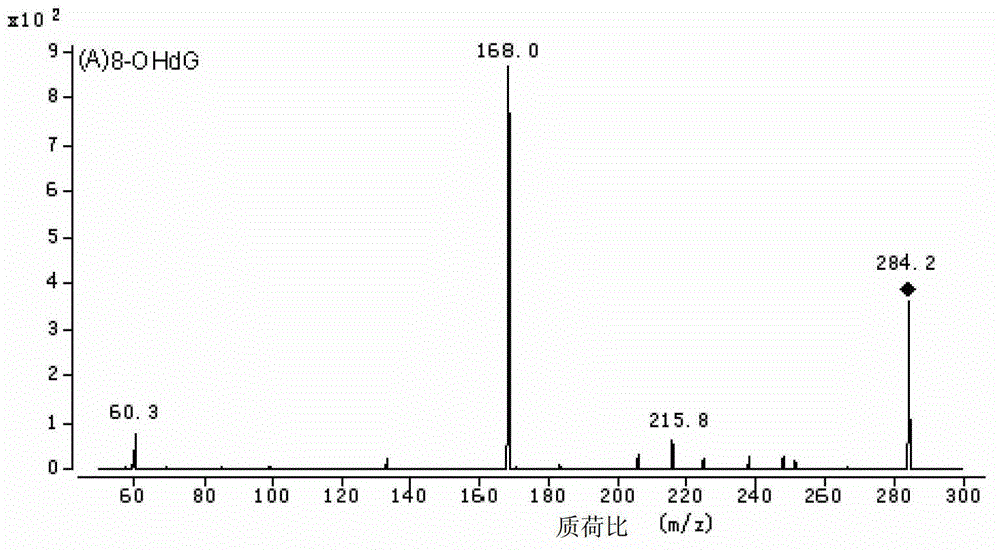
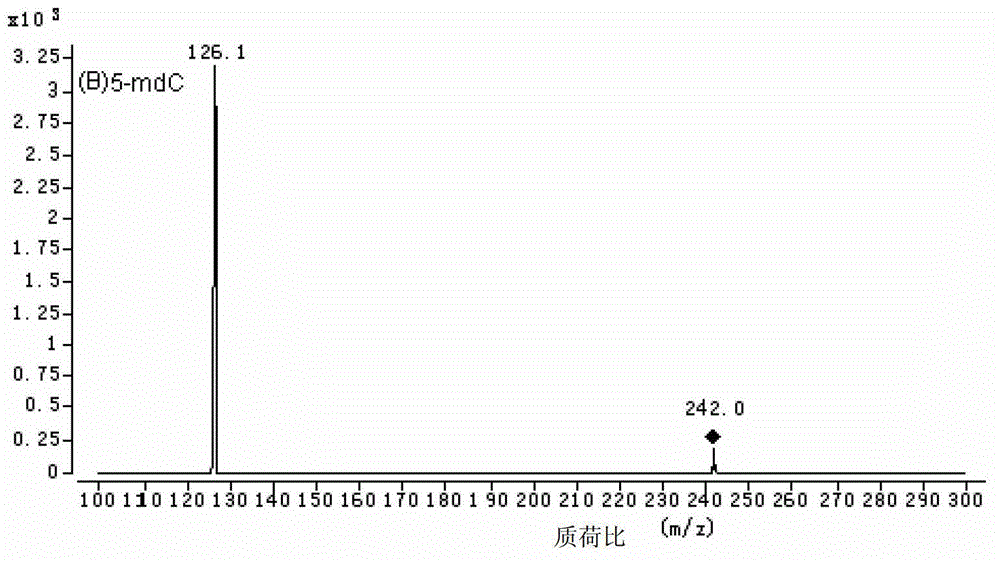
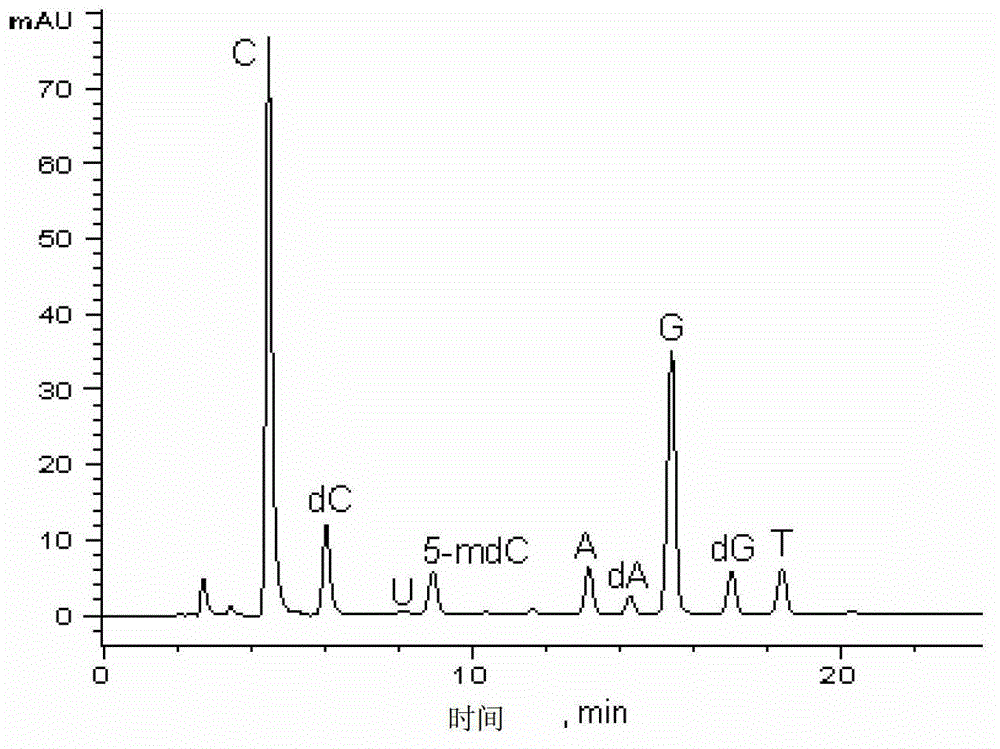
The invention discloses a method for high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-mass spectrometry (MS) detection of DNA oxidation and DNA methylation, and the method comprises the following steps: hydrolyzing DNA, measuring the content of 5-methyl cytosine (5-mdC) and 8-hydroxy deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in the DNA hydrolysis product by HPLC-ESI (electrospray ionization)-MS / MS; wherein the high performance liquid chromatography is performed as follows: a mobile phase A is formic acid / methanol with the volume ratio of 0.01-0.3, a mobile phase B is a formic acid water solution with the volume ratio of 0.01 to 0.3%, and under the conditions of the flow velocity of 0.2-0.4ml / min and the column temperature of 15 to 40 DEG C, separation is performed by a liquid chromatography column; ESI (electrospray ionization)-MS is performed as follows: an electrospray ion source is ionized, and mass spectrometric analysis is performed in the positive electrode mode by a multiple reaction monitoring system. The method for high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-mass spectrometry (MS) detection of DNA oxidation and DNA methylation can simultaneously detect the content of 8-OHdG and 5-mdC in a DNA sample.
Owner:柯跃斌
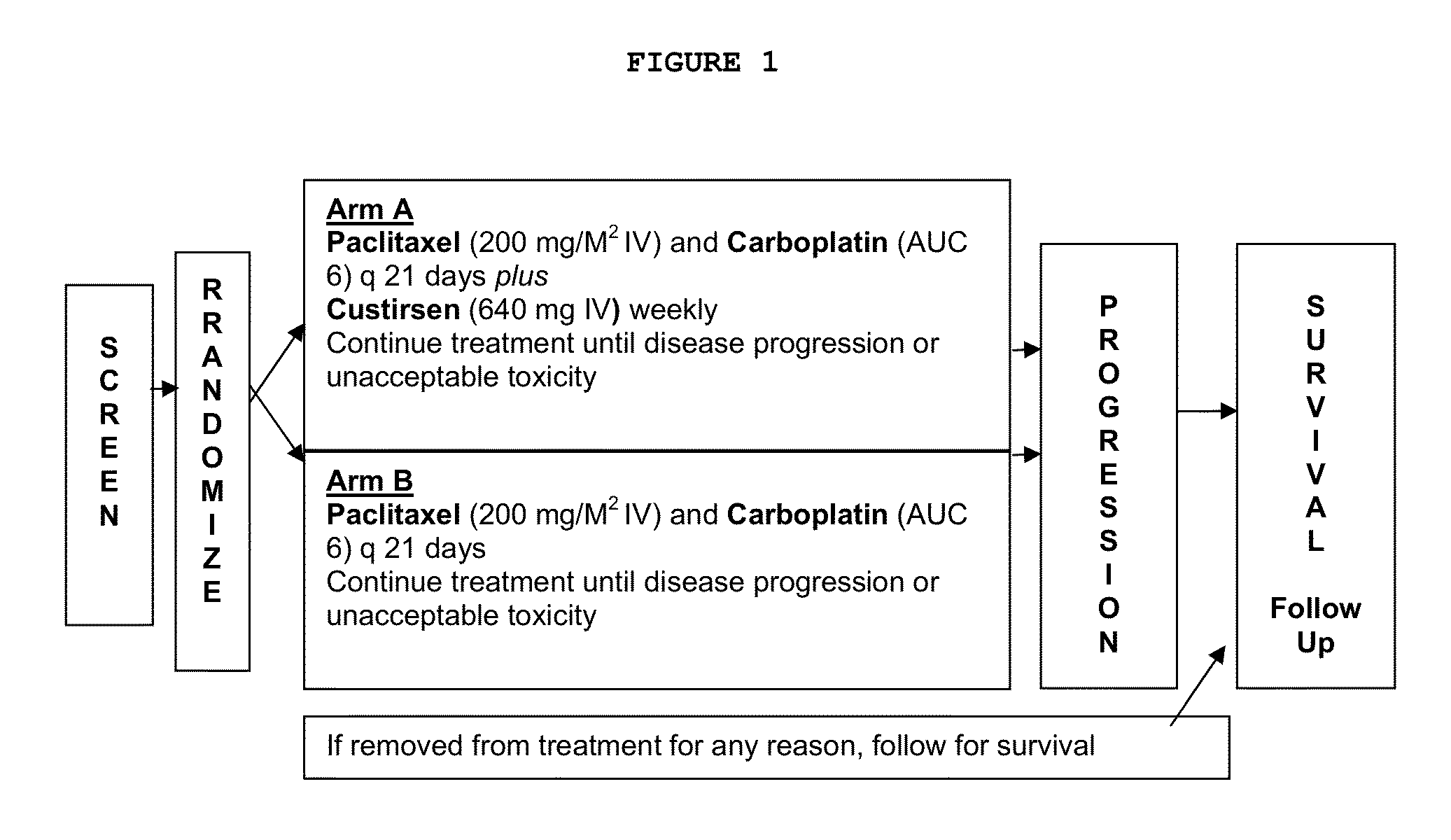
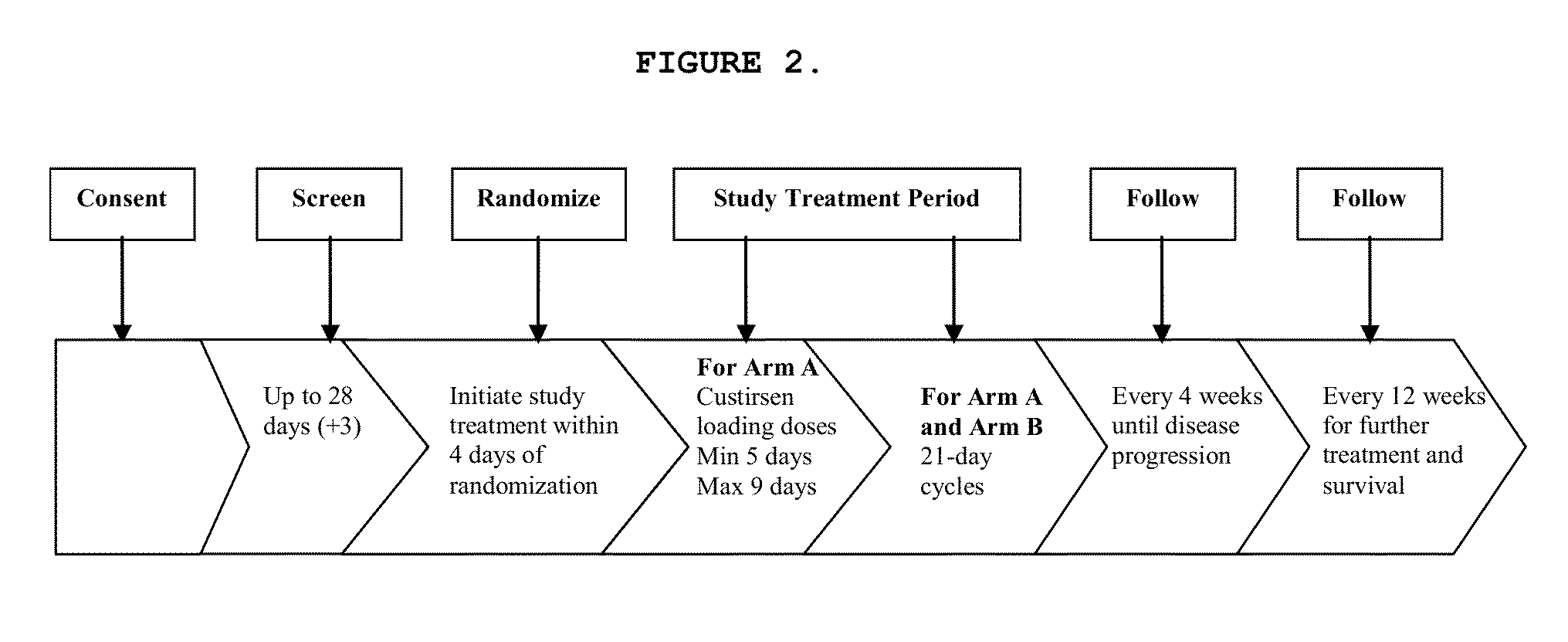
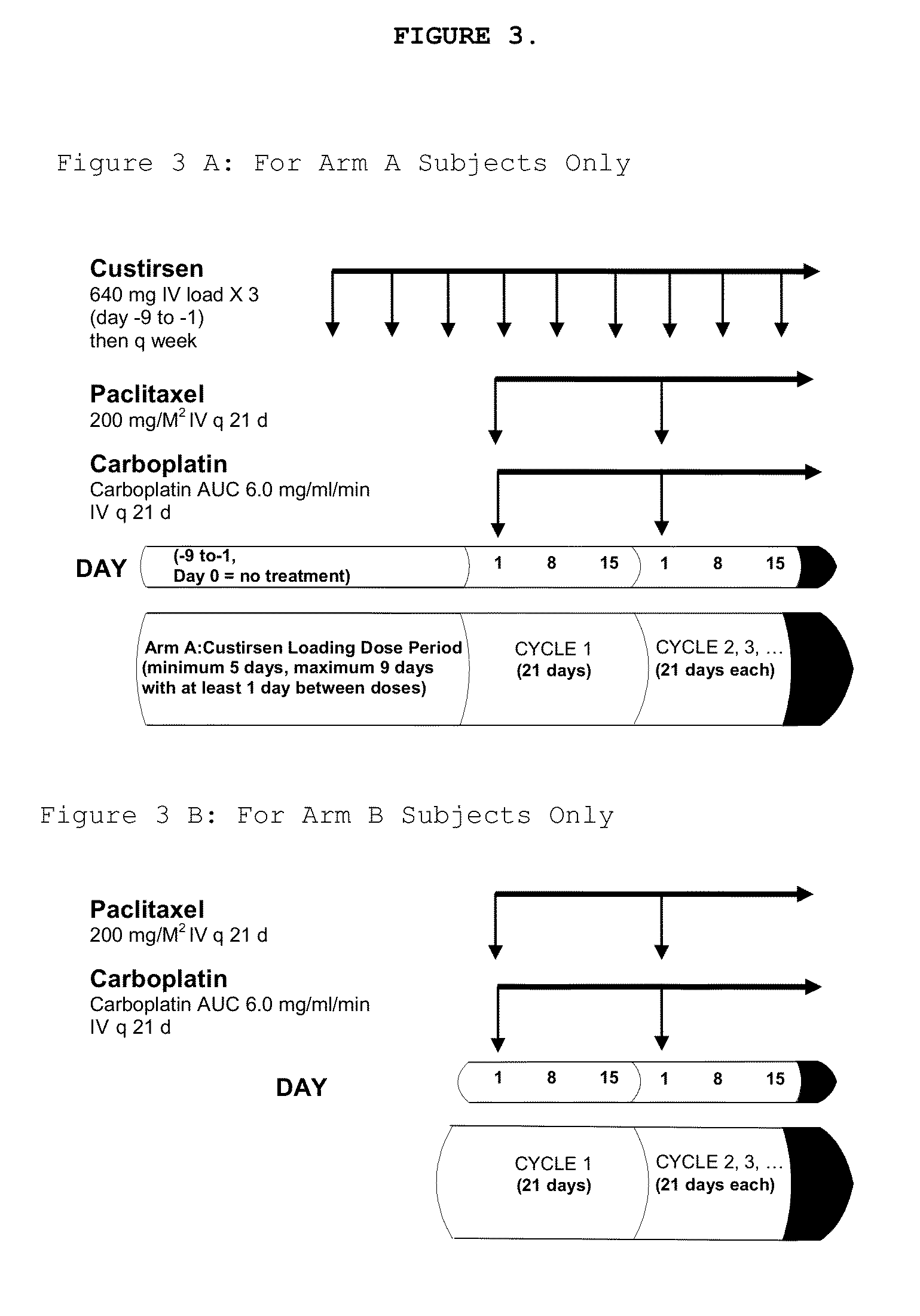
Method for treating non-small cell lung cancer
A method of treating a human patient afflicted with lung cancer comprising periodically administering to the human patient chemotherapy comprising an amount of a taxane and 640 mg of an anti-clusterin oligonucleotide having the sequence CAGCAGCAGAGTCTTCATCAT (Seq. ID No.: 1), wherein the anti-clusterin oligonucleotide has a phosphorothioate backbone throughout, has sugar moieties of nucleotides 1-4 and 18-21 bearing 2′-O-methoxyethyl modifications, has nucleotides 5-17 which are 2′ deoxynucleotides, and has 5-methylcytosines at nucleotides 1, 4, and 19, thereby treating the human patient afflicted with cell lung cancer.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
Method for detecting cytosine methylations
InactiveUS8241855B2Easy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGenomic DNAPolymerase L
A method is described for the detection of 5-methylcytosine in genomic DNA samples. First, a genomic DNA from a DNA sample is chemically converted with a reagent, whereby 5-methylcytosine and cytosine react differently. Then the pretreated DNA is amplified with the use of a polymerase with primers of different sequence. In the next step, the amplified genomic DNA is hybridized to an oligonucleotide array and PCR products are obtained, which must be provided with a label. Alternatively, the PCR products can be extended in a primer extension reaction, wherein the extension products are also provided with a label. In the last step, the extended oligonucleotides are investigated for the presence of the label.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Unmethylated CpG dinucleotide content detection method
InactiveCN101187652AImmunocompetentComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaHplc method
The invention provides a method for testing non-ethylating CpG content, which comprises adopting specific methylaseSssI to modify CpG dinucleotide aracytidine into 5-methylcytosine, then using nucleicacidase P1 and bacterial alkaline phosphatase to hydrolyze DNA into single deoxynucleoside, using a reversed-phase hplc method to test quantity of the 5-methylcytosinein DNA hydrolytic samples which are both modifying and un-modifying, and testing the CpG through differences of the 5-methylcytosine detectable amount between the modifying DNA hydrolytic sample and the un-modifying DNA hydrolytic samples.
Owner:NAT INST FOR THE CONTROL OF PHARMA & BIOLOGICAL PROD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com