Patents
Literature
60 results about "5-Methylcytosine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
5-Methylcytosine is a methylated form of the DNA base cytosine that may be involved in the regulation of gene transcription. When cytosine is methylated, the DNA maintains the same sequence, but the expression of methylated genes can be altered (the study of this is part of the field of epigenetics). 5-Methylcytosine is incorporated in the nucleoside 5-methylcytidine.
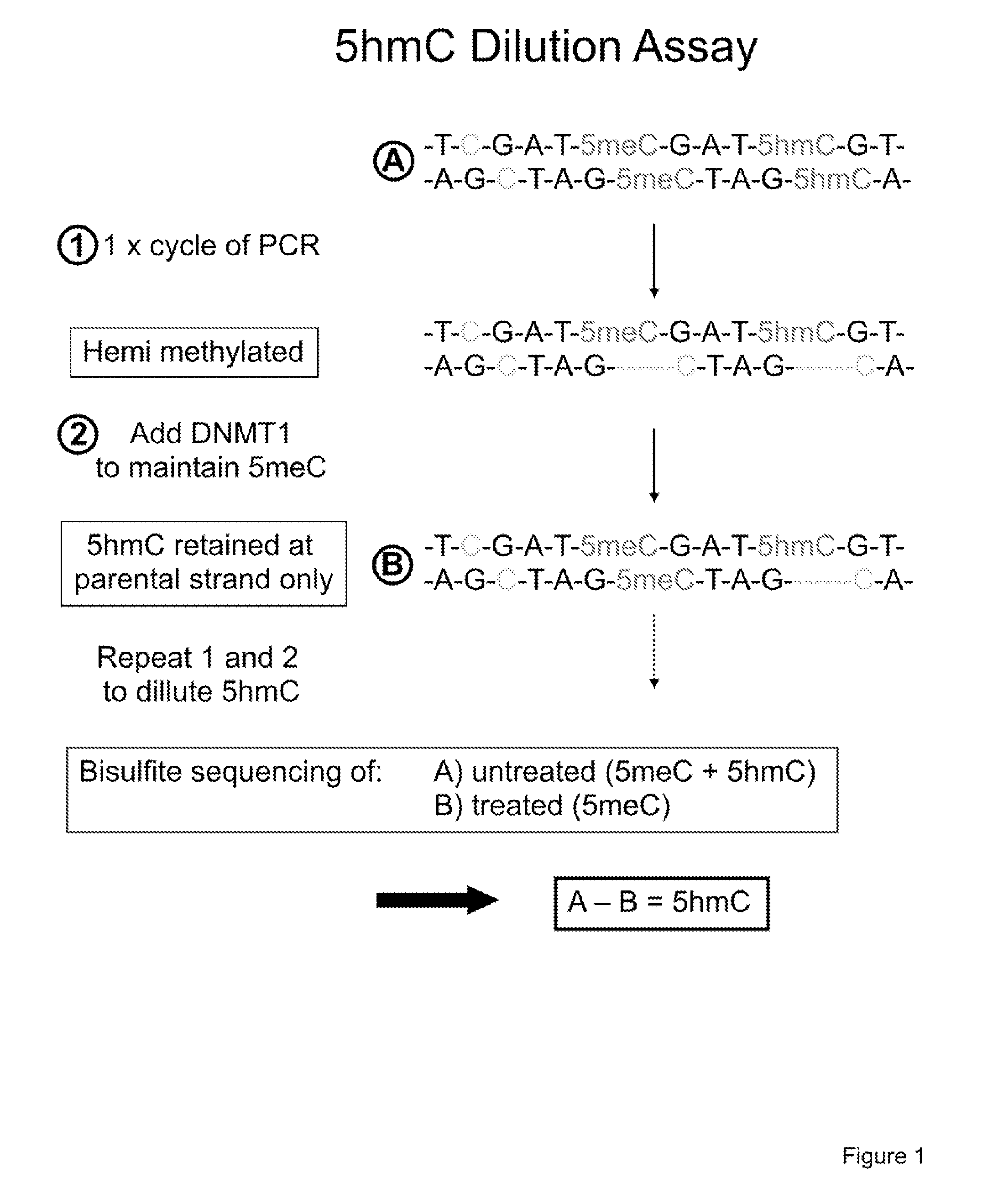
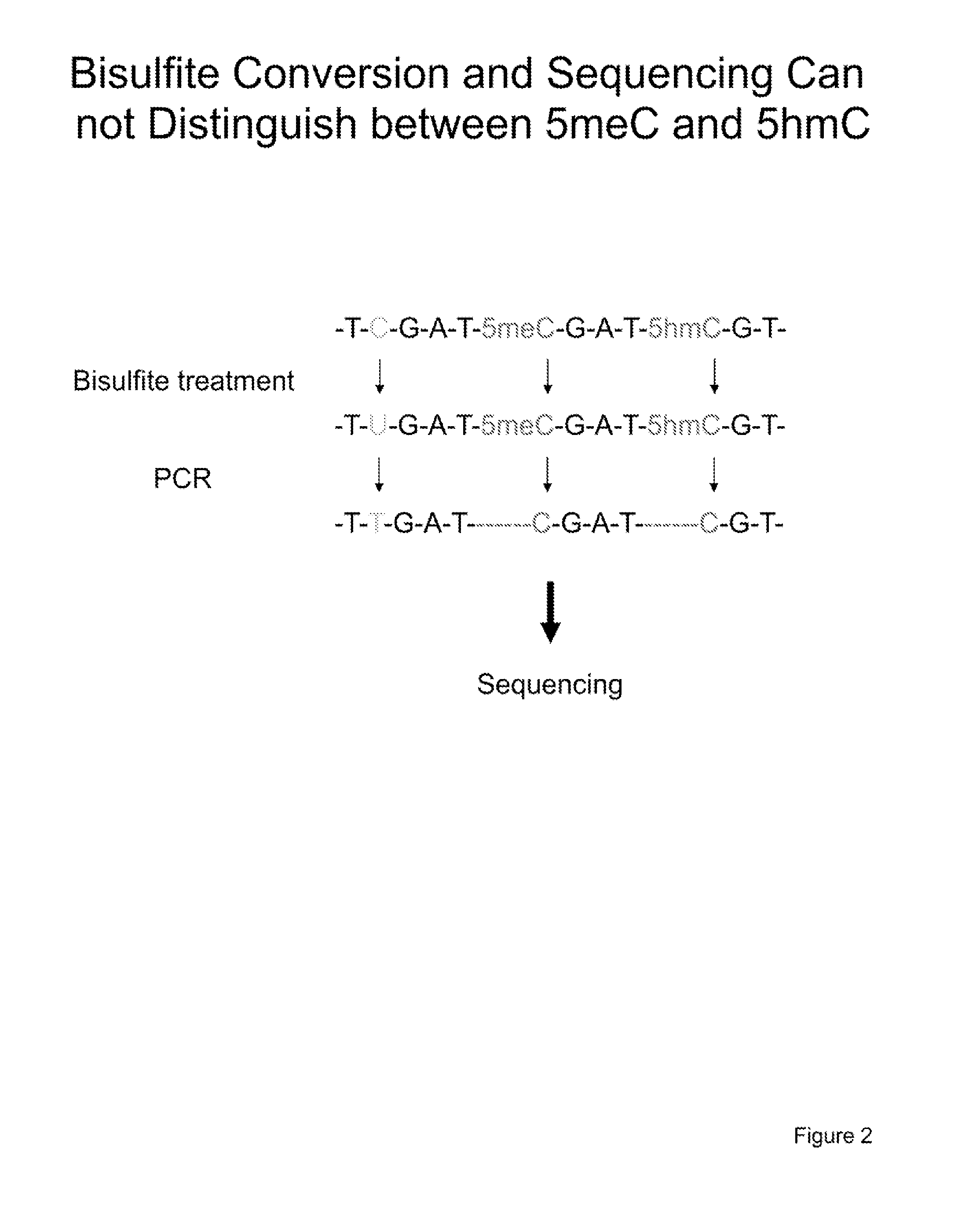
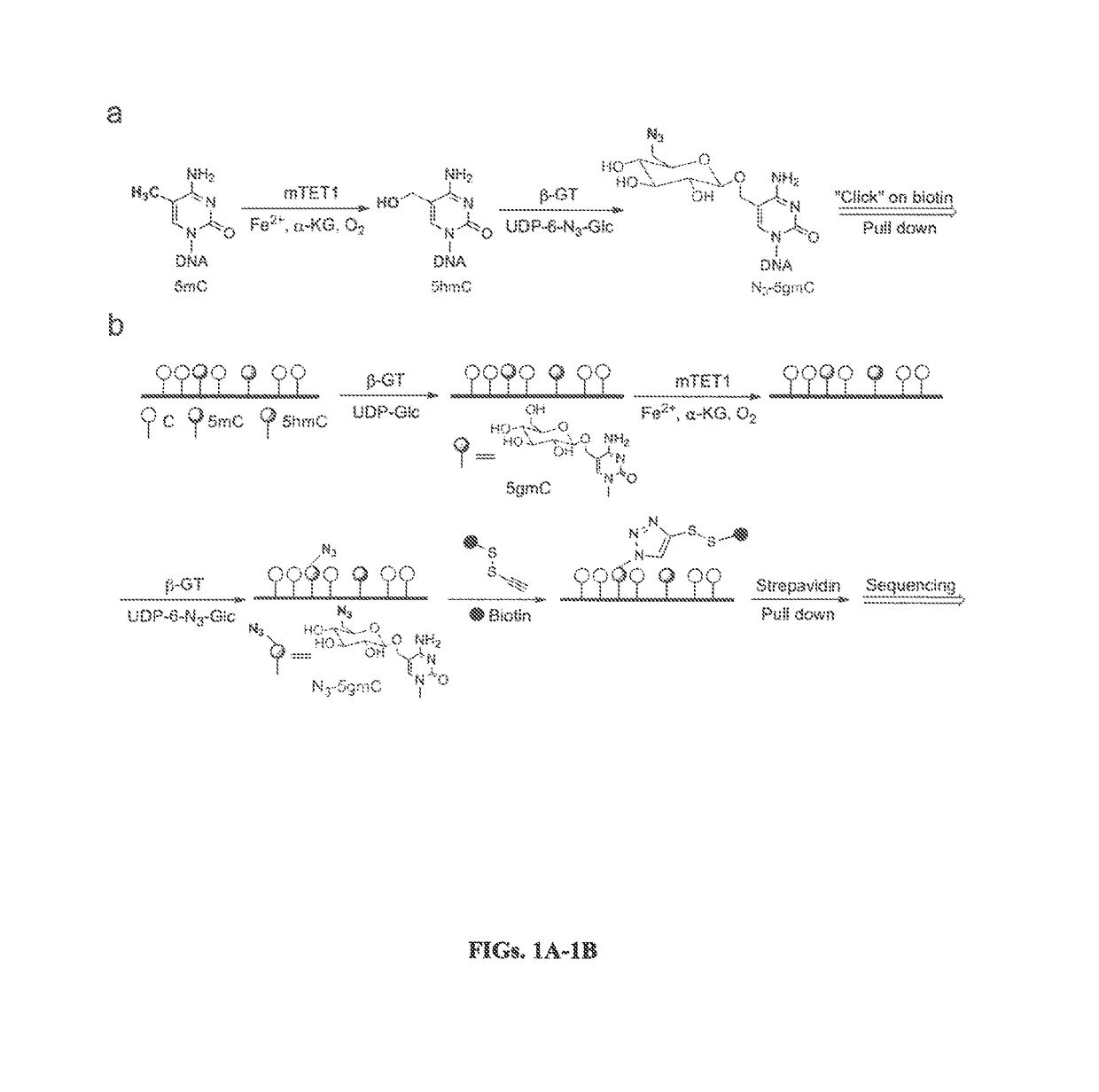
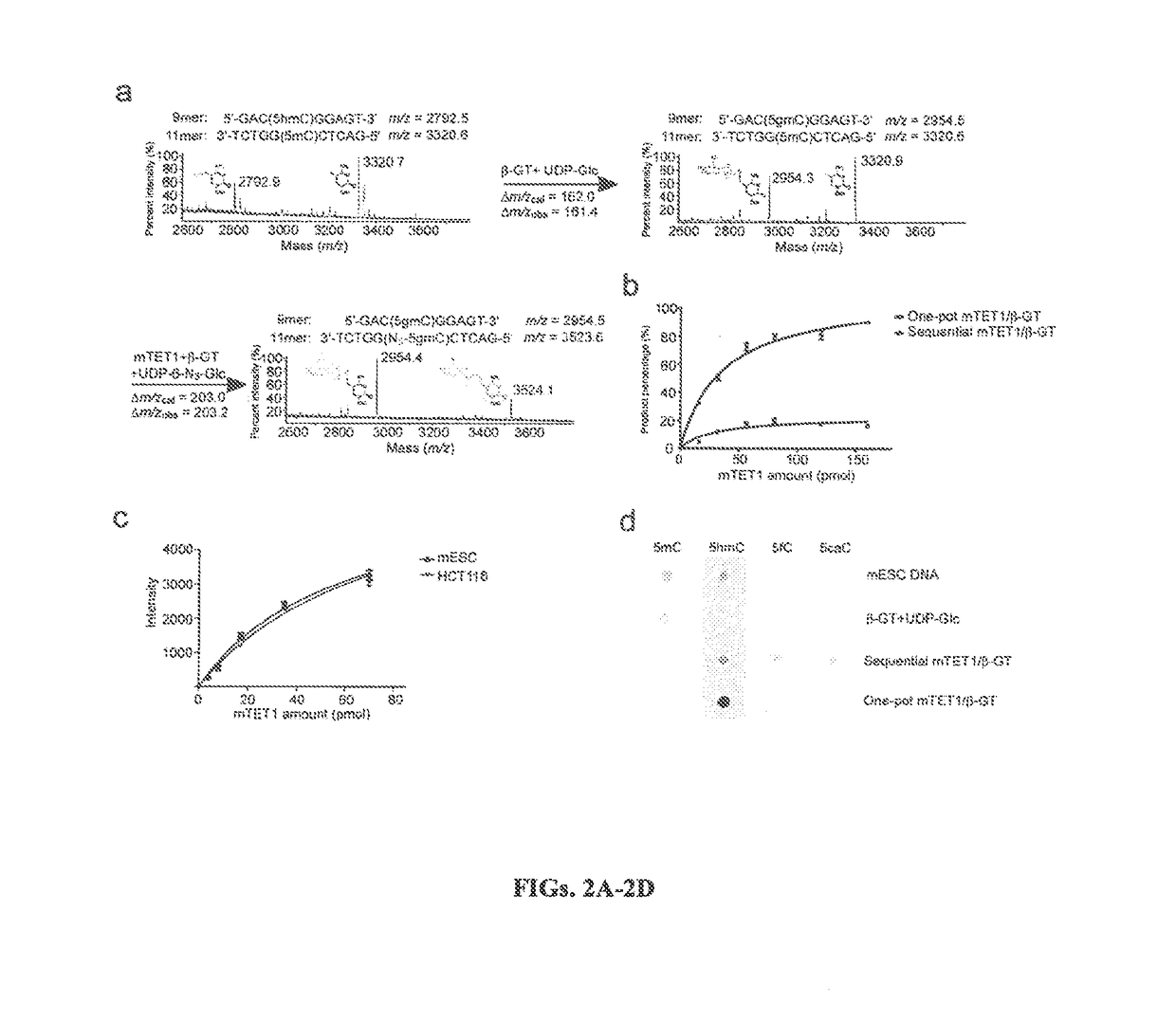
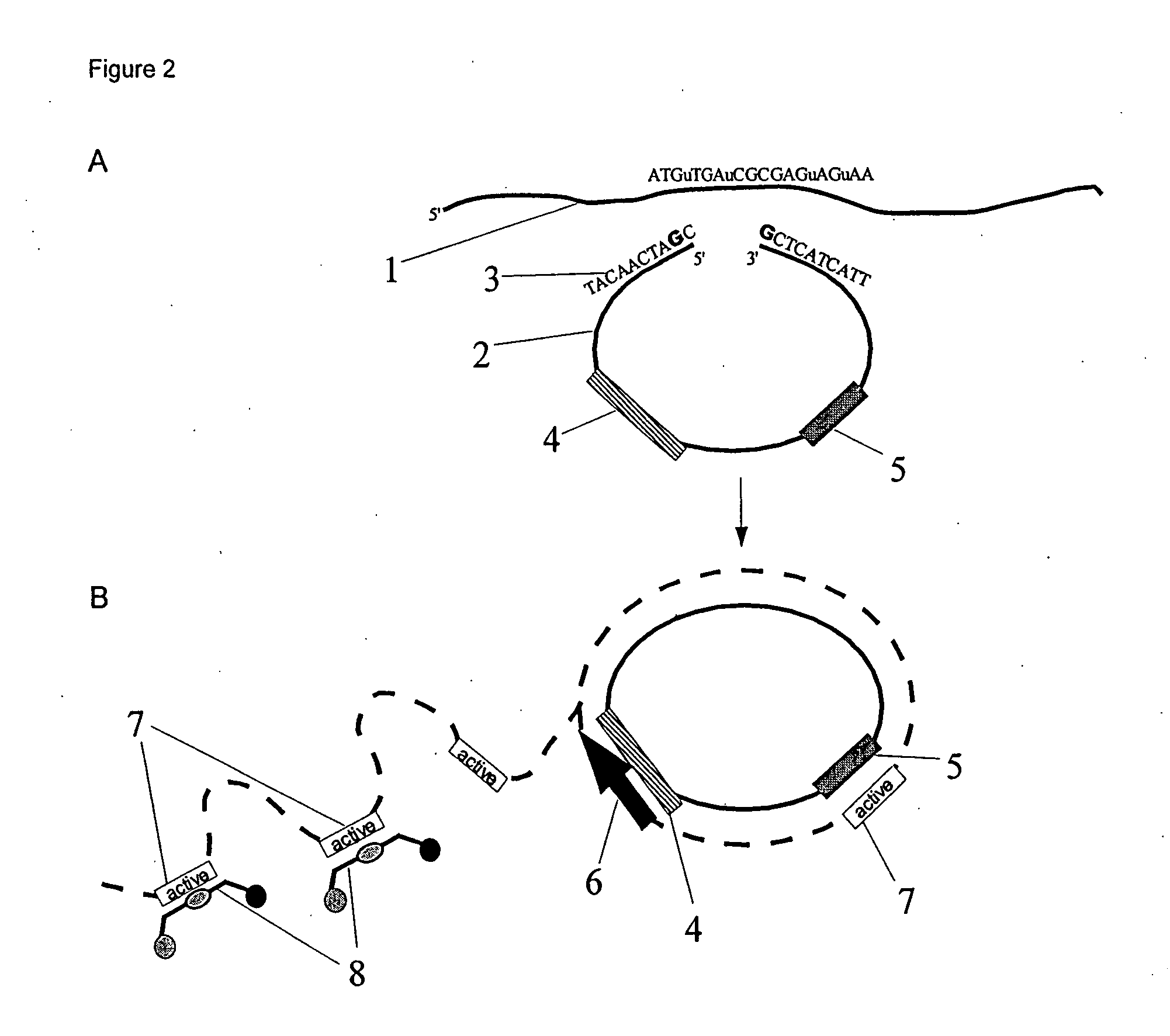
COMPOSITION AND METHODS RELATED TO MODIFICATION OF 5-METHYLCYTOSINE (5-mC)
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for detecting, evaluating, and / or mapping 5-methyl-modified and / or 5-hydroxylmethyl-modified cytosine bases within a nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
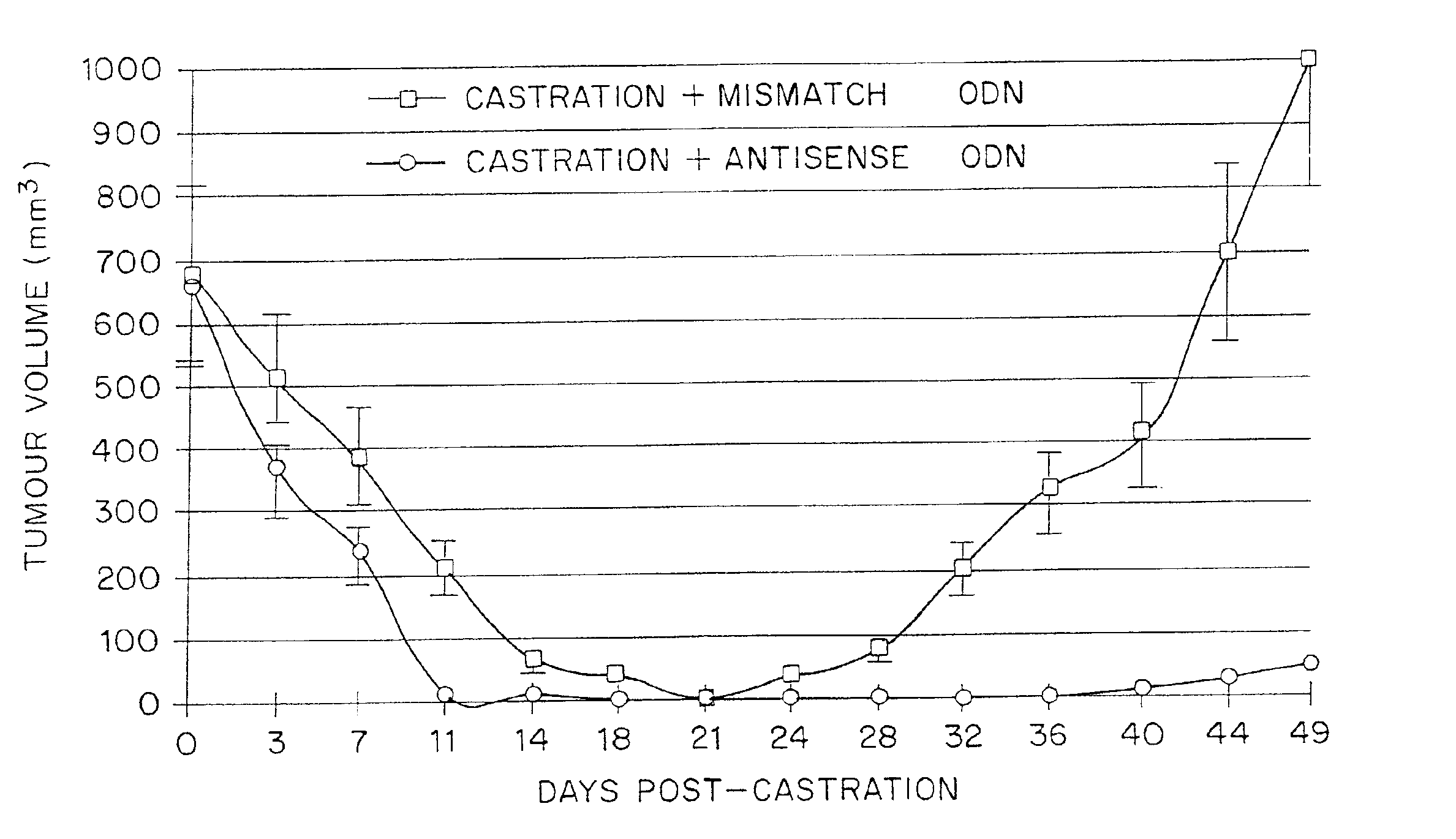
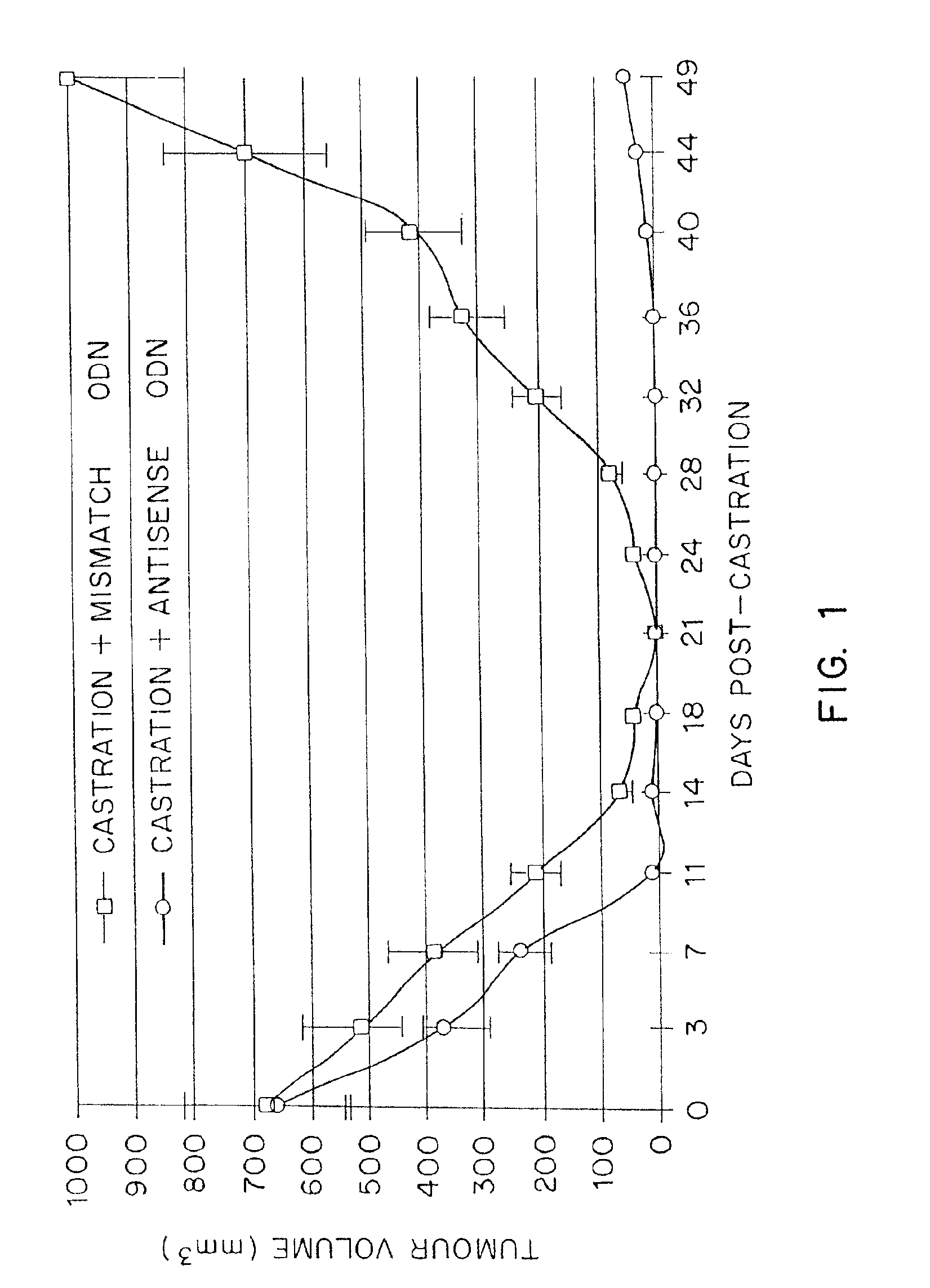
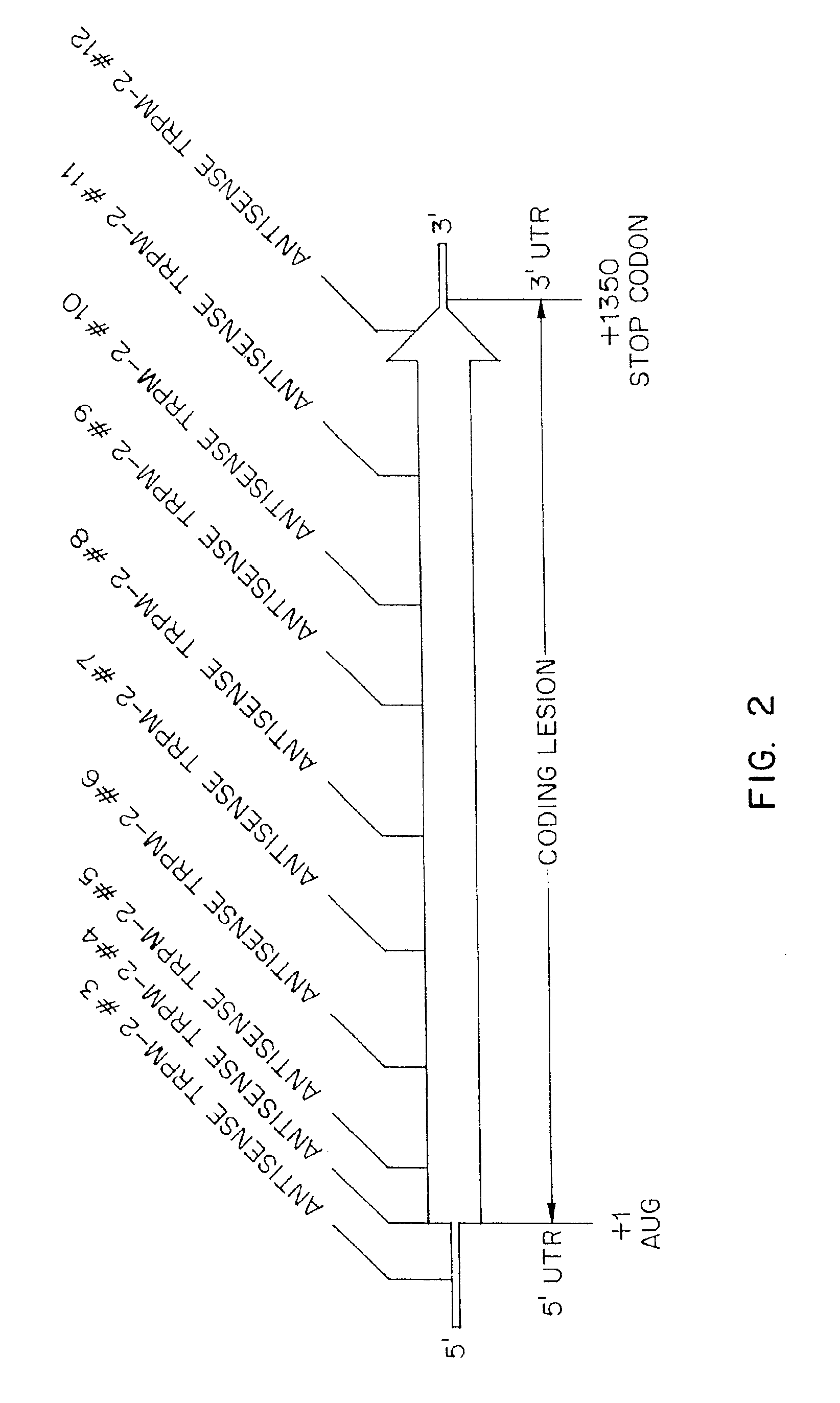
TRPM-2 antisense therapy using an oligonucleotide having 2′-O-(2-methoxy)ethyl modifications
InactiveUS6900187B2Improve in vivo stabilityImproved in vitroPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsIn vivoOligonucleotide
A compound consisting of an oligonucleotide of sequence CAGCAGCAGAGTCTTCATCAT, where the oligonucleotide has a phosphorothioate backbone throughout, the sugar moieties of nucleotides 1-4 and 18-21 bear 2′-O-methoxyethyl modifications, and the remaining nucleotides (nucleotides 5-17) are 2′-deoxynucleotides, and where the cytosines of nucleotides 1, 4 and 19 are 5-methylcytosines. The compound has increased stability in vivo and improved in vitro and in vivo antitumor activity.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
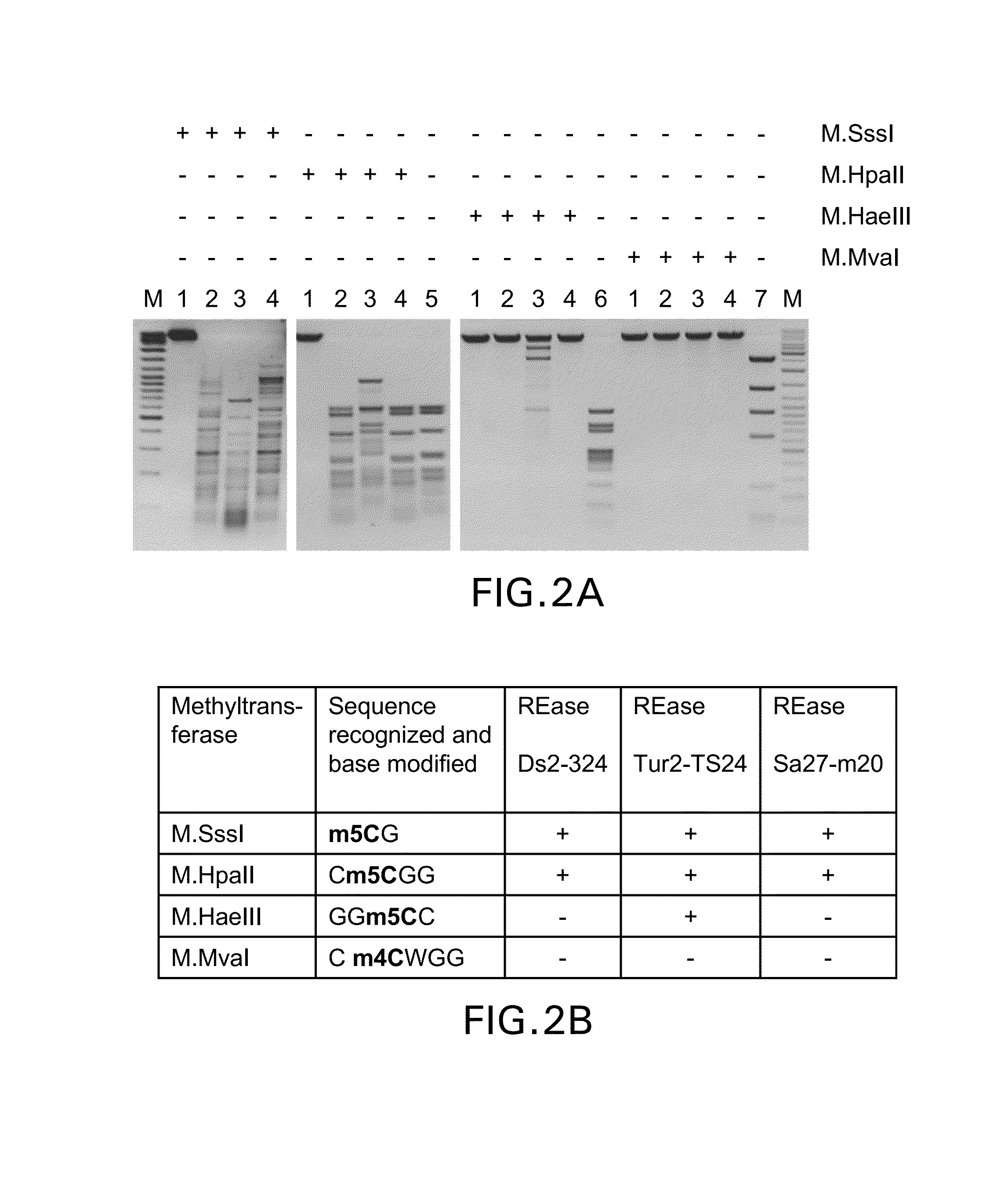
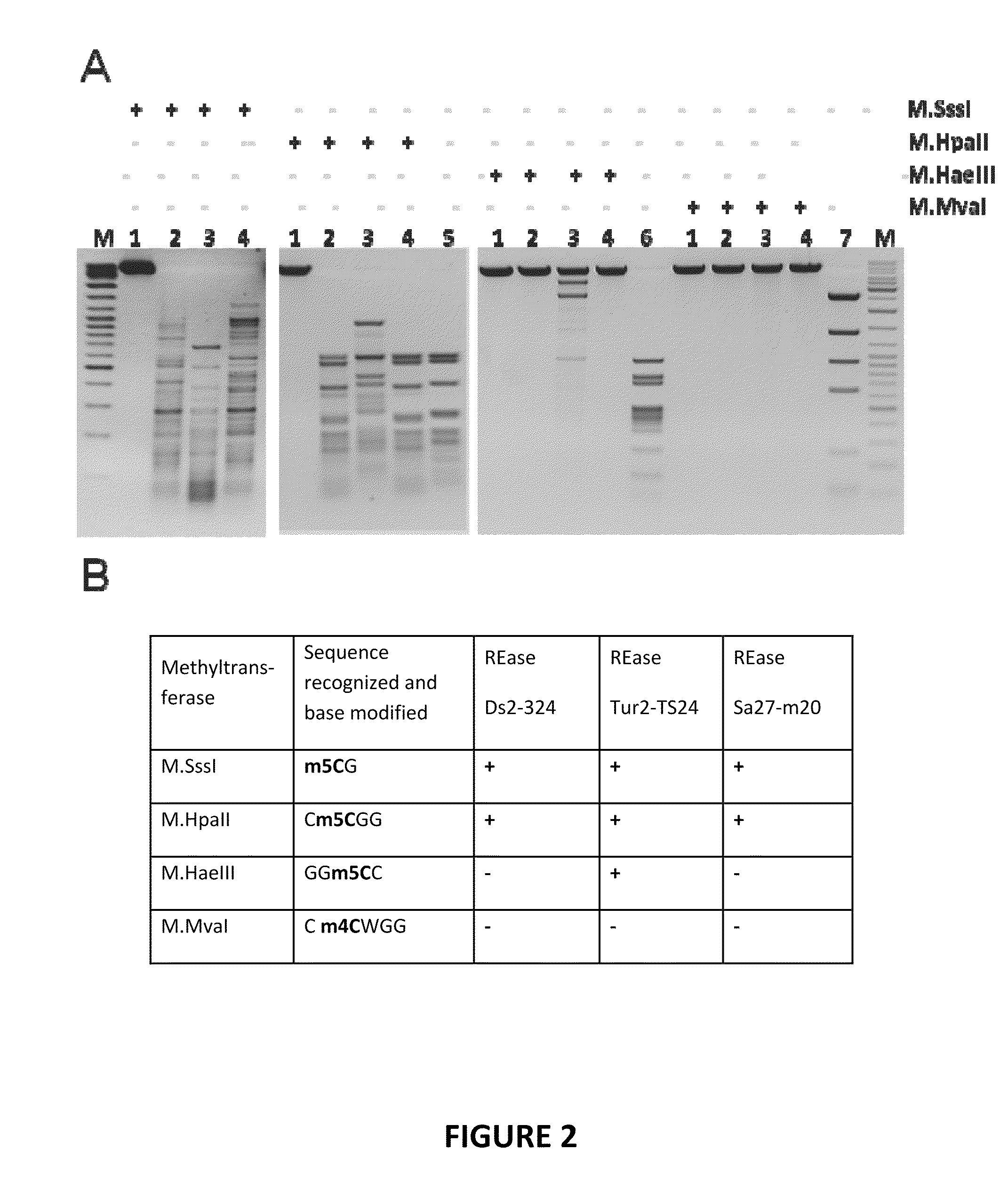
Restriction endonucleases and their applications
Provided is a methylation-specific restriction endonuclease for a DNA duplex substrate, which endonuclease recognizes in a strand of the duplex a 2 to 6 nucleotide recognition sequence comprising a 5-methylcytosine, and cleaves each strand of the duplex at a fixed position outside the recognition sequence.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BALTICS UAB
Methods and kits for detection of methylation status
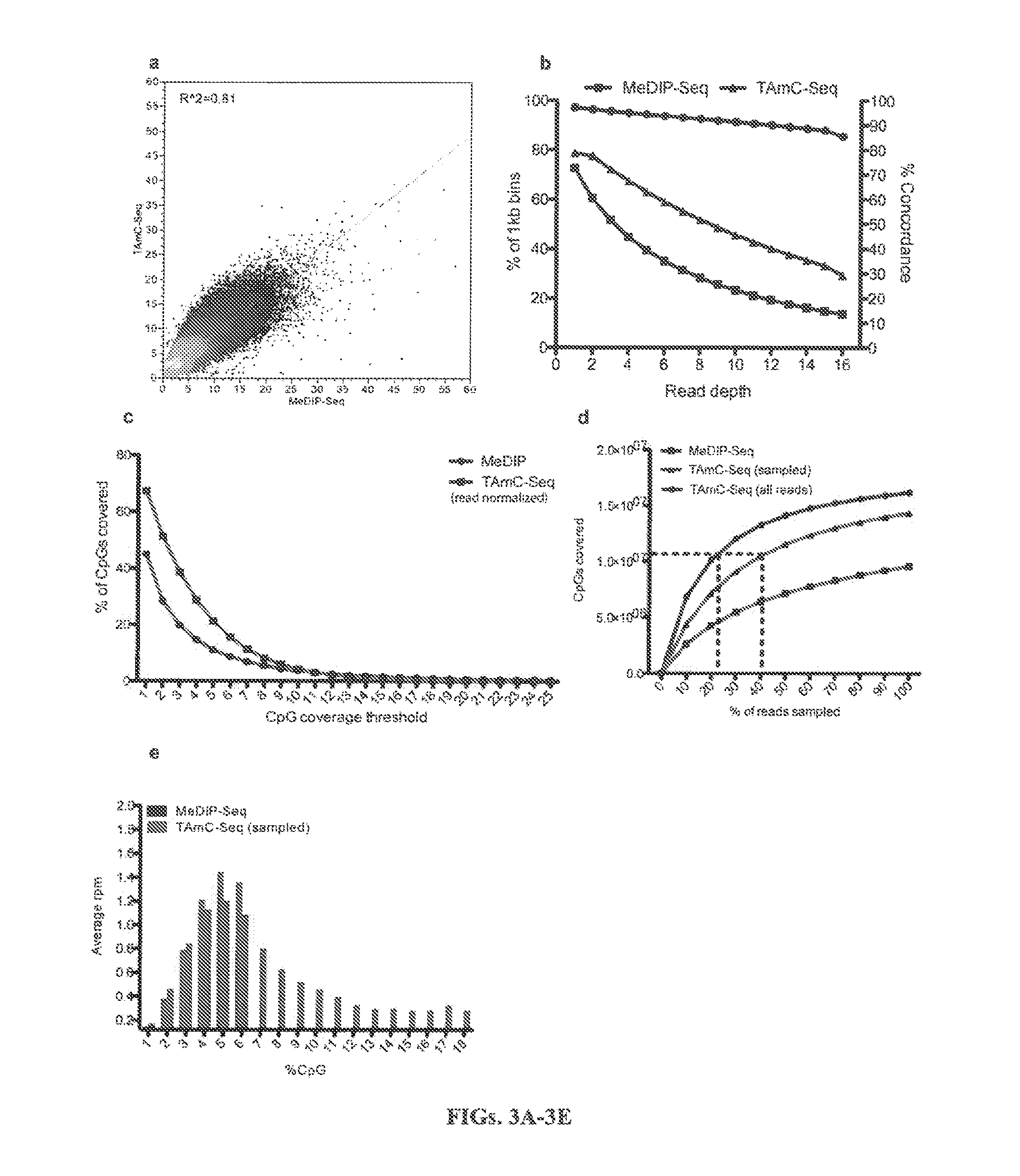
The present invention relates to methods and kits for the detection of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) and / or 5-methylcytosine (5meC). In some embodiments, the present invention relates to methods and kits for detection of 5hmC and / or 5meC in nucleic acid (e.g., DNA, RNA). In some embodiments, the present invention relates to detection of 5hmC in genomic DNA, e.g., mammalian genomic DNA
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
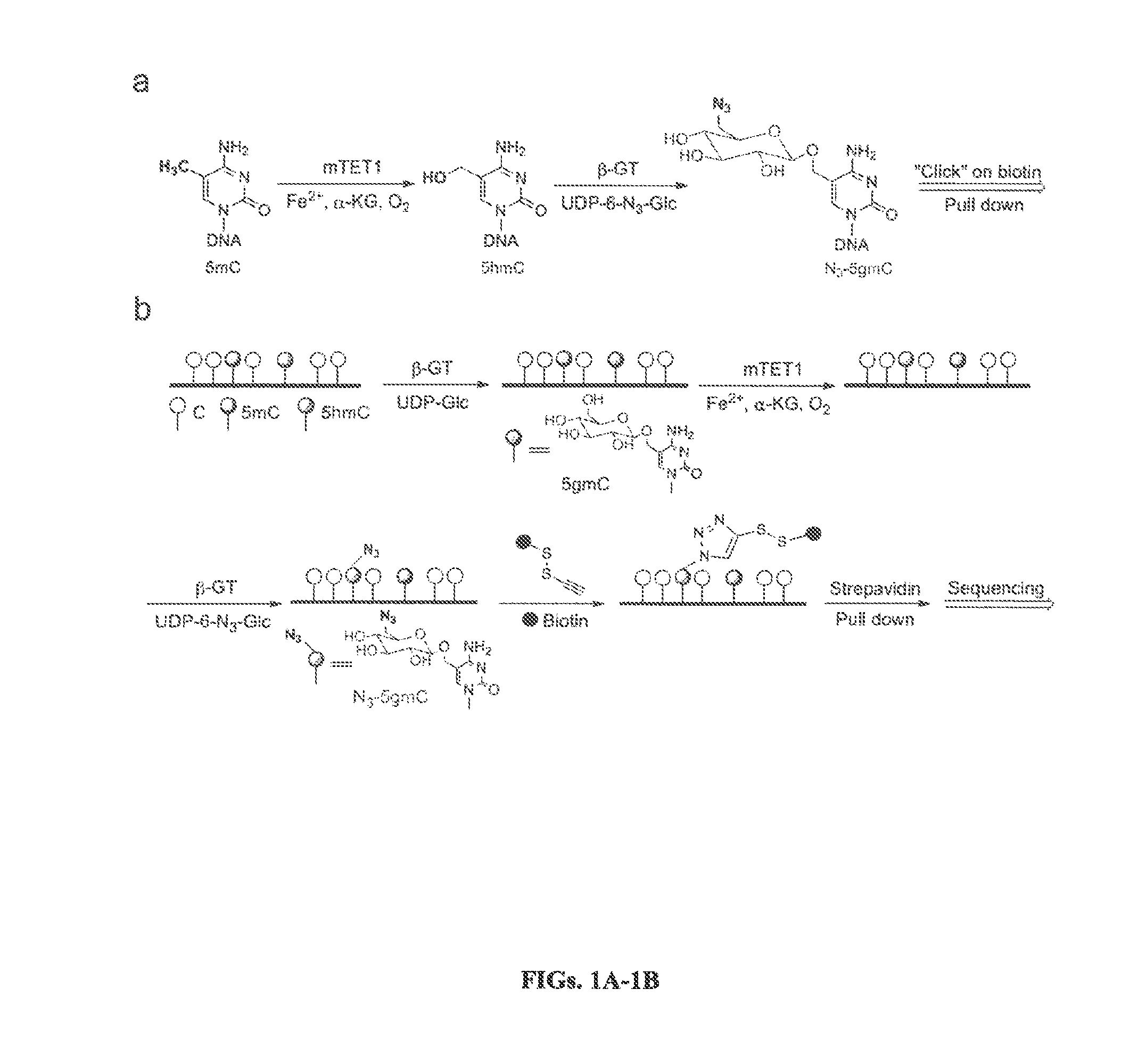
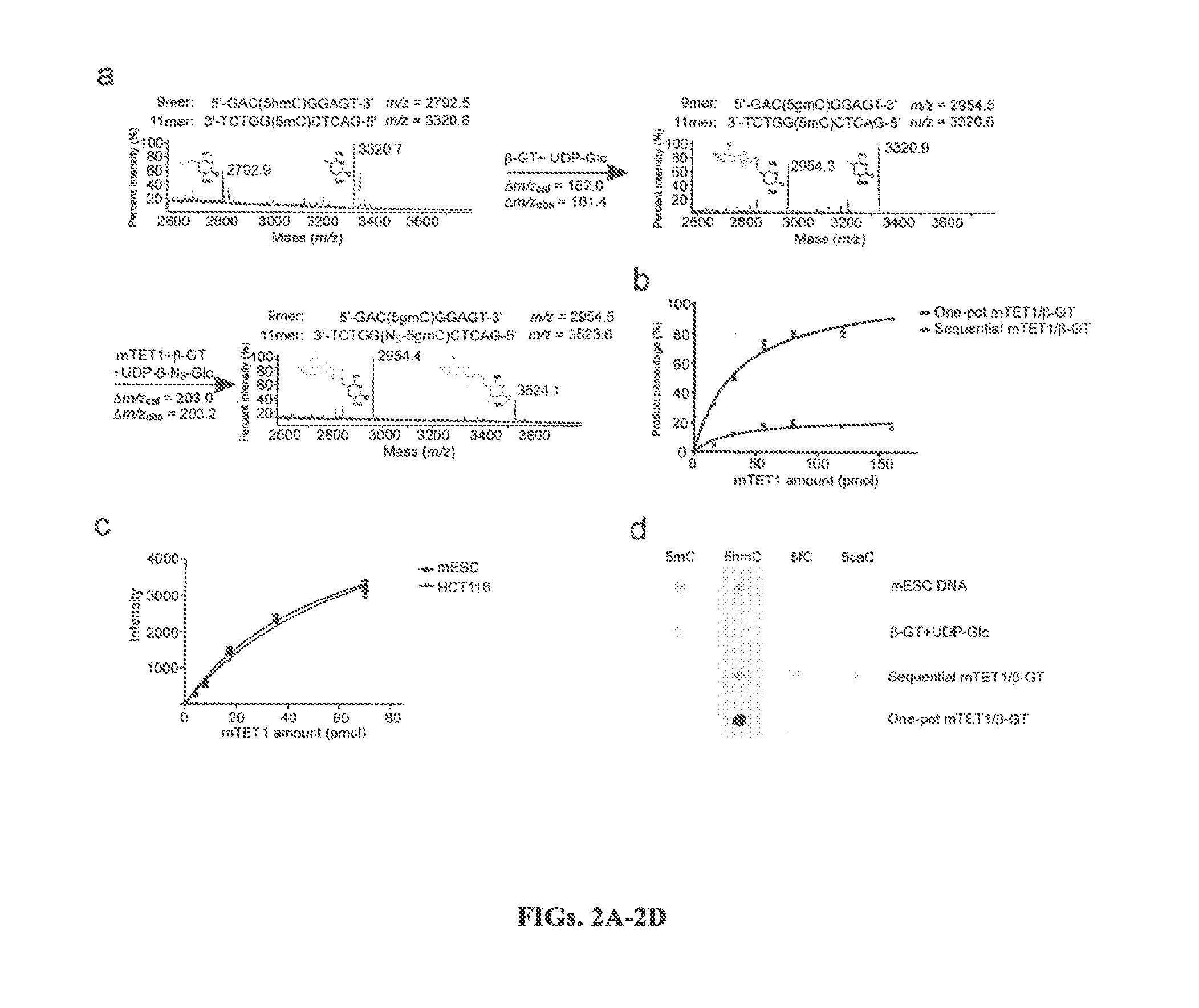
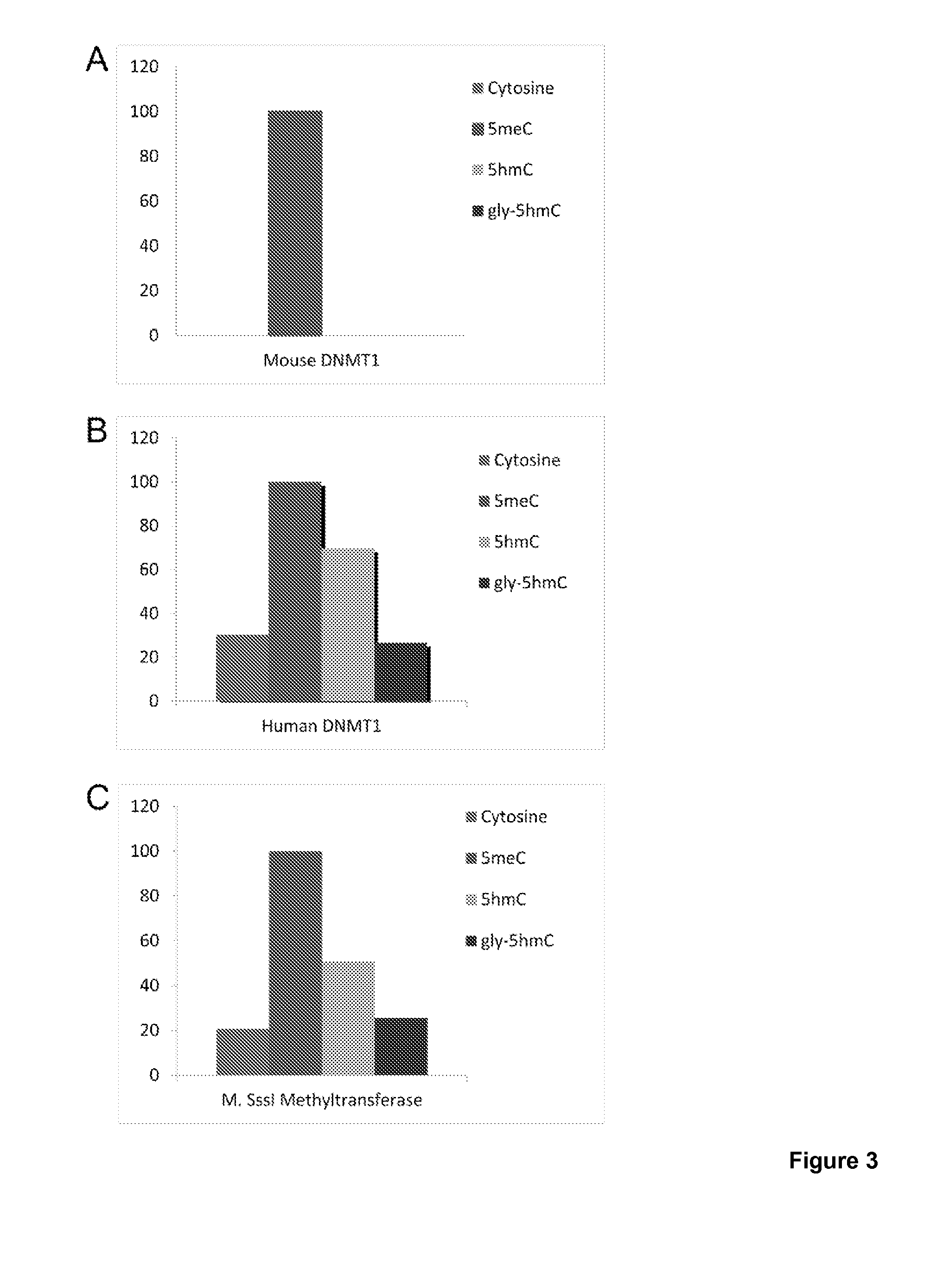
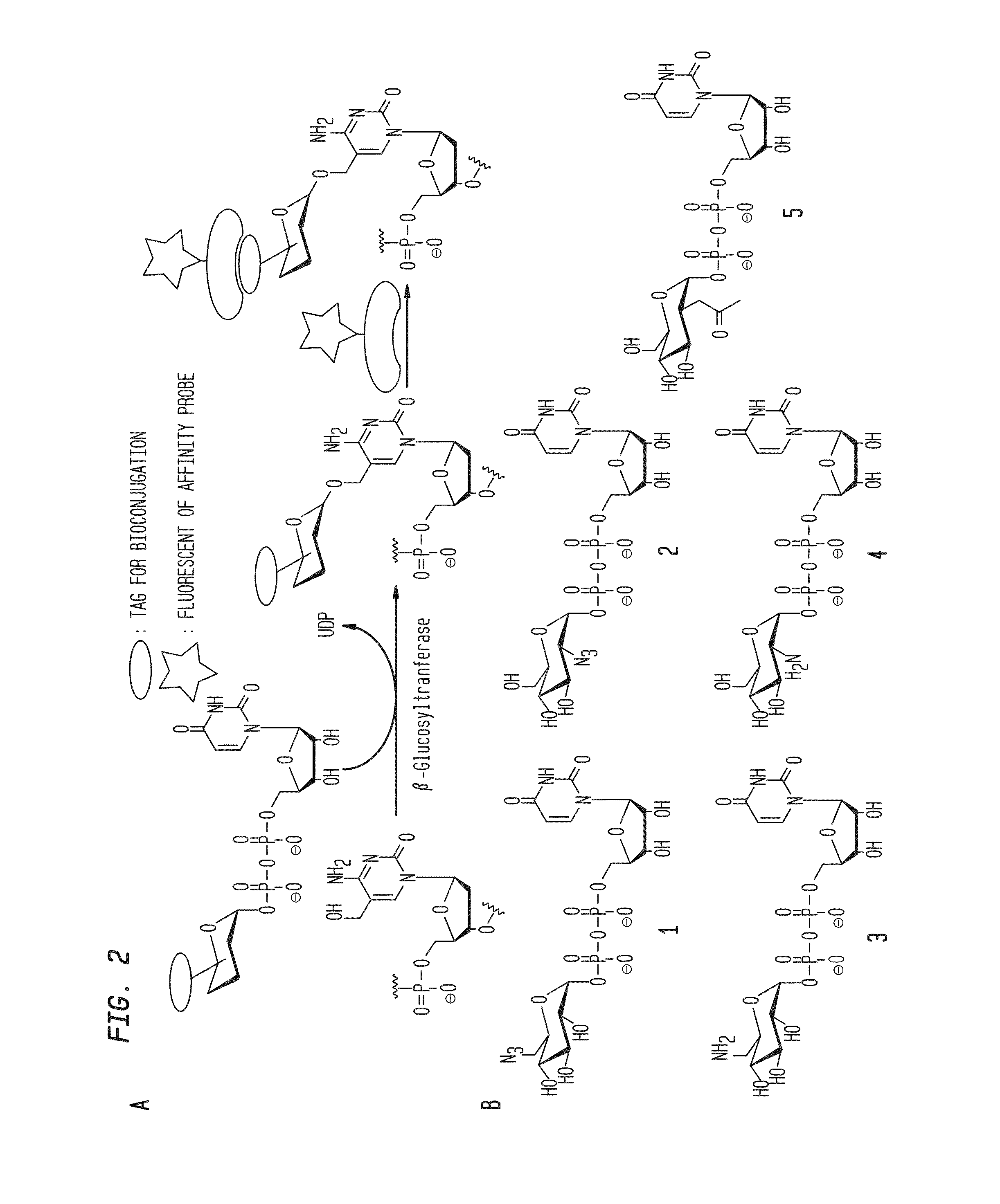
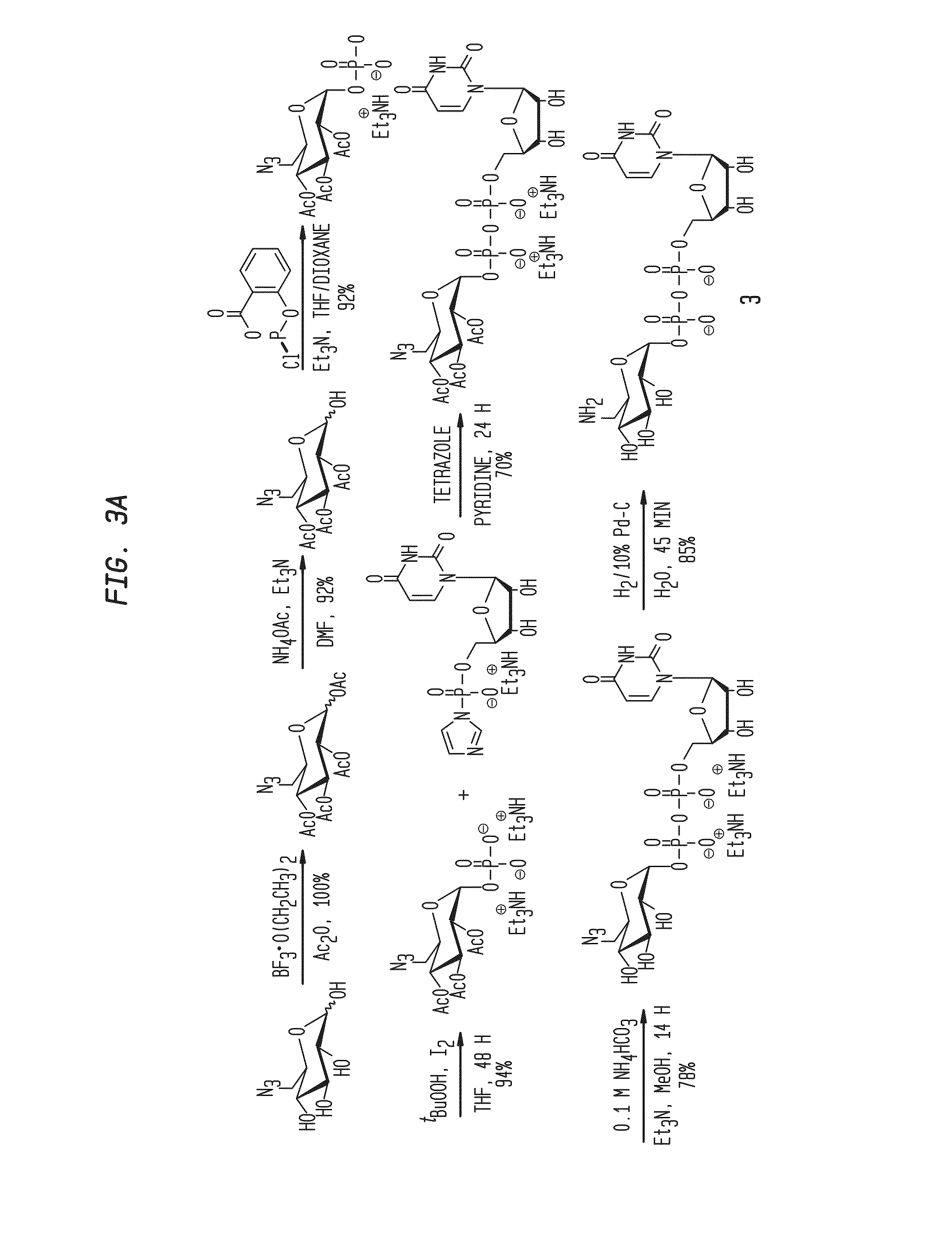
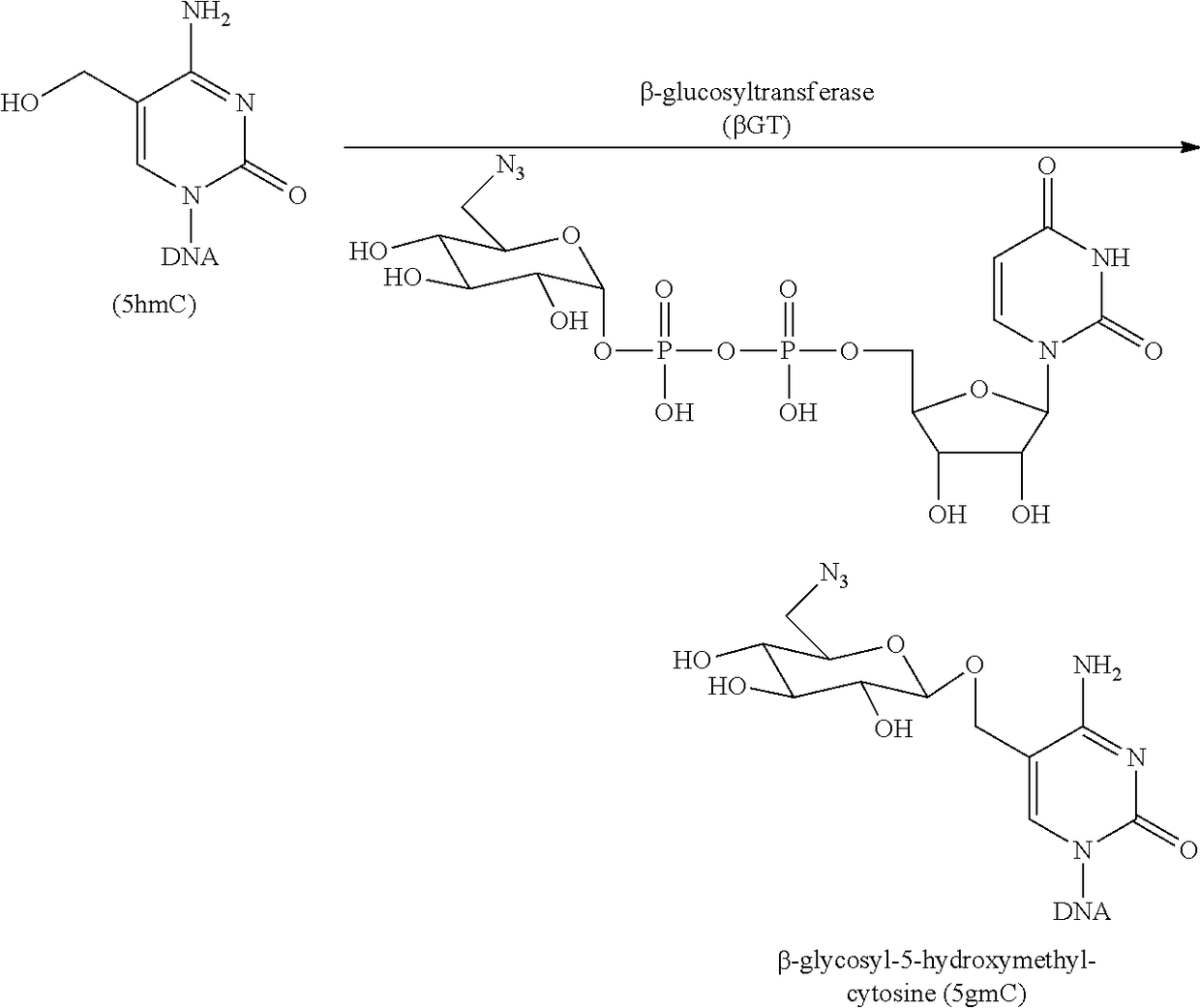
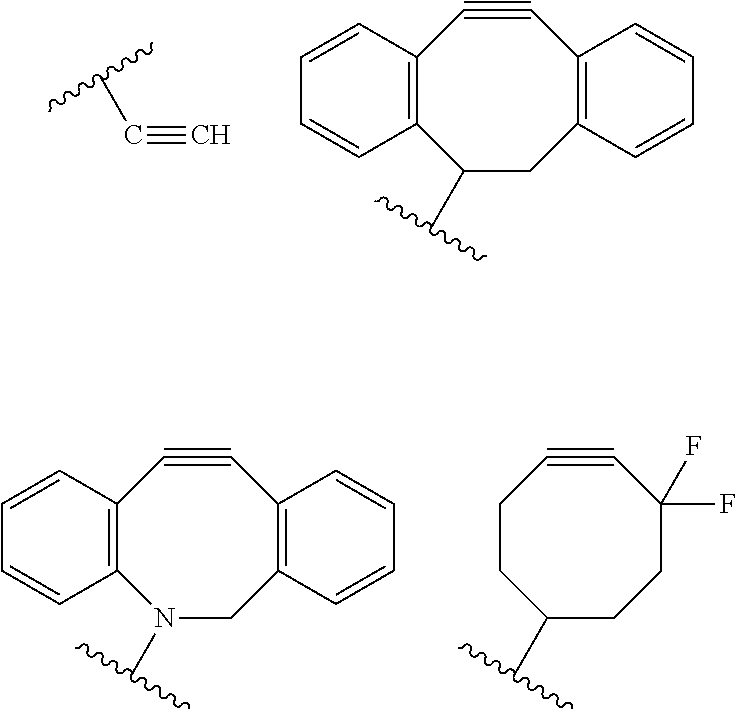
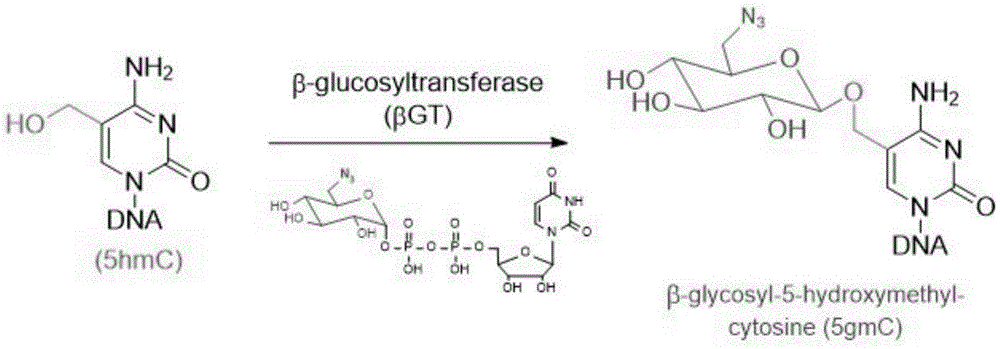
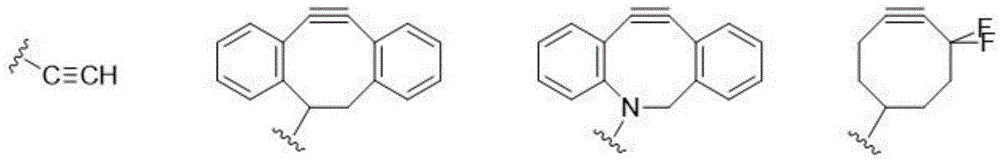
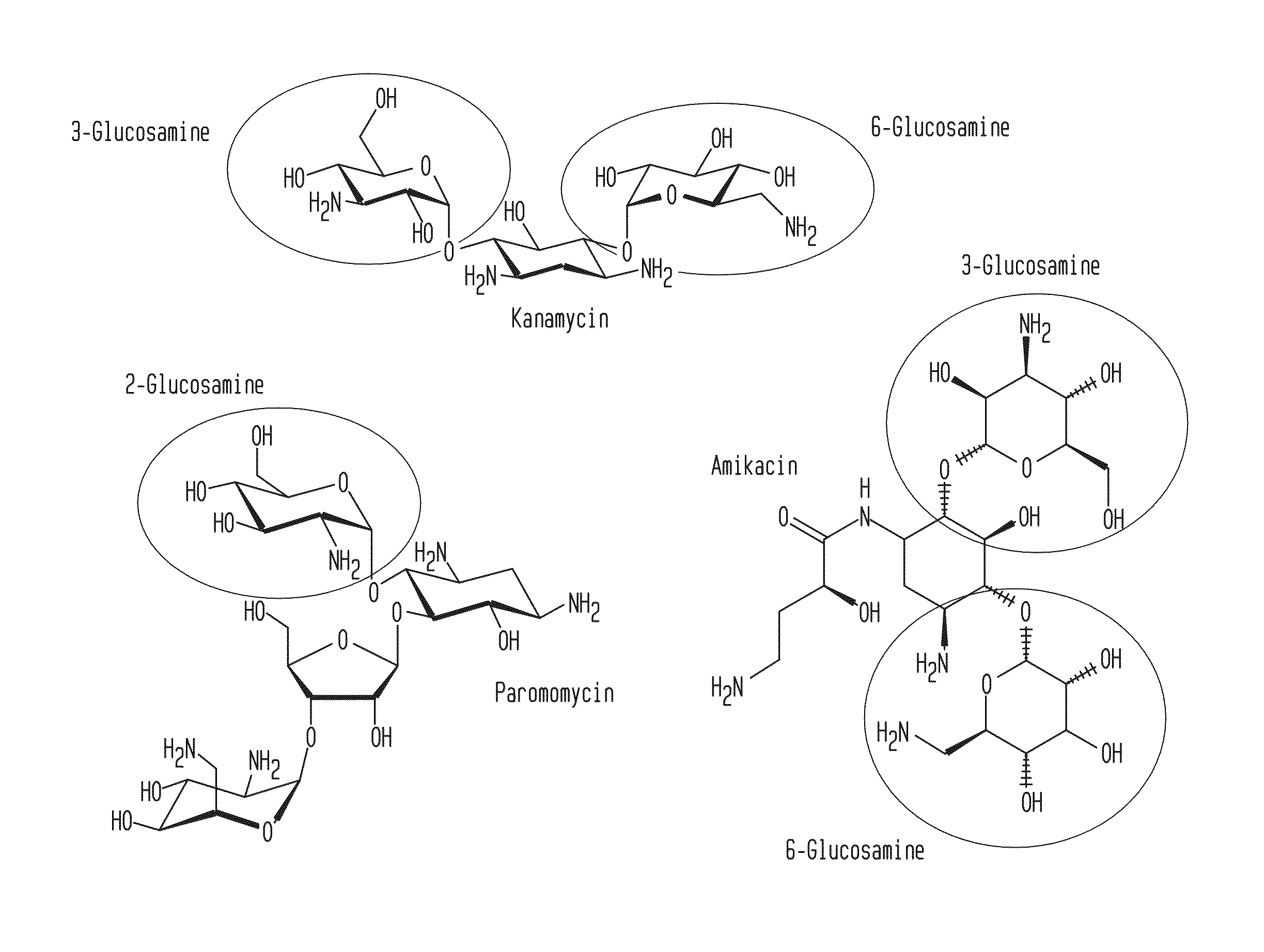
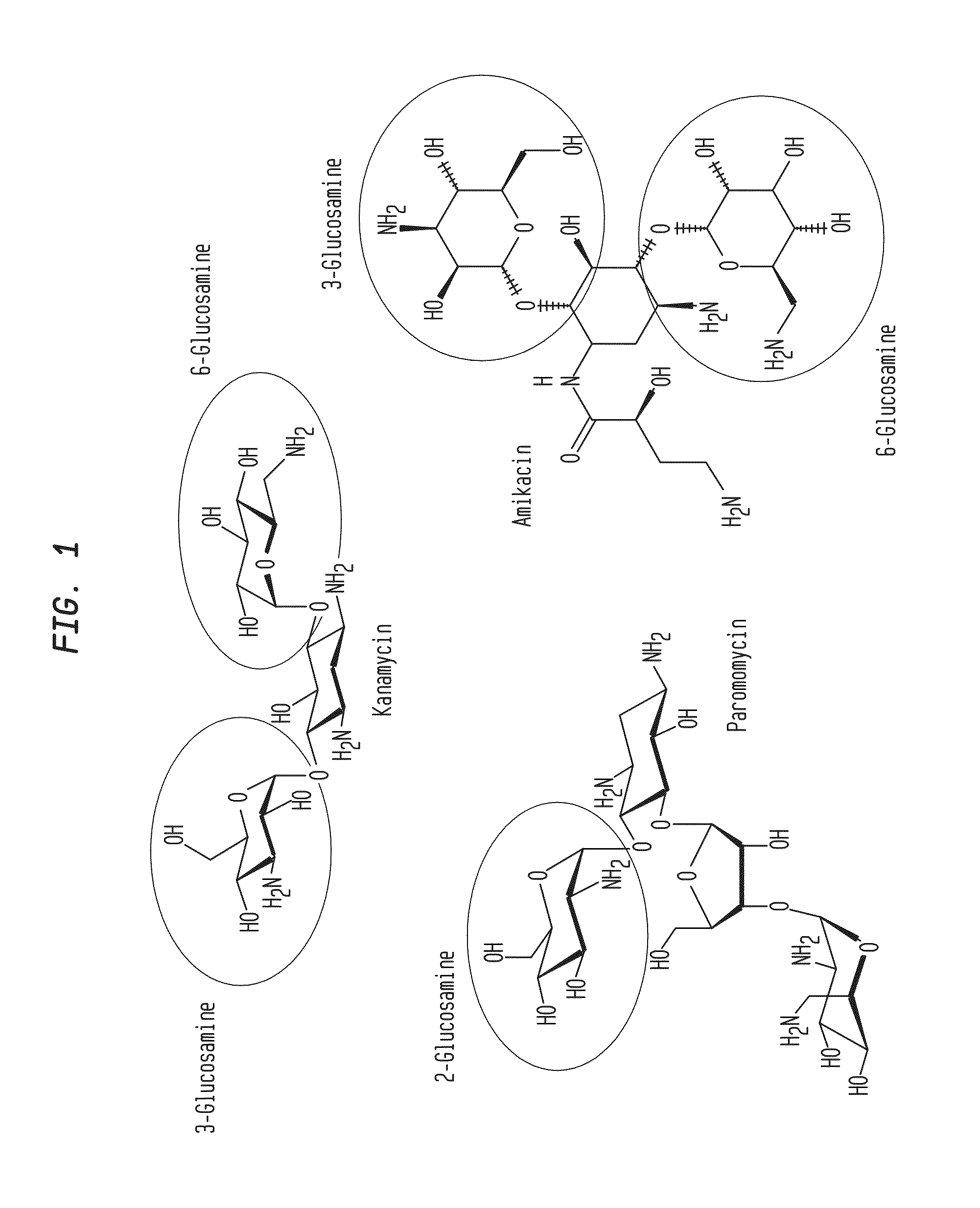
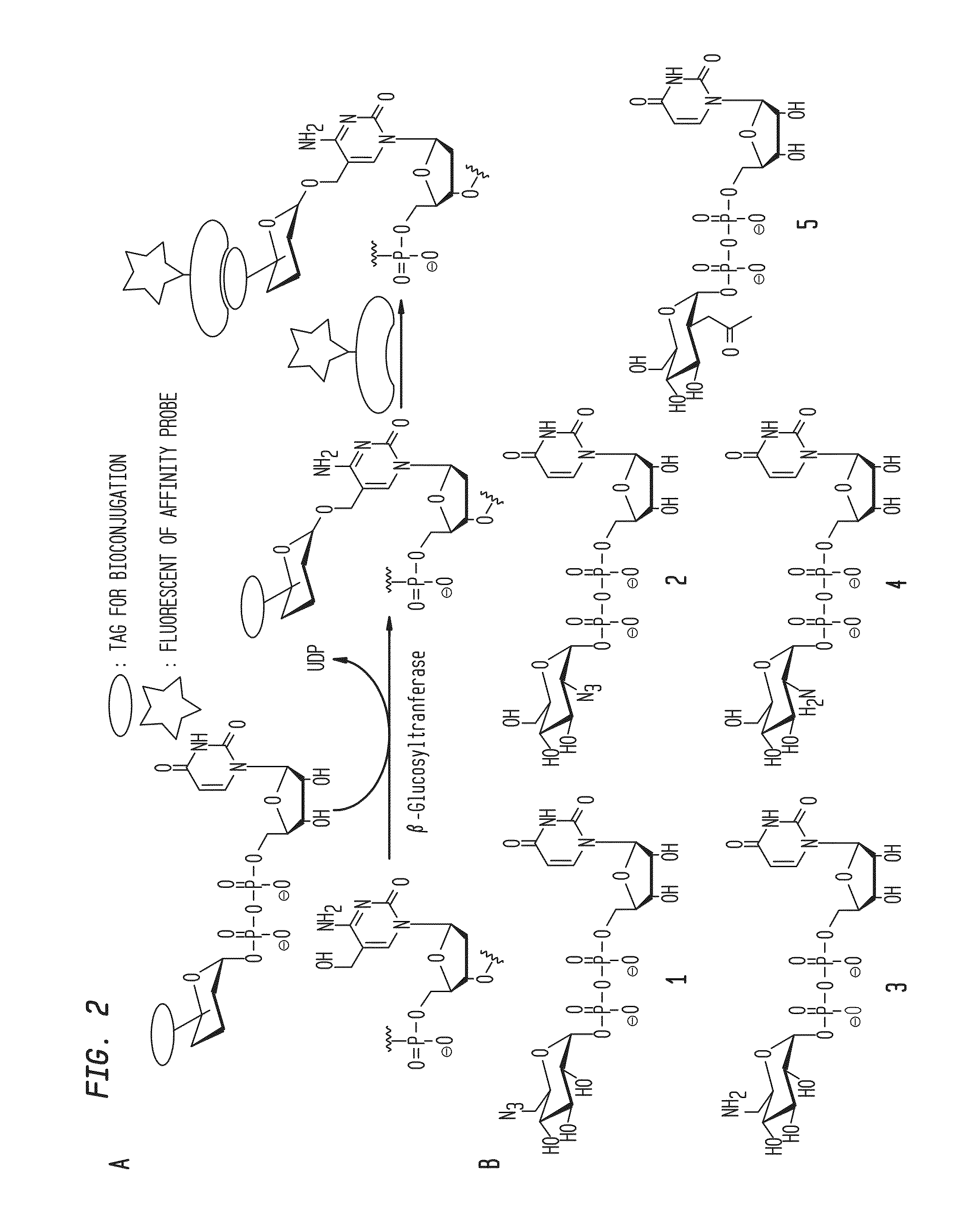
Compositions and Methods for the Transfer of a Hexosamine to a Modified Nucleotide in a Nucleic Acid
ActiveUS20140127677A1Well representedSelective control over cleavage of the nucleic acidFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesNucleotideHexosamines
Nucleic acids comprising β-glucosaminyloxy-5-methylcytosine; compositions, kits and methods of producing the nucleic acids using a glycosyltransferase; and methods of using the nucleic acids are described.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Method for genomic profiling of DNA 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine
ActiveUS20170253924A1Improve sequencing efficiencySufficient selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideDNA fragmentation
The present invention provides a method for genomic profiling of DNA 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, comprising the following steps: (1) DNA purification and fragmentation pretreatment: the target DNA is extracted and then broken to an average of 50 nucleotides to 10,000 nucleotides in length; (2) the repair of trace amount of DNA and the ligation thereof to the adaptor: the pre-treated DNA fragments are repaired and ligated with the sequencing adaptor required for the second-generation sequencing, (3) covalently labeling 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, (4) solid-phase enrichment of the labeled DNA fragments having cytosine with 5-position modification; (5) the PCR amplification of the solid-phase enriched DNA fragments, the PCR product is obtained and purified to obtain a library for the second-generation sequencing, after mapping the sequencing reads to the genome, the distribution map of the cytosine with 5-position modification in the DNA sample could be generated. The present invention greatly enhances the selectivity and efficiency of binding of the solid-phase surface with the DNA modified base.
Owner:BEIJING XUANNIAO FEIXUN TECH CO LTD
DNA5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine genome sequencing method
ActiveCN105648537AHigh selectivityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSolid phases5-Methylcytosine
The invention provides a DNA5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine genome sequencing method, comprising the following steps: (1), purifying and fragmentation pretreating DNA: extracting targeted DNA, breaking it into fragments having an average length of 50 nucleotides to 10000 nucleotides; (2), repairing trace DNA and connecting linker-adaptors: repairing and connecting pretreated DNA fragments to sequencing linker-adaptors required for next-generation sequencing; (3), covalently labeling 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine; (4), enriching in solid phase DNA fragments of labeled 5-position modified cytosine, and in the solid phase, amplifying with PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplimers of the corresponding linker-adaptors; purifying obtained PCR products to obtain a distribution map of genome 5-position modified cytosine required for next-generation sequencing. The invention greatly enhances bonding selectivity and efficiency of solid phase surface with DNA modified bases.
Owner:SHANGHAI YIBIEN GENE TECH CO LTD +1
Highly sensitive method for the detection of cytosine methylation patterns
InactiveUS7229759B2Inhibit bindingSolution value is not highSugar derivativesComponent separationChemical treatmentPolymerase L
The present invention concerns a method for the detection of cytosine methylation in DNA samples, wherein the following steps are conducted: (a) a genomic DNA sample, which comprises the DNA to be investigated and background DNA, is chemically treated in such a way that all of the unmethylated cytosine bases are converted to uracil, whereas the 5-methylcytosine bases remain unchanged; (b) the chemically treated DNA sample is amplified with the use of at least 1 primer oligonucleotide as well as a polymerase, whereby the DNA to be investigated is preferred as the template over the background DNA, and (c) the amplified products are analyzed and the methylation status in the DNA to be investigated is concluded from the presence of an amplified product and / or from the analysis of additional positions.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Method for the quantification of methylated DNA
InactiveUS20050287553A1Reliable valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseProbe type
Particular aspects of the present invention provide a method for quantification of two different variations of a DNA sequence. Particularly, the invention relates to a quantification of methylated DNA, and for this purpose, the test DNA is converted so that cytosine is converted to uracil, while 5-methylcytosine remains unchanged. The converted DNA is amplified by means of a real-time PCR, wherein two labeled real-time probe types are utilized: one specific for methylated DNA; and one for unmethylated DNA. Preferably, the degree of methylation of the test DNA is calculated from the ratio of the signal intensities of the probes or from the Ct values. The inventive methods have substantial utility for diagnosis and prognosis of cancer and other disorders associated with altered or characteristic DNA methylation status, as well as having substantial utility for analysis of SNPs, allelic expression, and prediction of drug response, drug interactions, among other uses.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Method for the detection of cytosine methylations in dna with the aid of scorpion
The invention relates to a method for analyzing cytosine methylations in DNA sequences, according to which non-methylated cytosines are first converted into uracil while 5-methylcytosine remains unmodified. The DNA is then amplified by means of a polymerase and at least one primer whose 5 end is connected to a probe via a linker. The probe is intramolecularly hybridized onto the amplified products in accordance with the methylation state of the DNA, hybridization being detectable via different detection systems. The inventive method is particularly suitable for diagnosing and predicting cancer diseases and other diseases associated with a modification of the methylation state as well as for predicting undesired effects of medicaments.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Compositions and methods for the transfer of a hexosamine to a modified nucleotide in a nucleic acid
ActiveUS9200260B2Selective control over cleavage of the nucleic acidFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesNucleotideHexosamines
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Composition and methods related to modification of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC)
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for detecting, evaluating, and / or mapping 5-methyl-modified and / or 5-hydroxylmethyl-modified cytosine bases within a nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
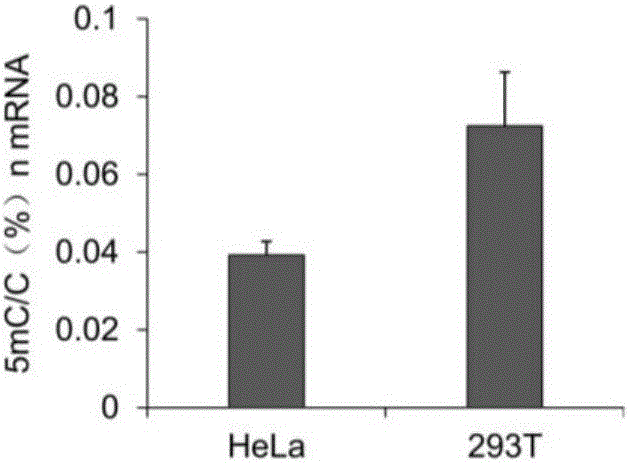
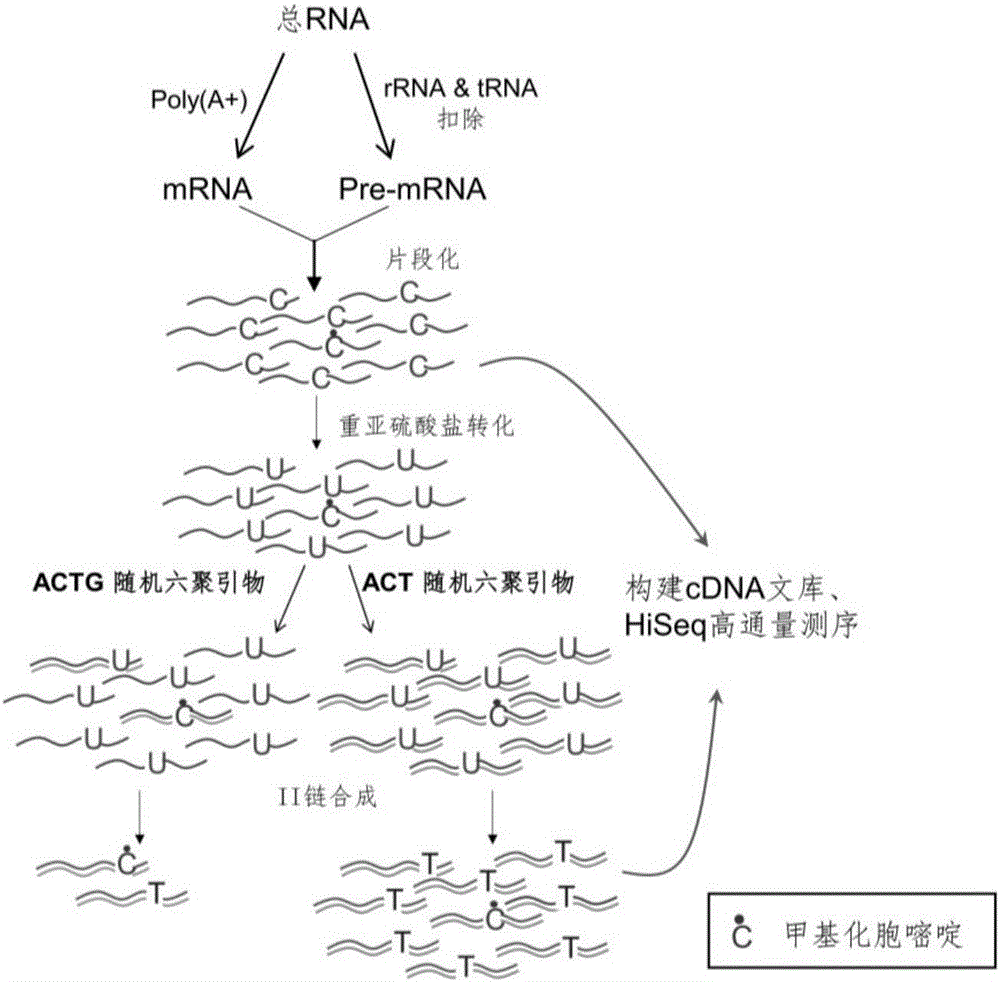
Library construction method for RNA 5mC bisulfite sequencing and application of library
ActiveCN105132409AEfficient matchingHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBisulfite sequencingRandom hexamer
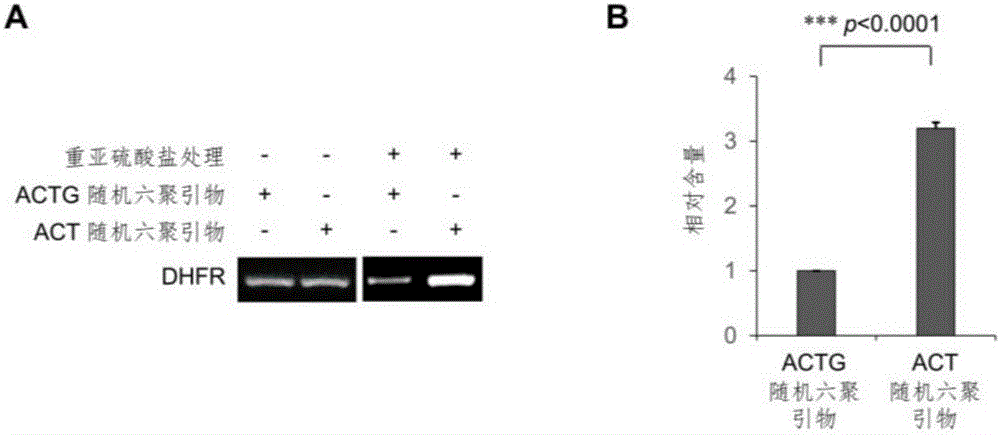
The invention relates to a library construction method, a sequencing method and a methylation detection method for sequencing 5-methylcytosine (5mC) modified bisulfite on RNA molecule. By designing and using triplet base random hexamers which contain ACT only, RNA fragment reverse transcription, PCR amplification efficiency and 5mC site detection efficiency after bisulfite treatment can be significantly improved, which is conducive to high-throughput sequencing of the 5mC site.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Method for relative quantification of methylation of cytosine bases in DNA samples
InactiveUS7153671B2Overcome disadvantagesMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyAmplification dnaGenomic DNA
A method is described for the relative quantification of the methylation of cytosine bases in DNA samples, wherein the following method steps are conducted:a) a genomic DNA sample is chemically converted with a reagent, wherein 5-methylcytosine and cytosine react differently and show a different base pairing behavior in the DNA duplex after the reaction;b) the DNA sample is amplified, whereby a fluorescently labeled dCTP or dGTP derivative is added;c) the amplified products are separated spatially from each other; andd) the fluorescence of the separated amplified products is measured quantitatively.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Restriction endonucleases and their applications
ActiveUS20110207139A1Well representedHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideGenetics
Provided is a methylation-specific restriction endonuclease for a DNA duplex substrate, which endonuclease recognizes in a strand of the duplex a 2 to 6 nucleotide recognition sequence comprising a 5-methylcytosine, and cleaves each strand of the duplex at a fixed position outside the recognition sequence.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BALTICS UAB
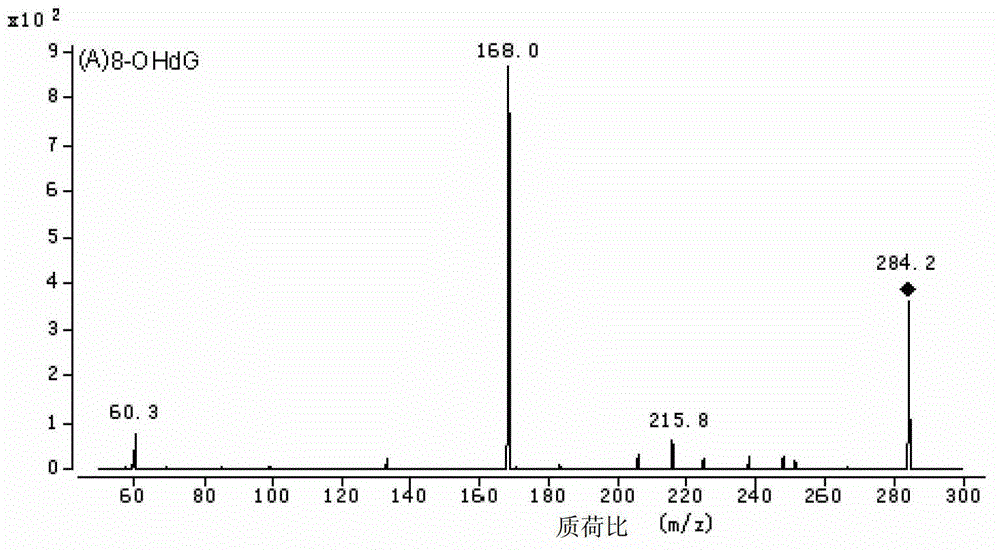
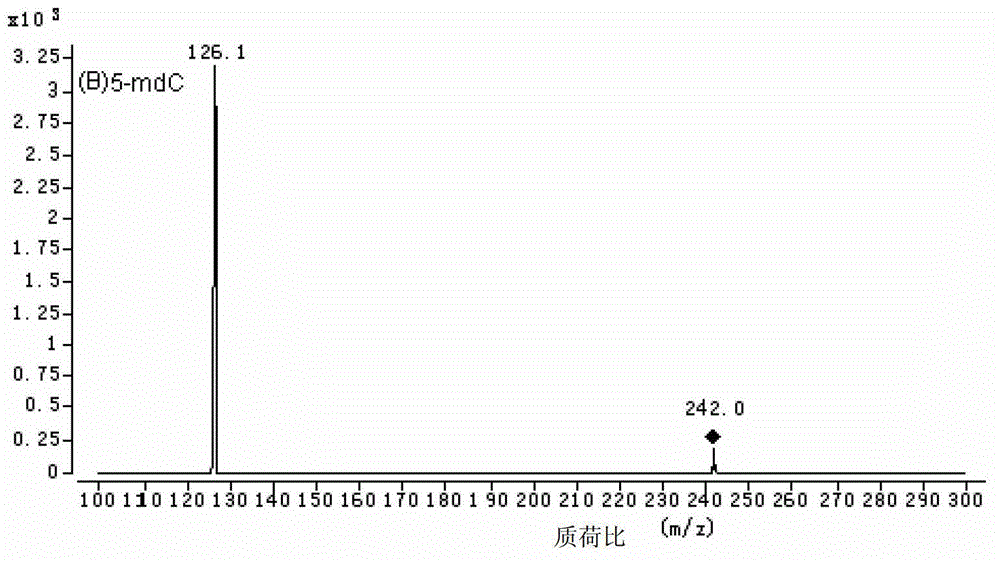
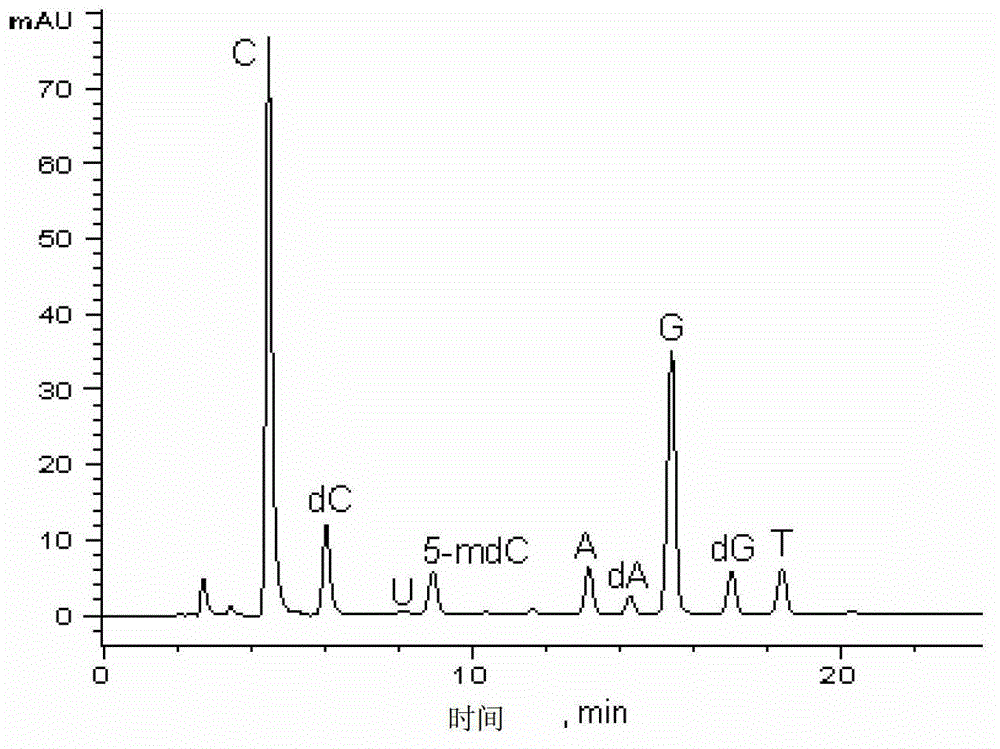
Method for high performance liquid chromatography(HPLC)-mass spectrometry (MS) detection of DNA oxidation and DNA methylation
The invention discloses a method for high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-mass spectrometry (MS) detection of DNA oxidation and DNA methylation, and the method comprises the following steps: hydrolyzing DNA, measuring the content of 5-methyl cytosine (5-mdC) and 8-hydroxy deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in the DNA hydrolysis product by HPLC-ESI (electrospray ionization)-MS / MS; wherein the high performance liquid chromatography is performed as follows: a mobile phase A is formic acid / methanol with the volume ratio of 0.01-0.3, a mobile phase B is a formic acid water solution with the volume ratio of 0.01 to 0.3%, and under the conditions of the flow velocity of 0.2-0.4ml / min and the column temperature of 15 to 40 DEG C, separation is performed by a liquid chromatography column; ESI (electrospray ionization)-MS is performed as follows: an electrospray ion source is ionized, and mass spectrometric analysis is performed in the positive electrode mode by a multiple reaction monitoring system. The method for high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-mass spectrometry (MS) detection of DNA oxidation and DNA methylation can simultaneously detect the content of 8-OHdG and 5-mdC in a DNA sample.
Owner:柯跃斌
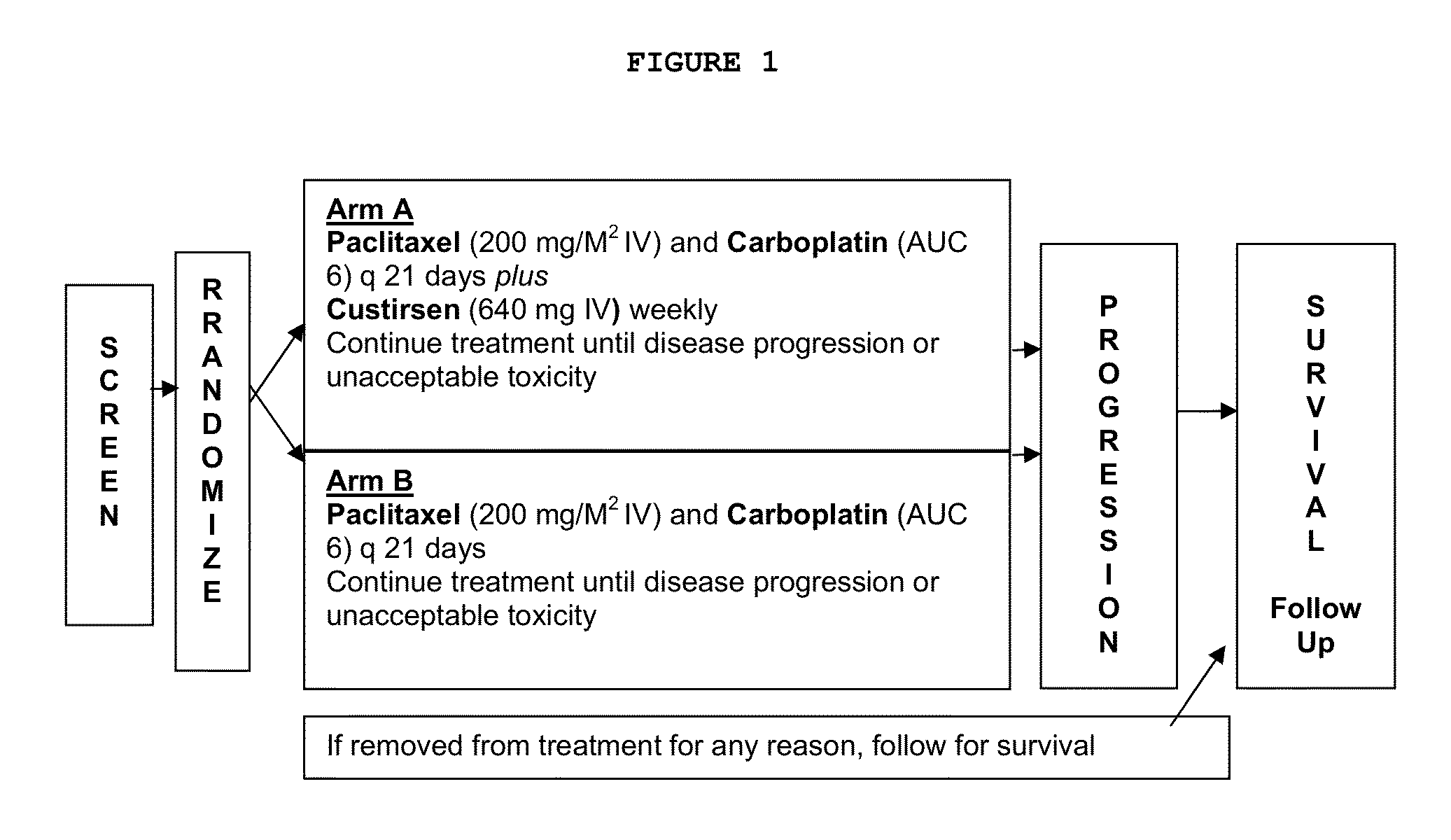
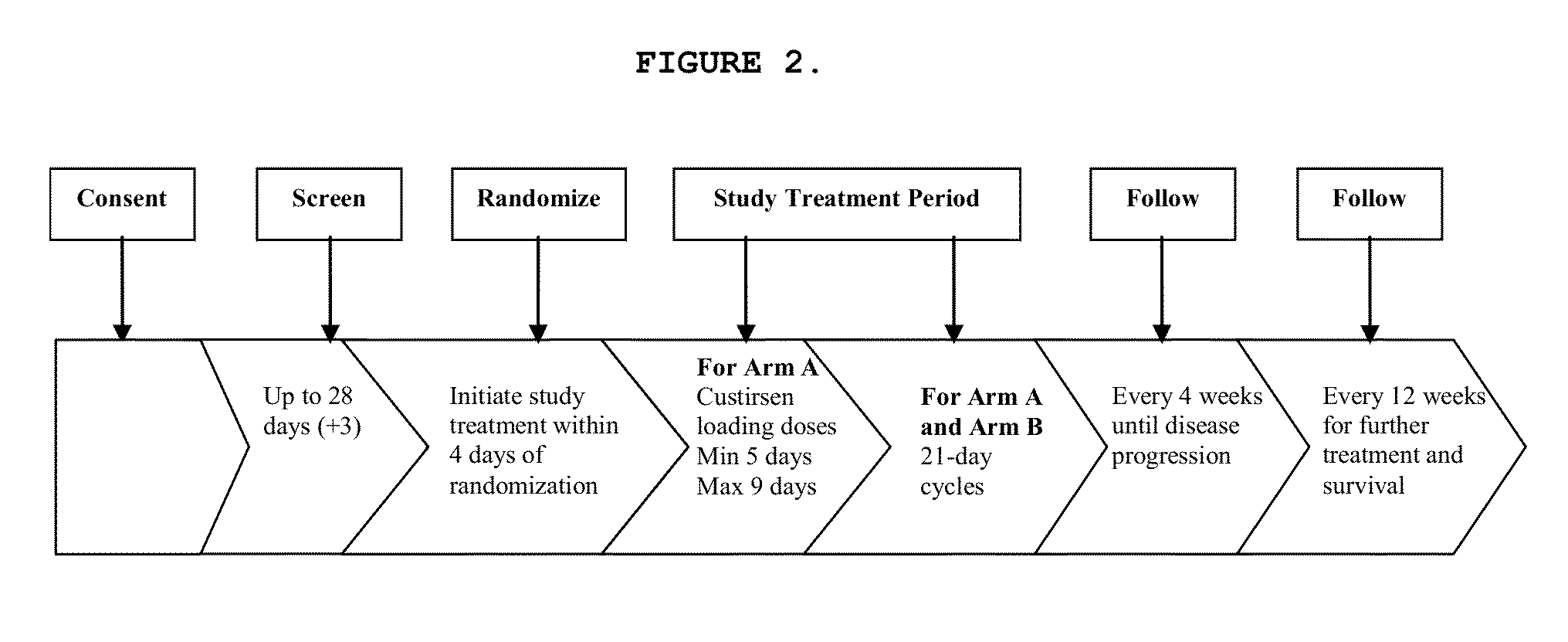
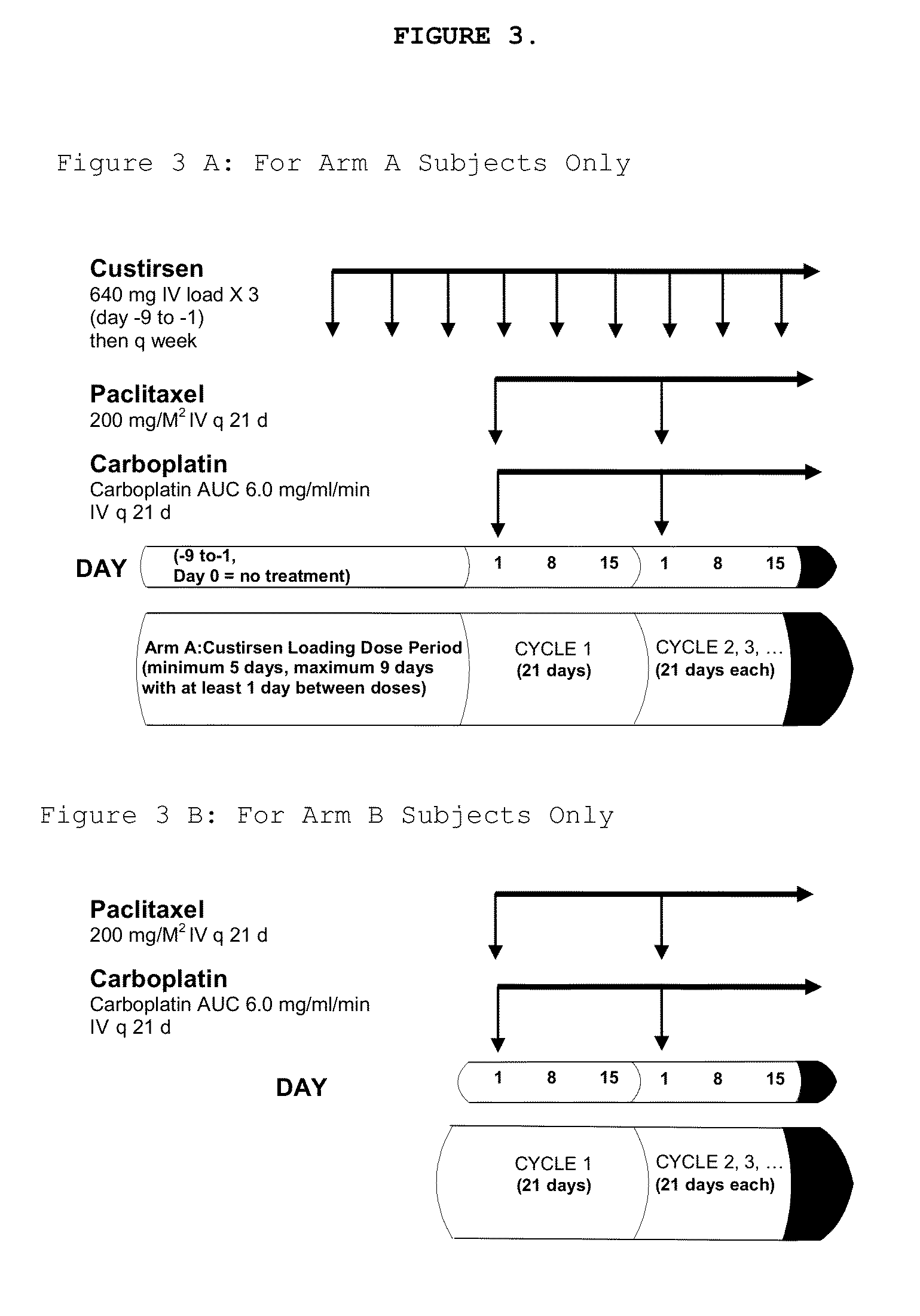
Method for treating non-small cell lung cancer
A method of treating a human patient afflicted with lung cancer comprising periodically administering to the human patient chemotherapy comprising an amount of a taxane and 640 mg of an anti-clusterin oligonucleotide having the sequence CAGCAGCAGAGTCTTCATCAT (Seq. ID No.: 1), wherein the anti-clusterin oligonucleotide has a phosphorothioate backbone throughout, has sugar moieties of nucleotides 1-4 and 18-21 bearing 2′-O-methoxyethyl modifications, has nucleotides 5-17 which are 2′ deoxynucleotides, and has 5-methylcytosines at nucleotides 1, 4, and 19, thereby treating the human patient afflicted with cell lung cancer.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
Method for detecting cytosine methylations
InactiveUS8241855B2Easy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGenomic DNAPolymerase L
A method is described for the detection of 5-methylcytosine in genomic DNA samples. First, a genomic DNA from a DNA sample is chemically converted with a reagent, whereby 5-methylcytosine and cytosine react differently. Then the pretreated DNA is amplified with the use of a polymerase with primers of different sequence. In the next step, the amplified genomic DNA is hybridized to an oligonucleotide array and PCR products are obtained, which must be provided with a label. Alternatively, the PCR products can be extended in a primer extension reaction, wherein the extension products are also provided with a label. In the last step, the extended oligonucleotides are investigated for the presence of the label.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Unmethylated CpG dinucleotide content detection method
InactiveCN101187652AImmunocompetentComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaHplc method
The invention provides a method for testing non-ethylating CpG content, which comprises adopting specific methylaseSssI to modify CpG dinucleotide aracytidine into 5-methylcytosine, then using nucleicacidase P1 and bacterial alkaline phosphatase to hydrolyze DNA into single deoxynucleoside, using a reversed-phase hplc method to test quantity of the 5-methylcytosinein DNA hydrolytic samples which are both modifying and un-modifying, and testing the CpG through differences of the 5-methylcytosine detectable amount between the modifying DNA hydrolytic sample and the un-modifying DNA hydrolytic samples.
Owner:NAT INST FOR THE CONTROL OF PHARMA & BIOLOGICAL PROD
Highly sensitive method for the detection of cytosine methylation patterns
InactiveUS20120107807A1Inhibit bindingSolution value is not highMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorComponent separationUracilPolymerase L
Owner:OLEK ALEXANDER +1
Method for quantification of methylated DNA
The present invention relates to a method for the quantification of methylated cytosines in DNA. In the first step of the invention unmethylated cytosines in the DNA to be analysed are chemically converted into uracil while 5-methylcytosines remain unchanged. In a second step the converted DNA is amplified methylation specifically in a real time PCR using a methylation specific probe. Finally the amount of uniformly methylated DNA is calculated by combining criteria derived from the shape of the real time curve and from the signal intensity. The method is preferably used for diagnosis and / or prognosis of adverse events for individuals, for distinguishing cell types and tissues, or for investigating cell differentiation.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Method for detecting 5-methylcystein in DNA
The invention relates to a method for detecting 5-methylcystein in DNA. The method is used for detecting the 5-methylcystein in the DNA based on an asymmetric PCR (polymerase chain reaction) theory by applying dGTP (deoxyguanosine triphosphate) containing a fluorophore. The method comprises the specific detection steps of treating the DNA containing the 5-methylcystein by a sodium hydrogen sulfite method, converting cytosine in the DNA into uracil, and obtaining complementary chains of a large amount of target DNAs through asymmetric PCR, wherein adenine without fluorescence is complementary to the cytosine in the DNA, and dGTP with fluorescence is compensatory to the 5-methylcystein; detecting 5-methylcystein in the DNA through DNA gel electrophoresis (PAGE). Therefore, the 5-methylcystein in the DNA can be subjected to fluorescence detection through excitation at 492 nanometers.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
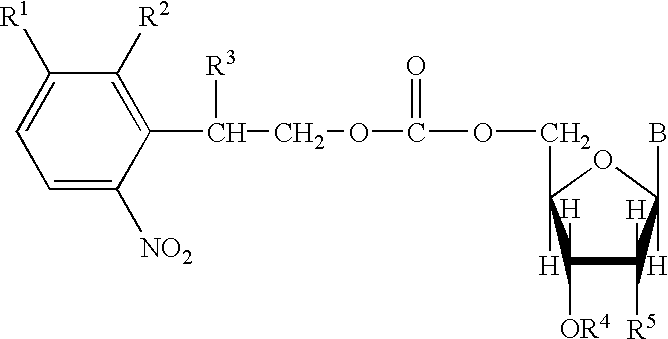
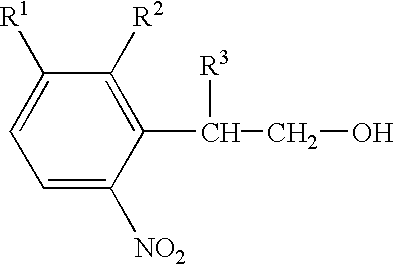
Nucleoside derivatives with photolabile protective groups
The invention relates to nucleoside derivatives with photolabile protecting groups of general formula (I), where R1=H, F, Cl, Br, I, NO2; R2=H, CN, where R1 and R2 are not simultaneously H; R3=H, 1-4 C alkyl, phenyl; R4=H or a conventional functional group for the synthesis of oligonucleotides; R5=H, OH, halogen or XR6, where X=O or S and R6=a conventional nucleotide protecting group; B=adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine, uracil, 2,6-diaminopurin-9-yl, hypoxanthin-9-yl, 5-methylcytosin-1-yl, 5-amino-4-imidazolcarboxamid-1-yl or 5-amino-4-imidazolcarboxamid-3-yl, where, if B=adenine, cytosine or guanine the primary amine functionality, optionally, carries a permanent protecting group. Furthermore, these derivatives may be used for the light-controlled synthesis of oligonucleotides on a DNA chip.
Owner:NIGU CHEM
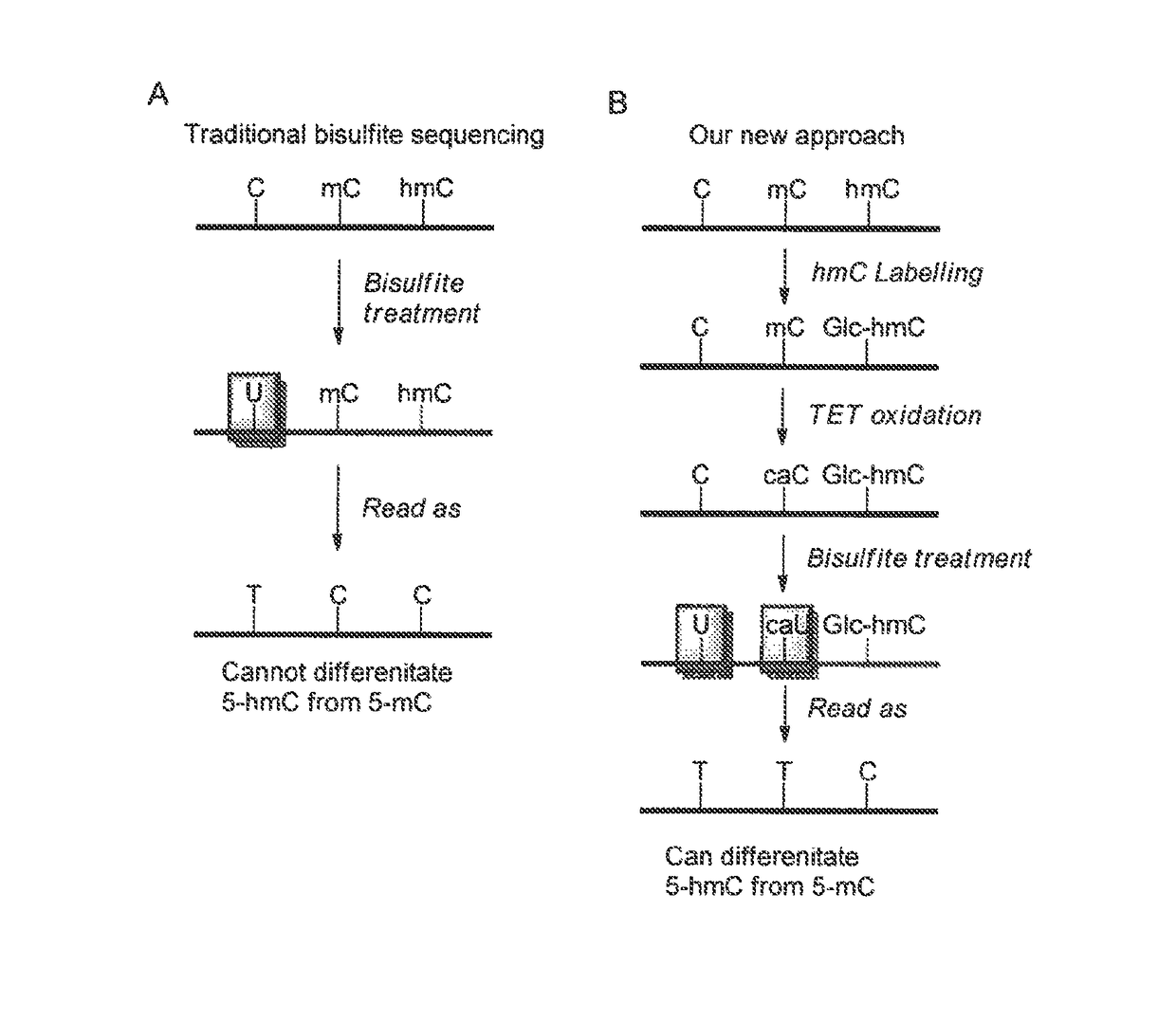
Method and reagent for adjusting methylation/demethylation state of nucleic acid
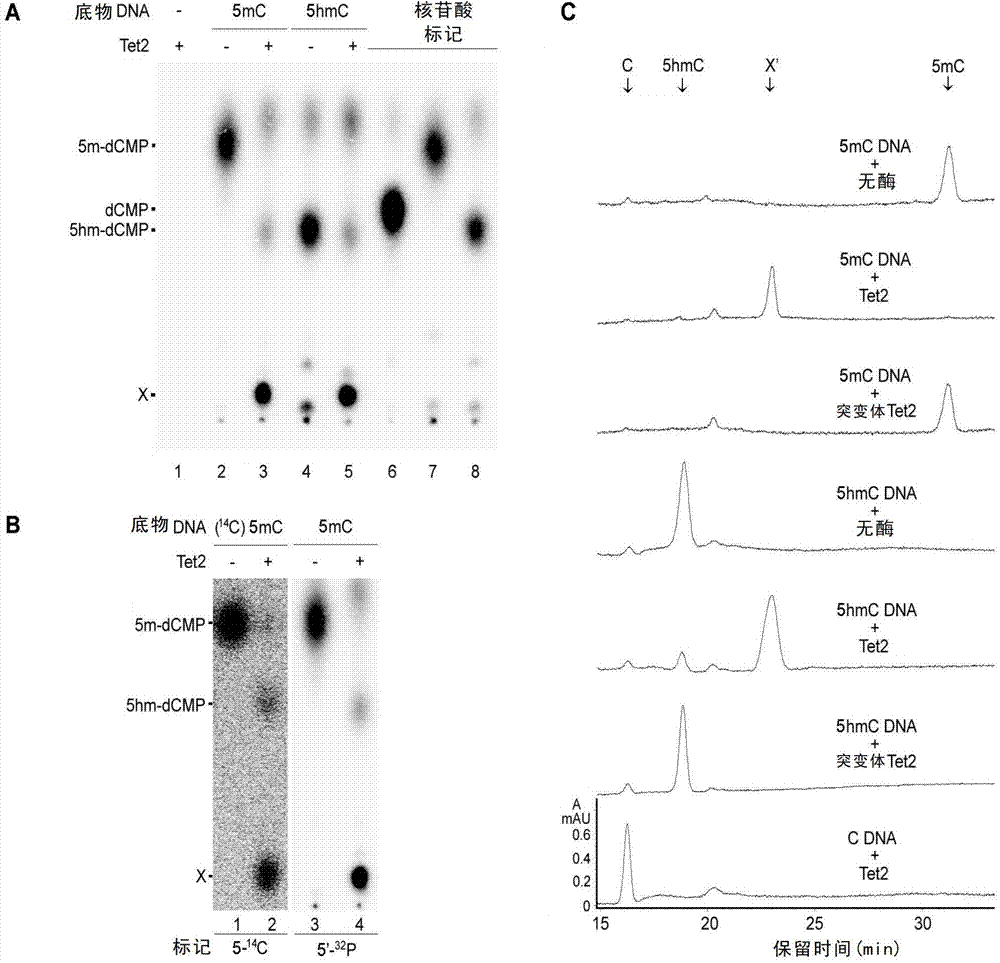
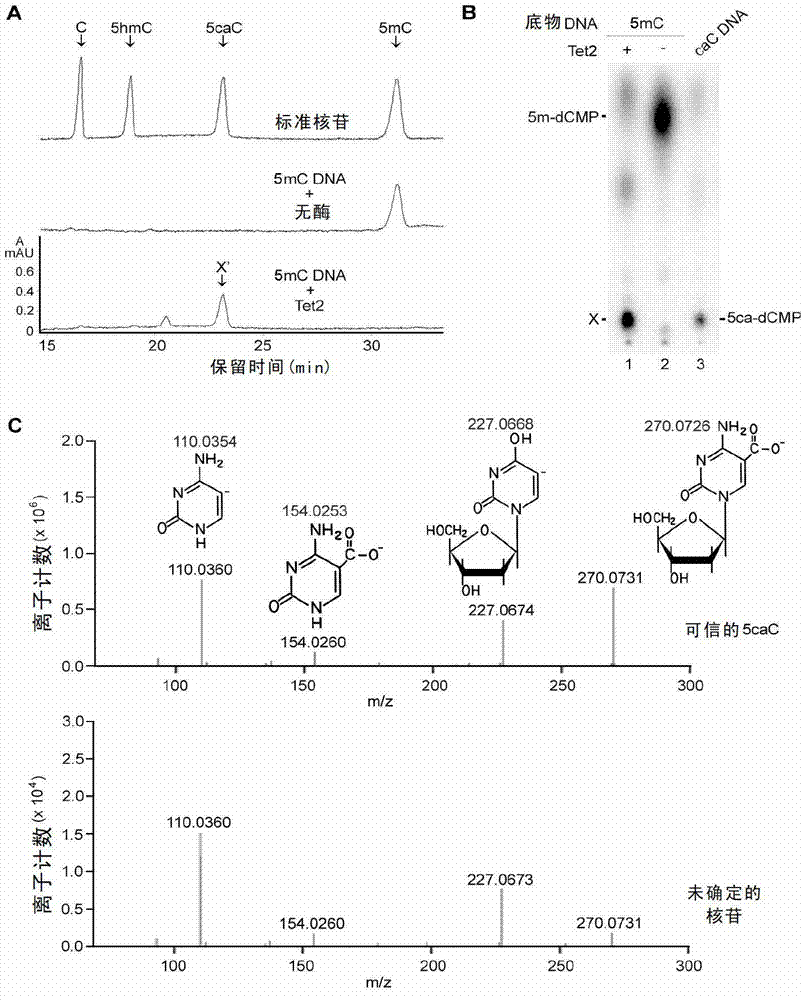
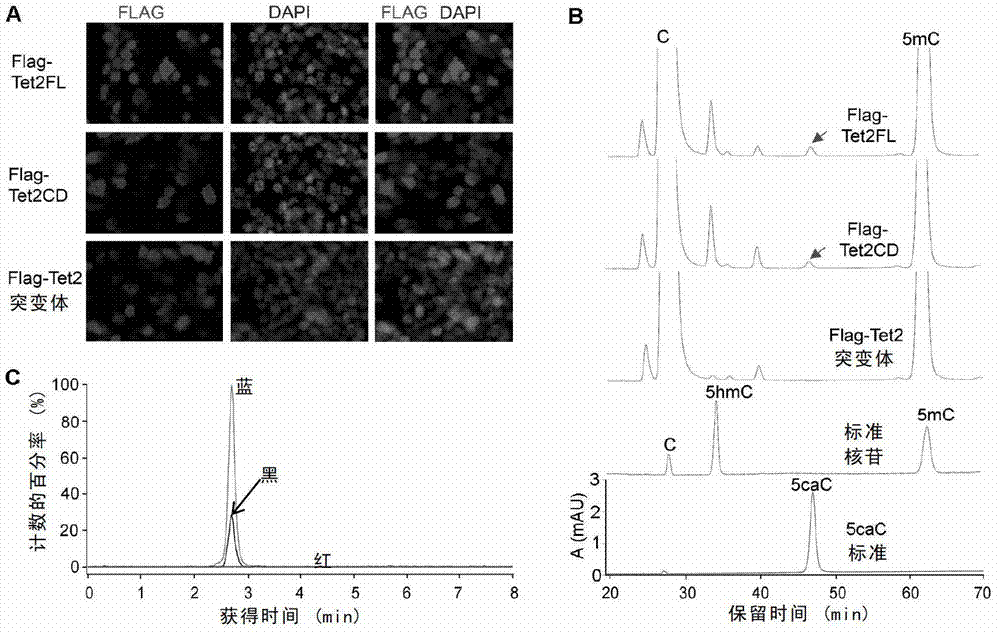
The invention relates to a method and a reagent for adjusting the methylation / demethylation state of nucleic acid. An inventor proves that 5-methylcystein (mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC) in genome deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) can be oxidized into 5-carboxyl cytosine (caC) by Tet dioxygenase for the first time. Thymine DNA glycosylase (TDG) can specifically identify the 5caC and remove the 5caC from the genome to ensure that DNA is demethylated actively. Therefore, the methylation / demethylation effect of DNA in the genome can be adjusted, and the reagent for adjusting methylation / demethylation effect of DNA in the genome can be prepared. Through verification, the genome DNA in a cell has 5caC modification, a 5caC modification spectrum can be used for monitoring the state of the cell, and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and analogues thereof can be used as regulators of Tet enzyme. Moreover, by Tet mutation in leukemia, the 5caC activity is reduced or the 5caC is inactivated.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ligase/polymerase method for detecting cytosine methylation in DNA samples
InactiveUS7405040B2Easy to detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHistone methylationNucleotide
Described is a method for detecting 5-methylcytosine in genomic DNA samples. First, a genomic DNA from a DNA sample is chemically converted with a reagent, 5-methylcytosine and cytosine reacting differently, and the pretreated DNA is subsequently amplified using a polymerase and at least one primer. In the next step, the amplified genomic DNA is hybridized to at least two oligonucleotides, the latter being joined by inserting at least one oligonucleotide. In the ligation product, one nucleotide carries a detectable label, and the elongation depends on the methylation status of the specific cytosine in the genomic DNA sample. In the next step, the elongated oligonucleotides are analyzed for the presence of the label.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Method for quantitatively detecting deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) demethylation capability of pollutant
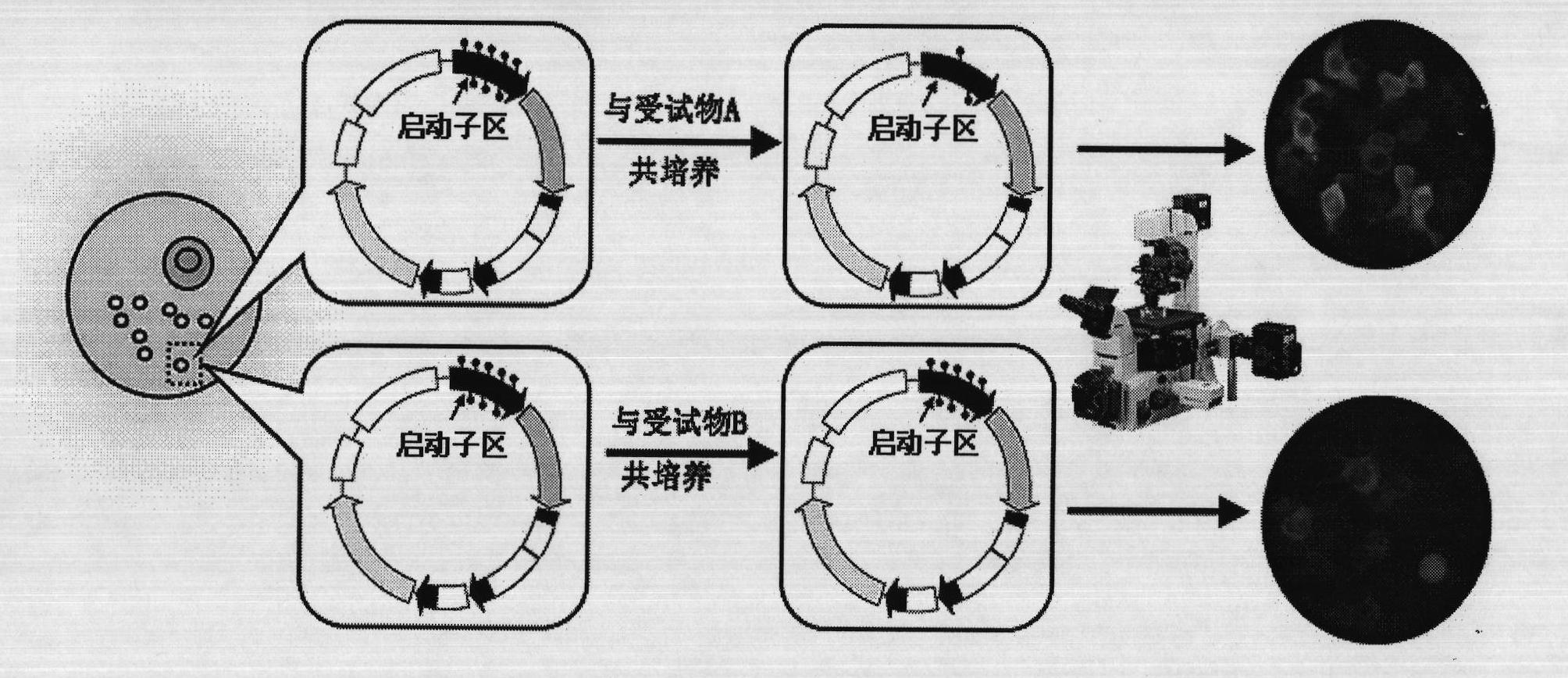
InactiveCN101886130AThe method is easy to operateSimple stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyBiology
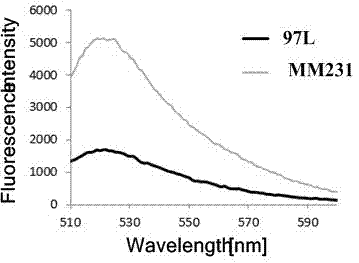
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively detecting the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) demethylation capability of pollutant, and belongs to the field of the methods for detecting the health damaging capability of the pollutant. At present, no mature detection technology is provided for evaluating the DNA demethylation capability of the pollutant. The method comprises the following steps of: manually methylating fluorescent plasmids; transferring Hela cells from highly-methylated fluorescent plasmids to prepare reconstitution cell strains; performing pretreatment on a pollutant sample; co-culturing 5-methylcystein standard series and the reconstitution cell strains and synchronously co-culturing the tested sample and the reconstitution cell strains; performing fluorescent photographing and fluorescence intensity treatment on the reconstitution cell strains; drawing a pollutant demethylation capability detection standard curve; and quantitatively detecting the demethylation capability of the tested sample pollutant. If green fluorescent light emitted from tested cells is brighter, the demethylation capability of the pollutant is higher and the risk of health damage to a human body is higher. A rapid, simple and quantitative detection method is provided for evaluating the human DNA demethylation capability of the pollutant.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Method for detecting a methylation pattern
The present invention relates to a method for detecting the presence of one or more methylation patterns. It comprises the conversion of nucleic acids and a catalytic nucleic acid activity. Here, the conversion of the nucleic acid is characterized such that the 5-methylcytosine remains unchanged while the unmethylated cytosine is converted into uracil or another base, which can be distinguished from cytosine in its base-pairing behavior.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Method for measuring DNA methylation content of floating fern by using high performance liquid chromatography
InactiveCN101813681ASimple methodLow costComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementRetention timeA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for measuring DNA methylation content of floating fern by using high performance liquid chromatography. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a floating fern sample to be measured and extracting DNA in the sample to obtain a DNA sample to be measured; storing the DNA sample at the temperature of -20 DEG C for later use after the DNA sample is dissolved in buffer liquid; hydrolyzing the DNA sample to be measured and centrifuging the hydrolyzed DNA sample; taking supernatant liquid so as to obtain the solution of the sample to be measured; preparing the mixed solution of standard samples of a cytosine standard sample and a 5-methylcytosine standard sample; and measuring the DNA methylation content of the DNA sample to be measured according to peak retention time and peak areas of the mixed solution of the standard samples and the solution of the sample to be measured under the same high performance liquid chromatography measurement condition. In the method, the DNA methylation content of the floating fern is measured by using the high performance liquid chromatography; and therefore, the method has the characteristics of simplicity, low cost, fast and accurate measurement, and good quantitative analysis effect. Simultaneously the high performance liquid chromatographic technology per se is used very widely, the technology is mature relatively, and the DNA extraction from the floating fern can be implemented by using a conventional method, so the method can be popularized and applied.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Unmethylated CpG dinucleotide content detection method
InactiveCN100526876CImmunocompetentComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaPyrimidine Nucleotides
The invention provides a method for testing non-ethylating CpG content, which comprises following steps: adopting specific methylating enzyme SssI to modify CpG dinucleotide cytosine which is 5-methylcytosine,then using nuclease P1 and bacterial alkaline phosphatase to hydrolyze DNA into single deoxynucleoside, using a reversed-phase high effective liquid phase method to test the content of the 5-methylcytosinein DNA hydrolytic samples which are both modifying and un-modifying, and testing the CpG through differences of the 5-methylcytosine detectable amount between the modifying DNA hydrolytic sample and the un-modifying DNA hydrolytic samples.
Owner:NAT INST FOR THE CONTROL OF PHARMA & BIOLOGICAL PROD
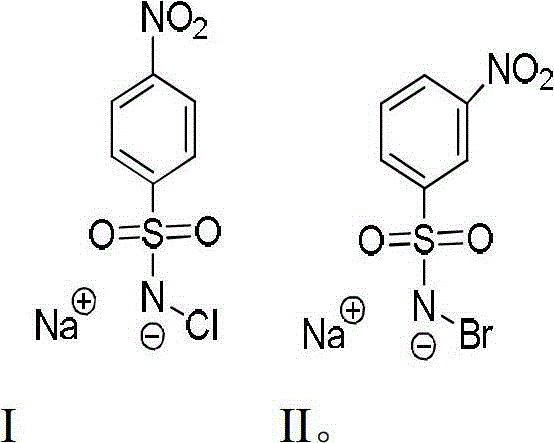
Chemical method for detecting 5-methylcystein in DNA
InactiveCN102912024AEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurement3-deoxyriboseDeoxyribose
The invention relates to a chemical method for detecting 5-methylcystein in DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid). Two compounds adopted in the method are substituted chloramine-B hydrate and substituted bromoamine-B hydrate. The method comprises the detection steps of allowing the substituted chloramine-B hydrate to react with cytosine in the fluorescently-labeled DNA, then allowing the substituted bromoamine-B hydrate to react with the cytosine and the 5-methylcystein in the fluorescently-labeled DNA, treating with piperidine, and comparing two reacted DNA zones in DNA polyacrylamide denatured gel to clearly observe the positions and the number of the 5-methylcystein.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com