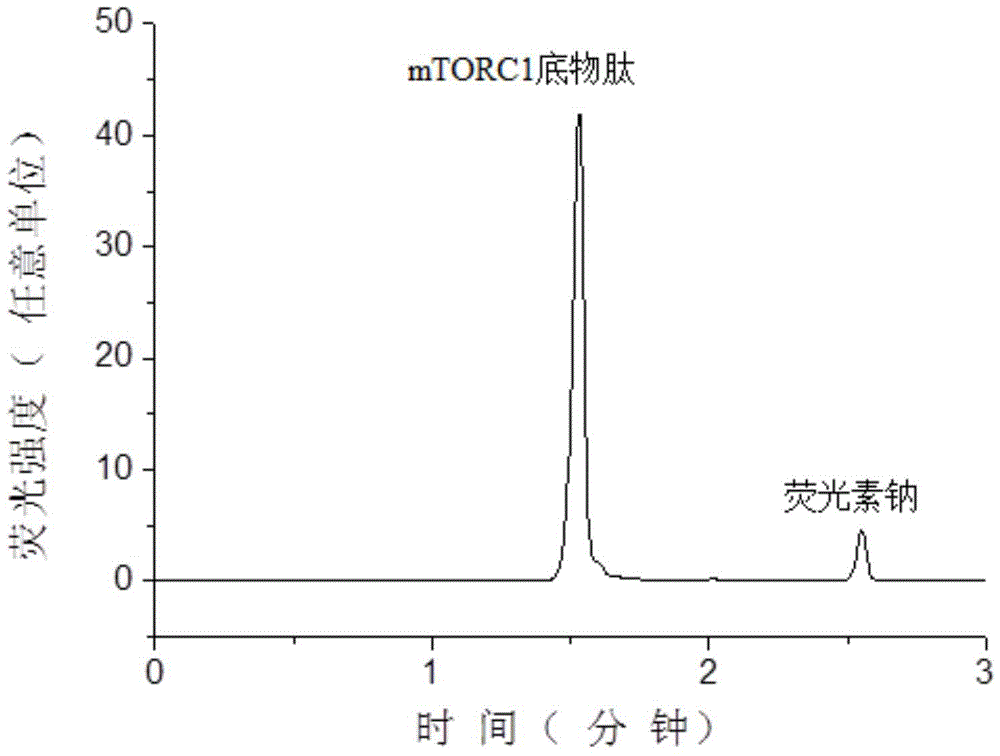
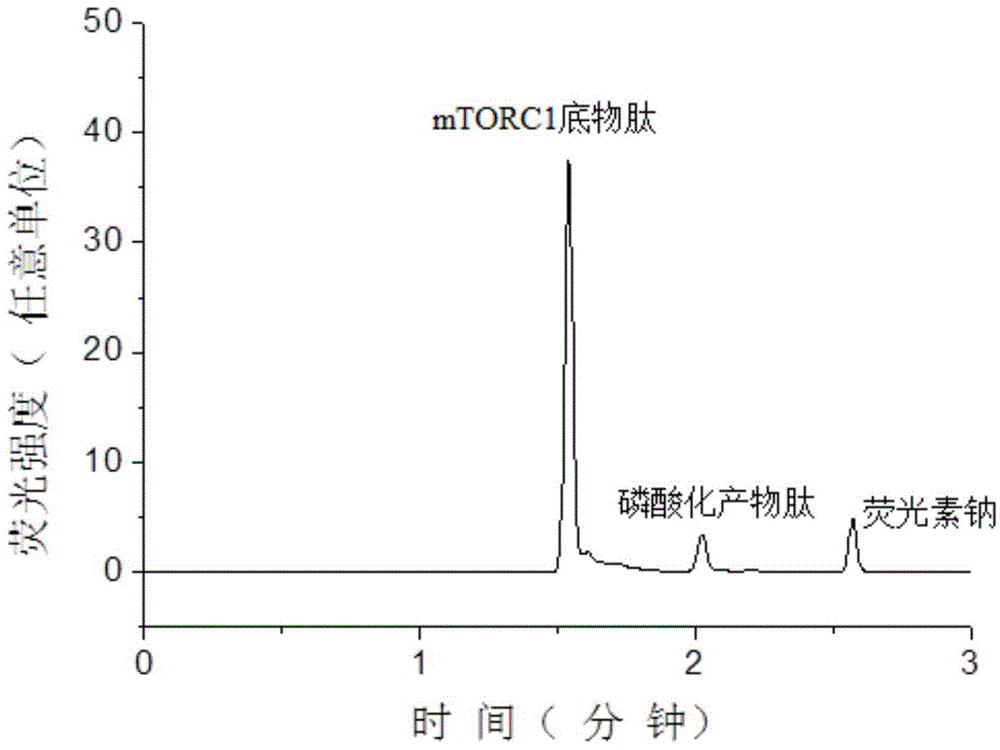
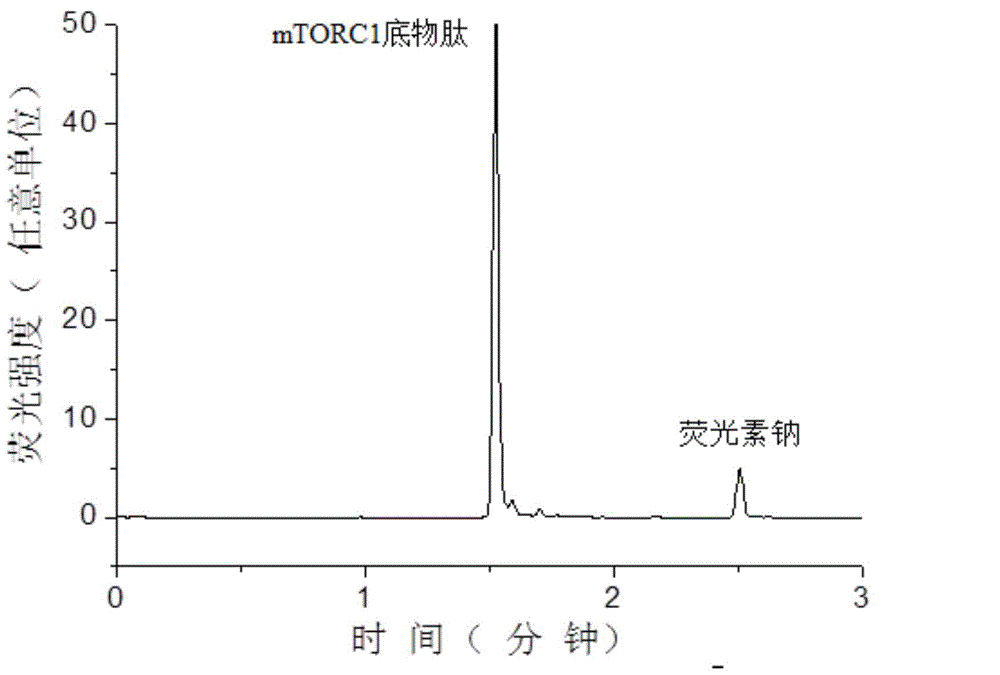
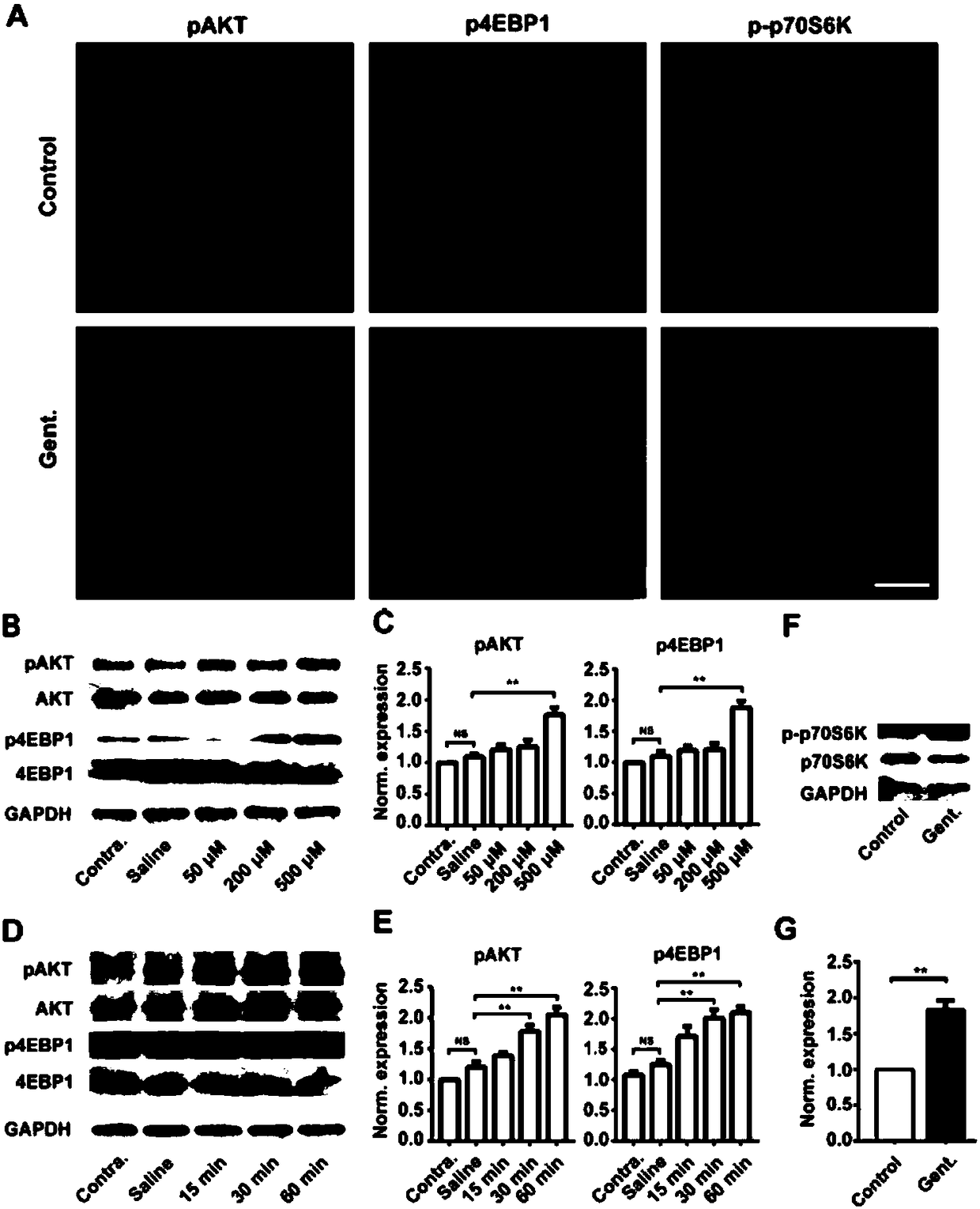
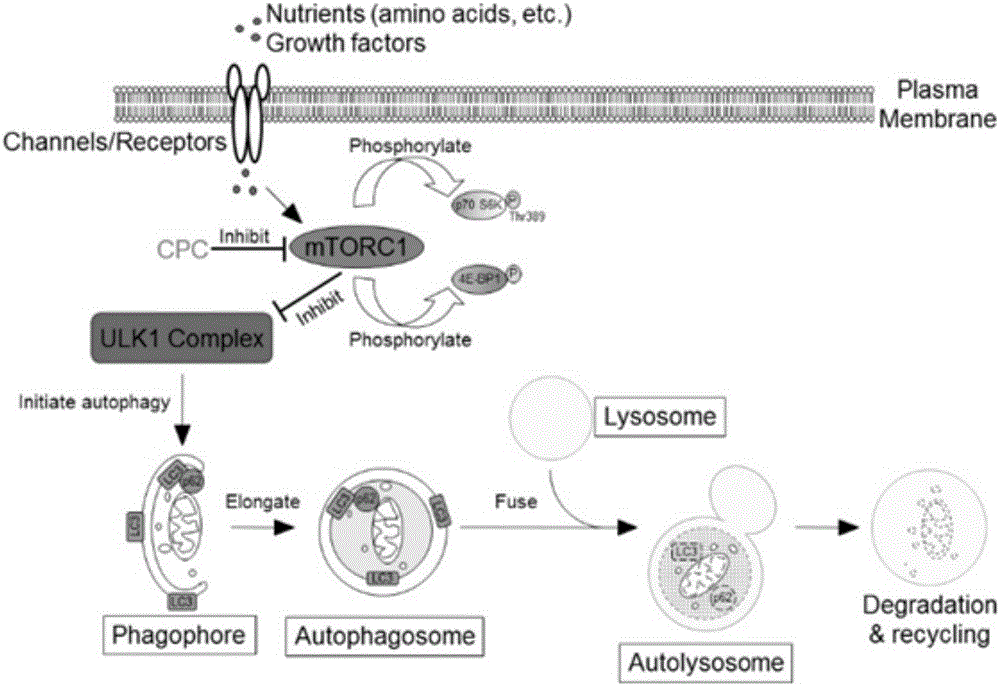
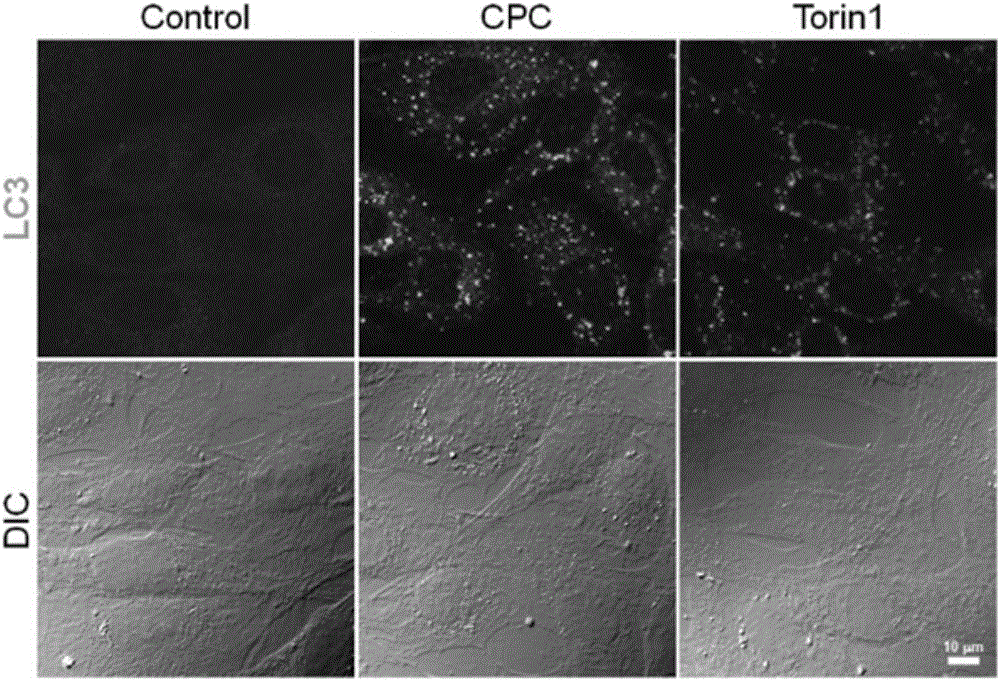
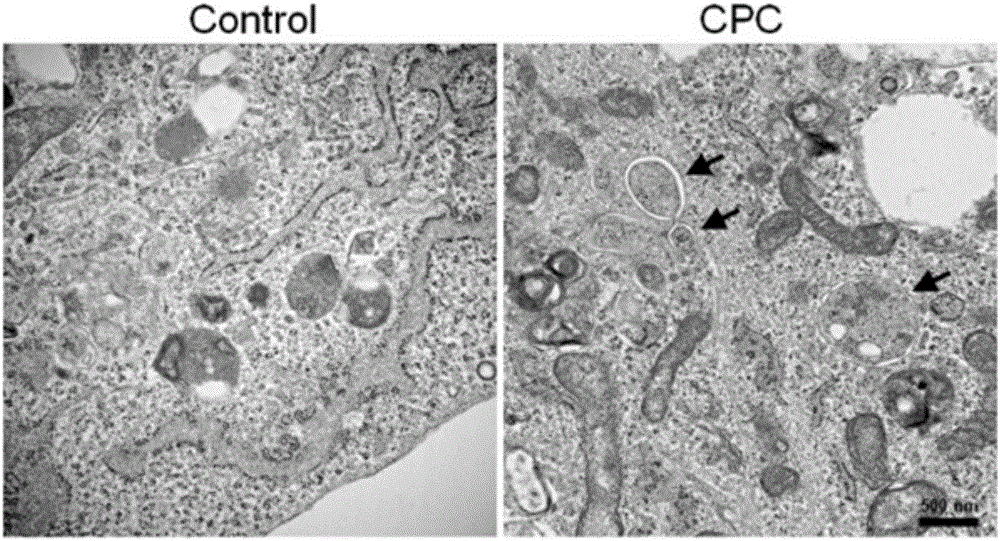
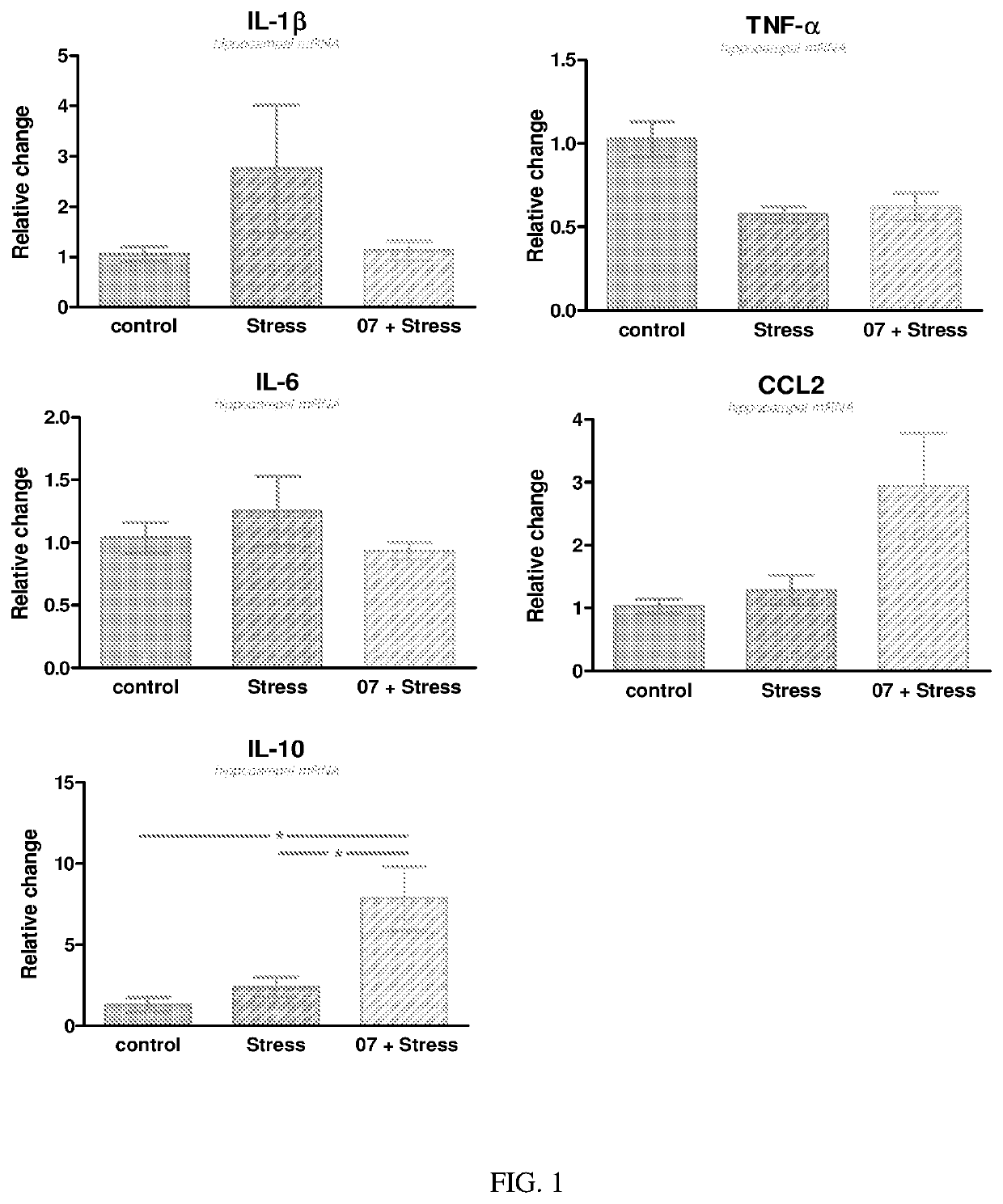
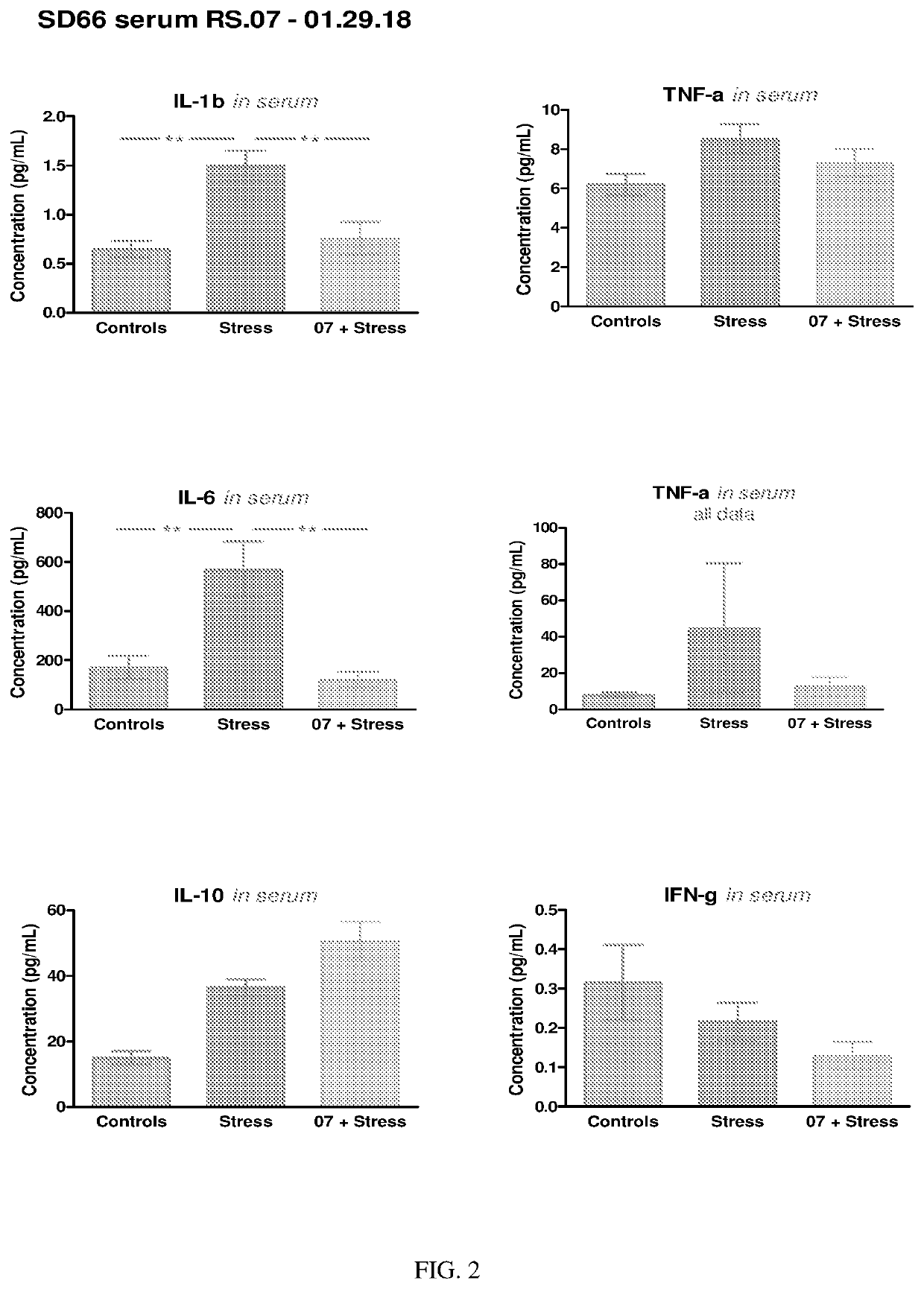
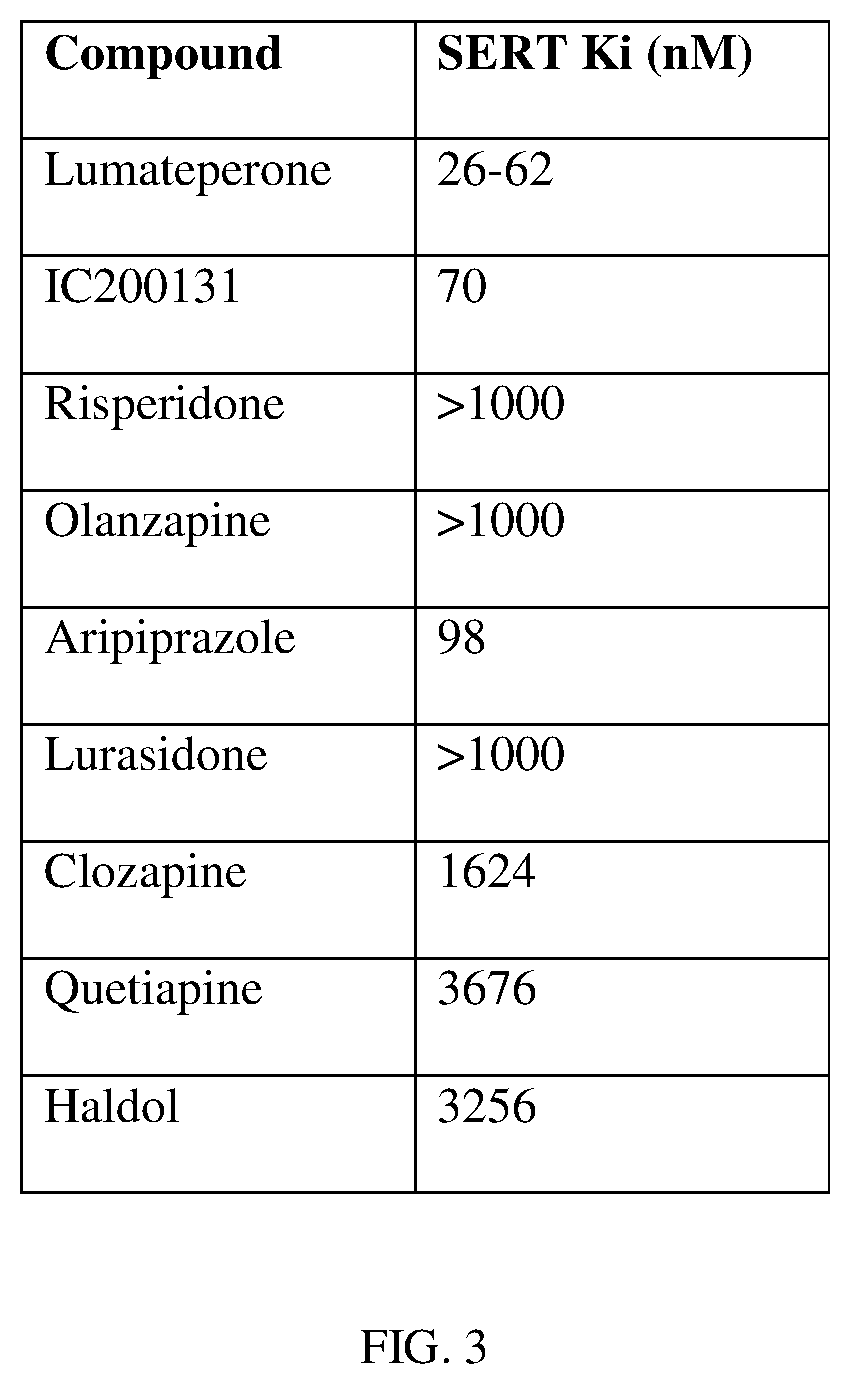
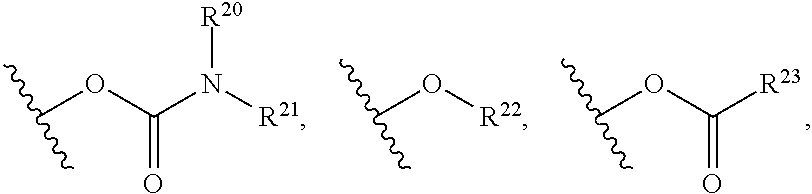
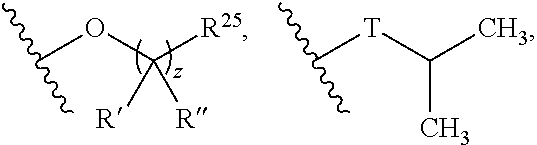
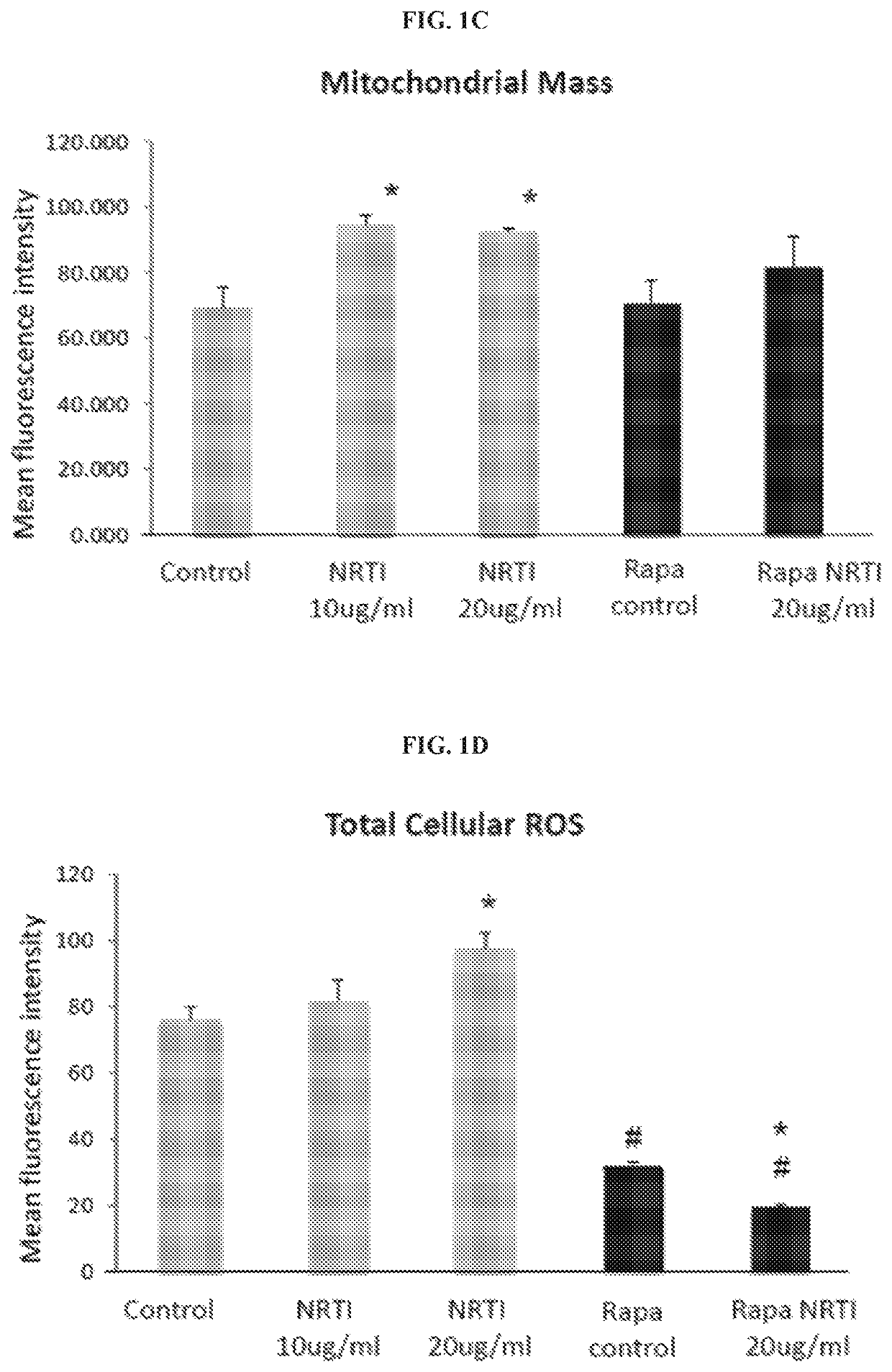
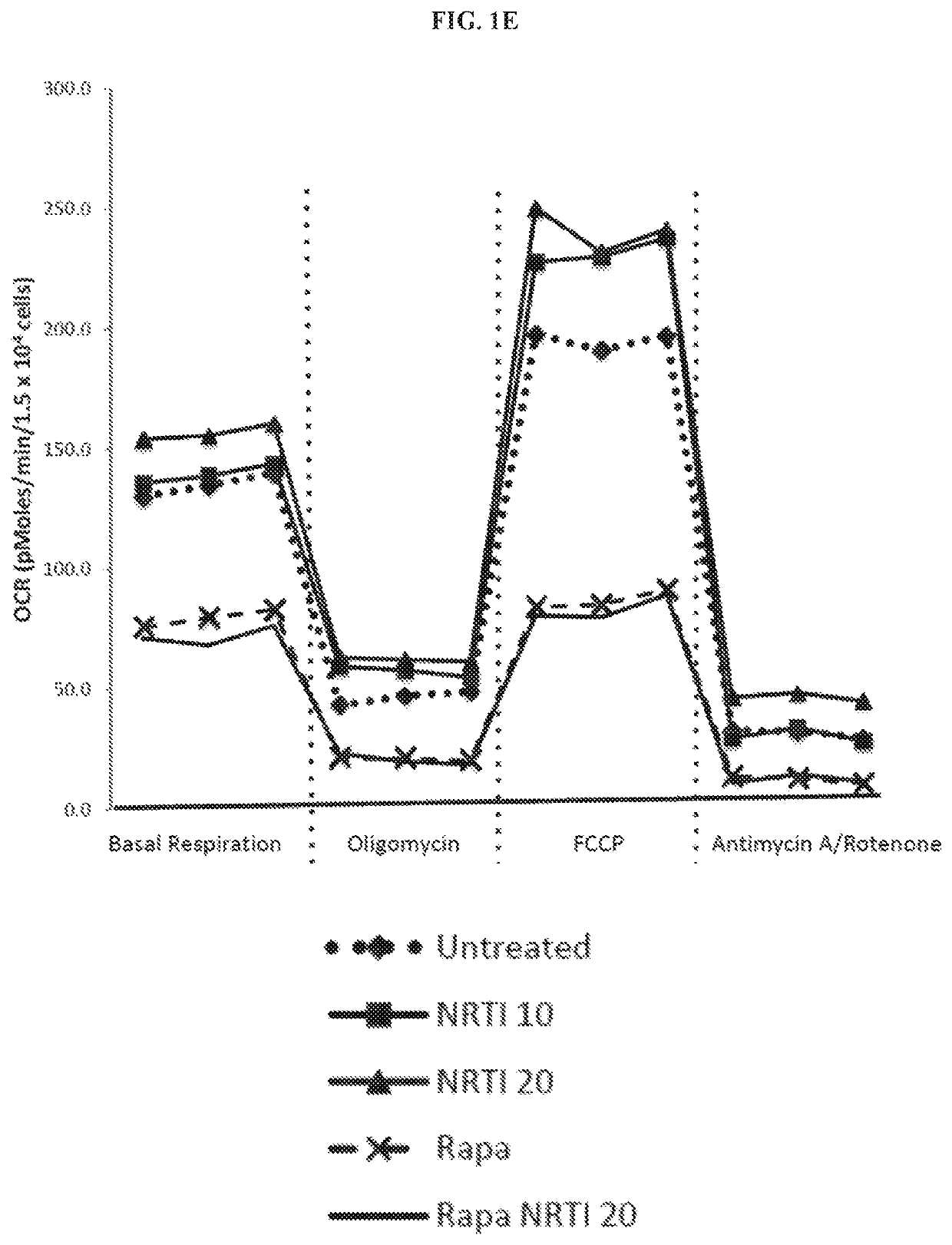
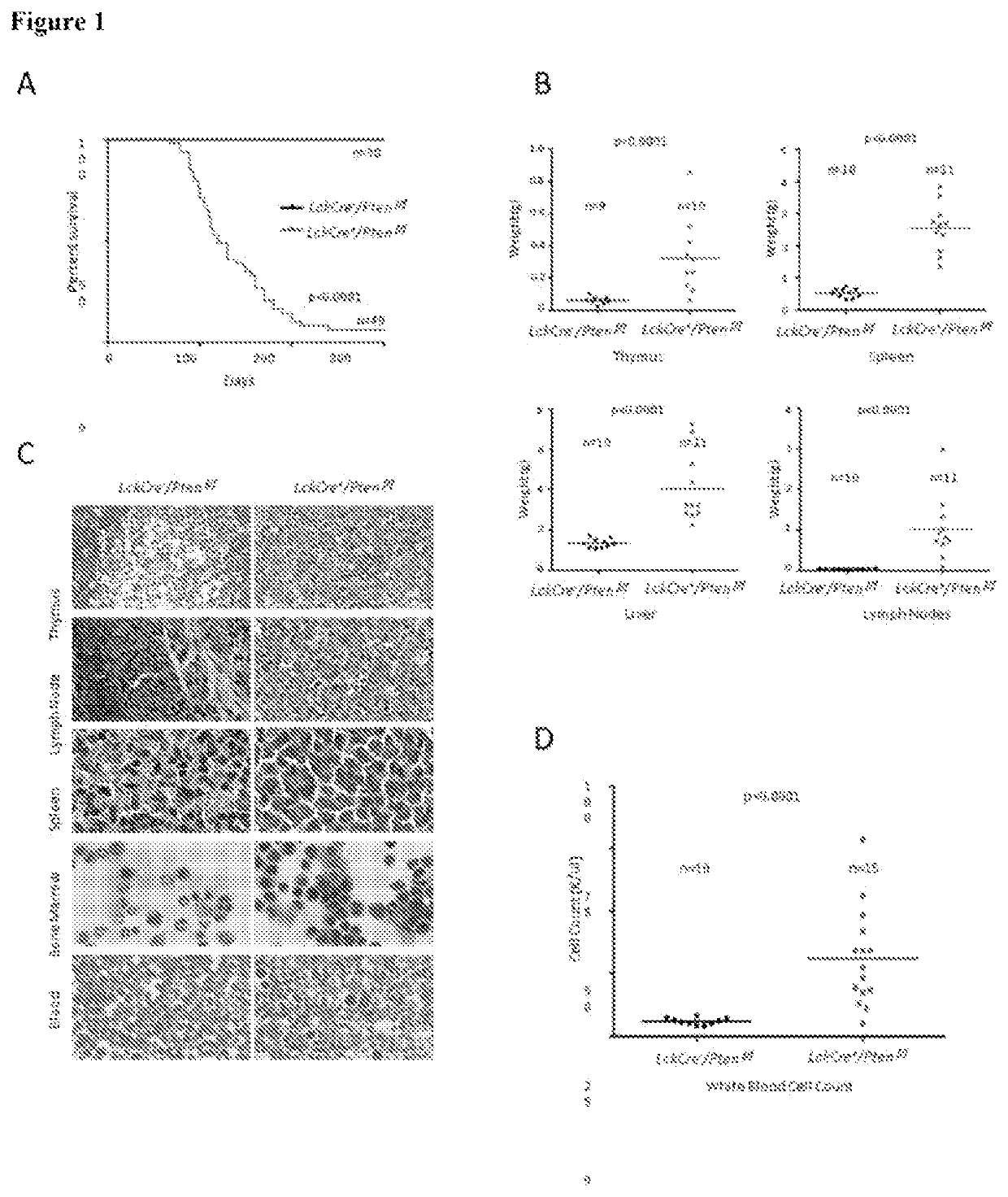
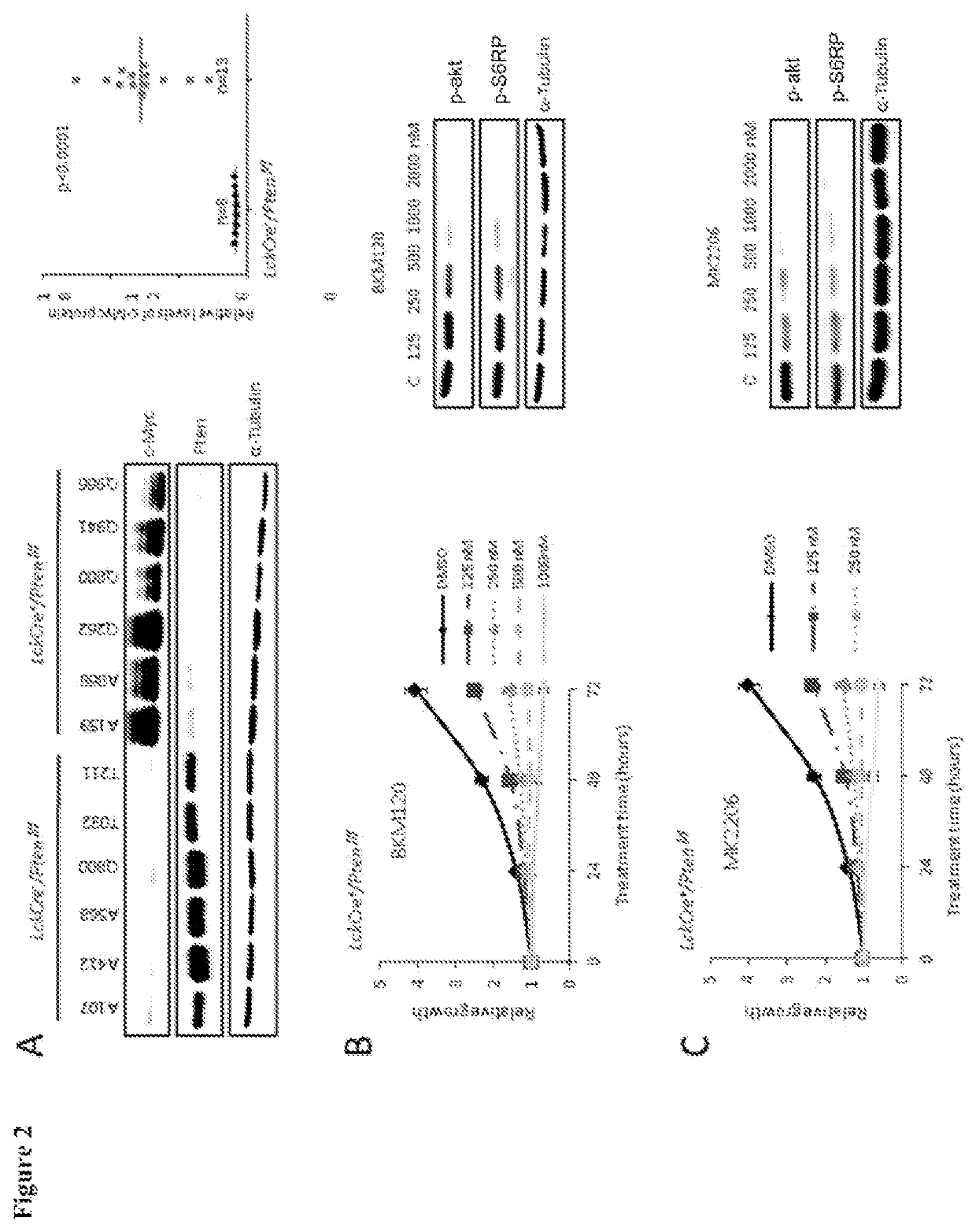
Patents
Literature
45 results about "MTORC1" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
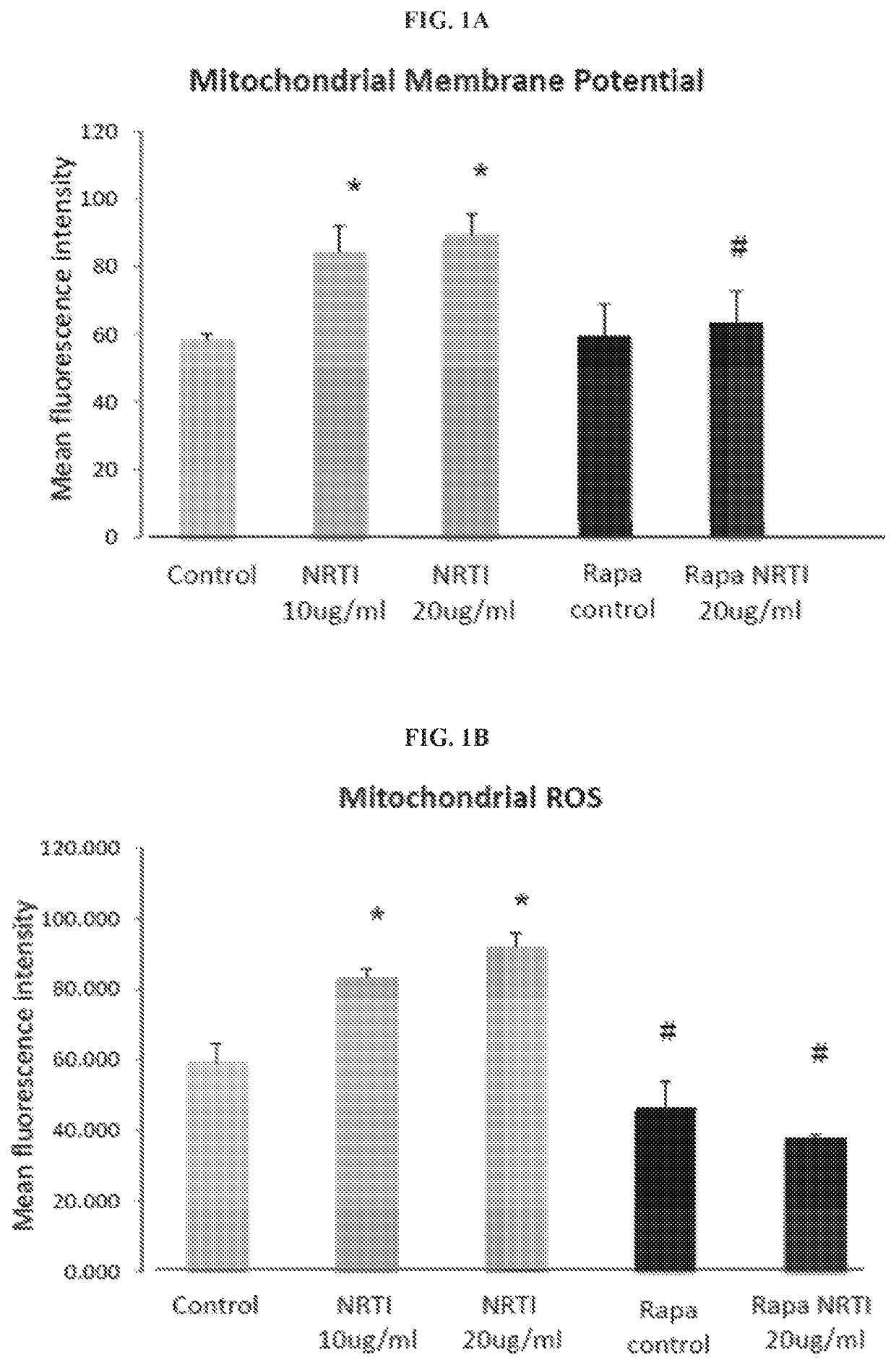
MTORC1, also known as mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 or mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1, is a protein complex that functions as a nutrient/energy/redox sensor and controls protein synthesis.
Application of polyphenolic compound
InactiveCN105213362AInhibition of enzyme catalytic activitySignificant effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicineCurative effect
The invention discloses application of a polyphenolic compound. The polyphenolic compound shown in formula I can be used for preparing an mTOR inhibitor, especially an mTORC1 inhibitor. The invention further discloses application of the polyphenolic compound in the preparation of medicine for preventing and / or treating cancer, metabolic disorder syndrome, neurodegenerative diseases or inflammation. The diseases include diseases which are prevented and / or treated by inhibiting the catalytic activity of the enzyme of mTORC1. Preferably, the diseases include cancer, metabolic disorder syndrome, neurodegenerative diseases or inflammation. The polyphenolic compound can effectively inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme of mTOR and is good in curative effect on the cancer, metabolic disorder syndrome, neurodegenerative diseases or inflammation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
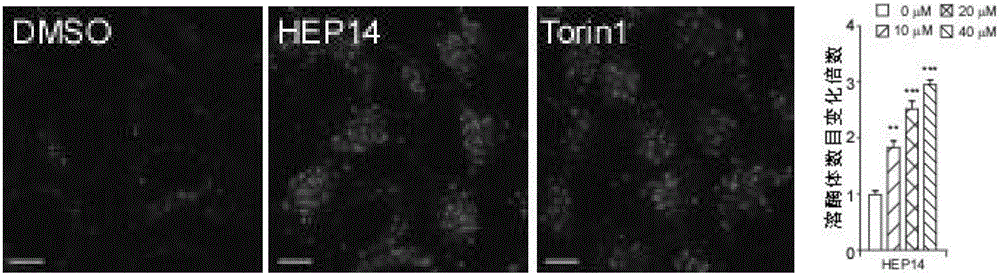
Ingenol and application of derivative of ingenol in enhancement of generation of lysosome
ActiveCN106619600AInterfering with metabolic balanceNervous disorderEster active ingredientsFunctional disturbanceDisease
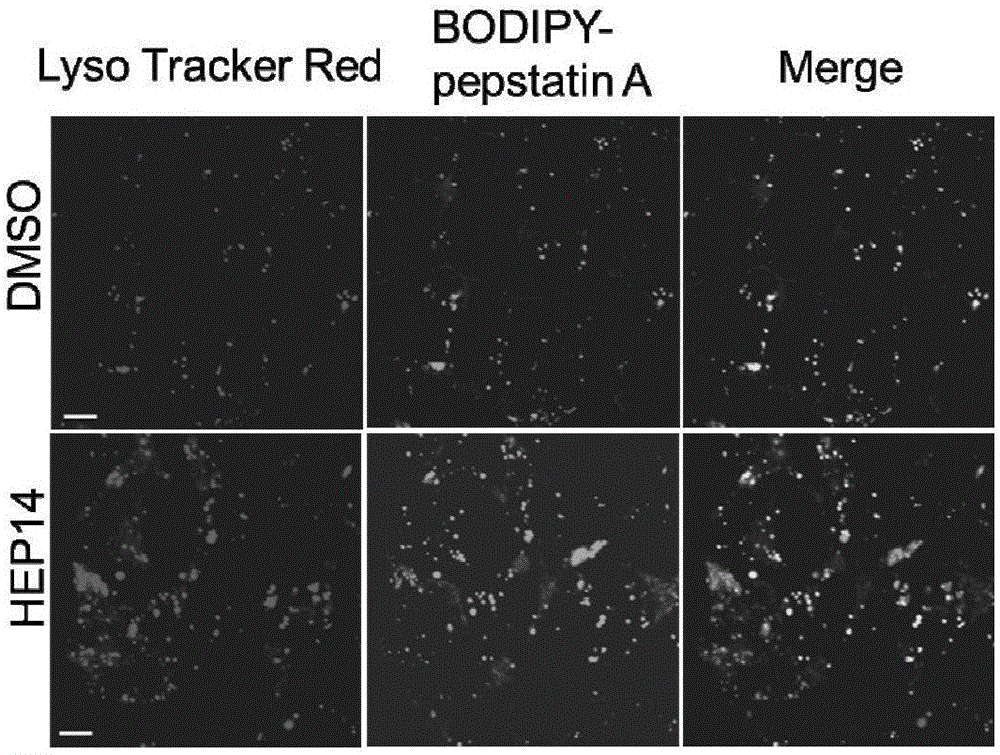
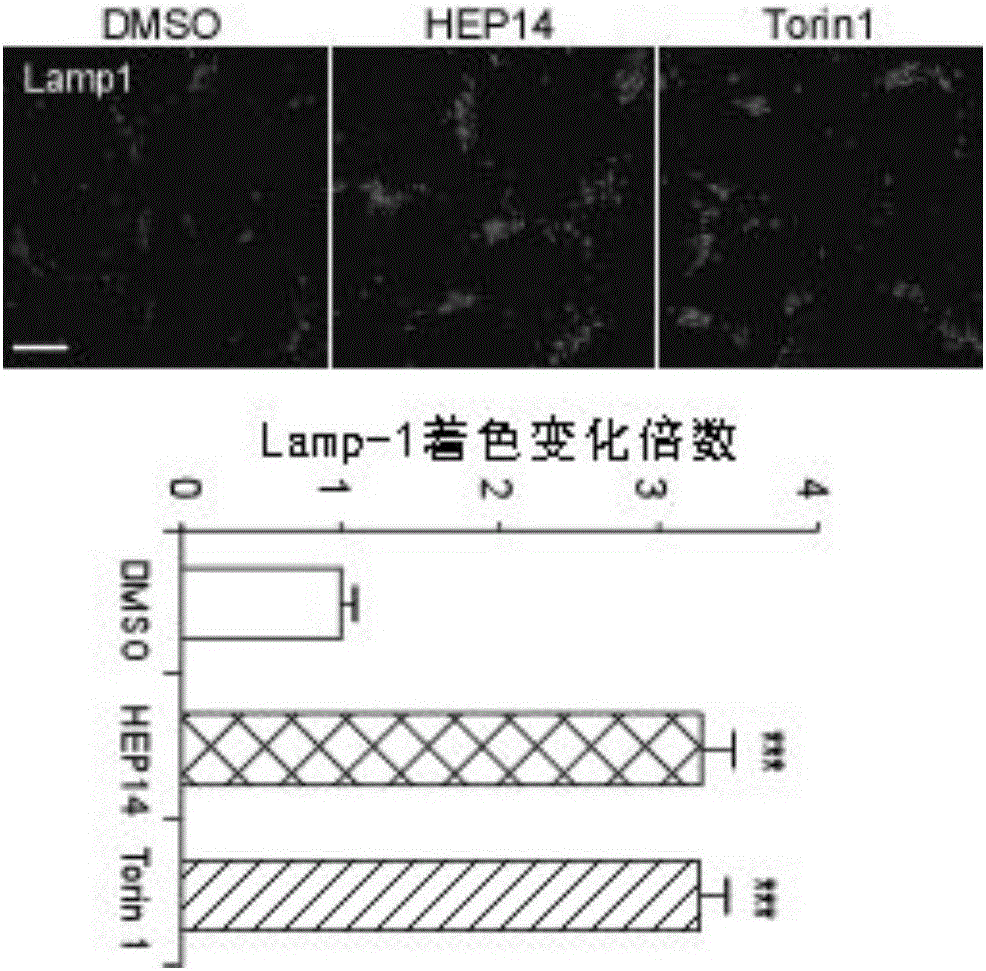
The invention discloses ingenol and application of a derivative of ingenol in enhancement of generation of lysosome. The application specifically comprises optional application of HEP14 or the derivative thereof in the following applications: induction of generation of the lysosome; preparation of drugs for induction of generation of the lysosome; and preparation of drugs for treating and / or preventing lysosome functional disturbance related diseases. HEP14 can activate PKC alpha and PKC delta, on one hand, transcription factors TFEB are activated through two parallel signal pathways, and on the other hand, transcription inhibitors are inactivated and are finally used as 'molecular switches' to control generation of the lysosome. Activation of PKC causes inactivation of GSK3 beta, then transfer of TFEB dephosphorylation to cell nucleus is caused, meanwhile, PKC which is in an activated state can further activate MAPK kinase JNK2 and p38 and phosphorylate ZKSCAN3, and ZKSCAN3 can be transferred to cytoplasm from cell nucleus. HEP14 does not affect activity of mTORC1, therefore, cell metabolism balance is not disturbed, and the ingenol is a perfect drug for treating lysosome related diseases possibly.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
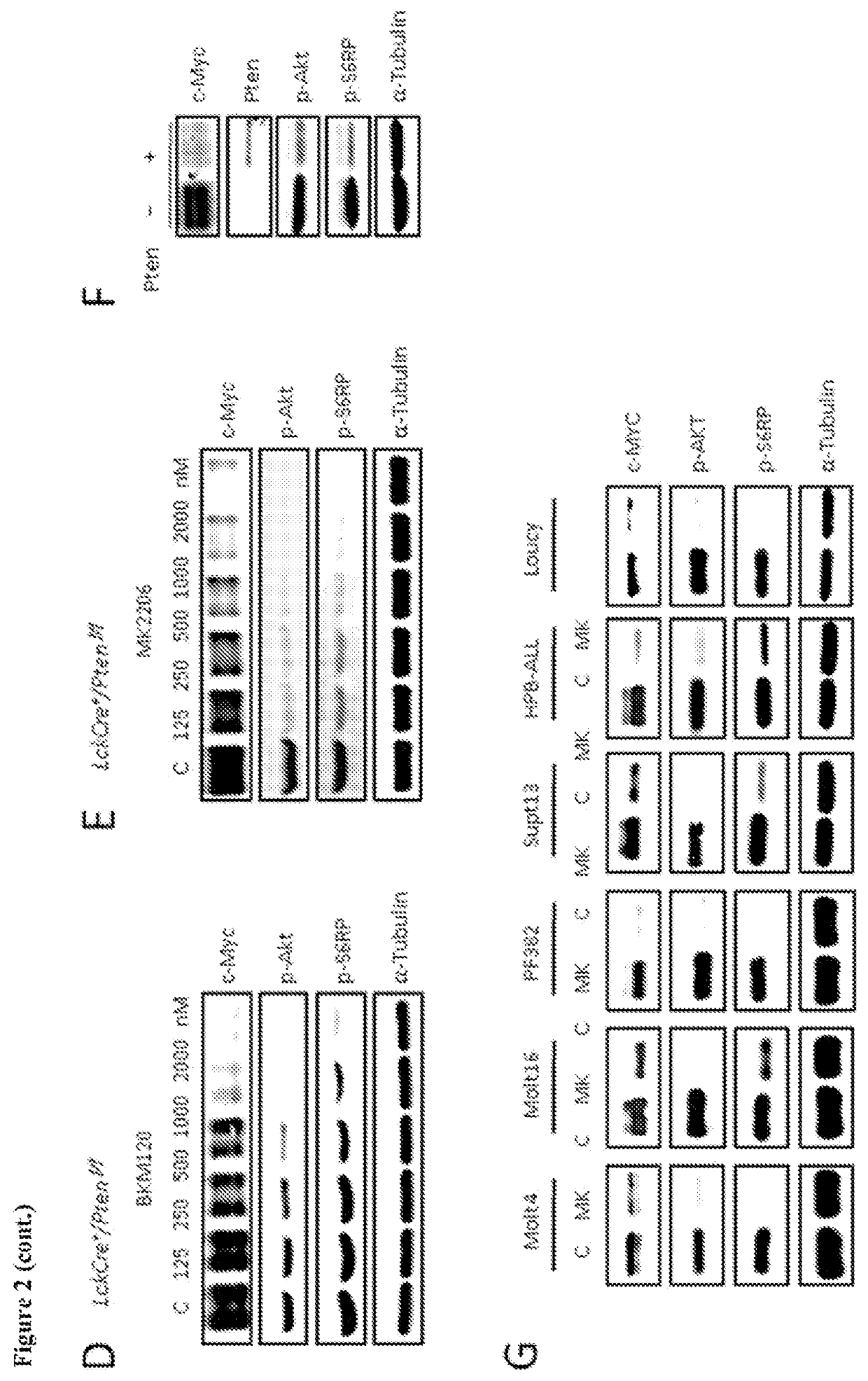
Mouse model for mTORC1 (mechanistic target of rapamycin 1) pathways and method for building mouse model
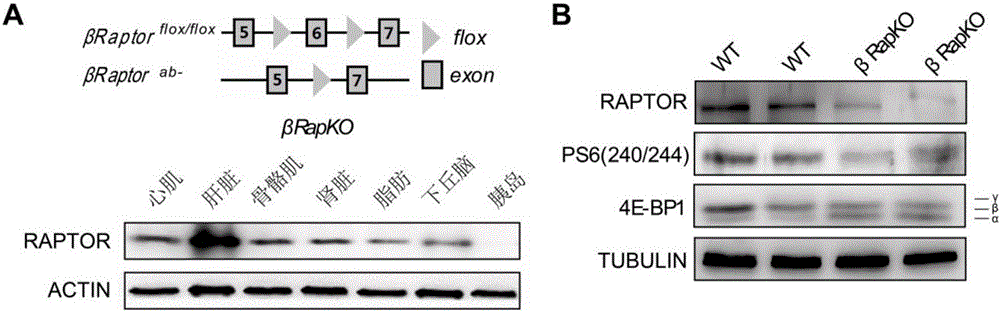
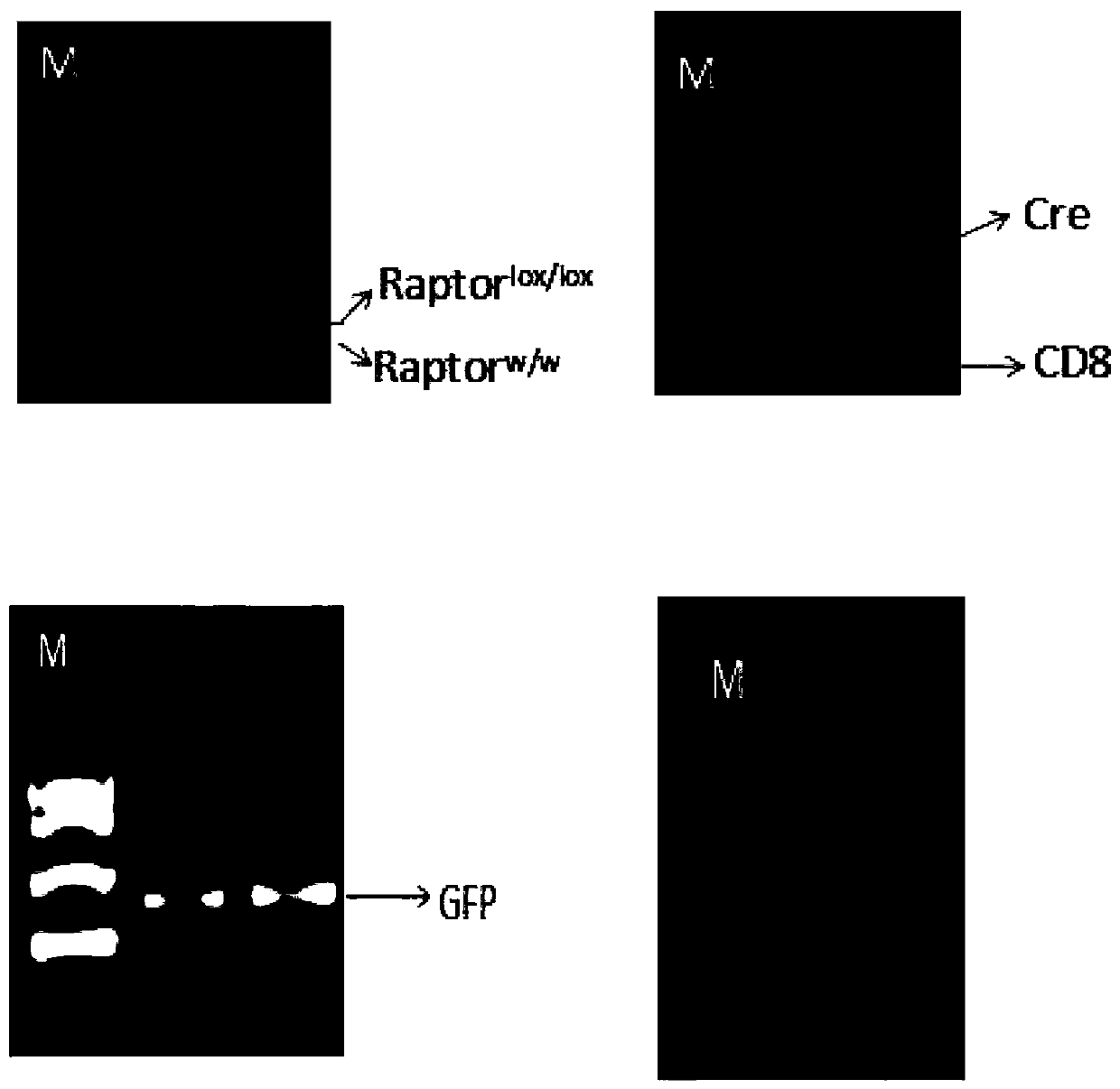
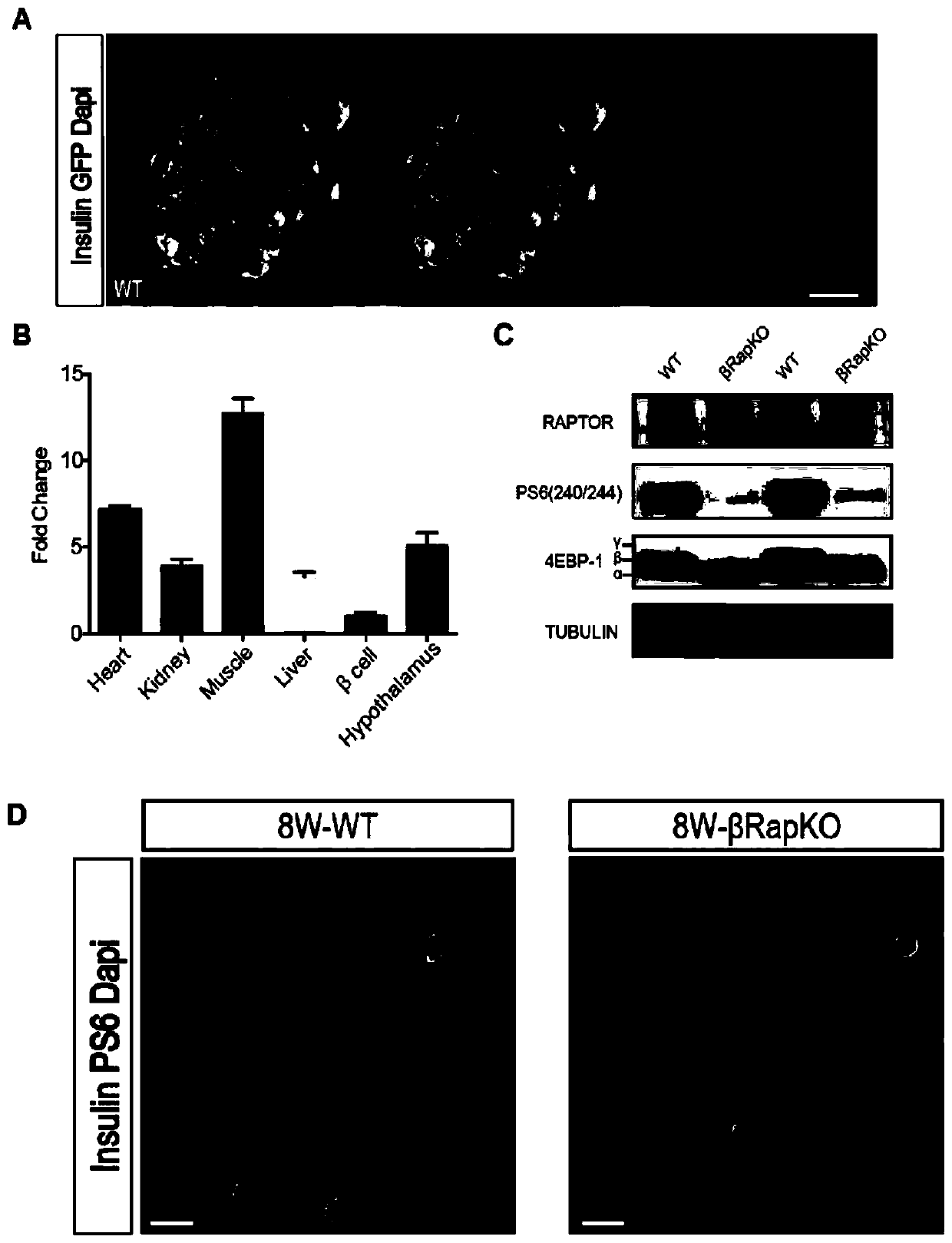
The invention relates to a mouse model for mTORC1 (mechanistic target of rapamycin 1) pathways and a method for building the mouse model. The mouse model is a mouse. Raptor is specifically knocked out of beta cells in the mouse. The method includes allowing Raptor lox / lox mice of C57 strains and RIP-Cre mice to carry out mating to obtain Raptor heterogeneous mice, namely RIP-Cre Raptor lox / w mice; allowing the Raptor heterogeneous mice to carry out mating to obtain Raptor lox / lox mice with RIP-Cre so as to obtain the mouse model. The mouse model and the method have the advantages that the method is simple; as discovered by means of comparison, the TORC1 signaling pathways in the mouse can be specifically inhibited after the Raptor is specifically knocked out by the beta cells in the mouse, accordingly, foundations can be laid for follow-up research, and the mouse model and the method have excellent application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST FOR ENDOCRINE & METABOLIC DISEASES +1
P13k-mtorc1-s6k1 signaling pathway biomarkers predictive of Anti-cancer responses
ActiveUS20170184565A1Reduce the amount requiredReduced activityCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsCancer therapyBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention is based, in part, on the identification of novel FI.3K-mTORCI-S6K 1 signaling pathway biomarkers predictive of responsiveness to anti-cancer therapies.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Application of flavonoids
InactiveCN105267200AInhibition of enzyme catalytic activitySignificant effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseMedicine
The invention discloses application of flavonoids. As shown in formula I, the flavonoids can be used for preparing an mTOR inhibitor, and in particular an mTORC1 inhibitor. The invention discloses application of the flavonoids in preparing medicines for preventing and / or treating cancers, metabolic disorder syndrome, neurodegenerative disease or inflammation. The diseases are prevented and / or treated by inhibiting the catalytic activity of enzyme of the mTORC1 in the field, and preferably the diseases are cancers, metabolic disorder syndrome, neurodegenerative disease or inflammation. The flavonoids disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively inhibiting the catalytic activity of the enzyme of the mTOR, and can show a good curative effect on cancers, metabolic disorder syndrome, neurodegenerative disease or inflammation.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Macrophage-targeted mTORC1 activator for controlling NASH progression
InactiveCN107693792AAccelerated disease progressionEnhanced disease progressionCompounds screening/testingDigestive systemAbnormal macrophageMedicine
The invention discloses a macrophage-targeted mTORC1 activator for controlling NASH progression. The invention provides the application of a substance capable of reducing the activity of mTORC1 in macrophages in the preparation of a product capable of promoting progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis to hepatic fibrosis. By studying the effect of mTORC1 in macrophages on the non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, it is found that the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis can be accelerated by inhibiting the activity of mTORC1 in macrophages. The invention is of great reference significancefor the research on the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and for the selection of future treatment strategies.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
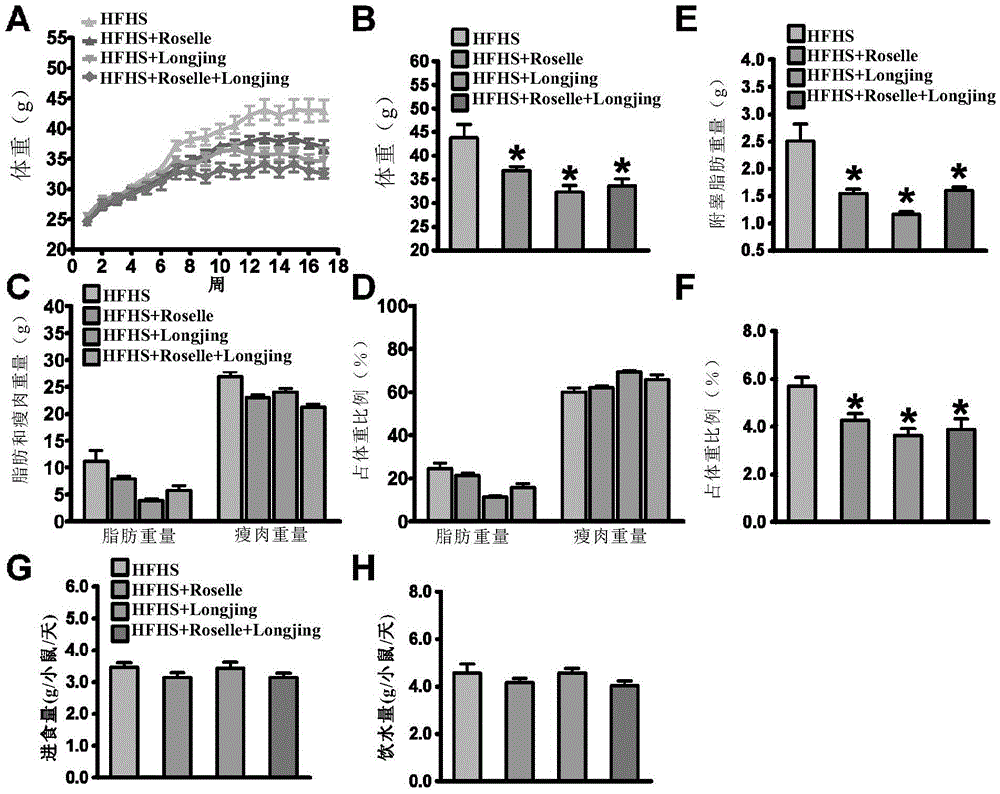
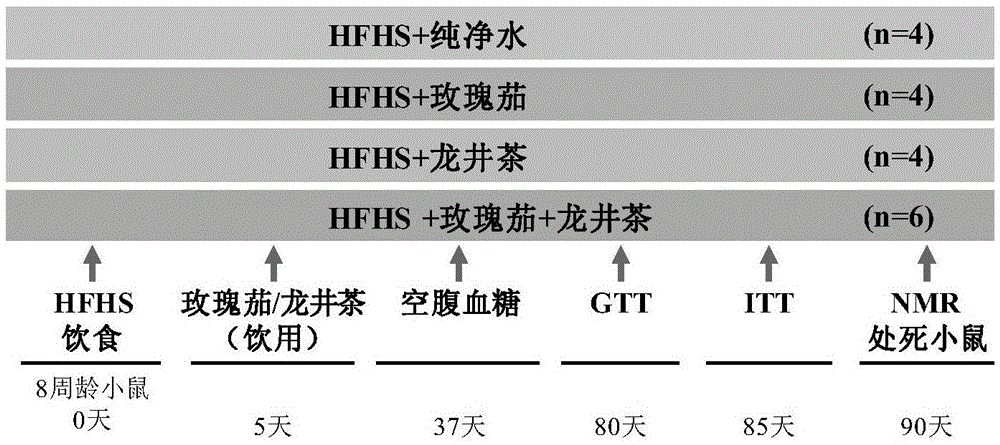
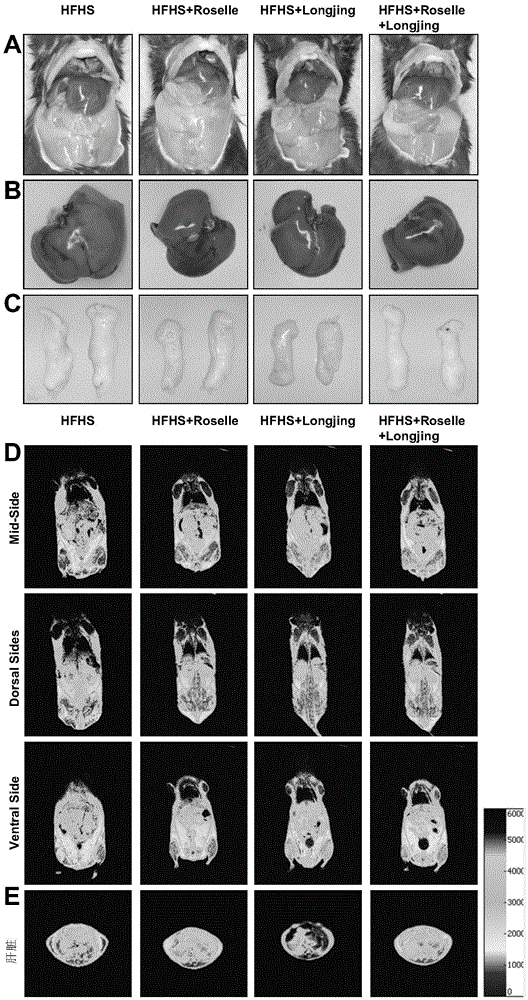
Application of hibiscus sabdariffa-green tea composition in relieving diet-induced metabolic disorders
ActiveCN105535267AImprove hyperlipidemiaNervous disorderPre-extraction tea treatmentMembrane lipid metabolismFatty acid
The invention relates to application of a hibiscus sabdariffa-green tea composition in relieving diet-induced metabolic disorders, and particularly provides an aqueous extract and a composition with the same. The aqueous extract is the aqueous extract of the mixture of hibiscus sabdariffa flower and green tea or is the mixture of a hibiscus sabdariffa aqueous extract and a green tea aqueous extract. It is found that the hibiscus sabdariffa aqueous extract and the green tea aqueous extract can remarkably relieve weight increment of the body and epididymis fat of a mouse induced by high-fat and high-sugar diet, lower blood glucose and blood fat, improve mouse liver fat deposition and increase insulin sensitivity, while has no obvious influence on the food intake and water intake of the mouse. It is also found that the hibiscus sabdariffa-longjing tea composition extracting solution can lower fatty liver by increasing liver fatty acid oxidation and lowering lipid synthesis; in addition, insulin resistance can be lowered in the way of restraining mTORC1 / S6K.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel Compositions and Methods for Treating or Preventing Dermal Disorders
ActiveUS20180280362A1Extend your lifePreserving cell organizationOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsWrinkle skinActinic keratosis
The present invention includes compositions and methods for treating or preventing certain dermal disorders including dermal atrophy, pseudoscars, actinic keratosis, seborrheic or actinic keratoses, lentigines, focal areas of dermal thickening, and coarse wrinkles. In certain embodiments, the compositions useful within the invention comprise a therapeutically effective amount of a mTORC1 inhibitor and a dermatologically acceptable carrier.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Application of mTOR signal path inhibitor to preparation of medicament for preventing or treating extragenetic hearing impairment
InactiveCN108310386AAvoid damageImprove hearingOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderEverolimusMTOR signaling pathway
The invention discloses application of a mTOR signal path inhibitor to preparation of a medicament for preventing or treating extragenetic hearing impairment. The mTOR signal path inhibitor is selected from at least one of sirolimus, sirolimus analogue and second-generation mTOR signal path inhibitor; the sirolimus analogue is selected from at least one of everolimus, temsirolimus and Deforolimus;the second-generation mTOR signal path inhibitor is selected from at least one of PI3K / mTOR double inhibitor, selective mTORC1 / 2 inhibitor and ATP competitive mTOR kinase inhibitor. As found by the inventor of the application, the mTOR signal path inhibitor can effectively relieve damage to inner ear hair cells and spiral ganglion cells caused by non-genetic factors such as ototoxic drug, remarkably improve the impaired listening ability, and effectively prevent and treat extragenetic hearing impairment.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Application of alkyl pyridine compound to preparation of medicine for inducing cell autophagy and method for inducing cell autophagy
ActiveCN106727548ALow working concentrationStrong specificityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderInducerPyridine
The invention discloses application of an alkyl pyridine compound to preparation of a cell autophagy inducer or application of an alkyl pyridine compound to preparation of a medicine for treating diseases capable of being benefit from autophagy induction and a method for inducing cell autophagy, and belongs to the field of biological medicines. The compound induces cell autophagy mainly by restraining the activity of mTORC1. When the compound serves as an autophagy inducer or an effective constituent of the medicine for treating diseases capable of being benefit from autophagy induction, the compound is low in working concentration and high in specificity, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:蒋培都
Novel methods
PendingUS20210060009A1Enhancing mTOR signalingReduce neuroinflammationNervous disorderOrganic chemistryLumateperoneReceptor
The disclosure provides methods for the acute treatment of depression and / or anxiety, for the enhancement of mTOR (e.g., mTORC1) signaling, and for the reduction of neuroinflammation, comprising administering to a patient in need thereof, a therapeutically effective amount of a 5-HT2A or 5-HT2A / D2 receptor ligand, e.g. lumateperone.
Owner:INTRA CELLULAR THERAPIES INC
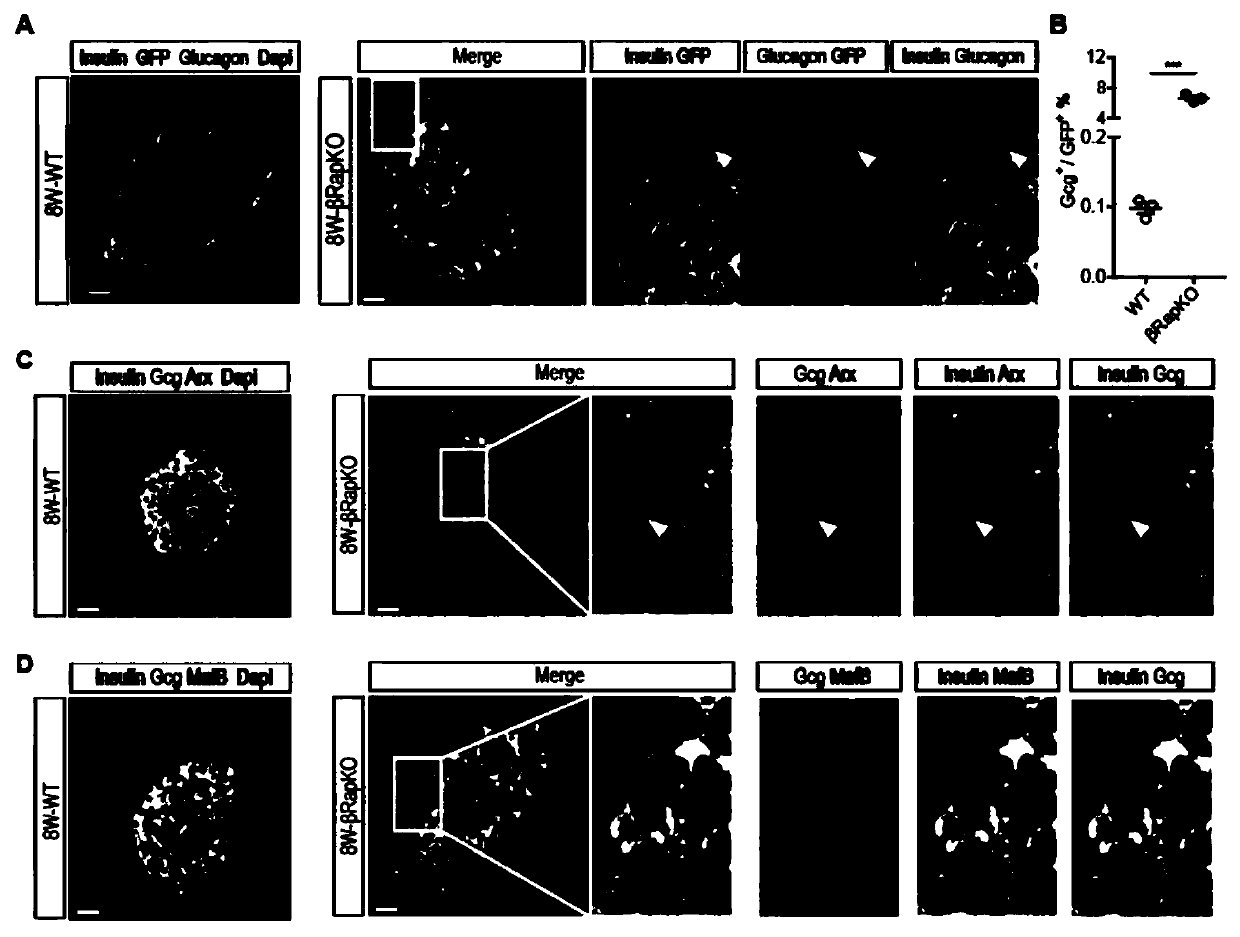
Application of mTORC1 in medicines for regulating and controlling functions and conversion of pancreatic beta cells
InactiveCN107684622AFunction increaseMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical active ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaPancreatic islets
The invention discloses application of mTORC1 in medicines for regulating and controlling the functions and conversion of pancreatic beta cells; and the functions of pancreatic beta cells are improvedby regulating the activity or regulation bypass of mTORC1 passages and / or the pancreatic non-beta cells are converted into new pancreatic beta cells. The conversion is gene recording without a differentiation process. The invention discloses that the mTORC1 passages are of an important role in identity maintenance of beta cells. The specific Raptor knockout of the beta cells can cause functionaldisorders and cell immaturity of the beta cells as well as hyperglycemia since metabolic requirements cannot be met, and simultaneously causes expression increase of MafB, so that transdifferentiationis caused. The activity of the mTORC1 passages is adjusted, or regulation bypasses of the mTORC1 passages can serve as a new target spot for beta cell therapy, and the functions of the beta cells areimproved, or new beta cells are generated by non-beta cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST FOR ENDOCRINE & METABOLIC DISEASES +1
Methods and Compositions for Neoadjuvant Therapy
InactiveUS20140271667A1Reduce metastatic migrationBiocideSugar derivativesCancer cellLymphatic Spread
A method for inhibiting tumor cell migration or metastasis of a cancer in a mammalian subject comprises one or more of the steps of administering to a subject a therapeutically effective amount of a composition comprising a molecule that: suppresses focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activity or phosphorylation; suppresses ULK1 kinase activity; suppresses activation or signaling of the mTORC1 (Ser757) pathway; activates AMPK; activates FIP200; or activates LKB1, in a cancer cell. Still another method of inhibiting tumor cell migration involves inhibiting phosphorylation of ULK1 on Ser757 in subjects with lung cancer. Suppressing activation or signaling of the mTORC1 (Ser757) pathway in subjects is in one aspect useful in treating lung cancer.
Owner:THE WISTAR INST OF ANATOMY & BIOLOGY
Use of glycine in aspect of preparation of drug delivery reinforcer and cell transplantation reagent
ActiveCN110152004AEnhancement effect is goodPromote proliferationOrganic active ingredientsMuscular disorderDiseaseGlycine
The invention relates to use of glycine in the aspect of preparation of a drug delivery reinforcer and a cell transplantation reagent and belongs to the field of biomedicines. The use of the glycine in the aspect of preparation of the drug delivery reinforcer is characterized in that drug delivery is reinforced through activating mTORC1 by the glycine; meanwhile, based on new use of the glycine, the invention further provides a novel drug for treating muscular diseases, use of the glycine in preparation of anti-aging drugs, use of the glycine in the aspect of preparation of drugs for muscularfrozen injury and a composition for reinforcing the drug delivery. According to the use, a novel mechanism for reinforcing the drug delivery by the glycine is discovered, the efficiency of drug delivery can be effectively increased, the drug effect is improved, the dosage of drugs is lowered, and the treatment effect is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Method for regulating exosome release, and medical application of method
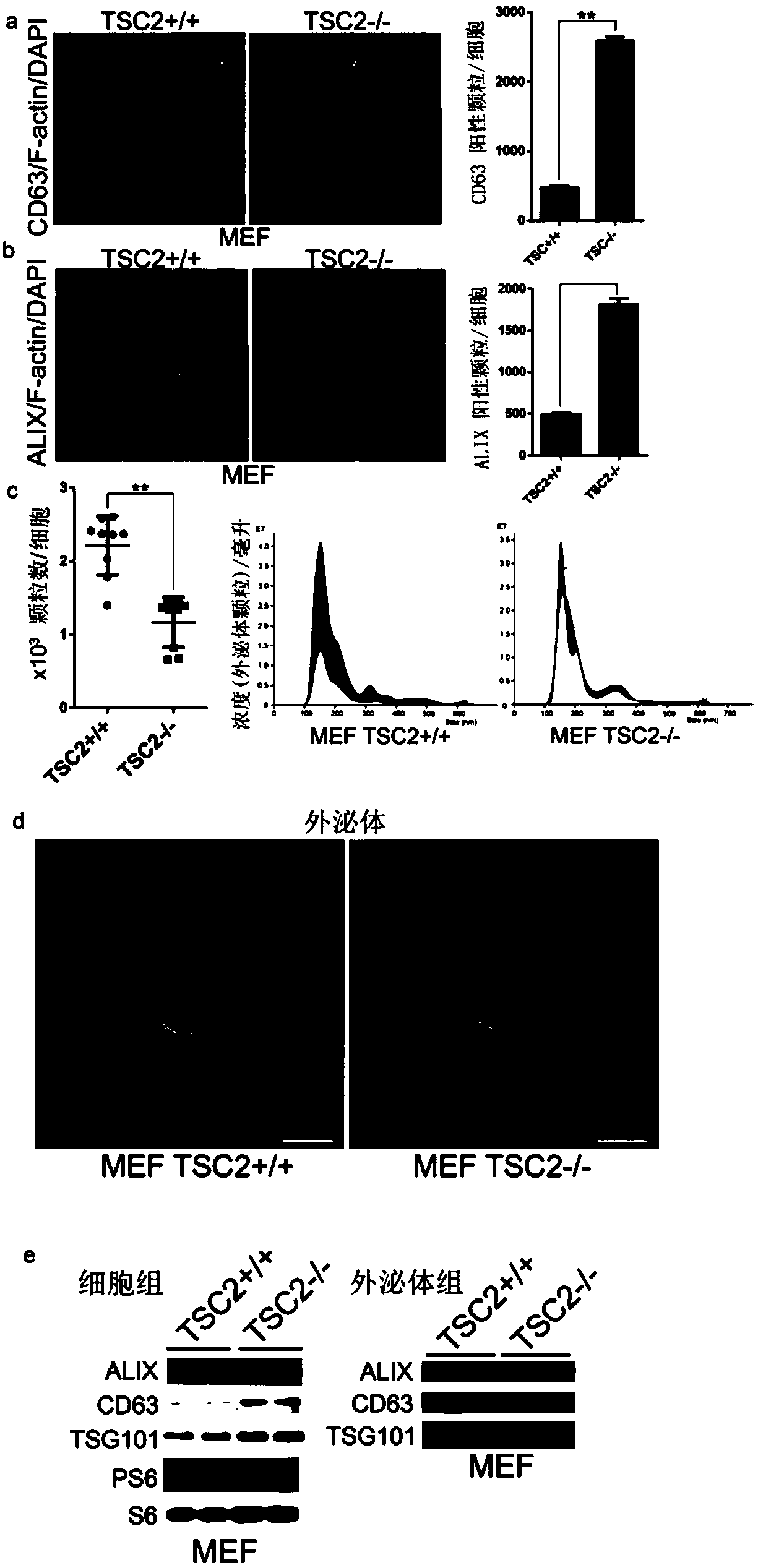
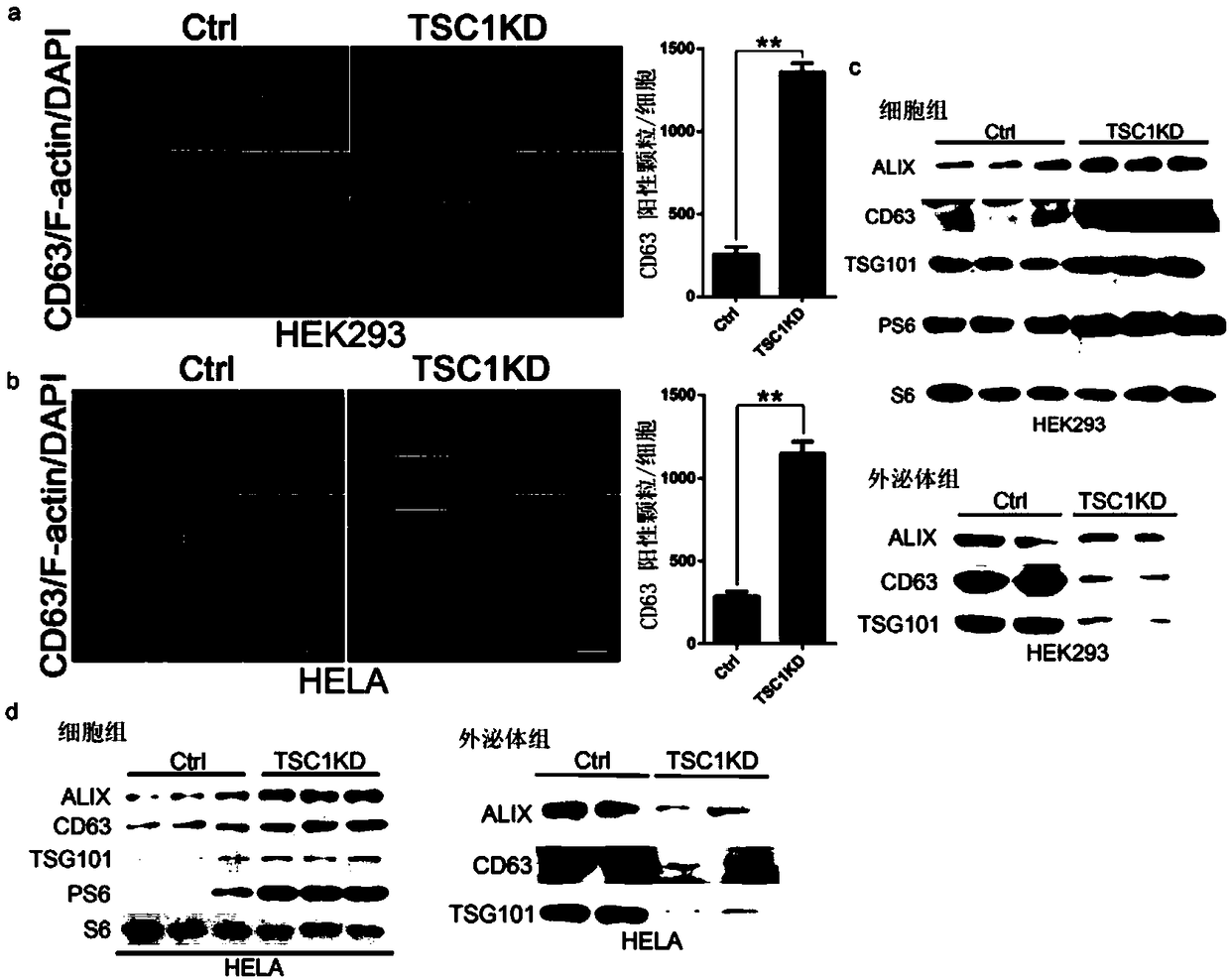
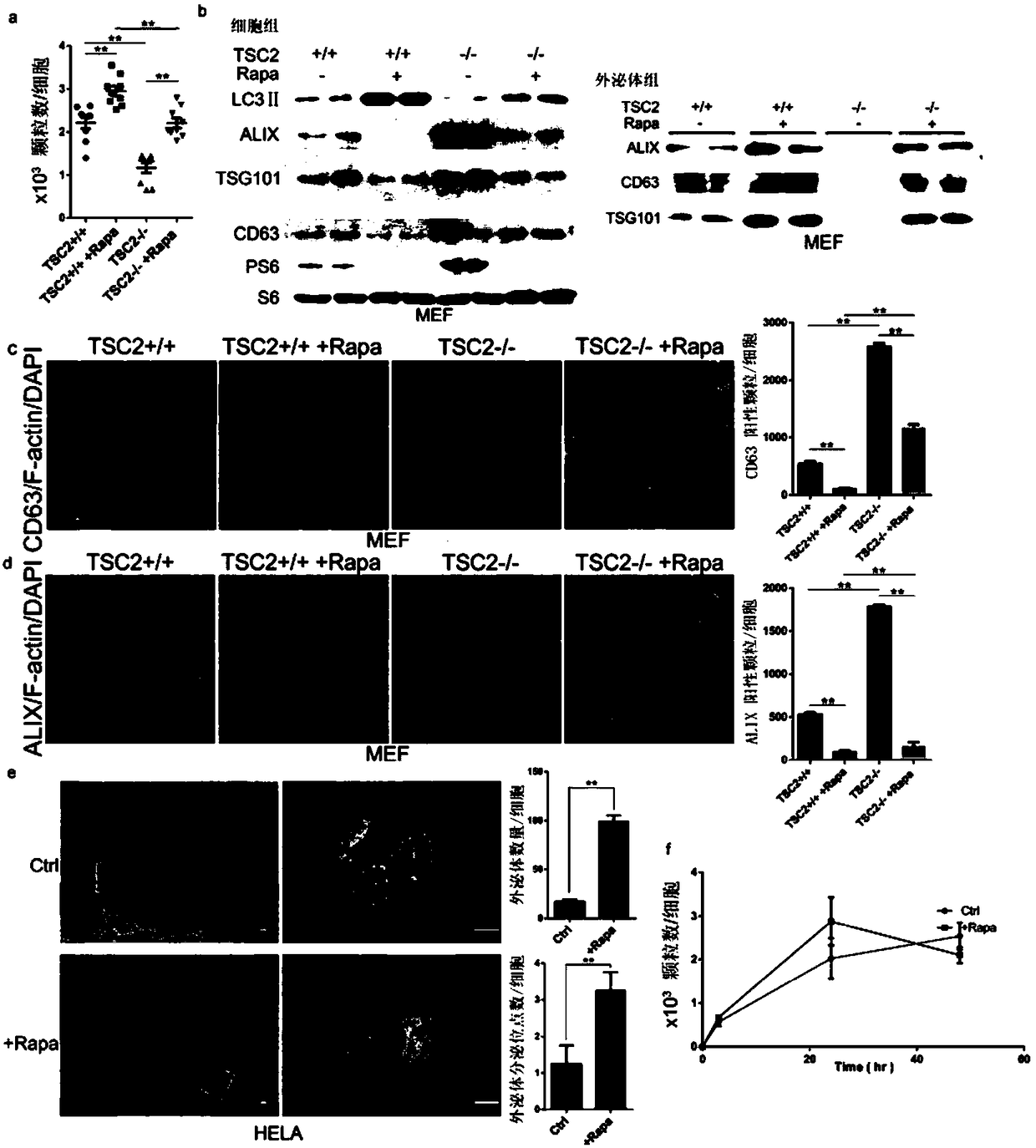
The invention provides a method for regulating exosome release, and medical application of the method in exosome release regulation. The exosome release is promoted by inhibiting the activity of rapamycin target protein mTORC1. The activation of the mTORC1 is inhibited by means of rapamycin, so that the exosome release is increased. By depriving nutrients, growth factors and dietary restrictions,the activity of the mTORC1 is inhibited, and the exosome release is promoted. The mTORC1 regulates the exosome release by means of a Rab27A-dependent mechanism. mTOR is associated with Rab27A, and theinteraction between the Rab27A and the mTOR is enhanced by means of rapamycin treatment. The exosome release, accompanied by autophagy, is affected by changes in nutrients and growth factor conditions. According to the exosome release, the cellular contents are released out of cells by means of fusion with the plasma membrane, so that the loss of the cellular contents is caused. The method can regulate the exosome release and provides a feasible scheme for medical application in the exosome release regulation.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Mtorc modulators and uses thereof
Owner:AEOVIAN PHARM INC
Preparation method of mouse with specific Raptor knocked out in beta cells during GFP tracing
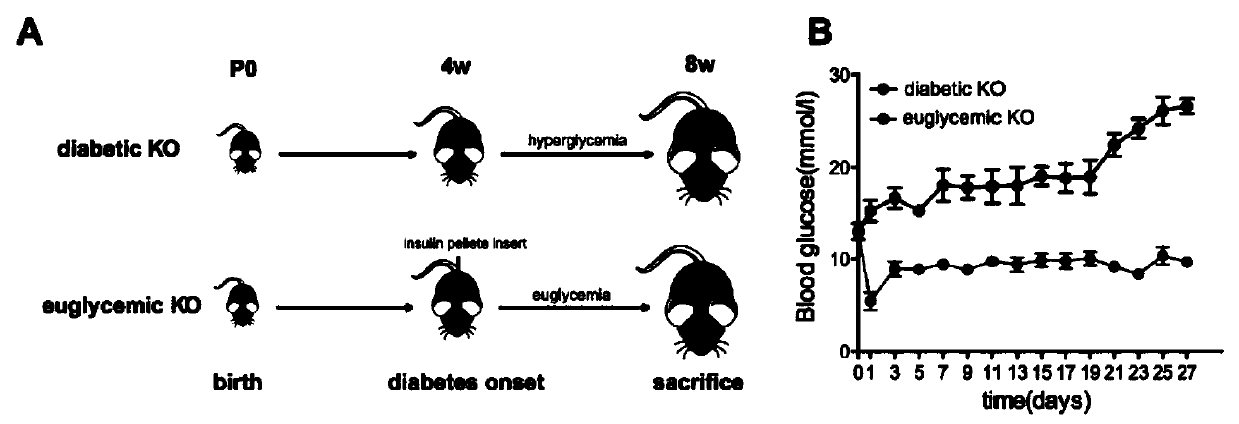
The invention relates to a preparation method of a mouse with specific Raptor knocked out in beta cells during GFP tracing. The method comprises the steps of mating an ROSA26-EGFPf mouse with an RIP-Cre mouse to obtain a homozygous mouse with RIP-Cre and EGFP sequences; then, mating the homozygous mouse with a Raptorlox / lox mouse to obtain a Raptorlox / w mouse with RIP-Cre and EGFP homozygous subsequences; then, selfing the Raptor heterozygous mouse to obtain a Raptorlox / lox mouse with RIP-Cre and EGFP homozygote sequences. The method aims to explain the direct effect of mTORC1 on beta cell identity and maintenance before the onset of diabetes, and provides a further basis for the mTORC1 serving as a drug action target.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
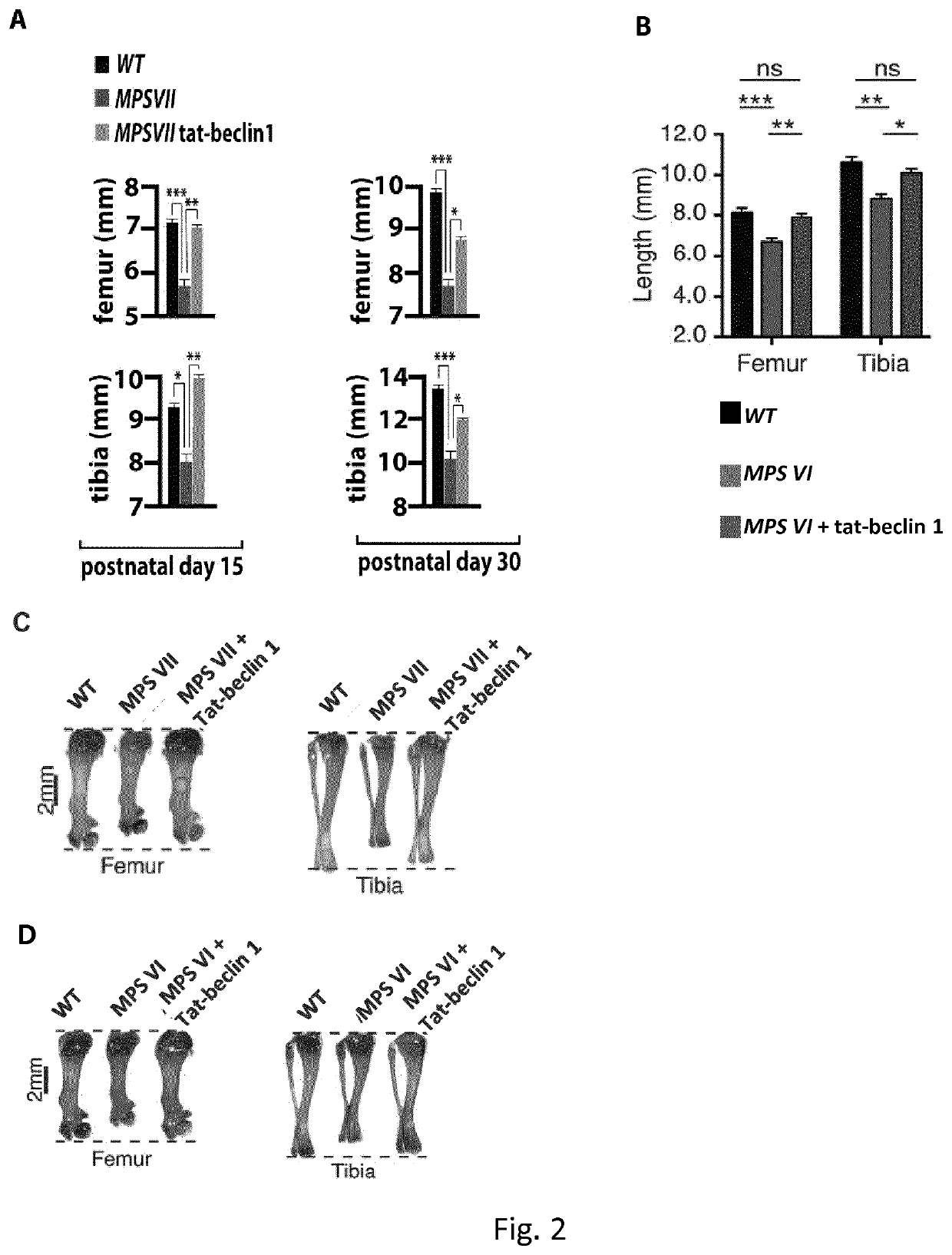
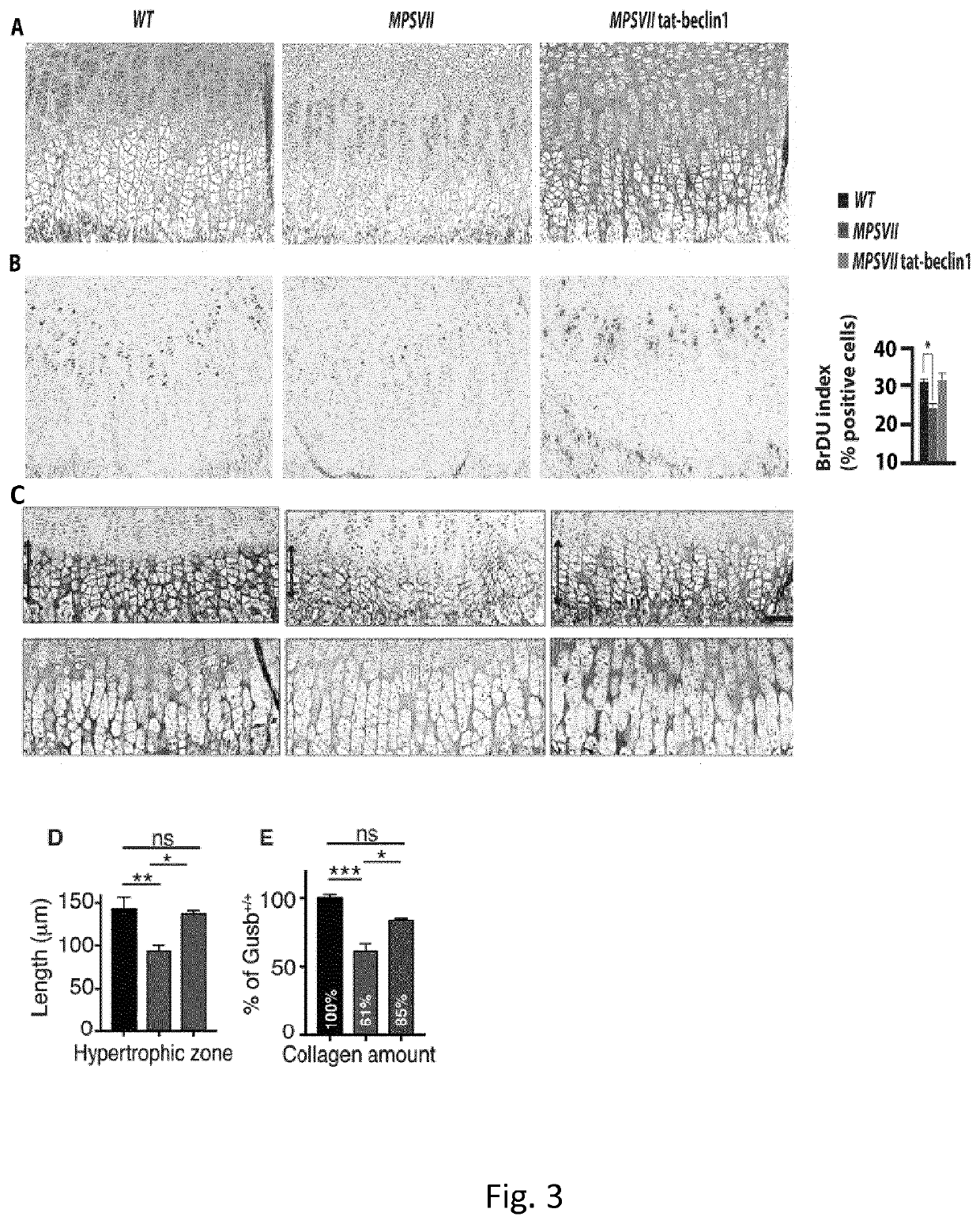
Treatment of bone growth disorders
PendingUS20200230207A1Increase productionEasy to measurePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsBh3 mimeticNucleotide
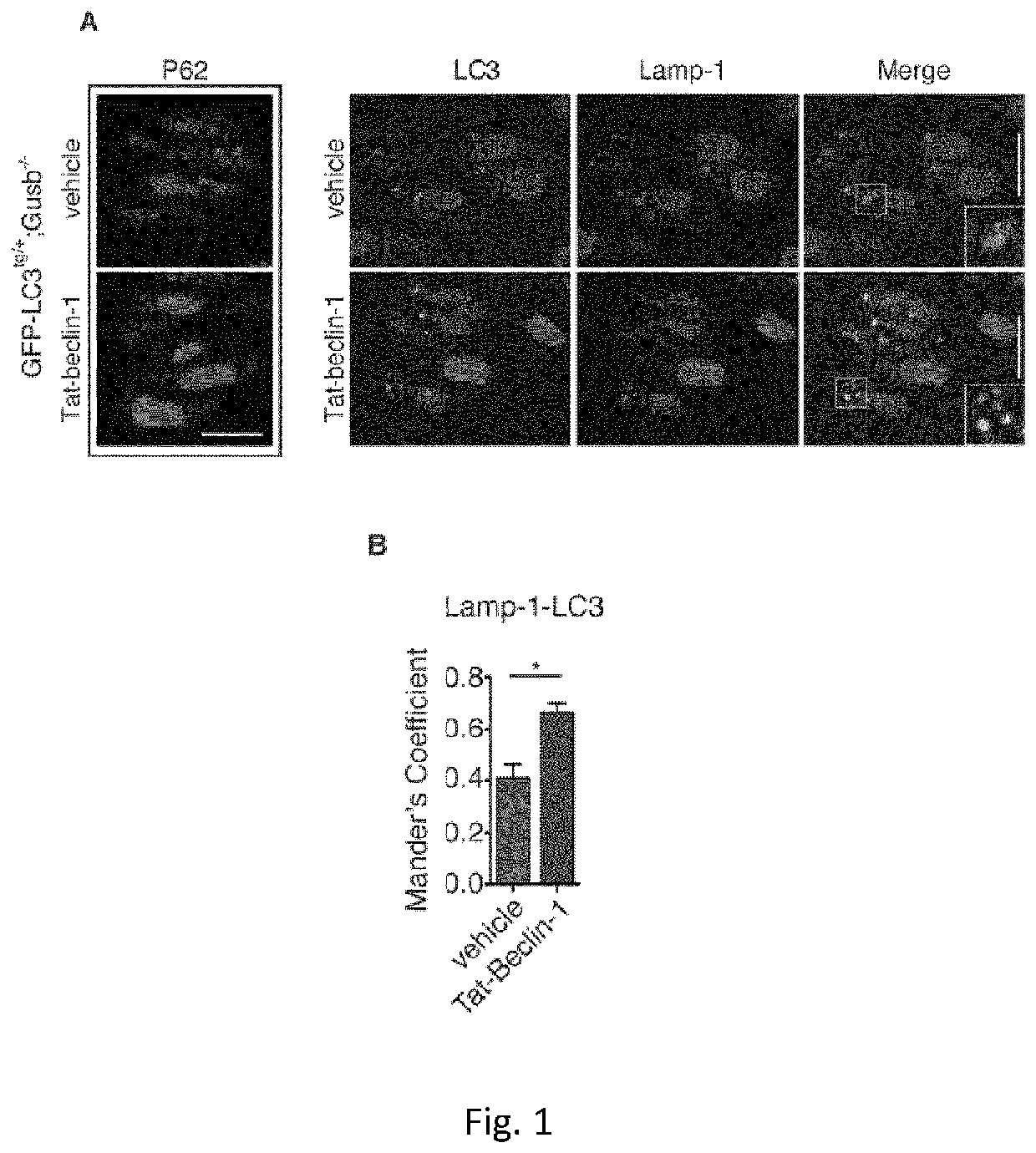
The present invention relates to an activator of beclin 1-Vps 34 complex for use in the treatment and / or prevention of a bone growth disorder. The activator may be a polypeptide, a polynucleotide, a vector, a host cell or a small molecule. In particular the activator may be a Beclin 1 peptide or a fragment or a derivative thereof, a mTORC1 inhibitor or a BH3 mimetic. The present invention also relates to pharmaceutical composition comprising said activator.
Owner:FOND AZIONE TELETHON
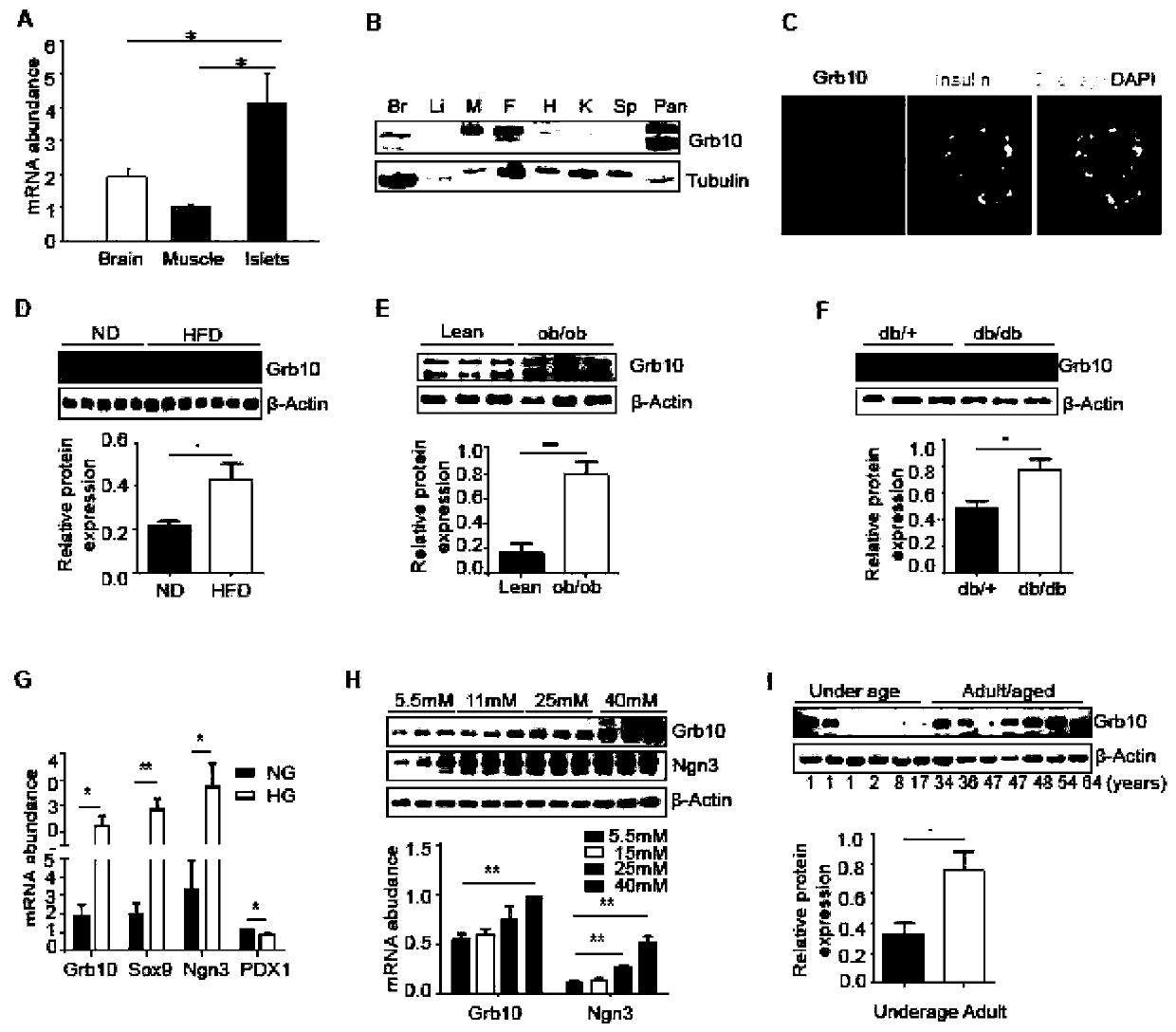
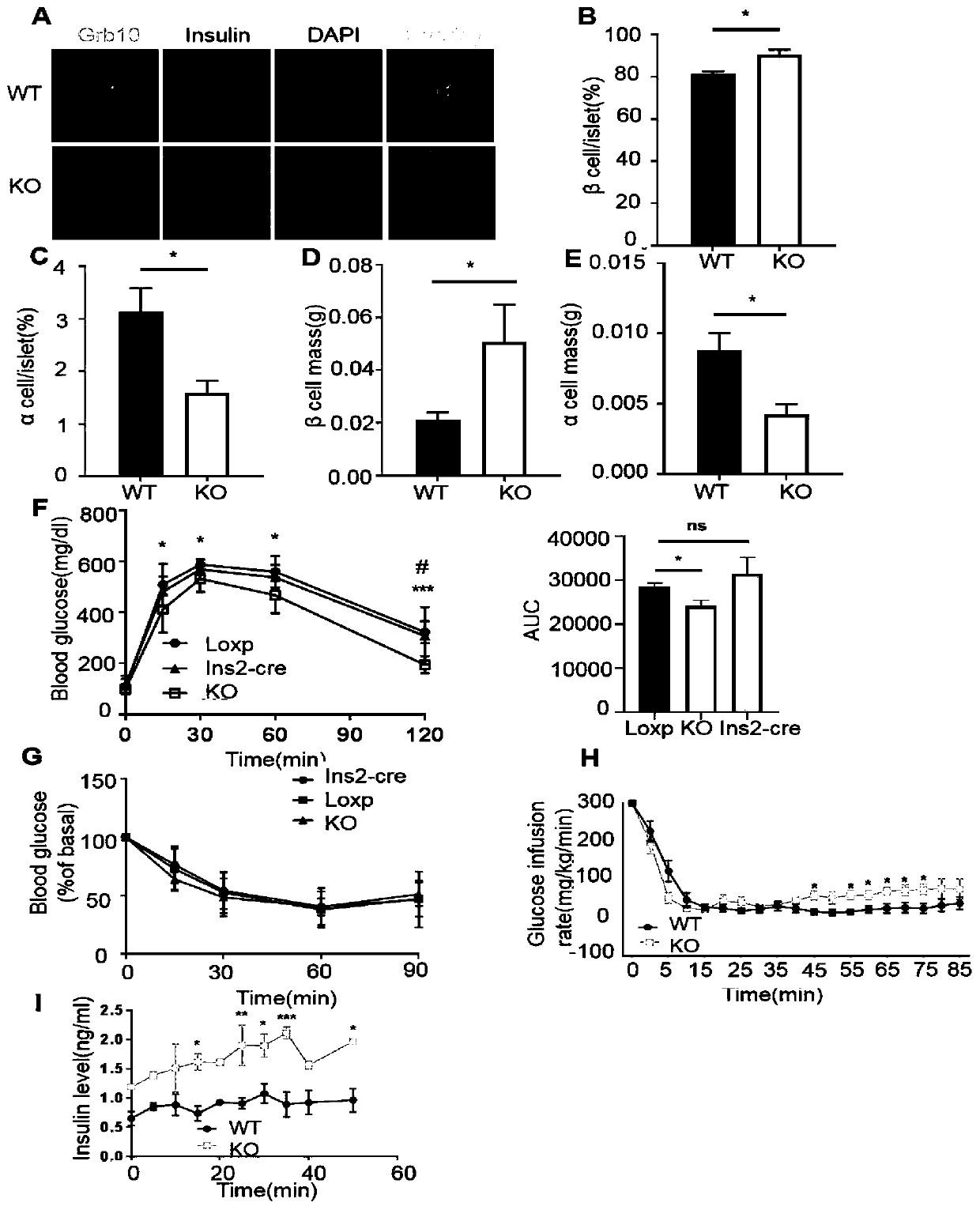
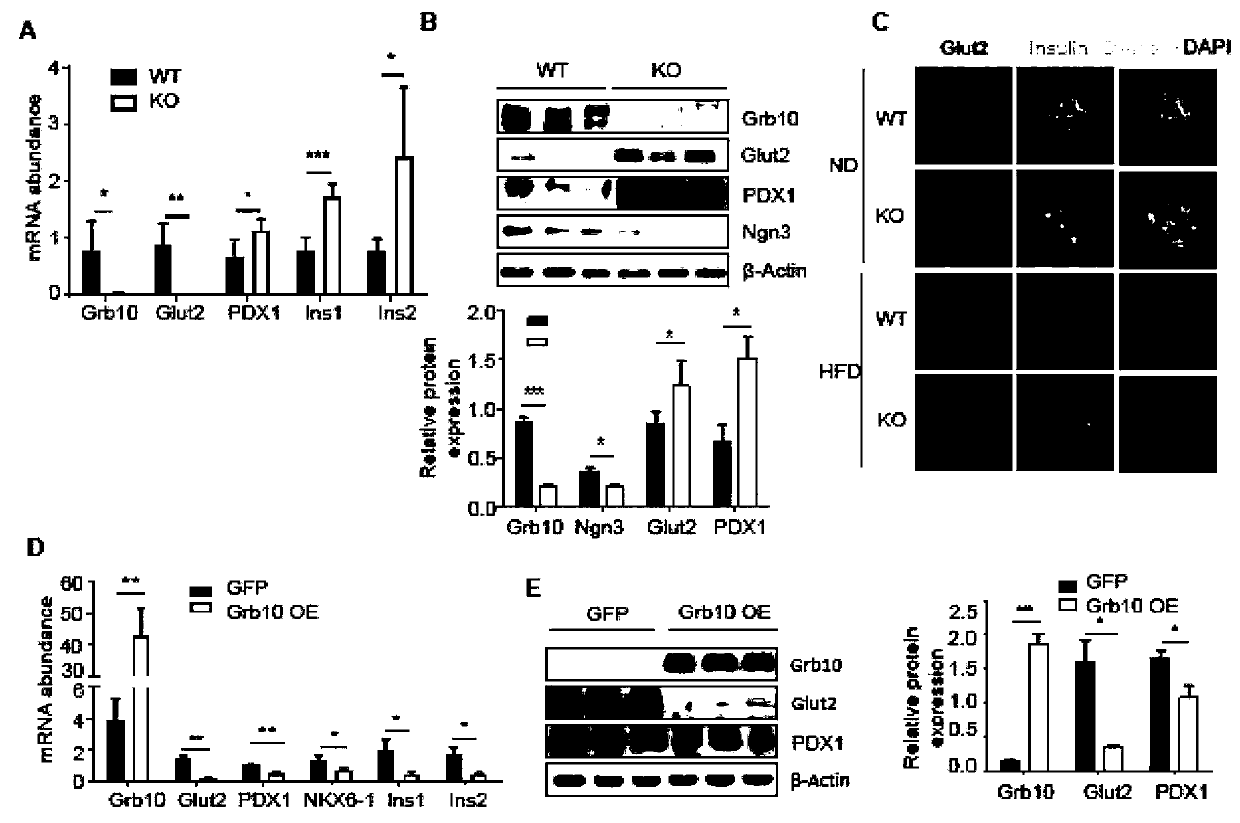
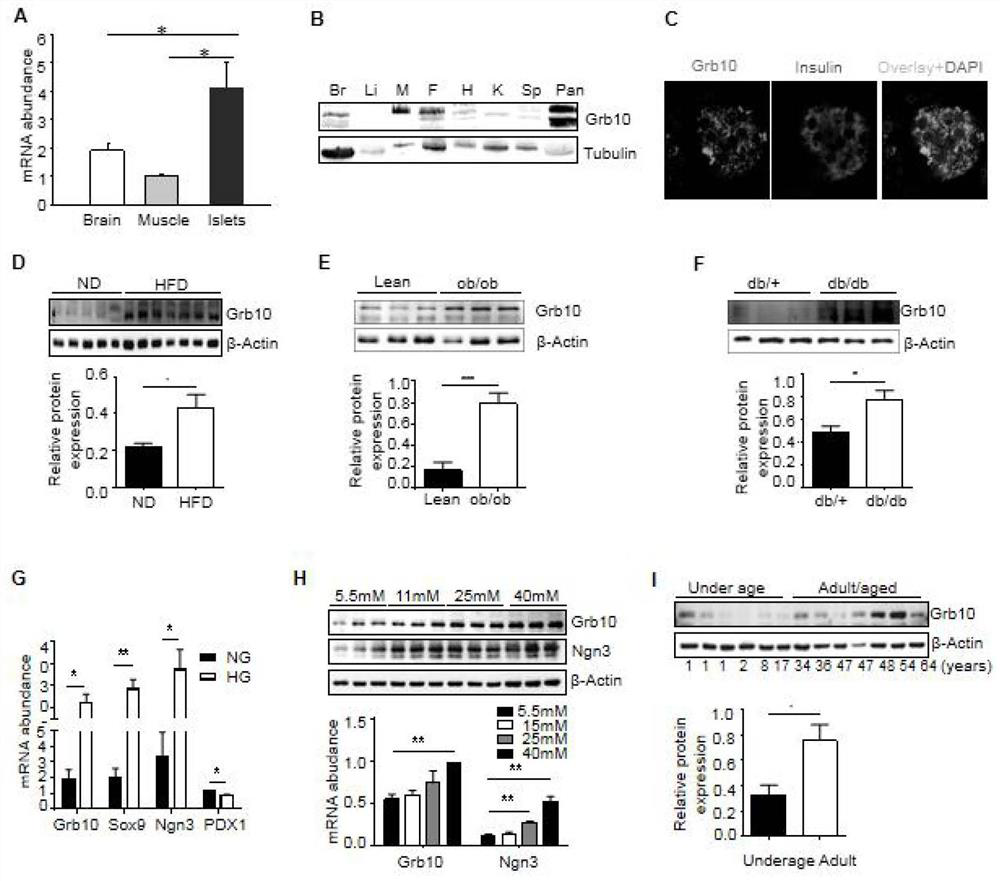
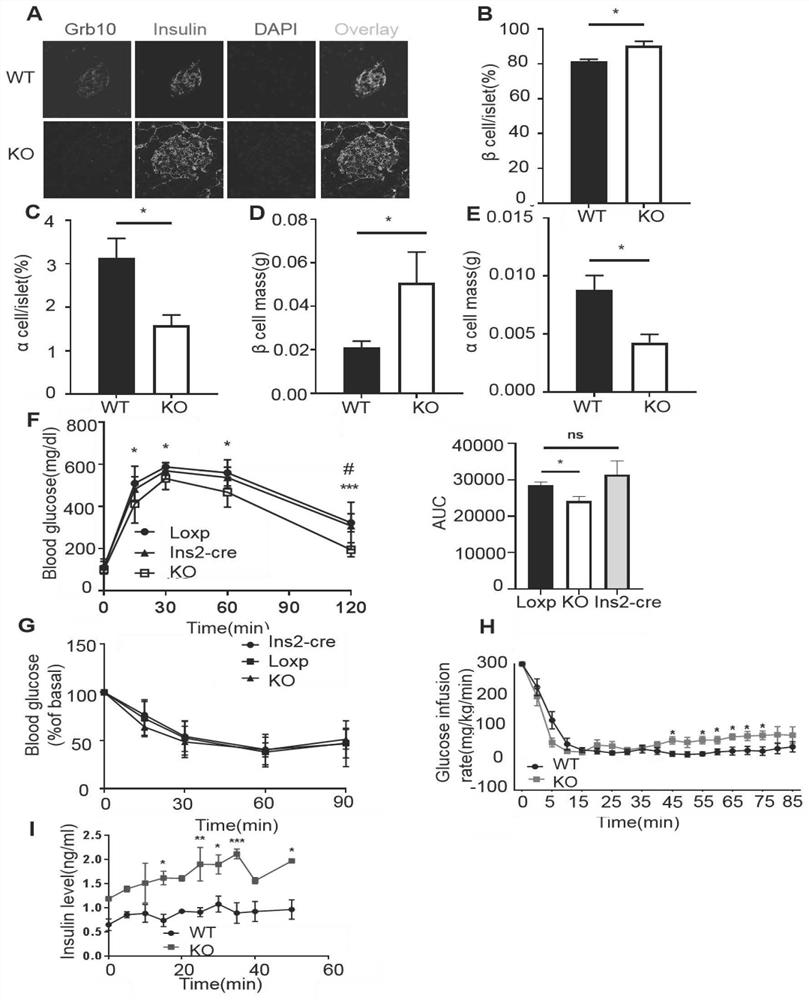
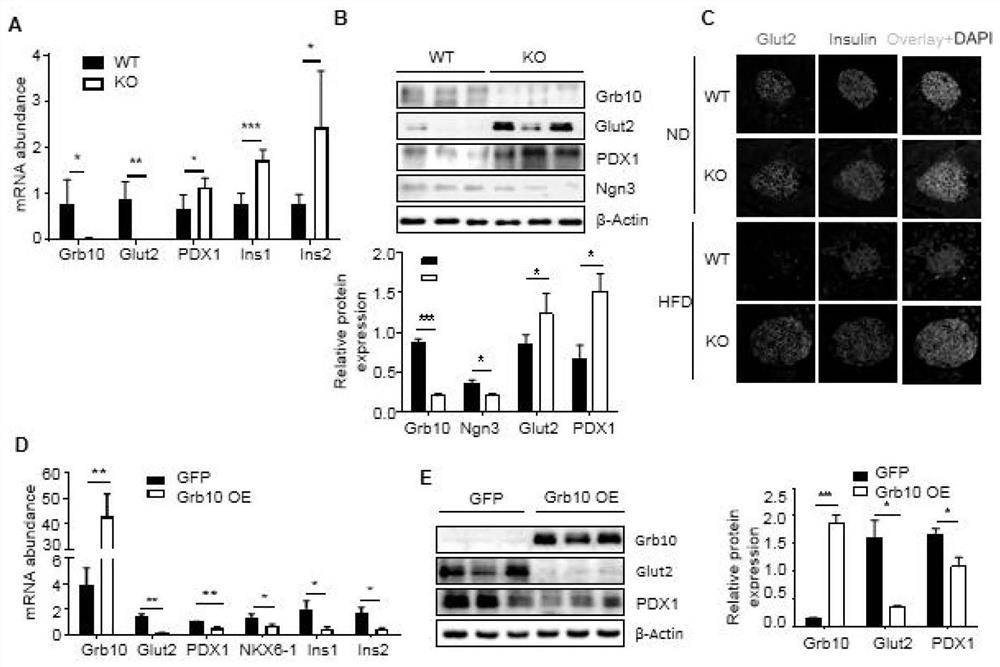
Application of Grb10 as key negative regulation factor of beta cell dysfunction
InactiveCN111494635APromote maturityInhibition of dedifferentiationMetabolism disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementBeta-cell FunctionGRB10
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, in particular to application of Grb10 as a key negative regulation factor for pancreatic beta cell dysfunction. According to the invention, the physiological function of Grb10 in beta cells is researched, wherein the results show that Grb10 is highly expressed in pancreas and islets of human and mice, and is highly expressed in islets of diabetic mouse models and islets of old people. In addition, the beta cell specific knockout Grb10 increases the beta cell quality and beta cell function of high fat diet (HFD) mice by promoting beta cell maturation and inhibiting beta cell dedifferentiation. According to the invention, the important role of Grb10-mTORC1 interaction in regulating beta cell dedifferentiation is highlighted, and a new insight is provided for a regulating mechanism of beta cell characteristics and functions.
Owner:THE SECOND XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
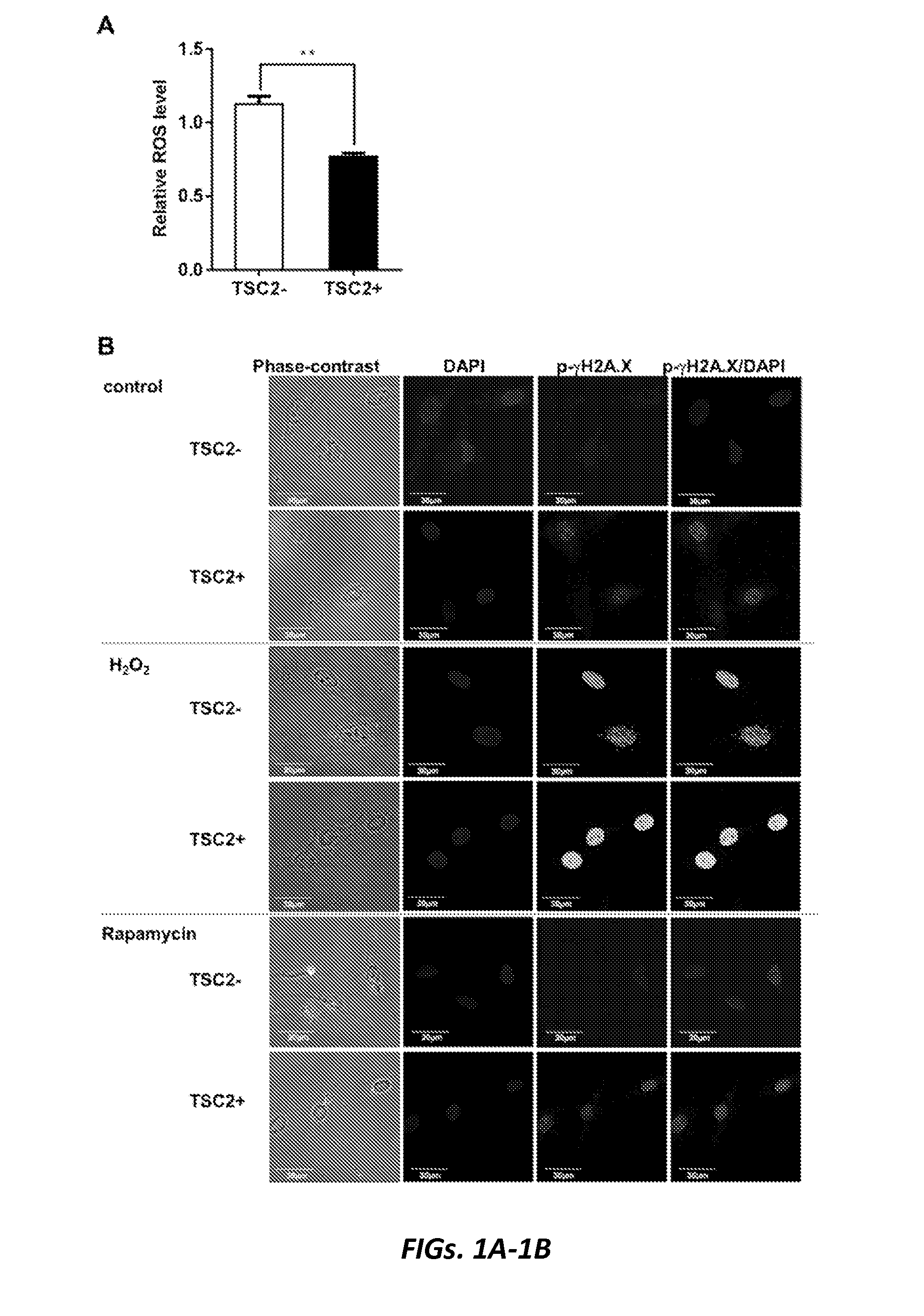
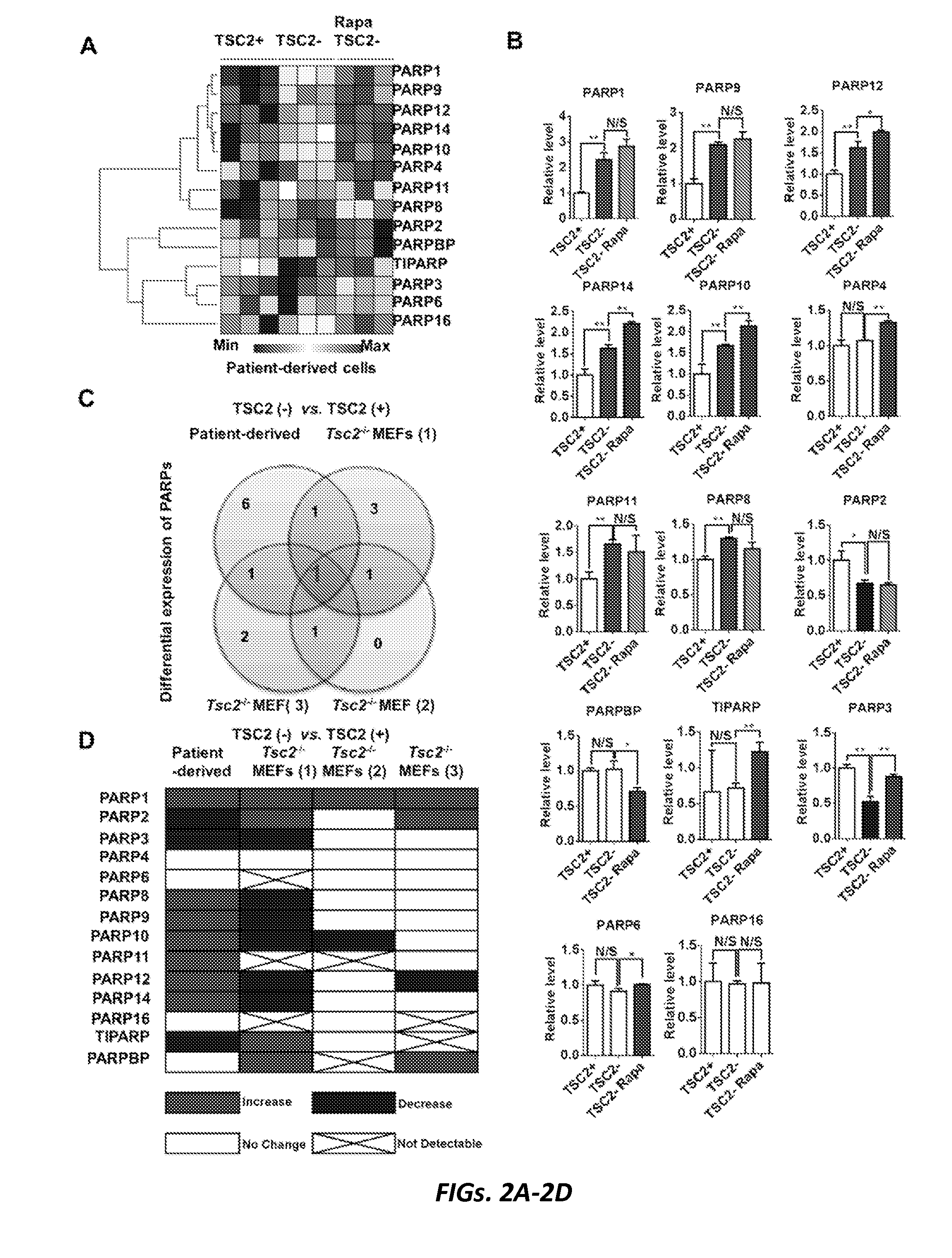
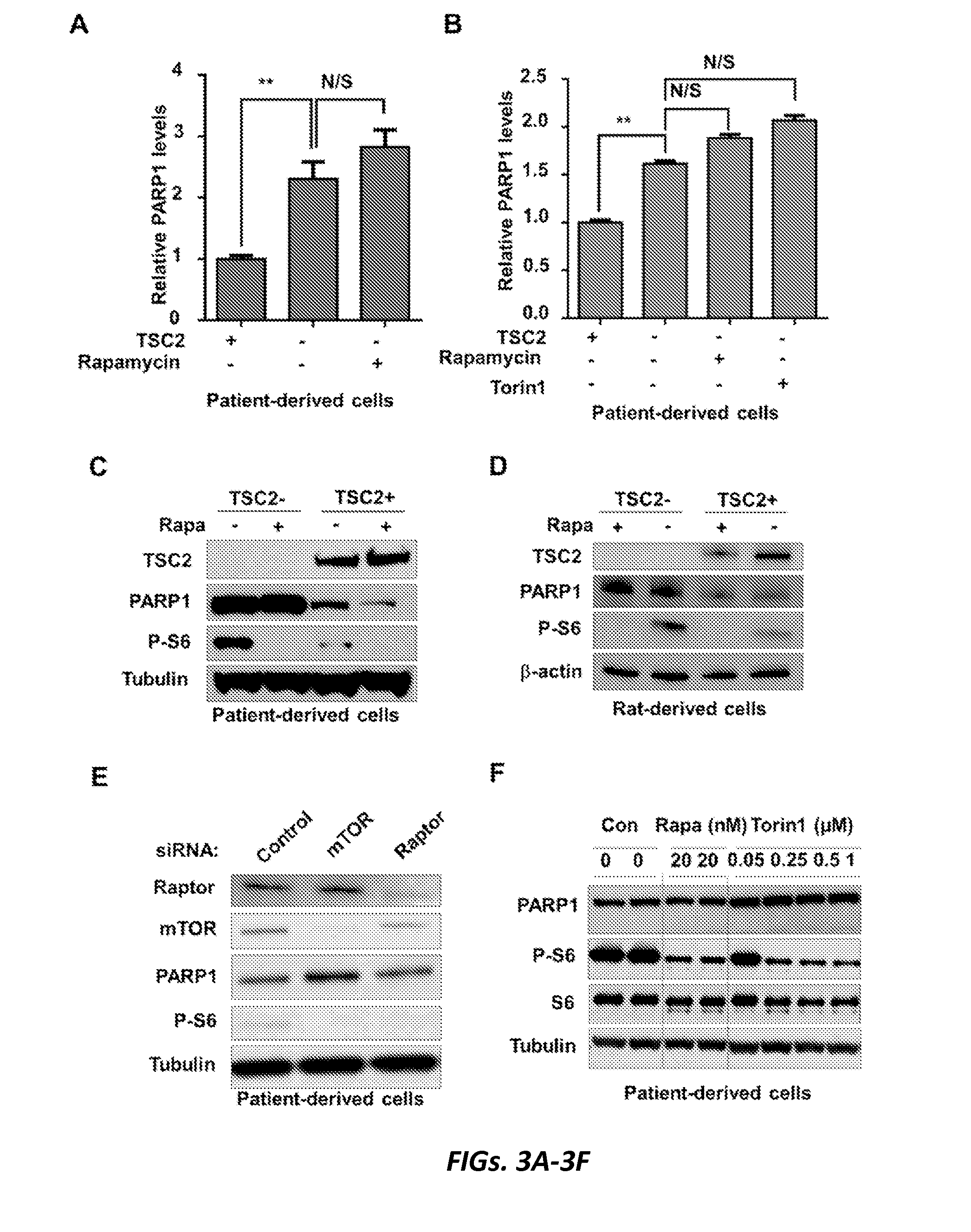
Targeting parp1 for treatment of tsc and cancers
The present invention relates to methods of treating a condition associated with mTORC1 hyperactivation or TSC2-deficient cancer, the method comprising administering to a subject having the cancer a pharmaceutically-effective amount of a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) inhibitor. In some embodiments, the condition associated with mTORC1 hyperactivation is tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC). In some embodiments, the condition associated with mTORC1 hyperactivation is lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM). In some embodiments, the condition associated with mTORC1 hyperactivation is TSC2-deficient cancer.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Grb10 used as key negative regulation factor of beta cell dysfunction
InactiveCN111920955APromote maturityInhibition of dedifferentiationMetabolism disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementBeta-cell FunctionGRB10
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, in particular to an application of Grb10 as a key negative regulation factor for pancreatic beta cell dysfunction. According to the invention, the physiological function of Grb10 in beta cells is studied. Experimental results show that Grb10 is highly expressed in pancreas and islets of human and mice, and is highly expressed in islets ofdiabetic mouse models and islets of old people. In addition, the beta cell specific knockout Grb10 increases the beta cell quality and beta cell function of high fat diet (HFD) mice by promoting betacell maturation and inhibiting beta cell dedifferentiation. According to the invention, the important role of Grb10-mTORC1 interaction in regulating beta cell dedifferentiation is highlighted, and a new insight is provided for a regulating mechanism of beta cell characteristics and functions.
Owner:THE SECOND XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
Biomarkers of renal disorders
InactiveUS20150018383A1High riskOvercome side effectsBiocideDisease diagnosisDiseaseBiological activation
The present invention is directed to the use of marker for Akt2 activation in podocytes as a biomarker to predict toxicity of mTOR inhibitors. Another aspect of the invention relates to a method for preventing graft rejection comprising administering a selective mTORC1 or Akt1 inhibitor in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Free raptor reduces aging- and obesity-induced fatty liver
InactiveUS20170014477A1Increase PHLPPLower Level RequirementsPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderFatty liverDrug carrier
The present invention provides a method of reducing a subject's hepatic and plasma triglyceride levels comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutical carrier and a compound that increases PHLPP2 in liver cells in an amount effective to reduce the subject's hepatic and plasma triglyceride levels.The present invention also provides a method of reducing a subject's hepatic and plasma triglyceride levels comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutical carrier and a compound that increases free Raptor in liver cells in an amount effective to reduce the subject's hepatic and plasma triglyceride levels.The present invention also provides a process for determining the amount of free Raptor in a subject's liver comprising:a) obtaining a biological sample comprising liver cells of the subject;separating free Raptor and mTORC1-associated Raptor in the sample; andc) determining the amount of free Raptor in the sample.The present invention also provides a method of reducing a subject's hepatic and plasma triglyceride levels comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutical carrier and a compound that prevents PHLPP2 degradation in liver cells in an amount effective to reduce the subject's hepatic and plasma triglyceride levels.The present invention also provides a method of reducing a subject's hepatic and plasma triglyceride levels comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a pharmaceutical composition comprising a pharmaceutical carrier and a compound that inhibits Glucagon signaling in liver cells in an amount effective to reduce the subject's hepatic and plasma triglyceride
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
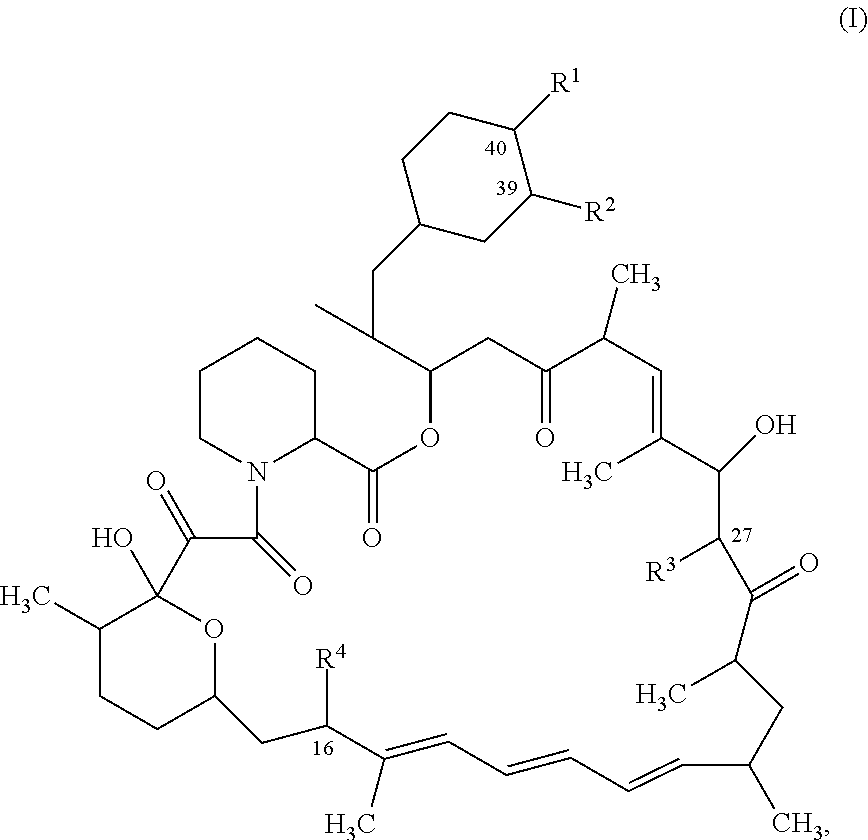
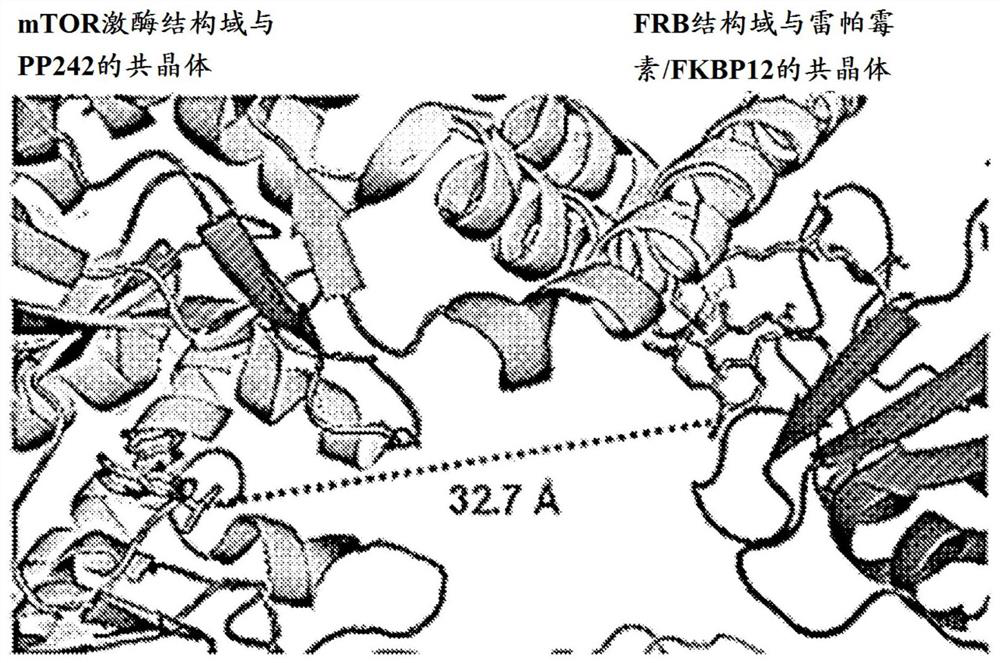
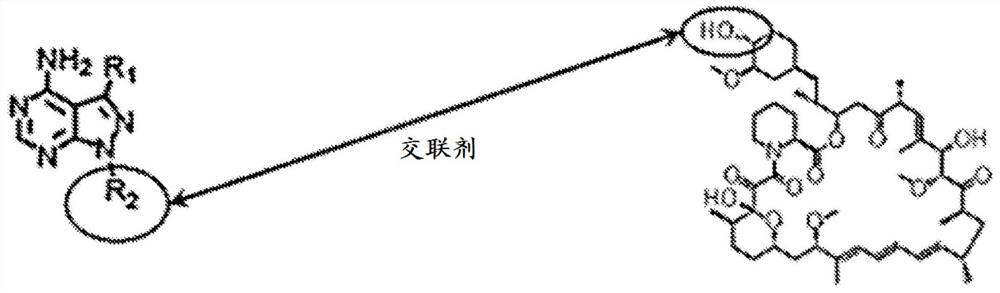
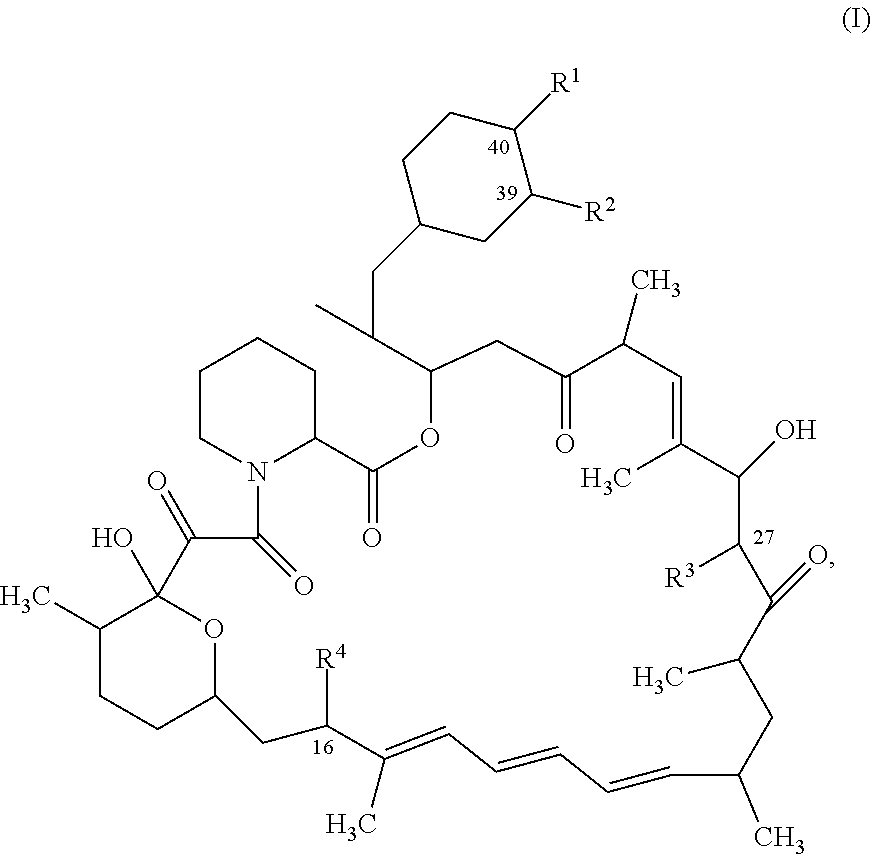
mTORC1 INHIBITORS
The present application relates to a compound, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, comprising a monovalent active site mTOR inhibitor covalently bound to monovalent rapamycin or a monovalent rapamycin analogue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
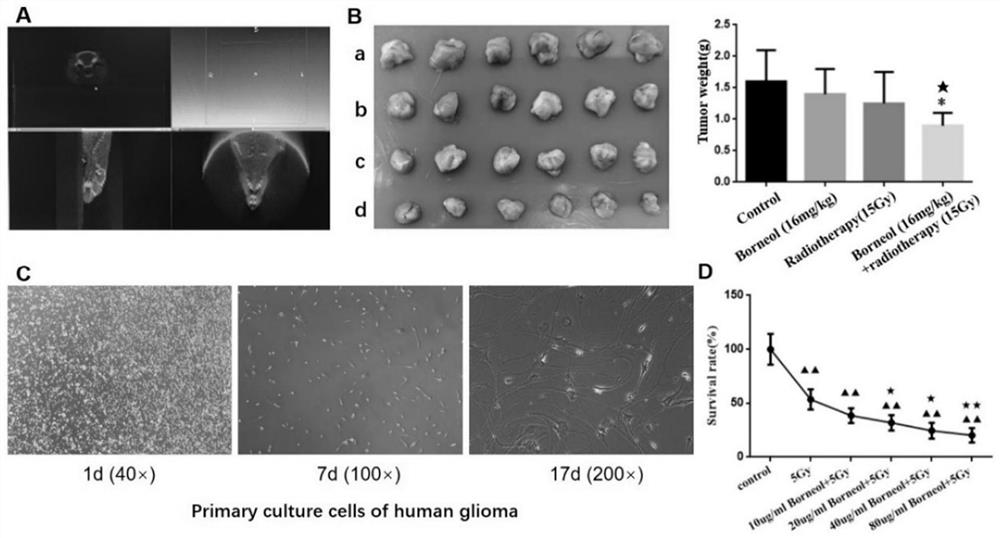
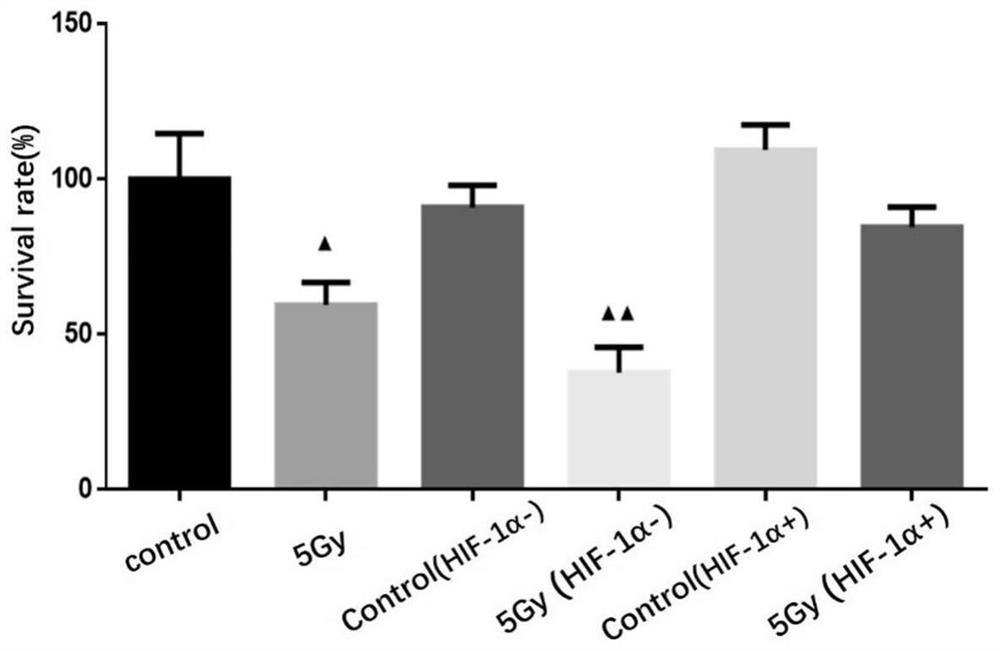
Application of borneol in preparation of brain glioma radiotherapy combined medicine
InactiveCN111870592AImprove targetImprove the molecular mechanismHydroxy compound active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismHIF1ASignalling pathways
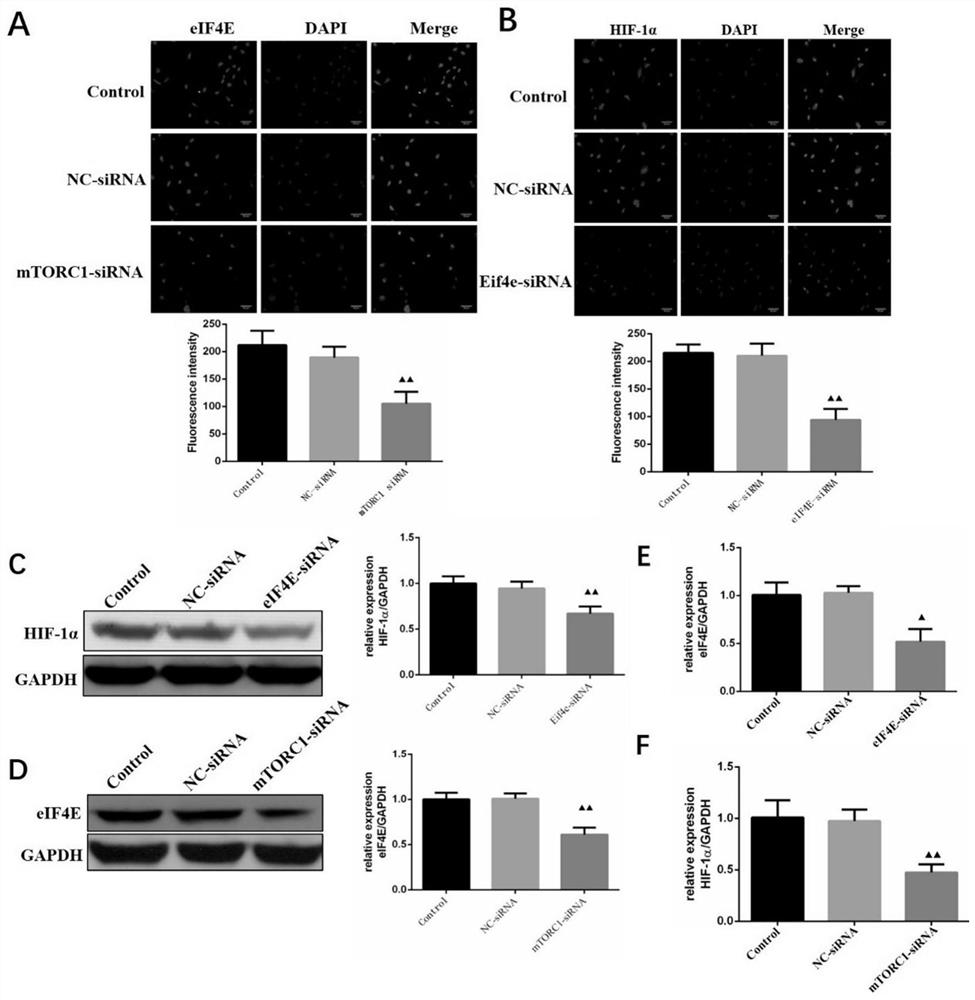
The invention relates to the field of tumor drugs, and discloses an application of borneol in preparation of a brain glioma radiotherapy combined drug. The inventor of the invention finds that borneolcan effectively enhance the sensitivity of malignant brain glioma radiotherapy, and the effect may be that the expression of HIF1a is regulated and controlled by mediating mTORC1 / eIF4E signaling pathways so as to reverse radiotherapy resistance, so that borneol can be used as a malignant brain glioma radiotherapy combined drug.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CANCER HOSPITAL
mTORC1 modulators
ActiveUS10807951B2Reduced activityLower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseBiochemistry
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Mtorc modulators and uses thereof
ActiveUS20210002300A1Impaired insulin sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderRapamycin AnalogBiochemistry
Owner:AEOVIAN PHARM INC
Compositions and methods for treating or preventing dermal disorders
ActiveUS10695326B2Treating or preventing an age-related dermal disorderExtend your lifeOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsActinic keratosesDisease
The present invention includes compositions and methods for treating or preventing certain dermal disorders including dermal atrophy, pseudoscars, actinic keratosis, seborrheic or actinic keratoses, lentigines, focal areas of dermal thickening, and coarse wrinkles. In certain embodiments, the compositions useful within the invention comprise a therapeutically effective amount of a mTORC1 inhibitor and a dermatologically acceptable carrier.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
P13K-MTORC1-S6K1 signaling pathway biomarkers predictive of anti-cancer responses
The present invention is based, in part, on the identification of novel FI.3K-mTORCI-S6K 1 signaling pathway biomarkers predictive of responsiveness to anti-cancer therapies.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
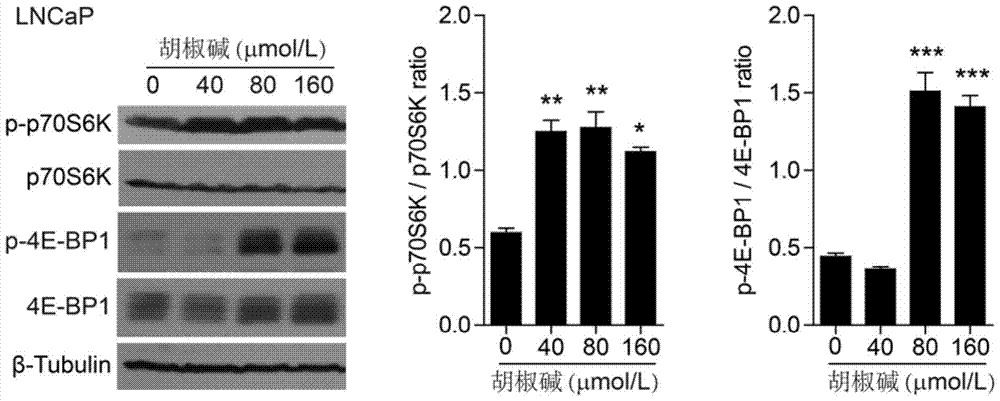
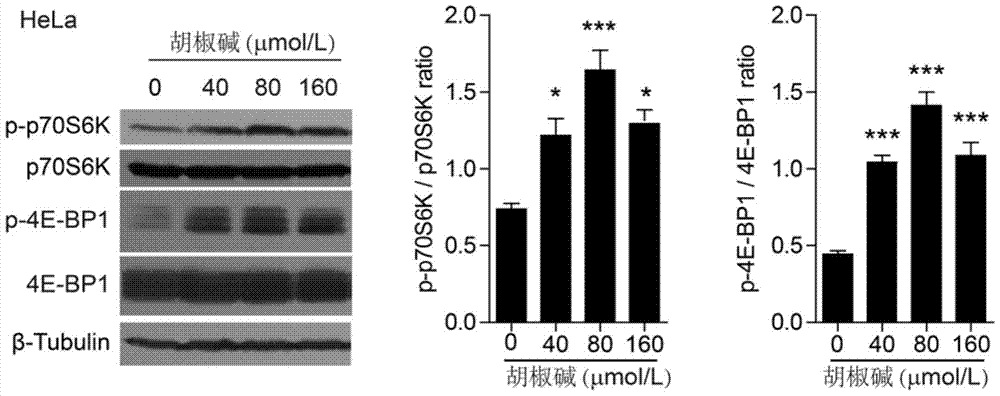
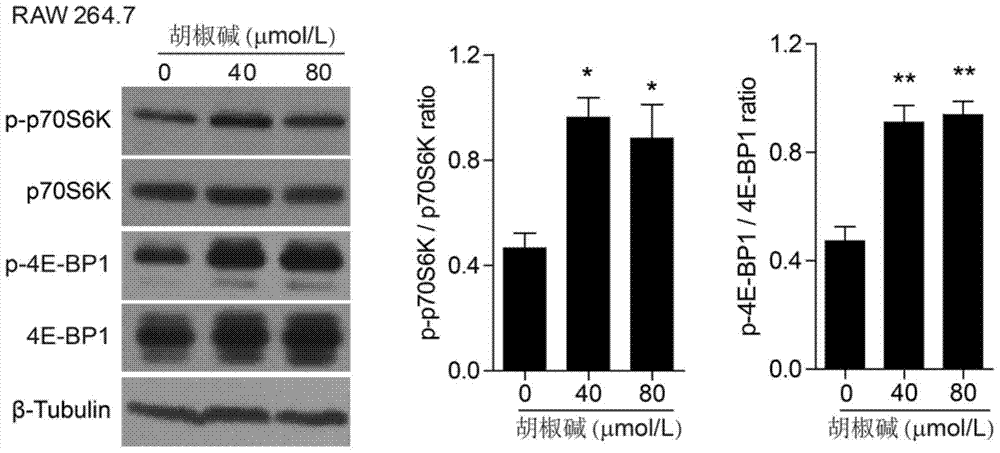
Application of piperine in the preparation of drugs for preventing and treating sepsis
ActiveCN105147684BPromote activationFunction increaseAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesBiological activation
The invention discloses application of piperine to the preparation of drugs for preventing and treating septicemia. Piperine can strongly enhance the leucine-induced activation of mTORC1. Piperine can prevent bacterial abdominal infection and further prevent septicemia, and can also enhance the functions of macrophages, including bacterial phagocytosis and TNF-alpha and IL-6 secretion capability, to prevent bacterial infection induced macrophage apoptosis. Therefore, piperine or the combination of piperine, leucine and glutamine can enhance the mTORC1 activity of bodies and be used for treating bacterial infections and septicemia.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com