Patents
Literature
150 results about "Velocity reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
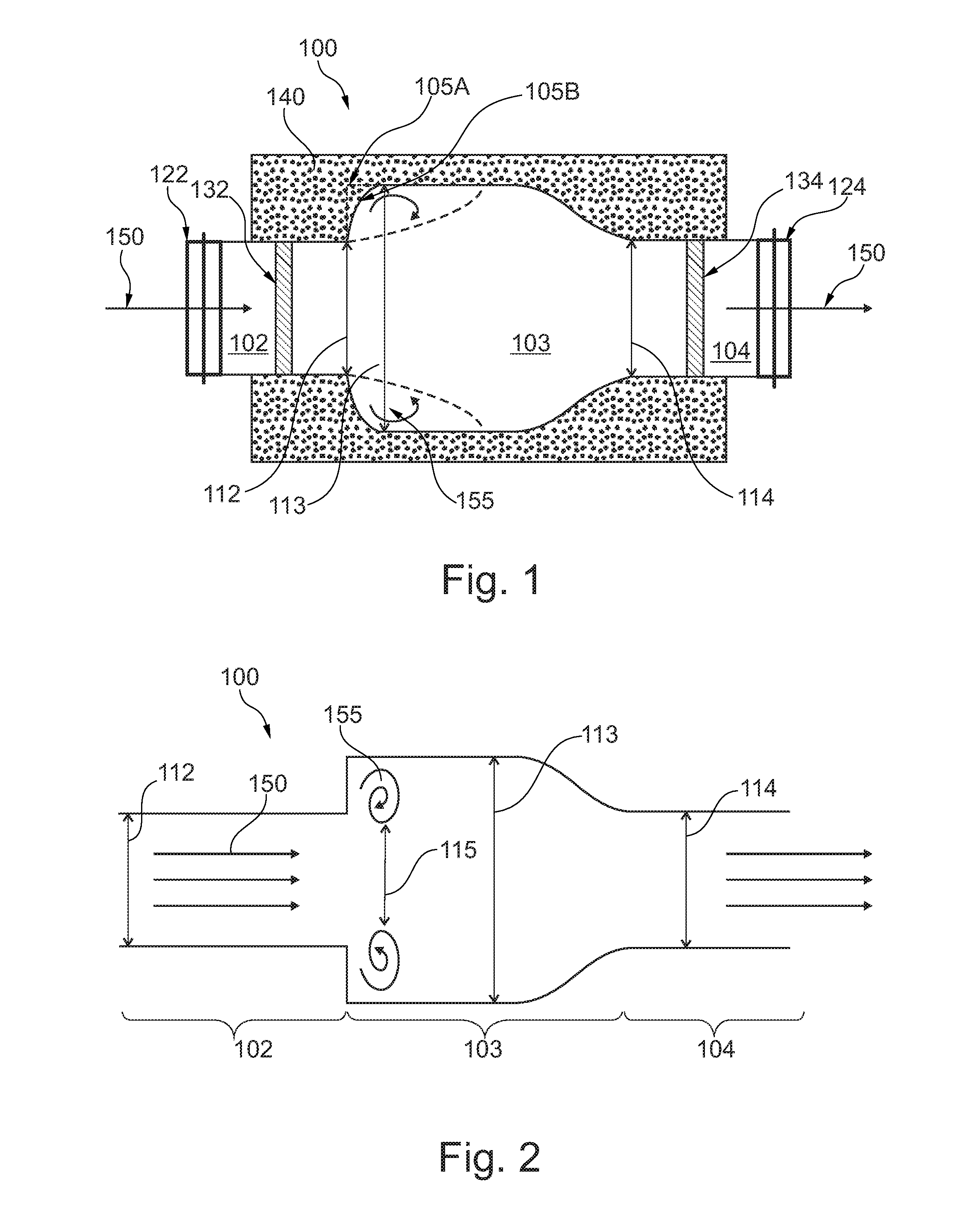
The average water velocity is multiplied by the reduction factor to account for areas of reduced velocity utilized by a swimming fish to conserve energy. The use of Velocity Reduction Factors is usually only applicable for small fish. Different Velocity Reduction Factors can be applied to the inlet, barrel, and outlet zones.
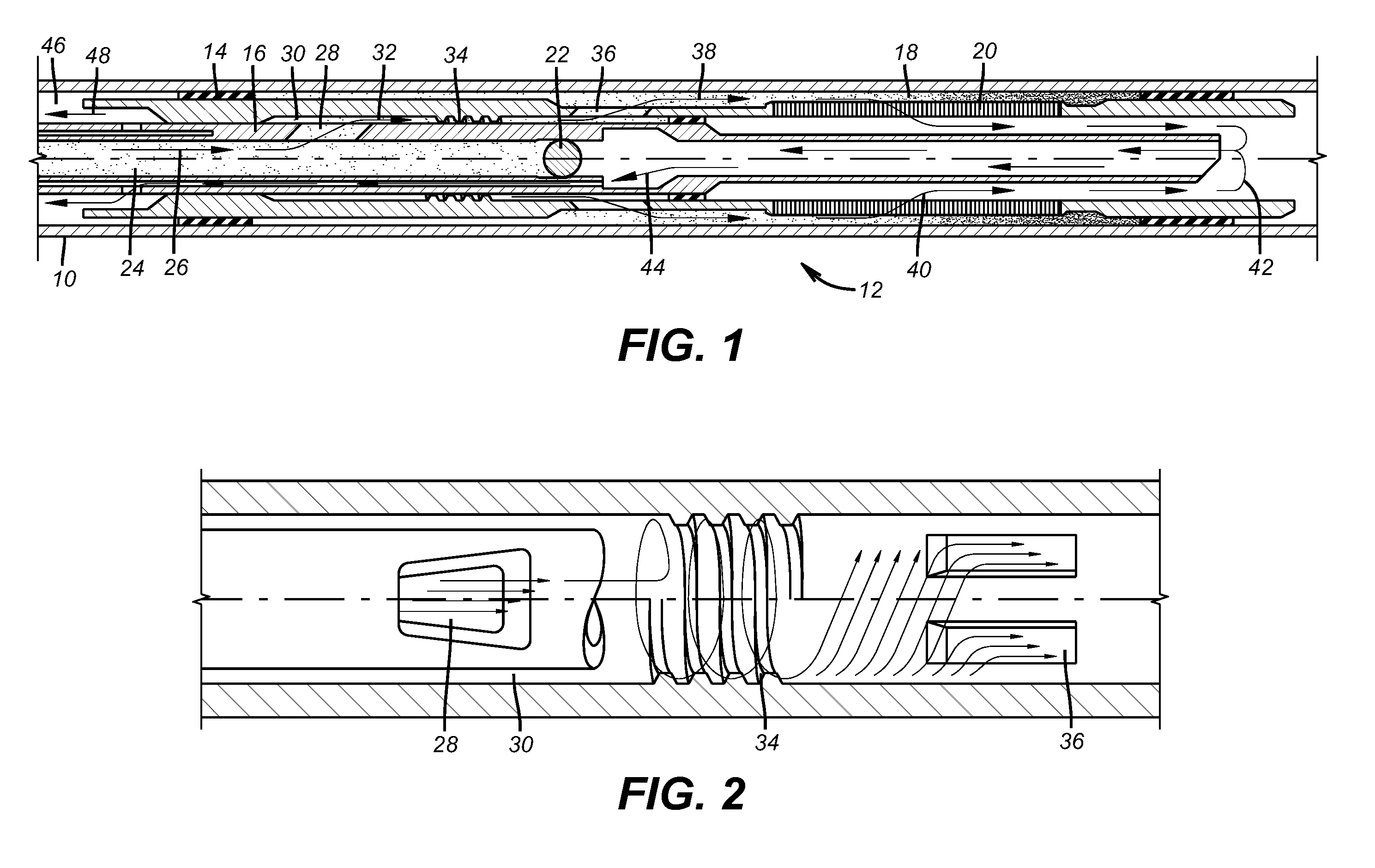
Prolonged Transit Time of Permeability-Enhancing Drug Eluting Pill
InactiveUS20080275430A1Promote absorptionShorten speedMedical devicesMicromachined deliveryPower flowMedicine
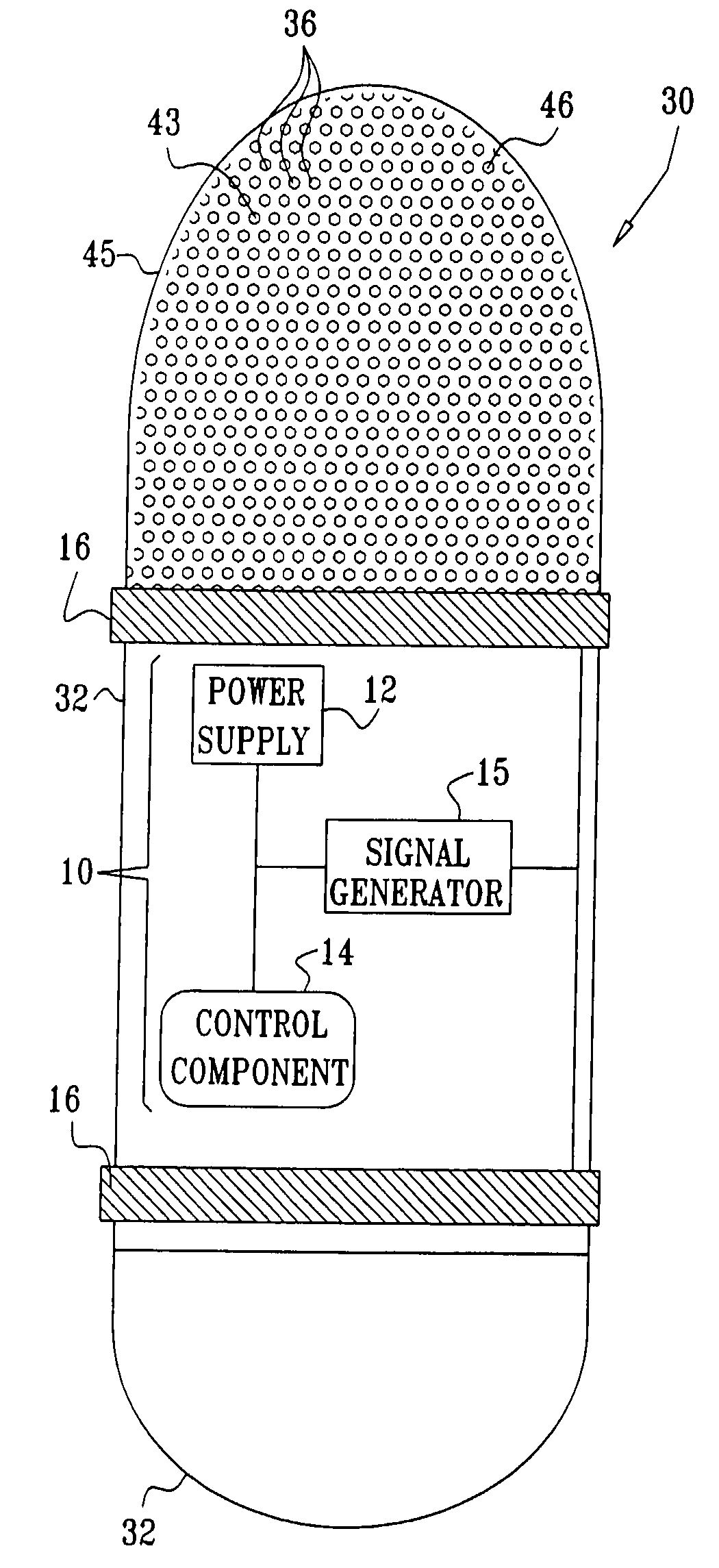
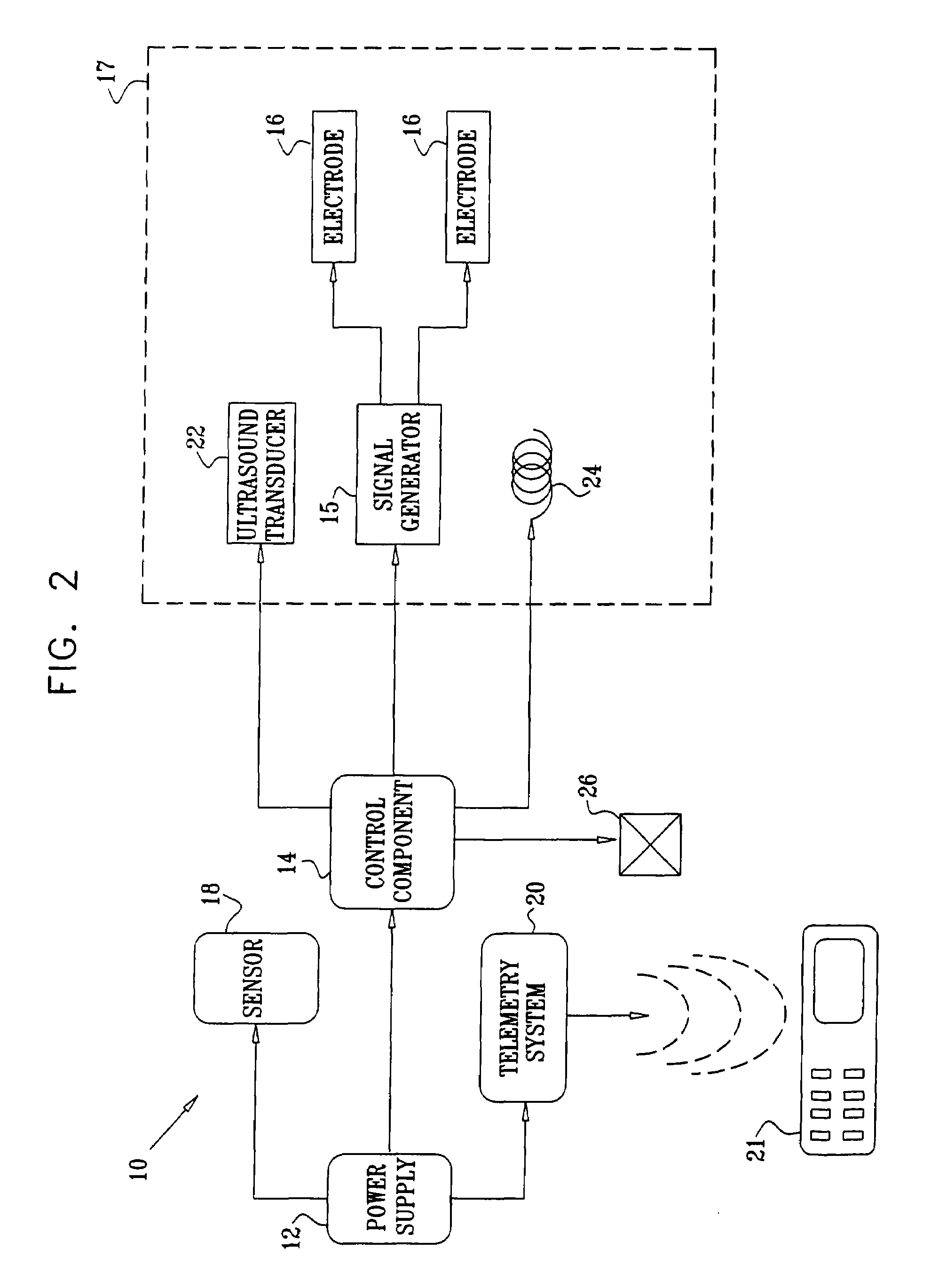
Apparatus is provided for drug administration. The apparatus includes an ingestible capsule, which includes a drug, stored by the capsule. The apparatus also includes an environmentally-sensitive mechanism, adapted to change a state thereof responsively to a disposition of the capsule within a gastrointestinal (GI) tract of a subject; one or more drug-passage facilitation electrodes; and a control component, adapted to facilitate passage of the drug, in response to a change of state of the environmentally-sensitive mechanism, by driving the drug-passage facilitation electrodes to apply an electrical current. The apparatus further includes a velocity-reduction element adapted to reduce a velocity of the capsule through the GI tract for at least a portion of the time that the control component is facilitating the passage of the drug. Additional embodiments are also described.
Owner:E PILL PHARMA
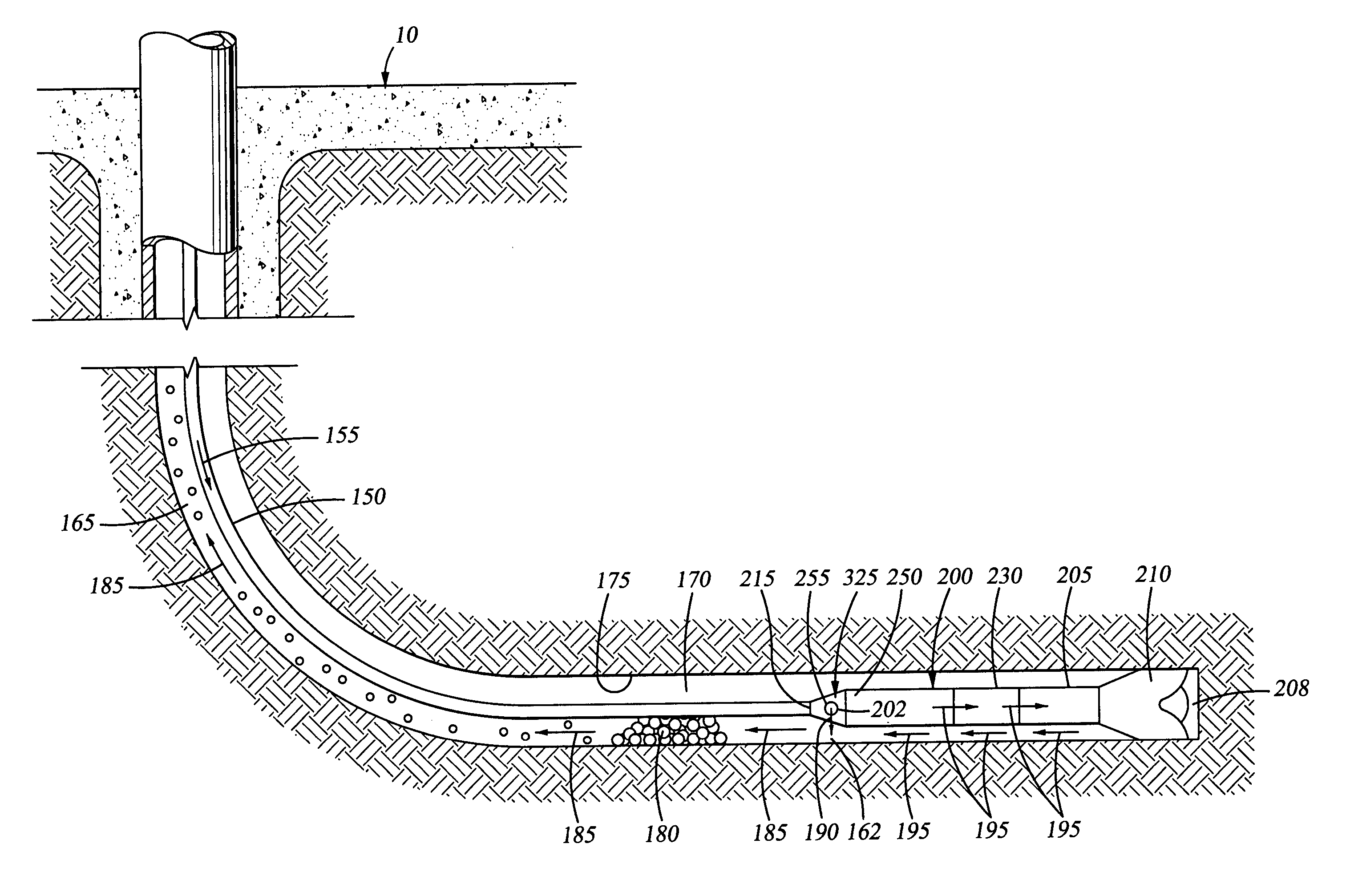
Method of creating a zonal isolation in an underground wellbore
A method of creating a zonal isolation above a target zone in an underground wellbore comprises: inserting a slurry injection tubing into the wellbore; arranging within an annular space surrounding said tubing an particle accumulation means, such as an expandable screen or an area where the slurry velocity is reduced; and pumping a slurry comprising a carrier fluid and granular material down via the slurry injection tubing and the target zone and then up into the annular space, such that at least some granular material accumulates and forms an elongate zonal isolation in the annular space between the target zone and the particle accumulation means, which zonal isolation is removable and exerts a limited radial force to the surrounding formation, thereby reducing the risk of formation damage.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
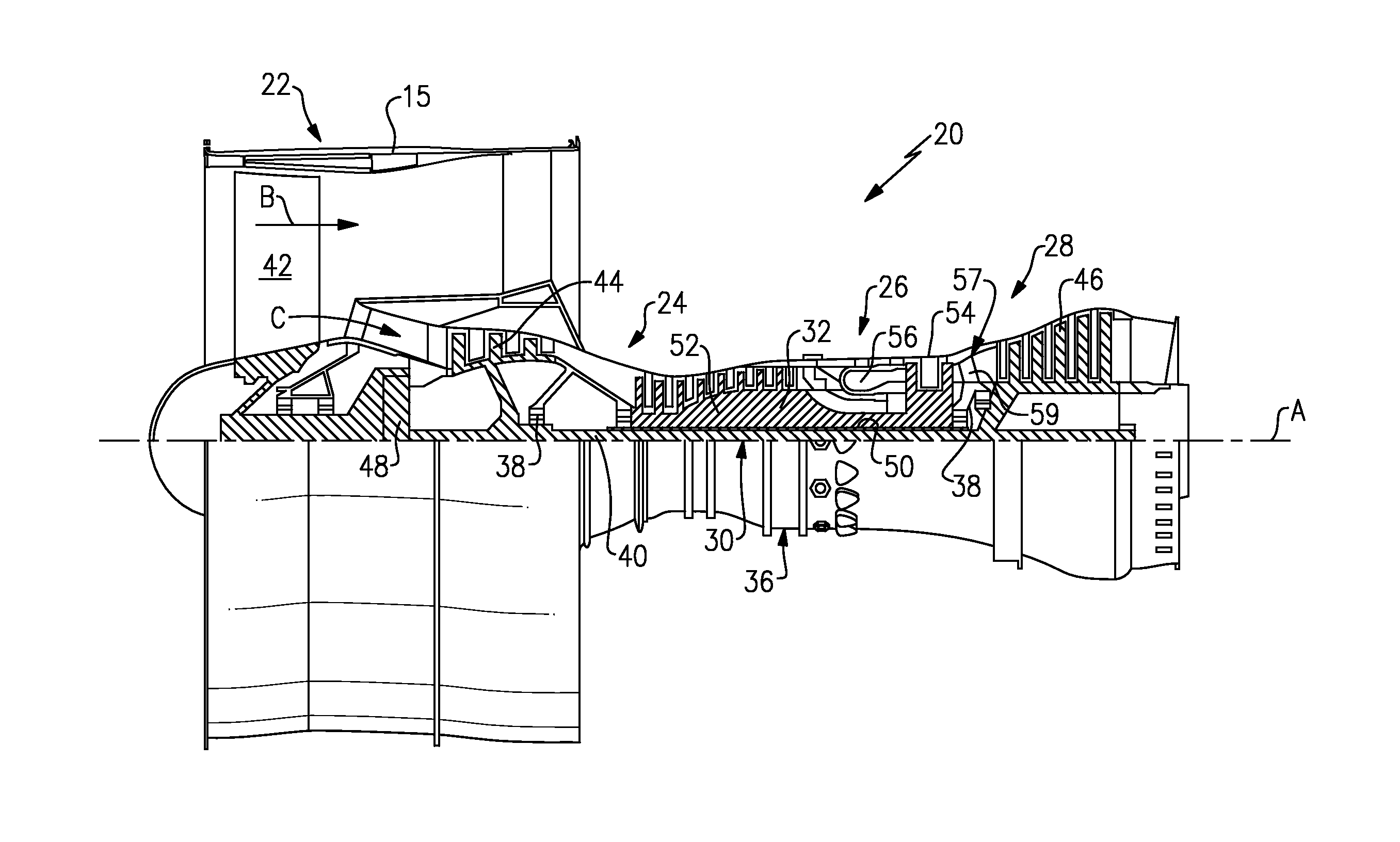
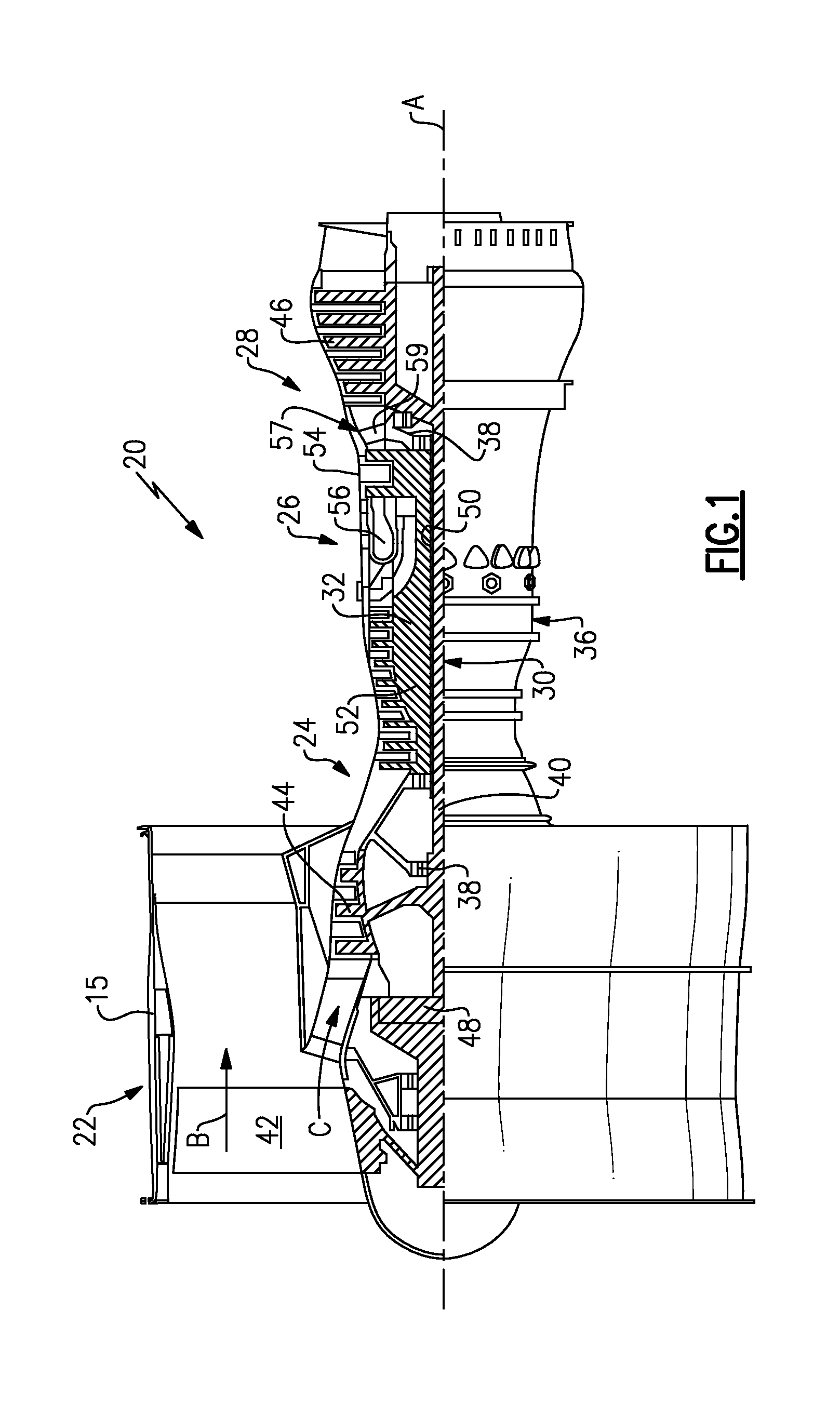
Low noise turbine for geared turbofan engine
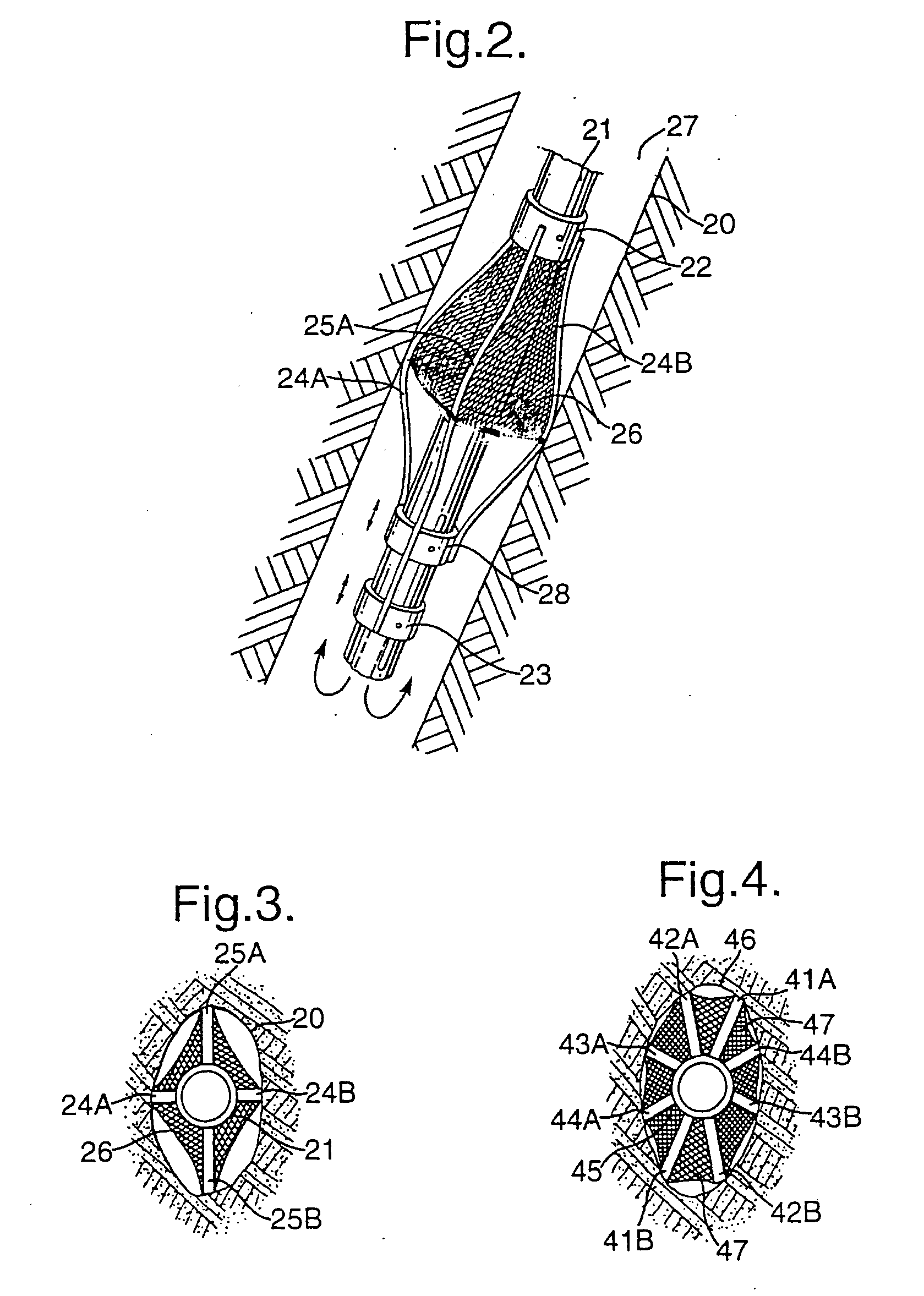
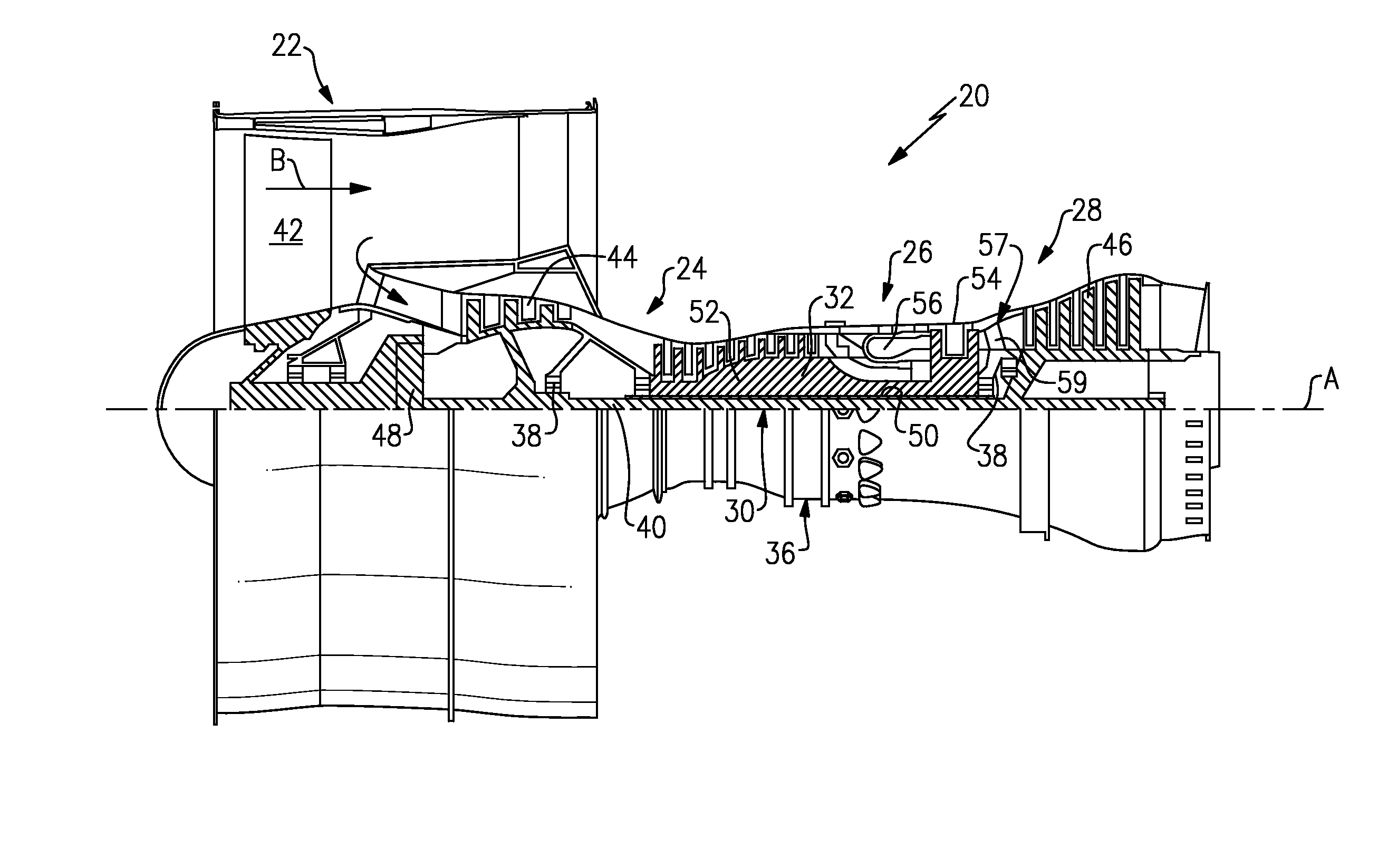
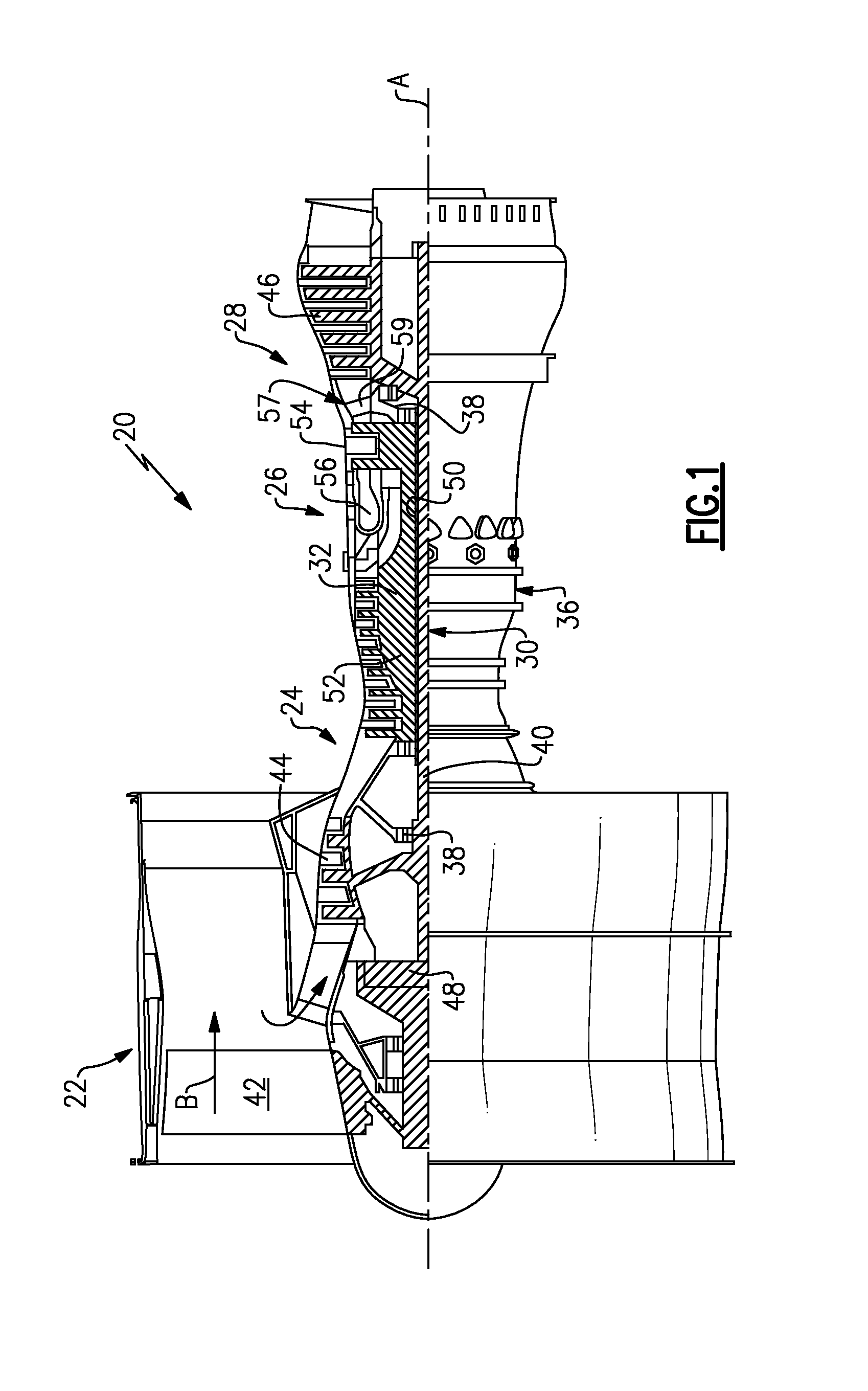
A gas turbine engine is utilized in combination with a gear reduction to reduce the speed of a fan relative to a low pressure turbine speed. The gas turbine engine is designed such that a blade count in the low pressure turbine multiplied by the speed of the low pressure turbine will result in operational noise that is above a sensitive range for human hearing. A method and turbine module are also disclosed.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
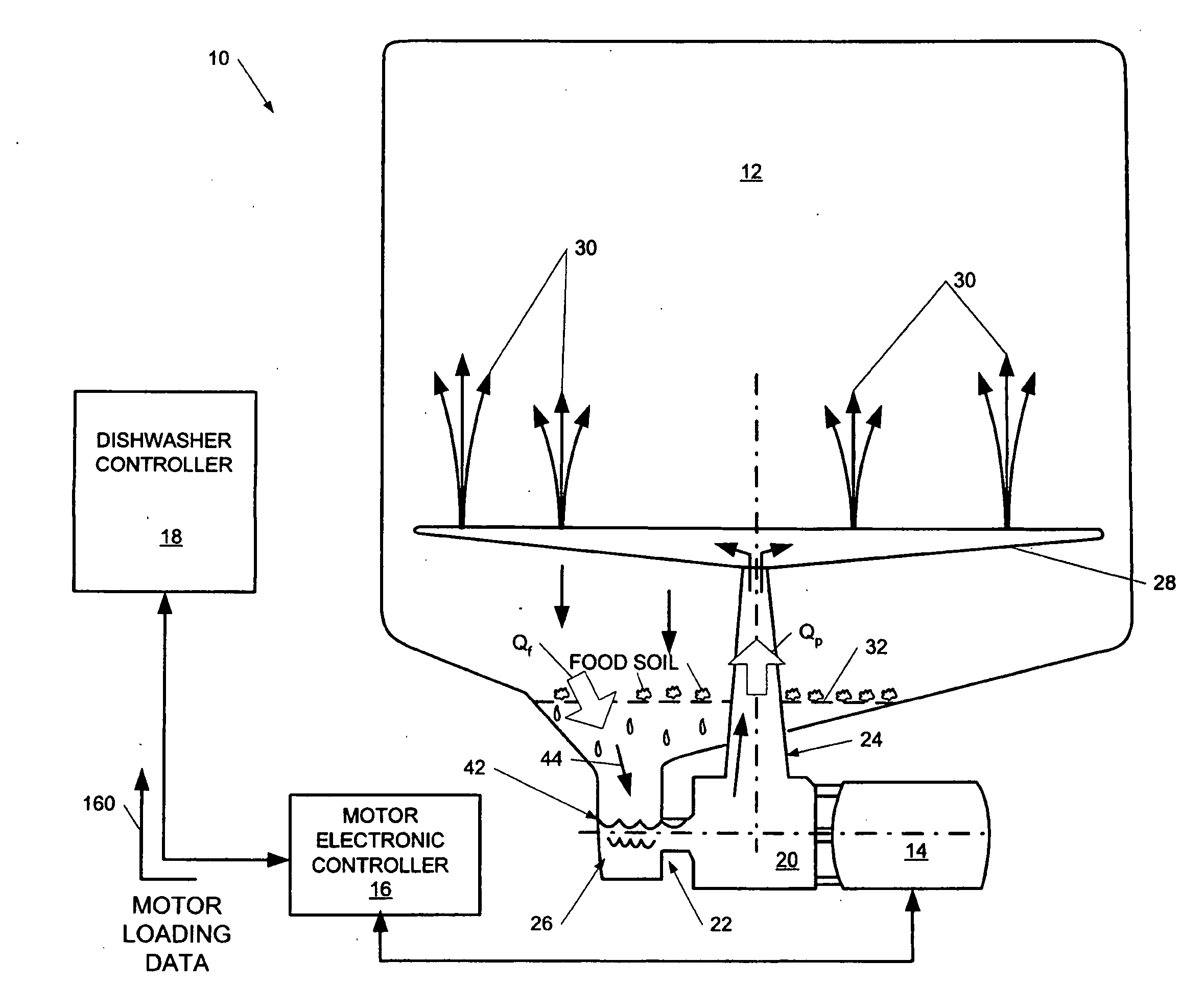
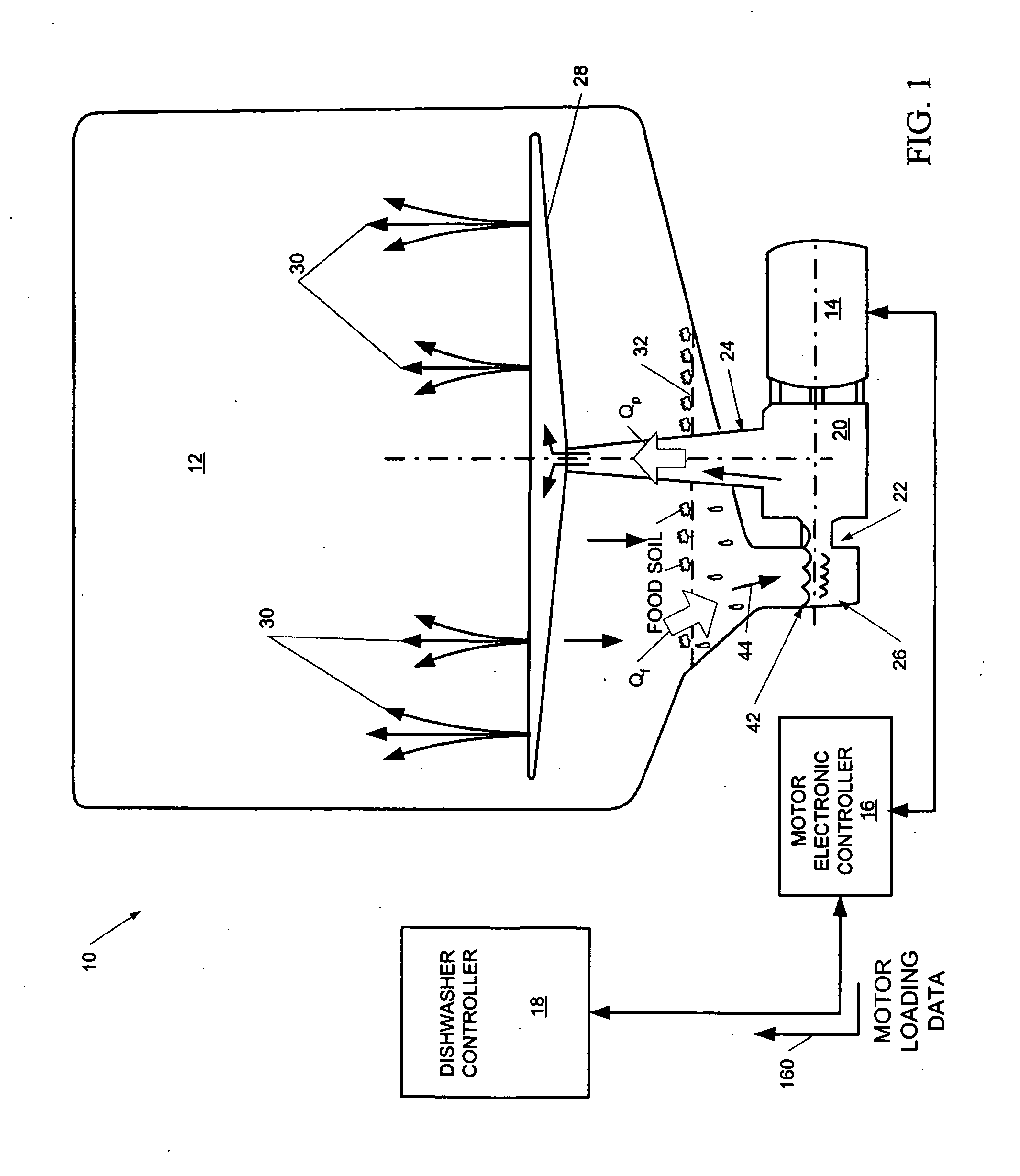
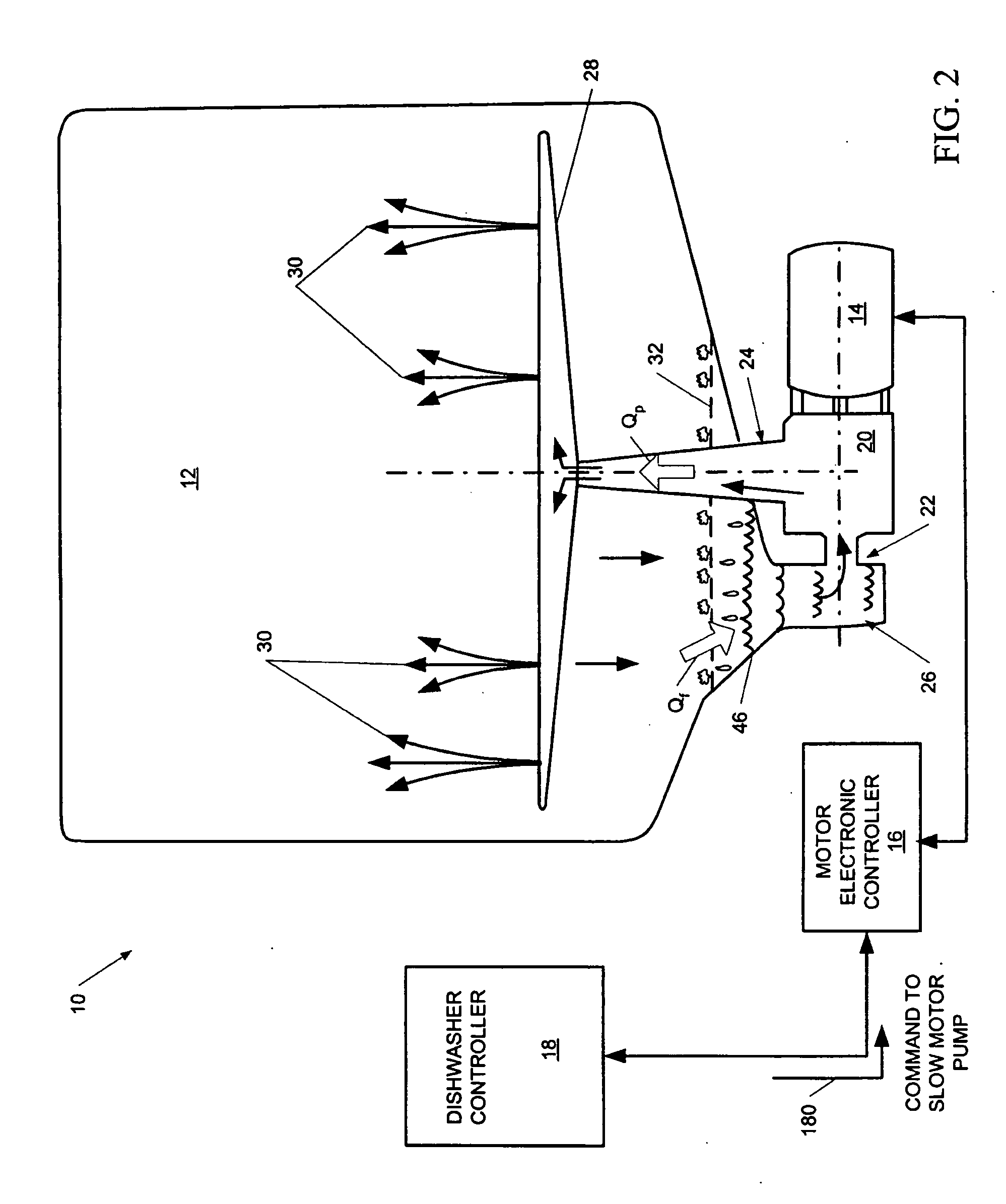
Dishwasher with controlled induction motor/pump
InactiveUS20060237044A1Easy to coverEasy to cleanAC motor controlAutomatic washing/rinsing machine detectionMotor speedMotor controller
A dishwasher having a speed-controlled induction motor coupled to a pump to drive the pump during dishwasher operation. A motor controller is connected to the induction motor to control the speed of operation of the induction motor. A dishwasher controller is connected to the motor controller for sending signals to, and receiving signals from, the motor controller during operation to control the motor speed. The flow rate of water through the pump discharge to a spray arm is controlled based on the phase of the wash cycle and the condition of the filter that blocks food debris from entering the sump. The motor speed is decreased to decrease the pump flow rate when the flow rate through the filter decreases in an early phase of the wash cycle. The motor speed is increased to increase the pump flow rate during later phases of the wash cycle. In steady state operation, the flow rate through the filter is matched to the flow rate through the pump discharge.
Owner:VIKING RANGE
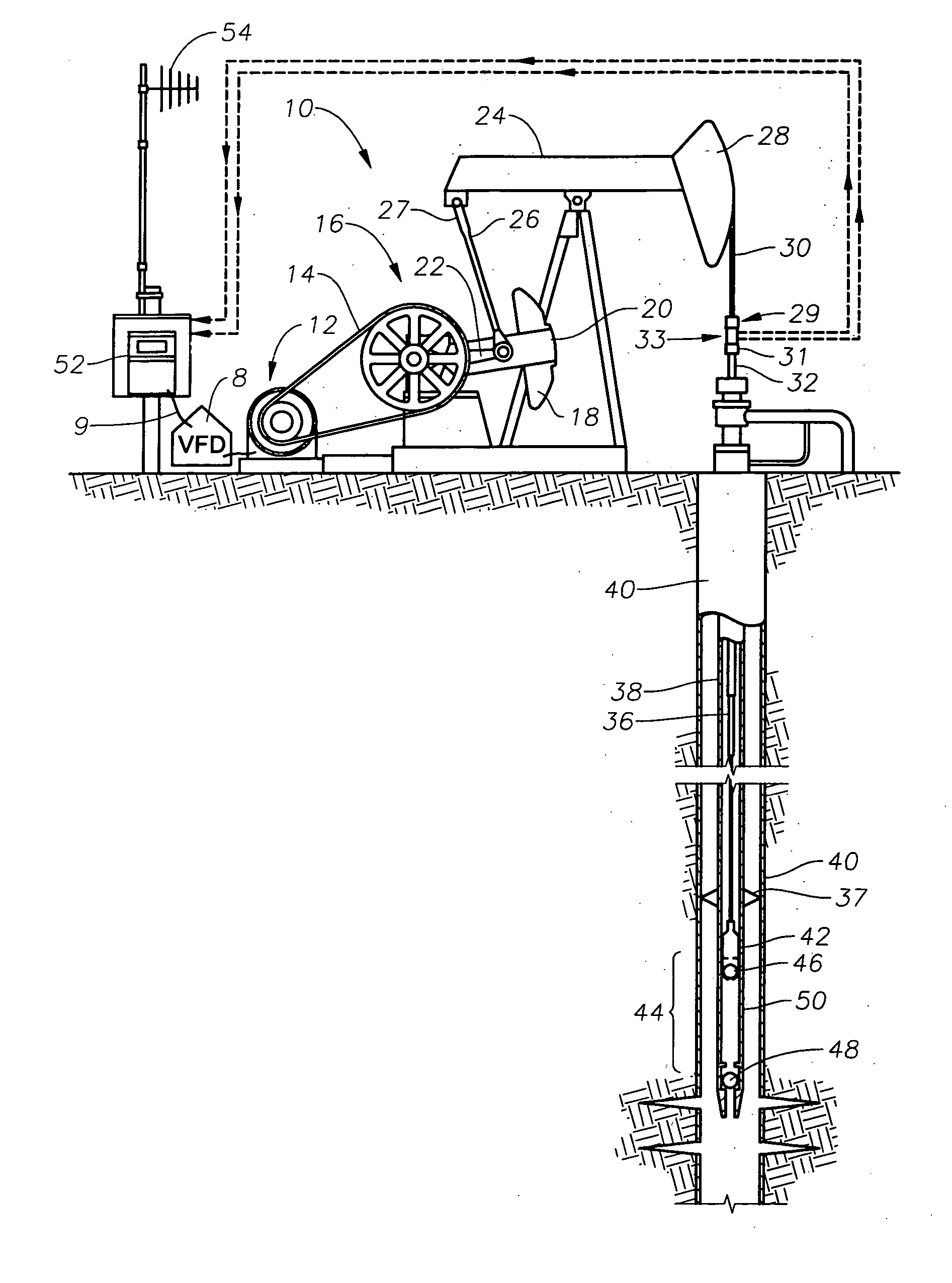
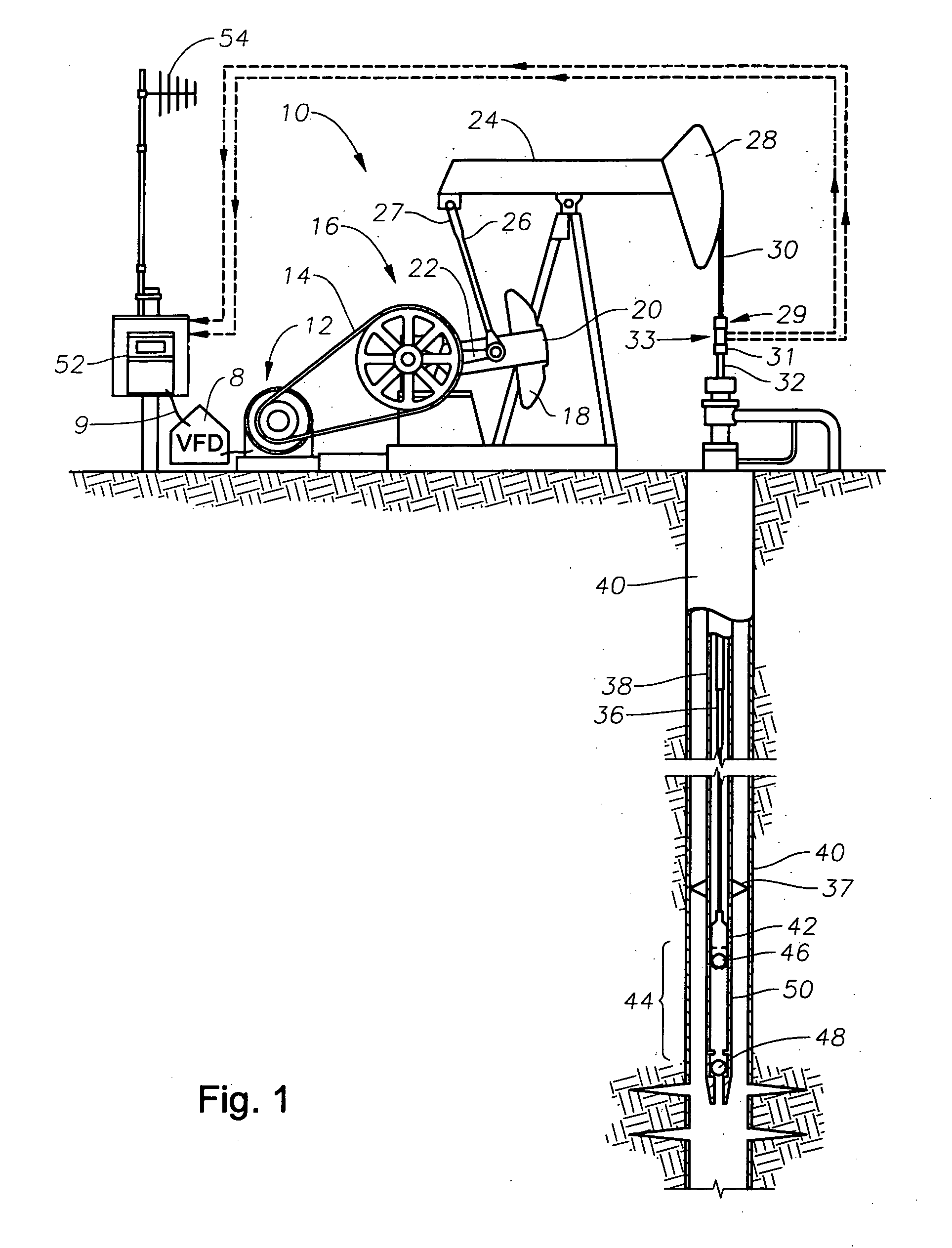
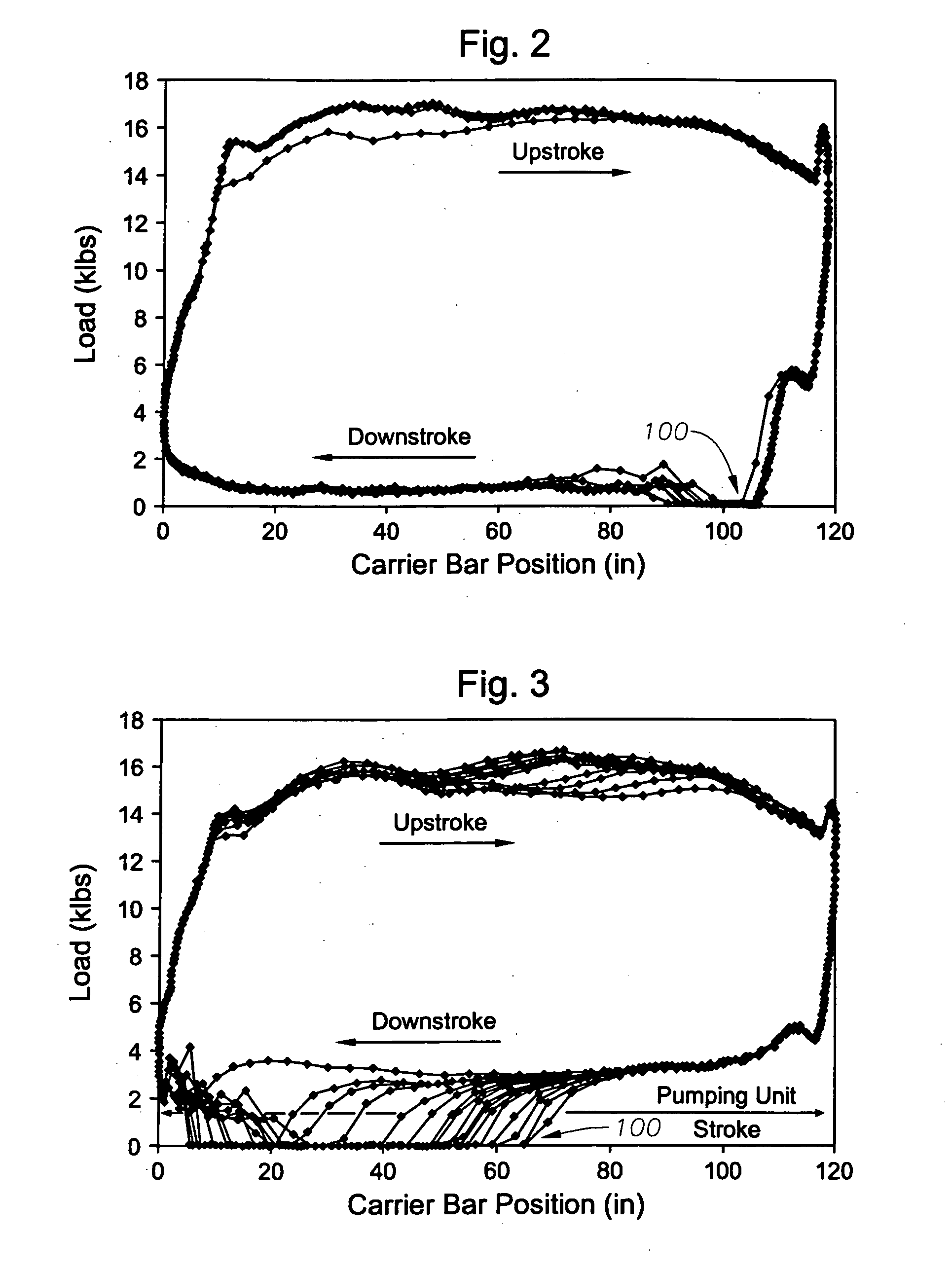
Method for mitigating rod float in rod pumped wells
ActiveUS20060067834A1Reduce harmMaximize productionFlexible member pumpsMotor parameterMotor speedVariable-frequency drive
Rod Float Mitigation (RFM) methods for rod-pumped oil wells having a variable frequency drive which controls the speed of the motor for the pump. Each method monitors rod loads or a similar condition and takes action only when rod load drops below a predefined minimum load. A first method reduces the speed of the motor to a preset level. A second method fixes the torque level on the pump downstroke by adjusting motor speed based on a calculated gearbox torque compared to a programmed fixed limit. Another method includes a program in the variable frequency drive which includes a preferred RFM Torque Curve for the pump to follow on its downstroke. When rod float occurs, the program monitors gearbox torque and adjusts the speed to follow the predetermined RFM Torque Curve thereby mitigating rod float with minimum decrease in production.
Owner:RAVDOS HLDG INC
Low noise compressor rotor for geared turbofan engine
A gas turbine engine comprises a fan and a turbine section having a first turbine rotor. The first turbine rotor drives a compressor rotor. A gear reduction effects a reduction in the speed of the fan relative to an input speed from a fan drive turbine rotor. The compressor rotor has a number of compressor blades in at least one of a plurality of rows of the compressor rotor. The blades operate at least some of the time at a rotational speed. The number of compressor blades in at least one row and the rotational speed are such that the following formula holds true for at least one row of the compressor rotor:(the number of blades×the rotational speed) / (60 seconds / minute)≧5500 Hz; andthe rotational speed being in revolutions per minute.A compressor module and a method of designing a gas turbine engine are also disclosed.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
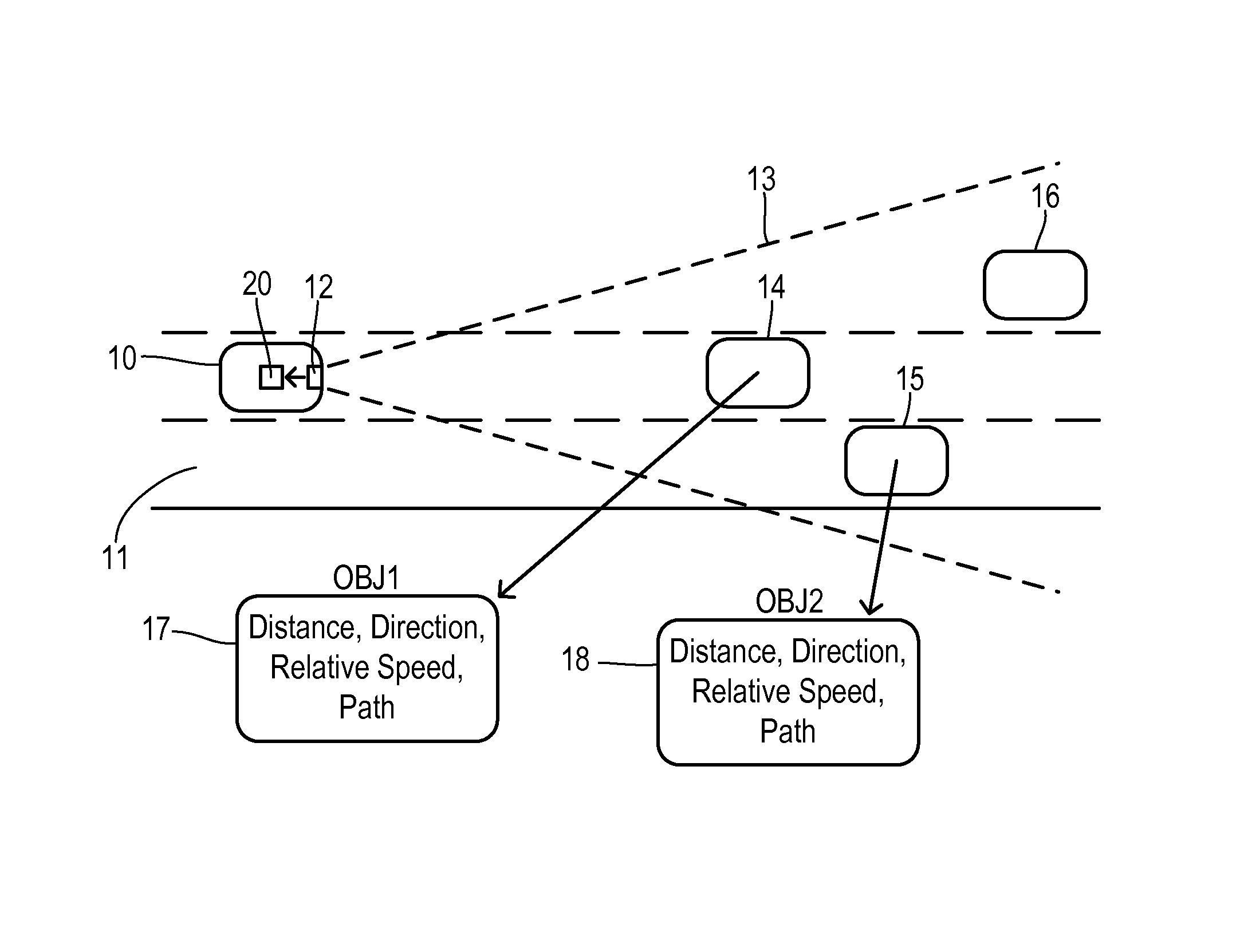
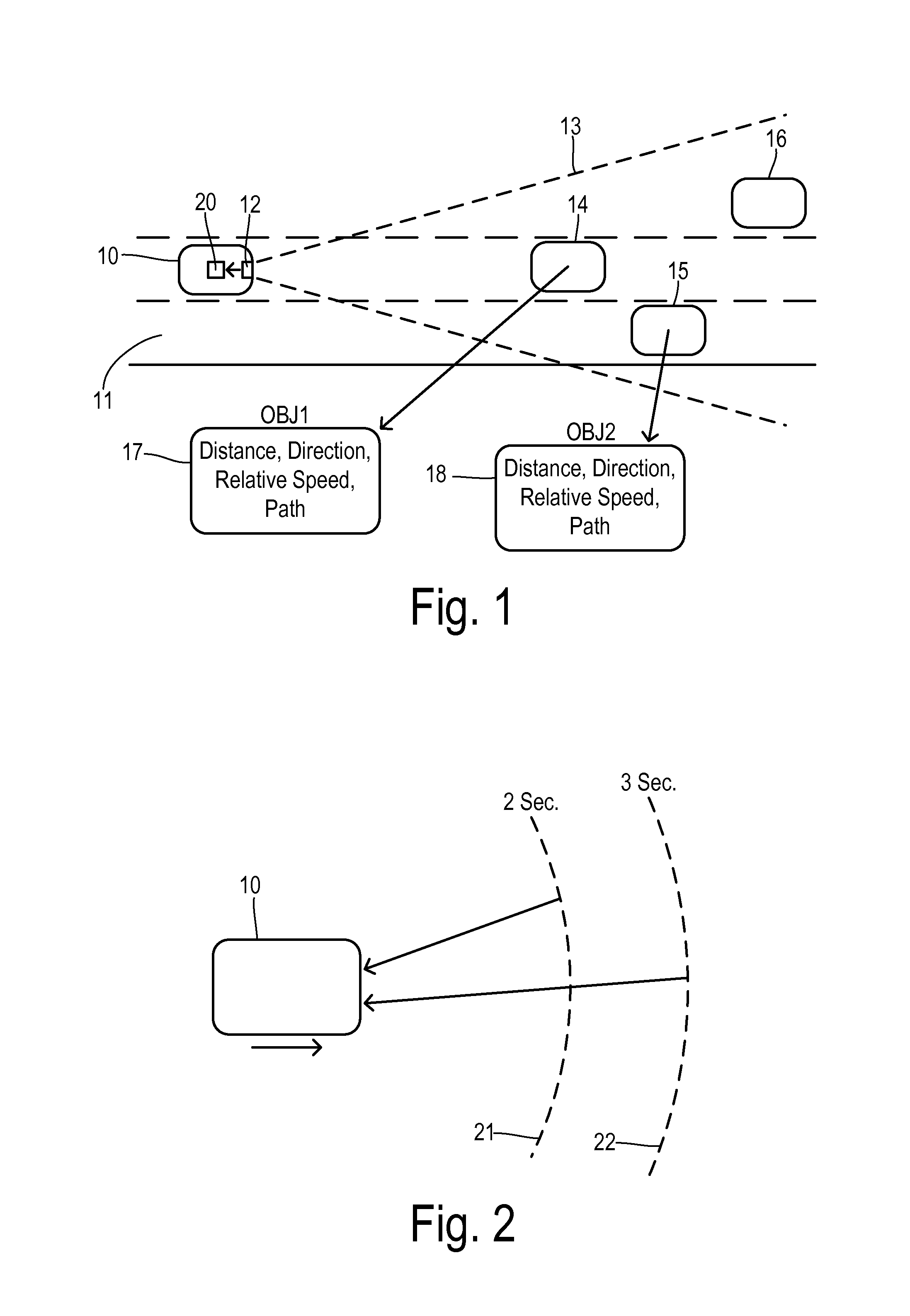
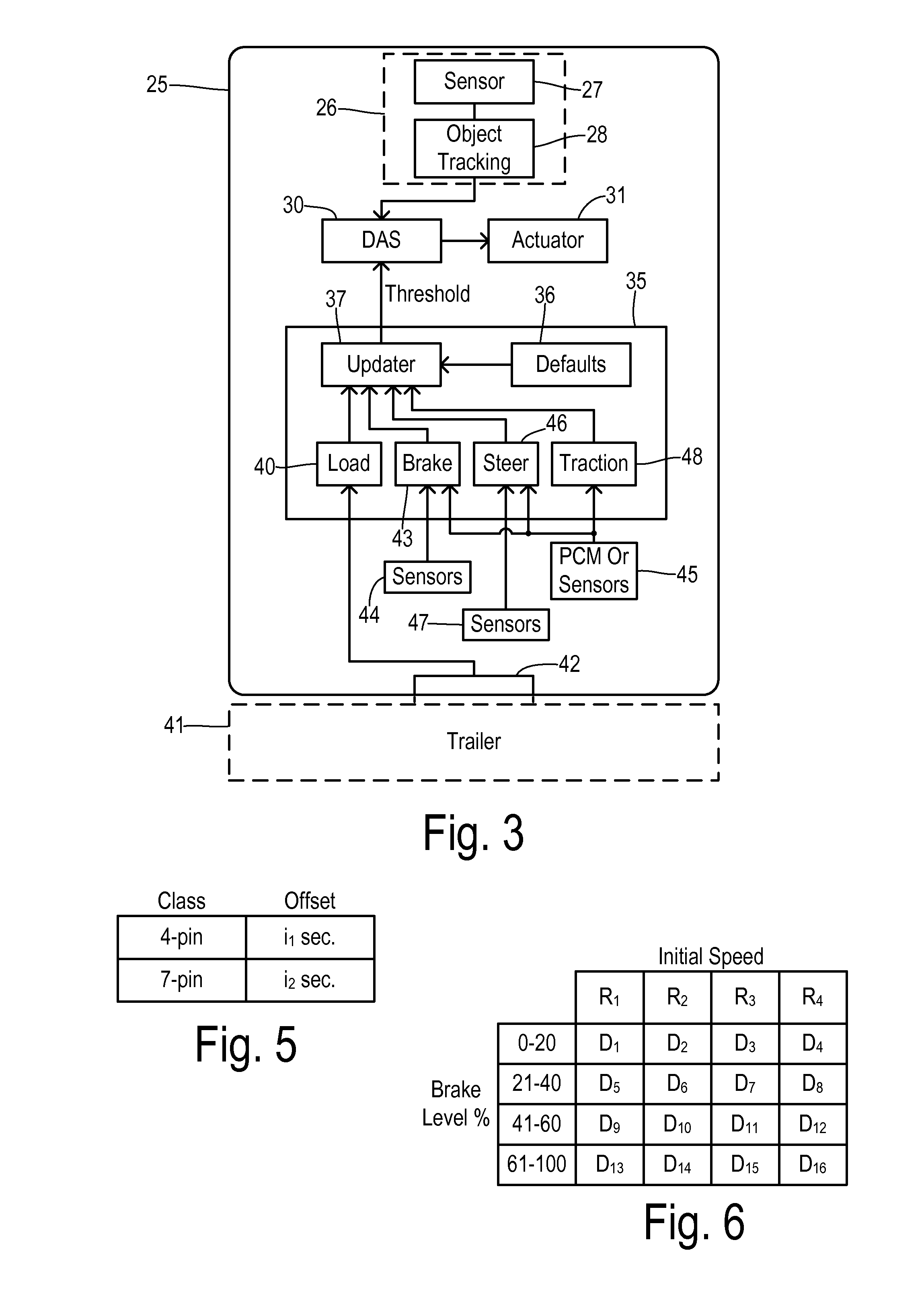
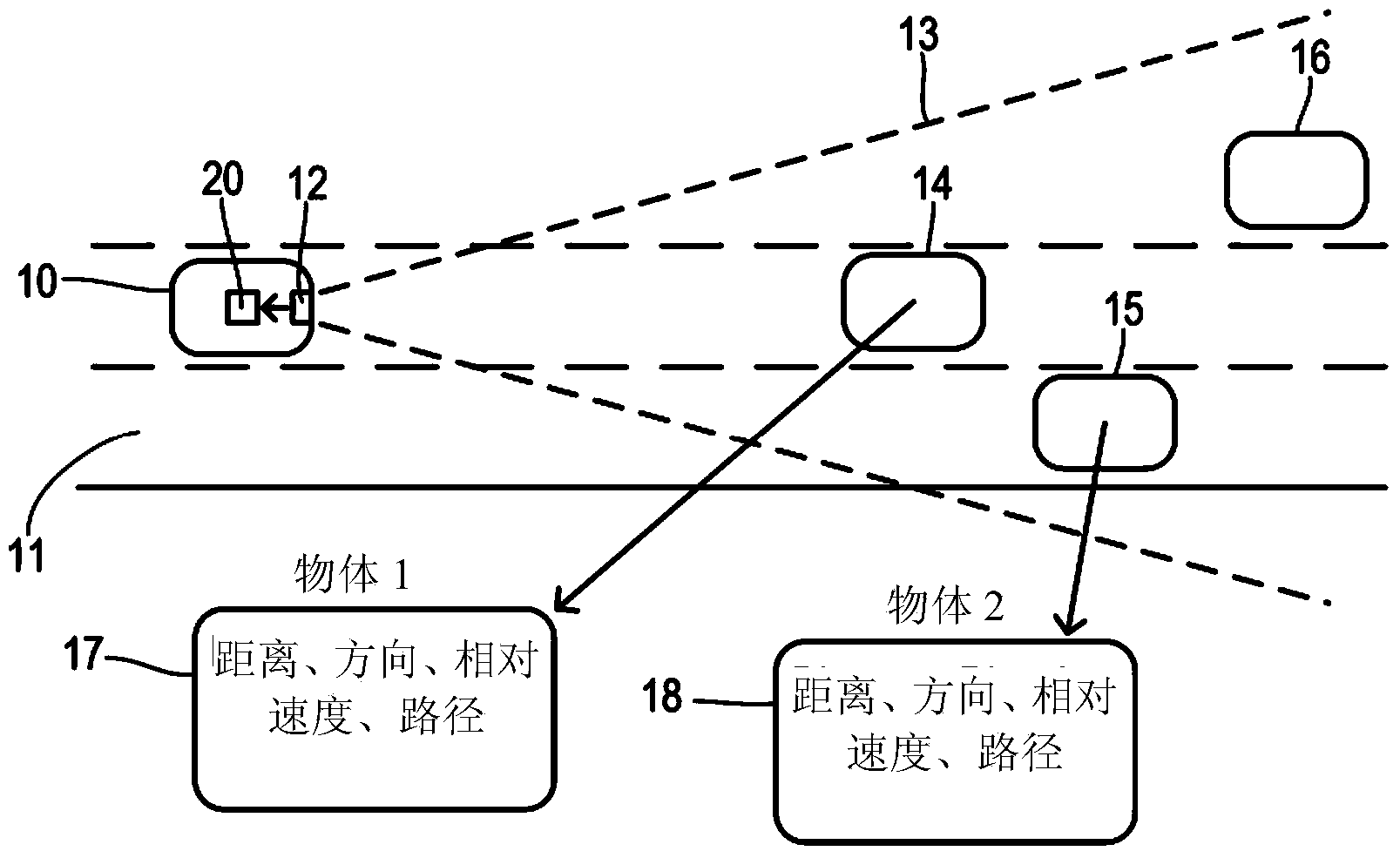
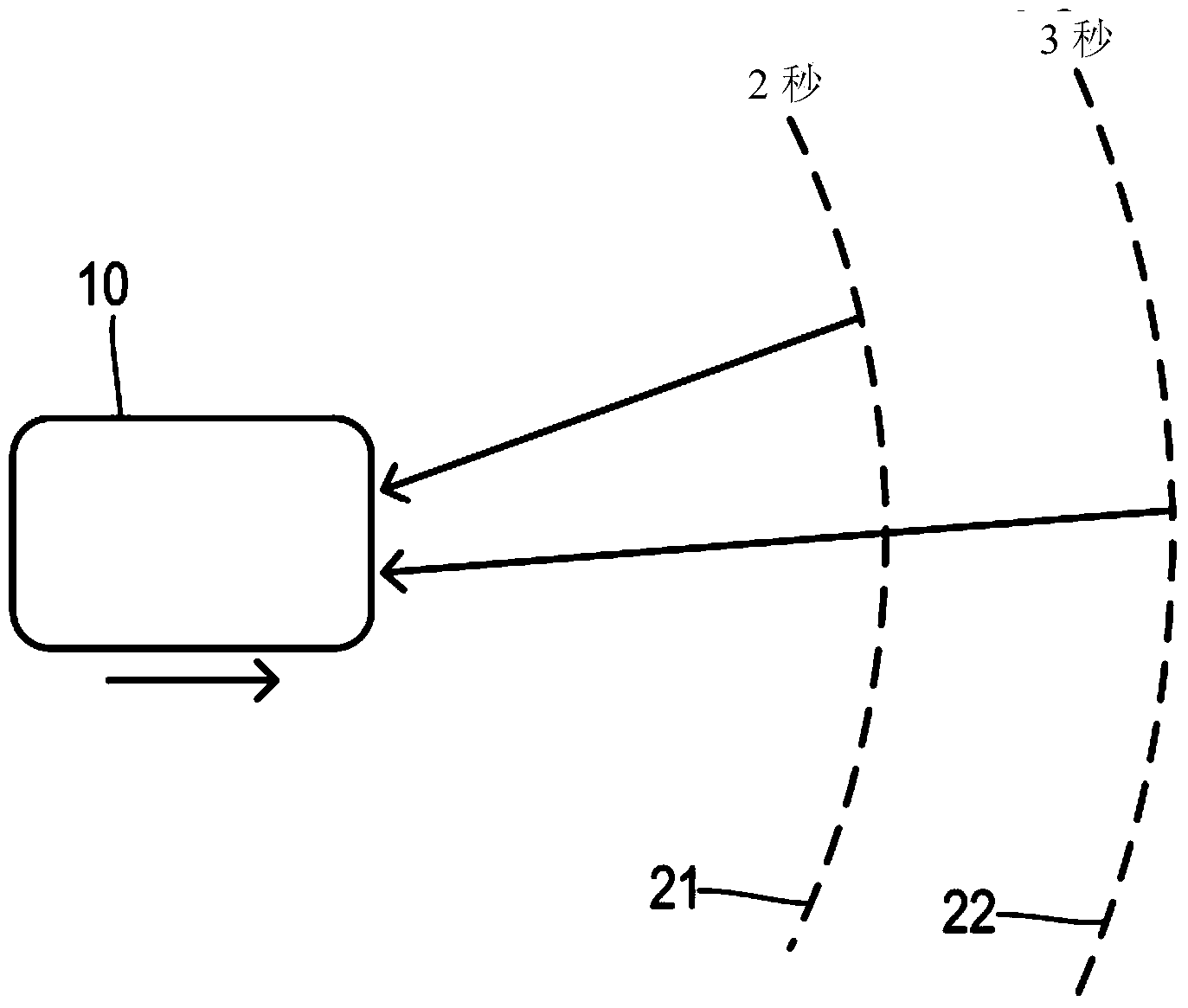
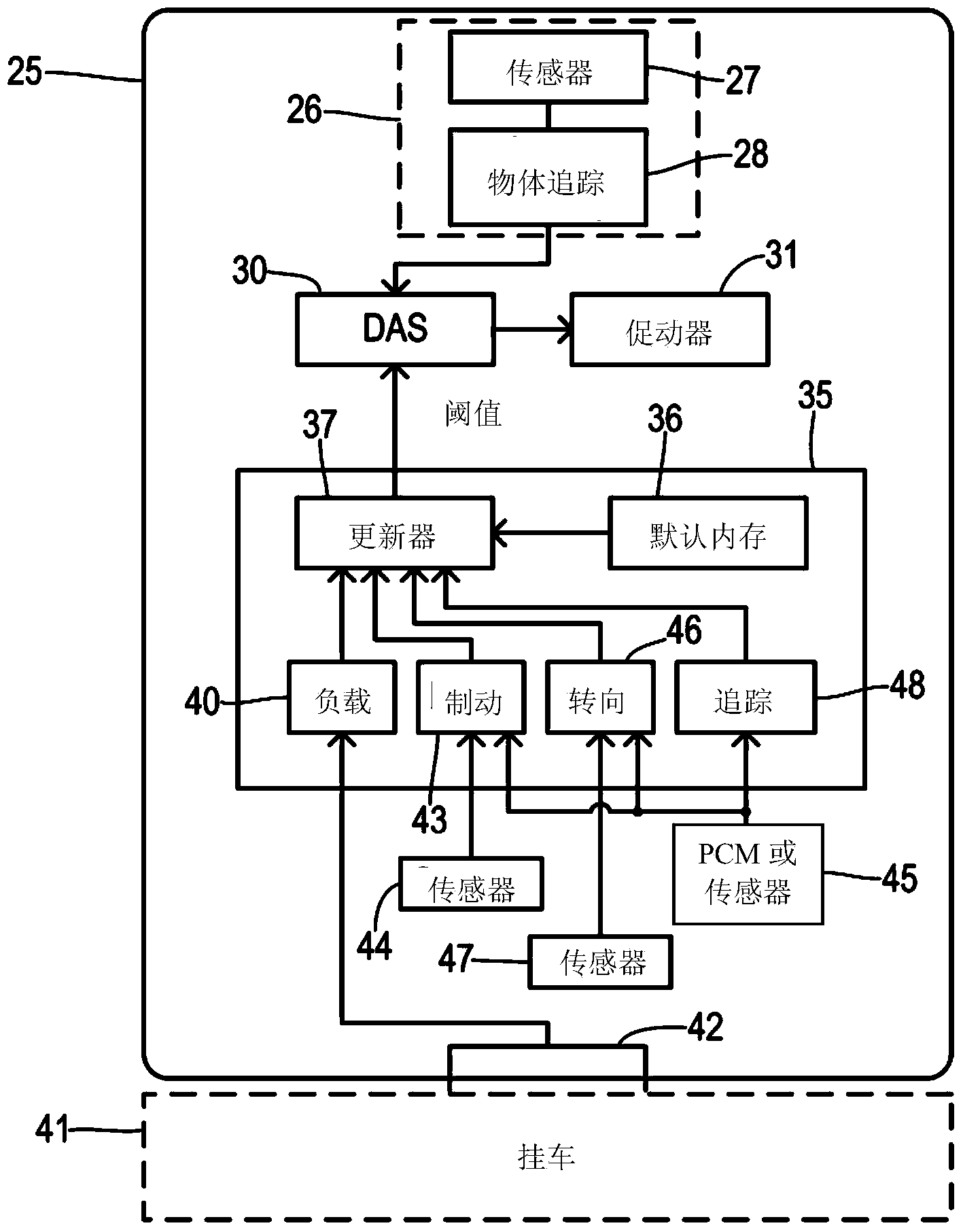
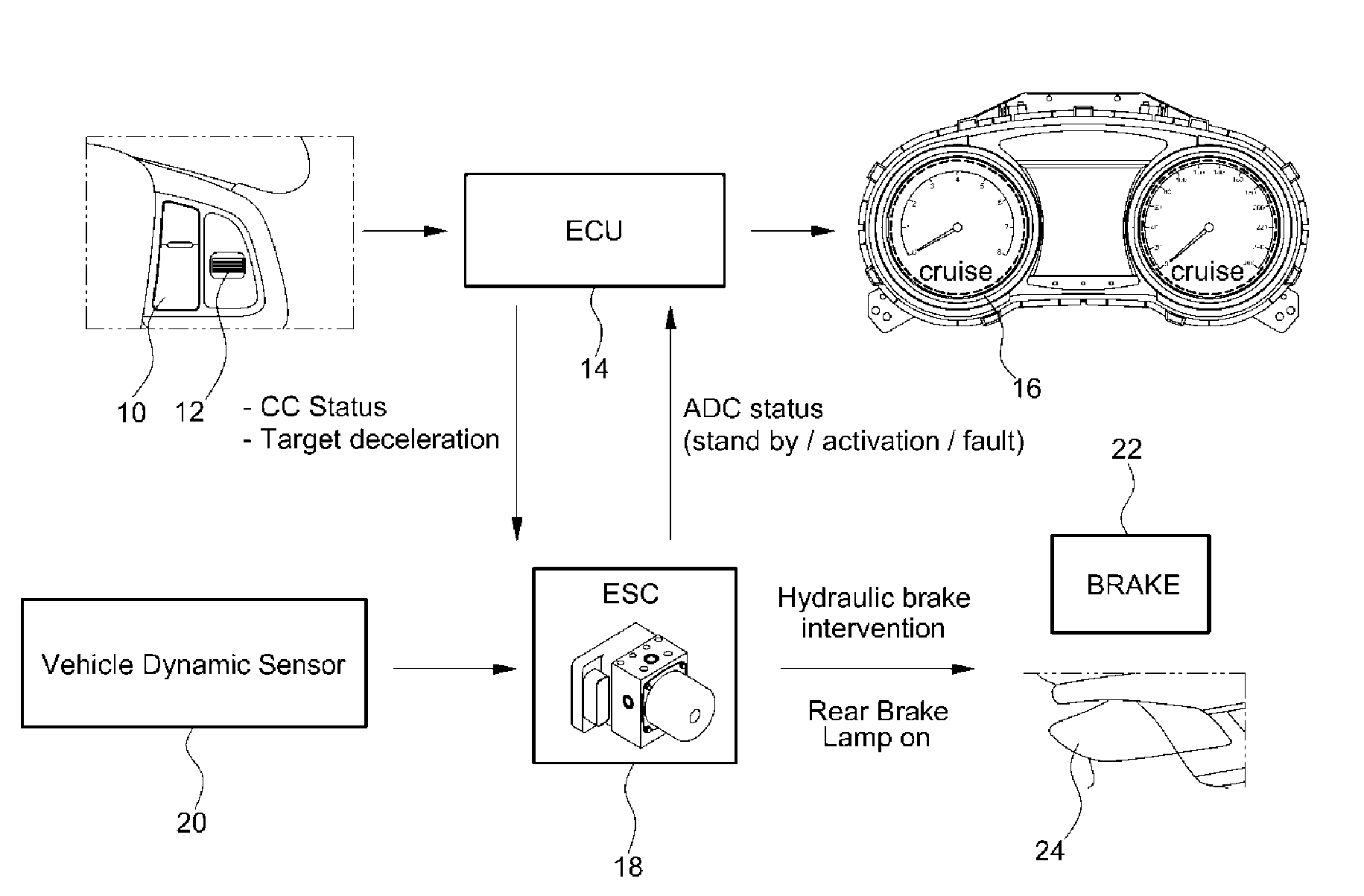
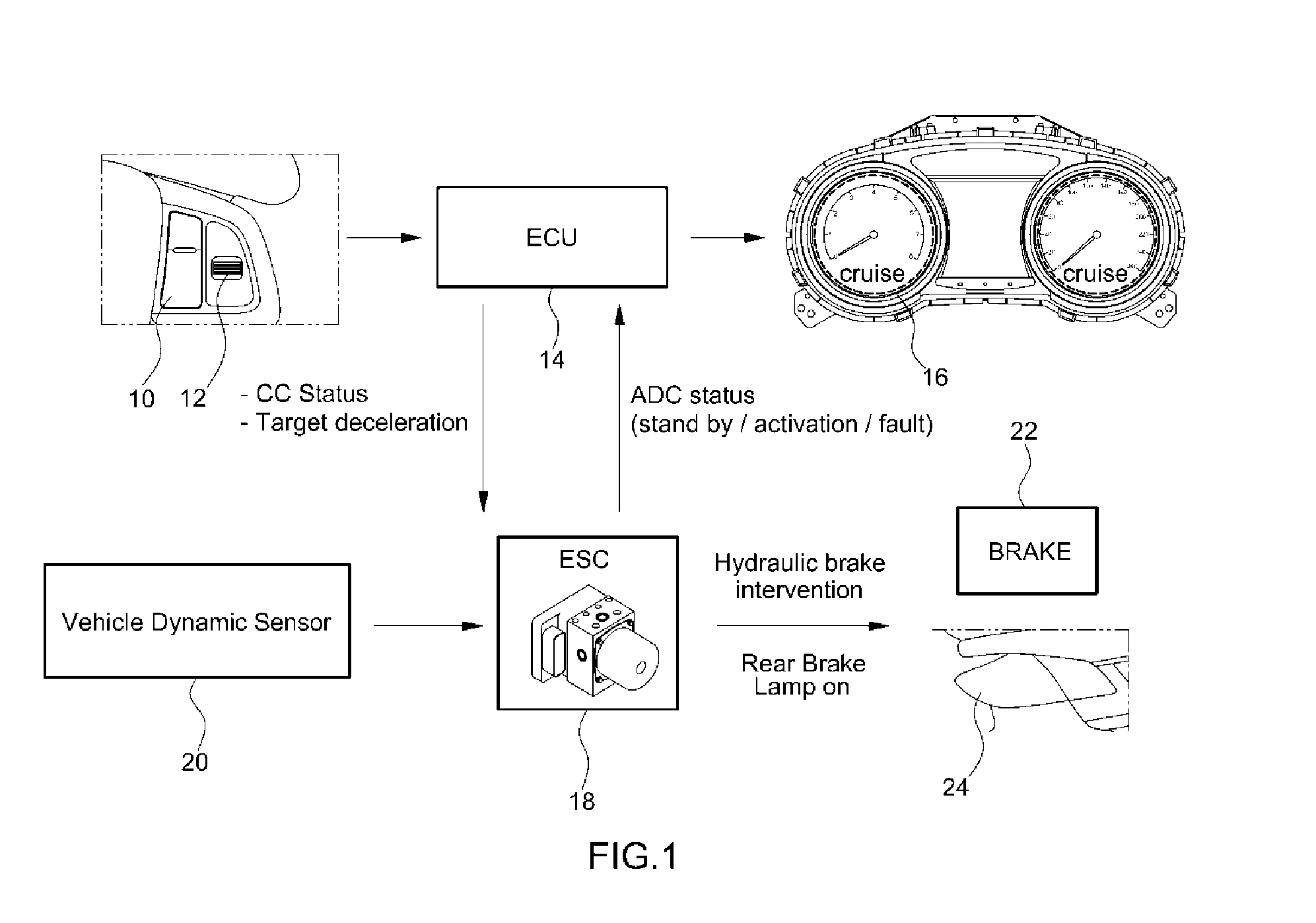
Adjustable threshold for forward collision warning system
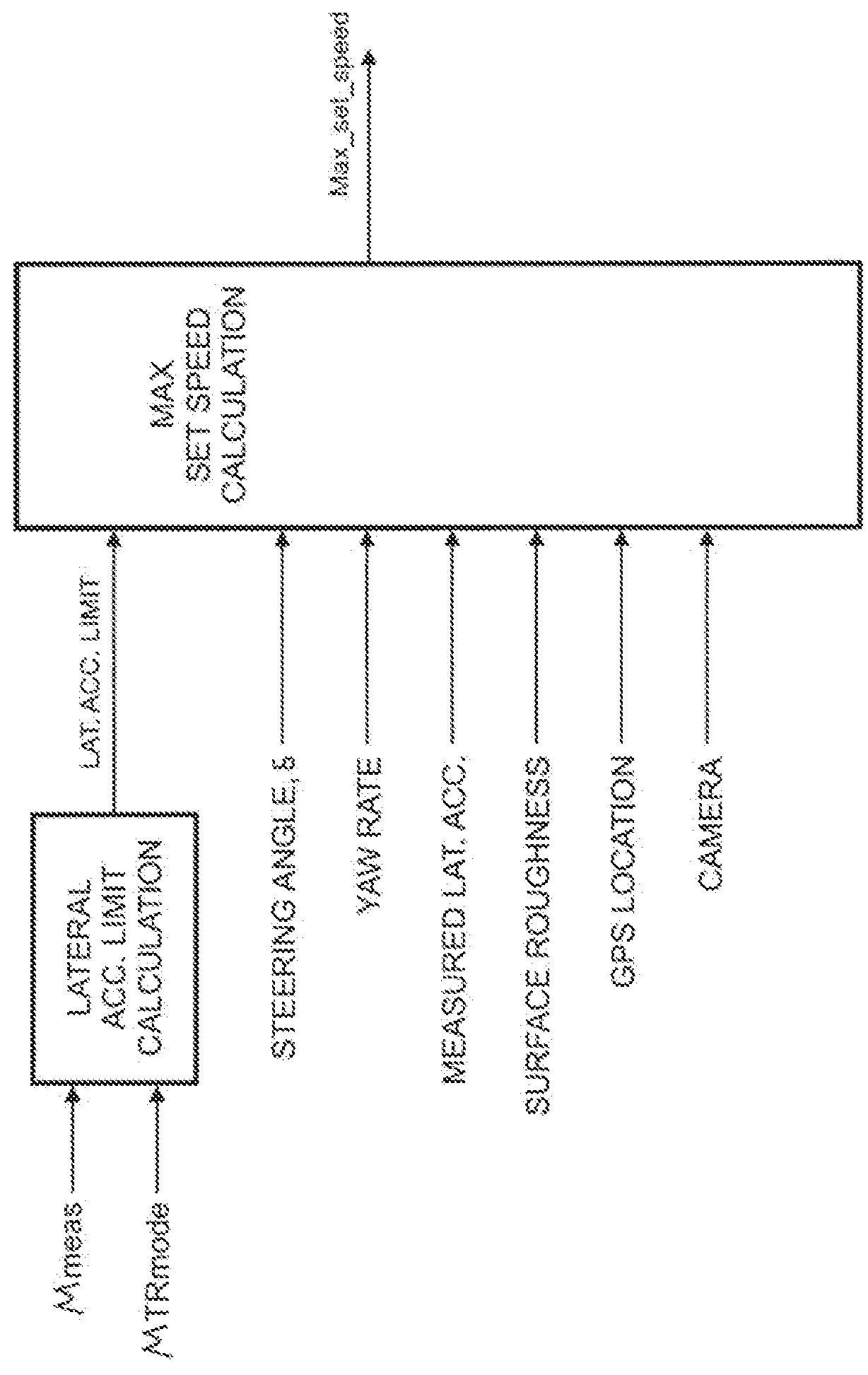
A driver assistance system for a motor vehicle monitors approaching objects around the vehicle in order to take a driver assistance action in response to a predicted impact with an approaching object according to a time-to-impact threshold. the time-to-impact threshold includes a nominal or default value that is adjusted according to several different measures of vehicle and driving conditions. Respective offsets determined by a load monitor, a braking monitor, and a steering monitor are added to the threshold in response to measured vehicle performance parameters being different from expected values. The driver assistance action may be a perceptible warning for a forward collision warning system, a speed reduction in an adaptive cruise control system, or a braking action in a brake-steer system.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
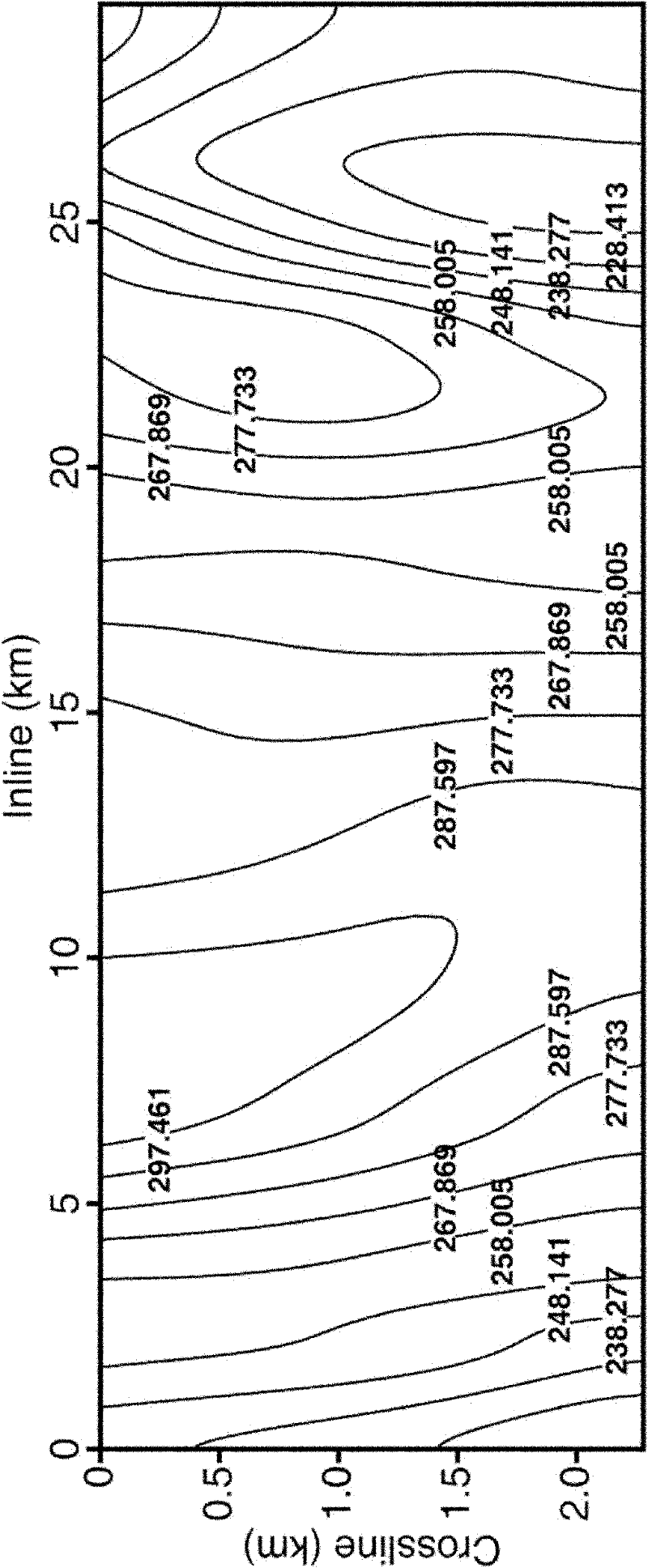
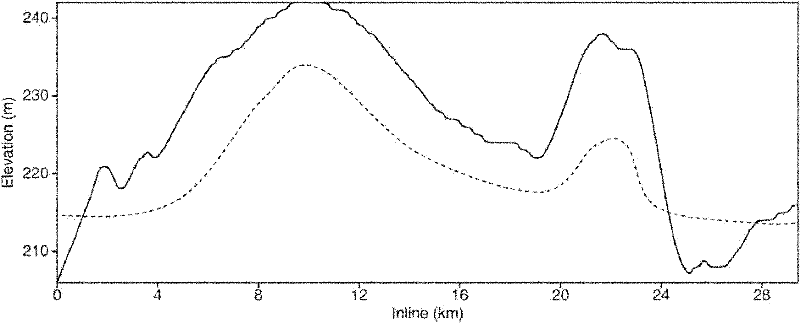
Direct prestack time migration method for three-dimensional seismic data acquired from irregular surfaces
InactiveCN102193109AAvoid difficultiesReduce processing linksSeismic signal processingLand acquisitionSurface velocity
The invention discloses a direct prestack time migration method for three-dimensional seismic data acquired from irregular surfaces, and the method is applied to the processing on reflected seismic information in seismic exploration. The method can be used for directly carrying out three-dimensional seismic data migration imaging (at different elevations) on shot points and geophone points acquired from irregular surfaces without statically correcting a processing process. In the method, no vertical emergence and incidence assumption is performed on nearsurface seismic wave propagation, therefore, the method can adapt to the situations which have no obvious low velocity region and velocity-reduction region such as high-velocity rock outcropping, and the like. In the method, the seismic wave propagation in near surfaces or stratums is described by using two equivalent speed parameters; and the two equivalent speed parameters can be determined according to the straightness of lineups inmigrated gathers, thereby avoiding the difficulties in near-surface velocity modeling. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the gathers subjected to migration can be subjected to remainingstatic correction, thereby effectively compensating the inherent errors existing in a land acquisition technology. The method has important application value in oil, gas and mineral resource exploration in complex surface areas.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of speed control for a vehicle
ActiveUS20160031444A1Reduce frictionMaximum speed control speedVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsTerrainVehicle driving
A vehicle is adapted to sense a condition of use in which a maximum speed control speed is reduced. The condition of use may be indicated by a sensor of the vehicle, or selected according to the kind of terrain across which the vehicle is travelling. Selection of terrain type may be manual or automatic, and may enable a selection of sensors appropriate to the terrain type. A vehicle driver may select a speed control speed lower than the permitted maximum.
Owner:JAGUAR LAND ROVER LTD
Industrial robot obstacle avoidance track planning method based on torque control
ActiveCN107139171ACollision prediction worksObstacle avoidanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorDynamic modelsCollision detection
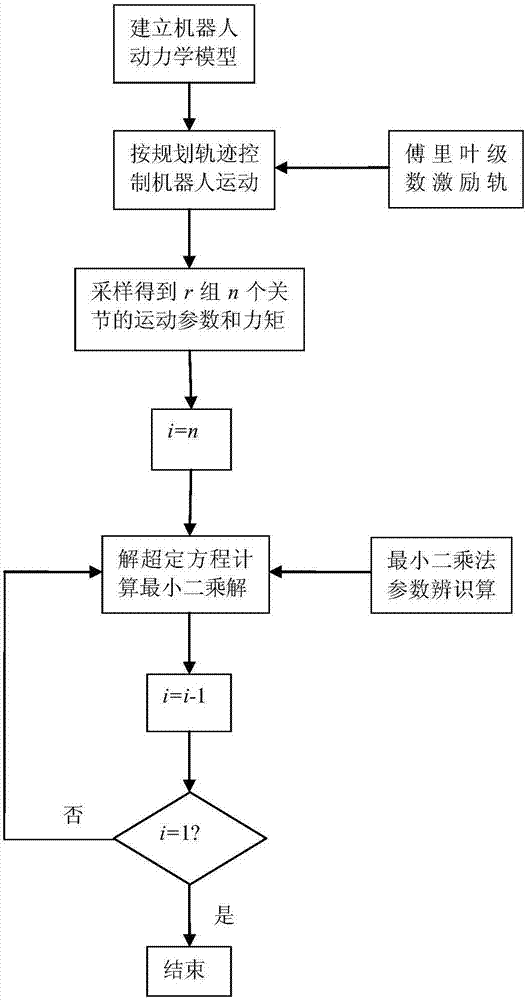
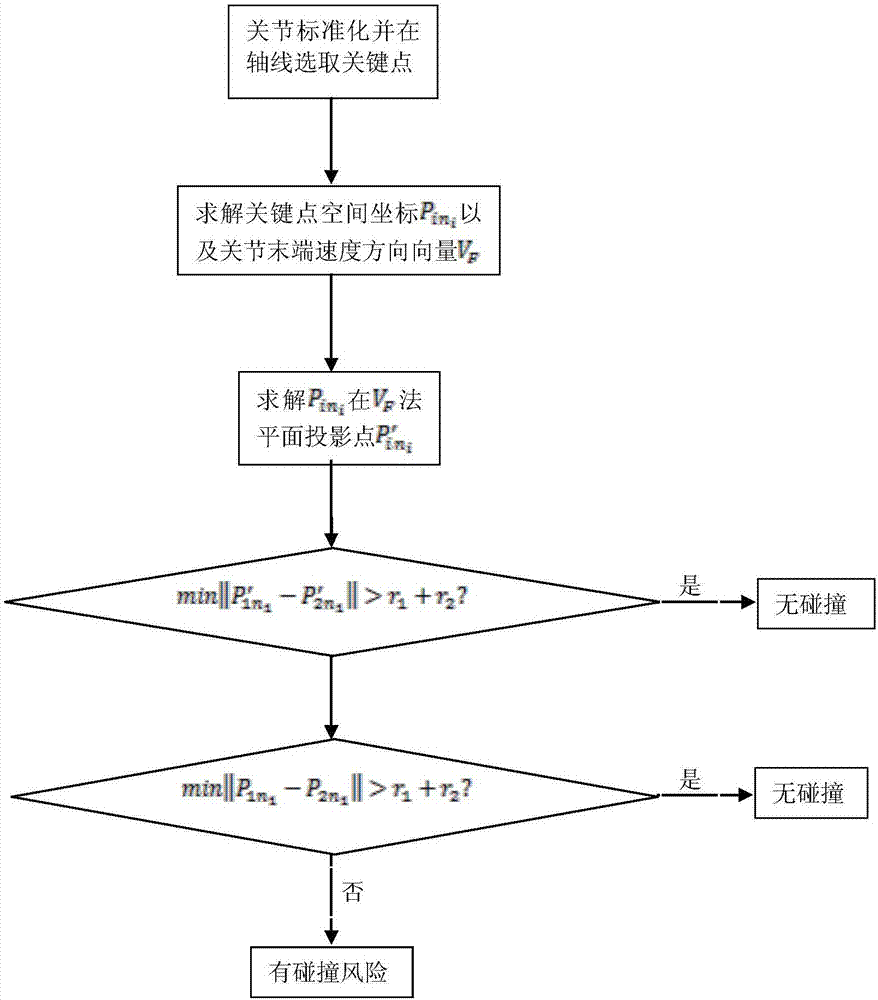
The invention discloses an industrial robot high-speed high-precision obstacle avoidance track planning method based on torque control. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a robot dynamics model is established by identifying kinematics and inertial parameters of all joints; 2, displacements of all joint angles are obtained through inverse kinematics solution when a robot moves to an end point; 3, the displacements of the joint angles are adopted as motion tracks, speeds and accelerated speeds of all joints are planned through a sine jerk planning method, the speeds and the accelerated speeds are substituted into the dynamics model so as to solve control torque in the motion tracks; 4, collision detection is carried out by adopting a method of judging the distance between key points after detecting the interference conditions of joint projections; and 5, when it is detected that the collision may occur, an impedance accelerated speed is applied to the dangerous joints to reduce the motion speed of the joints so as to achieve the obstacle avoidance. The industrial robot obstacle avoidance track planning method based on the torque control has the advantages that the control precision is high, the obstacle avoidance is effectively realized, and the safety is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
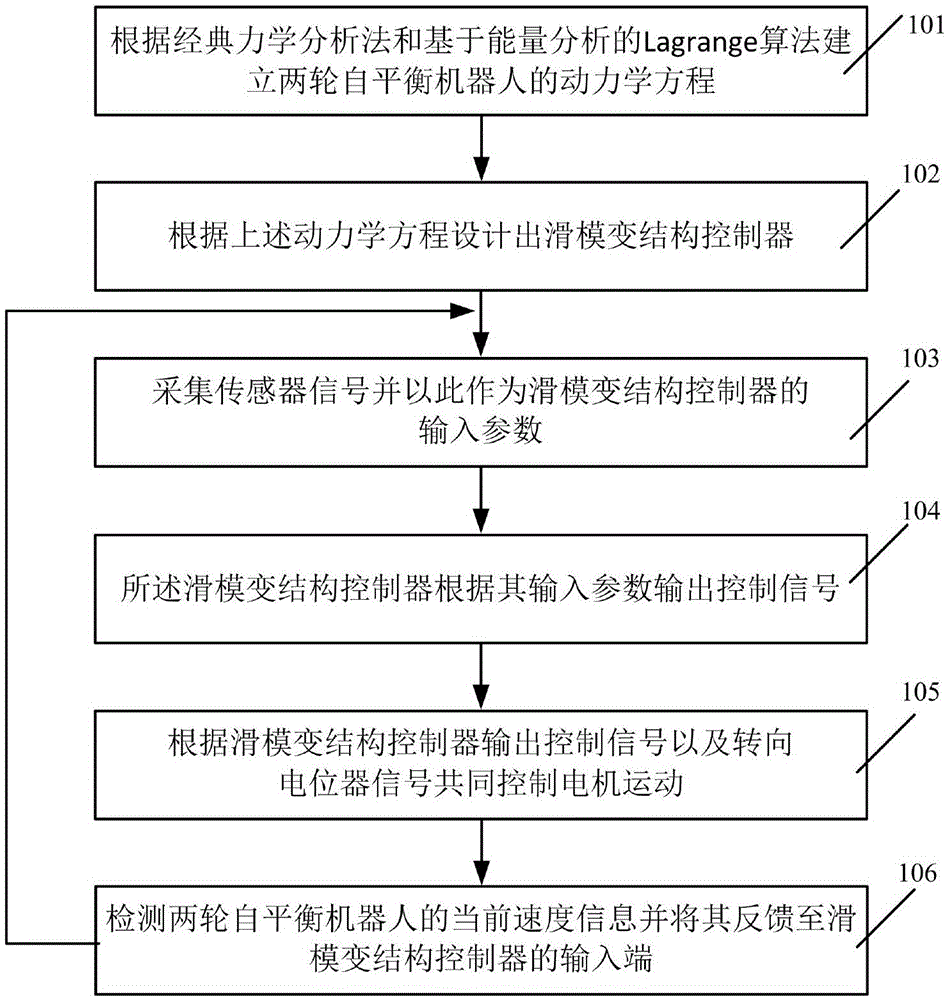
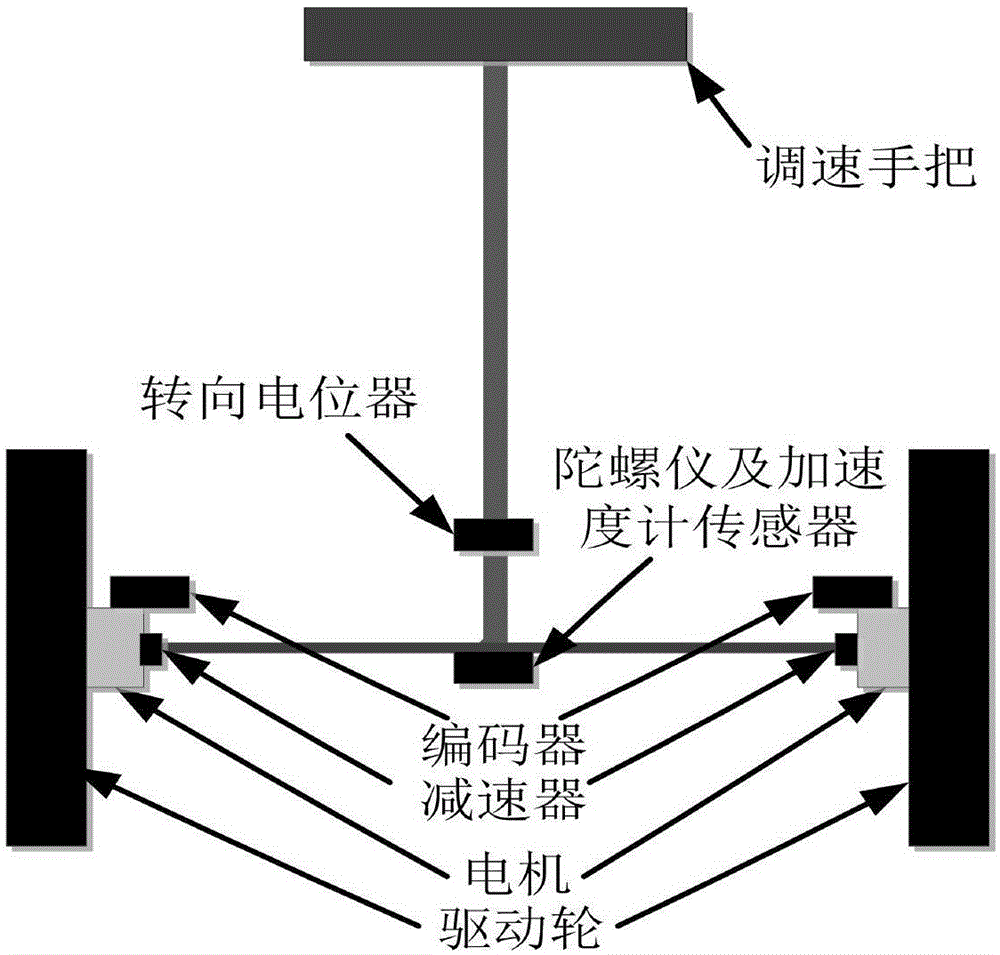
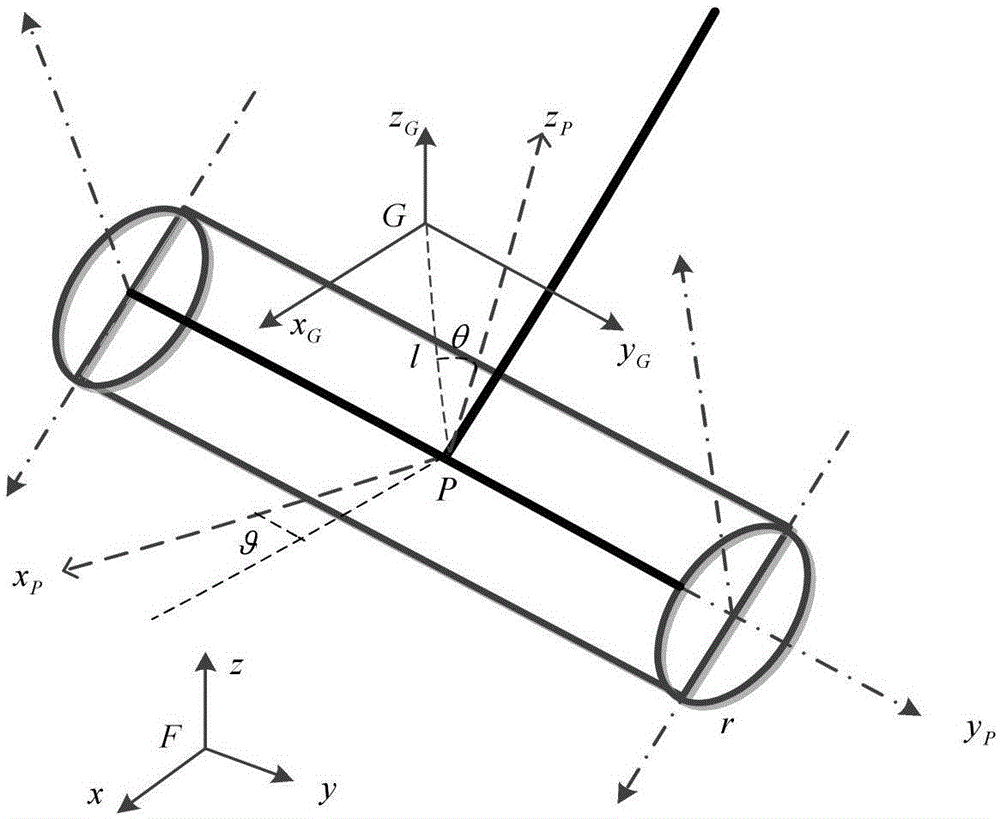
A two-wheeled self-balance robot self-adaptive sliding mode changing structure control method and system
The invention discloses a two-wheeled self-balance robot self-adaptive sliding mode changing structure control method and system. According to a classical mechanics analytic method and based on a Lagrange algorithm based on energy analysis, molding of a kinetic equation of a two-wheeled self-balance robot of is realized, a sliding mode changing structure controller is designed according to the kinetic equation. The sliding mode changing structure controller comprises a speed sliding mold changing structure controller and an angle sliding mold changing structure controller; the speed sliding mold changing structure controller and the angle sliding mold changing structure controller give each other feedbacks; a feedback equation is that theta r=beta V; and self-adaptive controlling is carried out on the system on the basis of a function approximation mode. Through adoption of the technical scheme of the present invention, the modeling process is enabled to be more simplified and comprehensive; the robustness and the respond speed of the system are raised; simultaneously, since a mutual feedback relation exists between the speed and the angle of the system, when an inclination angle of the system is overlarge, the system will automatically decelerate; while the speed is reduced, the system will return to the balance position; in a condition of facing different road surface conditions, the system can adapt to external environment and large scope load changes, thereby guaranteeing the safety and stability of the system.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
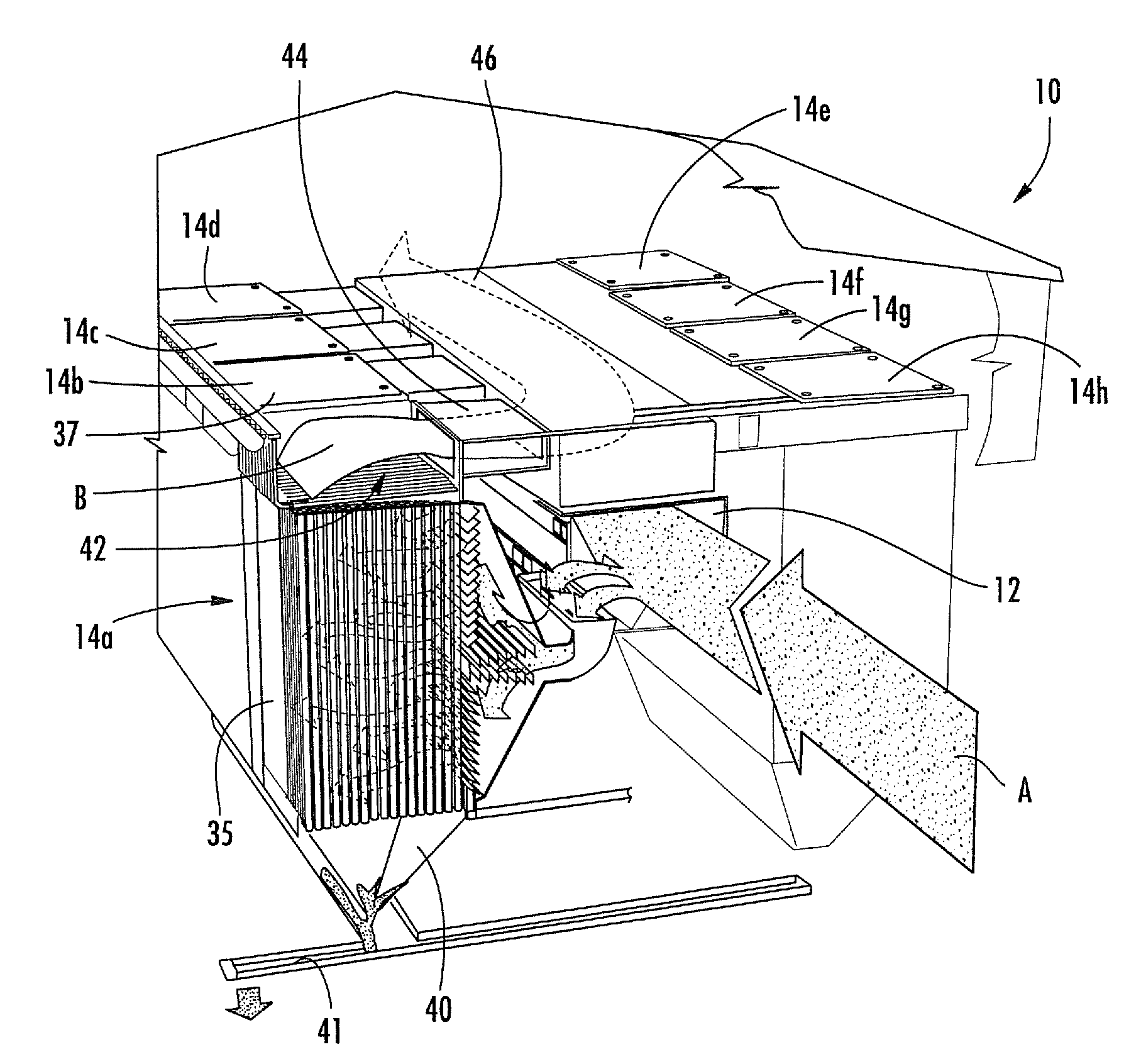
Airflow Reducing and Redirecting Arrangement For Industrial Baghouse
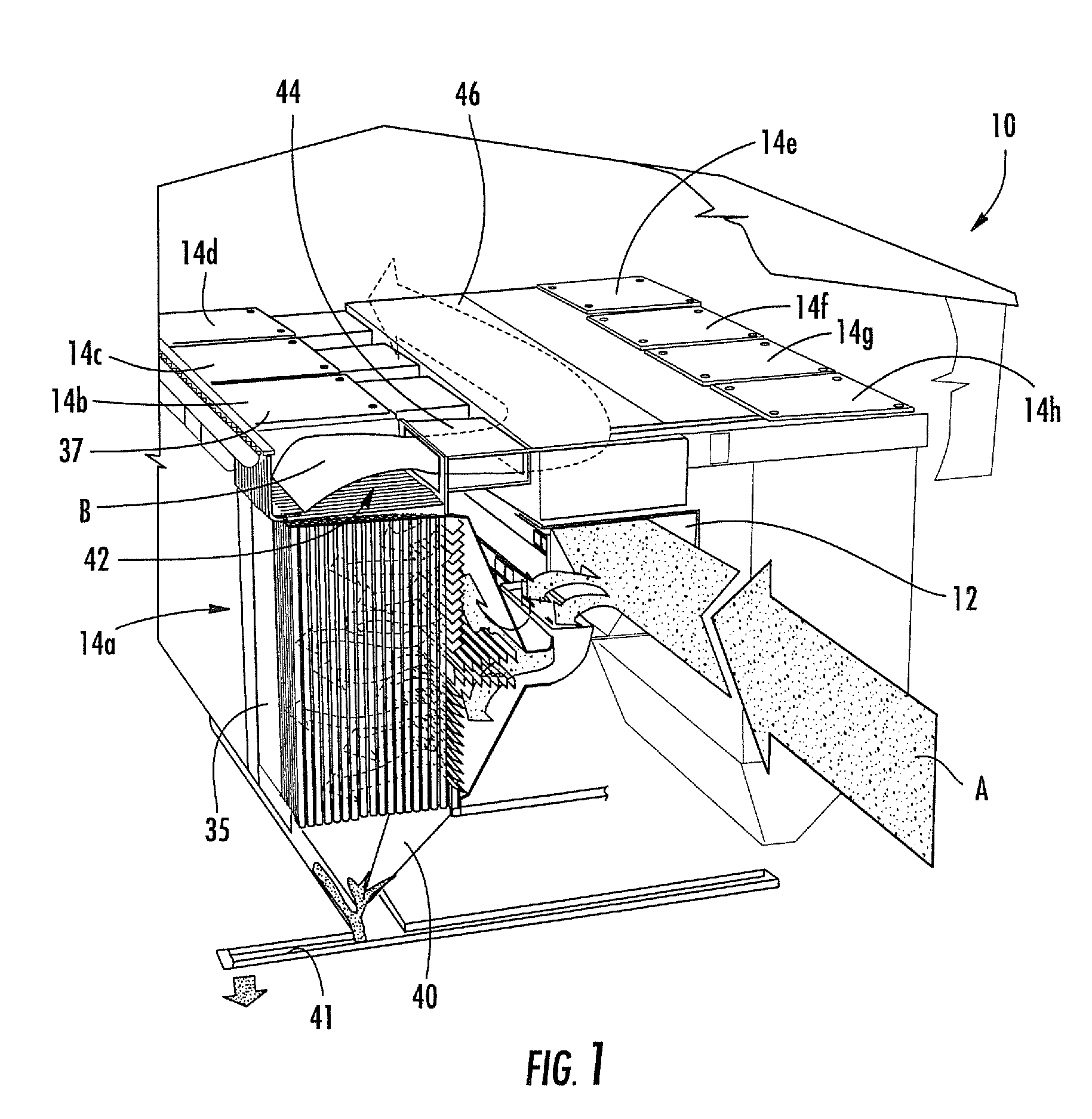
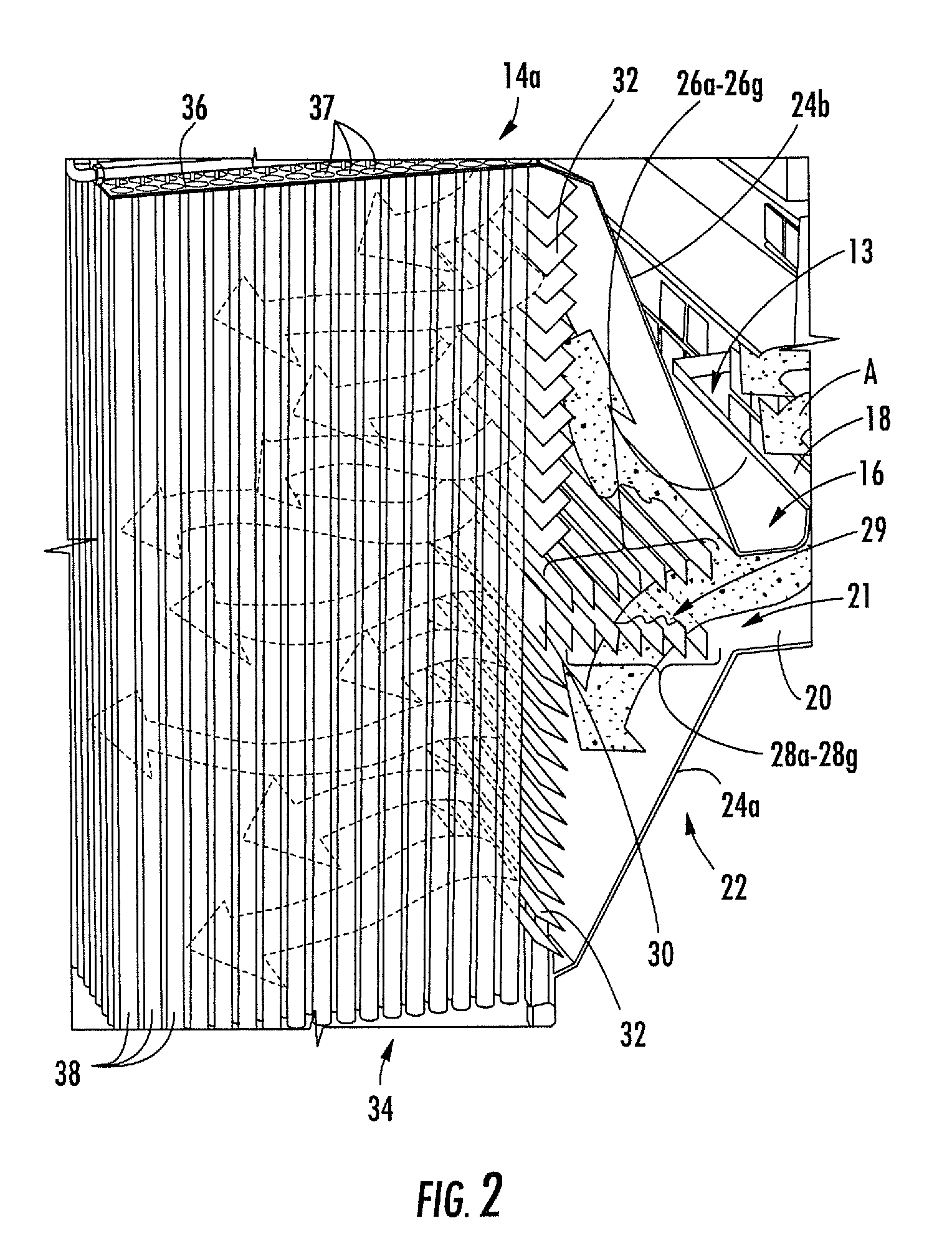
InactiveUS20090020011A1Shorten speedEfficient removalCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentAir filtrationBaghouse
An air filtering unit for a factory includes: an entry duct; a flow expander section fluidly connected with the entry duct, the flow expander section including a flow distribution unit and a flow velocity reduction unit; a filter unit fluidly connected with the flow expander section, the filter unit having a plurality of filter bags, the filter bags being suspended from a tube sheet; and an exit duct fluidly connected with the filter unit. The flow distribution unit comprises a series of flow distribution members positioned along a flow path, the flow distribution unit located and configured to substantially equally distribute an airstream along the length of the flow axis into a plurality of divided substreams. The flow velocity reduction unit includes a plurality of flow reduction members, each of the flow reduction members positioned and configured to confront at least one of the divided substreams and reduce the flow velocity thereof.
Owner:MENARDI MIKROPUL LLC
Adjustable threshold for forward collision warning system
ActiveCN104228836AAnti-collision systemsExternal condition input parametersMobile vehicleDriver/operator
A driver assistance system for a motor vehicle monitors approaching objects around the vehicle in order to take a driver assistance action in response to a predicted impact with an approaching object according to a time-to-impact threshold. The time-to-impact threshold includes a nominal or default value that is adjusted according to several different measures of vehicle and driving conditions. Respective offsets determined by a load monitor, a braking monitor, and a steering monitor are added to the threshold in response to measured vehicle performance parameters being different from expected values. The driver assistance action may be a perceptible warning for a forward collision warning system, a speed reduction in an adaptive cruise control system, or a braking action in a brake-steer system.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
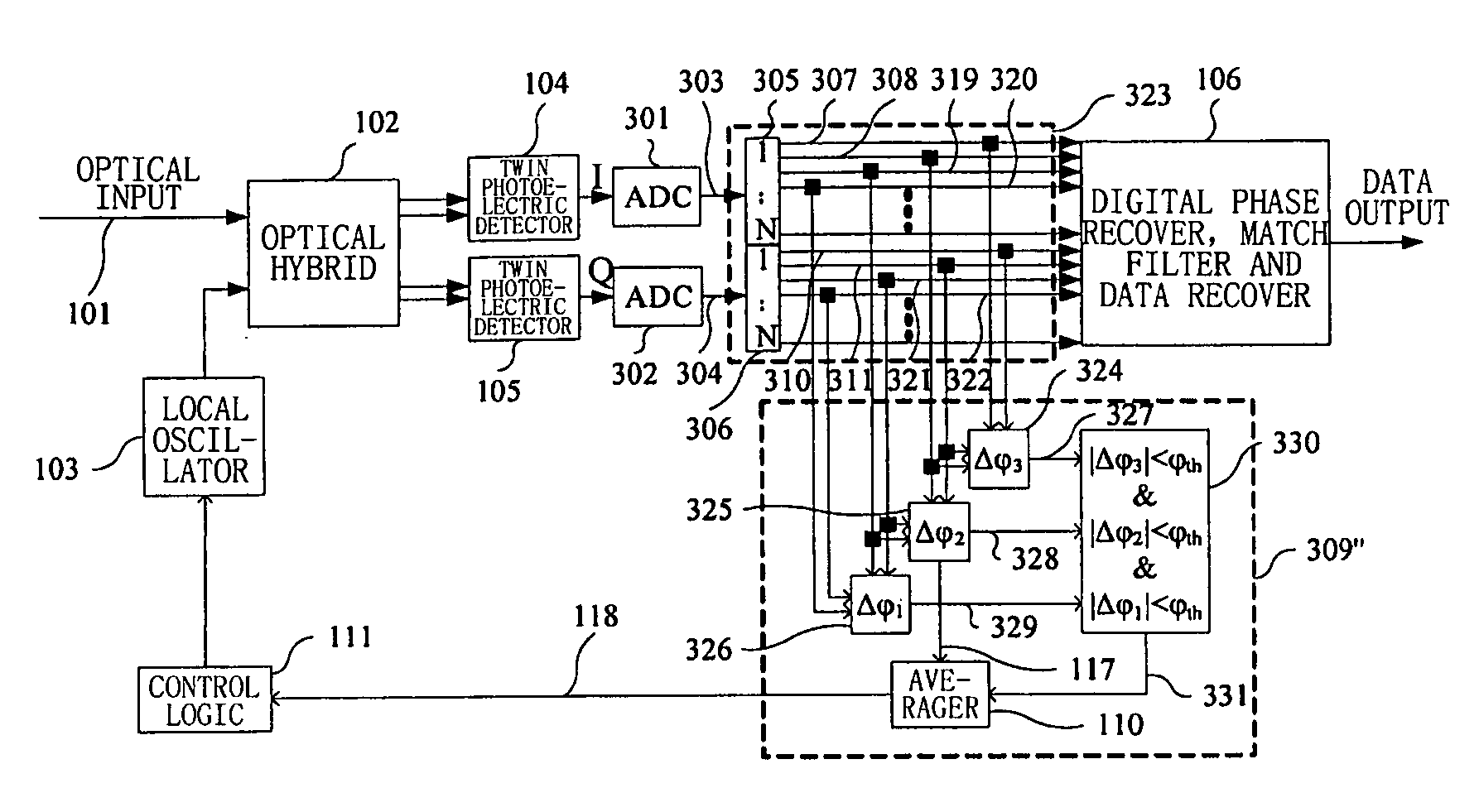
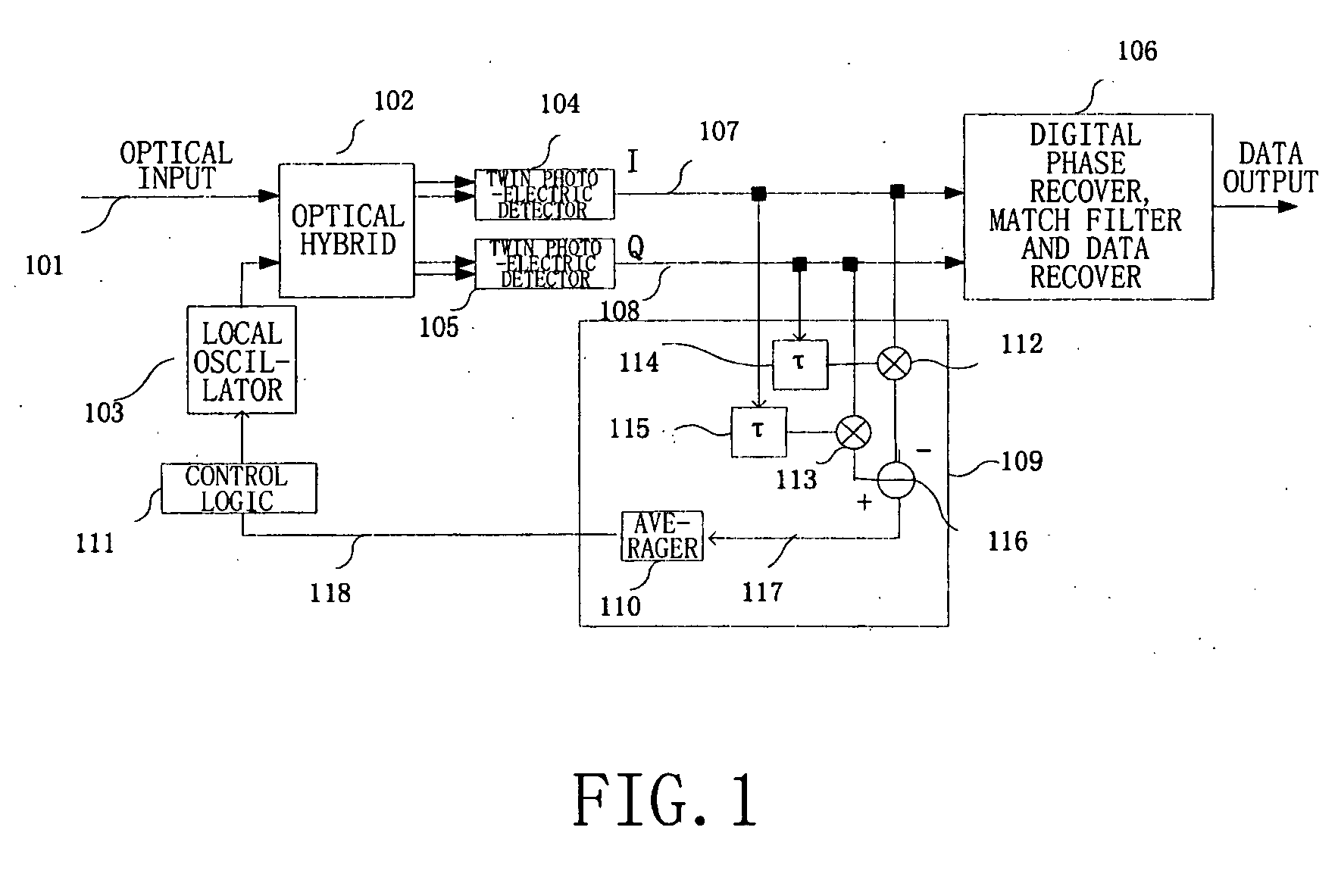
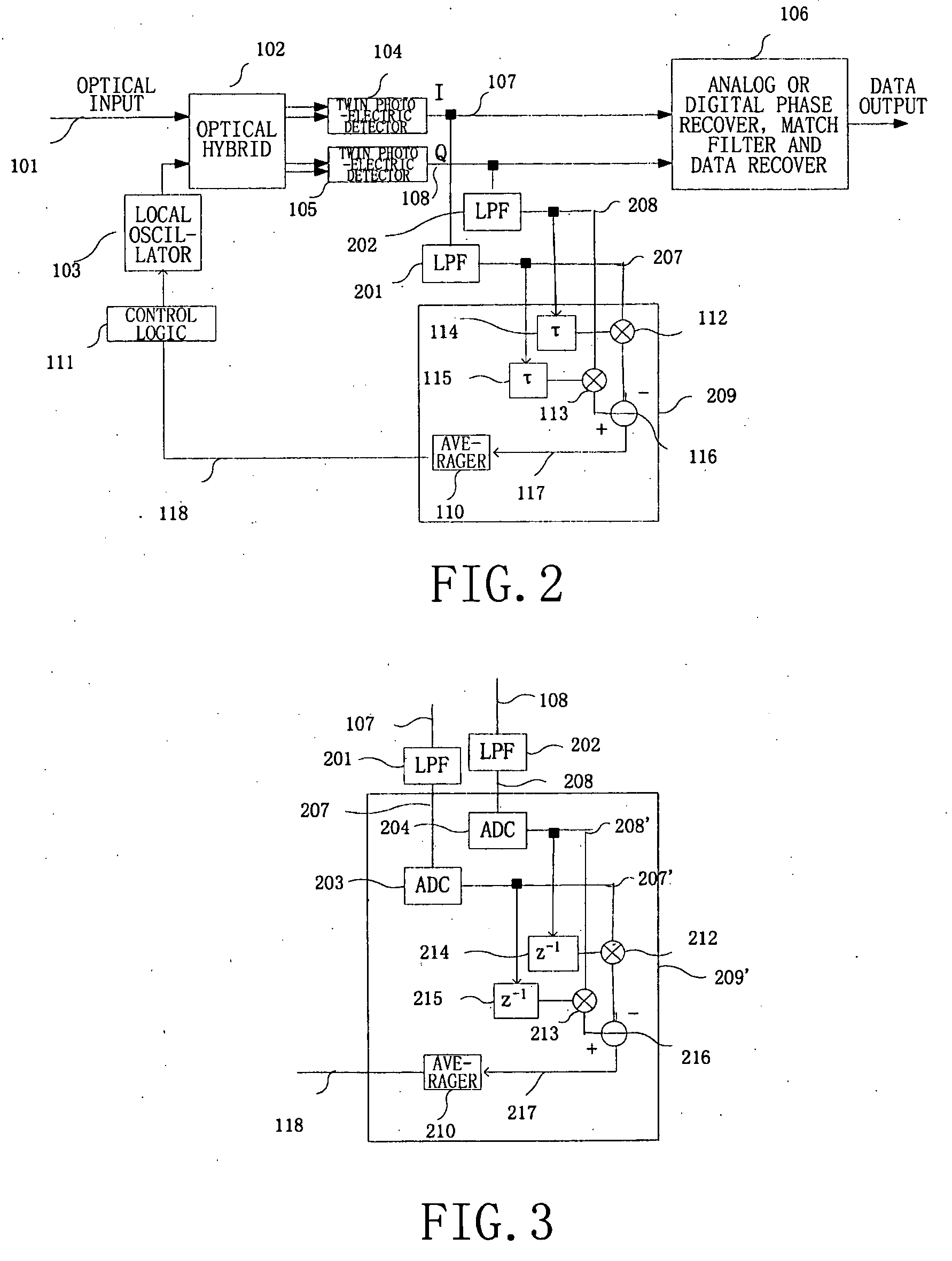
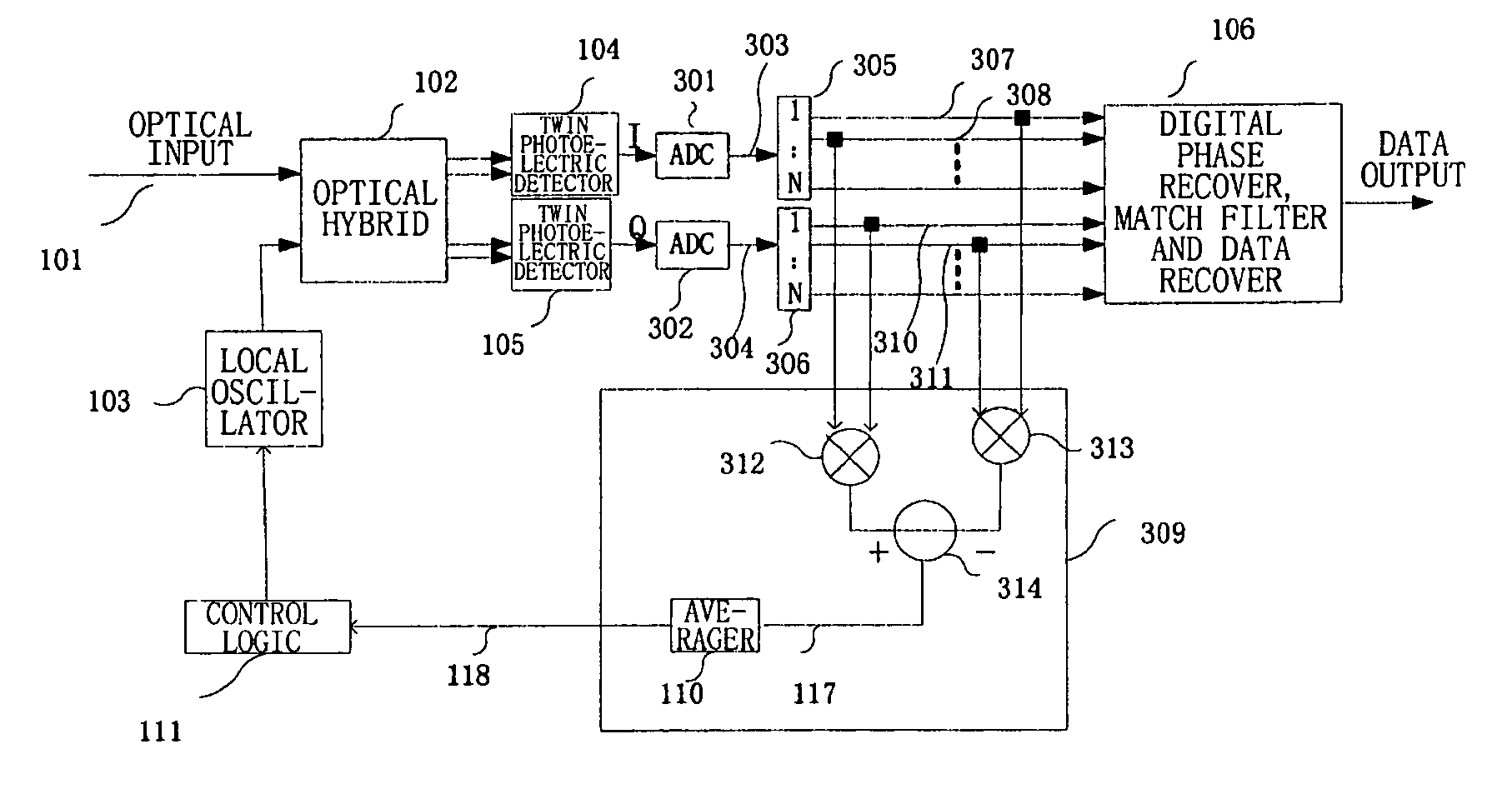
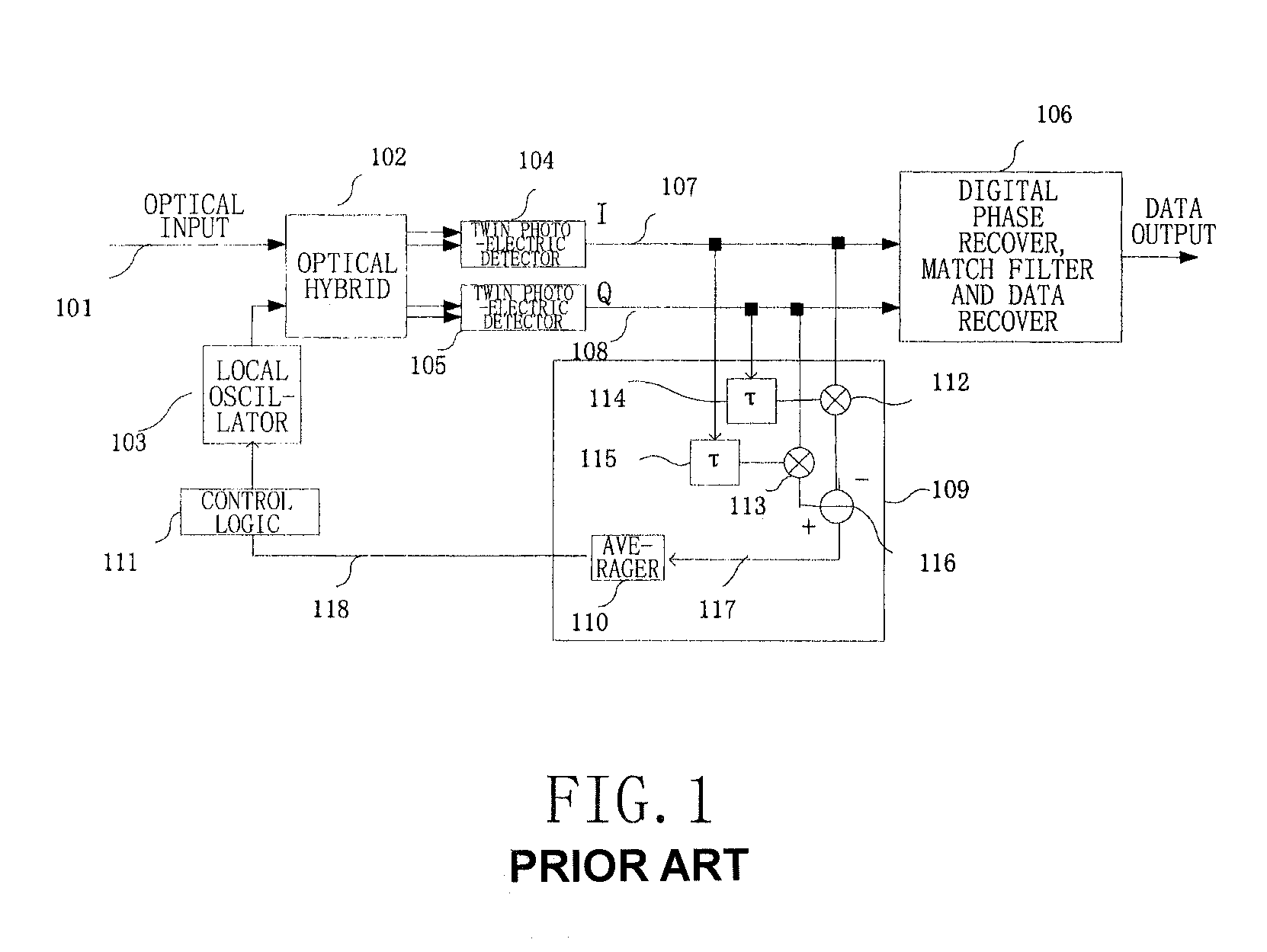
Frequency offset monitoring device and optical coherent receiver
ActiveUS20090080906A1Reduce demandReduce operating speedTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsLow speedFrequency offset
The present invention provides a frequency offset monitoring device and an optical coherent receiver. A low speed frequency offset monitoring device comprises a signal speed lowering section, for lowering the speed of an inputted signal and outputting the speed lowered signal, and a frequency offset monitor, for monitoring frequency offset of the speed lowered signal outputted by the signal speed lowering section.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for converting constant-volume supply fans to variable flow operation
ActiveUS7726582B2Shorten speedEffective conditioningMechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusWireless controlTemperature control mode
A control strategy for supply fans in constant-volume heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems that reduces the speed of the fan at part-load conditions is provided. The invention consists of a constant-volume HVAC system, wireless discharge air temperature sensors, wireless hot source and cold source temperature sensors, and a wireless controller coupled to a fan modulation device. The controller includes a finite state machine that switches between a high-temperature control mode and a low-temperature control mode. The controller also includes a calculator that calculates a high temperature setpoint and a low temperature setpoint as a function of the hot source and cold source temperatures. In high temperature control mode, the controller compares the maximum discharge air temperature with the high temperature setpoint, and it commands the fan modulating device so that the maximum discharge air temperature remains close to the high temperature setpoint. In low temperature control mode, the controller compares the minimum discharge air temperature with the low temperature setpoint, and it commands the fan modulating device so that the minimum discharge air temperature remains close to the low temperature setpoint. Alternatively, the controller includes a calculator that computes a largest load as a function of previous fan command, discharge air temperatures, and readings from wireless zone temperature sensors. The controller increases the speed of the fan as the largest load increases, and reduces the speed of the fan as the largest load decreases.
Owner:VIGILENT CORP
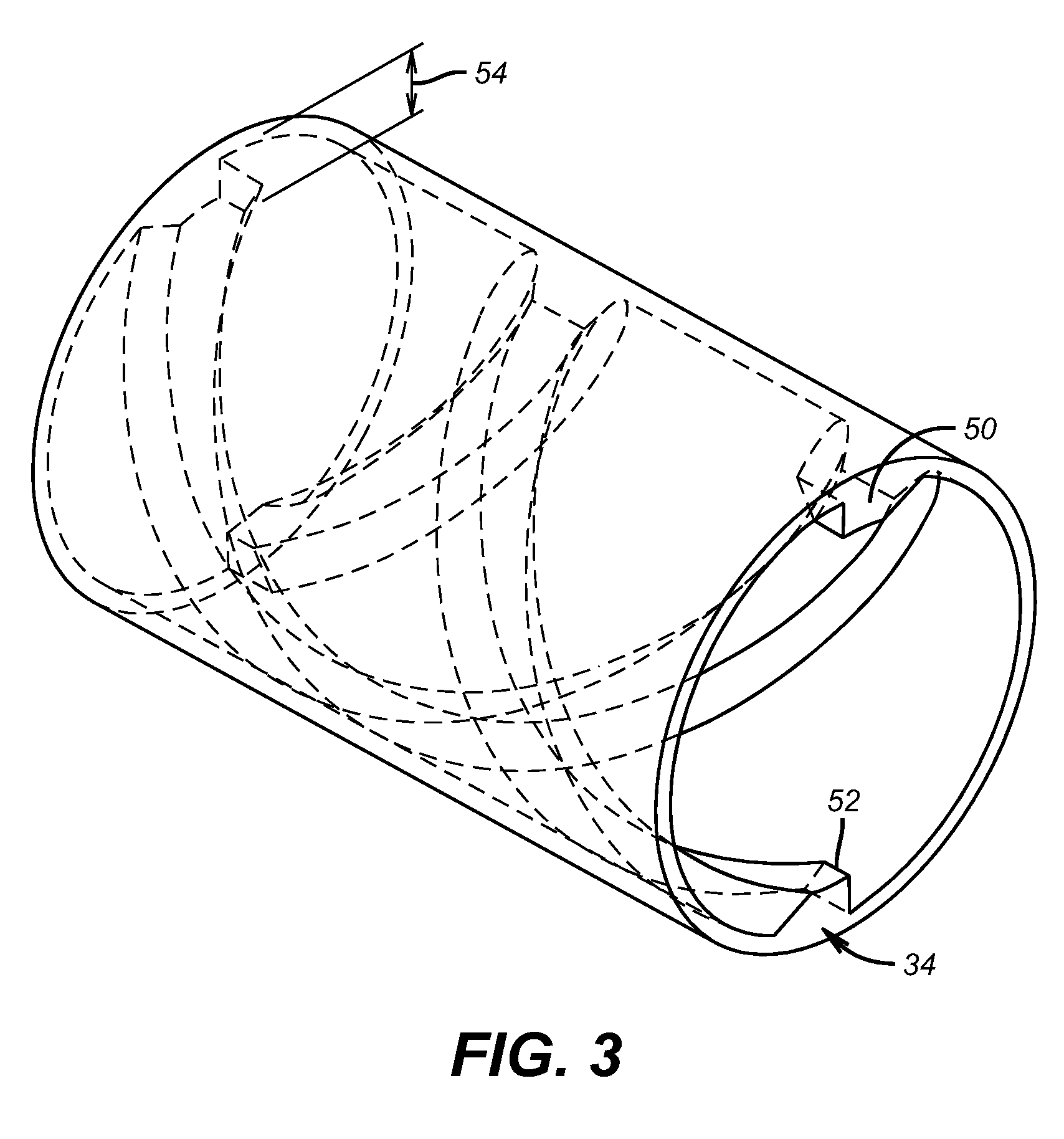
Signature velocity reduction device and method
Owner:MANROLAND GOSS WEB SYST AMERICAS LLC
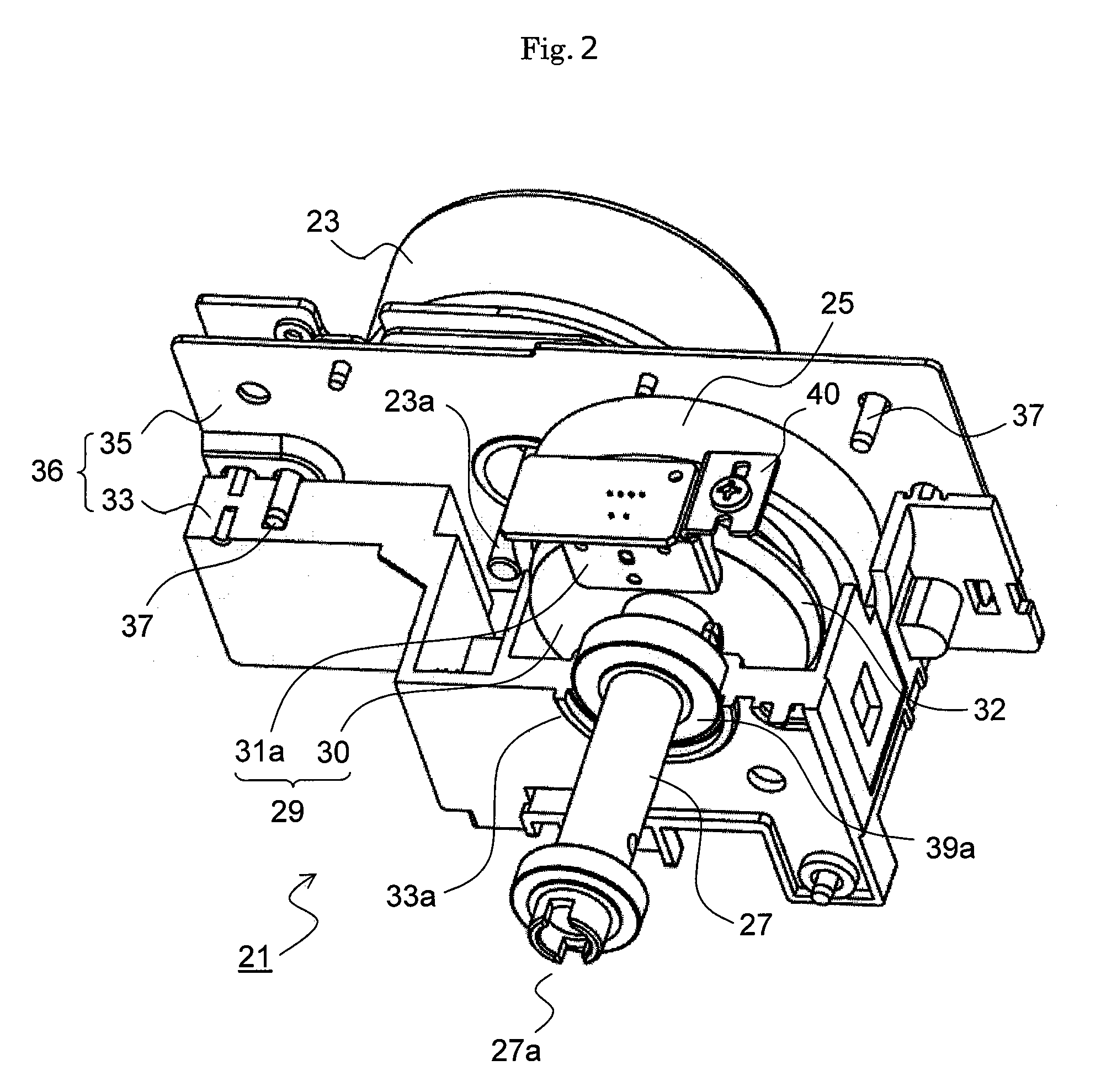
Drive Unit and Image Forming Apparatus Equipped with the Same
ActiveUS20090179528A1Avoid stickingEasy to produceDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesMagnetic measurementsMechanical engineeringEncoder
A drive unit includes a motor being a drive source, a velocity reduction gear for reducing the revolution of the motor, an output shaft for connecting the velocity reduction gear to the rotation shaft of a photosensitive drum, and a velocity detection mechanism including an encoder and sensor members and detecting the revolution of the output shaft. The velocity reduction gear and the velocity detection mechanism are placed in a unit housing including a housing body made of a resin with one end opened and a support plate made of metal closing the opening of the housing body, and the output shaft is rotatably supported by the housing body and the support plate.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
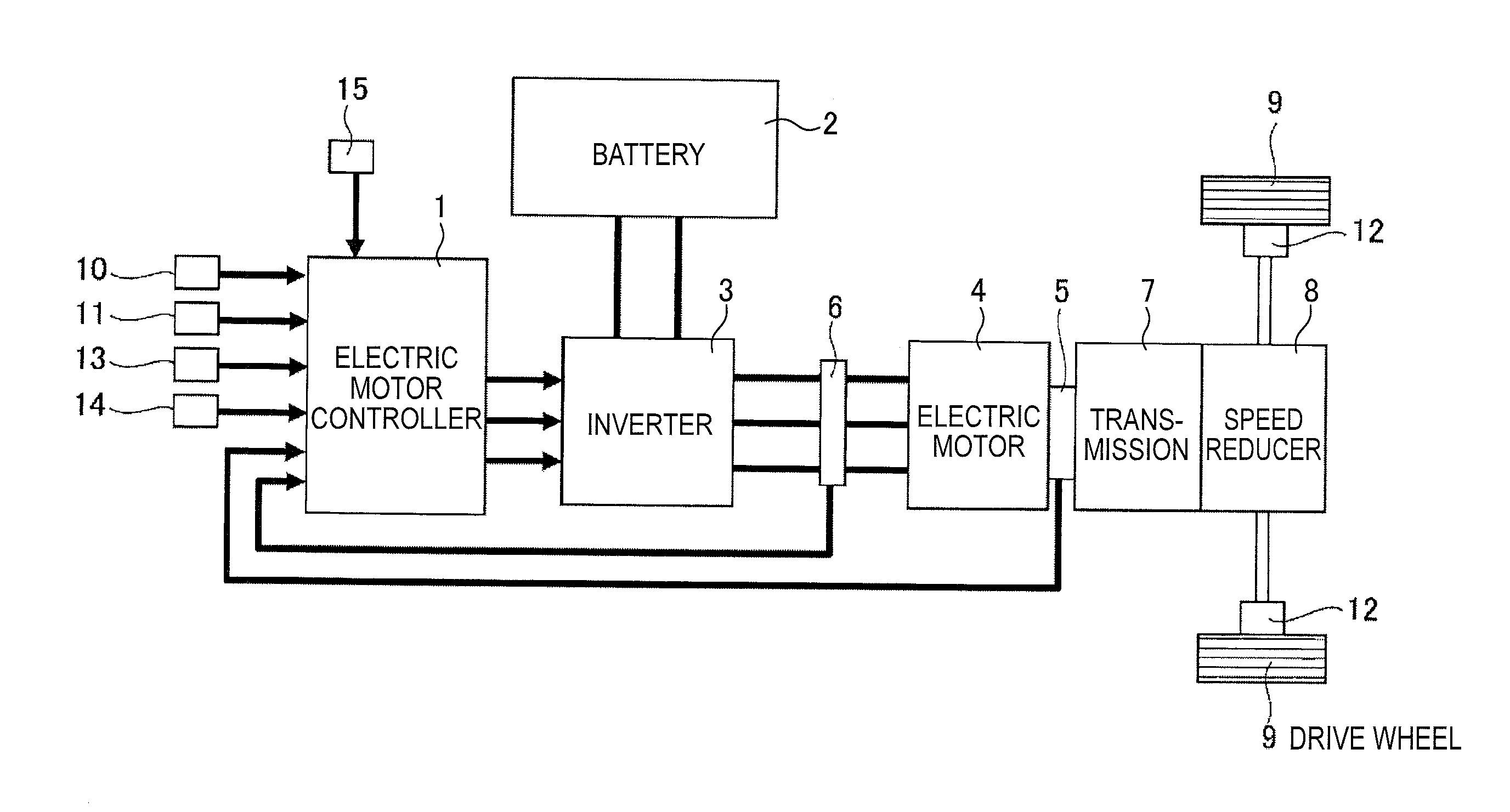
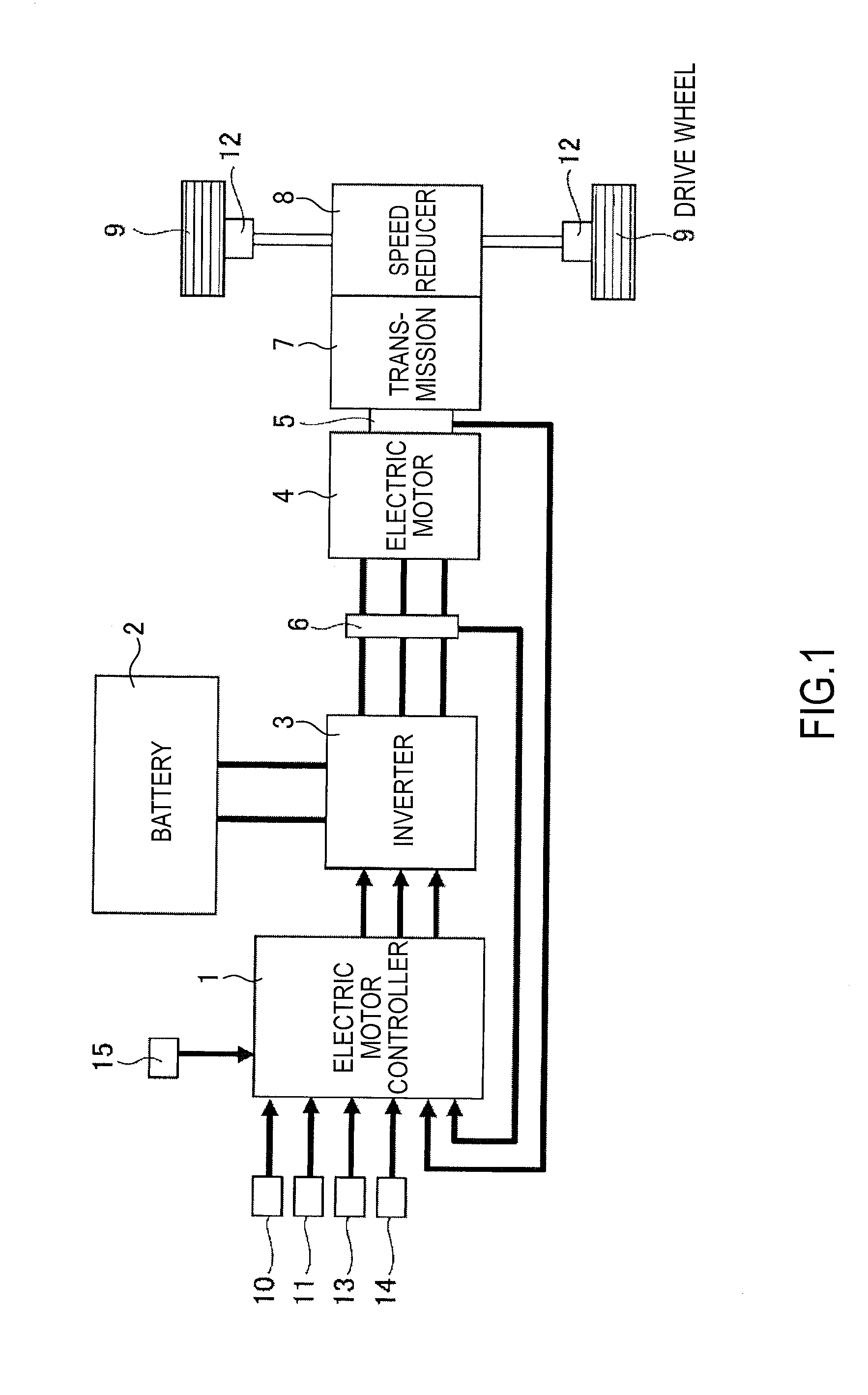
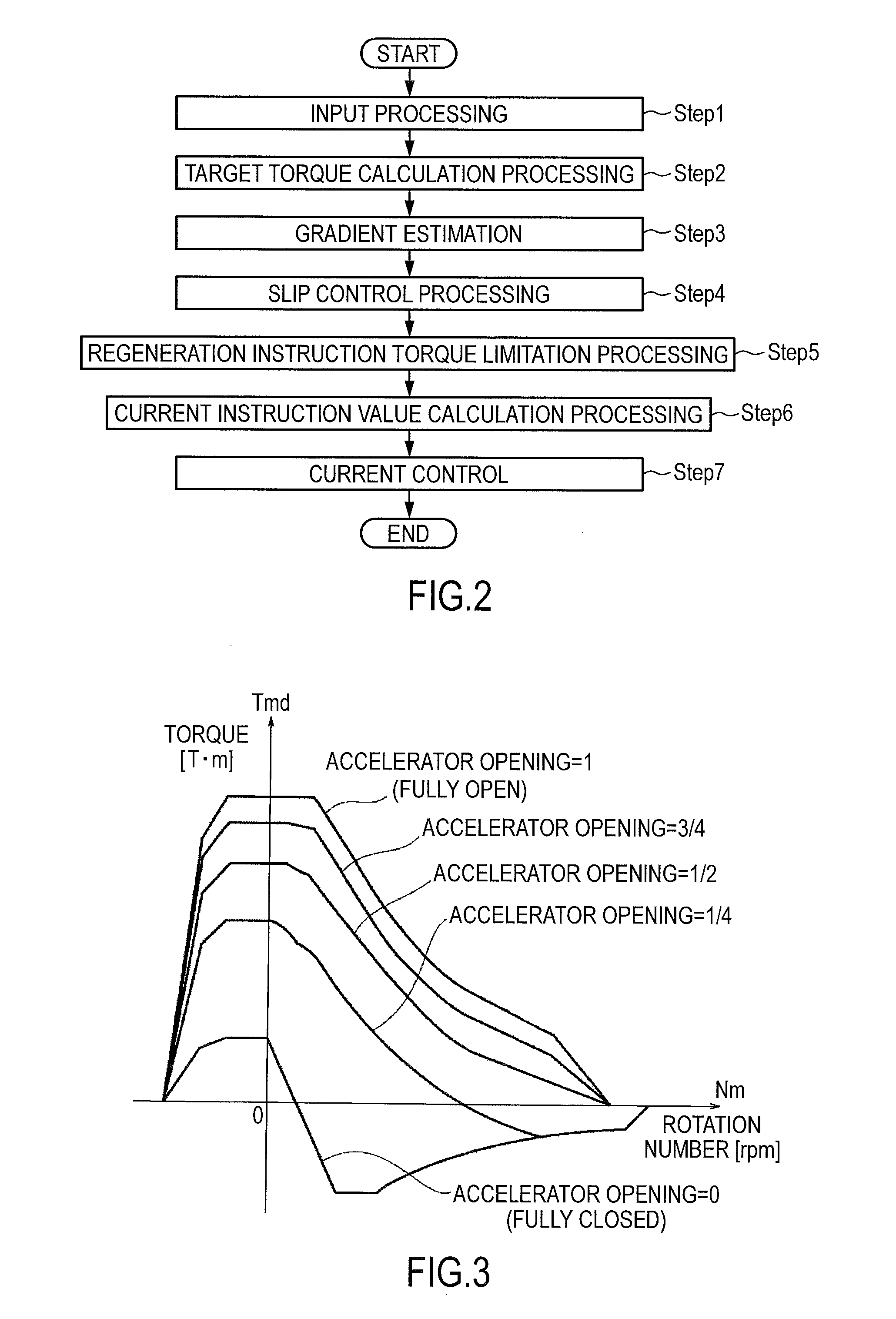
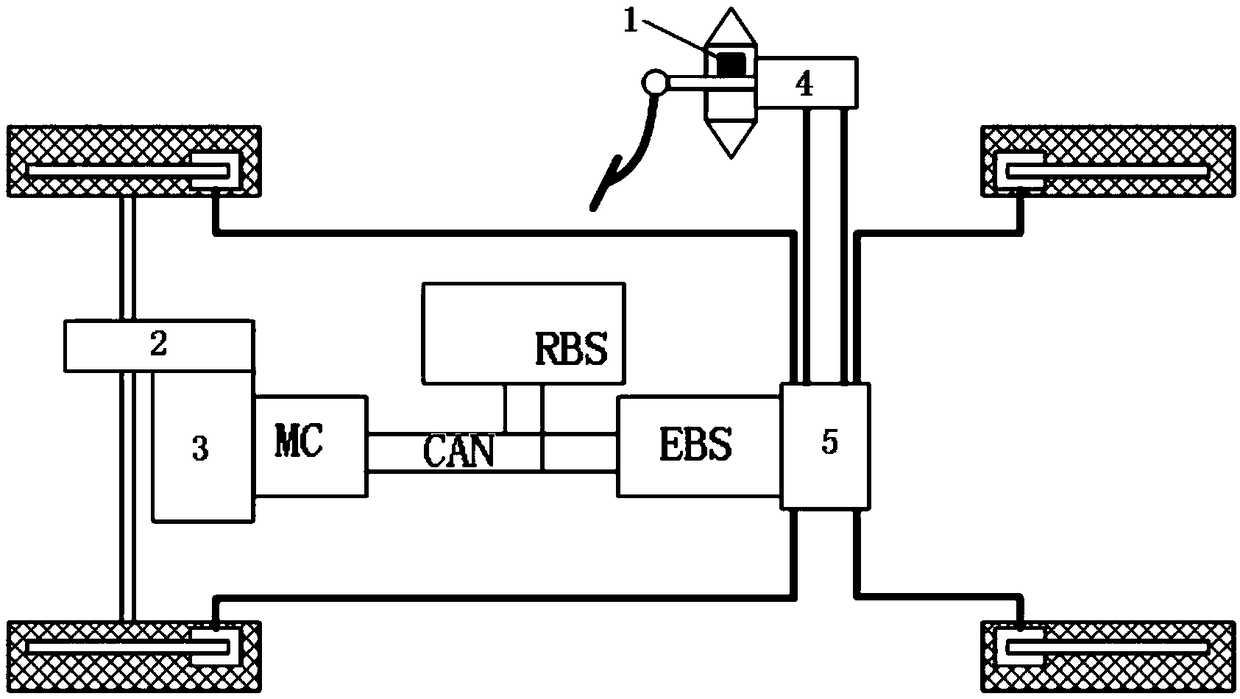
Regeneration braking control device of electric vehicle
A regeneration braking control device of an electric vehicle, wherein, in an electric vehicle system that includes an electric motor coupled to a drive wheel, the refernation braking control device has an electric motor controller that controls powering / regeneration of the electric motor, and a regeneration amount setting unit that sets a regeneration amount by a driver operation and that can change the regeneration amount according to an intention of a driver. The electric motor controller includes a regeneration instruction torque limitation unit that limits, immediately before stop of the vehicle with a motor rotation speed in a low-speed area, the regeneration amount to be decreased as a motor rotation speed is lowered.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
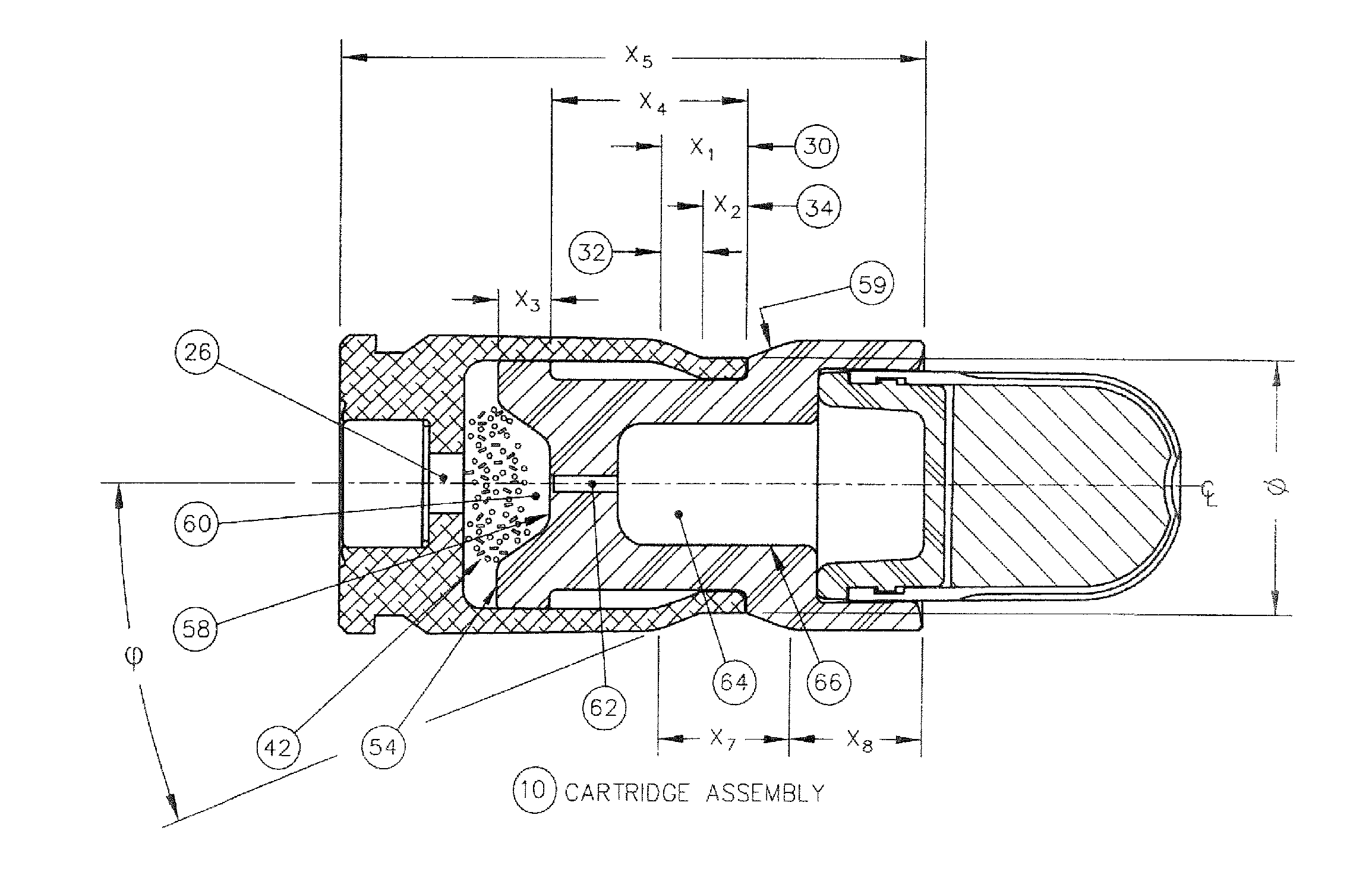
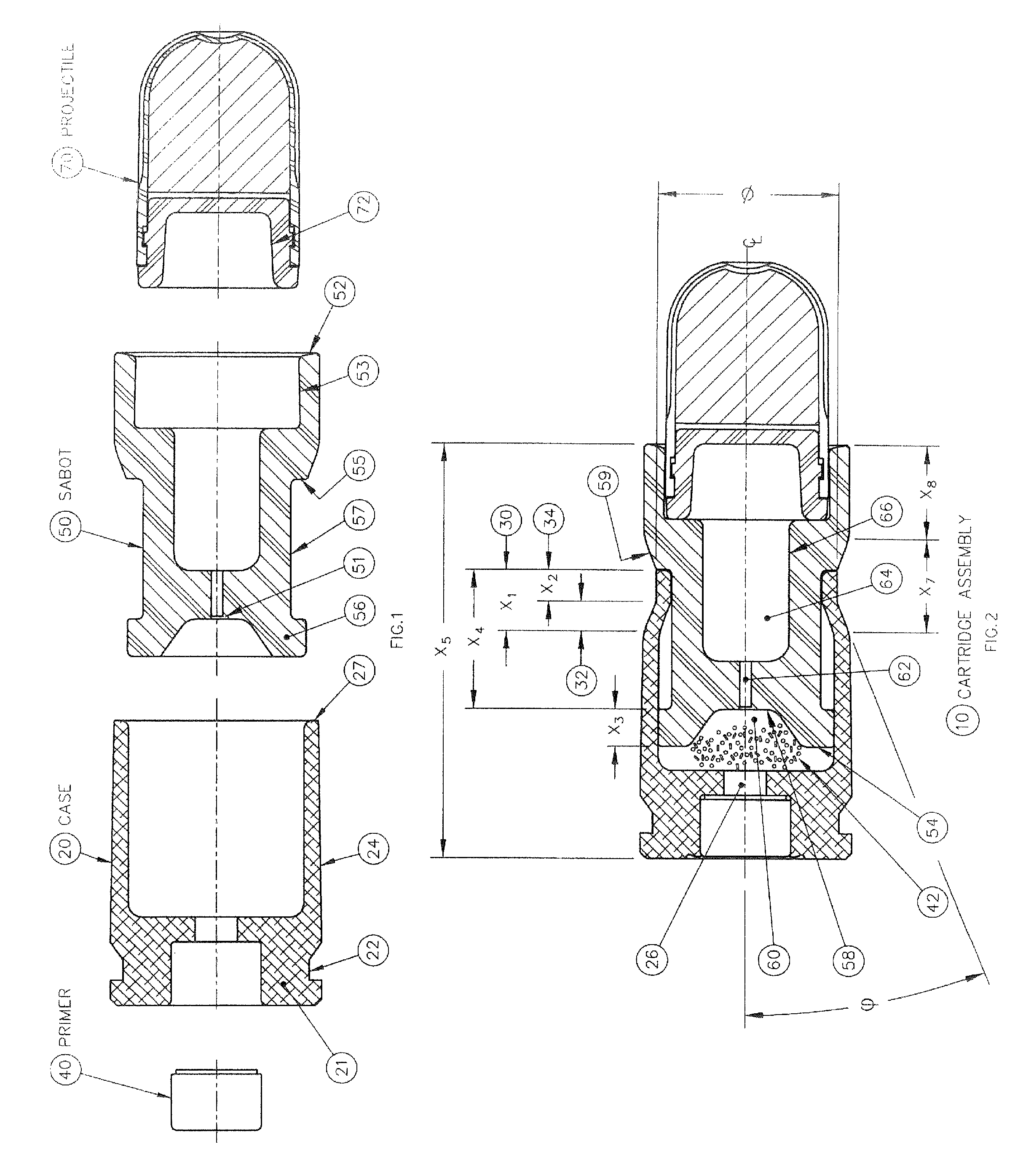
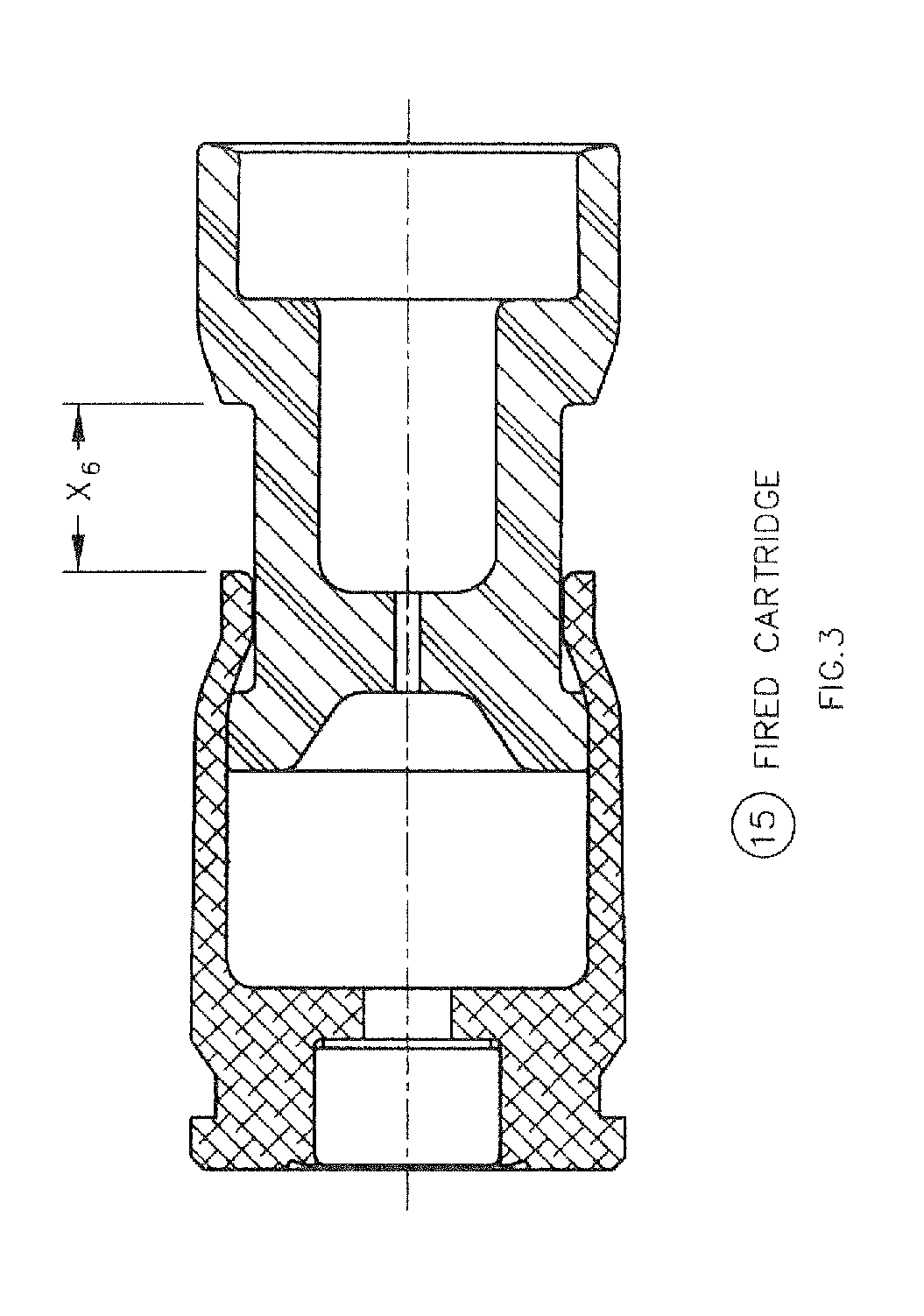
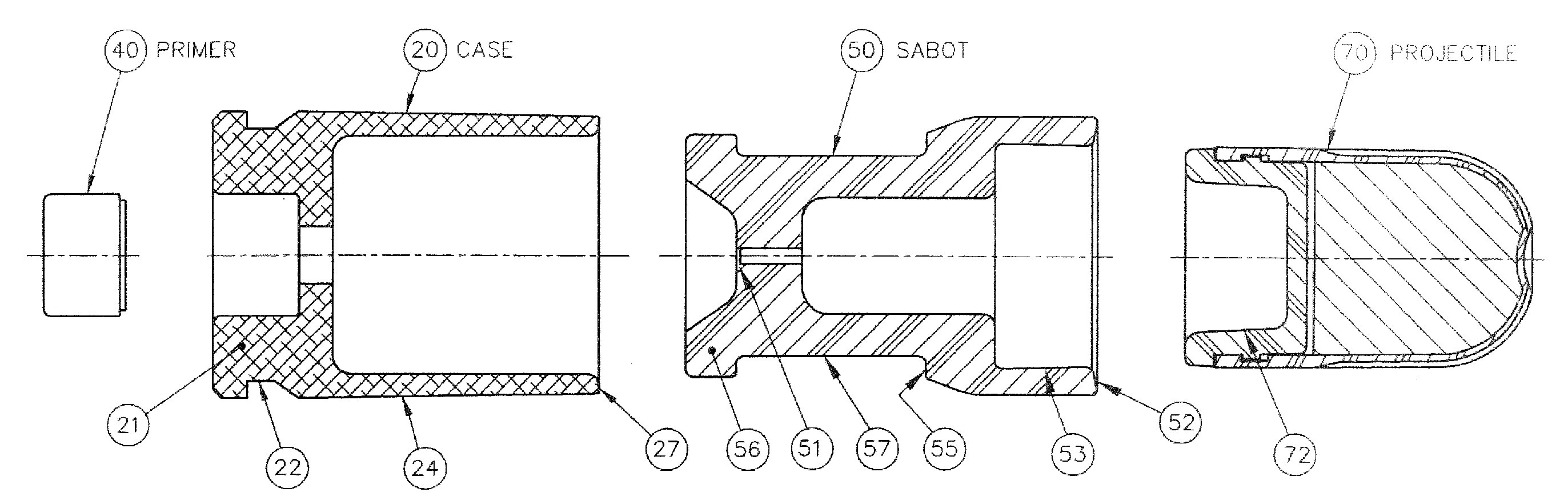
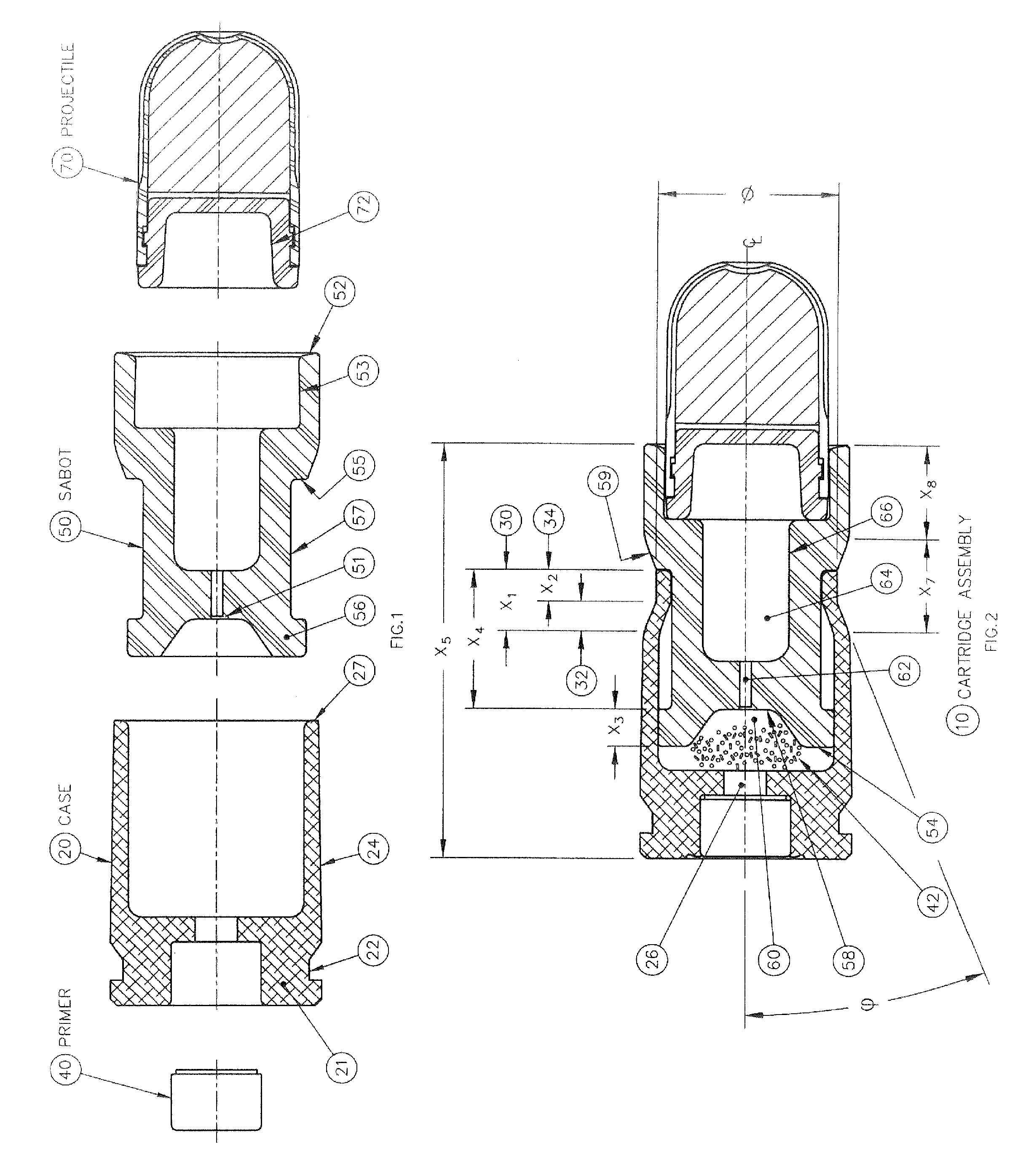
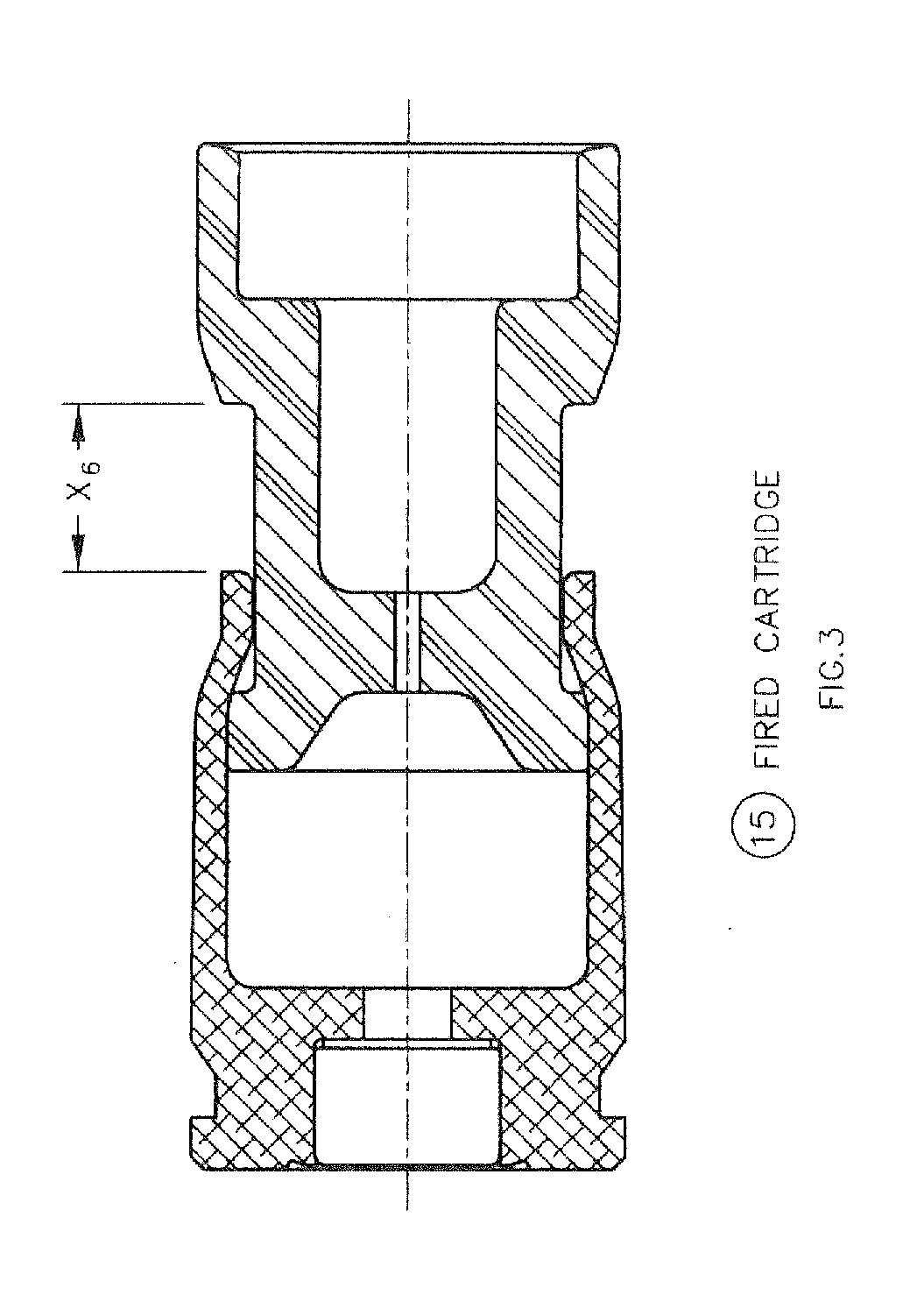
Reduced energy training cartridge for straight blow back operated firearms
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS ORDNANCE & TACTICAL SYST CANADA VALLEYFIELD INC
Noise reduction unit for vacuum suction drains
ActiveUS20130287505A1Improved noise damping characteristicBulk conveyorsSewage drainingNoise levelSuction drain
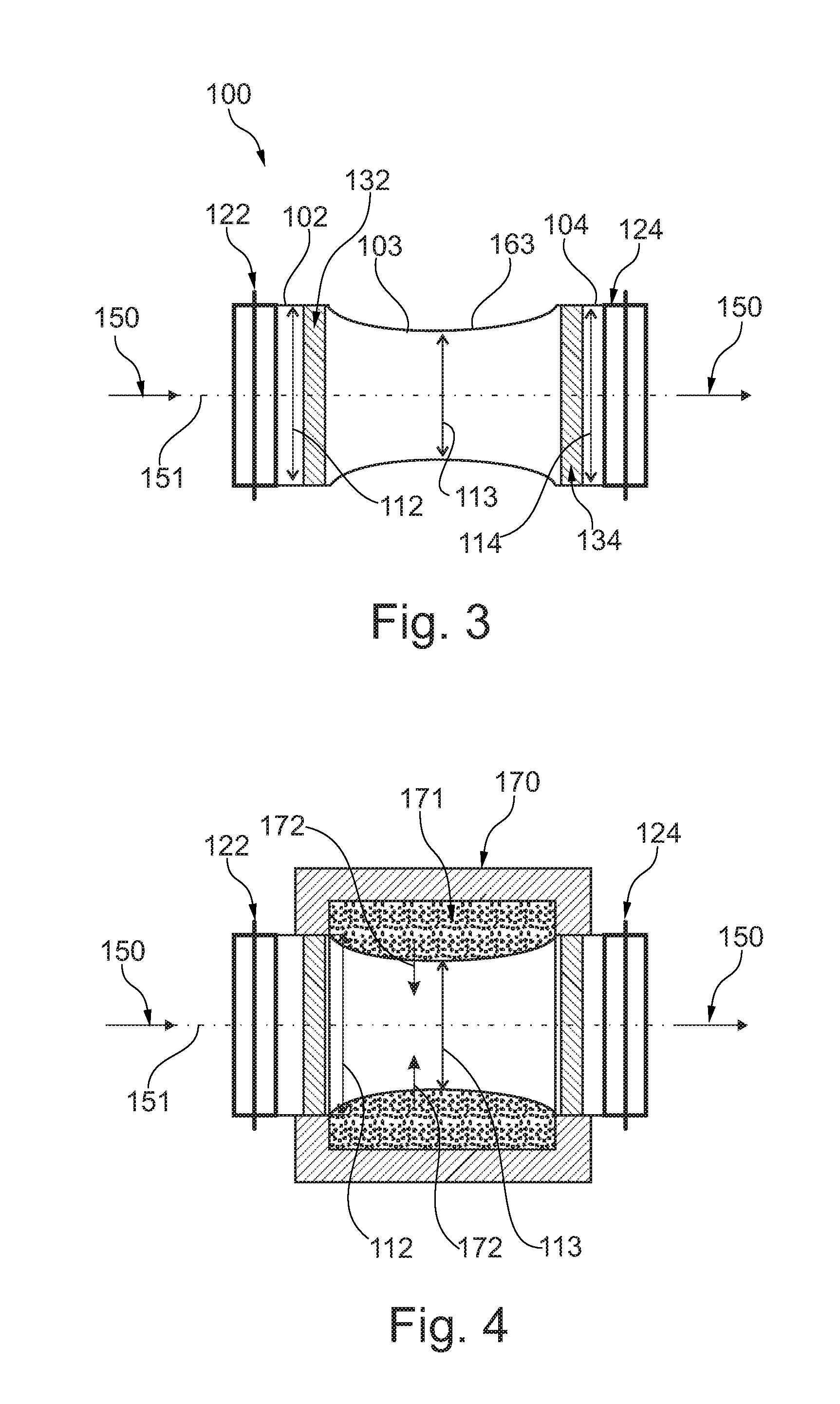
A noise reduction unit for inserting in a vacuum suction drain is adapted to be flown through by a material to be conveyed through the vacuum suction drain and comprises an inlet section with a first diameter, a middle section with a second diameter and an outlet section with a third diameter. The middle section is adapted to affect a flow velocity reduction of the material to be conveyed such that the noise level arising during the conveying process is being reduced.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Frequency offset monitoring device and optical coherent receiver
ActiveUS8374512B2Large capacityShorten speedTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsLow speedFrequency offset
The present invention provides a frequency offset monitoring device and an optical coherent receiver. A low speed frequency offset monitoring device comprises a signal speed lowering section, for lowering the speed of an inputted signal and outputting the speed lowered signal, and a frequency offset monitor, for monitoring frequency offset of the speed lowered signal outputted by the signal speed lowering section.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
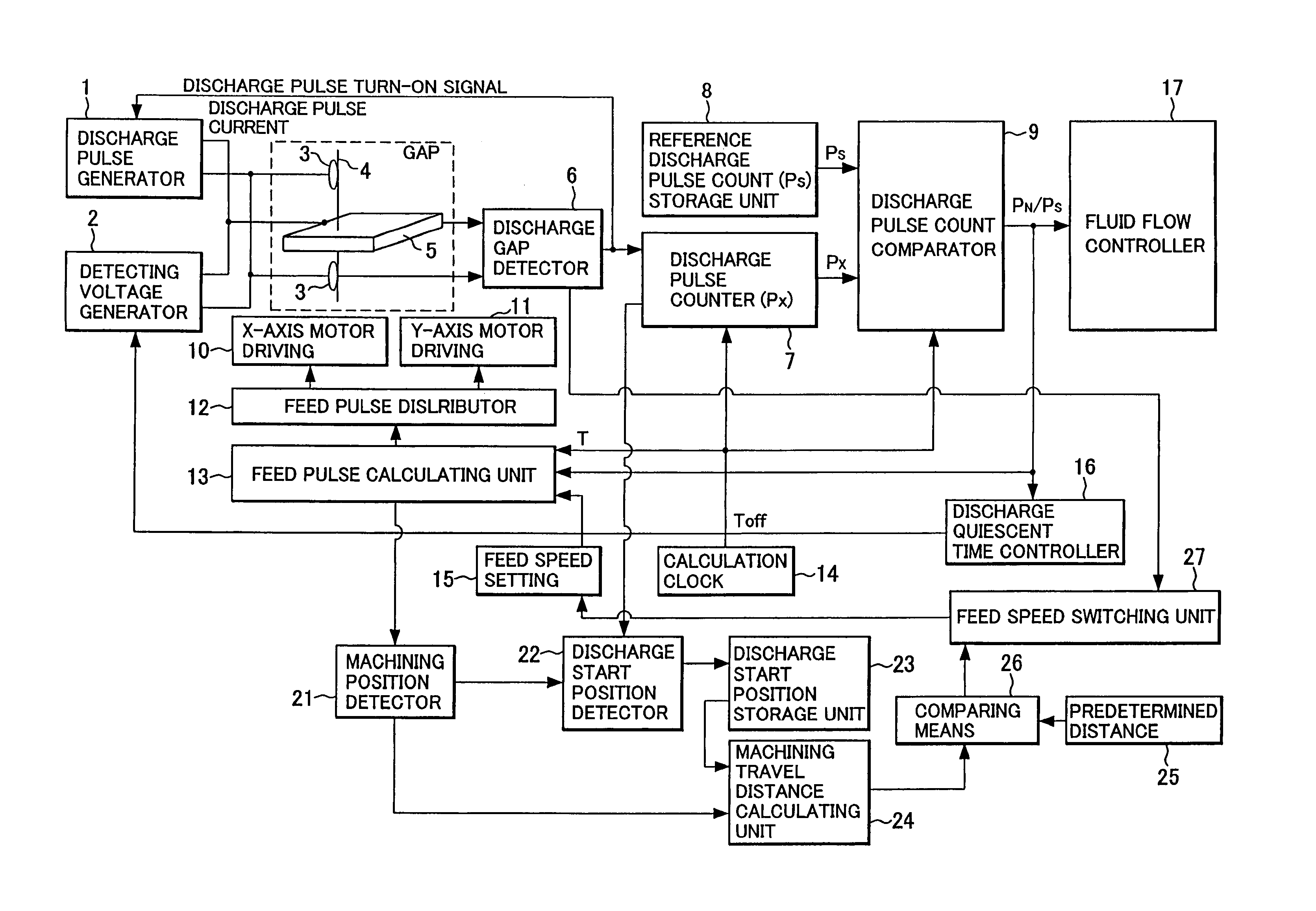
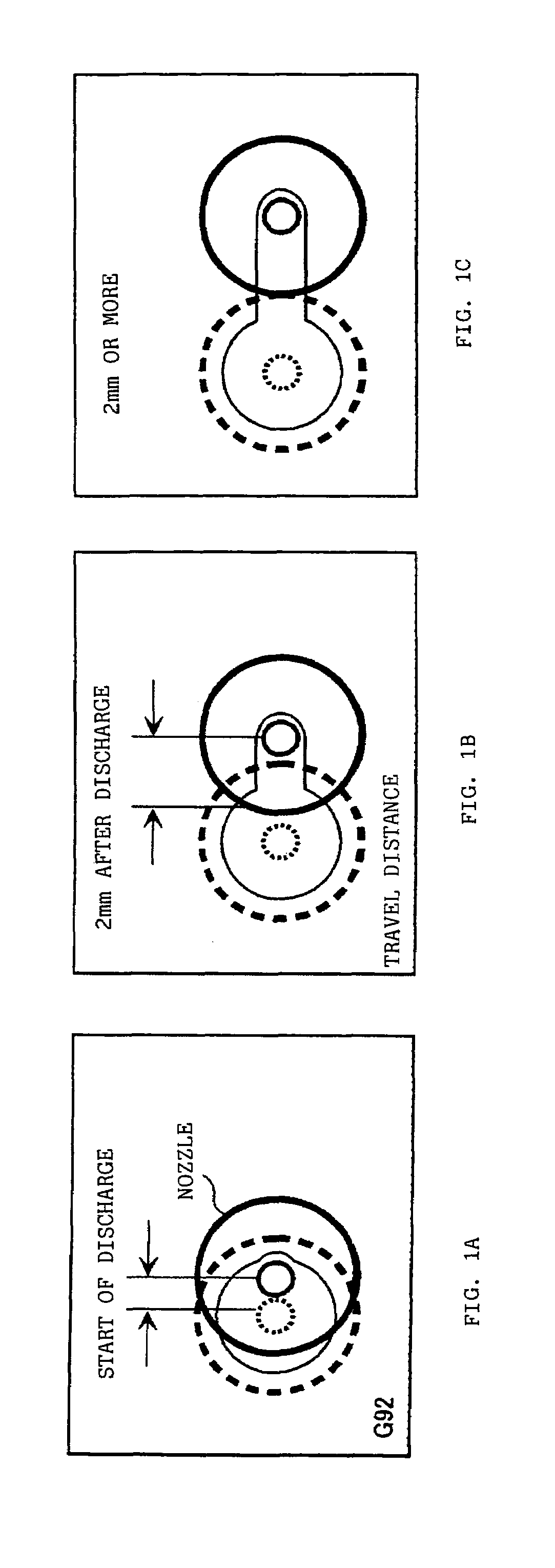
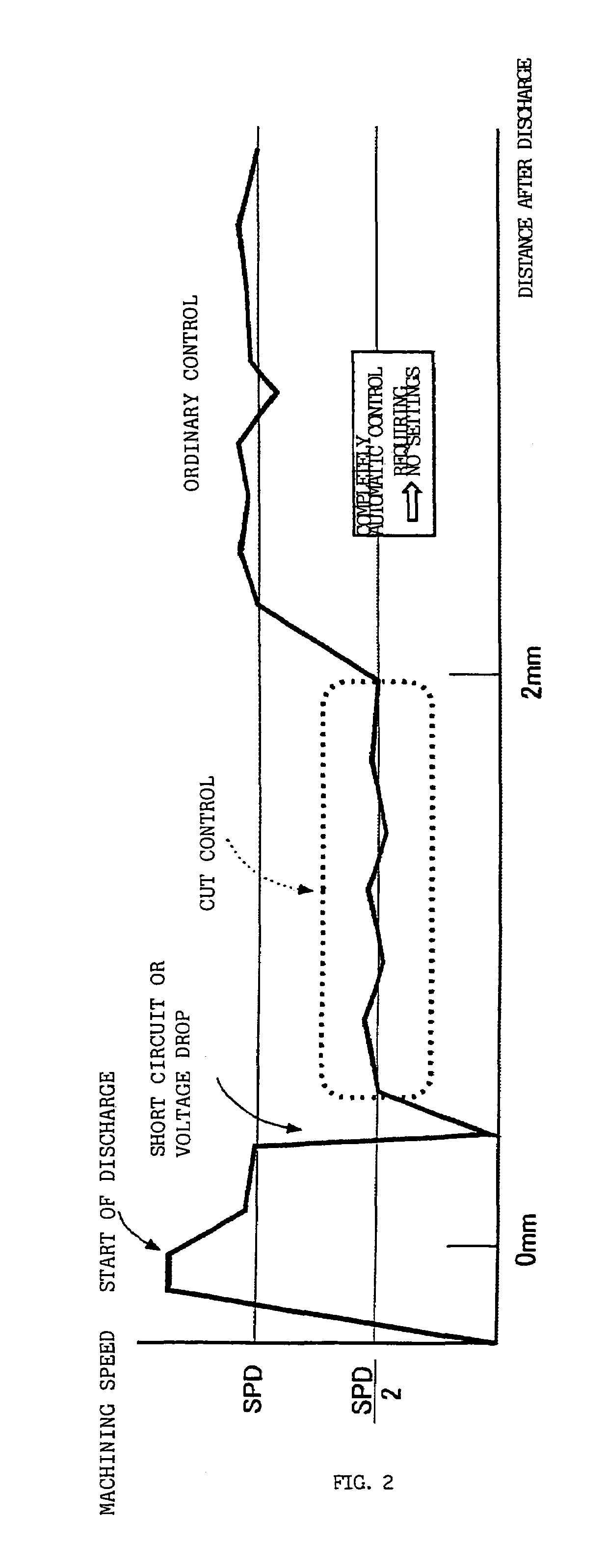
Controller for a wire electrical discharge machine
ActiveUS6998562B2Little riskShorten speedElectric circuitsElectrical discharge machiningVelocity reduction
Set feed speed is lowered when a short circuit is detected in a range within which machining is unstable, the range starting from the point at which discharge is detected after machining starts from a machining start point, thus control is carried our according to a machining rate, thereby preventing successive occurrence of short circuits. When machining proceeds beyond the unstable range, the lowered feed speed is returned to the normal feed speed.
Owner:FANUC LTD
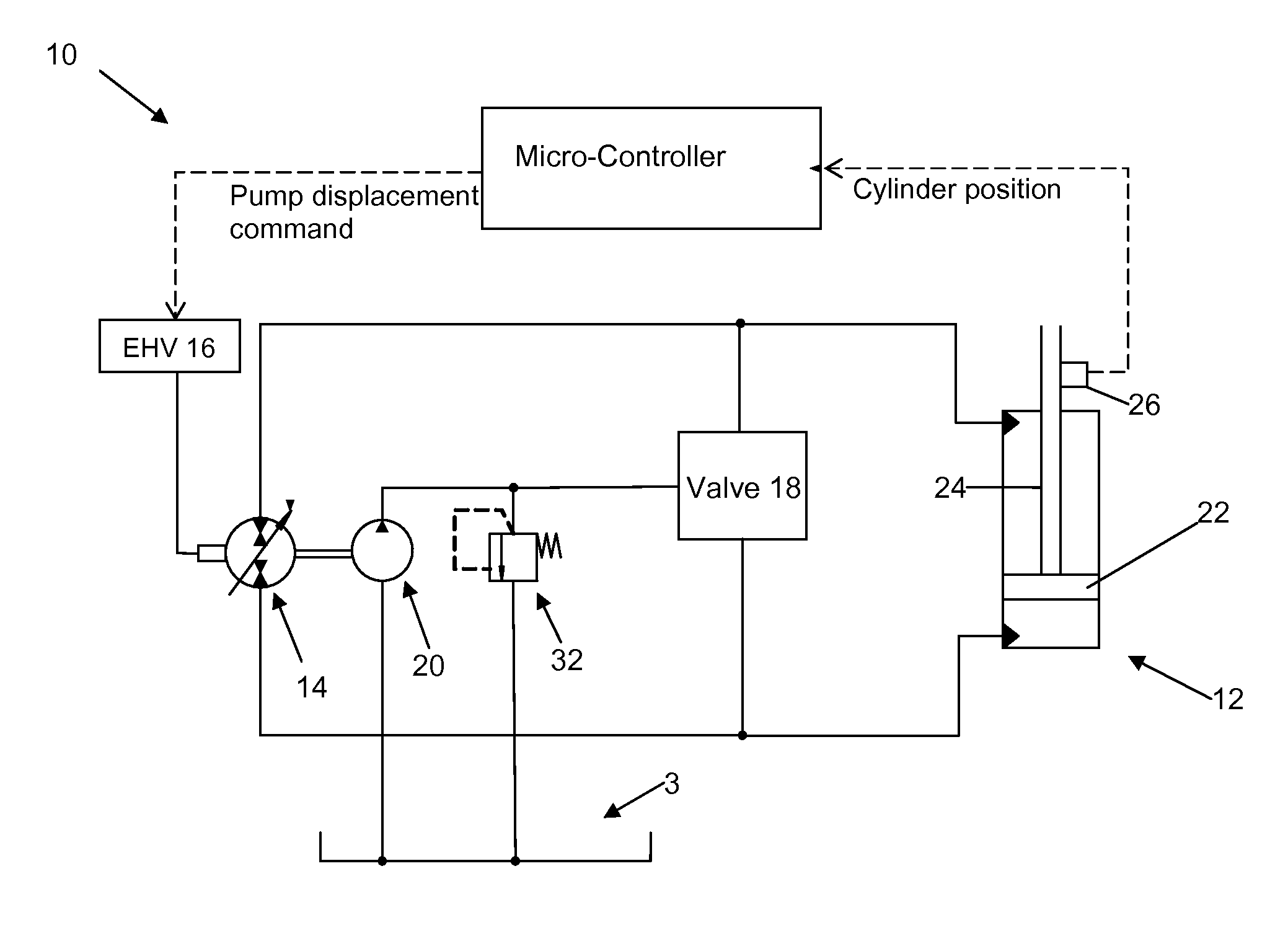
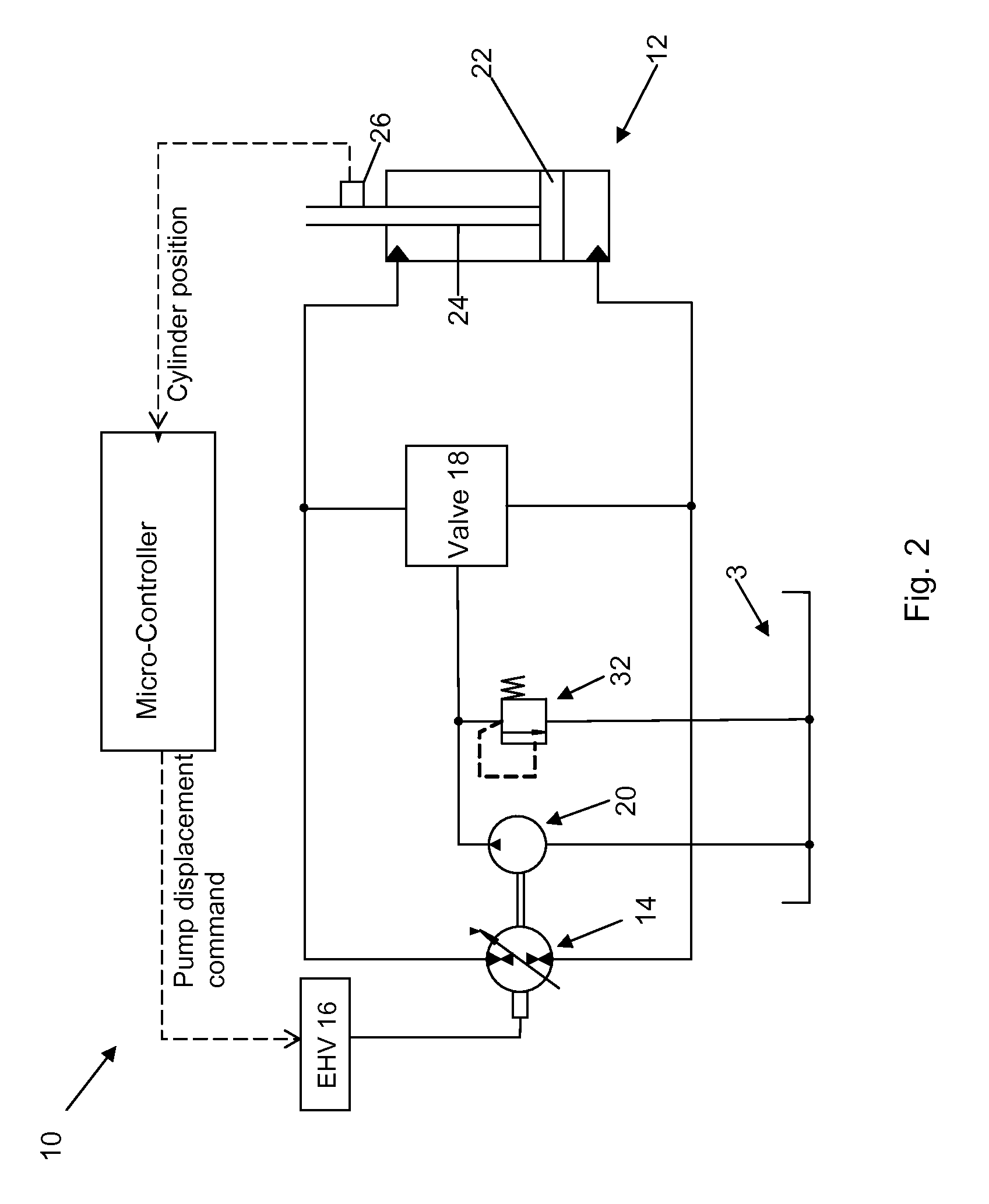
System and method for pump-controlled cylinder cushioning
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Low Noise Compressor Rotor for Geared Turbofan Engine
ActiveUS20130276424A1Reduce fan speedShorten speedEngine fuctionsGas turbine plantsLow noiseCombustor
A gas turbine engine has a fan, a compressor section having a low pressure portion and a high pressure portion, a combustor section, and a turbine having a low pressure portion. The low pressure turbine portion drives the low pressure compressor portion and the fan. A gear reduction effects a reduction in the speed of the fan relative to a speed of the low pressure turbine and the low pressure compressor portion. At least one of the low pressure turbine portion and low pressure compressor portion has a number of blades in each of a plurality of rows. The blades operate at least some of the time at a rotational speed. The number of blades and the rotational speed are such that the following formula holds true for at least one of the blade rows of the at least one of the low pressure turbine portion and / or the low pressure compressor sections: (number of blades×rotational speed) / 60≧5500. The rotational speed is an approach speed in revolutions per minute.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Auto cruise downhill control method for vehicle
InactiveUS20140156163A1Shorten speedVehicle fittingsDigital data processing detailsDriver/operatorAutomatic braking
Disclosed herein is an auto cruise downhill control (ADC) method for a vehicle, whereby, when a speed of the vehicle exceeds an auto cruise setting speed, the speed of the vehicle is automatically adjusted to be the auto cruise setting speed by using an engine control unit (ECU) and an electronic stability control (ESC) unit. In other words, when a current vehicle speed exceeds a predetermined value compared to a driver's setting speed for auto cruise, automatic braking activation control is performed by the ESC unit to adjust the speed of the vehicle to be the auto cruise setting speed when the vehicle is operating on a steep decline. Additionally, when a driver makes a steep downward adjustment of the setting speed, automatic braking activation control is performed by the ESC unit to decrease the speed of the vehicle to a downwardly adjusted level at an accelerated rate.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +2
Reduced Energy Training Cartridge for Straight Blow Back Operated Firearms
ActiveUS20120192751A1Reduce decreaseSlide fastAmmunition projectilesTraining ammunitionCombined useGun barrel
The present invention discloses a reduced energy training cartridge for use in a straight blowback operated firearm having a barrel with firing chamber, the cartridge comprising a cartridge case being defined by a rear portion with an external groove, a front portion having a velocity reduction structure and a wall with an outer surface and an inner surface, a sabot slideably engaged within the cartridge case, the sabot having a rear portion with an outside diameter substantially equal to the inside diameter of the inner surface of the cartridge case and which contains a gas sealing and braking structure and a primer disposed in the rear portion of the cartridge case where, upon percussion of the primer, the cartridge case rapidly slides relative to the sabot until such point when the velocity reduction structure of the cartridge case engages with the sealing and braking structure of the sabot, thereby stopping further movement of the cartridge case relative to the sabot, The present invention also contemplates using a metallic case in combination with a non-metallic or polymer sabot.
Owner:GENERAL DYNAMICS ORDNANCE & TACTICAL SYST CANADA VALLEYFIELD INC
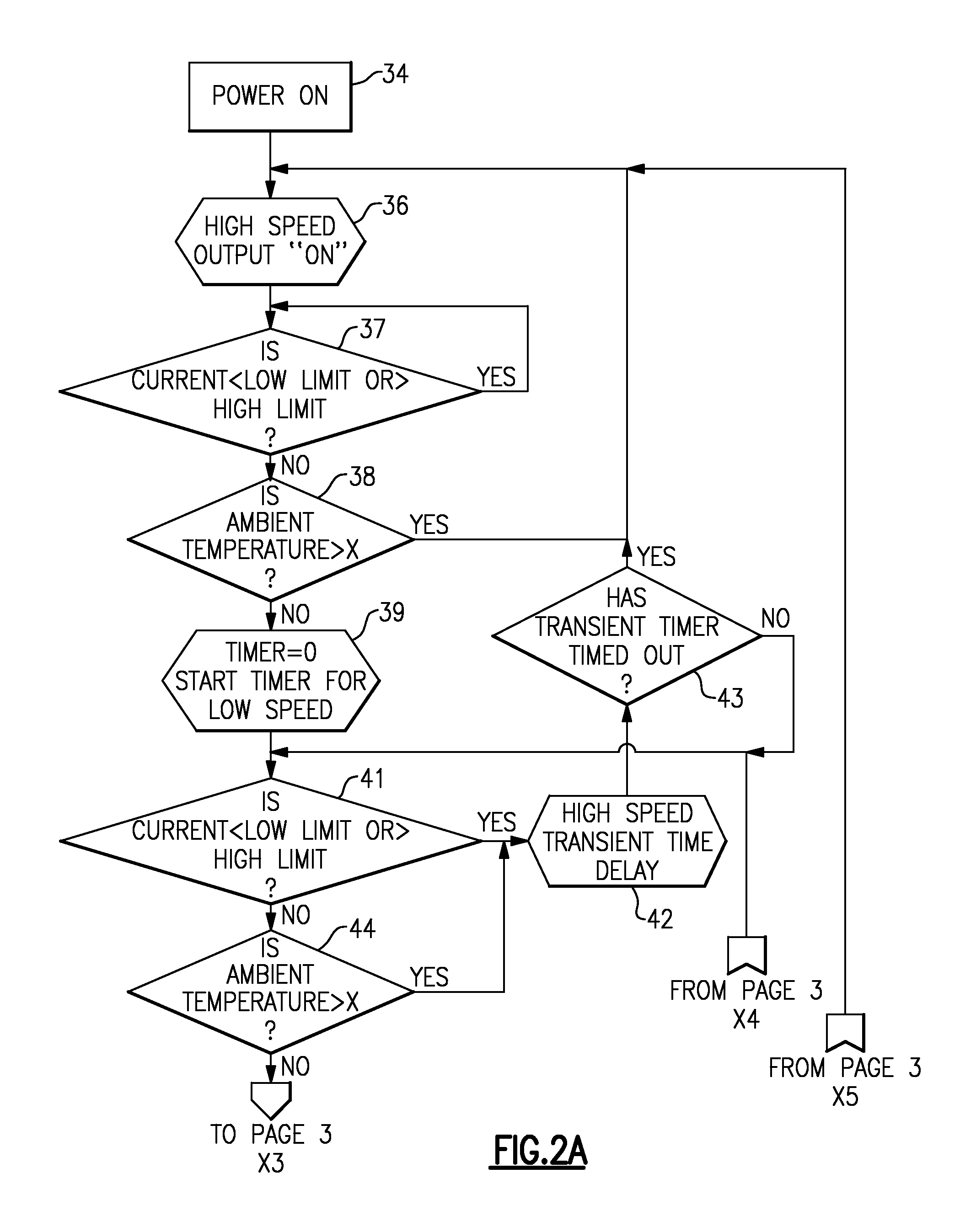
Two speed control for mobile refrigeration generators
ActiveUS20100289273A1Eliminate short cyclingEngine controllersMachines/enginesLow speedCurrent sensor
A current sensor is installed in a generator set to measure the current being delivered from the generator set to a refrigeration unit. A control is responsive to the current transformer to reduce the speed of the drive engine to a lower speed when the current being delivered to the refrigeration unit is determined to be below a predetermined higher level. Provision is made to override the system when the sensed current is determined to be transient caused or in the event that ambient temperature is determined to be above a predetermined temperature threshold.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
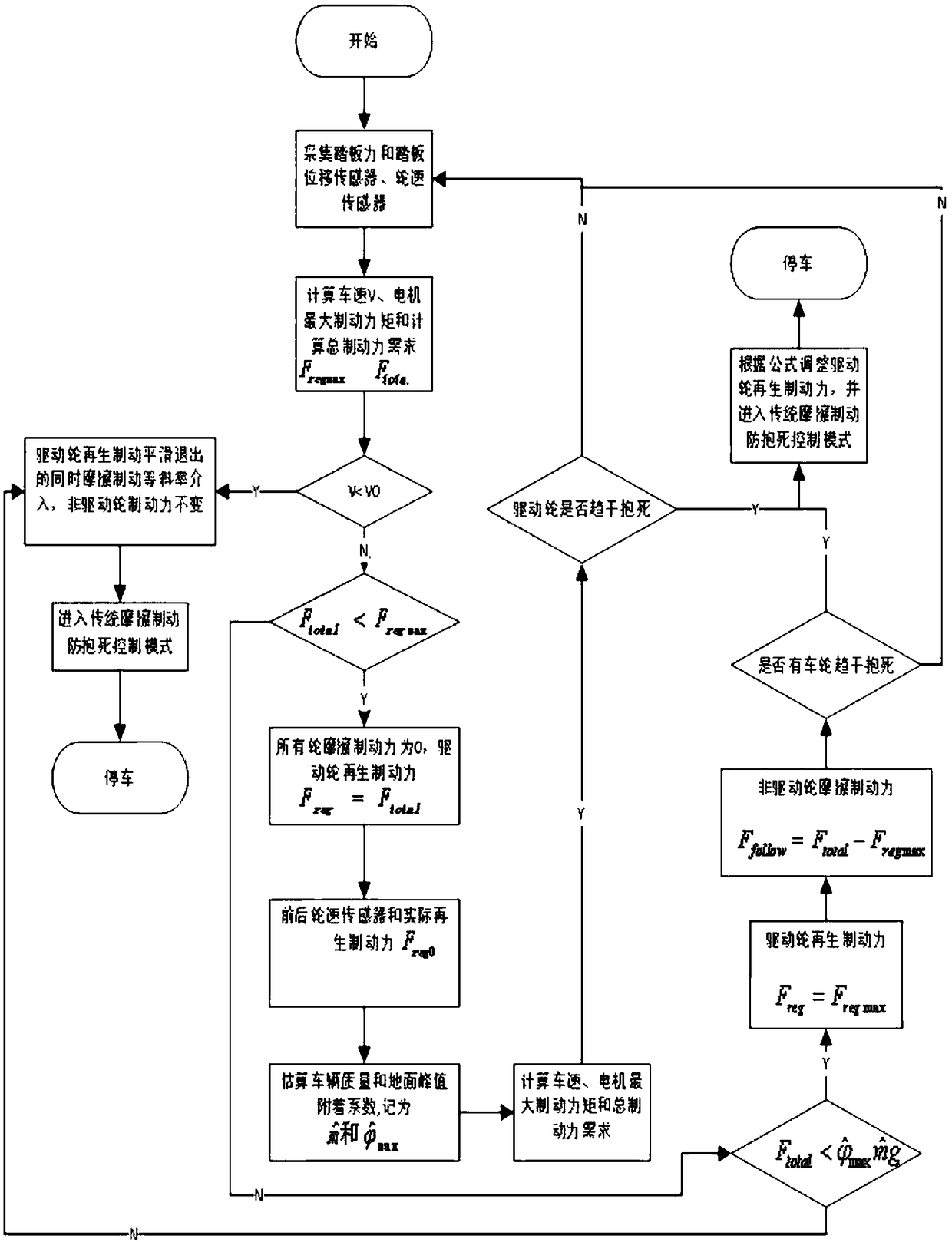
Electric vehicle braking energy recovery control algorithm
ActiveCN108688474AAvoid rough brakingMaximum braking energyElectrodynamic brake systemsEnergy recoveryEngineering
The invention relates to an electric vehicle braking energy recovery control algorithm. The electric vehicle braking energy recovery control algorithm is characterized by being composed of the following steps that in the initial stage of braking, only regenerative braking force of a motor is used for braking, and braking energy is recovered as much as possible, and at the same time, a road adhesion coefficient based on the least square method and a vehicle quality estimation algorithm are adopted to obtain road adhesion coefficient information and vehicle load condition information of vehiclebraking; in the middle stage of the braking process, a Kalman filter algorithm is used for estimating the slip ratio of front and rear wheels; in order to improve the accuracy of the slip rate estimation, the vehicle quality and the road adhesion coefficient obtained at the initial stage of braking are taken as initial values to put into the Kalman filter algorithm; at the end of the braking process, when the vehicle speed is reduced below V0, an algorithm of smoothly reducing the regenerative braking force while improving friction braking is adopted in order to improve the comfort of brakingand prevent generation of torque fluctuation caused by excessive low rotation speed of the motor, and braking is gradually transitioned to a pure friction braking mode to finally stop a vehicle.
Owner:刘清河
Method and apparatus for removing cuttings from a deviated wellbore
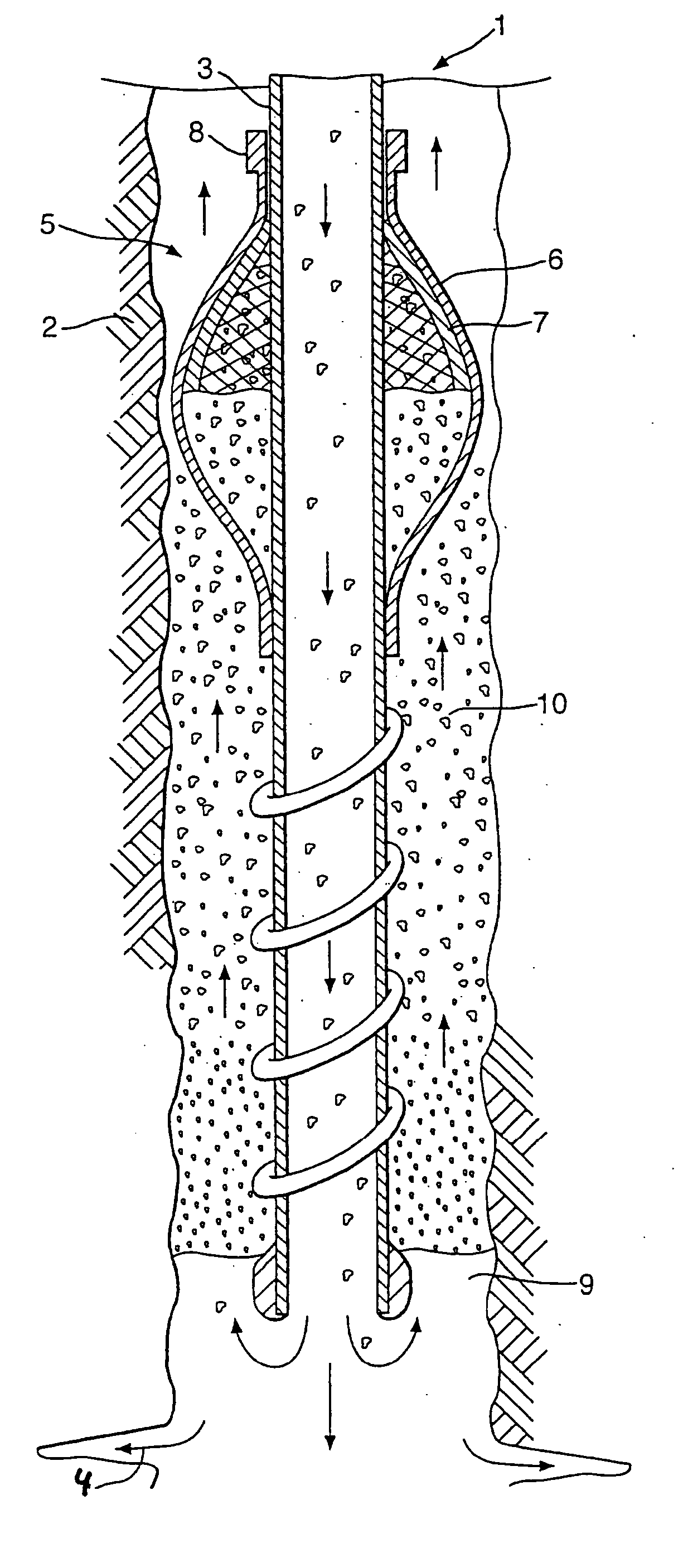
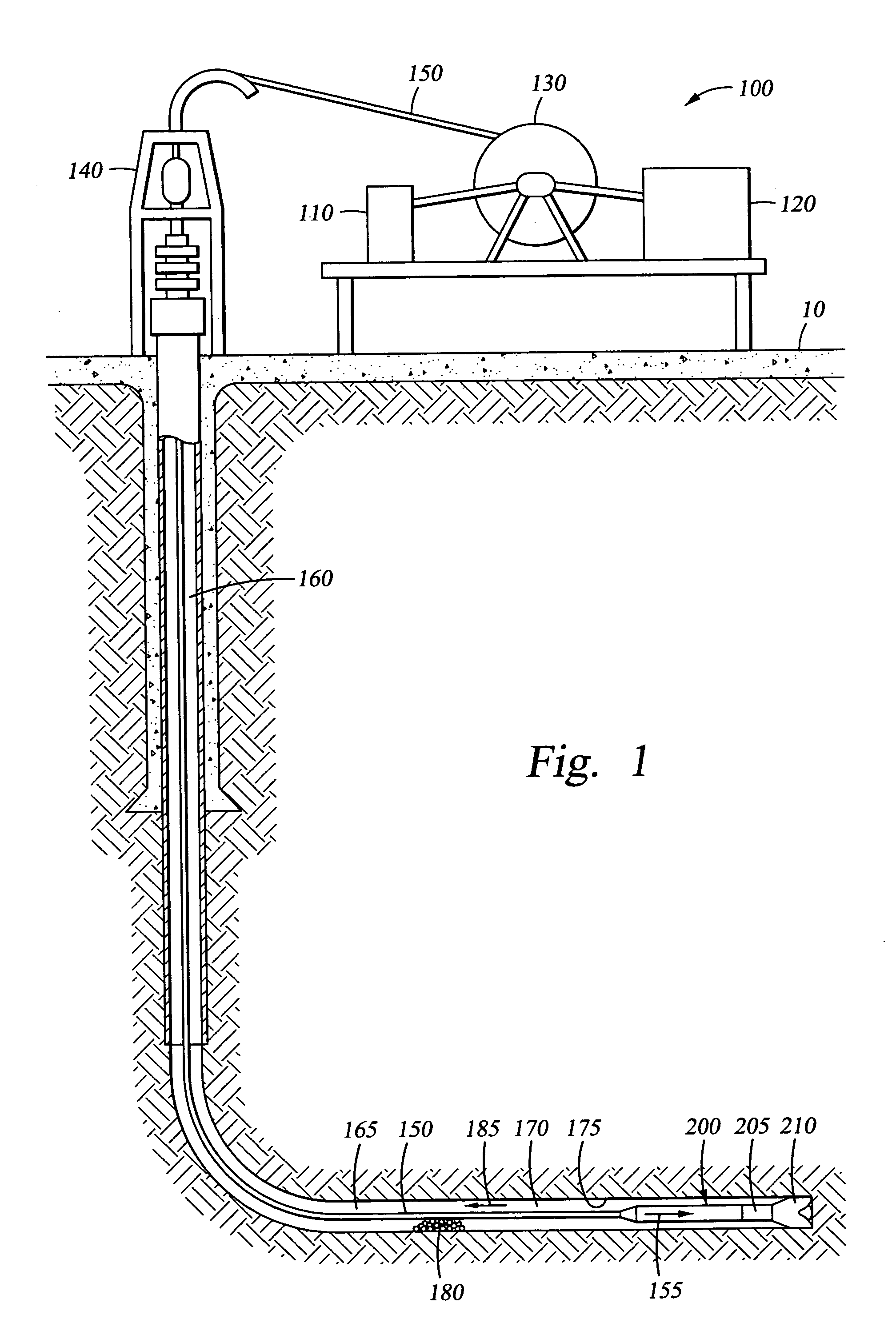
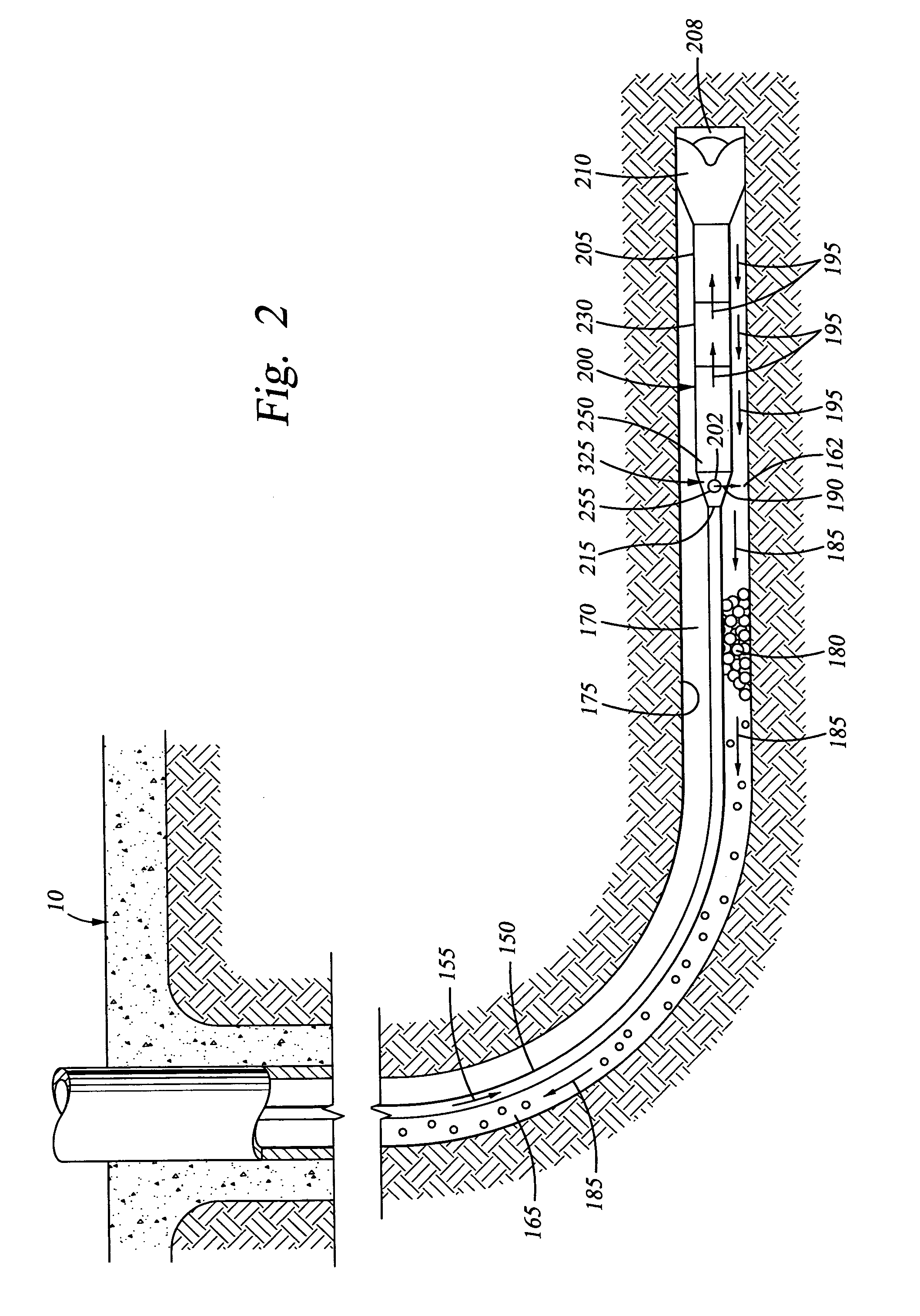
Apparatus and methods for diverting a portion of the drilling fluid that flows into a drilling assembly comprise diverting the drilling fluid into the annulus of a deviated wellbore at a flow rate corresponding to a velocity that is sufficient to transport cuttings to the surface while drilling progresses. The diverted drilling fluid is directed into the annulus at an angle to prevent erosion of the wellbore wall. The flow rate of the diverted drilling fluid is controlled to establish a fixed flow rate, or alternatively, a variable flow rate. Pressure is dissipated and fluid velocity is reduced as the diverted drilling fluid flows between a high fluid pressure within the drilling assembly to a lower pressure in the wellbore annulus.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Fixed Swirl Inducing Blast Liner
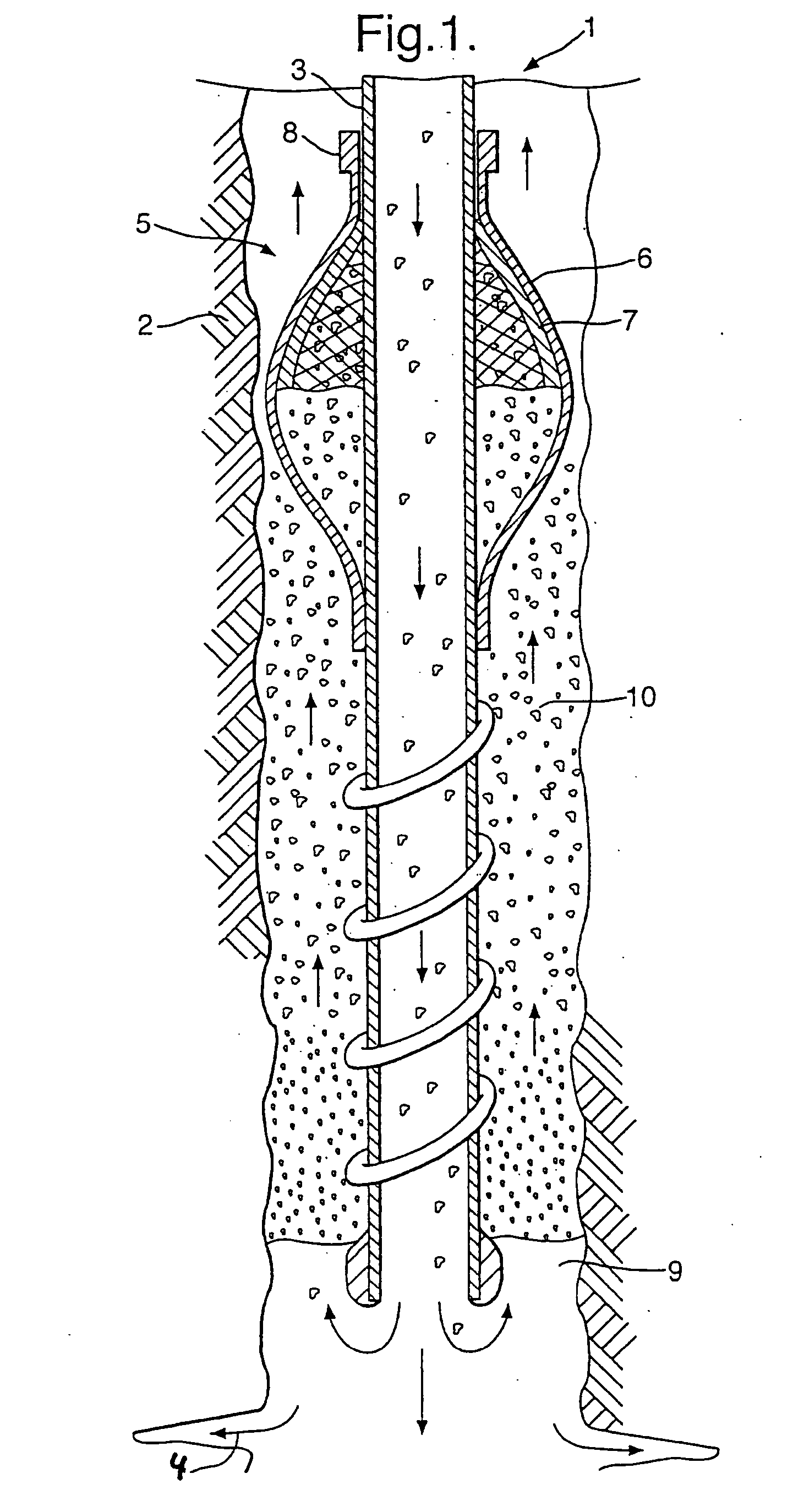
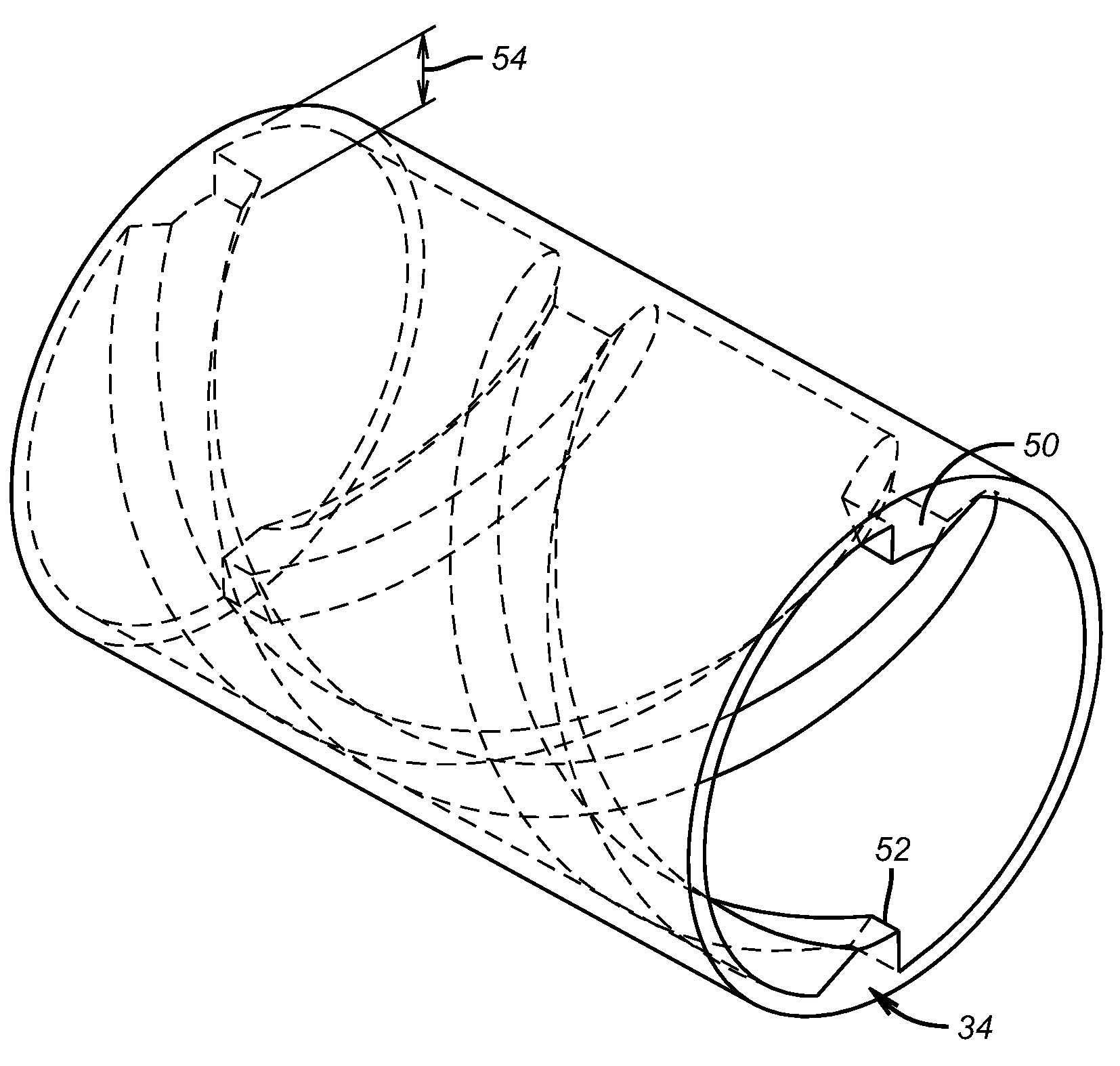
Wear is reduced in abrasive slurry service at an outlet into an annular space defined by the wellbore and around the tool. In a gravel packing application with a crossover, the slurry exits a central passage and goes into an internal annulus in the tool. Turning vanes that make at least one full turn and that have a height at least partially the height of the annular space are there to impart a swirl movement to at least a portion of the slurry stream. The swirling motion has beneficial effects of reducing turbulence which allows a velocity reduction for a comparable output volume. As a result of the lower turbulence leading to the final exit from the tool into the surrounding annulus, the exit ports experience reduced erosion and longer service life.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com