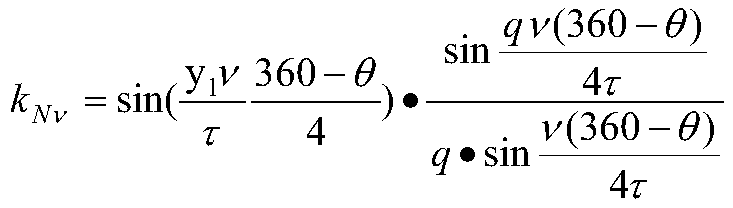Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Improve sinusoidality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Permanent magnet synchronous motor without stator iron core
InactiveCN101783557AReduce volumeReduce weightMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machinesHarmonicClosed loop
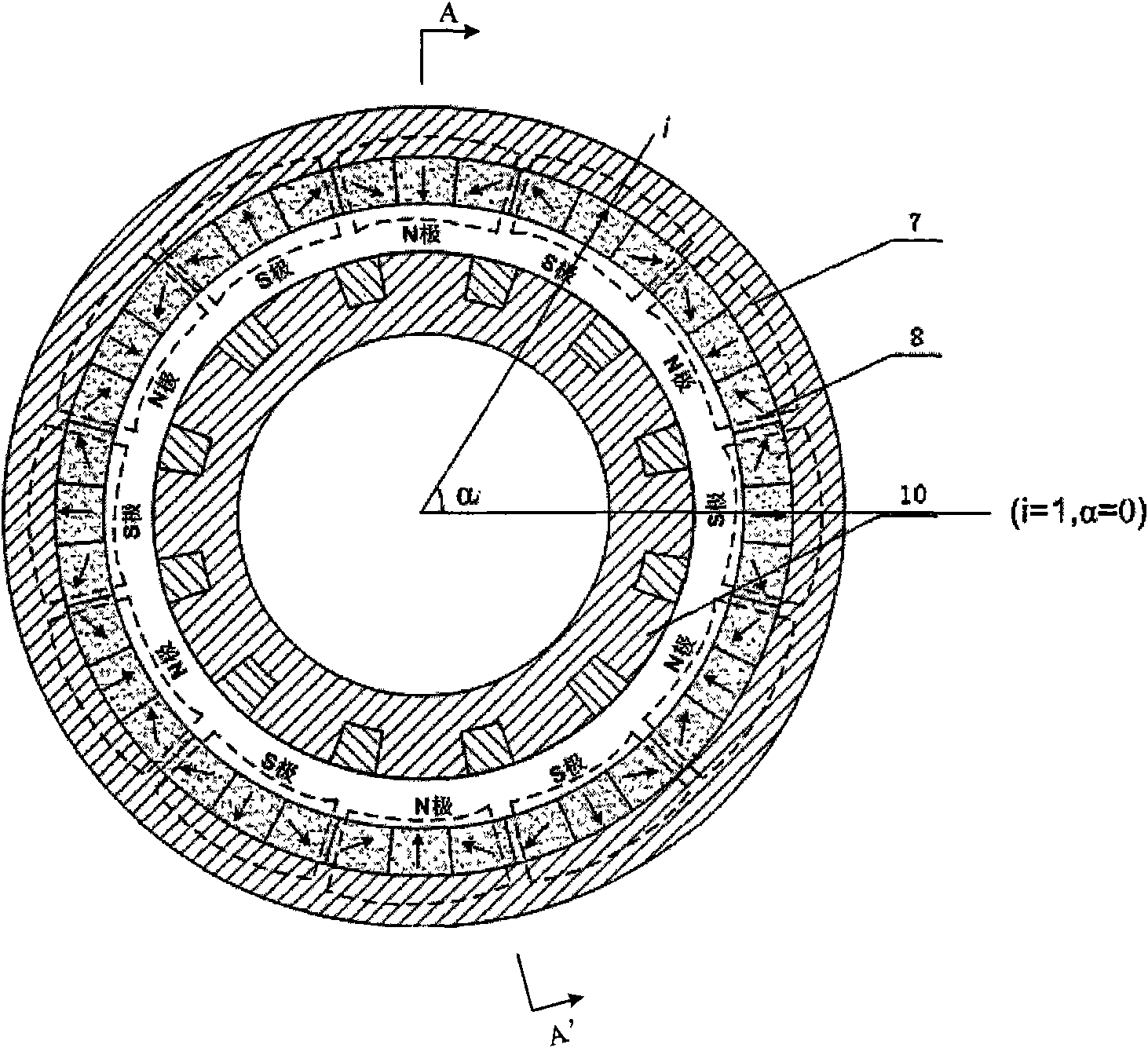
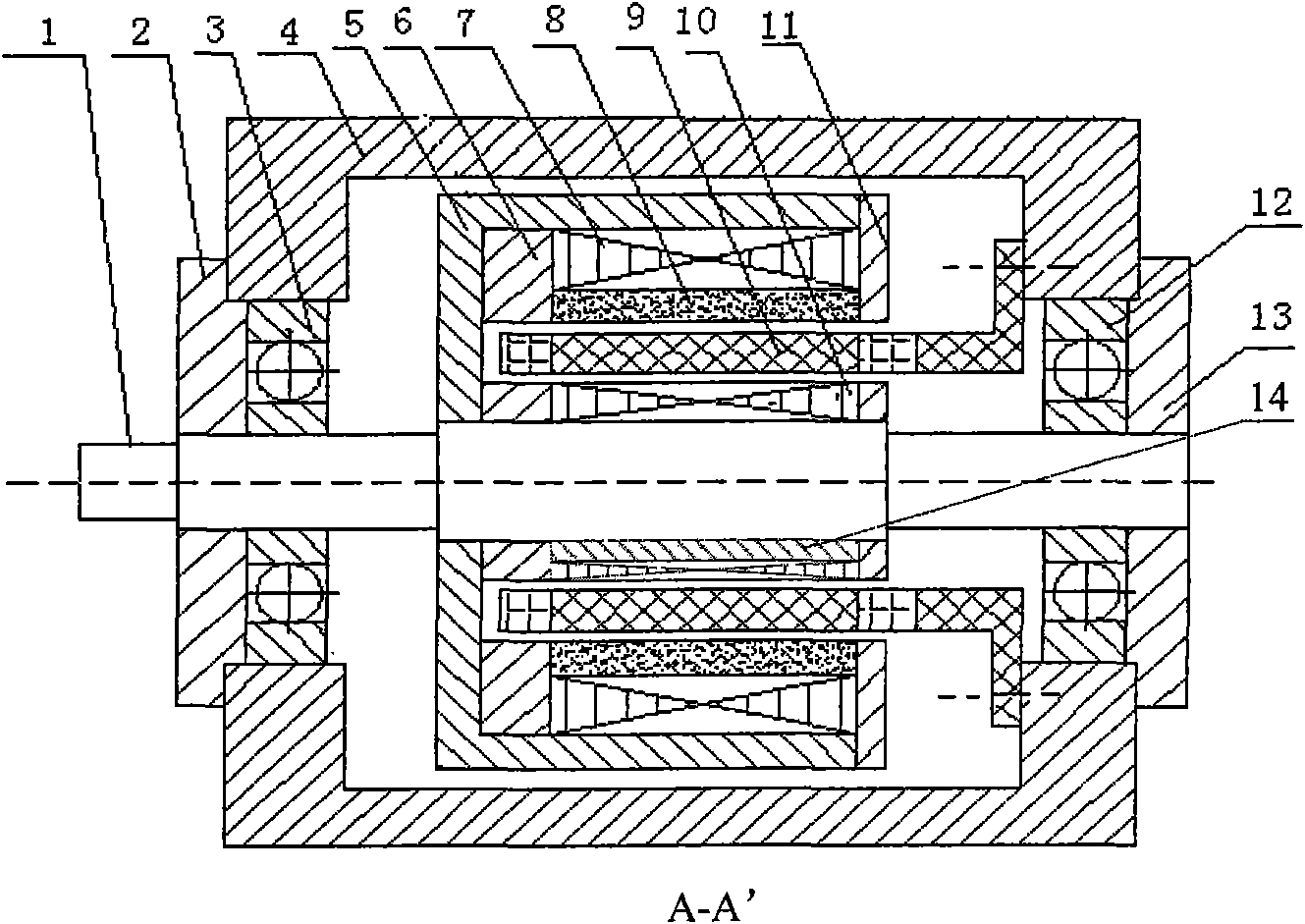
The invention relates to a permanent magnet synchronous motor without a stator iron core, which mainly comprises a rotor shaft, an inner rotor iron core, a magnetic isolation block, a hollow cup stator (including a skeleton and a fractional slot concentrated winding), a Halbach permanent magnet and an outer rotor iron core, wherein the magnetic isolation block is embedded in the inner rotor iron core and forms an inner rotor core component part with the inner rotor iron core, the inner rotor iron core, the outer rotor iron core and the permanent magnet are all connected with the rotor shaft, the Halbach permanent magnet is stuck to the outer rotor iron core, and the hollow cup stator is fixed on a motor shell. The permanent magnetic circuit is formed into a closed loop circuit via the inner rotor iron core, the magnetic air gap, the Halbach permanent magnet and the outer rotor iron core. The invention utilizes the magnetic isolation block to achieve a salient pole structure of the motor so as to realize control by the difference of A-axis and D-axis inductance, the concentrated winding is utilized to weaken harmonic content in winding induced electromotive force and greatly increase the sinusoidal property of the winding induced electromotive force and winding current, so the torque impulse is reduced, and the stationarity of the output torque is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
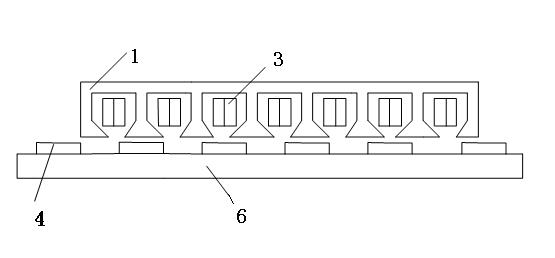
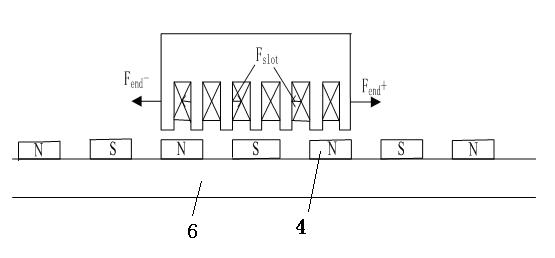
Thrust optimization design method for tubular permanent magnet synchronous linear motor
InactiveCN102013785AHigh force densityConvenient lengthPropulsion systemsPhase differenceFinite element method
The invention discloses a thrust optimization design method for a tubular permanent magnet synchronous linear motor, which comprises: firstly, building a solid model of the motor and setting run option parameters including the length of the primary iron core of the primary iron core stator of the motor; secondly, resolving the run option parameters by using a finite element method and building a finite element geometrical model; thirdly, calculating the optimization phase difference between the end forces at the two ends of the primary iron core stator according to a formula, and regulating the length of the primary iron core to obtain the optimal length of the primary iron core, which corresponds to the optimization phase difference; and finally, obtaining the tubular permanent magnet synchronous linear motor with the smallest thrust fluctuation through magnetization by the optimal length of the primary iron core, the half-open, half-closed, round-bottom grooved tooth-groove structure and a Halbach structure. In the invention, the thrust fluctuation is minimized by relieving the influences of magnetic drag produced by an end effect and a tooth-groove effect on the thrust fluctuation; the method is simple and effective; and the calculation accuracy is high, and the motor can serve as both an electrical motor and a generator.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
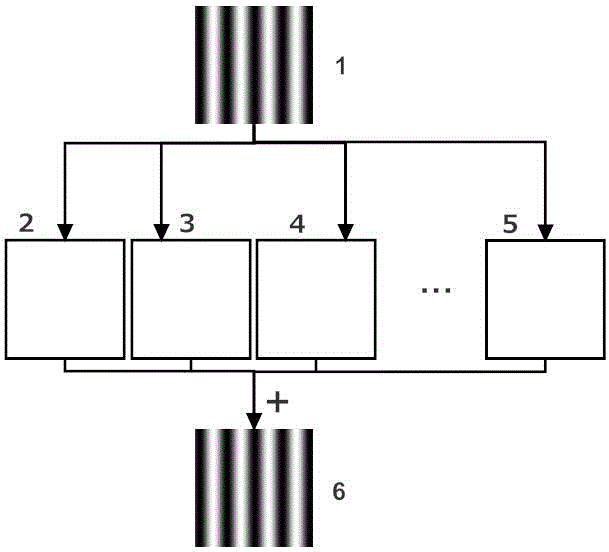
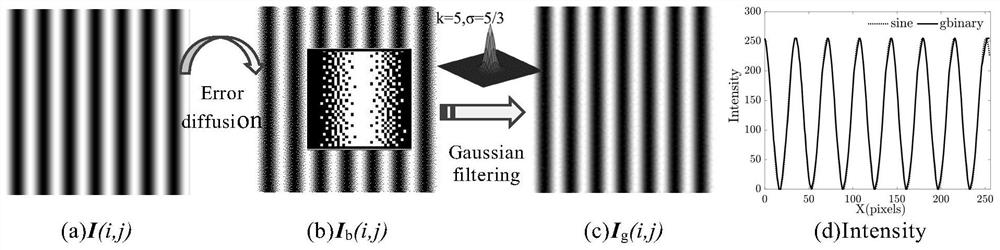
Method for generating light field with sine structure by means of space-time binary encoding
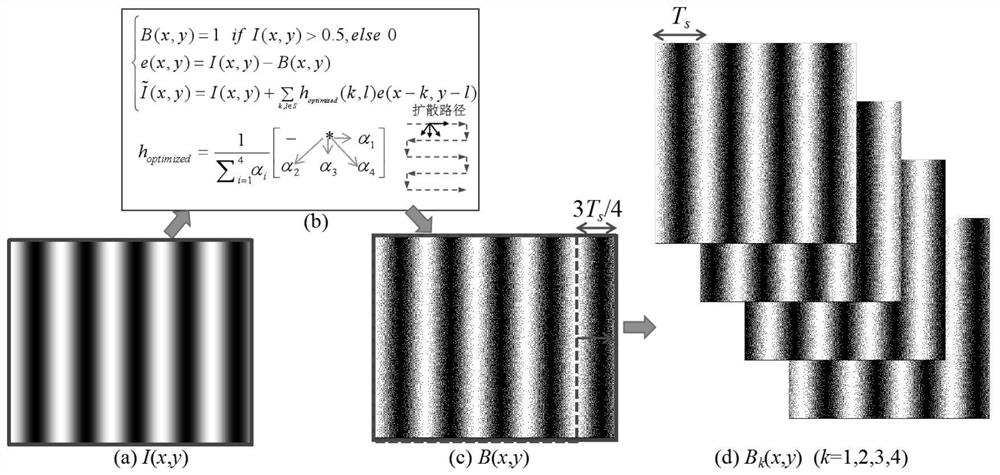
ActiveCN104567730AImprove sinusoidalityHigh-speed and high-precision 3D surface shape measurementUsing optical meansNon linear responseGray level
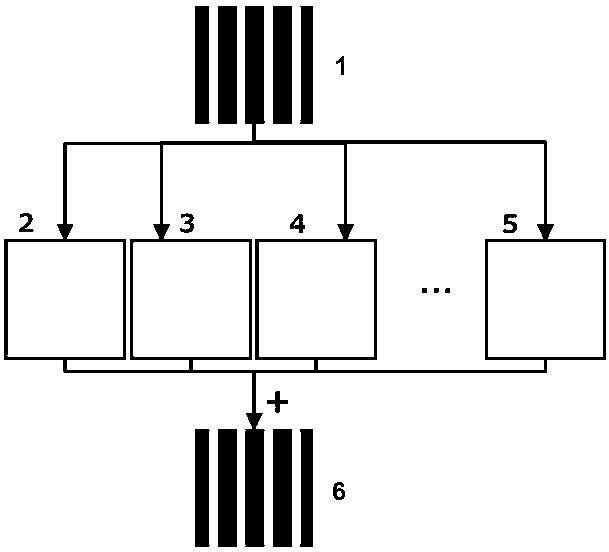
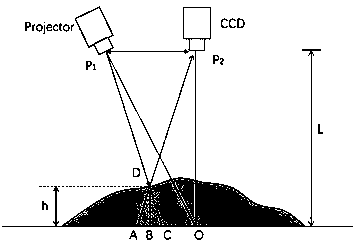
The invention belongs to the three-dimensional sensing technology and discloses a method for generating a light field with a sine structure by means of space-time binary encoding. According to the method, a standard sine fringe pattern 1 generated by a computer is equally divided into 2<n> (n>=2) sections according to gray-level distribution, then time and space encoding is conducted on each section by means of two-dimensional error diffusion to obtain 2<n> (n>=2) binary fringe patterns (2, 3, 4, ..., 5), and then linear superposition is conducted on the binary fringe patterns after the binary fringe patterns are projected and acquired through an imaging system, so that a high-quality sine fringe 6 is obtained. The projected binary fringe patterns are not affected by the non-linear response of a digital projector, the high-speed binary pattern switching function of the digital projector is fully utilized, and the speed and precision of three-dimensional surface measurement are improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
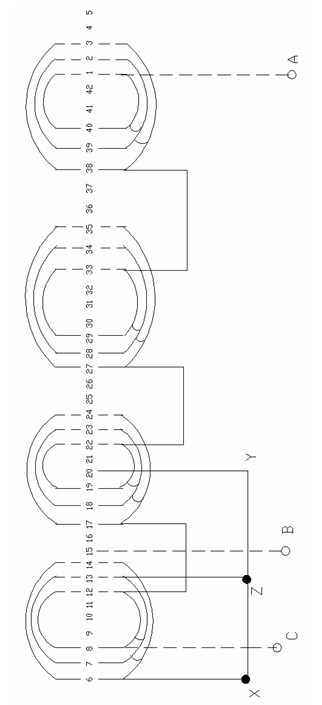
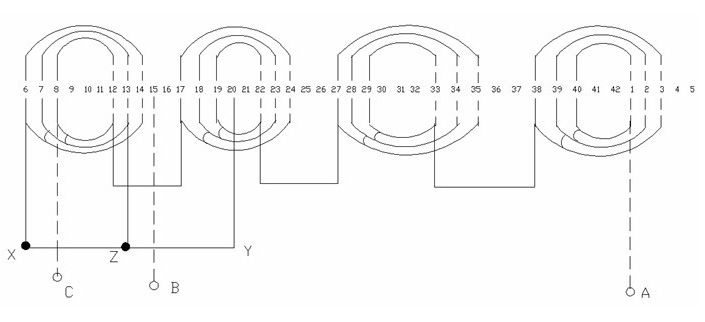
Mixed concentric single and two-layer winding for servo permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN101984540AImprove machining accuracyLess total harmonic contentSynchronous machine detailsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionHarmonicPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention relates to a mixed concentric single and two-layer winding for a servo permanent magnet synchronous motor. A motor stator winding is a single and two-layer winding formed by mixing two concentric windings, wherein the number of turns of the coil of each of the two concentric windings is 3, and the pitches and the numbers of turns of the two concentric windings are different. Compared with the short-pitch two-layer winding for the foreign similar motor, the formed mixed concentric single and two-layer winding has the advantages that the fundamental wave winding coefficient is improved by 2.08%, the phase belt harmonic waves are reduced by 45%, the magnetic potential sine property is better, the heating is small, the temperature rise is low, the vibration noise is small, the torque pulsation is small, the insulation between groove layers is reduced by 28.59%, the cost is reduced, the efficiency is improved, the operating quality of the motor is improved, and the machining precision is improved.
Owner:TELLHOW SCI TECH CO LTD
Built-in permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN108923560ASimple production processImprove structural strengthMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet motorConductor Coil
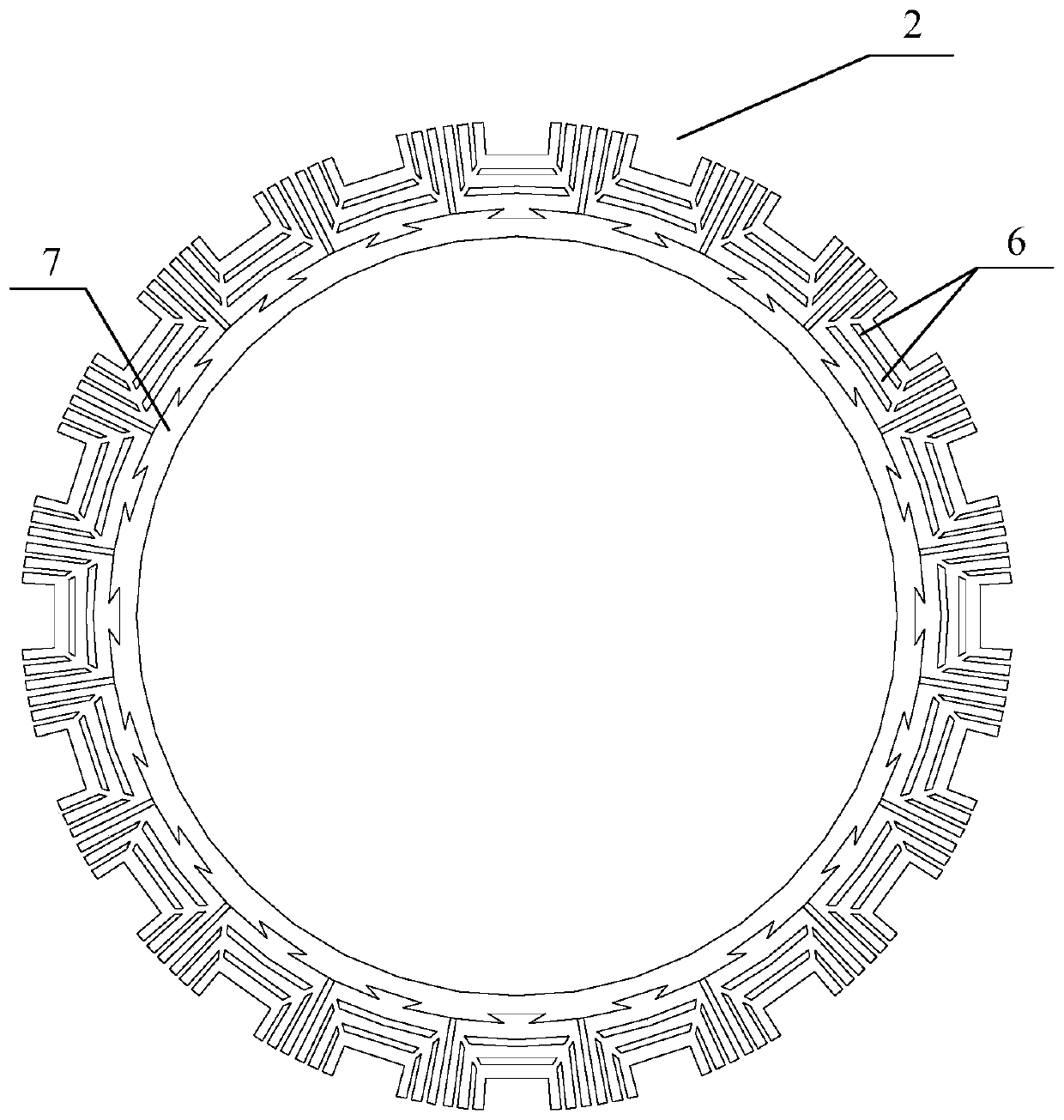
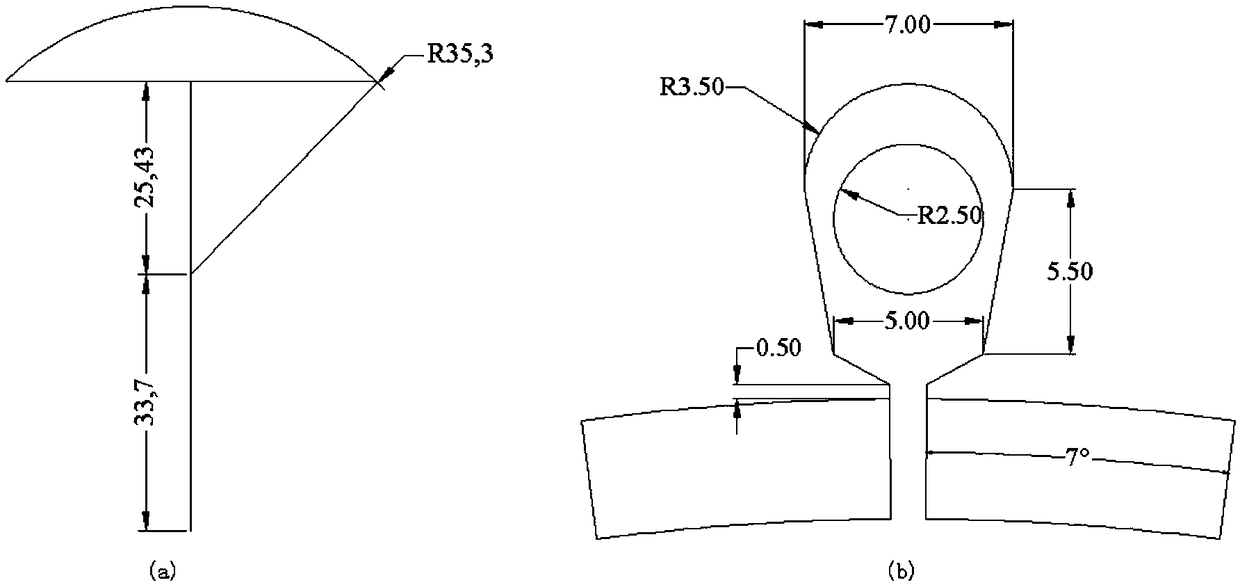
The invention relates to the field of permanent magnet motors, and discloses a built-in permanent magnet motor. The built-in permanent magnet motor comprises a case, a regular polygonal stator iron core, an asymmetric hybrid rotor iron core, permanent magnets, a shaft, windings and insulating frames. The regular polygonal stator iron core is defined by a plurality of T-shaped tooth connection yokes. The contact part of the regular polygonal stator iron core and the case forms a contact area, and a gap between the regular polygonal stator iron core and the case forms a filling area. The asymmetric hybrid rotor iron core comprises a shaft sleeve, a shaft hole, a fan area, connecting bridges and supporting protrusions and contains full-connecting-bridge-type laminations and a half-connecting-bridge-type lamination. The full-connecting-bridge-type laminations are located at the two ends of the asymmetric hybrid rotor iron core, and the half-connecting-bridge-type lamination is clamped by the full-connecting-bridge-type laminations in a wrapped mode in the axial direction. Tooth parts of all the T-shaped tooth connection yokes are wrapped with the insulating frames. The windings are wound around the insulating frames. According to the built-in permanent magnet motor, the production technology of the motor can be simplified, and the structural strength of the motor can also be improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG WELLING ELECTRIC MACHINE MFG
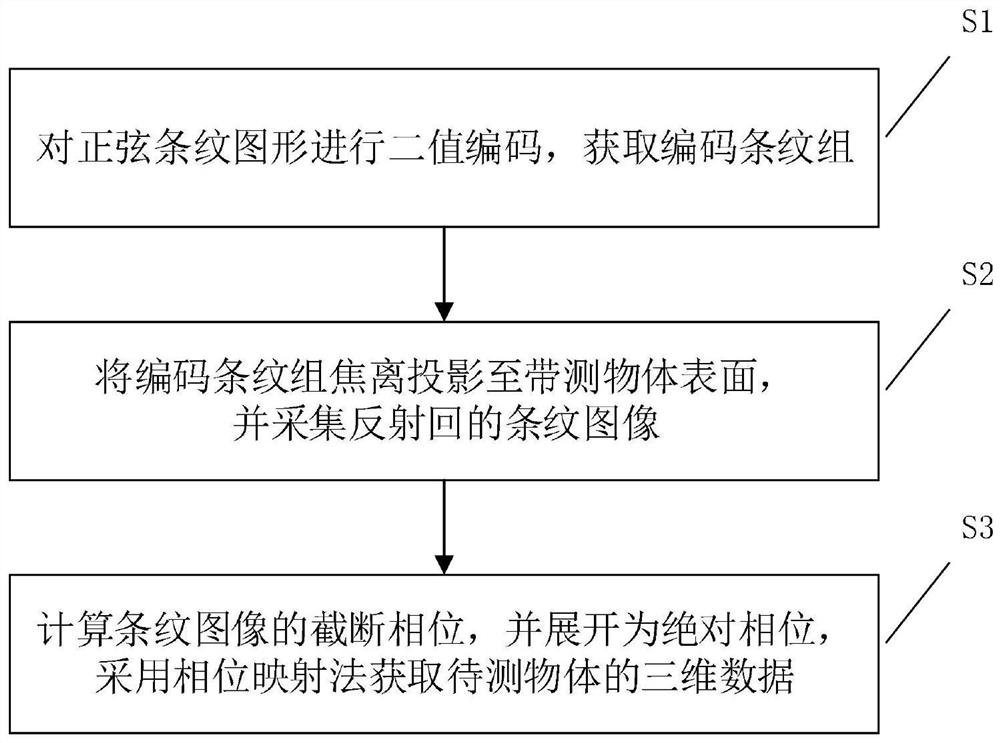
Three-dimensional measurement method based on binary coding and electronic equipment
ActiveCN113358065AImprove sinusoidalityLow species errorUsing optical meansAlgorithmProjection image
The invention relates to the field of three-dimensional measurement, in particular to a three-dimensional measurement method based on binary coding and electronic equipment. According to the invention, binary coding is carried out on the sine fringe image through the error diffusion algorithm, the sine property of the projection image is improved, the fringe group is coded by using the out-of-focus projection, and finally, the collected fringe image reflected by the object to be measured is processed to obtain the three-dimensional data of the object to be measured. Due to the fact that the projection image adopts binary coding and only has two gray values of 0-1, the digital projector is not influenced by nonlinearity, and high-speed and high-precision three-dimensional surface shape measurement is achieved under the limitation of limited frame frequency (120Hz).
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Ultrahigh-power servomotor
InactiveCN104682647AIncreased winding factorSmall positioning torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsShortest distanceElectric machine
The invention discloses an ultrahigh-power servomotor, which belongs to the field of servomotors. The ultrahigh-power servomotor comprises a stator and a rotor; the rotor is located in the stator; the central axis of the stator is superposed with the central axis of the rotor; a double-layer winding is wound in stator slots on the stator, so that the electromotive force of the motor is close to the sine-shaped winding; the distribution pattern of the winding on the stator is short-distance distribution; the rotor comprises a rotor shaft and steel magnets; the steel magnets are fixed on the periphery of the rotor shaft; the rotor shaft at which the steel magnets are fixed is of a non-cylindrical structure; the steel magnets are non-uniform-thickness steel magnets; the cross section of each steel magnet is shaped like a reaphook, and the magnetization method is parallel magnetization. The sinusoidality of the electromotive force of the ultrahigh-power servomotor disclosed by the invention is high, and the ultrahigh-power servomotor can realize low inertia, high rotational speed, short-time peak overload and other performance indexes under the condition of high specific power.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF PRECISE MECHATRONICS CONTROLS +1
High-power-density hub motor structure
ActiveCN113131700AReduce copper lossIncrease torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machinePower density
The invention discloses a high-power-density hub motor structure. The high-power-density hub motor structure comprises an outer rotor, a stator, an inner rotor and a hub which are coaxially arranged, the outer rotor and the inner rotor are connected through a fixing support, the outer rotor comprises an outer rotor iron core and a plurality of V-shaped magnetic steel grooves evenly formed in the outer rotor iron core in the circumferential direction, and a linear magnetic steel groove is formed between every two adjacent V-shaped magnetic steel grooves; a permanent magnet is embedded in each magnetic steel groove, the periphery of the outer rotor iron core is fixed with a hub; inner stator teeth and outer stator teeth are arranged on the stator, and an inner stator slot and an outer stator slot are respectively arranged between the adjacent inner stator teeth and between the adjacent outer stator teeth; the inner stator slot and the outer stator slot are respectively provided with two set of concentrated windings, the two sets of concentrated windings are connected in series; and the end part of each inner stator tooth and the end part of each outer stator tooth are each provided with at least one small slot, and therefore, a plurality of inner modulation teeth and outer modulation teeth can be formed. According to the high-power-density hub motor structure of the invention, the output torque and the power density of the motor can be improved under the condition that the stack length and the outer diameter of the hub are not changed.
Owner:台铃科技(江苏)股份有限公司
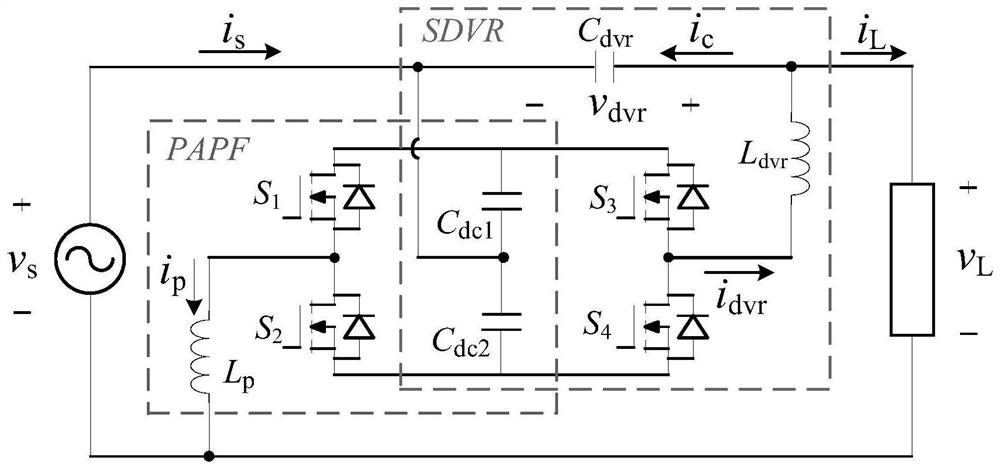
Single-phase UPQC voltage harmonic control method
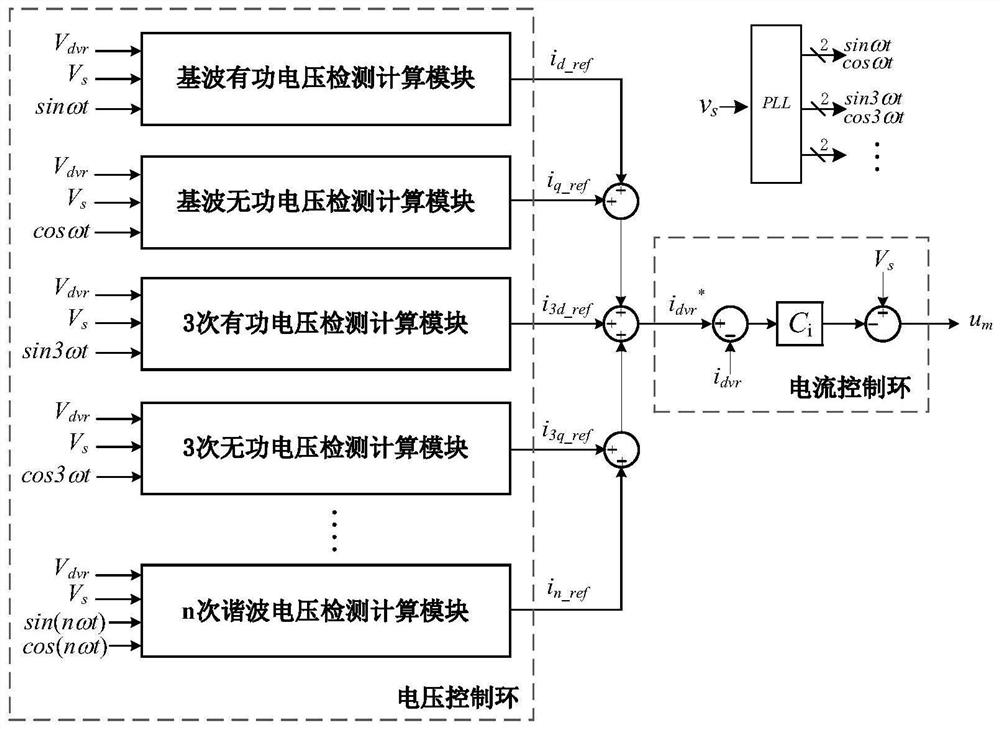
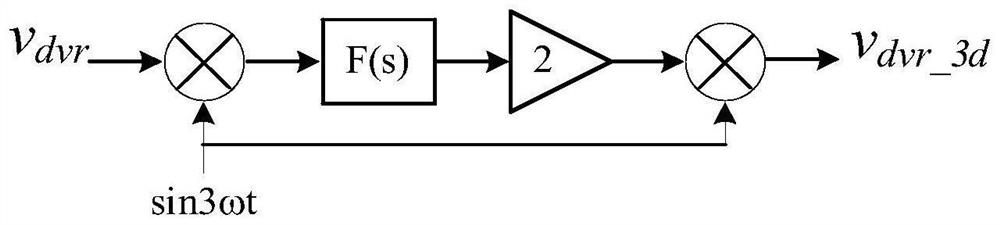
PendingCN114566965AReduce harmonic contentSimple control algorithmReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationAc network voltage adjustmentPower qualityControl engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric energy quality control, and particularly relates to a single-phase UPQC voltage harmonic control method. According to the invention, the harmonic component in the compensation voltage can be compensated, the control algorithm is simple and clear, the realization difficulty is low, the compensation effect on each harmonic is obvious, and the harmonic content of the compensation voltage and the load voltage is effectively reduced. According to the invention, reactive power and each harmonic wave in the compensation voltage can be compensated in a targeted manner; the control method is simple and clear, low in implementation difficulty and good in dynamic performance; the compensation effect is good, the sinusoidal property of the compensation voltage can be remarkably improved, and the UPQC system performance is improved; the method can enhance the stability and reliability of UPQC system compensation, and is suitable for various left-to-right serial UPQC topological structures.
Owner:GUANGXI COLLEGE OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
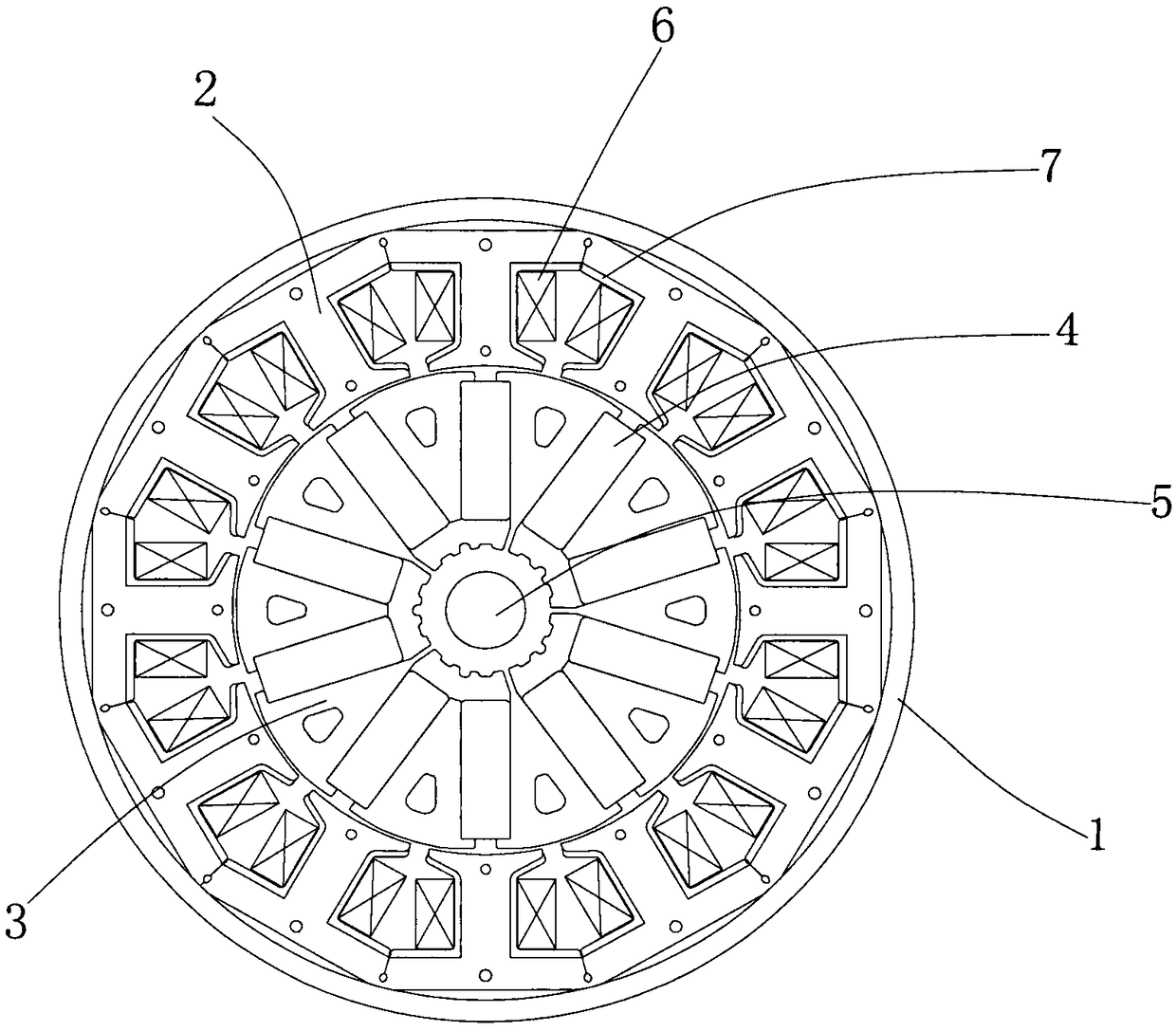
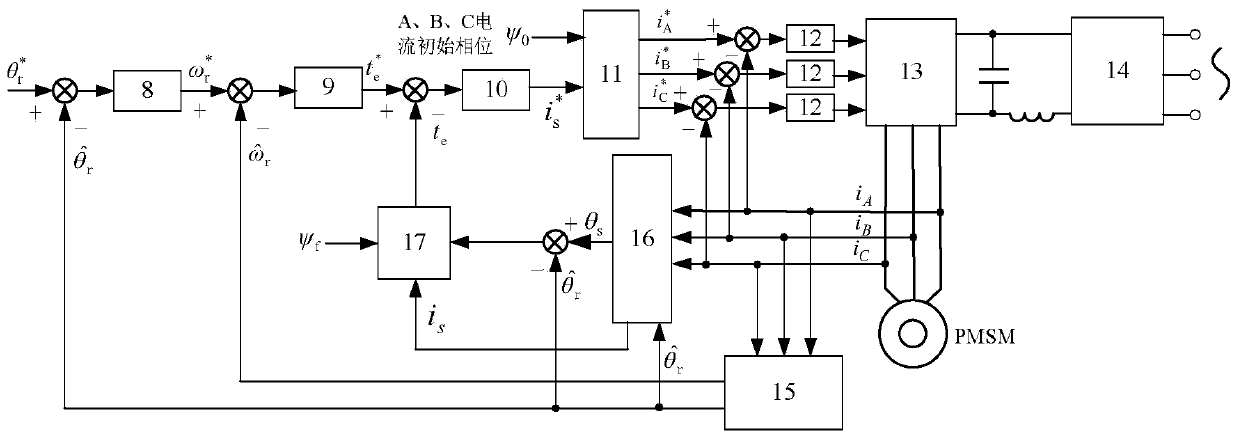
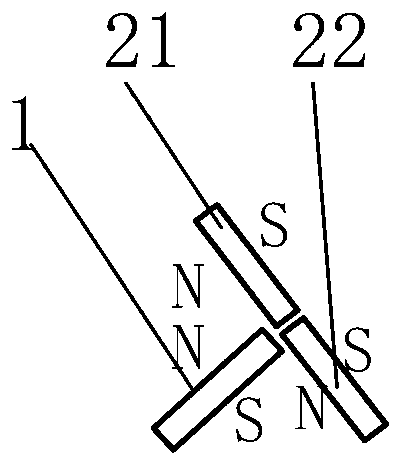
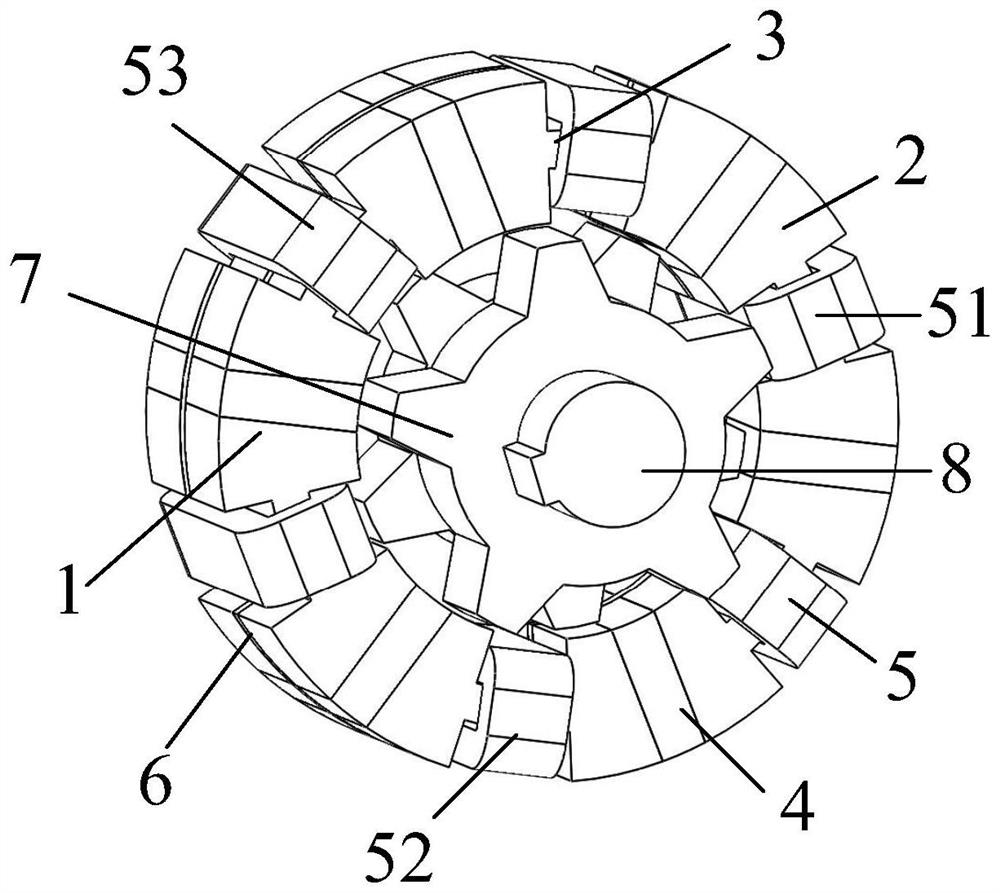
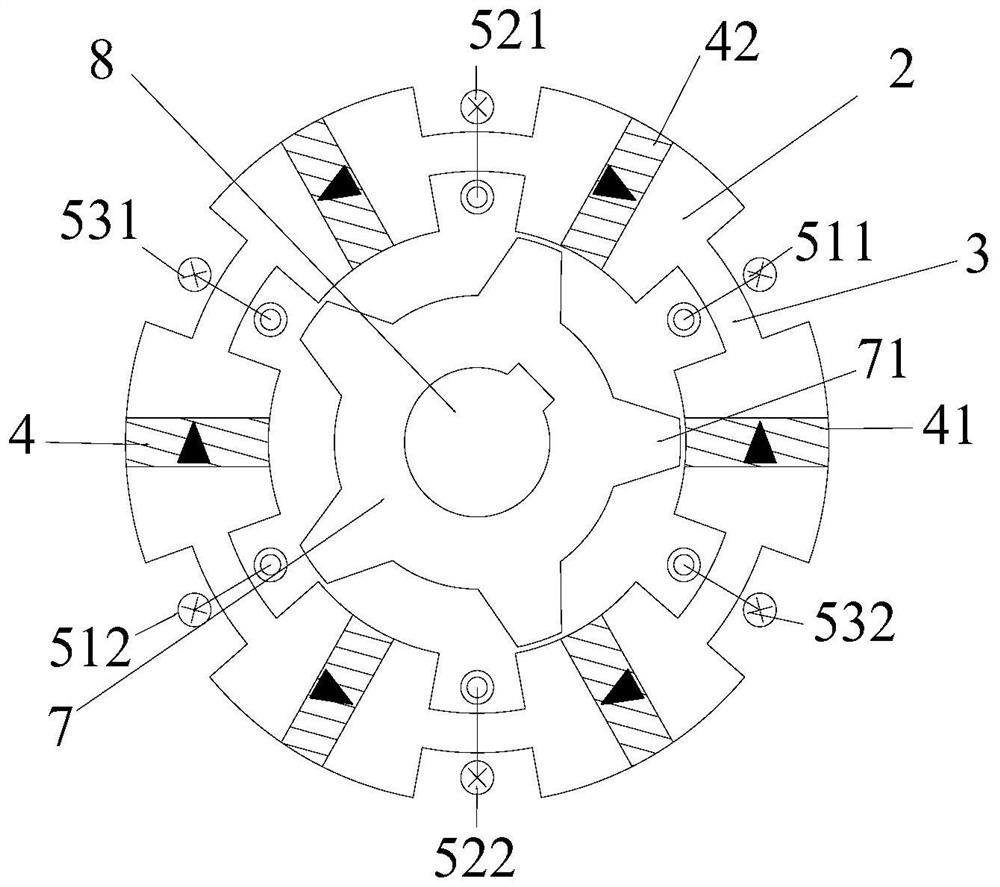
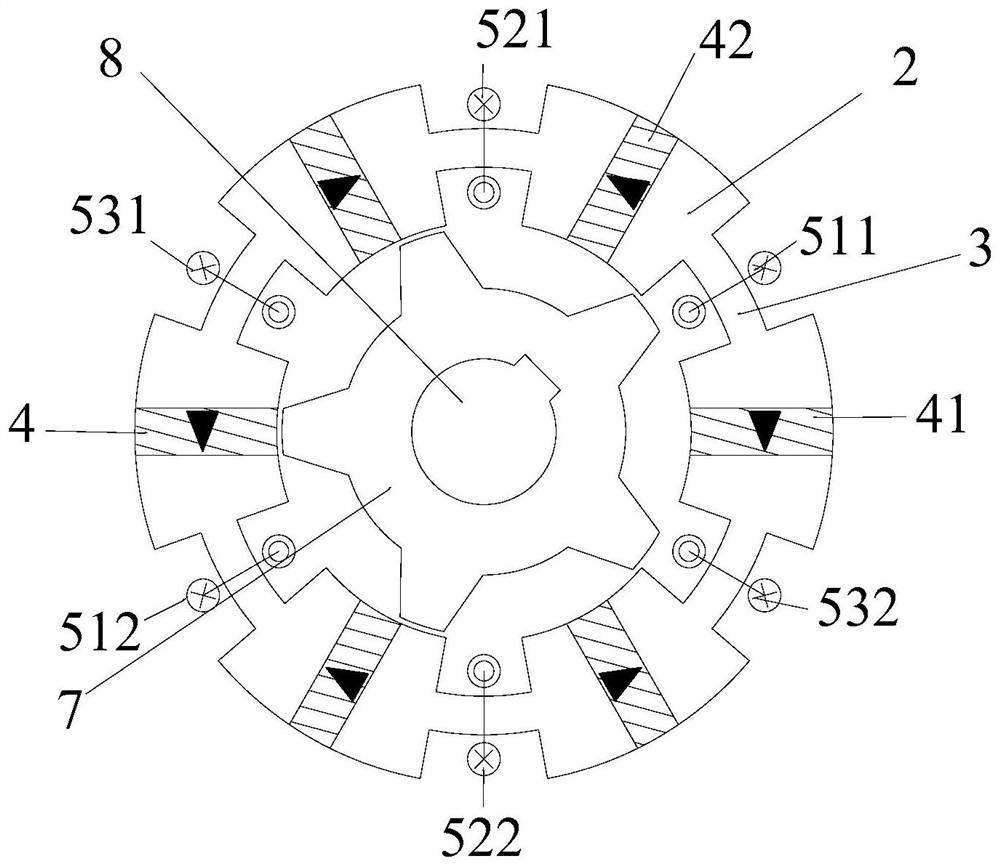
Permanent magnet/reluctance dual-rotor low-speed and high-torque synchronous motor and control system thereof
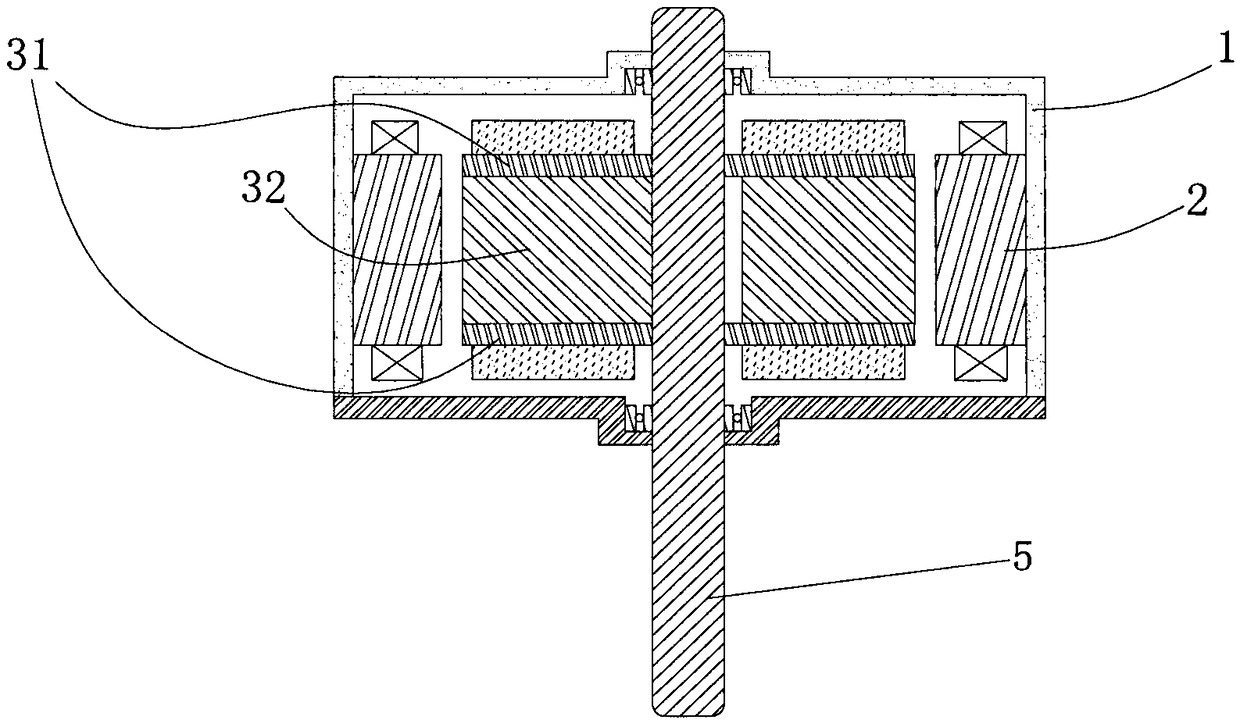
PendingCN109861477AStable structureIncreased torque densityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlSynchronous motorControl vector
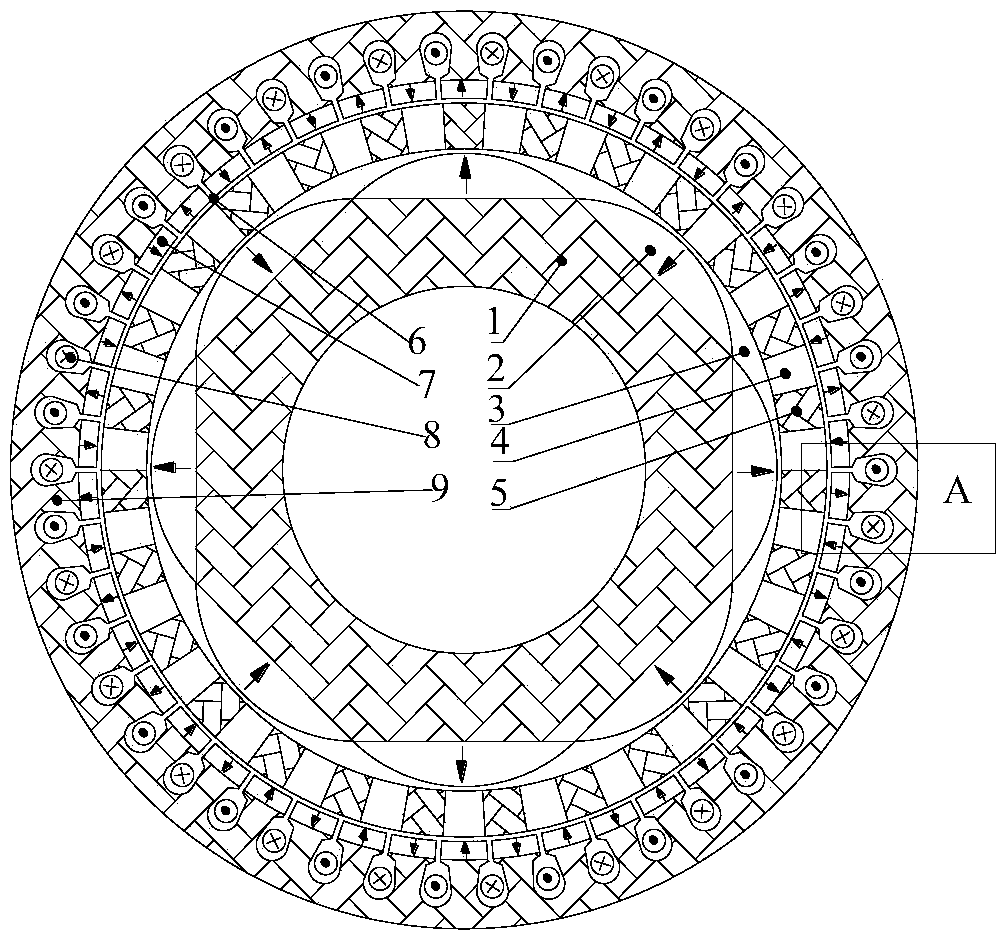
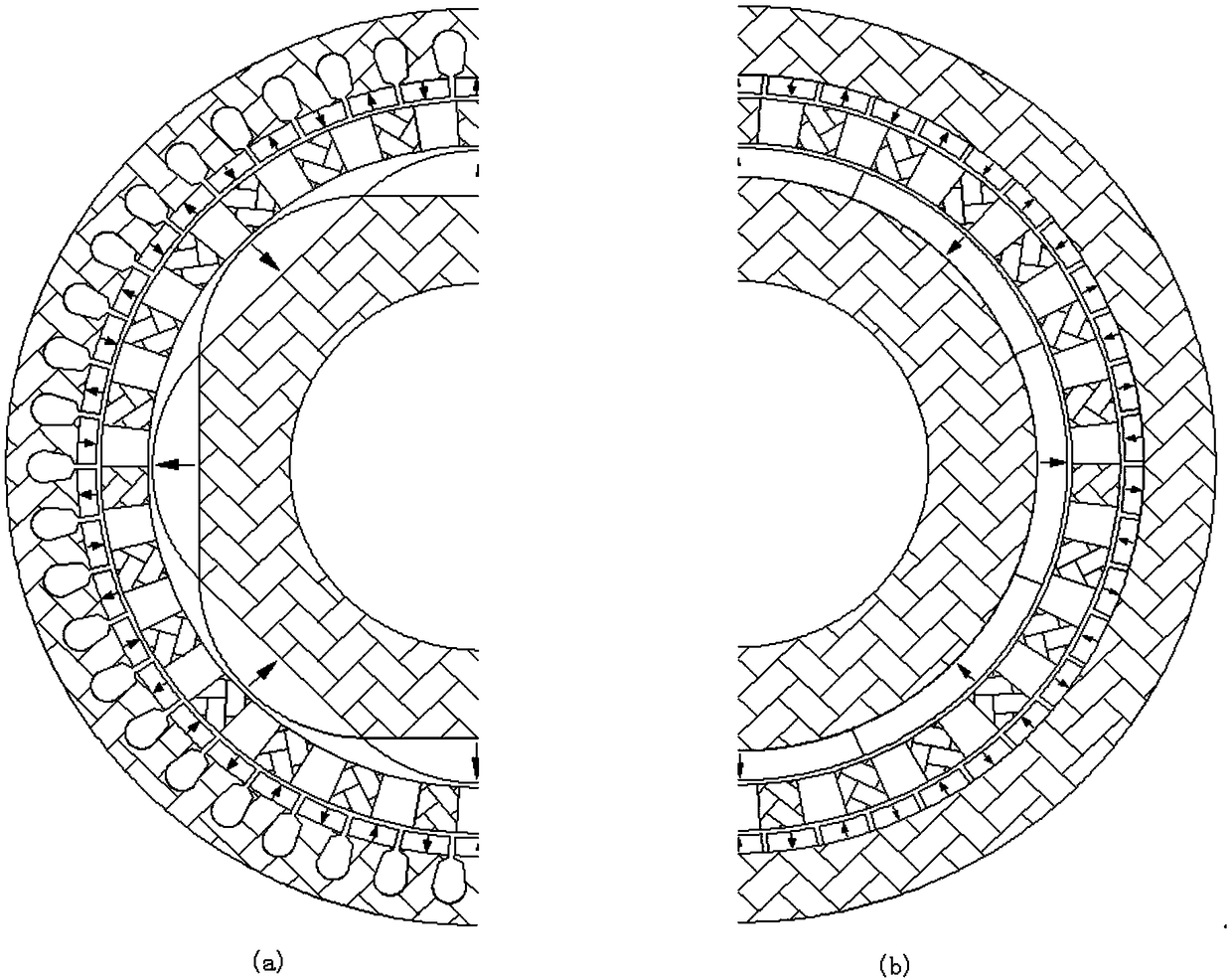
The present invention provides a permanent magnet / reluctance dual-rotor low-speed and high-torque synchronous motor and a control system thereof. The synchronous motor is mainly formed by an outer rotor (1), an inner rotor (2) and a stator (3). The stator (3) is arranged between the outer rotor (1) and the inner rotor (2). The method estimates the position of a reluctance rotor to obtain the position of the whole rotor to achieve sensorless control. The provided sensorless vector control method does not need coordinate transformation, is simple in structure and can overcome the problems of thecomplexity of the vector control and the high dependence on the motor parameters.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Magnetic gear device with improved transmission stability
InactiveCN108712056AImprove transmission stabilityReduce torque ripplePermanent-magnet clutches/brakesTorque densityConductor Coil
The invention discloses a magnetic gear device with improved transmission stability. The magnetic gear device comprises an inner rotor, a magnetism-adjusting ring and an outer stator which are arranged coaxially from inside to outside, wherein an inner-layer air gap exists between the inner stator and the magnetism-adjusting ring; an outer-layer air gap exists between the magnetism-adjusting ringand the outer stator; the inner stator comprises an inner yoke and an inner permanent magnet; the inner permanent magnet is attached to the surface of the inner yoke; the outer stator comprises an outer permanent magnet, a coil and an external yoke; the outer permanent magnet comprises a plurality of same permanent magnets; the plurality of permanent magnets constructing the outer permanent magnetare uniformly attached to an inner surface of the outer yoke at equal intervals in a non-eccentrical manner; a slot is formed in a gap between every two permanent magnets on an inner side of the outer yoke; the coil is arranged in the slots to form an exciting winding; both the inner permanent magnet and the outer permanent magnet are magnetized in a radial direction; and during working, the inner rotor and the magnetism-regulating ring rotate along the same direction, the outer stator is fixed, and the coil is electrified. Through adoption of the magnetic gear device, the transmission stability and torque density of the magnetic gear device can be improved, and the device mass is lowered.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
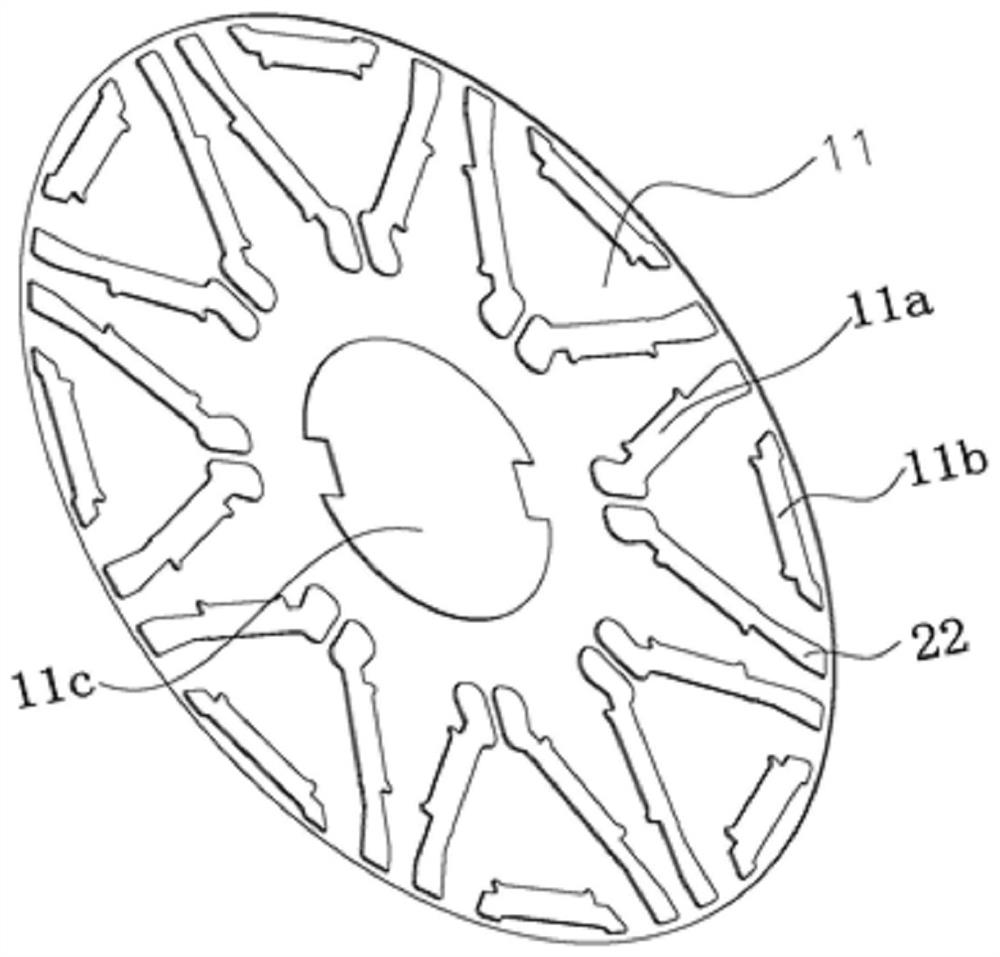
Novel stator winding structure based on axial coreless motor
InactiveCN110994849AHarmonic reductionSimple processWindings conductor shape/form/constructionElectric machineCounter-electromotive force
The invention discloses a novel stator winding structure based on an axial coreless motor, and the structure comprises at least three single coils with the same specification, the at least three single coils are annularly distributed to form a winding, and each single coil of the winding is arranged in an annular non-uniform manner. The novel stator winding structure based on the axial coreless motor can effectively reduce the higher harmonics of counter electromotive force of the motor and can improve the sinusoidal property of counter electromotive force waveforms. The stator winding is simple in process, convenient to assemble and low in cost, the working efficiency of the motor is improved, the cost performance and the flexibility of processing and manufacturing are also improved, andthe mechanical strength and the heat dissipation characteristic are better.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
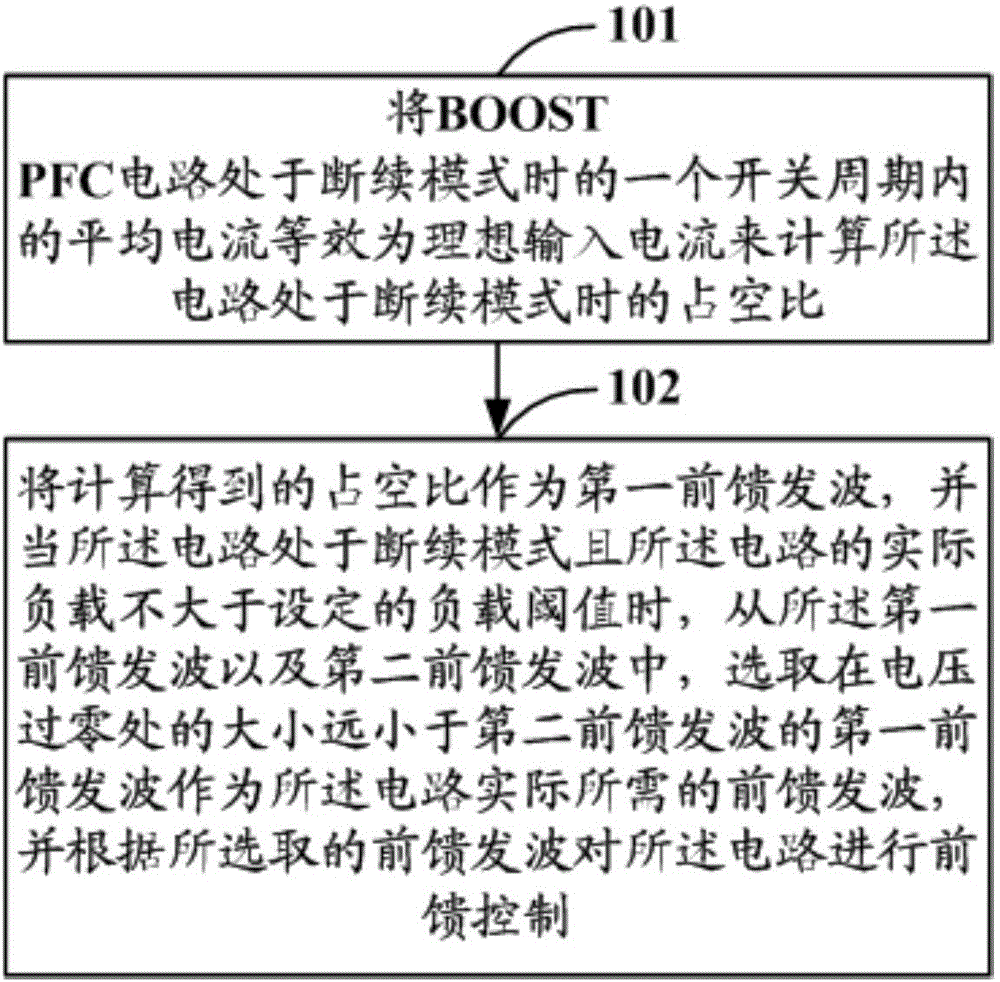
Circuit control method and device
ActiveCN106160449AImprove performanceImprove sinusoidalityEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsHarmonicAverage current
The invention discloses a circuit control method and device. The method includes the steps that the duty ratio of a boost power factor correction circuit in an intermittent mode is calculated with average current equivalence of the boost power factor correction circuit in the intermittent mode in a switching period as ideal input current; the duty ratio serves as a first feed-forward wave; when the circuit is in the intermittent mode and an actual load is not larger than a set load threshold, the first feed-forward wave with the amplitude at the voltage zero-crossing position much smaller than that of a second feed-forward wave is selected as a feed-forward wave of the circuit, feed-forward control is conducted on the circuit according to the selected feed-forward wave, wherein the second feed-forward wave is 1-Uin / UBus, so when the boost power factor correction circuit is in the intermittent mode and the load is small, the feed-forward wave of the circuit is much smaller than 1 at the voltage zero-crossing position, that is, the duty ratio is not full, the voltage of a bus cannot be increased, and the effects of improving the sinusoidal property of current, reducing the input current harmonic content, improving PF and the like can be achieved.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
Hybrid permanent magnet rotor for electric vehicles
ActiveCN109274187AWeaken Distortion EffectImprove sinusoidalityMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesPermanent magnet rotorHigh magnetic field strength
The invention provides a hybrid permanent magnet rotor for an electric vehicle, belonging to the technical field of electric vehicle motors. The rotor is an inner rotor structure, comprising a first permanent magnet, a second permanent magnet, a third permanent magnet, a non-magnetic conductive fixed core, a rotor iron core and a tightening ring, and the rotor iron core is fixed on the periphery of the non-magnetic conductive fixed core; The first permanent magnet, the second permanent magnet and the third permanent magnet are the same in number and even in number, and are combined into a shape. The outer side of the rotor is provided with a tightening ring to prevent deformation of the rotor. Compared with the existing permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor, it saves part of the scarcerare earth permanent magnet, has higher magnetic field strength, higher mechanical strength, effective use of reluctance torque, and higher output power.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Brushless generator without automatic voltage regulator
InactiveCN102810920AEasy maintenanceImprove cooling conditionsMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsFailure rateEngineering
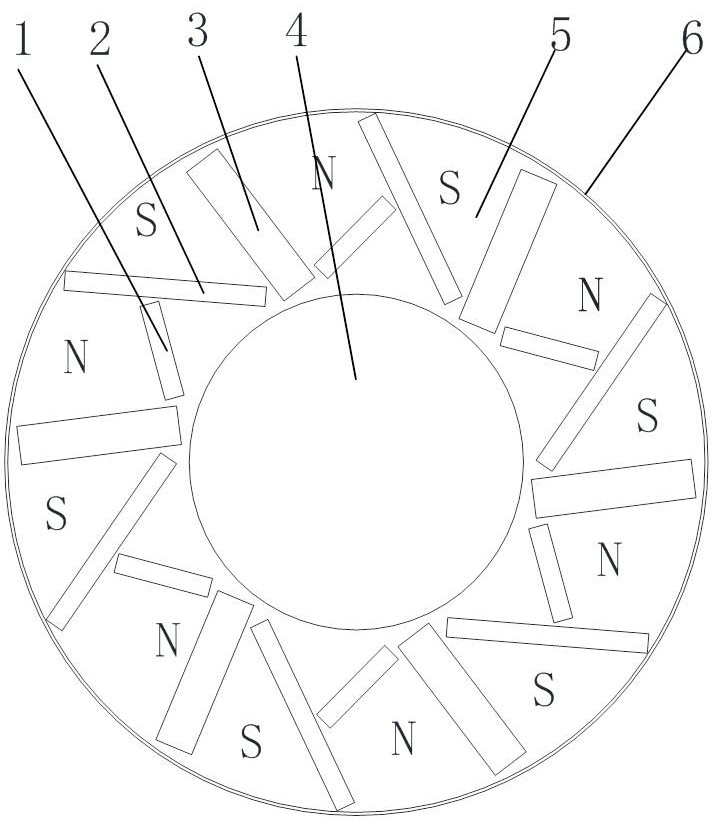
The invention provides a brushless generator without an automatic voltage regulator (AVR). The brushless generator comprises a main unit and an exciter. The main unit comprises a main unit rotor pole lamination. The exciter comprises an exciter stator pole lamination. The main unit rotor pole lamination is symmetrically provided with four permanent magnets. A non-salient pole rotating-armature mode is adopted for the magnetic circuit structure of the exciter stator pole lamination, and a magnetic field winding of the exciter is a three-phase magnetic field winding. The brushless generator is not provided with the AVR, so that cost is reduced, economic benefits are improved, the maintenance of the generator is facilitated, and a failure rate is decreased. In addition, the exciter stator pole lamination and the magnetic field winding are redesigned and reconfigured, so that the radiation area of the winding is enlarged, and a radiation condition is good; and moreover, due to the adoption of a distributed magnetic field winding, the brushless the sinusoid of an air gap magnetic field waveform is high, excitation power is high, an excitation winding is easily fixed, mechanical strength is strong, and a model machine is detected to have ideal effects.
Owner:福建一华电机有限公司
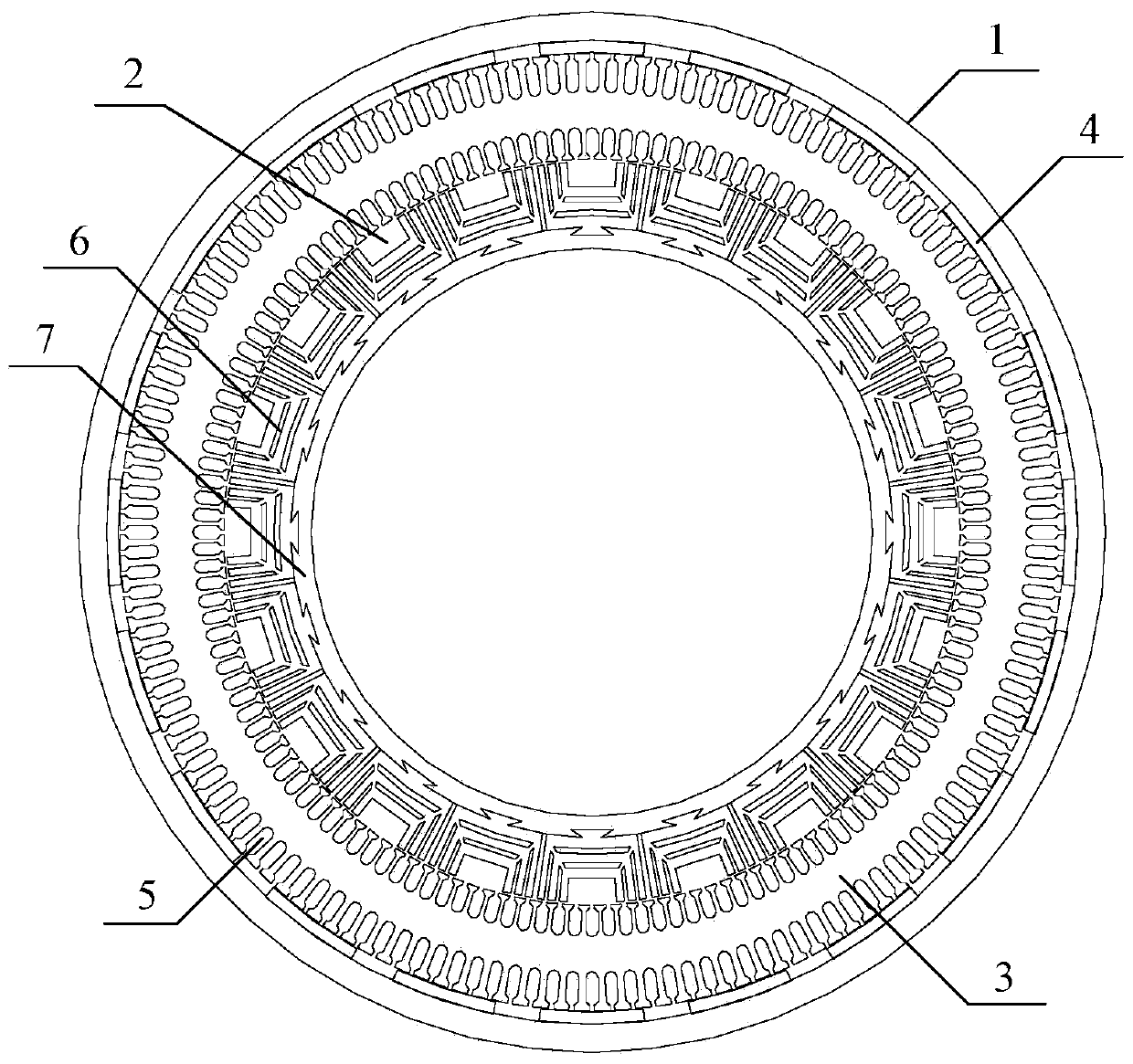
Permanent magnet motor
PendingCN113346643ASimple production processImprove structural strengthMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineBridge type
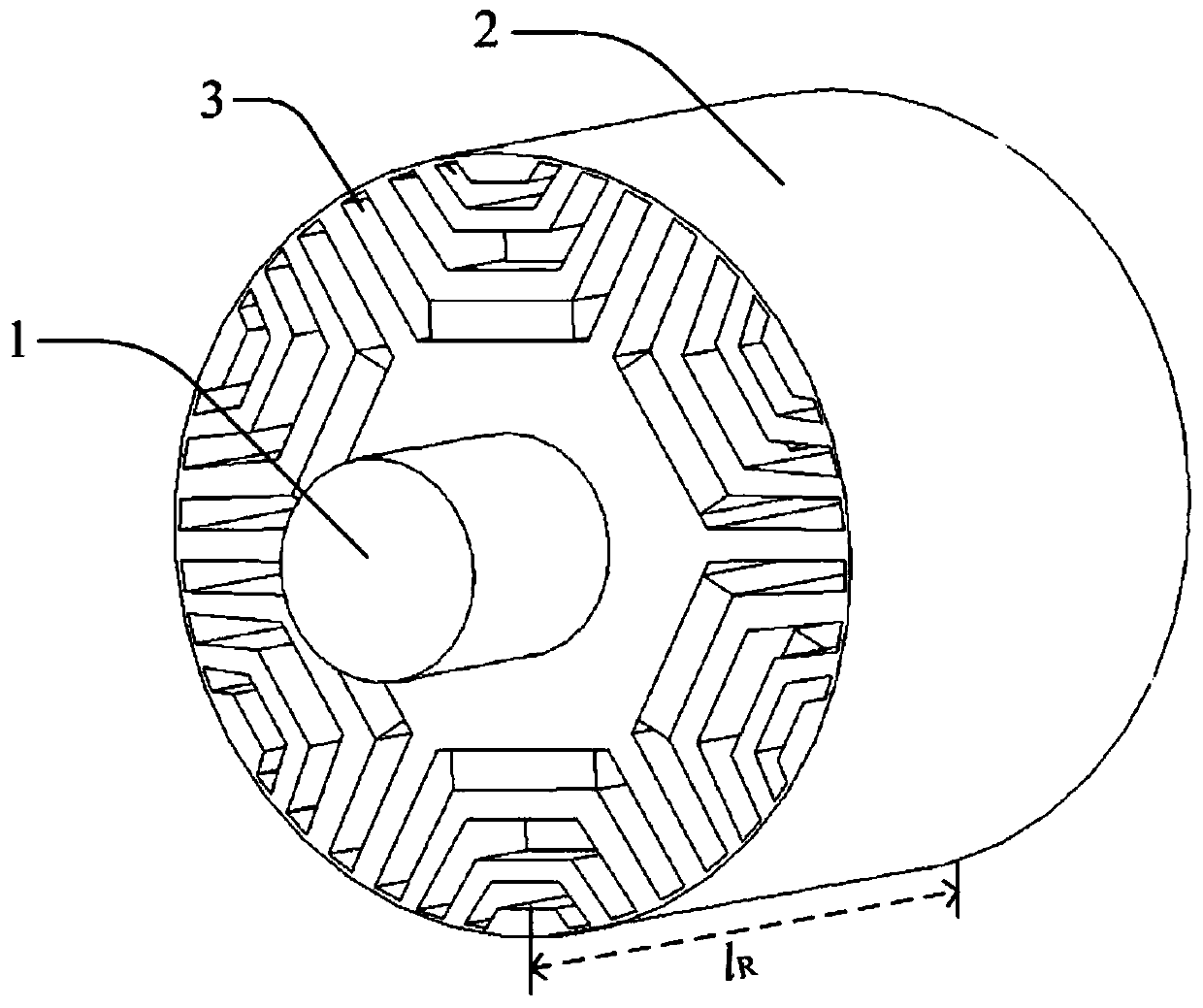
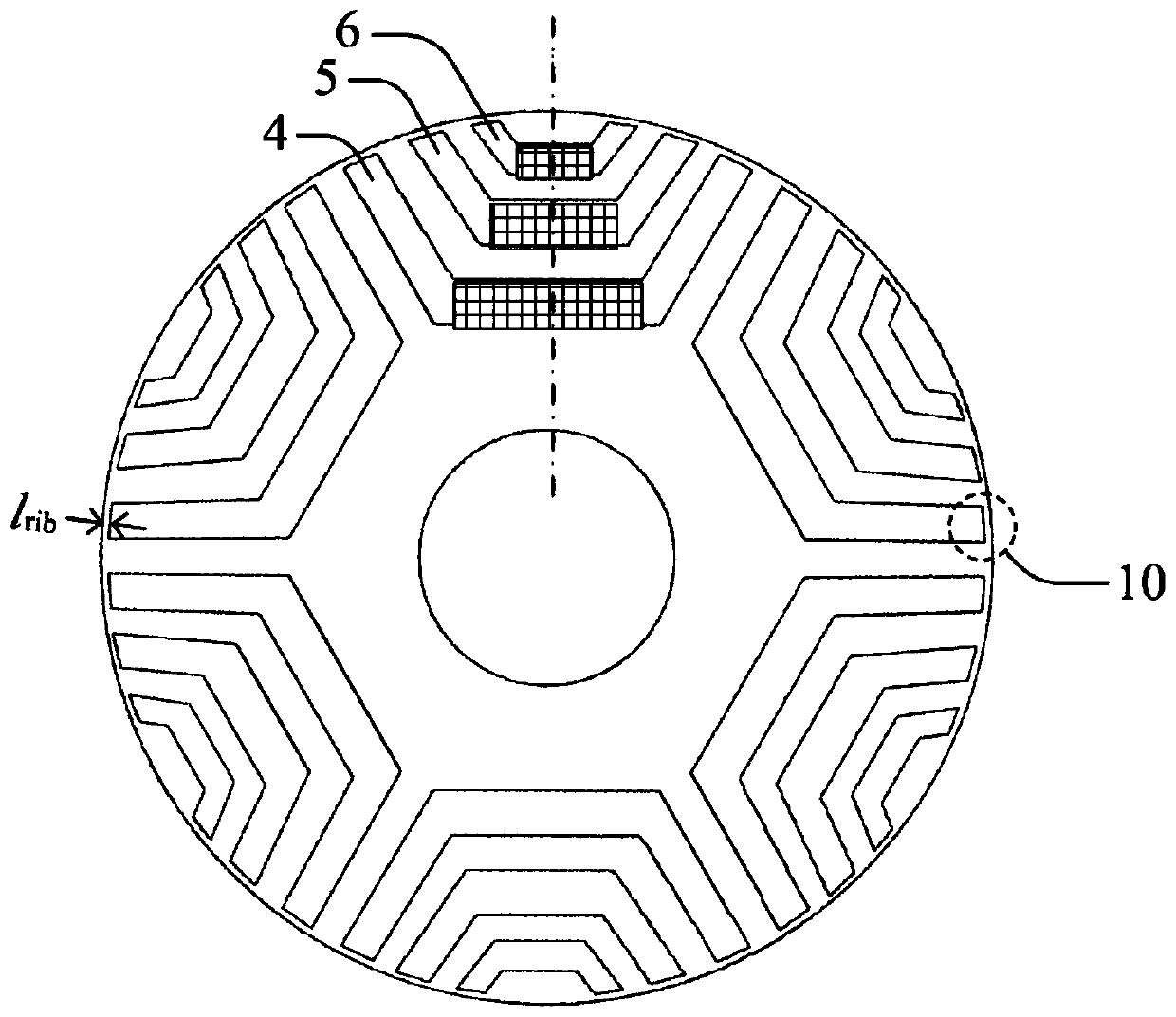
The invention relates to the field of permanent magnet motors and discloses a permanent magnet motor. The permanent magnet motor comprises a shell, a stator core and a rotor core, wherein the stator iron core is circumferentially arranged along the inner wall of the casing, and the rotor iron core is installed in a space enclosed by the stator iron core; the rotor iron core comprises at least two full-bridge type lamination groups and at least one half-bridge type lamination group, and the laminations in the full-bridge type lamination groups comprise a plurality of full-bridge punching sheets which are connected with the first central connection bridges and are distributed along the circumferential direction; the laminations in the half-bridge type lamination groups comprise at least one separation punching sheet which is disconnected from a second central connection bridge and is distributed along the circumferential direction, and the full-bridge type lamination groups and the half-bridge type lamination groups are laminated along the axial direction, so each half-bridge type lamination group is positioned between two full-bridge type lamination groups; therefore, the adjacent sectors of the rotor core are asymmetric. The power density of the motor can be improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG WELLING ELECTRIC MACHINE MFG
Electric vehicle permanent magnet synchronous driving motor
ActiveCN109391113AIncrease the magnetic field strengthIncrease output powerMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention provides an electric vehicle permanent magnet synchronous driving motor and belongs to the technical field of electric vehicles. The driving motor is an inner rotor structure and includes first permanent magnets, second permanent magnets, a nonmagnetic fixed core, a rotor core and a stator, wherein the rotor core is internally fixed to the nonmagnetic fixed core; the number of the first permanent magnets and the number of the second permanent magnets are the same and are both even numbers; the first permanent magnets and the second permanent magnets have different lengths and arein [lambda] shapes; the outer side of the rotor core has a high-strength steel hoop. Compared with the existing permanent magnet synchronous motor, the electric vehicle permanent magnet synchronous driving motor has higher magnetic field strength, larger output power, larger mechanical strength, and lower torque ripple, can utilize reluctance torque, and has better sinusoidality in the air gap flux density.
Owner:GANZHOU FORTUNE ELECTRONICS
Permanent magnet synchronous motor without stator iron core
InactiveCN101783557BReduce volumeReduce weightMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machinesHarmonicCore component
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Stator and motor using same
PendingCN113206561AImproved sinusoidalityImprove sinusoidalityMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic coreMagnet
The invention relates to a stator and a motor using the same. The stator comprises a stator magnetic core and a stator winding wound on the stator magnetic core, and the stator magnetic core comprises: an annular stator magnet yoke; stator teeth which extend from the stator magnet yoke in the radial direction, wherein the stator teeth are evenly distributed in the circumferential direction of the stator magnet yoke at intervals, and wire grooves used for containing wires of the stator winding are formed between the adjacent stator teeth. The plurality of stator teeth at least comprise a first type of stator teeth with a first length and a second type of stator teeth with a second length, and the second length is greater than the first length; and the first type of stator teeth and the second type of stator teeth are alternately arranged along the circumferential direction according to a preset rule. According to the embodiment of the invention, the sinusoidal property of the magnetomotive force generated by the winding can be improved, the harmonic electromagnetic force is weakened, and the electromagnetic performance of the motor is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU XIAOPENG MOTORS TECH CO LTD
A method for generating sinusoidal structured light field by spatio-temporal binary encoding
ActiveCN104567730BImprove sinusoidalityHigh precisionUsing optical meansError diffusionSpatial encoding
The invention belongs to the three-dimensional sensing technology and discloses a method for generating a light field with a sine structure by means of space-time binary encoding. According to the method, a standard sine fringe pattern 1 generated by a computer is equally divided into 2<n> (n>=2) sections according to gray-level distribution, then time and space encoding is conducted on each section by means of two-dimensional error diffusion to obtain 2<n> (n>=2) binary fringe patterns (2, 3, 4, ..., 5), and then linear superposition is conducted on the binary fringe patterns after the binary fringe patterns are projected and acquired through an imaging system, so that a high-quality sine fringe 6 is obtained. The projected binary fringe patterns are not affected by the non-linear response of a digital projector, the high-speed binary pattern switching function of the digital projector is fully utilized, and the speed and precision of three-dimensional surface measurement are improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
A hybrid permanent magnet rotor for electric vehicles
ActiveCN109274187BWeaken Distortion EffectImprove sinusoidalityMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesPermanent magnet rotorHigh magnetic field strength
The invention provides a hybrid permanent magnet rotor for an electric vehicle, belonging to the technical field of electric vehicle motors. The rotor is an inner rotor structure, comprising a first permanent magnet, a second permanent magnet, a third permanent magnet, a non-magnetic conductive fixed core, a rotor iron core and a tightening ring, and the rotor iron core is fixed on the periphery of the non-magnetic conductive fixed core; The first permanent magnet, the second permanent magnet and the third permanent magnet are the same in number and even in number, and are combined into a shape. The outer side of the rotor is provided with a tightening ring to prevent deformation of the rotor. Compared with the existing permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor, it saves part of the scarcerare earth permanent magnet, has higher magnetic field strength, higher mechanical strength, effective use of reluctance torque, and higher output power.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
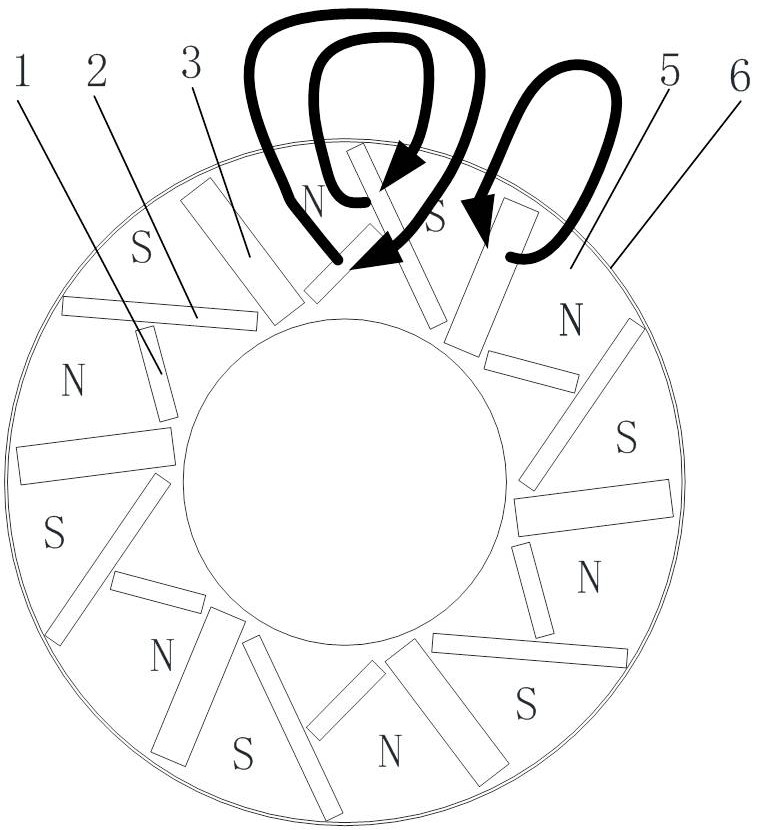
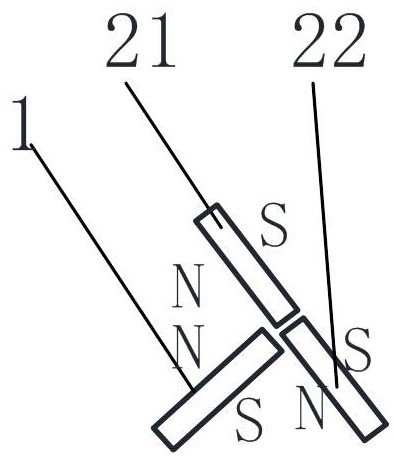
Permanent magnet synchronous motor and rotor thereof
PendingCN114744795AReduce dosageImprove sinusoidalityMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machinesPermanent magnet synchronous motorMagnetic poles
The invention discloses a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. Each group of magnetic pole slots is divided into two inner magnetic pole slots positioned on the inner layer and one outer magnetic pole slot positioned on the outer layer along the radial direction of a rotor iron core sheet; two of the magnetic pole groups are first permanent magnets, the other one of the magnetic pole groups is a second permanent magnet, after the first permanent magnets are matched with the inner magnetic pole grooves, the two first permanent magnets are arranged in a V shape, and a magnetic pole straight shaft which is axially symmetric about the two first permanent magnets is arranged between the two first permanent magnets; at least one end of the inner magnetic pole groove extends to form a magnetic isolation groove located on the outer side of the first permanent magnet. After the second permanent magnets are matched with the outer magnetic pole grooves, the symmetry axes of the second permanent magnets coincide with the magnetic pole straight axes, and the distance between the second permanent magnets and the peripheral face of the rotor iron core piece is smaller than the distance between the first permanent magnets and the peripheral face of the rotor iron core piece. According to the invention, the counter electromotive force can be reduced, the no-load counter electromotive force waveform sinusoidal property is improved, the reluctance torque is improved, and the cogging torque is reduced.
Owner:成都华川电装有限责任公司
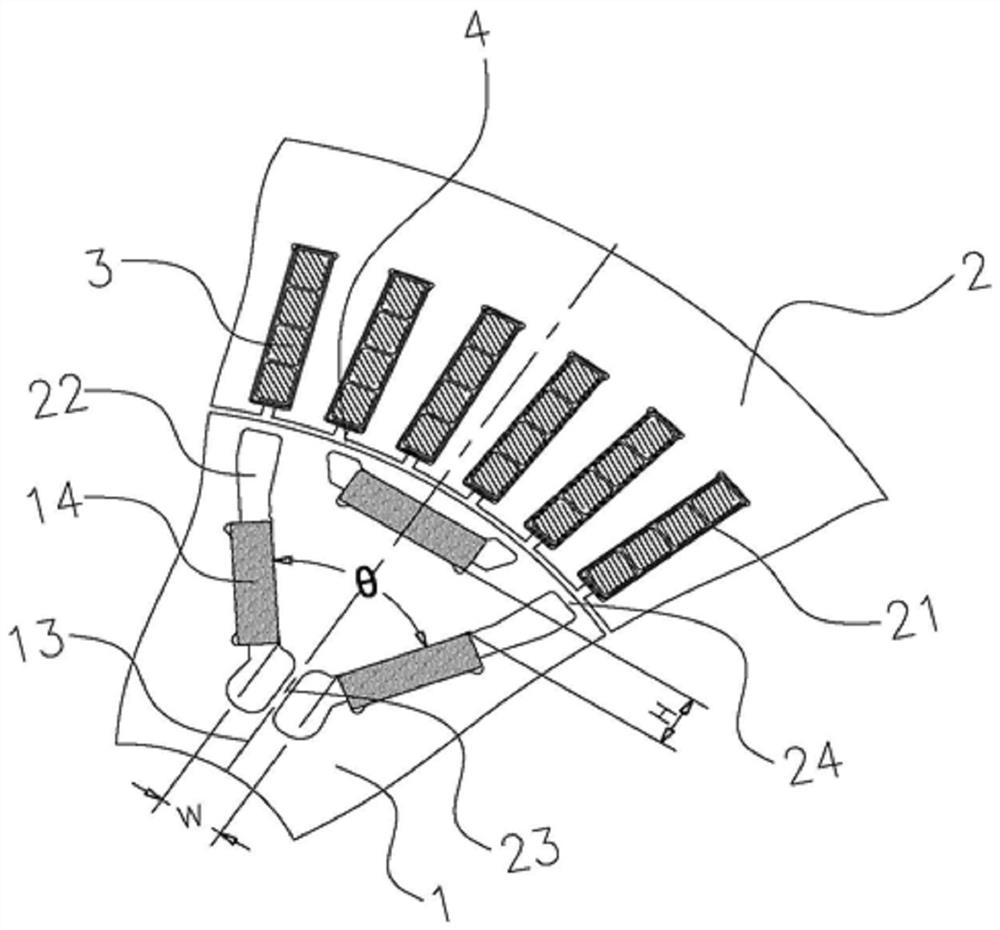
Novel stator structure based on axial flux motor
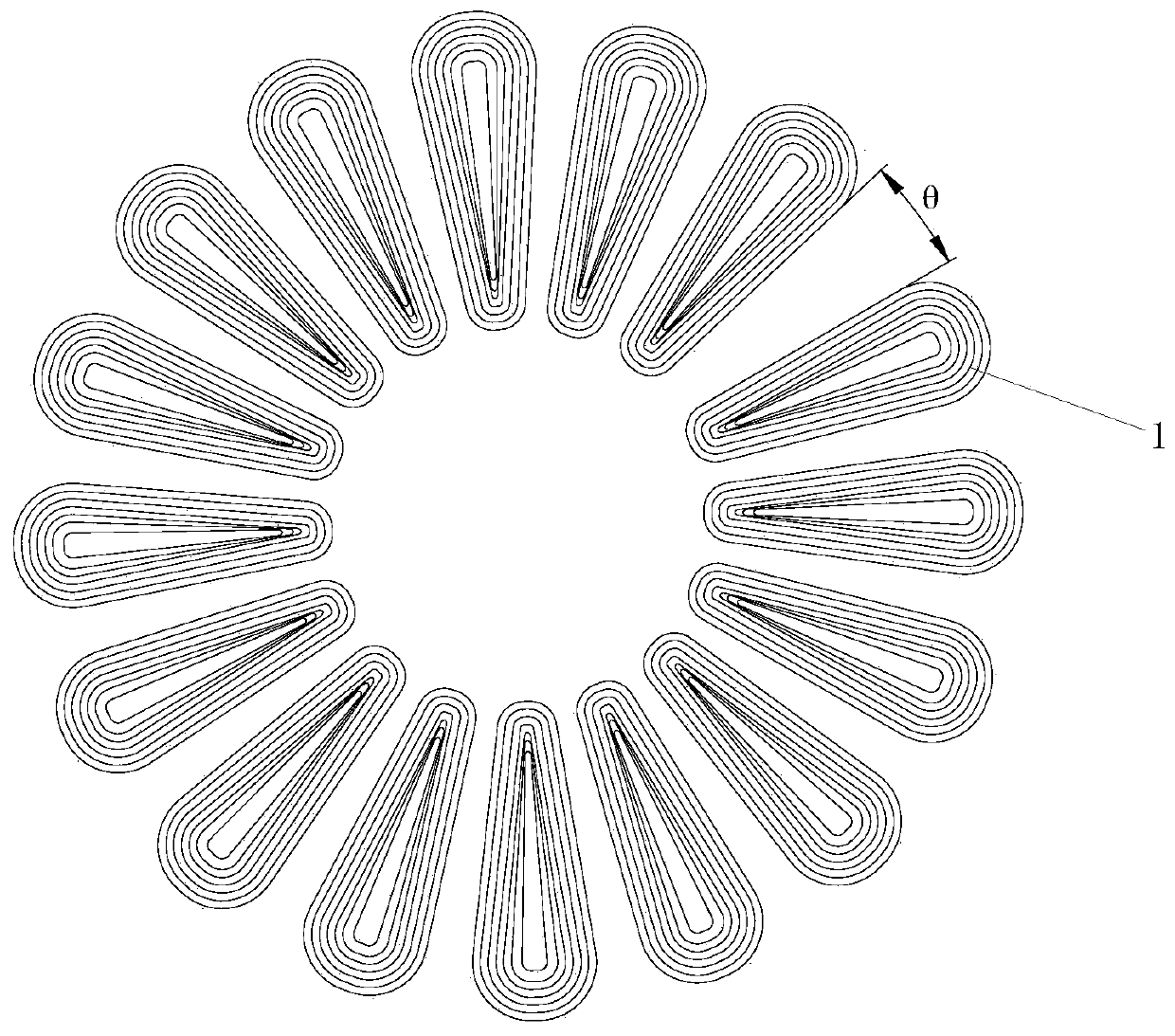
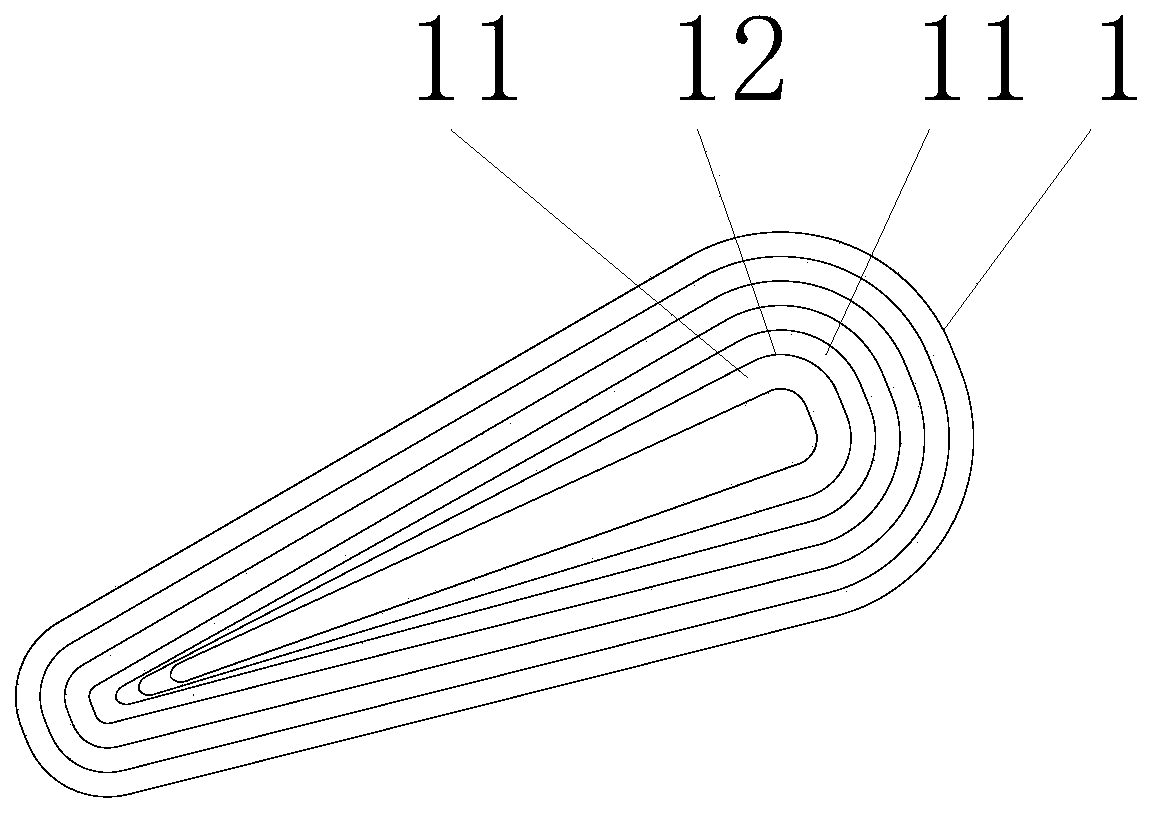
ActiveCN113691034AHarmonic reductionImprove work efficiencyWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineEngineering
The invention discloses a novel stator structure of an axial magnetic flux motor, which comprises more than three coil monomers which are annularly distributed in a stator and have the same specification, every N adjacent coil monomers form a coil unit, three coil units are arranged in the stator, the included angle between any two adjacent coil units is theta, and theta is greater than or equal to 1. The value range of theta is 2-35 degrees, and the coil monomers in each coil unit are annularly and uniformly distributed in an array at the angle of 360-3*theta. The invention provides a non-uniformly distributed stator structure of an axial magnetic flux motor, which is simultaneously suitable for an axial magnetic flux motor with an iron core and an axial magnetic flux motor without an iron core, can effectively reduce higher harmonics of counter electromotive force of the motor, and improves the sinusoidal property of the output voltage waveform of the motor.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Three-dimensional imaging method based on error diffusion dithering algorithm
InactiveCN110455219AImprove sinusoidalityReduce imaging errorsUsing optical means3D modellingGratingAlgorithm
The invention relates to a three-dimensional imaging method based on an error diffusion dithering algorithm. The method includes the following steps: acquiring a threshold value obtained based on an average gray value and an error compensation parameter in a matrix around a pixel in an error diffusion dithering algorithm; adding an original gray value of a to-be-detected pixel point to a quantization error introduced in the error diffusion process, calculating a temporary gray value of each pixel in a full image, comparing the temporary gray values with the threshold, indicating the pixel output to be 255 under the condition of being larger than the threshold by the temporary gray values, and otherwise, indicating the pixel output to be0; and carrying out defocusing on the output pixel toobtain three-dimensional imaging. On the basis of the threshold optimization method, the three-dimensional structured light imaging is optimized, so that the sinusoidal nature of the defocusing grating is improved effectively and the imaging errors are reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU JIANGAO OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Novel stator and rotor structure of surface-mounted permanent magnet motor
InactiveCN112838695ASafe and stable operationReduce lossMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic polesElectric machinery
The invention discloses a stator and rotor structure of a surface-mounted permanent magnet motor, which comprises a stator, a rotor, stator water holes, permanent magnets and permanent magnet auxiliary grooves. In order to output high torque and stably operate the motor, the structure adopts an inner rotor and outer stator mechanism, the inner rotor adopts a magnetic pole surface-mounted type, and the magnetic pole adopts two non-uniform permanent magnets, the inner side arc and the outer side arc are located on the same circle with the proportion of 6:5, auxiliary grooves are formed in magnetic poles, excitation windings are placed in inner stator winding grooves, and two round holes are formed in stator teeth to be connected with water pipes to facilitate heat dissipation of the motor. According to the invention, the asymmetric structure of the magnetic poles is used to reduce eddy current loss and optimize the air-gap flux density waveform, reduce magnetic leakage and enhance the sinusoidal property of the air-gap magnetic field; the permanent magnets are used for forming auxiliary slots to reduce cogging torque pulsation; and the purposes of reducing the waveform irregularity and controlling the temperature rise are achieved by using the water holes formed in the stator, so that the motor can operate more safely and stably.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A permanent magnet synchronous drive motor for electric vehicles
ActiveCN109391113BIncrease the magnetic field strengthIncrease output powerSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsPermanent magnet synchronous motorEngineering
The invention provides an electric vehicle permanent magnet synchronous driving motor and belongs to the technical field of electric vehicles. The driving motor is an inner rotor structure and includes first permanent magnets, second permanent magnets, a nonmagnetic fixed core, a rotor core and a stator, wherein the rotor core is internally fixed to the nonmagnetic fixed core; the number of the first permanent magnets and the number of the second permanent magnets are the same and are both even numbers; the first permanent magnets and the second permanent magnets have different lengths and arein [lambda] shapes; the outer side of the rotor core has a high-strength steel hoop. Compared with the existing permanent magnet synchronous motor, the electric vehicle permanent magnet synchronous driving motor has higher magnetic field strength, larger output power, larger mechanical strength, and lower torque ripple, can utilize reluctance torque, and has better sinusoidality in the air gap flux density.
Owner:GANZHOU FORTUNE ELECTRONICS
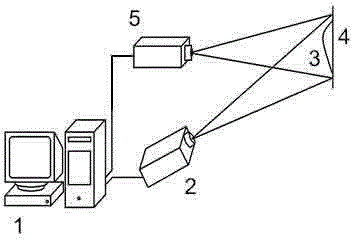
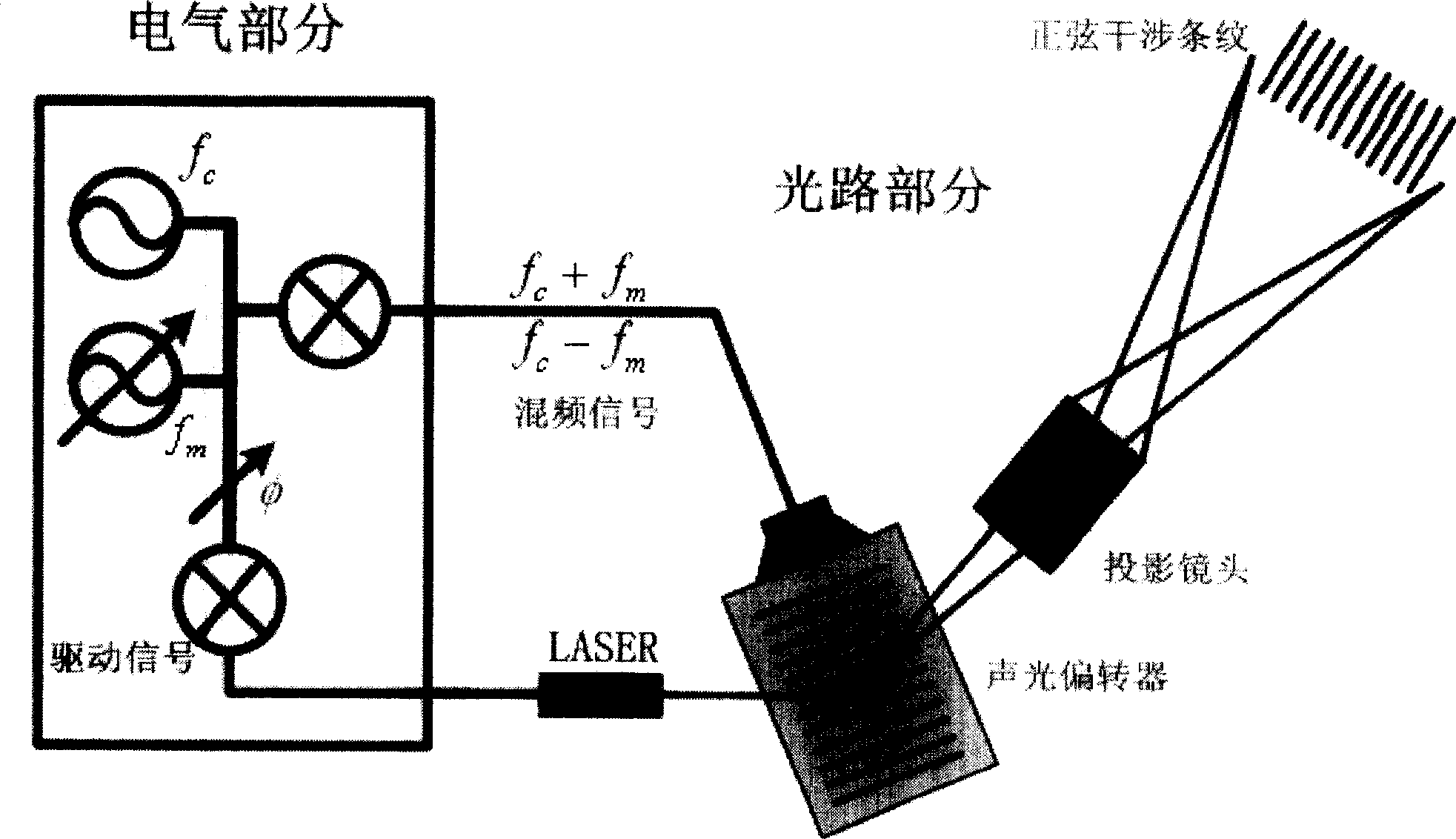
Sinusoidal fringe structural light projector based on acousto-optic deflection device
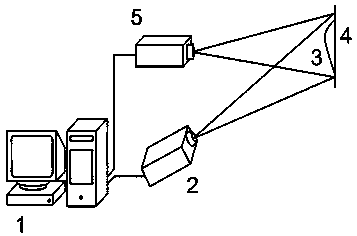
InactiveCN100494887CIncrease flexibilityImprove 3D measurement accuracyUsing optical meansNon-linear opticsAcousto-opticsEngineering
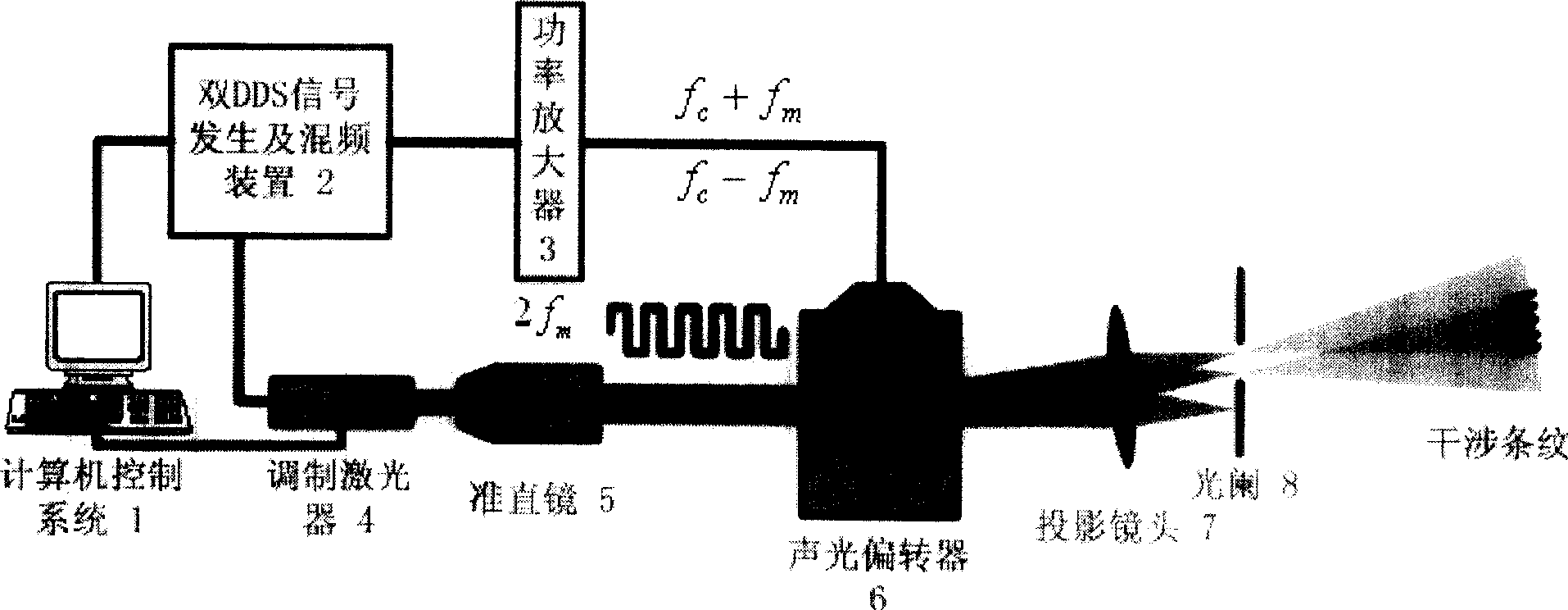
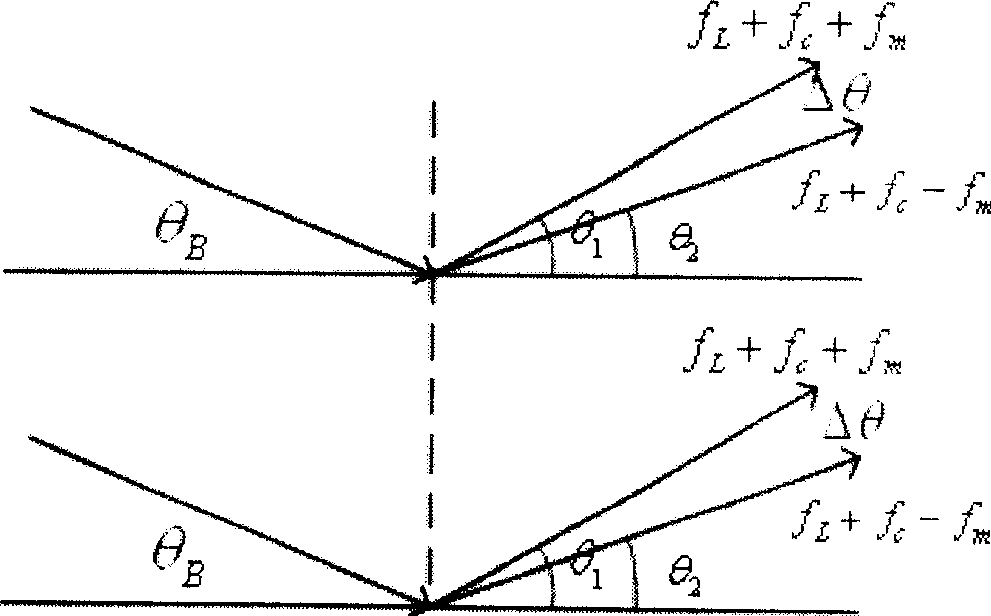
A sine stripe configuration light project equipment based on acousto-optic deflector relates to acousto-optic deflector, double DDS signal generator equipment, mixing multiplier, power amplifier, confection laser, light system and computer controlling system. The acousto-optic deflector produces intervened stripe. Double DDS signal generator equipment produces two-way driving signal. Mixing multiplier mixes the center frequency of the acousto-optic deflector and the confection signal of the DDS. Power amplifier amplifies the power of the mixing signal. Confection laser offers coherent light source and incepts driving signal of laser from DDS. Light system relates to collimating mirror, projection lens and diaphragm which filtrates the 0 level diffraction light from the acousto-optic deflector. Computer control system controls the frequency and phase of the double DDS signal generator equipment to bring the signal, adjusts and controls the brightness and duty ratio of the high frequency confection laser.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Rotor magnetic-field sine permanent-magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure
ActiveCN109861426AImprove sinusoidalityRipple torque reductionMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorPhysics
The invention discloses a rotor magnetic-field sine permanent-magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure. The rotor magnetic-field sine permanent-magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure comprises a central rotation shaft and a rotor core, wherein the rotor core sleeves the central rotation shaft, P through groove groups are uniformly formed in positions, encircling the centralrotation shaft, of the rotor core and are same in shape and size, P is rotor magnetic poles, each through groove group comprises a plurality of through grooves, permanent magnets are arranged in thethrough grooves, the polarities of the permanent magnets in the same through groove group are same, the polarities of permanent magnets in two adjacent through groove groups are different, and the lengths of the permanent magnets in the same through groove group are different. By arranging the lengths of the permanent magnets in the same through groove group to be different, the sine performance of a rotor magnetic field can be improved, and the ripple torque is reduced. By the rotor magnetic-field sine permanent-magnet reluctance synchronous motor rotor structure, the harmonic content of an air gap magnetic field can be reduced, the eddy-current loss is reduced, and the running efficiency of the motor is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A New Stator Winding Structure Based on Axial Ironless Motor
InactiveCN110994849BHarmonic reductionSimple processWindings conductor shape/form/constructionElectric machineCounter-electromotive force
The invention discloses a novel stator winding structure based on an axial coreless motor, and the structure comprises at least three single coils with the same specification, the at least three single coils are annularly distributed to form a winding, and each single coil of the winding is arranged in an annular non-uniform manner. The novel stator winding structure based on the axial coreless motor can effectively reduce the higher harmonics of counter electromotive force of the motor and can improve the sinusoidal property of counter electromotive force waveforms. The stator winding is simple in process, convenient to assemble and low in cost, the working efficiency of the motor is improved, the cost performance and the flexibility of processing and manufacturing are also improved, andthe mechanical strength and the heat dissipation characteristic are better.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
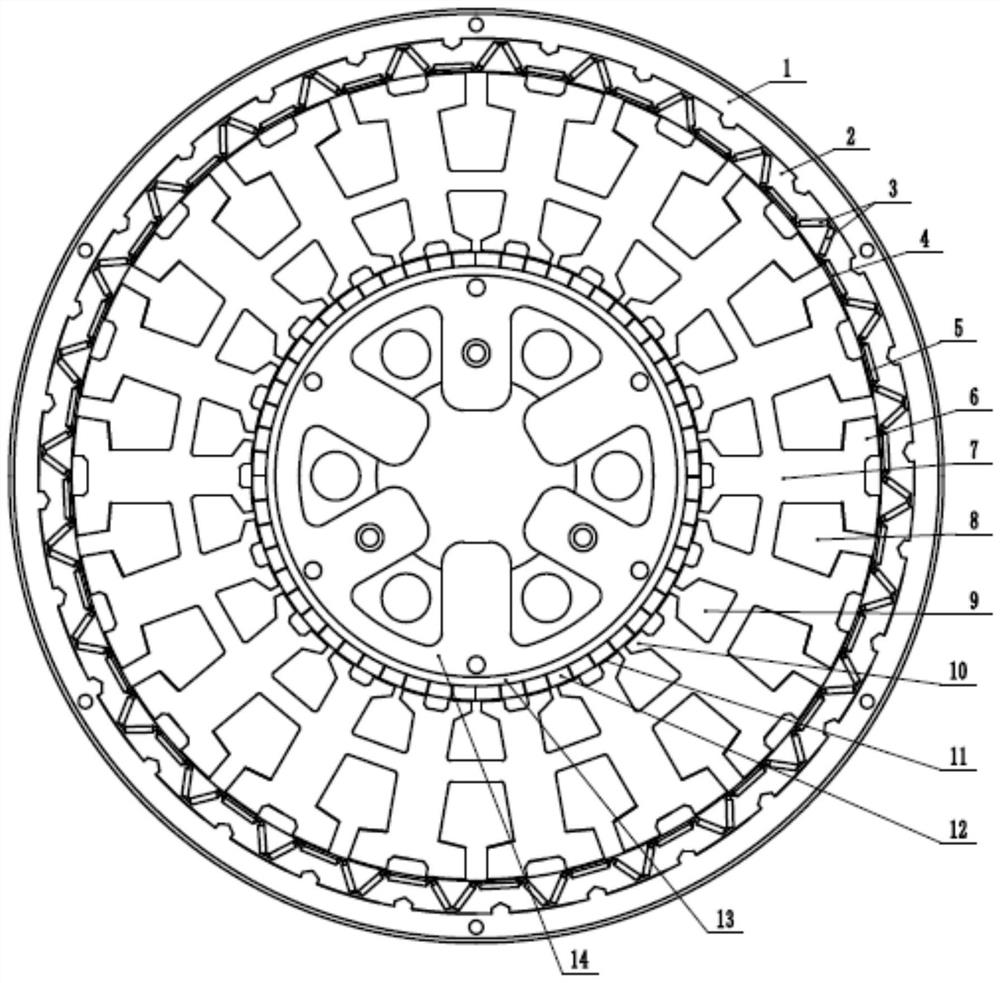
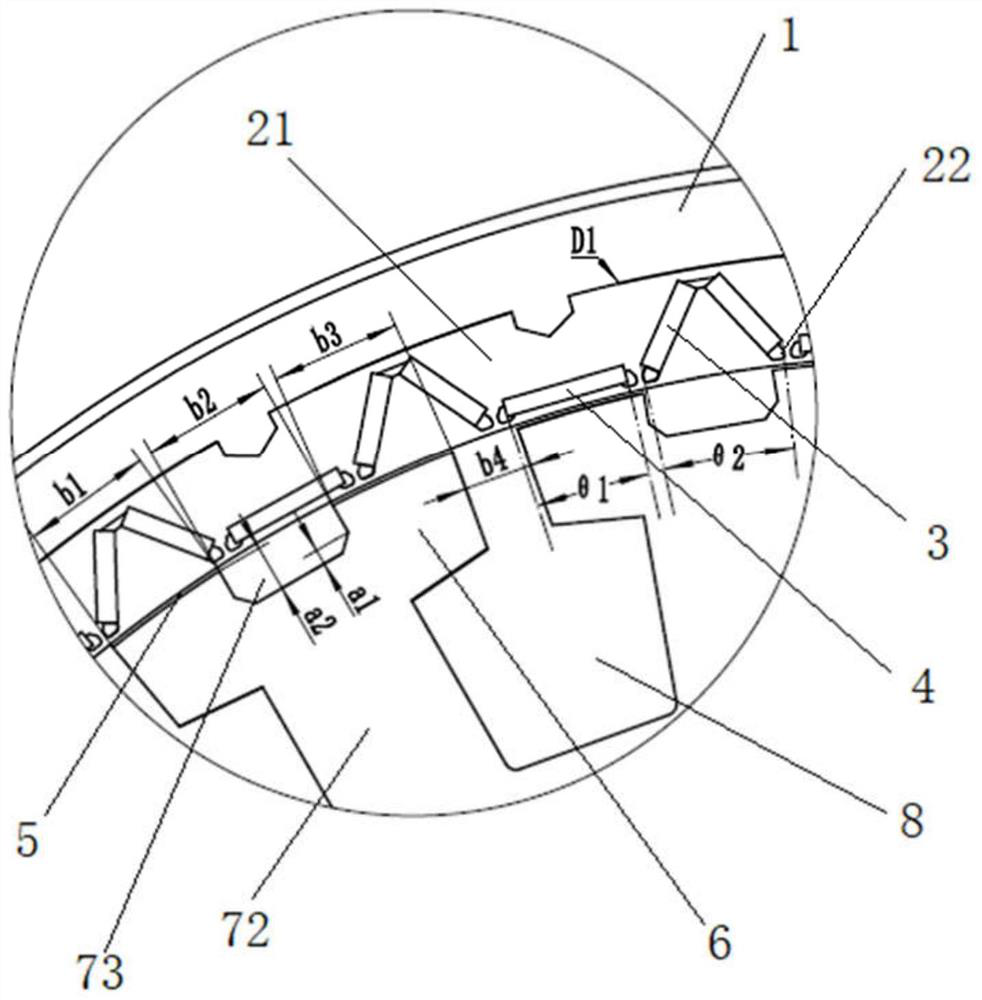
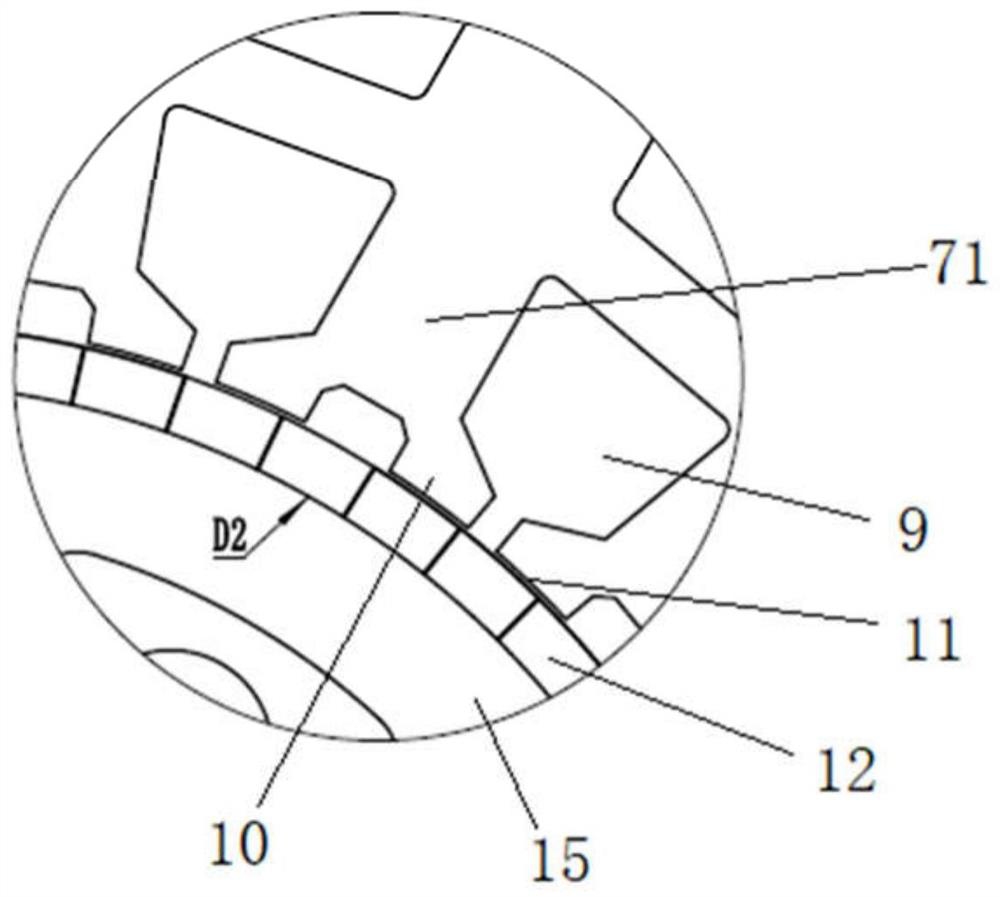
Radial and axial dual-modular magnetic flux switching motor
ActiveCN113178963ALess odd harmonic contentSuppresses unilateral magnetic pullWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectric machineEngineering
The invention relates to a radial and axial dual-modular magnetic flux switching motor. The radial and axial dual-modular magnetic flux switching motor comprises a stator and a rotor; the stator comprises an armature winding and at least one stator module arranged in the axial direction, each stator module comprises two stator units, and magnetic isolation rings are embedded between the two stator units of each stator module and between the two adjacent stator units of the two adjacent stator modules; each stator unit comprises a permanent magnet and a plurality of stator iron cores which are arranged in a circumferential manner, and the permanent magnet is embedded between two adjacent stator iron cores; the same armature coil of the armature winding is wound on the magnetic conductive bridge arms of the stator cores at the same positions of all the stator units along the axial direction of the motor; and the rotor comprises rotor modules with the same number as the stator modules, each rotor module comprises two rotor units, and the difference between the central angles of the installation positions of the two rotor units of each rotor module is 180 DEG. The harmonic waveform of the permanent magnet flux linkage of the motor is closer to sine waves, pulsation of output torque of the motor is reduced, and vibration and noise are reduced.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com