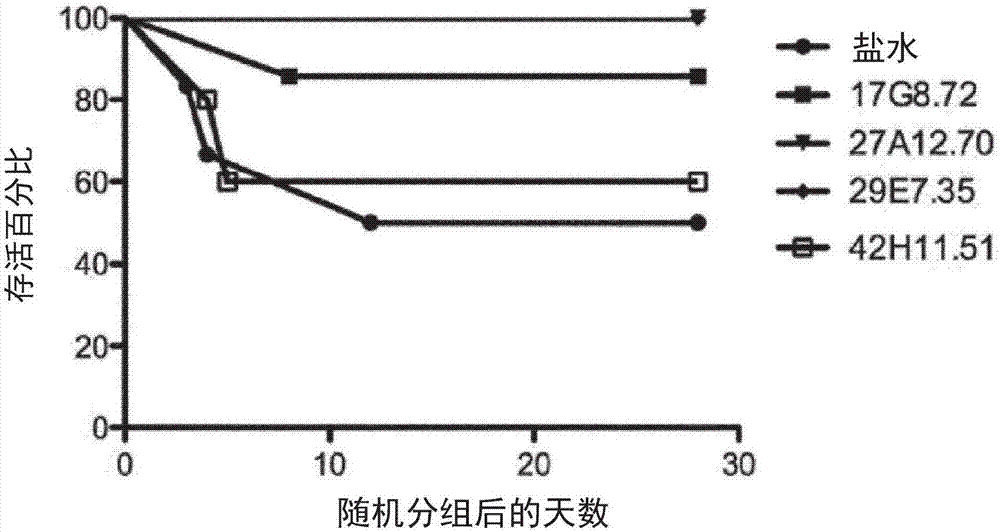
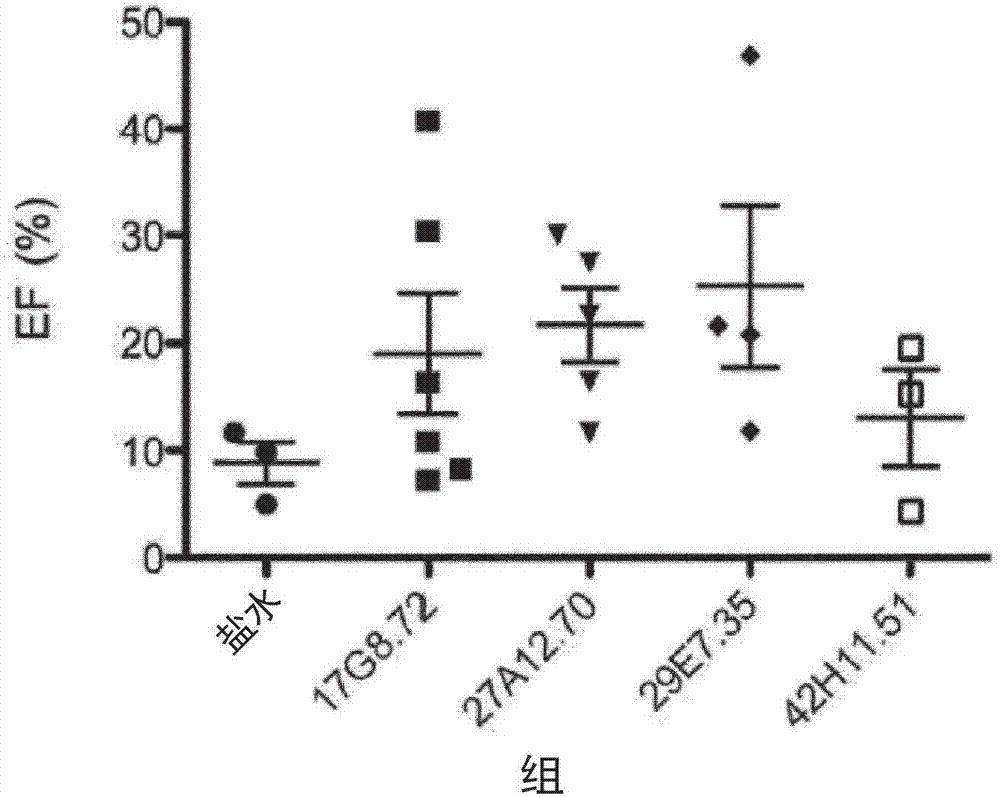
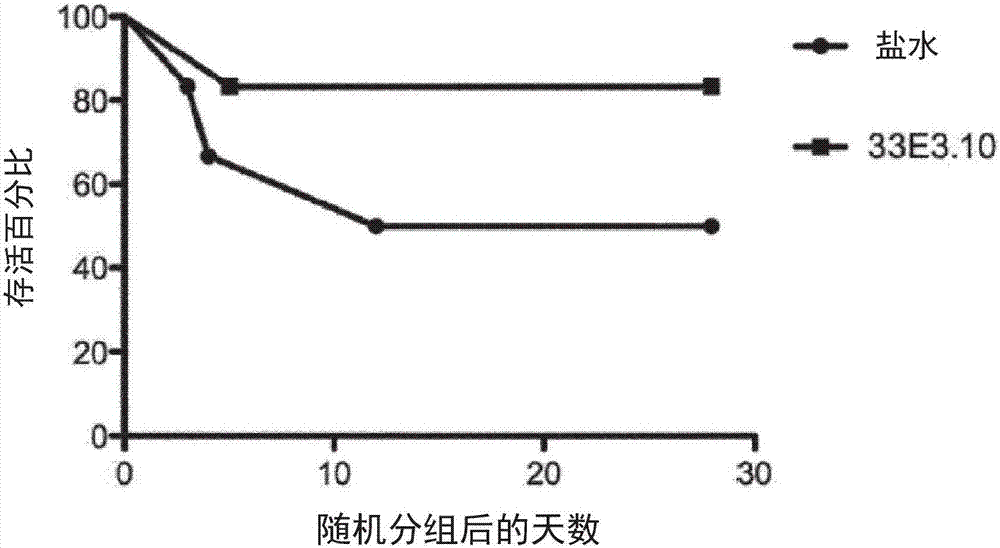
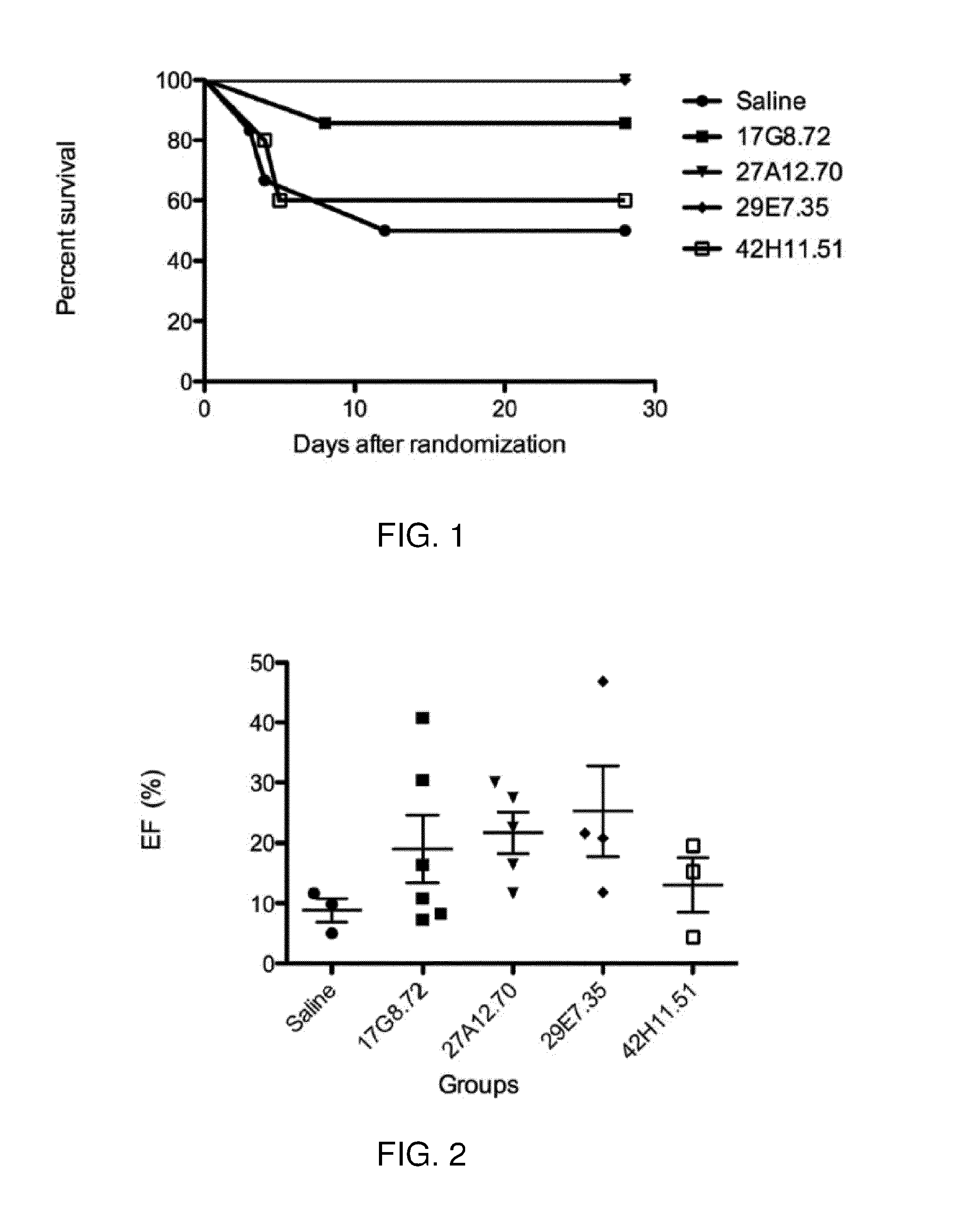
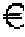Patents
Literature
31 results about "Aneurysm formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
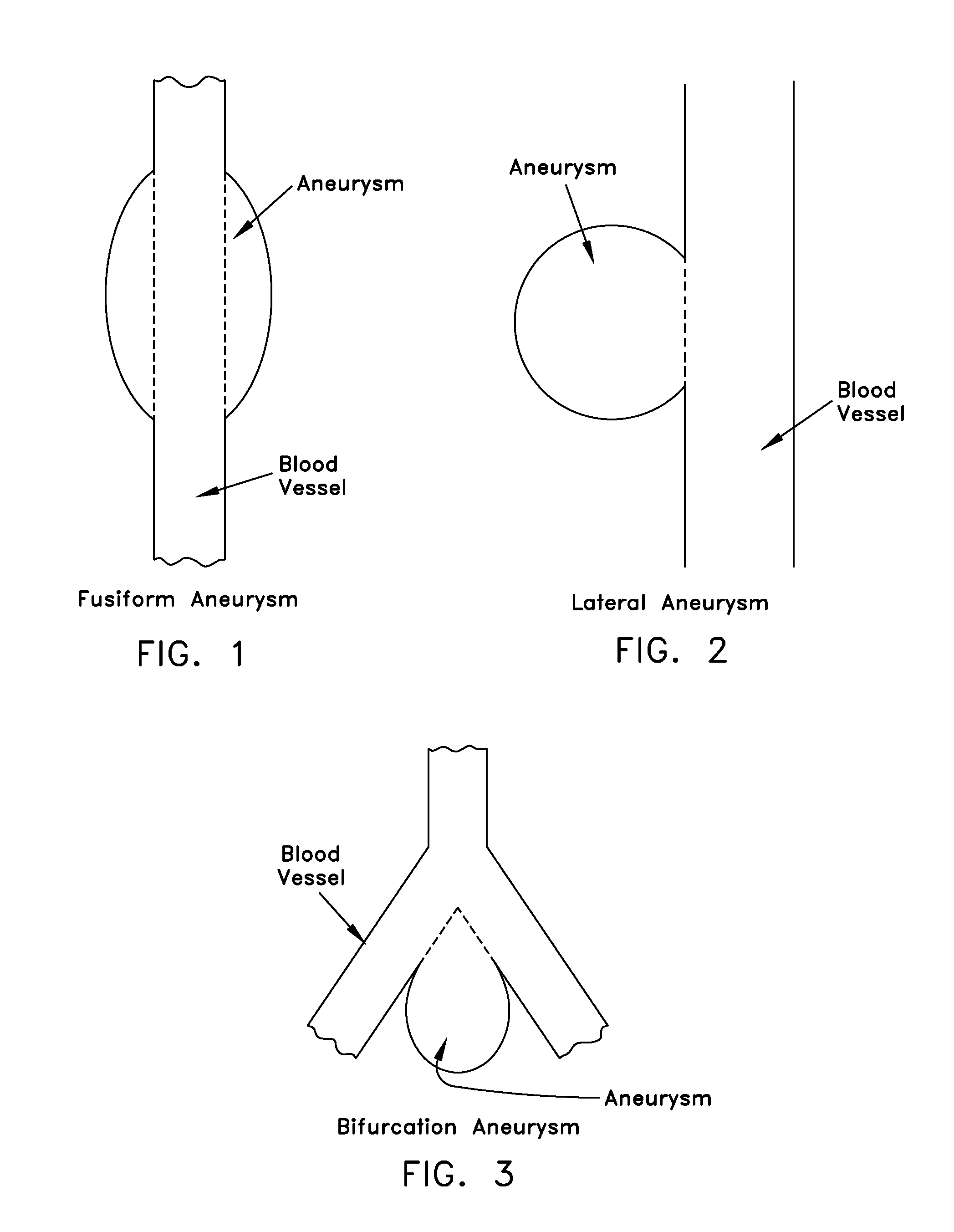
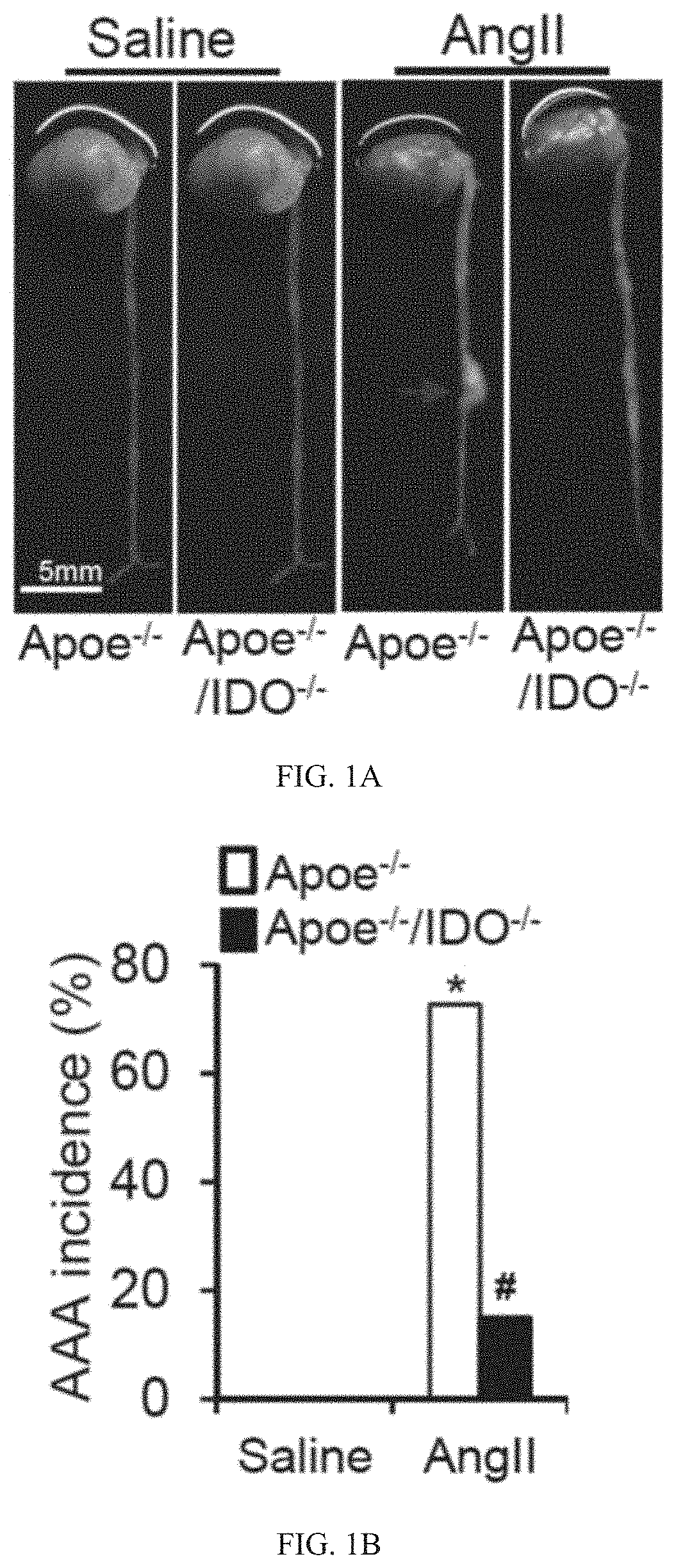
Aneurysm formation is due to multiple factors affecting the arterial segment and its local environment. Many aneurysms are atherosclerotic in nature. As the aneurysmal dilatation increases, the arterial wall tension also increases and this can result in rupture of the aneurysm.
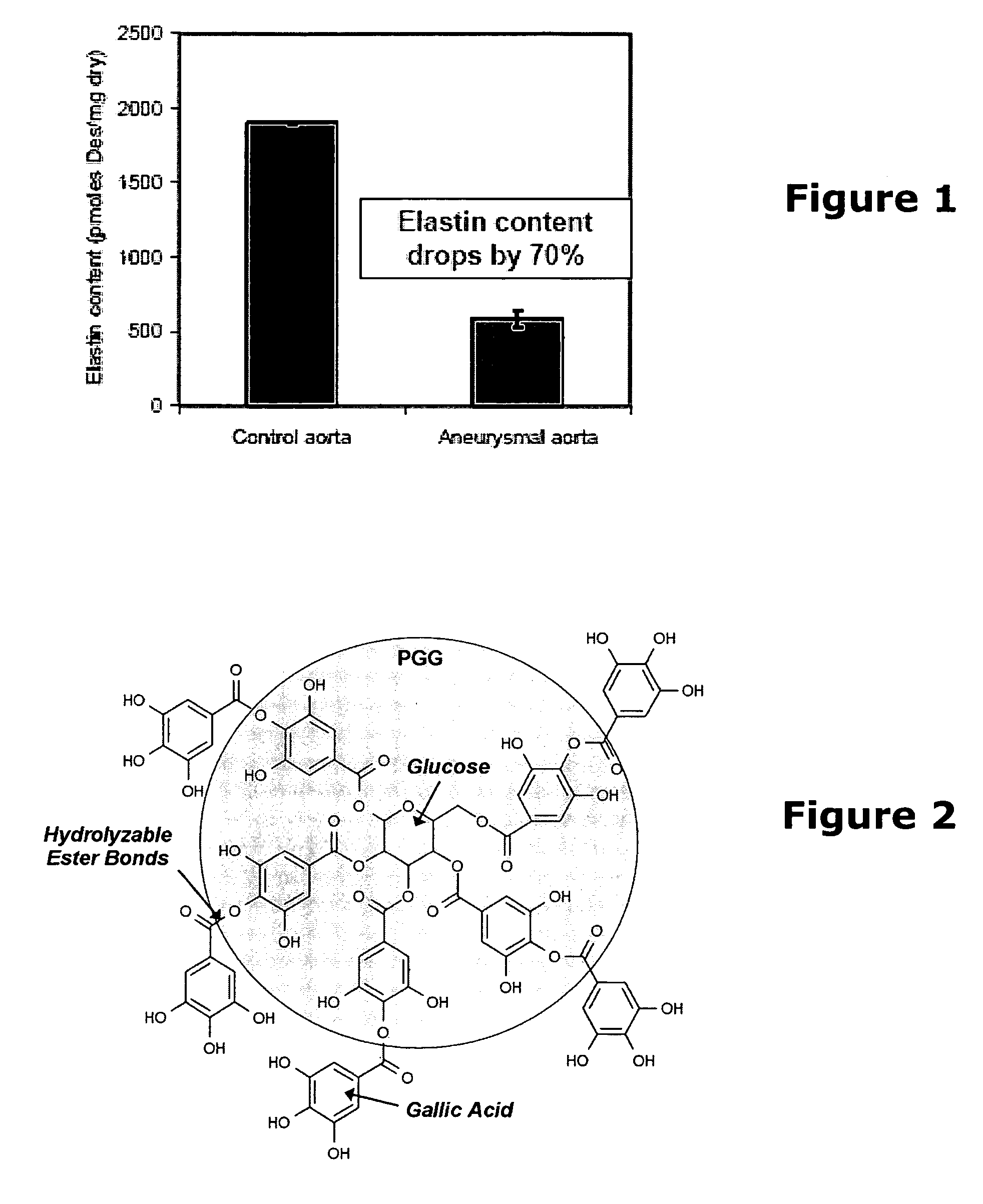
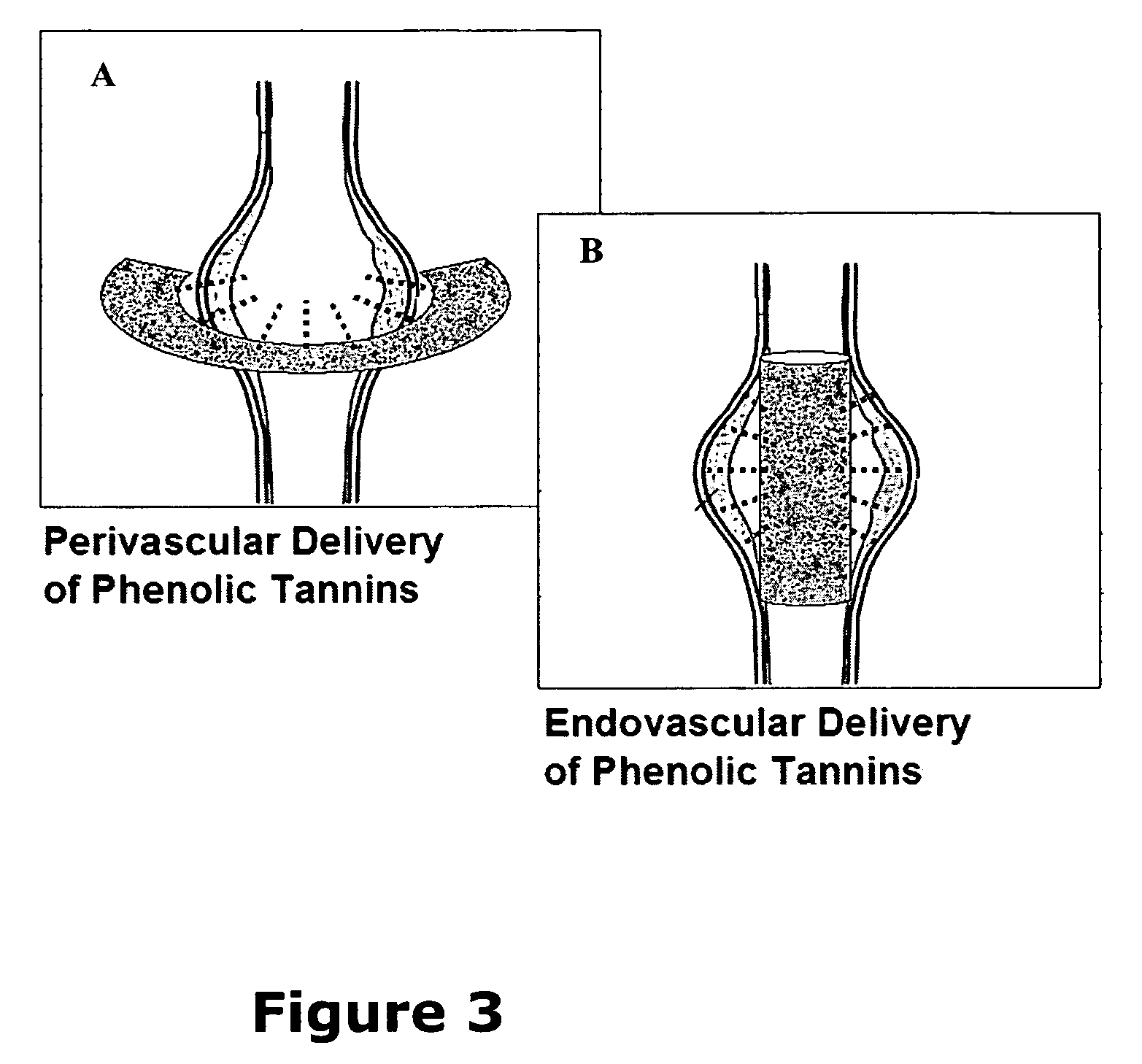
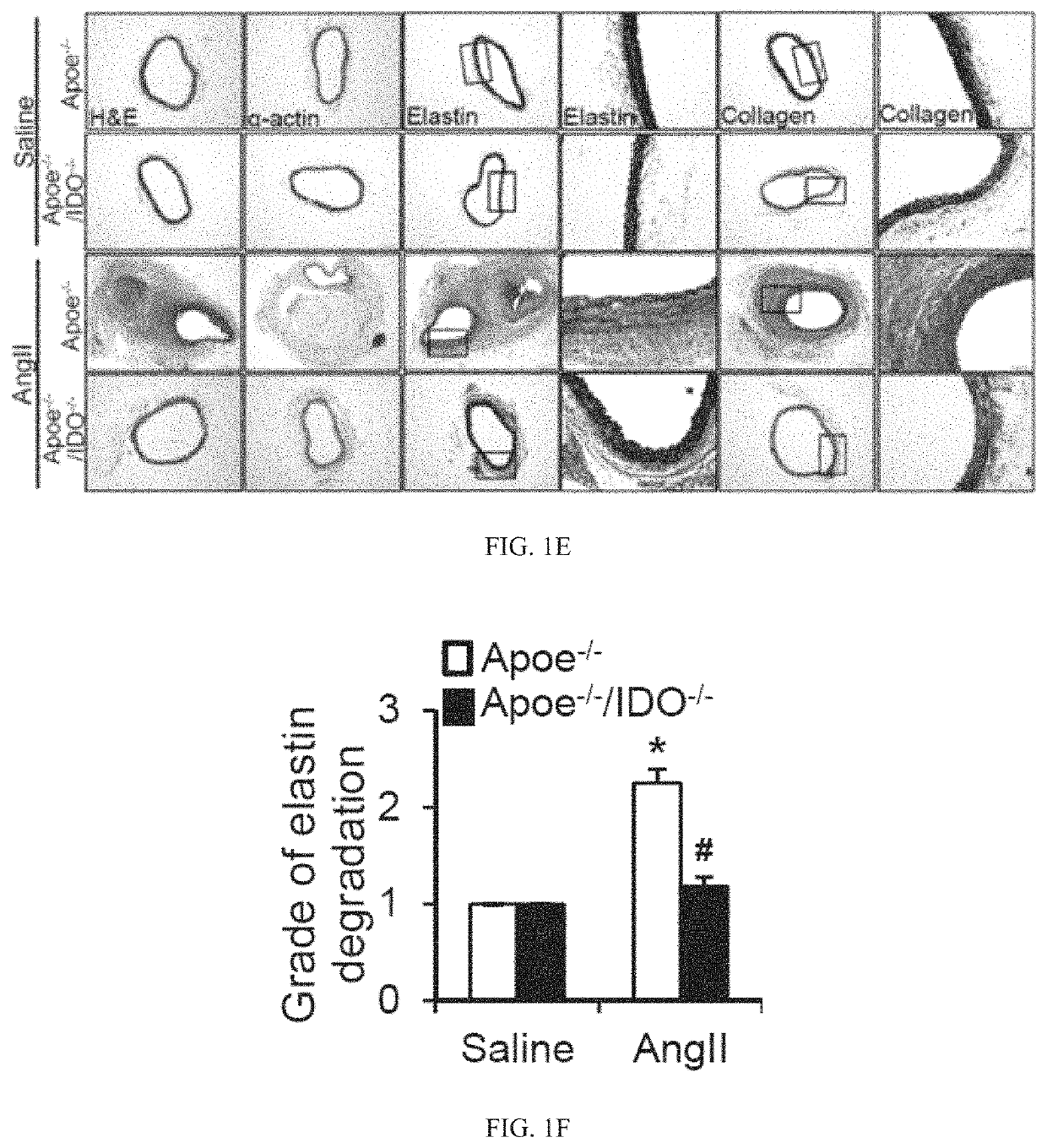
Elastin stabilization of connective tissue
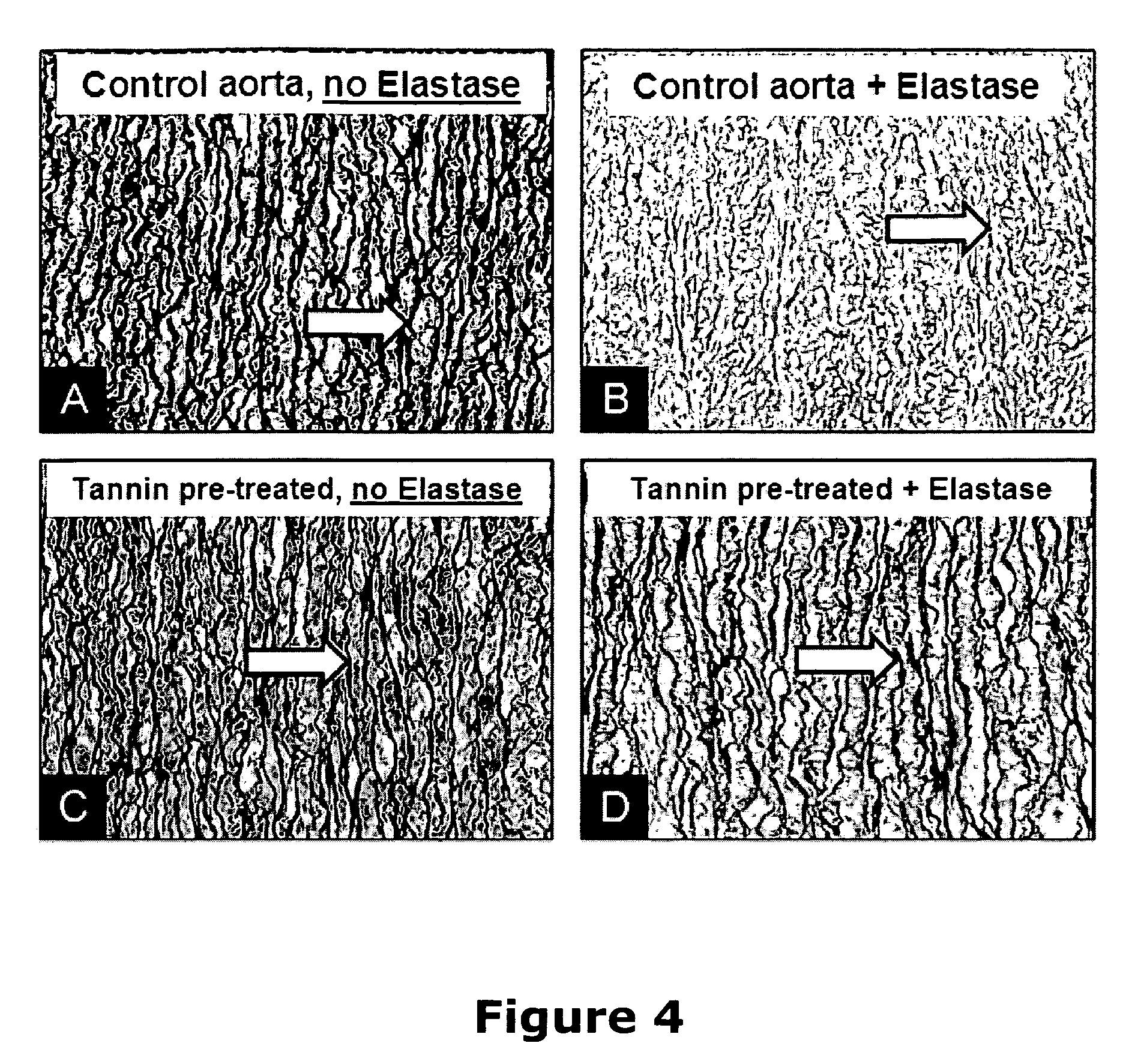
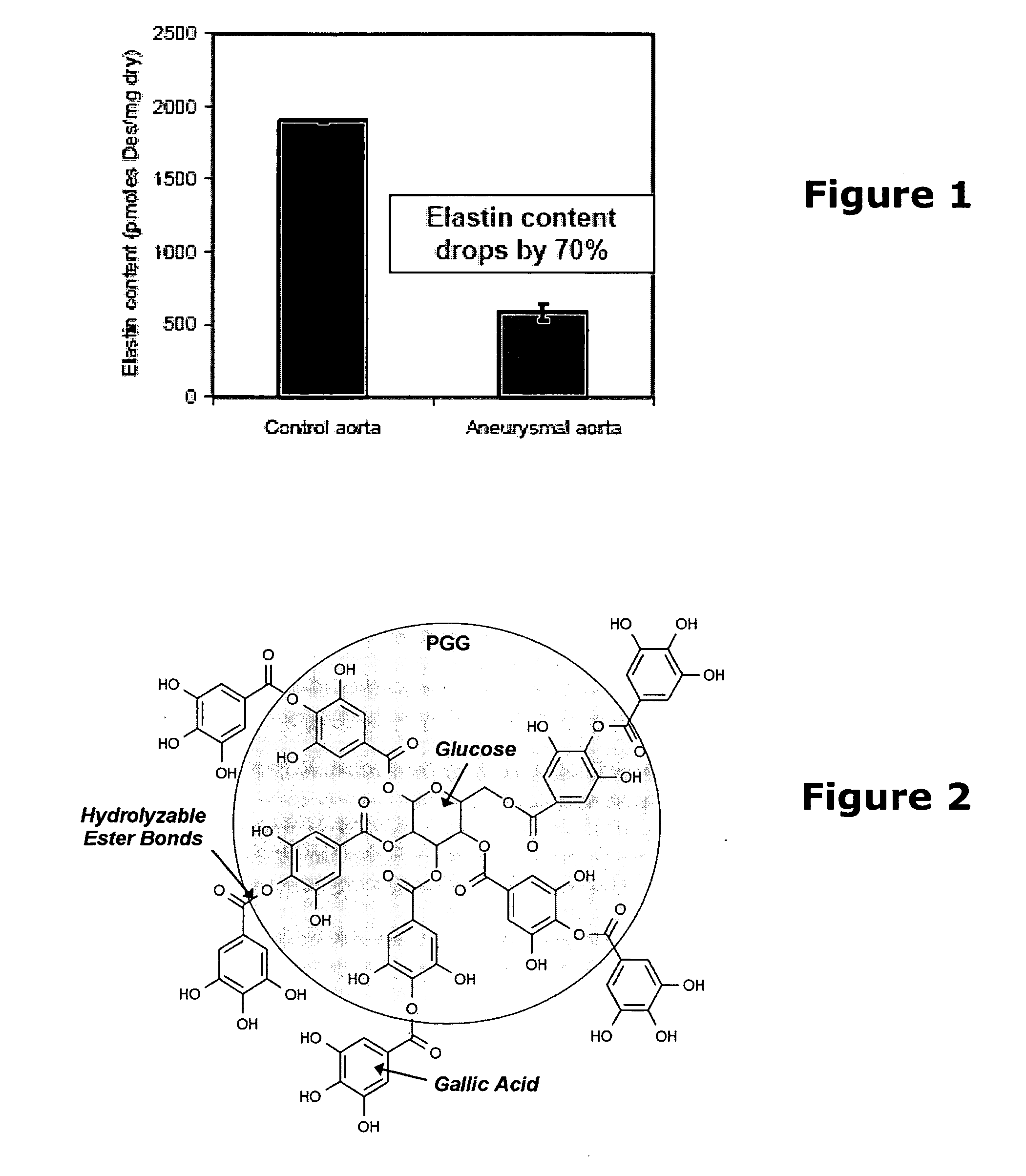
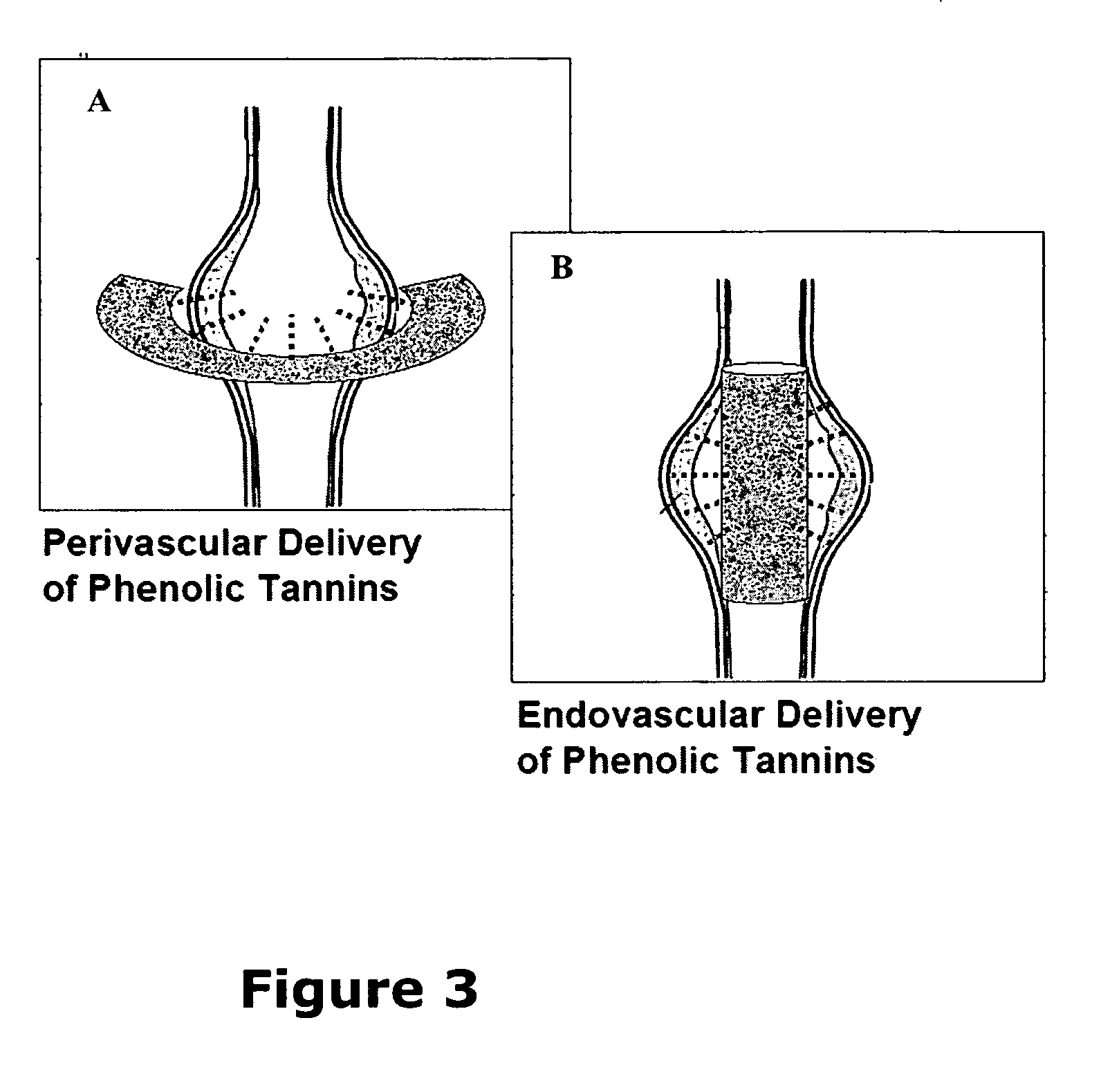
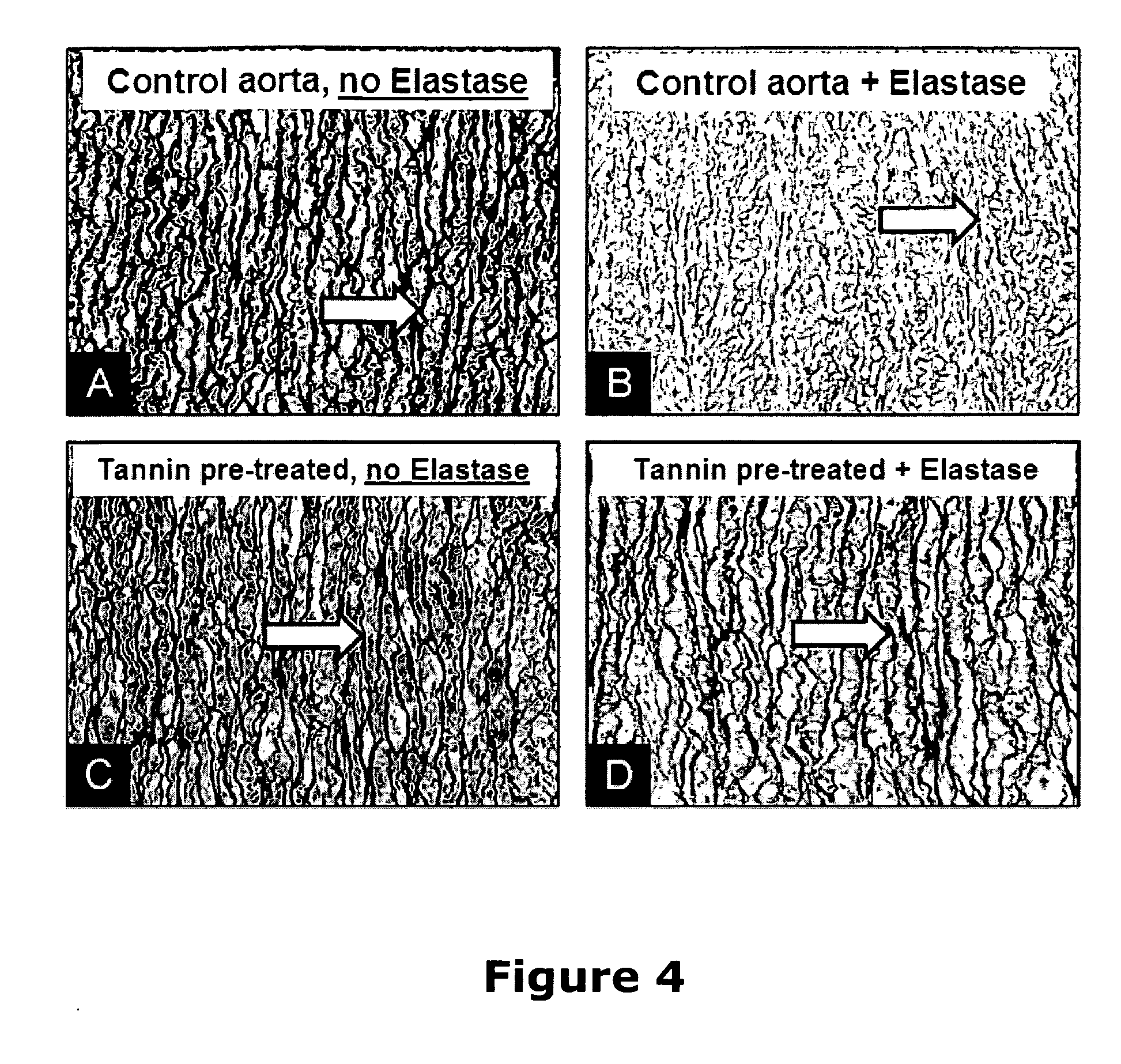
A method and product are provided for the treatment of connective tissue weakened due to destruction of tissue architecture, and in particular due to elastin degradation. The treatment agents employ certain unique properties of phenolic compounds to develop a protocol for reducing elastin degradation, such as that occurring during aneurysm formation in vasculature. According to the invention, elastin can be stabilized in vivo and destruction of connective tissue, such as that leading to life-threatening aneurysms in vasculature, can be tempered or halted all together. The treatment agents can be delivered or administered acutely or chronically according to various delivery methods, including sustained release methods incorporating perivascular or endovascular patches, use of microsphere carriers, hydrogels, or osmotic pumps.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
Elastin stabilization of connective tissue
A method and product are provided for the treatment of connective tissue weakened due to destruction of tissue architecture, and in particular due to elastin degradation. The treatment agents employ certain unique properties of phenolic compounds to develop a protocol for reducing elastin degradation, such as that occurring during aneurysm formation in vasculature. According to the invention, elastin can be stabilized in vivo and destruction of connective tissue, such as that leading to life-threatening aneurysms in vasculature, can be tempered or halted all together. The treatment agents can be delivered or administered acutely or chronically according to various delivery methods, including sustained release methods incorporating perivascular or endovascular patches, use of microsphere carriers, hydrogels, or osmotic pumps.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
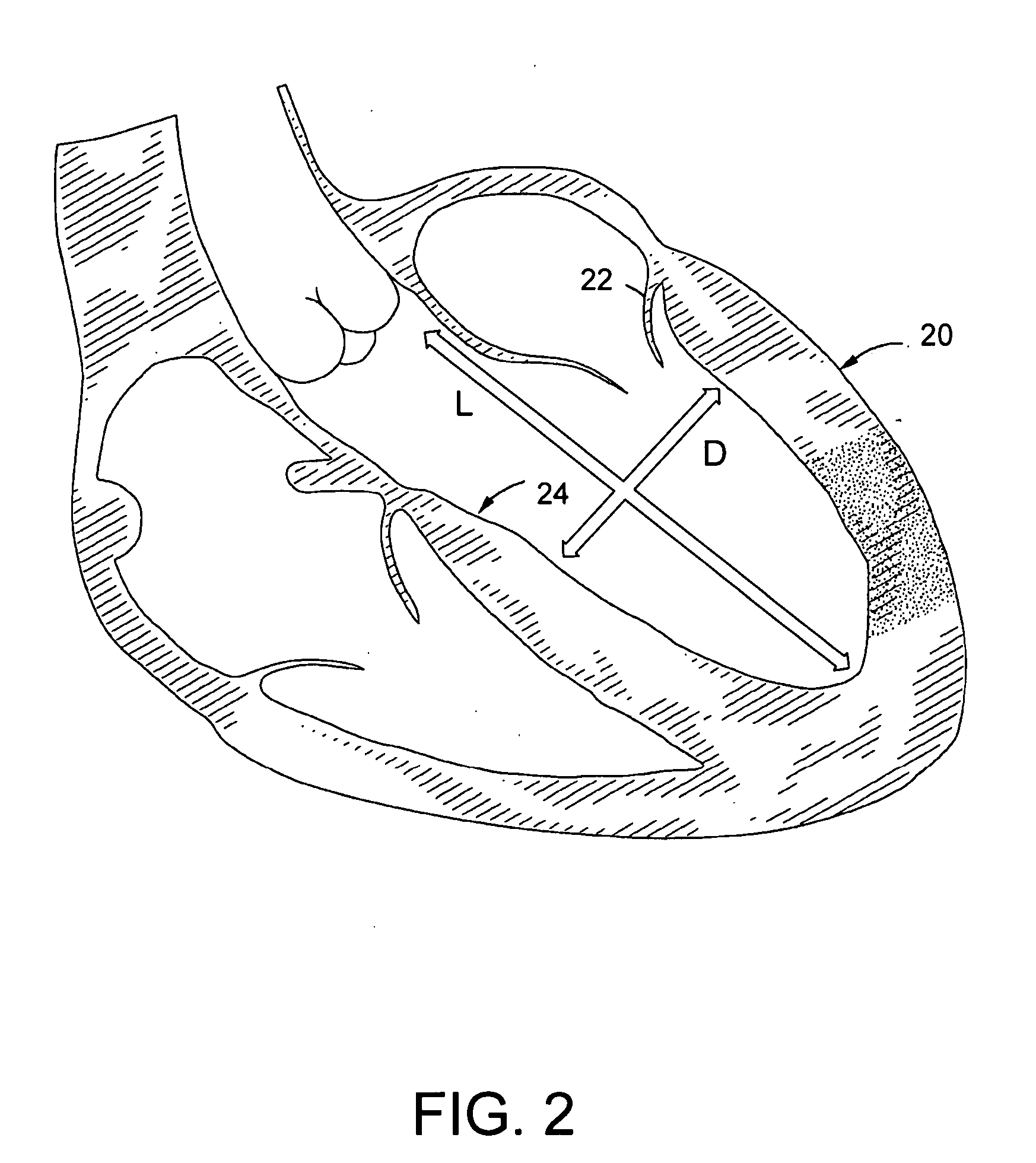
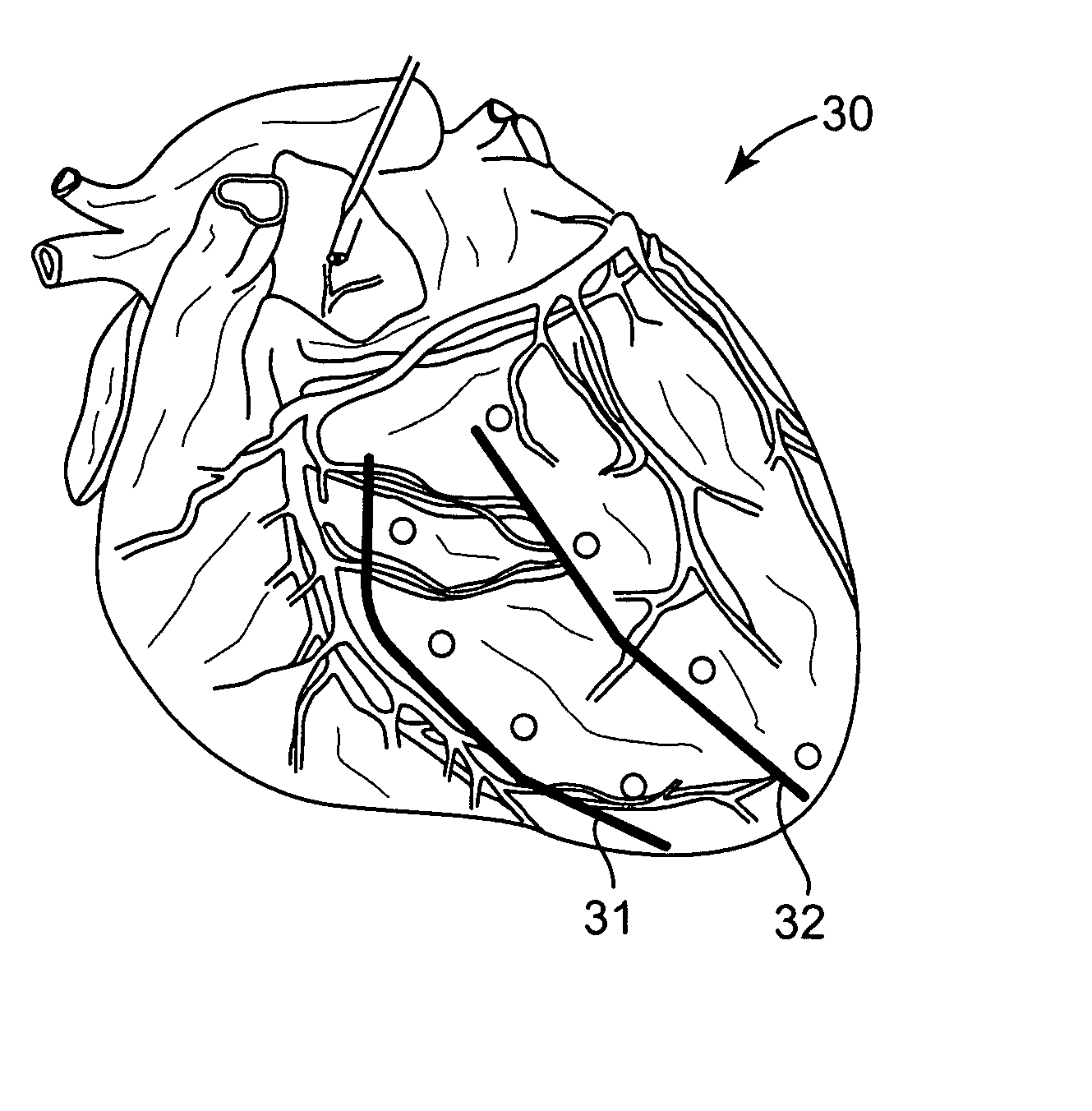
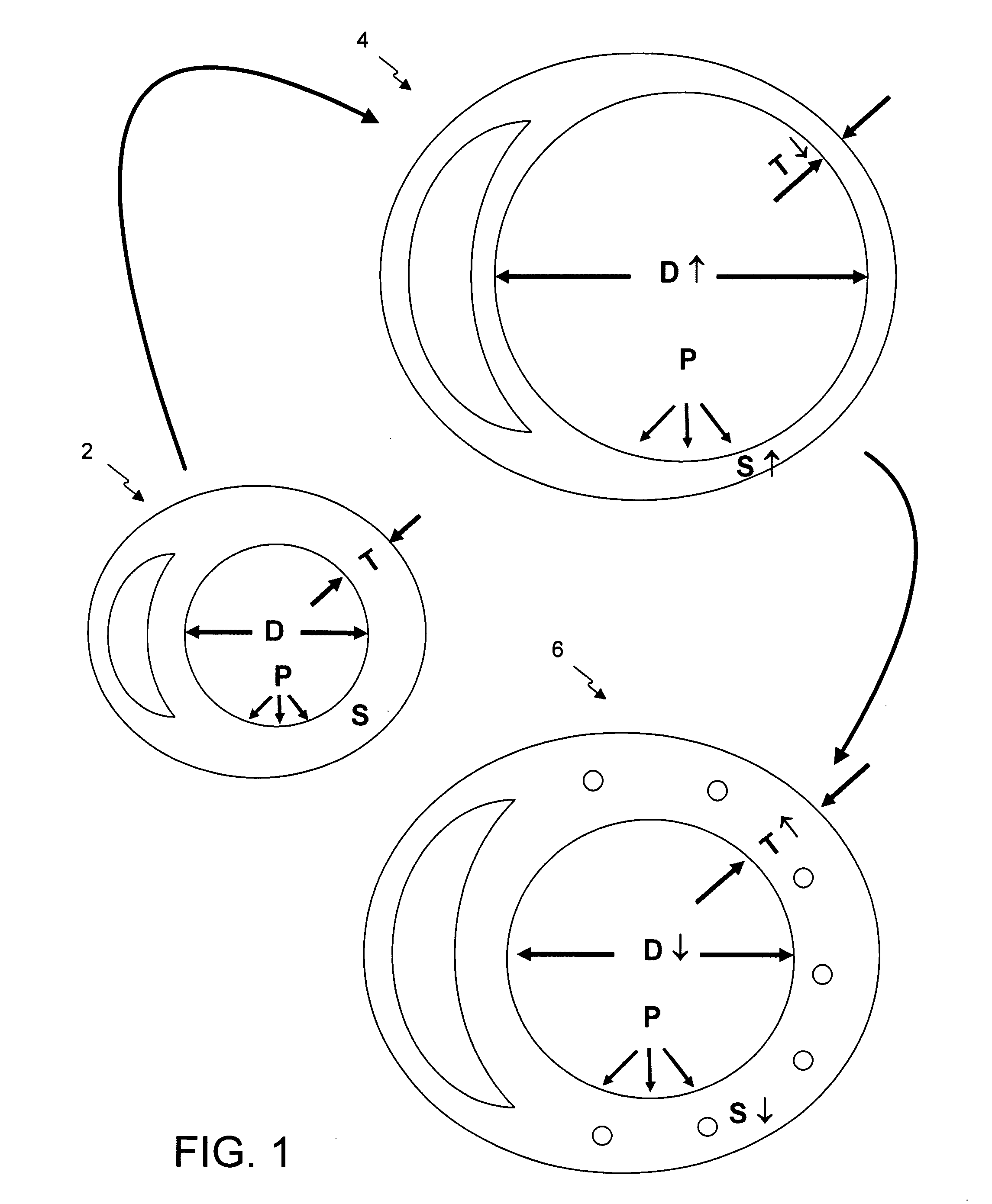
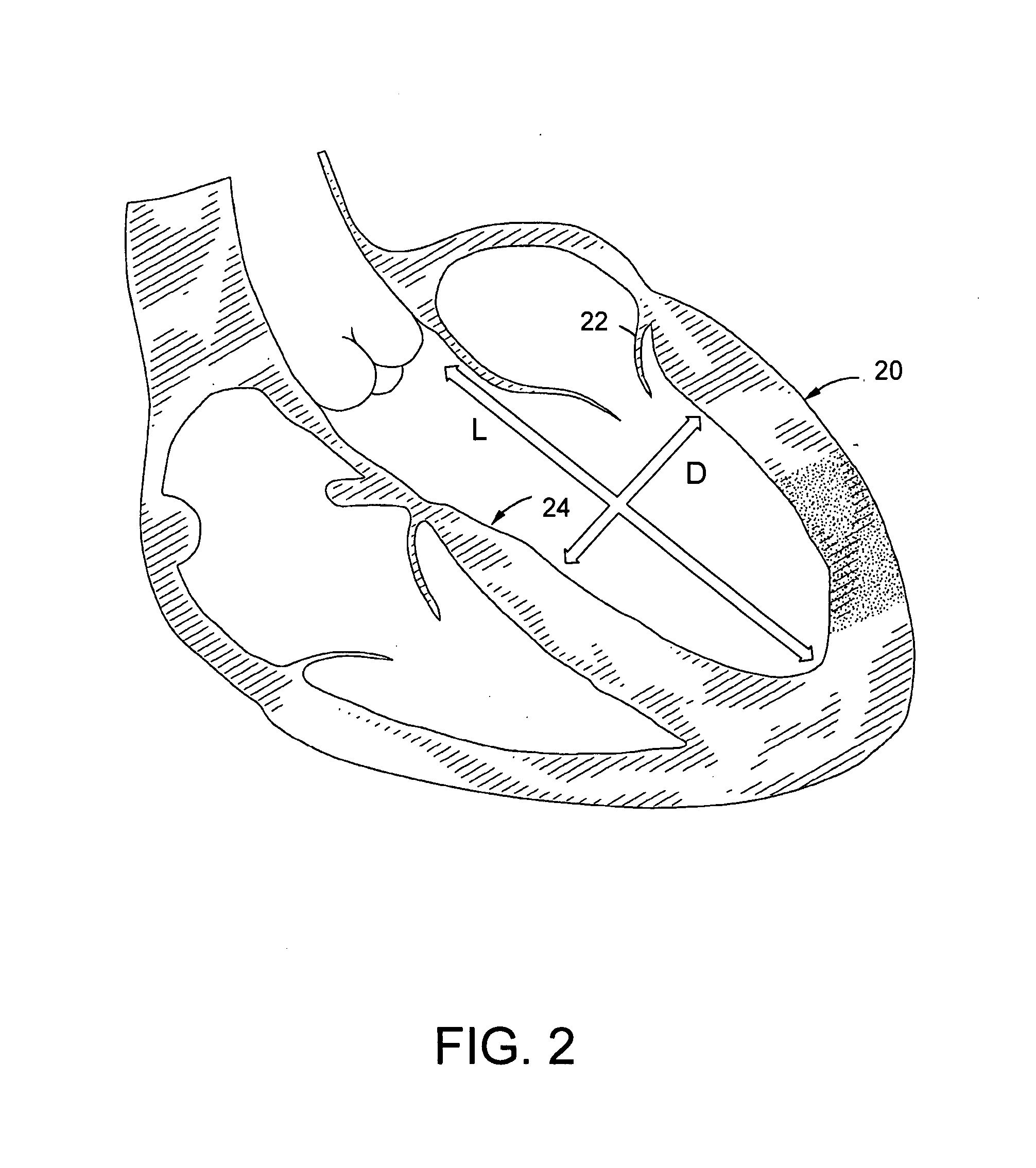
Intramyocardial patterning for global cardiac resizing and reshaping
ActiveUS20080065048A1Thickening myocardiumReducing systolic volumeInfusion syringesHeart valvesVentricular dysrhythmiaCardiac wall
Cardiomyopathy may be treated by distributing space-occupying agent within the myocardium in a pattern about one or more chambers of the heart, such that the space-modifying agent integrates into and thickens at least part of the cardiac wall about the chamber so as globally to reduce wall stress and stabilize or even reduce chamber size. Some patterns also cause a beneficial global reshaping of the chamber. These changes occur quickly and are sustainable, and have a rapid and sustainable therapeutic effect on cardiac function. Over time the relief of wall stress reduces oxygen consumption and promotes healing. Moreover, various long-term therapeutic effects may be realized depending on the properties of the space-occupying agent, including combinations with other therapeutic materials. Specific cardiac conditions treatable by these systems and methods include, for example, dilated cardiomyopathy (with or without overt aneurismal formations), congestive heart failure, and ventricular arrhythmias. Patterns of distribution of space-occupying agent within the myocardium for global resizing may also be used or augmented to treat localized conditions such as myocardial infarctions, overt aneurysm of the ventricular wall as typically forms in response to large transmural myocardial infarctions, and mitral regurgitation due to a noncompliant mitral valve. These techniques may also be used to treat localized conditions that may not yet have progressed to cardiomyopathy.
Intramyocardial patterning for treating localized anomalies of the heart
Cardiomyopathy may be treated by distributing space-occupying agent within the myocardium in a pattern about one or more chambers of the heart, such that the space-modifying agent integrates into and thickens at least part of the cardiac wall about the chamber so as globally to reduce wall stress and stabilize or even reduce chamber size. Some patterns also cause a beneficial global reshaping of the chamber. These changes occur quickly and are sustainable, and have a rapid and sustainable therapeutic effect on cardiac function. Over time the relief of wall stress reduces oxygen consumption and promotes healing. Moreover, various long-term therapeutic effects may be realized depending on the properties of the space-occupying agent, including combinations with other therapeutic materials. Specific cardiac conditions treatable by these systems and methods include, for example, dilated cardiomyopathy (with or without overt aneurismal formations), congestive heart failure, and ventricular arrhythmias. Patterns of distribution of space-occupying agent within the myocardium for global resizing may also be used or augmented to treat localized conditions such as myocardial infarctions, overt aneurysm of the ventricular wall as typically forms in response to large transmural myocardial infarctions, and mitral regurgitation due to a noncompliant mitral valve. These techniques may also be used to treat localized conditions that may not yet have progressed to cardiomyopathy.
Owner:CARDIOPOLYMERS +2
Method and system for monitoring a condition of cerebral aneurysms
ActiveUS20200085318A1Avoid developmentSaves populationMedical simulationImage enhancementRadiologyBrain aneurysm
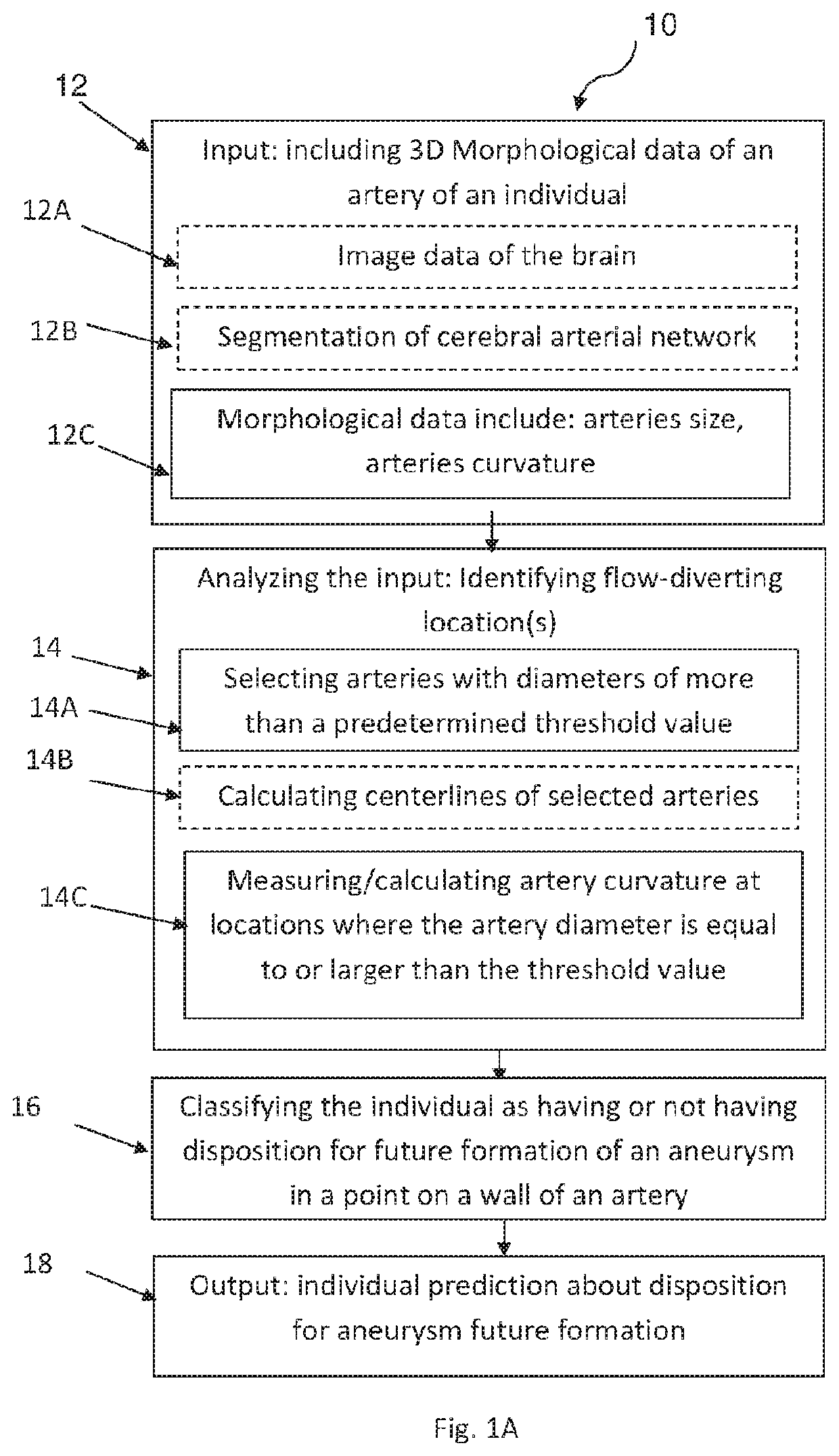
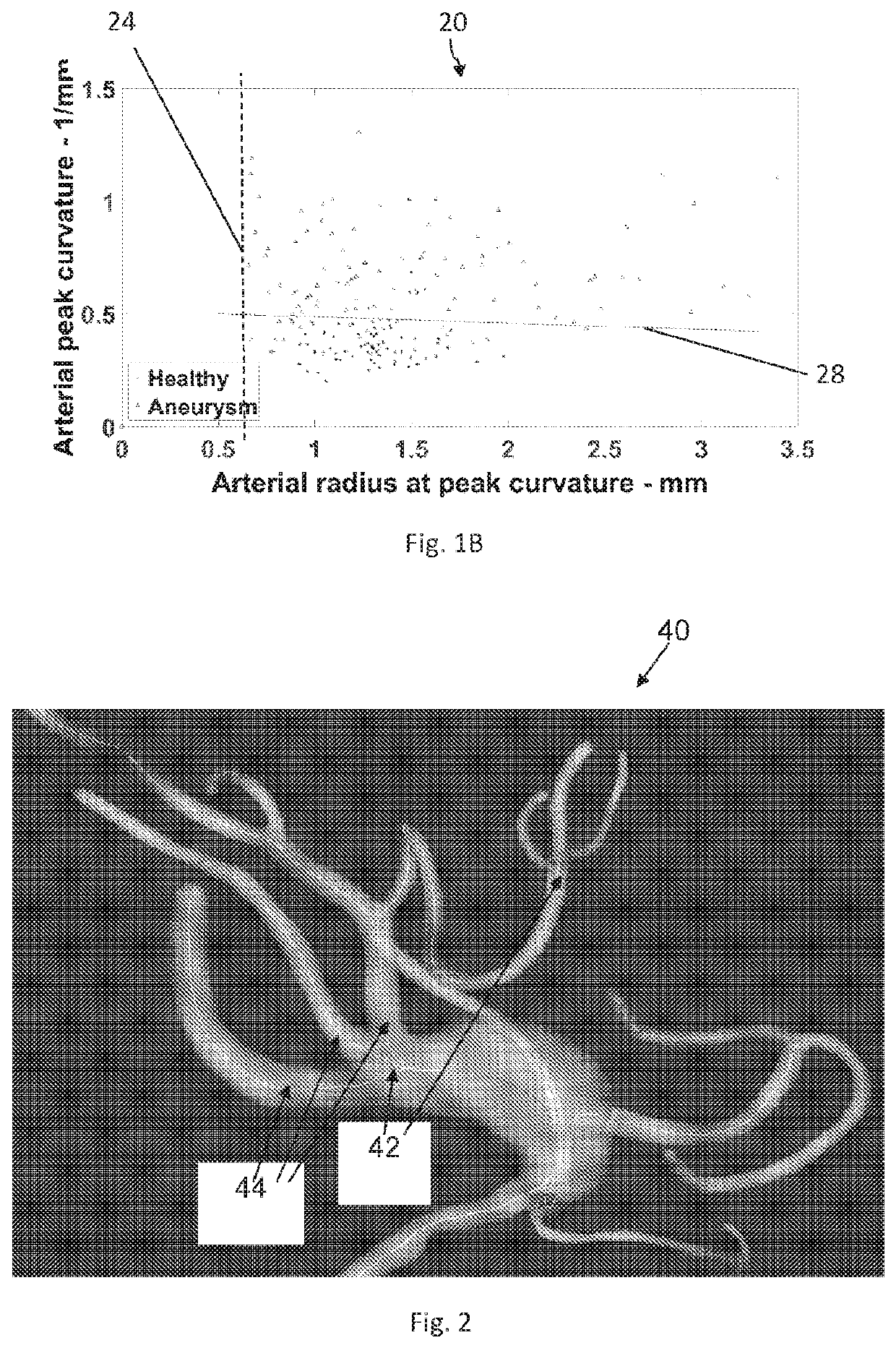
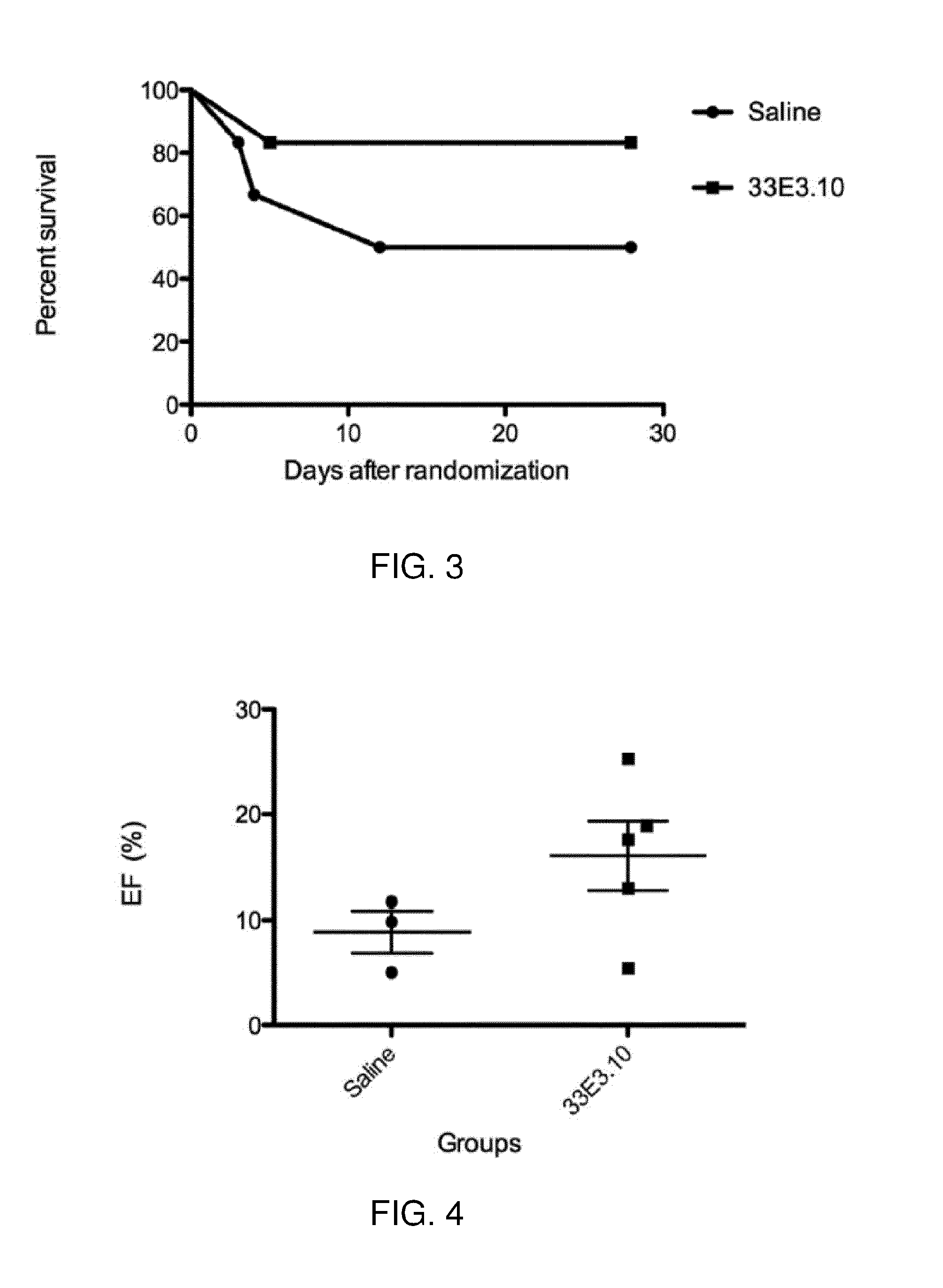
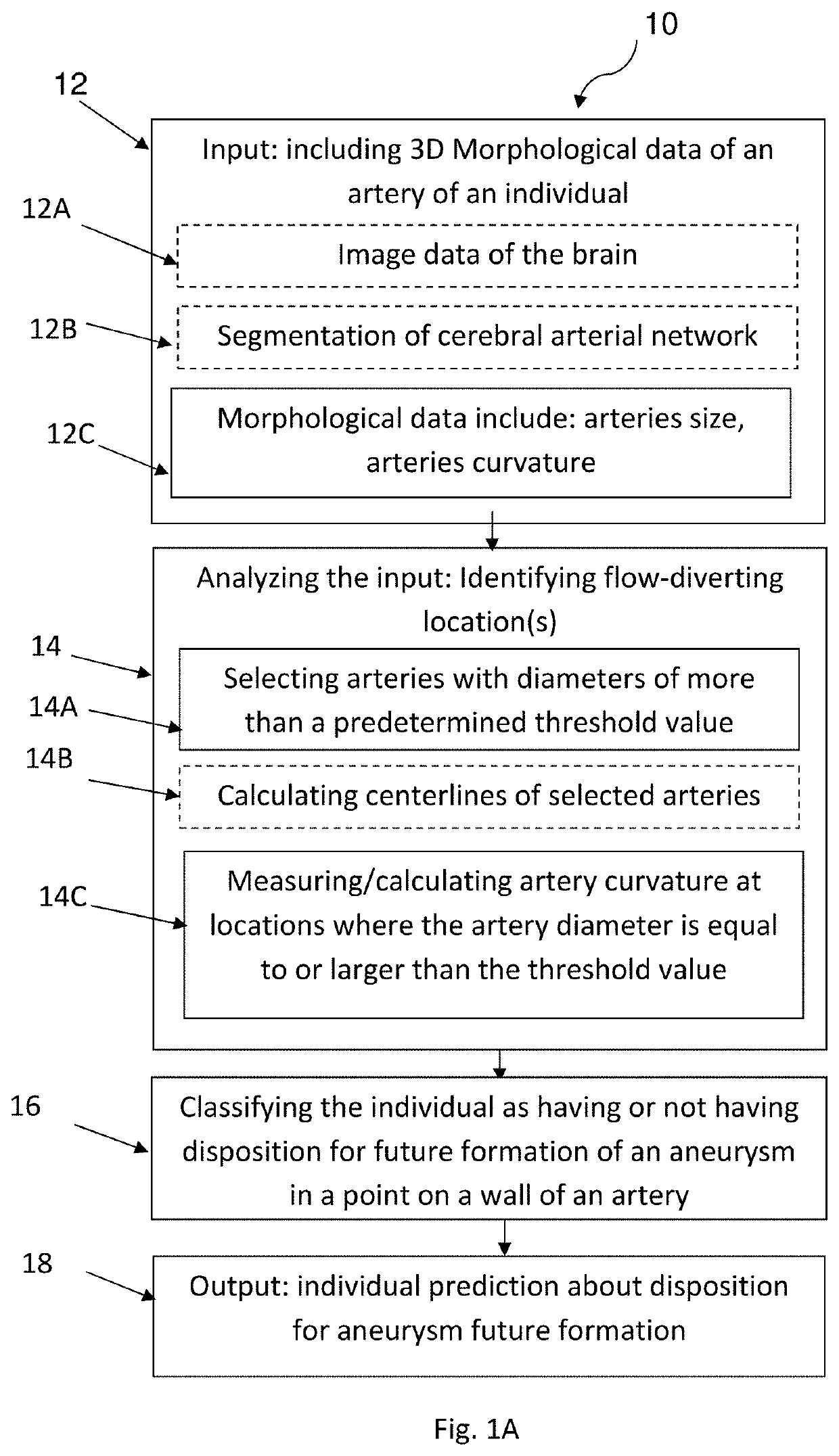
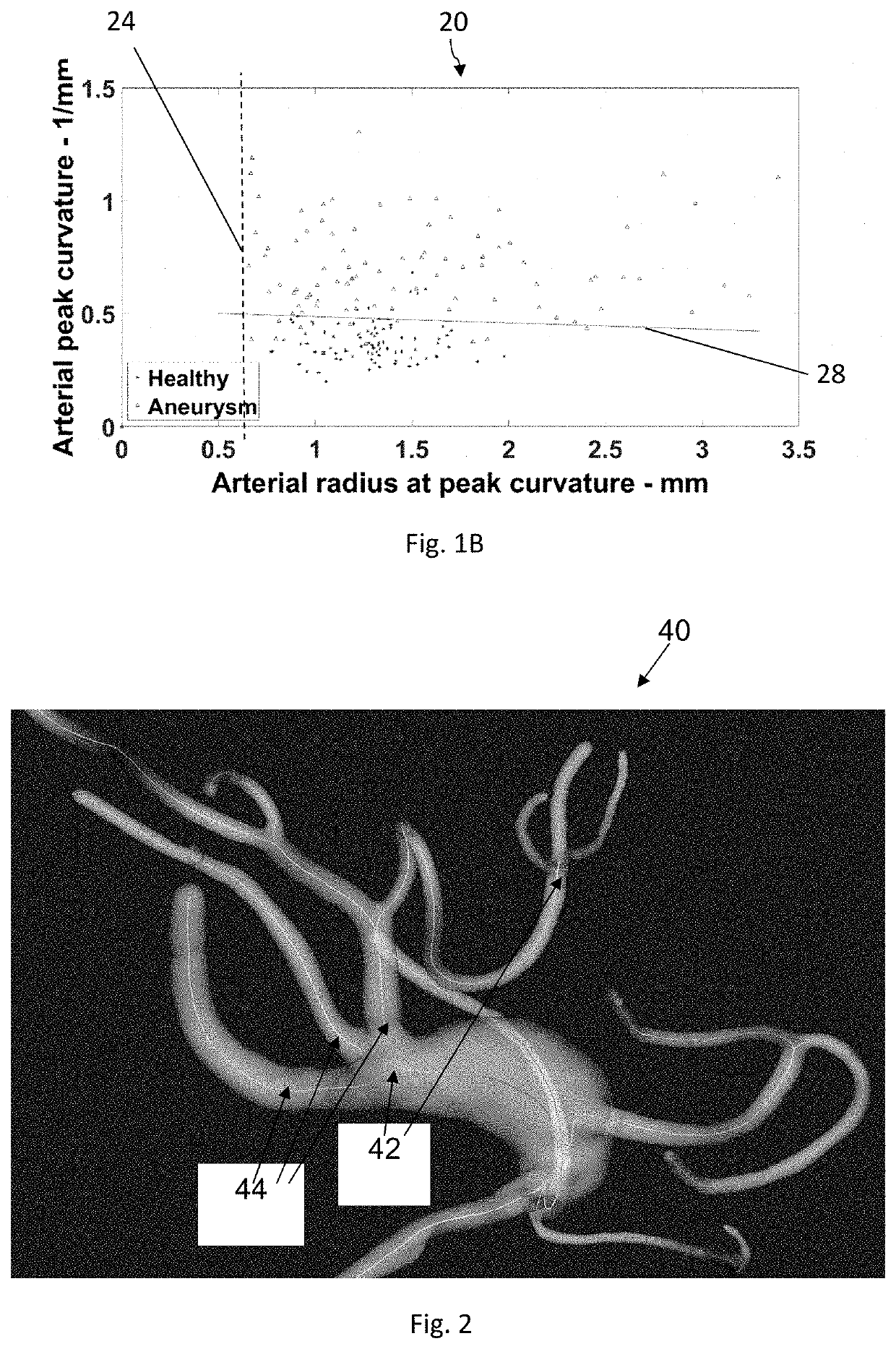
Methods and systems for controlling aneurysm initiation or formation in an individual are presented; the technique comprises receiving morphological data of an artery being indicative of at least first and second geometrical parameters of the artery along its trajectory; analyzing the data to identify at least one flow-diverting location along the artery satisfying first and second predetermined conditions of the geometrical parameters; classifying the individual as having or not having disposition for future formation of an aneurysm, depending respectively on whether the at least one flow-diverting location is identified or not and generating classification data; and generating prediction data for the individual with regard to future aneurysm formation.
Owner:ANEUSCREEN LTD
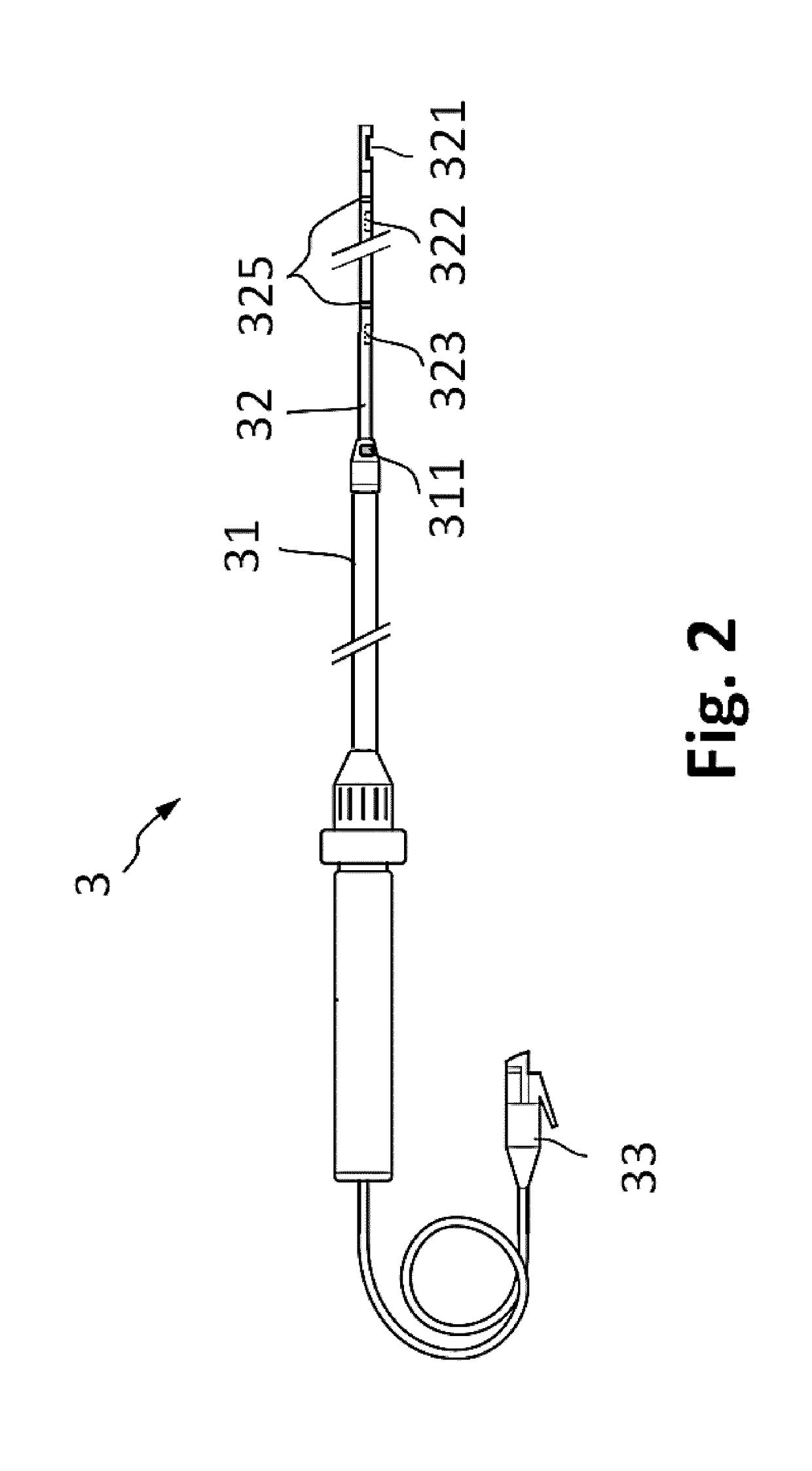
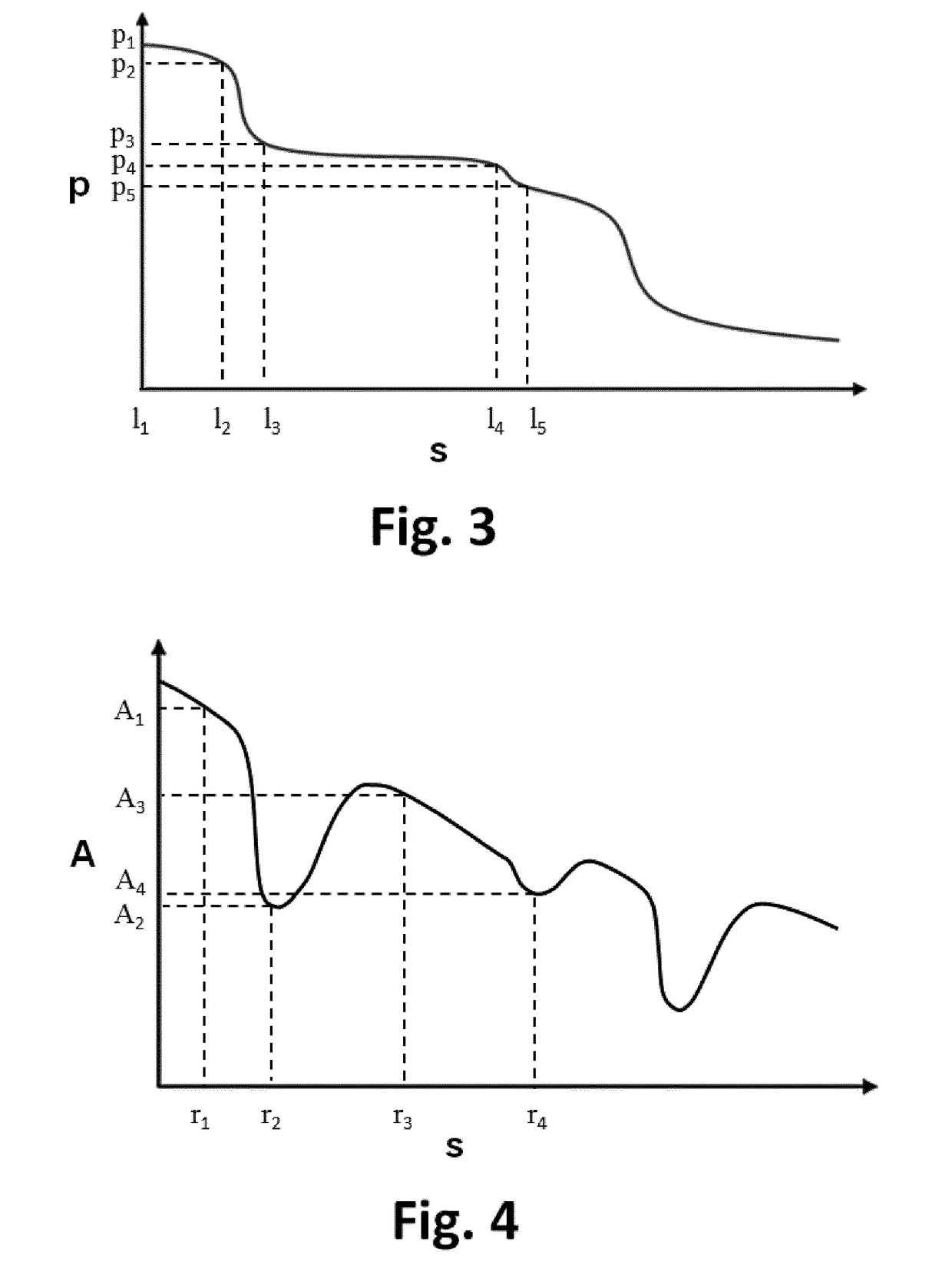
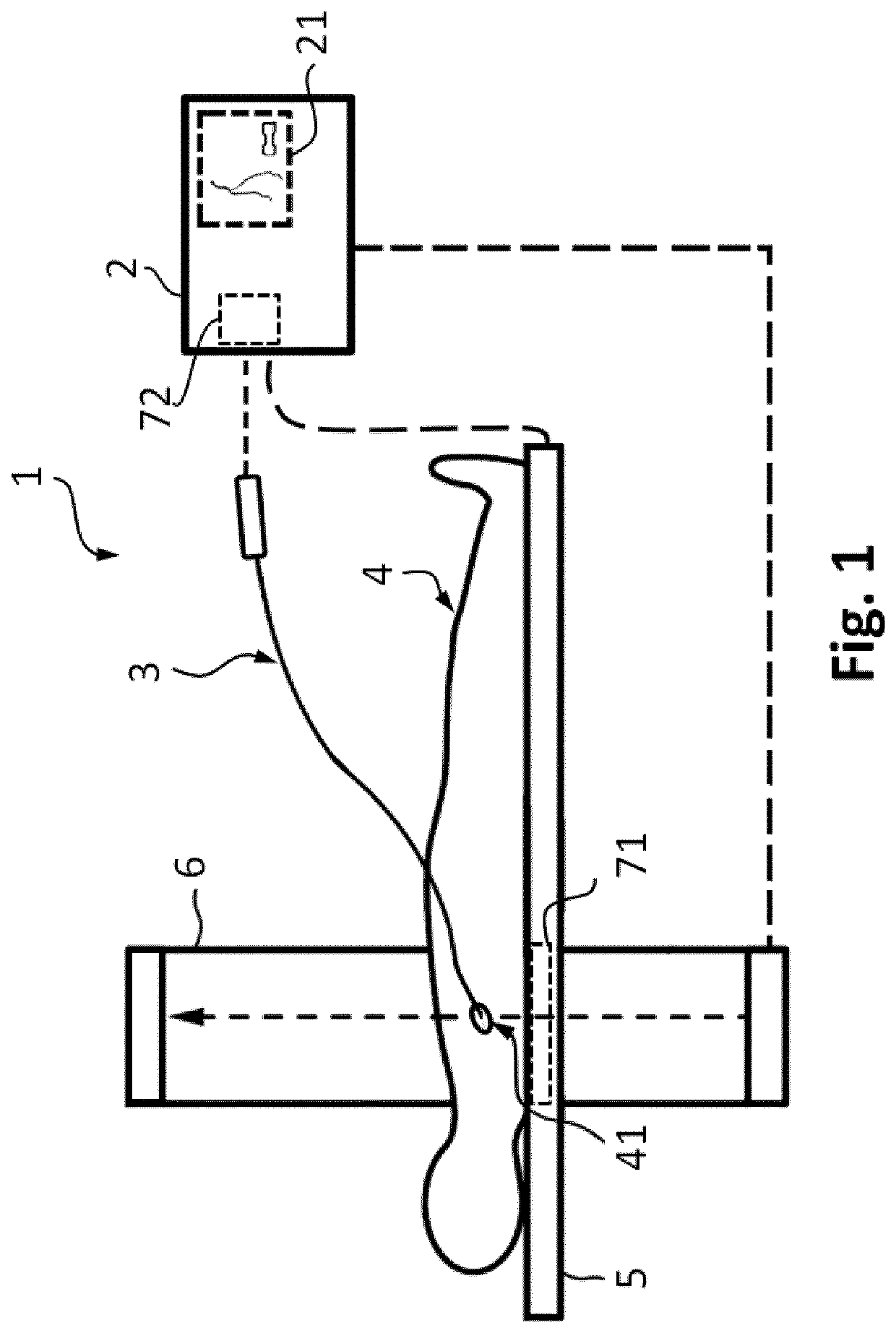
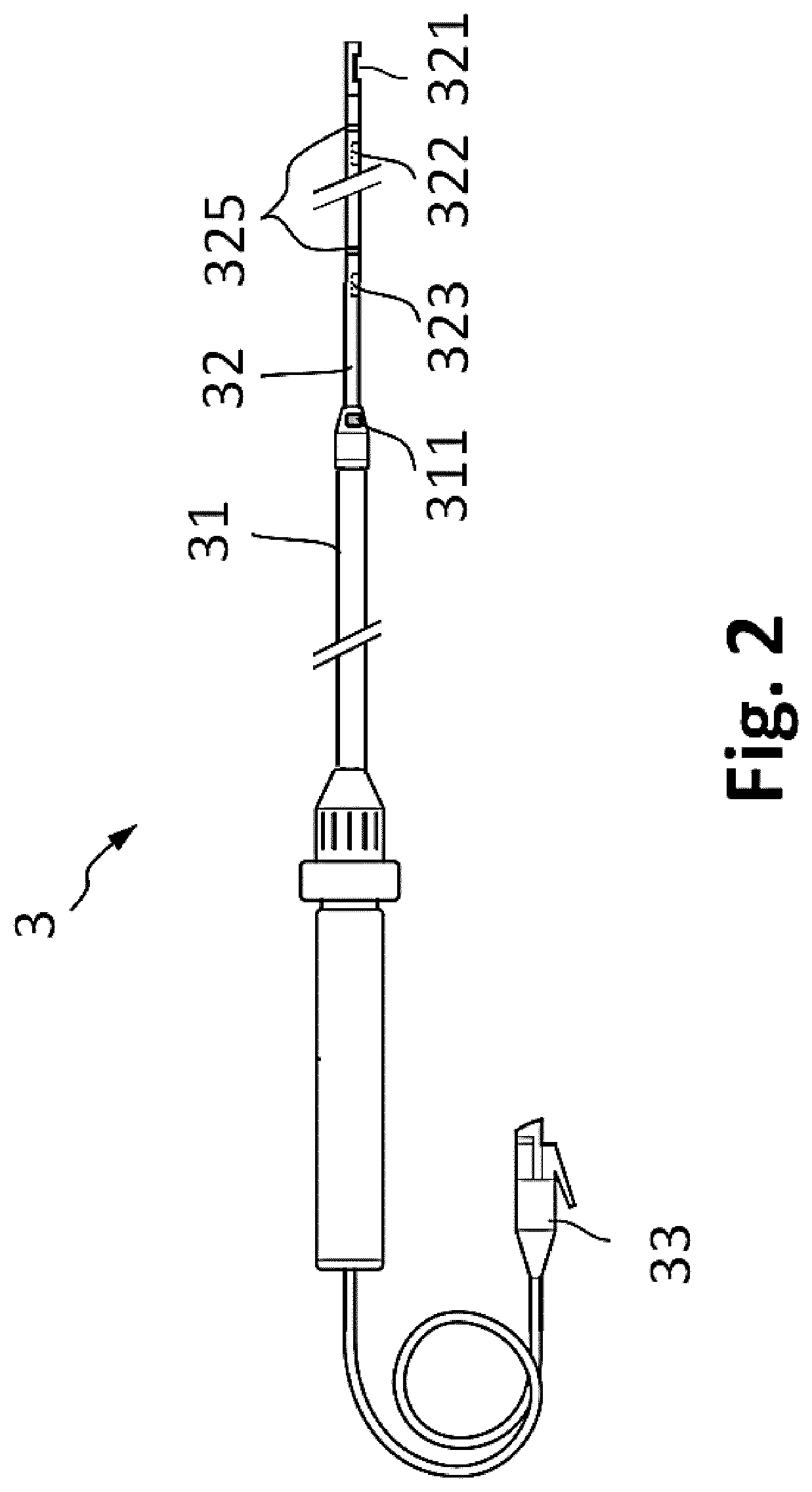
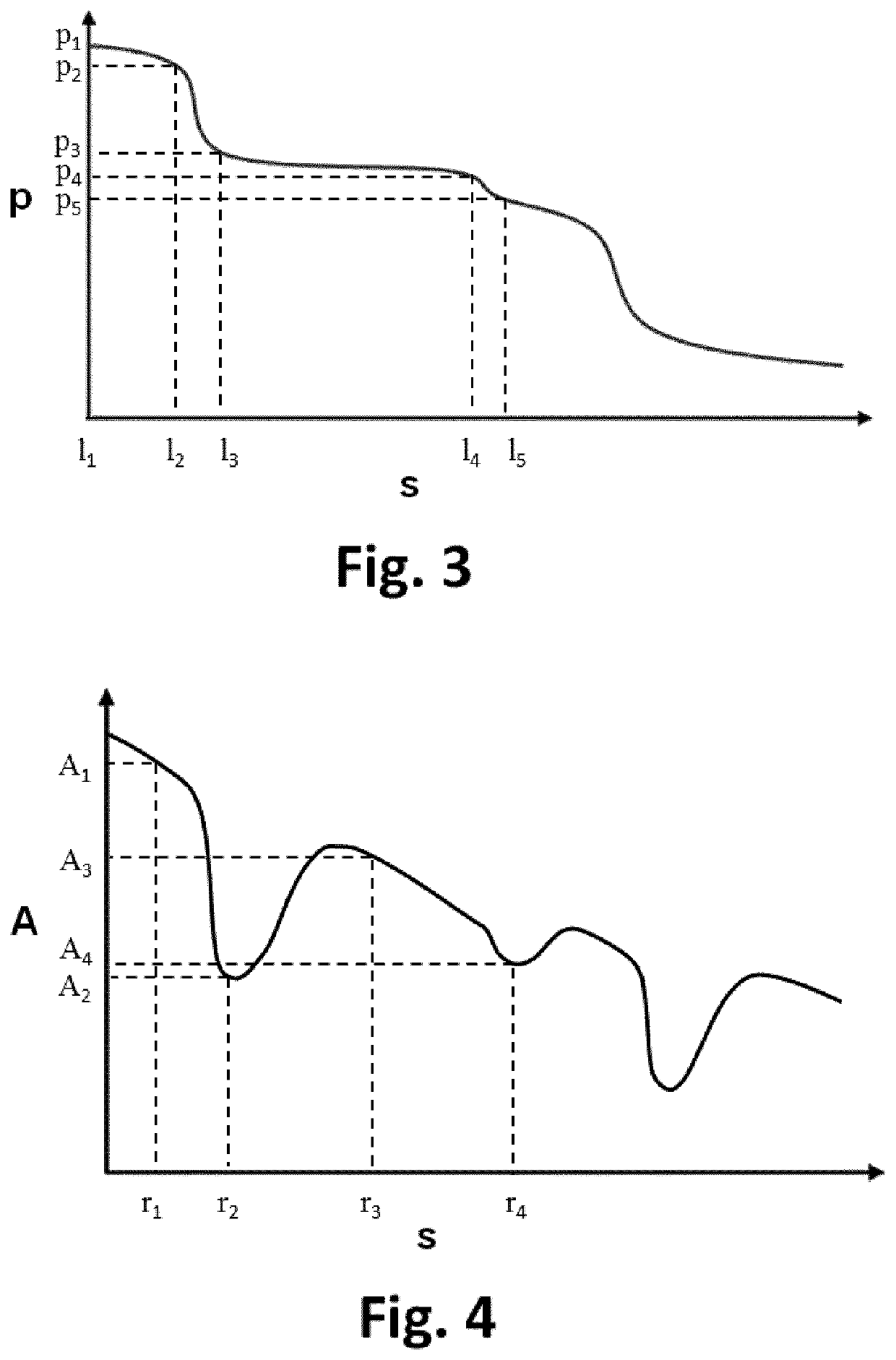
Apparatus for vessel characterization
ActiveUS20190046047A1Easy constructionReplacement is neededUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPulsatile blood flow
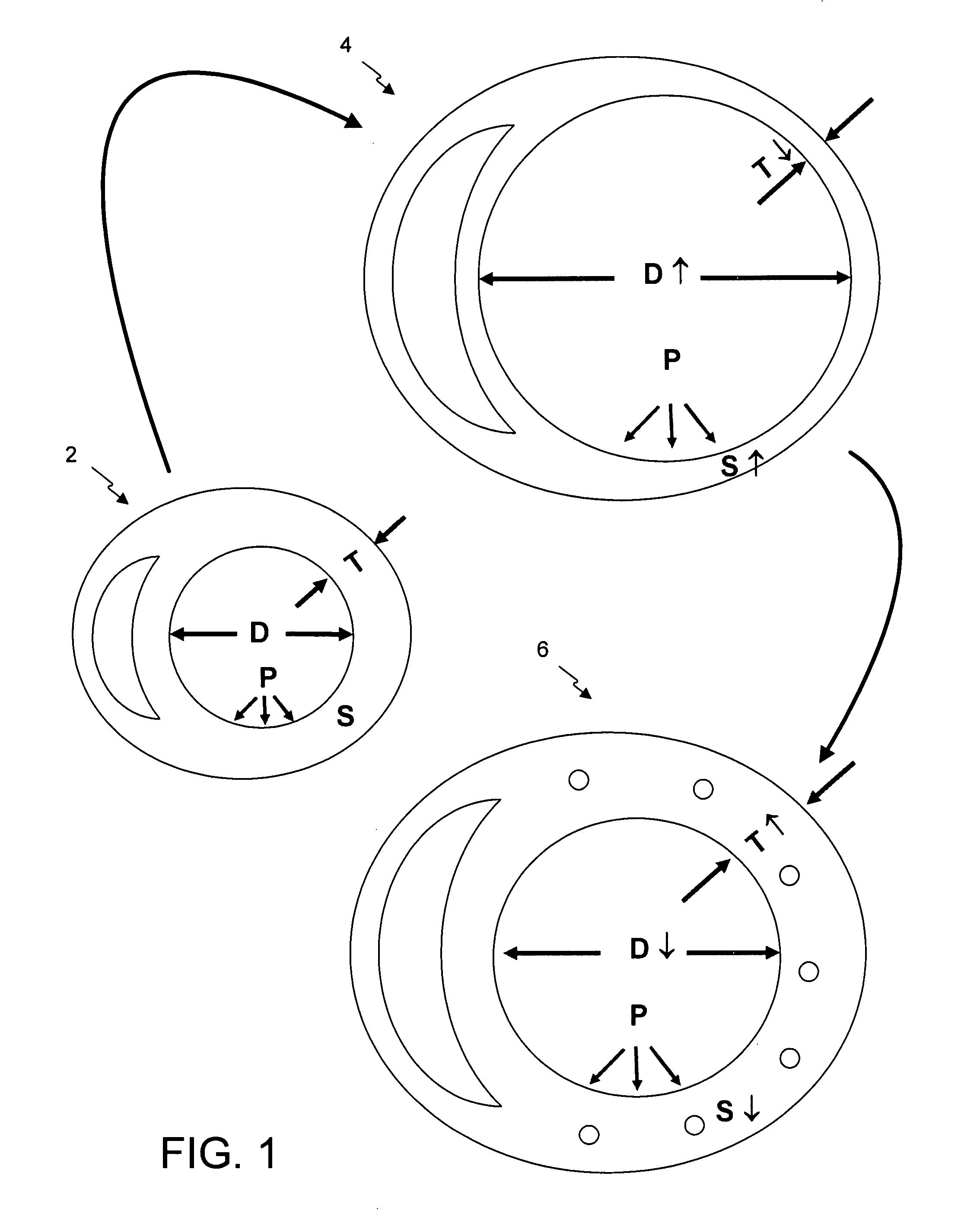
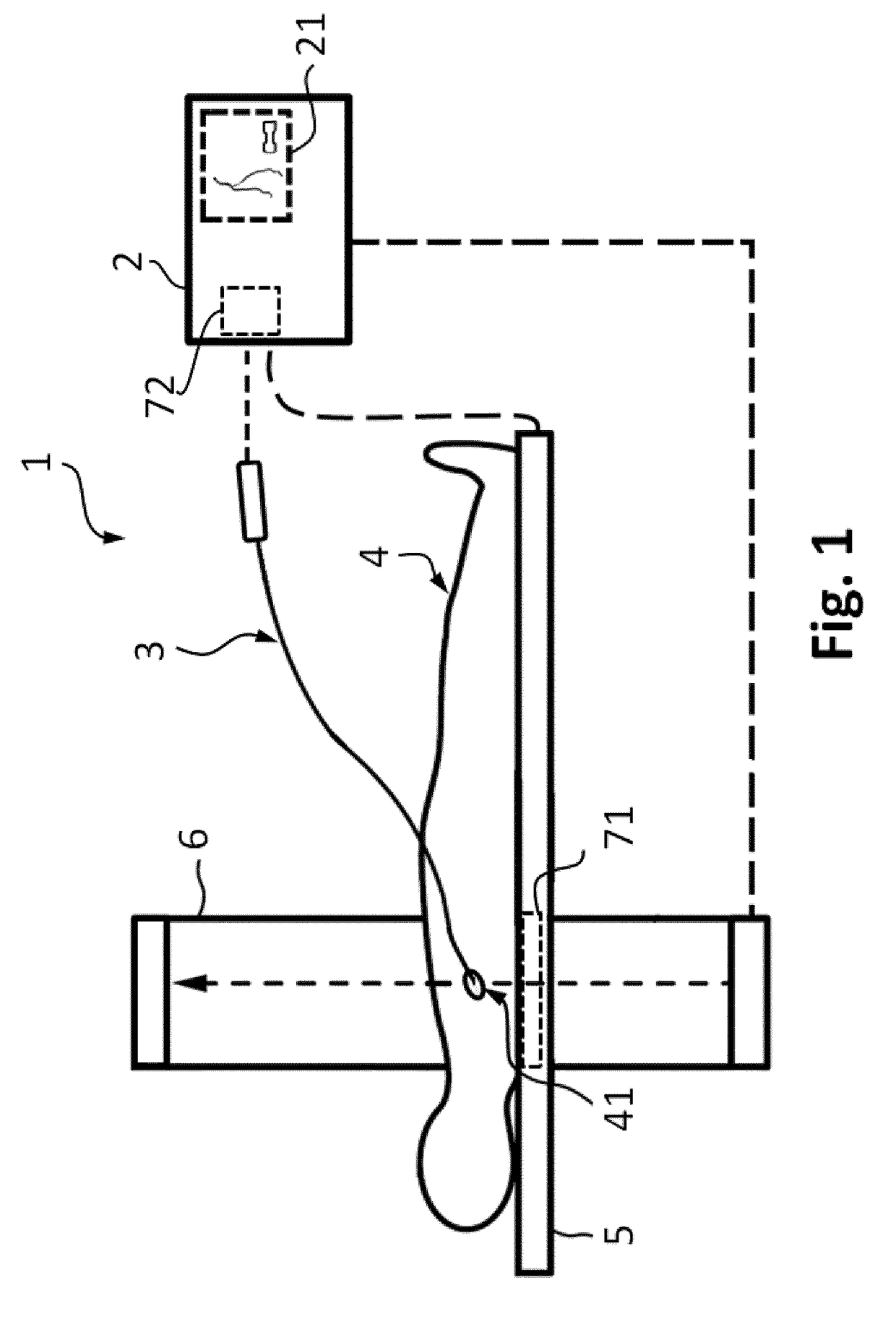
The invention discloses an apparatus (2), a system (1) and a method (100) for characterization of vessels and for vessel modeling. The cross sectional area (A1) of the vessel is derived from pressure measurements (p1, p2) obtained by an instrument (3) from within the vessel. When multiple cross sectional areas (A1, A2) are derived for multiple reference positions (r1, r2) based on pressure measurements (p1, p2, p3) along the vessel, a representation (20, 30) of the vessel can be rendered, without requiring any imaging modality. Furthermore, the effect of the pulsatile blood flow on the elasticity of the vessel walls can be visualized, supporting assessment of a stenosis or an aneurysm formation along the vessel.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
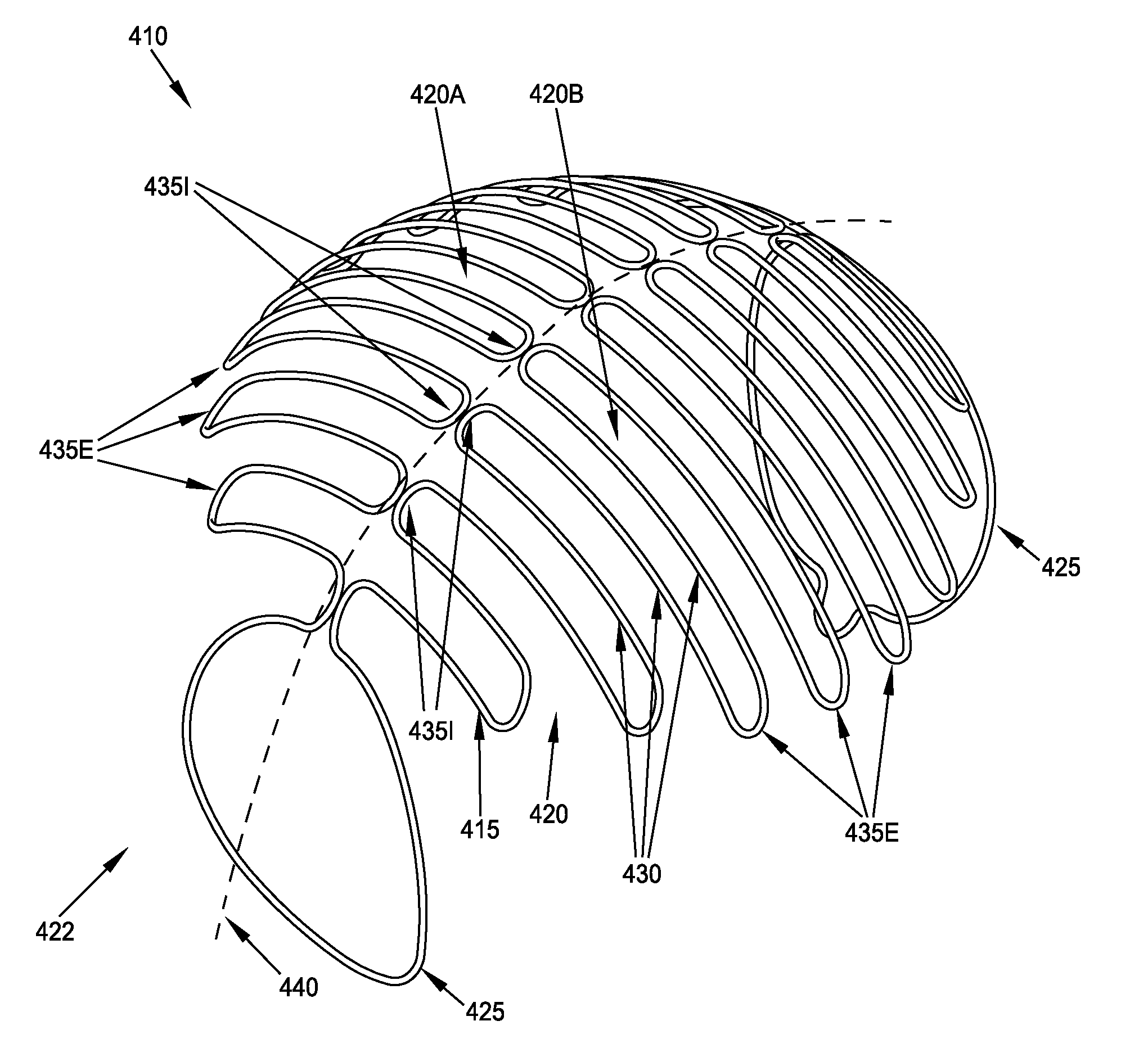
Method and apparatus for restricting flow through an opening in the side wall
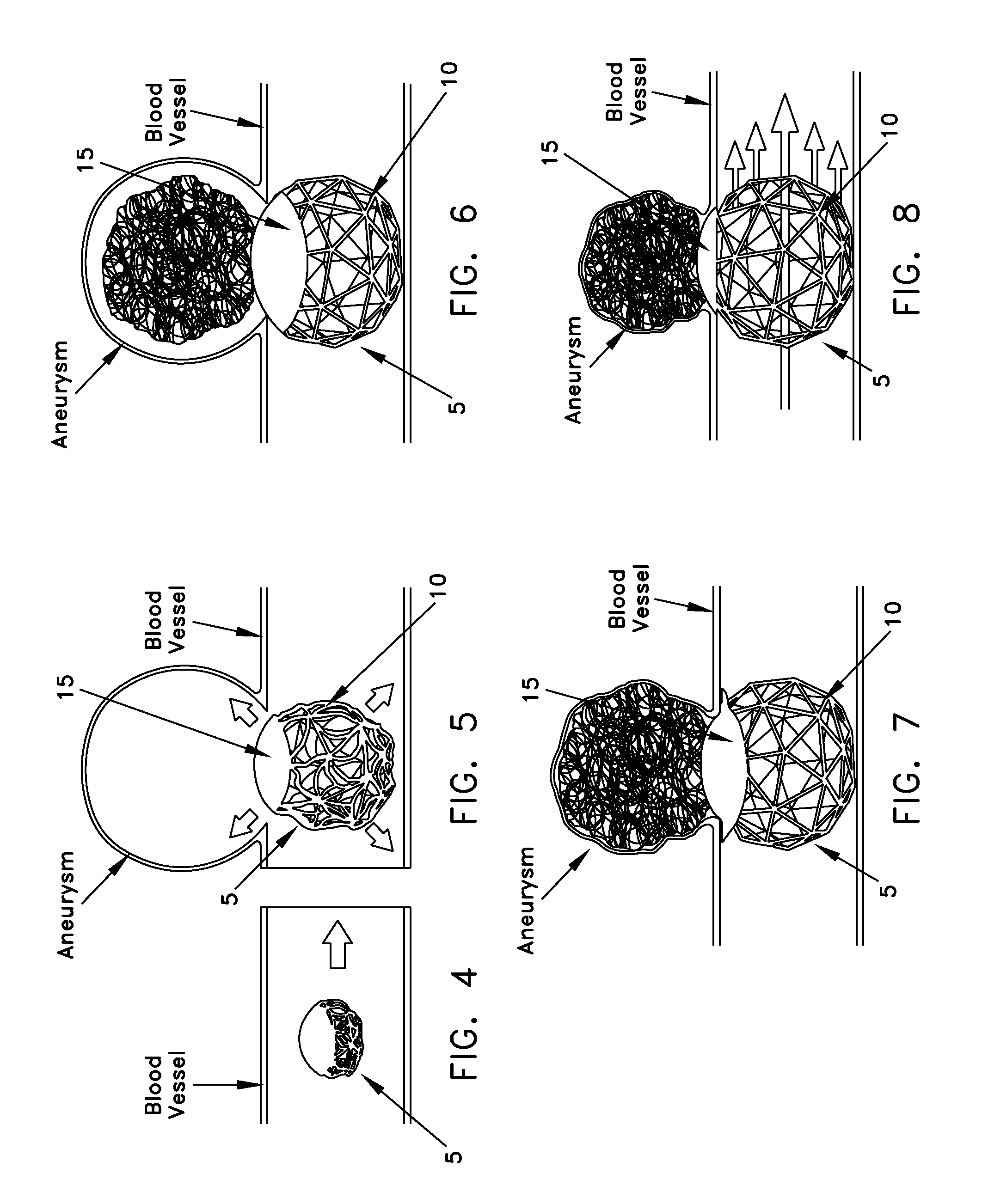
A device comprising a single closed loop of elastic filament configurable between (i) a first configuration for movement along a blood vessel; and (ii) a second configuration for lodging within a blood vessel, the second configuration providing a single flow-restricting face sized and configured to cover the mouth of the aneurysm and obstruct blood flow to the aneurysm while permitting substantially normal blood flow through the blood vessel, with the degree of obstruction at the mouth of the aneurysm being such that the aneurysm thromboses when the face is positioned over the aneurysm, the flow-restricting face comprising a plurality of lengths of the closed loop of filament disposed in close proximity to one another in a switchback configuration, and at least one leg for holding the flow-restricting face adjacent the mouth of the aneurysm, the leg configured so as to maintain substantially normal blood flow through the blood vessel.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Cell-Free Tissue Engineered Vascular Grafts
ActiveUS20140147484A1Convenient and smoothReduced graft stenosisBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsRestenosisCell free
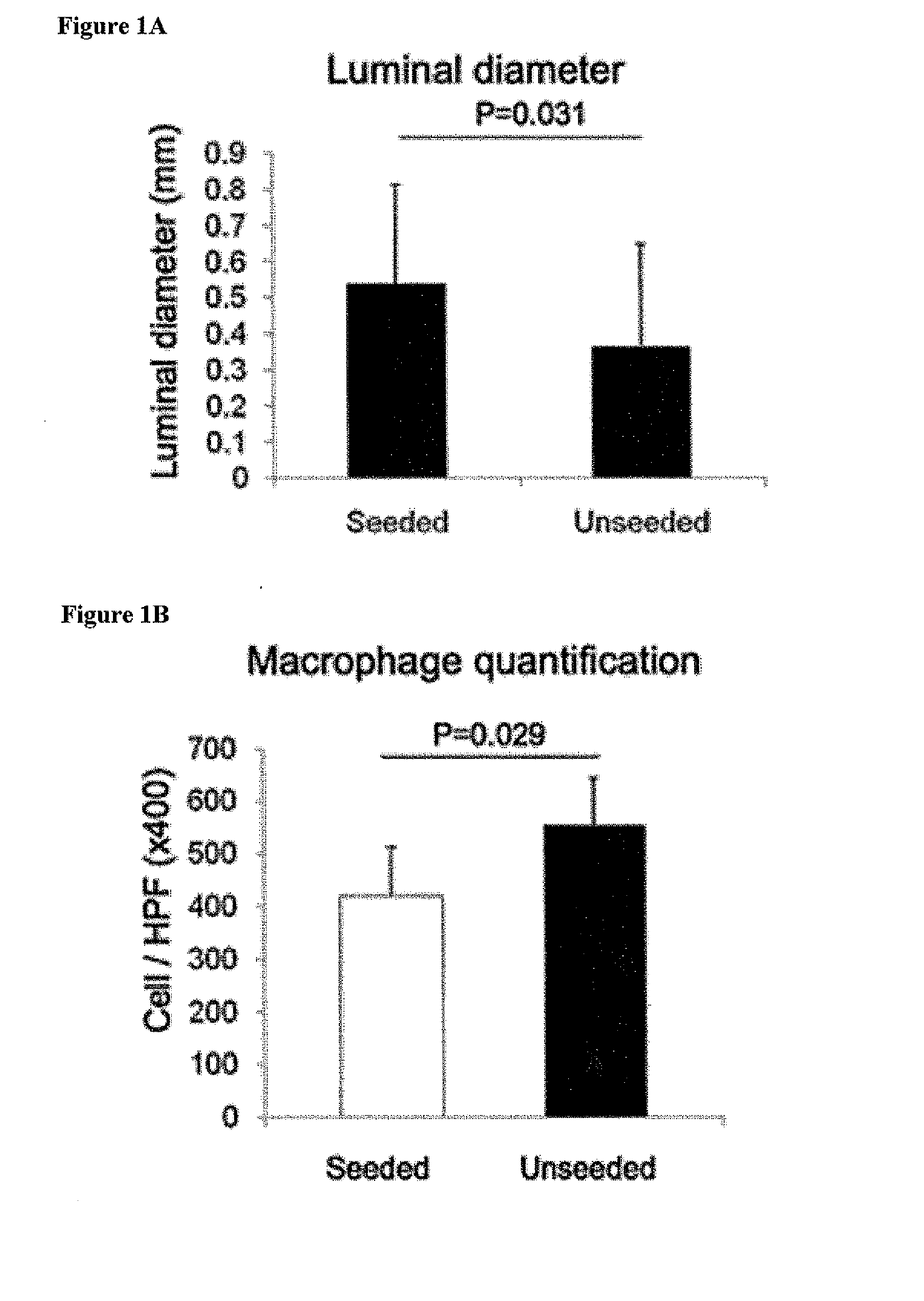
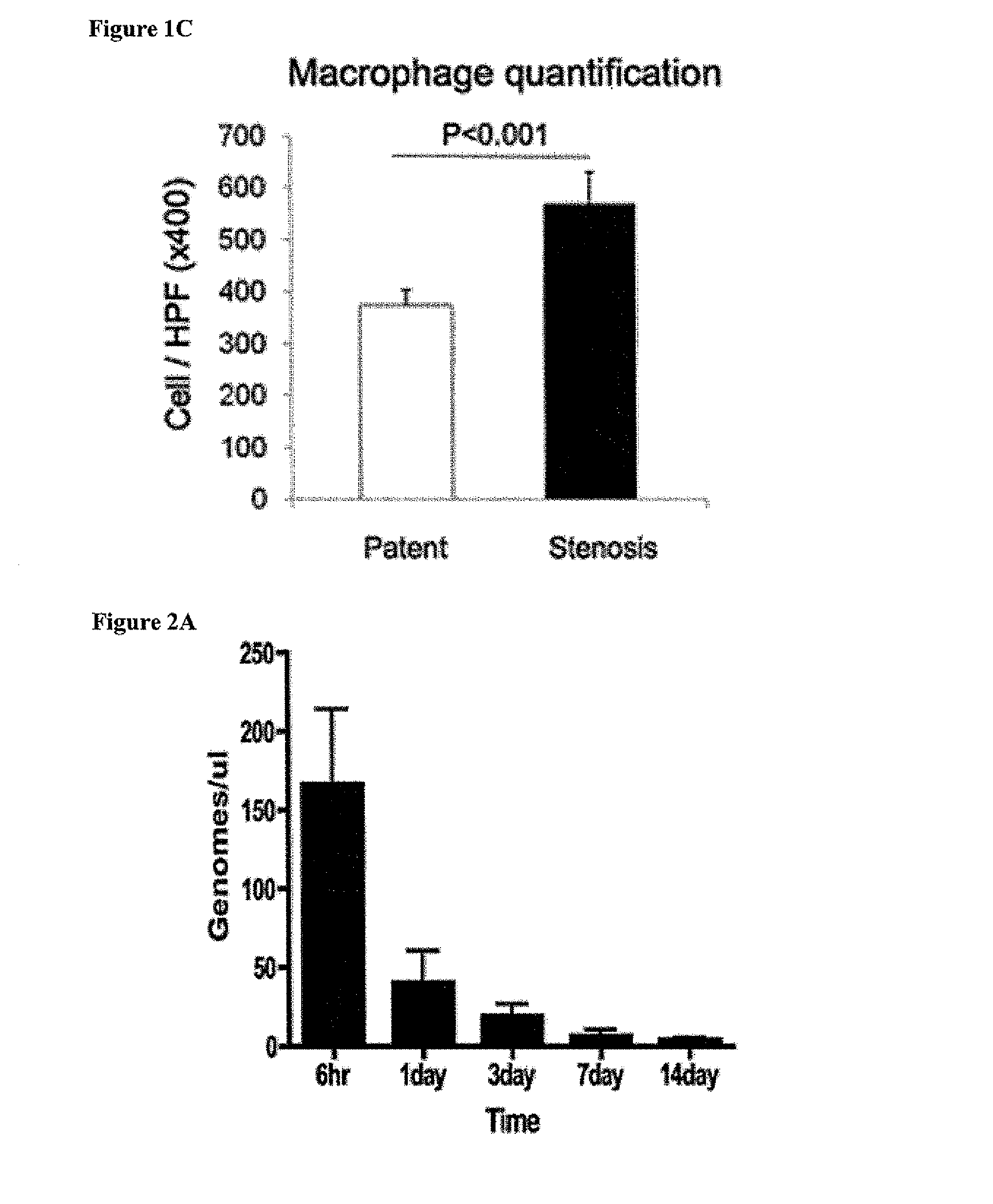
A composition containing a macrophage inhibitor may be administered in an effective amount to prevent, inhibit or reduce restenosis, thrombus or aneurysm formation in implanted polymeric vascular grafts. The composition may be administered prior to vascular graft implantation, at the same time as vascular graft implantation, following vascular graft implantation, or any combination thereof. Examplary macrophage inhibitors include bisphosphonates, anti-folate drugs and antibodies, preferably in a controlled release or liposomal formulation.
Owner:YALE UNIV
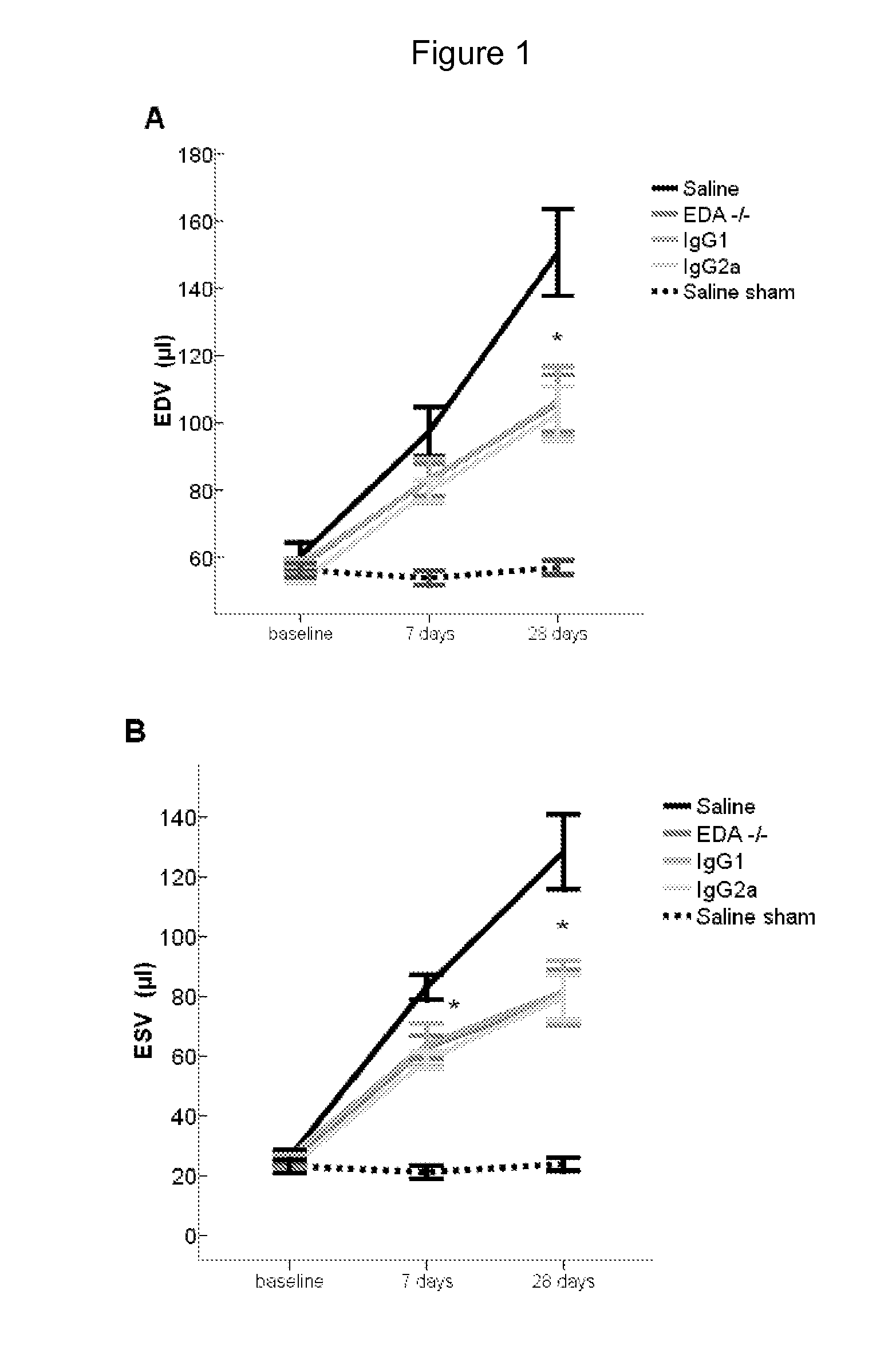
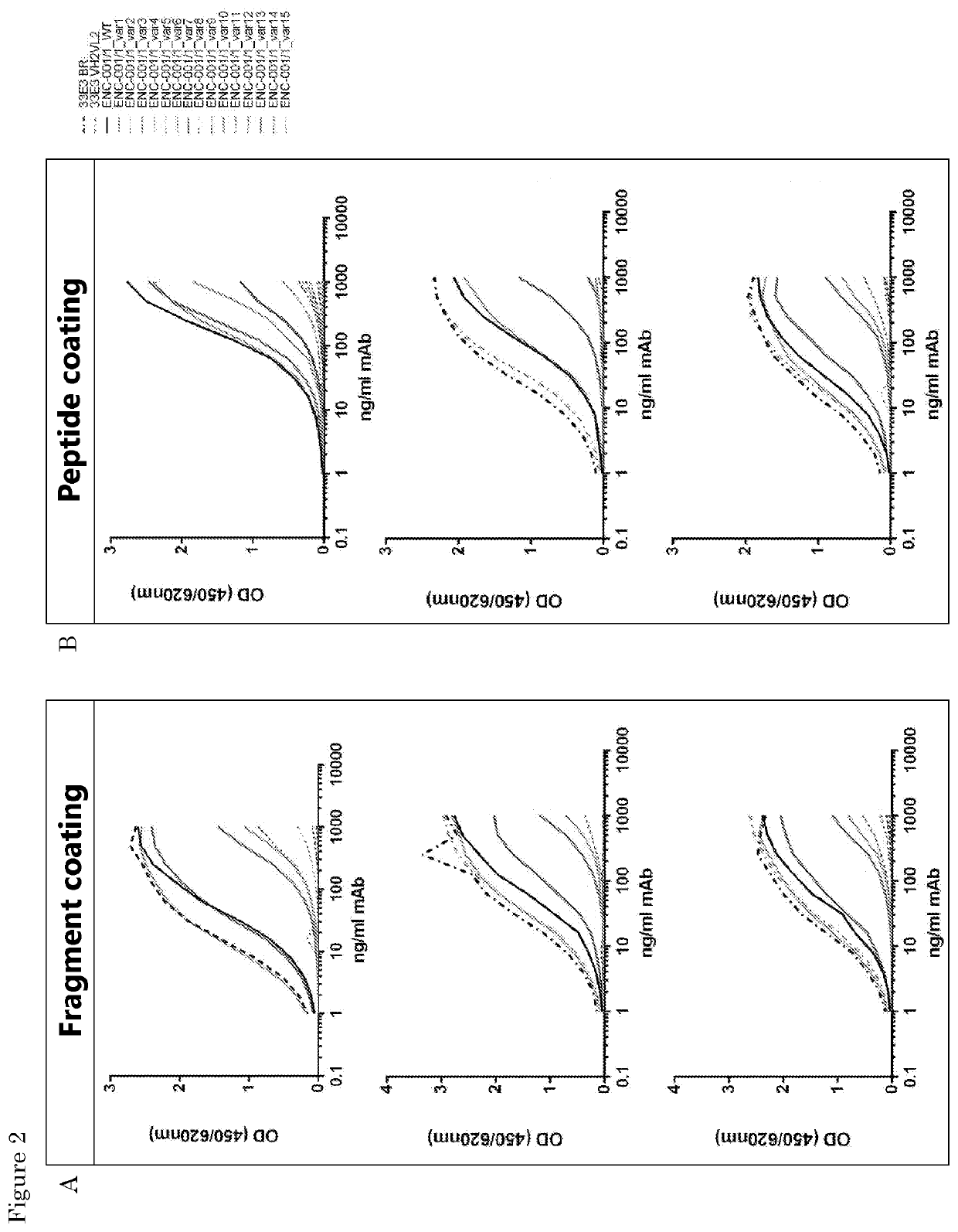
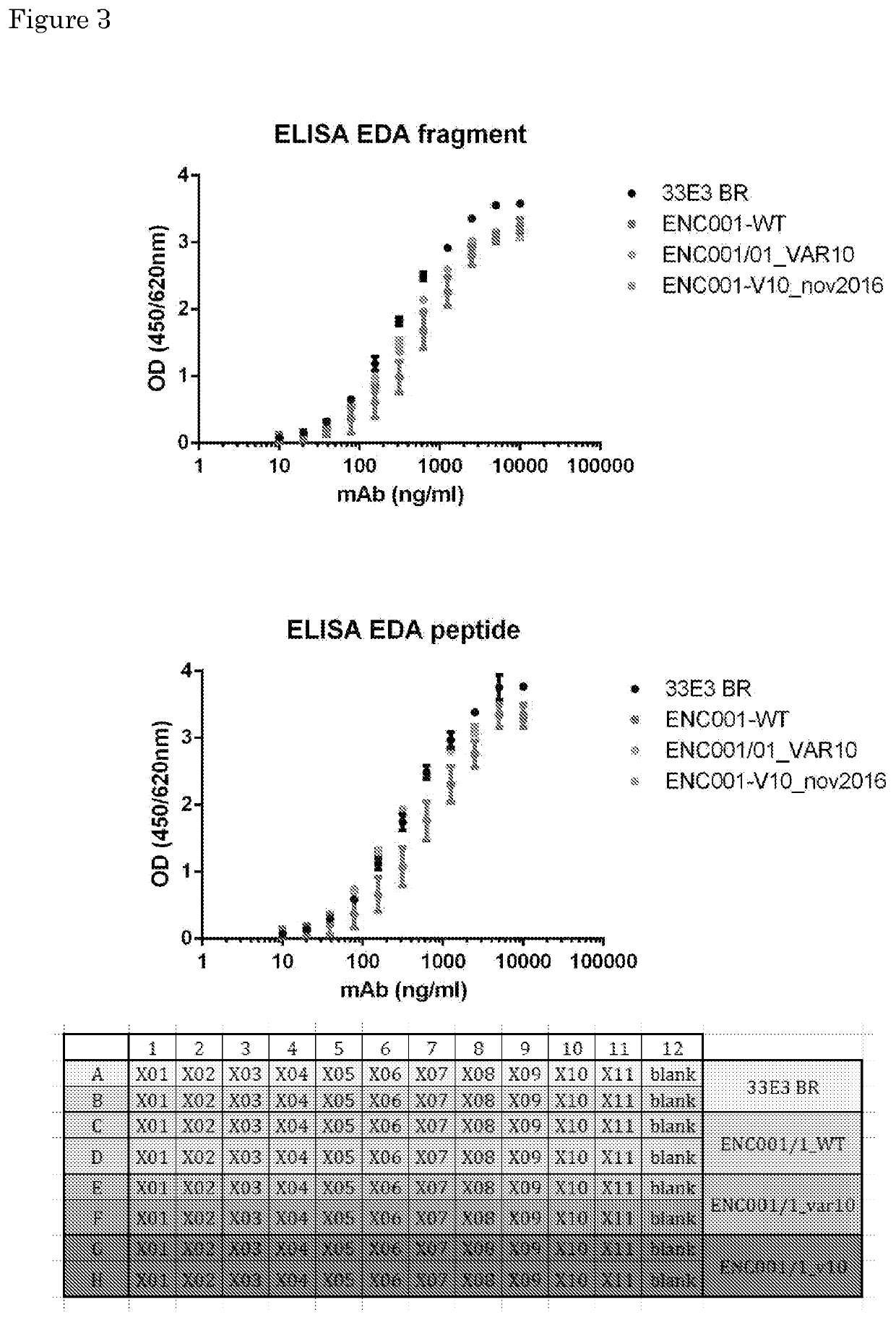
Immunoglobulin-like molecules directed against fibronectin-eda
InactiveCN107406498AImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntibody ingredientsPressure overloadIschemic injury
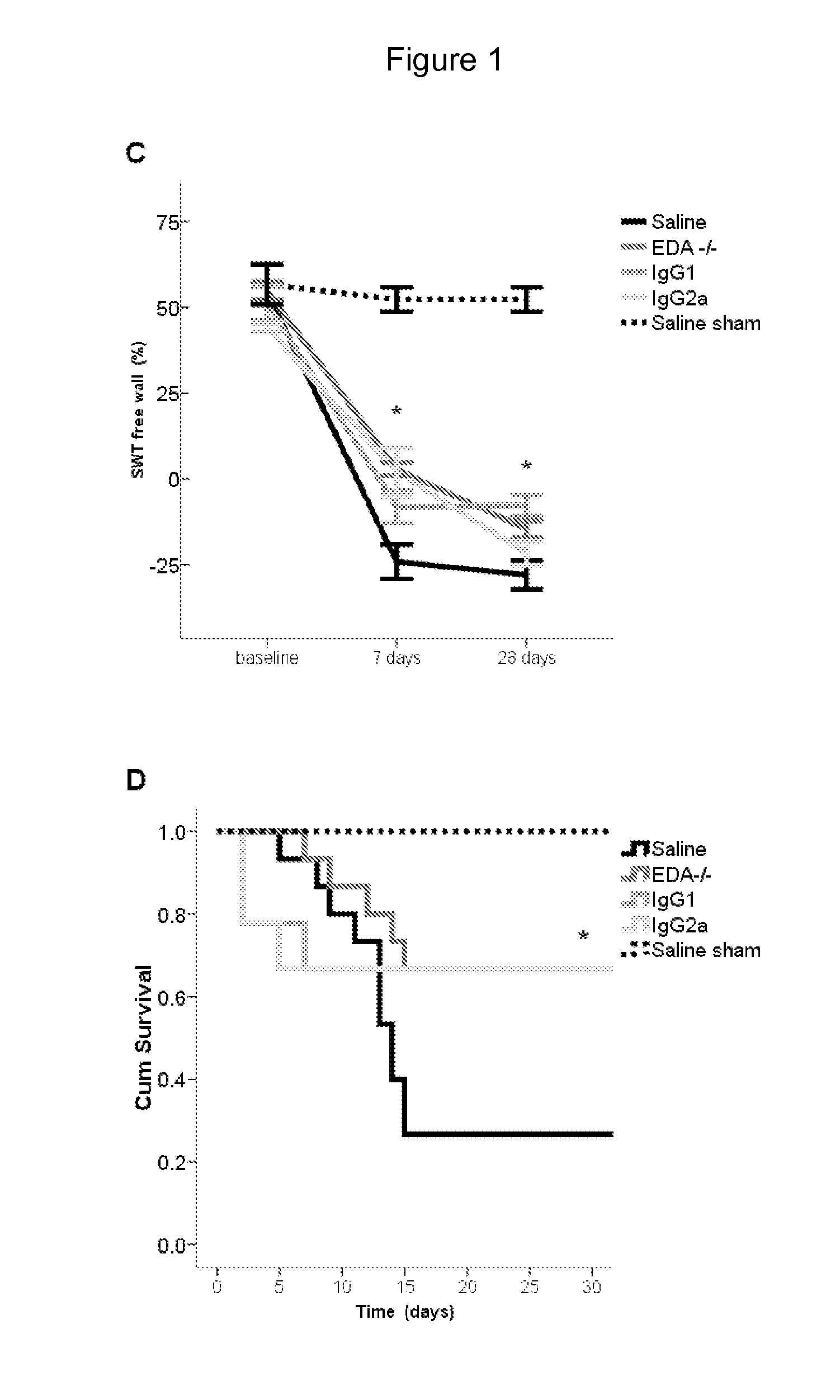
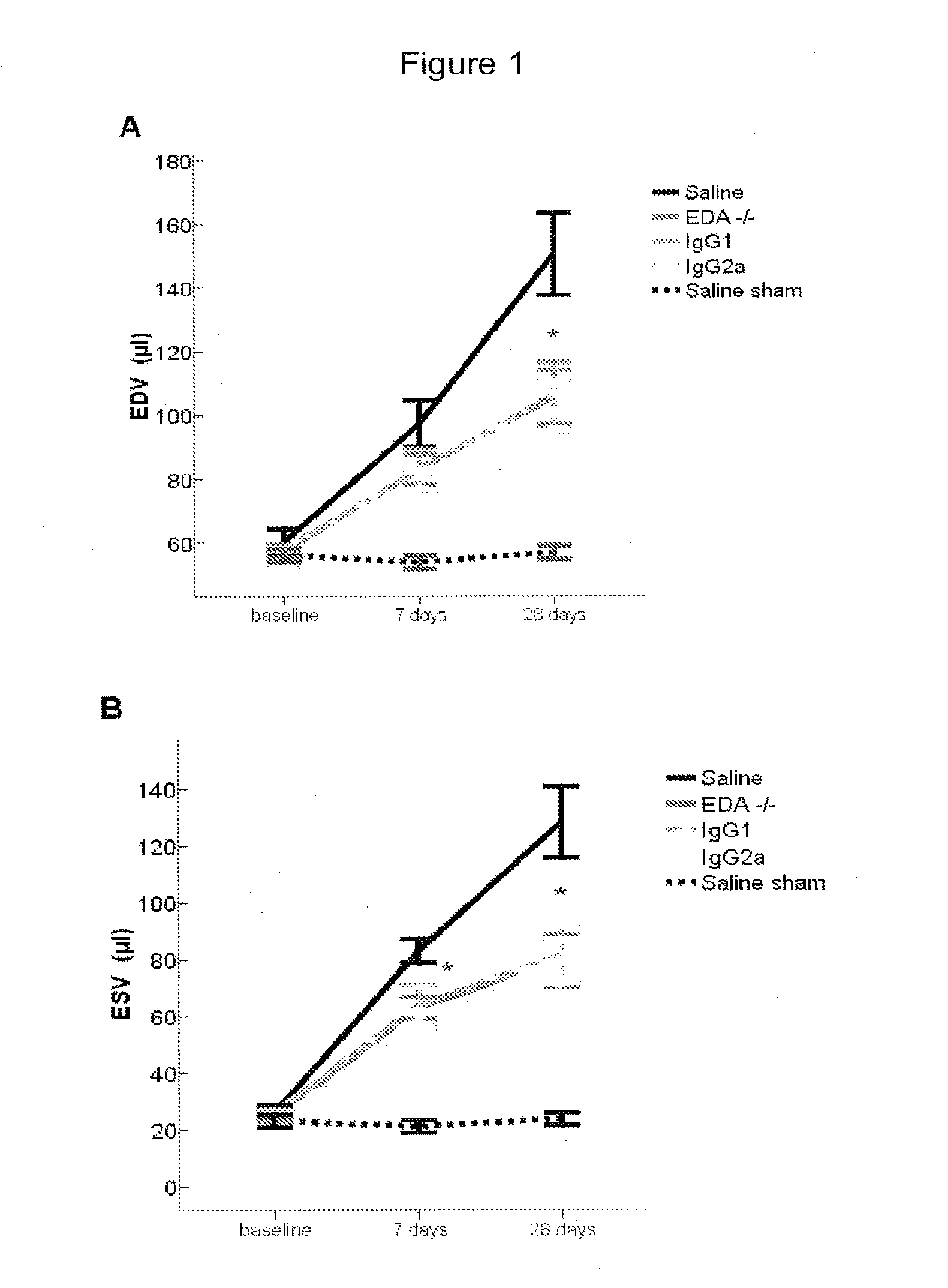
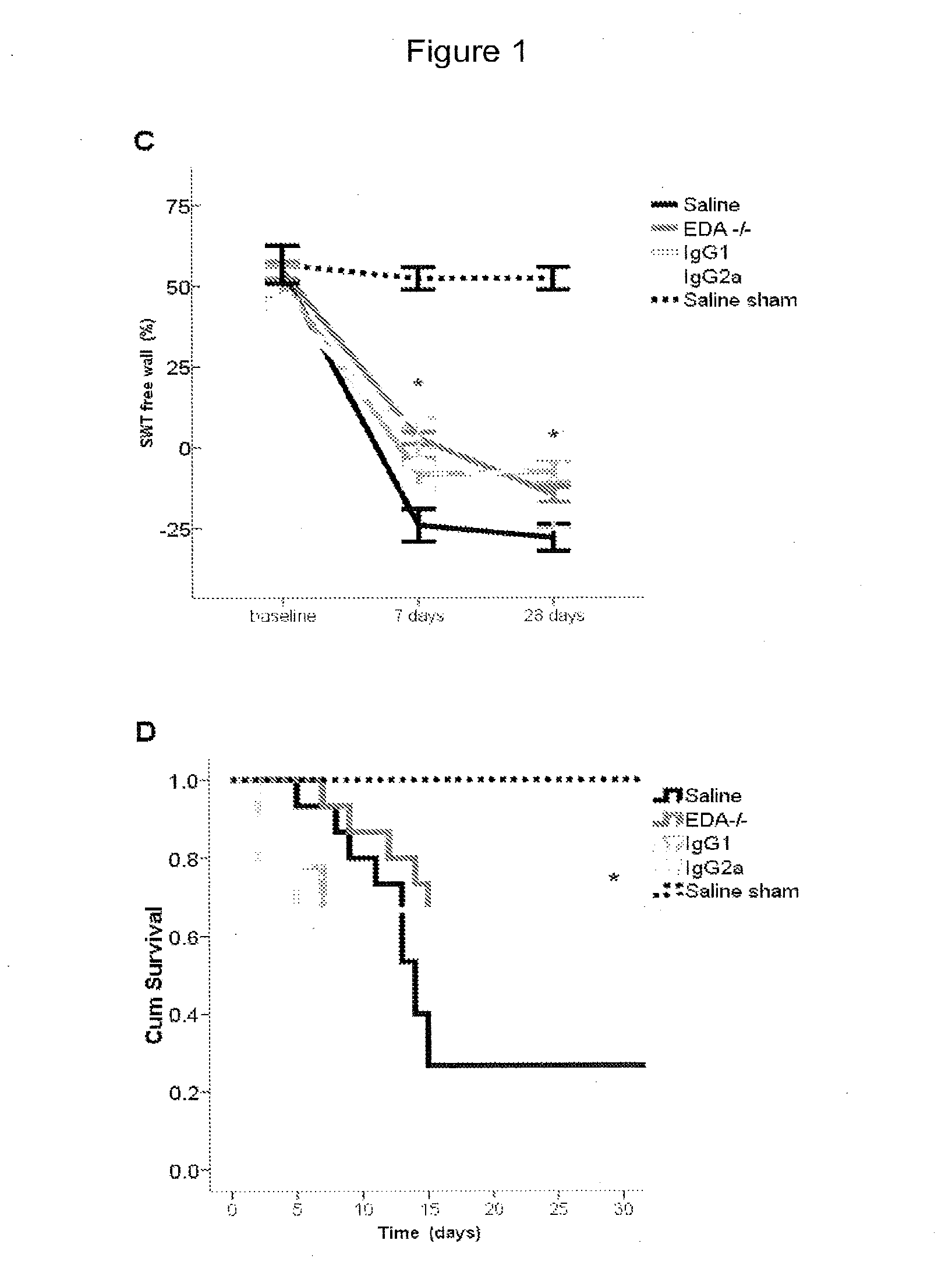
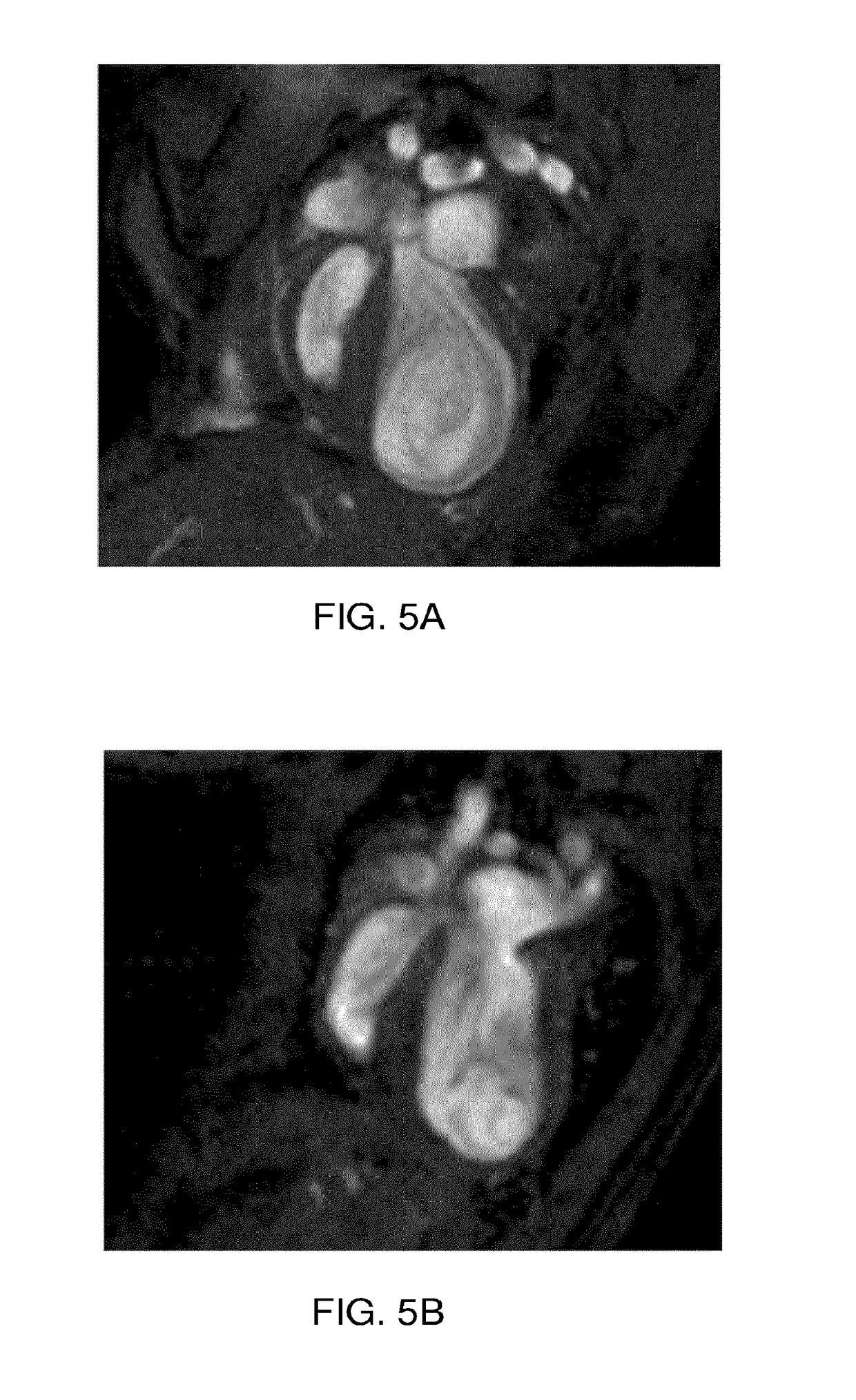
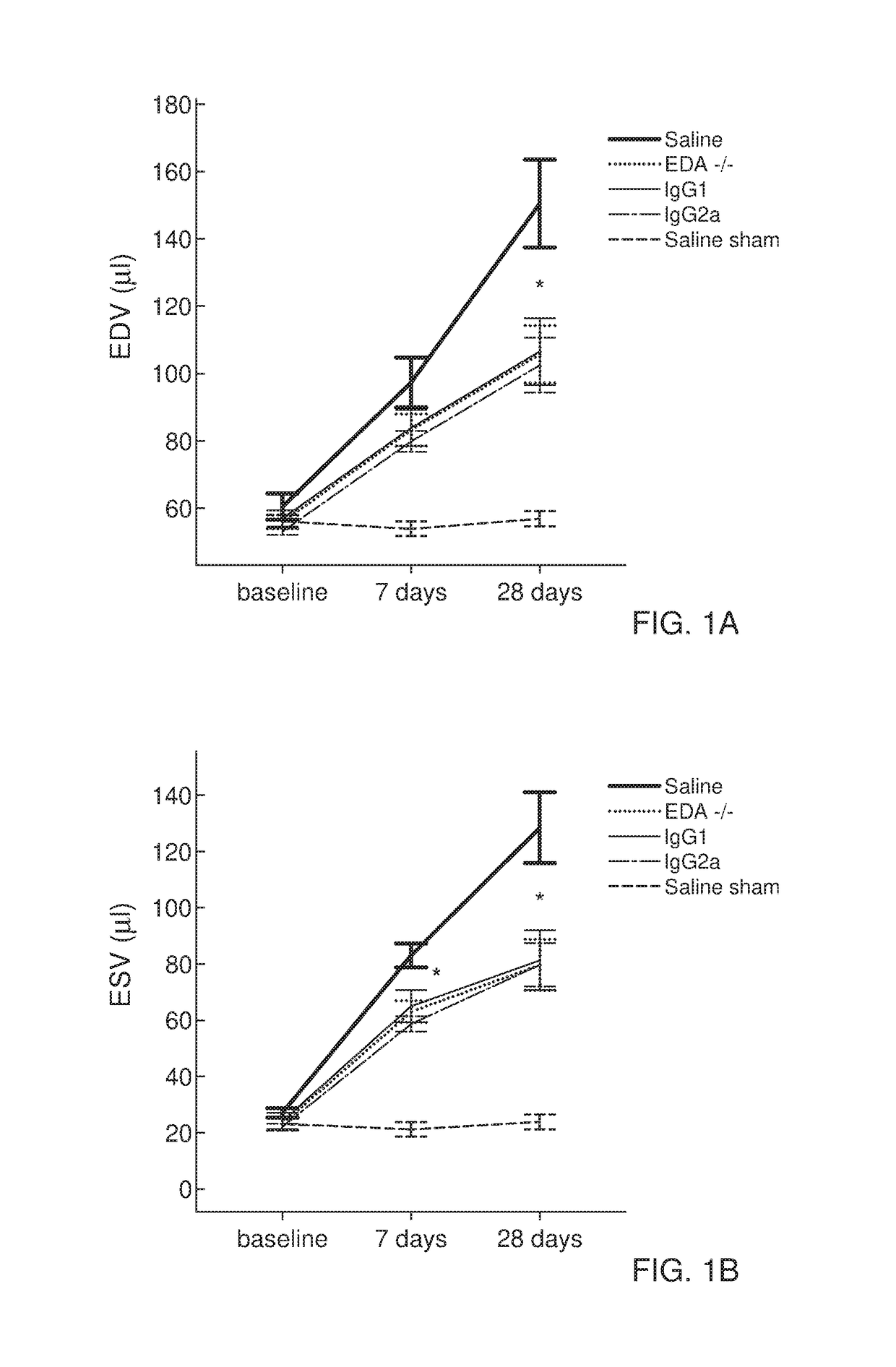
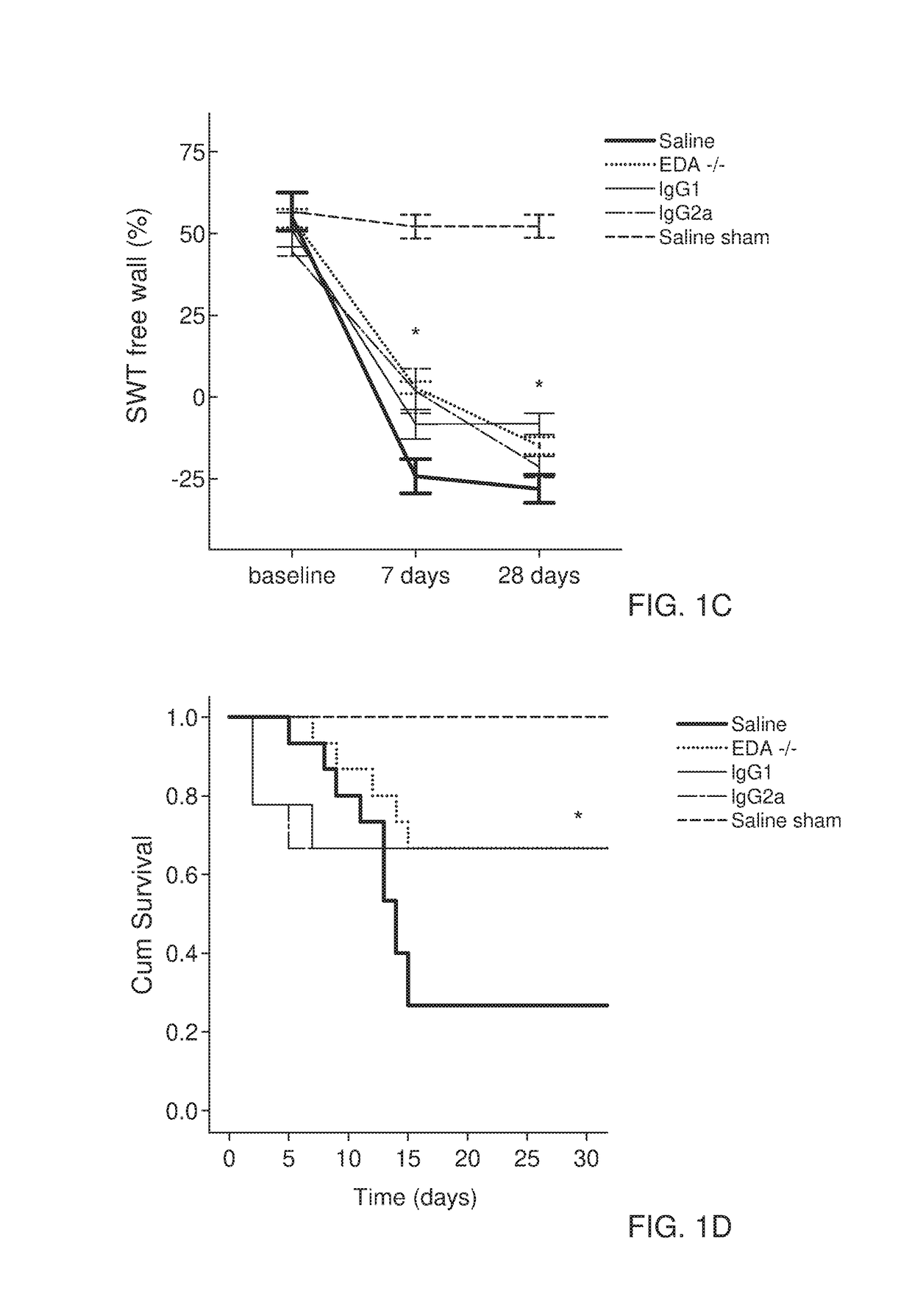
The present invention is concerned with immunoglobulin (Ig)-like molecules or fragments thereof for use in treatment, prevention, or prevention of progression of adverse cardiac remodelling and conditions resulting from or relating to pressure-overload, such as heart failure, aneurysm formation and remote myocardial fibrosis and for use in improving angiogenesis, preferably after ischemic injury. The invention also provides nucleic acid molecules encoding said Ig-like molecules, vectors comprising same, and host cells comprising same.
Owner:ENCARE BIOTECH BV
Immunoglobulin-like molecules directed against fibronectin-eda
InactiveUS20160368974A1Improve angiogenesisMinimize and eliminate occurrenceImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsPressure overloadIschemic injury
The present invention is concerned with immunoglobulin (Ig)-like molecules or fragments thereof for use in treatment, prevention, or prevention of progression of adverse cardiac remodelling and conditions resulting from or relating to myocardial infarction and pressure-overload, such as heart failure, aneurysm formation and remote myocardial fibrosis and for use in improving angiogenesis, preferably after ischemic injury. The invention also provides nucleic acid molecules encoding said Ig-like molecules, vectors comprising same, and host cells comprising same.
Owner:UMC UTRECHT HLDG BV
Method and system for monitoring a condition of cerebral aneurysms
ActiveUS20210212573A1Avoid developmentSaves populationMedical simulationImage enhancementRadiologyEngineering
Owner:ANEUSCREEN LTD
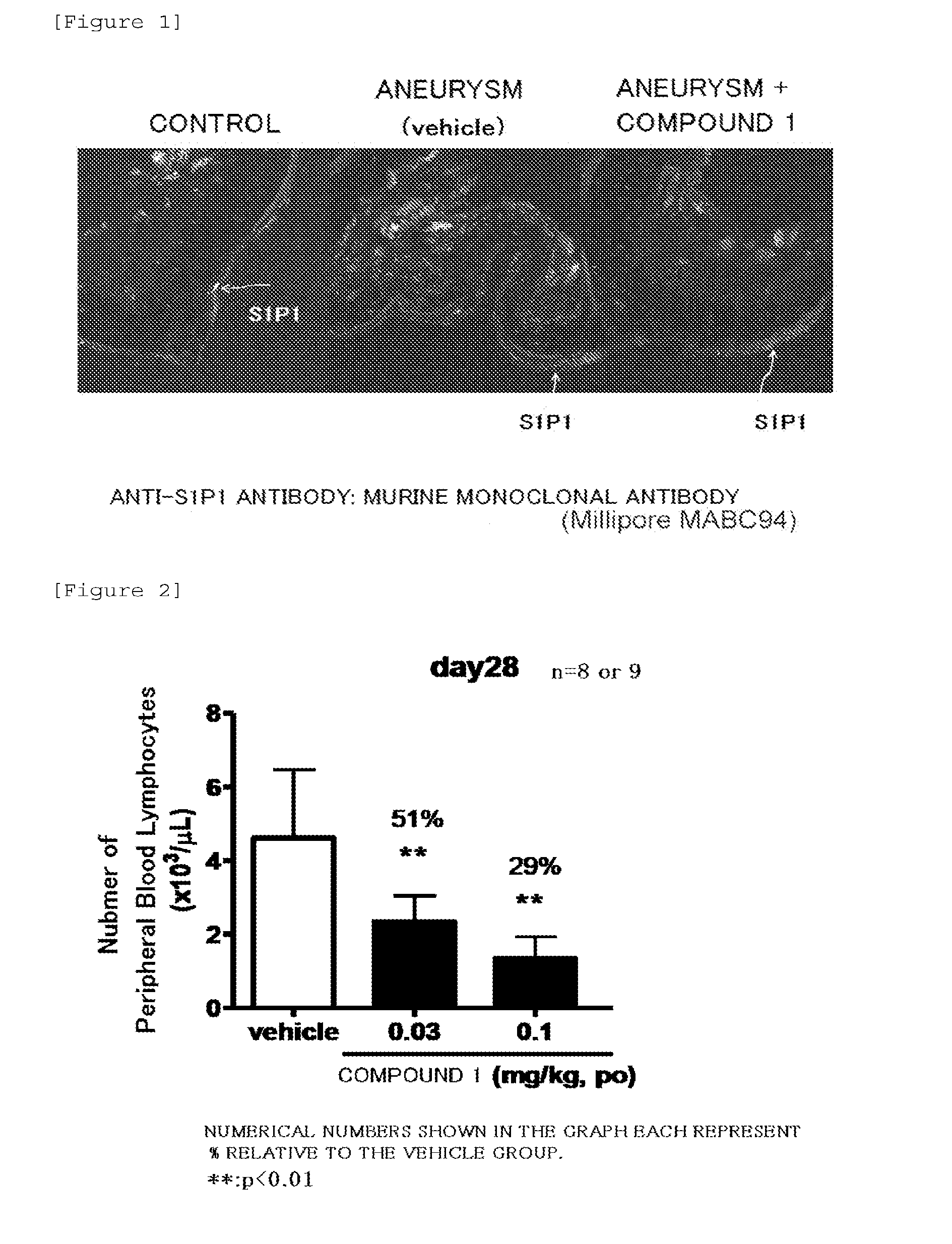
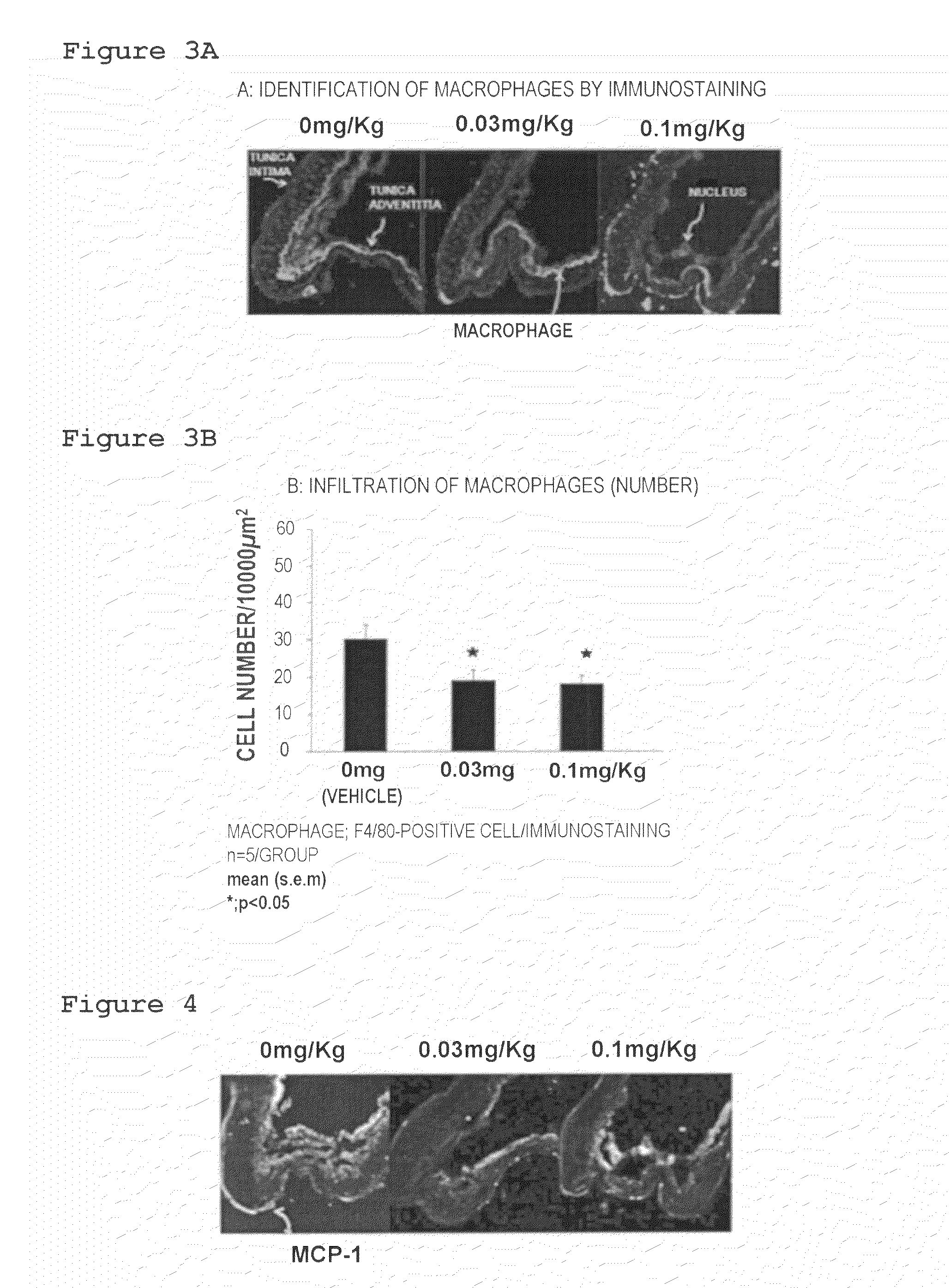
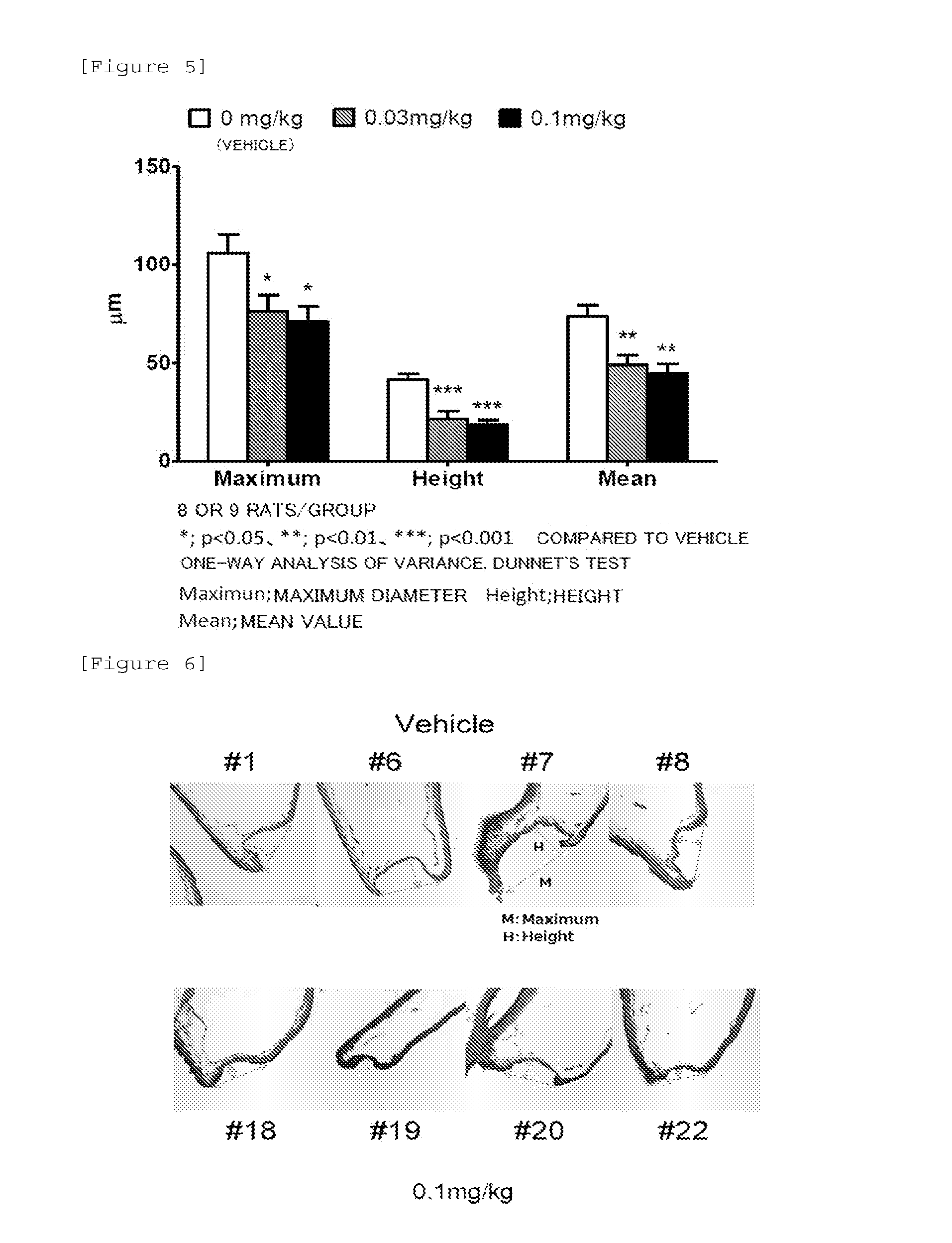
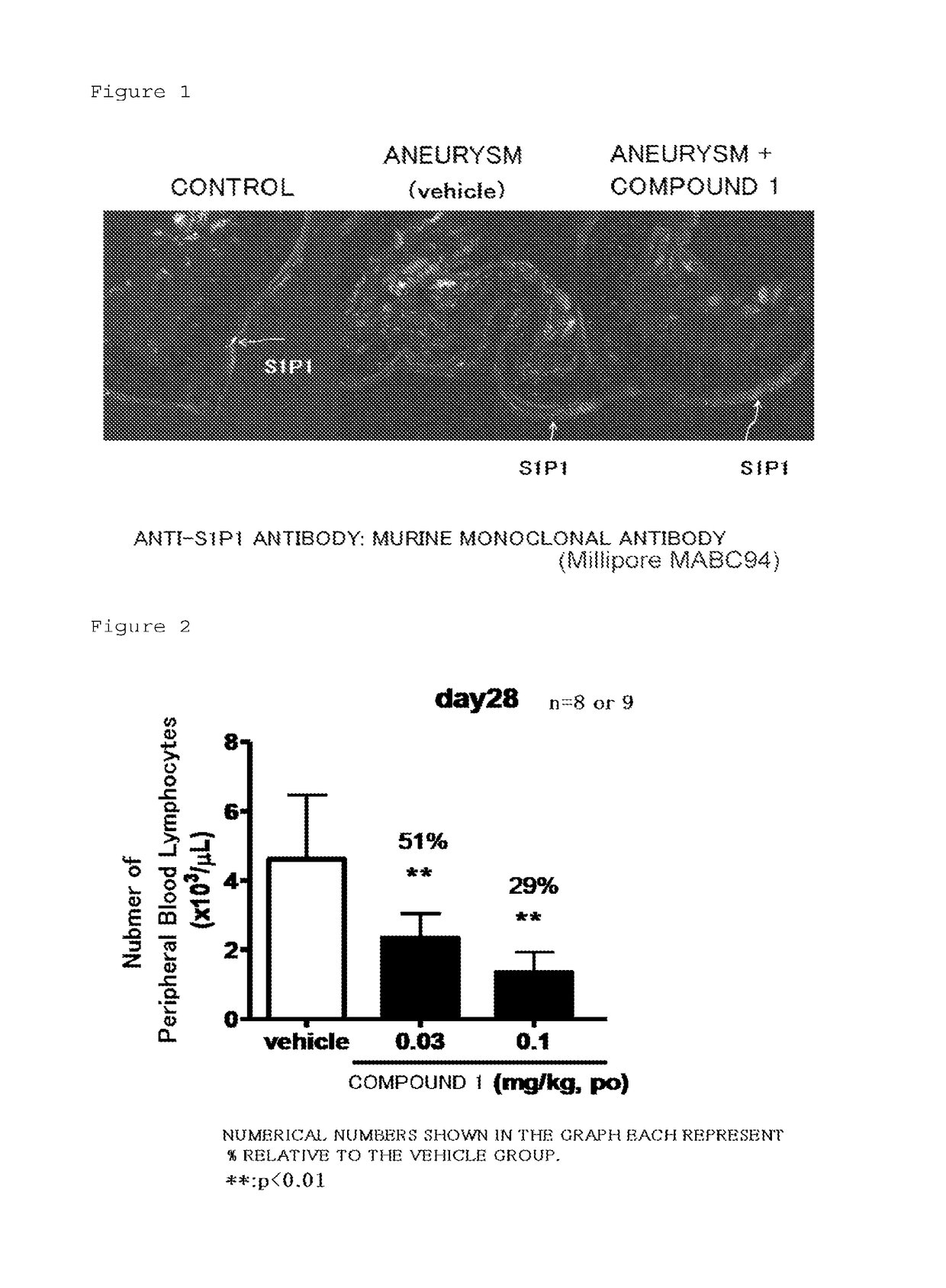
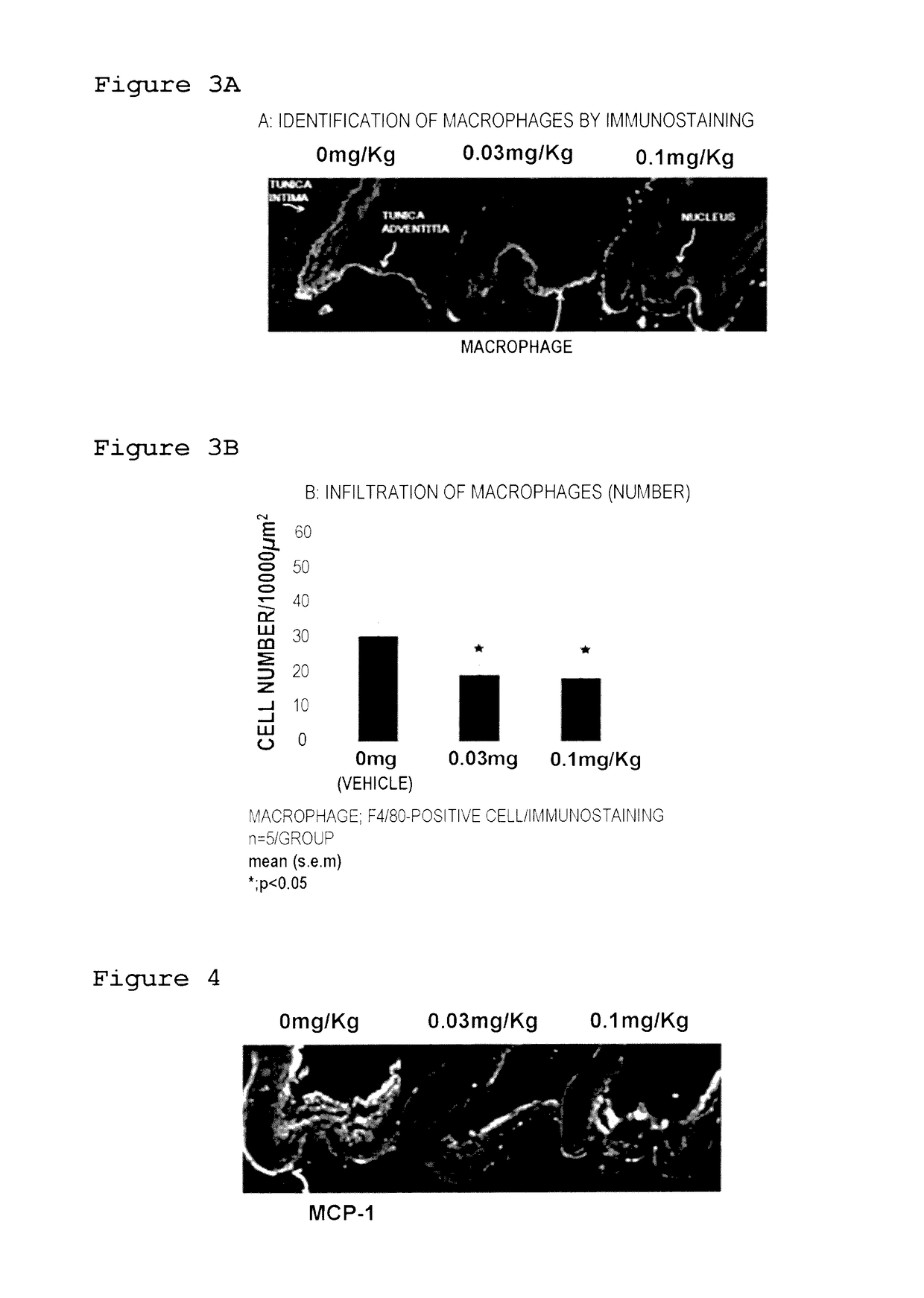
Medicinal composition for inhibiting formation and/or enlargement of cerebral aneurysm or shrinking same
Provided is a pharmaceutical composition which enables the inhibition of formation and / or enlargement of cerebral aneurysm or the regression of cerebral aneurysm. The pharmaceutical composition for the inhibition of formation and / or enlargement of cerebral aneurysm or for the regression of cerebral aneurysm of the present invention, which includes a S1P1 receptor agonist as an active ingredient, enables the inhibition of formation and / or enlargement of cerebral aneurysm or the regression of cerebral aneurysm, and enables the prevention and / or treatment of a disease associated with cerebral aneurysm.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
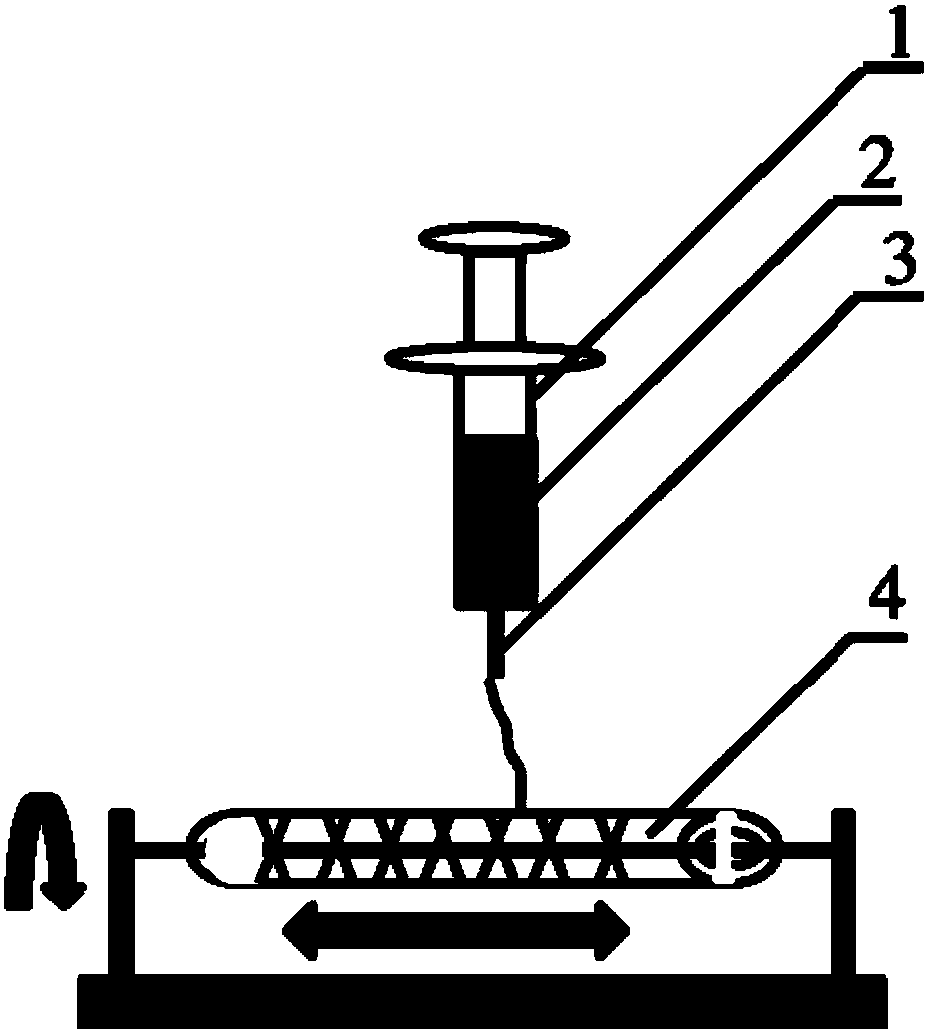
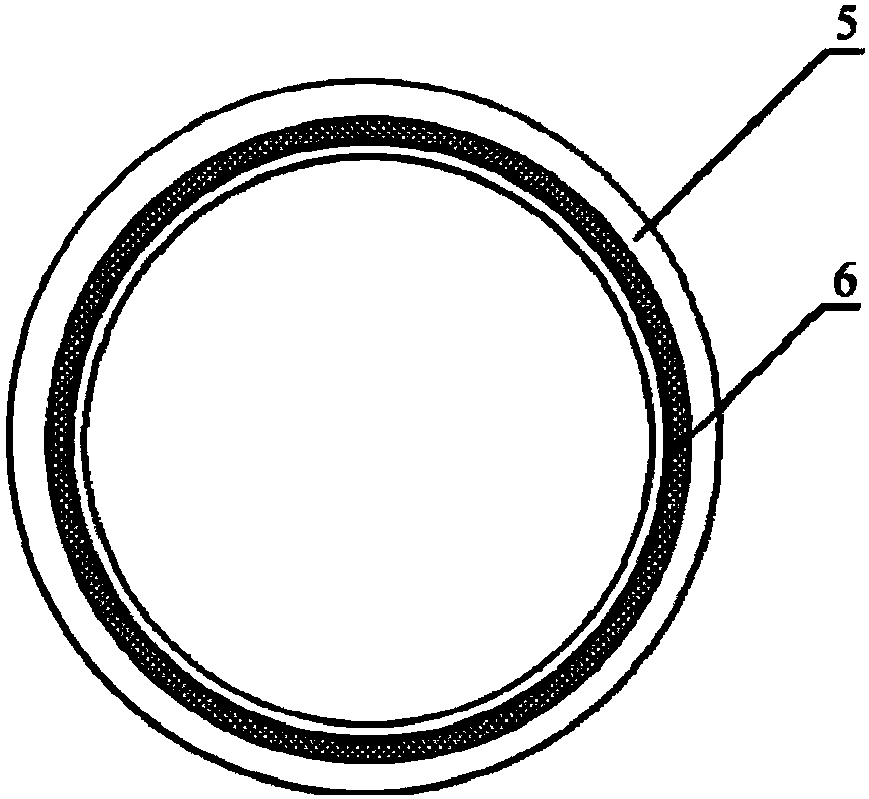
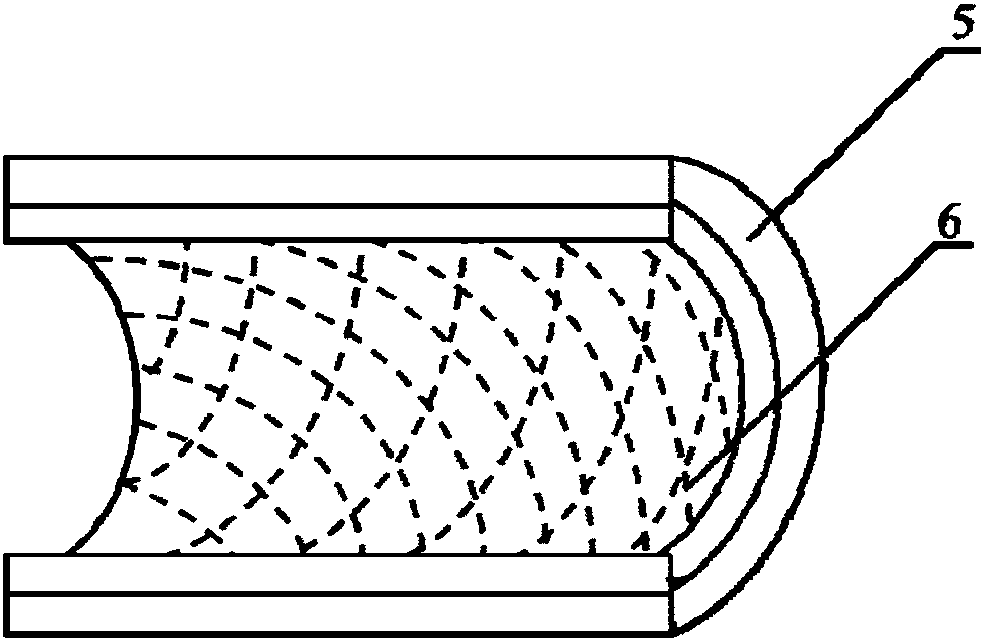
Method for constructing engineered artery blood vessel in vivo by taking melt-spun fibers as framework
InactiveCN108525015AConvenient and smoothGuaranteed unobstructedMelt spinning methodsNon-woven fabricsMedical equipmentIn vivo
The invention belongs to the field of medical equipment and in particular relates to a method for constructing an engineered artery blood vessel in vivo by taking melt-spun fibers as a framework. Theframework comprises a cylindrical receiver and a plurality of spun fibers which are wound on the cylindrical receiver; the diameter of the spun fibers is 5 to 200mu m; the spun fibers comprise warp fibers and weft fibers; a longitudinal included angle between the warp fibers and the weft fibers is alpha and the alpha is greater than or equal to 30 degrees and less than or equal to 130 degrees; thewarp fibers and the weft fibers are staggered for a plurality of layers up and down to form a cylindrical structure. According to the method provided by the invention, the finally-obtained melt-spunfiber framework has good mechanical strength, toughness and compliance through adjusting the diameter of the spun fibers, a winding angle and the winding density, and is suitable for surgical suturingoperation; the framework has good elasticity and can be shrunk or expanded along changes of blood pressure in an application process, the smoothness of the blood vessel is kept, the binary restenosisis reduced and arterial aneurysm is prevented from being formed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for preventing myocardial infarction-related complications
InactiveUS20130274448A1Prevents left ventricular dilatationImprove survivalImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCardiac muscleNeutralizing antibody
The present invention is concerned with treatment, prevention, or prevention of progression of myocardial infarction or adverse cardiac remodeling related conditions such as heart failure, aneurysm formation and remote myocardial fibrosis by administering a binding member such as, for example, a neutralizing antibody, binding to fibronectin-EDA, in particular the EDA domain of fibronectin-EDA to a subject in need thereof.
Owner:UMC UTRECHT HLDG BV
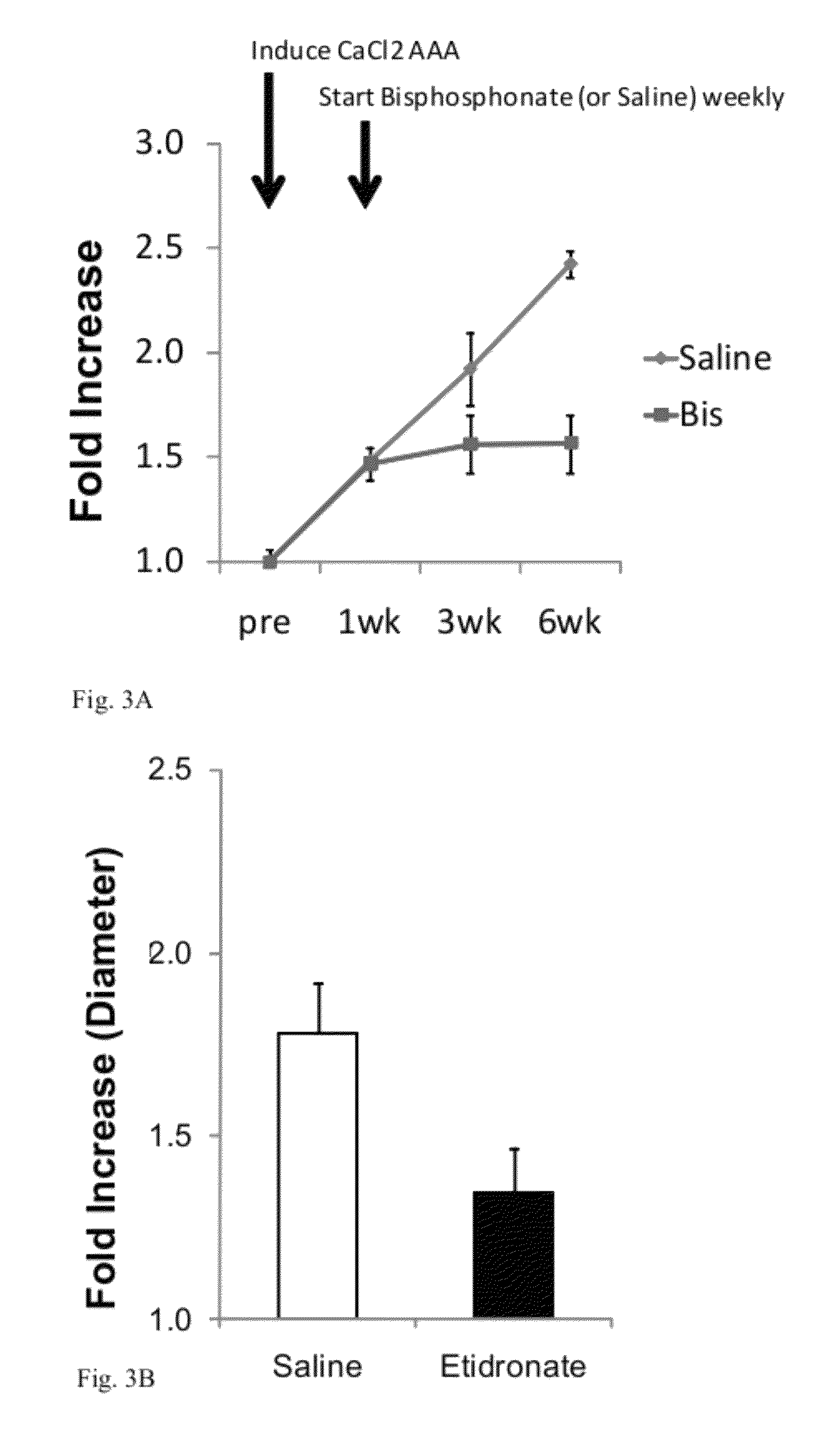
Methods of treating aneurysm
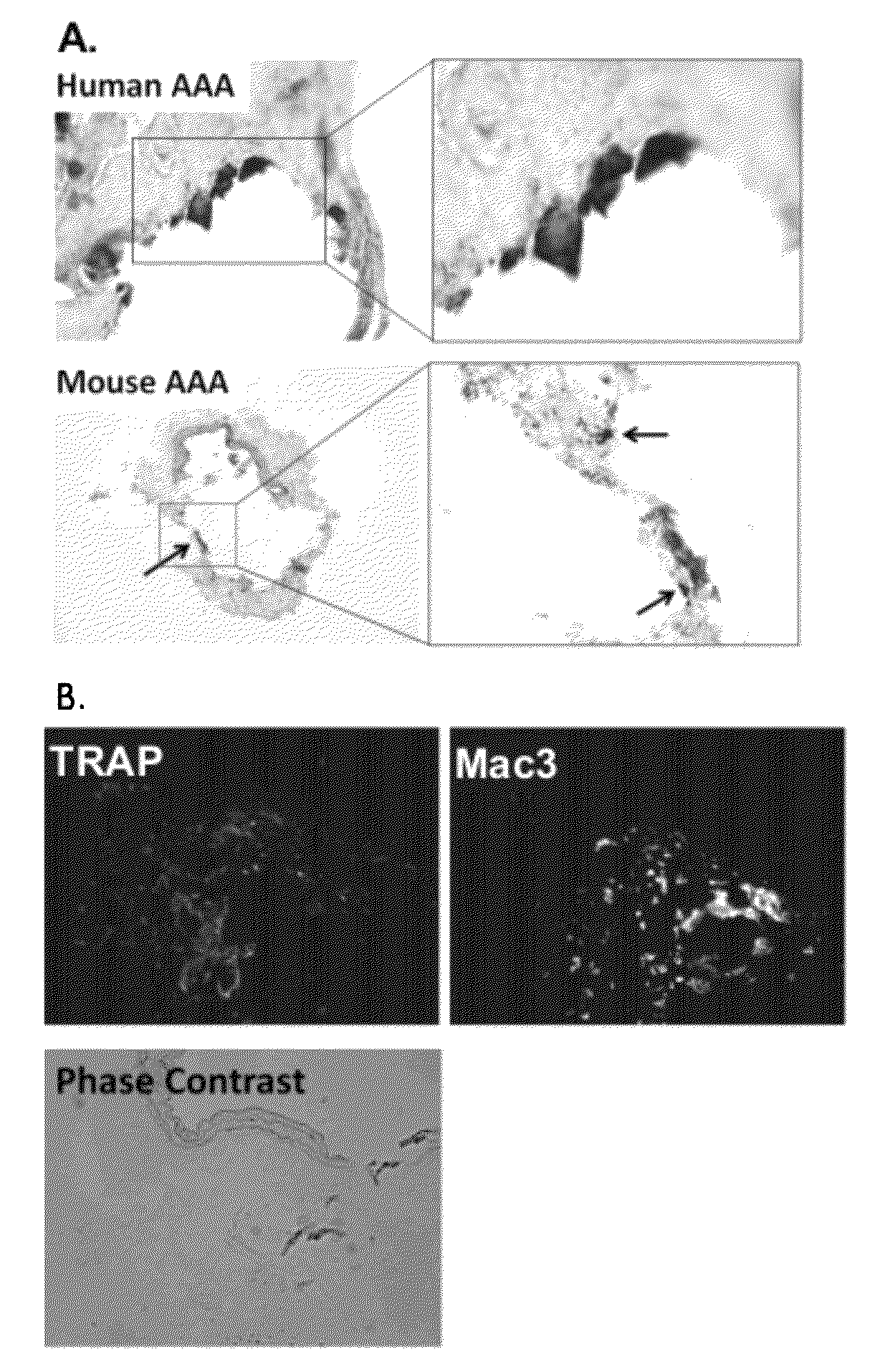
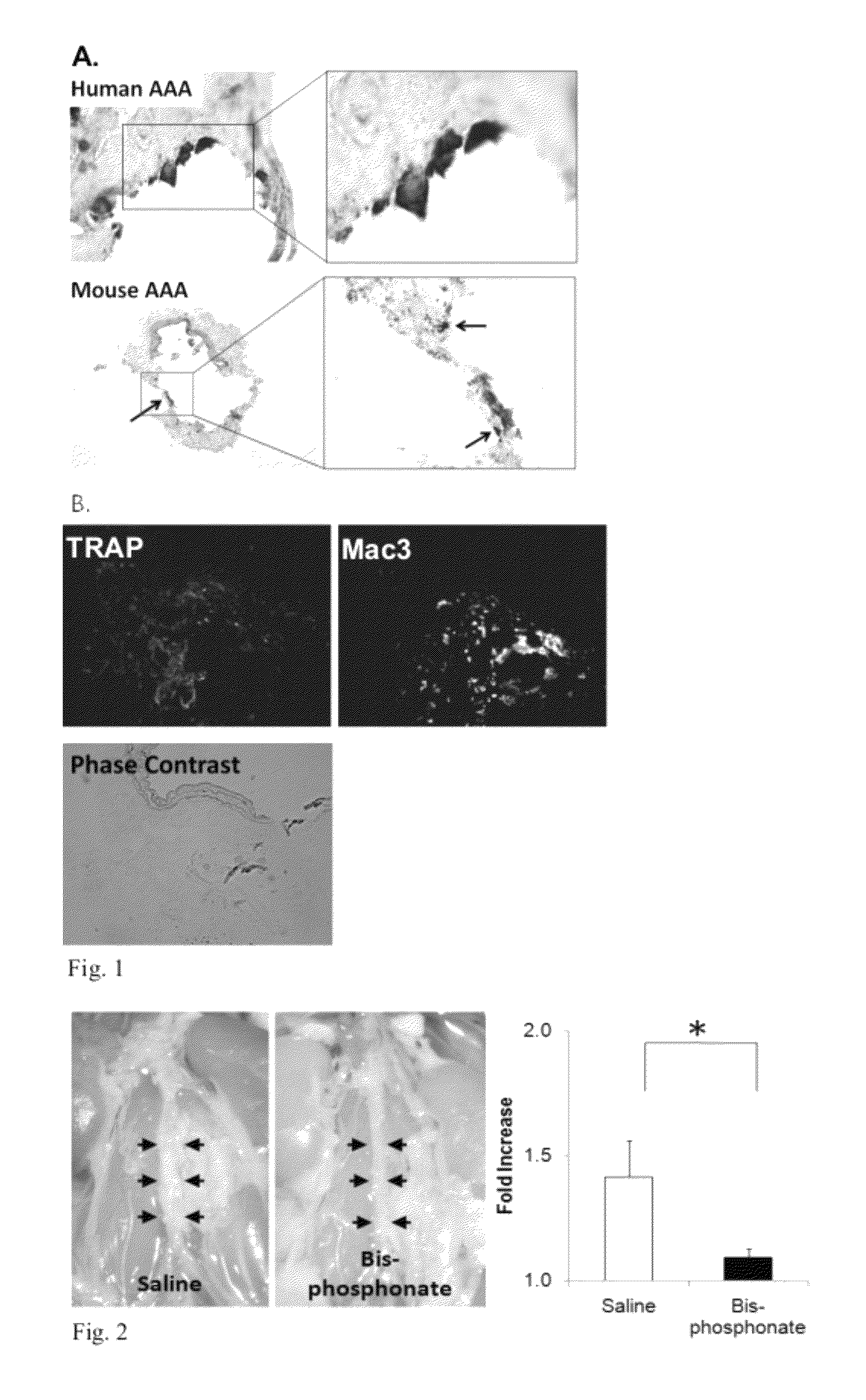
The present invention is directed to a method for treating aneurysms in vascular tissue. The method includes administering a bisphosphonate compound to a subject in an amount which is effective against the formation or progression of aneurysm, or which is effective to induce regression of an established aneurysm. In alternative methods, an anti-RANKL neutralizing antibody is administered to the subject to achieve analogous anti-aneurysm effect. The methods of particular advantage in the treatment of subjects having an abdominal aortic aneurysm, a relatively common, and life-threatening, condition.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Improved Anti-fibronectin eda antibodies
InactiveUS20210095011A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesMyofibrosis
The disclosure concerns antibodies that bind fibronectin-EDA. These antibodies are particularly useful for use in treatment, prevention, or prevention of progression of fibrosis, adverse cardiac remodeling and conditions resulting from or relating to myocardial infarction and pressure-overload, such as heart failure, aneurysm formation and remote myocardial fibrosis and for use in improving angiogenesis, preferably after ischemic injury.
Owner:ENCARE BIOTECH BV
Treatment of aneurysms
ActiveUS20200138810A1Effective biomarkerReduce mortalityOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderKynureninaseMetabolite
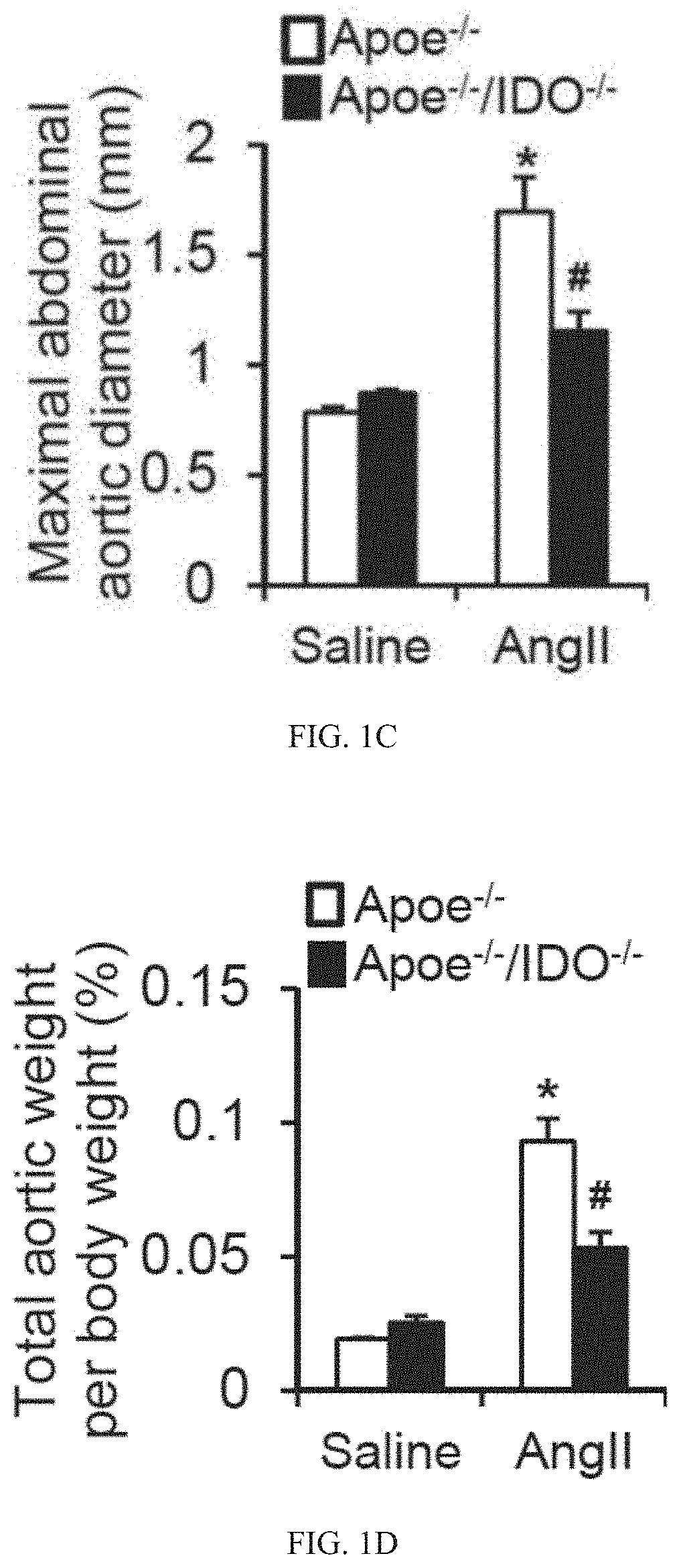
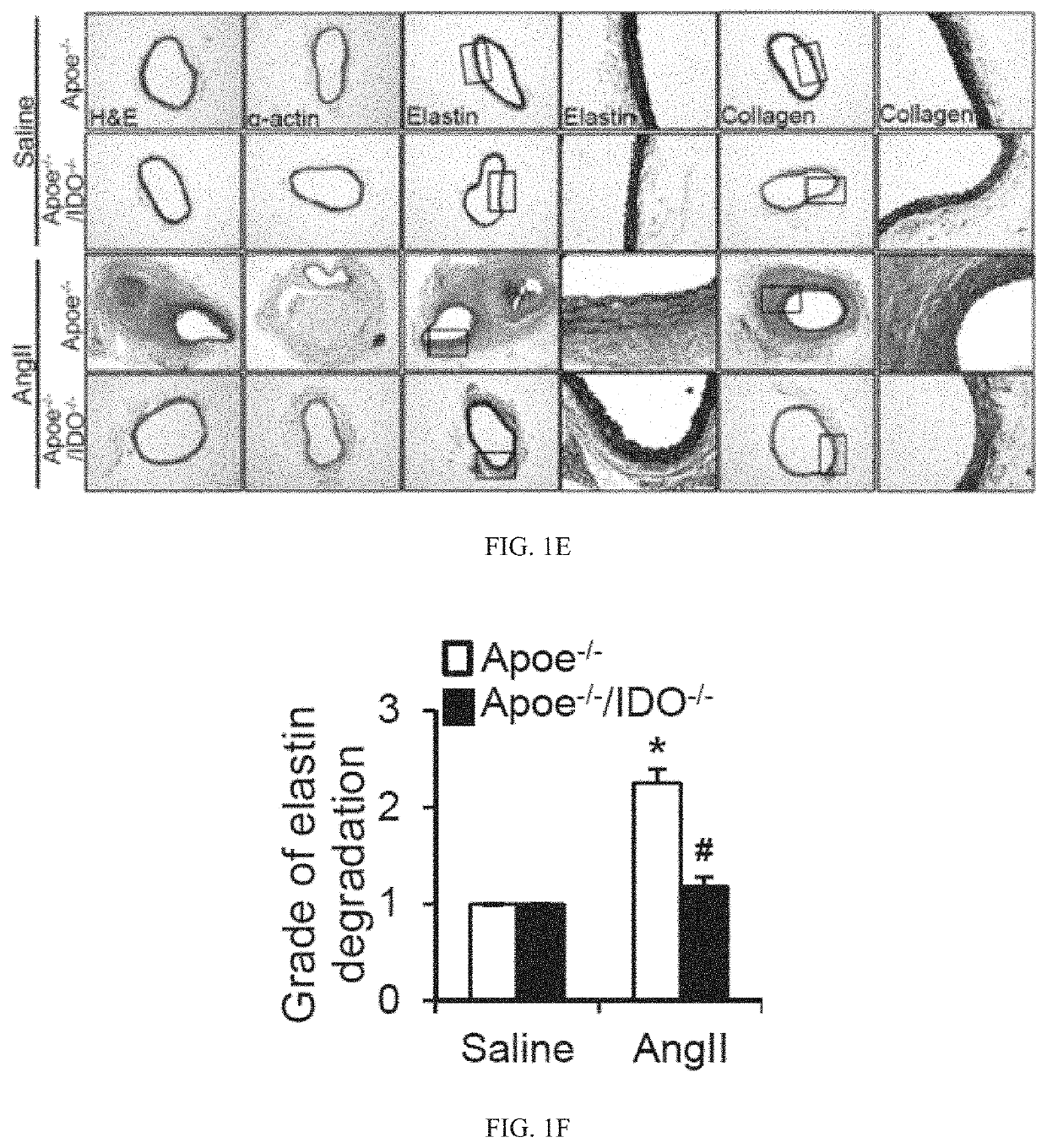
The present invention provides methods for detecting and / or treating a subject having an aneurysm or at risk for developing an aneurysm. It has been discovered that a key metabolite of the kynurenine (Kyn) pathway, a major route for the metabolism of essential amino acid tryptophan (Trp) into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), plays a critical role in the formation of aneurysms, for example abdominal aortic aneurysms. In particular, it has been discovered that 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid (3-HAA), a product of kynureninase (KYNU), plays a causative role in the formation of aneurysms by, for example exerting pro-inflammatory effects on vascular smooth muscle cells. It has further been discovered that elevated levels of 3-HAA are indicative of the presence and / or progression of an aneurysm, and 3-HAA levels correlate with the size (aortic diameter) of the aneurysm.
Owner:GEORGIA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
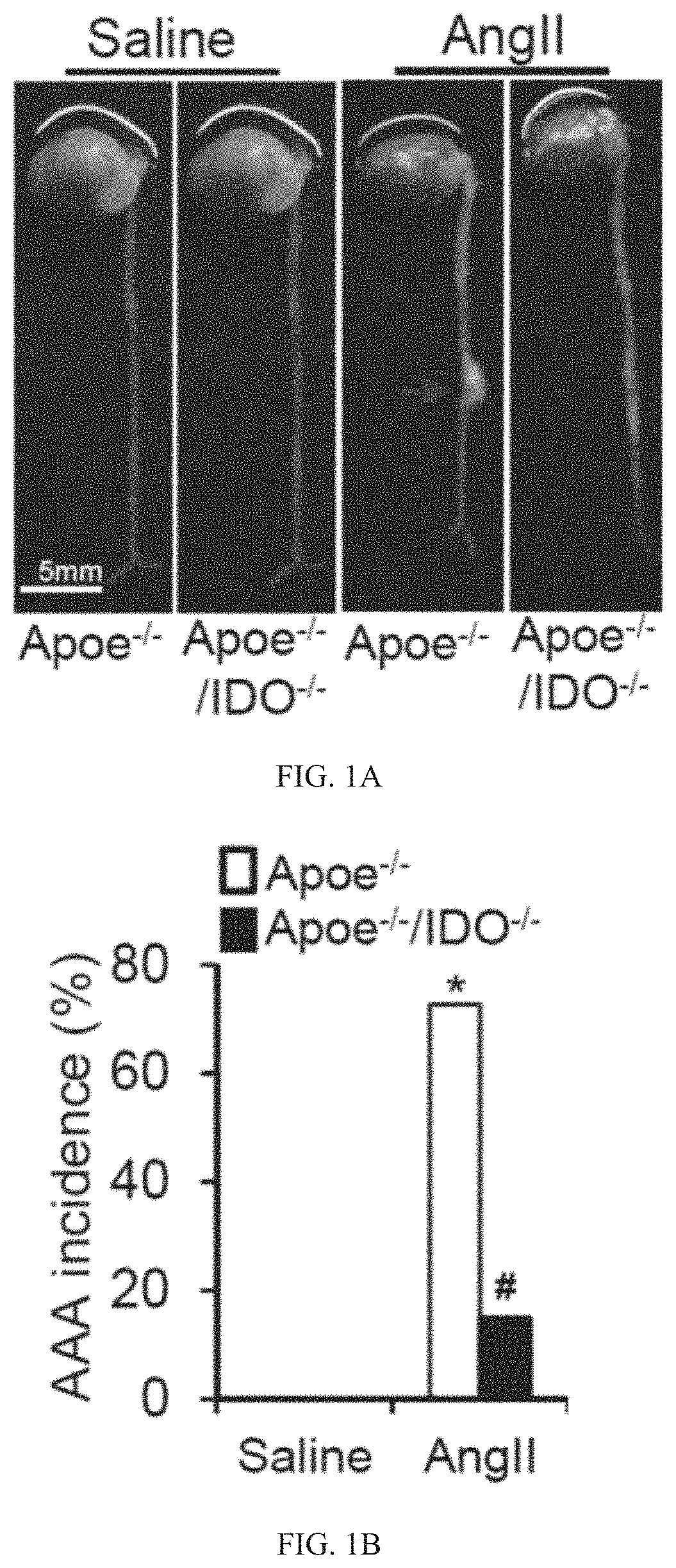
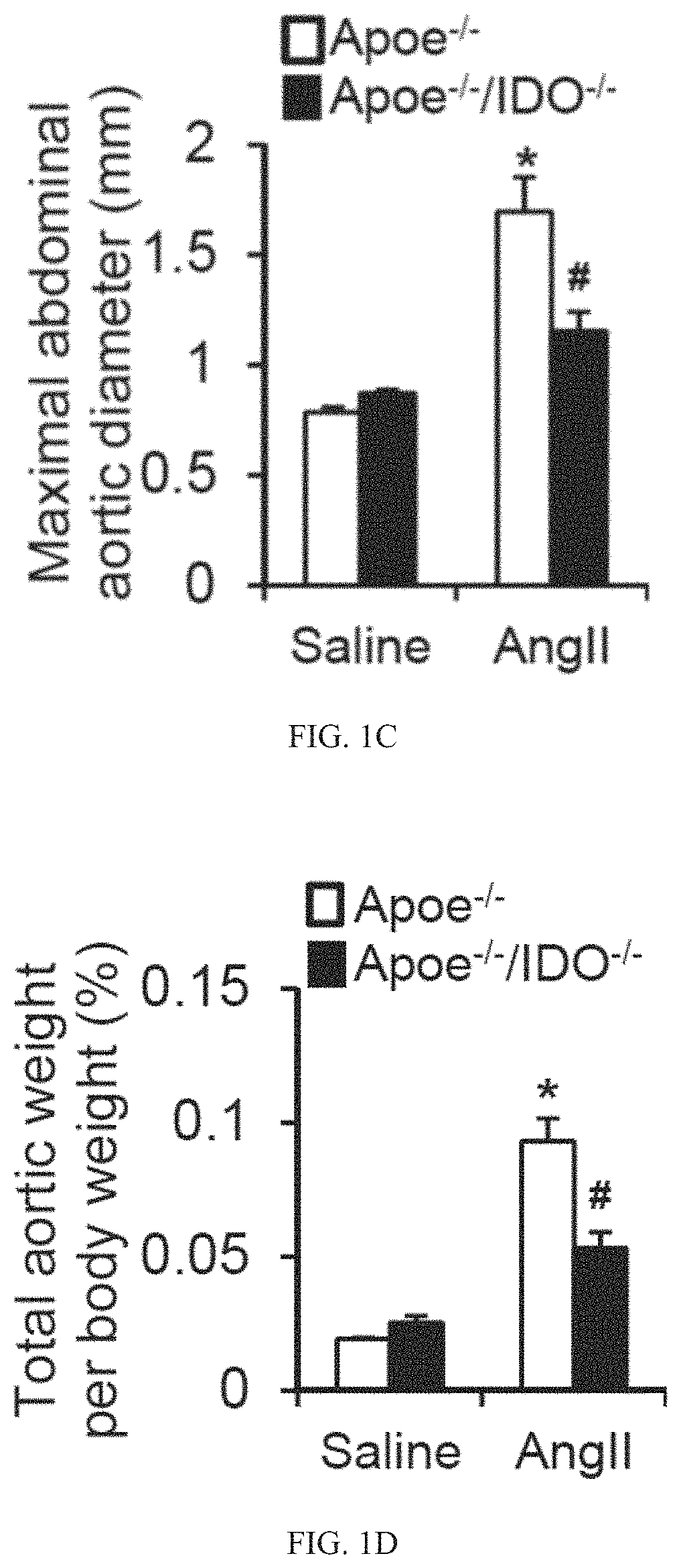
Application of h.hathewayi or taurine as a medicine for preventing and treating intracranial aneurysm formation and rupture
ActiveCN111450123BReduce formationInhibition of activationAntipyreticBacteria material medical ingredientsInternal iliac aneurysmPharmaceutical drug
The invention provides an application of H. hathewayi or taurine as a medicine for preventing and treating intracranial aneurysm formation and rupture. The present invention discloses that supplementation of H. hathewayi promotes the increase of plasma taurine level, and ultimately reduces the formation and rupture of intracranial aneurysm. Direct supplementation of taurine can also reduce the formation and rupture of intracranial aneurysms.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Cell-free tissue engineered vascular grafts
ActiveUS9326951B2Greater off-the-shelf availabilityImprove clinical utilityOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsRestenosisControl release
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method for preventing myocardial infarction-related complications
InactiveUS20150218263A1Prevents left ventricular dilatationImprove survivalImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCardiac muscleNeutralizing antibody
The present invention is concerned with treatment, prevention, or prevention of progression of myocardial infarction or adverse cardiac remodeling related conditions such as heart failure, aneurysm formation and remote myocardial fibrosis by administering a binding member such as, for example, a neutralizing antibody, binding to fibronectin-EDA, in particular the EDA domain of fibronectin-EDA to a subject in need thereof.
Owner:UMC UTRECHT HLDG BV
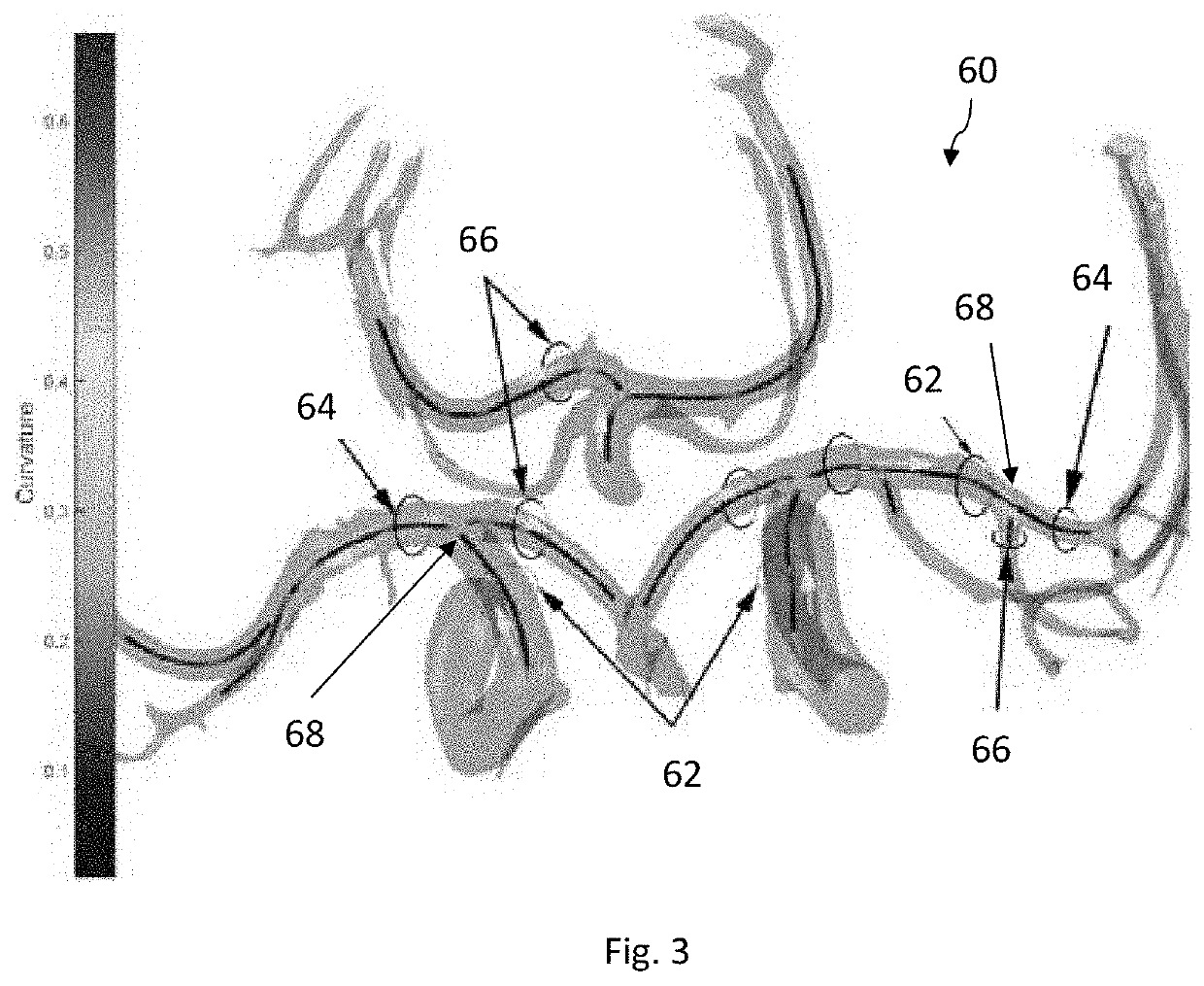
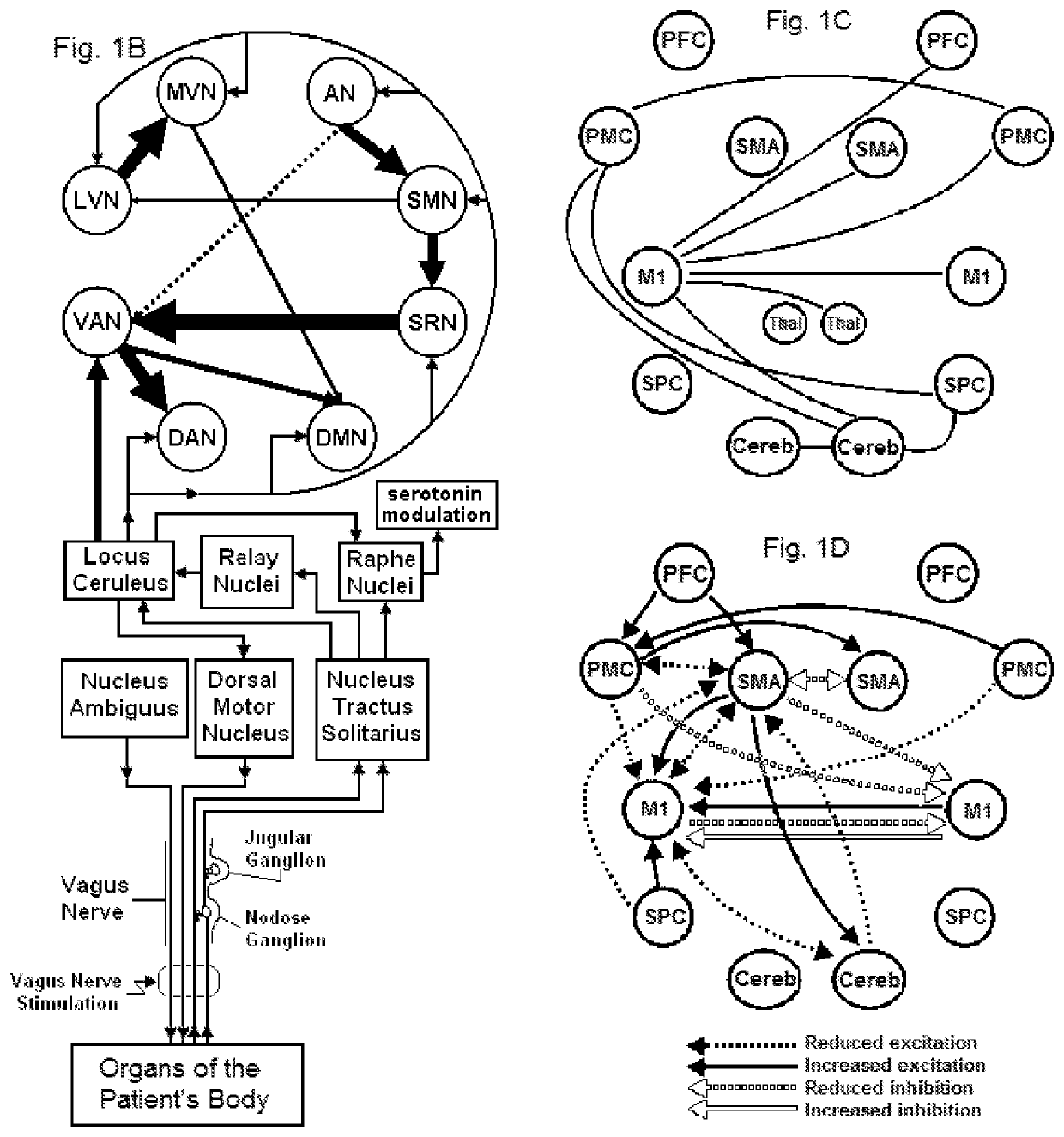
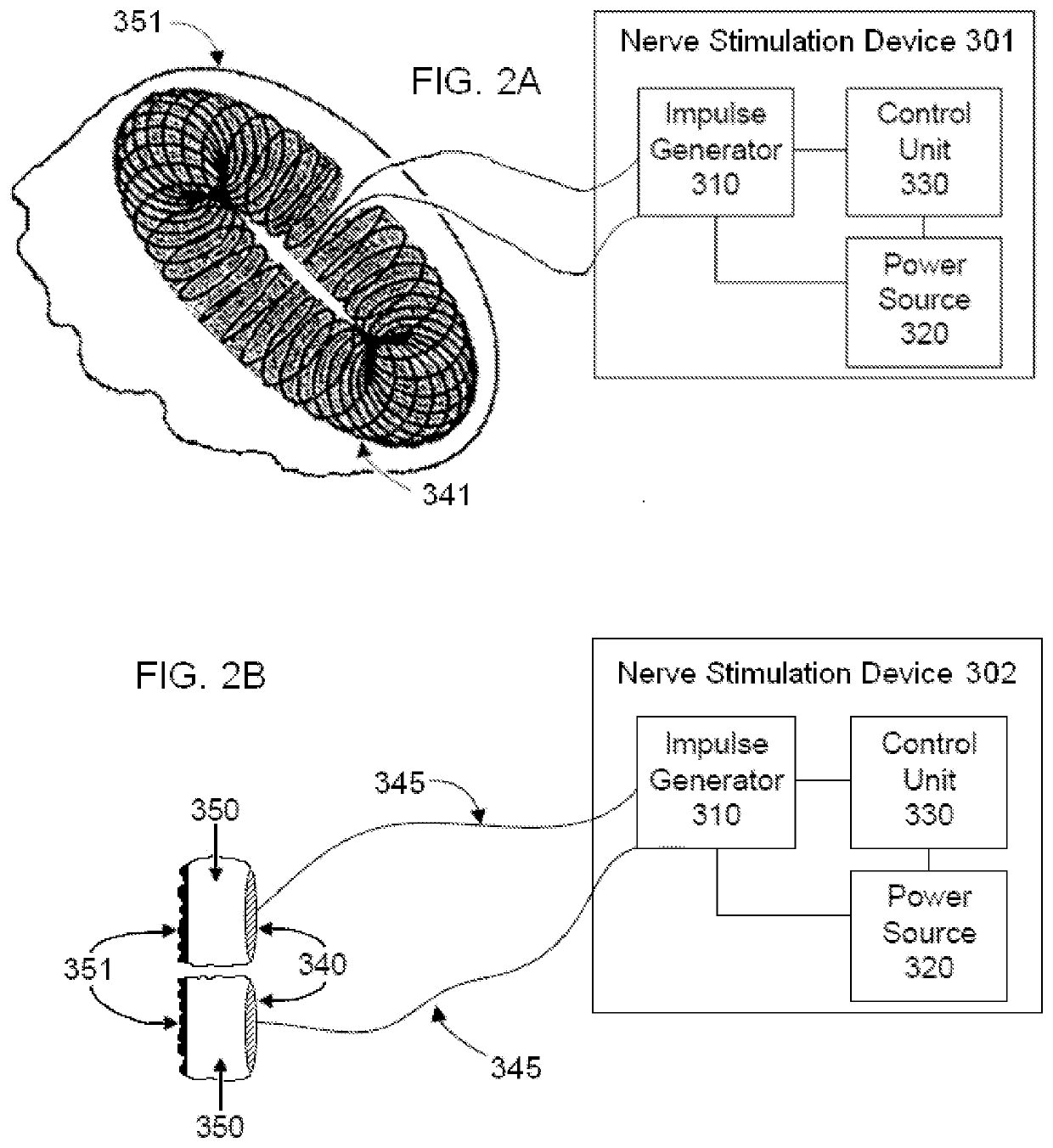
Systems and methods for controlling against aneurysm formation, growth and rupture, and improving post-rupture outcomes
PendingUS20220016424A1Improve patient outcomesPrevent further growthExternal electrodesArtificial respirationAneurysm ruptureElectro stimulation
A system and method is provided for improving the patient outcome for a subject having an aneurysm. The method includes determining that the subject has the aneurysm, positioning a vagus nerve stimulation system on the subject, the vagus nerve stimulation system being configured to provide an electrical stimulation to the vagus nerve of the subject. Stimulating the vagus nerve of the subject with the vagus nerve stimulation system to at least one of: prevent further growth of the aneurysm; decrease the likelihood that the aneurysm ruptures; and decrease effects of rupture, when the aneurysm of the subject ruptures.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Medicinal composition for inhibiting formation and/or enlargement of cerebral aneurysm or shrinking same
Provided is a pharmaceutical composition which enables the inhibition of formation and / or enlargement of cerebral aneurysm or the regression of cerebral aneurysm. The pharmaceutical composition for the inhibition of formation and / or enlargement of cerebral aneurysm or for the regression of cerebral aneurysm of the present invention, which includes a S1P1 receptor agonist as an active ingredient, enables the inhibition of formation and / or enlargement of cerebral aneurysm or the regression of cerebral aneurysm, and enables the prevention and / or treatment of a disease associated with cerebral aneurysm.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Immunoglobulin-like molecules directed against fibronectin-eda
InactiveUS20180264108A1Improve angiogenesisPromote angiogenesisImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntibody ingredientsPressure overloadIschemic injury
The present invention is concerned with immunoglobulin (Ig)-like molecules or fragments thereof for use in treatment, prevention, or prevention of progression of adverse cardiac remodelling and conditions resulting from or relating to pressure-overload, such as heart failure, aneurysm formation and remote myocardial fibrosis and for use in improving angiogenesis, preferably after ischemic injury. The invention also provides nucleic acid molecules encoding said Ig-like molecules, vectors comprising same, and host cells comprising same.
Owner:ENCARE BIOTECH BV
Immunoglobulin-like molecules directed against fibronectin-EDA
InactiveUS10011652B2Minimize and eliminate occurrenceMinimize and eliminate and riskHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPressure overloadIschemic injury
Owner:UMC UTRECHT HLDG BV
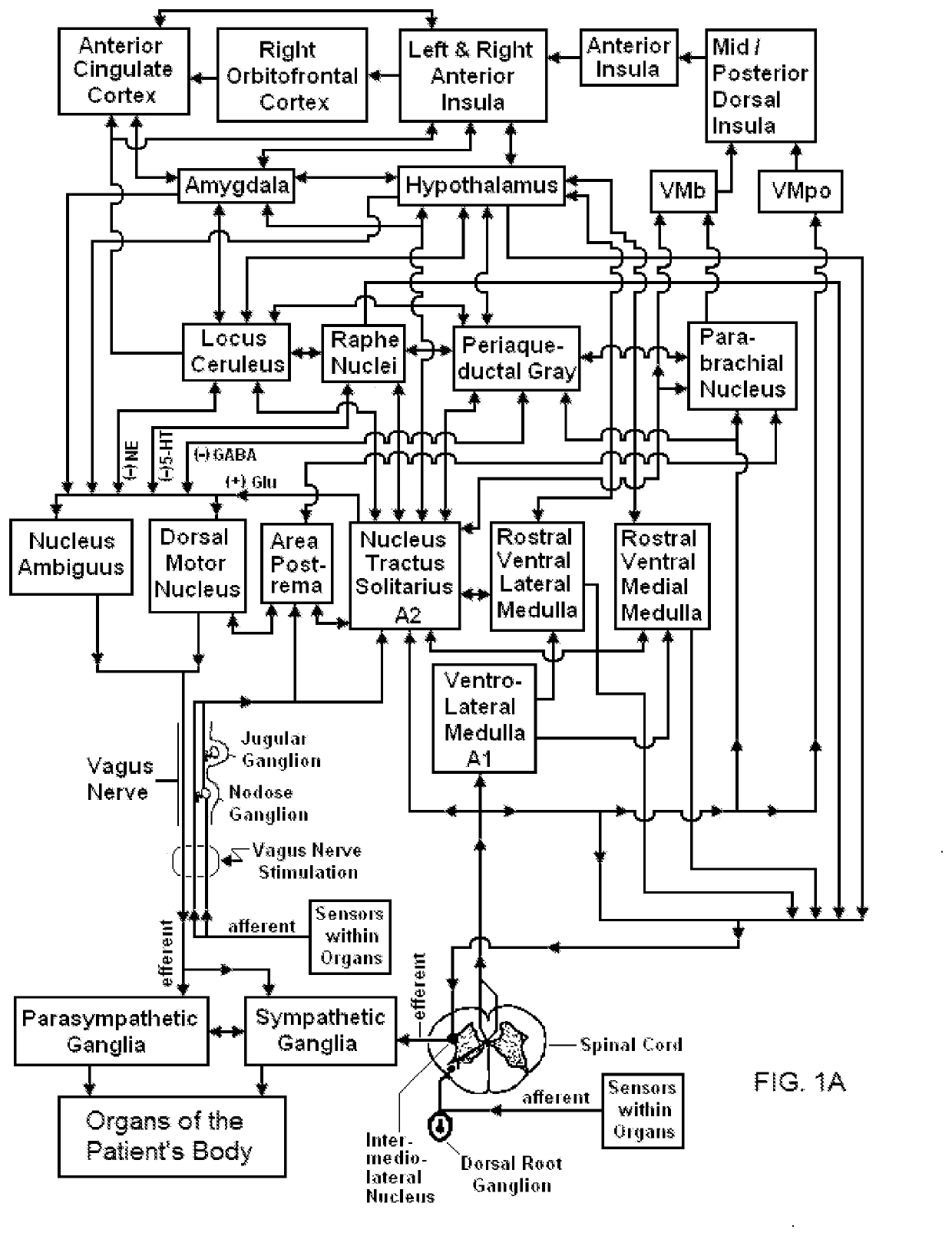
Vagal nerve stimulation for treating or preventing stroke or transient ischemic attack
PendingUS20210299435A1Reduce inflammationInhibition of excitementSpinal electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsNerve fiber bundleTransient ischemic attack (TIA)
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for reducing inflammation associated with an aneurysm in a patient. The methods comprise transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers, particularly those in the vagus nerve. Vagus nerve stimulation is used to modulate the release of neurotransmitters in the brain and to reduce inflammation that may lead to the formation, growth, rupture or hemorrhage of an aneurysm.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Immunoglobulin-like molecules directed against fibronectin-eda
ActiveUS20180346557A1Minimize and eliminate occurrenceMinimize and eliminate and riskImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsIntravenous gammaglobulinZonulin
The present invention is concerned with immunoglobulin (Ig)-like molecules or fragments thereof for use in treatment, prevention, or prevention of progression of adverse cardiac remodelling and conditions resulting from or relating to myocardial infarction and pressure-overload, such as heart failure, aneurysm formation and remote myocardial fibrosis and for use in improving angiogenesis, preferably after ischemic injury. The invention also provides nucleic acid molecules encoding said Ig-like molecules, vectors comprising same, and host cells comprising same.
Owner:UMC UTRECHT HLDG BV
Method for preventing myocardial infarction-related complications
InactiveUS20180362627A1Prevents left ventricular dilatationImprove survivalImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCardiac muscleNeutralizing antibody
The present invention is concerned with treatment, prevention, or prevention of progression of myocardial infarction or adverse cardiac remodeling related conditions such as heart failure, aneurysm formation and remote myocardial fibrosis by administering a binding member such as, for example, a neutralizing antibody, binding to fibronectin-EDA, in particular the EDA domain of fibronectin-EDA to a subject in need thereof.
Owner:UMC UTRECHT HLDG BV
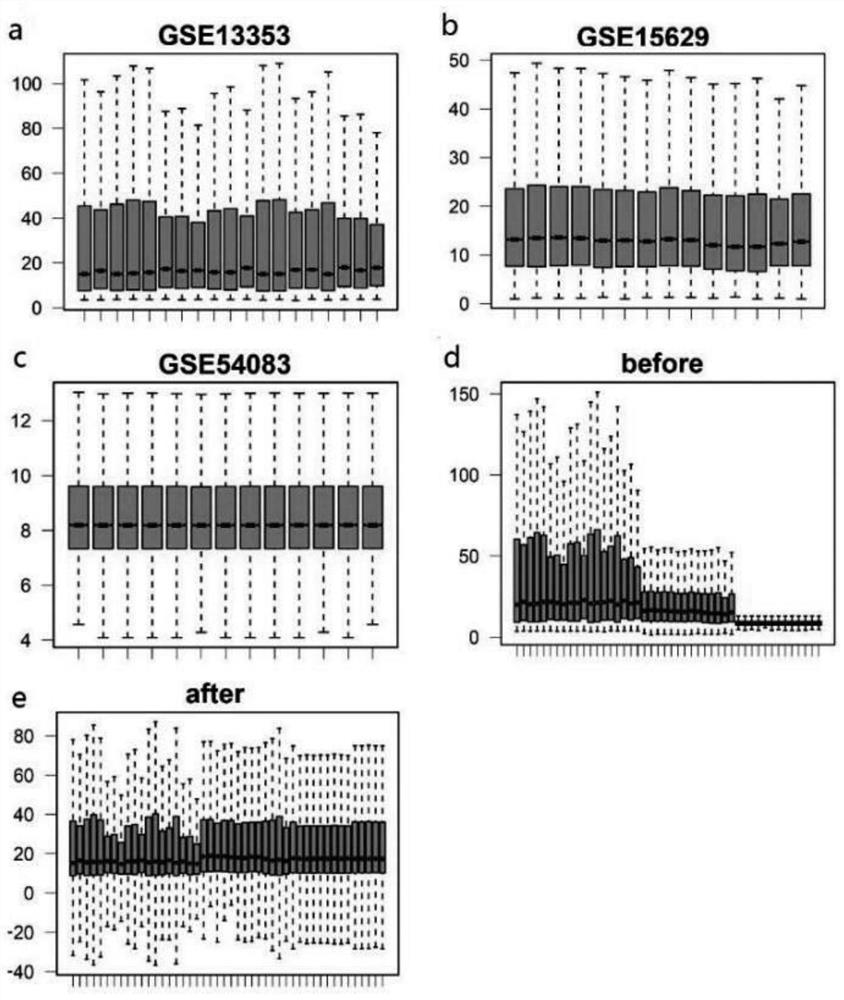
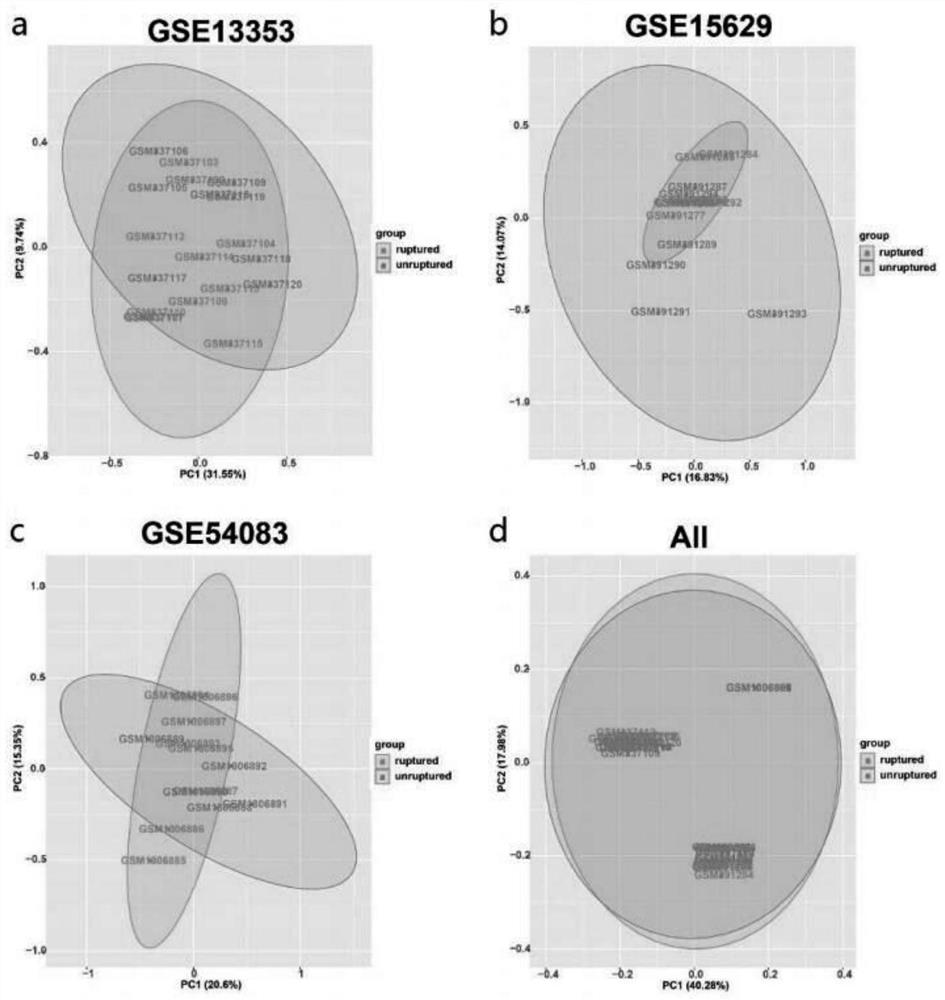
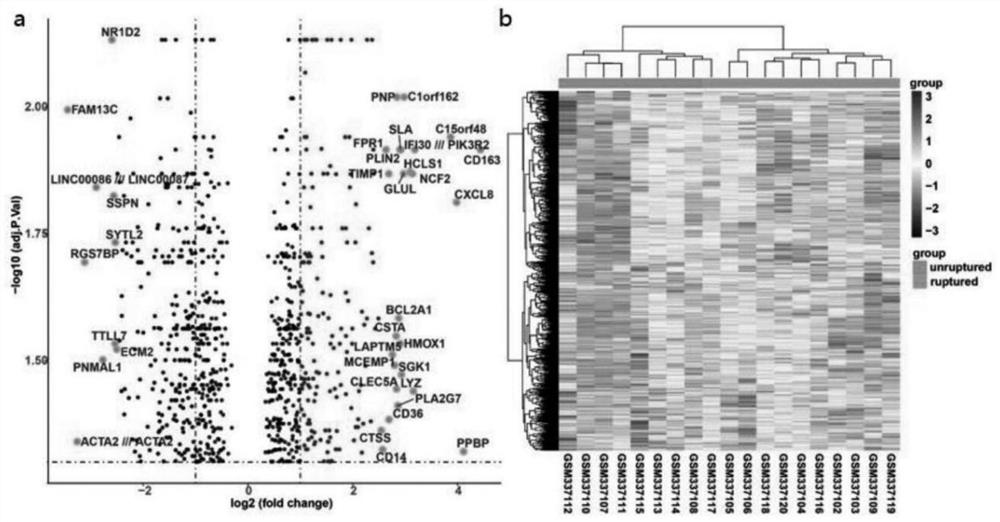
Research method for key genes of intracranial aneurysm formation and rupture
The invention relates to the field of bioinformatics, in particular to a research method of key genes of intracranial aneurysm formation and rupture, which comprises the following steps: S1, chip data acquisition and chip data pretreatment; s2, screening key genes; s3, gene function enrichment analysis and immune microenvironment analysis, on the basis of screening of key genes, a method combining differential expression gene analysis and WGCNA is adopted, on the basis, the key genes obtained after intersection of results of the two methods are subjected to protein interaction network analysis, the gene with the most core of IAs formation and rupture is screened out, and the key genes with the core of IAs formation and rupture are screened out. The method realizes identification of potential key genes causing formation and rupture of IAs through a weight gene co-expression network analysis method.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Treatment of aneurysms
ActiveUS11376248B2Effective biomarkerReduce morbidityOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderKynureninaseMetabolite
The present invention provides methods for detecting and / or treating a subject having an aneurysm or at risk for developing an aneurysm. It has been discovered that a key metabolite of the kynurenine (Kyn) pathway, a major route for the metabolism of essential amino acid tryptophan (Trp) into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), plays a critical role in the formation of aneurysms, for example abdominal aortic aneurysms. In particular, it has been discovered that 3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid (3-HAA), a product of kynureninase (KYNU), plays a causative role in the formation of aneurysms by, for example exerting pro-inflammatory effects on vascular smooth muscle cells. It has further been discovered that elevated levels of 3-HAA are indicative of the presence and / or progression of an aneurysm, and 3-HAA levels correlate with the size (aortic diameter) of the aneurysm.
Owner:GEORGIA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Apparatus for vessel characterization
ActiveUS10694955B2Well representedEase of evaluationImage analysisOrgan movement/changes detectionImaging modalitiesPulsatile blood flow
The invention discloses an apparatus (2), a system (1) and a method (100) for characterization of vessels and for vessel modeling. The cross sectional area (A1) of the vessel is derived from pressure measurements (p1, p2) obtained by an instrument (3) from within the vessel. When multiple cross sectional areas (A1, A2) are derived for multiple reference positions (r1, r2) based on pressure measurements (p1, p2, p3) along the vessel, a representation (20, 30) of the vessel can be rendered, without requiring any imaging modality. Furthermore, the effect of the pulsatile blood flow on the elasticity of the vessel walls can be visualized, supporting assessment of a stenosis or an aneurysm formation along the vessel.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com