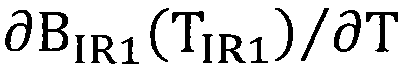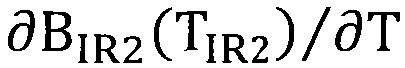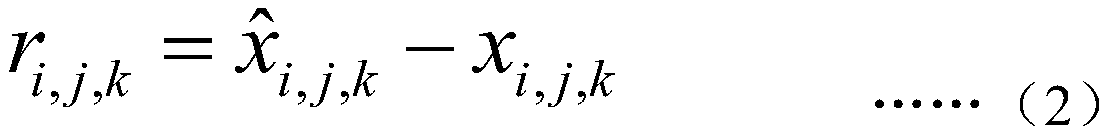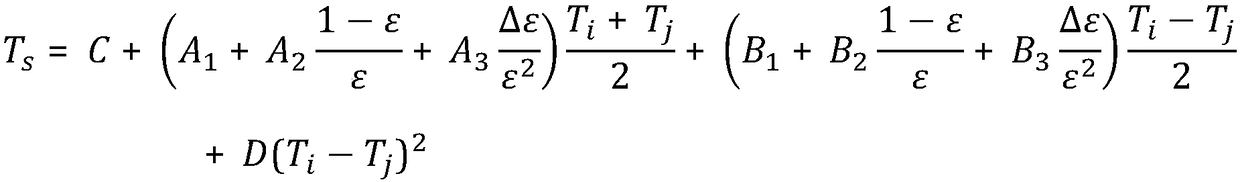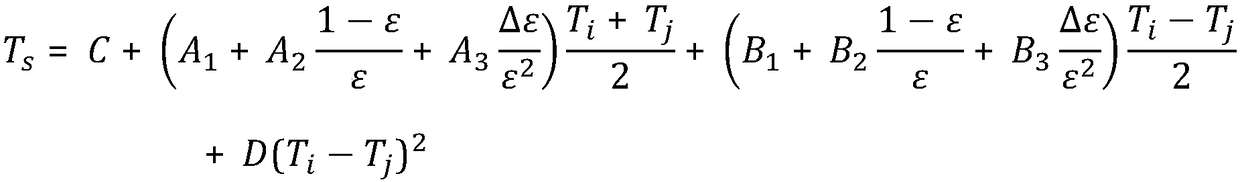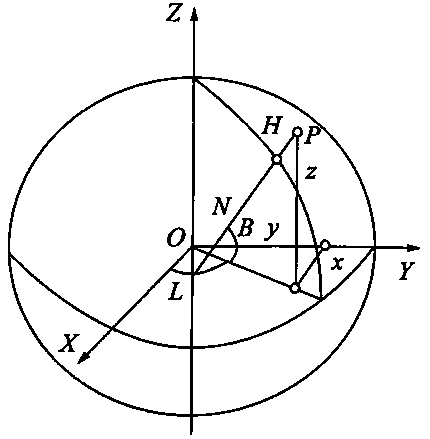Patents
Literature
45 results about "Atmospheric profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Atmospheric temperature and humidity profile processing method and system with active and passive remote sensing combined
ActiveCN104007486AReduce mistakesImprove accuracyIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesAtmospheric temperatureMicrowave radiometer
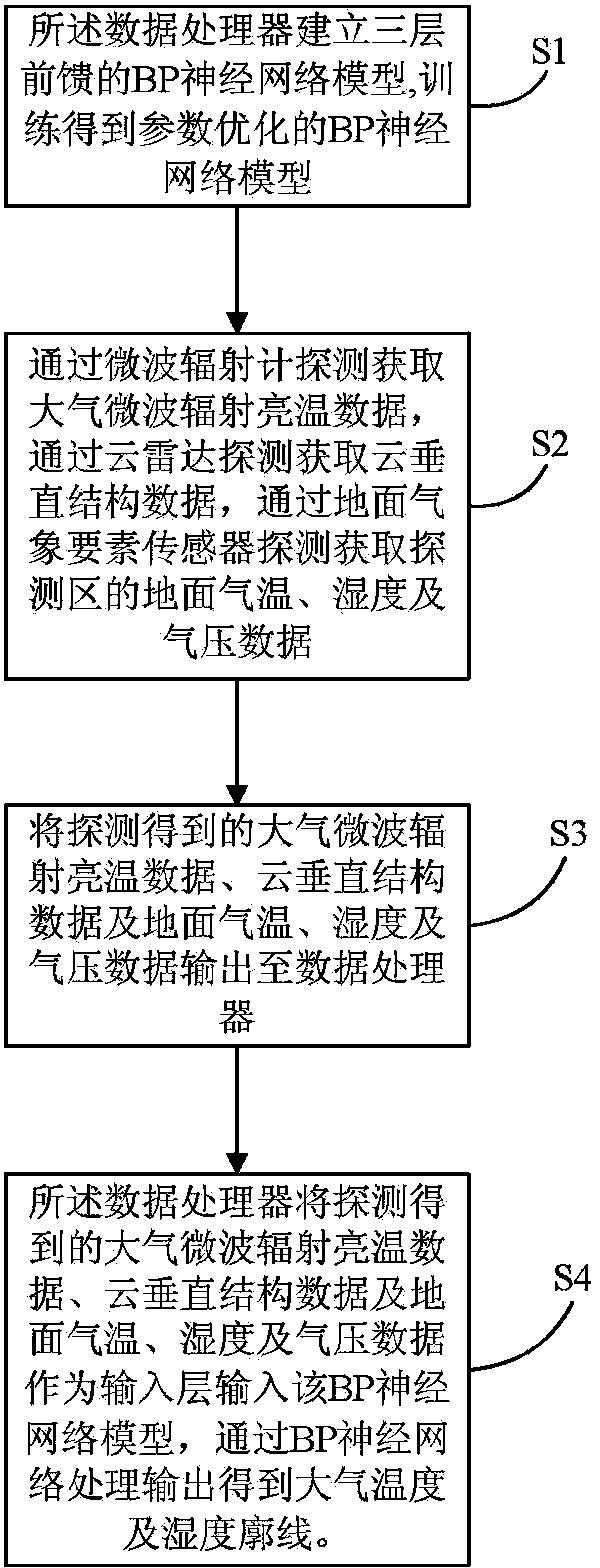
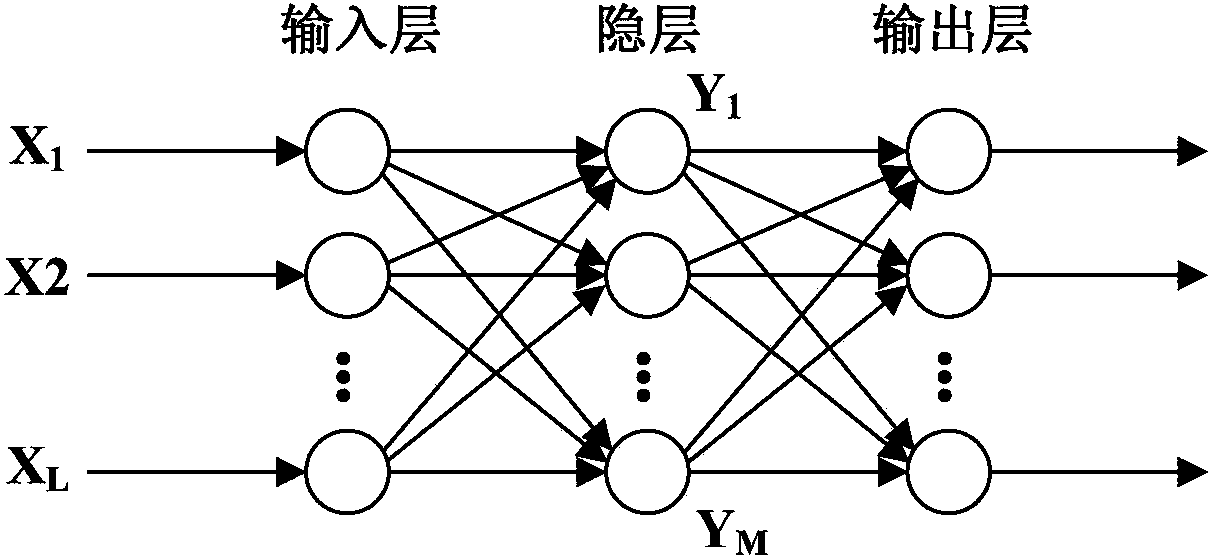
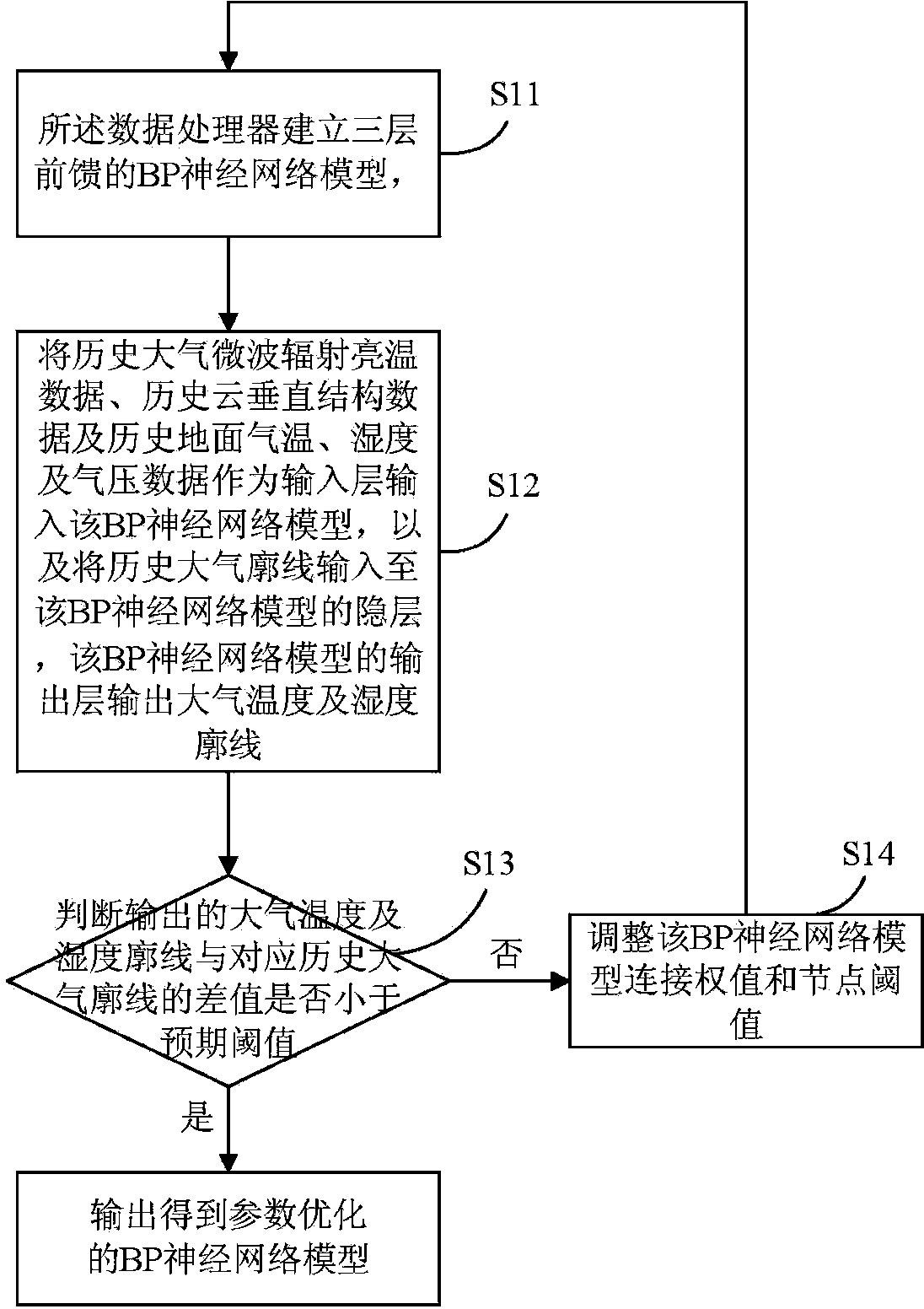
The invention provides an atmospheric temperature and humidity profile processing method and system with active and passive remote sensing combined. The system relates to the following steps that atmospheric microwave radiation brightness temperature data are detected and acquired through a microwave radiometer, cloud vertical structure data are detected and acquired through a cloud radar, and ground surface air temperature, humidity and air pressure data of a detecting area are detected and acquired through a ground surface meteorological element sensor; a data processor builds a three-layer feedforward BP neural network model for processing and training, and the BP neural network model with parameters optimized is obtained; the detected atmospheric microwave radiation brightness temperature data, the detected cloud vertical structure data and the detected ground surface air temperature, humidity and air pressure data are input into the BP neural network model by the data processor to serve as input layers, and the atmospheric temperature and humidity profile is obtained through processing and output of a BP neural network. Due to the atmospheric temperature and humidity profile processing method and system with active and passive remote sensing combined, the error for processing the atmospheric temperature and humidity profile in cloud weather is effectively reduced, and the accuracy and the effectiveness of the atmospheric profile are improved.
Owner:CMA METEOROLOGICAL OBSERVATION CENT
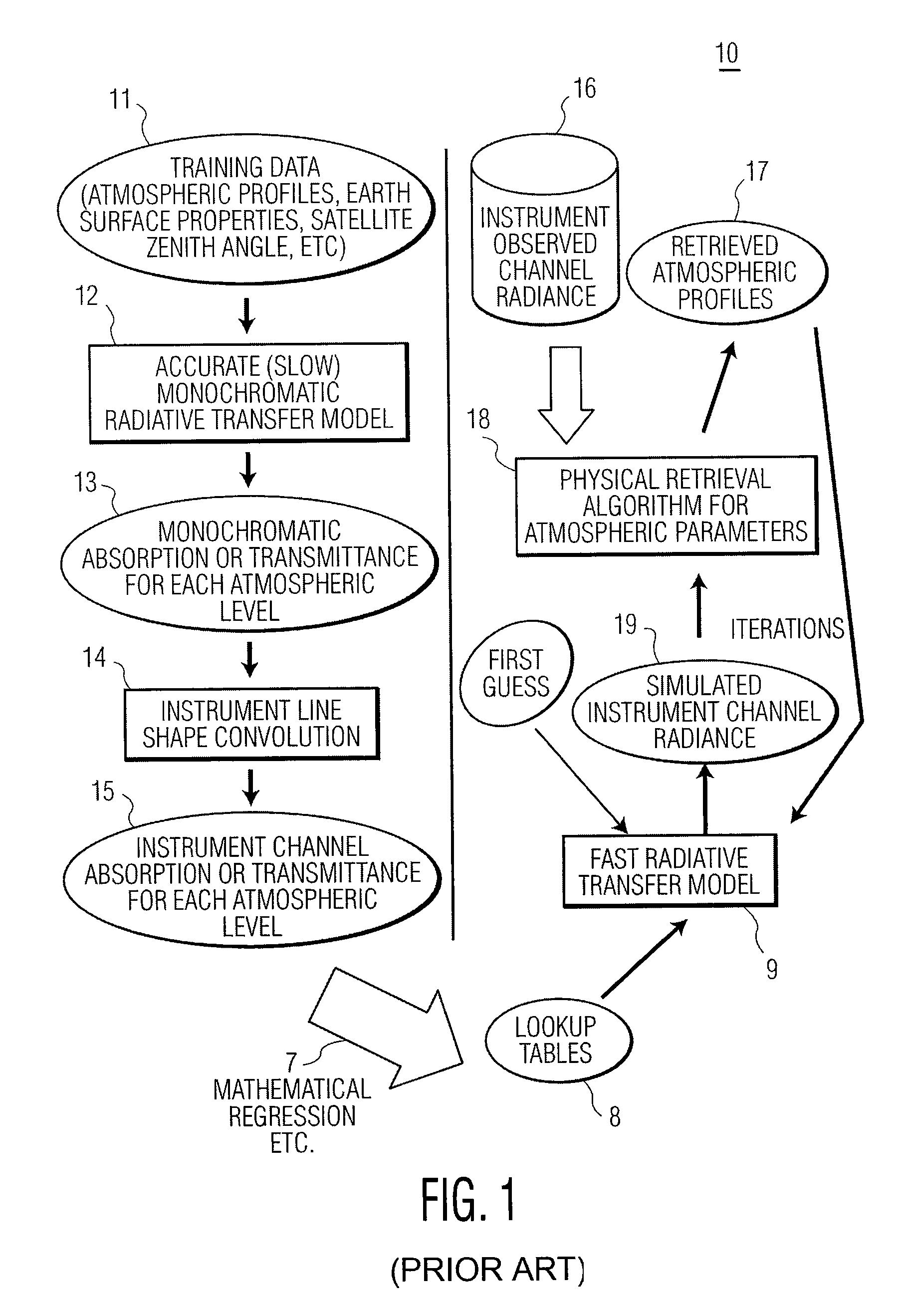
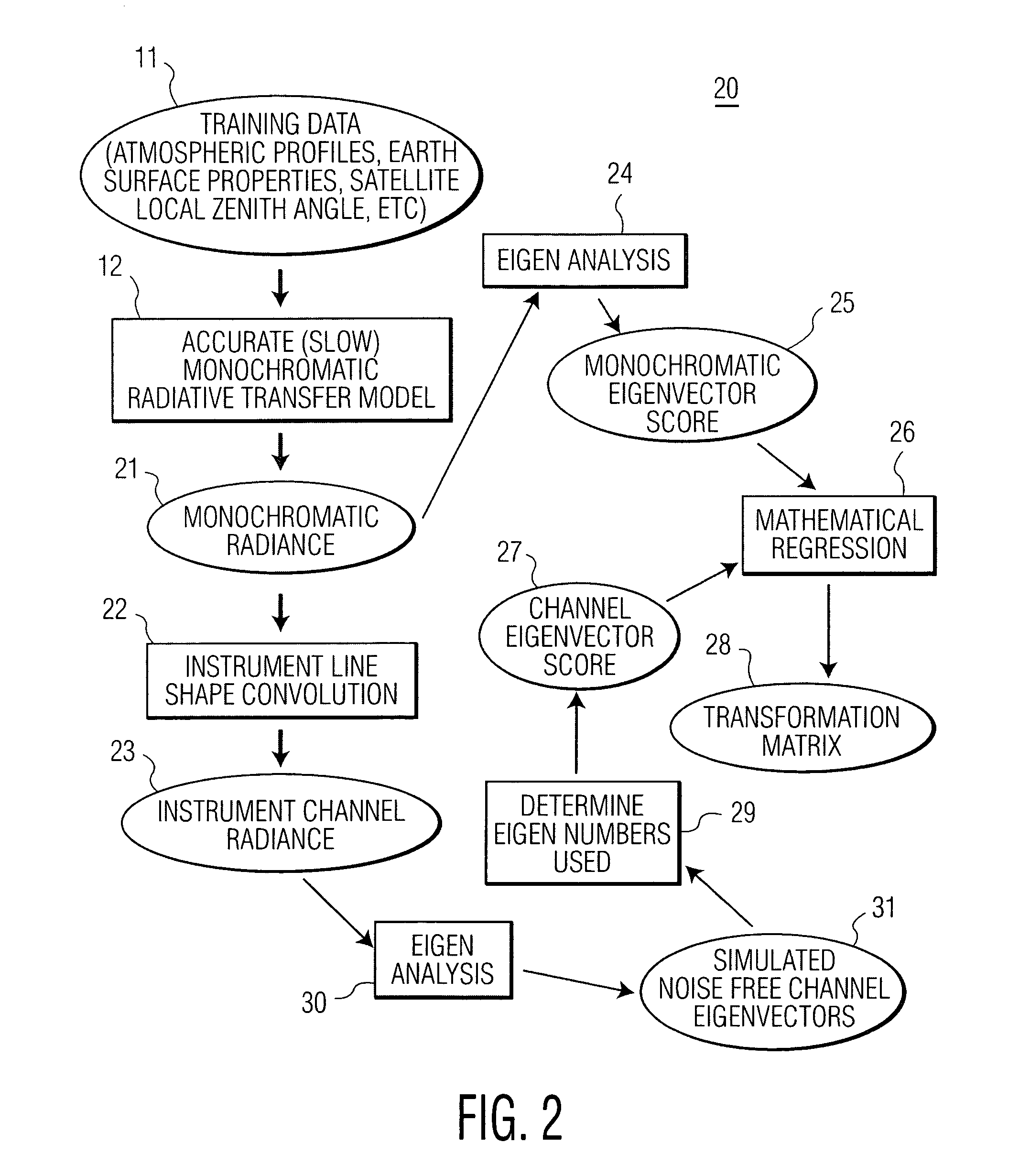
Method and system for determining atmospheric profiles using a physical retrieval algorithm
ActiveUS7558673B1Indication of weather conditions using multiple variablesThermometerFrequency spectrumNoise level
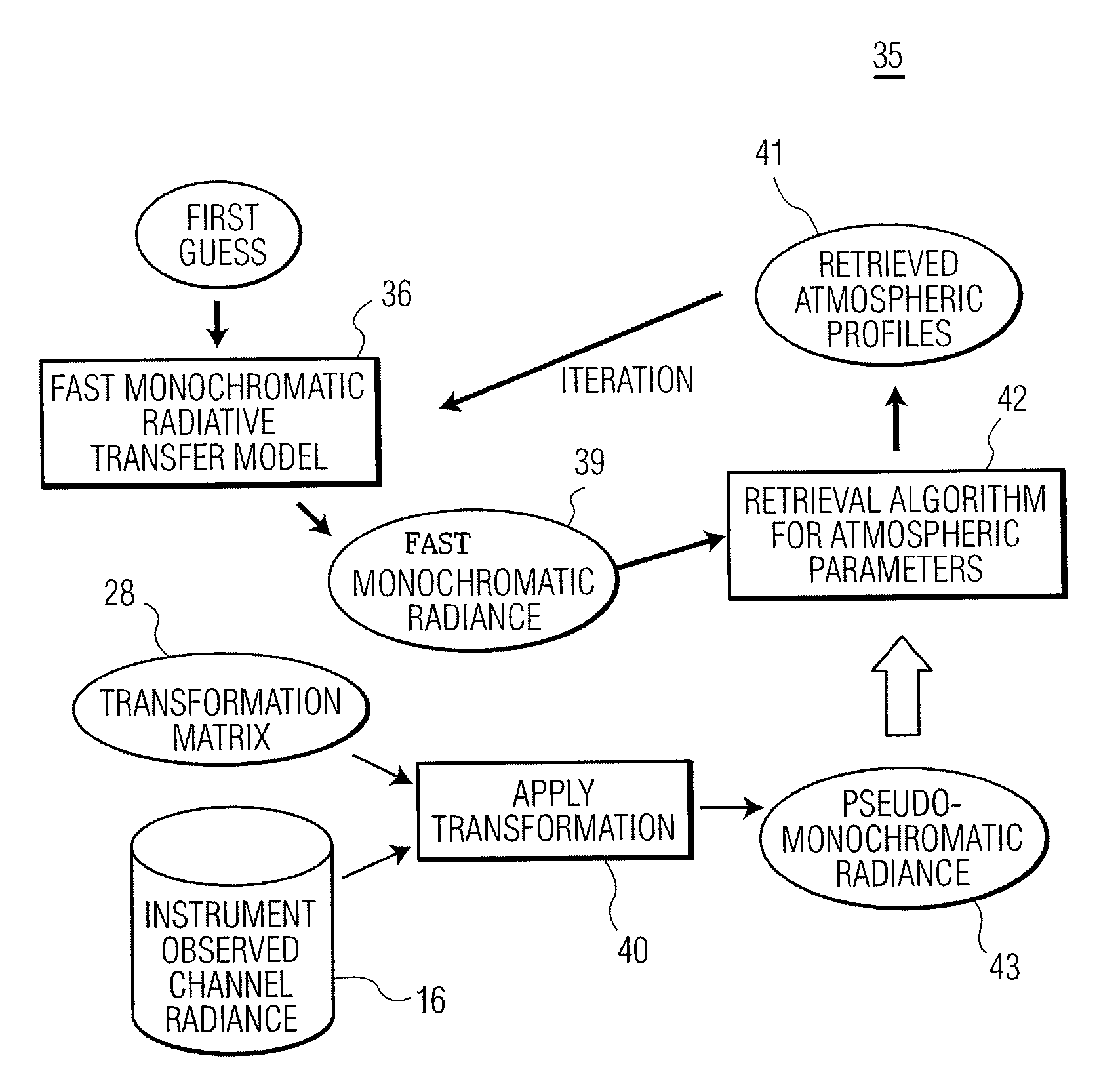
The present invention provides a new approach for processing hyper-spectral radiance data. It uses a transformation matrix to convert an instrument radiance spectrum into a pseudo-monochromatic radiance spectrum. The pseudo-monochromatic radiance spectrum is produced by an empirical transform of the instrument channel spectrum to a monochromatic equivalent spectrum (i.e., a pseudo-monochromatic spectrum). Eigenvector regression is used to produce the empirical transformation. Although the transformation does not produce the monochromatic radiance spectrum without error, the transformation error is generally well below nominal instrument noise levels for most spectral channels. The reduction in instrument noise results from a noise filtering effect of the eigenvector transformation. One of the advantages of the present invention is that it eliminates the need to build different fast radiative transfer models (RTMs) for different observing instruments, since the retrieval of geophysical parameters is based on an inversion of the monochromatic radiative transfer model. Although a different transformation matrix is required for different instrument spectral channel characteristics, the production of this transformation matrix is straightforward and simpler than the production of an accurate channel radiance fast model.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Near-surface temperature inversion method based on FY-2C thermal-infrared waveband
The invention relates o a near-surface temperature inversion method based on FY-2C thermal-infrared waveband data as well as NCEP (National Centers for Environmental Prediction) atmospheric profile data. The inversion method comprises the steps of A) calculating an atmospheric transmittance tau[i](theta), wherein the tau[i](theta) represents the atmospheric transmittance at the waveband i when the observation zenith angle is theta; B) respectively calculating land surface emissivity epsilon[IR1] and epsilon[IR2] of FY-2C at the wavebands IR1 and IR2; C) calculating a temperature change rate Rt(h) in different atmospheric layers, wherein Rt(h) is the reduced rate of temperature at the height h; D) calculating steam content proportion Rw(h) in different atmospheric layers, wherein the Rw(h) represents the percentage of steam in total water content at the layer whose height is h; and E) calculating the near-surface temperature Ta via the formula Ta=(B0+B1TIR1+B2TIR2-bT0) / a.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
System and Method for Atmospheric Correction of Information
ActiveUS20130006534A1Electromagnetic finder monitoring/testingDigital computer detailsAtmospheric correctionAtmospheric sciences
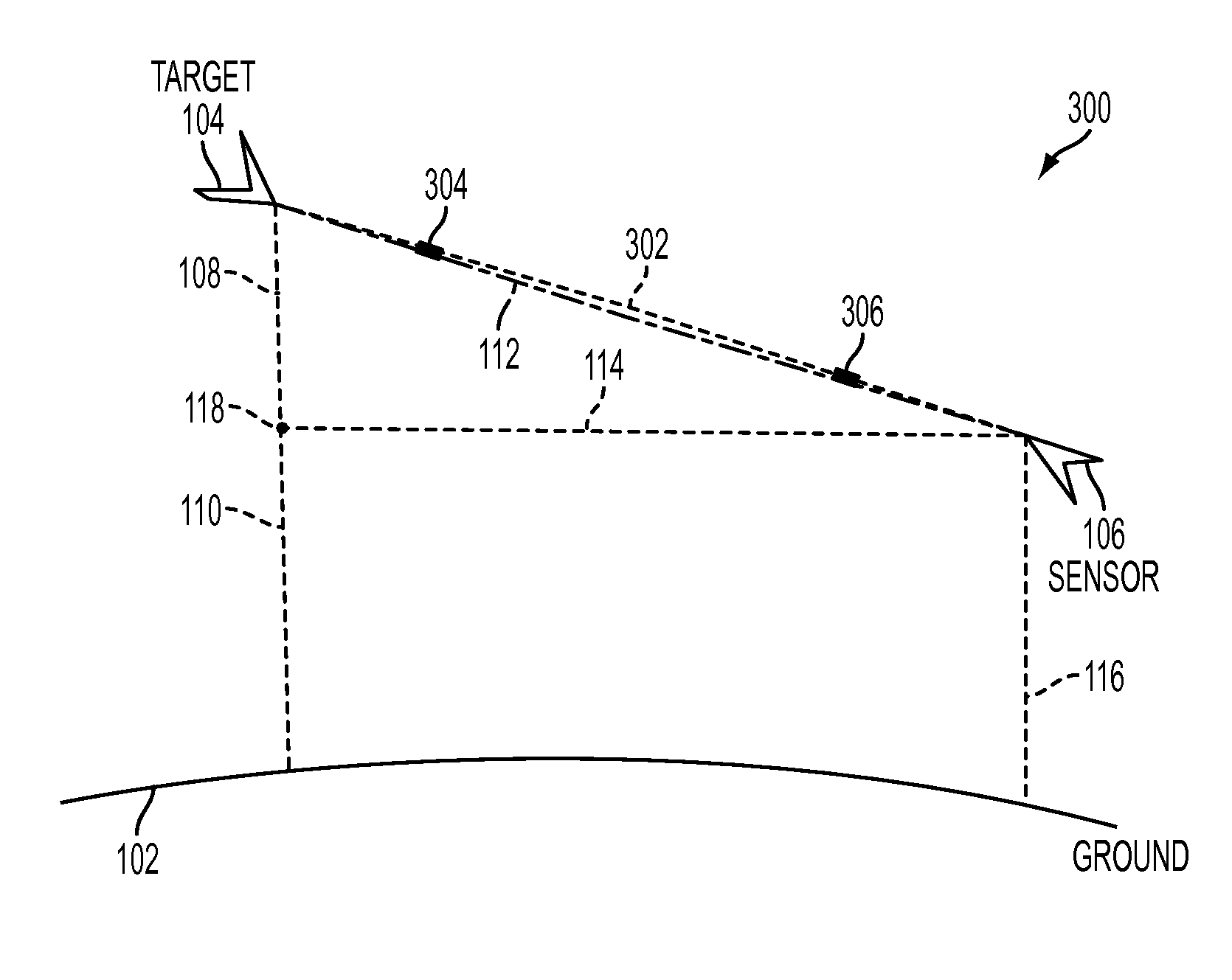
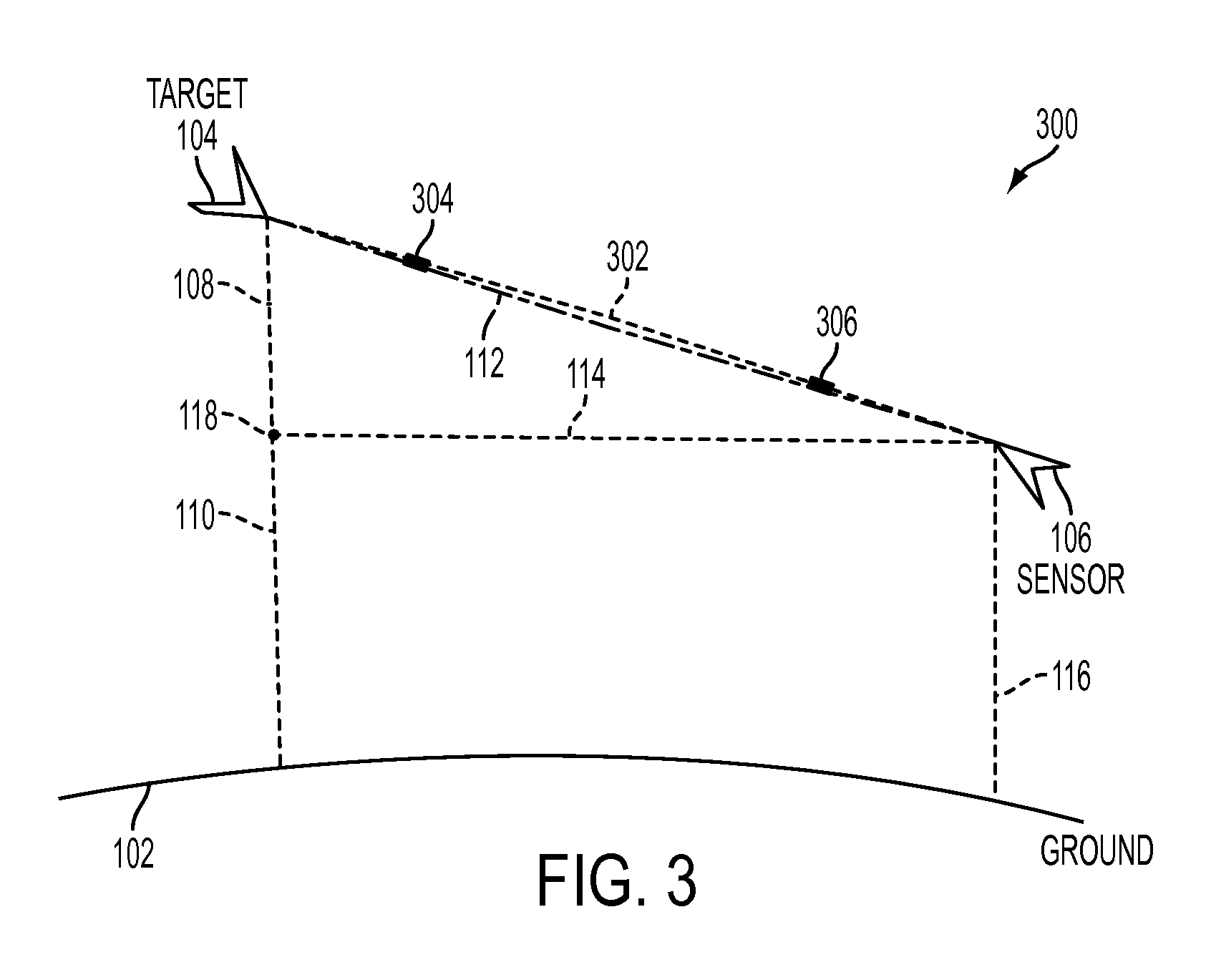
An atmospheric correction system (ACS) is proposed, which accounts for the errors resulting from the in-homogeneities in the operational atmosphere along the slant path by constructing atmospheric profiles from the data along the actual target to sensor slant-range path. The ACS generates a slant-range path based on the arbitrary geometry that models the sensor to target relationship. This path takes the atmosphere and obstructions between the two endpoints into account when determining the atmospheric profile. The ACS uses assimilation to incorporate weather data from multiple sources and constructs an atmospheric profile from the best available data. The ACS allows the user to take advantage of variable weather and information along the path that can lead to increased accuracy in the derived atmospheric compensation value.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
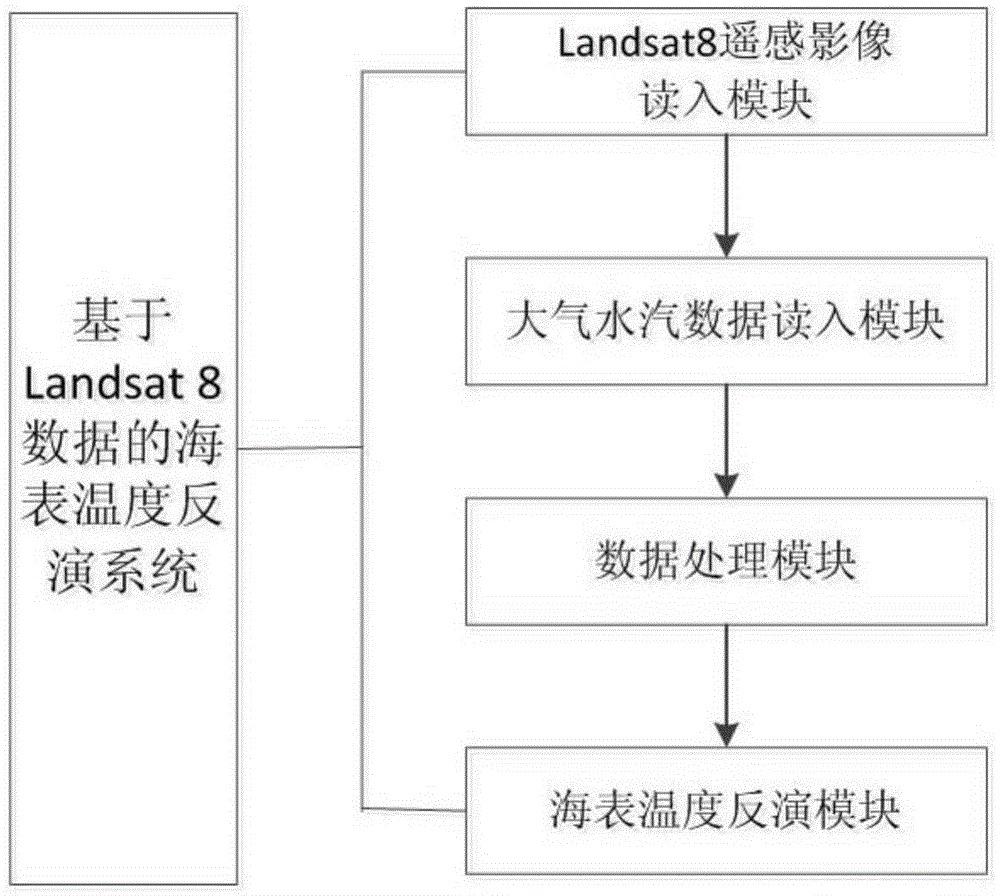
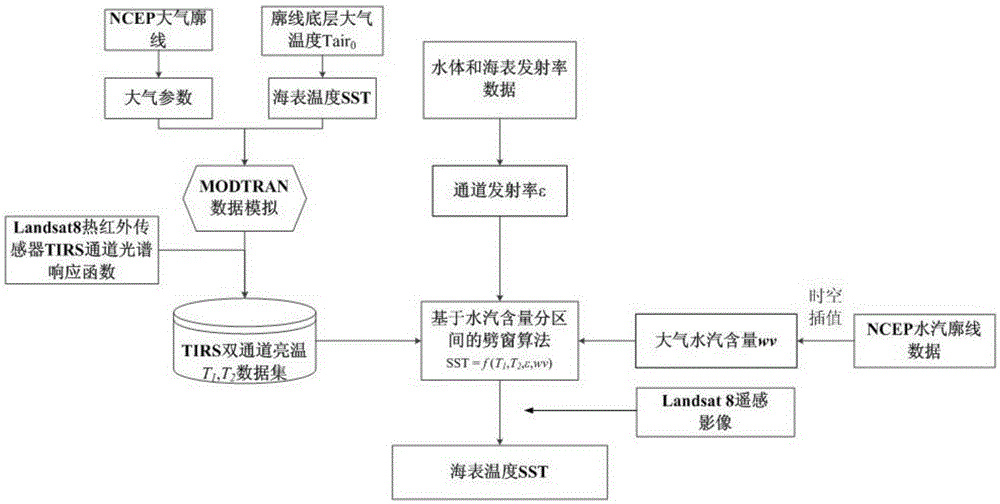
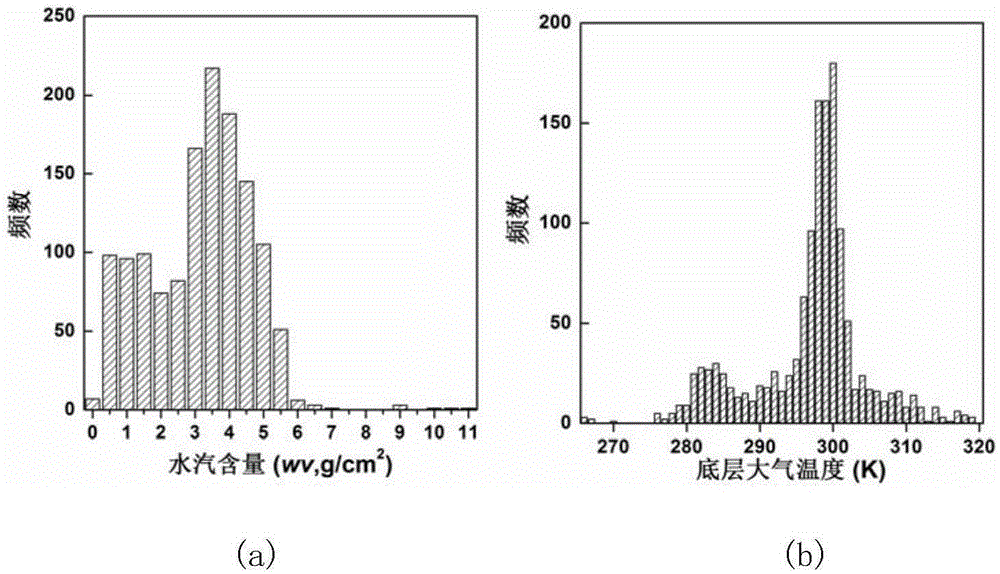
SST (Sea Surface temperature) inversion method and system based on Landsat 8 data
ActiveCN106768393AHigh precisionThe calculation process is simpleRadiation pyrometrySplit windowThermal infrared
The invention relates to an SST inversion method and system based on Landsat 8 data. The method comprises that Landsat 8 optical and thermal-infrared remote sensing images and corresponding atmospheric contour data are read; on the basis of water-body and seawater emissivity data and a spectral response function of a Landsat 8 TIRS (Thermal Infrared Sensor), the atmospheric contour is used for driving, and channel brightness temperatures in the aerosphere top of two channels of the TIRS under different combined conditions of atmospheric conditions, SSTs and emissivities are simulated; and the obtained total atmospheric column water vapor content is used to divide the atmospheric column water vapor content into intervals, a split-window algorithm is used to construct SST inversion algorithms of the different water vapor content intervals, the SST is calculated, and a result is output. The system comprises a remote-sensing image reading module, an atmospheric water vapor data reading data, a data processing module and an SST inversion module. The system and method can be used to obtain high-precision SST.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
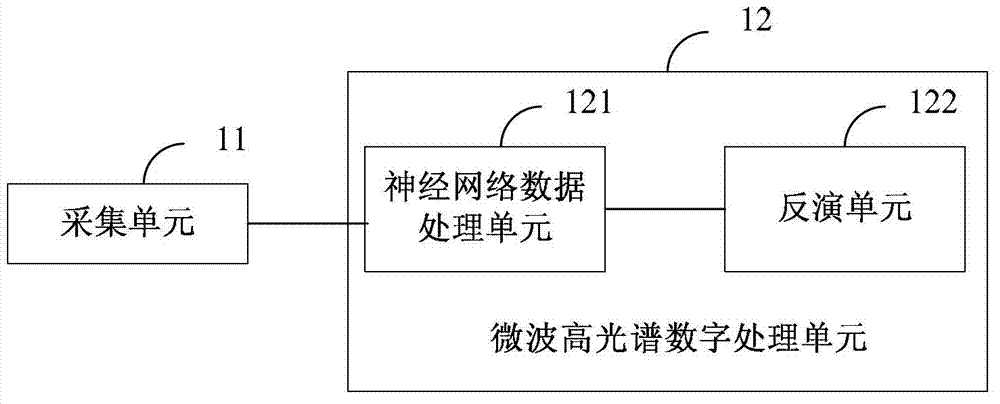
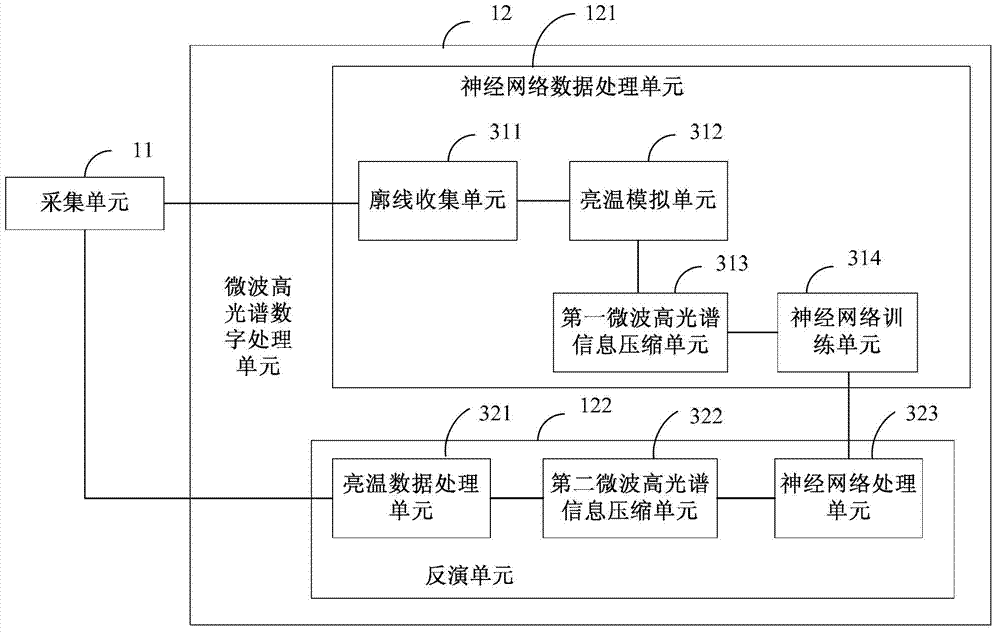
Microwave hyperspectral digital processing and control method and device
InactiveCN102819024AInversion realizationHigh speed acquisitionElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationFrequency spectrumData acquisition
Owner:BEIJING KUNQI ELECTRONICS SYST
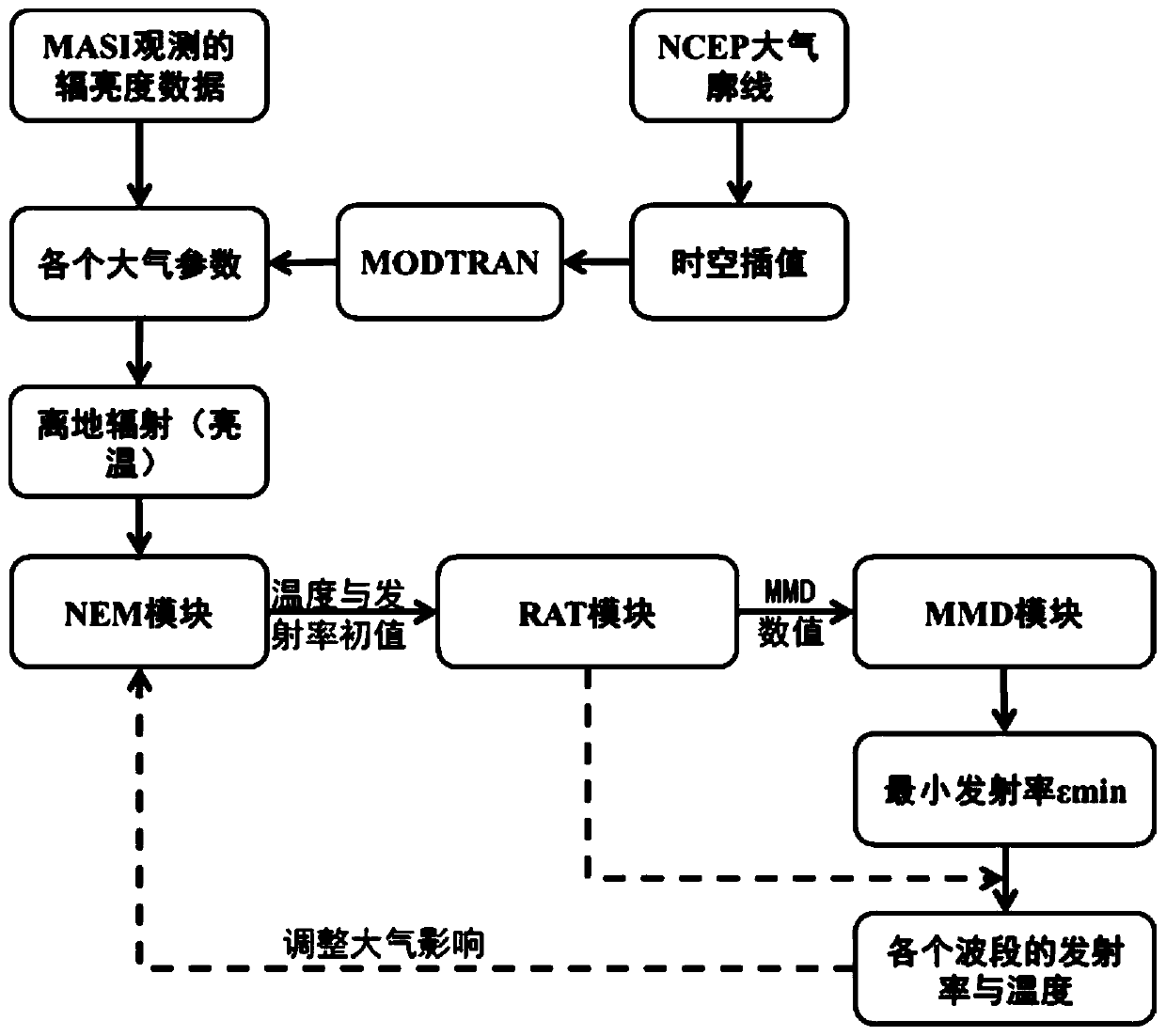
Aviation mid-infrared hyperspectral data temperature and emissivity inversion method
PendingCN110866467AHigh precisionSolving the temperature emissivity inversion problemScene recognitionComplex mathematical operationsMiddle infraredAtmospheric radiation
The invention belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image processing, and particularly relates to an aviation mid-infrared hyperspectral data temperature and emissivity inversion method, which comprises the following steps: 1, preprocessing aviation mid-infrared hyperspectral remote sensing data to select a minimum noise wave band; 2, analyzing an intermediate infrared radiation transmission process, and deriving an intermediate infrared radiation transmission equation; 3, carrying out space-time interpolation by utilizing the atmospheric profile data to simulate each atmospheric parameter; 4, eliminating solar radiation and atmospheric thermal radiation effects according to an intermediate infrared atmospheric radiation transmission equation to obtain off-ground radiation; 5, iteratively eliminating downlink radiation in the ground clearance by using an NEM module to obtain the surface temperature and emissivity; 6, calculating the relative emissivity by using the RAT module, and keeping the emissivity spectrum shape inverted by the NEM module unchanged; and 7, acquiring the surface temperature and emissivity by using the empirical relationship between the emissivity spectrum shape parameters of the MMD module and the RAT module and the minimum value of the channel emissivity.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY +1
Estimation method and system for observing brightness temperature data errors by satellite-borne microwave radiometer
ActiveCN112197865AHigh precisionRadiation pyrometryComplex mathematical operationsMathematical modelBrightness temperature
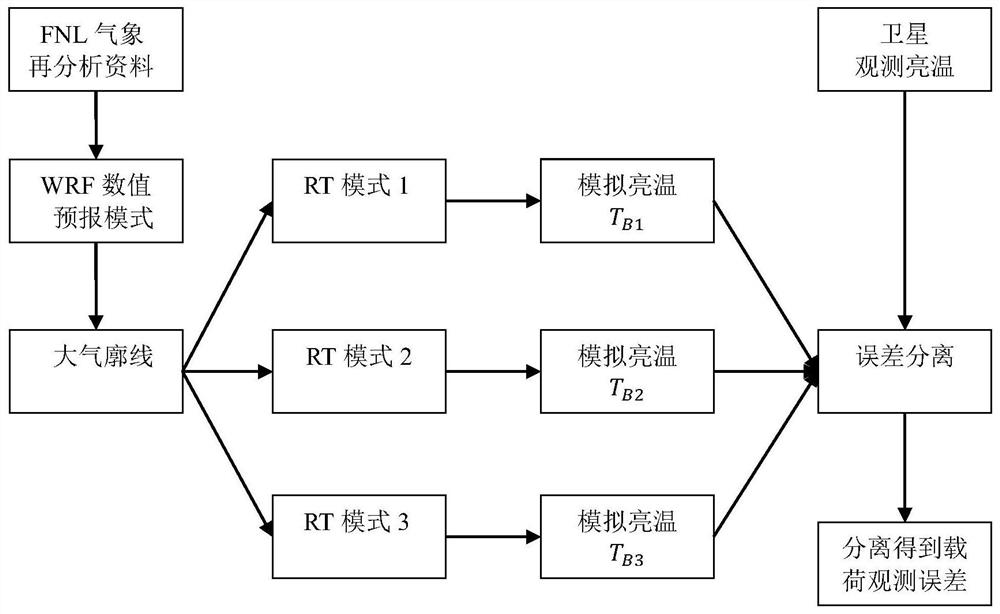
The invention discloses an estimation method and system for observing brightness temperature data errors by satellite-borne microwave radiometer. The method comprises the steps: obtaining a group of atmospheric profiles covering a satellite-borne microwave radiometer observation brightness temperature data region through the prediction of a numerical prediction mode, and carrying out interpolationto obtain a satellite-borne microwave radiometer observation brightness temperature TA; sending the atmospheric profile parameters output by the numerical prediction mode into a plurality of different RT modes to obtain a radiation transmission RT mode simulation brightness temperature TB matched with the observation brightness temperature space-time; establishing an equation based on the mathematical model for observing the brightness temperature subtraction simulation brightness temperature OB error and statistical data to carry out error term separation solution, and calculating an observation error of the satellite-borne microwave radiometer; and quantitatively evaluating the observation brightness temperature data quality of the satellite-borne microwave radiometer by solving the estimated observation error of the satellite-borne microwave radiometer. According to the method, the real observation brightness temperature error of the satellite-borne microwave radiometer is separated and estimated from the 'O-B' error, and the evaluation precision of the observation brightness temperature data quality of the satellite-borne microwave radiometer can be improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
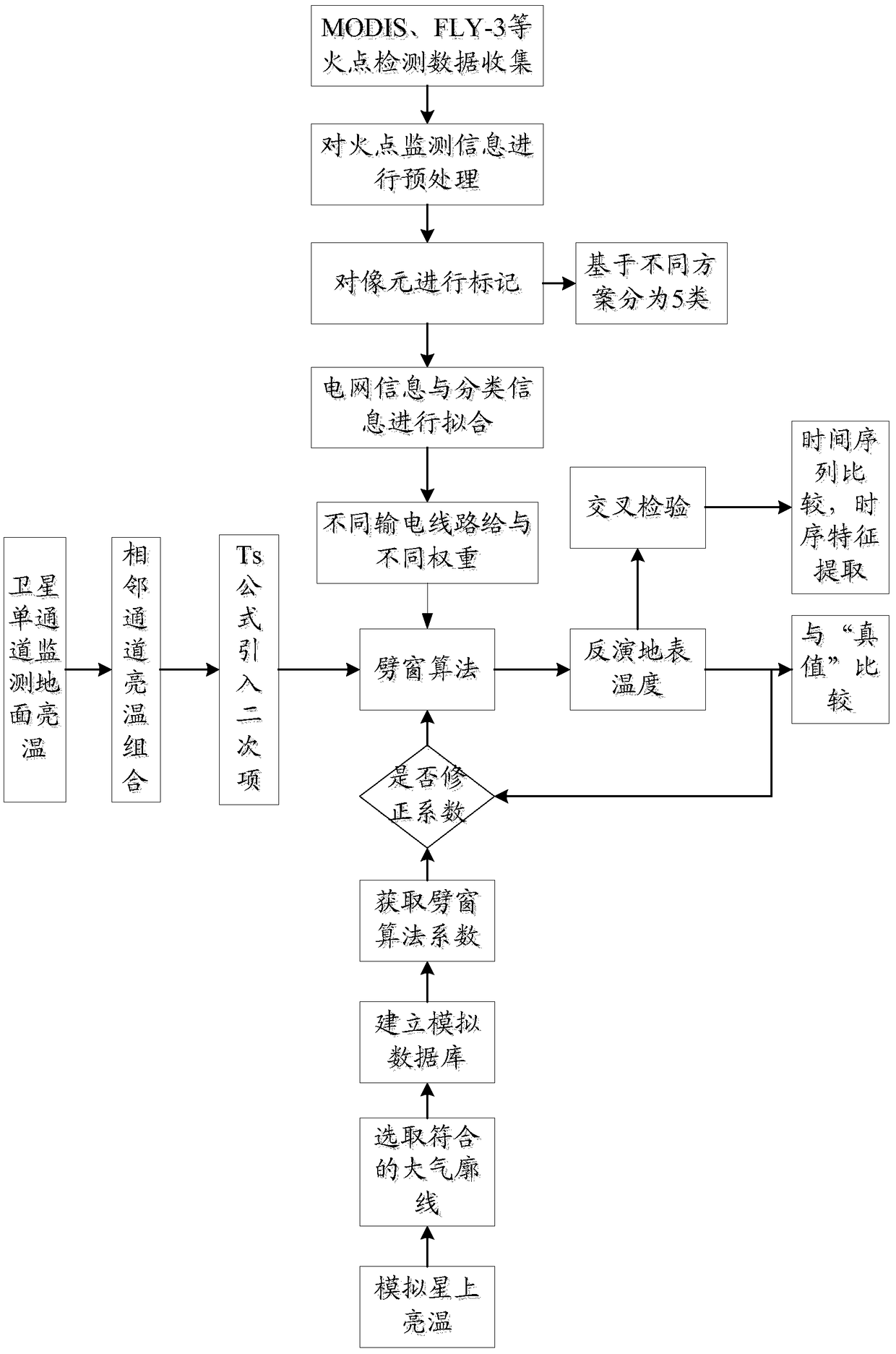
Power transmission line vegetation fire monitoring and early warning method based on geostationary satellite monitoring data
ActiveCN109509319AImprove accuracyHigh precisionForest fire alarmsFire alarm radiation actuationVegetationNatural satellite
The invention provides a power transmission line vegetation fire monitoring and early warning method based on geostationary satellite monitoring data. The method includes the steps that land cover types corresponding to the pixels of a landform picture are determined, and the weights of power transmission line units are calculated; the atmospheric profile of a monitoring area during monitoring isdetermined in real time; ground brightness temperature values measured by satellites in adjacent channels respectively are determined; inverse surface temperatures corresponding to the pixels are calculated; after being obtained, the inverse surface temperatures corresponding to the pixels are marked on the landform picture, centralized analysis of the distribution of the inverse surface temperatures on the landform picture is conducted, and then vegetation fire monitoring and early warning are conducted. The power transmission line vegetation fire monitoring and early warning method based onthe geostationary satellite monitoring data has the advantages that the precision of the inverse surface temperatures can be improved, and thus the accuracy of vegetation fire monitoring and early warning can be effectively improved when vegetation fire monitoring and early warning are conducted according to the inverse surface temperatures.
Owner:BEIJING E TECHSTAR
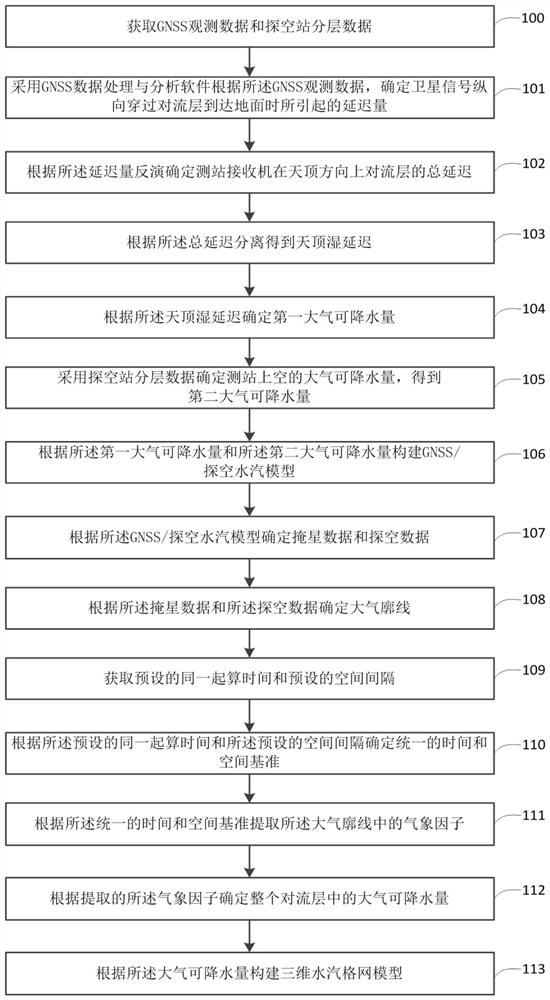
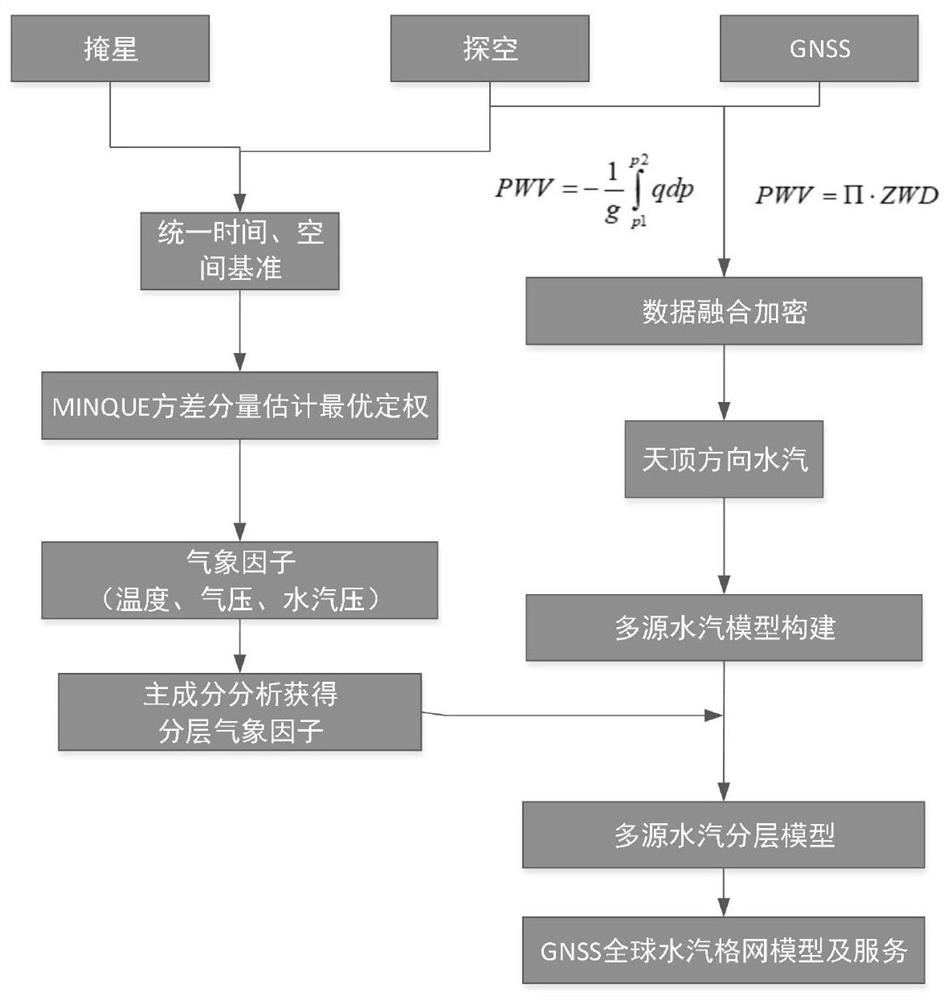
Method and system for establishing three-dimensional water vapor grid model
PendingCN111881581ARealize refined extractionWeather condition predictionDesign optimisation/simulationTroposphereWater vapor
According to the method and the system for establishing the three-dimensional water vapor grid model, the GNSS data is utilized to invert the ZWD so as to calculate the PWV, the sounding station datais utilized to calculate the PWV, and the least square variance estimation is utilized to perform data fusion on the two. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an atmospheric profile byutilizing occultation data and sounding data, extracting meteorological factors in the atmospheric profile, determining time and space references of depth fusion on the basis of GNSS / sounding / occultation inversion water vapor, and establishing a grid water vapor model based on multi-source data. According to the technical scheme, the limitation that the whole troposphere serves as a research object is broken through, the established layered water vapor model can conduct refined extraction on water vapor data, a theoretical basis is provided for refined weather forecast, and certain practical significance is achieved.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF SURVEYING & MAPPING
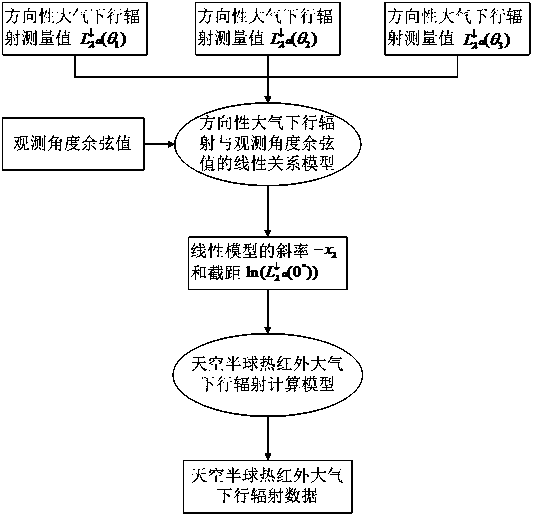
Sky hemisphere thermal infrared atmospheric downward radiation ground measurement method
InactiveCN109959970ASave complex calculationsSimple methodNuclear radiation detectionReduced modelLinear relationship
The invention discloses a sky hemisphere thermal infrared atmospheric downward radiation ground measurement method. through approximate expression of thermal infrared directional atmospheric downwardradiation, a linear relationship model between directional atmospheric downward radiation and an observation angle cosine value is constructed; and further in combination of an angular integral relationship between the directional atmospheric downward radiation and sky hemisphere atmospheric downward radiation, a simplified model for using a slope and an intercept in the linear relationship modelto calculate the sky hemisphere atmospheric downward radiation is developed. As long as an infrared radiometer on the ground is used to perform three times of measurement on different observation angles of the sky, the slope and the intercept can be fit according to the constructed linear relationship model, and thus, the sky hemisphere thermal infrared atmospheric downward radiation is calculated. The complicated calculation of the hemisphere integral is saved, release of a sounding balloon in the field to acquire atmospheric profile data is not needed either, the infrared radiometer is onlyused on the ground to perform three times of measurement in different directions of the sky, the sky hemisphere thermal infrared atmospheric downward radiation data can thus be quickly obtained, materials and financial resources are saved, and a great significance is achieved in ground verification of a thermal infrared surface temperature remote sensing inversion product.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS +1
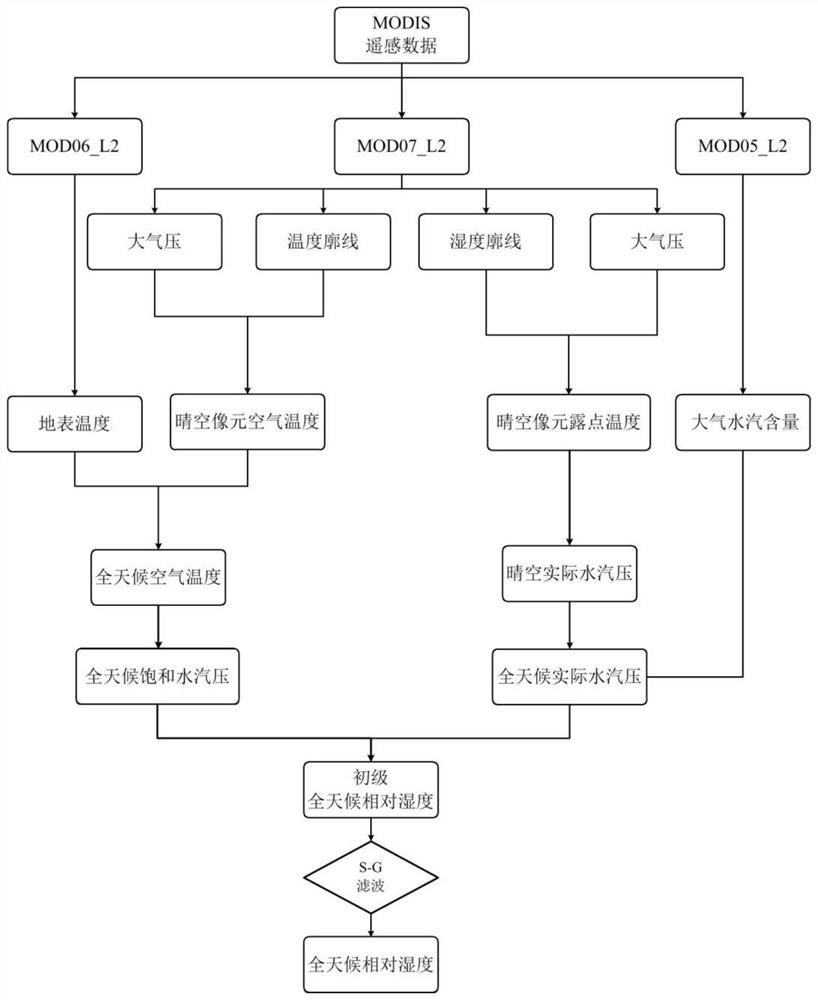
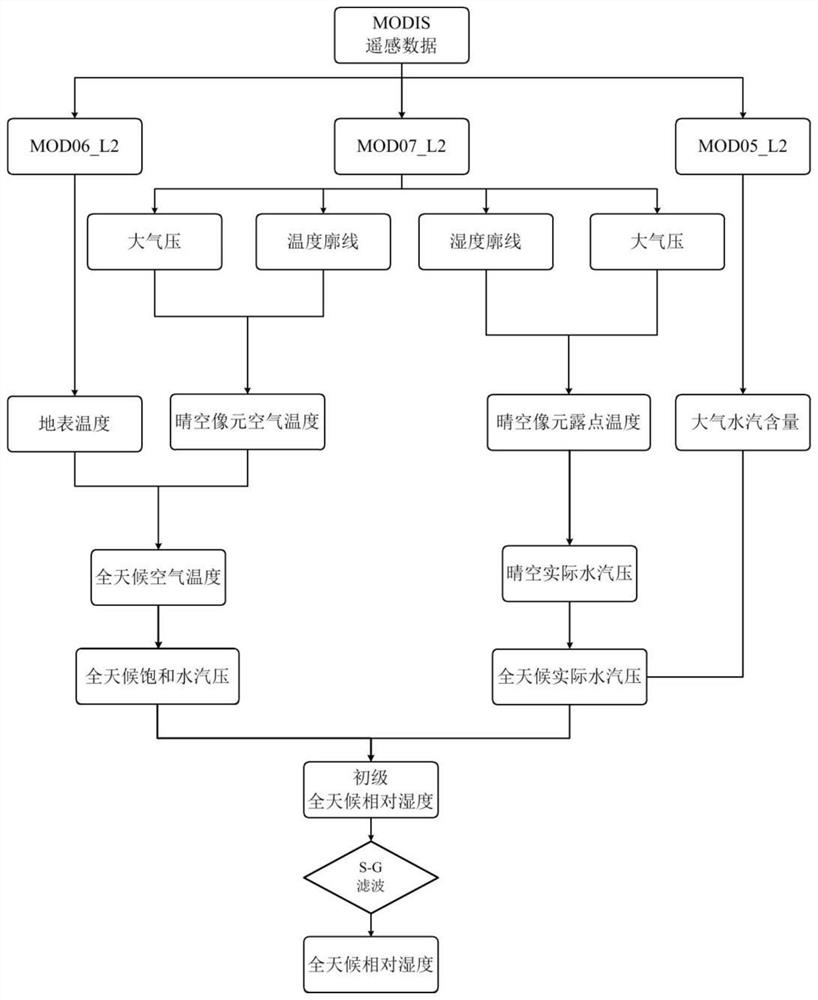
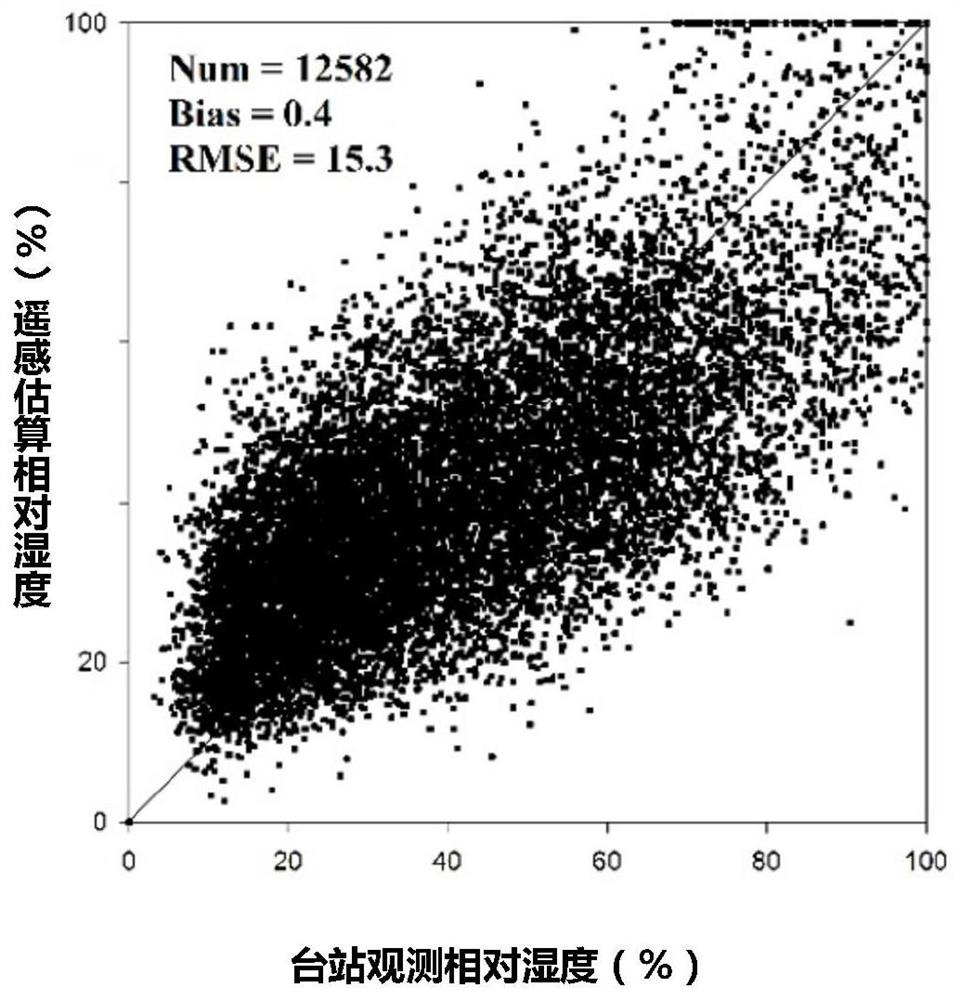
All-weather relative humidity estimation method based on full remote sensing data
ActiveCN112327388AImprove accuracyWeather condition predictionComplex mathematical operationsSensing dataSaturated water vapor
The invention discloses an all-weather relative humidity estimation method based on full remote sensing data. The method comprises the steps: reading the atmospheric water vapor content, the surface temperature, the temperature profile, the humidity profile and the atmospheric pressure profile from MODIS satellite remote sensing water vapor product data, cloud product data and atmospheric profileproduct data respectively; deriving the all-weather saturated water vapor pressure by utilizing the surface temperature, the atmospheric pressure profile and the temperature profile; deducing the all-weather actual vapor pressure according to the atmospheric vapor content, the atmospheric pressure profile and the humidity profile; and calculating the all-weather relative humidity by utilizing theobtained all-weather saturated water vapor pressure and actual water vapor pressure, and carrying out Savitzky-Golay filtering to obtain the final all-weather relative humidity. According to the all-weather relative humidity estimation method based on the full remote sensing data, the all-weather relative humidity is calculated by completely utilizing the MODIS satellite remote sensing data on thebasis of not depending on any auxiliary data, so that the method is simple, and the result is accurate.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
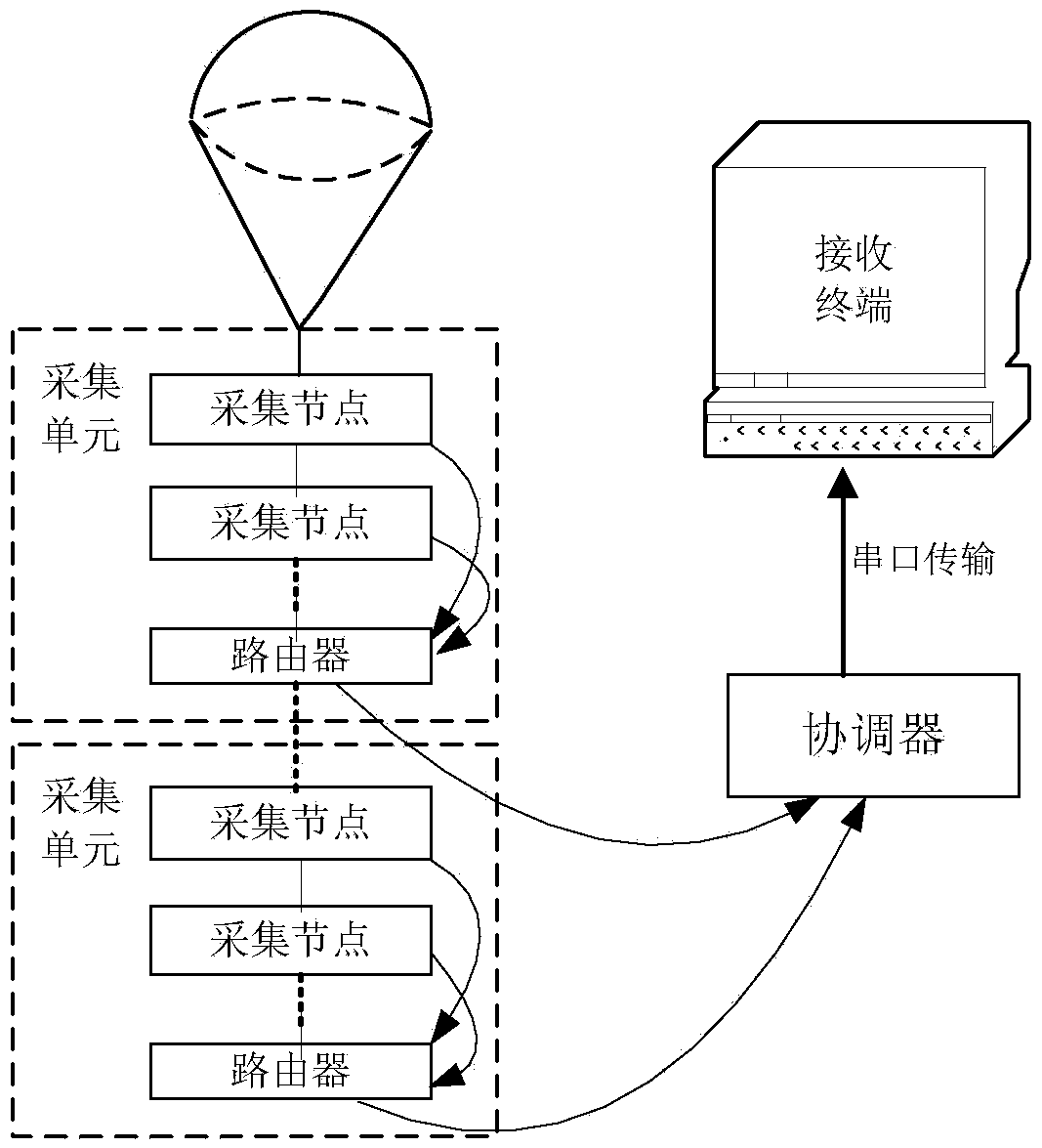
Acquisition system of atmospheric profile parameters including temperature, humidity and pressure
InactiveCN105374189AStrong collection abilityImprove real-time performanceNon-electrical signal transmission systemsLongitudeData acquisition
The invention discloses an atmospheric profile parameter acquisition system. The system includes a captive balloon, a coordinator, a receiving terminal and at least one group of acquisition unit. The at least one group of acquisition unit is sequentially fastened on the captive rope of the captive balloon; the acquisition unit includes a router and multiple acquisition nodes connected sequentially; the acquisition nodes are for the acquisition of three meteorological parameters including temperature, humidity and air pressure of an atmospheric profile, whose height the acquisition nodes are on; the router is used to collect the meteorological parameters of all acquisition nodes in the unit, in which the router locates; a coordinator and the router of the acquisition unit are in a wireless network; the coordinator receives meteorological parameters collected by each router and forwards the meteorological parameters to the receiving terminal. The system of the invention can realize real-time acquisition of three meteorological parameters including temperature, humidity and air pressure of the sea surface on the same longitude and latitude and obtain gradient distribution values concerning the three meteorological parameter values of the profile, and is conductive to accurate prediction of the time and region of atmospheric duct.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
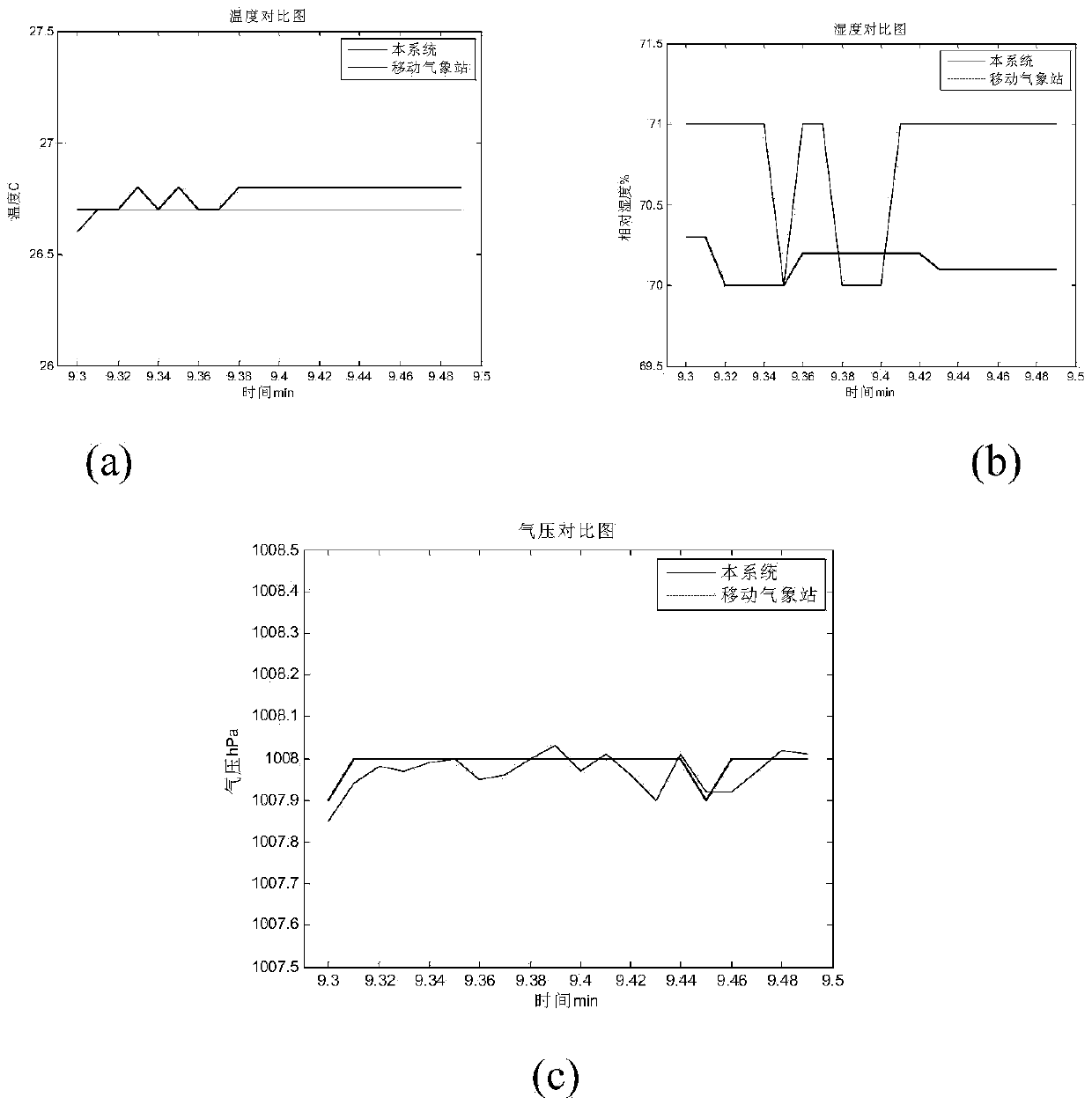
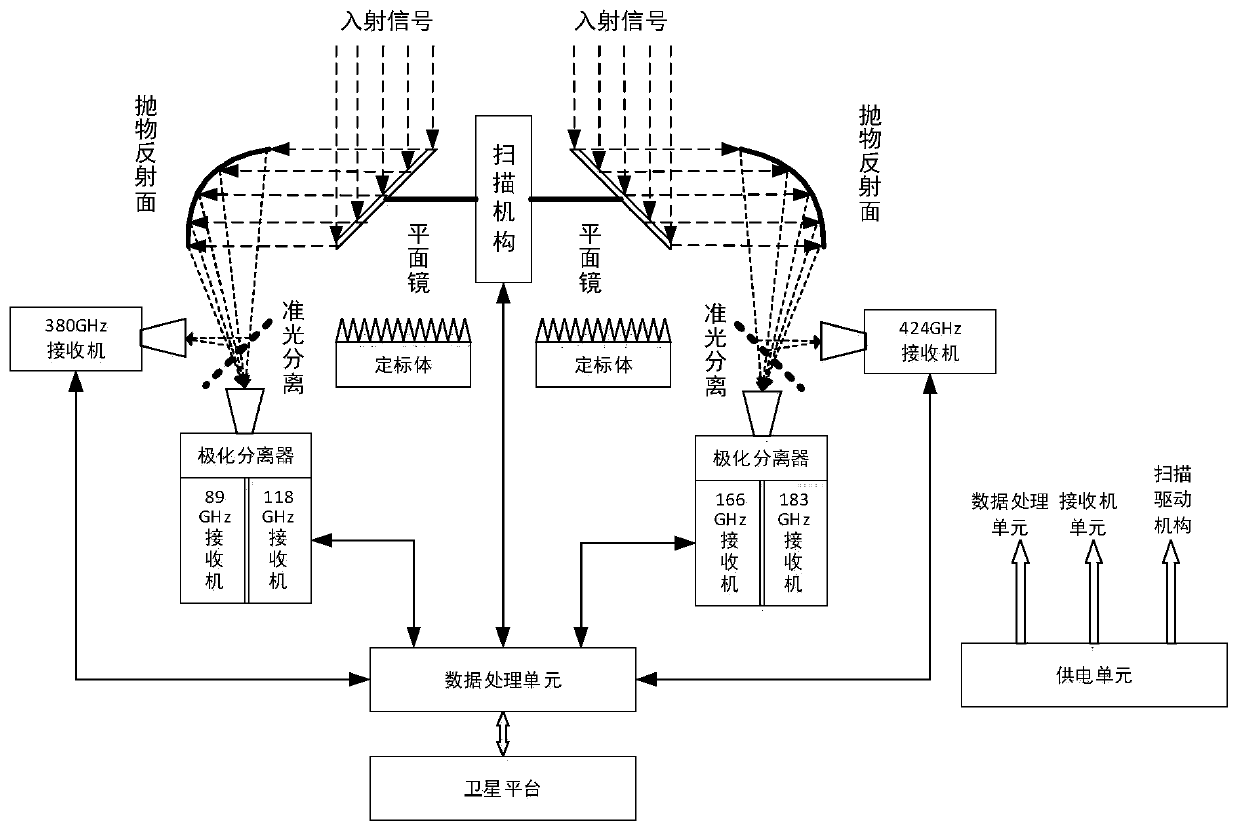
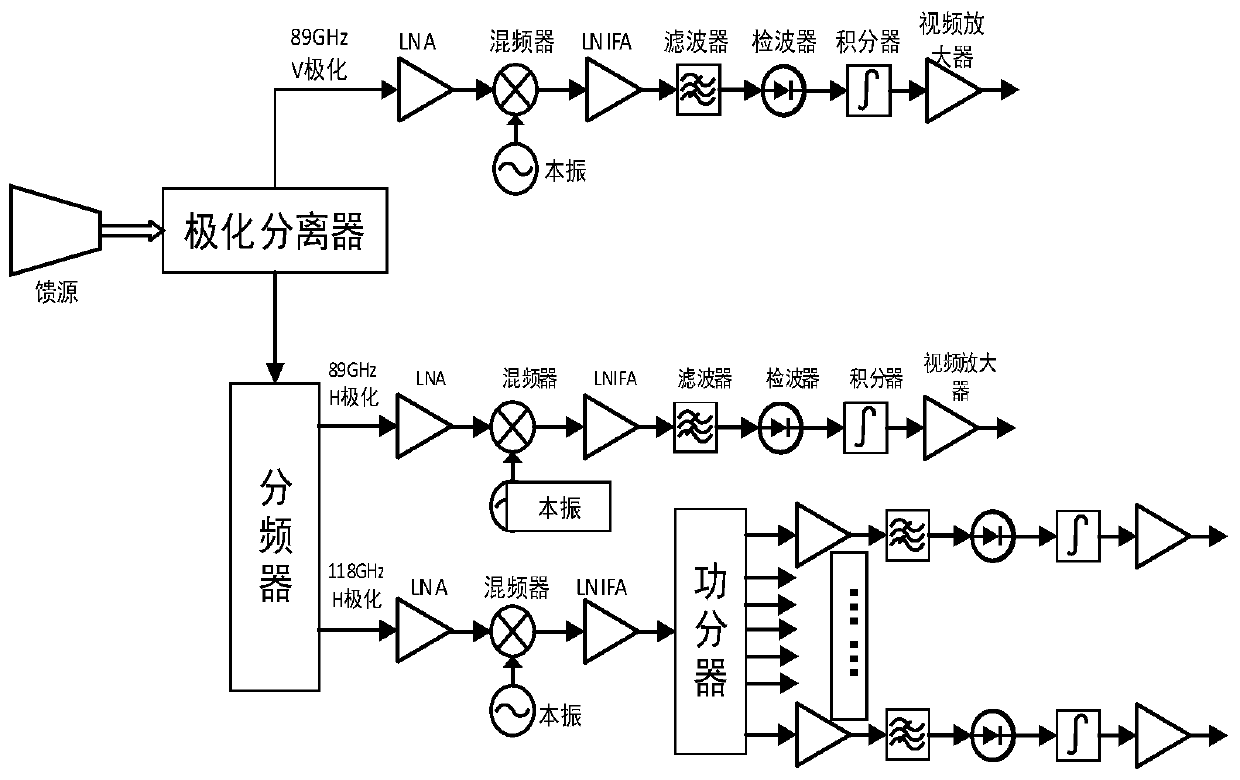
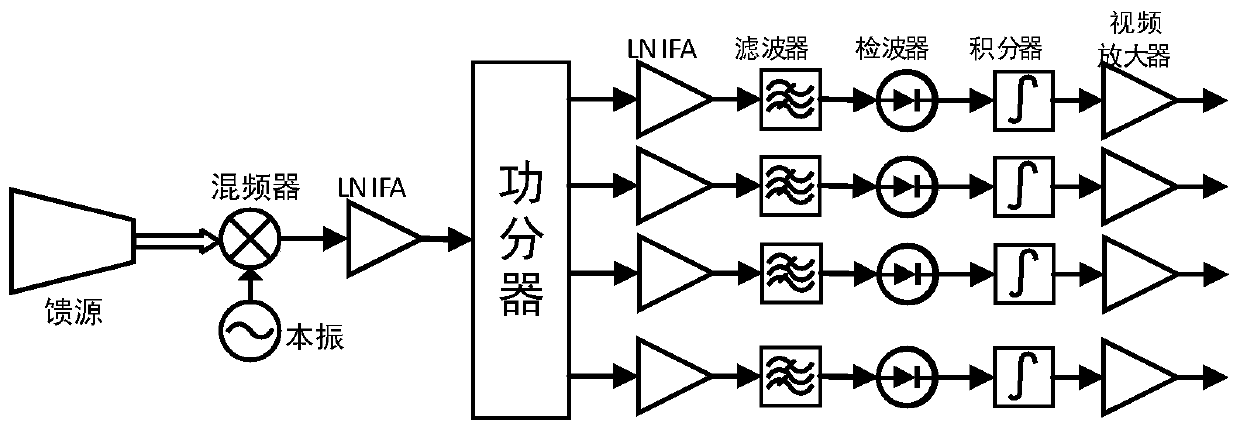
Satellite-borne terahertz atmospheric profile detector
ActiveCN111487623AOvercome temperatureOvercome humidityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationReflected wavesAtmospheric temperature
The invention discloses a satellite-borne terahertz atmospheric profile detector. The detector comprises an antenna and feed network, a receiver module, two calibration bodies and a data processing unit, wherein the antenna and feed network is used for respectively carrying out reflection and quasi-optical separation on two paths of atmospheric brightness temperature signals, respectively formingtwo paths of high-frequency reflected waves and two paths of low-frequency transmitted waves, and inputting the two paths of high-frequency reflected waves and the two paths of low-frequency transmitted waves into the receiver module; the receiver module comprises receivers of six detection frequency bands; the receivers of two detection frequency bands are combined into a temperature detection channel for detecting vertical distribution of the atmospheric temperature; the receivers of two detection frequency bands are combined into a humidity detection channel for detecting vertical distribution of the atmospheric humidity; the receivers of two detection frequency bands are used for detecting cirrus cloud, liquid water content and heavy rainfall; and the data processing unit is used for providing a normal working time sequence, controlling the reflection angle of the antenna and feed network, and carrying out acquisition quantification, storage and downloading on the data of the receiver module.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
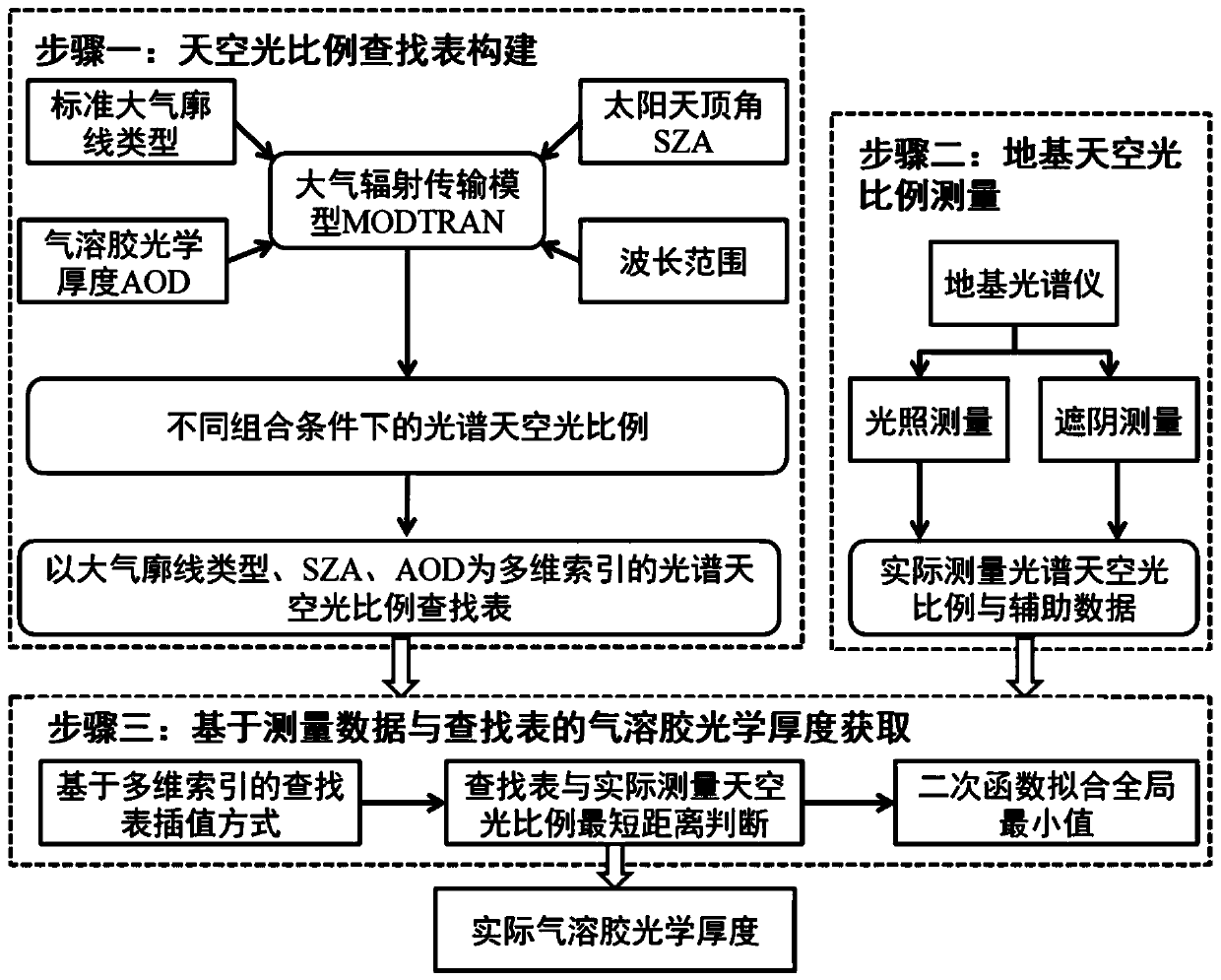
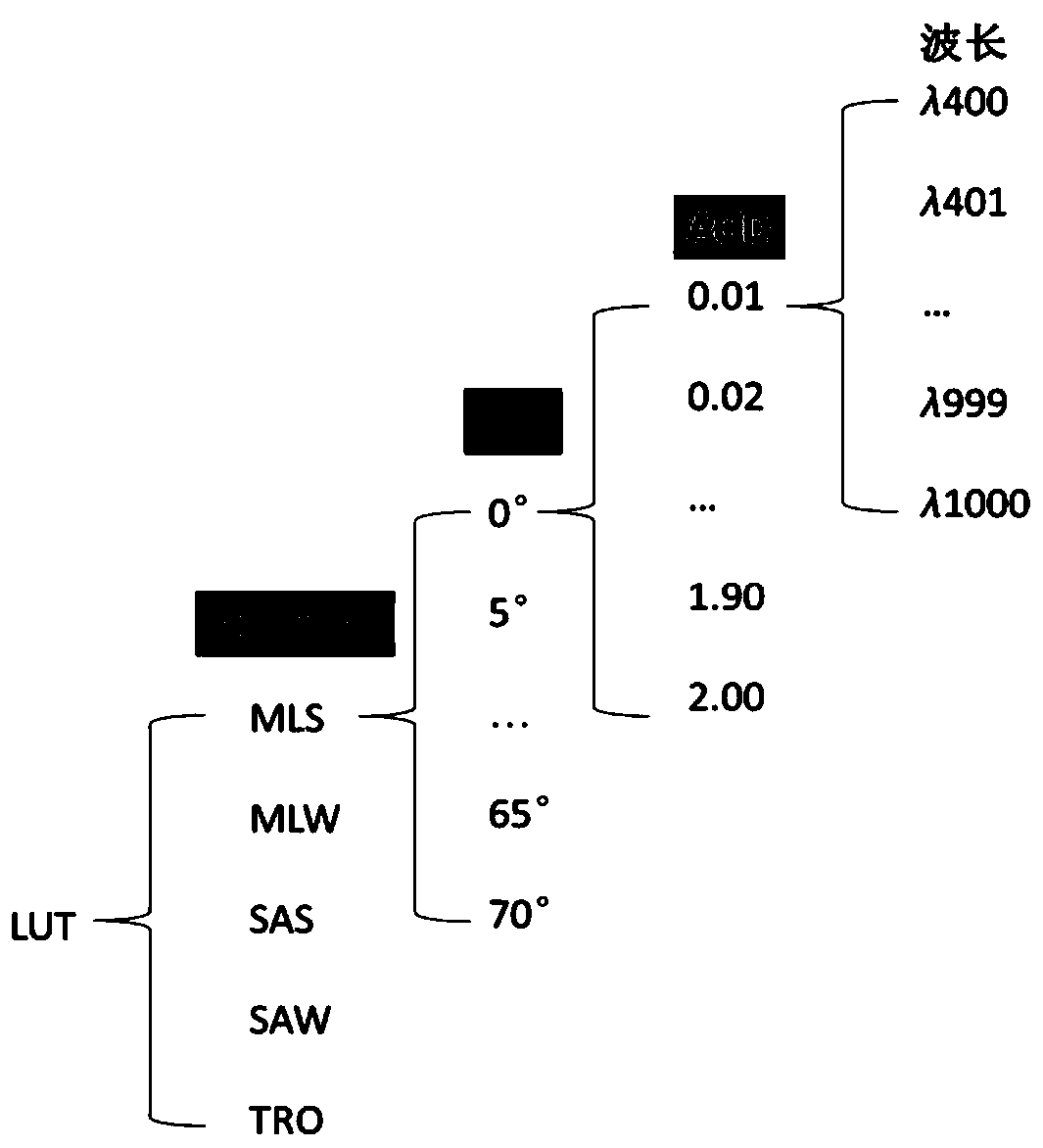
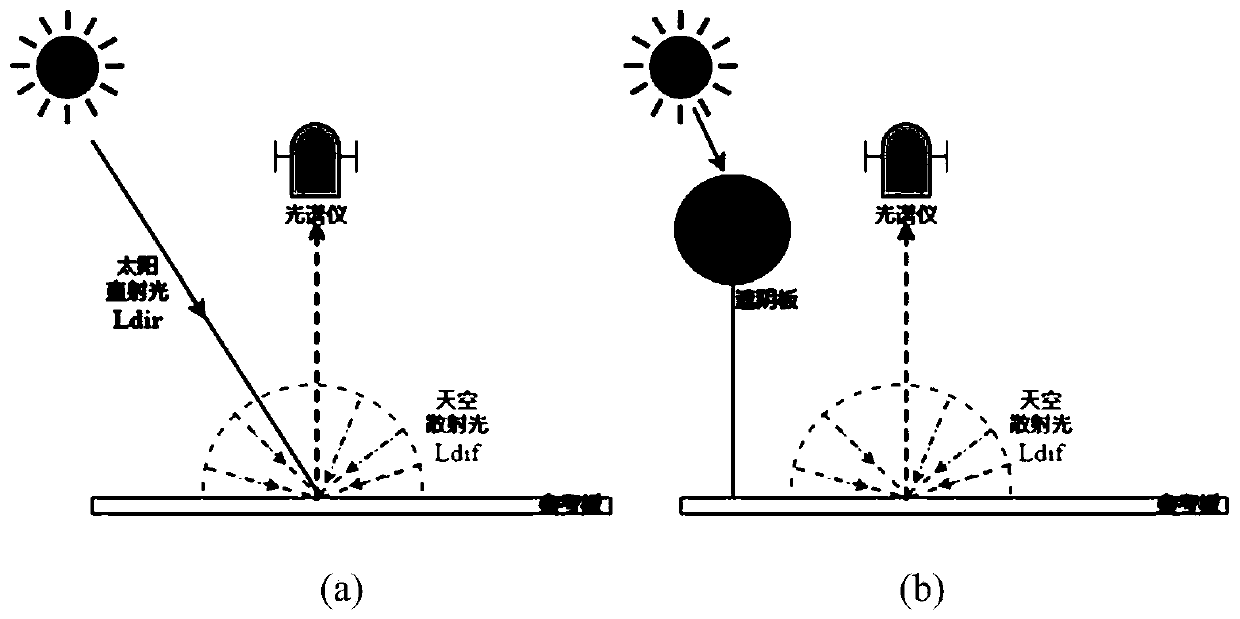
Atmospheric aerosol optical thickness estimation method and device based on measurement data of ground-based spectrometer
The invention discloses an atmospheric aerosol optical thickness estimation method and a device based on measurement data of a ground-based spectrometer. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a spectral sky light proportion lookup table corresponding to a single wavelength between 400nm and 1000nm by taking an atmospheric profile type, a solar zenith angle and aerosol optical thickness as multi-dimensional indexes based on sky light proportions simulated by atmospheric radiation transmission software under different combination conditions; 2) measuring the sky light proportions by using a ground-based spectrometer and a standard reference board; and 3) extracting local lookup table data corresponding to the observation time from the lookup table established in the step1) based on the multi-dimensional indexes, and calculating the distance between the sky light proportion corresponding to different atmospheric aerosol optical thicknesses in the lookup table and theactually measured sky light proportion, and fitting by using a quadratic function to obtain a final aerosol optical thickness estimated value. The optical thickness of the atmospheric aerosol can be estimated by utilizing the spectral sky light proportion measured on the ground.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
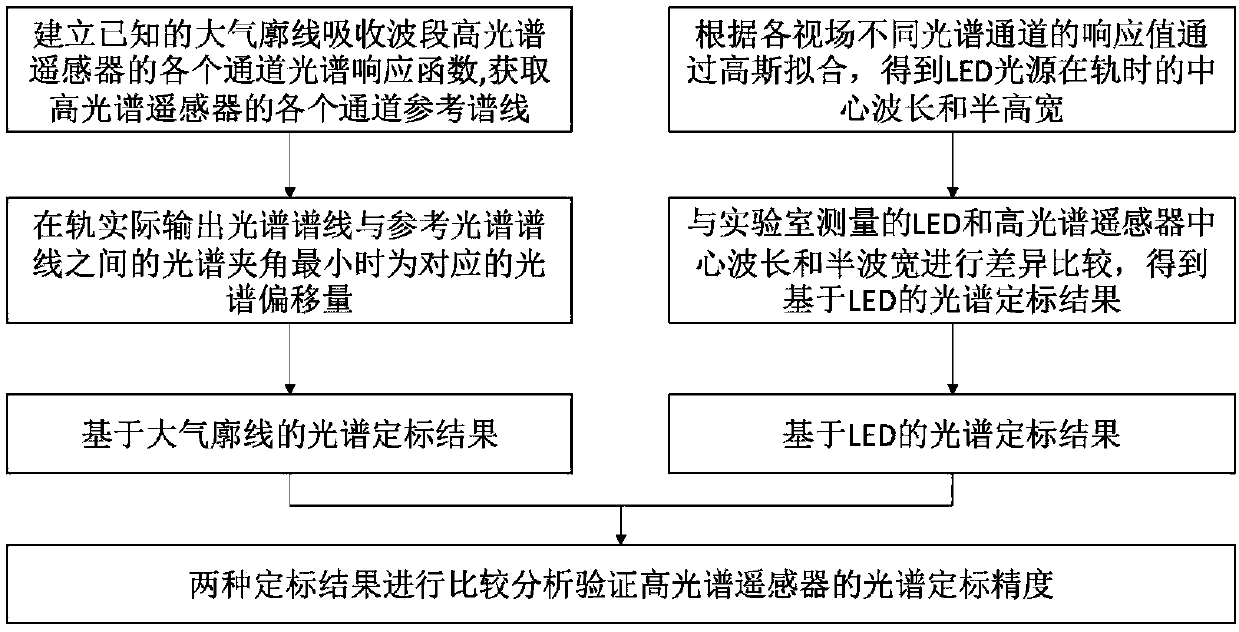
On-orbit spectrum calibration method of hyperspectral remote sensor based on atmospheric profile and LED
ActiveCN109655158AImprove stabilityHigh precisionSpectrum investigationSensing dataCalibration result
The invention discloses an on-orbit spectrum calibration method of a hyperspectral remote sensor based on an atmospheric profile and an LED. The method includes the steps of separately utilizing the known atmospheric profile and an LED spectrum to calibrate and correct spectrum deviation of the hyperspectral remote sensor, comparing a spectral calibration result based on the atmospheric profile with a spectral calibration result based on the LED, analyzing the comparison result, and determining that the spectral calibration precision of the hyperspectral remote sensor is reached if the difference between the two calibration results is not greater than 5%. The method aims to overcome the defects of existing on-orbit calibration technologies of the hyperspectral remote sensors, combine an atmospheric profile calibration technology with an LED calibration technology, mutually verify the calibration results of different spectra, improve the on-orbit spectrum calibration precision of the hyperspectral remote sensor, and correspondingly ensure the reliability and value of quantitative application of remote sensing data.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Real-time automated method and system enabling continuous supersonic flight while preventing ground level sonic boom
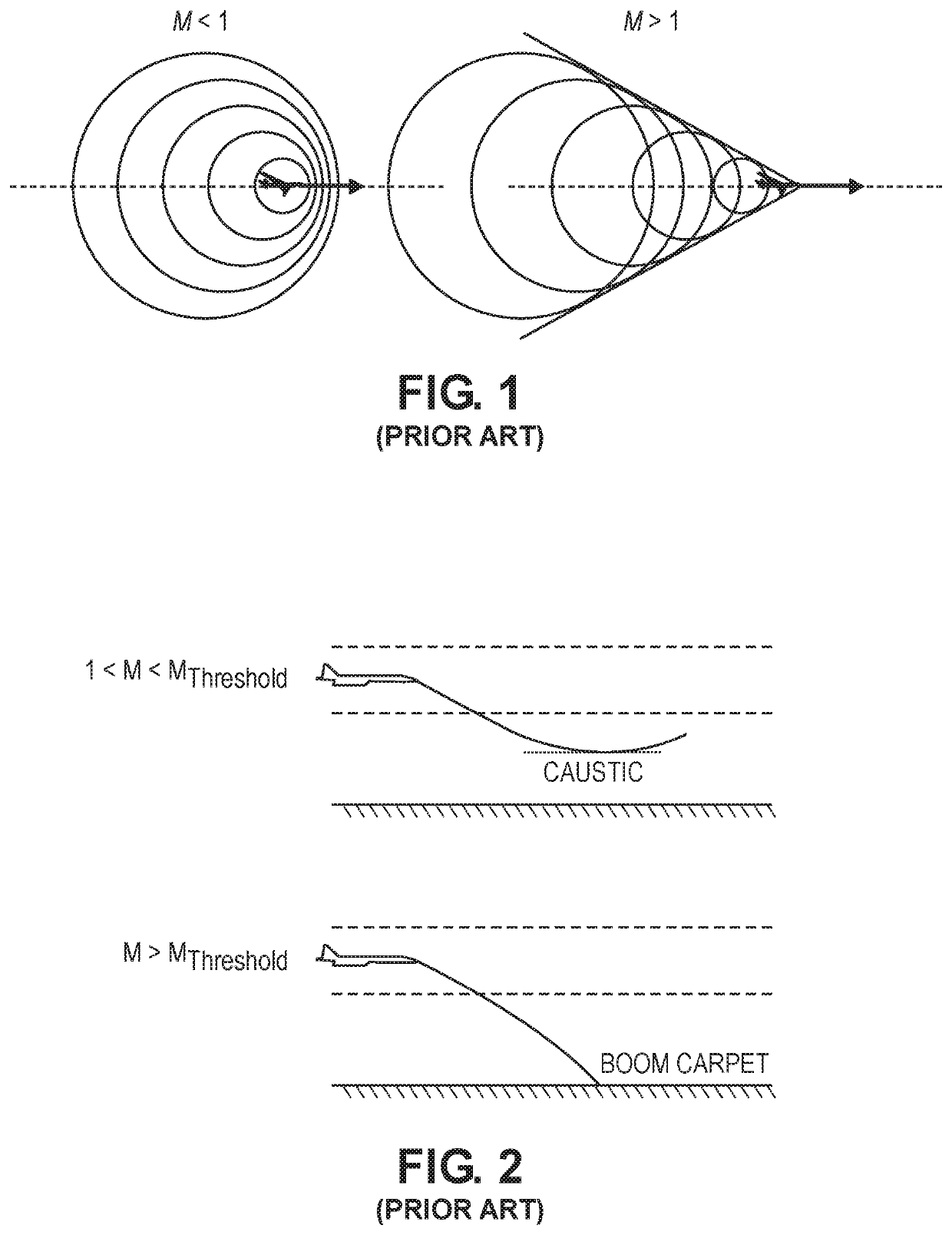
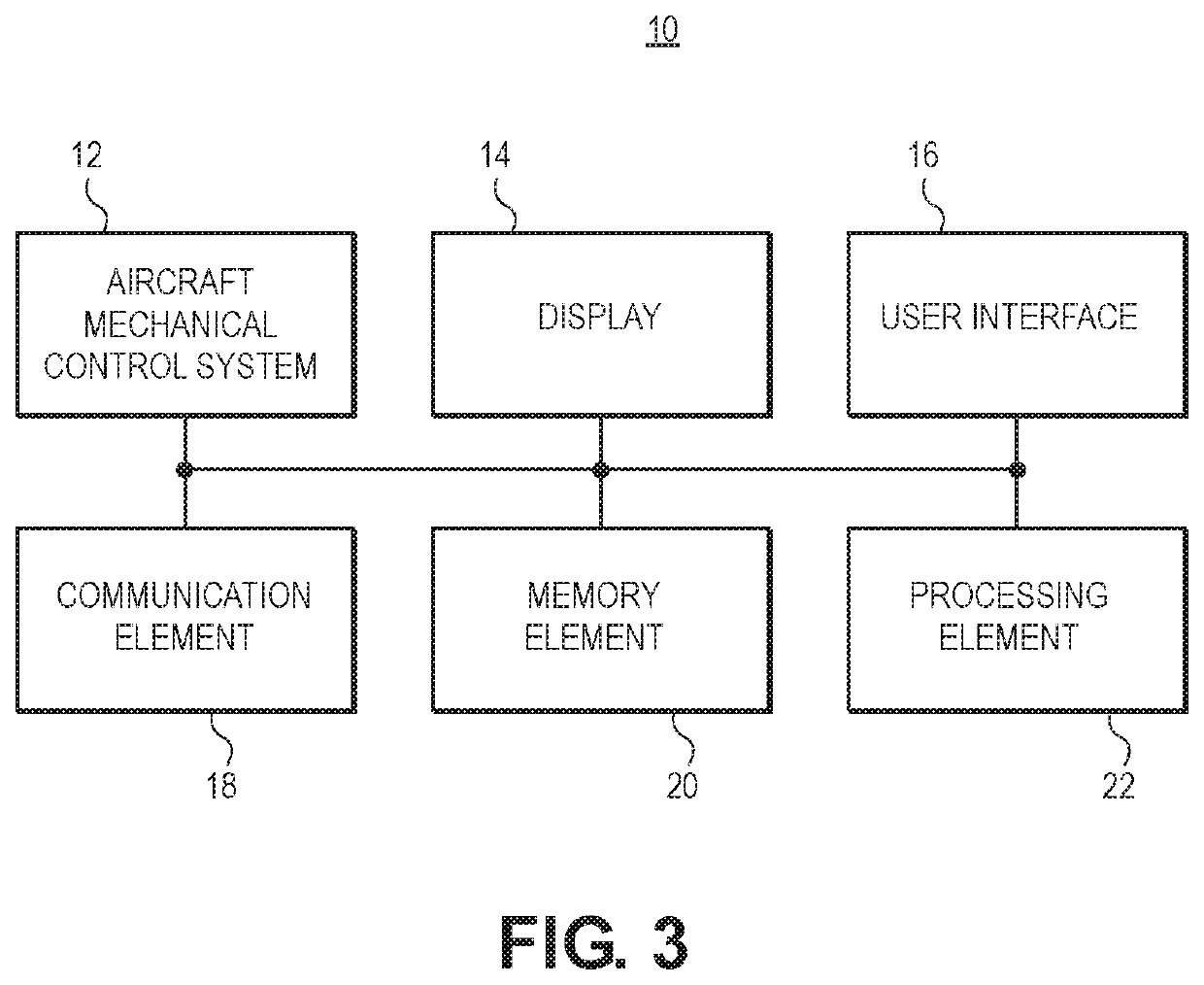
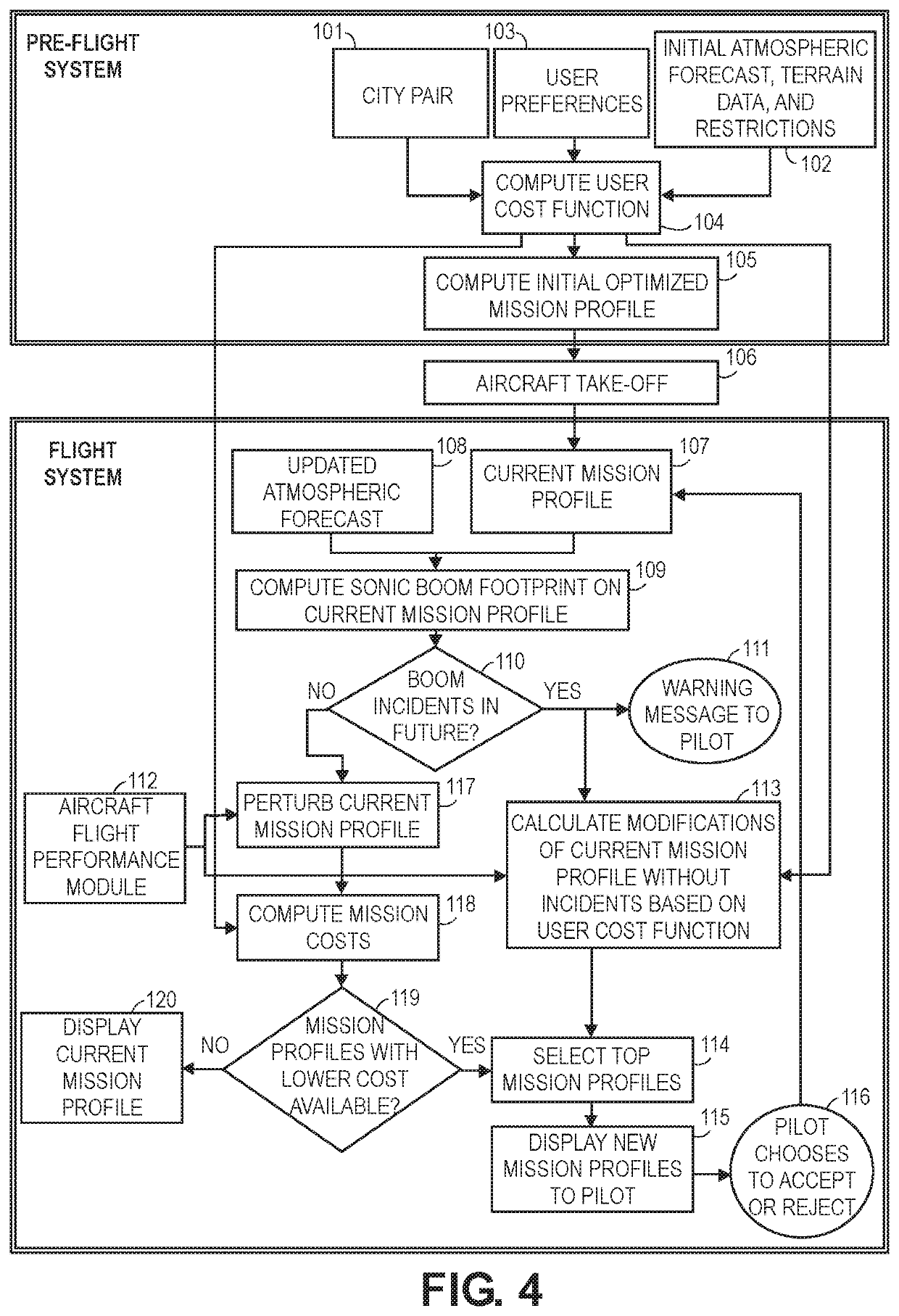
InactiveUS20210233413A1Avoid it happening againReduce user costsVehicle position/course/altitude controlAircraft traffic controlAtmospheric sciencesAutomated method
A method for determining a Mach cutoff flight profile for an aircraft comprises receiving a flight origination and destination; receiving an initial atmospheric profile forecast; receiving user preferences on flight parameters to be optimized; computing a user cost function; determining a flight profile which implements Mach cutoff; receiving updates on the atmospheric profile forecast; determining potential sonic boom incidents; determining one or more sonic boom avoidance modifications to the flight profile that will avoid sonic boom incidents and not exceed the user cost function if potential sonic boom incidents are determined; presenting one or more sonic boom avoidance modifications to a pilot of the aircraft if potential sonic boom incidents are determined; receiving selection of one of the sonic boom avoidance modifications if potential sonic boom incidents are determined; and updating the flight profile with the selected sonic boom avoidance modification if potential sonic boom incidents are determined.
Owner:AERION INTPROP MANAGEMENT CORP
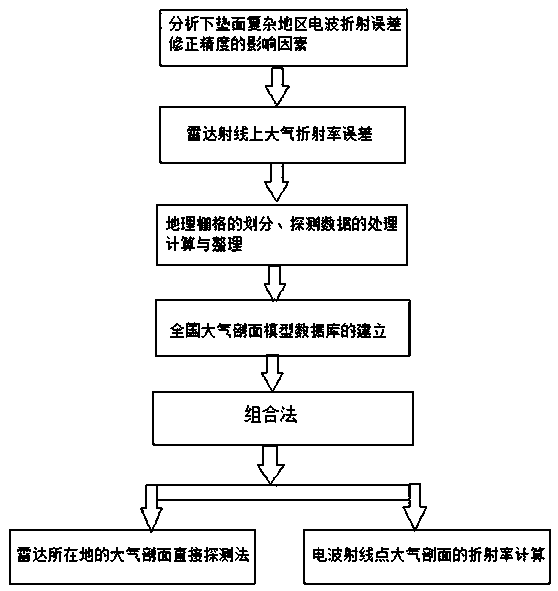
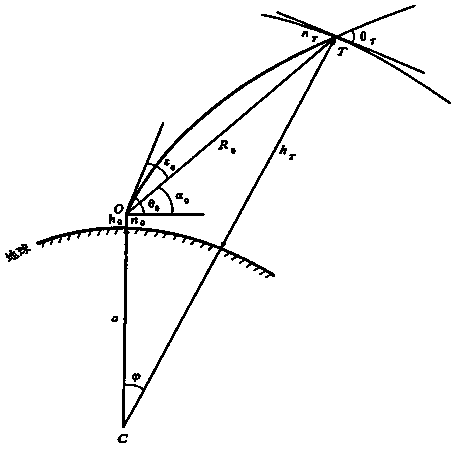
Calculation method for atmospheric refractivity on electric wave ray
InactiveCN109164439AImprove calculation accuracyReduce calculation errorsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarCalculation error
The invention discloses a calculation method for atmospheric refractivity on an electric wave ray, comprising the following steps: according to a geographic position range of China and characteristicsof radio meteorological environmental changes, building a nationwide atmospheric refractivity profile database; for a uniform atmospheric structure region, obtaining an atmospheric profile of a placewhere a radar is located by utilizing a direct detection method, and acquiring refractivity of the electric wave ray by virtue of translation of the actually measured refractivity at the same height;for a non-uniform atmospheric structure region, when a starting position of the electric wave ray is in a grid where the radar is located, obtaining an atmospheric refractivity profile of a place where the radar is located by utilizing the direction detection method; when the electric wave ray falls in other grids, firstly calculating a position of a ray point, then obtaining the atmospheric refractivity profile of the ray point by utilizing a nationwide atmospheric profile model database, and obtaining the atmospheric refractivity on the electric wave ray by utilizing the refractivity profile. The calculation method disclosed by the invention can be easily realized in engineering application, a calculation error of the calculation method is small, and then calculation accuracy of electric wave refractivity can be effectively improved.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
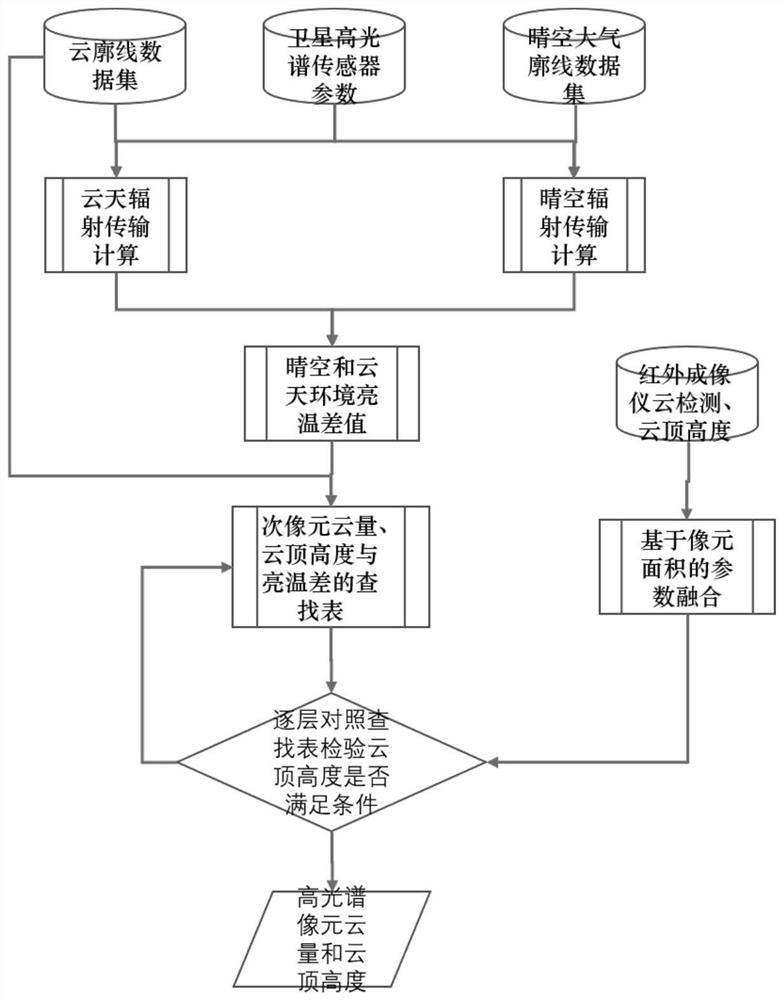
Cloud top height real-time calculation method based on satellite infrared detection element parameters
The invention discloses a cloud top height real-time calculation method based on satellite infrared detection element parameters, and the method comprises the steps: firstly collecting a cloud profile data set, satellite hyperspectral sensor parameters and a clear sky atmosphere profile data set, and carrying out cloud sky radiation transmission calculation and clear sky radiation transmission calculation on the data sets to obtain a clear sky environment brightness temperature difference value and a cloud sky environment brightness temperature difference value; calculating by combining the calculated bright temperature difference value of the clear sky and the cloud sky environment with the cloud profile data set to obtain a lookup table of the sub-pixel cloud cover, the cloud top height and the bright temperature difference; checking whether the cloud top height meets conditions or not by comparing the lookup table layer by layer; if yes, the cloud cover and the cloud top height of the hyperspectral pixel are obtained; and if not, continuing to execute the steps. The method is reliable in data calculation.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT +3
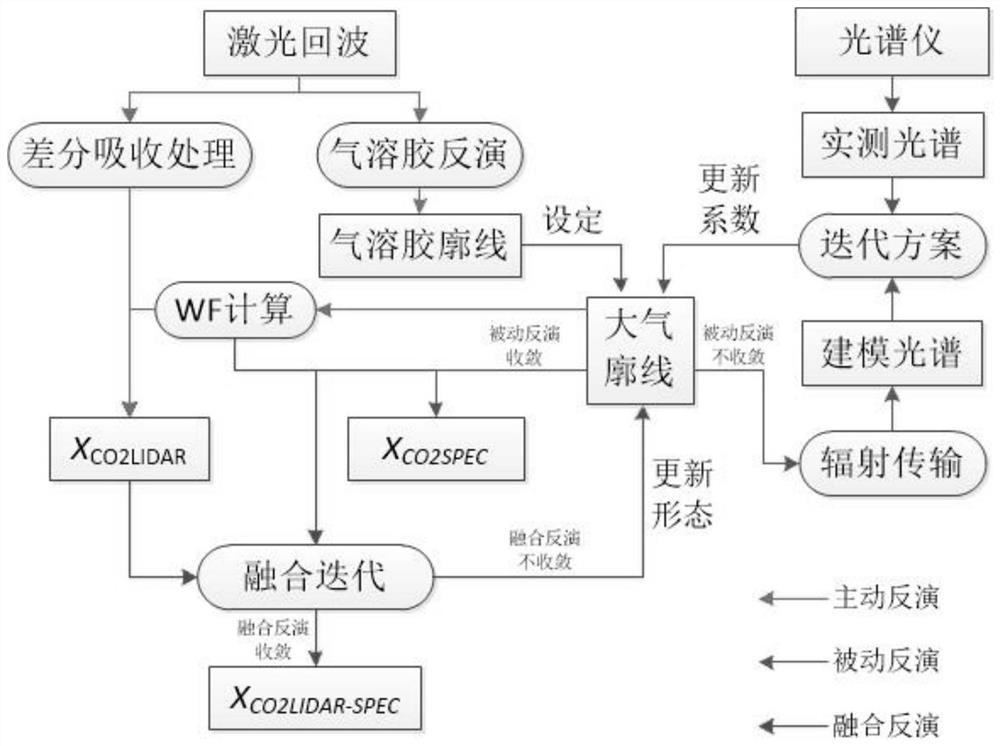
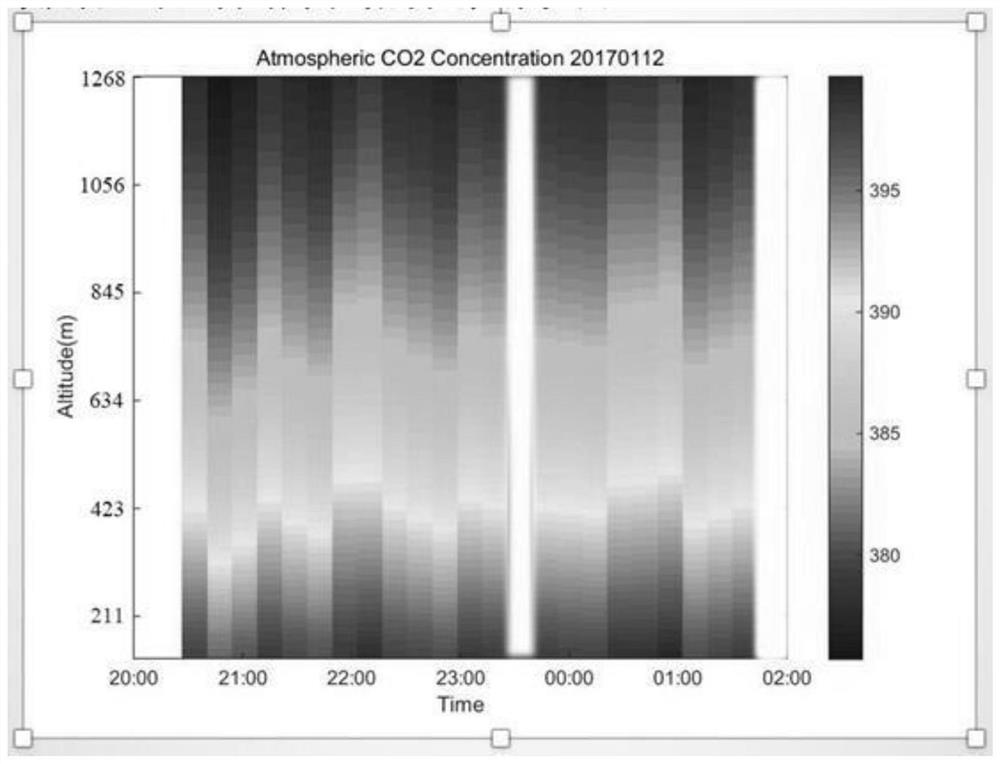
Atmospheric CO2 concentration collaborative inversion method for satellite-borne laser radar and hyperspectrometer
PendingCN114114324ATake advantage ofElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationSpectrographSolar spectra
The invention relates to an atmospheric CO2 concentration coordinated inversion method for a satellite-borne laser radar and a hyperspectrometer. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out inversion by using a laser radar 1064nm echo signal to obtain an aerosol atmospheric profile, calculating the weighted concentration of a CO2 column according to a laser radar 1572nm echo signal, carrying out modeling on atmospheric radiation by using a scriatran model, carrying out least square fitting on a solar spectrum obtained by observation and an analog value output by the scriatran model to obtain a CO2 vertical concentration profile, and then taking the vertical profile as an absolute constraint to obtain a CO2 vertical concentration curve. Constructing a loss function, setting the weight of the loss function through a priori observation value, obtaining an optimal solution enabling the loss function to be minimum, updating an atmosphere profile, and calculating to obtain a final XCO2 product. According to the invention, the advantages of high detection precision and high availability of the laser radar and the advantages of high detection light coverage and high resolution of the high spectrograph are fused, so that an atmospheric CO2 column concentration product with the characteristics of high resolution, high coverage, high precision and high availability is obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
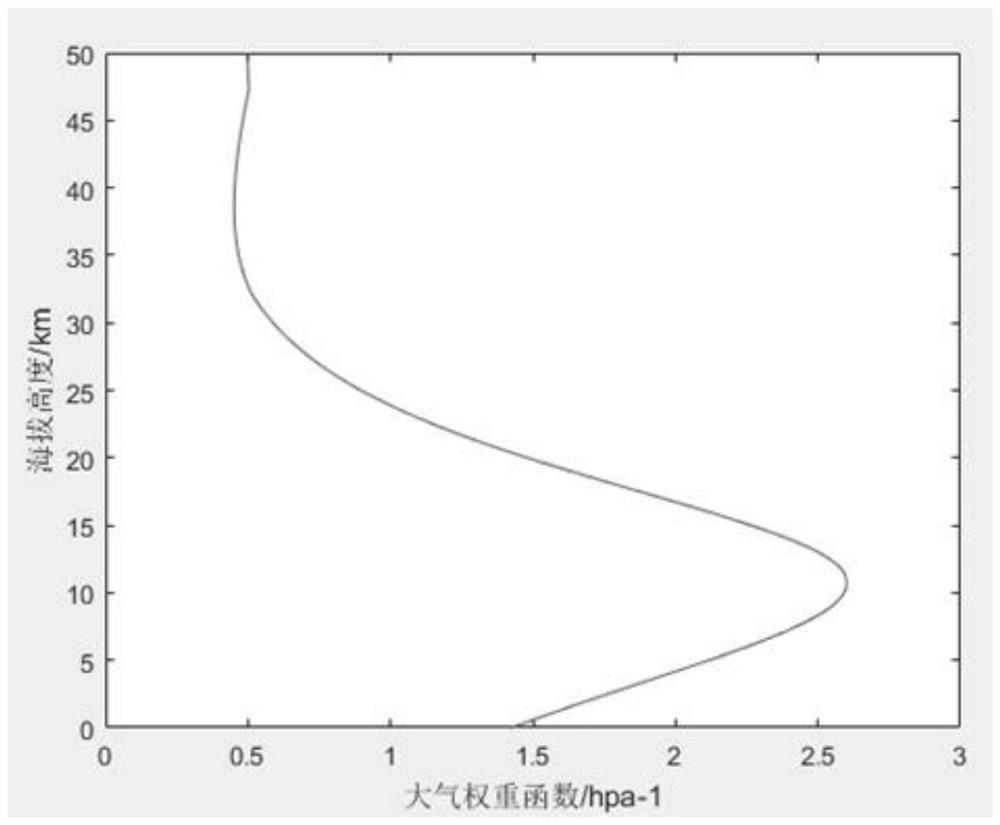
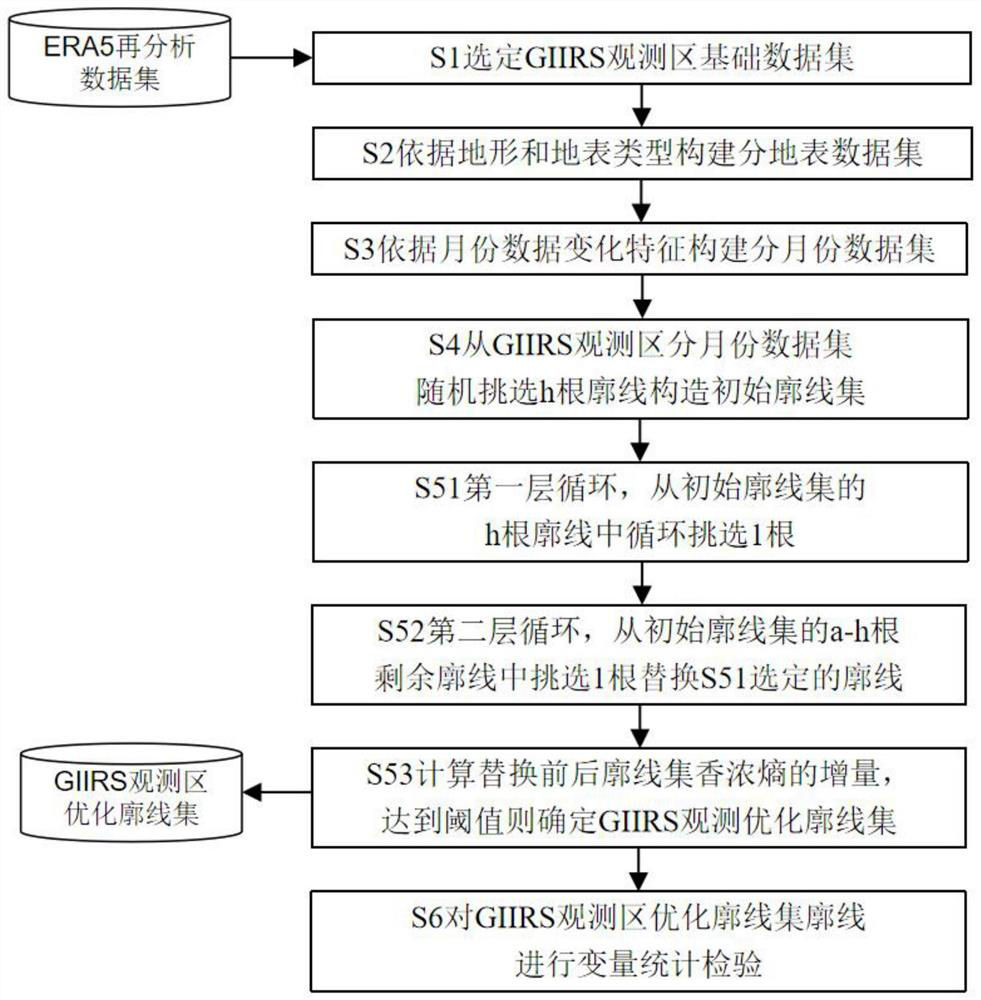
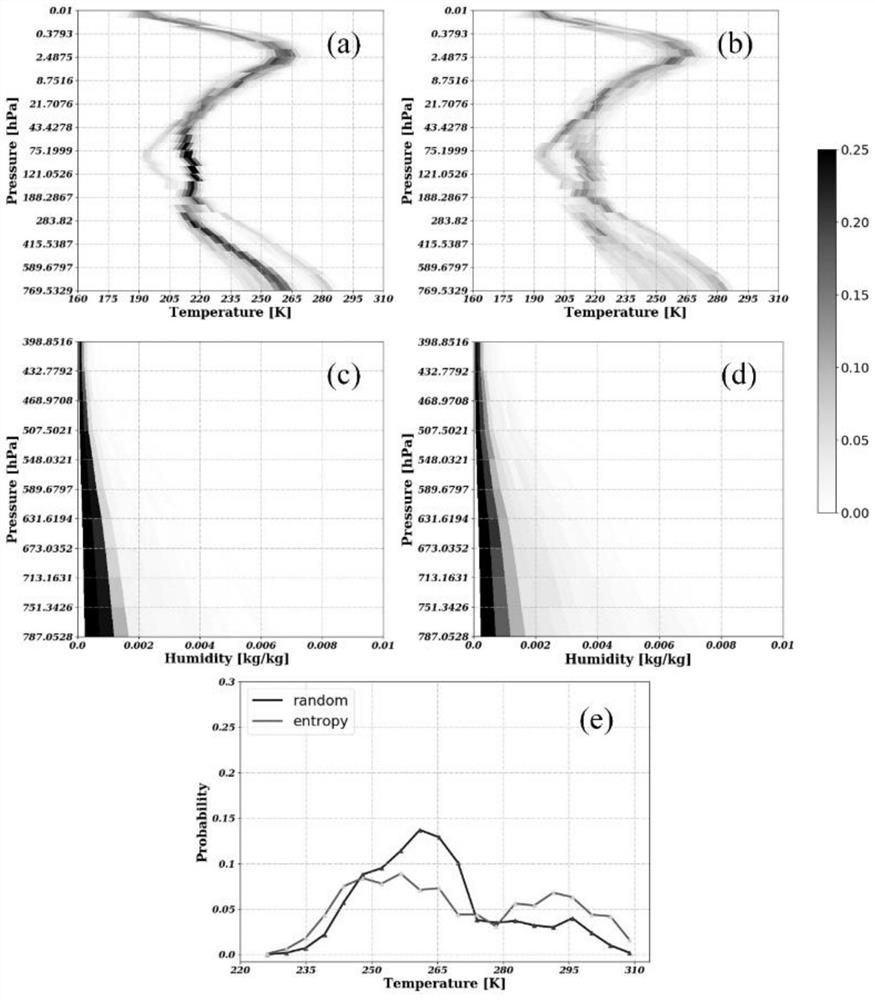
GIIRS observation area atmospheric profile set sampling method based on Shannon entropy
PendingCN112730300AGuaranteed uniformityMaterial analysis by optical meansData setAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses a GIIRS observation area atmospheric profile set sampling method based on Shannon entropy. The method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a GIIRS observation area basic atmospheric data set; S2, dividing the ground surface of the GIIRS observation area into a plurality of different ground surface types, and correspondingly dividing the basic data set of the GIIRS observation area into different atmospheric data sets according to the ground surface types; S3, dividing each data set obtained in the step S2 into atmosphere sub-data sets by months; S4, randomly selecting h profiles from each sub-data set, and constructing an initial sampling profile set of the GIIRS observation area; S5, utilizing the initial profile set of the GIIRS observation area to construct an optimized profile set of the GIIRS observation area; and S6, performing statistical test on the optimized profile set in step S5. On the basis of combining factors of surface types and atmospheric monthly changes, a Shannon entropy sampling method is applied to construct a GIIRS observation area profile data set, and the problem that it is difficult for a profile database publicly published at present to accurately characterize atmospheric change characteristics of an infrared hyperspectral GIIRS observation area is solved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
FY-3D passive microwave data under-cloud surface temperature inversion and verification method
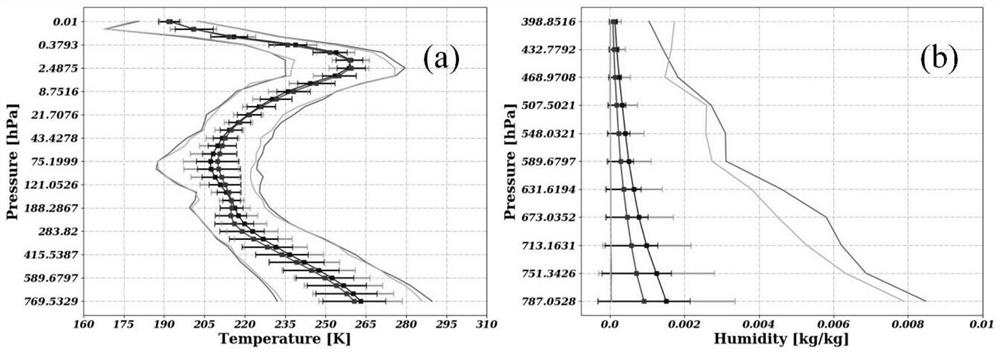
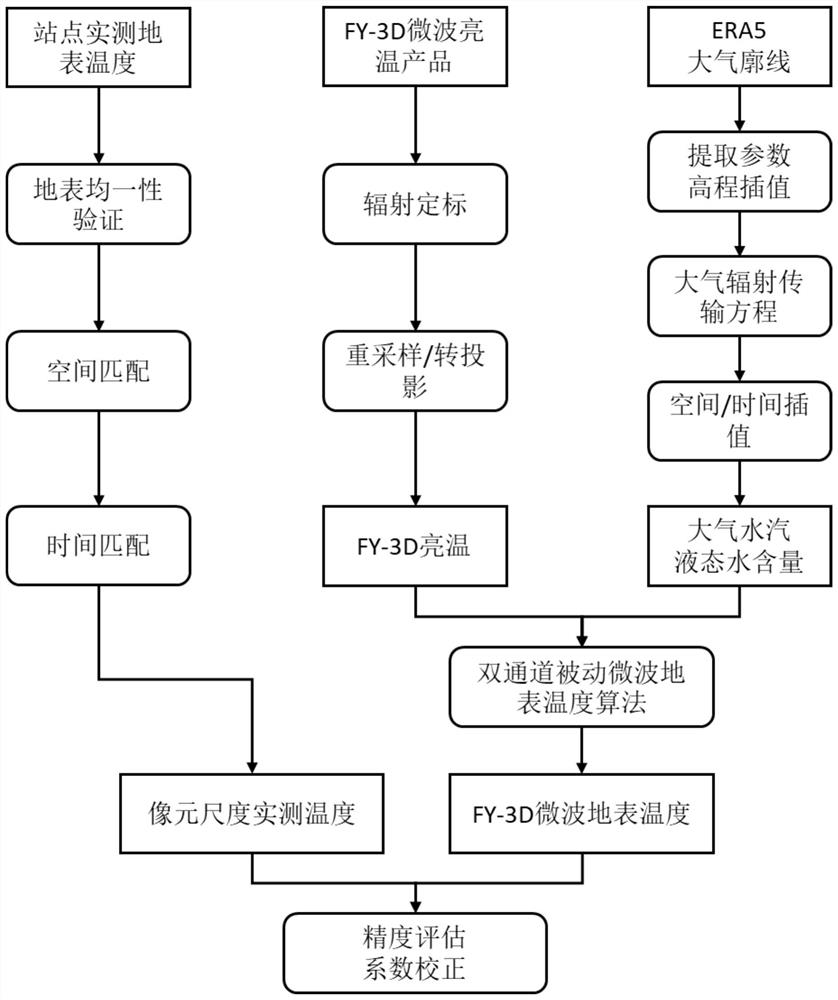
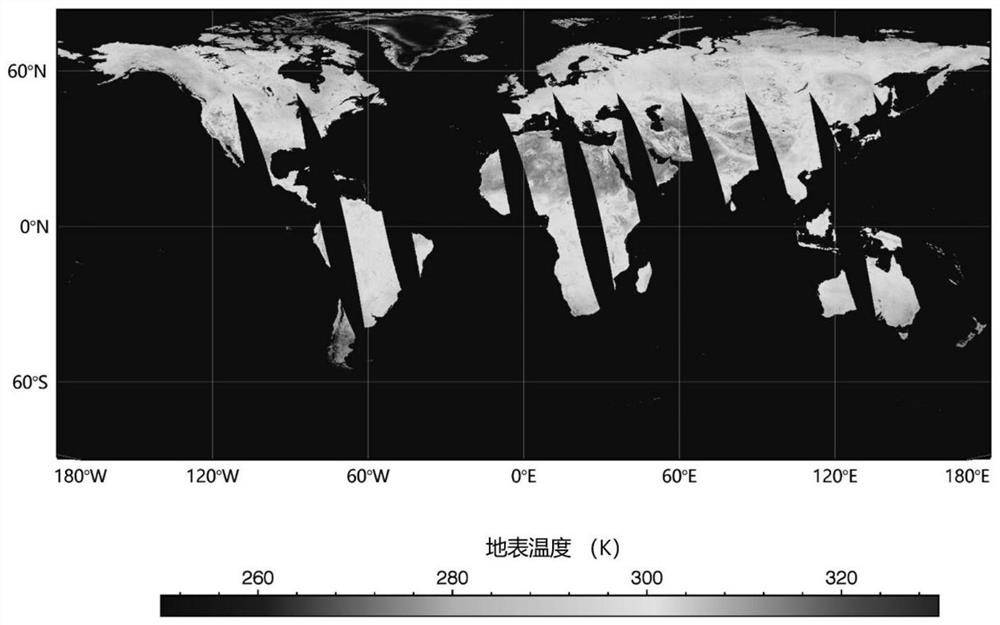
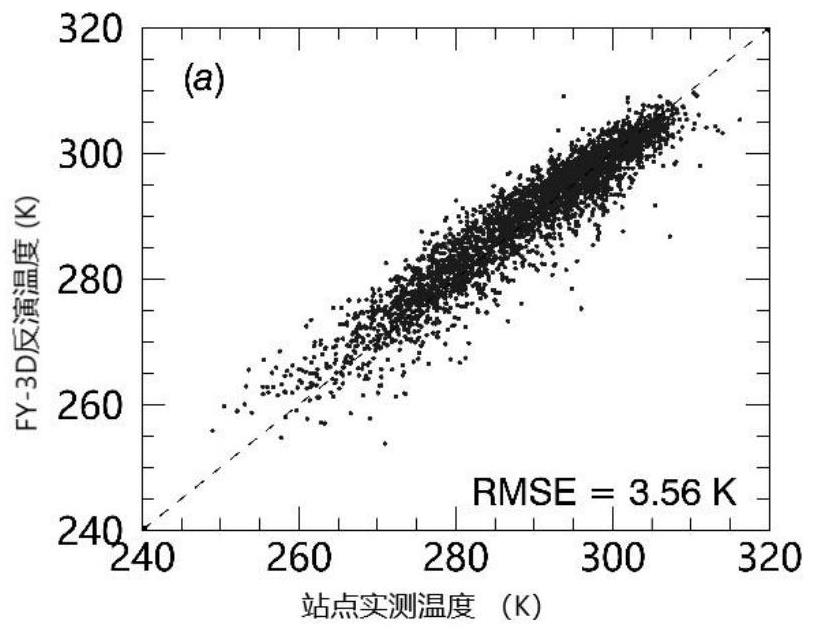
PendingCN114722350AAchieving High-Precision EstimationRealize accuracy comparison verificationRadiation pyrometryComplex mathematical operationsBrightness temperaturePerpendicular polarization
The invention provides an FY-3D passive microwave data under-cloud surface temperature inversion and verification method, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining FY-3D passive microwave data, carrying out the data preprocessing, and extracting the dual-channel brightness temperature of 18.7 GHz and 23.8 GHz vertical polarization channels; eRA5 atmosphere profile data are obtained, and data processing is carried out to extract the content of atmosphere water vapor and liquid water; based on the dual-channel brightness temperature of the 18.7 GHz and 23.8 GHz vertical polarization channels, combining the corresponding atmospheric water vapor and liquid water content data, and adopting a dual-channel physical algorithm to estimate the surface temperature under the clouded condition; and verifying and correcting the estimated surface temperature by using the surface temperature data under the cloud measured by the site. According to the method, the influence of the atmospheric water vapor and the liquid water content in the cloud on passive microwave radiation is quantified, the estimation precision of the under-cloud surface temperature is improved, and the precision comparison verification of the under-cloud surface temperature of the ground point data and the FY-3D passive microwave data is realized.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Automatic observation meteorological satellite thermal infrared channel on-orbit site radiometric calibration method
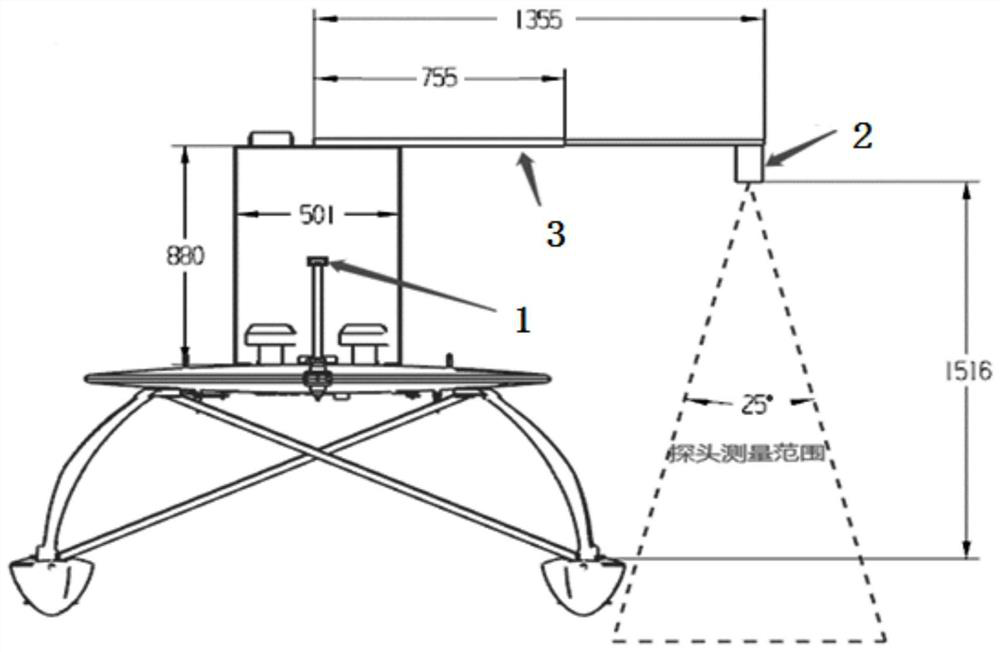
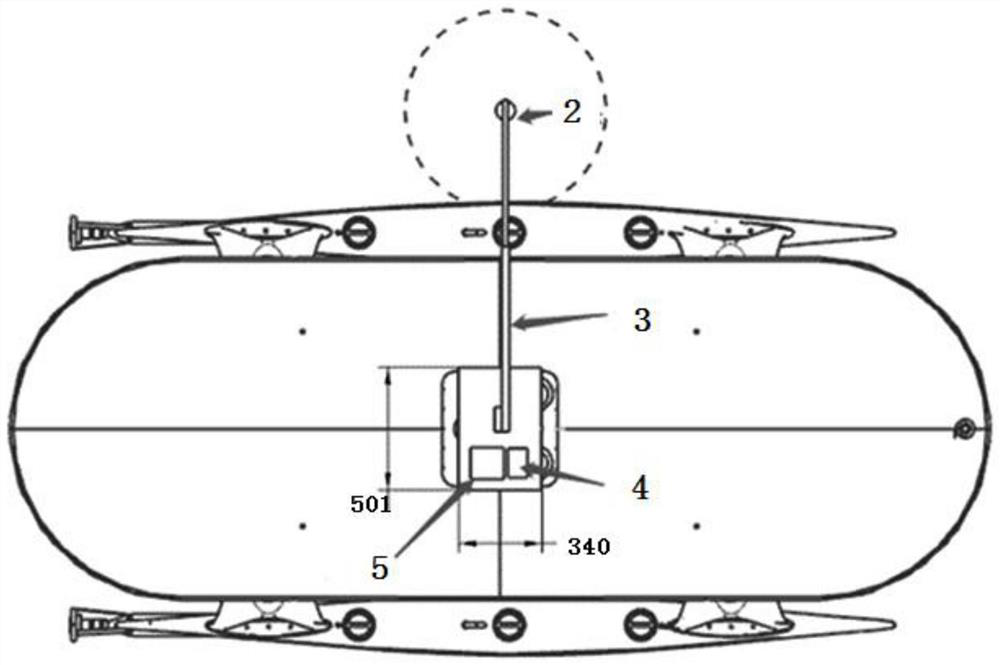
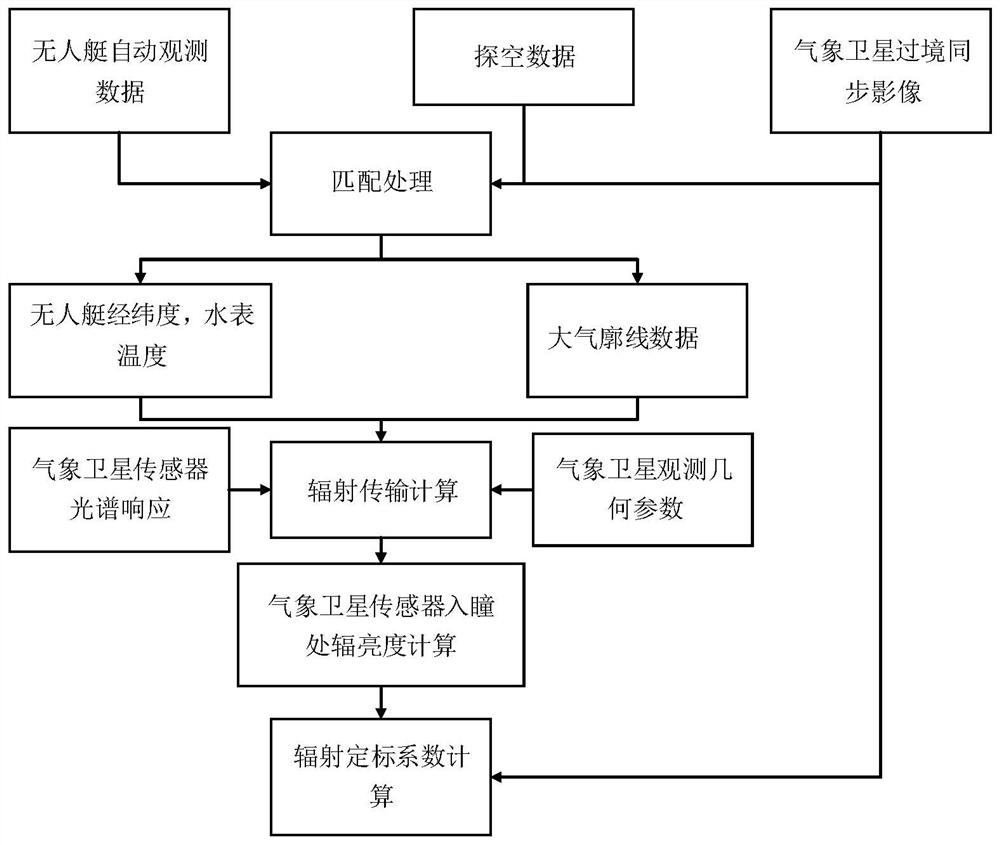
The invention discloses an automatic observation meteorological satellite thermal infrared channel on-orbit site radiometric calibration method, which comprises the following steps that: acquiring lake surface water temperature observation data synchronously measured by a satellite and the ground by an unmanned ship water surface automatic observation system in an automatic data acquisition mode, and reading the observation data; after reading the observation latitude and longitude data of the unmanned ship, matching the observation latitude and longitude data with the observation data of a meteorological satellite; during matching, firstly, selecting matching points of a cloudless area, acquiring observation data on the matching points, and averaging pixel DN values of windows around meteorological satellite data; reading and processing sounding data, and performing matching; simulating to obtain the apparent radiance of an atmosphere top channel on each matching point; and performing linear regression calculation to obtain an absolute radiometric calibration coefficient of a to-be-calibrated channel. According to the method, the calibration frequency can be improved to a great extent by acquiring the encrypted sounding atmosphere profile data, and the calibration precision can be further improved.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT
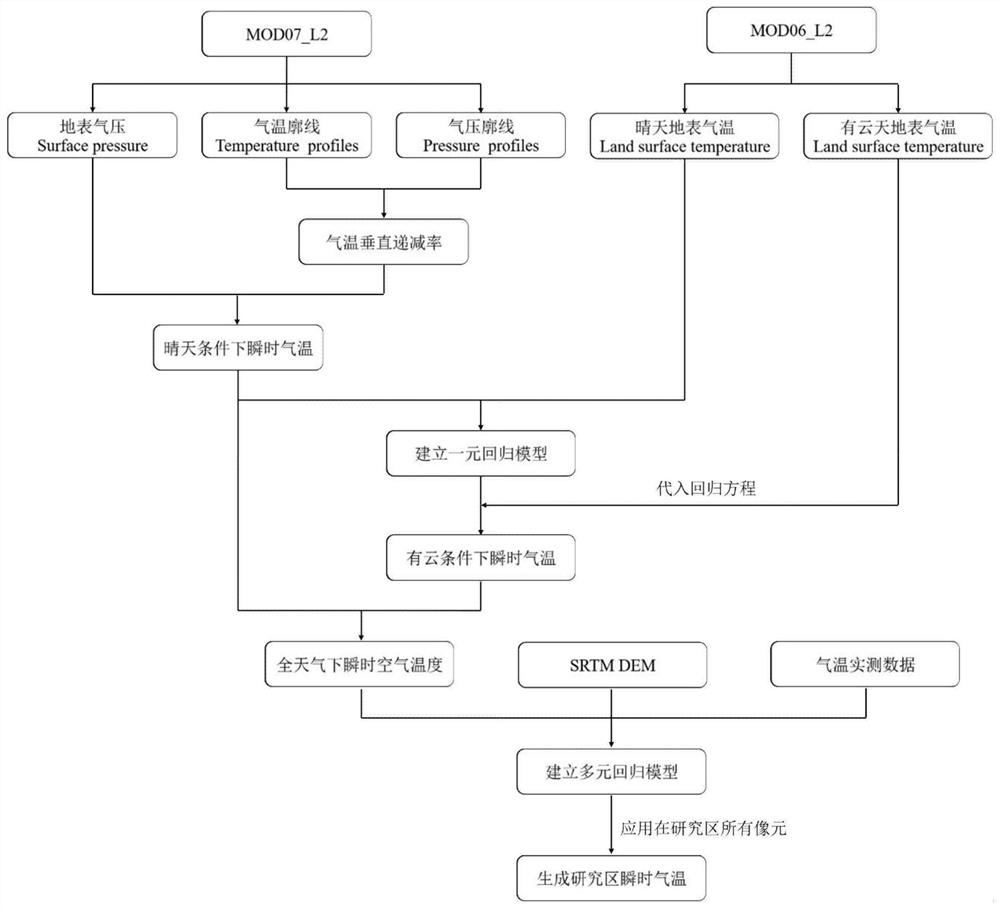
Method for estimating all-weather temperature and spatial and temporal distribution thereof based on MODIS product data
PendingCN113255148AGet rid of dependenceWeather condition predictionDesign optimisation/simulationAtmospheric sciencesAccurate estimation
The invention provides a method for estimating all-weather temperature and spatial and temporal distribution thereof based on MODIS product data, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining MOD07L2 and MOD06L2 product data, SRTM DEM data and site actual measurement data of a research area, carrying out the preprocessing of the data, guaranteeing the time consistency of the MODIS product data and the site actual measurement data, and enabling the SRTM DEM data and the MODIS product data to have the same spatial resolution; using an atmosphere profile extrapolation method to obtain a sunny day air temperature, and averaging the sunny day air temperature with the surface temperature to obtain air temperature instantaneous data under the sunny day condition; and establishing a regression model of the sunny air temperature and the sunny land surface temperature, substituting the land surface temperature under the cloudy condition into a regression equation to obtain the instantaneous air temperature under the cloudy condition, and further synthesizing the instantaneous air temperature into the air temperature under all weather conditions. According to the invention, continuous estimation of all-weather temperature in instantaneous time is realized; the spatial and temporal distribution information of the air temperature of the research area can be quickly obtained, and continuous and accurate estimation of the all-weather air temperature on different spatial and temporal scales is realized.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
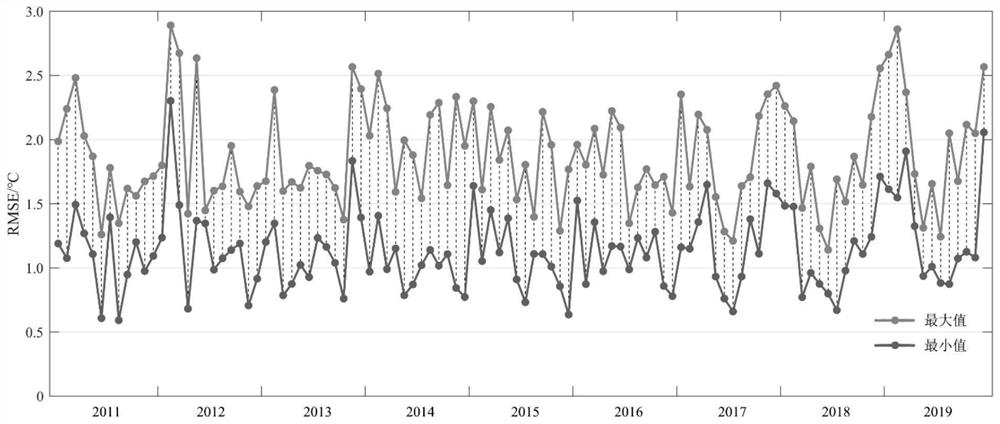
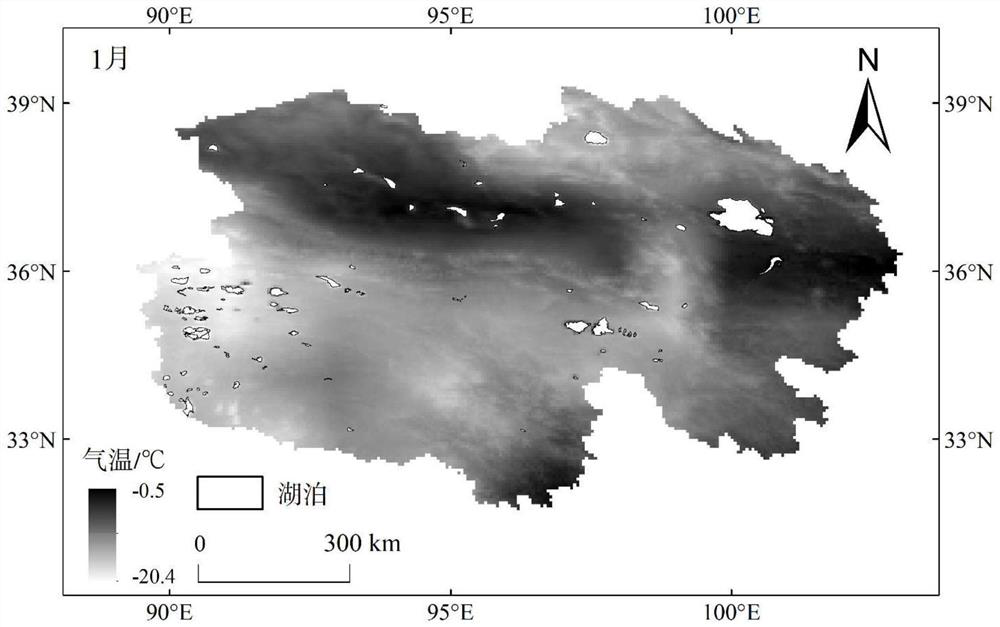
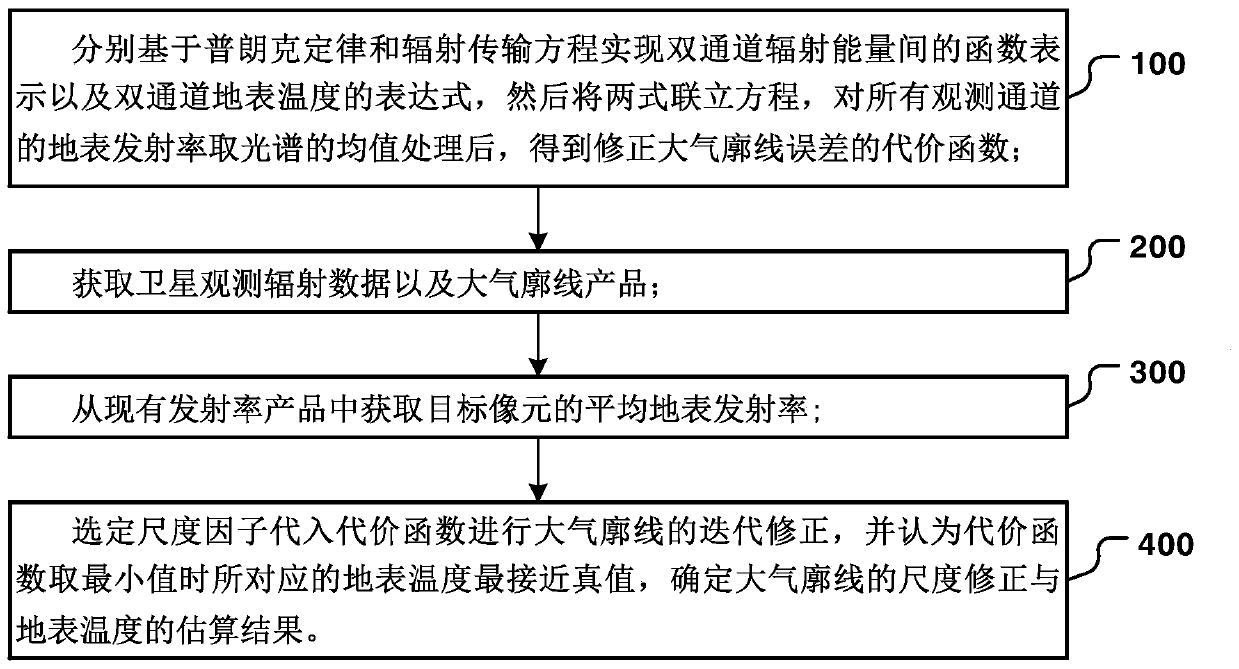
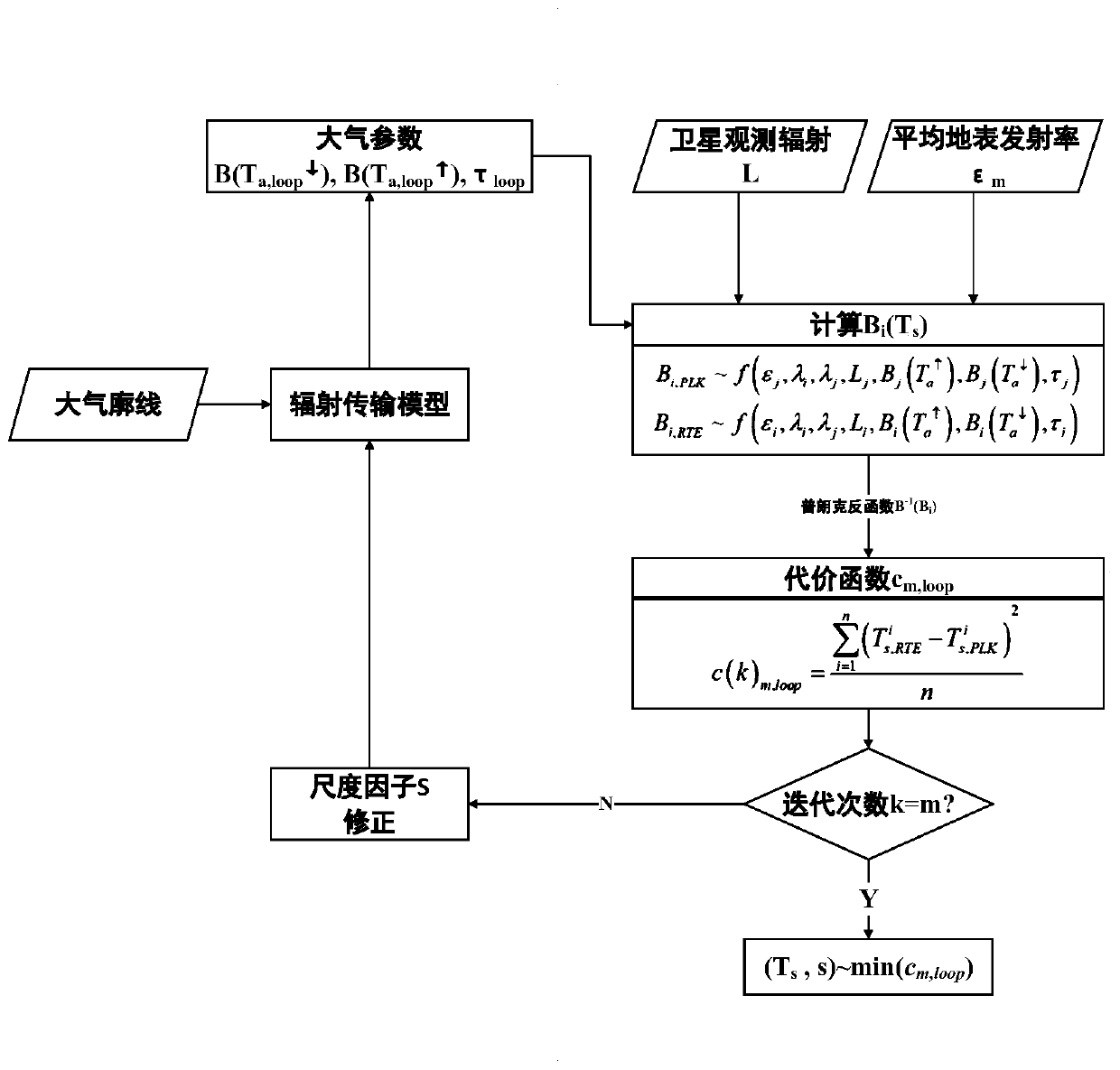
Surface temperature estimation method based on atmospheric scale factor
ActiveCN110990763ARealize the second inversionImprove stabilitySensing radiation from gases/flamesComplex mathematical operationsEmissivitySatellite observation
The invention provides a surface temperature estimation method based on an atmospheric scale factor, and the method comprises the steps: firstly achieving the function expression of dual-channel radiation energy and the expression of dual-channel surface temperature based on a Planck law and a radiation transmission equation, and obtaining a cost function for correcting an atmospheric profile error; acquiring satellite observation radiation data and an atmospheric profile product; obtaining the average surface emissivity of a target pixel from an existing emissivity product; and selecting a scale factor, substituting the scale factor into the cost function to carry out iterative correction on an atmospheric profile, and determining the scale correction of the atmospheric profile and the estimation result of the surface temperature by taking the surface temperature corresponding to a minimum value of the cost function as an approximate truth value. According to the method, atmospheric water vapor correction and surface temperature estimation under various observation conditions are realized through an iterative correction mode, the method does not depend on any empirical relationship, higher inversion stability and universality are achieved, and the method is not only suitable for extremely-dry and extremely-wet atmospheric environments, but also can ensure the precision under multiple observation angles.
Owner:中交信息技术国家工程实验室有限公司 +1
System and method for atmospheric correction of information
ActiveUS9097792B2Electromagnetic finder monitoring/testingDigital computer detailsAtmospheric correctionAtmospheric sciences
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
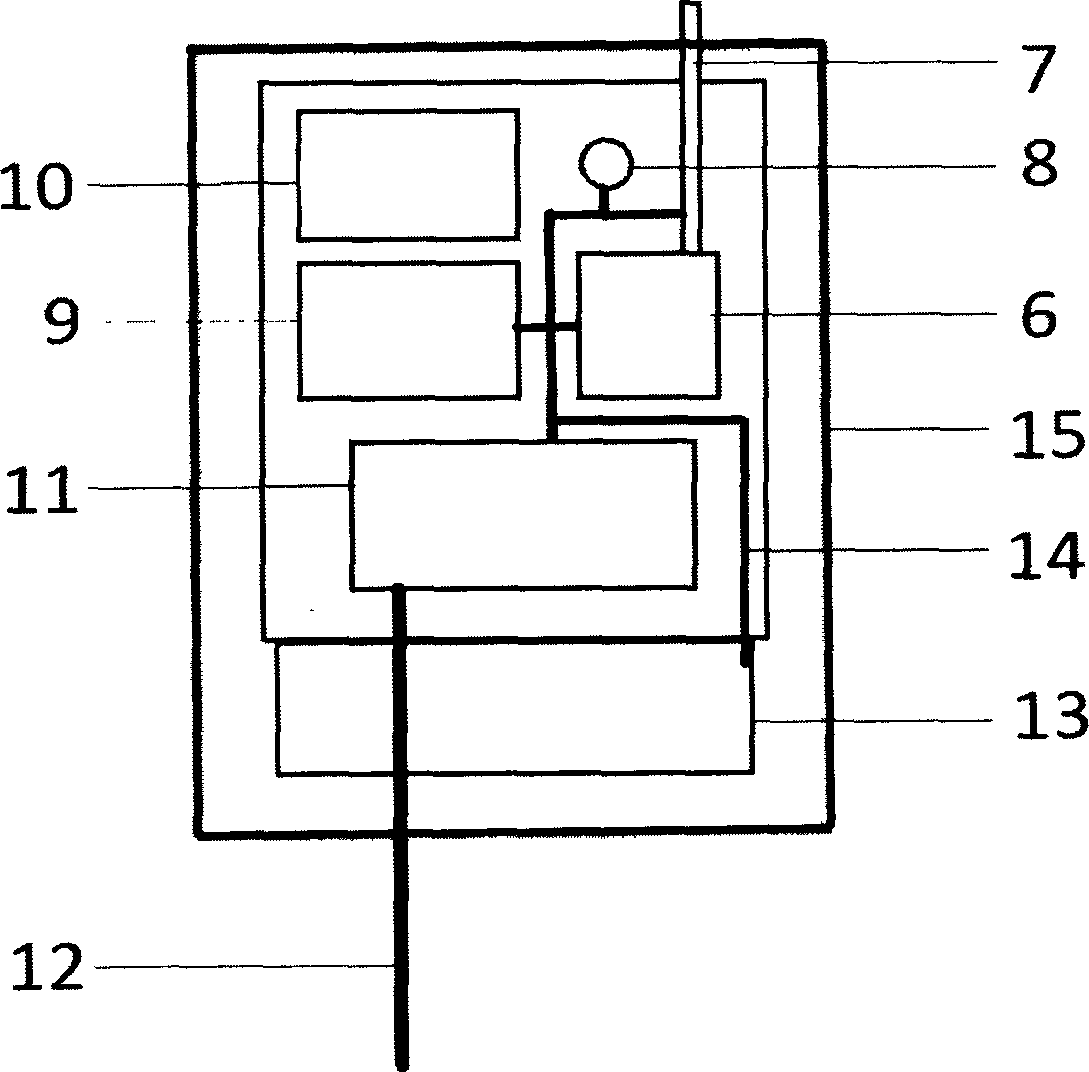
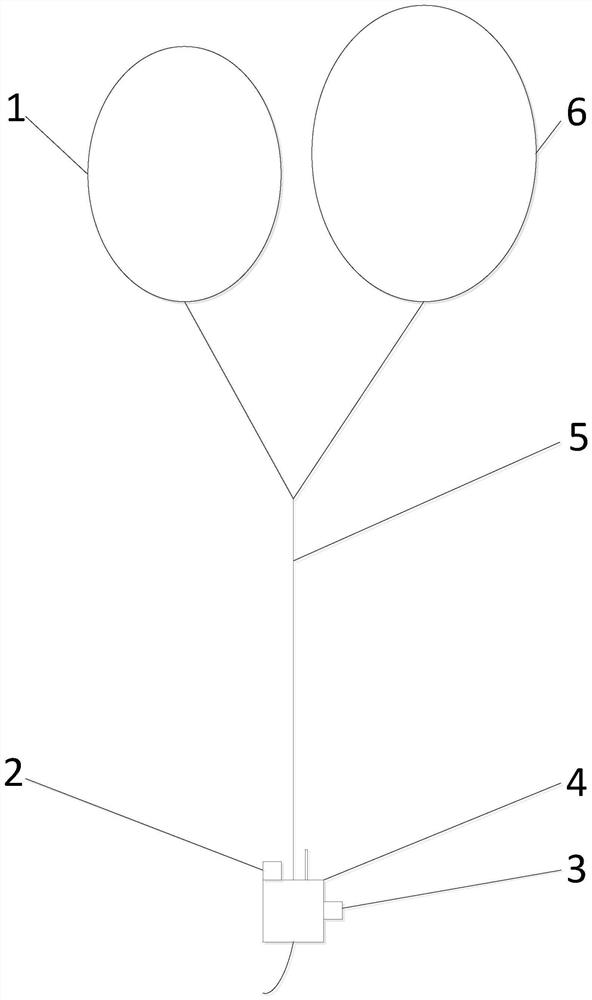
Onboard cruising low-altitude atmospheric profile measuring instrument
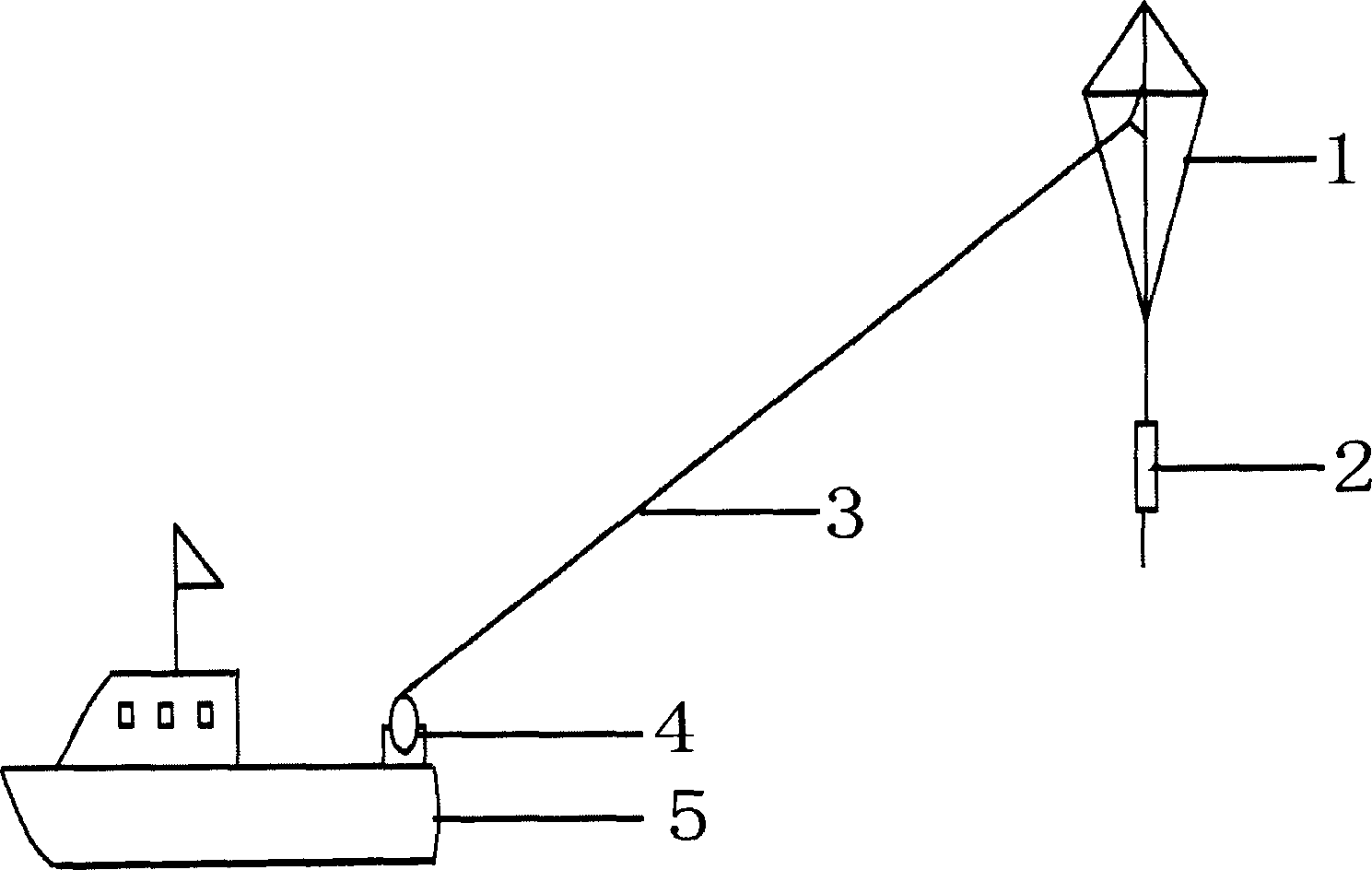
InactiveCN104375206ARealize continuous weather observationRainproofIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesICT adaptationFiberMeasuring instrument
The invention provides an onboard cruising low-altitude atmospheric profile measuring instrument. The onboard cruising low-altitude atmospheric profile measuring instrument comprises a specially-made kite 1, a mini-type meteorological acquisition system 2, a mooring rope 3 and an onboard winch 4. The onboard cruising low-altitude atmospheric profile measuring instrument is characterized in that the specially-made kite 1 is a special kite with high-strength carbon fiber rods serving as a supporting framework and rainproof silk fabric serving as shell fabric; the mooring rope 3 is a special Kevlar line for a large kite on the market and can bear 2500-pound tension to the maximum degree; the onboard winch 4 is installed at the tail of a ship 5, take-up and pay-off operation of the winch is driven and controlled by an alternating current motor, and the mooring rope 3 for taking up and paying off the large kite is arranged on a windlass of the winch. The onboard cruising low-altitude atmospheric profile measuring instrument has the following advantages that the height of the mini-type meteorological acquisition system 2 in air is controlled by taking up and paying off the mooring rope 3 by the onboard winch 4, and continuous meteorological observation at the ascent or descent height of low-altitude atmosphere can be achieved; the meteorological acquisition system adopted in the instrument can acquire high-accuracy data of air temperature, air humidity, atmospheric pressure and the like, and the system has the advantages of being light in weight, low in cost, small in power consumption and the like.
Owner:王海员
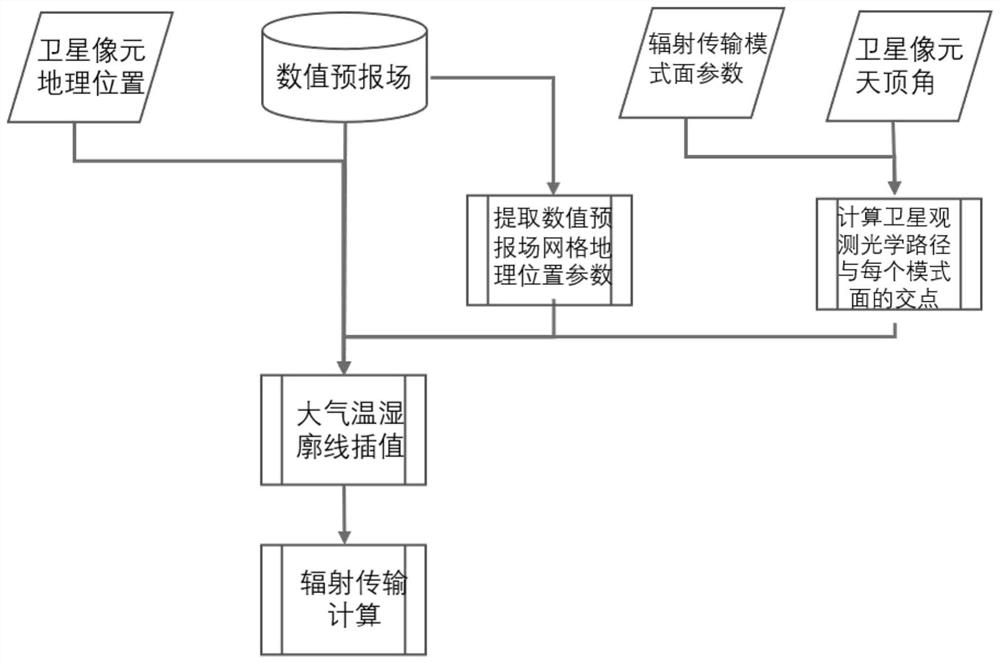
Method for correcting zenith angle simulation error of positive orbit satellite based on optical tracking
PendingCN114706104AElimination of simulated satellite observationsEliminate bias from actual satellite observationsSatellite radio beaconingAtmospheric layerSatellite observation
The invention discloses a method for correcting a zenith angle simulation error of a positive orbit satellite based on optical tracking. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating projections of intersection points of a radiation transmission mode layer and a satellite observation optical path on the ground one by one; according to the geographic position of the intersection point, interpolating from the numerical forecasting field grid points to obtain an atmospheric profile of the intersection point position; intercepting and interpolating an atmospheric temperature and humidity profile from the mode surface height of the radiation transmission mode to interpolate a profile of a corresponding height layer; repeating the steps on the radiation transmission mode surfaces one by one from the ground until the top of the atmosphere; and recombining the atmospheric profile between each radiation transmission mode surface into an atmospheric profile of a continuous height from the ground to the atmosphere top according to the corresponding mode surface, and inputting the atmospheric profile into a radiation transmission mode for calculation. According to the invention, deviation calculation is more accurate.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT +2
An all-weather relative humidity estimation method based on full remote sensing data
ActiveCN112327388BImprove accuracyWeather condition predictionComplex mathematical operationsSensing dataSaturated water vapor
The invention discloses an all-weather relative humidity estimation method based on full remote sensing data. The method reads atmospheric water vapor content, surface temperature and temperature profile from MODIS satellite remote sensing water vapor product data, cloud product data and atmospheric profile product data respectively. , humidity profile and atmospheric pressure profile; use the surface temperature, atmospheric pressure profile and temperature profile to derive the all-weather saturated water vapor pressure; atmospheric water vapor content, atmospheric pressure profile and humidity profile to derive the all-weather actual water vapor pressure; use the obtained The all-weather relative humidity is calculated from the all-weather saturated water vapor pressure and the actual water vapor pressure, and the Savitzky‑Golay filter is performed to obtain the final all-weather relative humidity. The all-weather relative humidity estimation method based on all remote sensing data provided by the present invention completely utilizes MODIS satellite remote sensing data to calculate all-weather relative humidity without any auxiliary data, and the method is simple and the result is accurate.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
A round-trip meteorological sounding balloon
Owner:中国人民解放军63660部队
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com