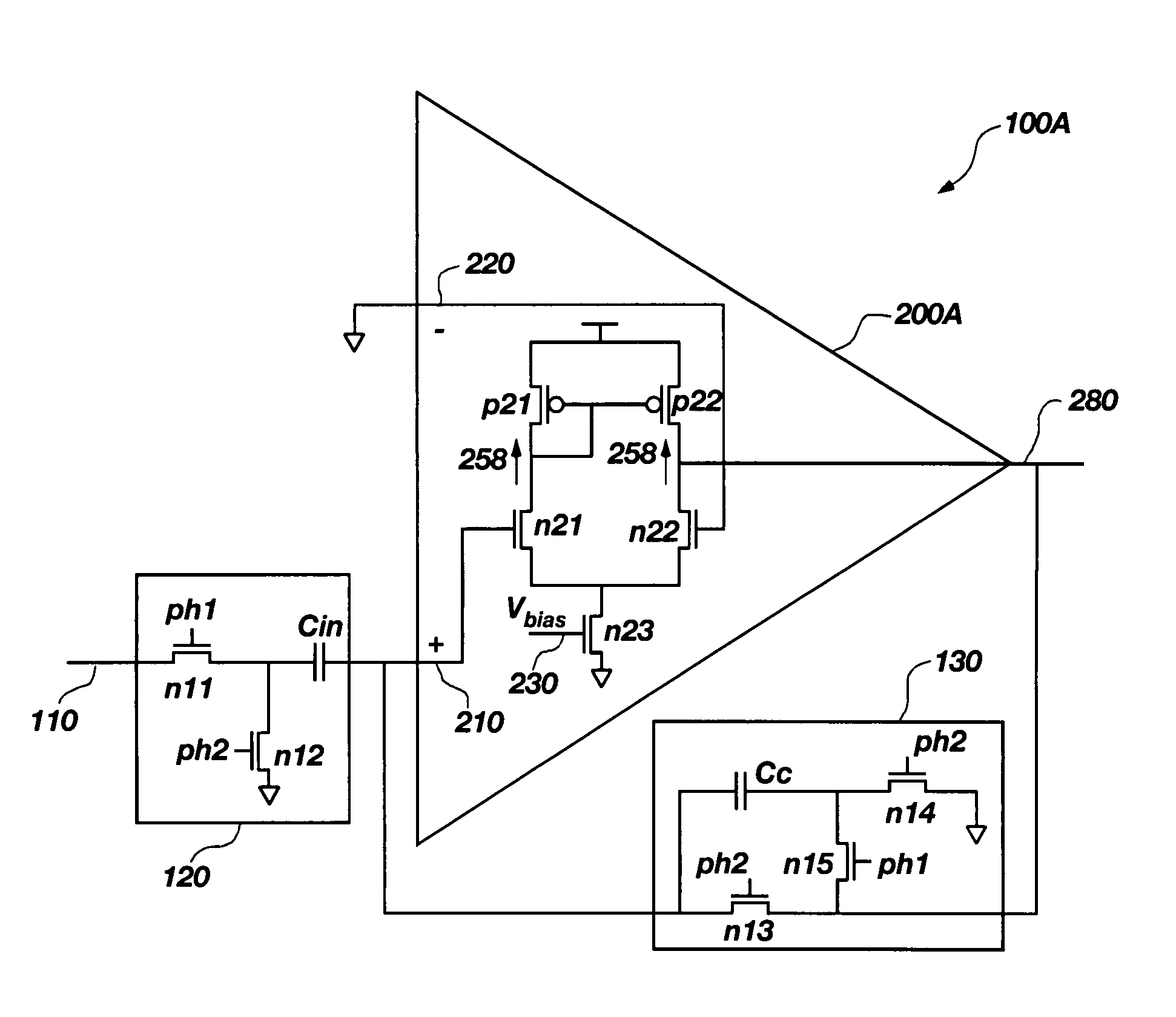
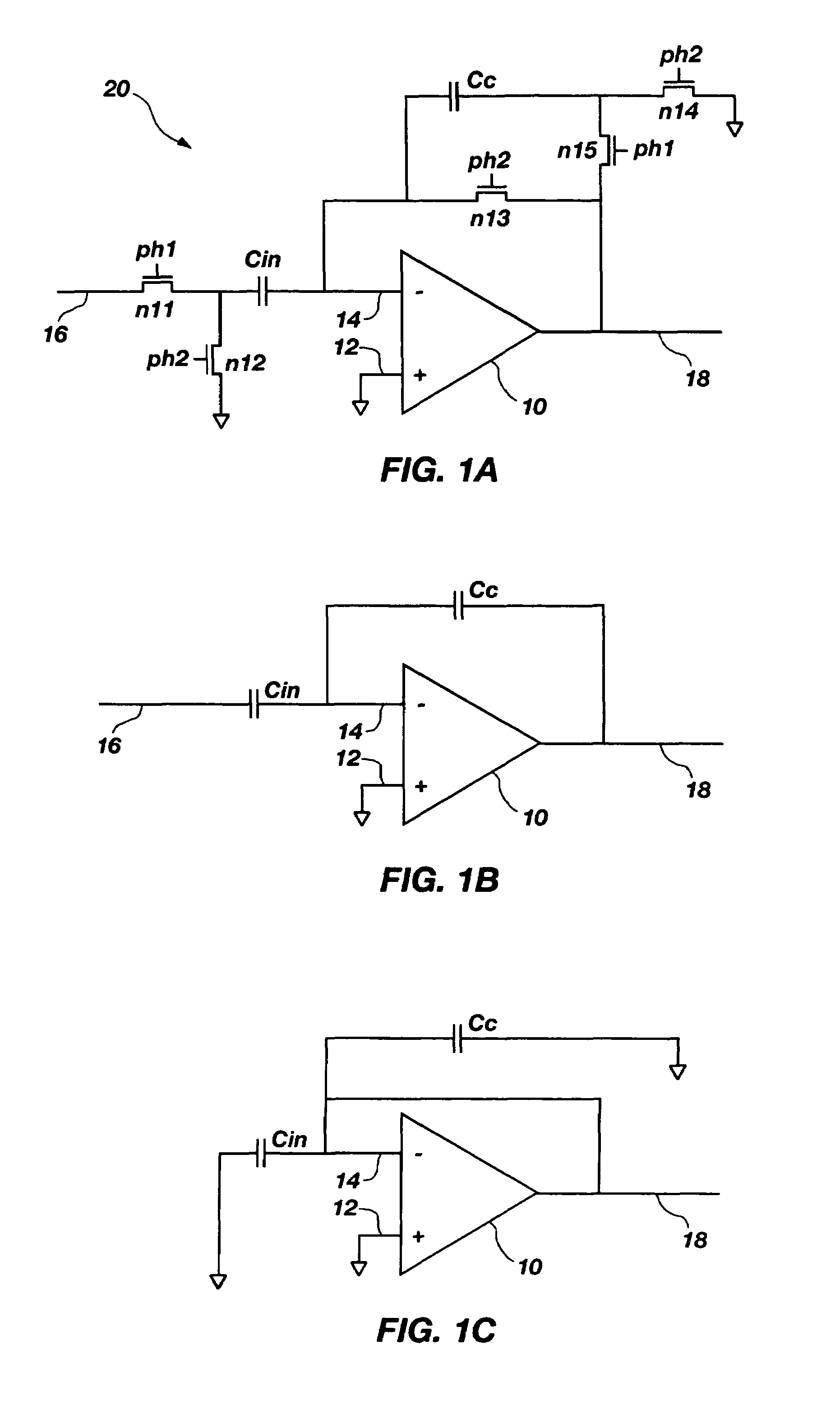
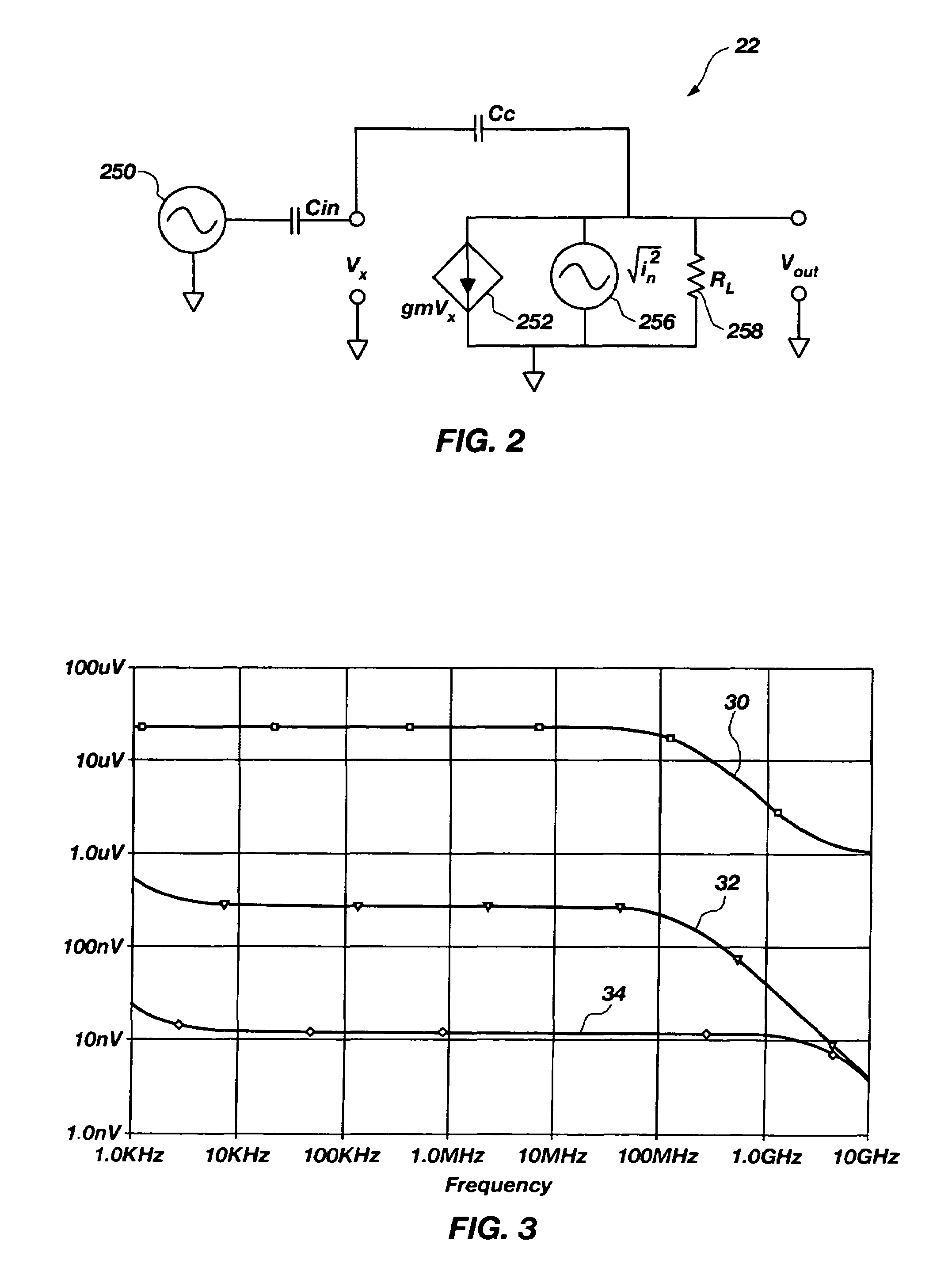
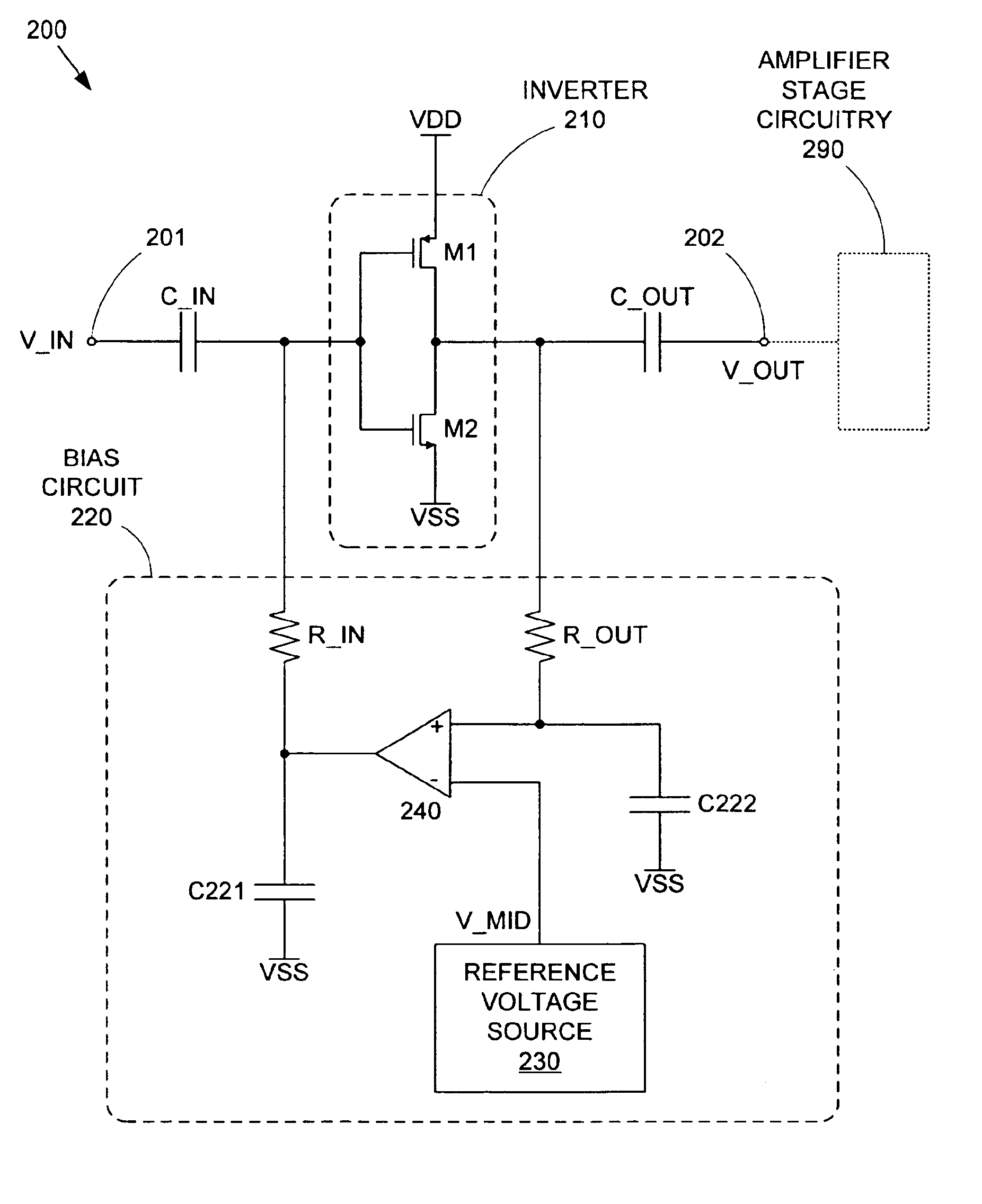
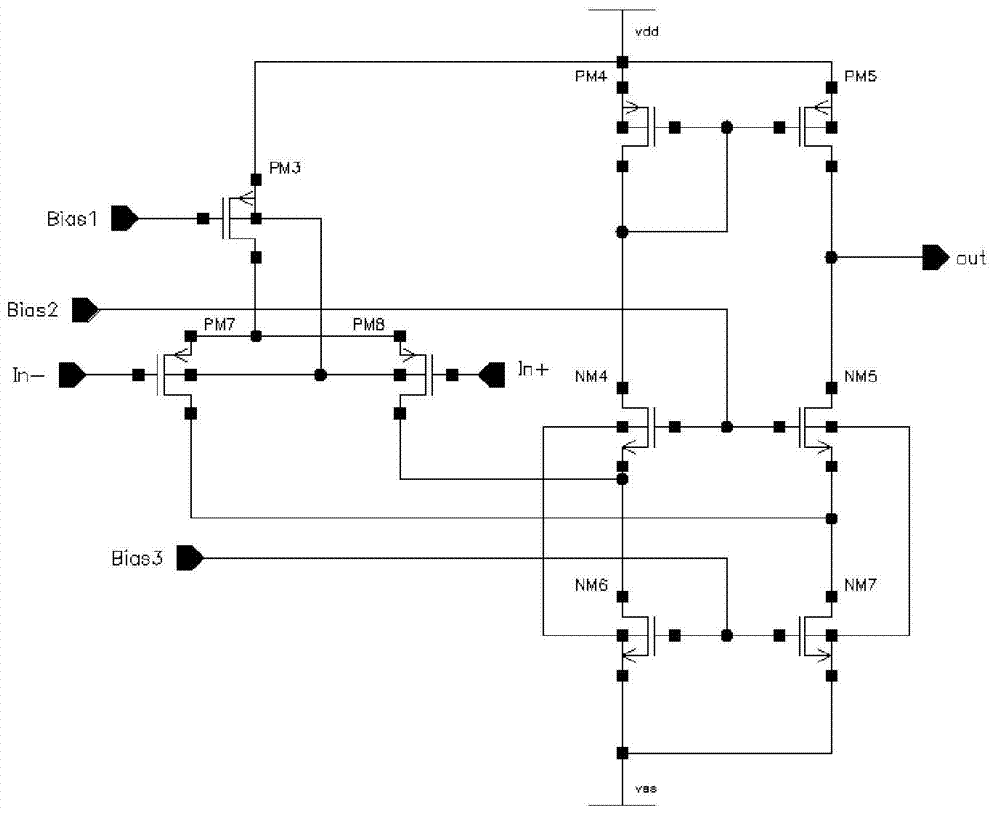
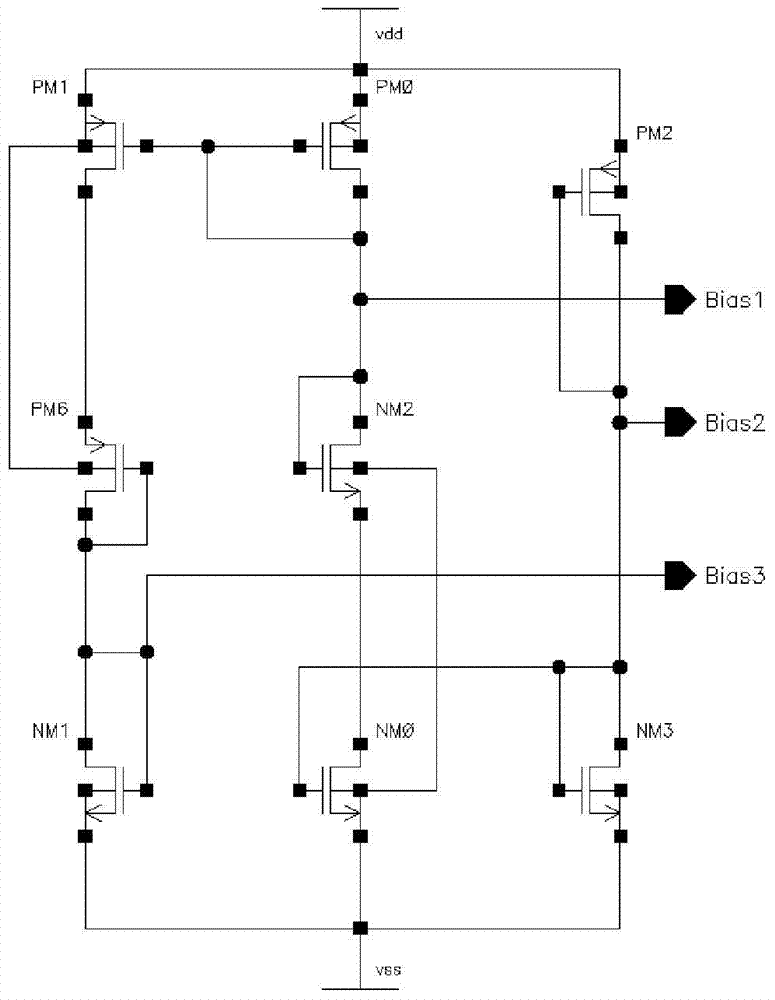
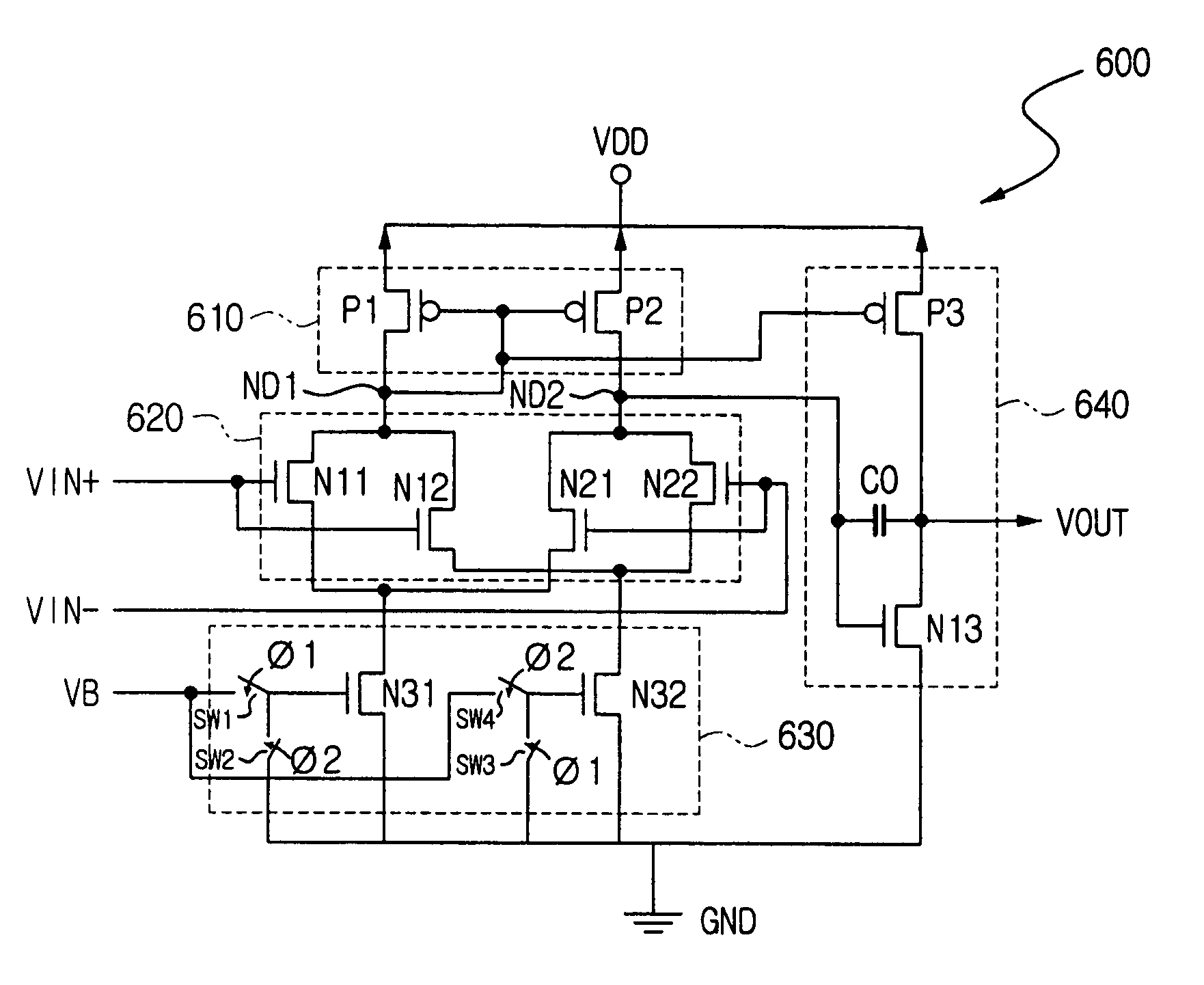
Patents
Literature
54 results about "Cmos amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
CMOS amplifiers are ubiquitous analog circuits which are used in computers, audio systems, smart phones, cameras, telecommunication systems, biomedical circuits and many other systems, and their performance has great impact on the overall specifications of the systems.
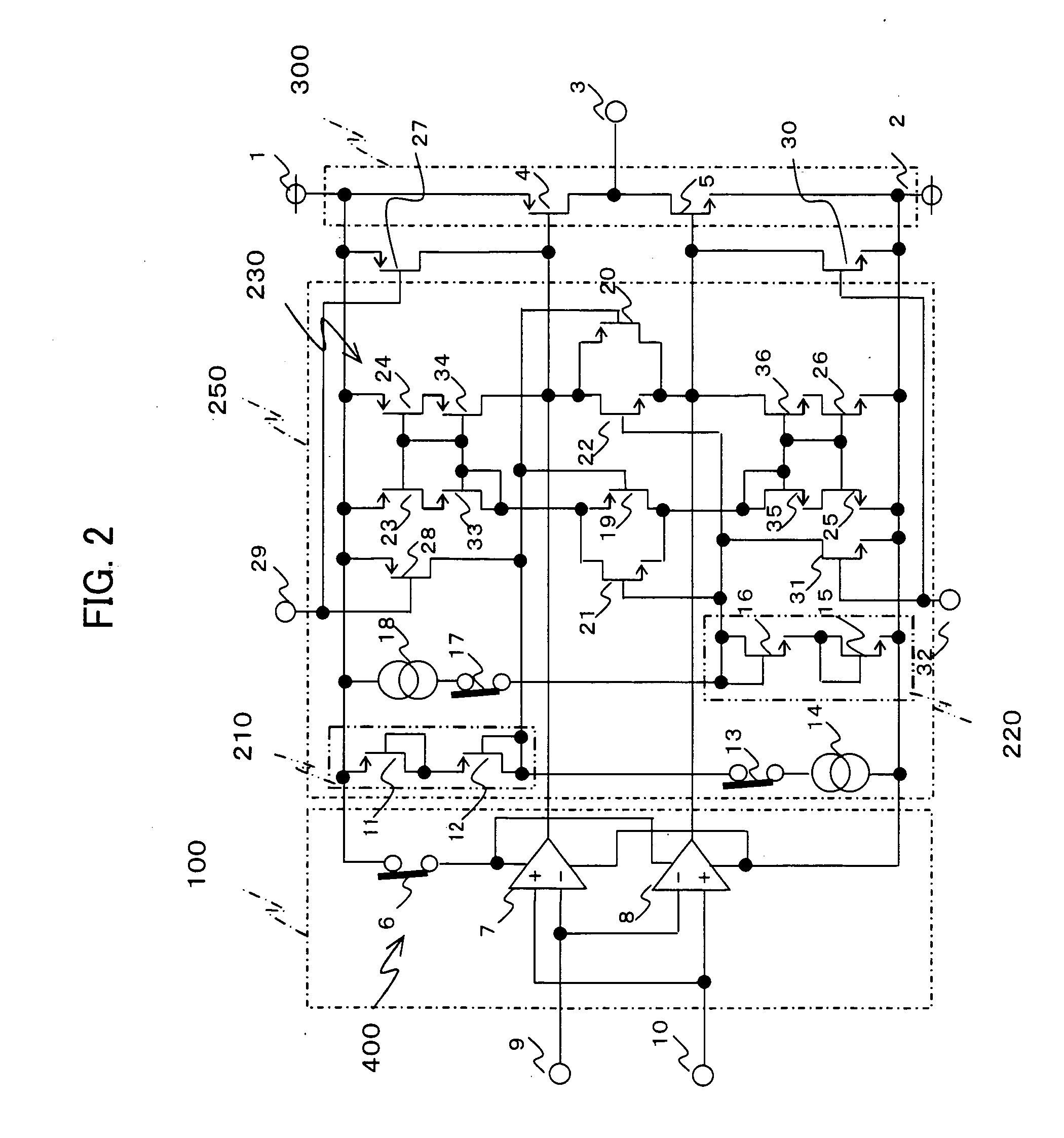
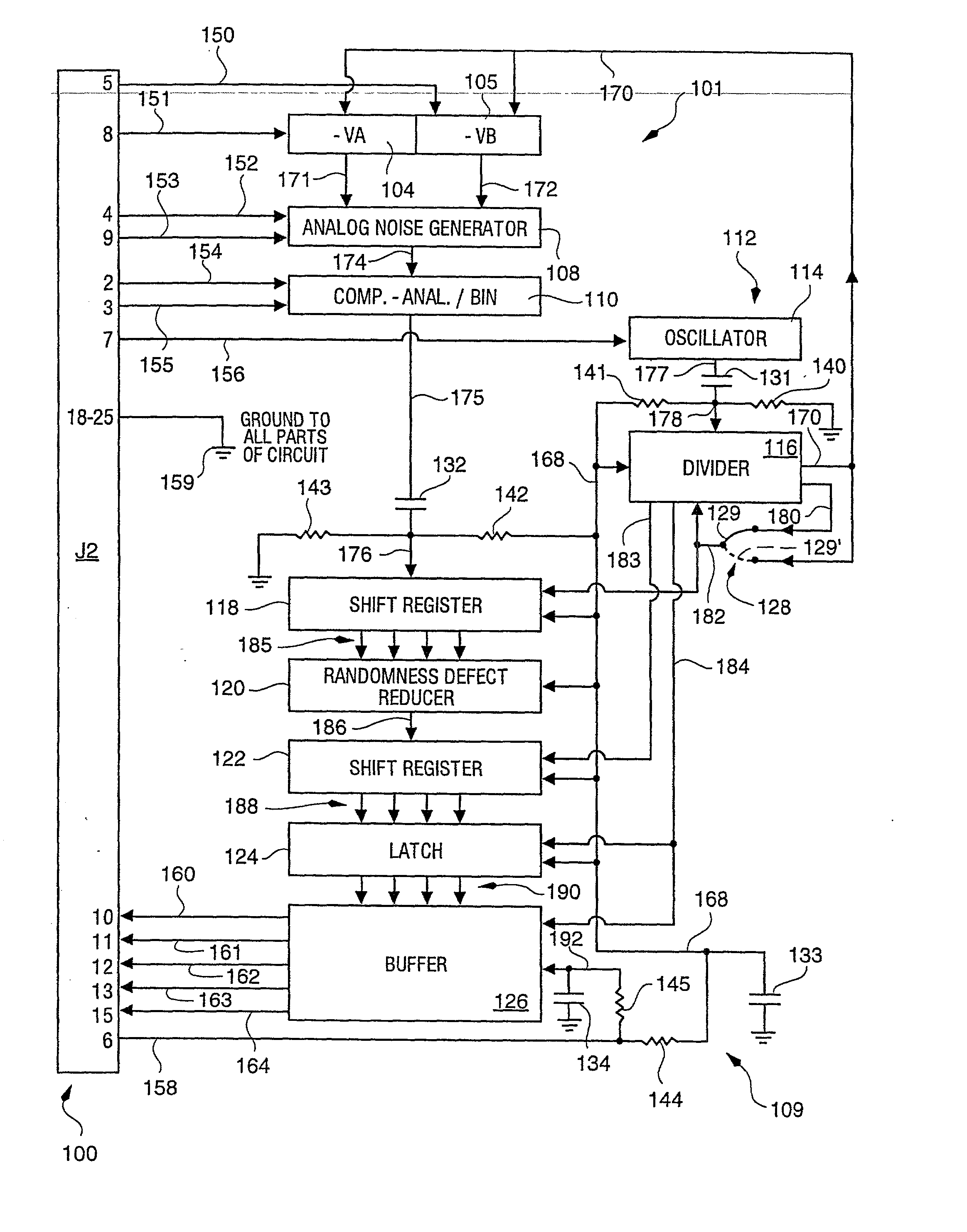
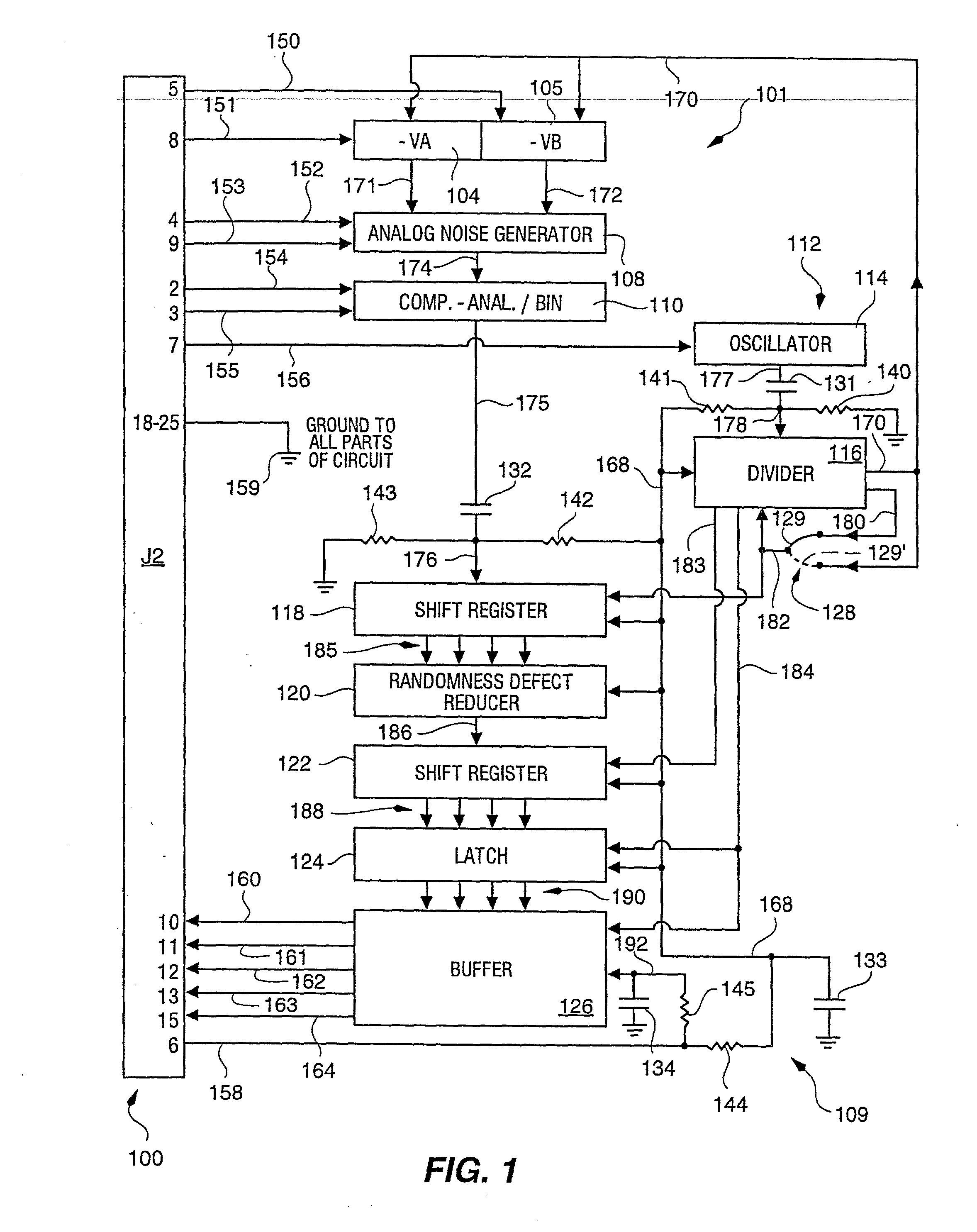
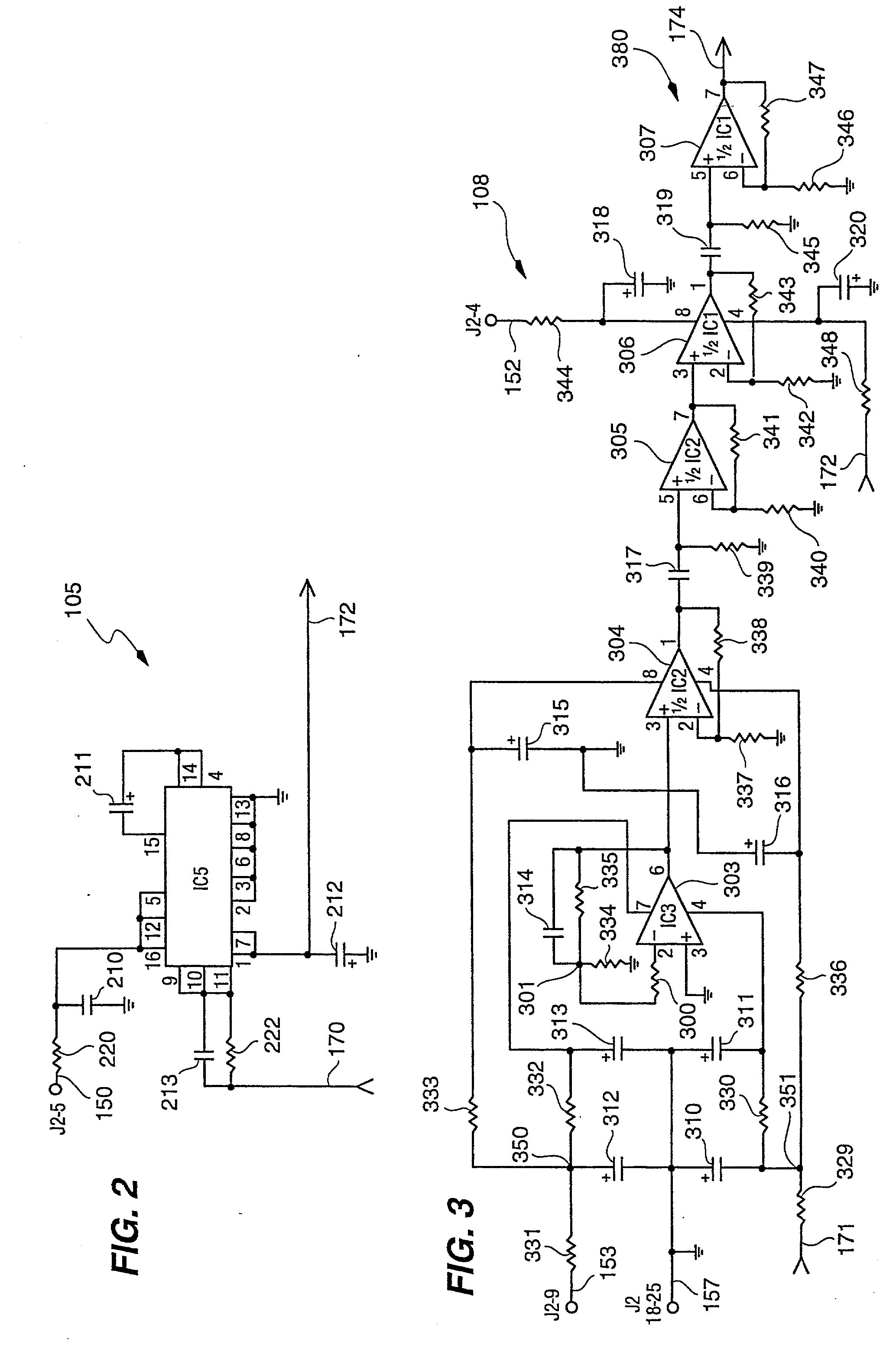
Random number generator and generation method
InactiveUS6324558B1Improve its ability to generateReduce defectsRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsCmos comparatorShift register
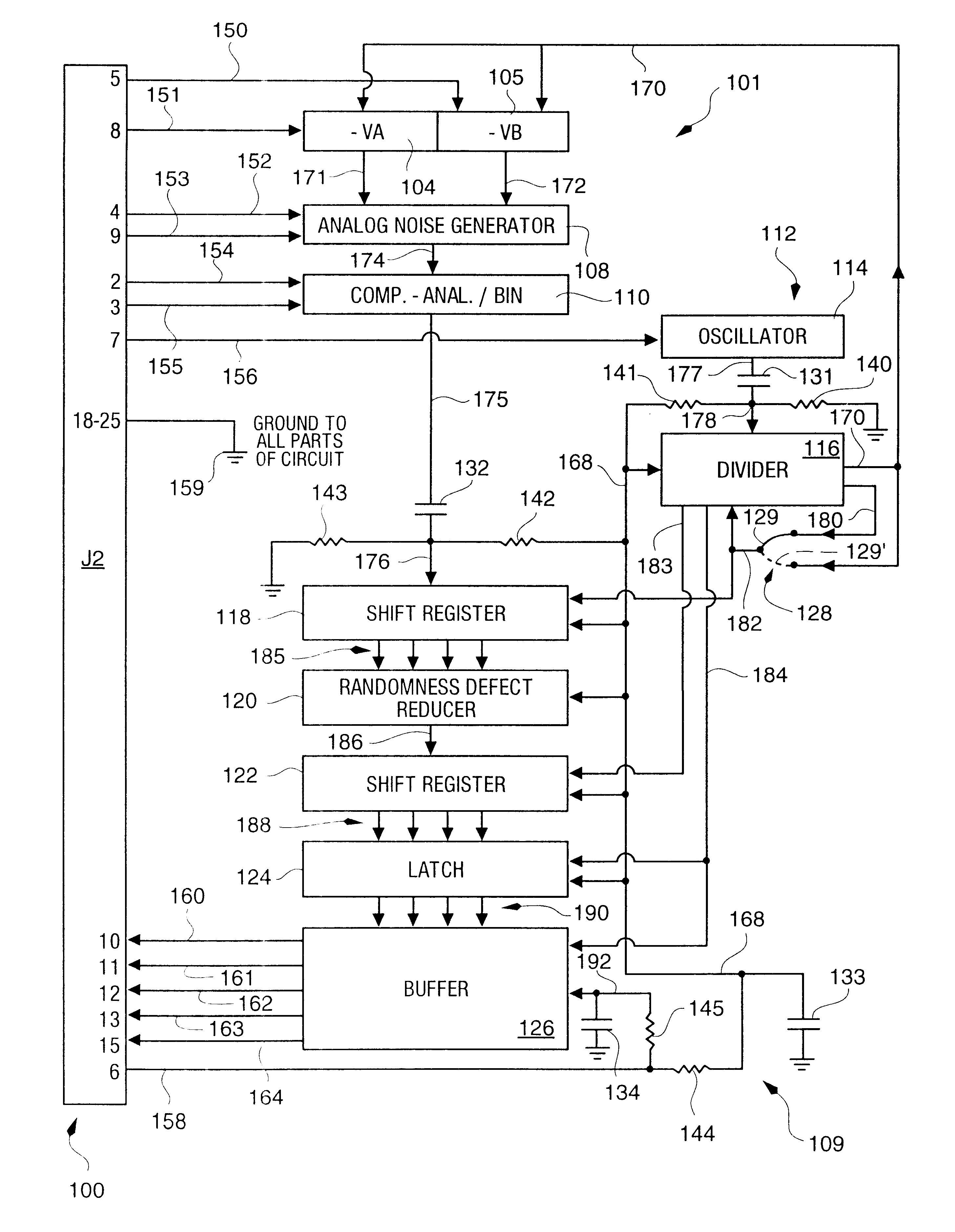
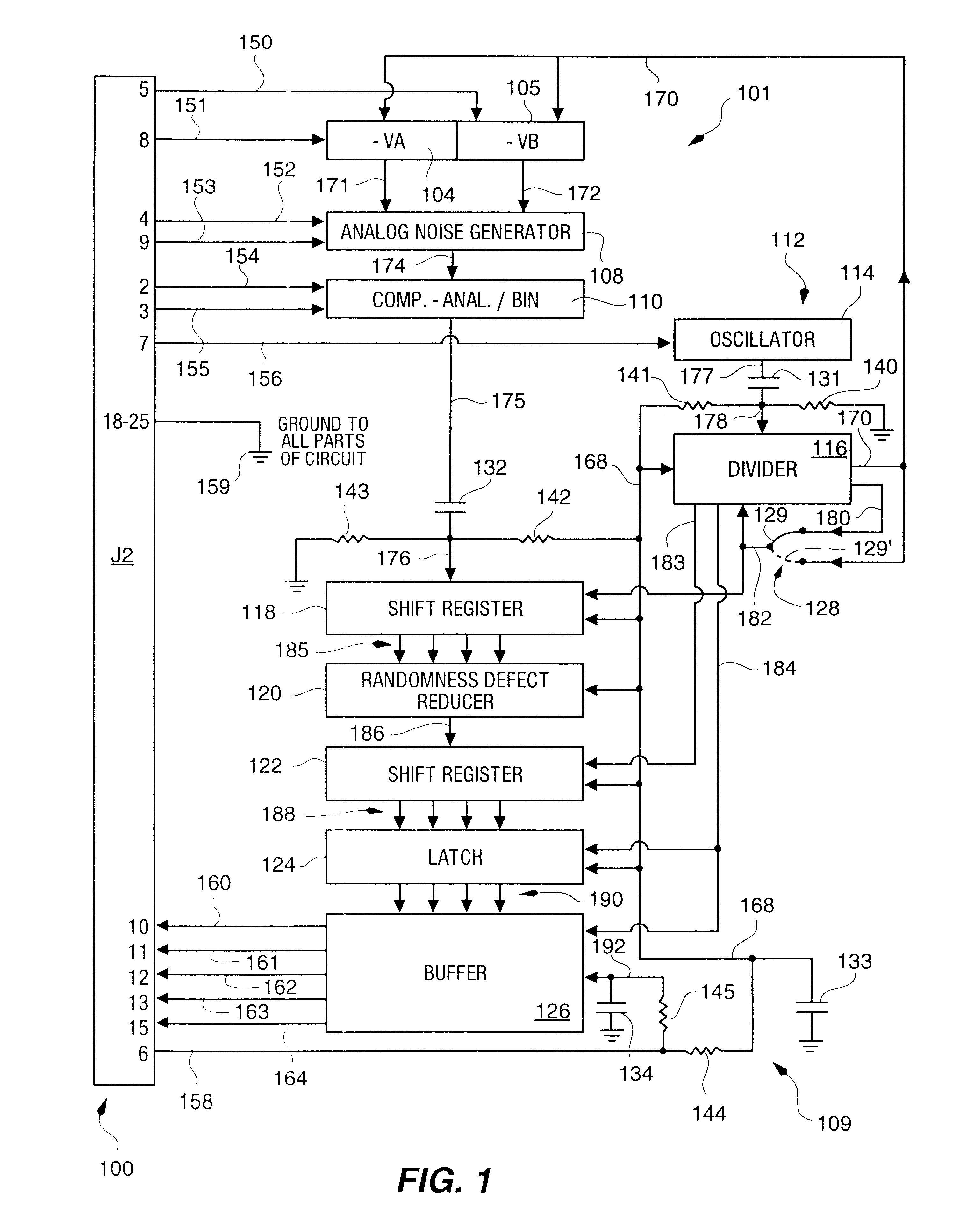
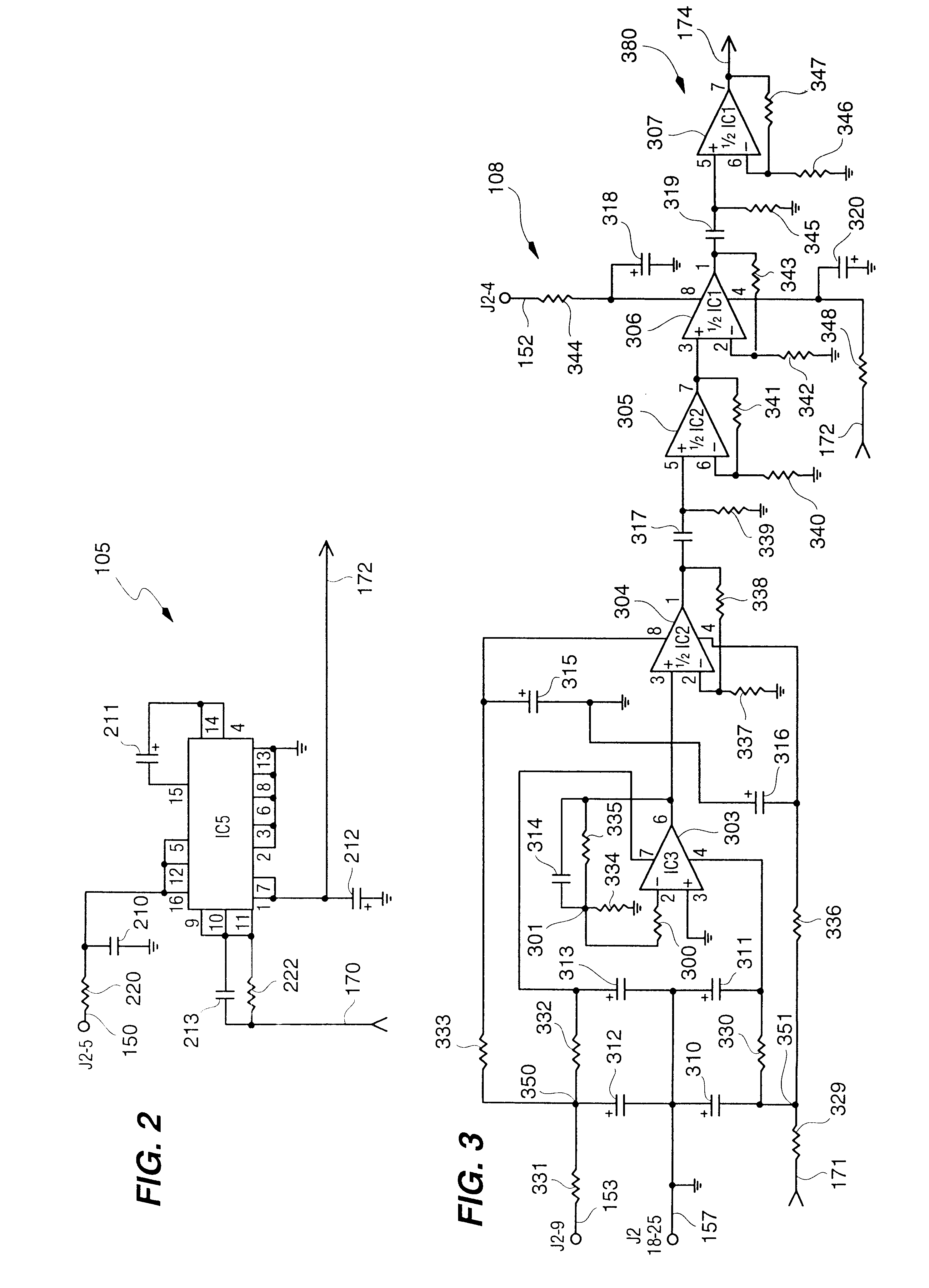
An RNG circuit is connected to the parallel port of a computer. The circuit includes a flat source of white noise and a CMOS amplifier circuit compensated in the high frequency range. A low-frequency cut-off is selected to maintain high band-width yet eliminate the 1 / f amplifier noise tail. A CMOS comparator with a 10 nanosecond rise time converts the analog signal to a binary one. A shift register converts the serial signal to a 4-bit parallel one at a sample rate selected at the knee of the serial dependence curve. Two levels of XOR defect correction produce a BRS at 20 kHZ, which is converted to a 4-bit parallel word, latched and buffered. The entire circuit is powered from the data pins of the parallel port. A device driver interface in the computer operates the RNG. The randomness defects with various levels of correction and sample rates are calculated and the RNG is optimized before manufacture.
Owner:QUANTUM WORLD
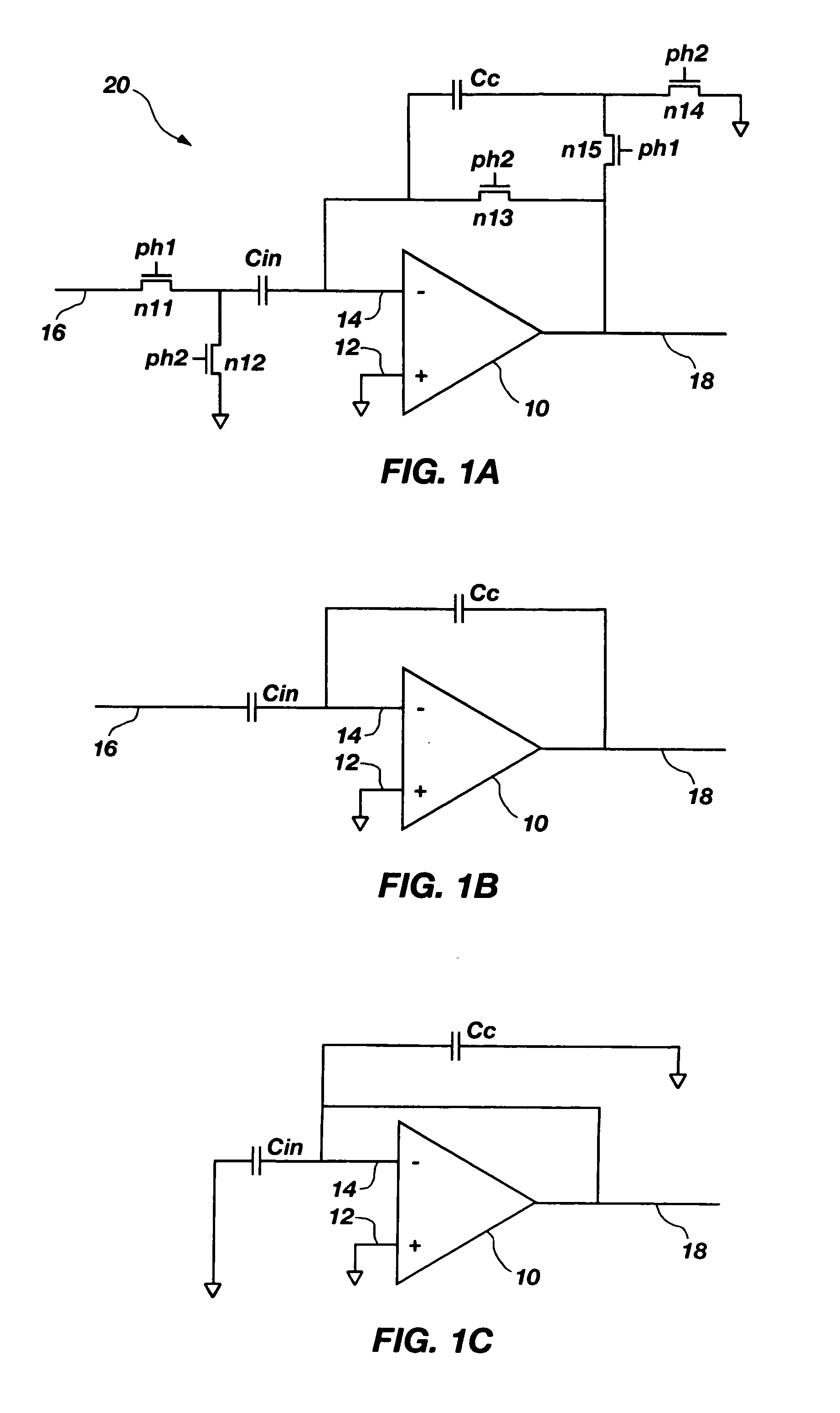
Switched capacitor amplifier with higher gain and improved closed-loop gain accuracy
ActiveUS20080186093A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
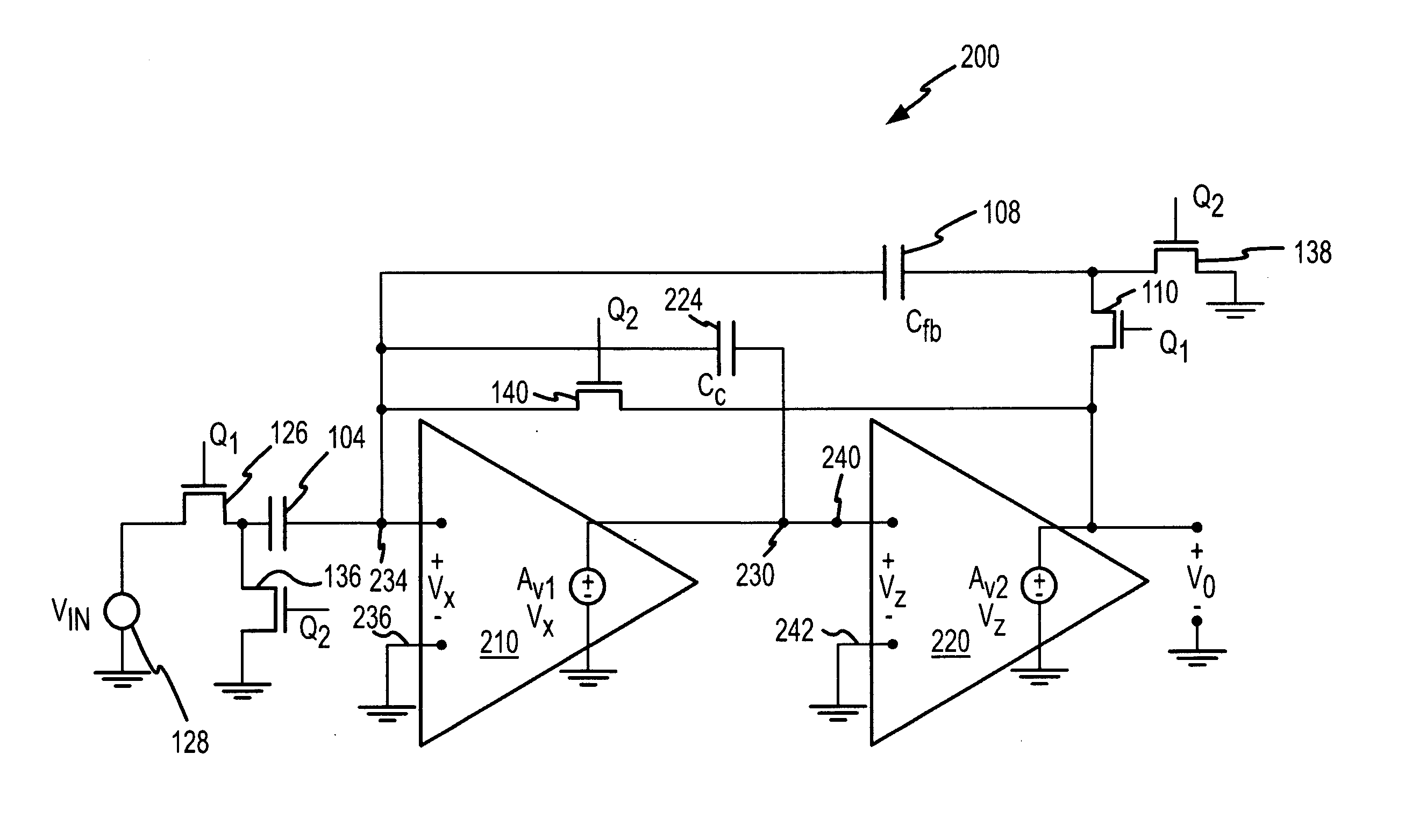
A switched capacitor CMOS amplifier uses a first stage non-inverting CMOS amplifier driving a second stage inverting CMOS amplifier. The first stage amplifier is provided with positive feedback to substantially increase the gain of the first stage amplifier. In the described examples, the positive feedback is provided either by connecting a capacitor from the output to the input of the first stage amplifier or by connecting a shunt transistor in parallel with an input transistor and driving the transistor from the output of the first stage amplifier. The substantially increased gain resulting from the positive feedback allows the gain of the switched capacitor amplifier to be set by the ratio of the capacitance of an input capacitor to the capacitance of a feedback capacitor. The amplifier also includes switching transistors for periodically discharging the input capacitor and the feedback capacitor.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
System and method for providing slew rate enhancement for two stage CMOS amplifiers
A slew rate enhancement circuit is disclosed for increasing a slew rate in a two stage CMOS amplifier. The slew rate enhancement circuit detects an input signal transition in the two stage CMOS amplifier. Depending on the polarity of the input signal transition the slew rate enhancement circuit turns on either (1) a first current source to charge a first compensation capacitor, or (2) a second current source to charge a second compensation capacitor. The slew rate enhancement circuit increases the slew rate by a factor of four to five and decreases the settling time of a voltage transition by a factor of three.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Physical unclonable chip circuit
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
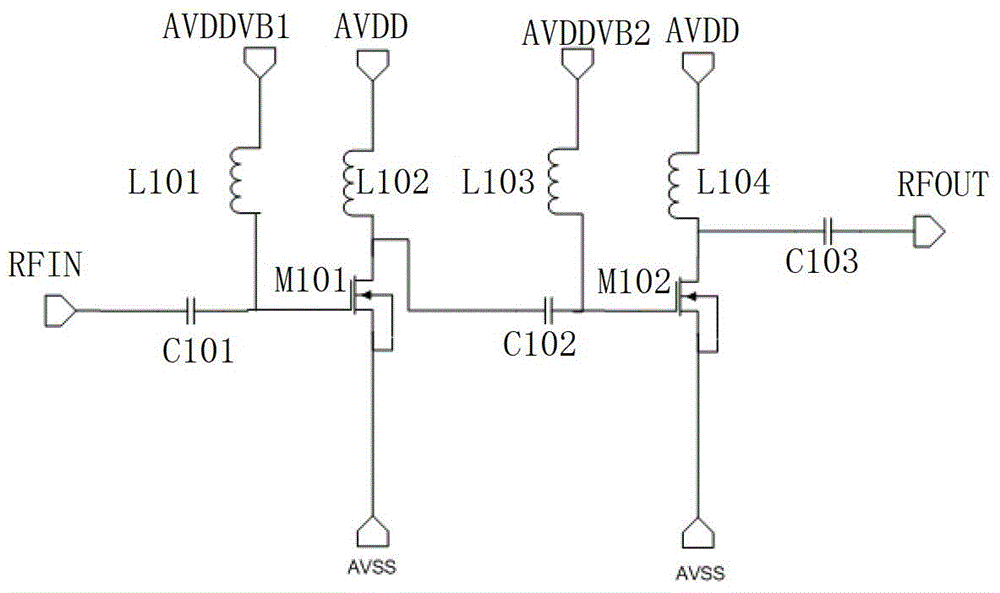
Radio frequency power amplifier
ActiveCN104158500AImprove pressure resistanceImprove isolationHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthCommon emitterAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a radio frequency power amplifier integrated on a same chip. The radio frequency power amplifier comprises two stages of amplifying circuits. An automatic biasing cascode CMOS amplifier is adopted in the first-stage amplifying circuit, and a SiGe HBT connected through a common emitter is adopted in the second-stage amplifying circuit. According to the radio frequency power amplifier, the withstand voltage, the isolation and the bandwidth of the circuits can be improved, the voltage swing and working current of the circuits can be improved, the gain and the maximum output power of the circuits can be improved, the frequency performance of the power amplifier can be improved, full-chip integration can be achieved, and accordingly, the integration degree is improved, cost is reduced, and the application is simplified.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
CMOS amplifier
InactiveUS20070096819A1Interrupting currentGated amplifiersDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierHemt circuits
A CMOS amplifier according to the present invention includes an input stage, an output stage, a feedforward type idling current control circuit, and an interrupter circuit. The output stage includes a grounded-source push-pull circuit having an output P-channel MOS transistor and an output N-channel MOS transistor. The input stage includes two differential amplifier circuits. The idling current control circuit supplies idling currents to the MOS transistors of the output stage so that the MOS transistors of the output stage perform class AB amplification operations. The interrupter circuit includes a plurality of switches which are off in a stand-by state to stop power supply to the differential amplifier circuits, stop operations of constant current circuits included in the idling current control circuit, and cancel gate-source voltages at the MOS transistors of the output stage.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Random number generator and generation method
InactiveUS20020169810A1Improve its ability to generateReduce defectsRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsCmos comparatorShift register
An RNG circuit is connected to the parallel port of a computer. The circuit includes a flat source of white noise and a CMOS amplifier circuit compensated in the high frequency range. A low-frequency cut-off is selected to maintain high band-width yet eliminate the 1 / f amplifier noise tail. A CMOS comparator with a 10 nanosecond rise time converts the analog signal to a binary one. A shift register converts the serial signal to a 4-bit parallel one at a sample rate selected at the knee of the serial dependence curve. Two levels of XOR defect correction produce a BRS at 20 kHZ, which is converted to a 4-bit parallel word, latched and buffered. The entire circuit is powered from the data pins of the parallel port. A device driver interface in the computer operates the RNG. The randomness defects with various levels of correction and sample rates are calculated and the RNG is optimized before manufacture.
Owner:QUANTUM WORLD
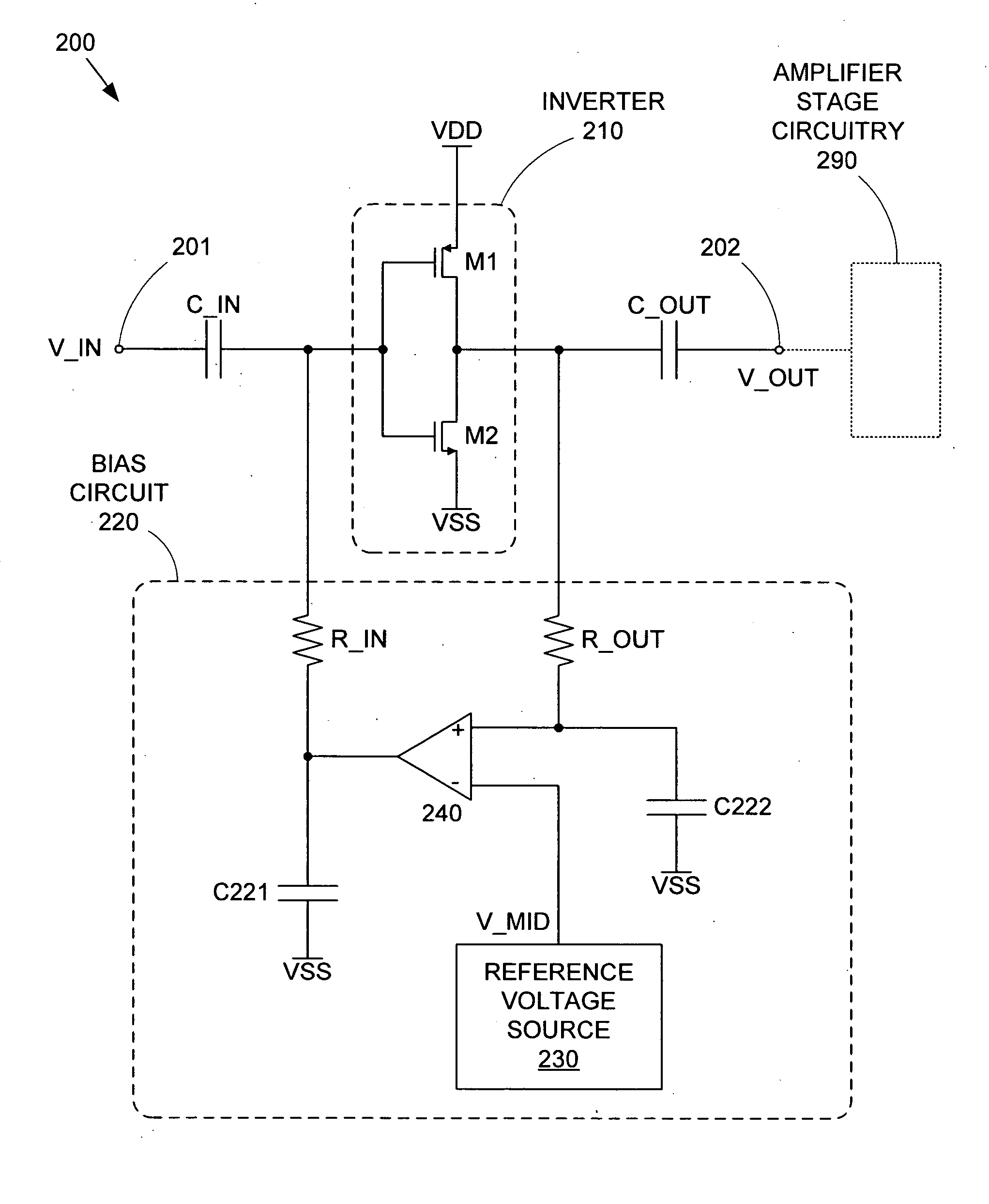
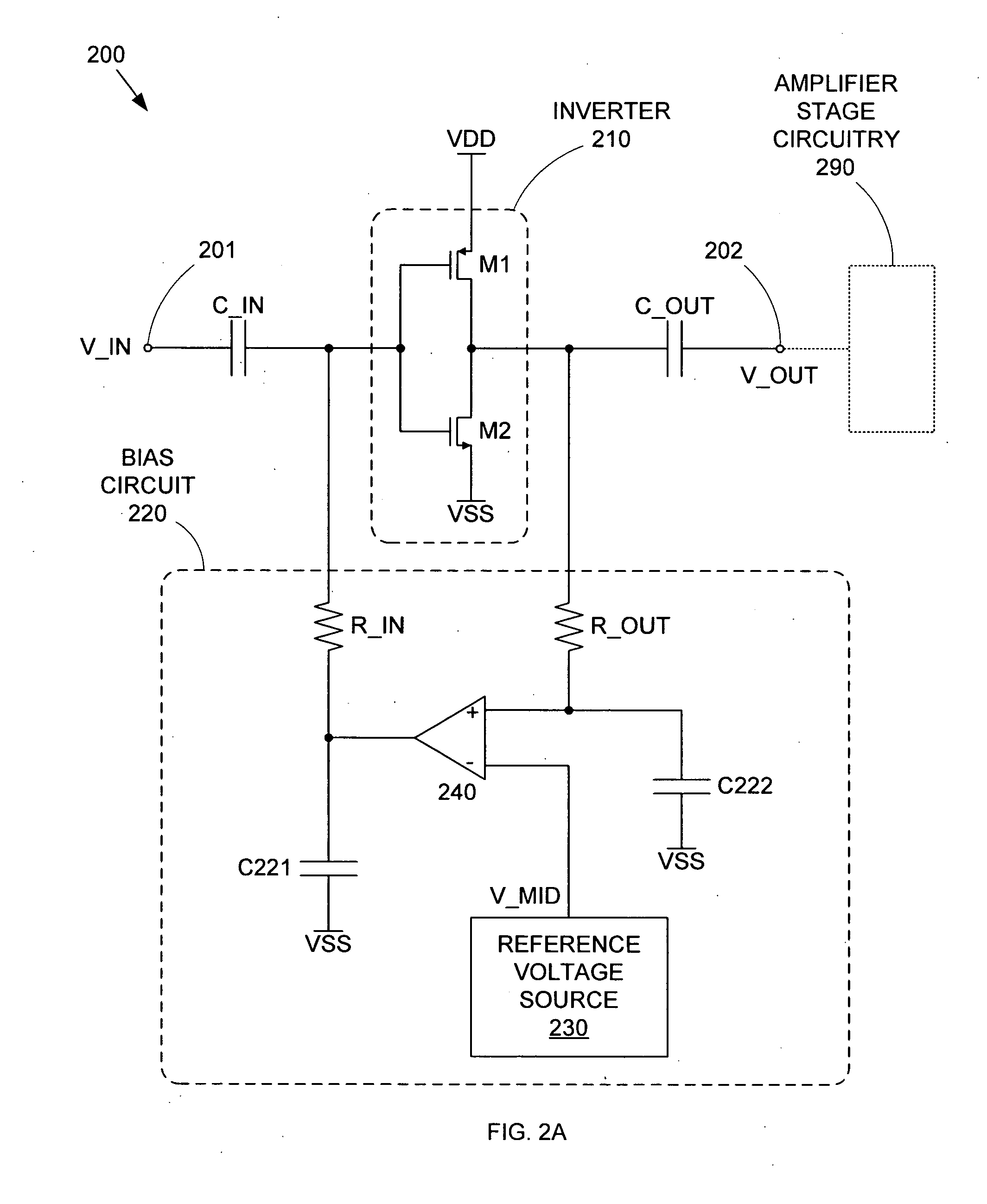
High frequency differential power amplifier
ActiveUS20050206412A1Without consuming excessive powerAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsCMOSAudio power amplifier
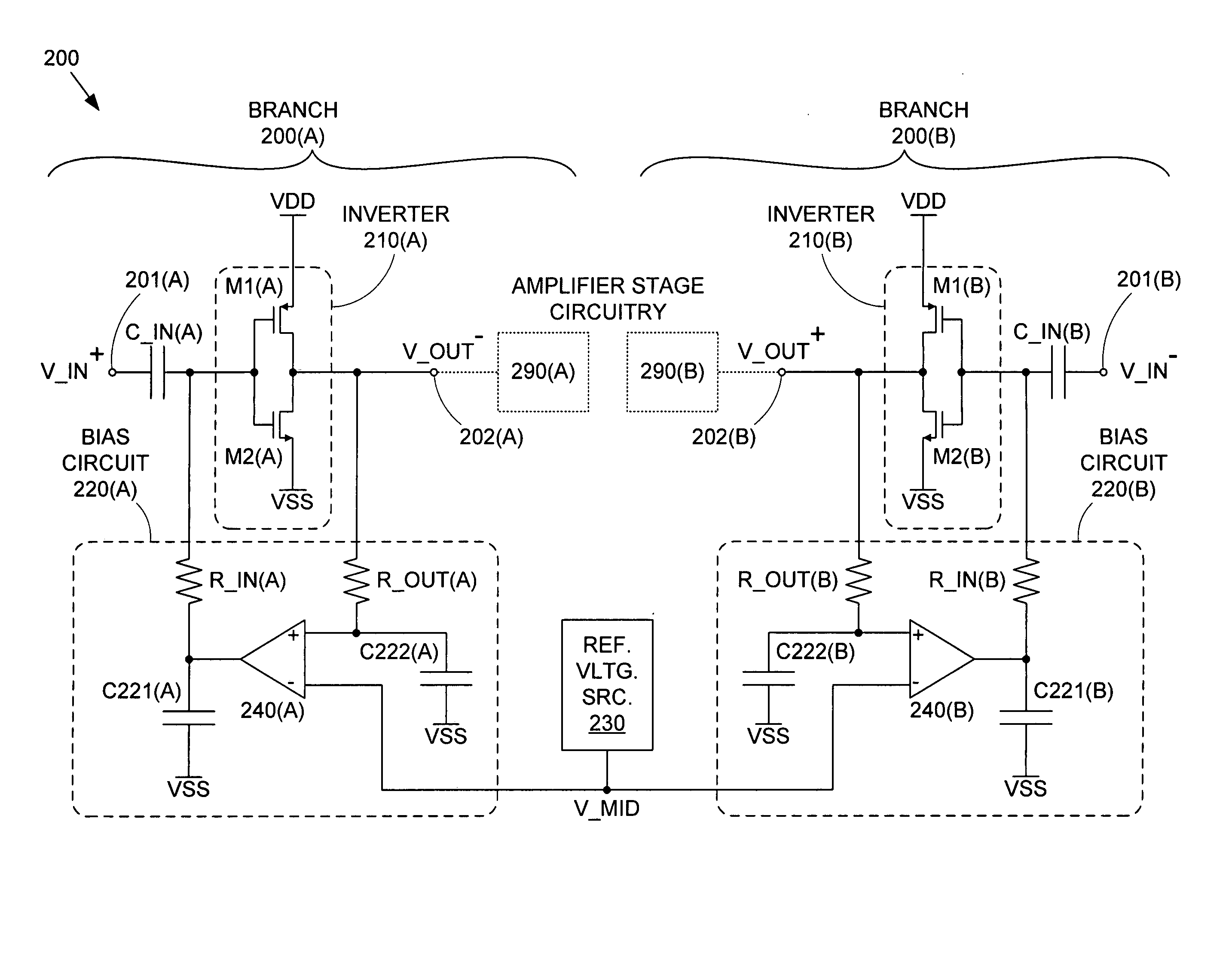
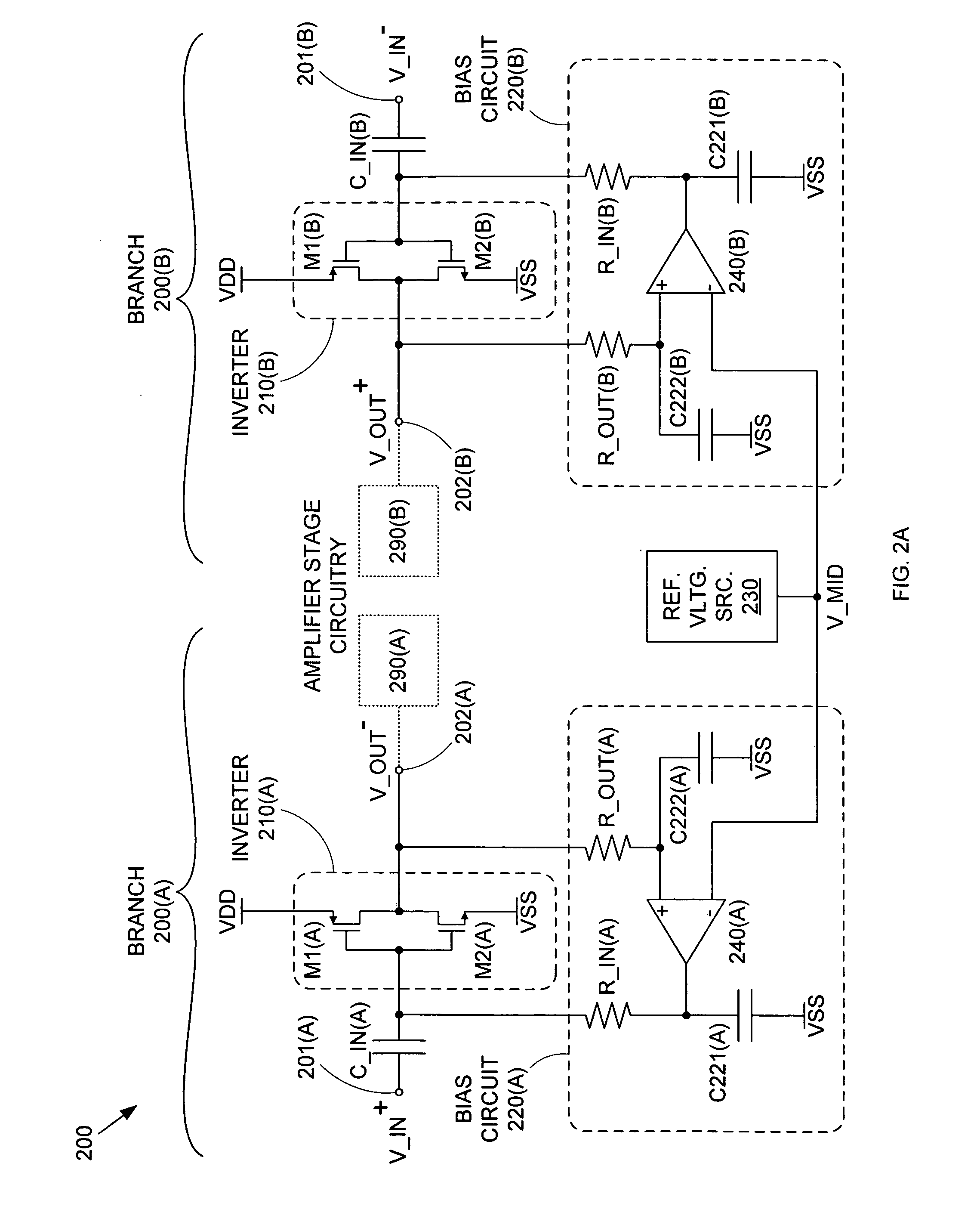
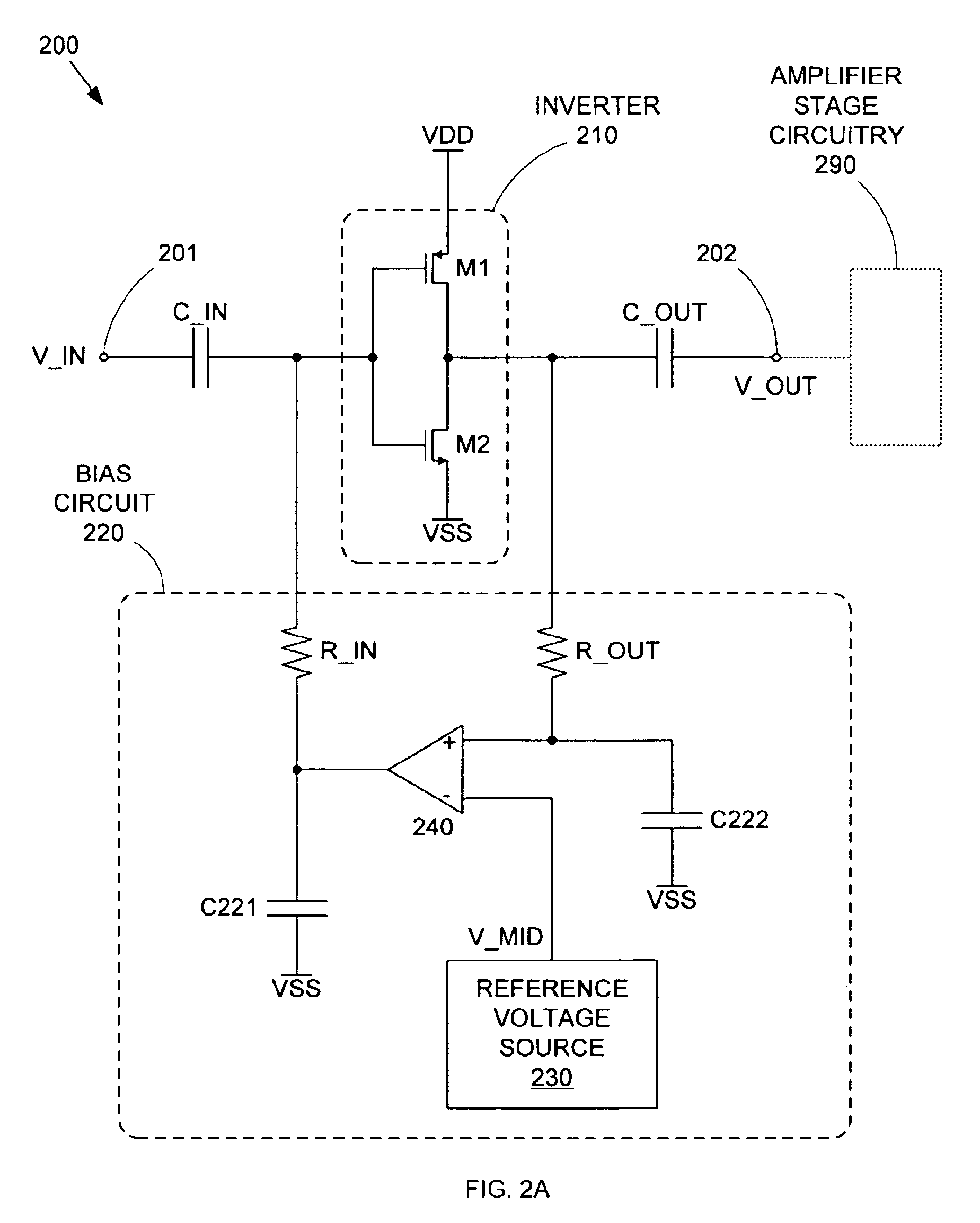
A differential CMOS amplifier includes two CMOS inverters and biasing circuitry providing feedback loops across the output and input of each inverter. The biasing circuitry provides linear biasing so that the inverters can apply a desired gain to a pair of high frequency input signals (i.e., a differential input signal). The biasing circuitry can include operational amplifiers (op-amps) for providing positive feedback control between the output and input of the inverters. The inputs of the inverters can be regulated by this feedback loop such that their outputs are driven to the reference voltage, thereby forcing the inverters to operate in their linear regions so that non-distorting amplification can be applied to the input AC signals.
Owner:SONRAI MEMORY LTD
System and method for linearizing a CMOS differential pair
InactiveUS7276970B2Resonant circuit detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLocal oscillator signalFilter tuning
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Class AB CMOS amplifiers
ActiveUS7078971B2Reduce variationDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCMOSLevel shifting
A class AB output stage of a CMOS amplifier has a level-shifting voltage follower constituted by a level-shifting transistor and a current source. A bias circuit replicates the level-shifting voltage follower in a feedback arrangement to produce a variable bias voltage for the current source of both the main and replica level-shifters. The arrangement serves to control the output voltage of the level-shifter such that it provides the amplifier with a relatively constant quiescent current of the output stage over variations of manufacturing process, supply voltage, and temperature. The level shifting function can be facilitated by a resistive on-state of a power-down transistor between the level-shifting and load transistors.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC +1
High frequency differential power amplifier
ActiveUS6937071B1Without consuming excessive powerAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPower inverterCMOS
A differential CMOS amplifier includes two CMOS inverters and biasing circuitry providing feedback loops across the output and input of each inverter. The biasing circuitry provides linear biasing so that the inverters can apply a desired gain to a pair of high frequency input signals (i.e., a differential input signal). The biasing circuitry can include operational amplifiers (op-amps) for providing positive feedback control between the output and input of the inverters. The inputs of the inverters can be regulated by this feedback loop such that their outputs are driven to the reference voltage, thereby forcing the inverters to operate in their linear regions so that non-distorting amplification can be applied to the input AC signals.
Owner:SONRAI MEMORY LTD
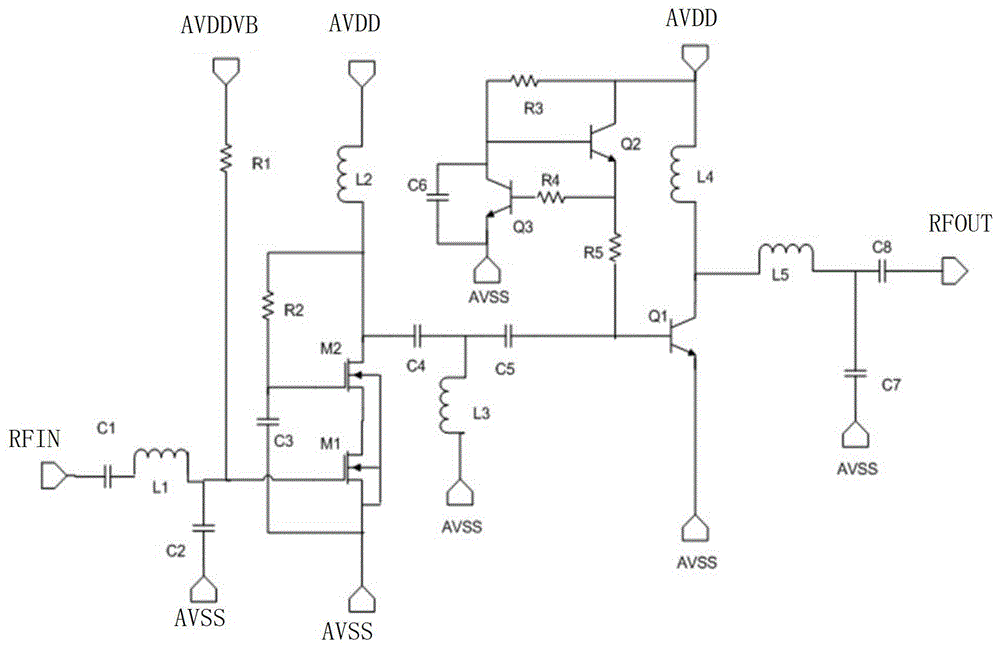
Low noise amplifier
ActiveCN104158497AHigh gain performanceHigh gainAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTotal impedanceResistor
The invention discloses a low noise amplifier. The low noise amplifier comprises a first-stage amplifying circuit, a second-stage amplifying circuit, a first-stage biasing circuit, a second-stage biasing circuit and an output impedance matching circuit, wherein the first-stage amplifying circuit and the second-stage amplifying circuit are cascaded. The first-stage amplifying circuit comprises first NMOS pipes with the common sources connected, and a first resistor and a first inductor are connected between the drain electrodes of the first NMOS pipes and a supply voltage. The second-stage amplifying circuit comprises a cascode CMOS amplifier. According to the low noise amplifier, the first-stage amplifying circuit and the second-stage amplifying circuit are cascaded so that the gain performance and the noise performance of the circuits can be greatly improved; a first inductive load at the drain end of the first-stage amplifying circuit enables the total impedance of the load end of the first-stage amplifying circuit to keep roughly unchangeable within a wide frequency range, and therefore the high frequency gain of the whole circuit can be improved and can be stable; the cascode amplifier is adopted in the second-stage amplifying circuit so that the whole low noise amplifier can obtain the good noise performance and gain performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Switched capacitor amplifier with higher gain and improved closed-loop gain accuracy
ActiveUS7365597B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A switched capacitor CMOS amplifier uses a first stage non-inverting CMOS amplifier driving a second stage inverting CMOS amplifier. The first stage amplifier is provided with positive feedback to substantially increase the gain of the first stage amplifier. In the described examples, the positive feedback is provided either by connecting a capacitor from the output to the input of the first stage amplifier or by connecting a shunt transistor in parallel with an input transistor and driving the transistor from the output of the first stage amplifier. The substantially increased gain resulting from the positive feedback allows the gain of the switched capacitor amplifier to be set by the ratio of the capacitance of an input capacitor to the capacitance of a feedback capacitor. The amplifier also includes switching transistors for periodically discharging the input capacitor and the feedback capacitor.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
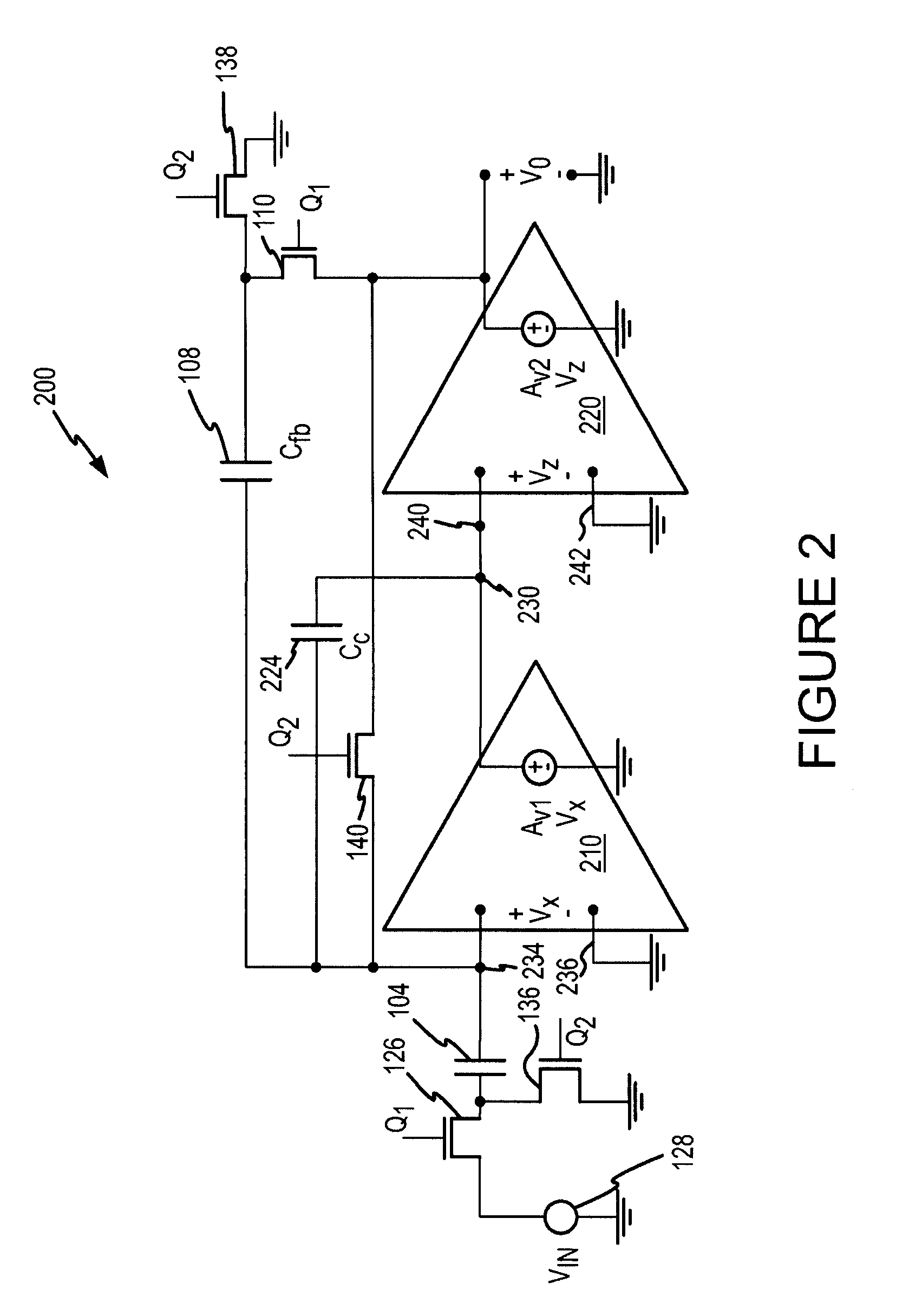
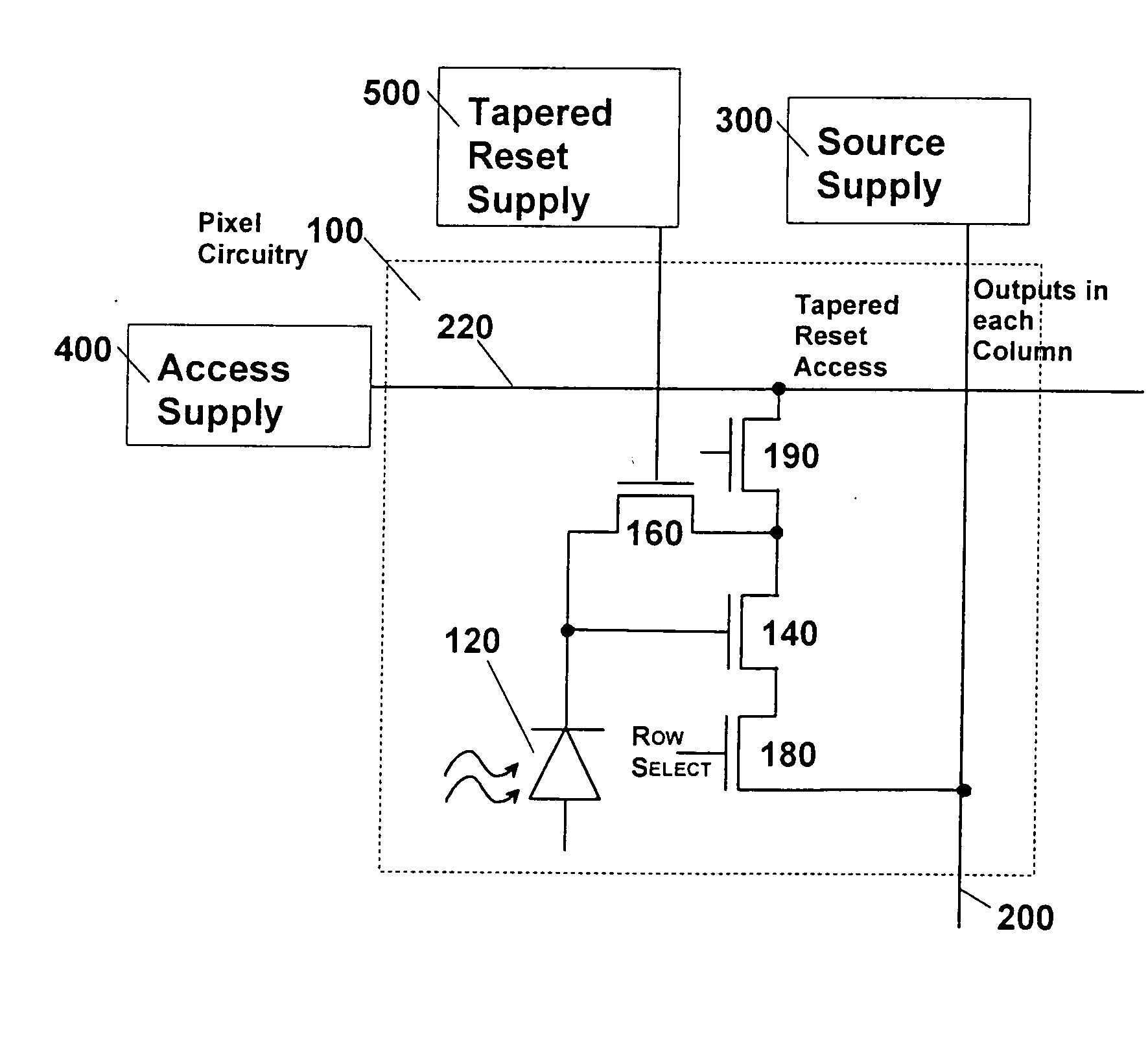
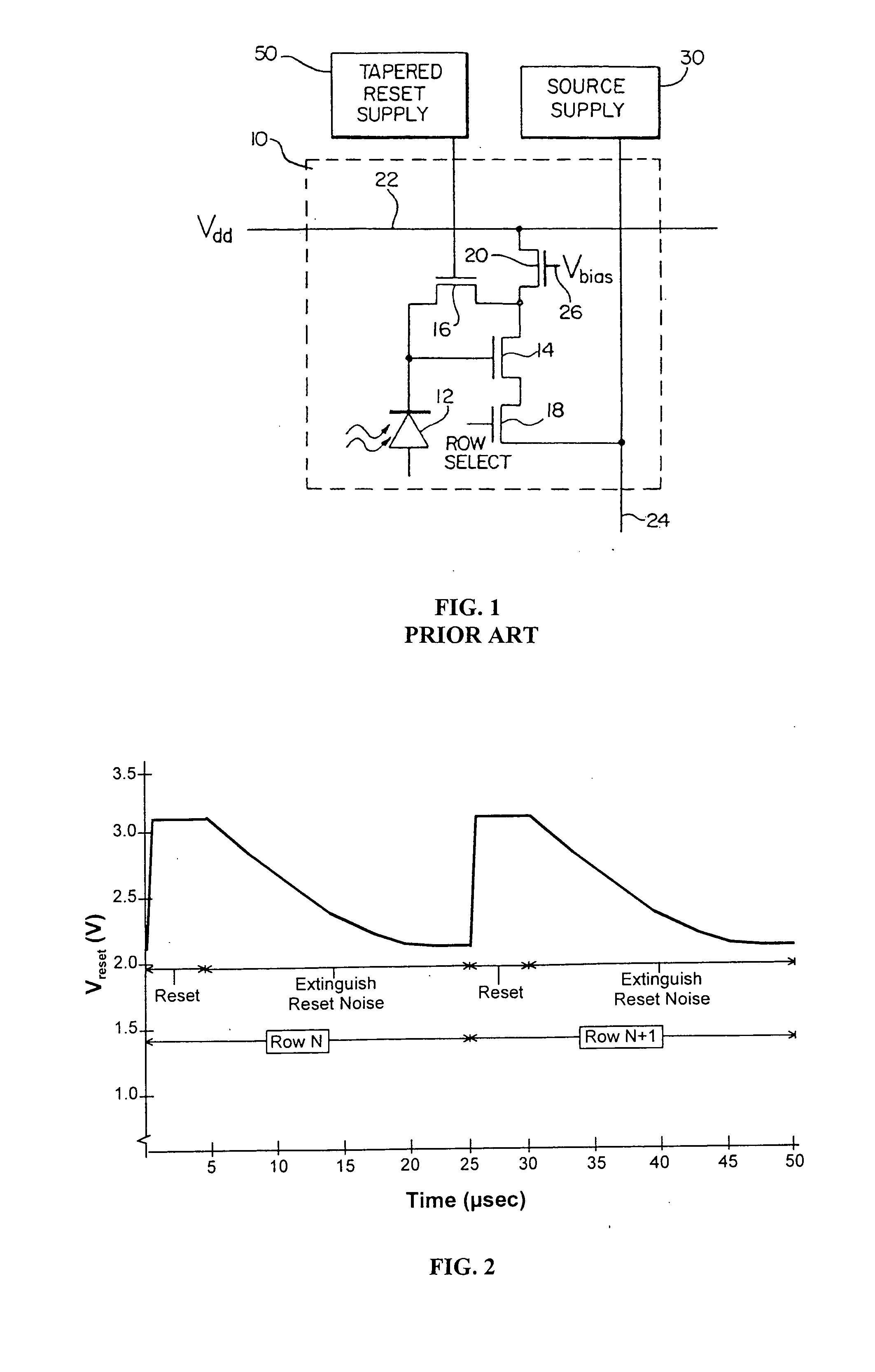
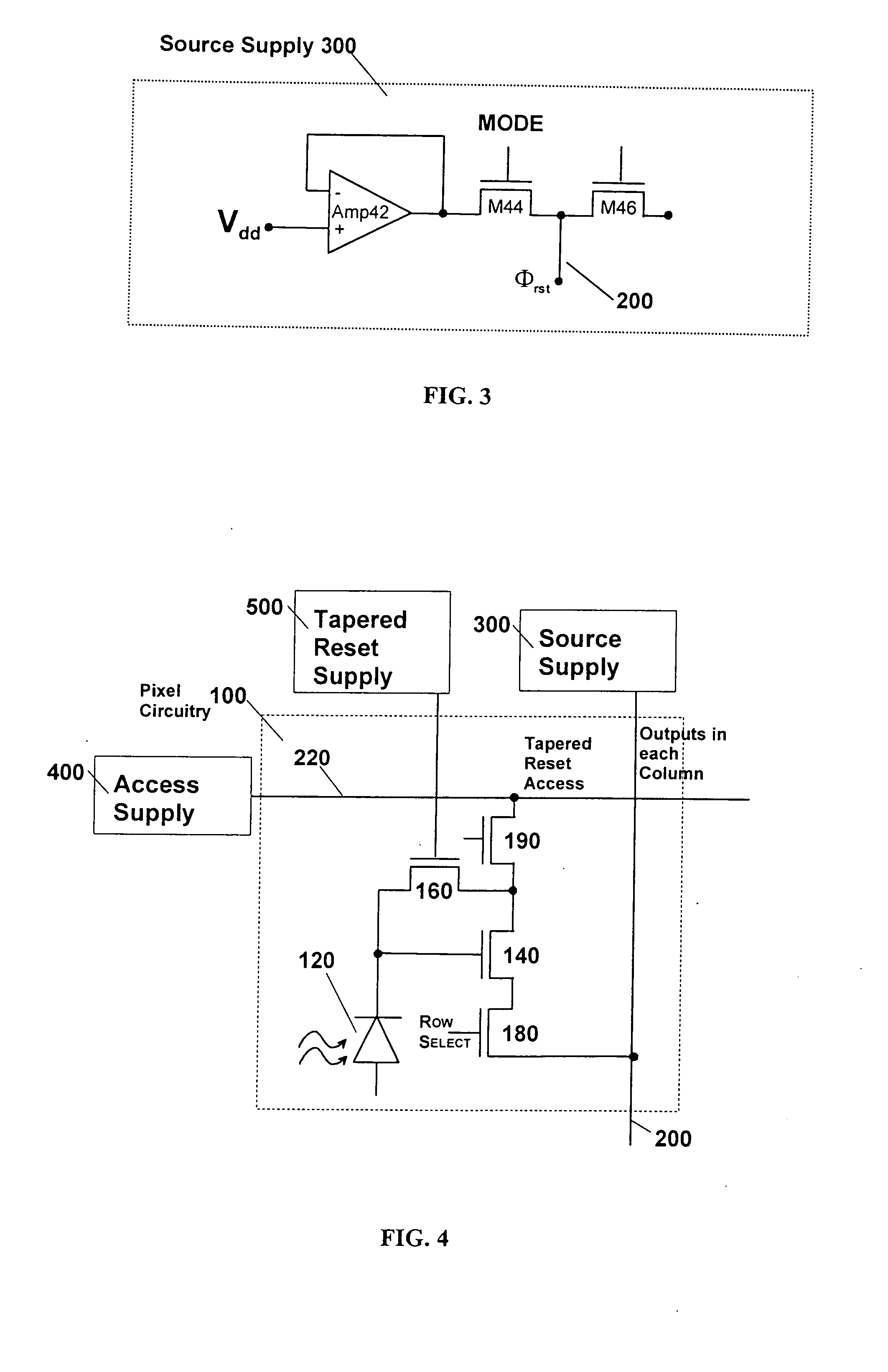
Low noise CMOS amplifier for imaging sensors
InactiveUS20050068438A1Increased amplifier gainImprove low noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMOSFETCMOS
A CMOS pixel amplifier circuit includes four transistors having the same polarity, and a photodetector. An access supply connects to the pixel circuit via a bus and is configured as a current source that acts as a distributed feedback amplifier, when it is connected to the pixel transistors. The access supply connects to an access MOSFET that isolates a common node from an output node. In this configuration, the feedback amplifier is a cascoded inverter, which provides gains 100-1000 times greater than prior circuits.
Owner:INNOVATIVE TECH LICENSING
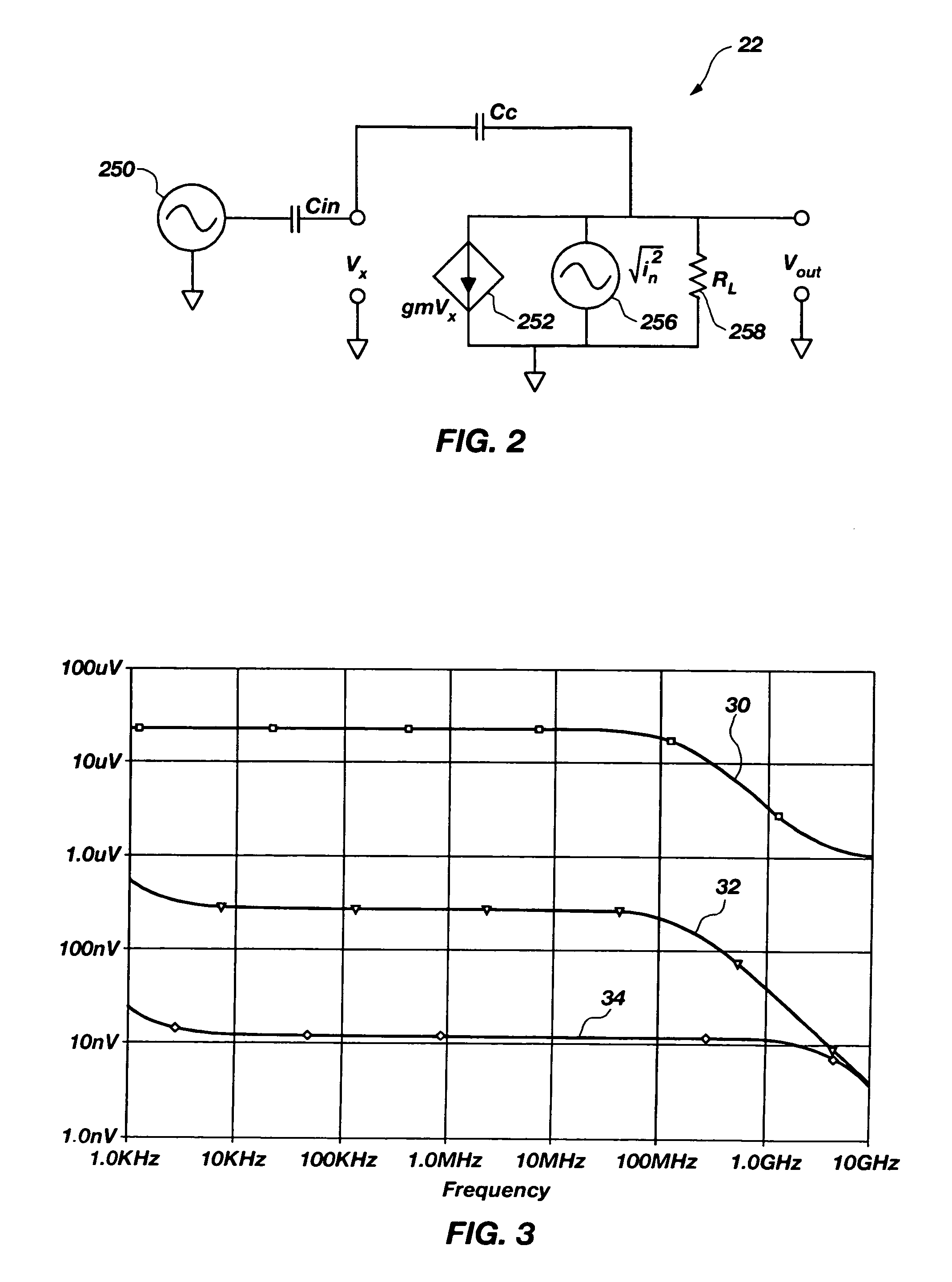
Technique to improve the gain and signal to noise ratio in CMOS switched capacitor amplifiers
InactiveUS7230479B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioEasy to switchAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyCapacitanceEngineering
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
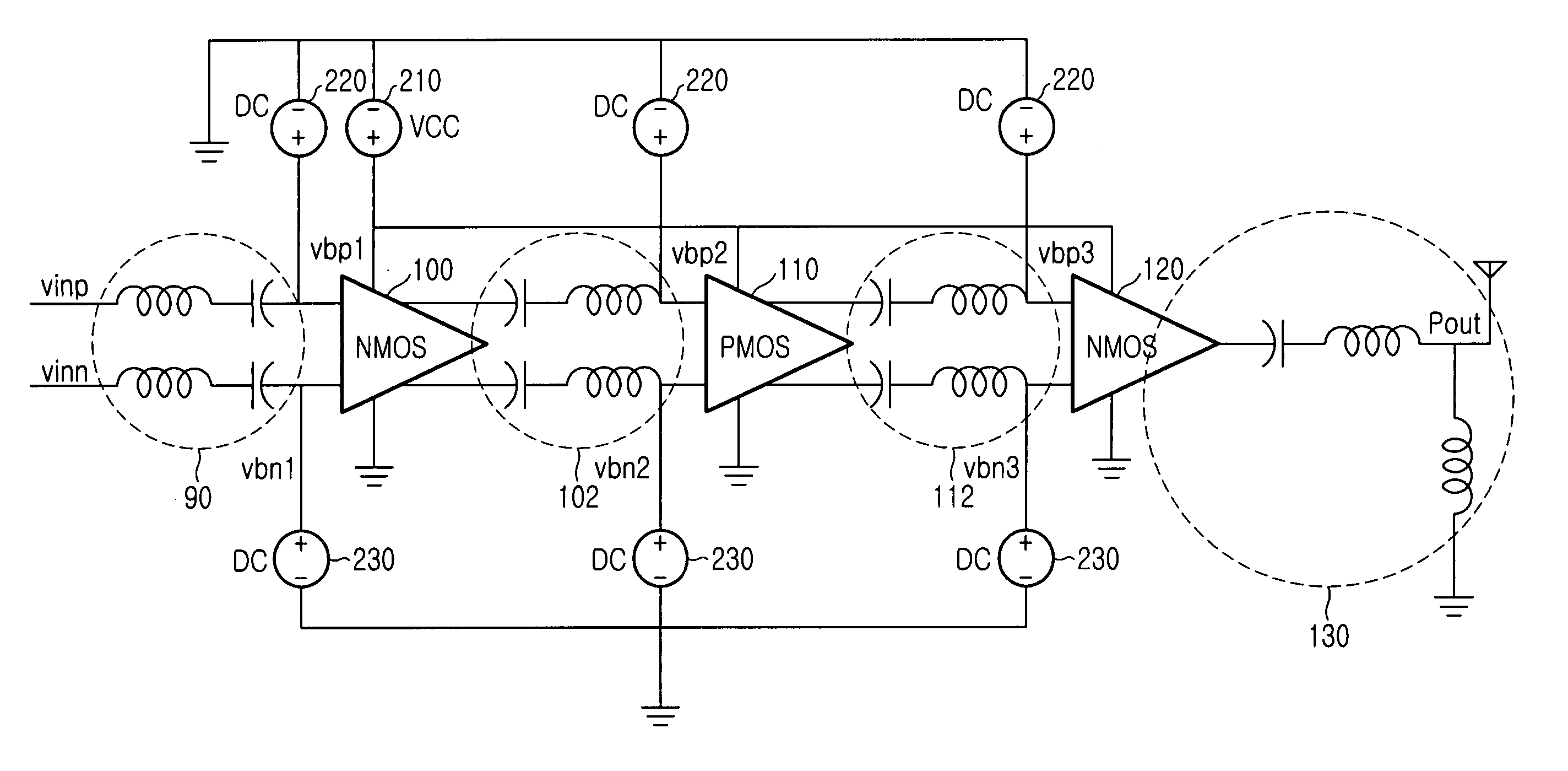
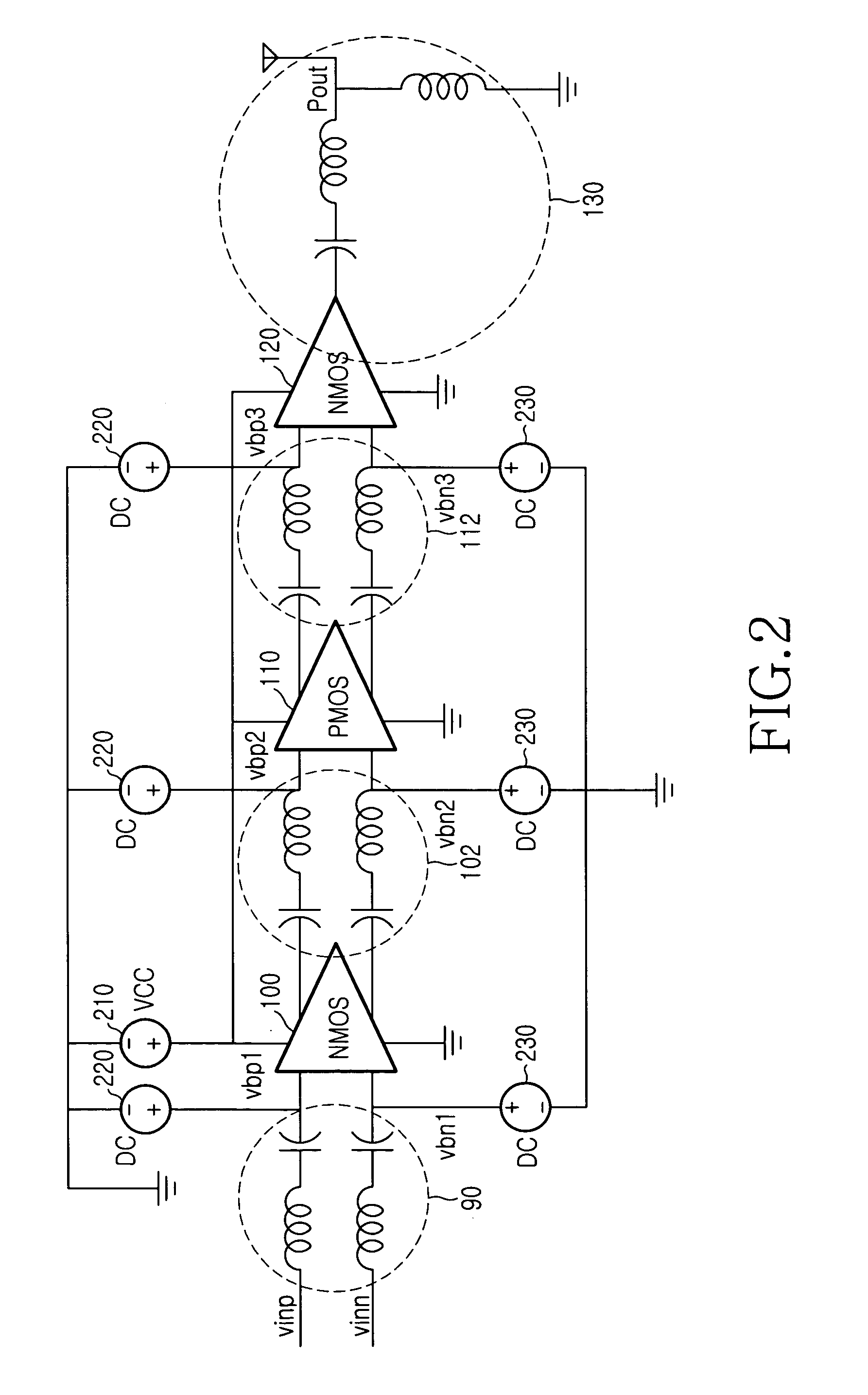
High frequency power amplifier
InactiveUS6940353B2Output maximizationPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersHigh frequency powerEngineering
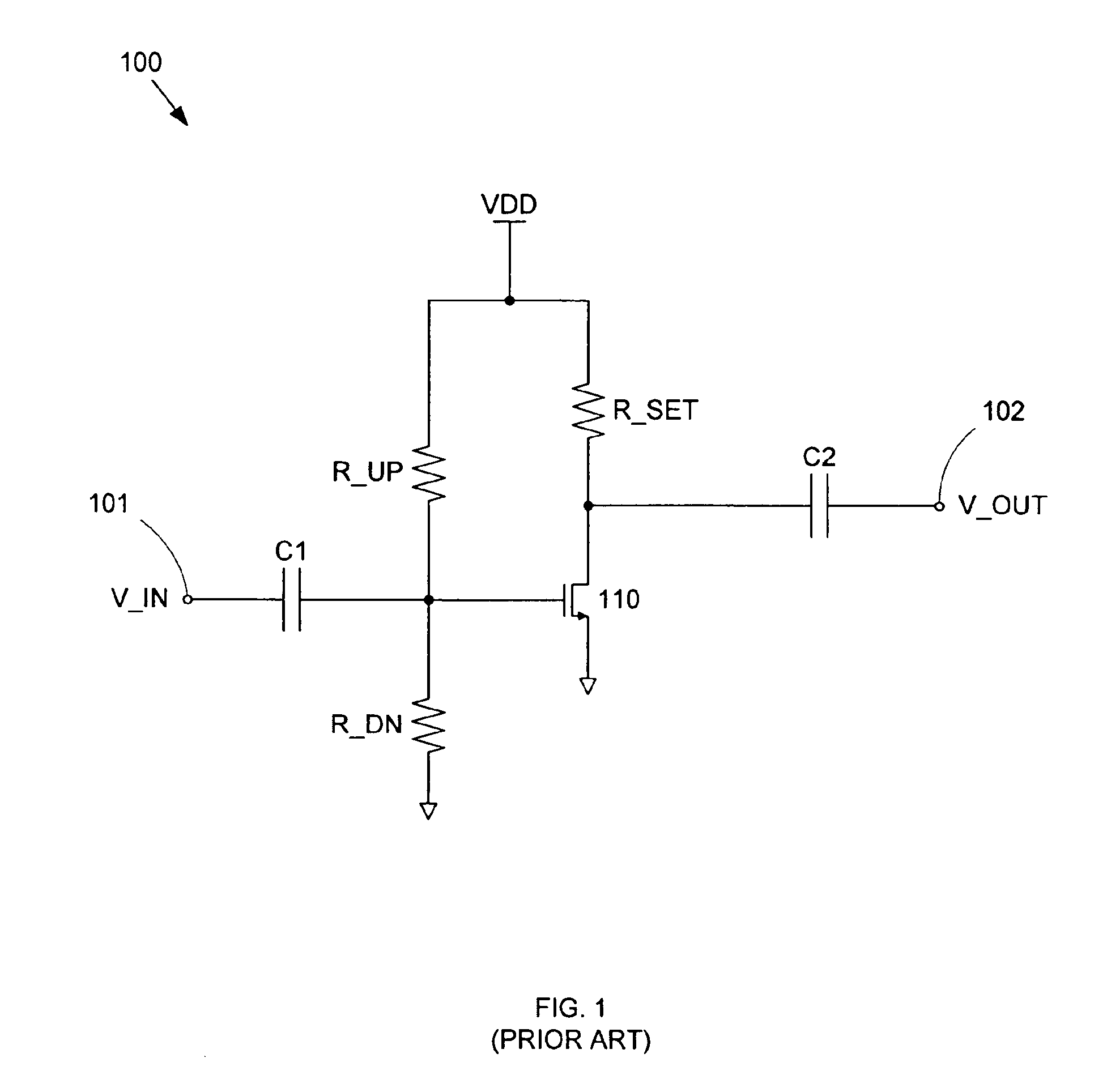
A CMOS amplifier includes a CMOS inverter and a bias circuit coupled in a feedback loop between the output and input of the inverter. The bias circuit provides linear biasing so that the inverter can apply a desired gain to a high frequency input signal. The bias circuit can include an operational amplifier (op-amp) providing positive feedback control between the output and input of the inverter. By providing a reference voltage to the other input of the op-amp, the input of the inverter is regulated such that its output is driven to the reference voltage. This in turn forces the inverter to operate in its linear region, so that the inverter applies non-distorting amplification to the input AC signal. The AC signal is prevented from affecting the operation of the bias circuit by resistors coupling the bias circuit to the op-amp.
Owner:MICREL
System and method for linearizing a CMOS differential pair
InactiveUS7696823B2Multiple-port networksSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLocal oscillator signalFilter tuning
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers provide image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. Active filters utilize multi track spiral inductors with shields to increase circuit Q. The filters incorporate a gain stage that provides improved dynamic range through the use of cross coupled auxiliary differential pair CMOS amplifiers to cancel distortion in a main linearized differential pair amplifier. Frequency planning provides additional image rejection. Local oscillator signal generation methods on chip reduce distortion. A PLL generates needed out of band LO signals. Direct synthesis generates in band LO signals. PLL VCOs are centered automatically. A differential crystal oscillator provides a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission throughout the receiver is used. ESD protection is provided by a pad ring and ESD clamping structure. Shunts utilize a gate boosting at each pin to discharge ESD build up. An IF VGA utilizes distortion cancellation achieved with cross coupled differential pair amplifiers having their Vds dynamically modified in conjunction with current steering of the differential pairs sources.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Amplifying device
InactiveUS20100295614A1Low costShorten the timeGain controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierInput impedance
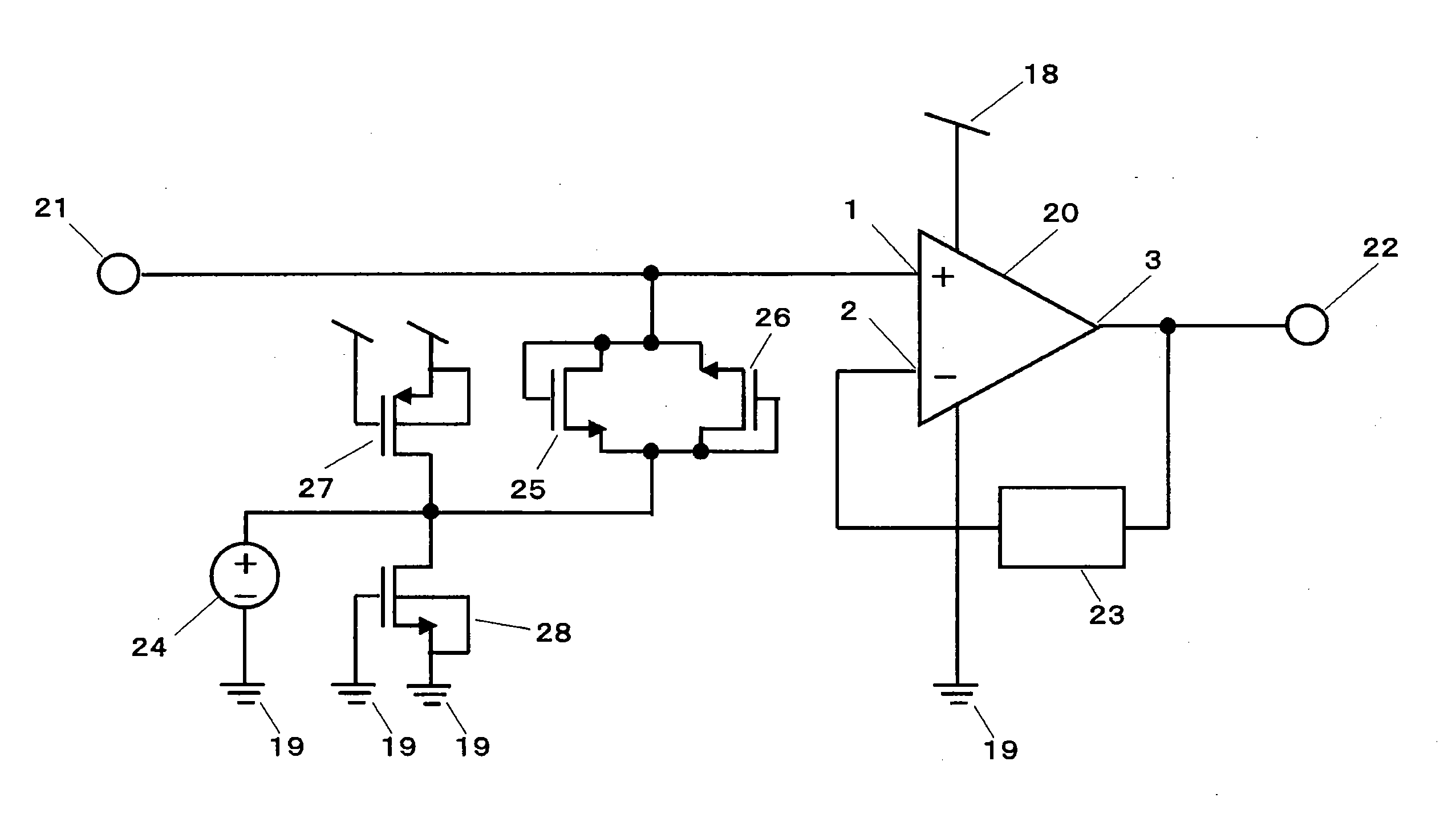
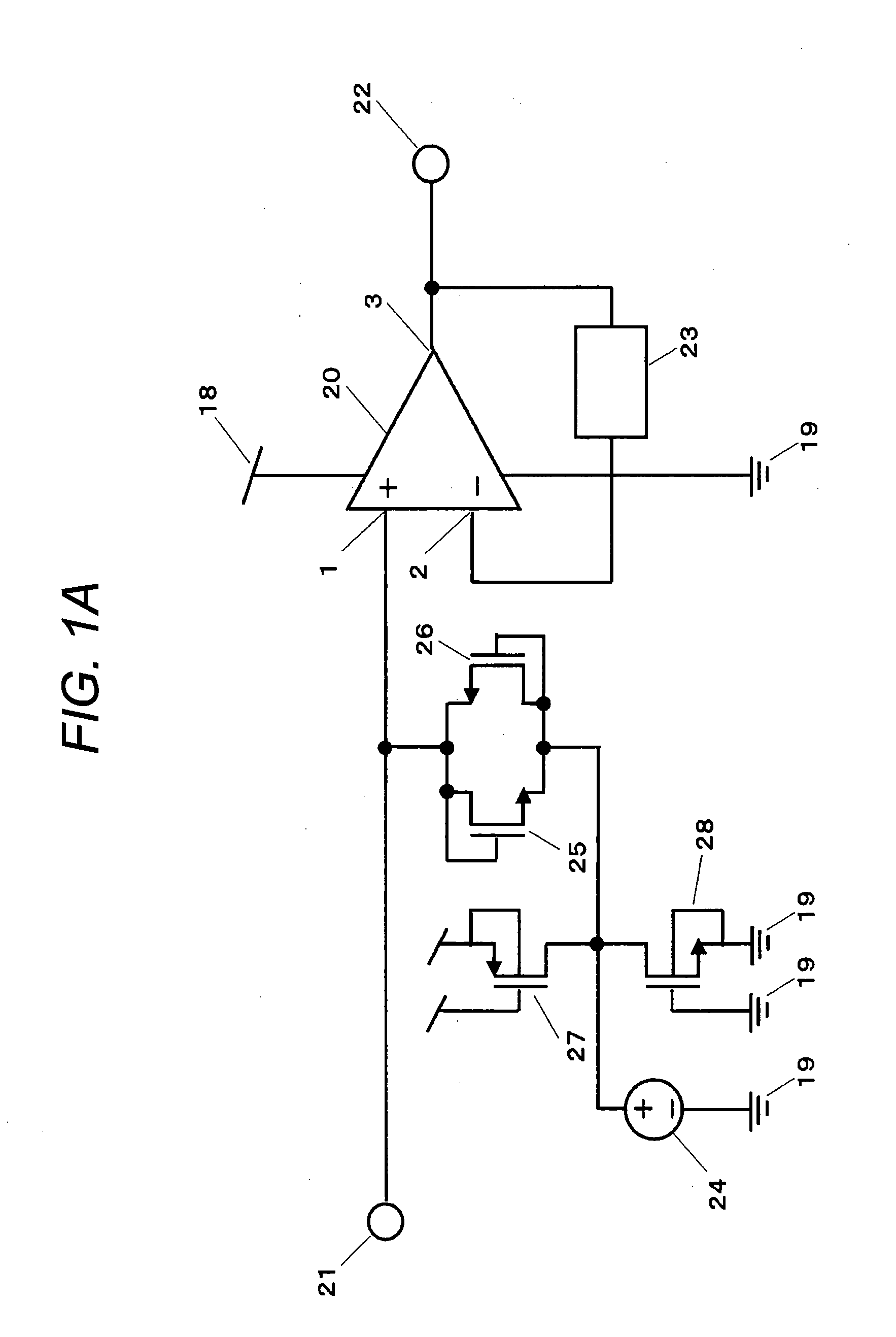
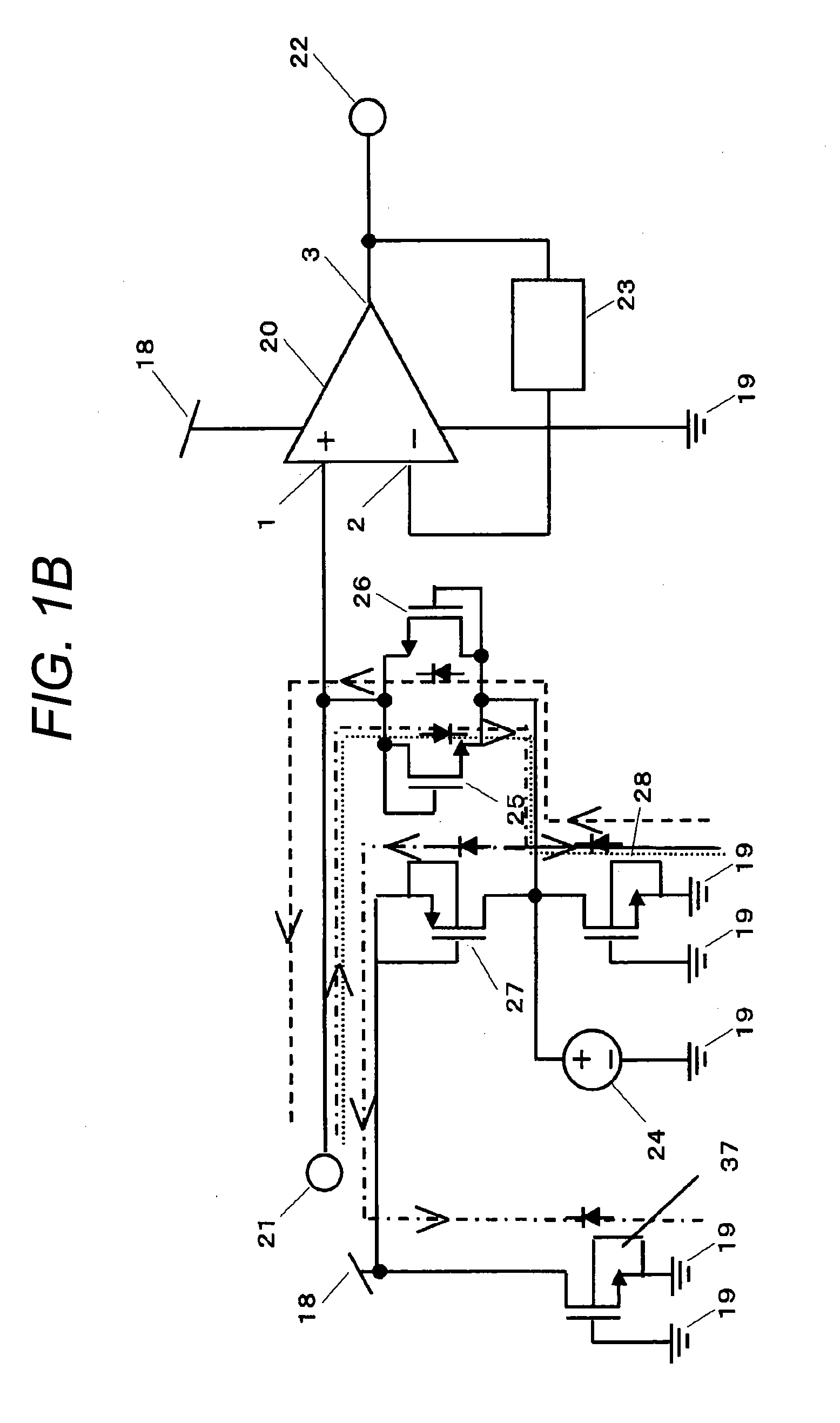
An amplifying device for setting input impedance at several GΩ to several tens of GΩ and improving an ESD withstand current rating is provided.An ECM is connected to an input terminal 21 and frequency characteristics become flat to a voice band by high input impedance of a CMOS amplifier 20 and the input impedance is set at several GΩ to several tens of GΩ and thereby, response time after detecting a loud voice or turning on a power source of the ECM is speeded up and desired electrical characteristics are achieved. A path for releasing a surge voltage which occurs during assembly in the outside of an IC and intrudes from the input terminal 21 to a power source terminal or an earth terminal without an influence on a signal (20 Hz to 20 kHz) of a voice band entering from the input terminal 21 can be constructed by connecting a P-channel MOS transistor 27 and an N-channel MOS transistor 28 as an ESD protective element.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Class ab CMOS amplifiers
ActiveUS20060109056A1Reduce variationDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCMOSLevel shifting
A class AB output stage of a CMOS amplifier has a level-shifting voltage follower constituted by a level-shifting transistor and a current source. A bias circuit replicates the level-shifting voltage follower in a feedback arrangement to produce a variable bias voltage for the current source of both the main and replica level-shifters. The arrangement serves to control the output voltage of the level-shifter such that it provides the amplifier with a relatively constant quiescent current of the output stage over variations of manufacturing process, supply voltage, and temperature. The level shifting function can be facilitated by a resistive on-state of a power-down transistor between the level-shifting and load transistors.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC +1
Logarithmic linear variable gain CMOS amplifier
ActiveUS7737759B2Multiple input and output pulse circuitsVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesEngineeringCmos amplifier
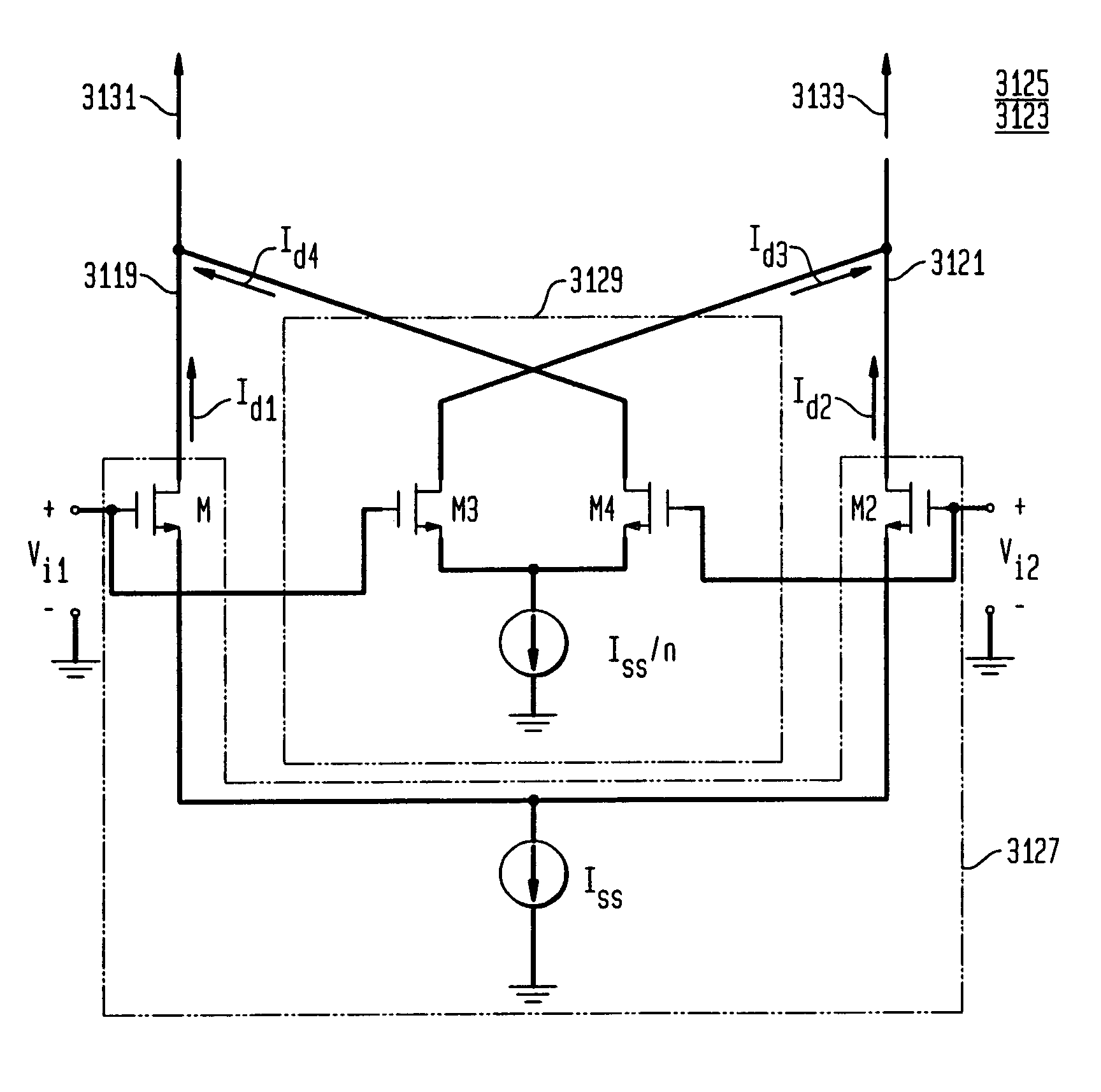
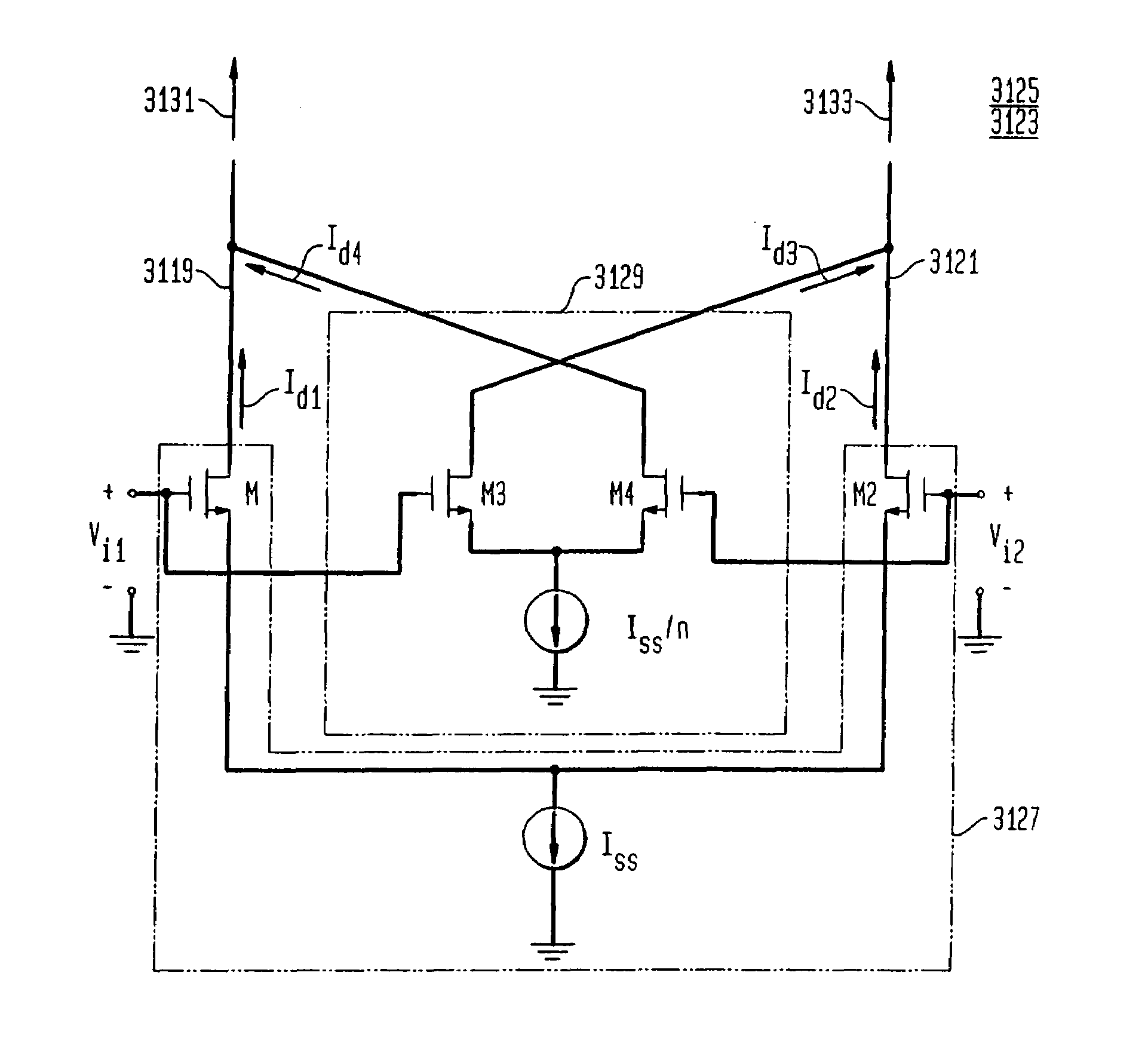
A logarithmic linear variable gain CMOS amplifier includes first and second differential pairs of transistors forming a differential input, with each differential pair of transistors including a common source node. A pair of diode-connected load transistors is connected to the first and second differential pairs of transistors, and a third differential pair of transistors is connected to the pair of diode-connected load transistors. The third differential pair of transistors include respective gates connected together and in parallel to gates of the first and second differential pairs of transistors. First and second current mirrors are respectively connected to the common source nodes of the first and second differential pairs of transistors for programmably injecting respective bias currents thereto, with a sum of the respective bias currents remaining constant.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
CMOS amplifier with integrated tunable band-pass function
InactiveCN102119486AMultiple-port active networksLow frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierCmos amplifier
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
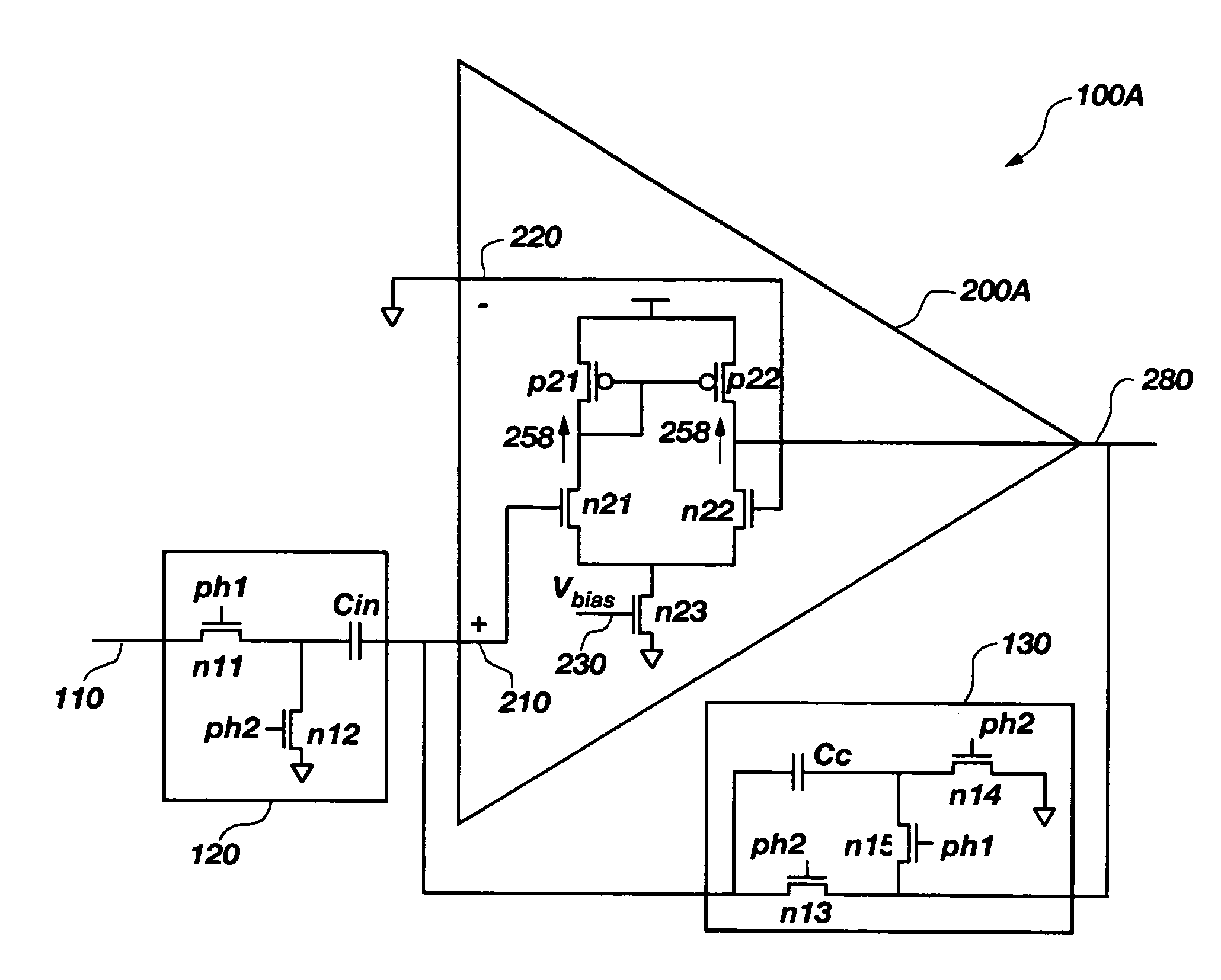
Apparatus and method for reducing flicker noise of CMOS amplifier
ActiveUS20070159253A1Reduce low frequency flicker noiseReduce flicker noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersLoad circuitMOSFET
An apparatus and method of reducing a flicker noise of a CMOS amplifier is provided. In the CMOS amplifier, a load circuit is connected to a signal input circuit which includes two pairs of MOSFETs which simultaneously receive differential signals. In this instance, a first MOSFET included in a switch-bias circuit is connected to one pair of MOSFETs which receive the differential signals and functions as a current source in the case of activation of a clock signal Ø1. A second MOSFET included in the switch-bias circuit is connected to another pair of MOSFETs which receive the differential signals and functions as a current source in the case of activation of a clock signal Ø2.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
CMOS low-temperature small-noise operation amplifying circuit
InactiveCN104765399AHigh voltage rejection ratioReduce noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesLow noiseCapacitance
The invention discloses a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) low-temperature low-noise operational amplifier circuit. A biasing circuit part adopts a multi-stage current mirror sleeving mode, and reference current is generated by an active resistor of an MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube comprising two connected diodes, so that the reference current of an amplifier has better temperature characteristics; an amplification part is of a differential input folded cascode structure, the open loop gain of the amplifier can be greater than 80dB by virtue of one-stage amplification, and the defect that oscillation is easily caused by a Miller compensation capacitor used by the conventional two-stage amplification at the low temperature of 77K is overcome; a large tube of which the width to length ratio is greater than 100 is adopted for differential input, the noise performance of a CMOS amplifier is improved favorably, and a differential operational amplifier can normally work at the normal temperature and the low temperature of 77K, can be used as a standard amplifier module designed for a low-temperature CMOS circuit, can be applied to a photovoltaic infrared detector circuit, and can also be applied to a long-wave infrared optical guide detector circuit.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and method for reducing flicker noise of CMOS amplifier
ActiveUS7453317B2Reduce flicker noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersMOSFETLoad circuit
An apparatus and method of reducing a flicker noise of a CMOS amplifier is provided. In the CMOS amplifier, a load circuit is connected to a signal input circuit which includes two pairs of MOSFETs which simultaneously receive differential signals. In this instance, a first MOSFET included in a switch-bias circuit is connected to one pair of MOSFETs which receive the differential signals and functions as a current source in the case of activation of a clock signal Ø1. A second MOSFET included in the switch-bias circuit is connected to another pair of MOSFETs which receive the differential signals and functions as a current source in the case of activation of a clock signal Ø2.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Differential line driver
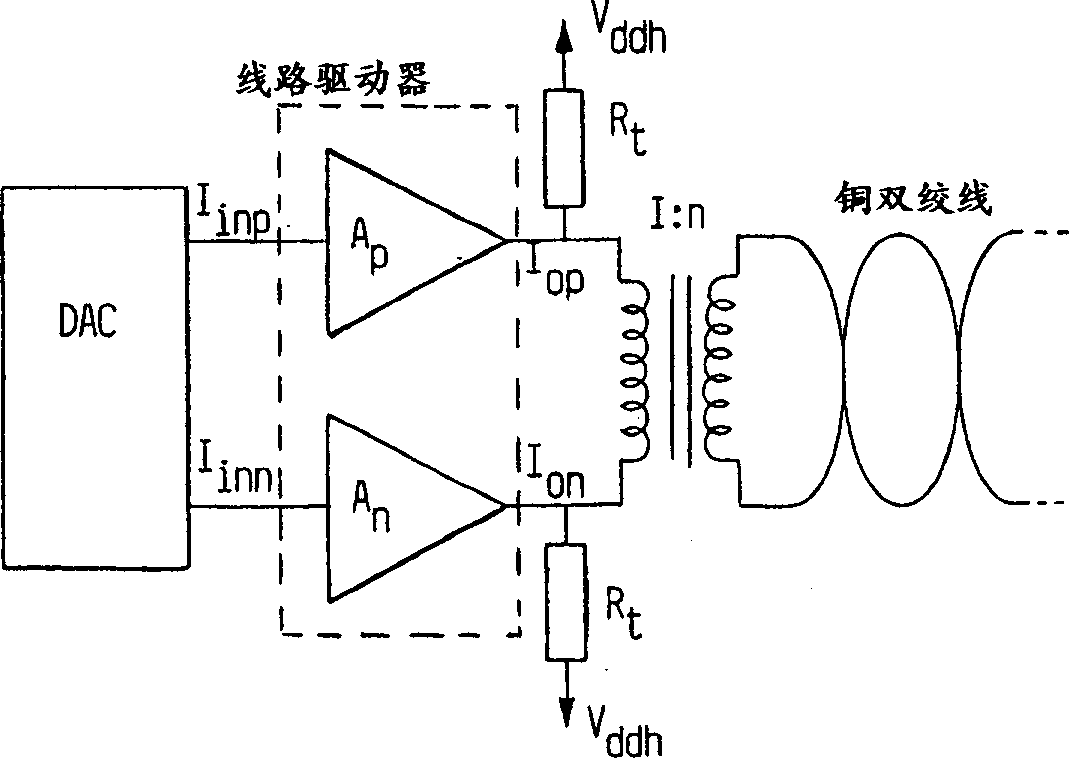
InactiveCN1304585ALower input impedanceIncrease output impedanceAnalogue/digital conversionSolid-state devicesModem deviceInstability
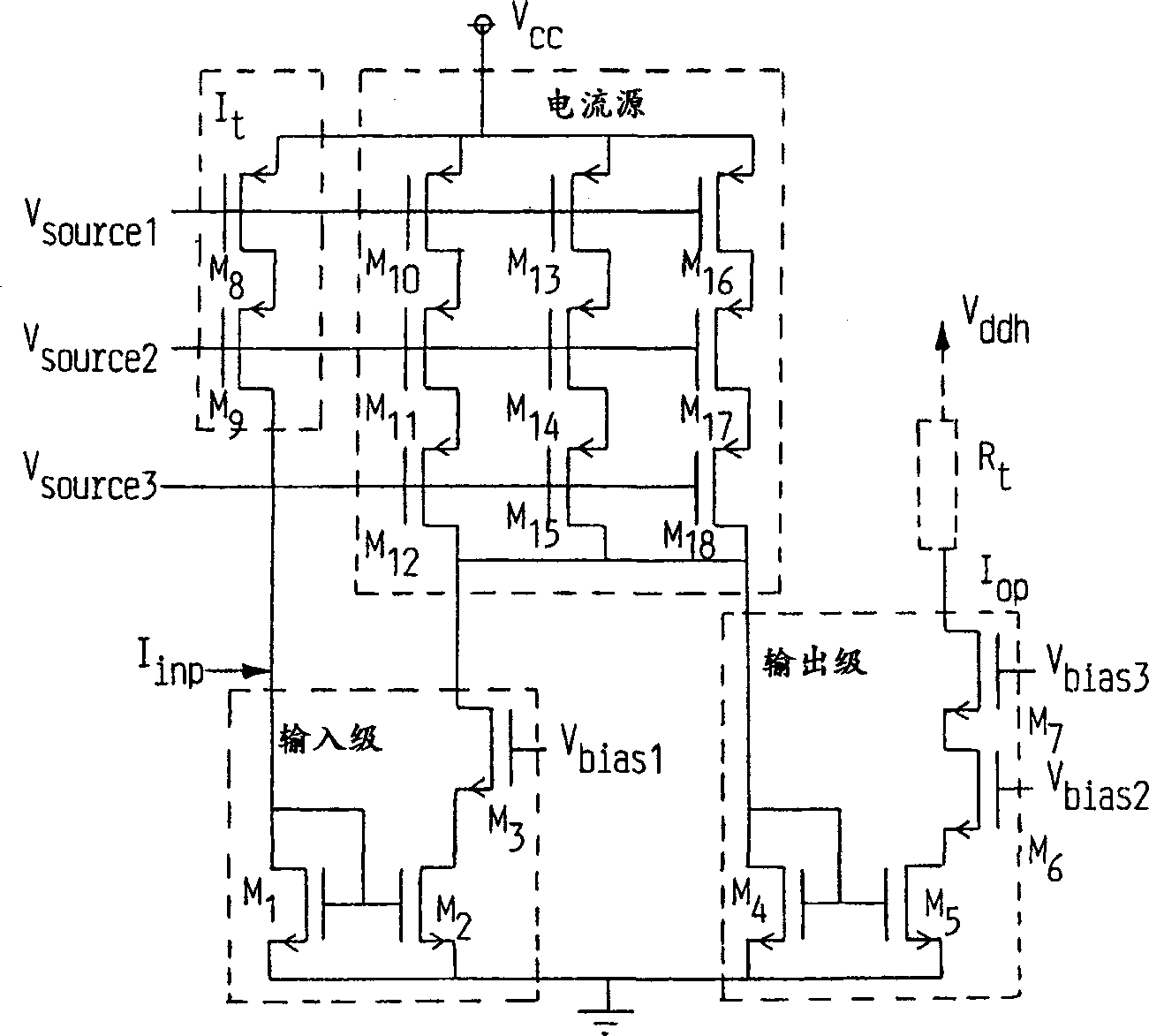
A fully differential line driver, especially for twisted copper pairs. It comprises two current amplifiers (Ap, An), made in standard CMOS technique, each having an input (Iinp, Iinn) and an output (Iop, Ion), which latter are connected via terminal resistors (Rt) to a voltage source, which may be set to a larger voltage than that used for driving the CMOS amplifiers. With this invention, a low output impedance can be combined with a large swing. Further, feedback is not necessary, avoiding problems like potential instability. A preferred embodiment also has a very low-impedance input, making it appropriate for connecting to a DAC, thus reducing distortion of its output signal. The invention is suitable for very-high-speed-digital-subscriber-line modems.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Apparatus for a differential self-biasing CMOS amplifier
InactiveUS7227411B2Differential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCmos amplifierDifferential amplifier
Aspects of the invention provide a self-biasing differential amplifier. The self-biasing differential amplifier may include a first input stage and a biasing transistor pair coupled to the first input stage. A second input stage may be coupled to the first input stage and the biasing transistor pair. The first input stage of the self-biasing differential amplifier may include a first PMOS transistor coupled to a first NMOS transistor in an inverter arrangement. The second input stage may include a second PMOS transistor coupled to a second NMOS transistor. The biasing transistor pair may include a third PMOS transistor coupled to a third NMOS transistor.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
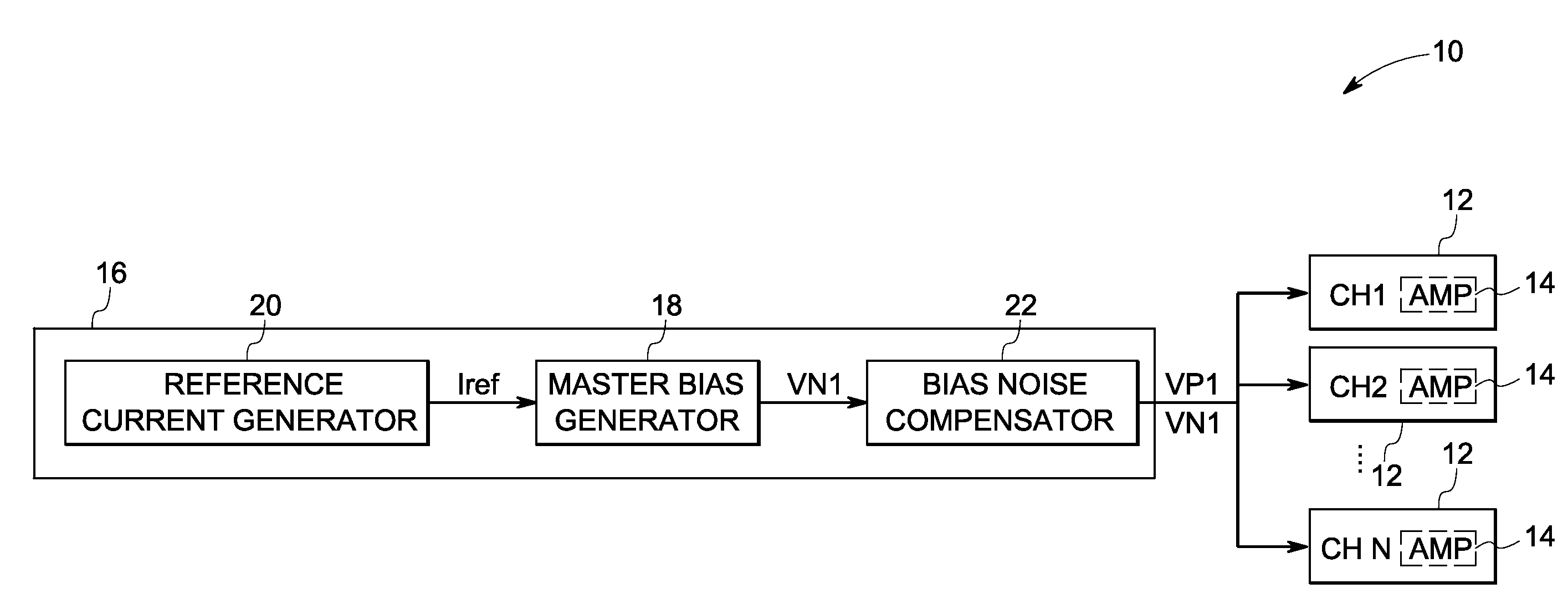
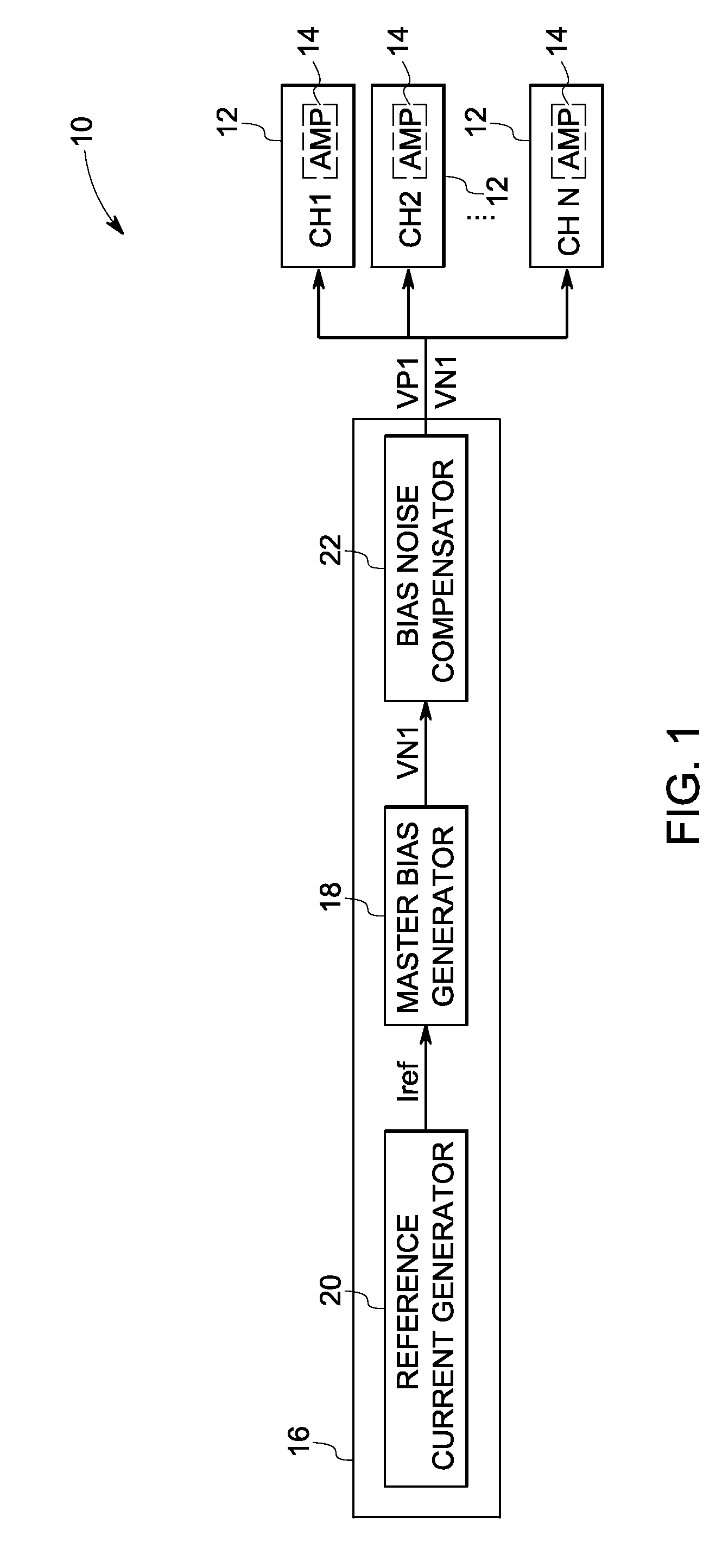
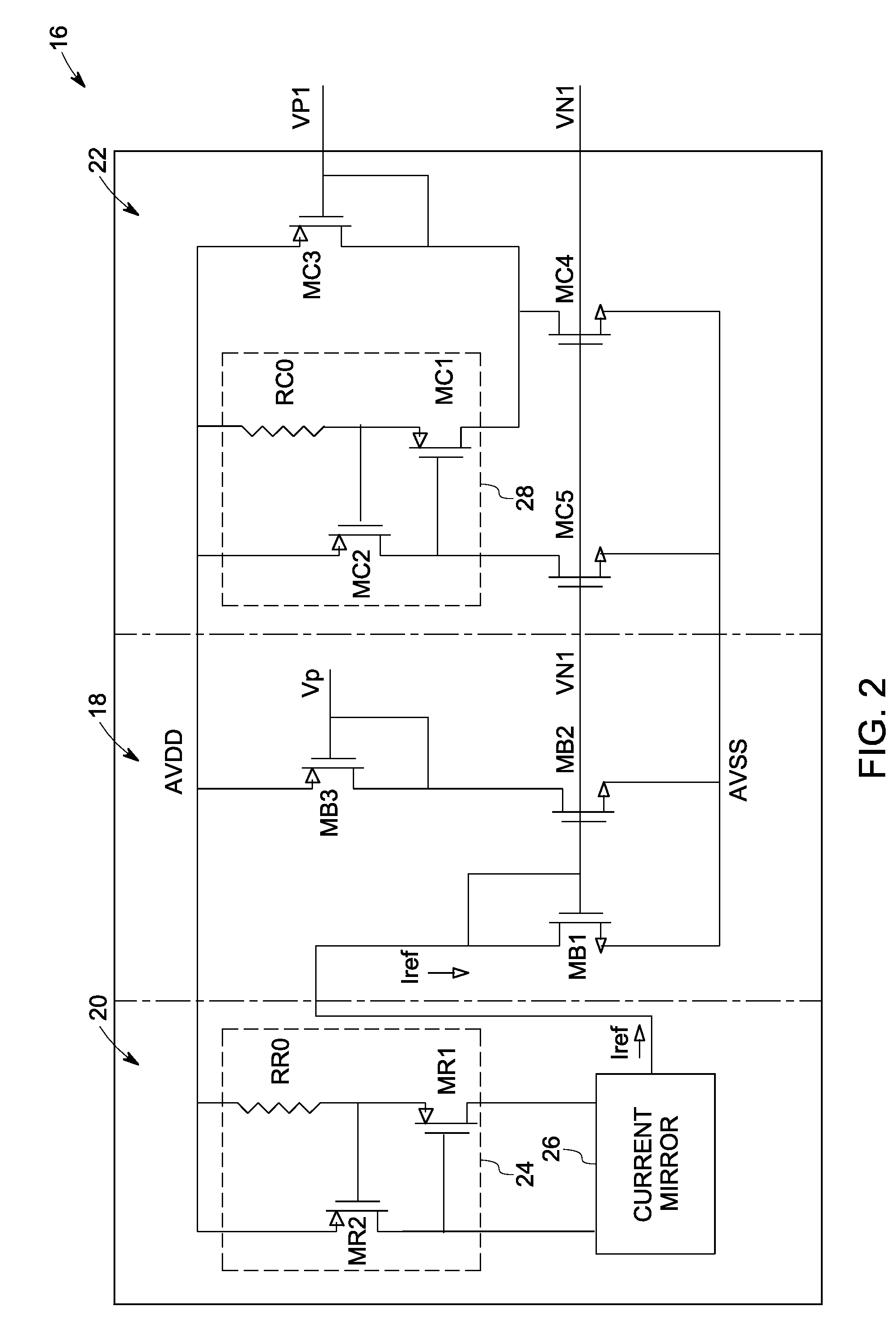
System and method for reducing flicker noise from CMOS amplifiers
InactiveUS20100013560A1Reduce correlated low frequency noiseReduce low frequency noiseAmplifier detailsAmplifiers with semiconductor devices onlyCMOSAudio power amplifier
A technique is provided for acquiring data with reduced correlated low frequency noise interference via a data acquisition circuit. The data acquisition circuit includes a plurality of data channels comprising a plurality of amplifiers and a biasing circuit for providing bias voltages to the plurality of amplifiers. The biasing circuit is configured to generate the bias voltages and establish a relationship between the bias voltages so as to reduce correlated low frequency noise in the plurality of amplifiers.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Technique to improve the gain and signal to noise ratio in CMOS switched capacitor amplifiers
InactiveUS20070030059A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEasy to switchAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyCapacitanceDevice material
The present invention comprises switched capacitor amplifiers including positive feedback, semiconductor devices, wafers and systems incorporating same and methods for amplifying signals using positive feedback, while maintaining a stable gain and producing an improved signal-to-noise ratio. One embodiment includes a switched capacitor amplifier comprising a Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) amplifier, a feed-in switched capacitor, and a feedback switched capacitor. The feed-in switched capacitor operably couples an input signal to the non-inverting input of the CMOS amplifier. Similarly, the feedback switched capacitor operably couples the amplifier output to the non-inverting input to create a positive feedback loop. A capacitance of the feedback switched capacitor relative to a capacitance of the feed-in switched capacitor comprises a feedback proportion. This feedback proportion may be configured to maintain a stable gain of the switched capacitor amplifier and increase a signal-to-noise ratio of the switched capacitor amplifier, even with the switched capacitor amplifier configured in a positive feedback arrangement.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Power amplifier for a transmitter
InactiveUS20060066411A1Improve linearityReduce distortion problemsPower amplifiersAmplifier combinationsCMOSAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier for a transmitter includes a plurality of CMOS amplifiers of different types which are serially and alternately connected, and matching circuits for matching impedance discrepancies between the CMOS amplifiers of different types.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High frequency power amplifier
ActiveUS20050083127A1Output range can be maximizedOutput maximizationPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersCMOSHigh frequency power
A CMOS amplifier includes a CMOS inverter and a bias circuit coupled in a feedback loop between the output and input of the inverter. The bias circuit provides linear biasing so that the inverter can apply a desired gain to a high frequency input signal. The bias circuit can include an operational amplifier (op-amp) providing positive feedback control between the output and input of the inverter. By providing a reference voltage to the other input of the op-amp, the input of the inverter is regulated such that its output is driven to the reference voltage. This in turn forces the inverter to operate in its linear region, so that the inverter applies non-distorting amplification to the input AC signal. The AC signal is prevented from affecting the operation of the bias circuit by resistors coupling the bias circuit to the op-amp.
Owner:MICREL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com