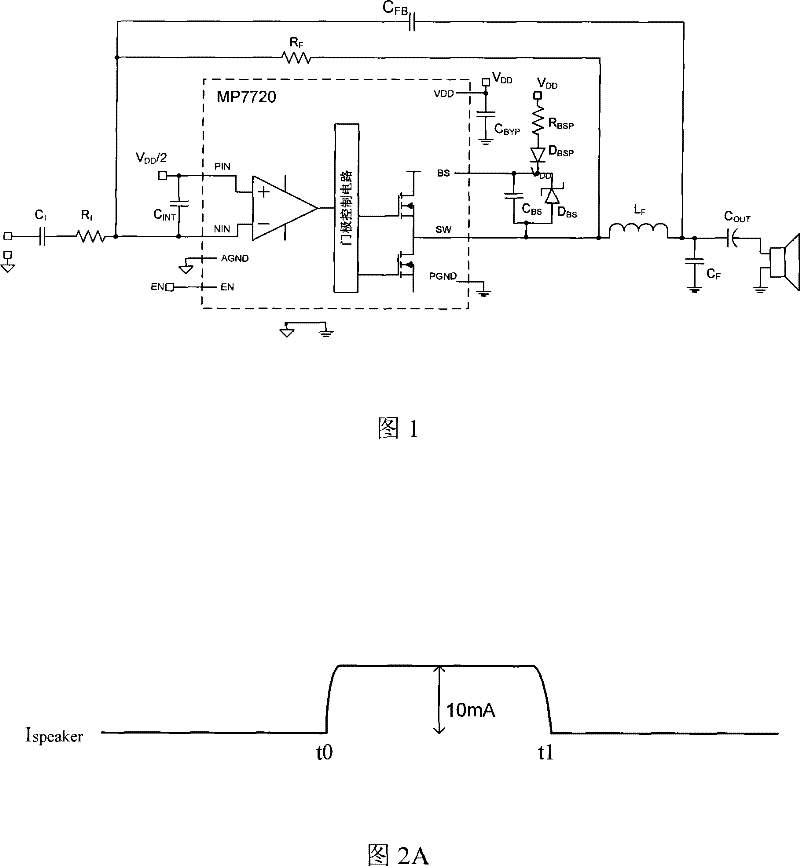
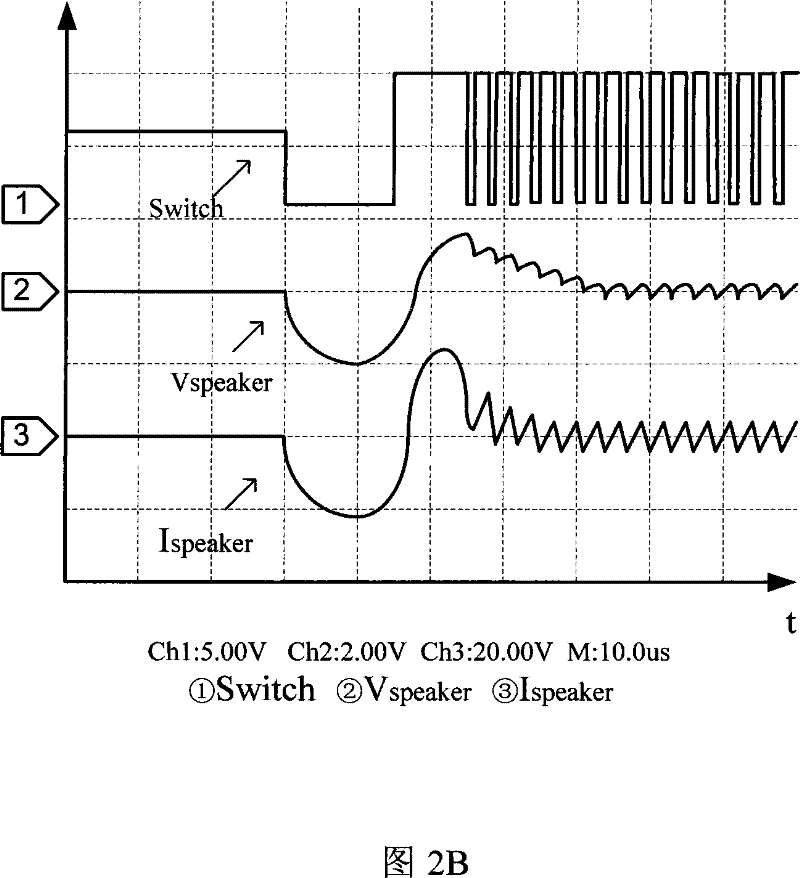
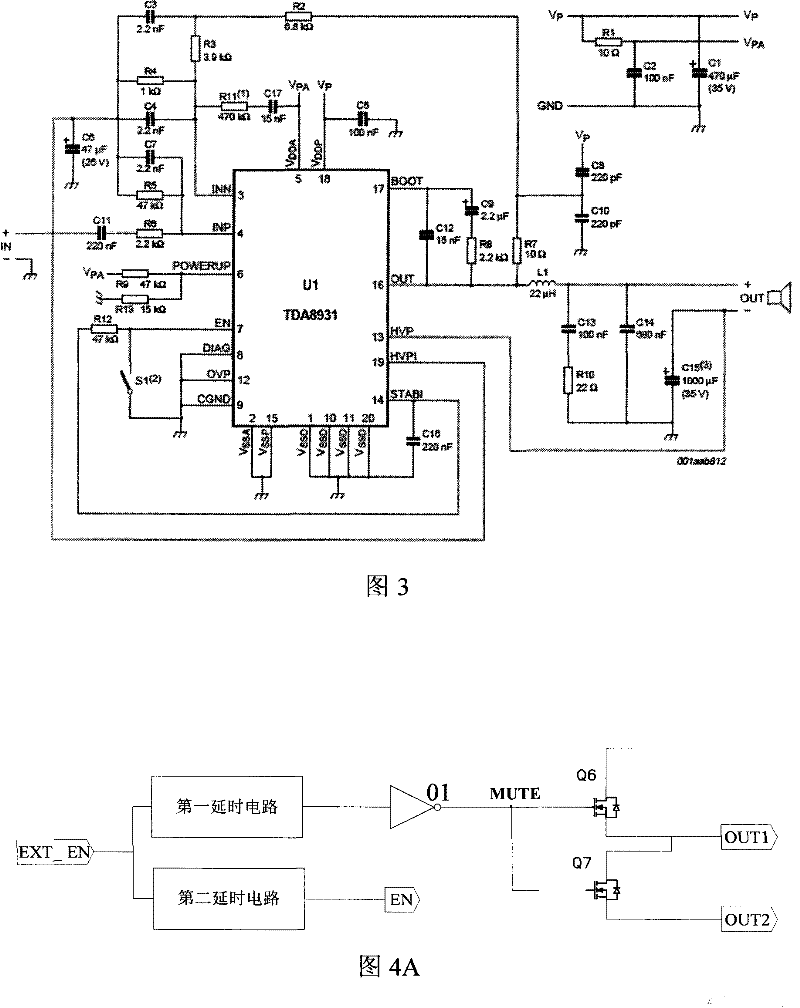
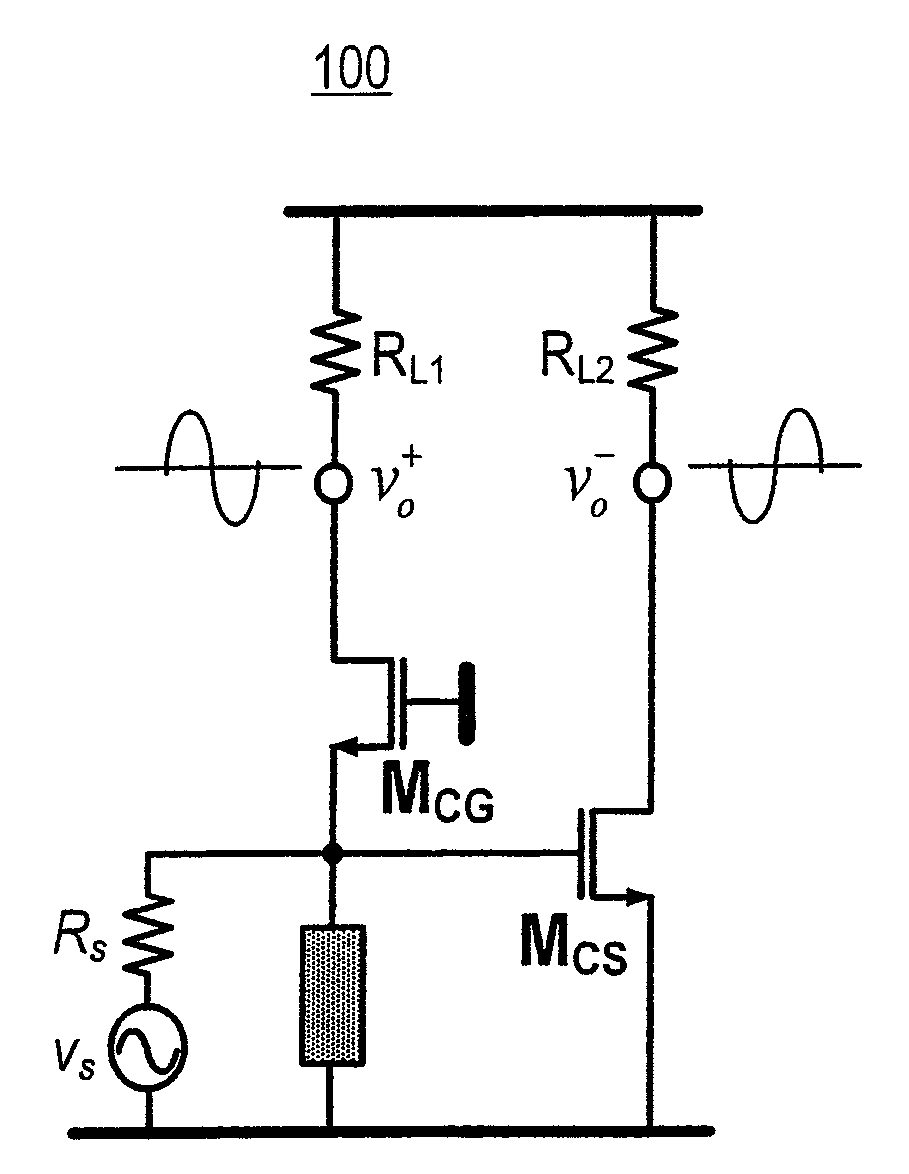
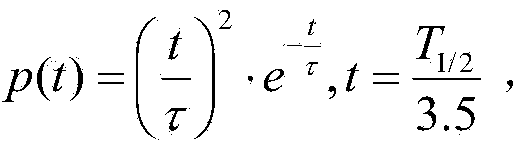Patents
Literature
36 results about "Amplifier noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
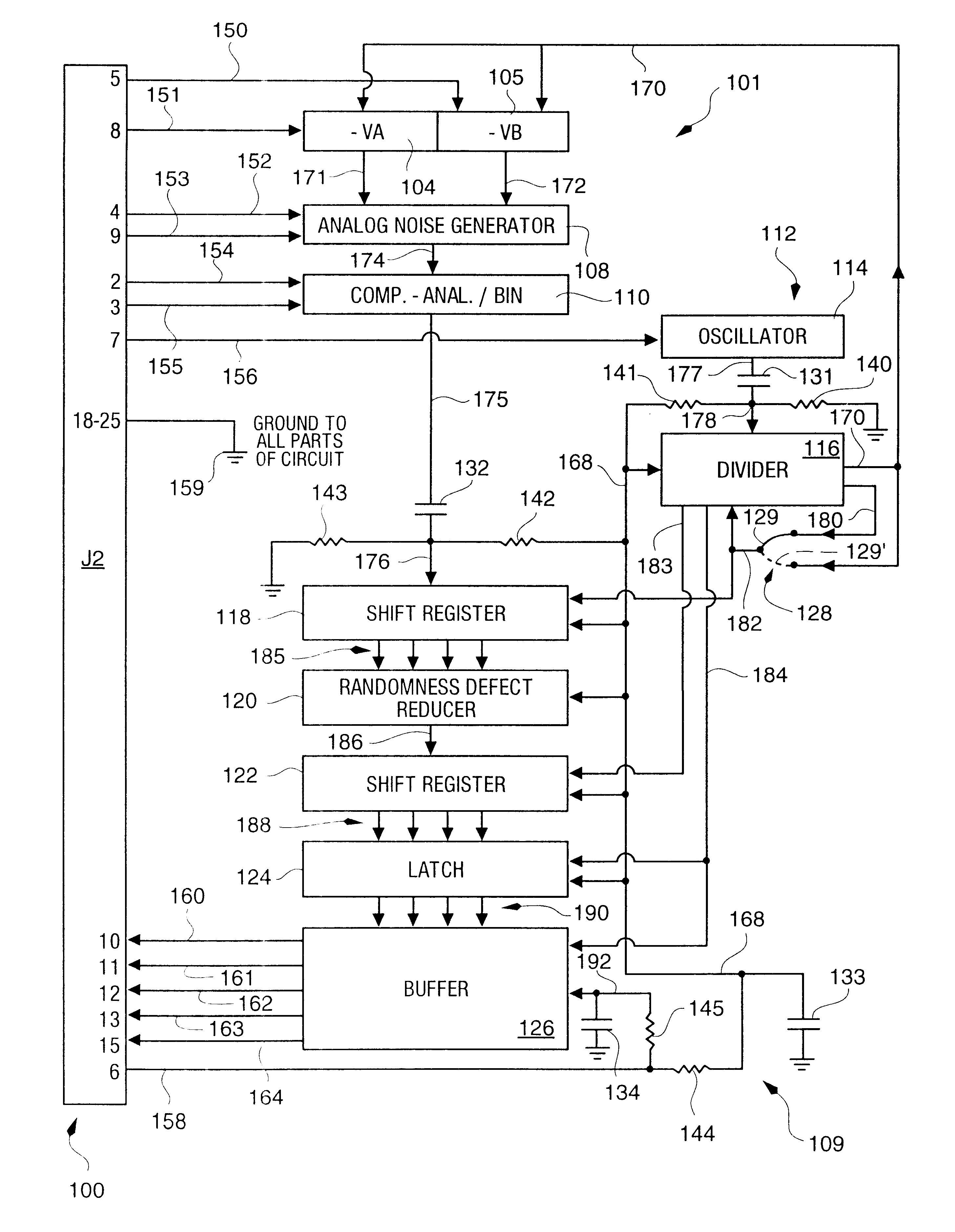
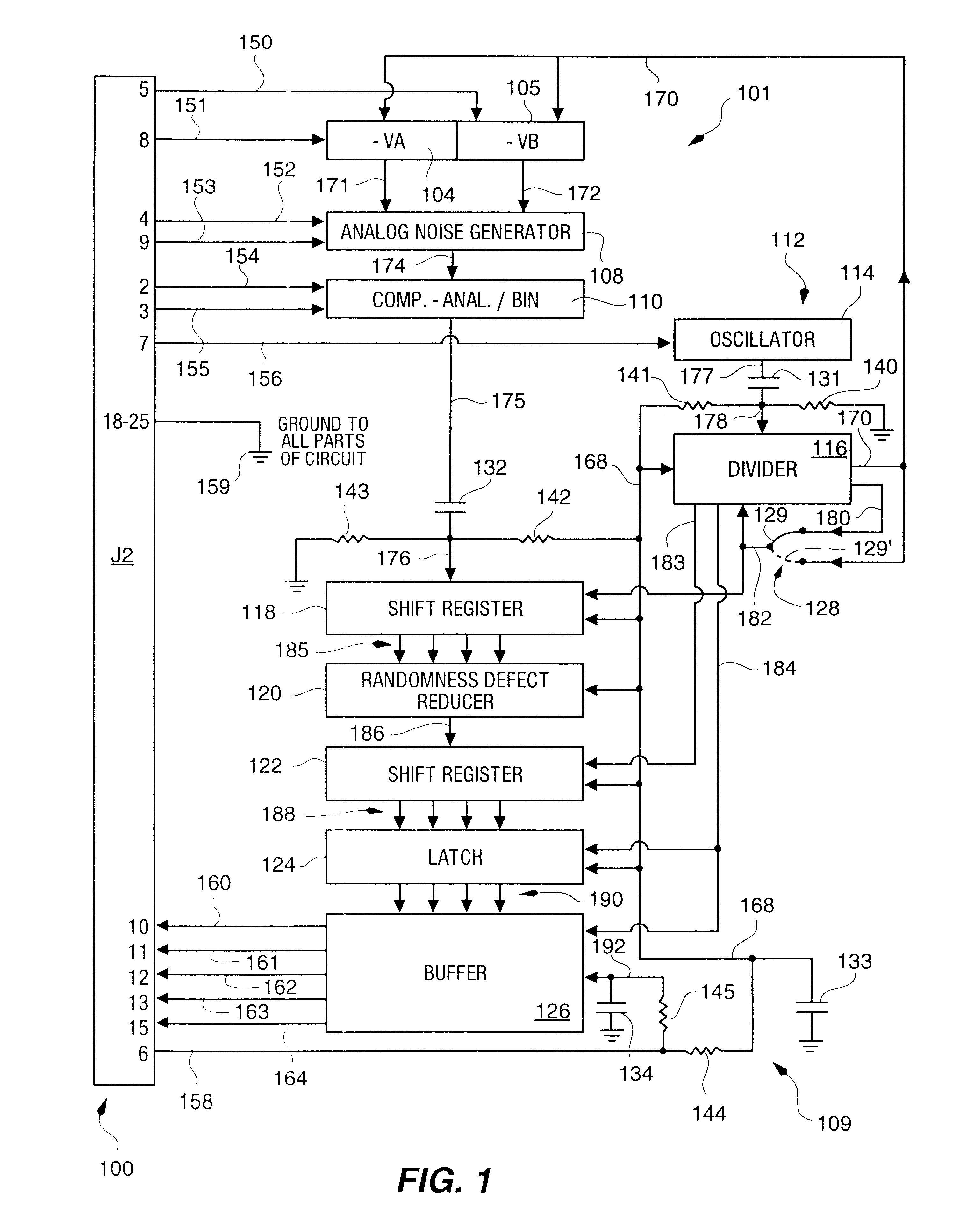
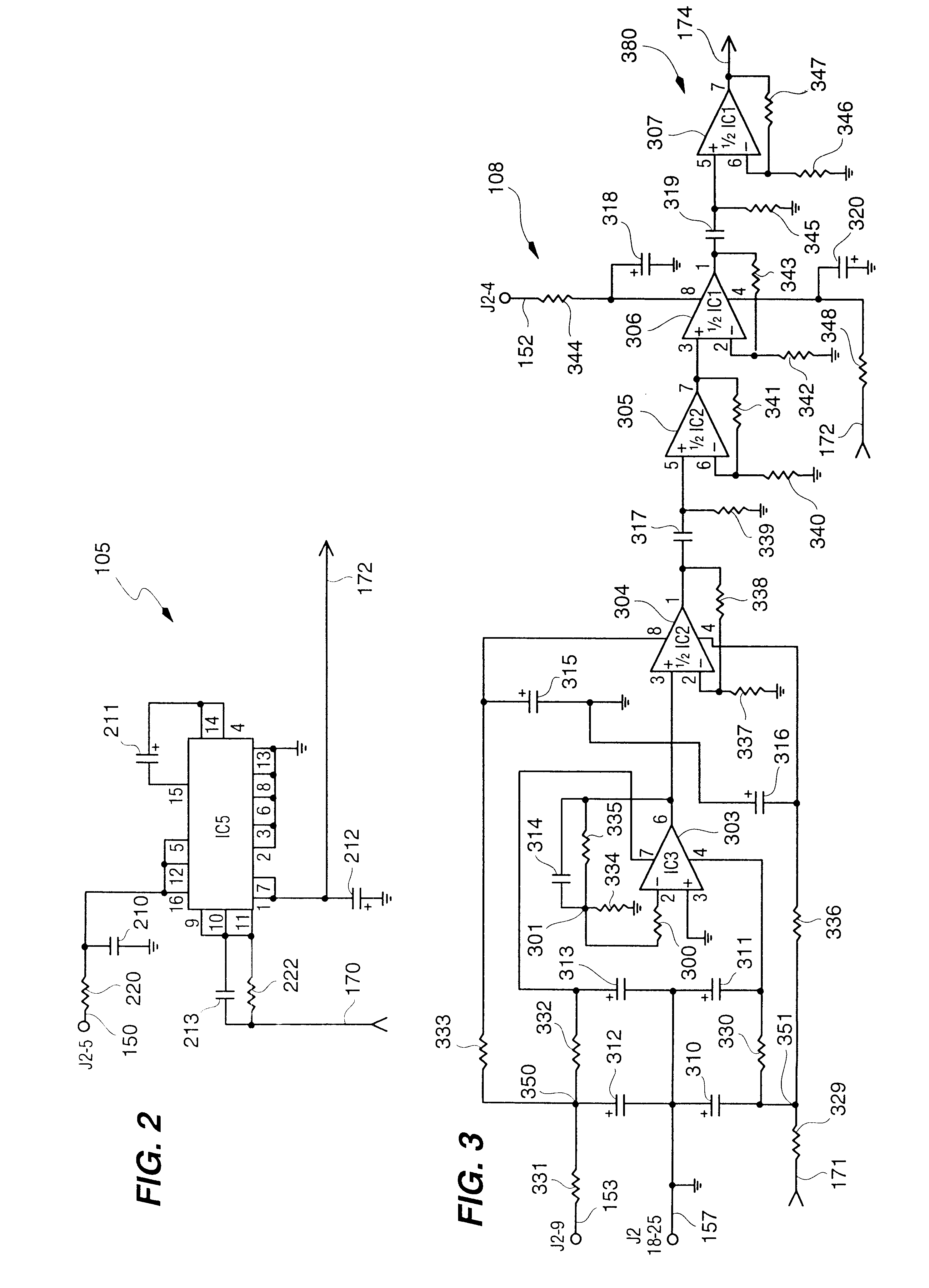
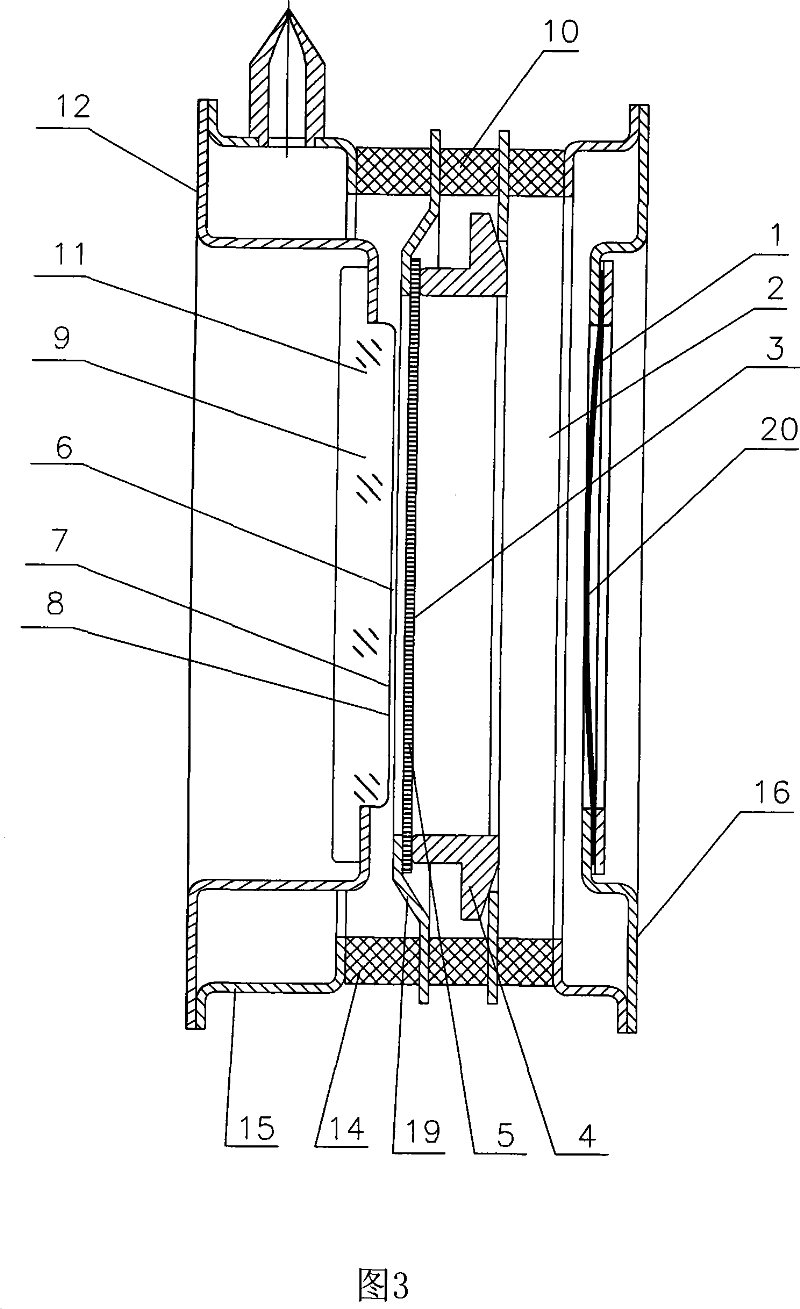
Random number generator and generation method
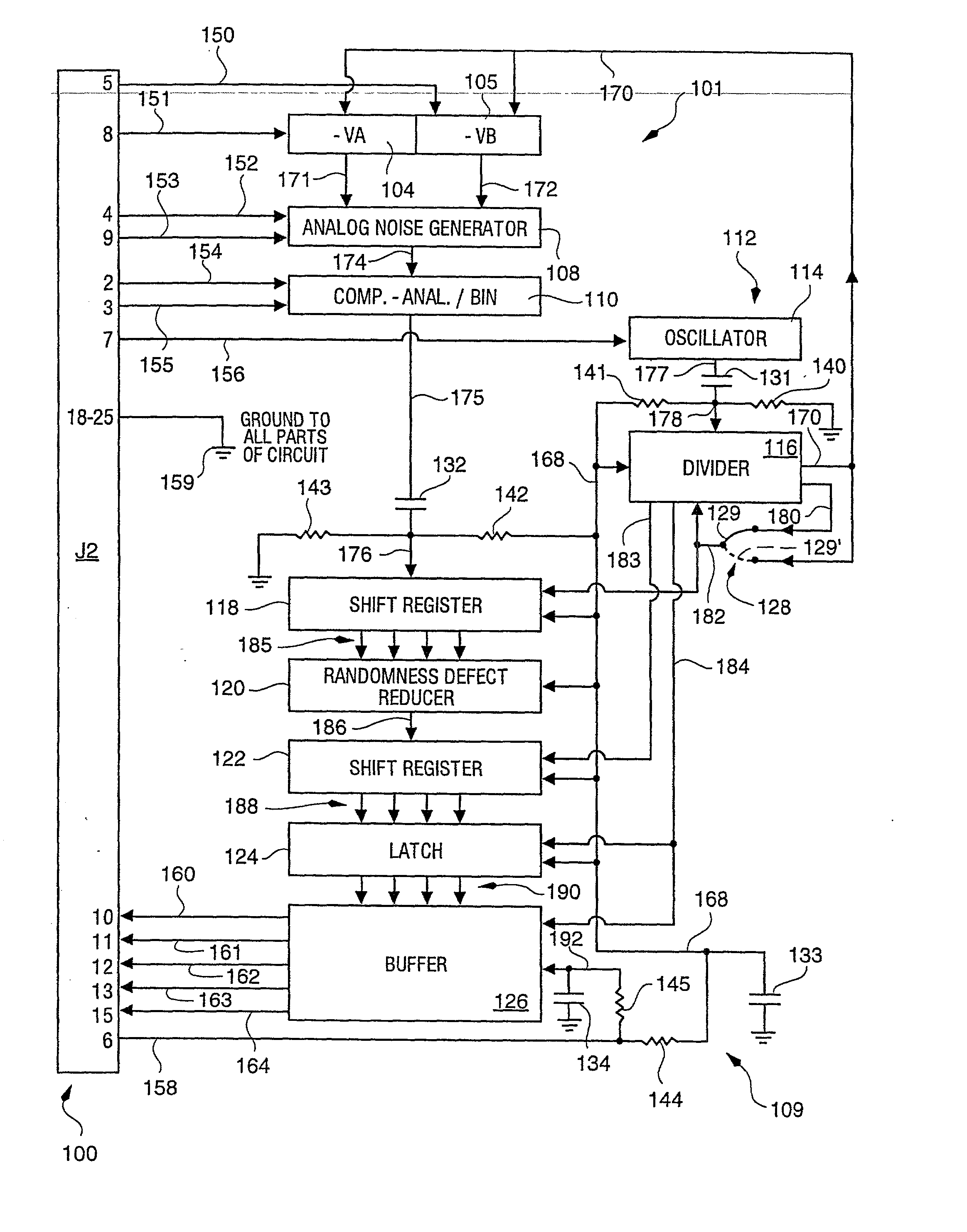
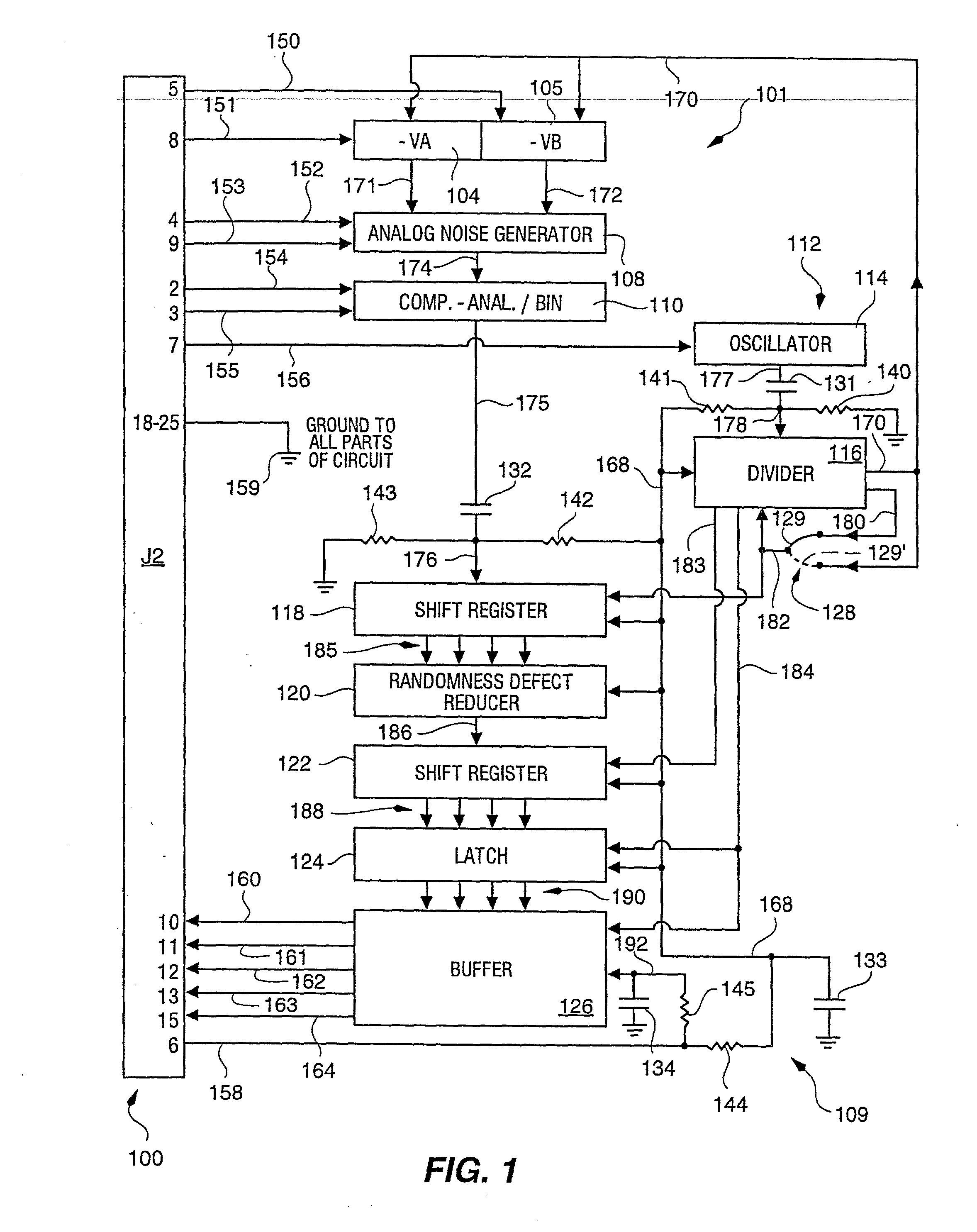
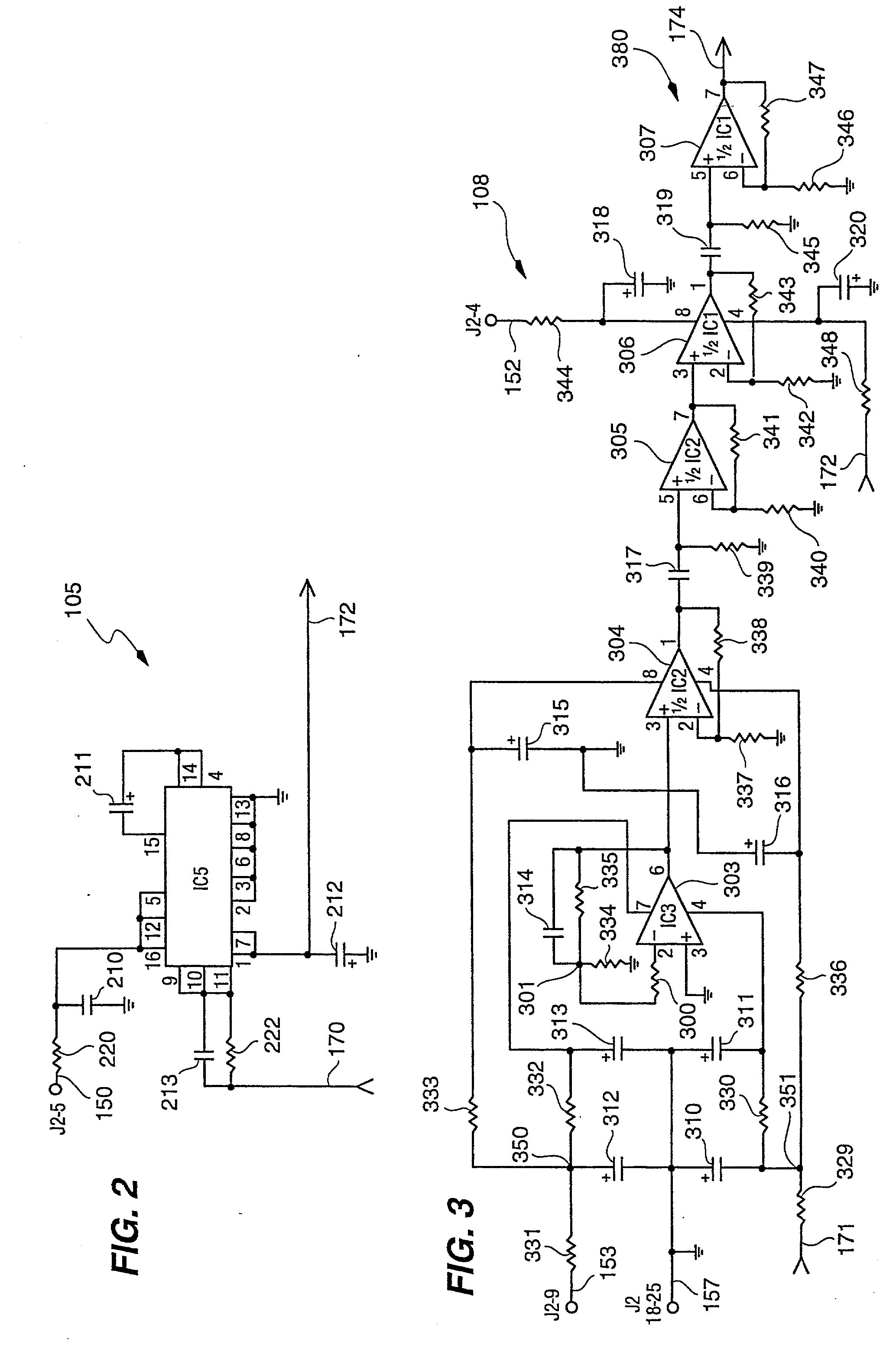
InactiveUS6324558B1Improve its ability to generateReduce defectsRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsCmos comparatorShift register
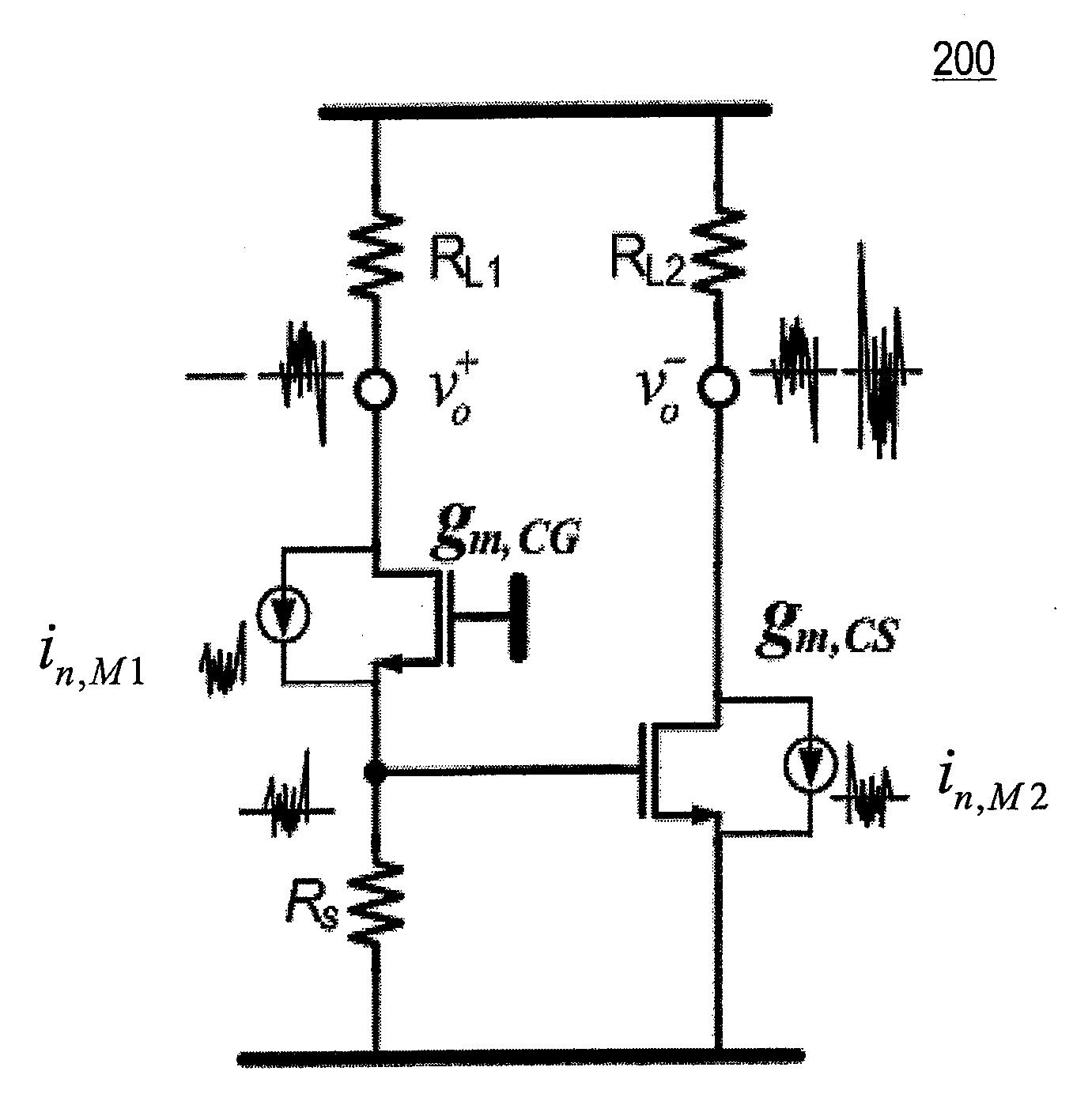
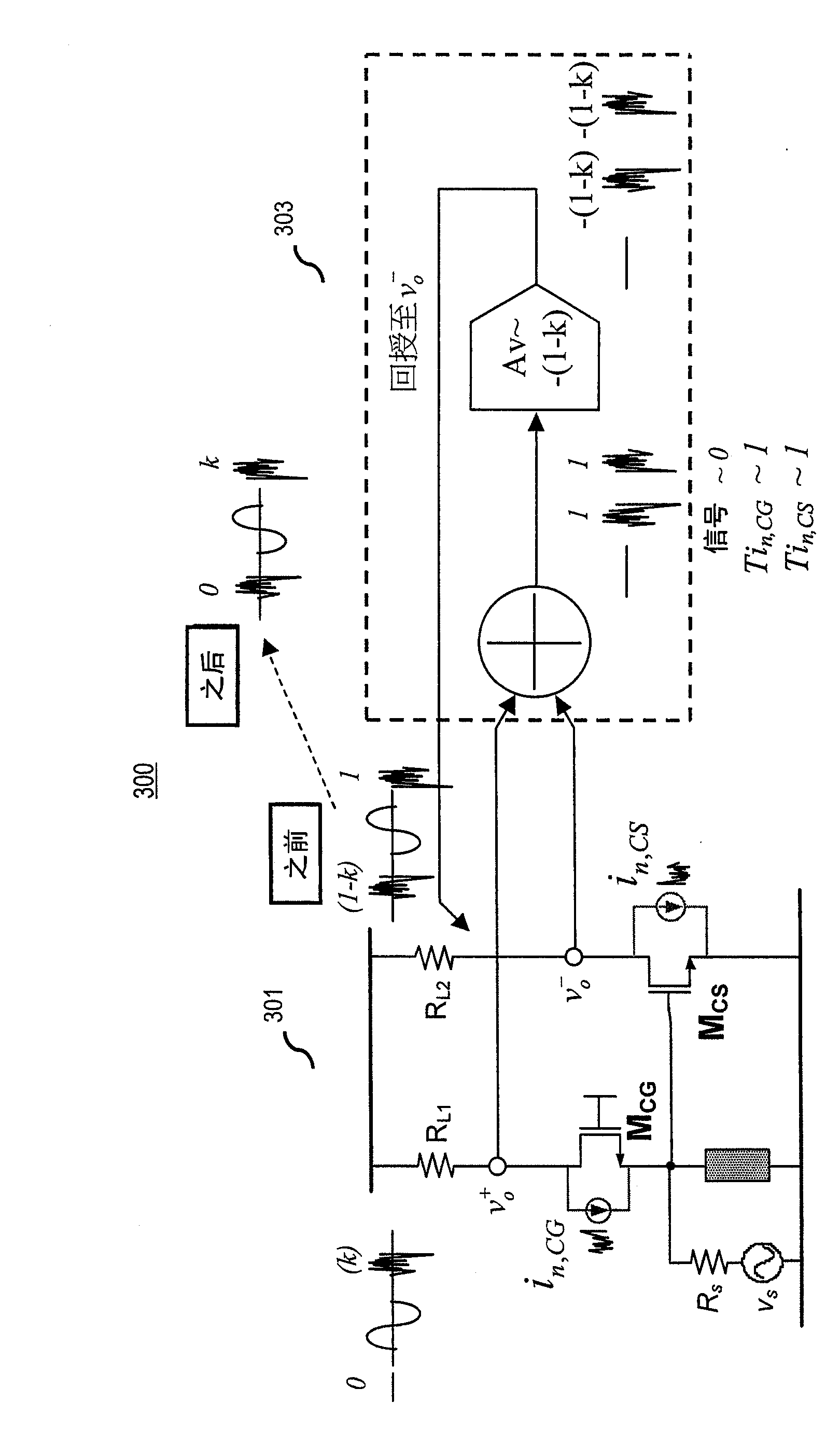
An RNG circuit is connected to the parallel port of a computer. The circuit includes a flat source of white noise and a CMOS amplifier circuit compensated in the high frequency range. A low-frequency cut-off is selected to maintain high band-width yet eliminate the 1 / f amplifier noise tail. A CMOS comparator with a 10 nanosecond rise time converts the analog signal to a binary one. A shift register converts the serial signal to a 4-bit parallel one at a sample rate selected at the knee of the serial dependence curve. Two levels of XOR defect correction produce a BRS at 20 kHZ, which is converted to a 4-bit parallel word, latched and buffered. The entire circuit is powered from the data pins of the parallel port. A device driver interface in the computer operates the RNG. The randomness defects with various levels of correction and sample rates are calculated and the RNG is optimized before manufacture.
Owner:QUANTUM WORLD
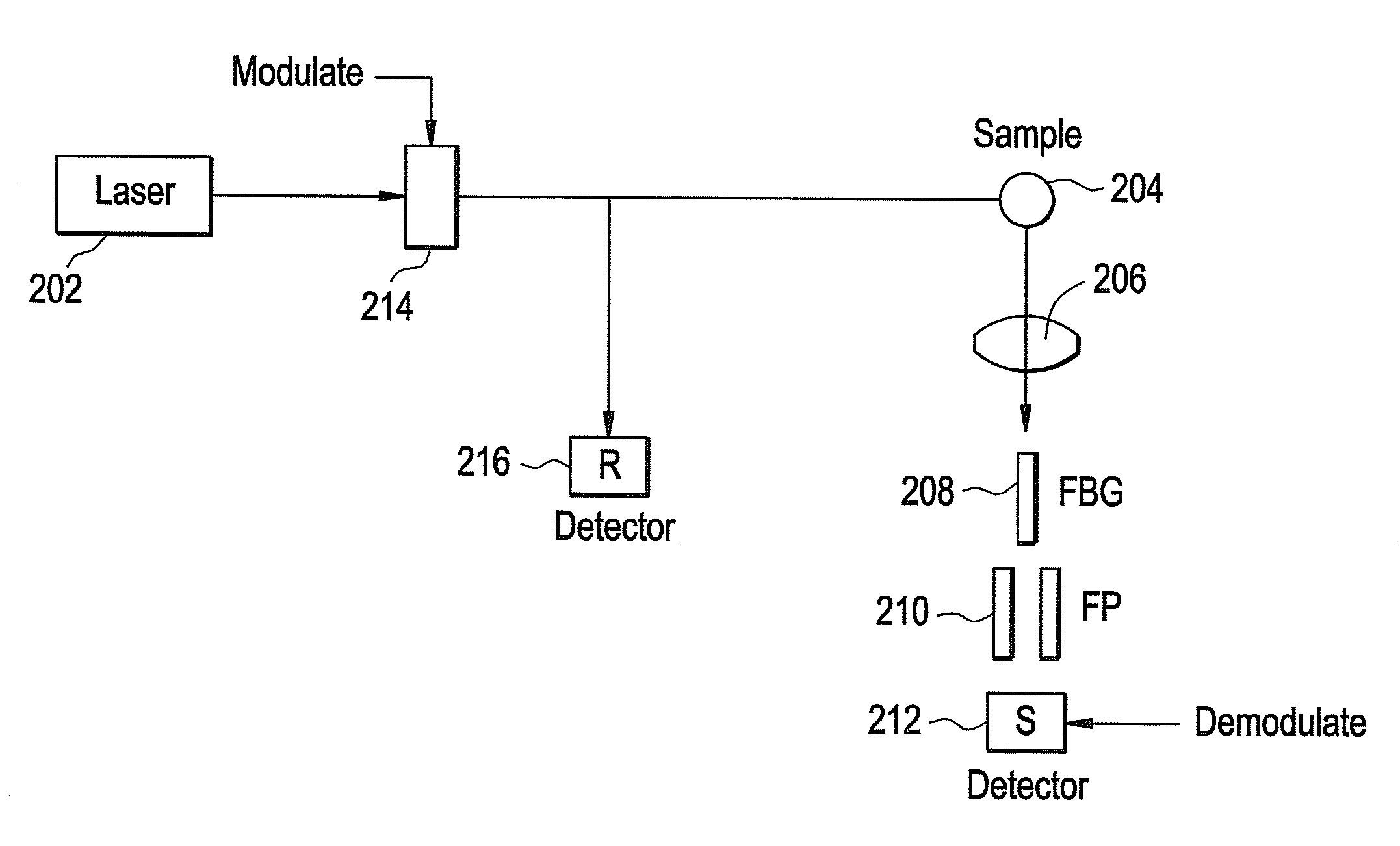
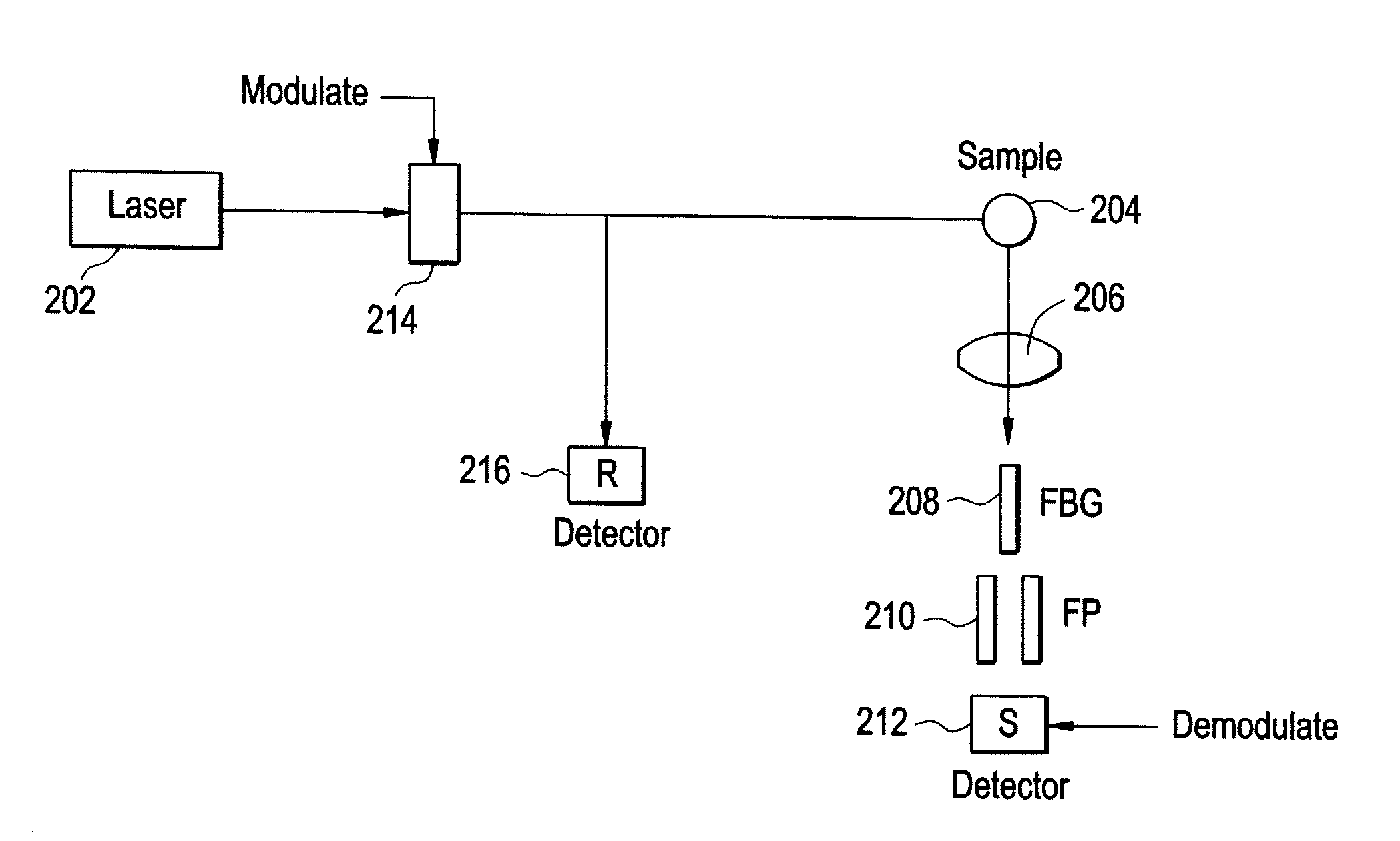
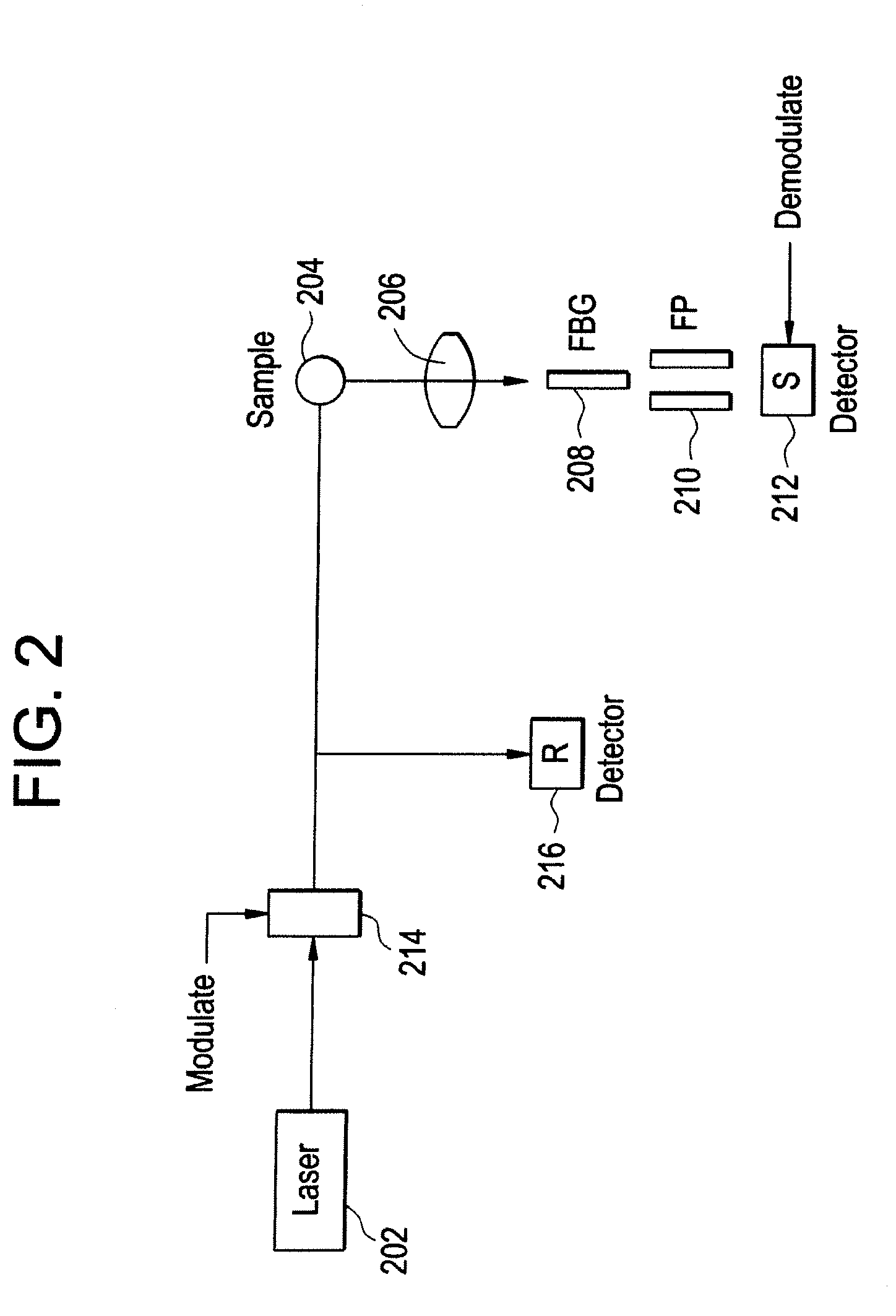
Method and apparatus for improved signal to noise ratio in raman signal detection for MEMS based spectrometers
InactiveUS20080018890A1Radiation pyrometryPhotometry electrical circuitsDiscriminatorAudio power amplifier
A method of Raman detection for a portable, integrated spectrometer instrument includes directing Raman scattered photons by a sample to an avalanche photodiode (APD), the APD configured to generate an output signal responsive to the intensity of the Raman scattered photons incident thereon. The output signal of the APD is amplified and passed through a discriminator so as to reject at least one or more of amplifier noise and dark noise. A number of discrete output pulses within a set operational range of the discriminator is counted so as to determine a number of photons detected by the APD.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Lidar three-dimensional imaging system based on virtual instrument
ActiveCN104049259AAchieve seamless integrationShorten the development cycleElectromagnetic wave reradiationMirror reflectionFull waveform
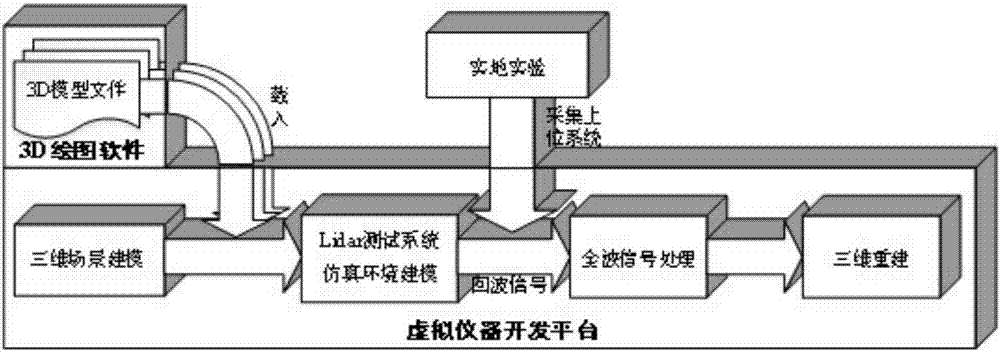
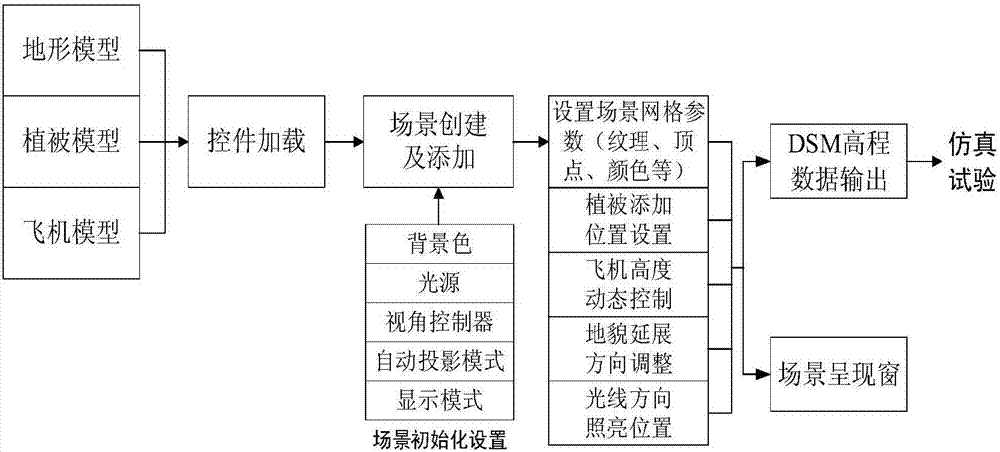
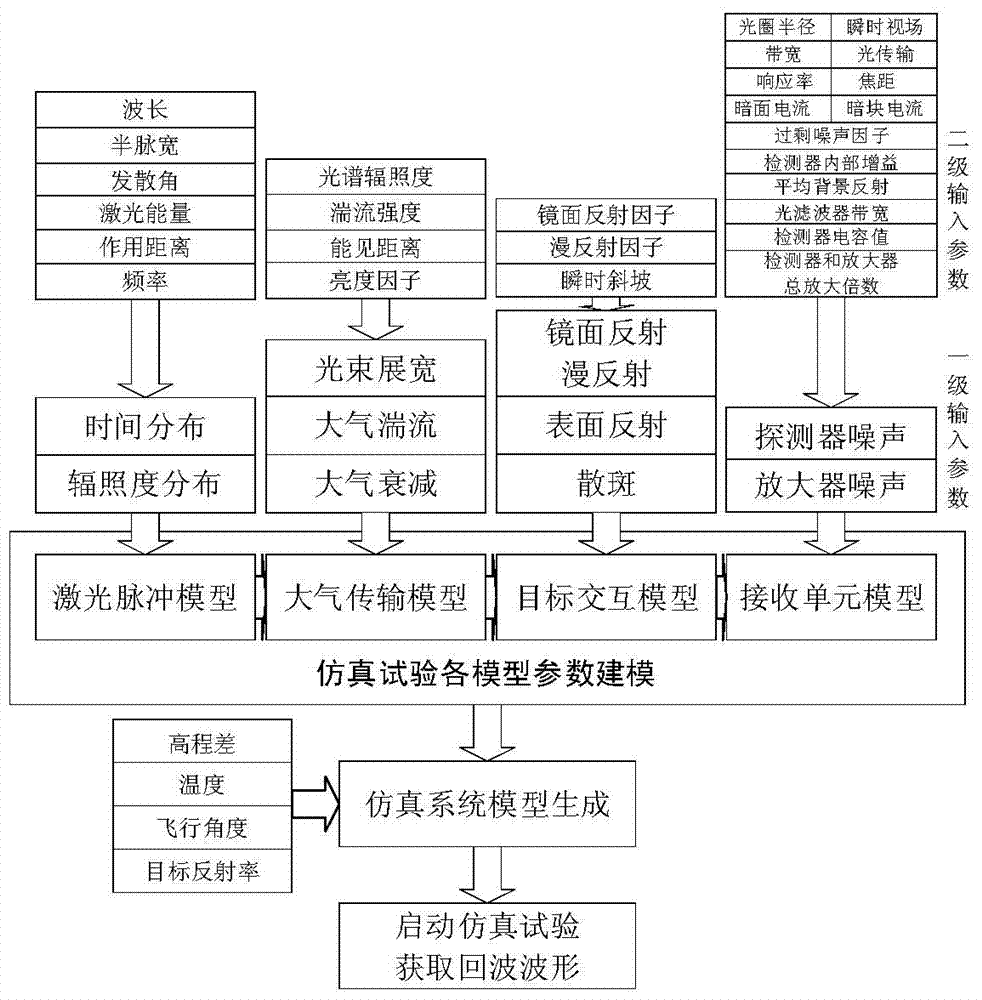
A lidar three-dimensional imaging system based on a virtual instrument comprises a three-dimensional scene modeling module, a lidar testing system simulation environment modeling module, a full-waveform signal processing module and a three-dimensional reconstruction module. The three-dimensional scene modeling module comprises a three-dimensional model loading element used for setting background colors, visual angle control, illumination, a projection mode, a display model and other basic scene projects. The lidar testing system simulation environment modeling module comprises four modeling sub-modules which are a laser pulse model, an atmospheric transmission model, an object interaction model and a receiving unit model. The laser pulse model is used for simulating a laser source according to the wavelength, pulse width, energy and other characteristics of a laser. The atmospheric transmission model is used for simulating a tested atmospheric environment, so that a noise model is generated for acting on the laser. The object interaction model is used for simulating effects of the laser and a detected object, and the effects comprise mirror reflection, diffuse reflection, surface reflection and speckles. The receiving unit model is used for simulating detector noise and amplifier noise which are generated after sensing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method and apparatus for restraining D-genus power amplifier noise and D-genus power amplifier with noise suppression
InactiveCN101465619ASuppress noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a noise suppression method for class D power amplifier, which includes a step S1 and a step S2; wherein, in step S1, an external enabling signal is received; in step S2, when the state of external enabling signal is changed, an enabling signal for a class D power amplifier is generated according to the external enabling signal; meanwhile, a silencing signal used for controlling the load of a class D power amplifier is generated according to the external enabling signal. The noise suppression method for class D power amplifier can effectively suppress POP or CLICK noise generated in capacitor charge-discharge process without increasing or modifying chip pins.
Owner:HANGZHOU MPS SEMICON TECH
Random number generator and generation method
InactiveUS20020169810A1Improve its ability to generateReduce defectsRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsCmos comparatorShift register
An RNG circuit is connected to the parallel port of a computer. The circuit includes a flat source of white noise and a CMOS amplifier circuit compensated in the high frequency range. A low-frequency cut-off is selected to maintain high band-width yet eliminate the 1 / f amplifier noise tail. A CMOS comparator with a 10 nanosecond rise time converts the analog signal to a binary one. A shift register converts the serial signal to a 4-bit parallel one at a sample rate selected at the knee of the serial dependence curve. Two levels of XOR defect correction produce a BRS at 20 kHZ, which is converted to a 4-bit parallel word, latched and buffered. The entire circuit is powered from the data pins of the parallel port. A device driver interface in the computer operates the RNG. The randomness defects with various levels of correction and sample rates are calculated and the RNG is optimized before manufacture.
Owner:QUANTUM WORLD
Apparatus and method to reduce power amplifier noise generation in a multiplexed communication system
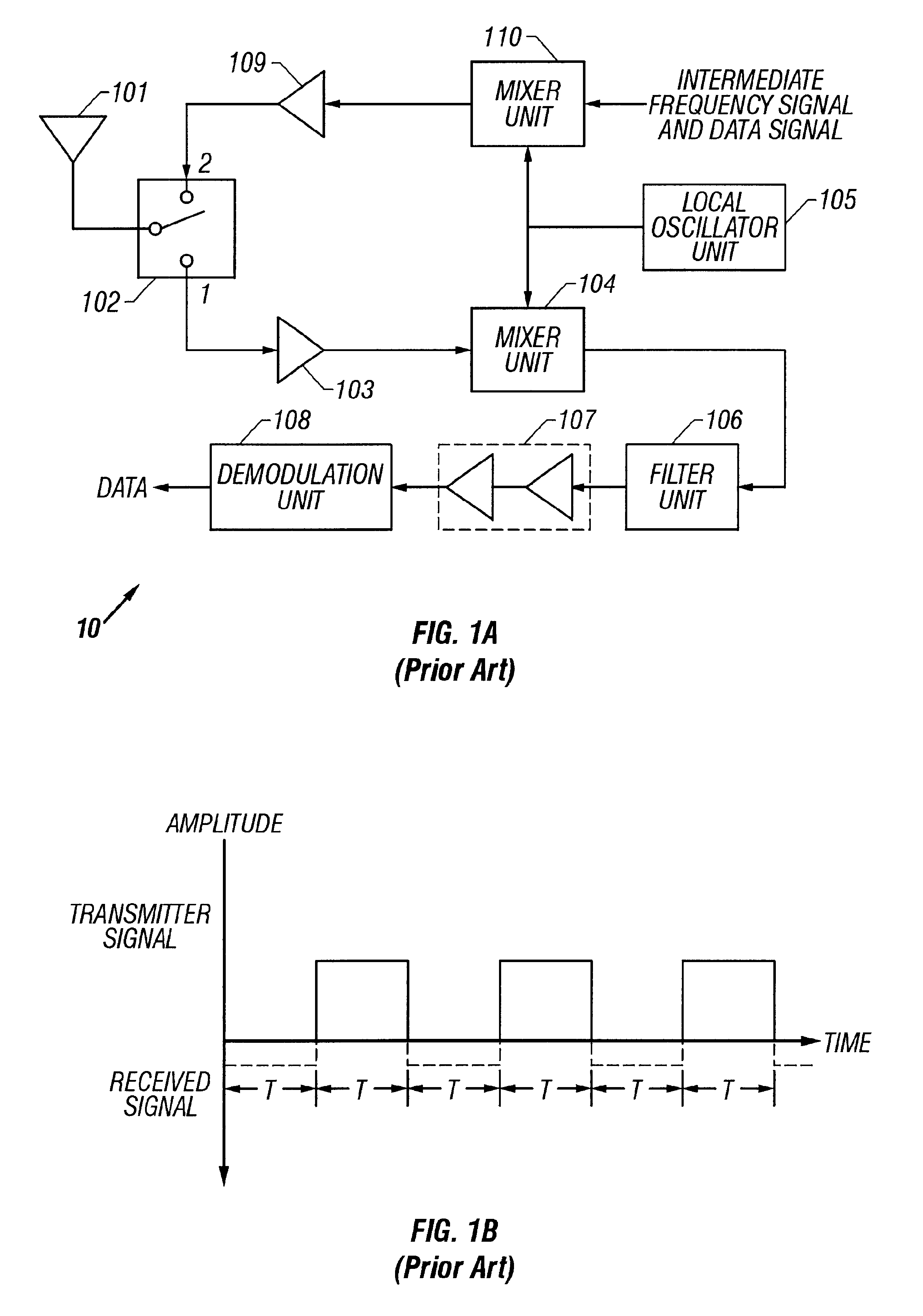
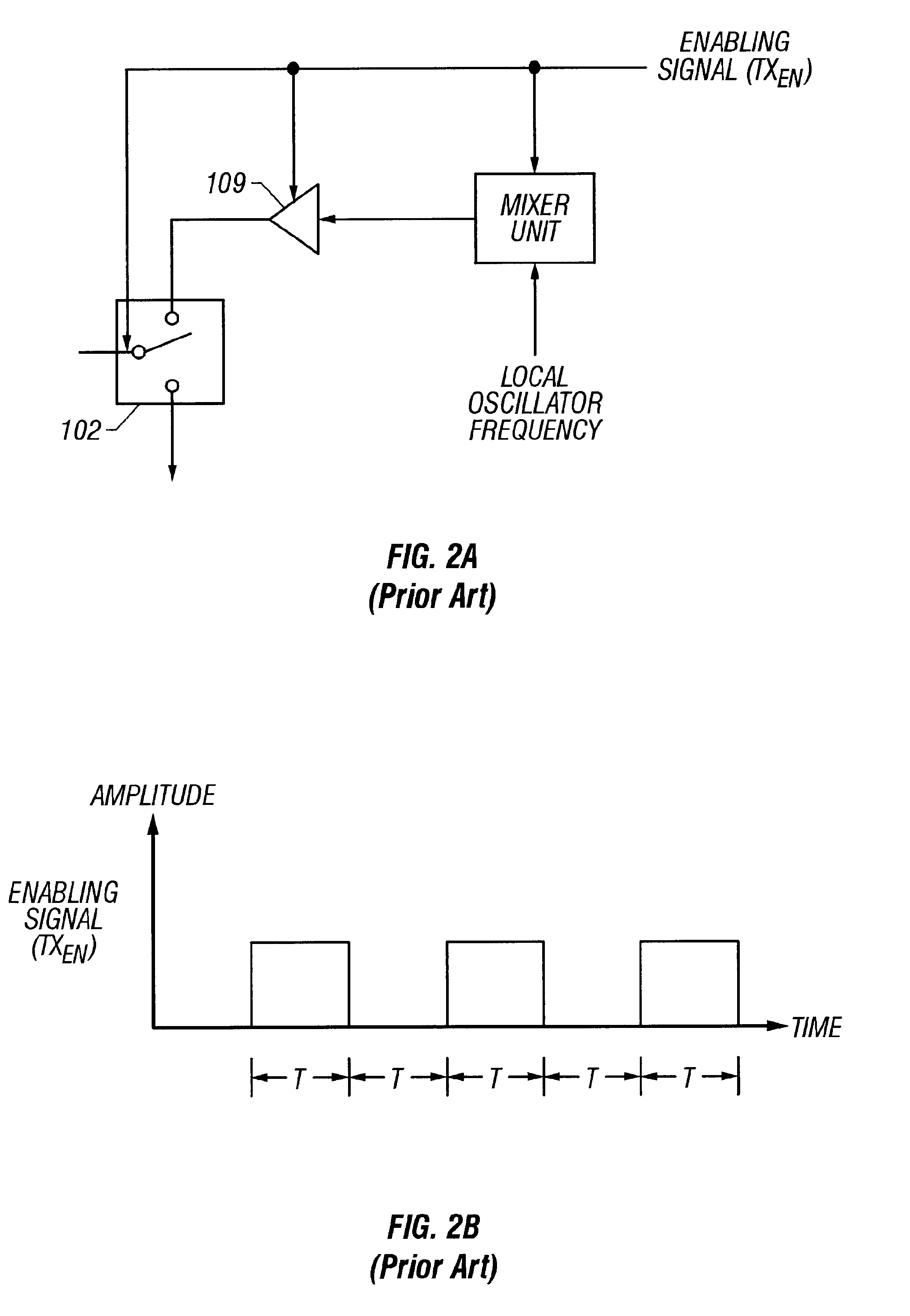
InactiveUS6404824B1Resonant long antennasTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
In order to reduce the noise components in a multiplexed communication system, noise components generally referred to as splatter that from the rapid transition between the transmitting state and the non-transmitting state, this power transition in the transmitted signal is provided with a ramped envelope. In the preferred embodiment, the ramped power transition is the result of a ramped enabling signal applied to the power amplifier generating the transmitted signal. The use of a ramped power transition reduces the noise introduced as a result of an abrupt power transition. In addition, the transmitted signal is provided with a preamble so that no data is transmitted during the transition period.
Owner:MICROSEMI SEMICON U S
High-resolution X-ray image enhancer
InactiveCN101034653AReduce scatterImprove transmittanceCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersImage-conversion/image-amplification tubesFluorescenceX ray image
The invention relates to a high resolution X radial image amplifier, it includes input window, photoelectricity cathode, micro channel board module, output window and shell; output window includes in turn axial connected fluorescent screen, luminous powder level and aluminum membrane; the shell includes seal ring, the ceramic shell and the output window metal shell; the output window seal fixes in the output window metal shell; the input window seal fixes in the metal window of the middle of seal ring front end; the input window material is the aluminum or beryllium metal, the material of seal ring ia the cut down alloy 4J33, the input window connect seal ring with the aluminum braze welding. This invention solved the technical problem of the existing X radial image amplifier to X radial low transmissibility, the difference contrast gradient, the serious scattering, the big noise; the invention has high transmissibility and the small scattering power to X radial, can reduced electronic dissemination time, the transit time and the space charge effect, reduced X radial image amplifier noise, enhanced the contrast gradient.
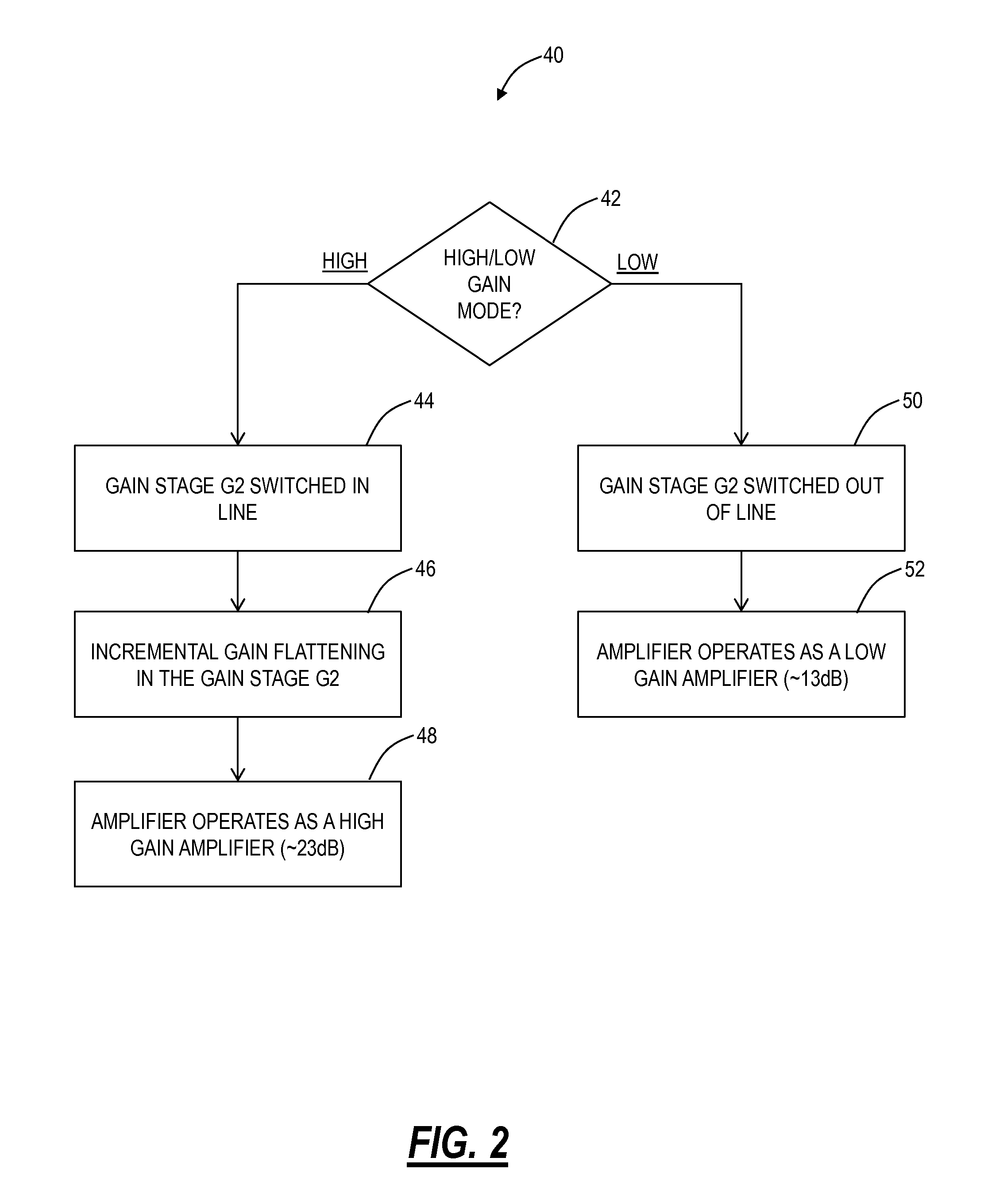
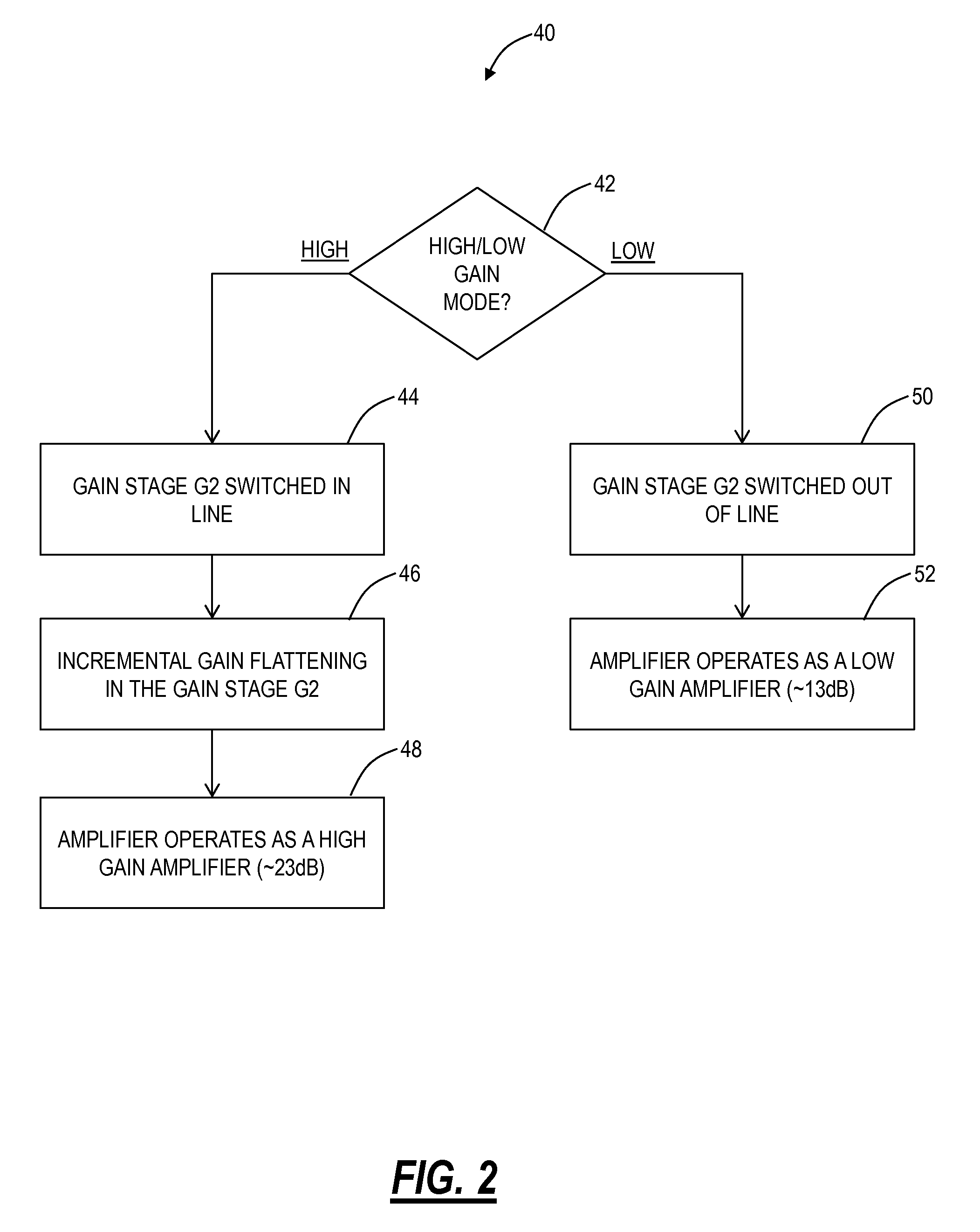
Owner:陕西光电子先导院科技有限公司
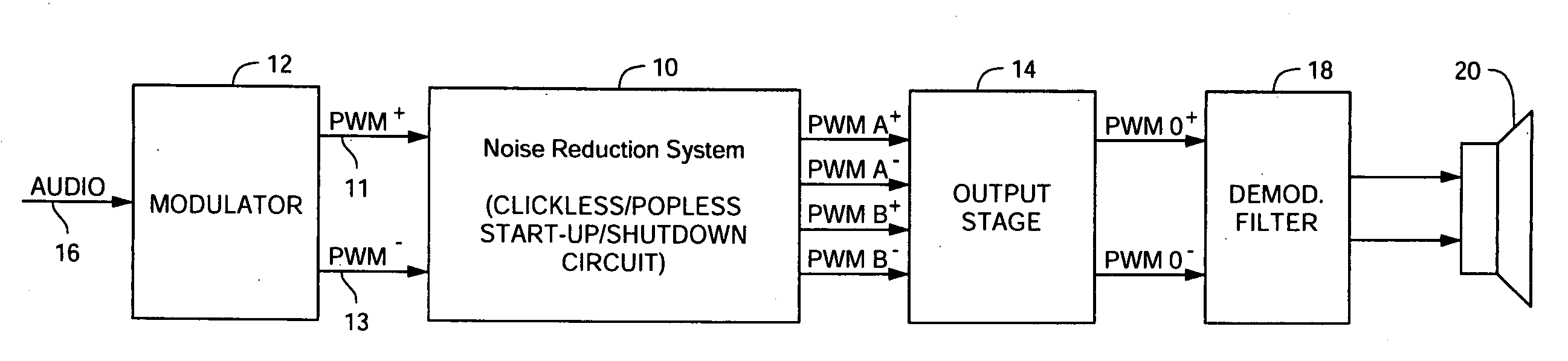
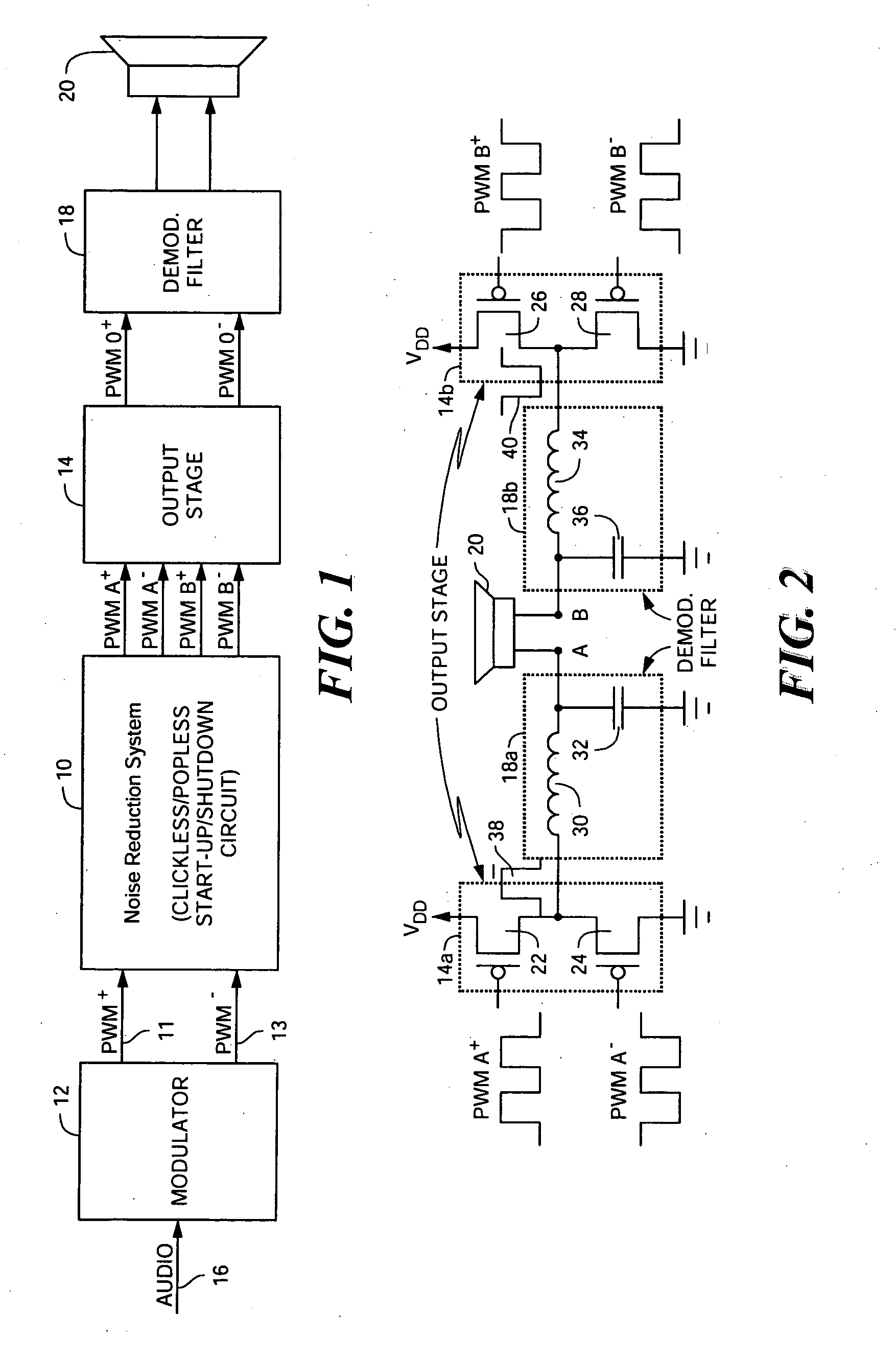
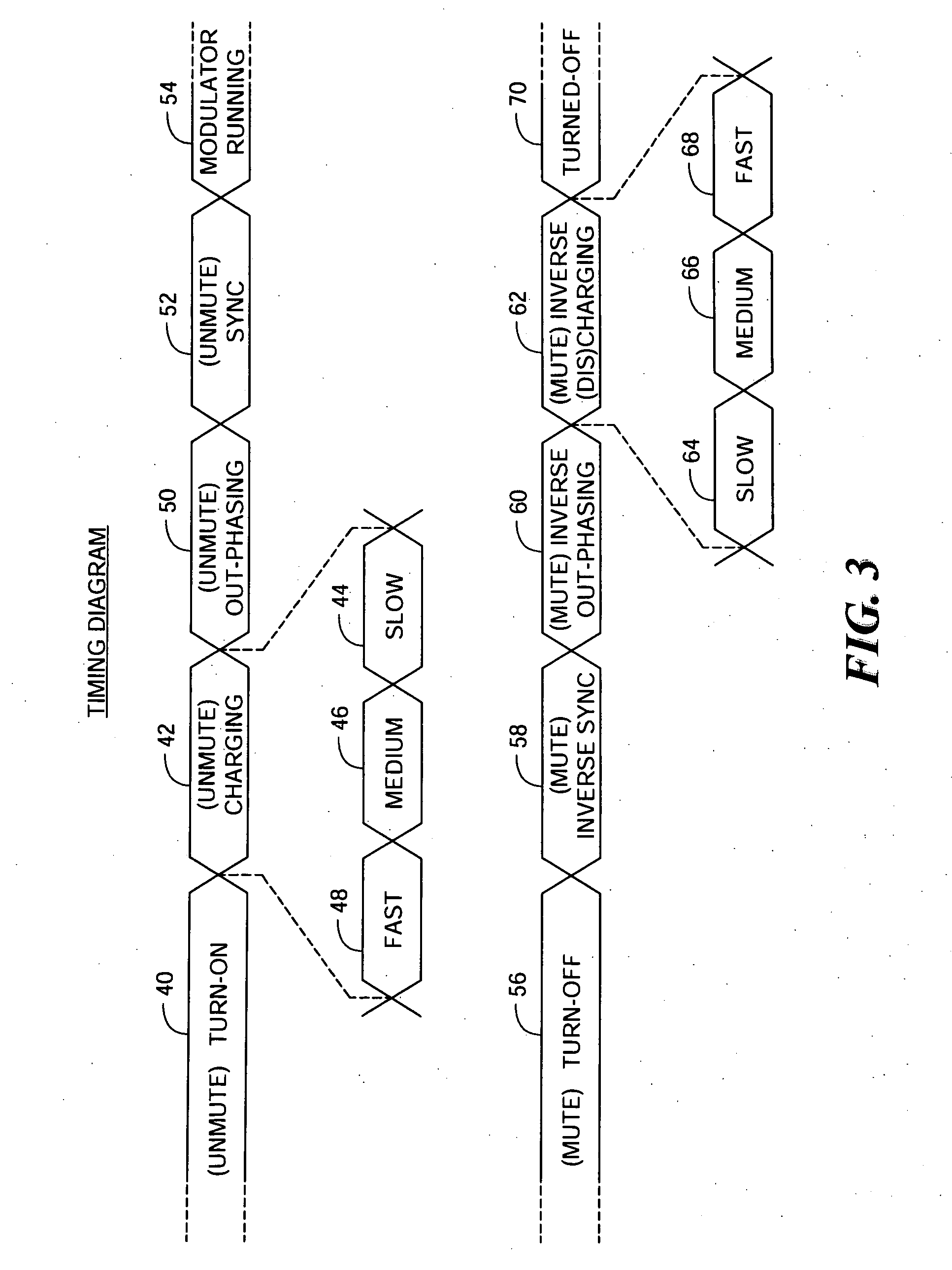
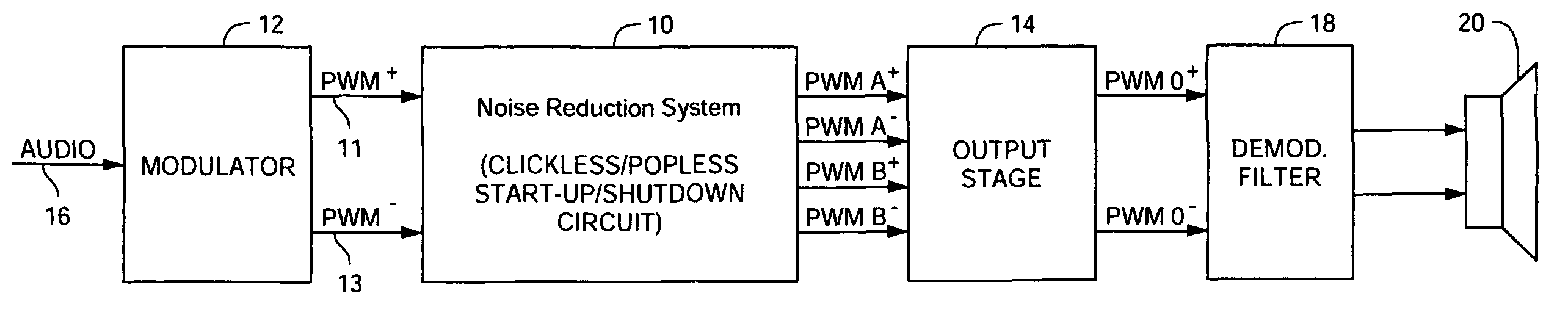
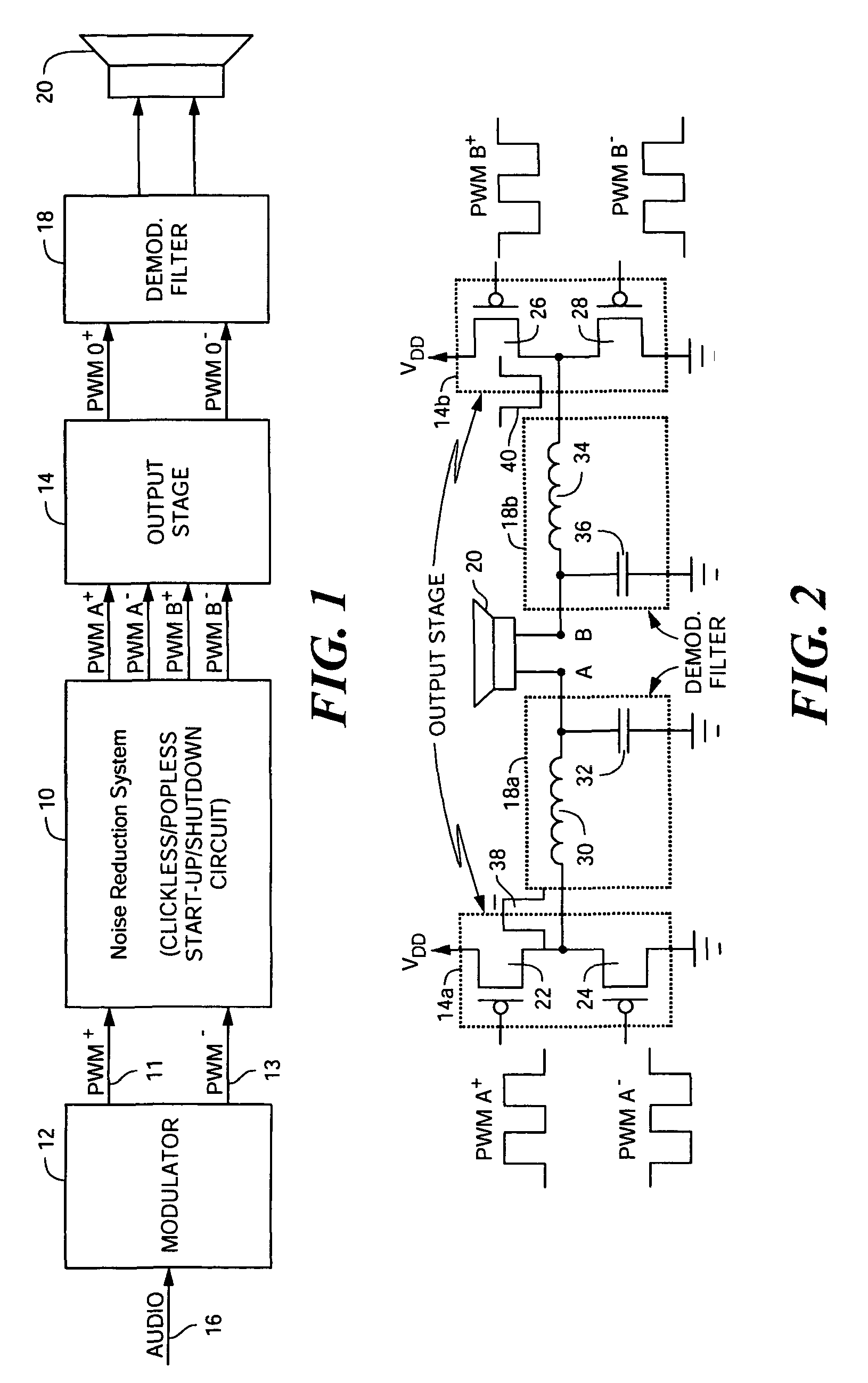
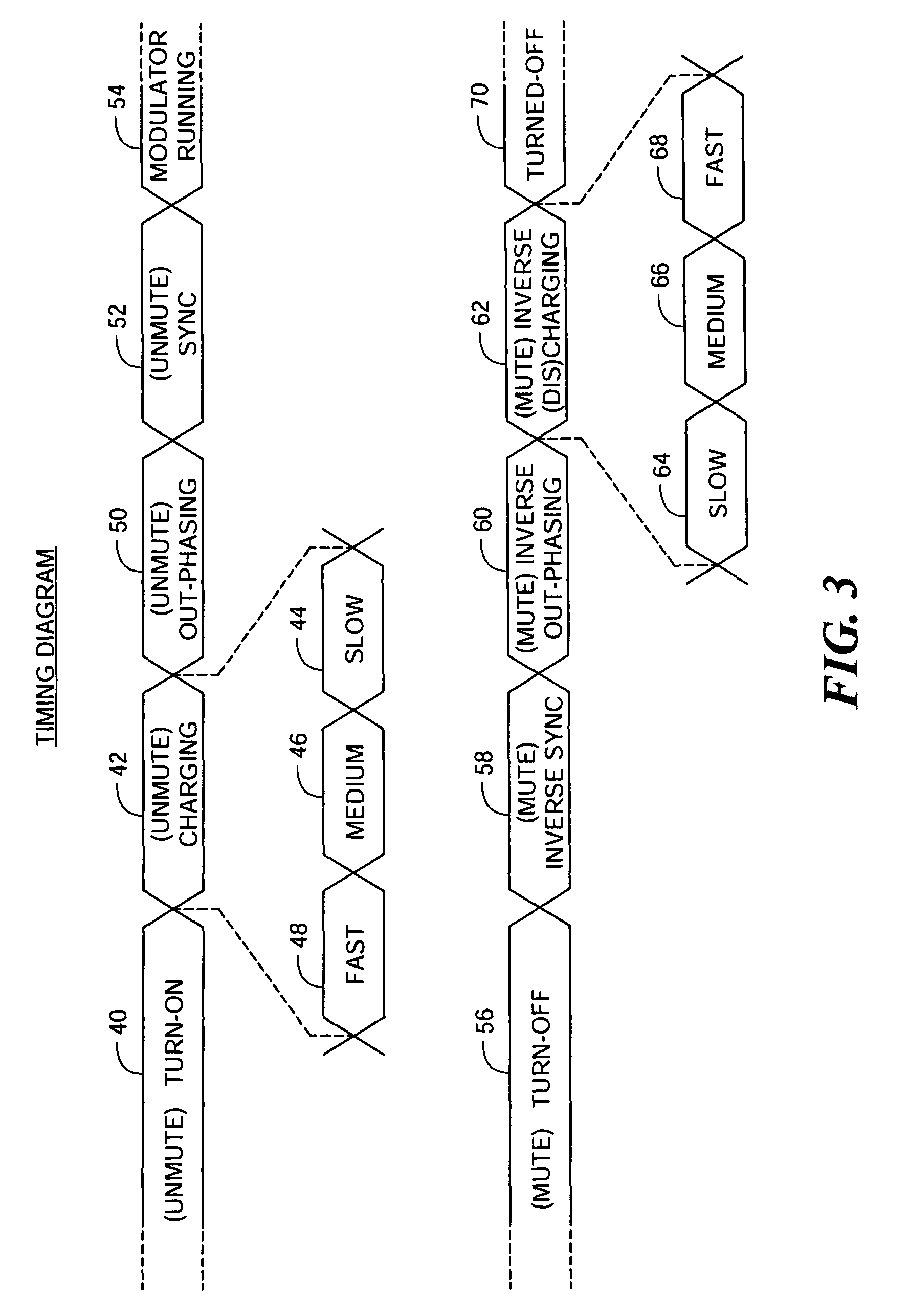
Noise reduction system and method for audio switching amplifier
InactiveUS20080111620A1Improve noiseReduce audible noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlAudio power amplifierRelative phase
Noise reduction for a switching amplifier system having a differential output stage and demodulator filter responsive to complementary PWM signals includes generating in-phase PWM signals and gradually adjusting their duty cycle between a low duty cycle and the full duty cycle of the complementary PWM signals, generating full duty cycle PWM signals and gradually shifting their relative phase between in-phase and out-of-phase; and in response to a turn-on signal, adjusting the in-phase PWM signals from low to full duty cycle and shifting the relative phase from in-phase to out-of-phase, and in response to a turn-off signal shifting the relative phase from out-of-phase to in-phase and adjusting the in-phase PWM signals from full to low duty cycle for maintaining balanced charge on the demodulation filter to reduce audible noise.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
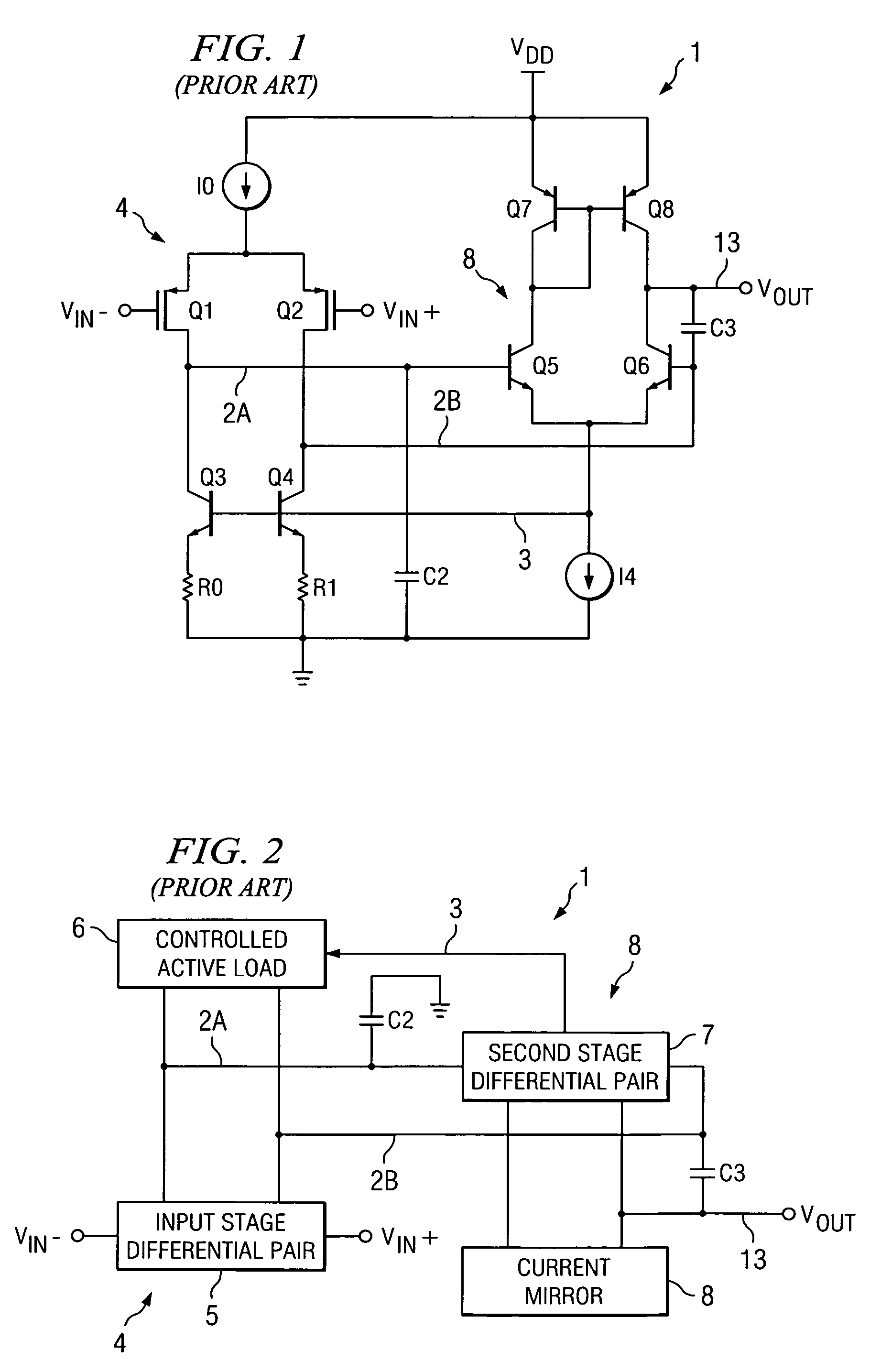
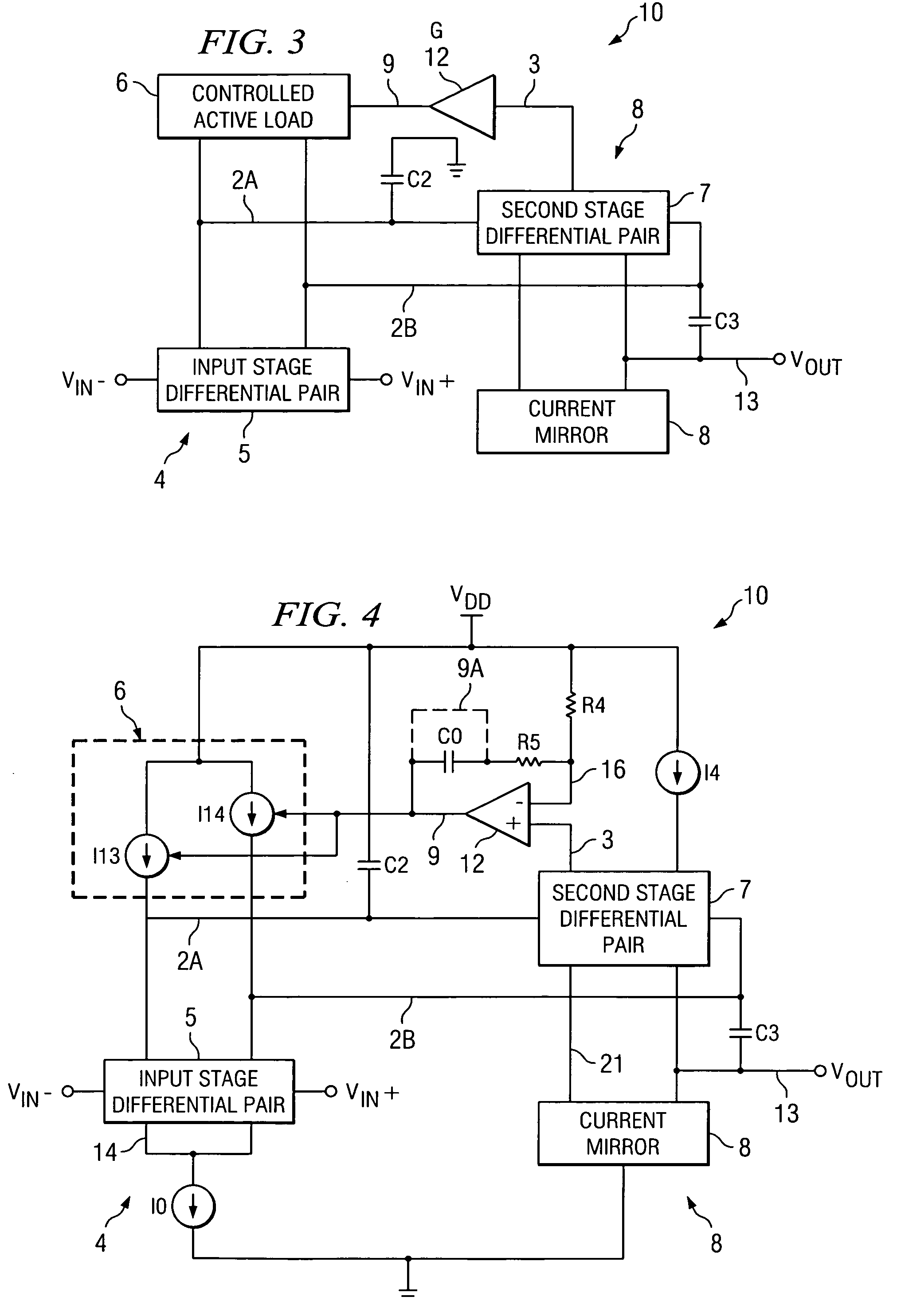
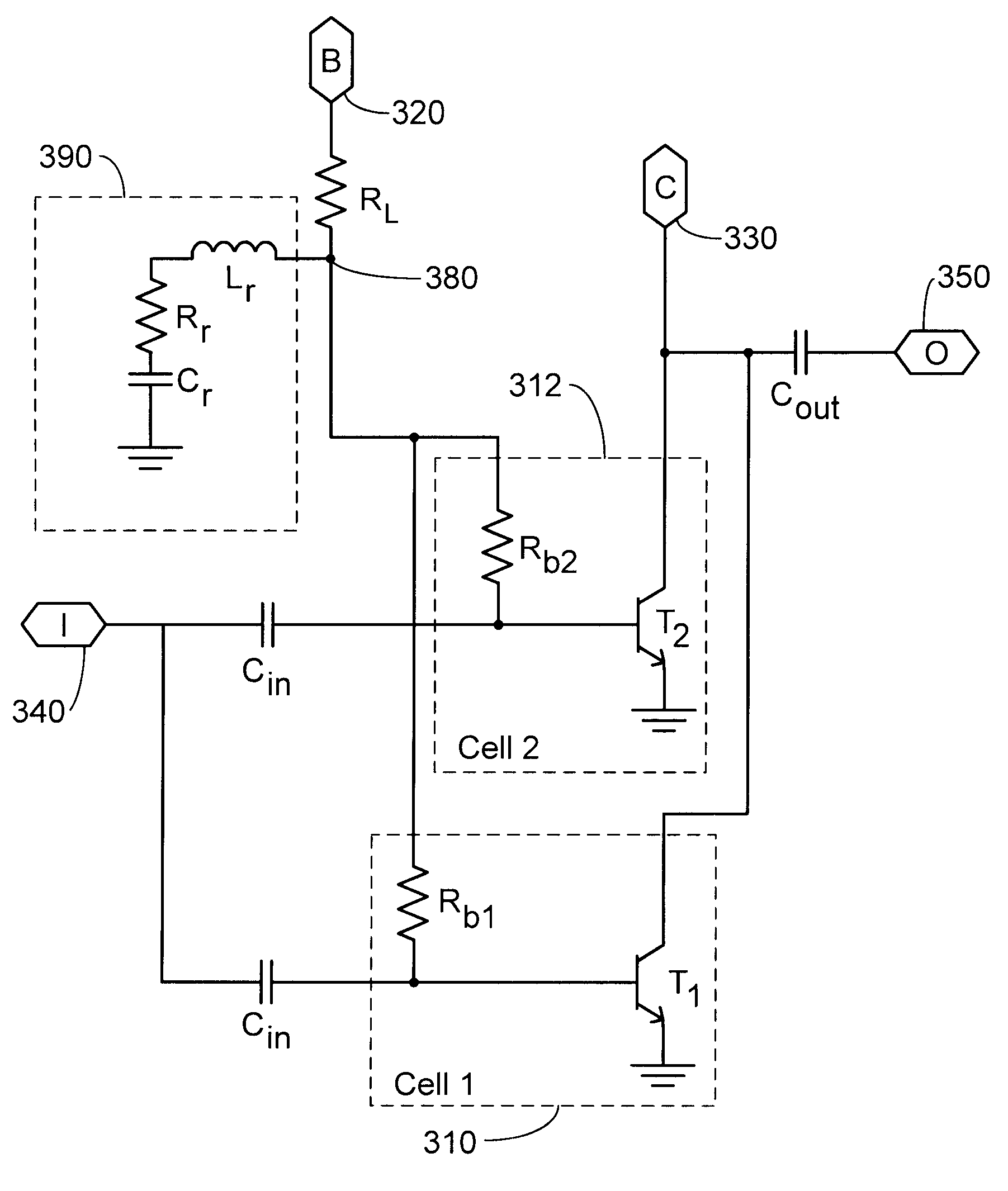
Fast settling, low noise, low offset operational amplifier and method
ActiveUS20060267685A1Settling fastReduce noiseAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersLow noiseLoad circuit
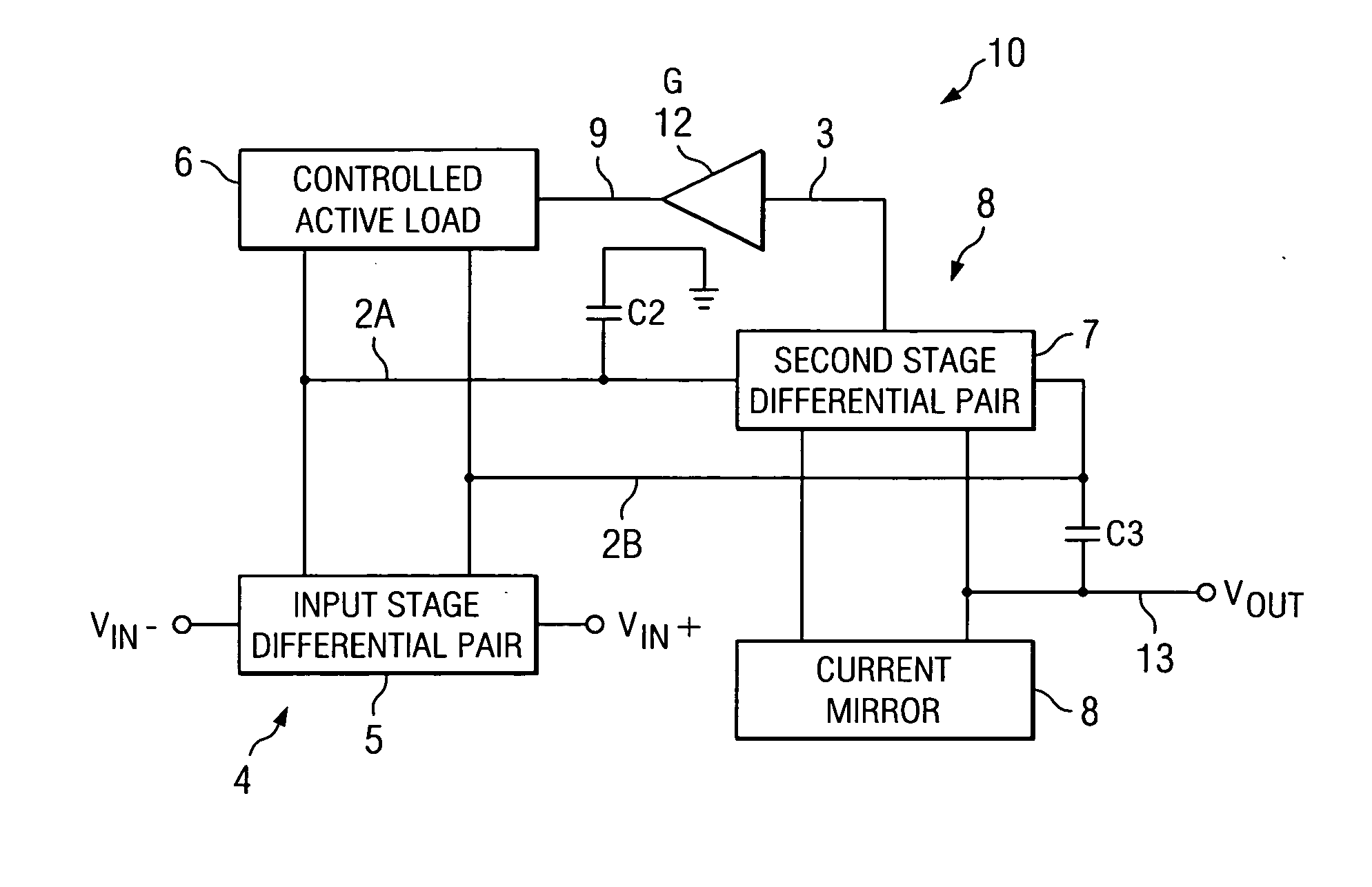
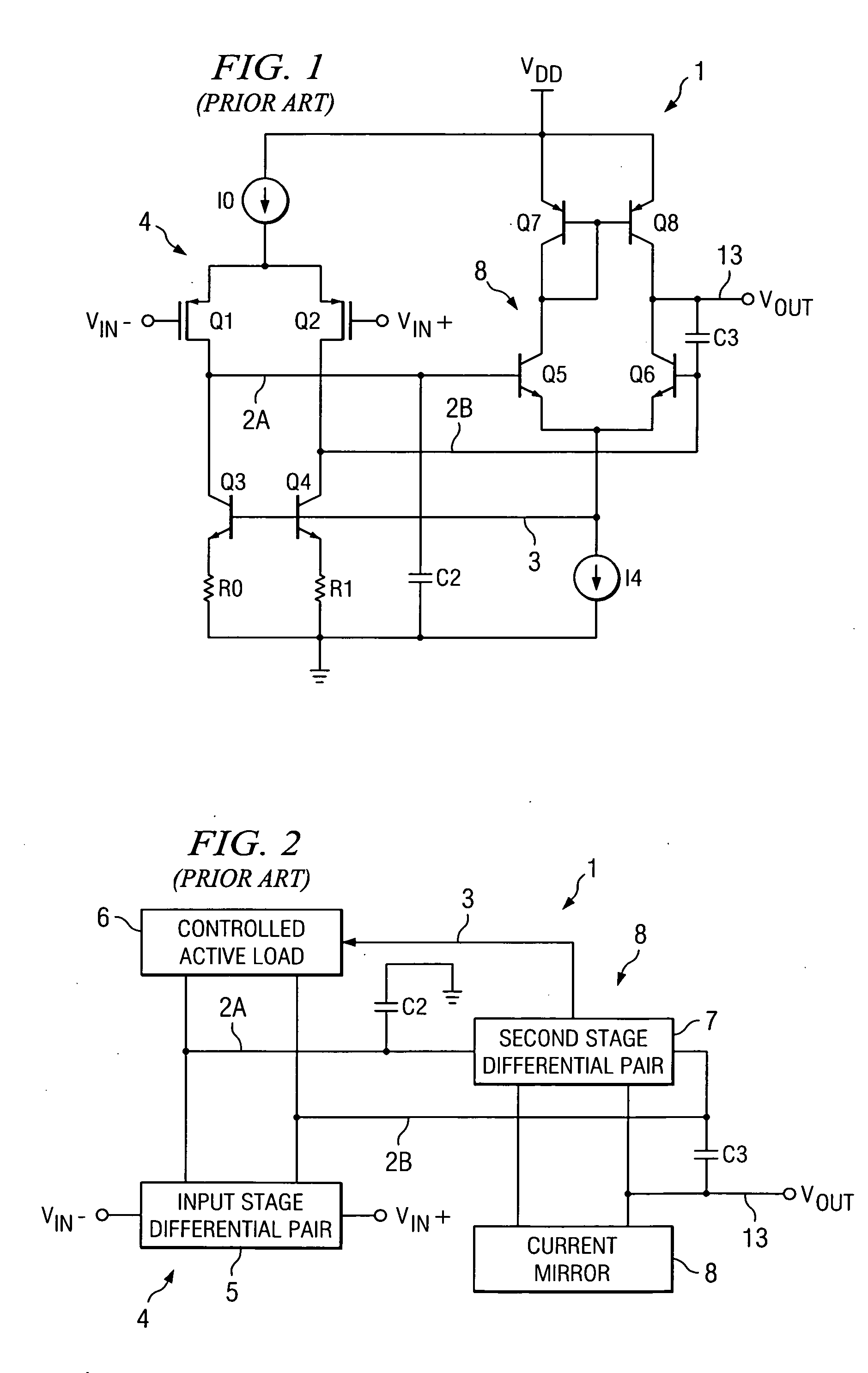
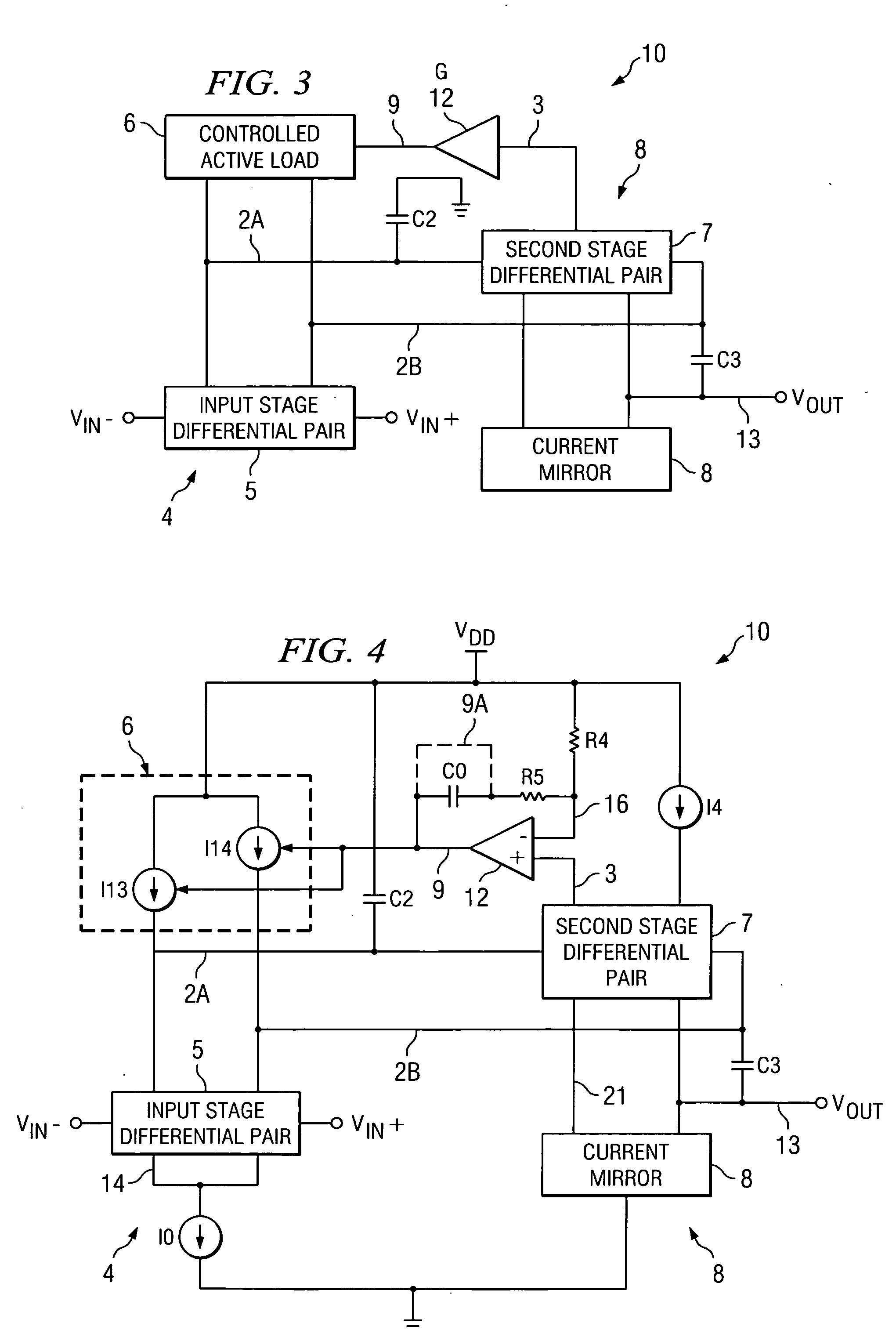
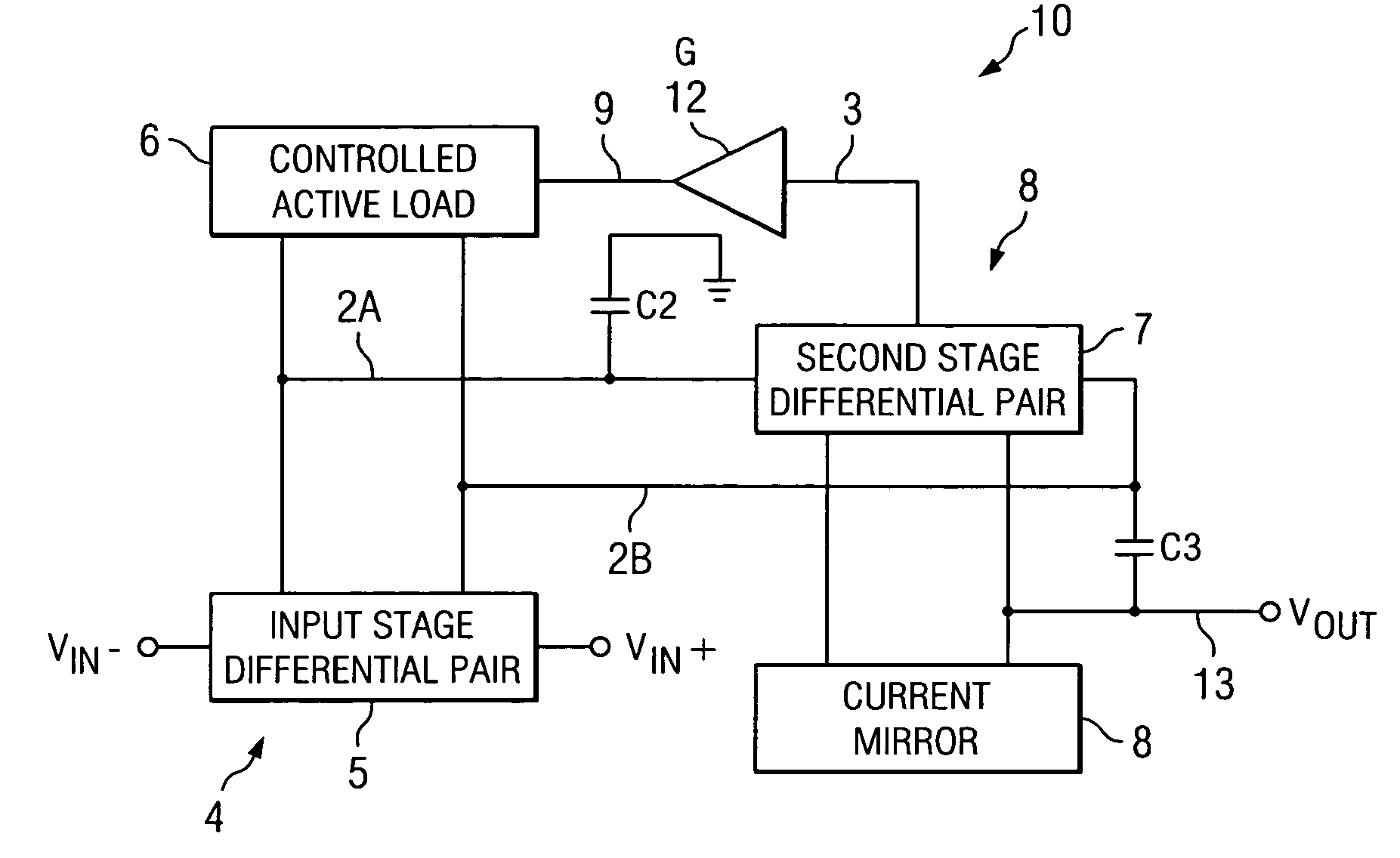
An amplifier (10) includes a first stage (4) including differentially coupled first (Q1) and second (Q2) input transistors and a controlled active load circuit (6). A second stage (8) includes differentially coupled third (Q5) and fourth (Q6) input transistors and a load circuit (Q7,8). A first output (2A) of the first stage (4) is coupled to a first input of the second stage (8), a second output (2B) of the first stage (4) being coupled to a second input of the second stage (8). A common mode feedback amplifier (12) has an input coupled to receive a common mode signal (3) from the second stage (8) for producing an amplified common mode signal (9) on a control input of the controlled active load circuit (6) to provide fast settling of an output (Vout) of the second stage without substantially increasing amplifier noise.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Fast settling, low noise, low offset operational amplifier and method
ActiveUS7298210B2Settling fastReduce noiseAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersLow noiseLoad circuit
An amplifier (10) includes a first stage (4) including differentially coupled first (Q1) and second (Q2) input transistors and a controlled active load circuit (6). A second stage (8) includes differentially coupled third (Q5) and fourth (Q6) input transistors and a load circuit (Q7,8). A first output (2A) of the first stage (4) is coupled to a first input of the second stage (8), a second output (2B) of the first stage (4) being coupled to a second input of the second stage (8). A common mode feedback amplifier (12) has an input coupled to receive a common mode signal (3) from the second stage (8) for producing an amplified common mode signal (9) on a control input of the controlled active load circuit (6) to provide fast settling of an output (Vout) of the second stage without substantially increasing amplifier noise.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Extended dynamic range optical amplifier
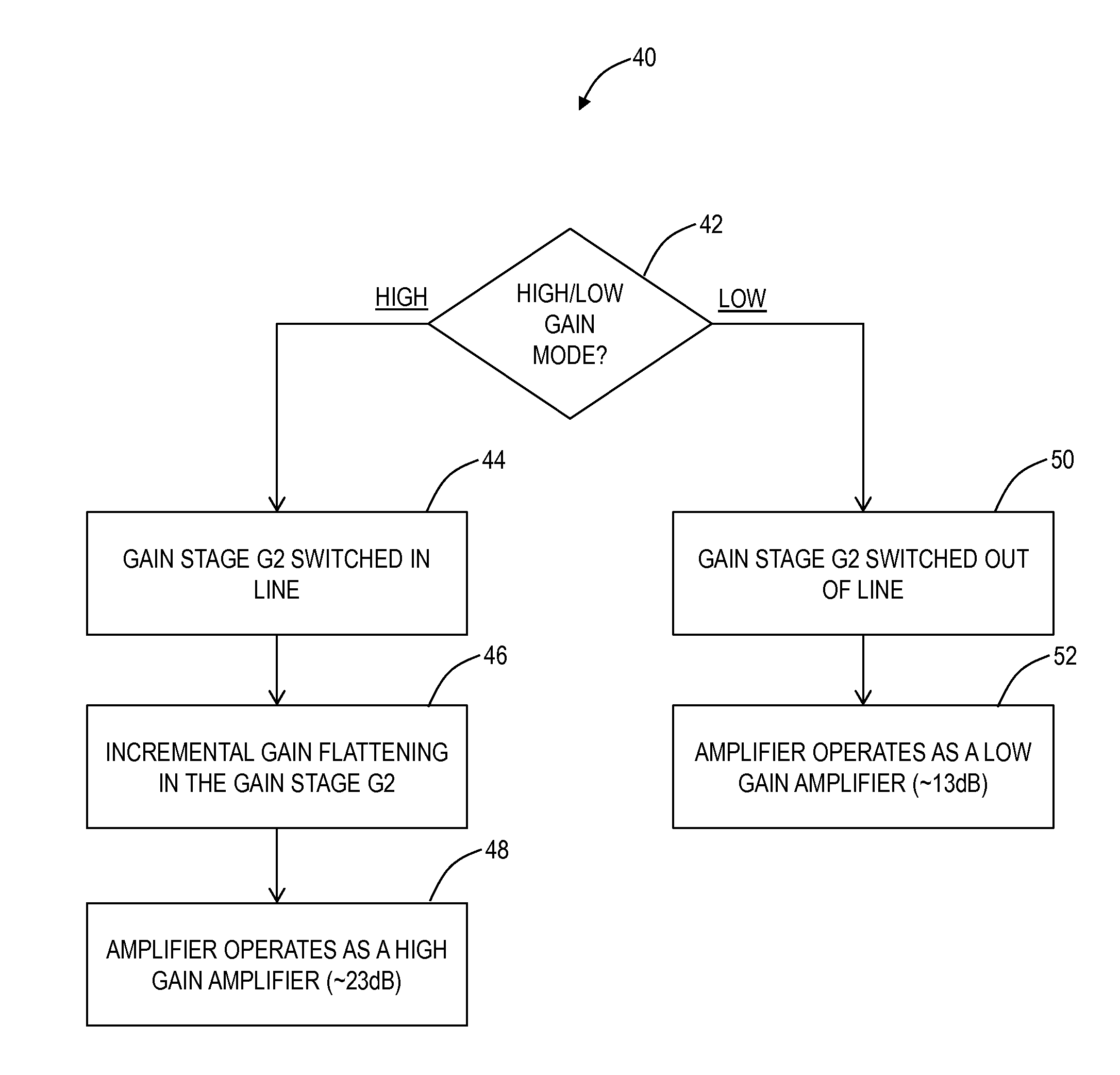
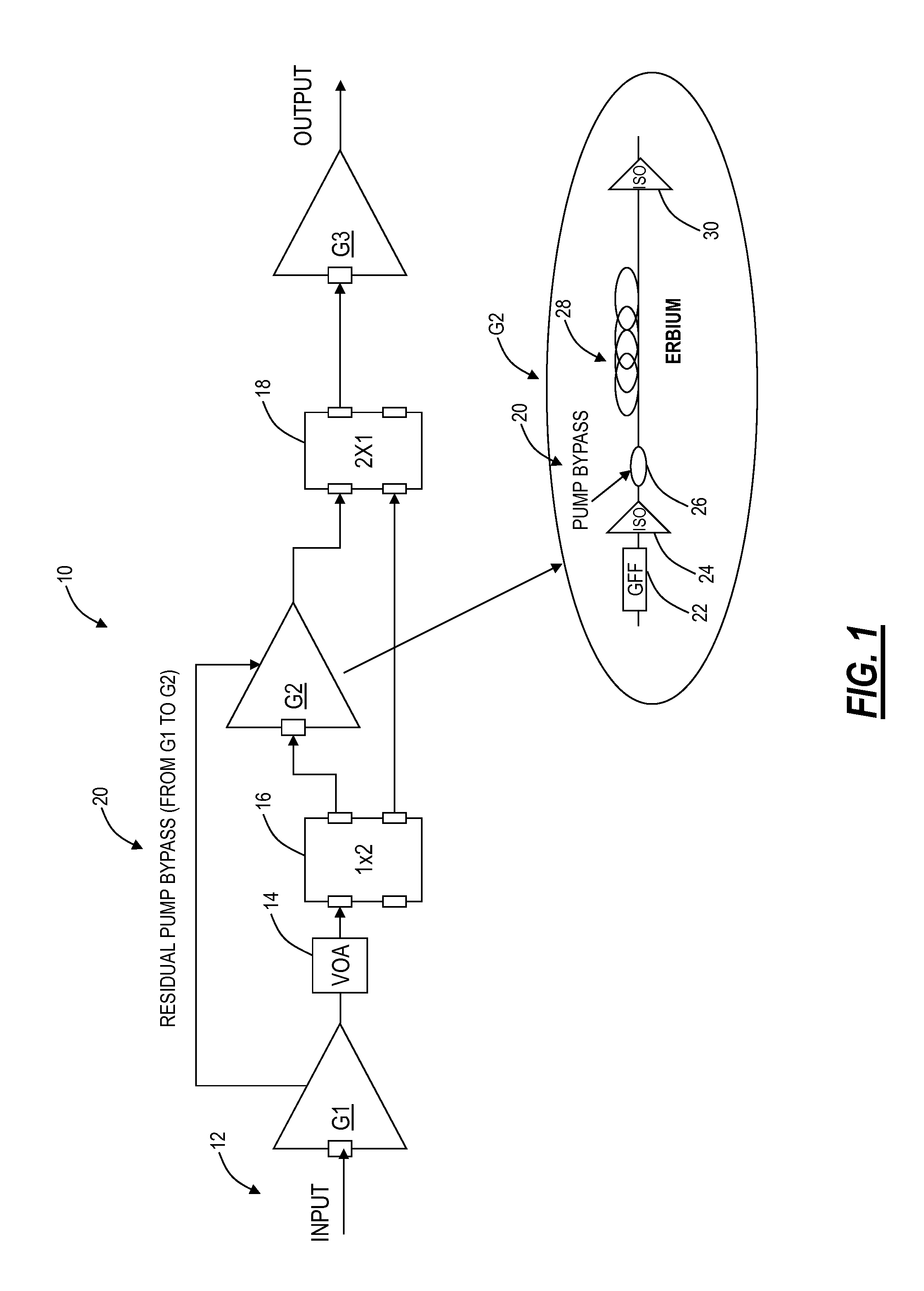
ActiveUS20140177037A1High gainIncrease choiceLaser detailsOptical transmission with multiple stagesAudio power amplifierIntermediate stage
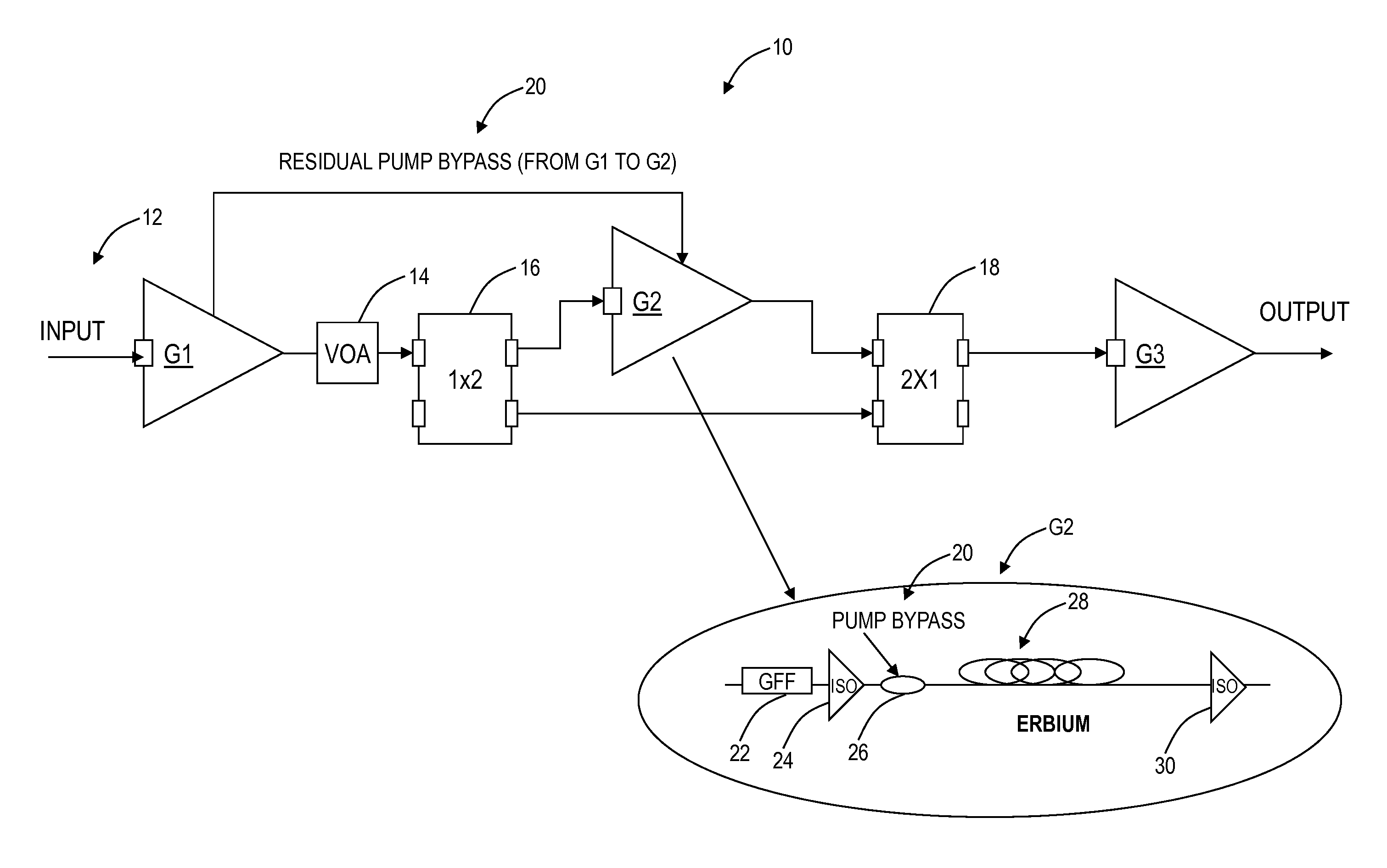
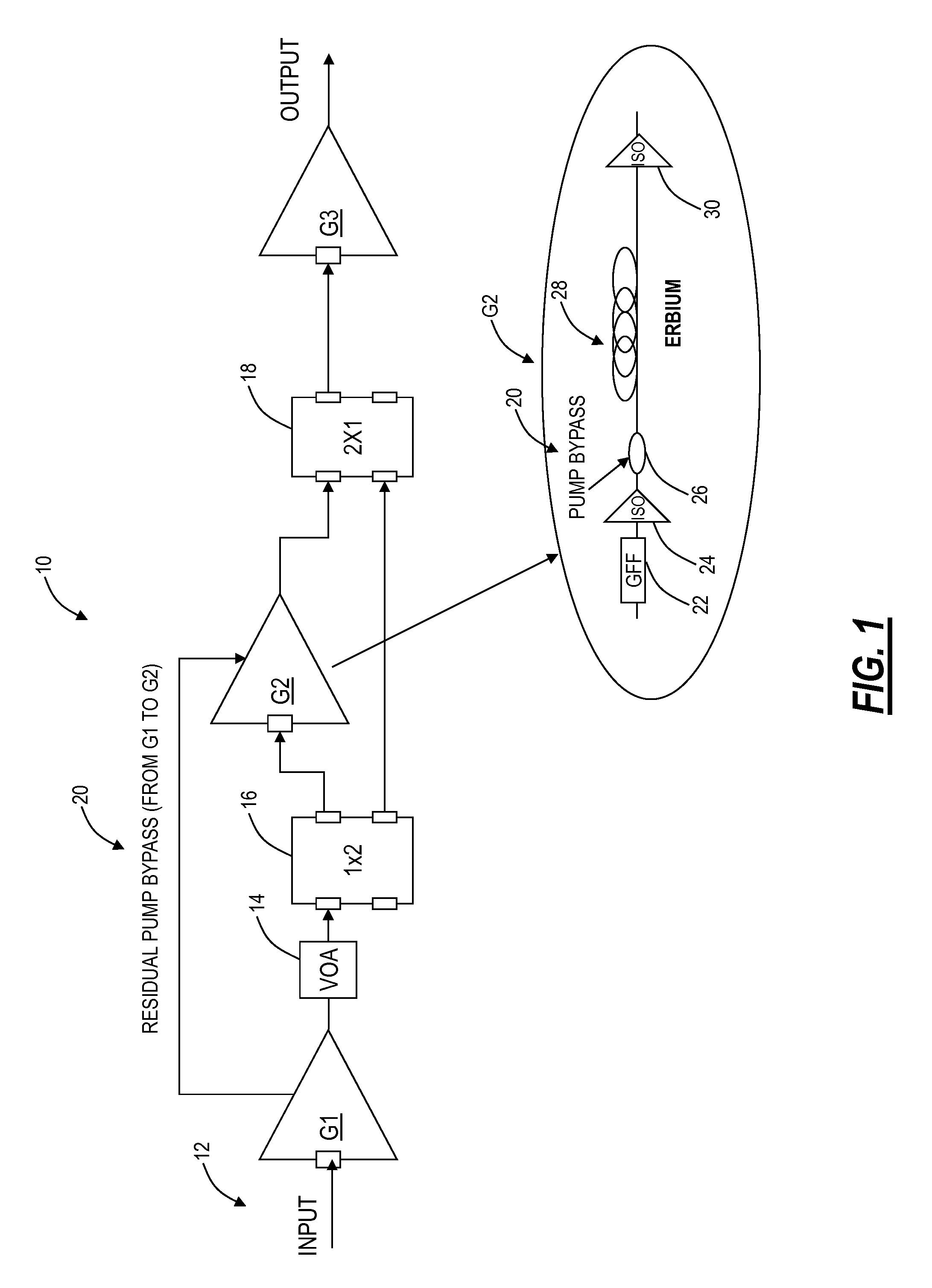
An extended dynamic range optical amplifier, a method of operation, and a line amplifier configuration include an optical amplifier that can be optimized for high or low span loss conditions by switching an internal stage in or out of an internal light path within the amplifier. The extended dynamic range optical amplifier can include a low gain mode and a high gain mode with an internal switch to switch out a gain mid-stage in a low gain mode to extend the useful dynamic range of the amplifier. Further, the extended dynamic range optical amplifier can use residual pump power from an initial stage to pump the gain mid-stage in the high gain mode. Additionally, the extended dynamic range optical amplifier includes remapping of gain in the initial stage and the gain mid-stage to optimize the amplifier noise performance based on the maximum output power of the amplifier.
Owner:CIENA
Extended dynamic range optical amplifier
ActiveUS8873135B2Optical transmission with multiple stagesActive medium materialAudio power amplifierIntermediate stage
An extended dynamic range optical amplifier, a method of operation, and a line amplifier configuration include an optical amplifier that can be optimized for high or low span loss conditions by switching an internal stage in or out of an internal light path within the amplifier. The extended dynamic range optical amplifier can include a low gain mode and a high gain mode with an internal switch to switch out a gain mid-stage in a low gain mode to extend the useful dynamic range of the amplifier. Further, the extended dynamic range optical amplifier can use residual pump power from an initial stage to pump the gain mid-stage in the high gain mode. Additionally, the extended dynamic range optical amplifier includes remapping of gain in the initial stage and the gain mid-stage to optimize the amplifier noise performance based on the maximum output power of the amplifier.
Owner:CIENA
LiDAR 3D Imaging System Based on Virtual Instrument
ActiveCN104049259BAchieve seamless integrationShorten the development cycleElectromagnetic wave reradiationMirror reflectionFull waveform
A lidar three-dimensional imaging system based on a virtual instrument comprises a three-dimensional scene modeling module, a lidar testing system simulation environment modeling module, a full-waveform signal processing module and a three-dimensional reconstruction module. The three-dimensional scene modeling module comprises a three-dimensional model loading element used for setting background colors, visual angle control, illumination, a projection mode, a display model and other basic scene projects. The lidar testing system simulation environment modeling module comprises four modeling sub-modules which are a laser pulse model, an atmospheric transmission model, an object interaction model and a receiving unit model. The laser pulse model is used for simulating a laser source according to the wavelength, pulse width, energy and other characteristics of a laser. The atmospheric transmission model is used for simulating a tested atmospheric environment, so that a noise model is generated for acting on the laser. The object interaction model is used for simulating effects of the laser and a detected object, and the effects comprise mirror reflection, diffuse reflection, surface reflection and speckles. The receiving unit model is used for simulating detector noise and amplifier noise which are generated after sensing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Optimization method of transmission performance of long-distance coherent optical communication system
InactiveCN104410452AImprove performanceReduce the numberElectromagnetic transmissionTelecommunications linkTime delays
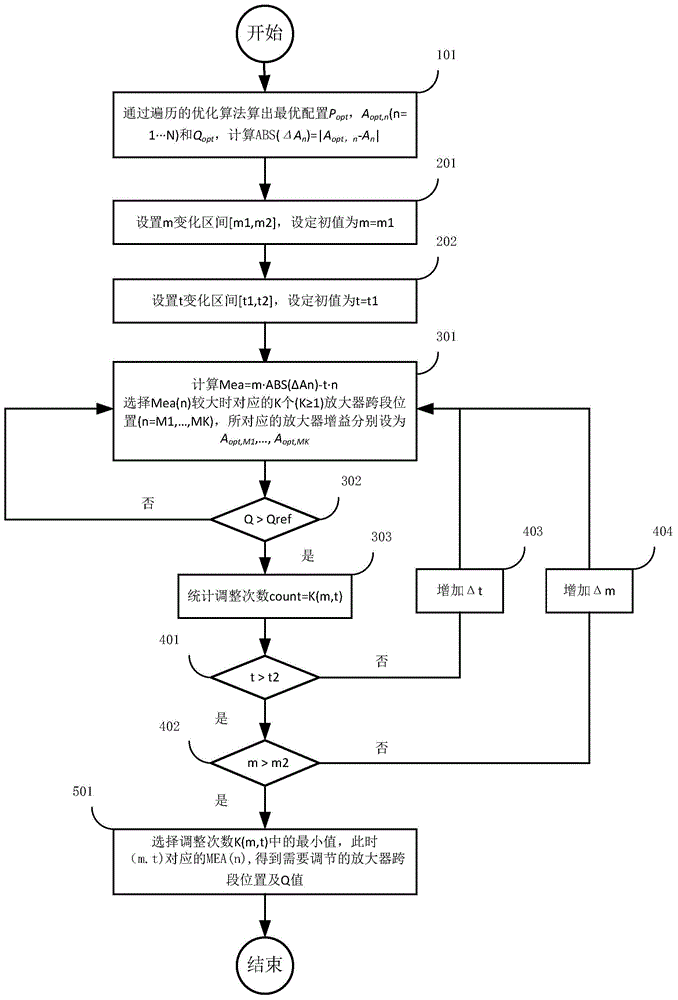
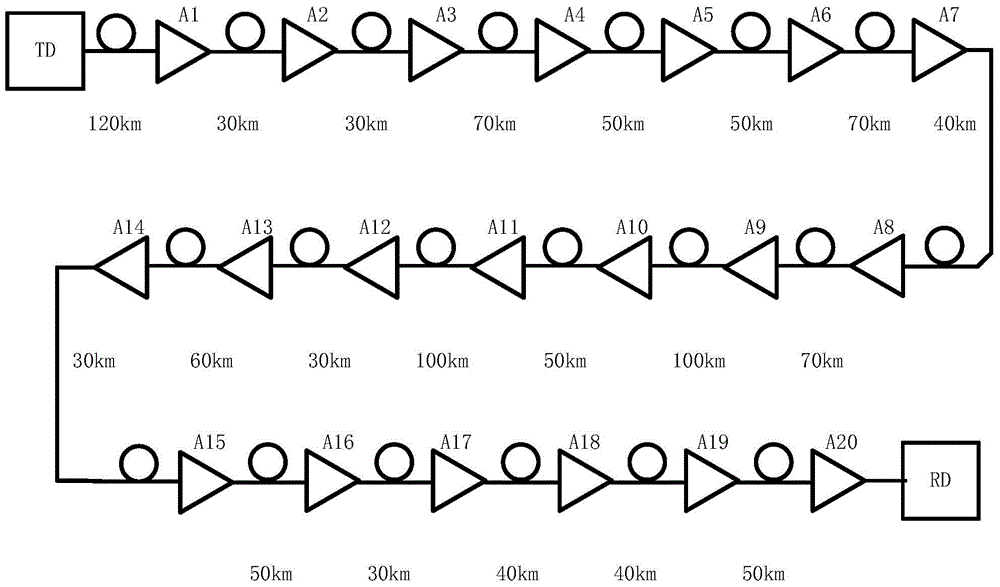
The invention provides an optimization method of transmission performance of a long-distance coherent optical communication system for solving the problem of difficulty in quickly carrying out global optimization on the transmission performance of the coherent optical communication system with a long distance, a large cross-section number, unequal cross-section indexes and no dispersion compensation. The optimization method comprises the following steps that an optimal performance parameter of the whole optical communication link is computed based on link attention and amplifier noise characteristics; ranges and initial values of one group of weighting coefficients (m, t) are arranged; two factors including an optimal difference value of amplifier gain and an amplifier cross-section position are considered to arrange a module Mea (m, t, n), the corresponding Kminth amplifier cross-section position Mk is selected when the Mea is larger, the amplifier gain is Aopt, Mt, wherein k is equal to 1-Kmin, and the other amplifier gain is the initial value thereof. According to the optimization method, promotion of a light path performance index factor Q is considered, instantaneous characteristics, such as shake and time delay, which are caused by overlarge regulated quantity or overlarge regulation number, are avoided, and the performance of the optical transmission system is quickly optimized under the conditions of the extra-long distance and the large cross-section number.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
An apparatus and method to calculate a noise figure of an optical amplifier for wavelength channels in a partial-fill scenario to account for channel loading
An apparatus comprising a processor configured to calculate a noise figure of an optical amplifier for a plurality of selected wavelength channels in a partial-fill scenario that accounts for channel loading. The noise figure is calculated using a plurality of corresponding noise figure correction values at a plurality of wavelengths based on an effective number of channels.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
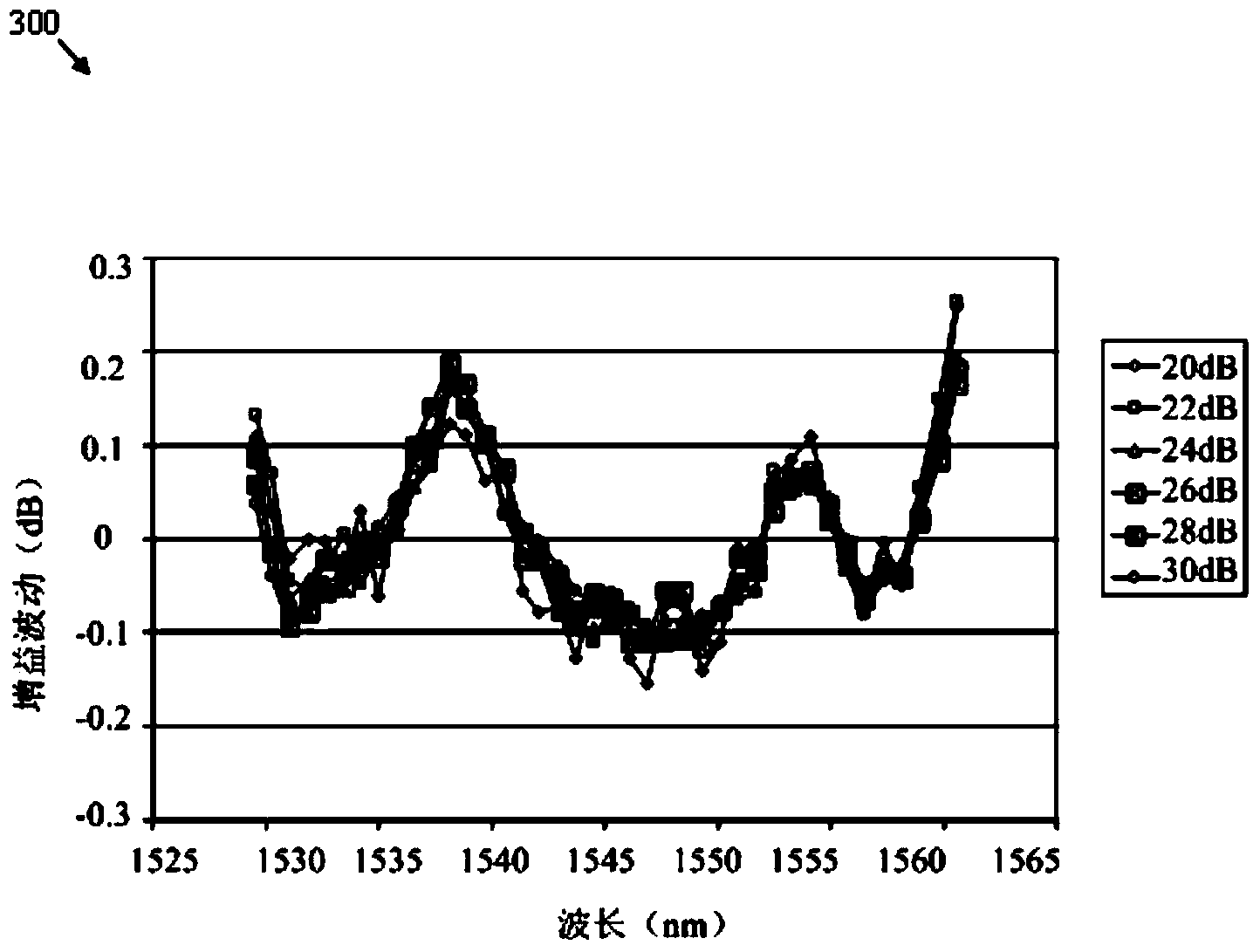
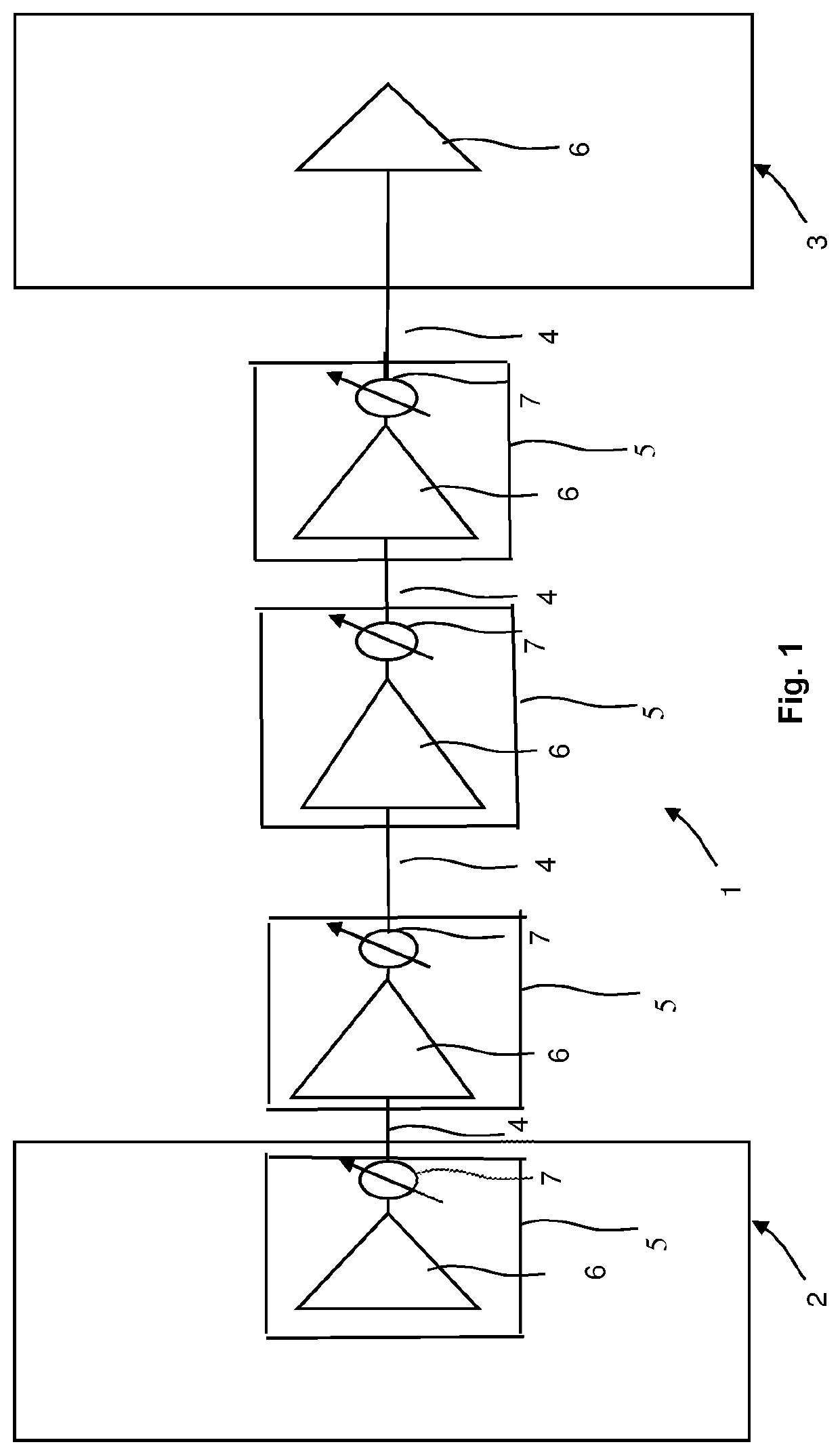
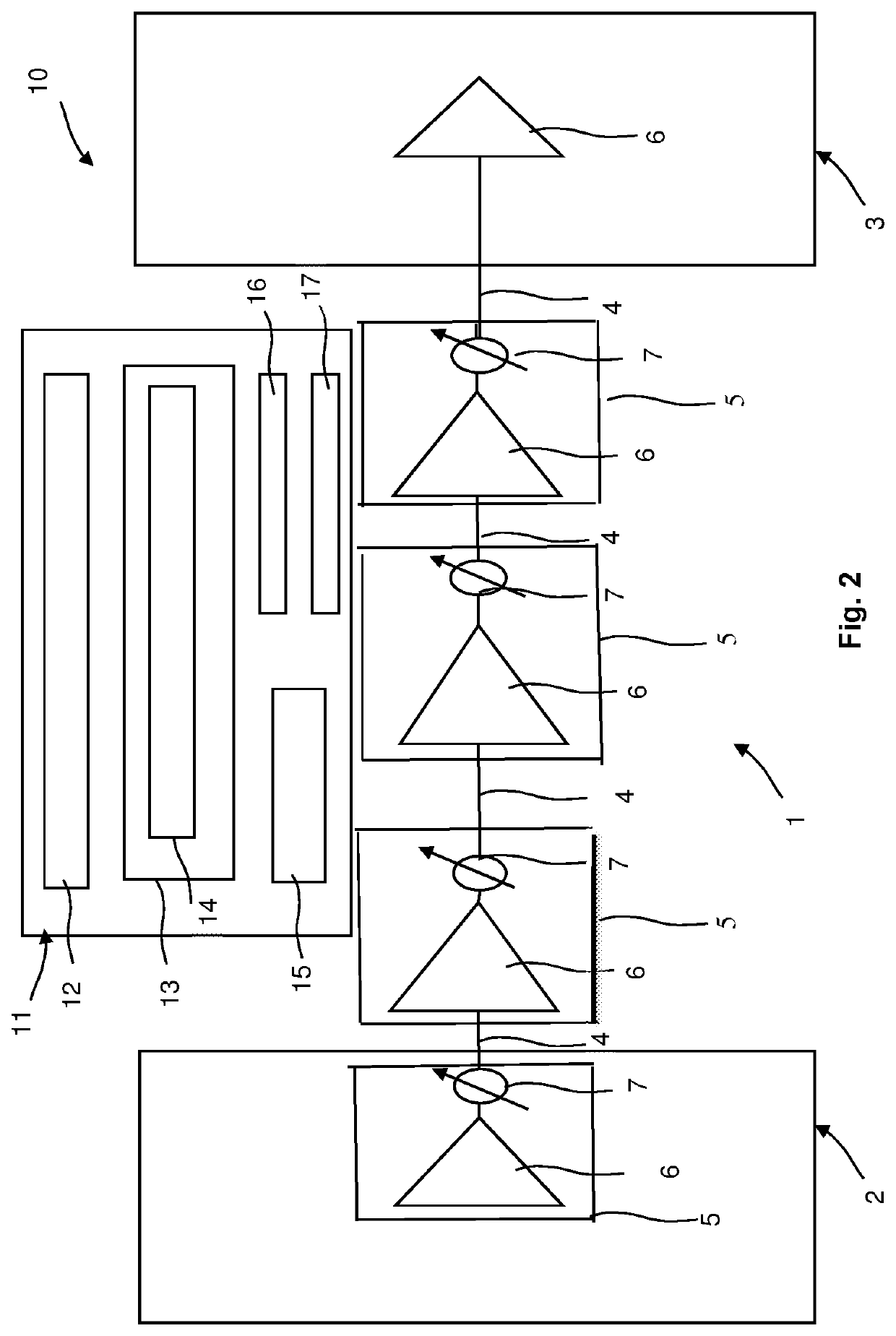
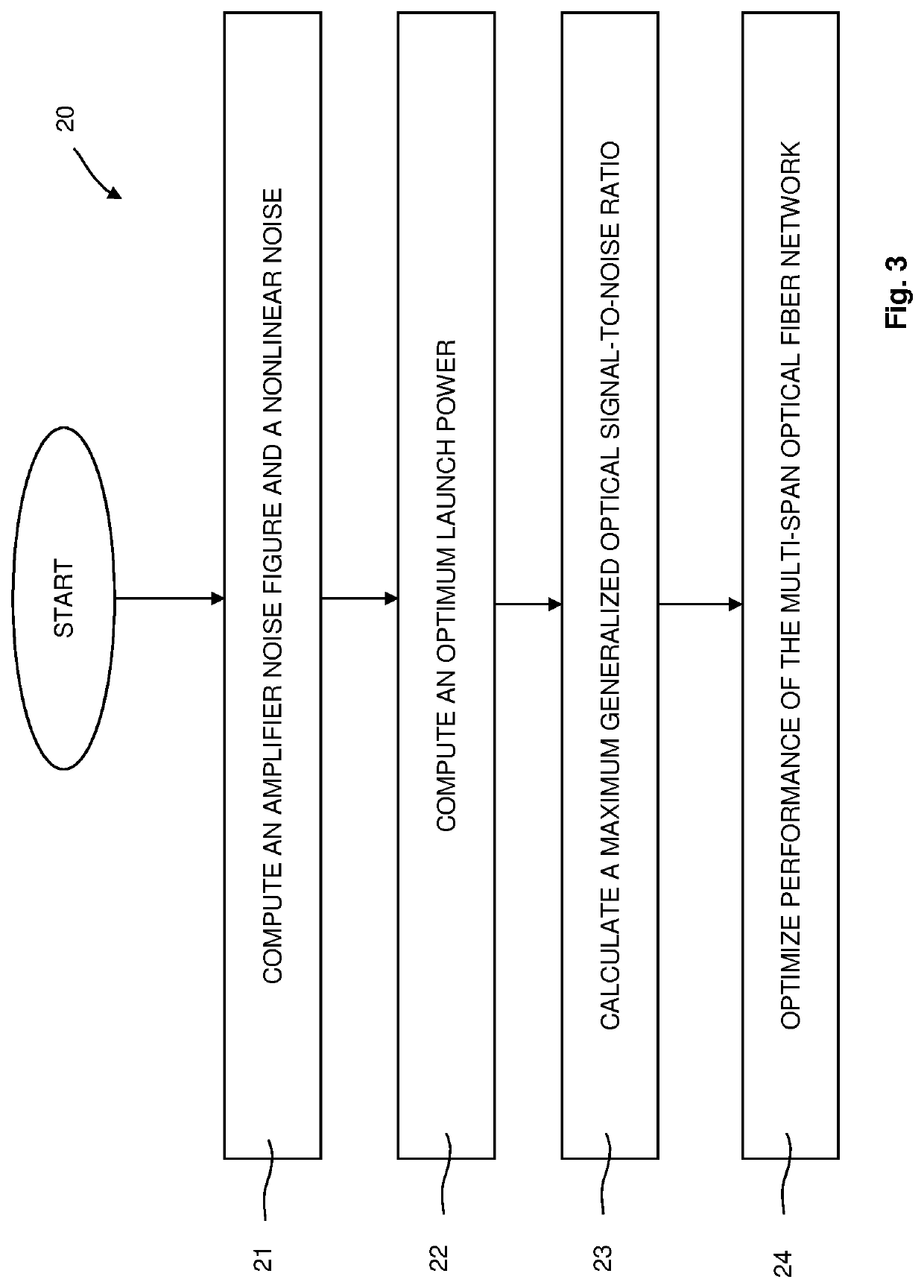
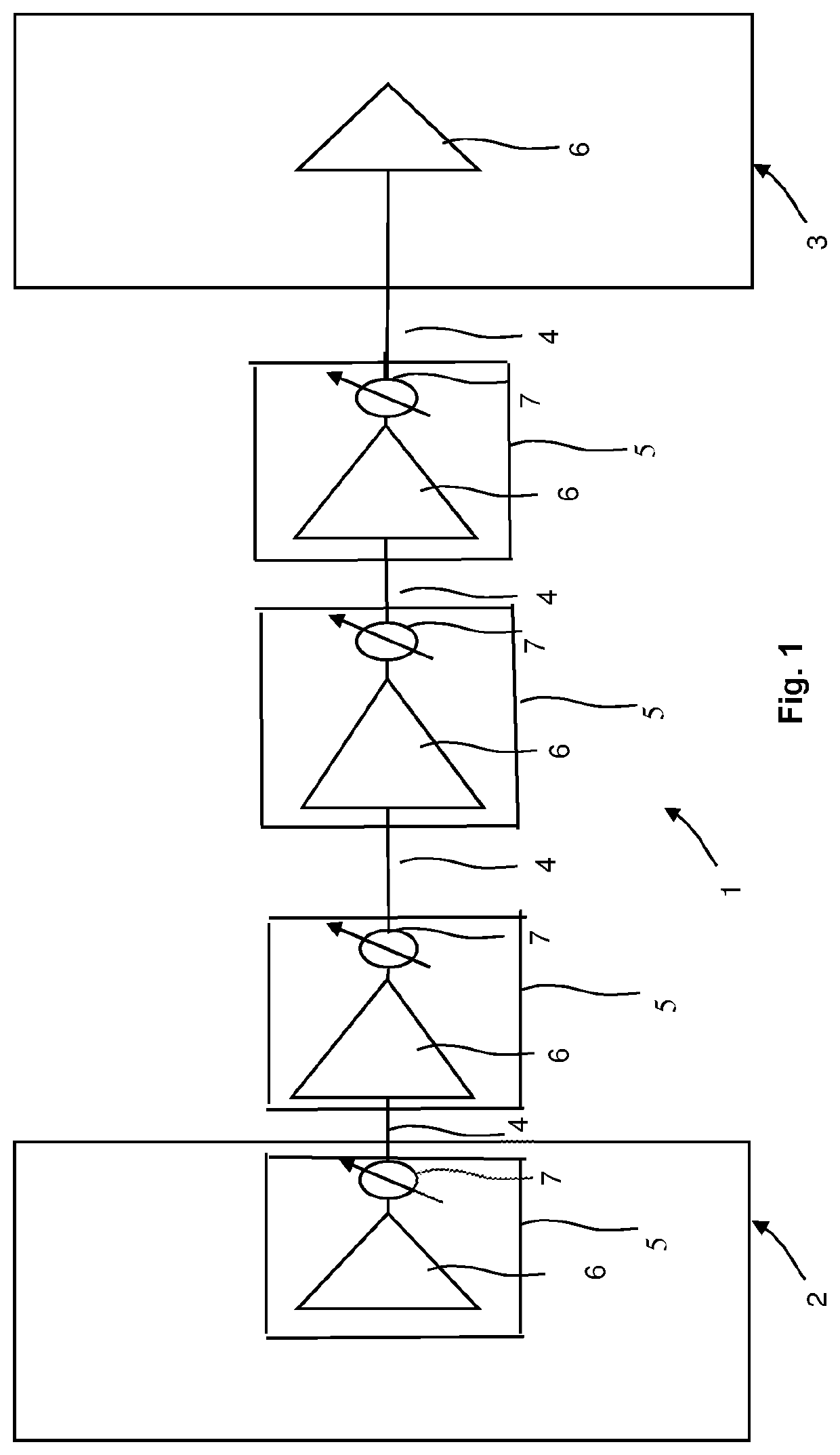
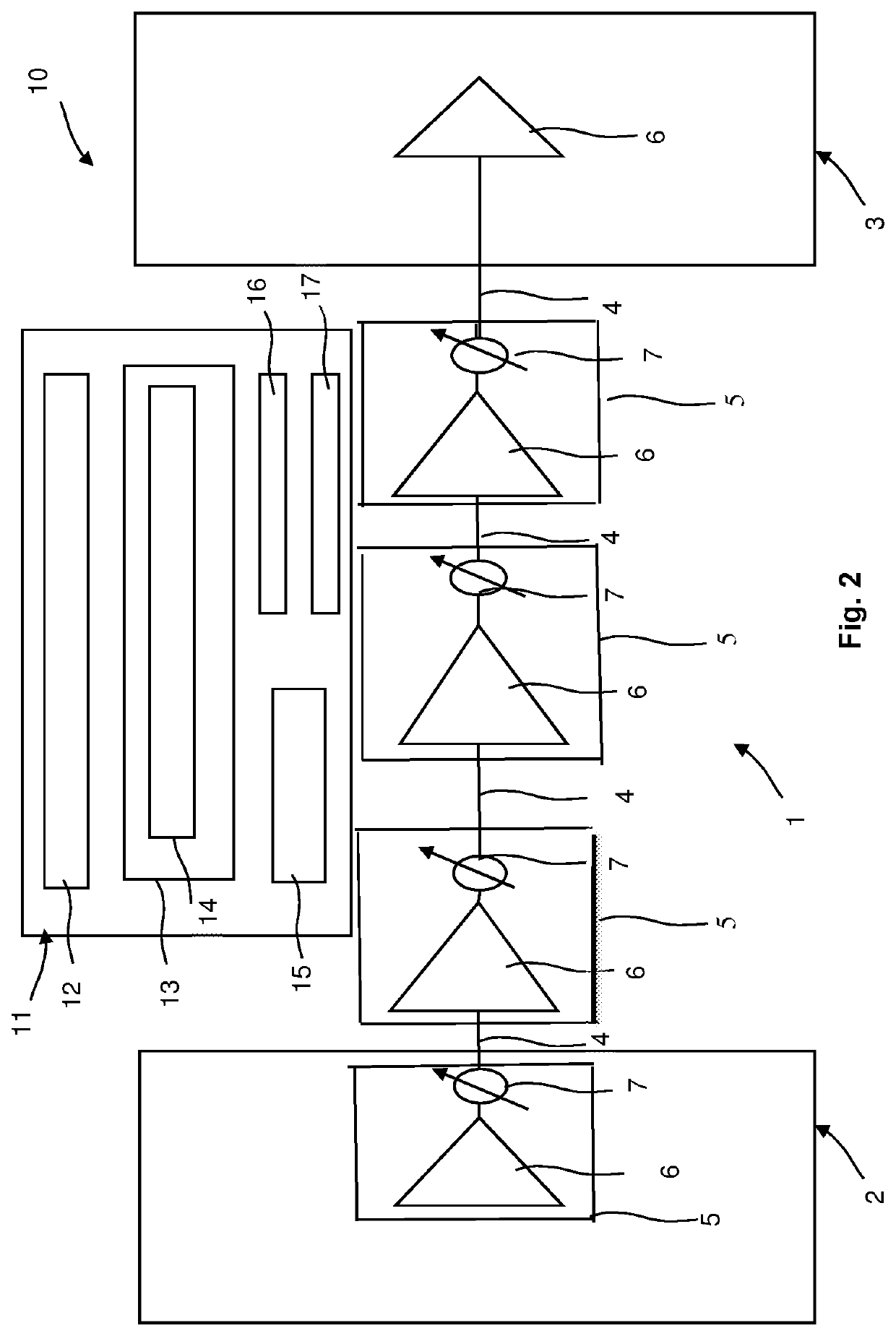
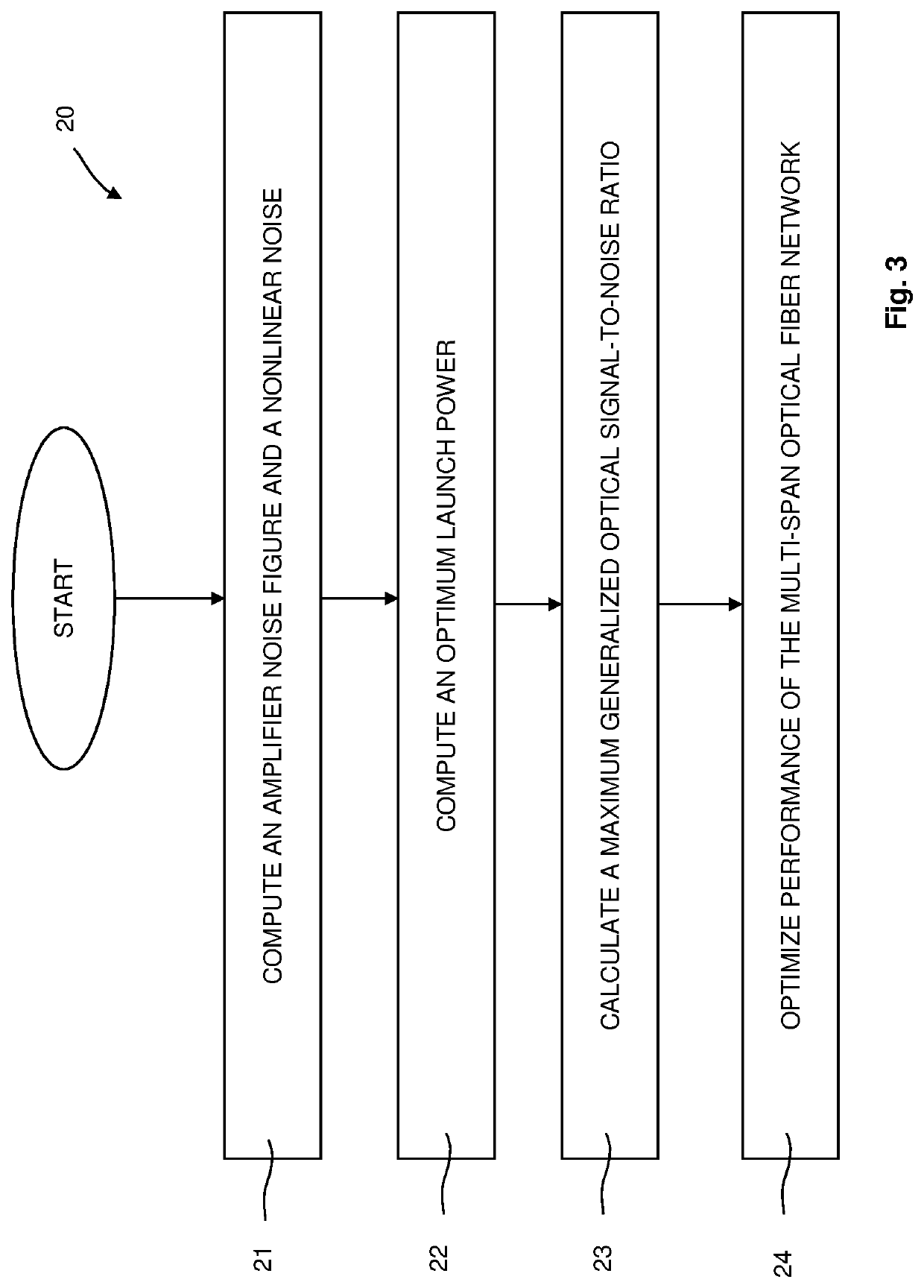
Method and Network Control Device for Optimizing Performance of a Multi-Span Optical Fiber Network
ActiveUS20220109509A1Improve performanceComputational effortOptical transmission with multiple stagesElectromagnetic network arrangementsGainFiber network
The present invention relates to a method for optimizing performance of a multi-span optical fiber network. Each span has an associated optical transmission fiber connected to an associated optical amplifier. Gain and output power of the associated optical amplifier are respectively controlled independently. An amplifier noise figure respectively depends on the gain of the associated optical amplifier, with each associated optical amplifier further connected to launch optical signals into a remainder of a corresponding optical transmission line. The method includes the steps of for each span, computing the amplifier noise figure and a non-linear noise generated in the span based on information about the span and using the computed amplifier noise figure and the computed non-linear noise to compute an optimum launch power, and optimizing performance of the multi-span optical fiber network based on the computed optimum launch powers of all spans.
Owner:ADVA OPTICAL NETWORKING SE
Noise reduction system and method for audio switching amplifier
InactiveUS7872522B2Improve noiseReduce audible noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlAudio power amplifierRelative phase
Noise reduction for a switching amplifier system having a differential output stage and demodulator filter responsive to complementary PWM signals includes generating in-phase PWM signals and gradually adjusting their duty cycle between a low duty cycle and the full duty cycle of the complementary PWM signals, generating full duty cycle PWM signals and gradually shifting their relative phase between in-phase and out-of-phase; and in response to a turn-on signal, adjusting the in-phase PWM signals from low to full duty cycle and shifting the relative phase from in-phase to out-of-phase, and in response to a turn-off signal shifting the relative phase from out-of-phase to in-phase and adjusting the in-phase PWM signals from full to low duty cycle for maintaining balanced charge on the demodulation filter to reduce audible noise.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
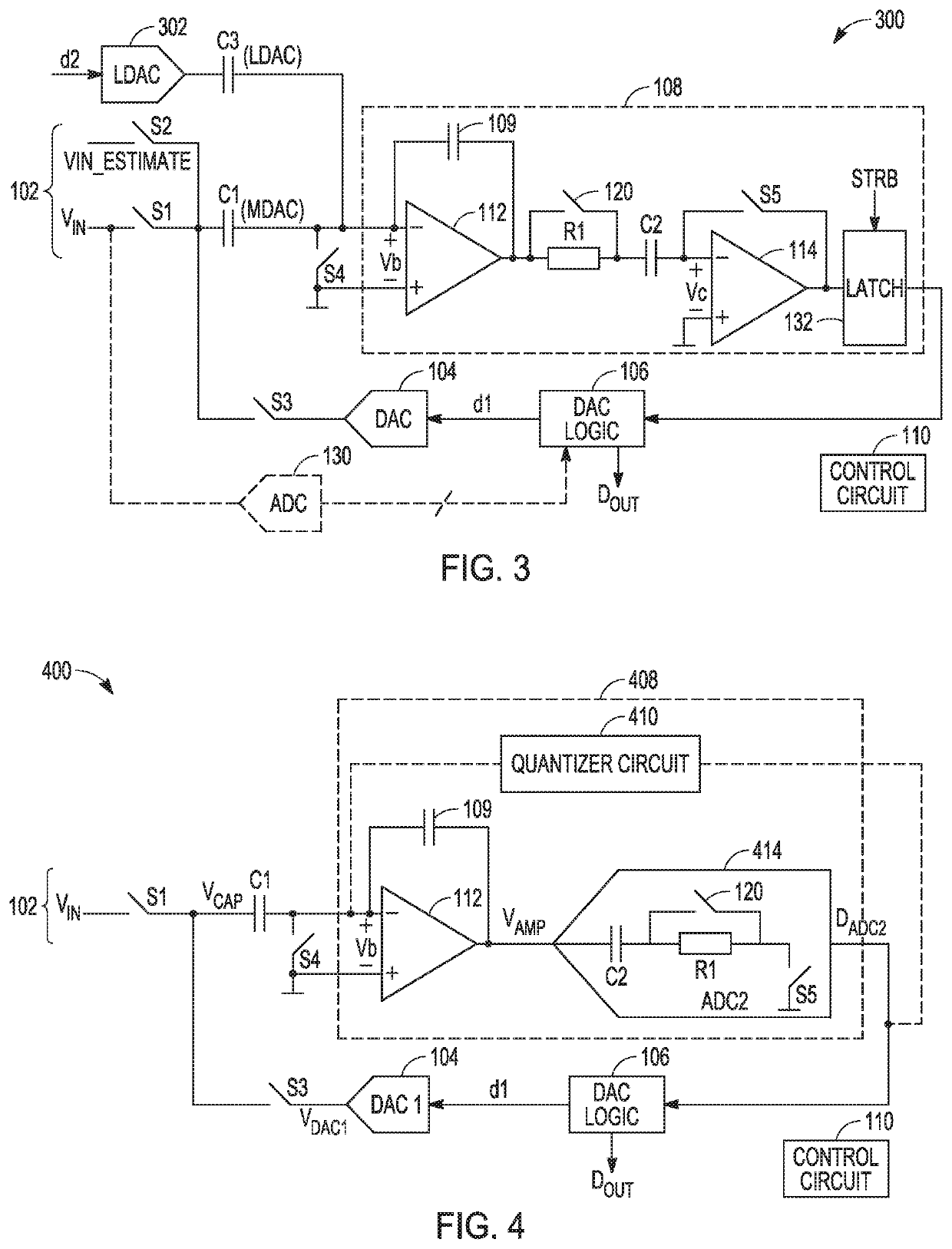
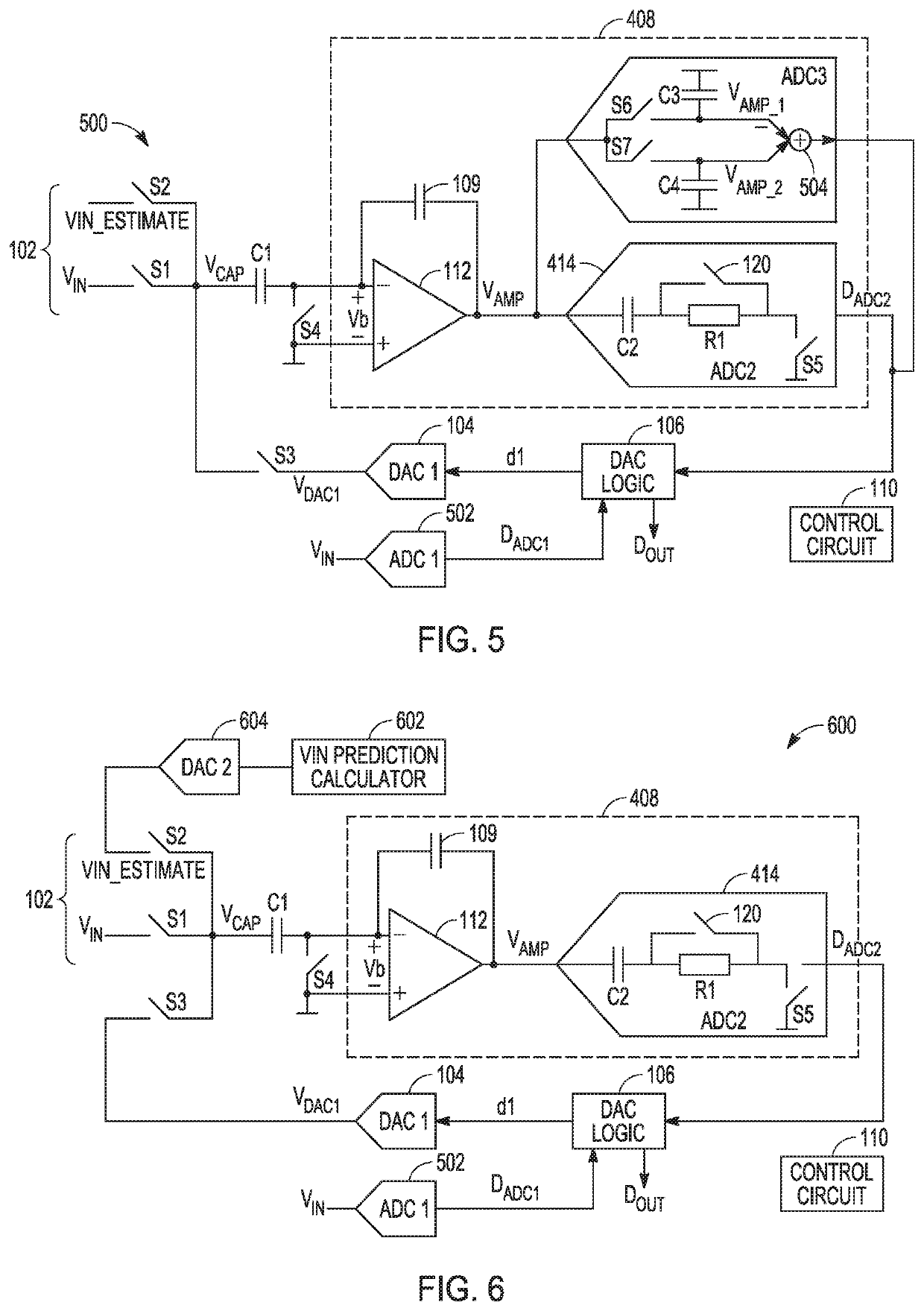
Low noise analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS10715160B1Reduce noiseReduce the impact of noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital/analogue conversionLow noiseConverters
Noise sources in an ADC circuit can include kT / C noise of a sampling capacitor, noise coupling on to sampling capacitors from digital circuits, and amplifier noise. Also, charge injection from mismatch in sample switches can cause offsets. These various noise sources can be largely canceled or reduced using described techniques. As a result, the size of the sampling capacitors can be greatly reduced, while still achieving significantly improved noise performance and power efficiency for the overall converter.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Method and apparatus for canceling balun amplifier noise
ActiveCN102545790AReduced Noise Figure NFAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceRF amplifierImpedance matchingVoltage sensing
The noise figure of a low noise amplifier (LNA) is reduced without sacrificing performance such as gain, IIP3, and wideband impedance matching. Embodiments include configuring a control module of the LNA to sum and scale an output from a current-sensing branch of the LNA and an output from a voltage sensing branch of the LNA into one or more summed and scaled outputs. The control module also feeds the one or more summed and scaled outputs back to at least one of the outputs of the branches of the LNA.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Low noise signal reproducing method for a solid state imaging device
InactiveUS20110050970A1Avoid saturationReduce noise signalTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow noiseAudio power amplifier
A method for reproducing a low noise signal for a solid state imaging device which can reduce not only the reset noise but the amplifier noise around frequency zero, avoiding the saturation of the voltage conversion part in a bright scene, is accomplished by controlling a reset pulse of a CCD imaging device according to the result of comparing the output signal of the CCD imaging device with a reference signal value. When the output signal of the CCD imaging device is smaller than the reference signal value, the reset pulse is not applied to the CCD imaging device. Thereat, a pixel signal is reproduced as a differential signal between two signals sampled at two points with an interval of T0, the amplifier noise around frequency zero being reduced in the pixel signals.
Owner:OZAWA NAOKI
Method and apparatus for improved signal to noise ratio in raman signal detection for MEMS based spectrometers
InactiveUS20080204743A1Radiation pyrometryPhotometry electrical circuitsDiscriminatorAudio power amplifier
A method of Raman detection for a portable, integrated spectrometer instrument includes directing Raman scattered photons by a sample to an avalanche photodiode (APD), the APD configured to generate an output signal responsive to the intensity of the Raman scattered photons incident thereon. The output signal of the APD is amplified and passed through a discriminator so as to reject at least one or more of amplifier noise and dark noise. A number of discrete output pulses within a set operational range of the discriminator is counted so as to determine a number of photons detected by the APD.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Device and method for power amplifier noise reduction
ActiveUS7545218B1Reduce noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
A power amplifier for use in wireless communication devices is disclosed that reduces the noise generated at the output of the amplifier in the receive band of the wireless communication device. A resonant circuit is inserted between the base ballast resister and the lumped resister. The resonant frequency of the resonant circuit is adjusted to correspond to the frequency offset between the transmission frequency and the frequency corresponding to the peak noise in the receive band of the communication device.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
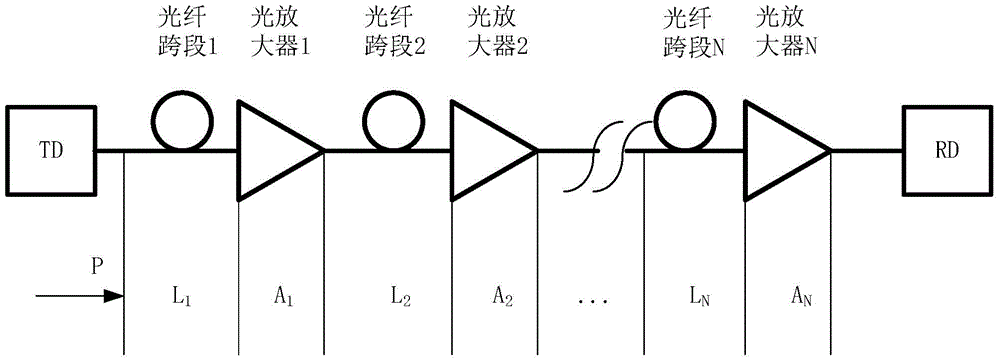
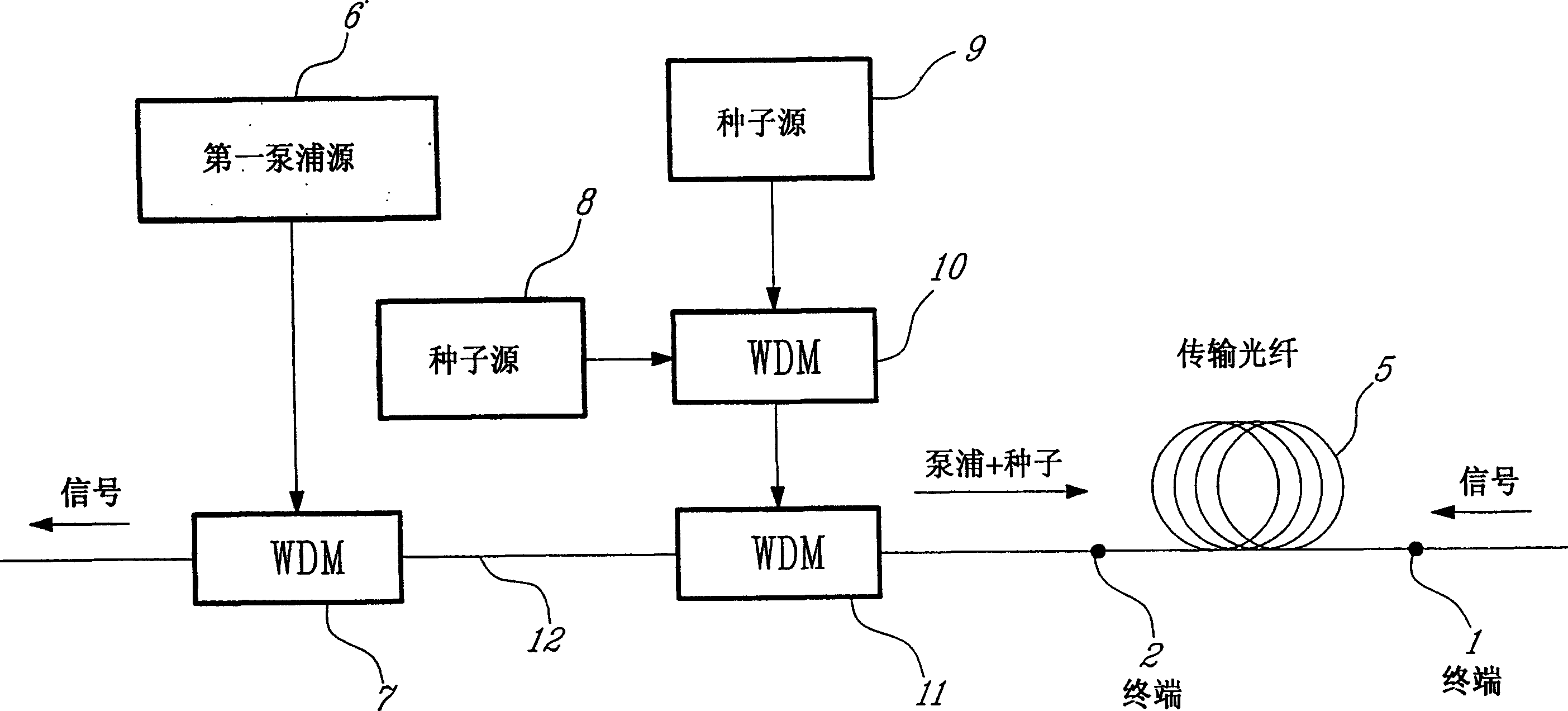
Cascaded pumping system and method for distributed Raman amplification in optical fiber telecommunication system
A pumping scheme for distributed Raman amplification (DRA) in optical fiber telecommunication systems is disclosed in which pump energy at the wavelength(s) required for DRA of the transmitted optical signal(s) is developed within the transmission fiber from a primary pump source through a series, n, where n >= 1, of Raman conversions resulting from the launch into the fiber of a primary pump source along with low-power seed sources. Alternatively, seed sources can be replaced by reflecting means to return, into the fiber, backward-travelling amplified spontaneous Raman scattered light resulting from high power in the fiber at a wavelength one Raman shift below the desired seed wavelength. The peak Raman gain thus occurs some distance from the primary pump launch terminal and leads to improved amplifier noise performance. Dynamic control of the magnitude and / or the spectral profile of the distributed Raman gain at, or near, a signal launch terminal can also be provided.
Owner:MPB TECH
Enhanced light detector
ActiveUS20210372850A1Increase signal amplitudeLess effect on signal detectionOptical measurementsPhotometry electrical circuitsFrequency spectrumEngineering
Methods for design and production of highly sensitive active and passive light detecting devices and systems. Orders of magnitude improvement in optical signal detection is made possible in high noise or low contrast scenes. The current invention creates a small spectral difference between two parts of a split light stream. When recombined, the altered light streams partially correlate, and that generates full amplitude signal oscillation at a frequency that depends on the constituent spectrum. The full amplitude signals and spectrum dependent oscillation make signal discrimination much better than intensity-only methods. The effect of read noise, amplifier noise, dark current noise, and thermal noise due to photo detector shunt resistance, become less important when compared to light detection using prior art methods
Owner:VOLLMERHAUSEN RICHARD H
Method and apparatus for restraining D-genus power amplifier noise and D-genus power amplifier with noise suppression
InactiveCN101465619BSuppress noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCapacitanceCharge discharge
The invention discloses a noise suppression method for class D power amplifier, which includes a step S1 and a step S2; wherein, in step S1, an external enabling signal is received; in step S2, when the state of external enabling signal is changed, an enabling signal for a class D power amplifier is generated according to the external enabling signal; meanwhile, a silencing signal used for controlling the load of a class D power amplifier is generated according to the external enabling signal. The noise suppression method for class D power amplifier can effectively suppress POP or CLICK noisegenerated in capacitor charge-discharge process without increasing or modifying chip pins.
Owner:HANGZHOU MPS SEMICON TECH
Method and apparatus for canceling balun amplifier noise
ActiveCN102545790BReduced Noise Figure NFAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceRF amplifierPower flowEngineering
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Feed back type active noise eliminating earpiece
InactiveCN100531450CGuaranteed stabilityCancel noiseTransducer circuitsClosed loop feedbackEngineering
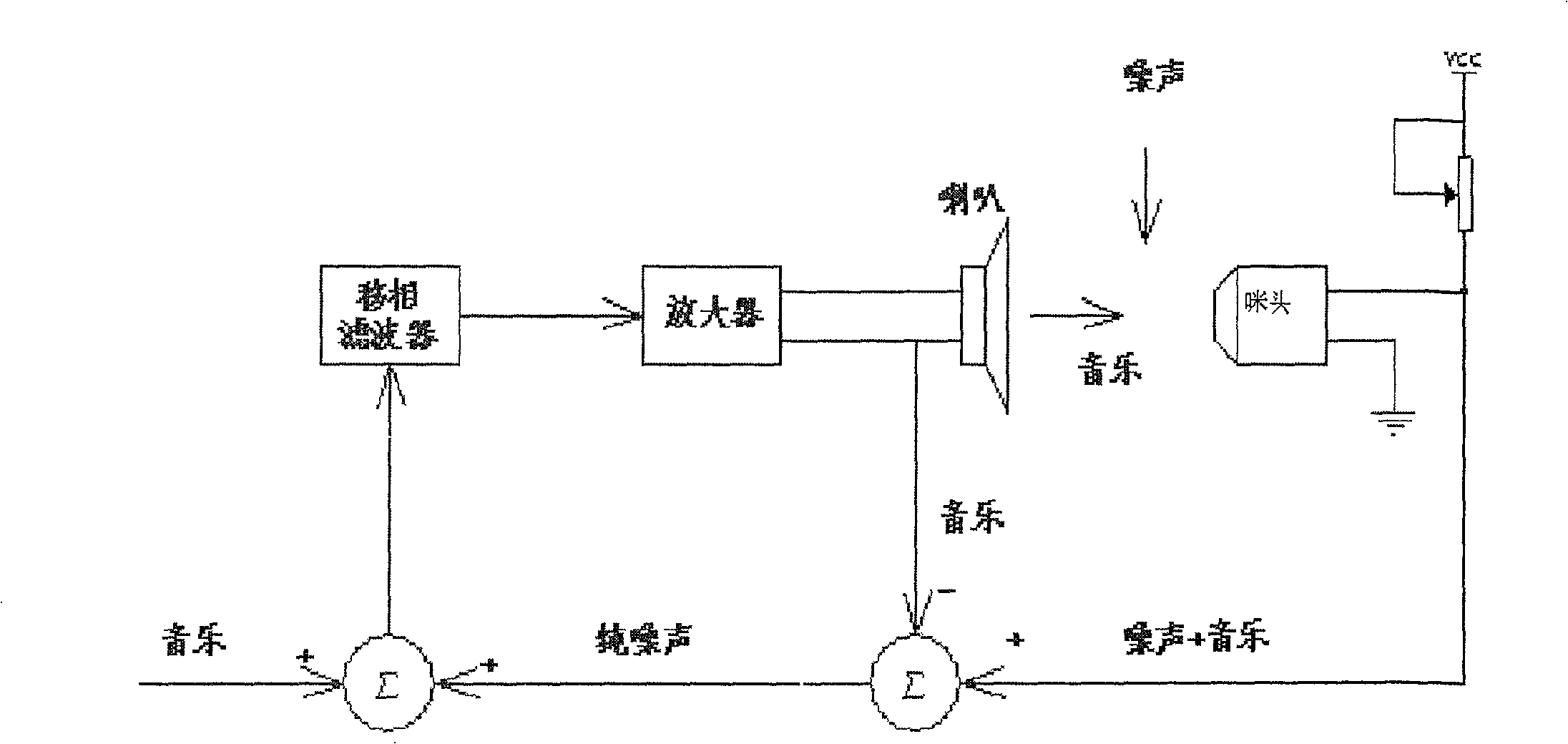
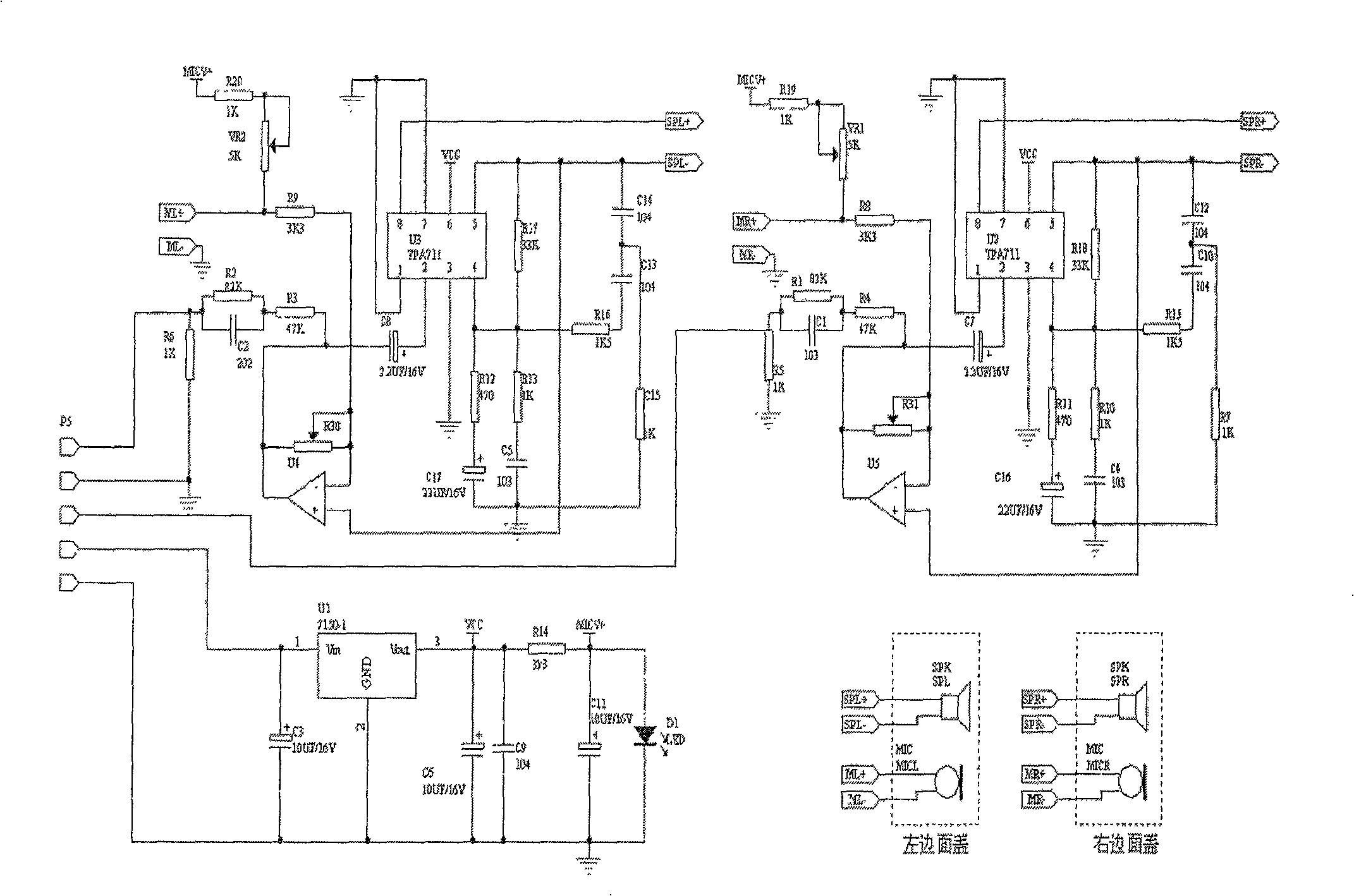
The invention relates to a feedback type active noise canceling earphone which is mainly composed of a microphone, a phase-shifting filter, an amplifier and a speaker, wherein the noise received by the microphone and the music are subtracted from the music signal output by the audio amplifier to obtain pure noise , the pure noise is superimposed with the music signal, and the high and low frequencies are filtered out through the phase-shift filter, and then amplified and inverted by the audio amplifier to drive the speaker, thereby canceling the external noise. The invention adopts the principle of feedback active closed-loop denoising to design filtering, phase shifting, amplification and compensation circuits, and improves the physical structure of the earphone, the arrangement of the feedback loop, the selection of components and earphone materials, so that the performance of the earphone is more stable , the noise cancellation effect is better, the average noise attenuation of the earphone is 20db in the range of 100-400HZ, and the maximum noise attenuation is 35db.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
Enhanced light detector
ActiveUS11391623B2High sensitivityImprove abilitiesOptical measurementsPhotometry electrical circuitsFrequency spectrumEngineering
Methods for design and production of highly sensitive active and passive light detecting devices and systems. Orders of magnitude improvement in optical signal detection is made possible in high noise or low contrast scenes. The current invention creates a small spectral difference between two parts of a split light stream. When recombined, the altered light streams partially correlate, and that generates fall amplitude signal oscillation at a frequency that depends on the constituent spectrum. The full amplitude signals and spectrum dependent oscillation make signal discrimination much better than intensity-only methods. The effect of read noise, amplifier noise, dark current noise, and thermal noise due to photo detector shunt resistance, become less important when compared to light detection using prior art methods.
Owner:VOLLMERHAUSEN RICHARD H
Method and network control device for optimizing performance of a multi-span optical fiber network
ActiveUS11489597B2Improve performanceImprove efficiencyOptical transmission with multiple stagesElectromagnetic network arrangementsEngineeringGain
The present invention relates to a method for optimizing performance of a multi-span optical fiber network. Each span has an associated optical transmission fiber connected to an associated optical amplifier. Gain and output power of the associated optical amplifier are respectively controlled independently. An amplifier noise figure respectively depends on the gain of the associated optical amplifier, with each associated optical amplifier further connected to launch optical signals into a remainder of a corresponding optical transmission line. The method includes the steps of for each span, computing the amplifier noise figure and a non-linear noise generated in the span based on information about the span and using the computed amplifier noise figure and the computed non-linear noise to compute an optimum launch power, and optimizing performance of the multi-span optical fiber network based on the computed optimum launch powers of all spans.
Owner:ADVA OPTICAL NETWORKING SP ZOO
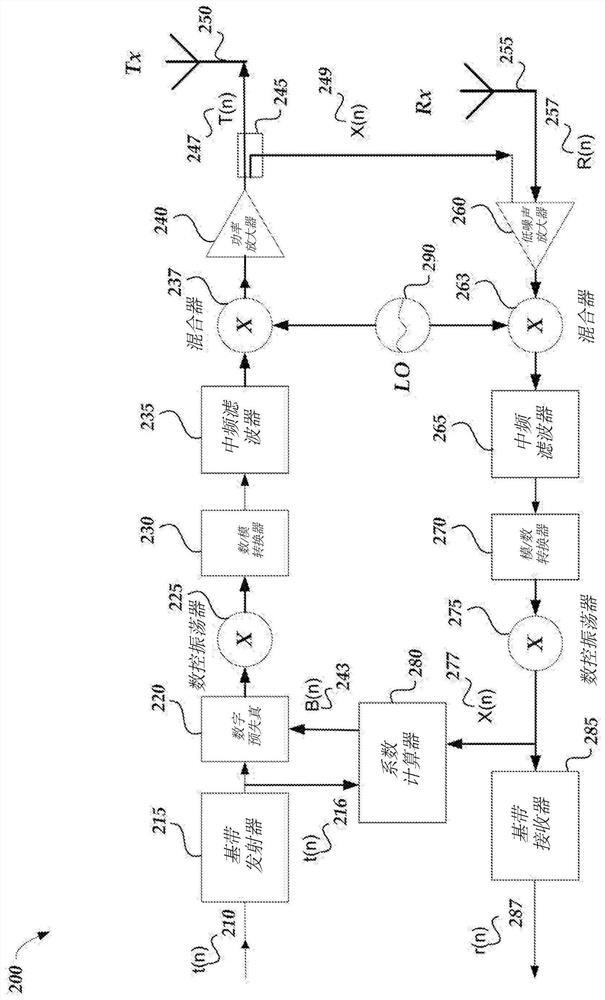
Wireless devices and systems including examples of compensating power amplifier noise
Examples described herein include methods, devices, and systems which may compensate input data for non-linear power amplifier noise to generate compensated input data. In compensating the noise, during an uplink transmission time interval (TTI), a switch path is activated to provide amplified input data to a receiver stage including a coefficient calculator. The coefficient calculator may calculate an error representative of the noise based partly on the input signal to be transmitted and a feedback signal to generate coefficient data associated with the power amplifier noise. The feedback signal is provided, after processing through the receiver, to a coefficient calculator. During an uplink TTI, the amplified input data may also be transmitted as the RF wireless transmission via an RF antenna. During a downlink TTI, the switch path may be deactivated and the receiver stage may receive an additional RF wireless transmission to be processed in the receiver stage.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com