Patents
Literature
45 results about "Cmos voltage controlled oscillator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
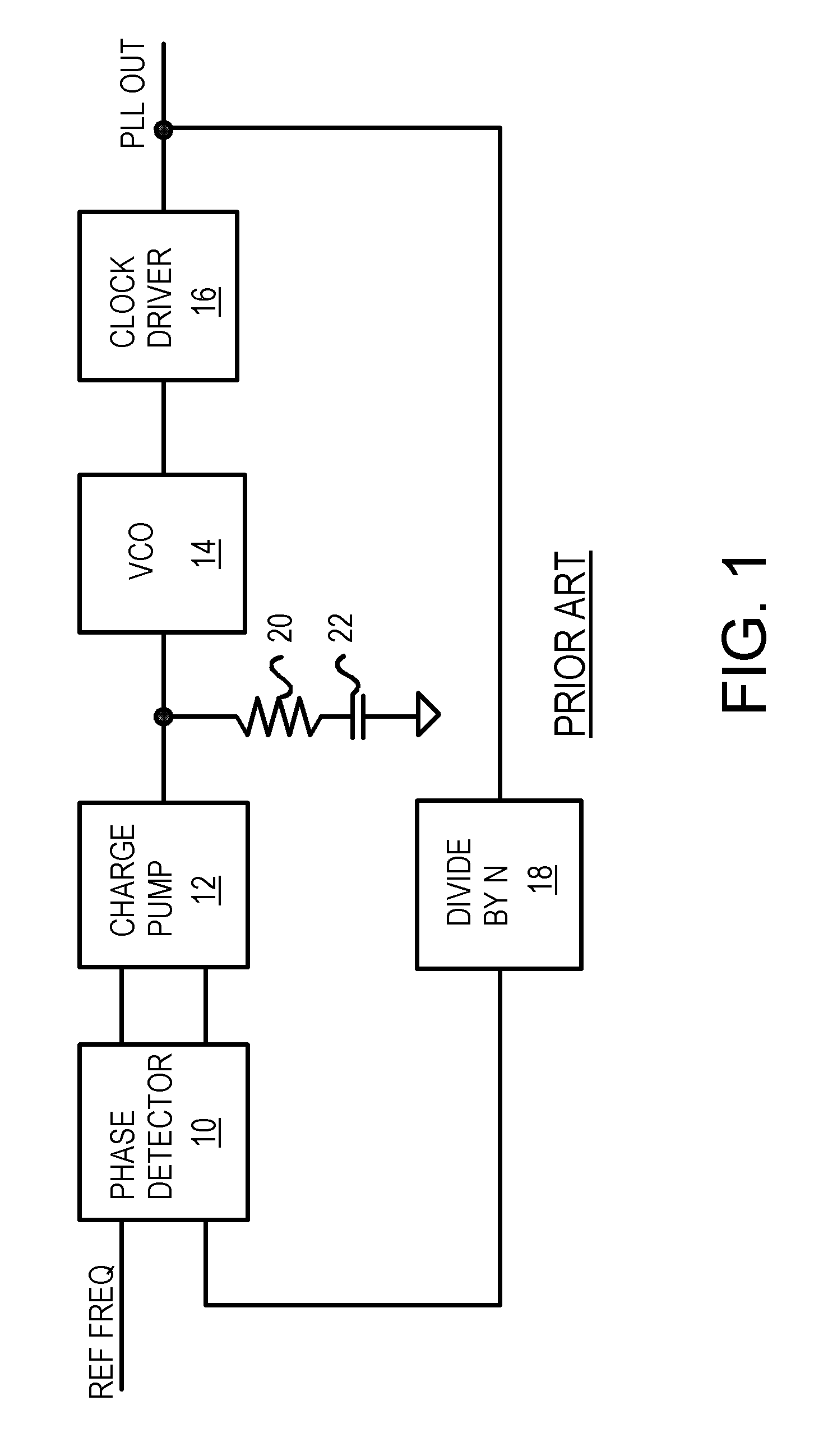
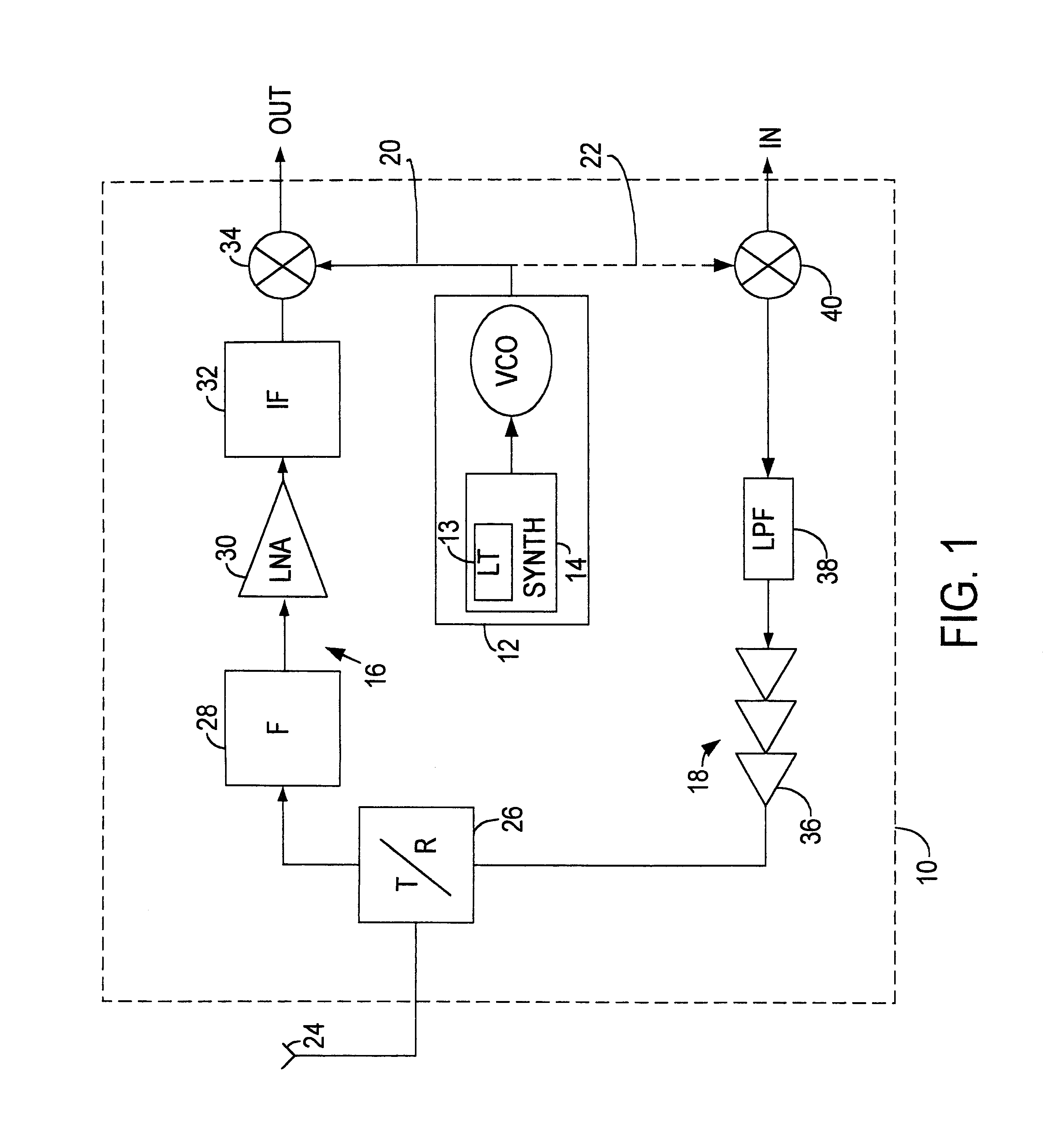
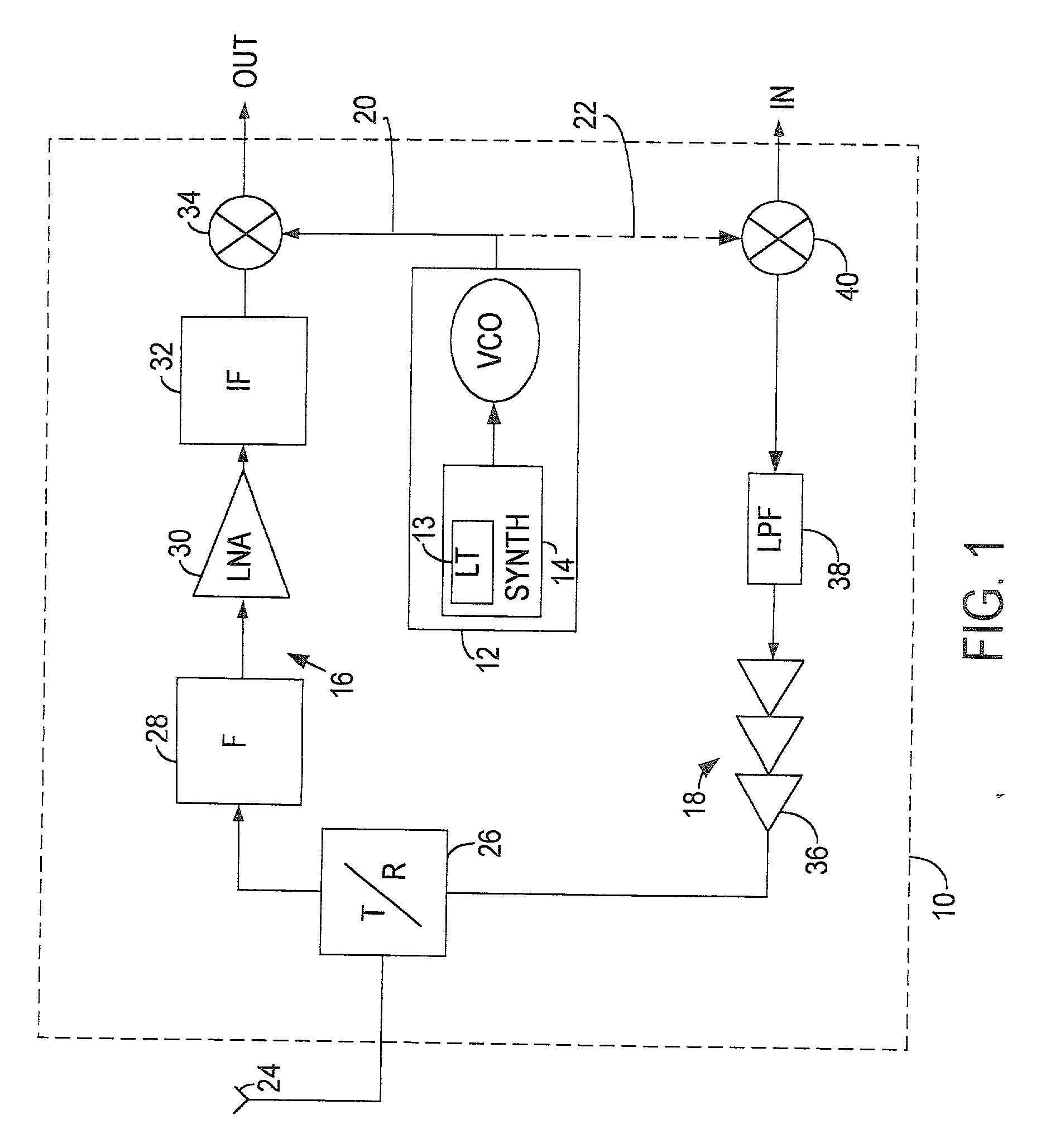
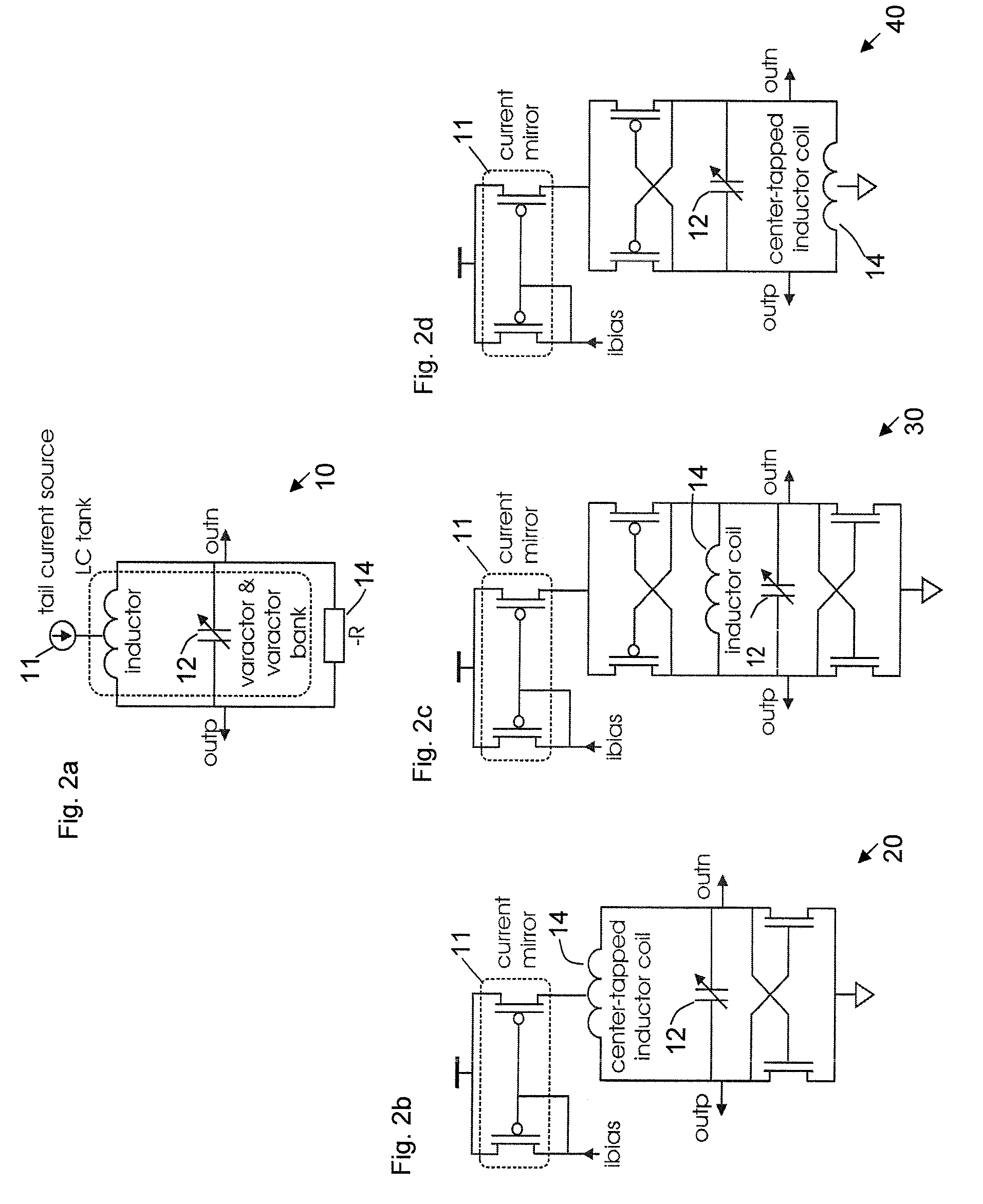
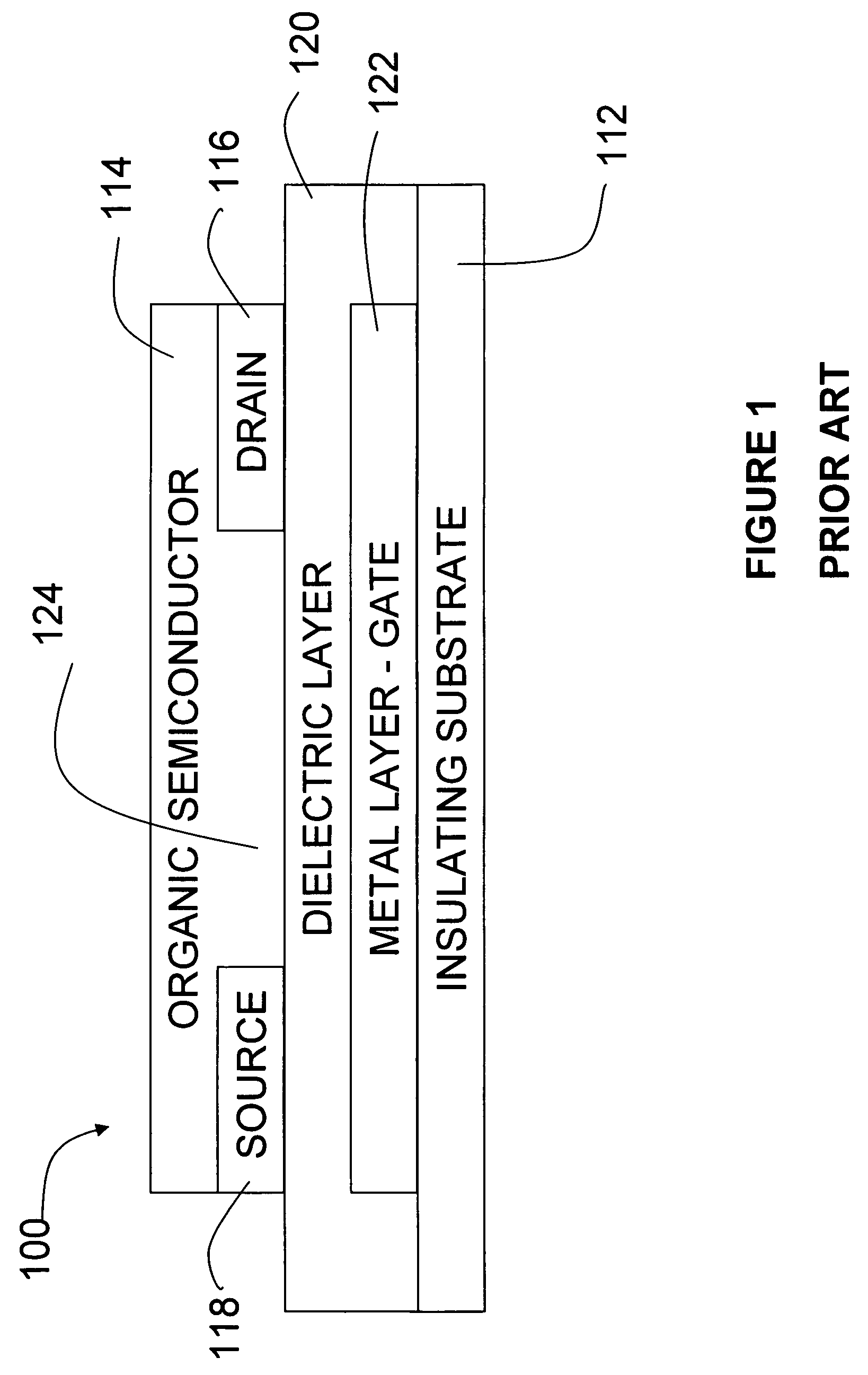
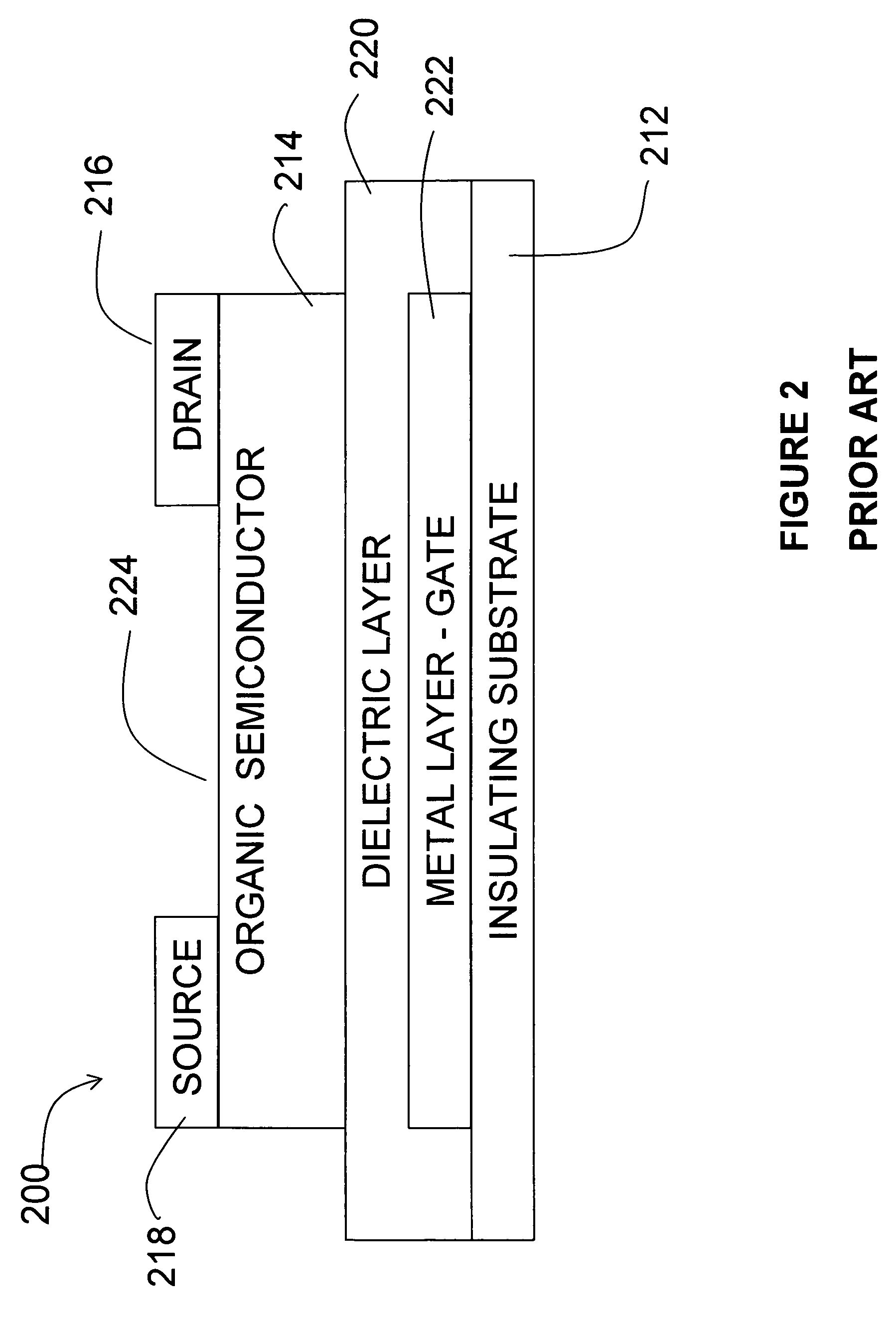
A CMOS voltage controlled oscillator is described. This CMOS voltage controlled oscillator is a linear CMOS circuit and exhibits an infinite current gain, a near infinite input impedance, a very high voltage gain with a corresponding low power consumption.
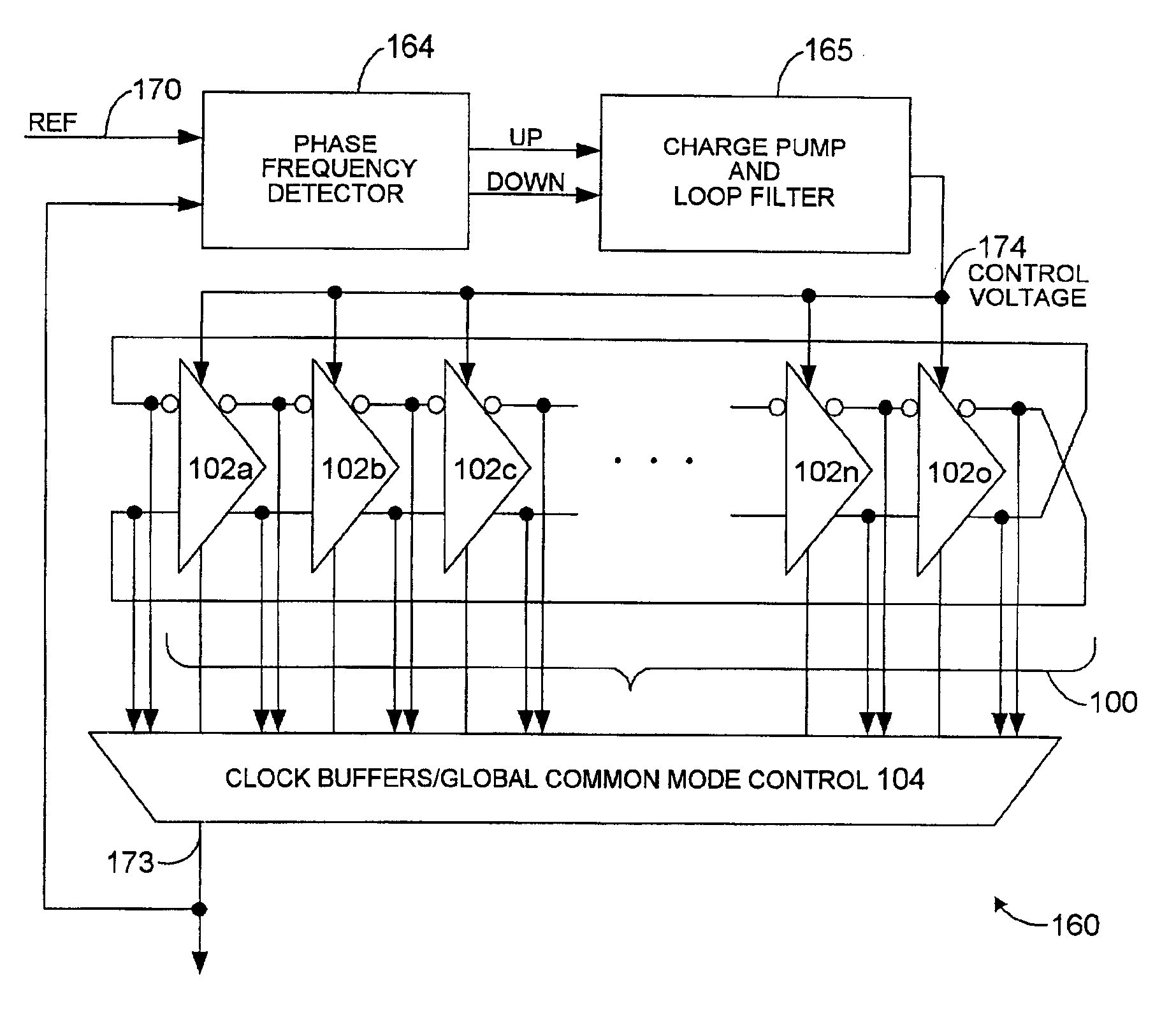
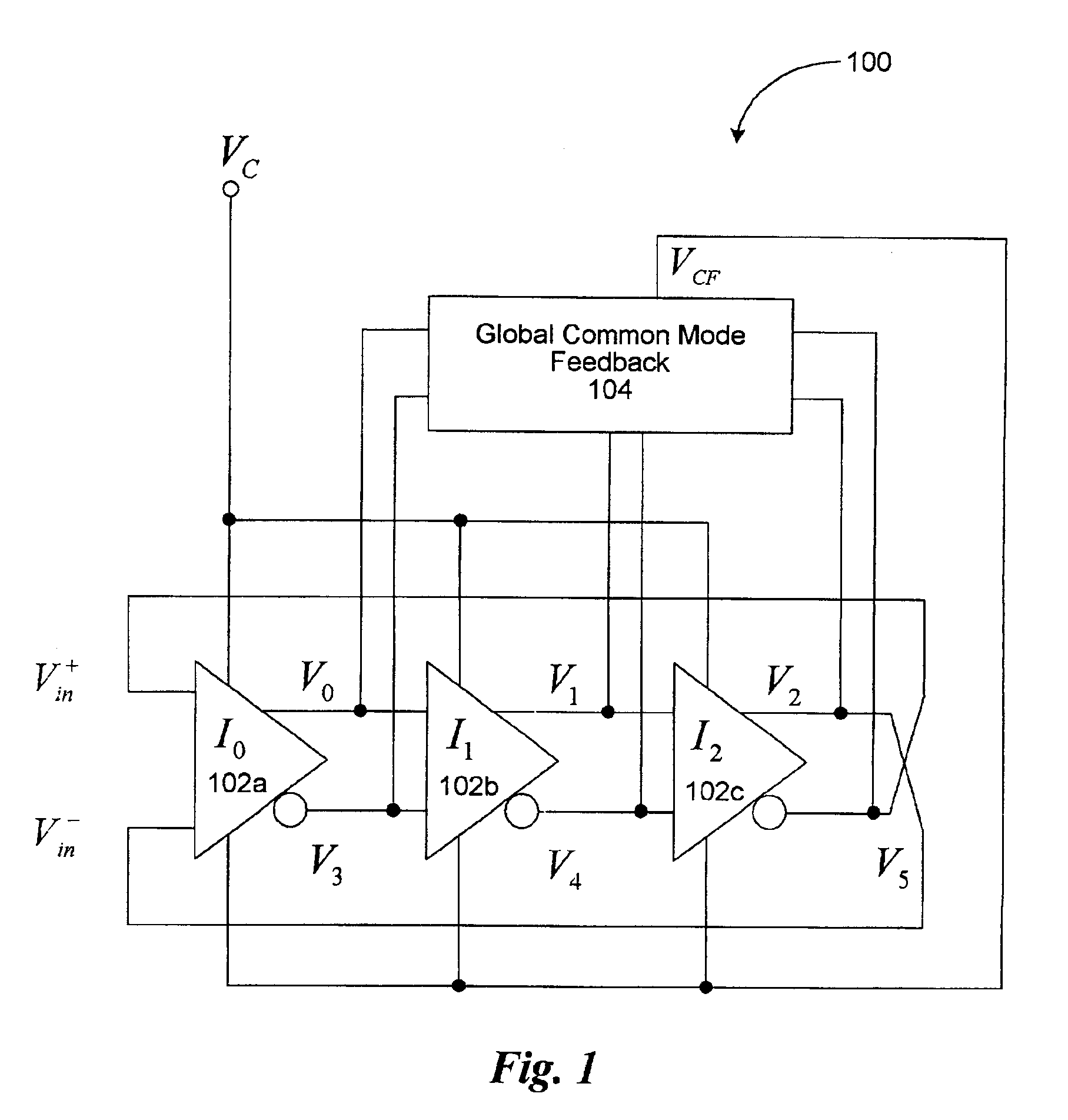
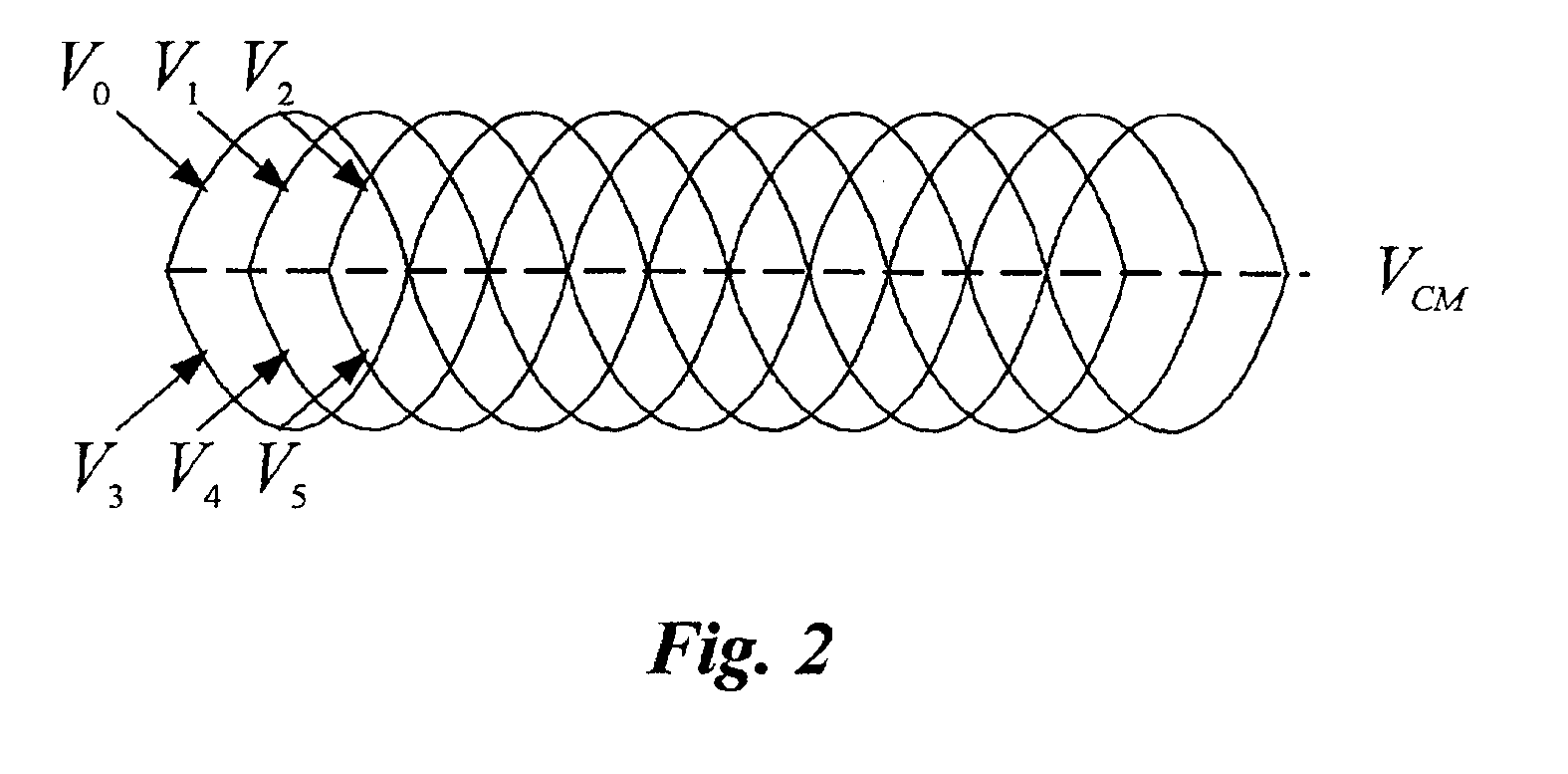
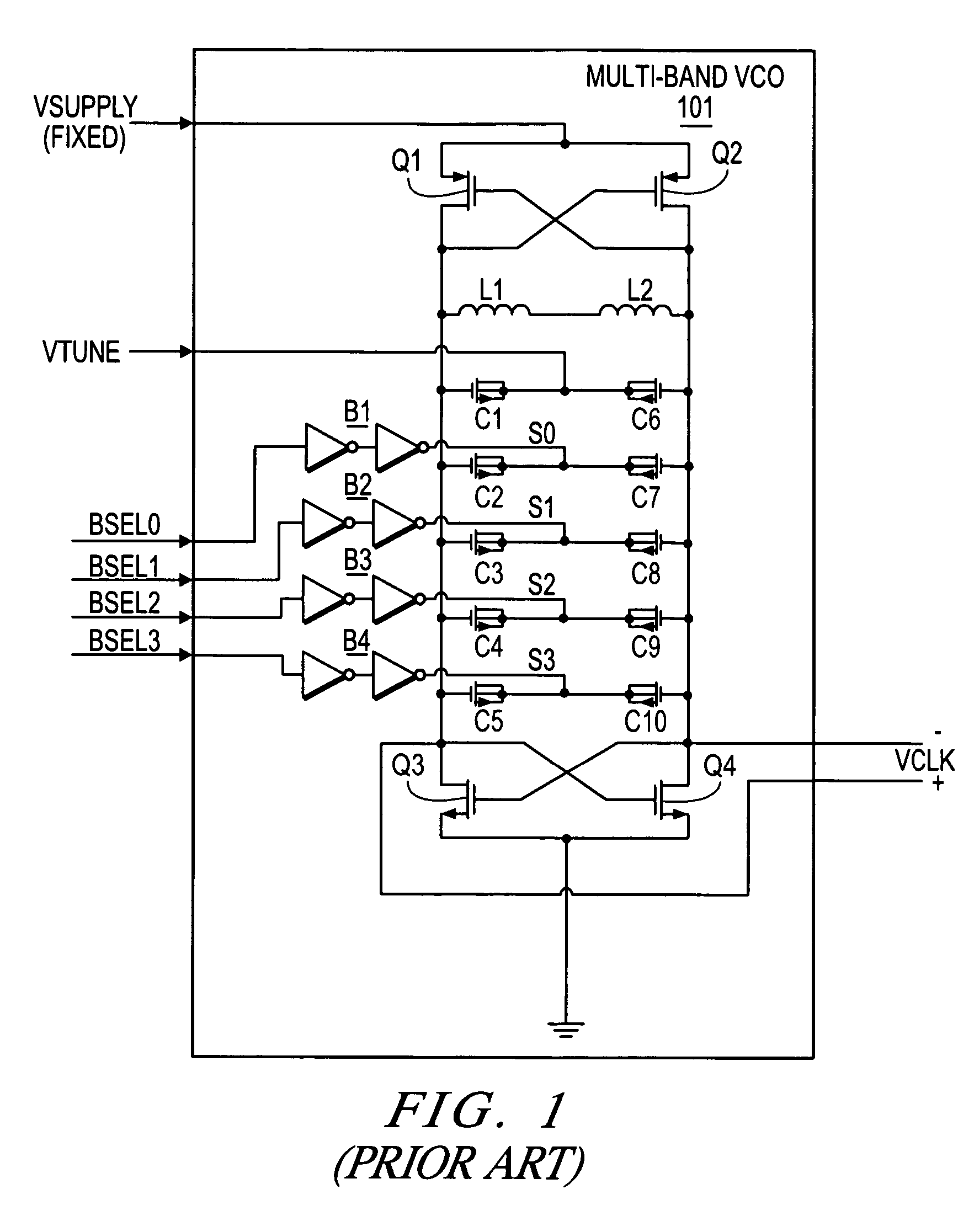
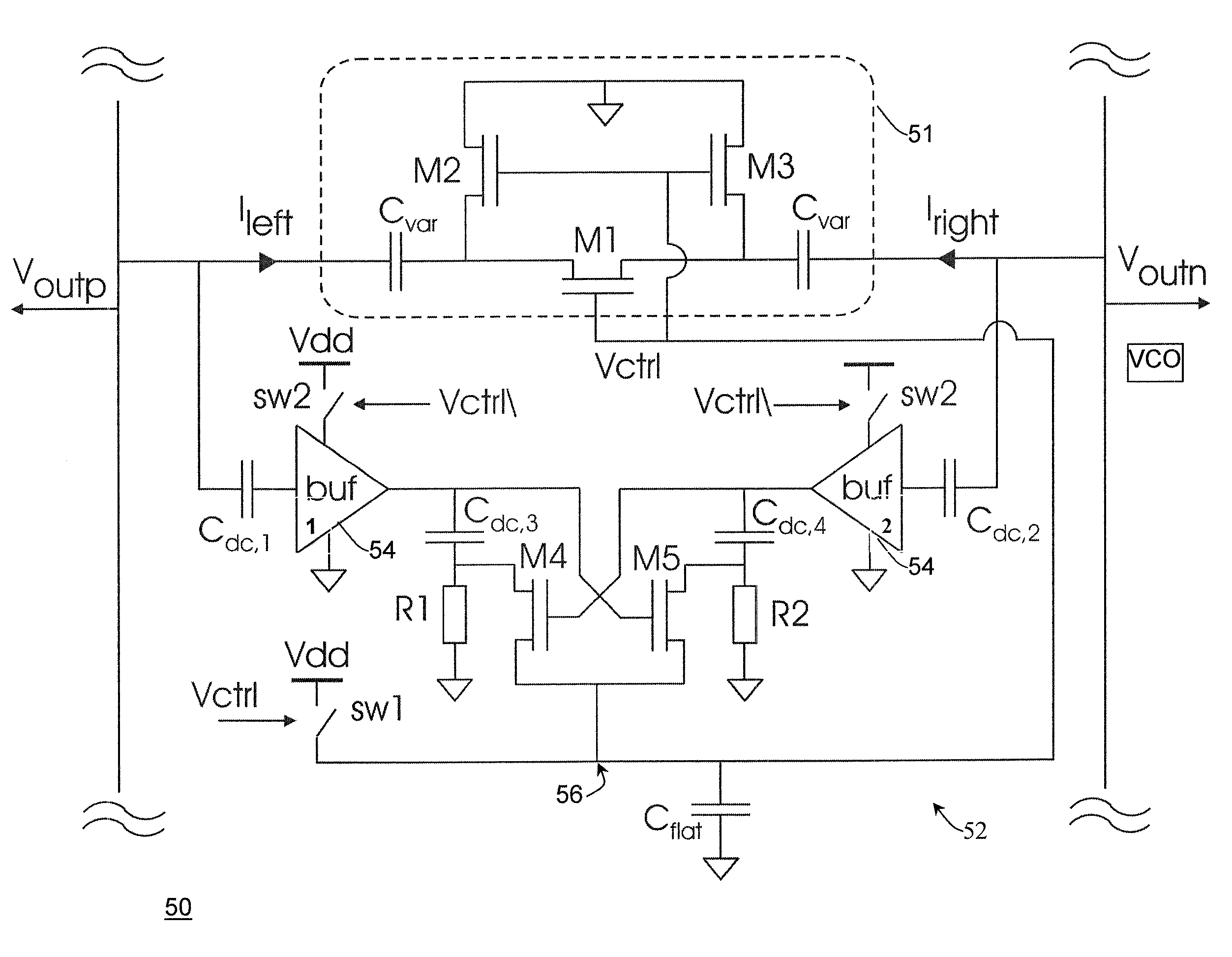
Multi-phase voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) with common mode control
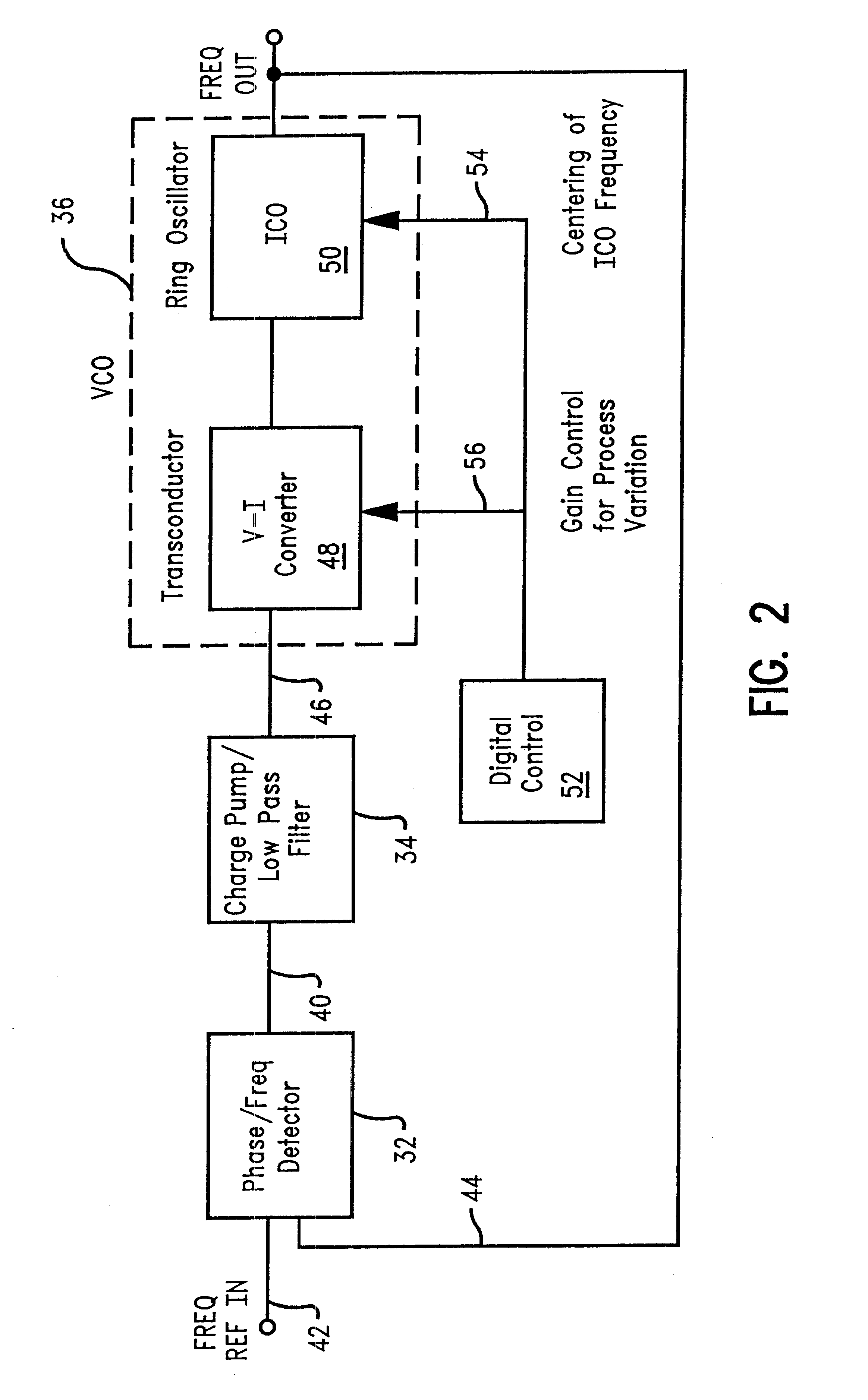
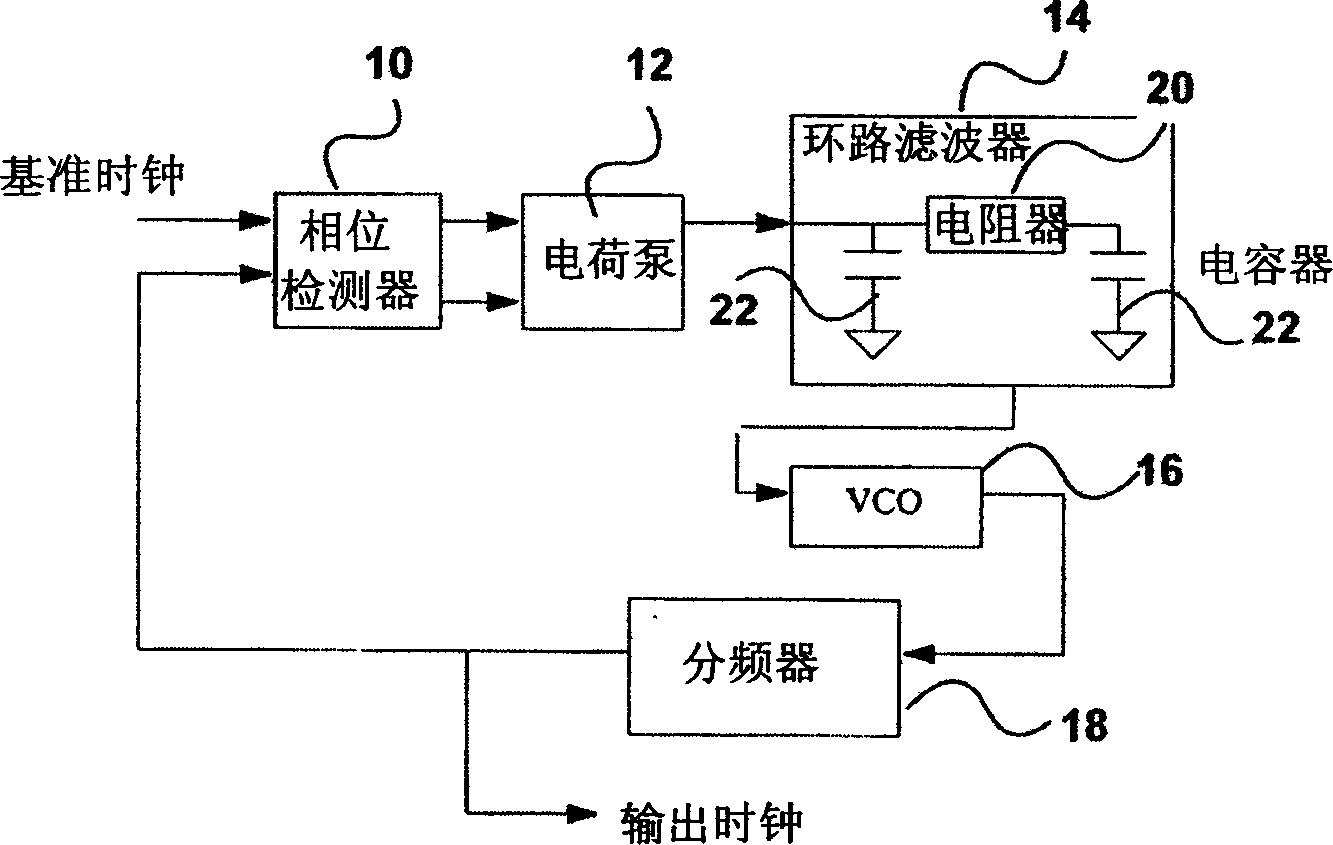
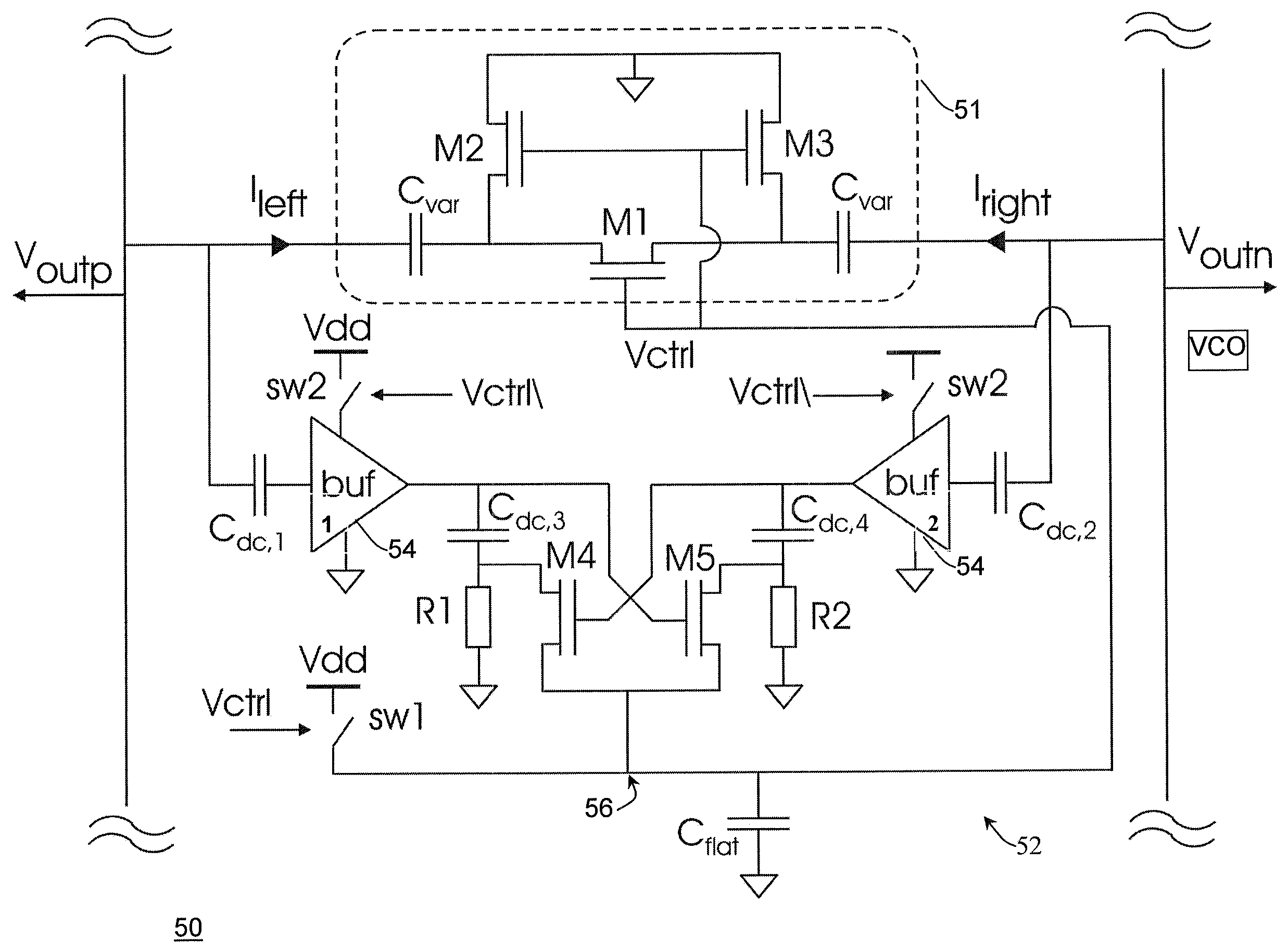
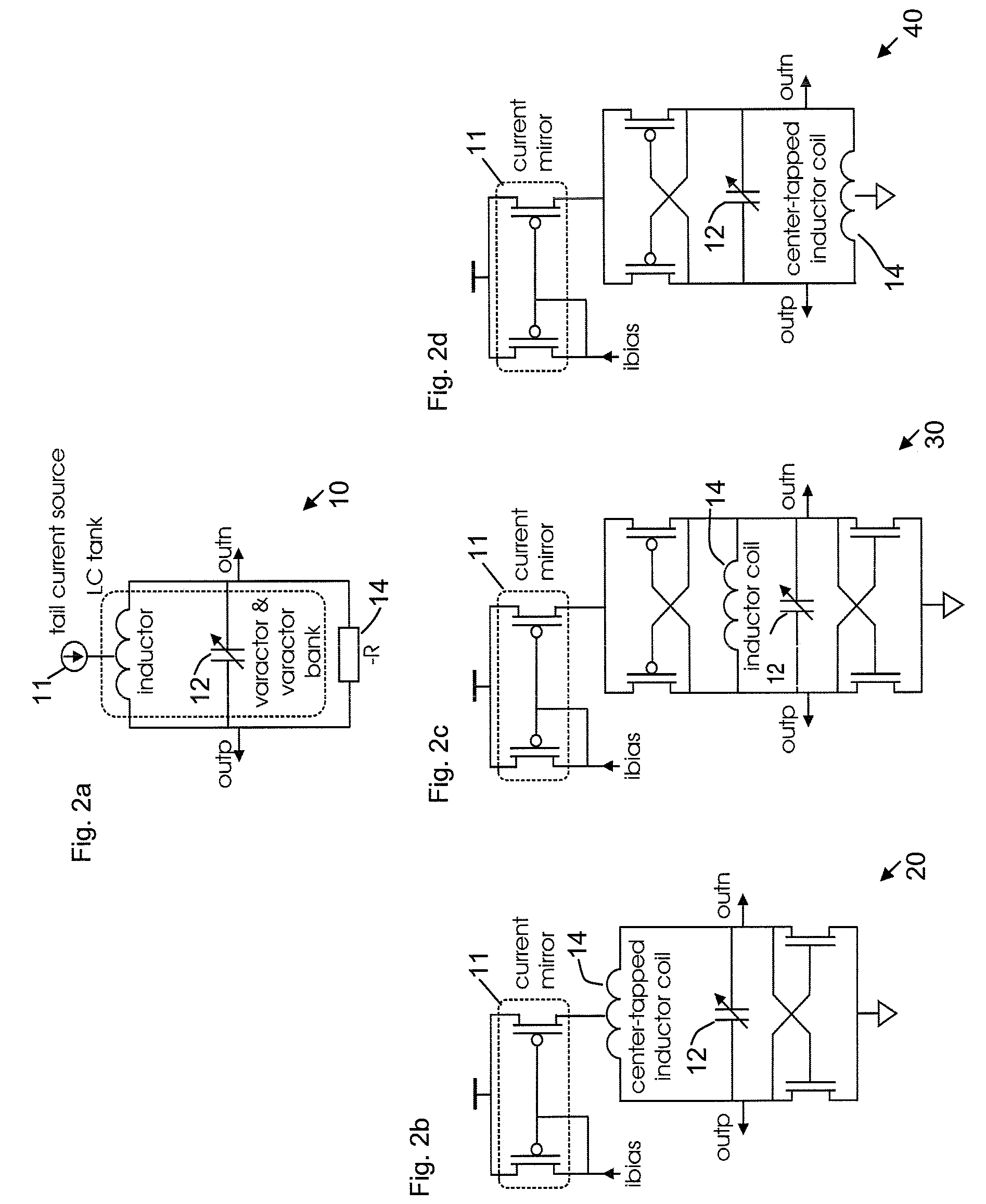
A voltage controlled oscillator ("VCO") circuit capable of generating signals with reduced jitter and / or low-phase noise is provided. One embodiment provides a plurality of cascaded VCO cells, where each VCO cell can include a source coupled differential pair, a bias transistor connected to the differential pair for biasing the differential pair, a resistive load pair connected to the differential pair, and a voltage controlled capacitor pair or varactor pair connected to the differential pair. The varactors provide control over the frequency of the oscillations produced by the VCO circuit in combination with a control voltage. A phase frequency detector combined with a charge pump and loop filter provide the control voltage.
Owner:UNIVERSAL CONNECTIVITY TECH INC
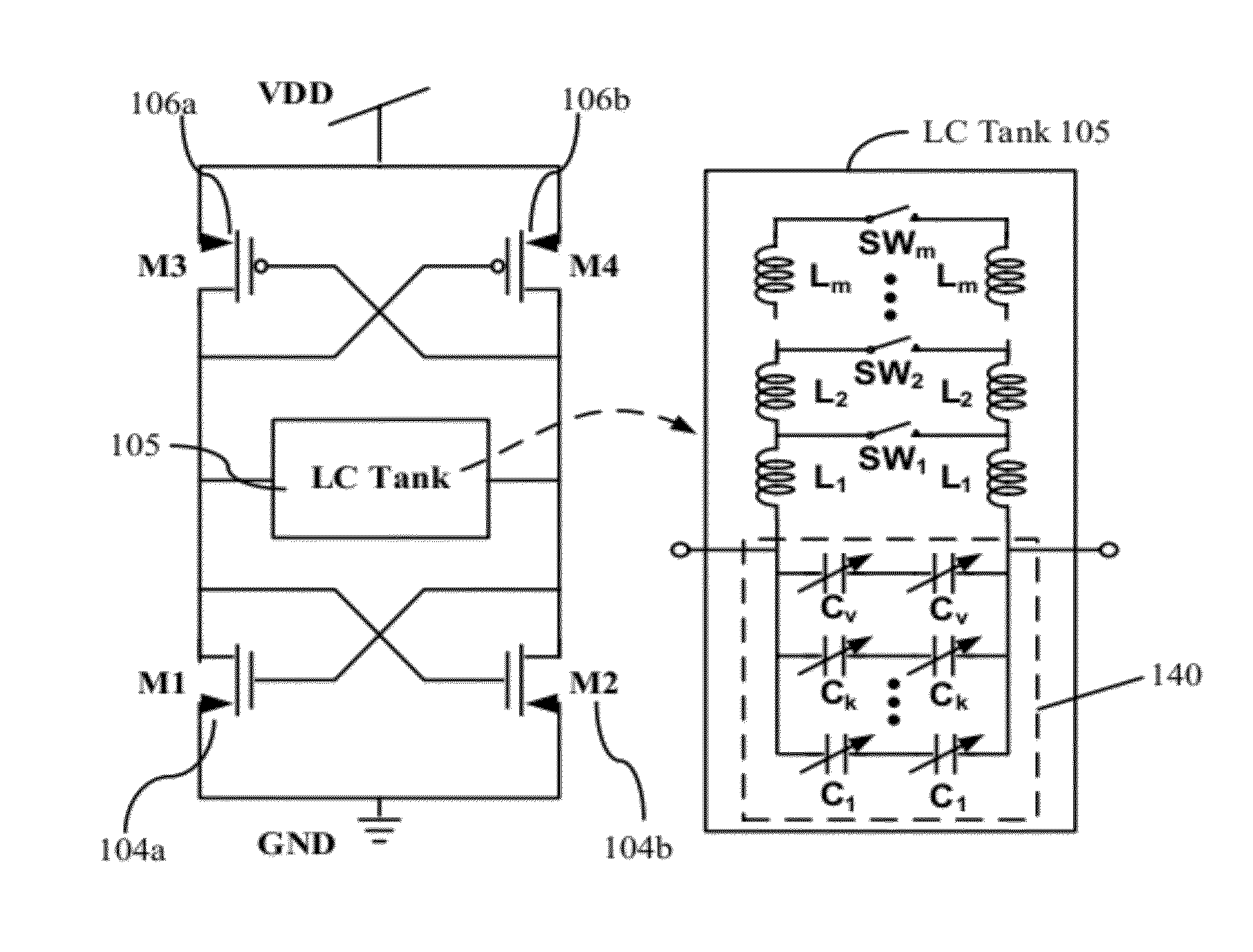
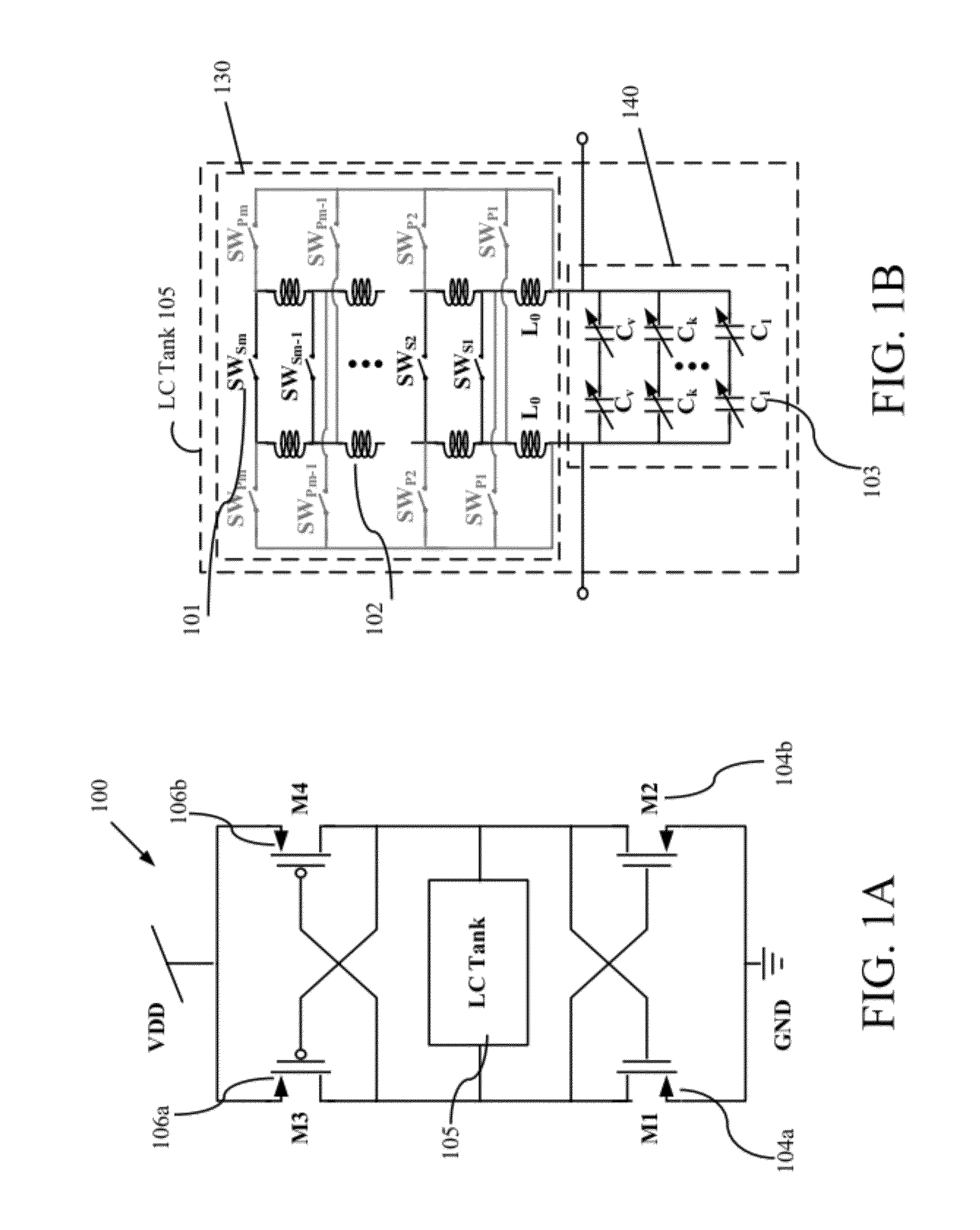
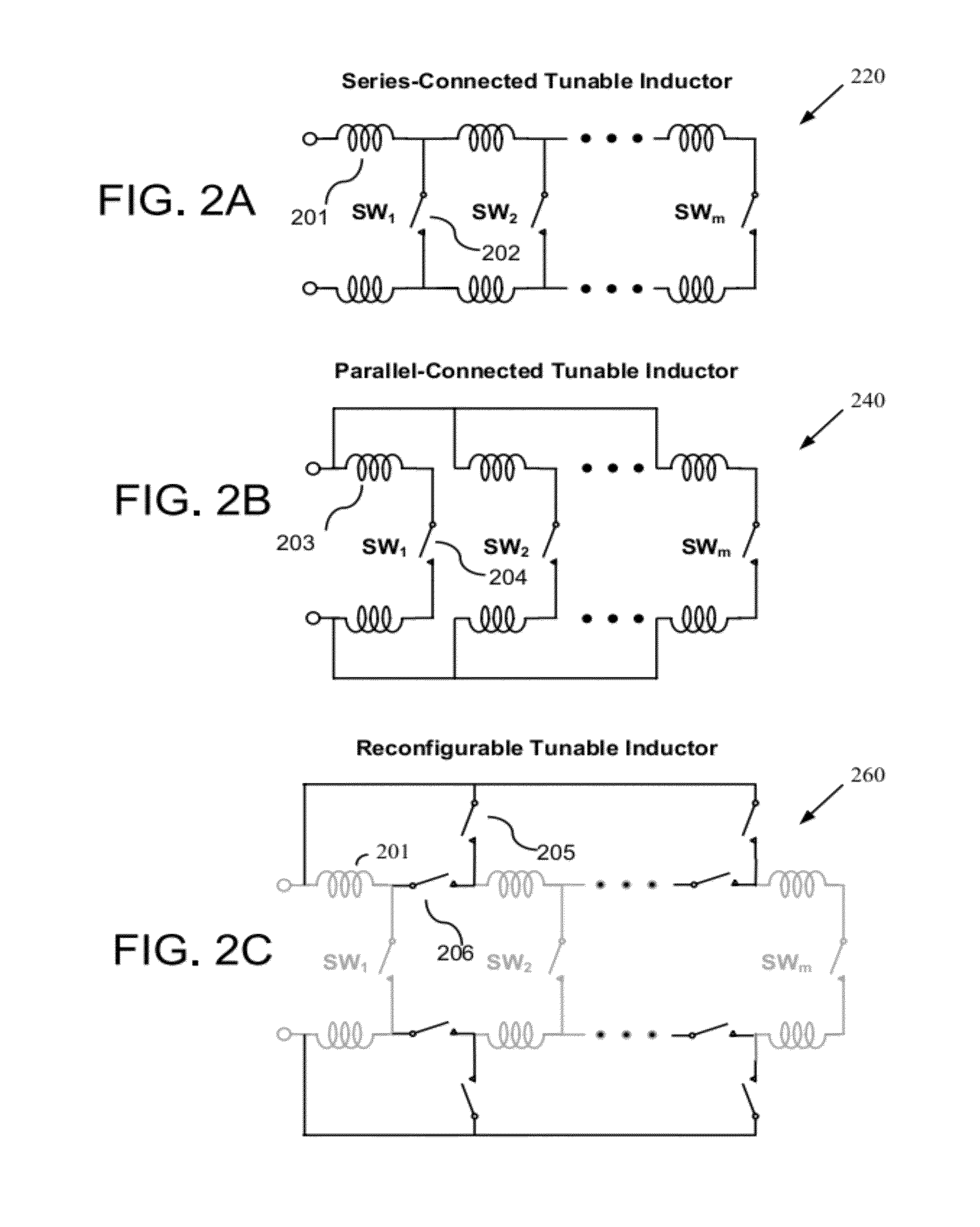
Systems and Methods for Wideband CMOS Voltage-Controlled Oscillators Using Reconfigurable Inductor Arrays
InactiveUS20120286889A1Adjust capacitanceElectric pulse generatorOscillations generatorsUltra-widebandCapacitance
As wireless communication technology evolves, various transceivers become integrated into a single system, which implements a seamless connection to search available frequency bands and to provide wireless connections regardless of their wireless standards. One of the key technologies for seamless implementation is an ultra-wideband local oscillator, which can overcome the restriction of limited tuning range in typical RF local oscillators. Many RF oscillators incorporate LC-tuned oscillators because of their good noise performance while their tuning range is limited by fixed inductance and varied capacitance. The planar inductor fabricated on the CMOS process occupies a large area as well. By replacing the planar inductor with the array of bondwires, and including switches to provide proper impedance for the circuit to generate negative impedance, the tuning range of a CMOS voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is extended more than 100%, which number can not be achieved in a convention VCO.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Linear voltage controlled oscillator transconductor with gain compensation
InactiveUS6466100B2More of the gainLess of the gainPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase locked loop circuitLow-pass filter
A voltage controlled oscillator of a phase locked loop circuit having digitally controlled gain compensation. The digital control circuitry provides binary logic input to the voltage controlled oscillator for a digitally controlled variable resistance circuit, a digitally controlled variable current transconductor circuit, or differential transistor pairs having mirrored circuitry for adjusting the V-I gain. The latter configuration requires the voltage controlled oscillator to incorporate a source-coupled differential pair which is driven by a low pass filter capacitor output voltage, and connected to load transistors; a current source and a current mirror for generating a tail current; individual banks of transistors to mirror the load transistor currents; a digital-to-analog converter with control lines outputted there from, the digital-to-analog converter used to increase the amount of current allowed to flow to the transconductor output, the current being digitally increased and decreased corresponding to an amount of current pulled from the current source, and mirroring the current through at least one transistor mirror circuit.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Voltage control oscillator with low tuning gain variance
InactiveCN101483434ACounteract the effects of tuning gainRealize the designPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsCapacitanceControl signal
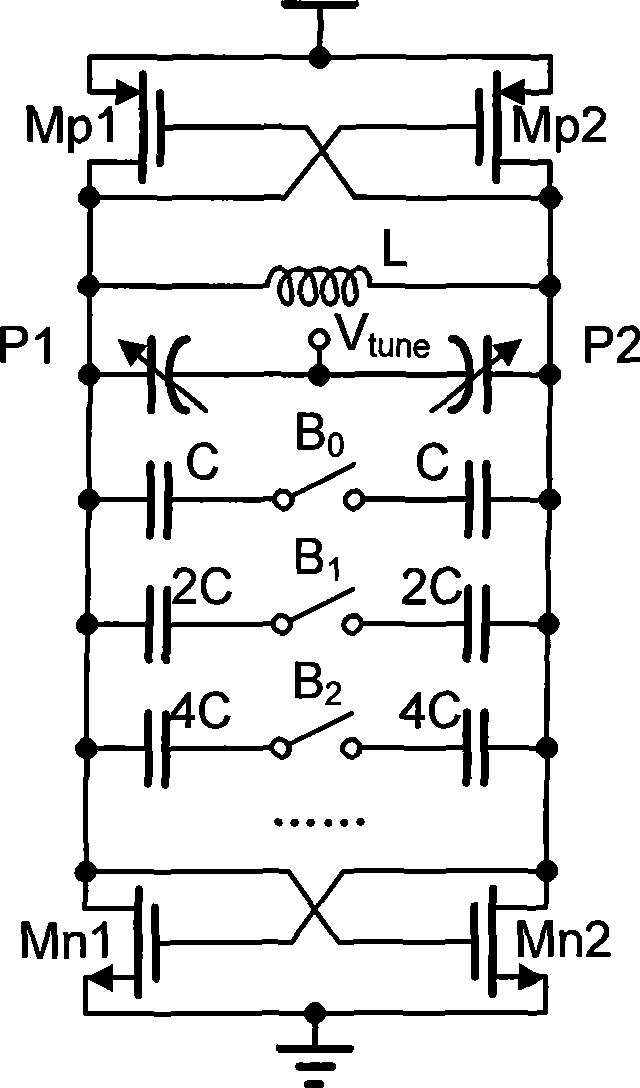
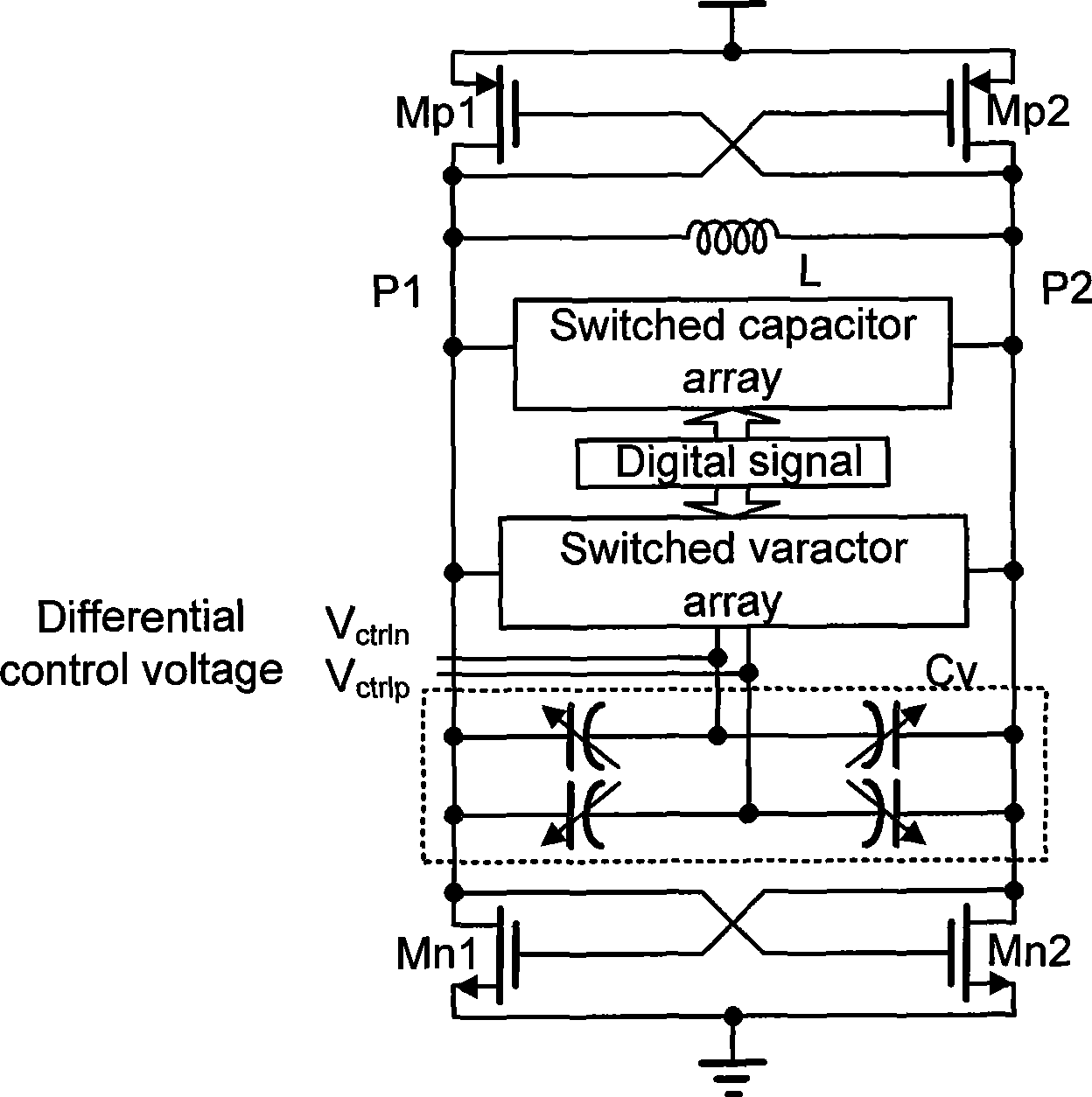
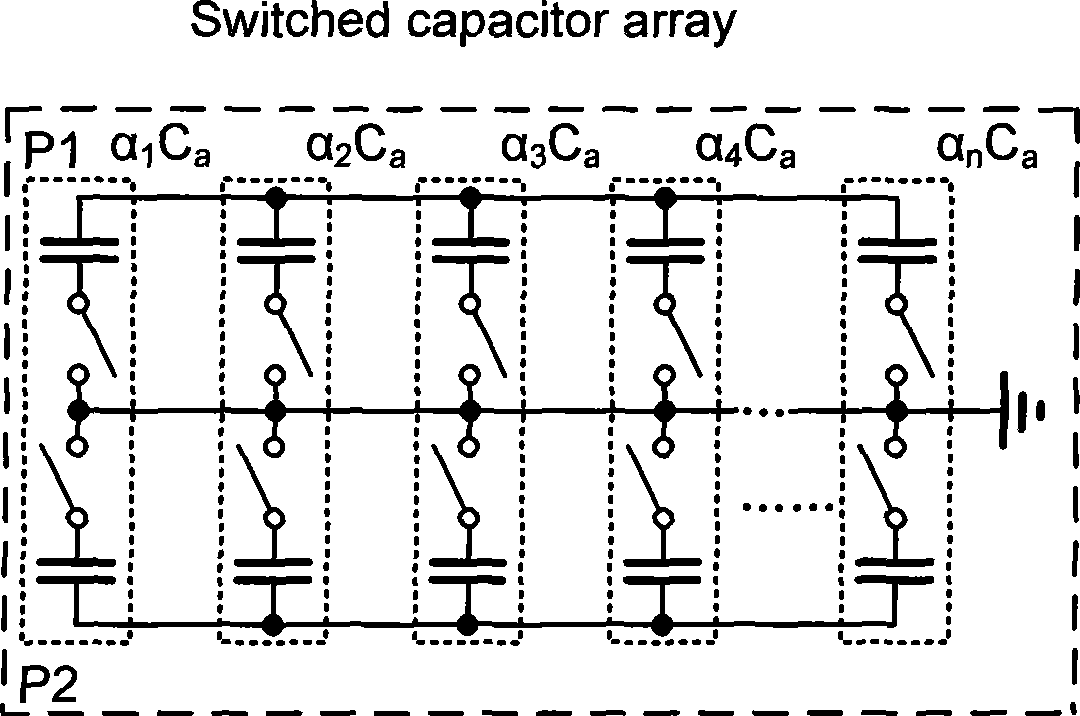
The present invention discloses an LC voltage-controlled oscillator with low tuning gain variation. The LC voltage-controlled oscillator comprises a parallel inductance-capacitance resonance circuit, two pairs of transistors which are crossly coupled and connected, a pressure controlled variable capacitor, a switch variable capacitor array and a switching capacitor array. The variation range of pressure controlled variable capacitor is adjusted through the switch variable capacitor array for counteracting the effect of oscillation frequency to tuning gain. The invention adjusts the magnitude of variable capacitor switched into the resonant circuit with a digital control signal according to the variation of oscillation frequency, and changes the regulation range of equivalent variable capacitor along with the difference of sub-band thereby counteracting the effect of oscillation frequency change to the tuning gain of voltage controlled oscillator, realizing the design of wideband voltage controlled oscillator with low tuning gain variation, and simultaneously not adding additional power consumption.
Owner:SHANGHAI RUIXIE MICROELECTRONICS TECH
CMOS voltage controlled oscillator circuit for operation with low supply voltage and method for same
InactiveUS6859112B2Angle modulation by variable impedenceGenerator stabilizationCapacitancePhase noise
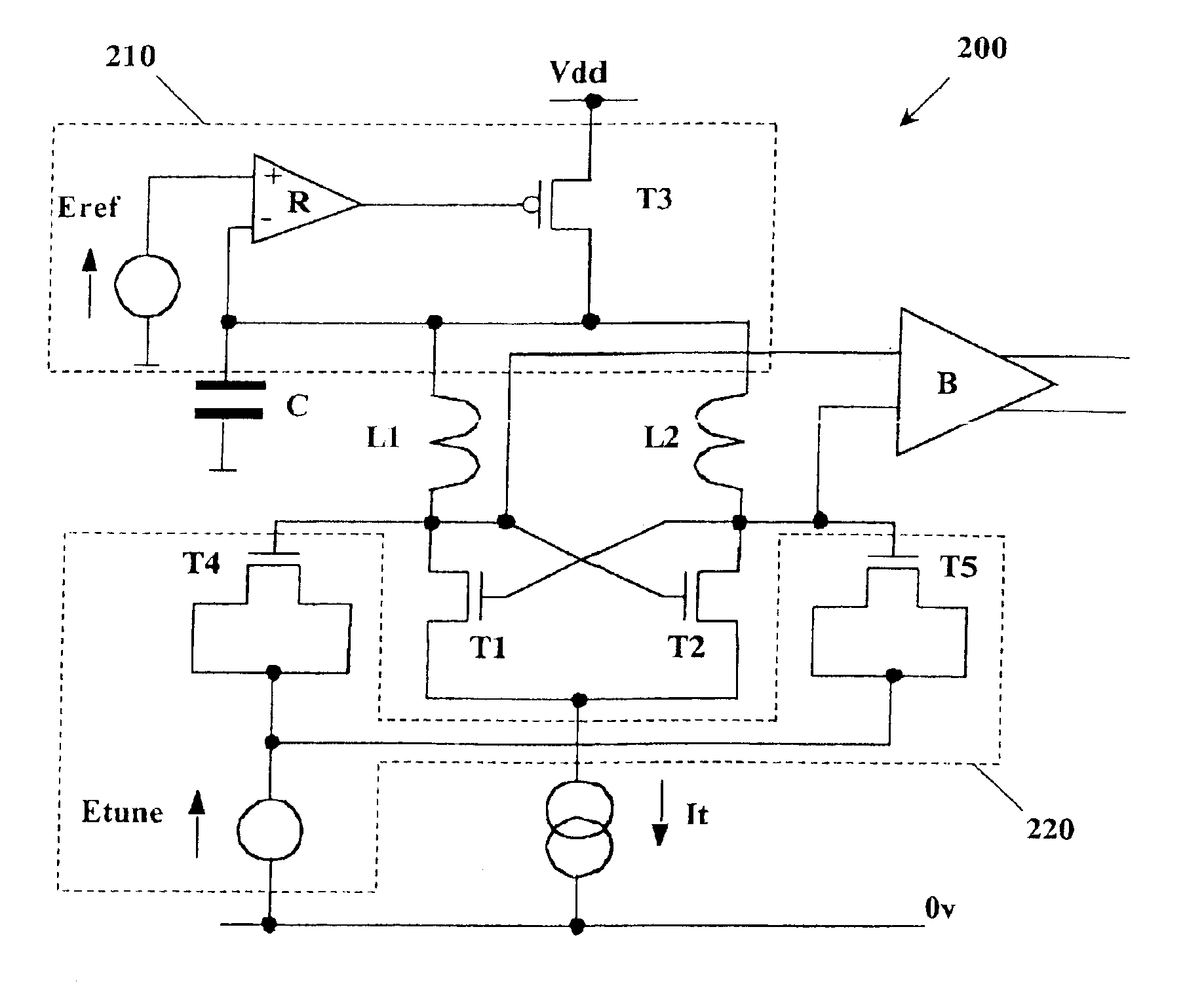
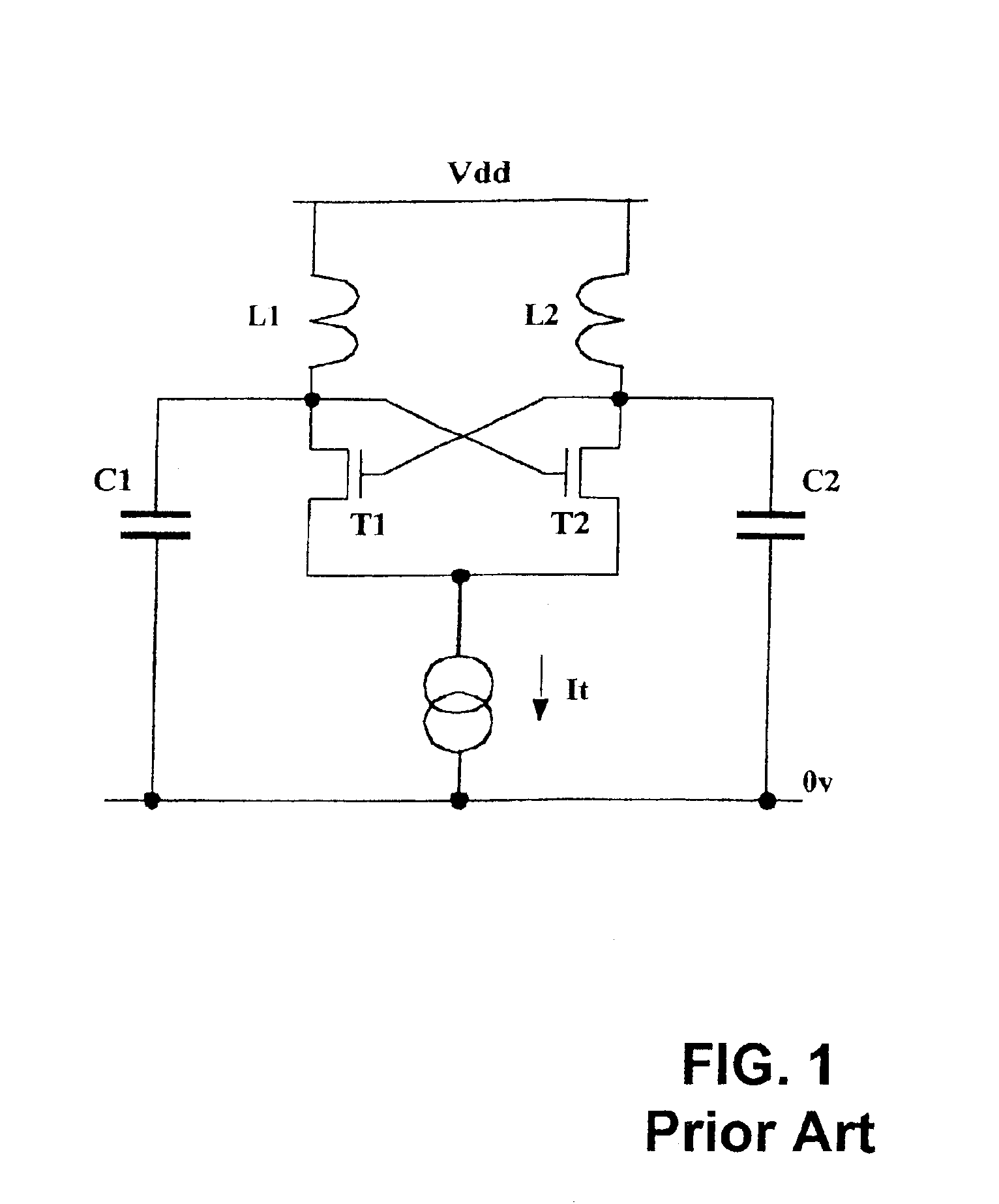
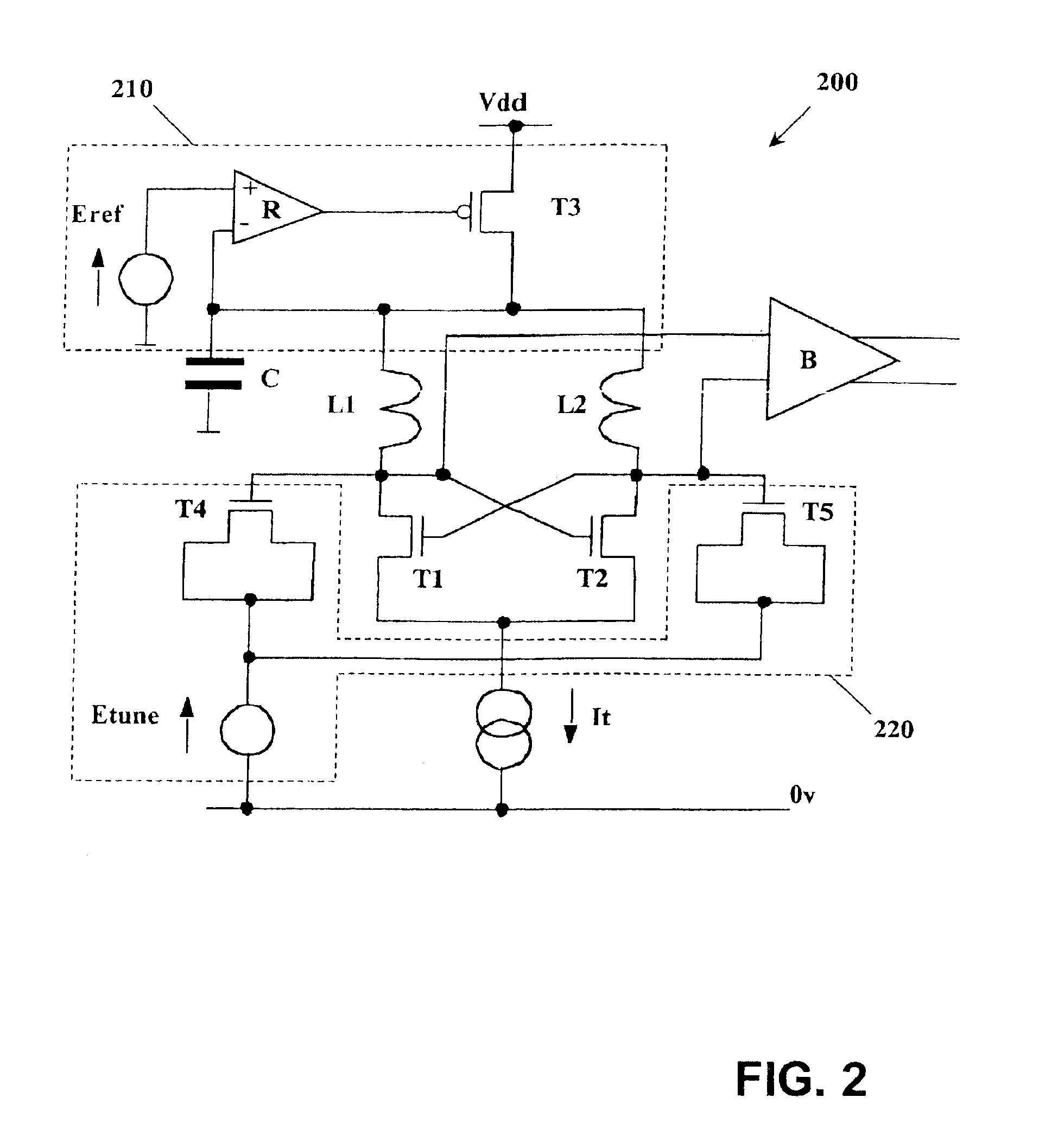
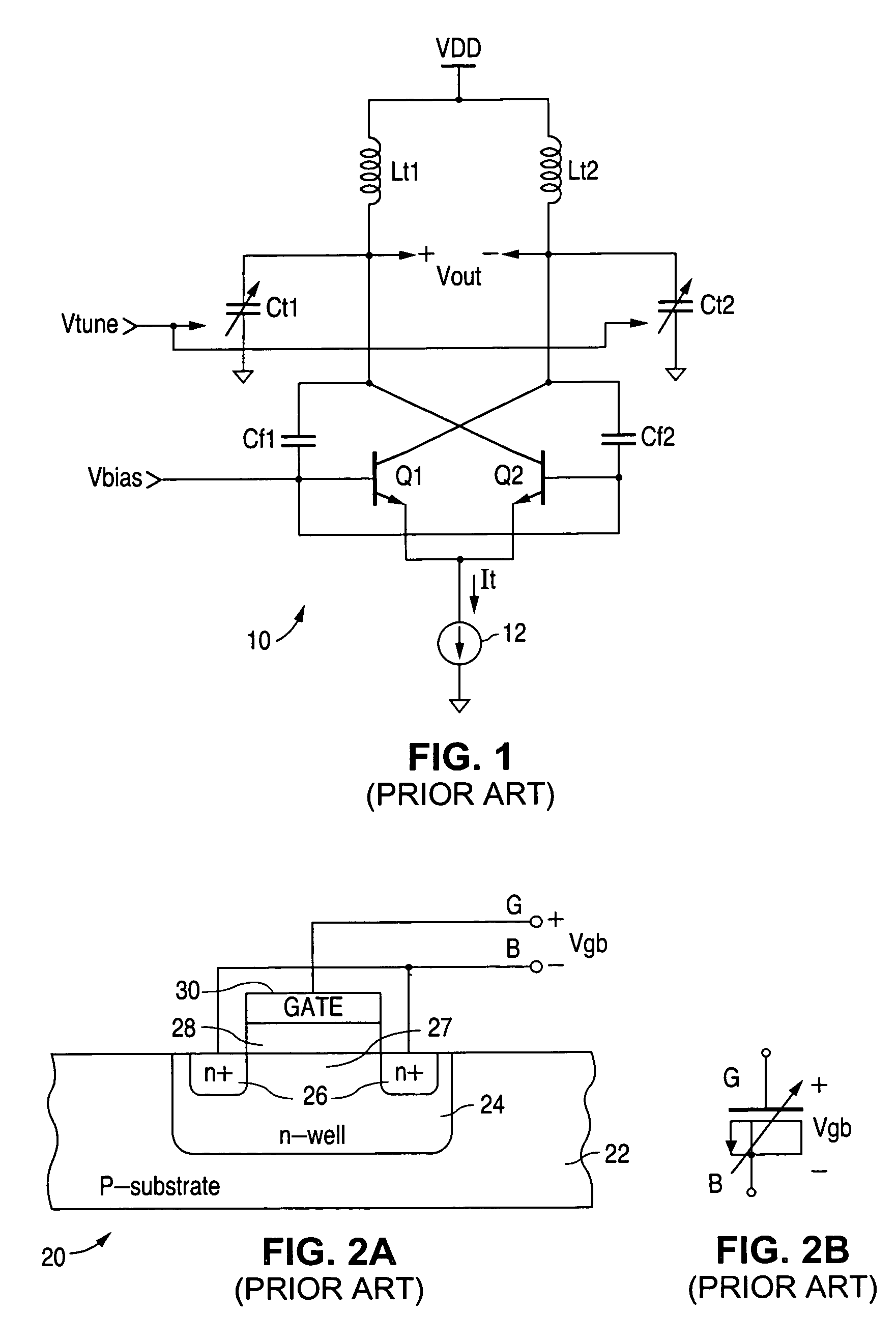
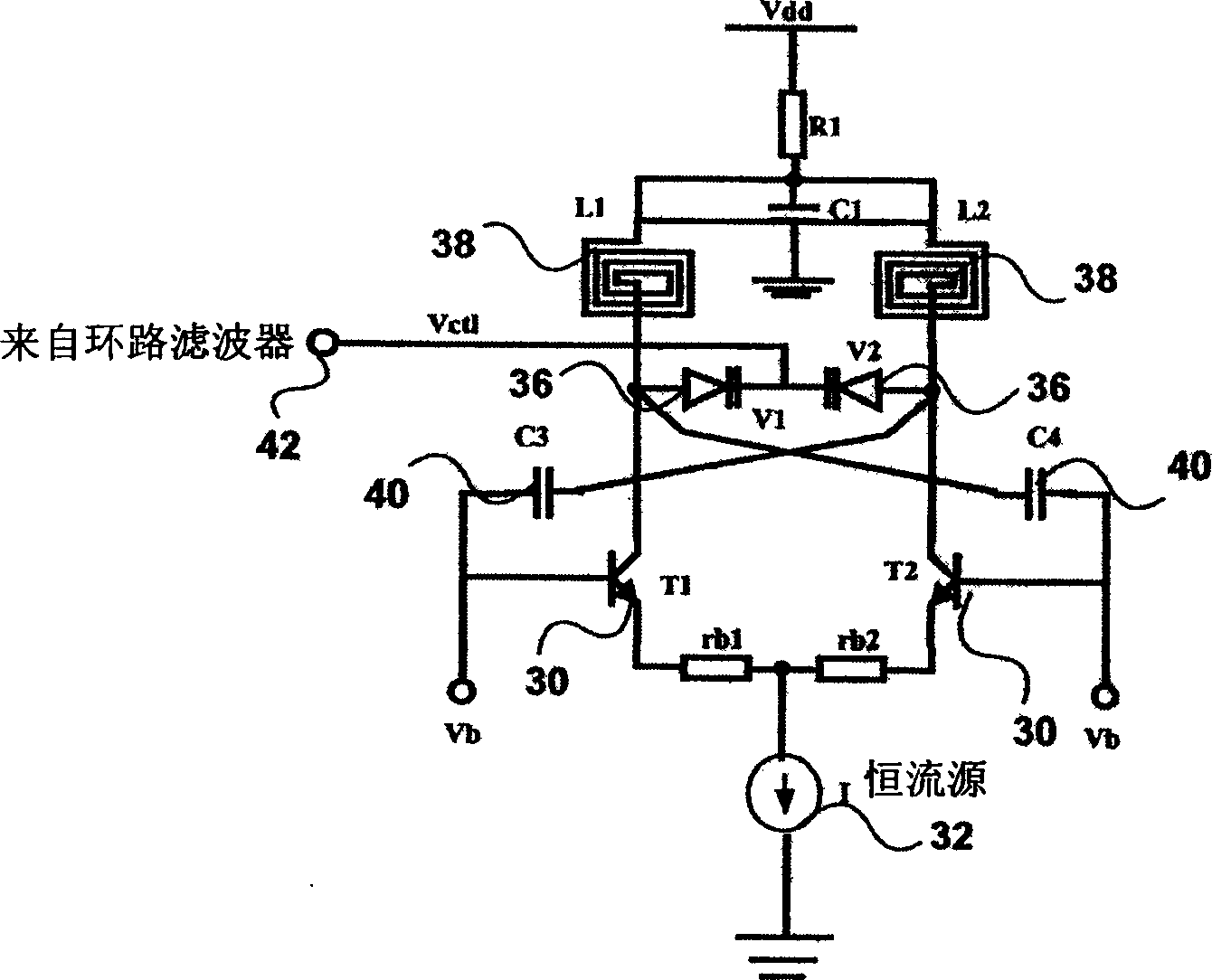
A voltage controlled oscillator circuit and method comprising: a harmonic oscillator having a cross-coupled NFET devices (T1, T2) and an LC tank circuit (L1, L2, C) performing oscillation; a series voltage regulator (210) regulating voltage applied to the harmonic oscillator via a PFET device (T3) and differential amplifier (R); and a tuning circuit (220) having voltage controlled capacitance ‘Zero-Vt’ NFET devices (T4, T5) controlling oscillation of the harmonic oscillator. A differential output buffer (B) provides output buffering to a subsequent stage. This provides advantages that: operation at low supply voltages is facilitated and the sensitive oscillator cell is decoupled from the main supply noise offering improved phase noise performance; the output swing of the oscillator has a well controlled common-mode value which can be selected to most efficiently drive a following stage; and using ‘Zero-Vt’ NFETs facilitates the use of a lower supply voltage.
Owner:IBM CORP
Switching capacitor type DC-DC converter
InactiveCN101478234AImprove efficiencySmall output rippleApparatus without intermediate ac conversionDc dc converterEngineering
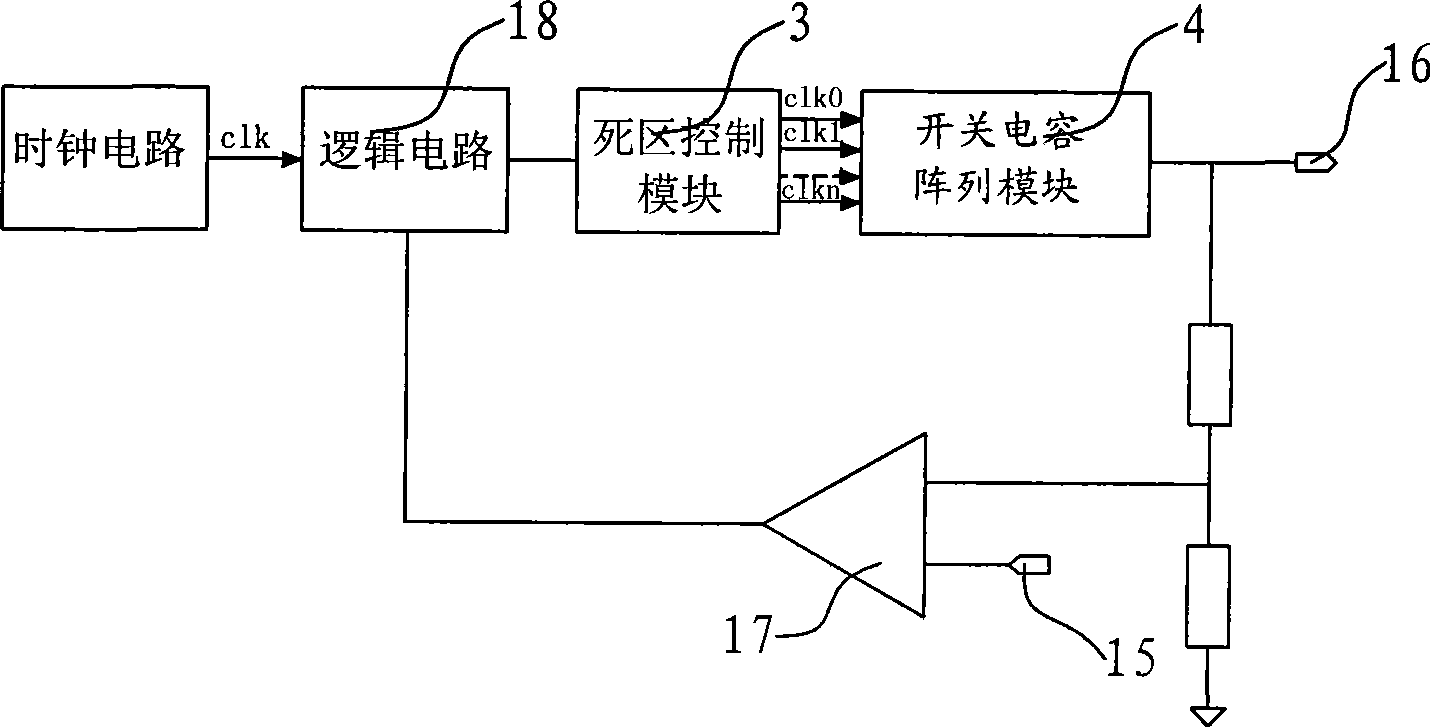
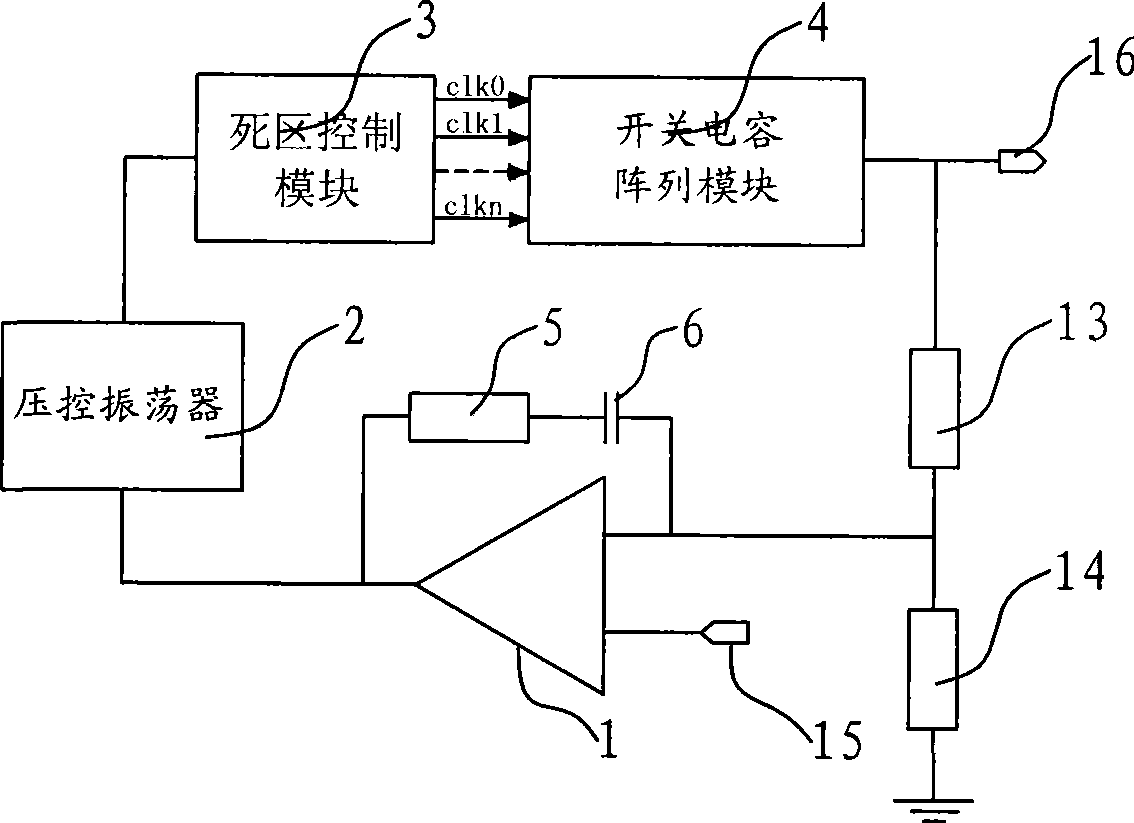
The invention provides a switched capacitor DC-DC converter. The switched capacitor DC-DC converter comprises an output sampling branch, a dead area control module for generating the dead area and outputting multiunit clock signals which has the same frequency as the input clock, a switched capacitor array module for receiving multiunit clock signals which are not overlapped and sent by the dead area control module, an error amplifier for receiving the voltage signal from the output sampling branch and the reference voltage signals, and a voltage controlled oscillator for receiving the output voltage signals of the error amplifier and for outputting the clock signals with corresponding frequency. The voltage controlled oscillator sends the clock signals to the dead control module. The frequency variation of the clock signals is in proportion to the output voltage variation of the error amplifier. The converter has low output voltage ripple and high efficiency in full load range.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
PLL circuit having a variable output frequency
InactiveUS6587005B2Compensation deviationPulse automatic controlAngle modulation detailsCapacitanceMos capacitor
Owner:NEC CORP
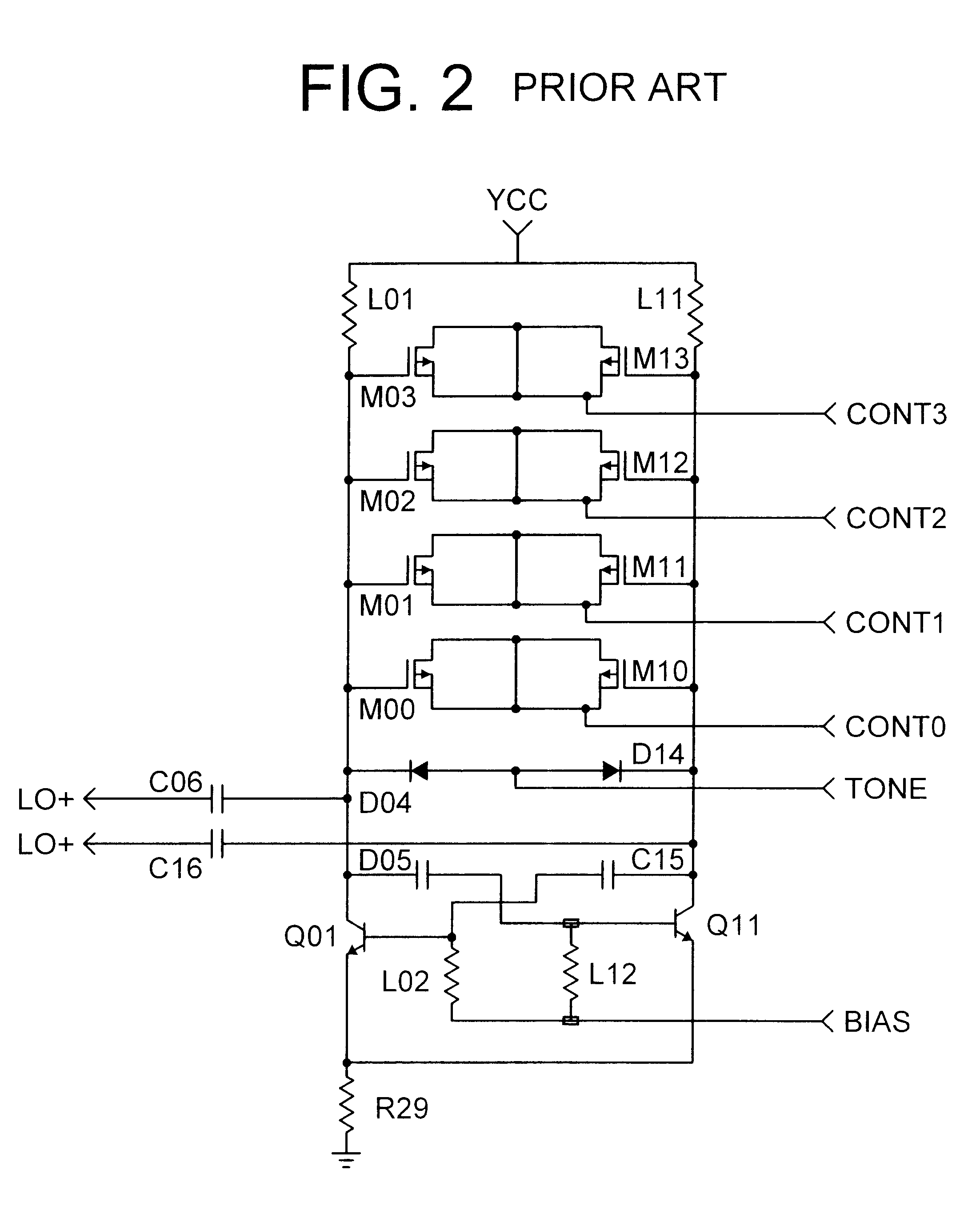
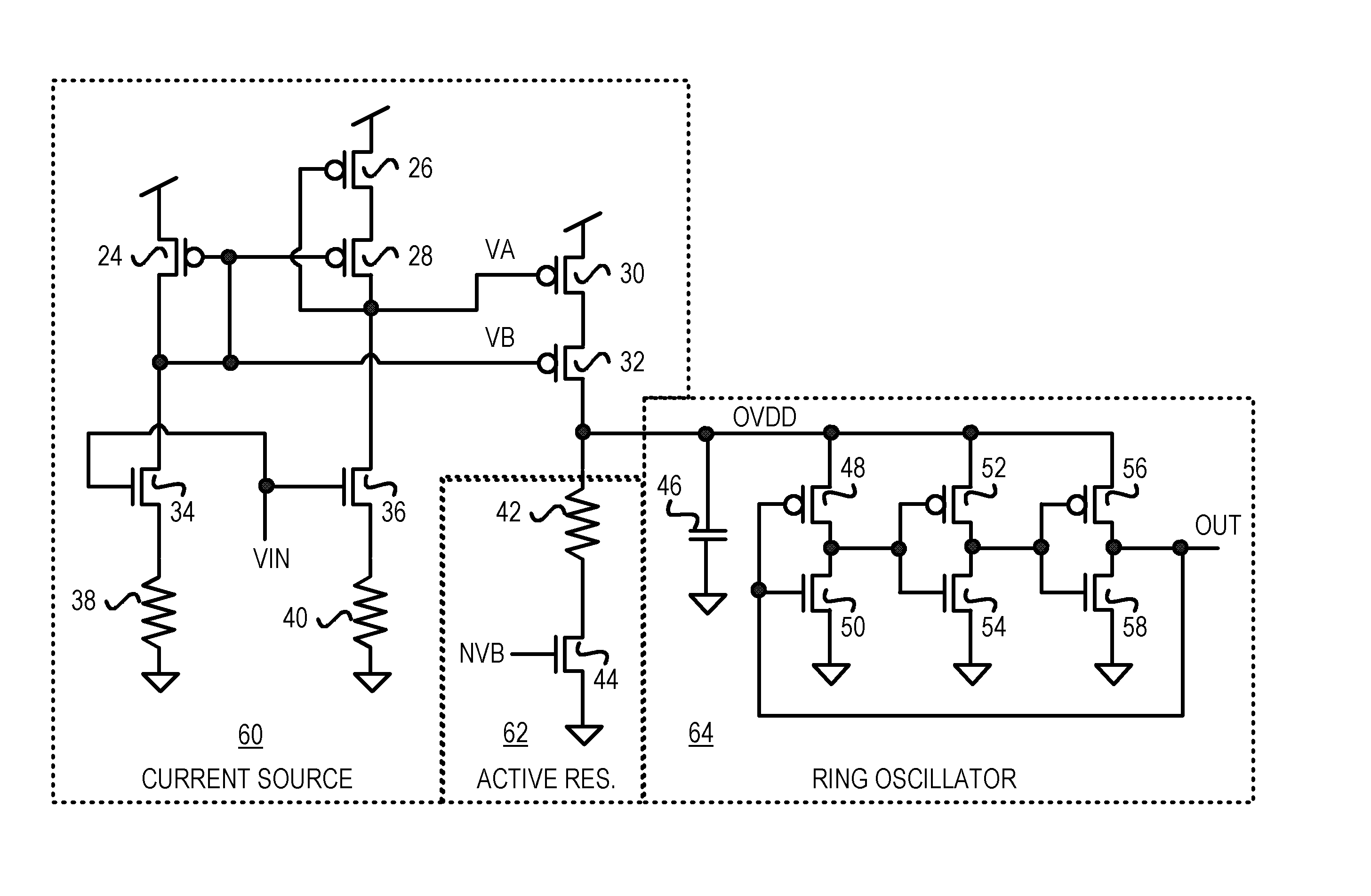
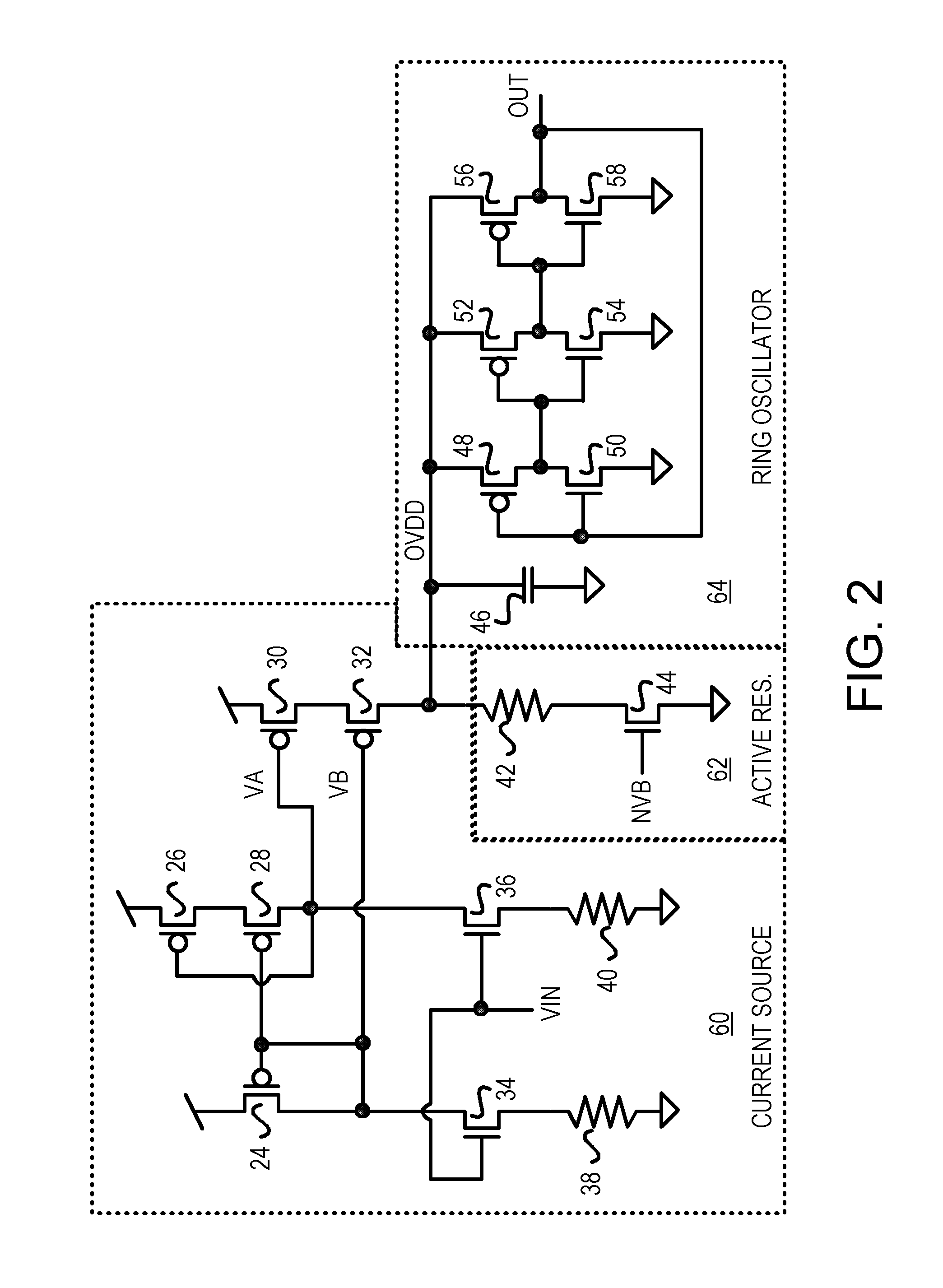
CMOS voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) with a current-adaptive resistor for improved linearity
A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) for a phase-locked loop (PLL) has improved bandwidth and performance at lower frequency. A variable current source supplies a current to an internal oscillator-power node. The current varies with the VCO input voltage. The internal oscillator-power node drives the sources of p-channel transistors in inverter stages in the ring oscillator. The variable current causes the internal oscillator-power node's voltage to vary, which varies the output frequency. An active resistor is in parallel with the ring oscillator. The active resistor has a resistor and an n-channel transistor in series between the oscillator-power node and ground. The n-channel transistor has a fixed bias voltage on its gate and is non-linear. The non-linear effective resistance of the n-channel transistor improves overall linearity of the ring oscillator. The parallel effective resistance of the active resistor lowers overall effective resistance of the ring oscillator. Oscillator bandwidth at lower frequencies improves.
Owner:DIODES INC
Tunable capacitance circuit for voltage control oscillator
ActiveUS7098751B1Improve bindingAngle modulation by variable impedenceAngle modulation detailsCapacitancePhase noise
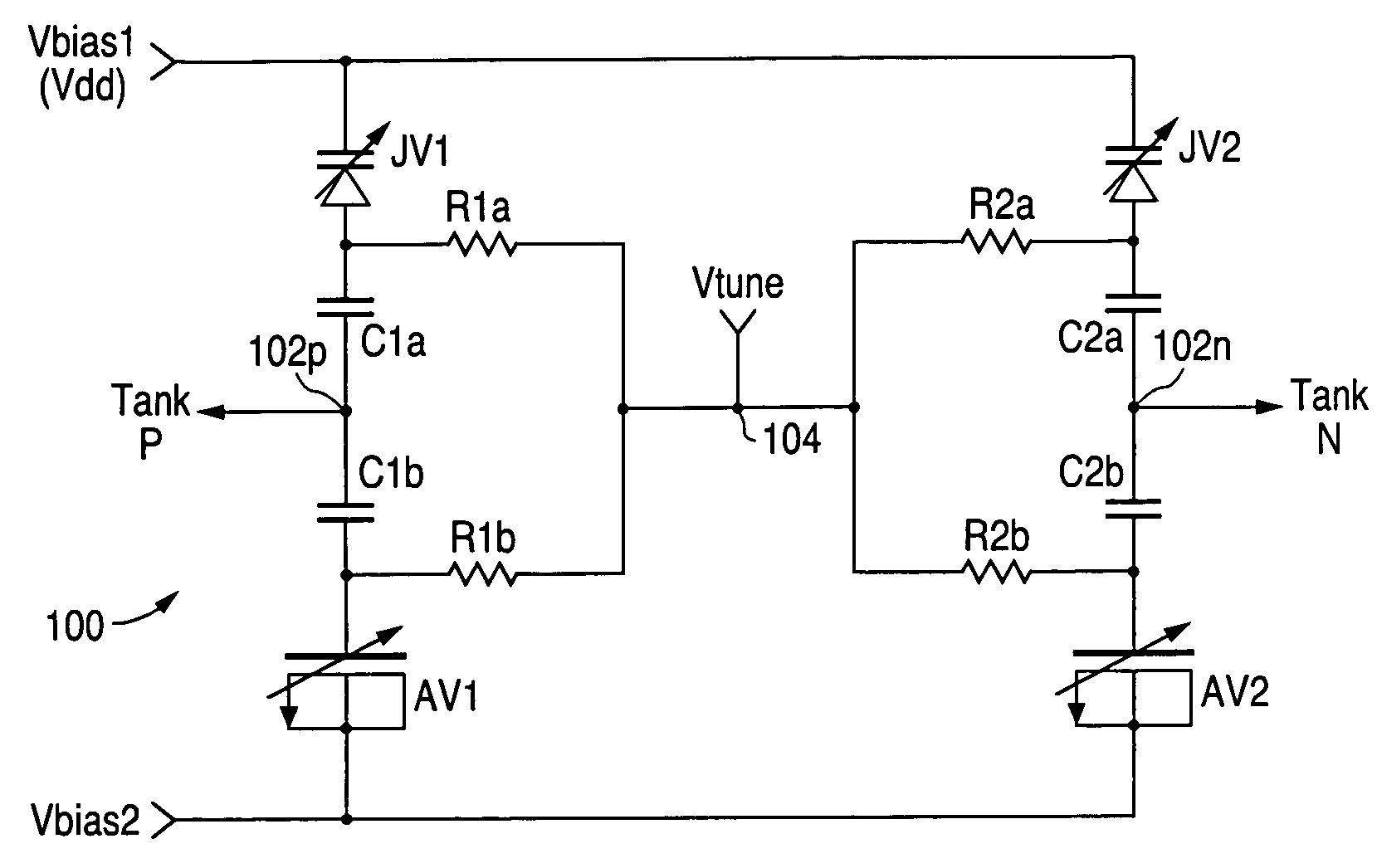
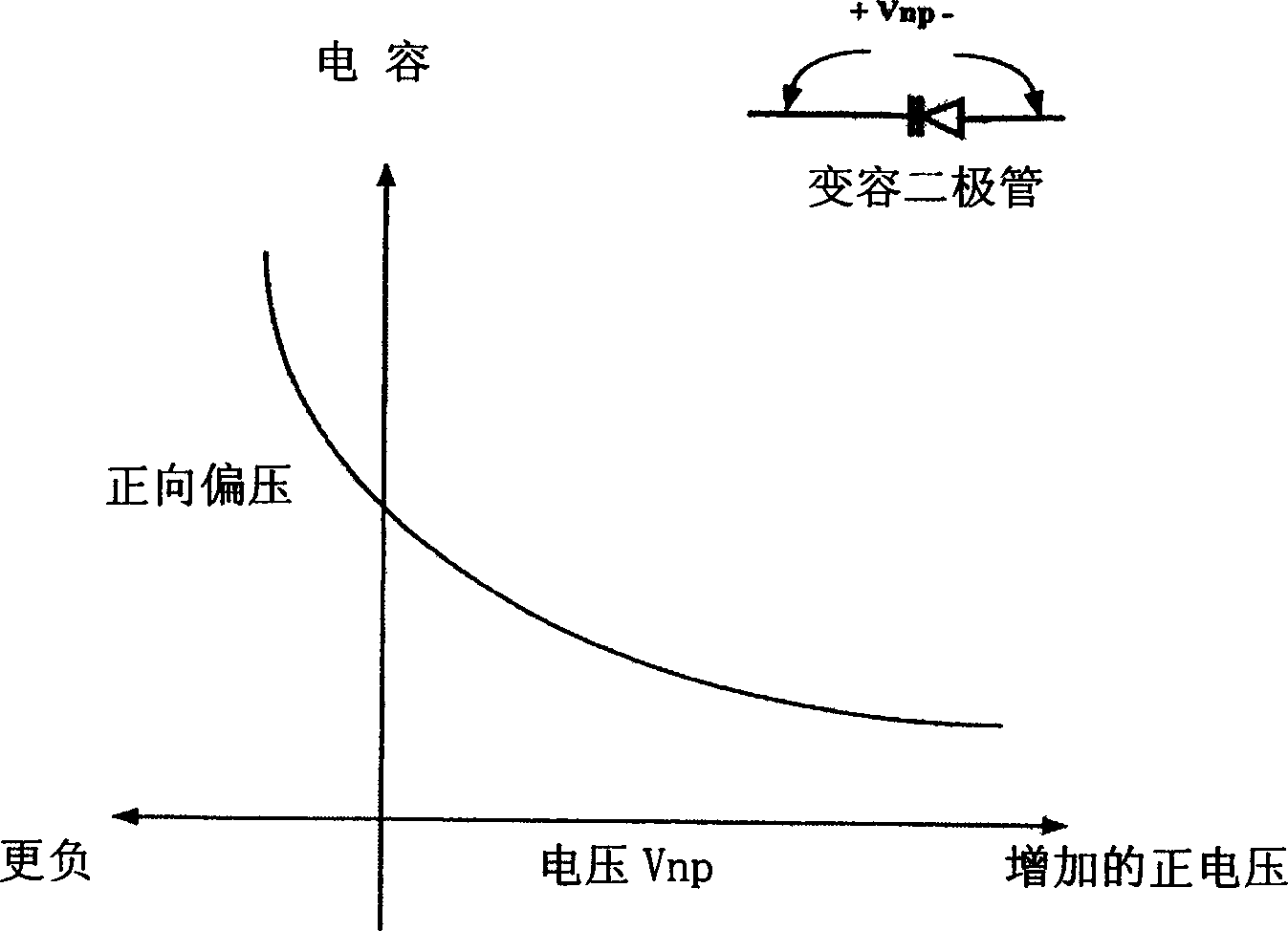
A circuit and method for providing a tunable capacitance for a voltage control oscillator (VCO) in which at least one P-N junction varactor and at least one metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) accumulation-mode varactor are effectively coupled and tuned in parallel, thereby providing a net tunable capacitance with which the VCO will realize an optimal combination of quality factor, phase noise, and gain characteristics.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
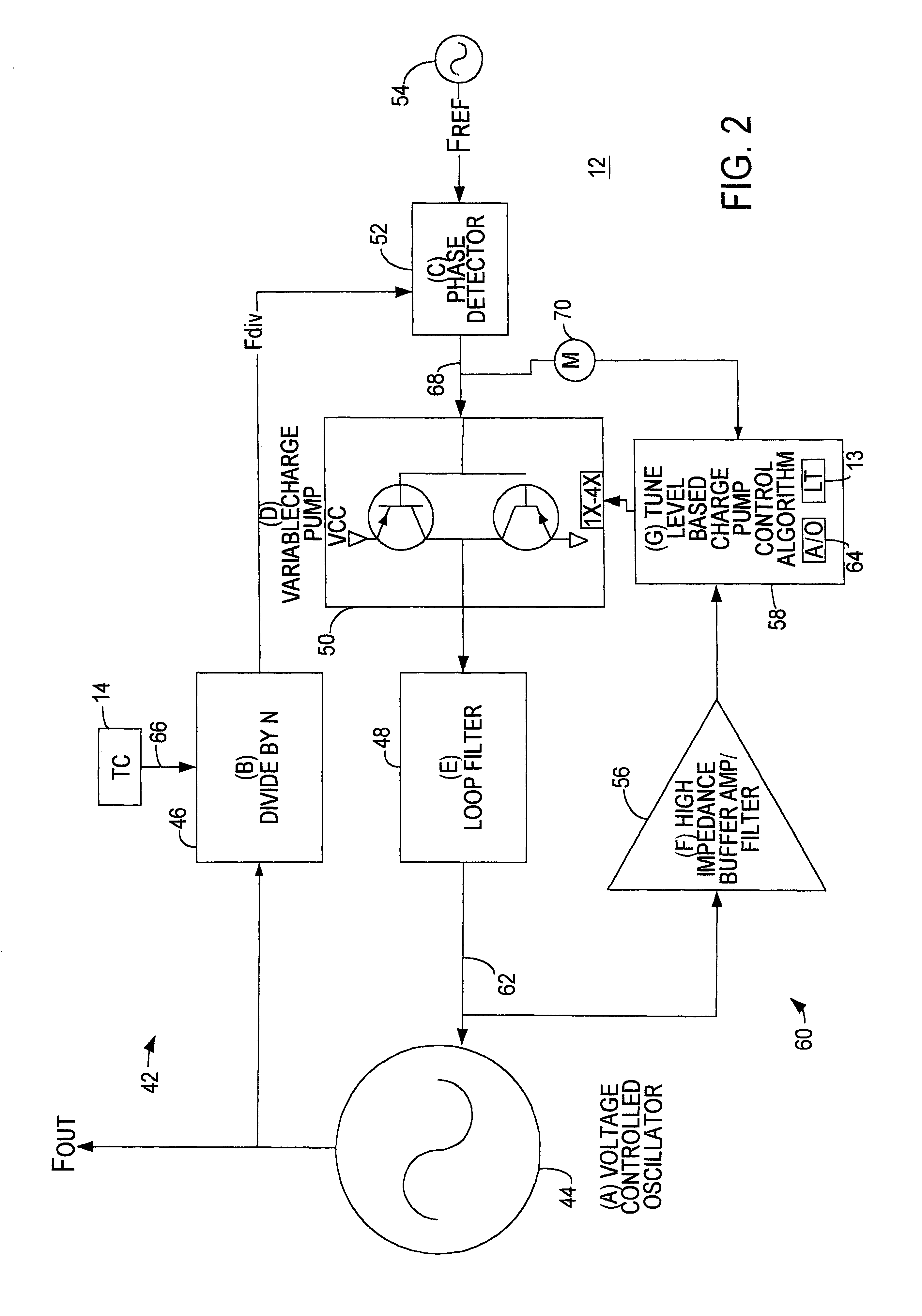
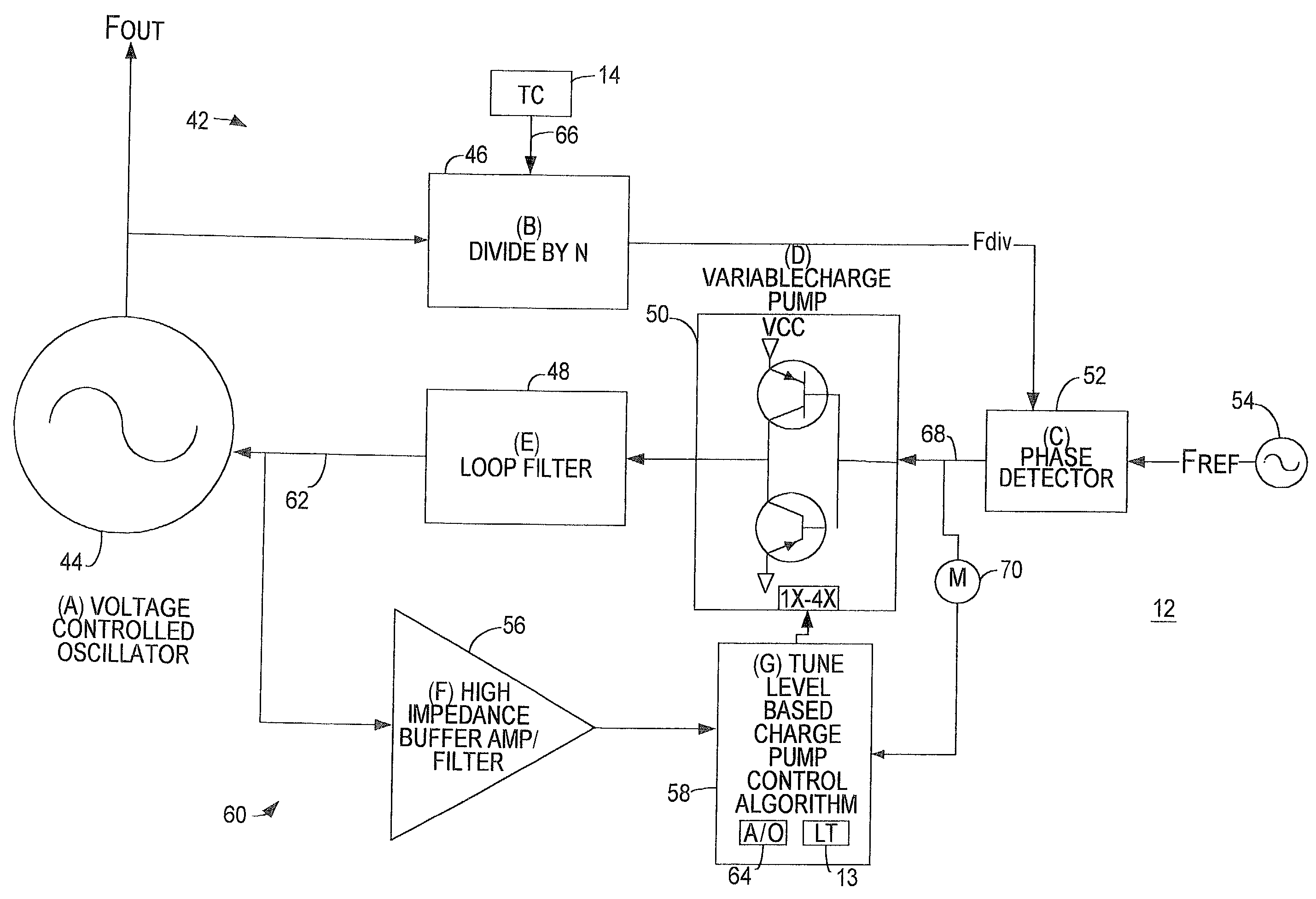
VCO tuning curve compensated charge pump current synthesizer
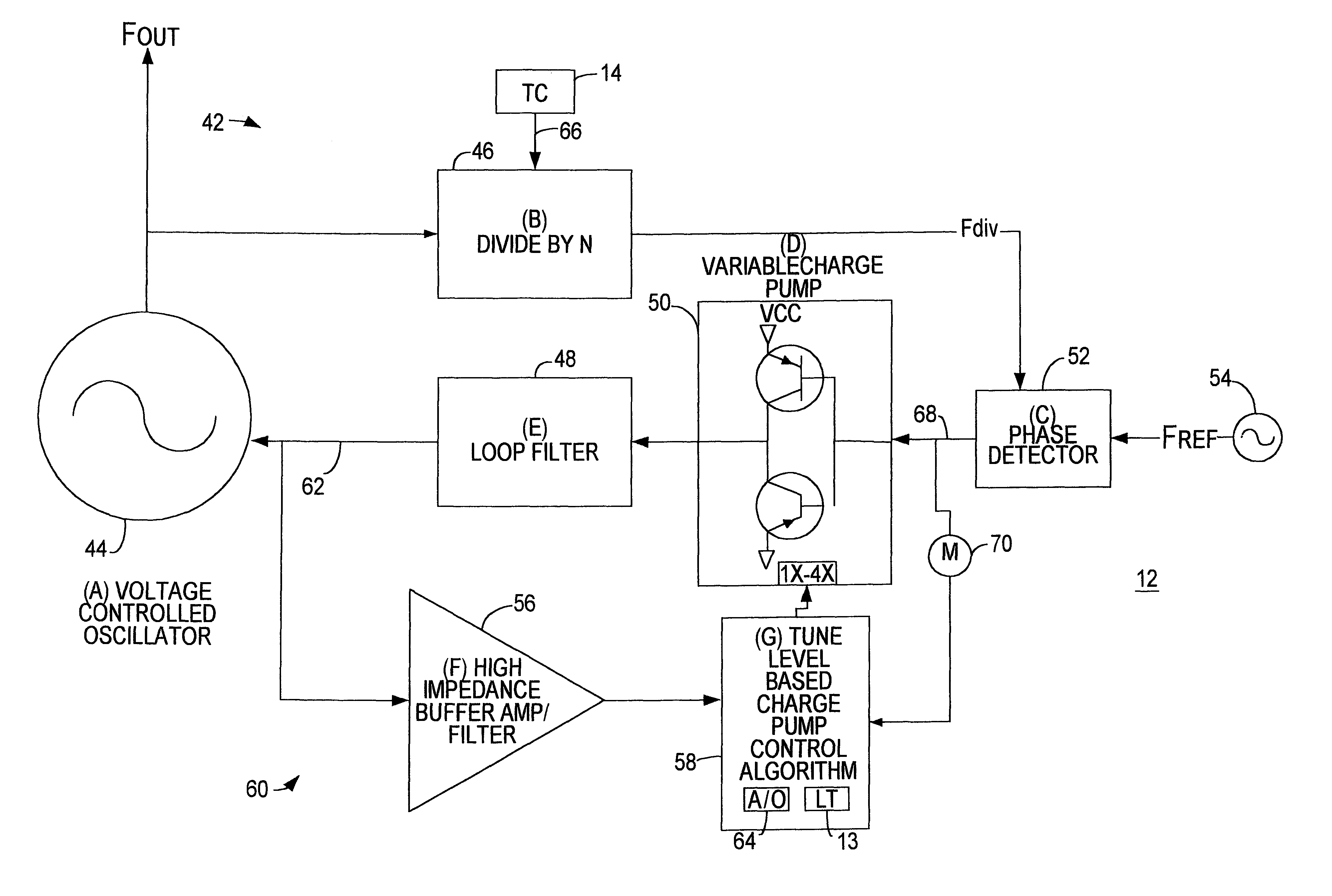
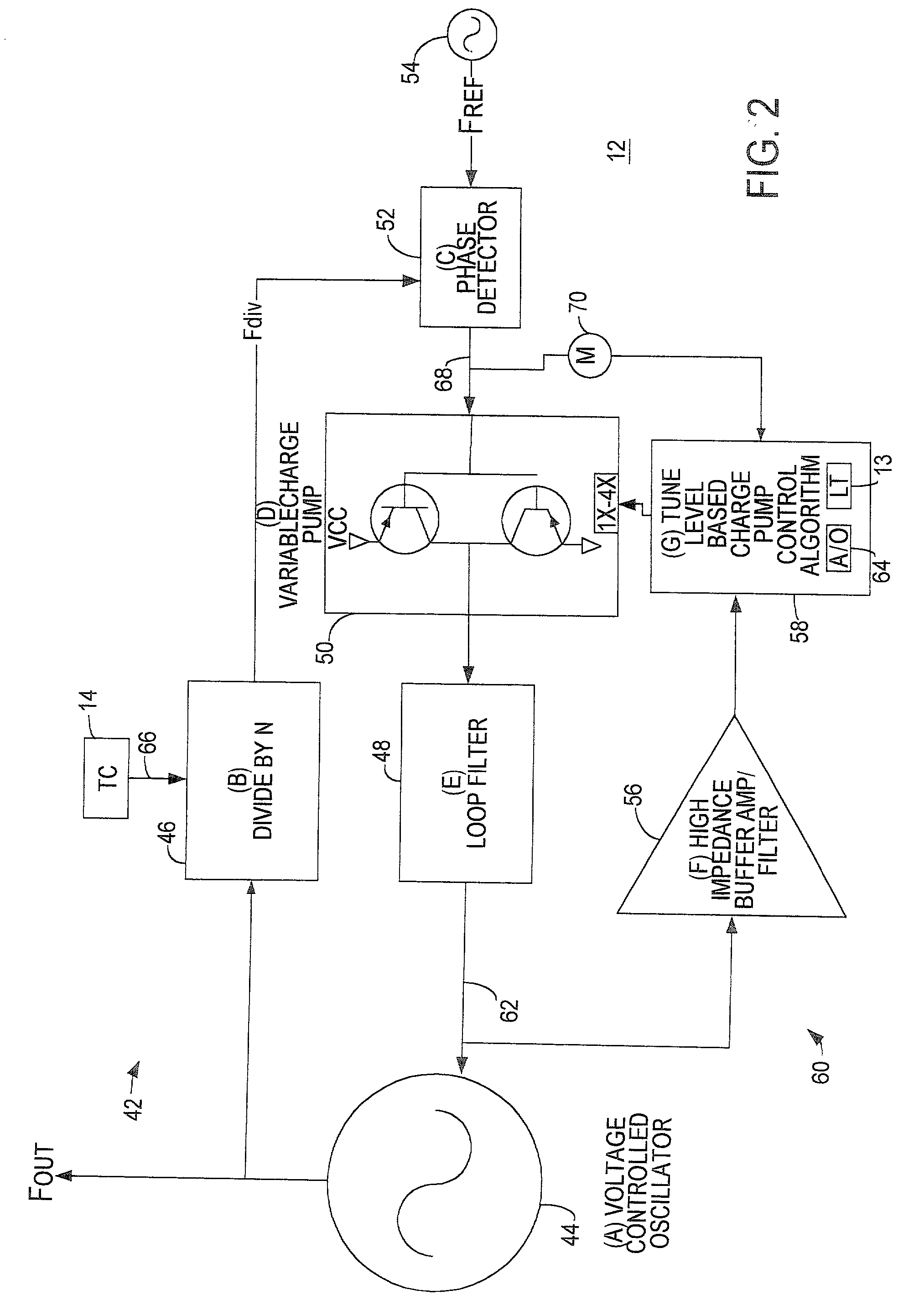
A system provided for controlling an output frequency of a voltage controlled oscillator relative to a reference frequency. A method includes the steps of detecting a phase error between a divided output of the voltage controlled oscillator and the reference frequency, pumping a frequency control input of the voltage controlled oscillator with the phase error and adjusting a pumping gain based upon a magnitude of the frequency control input to the voltage controlled oscillator.This apparatus includes a phase detector adapted to detect the phase error between the divided output of the voltage controlled oscilator and the reference frequency and a charge pump adapted to pump the frequency control input of the voltage controlled oscillator with the phase error. The apparatus also includes a gain controller adapted to adjust the pumping gain based upon the magnitude of the frequency control input to the voltage controlled oscillator.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
VCO tuning curve compensated charge pump current synthesizer
InactiveUS20020039050A1Modulated-carrier systemsPulse automatic controlPhase detectorVoltage control
A system provided for controlling an output frequency of a voltage controlled oscillator relative to a reference frequency. A method includes the steps of detecting a phase error between a divided output of the voltage controlled oscillator and the reference frequency, pumping a frequency control input of the voltage controlled oscillator with the phase error and adjusting a pumping gain based upon a magnitude of the frequency control input to the voltage controlled oscillator. The apparatus includes a phase detector adapted to detect the phase error between the divided output of the voltage controlled oscilator and the reference frequency and a charge pump adapted to pump the frequency control input of the voltage controlled oscillator with the phase error. The apparatus also includes a gain controller adapted to adjust the pumping gain based upon the magnitude of the frequency control input to the voltage controlled oscillator.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Linear voltage controlled oscillator transconductor with gain compensation
InactiveUS20020089381A1Decrease resistance of variable resistanceMore of the gainPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase locked loop circuitLow-pass filter
A voltage controlled oscillator of a phase locked loop circuit having digitally controlled gain compensation. The digital control circuitry provides binary logic input to the voltage controlled oscillator for a digitally controlled variable resistance circuit, a digitally controlled variable current transconductor circuit, or differential transistor pairs having mirrored circuitry for adjusting the V-I gain. The latter configuration requires the voltage controlled oscillator to incorporate a source-coupled differential pair which is driven by a low pass filter capacitor output voltage, and connected to load transistors; a current source and a current mirror for generating a tail current; individual banks of transistors to mirror the load transistor currents; a digital-to-analog converter with control lines outputted there from, the digital-to-analog converter used to increase the amount of current allowed to flow to the transconductor output, the current being digitally increased and decreased corresponding to an amount of current pulled from the current source, and mirroring the current through at least one transistor mirror circuit.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Voltage controlled oscillator with gain control
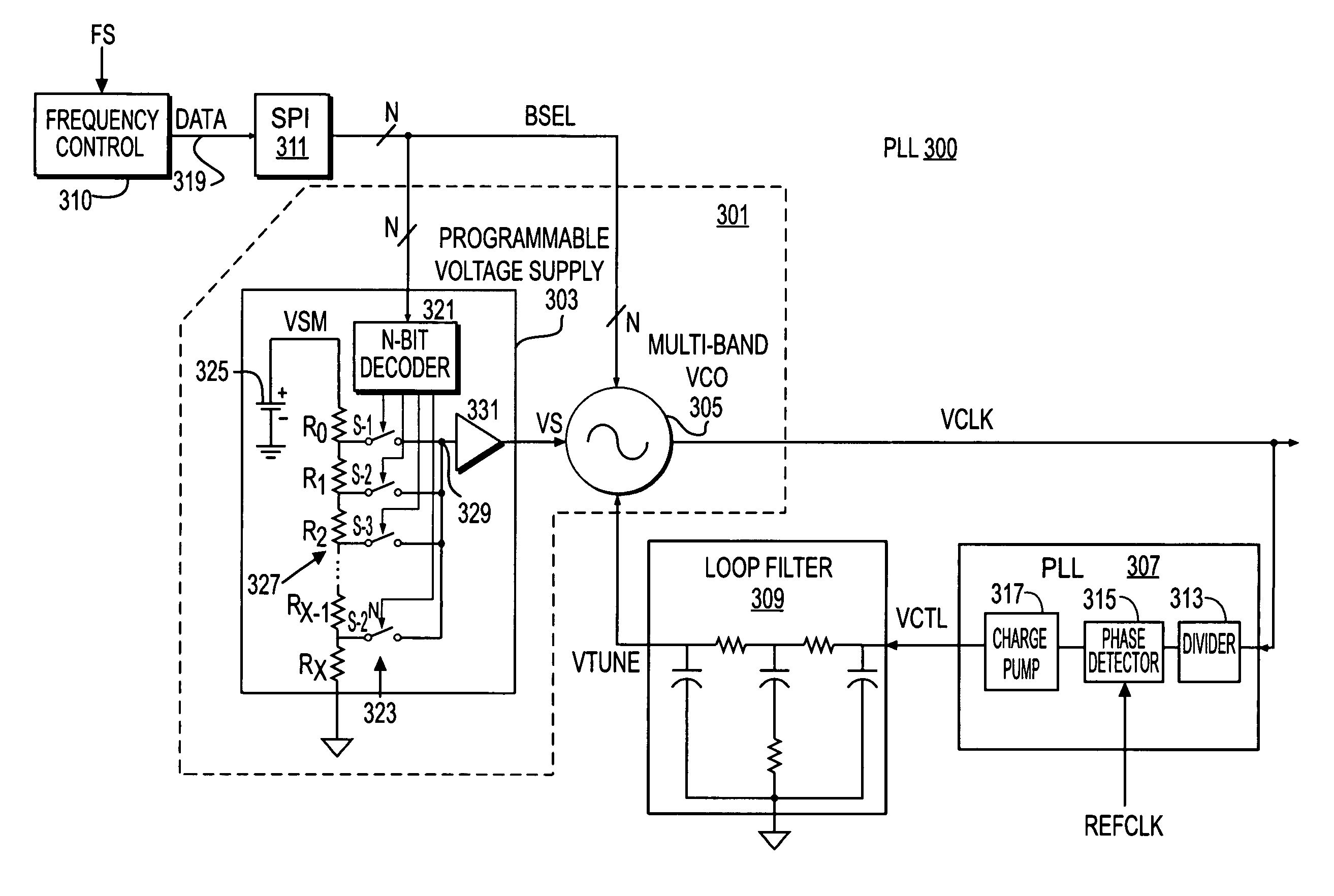
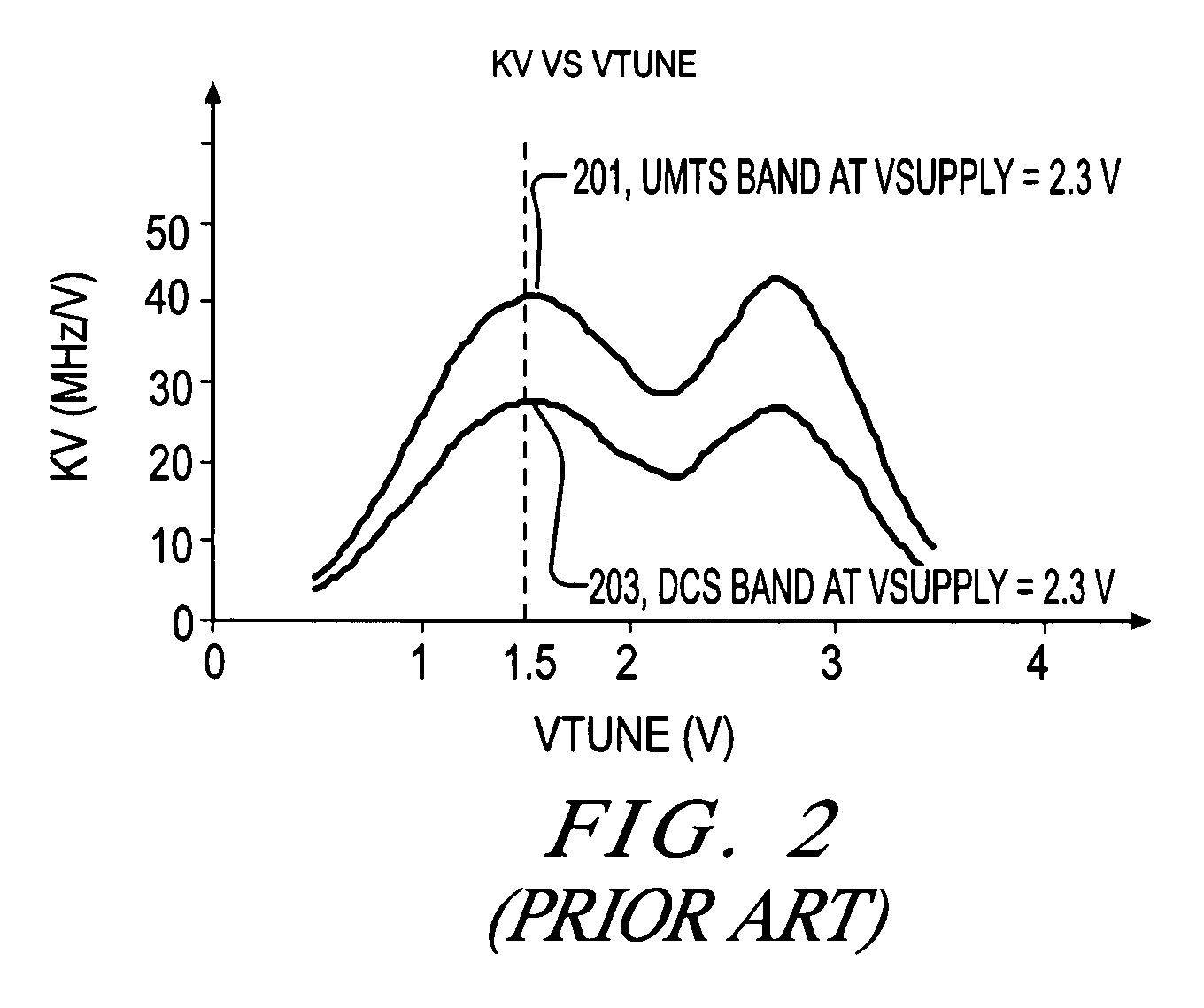
A VCO circuit including a VCO, a voltage supply and a control circuit. The VCO has a supply voltage input and a gain that changes with its supply voltage. The voltage supply has an adjust input and an output coupled to the supply voltage input of the VCO. The voltage supply adjusts the voltage level of its output in response to changes of the adjust input. The control circuit has a first adjust output coupled to the adjust input of the voltage supply to adjust the gain of the VCO. The VCO may include a frequency range adjust input controlled by the control circuit so that the gain of the VCO is adjusted when the frequency range is changed. For a multi-band VCO, the gain is adjusted for different frequency bands to maintain a relatively constant gain for each frequency band.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Linearized fractional-N synthesizer having a current offset charge pump
InactiveUS7171183B2Easy to makePulse generation by bipolar transistorsPulse automatic controlLoop filterPhase difference
A linear fractional-N synthesizer includes phase and frequency detection module, a charge pump circuit, a loop filter, a voltage controlled oscillator, and a fractional-N divider. The phase and frequency detection module is operably coupled to produce a charge up signal, a charge down signal, or an off signal based on a phase difference and / or a frequency difference between a reference oscillation and a feedback oscillation. The charge pump circuit is operably coupled to produce a positive current when the charge up signal is received, a negative current when the charge down signal is received, and a non-zero offset current when the off signal is received. The charge pump includes a resistor and a control module. The resistor provides the non-zero offset current and the control module maintains the non-zero offset current at a substantially constant value. The loop filter is operably coupled to produce a control voltage based on at least some of: the positive current, the negative current, and the non-zero offset current. The voltage controlled oscillator produces an output oscillation based on the control voltage. The fractional-N divider module operably coupled to divided the output oscillation by a fractional N value to produce the feedback oscillation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Numerical control LC voltage controlled oscillator with amplitude detection
InactiveCN106549636AChange bandwidthEasy output rangeOscillations generatorsNumerical controlLow noise
The invention discloses a numerical control LC voltage controlled oscillator with amplitude detection. The numerical control LC voltage controlled oscillator comprises an LC oscillator and an oscillation signal amplitude detection unit. The LC oscillator is composed of an LC frequency resonant unit, a capacitor array unit and a varactor array unit; and an output amplitude detection unit is composed of a differential amplification circuit with a tail current source and a transmission gate with a switch controller. The LC voltage controlled oscillator generates a high-performance and low-noise differential oscillation signal, and changes the bandwidth and the voltage control gain through a numerical control signal provided by an external circuit. The output amplitude detection unit receives an oscillated high-frequency differential signal and outputs the maximum value of the differential signal, and the amplitude of an oscillation signal can be obtained by subtracting a DC offset from the maximum value. The numerical control LC voltage controlled oscillator disclosed by the invention can not only realize a large variable capacitance range and a highly linear voltage control gain, and can further judge whether the circuit can perform normal oscillation work, obtain the amplitude of the high-frequency oscillation signal, and solve the problem of monitoring the oscillation circuit and the oscillation signal in real time.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
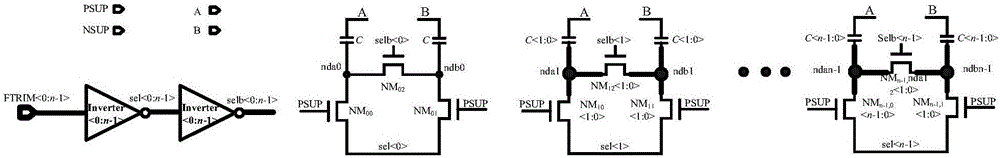
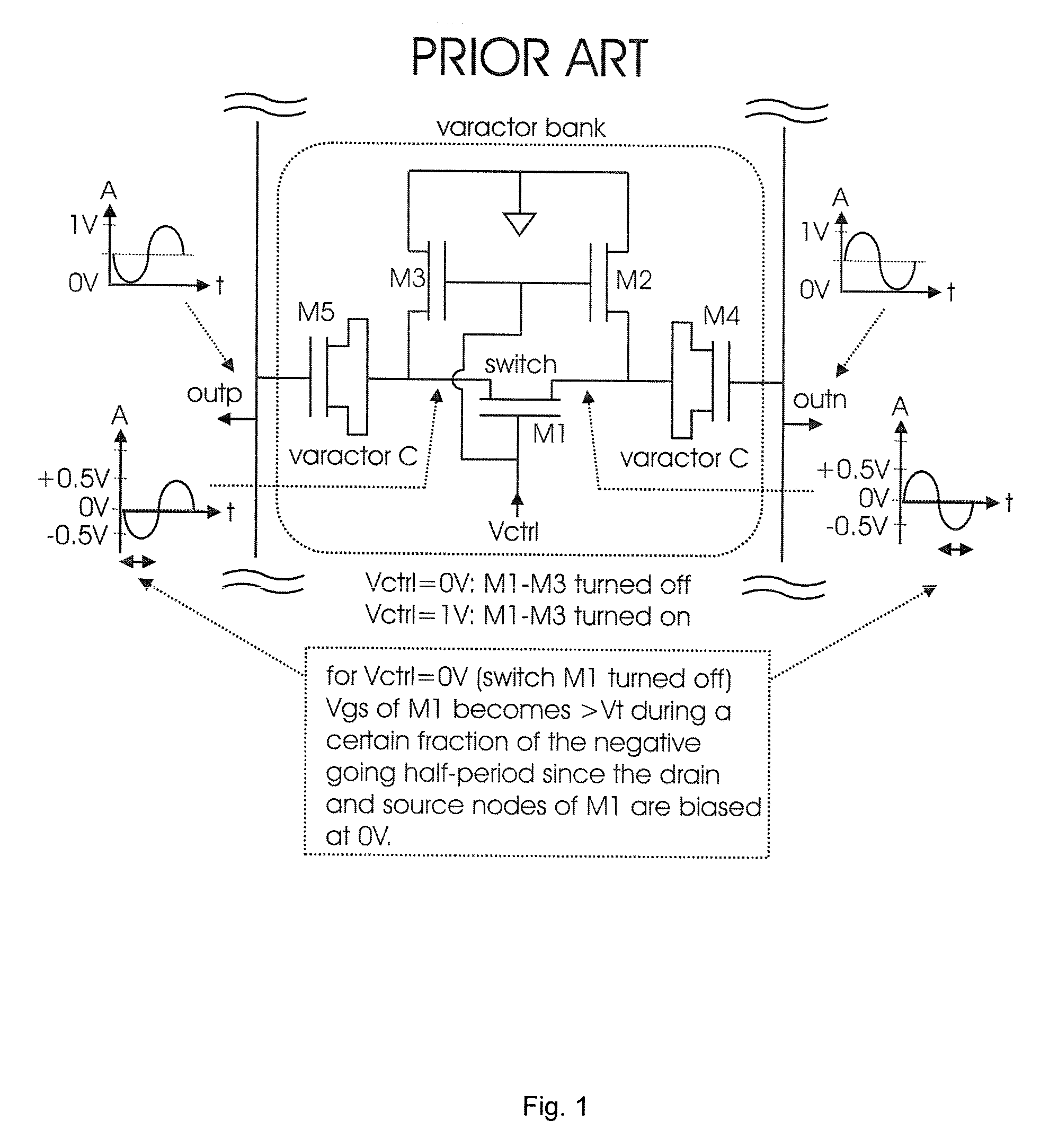
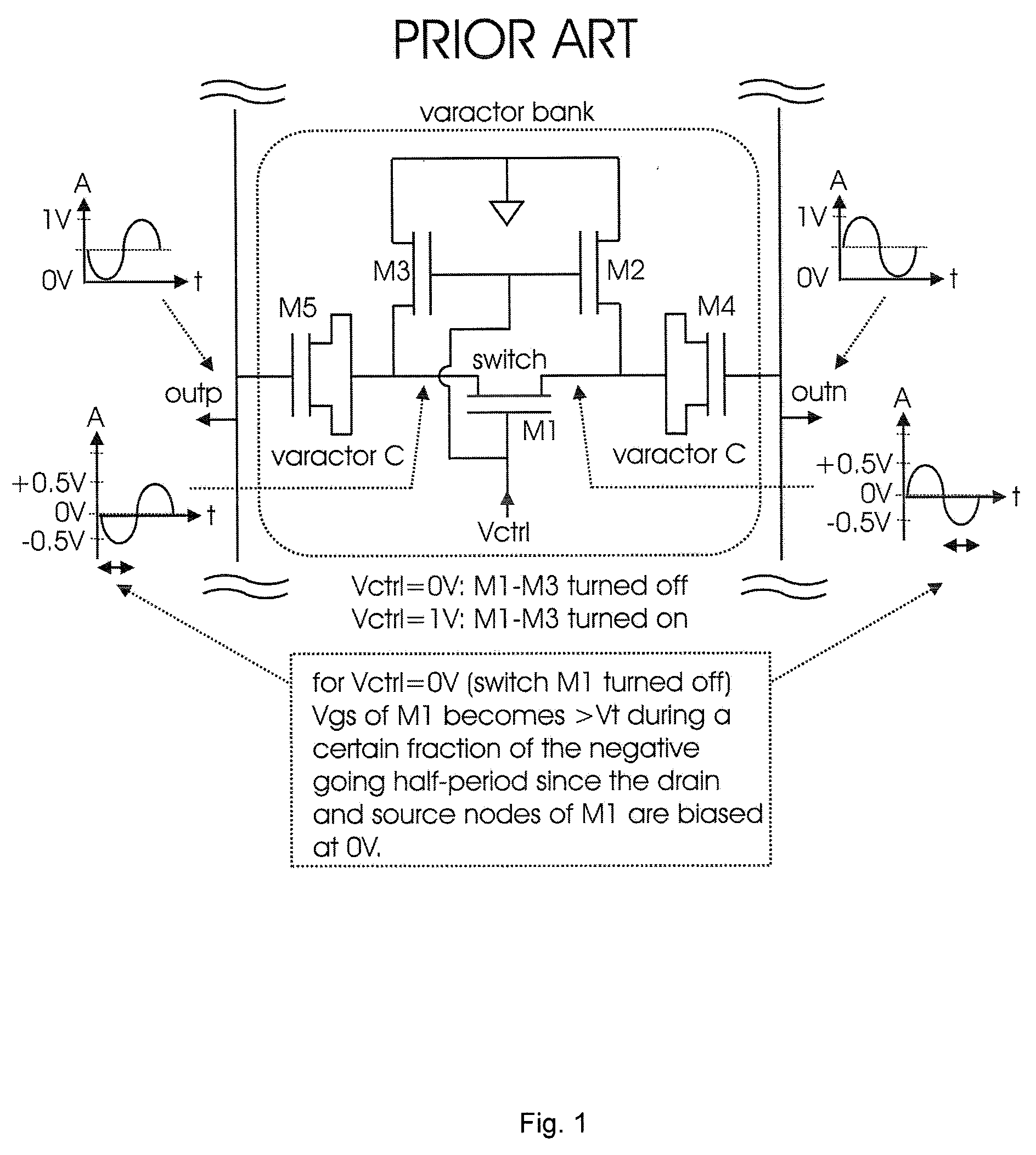
Varactor bank switching based on negative control voltage generation
InactiveUS7479839B1Angle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlControl signalPass gate
A method and apparatus for varactor bank switching for a voltage controlled oscillator is disclosed. Varactor bank switching involves generating a negative bias voltage signal as a control signal for a varactor bank switch in an off-state, the varactor bank switch comprising a pass-gate circuit including switching transistors. Generating the negative bias voltage signal includes employing an active rectifier circuit running at the speed of an oscillation signal, the negative bias voltage signal maintaining the gate-source voltage of the pass-gate circuit below a threshold voltage to prevent said switching transistors from becoming conductive in an off-state.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
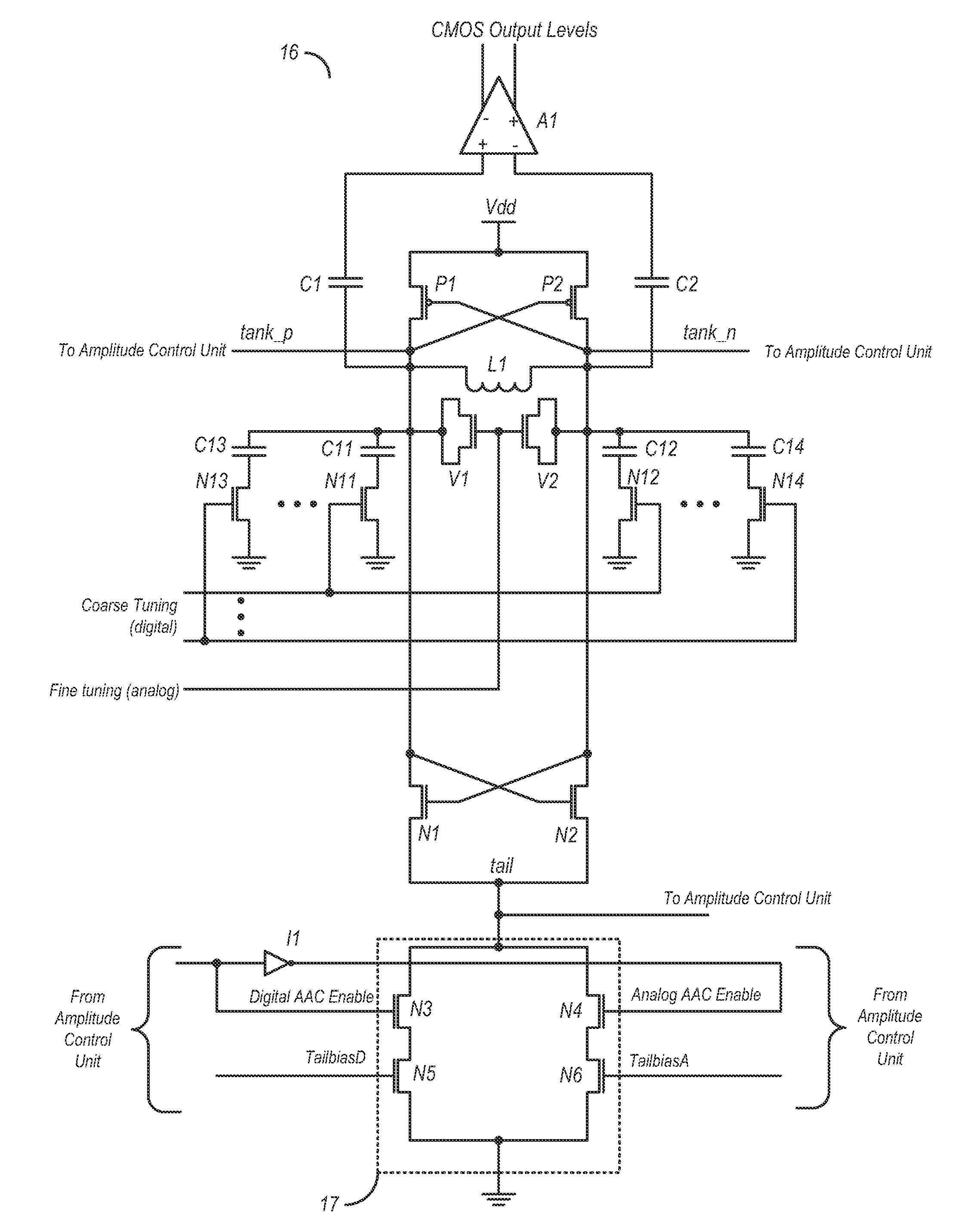
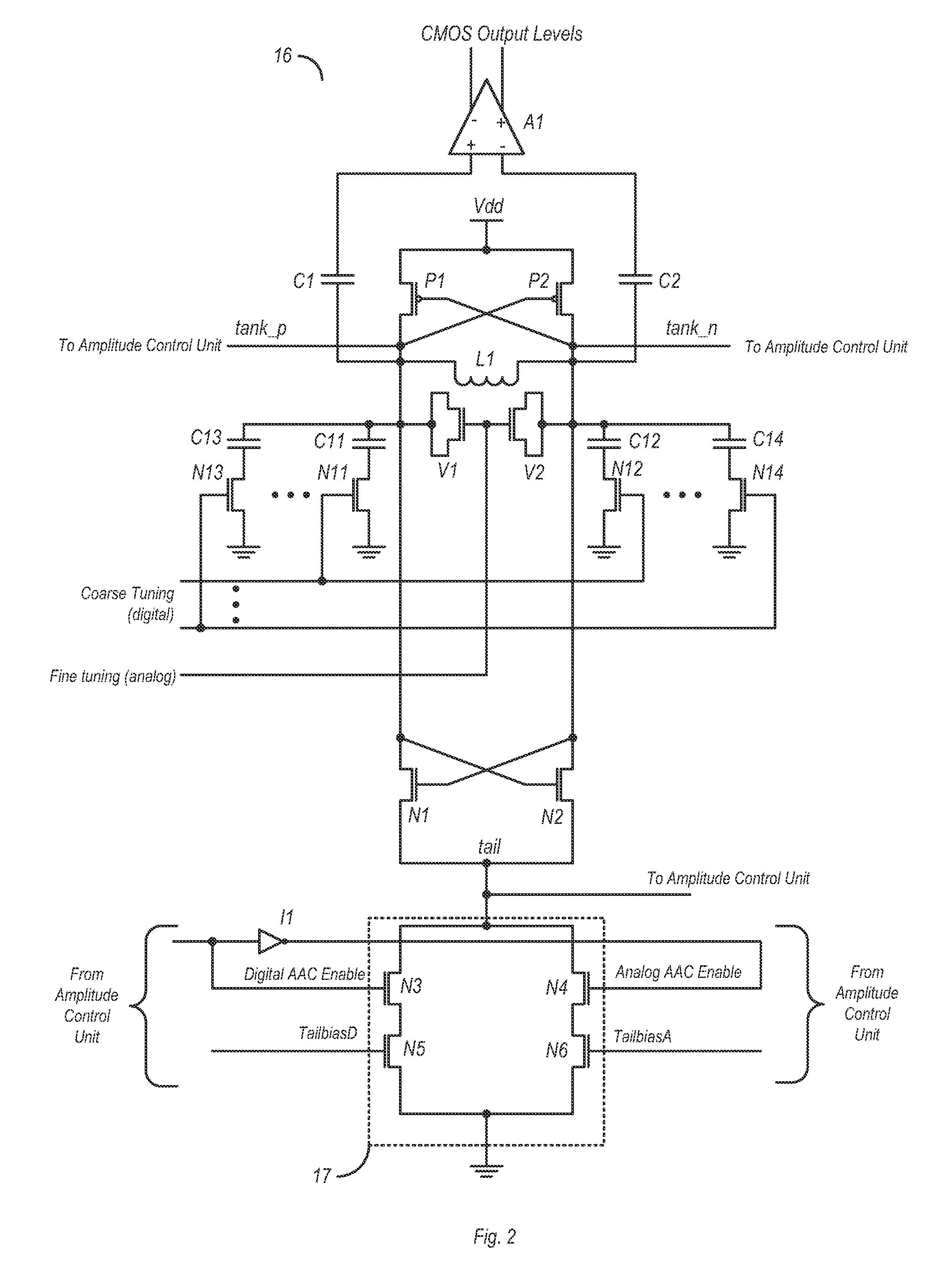
Automatic amplitude control for voltage controlled oscillator
ActiveUS8134417B2Angle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlAmplitude controlEngineering
A circuit and method for calibrating a VCO (voltage controlled oscillator) is disclosed. In one embodiment, a circuit includes a VCO and a bias control circuit coupled to a tail node of the VCO. An amplitude control unit may also be coupled to the tail node, wherein the amplitude control unit is configured to determine the amplitude of a VCO output signal based on a voltage present on the tail node. The amplitude control unit may also be configured to generate a bias voltage based on the amplitude of the VCO output signal and a target voltage. The bias control circuit may be coupled to receive the bias voltage from the amplitude control unit and may be further configured to adjust the voltage on the tail node based on the received bias voltage.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
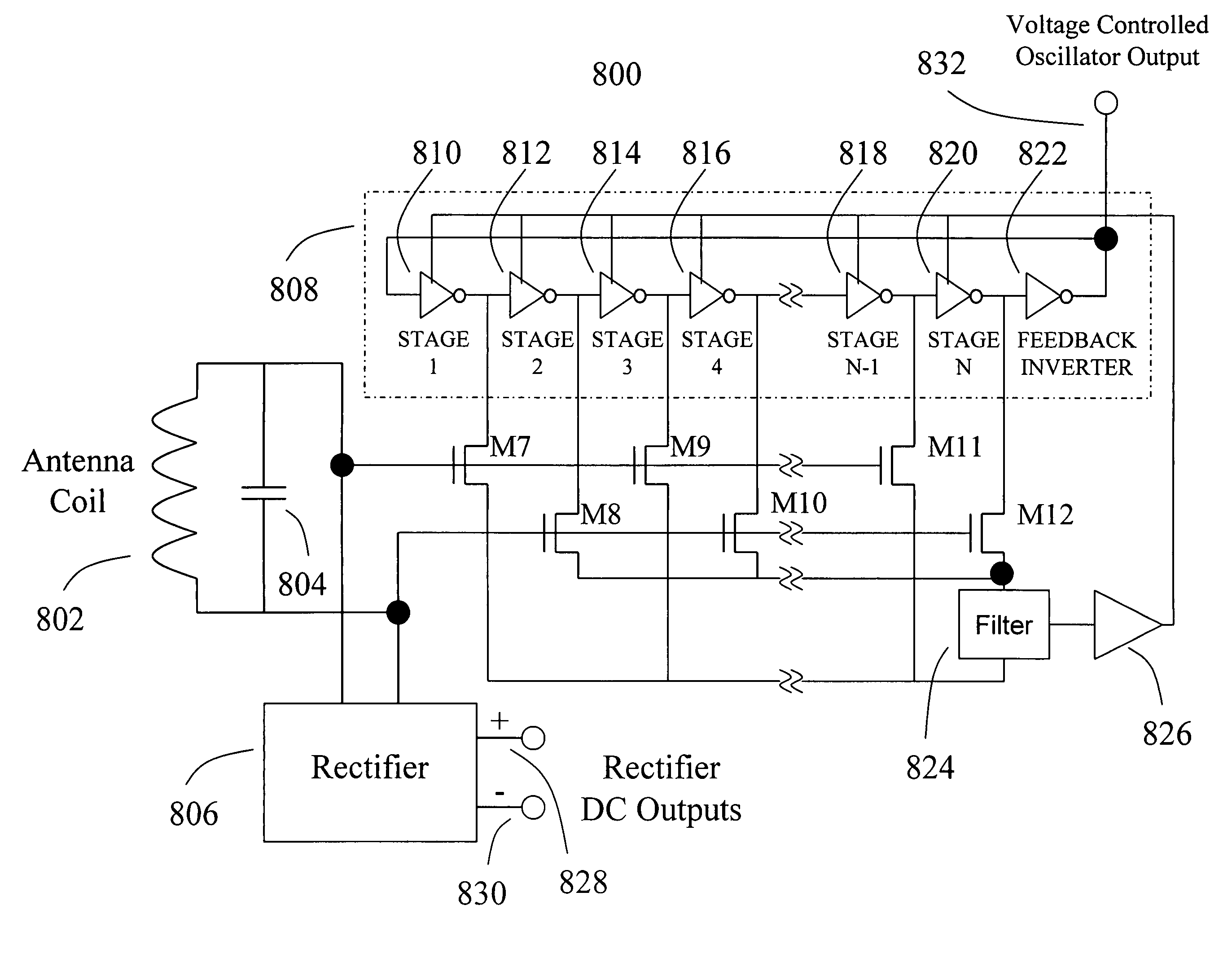
Non-quasistatic phase lock loop frequency divider circuit
A non-quasistatic MOS frequency divider circuit uses a phase lock loop configuration including an antenna coil to induce a differential input signal, an antenna resonating capacitor, a rectifier, a voltage controlled ring oscillator, a phase detector and a loop filter. All transistors used are organic MOS devices of PMOS, NMOS or both PMOS and NMOS varieties. The voltage-controlled oscillator includes a multiple delay stage ring oscillator. The phase detector includes transistors connected as sampling switches to sample the individual oscillator stage voltages into the loop filter. The sampling transistors have gates connected to the coil. The loop filter provides a substantially direct current to a loop amplifier and then to the voltage controlled oscillator delay control input. This configuration results in the voltage controlled oscillator frequency being synchronous to—and at a sub-multiple of the antenna signal frequency. The sampling transistor gates are all connected to the coil and thereby become part of the capacitance of the radio frequency parallel resonant network. The transistor gates are then efficiently switched at the rate of the radio frequency signal with no delay relative to the coil voltage. Operation of the phase detector organic transistors is based on non-quasistatic behavior of the transistor. Non-quasistatic operation results in phase detection at a frequency much higher than the quasistatic limit of transistor unity gain bandwidth.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
PLL circuit
InactiveUS20090245450A1Improve featuresSimple configurationPulse transformerPulse automatic controlLoop filterPhase locked loop circuit
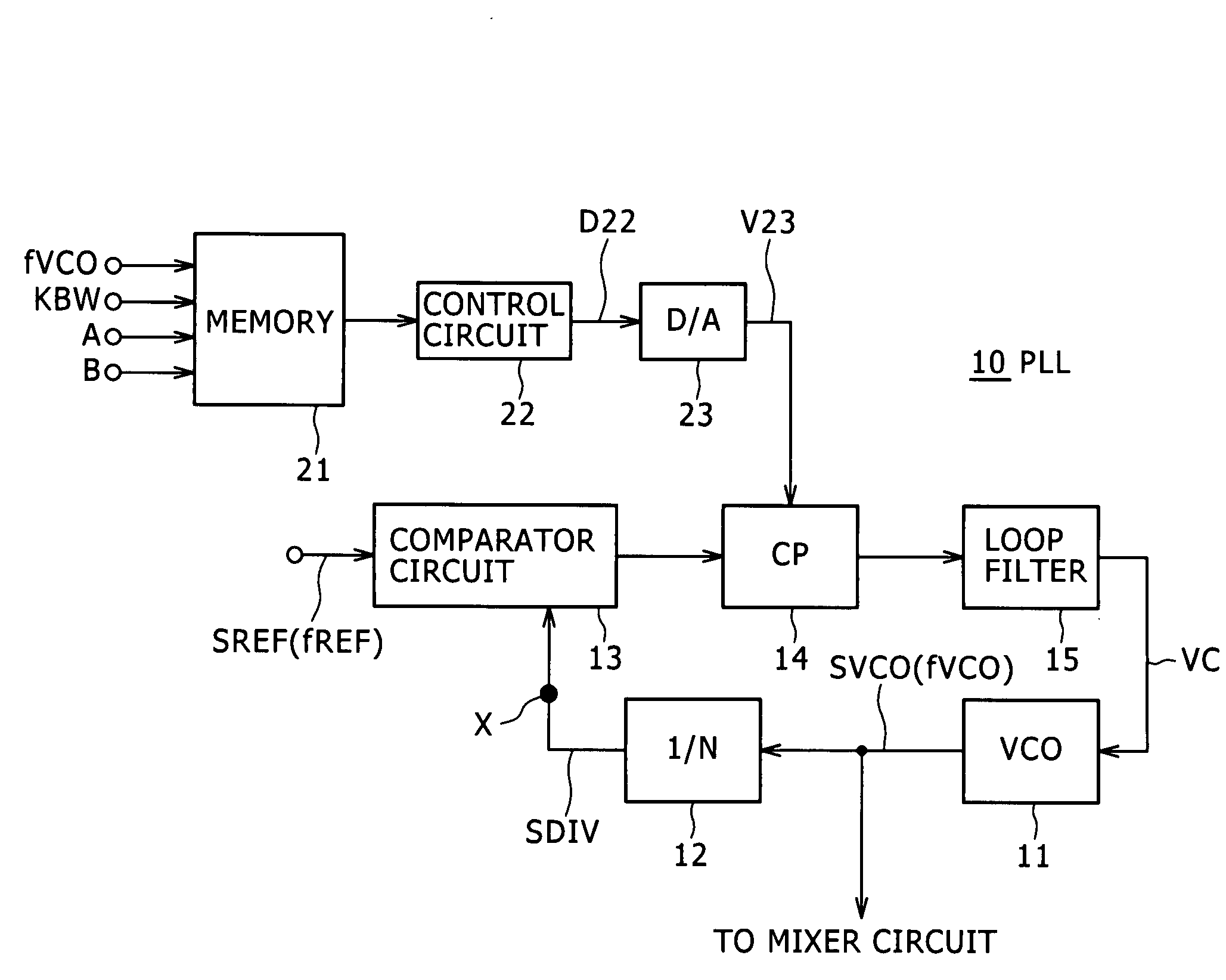
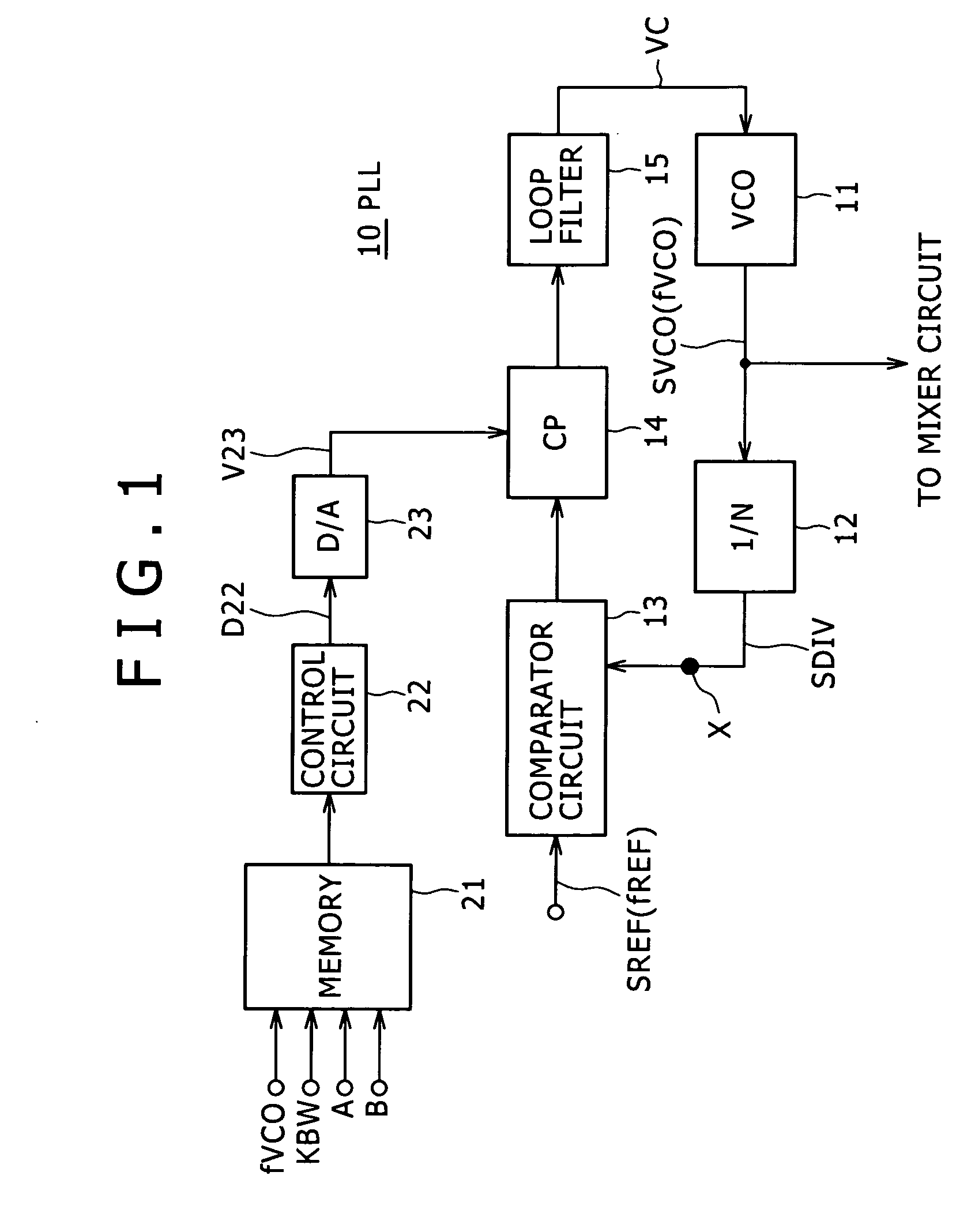
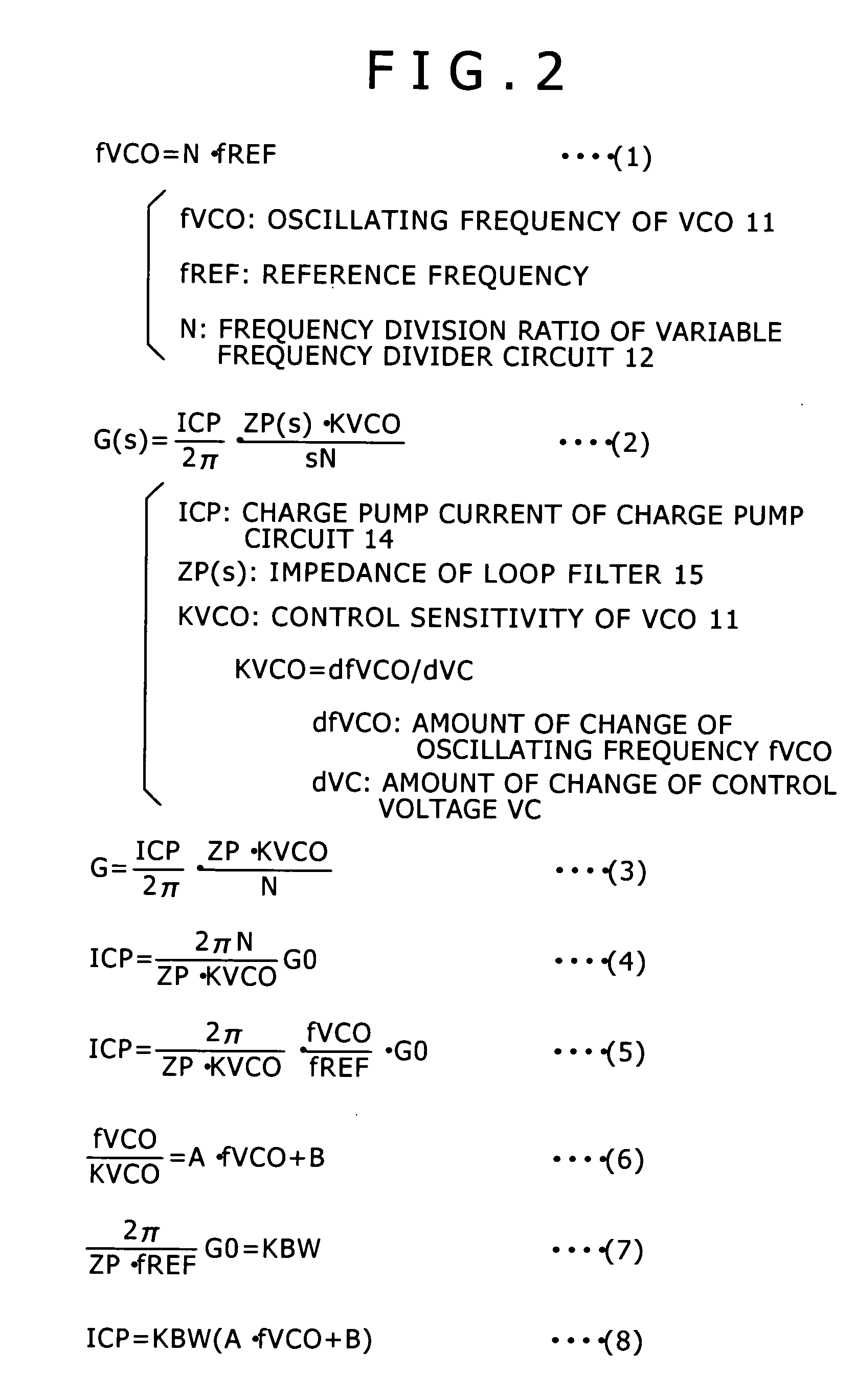
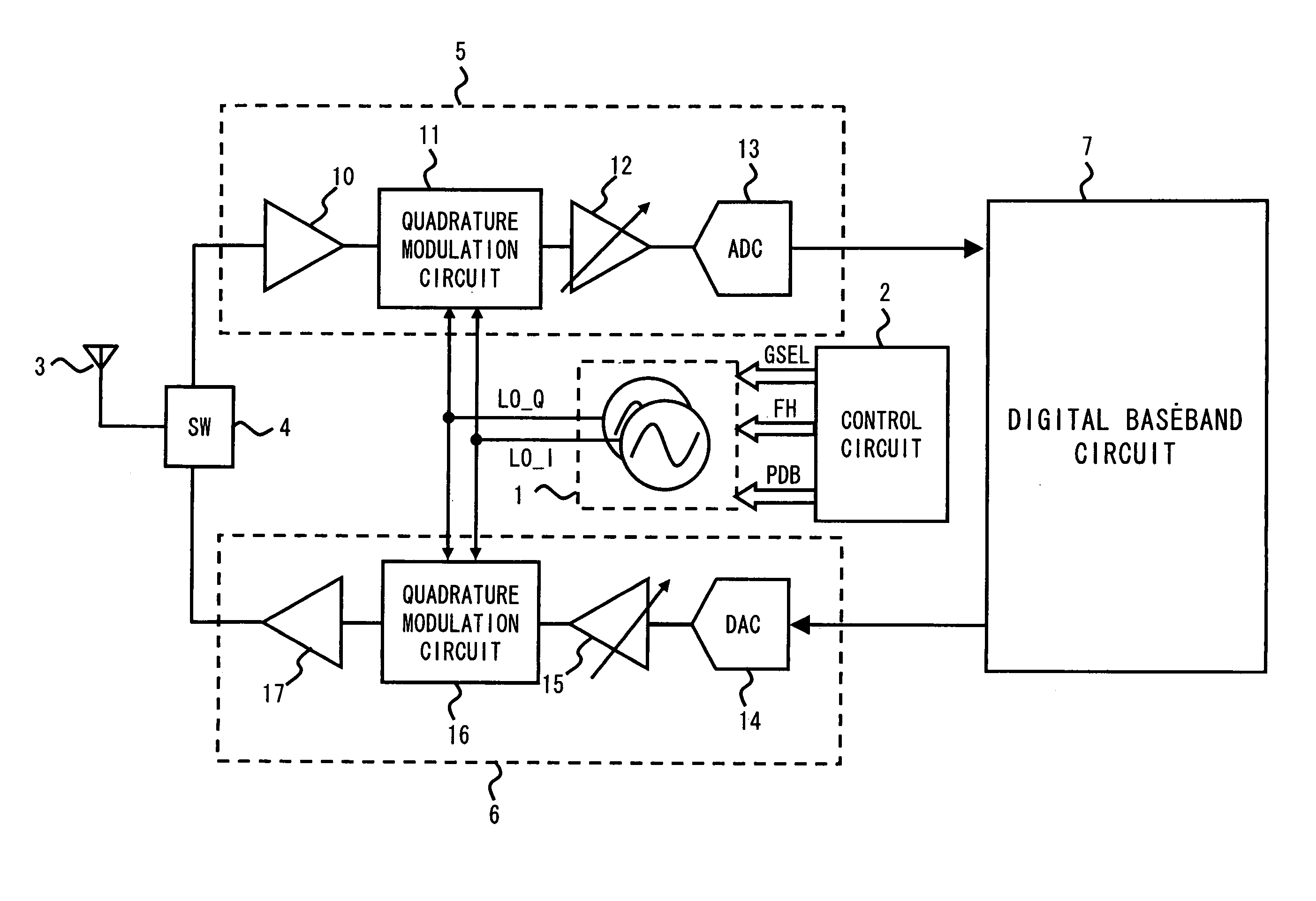
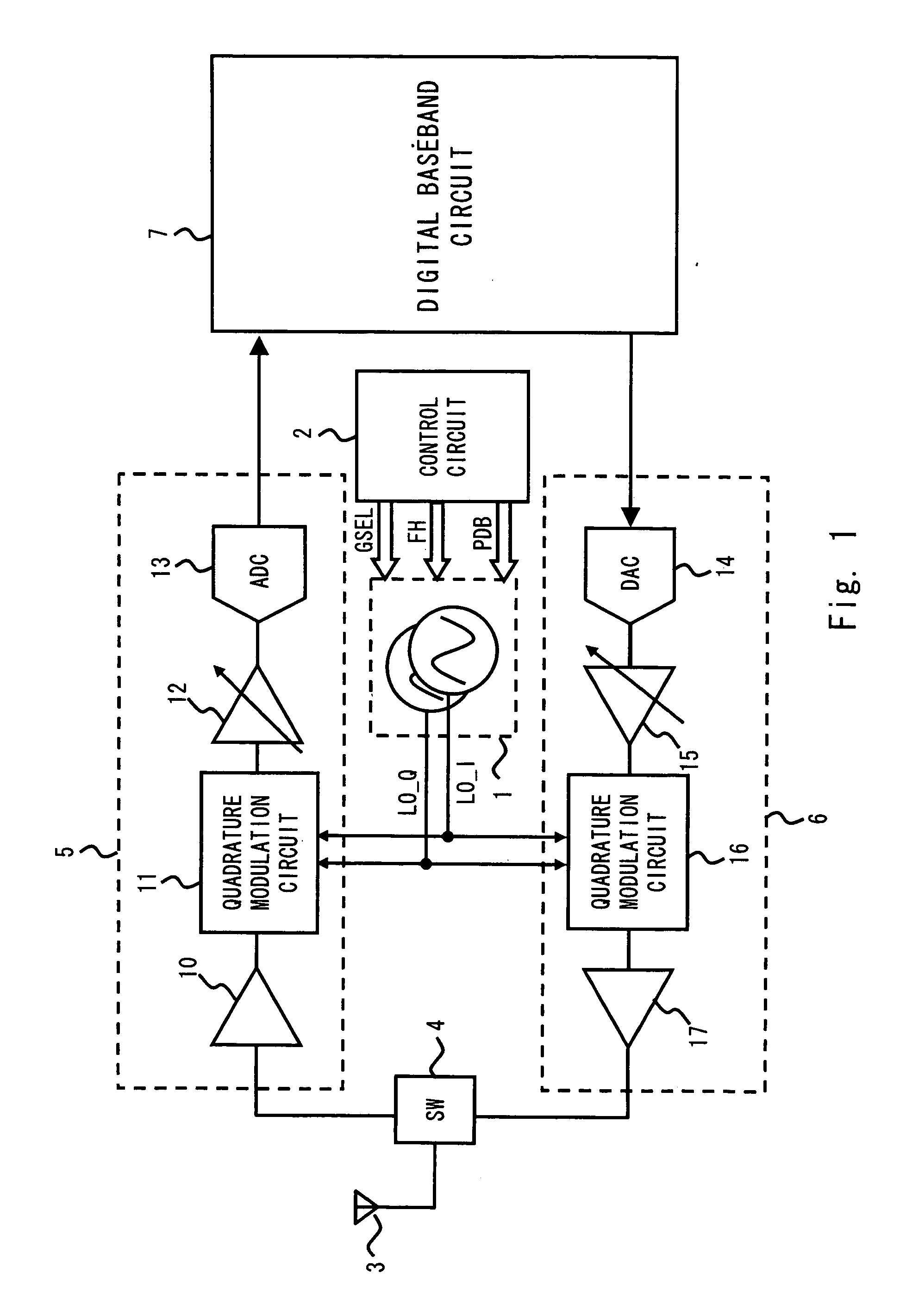
Disclosed herein is a phase-locked loop circuit including: a voltage controlled oscillator; a variable frequency divider circuit for frequency-dividing an oscillating signal of the voltage controlled oscillator into a 1 / N (N is an integer) frequency; a phase comparator circuit for comparing phases of a frequency-divided signal and a reference signal of a reference frequency with each other; a charge pump circuit for outputting a charge pump current changed in pulse width; a loop filter for being supplied with the charge pump current and outputting a direct-current voltage changed in level; and a control circuit for calculating a value of the charge pump current as a function of the oscillating frequency of the voltage controlled oscillator and a coefficient for setting a phase locked loop band, and setting the value of the charge pump current in the charge pump circuit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Local signal generation circuit
InactiveUS20090201065A1Reducing area consumptionReduce circuit areaPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorLoop filterPhase difference
A local signal generation circuit in accordance with one aspect of the present invention includes a phase comparator that detects a phase difference between a reference signal and a feedback signal and outputs a error signal, a charge-pump circuit that receives the error signal and generates a step-up voltage, a loop filter that generates a tuning voltage by changing the shape of the step-up voltage, a voltage control oscillator that generates a first output signal having a predefined frequency based on the tuning voltage, and a prescaler that outputs a second output signal generated by dividing the frequency of the first output signal to a predefined frequency and also outputs a frequency-division signal generated by dividing the frequency of the first output signal to the predefined frequency to a frequency divider that generates the feedback signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Voltage controlled oscillator with body of transistors bias control
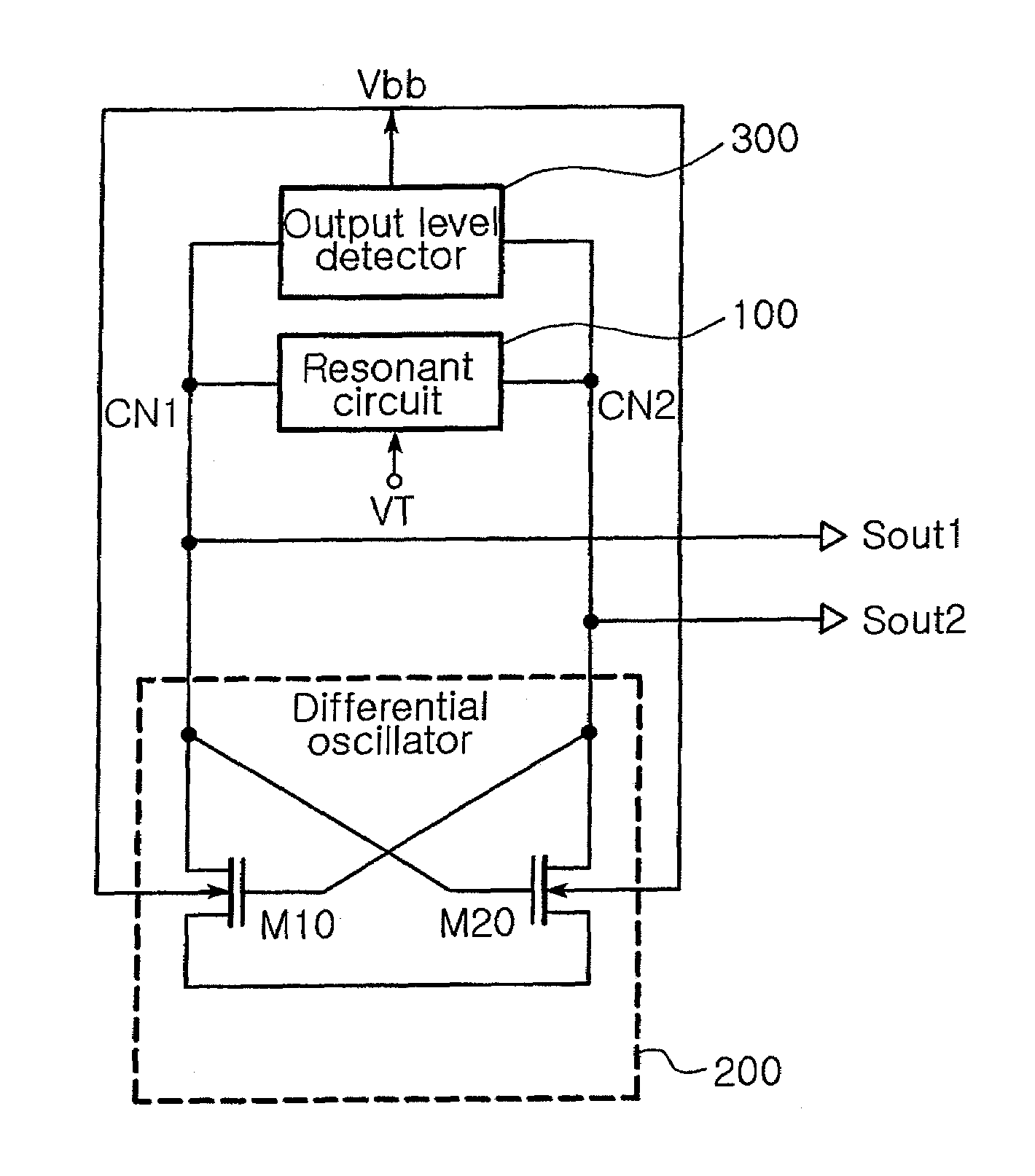
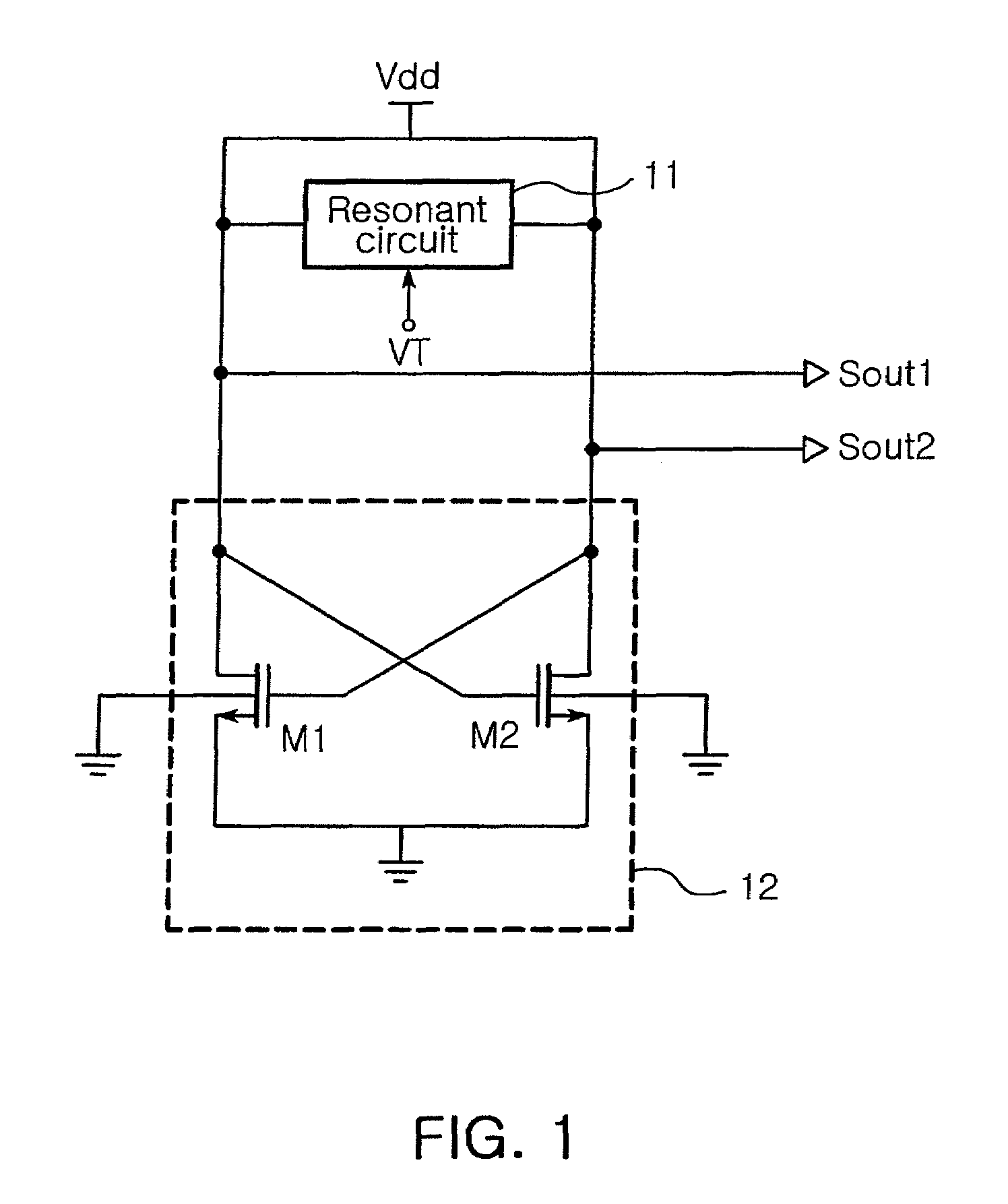
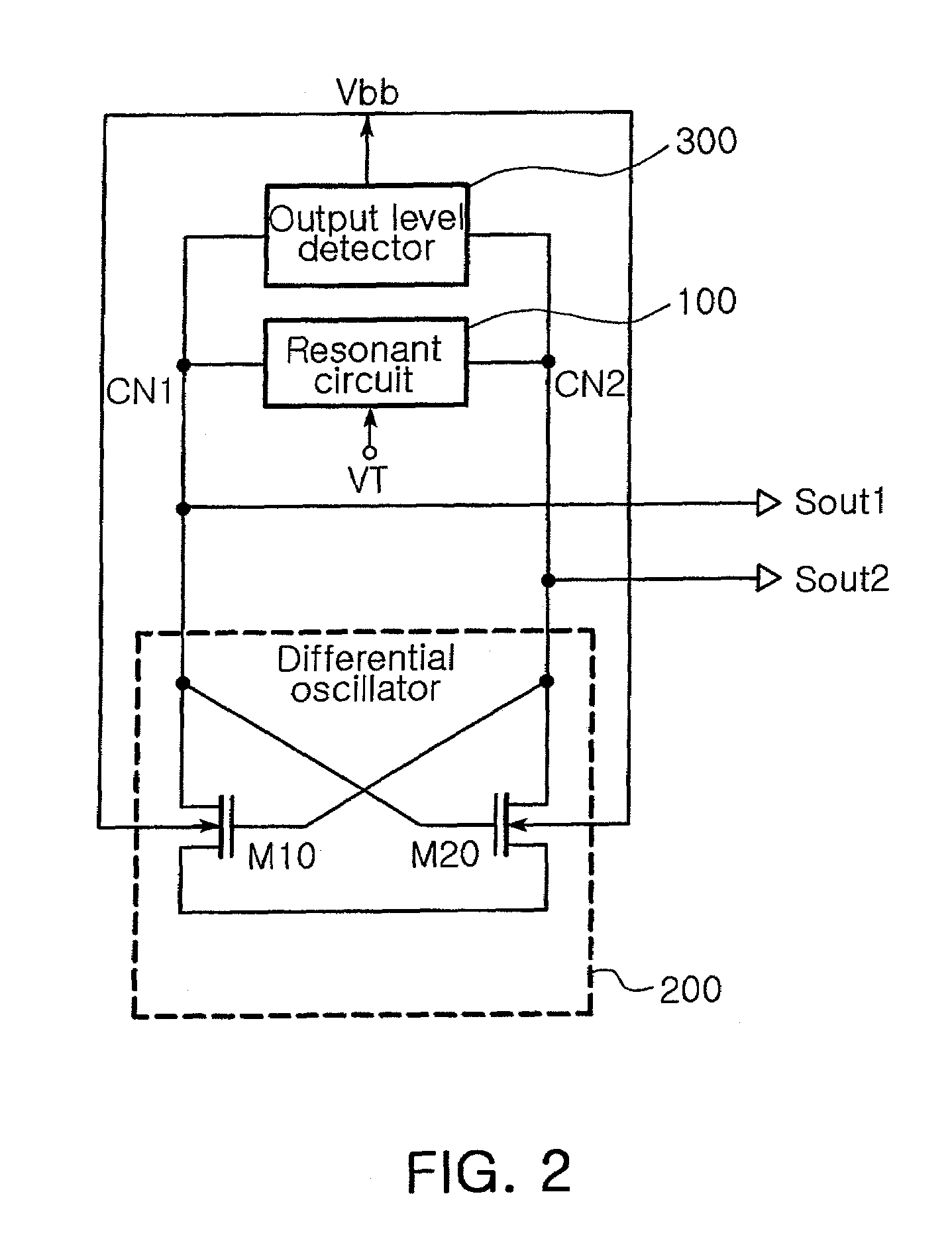
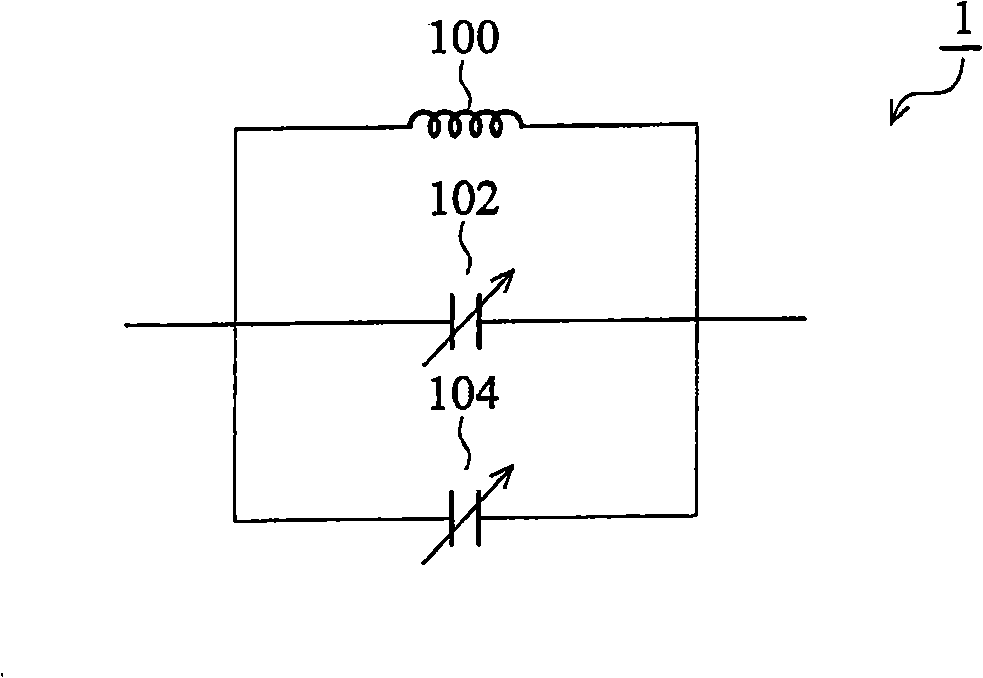
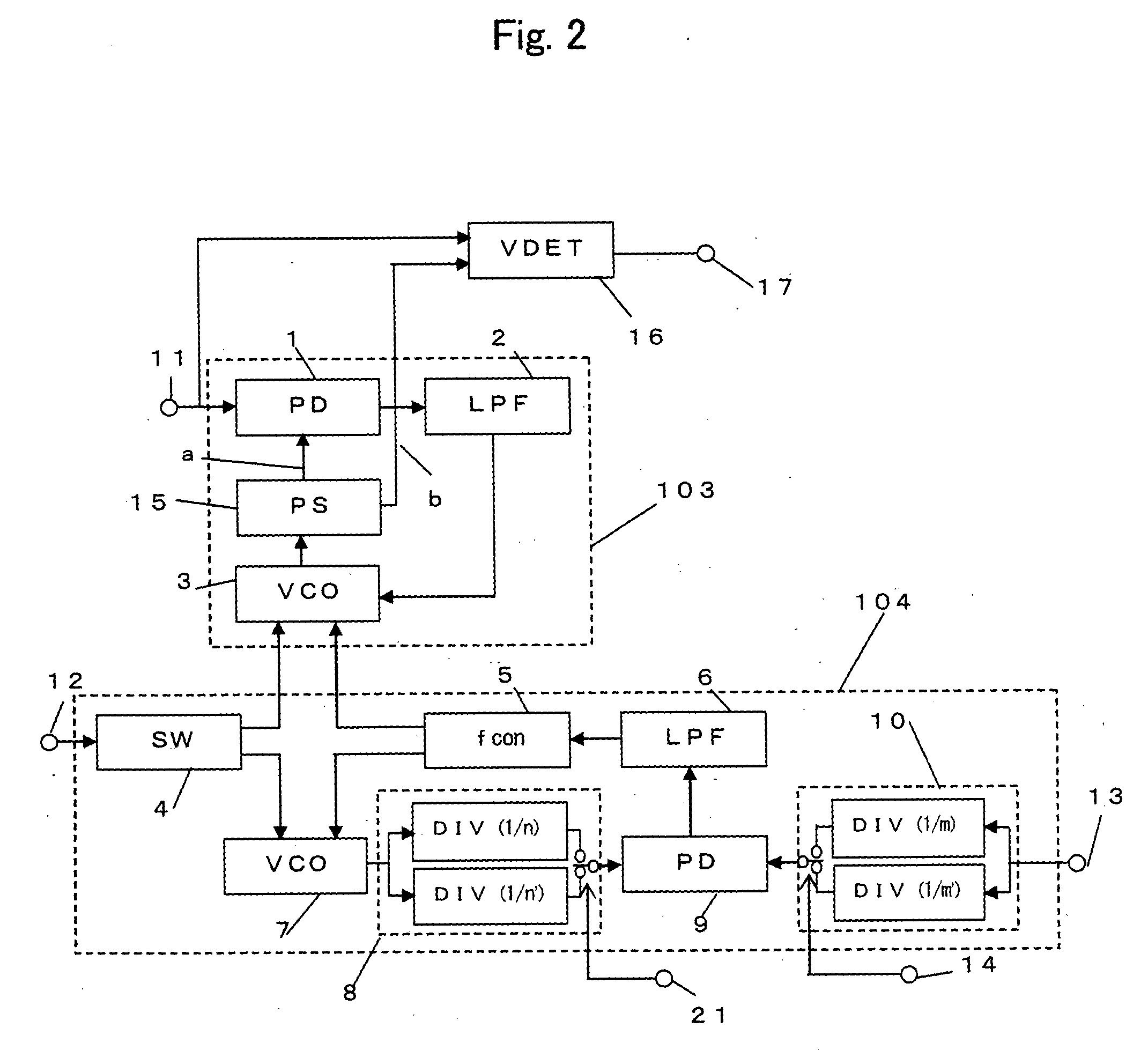
In a voltage controlled oscillator, a resonant circuit generates a resonant frequency in response to a tuning voltage. A differential oscillator includes first and second transistors differentially cross-coupled to the resonant circuit. The first and second transistors supply energy to the resonant circuit to oscillate the resonant frequency from the resonant circuit, thereby generating first and second oscillation signals having a phase difference of 180 degree. Also, the first and second transistors adjust the first and second oscillation signals to a uniform level in response to a body bias voltage. In addition, an output level detector detects a level of the first and second oscillation signals from the differential oscillator and supplies the body bias voltage corresponding to the detected level to a body of each of the first and second transistors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Integrate circuit
InactiveCN101359897AReduce frequency driftPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsCapacitanceNegative temperature
An integrated circuit is provided. The integrated circuit comprises a voltage controlled oscillator and a first compensation capacitor. The voltage controlled oscillator generates an oscillation signal. The first compensation capacitor, coupled in parallel to the voltage controlled oscillator, receives a control voltage to generate a negative temperature coefficient capacitance to compensate for frequency drift of the oscillation signal. The control voltage is temperature dependent.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
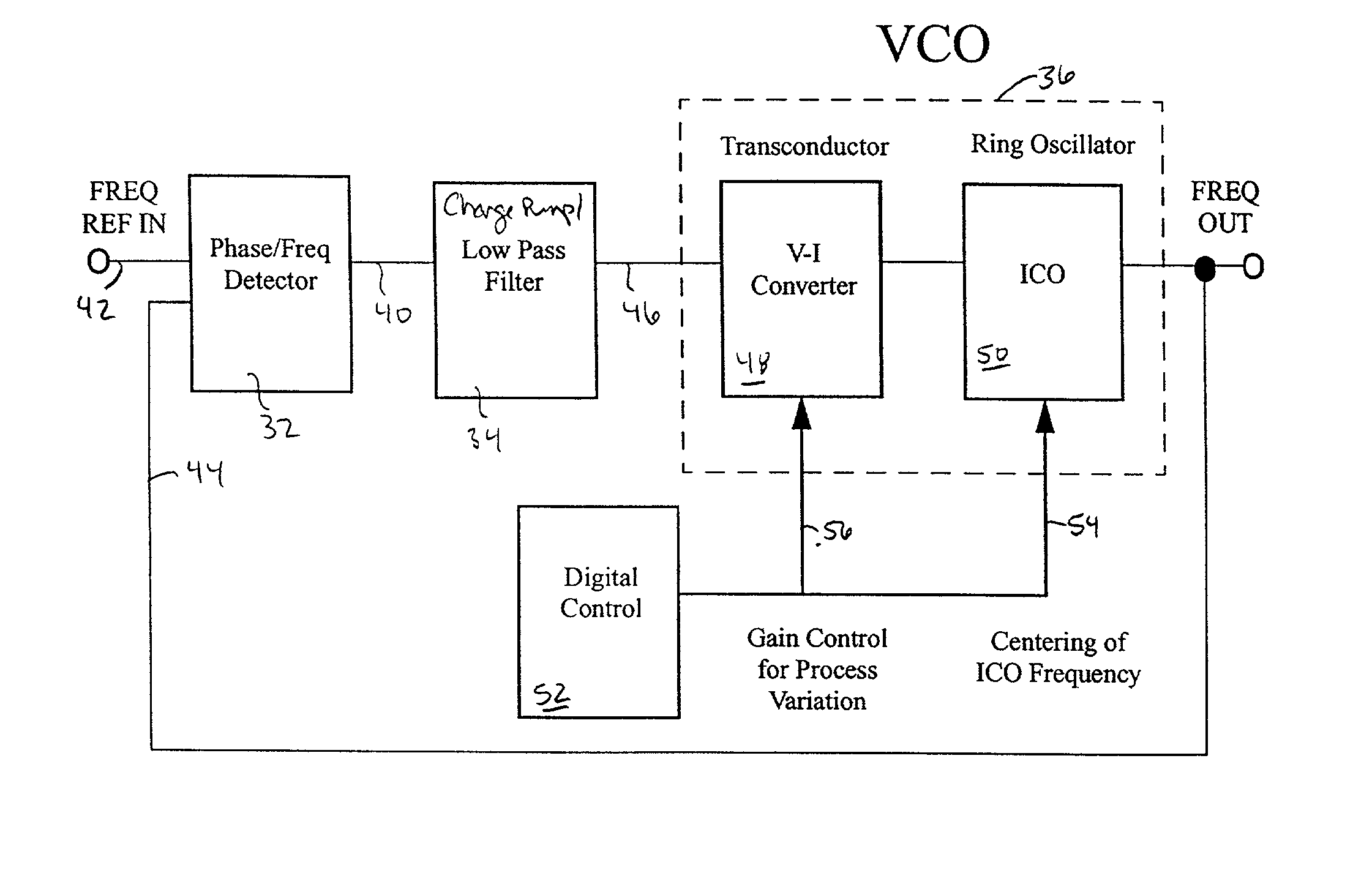
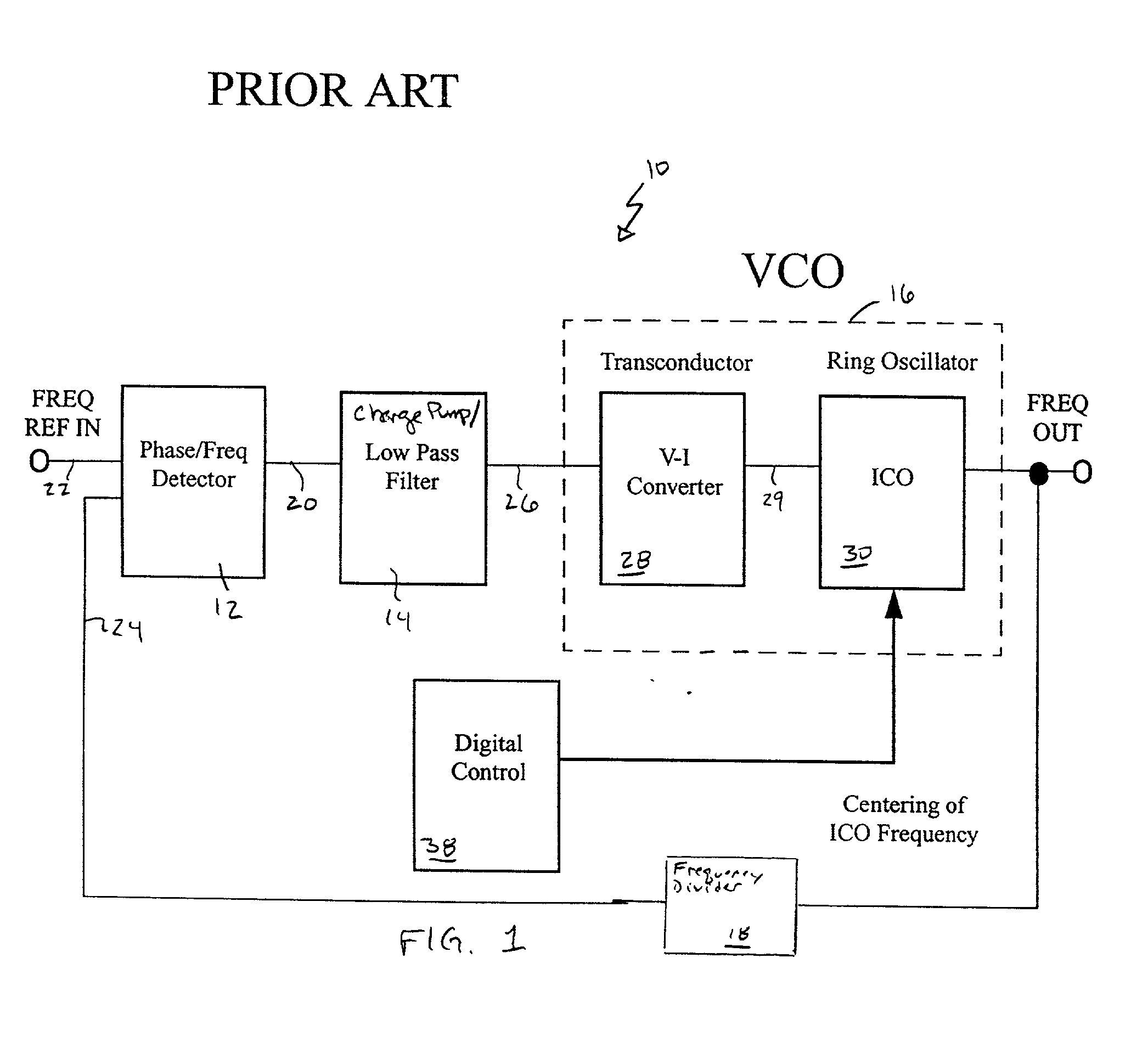
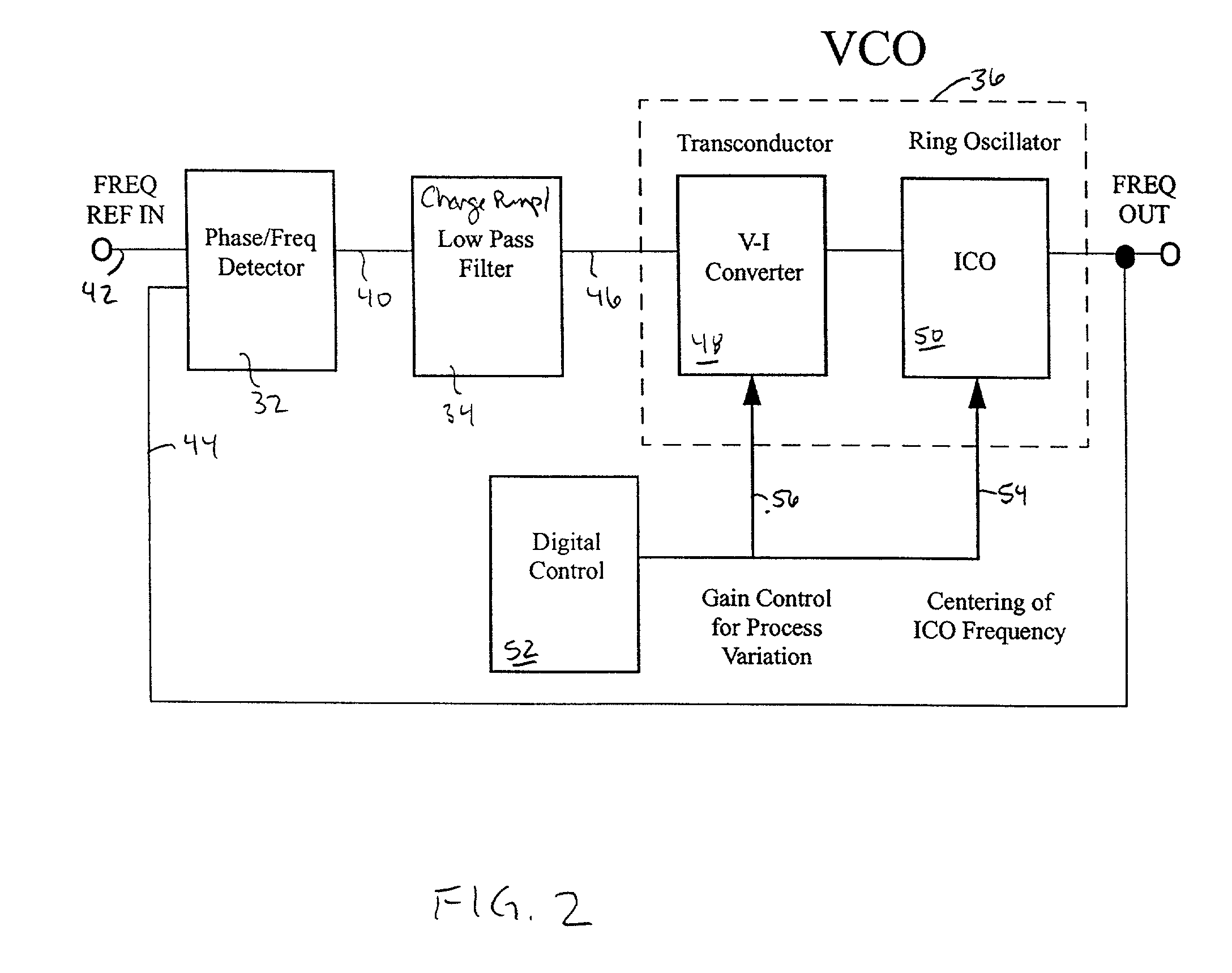
Multiple status e-fuse based non-volatile voltage control oscillator configured for process variation compensation, an associated method and an associated design structure
InactiveUS7609121B2Angle modulation by variable impedencePulse automatic controlInductorSelf correction
Disclosed are embodiments of a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) capable of non-volatile self-correction to compensate for process variations and to ensure that the center frequency of the oscillator is maintained within a predetermined frequency range. This VCO incorporates a pair of varactors connected in parallel to an inductor-capacitor (LC) tank circuit for outputting a periodic signal having a frequency that is proportional to an input voltage. A control loop uses a programmable variable resistance e-fuse to set a compensation voltage to be applied to the pair of varactors. By adjusting the compensation voltage, the capacitance of the pair of varactors can be adjusted in order to selectively increase or decrease the frequency of the periodic signal in response to a set input voltage and, thereby to bring the frequency of that periodic signal into the predetermined frequency range. Also disclosed are embodiments of an associated design structure for such a VCO and an associated method for operating such a VCO.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Capture range control mechanism for voltage controlled oscillators
A voltage controlled oscillator generates an output signal whose frequency varies as a first function of a control voltage applied to a control terminal. The voltage controlled oscillator has a wide range of frequency of operation. A gain adjust circuit adjusts the gain of the voltage controlled oscillator such that the first function varies as a second function of the gain. In a preferred embodiment the gain adjust circuit includes a variable impedance that may be external or integrated onto a common chip with the oscillator core.
Owner:ZARLINK SEMICON LTD
PLL circuit having a variable output frequency
InactiveUS20020089384A1Compensation deviationPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsCapacitanceEngineering
A phase locked loop (PLL) circuit includes a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) having a parallel resonant circuit including a first capacitance implemented by a reverse-biased diode and a second capacitance implemented by MOS capacitors. Upon lock-in of the oscillation frequency with respect to the reference frequency, whether the oscillation frequency has a deviation is examined based on the tune voltage controlling the first variable capacitance. If a deviation is observed due to a temperature fluctuation etc., the control voltage for the second variable capacitance is corrected for compensating the deviation.
Owner:NEC CORP
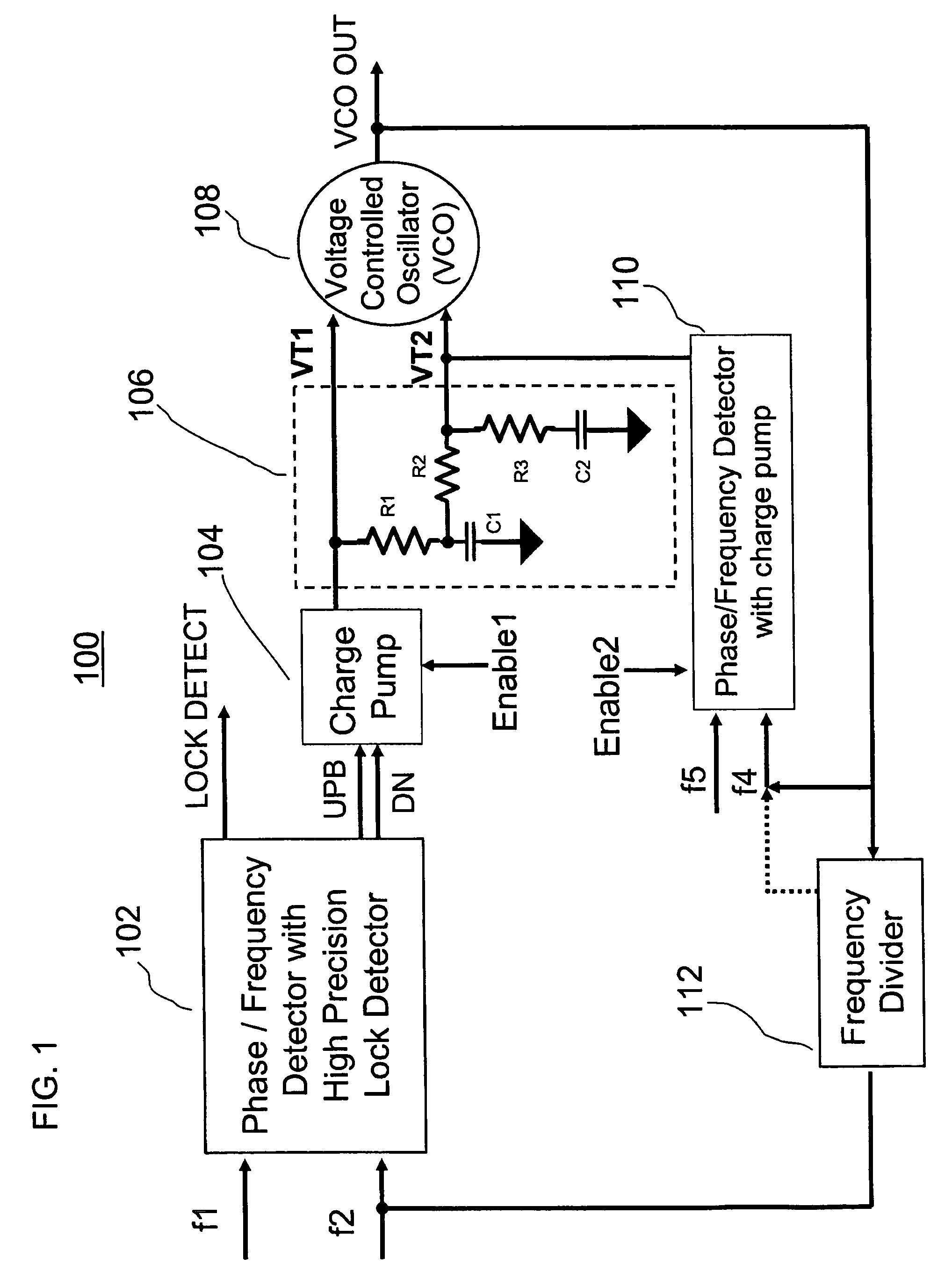
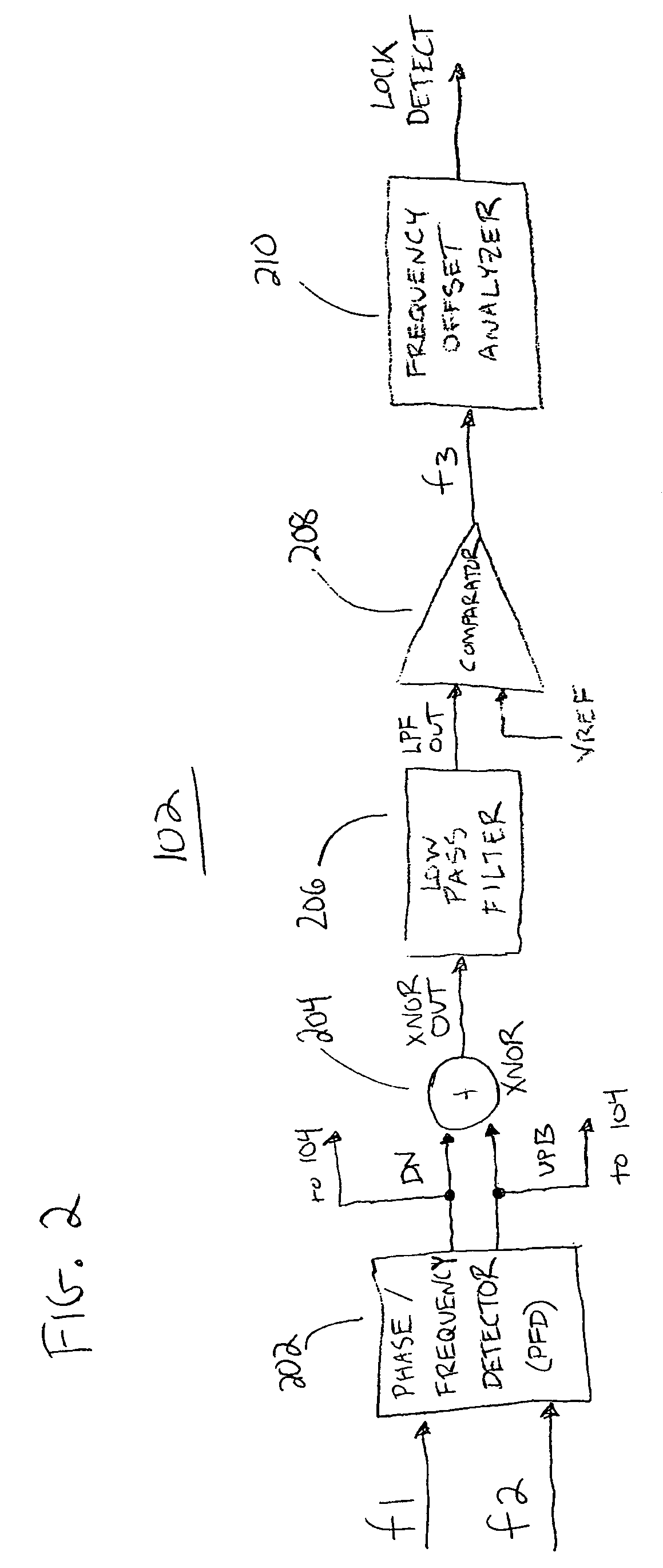
Low noise phase locked loop with a high precision lock detector
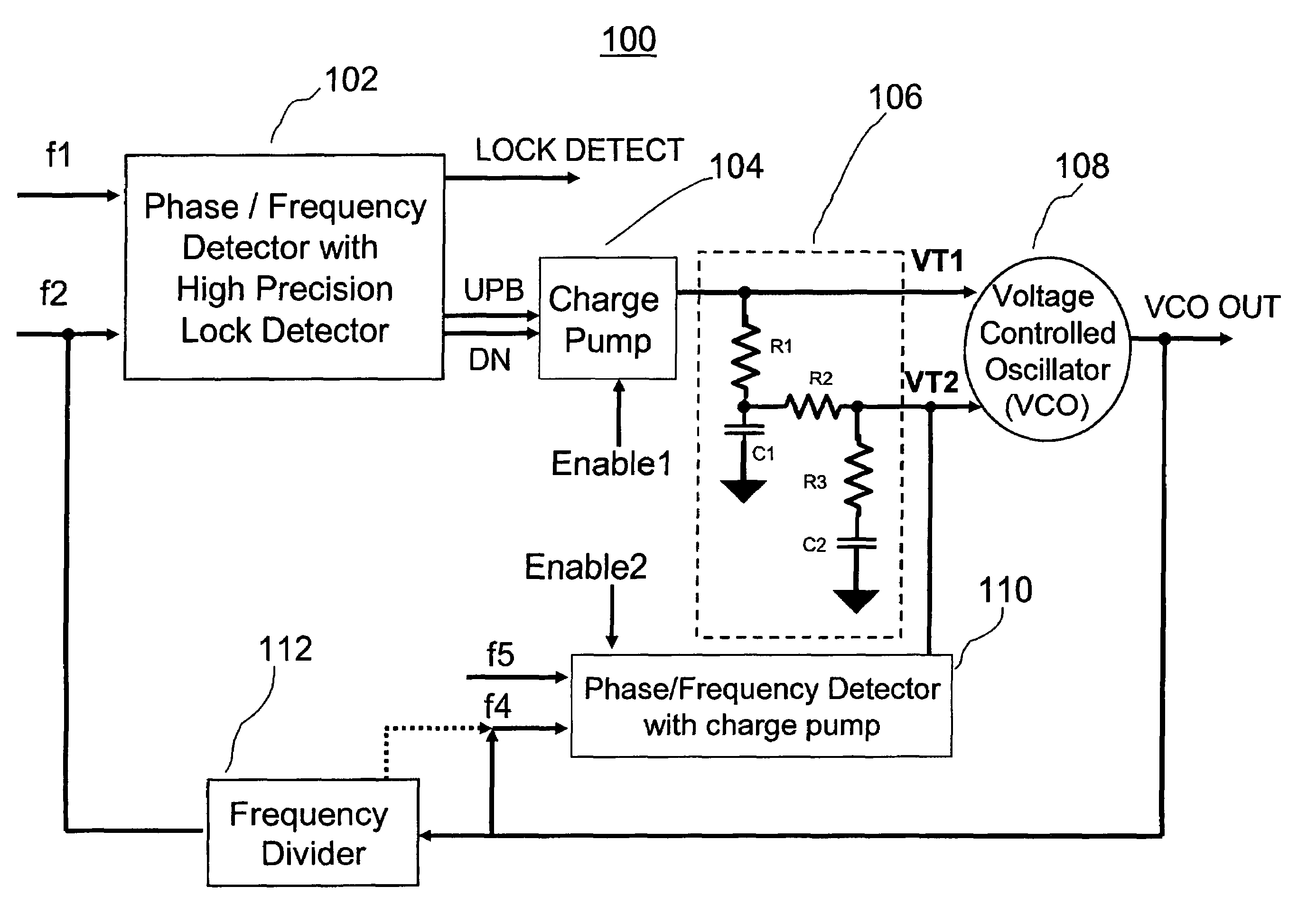
ActiveUS7420428B2Reducing overshoot of the second voltage tuning signalPulse automatic controlLow noiseVoltage controlled ring oscillator
A phase lock loop (PLL) includes a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) for providing a VCO output signal. A first phase / frequency detector (PFD) for providing a first voltage tuning signal is included for controlling a frequency of the VCO output signal by comparing a first reference signal to the VCO output signal. A second phase / frequency detector (PFD) for providing a second voltage tuning signal is included for controlling the frequency of the VCO output signal by comparing a second reference signal to the VCO output signal. The first and second voltage tuning signals provide, respectively, first and second gains of frequency per volt for controlling the frequency of the VCO output signal. The first voltage tuning signal has a higher gain than the second voltage tuning signal. The first voltage tuning signal provides coarse frequency control of the VCO output signal and the second voltage tuning signal provides fine frequency control of the VCO output signal.
Owner:HARRIS GLOBAL COMM INC
Voltage controlled oscillator circuit
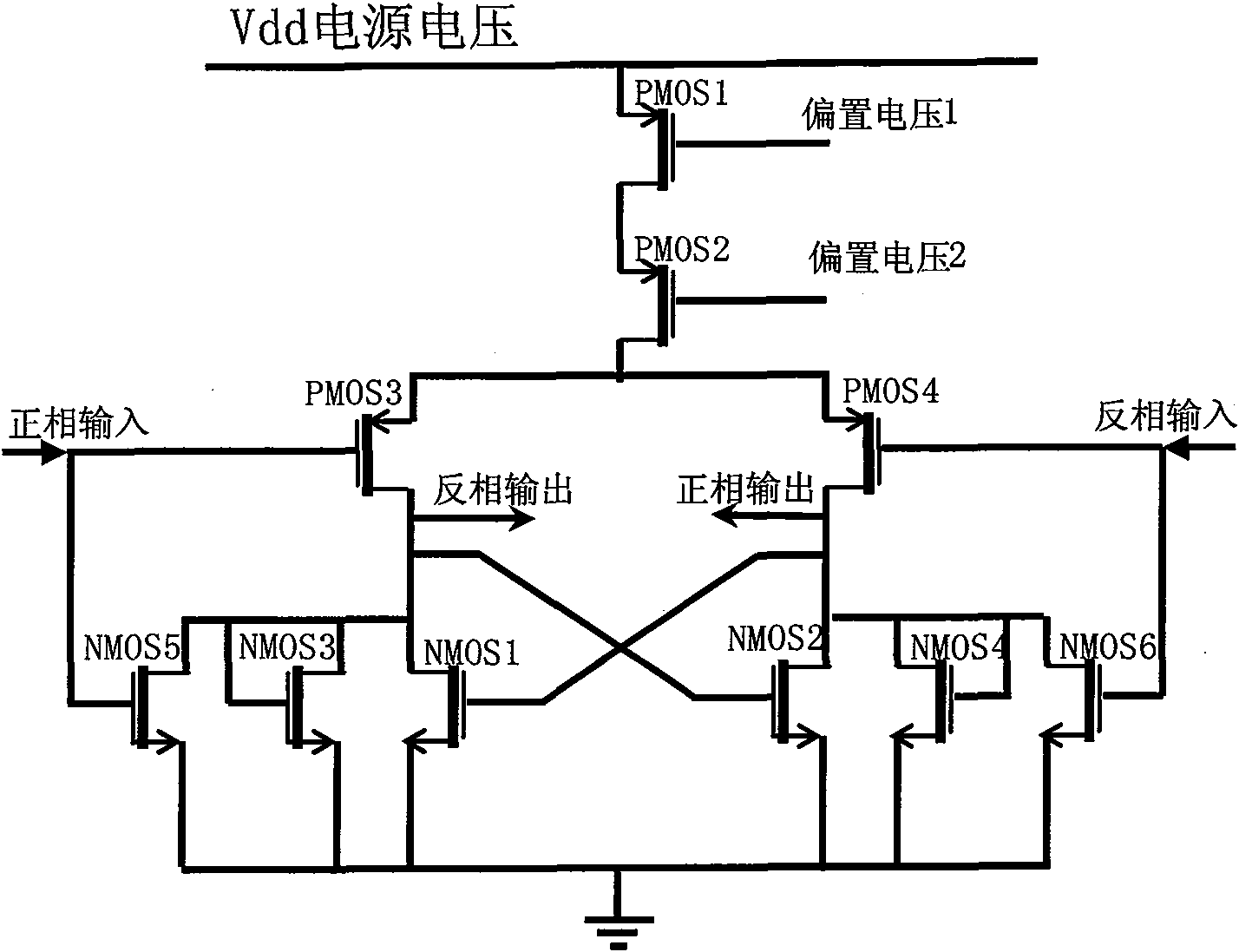
InactiveCN101630942ASimple structureImprove reliabilityPulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsEngineeringFrequency regulation
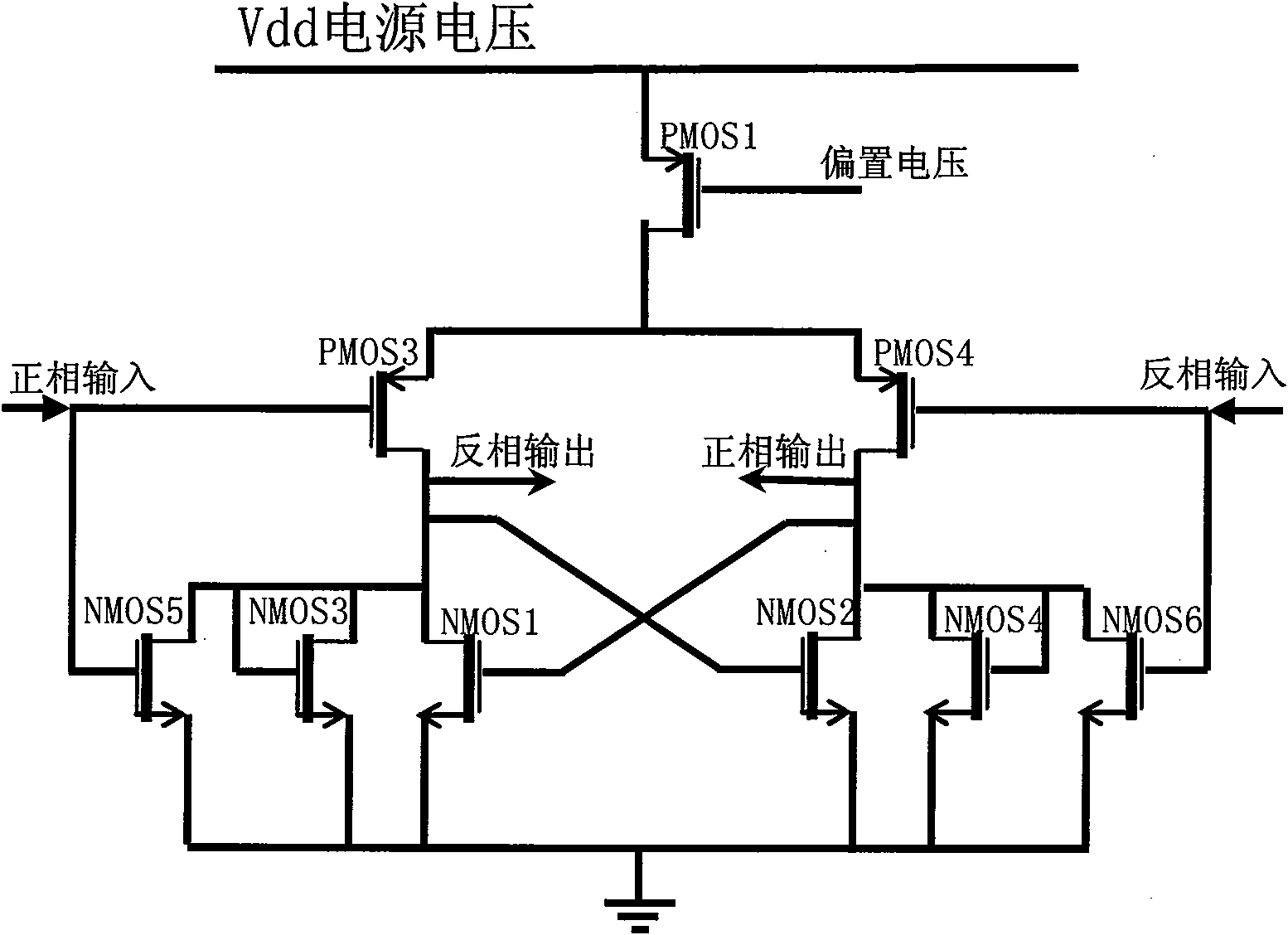
The invention provides a voltage controlled oscillator circuit, which consists of at least three stages of total difference unit circuits which are cascaded mutually and are completely same. The circuit has the advantages that: 1, the circuit is a CMOS voltage controlled oscillator circuit which has simple structure, high reliability, wide frequency regulating range, and can operate normally under extremely low power supply voltage; 2, the circuit can select a cascade mode of three-stage and above three-stage total difference units which are completely same; 3, source electrodes of positive feedback active load are directly earthed for improving one pass gain of the total difference units, thereby ensuring that the oscillator circuit can normally start oscillation under any condition; 4, a voltage clamping circuit plays a role of stabilizing amplitude of an output signal of the oscillator; and 5, when control voltage controls current in a tail current source of the difference unit to generate variation through certain V-I converting circuit, the oscillator circuit can generate output waveforms with different frequencies along with the magnitude of the tail current, as long as the current in the tail current source is invariable, the frequency of the output waveform of the oscillator circuit can be invariable.
Owner:天津南大强芯半导体芯片设计有限公司
PLL frequency synthesizer
InactiveCN1820417AConstant loop gain characteristicSimple structurePulse automatic controlCapacitanceLoop filter
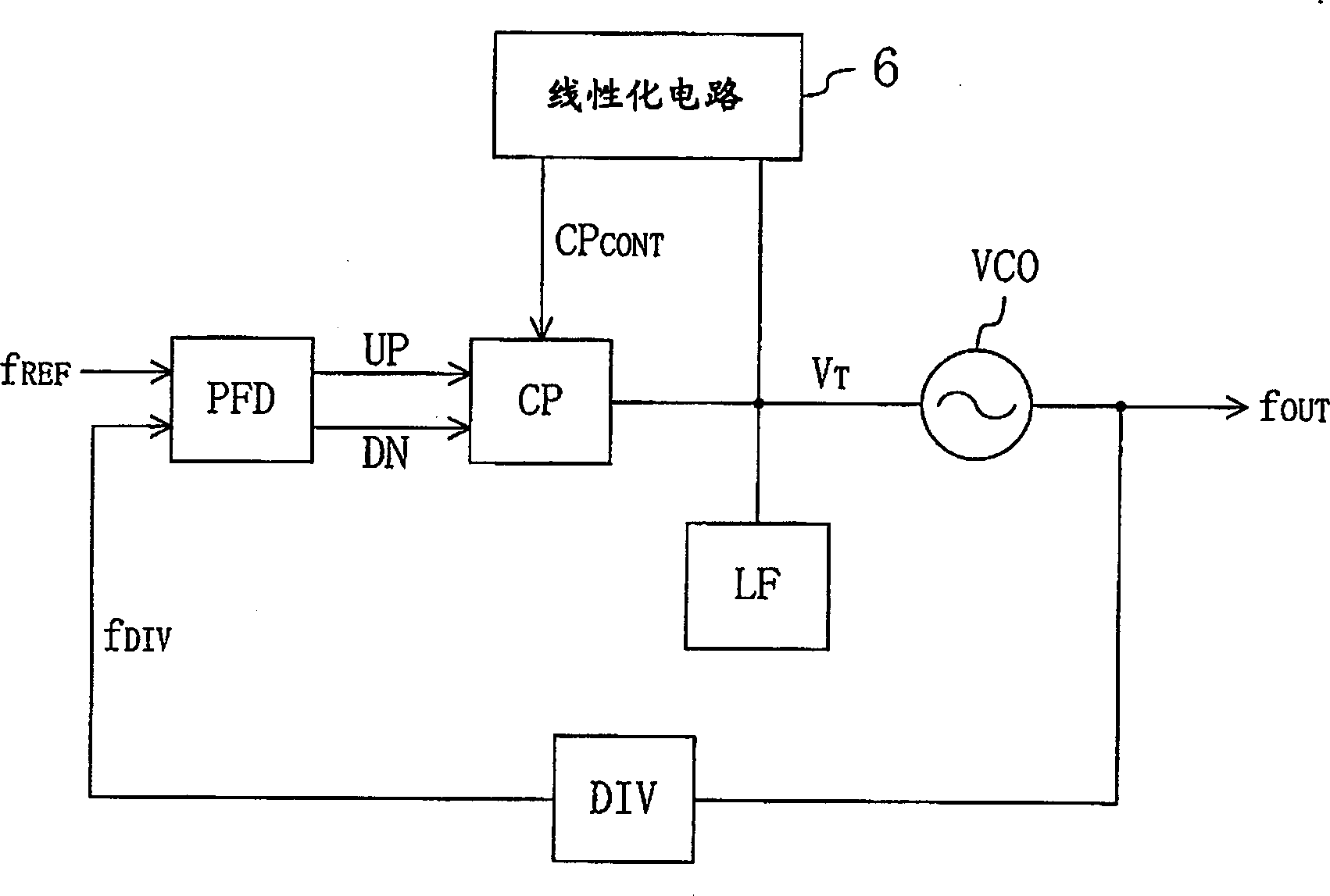
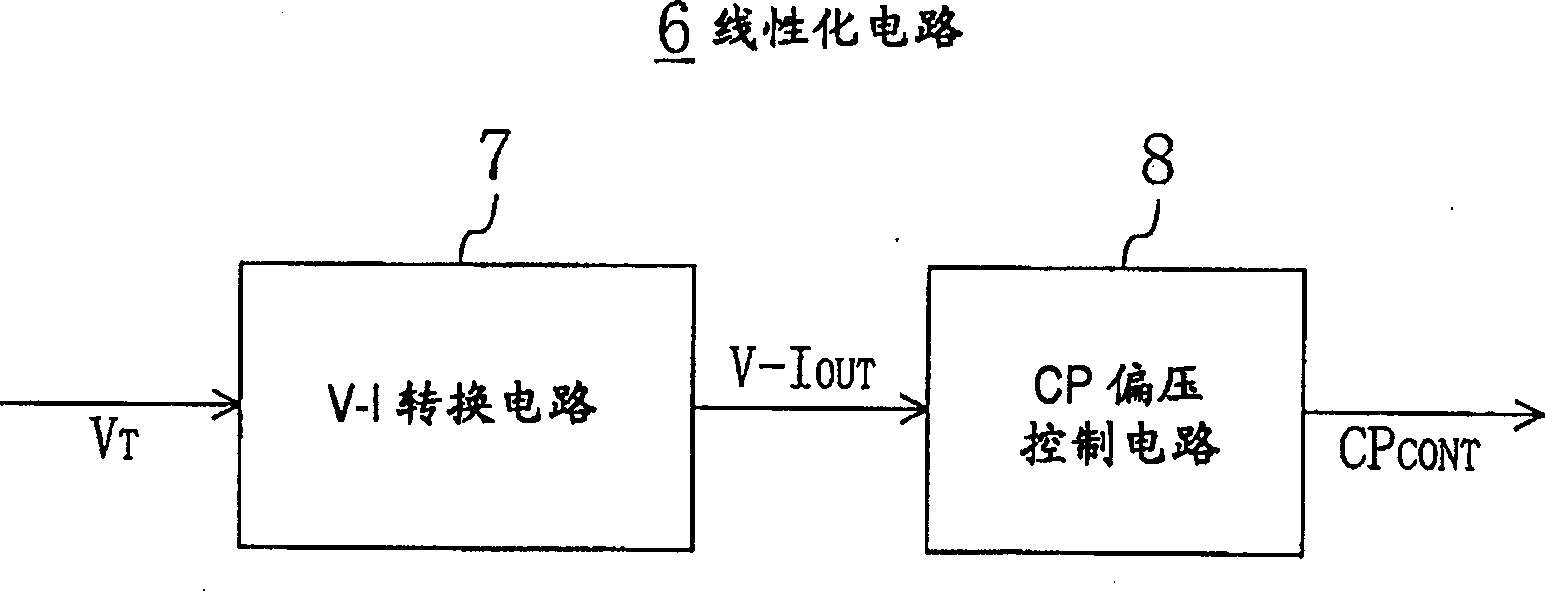
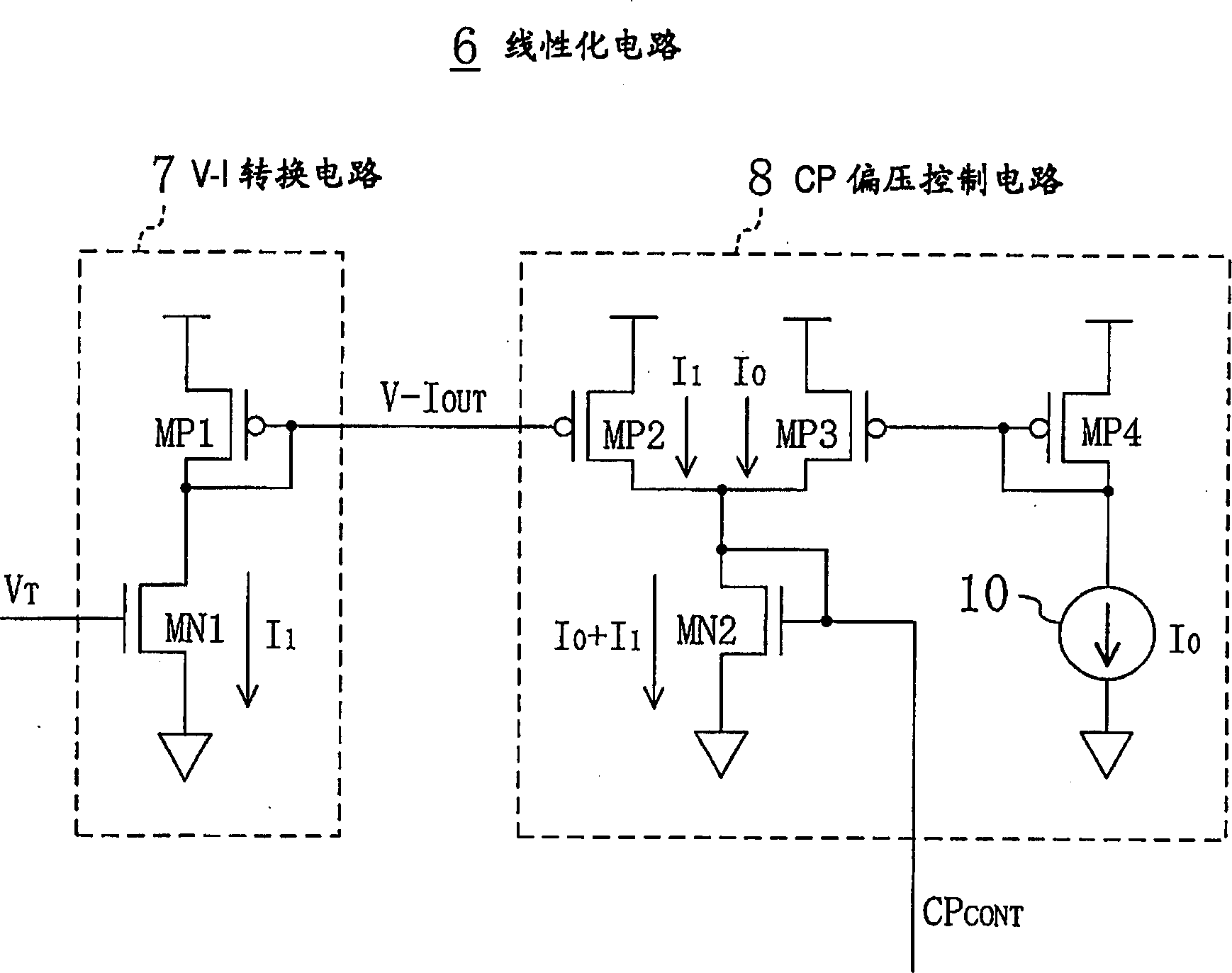
In a PLL frequency synthesizer, a linearization circuit (6) is provided which receives an oscillation frequency control signal (VT) from a loop filter (LF). The linearization circuit (6) outputs, in accordance with the potential level of the oscillation frequency control signal (VT), a charge pump current control signal (CPCONT) that exhibits the higher value, the higher the potential level. The charge pump (CP) receives the charge pump current control signal (CPCONT) to cause a current in accordance with the value of the received charge pump current control signal (CPCONT) to flow in or flow out. Thus, a simple circuit arrangement can be used to adjust and maintain constant the loop gain characteristic of the PLL frequency synthesizer. Accordingly, even when a variable capacitance element included in the a voltage controlled oscillator has a nonlinear characteristic for the potential of the input oscillation frequency control signal, the loop gain of the PLL frequency synthesizer having this voltage controlled oscillator can be adjusted and maintained constant.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
PLL circuit
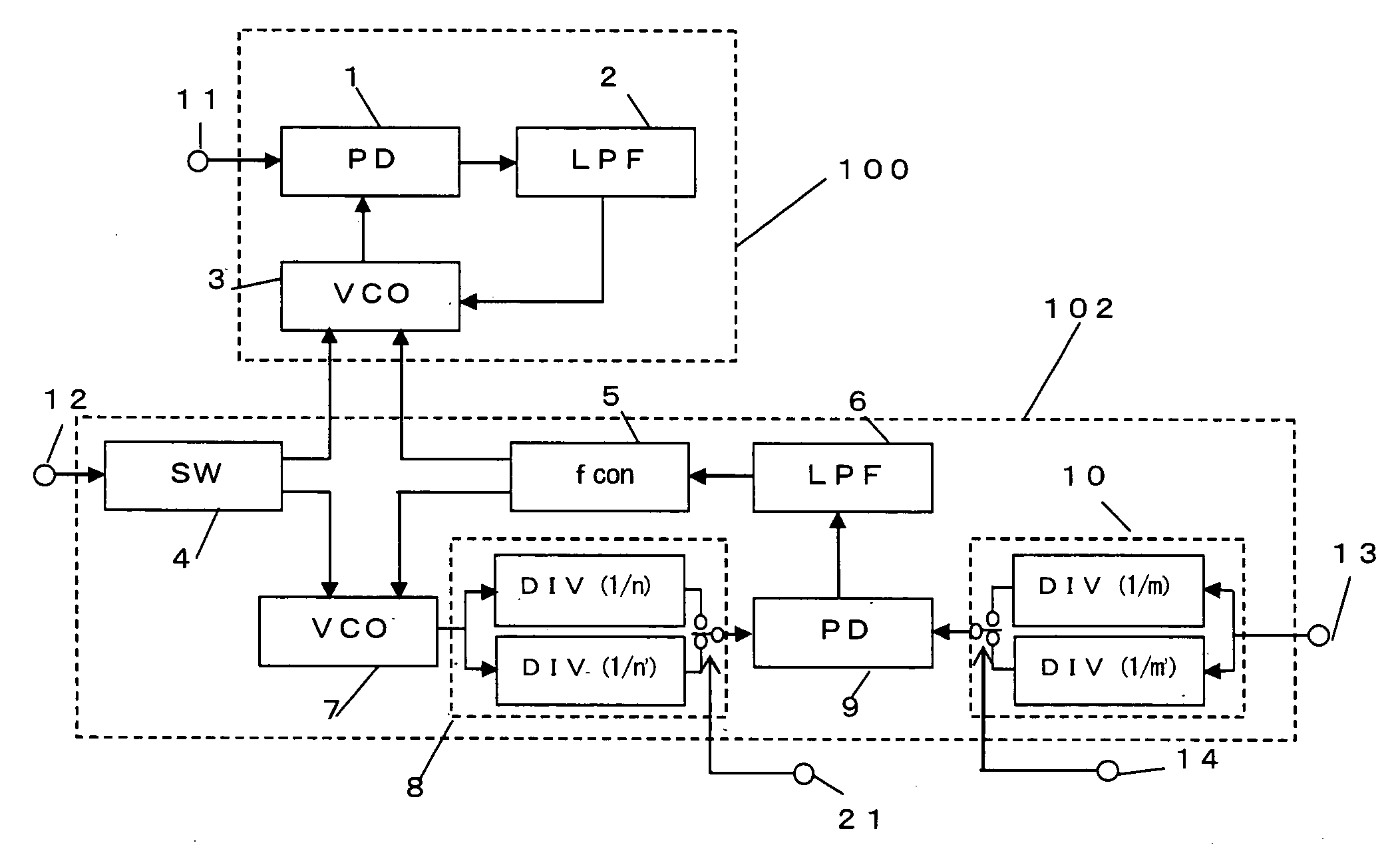
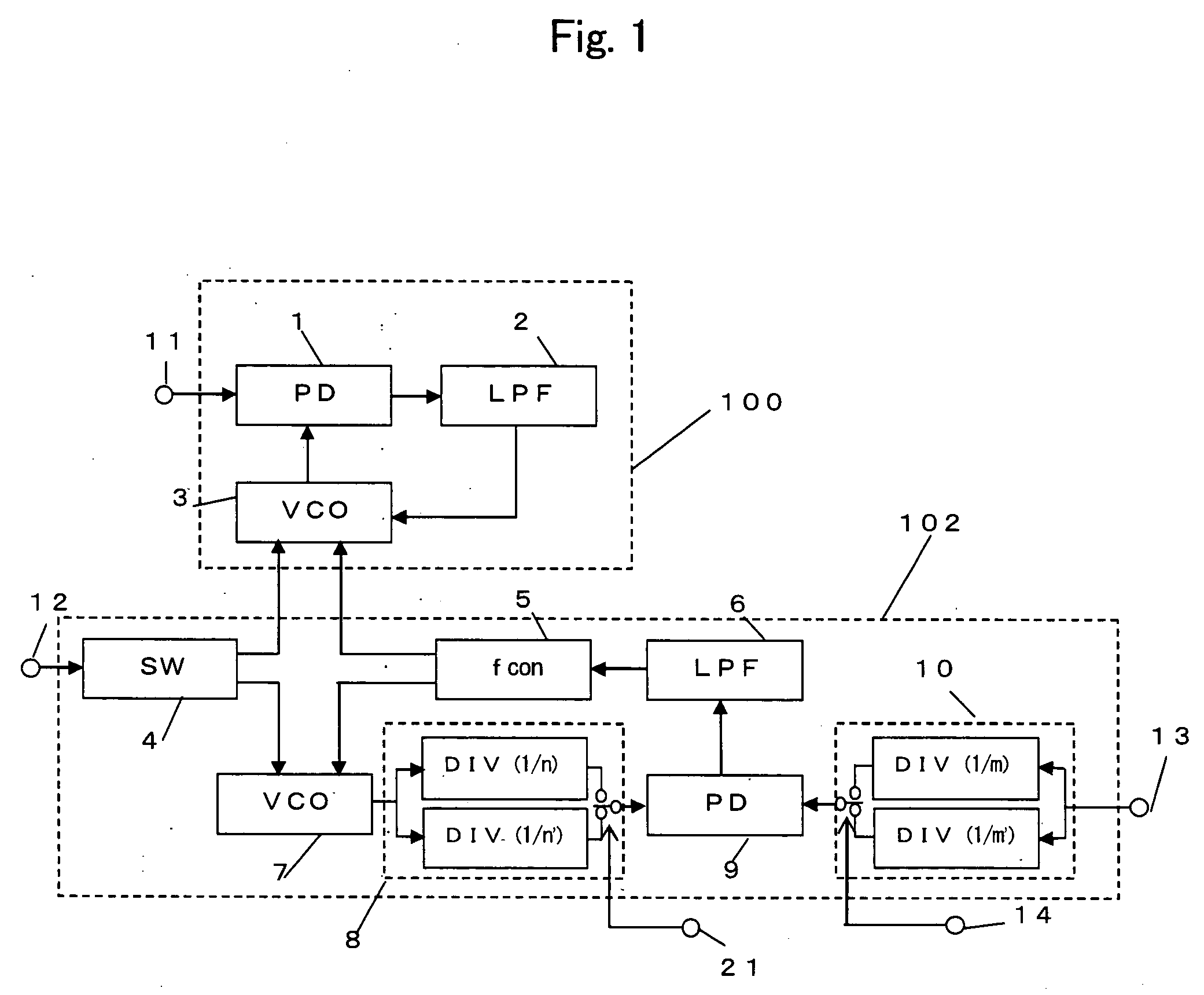
InactiveUS20050184810A1Improve accuracyMaintain good propertiesPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsEngineeringCmos voltage controlled oscillator
The frequency of a first voltage controlled oscillator is stabilized in a first PLL circuit part into which a reference frequency signal is inputted. In addition, a second PLL circuit part is formed by inputting a control voltage which is the same as the frequency control voltage of the first voltage controlled oscillator into a second voltage controlled oscillator having the same configuration as the first voltage controlled oscillator. The first PLL circuit part is provided with first and second variable frequency dividers which respectively divide the reference frequency signal and the output of the first voltage controlled oscillator. In response to an input signal into the second PLL circuit part, the free-running frequencies of the second and first voltage controlled oscillators are switched, and at the same time, the division ratio of first and second variable frequency dividers are switched.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Varactor bank switching based on negative control voltage generation
InactiveUS20090243702A1Discontinuous tuning for band selectionElectronic switchingControl signalPass gate
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com