Patents
Literature
59 results about "Edge function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and apparatus for converting RF signals to baseband
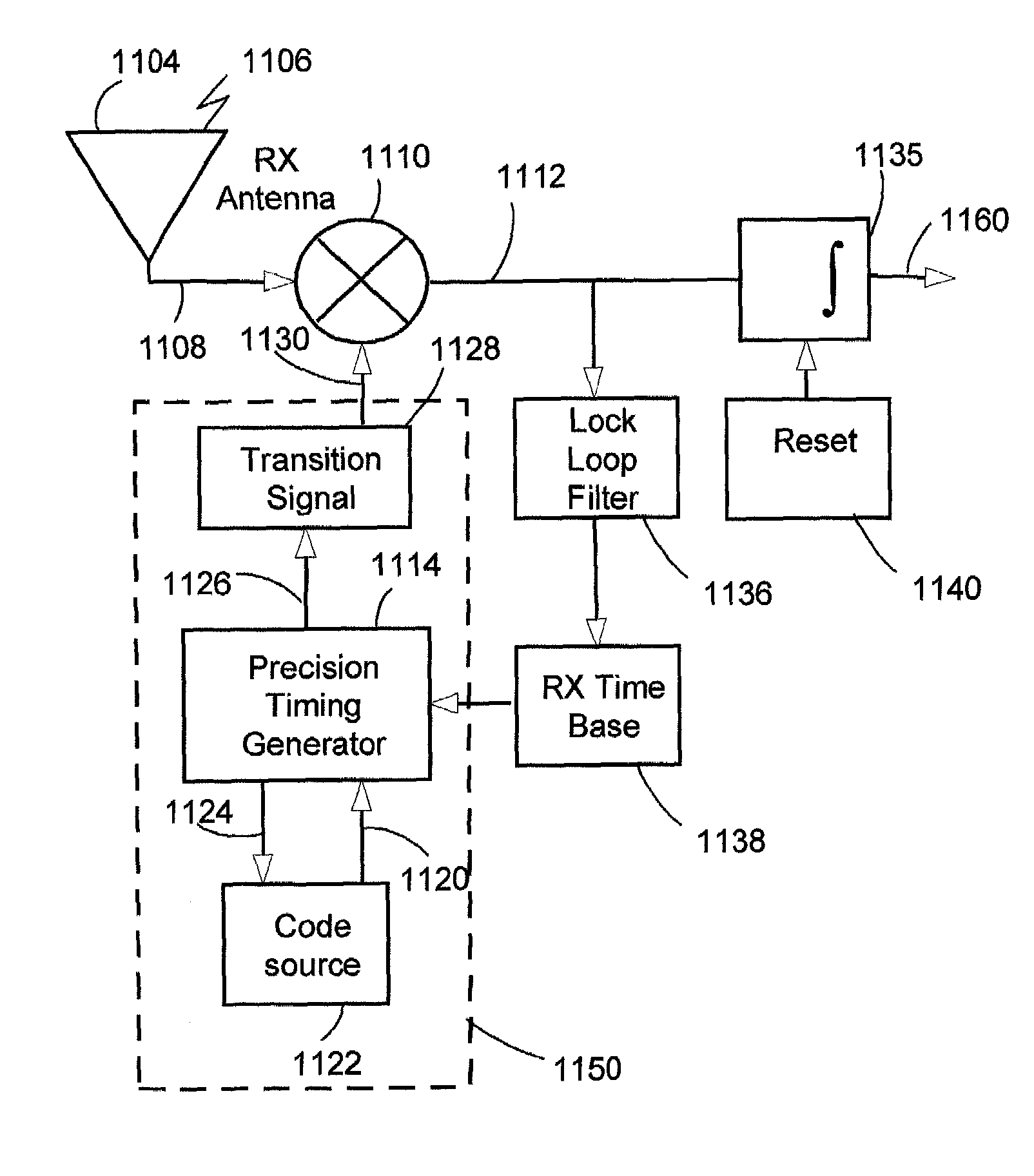
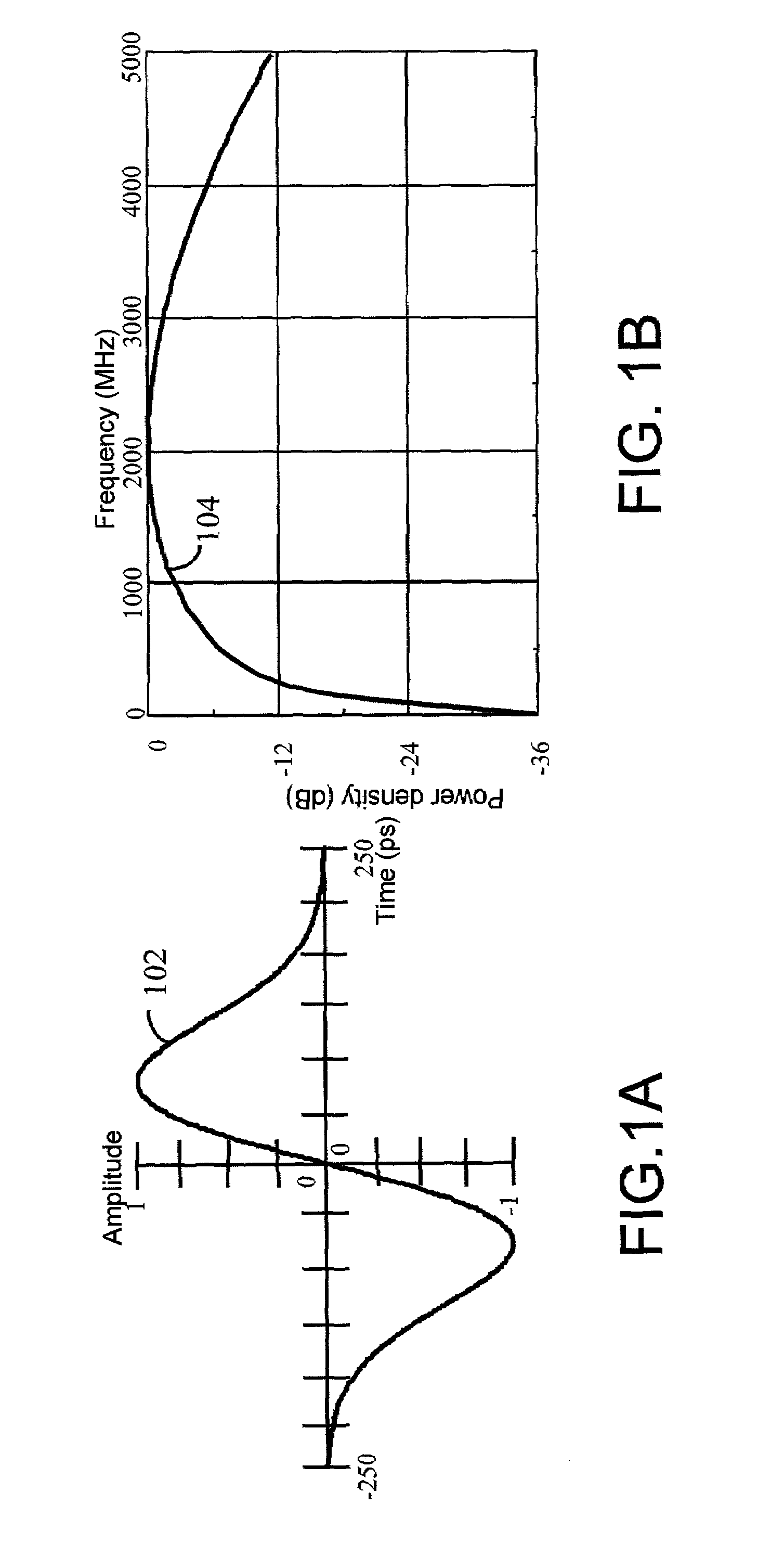
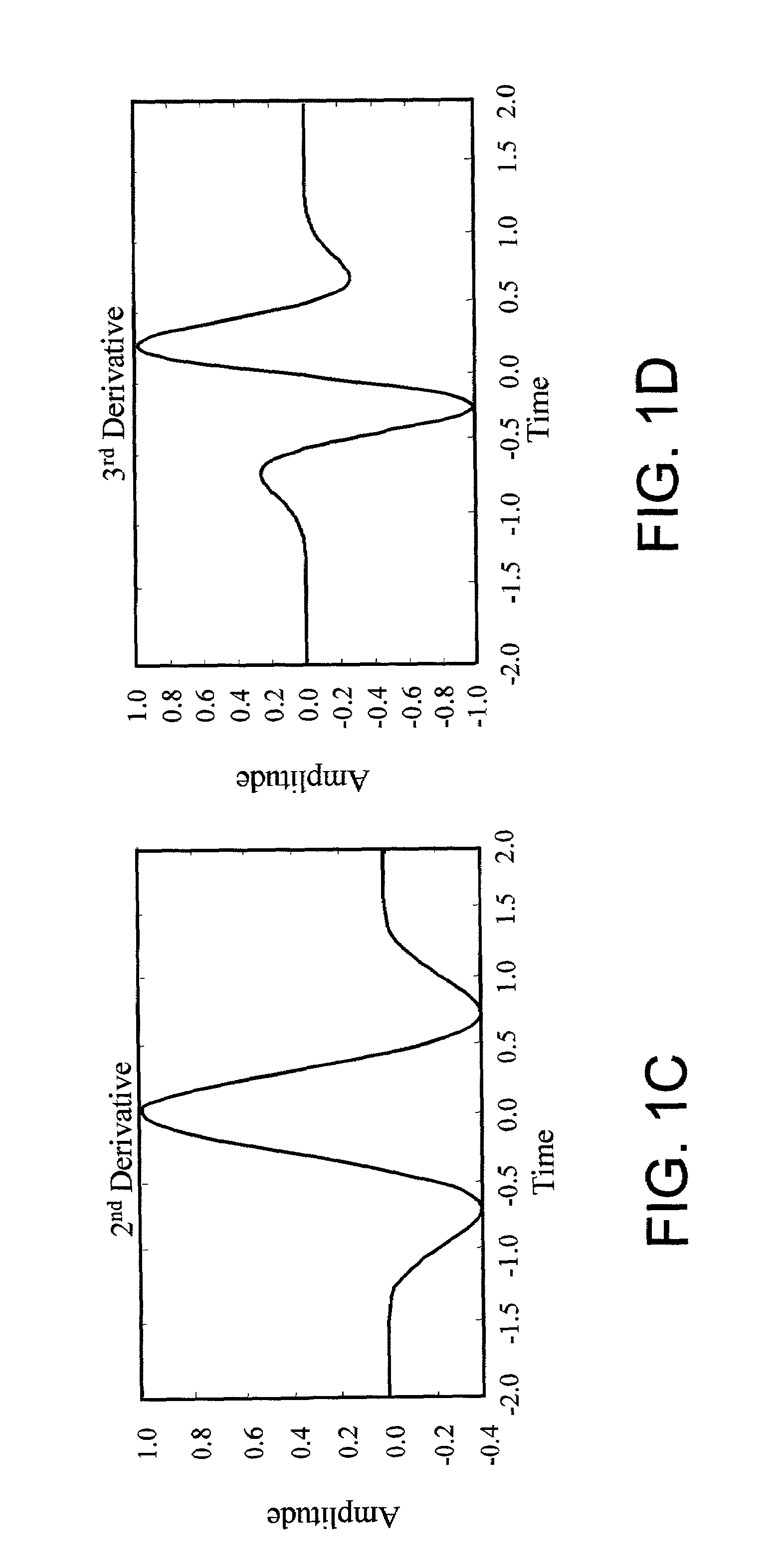
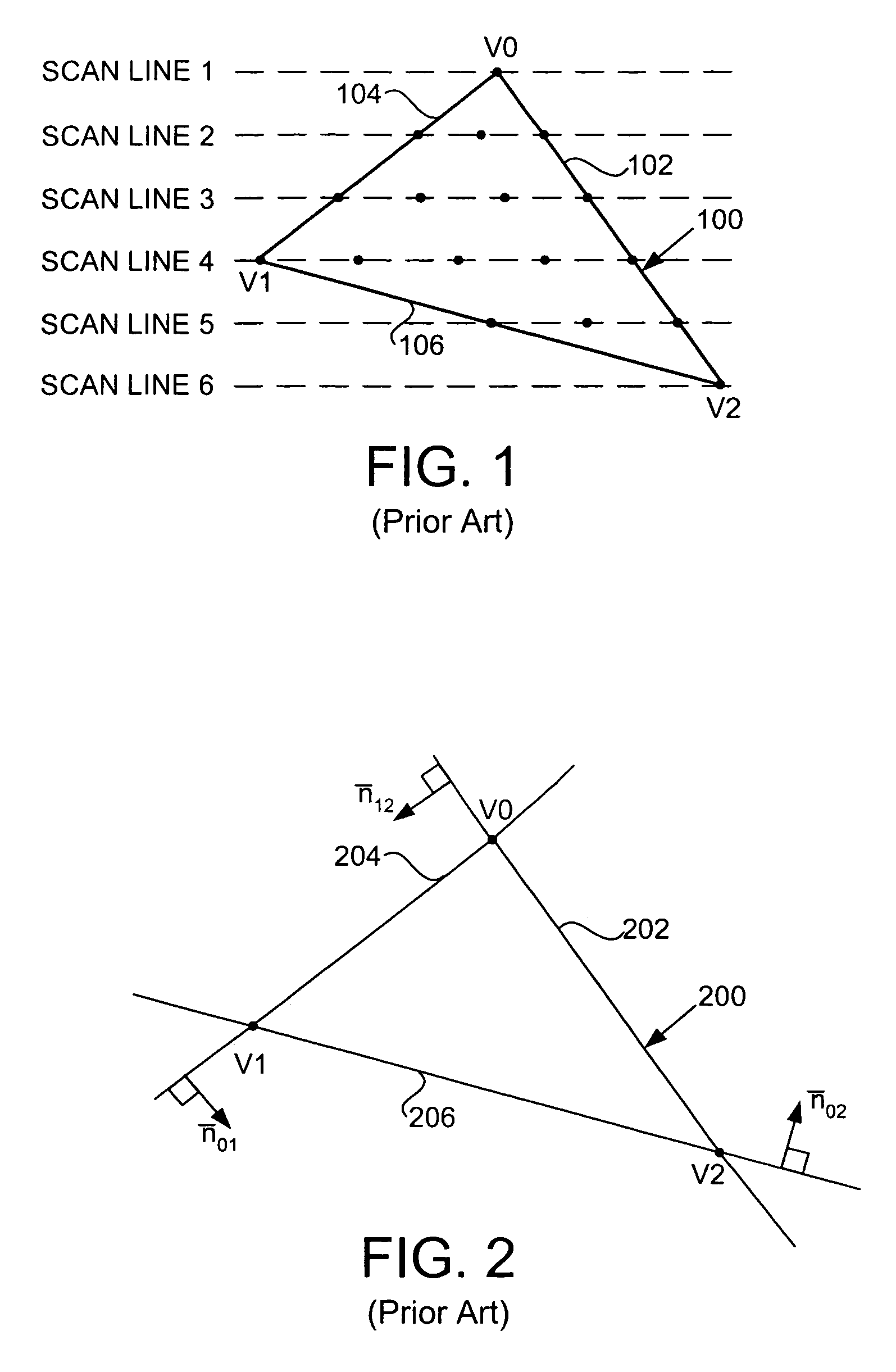
The present invention relates to the conversion of signals from RF to baseband using transition functions, or edge functions. These functions typically transition from positive to negative, or from negative to positive, synchronously with the transition of the received pulse signal, effecting detection essentially by synchronously rectifying a signal cycle of the received pulse, producing a net signal at baseband that can be further processed to detect modulation according to the modulation format. It is further disclosed how to configure these systems for optimal reception with a filter optimized for a given detect signal function. Generalizations of the matched filter embodiment lead to further embodiments employing alternative detection functions. Also disclosed is a two-stage version which applies a decode signal to the rectified signal. This step can be performed by a single correlator or by a plurality of correlators in parallel. Coding methods are disclosed to employ two-stage systems for enhanced channelization, and interference rejection.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
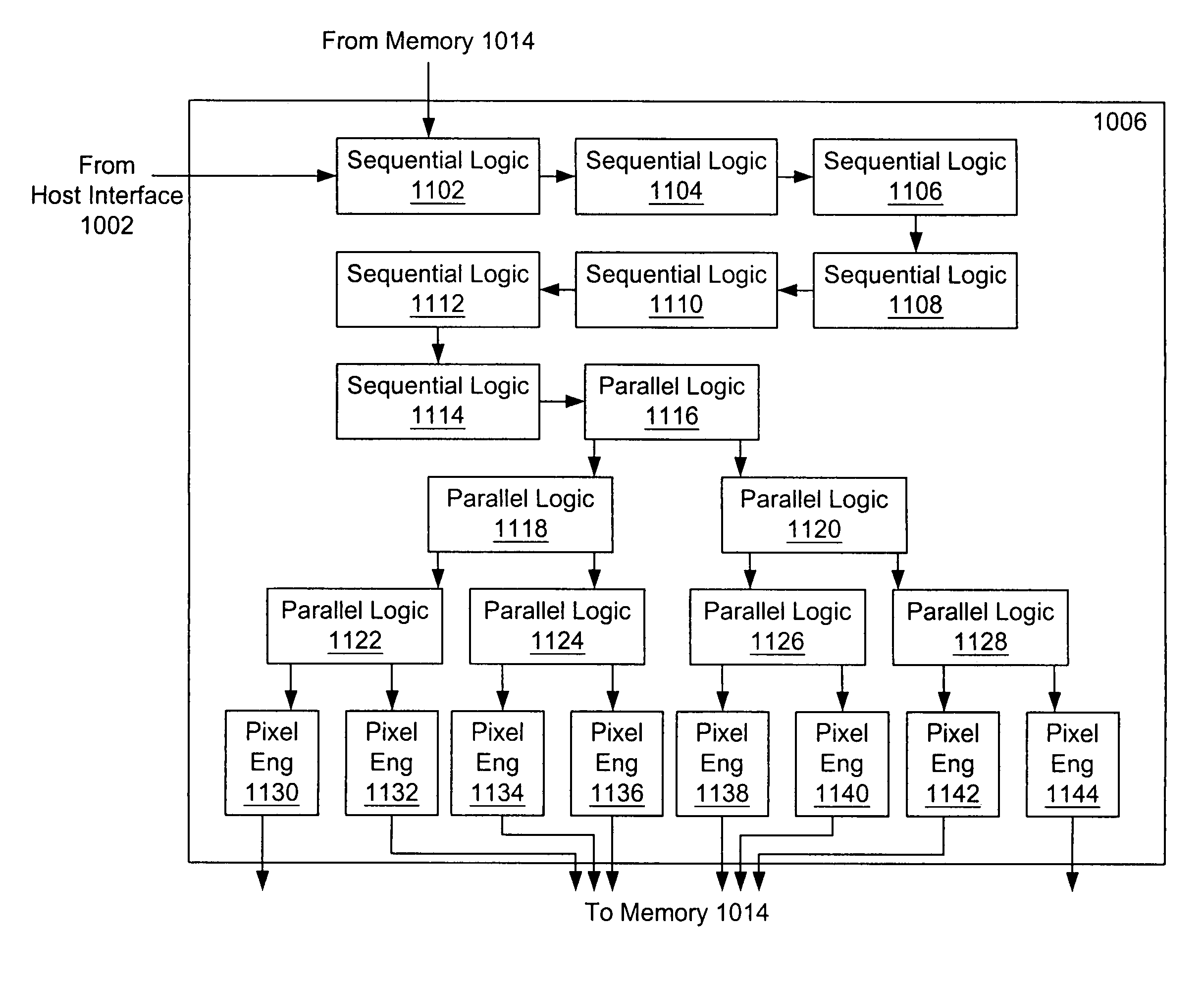
Parallel architecture for graphics primitive decomposition
InactiveUS7119809B1Efficient decompositionProcessor architectures/configurationFilling planer surface with attributesGraphicsDecomposition
A parallel architecture for determining pixels inside a graphics primitive is provided. The architecture is a pipeline structure having a predetermined number of sequential logic circuits connected in series followed by a predetermined number of parallel logic circuits arranged in a pyramid structure. Each sequential logic circuit uses arithmetic edge functions corresponding to edges of a graphics primitive to determine whether a polygonal portion of a raster image is inside the graphics primitive. If the polygonal portion is at least partly inside the graphics primitive, the sequential logic circuit divides the polygonal portion into a predetermined number of subportions and computes descriptors (e.g., vertices and translated edge functions) for each subportion sequentially. Descriptors are then transferred sequentially to the next stage. Each parallel logic circuit performs the same functions as that of a sequential logic circuit except that a parallel logic circuit computes descriptors of the subportions in parallel and transfers them to the next stage in parallel.
Owner:S3 GRAPHICS
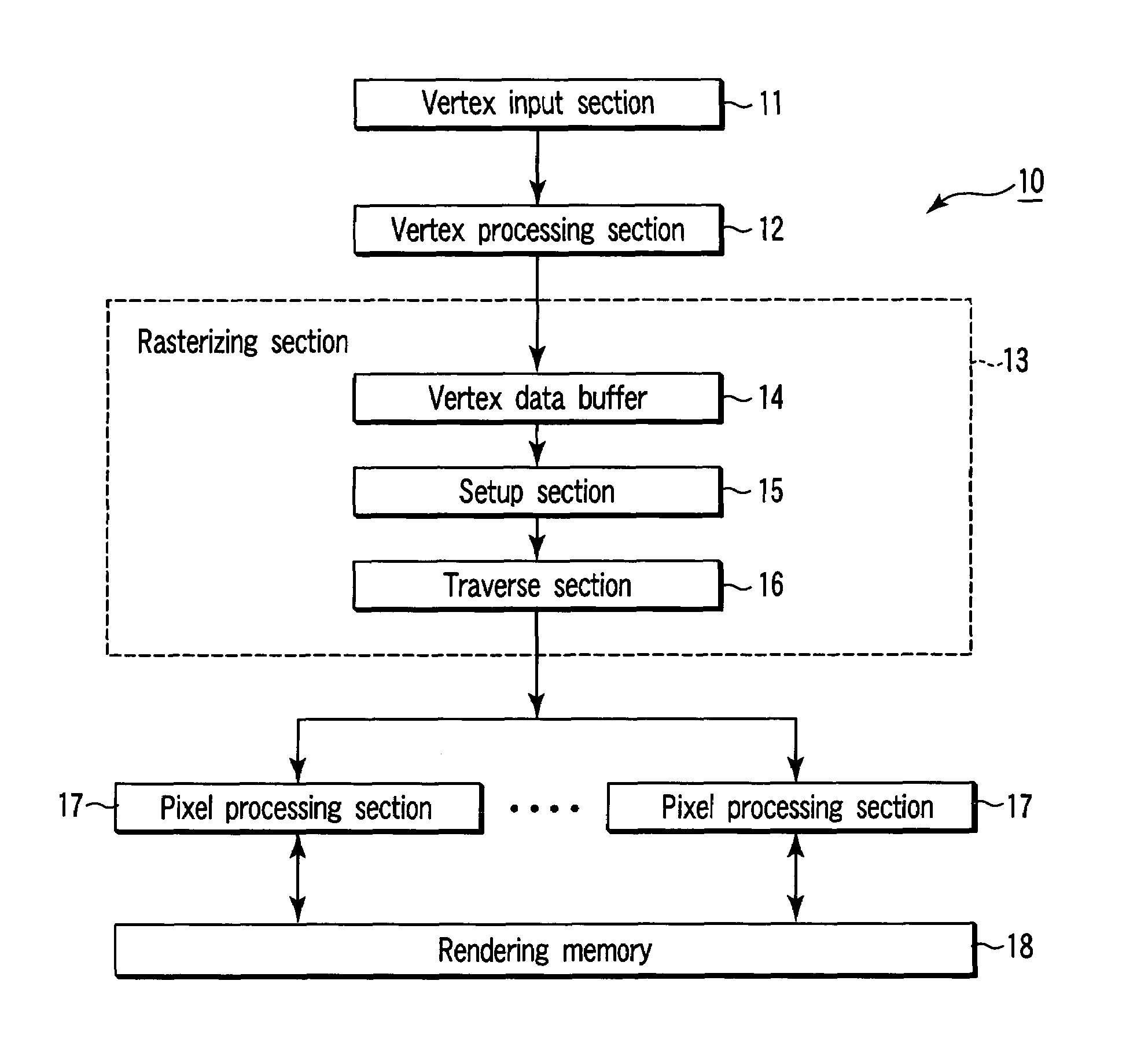
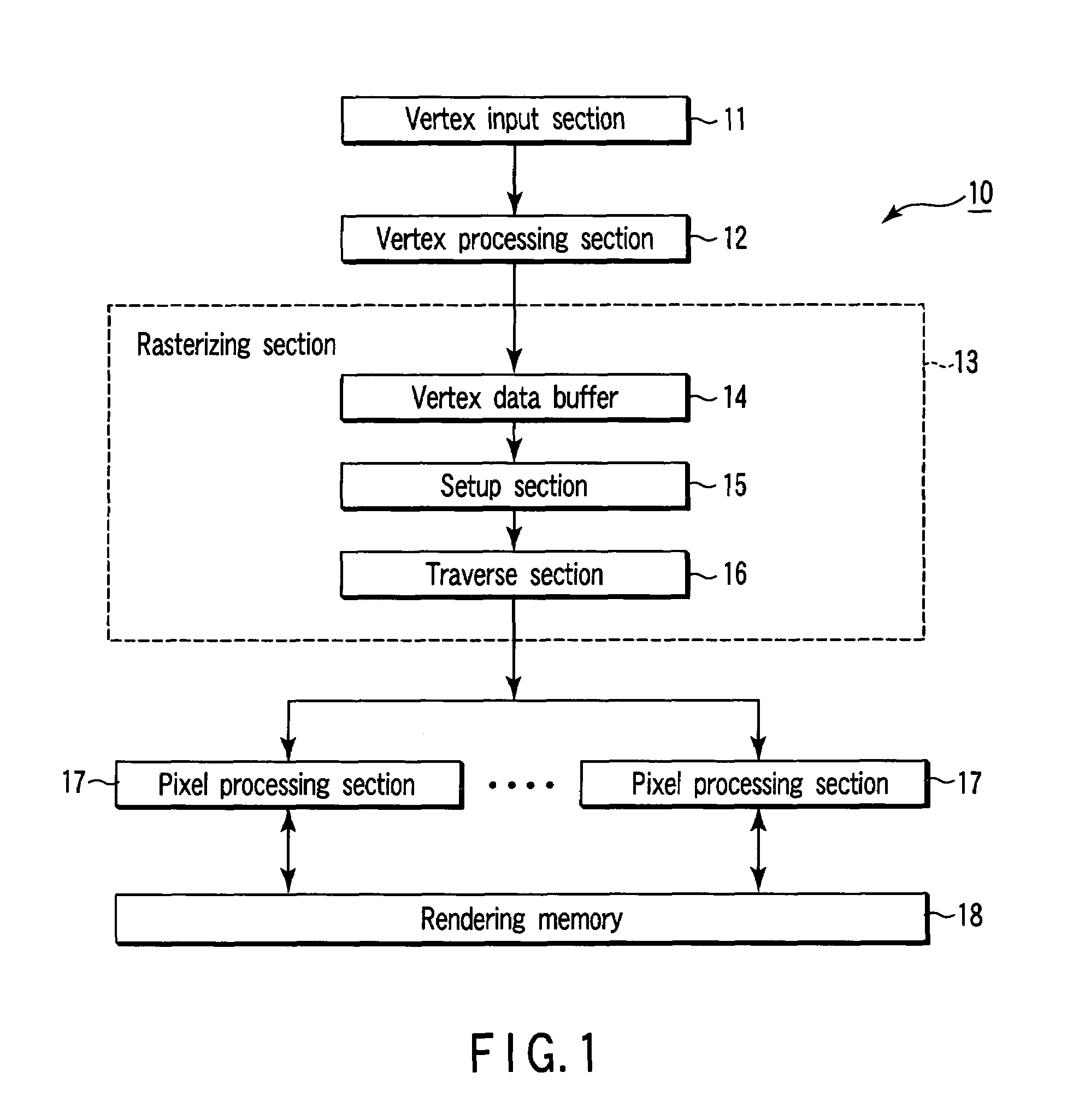
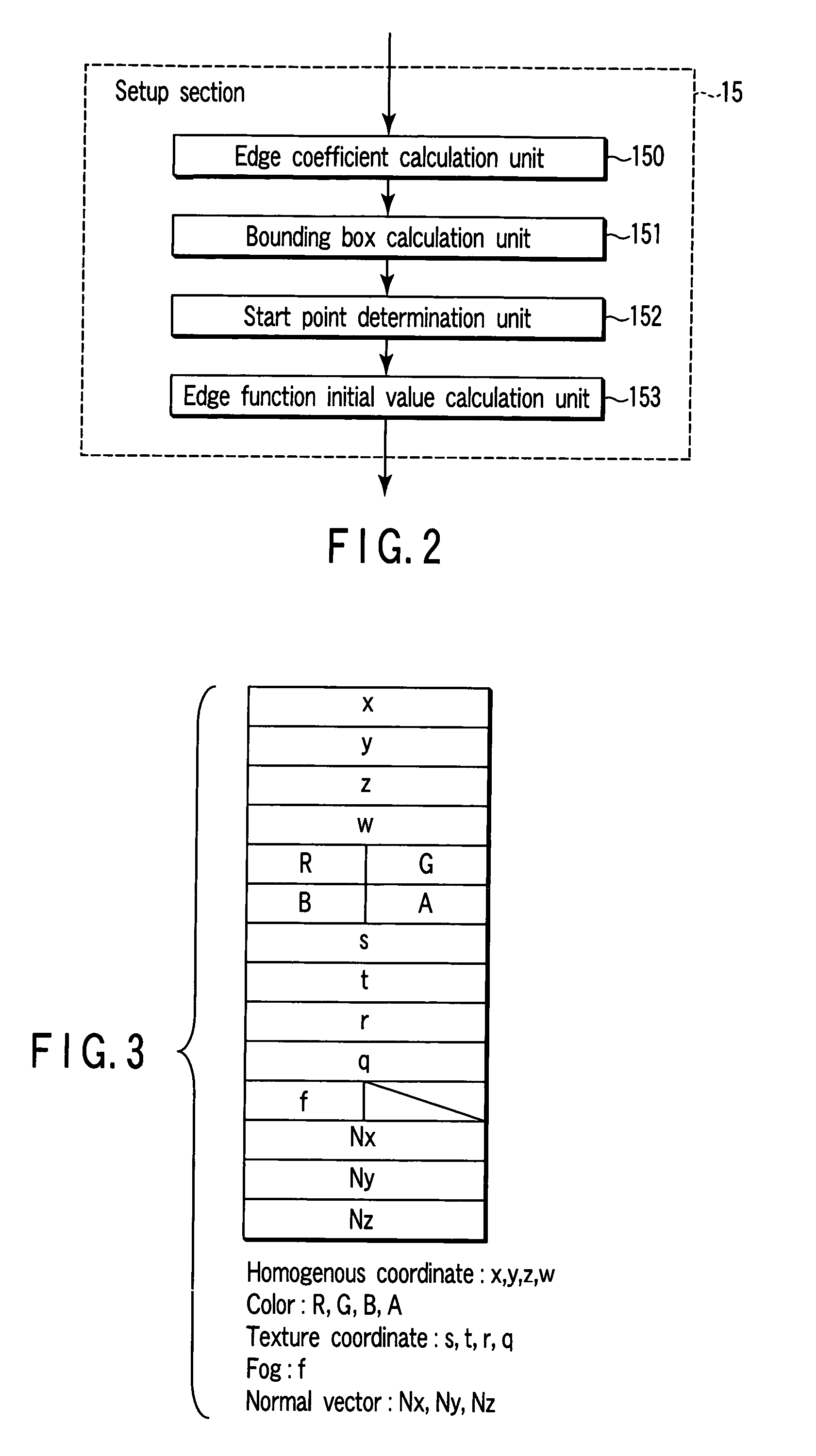
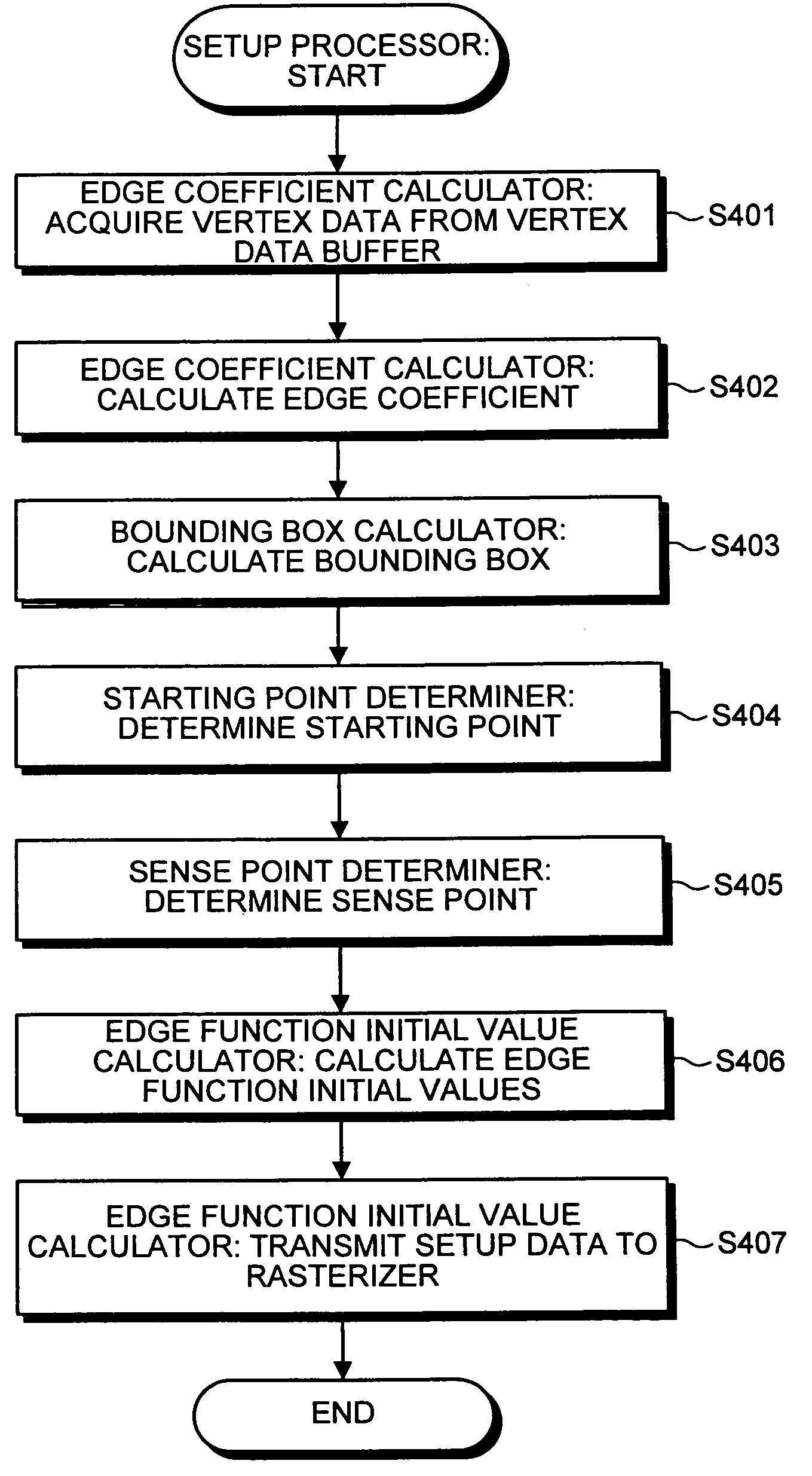
Rendering apparatus, rendering processing method and computer program product
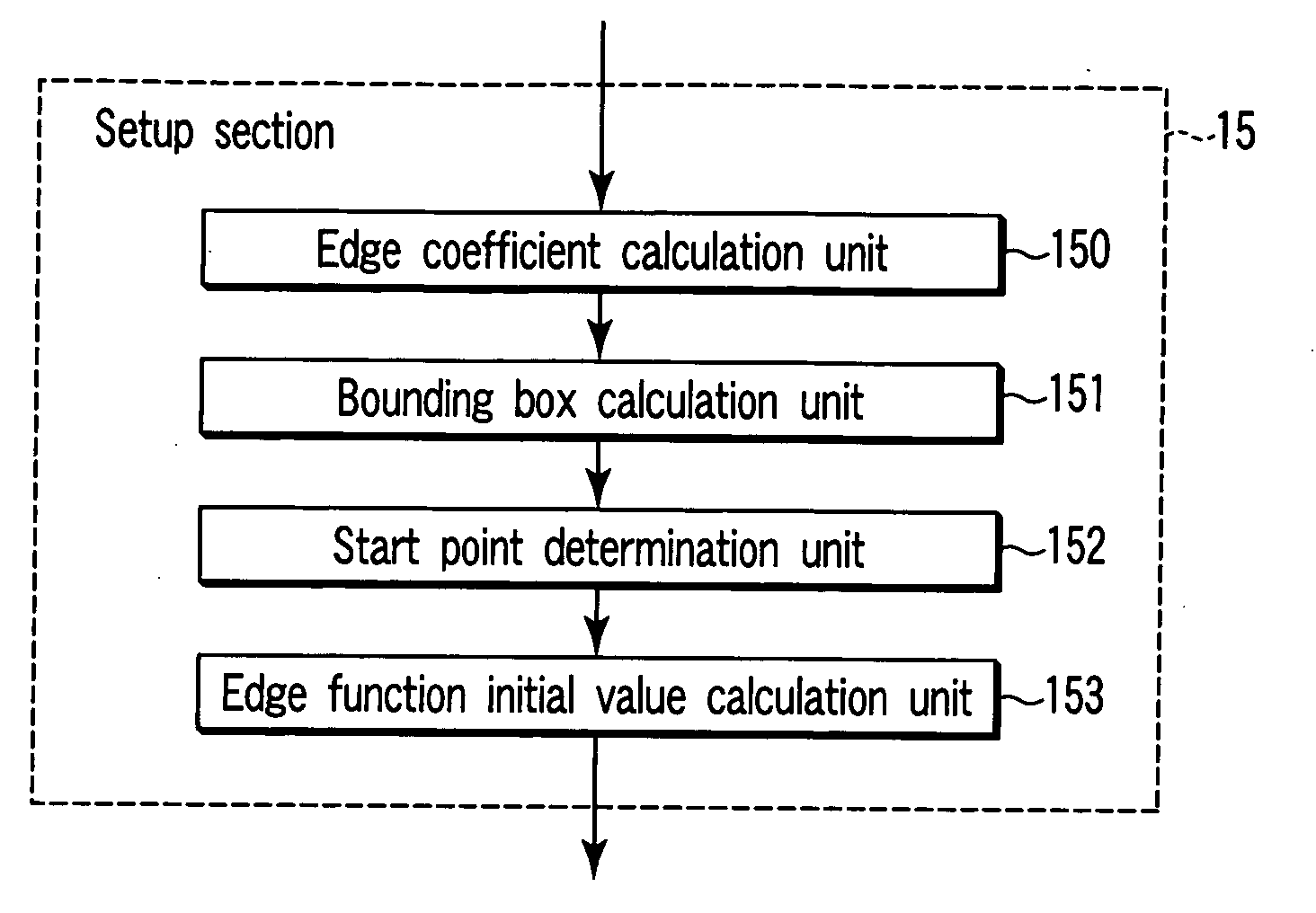
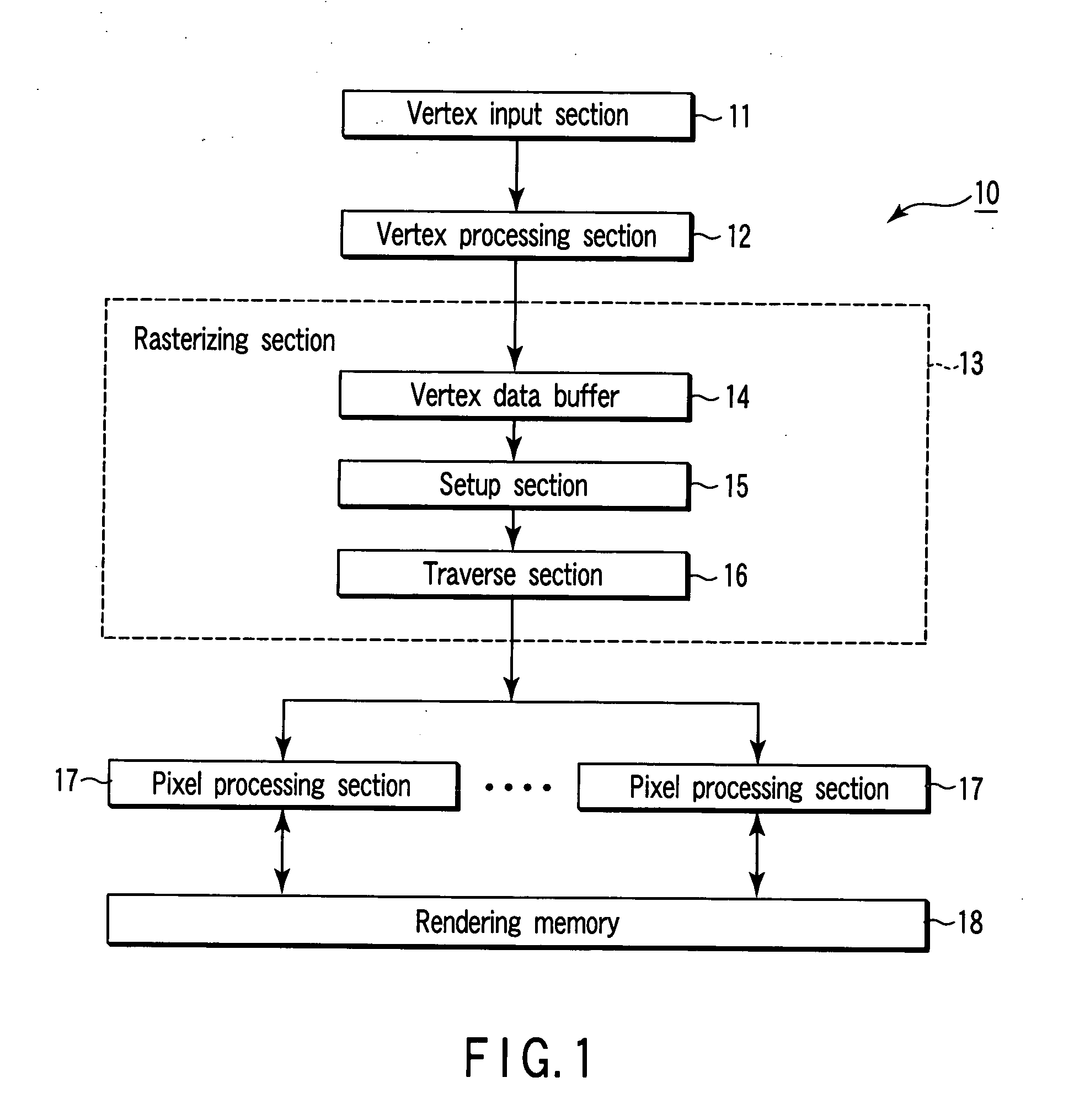
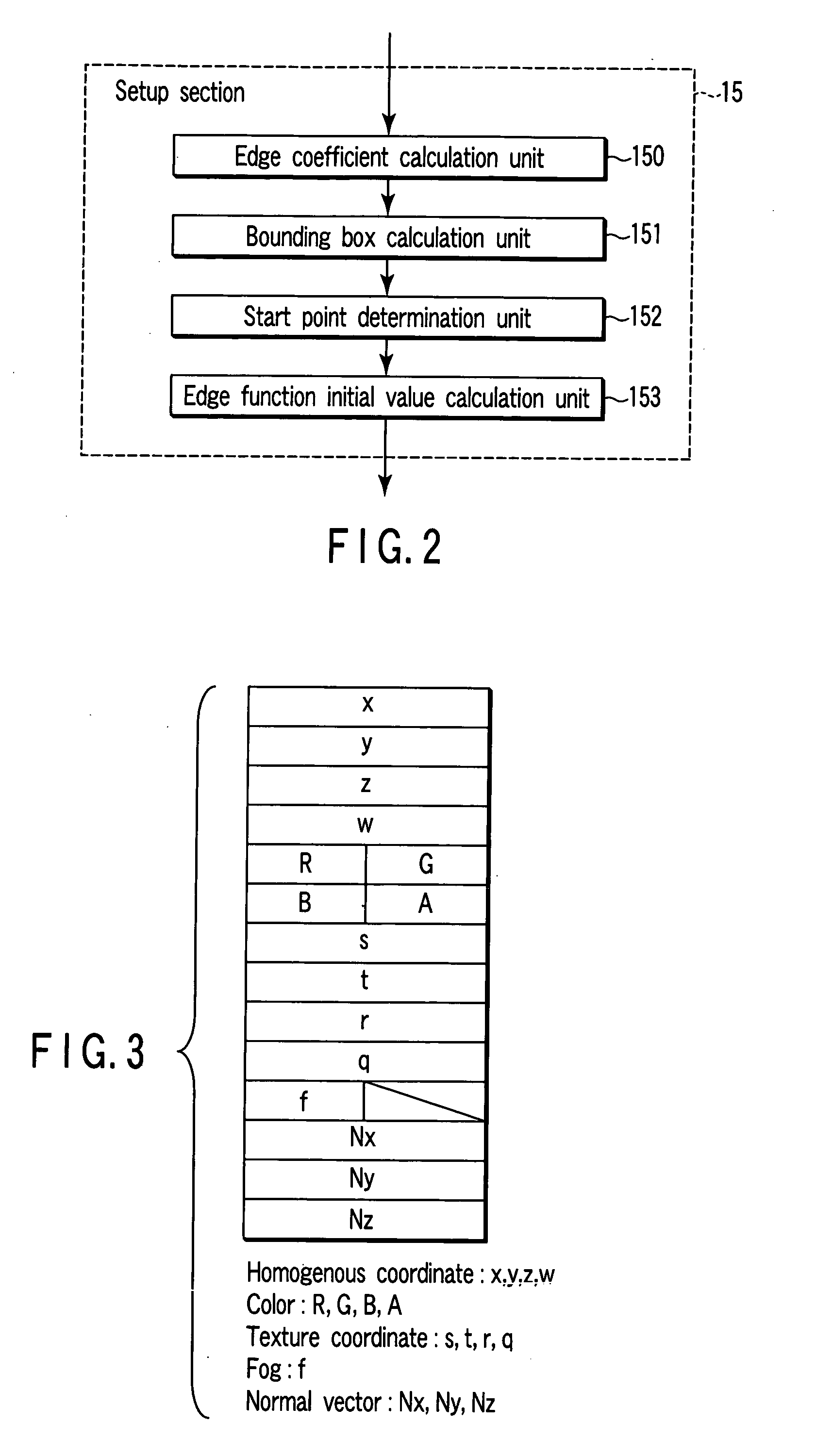
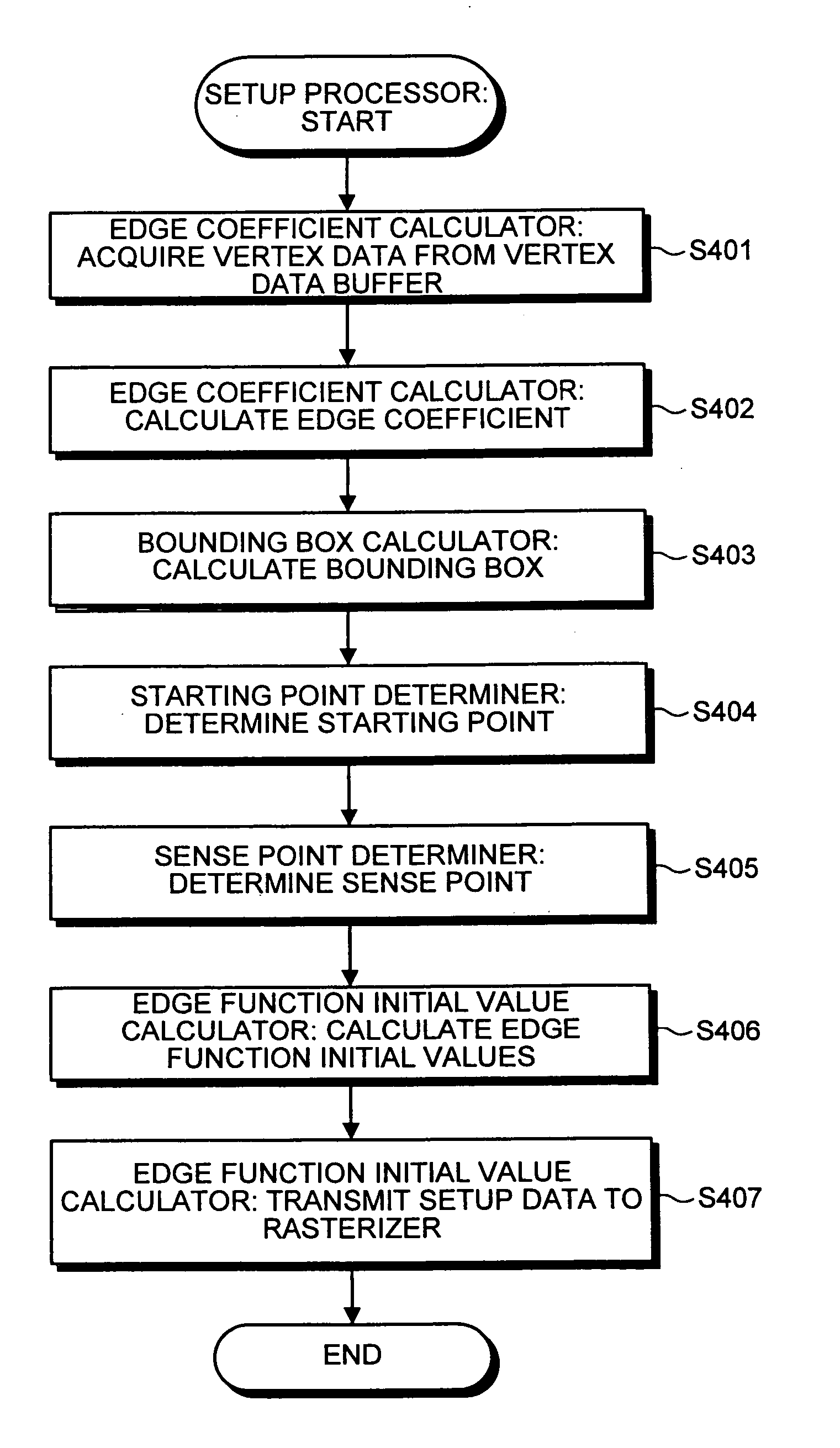
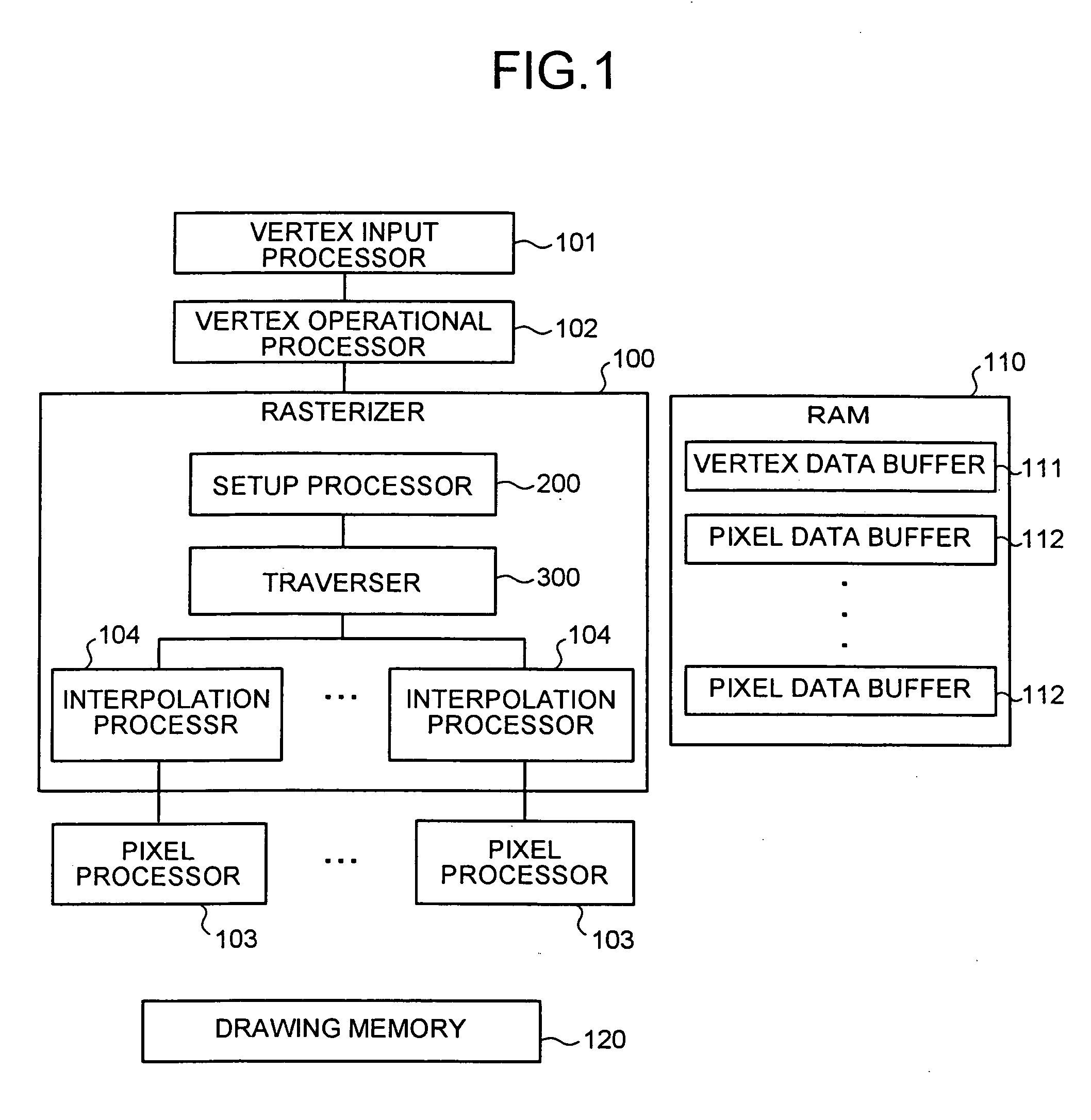
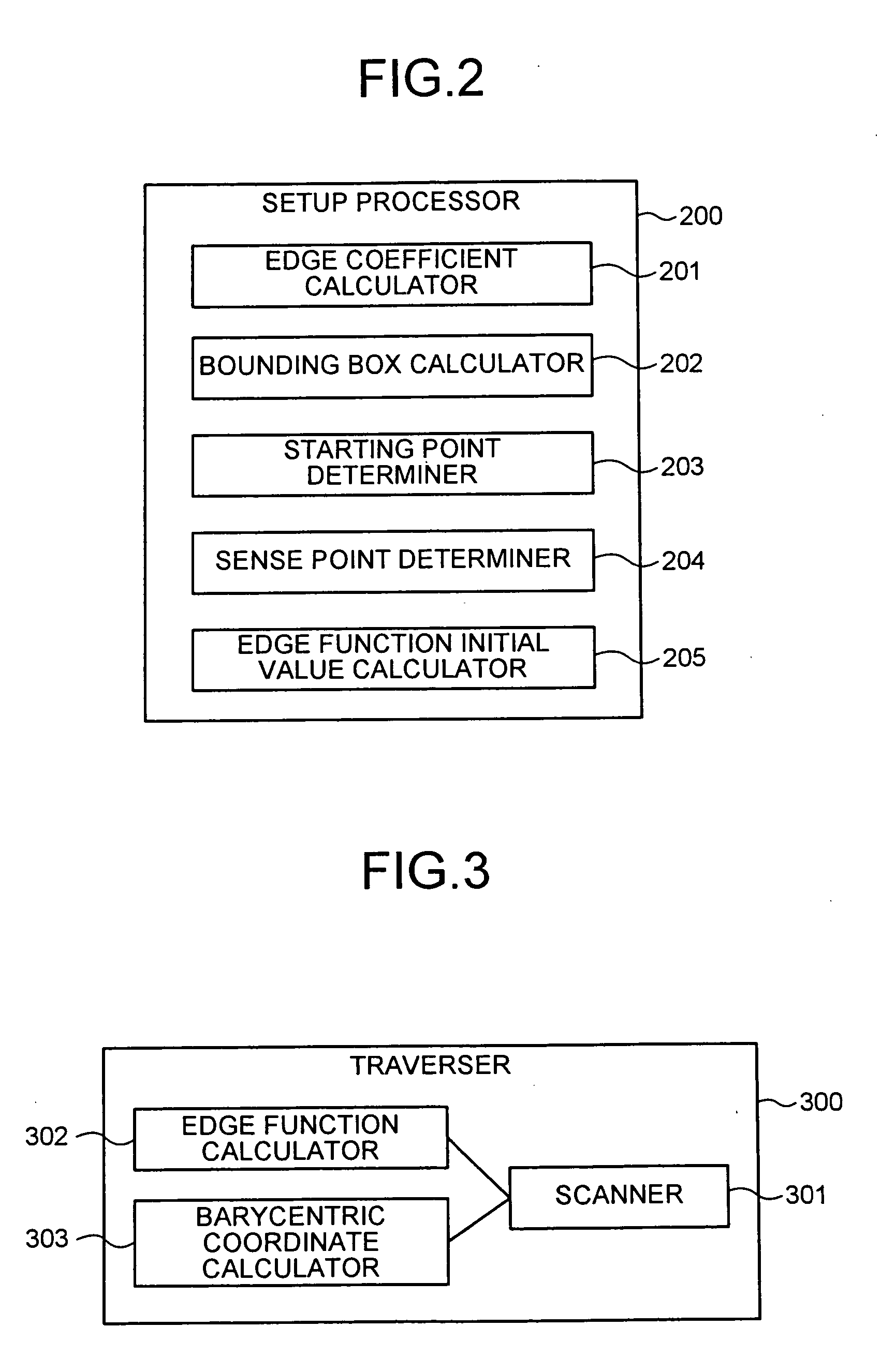
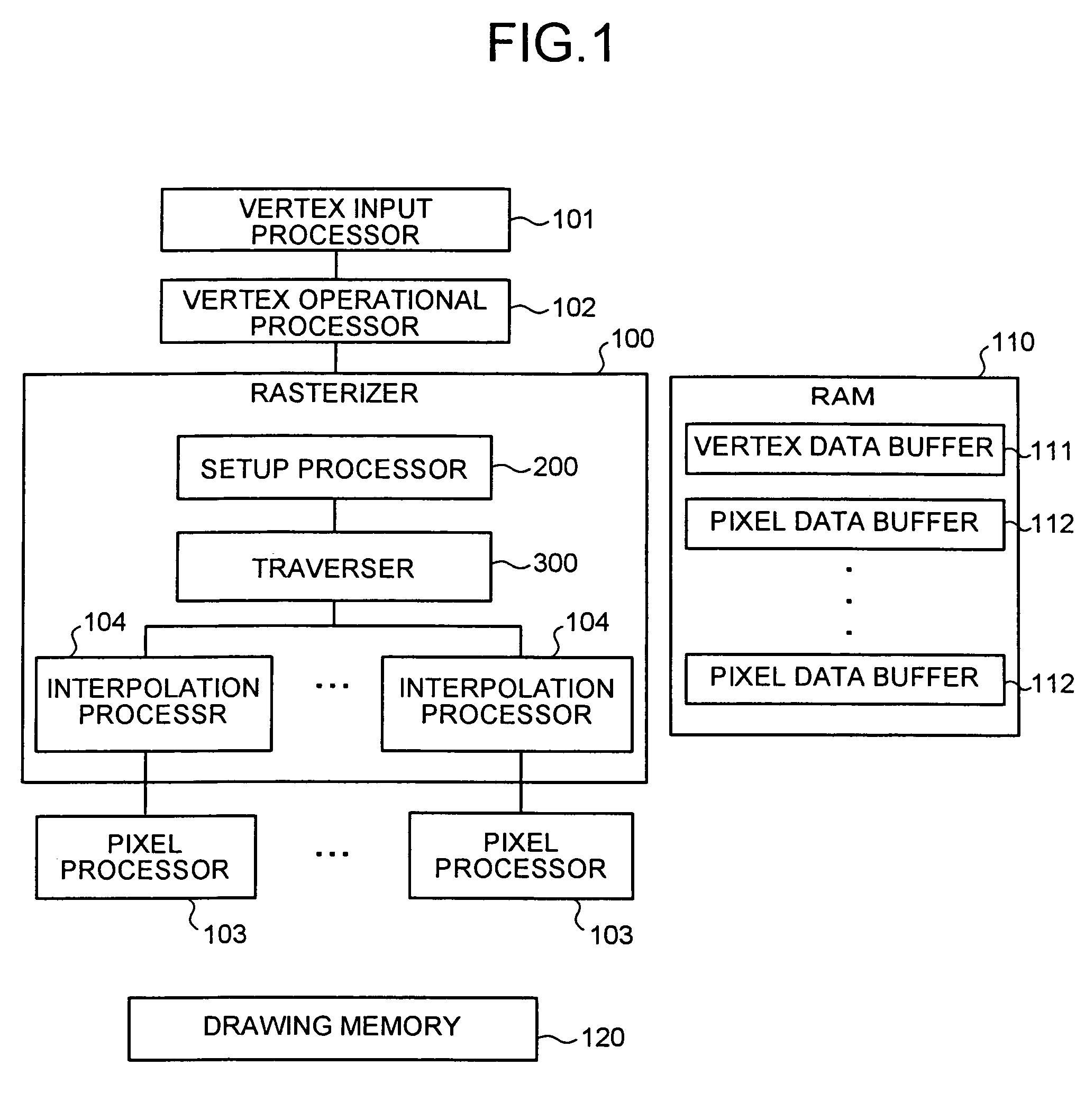
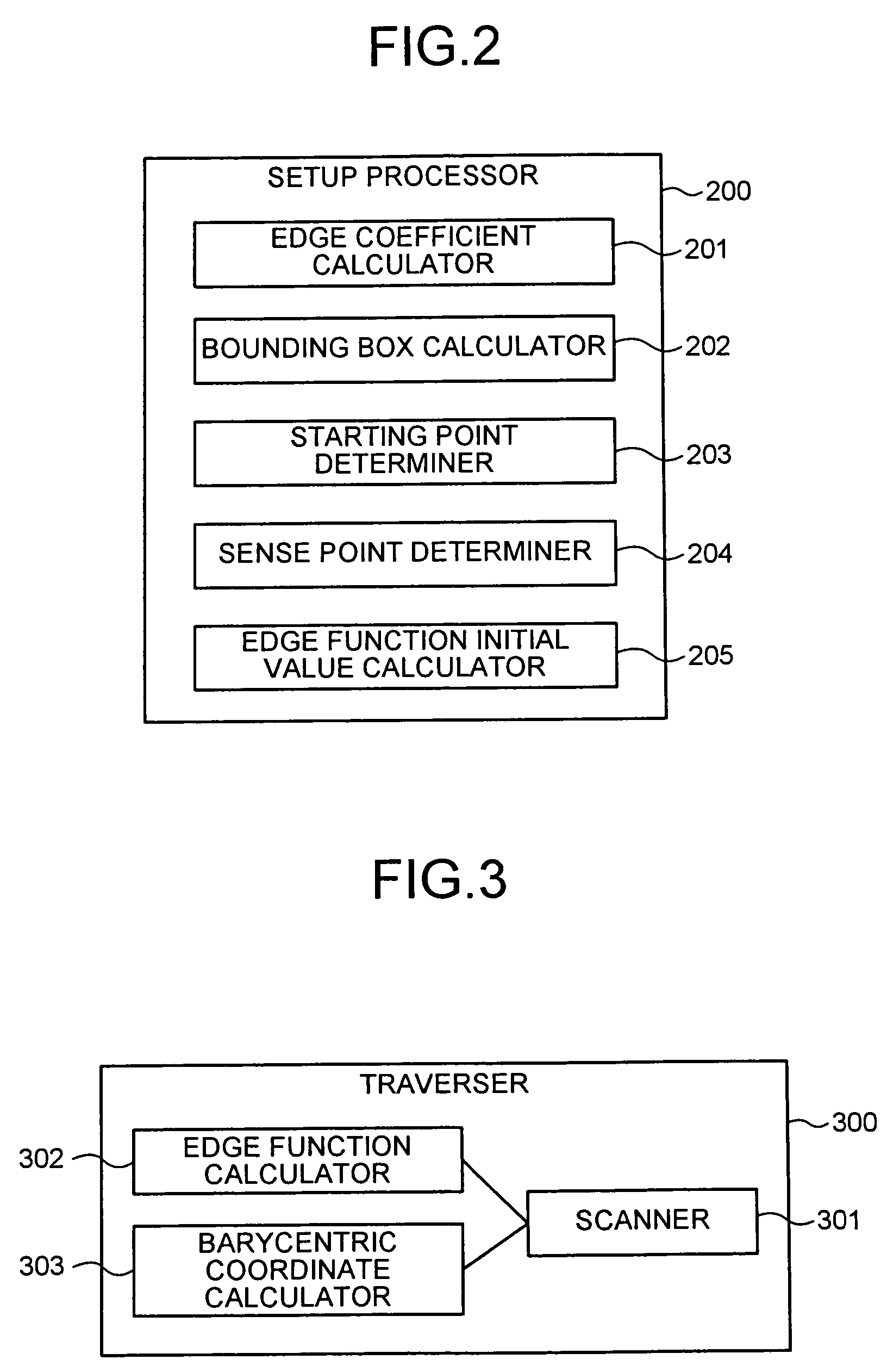
A setup section acquires vertex data including at least homogeneous coordinate and window coordinate relevant to two vertexes of rendering primitive, that is, segment. An edge coefficient calculation unit calculates an edge coefficient used for determining whether or not a pixel exists inside a projection area (parallelogram) of the segment. A bounding box calculation unit calculates a bounding box of the projection area from at least one vertex data of two vertexes and the edge coefficient. A start point determination unit classifies the projection area based on a combination of the edge coefficient, and determines scan start point and scan performing direction of the bounding box in accordance with the classification. An edge function initial value determination unit determines an edge function of the pixel corresponding to the scan start point as an initial value, and carries out a DDA, and thereby, generates setup data for rasterizing.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Drill and sharpening fixture
InactiveUS6030156AFacilitates central positioningEasy to GrindThread cutting toolsWood turning toolsFluteEngineering
A single point drill particularly adapted to producing small diameter deep holes utilizing a peck feed cycle routine. The preferred embodiment features a limited flute length with a depth approximately +E,fra 1 / 3+EE the drill diameter and a dual point edge consisting of a shallow cutting angle and a steep relief angle. A negative rake angle runs along this edge functioning as a knife edge that will cut on opposite rotation, countering the unbalanced forces inherent in a single point tool. A sharpening fixture consisting of 2 parallel slates secured with a T-headed bolt and an anti-rotation pin. The lower plate features a central groove to locate the drill, the upper plate having a short land that facilitates orienting and clamping the drill flute. The forward end of the fixture mimics the drill point allowing the drill to be sharpened on a grinder table or by hand with a suitable abrasive stone or file.
Owner:ANDRONICA RANDALL
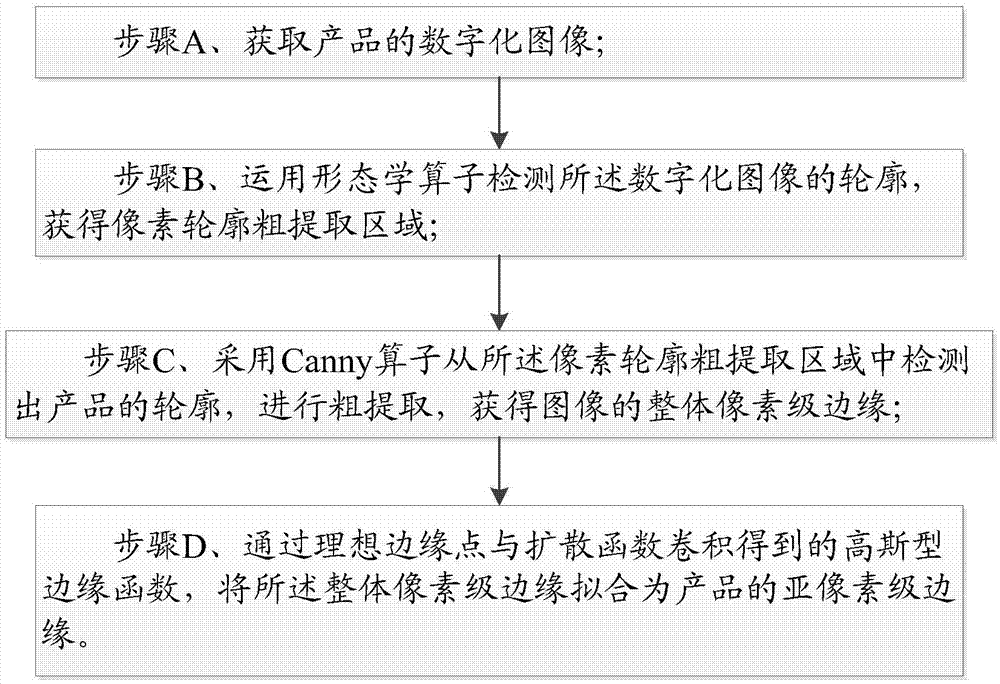
Sub-pixel edge detection method based on improved morphology
InactiveCN104732536ASmooth Outline EdgesAccurate detectionImage analysisDiffusion functionImage edge
The invention provides a sub-pixel edge detection method based on improved morphology. The method comprises the steps that a digitized image of a product is obtained; morphology operators are applied for detecting the outline of the digitized image to obtain a pixel outline rough extraction region; Canny operators are adopted for detecting the whole pixel-level edge of the product from the pixel outline rough extraction region; by means of Gaussian edge functions obtained through ideal edge points and diffusion function convolution, the whole pixel-level edge is fitted into a sub-pixel-level edge of the product. According to the method, the edge detection operators of the morphology are improved, the edge of the image outline can be smoothed, edge details are kept better, anti-noise performance is improved, image edge information is kept, the smoothness and the continuity of the edge are kept, the image edge can be detected accurately, the connectivity of an original image is ensured, an image edge extraction region is reduced, and the processing speed is increased.
Owner:GUANGDONG XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV ACADEMY +1
Rendering apparatus, rendering processing method and computer program product
InactiveUS7414636B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsFluid pressure computingComputer visionComputer science
A setup section acquires vertex data including at least homogeneous coordinate and window coordinate relevant to two vertexes of rendering primitive, that is, segment. An edge coefficient calculation unit calculates an edge coefficient used for determining whether or not a pixel exists inside a projection area (parallelogram) of the segment. A bounding box calculation unit calculates a bounding box of the projection area from at least one vertex data of two vertexes and the edge coefficient. A start point determination unit classifies the projection area based on a combination of the edge coefficient, and determines scan start point and scan performing direction of the bounding box in accordance with the classification. An edge function initial value determination unit determines an edge function of the pixel corresponding to the scan start point as an initial value, and carries out a DDA, and thereby, generates setup data for rasterizing.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Non-blocking parallel triangle rasterization unit structure
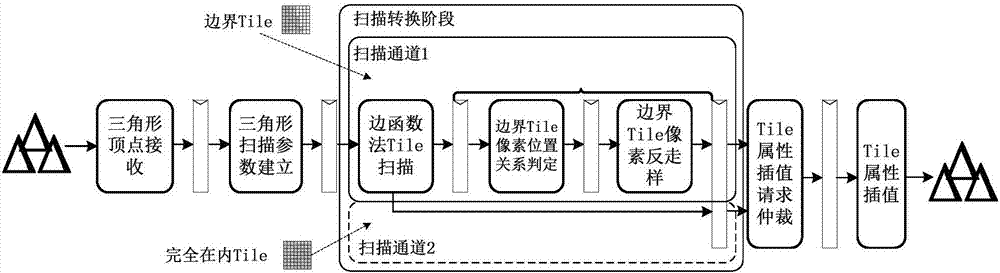
ActiveCN108009978AReduce scanEasy to handleProcessor architectures/configurationAnti-aliasingResource utilization
The invention provides a non-blocking parallel triangle rasterization unit structure. The triangle rasterization unit structure consists of 7 functional pipeline stages, which are a triangle vertex receiving unit, a triangle scanning parameter establishment unit, an edge function method Tile scanning unit, a boundary Tile pixel position relation judgment unit, a boundary Tile pixel anti-aliasing unit, a Tile attribute interpolation request arbitration unit and a Tile attribute interpolation unit in sequence from front to back. The triangle rasterization unit structure has capabilities of non-blocking parallel triangle block scanning and processing; pixel Tiles covered by a triangle are classified into two types including Tiles completely in the triangle and Tiles partially in the triangle;two parallel processing channels are set; on the premise of keeping a triangle Tile output sequence, non-blocking parallel scanning of the two types of the Tiles can be realized; the resource utilization rate, the triangle processing capability and the pixel generation capability are improved; and especially for relatively large triangle primitives, the structure is more effective.
Owner:XIAN AVIATION COMPUTING TECH RES INST OF AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
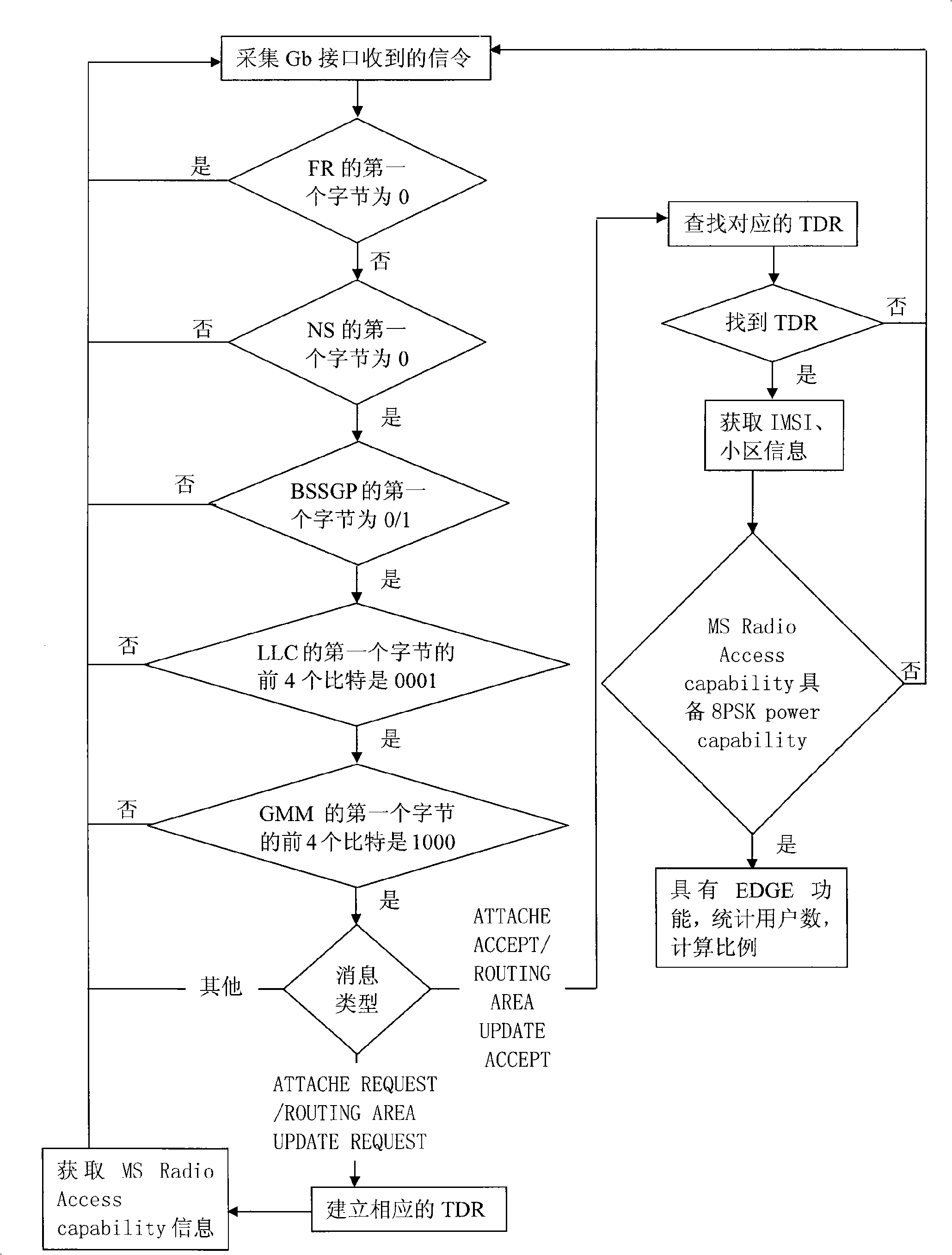
Method for detecting EDGE function of mobile phone user
The invention relates to a method for detecting whether a cell phone user has EDGE function or not, which comprises that signaling received by a Gb interface is collected; if the collected signaling is ATTACHE REQUEST or ROUTING AREA UPDATE REQUEST, the detail record of the corresponding event is established; MS Radio Access capability information is obtained and collecting is continued; if the collected signaling is ATTACHE ACCEPT or ROUTING AREA UPDATE ACCEPT, the detail record of the corresponding event is looked up; IMSI and subdistrict information of a user are gained; whether the user has 8PSK power capability or not is judged according to the MS Radio Access capability information, if yes, the user has EDGE function; if not, the user does not have EDGE function. The method can effectively look up the cell phone user having the EDGE function in the subdistrict.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Apparatus of and method for drawing graphics, and computer program product
InactiveUS20050134583A1Solve problemsDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsProjection image
An apparatus of drawing graphics includes an edge coefficient calculator calculating, from vertex data on vertices of a triangle, edge coefficients of edge functions used to determine whether a pixel is present in an inside region of the triangle, and a bounding box calculator calculating a bounding box of projected images of the triangle on a projection plane based on the edge coefficients. The apparatus also includes a starting point determiner and a traverser. The starting point determiner classifies the projected images of the triangle based on a combination of the edge coefficients for respective sides of the triangle, and determines a scan starting point from a corner of the bounding box based on classification of the projected images. The traverser generates pixel data used in rasterization by scanning the bounding box from the scan starting point.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Apparatus and method for processing graphics primitives
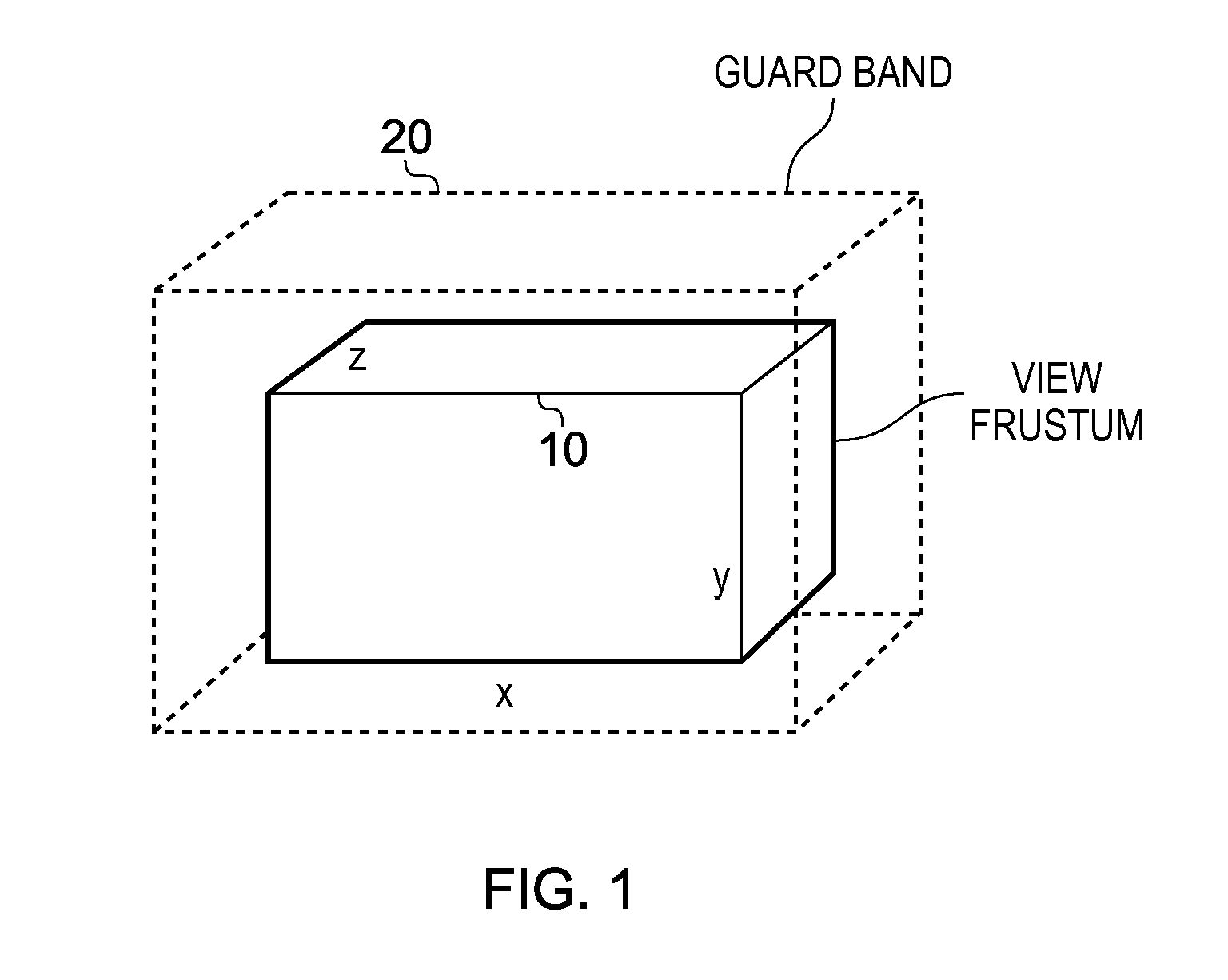
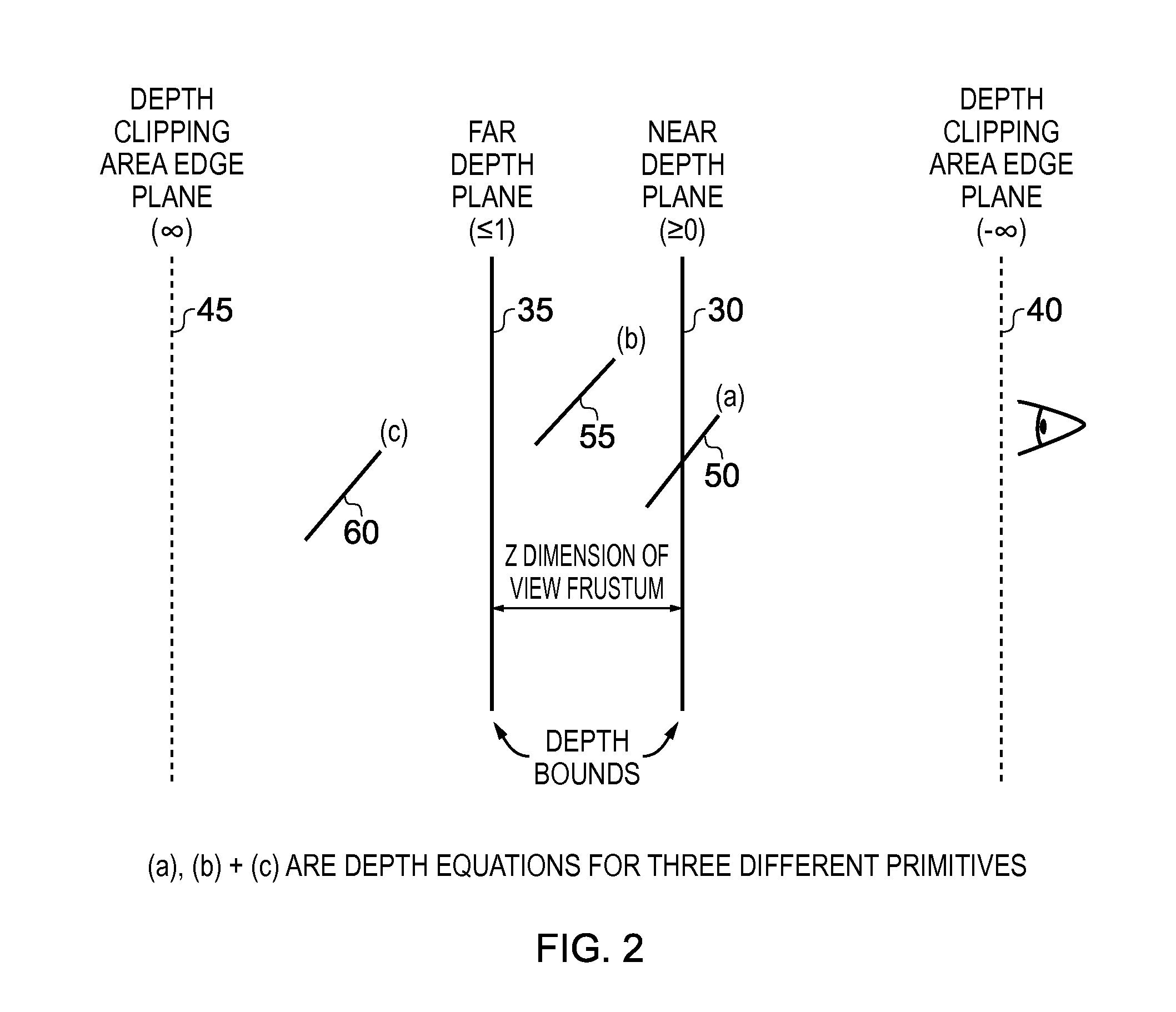
ActiveUS20140375637A1Improve performanceReduce area requirementsDetails involving image processing hardware3D-image renderingGraphicsViewing frustum
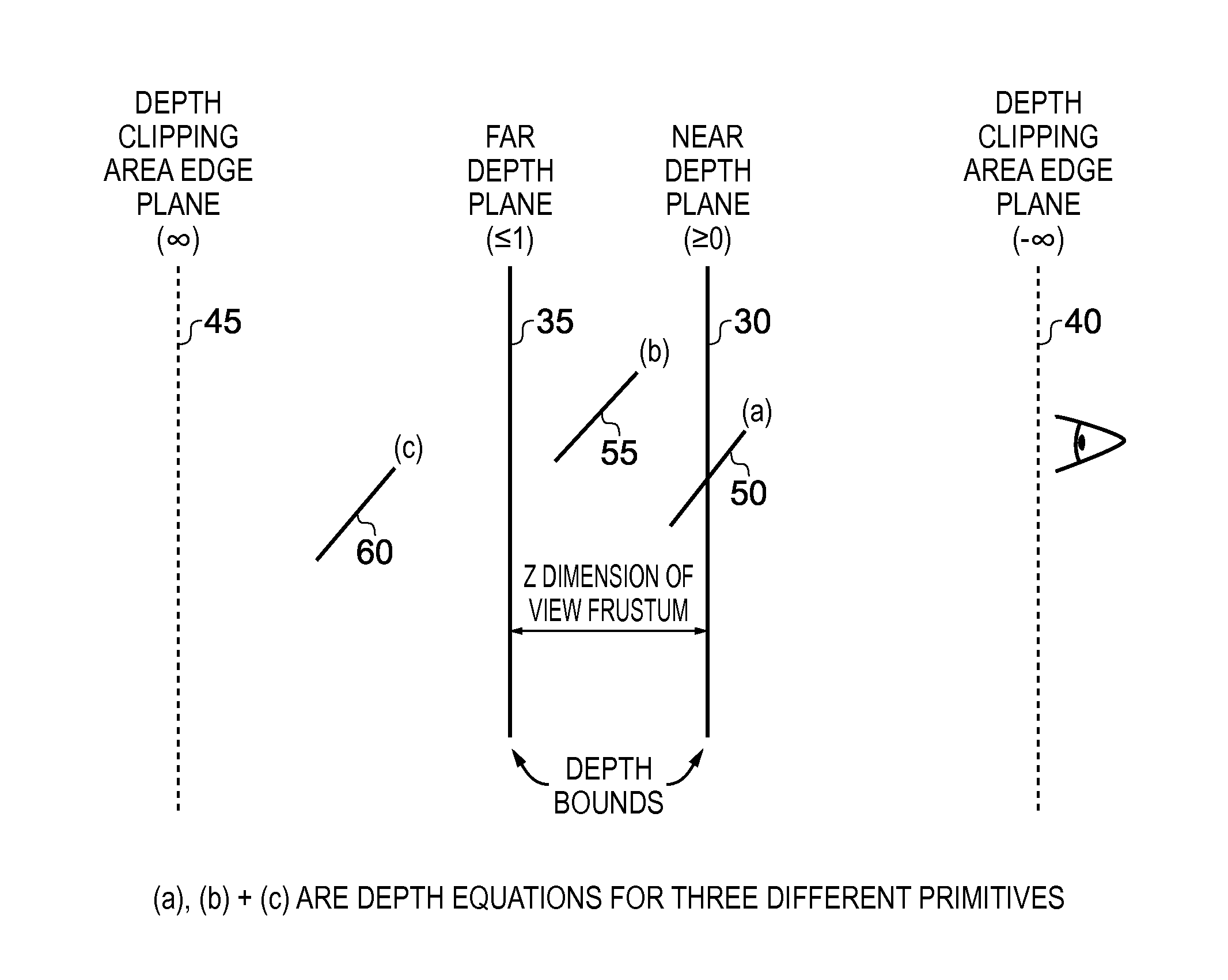
A method and apparatus includes primitive setup circuitry for determining a plurality of functions for an input graphics primitive, including an edge function associated with each edge of the input graphics primitive and a depth function associated with the input graphics primitive. Rasterization circuitry performs a rasterization operation in order to calculate position data for a plurality of graphics fragments to be used to represent the input graphics primitive. In a default mode of operation, depth bound clipping circuitry performs a depth bound clipping operation by determining, for each graphics fragment in said plurality of graphics fragments, a depth value for said graphics fragment using the depth function, and determining whether said depth value resides within a valid depth range of a view frustum, the graphics fragment being discarded from further processing if its depth value does not reside within said valid depth range.
Owner:ARM LTD
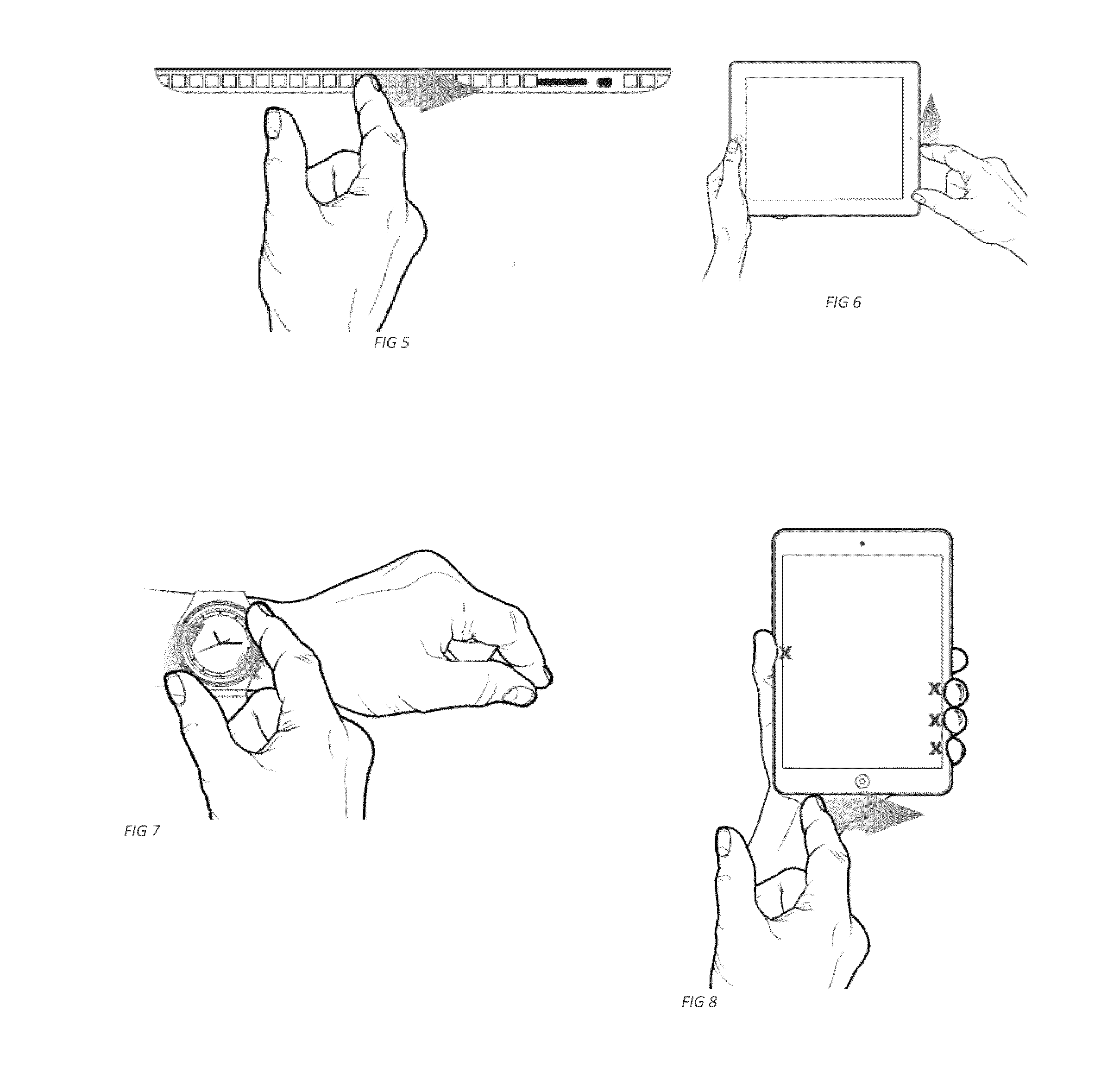
Touch sensitive edge input device for computing devices
InactiveUS20160154489A1Improve interactive experienceEasy to moveInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingCombined useHuman–computer interaction
A narrow strip for use in conjunction with a computing device which enables touch sensitive edge functionality in response to fingers in contact with the strip. The edge strip allows a user to control aspects of the computing device by using various touches and gestures without occluding the face of the computing device.
Owner:COLLINS ANTONIO R +1
Frequency domain self-adaptive non-linear earthquake imaging filtering method
InactiveCN106772588AEfficient removalKeep the detailsSeismic signal processingDecompositionSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
A frequency domain self-adaptive non-linear earthquake imaging filtering method comprises the steps as follows: firstly, earthquake data are input for calculation and analysis of frequency amplitude spectrum, original earthquake data are subjected to wavelet transformation scale component decomposition with a wavelet basis, components of the earthquake data on different scales are obtained, frequency domain transformation of the earthquake data is performed according to the corresponding relation between the scales and the frequency, single-frequency component earthquake data are extracted from the frequency domain earthquake data subjected to wavelet transformation, the single-frequency component earthquake data in which noise are mainly distributed are subjected to edge function solution of an improved self-adaptive non-linear diffusion equation, finally, all frequency component data can meet the requirement of the maximum signal-to-noise ratio, signal-to-noise ratio quality monitoring is performed on the iterative process of repeated self-adaptive non-linear diffusion filtering, so that the optimal iteration times of filtering is determined, all frequency component earthquake data after repeated iteration filtering are subjected to wavelet reconstruction synthesis, and the final earthquake data after imaging filtering are obtained.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
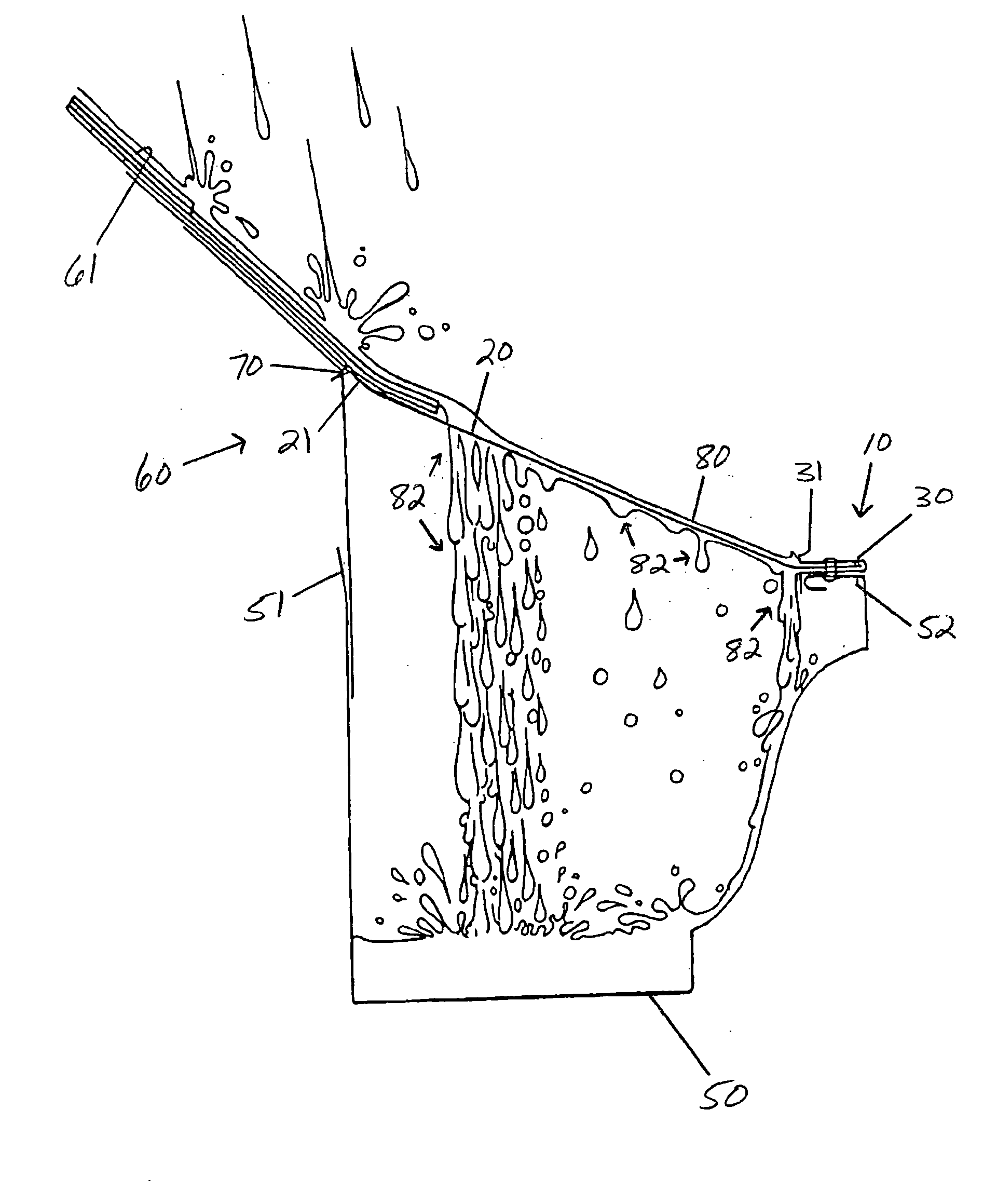
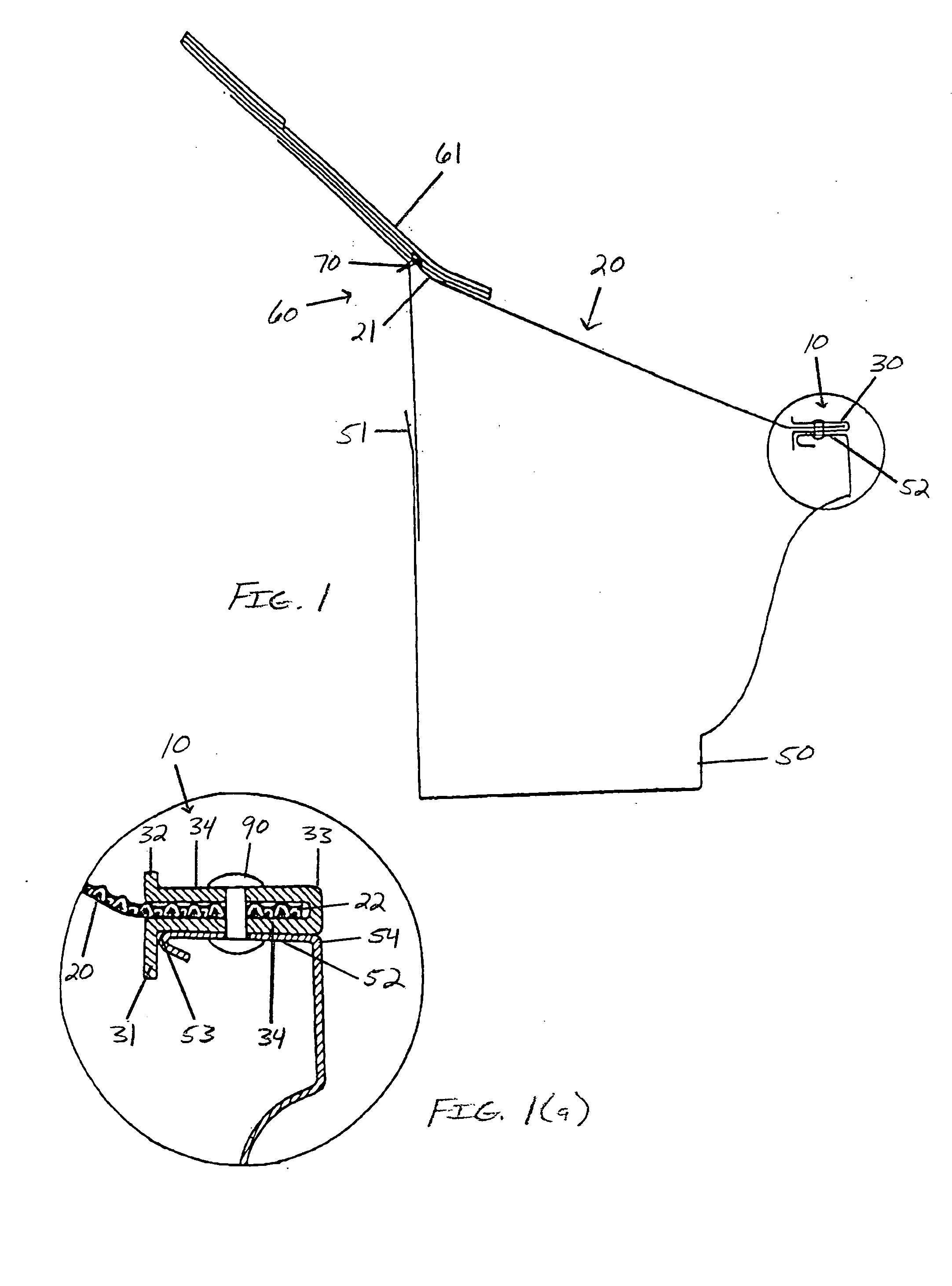
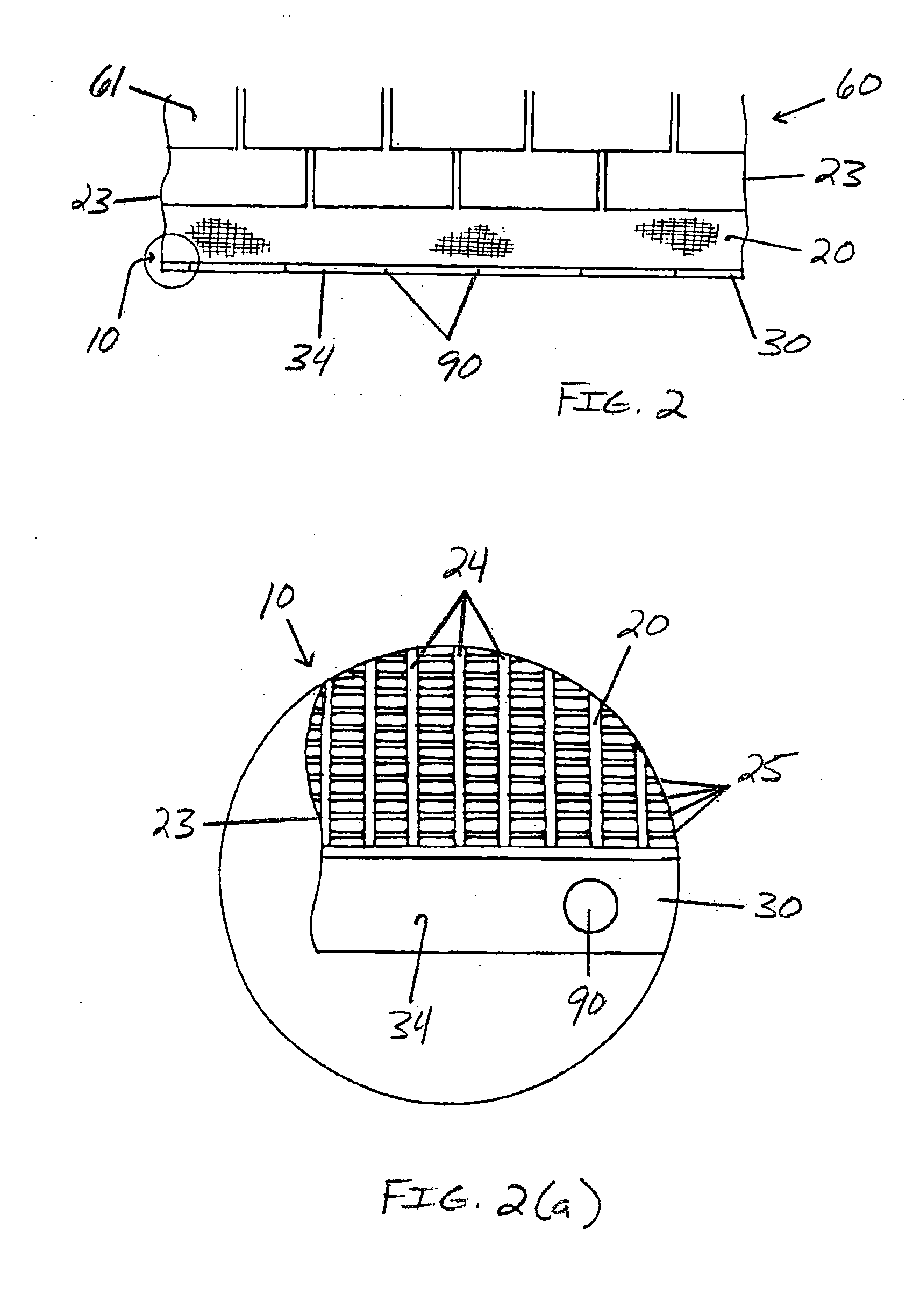
Gutter screen termination trim with water tension breaker
InactiveUS7056433B2Low costReducing “over-the-edge” roof water runoffRoof coveringFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater leakageEngineering
The present invention provides a gutter screen attachment for minimizing water film runoff and debris collection adjacent a screened gutter. The screen attachment comprises a superior breaker edge, an inferior breaker edge, and a screen-receiving region. The screen-receiving region comprises an edge-receiving fold that accepts the gutter-engaging edge of a gutter screen. The superior breaker edge extends upwardly opposite the inferior breaker edge and is designed to break the water tension of a water film formed upon the gutter screen. The inferior breaker edge is designed to prevent water leakage between the screen attachment and the gutter. The superior breaker edge is of minimized height so as to allow bulky debris to translate over the superior breaker edge. It is thus contemplated that the superior breaker edge functions to allow water to more properly permeate through the gutter screen.
Owner:SWISTUN KAZIMIERZ
Frameless supplemental window for fenestration incorporating infiltration blockers
ActiveUS9663983B2Improve rigidityHigh strengthLight protection screensRain/draught deflectorsThermal insulationPlastic film
A novel and useful frameless supplemental window for fenestration incorporating infiltration blockers suitable for use with existing windows. The supplemental window, in one embodiment, comprises plastic sheet material with bullnose edging around it. Corner braces add rigidity and strength to corners in several embodiments. An attachment mechanism secured either to the sheet material or the bullnose edge functions to fasten and / or seal the supplemental window to an existing window. Infiltration blockers fastened to the sheet or bullnose prevent or minimize air leakage around various window elements. The bullnose edging and infiltration blockers function to substantially enclose (i.e. trap) a volume of air between the window pane and the plastic sheet material. The supplemental window is configured such that the layer of air enclosed is of an optimum thickness within a preferred range of 0.15 to 0.75 inches to maximize thermal insulation properties of the supplemental window.
Owner:WEXENERGY
Partial guardband clipping
ActiveUS20060061596A1Reduce the amount of calculationDrawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputational scienceGraphics
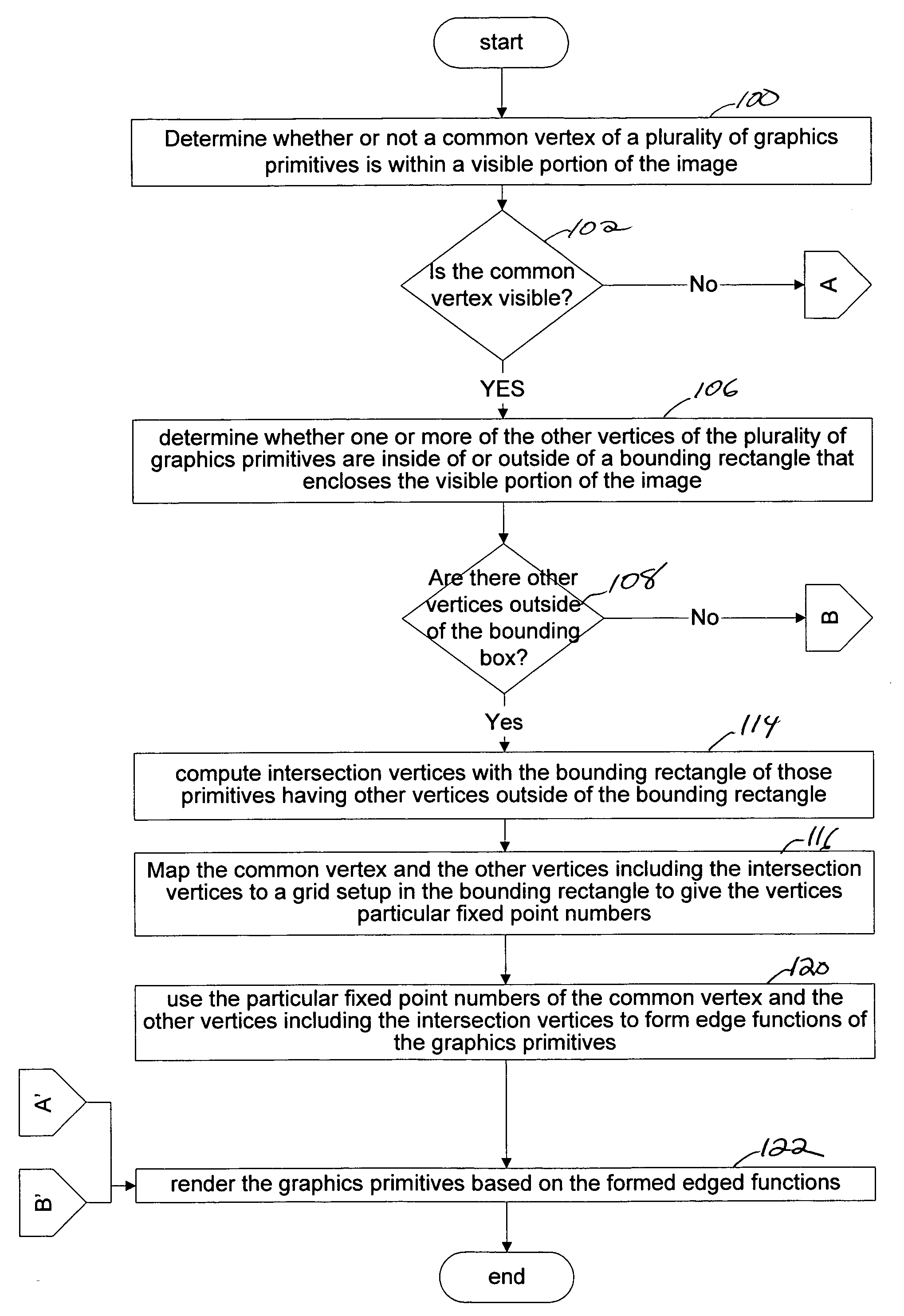
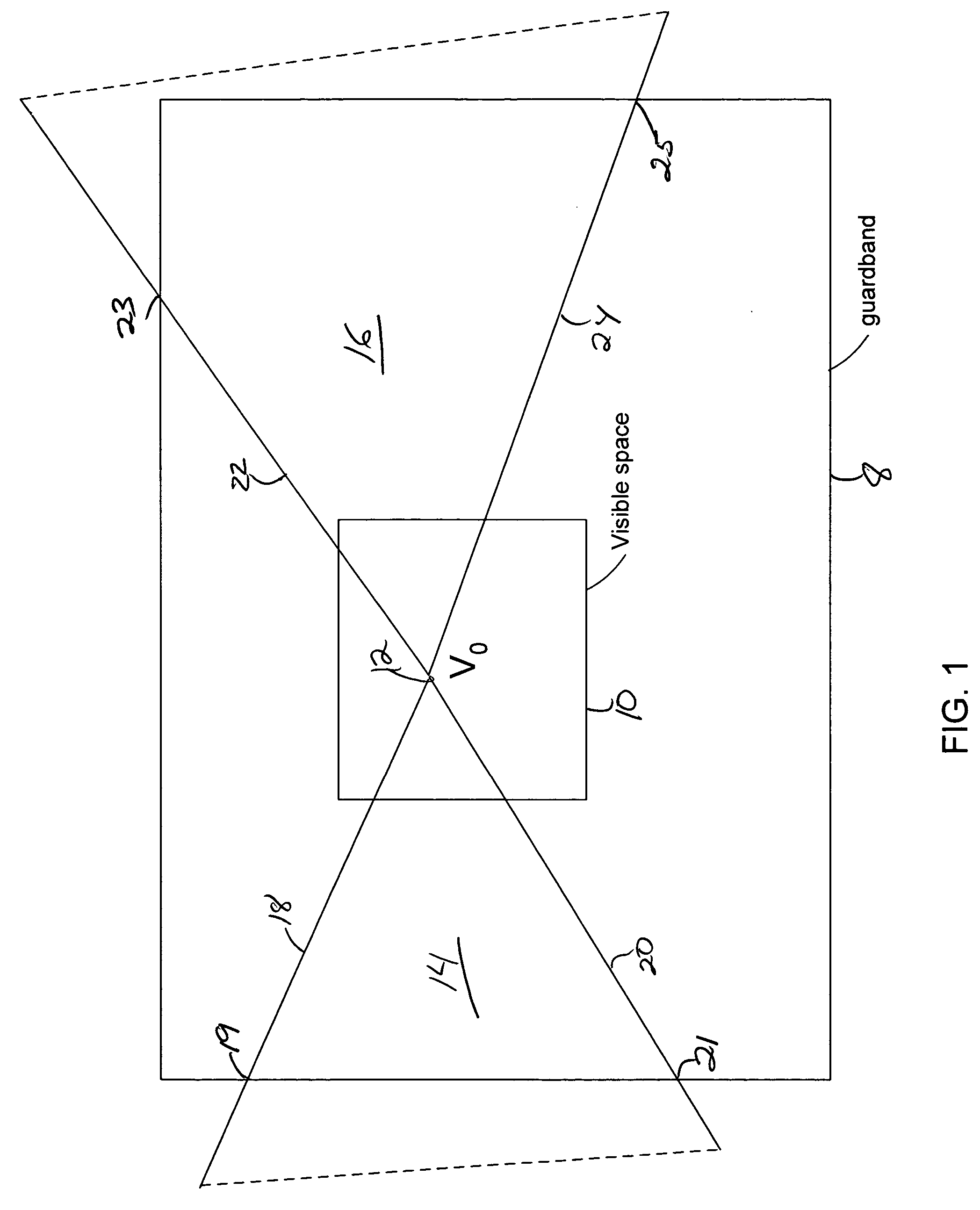
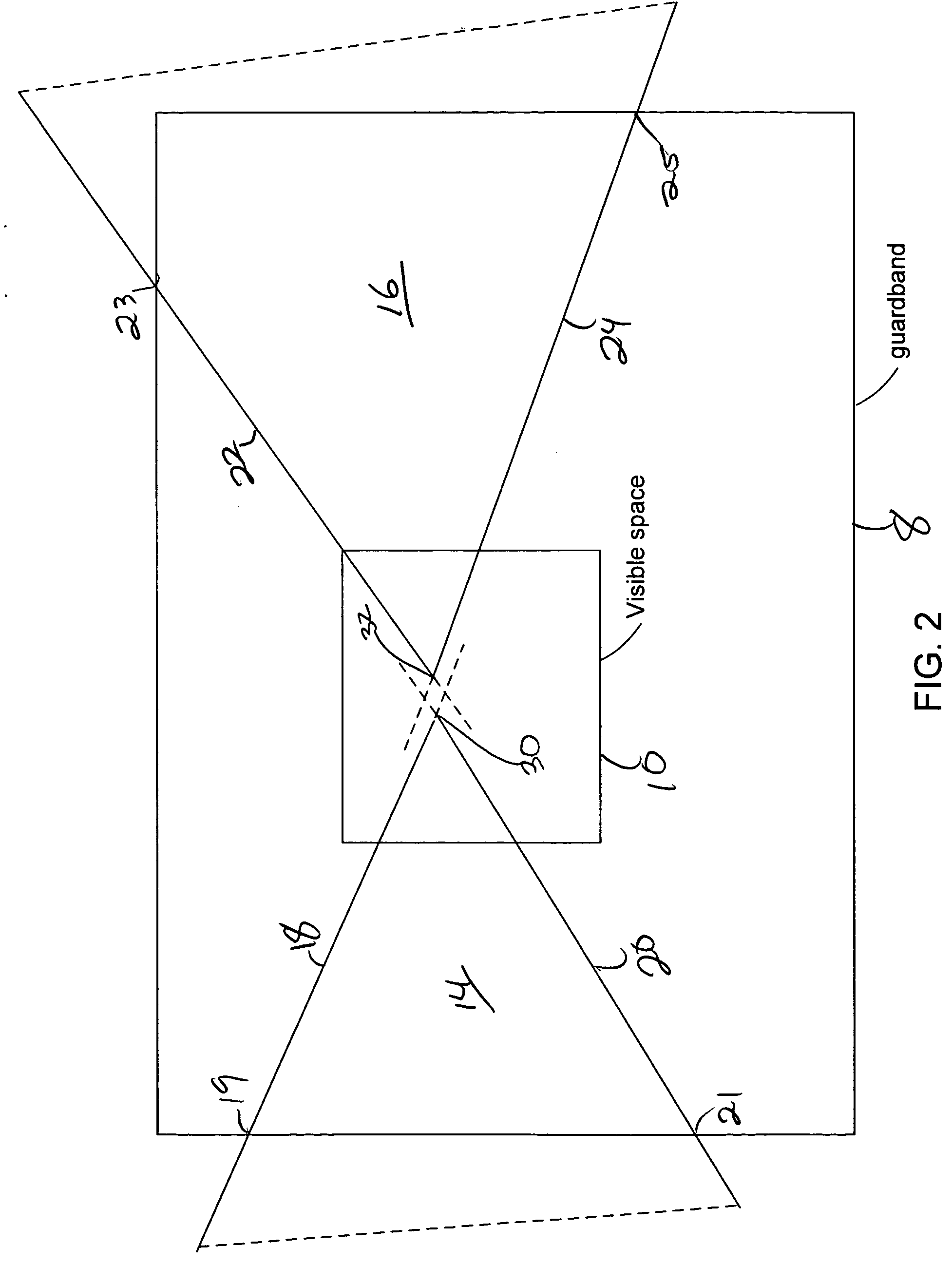
A method for rendering a visible portion of an image that includes a plurality of graphics primitives. The size of the graphics primitives may be large and require the use of floating point numbers to represent the vertices. When the graphics primitives have a common vertex that is visible, the edge functions for the primitive are computed so as to avoid the common vertex becoming different for the different primitives. If the other vertices of the graphics primitives lie outside a bounding rectangle, then a vertex is formed at the intersection of the bounding rectangle and the graphics primitive. Fixed point numbers for the common vertex and other vertices including intersection vertices are then used to compute edge functions of the primitive and the primitive is rendered using the edge functions. If the common vertex is not visible, then floating point numbers are used to compute the edge functions.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
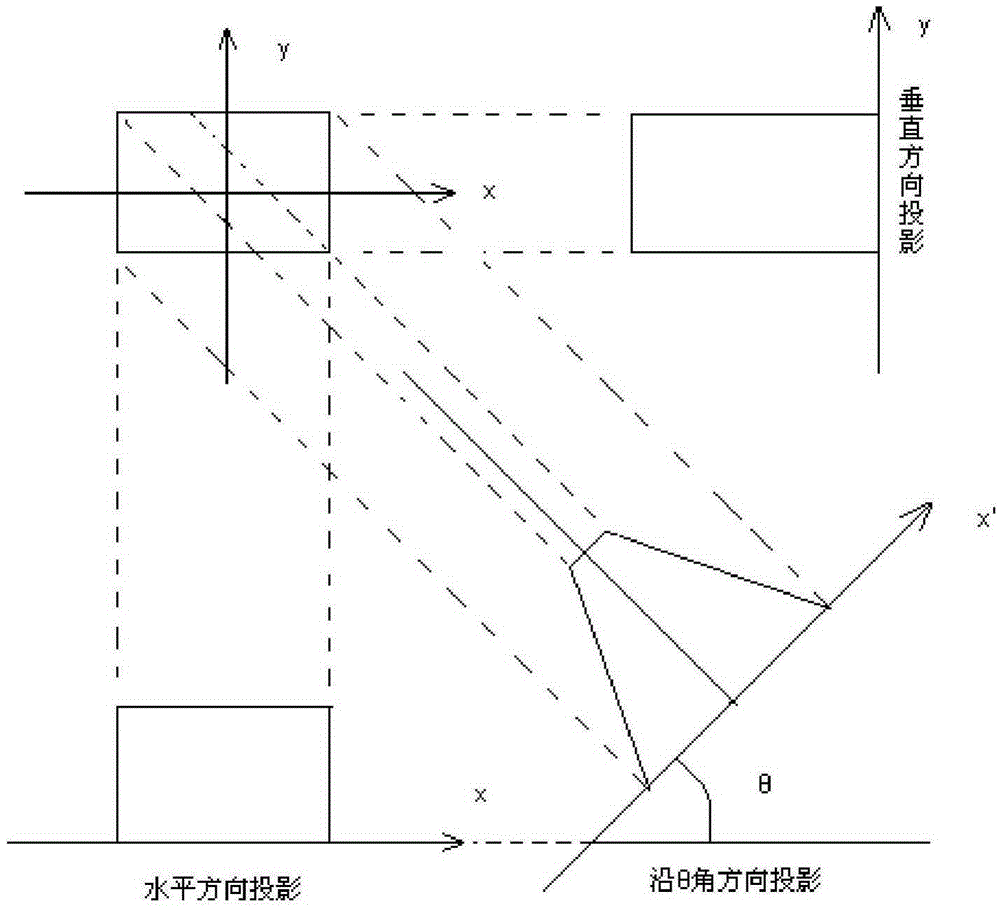
License plate inclination angle correction method based on Radon transform
InactiveCN105426888AImprove the accuracy of number plate recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionPeak value
The invention provides a license plate inclination angle correction method based on Radon transform, which relates to the field of license plate identification and is used for correcting identified inclined license plates. The license plate inclination angle correction method comprises the following steps: calculating a binary edge image of an image by using an edge function, and a detecting straight lines in an original image; calculating the Radon transform of the edge image, respectively projecting each point with a pixel 1 on directions of 0-179 degrees, calculating the Radon transform of the edge image, and displaying a transform effect picture; and detecting peak values in a Radon transform matrix, wherein these peak values correspond to the straight lines in the original image, the column coordinates theta of these peak values in the Radon transform matrix are the inclination angles of straight lines vertical to the straight lines in the original image, and the inclination angles of the straight lines are 90-theta.
Owner:SICHUAN HAOTEL COMM
Frameless supplemental window for fenestration
ActiveUS9845636B2Improve rigidityHigh strengthLight protection screensWindow/door framesThermal insulationPlastic film
A novel and useful frameless supplemental window for fenestration suitable for use with existing windows. The supplemental window, in one embodiment, comprises plastic sheet material with bullnose edging around it. Corner braces add rigidity and strength to corners in several embodiments. An attachment mechanism secured either to the sheet material or the bullnose edge functions to fasten and / or seal the supplemental window to an existing window. The bullnose edging functions to substantially enclose (i.e. trap) a volume of air between the window pane and the plastic sheet material. The supplemental window is configured such that the layer of trapped air is of an optimum thickness within a preferred range of 0.15 to 0.75 inches to maximize thermal insulation properties of the supplemental window.
Owner:WEXENERGY
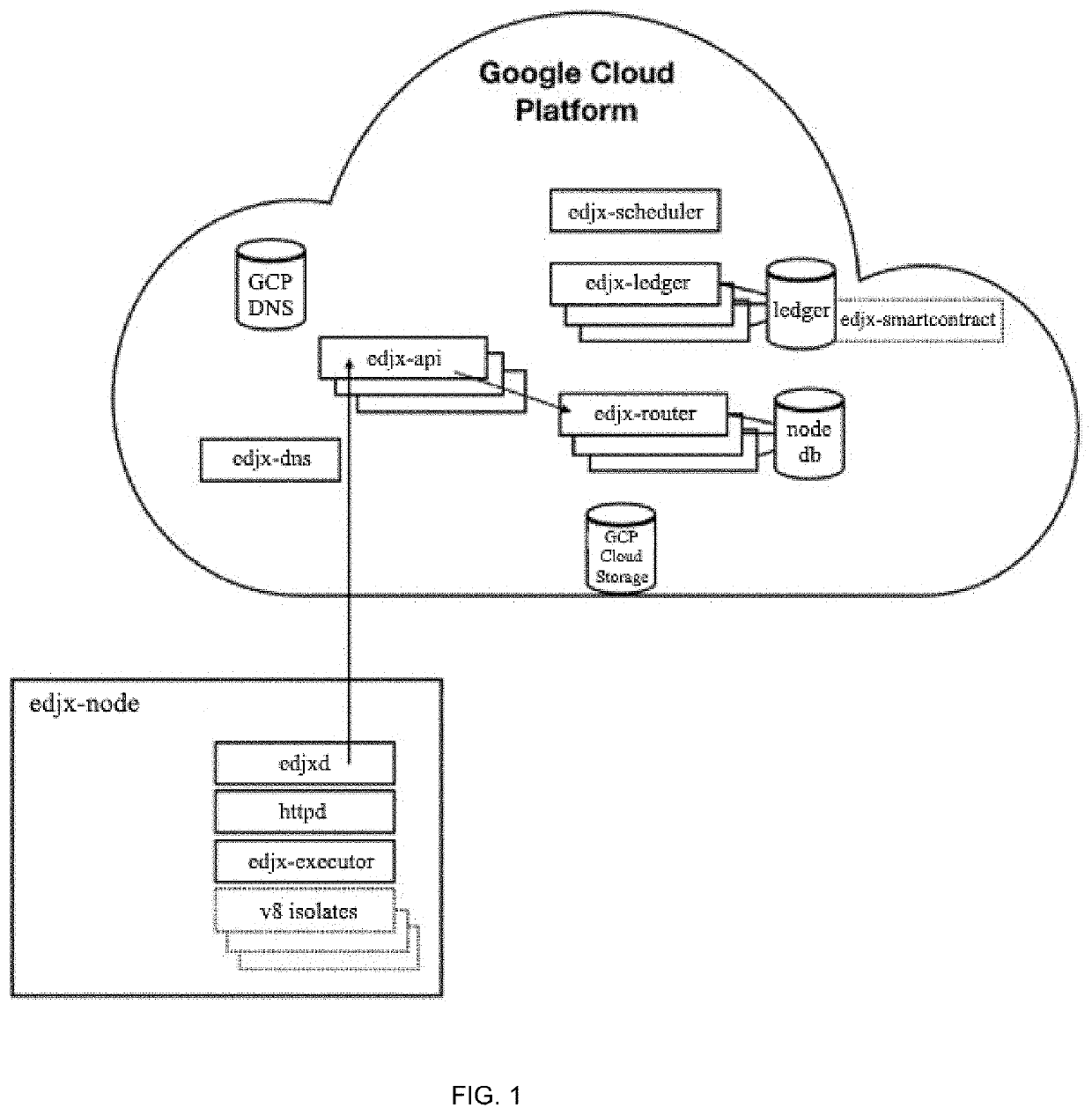
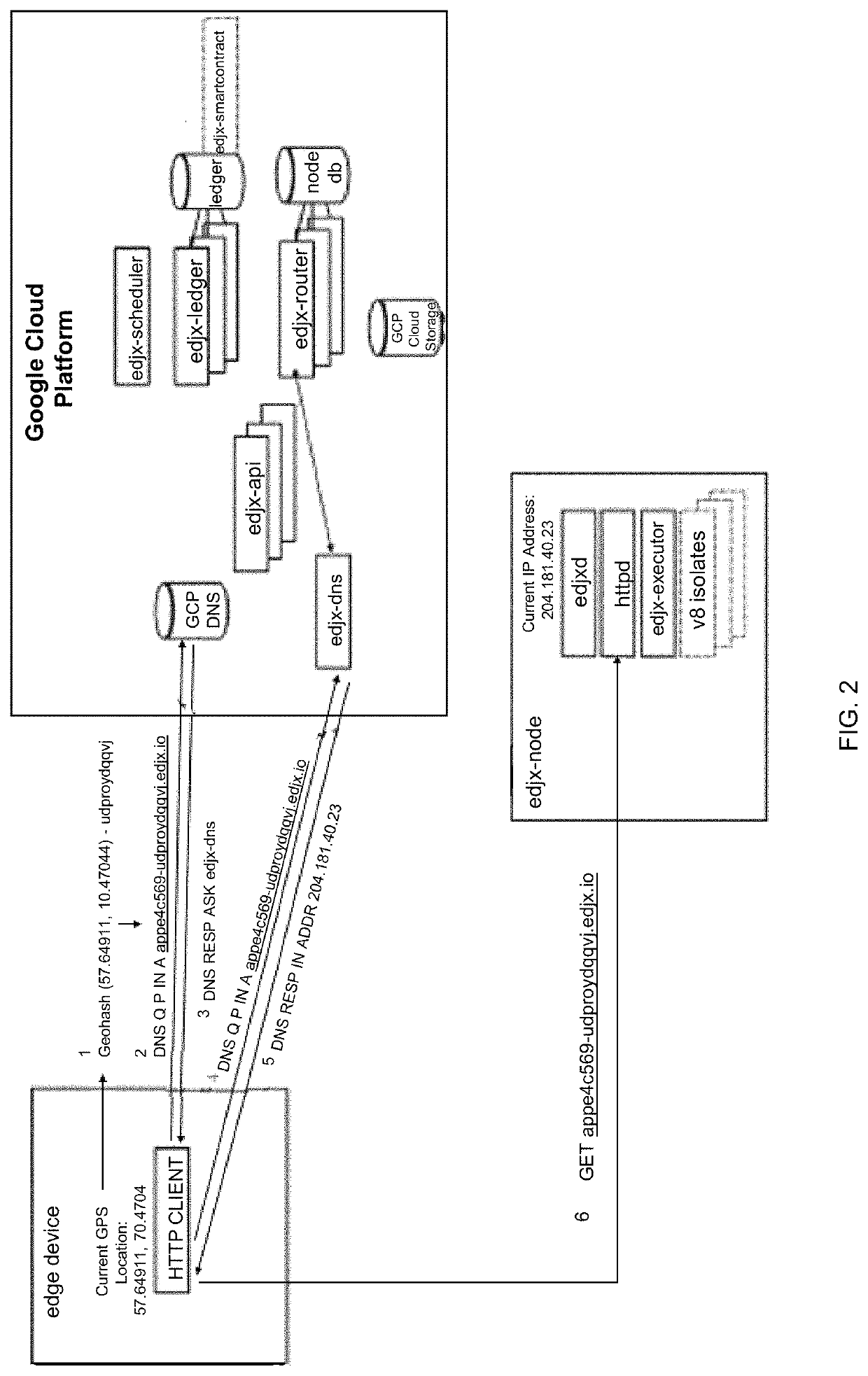
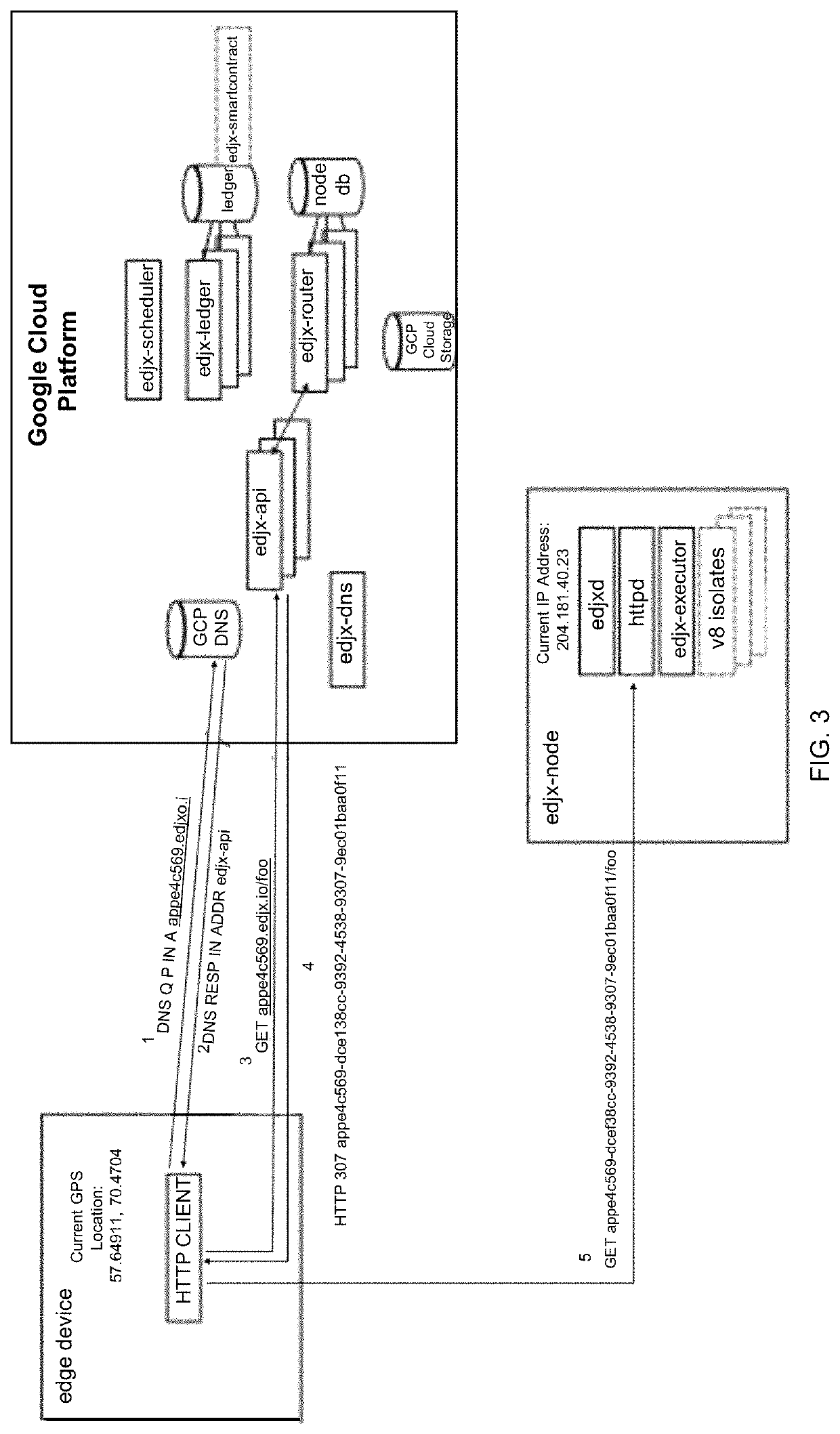
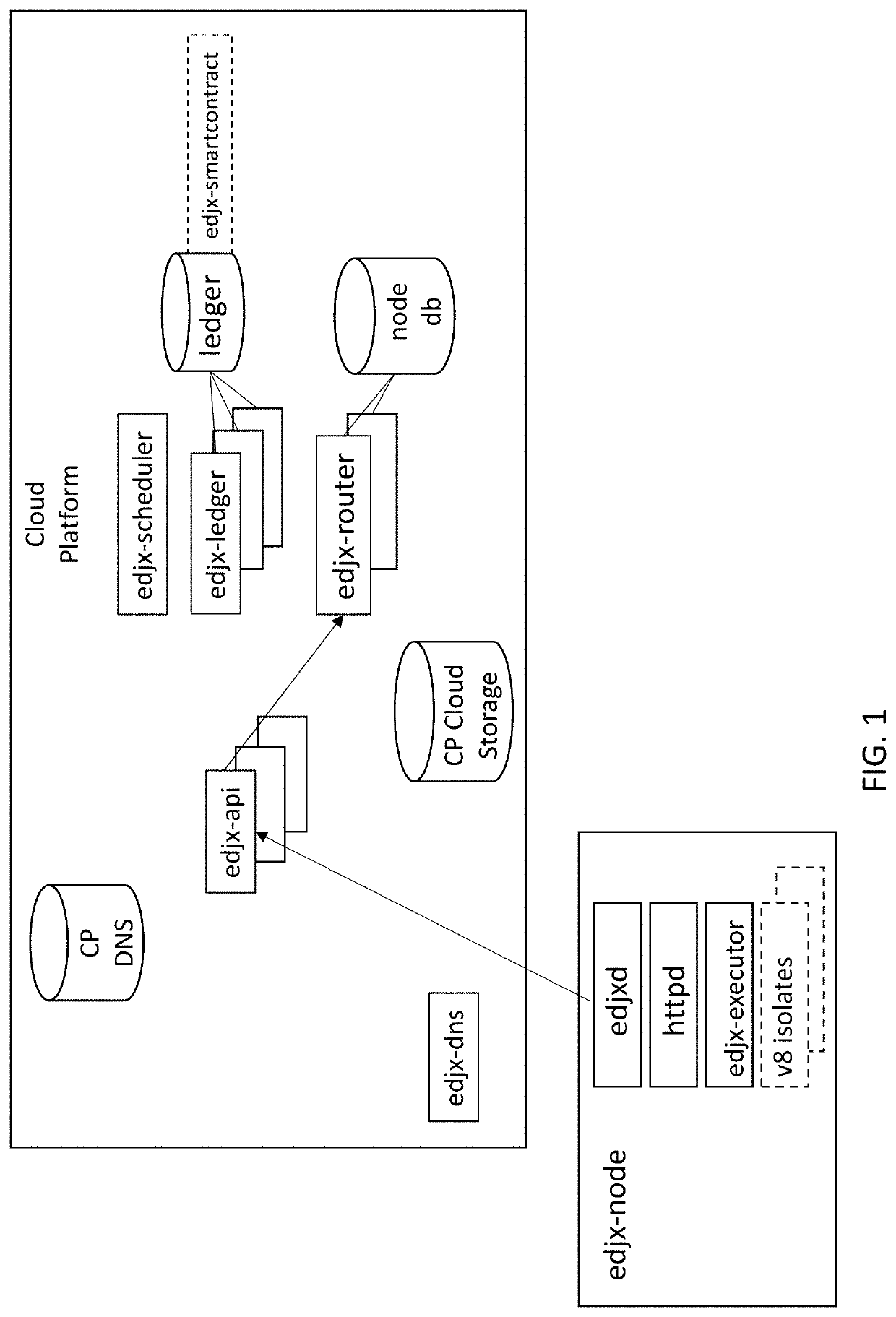
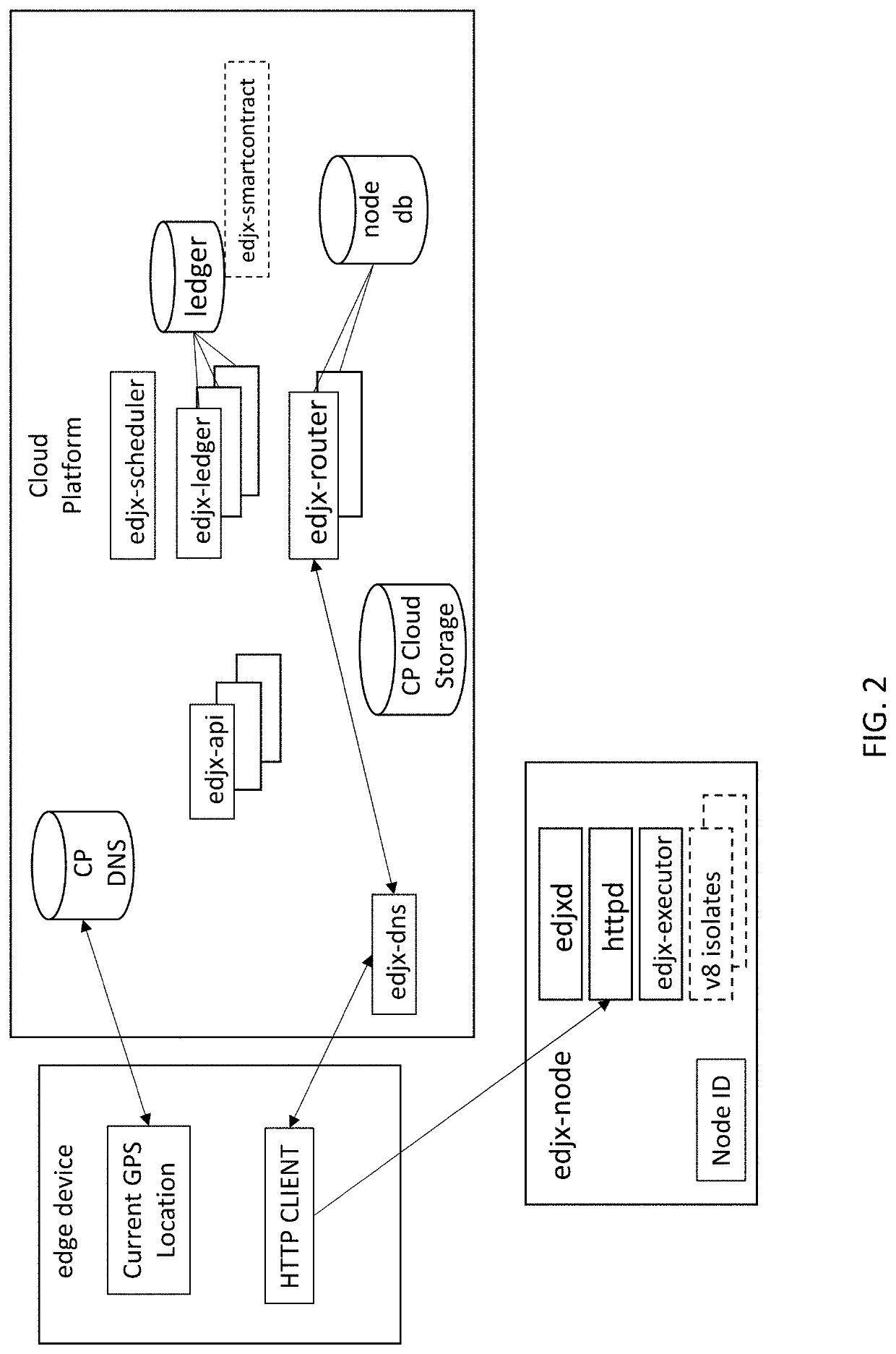
Systems and methods for locating microserver nodes in proximity to edge devices using georouting
ActiveUS11089083B1Encryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer security arrangementsTransmission protocolEdge node
Systems and methods for locating microserver nodes in proximity to edge devices using georouting. Microservers automatically form a global peer-to-peer network to serve edge functions and content to edge devices. Edge devices use HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to execute serverless functions or otherwise retrieve data from edge nodes and / or microservers located in proximity to the HTTP client. The cloud platform locates the nearest edge node and / or microserver. Edge devices georoute HTTP requests to the nearest edge node and / or microserver. Serverless functions are implemented in secure, isolated environments using a blockchain.
Owner:EDJX INC
Apparatus of and method for drawing graphics, and computer program product
An apparatus of drawing graphics includes an edge coefficient calculator calculating, from vertex data on vertices of a triangle, edge coefficients of edge functions used to determine whether a pixel is present in an inside region of the triangle, and a bounding box calculator calculating a bounding box of projected images of the triangle on a projection plane based on the edge coefficients. The apparatus also includes a starting point determiner and a traverser. The starting point determiner classifies the projected images of the triangle based on a combination of the edge coefficients for respective sides of the triangle, and determines a scan starting point from a corner of the bounding box based on classification of the projected images. The traverser generates pixel data used in rasterization by scanning the bounding box from the scan starting point.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
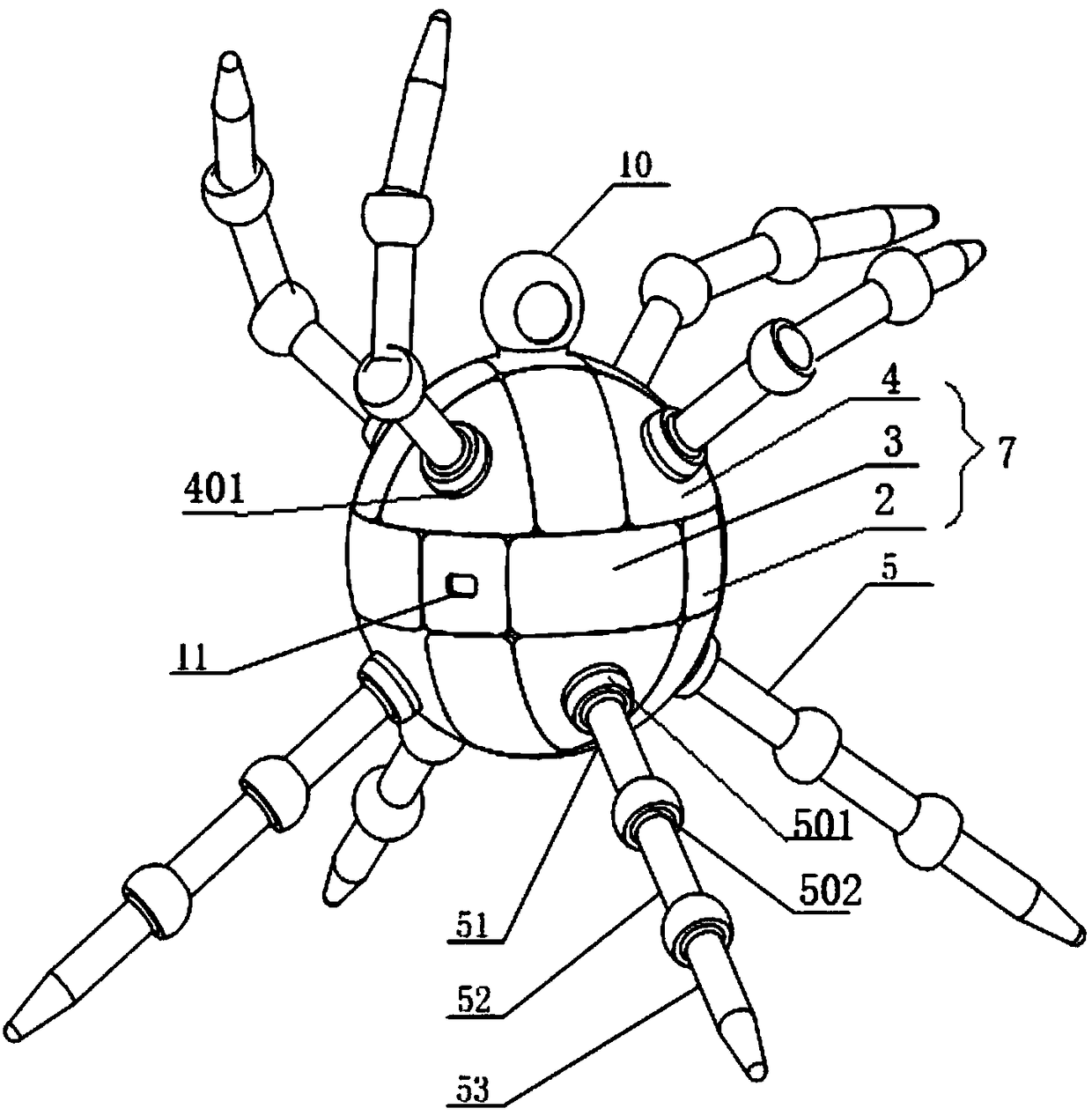
Magic cube type eight-foot metamorphic robot
ActiveCN108583718ADegrees of freedom achievedAchieve freedomVehiclesMetamorphic robotsRelative motion
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots, and relates to a magic cube type eight-foot metamorphic robot. The magic cube type eight-foot metamorphic robot comprises a spherical outer body, a center inner body and walking execution supporting legs. The spherical outer body comprises six axis driving assemblies, twelve seamed edge function assemblies and eight vertex angle branch assemblies, the axis driving assemblies, the seamed edge function assemblies and the vertex angle branch assemblies are interlocked to form a space six-circle orthogonal bearing inside the spherical outer body in an inlay mode, and the spherical outer body realizes own relative motion reconstruction by means of the space six-circle orthogonal bearing. Visual devices are arrange on the outer surfaces ofthe axis driving assemblies, motors are arranged in the axis driving assemblies, control devices and communication devices are arranged on the outer surfaces of the seamed edge function assemblies, and supporting leg connecting ends used for connecting the walking execution supporting legs are arranged on the outer surfaces of the vertex angle branch assemblies. The spherical outer body covers theexterior of the center inner body, the spherical outer body can be rotatably connected with the center inner body through the axis driving assemblies, and a battery is arranged in the center inner body.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Edge image extraction method and system based on correlated imaging
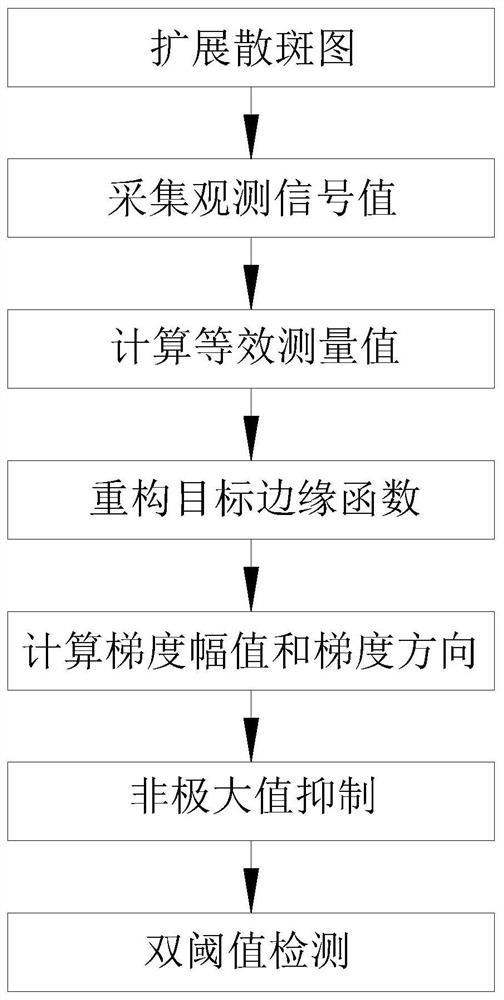
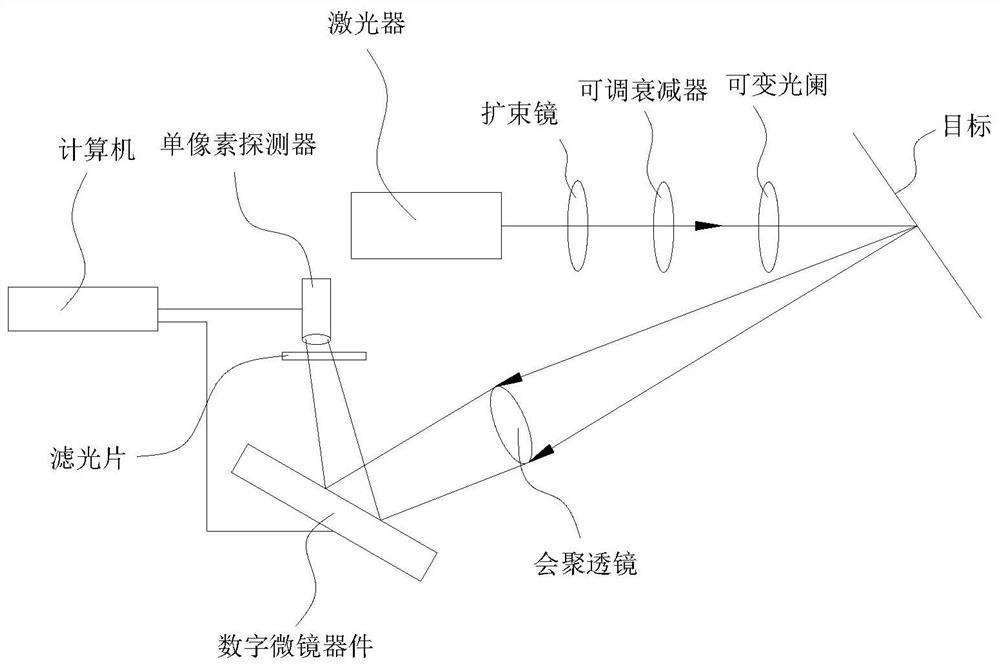
InactiveCN111968143ASuppress refinementSuppress blurImage enhancementImage analysisImage extractionEdge maps
The invention provides an edge image extraction method and system based on correlated imaging, and relates to the technical field of edge image extraction. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an observation signal value and a corresponding illumination light field intensity distribution function Ik(x, y) based on an imaging system; calculating the sum of equivalent measurement values; reconstructing a vertical edge function Nabla Rv(x, y) and a horizontal edge function Nabla Rh(x, y) of the target; calculating the gradient amplitude Nabla R(x, y) and the gradient direction theta(x, y) of the target; refining the edge and suppressing edge blur by adopting non-maximum suppression, eliminating a pseudo edge and discontinuous lines generated by non-maximum suppression through double-threshold detection, and finally, directly extracting a clear edge image of a thin edge, thereby being beneficial to accurate extraction of angular point information of the target in the later period.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Gutter screen termination trim with water tension breaker
InactiveUS20050155920A1Low costReducing “ over-the-edge ” roof water runoffRoof coveringFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater leakageEngineering
The present invention provides a gutter screen attachment for minimizing water film runoff and debris collection adjacent a screened gutter. The screen attachment comprises a superior breaker edge, an inferior breaker edge, and a screen-receiving region. The screen-receiving region comprises an edge-receiving fold that accepts the gutter-engaging edge of a gutter screen. The superior breaker edge extends upwardly opposite the inferior breaker edge and is designed to break the water tension of a water film formed upon the gutter screen. The inferior breaker edge is designed to prevent water leakage between the screen attachment and the gutter. The superior breaker edge is of minimized height so as to allow bulky debris to translate over the superior breaker edge. It is thus contemplated that the superior breaker edge functions to allow water to more properly permeate through the gutter screen.
Owner:SWISTUN KAZIMIERZ
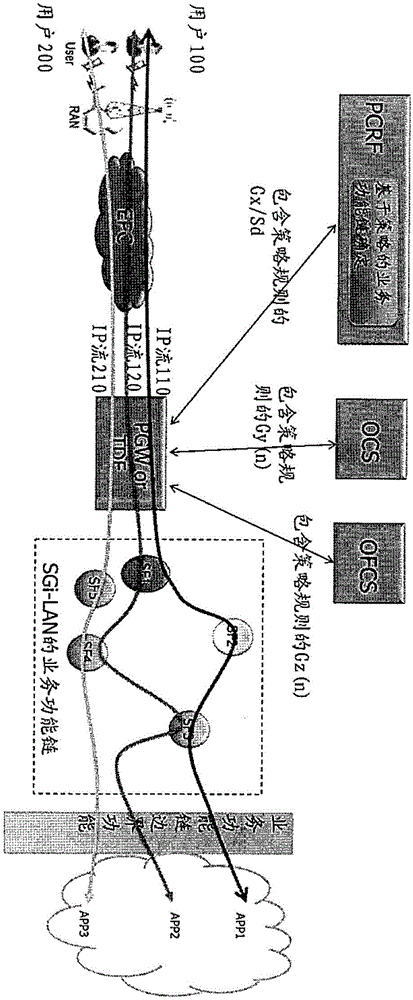
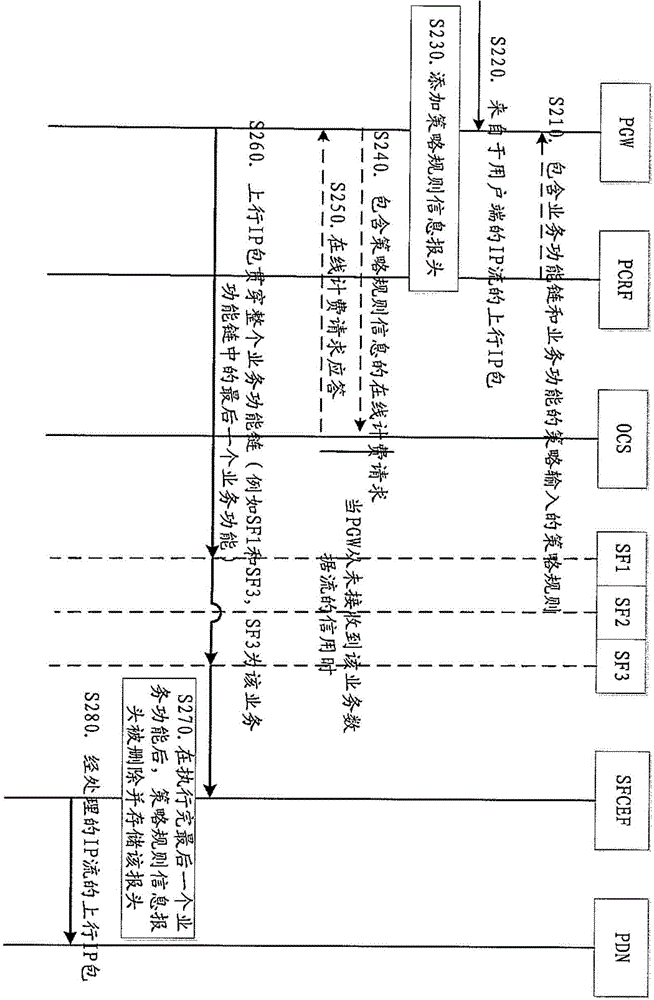
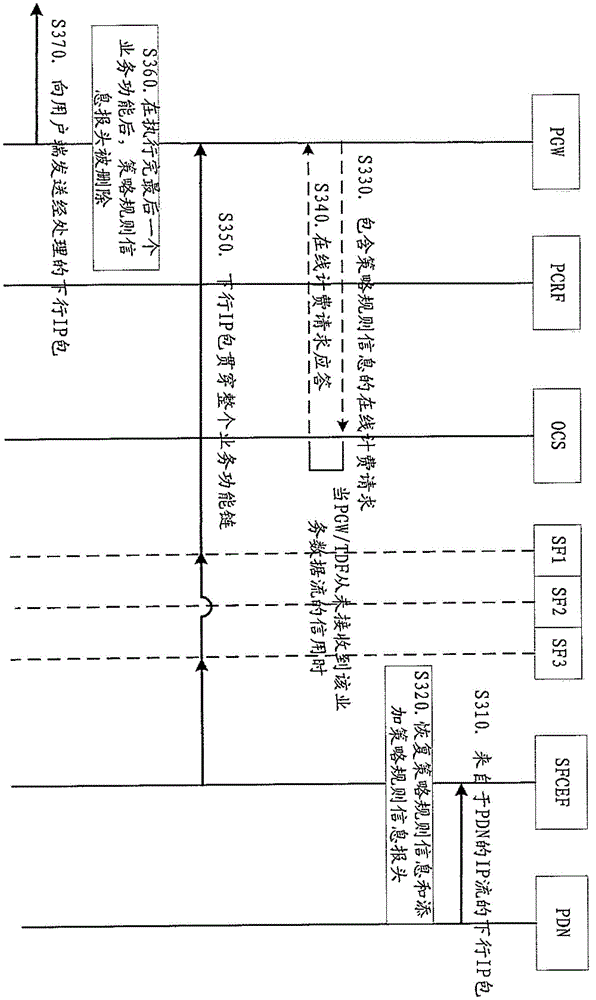
PCC-framework-based service function chain control method and device
ActiveCN105451207AMore incomeImprove performanceService provisioningAccounting/billing servicesComputer networkExecution unit
The invention provides a PCC-framework-based service function chain control method and device. The method comprises PGW receives policy rule information, at least comprising service function chain information, of IP flow from a PCRF, and adds a policy rule information header to an uplink IP packet of IP flow from a user side; a service function execution unit carries out service function on the uplink IP packet according to the policy rule information and transmits the uplink IP packet obtained after execution of the service function to a service function edge function unit; and the service function edge function unit deletes and stores the policy rule information header, wherein the service function edge function unit can serve as an independent entity or be integrated into the PGW. A downlink IP packet corresponding to the IP flow executes the similar scheme. Technical scheme enables a service function chain can be updated dynamically, and provides capability for defining more flexible price plan and more flexible commercial charging mode for service providers.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
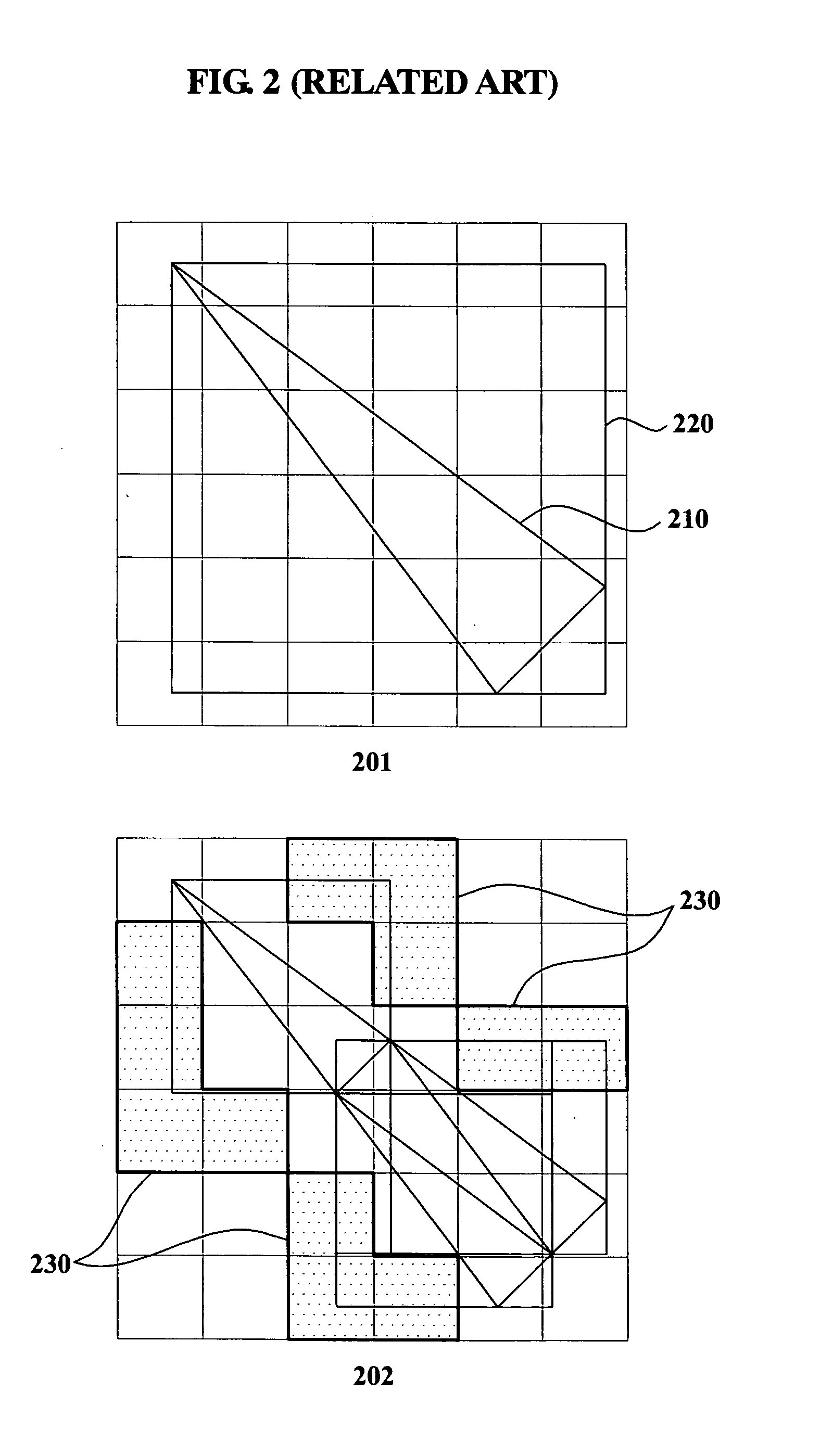
Method and system for tile binning using half-plane edge function
ActiveUS20080018664A1Accurate identification2D-image generationCathode-ray tube indicatorsPattern recognitionEdge function
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ga2O3 material-based cap layer composite double-gate P-type metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (PMOSFET) and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106783979AIncrease transfer rateImprove transconductanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricField-effect transistor
The invention relates to a Ga2O3 material-based cap layer composite double-gate P-type metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (PMOSFET) and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of selecting an N-type semi-insulation substrate, growing an N-type Beta-Ga2O3 layer by molecular beam epitaxy, and forming a table surface by dry etching; forming a source region and a drain region at two side positions of the table surface by an ion injection process; forming a source electrode and a drain electrode at two side positions near to the source region and the drain region; forming a first gate dielectric layer and a second gate dielectric layer at inclined surface positions of the other two sides, near to a source region side, of the table surface by a magnetron sputtering process; forming cap layers on surfaces of the first gate dielectric layer and the second gate dielectric layer; and forming gate electrodes on surfaces of the cap layers. Two materials with different dielectric constants are used as composite gate oxide layers to transmit holes and block electrons so as to improve the transmission efficiency; and the relatively thin cap layers are used, a dipole layer is formed at a gate oxide layer / Ga2O3 interface by a high-temperature process, thus, the adjustment of a band edge function is achieved, and the device reliability is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
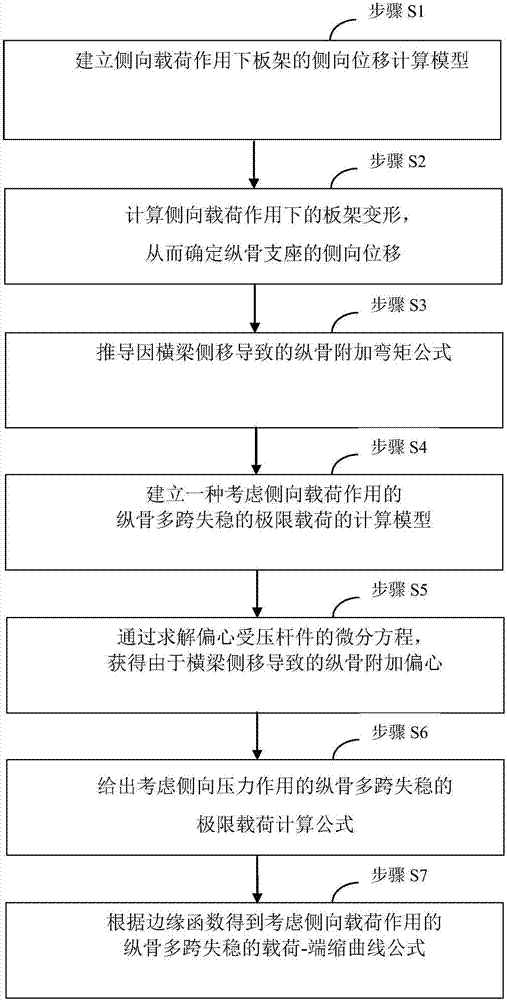
Lateral load action-considered longitudinal multi-span instability load-end shrink curve determination method.
ActiveCN107273560AHigh precisionHigh speedGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationInstabilityEngineering
The invention relates to the field of ship structure design, and discloses a lateral load action-considered longitudinal multi-span unstable load-end shrink curve determination method. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a theoretical model which considers the influences of lateral migration, of a crossbeam or ribbed plate (hereinafter uniformly referred to as crossbeam), caused by overall deformation of a grillage, and longitudinal multi-span instability due to actions of bearing longitudinal axial force and lateral pressure; obtaining longitudinal additional eccentricity caused by lateral migration of the crossbeam through solving a differential equation; giving an extreme load calculation formula which considers longitudinal multi-span instability caused by lateral load action; and obtaining a longitudinal multi-span instability load-end shrink curve formula which considers the lateral load action through an edge function and plastically-corrected extreme load of longitudinal multi-span instability. The method can be used for expanding the existing Smith method for ship beam extreme load calculation, determining the double-bottom effect of ship beam extreme load and improving the precision and speed of ship beam ultimate bending moment calculation.
Owner:708TH RES INST OF CSSC
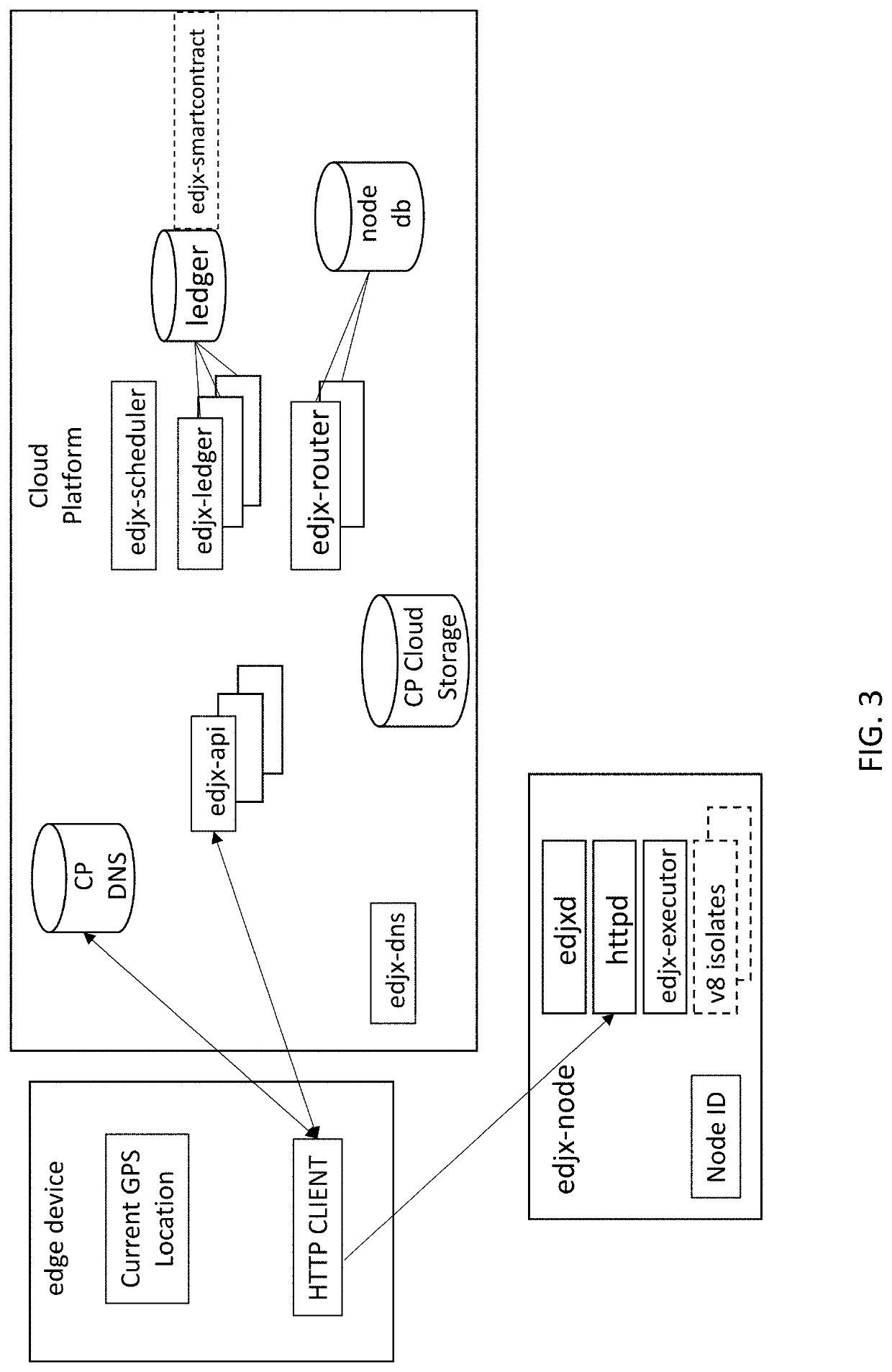
Systems and methods for locating server nodes in close proximity to edge devices using georouting
Systems and methods for locating server nodes in close proximity to edge devices using georouting. Microservers automatically form a global peer-to-peer network to serve edge functions and content to edge devices. Edge devices use HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to execute serverless functions or otherwise retrieve data from edge nodes located in close proximity to the HTTP client. Serverless functions are implemented in secure, isolated environment utilizing a blockchain.
Owner:EDJX INC
Method and system for tile binning using half-plane edge function
ActiveUS8345064B2Accurate identification2D-image generationCathode-ray tube indicatorsPattern recognitionEdge function
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
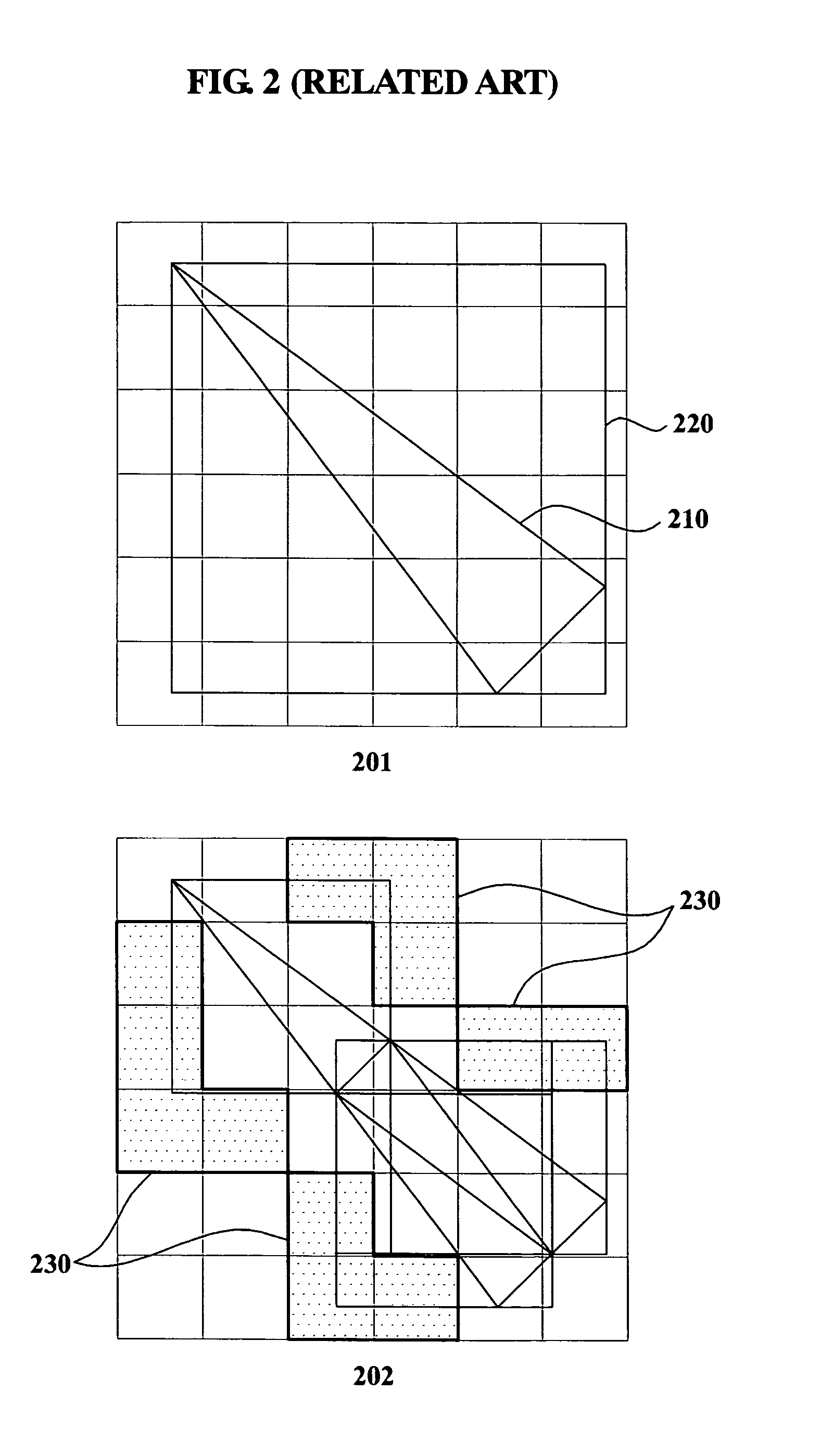
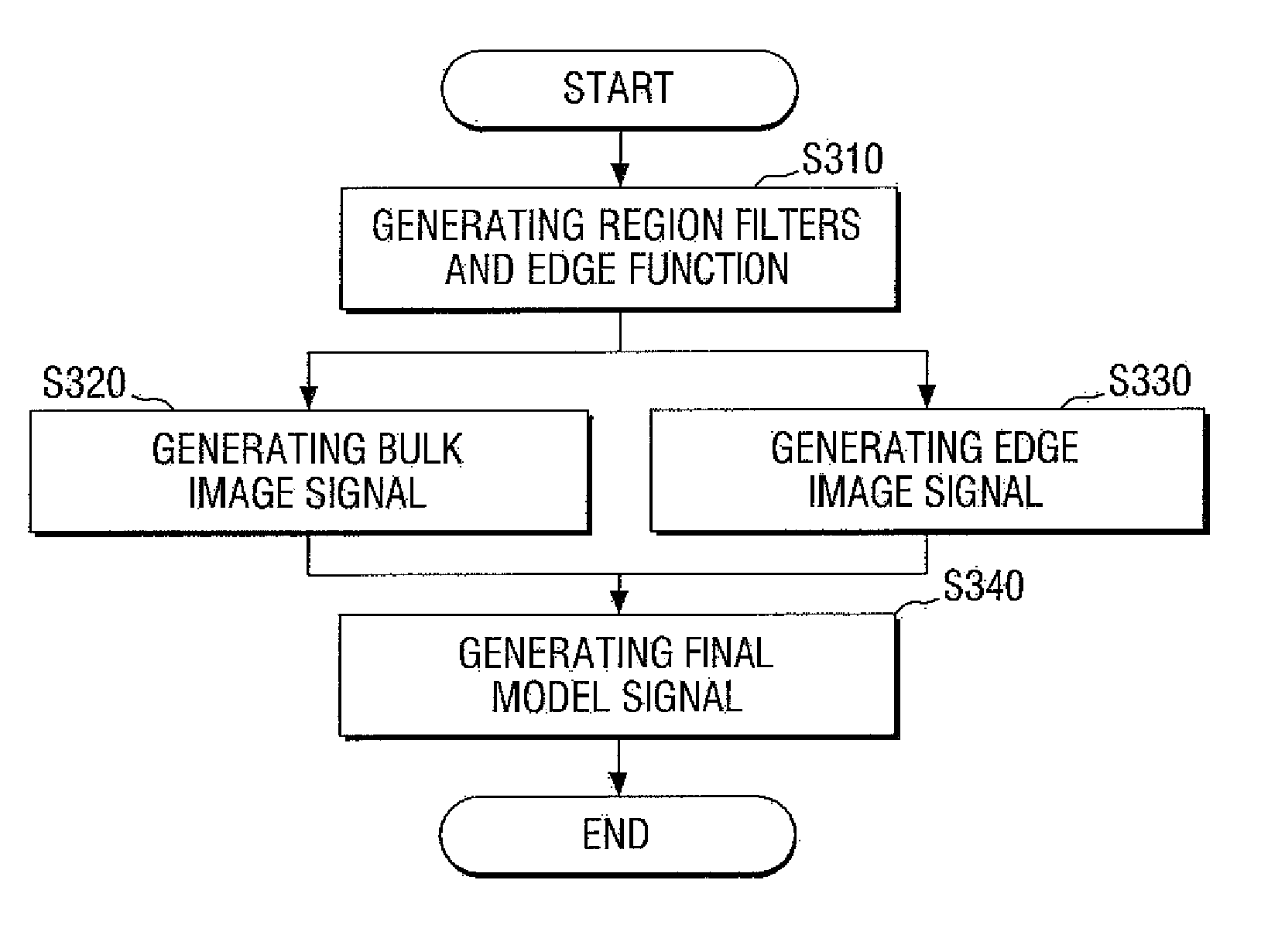
Optical proximity correction modeling method and system
An optical proximity correction modeling method for predicting a topography effect due to a pattern stack structure that includes a first material pattern, a second material pattern, and a boundary region between the first material pattern and the second material pattern. The method includes generating a first region filter that corresponds to the first material pattern, a second region filter that corresponds to the second material pattern, and an edge function corresponding to the boundary region; generating a bulk image signal from a layout using the first region filter and the second region filter; generating an edge image signal from the layout using the edge function, a characteristic kernel that represents characteristics of the boundary region, the first region filter, and the second region filter; and generating a final model signal from the bulk image signal and the edge image signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Gauze edge covering equipment having edging function
InactiveCN110158245AWith stroke functionImprove efficiencyWork-feeding meansSewing-machine control devicesEngineeringLens plate
The invention discloses gauze edge covering equipment having an edging function and relates to the technical field of textile equipment. The gauze edge covering equipment comprises a base, a reflecting support is fixed on one surface of the base, a lens is fixedly connected on one surface of the reflection support, a supporting rod is fixed on one surface of the base, one end of the supporting rodis rotatably connected with a turntable, a fixed rod is fixed on one surface of the turntable, a fixed support is fixed at one end of the fixed rod, and a photoelectric sensor is fixed on each of twosides of the fixed support; a plurality of transverse guide rails are arranged on one surface of the base, one surface of each transverse guide rail is slidably connected with a moving support, and afirst driving device is arranged on one side face of the moving support. Automatic edging and edge covering of the equipment are realized through automatic recognition of the photoelectric sensors, and the equipment stops automatically after edge covering is completed, so that edge covering work is enabled to break away from manpower intervention, and the equipment has the advantage that edge covering efficiency is improved.
Owner:利辛县缘艺纱网有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com