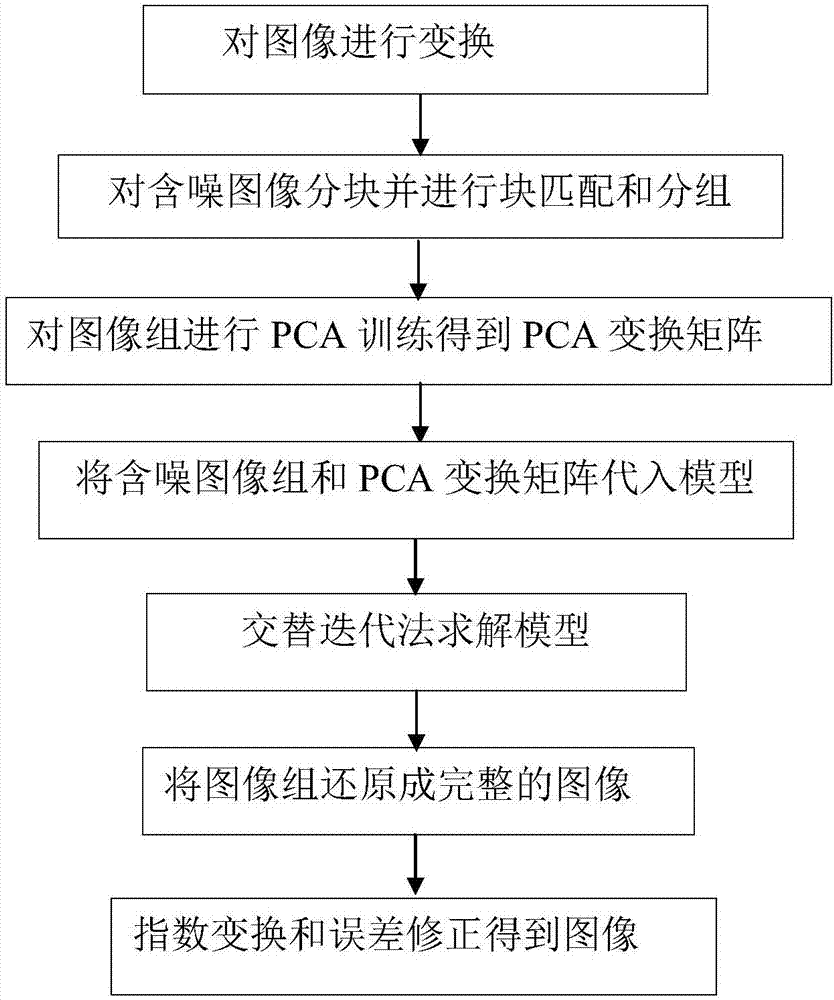
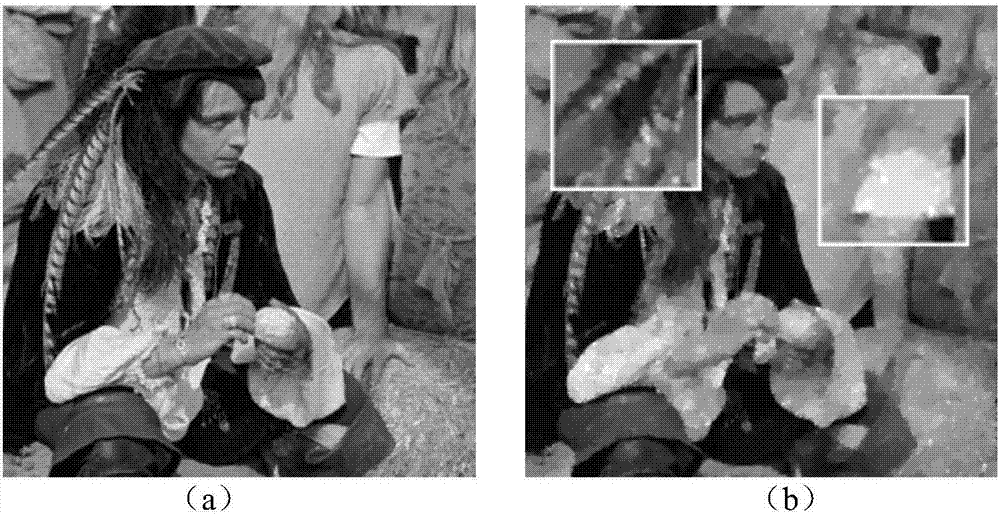
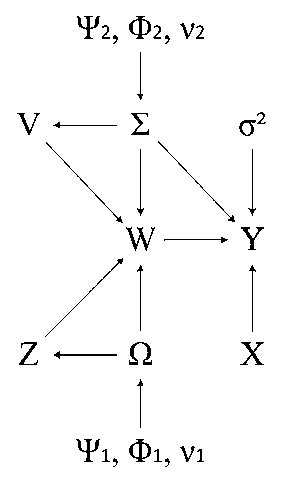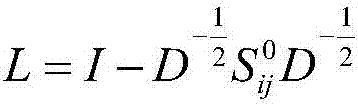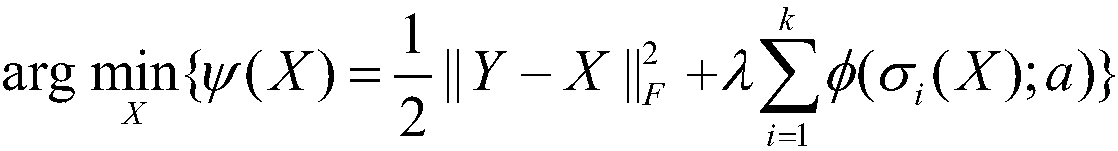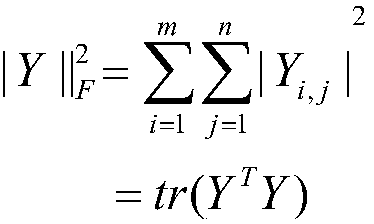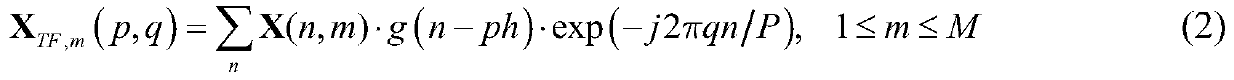Patents
Literature
54 results about "Low-rank approximation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
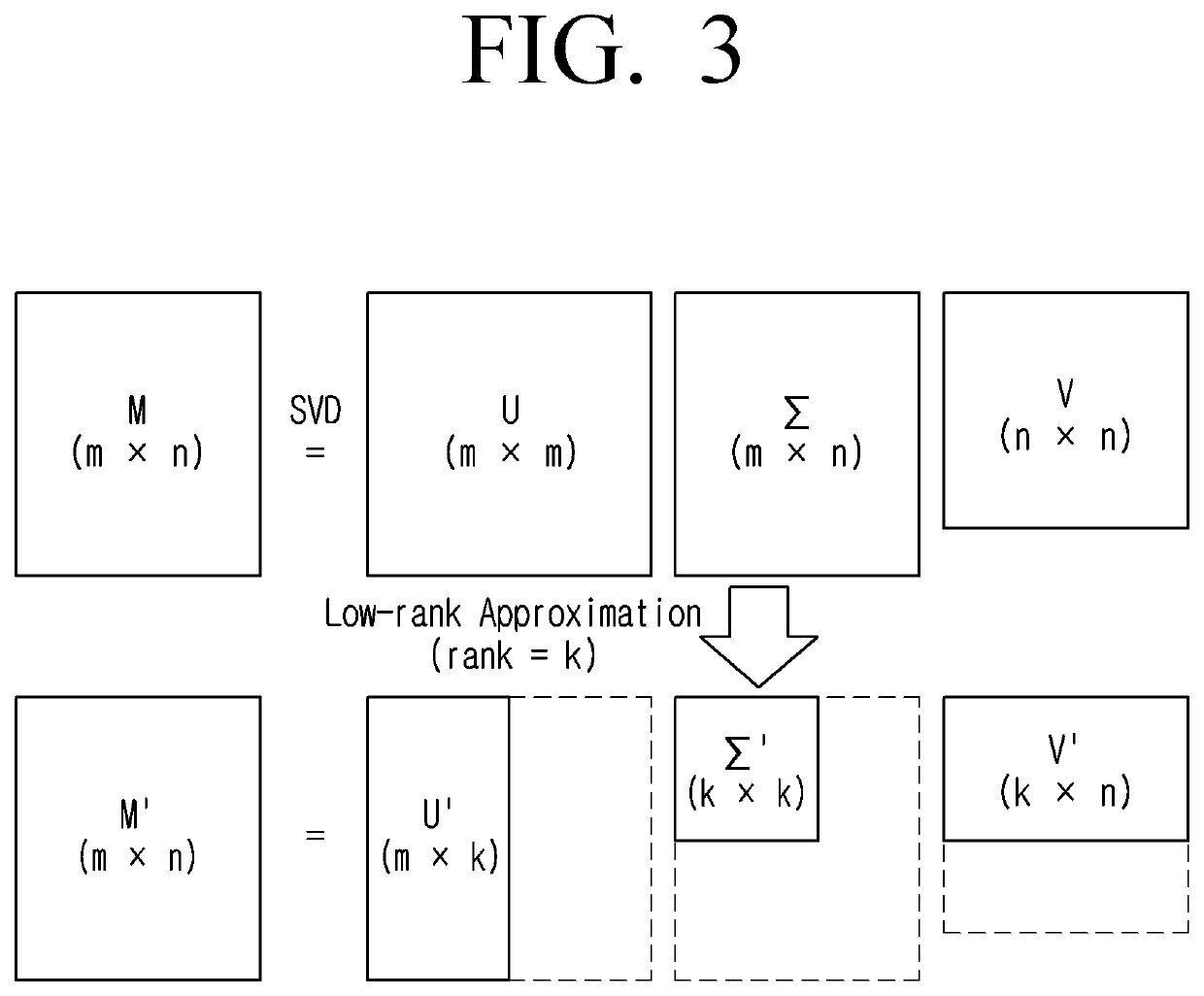
In mathematics, low-rank approximation is a minimization problem, in which the cost function measures the fit between a given matrix (the data) and an approximating matrix (the optimization variable), subject to a constraint that the approximating matrix has reduced rank. The problem is used for mathematical modeling and data compression. The rank constraint is related to a constraint on the complexity of a model that fits the data. In applications, often there are other constraints on the approximating matrix apart from the rank constraint, e.g., non-negativity and Hankel structure.
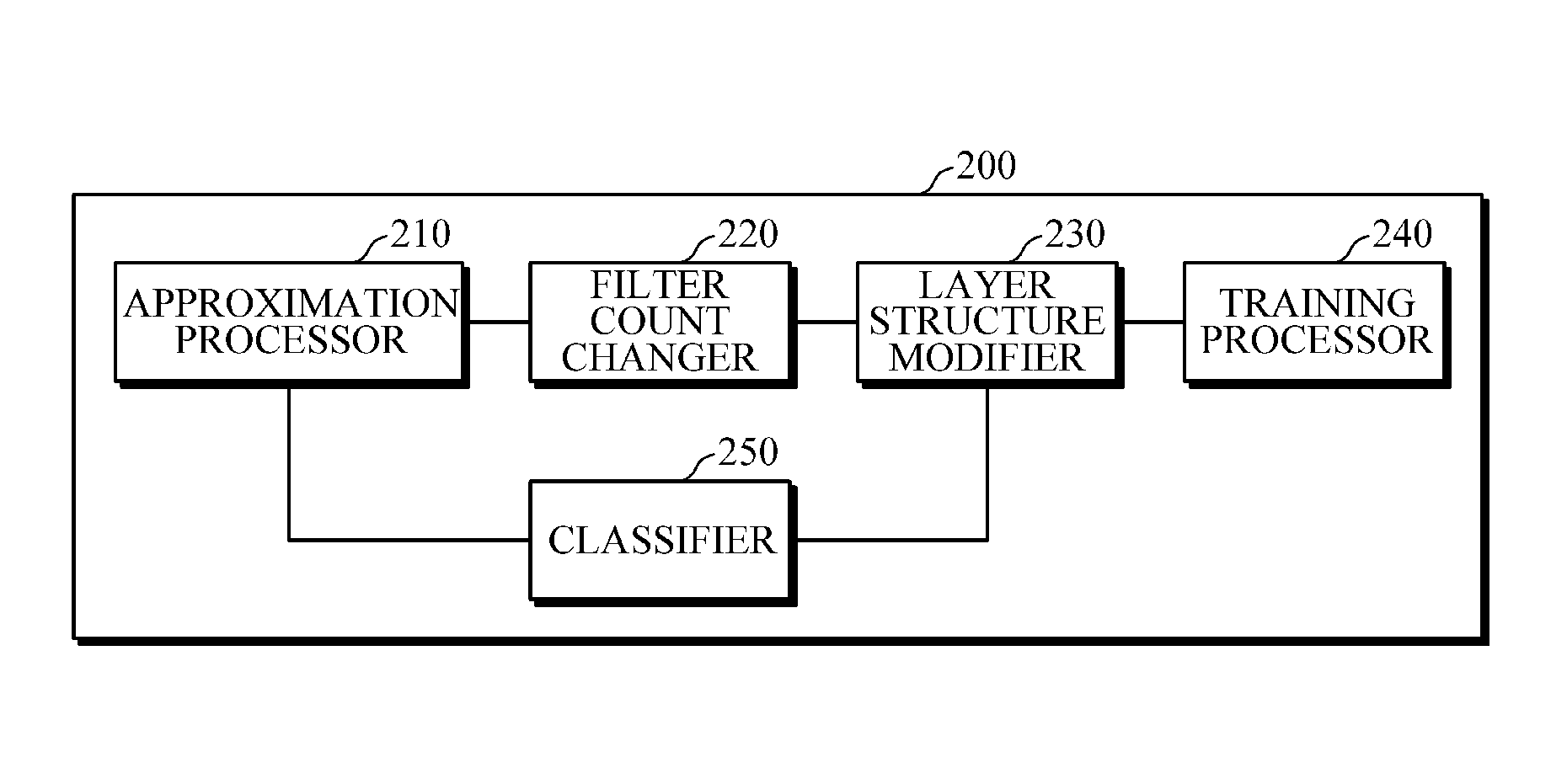
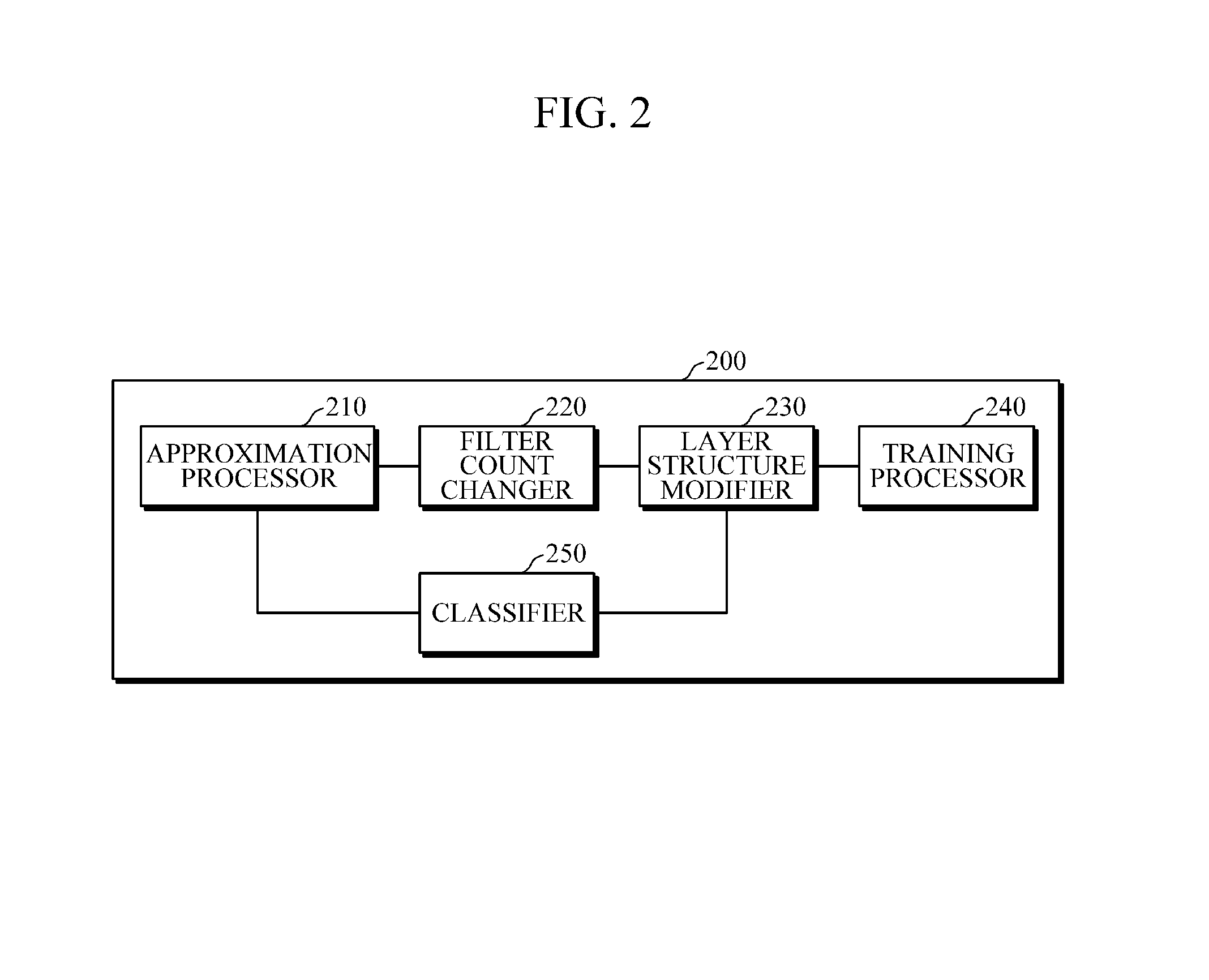
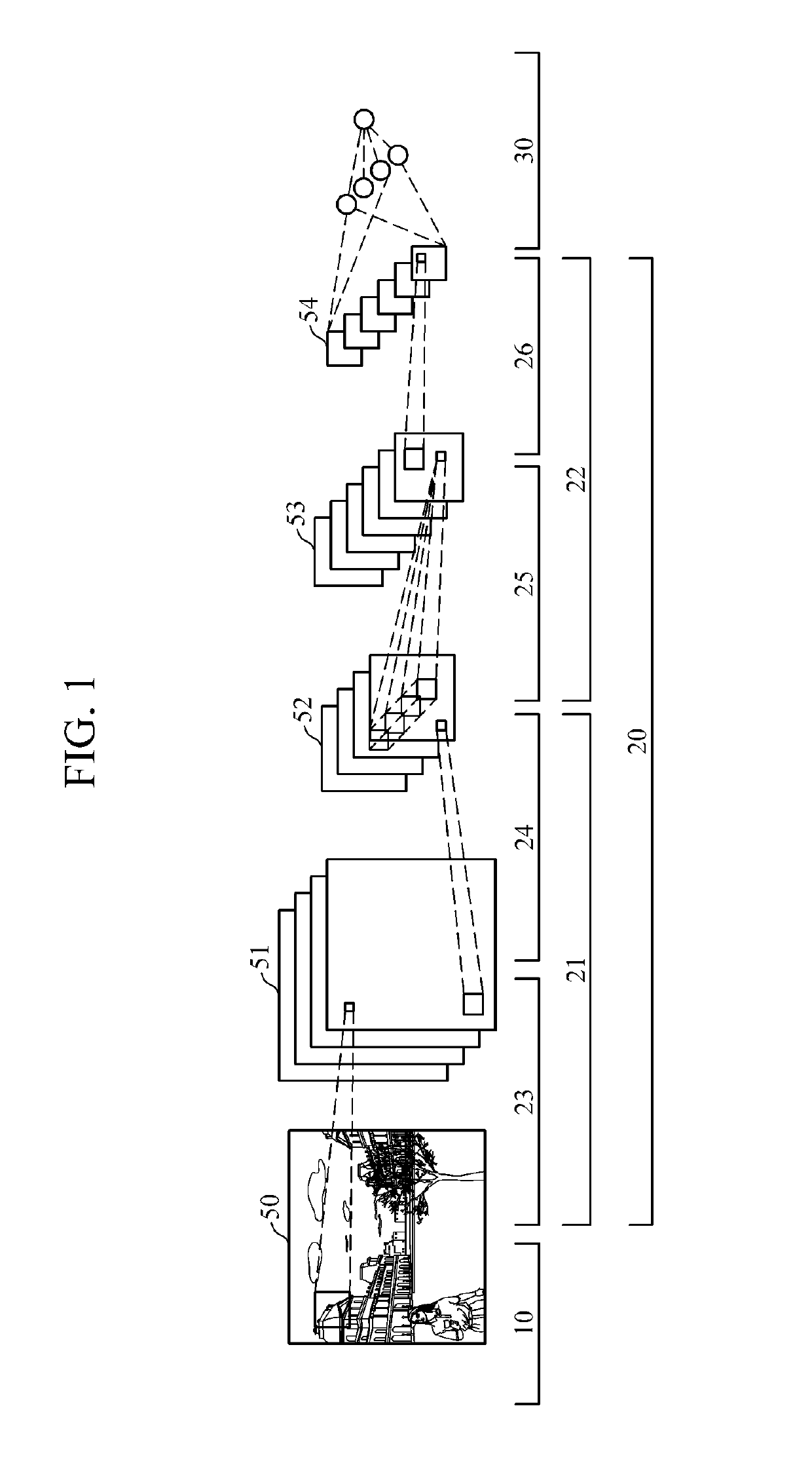
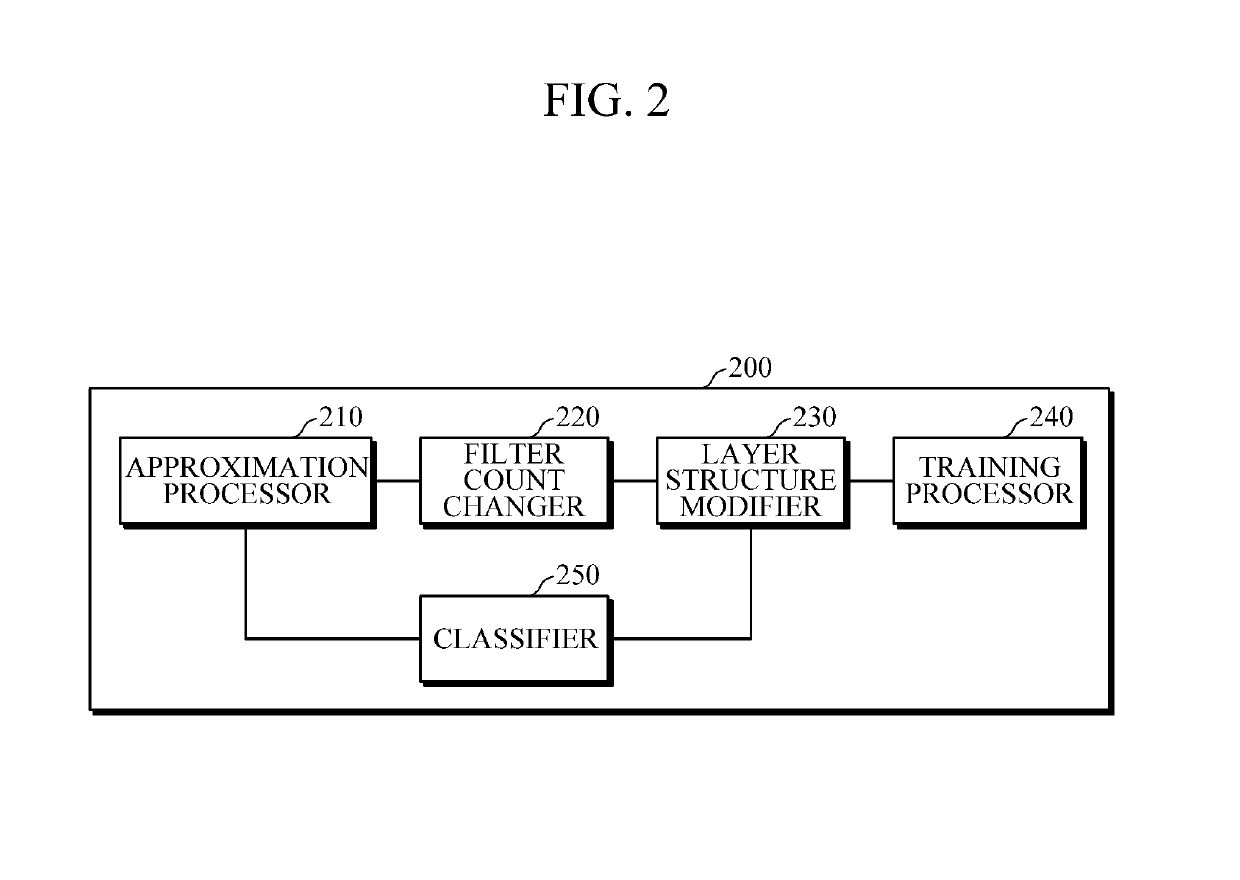
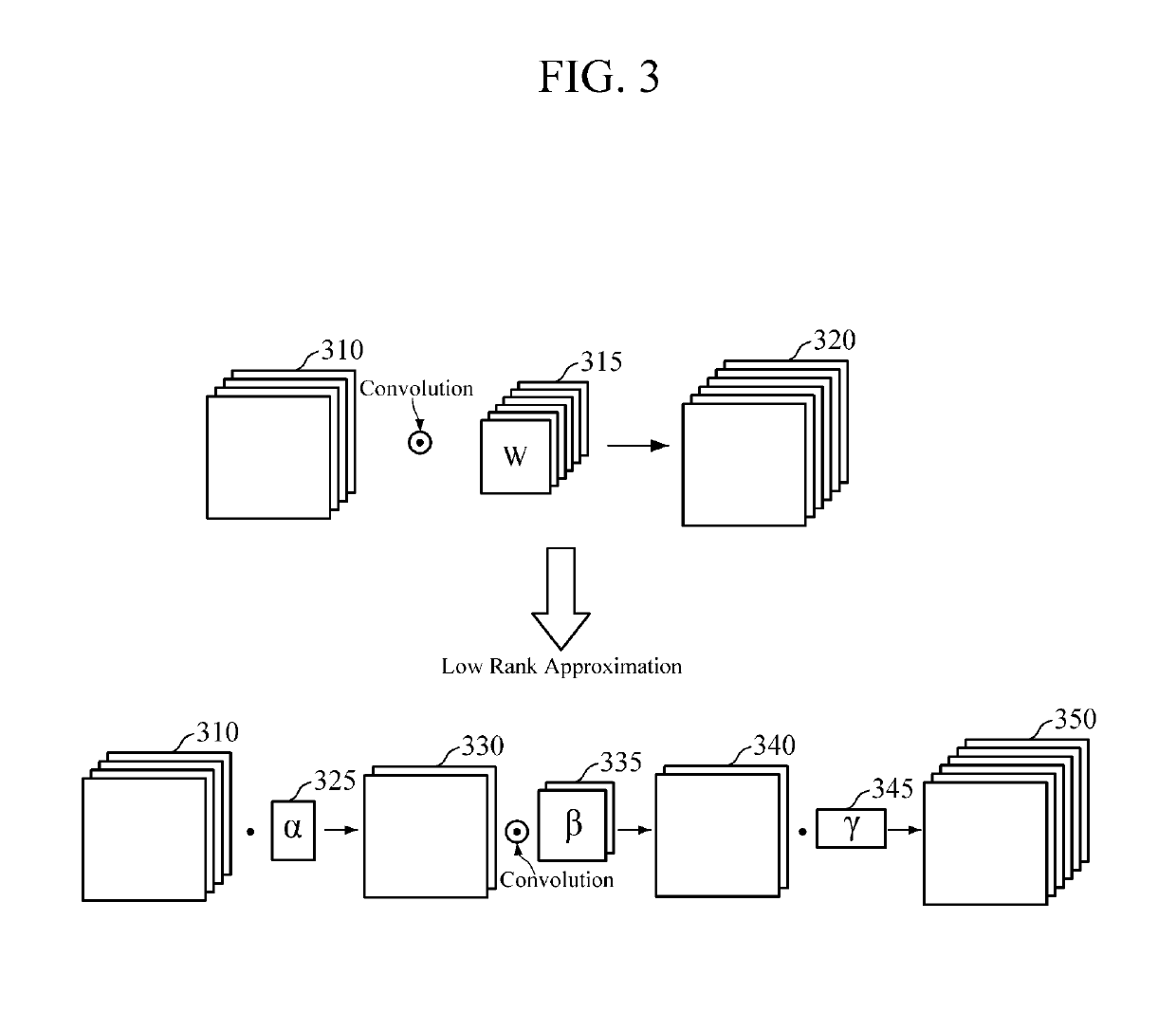
Convolution neural network training apparatus and method thereof
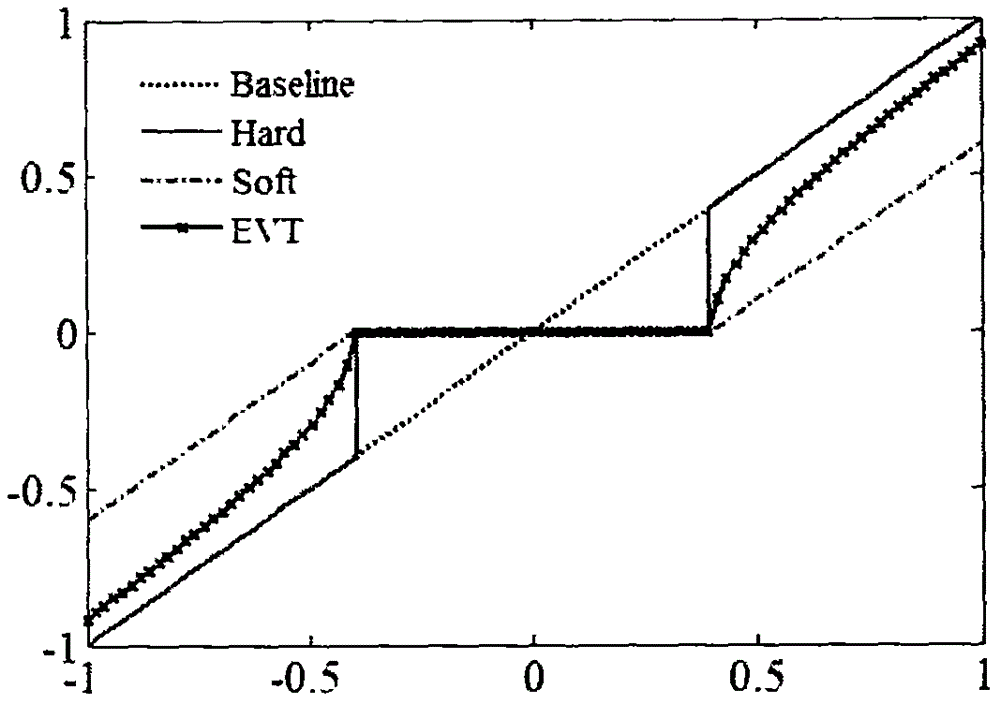
ActiveUS20160162782A1Reduce in quantityReduce the number of outputsImage enhancementImage analysisReconstruction filterLow-rank approximation
An apparatus and method of training a convolutional neural network (CNN) are provided. A method of training a CNN including a plurality of convolution layers stored in a memory involves approximating, using a processor, a convolution layer among the plurality of convolution layers using a low-rank approximation; reducing the number of output reconstruction filters of the approximated convolution layer; and modifying a structure of the CNN based on an approximation result and the reduced number of output reconstruction filters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Neural network training method, neural network training device, data processing method and data processing device
InactiveCN106326985AImprove processing efficiencySmall amount of calculationNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsNerve networkAlgorithm
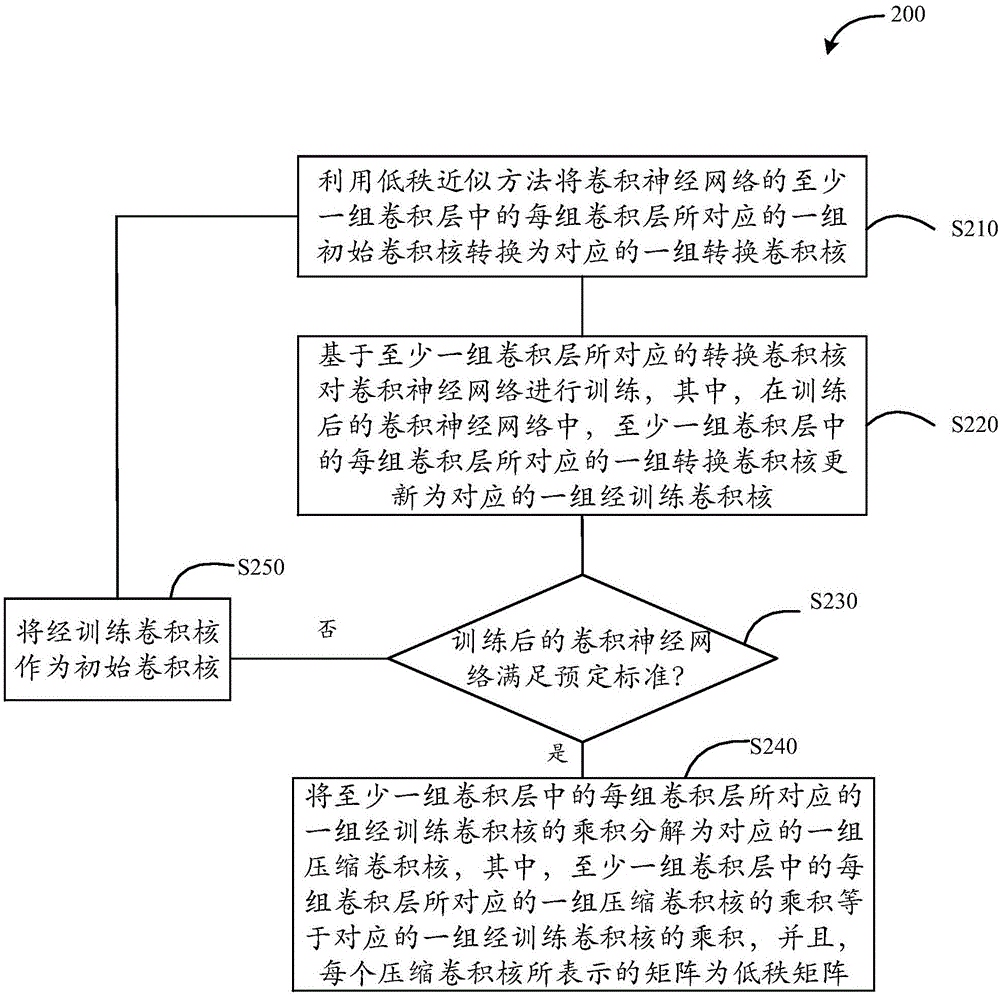
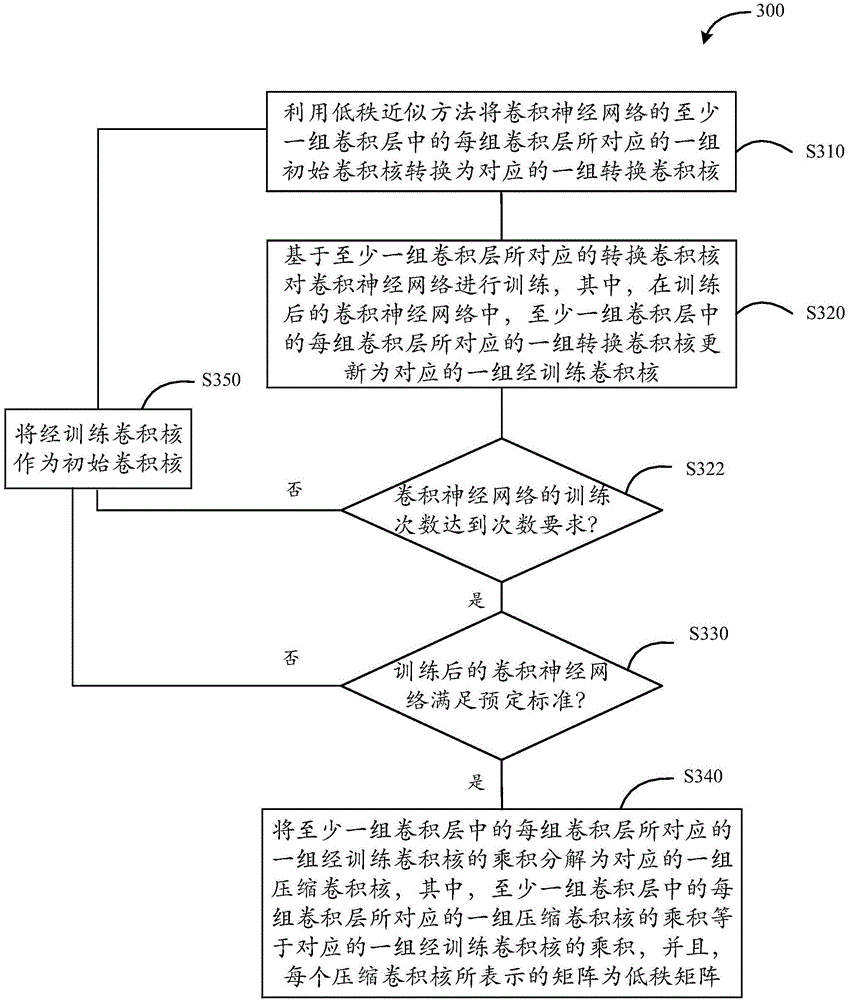
The invention provides a neural network training method, a neural network training device, a data processing method and a data processing device. The neural network training method comprises the following steps: S210, transforming a set of initial convolution kernels corresponding to each of at least one set of convolution layers of a convolutional neural network into a corresponding set of transformed convolution kernels by use of a low-rank approximation method; S220, training the convolutional neural network based on the transformed convolution kernels corresponding to the at least one set of convolution layers; S230, judging whether the trained convolutional neural network meets a predetermined standard, going to S240 if the trained convolutional neural network meets the predetermined standard, or going to S250; S240, decomposing the product of the set of trained convolution kernels corresponding to each of the at least one set of convolution layers into a corresponding set of compressed convolution kernels; and S250, taking the set of trained convolution kernels corresponding to each of the at least one set of convolution layers as a set of initial convolution kernels corresponding to the set of convolution layers, and returning to S210. Through the methods and the devices, the amount of computation can be saved.
Owner:BEIJING KUANGSHI TECH +1
Method and apparatus for spatio-temporal compressive sensing
InactiveUS20100306290A1Large datasetsConfirm its effectivenessDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionAnomaly detectionTomography
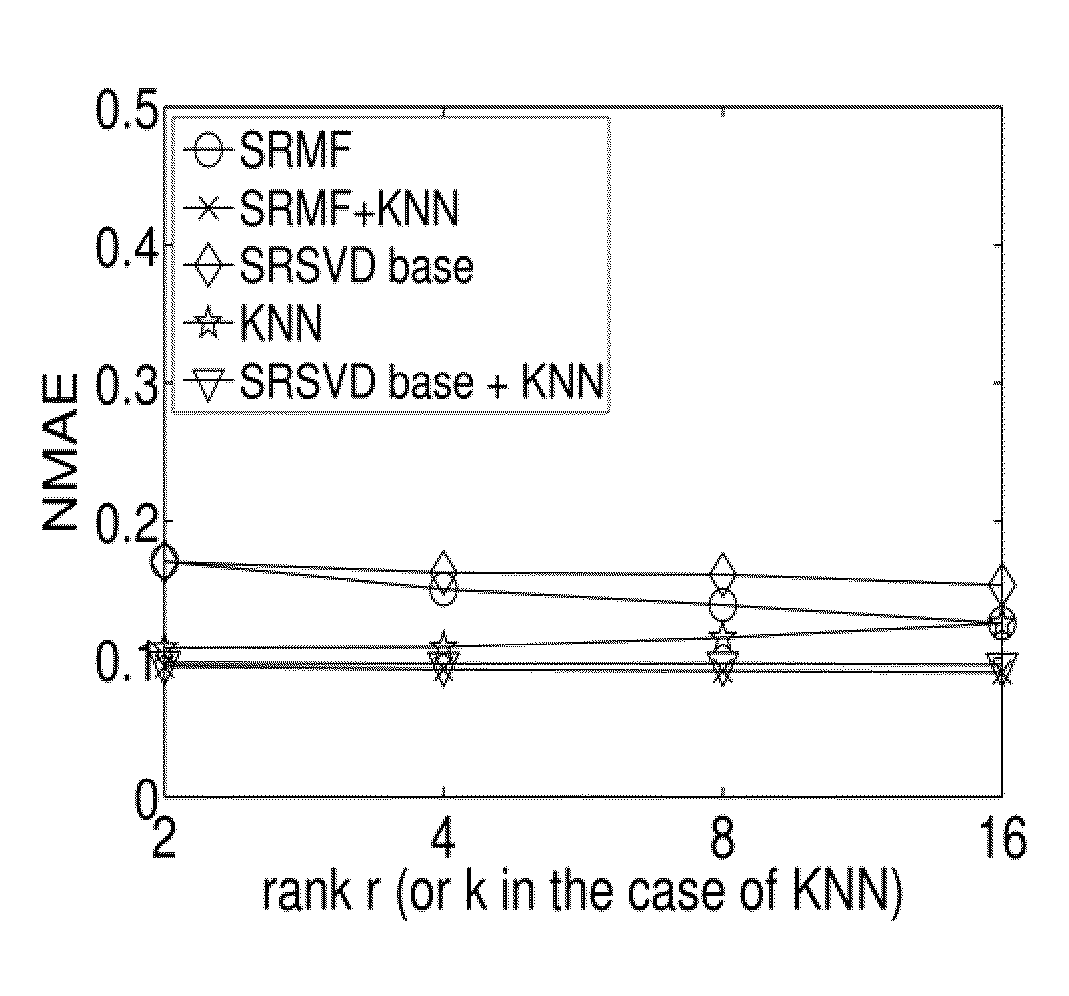
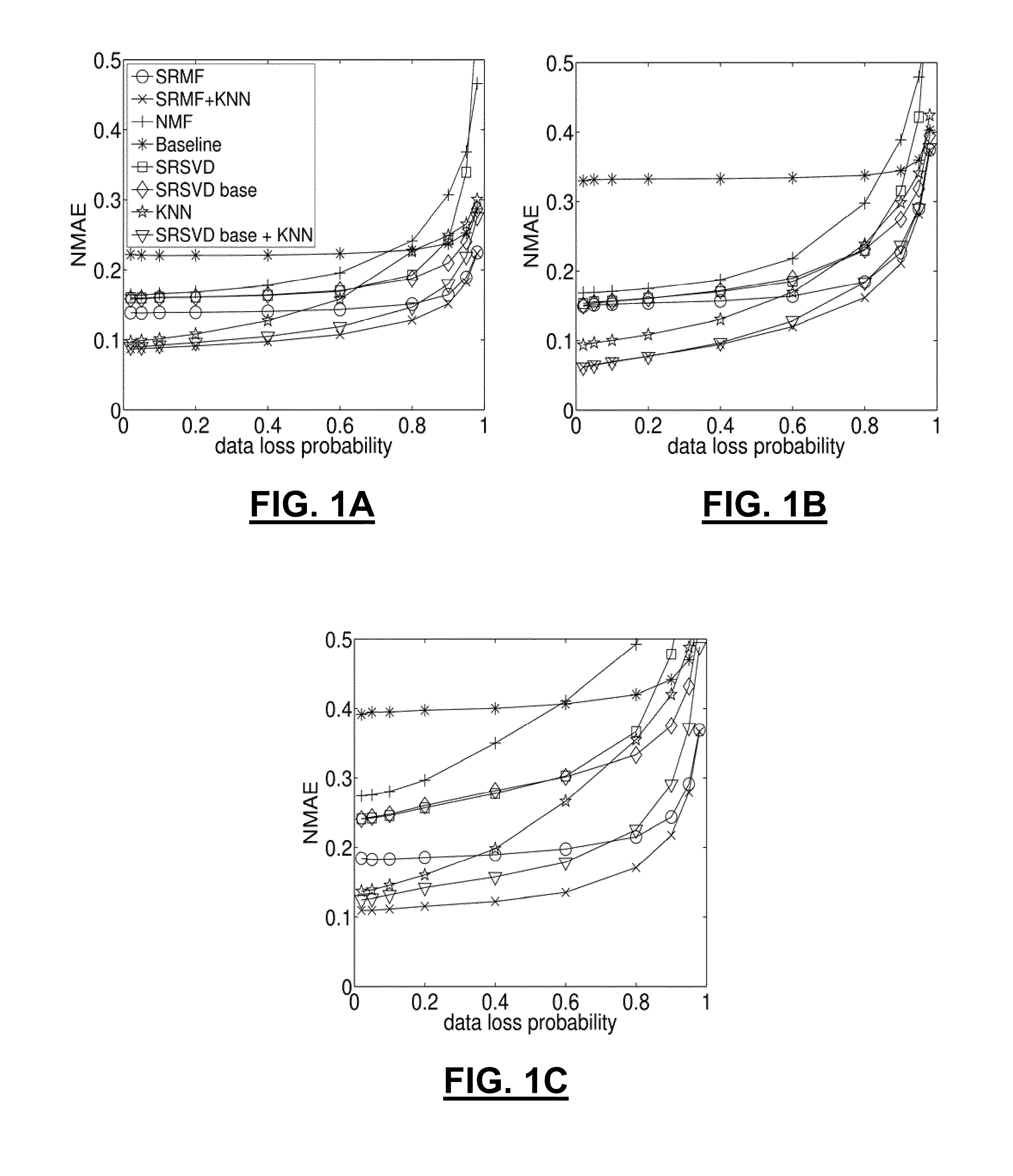
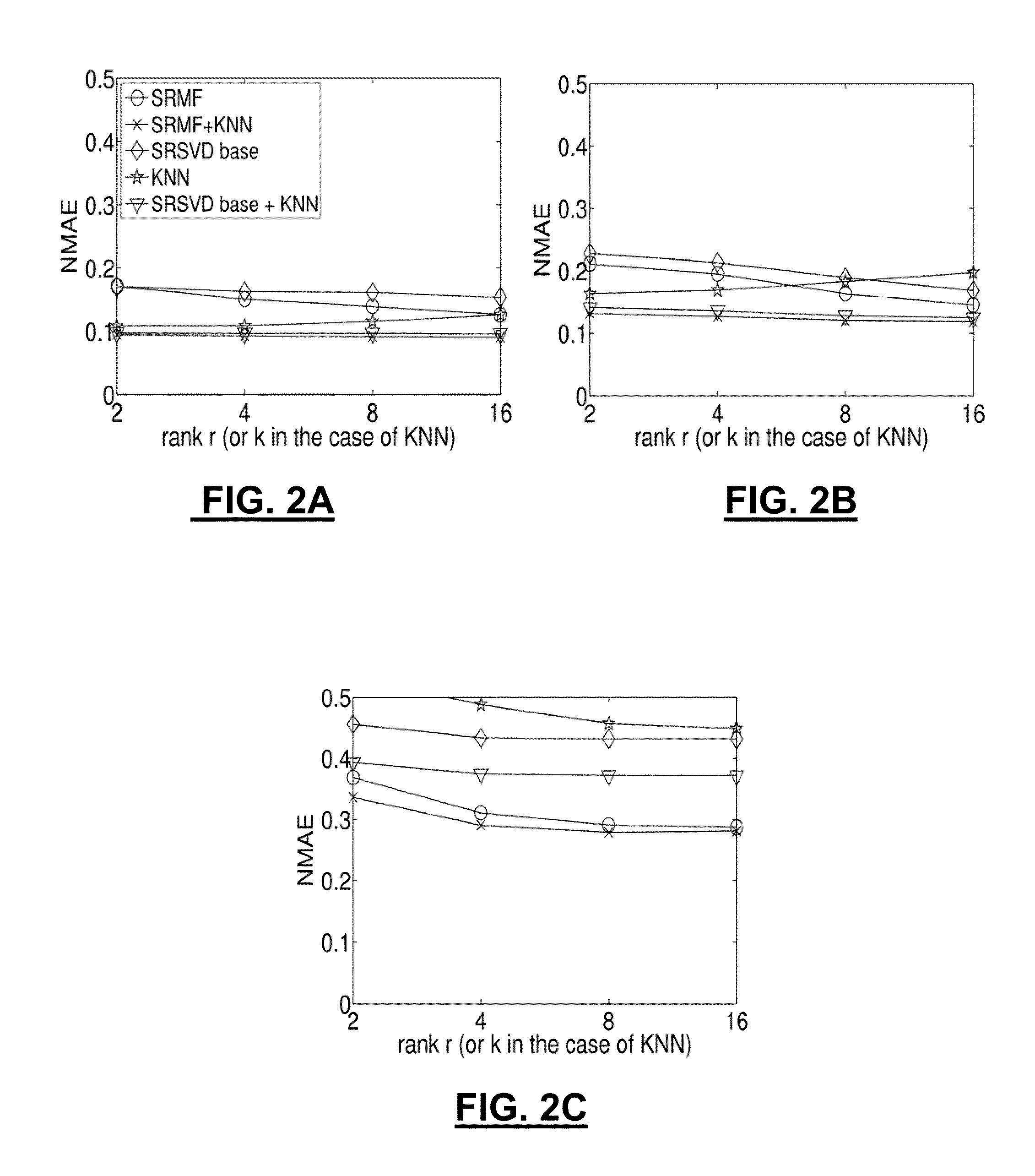
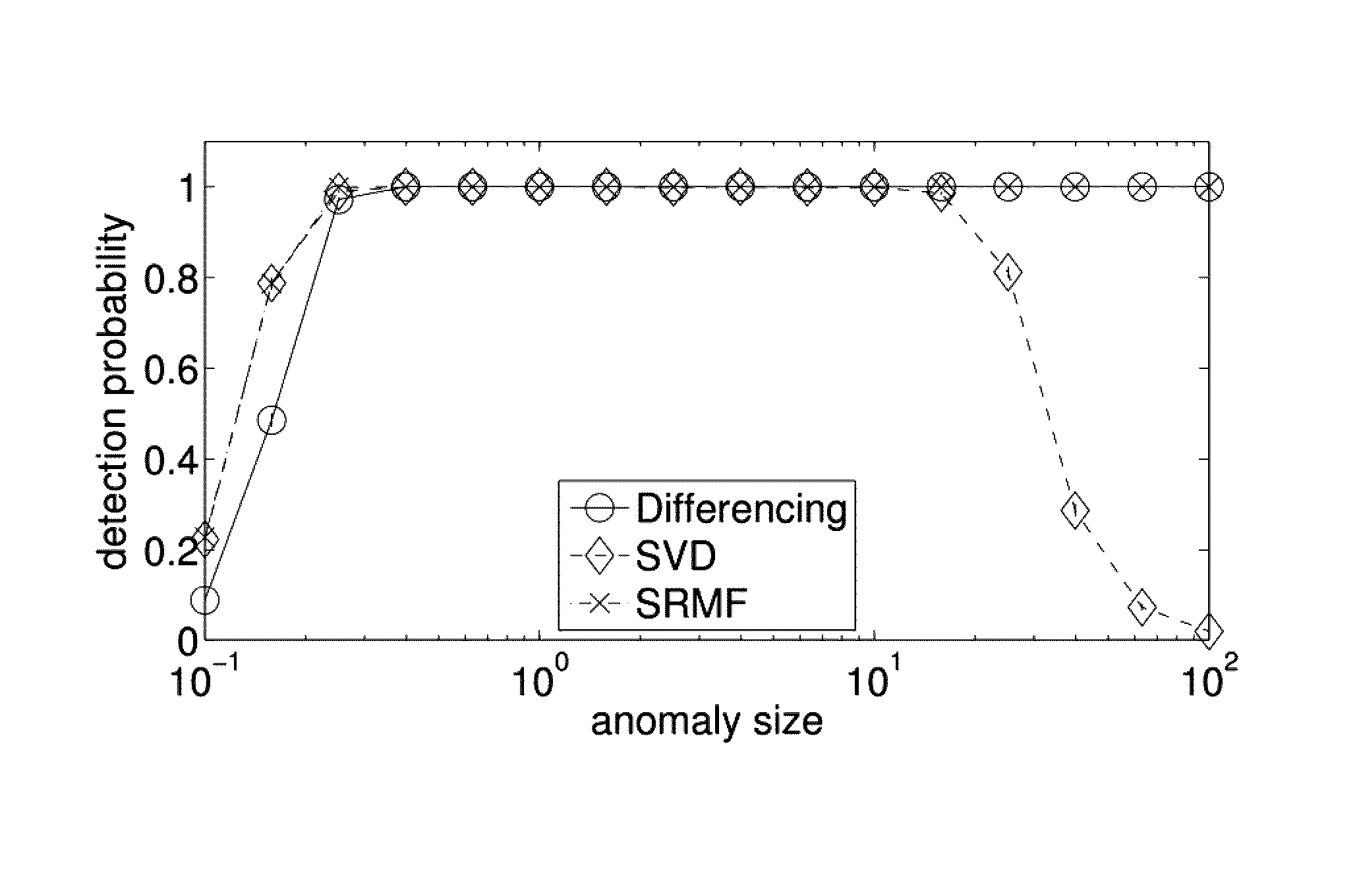
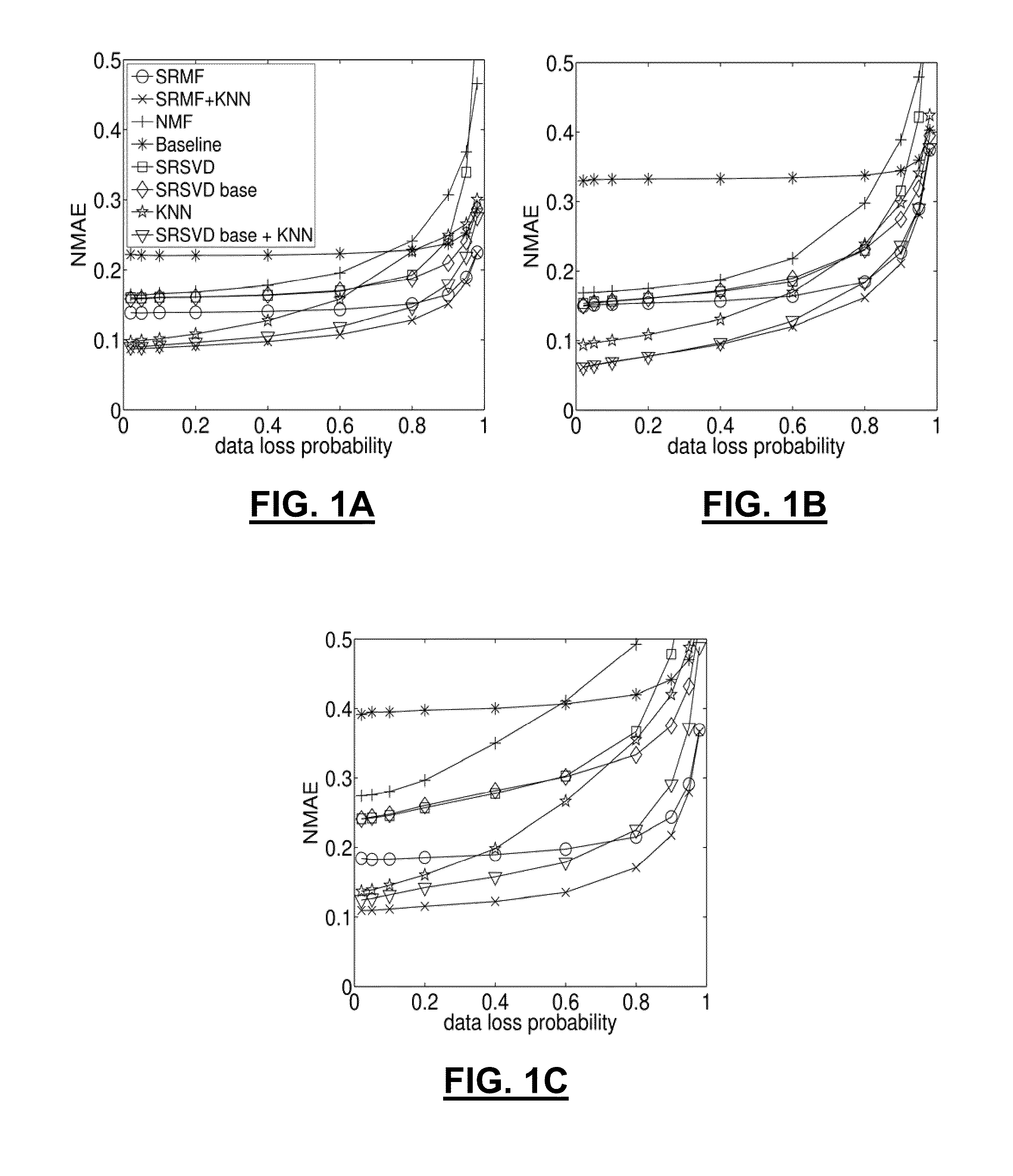
A method and apparatus for spatio-temporal compressive sensing, which allows accurate reconstruction of missing values in any digital information represented in matrix or tensor form, is disclosed. The method of embodiments comprises three main components: (i) a method for finding sparse, low-rank approximations of the data of interest that account for spatial and temporal properties of the data, (ii) a method for finding a refined approximation that better satisfies the measurement constraints while staying close to the low-rank approximations obtained by SRMF, and (iii) a method for combining global and local interpolation. The approach of embodiments also provides methods to perform common data analysis tasks, such as tomography, prediction, and anomaly detection, in a unified fashion.
Owner:ZHANG YIN +1
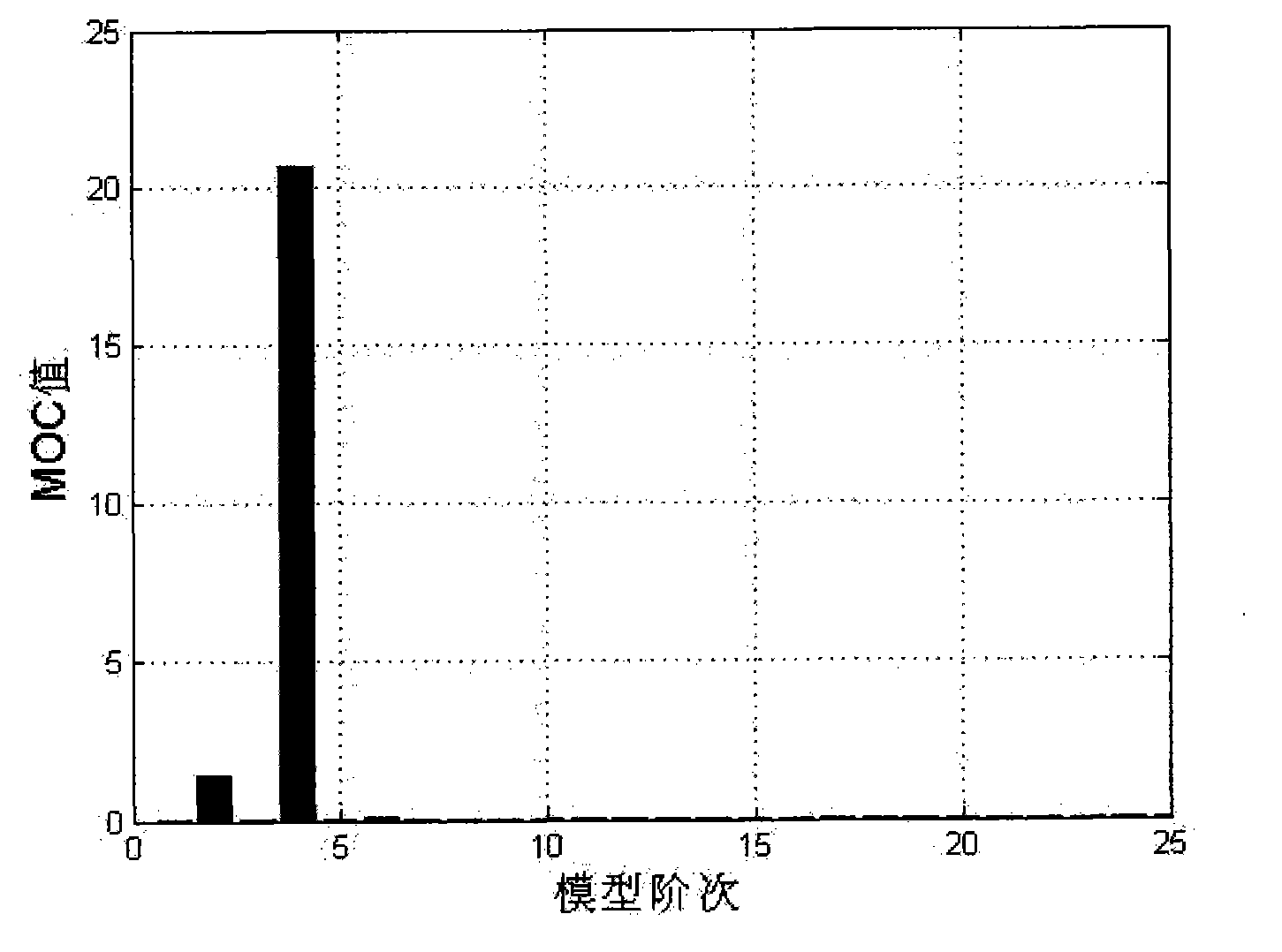
Method for identifying modal parameter based on model order determination and signal noise elimination
InactiveCN101964050ATo achieve the purpose of noise reductionAvoid it happening againCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionAlgorithm
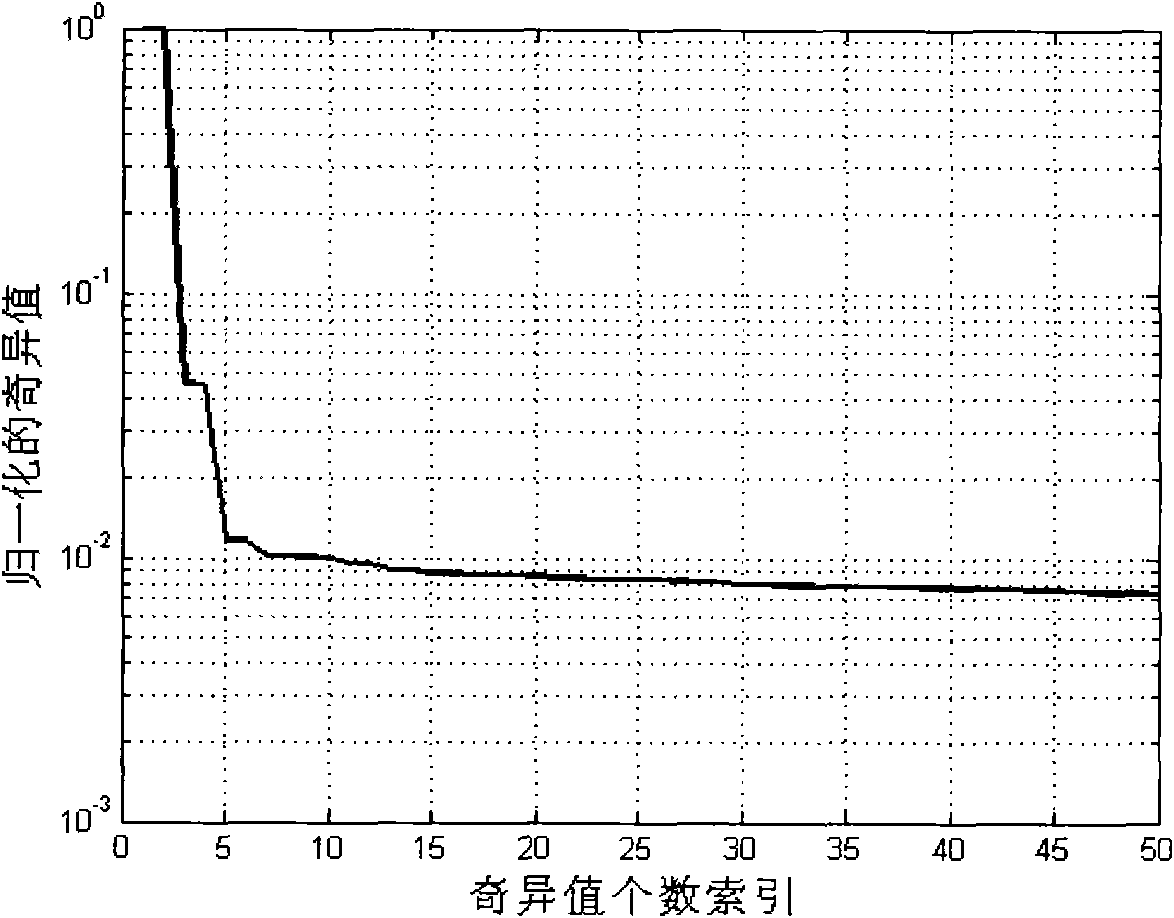
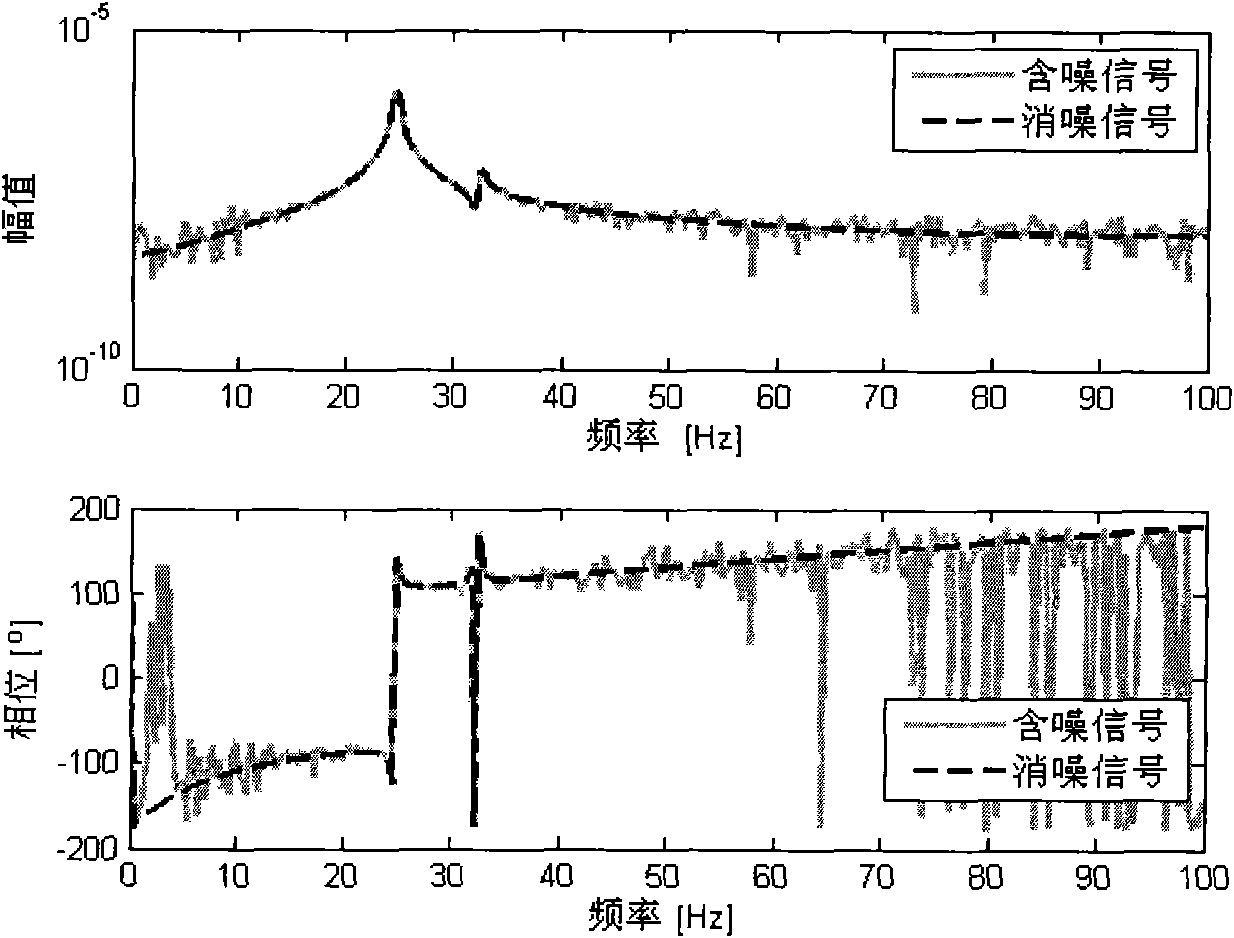
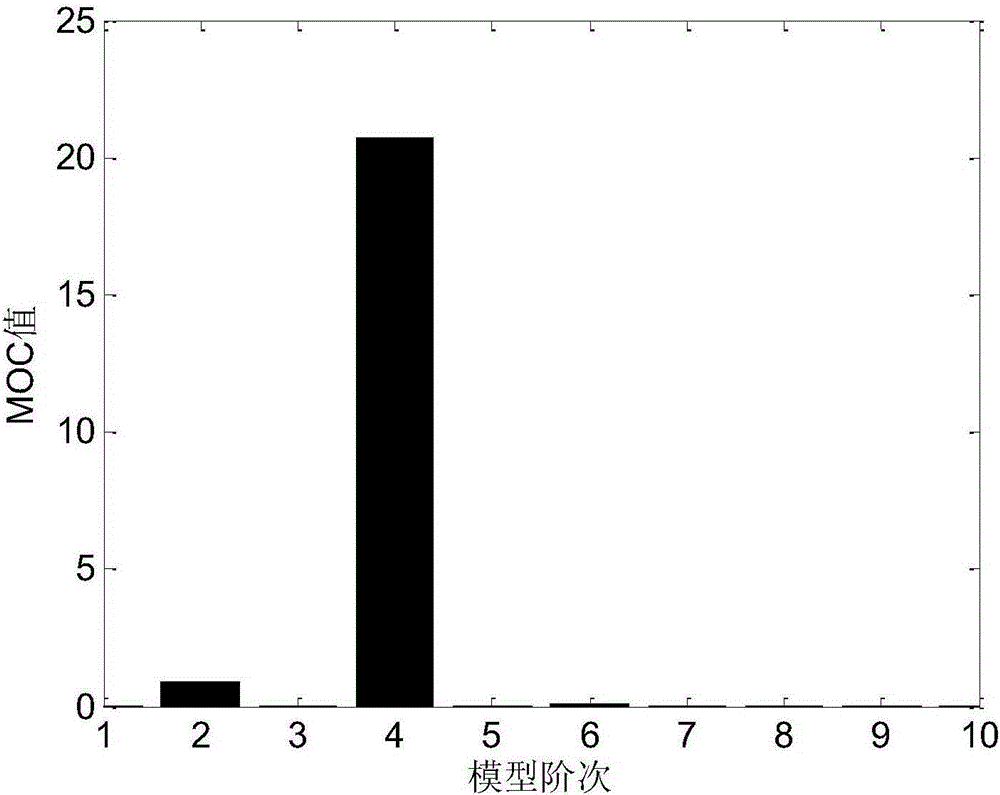
The invention provides a method for identifying a modal parameter based on model order determination and signal noise elimination, which comprises the following steps of: accurately determining the order of a model by singular value decomposition technology, eliminating noise from a measured signal by mathematical low-rank approximation technology, and identifying the modal parameter based on the determined order of the model and the signal from which the noise is eliminated. Compared with the prior art, the method for identifying the modal parameter based on the model order determination and signal noise elimination saves computation time, improves work efficiency and the identification accuracy of the modal parameter, therefore has higher practical application value.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
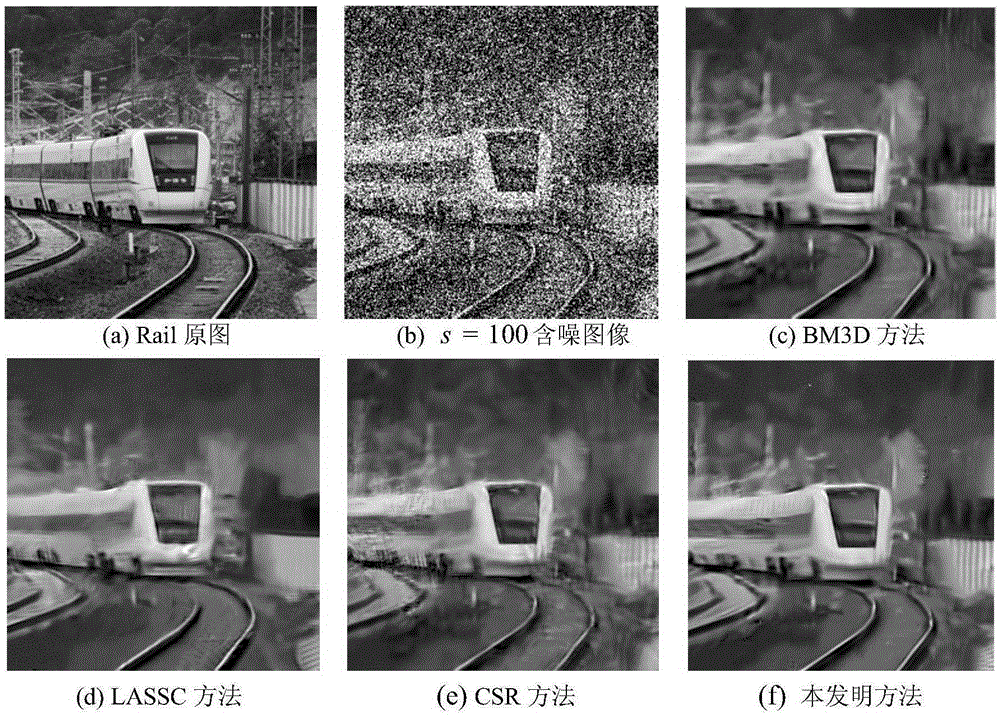
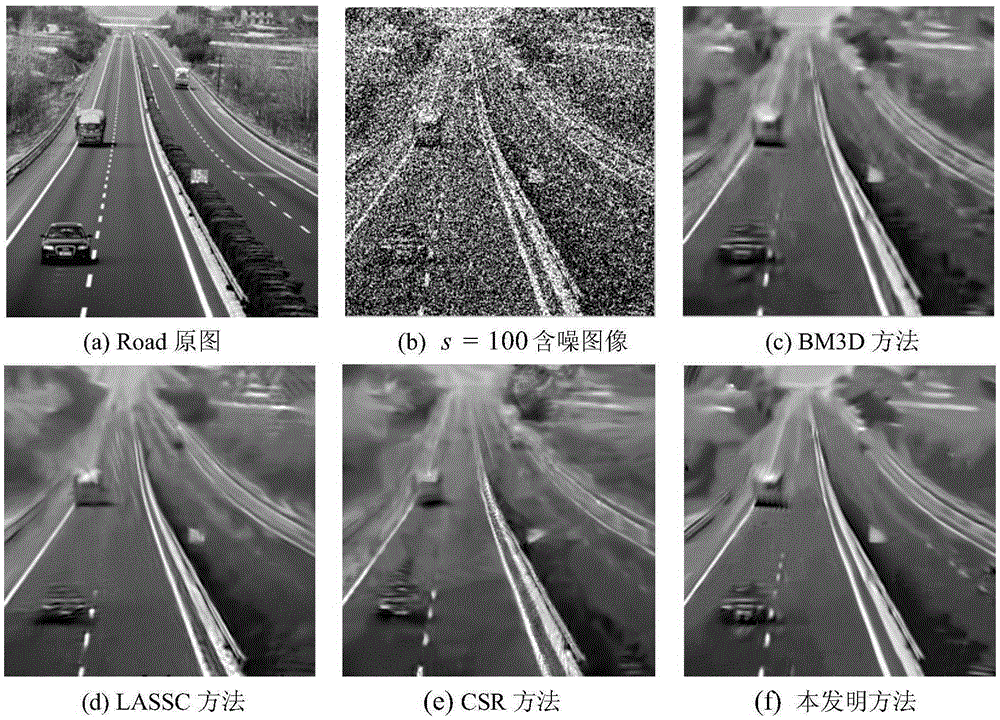
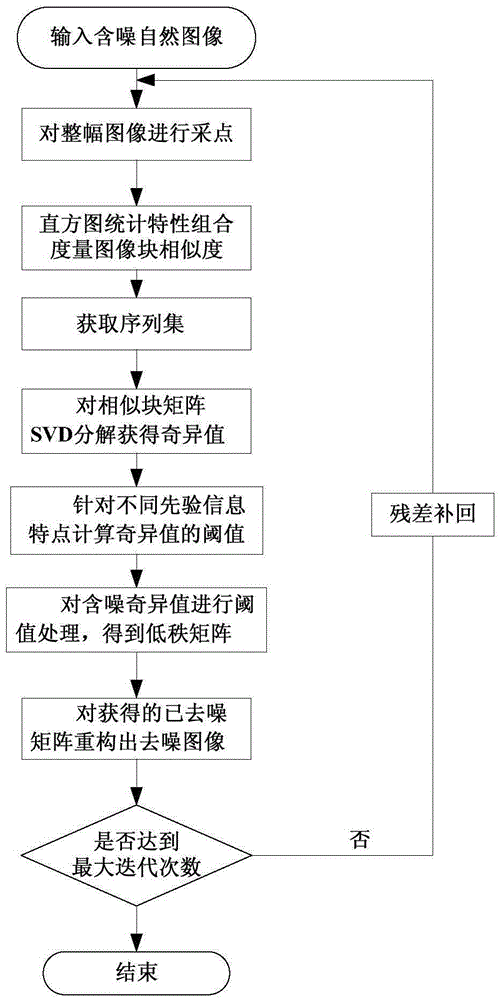
MCMC sampling and threshold low-rank approximation-based image de-noising method
InactiveCN105260998AEasy to keepPreserve texture detail informationImage enhancementSingular value decompositionHigh dimensional
The invention discloses an MCMC sampling and threshold low-rank approximation-based image de-noising method. According to the method, firstly, during the denoising process, an image block is generated through the MONTE-CARLO sampling process. Secondly, based on a plurality of statistical features in a histogram, a similarity judging function that meets the condition of the Markov chain can be obtained. Thirdly, the singular value decomposition on all kinds of image block clusters is conducted and the self-adaptive threshold estimation for singular values is conducted according to the prior information corresponding to an image. Fourthly, on the basis of a decomposed low-rank structure, the image reconstruction is conducted according to the low-rank approximation algorithm, so that the de-noising purpose is realized. According to the invention, the characteristics of the similar non-local geometric structure information of images and the better treatment of high-dimensional data based on a low-rank matrix are fully utilized. Meanwhile, the defect in the prior art that the conventional non-local mean-value traversing search method is high in block-selecting complexity can be overcome. The block-selecting robustness is therefore improved. moreover, to a certain extent, the algorithm operating period is shortened.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
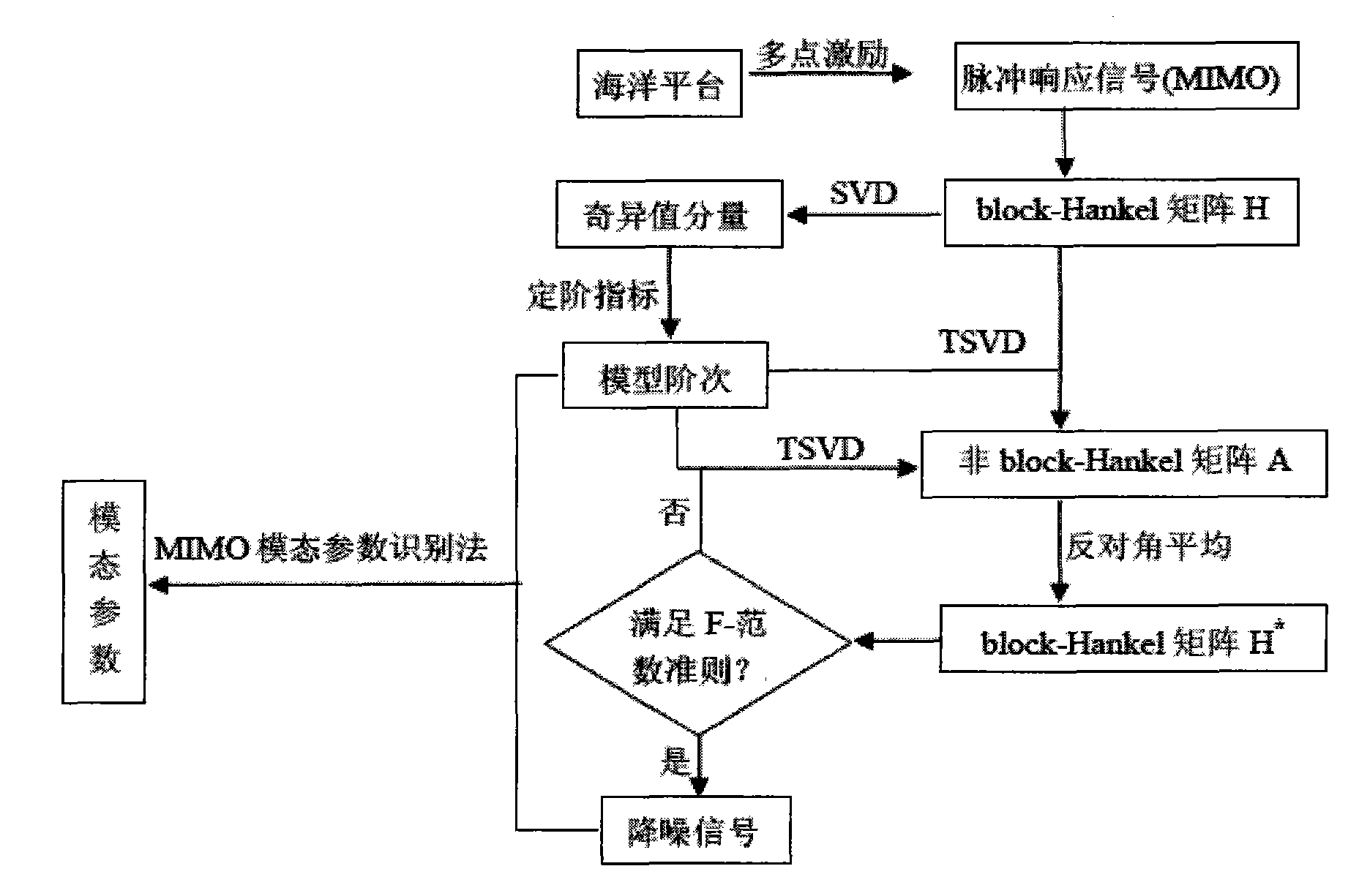
Modal parameter recognizing method based on multi-input multi-output signal noise reduction
InactiveCN103246890ASave machine timeImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti inputAlgorithm
The invention relates to a modal parameter recognizing method based on multi-input multi-output signal noise reduction. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of step 1, performing block-Hankel matrix conversion on noise-containing multi-point pulse responding signals to obtain a first block-Hankel matrix; step 2, processing the first matrix by utilizing structural low rank approximating according to the rank of the first matrix to obtain a first non-block-Hankel matrix after the low rank approximating; step 3, replacing the elements of each block in a second matrix with math average values of the block elements on a back-diagonal to obtain a second block-Hankel matrix; step 4, repeating the steps 2 and 3 until convergence, thus obtaining the noise-reduced multi-point pulse responding signal; and step 5, performing modal parameter recognizing. The modal parameter recognizing method based on multi-input multi-output signal noise reduction can save machine time and improve recognizing accuracy.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Image de-noising processing method and device
InactiveCN105761216ACancel noiseSolve the problem of not effectively removing noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionNoise reduction
The present invention discloses an image de-noising processing method and device, and relates to the field of image processing technology. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem that a noise reduction method aiming at the magnetic resonance image design cannot effectively remove noise in the prior art. The method comprises: performing variance stabilization transformation of obtained nuclear magnetic resonance image signals, and obtaining transformation data with Gaussian distribution noise; performing estimation of the transformation data with Gaussian distribution noise through low rank approximation, and obtaining a reference image of reconstruction estimation and a nucleus Wiener filtering coefficient; performing convolution of the nucleus Wiener filtering coefficient and the transformation data with Gaussian distribution noise, and obtaining the noise reduction data with biased estimation; and performing unbiased inverse transformation of the noise reduction data with biased estimation, and obtaining a noise-free and unbiased estimation nuclear magnetic resonance image.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Signal noise reducing method for modal parameter identification
The invention discloses a signal noise reducing method for modal parameter identification. The signal noise reducing method for modal parameter identification comprises the steps that 1, a Hankel matrix is built through a pulse response signal of a noise-containing structure; 2, a rank of the Hankel matrix is resolved, an order determination index is resolved according to the rank of the Hankel matrix, and a model order is determined through the order determination index; 3, the Hankel matrix is processed through the order determination index and structure low rank approximation to obtain a rebuilt matrix processed through low rank approximation; 4, the step 2 and the step 3 are repeatedly performed until the convergent standard is met, and therefore a noise reducing signal is obtained; 5, modal parameter identification is performed through the noise reducing signal. The signal noise reducing method for modal parameter identification has the advantages that the fact that a Frobenius norm of a difference between the Hankel matrix before being processed through noise reducing and the Hankel matrix after being processed through noise reducing approaches to be the minimum can be achieved by setting the mode of the convergent standard and structure low rank approximation, that is, the improvement of the precision of the noise reducing signal can be achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Multitask machine learning method and multitask machine learning device both used for image classification
InactiveCN103310229AImprove learning accuracyHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexityStudy methods
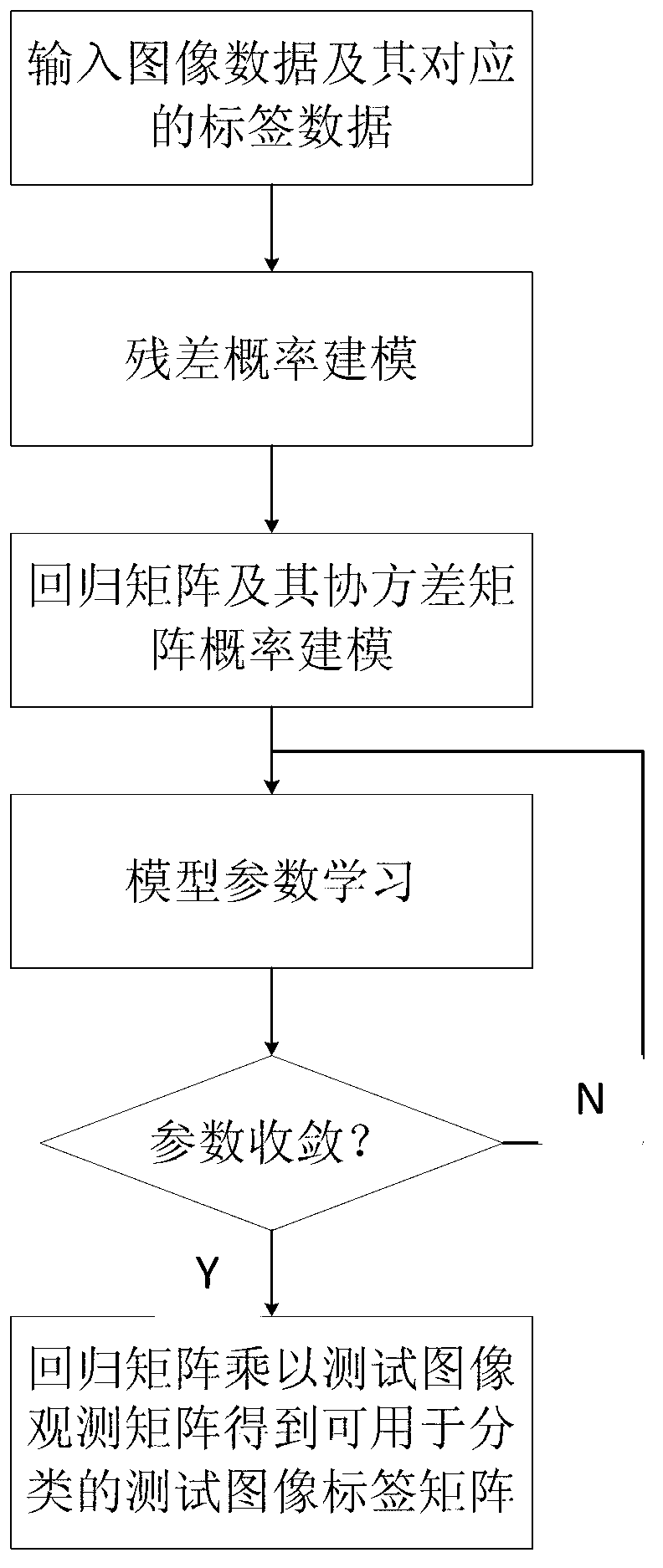
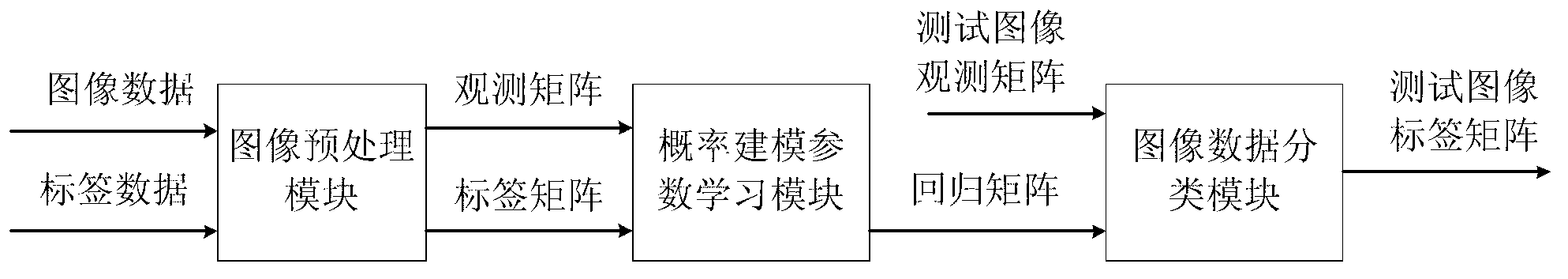
The invention discloses a multitask machine learning method and a multitask machine learning device both used for image classification. The method and the device are characterized in that low rank approximation of a residual structure and a covariance matrix of a regression matrix are utilized simultaneously, probability modeling is performed on the residual structure, the regression matrix, a low rank decomposition of the regression matrix and the covariance matrix of the regression matrix, learning of parameters of a probability model is performed through a variational deduction method or a sampling method, and a regression matrix high in accuracy is acquired finally and used for image classification. By the scheme, on one side, correlativity information among multitasks in the residual structure is utilized, so that parameter learning accuracy can be improved to improve classification accuracy; on the other side, by performing low rank approximation on the covariance matrix of the regression matrix, calculating complexity of an algorithm can be effectively lowered.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
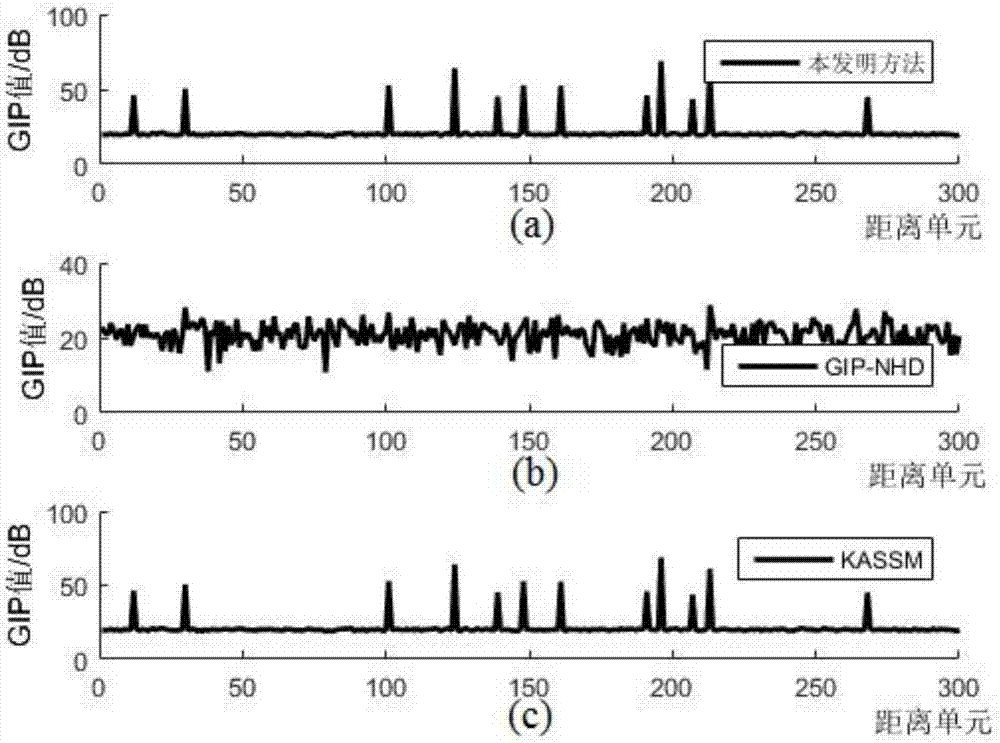
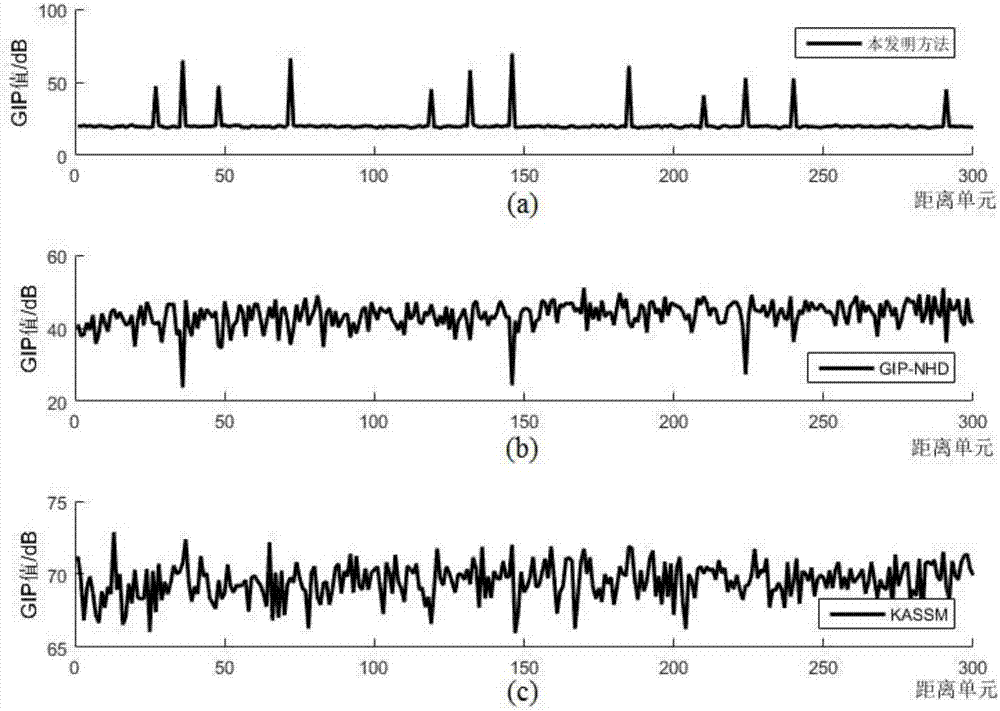
Interference sample eliminating method based on generalized inner-product arbitrary array
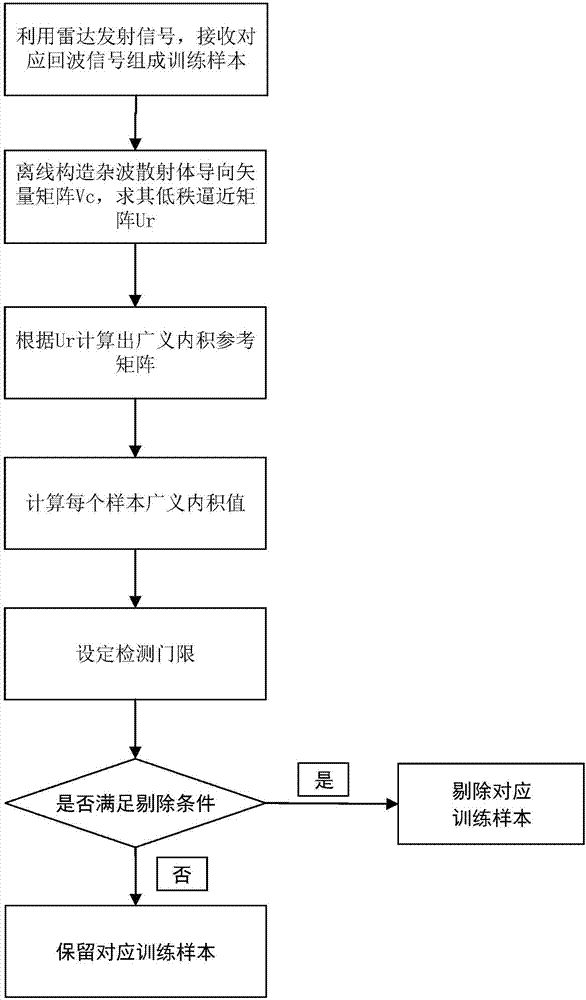
The invention provides an interference sample eliminating method based on a generalized inner-product arbitrary array, and solves the technical problem that the echo sample of an arbitrary array configurational antenna cannot be selected at present. The method comprises the following implementation steps: using a radar transmission signal, and selecting corresponding echo data as training samples; constituting the low-rank approximation matrix Ur of a clutter subspace in an off-line manner; calculating the inverse matrix of a clutter covariance matrix in the off-line manner; calculating the generalized inner-product value of each training sample; setting a detection threshold eta; carrying out elimination on disturbance samples, screening the training samples, and finally obtaining samples to be measured after the elimination of the disturbance samples so as to carry out space-time two-dimensional self-adaption processing in next step. The inverse matrix of the clutter covariance is constructed in the off-line manner, wherein the inverse matrix contains the position and beam pointing information of each array element, so that interference samples under the arbitrary array configurational antenna can be eliminated, the processing result is not influenced by the training samples, and the computational burden is low. The method is used for onboard and interspace radar space-time two-dimensional signal processing.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
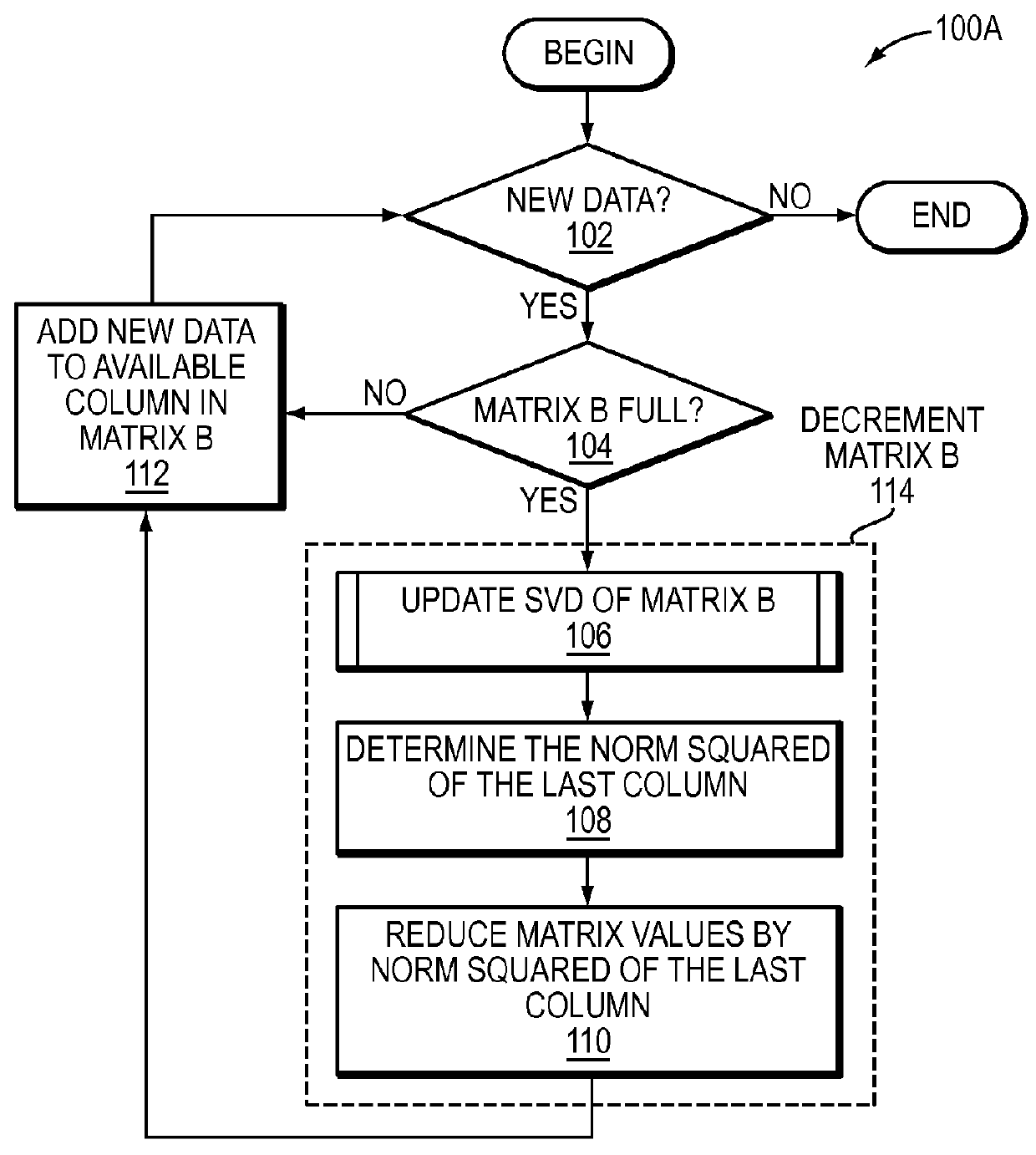
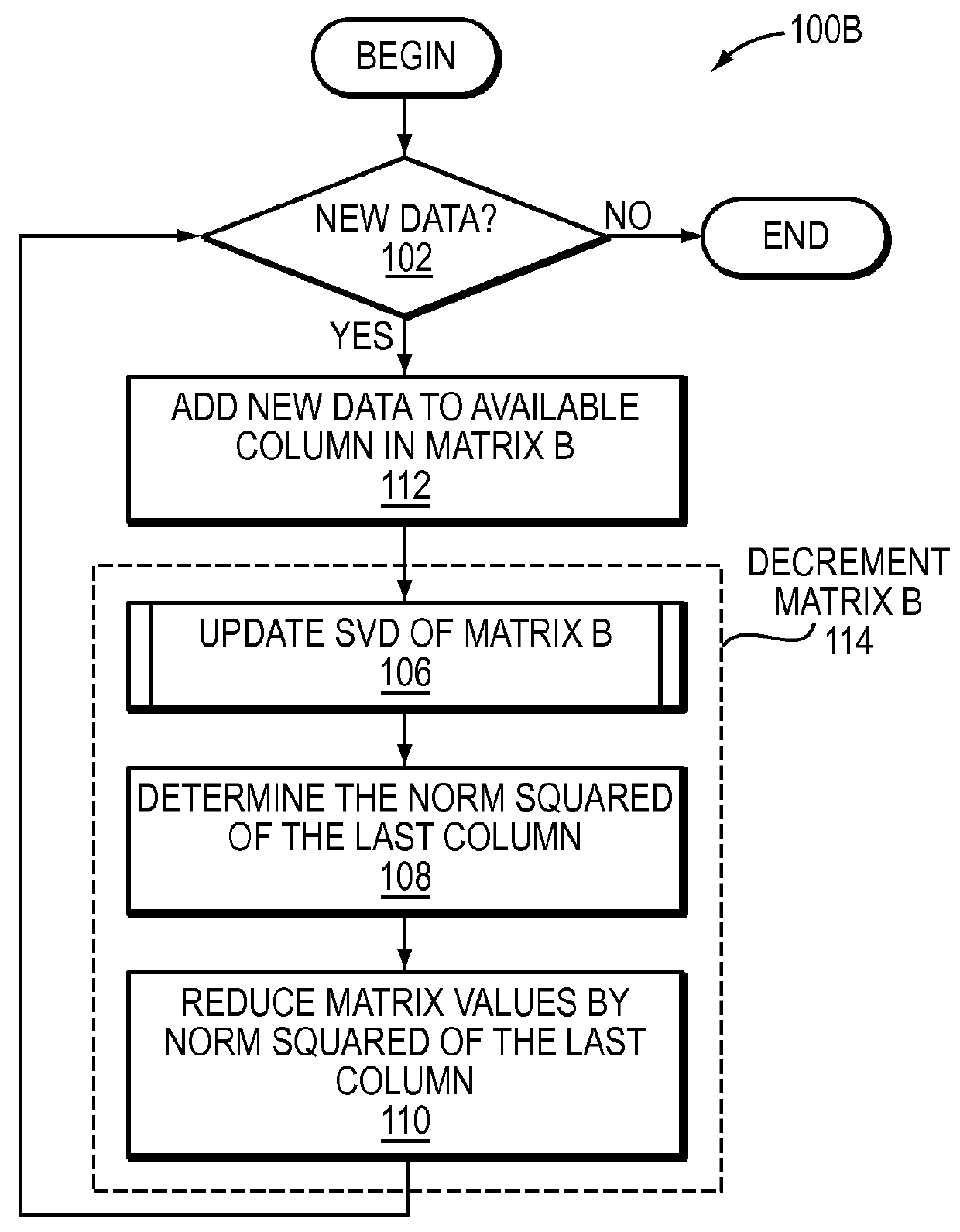
Systems and methods for low-rank matrix approximation
ActiveUS20160055124A1Reduce storageReduce computing requirementsDigital data information retrievalDigital computer detailsSingular value decompositionLow-rank approximation
Systems and methods for generating a low-rank approximation of a matrix are provided. The various systems and methods may identify at least a first set of right singular vectors and a first set of singular values of a subset of the matrix, reduce the subset by an amount of energy of a selected data entry of the subset based on the first set of right singular vectors and the first set of singular values, incorporate a new data entry from the matrix into the subset, update the first set of right singular vectors and the first set of singular values of the subset based on the new data entry by a singular value decomposition (SVD) update, and generate the low-rank approximation of the matrix based on the updated first set of right singular vectors and the updated first set of singular values.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
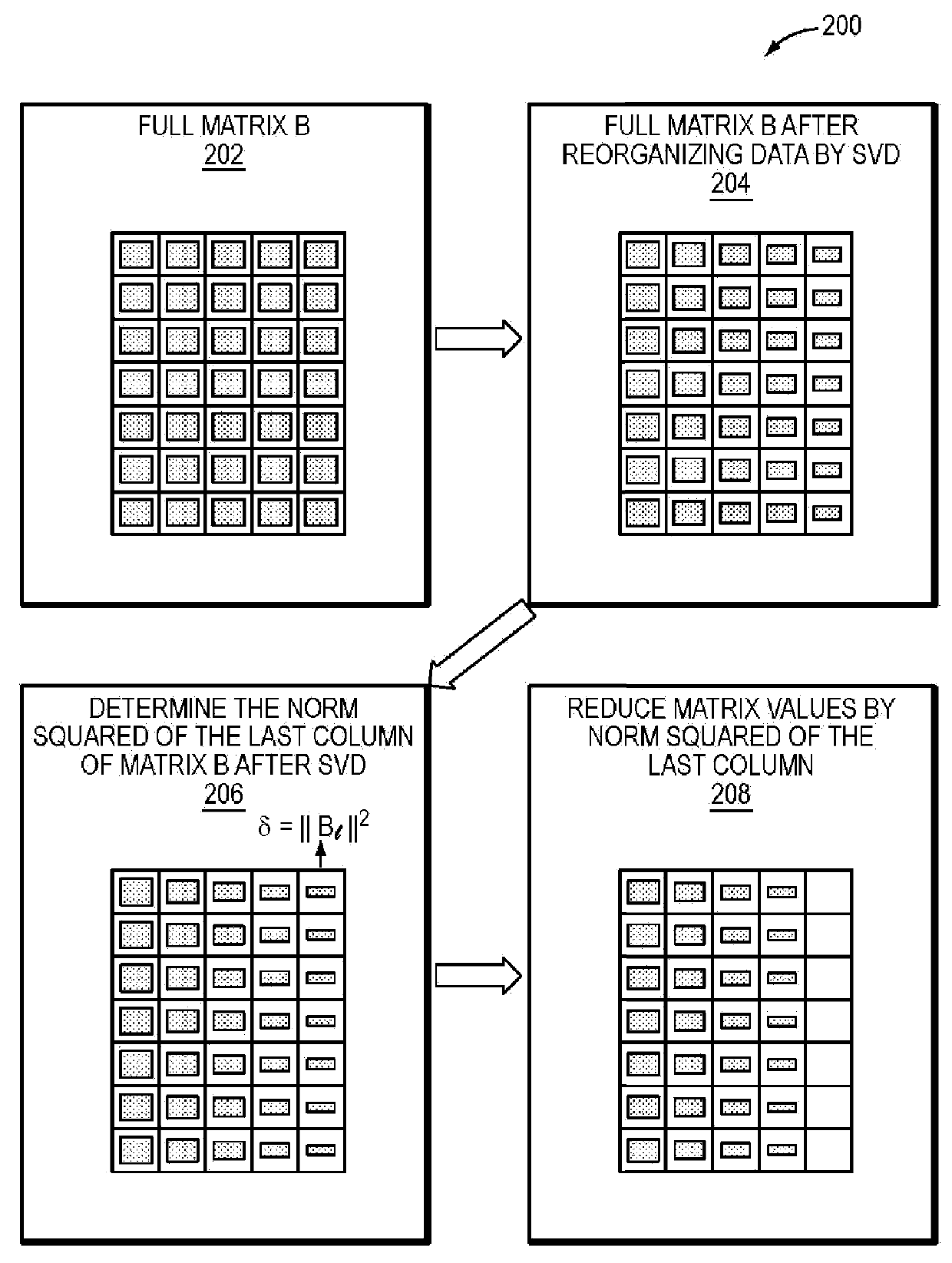
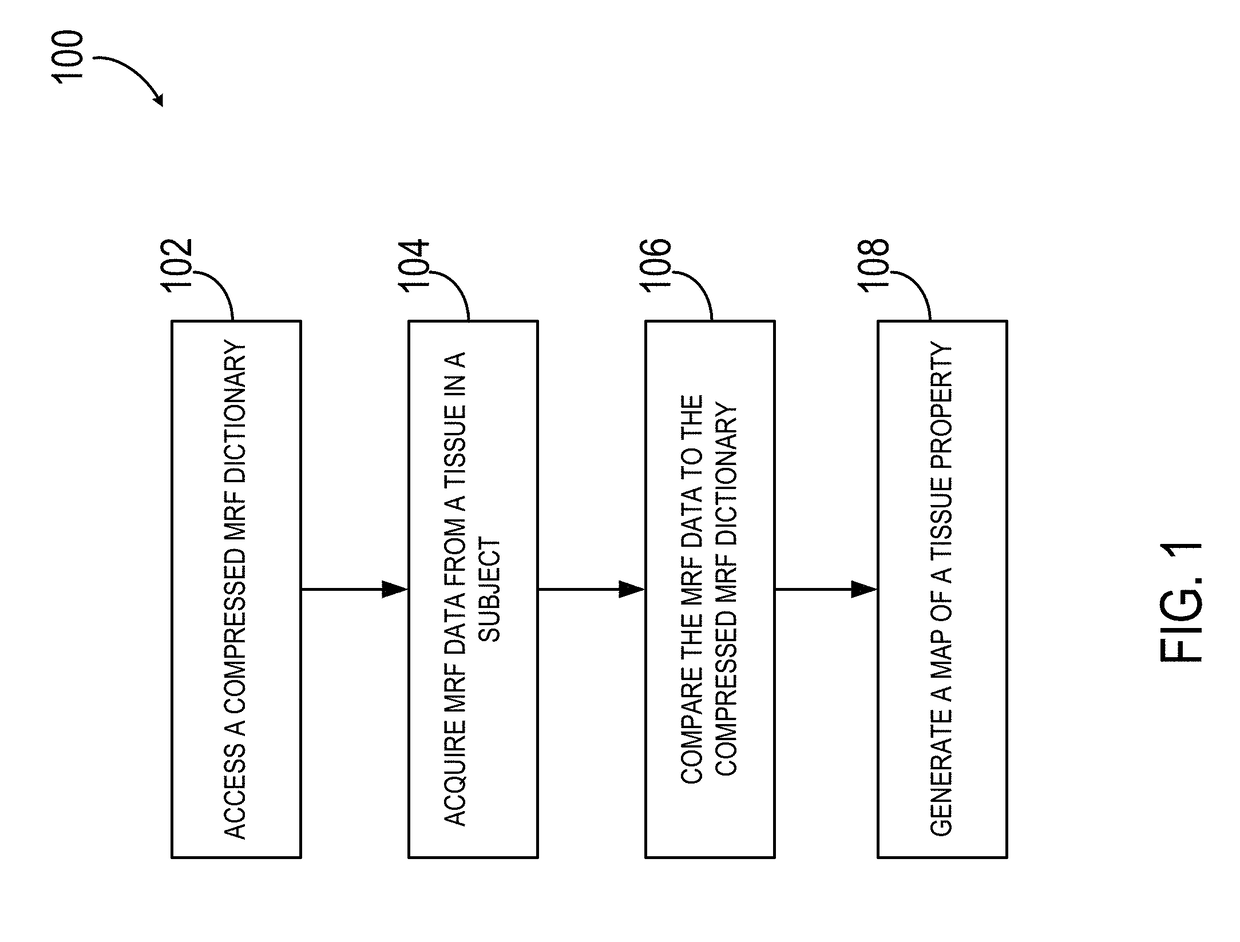
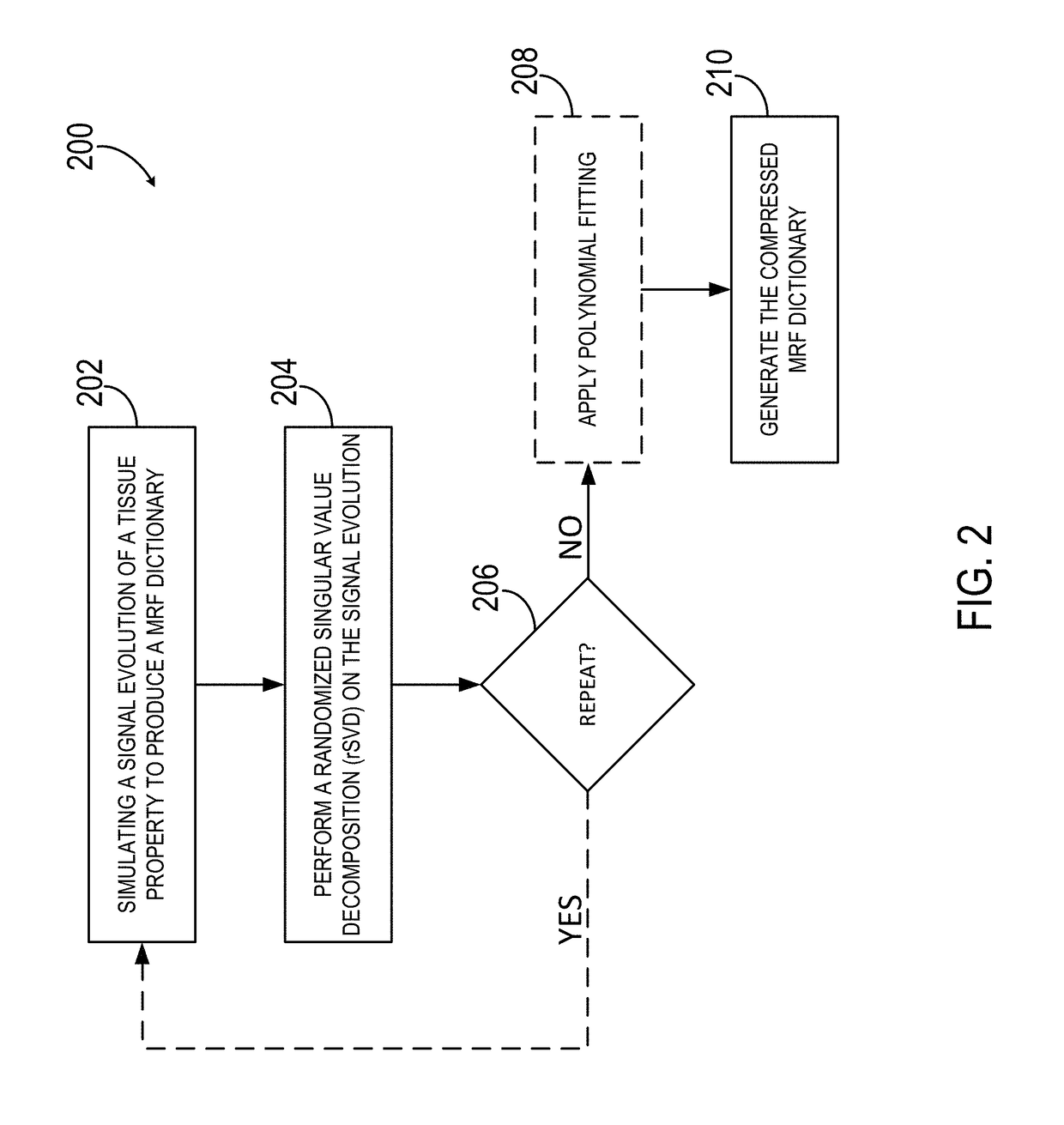
System and Method for Low Rank Approximation of High Resolution MRF Through Dictionary Fitting
ActiveUS20180203082A1High resolutionReduce memory requirementsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVectoral format still image dataSingular value decompositionResonance
A system and method is provided for generating a map of a tissue property in a subject using magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF) and a compressed MRF dictionary, where the compressed MRF dictionary has a significantly reduced memory requirement relative to a standard MRF dictionary. The method includes performing a randomized singular value decomposition (rSVD) on a MRF dictionary to produce the compressed MRF dictionary. MRF data is then acquired and compared to the MRF dictionary to identify the tissue property from the region of interest in the subject. A tissue property map is then generated based on the tissue in the region of interest of the subject.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
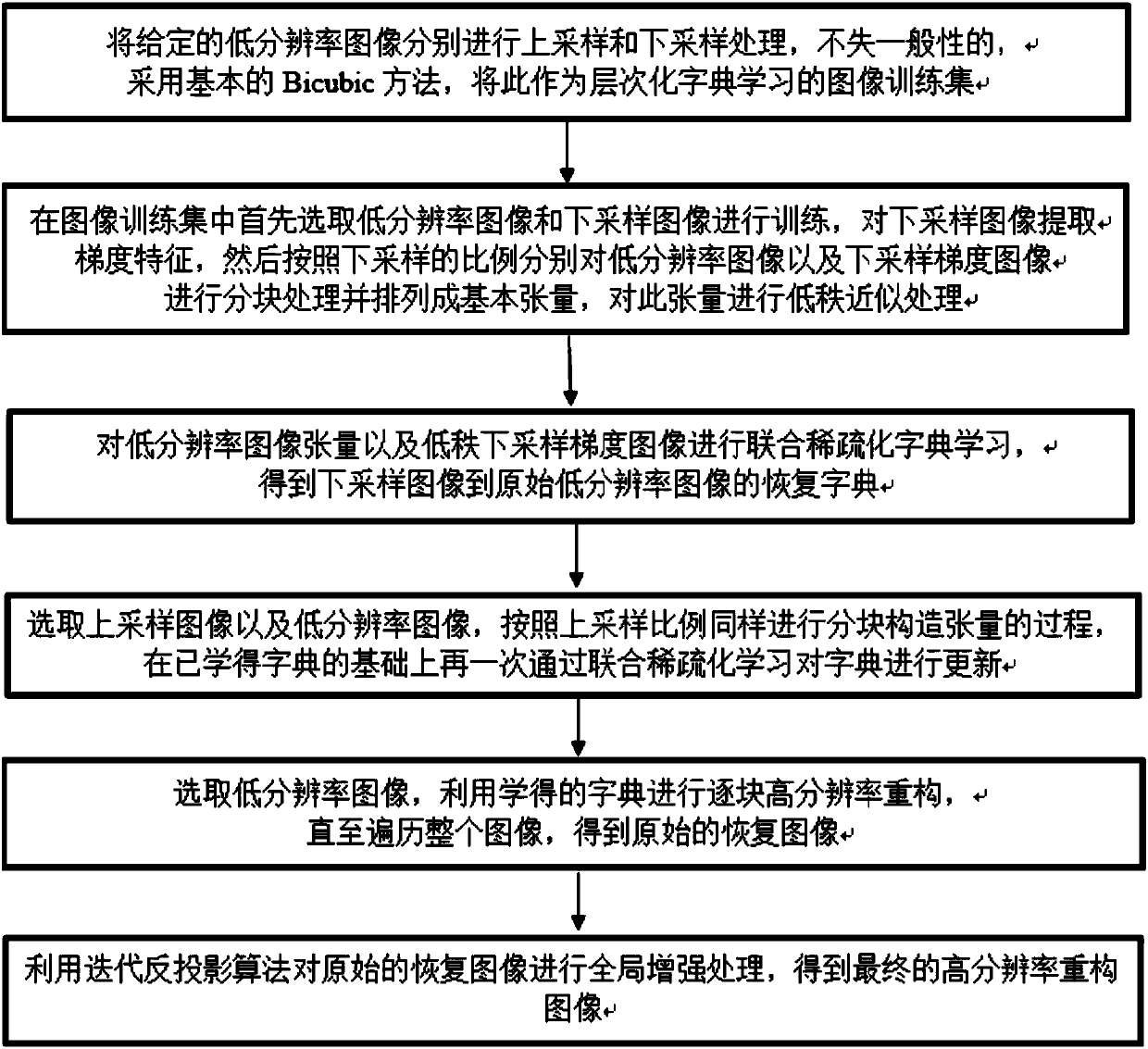
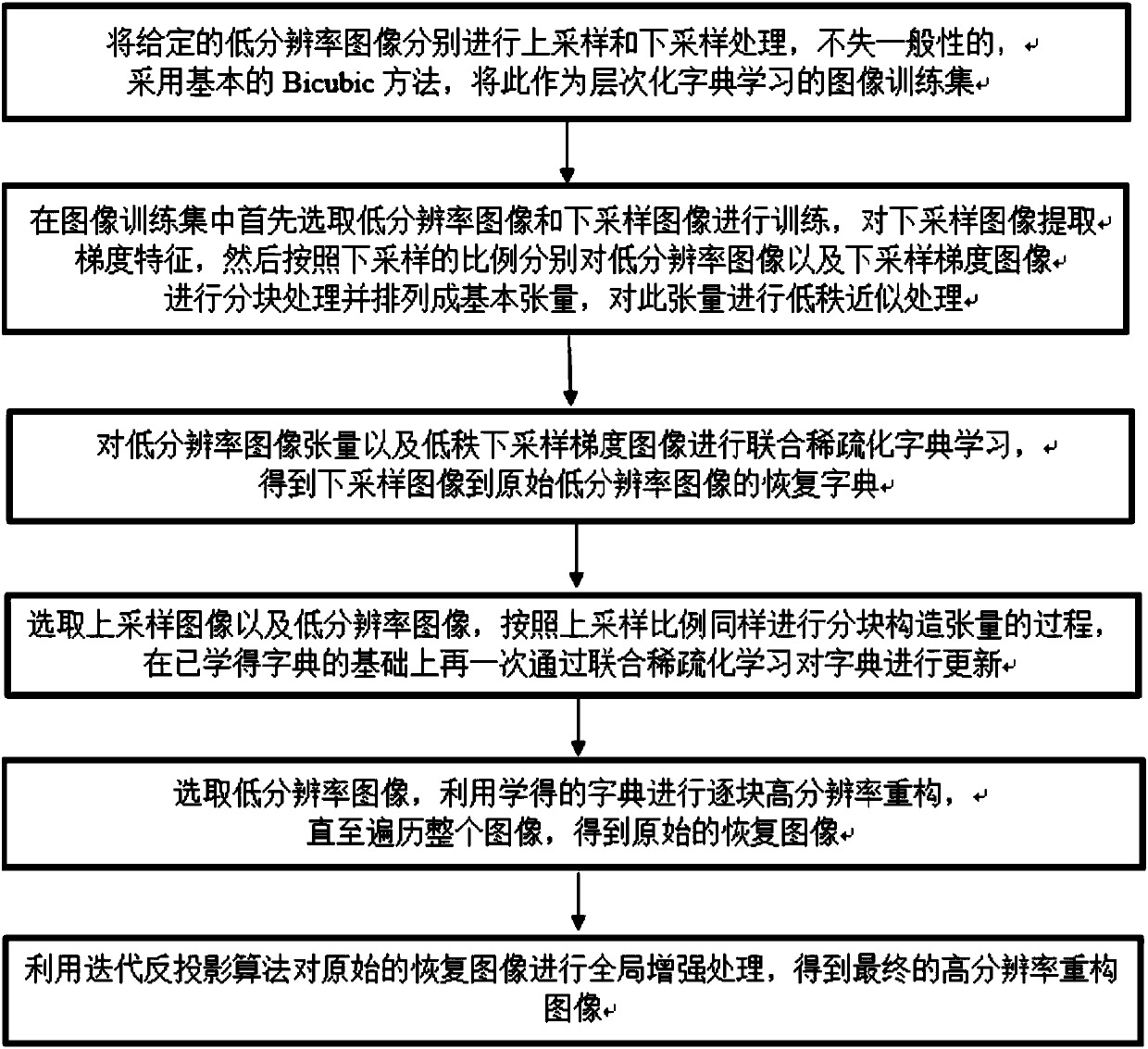
High-resolution image reconstruction method based on low-rank tensor and hierarchical dictionary learning
ActiveCN107067380AHigh precisionPreserve basic structural informationImage enhancementDictionary learningImage resolution
A high-resolution image reconstruction method based on a low-rank tensor and hierarchical dictionary learning is provided. The method comprises steps of: up-sampling and down-sampling an original image by using bilinear interpolation, and using a processed result and the original image as a dictionary learning training set; training the original image and a down-sampled image, extracting the down-sampled image gradient, arranging the original image and the down-sampled image gradient as the tensor, and subjecting the down-sampled image gradient tensor to low-rank approximation; subjecting the original tensor and the approximate down-sampled gradient tensor to sparse dictionary learning to obtain an image restoration dictionary; training a low-resolution image and the up-sampled image, extracting the low-resolution image gradient, arranging the low-resolution image gradient and up-sampled image as the tensor, learning to update the dictionary; transferring the original image to a YCbCr space, reconstructing the Y with the dictionary, reconstructing the Cb and the Cr by bilinear interpolation to obtain the original restored image; and subjecting the original restored image to global enhancement by using iteration back projection to obtain a final result. The method retains the structure information of the image by using the tensor and improves the precision of image reconstruction.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
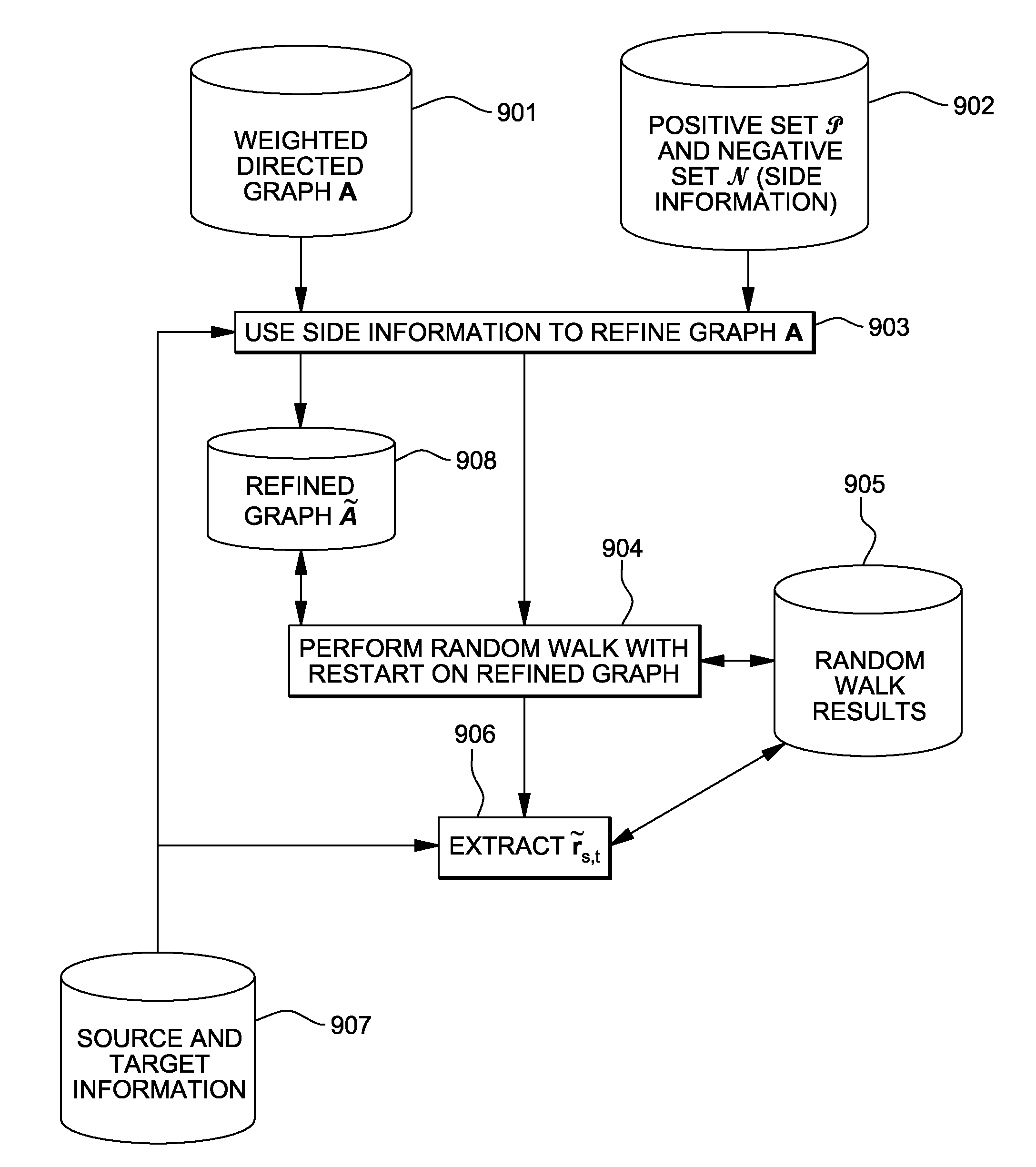
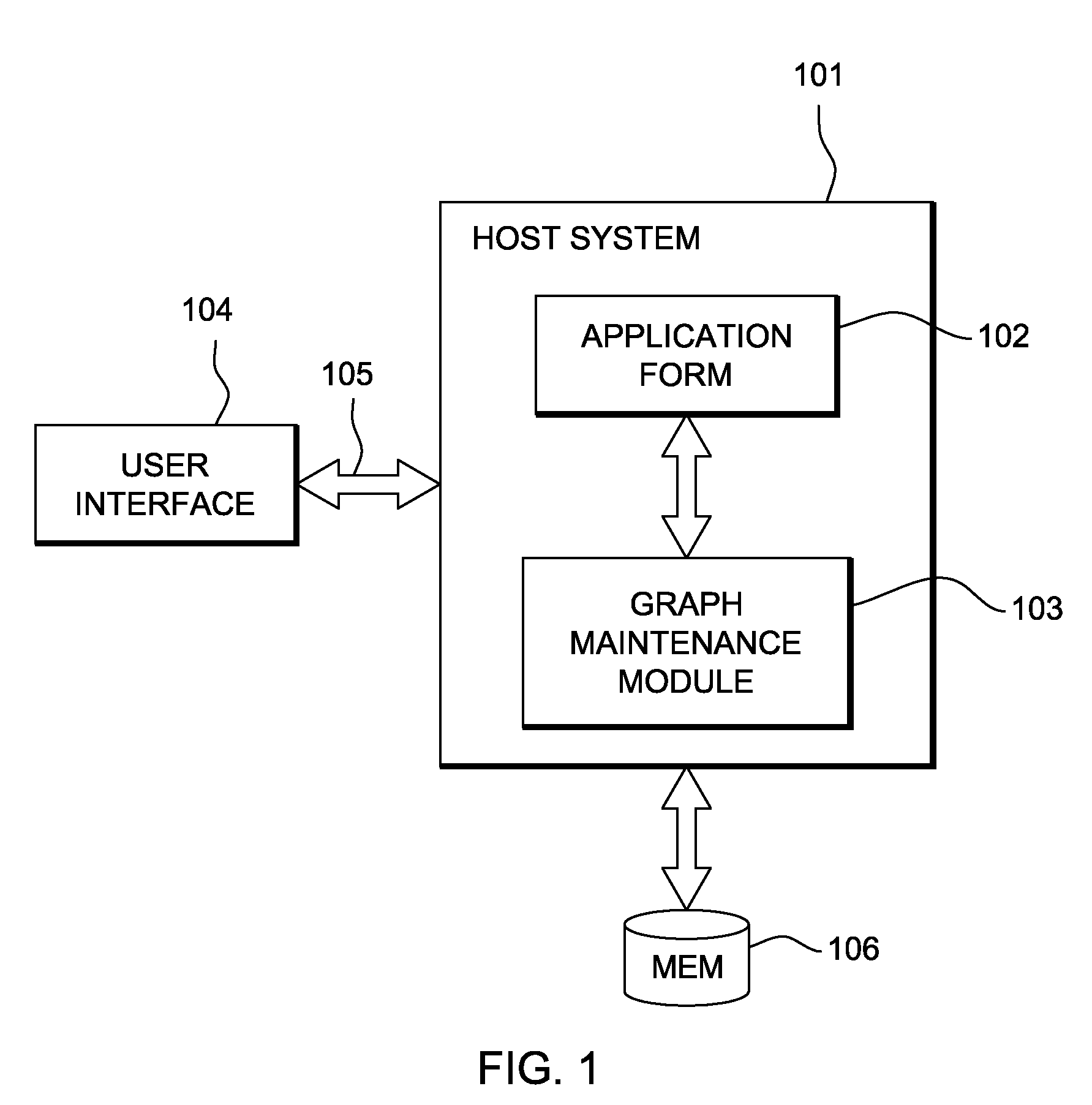
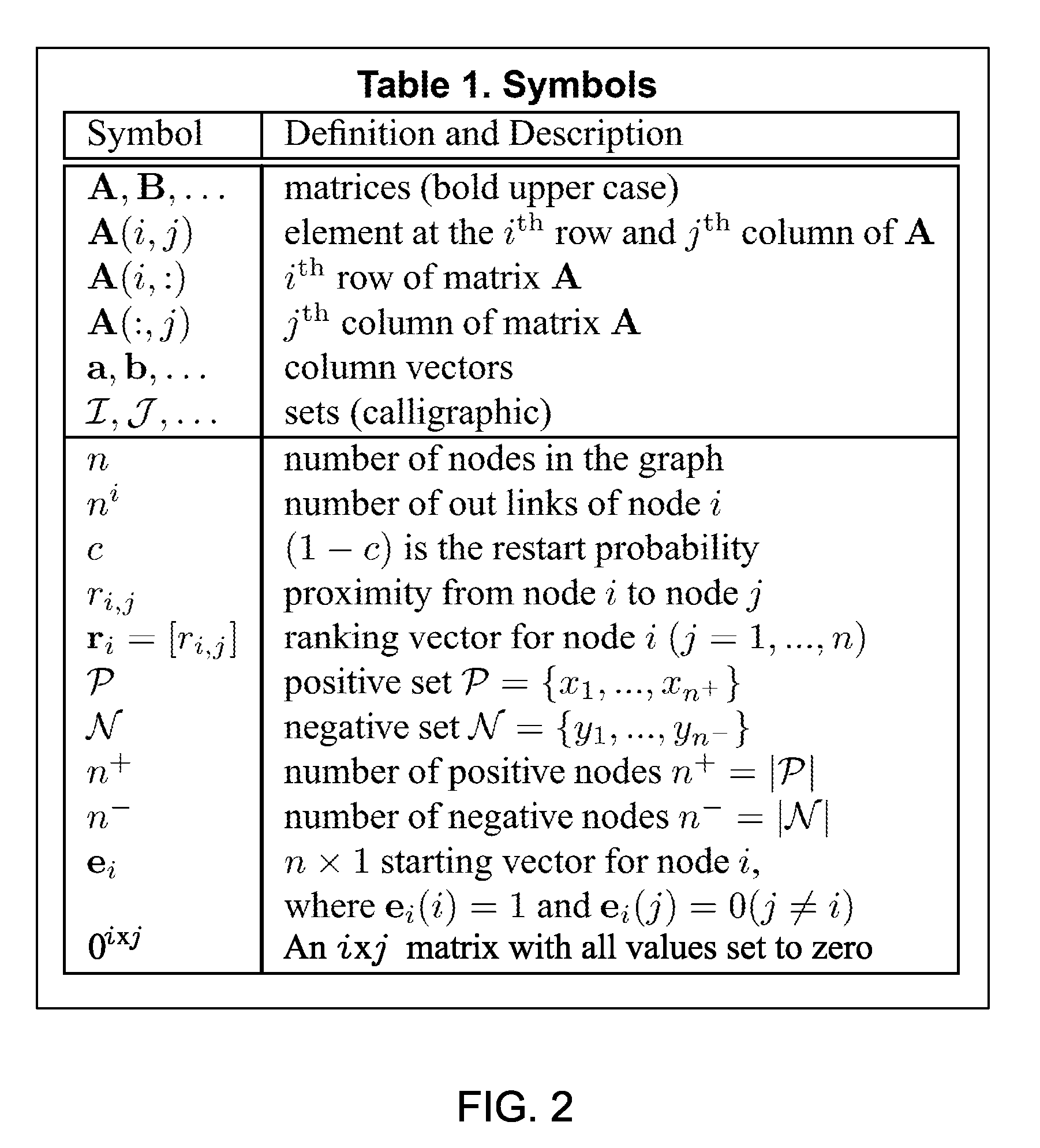
Efficient calculation of node proximity on graphs with side information
InactiveUS8346766B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDirected graphUser input
In a computerized data mining context, user input relating to positive and negative information is incorporated into node proximity measurements on a weighted, directed graph. Random walk results are updated without a full matrix inversion by using selective update to a low rank approximation and to inversion results.
Owner:IBM CORP
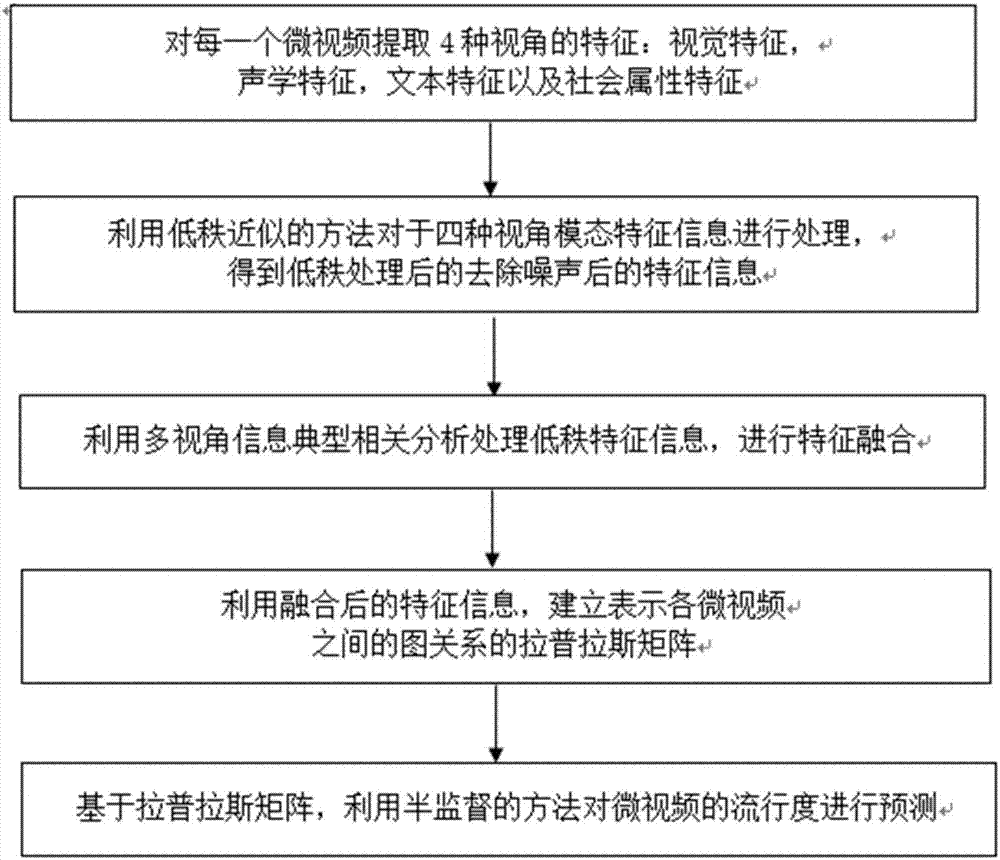
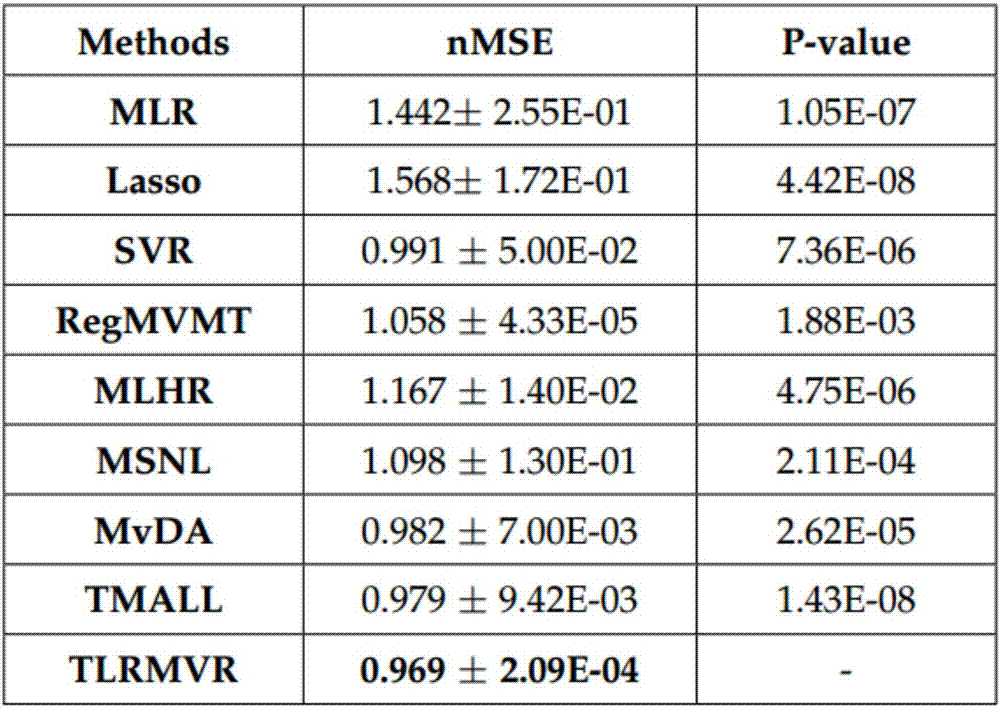
Micro-video popularity prediction method based on low-rank constraint and multi-view characteristic fusion
InactiveCN107229702AImprove stabilityTight structure featureForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmCorrelation analysis
The invention discloses a micro-video popularity prediction method based on low-rank constraint and multi-view characteristic fusion. The micro-video popularity prediction method includes the steps that four view modal characteristics are subjected to low-rank approximation processing respectively, and four kinds of noise-removing low-rank characteristic information are obtained; through multi-view-information typical correlation analysis, the four kinds of low-rank characteristic information are subjected to characteristic fusion; fused characteristic information is adopted, laplacian matrixes for expressing graph relationships between all micro videos are established; based on the laplacian matrixes, the popularity of the micro videos is predicted with the semi-supervised method. According to the micro-video popularity prediction method based on the low-rank constraint and multi-view characteristic fusion, the limitation of single-view characteristic on popularity prediction is avoided, the characteristics of all the views are processed through low-rank approximation processing, and the laplacian matrixes established between the characteristics have the higher stability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Video denoising method based on scale mixing model and low-rank approximation
InactiveCN106157259ASpatial statistical distribution is goodCharacterize the spatial statistical distributionImage enhancementImage analysisMixed noiseLow-rank approximation
The invention discloses a video denoising method based on a scale mixing model and low-rank approximation, and mainly aims to solve the problem that Gaussian pulse mixed noise is hard to be eliminated accurately in the prior art. The video denoising method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring an initial estimation of a video by adopting a median value filtering method, and searching a similar image block matrix in front and back frames of a test image; 2, modeling an abnormal point set by using the Laplace scale mixing model to convert the abnormal point estimation problem into a problem of joint solution for abnormal points and hidden factors so as to eliminate the abnormal points caused by the mixed noise; 3, performing low-rank approximation on the similar image block matrix, and calculating a denoised image by using a nonlocal low-rank model; 4, performing iterative calculating through the Laplace scale mixing model and the nonlocal low-rank model to obtain a recovered single-frame image; 5, repeating the steps 1 to 4 to obtain a denoised video. The video denoising method disclosed by the invention can eliminate the mixed noise and retain detailed information of the image, is good in visual effect, and can be used for denoising a video media, a remote-sensing image and a medical image.
Owner:西安电子科技大学昆山创新研究院 +1
Method and apparatus for spatio-temporal compressive sensing
InactiveUS8458109B2Accurate reconstructionImprove reconstruction accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsAnomaly detectionTomography
A method and apparatus for spatio-temporal compressive sensing, which allows accurate reconstruction of missing values in any digital information represented in matrix or tensor form, is disclosed. The method of embodiments comprises three main components: (i) a method for finding sparse, low-rank approximations of the data of interest that account for spatial and temporal properties of the data, (ii) a method for finding a refined approximation that better satisfies the measurement constraints while staying close to the low-rank approximations obtained by SRMF, and (iii) a method for combining global and local interpolation. The approach of embodiments also provides methods to perform common data analysis tasks, such as tomography, prediction, and anomaly detection, in a unified fashion.
Owner:ZHANG YIN +1
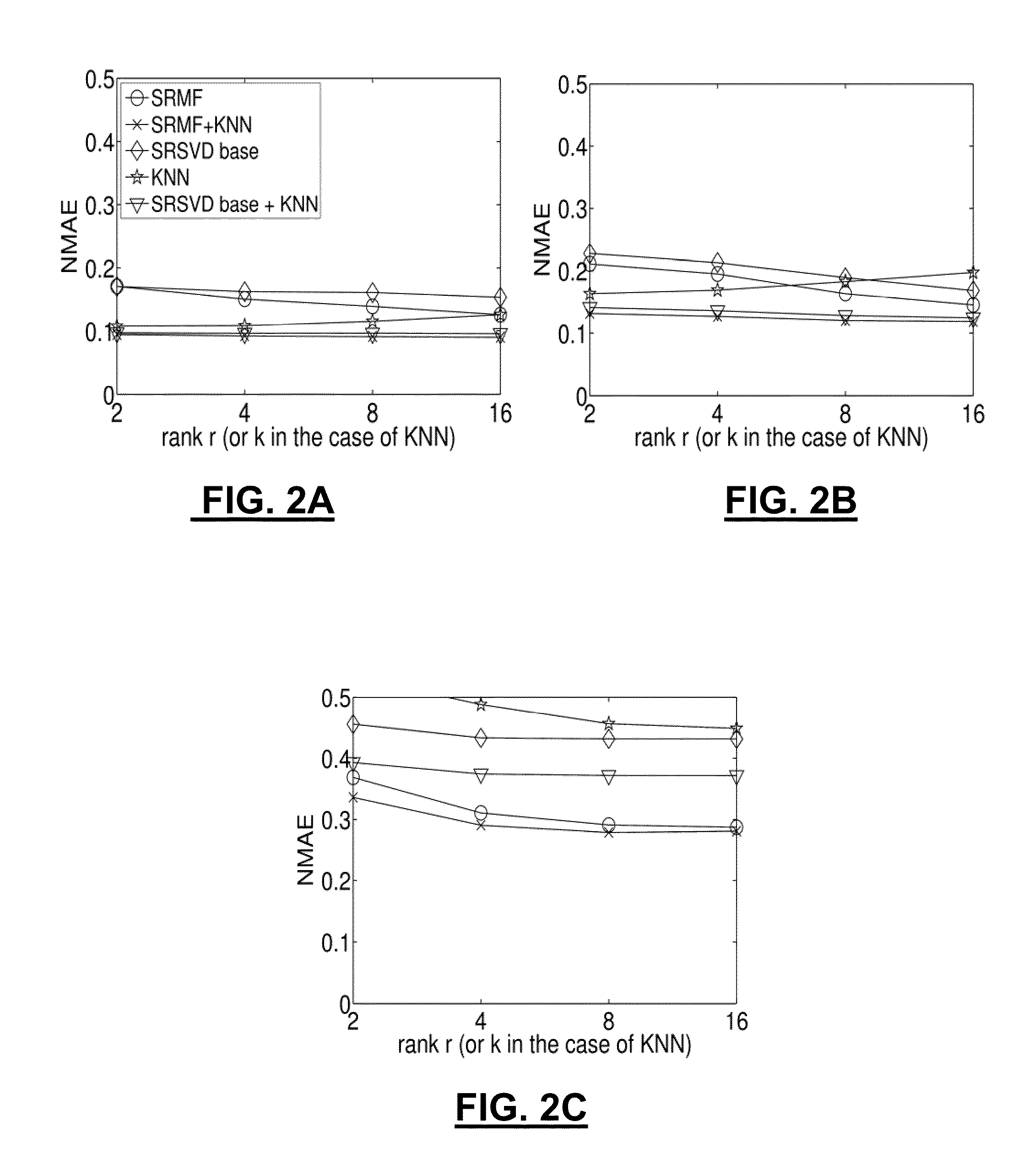
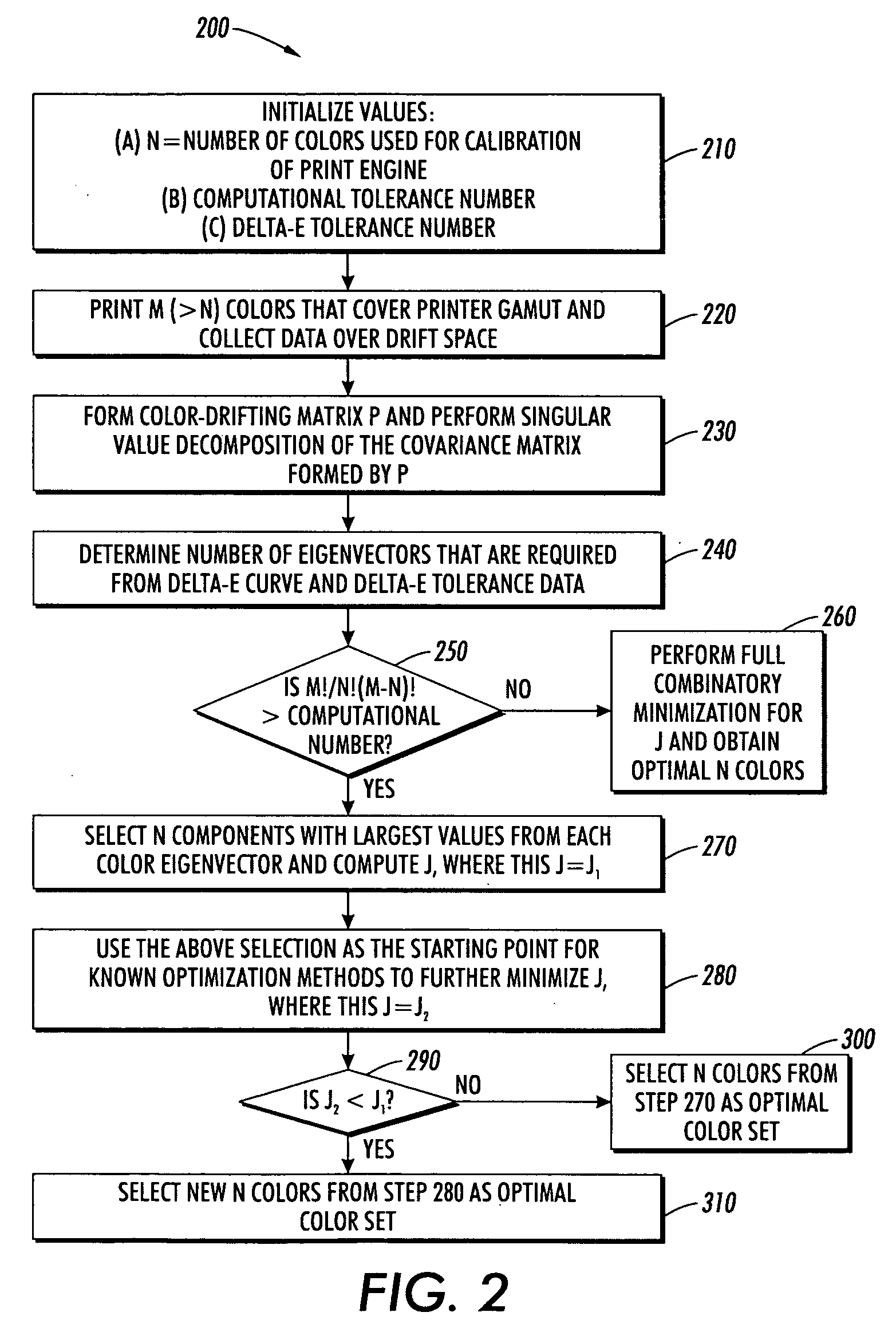
Optimal test patch selection for multi-media printing systems using low rank approximation
InactiveUS20080137150A1Colour-separation/tonal-correctionPictoral communicationPattern recognitionColor test
The exemplary embodiment disclosed herein comprises several aspects of defining and using optimal color test patches for calibrating a printing system for various purposes (e.g., multi-media, gamut extension, drifting correction, etc.). One aspect is the creation and use of color patches where the color patches are selected optimally to result in minimum mean square error when those color patches are used to determine weights of a limited number of basis vectors that model the system (e.g., model the print engine response). A joint optimization technique is given as a method to select the optimal color test patches for calibration.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Proton exchange membrane fuel cell non-linear state space model identification method
ActiveCN107632522ASimple designHigh simulationAdaptive controlSingular value decompositionSystem matrix
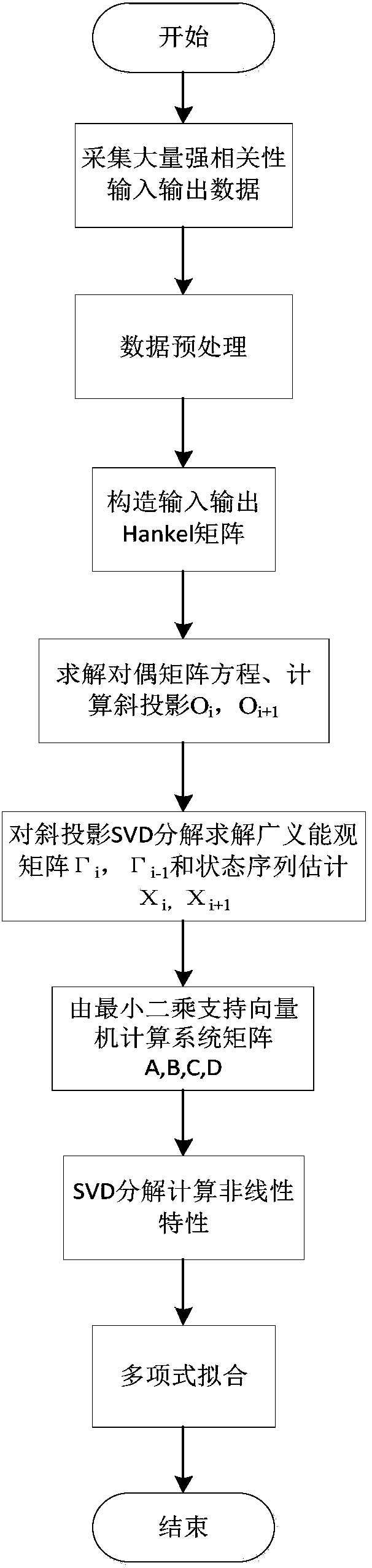
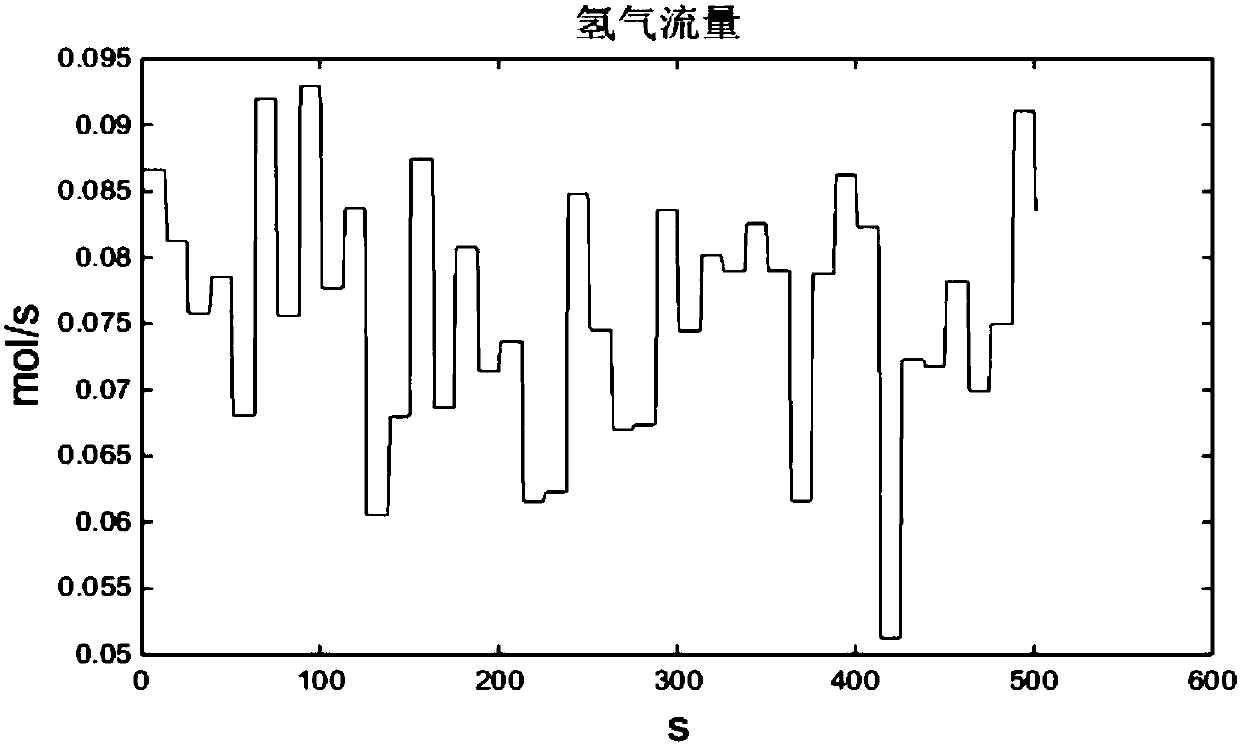
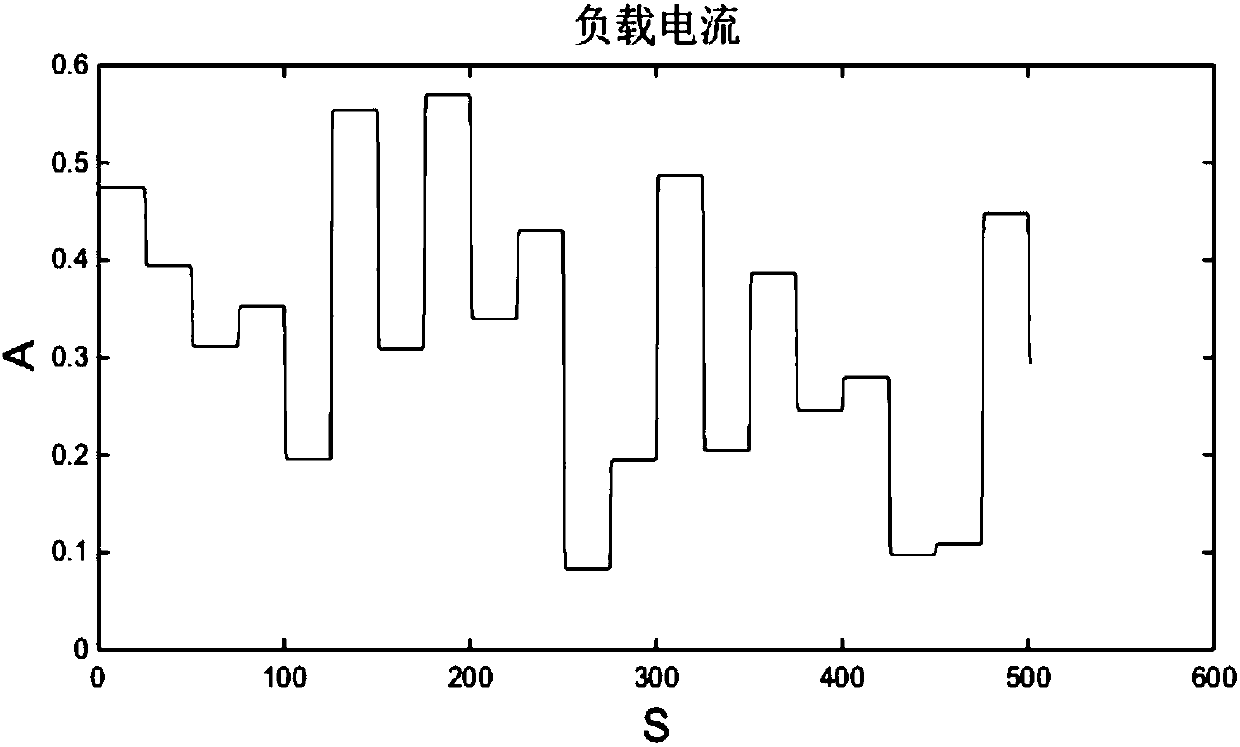
The invention discloses a proton exchange membrane fuel cell non-linear state space model identification method. According to the method, firstly, a hydrogen flow and a load current are selected as input variables, a voltage is selected as an output variable, and plenty of data is acquired; secondly, a Hankel matrix is constructed through the acquired data, and a dual matrix is solved; thirdly, amatrix projection is constructed through utilizing the result of a matrix equation; and lastly, inclined projection is decomposed through utilizing a singular value to acquire state sequence estimation of a system. The method is utilized repeatedly to solve the system matrix, and the low-rank approximation technology is utilized to acquire non-linear system characteristic estimation; actually-measured input data is taken as an abscissa, a non-linear identification characteristic is taken as an ordinate, and a MATLAB curve fitting tool is utilized to carry out polynomial fitting of the system non-linear characteristic. The method is advantaged in that the non-linear characteristic of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell can be quite accurately described, not only can solution schemes be provided for proton exchange membrane fuel cell modeling of actual engineering personnel and subsequent control system design, and relatively good reference values are for modeling of similar systems.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Abnormal event detection method based on low-rank approximation structured sparse representation
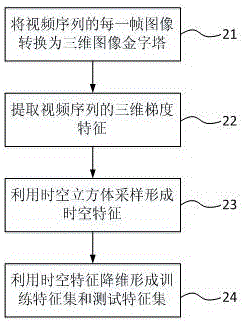
InactiveCN106503647ASparse reconstruction is accurateAccurate dynamic scene semantic understandingCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature setDimensionality reduction
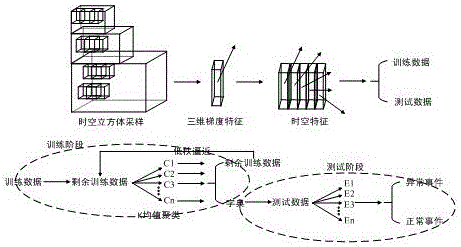
Disclosed in the invention is an abnormal event detection method based on low-rank approximation structured sparse representation. The method comprises three steps of feature extraction, training and testing. To be specific, step (1), a multi-scale three-dimensional gradient feature of a video sequence is extracted; step two, dimensionality reduction is carried out on the multi-scale three-dimensional gradient feature, thereby forming a training feature set and testing feature set; step three, a residual training feature and a correlated parameter are initialized; step four, iterative learning group sparse dictionary is carried out on the residual training feature, thereby obtaining a normal-mode dictionary; step five, sparse reconstruction is carried out on a testing feature by using the group sparse dictionary obtained by the training process; and step six, according to a reconstruction error, whether the testing feature is an abnormal feature is determined. Therefore, defects that the low-rank characteristic of video data is not dug fully and the detection is carried out slowly according to the abnormality detection technology can be solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Video image denoising processing method and apparatus
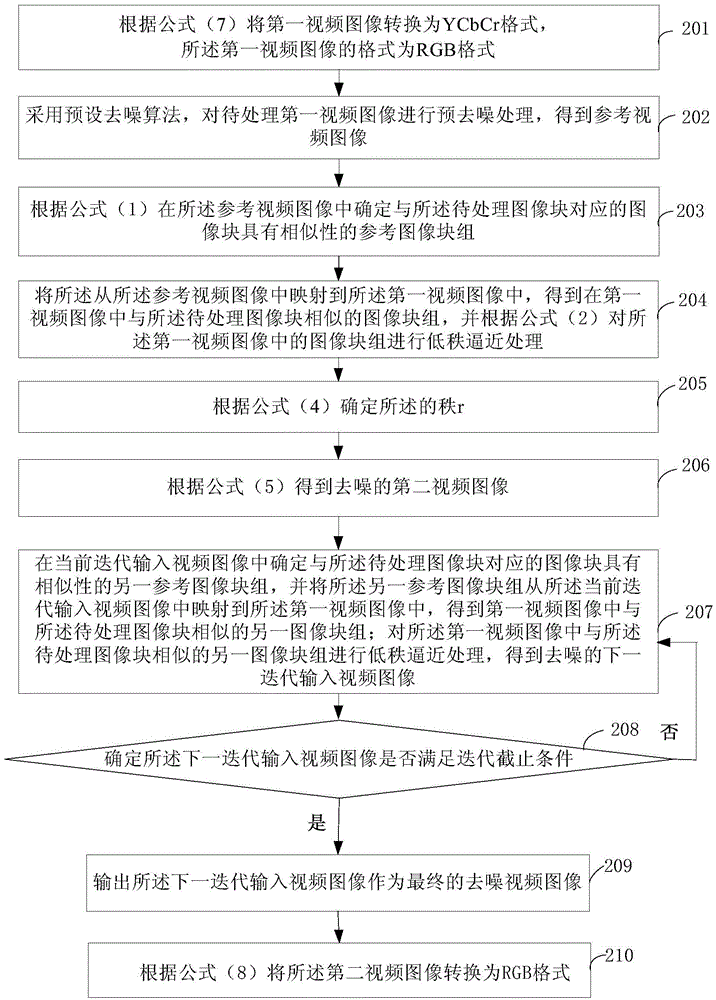
ActiveCN105338219AImprove denoising effectReduce adverse effectsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDenoising algorithmReference image
The invention provides a video image denoising processing method and an apparatus. The method comprises the following steps of using a preset denoising algorithm to carry out pre-denoising processing on a first video image to be processed so as to acquire a reference video image; determining a reference image block group possessing a similarity with an image block corresponding to an image block to be processed in the reference video image, mapping a coordinate position relation of the reference image block group into the first video image from the reference video image so as to acquire an image block group which is similar with the image block to be processed; and carrying out low rank approximation processing on the image block group in the first video image so as to acquire a second denoising video image. The reference video image after pre-denoising processing is taken as a basis of similarity measurement so that a similarity measurement result is accurate and quality of the final second denoising video image can be guaranteed. Based on a low rank approximation mode, the final second denoising video image is acquired so that a denoising effect of the video image is increased.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +2
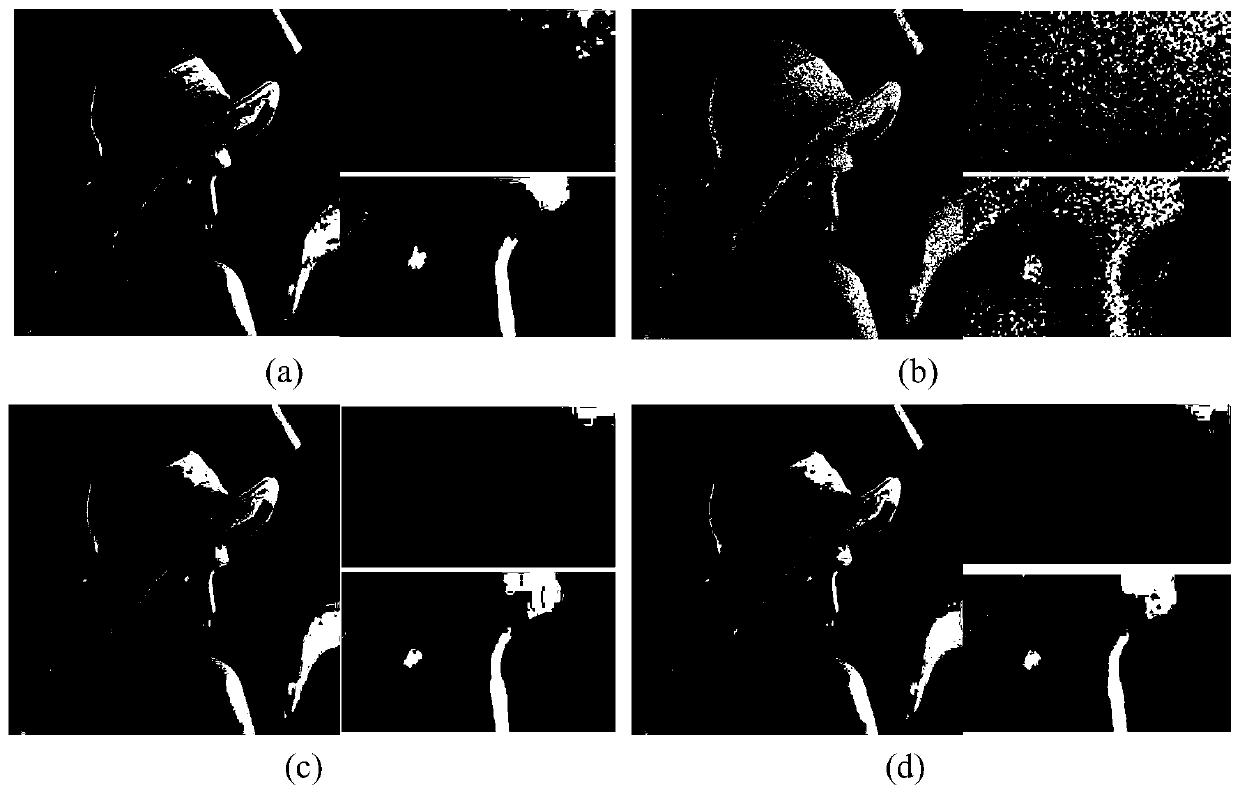
Tire defect detection method based on singular value decomposition
ActiveCN107194920AAvoid missing detectionAvoid false detectionImage enhancementImage analysisSingular value decompositionComputer vision
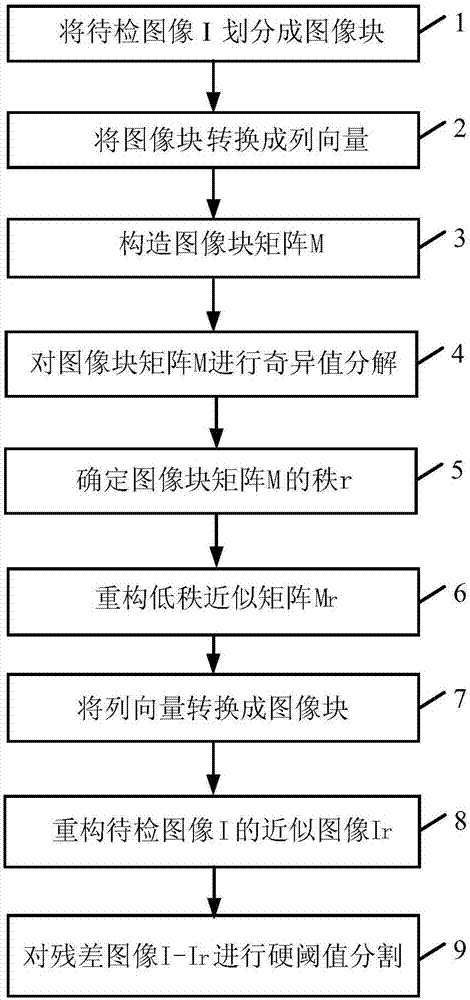
The invention provides a tire defect detection method based on singular value decomposition. A to-be-detected image I containing n pixels is divided to n m*m image blocks; each image block Pi is converted to a column vector ci; column vectors corresponding to all image blocks are used to construct an image block matrix M; through sequentially calculating the ratio of adjacent two singular values, the rank r of the image block matrix M is determined; the former r maximum singular values of the image block matrix M and the corresponding left singular vectors and right singular vectors are used to reconstruct a low-rank approximation matrix Mr of the image block matrix M; each column vector in the low-rank approximation matrix Mr is converted to an image block; all image blocks P<r> are used to reconstruct an approximate image Ir of the to-be-detected image I; hard threshold segmentation is carried out on a residual image I-Ir, a binary image Ib is obtained, and coordinates corresponding to a pixel with a gray value to be one in the image are the defect position. The detection method can position the specific defect position, missed detection and error detection caused by manual operation are avoided, and the defect detection accuracy is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF FINANCE & ECONOMICS
Image denoising method through combination of adaptive nonlocal samples and low rank
ActiveCN107292855AClear structureOvercome the edgeImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionPeak value
The invention discloses an image denoising method through combination of adaptive nonlocal samples and low rank. Firstly an image is transformed to a logarithmic domain by using logarithmic transformation, and a multiplicative noise model is transformed into an additive noise model; the image is partitioned and grouping is performed according to the similarity so as to obtain image groups having similar blocks; then low-tank approximation processing is performed on the image groups so as to obtain an initial estimation value; then adaptive nonlocal sample model processing is performed on the initial estimation value so as to obtain a logarithmic domain recovery result; and finally the logarithmic domain image is restored to a real number domain by using exponential transformation and corrected so as to obtain a final denoised image. The experiment result indicates that the method has great robustness for the multiplicative noise, and the great peak signal-to-noise ratio and the structural similarity can be obtained and the visual quality of the image can be greatly improved for the image having the multiplicative noise.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Convolution neural network training apparatus and method thereof
ActiveUS10452979B2Reduce in quantityReduce the number of outputsImage enhancementImage analysisReconstruction filterLow-rank approximation
An apparatus and method of training a convolutional neural network (CNN) are provided. A method of training a CNN including a plurality of convolution layers stored in a memory involves approximating, using a processor, a convolution layer among the plurality of convolution layers using a low-rank approximation; reducing the number of output reconstruction filters of the approximated convolution layer; and modifying a structure of the CNN based on an approximation result and the reduced number of output reconstruction filters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A matrix completion method
InactiveCN108537738AHigh precisionImage enhancementComplex mathematical operationsMagnetic resonance spectroscopicImaging processing
The invention relates to a high precision matrix completion method based on low-rank approximation. In actual use, large-scale data are often needed in fields such as image processing, commodity recommendation systems and magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Collection of large-scale data requires a lot of time. One way is to accelerate data collection by collecting partial signals and to recover complete signals based on low-rank characteristics of the data. The method comprises the steps of approximately calculating the rank of a matrix by using an approximation function, building a rebuilding model for missing signals of the matrix and finally rebuilding the signals through an iterative algorithm. A rebuilt matrix is high in precision, the operation is easy, and the method can recover complete signals from a small amount of data.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
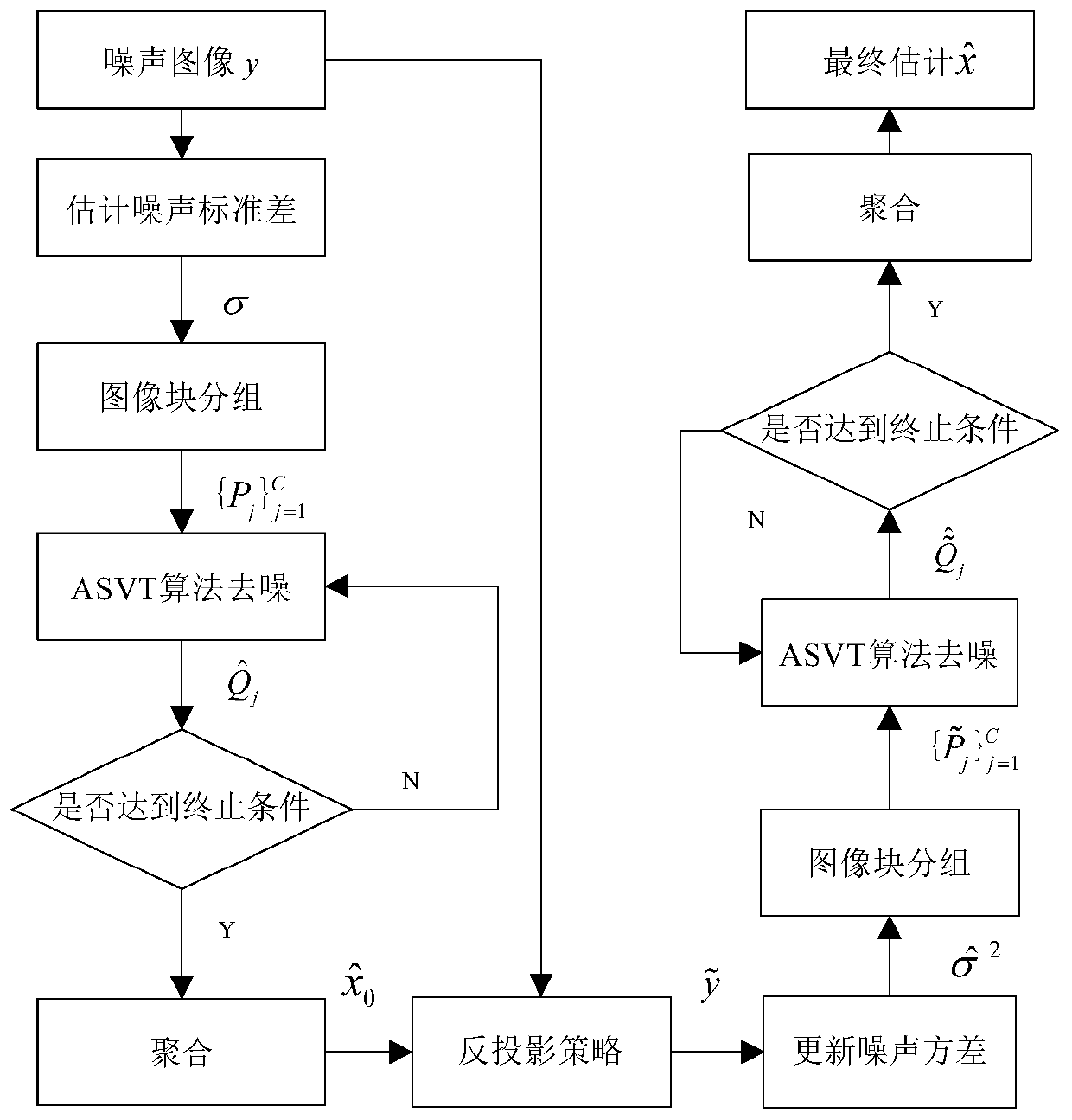
Two-stage image denoising method based on adaptive singular value threshold
PendingCN110349112ARestore textureReduce time complexityImage enhancementImage denoisingPattern recognition
The invention discloses a two-stage image denoising method based on an adaptive singular value threshold, which performs denoising estimation twice, and comprises the following steps of: dividing an original image to be denoised into a plurality of image blocks with the same size, and grouping similar image blocks through a block matching method to form a similar group matrix; converting a denoising problem into a low-rank approximation problem, and estimating similar image blocks of each group by using an adaptive singular value threshold; aggregating the estimated image blocks into an initial denoised image; in order to improve the first denoising result, adopting a two-stage strategy with a back projection step to further suppress noise residual errors, and generating a new noise image;and repeating the steps of the previous first stage to generate final denoising estimation. According to the method, more edge details which are easily blurred can be retained subjectively, the problem that a denoising result is too smooth is solved, the visual effect of the image is improved, and the calculation cost is reduced through fewer iterations.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF BUSINESS & TECH
Electronic apparatus and controlling method thereof
PendingUS20200364558A1Reduce power consumptionReduce response delayMemory architecture accessing/allocationNeural architecturesMatrix decompositionAlgorithm
Provided is an electronic apparatus. The electronic apparatus includes a memory and a processor. The processor is configured to apply a low rank approximation using a matrix decomposition for a first square matrix among a plurality of square matrices based on parameter values of a deep learning model, and obtain a first approximated matrix and a second approximated matrix for the first square matrix, obtain second approximated matrices for each of a plurality of remaining square matrices other than the first square matrix among the plurality of square matrices, based on the first approximated matrix for the first square matrix, and store the first approximated matrix the first square matrix and the second approximated matrices for each of the plurality of square matrices in the memory.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
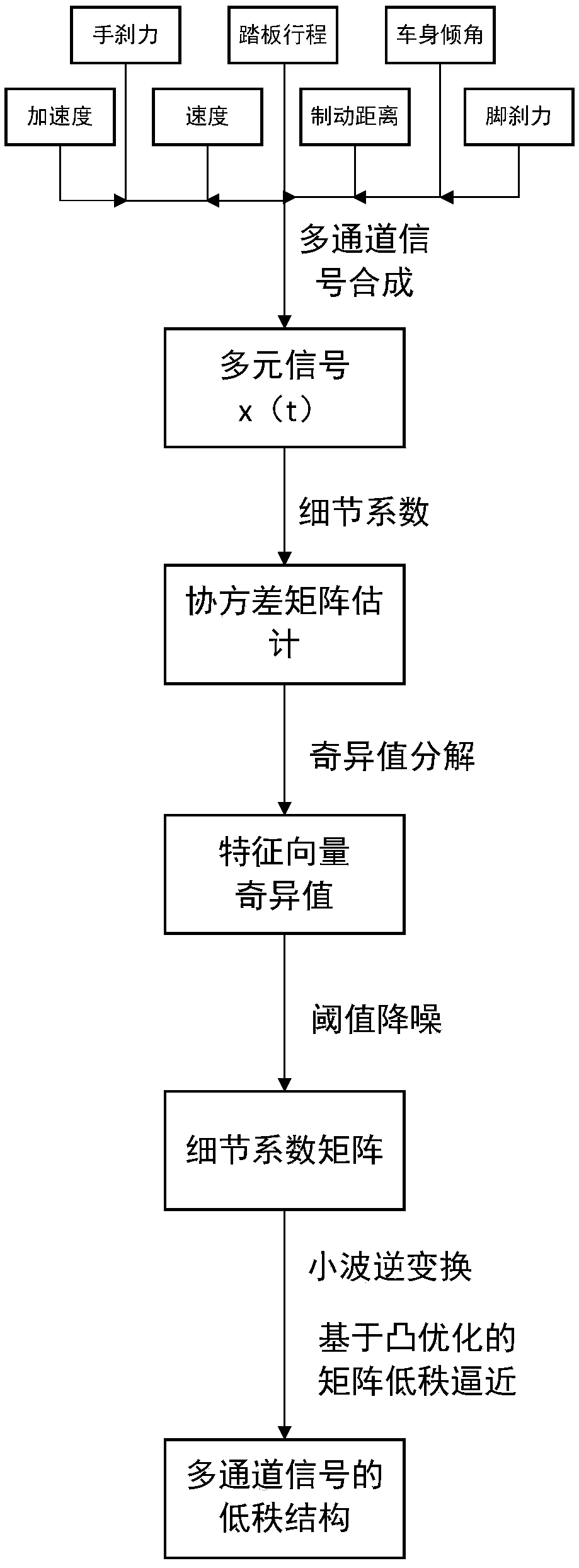
Multichannel wireless distributed braking data transmission method for a motor vehicle in defined field
ActiveCN108833024AReduce the impact of noiseAvoid interferenceRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTransmission noise reductionSingular value decompositionSignal quality
The invention discloses a multichannel wireless distributed braking data transmission method for a motor vehicle in a defined field, and the method comprises the steps: synthesizing a plurality of physical quantity signals in a process of detecting the braking performances of the motor vehicle in the defined field into one multi-element signal, and carrying out the discrete wavelet transform of the multi-element signal to achieve the noise reduction of the signal of each channel, thereby obtaining a discrete wavelet coefficient of each channel; obtaining covariance matrix estimation of noise through a detail coefficient, and carrying out the SVD (singular value decomposition) of the covariance matrix; determining a threshold value of noise reduction of the signal of each channel; carryingout the inverse wavelet transform of a detail coefficient matrix after threshold noise reduction; employing a matrix low-rank approximation method based on convex optimization for processing to obtaina low-rank structure of a multi-channel signal. The method can reduce the noise impact of each channel, can avoid the data interference between the channels, and guarantees the quality of the signal.Finally, the method achieves the compression of the signal to a certain degree, can reduce the difficulty of data transmission, and can improve the data transmission speed.
Owner:温州市特种设备检测研究院
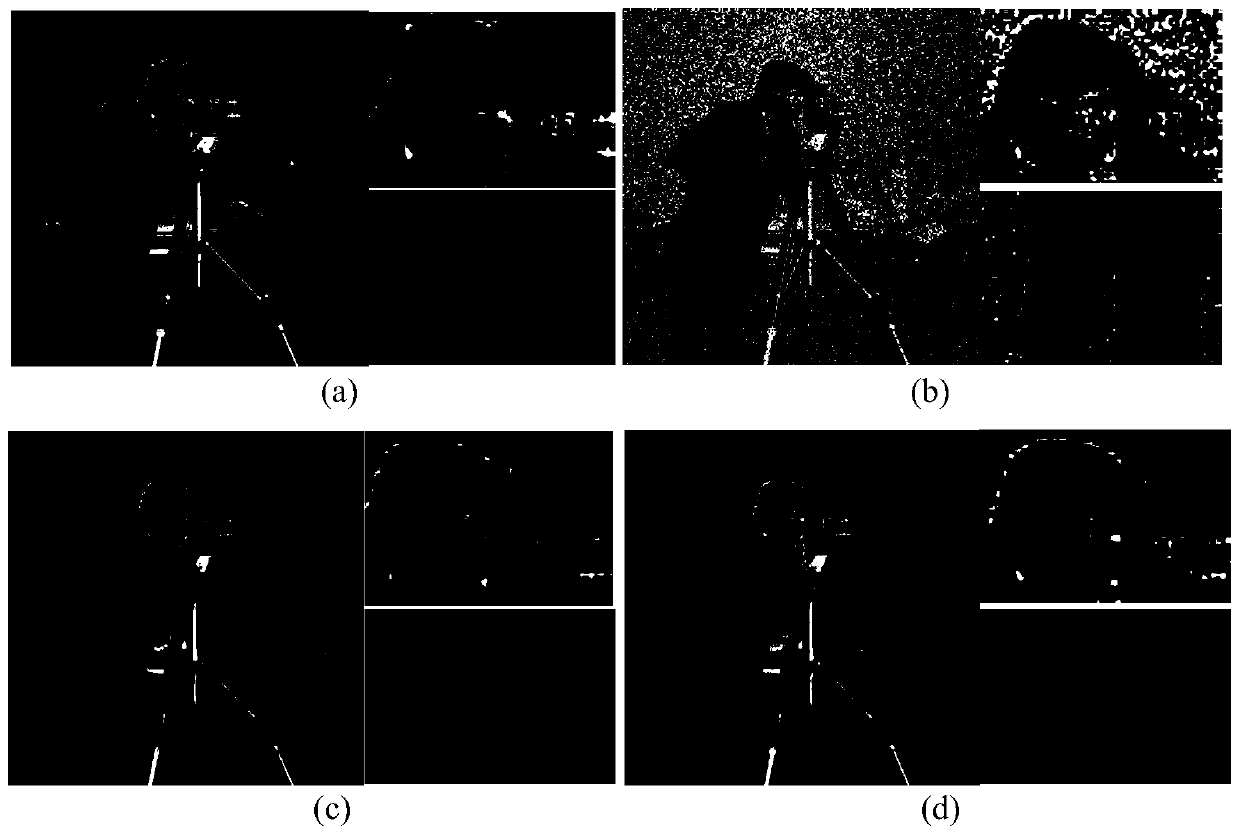
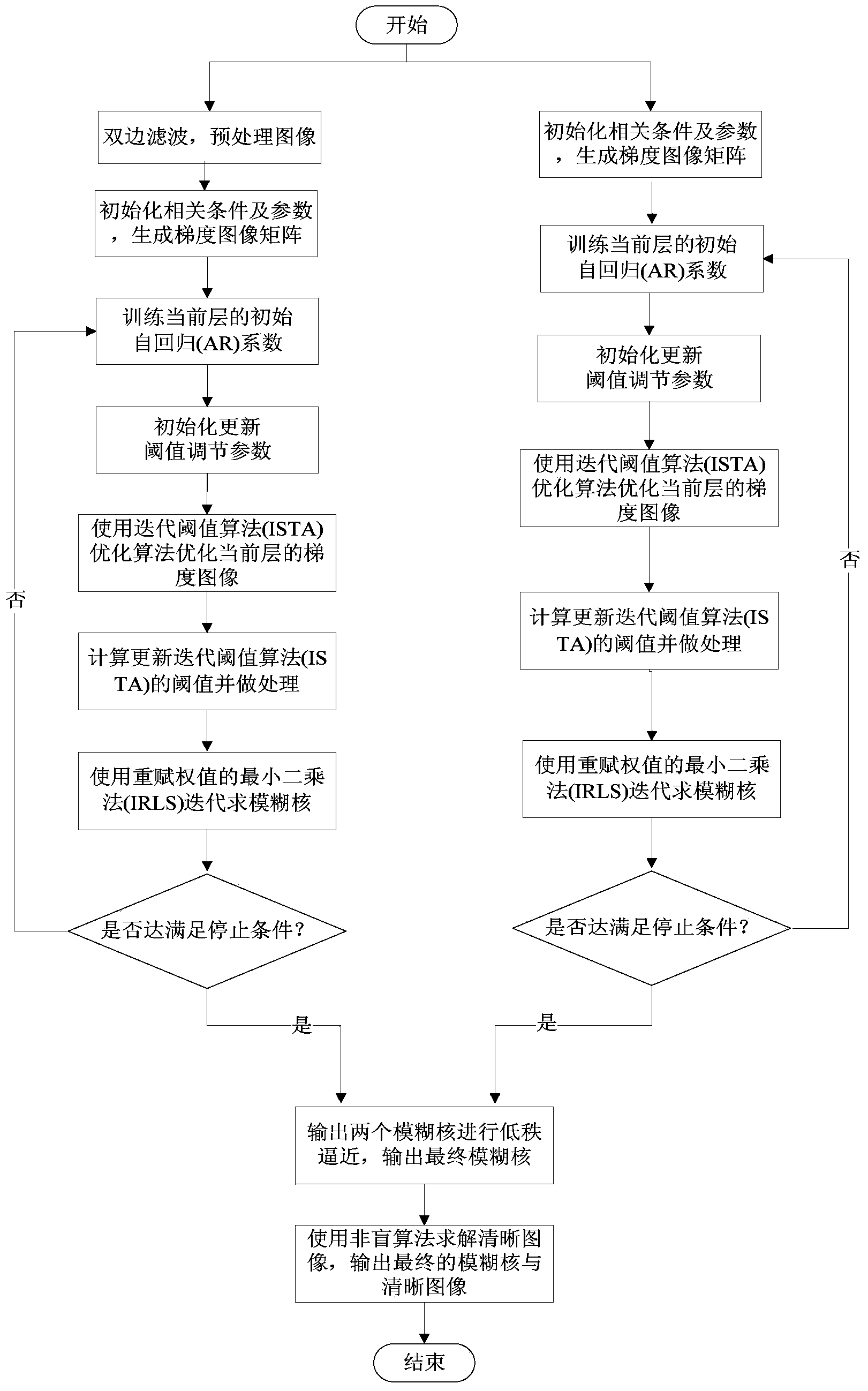
Low-rank approximation fuzzy nucleus estimation method for image blind restoration
ActiveCN104166961AReduce inaccuracyThe result of image blind restoration is goodImage enhancementIdeal imageNeighbor relation
The invention discloses a low-rank approximation fuzzy nucleus estimation method for image blind restoration, mainly for solving the problems of how to more accurately realize fuzzy nucleus estimation in a conventional image blind restoration method and how to accordingly restore an ideal image. The realization steps comprise: on one hand, taking a neighbor relation of a gradient image into consideration, and improving an iteration threshold strategy by use of an autoregression (AR) strategy so as to estimate a fuzzy nucleus; on the other hand, enhancing image margin information by use of a heuristic filter to estimate another fuzzy nucleus; afterwards, introducing a low-rank approximation strategy to a fuzzy nucleus estimation process to solve a more reliable fuzzy nucleus; and finally, restoring a clear image by use of an advanced image restoration method. Compared to some conventional methods, the method provided by the invention has the following advantages: PSNR, SSIM and FSIM values are higher, the visual effect is better, fuzziness is effectively removed, more details are maintained, and the designed fuzzy nucleus is also more accurate.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
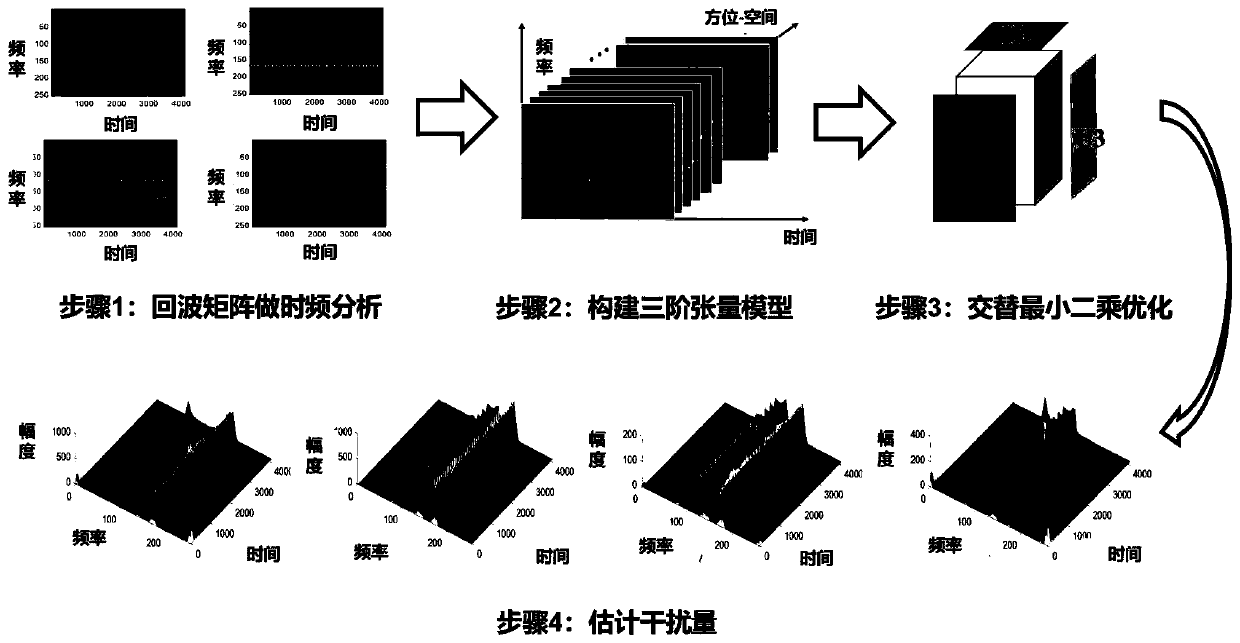
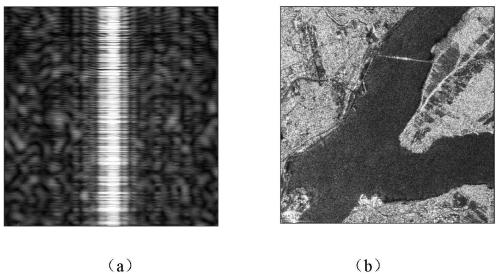
Synthetic aperture radar interference suppression method based on tensor low-rank approximation
ActiveCN111398912AImprove image qualityGuaranteed interference separation performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlternating least squaresSynthetic aperture radar
The invention provides a synthetic aperture radar interference suppression method based on tensor low-rank approximation. Correlation coupling between low rank of interference in a time-frequency representation space and azimuth echoes is deeply mined. A two-dimensional radar echo is constructed into a three-order frequency-time-azimuth tensor, the tensor low-rank approximation technology is combined, the energy of interference is estimated through alternating least square optimization iteration, and effective separation of the interference and a target echo is achieved in a tensor representation space. According to the invention, the tensor low-rank approximation technology is utilized to realize effective separation of interference and target echo, so as to improve image imaging quality.Compared with a traditional method for processing single azimuth echoes one by one at a specific moment, iterative optimization solving is conducted by comprehensively utilizing the low rank performance of the time-frequency space and the coupling relevance of the azimuth space, the interference separation performance can be guaranteed, and meanwhile the operation efficiency is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com