Patents
Literature
84results about How to "Drawback mentioned" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
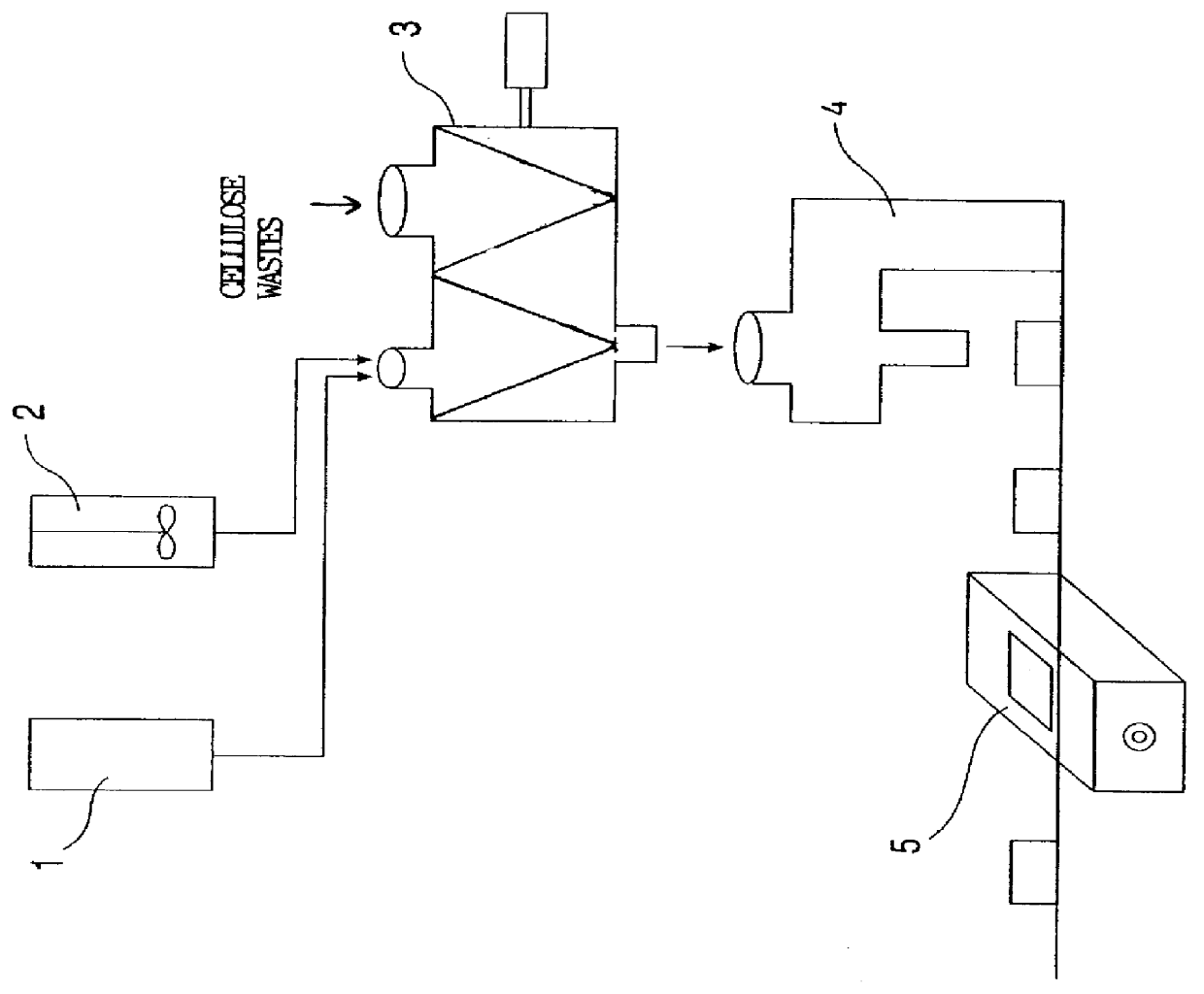
Method of bioconversion of industrial or agricultural cellulose containing wastes
InactiveUS6159510ADrawback mentionedHigh in proteinMilk preparationFood processingCelluloseMicroorganism
PCT No. PCT / IL98 / 00437 Sec. 371 Date Feb. 8, 2000 Sec. 102(e) Date Feb. 8, 2000 PCT Filed Sep. 10, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO99 / 12429 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 18, 1999A method of bioconversion of organic industrial or agricultural cellulose containing wastes into proteinaceous product. The method comprises comminution of the wastes with moistening and addition of a starting culture inducing their biological degradation and conversion into simple carbohydrates. The carbohydrates are fermented into digestible products. The starting culture comprises cleaving enzymes produced by edible microorganisms such as fungus and bacteria selected from the group consisting of Ilumicola grisea, Trichoderma harzanum, Ruminococcus albus.
Owner:BIOFEED
Upgraded inhalator for powder preparations
InactiveUS20120160241A1Improve efficiencyEasy and more functional loadingRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsInhalationInhalators
An upgraded inhalator for powder preparations comprises a main body having an inhalation channel, an external opening accessible by a user, and a tank adapted to receive a dose of powder preparation. The tank is opened to establish communication with the inhalation channel. At least one protuberance protrudes or extends towards the inside of the inhalation channel. Each protuberance defines substantially concave impact surface and is arranged on the opposite side to the external opening. The impact surface of each protuberance intercepts the powder preparation during its crossing of the inhalation channel towards the external opening.
Owner:OLIVA ROBERTO
Crosslinked polyethylene compositions
A method for making a polymer blend includes blending a thermoplastic polymer, a grafted polyolefin, a moisture source, and a crosslinking agent in a mixing zone to provide a thermoplastic polymer blend including a matrix phase of the thermoplastic polymer, a reinforcing phase of the at least partially crosslinked polyolefin, and having a gel content of from about 10% to about 50% by weight.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
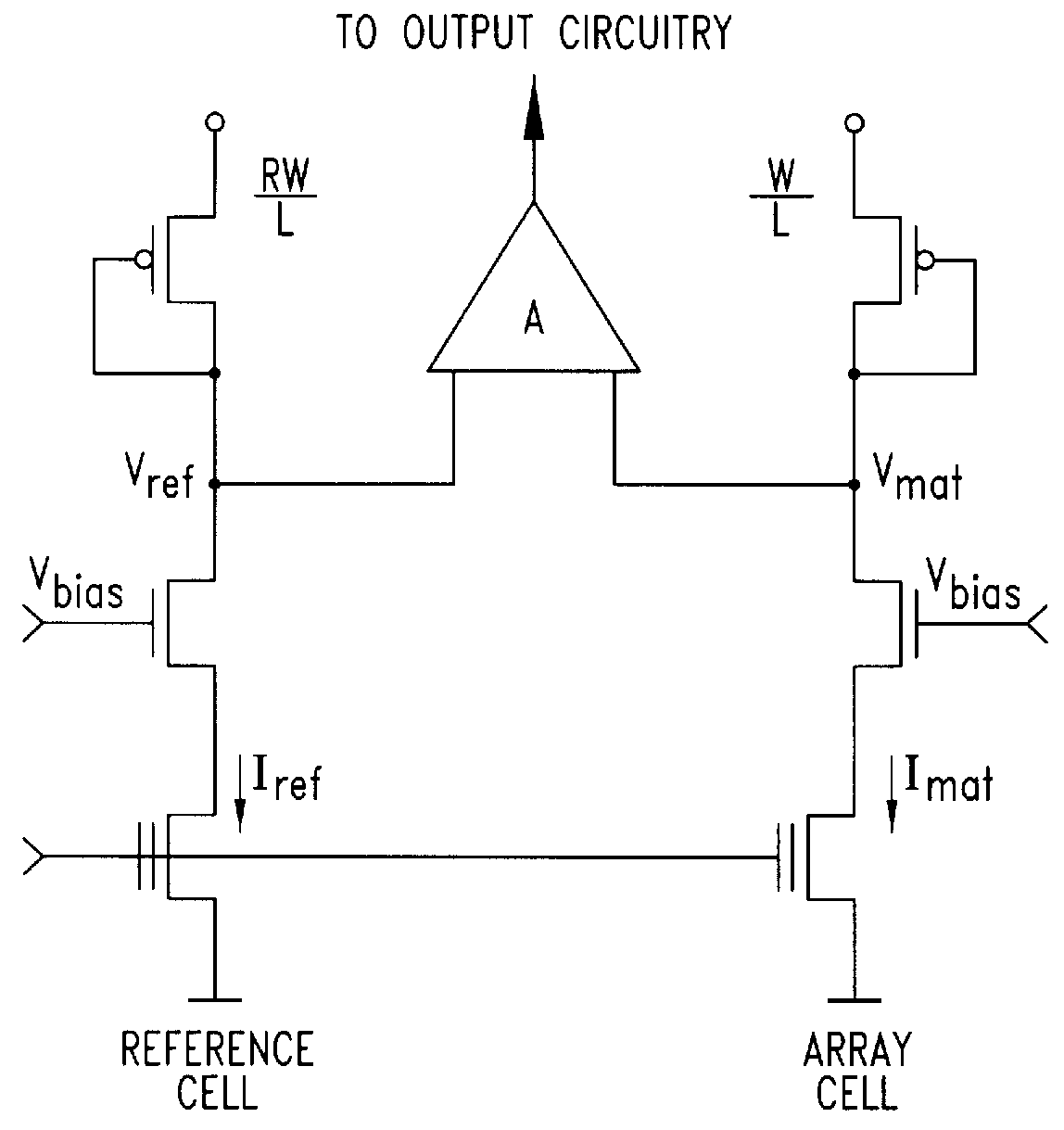
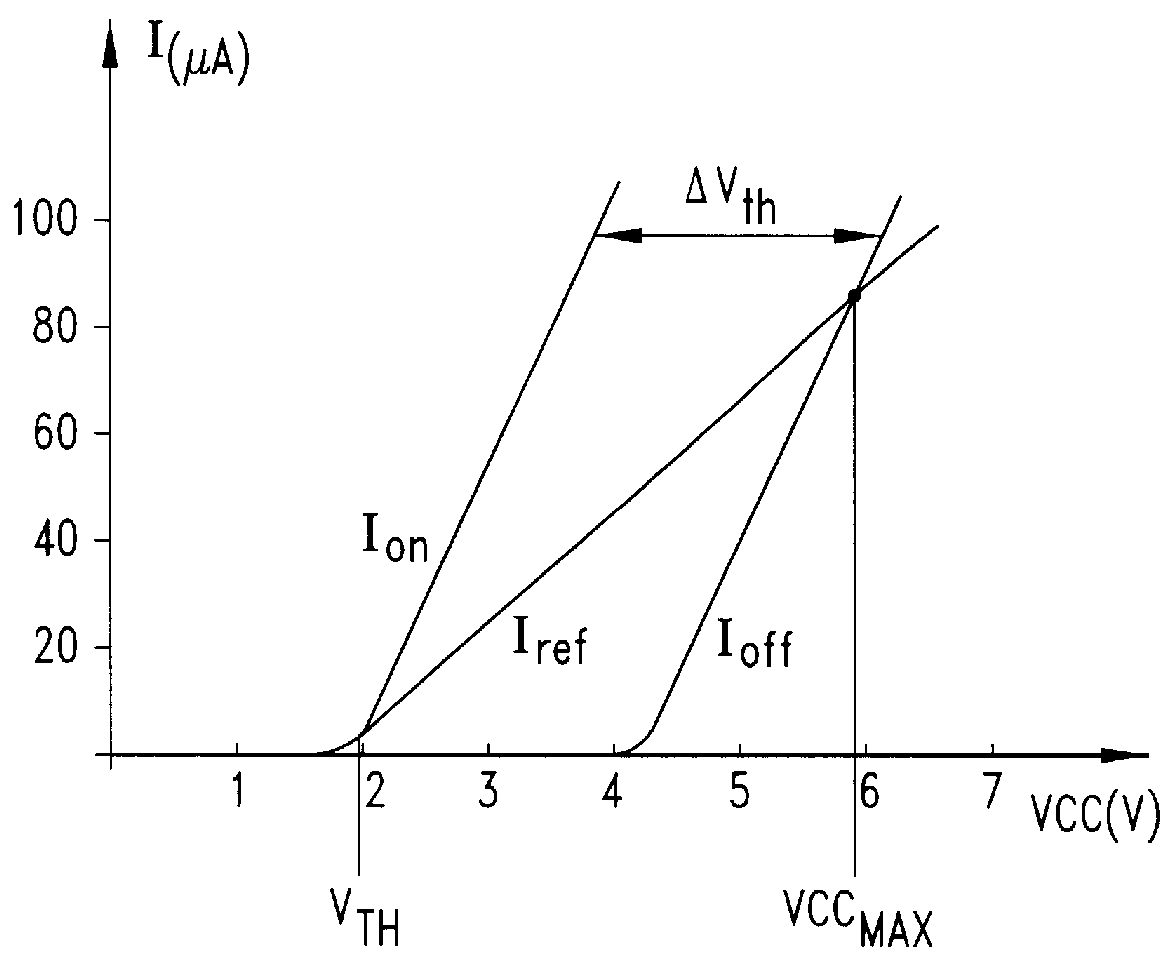
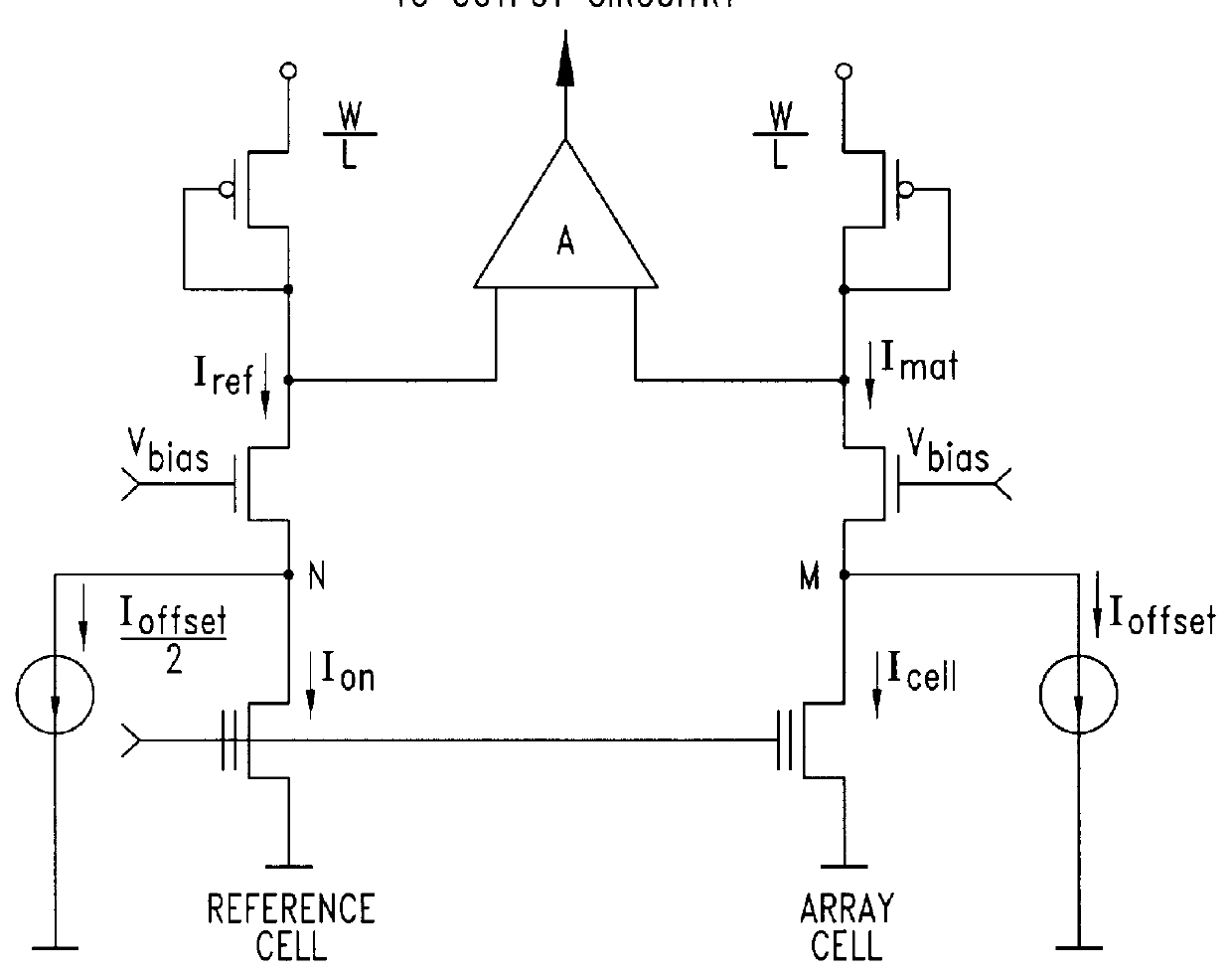
Sense circuit for reading data stored in nonvolatile memory cells
InactiveUSRE36579E1Avoid disadvantagesDrawback mentionedRead-only memoriesDigital storageAccess timeHemt circuits
A sense circuit for reading EPROM and ROM type memory cells employs a circuit for generating an offsetting current which is exempt of error during transients and which thus permits to achieve a reduced access time. On the other hand, the sense circuit maintains the intrinsic advantages of a current-offset sensing architecture which is represented by a substantially unlimited operating voltage range toward the maximum value VCCmax. The current generating circuit is driven by means of a supplementary row of cells which is decoded at every reading and which replicates, during transients, the behaviour of the row selected for the reading.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
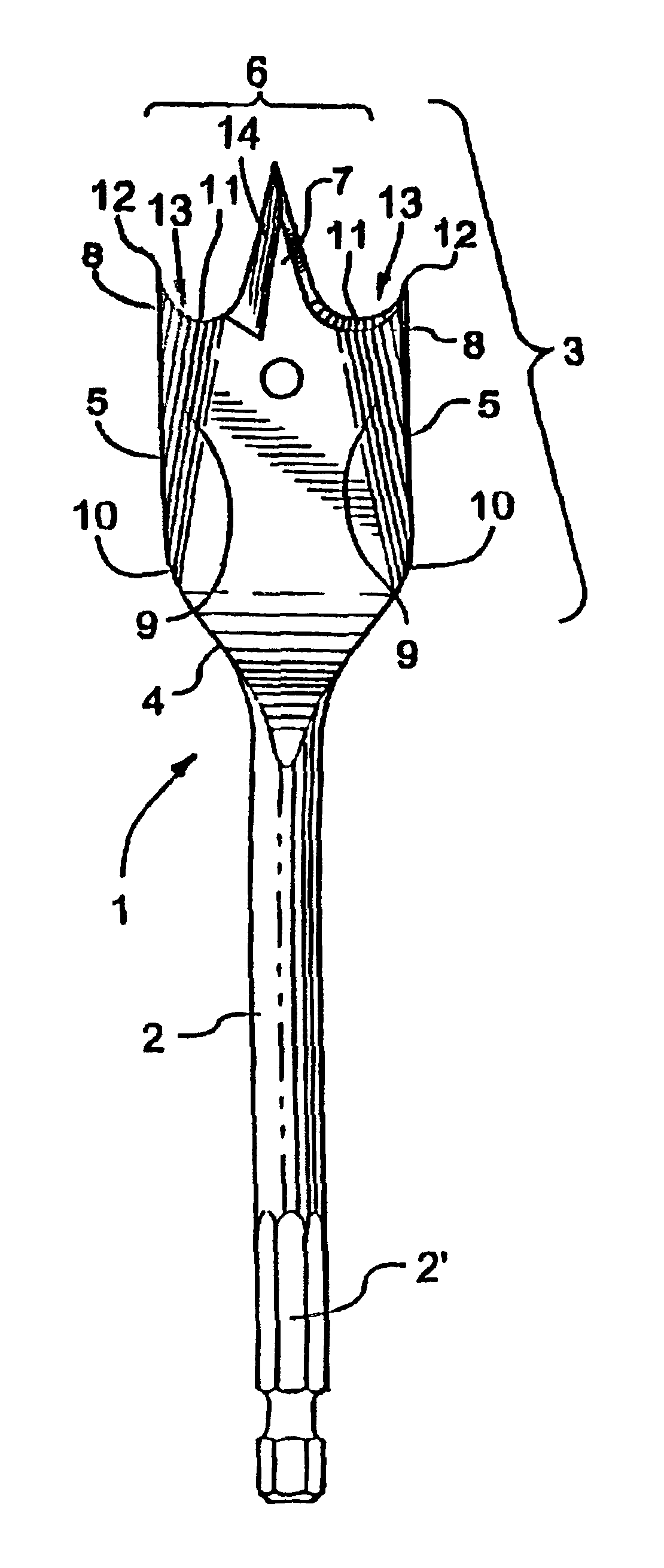
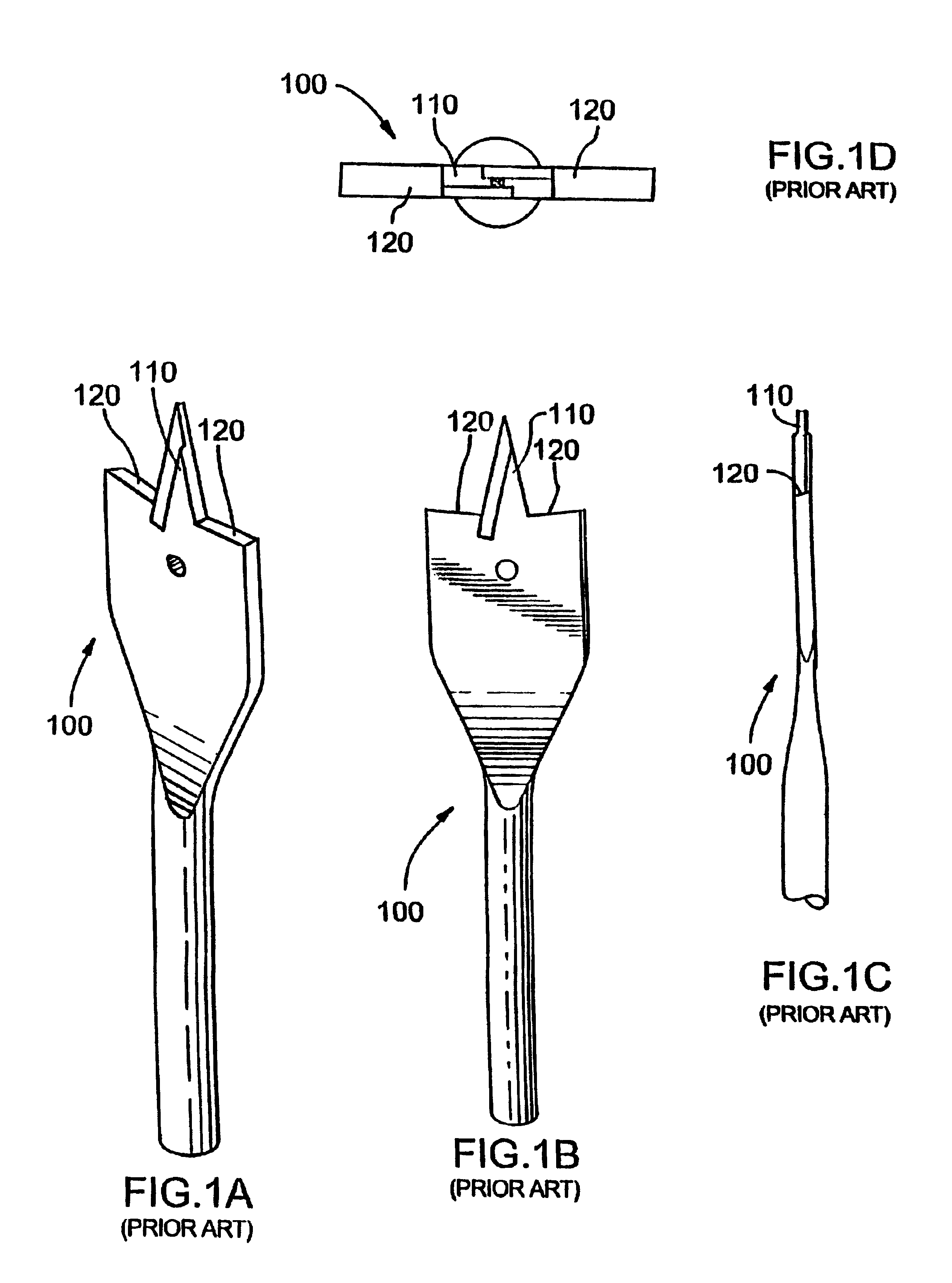
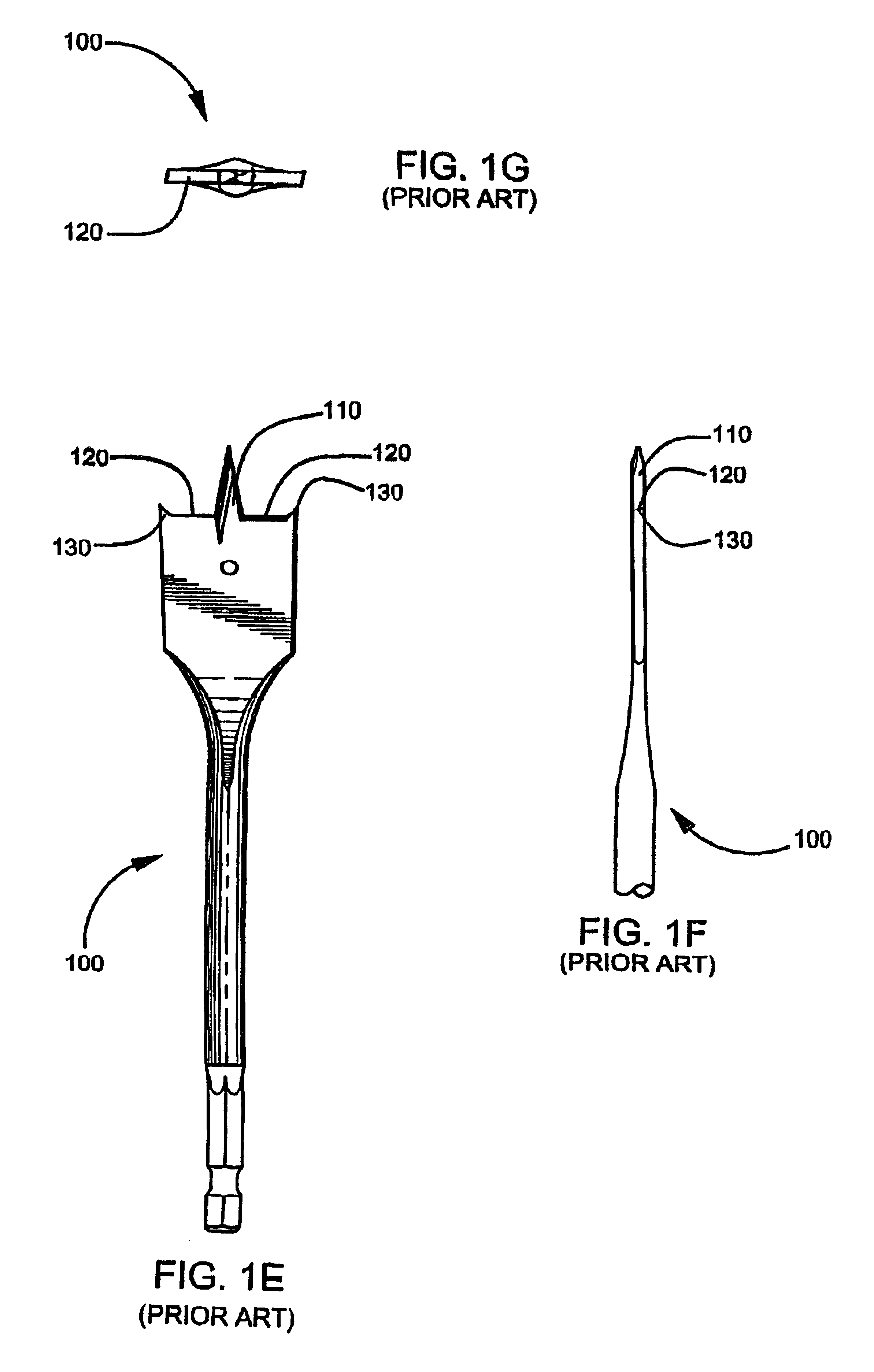
Spade bits with angled sides
InactiveUS6957937B2Improve Chip EvacuationDrawback mentionedWood turning toolsTransportation and packagingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A spade drill bit has a shaft and a spade head portion arranged on the shaft. The head portion has a rearward facing bottom edge, two longitudinal sides and a forward facing cutting edge. The cutting edge has a pointed, generally triangularly shaped tip and outer ends. The longitudinal sides of the head portion are bent along a bend in a direction of rotation of the drill bit during operation, so that the outer ends are bent forwards in the rotating direction. The bend runs from a first position at one of the longitudinal sides, closer to the bottom edge than to the cutting edge, and to a second position at the cutting edge between the outer end and the tip.
Owner:TEAM FAIR HLDG
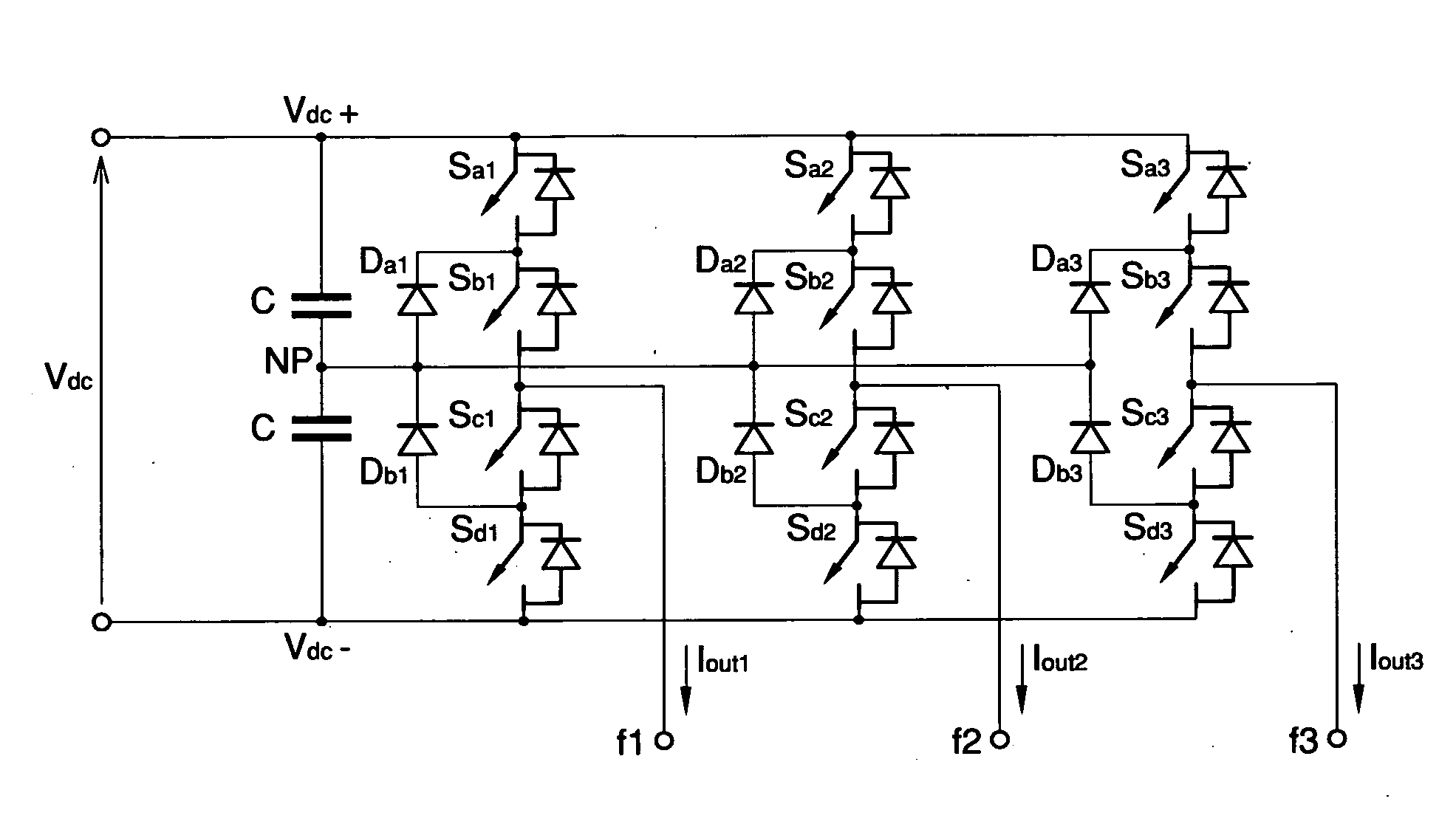
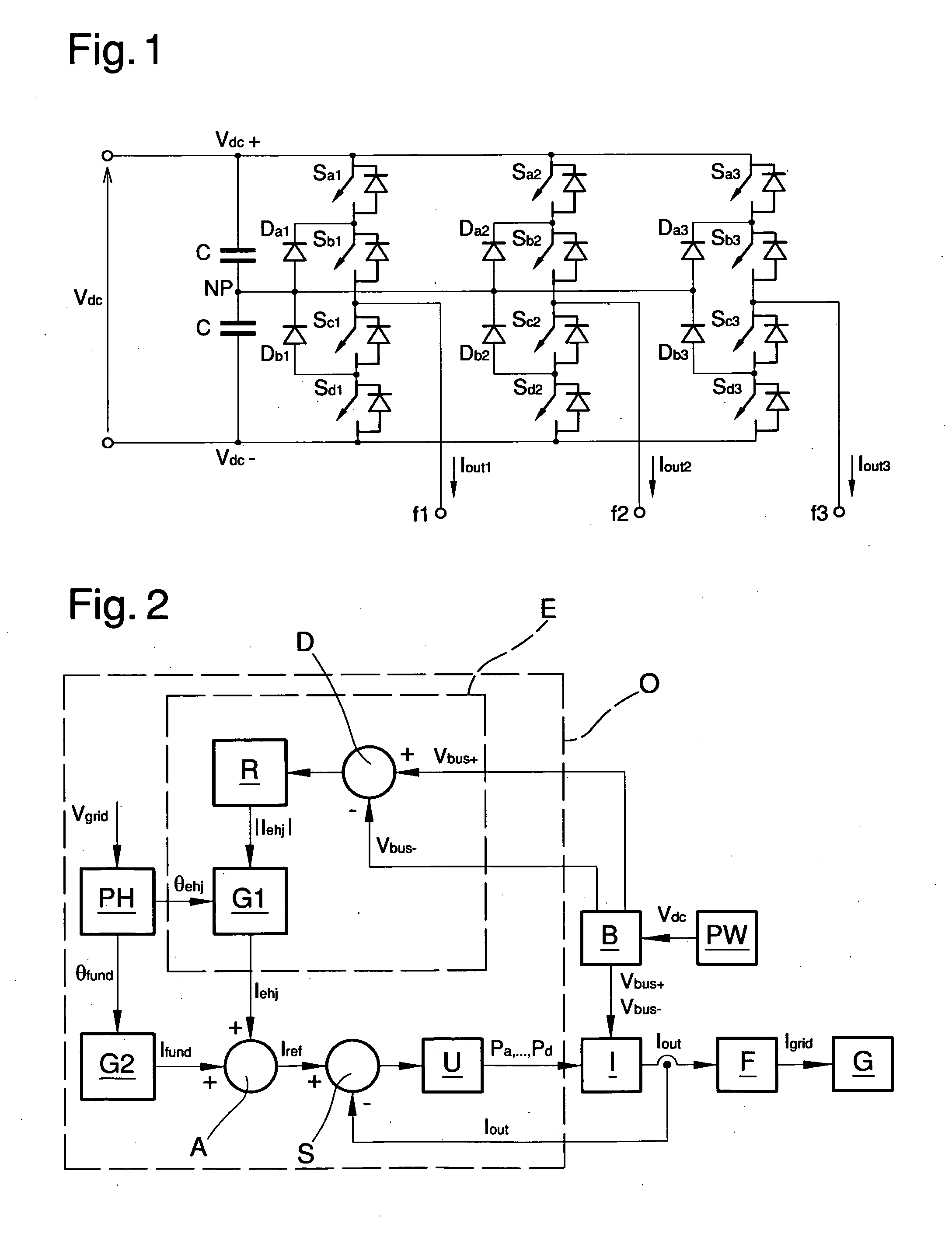
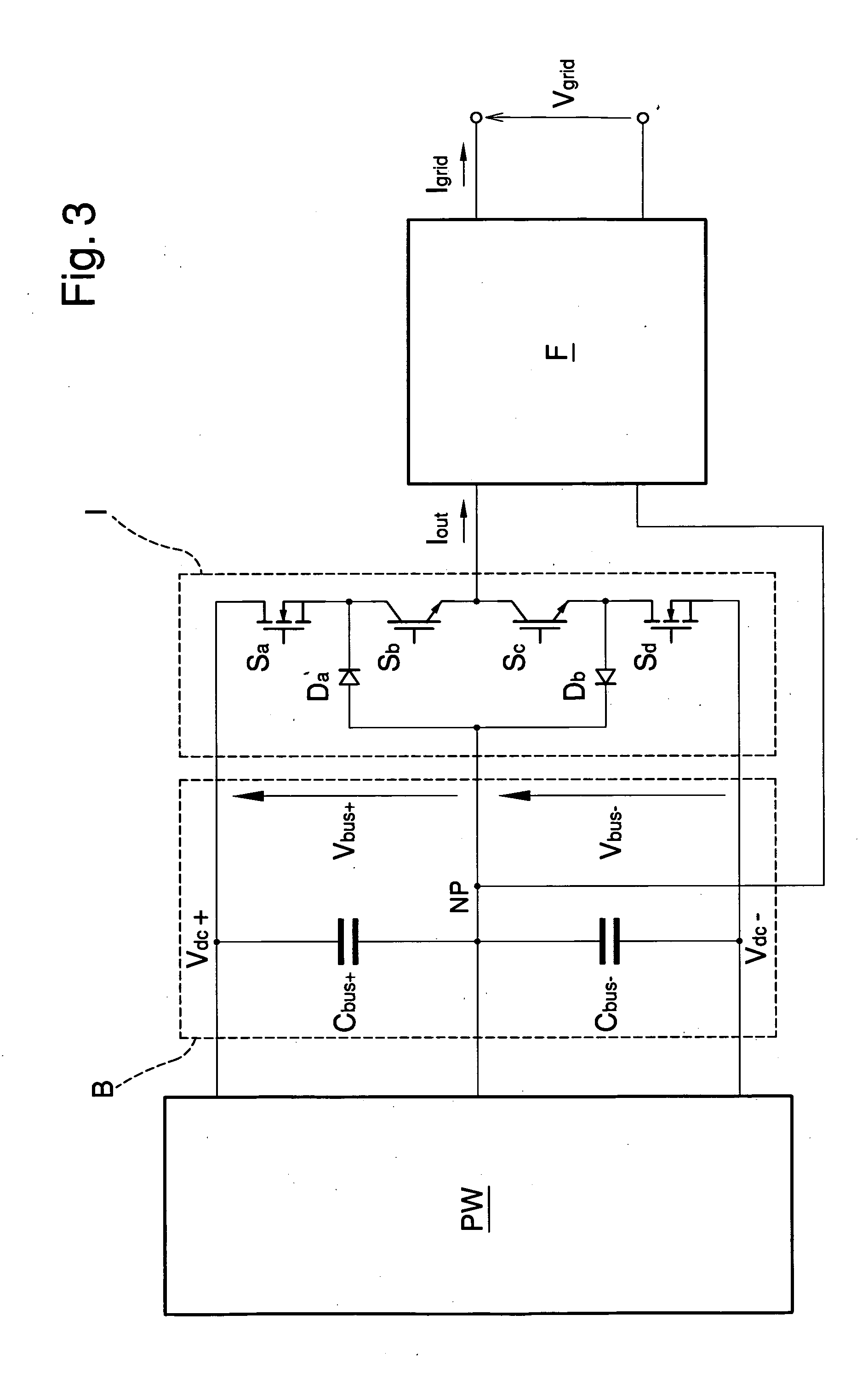
System and method for offsetting the input voltage unbalance in multilevel inverters or the like
InactiveUS20120281442A1Effective and easy to useIncrease costAc-dc conversionHarmonicReference current
The system for offsetting the input voltage unbalance in multilevel inverters or the like comprises a control unit operatively associated with a multilevel inverter for converting direct current into alternate current, the control unit being suitable for piloting the multilevel inverter for generating an output current depending on a reference current, and an equalisation unit for equalising the input voltages of the multilevel inverter having first generation means of a harmonic component of order equal to the reference current, out of phase with respect to the fundamental component of the reference current, detection means of the unbalance of the input voltages to the multilevel inverter, regulation means of the amplitude of the harmonic component depending on the detected unbalance, for offsetting the unbalance. The method for offsetting the unbalance of the input voltages in multilevel inverters or the like comprises a control phase of a multilevel inverter for converting direct current into alternate current, in which the multilevel inverter is piloted for generating an output current depending on a reference current, a generation phase of a harmonic component of order equal to the reference current, out of phase with respect to the fundamental component of the reference current, a detection phase of the unbalance of the input voltages to the multilevel inverter and a regulation phase of the amplitude of the harmonic component depending on the detected unbalance, for offsetting the unbalance.
Owner:META SYST
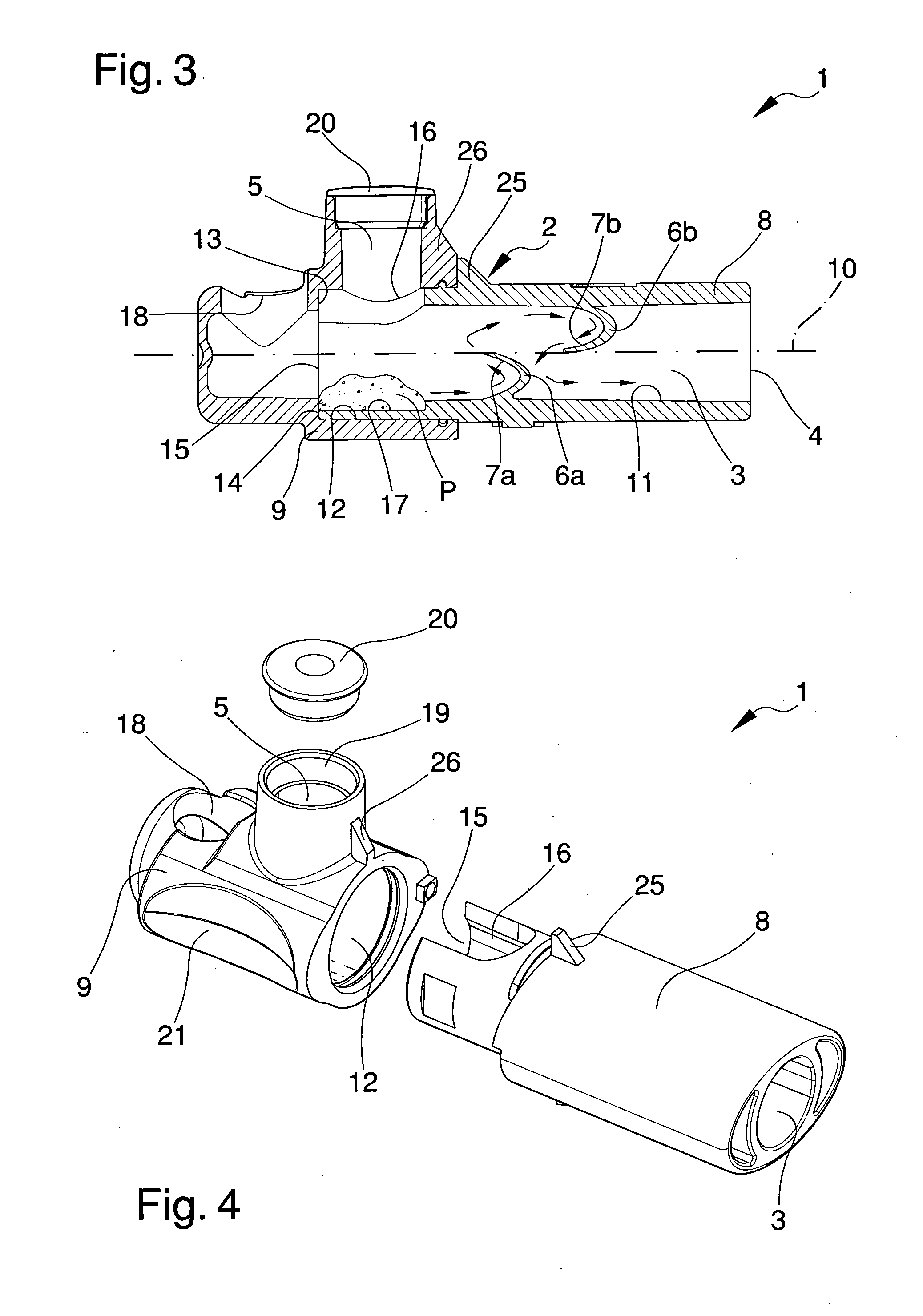
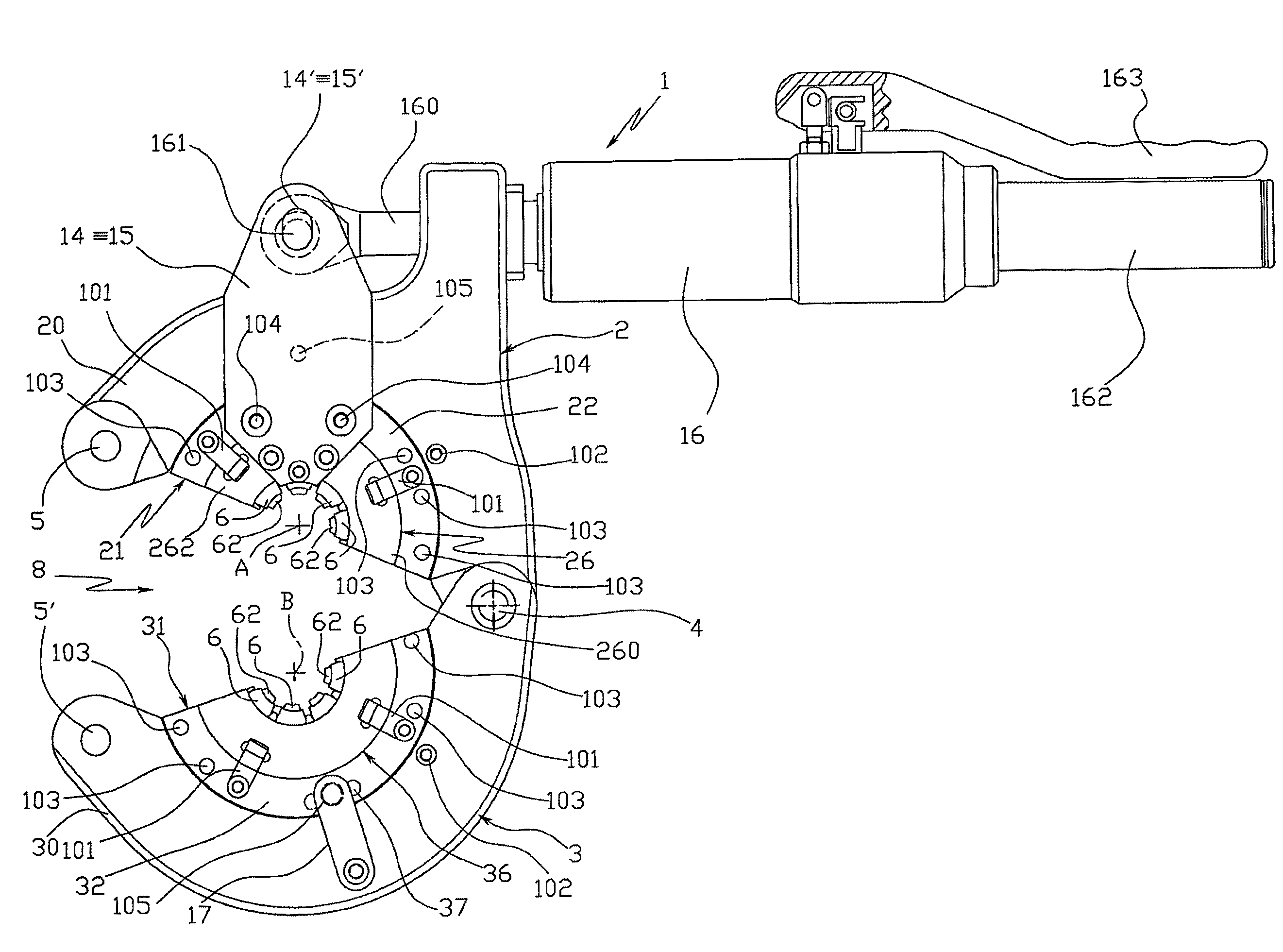
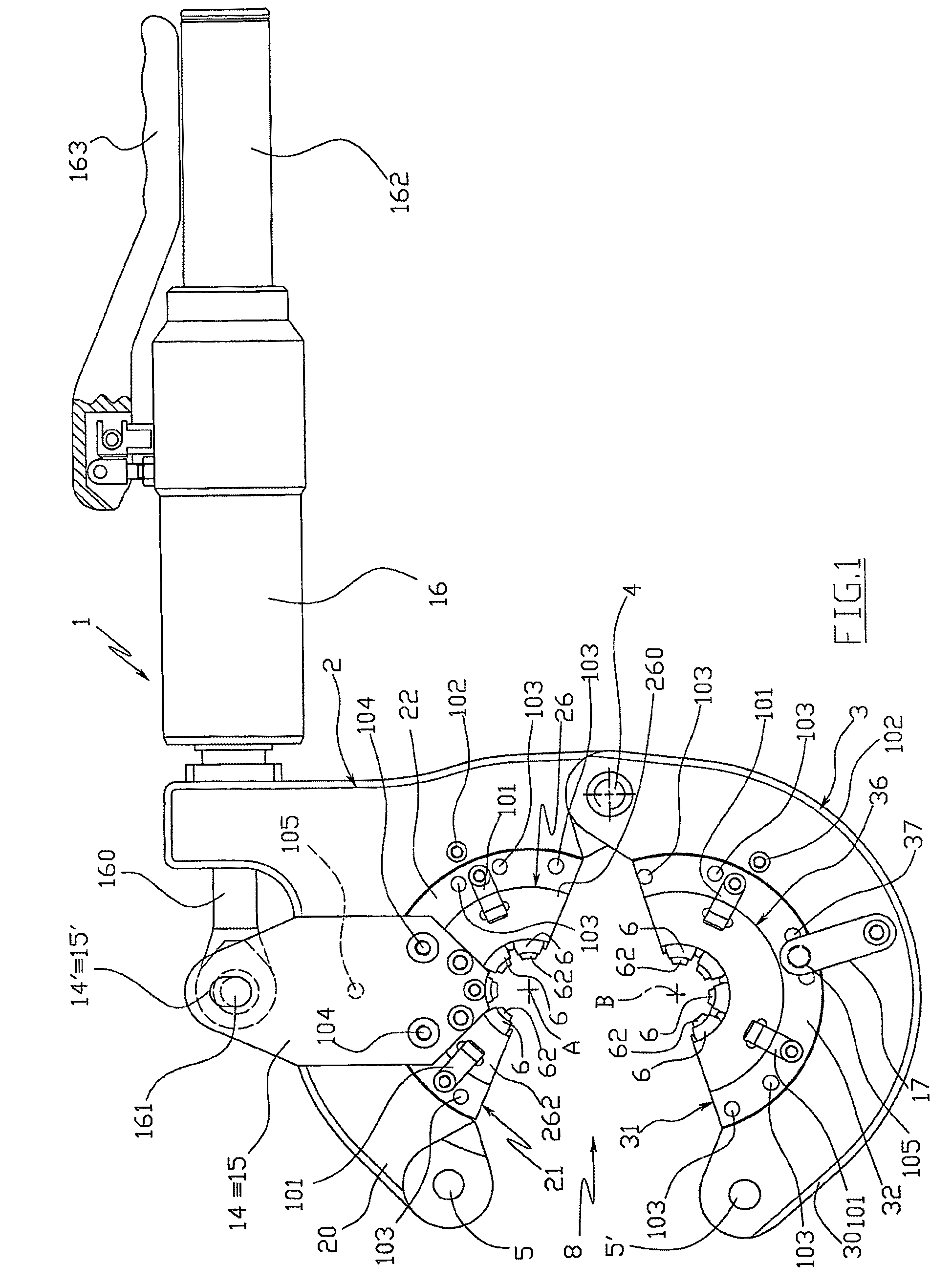
Tool for the connection of tubes by means of connection sleeves
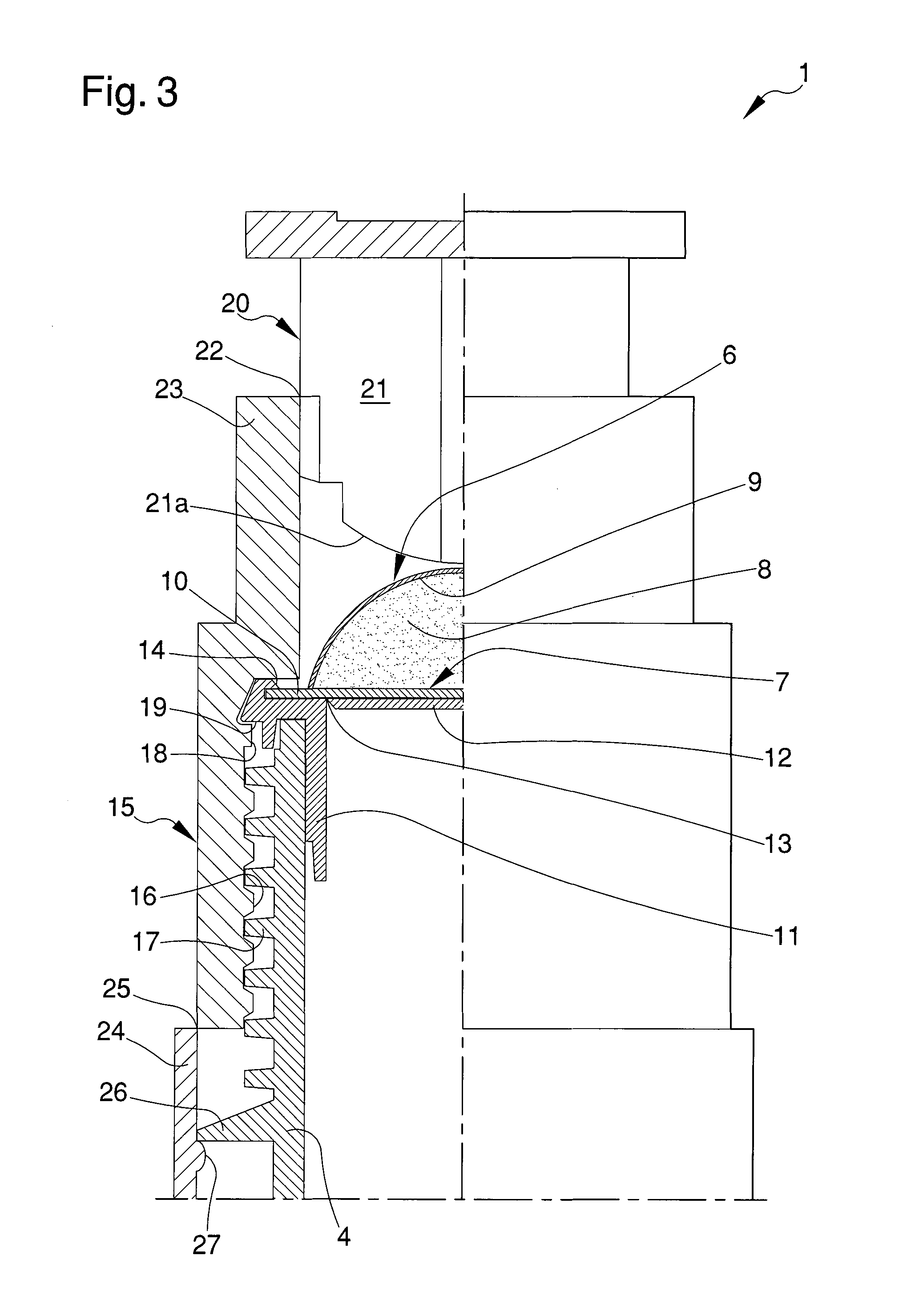
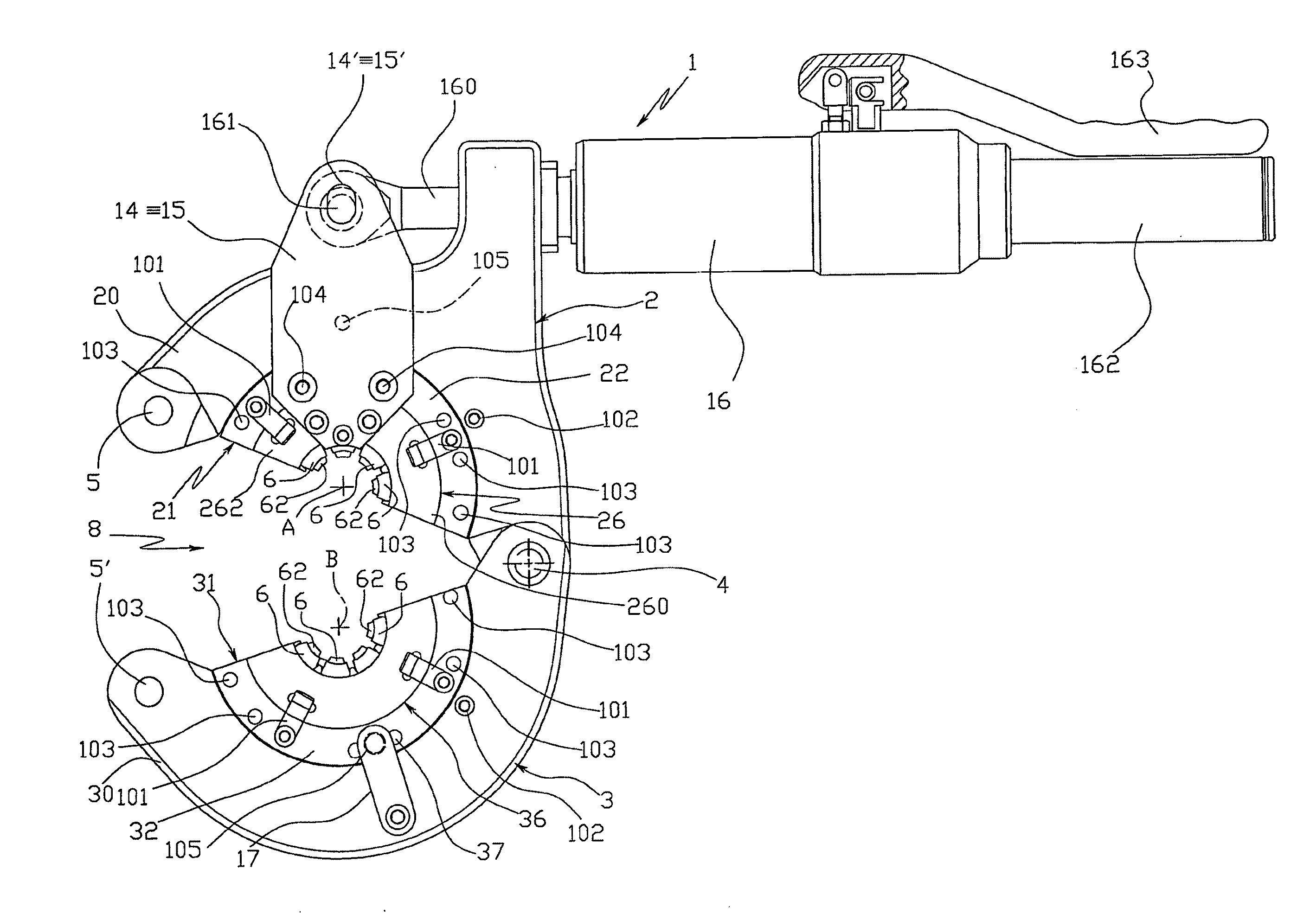
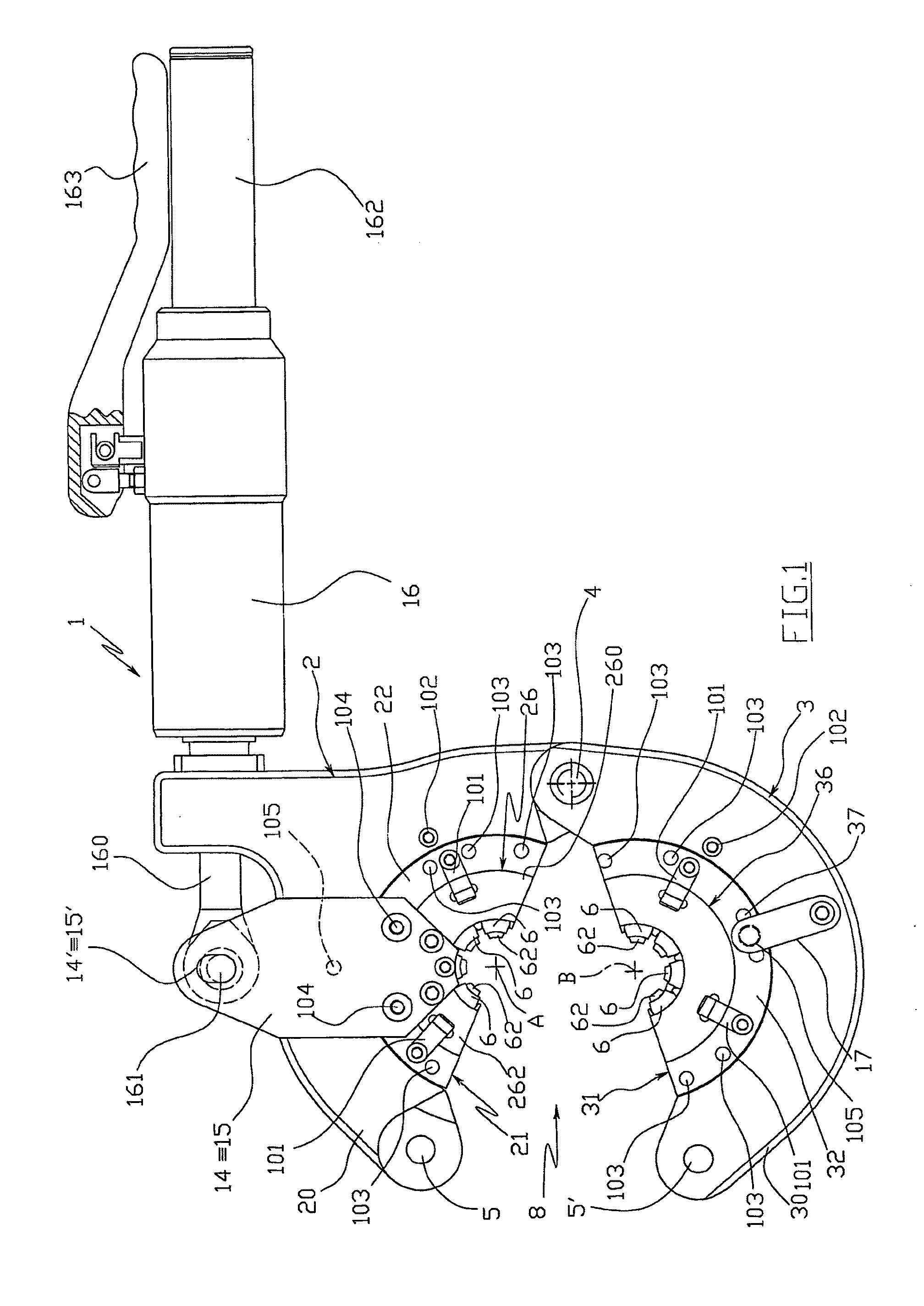
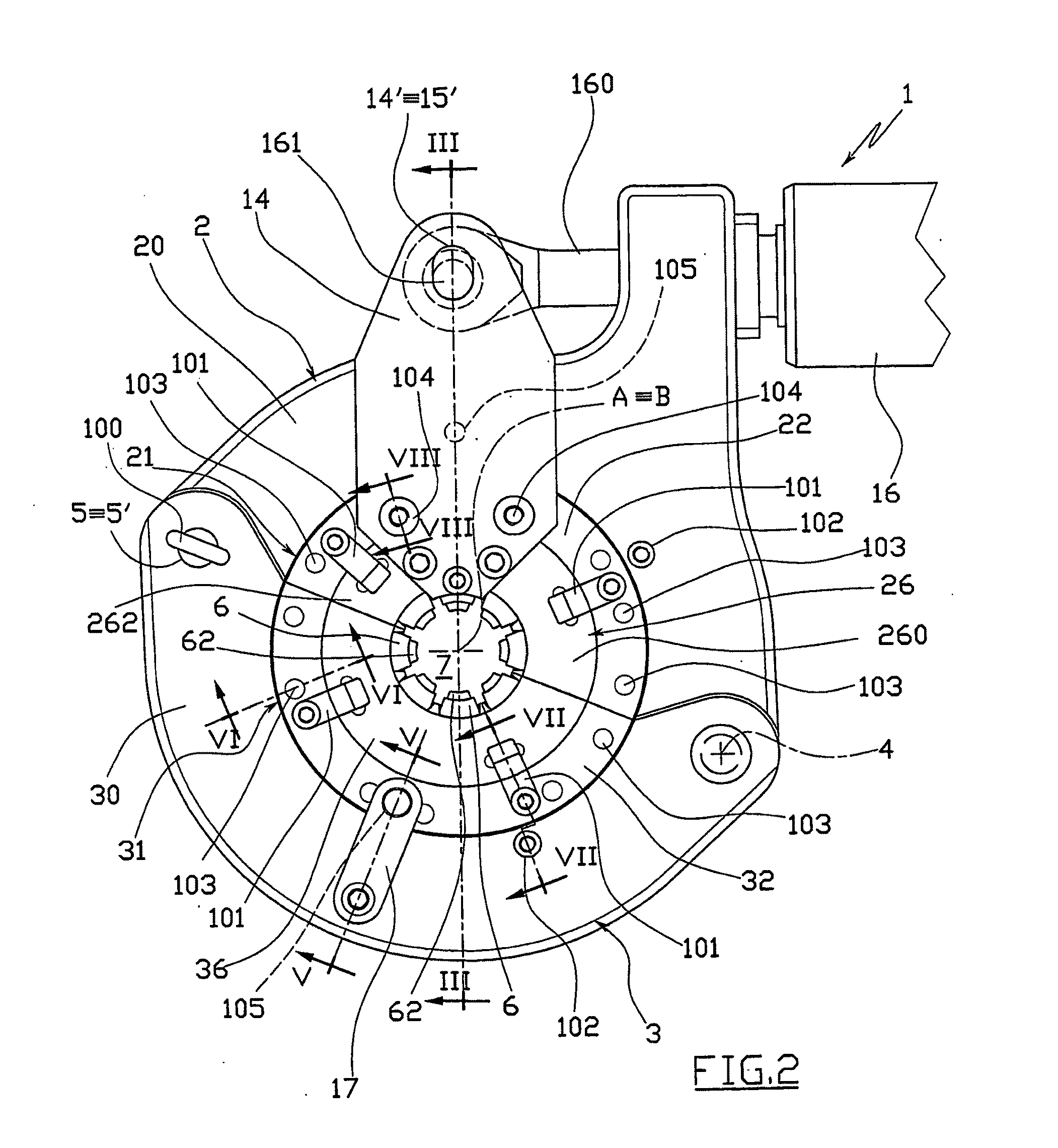
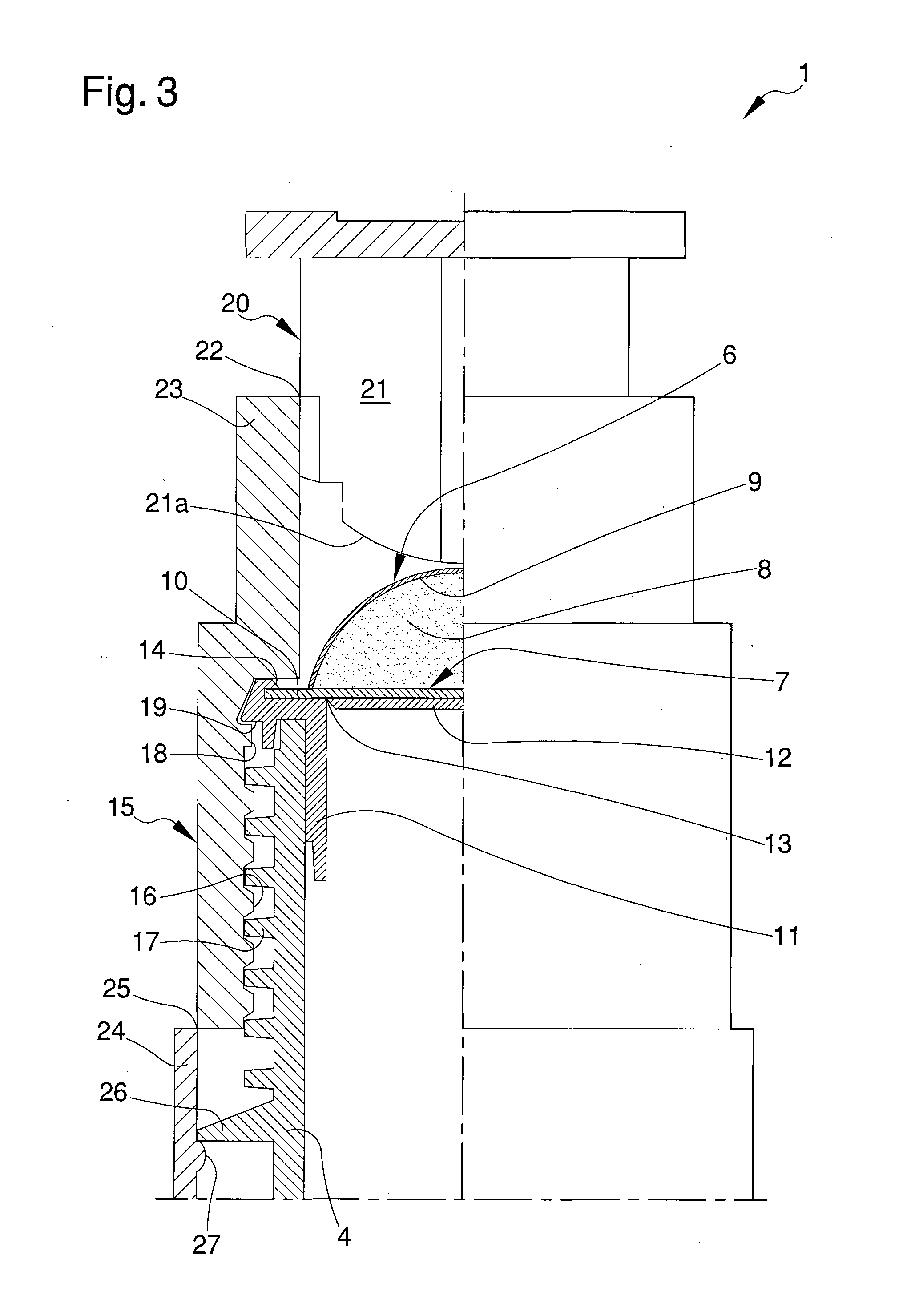
ActiveUS8336177B2Drawback mentionedLow costForging hammersPump installationsRest positionEngineering
A tool for the connection of tubes (T) by means of connection sleeves (C), comprising two jaws (2, 3) which are mutually movable between an open rest position, and a closed work position wherein they define an annular reception seat (7) of the connection sleeve (C), and wherein they turn a circumferential series of radial punches (6) towards the sleeve (C); said jaws (2, 3) each comprising at least one punch (6) sliding towards the center of said reception seat (7), and being mutually connected by means of a kinematic system which permits them, when they are found in said open rest position, to confer a generally open-ring shape to said reception seat (7), through whose lateral opening (8) the connection sleeve (C) can be inserted and extracted by lateral movement.
Owner:AUTOCONDIZIONATORI ZANI
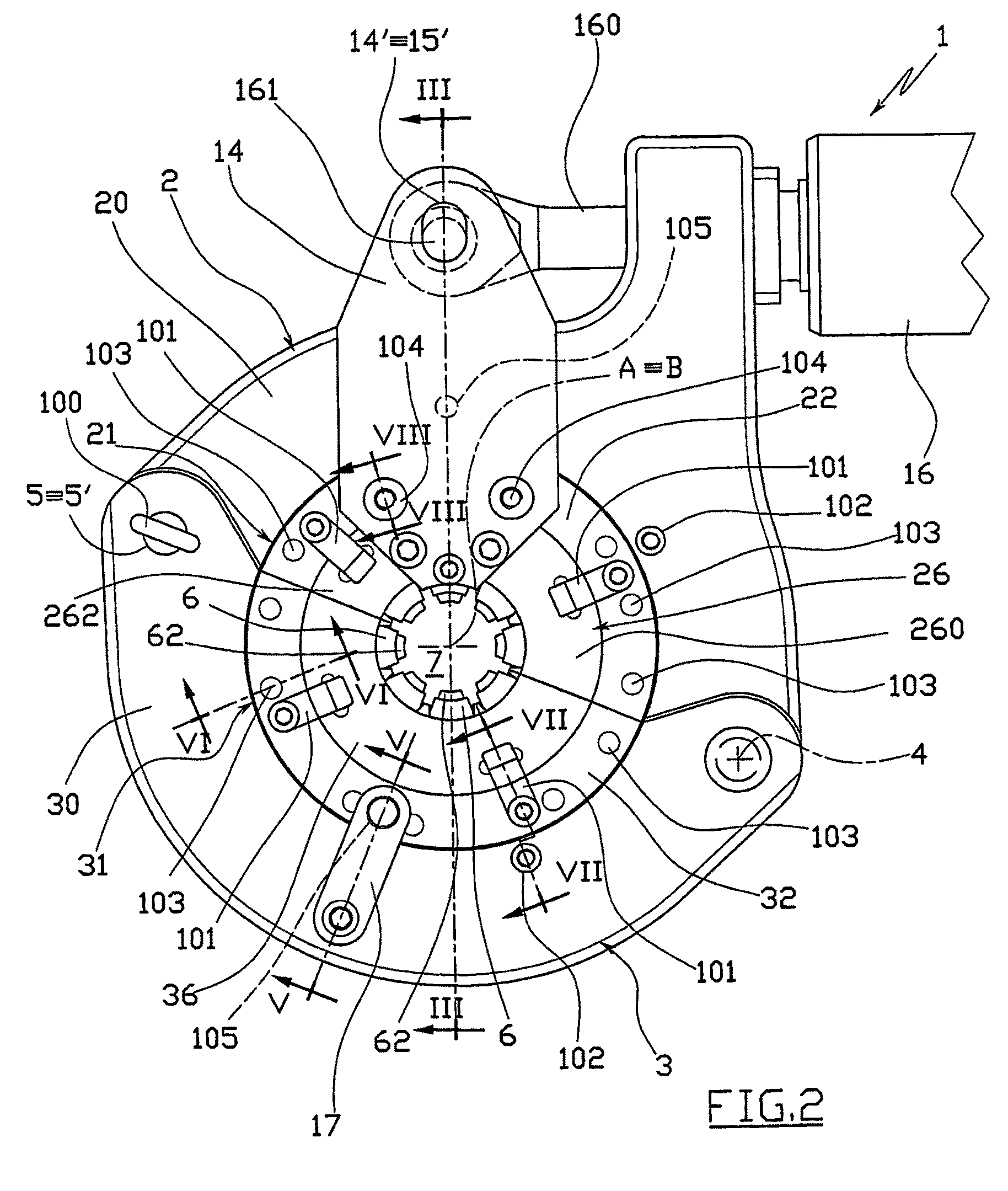
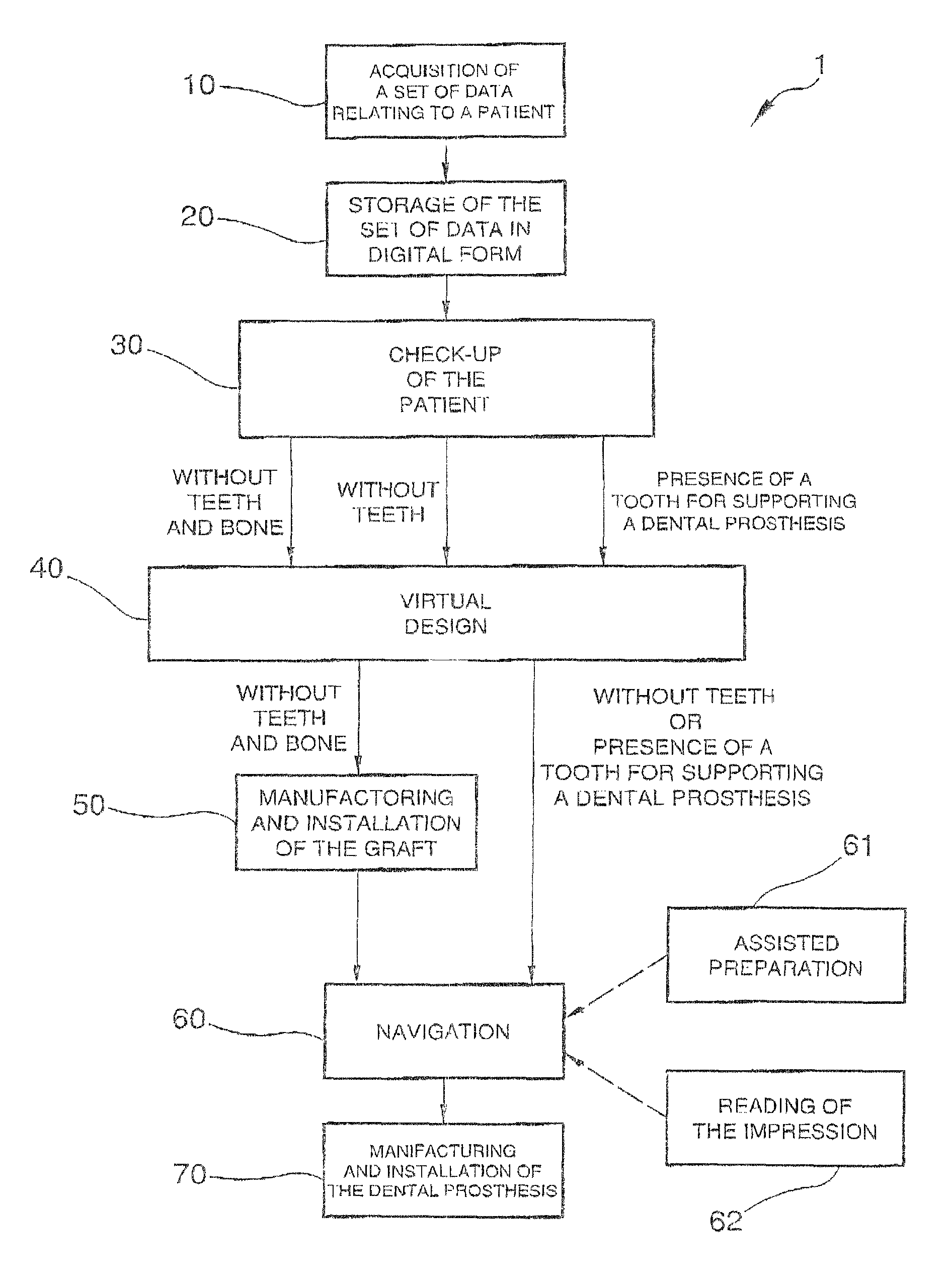
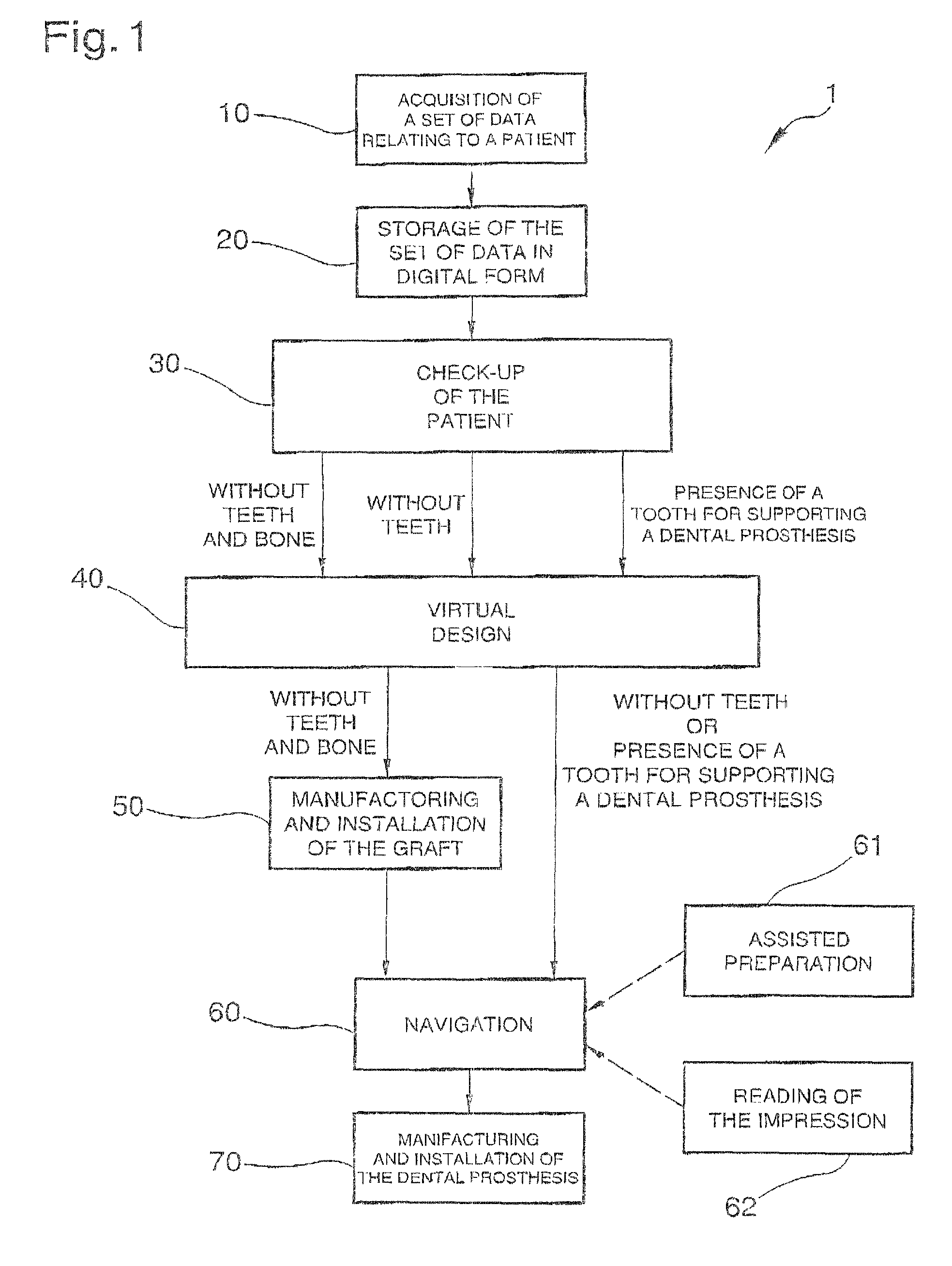
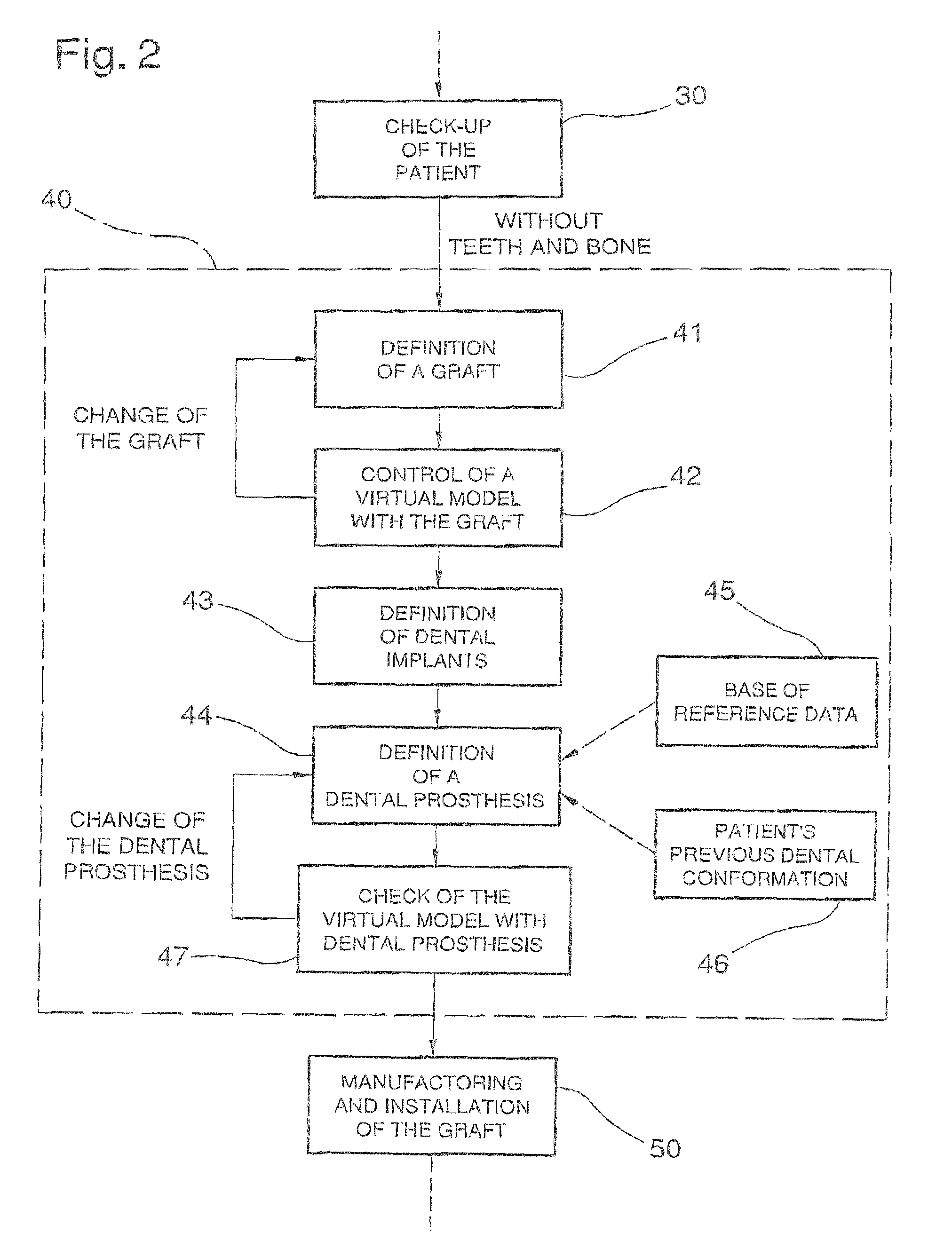
Method for planning and performing dental treatments
InactiveUS7909606B2Precise preparationEffective and easy to useImpression capsTeeth fillingData setDesign phase
Method for planning and performing dental treatments including an acquisition phase of a set of data relating to the position, to the conformation and to the dimension of at least one site inside the oral cavity of a patient who has to undergo a dental treatment and relating to the conformation of at least one portion of the patient's face; a design phase of a virtual prototype of at least one dental prosthesis that can be fitted at the site during the treatment, starting from the set of data and by means of a software program implemented on a computer; a determination phase, by means of the software program and starting from the set of data and from the virtual prototype of the dental prosthesis, of at least one virtual model suitable for visually reproducing the portion of the face following the fitting of the dental prosthesis; a preparation phase of the site by means of a dental instrument, with the assistance of the software and starting from the virtual prototype of the dental prosthesis and from the virtual model before the installation and the manufacture of the dental prosthesis.
Owner:MARCELLO MARCHESI
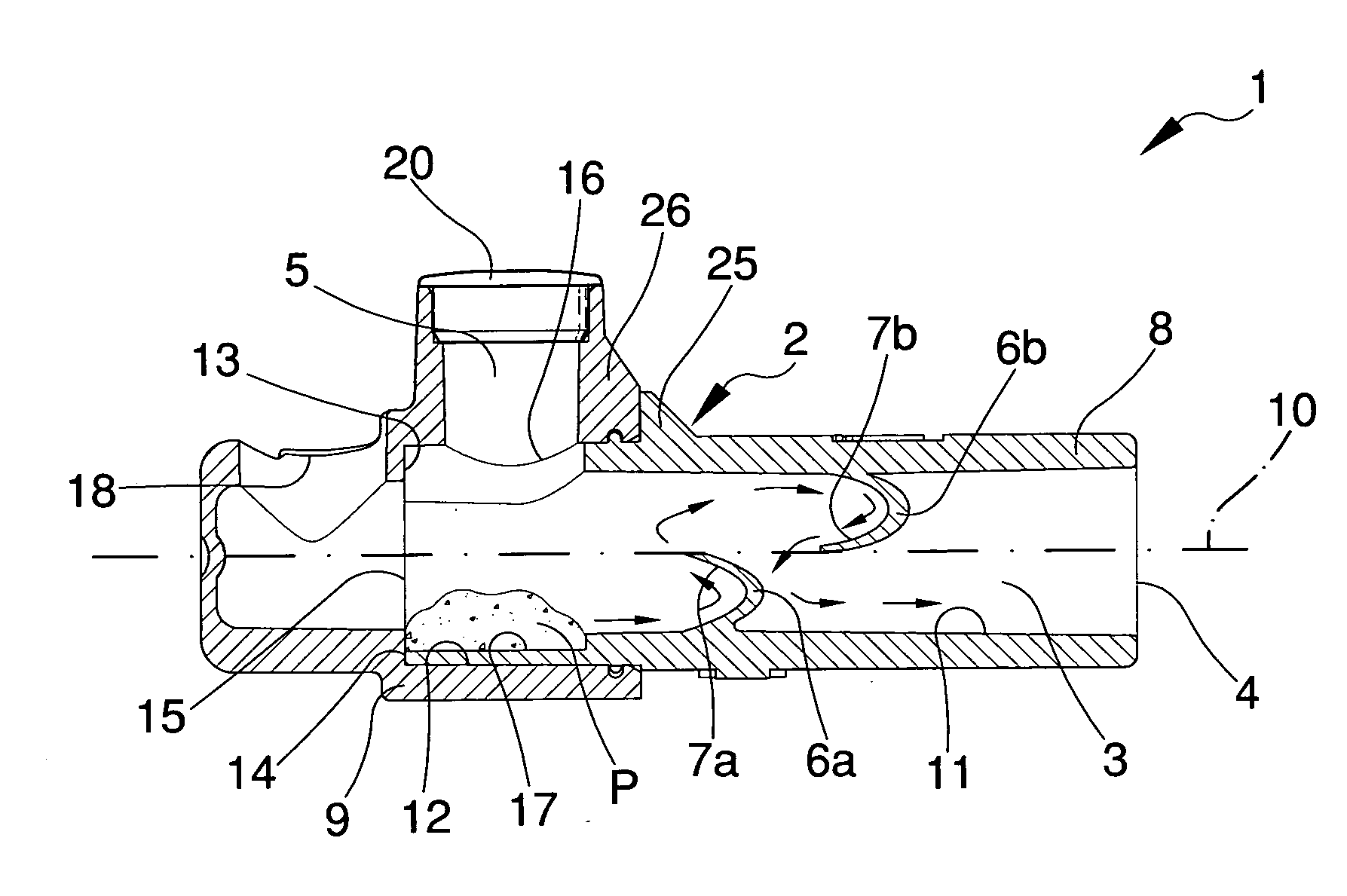
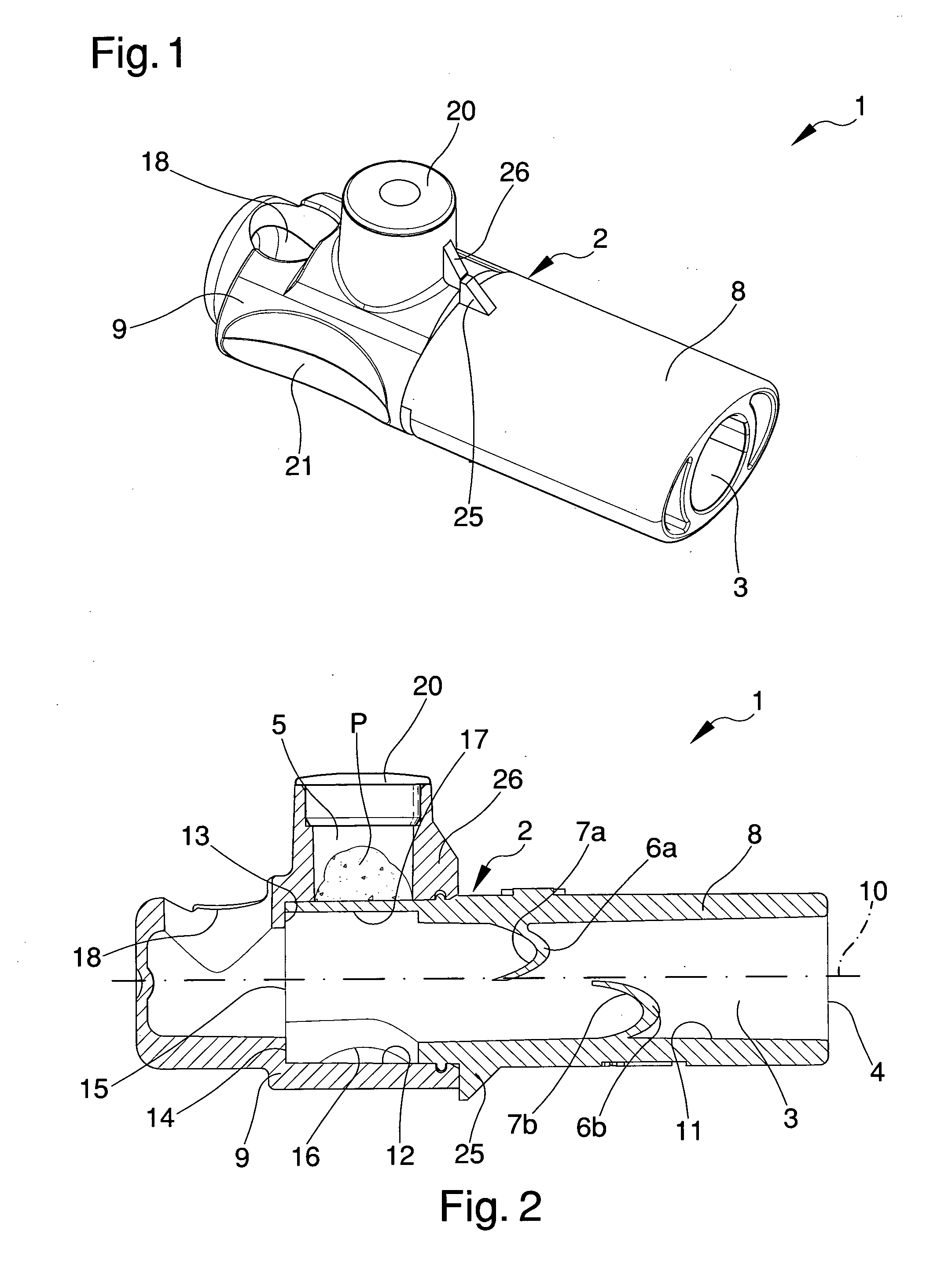
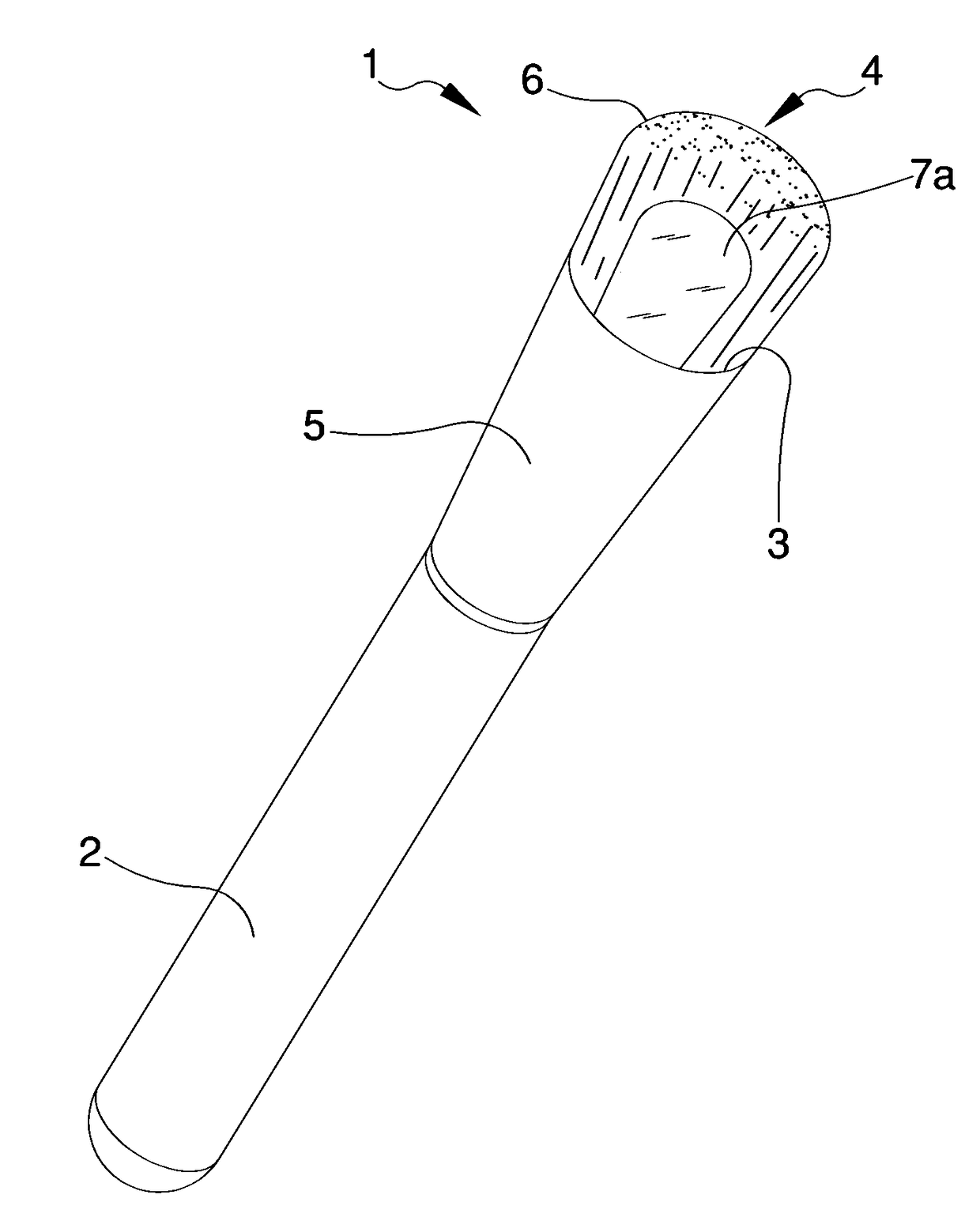
Ultrasonic type flowmeter apparatus and method of using the same
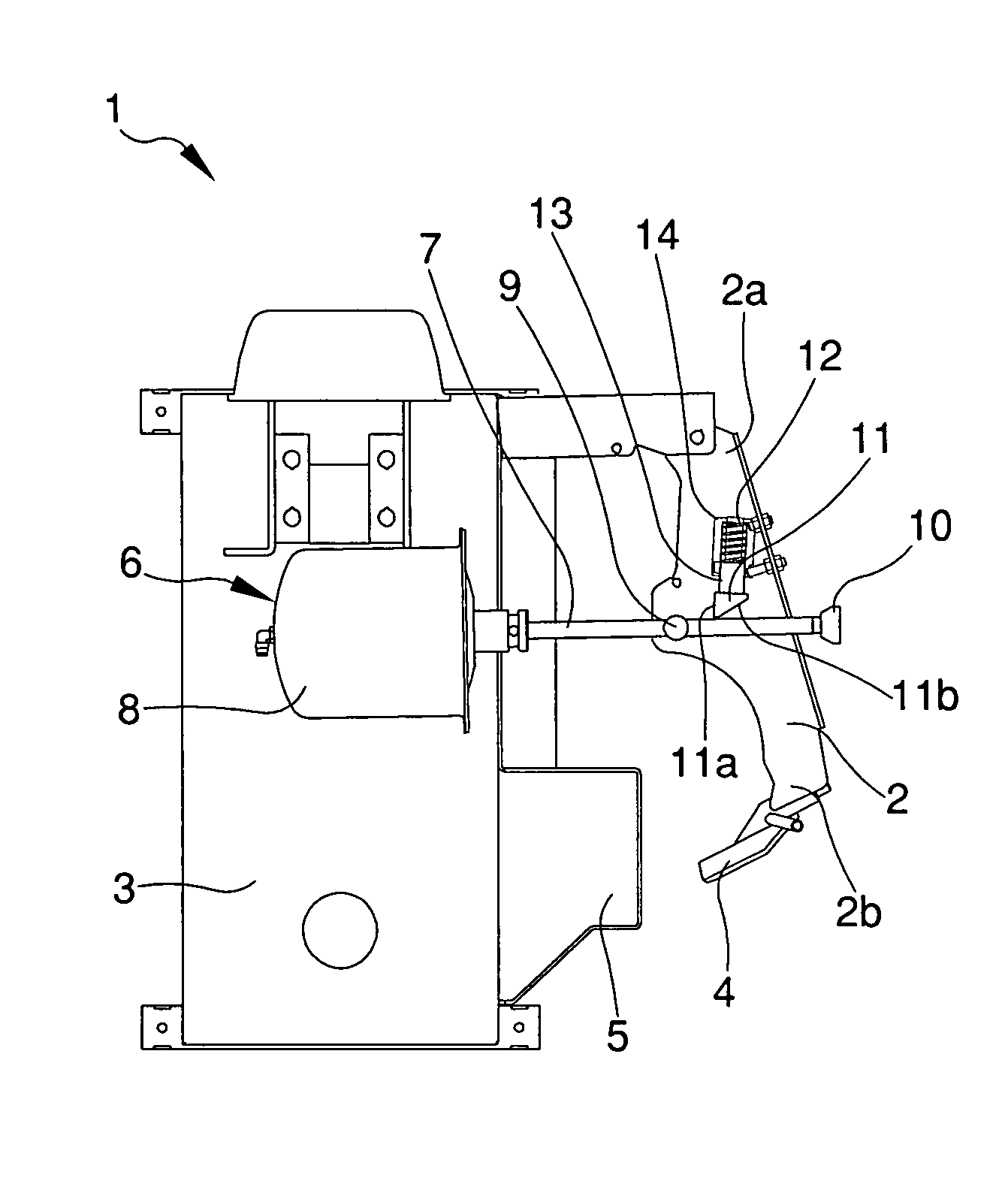
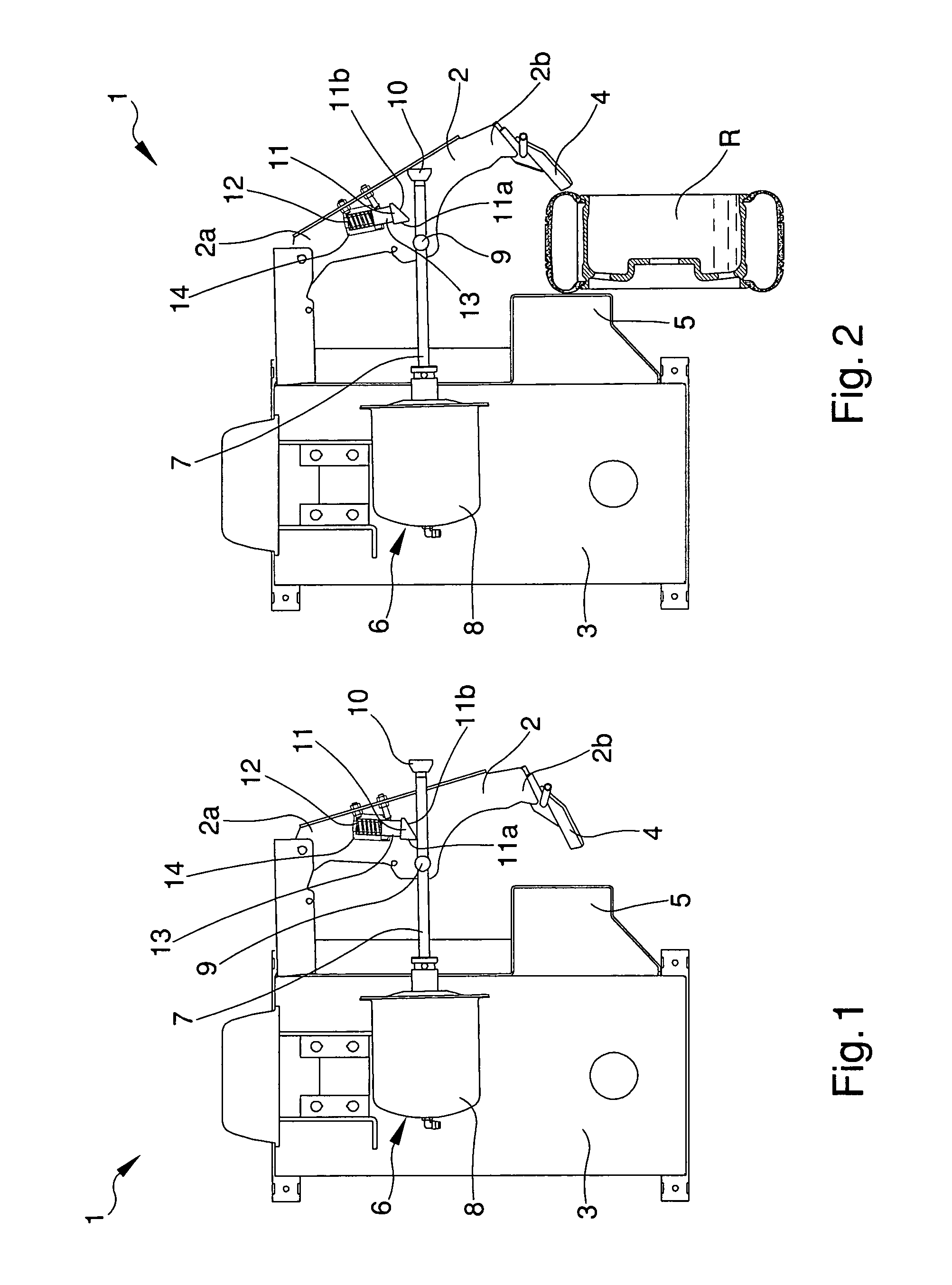
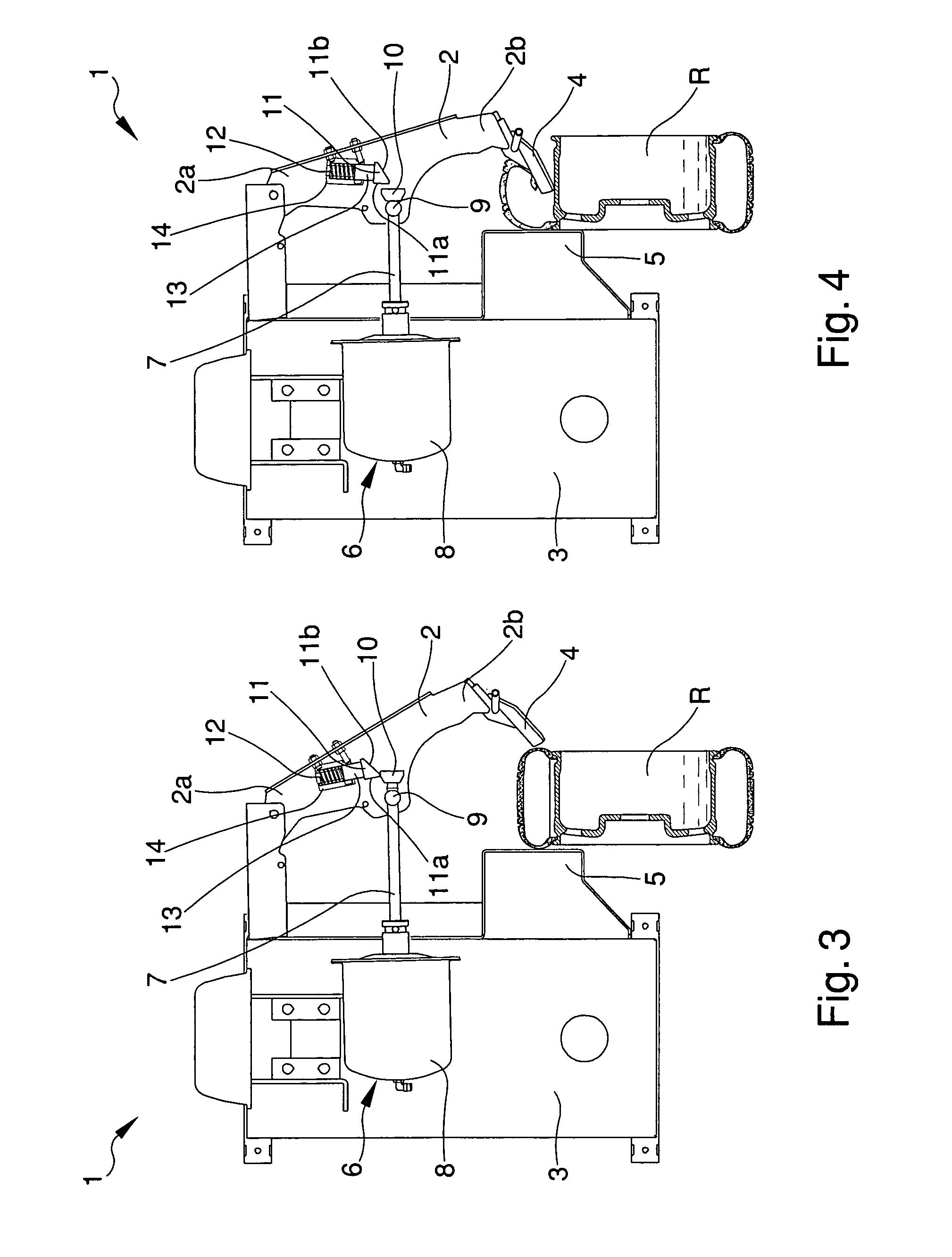
ActiveUS20130124131A1Accurate correctionRunning cost can be reducedDigital computer detailsFluid pressure measurementElectricityMemory chip
A disposable conduit 1 includes piezo-electric elements 2a and 2b and a memory chip 10 in which calibration data specific to the relevant conduit is stored. Before measurement, a non-disposable electrical measuring circuit reads the calibration data out of the memory chip 10 to prepare a calibrating equation or a calibration table. A flow speed of a blood passing through the conduit or a flow rate calculated from the flow speed is corrected in accordance with the calibrating equation or calibration table.
Owner:ATSUDEN
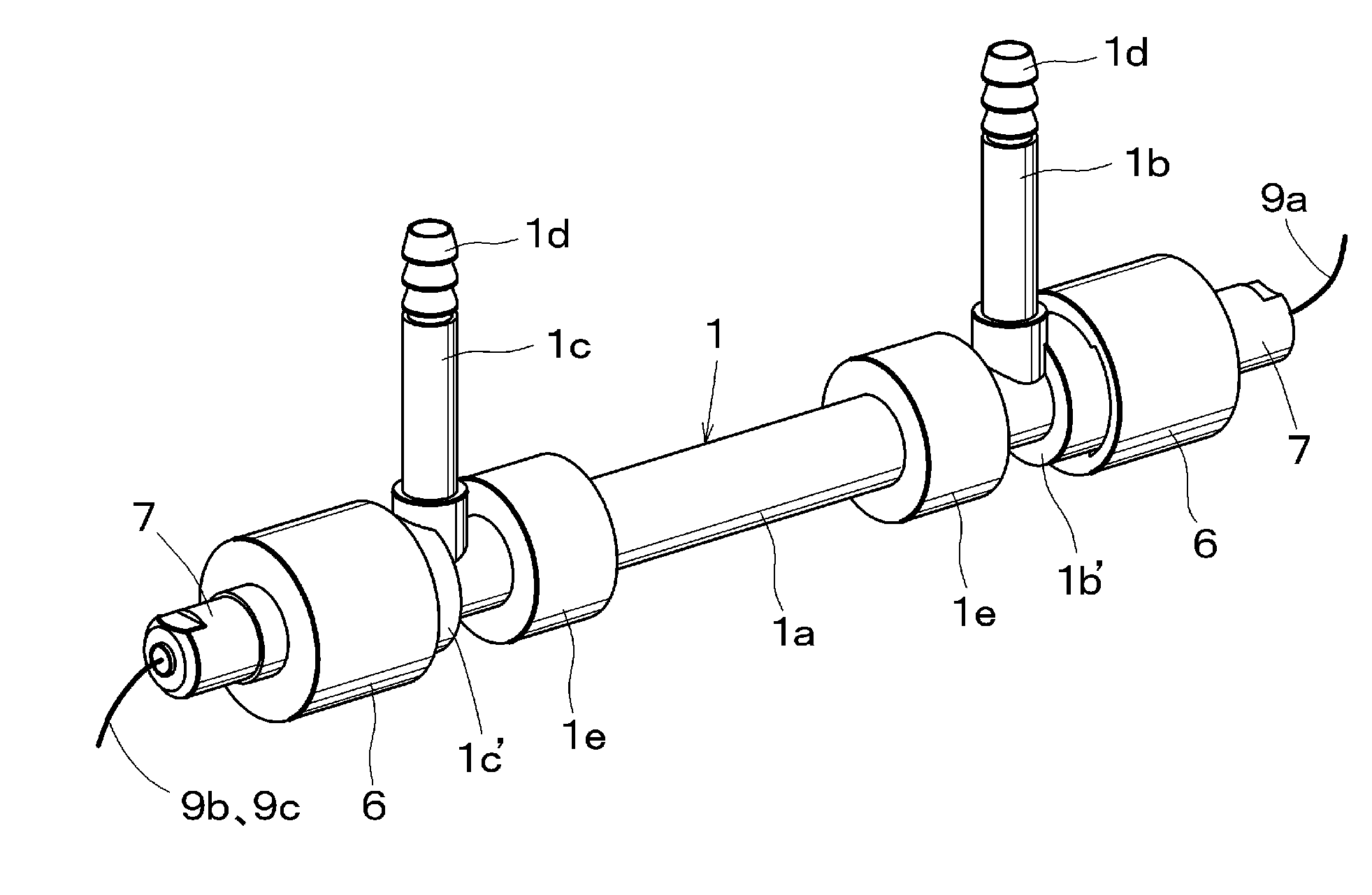
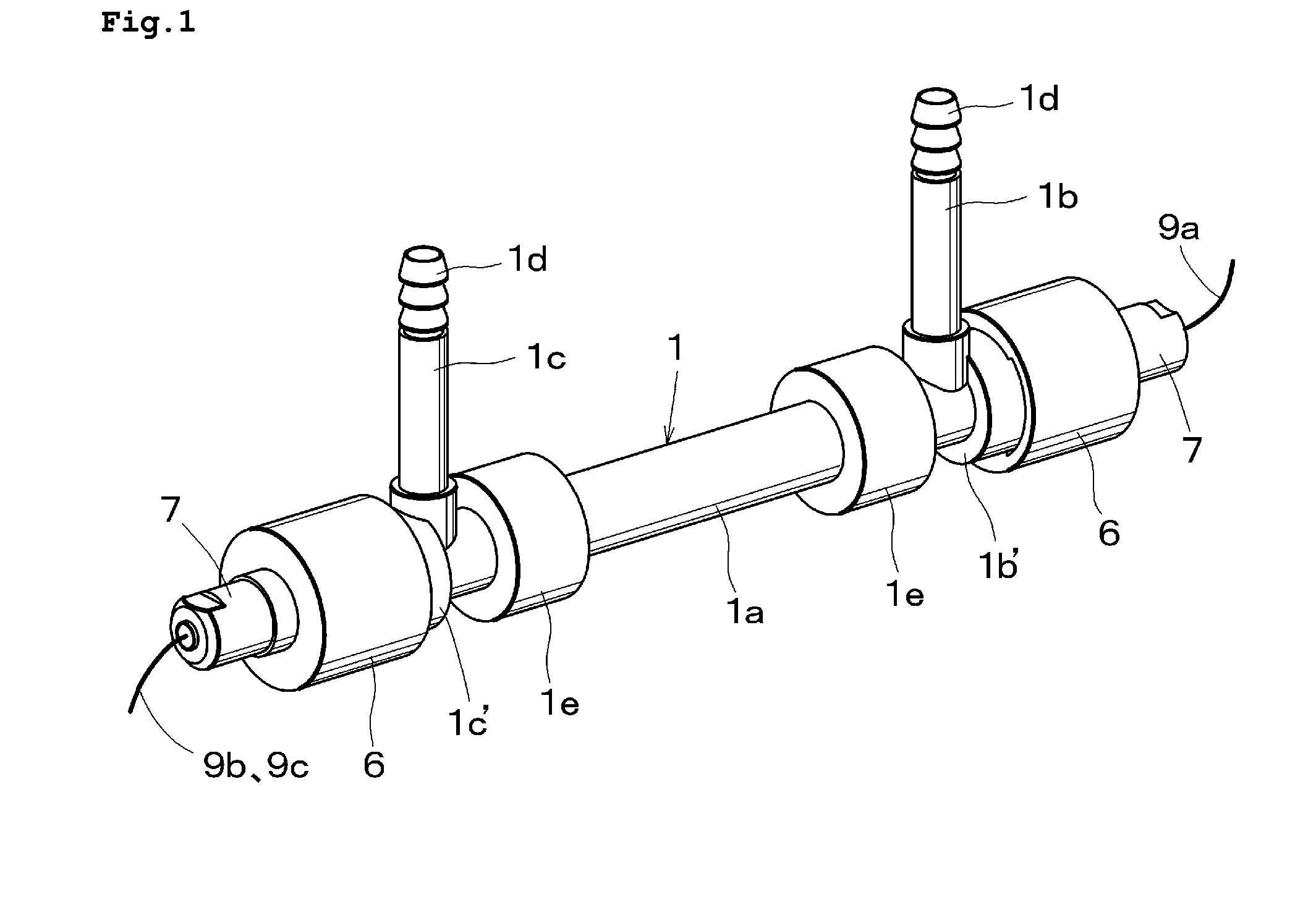
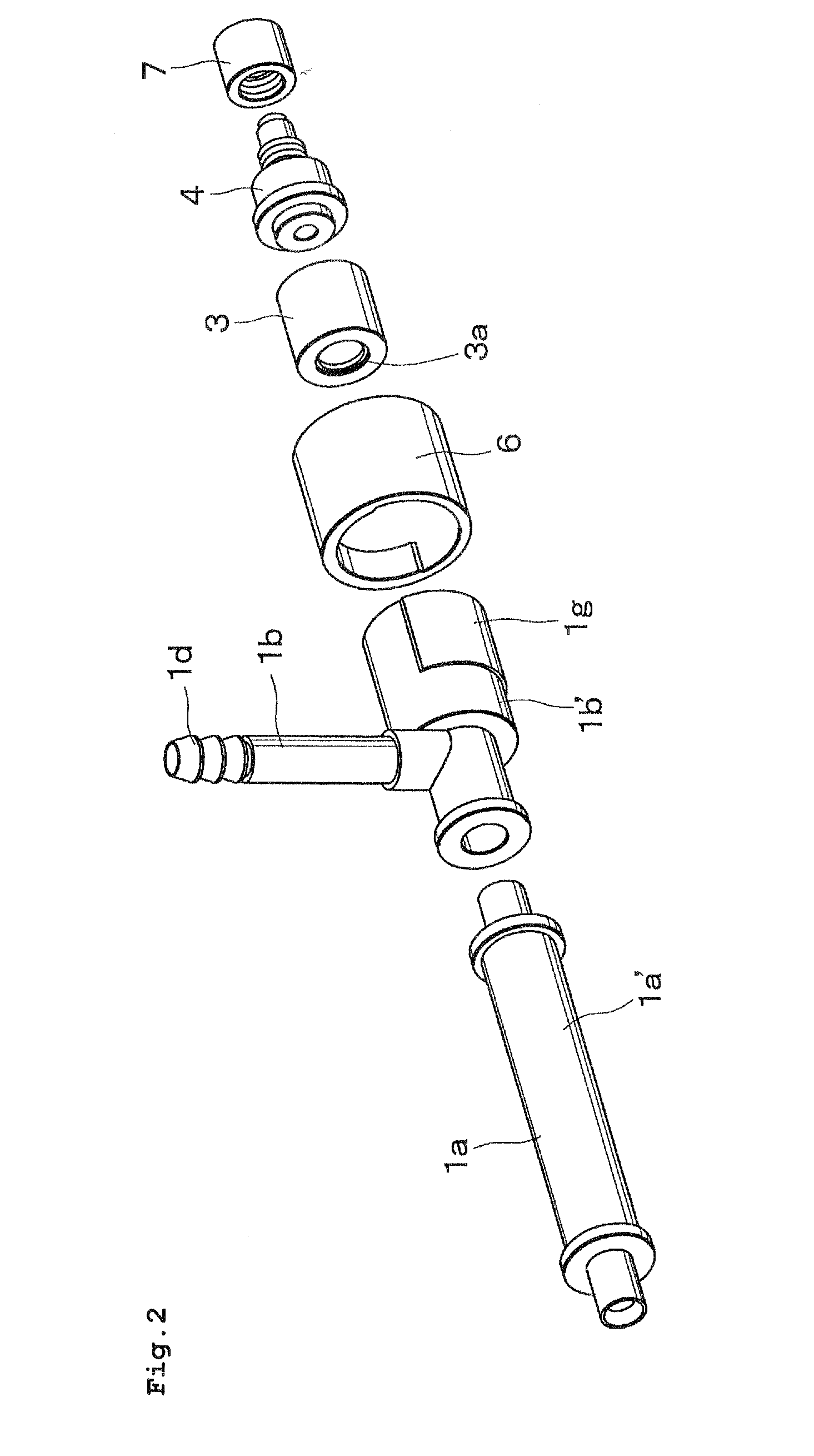
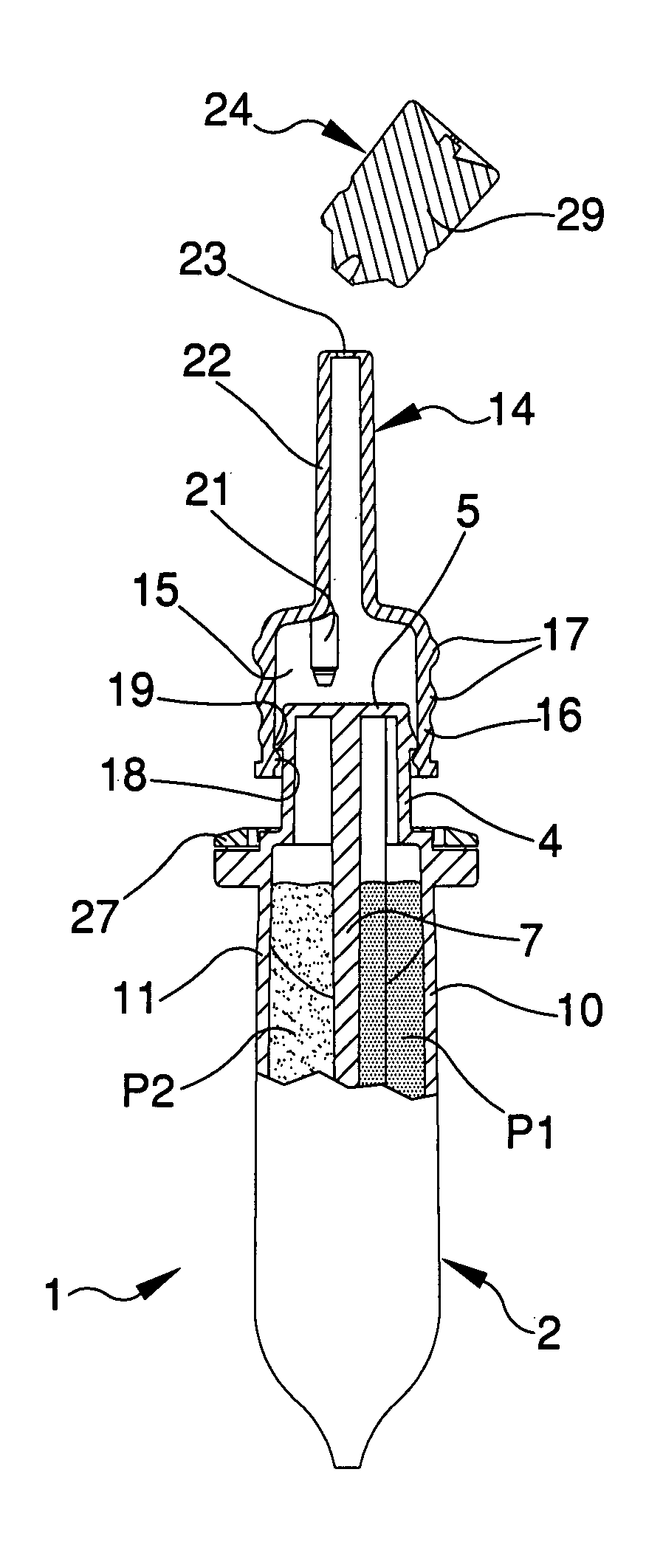
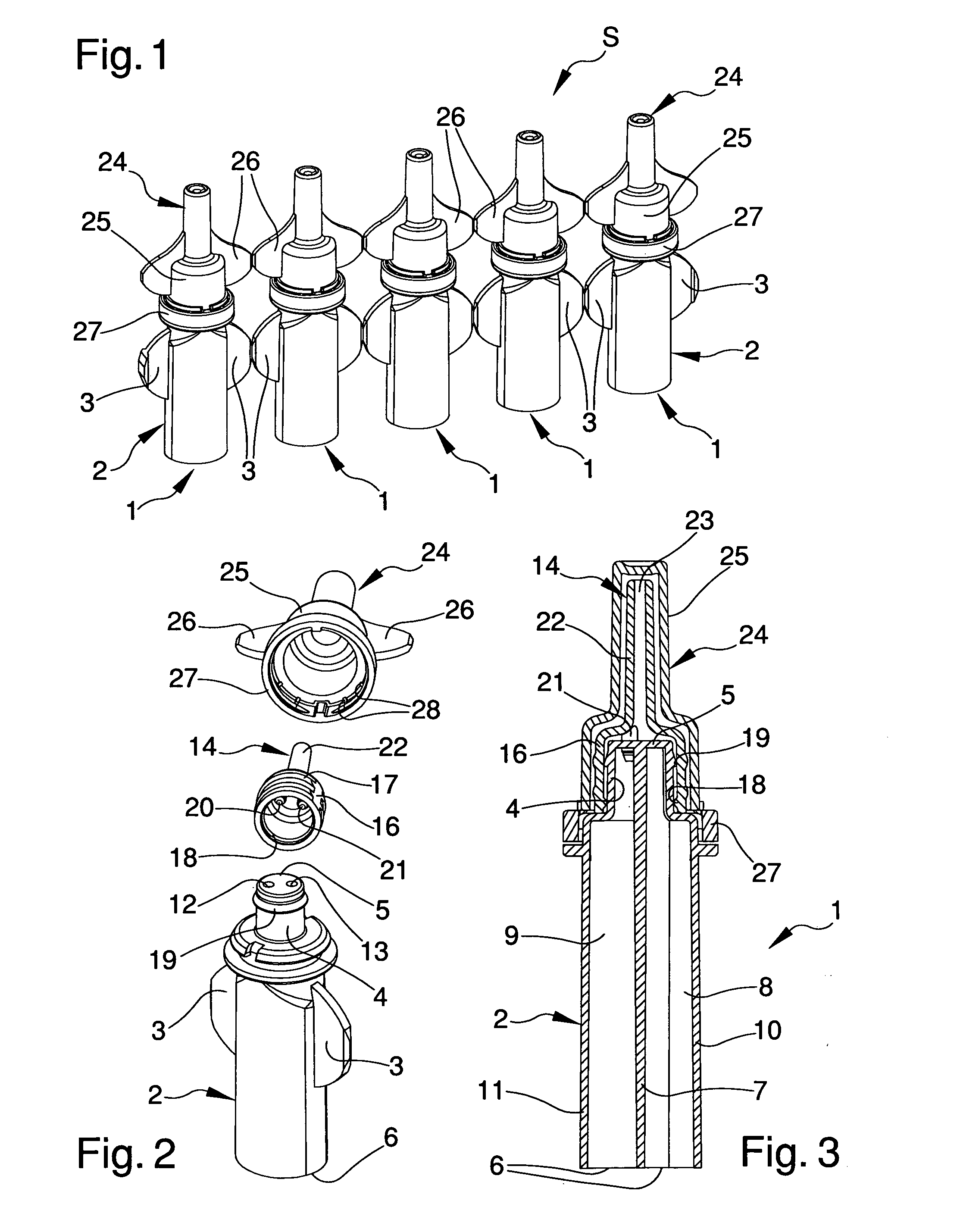
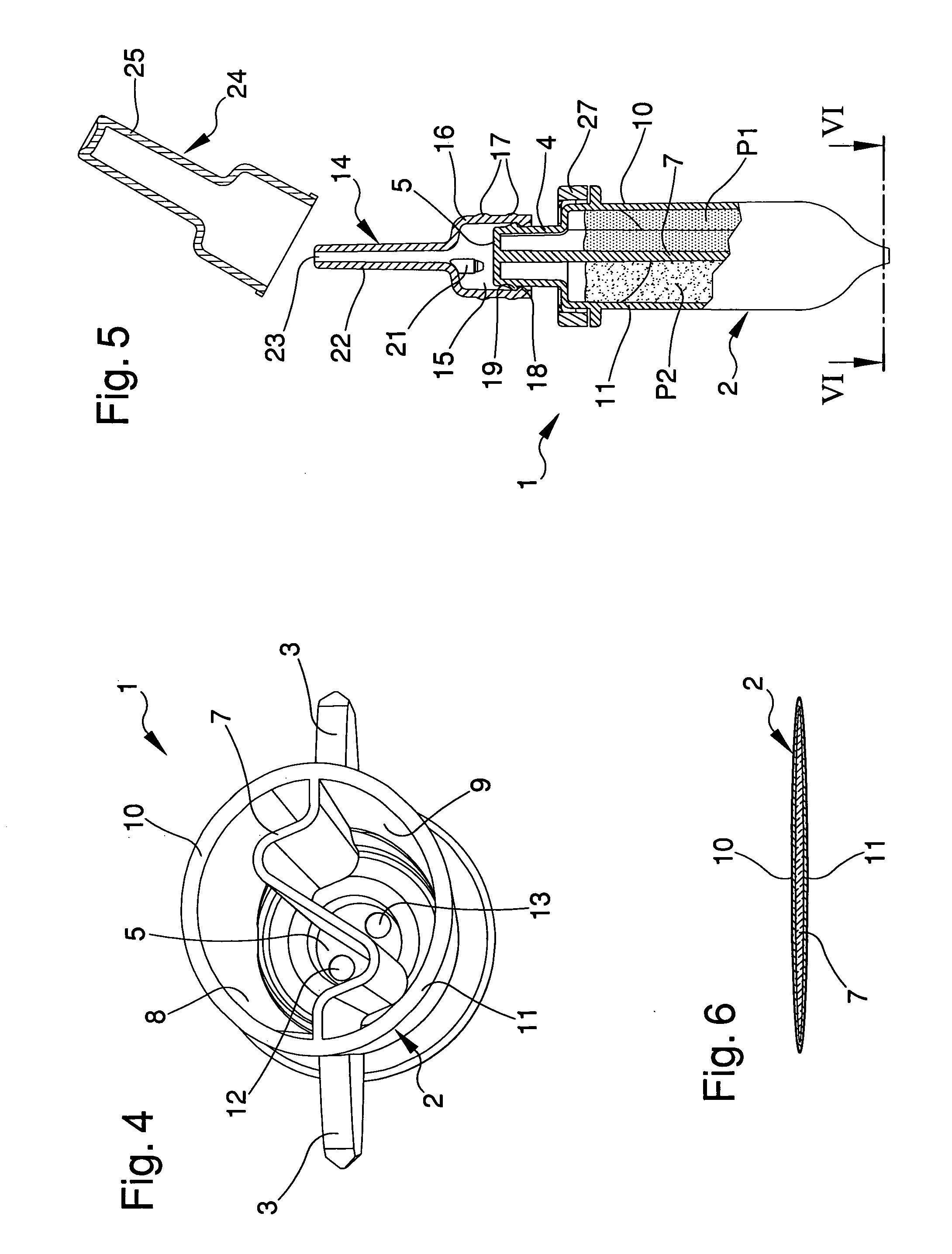
Container for fluid products, particularly pharmaceutical, cosmetic, food products or the like
InactiveUS20110186596A1Easy to operateReduced dimensionLiquid transferring devicesFlexible containersMechanical engineeringFood products
The container (1) for fluid products, particularly pharmaceutical, cosmetic, food products or the like, comprises a hollow body (2) inside which is defined a dividing wall (7) suitable for splitting up the inner volume of the hollow body (2) into two compartments (8, 9) for containing two fluid products (P1, P2), a neck (4) which extends from the hollow body (2) and which has two dispenser mouths (12, 13) for the fluid products (P1, P2), closing means (20, 21) for the dispenser mouths (12, 13) and a mixing element (14) which is associable with the neck (4) to define a mixing chamber (15) for the fluid products (P1, P2) exiting from the dispenser mouths (12, 13).
Owner:LAMEPLAST
Apparatus and method for servicing conveyor elements in a container treatment system
ActiveUS9676560B2Avoid pauseReduce installation and operation costDigital data processing detailsCleaningLoop controlState parameter
A conveyor arrangement for conveying containers in a container treatment system, including a conveyor track, at least one conveyor element movably arranged on the conveyor track and used for conveying one or a plurality of containers, a conveyor element servicing device connected to the conveyor track, and an open-loop and / or closed-loop control unit, where the conveyor track and the conveyor element are configured such that the conveyor element can be guided along the conveyor track in an individually controllable manner by means of the open-loop and / or closed-loop control unit, and where the open-loop and / or closed-loop control unit is configured to supply the conveyor element to the servicing device depending on at least one state parameter of the conveyor element.
Owner:KRONES AG
Draining device
InactiveUS20130327059A1Improve drainage capacityDrawback mentionedPressure pumpsGas turbine plantsPlenum chamberDrain tube
A draining device for draining a fluid from an aircraft engine support strut includes a suction arrangement having an inlet and extending along a longitudinal main axis to form a plenum chamber and a drain tube fluidly connected to the aircraft engine support strut and extending along the longitudinal main axis, the drain tube ending by an outlet, the outlet of the drain tube terminating within the plenum chamber of the suction arrangement. An air flow entering the inlet of the suction arrangement causes a low-pressure region to be created within the plenum chamber, substantially downstream the outlet of the drain tube.
Owner:SHORT BROTHERS
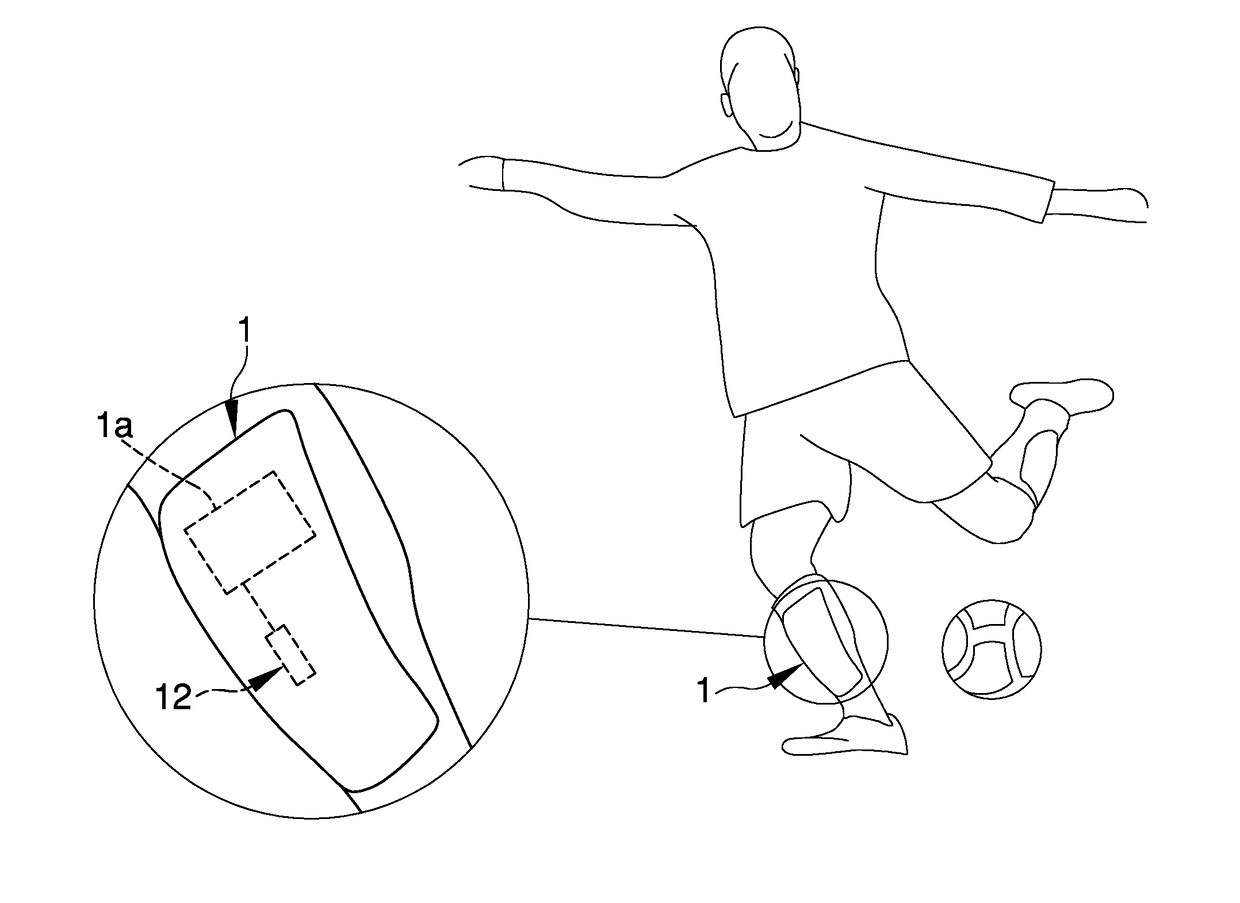
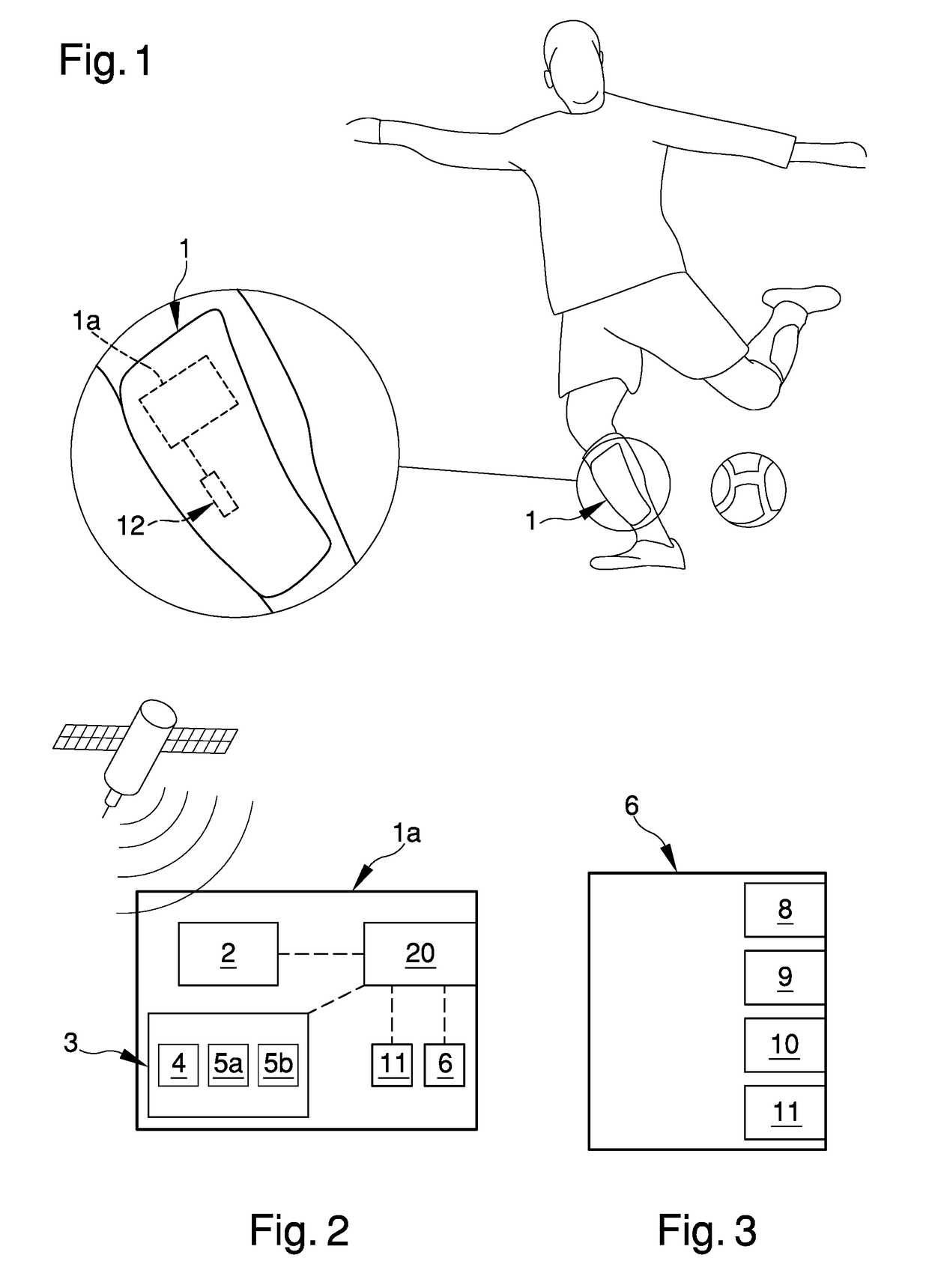
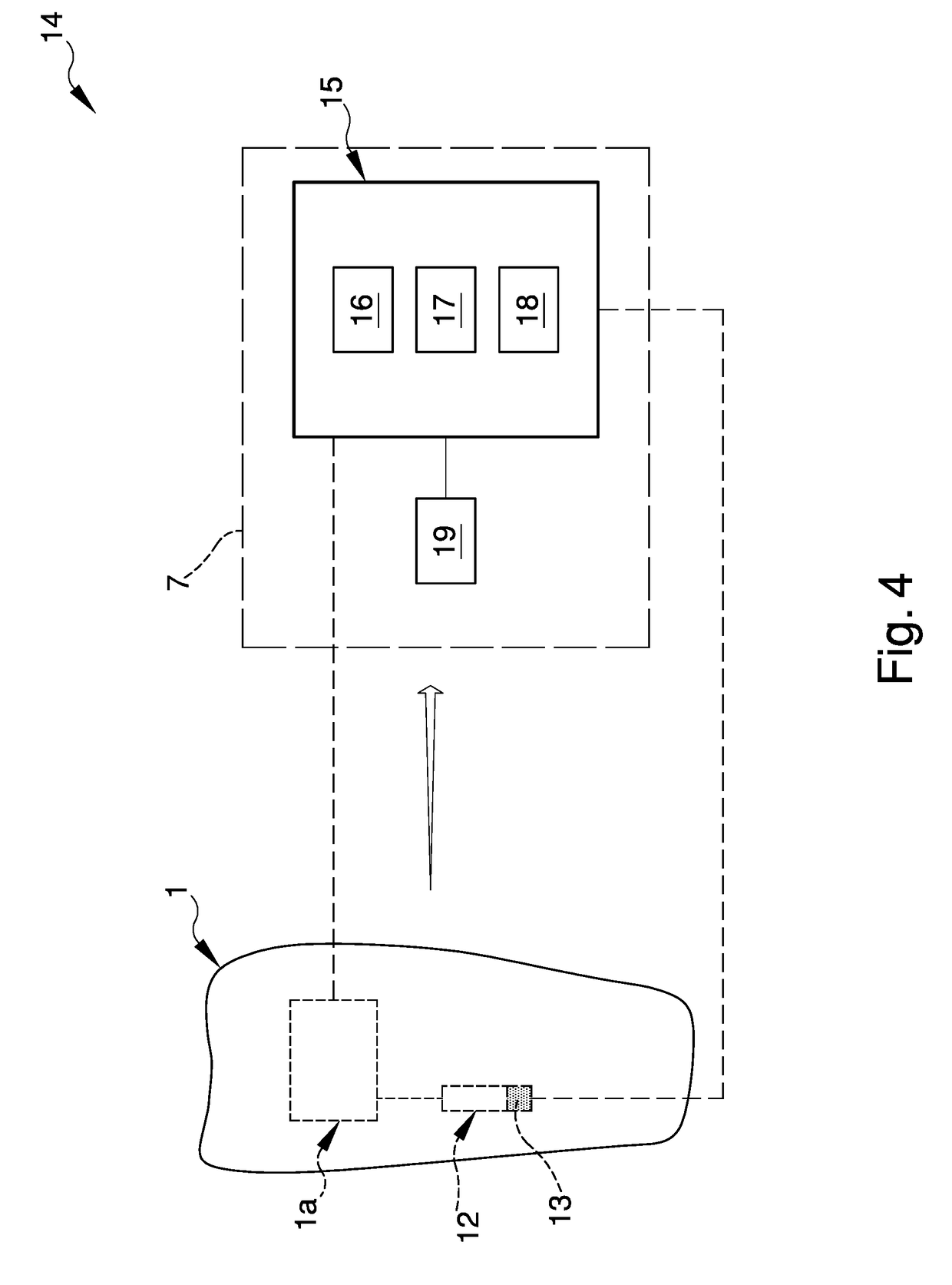
Protection device for carrying out sports activities usable in a data analysis and monitoring system, and relative system and method for processing and calculating the sent data
ActiveUS20180318694A1Improve accuracyDrawback mentionedGymnastic exercisingSports activityCommunication unit
Protection device (1) for sports activities, analysis and monitoring system (14) of data sent by a protection device and method for processing and calculating the data sent by a protection device where the protection device (1) comprises a localization unit (2) adapted to detect the positioning data (P) of the user, a detection unit (3) adapted to detect the movement data (A, M, W) of the user; at least a communication unit (6), operatively connected to the localization unit (2) and to the detection unit (3) and adapted to send / receive said positioning data (P) and movement data (A, M, W) to / from at least an external module (7).
Owner:GHST WORLD INC
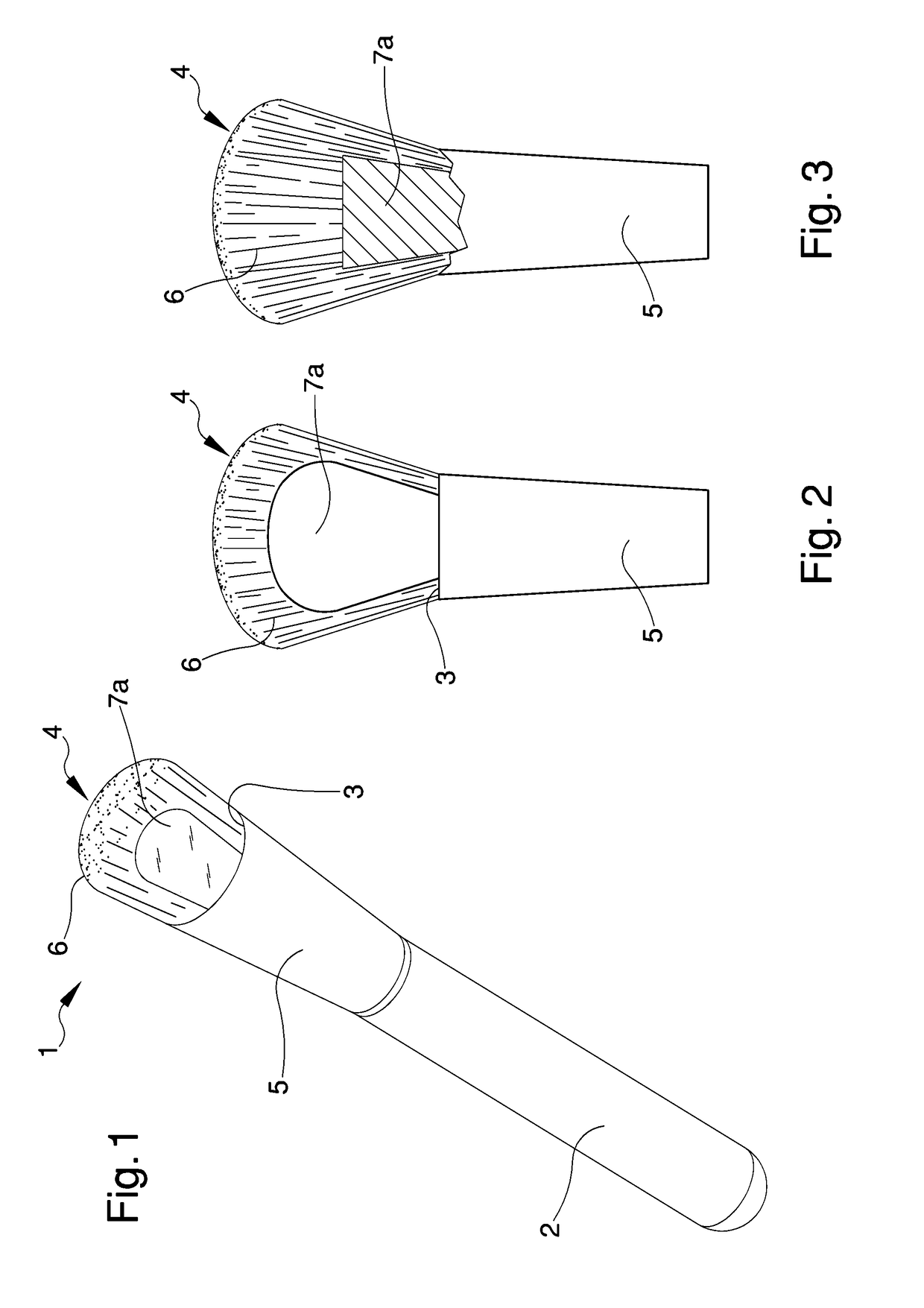
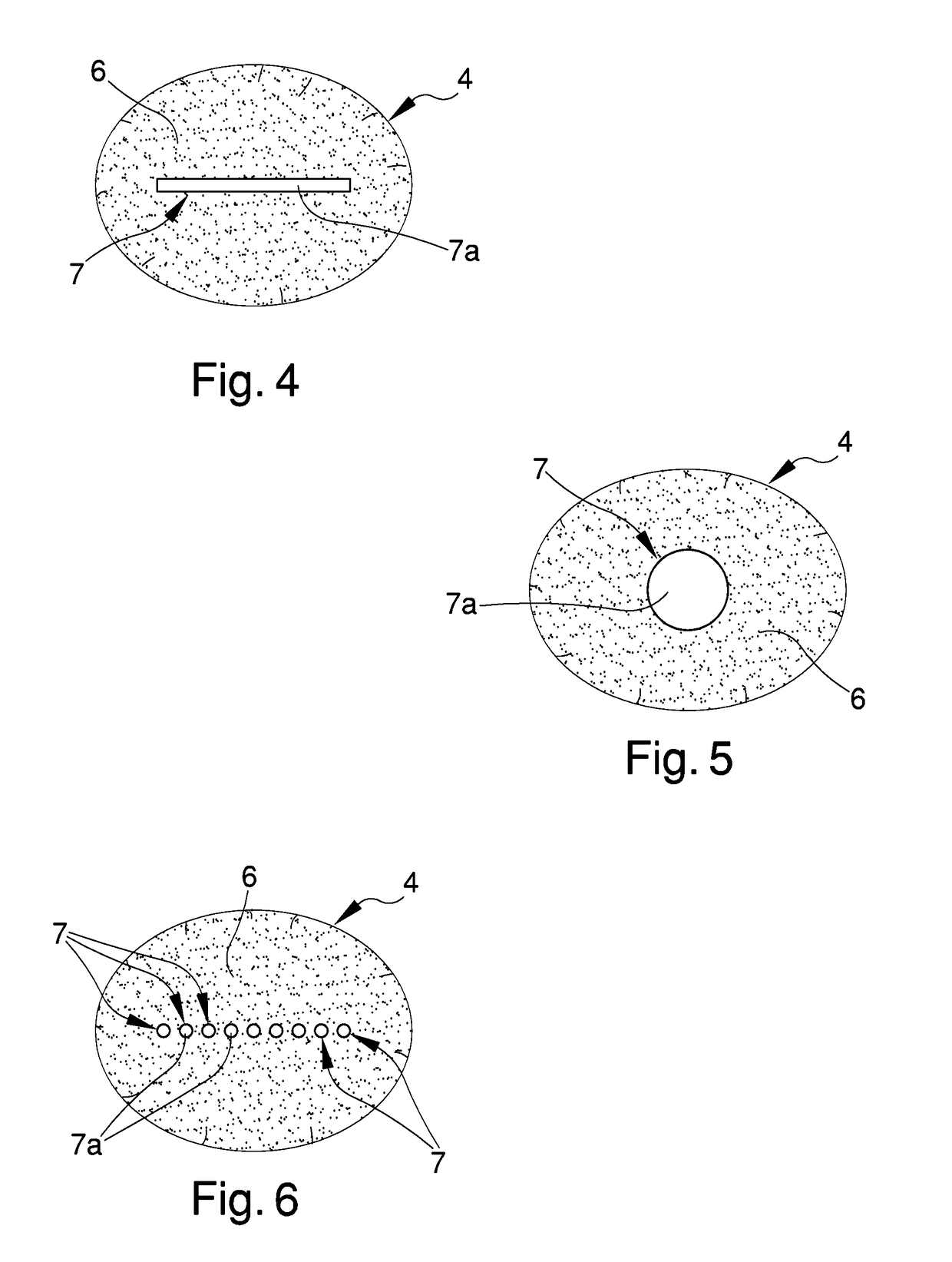
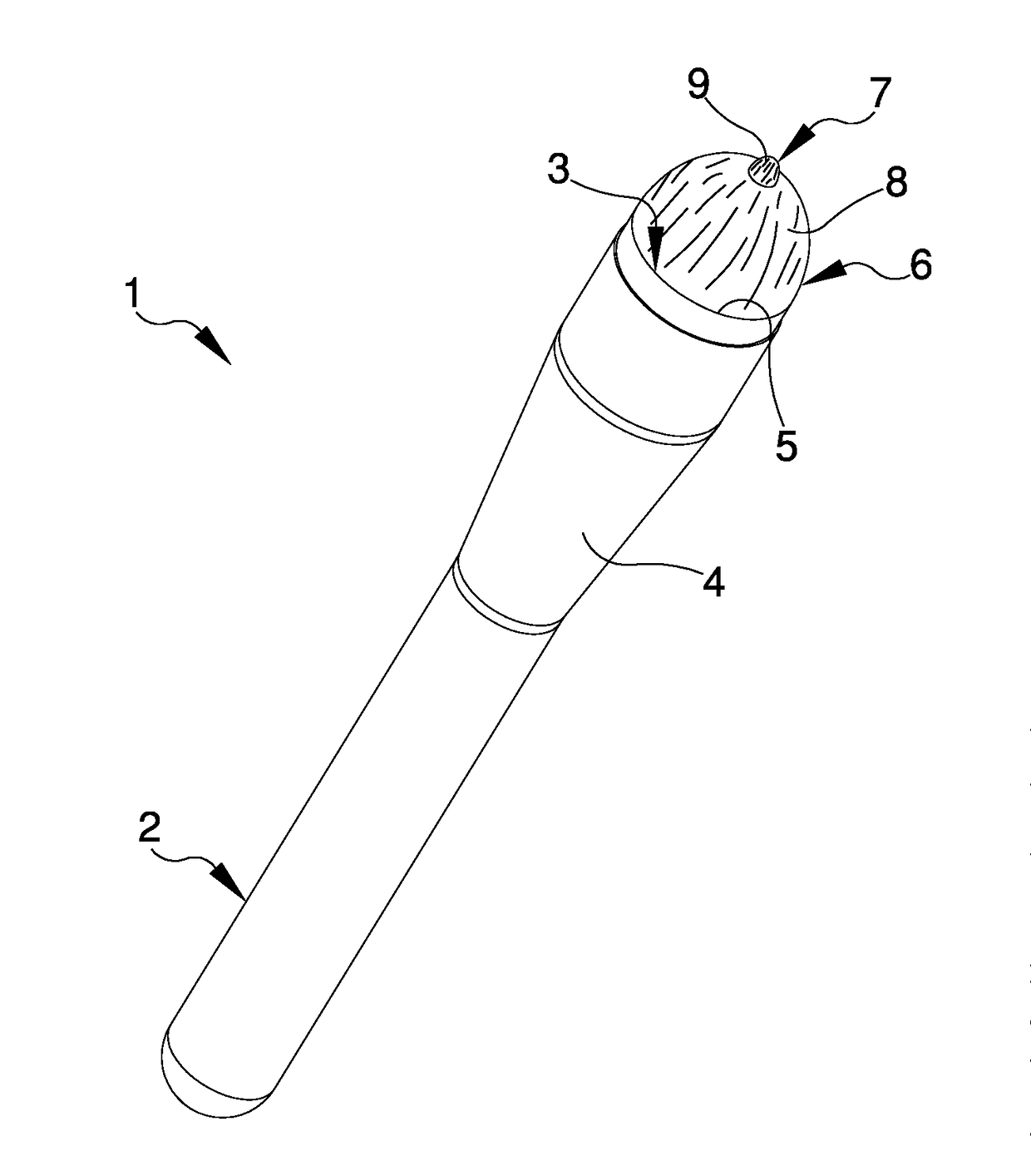
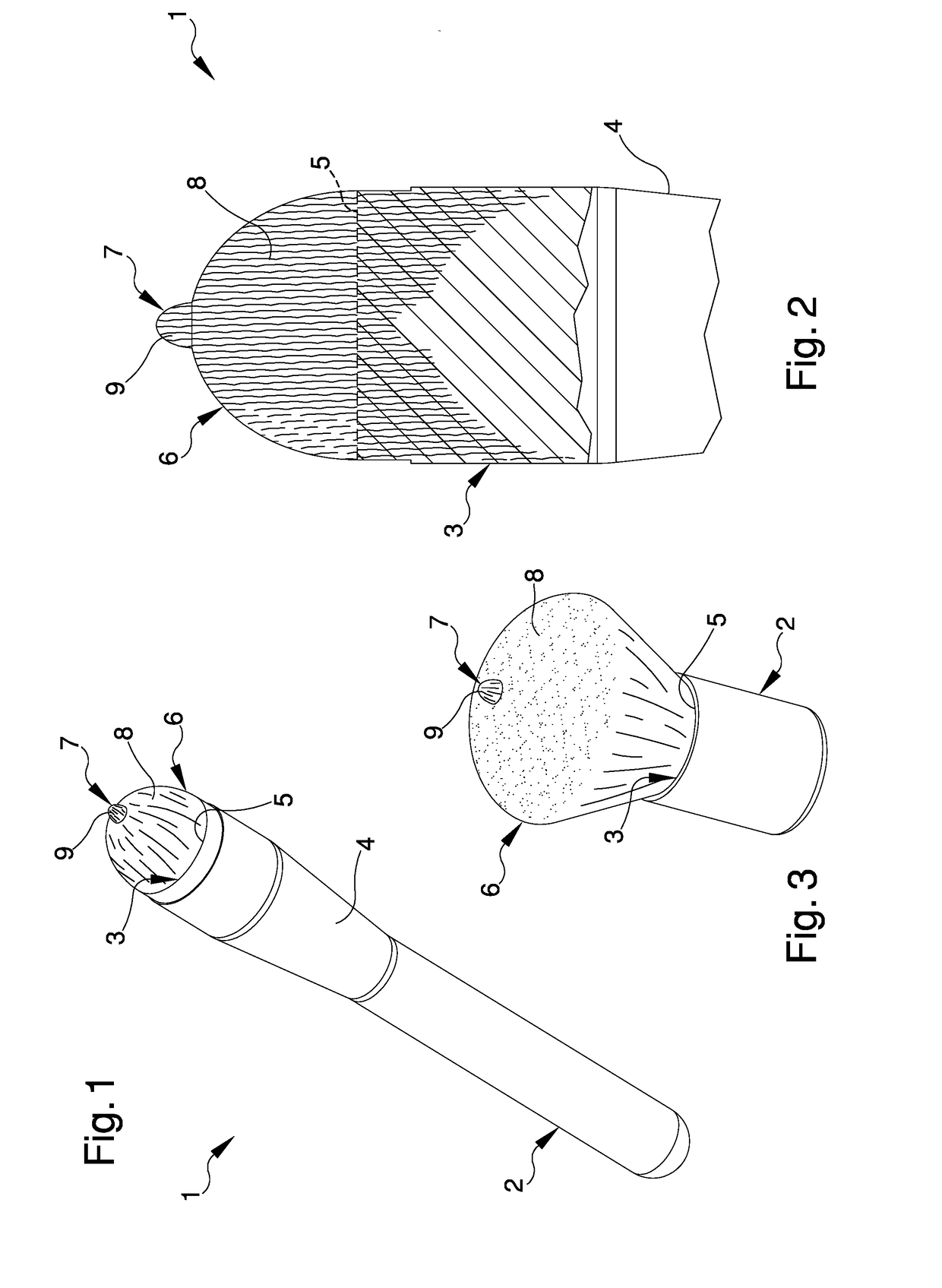
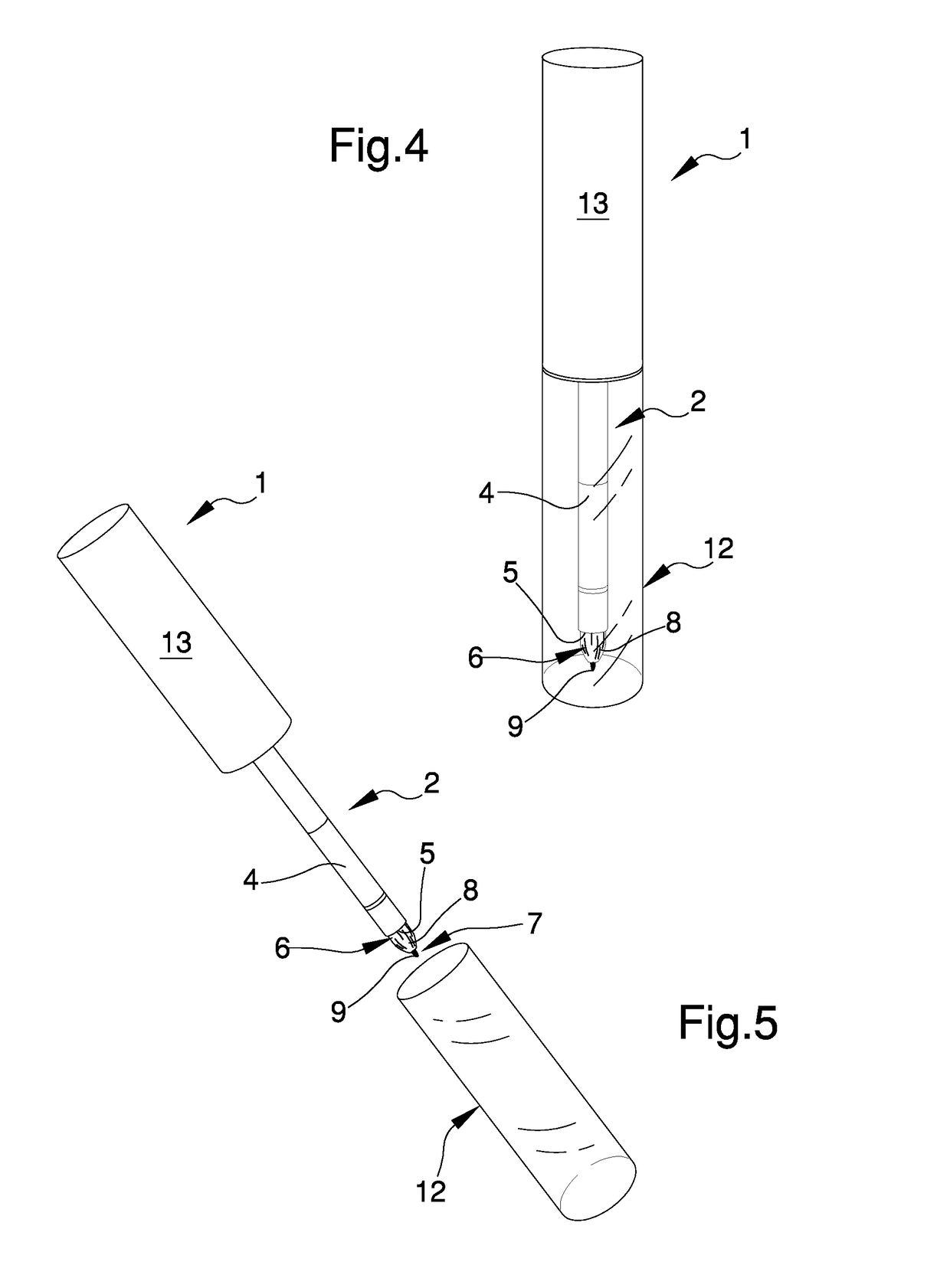
Upgraded brush
InactiveUS20180220786A1Fast and precise mannerSimplifying and speeding up operation of application and spreadingBristleScrub brushesMechanical engineering
The upgraded brush comprises an housing seat of a body of application comprising, in turn, a first plurality of hairs adapted to spread a product on a work surface, in which the body of application comprises at least one element with predefined stiffness adapted to direct the product on the work surface and defining at least a portion with different texture with respect to the first plurality of hairs.
Owner:PENNELLI FARO
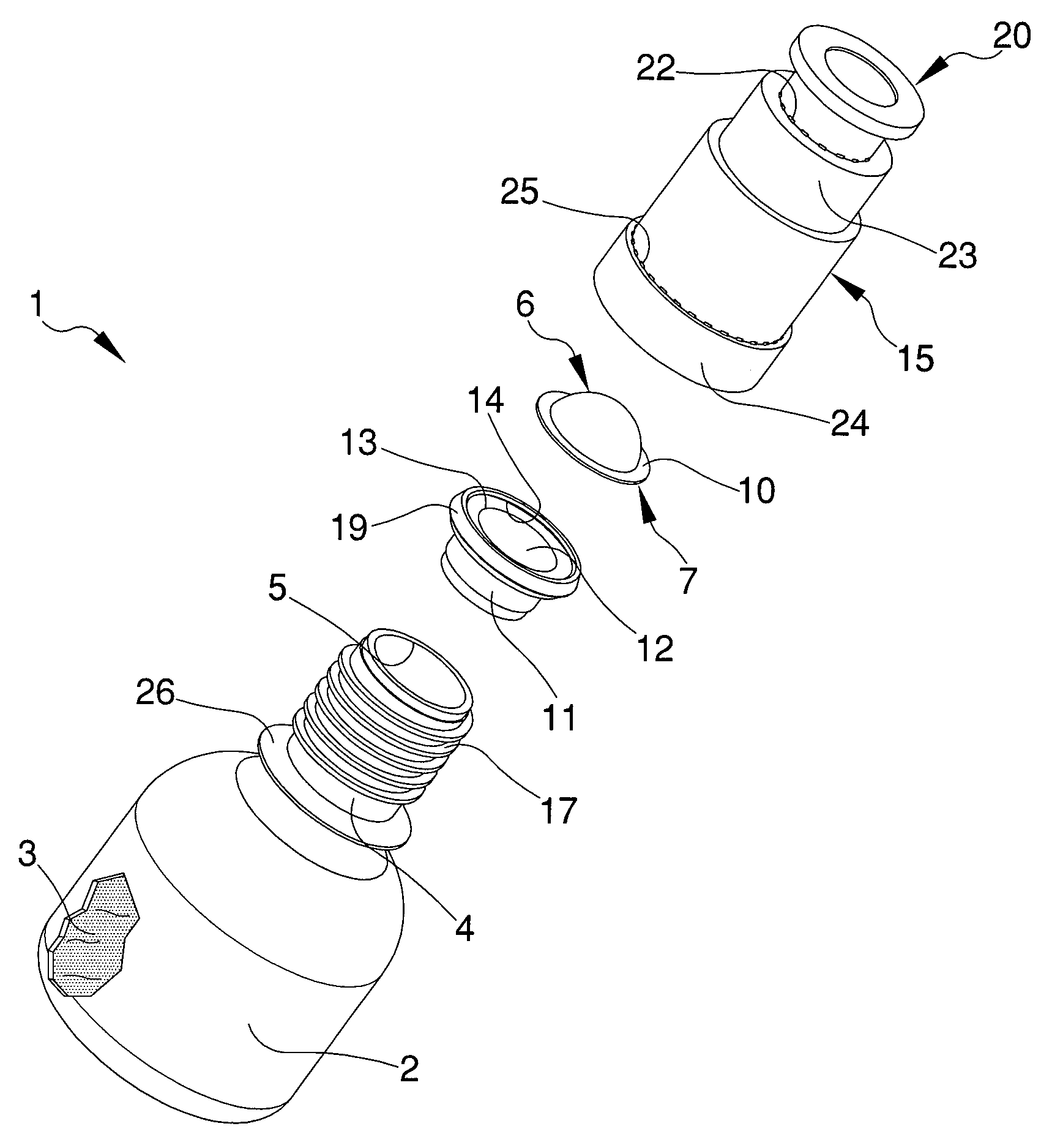
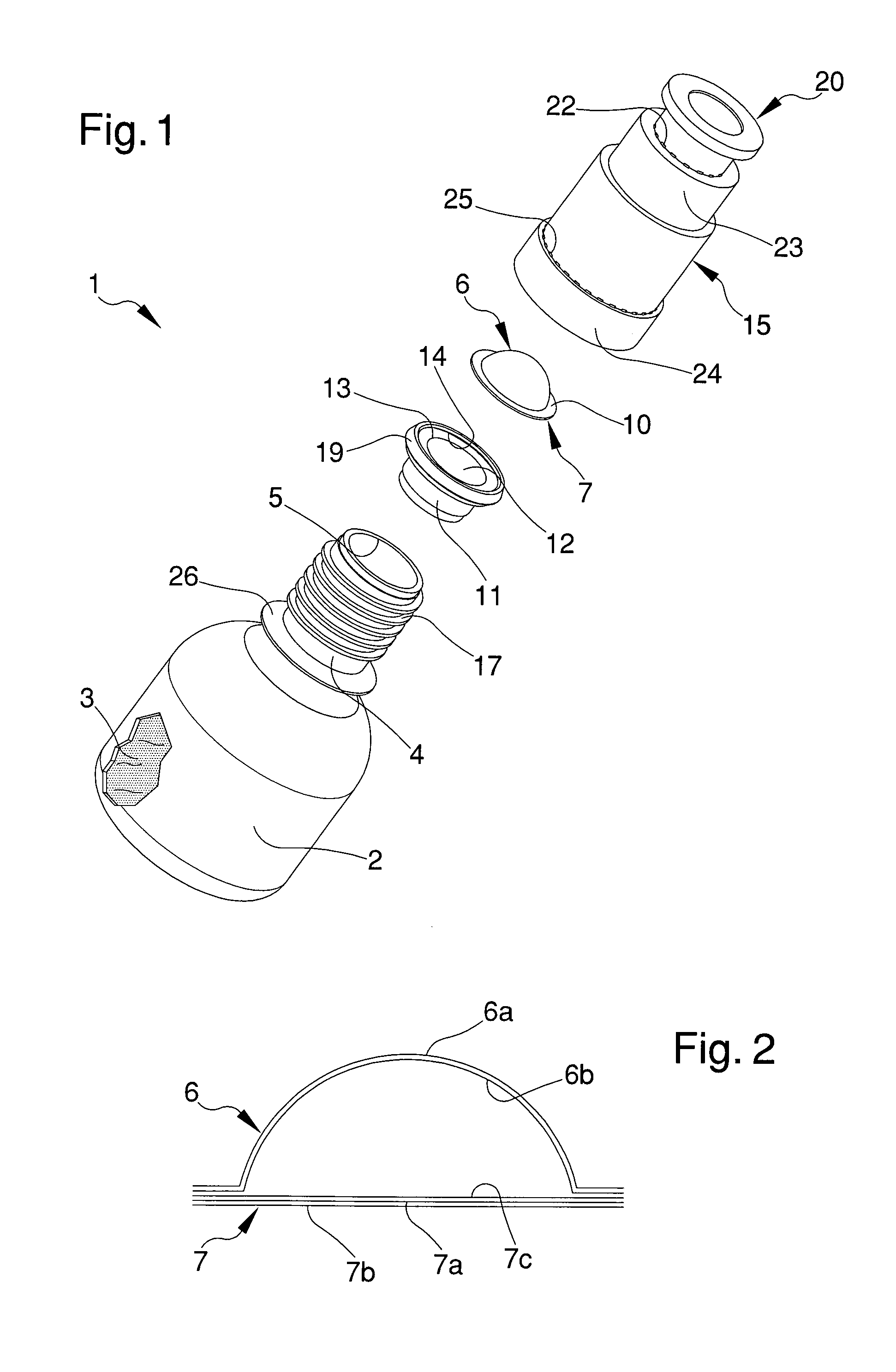
Bottle for extemporaneous preparation products, particularly medical, pharmaceutical, cosmetic products
InactiveUS9193517B2Easy to separateLow costDispensing apparatusClosure with auxillary devicesExtemporaneous preparationsBottle
Owner:LAMEPLAST
Tool for the connection of tubes by means of connection sleeves
ActiveUS20100107393A1Low costDrawback mentionedForging hammersPump installationsRest positionEngineering
A tool for the connection of tubes (T) by means of connection sleeves (C), comprising two jaws (2, 3) which are mutually movable between an open rest position, and a closed work position wherein they define an annular reception seat (7) of the connection sleeve (C), and wherein they turn a circumferential series of radial punches (6) towards the sleeve (C); said jaws (2, 3) each comprising at least one punch (6) sliding towards the centre of said reception seat (7), and being mutually connected by means of a kinematic system which permits them, when they are found in said open rest position, to confer a generally open-ring shape to said reception seat (7), through whose lateral opening (8) the connection sleeve (C) can be inserted and extracted by lateral movement.
Owner:AUTOCONDIZIONATORI ZANI
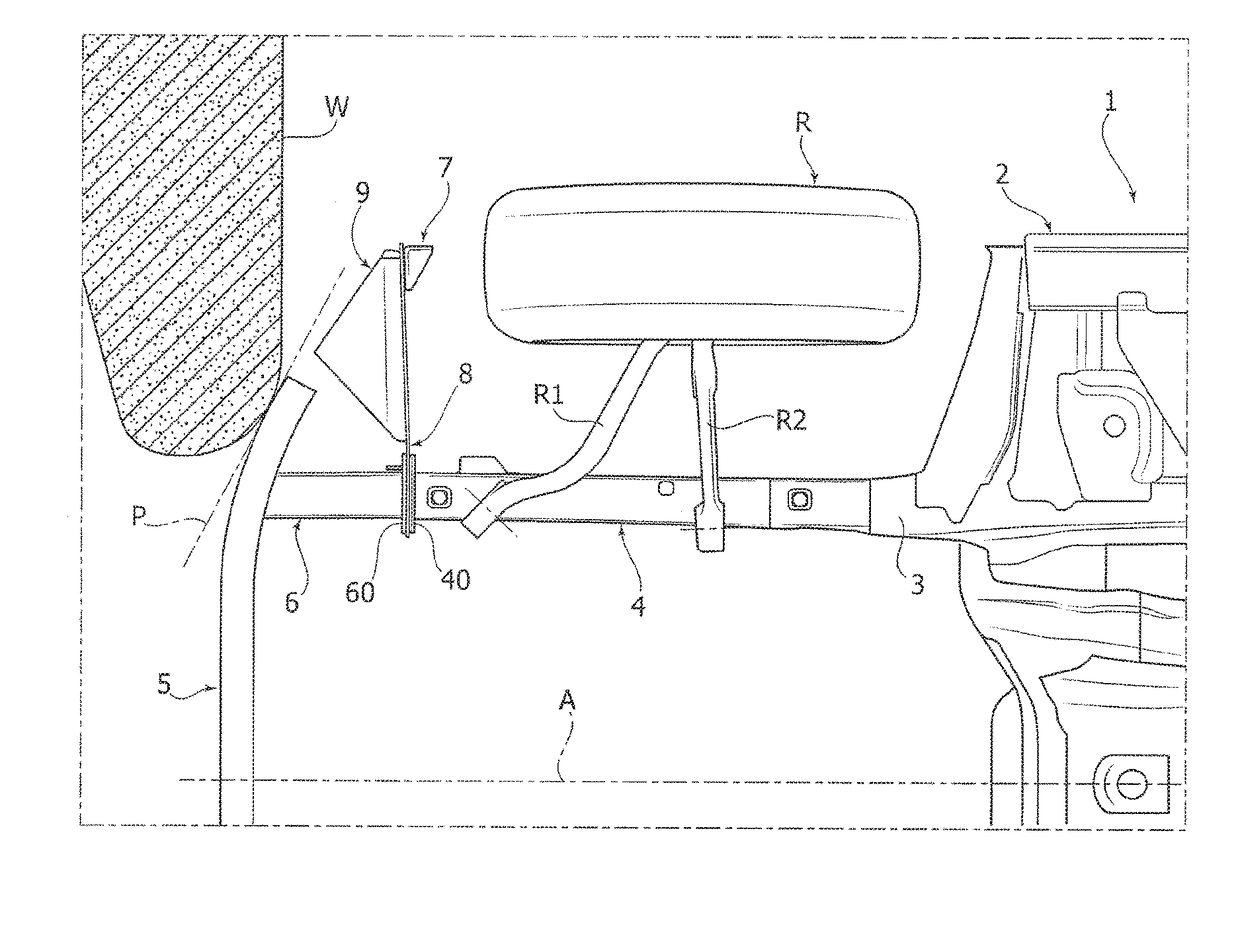
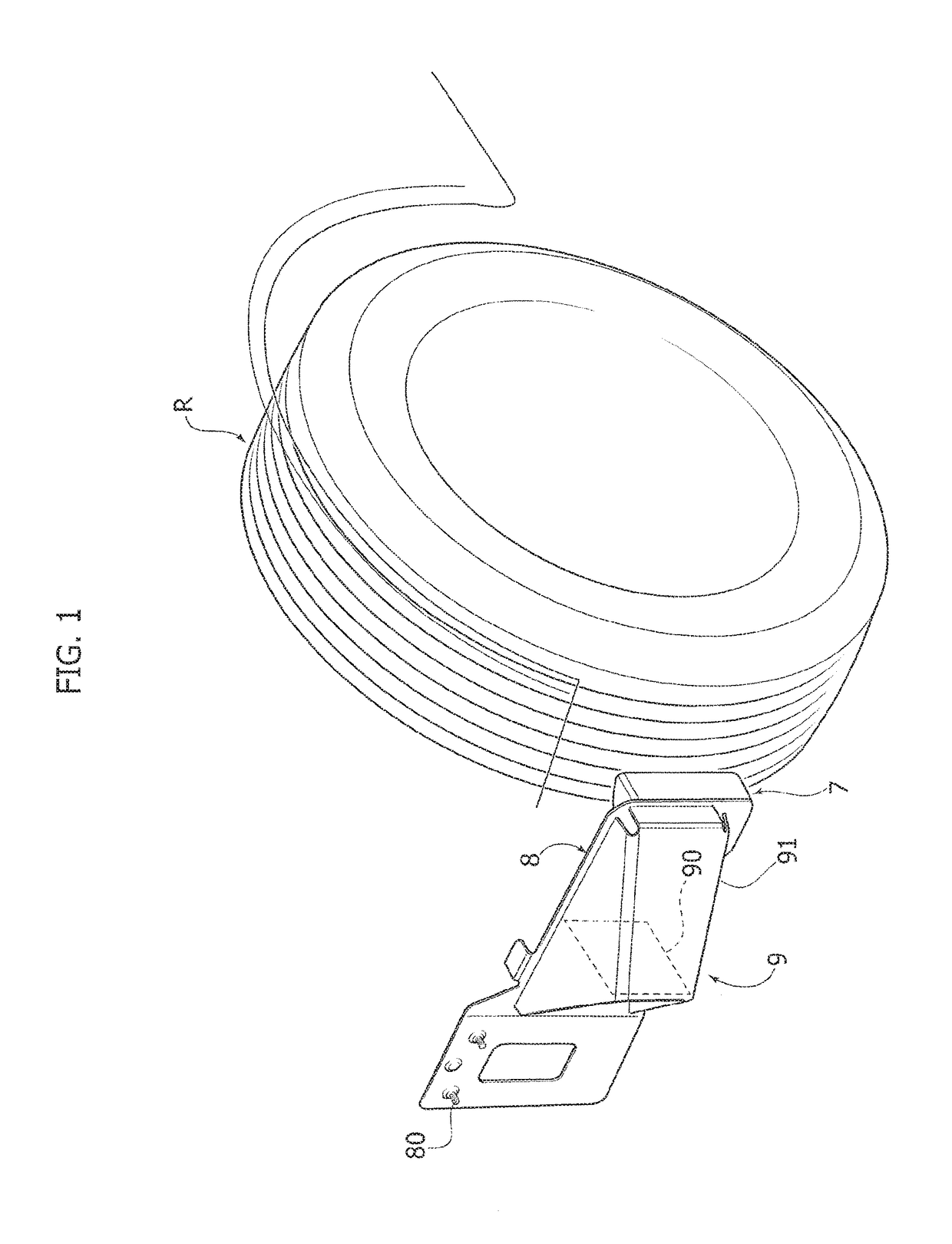
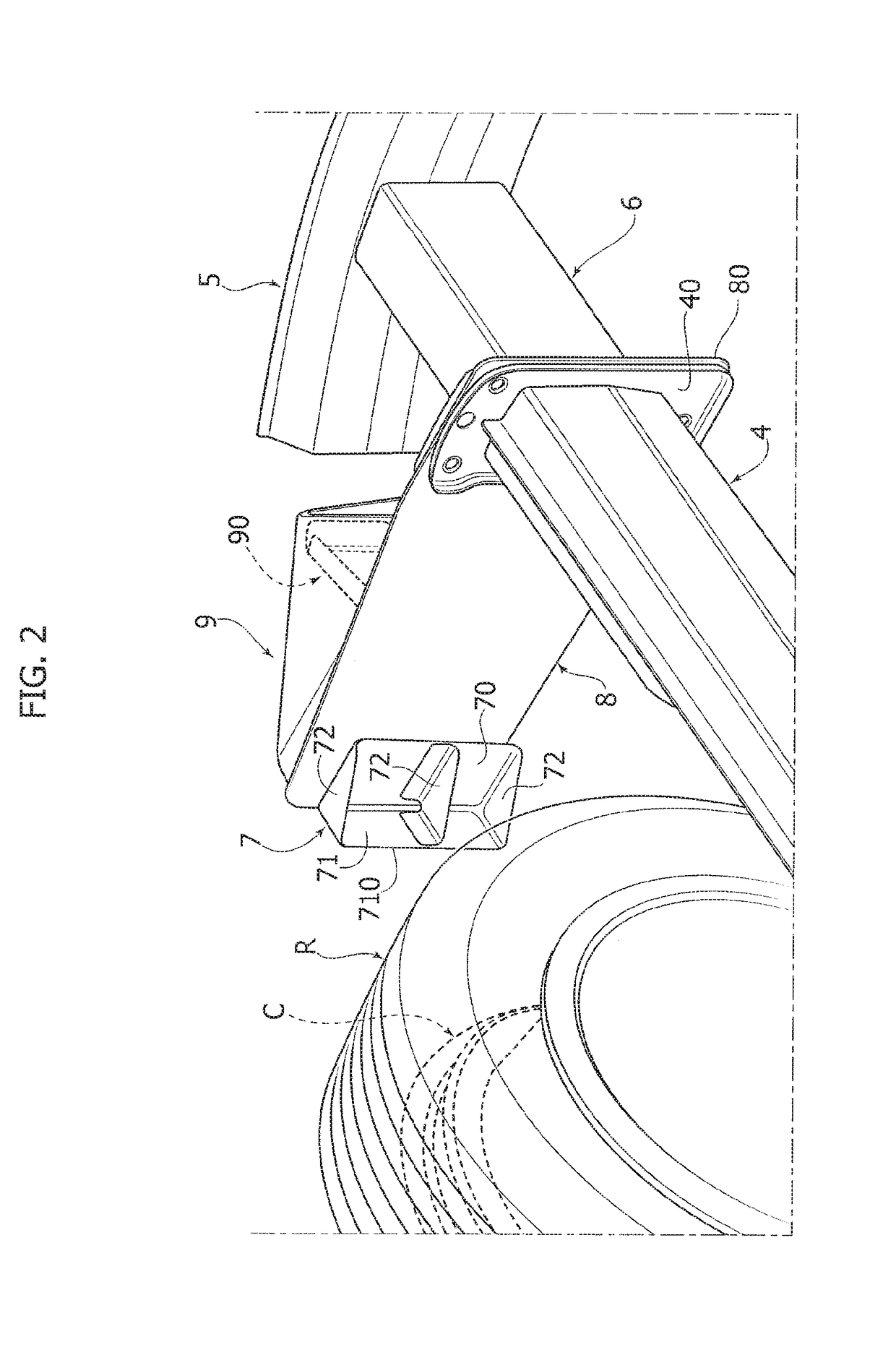
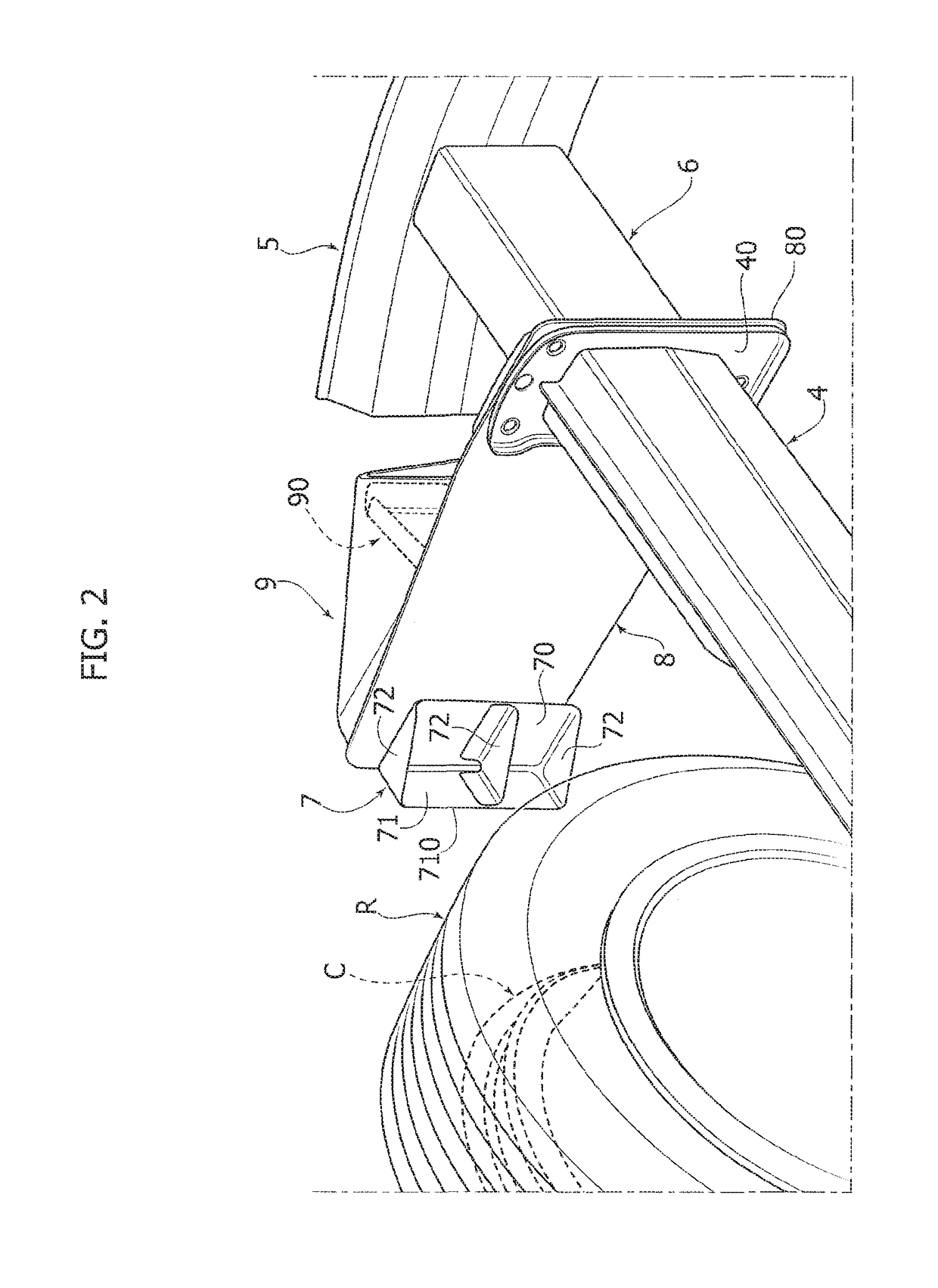
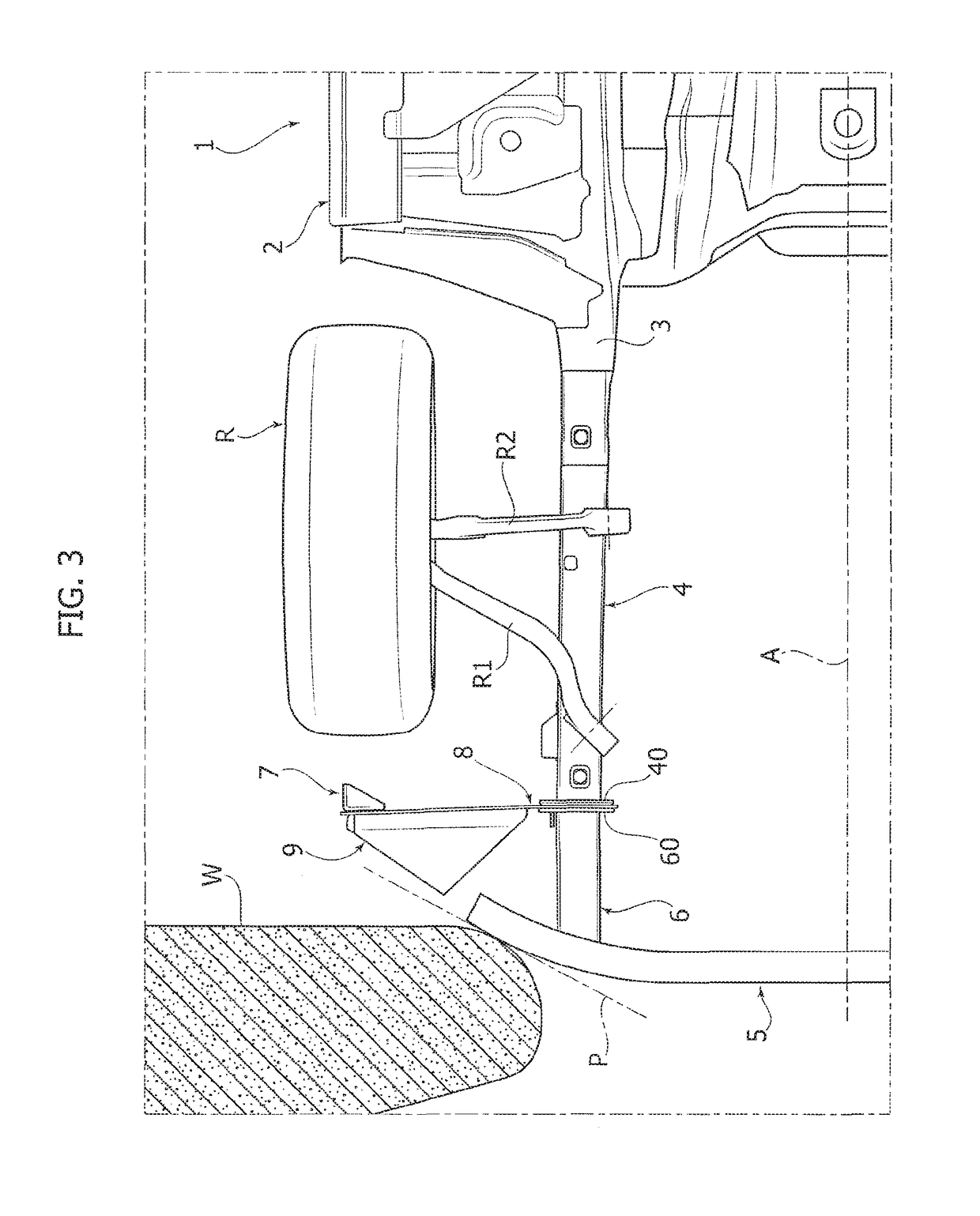
Safety device for orienting a motor-vehicle front wheel transversally to the longitudinal direction following a collision
ActiveUS20170297519A1Reduce riskSimple and inexpensive structurePedestrian/occupant safety arrangementUnderstructuresEngineeringMotorized vehicle
A safety device is described which is configured to orient a motor-vehicle front wheel transversely to the travel direction, following a collision of the motor-vehicle against a barrier. The device includes a ram member carried by a plate projecting laterally in a cantilever fashion from the motor-vehicle structure forwardly of the front wheel. The ram member is pushed against the front wheel following a collision of the motor-vehicle against the barrier. The ram member has a vertically elongated front portion, for engaging the wheel. With the transverse plate carrying the ram member there is associated a bumper structure located forwardly of the transverse plate and including a bumper element projecting forwardly from the transverse plate, at an intermediate position between the ram member and a connected end of the transverse plate.
Owner:FCA ITAL
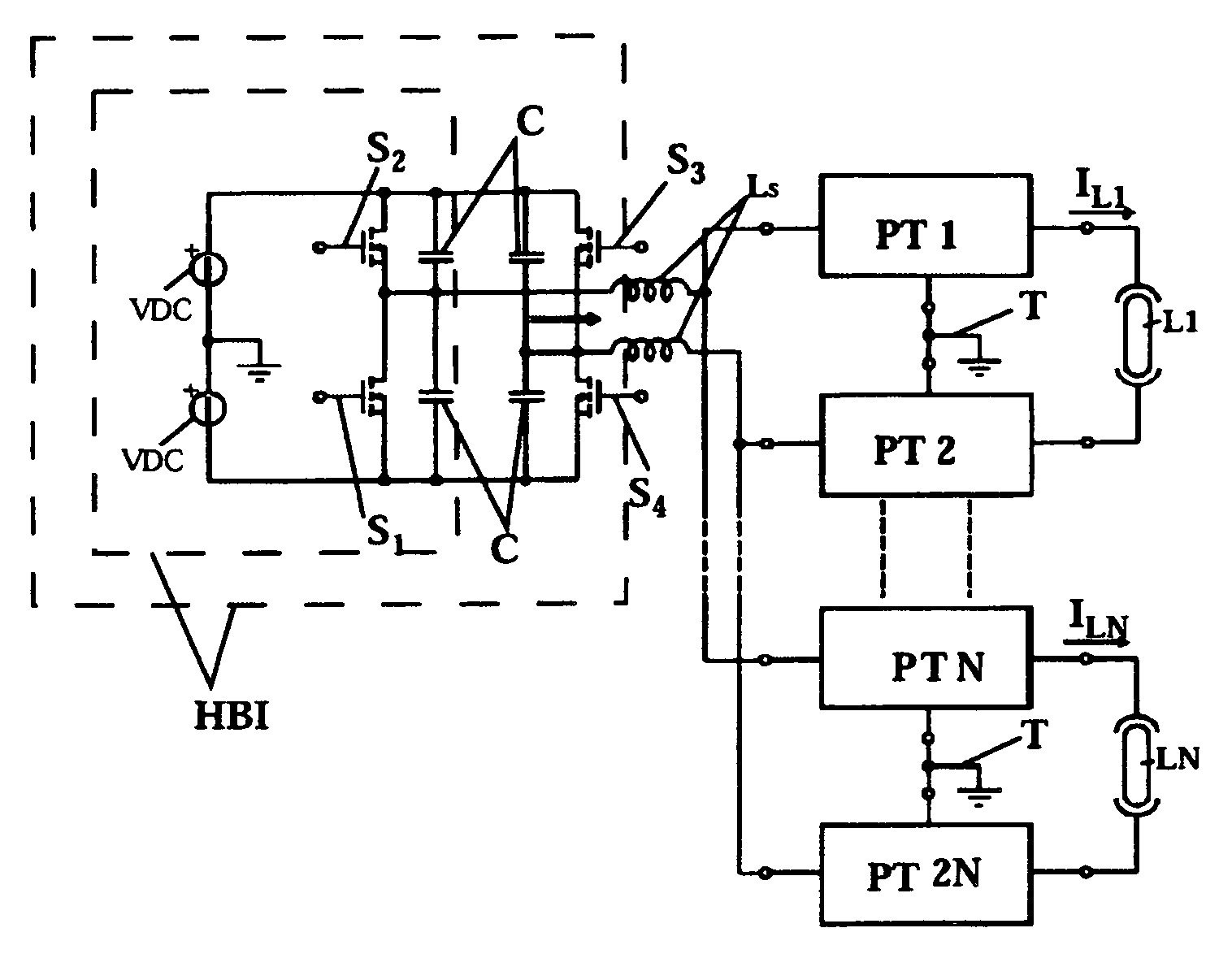
Power supply system for liquid crystal monitors
InactiveUS7233113B2Reduces component and complexityDrawback mentionedElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
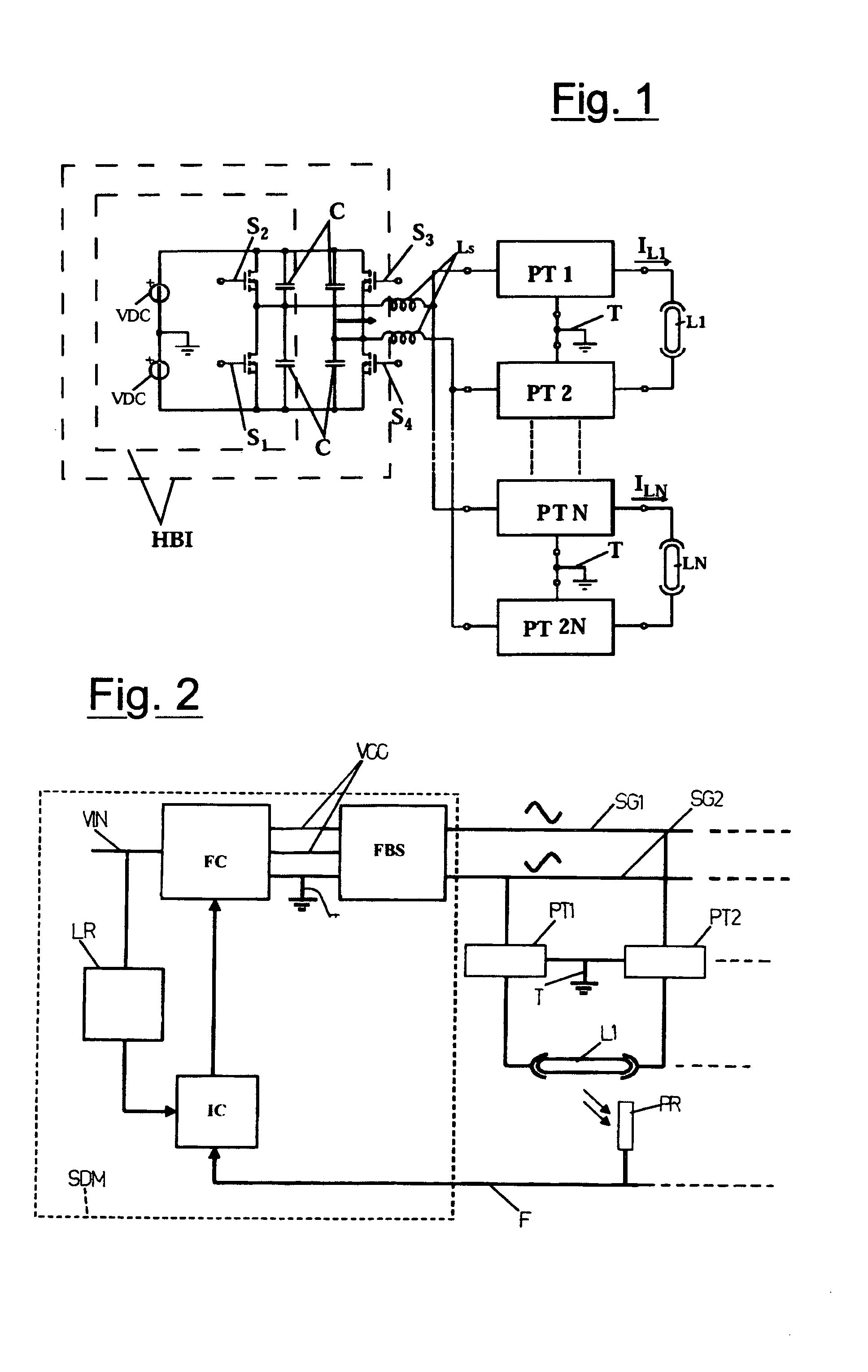
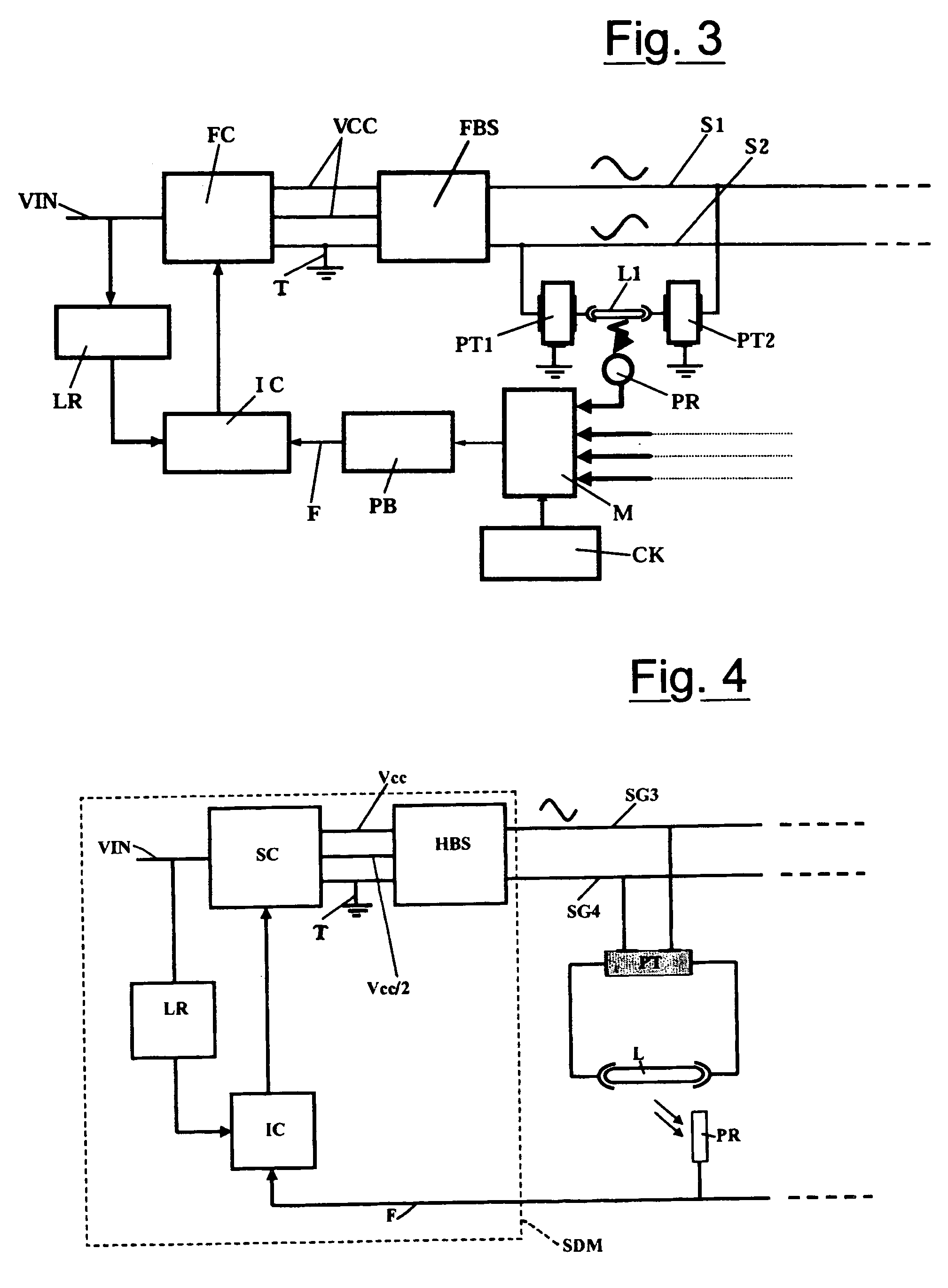
A power supply system for liquid crystal monitors includes a first DC / AC converter (FBS, HBS) operating at predetermined frequency and duty-cycles and being fed by a second DC / DC converter (FC) which regulates the circuit voltage. The feeding system can feed all the fluorescent lamps (L, L1, LN) in the monitor through a bus connection which transmits the output sinusoidal voltage (SG1, SG2, SG3) from the first DC / AC converter (FBS, HBS) to the primary windings of a plurality of parallel connected piezoelectric transformers (PT, PT1, PT2, PTN, PT2N) which are connected with the fluorescent lamps (L, L1, LN).
Owner:GLOBAL DISPLAY SOLUTIONS
Bottle for extemporaneous preparation products, particularly medical, pharmaceutical, cosmetic products
InactiveUS20140027322A1Easy to separateLow costClosuresDispensing apparatusExtemporaneous preparationsDrug product
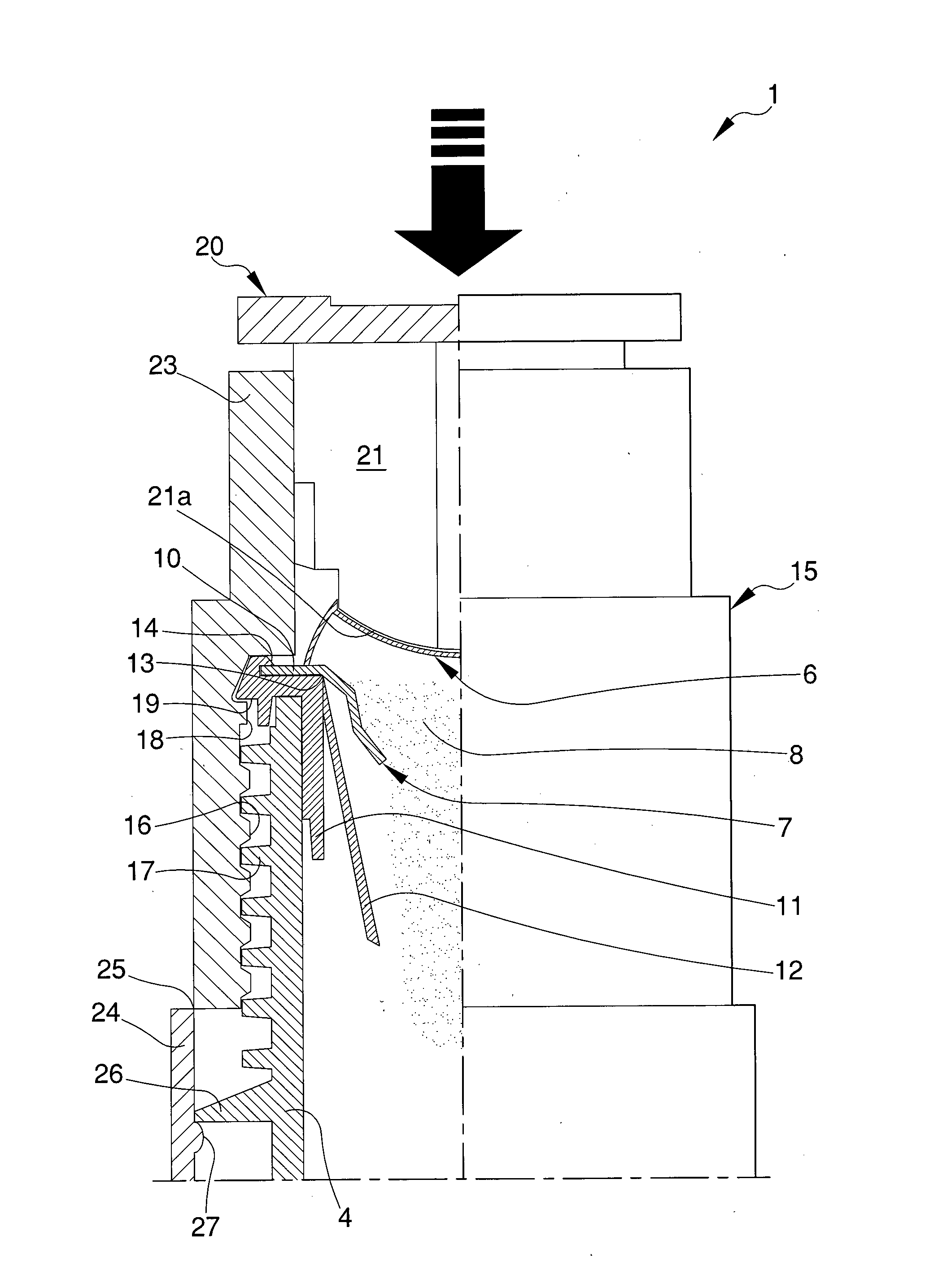
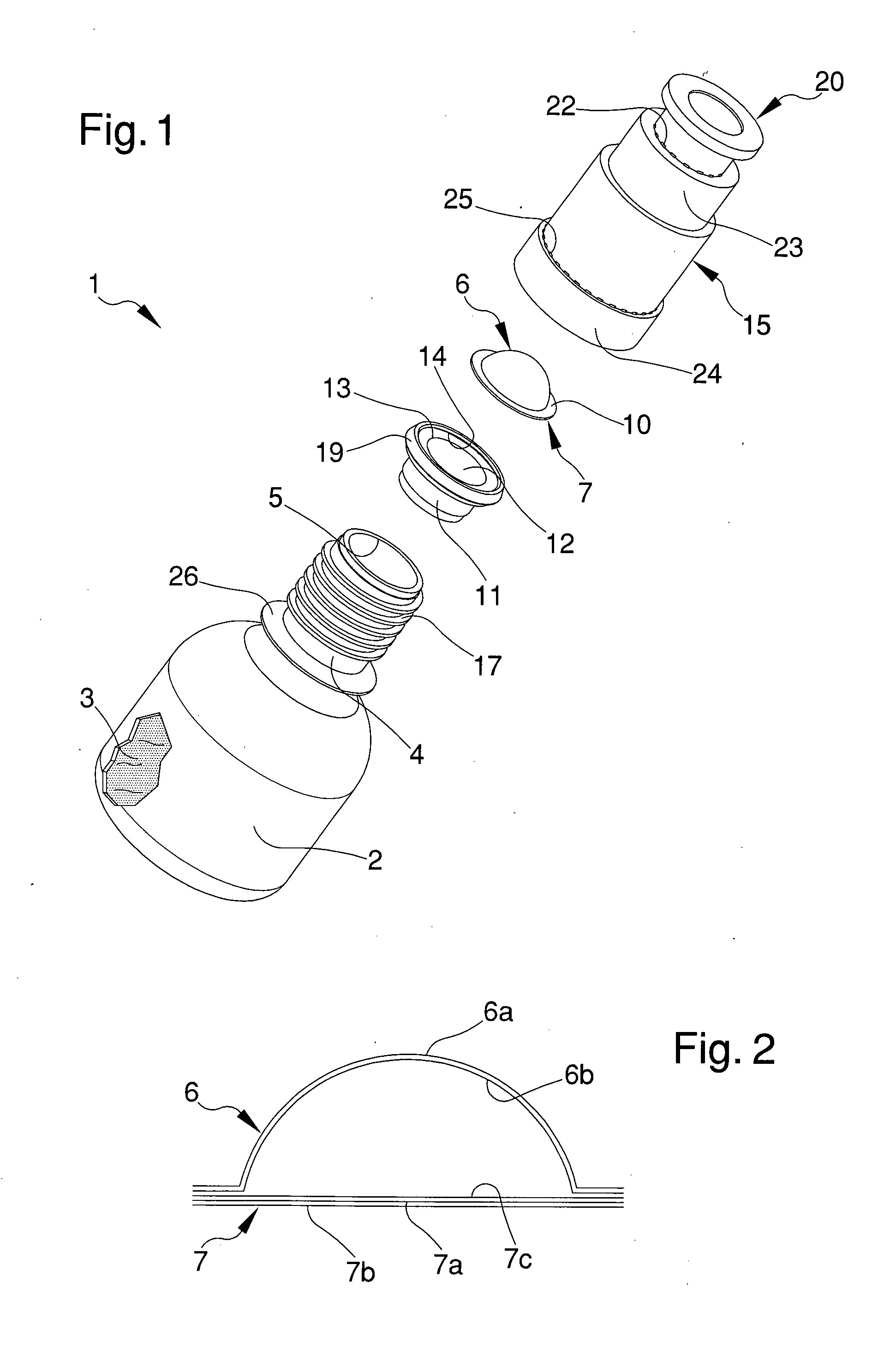
A bottle for extemporaneous-preparation products includes: a tank for containing a first substantially liquid substance, which has at least a dispensing mouth; and a container for containing a second substantially powdery substance associable with the tank substantially in proximity of the dispensing mouth, the inner volume of the container being temporarily separated from the inner volume of the tank and arranged to communicate therewith for mixing the first and second substances to form a product. The container includes a blistered capsule having: a first foil substantially deformable and shaped to define a containment cavity of the second substance; and a second foil substantially breakable, which is associated with the first foil to close the containment cavity and is turned towards the dispensing mouth, wherein applying pressure on the first foil causes the breaking of the second foil for the outflow and mixing of the first and of second substances.
Owner:LAMEPLAST
Bead breaking unit for tire changing machines
The bead breaking unit for tire changing machines includes an arm having a first extremity associated turnable with a support structure and a second extremity having a bead breaking tool, the arm being suitable for oscillating between an away position, wherein the bead breaking tool is positioned substantially at a distance from the support structure, and a work position, wherein the bead breaking tool is positioned substantially close to the support structure, at least an actuator device having a mobile element associated sliding with the arm, at least a drive element for driving the arm, associated with the mobile element and suitable for operating during the movement of the mobile element from an extracted position to a retracted position to move the arm towards the work position and an apparatus of temporary coupling between the mobile element and the arm, suitable for operating during the movement of the mobile element from the retracted position to the extracted position to move the arm from the work position to the away position.
Owner:GIULIANO GROUP
Modular gas-separating adsorbers
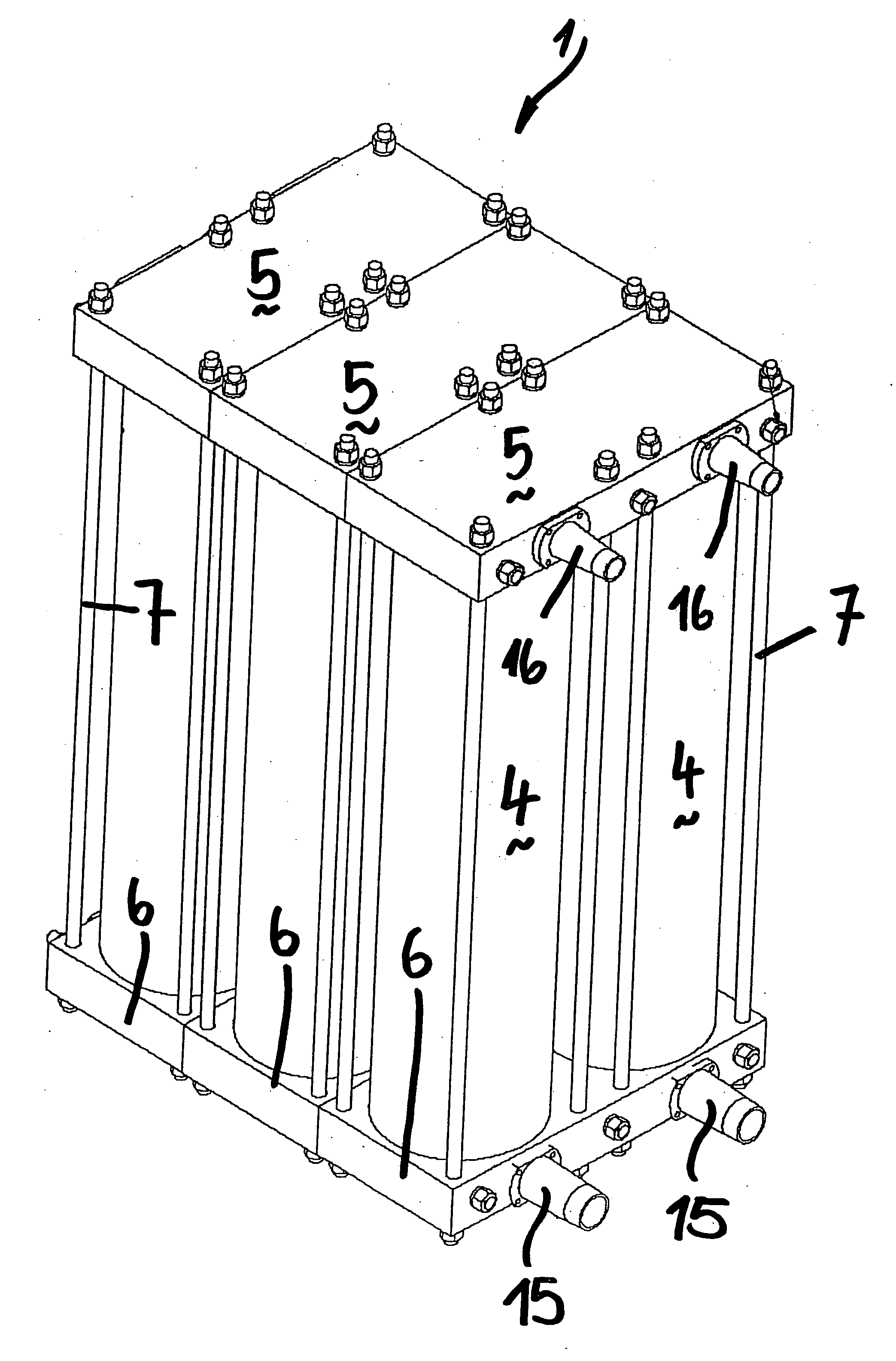
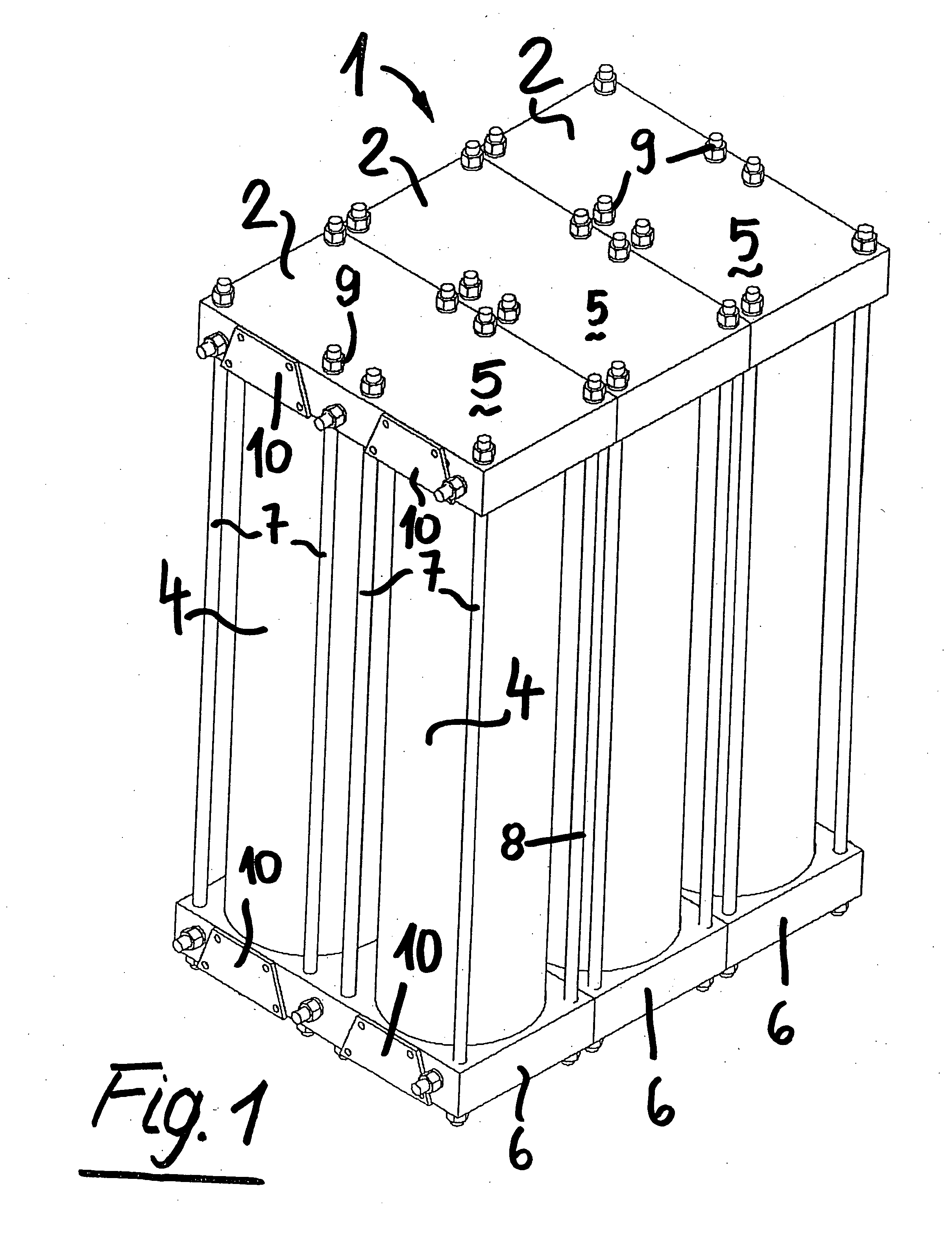
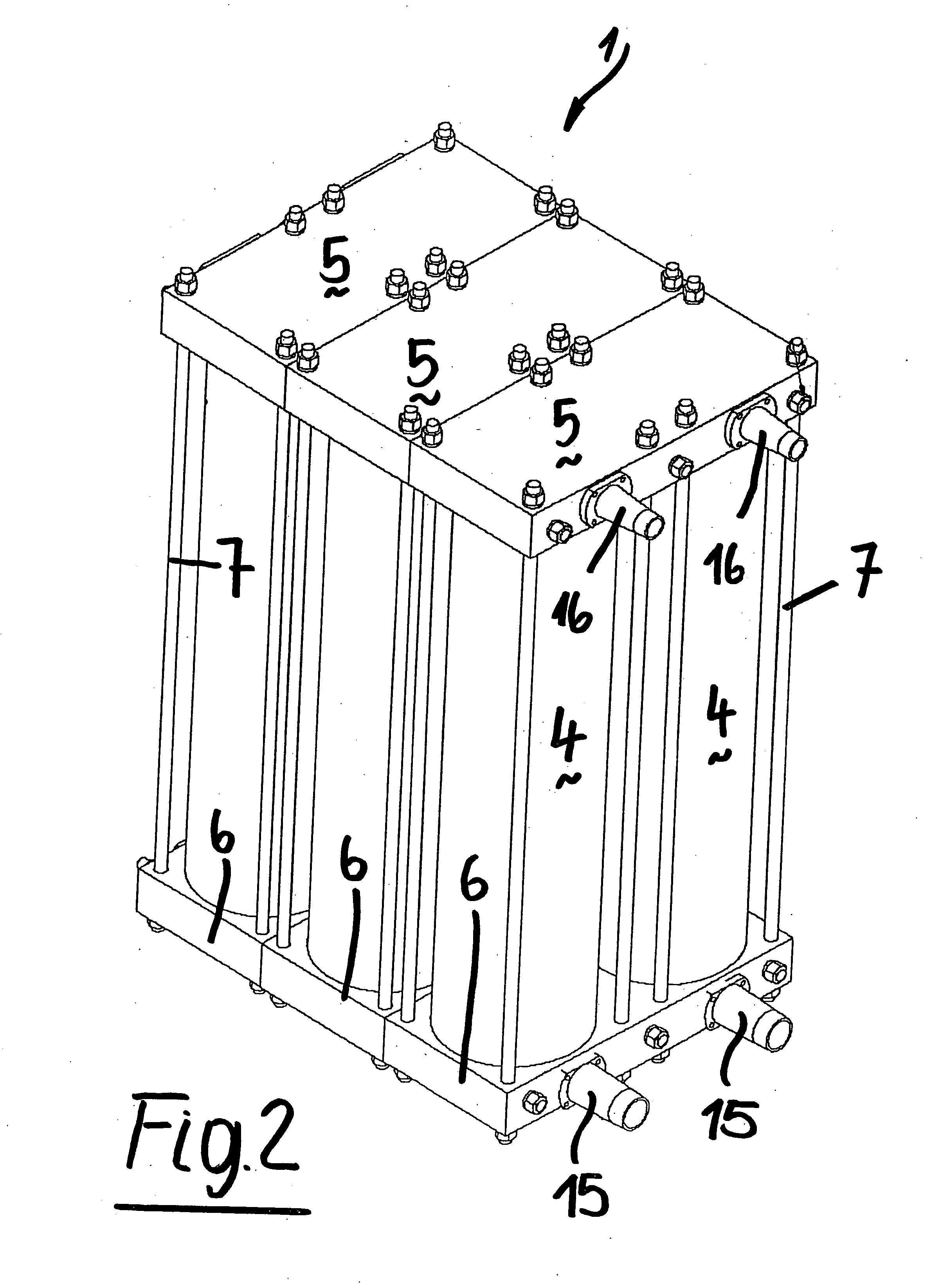
ActiveUS20090193774A1Drawback mentionedCombination devicesGas treatmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
In a modular gas-separating adsorber assembly, a pair of cylindric vessels, filled-in by a given amount of an adsorbing material (either a mainly adsorbing or a mainly adsorbing material) are always operatively assembled with a top plate and a bottom plate, the top and bottom plates being mutually coupled by tie rods, engaged in the plate corners, the bottom plates and top plates forming plate chambers and being operatively connected with the chamber formed by adjoining cylindric vessel, the plates having projecting fittings to be assembled with the plate chambers included in adjoining vessels.
Owner:NOXERIOR
Safety device for orienting a motor-vehicle front wheel transversally to the longitudinal direction following a collision
ActiveUS10059288B2Simple and inexpensive structureDrawback mentionedPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementUnderstructuresEngineeringMotorized vehicle
A safety device is described which is configured to orient a motor-vehicle front wheel transversely to the travel direction, following a collision of the motor-vehicle against a barrier. The device includes a ram member carried by a plate projecting laterally in a cantilever fashion from the motor-vehicle structure forwardly of the front wheel. The ram member is pushed against the front wheel following a collision of the motor-vehicle against the barrier. The ram member has a vertically elongated front portion, for engaging the wheel. With the transverse plate carrying the ram member there is associated a bumper structure located forwardly of the transverse plate and including a bumper element projecting forwardly from the transverse plate, at an intermediate position between the ram member and a connected end of the transverse plate.
Owner:FCA ITAL
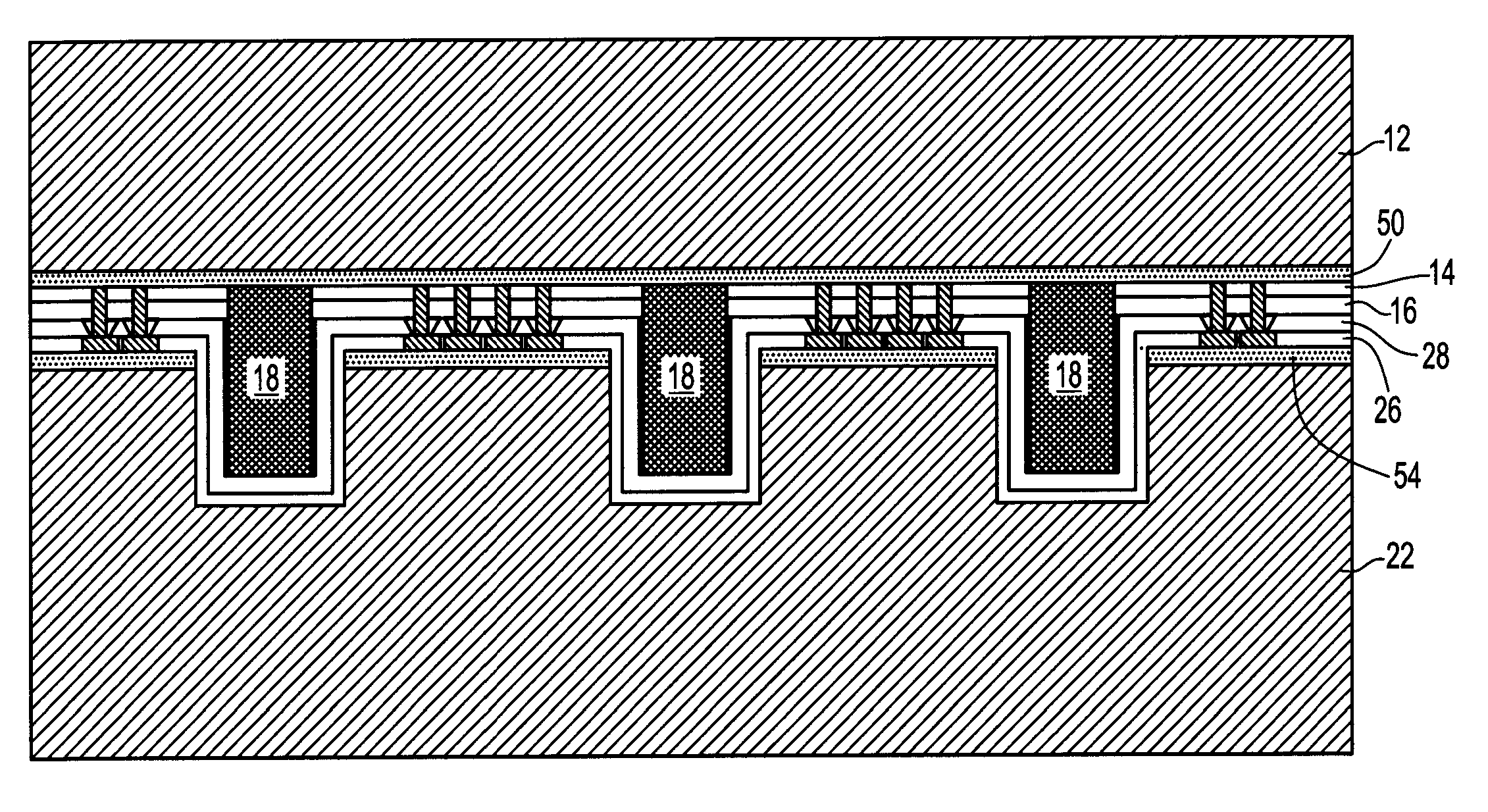
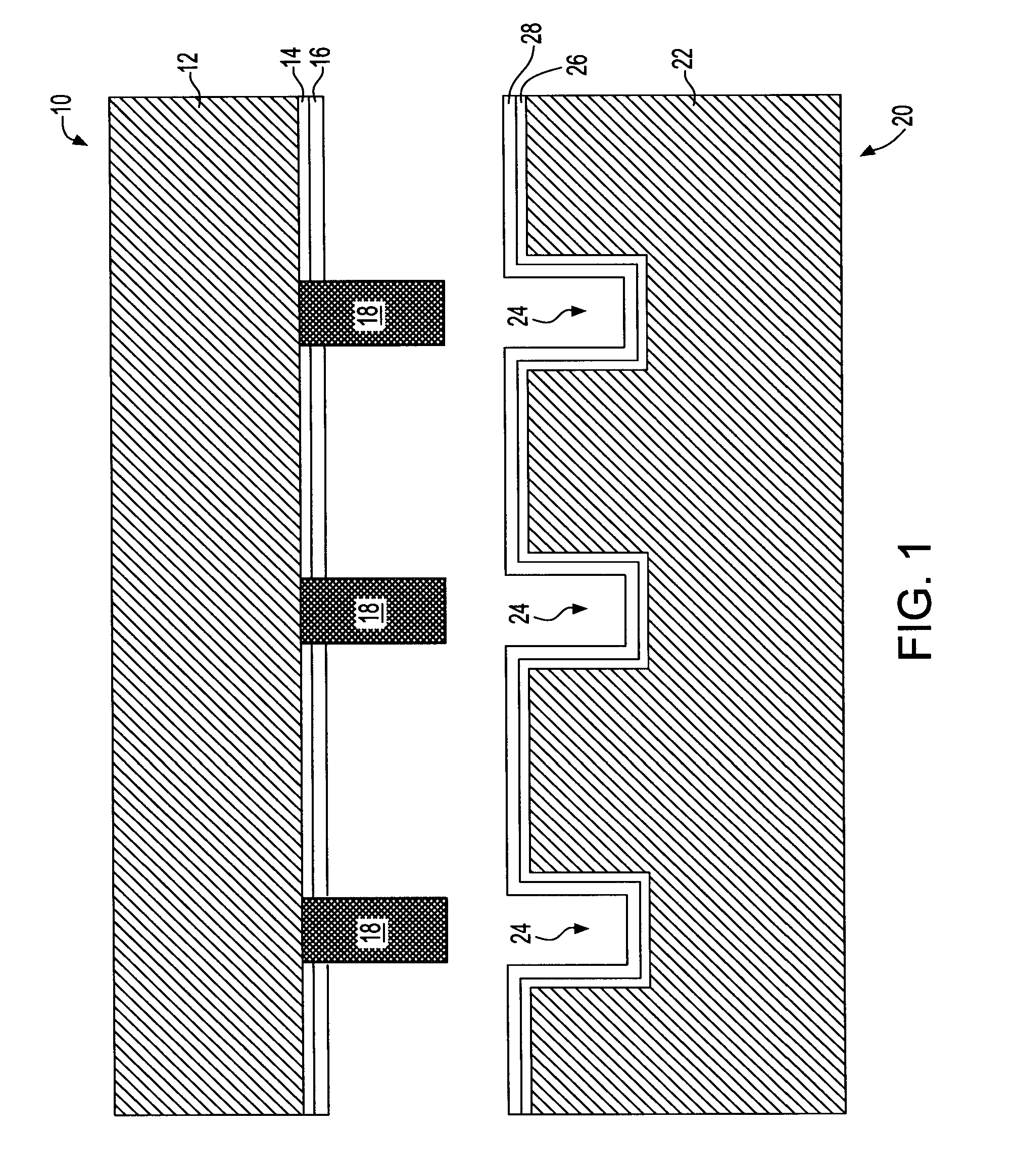
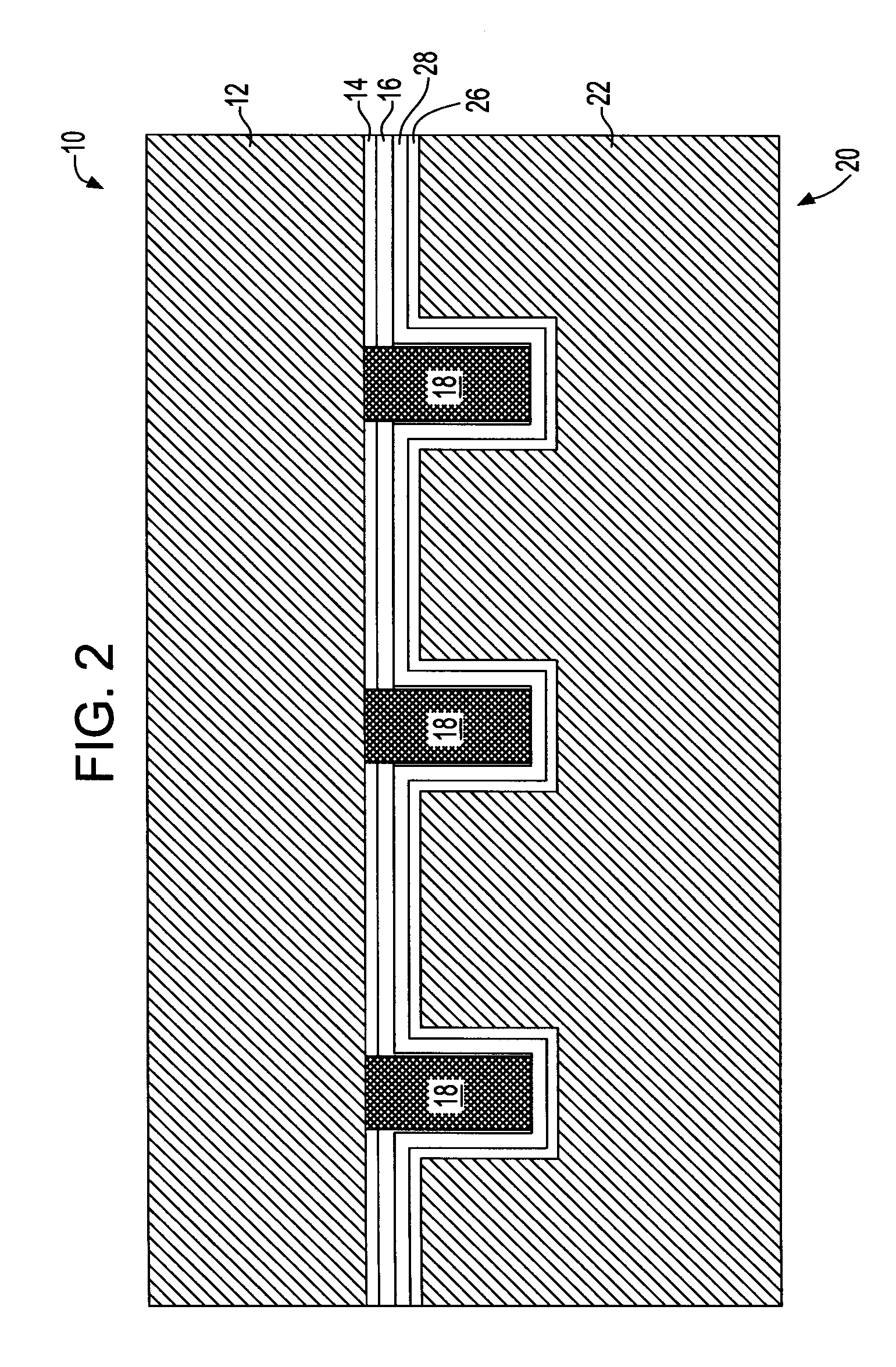
Metal filled through via structure for providing vertical wafer-to-wafer interconnection
ActiveUS20080105976A1Avoid radiationDrawback mentionedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInterconnectionEngineering
A vertical wafer-to-wafer interconnect structure is provided in which a first wafer and a second wafer are mated by way of metal studs that extend from a surface of the first wafer. The metal studs extend from the surface of the first wafer into a corresponding through via of the second wafer. A polyimide coating is present in the through via on mated surfaces of the first and second wafers and on another surface of the second wafer not mated to the first wafer, thus the metal studs provide a continuous metal path from the first wafer through the second wafer. Since only metal studs for the vertical connection are used, no alpha radiation is generated by the metal studs.
Owner:IBM CORP
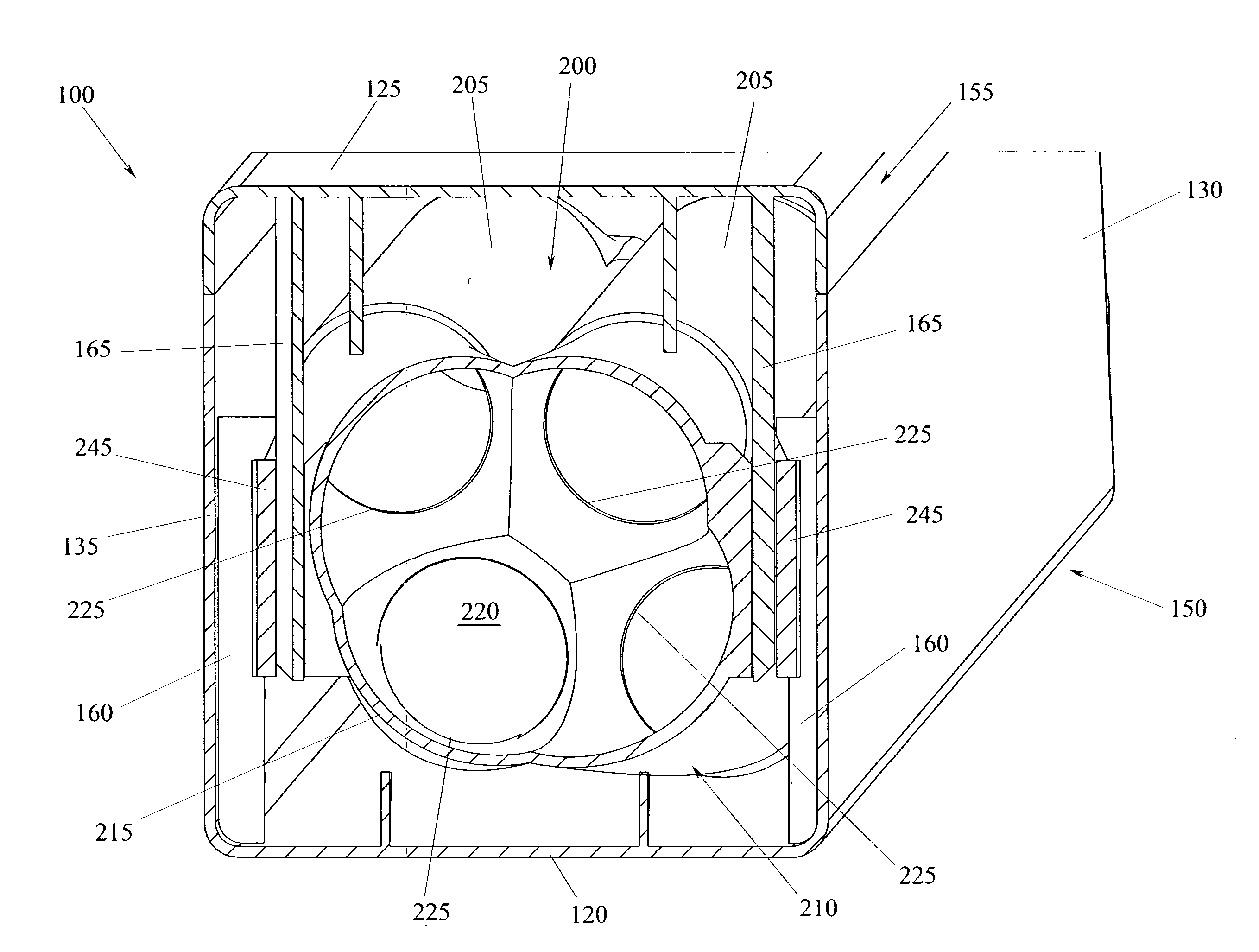
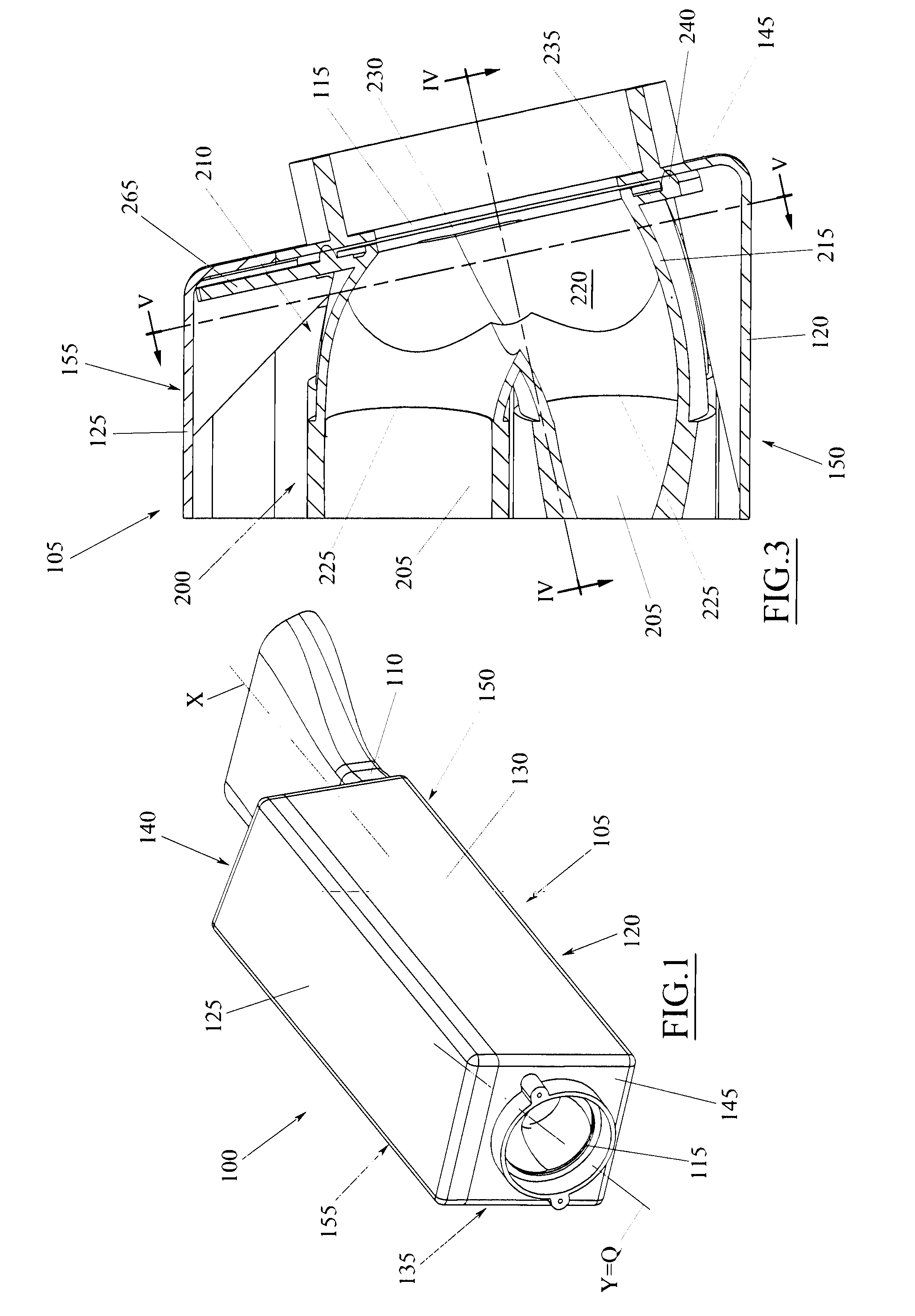
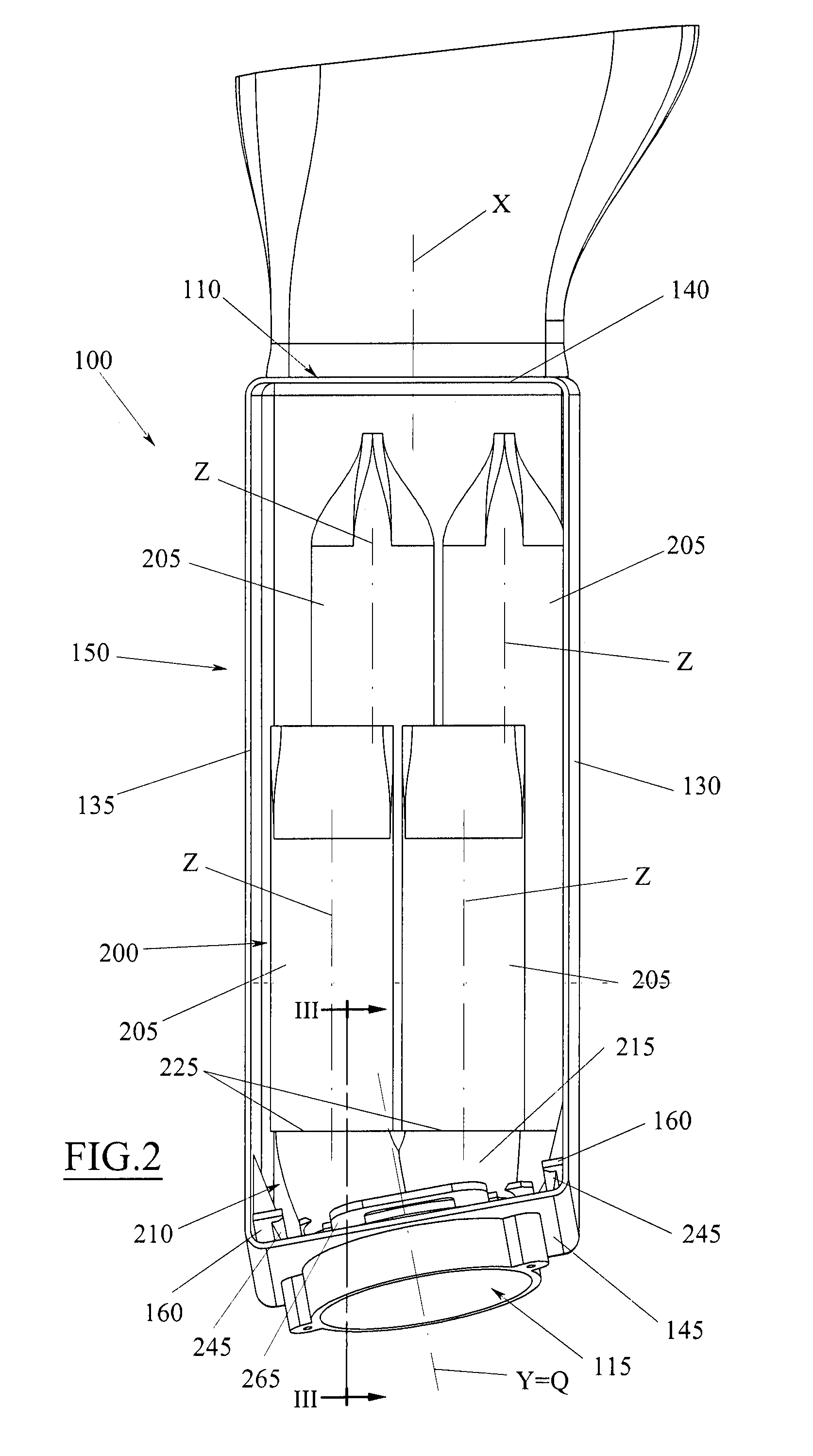
Manifold element for a filtering cartridge
ActiveUS20140230384A1Simple and reliable solutionSimple, rational and inexpensiveGas treatmentAuxillary pretreatmentTelecommunicationsAccess port
A manifold element (210) for a filtering cartridge (200) comprising a shaped shell (215) provided with an internal volume (220) and a plurality of access ports (225, 230) communicating with said internal volume, among which a plurality of first access ports (225) and at least one second access port (230), wherein each of said first access ports (225) is adapted to be coupled with a respective filtering material element (205) so as to support it and be occluded thereby.
Owner:UFI FILTERS SPA
Brush for the application of cosmetic products
ActiveUS20180084897A1Fast and accurate mannerFacilitate taking of requiredBristleBiomedical engineeringCosmetics
A brush for the application of cosmetic products, including a grip body having at least a housing seat made to measure for a plurality of hairs adapted to take, apply and spread cosmetic products on a user, in which the plurality of hairs is divided into: a first group of hairs adjacent to one another and fitted to measure in the housing seat and defining a convex spreading surface which is adapted to spread the cosmetic products on the user; and a second group of hairs adjacent to one another and inserted in the first group of hairs, defining a taking and application surface which is protruding with respect to the spreading surface and has a substantially pointed shape and is suitable for taking the cosmetic products and for their point-like application on the user.
Owner:PENNELLI FARO
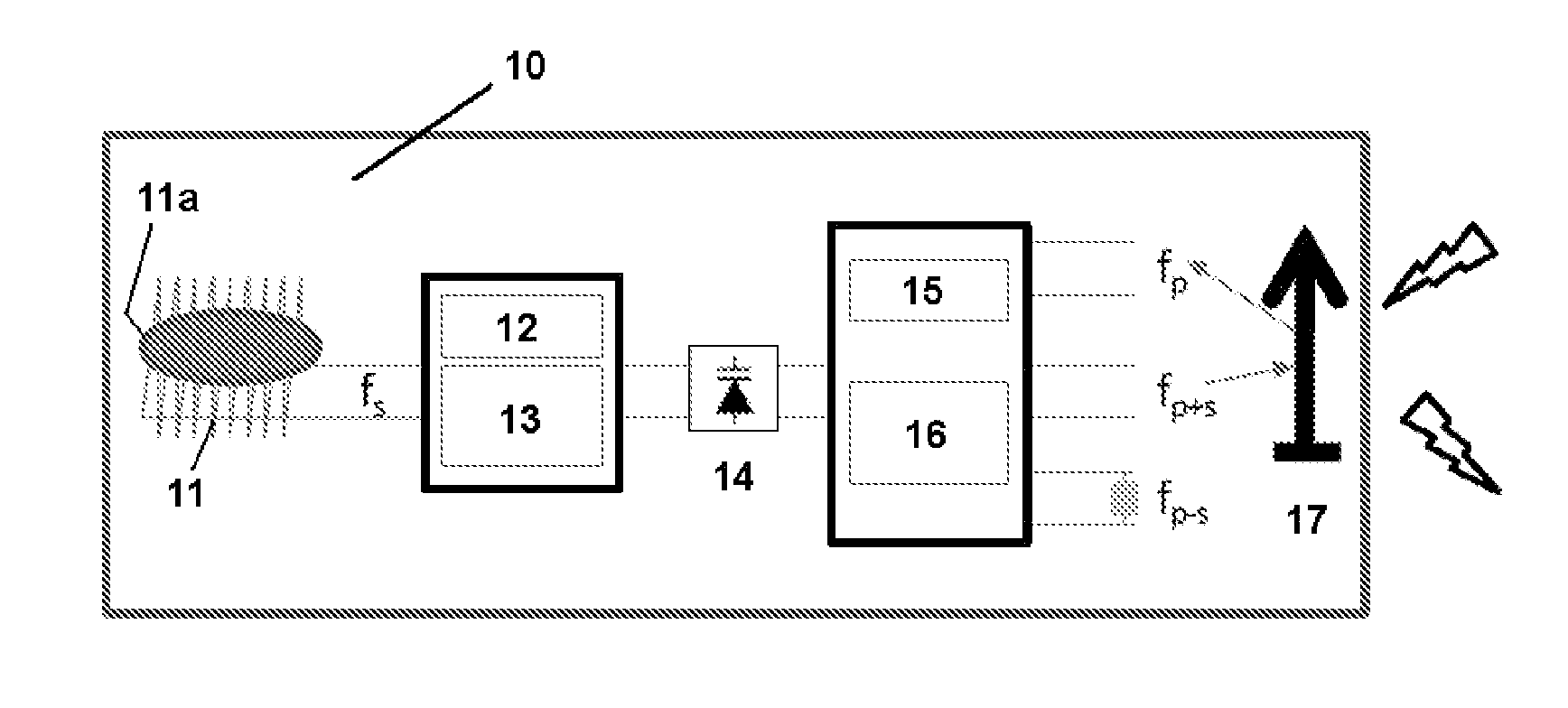
Active position marker system for use in an MRI apparatus
ActiveUS20150035533A1Simple and flexible operationDrawback mentionedSurgeryCatheterAudio power amplifierImaging processing
An active position marker system comprising at least one active position marker (10) and a remote transceiver unit (20) for communicating with the position marker is disclosed. Basically, the position marker (10) comprises a local RF receive coil (11) for receiving MR signals which are excited in a local volume, and a parametric amplifier (14) for amplifying and upconverting the frequency of the received MR signal into at least one microwave sideband frequency signal. This microwave signal is transmitted wirelessly or wire-bound to the transceiver unit for downconverting the same and supplying it to an image processing unit of an MR imaging apparatus.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Ultrasonic type flowmeter apparatus and method of using the same
ActiveUS9588934B2Easy to measureDrawback mentionedDigital computer detailsFluid pressure measurementMemory chipElectricity
A disposable conduit 1 includes piezo-electric elements 2a and 2b and a memory chip 10 in which calibration data specific to the relevant conduit is stored. Before measurement, a non-disposable electrical measuring circuit reads the calibration data out of the memory chip 10 to prepare a calibrating equation or a calibration table. A flow speed of a blood passing through the conduit or a flow rate calculated from the flow speed is corrected in accordance with the calibrating equation or calibration table.
Owner:ATSUDEN
Driving assistance system of motor vehicles
InactiveUS20170249845A1Easily installableEasily usableAnti-collision systemsSignalling/lighting devicesMobile vehicleBiological activation
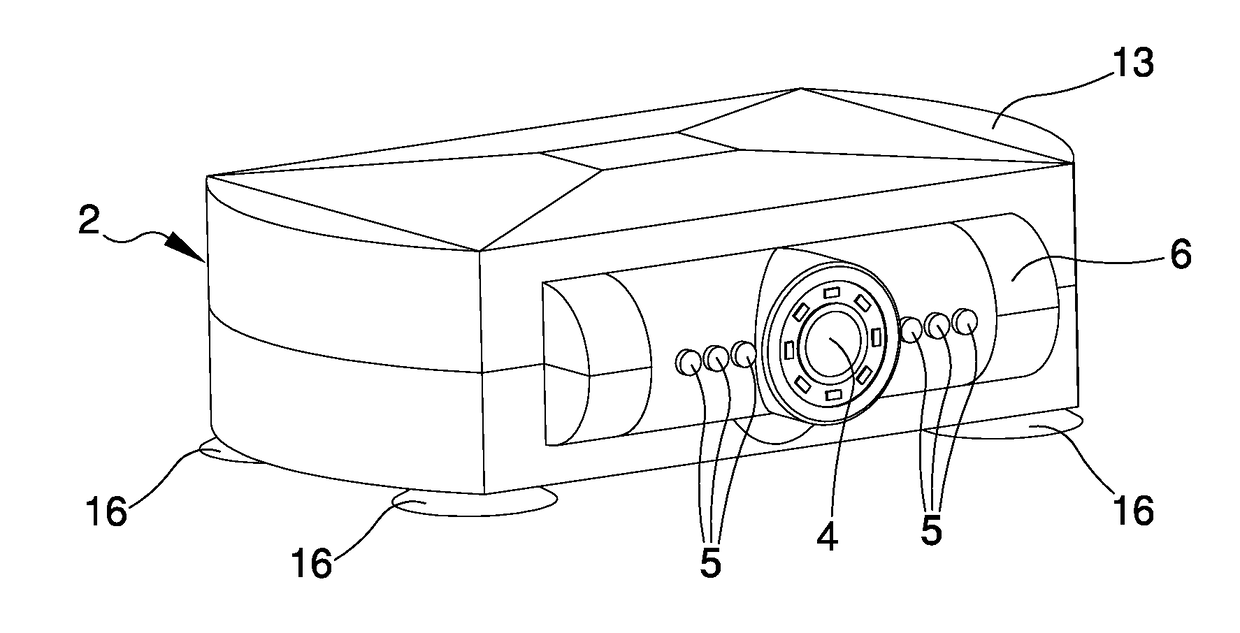
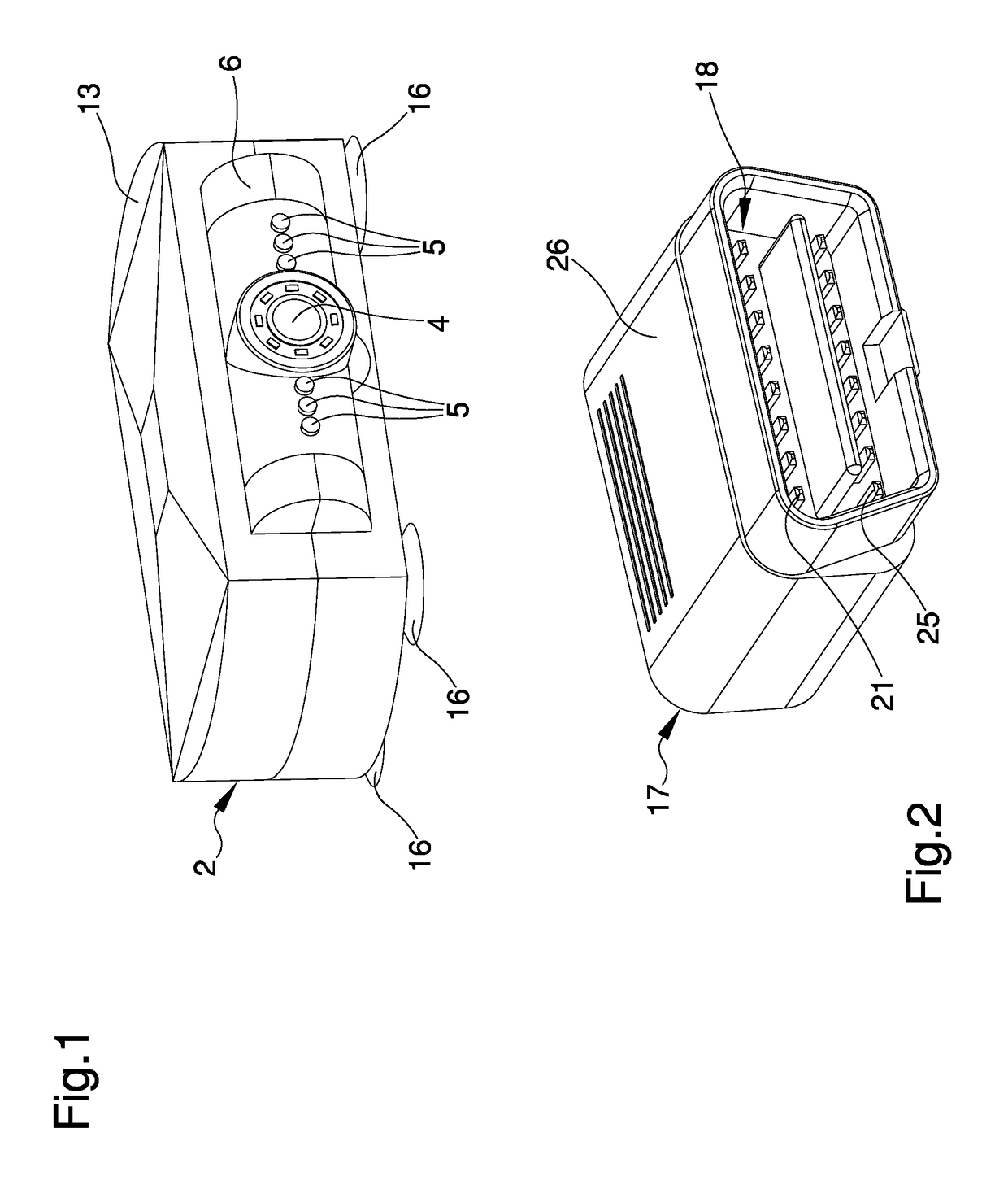
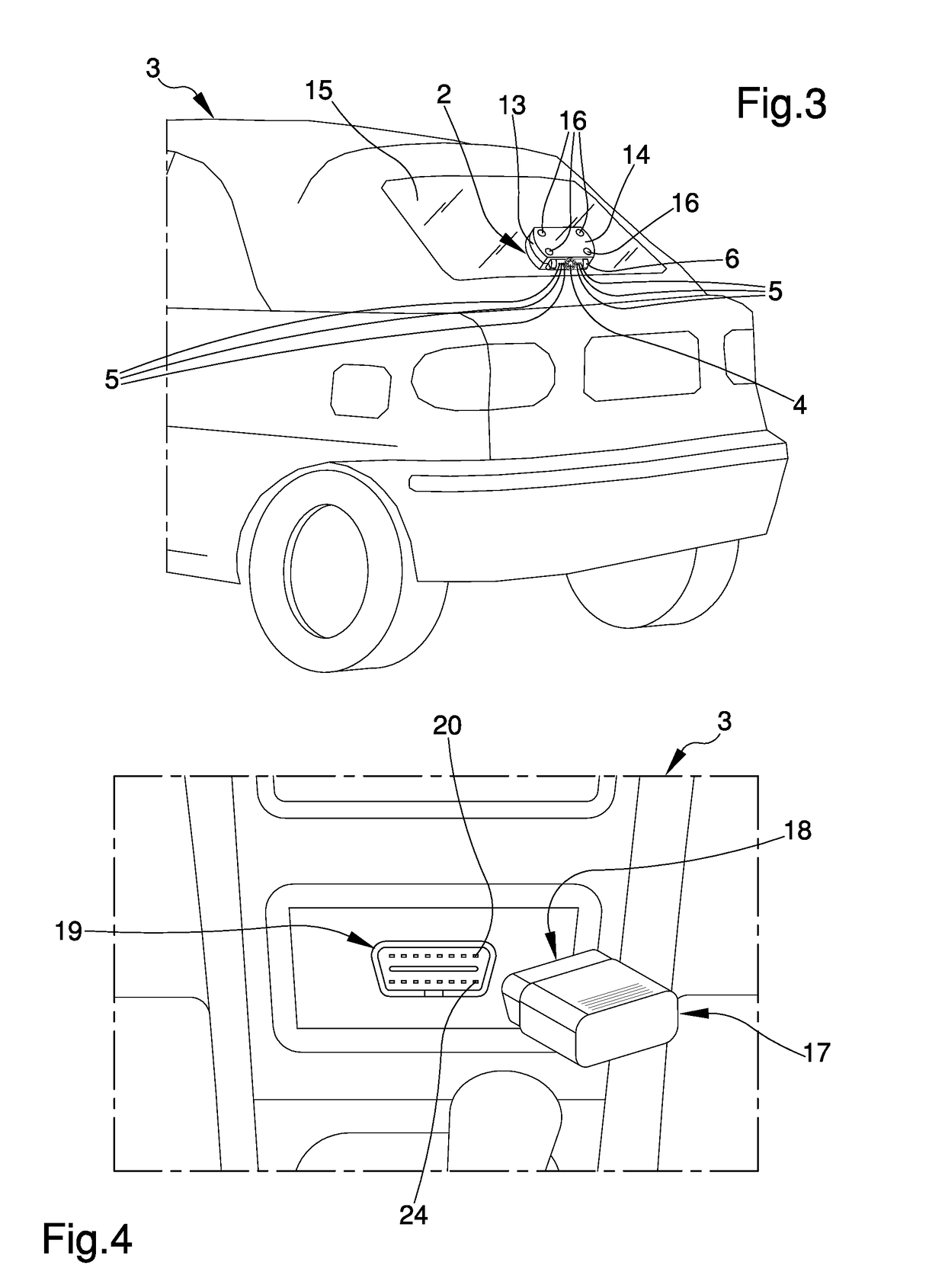
The driving assistance system of motor vehicles comprises a driving assistance device of a motor vehicle having at least a detection device for detecting the presence of possible obstacles on the outside of the motor vehicle, first activation / deactivation means operatively connected to the detection means and adapted to the activation / deactivation of the detection means, a first RF communication unit operatively connected to the first activation / deactivation means, removable fixing means of the assistance device to the motor vehicle, and wherein the system comprises a command device of the assistance device comprising an OBD type connector coupleable to an OBD type connection port of an on-board diagnostics system of the motor vehicle.
Owner:BREVETTI LAB
System for the distribution of radio frequency signals and relative combiner device
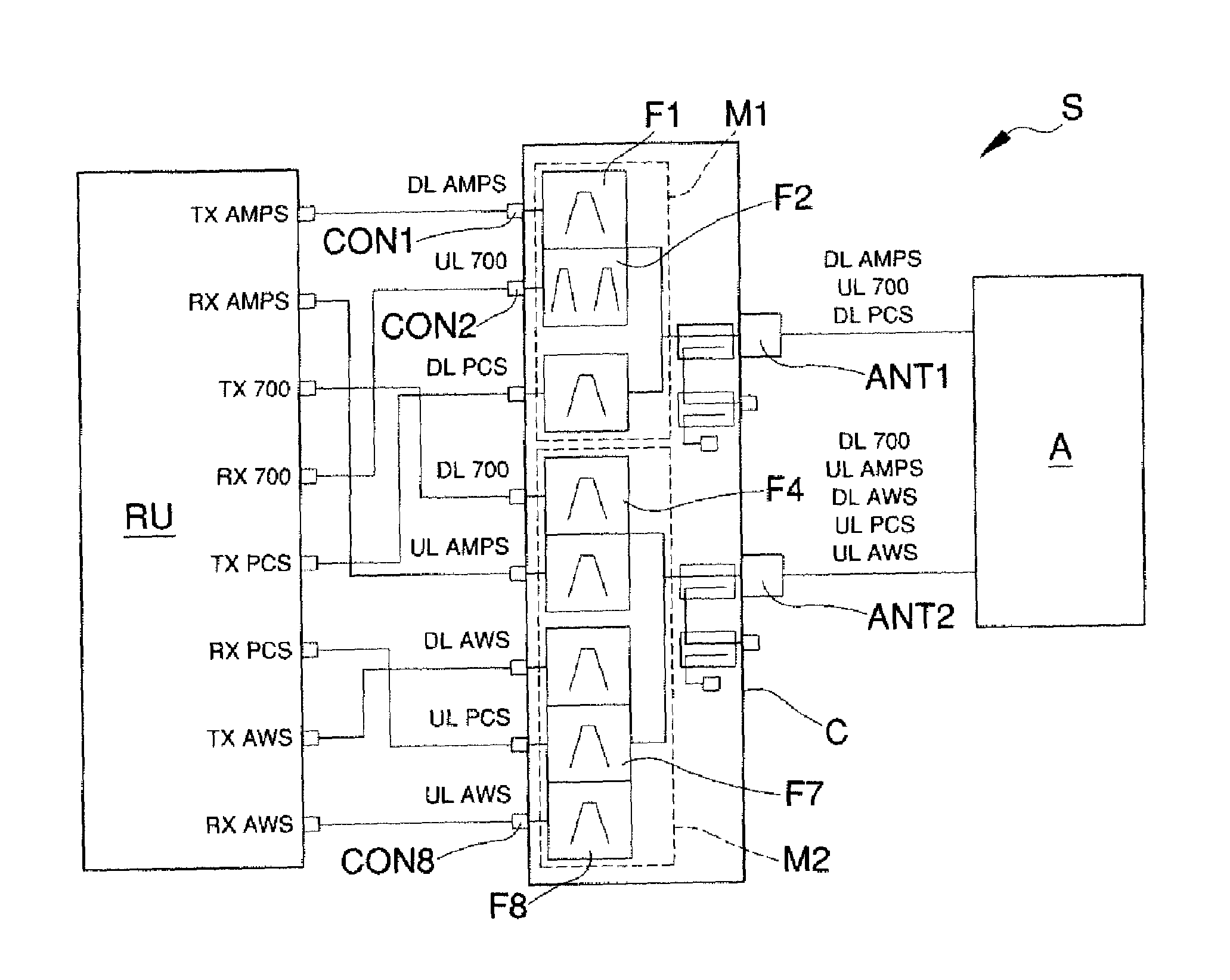
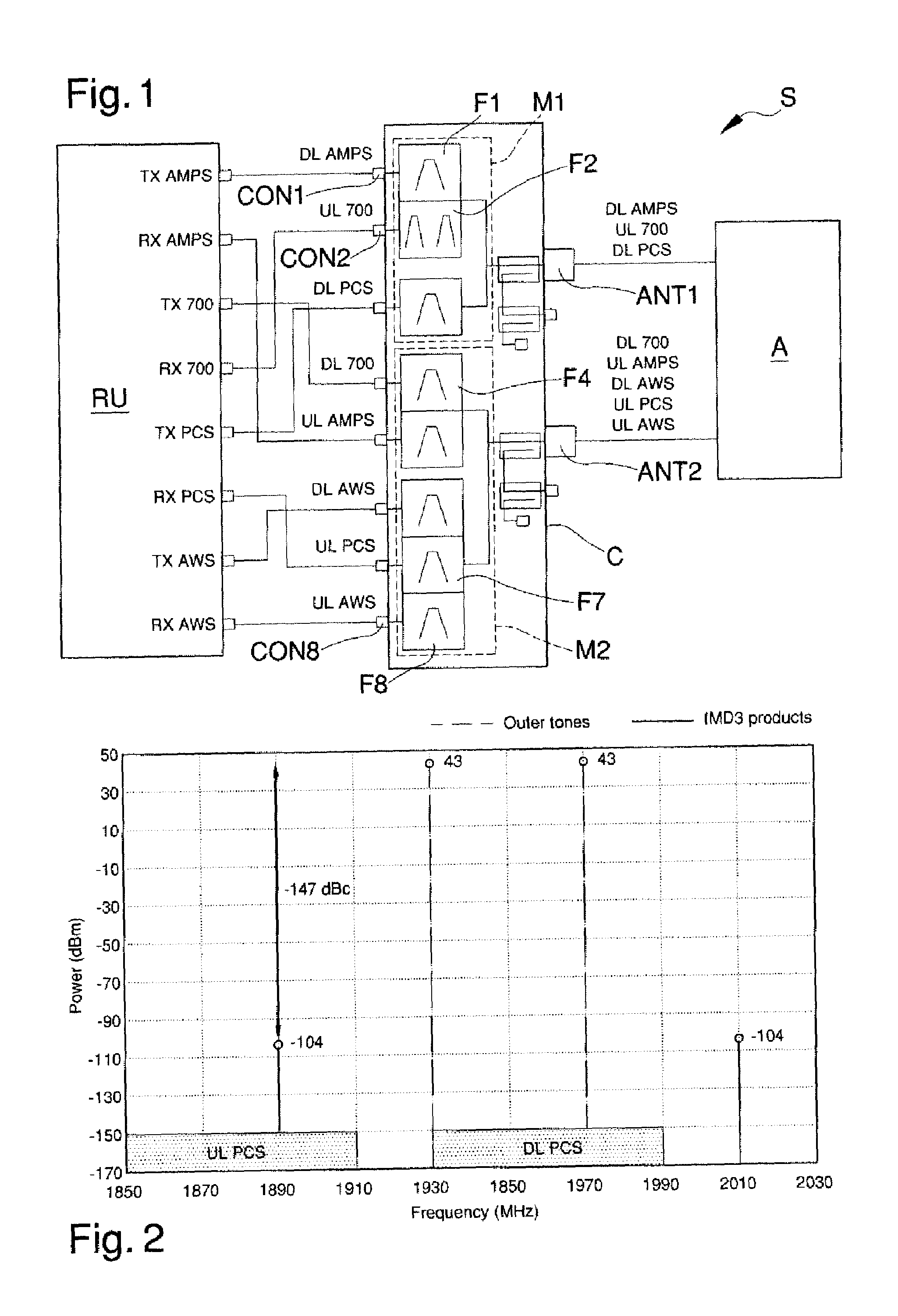
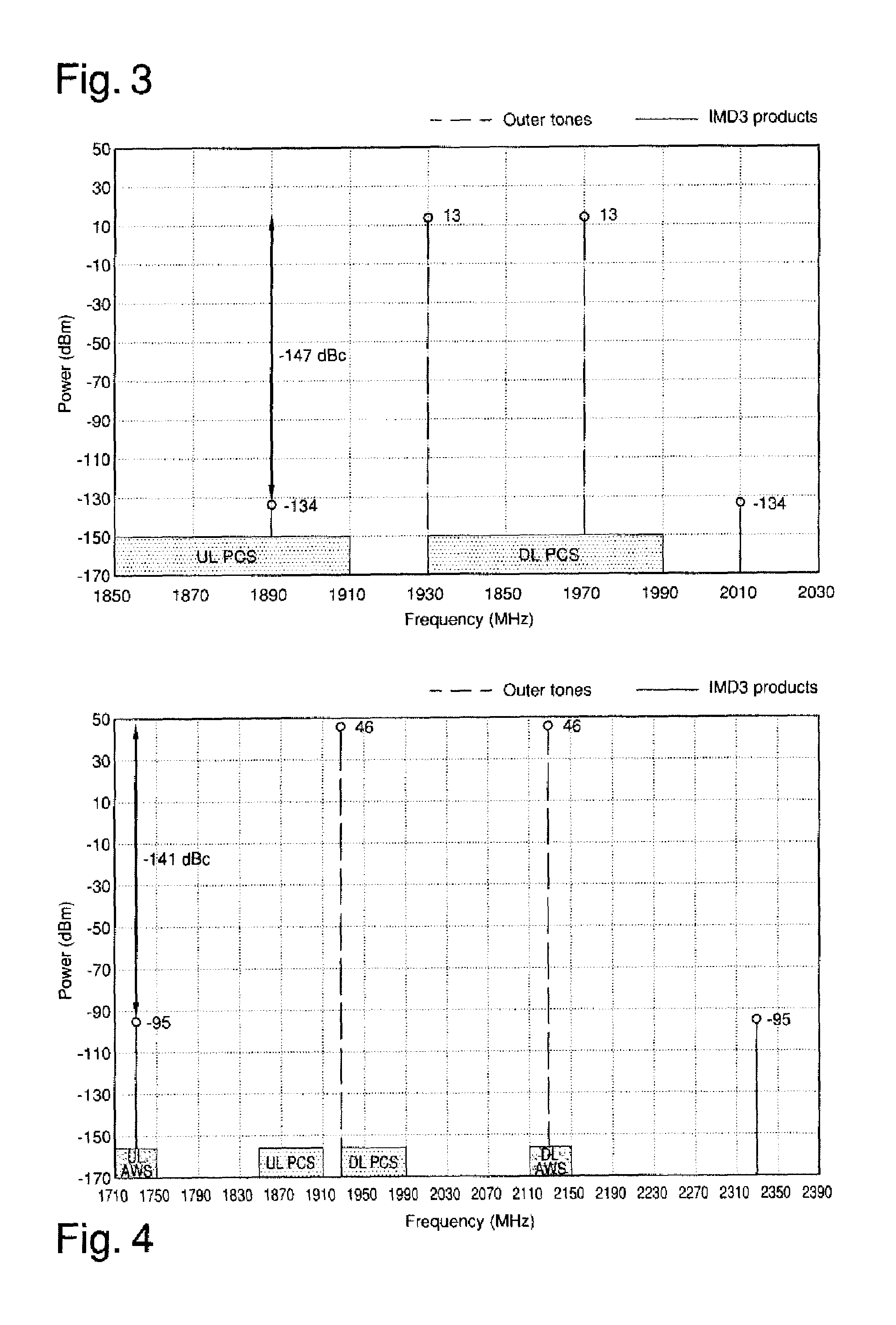
The system for the distribution of radio frequency signals, includes a combiner device of radio frequency signals having a plurality of signal connectors, a first antenna connector operatively connected to a first group of signal connectors and a second antenna connector operatively connected to a second group of signal connectors, and two antennas or a dual polarization antenna (A) connected to the antenna connectors, and a distribution device of radio frequency signals connected to the signal connectors Depending on the frequency band of the inter-modulation products of third order or higher generated by two downlink signals, one or more signal connectors from the first group or the second group is assigned to the downlink signals.
Owner:TEKO TELECOM
Method for displaying information from an id transmitter
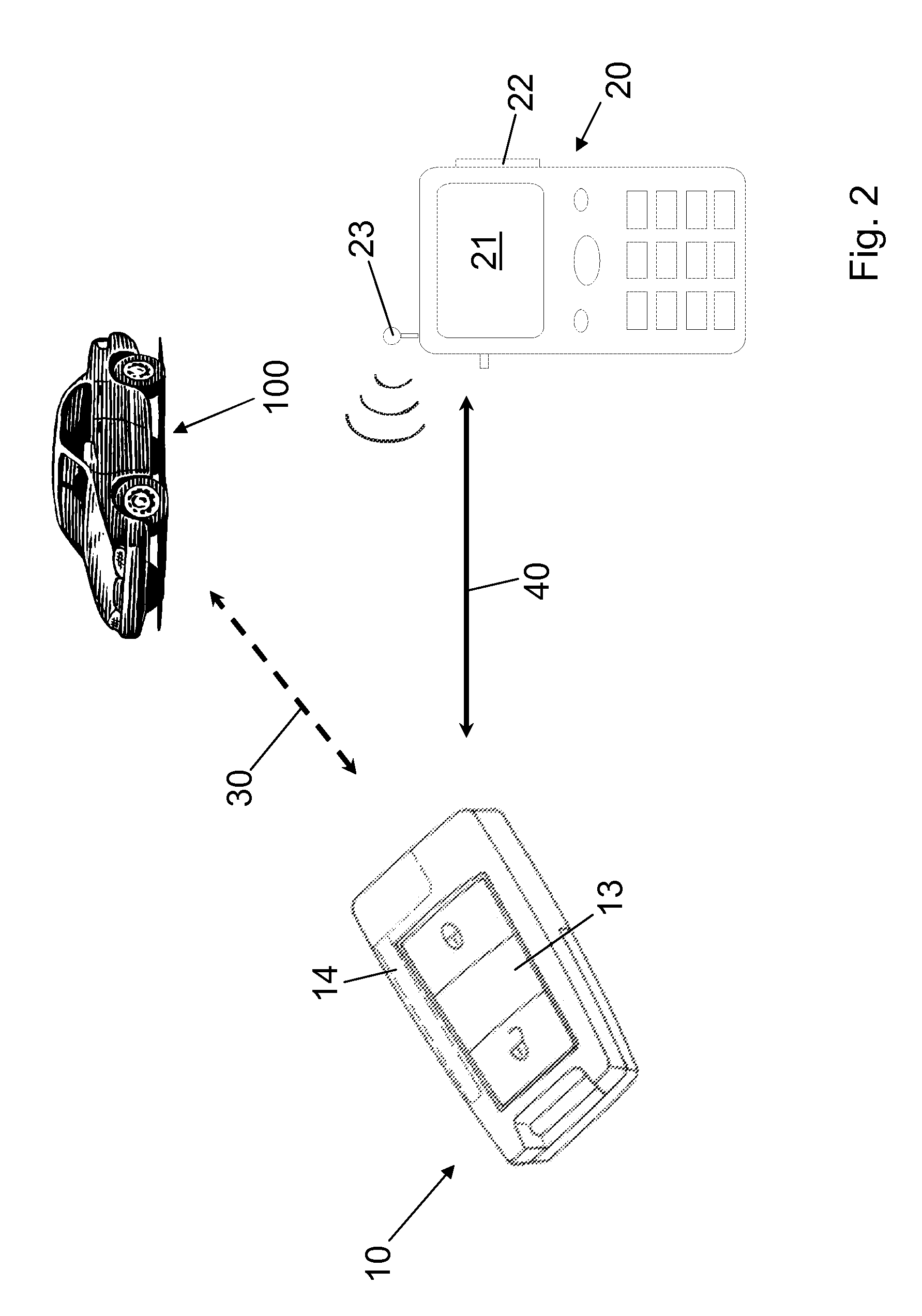
ActiveUS20120015636A1Drawback mentionedProgramme controlRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDisplay deviceData memory
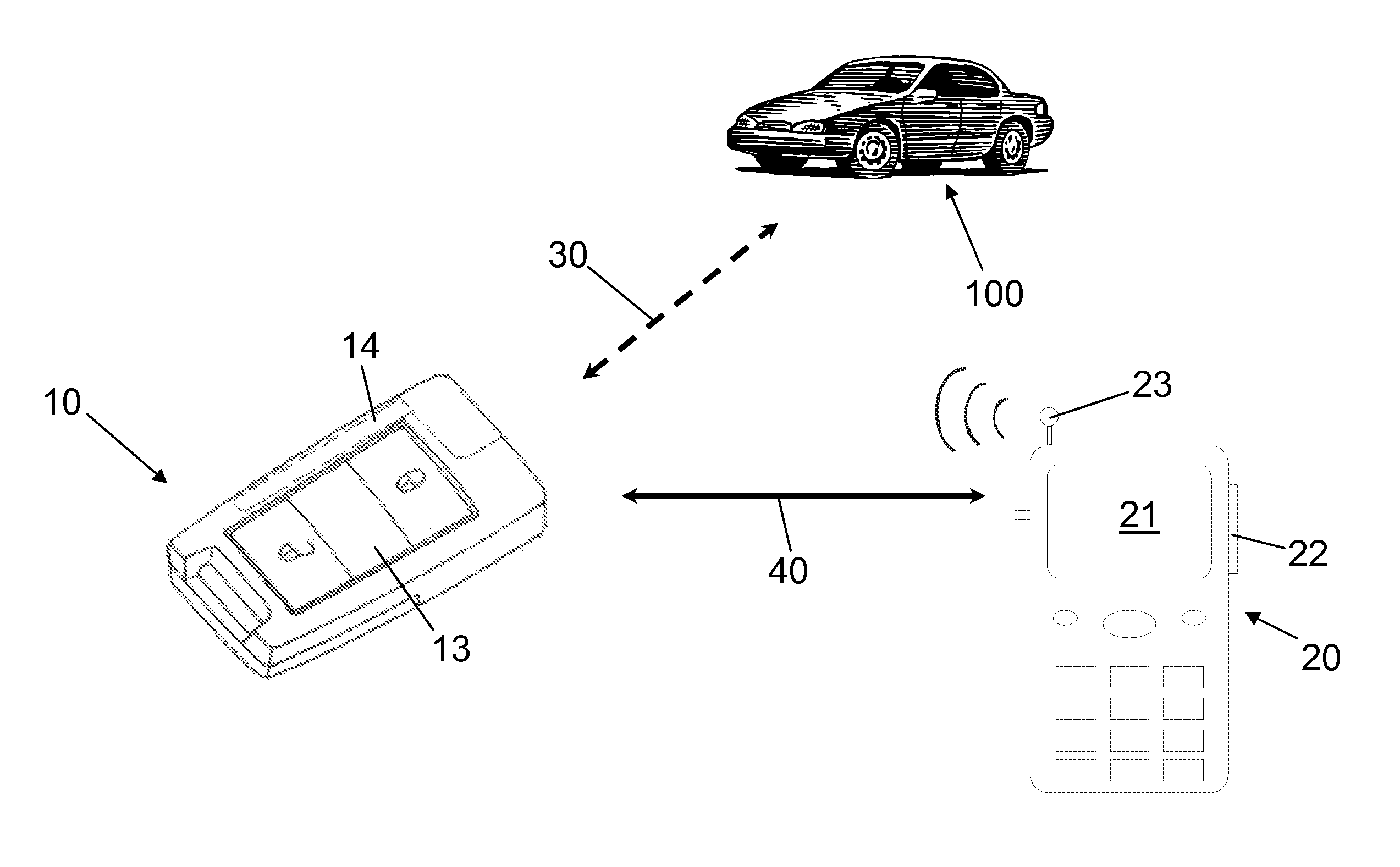
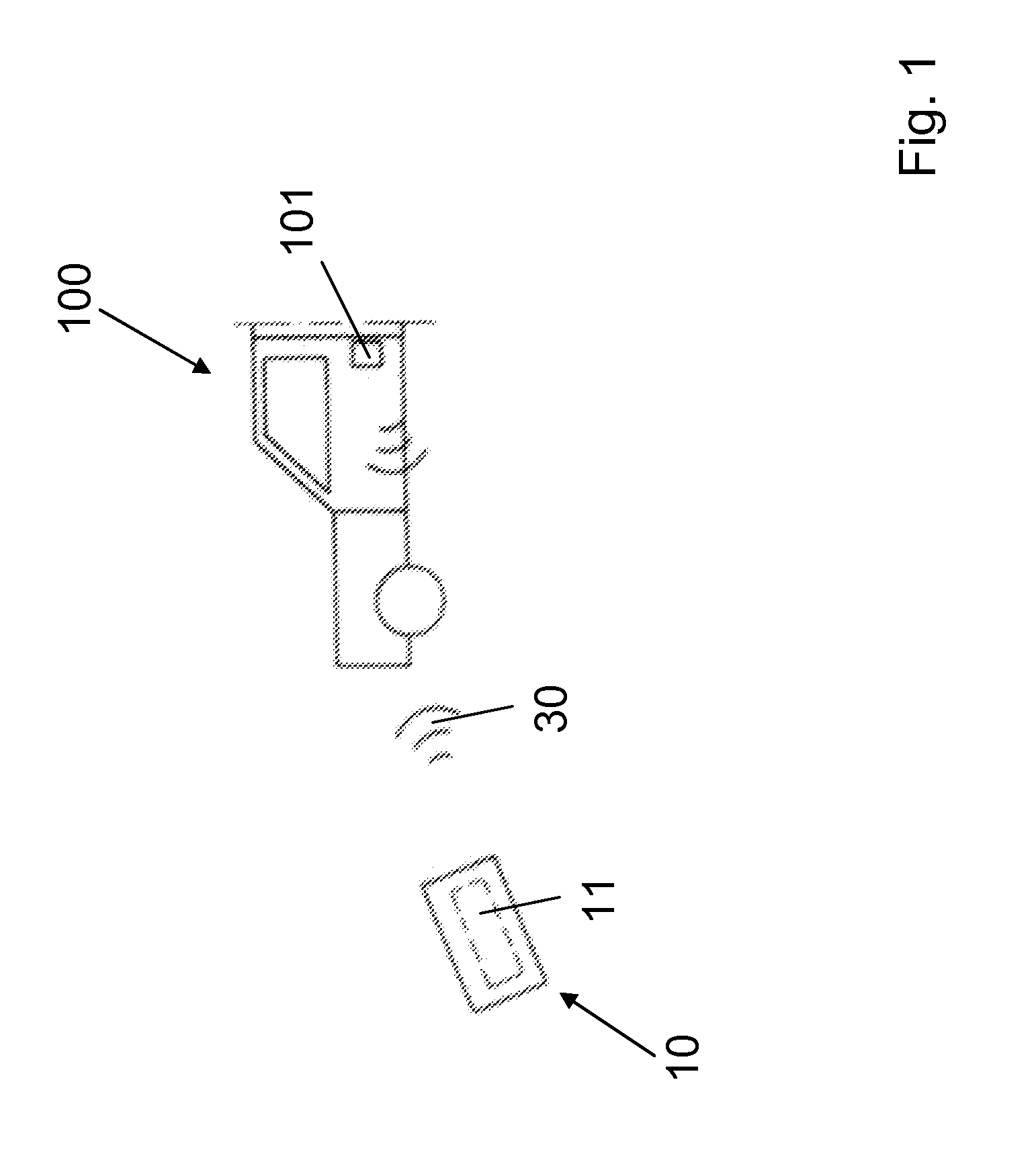
The invention relates to a method for displaying a piece of information, using a mobile ID transmitter (10) and a cellular telephone (20) having a display (21), wherein the mobile ID transmitter (10) is used to activate a security system of a motor vehicle, the mobile ID transmitter (10) has an electronics unit (11), the electronics unit (11) is used for data communication (30) with a vehicle-side device, a vehicle-side piece of information is transmitted from the vehicle-side device to the electronics unit (11) by means of the data communication (30), the vehicle-side piece of information is stored in a data memory (12), the electronics unit (11) communicates with the cellular telephone (20) by means of a communication connection (40), and the vehicle-side piece of information is transferred to the cellular telephone (20) by means of the communication connection (40) and displayed there by means of the display (21). Furthermore, the invention is also directed at a system for displaying a vehicle-side piece of information on a cellular telephone (20) by means of a mobile ID transmitter (10) and also only at an ID transmitter.
Owner:HUF HULSBECK & FURST GMBH & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com