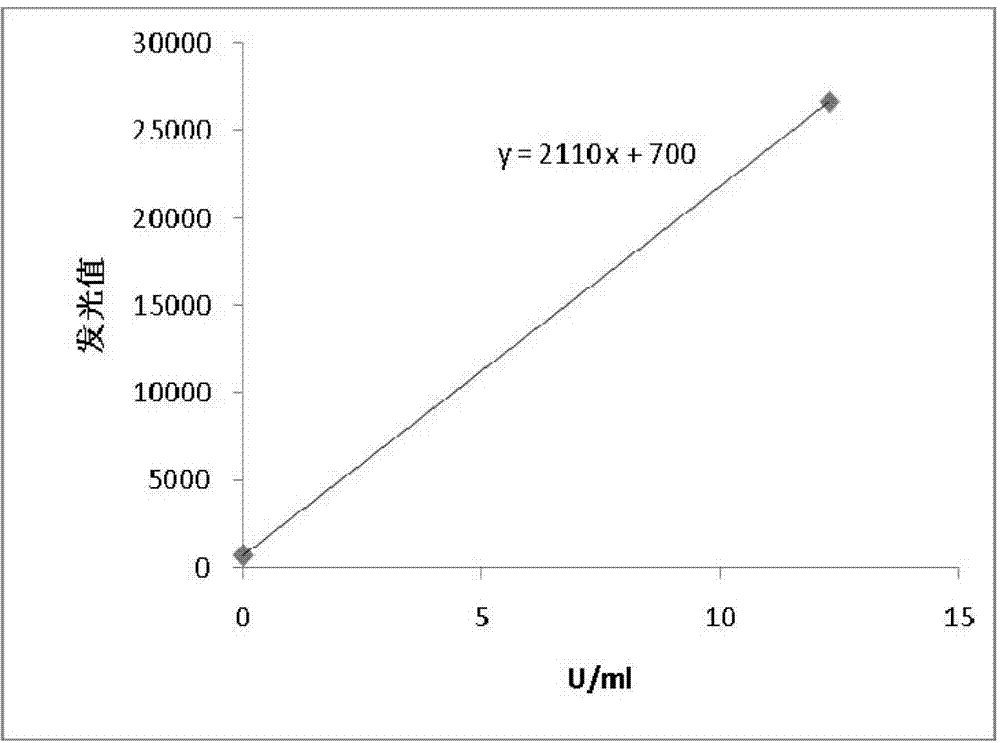
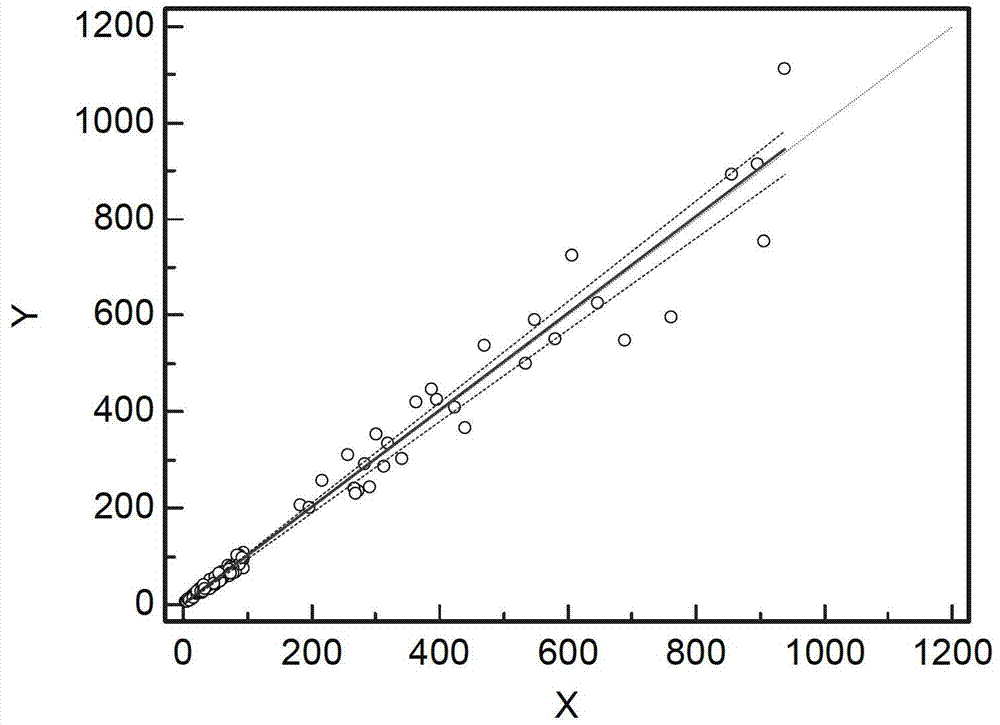
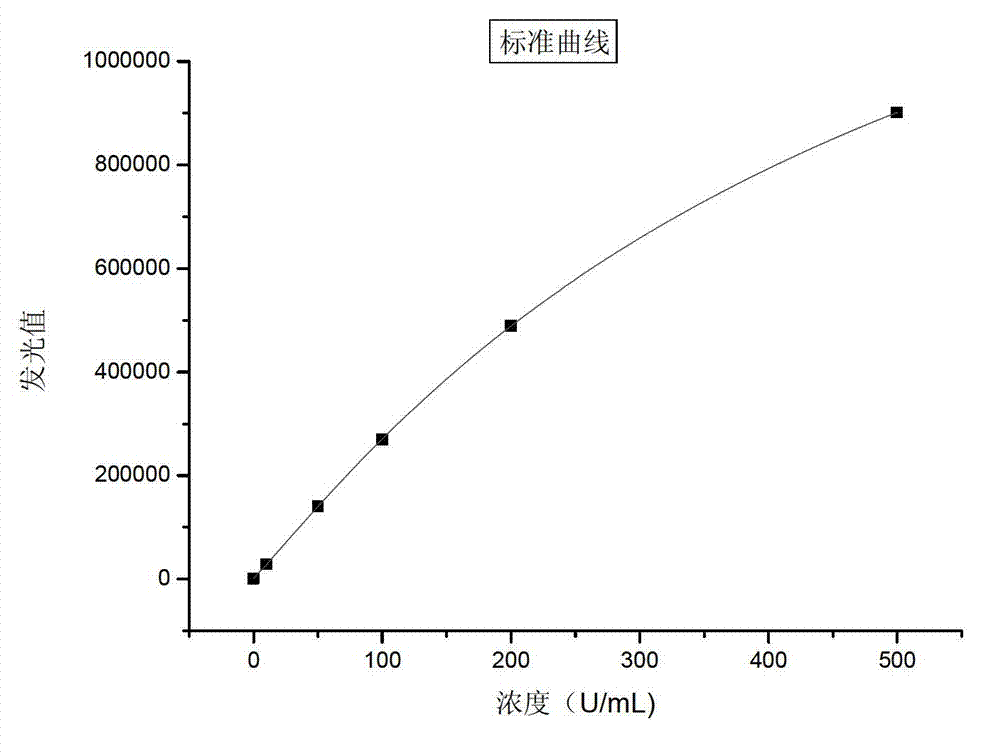
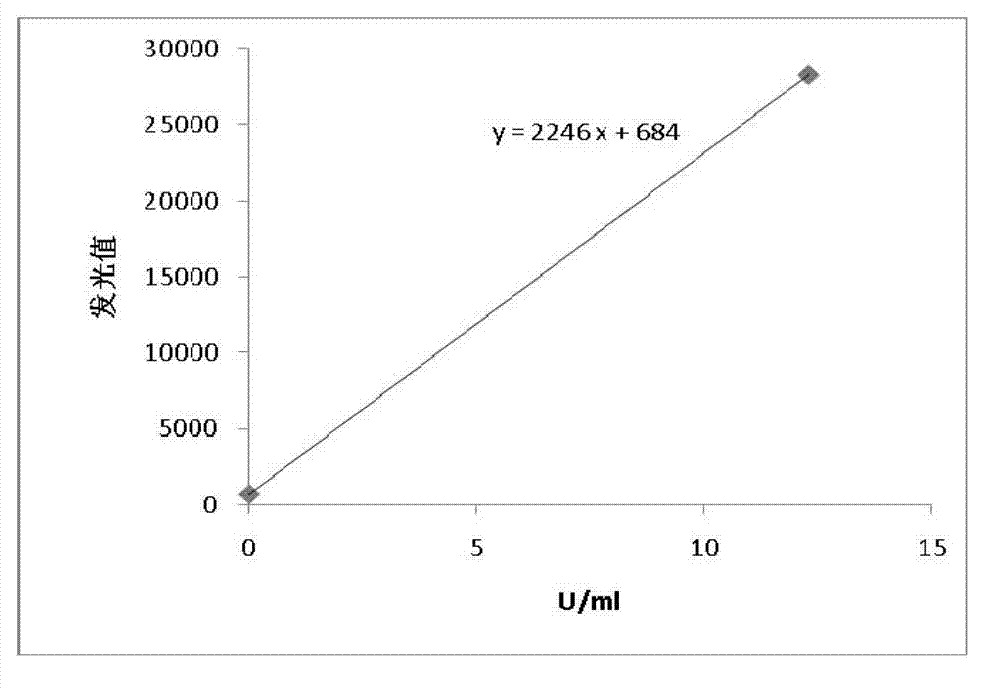
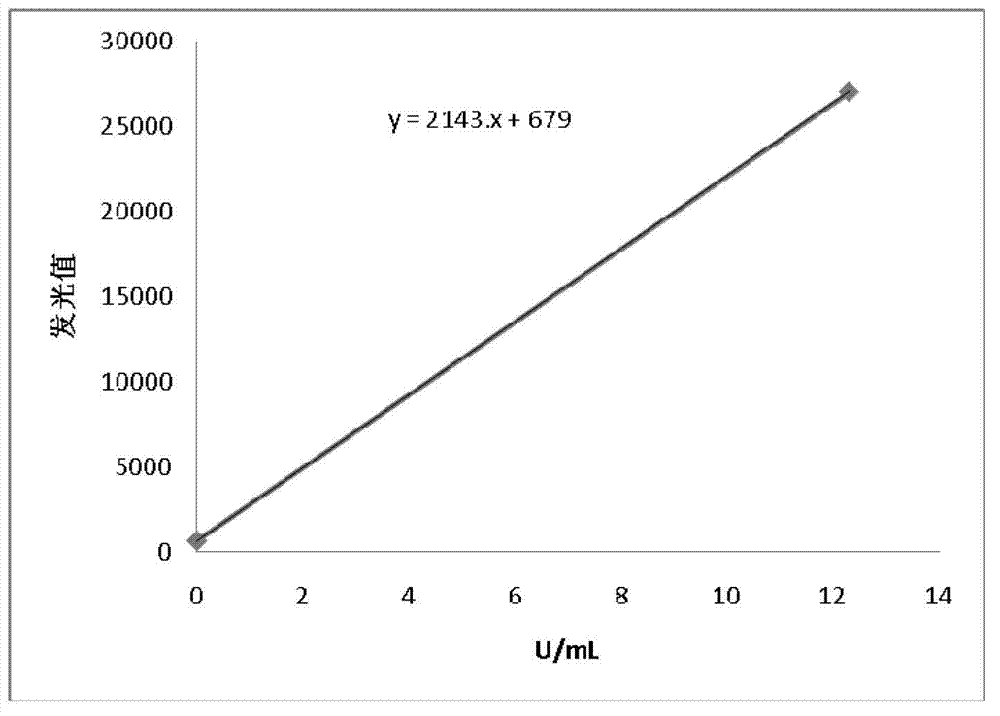
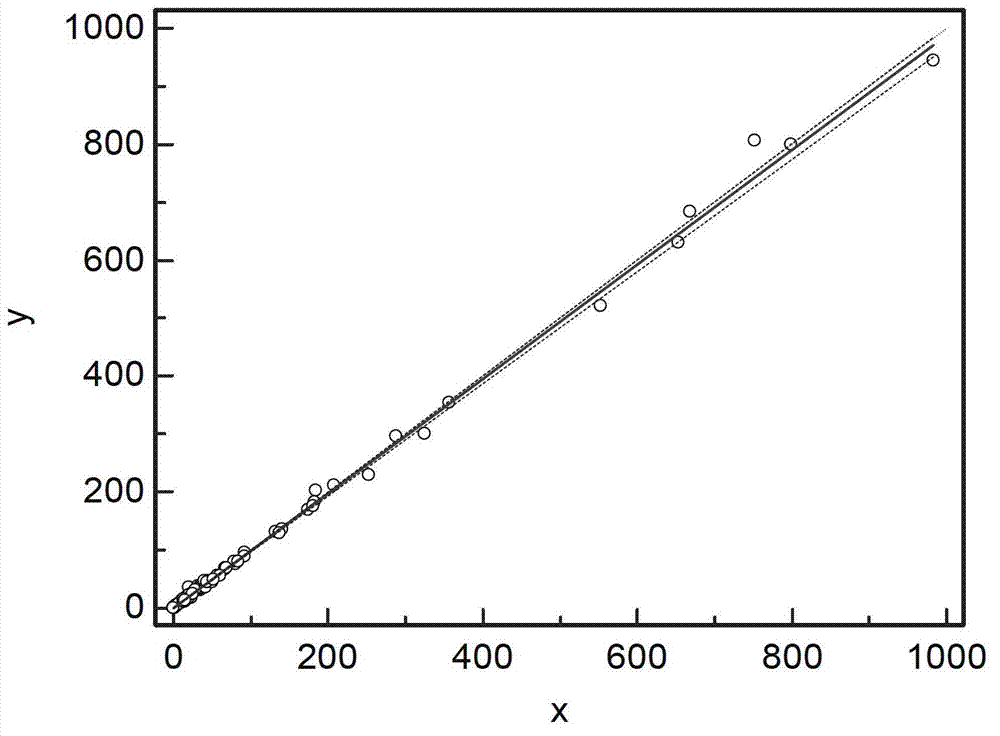
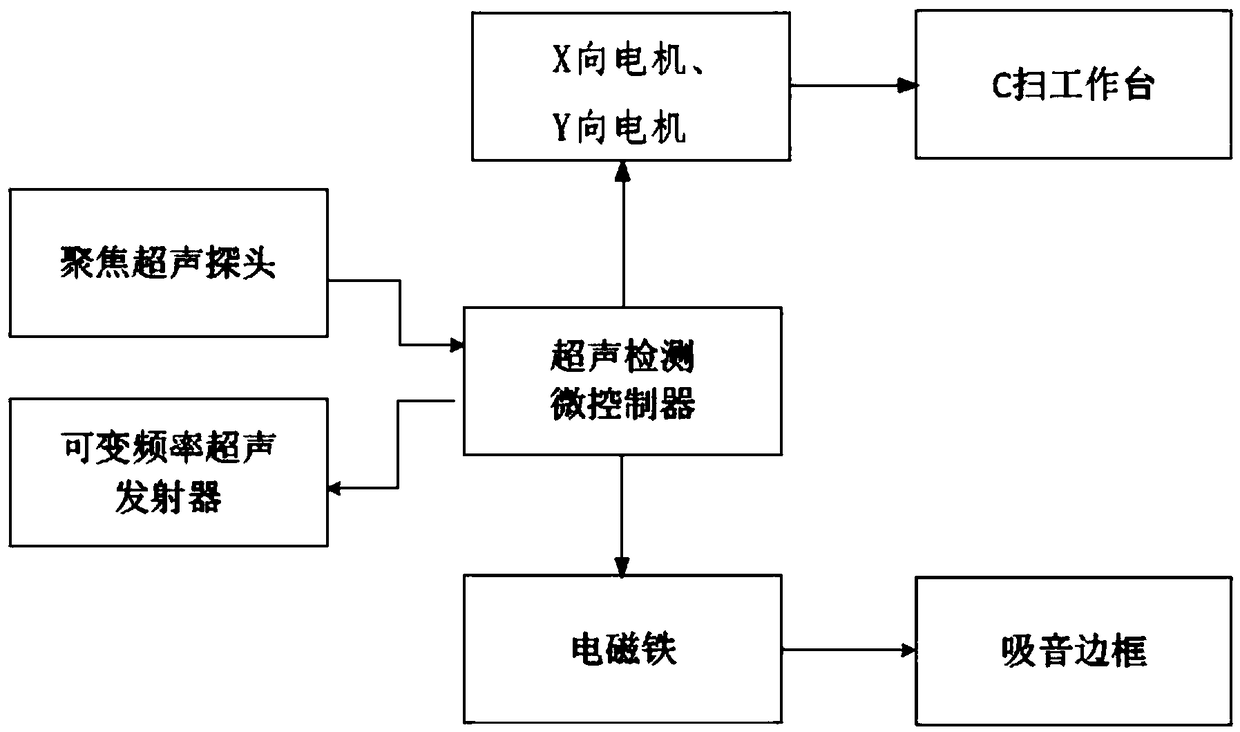
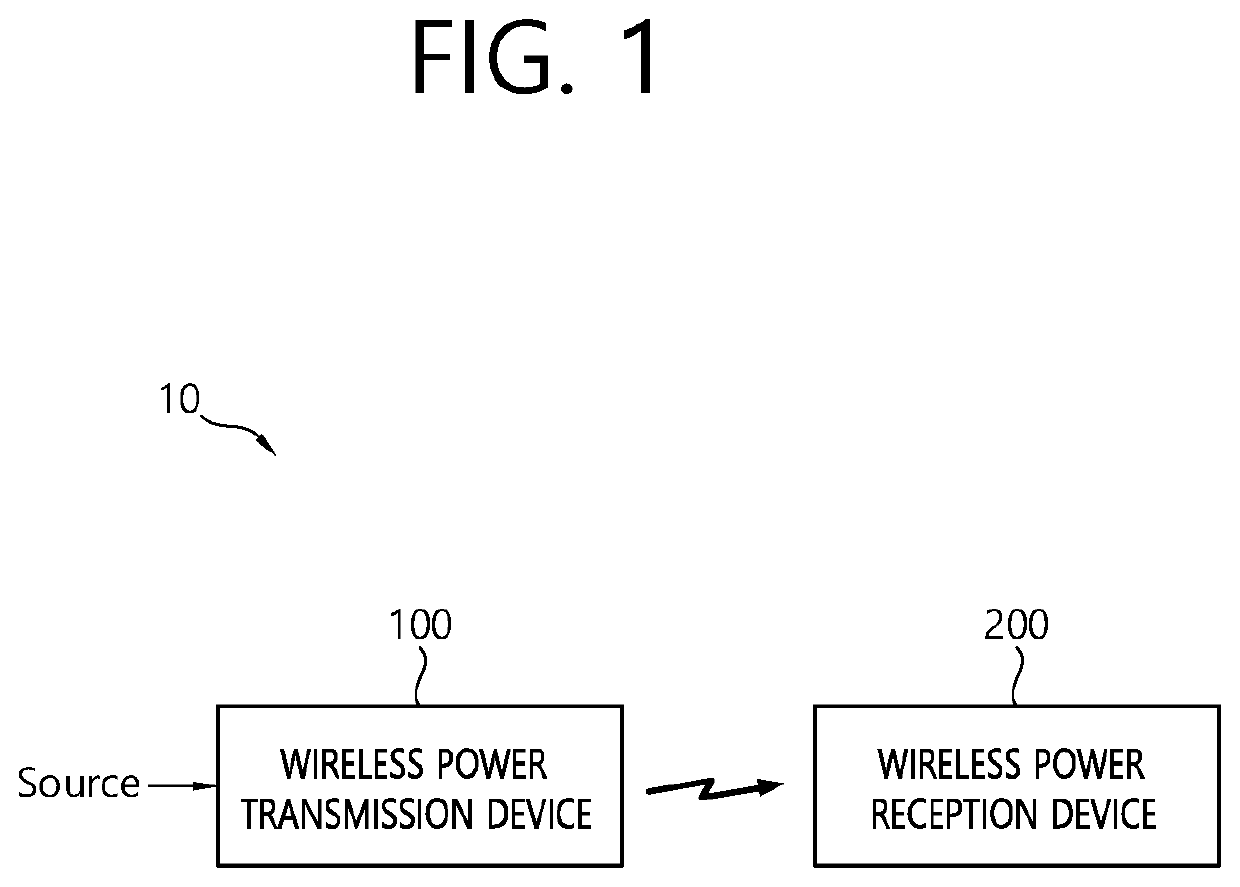
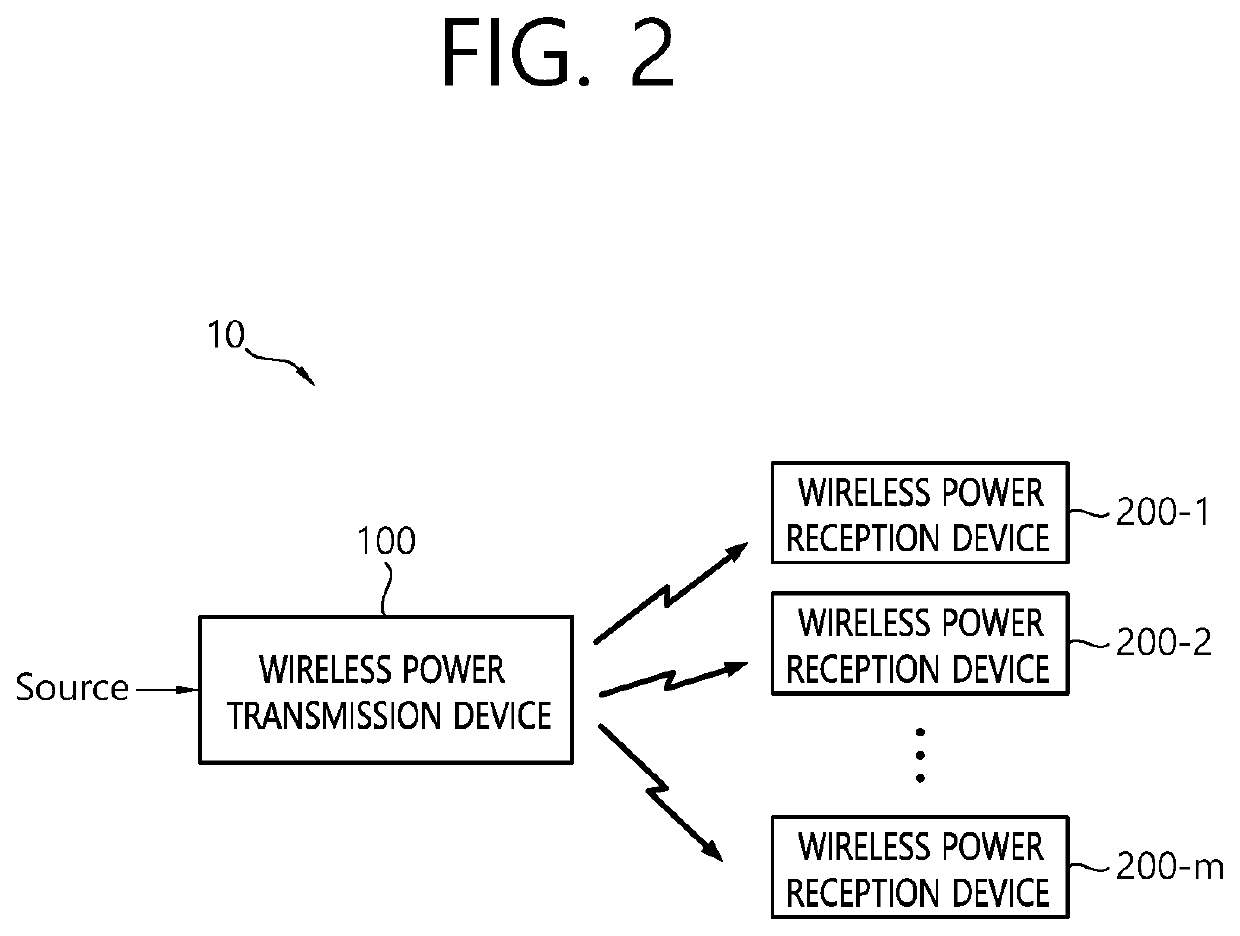
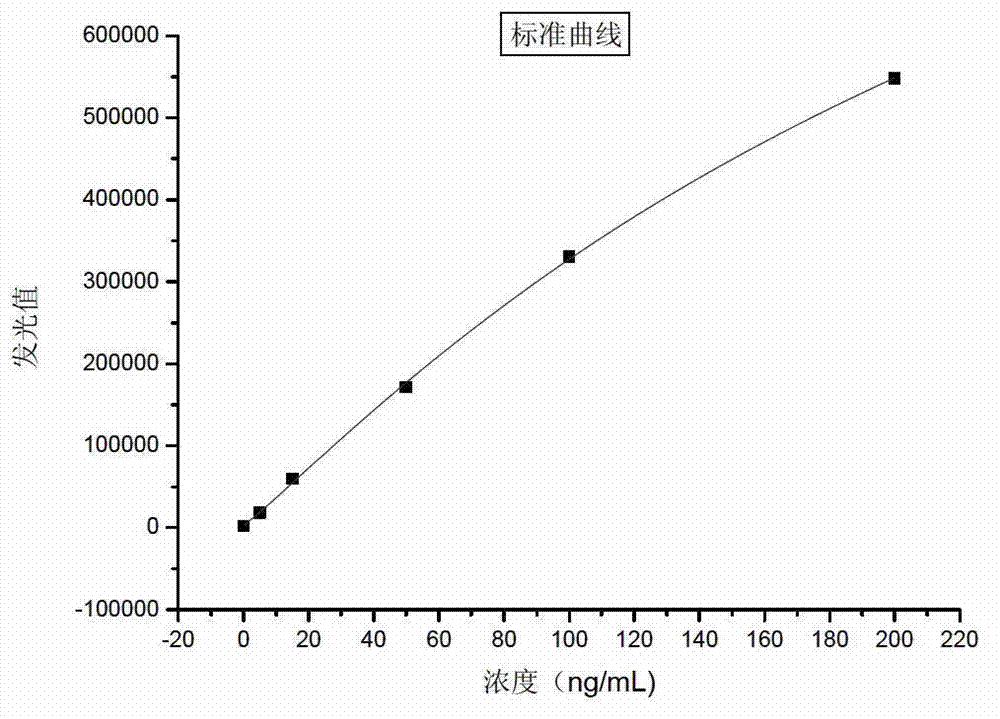
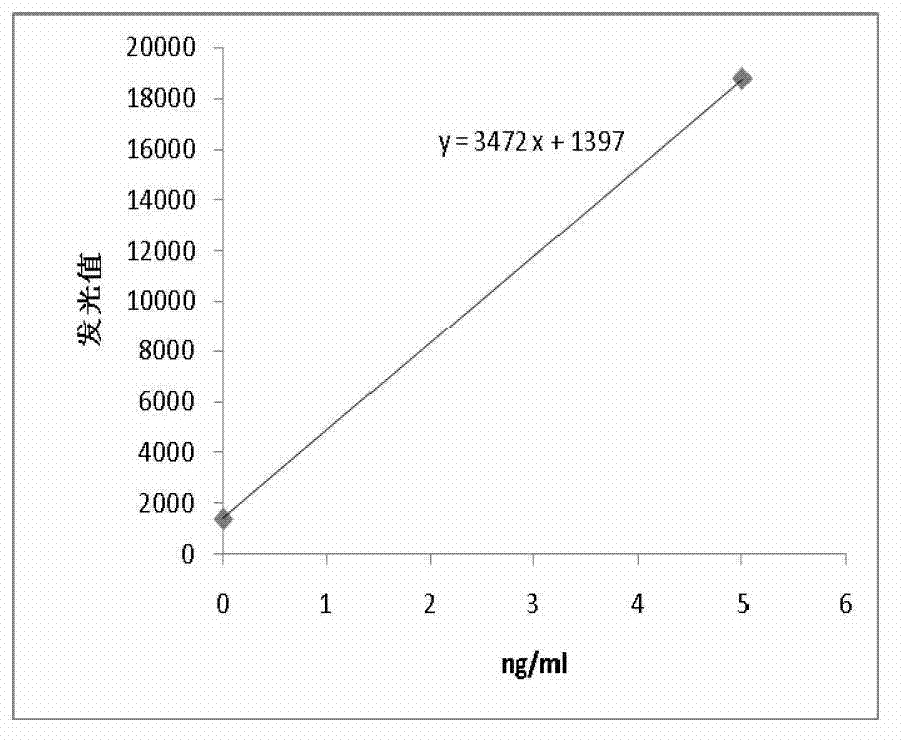
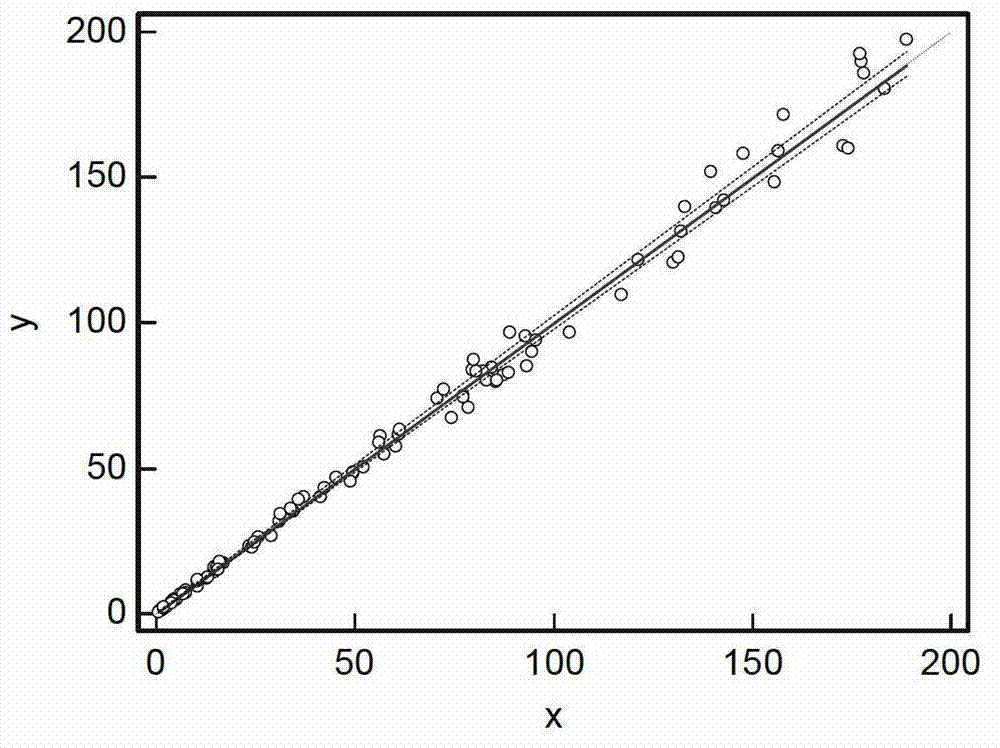
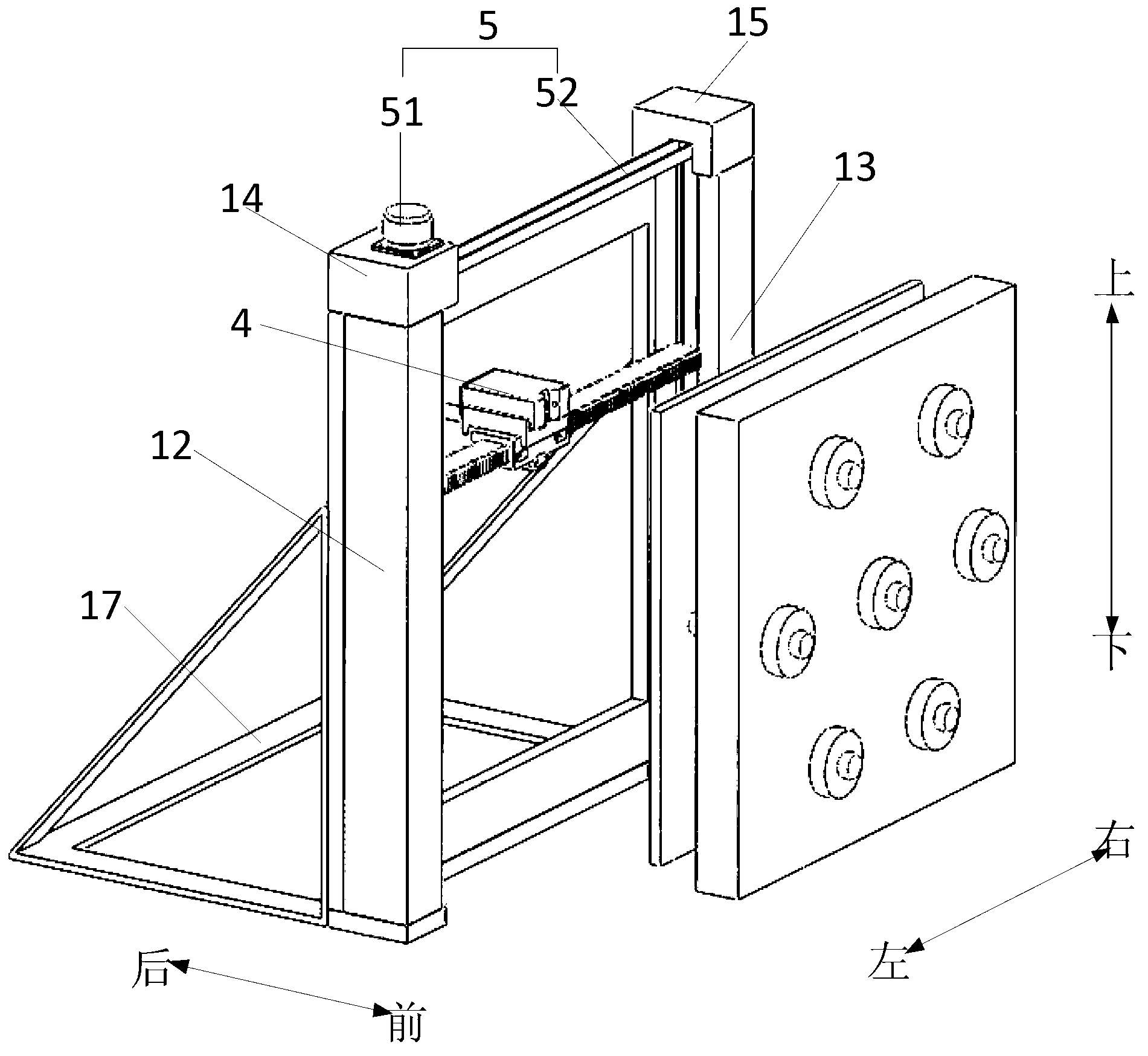
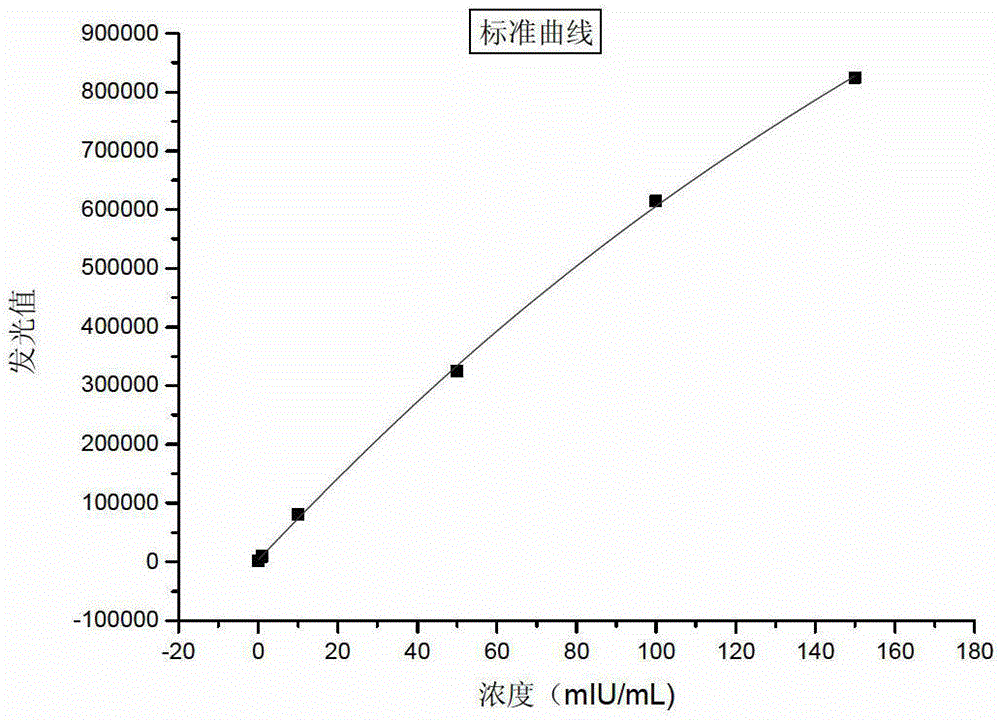
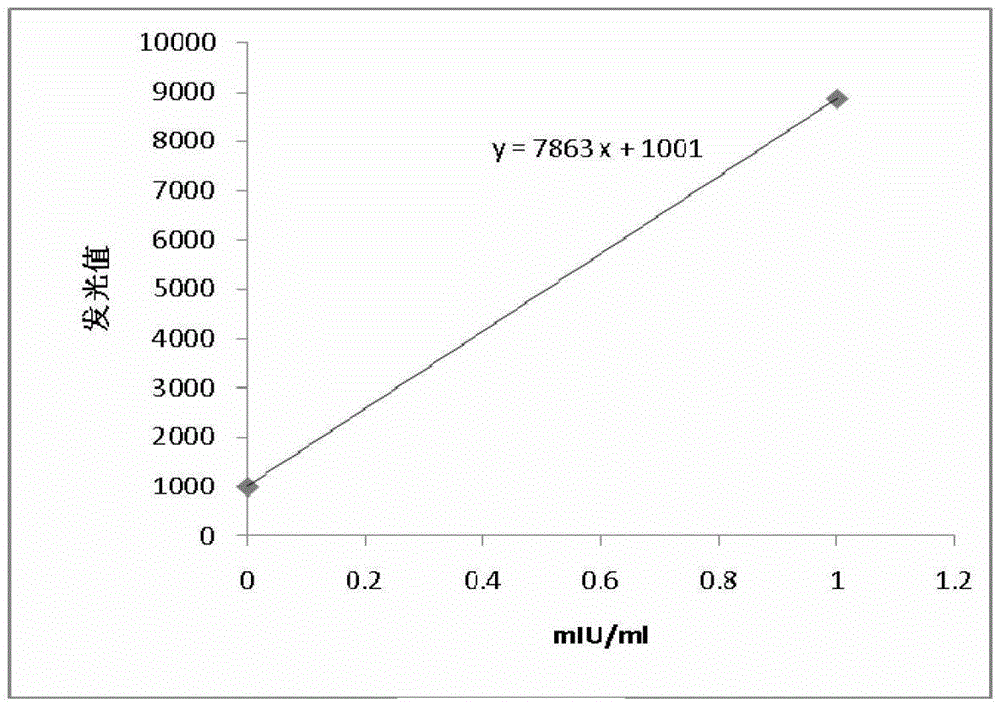
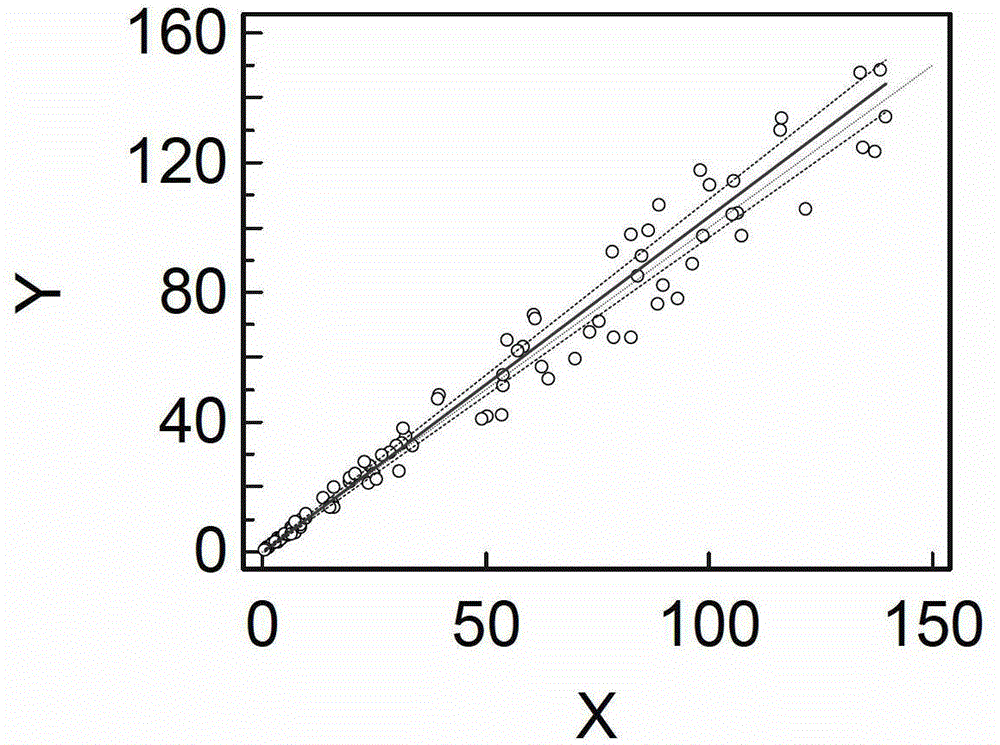
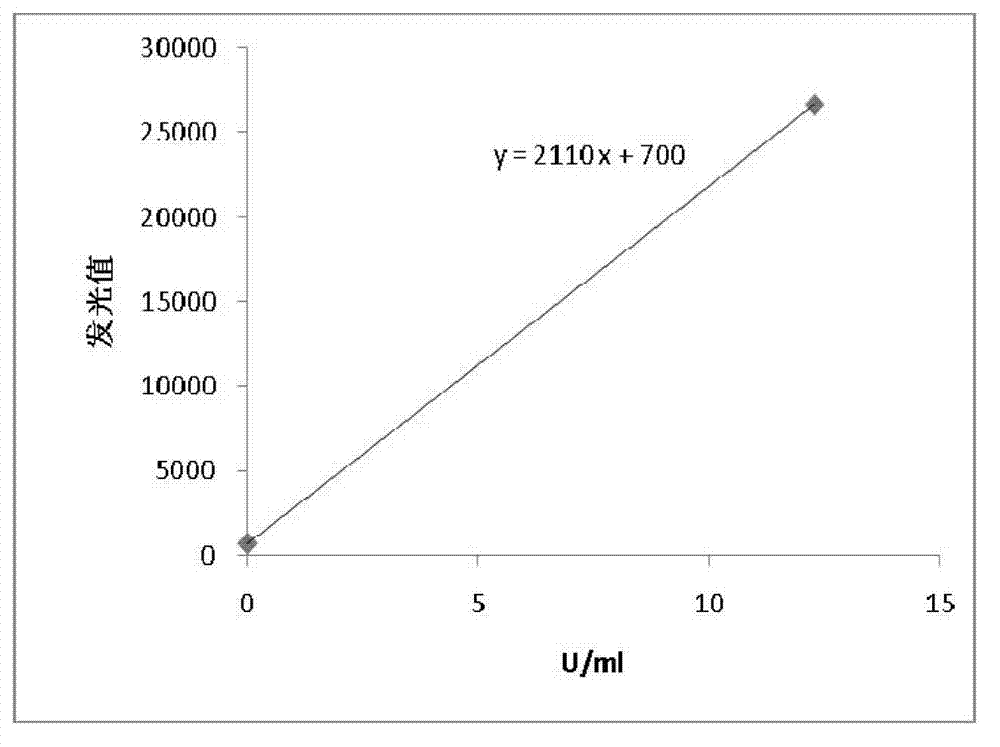
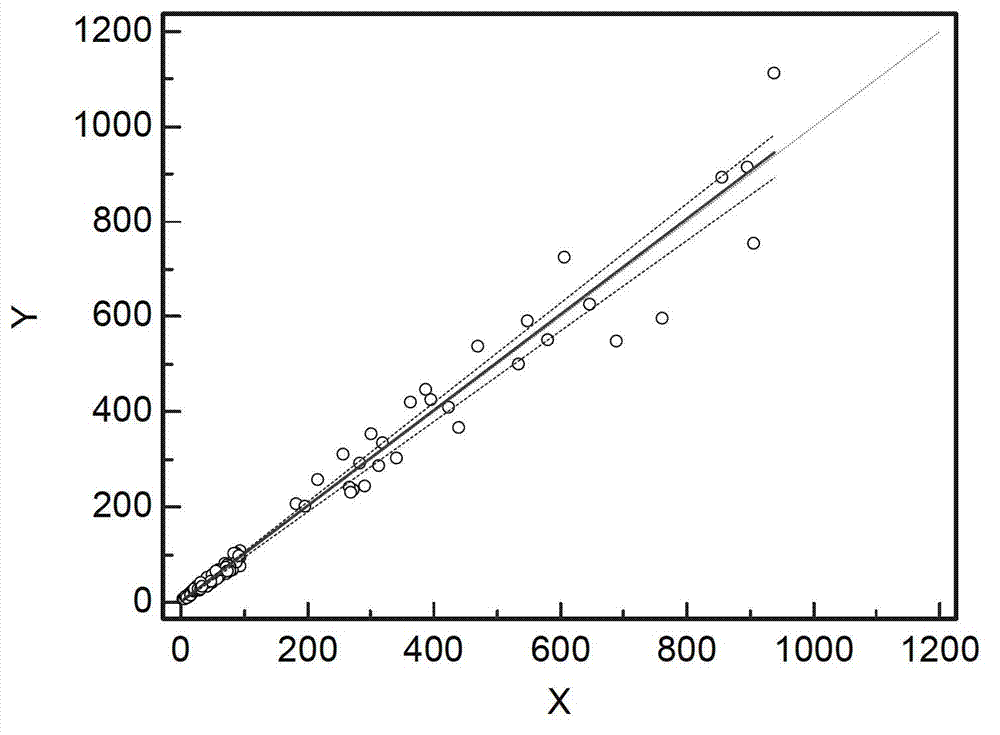
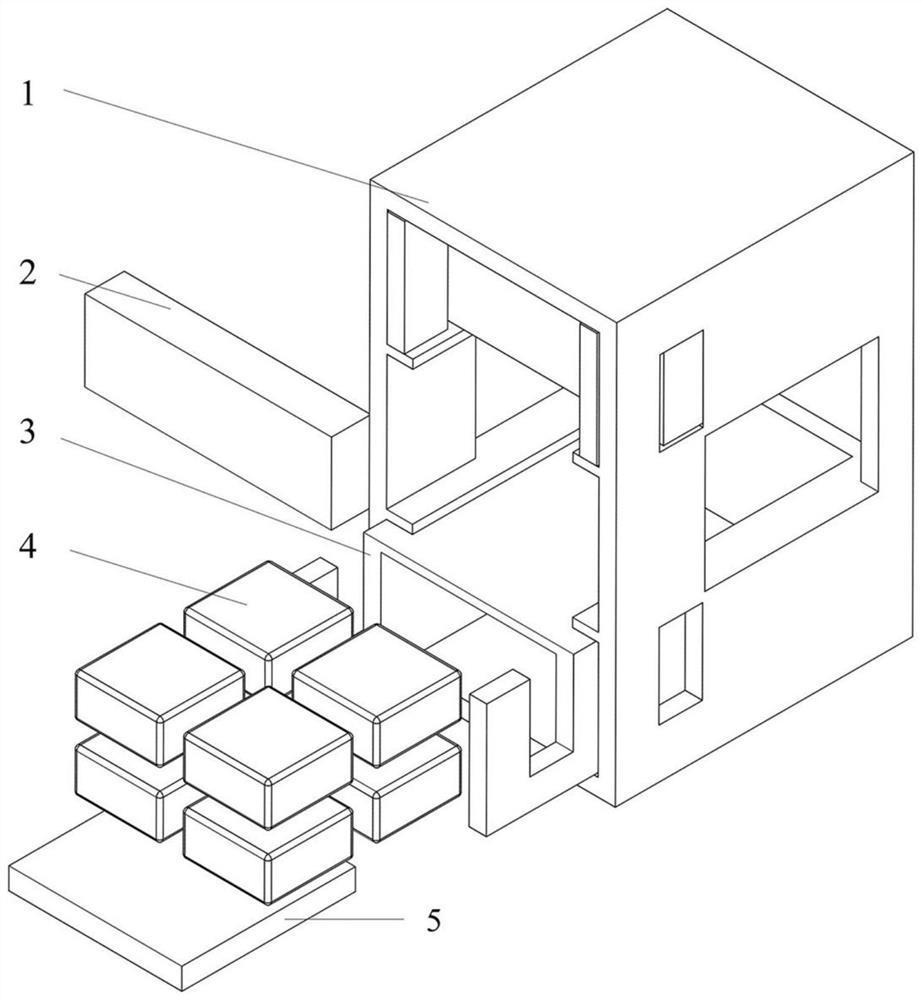
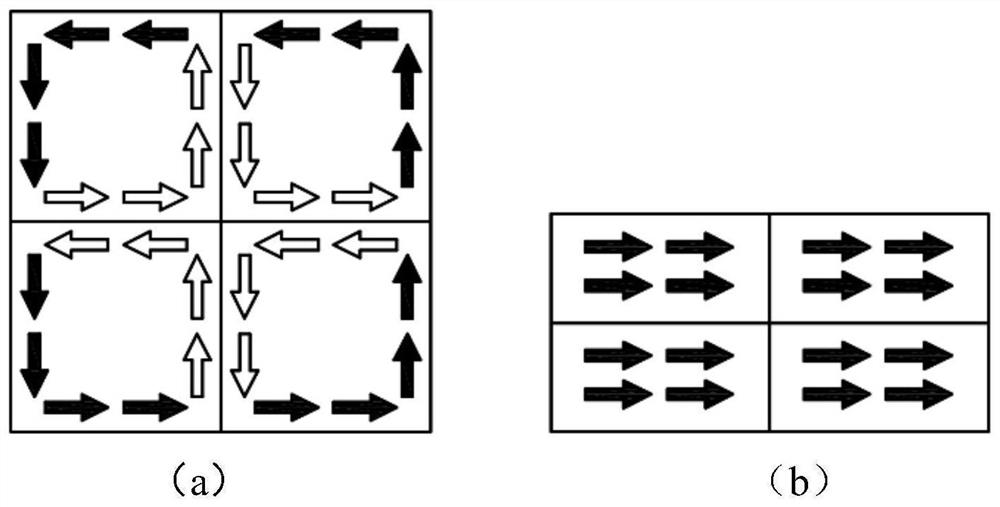
Patents
Literature
39results about How to "Precision testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semantically-aware network intrusion signature generator
ActiveUS20060212942A1Precision testingSimple methodError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic volumeProtocol for Web Description Resources
An automatic technique for generating signatures for malicious network traffic performs a cluster analysis of known malicious traffic to create a signature in the form of a state machine. The cluster analysis may operate on semantically tagged data collected by connection or session and normalized to eliminate protocol specific features. The signature extractor may generalize the finite-state machine signatures to match network traffic not previously observed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Semantically-aware network intrusion signature generator
ActiveUS8065722B2Precision testingSolve the high false alarm rateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFinite-state machineComputer science
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
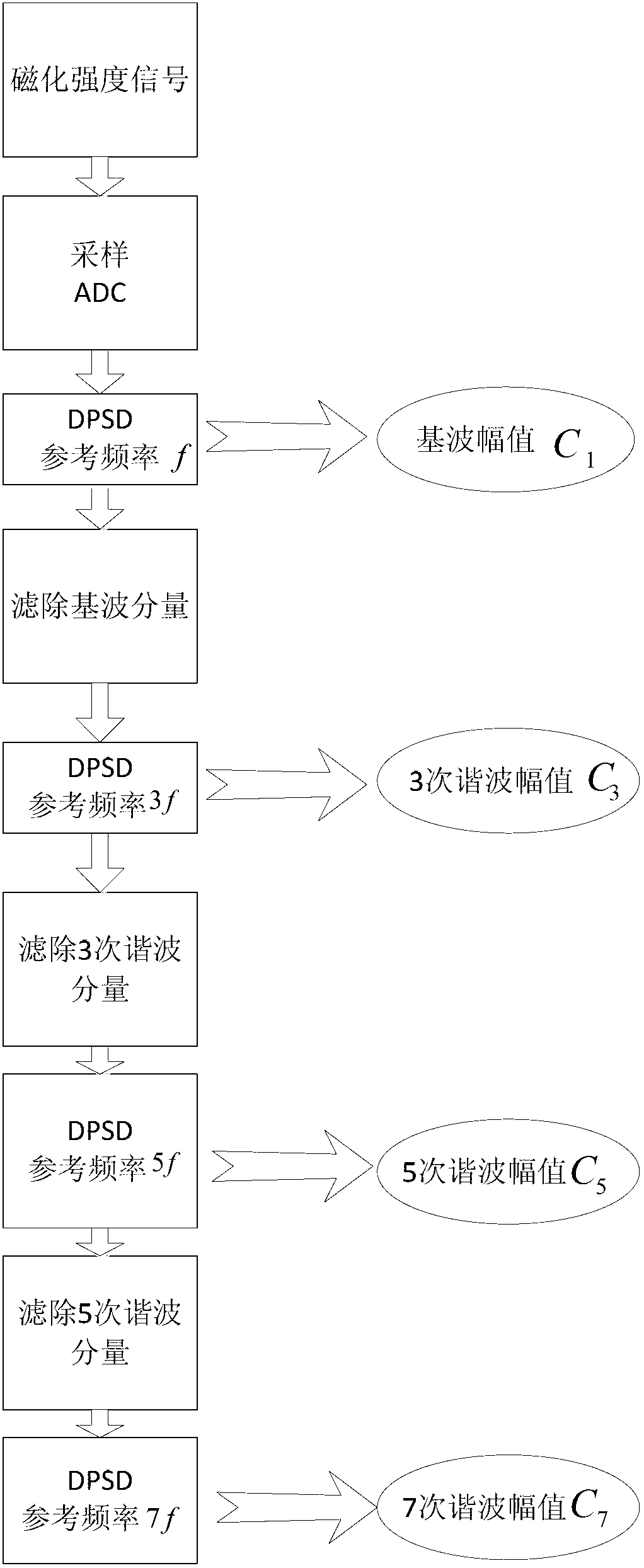
In vivo temperature measuring method and system based on alternating magnetization intensity of magnetic nanoparticles
InactiveCN103156581AAccurate detectionPrecision testingThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsBody temperature measurementMagnetizationMagnetite Nanoparticles
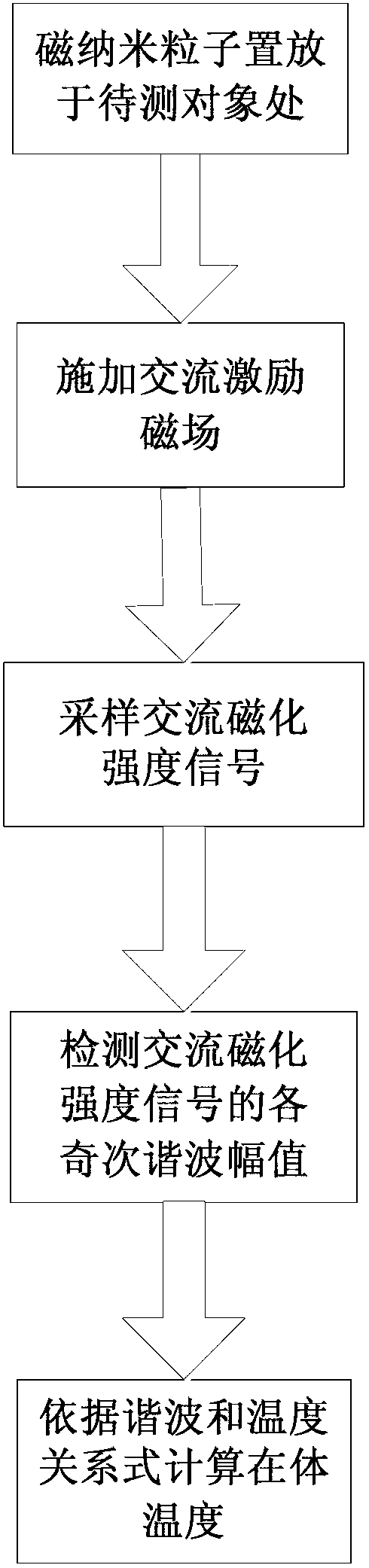
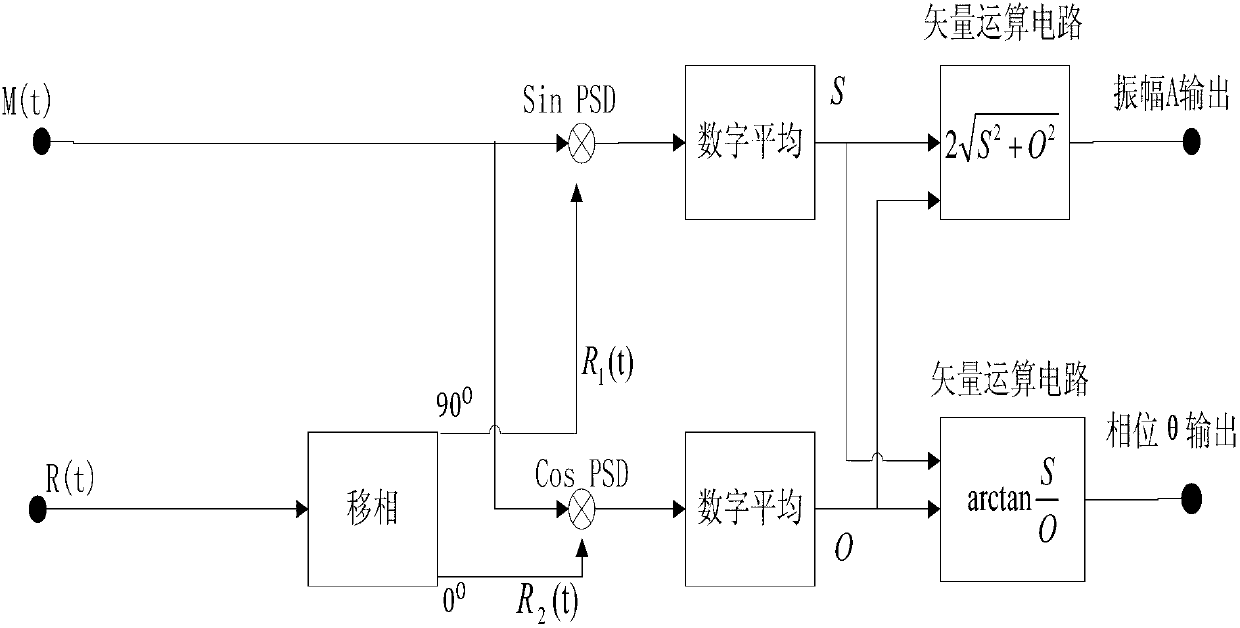
The invention discloses an in vivo temperature measuring method based on alternating magnetization intensity of magnetic nanoparticles and belongs to the technical field of nanometer testing. The method comprises the steps of putting a magnetic nanometer reagent at the position of a to-be-tested object, applying an alternating excitation field to an area of the magnetic nanometer reagent, collecting the alternating magnetization intensity of the magnetic nanometer reagent under action of the alternating excitation field, detecting all odd harmonic amplitudes in an alternating magnetization intensity signal, and finally calculating an in vivo temperature according to a relation of a harmonic and the temperature. The relation of all the odd harmonics and the in vivo temperature is preset through a discretization Langevin function and Fourier transform, and the in vivo temperature is solved through the relation without considering density information of the magnetic nanoparticles and variation, of effective magnetic moments, with the temperature during the solving process. Accurate detection of the in vivo temperature is achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
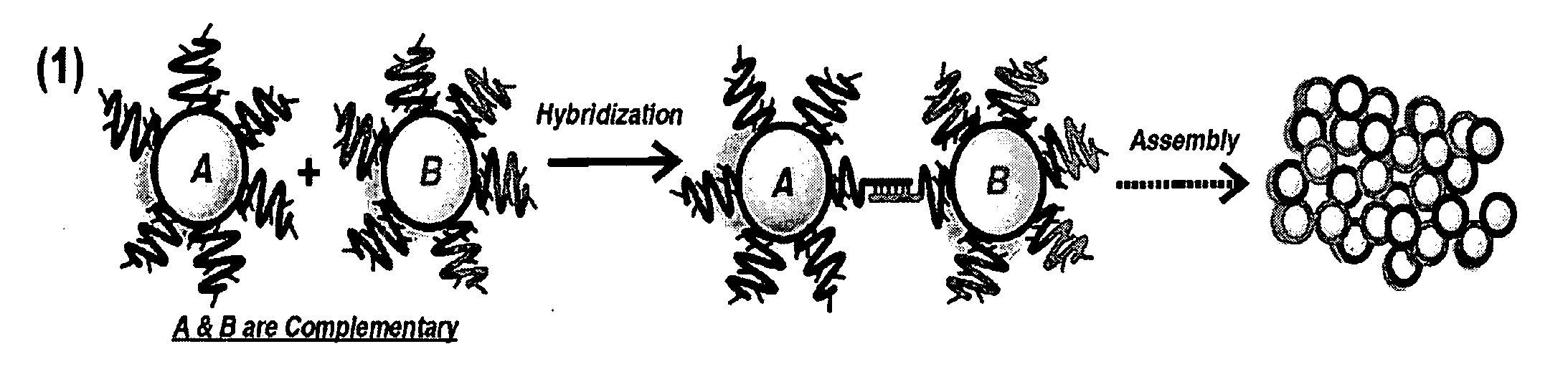
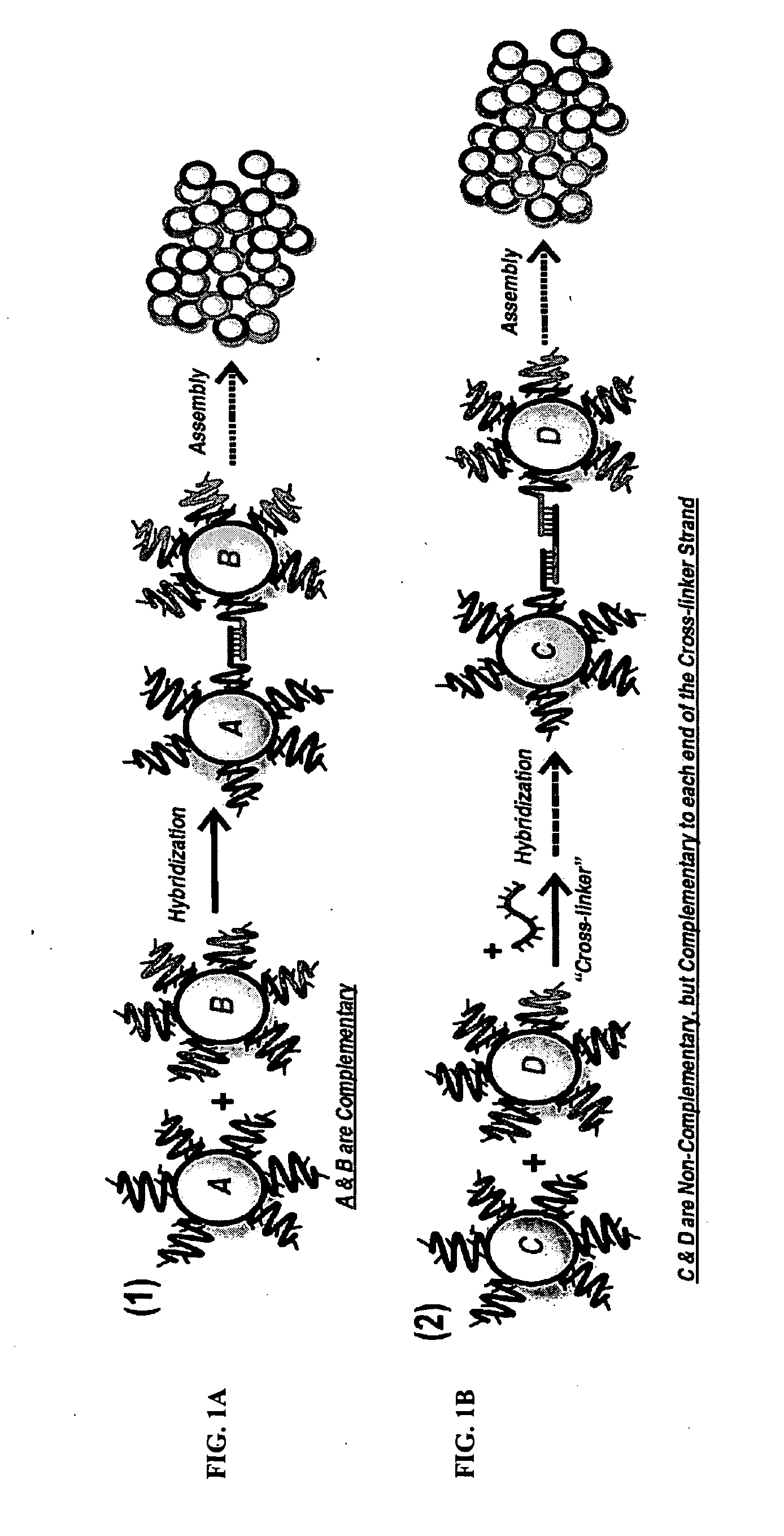
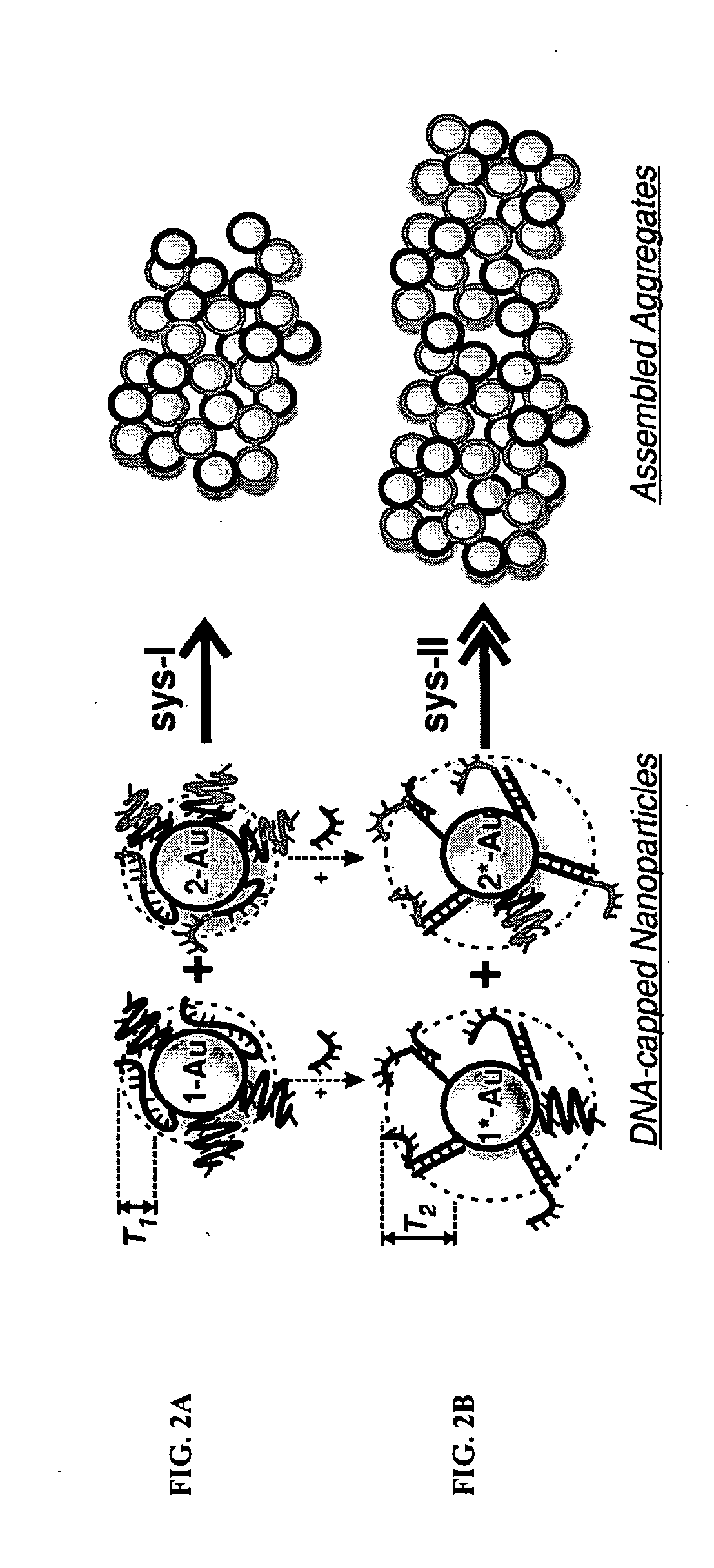
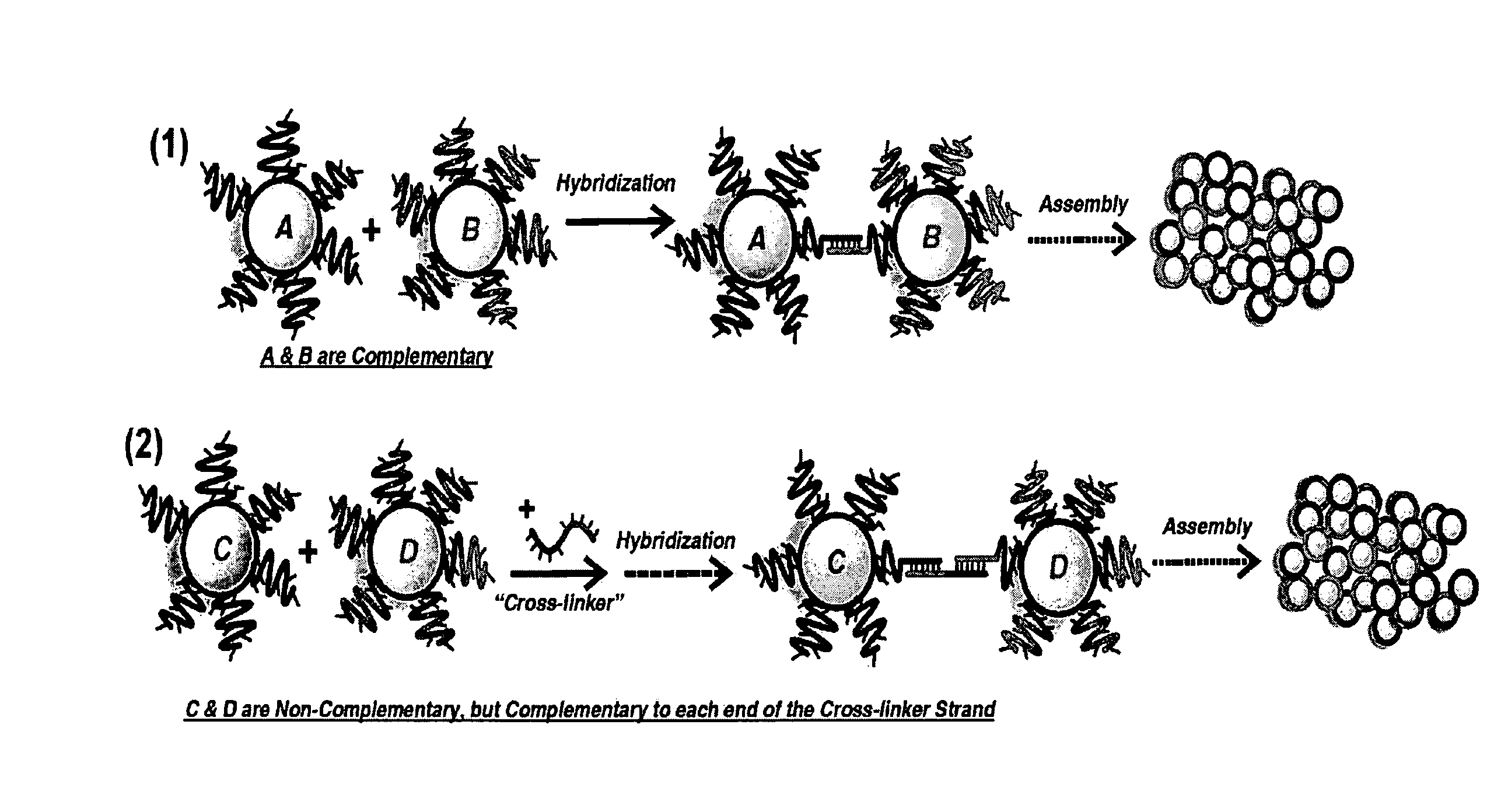
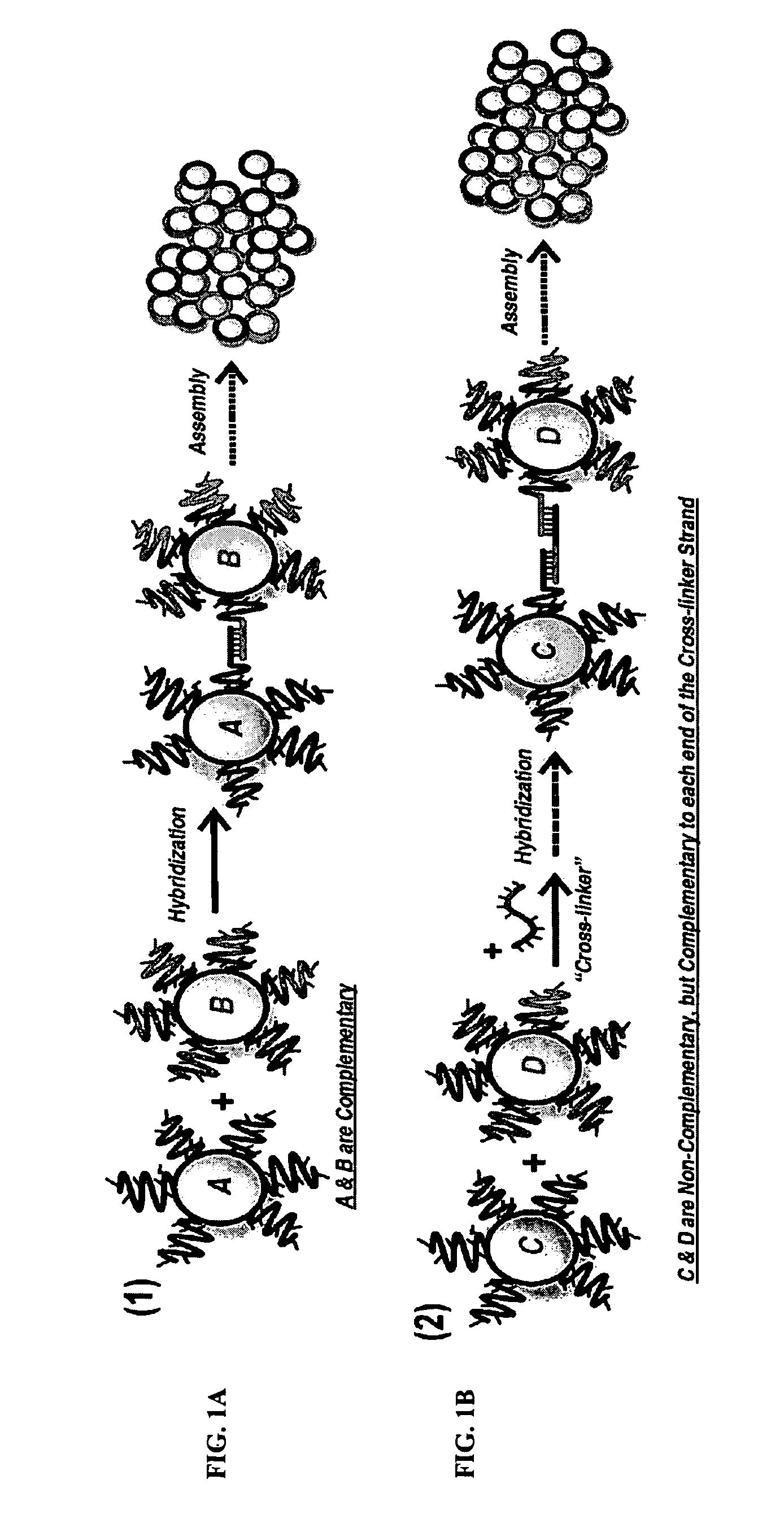
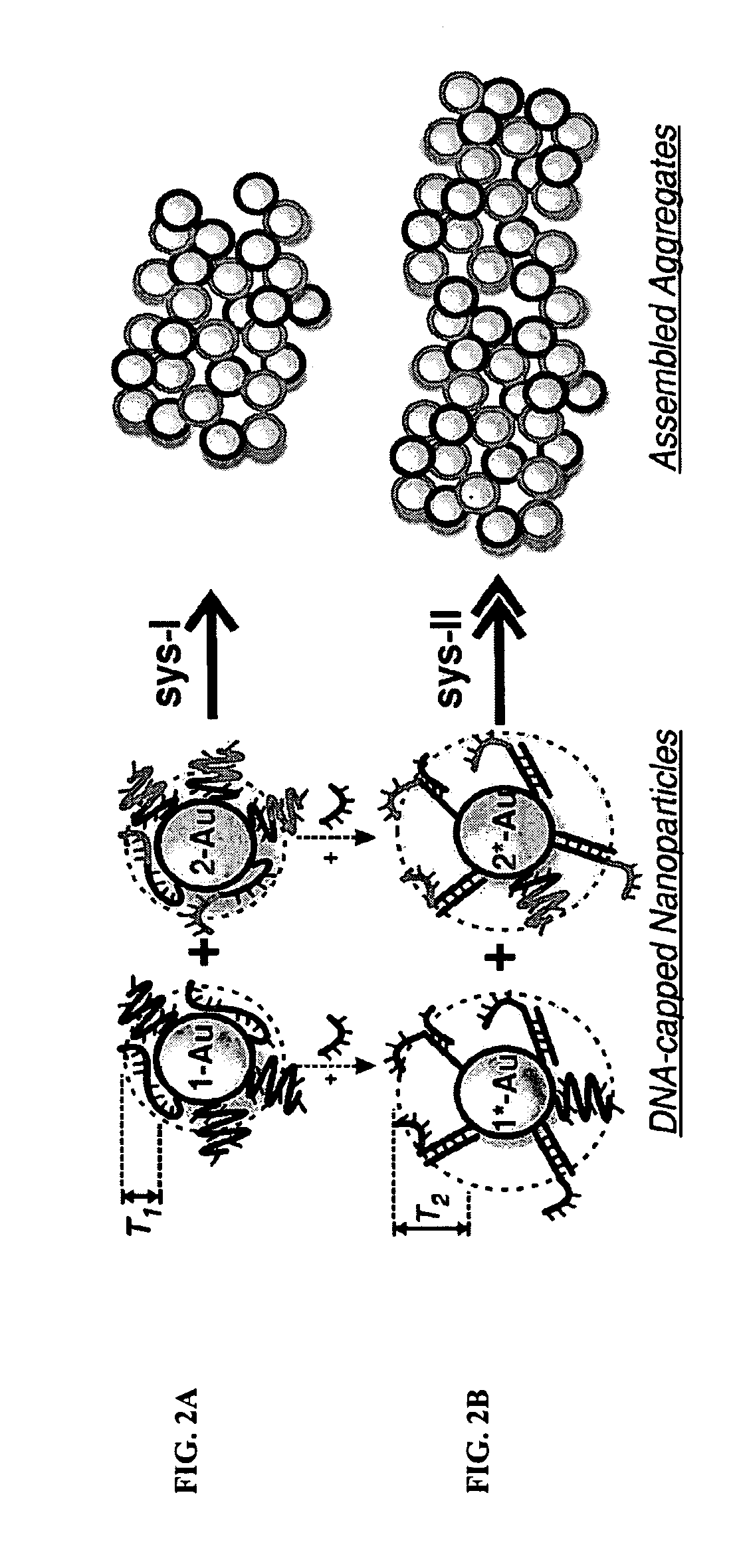
DNA-Guided Nanoparticle Assemblies
InactiveUS20090275465A1Little synthetic workloadPrecision testingNanostructure manufactureSugar derivativesActive agentNanoparticle
In some embodiments, DNA-capped nanoparticles are used to define a degree of crystalline order in assemblies thereof. In some embodiments, thermodynamically reversible and stable body-centered cubic (bcc) structures, with particles occupying <˜10% of the unit cell, are formed. Designs and pathways amenable to the crystallization of particle assemblies are identified. In some embodiments, a plasmonic crystal is provided. In some aspects, a method for controlling the properties of particle assemblages is provided. In some embodiments a catalyst is formed from nanoparticles linked by nucleic acid sequences and forming an open crystal structure with catalytically active agents attached to the crystal on its surface or in interstices.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
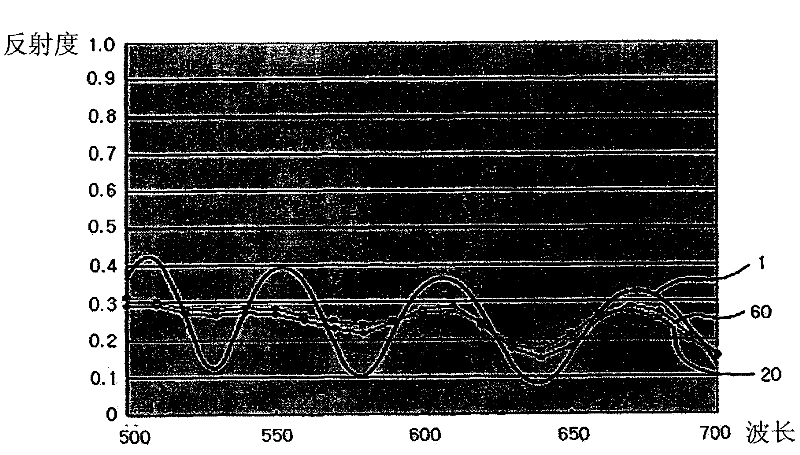
Reflectance distribution curve modeling method, thickness measurement scheme and thickness measurement reflectometer using same
ActiveCN102362146APrecision testingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementUsing optical meansComputational physicsLength wave
The reflectance distribution curve modeling method of the present invention is for modeling a reflectance distribution of a thin film layer according to a change in the wavelength of light with respect to a thin film layer having a uniform thickness, and comprises: a reflectance distribution curve preparation step whereby a reflectance distribution curve is prepared to represent reflectance distribution of the thin film layer according to a change in wavelength of light; an input intensity setting step whereby an intensity distribution curve is prepared to represent intensity of light in a certain wavelength band around a specific wavelength for which white light was band-passed, and then the intensity distribution curve is integrated within the wavelength band to set as an input intensity of the specific wavelength; an output intensity setting step whereby a combined intensity distribution curve of the reflectance and intensity distribution curves is integrated within the wavelength band to set an output intensity of the specific wavelength; an integrated reflectance setting step whereby a value obtained by dividing the output intensity of the specific wavelength by the input intensity of the specific wavelength is set as an integration reflectance of the thin film layer for the specific wavelength; and an integration reflectance distribution curve generating step whereby an integration reflectance distribution curve for reflecting the integration reflectance distribution according to a change in wavelength is generated by repeating the input intensity setting step, the output intensity setting step and the integration reflectance setting step, while changing the specific wavelength.
Owner:SNU PRECISION CO LTD
Nanometer magnetic particle chemiluminiscence determination kit for antigen CA125 relating to tumor, as well as preparation method and determining method of same
ActiveCN103048452AAnalysis of small differences between batchesAccurate detectionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntigenFluorescein
The invention relates to a nanometer magnetic particle chemiluminiscence determination kit for antigen CA125 relating to tumor, and the preparation method and the determining method of the kit. The kit comprises solution of tumor related antigen CA125 antibody containing fluorescein labels, suspending liquid of magnetic particles wrapped by fluorescent antibody, and solution of tumor related antigen CA125 antibody containing alkaline phosphatase labels. According to the invention, quantitative determination to the antigen CA125 relating to tumor can be performed with lower cost and higher degree of accuracy.
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
Nanometer magnetic particle chemiluminescent assay kit for cancer antigen CA15-3, and preparation method and detection method thereof
InactiveCN103048461ALow costAnalysis of small differences between batchesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntigenCA15-3
The invention relates to a nanometer magnetic particle chemiluminescent assay kit for a cancer antigen CA15-3, and a preparation method and a detection method thereof. The kit comprises a solution containing a fluorescein-mark labeled cancer antigen CA15-3 antibody, suspension of fluorescein antibody coated magnetic particles and a solution containing an alkaline phosphatase labeled cancer antigen CA15-3 antibody, wherein the alkaline phosphatase labeled cancer antigen CA15-3 antibody is formed by connecting alkaline phosphatase and the cancer antigen CA15-3 antibody through a crosslinking agent SMCC and 2-IT. According to the invention, the cancer antigen CA15-3 can be quantitatively detected with low cost, high accuracy degree and high precision degree.
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
Optical and thermal infrared multi-stage imaging detection method and device for defects of transparent component
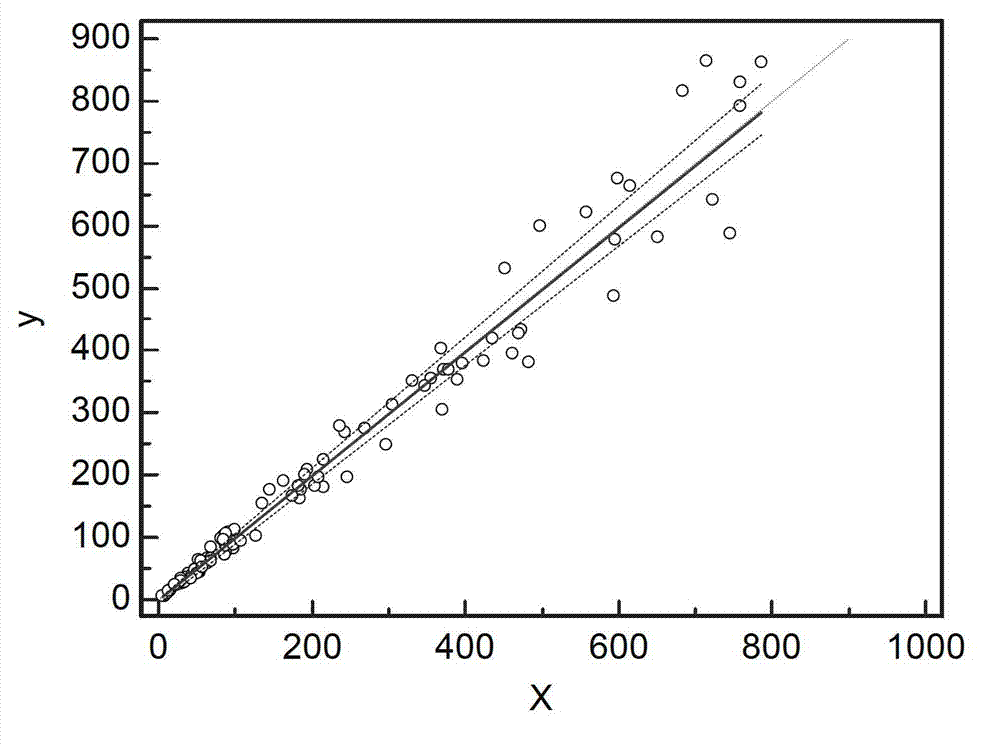
ActiveCN110827256AImprove accuracyInformativeImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryUltrasonic imagingEngineering
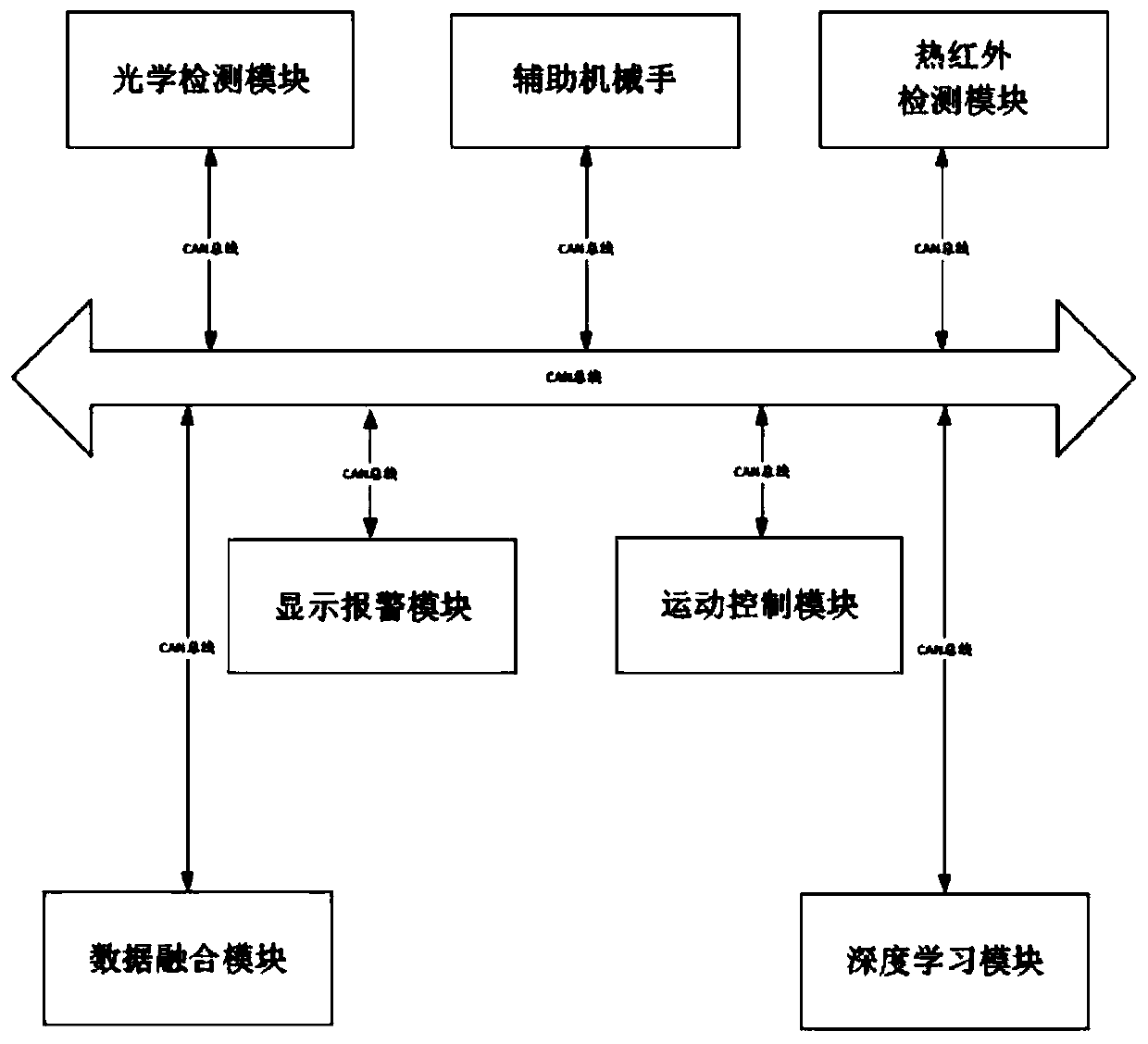
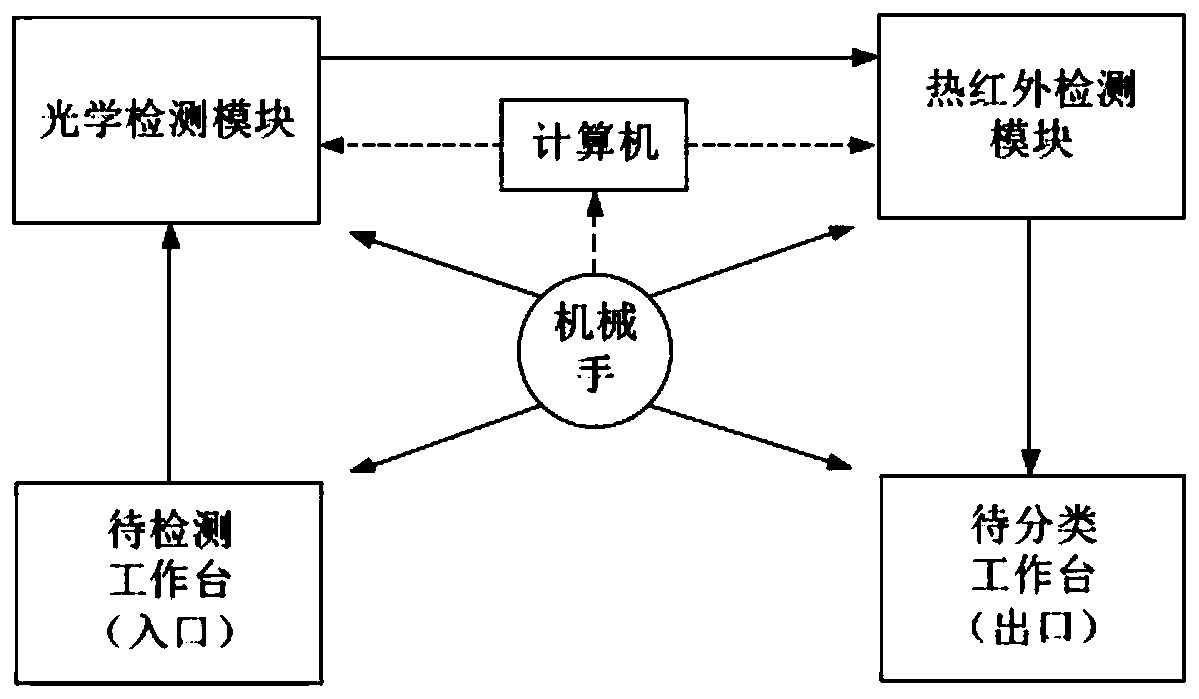
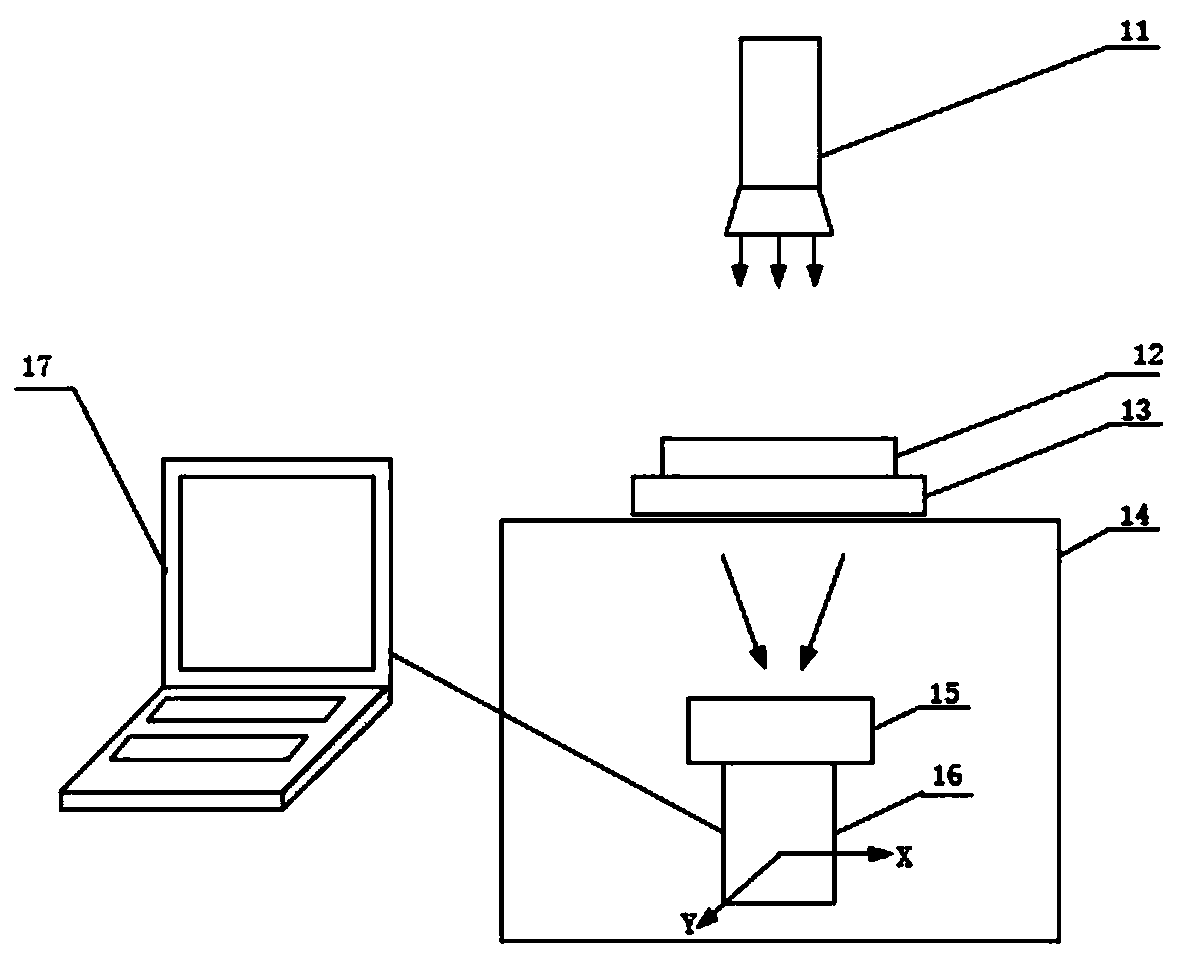
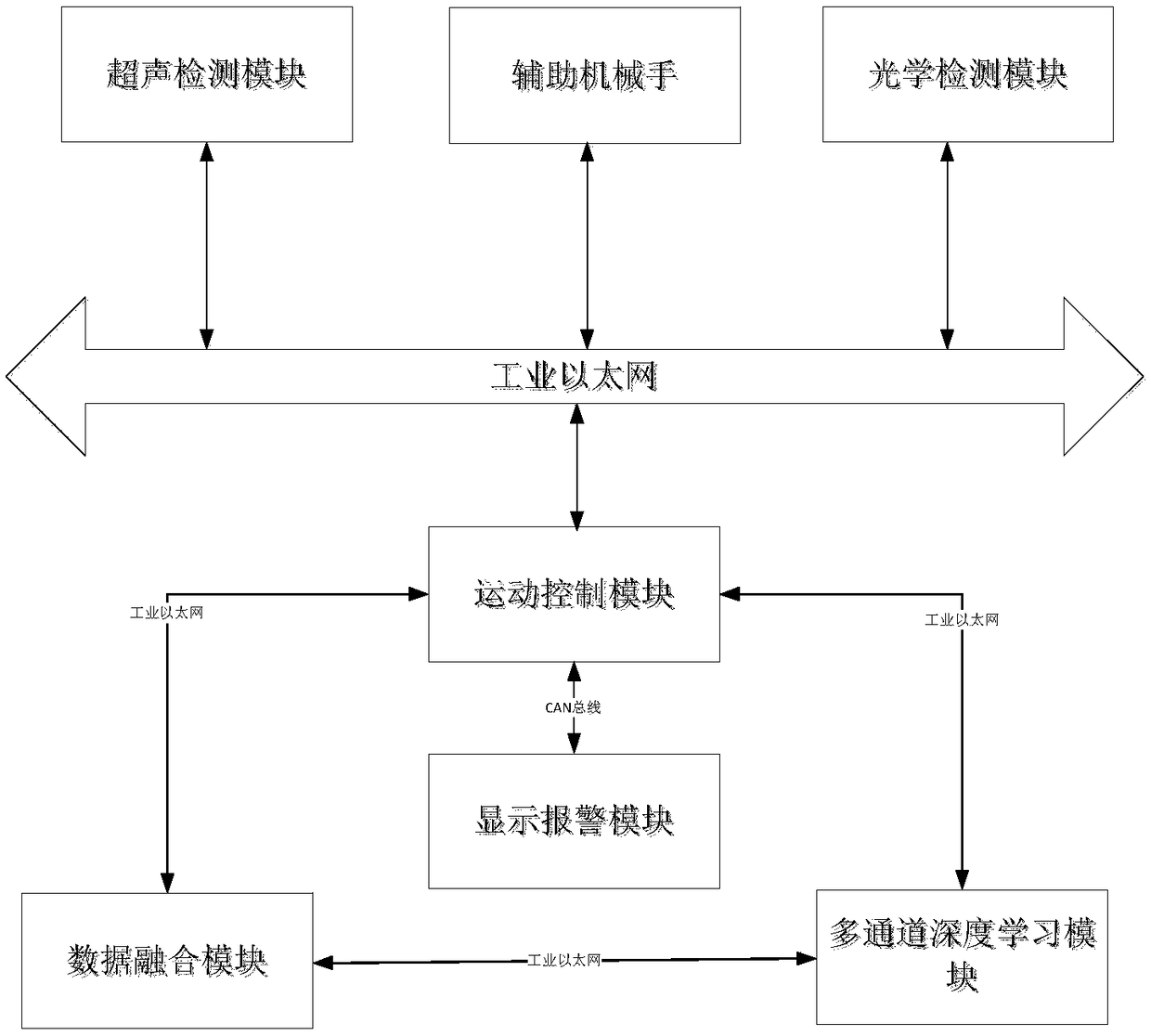
The invention discloses an optical and thermal infrared multi-stage imaging detection method and device for defects of a transparent component, and the method comprises the following steps: carrying out the optical imaging of a 3C transparent component, obtaining an optical image, and preliminarily judging the position and size of the defects of the 3C transparent component; using nitrogen to heatthe defect position of the 3C transparent component, carrying out thermal infrared imaging, and obtaining a thermal infrared image; and fusing the optical image and the thermal infrared image, and then recognizing the defect type of the 3C transparent component through deep learning. The device comprises an optical detection module, a thermal infrared detection module, a motion control module, adata fusion module, a deep learning module, an auxiliary manipulator and a display alarm module which are in communication connection with one another through a bus. Through optical imaging and thermal infrared ultrasonic imaging, multi-physical-quantity and multi-stage detection is carried out on a defective product, and then optical and infrared multi-source information fusion is completed through the convolutional neural network, so that the identification rate of defect detection of the 3C transparent component is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUST IND TECH RES INST
Nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence determining kit for promoting hormone generation by follicles and preparation and detection method thereof
ActiveCN103048473AEasy to manufactureAccurate detectionBiological testingFollicle-stimulating hormoneHormones regulation
The invention relates to a nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence determining kit for promoting hormone generation by follicles and preparation and detection method thereof. The kit comprises a first reagent which comprises a follicle-stimulating hormone antibody solution containing fluorescein isothiocyanate, a second reagent which comprises a follicle-stimulating hormone antibody solution containing an alkaline phosphatase mark, and a magnetic separation reagent which comprises a magnetic particle suspension coated by a fluorescein isothiocyanate antibody. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the kit and a detection method for detecting generated hormones by promoting the follicles by using the kit. Compared with the prior art, the kit is better in accuracy, higher in precision and higher in sensitivity, and samples to be tested are not needed to be pre-diluted, so that the kit is simple and time-saving to operate, wide in detection range and low in cost.
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
Nanometer magnetic particle chemiluminescence detection kit for carbohydrate antigen CA19-9 as well as preparation method thereof and detecting method thereof
ActiveCN103048453AReduce manufacturing costAnalysis of small differences between batchesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntigenAntibody
The invention relates to a nanometer magnetic particle chemiluminescence detection kit for a carbohydrate antigen CA19-9 as well as a preparation method thereof and a detecting method thereof. The kit comprises a solution, which contains a fluorescein labeled carbohydrate related antigen CA19-9, a suspension, which is coated with a fluorescein antibody, and a solution, which contains an alkaline phosphatase labeled carbohydrate related antigen CA19-9 antibody, wherein the alkaline phosphatase labeled carbohydrate related antigen CA19-9 antibody is obtained by connecting an alkaline phosphatase and the carbohydrate related antigen CA19-9 antibody through cross-linking agents SMCC and 2-IT. According to the invention, the carbohydrate related antigen CA19-9 can be quantitatively detected with lower cost, higher accuracy and higher precision.
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
Ultrasonic and optical double-imaging based transparent member defect detection device and method
PendingCN109115805AOvercome the shortcomings of a single detection technologyReduce Optical InterferenceAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansMovement controlManipulator
The invention discloses an ultrasonic and optical double-imaging based transparent member defect detection device and method. The device comprises an ultrasonic detection module, an optical detectionmodule, a movement control module, a data fusion module, a multi-channel deep learning module and an auxiliary manipulator; the ultrasonic detection module, the optical detection module and the auxiliary manipulator are in communication connection with the movement control module through the Ethernet; the data fusion module, the multi-channel deep learning module and the movement control module are in communication connection through the Ethernet in pairs; and the movement control module is also in communication connection with a display alarm module through a bus. By utilizing ultrasonic andoptical double-imaging detection, the ultrasonic and optical double-imaging based transparent member defect detection device and the method are more accurate in detection, and the device performs automatic operation and improves the detection efficiency.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUST IND TECH RES INST
Apparatus and method for performing power calibration in wireless power transmission system
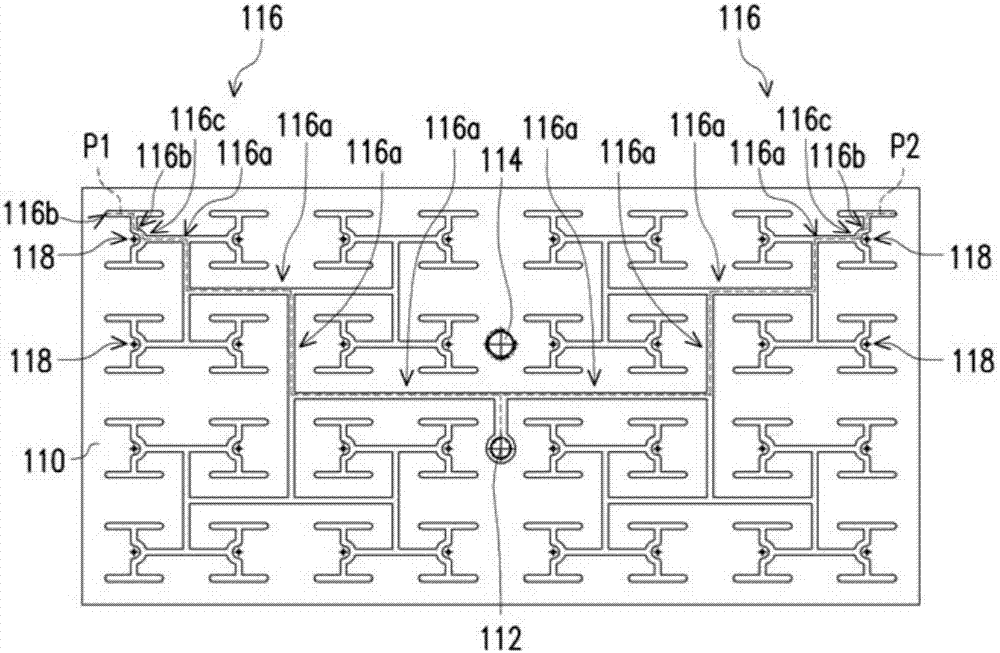
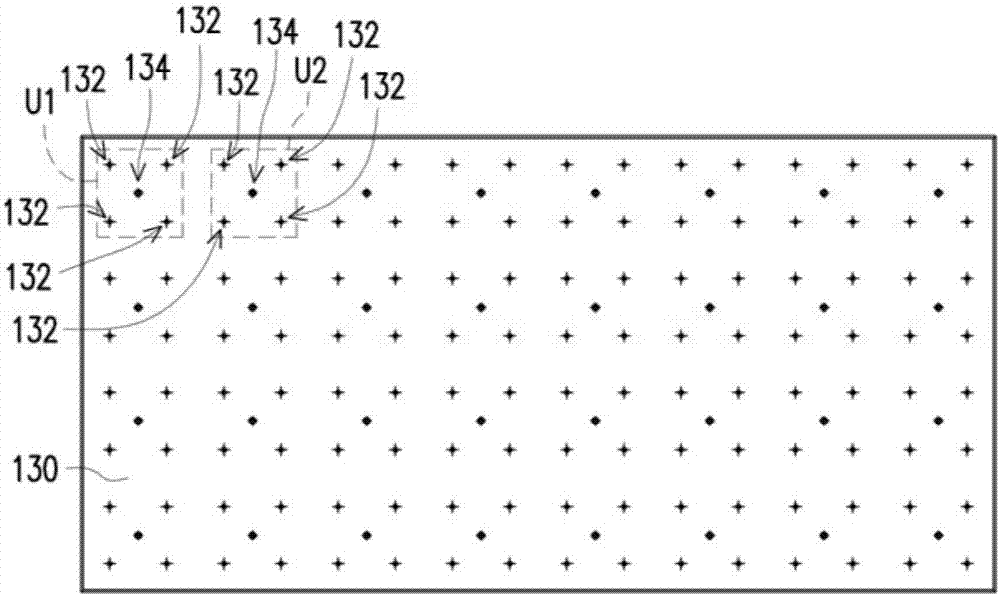
ActiveUS20210066973A1Precision testingCircuit arrangementsTransmissionElectric power transmissionTelecommunications
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for performing power calibration in a wireless power transmission system. The present specification provides a wireless power transmission apparatus comprising: a power conversion unit configured to transmit, in a power transfer phase, wireless power generated on the basis of magnetic coupling to a wireless power receiving device; and a communication / control unit configured to perform an initial calibration for a power parameter prior to the power transfer phase, receive a first received power packet from the wireless power receiving device indicating the power received by the wireless power receiving device during the power transfer phase, and detect foreign matter by using the received power and a first power loss determined on the basis of the initial calibration. It is possible to adaptively respond to a newly changed wireless charging environment to calibrate transmission power and reception power, and it is possible to detect foreign matter more precisely by detecting a power loss on the basis of the calibrated transmission and reception power.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence assay kit for free HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) beta subunit, preparation method for Nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence assay kit and detection method adopting Nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence assay kit
InactiveCN103048475AAccurate detectionPrecision testingChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingMicroparticleFluorescein isothiocyanate
The invention relates to a nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence assay kit for a free HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) beta subunit, a preparation method for the Nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence assay kit and a detection method adopting the Nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence assay kit. The kit comprises a first agent, a second agent and a magnetic separation agent, wherein the first agent comprises solution of free HCG beta subunit antibody marked with fluorescein isothiocyanate; the second agent comprises solution of free HCG beta subunit antibody marked with alkaline phosphatase; and the magnetic separation agent comprises suspension of magnetic particles coated with a fluorescein isothiocyanate resistance antibody. The invention further discloses the preparation method of the kit and the detection method for detecting the HCG beta subunit by adopting the kit. Compared with the prior art, the nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence assay kit has better accuracy, higher precision and higher sensitivity; a sample to be detected does not need to be pre-diluted; and the nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence assay kit is simple and time-saving to operate, has a wide detection range and is low in cost.
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
Displacement adjusting device
The invention discloses a displacement adjusting device which comprises a support, a guiding component, a micro-adjusting component, a micro-displacement meter and a driving component. Specifically, the guiding component is arranged on the support, the micro-adjusting component is arranged on the guiding component in a movable mode in a first straight line direction and a second straight line direction, the micro-displacement meter is movably arranged on the micro-adjusting component in a movable mode in a third straight line direction, wherein the first straight line direction, the second straight line direction and the third straight line direction are perpendicular to one another, the driving component is used for driving the micro-adjusting component to move, and the micro-adjusting component is respectively connected with the guiding component and the micro-adjusting component. The displacement adjusting device can be used for detecting the micro displacement of each actuating point of a deforming mirror quickly, efficiently and accurately, and accordingly high stress adjusting accuracy is achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Kit for detecting nano magnetic particle chemiluminescence of hormothyrin and preparation method and detection method thereof
ActiveCN103048474AAnalysis of small differences between batchesAccurate detectionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingMaterials scienceAbnormal alkaline phosphatase
The invention relates to a kit for detecting nano magnetic particle chemiluminescence of hormothyrin and a preparation method and a detection method thereof. The kit comprises a hormothyrin antibody solution containing a fluorescein mark, a magnetic particle suspension liquid coated by a magnetic particle antibody, and a hormothyrin antibody solution containing an alkaline phosphatase mark. According to the invention, hormothyrin can be quantitively detected with lower cost and higher accuracy and precision.
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
Unpowered pipeline inspection robot with controllable speed
ActiveCN111536367AAdjust travel speedImprove battery lifePigs/molesControl engineeringElectric machinery
The invention belongs to the technical field of pipeline inspection equipment, and particularly relates to an unpowered pipeline inspection robot with controllable speed. The unpowered pipeline inspection robot with controllable speed comprises a shell, and a first rotation device, a second rotation device and a drive device arranged in the shell, wherein the first rotation device and the second rotation device are respectively arranged at two ends of the shell; the first rotation device is connected with the drive device in a meshing way; the drive device drives the first rotation device so as to enable the shell to rotate axially; at least one group of wheel set module is arranged between the first rotation device and the second rotation device; and according to the wheel set modules, the advancing speed of the robot is adjusted through a first electromagnetic damping motor. Compared with the prior art, according to the unpowered pipeline inspection robot with controllable speed provided by the invention, the advancing speed of the robot is adjusted through the first electromagnetic damping motor, so that the stability in actively controlling the speed is realized; and in addition, the drive device drives the first rotation device to rotate, and the shell further keeps rotation in the advancing process, so that the detection area of a detection sensor on the surface of the shell is increased, and a large number of detection cost is saved.
Owner:李柏松 +1
Radiation detecting unit and radiation inspecting apparatus
InactiveCN101326449AEfficient configurationGood precisionRadiation intensity measurementSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
A detecting board (22) is provided with a wiring board (24), a semiconductor detecting element (25) firmly fixed on the upper plane of the wiring board (24) for detecting radiation and a spacer (28) firmly fixed on the upper plane of the wiring board (24), and a plurality of detecting boards are stacked and fixed. On each of the detecting boards (22), the semiconductor detecting element (25) and the spacer (28) are arranged to have a prescribed positional relationship. Furthermore, the detecting boards (22) are stacked by being aligned by the spacers (28) on an X-Y plane, and are fixed by fixing members (23a, 23b). The spacer (28) is provided with a step section (28e) so that the lower plane of the wiring board (24) is not brought into contact with the spacer (28) under the lower plane, and in the vertical direction, the spacers (28) are positioned by being brought into contact with each other.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
Flotation platform
The present invention provides an air flotation stage comprising at least a bottom layer and a top layer. The bottom layer has a first opening, a plurality of first channels, and a plurality of through holes. The top layer is disposed above the bottom layer and has a plurality of first air holes and a plurality of second air holes arranged in an array. The first opening communicates with the first air hole via the first passage to form a first air flow path. The through hole is correspondingly communicated with the second air hole to form a second air flow path. The airflow flows from the bottom layer to the outside of the top layer via one of the first airflow path and the second airflow path or from the top layer to the outside of the bottom layer via the other of the first airflow path and the second airflow path. The air flotation stage of the present invention is suitable for providing an air flow bearing substrate and for maintaining a horizontal effect of the substrate.
Owner:UTECHZONE CO LTD
Apparatus and method for performing power calibration in wireless power transmission system
ActiveUS11139702B2Precision testingCircuit arrangementsTransmissionElectric power transmissionTelecommunications
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for performing power calibration in a wireless power transmission system. The present specification provides a wireless power transmission apparatus comprising: a power conversion unit configured to transmit, in a power transfer phase, wireless power generated on the basis of magnetic coupling to a wireless power receiving device; and a communication / control unit configured to perform an initial calibration for a power parameter prior to the power transfer phase, receive a first received power packet from the wireless power receiving device indicating the power received by the wireless power receiving device during the power transfer phase, and detect foreign matter by using the received power and a first power loss determined on the basis of the initial calibration. It is possible to adaptively respond to a newly changed wireless charging environment to calibrate transmission power and reception power, and it is possible to detect foreign matter more precisely by detecting a power loss on the basis of the calibrated transmission and reception power.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
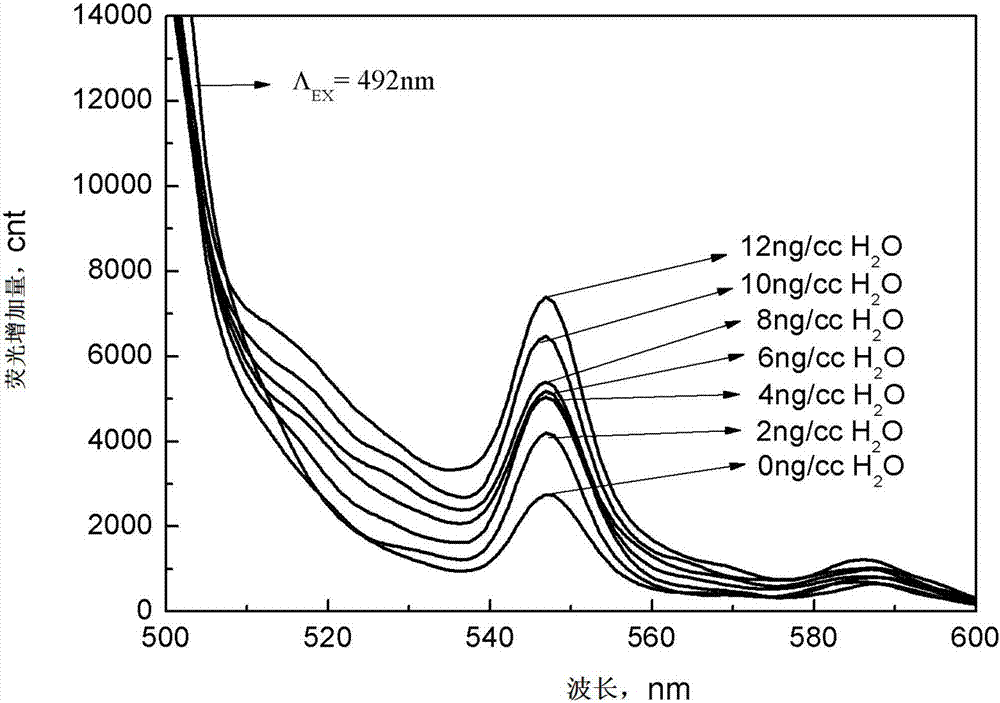
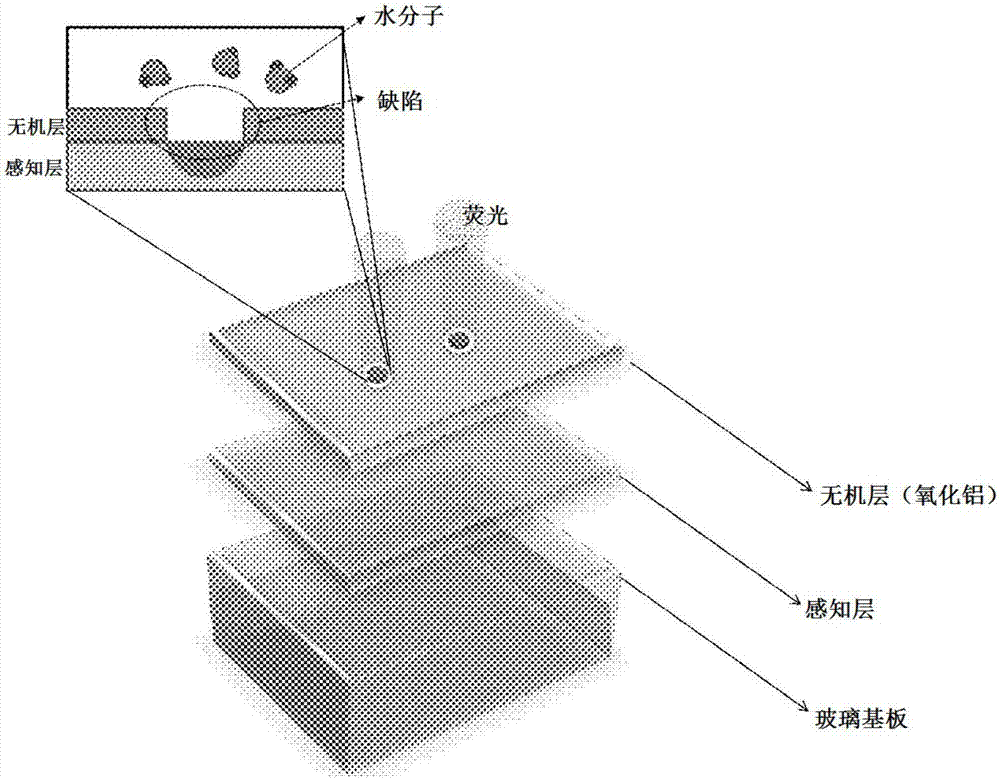
Moisture detection sensor, defect detection sensor, and sensor array using same
InactiveCN107209119AEffective monitoring of concentration changesGood choiceMaterial analysis using reversible reactionsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSensor arrayCalcein AM
The present invention provides a moisture detection sensor, a defect detection sensor, and a sensor array using the same, the moisture detector sensor comprising at least one moisture sensitive compound selected from the group consisting of Calcein, Calcein acetoxymethyl ester, Calcein-AM and Calcein blue. The moisture detection sensor and the defect detection sensor of the present invention have excellent selectivity, thereby being able to accurately quantify only moisture without being influenced by a coexisting gas, and are reversible so that the moisture detection sensor and the defect detection sensor can be re-used continuously, whereby it possible to reduce costs required and effectively monitor changes in moisture concentration. As such, the moisture detection sensor and the defect detection sensor can measure moisture barrier properties or water vapor transmission properties. In addition, the moisture detection sensor and the defect detection sensor have advantages of accurately detecting moisture due to excellent sensitivity and being very fast in response speed. Further, the present invention can easily monitor defects by utilizing the phenomenon whereby moisture easily penetrates into the defect detection sensor through a defect and thus fluorescence intensity increases.
Owner:KOREA INST OF CERAMIC ENG & TECH
Nano magnetic particle chemiluminiscence determining kit for promoting hormone generation by follicles and preparation and detection method thereof
ActiveCN103048473BAccurate detectionPrecision testingBiological testingFollicle-stimulating hormoneHormones regulation
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
DNA-guided nanoparticle assemblies
InactiveUS8487084B2Precision testingLittle synthetic workloadNanostructure manufactureSugar derivativesActive agentNanoparticle
In some embodiments, DNA-capped nanoparticles are used to define a degree of crystalline order in assemblies thereof. In some embodiments, thermodynamically reversible and stable body-centered cubic (bcc) structures, with particles occupying <˜10% of the unit cell, are formed. Designs and pathways amenable to the crystallization of particle assemblies are identified. In some embodiments, a plasmonic crystal is provided. In some aspects, a method for controlling the properties of particle assemblages is provided. In some embodiments a catalyst is formed from nanoparticles linked by nucleic acid sequences and forming an open crystal structure with catalytically active agents attached to the crystal on its surface or in interstices.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Kit for detecting nano magnetic particle chemiluminescence of hormothyrin and preparation method and detection method thereof
ActiveCN103048474BAnalysis of small differences between batchesAccurate detectionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBiological testingFluoresceinAntibody
The invention relates to a kit for detecting nano magnetic particle chemiluminescence of hormothyrin and a preparation method and a detection method thereof. The kit comprises a hormothyrin antibody solution containing a fluorescein mark, a magnetic particle suspension liquid coated by a magnetic particle antibody, and a hormothyrin antibody solution containing an alkaline phosphatase mark. According to the invention, hormothyrin can be quantitively detected with lower cost and higher accuracy and precision.
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
Reflectance distribution curve modeling method, thickness measurement scheme and thickness measurement reflectometer using same
ActiveCN102362146BPrecision testingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementUsing optical meansComputational physicsLength wave
The reflectance distribution curve modeling method of the present invention is for modeling a reflectance distribution of a thin film layer according to a change in the wavelength of light with respect to a thin film layer having a uniform thickness, and comprises: a reflectance distribution curve preparation step whereby a reflectance distribution curve is prepared to represent reflectance distribution of the thin film layer according to a change in wavelength of light; an input intensity setting step whereby an intensity distribution curve is prepared to represent intensity of light in a certain wavelength band around a specific wavelength for which white light was band-passed, and then the intensity distribution curve is integrated within the wavelength band to set as an input intensity of the specific wavelength; an output intensity setting step whereby a combined intensity distribution curve of the reflectance and intensity distribution curves is integrated within the wavelength band to set an output intensity of the specific wavelength; an integrated reflectance setting step whereby a value obtained by dividing the output intensity of the specific wavelength by the input intensity of the specific wavelength is set as an integration reflectance of the thin film layer for the specific wavelength; and an integration reflectance distribution curve generating step whereby an integration reflectance distribution curve for reflecting the integration reflectance distribution according to a change in wavelength is generated by repeating the input intensity setting step, the output intensity setting step and the integration reflectance setting step, while changing the specific wavelength.
Owner:SNU PRECISION CO LTD
Method for detecting grouting quality of bridge prestressed pipes based on combined seismic source method
ActiveCN104483389BAvoid disadvantagesAccurately determineAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave fieldClassical mechanics
The invention provides a source array method based detection method of grouting quality of a bridge prestressed pipeline. According to the detection method, a hammer source and a Chirp source are effectively combined together, advantages of the hammer source and the Chirp source are sufficiently played, meanwhile, disadvantages of the hammer source and the Chirp source are effectively avoided, so that the position of a first-motion wave can be accurately determined, an elastic wave field graph with high resolution can be obtained, and the grouting quality of a bridge prestressed pipeline can be accurately detected; the detection method further has the advantages as follows: the detection result is more accurate, the detection efficiency is high, requirements for the environment are low, the capacity of resisting disturbance is high, and the detection method can be used under the condition of absence of intensive vibration and impact; and besides, the operation is safe, and the detection method is harmless to human beings.
Owner:YUNNAN AEROSPACE ENG GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY INSPECTION
Nanometer magnetic particle chemiluminiscence determination kit for antigen CA125 relating to tumor, as well as preparation method and determining method of same
ActiveCN103048452BAnalysis of small differences between batchesAccurate detectionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntigenFluorescein
The invention relates to a nanometer magnetic particle chemiluminiscence determination kit for antigen CA125 relating to tumor, and the preparation method and the determining method of the kit. The kit comprises solution of tumor related antigen CA125 antibody containing fluorescein labels, suspending liquid of magnetic particles wrapped by fluorescent antibody, and solution of tumor related antigen CA125 antibody containing alkaline phosphatase labels. According to the invention, quantitative determination to the antigen CA125 relating to tumor can be performed with lower cost and higher degree of accuracy.
Owner:SUZHOU HAOOUBO BIOPHARML
Large-scale magnetic suspension detection method and device based on magnet arrays
PendingCN113203657AImplement density detectionImprove detection accuracySpecific gravity measurementParamagnetismMaterials science
The invention provides a large-scale magnetic suspension detection method and device based on magnet arrays. The detection method comprises the steps: constructing two groups of magnet arrays of which same poles are oppositely arranged; placing a diamagnetic sample in a container filled with a paramagnetic medium between the two groups of magnet arrays; after the diamagnetic sample suspends stably, measuring the suspension height of the diamagnetic sample; and determining a density calculation formula through a calibration experiment, and then obtaining the density of the diamagnetic sample through calculation. According to the detection method disclosed by the invention, the diamagnetic sample is detected in the form of the magnet arrays instead of large-size magnets, so that the density detection of the large-size sample is realized, and the detection precision is high; and the size of the magnet arrays can be adjusted according to the size of a sample to be detected, paramagnetic media with different densities can be replaced, the applicability is high, and the detectable density range is wide. The detection device comprises two groups of magnet arrays and a transparent container, wherein the same poles of the two groups of magnet arrays are arranged oppositely, and the transparent container is arranged between the two groups of magnet arrays and is filled with the paramagnetic media.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Air bearing
Owner:UTECHZONE CO LTD
Radar device comprising plurality of antennas arranged at horizontal and vertical intervals
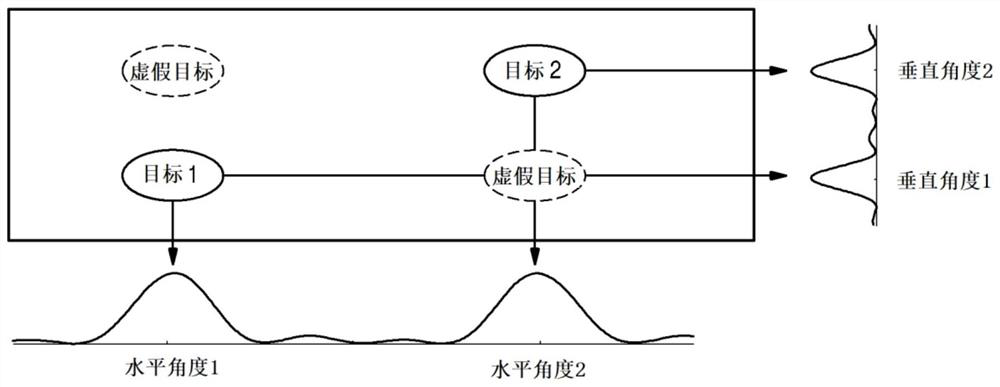
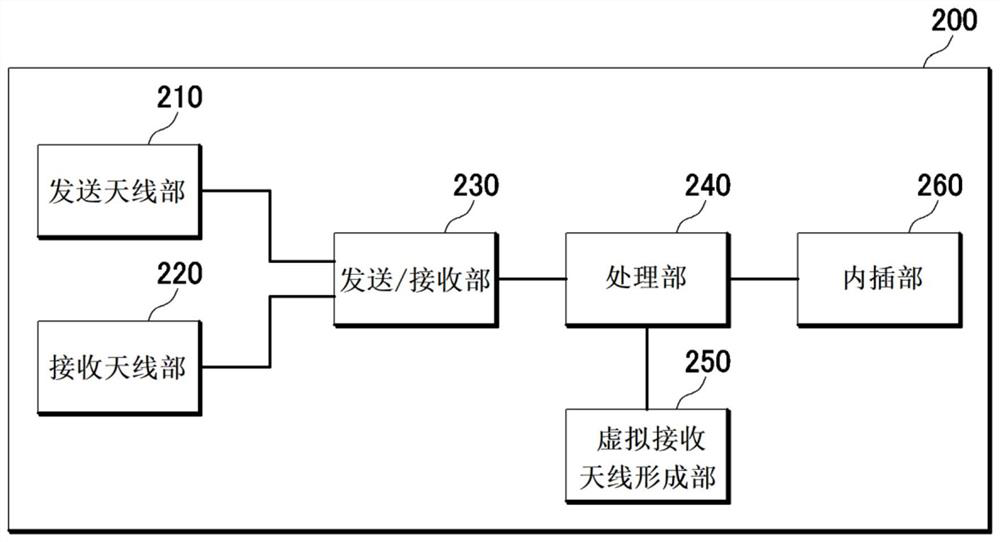
PendingCN114690167AImprove angular resolutionPrecision testingIndependent non-interacting antenna combinationsAntenna detailsRadarRemote sensing
The radar apparatus may include: a transmission antenna section including a plurality of transmission antennas arranged in a diagonal direction based on a first horizontal interval and a first vertical interval; the receiving antenna part comprises a first receiving antenna group and a second receiving antenna group which are arranged based on a first horizontal interval; a transmission / reception unit that transmits a transmission signal via the transmission antenna unit and receives a reflected signal reflected from a target object via the reception antenna unit; and a processing unit that processes the received reflected signal to derive information of the target object.
Owner:BITSENSING INC
Full-automatic detection security check device capable of blocking
InactiveCN111948731AReduce exposurePrecision testingGeological measurementsStructural engineeringSecurity check
The invention discloses a full-automatic detection security check device capable of blocking. The device comprises a main body box, a detection working cavity with a downward opening and extending upwards is formed in the main body box, a belt wheel working cavity with a downward opening and extending upwards is formed in the left side of the detection working cavity in a communicating mode, and abase is fixedly connected to the lower end wall of the main body box and internally provided with a standing plate moving cavity with an upward opening and communicating with the detection working cavity; a standing plate is connected into the standing plate moving cavity in a sliding fit mode, a standing plate spring is fixedly connected between the lower end face of the standing plate and the lower end wall of the standing plate moving cavity, a detected person is comprehensively and systematically examined through automatic operation of the detection plate, contact between people is reduced, and automation can be achieved in the detection process. And the detection of dangerous substances is more precise.
Owner:台州椒江彩格电子科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com