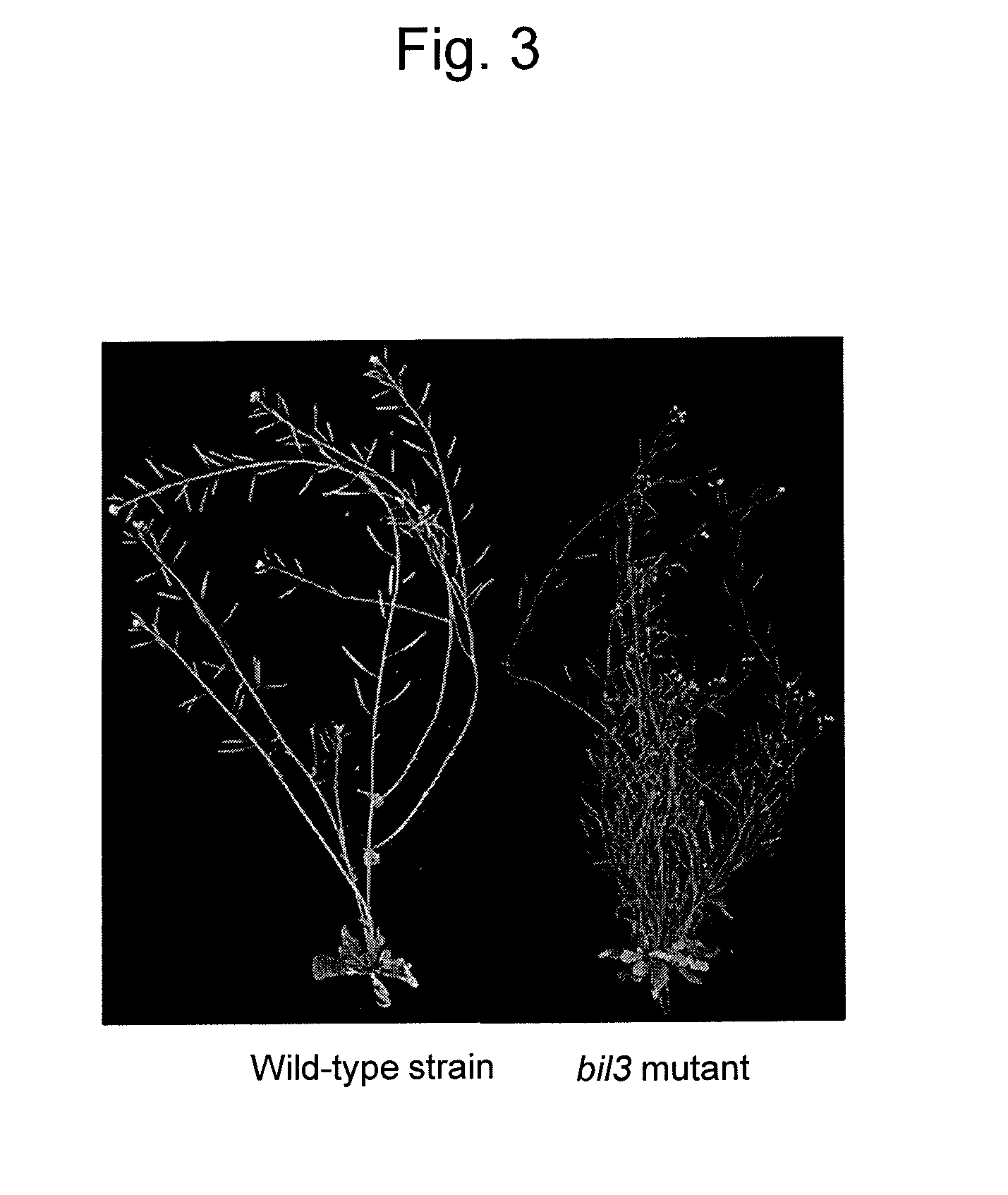Patents
Literature
33results about How to "Preventing and treating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
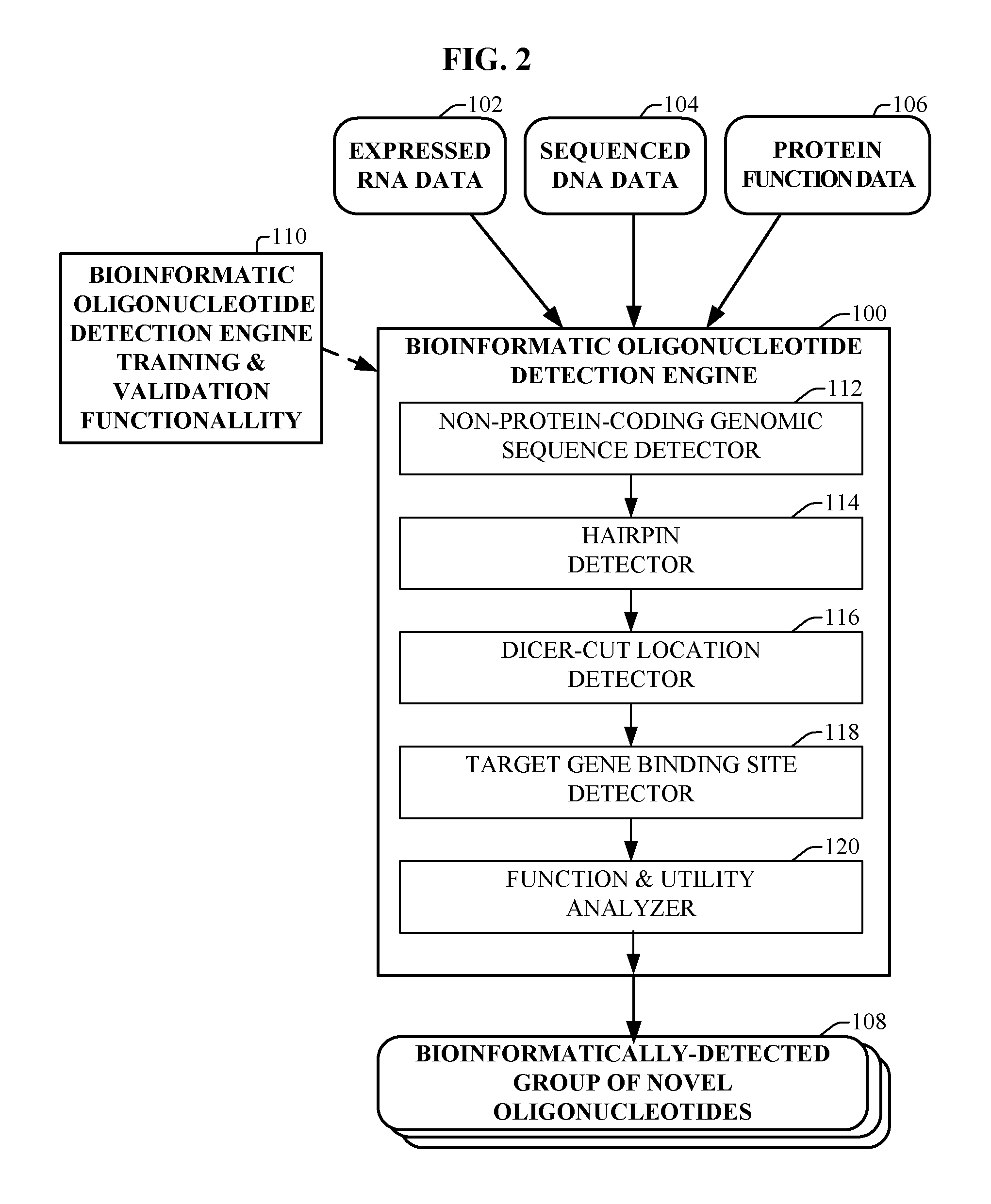
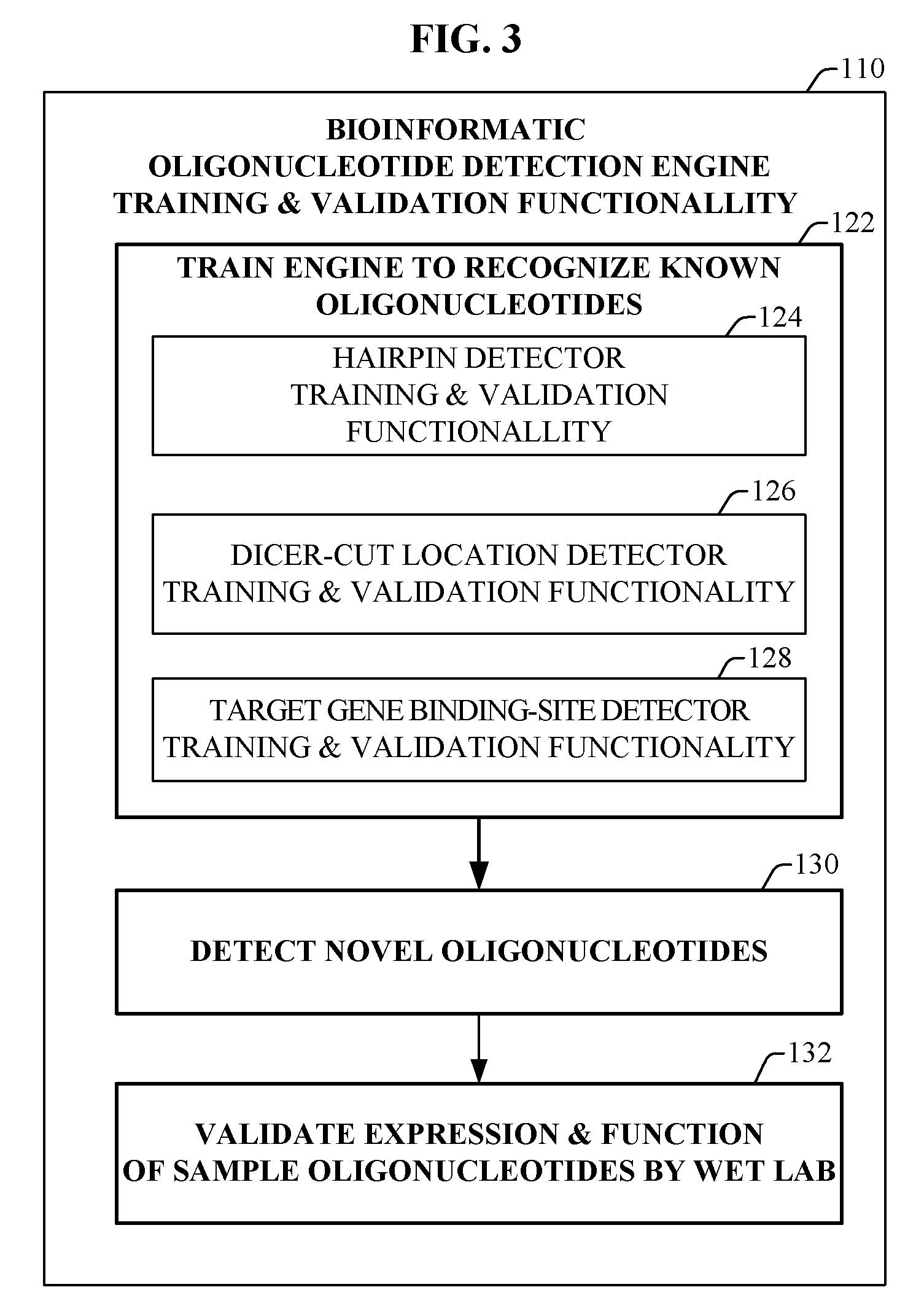
Bioinformatically detectable group of novel regulatory viral and viral associated oligonucleotides and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070042381A1Preventing and treating viral diseasesPreventing and treatingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideSpecific function
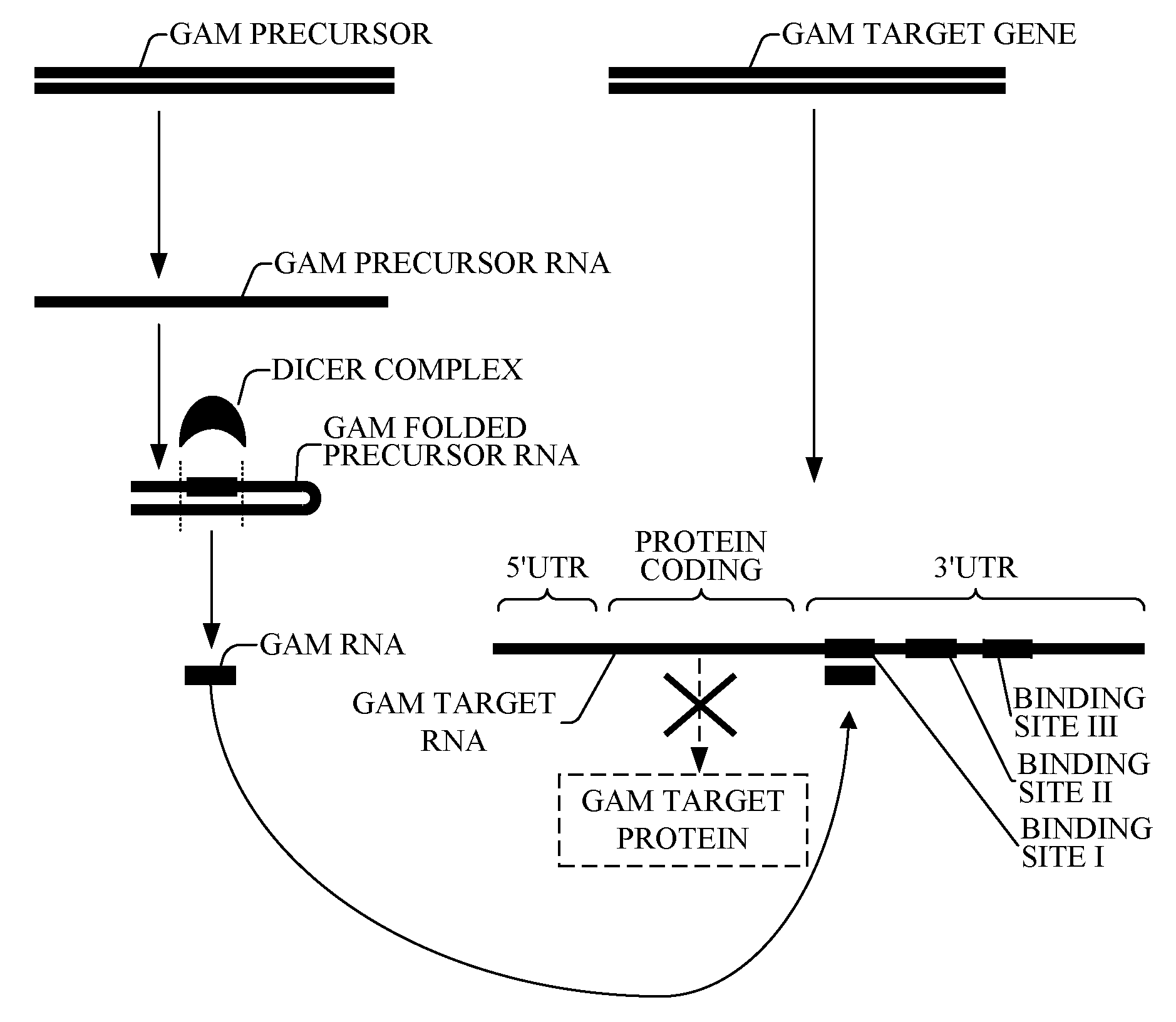
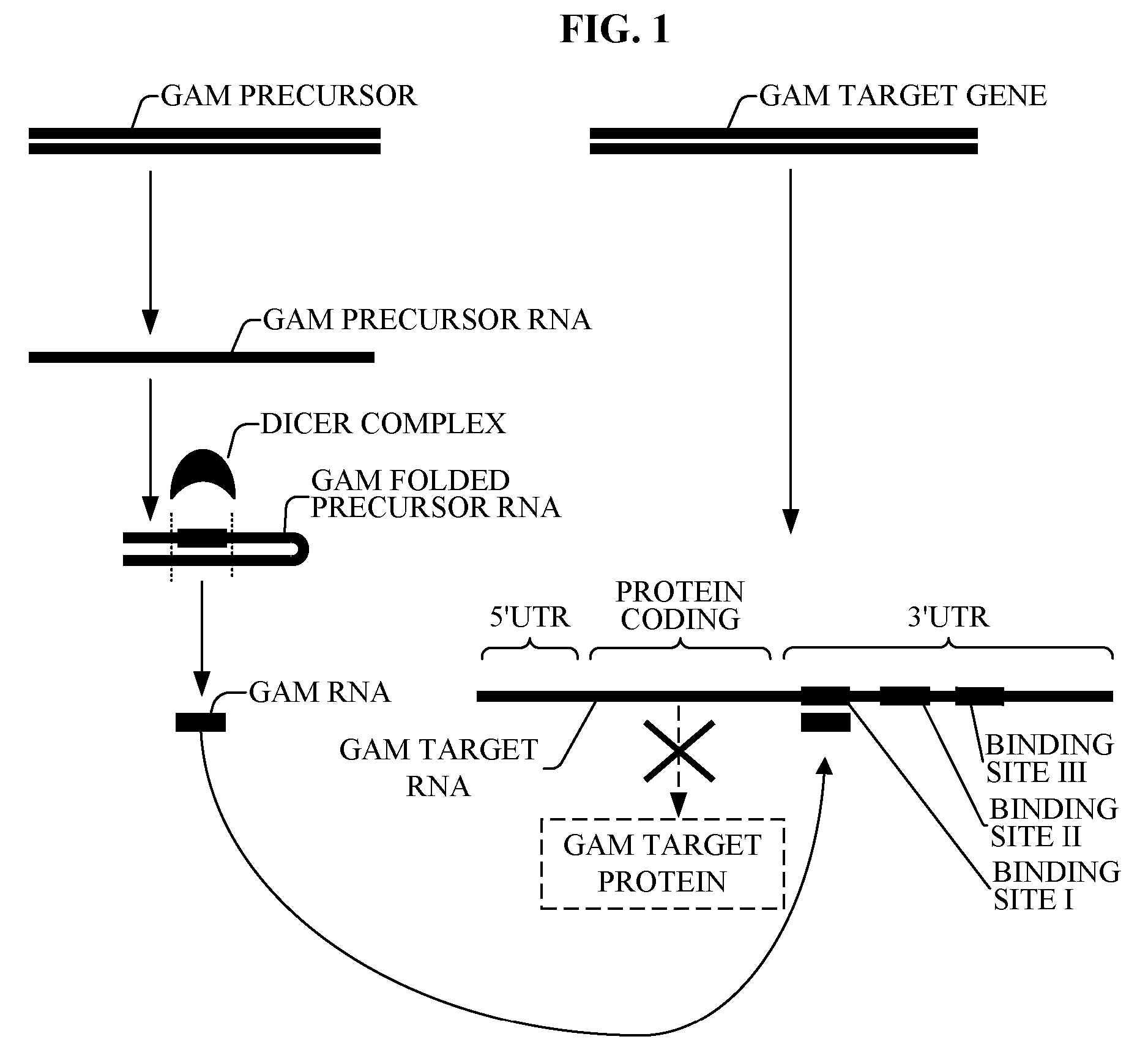
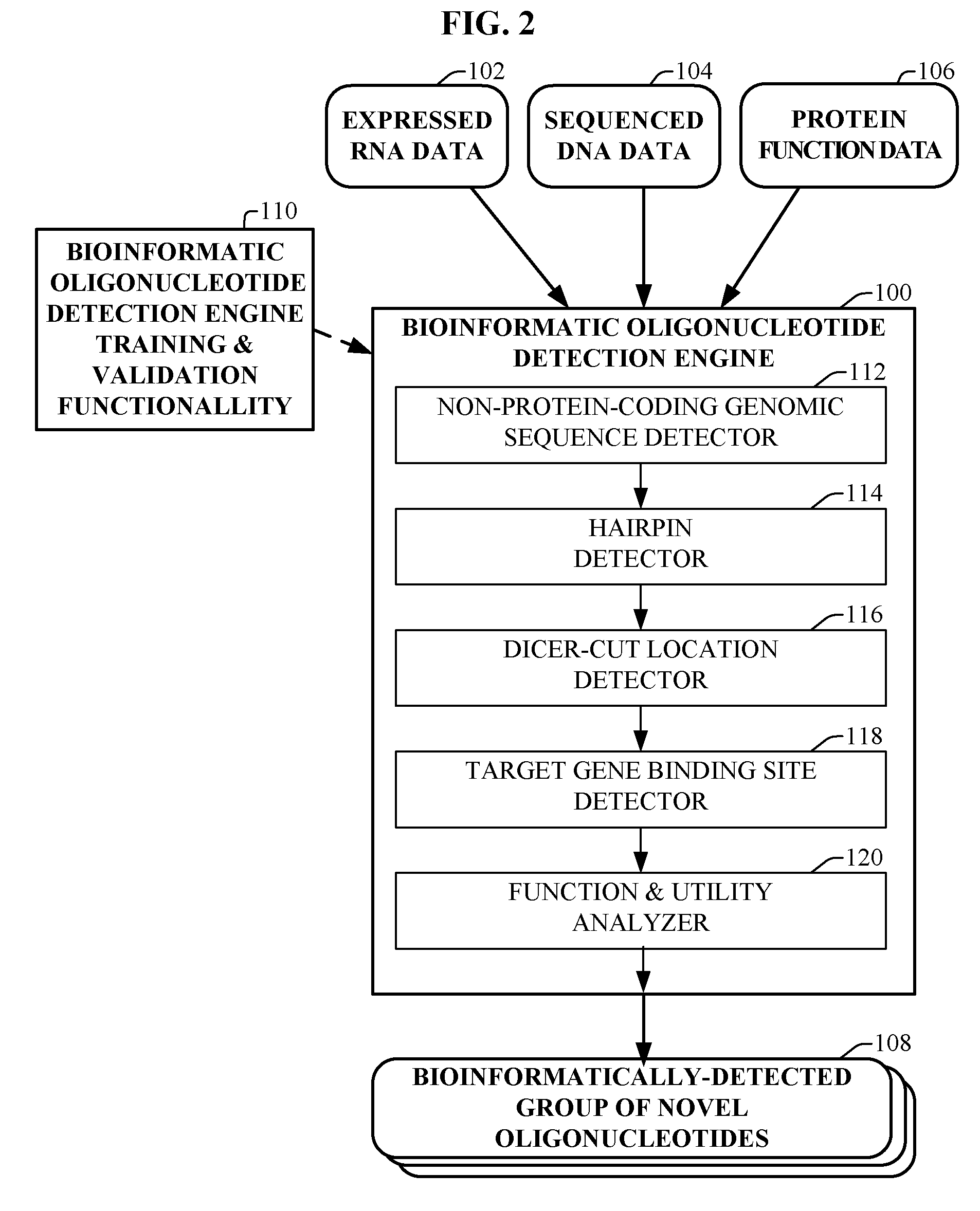
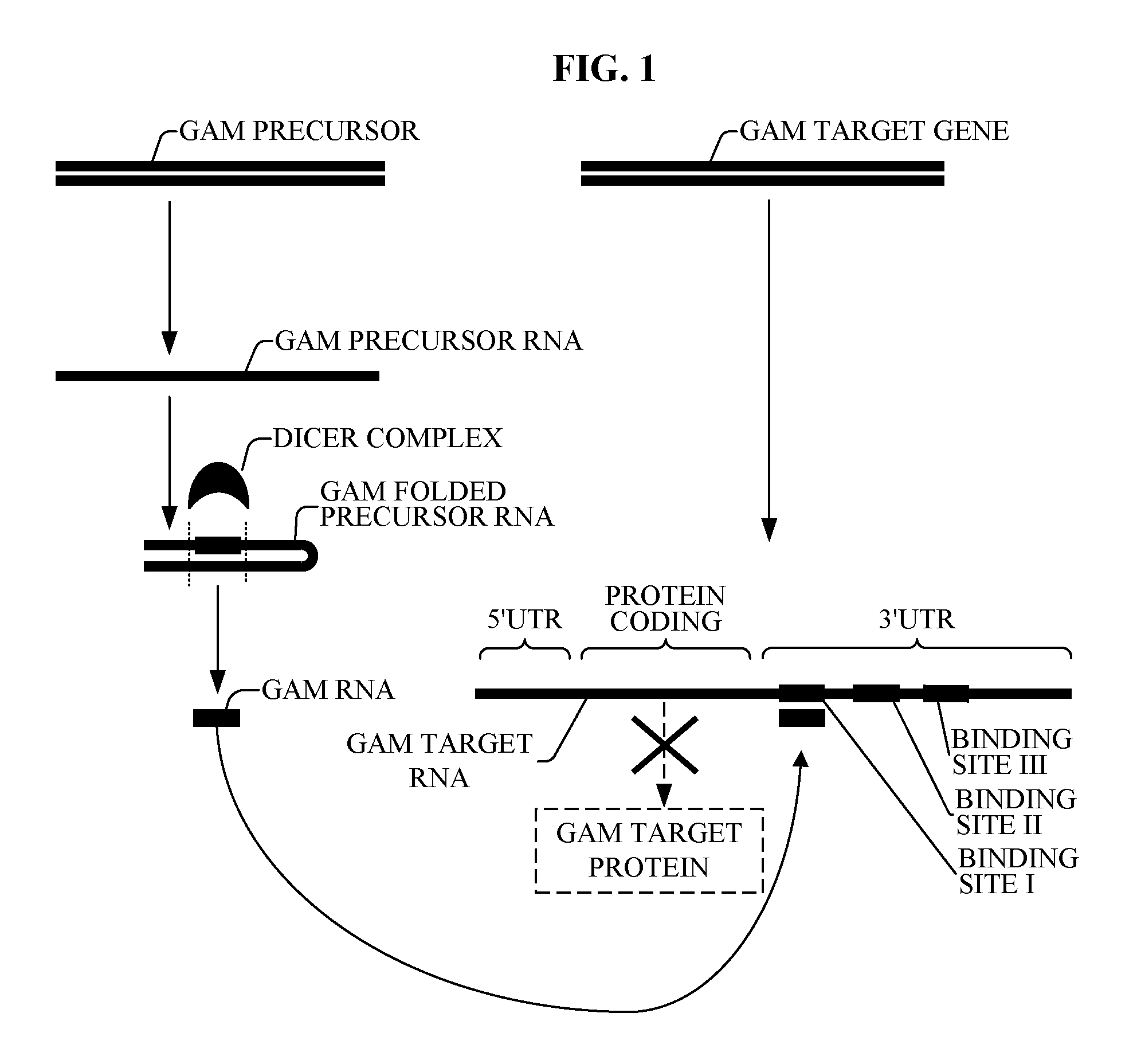
The present invention relates to a first group of novel viral and human associated oligonucleotides, here identified as “Genomic Address Messenger” or “GAM” oligonucleotide, and a second group of novel operon-like viral and human polynucleotides, here identified as “Genomic Record” or “GR” polynucleotide. GAM oligonucleotides selectively inhibit translation of known “target” genes, many of which are known to be involved in various viral diseases. Nucleic acid molecules are provided respectively encoding 1,655 viral and 105,537 human GAM precursor oligonucleotides, and 190 viral and 14,813 human GR polynucleotides, as are vectors and probes both comprising the nucleic acid molecules, and methods and systems for detecting GAM oligonucleotides and GR polynucleotides and specific functions and utilities thereof, for detecting expression of GAM oligonucleotides and GR polynucleotides, and for selectively enhancing and selectively inhibiting translation of the respective target genes thereof.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Compositions with Modified Nucleases Targeted to Viral Nucleic Acids and Methods of Use for Prevention and Treatment of Viral Diseases
ActiveUS20090047272A1Good antiviral effectPreventing and treatingHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsViral diseaseViral nucleic acid
Antiviral compositions comprising a modified nuclease, or a plurality of such modified nucleases having at least one non-natural amino acid residue substituted for a naturally occurring amino acid in a parent nuclease are provided, as are methods of use and kits providing unit dosages of such compositions.
Owner:NANONASE INC
Probiotic preparation for the prevention or treatment of canine gastrointestinal disorders
The present invention relates to a probiotic preparation for preventing and treating canine gastrointestinal disorders containing at least two dog-specific strains of lactic acid bacteria belonging to genus Lactobacillus, a calcium source in an amount of 20-99 weight-% expressed as CaCO3 of the dry weight of the preparation, and at least one prebiotic, and optionally additional dog-specific strains of lactic acid bacteria, excipients and carriers. The invention further relates to a process for the manufacture of the probiotic preparation, to dog food comprising the probiotic preparation, and to the use of the probiotic preparation for the manufacture of a pharmaceutical product or a dog food product for preventing and treating canine gastrointestinal disorders.
Owner:VETCARE
Methods and Compositions for the Prevention and Treatment of Sepsis
The present invention includes compositions comprising one or more complement inhibitors and one or more CD14 pathway inhibitors for the prevention or treatment of sepsis. The complement inhibitors may be antibodies that bind to and inhibit complement proteins such as C5a and the CD14 pathway inhibitors may be antibodies that bind to and inhibit CD14 pathway components, such as CD14 and LPS. The invention also relates to methods of treating subjects suffering from sepsis comprising administering these compositions, as well as kits for supplying the compositions for treatment.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Bioinformatically detectable group of novel regulatory viral and viral associated oligonucleotides and uses thereof
ActiveUS7777022B2Preventing and treating viral diseasesPreventing and treatingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific functionNucleotide
The present invention relates to a first group of novel viral and human associated oligonucleotides, here identified as “Genomic Address Messenger” or “GAM” oligonucleotide, and a second group of novel operon-like viral and human polynucleotides, here identified as “Genomic Record” or “GR” polynucleotide. GAM oligonucleotides selectively inhibit translation of known “target” genes, many of which are known to be involved in various viral diseases. Nucleic acid molecules are provided respectively encoding 1,655 viral and 105,537 human GAM precursor oligonucleotides, and 190 viral and 14,813 human GR polynucleotides, as are vectors and probes both comprising the nucleic acid molecules, and methods and systems for detecting GAM oligonucleotides and GR polynucleotides and specific functions and utilities thereof, for detecting expression of GAM oligonucleotides and GR polynucleotides, and for selectively enhancing and selectively inhibiting translation of the respective target genes thereof.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
LED Treatment of Dermatologic Toxicities Associated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors
InactiveUS20110196353A1Treating preventing toxicityAvoid managementSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyHuman epidermal growth factor receptorLight-emitting diode
The present invention relates generally to methods of preventing or treating toxicities of the skin, hair, and / or nails, which are associated with administration of one or more epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors, with light-emitting diode photomodulation treatment, either alone or in combination with other agents.
Owner:DELAND MAITLAND M +1
Glycosaminoglycan Compositions in Combination with Stem Cells
ActiveUS20120276173A1Improve efficiencyPreventing and treatingSuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsConnective tissue fiberCartilage repair
A pharmaceutical preparation for treating connective tissue damage in man and in animals, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a glycosaminoglycan composition comprising chondroitin sulfate, N-acetyl D-glucosamine, and hyaluronan, in combination with isolated stem cells. Methods of use and kits containing the glycosaminoglycan composition and materials for isolating stem cells and for treating connective tissue damage and repair of cartilage in man and in animals are also provided.
Owner:ARTHRODYNAMIC HLDG LLC
Methods, compositions and systems for the prevention and treatment of diaper rash
InactiveUS20050079229A1Preventing and treatingPreventing or treating diaper rashCosmetic preparationsBiocideSkin treatmentsPhysiology
Provided by the invention are systems for applying diaper rash treatment compositions to a selected skin treatment area without the need for the person administering the treatment to directly contact the composition or the skin of the patient. Application of the diaper rash treatment composition is accomplished by forming the composition into a mist or spray using an atomizing spray dispenser.
Owner:SYSTAGENIX WOUND MANAGEMENT (US) INC
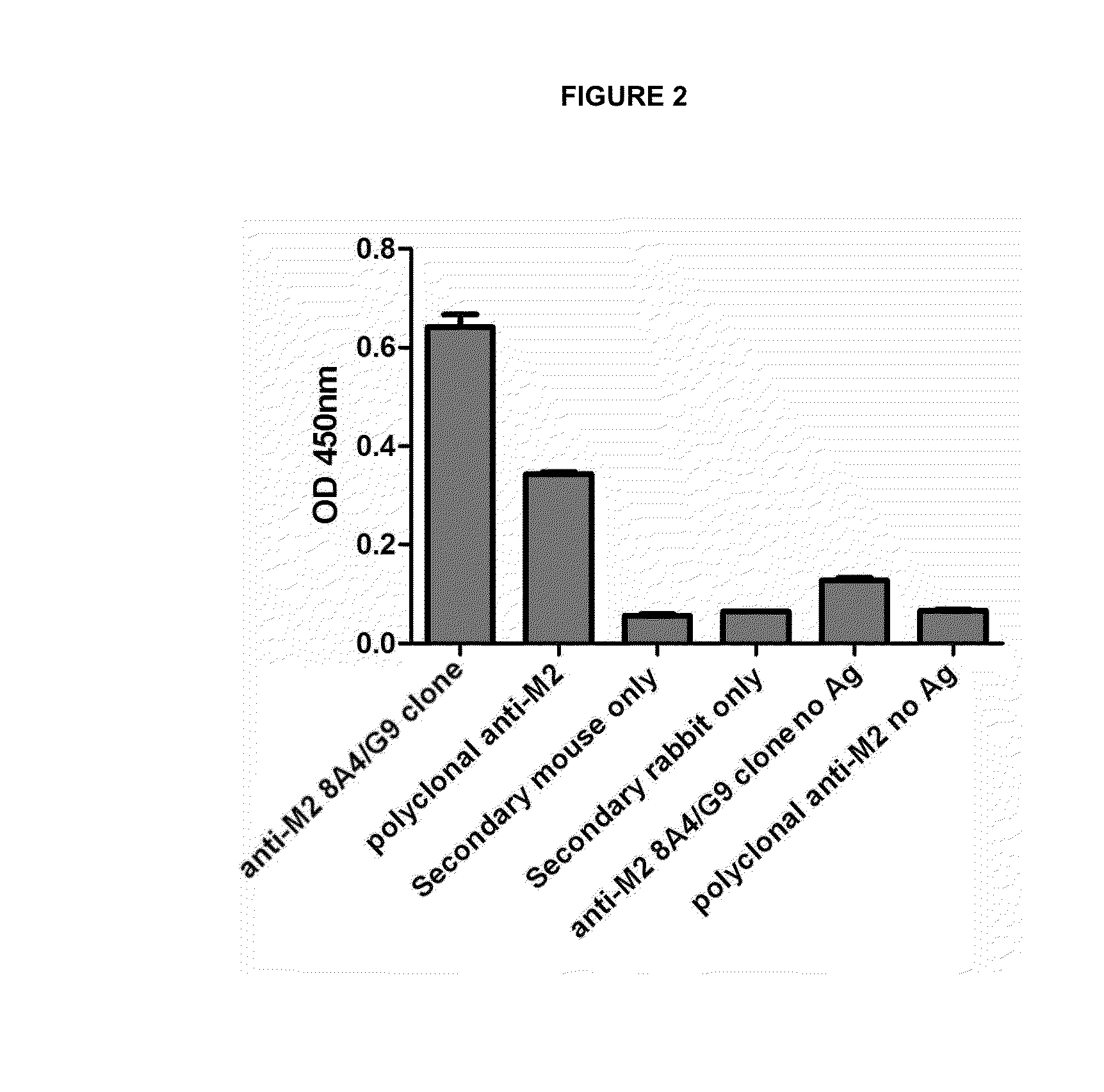
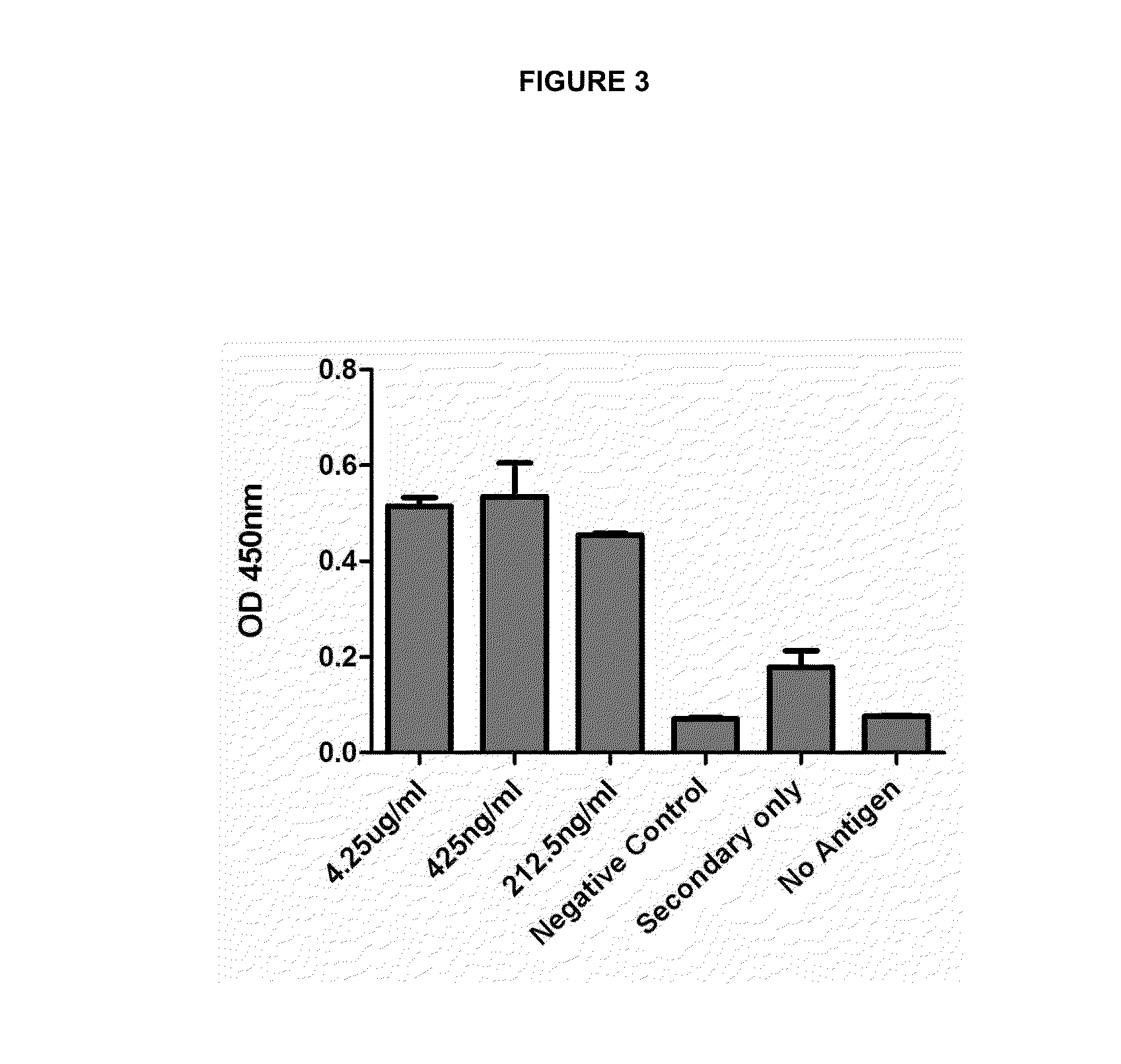
Monoclonal antibodies specific for the m2-1 antigen of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
ActiveUS20140348858A1Minimize the possibilityPreventing and treatingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementViral antigensDrug
The use of monoclonal antibodies specific for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Specifically, to a monoclonal antibody IgG2A secreted by the cell line of 8A4 / G9 hybridoma specifically directed to the M2-1 viral antigen, which is associated with the nucleocapside of the virus. The antibodies can be used for assays for the detection and / or determination of RSV infection. The antibodies are in the pure state and do not contain any other contaminating biological material. A method for preventing and treating the infection caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in a given host is provided, including the administration of a composition containing the monoclonal antibodies secreted by the 8A4 / G9 hybridoma in sufficient doses to prevent the disease. The antibody can be humanized in order to minimize the possibility of an immune response against the same in the patient. In addition, it can be used to obtain any pharmaceutical form of the formulation of the monoclonal antibodies secreted by the 8A4 / G9 hybridoma, which are suitable for the treatment or prevention of the disease caused by RSV. It also provides methods for detection and diagnosis of RSV viral antigens in biological samples using the monoclonal antibodies produced and secreted by cells of the 8A4 / G9 hybridoma.
Owner:PONTIFISIA UNIVERSIDAD KATOLIKA DE CHILE
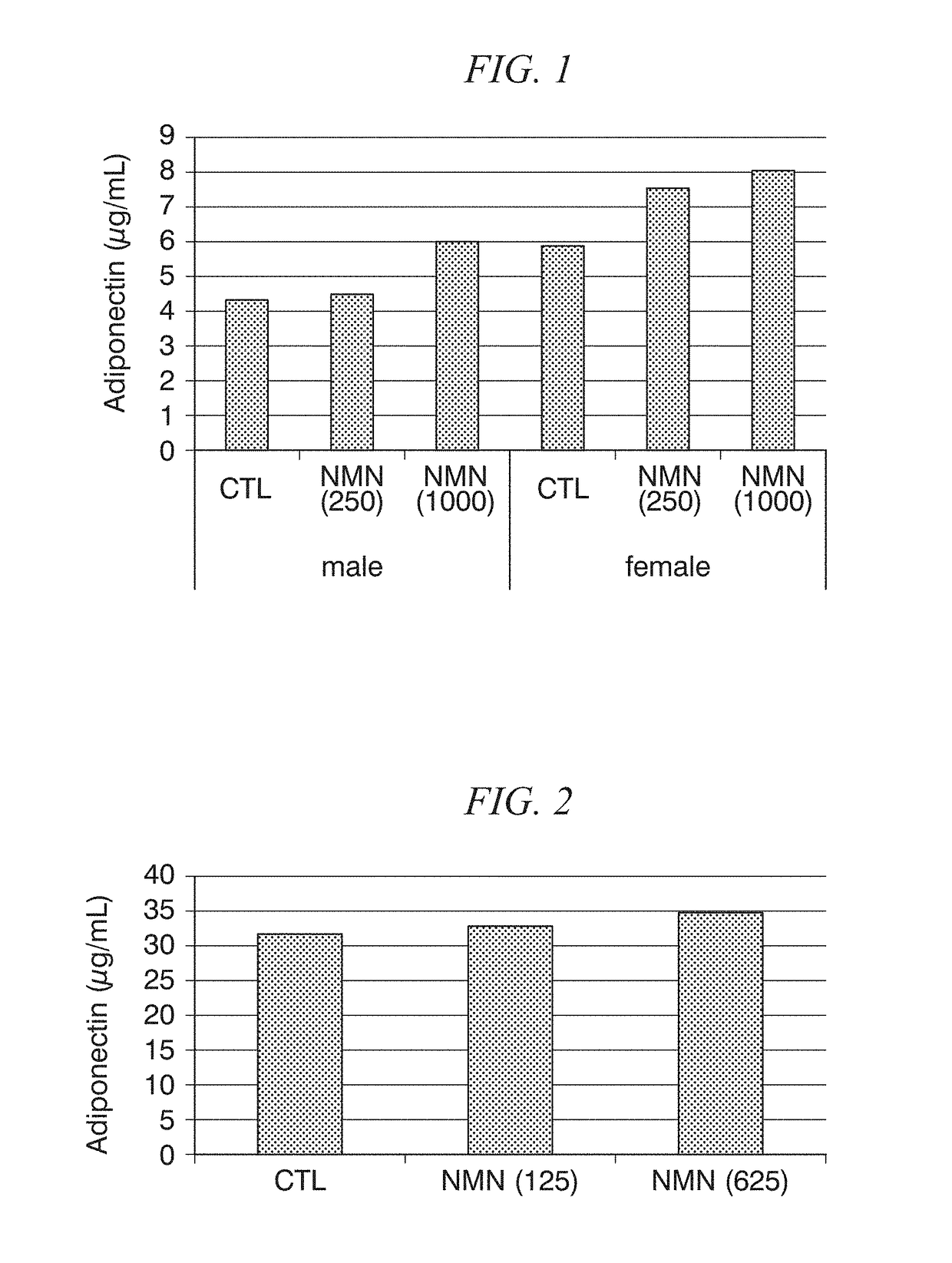
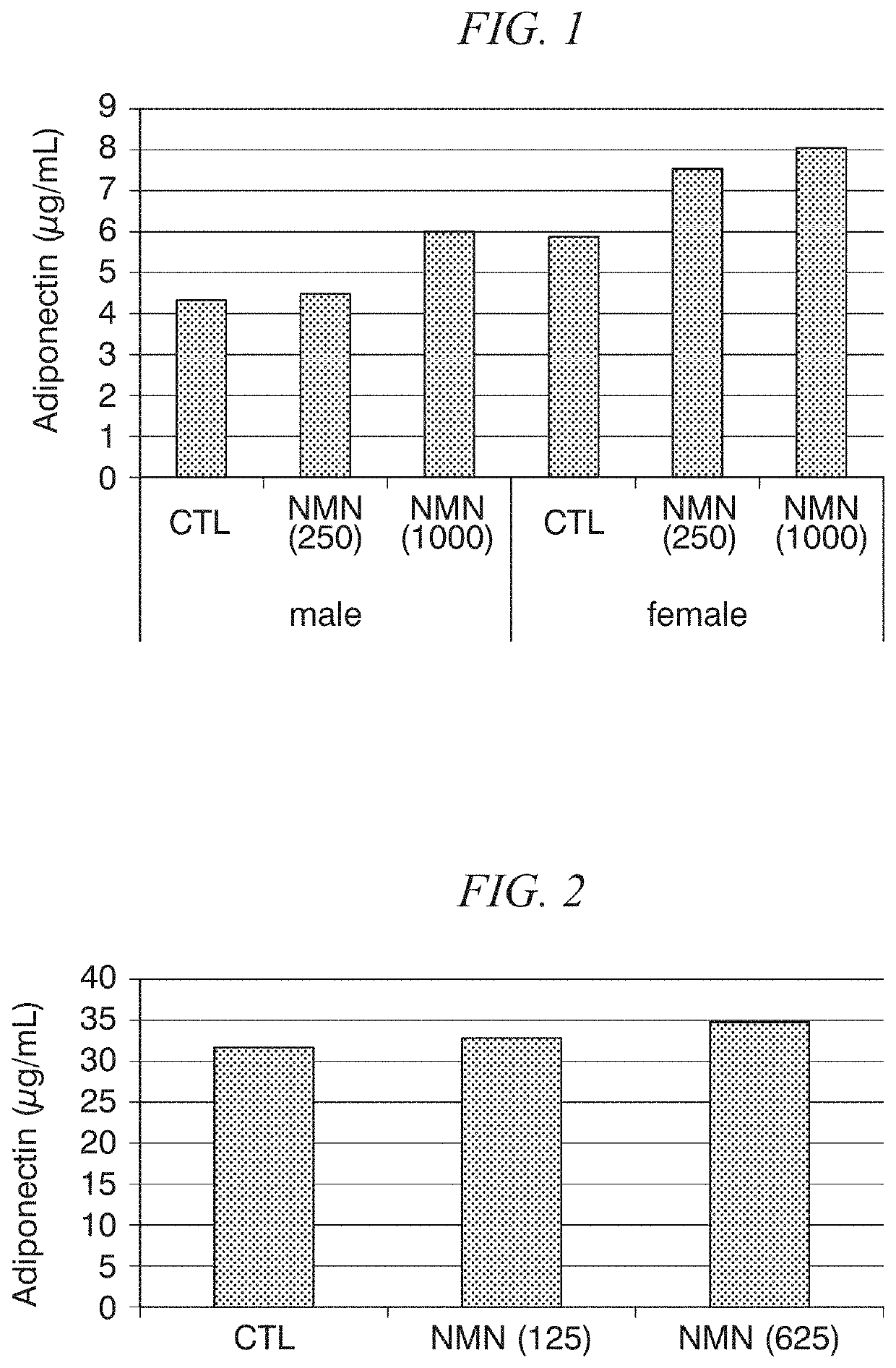
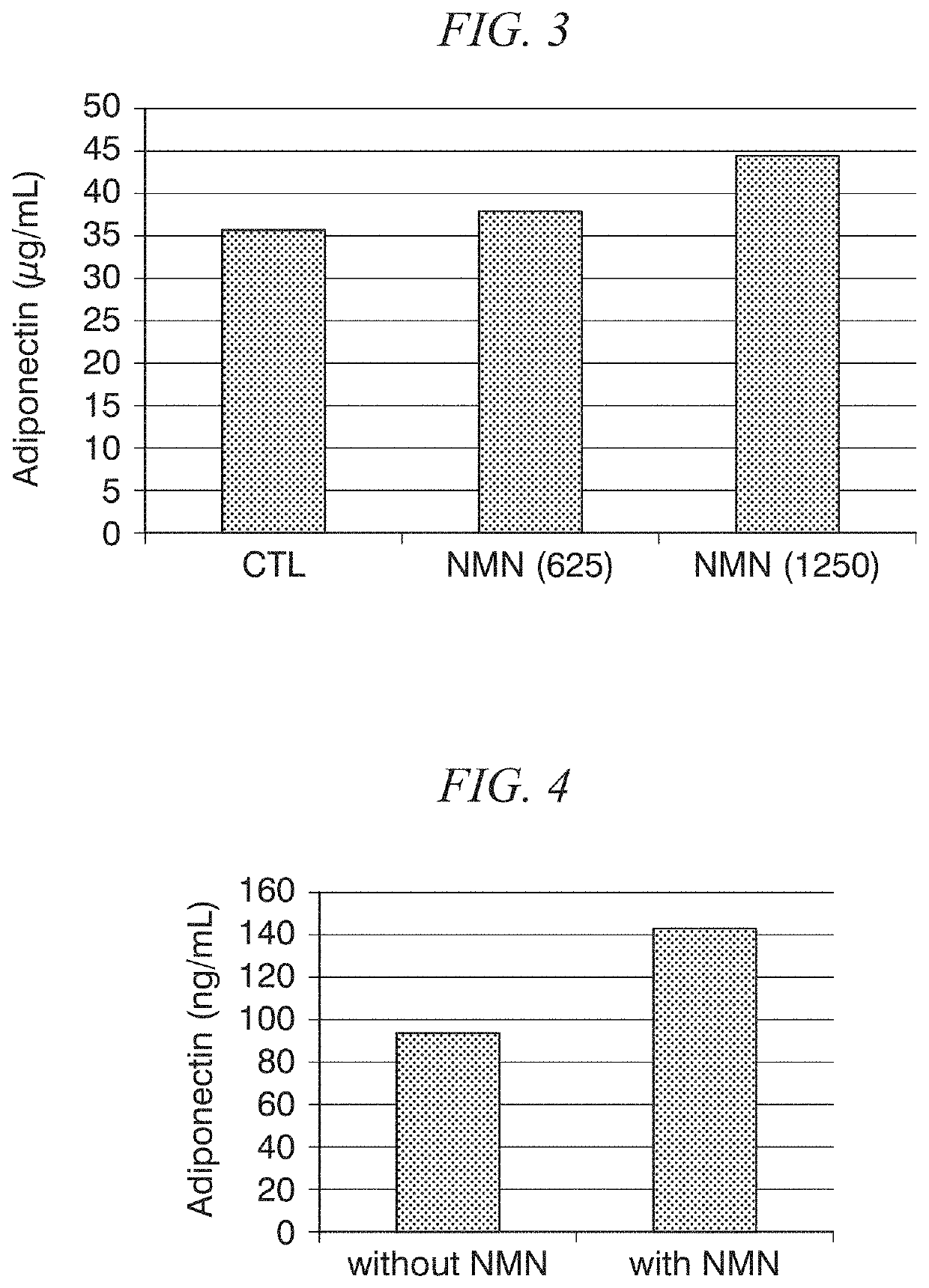
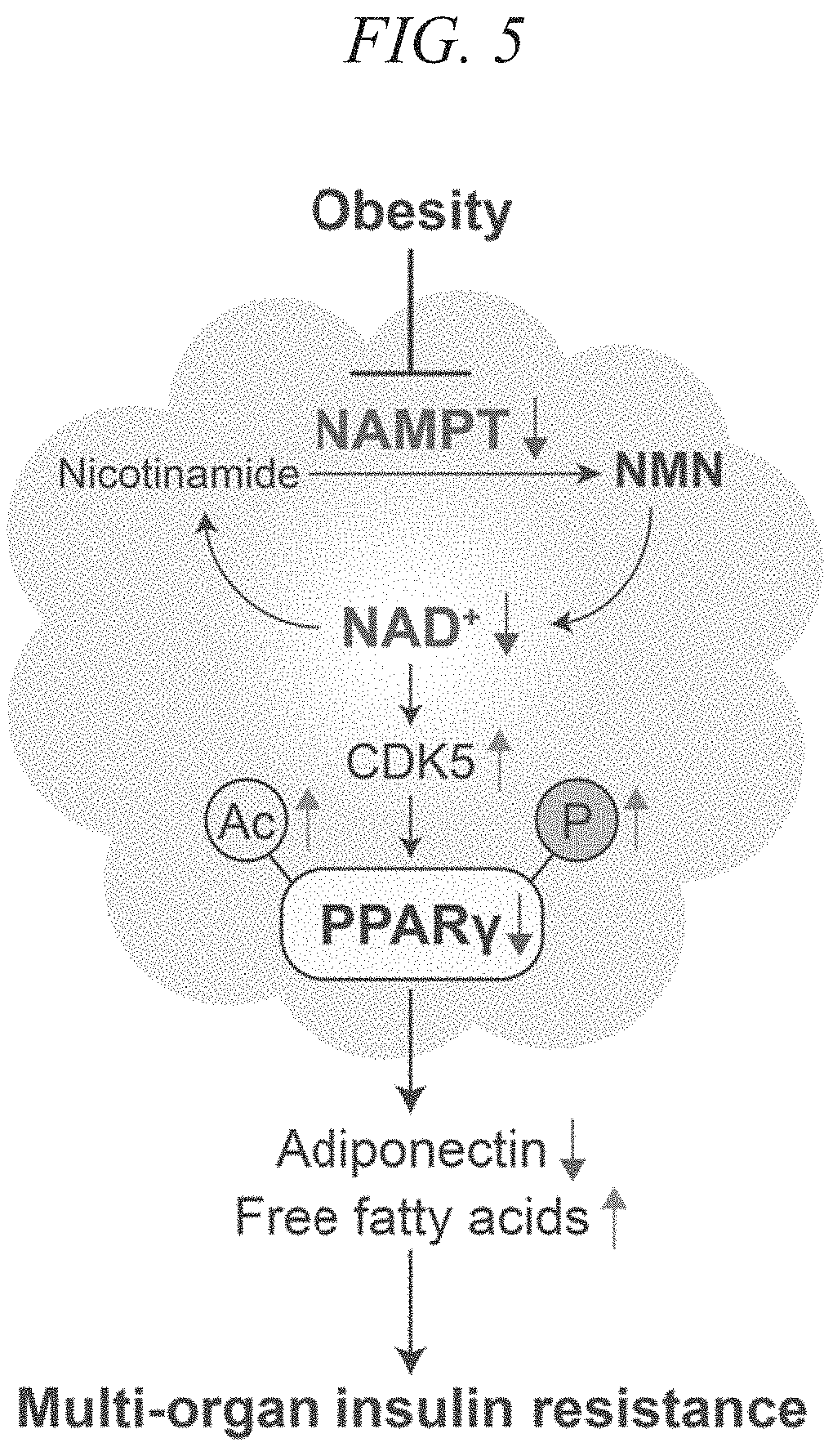
Adiponectin secretion enhancer
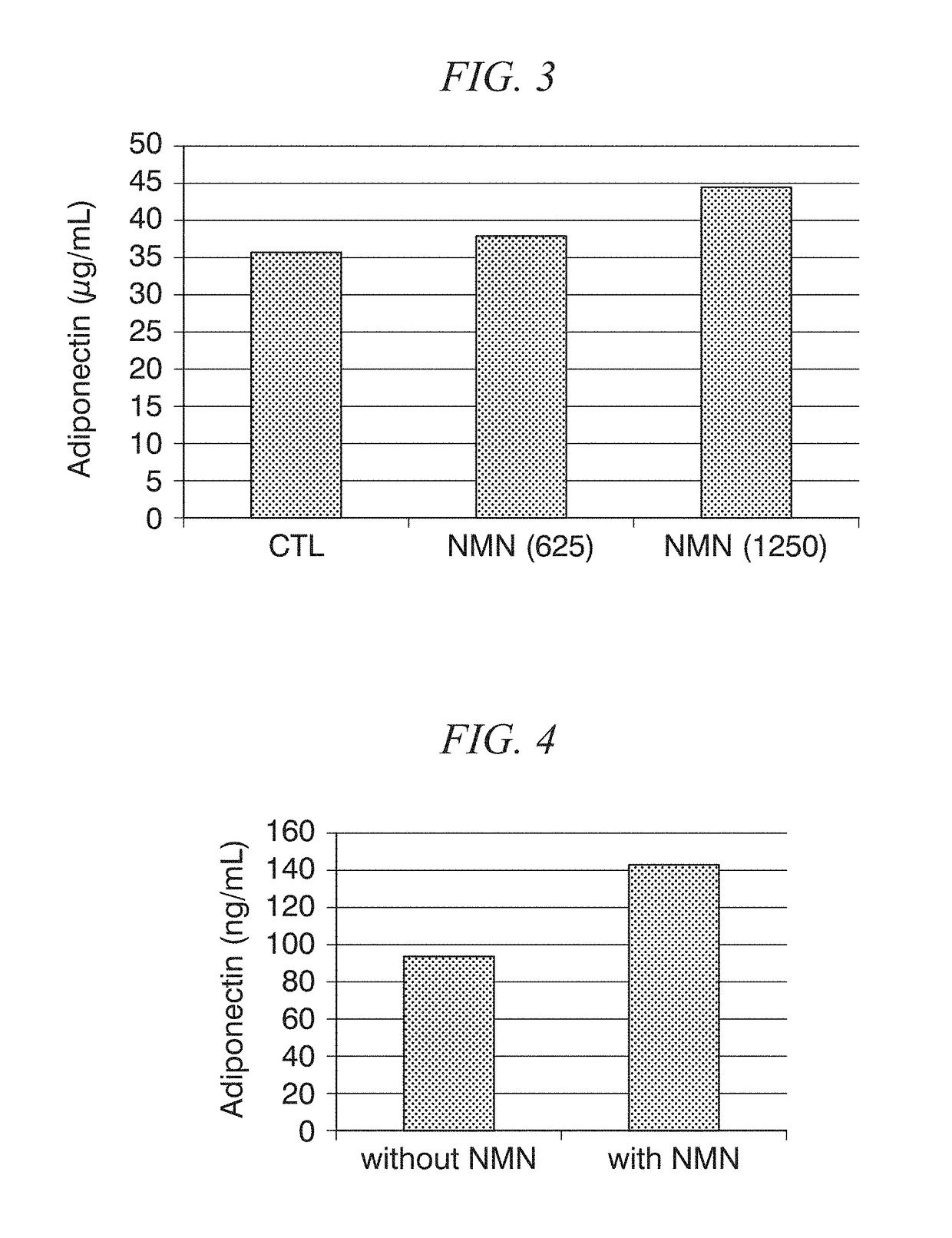
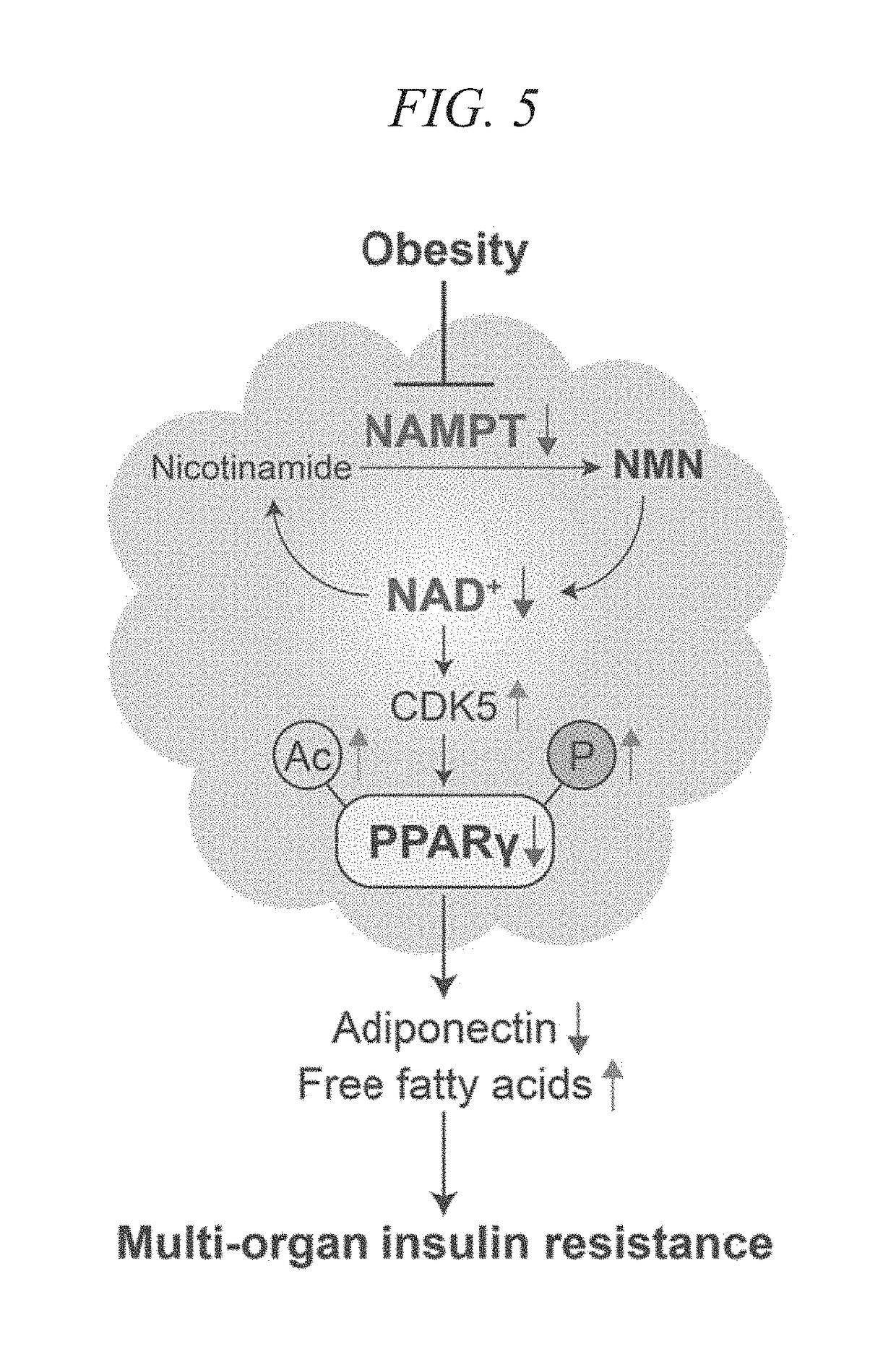
ActiveUS20180228824A1Increase secretionSafely ingestedCosmetic preparationsDispersion deliveryFatty liverDietary supplement
The present disclosure provides for the administration of β-NMN, which increases the secretion of adiponectin. The present disclosure also provides an adiponectin secretion enhancer comprising β-nicotinamide mononucleotide, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a solvate thereof, and a dietary supplement containing the aforementioned secretion enhancer, which can he ingested in order to increase the secretion of adiponectin. Also disclosed are methods of treating insulin resistance-related diseases such as of metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, fatty liver disease, hypertension, obesity, and arteriosclerosis.
Owner:ORIENTAL YEAST +1
Periplaneta americana extract or periplaneta americana medicinal powder as well as preparation method thereof and application in preparation for medicine used for preventing and treating radiation-induced damages
ActiveUS20170000829A1Preventing and treatingAvoid skin damageAnthropod material medical ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBreast tumoursLung cancer
The present invention provides an application of a periplaneta americana medicinal powder or a periplaneta americana extract in preparation for a medicine used for preventing and treating radiation-induced damages. The medicine is capable of preventing and treating the damages caused by radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, breast cancer, waldeyer's lymphoma, and other cancers. Through test verification, the medicine of the present invention has an obvious prevention and treatment effect for damages caused by radiation therapy for patients with breast tumours and breast cancer after surgery.
Owner:SICHUAN GOODDOCTOR PANXI PHARMA
Method for inhibiting yeast growth
InactiveUS20050271640A1Relieving yeast-related symptomInhibitory activityBiocideAntimycoticsYeastDisease
The invention relates to the use of microbes Lactobacillus rhamnosus LGG, ATCC 53103, Latobacillus rhamnosus LC705, DSM 7061, and Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp. shermanii PJS, DSM 7067 in inhibiting yeast growth, for preventing and treating diseases caused by yeast and for relieving yeast-related symptoms in animals or humans.
Owner:VALIO LTD
Anti-inflammatory method using gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogs
InactiveUS6887902B2Preventing and treatingEasy to prepareBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGabapentinDisease
GABA analogs such as gabapentin and pregabalin are useful to prevent and treat inflammatory diseases.
Owner:WARNER-LAMBERT CO +1
Method for preparing regulatory dendritic cells
InactiveUS20130052734A1Ensure large-scale productionEnsure safetyAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryCulture cellImmunology
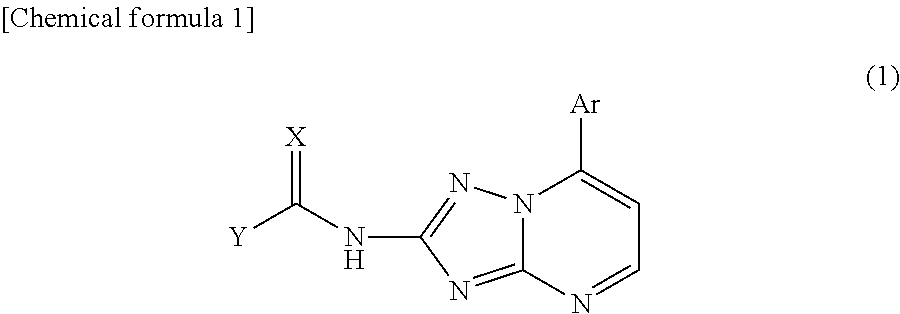
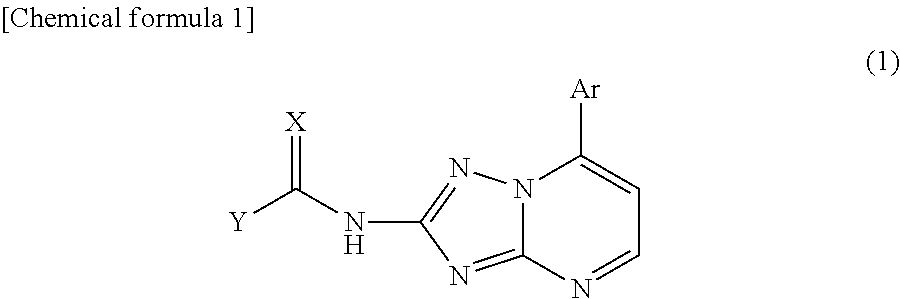
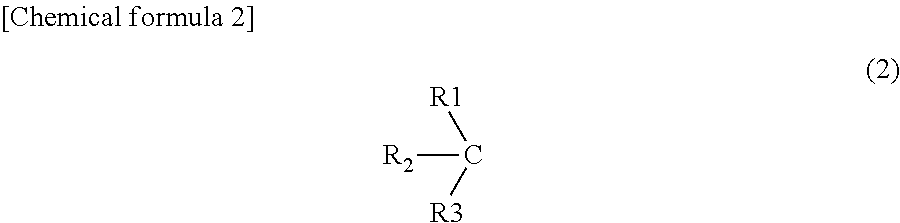
An object of the present invention is to establish a method that enables safe and convenient large-scale preparation of regulatory dendritic cells. The present invention provides a method for preparing regulatory dendritic cells, which comprises culturing cells that can be induced to result in regulatory dendritic cells in the presence of a [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivative.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD +1
Adiponectin secretion enhancer
ActiveUS10695360B2Increase secretionSafely ingestedCosmetic preparationsDispersion deliveryFatty liverDietary supplement
The present disclosure provides for the administration of β-NMN, which increases the secretion of adiponectin. The present disclosure also provides an adiponectin secretion enhancer comprising β-nicotinamide mononucleotide, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a solvate thereof, and a dietary supplement containing the aforementioned secretion enhancer, which can be ingested in order to increase the secretion of adiponectin. Also disclosed are methods of treating insulin resistance-related diseases such as of metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, fatty liver disease, hypertension, obesity, and arteriosclerosis.
Owner:ORIENTAL YEAST +1
Compositions with modified nucleases targeted to viral nucleic acids and methods of use for prevention and treatment of viral diseases
ActiveUS9592277B2Good antiviral effectPreventing and treatingHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsViral diseaseViral nucleic acid
Antiviral compositions comprising a modified nuclease, or a plurality of such modified nucleases having at least one non-natural amino acid residue substituted for a naturally occurring amino acid in a parent nuclease are provided, as are methods of use and kits providing unit dosages of such compositions.
Owner:NANONASE INC
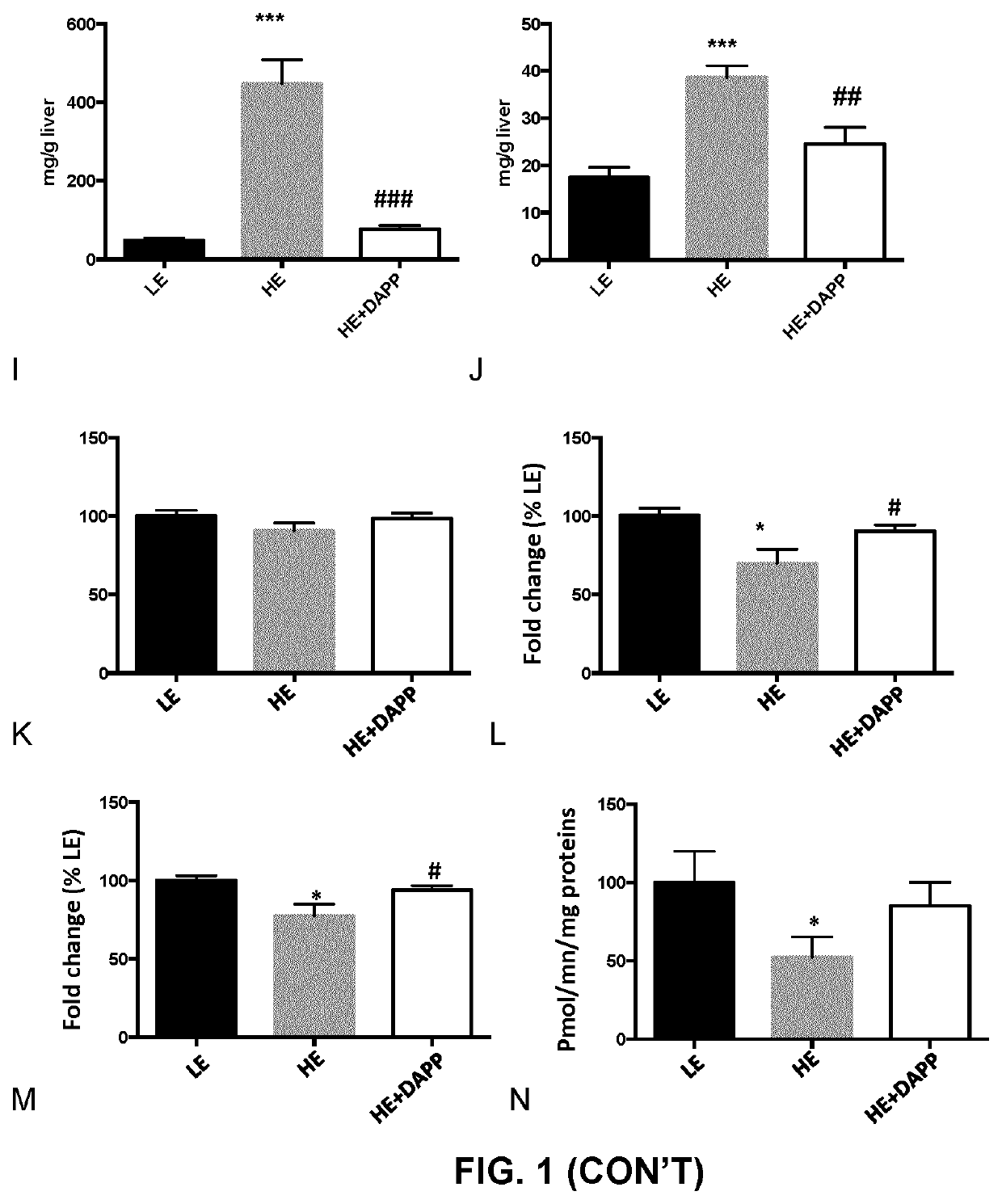
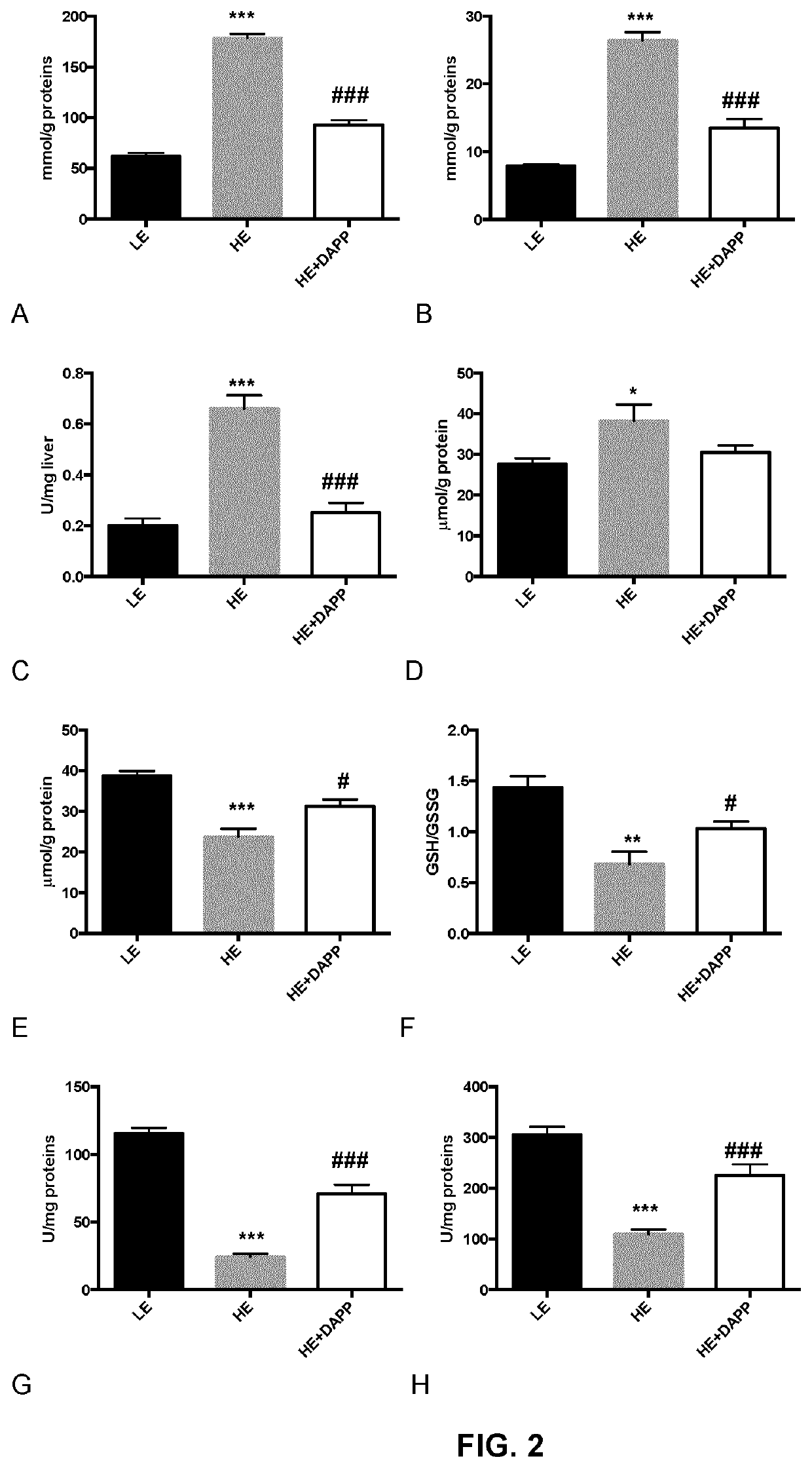
Apple peel polyphenol extract for the prevention and the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
PendingUS20220000959A1Avoid accumulationPreventing and treating insulin resistanceOrganic chemistryDigestive systemApple peelPancreatic hormone
The present document describes apple peel polyphenolic extract comprising a proanthocyanidin content of at least 15000 μg / g of dry weight, comprising about 30% to about 35% epicatechin content, and pharmaceutical composition comprising the apple peel polyphenolic extract. The present document also describes methods and use of the apple peel polyphenolic extract for preventing or treating conditions such as oxidative stress, inflammation and mitochondrial dysfunction of the liver, insulin resistance, intestinal endothelial tissue injury, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, and / or inhibition of de novo lipogenesis and β-oxidation of free fatty acids for preventing accumulation thereof in the liver. The present document also describes a process for extraction of at least a polyphenol content from dry apple peel powder.
Owner:LEAHY ORCHARDS
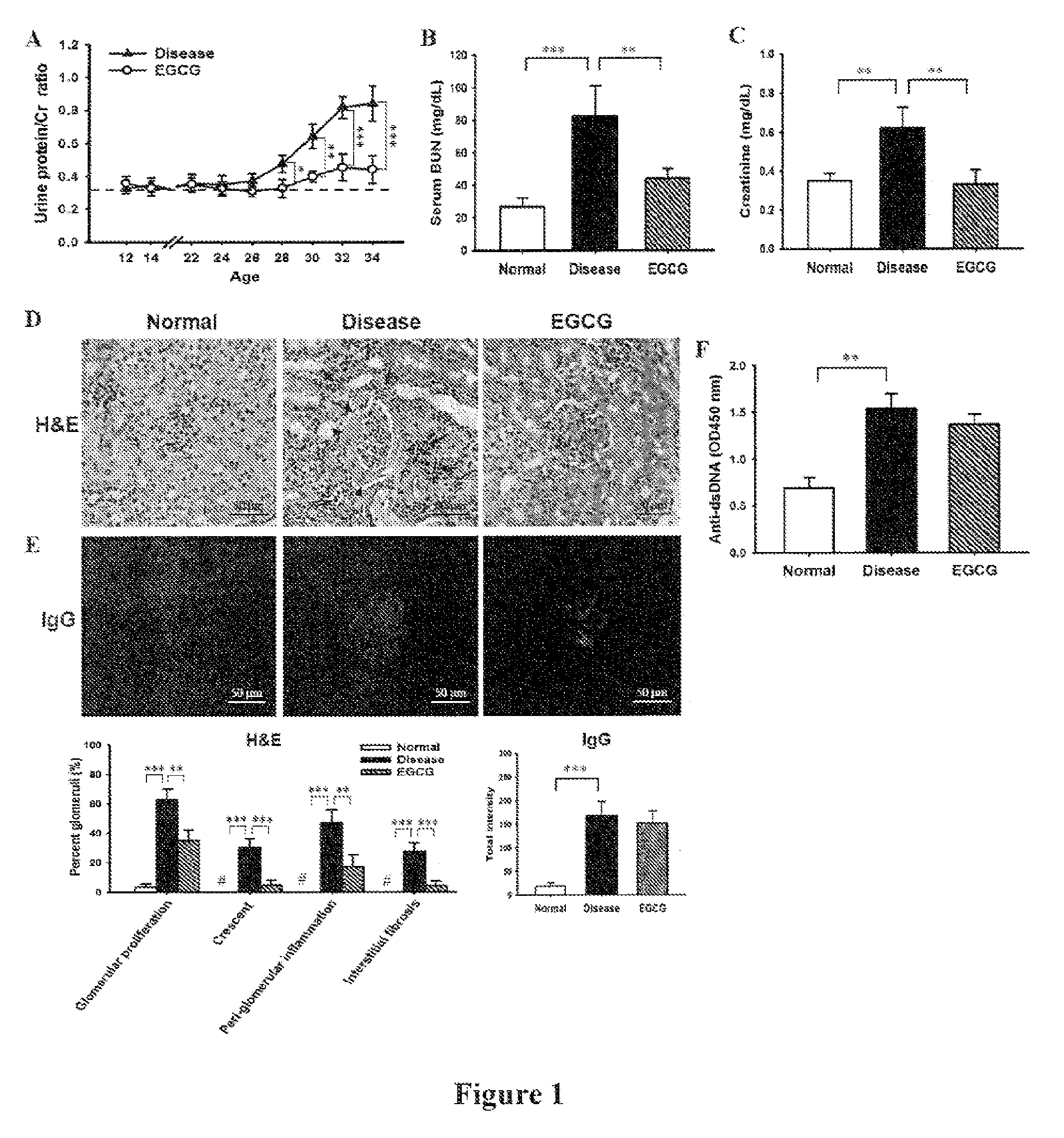
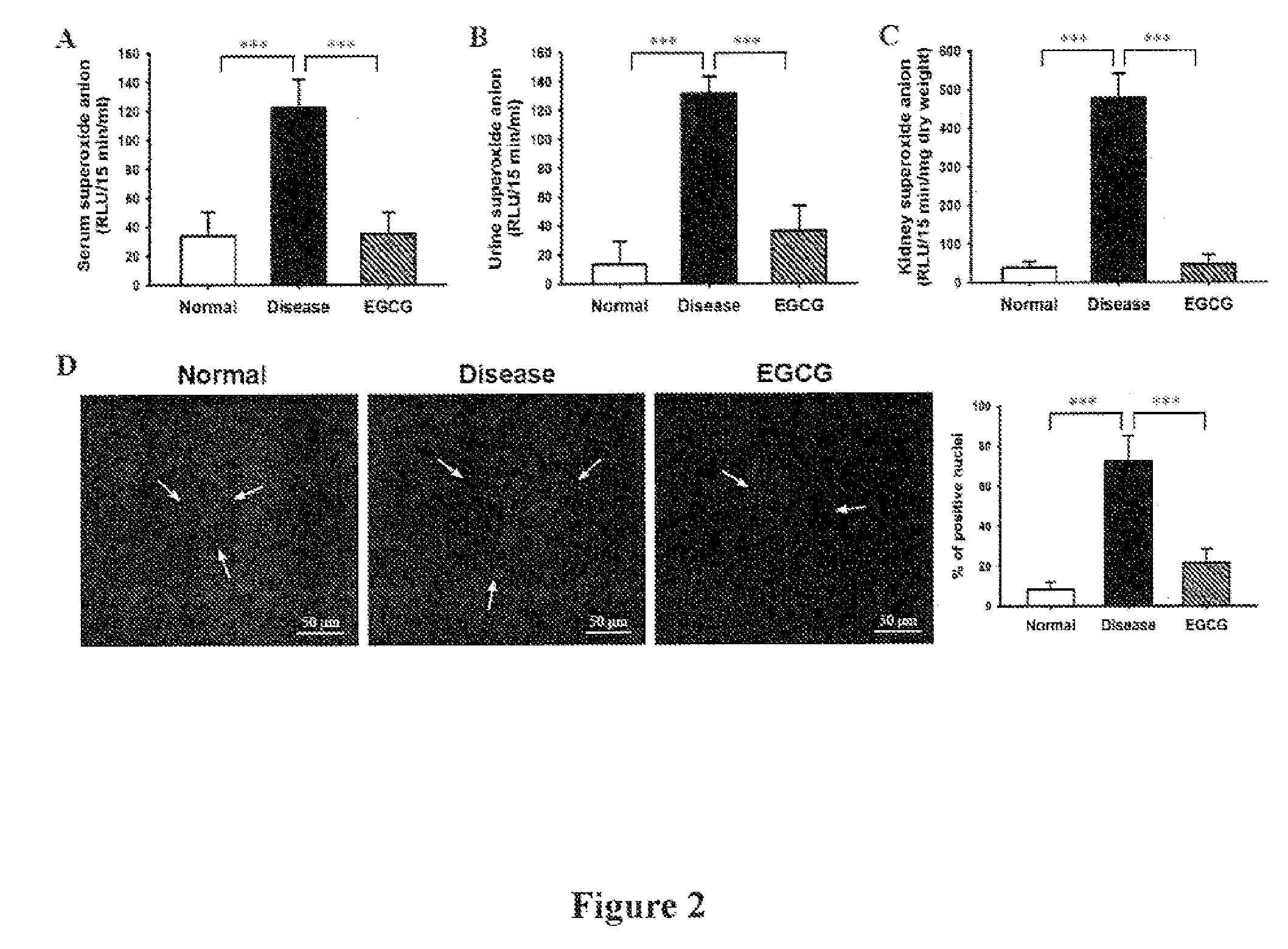
Use of epigallocatechin-3-gallate for immune regulation
InactiveUS20120309821A1Preventing and treatingAvoid developmentBiocideSkeletal disorderDiluentGallate
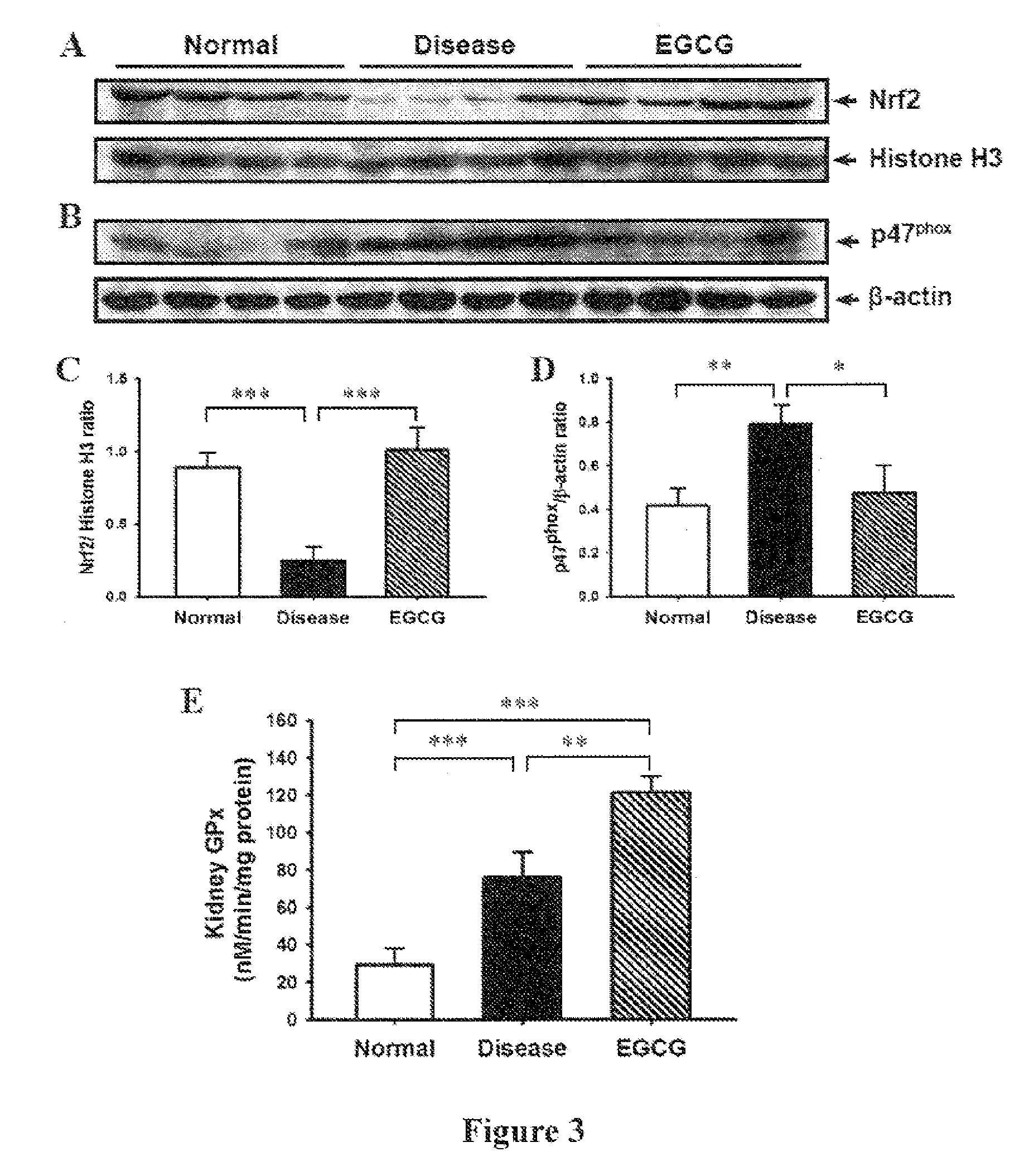
The preset invention relates to a method for treating lupus erythematosus, particularly lupus nephritis, comprising administering a subject in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or a physiologically functional derivative, together with one or more pharmaceutically acceptable carriers, diluents or excipients.
Owner:NAT DEFENSE MEDICAL CENT
Glycosaminoglycan compositions in combination with stem cells
ActiveUS9186375B2Improve efficiencyPreventing and treatingSuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsMedicineN Acetyl D Glucosamine
A pharmaceutical preparation for treating connective tissue damage in man and in animals, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a glycosaminoglycan composition comprising chondroitin sulfate, N-acetyl D-glucosamine, and hyaluronan, in combination with isolated stem cells. Methods of use and kits containing the glycosaminoglycan composition and materials for isolating stem cells and for treating connective tissue damage and repair of cartilage in man and in animals are also provided.
Owner:ARTHRODYNAMIC HLDG LLC
Induction of Arteriogenesis
InactiveUS20140057977A1Prevent diseaseReduce infarct sizeBiocideInorganic active ingredientsNo donorsSurgery
The present invention inter alia relates to a method of promoting collateral circulation comprising the step of exposing a subject to a therapeutically effective amount of an NO donor wherein the therapeutically effective amount of the NO donor promotes arteriogenesis sufficient to augment collateral circulation in a physiological or pathological condition.
Owner:DESMOID
Induction of arteriogenesis
InactiveUS20160367512A1Effective toolPreventing and treatingInorganic active ingredientsNitro compound active ingredientsNo donorsSurgery
The present invention inter alia relates to a method of promoting collateral circulation comprising the step of exposing a subject to a therapeutically effective amount of an NO donor wherein the therapeutically effective amount of the NO donor promotes arteriogenesis sufficient to augment collateral circulation in a physiological or pathological condition.
Owner:DESMOID
Method of preventing and treating brain infarction
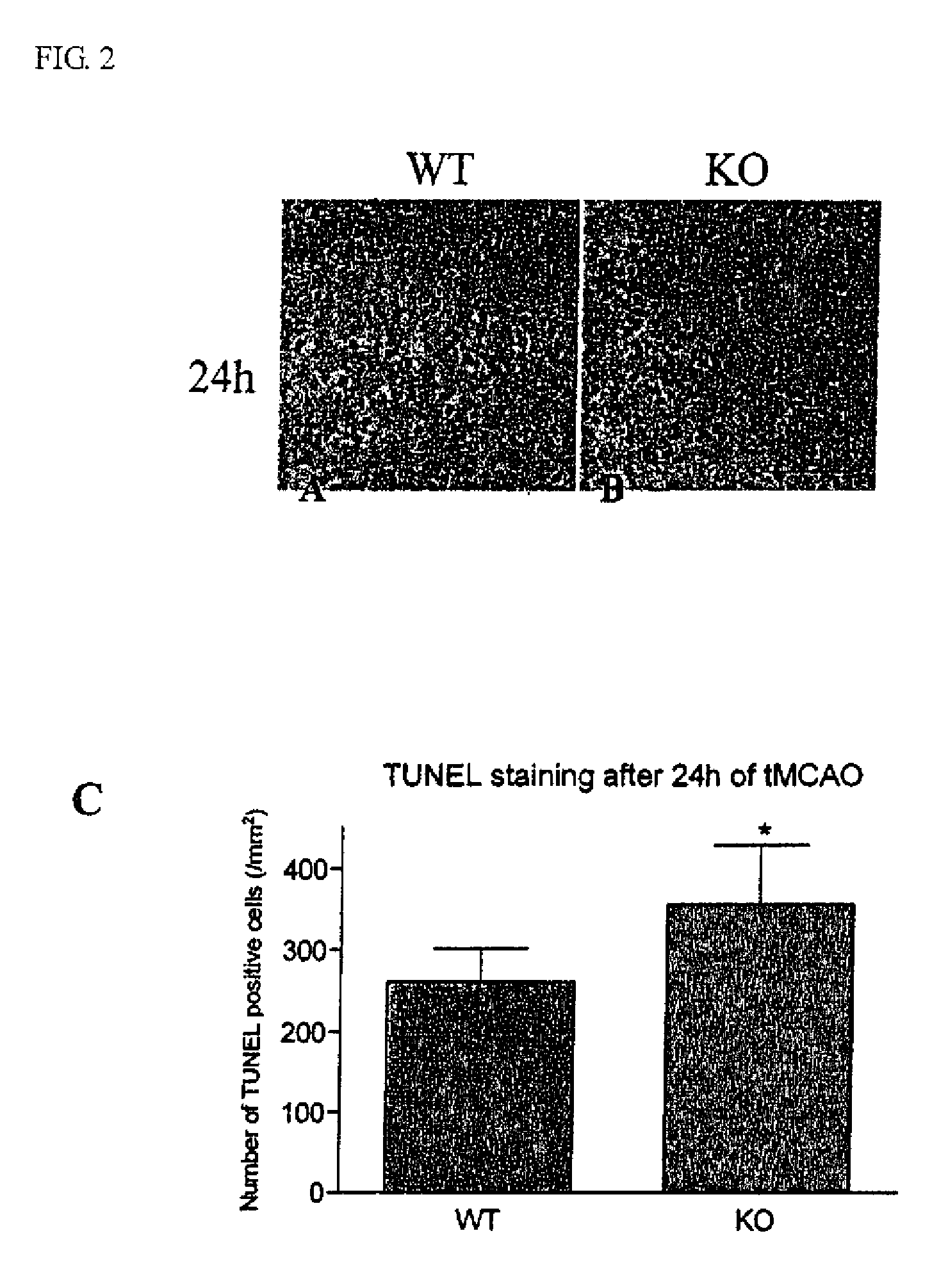
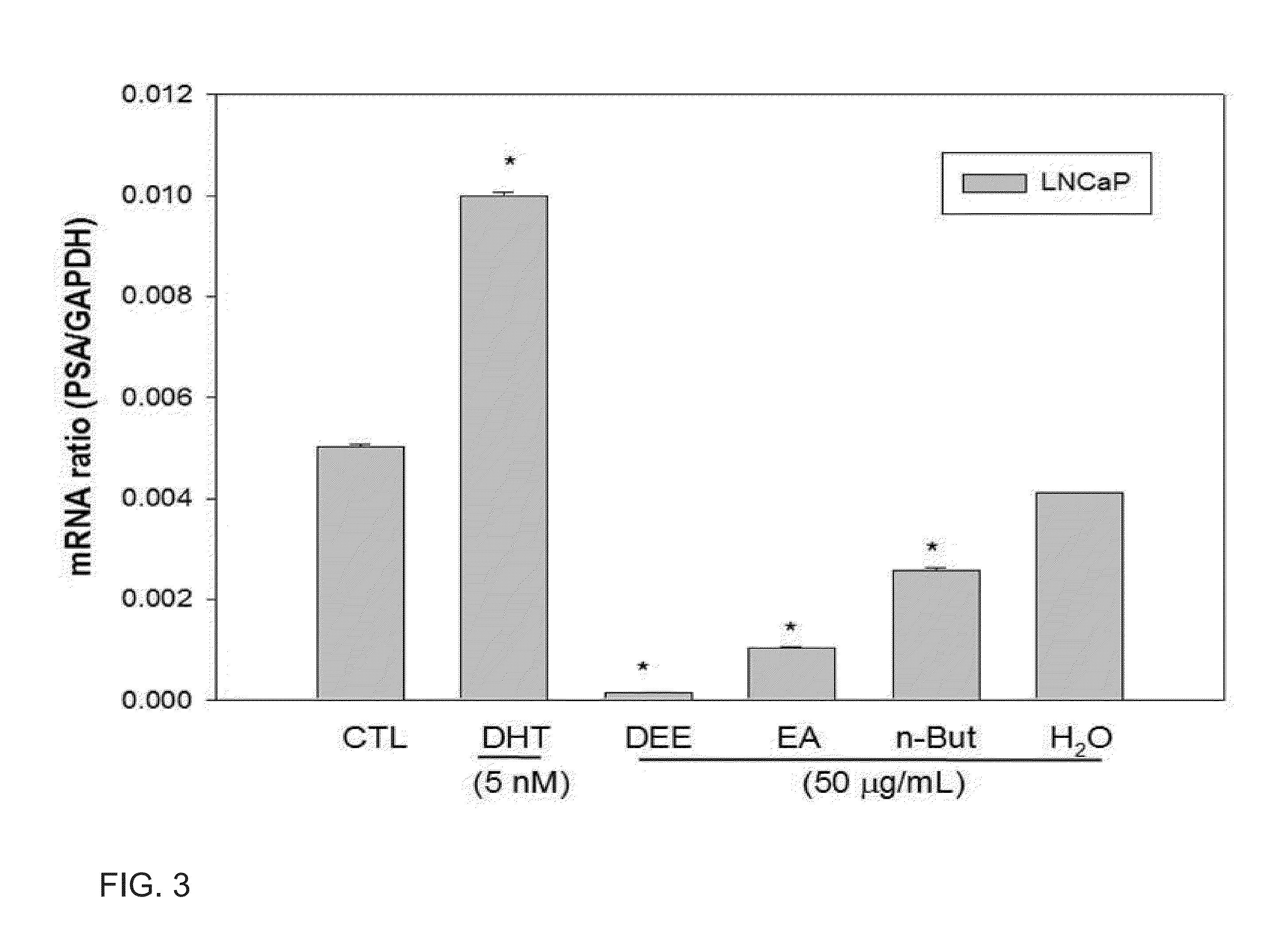
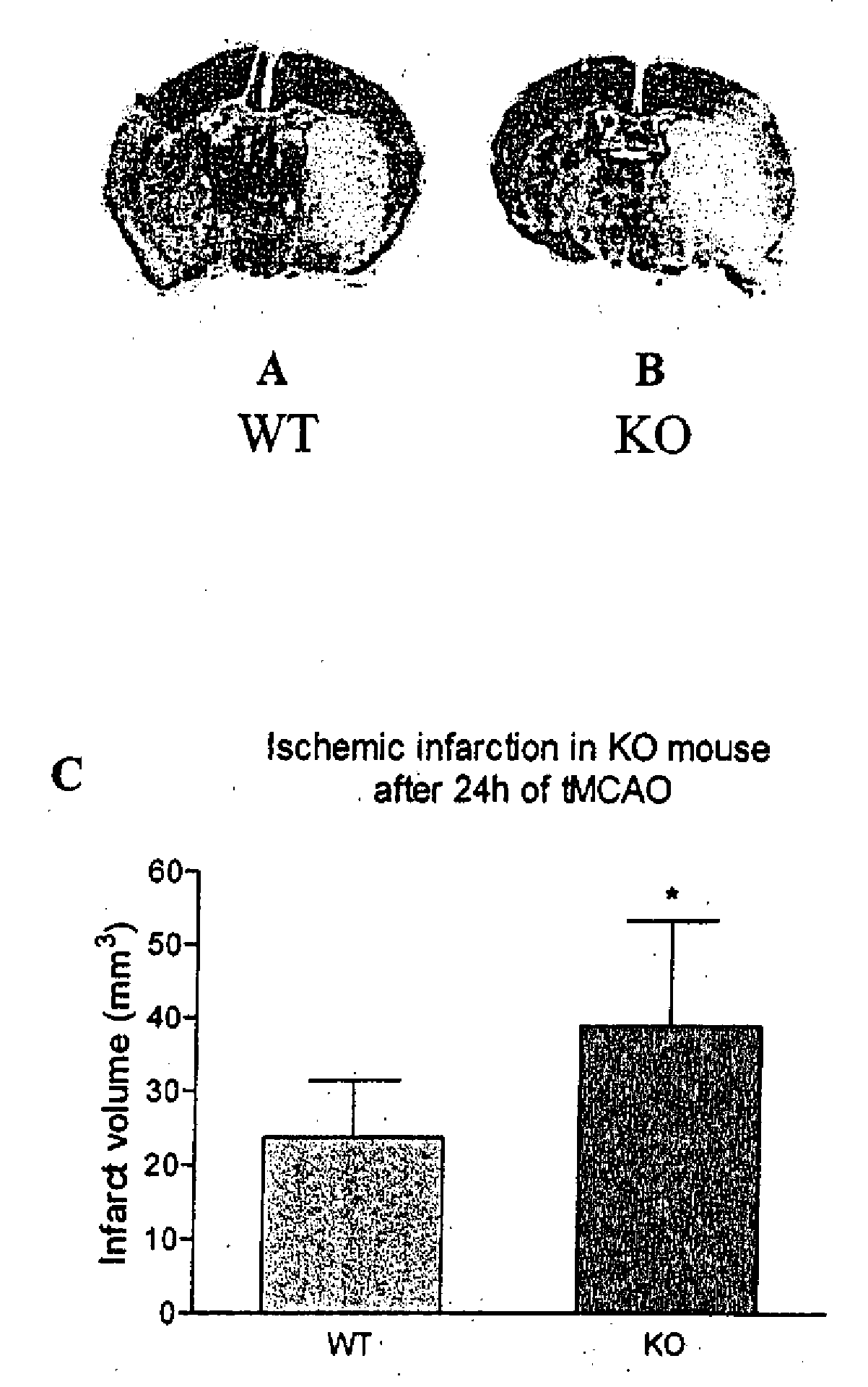
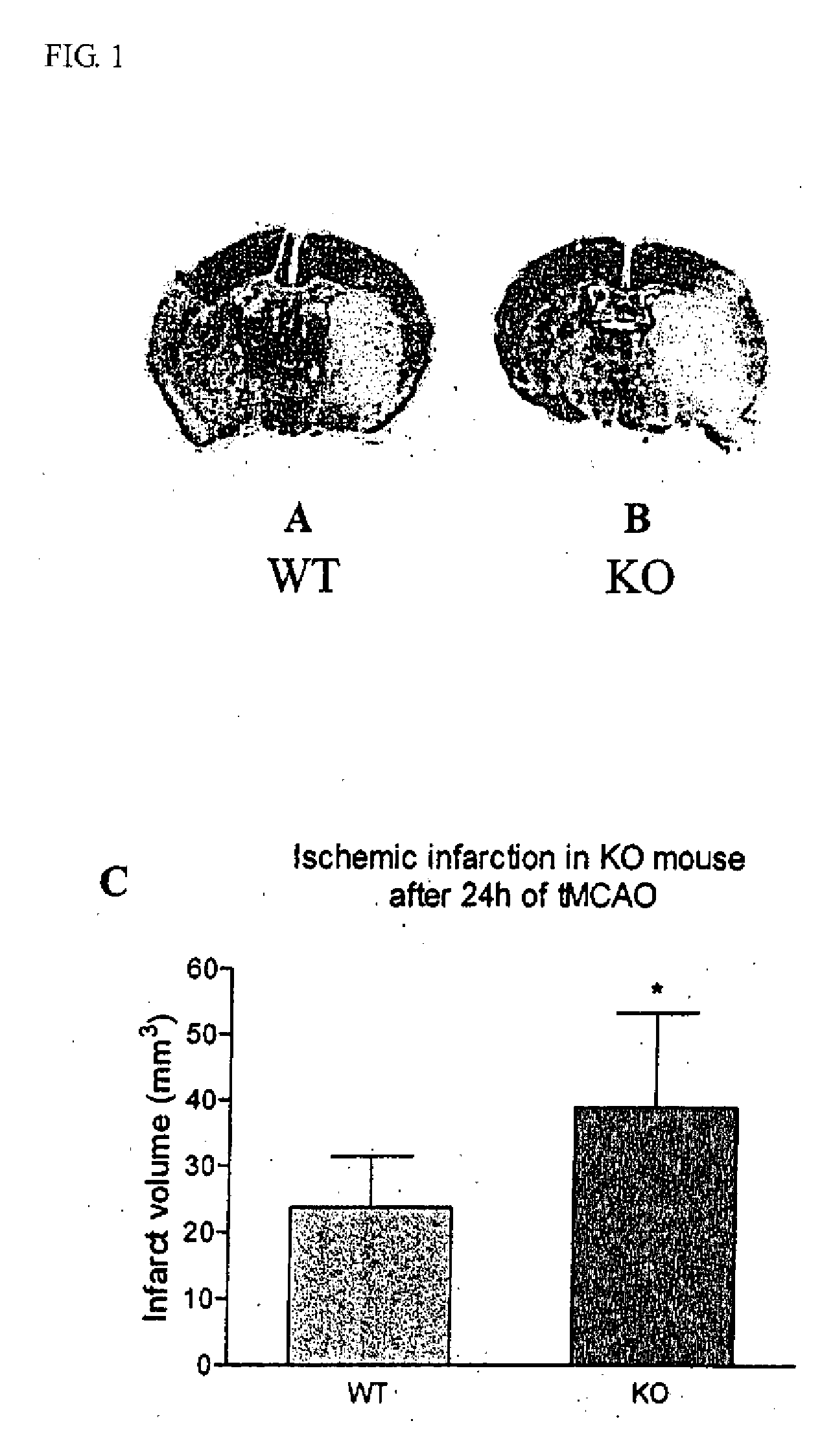
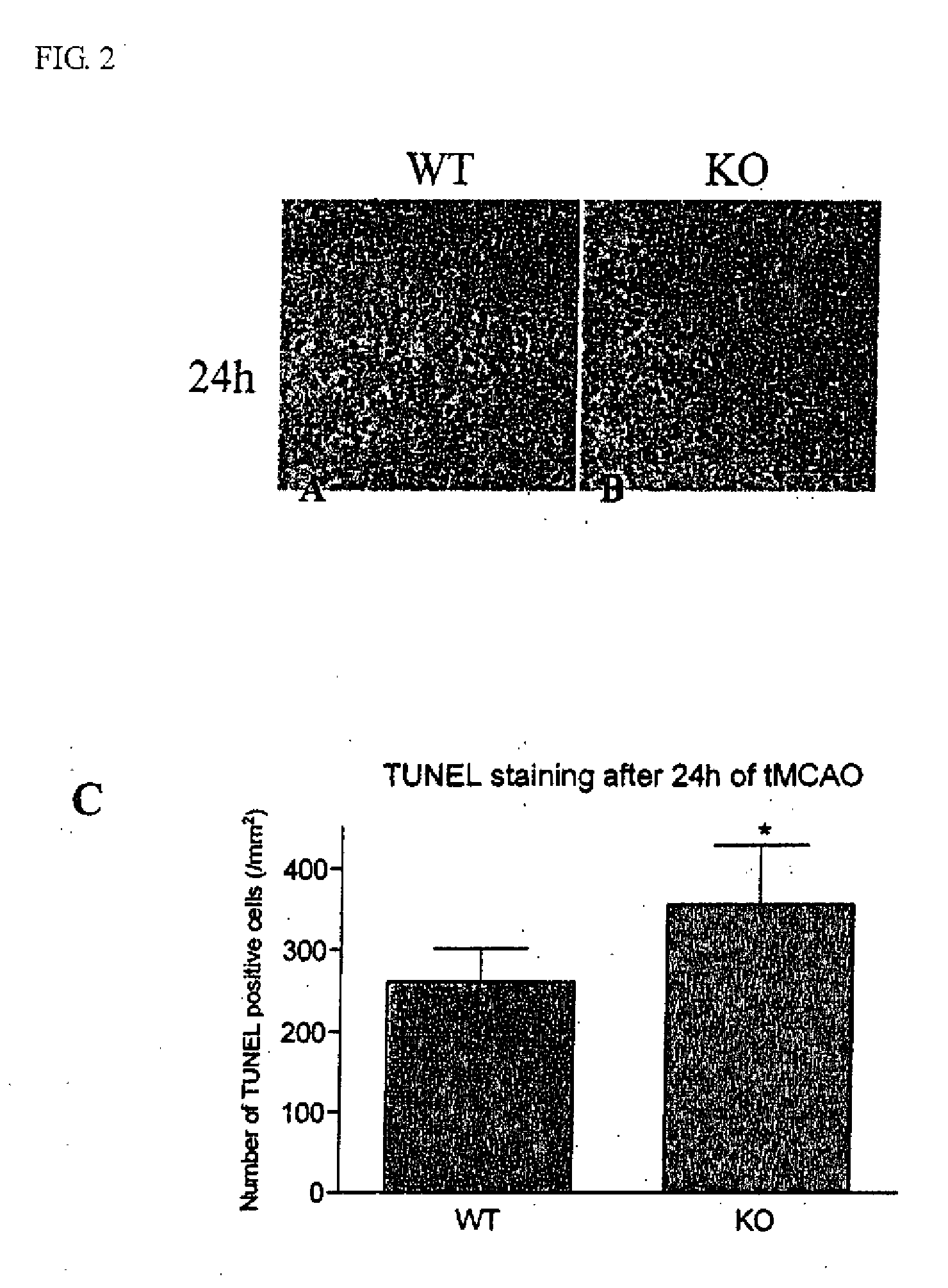
InactiveUS7976837B2Blockage and infarctionPreventing andNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAcute cerebral infarctionBiological activation
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
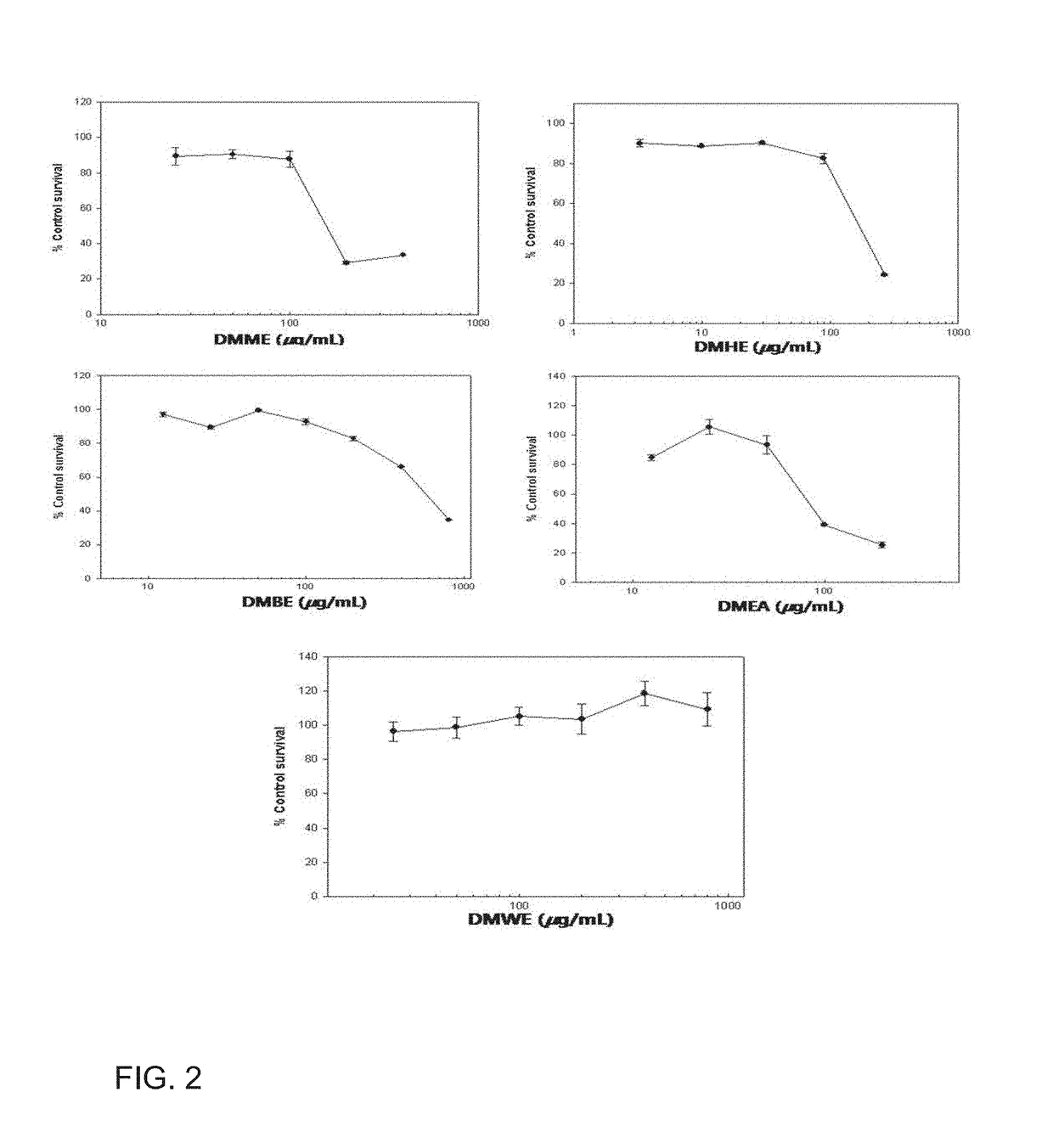
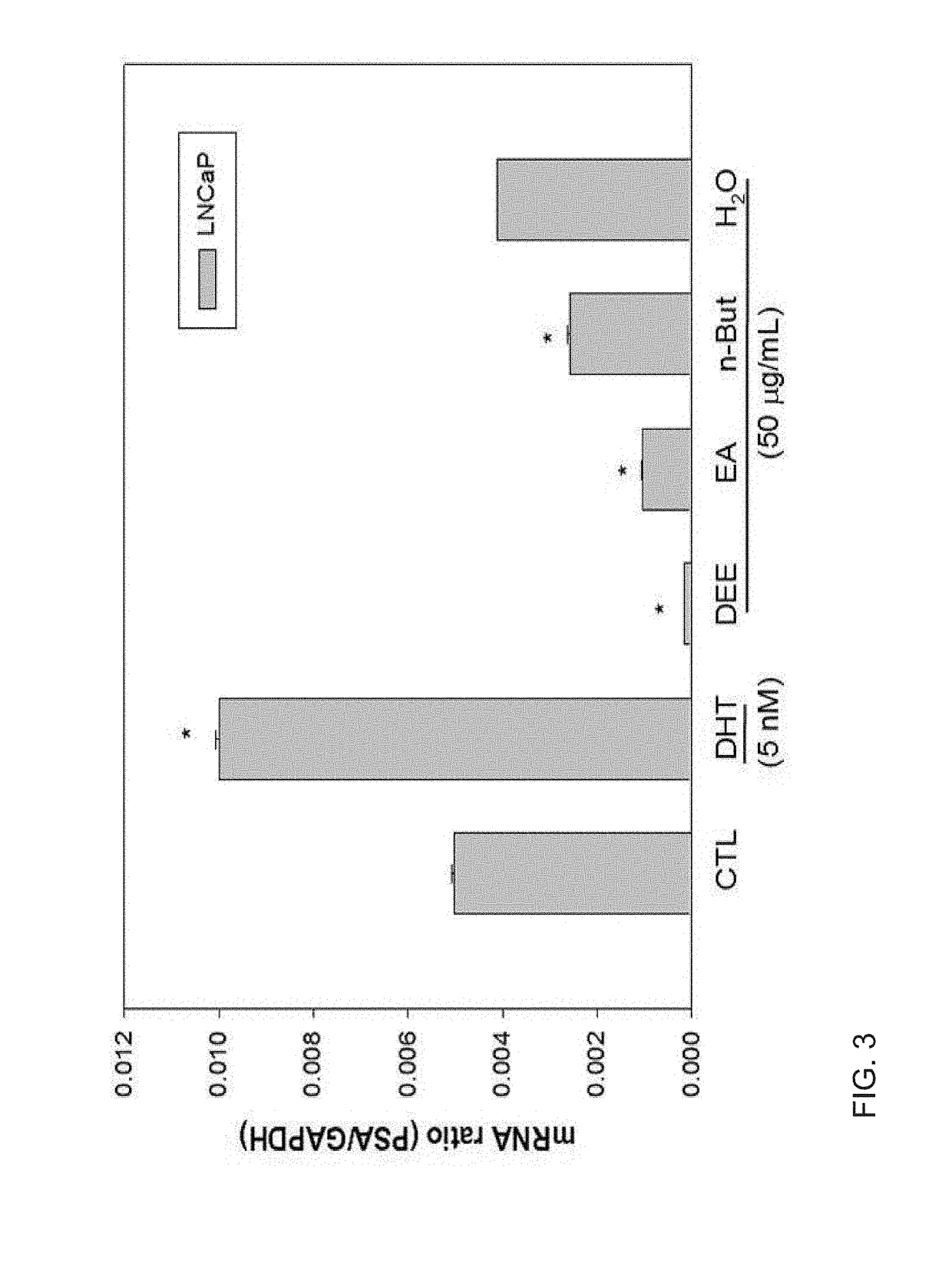
Composition comprising Dendropanax morbifera extract or compound derived therefrom as active ingredient for preventing and treating benign prostatic hyperplasia
ActiveUS10130668B2Preventing and relieving benign prostatic hyperplasiaPreventing and treatingUrinary disorderPlant ingredientsAdditive ingredientBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Composition for prevention or treatment of neurodegenerative disease
InactiveUS20210220340A1Preventing and treatingEasy to useNervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsSide effectAmyloid beta
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treatment of neurodegenerative disease, a composition employing amlexanox, which has been verified for safety through clinical trials. In addition, the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treatment of amyloid beta-caused cell damage, the composition employing a phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor inclusive of amlexanox. The composition of the present invention can be advantageously and safely used for ameliorating or treating amyloid beta-caused neurodegenerative disease and cell damage, without worry about side effects.
Owner:THE ASAN FOUND +1
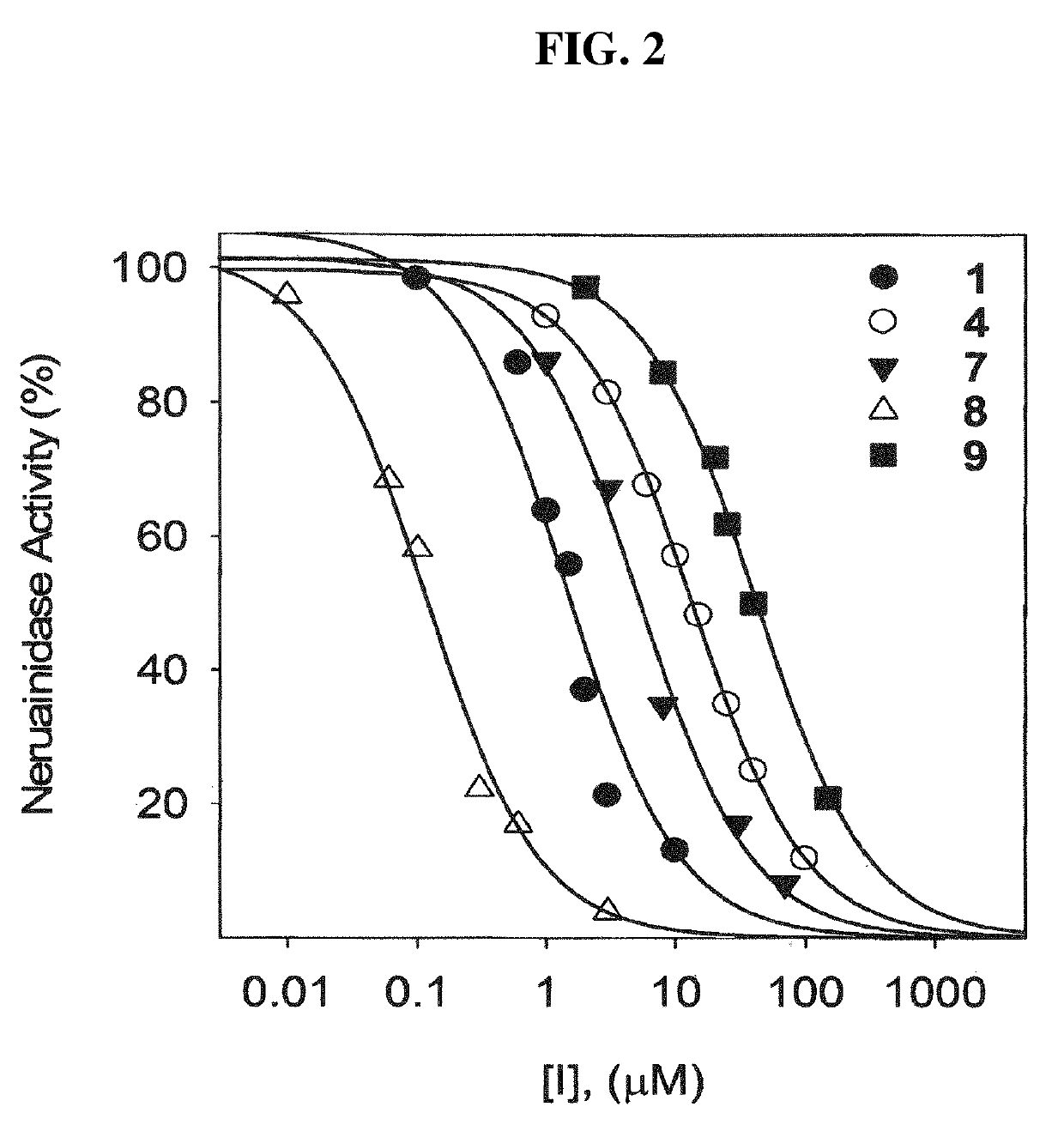
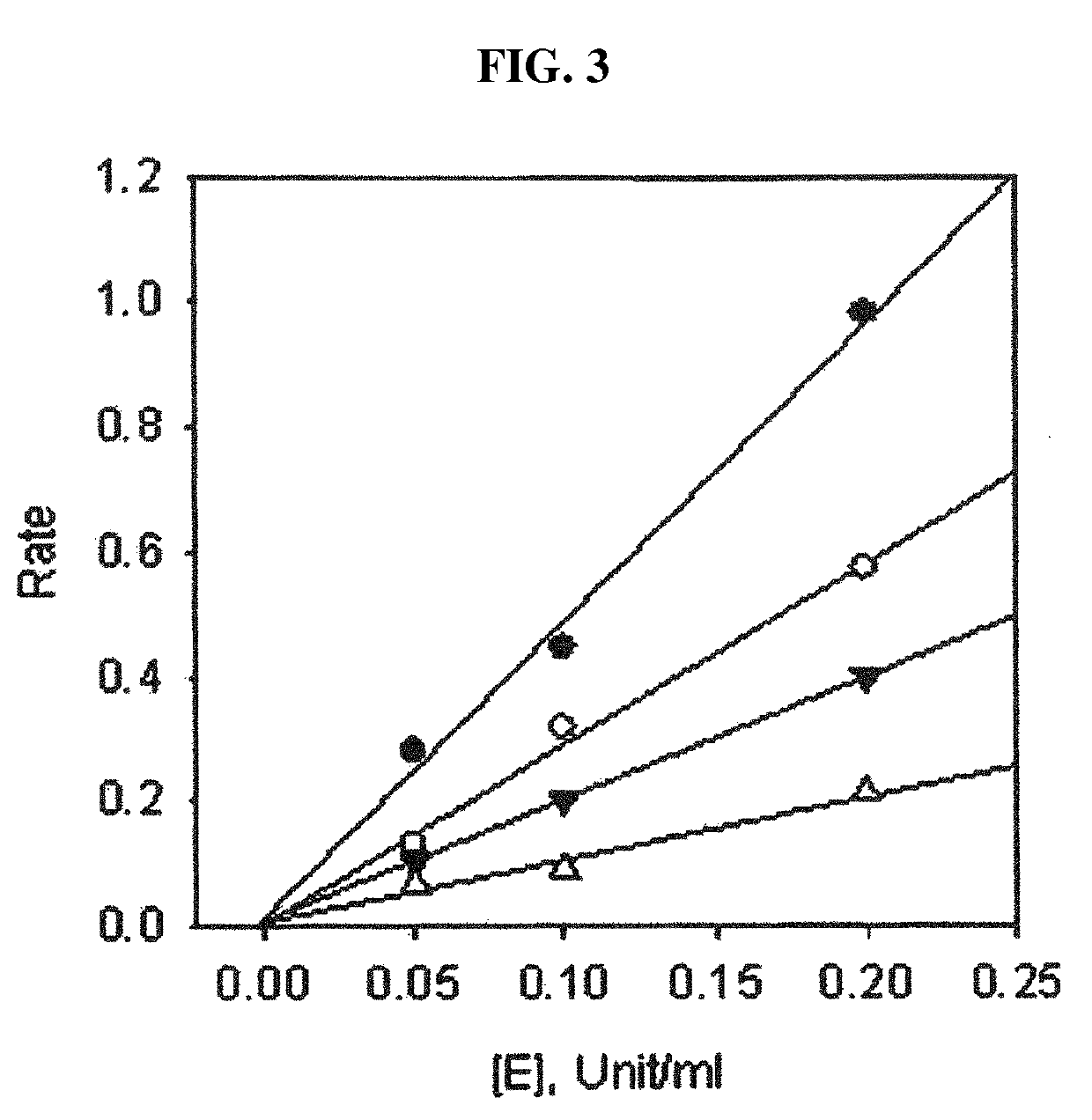
Composition for suppressing neuraminidase activity comprising geranylated flavonoid derived from Paulownia tomentosa as active ingredient
ActiveUS10406136B2Inhibitory activitySignificant inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTPaulownia tomentosa
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND GYEONGSANG NAT UNIV +1
Compounds for treatment of hepaci virus infection and method for determining therapy of hepaci virus infection, in particular, hcv infection
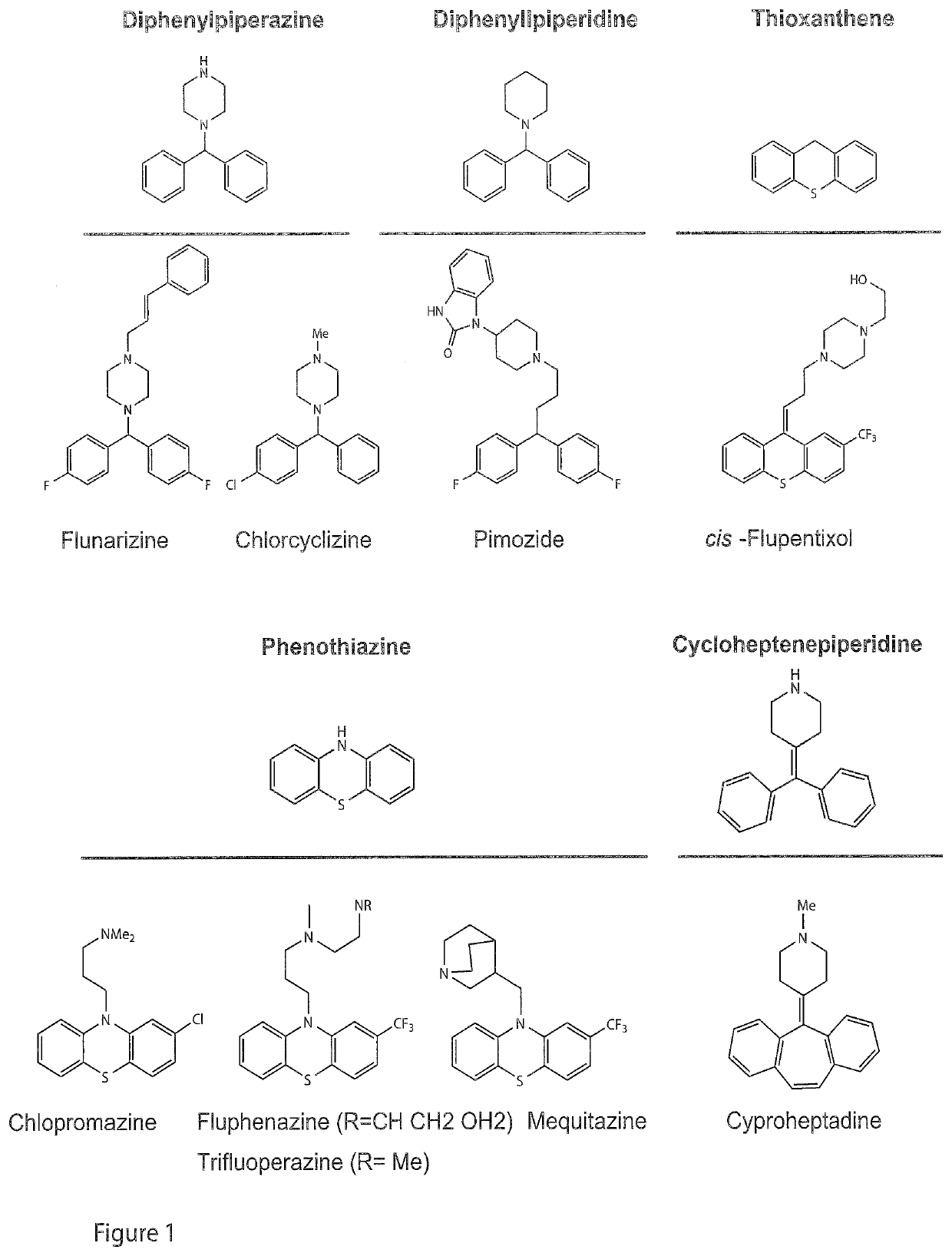
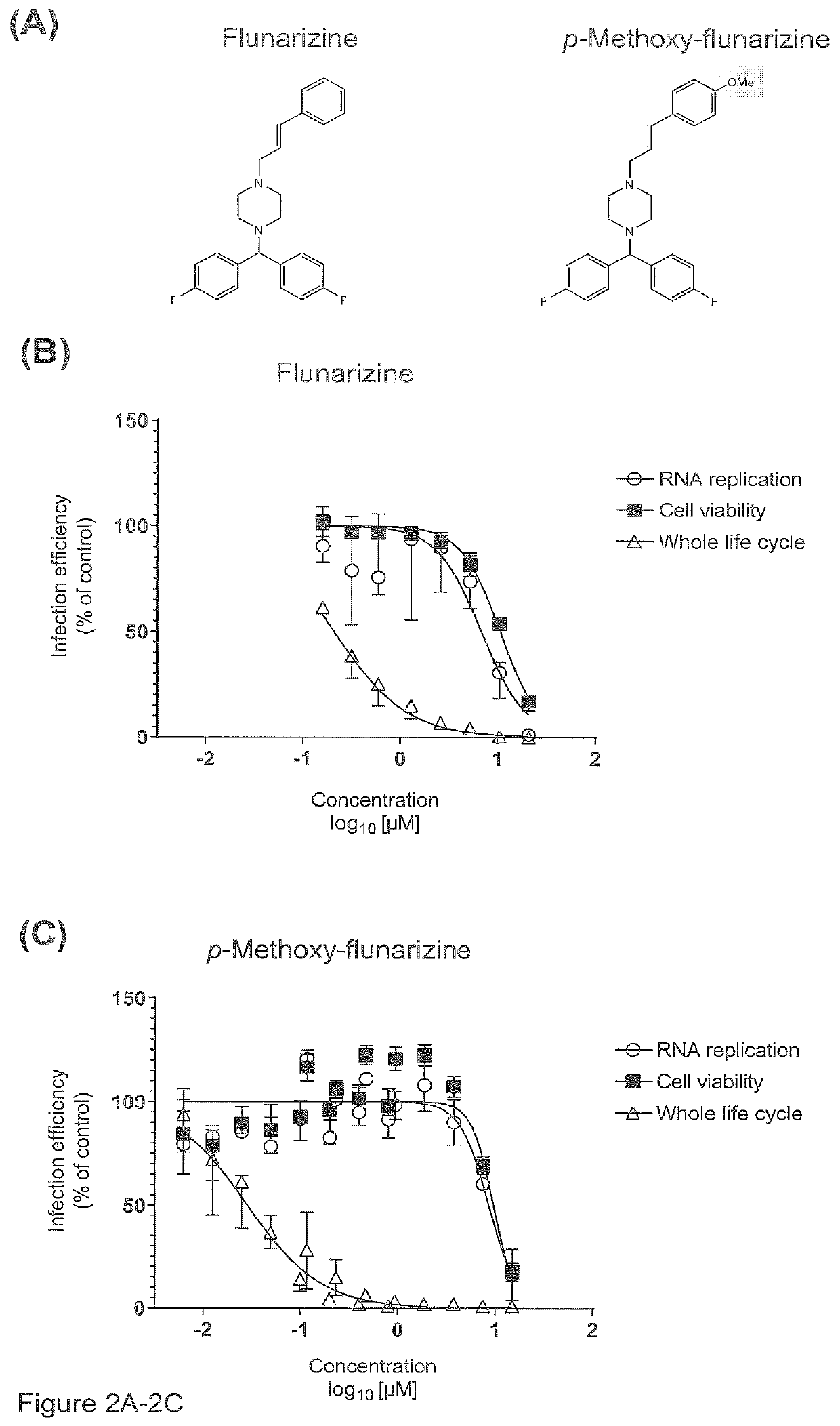
PendingUS20220024879A1Preventing and treatingOrganic chemistryAntiviralsHepatic inflammationVirus inhibitors
In a first aspect, the present invention relates to new compounds based on diphenylpiperazine and diphenylpiperidine structures. In particular, the present invention provides new flunarizine derivatives having improved hepaci virus infection inhibitory activity. In a further aspect, the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing said compound as well as the use of said pharmaceutical composition and the compounds according to the present invention in preventing or treating hepaci virus infection, in particular, HCV virus infection, like HCV of genotype 2. Moreover, a method for determining effectiveness of prophylactic or therapeutic treatment of hepaci virus, like HCV infection as well as a method for determining the therapy regimen of an individual afflicted with hepaci vims infection including HCV infection is provided. Said method is based on determining the sequence or interfacial hydrophobicity of the hepaci virus E1 protein. This may include determining the presence of mutations at predetermined positions of the E1 sequence. Based on determining the interfacial hydrophobicity of the E1 protein, the sensitivity to a diphenylpiperazine or diphenylpiperidine based hepaci virus inhibitor as well as a phenothiazine and cycloheptenepiperidine based hepaci virus inhibitor can be determined. When the central hydrophobicity region is disrupted or the hydrophobicity is below zero applying the Wimley-White hydropathy plot, or the mutations at positions 290, 299, 301 and 310 of SEQ ID No. 1 are present, it is submitted that the sensitivity against said compounds is reduced. Hence, it is possible to determine the therapy regimen of an individual afflicted with hepaci virus infection or being a risk of being afflicted with hepaci vims infection, in particular HCV infection like HCV genotype 2 infection.
Owner:TWINCORE ZENT FUR EXPERIMENTELLE & KLINISCHE INFEKTIONSFORSCHUNG
Method for preparing regulatory dendritic cells
InactiveUS20150139971A1Guarantee normal productionEnsure safetyAntibacterial agentsBiocideDendritic cellCulture cell
An object of the present invention is to establish a method that enables safe and convenient large-scale preparation of regulatory dendritic cells. The present invention provides a method for preparing regulatory dendritic cells, which comprises culturing cells that can be induced to result in regulatory dendritic cells in the presence of a [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivative.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD +1
Composition that augments plant disease resistance and/or branching
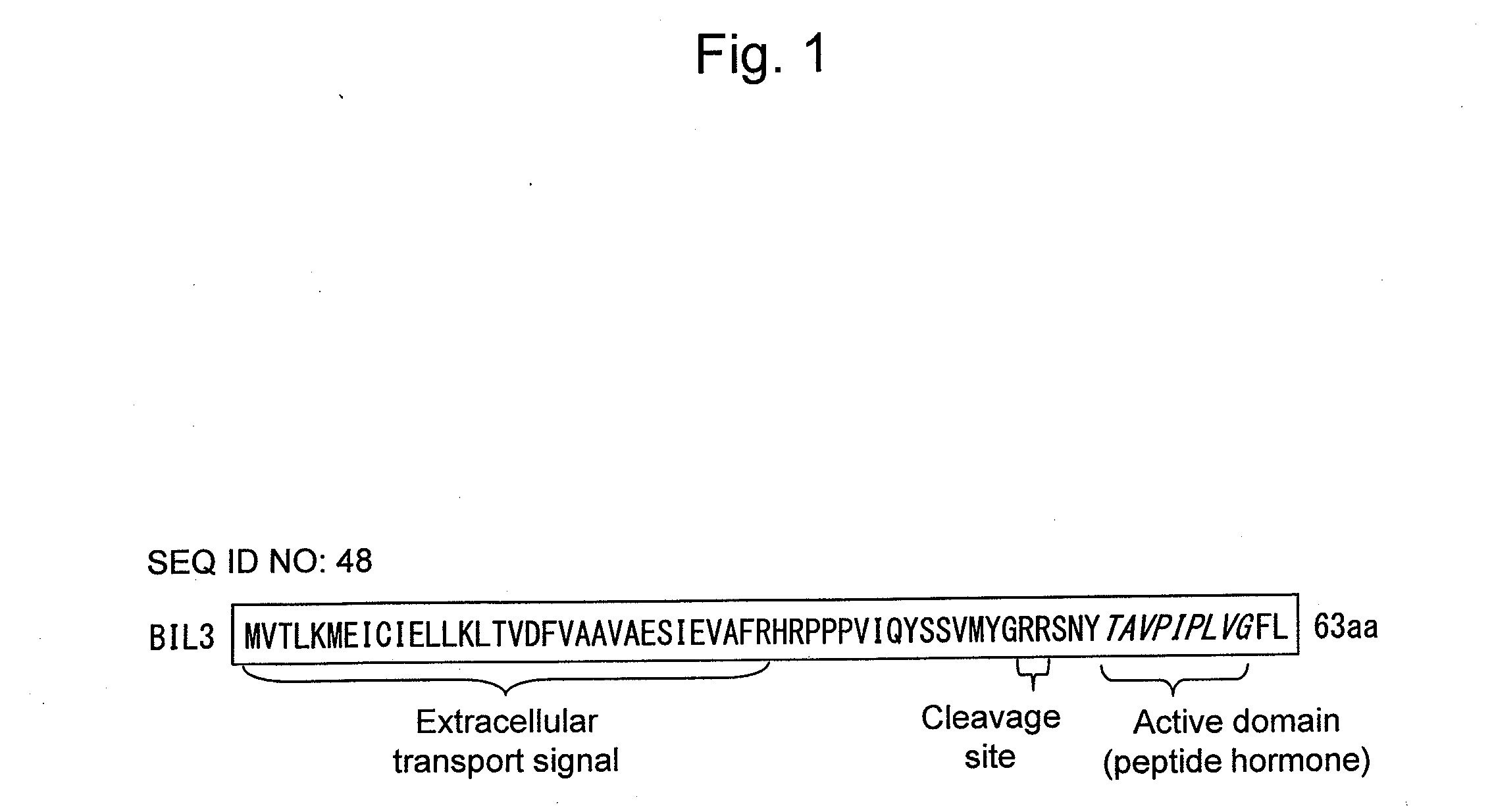
InactiveUS20140143910A1Enhanced yieldImprove disease resistanceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBrassinosteroidPeptide hormone
The objective of the present invention is to develop and provide: a composition that more inexpensively and safely augments plant disease resistance and / or plant branching by inducing new plant disease resistance via a brassinosteroids; and a method for suppressing microbial infection of plants and a method for augmenting branching using the composition. Provided is a composition containing as the active ingredient a peptide hormone obtained on the basis of isolating a disease resistant brassinosteroid variant and analyzing the causative gene thereof.
Owner:RIKEN
Composition comprising dendropanax morbiferaextract or compound derived therefrom as active ingredient for preventing and treating benign prostatic hyperplasia
ActiveUS20150182571A1Treating and preventing benign prostatic hyperplasiaPreventing and relieving benign prostatic hyperplasiaBiocideUrinary disorderAdditive ingredientBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Provided is a use of Dendropanax morbifera extract as an agent for preventing and treating benign prostatic hyperplasia, and more particularly, a composition for preventing and treating benign prostatic hyperplasia and a functional health food for preventing and reducing the effects of benign prostatic hyperplasia, in which the composition and food include, as an active ingredient, a Dendropanax morbifera extract or a compound which is isolated from the extract and then purified. The Dendropanax morbifera extract and the compound isolated from the extract have been demonstrated to be capable of effectively preventing and treating benign prostatic hyperplasia through a mechanism for inhibiting the androgen receptor signaling that induces benign prostatic hyperplasia. Therefore, the Dendropanax morbifera extract and the compound isolated from the extract according to the present invention can be effectively used in the production of medicines and functional foods capable of preventing, treating, and reducing the effects of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND CHOSUN UNIV
Method of preventing and treating brain infarction
InactiveUS20090263374A1Blockage and infarctionPreventing andNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAcute cerebral infarctionBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention is intended to clarify the relationship between PAR-2 and cerebral infarction and thereby provide an efficient method of preventing and treating cerebral infarction, as well as a pharmaceutical composition therefore. Namely, the present invention relates to a method of preventing and treating cerebral infarction by activating PAR-2 and / or promoting expression of PAR-2 gene. The present invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition for preventing and treating cerebral infarction, comprising one, or two or more of the active ingredients selected from the group consisting of a PAR-2 activator and / or a PAR-2 gene expression promoter; as well as a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. It further relates to a method of screening an active ingredient for preventing and treating cerebral infarction using as an indicator the PAR-2 activation promoted by a test substance.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com